Patents
Literature
606 results about "Pseudomonas fluorescens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pseudomonas fluorescens is a common Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It belongs to the Pseudomonas genus; 16S rRNA analysis has placed P. fluorescens in the P. fluorescens group within the genus, to which it lends its name.
rPA optimization
An optimized synthetic polynucleotide encoding a Bacillus anthracis protective antigen and an anthrax vaccine based on the encoded protective antigen. Furthermore, heterologous expression in a host Pseudomonas fluorescens bacteria of an optimized polynucleotide sequence encoding a Bacillus anthracis protective antigen.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Methods for production of plants resistant to HPPD herbicides
Methods for making transgenic plants that are resistant to HPPD herbicides are presented. Polynucleotides other than those from Pseudomonas fluorescens that encode resistant HPPD enzymes are enclosed for use in the process of making transgenic plants that are tolerant to HPPD-inhibiting herbicides.
Owner:SYNGENTA LTD
Bacteria-based and enzyme-based mechanisms and products for viscosity reduction breaking of viscoelastic fluids
ActiveUS7052901B2Low viscosityBreak viscosityDeodrantsFlushingIndirect actionPseudomonas fluorescens
It has been discovered that fluids viscosified with viscoelastic surfactants (VESs) may have their viscosities reduced (gels broken) by the direct or indirect action of a biochemical agent, such as bacteria, fungi, and / or enzymes. The biochemical agent may directly attack the VES itself, or some other component in the fluid that produces a by-product that then causes viscosity reduction. The biochemical agent may disaggregate or otherwise attack the micellar structure of the VES-gelled fluid. The biochemical agent may produce an enzyme that reduces viscosity by one of these mechanisms. A single biochemical agent may operate simultaneously by two different mechanisms, such as by degrading the VES directly, as well as another component, such as a glycol, the latter mechanism in turn producing a by-product (e.g. an alcohol) that causes viscosity reduction. Alternatively, two or more different biochemical agents may be used simultaneously. In a specific, non-limiting instance, a brine fluid gelled with an amine oxide surfactant can have its viscosity broken with bacteria such as Enterobacter cloacae, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and the like.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Compound microbial agent for degrading antibiotic and pesticide residues as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN106434430AEliminate pollutionAchieve biodegradableFungiBacteriaEcological environmentBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to a compound microbial agent for degrading antibiotic and pesticide residues as well as preparation and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology and environmental protection. Multi-thallus compound microbial powder is prepared from the compound microbial agent according to the weight percentage of living microbes to the total amount of compound microbial powder as follows: 10%-15% of bacillus subtilis, 10%-15% of aspergillus niger, 10%-15% of bacillus mucilaginosus, 10%-15% of enterococcus faecalis, 8%-12% of bacillus licheniformis, 8%-12% of bacillus megaterium, 8%-12% of pseudomonas fluorescens, 5%-8% of lactobacillus plantarum, 5%-8% of bacillus polymyxin and 6%-8% of streptococcus thermophiles. The compound microbial agent has the effects of degrading antibiotic and pesticide residues, fermenting and composting organic matter, acting as functional fertilizer and repairing the environment, and can solve the problems of secondary pollution caused by antibiotic residues in culture feces and resource utilization of organic waste and realizes biodegradation of the antibiotic and pesticide residues in soil when applied to the agricultural ecological environment, thereby being of great value and practical significance in restoration of agricultural ecological environment and protection of human health.
