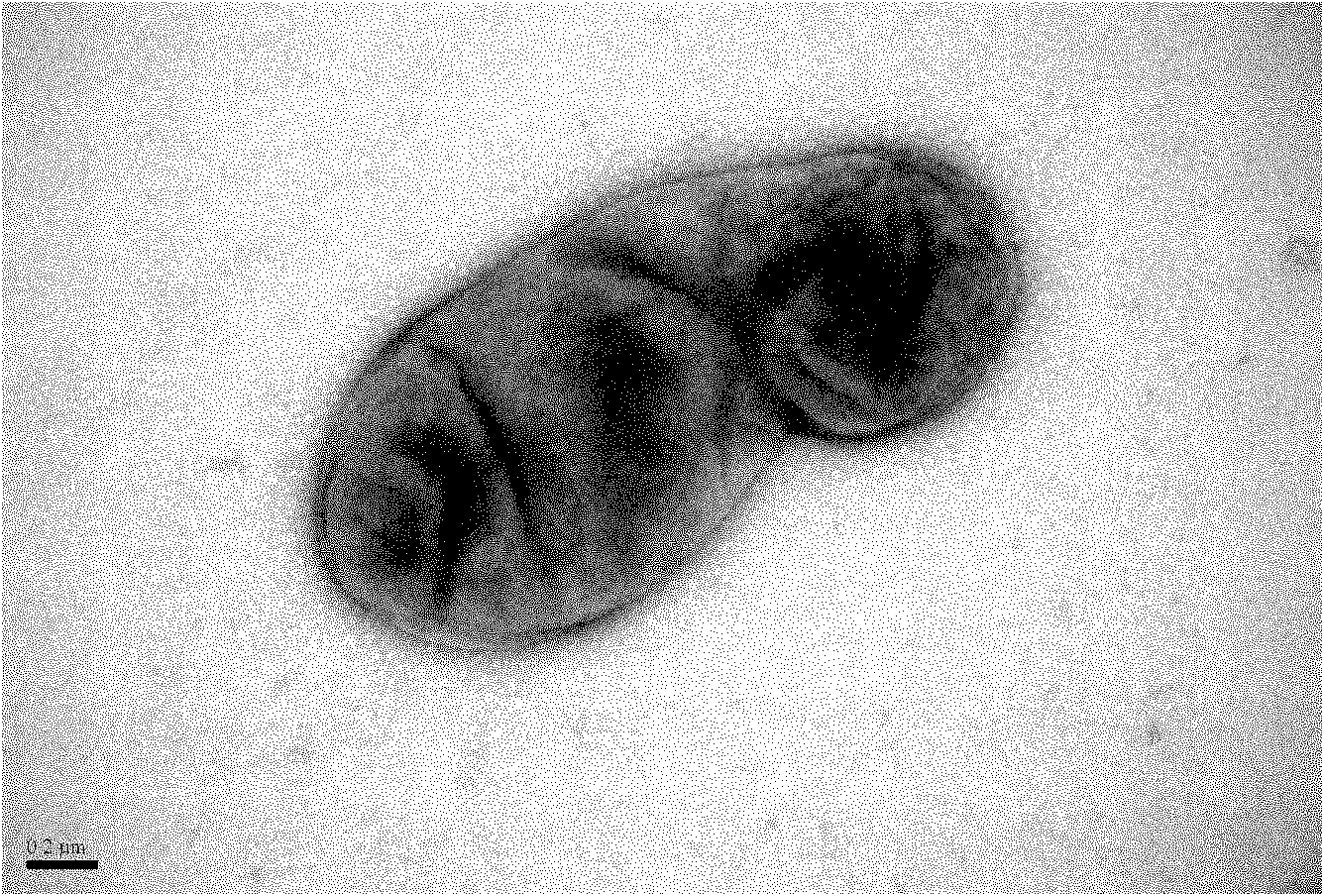
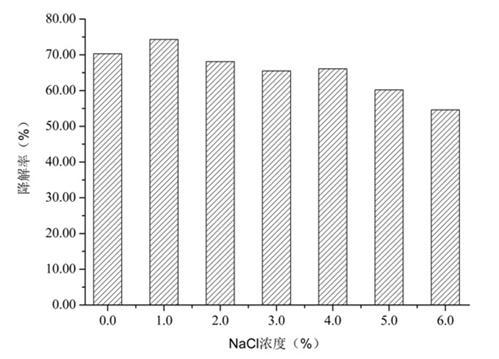
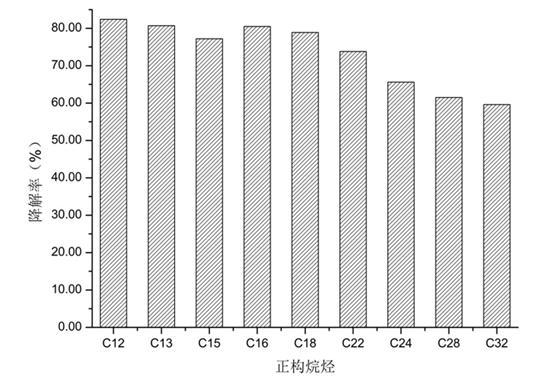
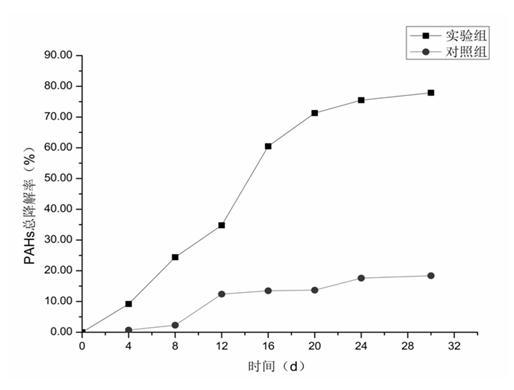
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Gram stain negative" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biocontrol bacteria strain preventing and curing plant disease
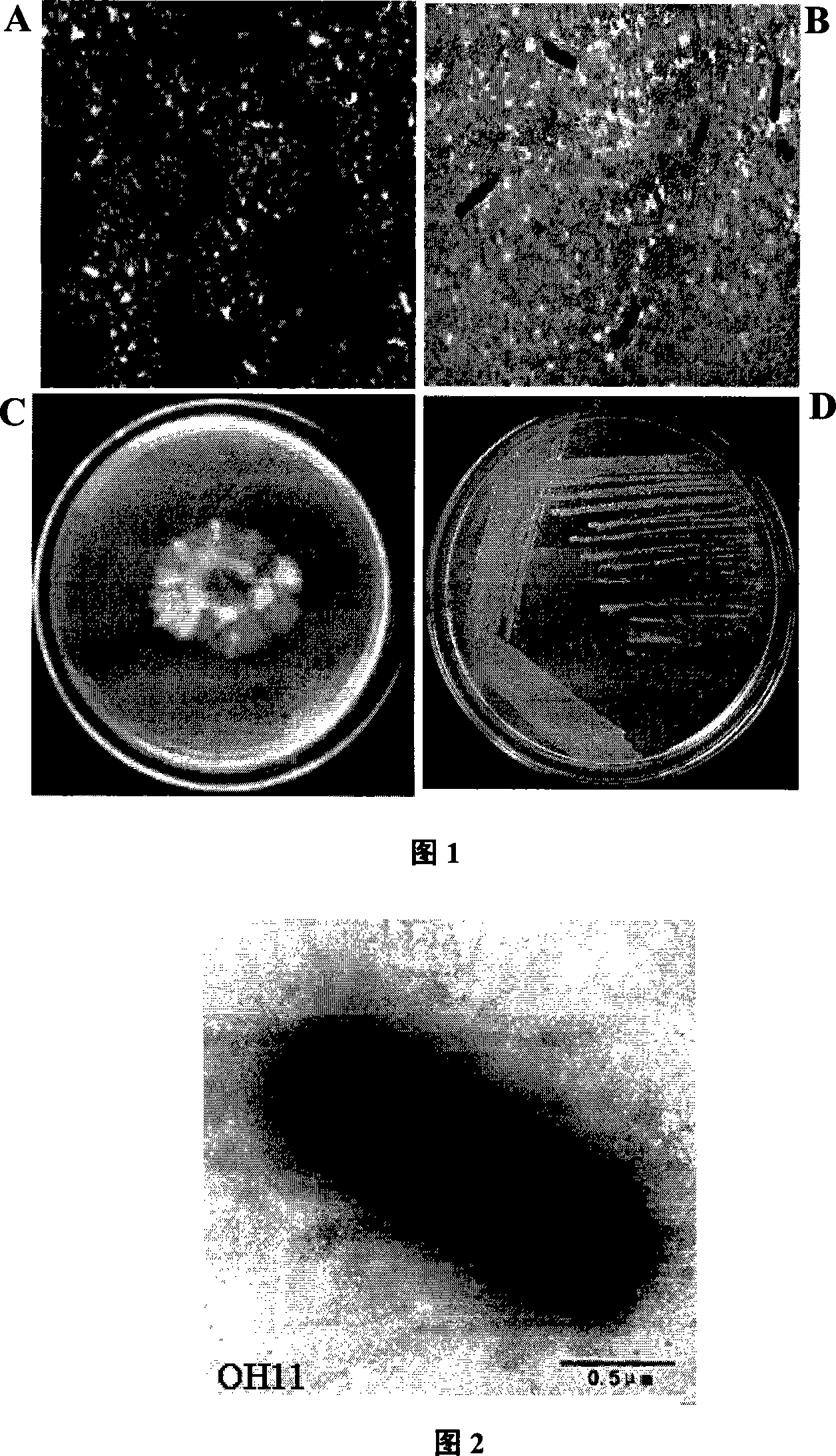
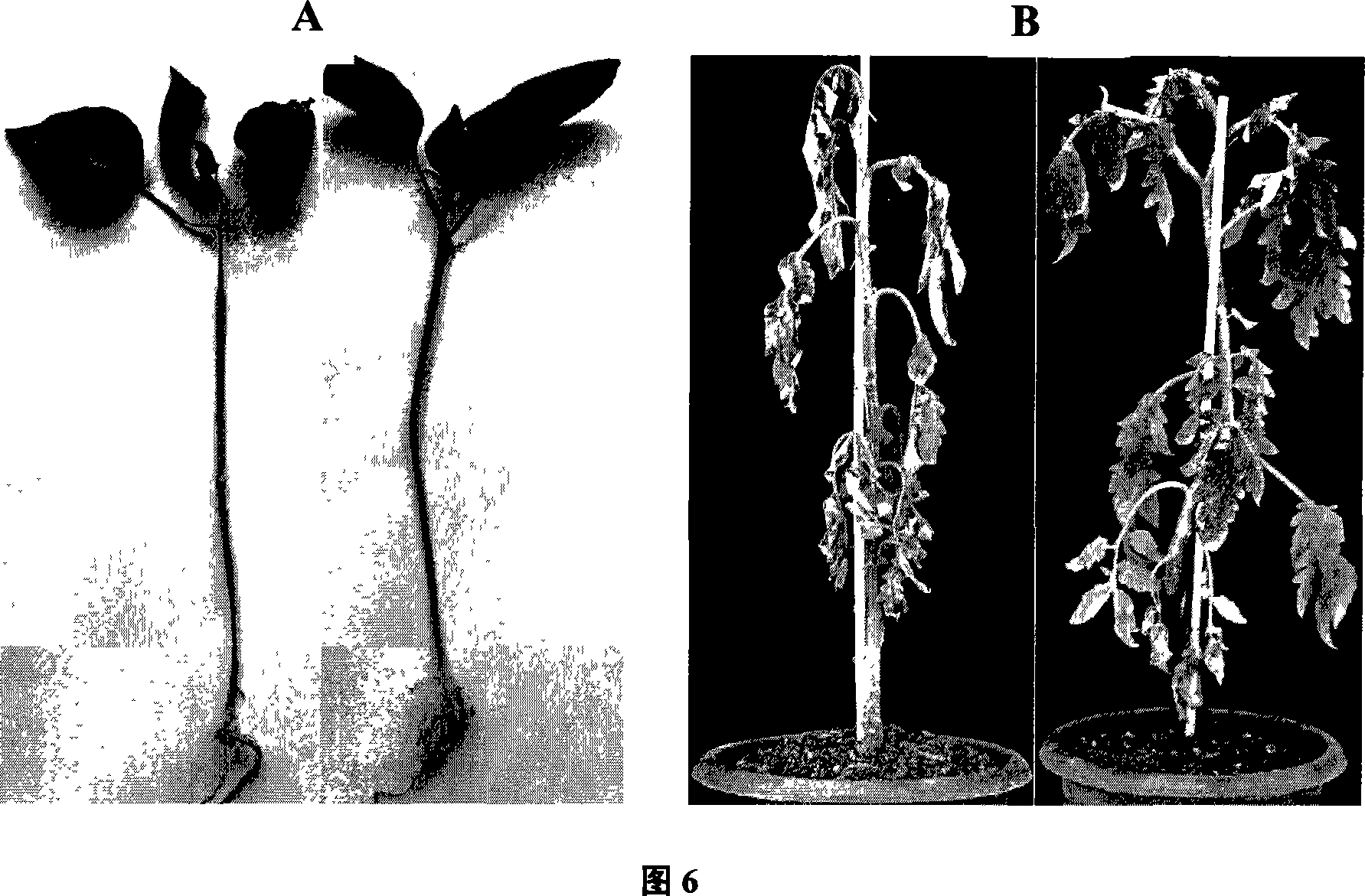
The invention provides a biocontrol bacterial strain for preventing and treating plant diseases and its bacterial agent, belonging to the field of biological control. The strains used are Gram-negative bacteria, identified as Lysobacter enzymogenes, and the strain code is OH11. Strain OH11 has no flagella but has slippage, can produce various extracellular hydrolytic enzymes including chitinase, β-1,3-glucanase and protease, and can effectively inhibit the growth of fungi and bacteria. The antibacterial zone diameters of strain OH11 against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Phytophthora capsici were both greater than 22.0 mm; the antagonism against potato ring rot was stronger, and the diameter of the inhibition zone reached 50 mm. The OH11 strain was inoculated into the seed tank, cultivated to the logarithmic growth phase, and the seed liquid was connected to the production tank for cultivation. The medium used in the production tank was the same as that of the seed tank. The liquid fermentation adopts aerobic submerged fermentation and fed-batch process, the dissolved oxygen is 15%-20%, the fermentation temperature is 30°C, the fermentation time is 72h, and the initial pH value is 7.5. After the fermentation is completed, the culture solution is taken out of the tank and directly packed into liquid dosage forms with plastic packaging barrels or packaging bottles, or subpackaged into solid dosage forms with peat adsorption packaging bags. The biocontrol strain OH11 can effectively control plant pathogenic fungi, bacteria, nematodes and other diseases, and the overall control effect is 50%-70%. In the greenhouse pot experiment, the control effects of OH11 on pepper blight and tomato bacterial wilt reached 83.6% and 86.4%, respectively. Strain OH11 has the characteristics of broad antibacterial spectrum, high activity, and environmental safety. In today's serious pesticide pollution, zymolysobacterium and its bacterial agent will be a good substitute.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Pseudomonas stutzeri strain and application thereof in degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with high molecular weight
InactiveCN101603022APromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesSpore structure
The invention relates to a novel strain of bacteria and application thereof in degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with high molecular weight. The strain is identified and named as Pseudomonas stutzeri MT-5 strain which has bacteriological characteristic of Gram-negative, has cells in a straight or bent rod shape but not spiral shape and not in a chain, has the size of 0.60-0.8*1.4-2.0mu m, has polar flagellum, can move, does not form spore or have sheath or protrusion, has no poly beta hydroxybutyrate observed, has round bacterial colony, not irregular edge, rough surface and irregular bump shape, and is white and opaque. The Pseudomonas stutzeri MT-5 strain can be applied to degrading PAHs, BAP / BGP with high molecular weight. The Pseudomonas stutzeri MT-5 strain has the degradation efficiency of 65 percent on the BGP and 59.6 percent on the BAP in 168h, and has the degradation capacity higher than related bacteria for degrading the BAP / BGP reported at home and abroad.