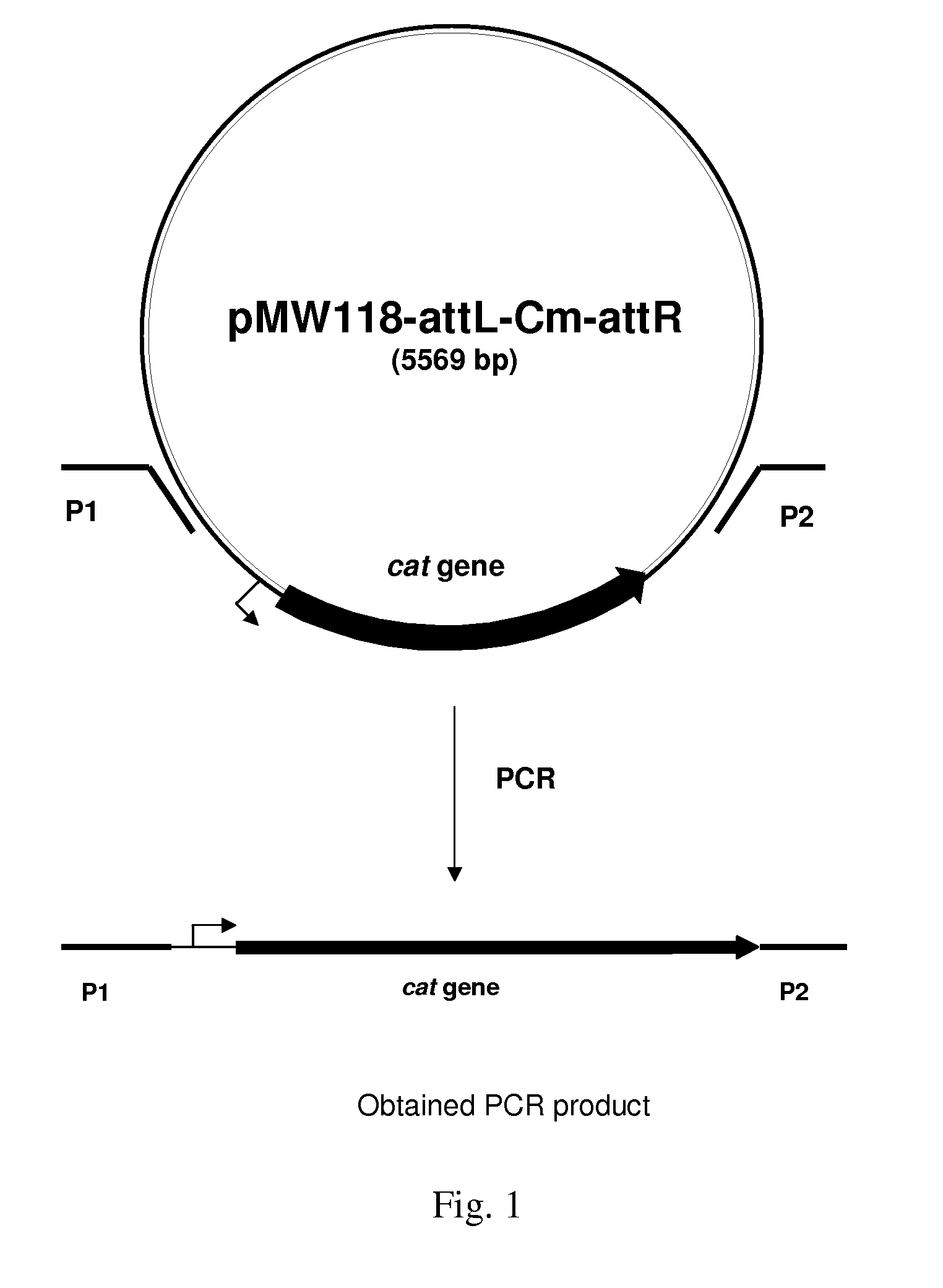
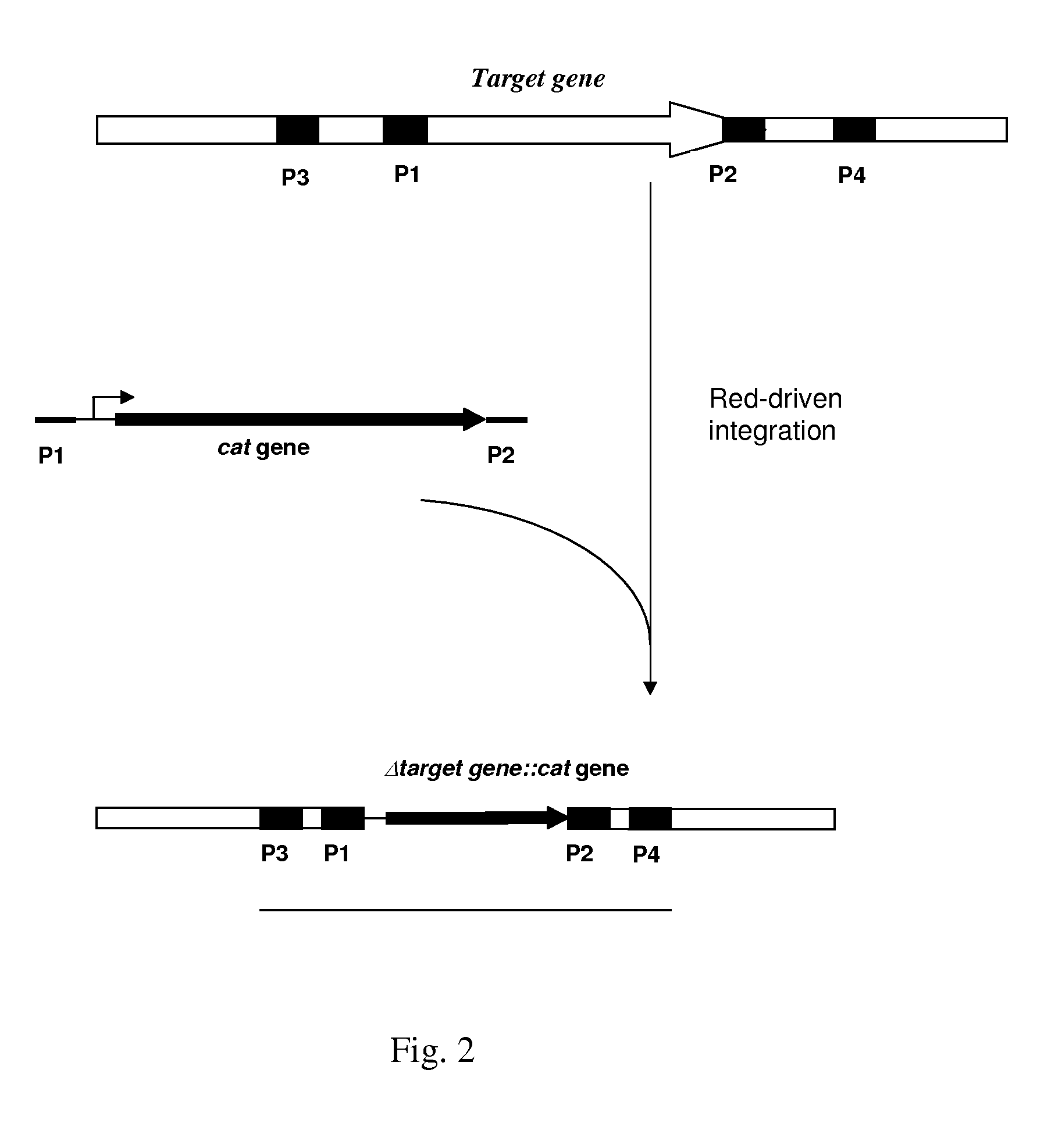
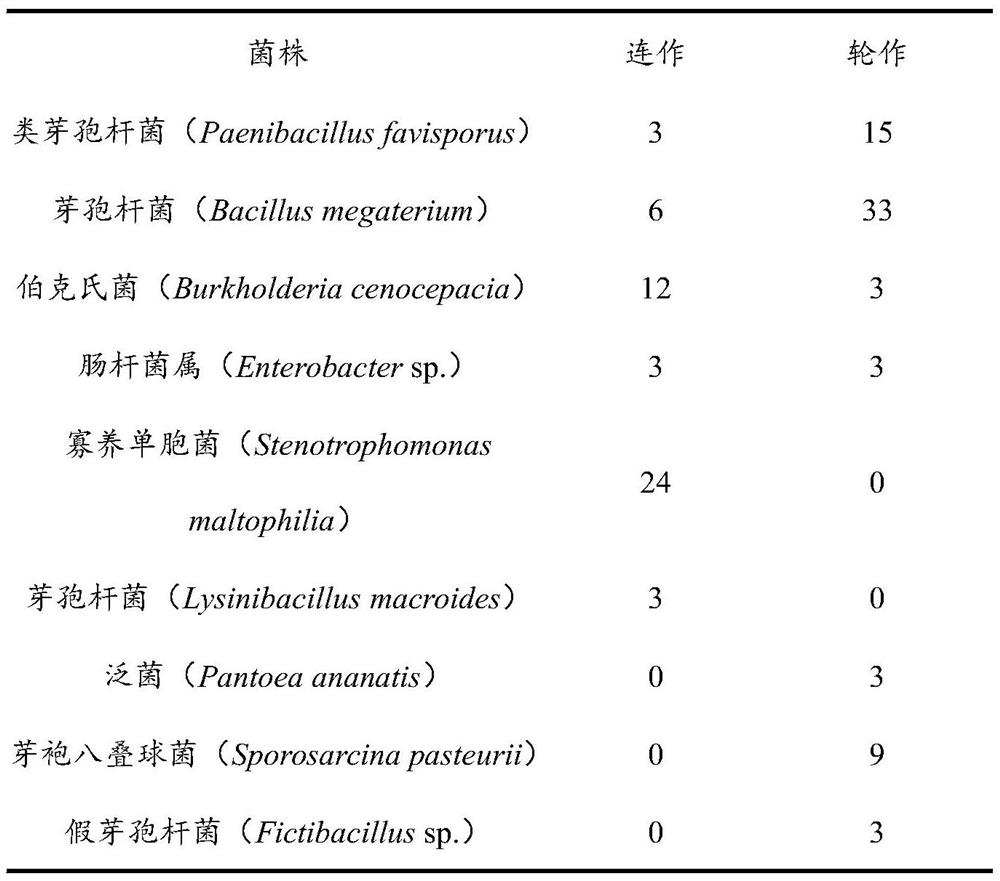
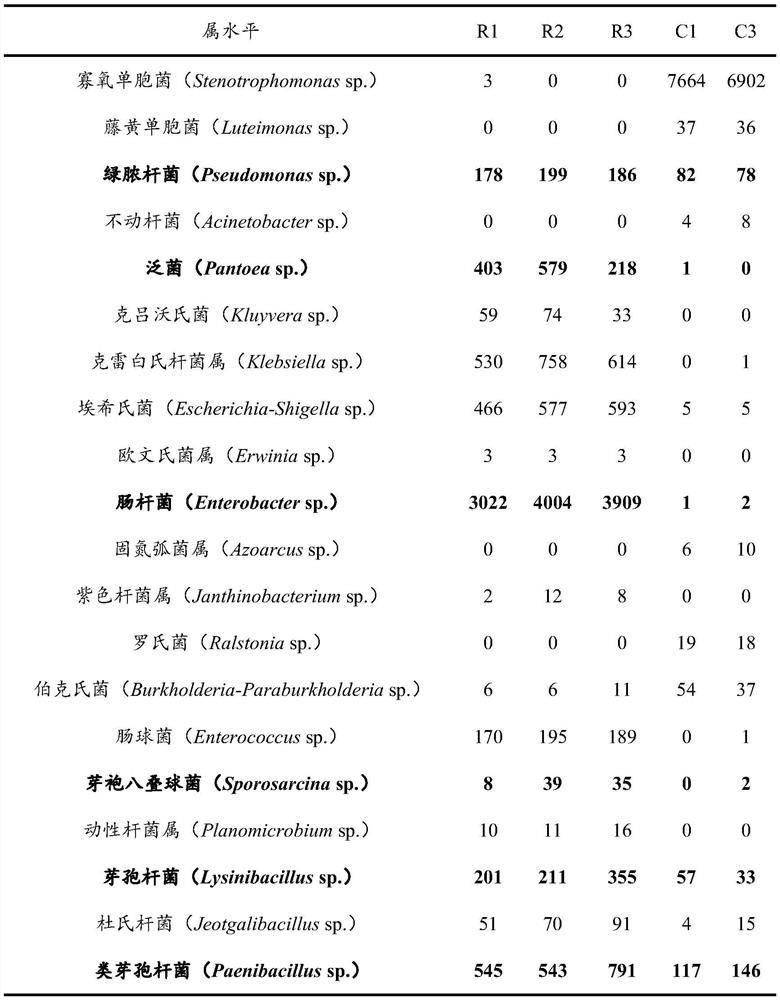
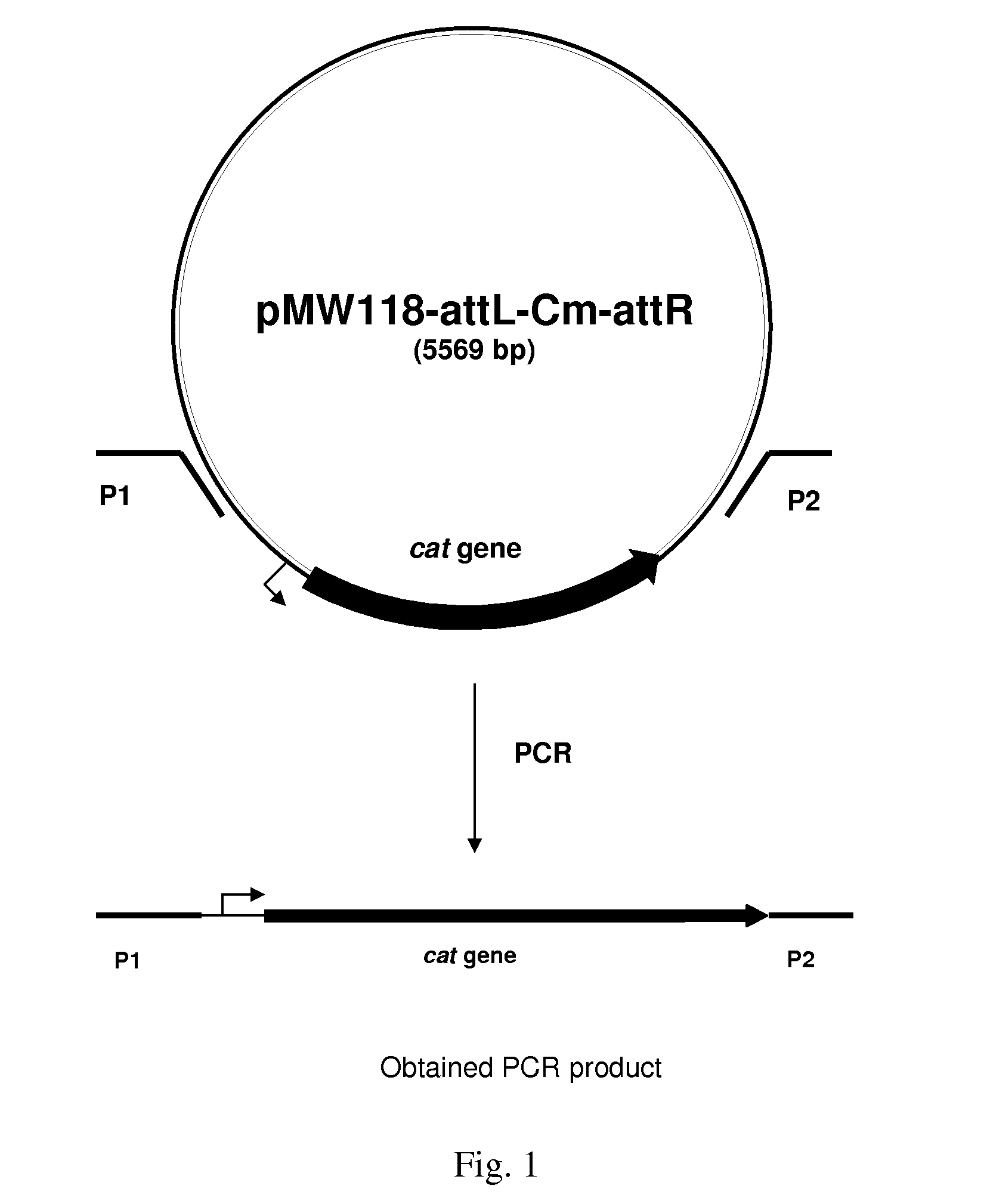
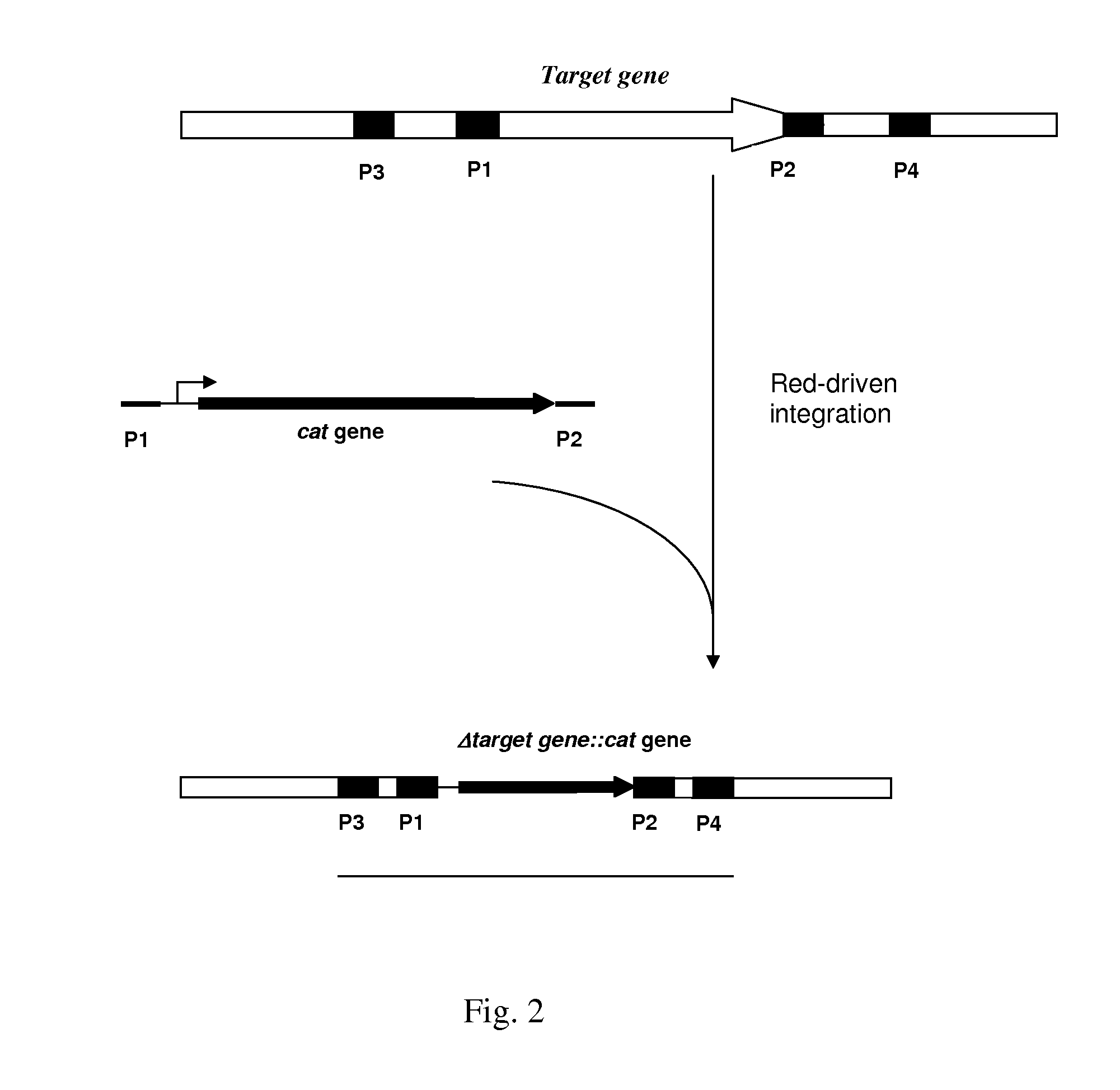
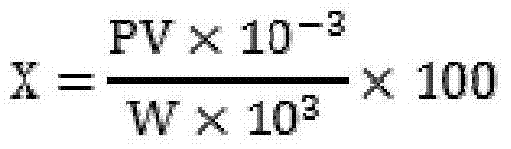Patents
Literature
118 results about "Pantoea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
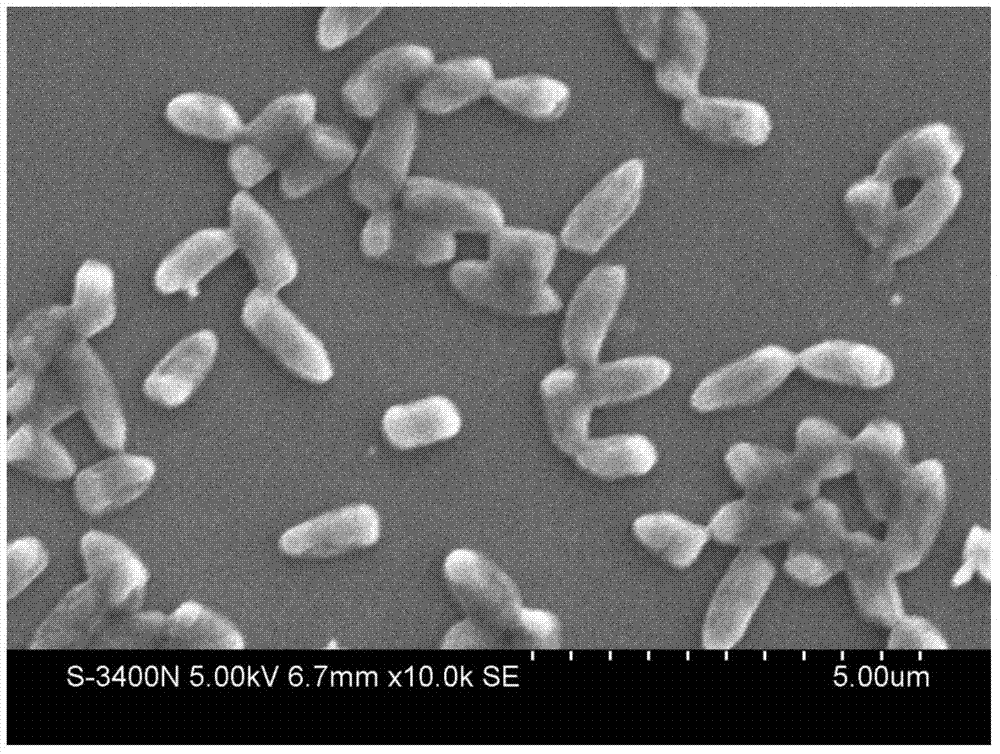
Pantoea is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria of the family Erwiniaceae, recently separated from the genus Enterobacter. This genus includes at least 20 species. Pantoea bacteria are yellow pigmented, ferment lactose, are motile, and form mucoid colonies. Some species show quorum sensing ability that could drive different gene expression, hence controlling certain physiological activities.
Method of reducing nitrosamine content in tobacco leaves
InactiveUS7549425B2Inhibit productionReduce contentTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentMicroorganismMicrobiology
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Biocontrol of plant diseases caused by Fusarium species with novel isolates of Bacillus megaterium and Pantoea agglomerans
Microbiological agents are provided for control of certain diseases of wheat and other cereals caused by Fusarium species, including Fusarium head blight of wheat and other cereals. These agents can also improve yield of wheat plants and cereals. The agents are novel isolates of Pantoea agglomerans and of Bacillus megaterium that exhibit the property of inhibiting fungal pathogens, particularly those produced by Fusarium species. Biocontrol compositions, and methods of using them to control plant pathogen development on wheat and cereal plants and for increasing plant yield, are also provided. The biocontrol compositions comprise a mixture of at least one microorganism selected from the group consisting of Pantoea agglomerans and Bacillus megaterium.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA
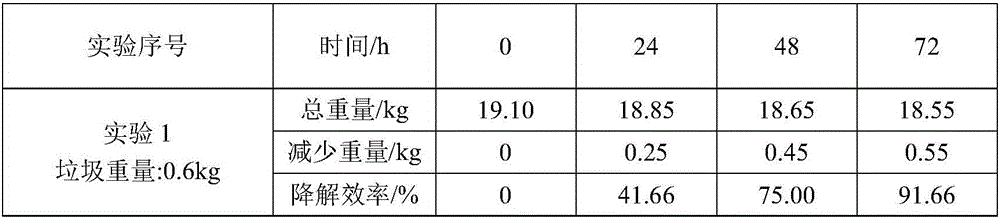
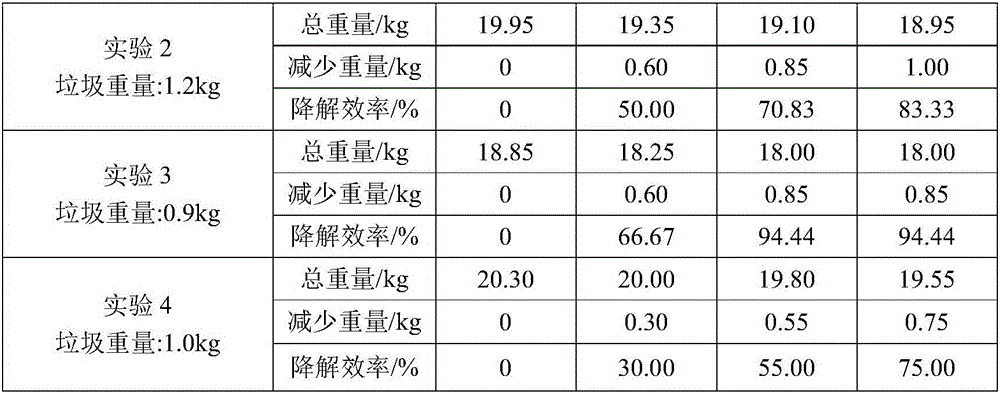
Kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106591178AEfficient degradationFast degradation rateBacteriaSolid waste disposalStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus xylosus
The invention relates to a kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and a preparation method and application thereof. The kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum is prepared by mixing a mixed inoculum of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, radiation-resistant methylobacterium, dispersed pantoea, pseudomonas oryzihabitans, citrobacter freundii and staphylococcus cohnii and a carrier, wherein the mass of the mixed inoculum accounts for 15-25% of the total mass of the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum; the mass ratio