Owner:中山市润泽生物科技有限公司
Expression of mammalian proteins in Pseudomonas fluorescens
The invention is a process for improved production of a recombinant mammalian protein by expression in a Pseudomonad, particularly in a Pseudomonas fluorescens organism. The process improves production of mammalian proteins, particularly human or human-derived proteins, over known expression systems such as E. coli in comparable circumstances Processes for improved production of isolated mammalian, particularly human, proteins are provided.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Bacterial preparation for degrading petroleum and restoring petroleum polluted soil ecology and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101603018ALarge specific surface areaRestoration of polluted soil ecologyFungiBacteriaColony numberBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to a bacterial preparation for degrading petroleum and restoring petroleum polluted soil ecology and a preparation method thereof. The bacterial preparation for degrading the petroleum and restoring the petroleum polluted soil ecology is a composite colony consisting of bacillus megaterium, pseudomonas fluorescens, streptococcus faecalis and candida tropicalis through optimized combination, wherein the matching ratio of the components is 1-2:1:1:0.5-1. The bacterial preparation has the advantage that the bacterial preparation can quickly form a micro-ecological advantage colony after the bacterial preparation is applied to the soil. If 2 to 5 percent of the bacterial preparation is added relative to the weight of surface soil (a cultivation layer of about 15 to 20 centimeters), the oil removal rate in three months is more than or equal to 75 percent (dichloromethane reflux extraction and gravimetric method), and the bacterial preparation has high effective colony number and strong adaptability and has remarkable effect of restoring the petroleum polluted soil ecological environment.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Expression of mammalian proteins in Pseudomonas fluorescens
The invention is a process for improved production of a recombinant mammalian protein by expression in a Pseudomonad, particularly in a Pseudomonas fluorescens organism. The process improves production of mammalian proteins, particularly human or human-derived proteins, over known expression systems such as E. coli in comparable circumstances Processes for improved production of isolated mammalian, particularly human, proteins are provided.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Compound bacterium for preventing and treating root-knot nematode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104357358AInhibition of reproductionReduce usageBiocideFungiAureobasidium sp.Paecilomyces lilacinus
The invention discloses a compound bacterium for preventing and treating root-knot nematode and a preparation method thereof. The compound bacterium for preventing and treating root-knot nematode is prepared by the following steps: carrying out high-density cultivation on raw material strains of bacillus thuringiensis, pseudomonas fluorescens, bacillus subtilis, streptomycete, aspergillus niger, paecilomyces lilacinus and fusarium oxysporum, inoculating activated and cultivated strains in a fermentation tank and implementing fermentation and extended cultivation; dehydrating and drying various single strains obtained from extended cultivation to obtain resting microorganism dry powder; and mixing 10-20 parts of bacillus thuringiensis, 5-10 parts of pseudomonas fluorescens, 10-20 parts of bacillus subtilis, 10-20 parts of streptomycete, 10-15 parts of aspergillus niger, 10-25 parts of paecilomyces lilacinus and 8-15 parts of fusarium oxysporum to obtain the compound bacterium for preventing and treating root-knot nematode. The compound bacterium disclosed by the invention is used for preventing and treating root-knot nematode; and compared with an existing product, the compound bacterium is environment-friendly, harmless and non-toxic to a human body and good in control efficiency.
Owner:SHANDONG SUKAHAN BIO TECH
Composite bacterial preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102199562AImprove decomposition abilityPromote degradationBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyDecomposition
The invention discloses a composite bacterial preparation as well as a preparation method and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of agricultural biochemistry. The composite bacterial preparation comprises the following components in parts by volume: 10-40 parts of brevibacillus brives fermentation bacterial liquid, 10-40 parts of pseudomonas fluorescens fermentation bacterial liquid and 15-45 parts of sugarcane thermophilic actinomyces, wherein the bacterial count in each mol of fermentation liquid is 0.4-0.7 billion. The strains of brevibacillus brives, pseudomonas fluorescens and sugarcane thermophilic actinomyce are separated from rabbit dung and fungi residues; and fermentation bacterial liquids of the separated strains are mixed according to a proper proportion to form the composite bacterial preparation. The composite bacterial preparation disclosed by the invention can be used for accelerating the degradation of organic materials and reducing the conversion of organic nitrogen into gaseous nitrogen, so that the composite bacterial preparation can present stronger ammonia-suppressing and decomposing capabilities in the fermentation process of pig manurecompost; and a smaller amount of ammonia gas is released while thorough decomposition of pig manure is accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method of reducing nitrosamines content in tobacco leaves
ActiveUS7556046B2Reduce contentTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentMicroorganismSphingomonas paucimobilis
A method of reducing the content of TSNA in tobacco leaves, comprising treating tobacco leaves with a microorganism which has the capability to reduce TSNA and which is selected from the group consisting of Sphingomonas paucimobilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Composite microbial preparation for methane tank and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101372666AGood repeatabilityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiogasPseudomonas fluorescens
The invention relates to a composite microbial inoculum used in a biogas generating pit, which consists of four kinds of microbial fermentation liquor, namely, 0.06-0.15 part of pseudomonas fluorescens solution, 0.04-0.08 part of waxen bacillus solution, 0.06-0.10 part of bacillus subtillis solution and 0.05-0.08 part of bacillus circulans solution, which are mixed in proportion. The composite microbial inoculum can promote the biogas generating pit to generate biogas normally in winter and can prepare the biogas by taking straws as main raw material.