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MEP
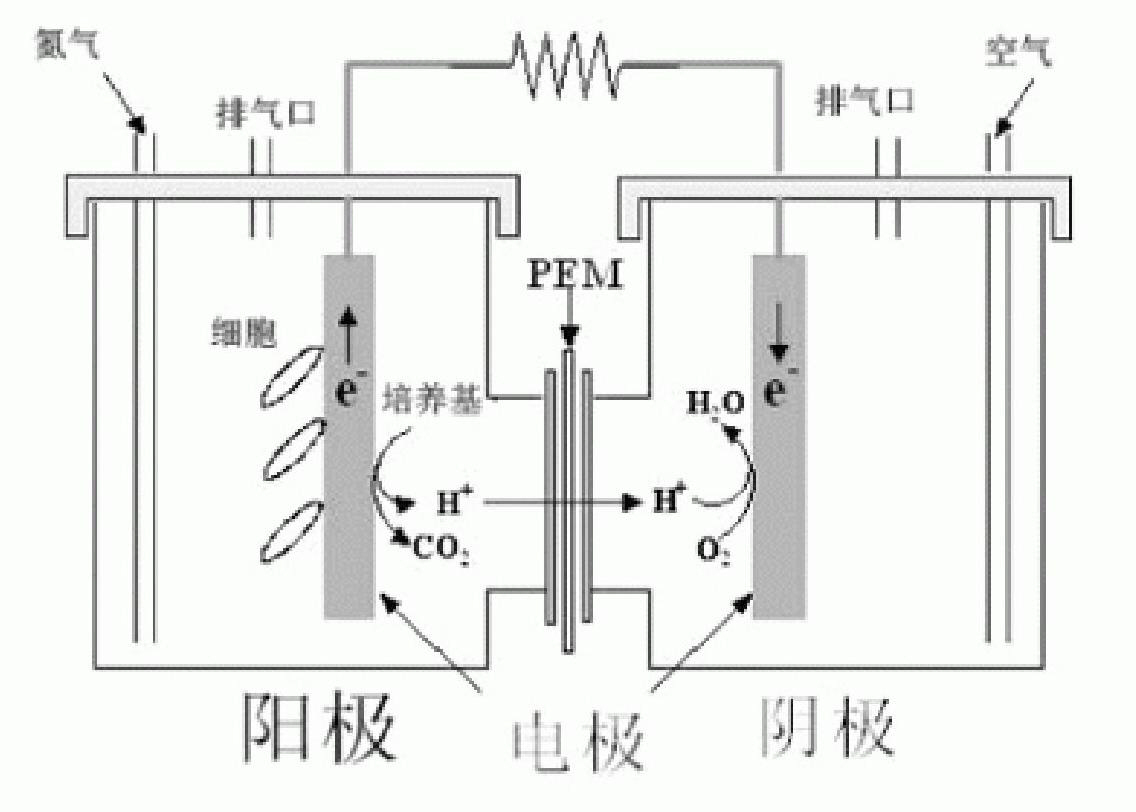
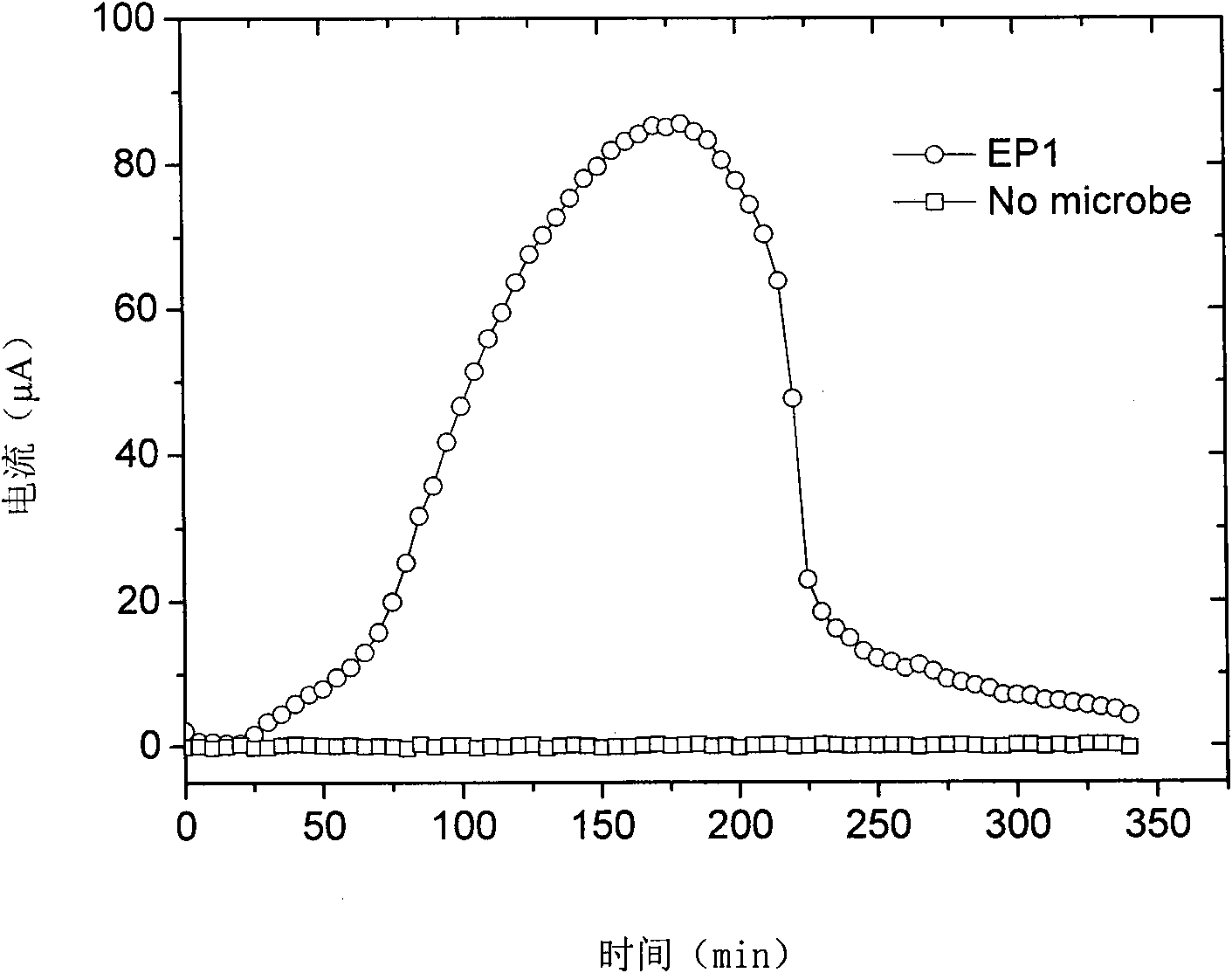
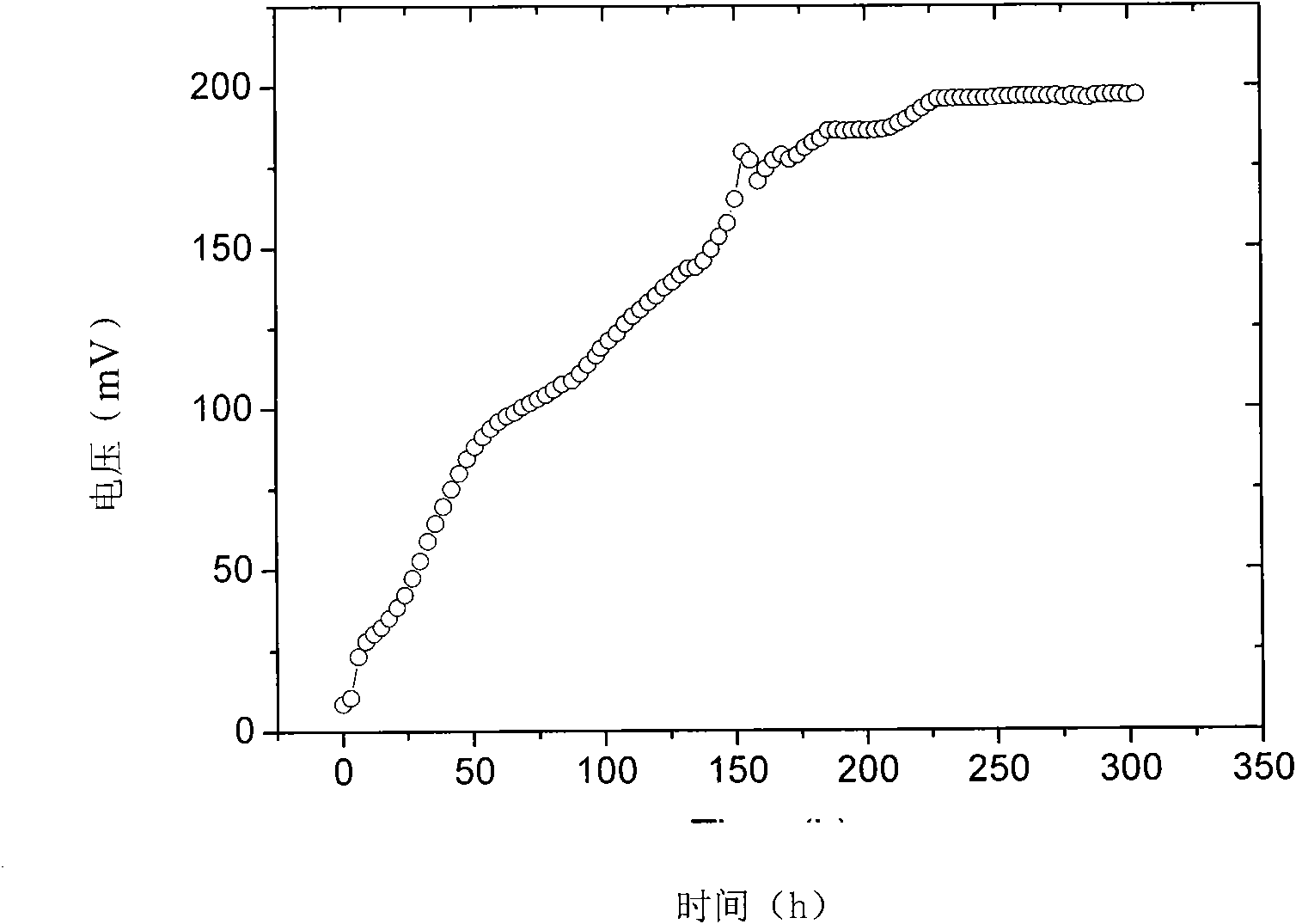
Shewanella spp and application thereof in microbial fuel cell
InactiveCN101838622AHas electricity-generating propertiesHigh electroactivityBacteriaCell electrodesShewanella putrefaciensBiology
The invention discloses shewanella spp and application thereof in a microbial fuel cell and relates to the technical field of biology. The shewanella spp is shewanella xiamenensis sp.nov.S4 preserved in the 'China Center for Type Culture Collection' in January, 2009 with the preservation number of CCTCC M 209017. The shewanella spp has the characteristics of negative Gram stain, rod-shaped and straight thallus, two circular ends, diameter of 0.3 to 1.2mu m, length of 2.5 to 5.8mu m, single or paired existence and short-chain arrangement, single flagella on the thallus, mobility, capability of producing electricity in a seawater environment and higher electricity production activity and is obtained by separating marine sediments near the sea.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
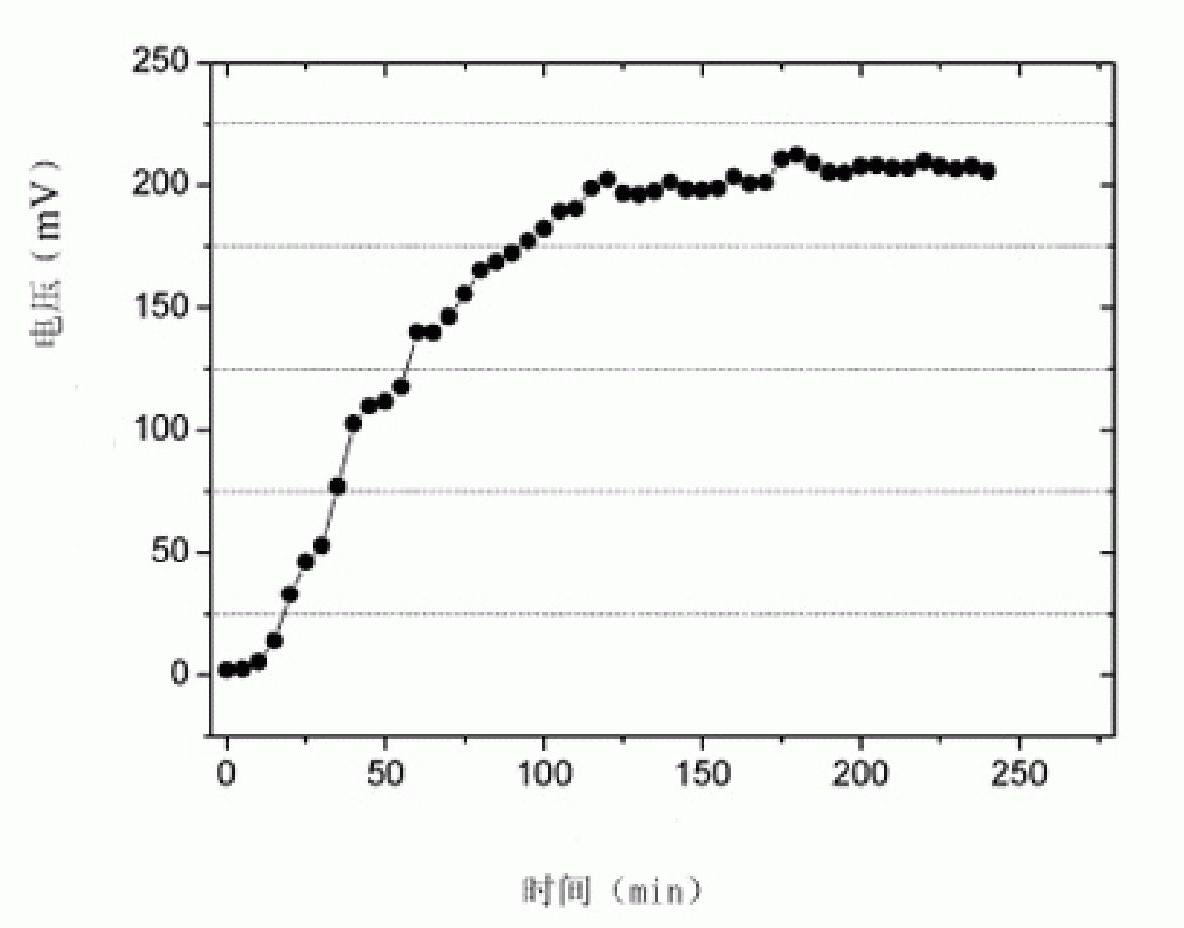
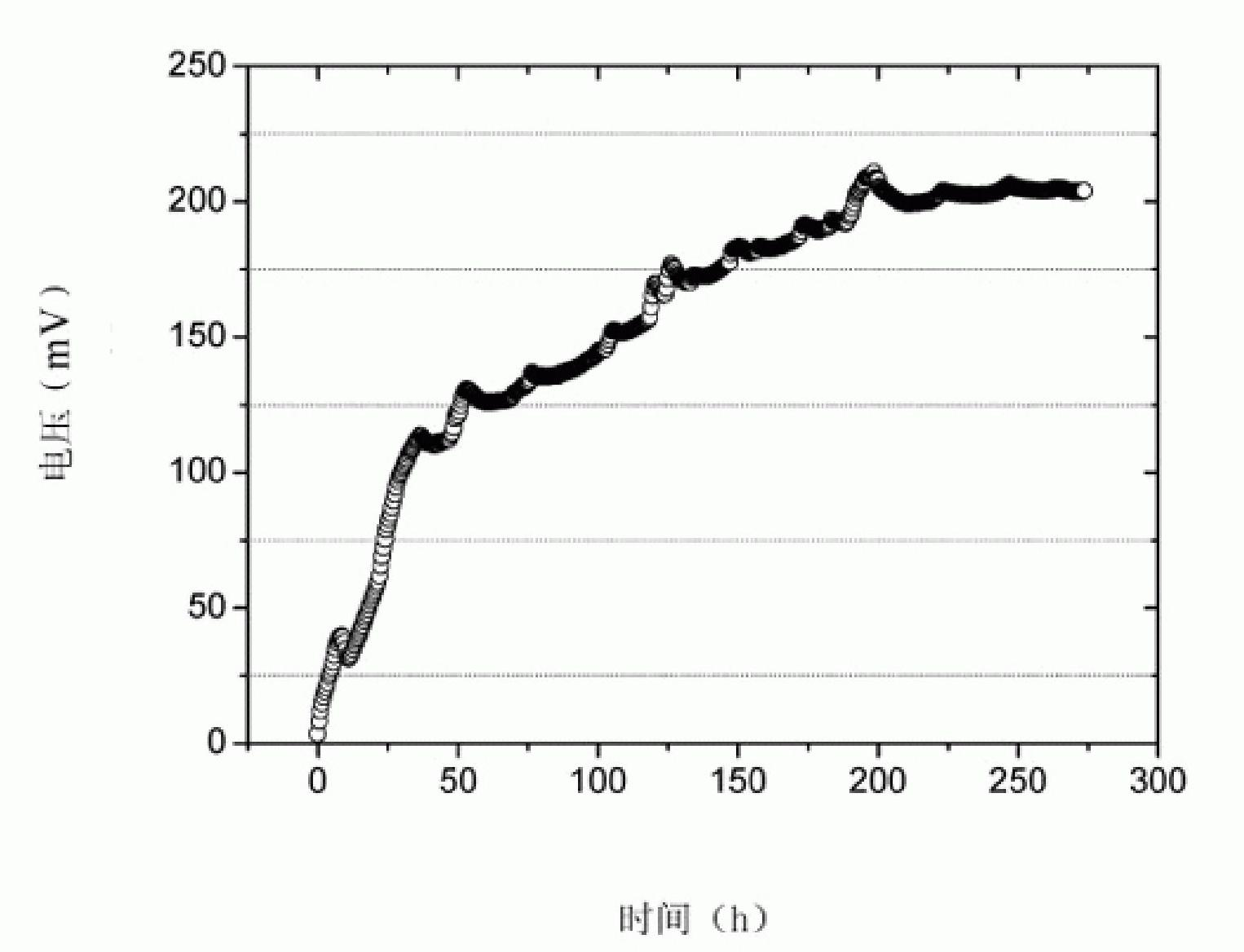
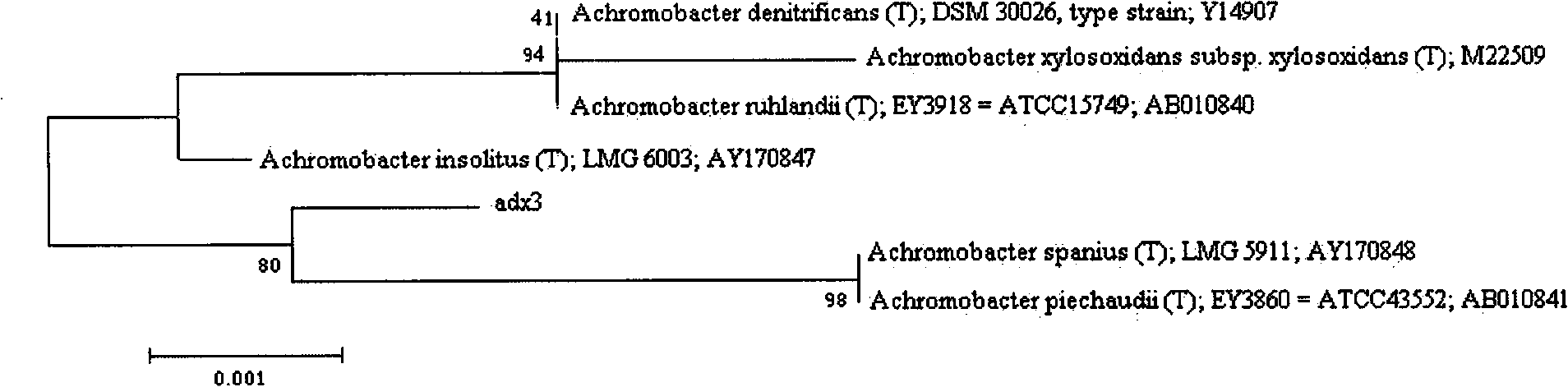
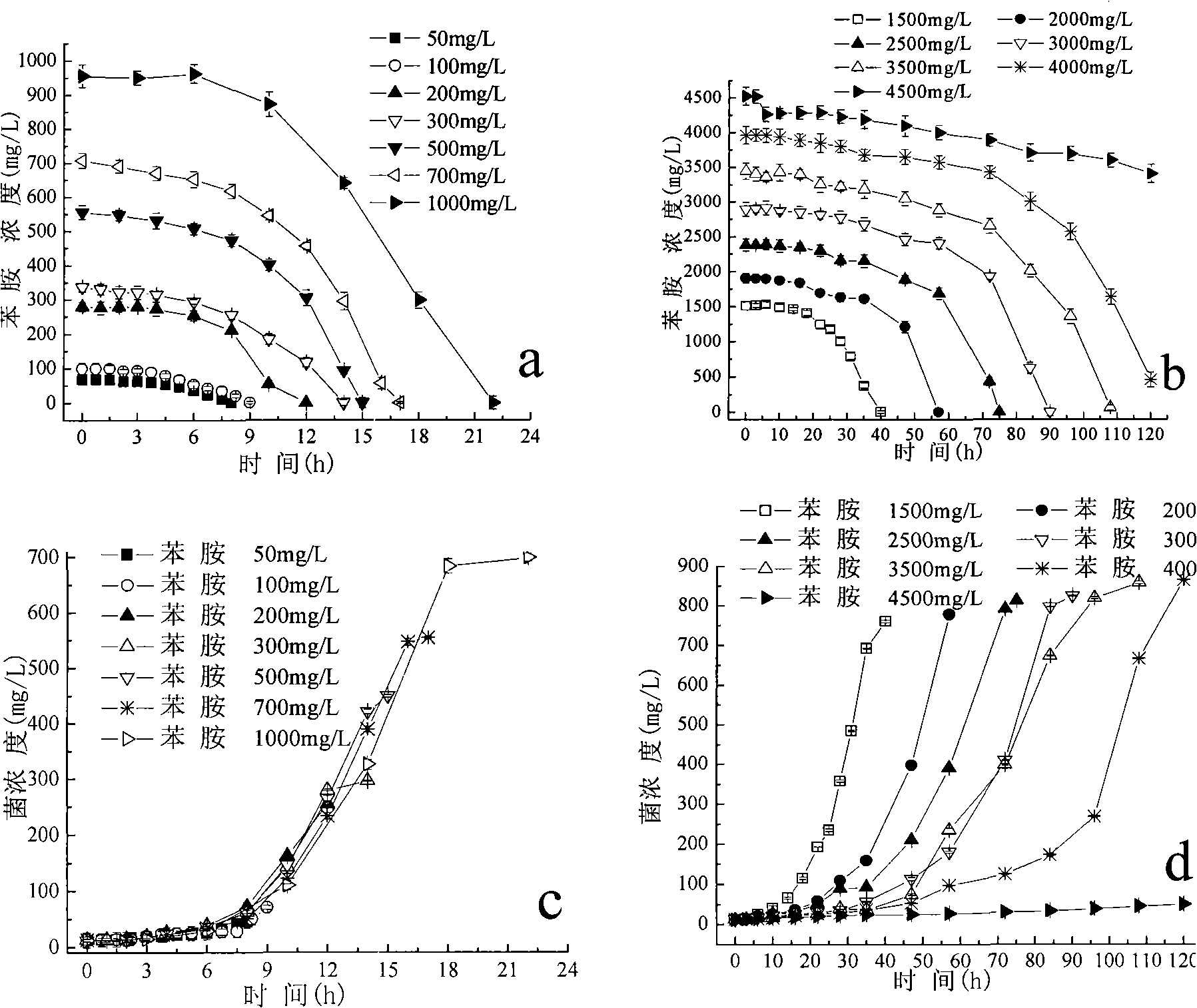
Achromobacter capable of degrading aniline and application thereof
InactiveCN101514330AGood self-flocculation propertiesImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaWater contaminantsGram stain negativeWastewater
The invention discloses an achromobacter capable of degrading aniline, wherein the 16S rDNA of the achromobacter has a sequence of SEQ ID No.1. Colonies are yellow, round, smooth and humid with neat edges and convex bulges. Through electron microscope observation, the achromobacter does not have flagellum and spore bacteria; and under the observation of the electron microscope, the form of the achromobacter is a thicker bacillus which is gram staining negative and oxidase and catalase negative, and is reduced by nitrate to generate gas. The achromobacter can achieve the efficient degradation of aniline pollutants under an aerobic condition, the maximum tolerance concentration to the aniline is up to 4,500 milligrams per liter, the aniline of which the concentration is less than or equal to 4,000 milligrams per liter can be completely removed, thus the achromobacter plays an important role in the controlling practice of aniline industrial wastewater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
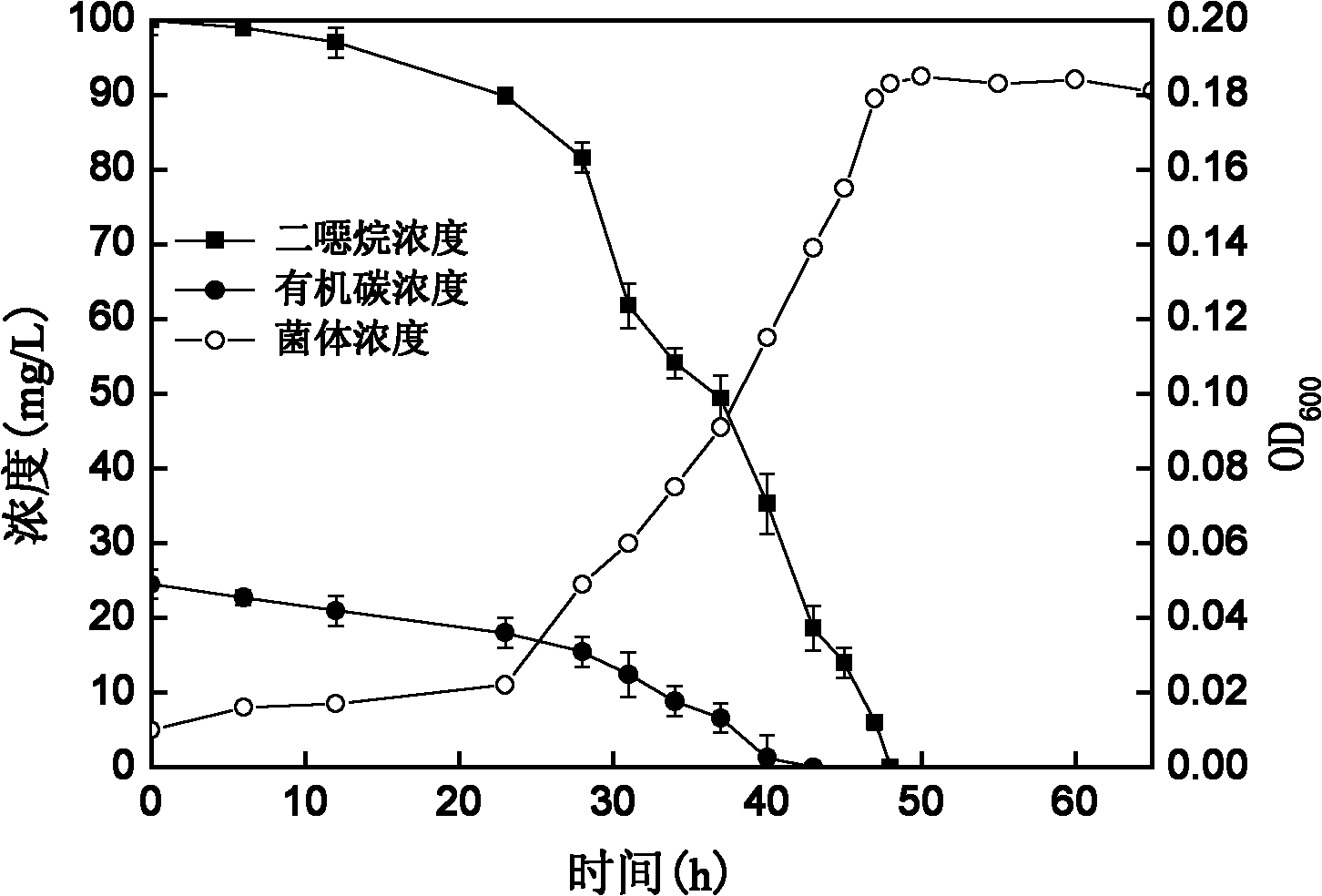
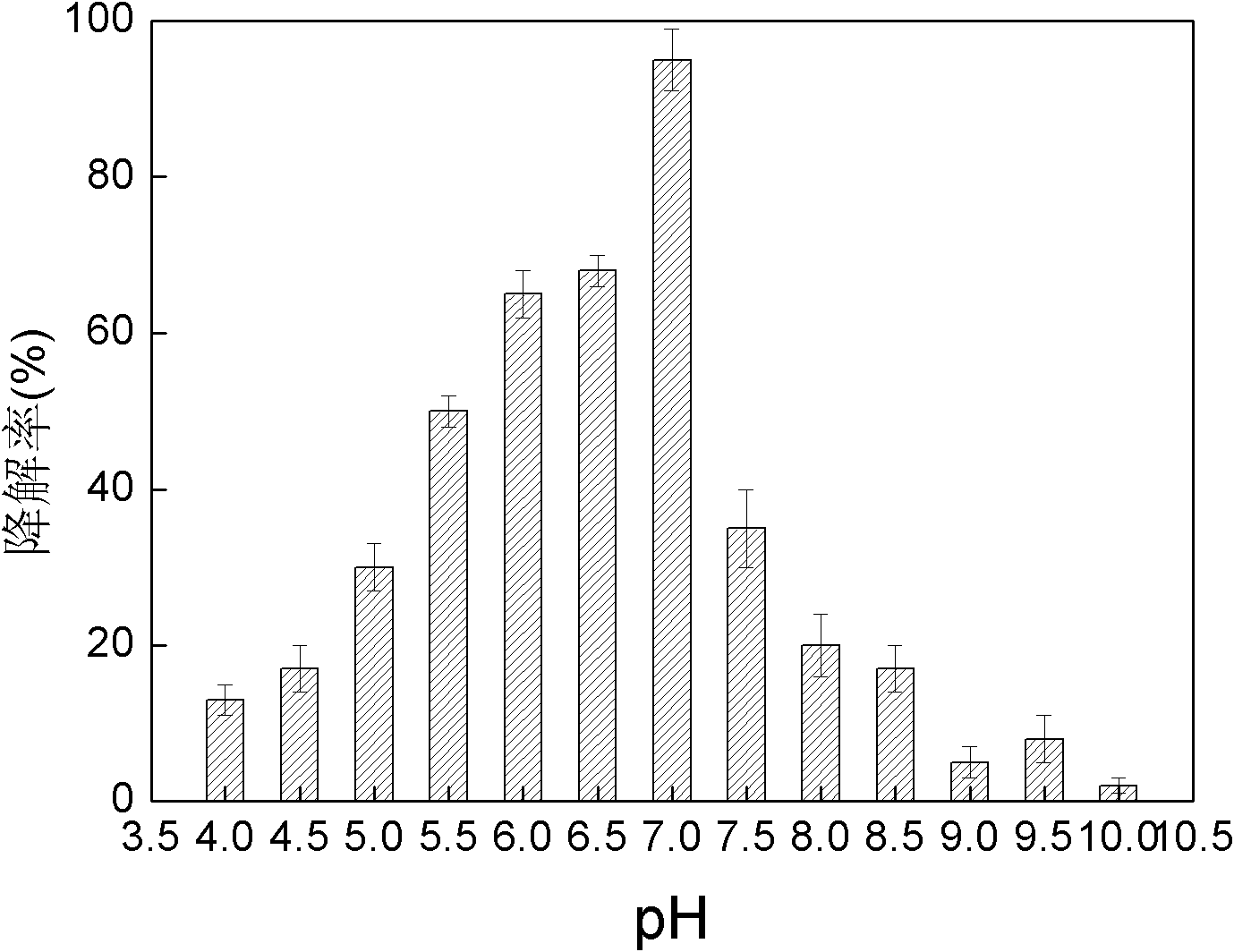
Xanthobacter sp. D7 capable of degrading dioxane and application thereof
