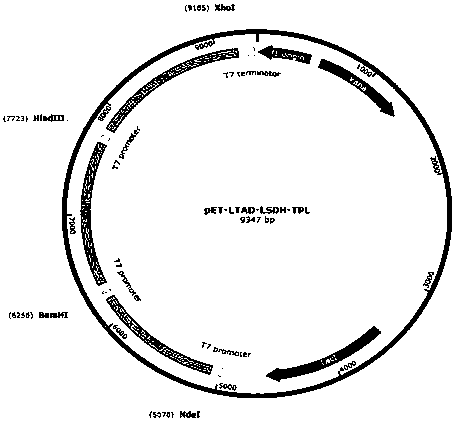
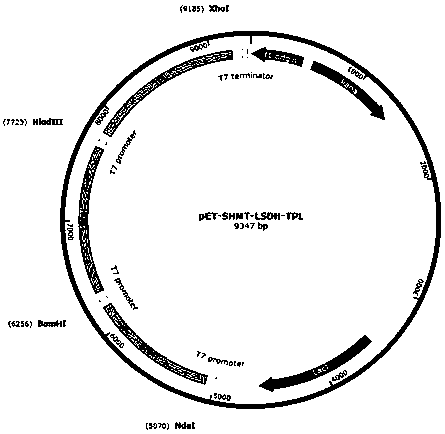
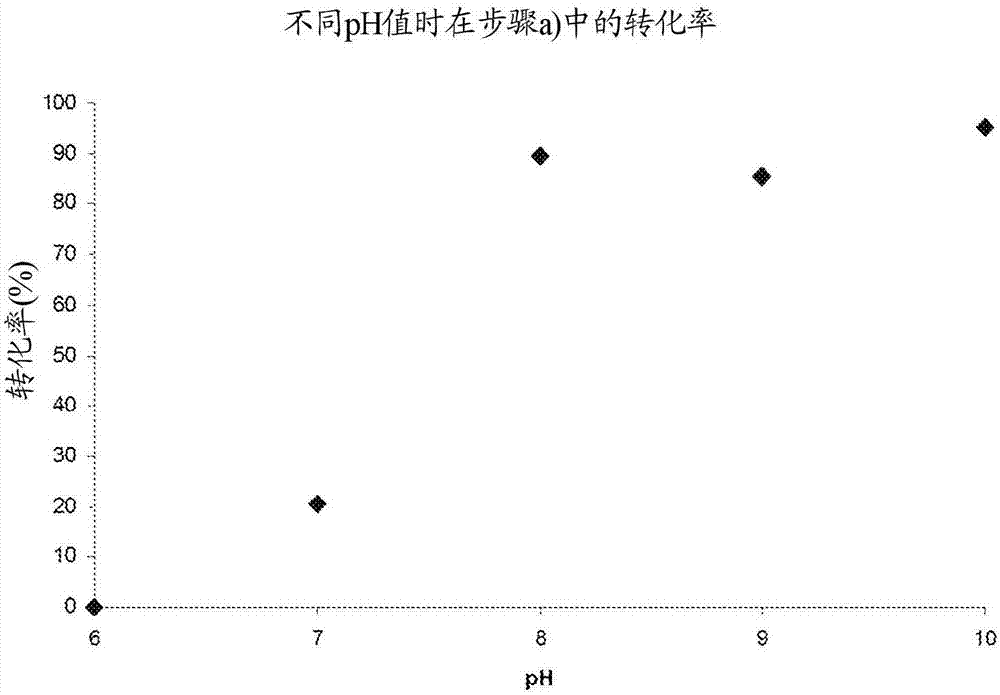
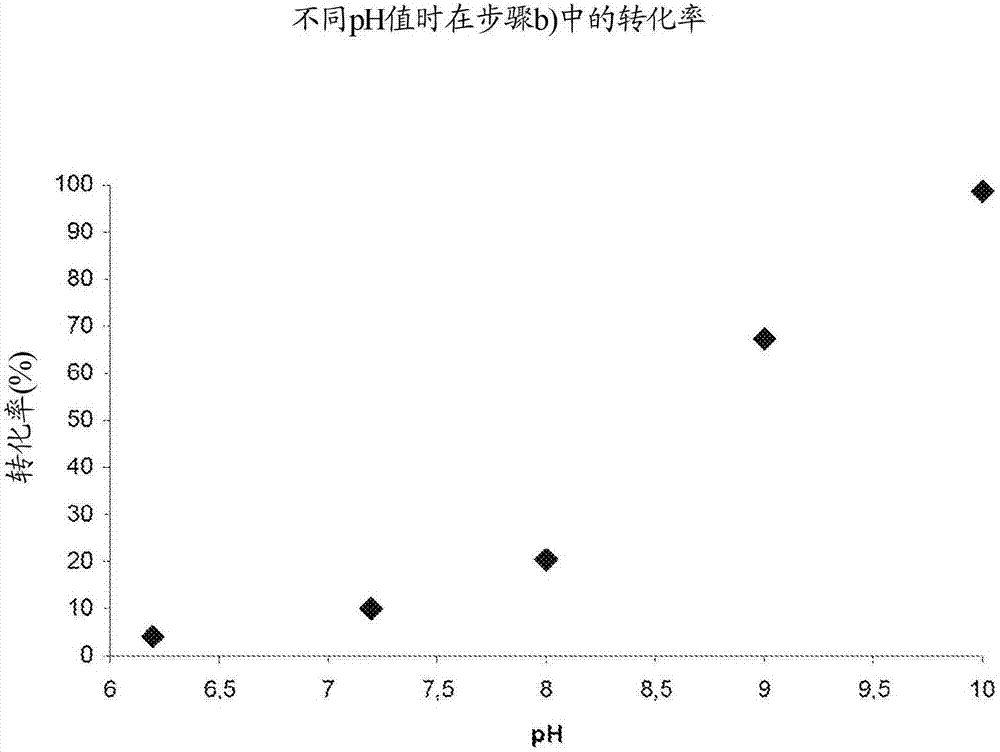
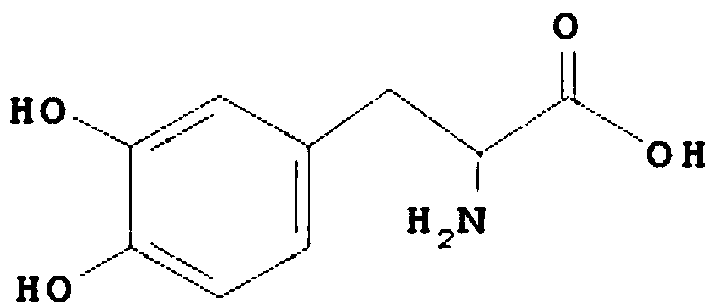
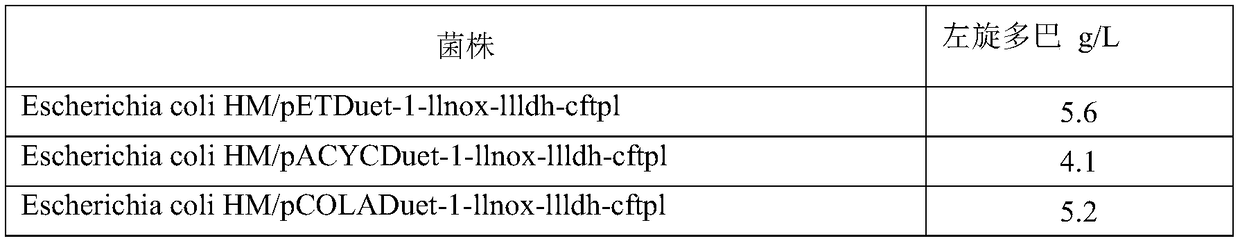
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Tyrosine phenol-lyase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
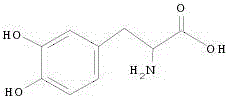
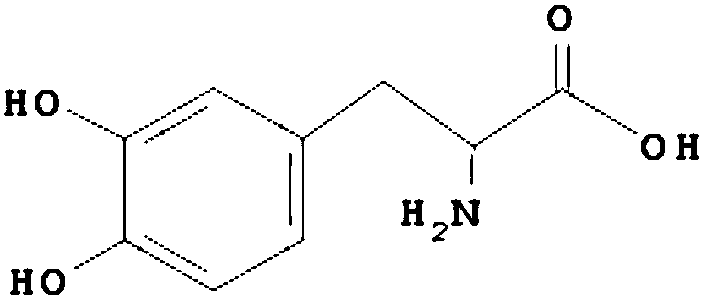
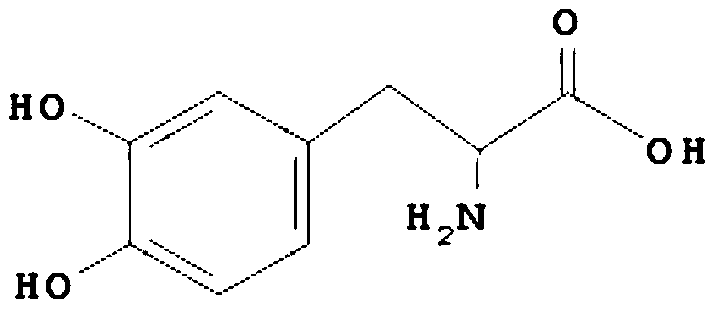
In enzymology, a tyrosine phenol-lyase (EC 4.1.99.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction L-tyrosine + H₂O ⇌ phenol + pyruvate + NH₃ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are L-tyrosine and H₂O, whereas its 3 products are phenol, pyruvate, and NH₃. This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically in the "catch-all" class of carbon-carbon lyases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-tyrosine phenol-lyase (deaminating; pyruvate-forming).
Trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria as well as construction method thereof and application thereof
The invention relates to trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria as well as a construction method thereof and application thereof. A tyrosine phenol lyase gene is constructed to express plasmids; chaperonin is introduced to express the plasmids to obtain the trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria which are identified as escherichia coli FPLF8 (Escherichia coli HPLF8) preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on February 19, 2016, with a preservation number being CCTCCNO:M 2016065. The engineering bacteria can be synthesized into levodopa by fermentation and conversion, and are efficiently expressed; the expressed product is stable and high in activity, and can be synthesized into levodopa by conversion in the presence of related substrates; and the process is simple, the cost is low, the yield is high, emission of three wastes is a little, and the application value for industrial production is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Tyrosine phenol-lyase (TPL) mutant of fusobacterium nucleatum, gene, carrier, engineered bacteria strain, and applications of TPL mutant of fusobacterium nucleatum
ActiveCN106754846AHigh cumulative concentration of synthetic levodopaHigh cumulative concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWild typeFusobacterium nucleatum
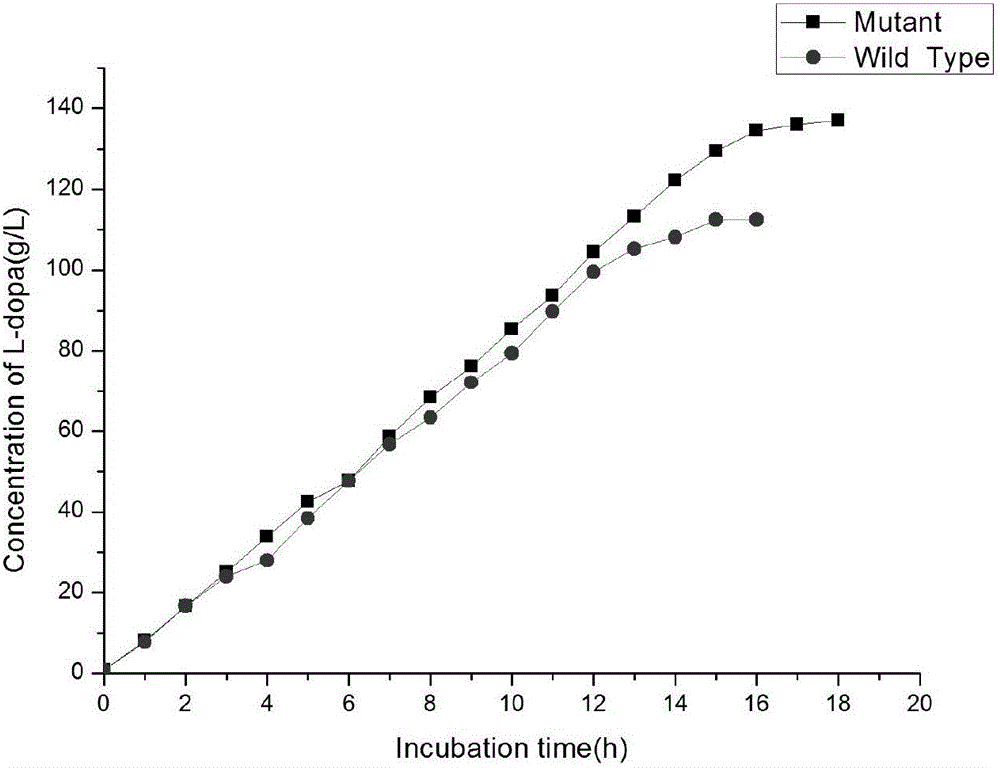
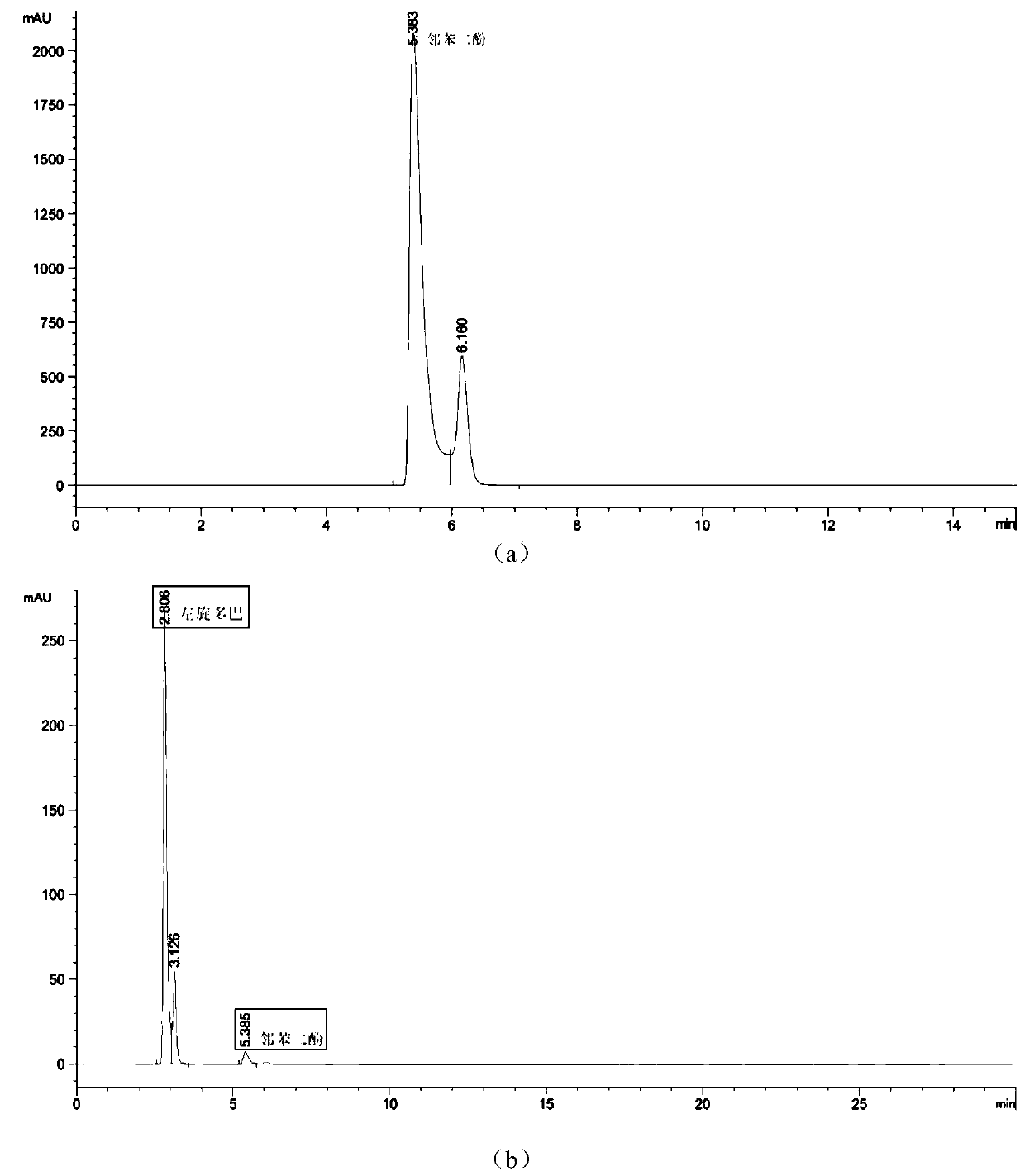
The invention discloses tyrosine phenol-lyase (TPL) mutant of fusobacterium nucleatum, a gene, a carrier, an engineered bacteria strain, and applications of the TPL mutant of fusobacterium nucleatum in synthetizing levodopa. Compared with the wild type, the TPL mutant of fusobacterium nucleatum provided by the invention has the more excellent catalytic performance. The accumulated concentration in synthesizing levodopa of the TPL mutant of fusobacterium nucleatum achieves 140g / L or above, compared with that of the wild type, the accumulated concentration is improved by 17-25 %, and the optical purity is greater than 99.5%; the conversion rate of the substrate, namely, catechol achieves 99.8% or above, and compared with that of the wild type, the conversion rate is improved by 15-20 %.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
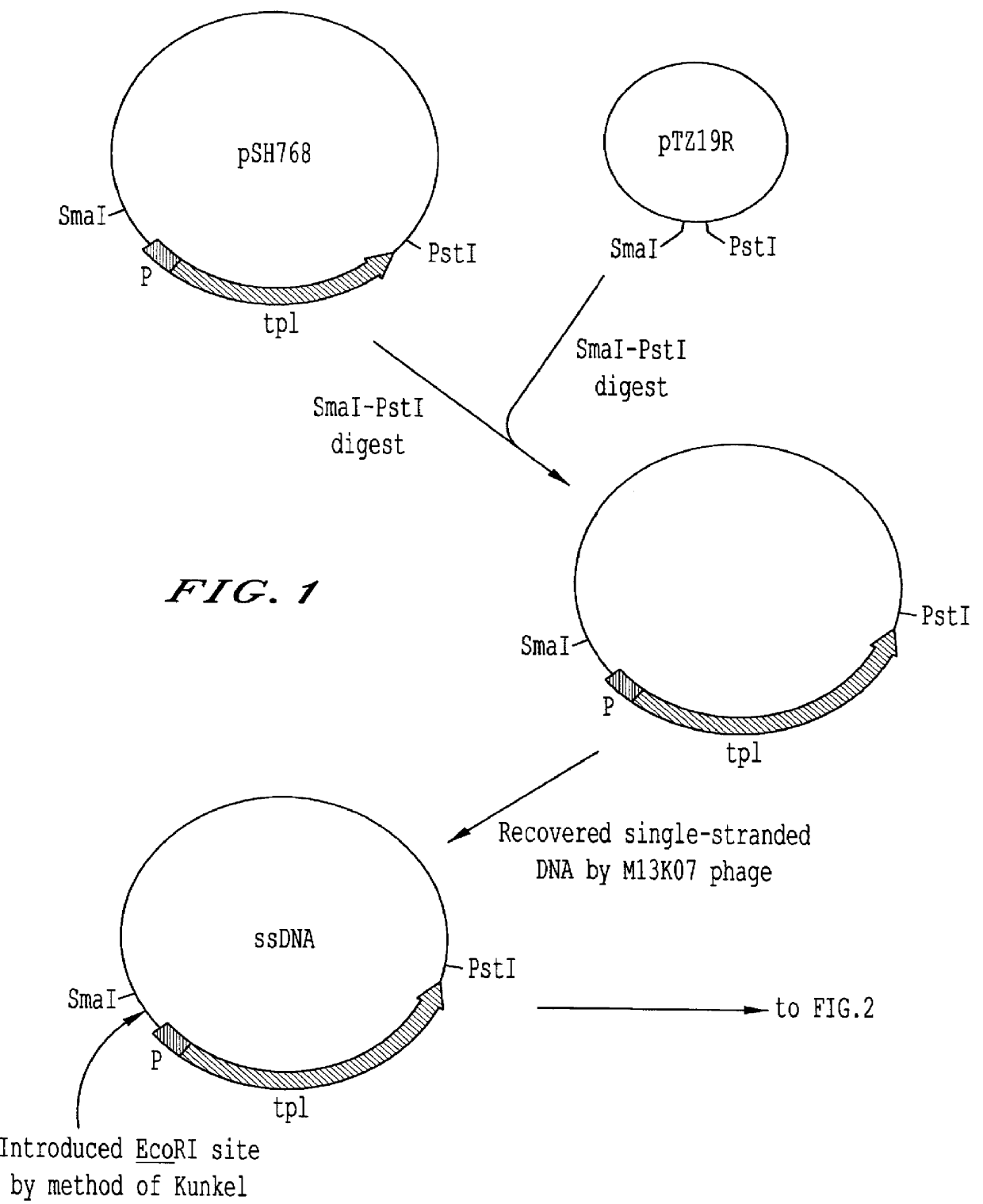
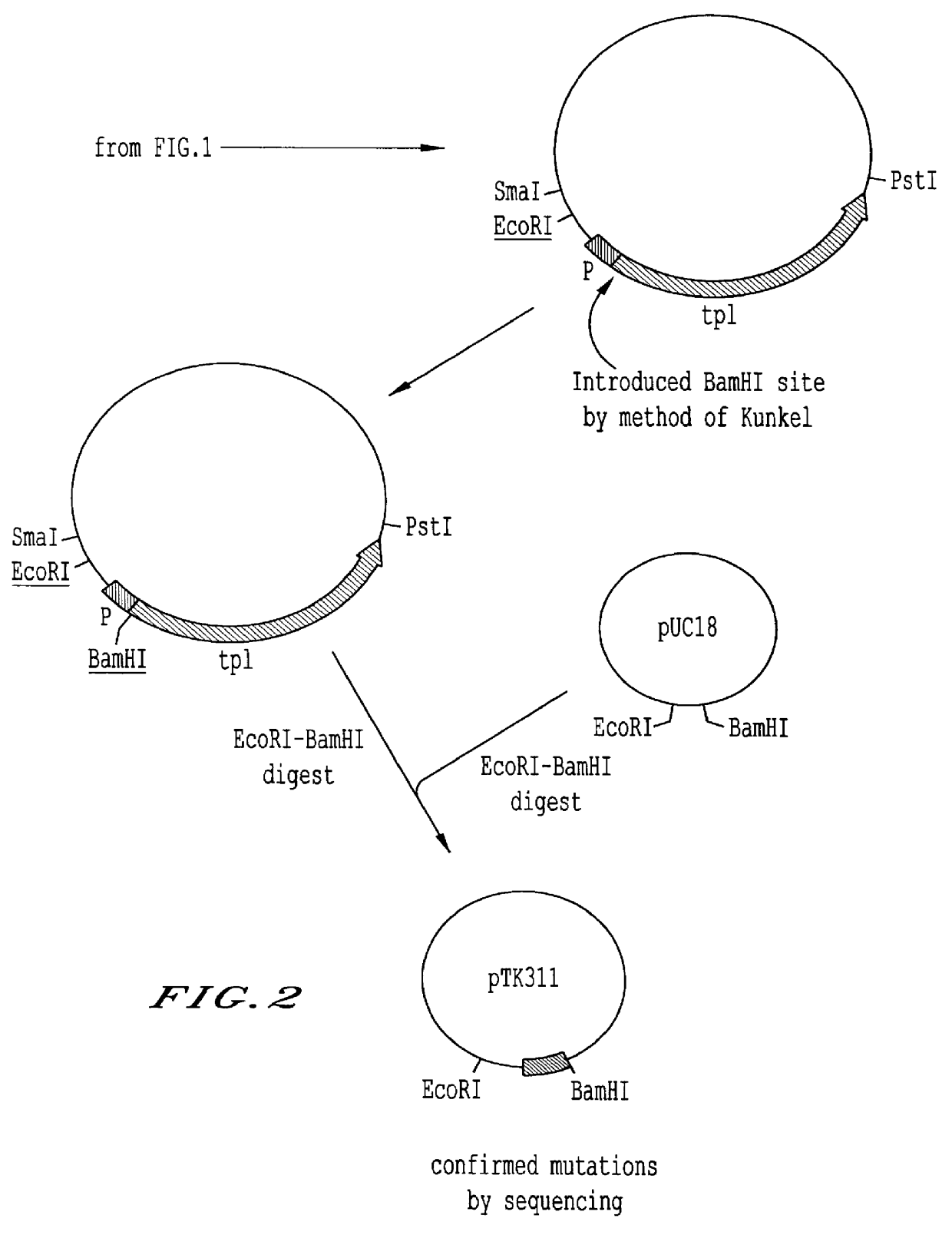
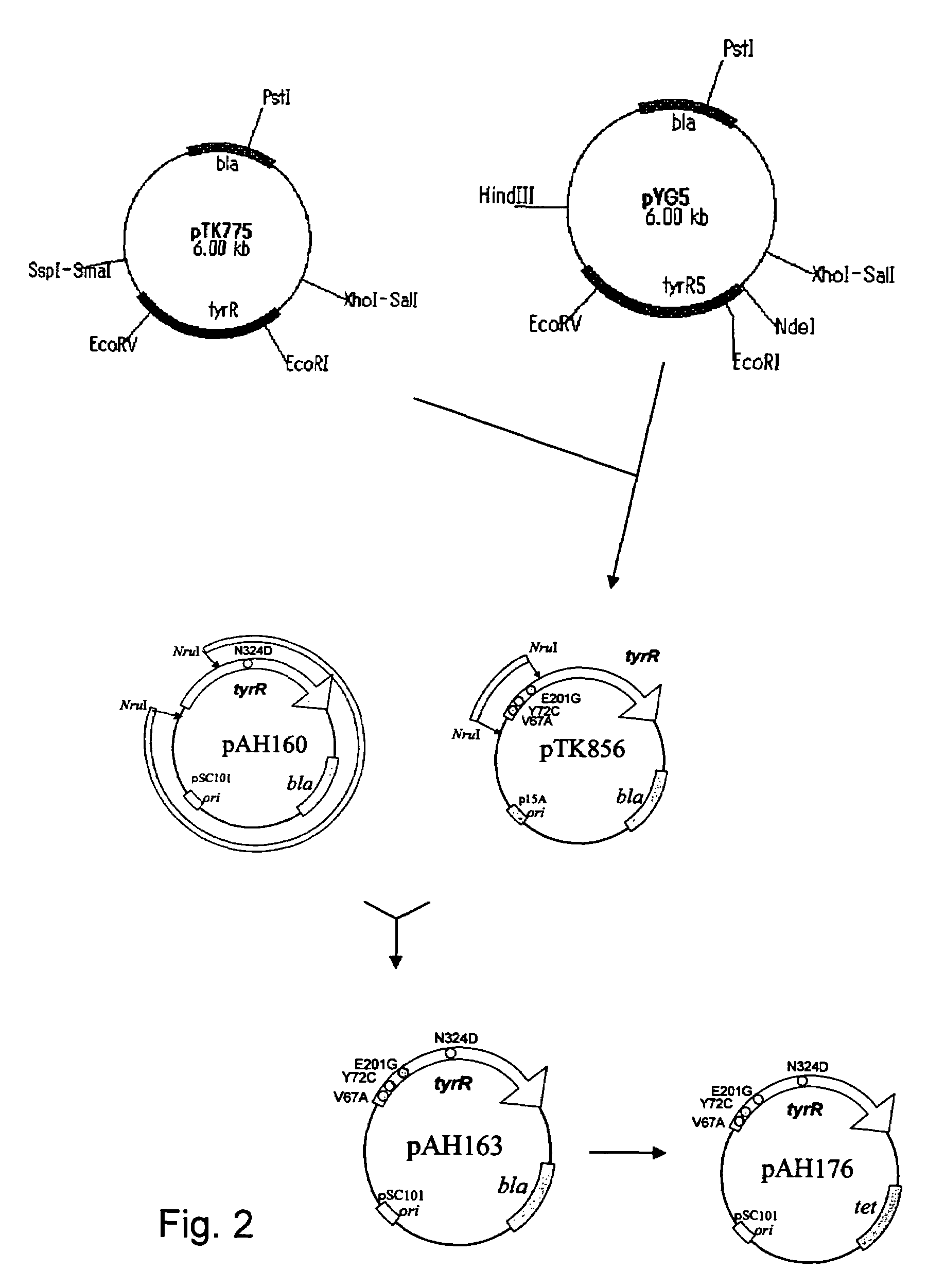
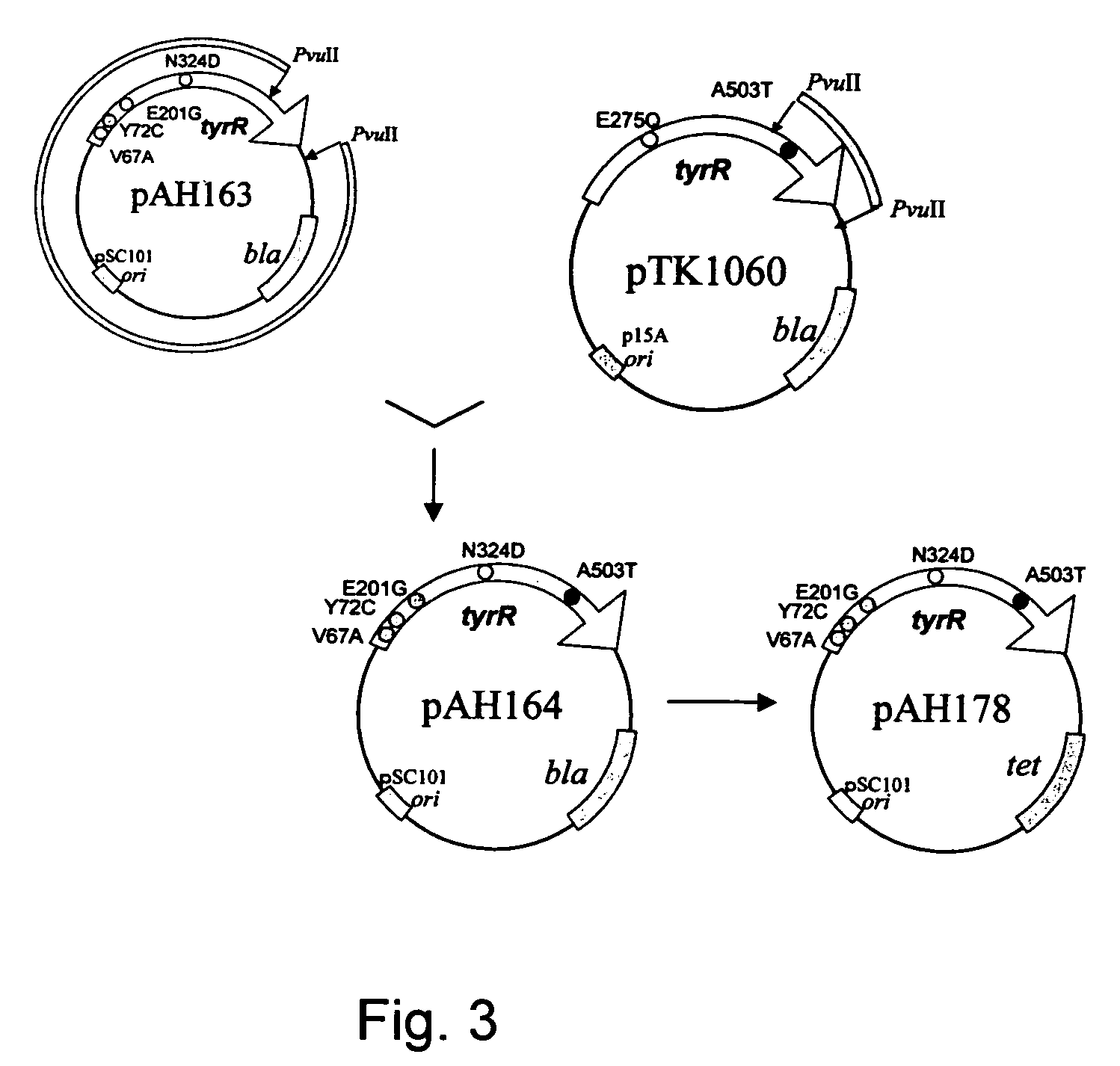
Mutant tyrosine repressor, a gene encoding the same, and a method for producing L-DOPA
A mutant tyrosine repressor that does not require tyrosine to induce expression of tyrosine phenol-lyase gene is obtained by introducing a mutation into a tyrosine repressor. A microorganism which is able to express large amounts of tyrosine phenol-lyase is obtained by introducing the mutant tyrosine repressor into the microorganism. The microorganism is useful for producing L-DOPA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