of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the radiation-resistant methylobacterium, the dispersed pantoea, the pseudomonas oryzihabitans, the citrobacter freundii and the staphylococcus cohnii is (1.5-3):(1-1.5):(1-1.5): (1-1.5):(1-1.5):(1-1.5); the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum is used for degrading kitchen garbage. Compared with the prior art, the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum has the advantages as follows: the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum can effectively degrade common vegetables, grains, fish, poultry meat and other kitchen garbage, has the degradation rate being above 80%, is high in degradation speed rate and small in odor, does not produce pollutants or poisonous substances, and is low in cost and stable in performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
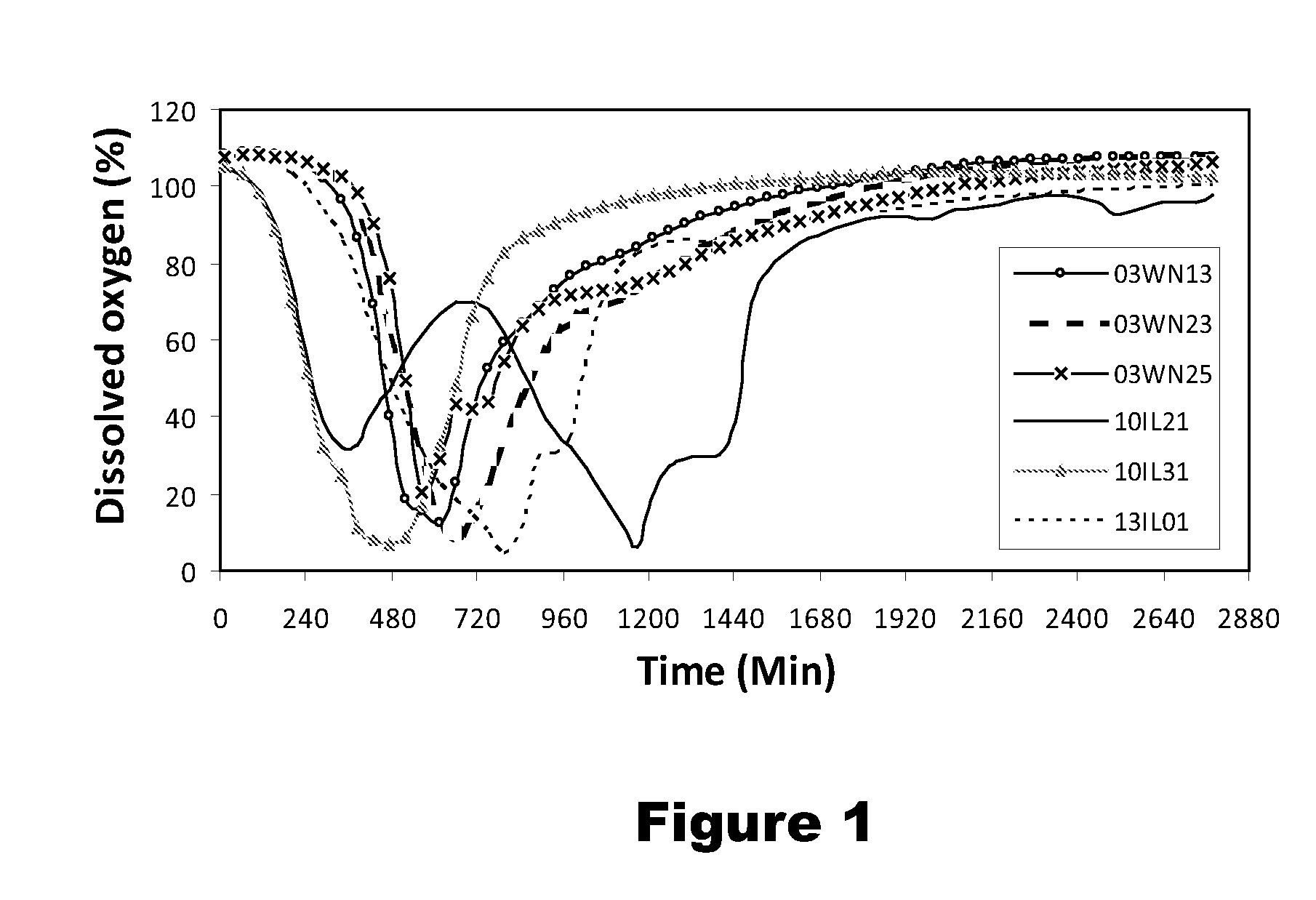
Use of Novel Strains for Biological Control of Pink Rot Infections in Potato Tubers
ActiveUS20120076765A1Inhibition is effectiveEffective for suppression and controlBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBacterial strain
Six bacterial strains: Bacillus simplex strain 03WN13, Bacillus simplex strain 03WN23, Bacillus simplex strain 03WN25, Pseudomonas koreensis strain 10IL21, Pantoea agglomerans strain 10IL31, and Pseudomonas lini strain 13IL01, are superior antagonists of Phytophthora erythroseptica Pethybr., the causative agent of pink rot on potatoes. These bacterial strains are effective for suppression and control of pink rot on potatoes.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Method for producing an l-amino acid using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS20090098621A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesGemella
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a gene coding for sRNA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-glutamic acid producing bacterium and a method for producing l-glutamic acid
ActiveUS20090215131A1Efficient productionImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesEnterobacter
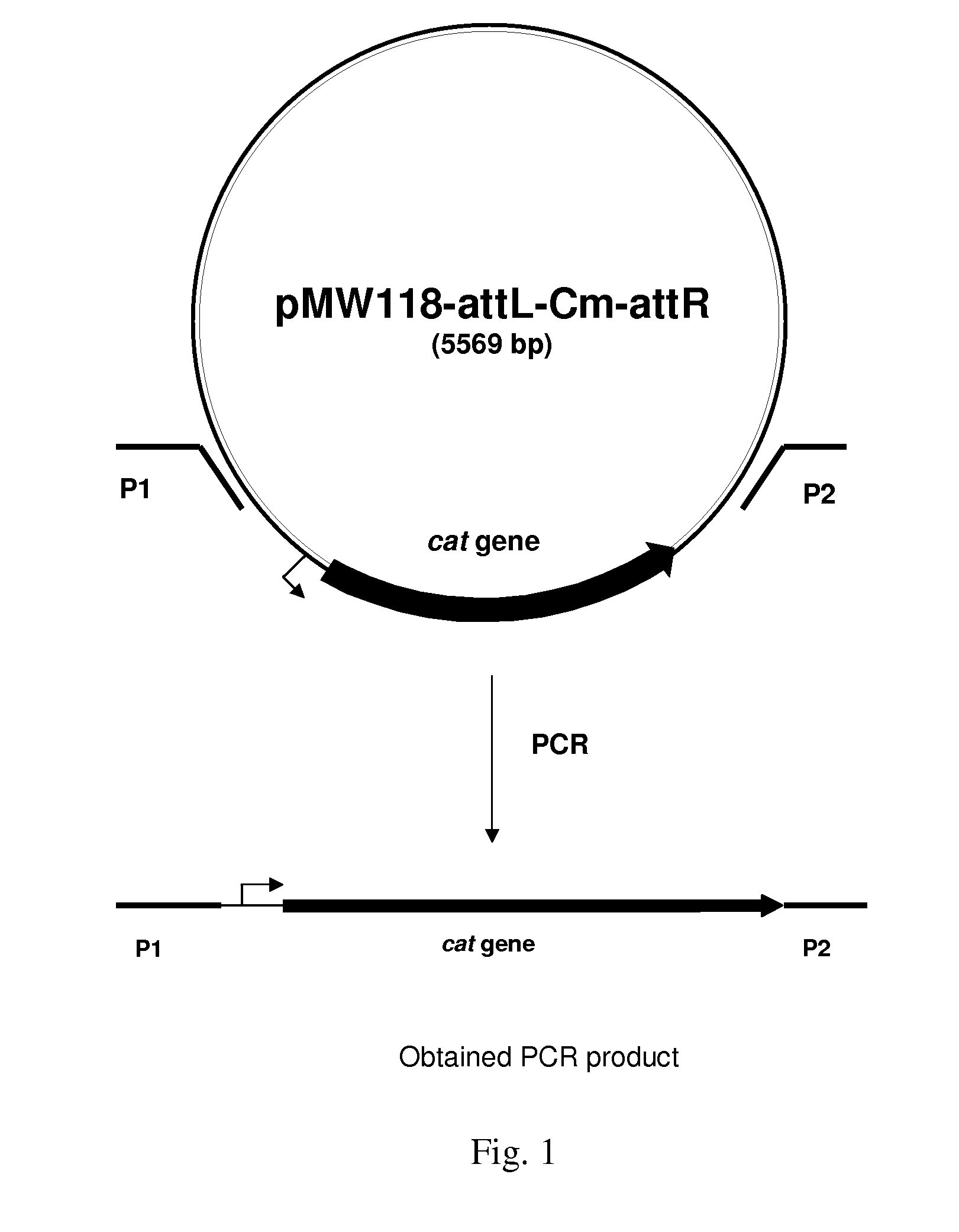
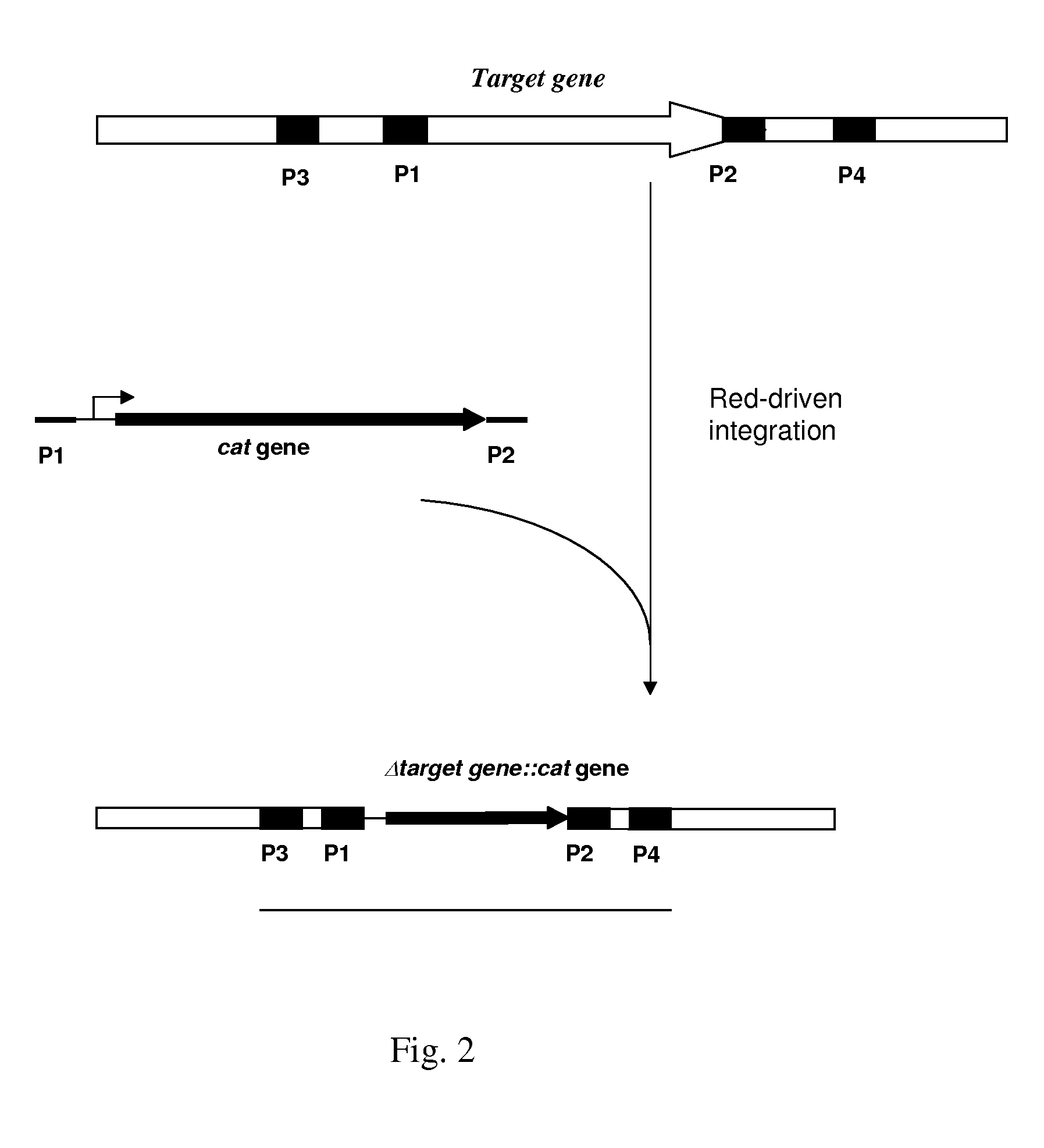
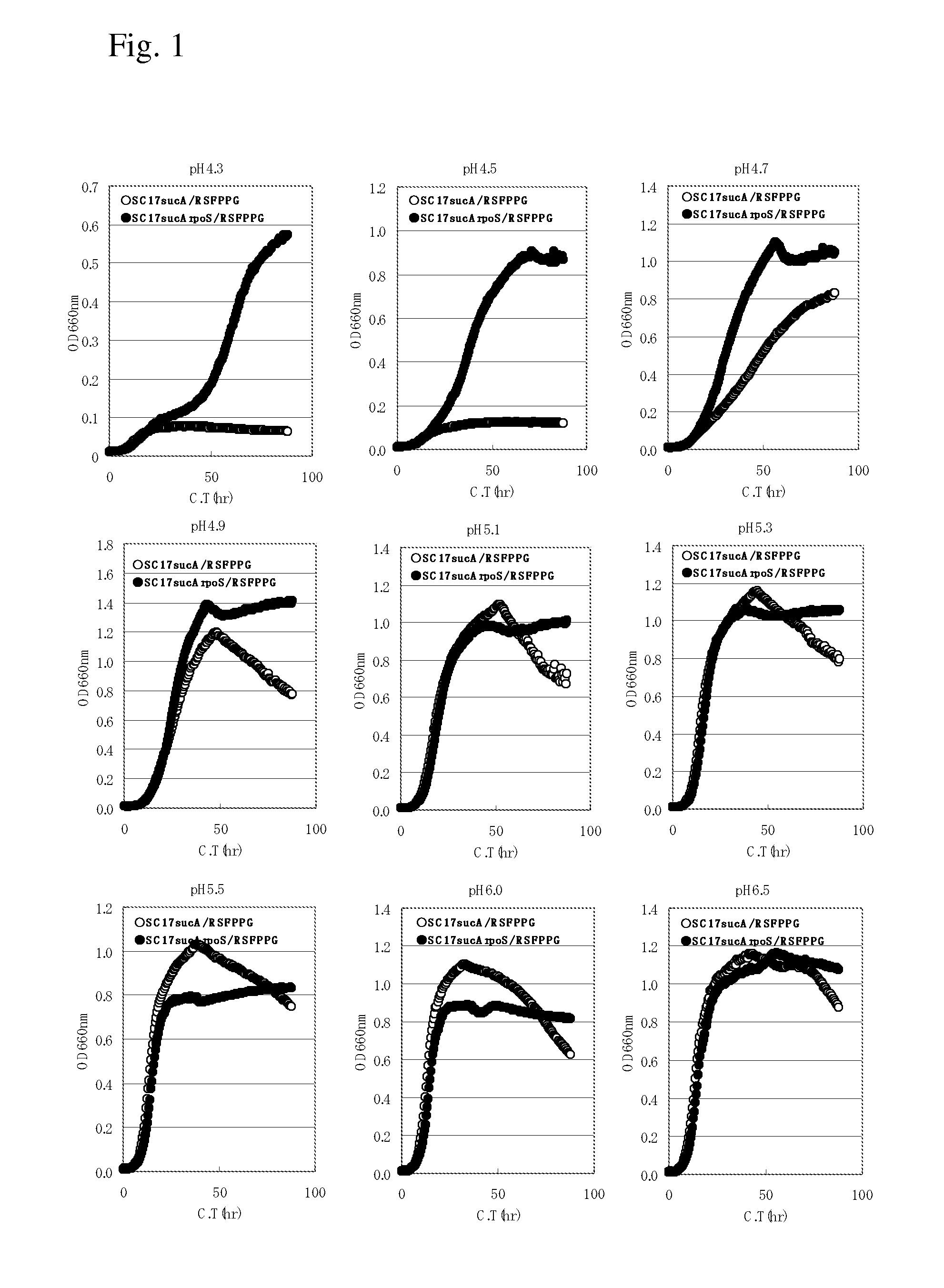
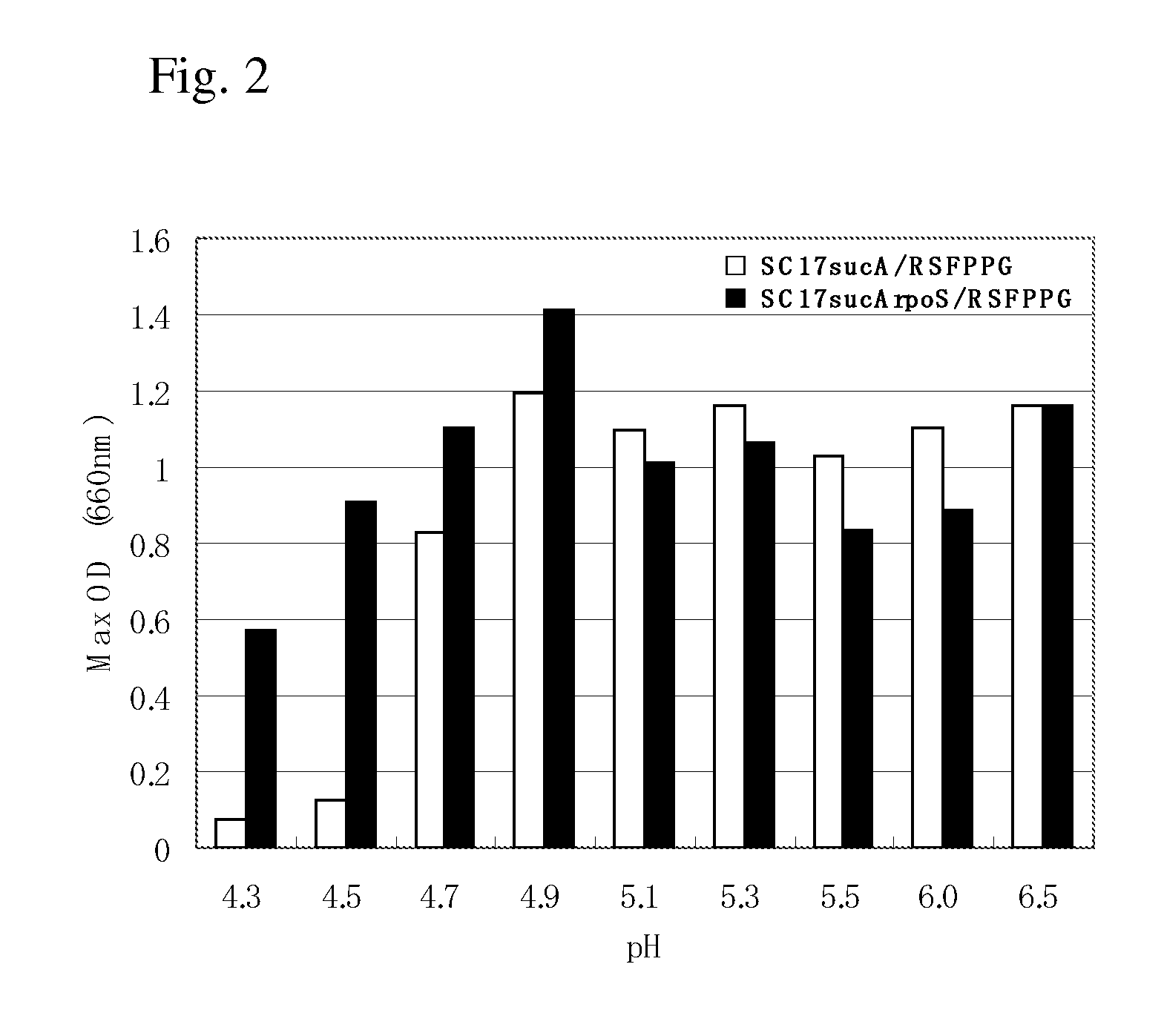
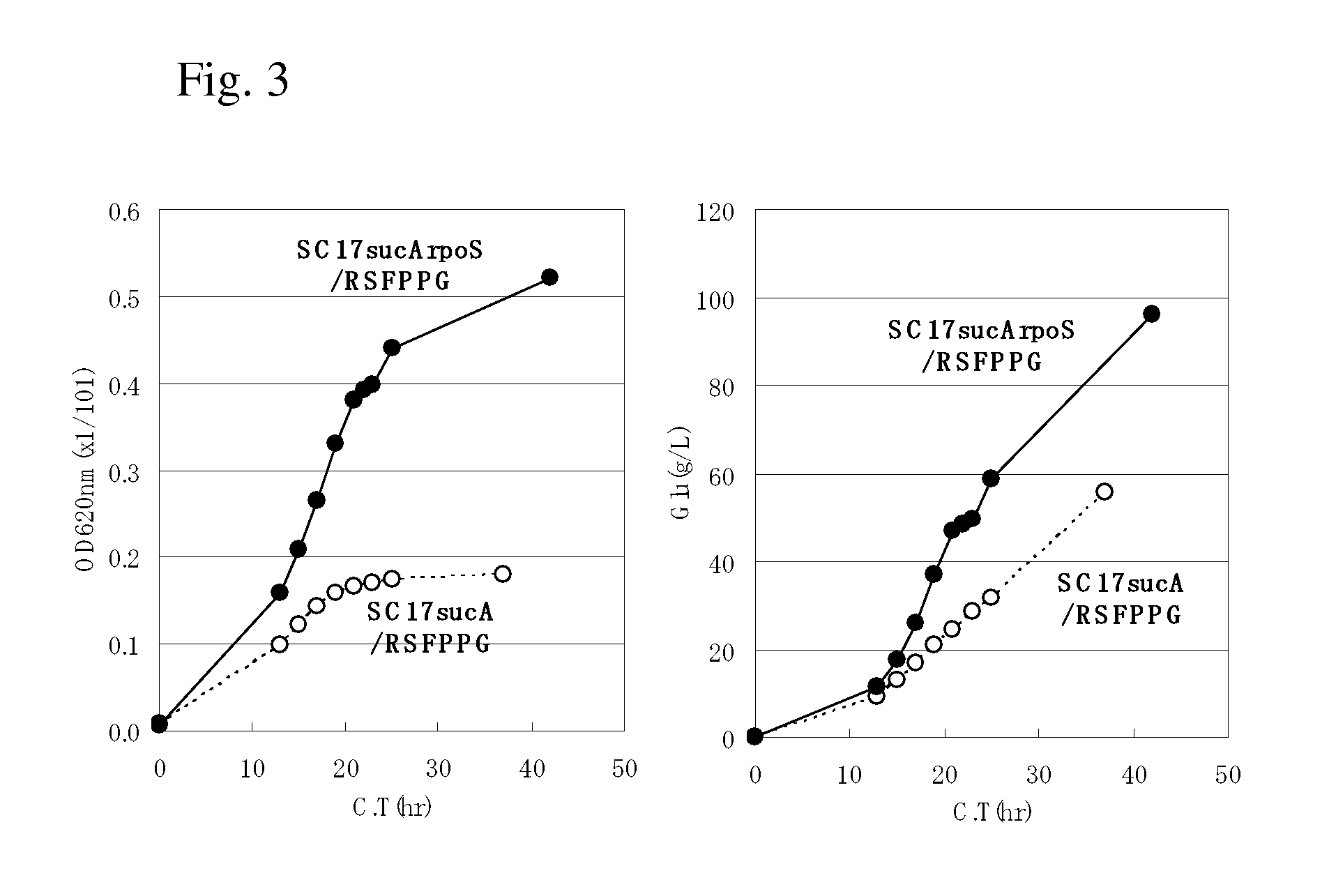
The present invention describes an L-glutamic acid-producing bacterium which belongs to the genus Pantoea, Enterobacter, Klebsiella or Erwinia, wherein the bacterium has been modified by gene recombination to inactivate the rpoS gene. A method is also described for culturing the bacterium in a medium to cause accumulation of L-glutamic acid in the medium, and collecting L-glutamic acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
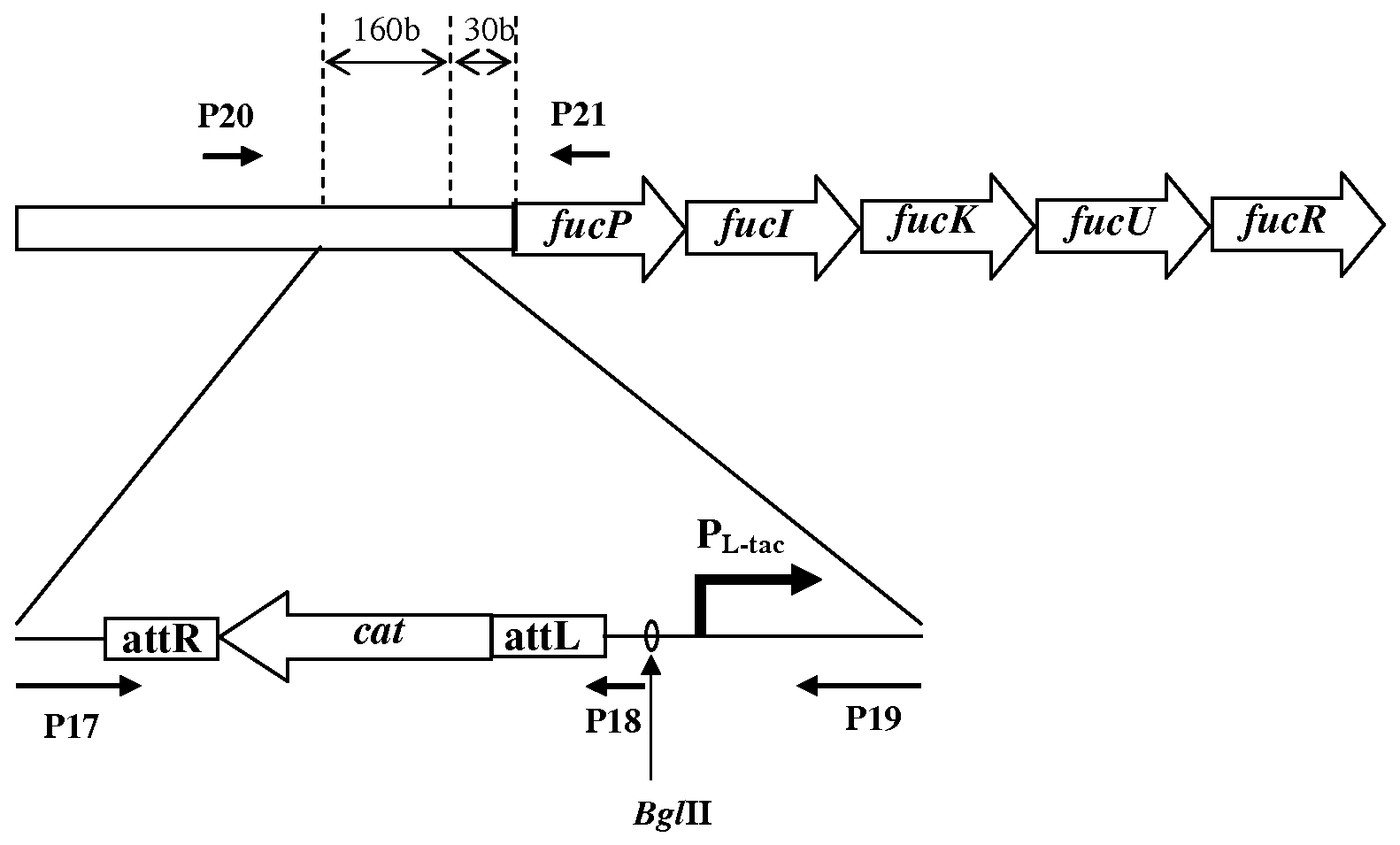
Method for Producing an L-Amino Acid Using a Bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae Family With Enhanced Expression of the fucPIKUR Operon