ActiveCN102168038AEfficient degradationStable degradationBacteriaDispersed particle separationXanthobacter sp.Bioremediation
The invention provides a novel strain-xanthobacter sp. D7 capable of degrading dioxane and application thereof to the decomposing treatment of dioxane by microorganisms. The xanthobacter sp. D7 is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection, of which the address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China and the zip code is 430072, the collection date is Sept. 9th, 2010, and the collection number is CCTCC No: M2010225. The bacteria capable of degrading dioxane are aerobic non-fermented type gram negative bacteria and the diozane can be used as the unique carbon source and energy for breeding and mineralizing the substrate into carbon dioxide and water; under the condition of pure culture, the bacteria can degrade the dioxane at the pH value of between 4.0 to 10 and the temperature of between 25 and 40 DEG C; the strain has relatively high adaptive capacity to environment, can be used for biological repair of polluted environment and lays a foundation for the project of purifying wastewater and waste gas which contain the dioxane by the biological method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Shewanella and application thereof in microbiological fuel cell
InactiveCN101880638AHas electricity-generating propertiesWide salt ion concentration toleranceBacteriaCell electrodesGram stain negativeMicroorganism
The invention discloses shewanella and application thereof in a microbiological fuel cell, and relates to the technical field of biology. The shewanella is Shewanella marisflavi EP1 which is preserved in 'China Center for Type Culture Collection' in January 2009 with the preservation number of CCTCC M 209016. The shewanella is characterized in that: the shewanella is gram-negative; the thalli are rod-shaped and straight; two ends are circular; the diameter is 0.3 to 1.0 micro; the length is 2.5 to 6.0 micros; the thalli can singly exist or are arranged in pair or in a short-chain shape; and the thalli have autogenetic flagella and can move. The shewanella is separated from offshore ocean sediments, has wide salt ion concentration tolerance activity, and can generate power in electrode liquid at the concentration of up to 8 percent. Therefore, the internal resistance of the microbiological fuel cell is effectively reduced.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
Efficient phosphate-dissolving bacterium and produced bacterial agent thereof
ActiveCN103911311AEasy to useReduce production and use costsAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaBiotechnologyOxidative enzyme
The invention provides an autonomously-screened efficient phosphate-dissolving bacterium and a produced bacterial agent thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The bacterial strain of the phosphate-dissolving bacterium is named as 21-III, is identified as burkholderia sp., and is preserved in China General Microbiology Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 7873. 16SrDNA sequence of the bacterial strain is submitted to GenBank, and the registration number is JX857813. The main biological characteristics of the bacterial strain comprise that Gram staining is negative, thallus is in the shape of a rod, catalase reaction is positive, oxidase reaction is positive and methyl red reaction is negative. The bacterial agent has obvious promotion effect on dissolution rate of phosphorus in soil, and is applicable to improve soil fertility of crops and beneficial for environment protection.