High efficiency biosynthesis method of caffeic acid with catechol as substrate
InactiveCN106701843AEase of mass productionEfficient synthesisCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaChemical synthesisCaffeic acid
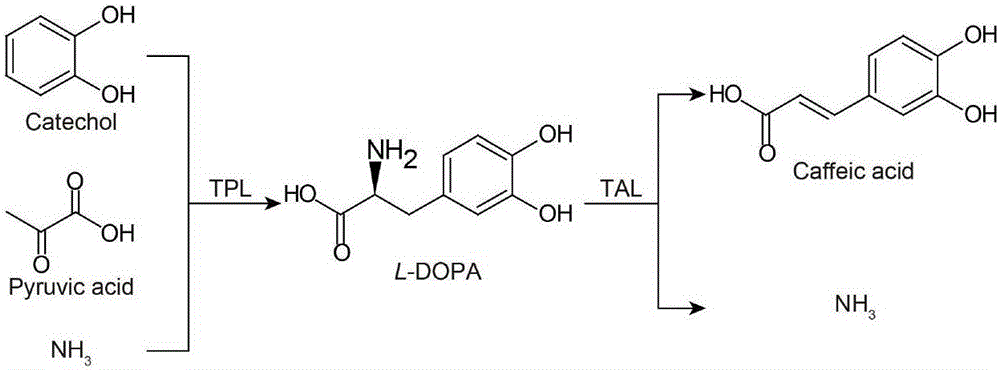
Belonging to the field of biochemical engineering, the invention discloses a high efficiency biosynthesis method of caffeic acid with catechol as the substrate. According to the invention, tyrosine phenol-lyase takes catechol, pyruvic acid and ammonia as the substrate to synthesize levodopa, tyrosine ammonia-lyase converts levodopa into trans-caffeic acid and NH3. Catechol, sodium pyruvate and ammonium chloride are relatively cheap compounds, therefore the caffeic acid biosynthesis method provided by the invention has large potential. Compared with the previous conversion methods taking L-tyrosine as the substrate, the substrate used by the method are cheaper and easier for large-scale production. Compared with chemical synthesis methods, the product of the method provided by the invention is single trans-caffeic acid, and further separation of an isomer is unnecessary.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Levodopa crystalline powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106117072AHigh yieldImprove uniformityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCrystallinityDrug biotransformation
The invention discloses levodopa crystalline powder and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes: obtaining a mixed solution containing levodopa through tyrosine phenol lyase biotransformation; using acidic liquid to adjust pH of the mixed solution to be on the acidic side; centrifuging or filtering and collecting coarse crystal; continuing acid adjusting and redissolving; adding activated carbon, and heating and stirring for decoloring; filtering clean liquid, performing adjusting alkali and crystallizing, filtering, and drying to obtain the levodopa crystalline powder. By using the method, on the basis that industrial production is realized, and residual substrate, protein and pigment in the process of transformation are filtered away effectively; vacuum microwave drying technology is adopted, so that product loss caused by exogenic action of hot air blowing and material turning during conventional drying is reduced, product appearance browning caused after levodopa is damaged or decomposed through high-temperature oxidation is avoided, and moisture uniformity of the crystalline powder after being dried. The crystalline powder obtained by the method is high in quality, total impurities calculated by HPLC peak appearing area percentage is not more than 0.05%, and crystallinity of the crystalline powder is higher than 90%.