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to enhance expression of at least one gene of the fucPIKUR operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Pantoea for degrading organic phosphorus and inorganic phosphorus and application of pantoea
The invention discloses pantoea for degrading organic phosphorus and inorganic phosphorus and application of the pantoea. The preservation number of the pantoea (Pantoea sp.)S-32 in a general microorganism center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms is CGMCC No.10017. According to the pantoea, the phosphorus solubility for degrading calcium phosphate reaches 24.19% and is equal to 3.64 times of that of bacillus megatherium As1,223; the phosphorus solubility for degrading lecithin reaches 2.47% and is equal to 1.46 times of that of bacillus megatherium As1,223; the pantoea has relatively strong environmental suitability and can adapt to relatively wide ranges of temperature, pH value and salinity. Experiments prove that the pantoea (Pantoea sp.)S-32 CGMCC No.10017 can serve as a strain resource of microbial fertilizers so as to increase the crop yield and accelerate the ecological restoration of soil of mining areas.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
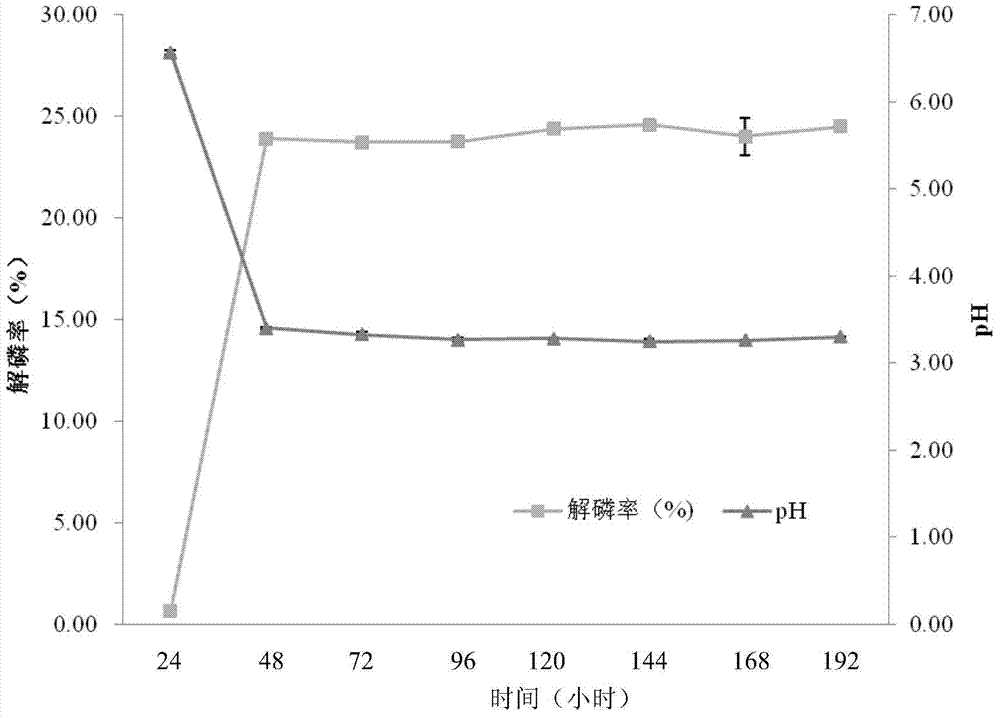
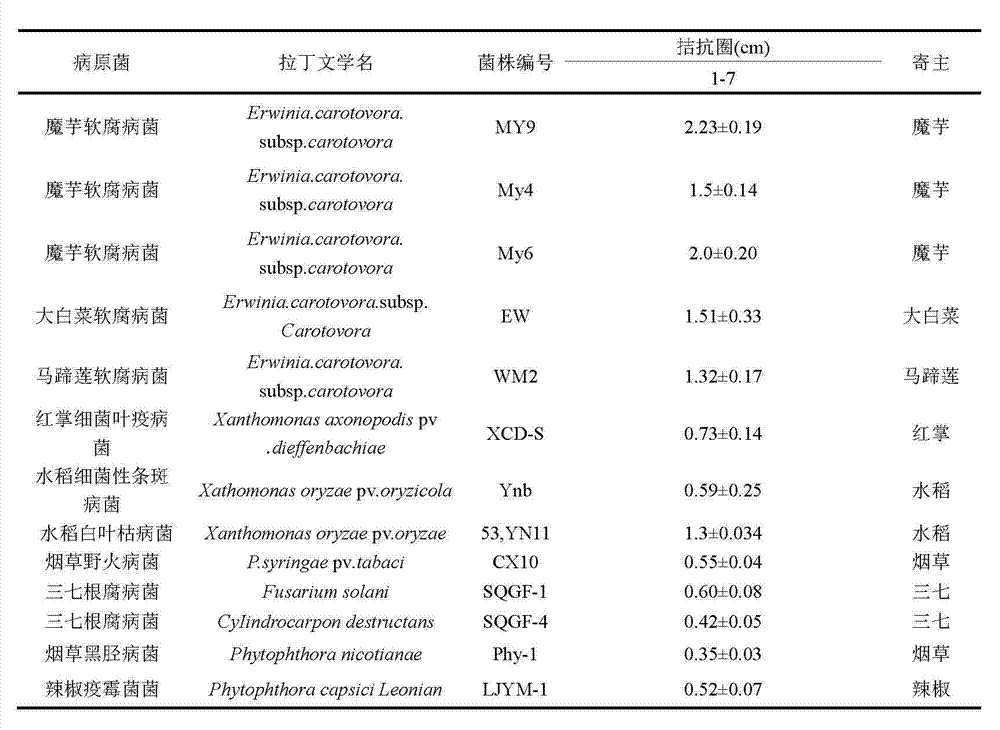
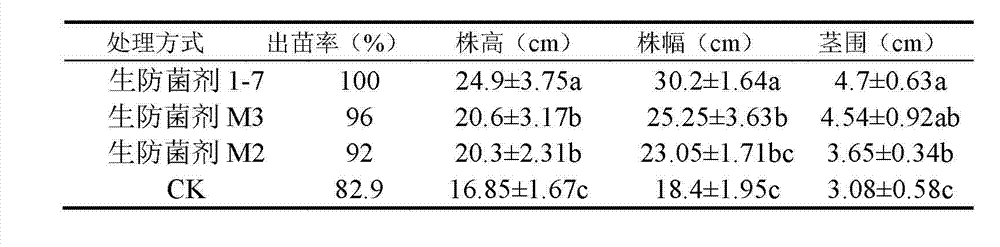
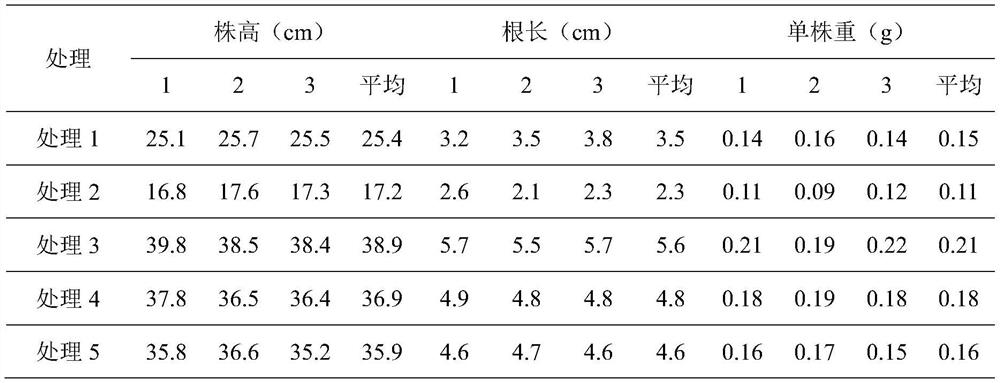
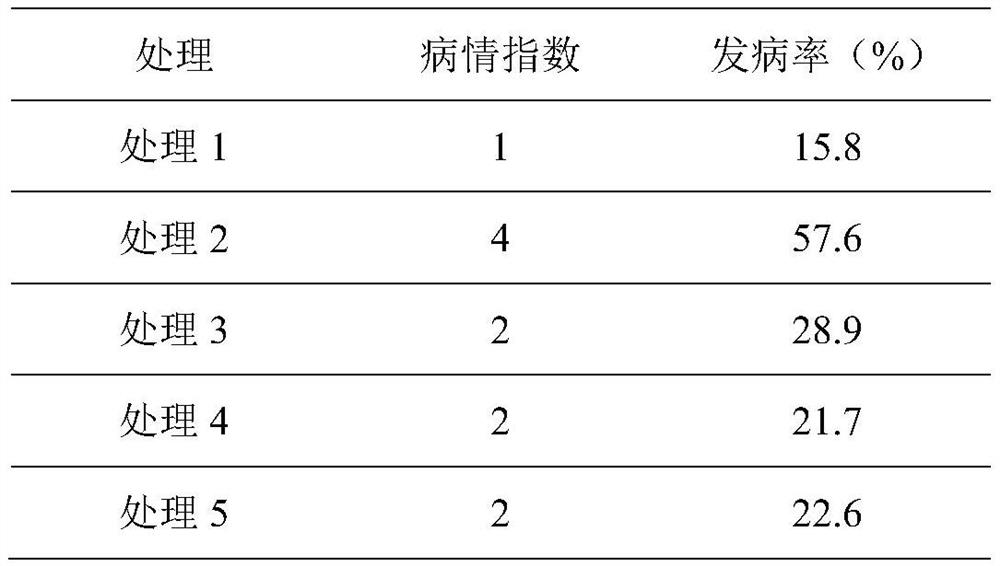
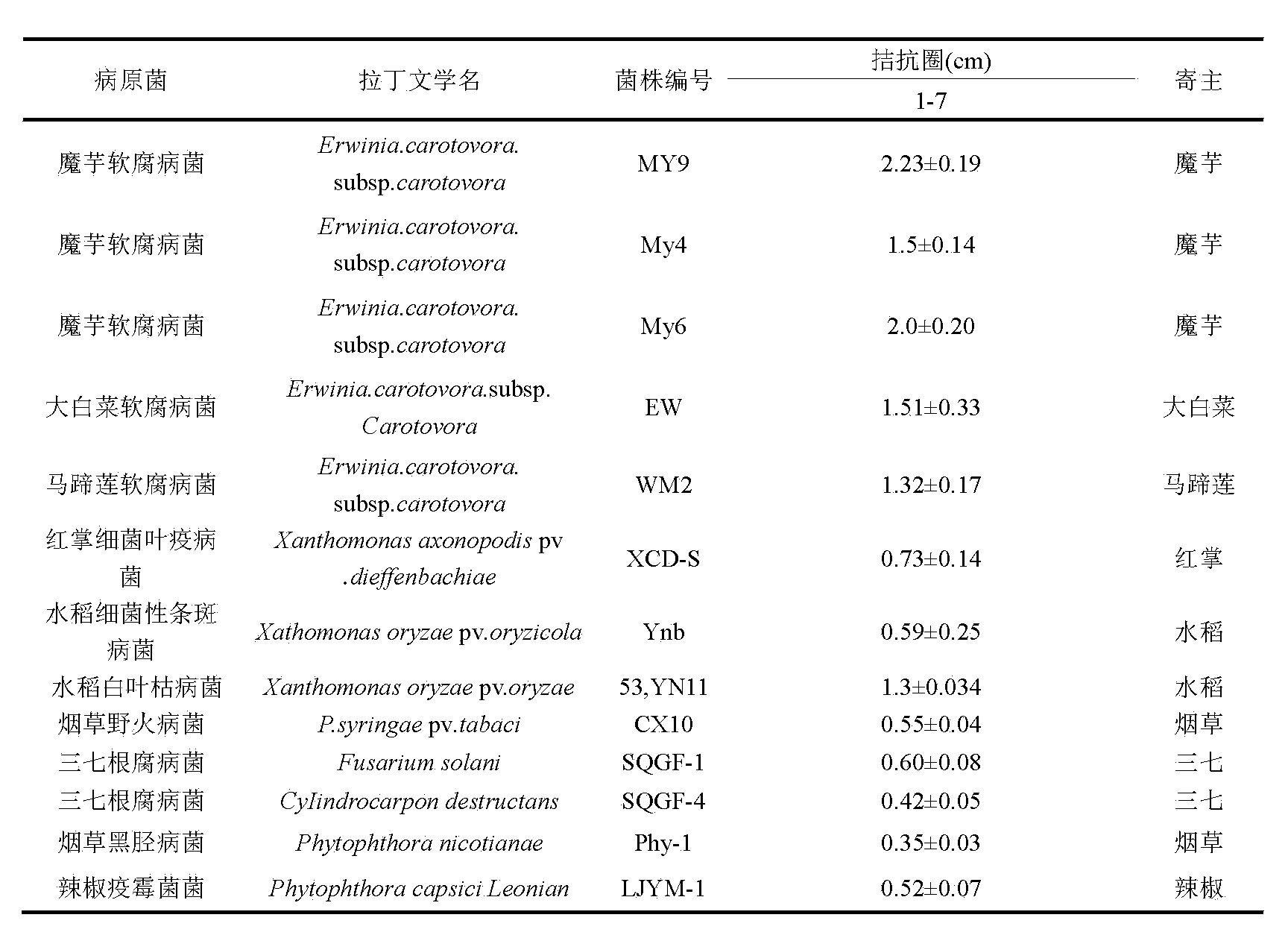
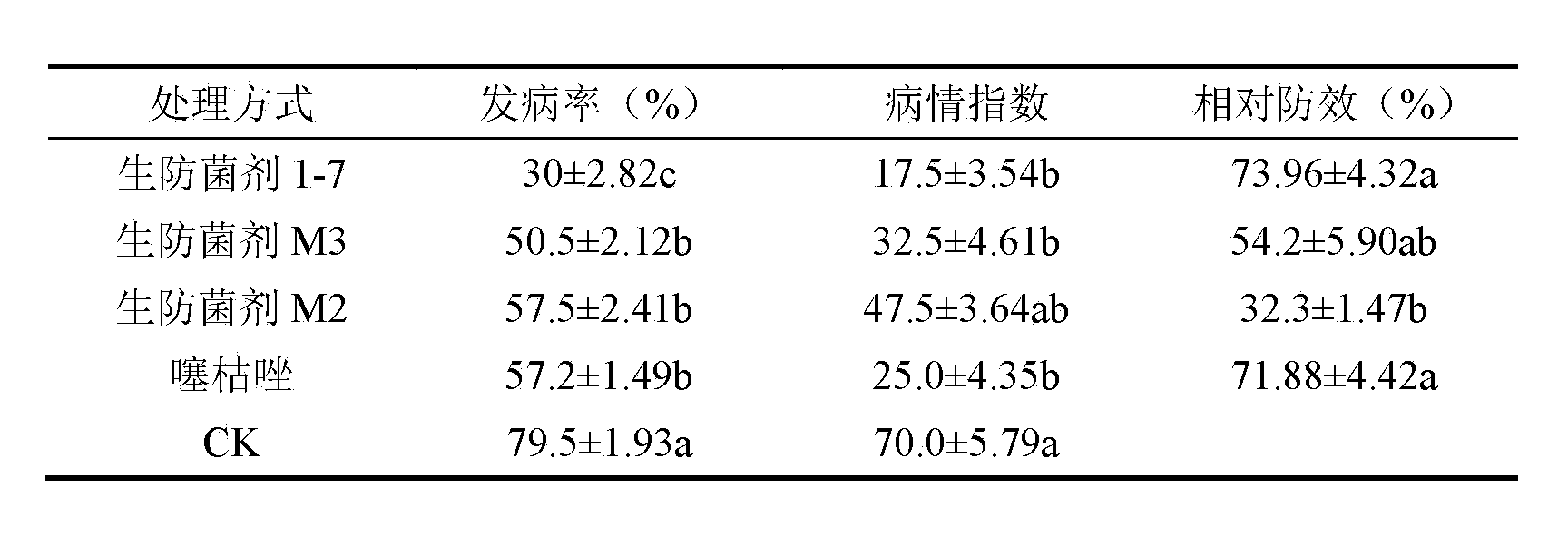
Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 and application
InactiveCN102899266AGood growth promoting effectGood characterBiocideBacteriaBacterial soft rotMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to a Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 and an application, which belongs to the biology technical field. The Pantoea agglomerans1-7 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 28th, 2012 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.6160. The Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 is used for preparing the preparations used for preventing and treating bacterial soft rot of konjak and clubroot disease on cruciferous vegetable club root in fields. The Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 has the advantages of high efficiency, no toxicity, safety and no residue, the bacterial strain1-7 has the characteristics of good disease control, better growth promotion effect, better comprehensive characters and easy industrial production, and the Pantoea agglomerans1-7 can be applied to preparation of preparations for controlling cruciferous vegetable club root in fields.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing l-arginine using a bacterium of enterobacteriaceae family, having attenuated expression of a gene encoding an l-arginine transporter