Owner:河南金百合生态农业科技有限公司
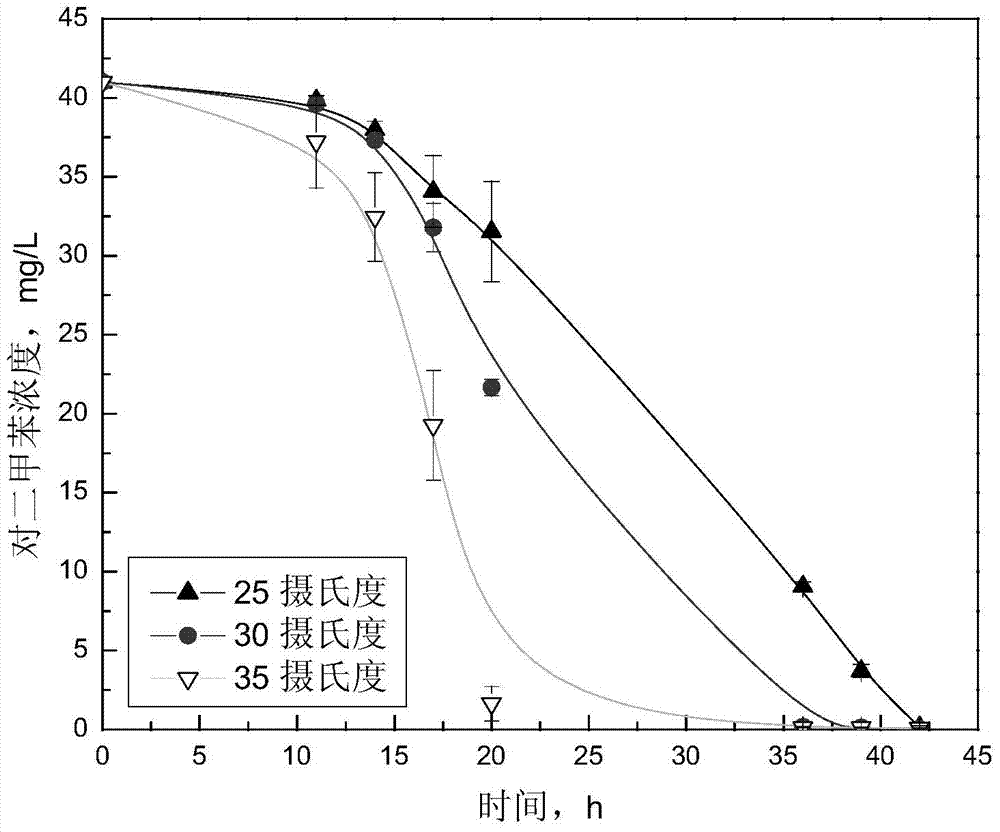
Bacterial strain for degradation of p-xylene and culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN103756928AGood substrate breadthStrong substrate adaptabilityBacteriaDispersed particle separationBacterial strainPure culture
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for degradation of p-xylene and a culture method and application thereof, the bacterial strain is named as Pandoraea sp WL1, the bacterial strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center(CGMCC), wherein the accession number is CGMCC NO.7897, and the accession date is July 8th, 2013. The bacterial strain for the degradation of the p-xylene is aerobic-type gram-negative bacteria, can grow by use of the p-xylene as a unique carbon source and energy, and can be completely mineralized into carbon dioxide and water; under the pure culture condition, the bacterial strain can degrade the p-xylene under the conditions of the temperature of 25-35 DEG C and the pH value of 4 to 8; the bacterial strain has good adaptive capacity to a substrate and the broadness to the substrate, can simultaneously degrade the p-xylene and methylbenzene. The bacterial strain lays a foundation for the industrial application of a biological method for disposing organic waste gases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
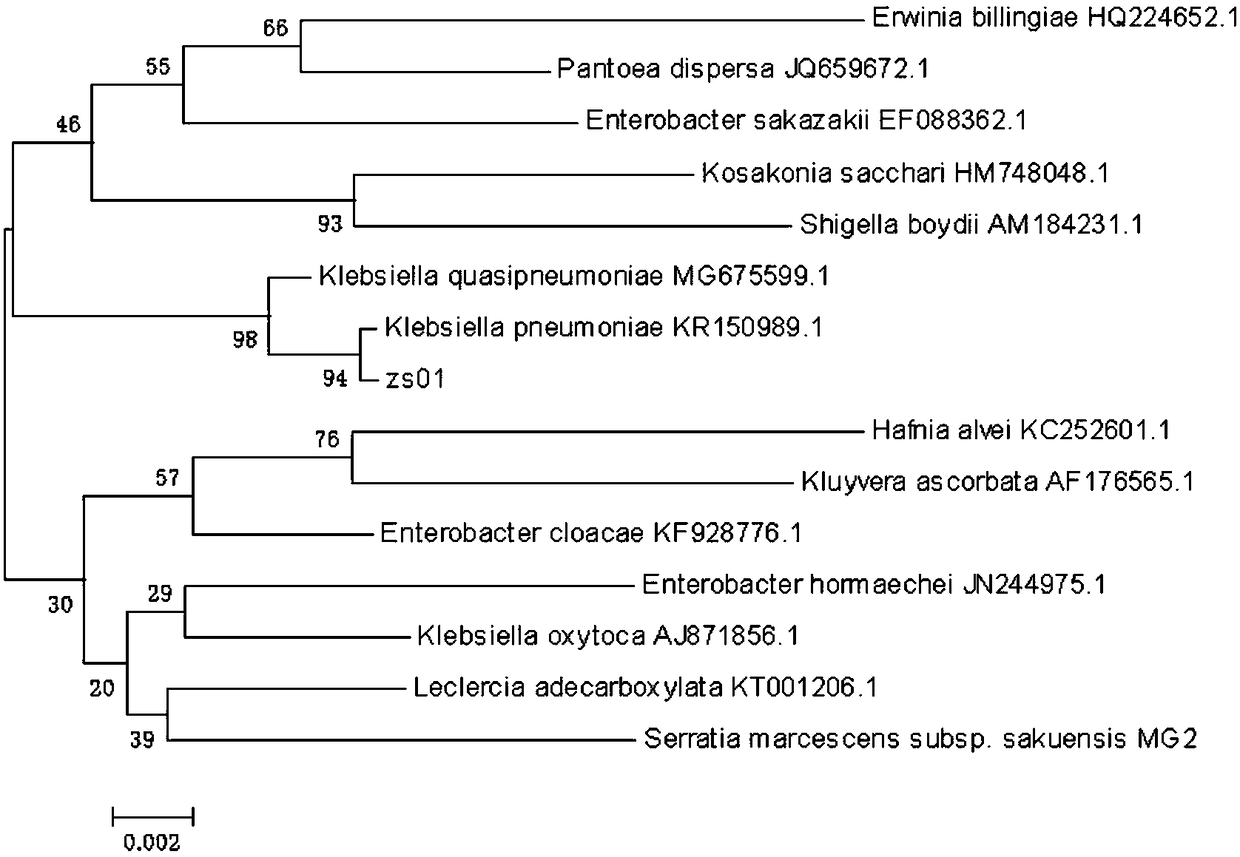
Novel klebsiella pneumoniae strain as well as isolation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109055282AHas the ability to degradeImprove toleranceBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationK pneumoniae
The invention discloses a novel klebsiella pneumoniae strain as well as an isolation method and application thereof. The novel strain is isolated and screened from activated sludge in an aeration tankof a papermaking sewage treatment plant and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection name is ZS-01, the collection number is 16041, and the collection date is June 30, 2018. The strain has the characteristics and performance as follows: (1), the characteristics are: colonies formed on a phenol MedA solid culture medium are relatively short and thickbacilli, have the sizes of (0.5-0.8)*(1-2)[mu]m, are arranged separately or in pairs, and are pale yellow, uniform in texture and opaque; relatively large gray white sticky colonies are formed on an MPYE solid culture medium, are flagella-free, have capsules, belong to enterobacteriaceae and are Gram-negative short and thick bacilli; (2), the performance is: the strain has certain phenol degradingcapability and has relatively high tolerance to phenol. The strain has the advantages as follows: the strain can degrade the phenol with relatively high concentration, and provides a new bacterial source for effectively treating phenol-containing wastewater with relatively high concentration.