Owner:INST OF SOIL & FERTILIZER SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Dedicated composite bacterial fertilizer for saline-alkali soil and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104609992ALower pHReduce salt contentOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesBacillus thuringiensisAlkali soil
The invention relates to a dedicated composite bacterial fertilizer for saline-alkali soil and a preparation method of the composite bacterial fertilizer, and belongs to the technical field of composite bacterial fertilizers. The composite bacterial fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 10-20% of a phosphate-solubilizing potassium-solubilizing composite bacterial inoculant, 40-60% of kitchen waste, and 30-40% of diatomite, wherein the phosphate-solubilizing potassium-solubilizing composite bacterial inoculant is prepared by the following steps: respectively culturing and centrifuging bacillus megatherium, bacillus thuringiensis, pseudomonas fluorescens, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, bacillus mucilaginosus and azotobacter chroococcum, performing freeze drying on the centrifuged bacteria, drying, and performing balanced mix on the dried bacteria; the kitchen waste is prepared by the following steps: sorting the kitchen waste, removing impurities, dehydrating and removing oil from the kitchen waste, then crushing the kitchen waste, adding the composite bacterial inoculant and a mixed enzyme preparation, and at last performing aerobiotic solid state fermentation. The composite bacterial fertilizer is prepared by recycling the wastes such as the kitchen waste and the waste diatomite, so that the saline-alkali soil can be improved fundamentally.
Owner:天津北洋百川生物技术有限公司
Control of phytopathogenic microorganisms with pseudomonas sp. and substances and compositions derived therefrom
Provided are compounds and compositions derived from Pseudomonas sp., particularly, Pseudomonas fluorescens or Pseudomonas protegens and more particularly strain having the identifying characteristics of Pseudomonas ATCC 55799 having antimicrobial properties and particularly, antibacterial properties.
Owner:MARRONE BIO INNOVATIONS
Method for recovering cadmium polluted soil by combining compound microorganism bacterium agent with houttuynia cordata
InactiveCN103071672AImprove the effect of bioremediationImprove repair effectContaminated soil reclamationHouttuyniaCombined method
The invention discloses a method for recovering cadmium polluted soil by combining a compound microorganism bacterium agent with houttuynia cordata. The compound microorganism bacterium agent comprises the following components by count: 1*10<9>-9*10<9>CFU (colony forming unit) / m<3> pseudomonas fluorescens, 1*10<8>-6*10<8>CFU / m<3> actinomyces ruminicola, and 1*10<9>-9*10<9>CFU / m<3> glomus mosseae. The method for recovering the soil comprises the following steps that the houttuynia cordata is planted in cadmium soil and the compound microorganism bacterium agent is inoculated into the soil, or the houttuynia cordata is soaked in the compound microorganism bacterium agent and then planted into the cadmium soil; when branches and leaves of the houttuynia cordata are luxuriant, the branches and the leaves of the houttuynia cordata are harvested; and cadmium in the soil can be removed. The compound microorganism bacterium agent can better improve the tolerance of the houttuynia cordata, promote growth of a plant in the high-cadmium-content soil, improve the absorbility of the plant to cadmium, and enhance a soil heavy metal removal effect. The method for recovering the soil is a safe, environment-friendly, high-efficiency, economical and practical plant-microorganism combined method for recovering the heavy metal polluted soil, and has a significant application value.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Strong promoter and plasmid vector containing strong promoter and application of strong promoter and plasmid vector
According to the invention, through amplifying a strong promoter in Ensifer adhaerens and carrying out bioinformatics analysis and functional verification, a strong promoter is obtained, and the strong promoter can be widely used for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum, Ensifer adhaerens and other alpha-proteobacteria and has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using the strong promoter, and an application of the corresponding strain and ahost cell in starting expression of a target gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Complex endophytic bacterial inoculant and application thereof in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN105950502AOvercoming Weaknesses of RepairImprove repair efficiencyBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacteroidesSedum alfredii