Owner:CHANGXING PHARMA
Method for preparing levodopa with one-pot enzymatic method
The invention discloses a method for preparing levodopa with a one-pot enzymatic method. The method is characterized in that formaldehyde, glycine and catechol are taken as substrates; formaldehyde and glycine are subjected to a catalytic reaction in the presence of aldolase and other enzymes to be converted into serine, then, serine is converted into pyruvic acid and ammonia under the action of anhydrase, and finally, pyruvic acid and catechol react under the action of tyrosine phenol lyase to produce levodopa. The method adopts novel catalysis routh design and has the advantages of being simple to operate, short in production cycle, low in production cost, high in yield, low in environmental protection pressure, suitable for mass industrial production and the like.
Owner:CHANGXING PHARMA
Method for producing p-vinylphenols
The invention relates to a biocatalytic method for producing p-vinylphenols, comprising a three-stage one-pot reaction according to the following reaction scheme: (A) wherein a) an optionally substituted phenol (1) is bound to pyruvic acid (BTS) to form the optionally substituted tyrosine (2) by means of catalytic action of a tyrosine phenol-lyase (TPL) and in the presence of ammonium ions, b) ammonia is eliminated from the tyrosine (2) by means of catalytic action of a tyrosine-ammonia-lyase (TAL) or phenyl-ammonia-lyase (PAL), in order to produce an optionally substituted p-coumaric acid (3), and c) the p-coumaric acid (3) undergoes a decarboxylation by means of catalytic action of a phenolic acid decarboxylase (PAD), in order to produce the desired, optionally substituted p-vinyl phenol(4); d) wherein the resultant CO2 is removed from the reaction system, in order to move the chemical equilibrium of all three reaction steps in the direction of the products.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GRAZ
Membrane filtration, separation and purification method of levodopa conversion solution
ActiveCN106117071AImprove qualityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPurification methodsCrystallinity
The invention discloses a membrane filtration, separation and purification method of a levodopa conversion solution. The conversion solution containing levodopa is obtained through tyrosine phenol-lyase biological conversion, the pH of the conversion solution is adjusted to be strongly acidic by means of acid fluid, clear liquid is collected through a ceramic membrane filtration system after proper temperature increasing, and after activated carbon is added into the collected ceramic membrane filtration clear liquid, stirring, temperature increasing and decoloring are conducted; after clear liquid is filtered, alkali adjustment and crystallization are conducted, then filtering is conducted to obtain crystal, the crystal is dried, and levodopa anhydrous crystal powder is obtained. The method effectively removes residual substrates, protein and pigment in the conversion process on the basis of industrial production, the anhydrous crystal powder obtained during production is high in quality and high in light transmittance, total impurities are not larger than 0.1% by HPLC peak area percentage, and the crystallization degree of the crystal powder is 90% or above.
Owner:CHANGXING PHARMA
Method for improving quality and yield of 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-L-ananine products
InactiveCN109161568AReduce or avoid oxidationImprove conversion rateFermentationAntioxidantSulfite salt
The invention relates to a method for improving quality and yield of 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-L-ananine products. The method comprises the following steps of (1) performing fermentation to obtain tyrosinephenol lyase; (2) preparing a substrate solution; (3) preparing material complementing liquid: after running water is boiled over, introducing nitrogen, lowering the temperature to be 10-25 DEG C, firstly, adding an antioxidant, adding 2-5g / L of sodium sulfite and 0.5-2g / L of ascorbic acid, then adding 100-160g / L of sodium pyruvate, 100-160g / L of catechol, 10-20g / L of ammonium acetate and 1-3g / L of EDTA, and regulating the pH to be 7.5-8.5; and (4) continuously introducing nitrogen for the substrate solution, adding the substrate solution to enzymes, sealing a reaction container for oxygen separation, introducing small amount of nitrogen for maintaining positive pressure, performing uniform stirring, performing sealing at 16-25 DEG C, performing vibration for a reaction, adding the material complementing liquid (sealing a material complementing container in a flowing manner, and continuously introducing small amount of nitrogen for maintaining positive pressure ), and when the flowingaddition of the material complementing liquid is finished and the concentration of catechol is lower than 0.05g / L, stopping the reaction. The product quality is improved, the conversion rate of the catechol is increased, and the product yield is increased. The method has high application value during industrialized production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
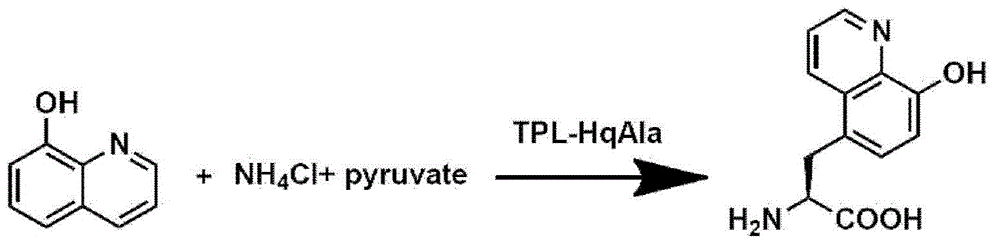
8-hydroxyquinoline alanine translation system and application thereof
ActiveCN104059891AEasy to foldHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase mutant which has an amino acid sequence selected from a group comprising an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:4 and conservative variants of the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:4, wherein the conservative variants have the same enzymatic activity as the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:4. The The invention also provides a translation system which comprises: (i) 8-hydroxyquinoline alanine or its structure analogs; (ii) an orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase of the invention; (iii) orthogonal tRNA, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase realizes prior aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA by the 8-hydroxyquinoline alanine or its structure analogs; and (iv) nucleic acid coding target protein, wherein the nucleic acid contains at least one selection codon specifically recognized by the orthogonal tRNA. Finally, the invention provides a tyrosine phenol lyase mutant which can catalyze 8-hydroxyquinoline to generate 8-hydroxyquinoline alanine, and has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:5.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