Owner:XIAN LONGHUA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCO LTD
Buprofezin pesticide residual degrading bacteria and produced microbial inoculum thereof
InactiveCN101560482AWill not affect the use effectEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGram stain negativeBiological property
The invention provides a degrading residual microbial inoculum of buprofezin pesticide, belonging to the field of biological high technology. The used bacterial strain is gram staining negative bacteria BF3, and is identified as Paracoccus (Paracoccus sp.). The main biological characteristic is gram-negative and cell is clubbed. Bacterial colony is milky yellowish, round, swollen and opaque, with neat margin and smooth surface. The bacterial strain is facultative anaerobic and chemoheterotropic. The culture solution obtained by fermenting BF3 strain is the microbial inoculum. The application of degrading bacteria product can ensure that buprofezin pesticide residue quantity in soil is reduced by more than 90%, and can solve the overproof problem of buprofezin pesticide residue in agricultural production.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Peanut rhizosphere pseudomonas fluorescens and application thereof
ActiveCN109666608AHas a growth-promoting effectImprove Iron NutritionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPotassiumGrowth promoting
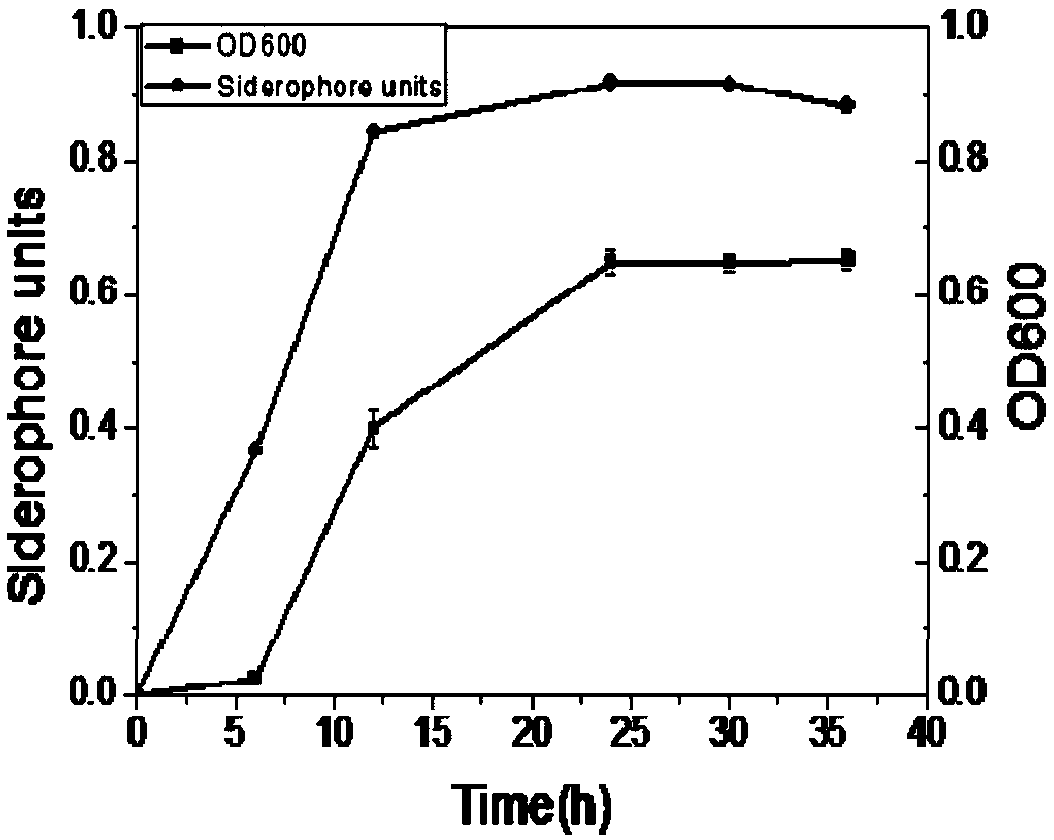
The invention discloses a peanut rhizosphere pseudomonas fluorescens and application thereof, wherein the pseudomonas fluorescens is named as 1502 IPR-01, and the preservation number is CGMCCNO. 16925. The peanut rhizosphere pseudomonas fluorescens 1502 IPR-01 is Gram-stained negative bacteria, has no spore, and has strong iron production carrier capacity; and the generated iron carrier has betteriron chelation capacity. The pseudomonas fluorescens 1502 IPR-01 and the microbial inoculum thereof have the capability of producing high-yield iron carriers, thereby improving the active iron content of new leaves of the peanuts obviously, improving the iron nutrition of the peanuts, generating auxin to promote the development of side root systems, improving the configuration of the root systems, promoting the improvement of the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium content of plants, reducing the sodium content of plants, improving the salt stress resistance, promoting the growth of peanuts obviously, improving the biomass and the yield of the peanuts and other growth promoting functions. Pseudomonas fluorescens 1502 IPR-01 of the present invention has a positive effect on plant growth promotion.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
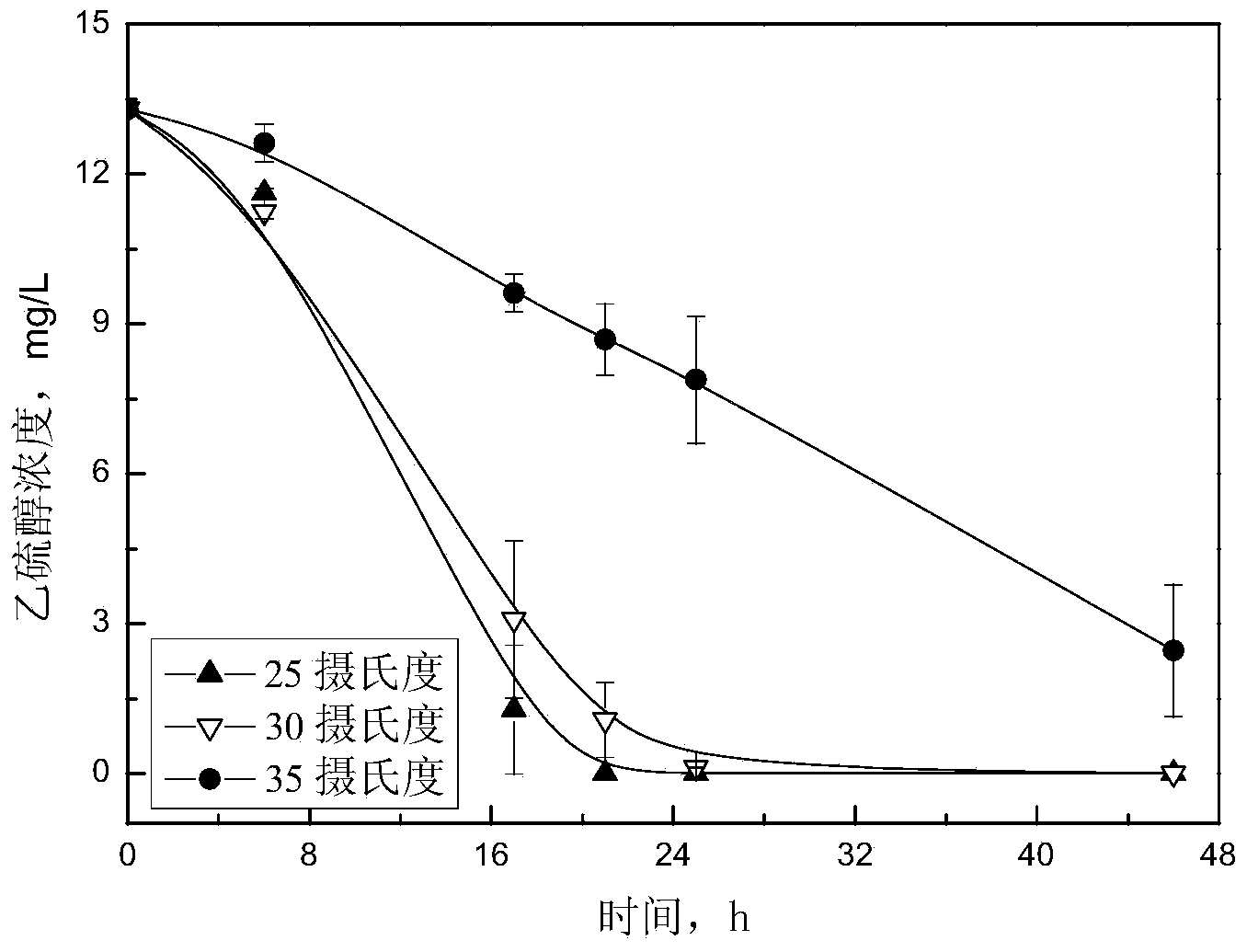
Stain for degrading ethanethiol, as well as culture method and application of strain
The invention discloses a strain for degrading ethanethiol as well as a culture method and application of the strain. The strain is named as Pseudomonas sp. WL2; the preservation number is CGMCC NO. 7898; the strain is preserved in the Common Microorganism Center of the Chinese Microorganism Strain Preservation Administration Committee(CGMCC), and the preservation date is 8th June, 2013. The strain for degrading ethanethiol is an aerobiotic Gram-negative bacterium, which can be grown by taking ethanethiol as a sole carbon source and energy, and can be thoroughly mineralized into CO2 and H2O. Under a pure culture condition, the strain is capable of degrading ethanethiol under the conditions that the temperature is 25-30 DEG C and the pH is 6-8. The strain has good substrate adaptive capacity and substrate extensiveness, and is capable of degrading propanethiol and methanol. The strain establishes the basis for industrial application in treating sulfur-containing stink organic waste gases by using a biologic method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
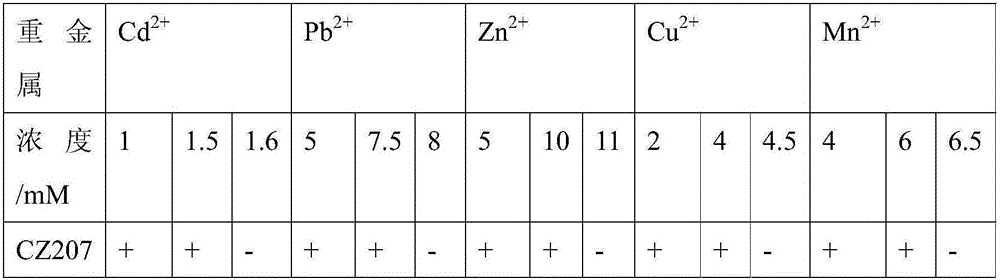
Achromobacter CZ207 strain capable of resisting heavy metal and promoting plant growth and application thereof
The invention provides an achromobacter sp CZ207 strain capable of resisting heavy metal such as cadmium, copper, lead, nickel and manganese and promoting the plant growth. The achromobacter sp CZ207 strain is preserved in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) on March 7, 2016, the address is Wuhan University, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2016091; a 16S rDNA (Ribosomal Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence of the achromobacter sp CZ207 strain is as shown in an SEQ ID NO.1. Through observation on an LB solid culture medium, bacterial colonies are light yellow, tidy and moist, and the center parts of the bacterial colonies bulge; through microscopy observation, the bacterial colonies are in gram-negative, are rod-shaped and have no spores. The achromobacter sp CZ207 strain provided by the invention can tolerate multiple heavy metals, can secrete nutrient elements such as plant growth hormone, dissolved inorganic phosphorus and solid nitrogen and has the function of promoting the plant growth.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Ralstoniasp. and application thereof in bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated saline-alkali soil
The invention discloses a Ralstoniasp. and application thereof in bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated saline-alkali soil. The Ralstoniasp. is collected by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation data is 4 November, 2009, and the preservation number is CGMCCNo.3389. The Ralstoniasp. is grown on an LB solid culture medium to form a white bacterial colony which is round and has regular edge and dry surface and is non-transparent; and the bacterial colony is in a round bar shap, dose not generate spores, is Gram-negative and has the highest growth temperature of 50 DEG C and the NaCl tolerance of 0-5%. The invention also discloses a nucleotide sequence of the Ralstoniasp. The Ralstoniasp. of the invention can degrade pollutants, such as petroleum hydrocarbon, polyaromatic hydrocarbon and the like in soil under the high salt environment; and the crude oil degradation rate can be above 60.0%. Thus, the invention can be applied in the biological control technology of soil pollution brought by polyaromatic hydrocarbon and petroleum.
