Patents
Literature
68 results about "Zymomonas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
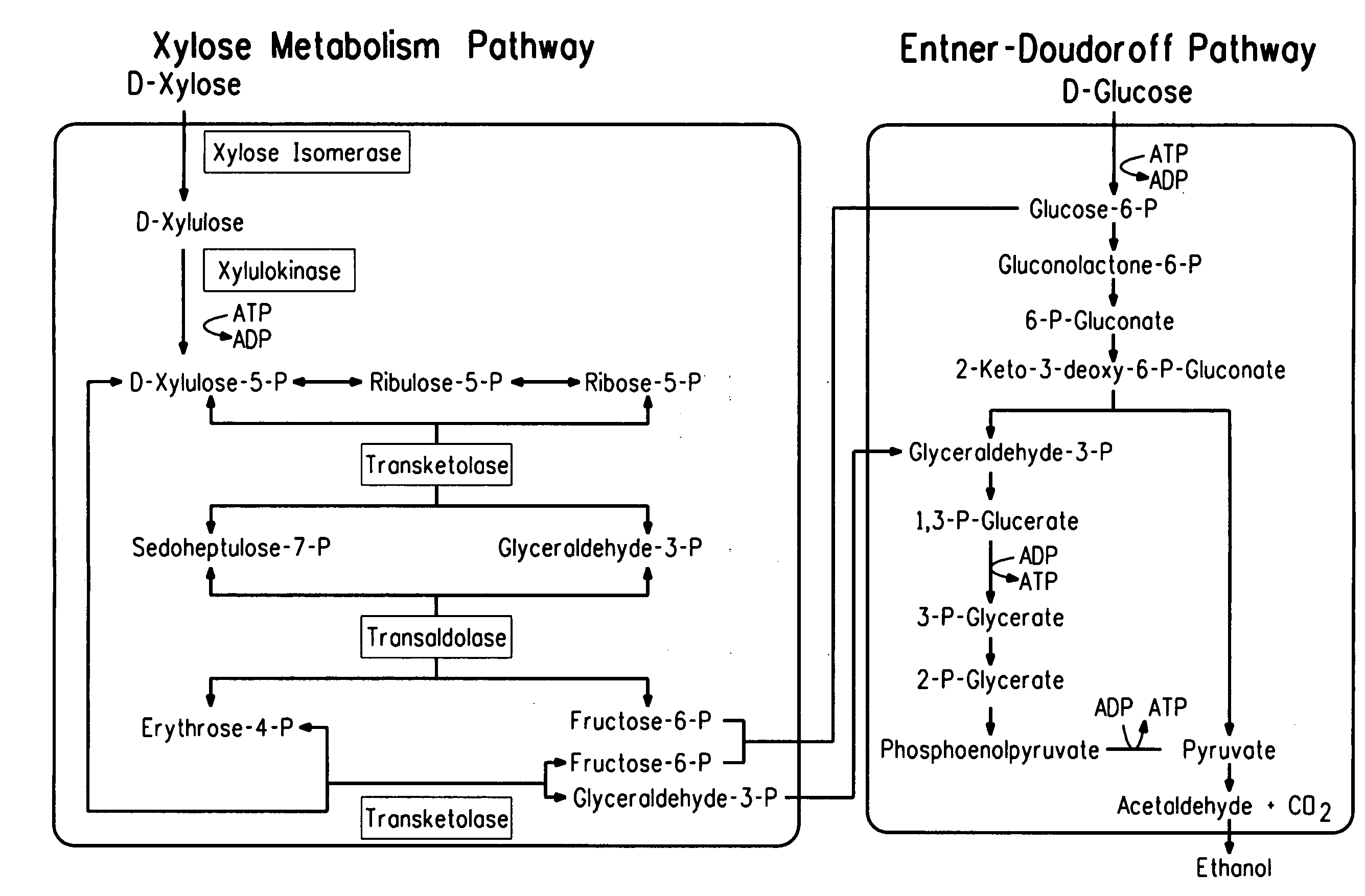
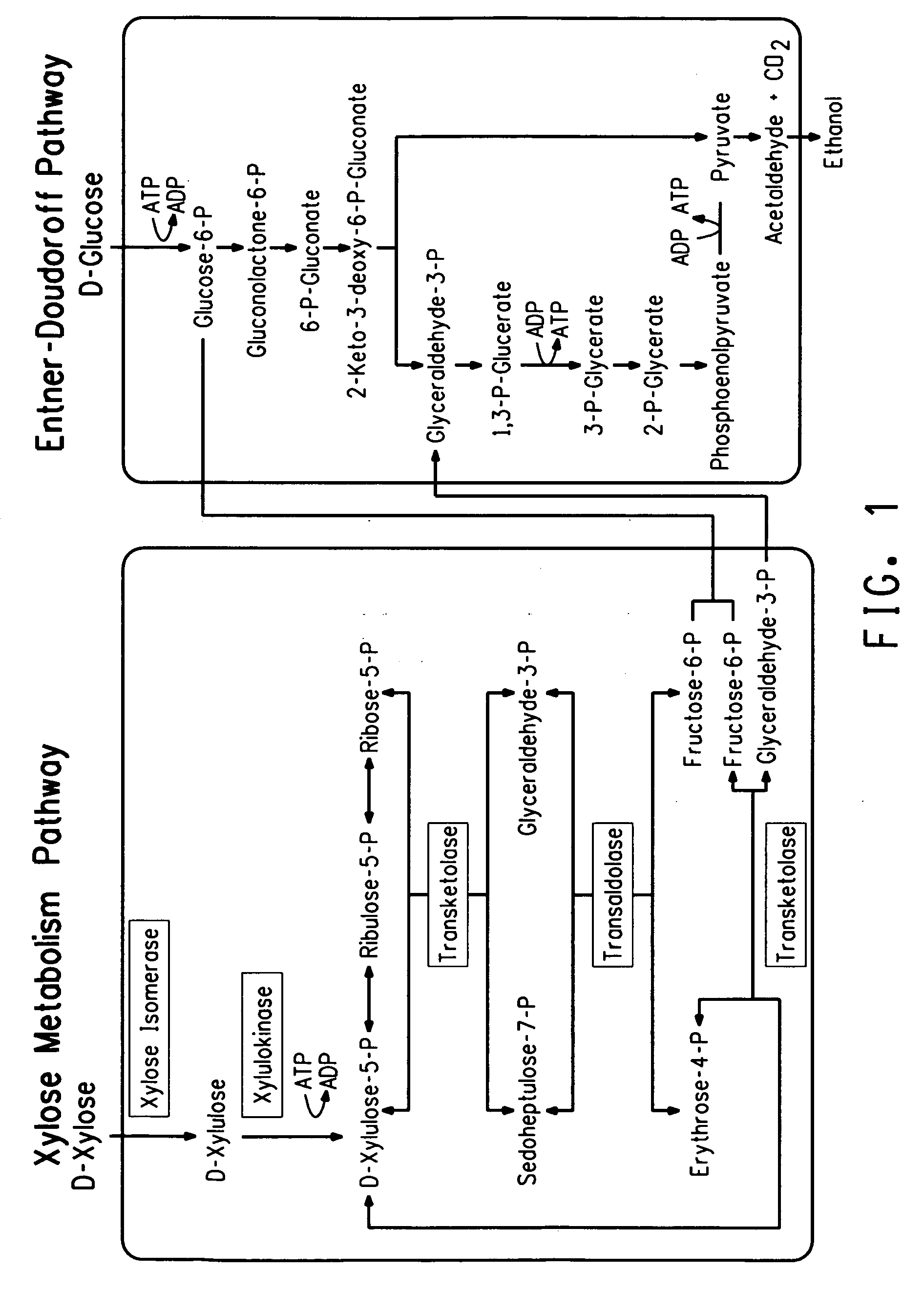
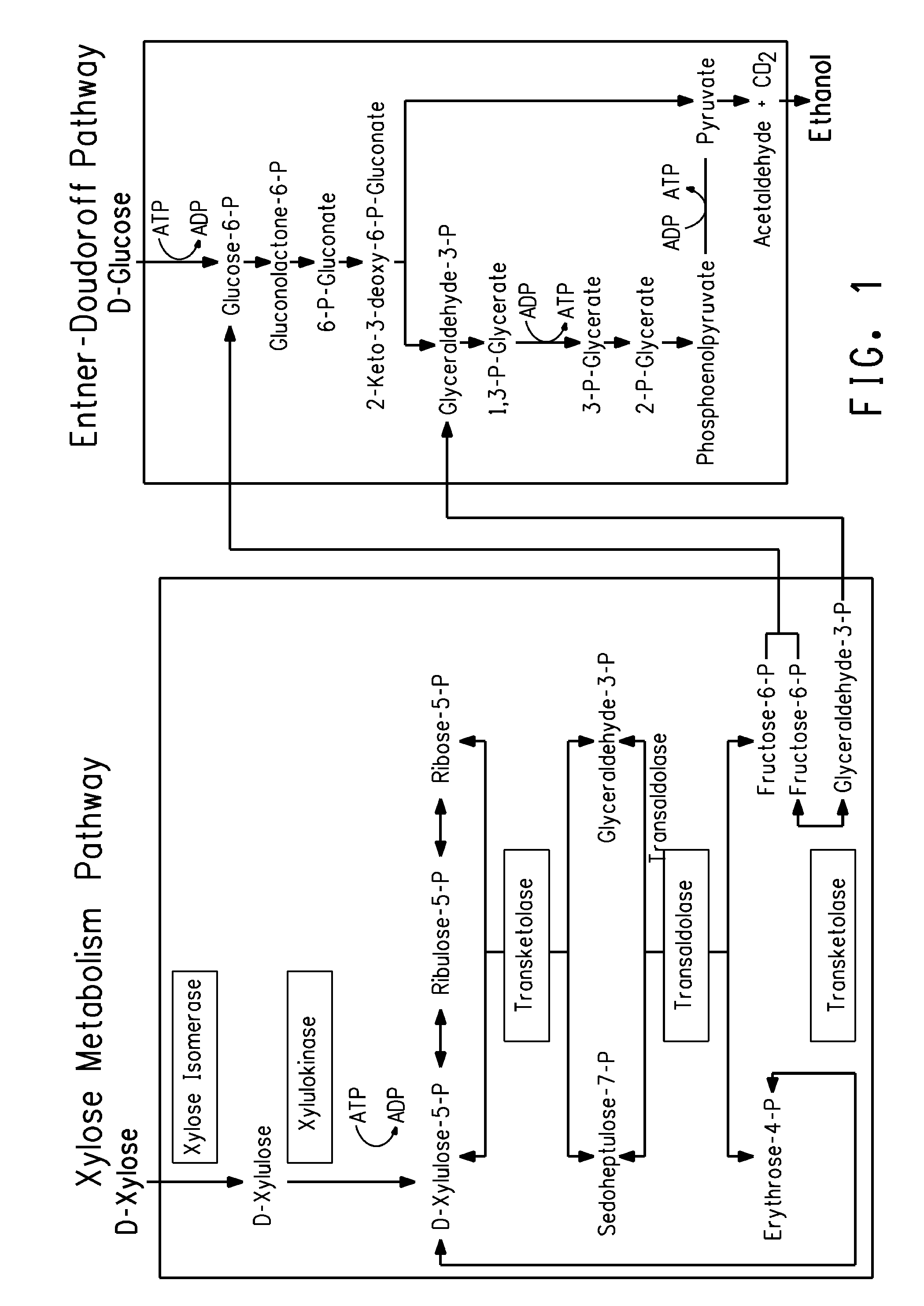
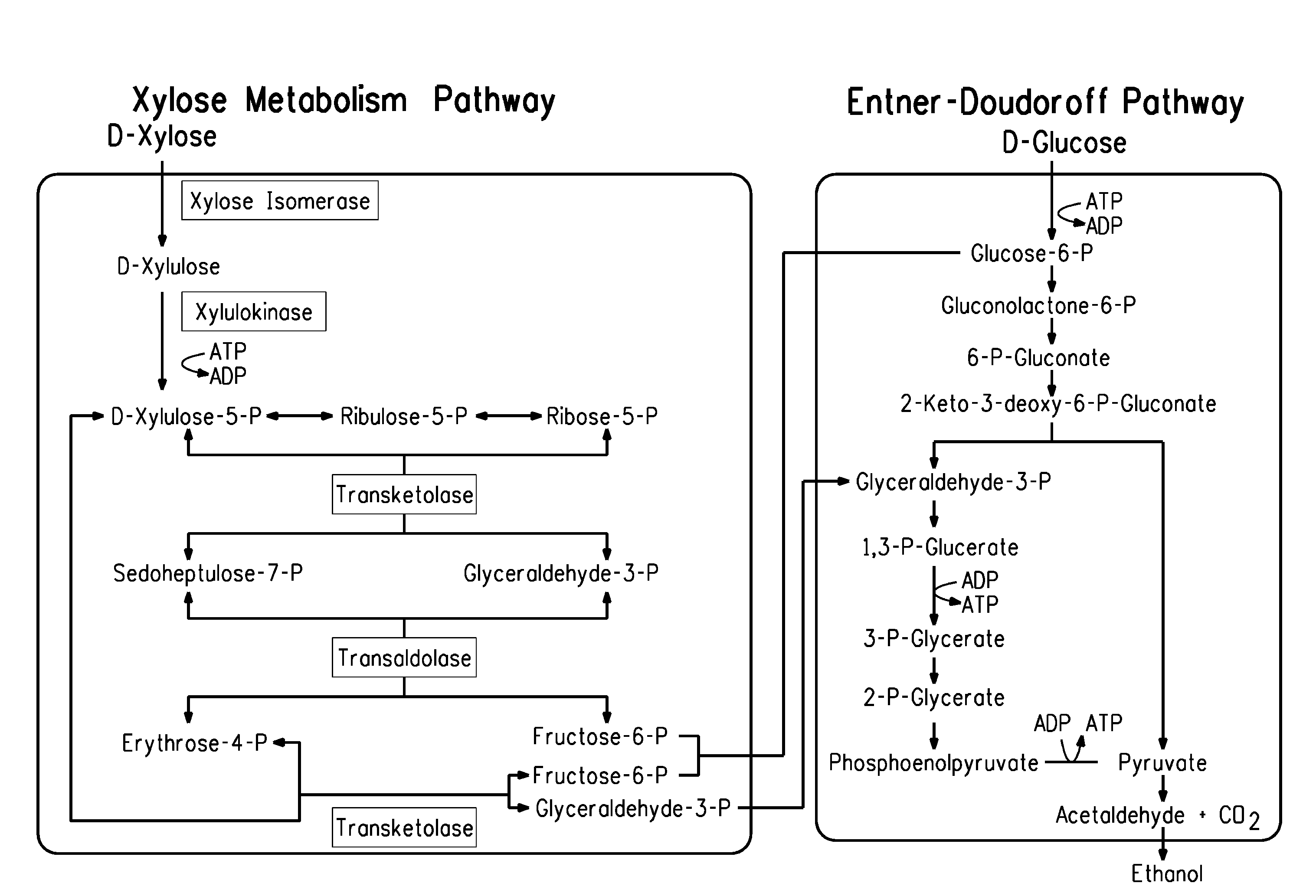
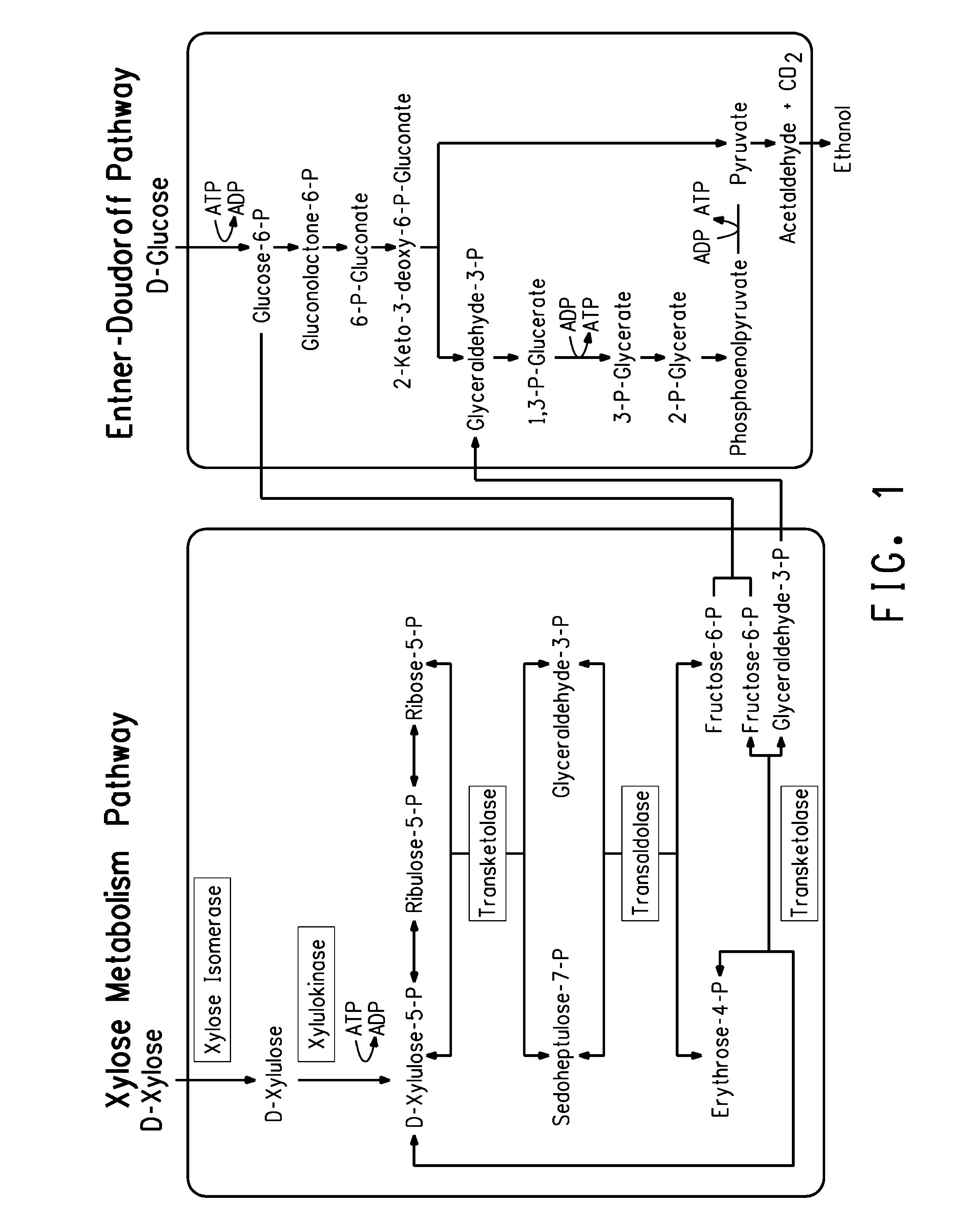
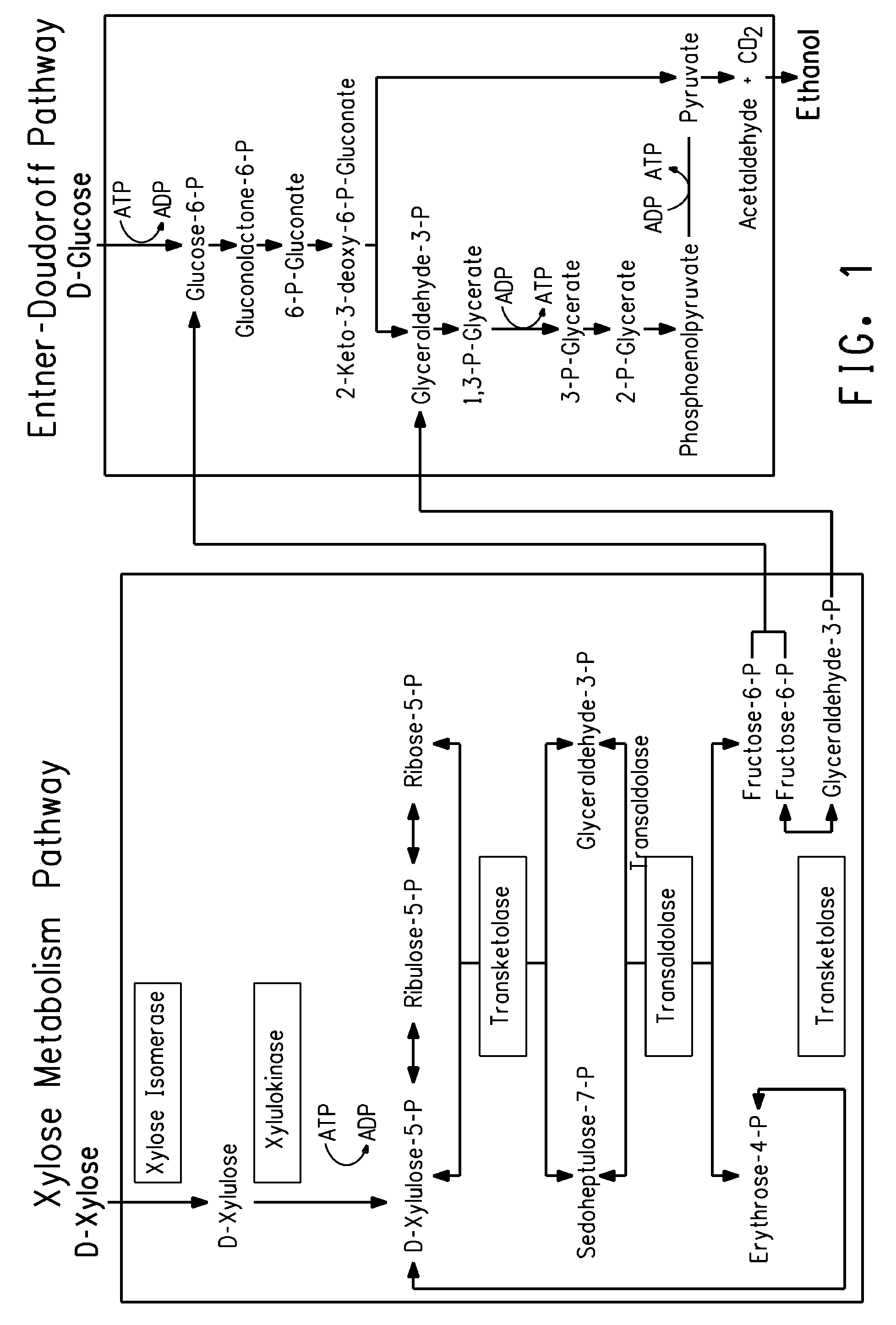
Zymomonas is a genus of bacteria. Members of this genus are gram negative, facultative anaerobic, non-sporulating, polarly-flagellated, rod-shaped bacteria. The best-known species from this genus is Zymomonas mobilis. It is a fermenting bacteria that contributes to cider sickness and beer spoilage. It has a near theoretical ethanol yield from glucose, no oxygen