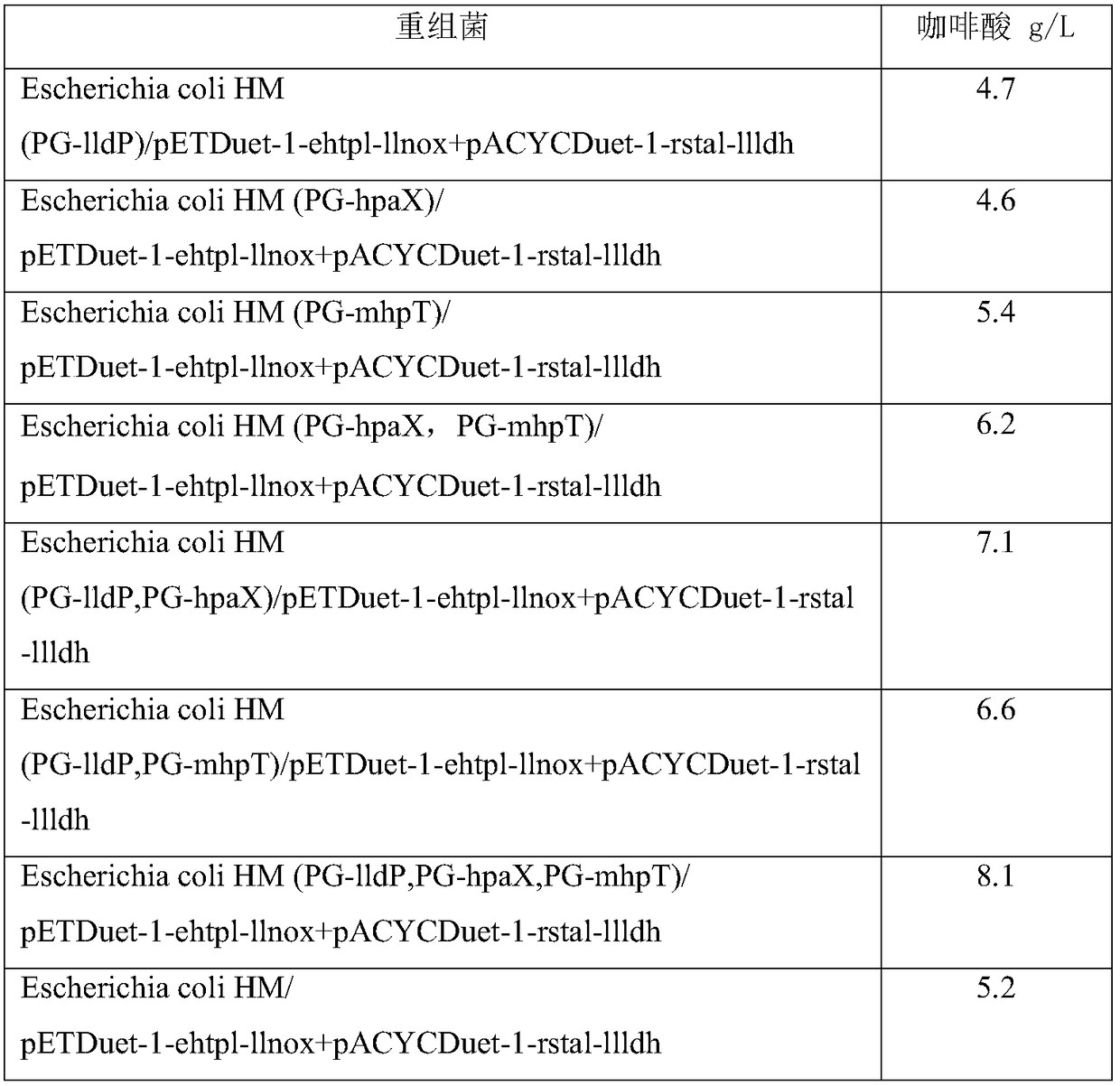
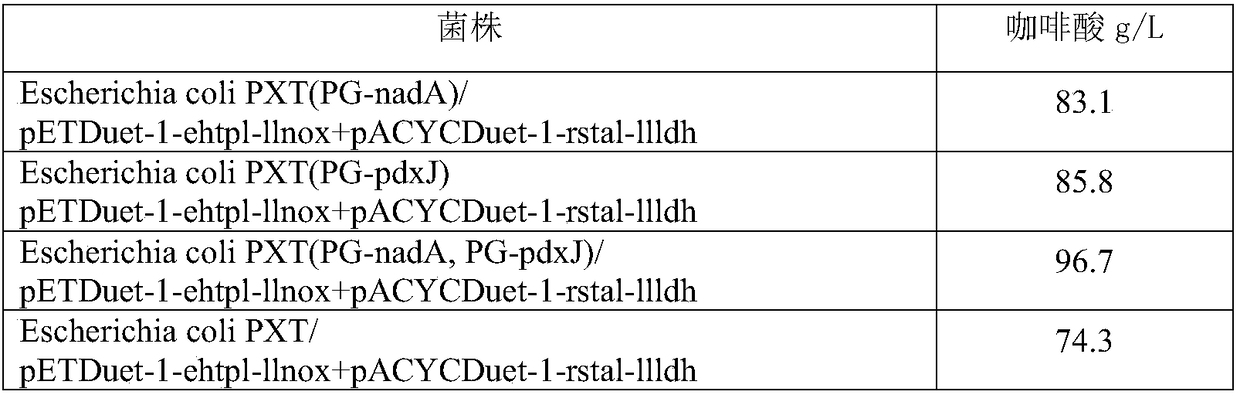
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of caffeic acid
ActiveCN108949652AEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-Lactate dehydrogenaseCaffeic acid
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of caffeic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium providedby the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing caffeic acid at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium has the advantages of realization of the efficient production ofcaffeic acid, simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Tyrosine repressor gene of a bacterium belonging to the genus Erwinia
Using as a host Escherichia coli which expresses lactose operon under the control of the promoter / enhancer of tyrosine phenol lyase gene derived from Erwinia herbicola, a DNA fragment coding for tyrosine repressor (tyrR) having an amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing is obtained from the chromosome gene library of Erwinia herbicola.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
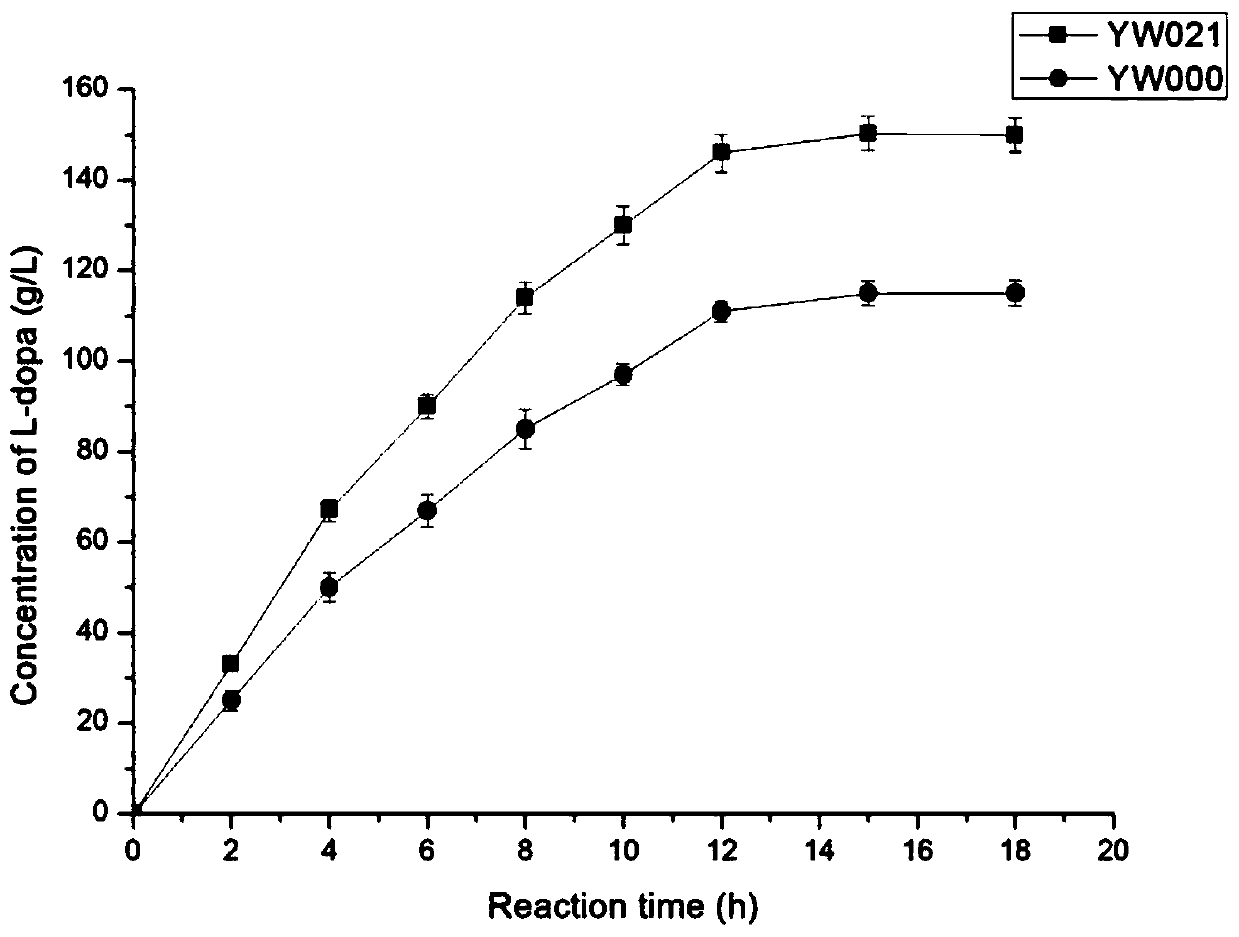
Kluyvera intermedia tyrosine phenol-lyase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110331153ASimple processEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRandom mutation
The invention discloses a kluyvera intermedia tyrosine phenol-lyase mutant and an application thereof. A tyrosine phenol-lyase gene from the kluyvera intermedia is cloned, random mutation is conductedon the tyrosine phenol-lyase gene, and the mutated gene is expressed in escherichia coli to obtain an engineering bacterium YW021 of which the enzyme activity is greatly improved. The maximum concentration of levodopa synthesized by the engineering bacterium YW021 provided by the invention is as high as 150g / L which is improved by about 30% than that of a wild type, and the conversion rate of zymolyte catechol is 99.9% or more.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Engineered bacterium to improve stability of tyrosine phenol-lyase and construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to an engineered bacterium and a construction method thereof, in particular to an engineered bacterium to improve stability of tyrosine phenol-lyase and a construction method andapplication thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The engineered bacterium is identified as Escherichia coli CBD-TPL, collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection at Wuhan university in Wuhan, China on 13th, 11, 2017; its collection number is CCTCC NO: M2017685. Two tyrosine phenol-lyase genes are linked with a cellulose binding domain gene to construct expression plasmids; target enzymes can be extracted effectively and immobilized; levodopa can be catalytically produced at the premise of providing a related substrate; purification yield is greatly increased; product quality is improved; the process is simple; the cost is low; the yield is high; the engineered bacterium herein is worthy of application in industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Extracellular expression and application of tyrosine phenol lyase
ActiveCN108715827ALow toxicityIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses extracellular expression and application of tyrosine phenol lyase and belongs to the technical field of biology. A method for extracellular expression includes: cloning high-activity tyrosine phenol lyase gene, co-expressing with signal peptide signal, converting Escherichia coli competent cells, and building a tyrosine phenol lyase extracellular secretion engineering strain mediated by signal peptide to realize extracellular expression, wherein obtained tyrosine phenol lyase fermentation liquid is used for converting and synthesizing tyrosine and derivatives. An extracellular expression mode is adopted to build the tyrosine phenol lyase engineering strain, and enzyme release quantity reaches higher than 50%, so that toxicity caused to cells due to excessive accumulation of protein in the cells is reduced, and total enzyme activity is improved by 36% when compared with common expression. Part of enzyme generated by fermentation is released into the fermentationliquid, thallus cells are high in permeability, contact of a substrate with enzyme is facilitated, and catalytic efficiency of the enzyme is improved substantially. The fermentation liquid can be directly adopted to catalyze the substrate to product L-tyrosine and the derivatives, and the cells do not need to be broken to extract pure enzyme for reaction, so that using cost of the enzyme is saved.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of levodopa
ActiveCN108949649ANot easy to decomposeHigh NAD contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of levodopa, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium is a recombinant Escherichia coli capable of producing pure levodopa at low cost; the recombinant Escherichia coli simultaneously expresses exogenous L-lactate dehydrogenase, NADH oxidase and tyrosine phenol lyase, and is obtained by knocking out an aromatic compound-degrading gene from host Escherichia coli; and the recombinant Escherichia coli can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, an ammonia ion transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene, an NAD synthesis gene and a pyridoxal phosphate synthesis gene. A bacterium can be applied to the production of levodopa, and a method for producing the levodopa has the advantages of simple production process, few impurities, easily available raw materials and good industrial application prospect.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Engineered bacterium to improve stability of tyrosine phenol-lyase and construction method and application thereof