Owner:BINZHOU UNIV
Salmonella abortus equi strain SMXJ-97 and application thereof in salmonella abortus equi vaccine
ActiveCN108220183AImprove securityNo danger of spreading poisonAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacteroidesMalonate
The invention relates to a Salmonella abortus equi strain SMXJ-97 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.9047. The strain has 16S rRNA gene sequences in a sequence table 1. The stain is separated from abortion sick horses in Xinjiang, the bacterium takes the shapes of a straight rod, the size is 0.7-1.6 [mu]m*2.0-5 [mu]m, and the bacterium is a negative Gram bacterium. The strain is an aerobic facultative anaerobic bacterium and can grow on a common culture medium, the growth temperature is 25-40 DEG C, the most appropriate temperature is 37 DEG C, the pH growth range is 5-9, and the most appropriate pH value is 7.4-7.6. The strain can be adopted to ferment mannitol and decompose lysine, urea cannot be decomposed with the strain, and tryptophan, malonate, saligenin and sorbitol cannot beutilized with the strain. The strain can be used for preparing salmonella abortus equi inactivation vaccines. The vaccines prepared from the strain are high in disease specificity, low in cost, highin security and good in protection effect.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Phosphate solubilizing bacterium and extraction method thereof
InactiveCN110669696AAbundant resourcesPhosphorus dissolving ability is strongBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologySucrose
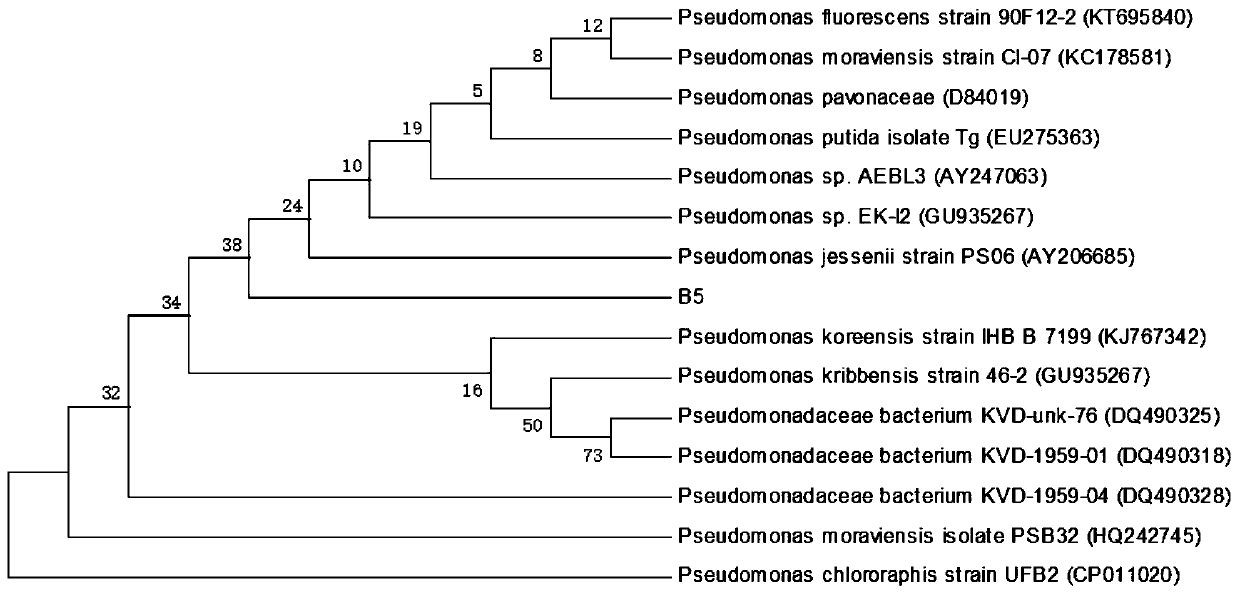
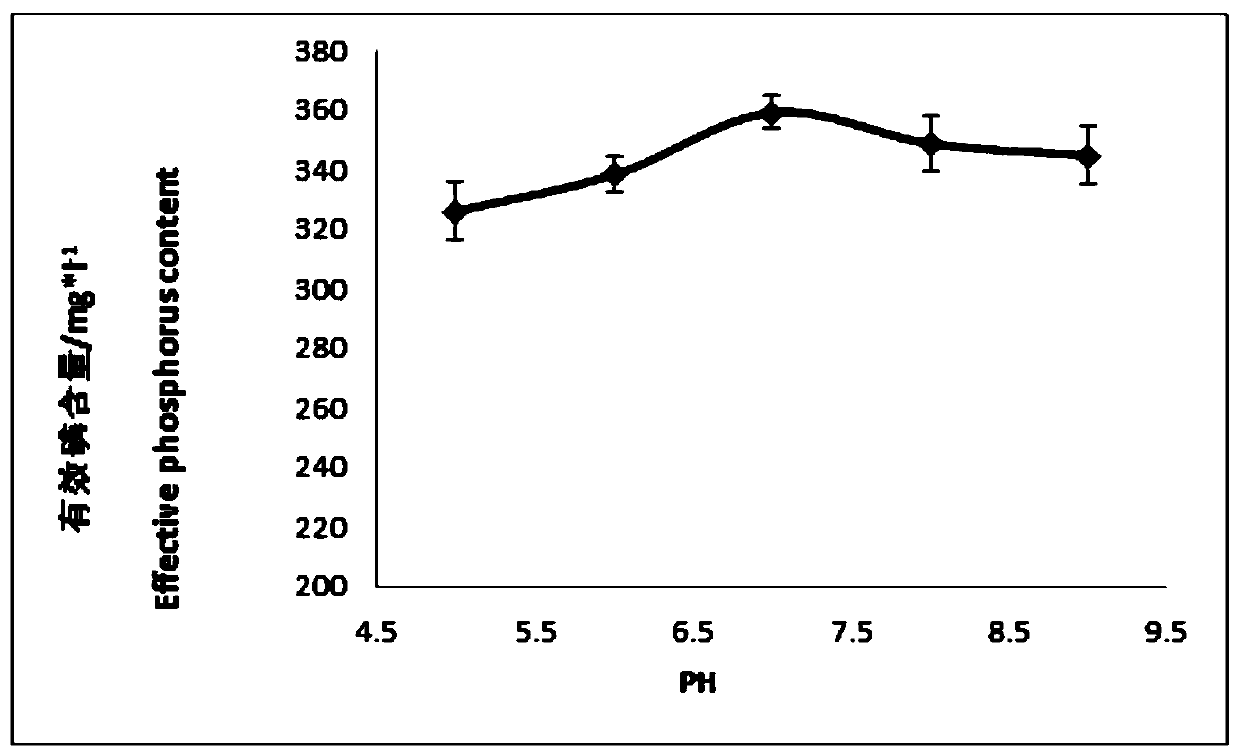
The invention discloses a phosphate solubilizing bacterium and an extraction method thereof. The phosphate solubilizing bacterium is named a strain B5, the strain B5 is a pseudomonas bacterium, determination results of biochemical criterion are gram staining is negative, a methyl red test is negative, a V-P reaction is negative, an indole test is negative, an oxidase test is negative, the strain B5 can use citrate as a carbon source to produce extracellular enzyme-gelatinase liquidation gelatin, catalase and indole are produced, and H2S is generated; the order of the phosphate solubilizing ability of the strain B5 from high to low under different carbon sources is that glucose is greater than galactose, the galactose is greater than lactose, the lactose is greater than sucrose, and the sucrose is greater than soluble phosphate starch, and the order of the phosphate solubilizing ability under different nitrogen sources is that ammonium sulfate is greater than ammonium chloride, the ammonium chloride is greater than urea, and the urea is greater than potassium nitrate; and the optimum growth temperature of the strain B5 is 28-32 DEG C, and the optimum growth pH of the strain B5 is 7-9.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
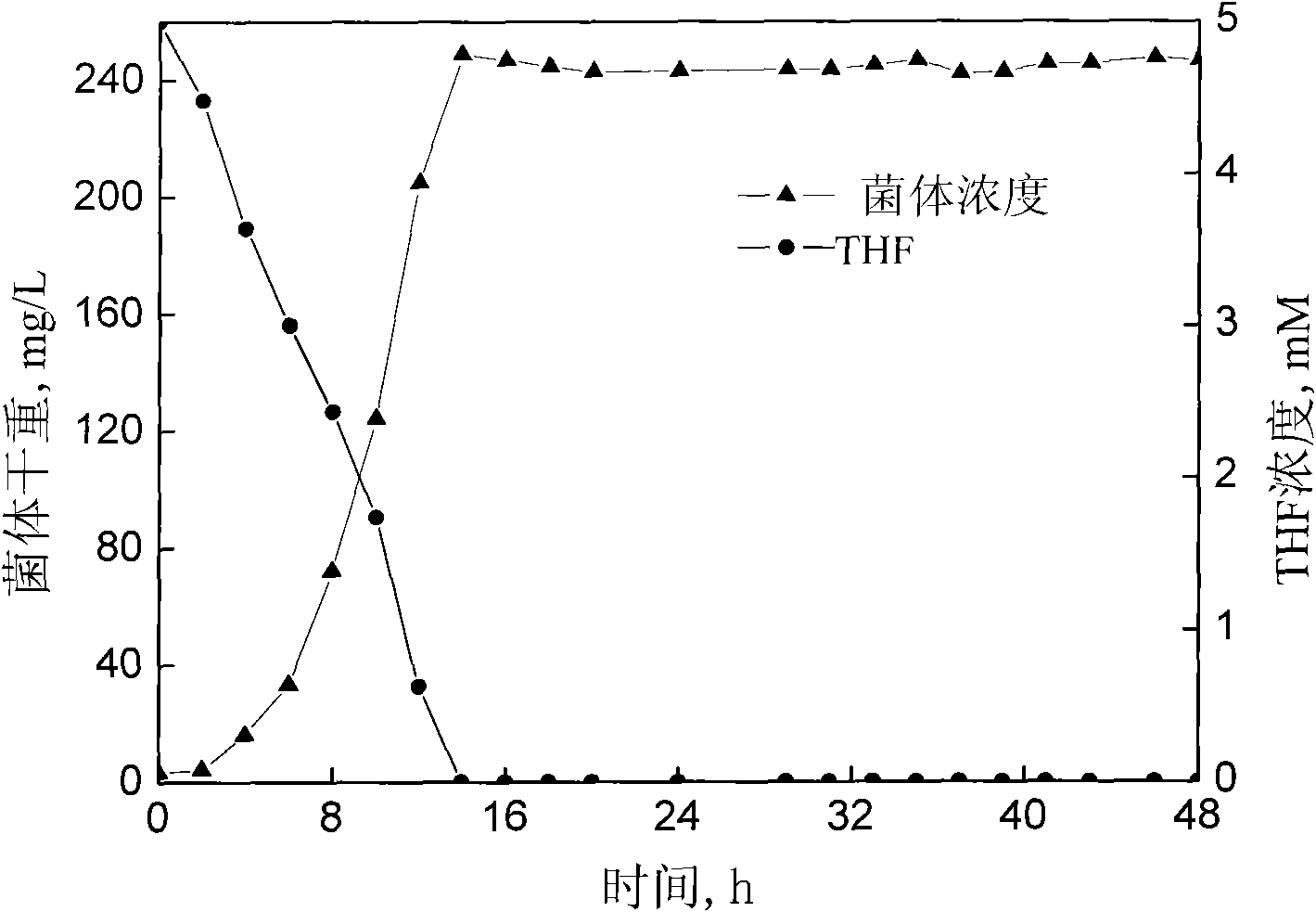
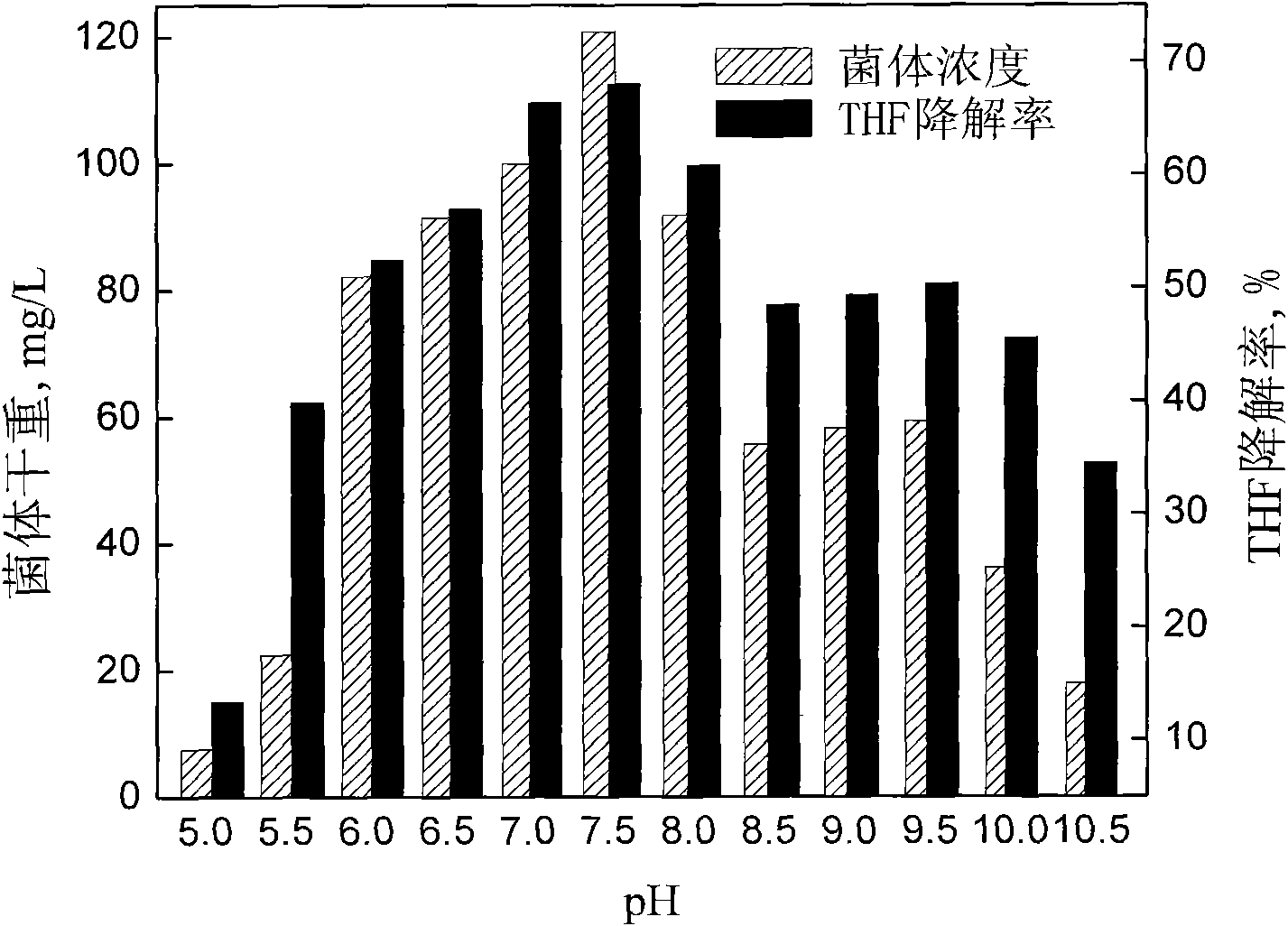
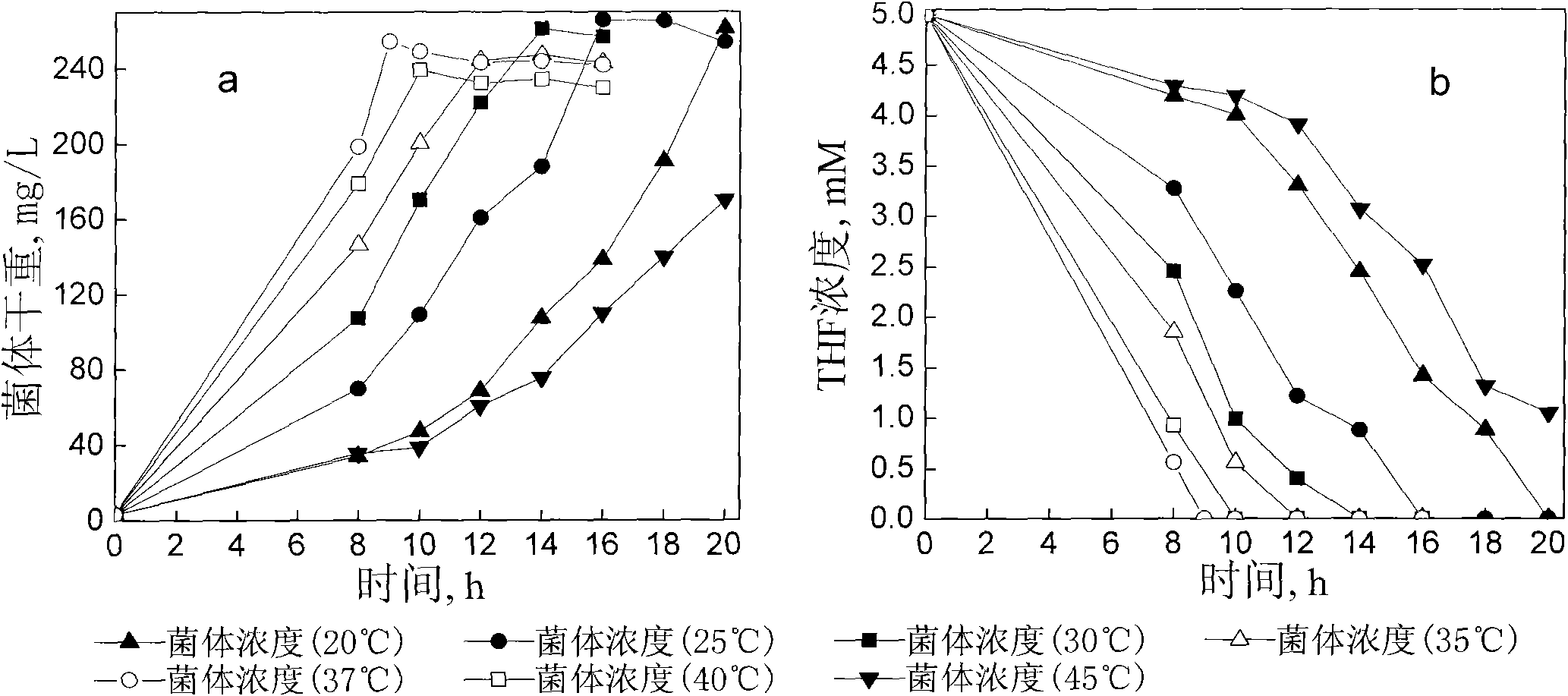
Tetrahydrofuran-degrading Pseudomonas Oleovorans DT4 and applications thereof
ActiveCN101845408AEfficient degradationTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaGram stain negativePseudomonas oleovorans
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas Oleovorans DT4 capable of degrading tetrahydrofuran effectively, which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, Address: Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 430072, Preservation Date: 07.15.2009, Preservation Number: CCTCC NO: M 209151. The tetrahydrofuran-degrading strain according to the invention, which is aerobic non-fermented Gram negative bacteria, can effectively degrade the substrate by taking tetrahydrofuran as carbon source during energy growth; the strain can degrade benzene and methylbenzene, and degrade ethylbenzene and dimethylbenzene in a manner of cometabolism; and the invention lays a foundation for application in purifying THF wastewater and waste gas containing projects by biological method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Salt-resistant Serratiasp. strain and application thereof in restoration of salinized petroleum-contaminated soil
The invention belongs to the fields of microbial application technology and biological restoration of contaminated soil, and particularly relates to a Serratiasp. strain and application thereof in the restoration of salinized petroleum-contaminated soil. The Serratiasp. strain disclosed by the invention was preserved by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on September 9th, 2011, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.5236; and the strain can efficiently degrade petroleum in a high-salt liquid environment and salinized soil. The strain is separated out from salinized petroleum-contaminated soil under salt stress conditions. The strain has regular edges, and is round in colony, non-transparent and white in color; and the thallus is a short rhabditiform and gram negativeone having a small size. The invention also discloses a nucleotide sequence of the Serratiasp. strain. The strain can degrade petroleum in a high-salt liquid environment, has a petroleum degradation rate of 60% or above in salinized soil, and has an obvious application effect in the restoration of salinized soil in the field.