The invention discloses a complex endophytic bacterial inoculant and an application thereof in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. The complex inoculant is composed of acinetobactercalcoaceticus, pseudomonas fluorescens, bacillusmegaterium, stenotrophomonasmaltophilia, bacillus pumilus and pseudomonas putida. The complex inoculant disclosed by the invention, when applied to heavy metal pollution remediation, integrates advantages of various endophytic bacteria and overcomes disadvantages of phytoremediation; and the complex inoculant can promote the growth of sedum alfredii hance, enhance the absorbing capacity of the sedum alfredii hance to heavy metals and improve the efficiency of phytoremediation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Microorganism which reduces nitrosamines and method of reducing nitrosamines using the same
InactiveCN1652702AQuality assuranceMaintain the smellTobacco treatmentMicroorganismsNitrosaminePseudomonas fluorescens
The invention relates to a method for reducing the SNA content in tobacco leaf, which is characterized in adopting microorganism for treatment. The microorganism is selected from the group formed with sphingomonas paucimobolis and pseudomonas fluorescens and can reduce the SNA content.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Method of growing bacteria for use in wastewater treatment
ActiveUS7658851B2Simple and cost-effectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacillus licheniformisBacteroides
A device and method for growing aerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacteria such as Pseudomonas Fluorescens, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Starkeya novella and various autotrophic sulfur metabolizing bacteria, along with methods for releasing these bacteria into suspended growth or fixed film wastewater treatment zones such as soil or media, for the purposes of bioremediation and the removal of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon wastes.
Owner:PSEUDONYM CORP
Method for treating polymer-containing sewage of oil field
ActiveCN101993177AEasy to separateExtend the filter cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeBacillus cereus
The invention relates to the improvement of a method for treating polymer-containing sewage of an oil field. The method is characterized in that microorganisms are formed by mixing bacillus cereuses, bacillus megateria, bacillus subtilis, candida lipolytica, bacillus brevis and pseudomonas fluorescens; after microorganism aerobic degradation, post filter treatment is carried out; obligate microorganisms are used for degrading oil and organic pollutants bonded on polymers, thereby improving the separability of surplus inorganic substances and polymer-containing substances; and meanwhile, the degradation of the oil and the organic pollutants creates a condition for subsequently prolonging the filter period of a filter material. The invention has the advantages of simple process, simplified flows, convenient running and management, good treatment effect, low treatment and running cost (0.65-0.7yuen / ton of water, which is 2 / 3 of that of conventional treatment), no need of adding any drug,no treatment secondary pollution and stable treatment effect, can guarantee that treated yield water can stably reach 5.5.2, has small sludge quantity and does not need a sludge treatment system, thereby solving the treatment problem of polymer-containing sewage of an oil field.
Owner:JIANGSU BODA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN103146610AIncrease profitImprove utilization efficiencyBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant rootsPhosphate
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology, and relates to plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and an application thereof. The plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (Pseudomonas fluorescens Y1) was collected in the General Microbiological Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee on January 11th, 2013, and is named Pseudomonas fluorescens in a classified manner, and the collection number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO. 7130. The strain utilizes insoluble phosphate as a phosphorus source for strong growth ability, can improve the utilization ratio of the fertilizer, promotes the development of plant roots and uptake of a fertilizer and increases the phosphorus content of the plant. The plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria disclosed by the invention has a good growth promoting effect for peanuts, and the efficient phosphate solubilisation of the strain promotes the growth and the development of the peanuts and the utilization ratio of a phosphorus fertilizer.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Biological agent for treating ammonia-nitrogen-containing wastewater and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104630101APromote degradationIncrease contact areaBacteriaWater contaminantsPseudomonas fluorescensAniline
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms and discloses a biological agent for treating ammonia-nitrogen-containing wastewater. The biological agent comprises rhodococcus ruber, micrococcus luteus, enterococcus faecalis, acinetobacter baumannii, arthrobacter crystallopoietes, thiobacillus denitrificans and pseudomonas fluorescens. The biological agent comprises multiple strains, has the advantages of reasonable compatibility and strong synergic effect and can be used for effectively removing ammonia nitrogen, sulfide, aniline substances and industrial COD in wastewater.