PendingCN109439605AImprove stabilityIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLarge intestine
The invention relates to an engineered bacterium and a construction method thereof, in particular to an engineered bacterium to improve stability of tyrosine phenol-lyase and a construction method andapplication thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The engineered bacterium is identified as Escherichia coli Trx-TPL, collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection at Wuhan university in Wuhan, China on 13th, 11, 2017; its collection number is CCTCC NO: M2017684. Two tyrosine phenol-lyase genes are linked with a thioredoxin gene to construct expression plasmids; stability, particularly thermal stability, of expressed enzymes can be effectively improved; conversion synthetic time of levodopa can be extended at the premise of providing a related substrate;substrate concentration is improved; the process is simple; the cost is low; the yield is high; the engineered bacterium herein is worthy of application in industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of Danshensu by using cheap substrate
ActiveCN108949648APoor substrate specificityEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseL-amino-acid oxidase
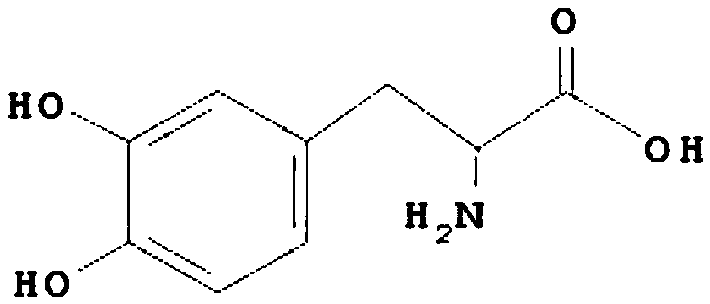
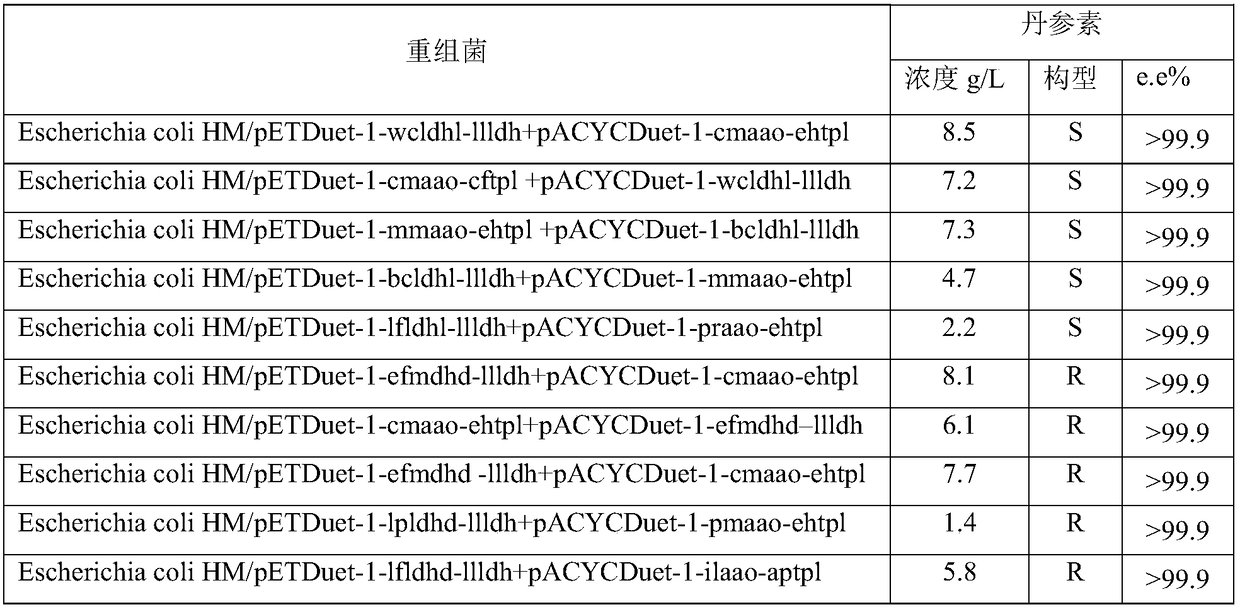
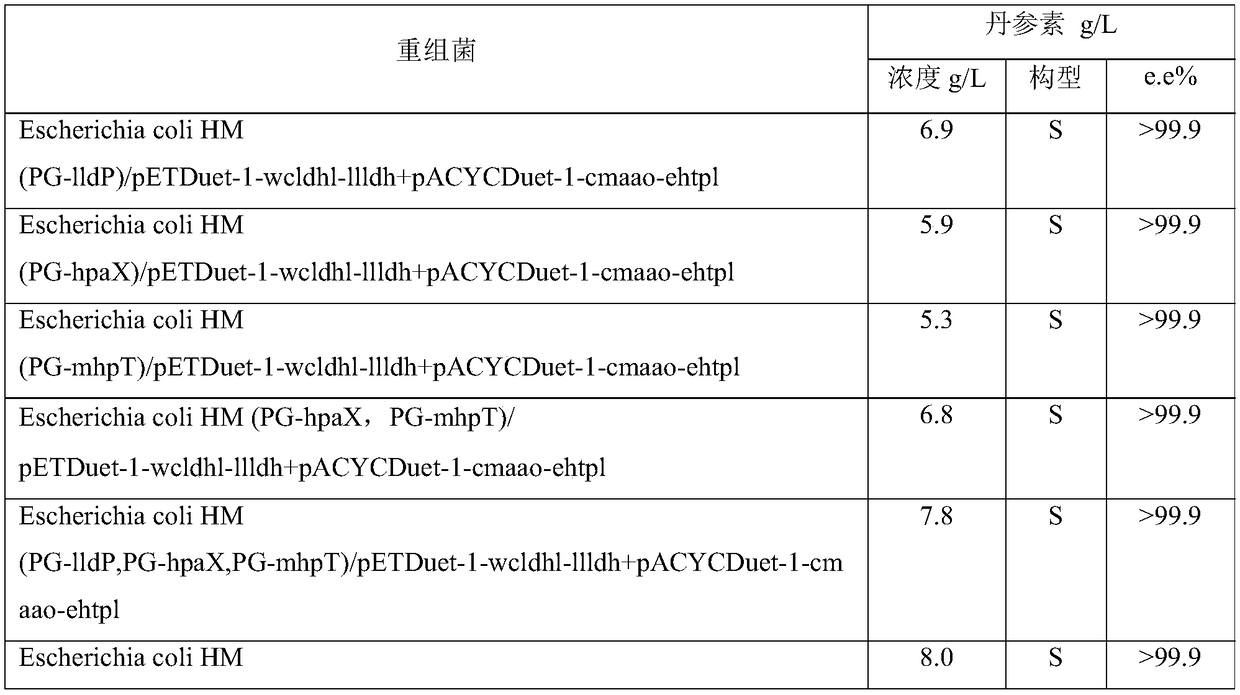
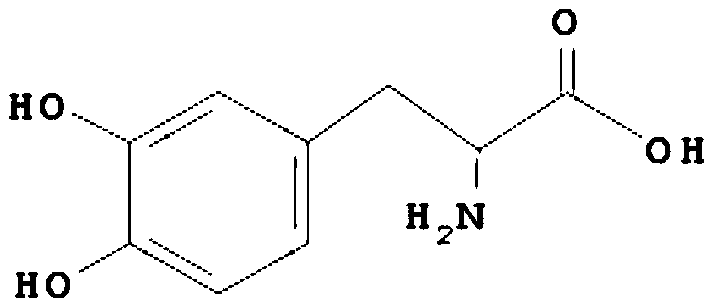
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of Danshensu by using a cheap substrate, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium provided by the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing Danshensu at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosinephenol lyase, L-amino acid oxidase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and alpha-hydroxycarboxylic acid oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium has the advantages ofrealization of the efficient production of Danshensu, simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:HONGTAOSIM RES INST OF ANALYCAL SCI & TECH LTD CO
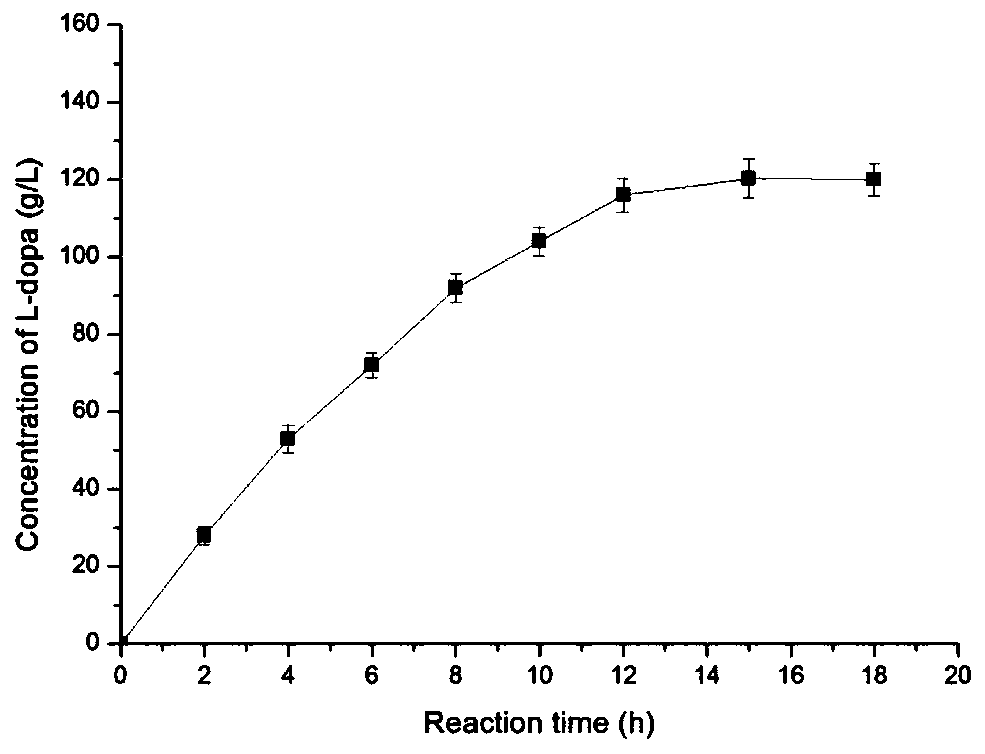
Pyruvic acid and L-dopa co-production process and application
ActiveCN110055292ALow costThree wastes lessMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a pyruvic acid and L-dopa co-production process and application. The process comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a pyruvic acid feed liquid by fermentation with torulopsis glabrata, sterilizing the feed liquid by a ceramic membrane, and removing proteins, nucleic acids, pigments and other macromolecules by an ultrafiltration membrane; (2) adding a certain amount of catechol, ammonium acetate, EDTA, sodium sulfite and other compounds to a pyruvic acid concentrate according to the molar amount of pyruvic acid, adjusting the pH to 7.0-9.0, and preparing an enzyme-catalyzed substrate solution; (3) fermenting with tyrosine-phenol lyase genetic engineering bacteria to obtain a tyrosine-phenol lyase bacterial solution, centrifuging to collect thalli, breaking cells by a high-pressure homogenizer, centrifuging, and collecting an enzyme solution; and (4) adding a certain amount of substrate solution to the enzyme solution, stirring evenly, and at the temperature of 25 DEG C, carrying out seal shock reaction. The substrate solution is prepared from the pyruvic acid concentrate, and the concentration of catechol is controlled at 0-10 g / L by fed-batching the substrate solution, the product reaches 120 g / L or more, and fed-batch of the substrate solution is stopped; when the content of catechol in the reaction solution is less than 0.2 g / L, and the reactionis stopped.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Protein fiber antibacterial finishing method based on enzymatic grafting copolymerization
ActiveCN109281166AReduce production energy consumptionReduce energy consumptionBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsAnimal fibresProtein fiberSerine
The invention discloses a protein fiber antibacterial finishing method based on enzymatic grafting copolymerization. Protein fiber antibacterial finishing is performed by using of tyrosine phenol lyase for catalyzing serine in protein fiber macromolecules to be converted into tyrosine and use of horseradish peroxidase for catalyzing graft copolymerization of the tyrosine in protein fiber and vinyl-containing quaternary ammonium salt monomers. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) oxidizing pretreatment; (2) enzyme-catalyzed amino acid conversion; and (3) enzyme-promoting graft copolymerization of the protein fiber and the vinyl-containing quaternary ammonium salt monomers. Compared with a traditional method for carrying out the protein fiber antibacterial finishing through padding baking, high-temperature bonding or coating finishing, the method has the advantages of being low in energy consumption, good in antibacterial effect and small in fiber damage.
Owner:无锡市奥菲超细织物有限公司
Inducible expression method in fermentation process of tyrosine phenol-lyase
The invention provides an inducible expression method in a fermentation process of tyrosine phenol-lyase, which belongs to the technical field of biological fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly fermenting a culture strain to OD600 of 25 to 30 under the condition of 36 to 38 DEG C, and obtaining to-be-induced fermentation solution; then cooling the to-be-induced fermentation solution in different phases, and adding an induction agent, observing an adaptation state of thallus according to the change of an oxygen dissolving level, obtaining a final induction fermentation solution after the dissolved oxygen amount is stable, and keeping the fermentation state until the fermentation is ended. The thallus is induced by virtue of the method of the invention, so that theharm of the induction agent for the thallus can be maximally reduced, and the problem that the thallus is poor in adaptability to the low temperature and the induction agent can be effectively solved. The thallus OD600 after the fermentation is ended is not less than 100, the wet weight of the thallus is 180 g / L or more, and the expression amount of the tyrosine phenol-lyase in the fermentation solution is greater than 15 g / L.