InactiveUS20100143983A1Improve productivityIncreased ability to produce L-arginineBacteriaHydrolasesBacteroidesMicrobiology
The present invention provides a method for producing L-arginine using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of one or several genes encoding an L-arginine transporter.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium having an enhanced ability to utilize glycerol
InactiveUS20090317876A1Improve abilitiesProducing L-aminoBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesGlycerol kinase
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to have glycerol kinase in which feedback inhibition by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is desensitized, thereby having enhanced ability to utilize glycerol.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Complex microbial agent for low-temperature methane fermentation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102433262AImprove reproductive abilityStrong digestionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses a complex microbial agent for low-temperature methane fermentation. According to the ccomplex microbial agent, fermentation broths obtained by fermenting pseudomonas sp. CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) No.4764, pantoea agglomerans CGMCC No.4765 and pantoea agglomerans are uniformly mixed according to the weight ratio of 1:1:1, so that a liquid formis obtained. The complex microbial agent disclosed by the invention can be directly fed into a methane tank, so that the methane tank can be used for normally producing gas in winter; and in addition, the complex microbial agent has a wide application value.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Using Pantoea agglomcrans KFS-9 fungus to produce 2, 3 butanediol, and application in cosmetic
InactiveCN1958785AShorten the growth cycleLow costCosmetic preparationsBacteriaMangroveRadiation tolerance
This invention provides a strain for producing 2, 3-butanediol, and its application as anti-UV and anti-oxidation agent in cosmetics. The strain with strong UV tolerance is separated from mangrove, and can produce 2, 3-butanediol. The strain has such advantages as wide nutrition range, short culture period, low cost and high yield. 2, 3-butanediol has good anti-UV and anti-oxidation effects, and can eliminate active oxygen free radicals and block lipid peroxidation, thus can be used as anti-UV and anti-oxidation agent in cosmetics.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for producing an L-amino acid using bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS7803584B2Improve productivityIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesPantoea
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Complex flora for preventing and treating peanut root rot and application thereof