Owner:江苏睿智建筑工程有限公司
Fermentation liquor composition for preparing biological organic fertilizer and preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101463334AHas a growth-promoting (fertilizer) effectHas antagonistic effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDiseaseGrowth promoting
The invention discloses a fermentation liquor composition used for preparing microbial organic fertilizer, which comprises the components based on the weight percentage: 60-70% of bacillus subtilis fermentation liquor, 15-20 % of bacillus pumilus fermentation liquor and 15-20 % of pseudomonas fluorescens fermentation liquor. The invention also provides a preparation method of the fermentation liquor composition, which comprises: bacillus subtilis, bacillus pumilus and the pseudomonas fluorescens are respectively fermented separately, and then the obtained fermentation liquors are mixed. The strain of the fermentation liquor composition has optimal combination, so as to realize versatility. The selected strain not only has effect of growth promotion, but also has antagonism effect for multiple plant soil-borne diseases. The bacillus subtilis and the pseudomonas fluorescens in the product are plant rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria which can stimulate and induce the systemic resistance of the crops, improve the self immunity and enhance disease resistance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of growing bacteria for use in wastewater treatment
ActiveUS20090321350A1Simple and cost-effectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiBacteroidesSulfur metabolizing bacteria
A device and method for growing aerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacteria such as Pseudomonas Fluorescens, Bacillus subtilus, Bacillus lichenoformis, Starkeya novella and various autotrophic sulfur metabolizing bacteria, along with methods for releasing these bacteria into suspended growth or fixed film wastewater treatment zones such as soil or media, for the purposes of bioremediation and the removal of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon wastes.
Owner:PSEUDONYM CORP
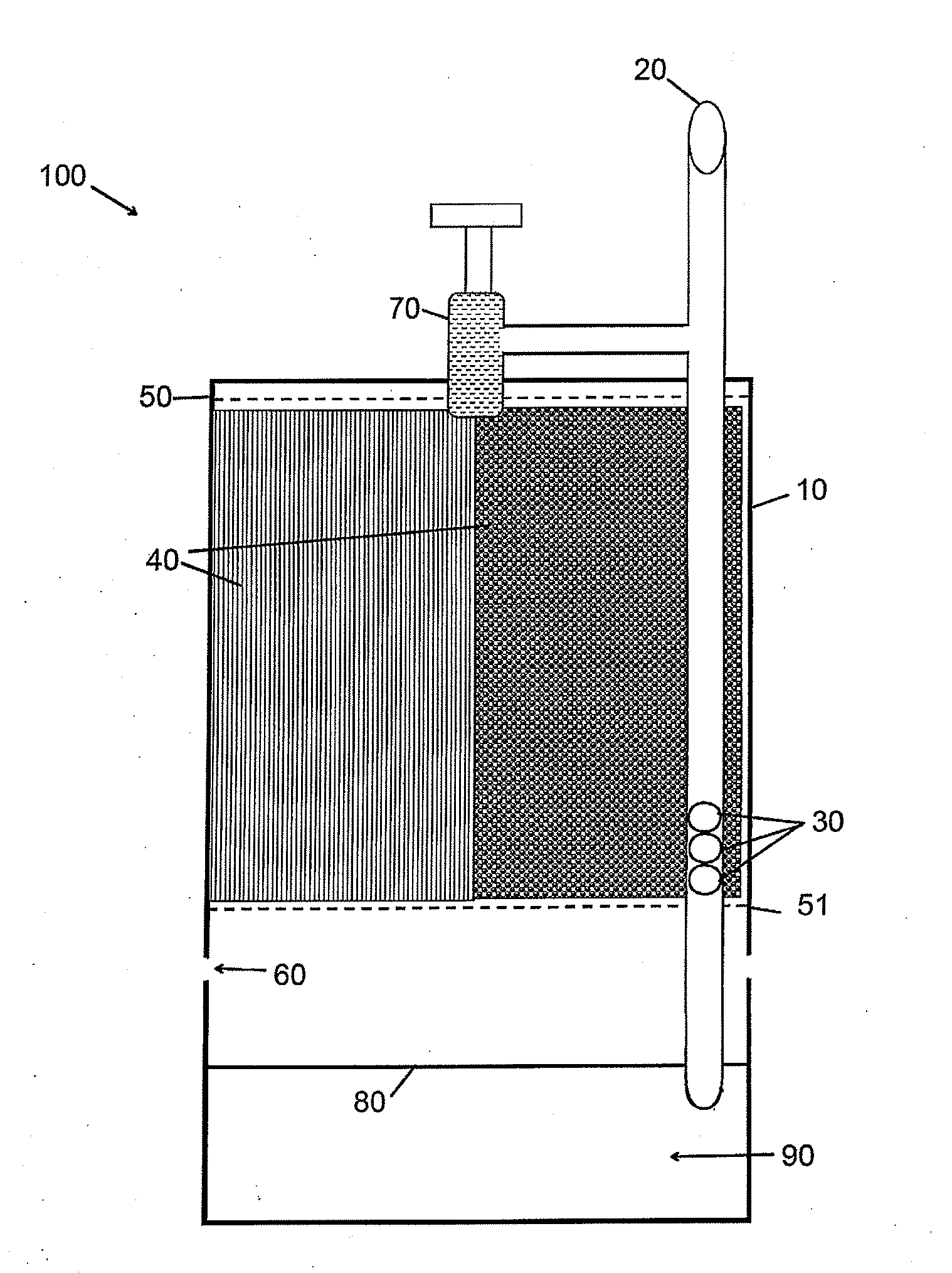
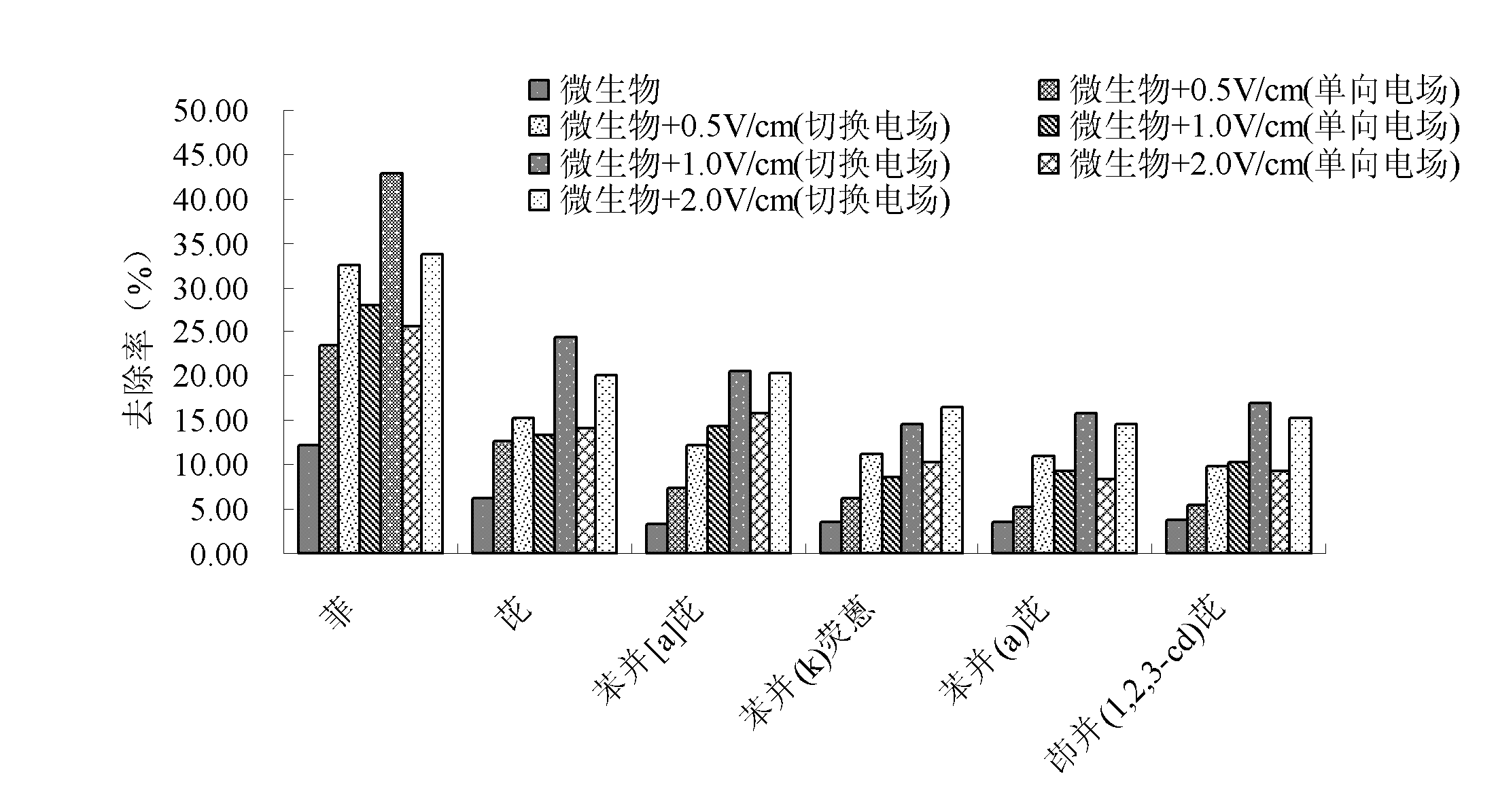
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium suitable for electric field condition and application thereof