Owner:SHANDONG LUKANG PHARMA
Method for improving efficiency of catalytic production of L-dopa by tyrosine phenol lyase
PendingCN110055291AImprove conversion rateHigh product concentrationFermentationCarbon-carbon lyasesKanamycinSulfite salt
The invention relates to a method for improving the efficiency of catalytic production of L-dopa by tyrosine phenol lyase. The method is characterized by comprising the steps: (1) selecting a single colony, inoculating a test tube containing an LB culture medium with the single colony, adding kanamycin (50 mg / L) at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C, at the speed of 220 rpm, culturing for 12-16 h, andthus obtaining primary seeds; (2) inoculating a shaking flask containing a fermentation culture medium with the primary seeds, and culturing for 10-12 h; (3) centrifuging, collecting bacteria to obtain the bacteria, breaking cells by ultrasound, and centrifuging at high speed to obtain a supernatant enzyme liquid; and (4) adding an enzyme solution into a substrate solution, stirring evenly, and carrying out sealed oscillation reaction at the temperature of 25 DEG C, wherein the substrate solution comprises 14-16 g / L of sodium pyruvate, 10-12 g / L of catechol, 50-60 g / L of ammonium acetate, 2-5g / L of sodium sulfite, and 1-3 g / L of EDTA, and the pH is adjusted to 7.5-8.5. The concentration of the reaction product reaches 20 g / L or more, and 10-30 g / L of L-dopa crystals are added to induce the product to crystallize in advance. The method greatly improves the conversion rate and the product concentration, improves the product quality, has simple process, low cost and high yield, and hasthe application value of industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Biosynthesis method of levodopa
ActiveCN110791536AReduce the cost of separation and purificationHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliResting Cell
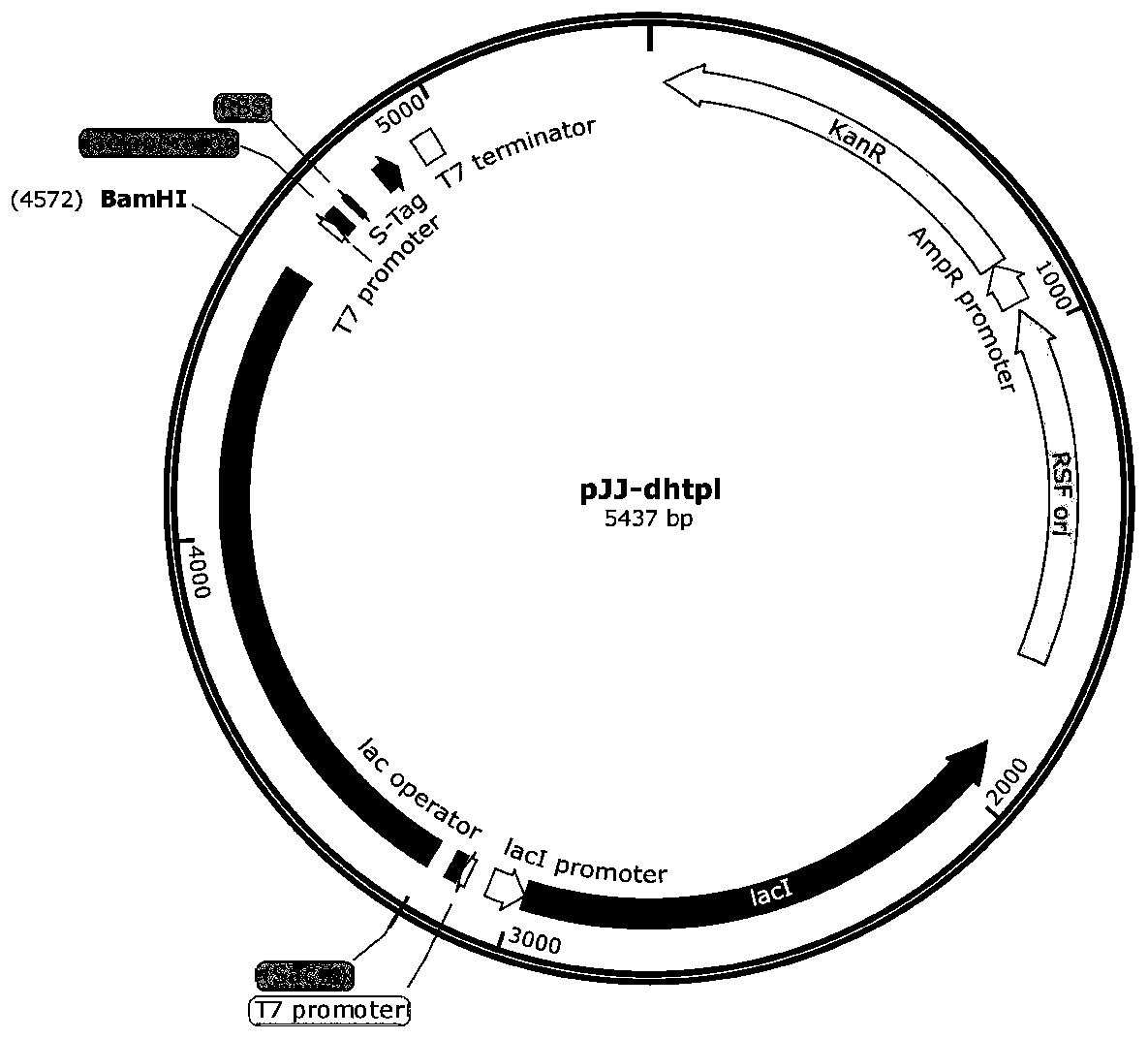
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of levodopa, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method constructs a recombinant expression vector pJJ-dhtpl containing a tyrosine phenol lyase gene dhptl, and realizes the high-efficiency expression of the tyrosine phenol lyase in Escherichia coli BL21. Recombinant Escherichia coli resting cells expressing tyrosine phenollyase can be used to catalyze synthesis of levodopa from cheap catechol and ammonium pyruvate in one step under the conditions of 16 DEG C, pH 7.5-8.0, and vacuum. Levodopa is difficult to dissolve in water, and can be precipitated in the form of crystals in the reaction system, the reaction is carried out thoroughly, and a molar conversion rate of the major reactant, catechol, is up to 96% or more. The recombinant Escherichia coli resting cells expressing tyrosine phenol lyase have good catalytic stability, and levodopa can be continuously accumulated by adding catechol and ammonium pyruvatemultiple times and in batches. The production process is simple, the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the product is easy to separate and purify, so that the method has a good application prospect for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Efficient biosynthesis method for transforming low-value compounds into caffeic acid
ActiveCN106497990AEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisCaffeic acid
The invention discloses an efficient biosynthesis method for transforming low-value compounds into caffeic acid, and belongs to the field of biochemical engineering. The method includes that tyrosine phenol lyase takes catechol, pyruvic acid and ammonia as substrates to synthesize levodopa, and tyrosine amino lyase converts levodopa into trans-caffeic acid and NH3. Since catechol, sodium pyruvate and ammonium chloride are all relatively cheap compounds, the efficient biosynthesis method is created for transforming low-value compounds into caffeic acid and is easy for large-scale production. Compared with a chemical synthesis method, the efficient biosynthesis method has the advantages that the product of the method is single trans-caffeic acid, and further separation of structural isomers is not required.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
In-situ coupled dyeing method for enzymatic protein fiber
InactiveCN109371710AAvoid damageReduce production energy consumptionDyeing processAcid dyeCoupling reaction
The invention discloses an in-situ coupled dyeing method for an enzymatic protein fiber. Serine in the protein fiber is catalyzed by tyrosine phenol-lyase so as to be converted into tyrosine, and then, the in-situ coupled dyeing of the protein fiber is accelerated due to a coupled reaction of tyrosine in the protein fiber and an aromatic diazonium salt. The in-situ coupled dyeing method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) oxidation pretreatment of the protein fiber; (2) enzymatic amino acid conversion; (3) protein fiber padding in an alkaline solution; and (4) in-situ coupled dyeing of the protein fiber. Compared with conventional acid dye dyeing and unmodified protein fiber and aromatic diazonium salt coupled dyeing of a protein fiber product, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low energy consumption, high enzymatic reaction efficiency and high dyeing depth and fastness.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
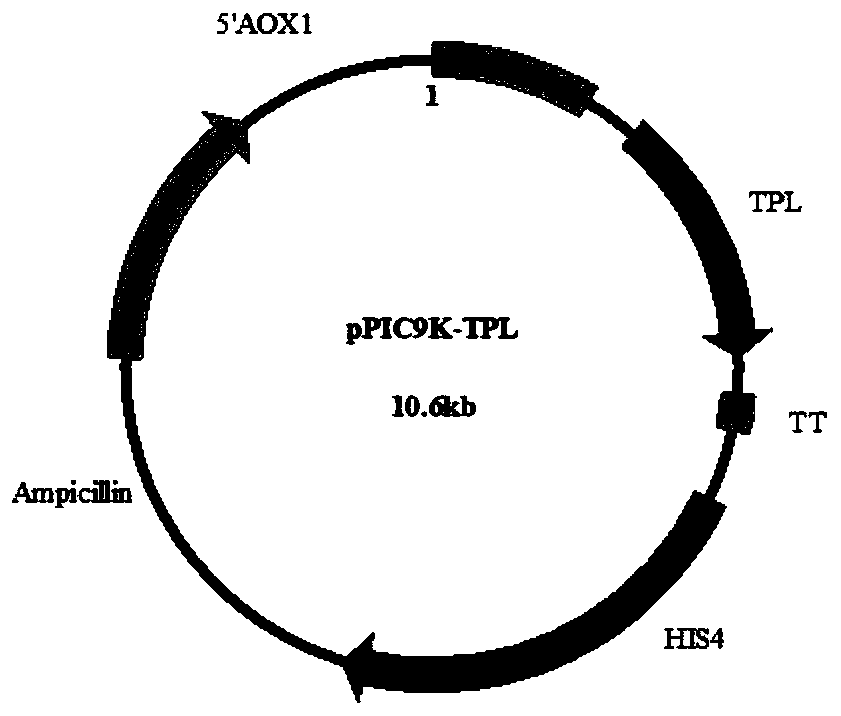
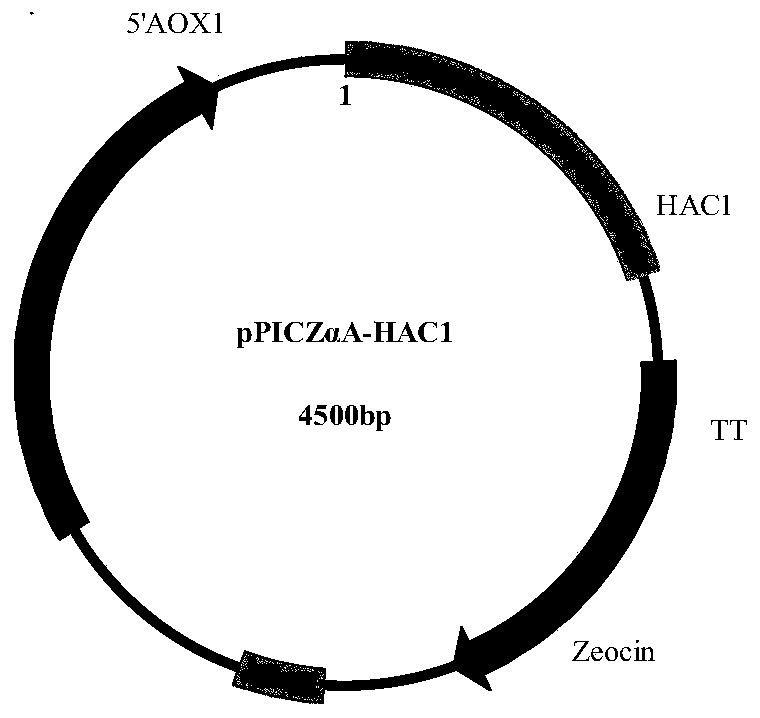
Recombinant Pichia pastoris engineering strain and its application in synthesizing levodopa
ActiveCN110305805AMeet the needs of industrializationReduce the degree of processingFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a recombinant Pichia pastoris engineering strain and its application in synthesizing levodopa. The recombinant Pichia pastoris engineering strain of the present invention is obtained by the following method: a DNA sequence of tyrosine phenol lyase (TPL) shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 is codon-optimized and transferred to Pichia pastoris GS115 to construct recombinant Pichia pastorisYZ001, then HAC1 shown in SEQ ID NO. 4 is overexpressed in Pichia pastoris YZ001, and the recombinant Pichia pastoris engineering strain YZ002 is constructed. A supernatant of the recombinant Pichiapastoris engineering bacteria fermented by centrifugation can be effectively used for the synthesis of levodopa, and the thalline after centrifugation can be used for the next batch of fermentation, which not only improves the synthesis efficiency and utilization rate of levodopa, saves production costs, but also opens up a new industrialization route for the production and processing of levodopa.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Mutant tyrosine repressor which does not require tyrosine to induce expression of the tyrosine phenol-lyase gene
InactiveUS7365161B2Efficient productionSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismEnterobacter agglomerans
A mutant tyrosine repressor that does not require tyrosine to induce expression of tyrosine phenol-lyase gene is obtained by introducing a mutation into a tyrosine repressor (tyrR), isolated from Pantoea agglomerans, or a tyrosine repressor (tyrR) which is encoded by SEQ ID NO. 1 and its derivative. A microorganism which is able to express large amounts of tyrosine phenol-lyase is obtained by introducing the mutant tyrosine repressor into the microorganism. The microorganism is useful for producing L-DOPA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Conversion and extraction method for producing levodopa by enzyme method
PendingCN111411132APrevent oxidationReduced post-processing timeOrganic compound preparationMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliUltrafiltration
The invention provides a conversion and extraction method for producing levodopa by an enzyme method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, preparing tyrosine phenol lyase, that is, centrifuging and collecting escherichia coli by a fermentation liquid, resuspending thalli by using a phosphate buffer solution, and carrying out wall breaking treatment through a high-pressure homogenizer; passing a wall-breaking liquid through a ceramic membrane, removing thallus fragments, and collecting filtrate; passing the filtrate through an ultrafiltration membrane, removing small-molecule impurities in the cells, and collecting entrapment liquid; and treating the retentate through decolorization resin, and collecting the effluent to obtain the tyrosine phenol lyase; 2, producing levodopa through enzymatic conversion, adding tyrosine phenol lyase into a reaction system based on 3000-10000U / L, adding a reaction bed charge, and supplementing catechol, sodium pyruvate and ammonium chloride inthe conversion process in different patches, wherein the yield of levodopa in the conversion liquid is 120-150g / L; and 3, carrying out extraction of levodopa, that is, adjusting the pH of the conversion liquid to be 3-4, and performing standing for 8-16h at a temperature of 4-8 DEG C; carrying out centrifugation collection of precipitation, carrying out pulping by 5-10 times of pure water and thencarrying out suction filtration, and repeating the steps for 2-5 times; eluting crystals by ethyl alcohol for 1-5 times and performing suction filtration to a dry state; and placing the crystals at atemperature of 40-80 DEG C and performing drying 1-4h to obtain a levodopa. The content of the levodopa reaches 98% or above, and the total yield reaches 80% or above.