requirement thus negating the need for expensive oxygen transfer, and high ethanol tolerance making it an effective microbe for ethanol biofuel production. However, in spite of these attractive advantages, several factors prevent the commercial usage of Z. mobilis in cellulosic ethanol production. The foremost hurdle is that its substrate range is limited to glucose, fructose and sucrose. Wild-type Z. mobilis cannot ferment C5 sugars like xylose and arabinose, which are important components of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. Unlike E. coli and yeast, Z. mobilis cannot tolerate toxic inhibitors present in lignocellulosic hydrolysates such as acetic acid and various phenolic compounds. Concentration of acetic acid in lignocellulosic hydrolysates can be as high as 1.5%, which is well above the tolerance threshold of Z. mobilis.
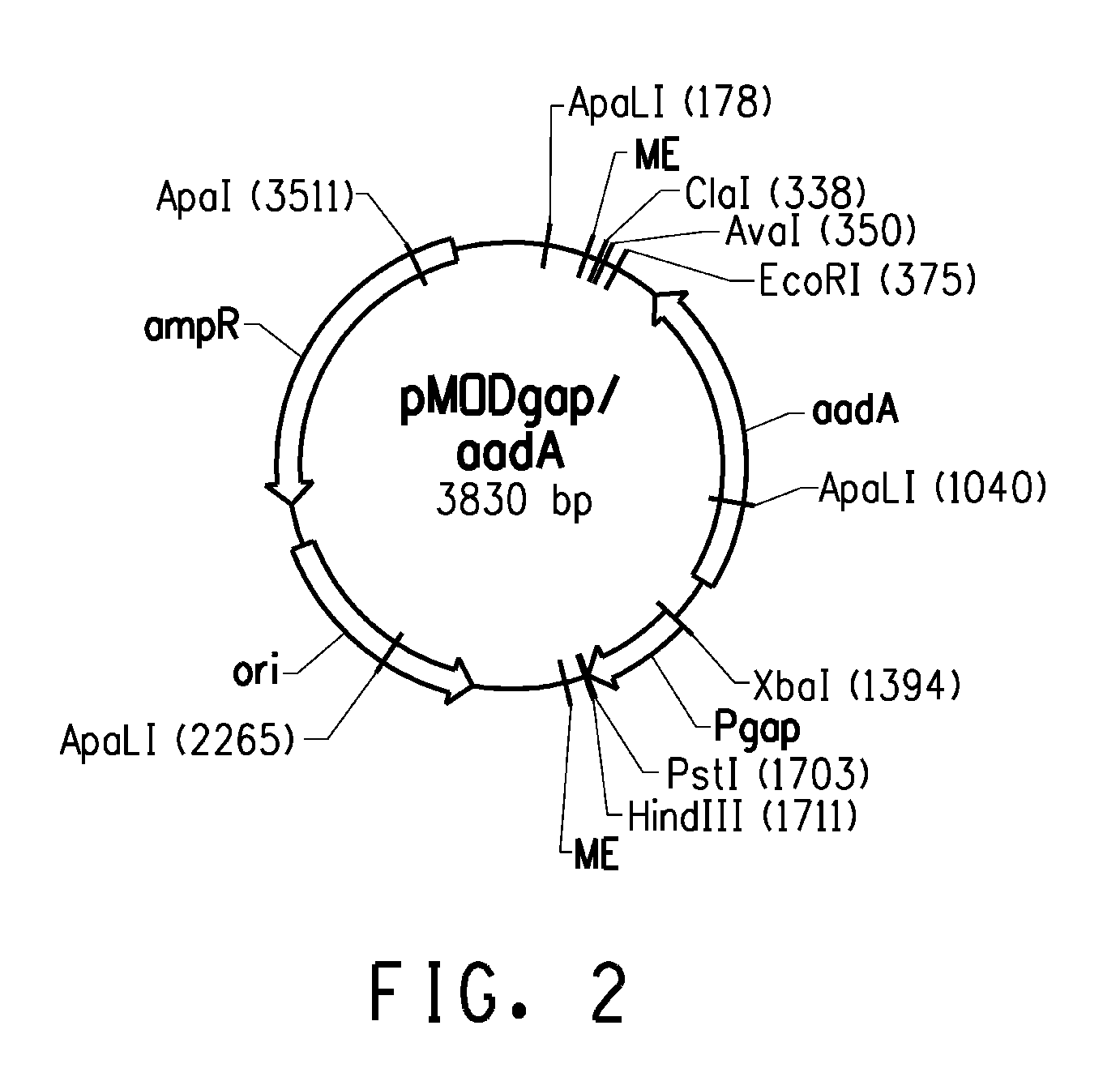
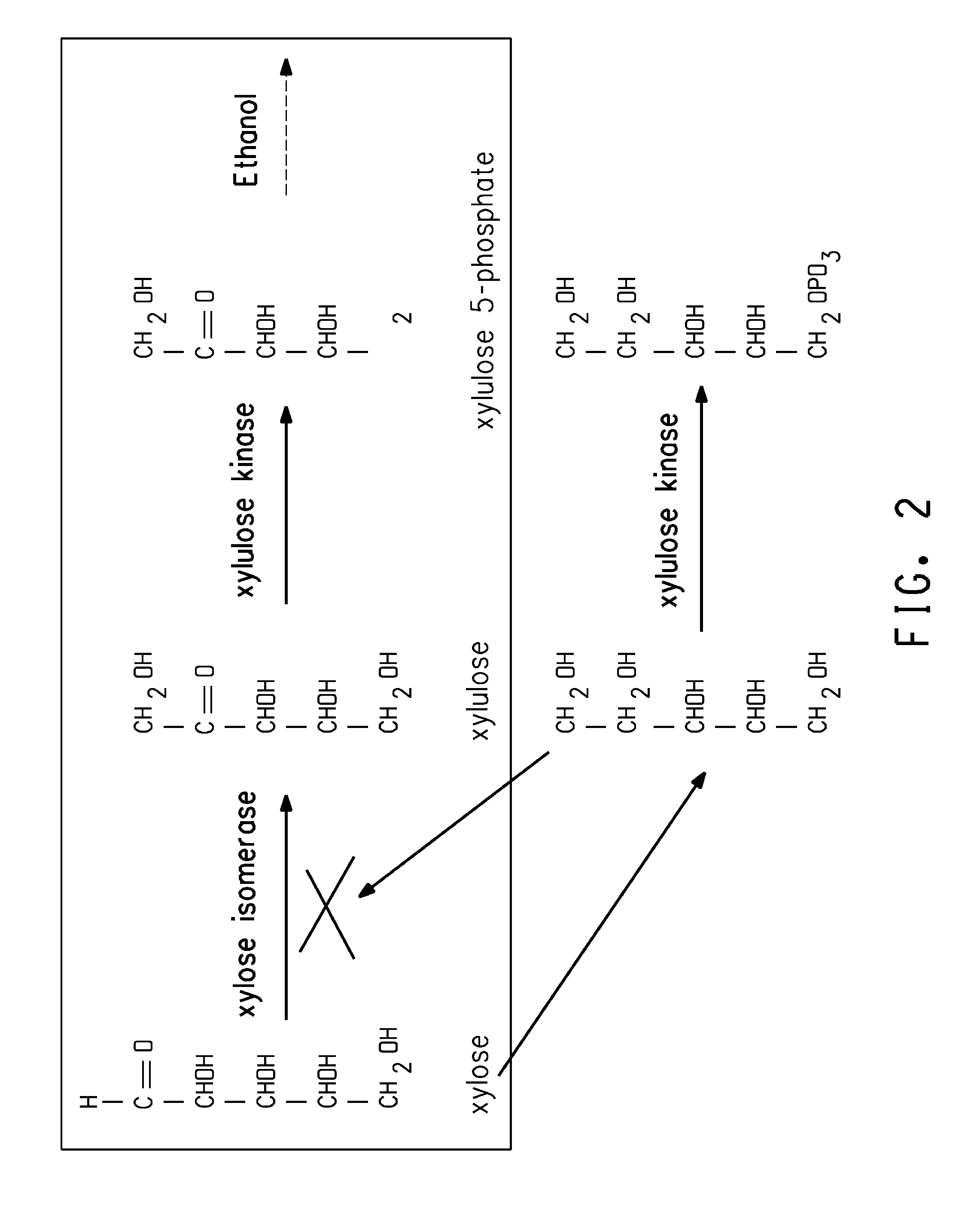
Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization
ActiveUS20090246846A1High expressionImproved xylose utilizationSugar derivativesBacteriaTransketolaseGlyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene
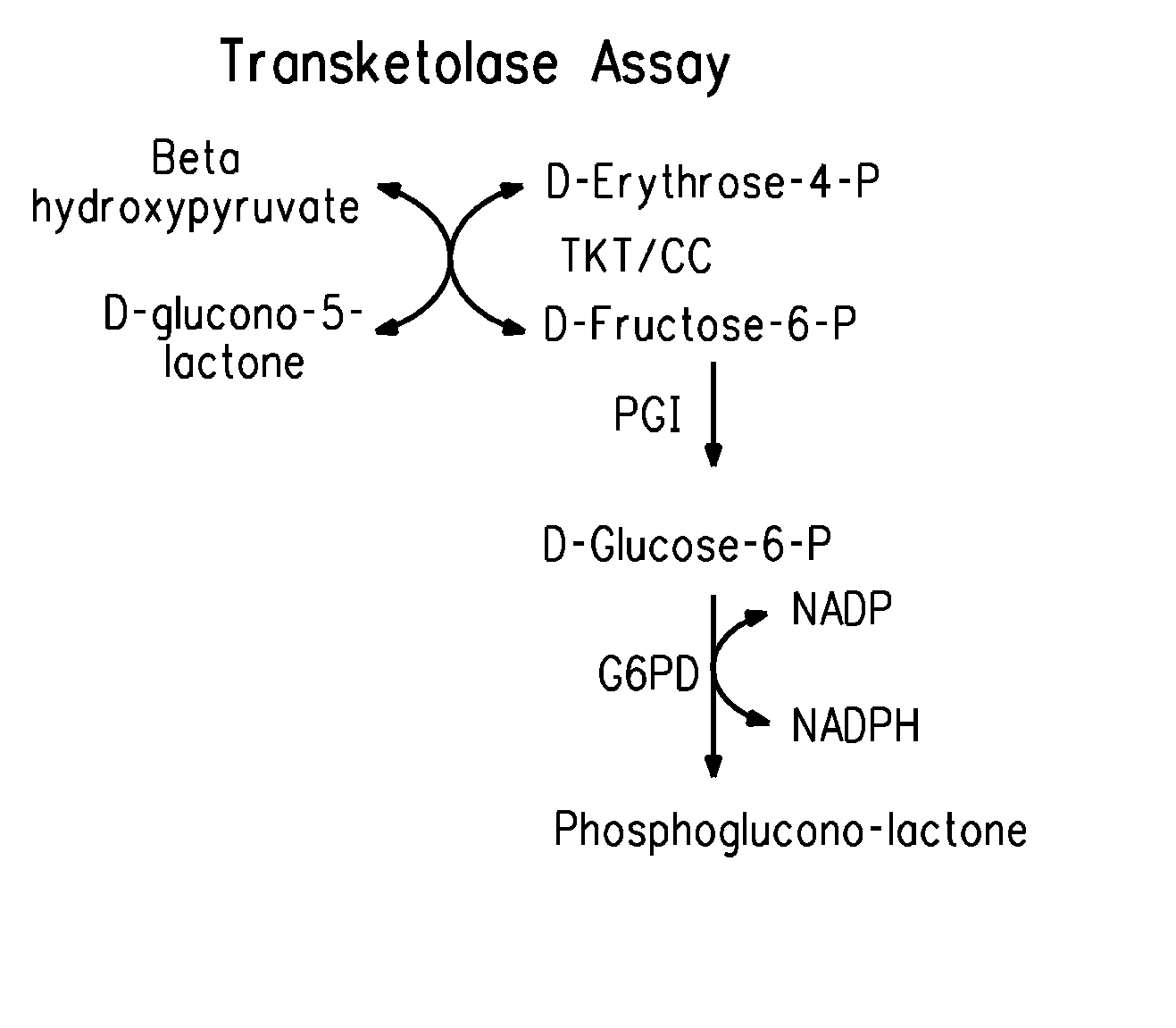
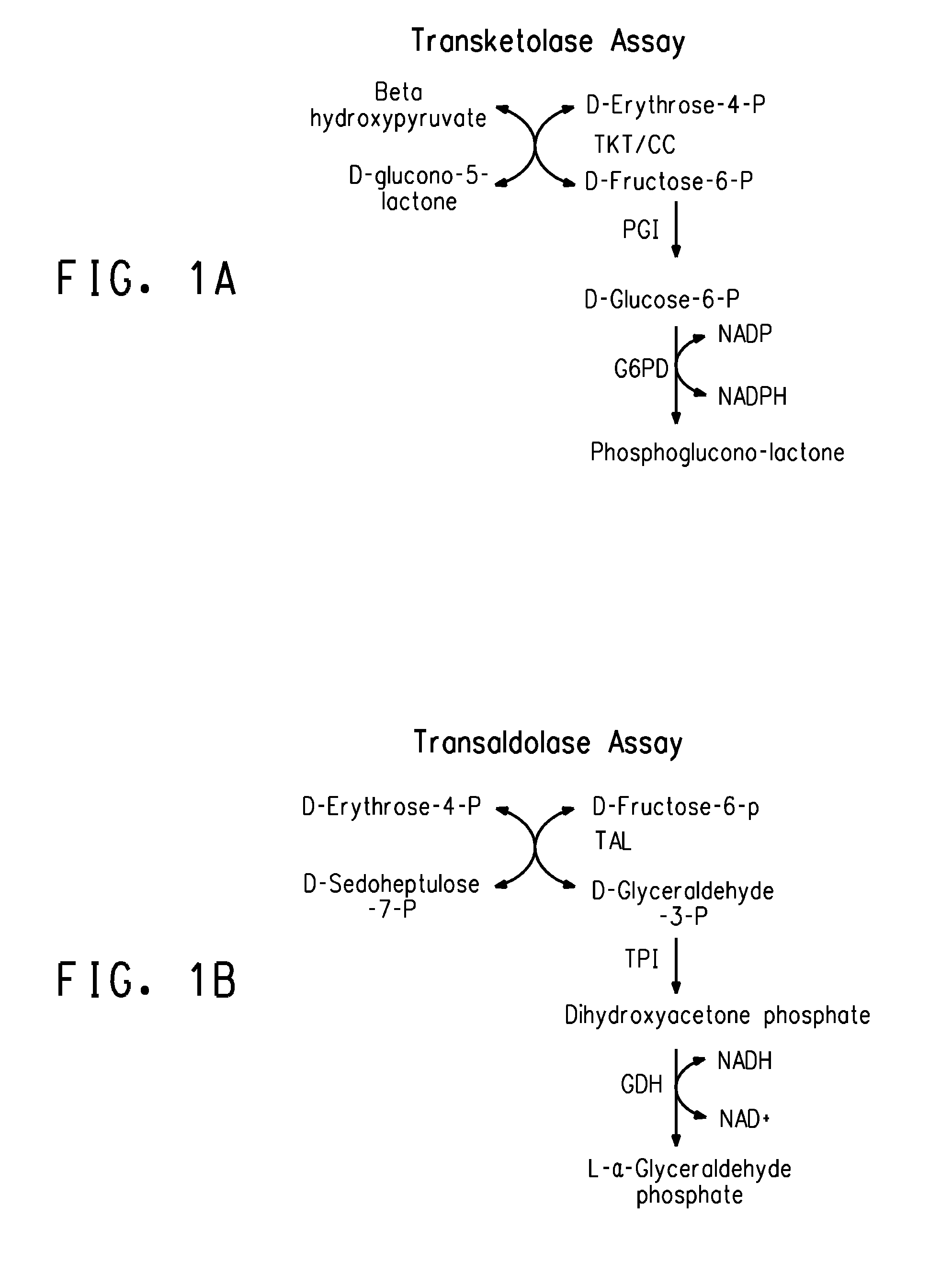
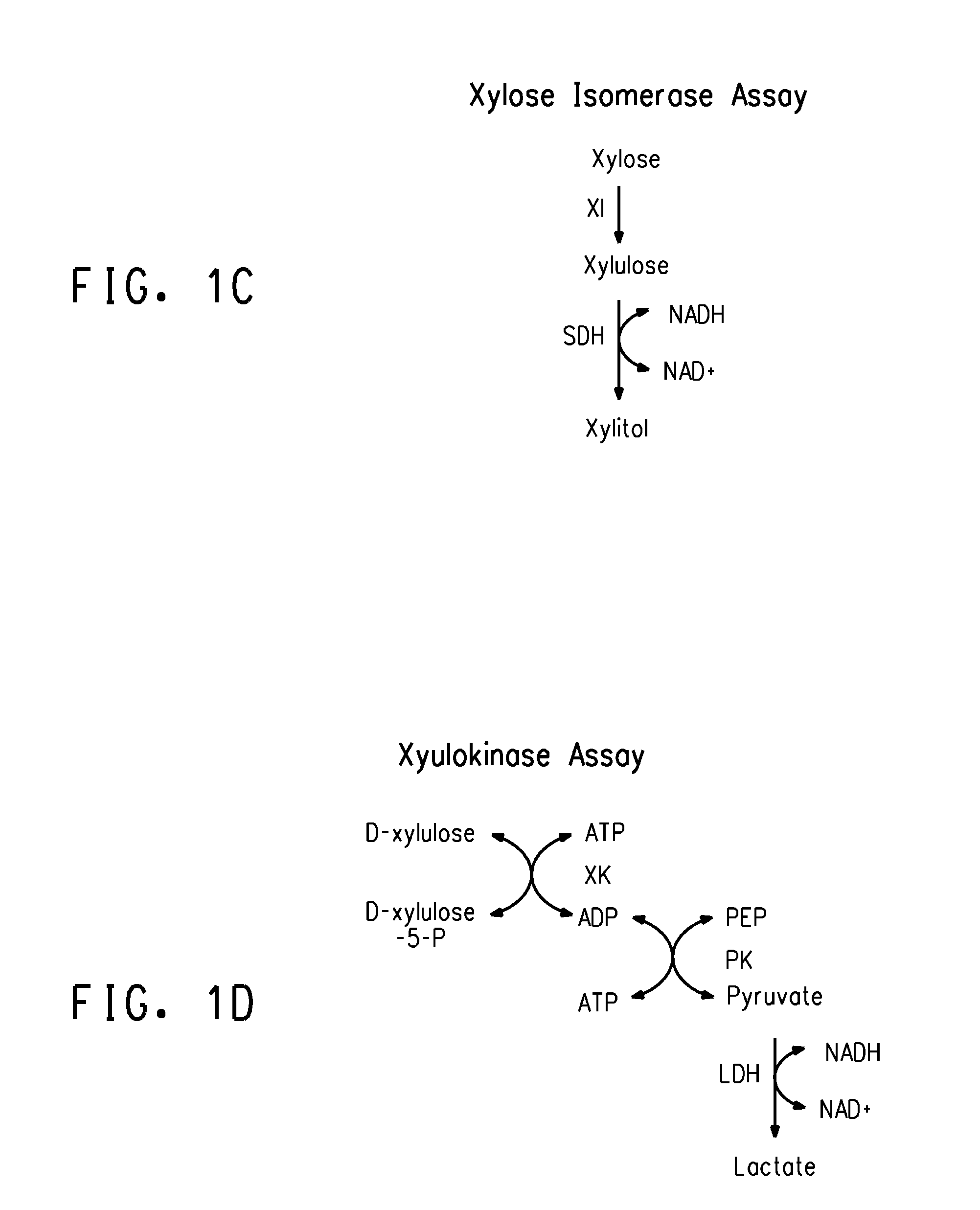
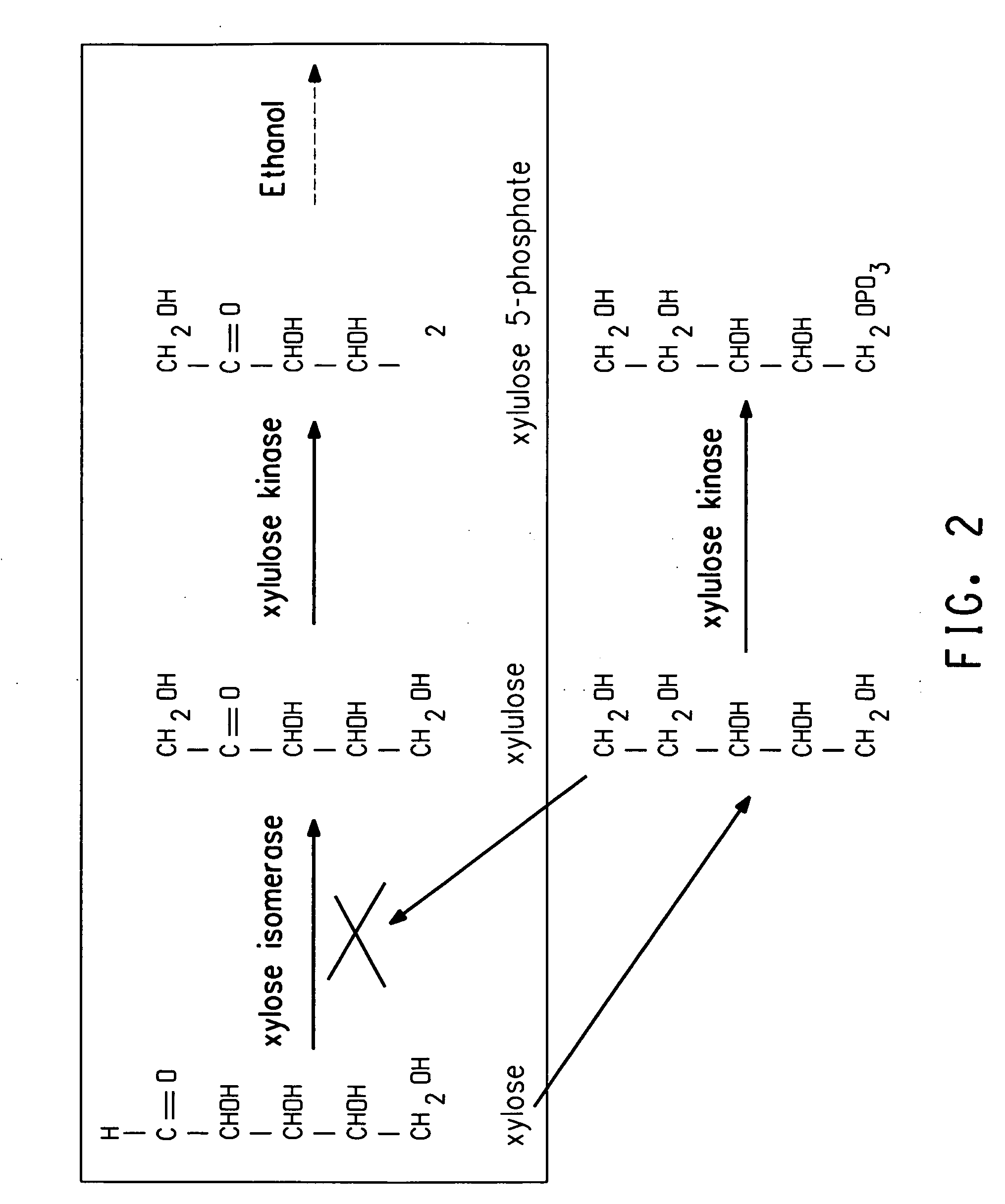
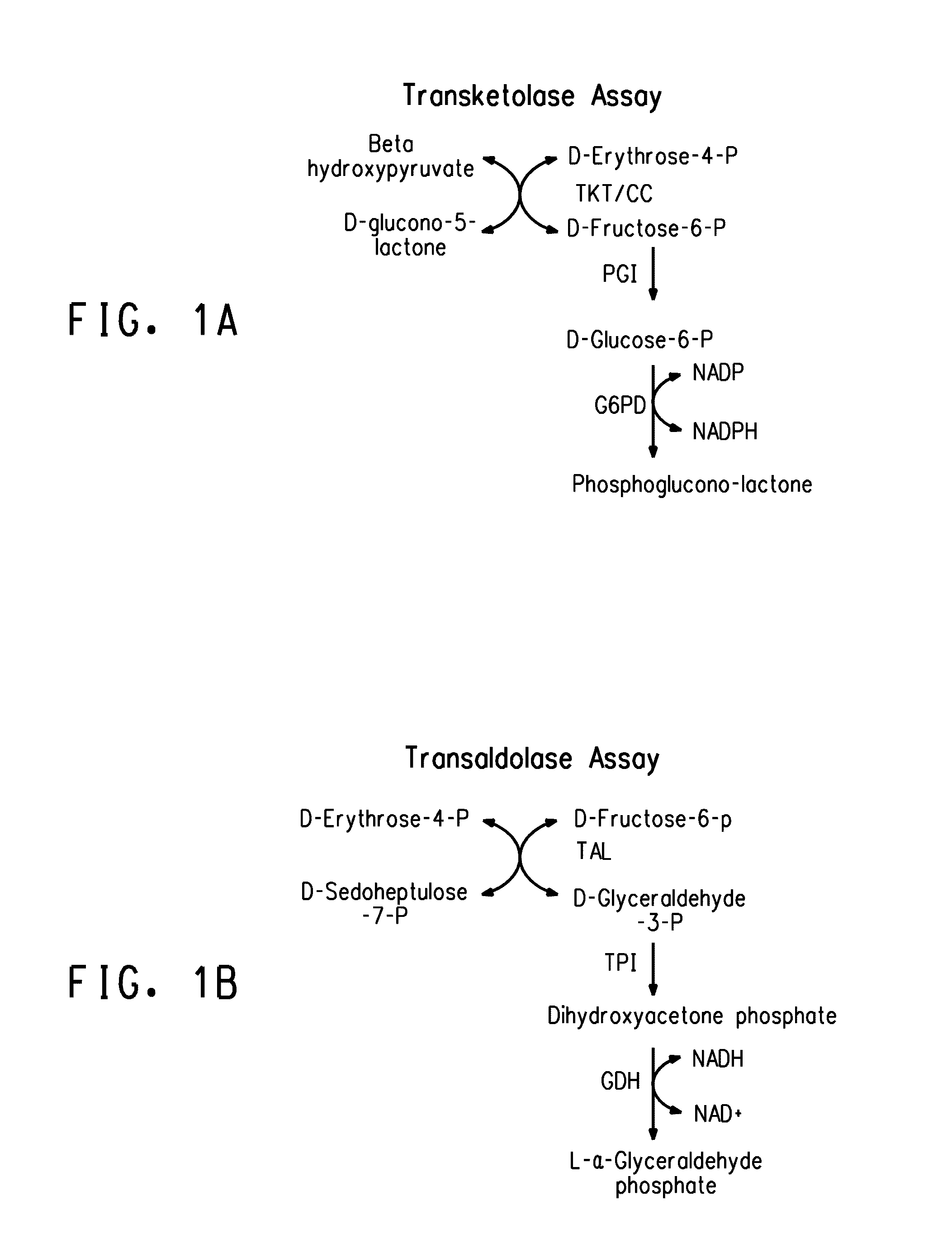
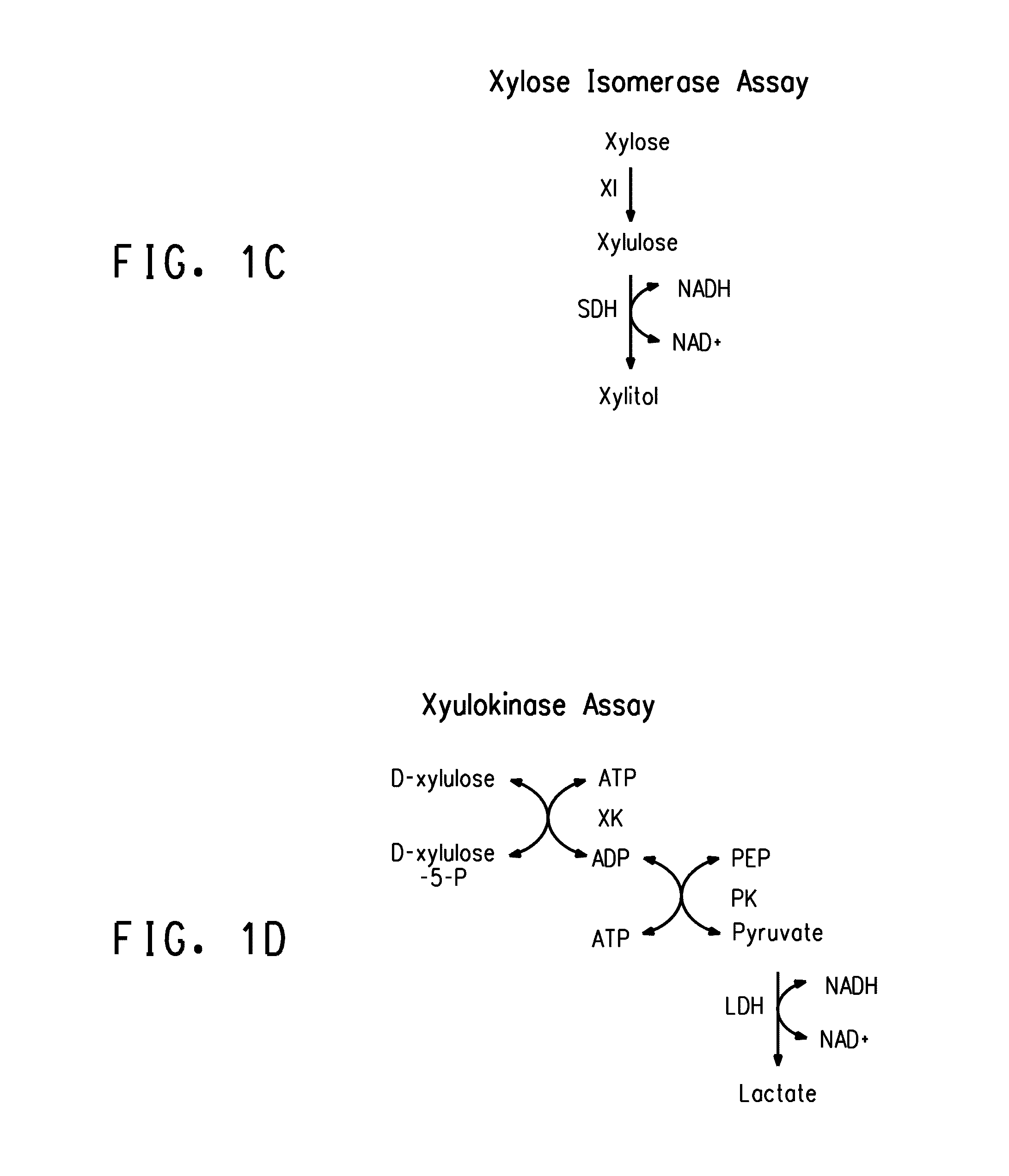