PendingCN111763643AEnhancement of rhizosphere colonizationThe disease prevention effect is stableBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyEcological environment
The invention provides a complex flora for preventing and treating peanut root rot and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of soil-borne disease prevention and treatment. The complex flora comprises pantoea, pseudobacillus, enterobacter, paenibacillus, sporosarcina, bacillus and pseudomonas aeruginosa. The pantoea, the pseudobacillus, the enterobacter, the paenibacillus, thesporosarcina, the bacillus and the pseudomonas aeruginosa in the complex flora have a synergistic interaction effect on inhibition of pathogenic fungi; compared with a single strain, the complex flora has the advantages that the rhizosphere colonization capacity is obviously improved, and the rhizosphere micro-ecological environment can be effectively optimized. The complex flora is inoculated topeanut roots, so that the peanut roots can be effectively prevented from being infected by fusarium oxysporum, and the health of the peanut roots is protected.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing an l-amino acid using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS20100311129A1Improve productivityIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesPantoea
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a gene coding for sRNA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
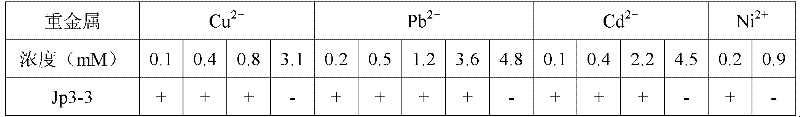
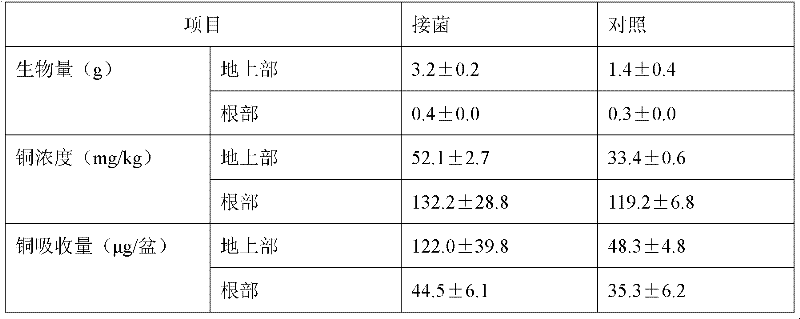
Endophytic bacteria capable of producing ACCD, its soil renovation bacterium agent and its application
InactiveCN102391974APromote growthImprove stress resistanceBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacteroidesEnterobacter agglomerans
The present invention belongs to the technical fields of agriculture and environmental pollution treatment, and relates to endophytic bacteria capable of producing ACCD, its soil renovation bacterium agent and an application thereof. The endophytic bacteria Jp3-3 which is named as Pantoea agglomerans Jp3-3 and preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the preservation date is 13th July, 2011, and the collection number of CCTCC is No: M 2011250. The ACCD enzymatic activity of the bacteria can reach as high as 402umM alpha-KB.h<-1>.mg<-1>; a liquid preparation contains effective live bacteria with amount of more than 1 billion / milliliter, a solid preparation contains live bacteria with amount of more than 0.2 billion / gram. The direct application of the soil renovation bacterium agent is capable of promoting the growth of the plants, absorbing the heavy metal and reinforcing the efficiency of plants for restoring the soil polluted by the heavy metal.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
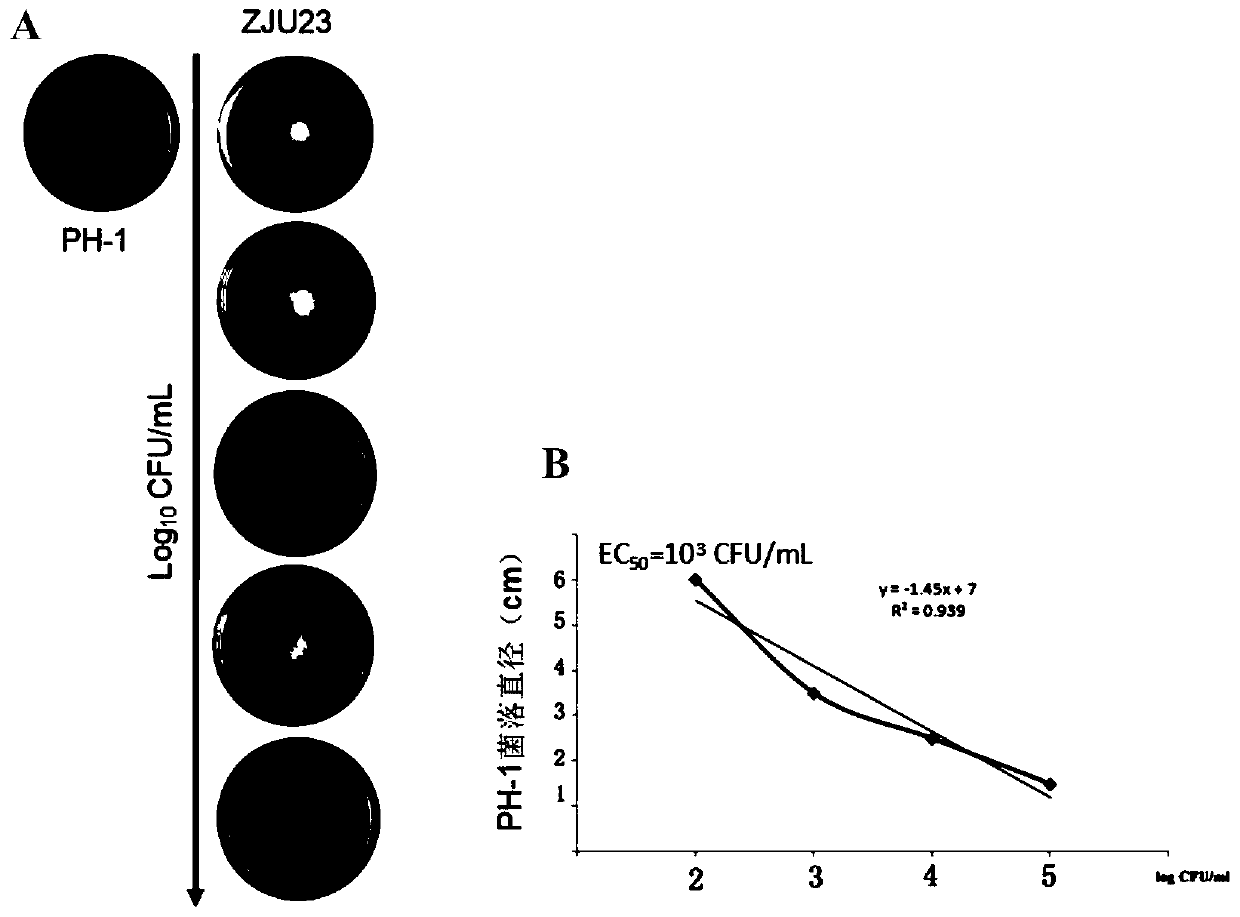
Pantoea agglomerans strain and application thereof