Owner:BINZHOU UNIV
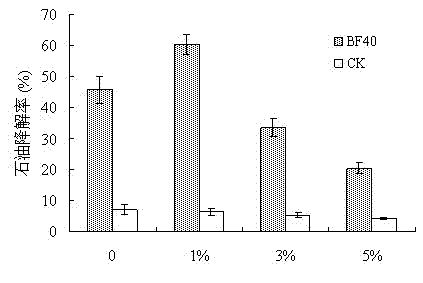
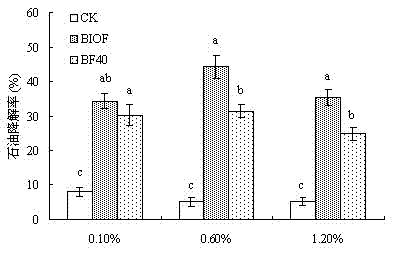
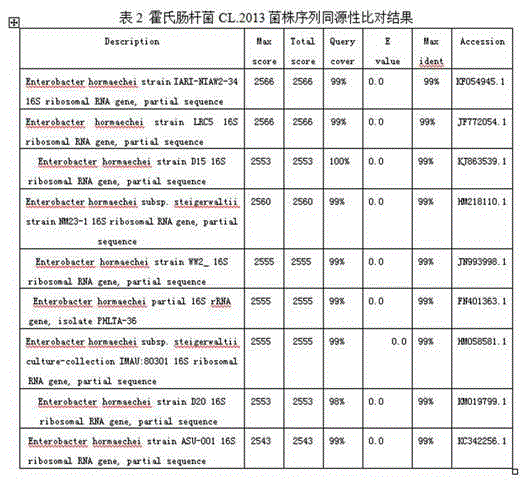
Enterobacter hormaechei CL2013 as well as method for preparing hexavalent chromium restoring bactericide
InactiveCN104928207AStrong reductionStrong reduction effect of hexavalent chromiumBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBiotechnologyGram stain negative
The invention relates to enterobacter hormaechei CL2013 separated from chromium slag storage yard soil, the strain of which is preserved on January 27, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.10451. The strain is cultured on an LB culture medium, and the cell is in a rod shape and is Gram-negative; the stain is cultured for 3 days, bacteria colony is in milky white color, the shape of the bacteria colony is circular and smooth, and the strain is determined as the enterobacter hormaechei by virtue of physiological and biochemical reaction and molecular biology. The enterobacter hormaechei CL2013 has good effect for reducing the hexavalent chromium. The invention also discloses a method for preparing hexavalent chromium repairing bactericide by utilizing the enterobacter hormaechei CL2013 strain and marigold processing waste liquid and waste slag. The method is simple, low in cost, free from secondary pollution, convenient to use and wide in market prospect.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
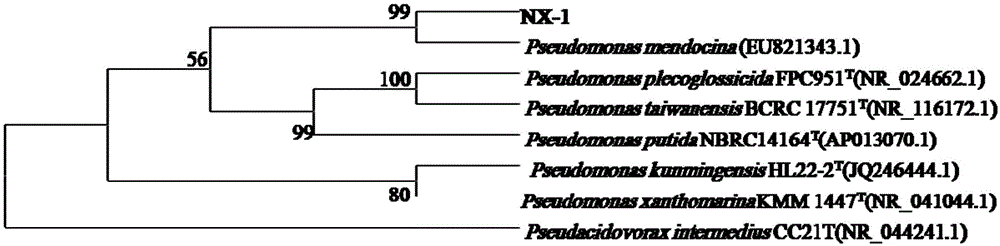
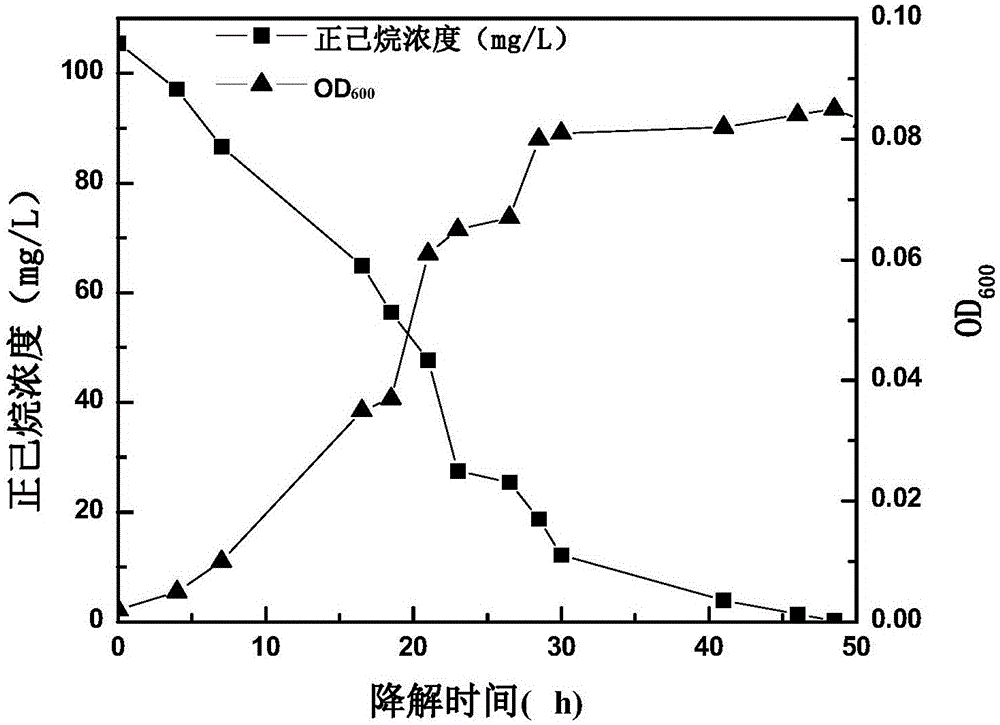
Pseudomonas mendocina NX-1 and application thereof to degradation of n-hexane
ActiveCN105087440APromote degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiologyPure culture
The invention provides a novel efficient n-hexane degrading bacterium-pseudomonas mendocina NX-1 and an application thereof to microbial degradation of n-hexane. Pseudomonas mendocina NX-1 is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan University in China, 430072, with collection date of March 15, 2015 and collection number of CCTCC NO:M2015114. The n-hexane degrading bacterium provided by the invention is an aerobic non-fermentation Gram-negative bacterium and can utilize n-hexane as an only carbon source for reproduction and completely mineralize the substrate into CO2 and H2O. Under the condition of pure culture, the bacterium can be used for degrading n-hexane in the pH value range of 4.0-10.0. The strain has stronger adaptive capacity to environment and lays the foundation for engineering application to purifying n-hexane containing wastewater and waste gases by a biological method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for extracting bacteria plasmid DNA
InactiveCN101235379AHarm reductionReduce pollutionGenetic engineeringFermentationMicroorganismGram stain negative
The invention relates to molecular biology, which particularly relates to an extracting method of bacterial plasmid DNA. The extracting method comprises the following steps: jolting and overnight culturing microbial thallus in fluid medium under the temperature which is 25 DEG C-30 DEG C, adding buffer solution in bacterial liquid which is overnight cultured, centrifuging to gather and wash to get cracking thallus, separating and purifying plasmid DNA, directly using plasmid DNA which is got in various molecular biology tests such as restriction enzyme, PCR and the like. The extracting method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation and high quality, and meanwhile, the invention is suitable for the extraction of Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria plasmid DNA, therefore, the extracting method has wide adaptability.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pantoea agglomerans and application thereof
ActiveCN105219678AGrowth inhibitionAvoid pollutionBiocideBacteriaEnterobacter agglomeransGram stain negative
The invention provides pantoea agglomerans and application thereof. A preservation number of the pantoea agglomerans is CCTCC NO: M2015563. The thallus of the pantoea agglomerans is rod-shaped and is negative when being treated by Gram staining; the pantoea agglomerans can be prepared into a liquid bacterial agent or wettable powder and is used for preventing and treating wheat scab and reducing the content of wheat gibberellin; in a process of solving toxin pollution, no toxic byproducts are generated and secondary pollution is not caused, so that the quality of agricultural products is improved and the edible safety of people and livestock is ensured.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
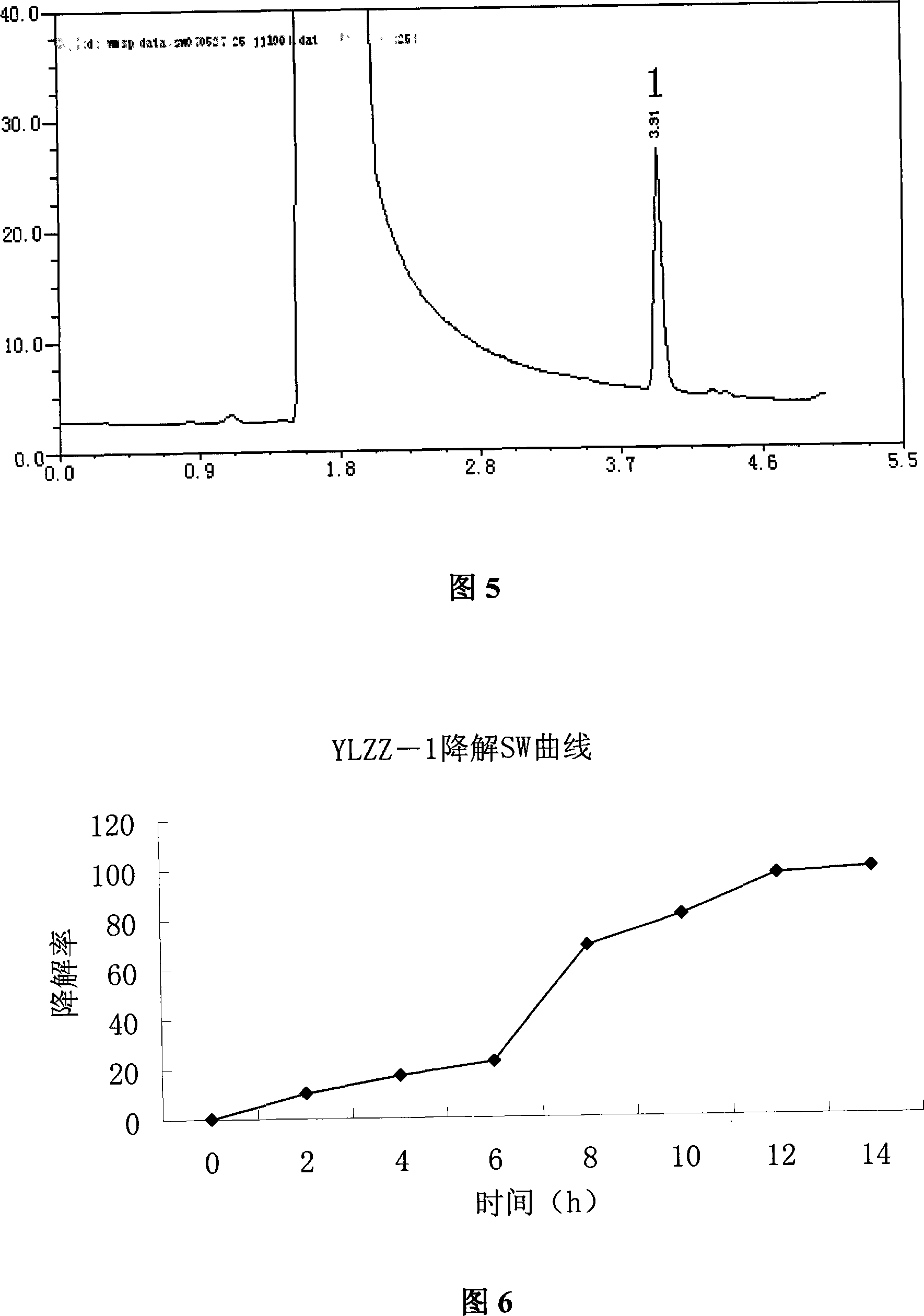
Spherosinin degradation bacterium calcium acetate fixed bacillus YLZZ-1 and method for producing the same
The invention discloses a swainsonine degradation bacteria acetic acid calcium acinetobacter YLZZ-1, which is of short rod shape, 0.2 to 0.3Mum x 0.5 to 1.0Mum, gram-negative without capsule, germ andmotion; bacterial colony is circular, ivory-white, smooth on the surface, wet, elevated and regular in edge and not transparent; bacterial strain is artificially separated and screened out from locoweed growing soil in areas such as Ganshu, Tibet, Inner Mongolia and Qinghai and is preserved at the preservation center for typical culturing in China on Jul., 20, 2007 with preservation No. of CCTCCNO: M 207108. The invention has the advantages of degrading swainsonine which is main toxin of locoweed (Swainsonine, SW).