ActiveCN103031256AReduce contentPromote degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonBacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental organic pollutant biological treatment and particularly relates to a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium suitable for an electric field condition and application of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium. The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium is pseudomonas fluorescens PB4, and has been already collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on July 19th, 2011, and the collection register number of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium is CCTCC No: M2011260. The pseudomonas fluorescens PB4 is used for repairing contaminated soil. A bacterial strain obtained by separating the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium is higher in activity under the action of the electric field condition, and thus, the ability of degradation of single polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon can be improved. After an electric field of 0.5-2.0V / cm is applied, the degradation activity of the pseudomonas fluorescens is enhanced, and the removal rate of the single polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the removal rate of the mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon are respectively increased by 12.46-30.62 percent and 8.11-20.20 percent after 28 days.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Expression of mammalian proteins in Pseudomonas fluorescens
The invention is a process for improved production of a recombinant mammalian protein by expression in a Pseudomonad, particularly in a Pseudomonas fluorescens organism. The process improves production of mammalian proteins, particularly human or human-derived proteins, over known expression systems such as E. coli in comparable circumstances Processes for improved production of isolated mammalian, particularly human, proteins are provided.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Recombinant nitrogen-fixing bacterial strain, inoculum containing the same and application methods
Recombinant bacterial strains comprising heterologous nif genes in its genome, and capable of fixing nitrogen. The strain may be, for example, a recombinant Pseudomonas fluorescens strain comprising heterologous nif genes in its genome. An inoculum and a method for increasing plant productivity are further described.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH CONICET +2
Pseudomonas fluorescens and application thereof in promoting growth of poplar
ActiveCN101575583AStrong dissolving effectPromote growth and developmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFertilizerRhizosphere
The invention discloses pseudomonas fluorescens separated from rooting zone soil and capable of dissolving difficultly soluble inorganic phosphorus in high efficiency. The pseudomonas fluorescens is classification-named as pseudomonas fluorescens JW-JS1 and has been stored in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the storage No. is M 209027, and the storage data is Feb. 18, 2009. The invention also discloses application of the pseudomonas fluorescens in promoting growth of poplar. Under the condition of liquid shaking culture, JW-JS1 strains have stronger effect of dissolving tricalcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite; and the pseudomonas fluorescens JW-JS1 can be inoculated to cuttage seedlings of NL-895poplar and tree seedlings of eastern cottonwood. Results show that the pseudomonas fluorescens obviously promotes the growth of the poplar. Therefore, the invention provides a desirable strain resource for developing a phosphorus-dissolving bacteria fertilizer special for the poplar.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Production method using food residues to prepare functional microorganism organic fertilizer
InactiveCN105753537ACutting costsShorten the "rotten" timeFungiBio-organic fraction processingLiquid wastePseudomonas fluorescens
The invention discloses a production method using food residues to prepare functional microorganism organic fertilizer.The production method includes the steps of a, collecting fresh kitchen wastes, and performing solid-waste separation to obtain solid wastes and liquid wastes; b, preparing fermentation substrates; c, respectively inoculating candida mycoderma bacteria, bacillus subtilis, lactobacillus and aspergillus niger into the fermentation substrates to perform first fermentation compost; d, turning piles and inoculating bacillus subtilis, pseudomonas fluorescens and streptomyces, turning piles, fermenting, and drying with cold air to obtain the finished functional microorganism organic fertilizer, wherein pH is 6.5-7.5, and moisture content is 35-50%.The production method has the advantages that the food residues are processed reasonably, and the functional microorganism organic fertilizer is prepared at low cost; the food residues are processed reasonably and thoroughly, the functional microorganism organic fertilizer with high practicality and high value is produced by using the functional strains, the utilization value of the wastes is maximized, and the method is green and free of pollution.
Owner:湖南富丰环保机械有限公司