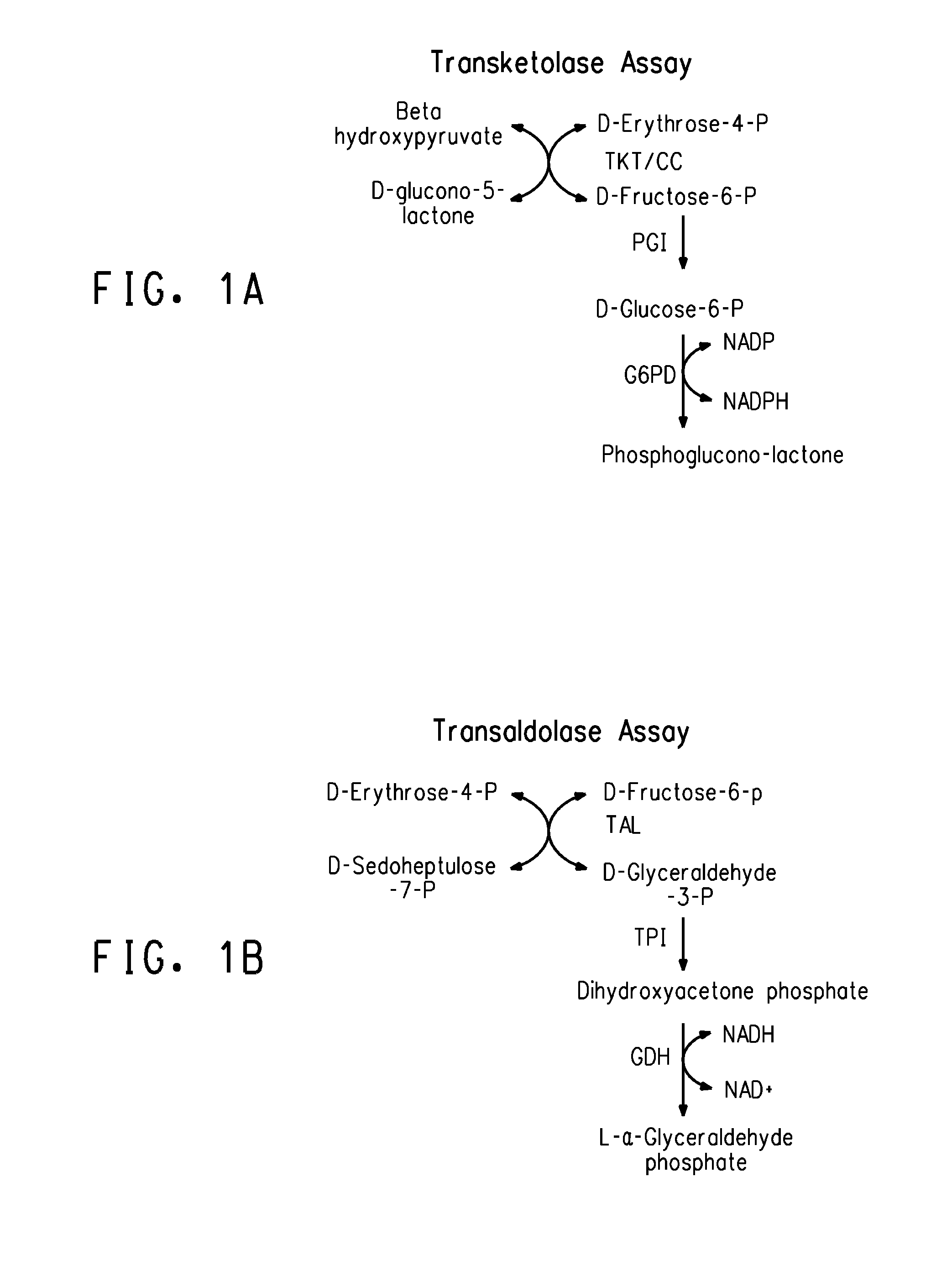
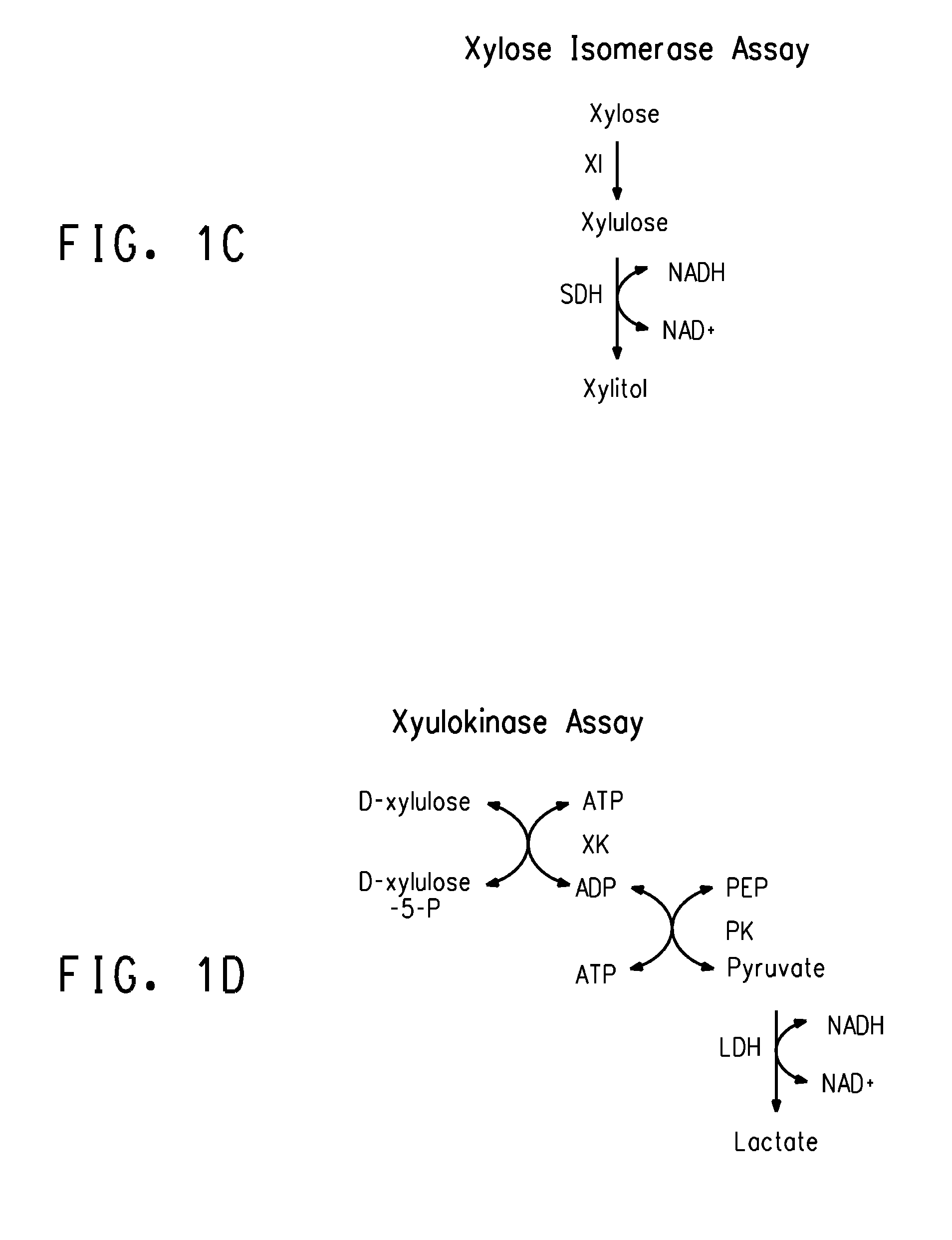
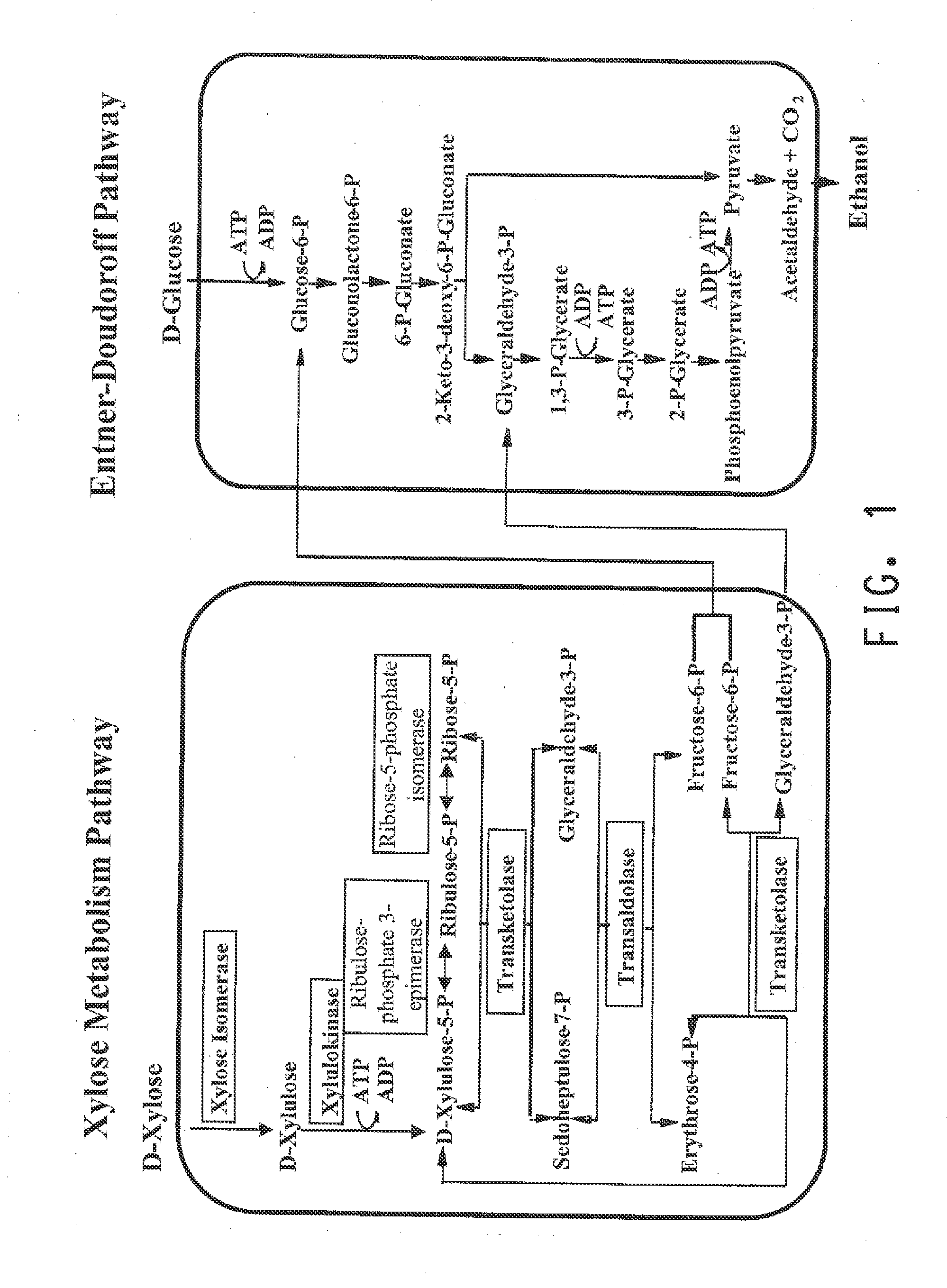
Strains of Zymomonas were engineered by introducing a chimeric xylose isomerase gene that contains a mutant promoter of the Z. mobilis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. The promoter directs increased expression of xylose isomerase, and when the strain is in addition engineered for expression of xylulokinase, transaldolase and transketolase, improved utilization of xylose is obtained.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Xylitol synthesis mutant of xylose-utilizing zymomonas for ethanol production