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
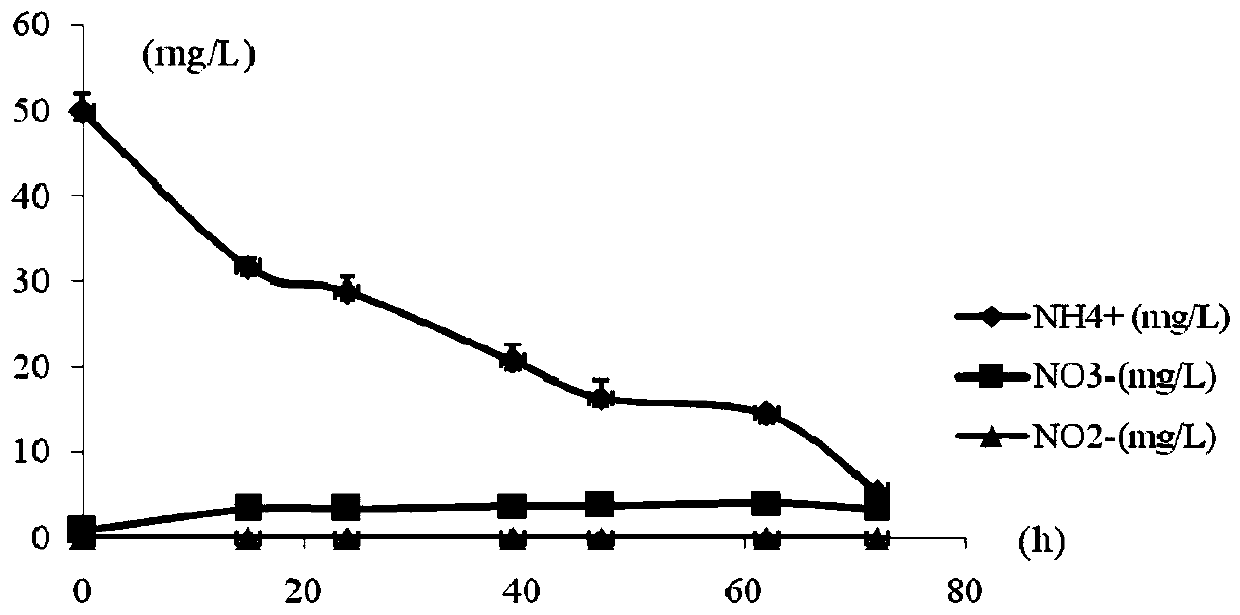
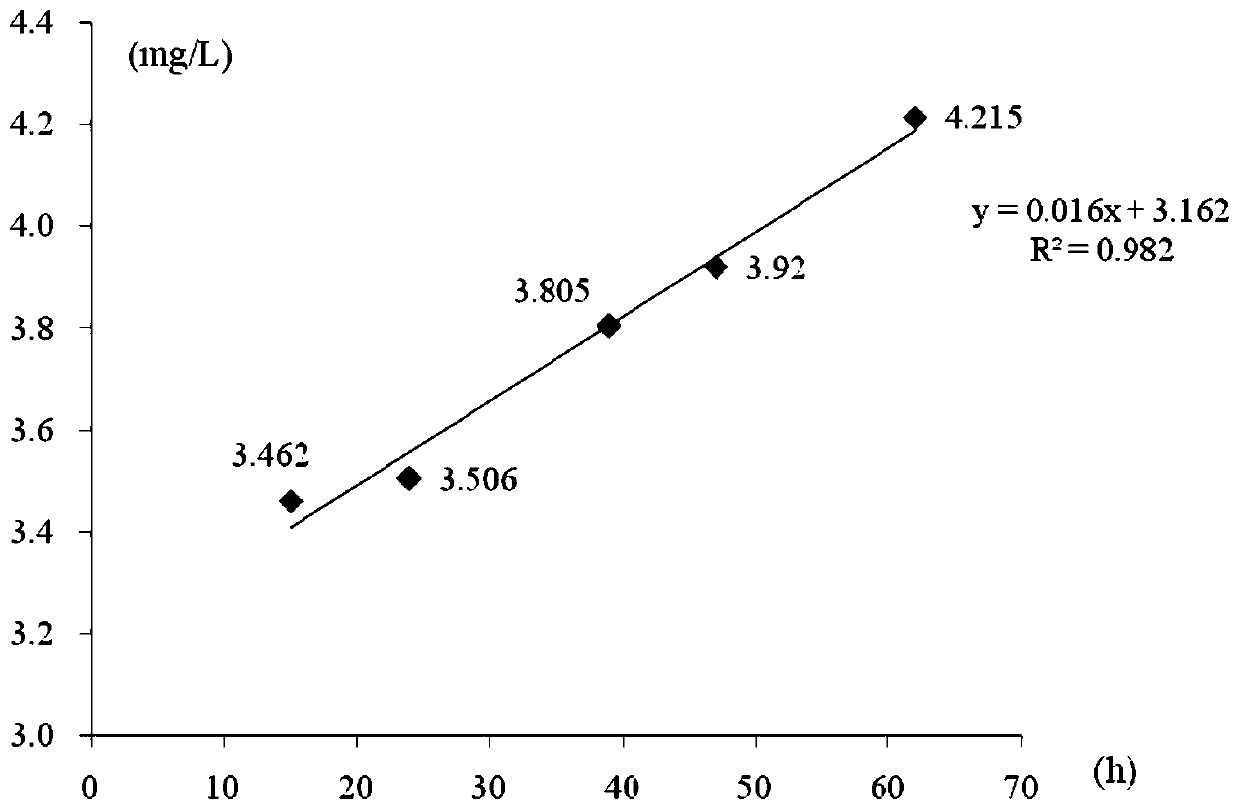
Heterotrophic ammonia oxidizing bacteria and application thereof
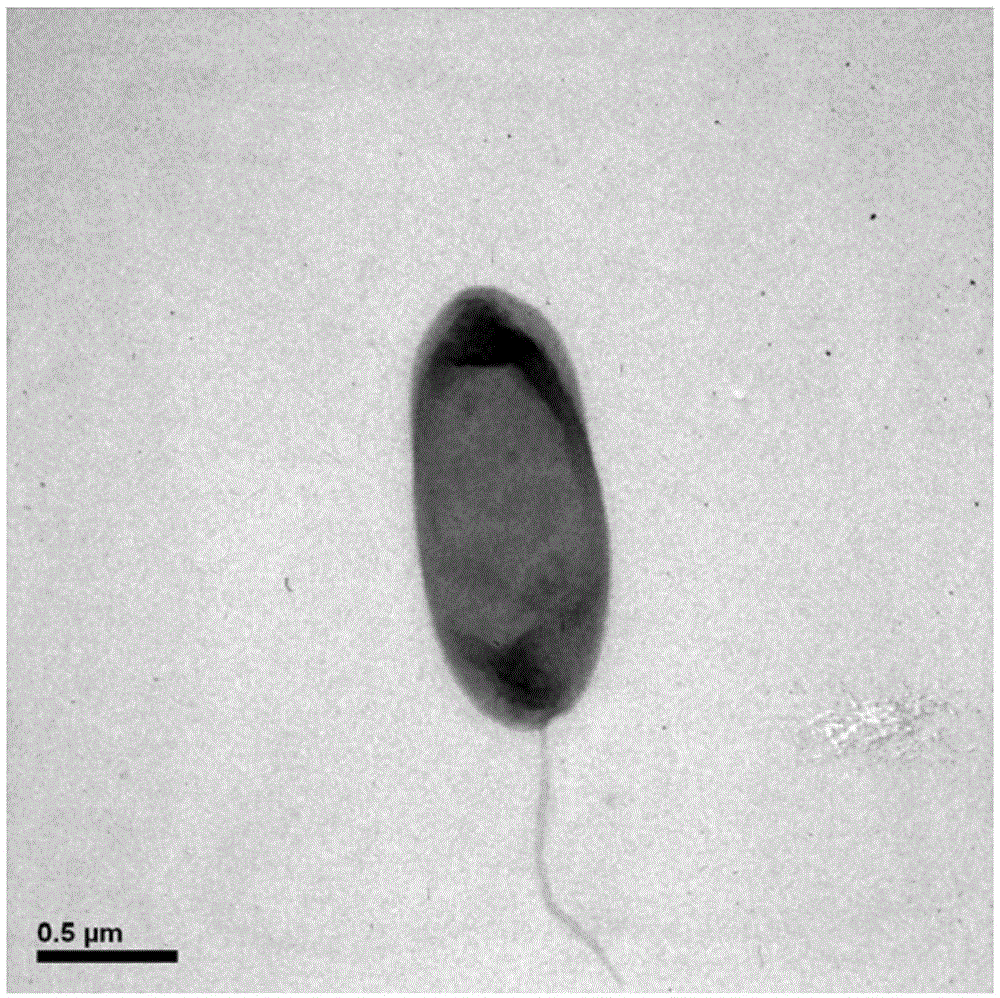
The invention discloses heterotrophic ammonia oxidizing bacteria and application thereof and relates to the technical field of biological treatment of environmental pollutants. The heterotrophic ammonia oxidizing bacteria come from penaeus vanmamei culture seawater and are obtained after artificial enrichment culture, separation and purification, which are strain MA-ZP17-13 gram-negative Halomonavenusta. Sequencing of genome of the strain MA-ZP17-13 gram-negative Halomona venusta finds that the strain contains an ammonia nitrogen oxygenase gene. The biological characteristics of the heterotrophic ammonia oxidizing bacteria are catalase and oxidase positive, obligate aerobic, rod-like strain form, milk white and opaque colonies, regular edges, surface bulge, no aureole and diameter of 1-2mm. The heterotrophic ammonia oxidizing bacteria can be applied to removal of ammonia nitrogen from salt-containing sewage.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Nicosulfuron pesticide residue degrading bacterium and inocula produced therefrom
InactiveCN101486985AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationCulture fluidPesticide residue
The invention provides a decomposing microbial inoculum that is used for eliminating nicosulfuron pesticide residue and belongs to the advanced technical field of biology. A Gram-negative bacteria strain YM3 identified as Pseudomonas sp. is used. The strain has following main biological characteristics: G, bacilliform thallus with size of (0.5-1.0) multiplied by (1.5-5.0) num, and positive in reduction reaction of catalase and nitrate; negative in oxidase and V.P. reaction and methyl red and indole reaction; non-hydrolysis of starch and isinglass, and non-utilization of citrate. A culture fluid that is obtained after fermentation of the YM3 strain is the microbial inoculum. By applying the product of the decomposing microbial inoculum, the residue amount of the nicosulfuron pesticide in soil can be lowered by over 72 percent, thus solving the problem of overproof nicosulfuron pesticide residue in agricultural industry.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
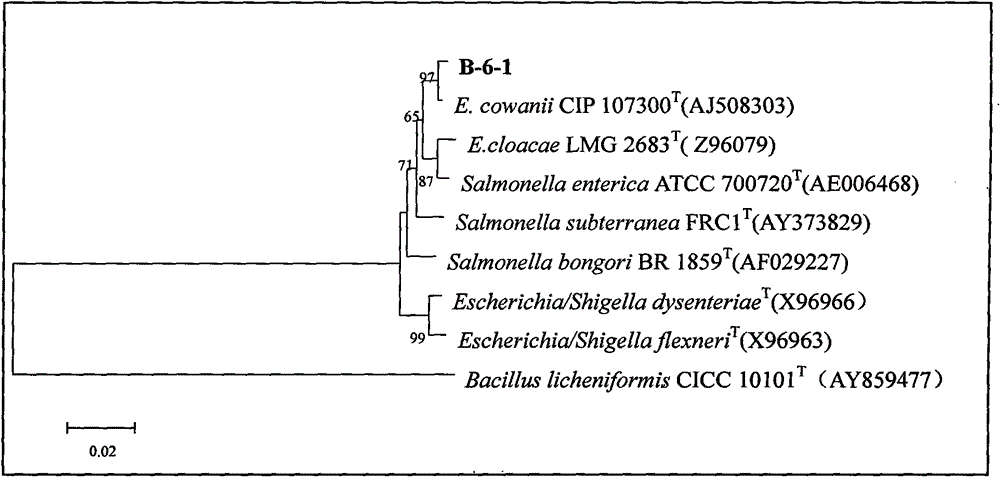
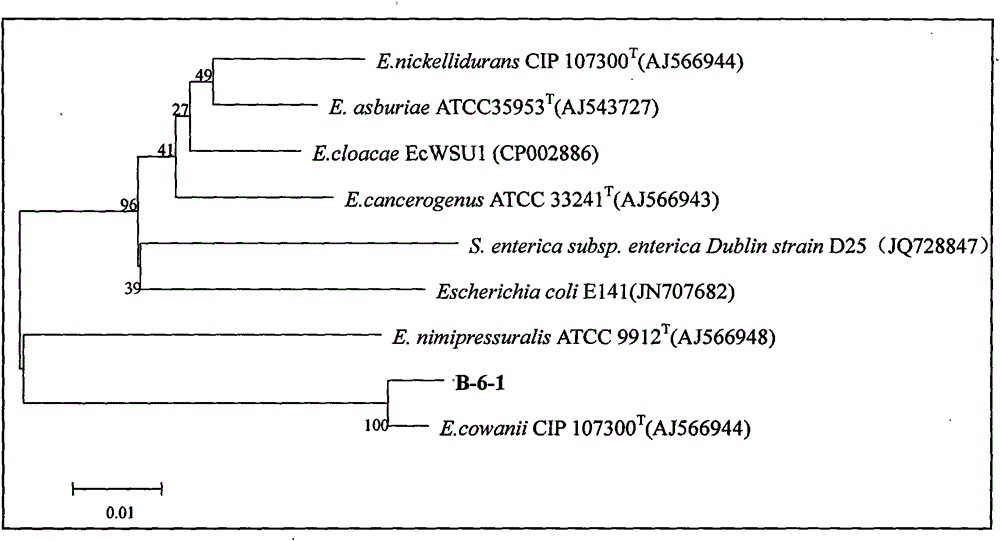
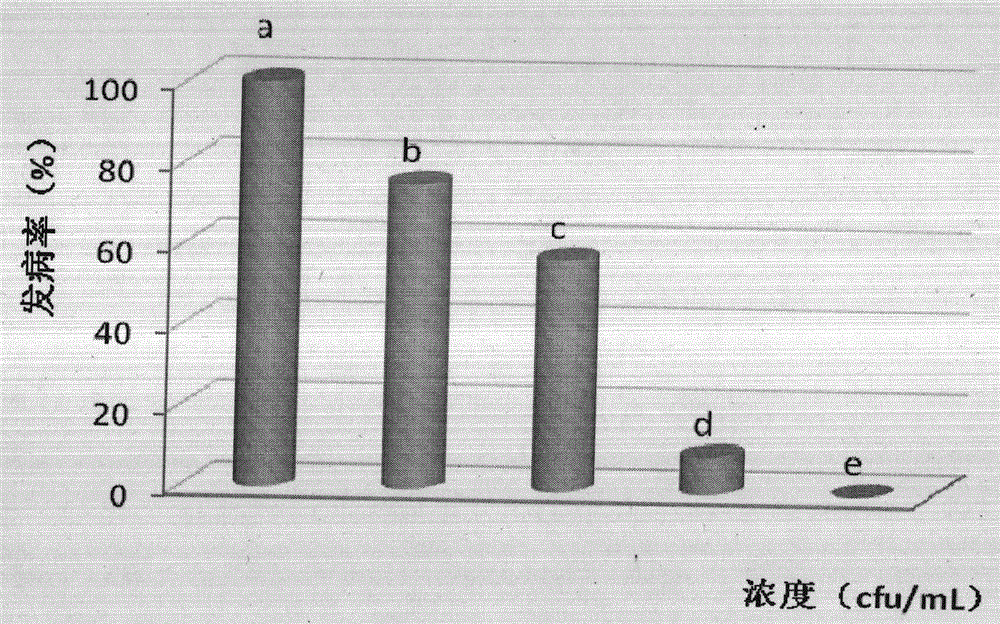
Biological antagonistic bacterial strain for controlling postharvest disease of fruit and vegetable, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103952327AStrong disease resistanceImprove disease resistanceFruit and vegetables preservationBacteriaBacterial strainPlant disease
Belonging to the field of microorganisms and biological control, the invention relates to a biological antagonistic bacterium, and a preparation method and application thereof. The bacterial strain is named as Enterobacter cowanii B-6-1, and belongs to Enterobacter Enterobacteriaceae. The main morphological characteristics include rod shape, short rod-like shape, length of 0.8-1.2 mum, width of 1-1.6 mum, Gram-negative bacterium, white colonies, smooth surface, and good growth at room temperature. The bacterial strain provided by the invention has excellent disease resistance performance, and the best formula comprising antagonistic bacterium liquid with concentration more than 1*10<8> cfu / mL and additional 50 m mol / L Na2SiO3 achieves the best disease resistance effect; therefore, the invention has great value to the development of fruit and vegetable farming.
Owner:FARM PROD STORAGE & FRESHENING INST SHANXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacterium and culturing, screening and applying method thereof
The invention provides a petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacterium and a culturing, screening and applying method thereof, and relates to a marine petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacterium. The petroleum hydrocarbon degradation strain is Martelella mediterranea( Martelella mediterranea ) MM-45, the Martelella mediterranea is a bacterial strain belonging to Martelella, showing negative of Gram's staining, the biological characteristics are a non-fermentation type, the Martelella mediterranea is obligate aerobic, the shape of the strain is non spore bearing, colonies are in the shape of a circle, yellow and opaque, the surface is smooth and moistening, the edges are regular, haloes do not exist, centers are in protrusion and the diameter is 2-3mm. The petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacterium can be applied to degradation organic compounds. Through identification, the 16S rDNA gene order of the Martelella mediterranea is a type strain Martelella mediterranea DSM 17316, and the similarity is 99.61%.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES +1
Styrene-degrading bacteria MJ001 and separating method thereof
InactiveCN101638630ALarge biomassPromote growthBacteriaWater contaminantsActivated sludgeIndustrial waste water
Owner:天津市天人合环保技术研发中心
2,4-dichlorobenzene oxygen butyl acetate pesticide residue degradation bacterium and produced bacterium agent thereof
InactiveCN101402927AWill not affect the use effectEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPesticide residueOxygen
The invention provides a degradation bacterium which can degrade butyl 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetate pesticide residue and a microbial inoculum produced by the degradation bacterium, pertaining to the high biotechnology field, wherein, the applied strains are Gram-stain negative bacteria Ld1 which are identified as Pseudomonas sp.; the degradation bacterium is mainly and biologically characterized in that: the main biological characteristic is G<->; thallus takes the shape of short rods, and the size of the thallus is about 0.5 Mum to 1.0 Mum multiplied by 1.5 Mum to 5.0 Mum; oxidase, catalase, nitrate reduction and citrate utilization reactions are positive; lipase reactions, V.P. reactions, MR reactions, indophenol reactions are negative; and starch can not be hydrolyzed. The microbial inoculum is obtained after the completion of the fermentation of the Ld1 strains. The application of the degradation bacterium products can reduce the residual quantity of butyl 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetate pesticides by more than 70 percent and can solve the problem that butyl 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetate pesticide residue in the agricultural production exceeds the standard.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacterium strain of reducing trivalence ferric and application thereof
The invention discloses reducing ferric iron bacteria strain and its using. It belongs to klebsiella trevisan sp. It is baculiform, single, pairs or short chain arrangement, non spore, and capsule. Gram staining is negative. Concurrently character does not like oxygen. Ferric iron is the final electron acceptor. The invention regenerates Fe(II)EDTA solution by biology method. In NOx complexation absorption process, part of the Fe(II)EDTA is oxidized to Fe(III)EDTA. And the Fe(III)EDTA is reduced to Fe(II)EDTA to regenerate to realize the cyclic utilization of the complexation absorption process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com