Owner:山东惠仕莱生物科技有限公司
A membrane filtration separation and purification method for levodopa conversion liquid
ActiveCN106117071BImprove qualityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPurification methodsCrystallinity
The invention discloses a membrane filtration, separation and purification method of a levodopa conversion solution. The conversion solution containing levodopa is obtained through tyrosine phenol-lyase biological conversion, the pH of the conversion solution is adjusted to be strongly acidic by means of acid fluid, clear liquid is collected through a ceramic membrane filtration system after proper temperature increasing, and after activated carbon is added into the collected ceramic membrane filtration clear liquid, stirring, temperature increasing and decoloring are conducted; after clear liquid is filtered, alkali adjustment and crystallization are conducted, then filtering is conducted to obtain crystal, the crystal is dried, and levodopa anhydrous crystal powder is obtained. The method effectively removes residual substrates, protein and pigment in the conversion process on the basis of industrial production, the anhydrous crystal powder obtained during production is high in quality and high in light transmittance, total impurities are not larger than 0.1% by HPLC peak area percentage, and the crystallization degree of the crystal powder is 90% or above.
Owner:CHANGXING PHARMA
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid
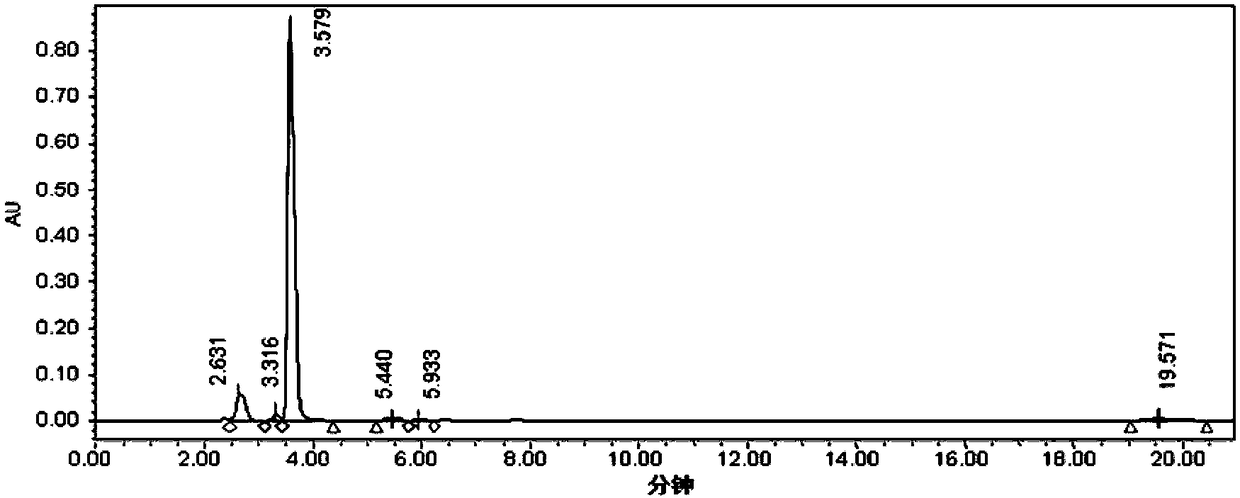
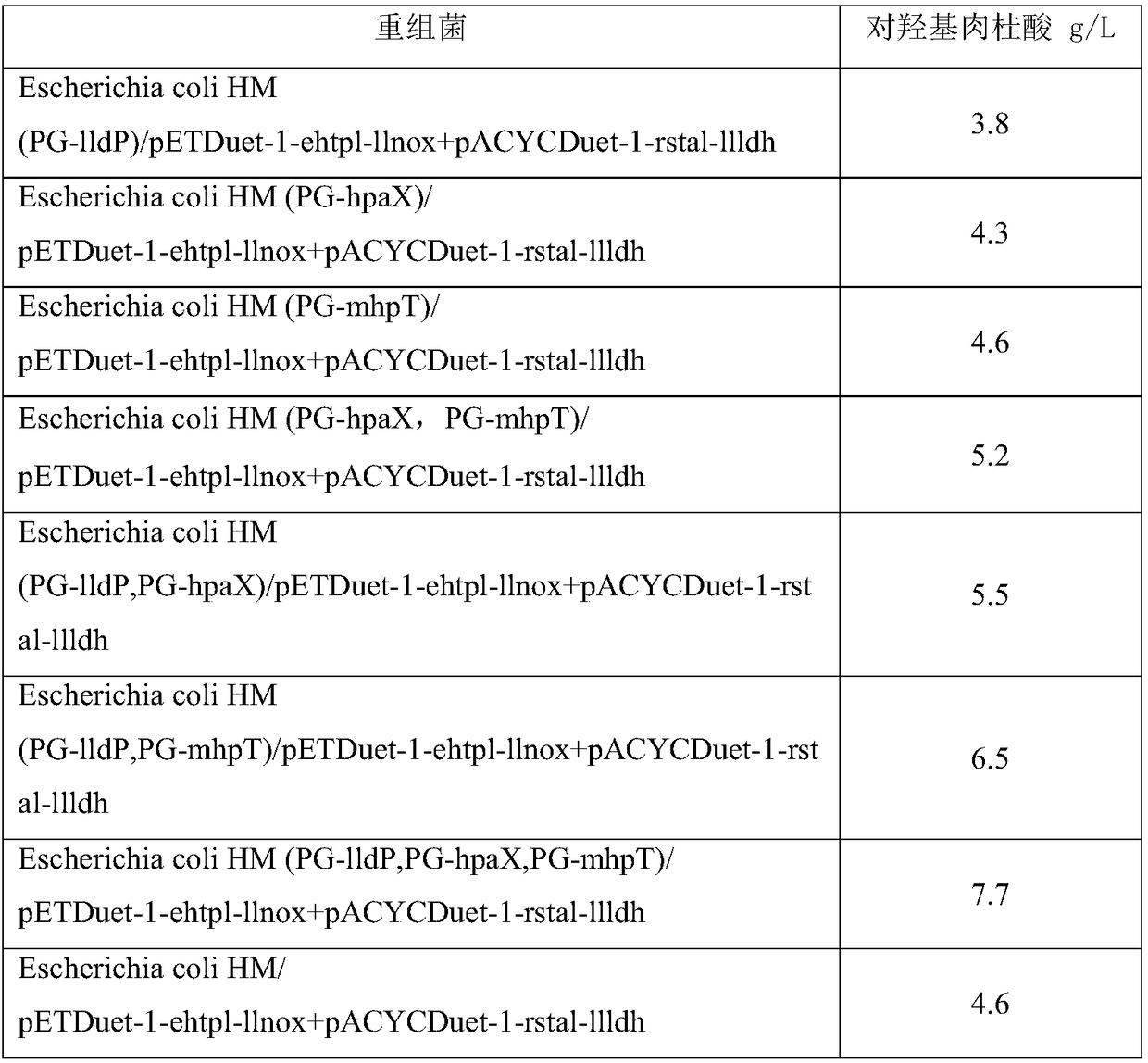
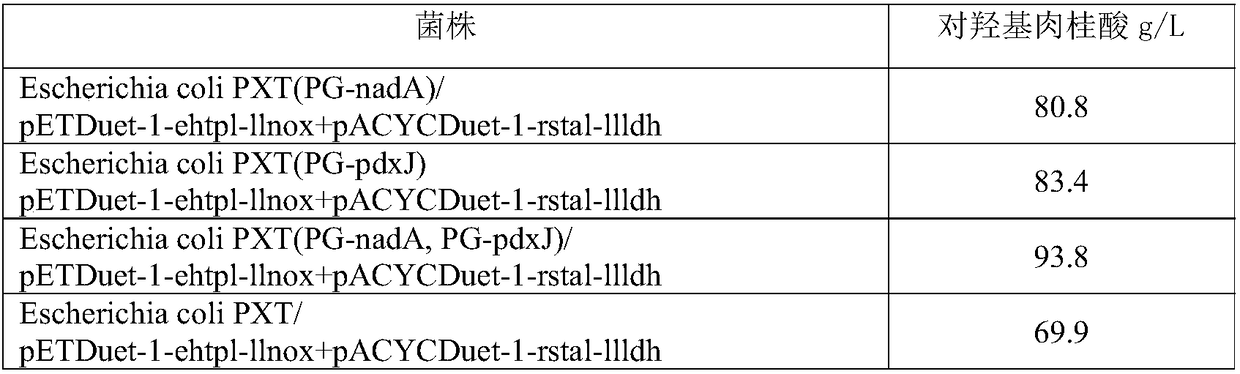
ActiveCN108949840AEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-Lactate dehydrogenaseBio engineering
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium provided by the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing p-hydroxycinnamic acid at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a phenol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium can realize the efficient production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid, and a method for producing the p-hydroxycinnamic acid has the advantages of simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com