InactiveUS20080286870A1Reduce productionIncreased ethanol productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeSugarGlucose-fructose oxidoreductase
A strain of xylose-utilizing Zymomonas was engineered with a genetic modification to the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene resulting in reduced expression of GFOR enzyme activity. The engineered strain exhibits reduced production of xylitol, a detrimental by-product of xylose metabolism. It also consumes more xylose and produces more ethanol during mixed sugar fermentation under process-relevant conditions.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
Inorganic-organic microbial compound fertilizer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102001870AAvoid competitionPromote growthOrganic fertilisersBacillus licheniformisHigh concentration
The invention relates to an inorganic-organic microbial compound fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The inorganic-organic microbial compound fertilizer is characterized by comprising ordinary high-concentration three-element compound fertilizer, humic acid, fly ash, microbial compound bacteria powder and other elements, wherein the microbial compound bacterial powder is obtained by mixing bacterial powders which are prepared by respectively fermenting and culturing photosynthetic bacteria, yeast, lactic acid bacteria, bifidobacterium, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, bacilluslaterosporus, bacillus megaterium, bacillus mucilaginosus, azotbacteria chroococum and actinomycetes. In the inorganic-organic microbial compound fertilizer, the microbial content of the yeast is no less than 2.0*108cfu / g, and the microbial contents of the other strains are all no less than 2.0*109cfu / g. The inorganic-organic microbial compound fertilizer can centralize the advantages of an organic fertilizer, an inorganic fertilizer and microorganisms, thereby enhancing the stress resistance and the disease resistance of crops, enhancing the fertilizer absorption ability of the crops, lowering the soil hardening degree and improving the soil ecological environment and the quality of the crops.