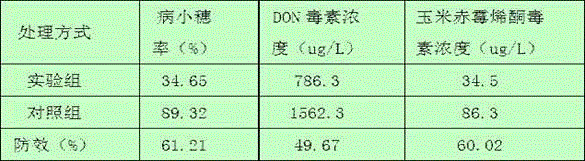
ActiveCN110713951AImprove the effect of prevention and controlVomitoxin reductionBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a pantoea agglomerans strain and application thereof. The pantoea agglomerans strain is named as Pantoea agglomerans ZJU23, with a preservation number of CGMCC No.16174 and a preservation date of July 30, 2018. According to the pantoea agglomerans strain, the control effect on wheat scab is up to 50-70%, vomitoxin is reduced by 50-80%, diseases caused by plant pathogenic fungi such as gibberellic disease, gray mold, rice blast, colletotrichum destructivum and rice sheath blight disease can also be simultaneously controlled, and the range of controlling is wide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
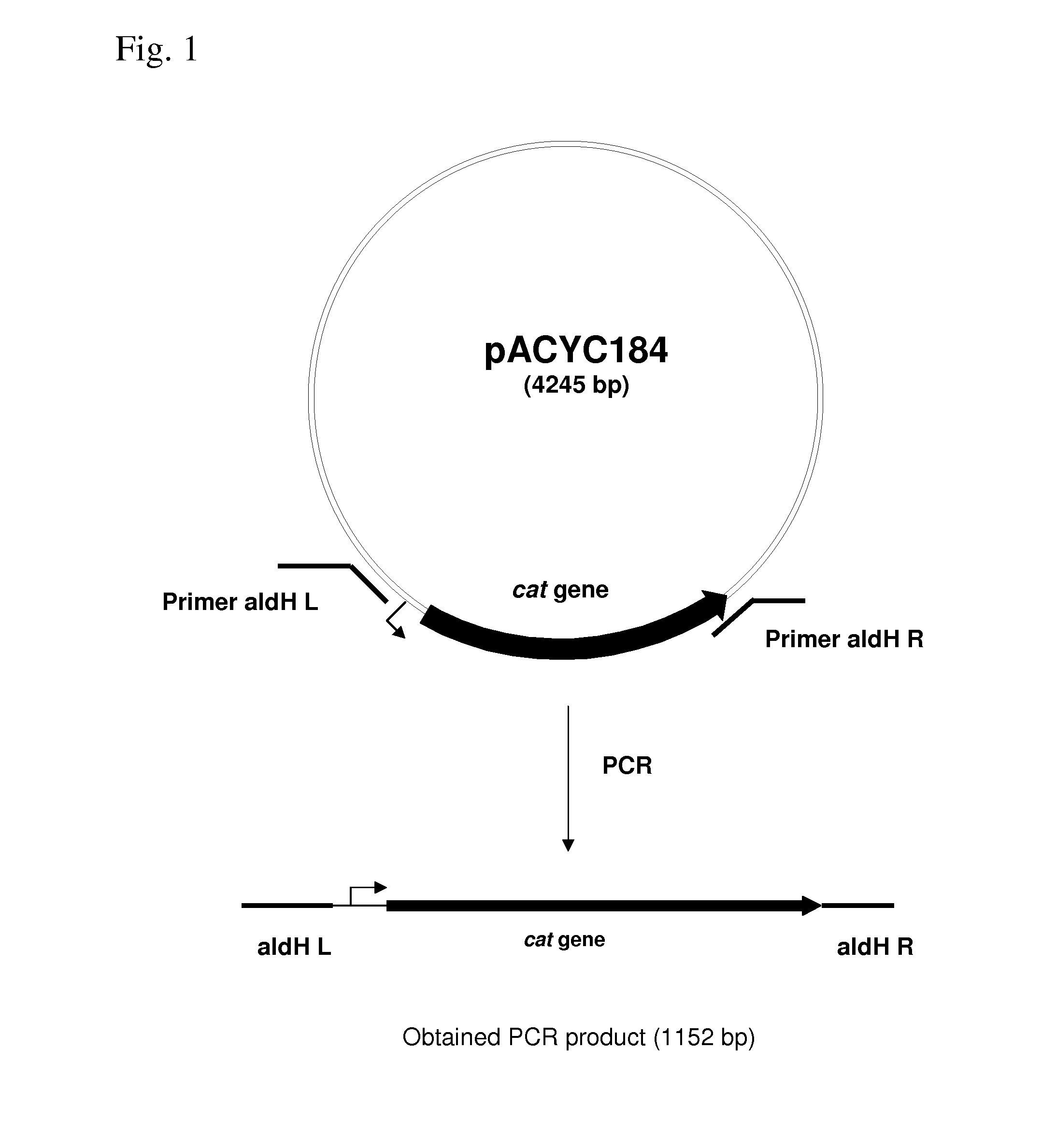
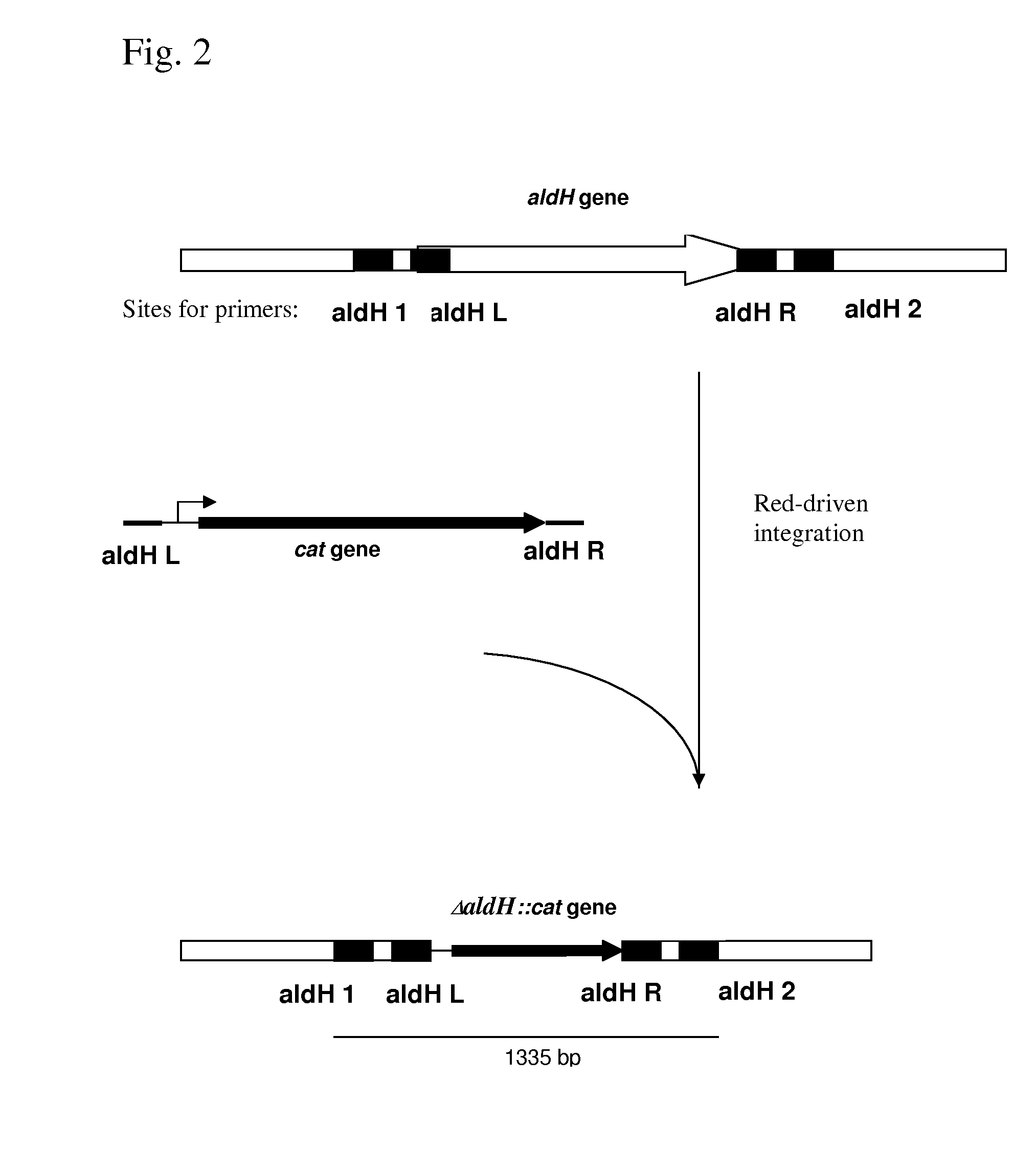
METHOD FOR PRODUCING AN L-AMINO ACID USING A BACTERIUM OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE FAMILY WITH ATTENUATED EXPRESSION OF THE aldH GENE
InactiveUS20100143982A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesEnterobacter
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of the aldH gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
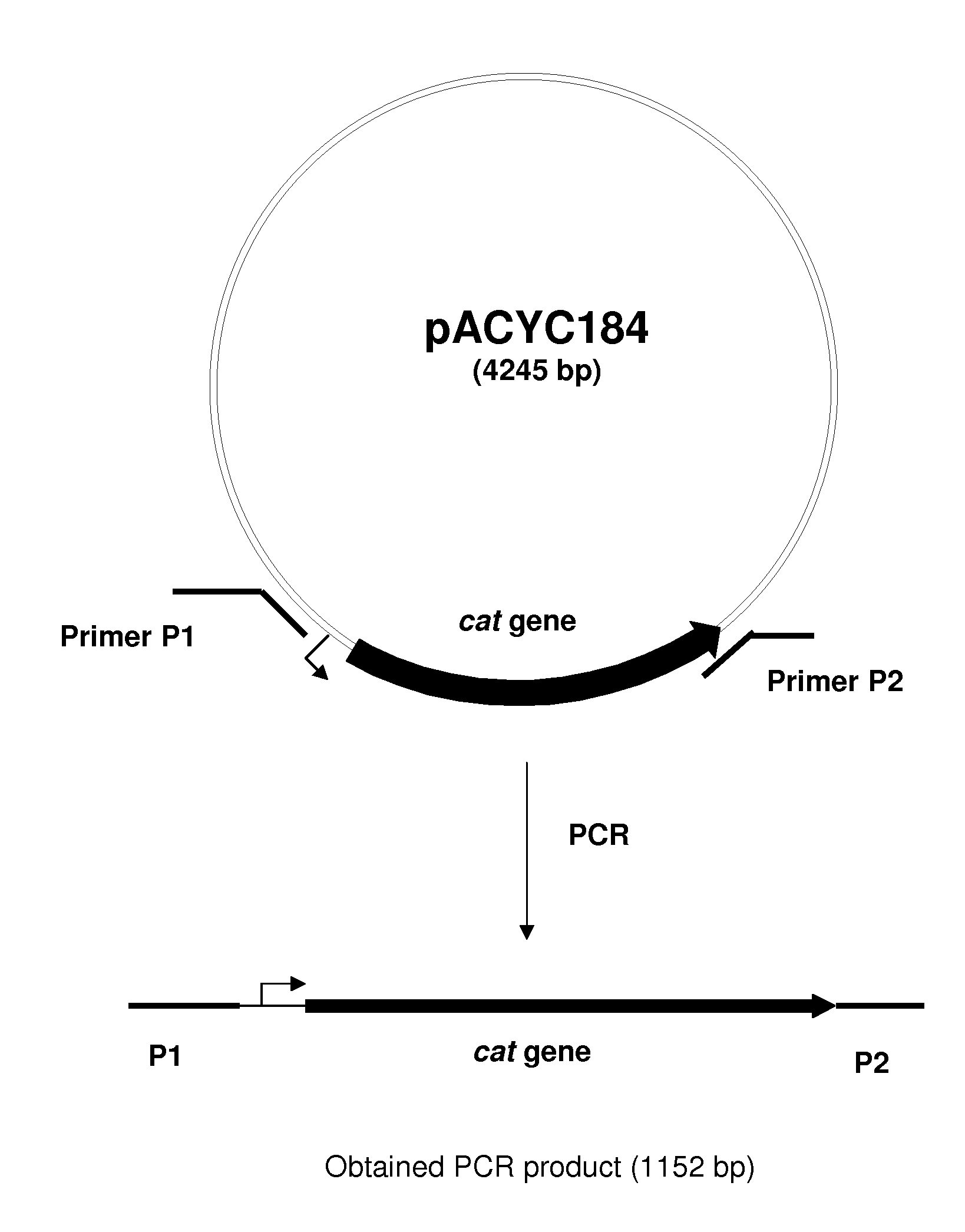
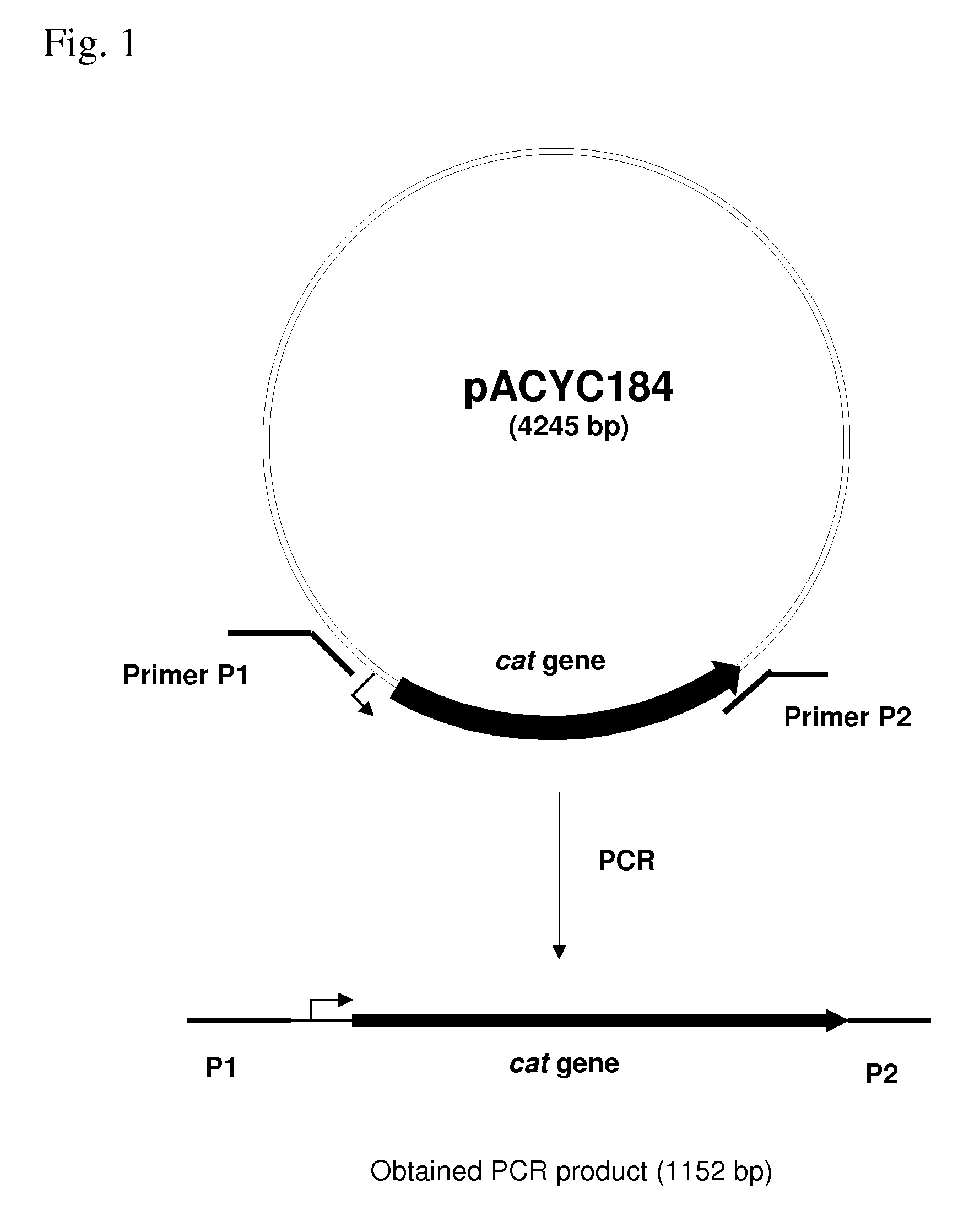
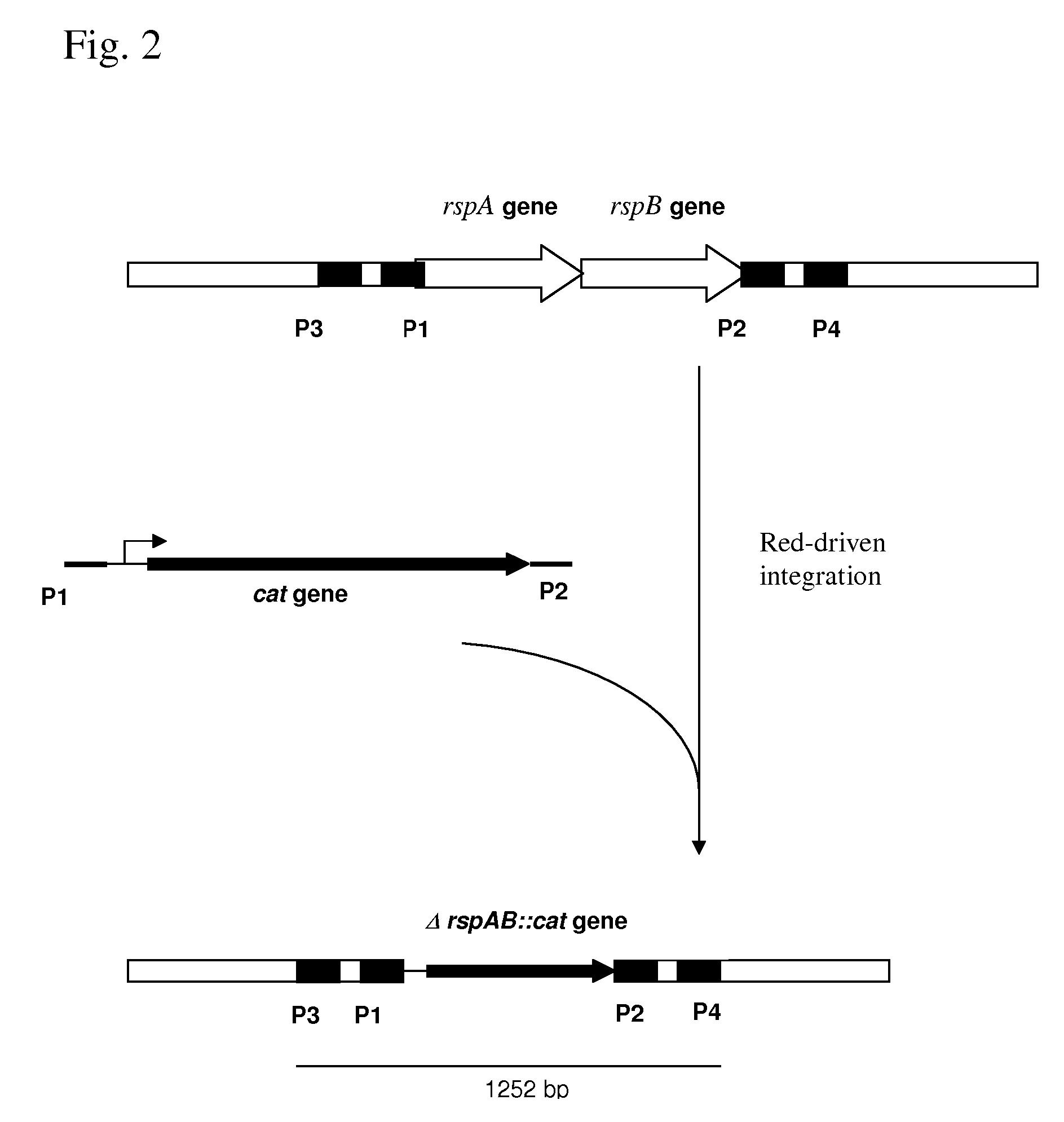
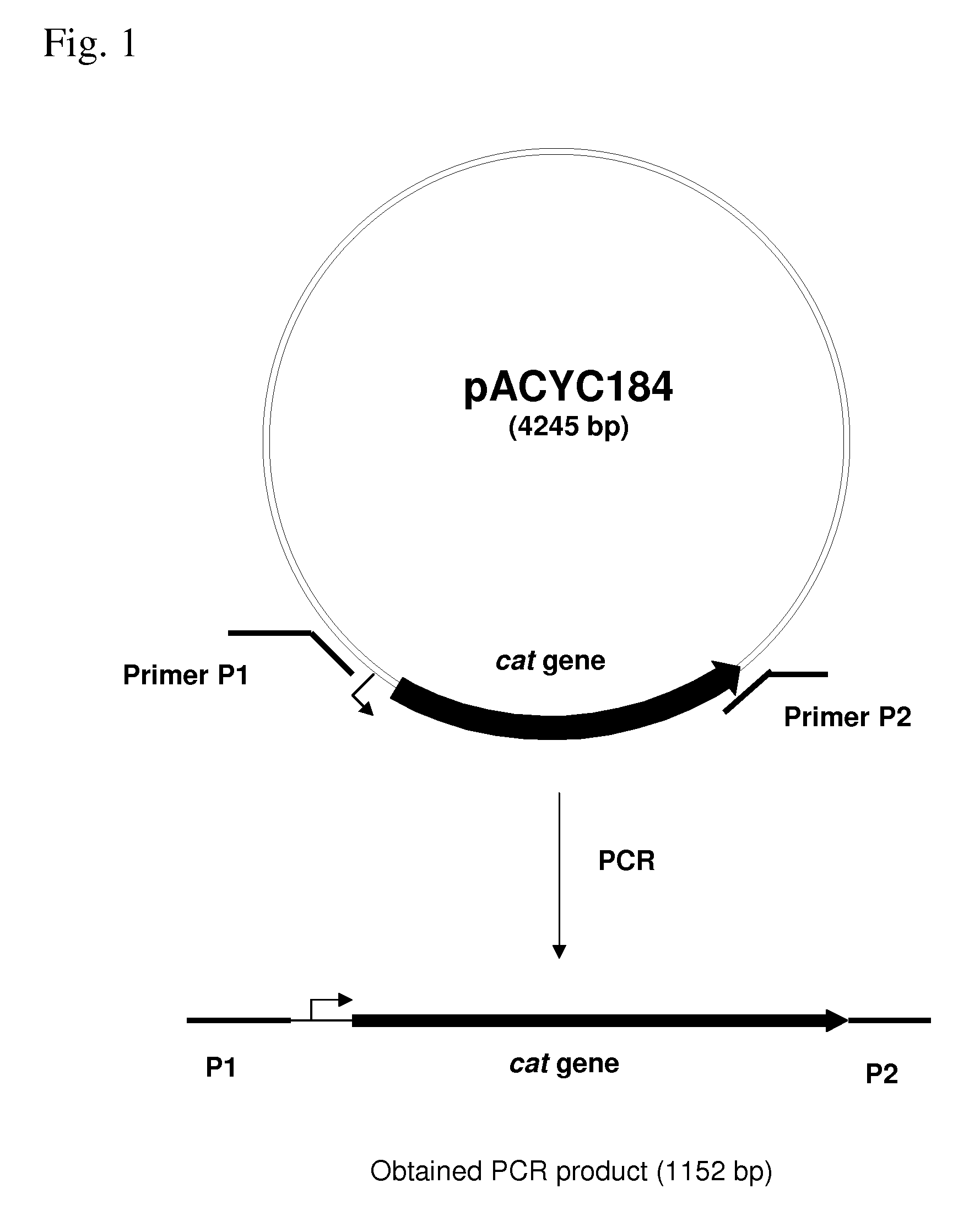
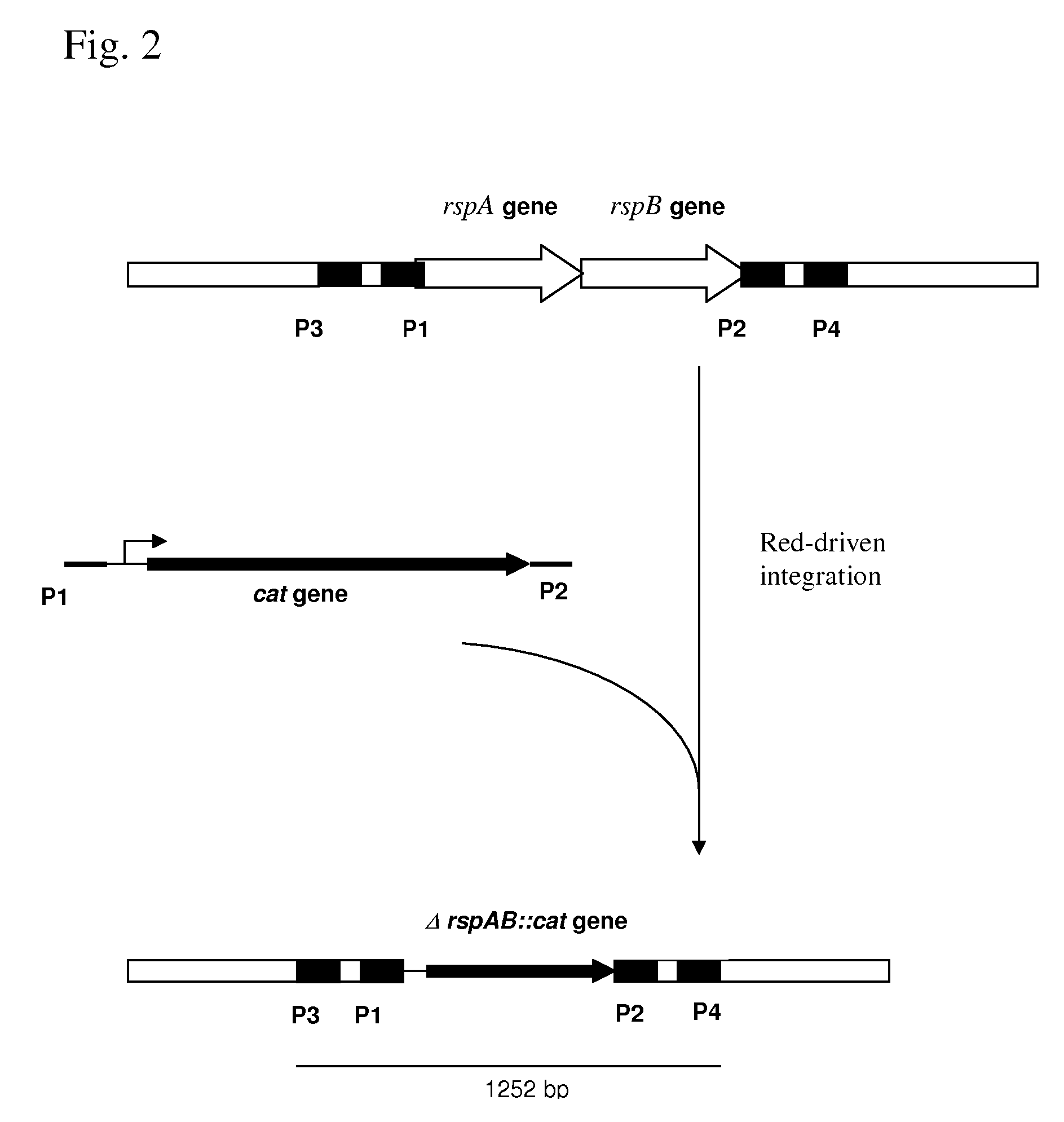
METHOD FOR PRODUCING AN L-AMINO ACID USING A BACTERIUM OF THE ENTEROBACTERIACEAE FAMILY WITH ATTENUATED EXPRESSION OF THE rspAB OPERON
InactiveUS20090170169A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesArs operon
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of the rspAB operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Sucrose isomerase mutant with improved stability and construction method thereof
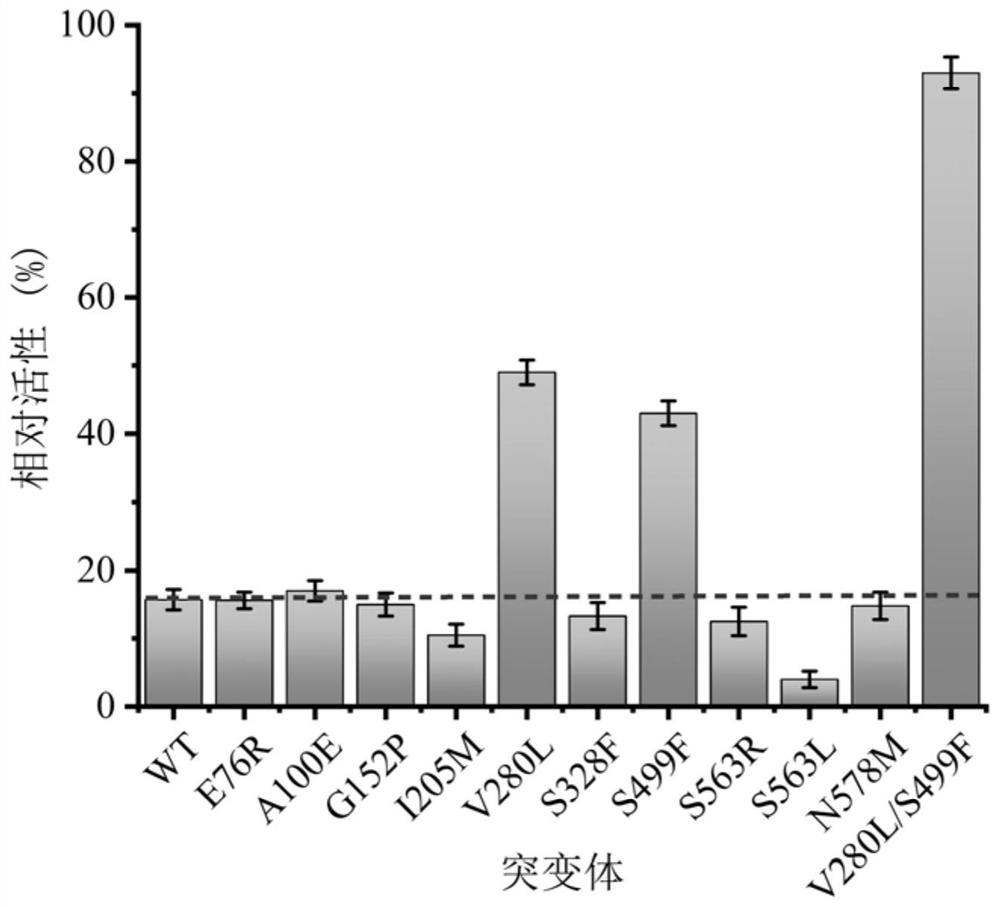
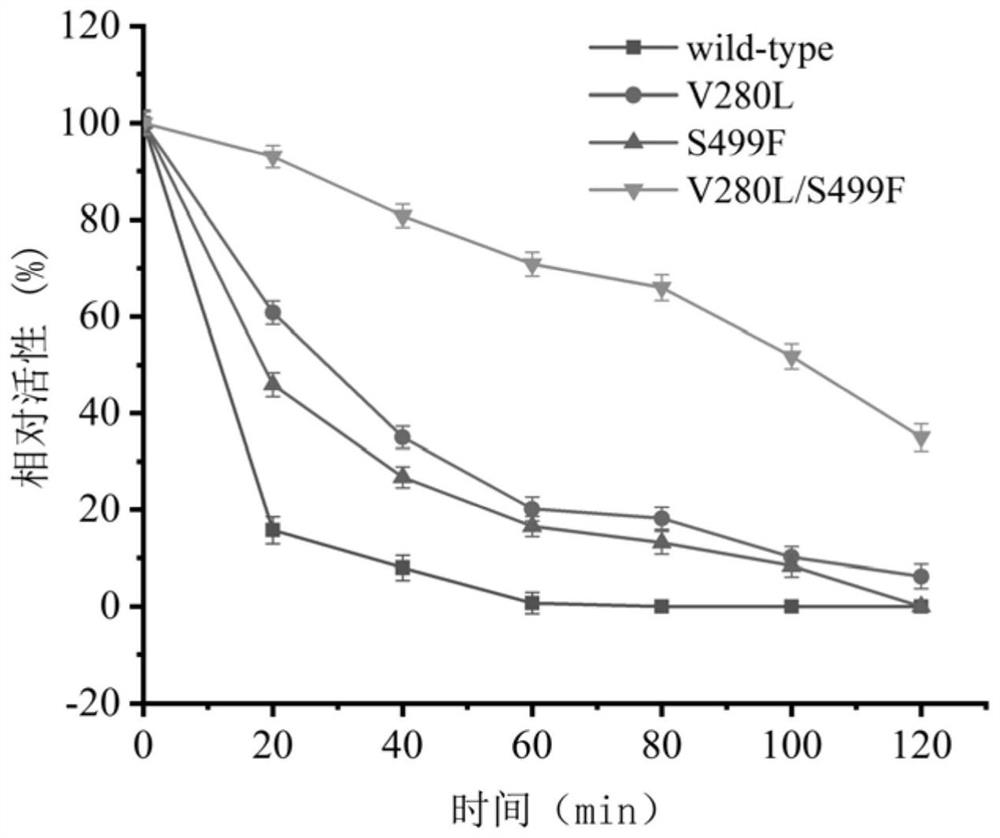
ActiveCN113151237AIncreased stability of single point mutationsHigh thermal stabilityBacteriaTransferasesSucroseIsomerase
The invention discloses a sucrose isomerase mutant with improved stability and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. On the basis of high-enzyme-activity dispersed pantoea-derived sucrose isomerase, two mutant strains V280L and S499F with improved single-point thermal stability and a combined mutant V280L / S499L are obtained through screening. The thermal stability of the three mutants is obviously improved, and the enzyme activity is not influenced. The mutants provided by the invention are more suitable for industrial production than natural sucrose isomerase, and have very huge application prospects and industrial values.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microbial-conversion-based method for synthesizing 3-hydroxy beta-ionone and beta-ionone