Soil conditioner for degrading pesticides in soil with microorganisms
InactiveCN106478288ARepair pollutionRich in organic matterExcrement fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersCompound organicBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a soil conditioner for degrading pesticides in soil with microorganisms. The soil conditioner is prepared from, by mass, 100-200 parts of organic fermented manure, 3-5 parts of trace fertilizer, 2-5 parts of bentonite, 5-7 parts of phosphate rock powder, 3-5 parts of amino acid and 0.1-1 part of microbial flora, wherein the microbial flora is composed of pseudomonas fluorescens, rhodopseudomonas palustris, alcaligenes faecalis, pseudomonas putida, bacillus licheniformis, spherical lysine bacillus, bacillus subtilis and bacillus cereus. The soil conditioner is prepared by compounding various microbial strains, the organic fermented manure, the trace fertilizer, amino acid, the bentonite and the phosphate rock powder, and can degrade the chemical pesticides in the soil, such as organic phosphorus pesticides, heterocyclic pesticides, phenol pesticides and aromatic pesticides, and remedy the pesticide-contaminated soil.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Bio-control composite bacterial agent and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN106804628APrevent decayDifferent functionsBiocideFungiBacillus megateriumBacillus thuringiensis
The invention discloses a bio-control composite bacterial agent which comprises, by weight, bacterial strains including 8-12 parts of purpureocillium lilacinum, 18-22 parts of pseudomonas fluorescens, 18-22 parts of bacillus cereus, 8-12 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus, 18-22 parts of bacillus subtilis, 8-12 parts of bacillus megaterium, 4-6 parts of bacillus thuringiensis and 4-6 parts of trichoderma viride and a culture medium comprising 0.8-1.2 parts of beef extract, 2.5-4 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.3-1.8 parts of urea, 10-12 parts of molasses, 1.5-2.5 parts of amino acid, 2.5-3.5 parts of glucose, 0.3-0.6 part of peptone, 0.25-0.4 part of sodium chloride and 0.35-0.6 part of potassium nitrate. The invention further comprises a preparation method of the bacterial agent. The bio-control composite bacterial agent has good effect on solving current problems of soil improvement, environment protection of agriculture and waste straw rubbish and can improve soil and accelerate crop growth and organic matter decomposition.
Owner:北京金必来生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com