InactiveCN105154479AImprove qualityMicroorganism based processesFermentationLuteinMicrobial transformation
The invention discloses a microbial-conversion-based method for synthesizing 3-hydroxy beta-ionone and beta-ionone. The method includes the following steps: (1), culturing scattered pantoea, inoculating a triangular bottle filled with a seed culture medium with a scattered pantoea strain, and oscillating at 180-200r / min under the conditions of pH being 6.5 and temperature being 30-34 DEG C for culture for 10-18h to obtain seed liquid; (2), fermenting in a seed tank; (3), obtaining 3-hydroxy beta-ionone and beta-ionone. By searching fermentation culture media, an optimal fermentation culture medium capable of efficiently degrading lutein is obtained, and 3-hydroxy beta-ionone and beta-ionone which have aromatic substances can be generated. The 3-hydroxy beta-ionone and beta-ionone are important aromatic substances, and tobacco quality can be improved greatly by adding a small amount of the aromatic substances into tobacco. The microbial-conversion-based method has huge application prospect in utilizing biologically-degraded lutein and generating natural aromatic substances.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Method for producing an L-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium having an enhanced ability to utilize glycerol
InactiveUS7811798B2Improve abilitiesProducing L-aminoBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesGlycerol kinase
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to have glycerol kinase in which feedback inhibition by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is desensitized, thereby having enhanced ability to utilize glycerol.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing beta-carotene and construction method thereof
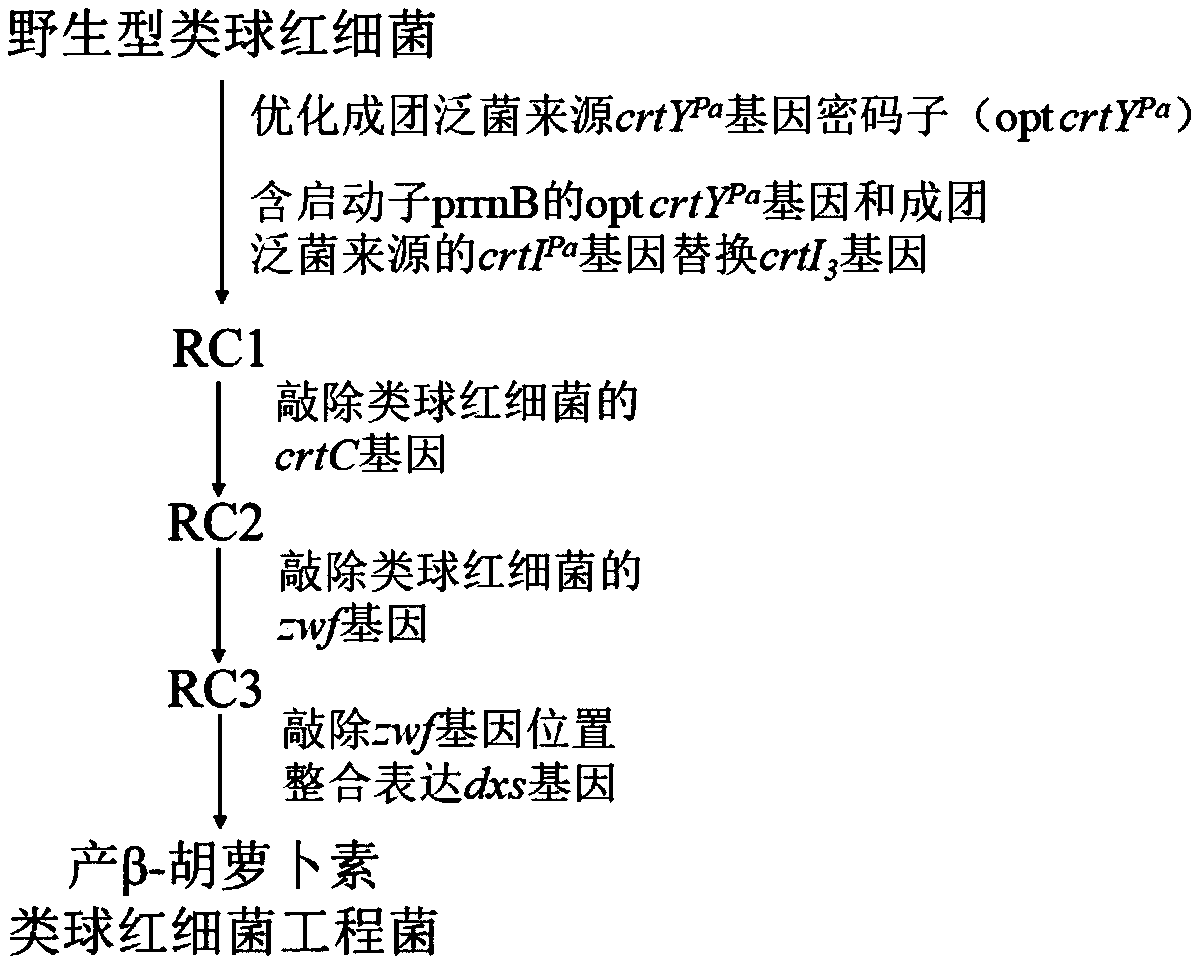
The invention discloses a rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing beta-carotene and a construction method thereof. The method includes first optimizing a codon of a lycopene cyclase gene crtYPa derived from pantoea agglomerans to obtain an opt crtYPa gene, then replacing an endogenous phytoene three-step dehydrogenase gene crtI3 of rhodobacter sphaeroides with the opt crtYPa genecontaining a promoter prrnB and a phytoene four-step dehydrogenase gene crtIPa gene derived from the pantoea agglomerans in a traceless mode, then knocking out an endogenous neurosporene hydroxylase gene crtC of the rhodobacter sphaeroides and a 6-phosphoglucose dehydrogenase gene zwf and finally knocking out an endogenous 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene dxs of the rhodobacter sphaeroides with integration expression at zwf position to obtain the rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing the beta-carotene. The strain is cultured by fermentation, and the content of the beta-carotene can reach 30mg / g DCW.
Owner:SHAANXI HEALTHFUL BIOLOGICAL ENG
Pantoea agglomerans and application thereof
ActiveCN105219678AGrowth inhibitionAvoid pollutionBiocideBacteriaEnterobacter agglomeransGram stain negative
The invention provides pantoea agglomerans and application thereof. A preservation number of the pantoea agglomerans is CCTCC NO: M2015563. The thallus of the pantoea agglomerans is rod-shaped and is negative when being treated by Gram staining; the pantoea agglomerans can be prepared into a liquid bacterial agent or wettable powder and is used for preventing and treating wheat scab and reducing the content of wheat gibberellin; in a process of solving toxin pollution, no toxic byproducts are generated and secondary pollution is not caused, so that the quality of agricultural products is improved and the edible safety of people and livestock is ensured.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
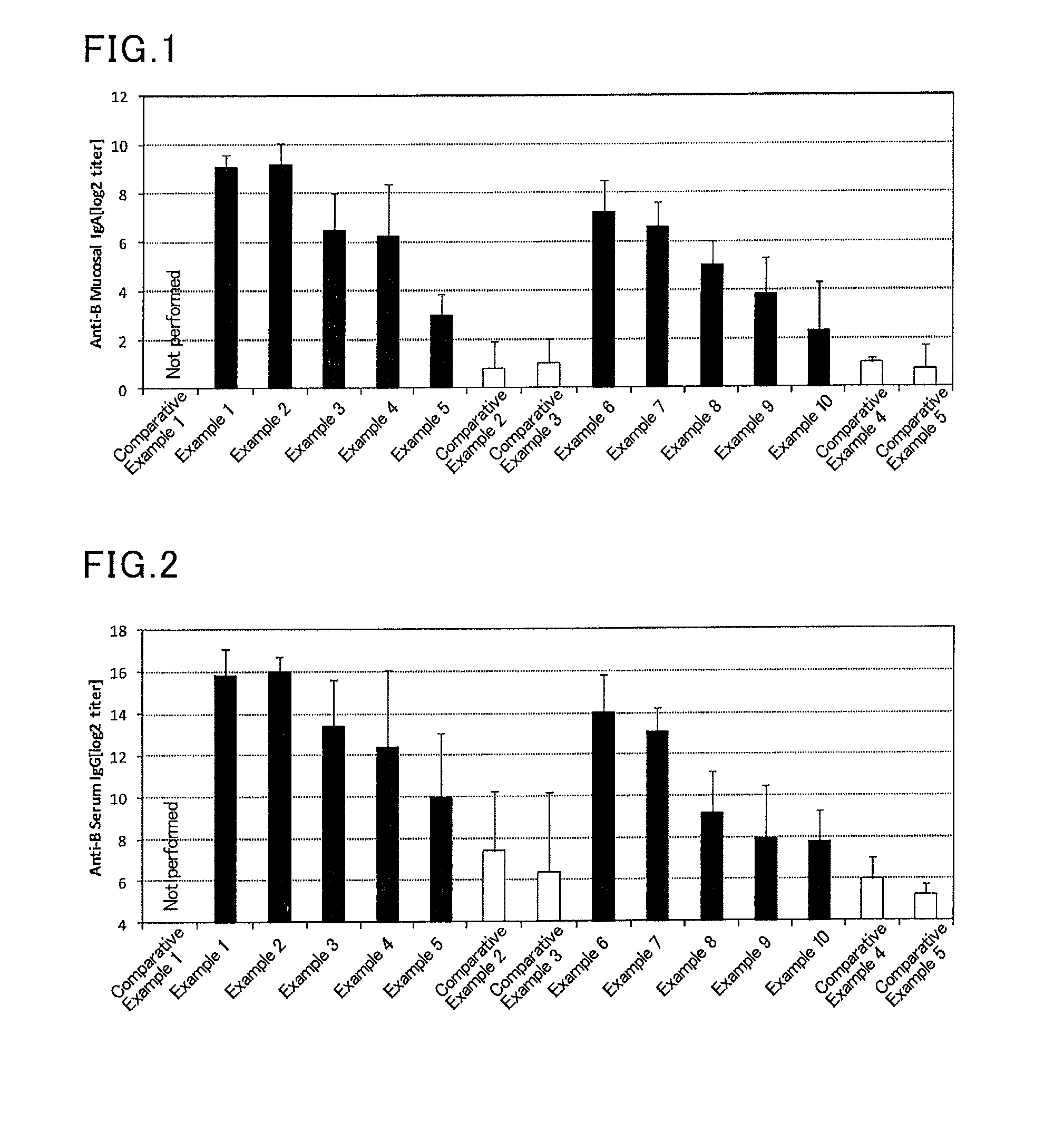
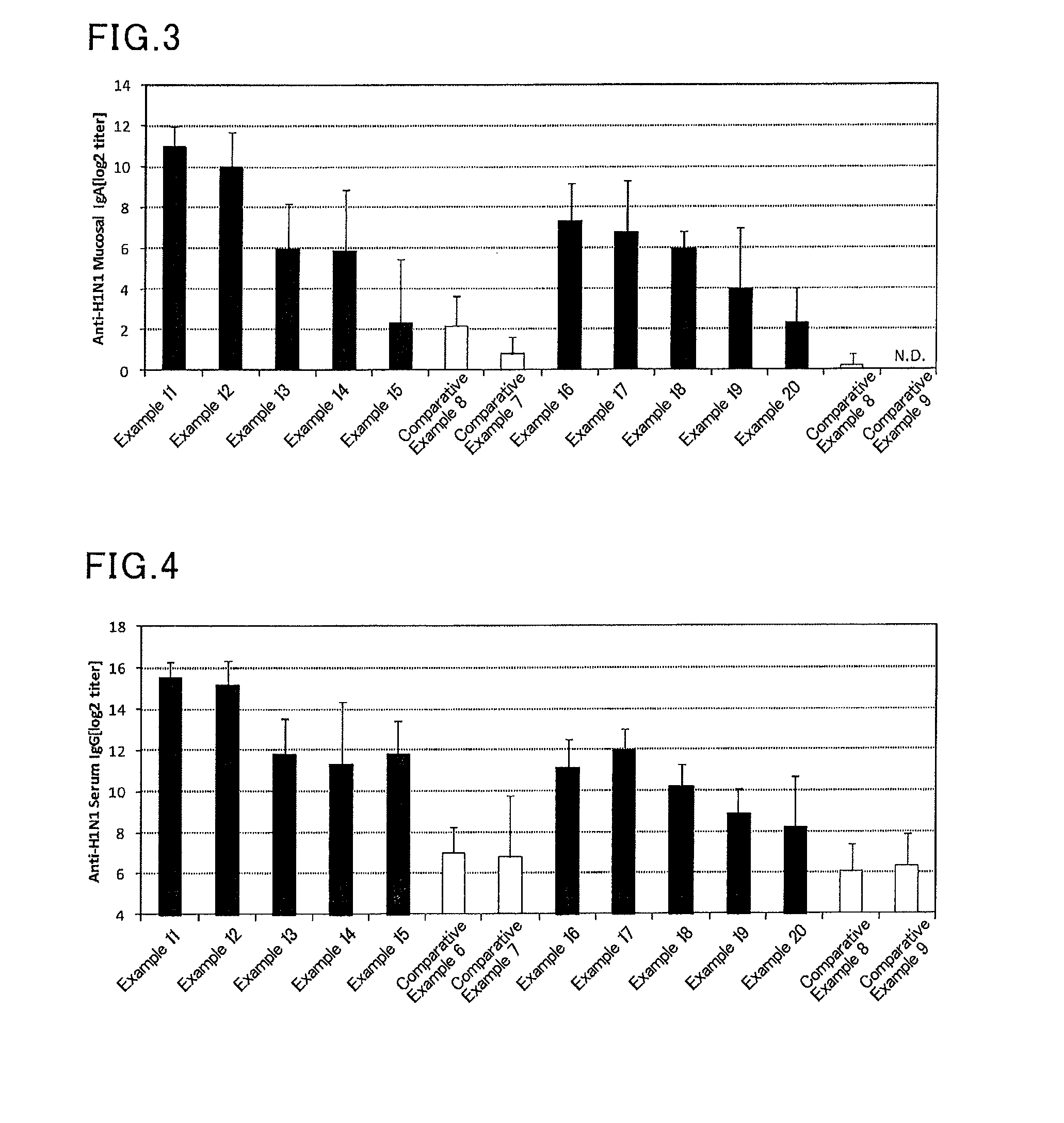
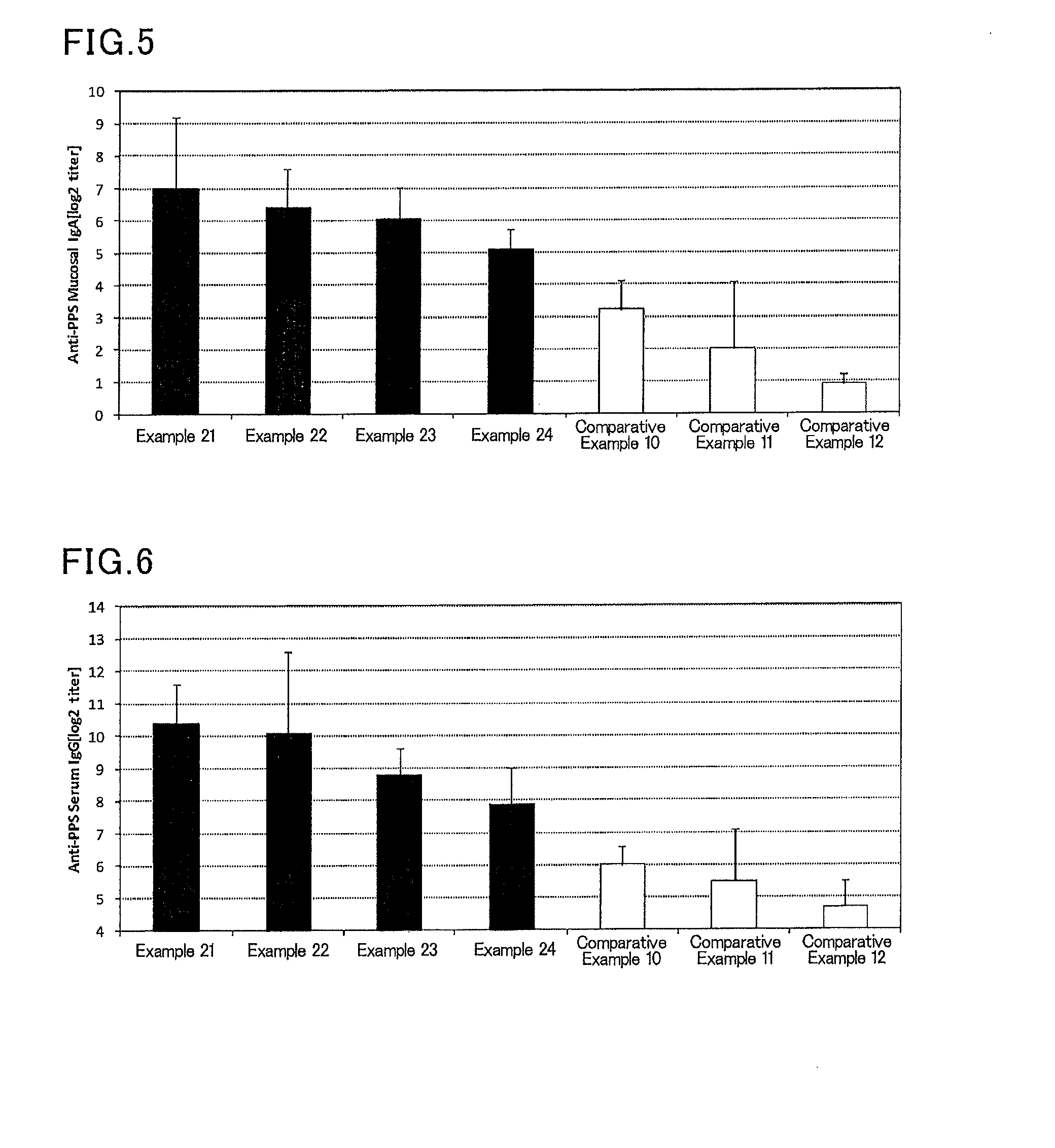
Mucosal vaccine composition
InactiveUS20160213773A1Safe and effectiveSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesXanthomonas
The present invention aims at providing a vaccine composition capable of being administered to an intraoral mucous membrane, ocular mucous membrane, ear mucous membrane, genital mucous membrane, pharyngeal mucous membrane, respiratory tract mucous membrane, bronchial mucous membrane, pulmonary mucous membrane, gastric mucous membrane, enteric mucous membrane, or rectal mucous membrane, that is safe, useful as a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for infectious diseases or cancers, and capable of effectively inducing the systemic immune response and mucosal immune response. The present invention provides a mucosal vaccine composition to be administered to at least one mucous membrane selected from the group consisting of a human or animal intraoral mucous membrane, ocular mucous membrane, ear mucous membrane, genital mucous membrane, pharyngeal mucous membrane, respiratory tract mucous membrane, bronchial mucous membrane, pulmonary mucous membrane, gastric mucous membrane, enteric mucous membrane, and rectal mucous membrane, the mucosal vaccine composition containing: at least one antigen; and as an adjuvant, a lipopolysaccharide derived from at least one gram-negative bacterium selected from the group consisting of Serratia, Leclercia, Rahnella, Acidicaldus, Acidiphilium, Acidisphaera, Acidocella, Acidomonas, Asaia, Belnapia, Craurococcus, Gluconacetobacter, Gluconobacter, Kozakia, Leahibacter, Muricoccus, Neoasaia, Oleomonas, Paracraurococcus, Rhodopila, Roseococcus, Rubritepida, Saccharibacter, Stella, Swaminathania, Teichococcus, Zavarzinia, Pseudomonas, Achromobacter, Bacillus, Methanoculleus, Methanosarcina, Clostridium, Micrococcus, Flavobacterium, Pantoea, Acetobacter, Zymomonas, Xanthomonas, and Enterobacter, or a salt thereof, wherein a mass ratio between the adjuvant and the antigen (total mass of the adjuvant / total mass of the antigen) is 0.002 to 500.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of the rspAB operon
InactiveUS7794988B2Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesOperonMicrobiology
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of the rspAB operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an organic acid
InactiveUS8247201B2Improve production efficiencyImprove production yieldSugar derivativesFermentationOrganic acidEnterobacter
An organic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an ability to produce an organic acid and has been modified so that the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity is enhanced, which is selected from Enterobacter, Pantoea, Erwinia, Klebsiella and Raoultella bacteria, or a product obtained by processing the bacterium, to act on an organic raw material in a reaction mixture containing carbonate ions, bicarbonate ions, or carbon dioxide gas to produce the organic acid, and collecting the organic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Microbial source combined biostimulant and application thereof
InactiveCN111747792AIncrease profitImprove disease and stress resistanceNitrogenous fertilisersOrganic fertilisersBiotechnologyOligosaccharide
The invention discloses a microbial source combined biostimulant. The microbial source combined biostimulant is characterized by being prepared from the following components, by mass: 0.1 to 17.5 percent of polyglutamic acid, 0 to 5.0 percent of amino-oligosaccharin, 0.05 to 2.0 percent of pantoea polysaccharide, 0 to 1.5 percent of gamma-aminobutyric acid and the balance of auxiliary materials. The microbial source combined biostimulant can effectively improve the utilization rate of a plant fertilizer, improve the disease resistance and stress resistance of the plant fertilizer and induce aself-defense system of the plant fertilizer, can be completely biodegraded in soil, and is non-toxic, harmless and pollution-free to plants and the soil environment.
Owner:轩凯生物科技(山东)有限公司
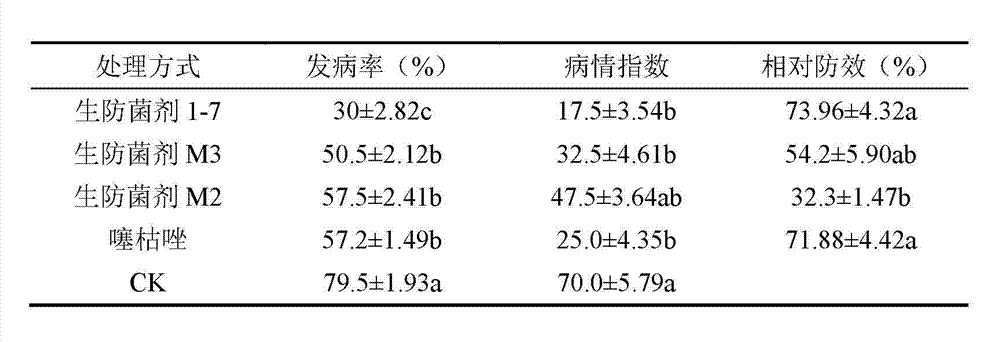
Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 and application
InactiveCN102899266BGood growth promoting effectGood characterBiocideBacteriaDiseaseBacterial soft rot
The invention relates to a Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 and an application, which belongs to the biology technical field. The Pantoea agglomerans1-7 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 28th, 2012 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.6160. The Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 is used for preparing the preparations used for preventing and treating bacterial soft rot of konjak and clubroot disease on cruciferous vegetable club root in fields. The Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 has the advantages of high efficiency, no toxicity, safety and no residue, the bacterial strain1-7 has the characteristics of good disease control, better growth promotion effect, better comprehensive characters and easy industrial production, and the Pantoea agglomerans1-7 can be applied to preparation of preparations for controlling cruciferous vegetable club root in fields.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com