Owner:山西晨雨晋中肥业有限公司
Zymomonas with improved ethanol production in medium containing concentrated sugars and acetate
InactiveUS20090203099A1Improve performanceIncreased acetate toleranceBacteriaBiofuelsAcetic acidSugar
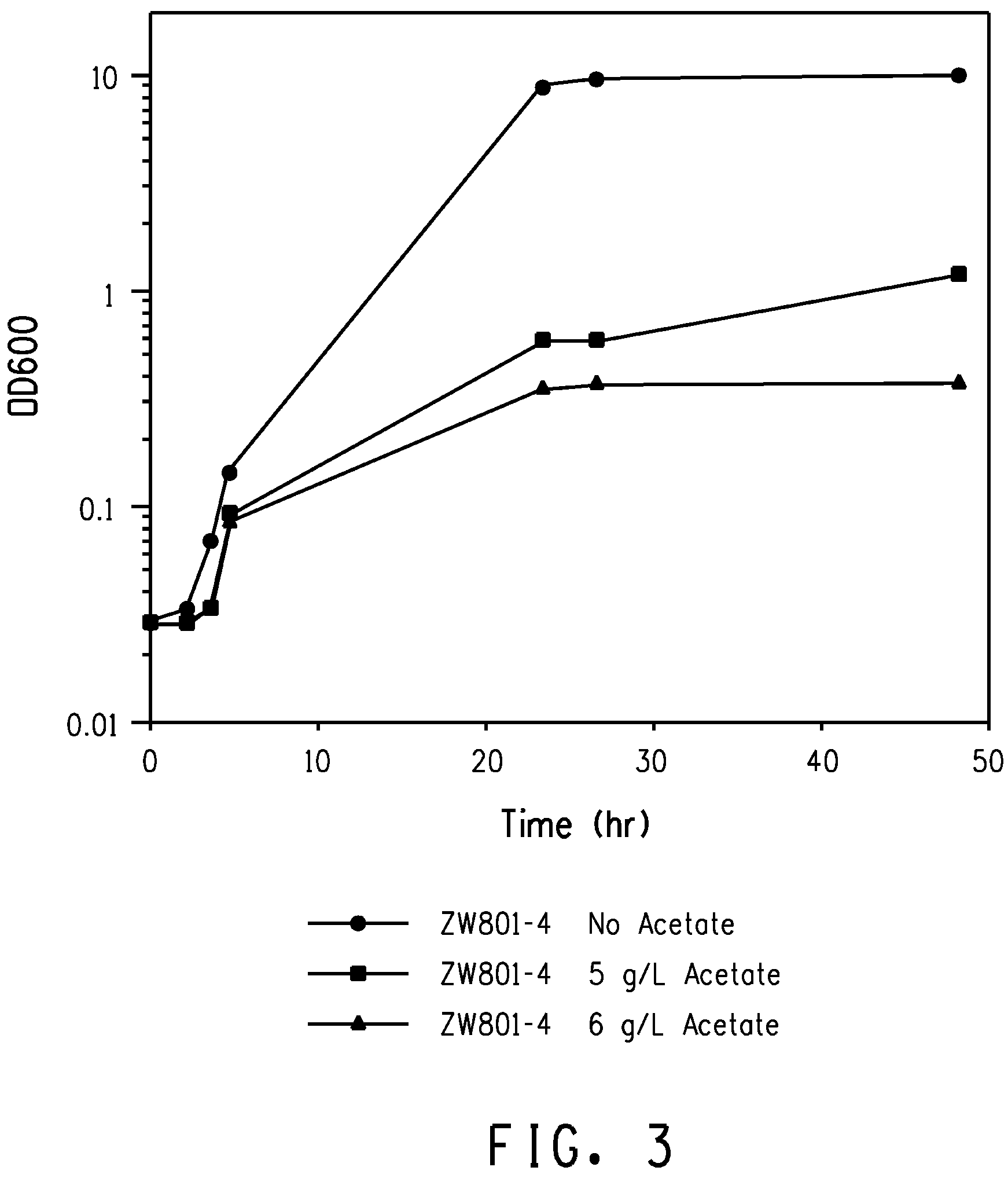
Through screening of a Zymomonas mutant library the himA gene was found to be involved in the inhibitory effect of acetate on Zymomonas performance. Xylose-utilizing Zymomonas strains further engineered to reduce activity of the himA gene were found to have increased ethanol production in comparison to a parental strain, when cultured in mixed-sugars medium comprising xylose, and, in particular, in the presence of acetate.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
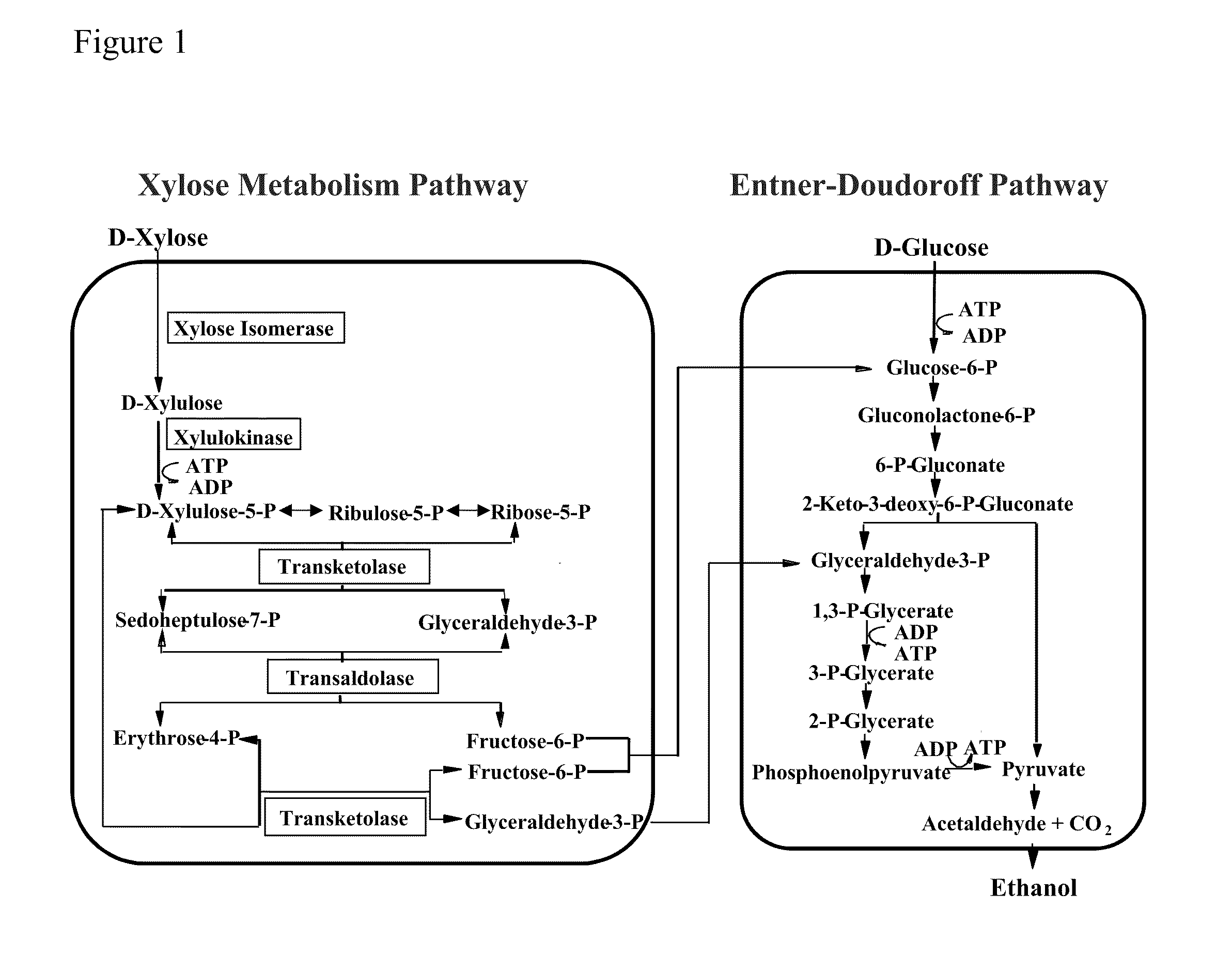
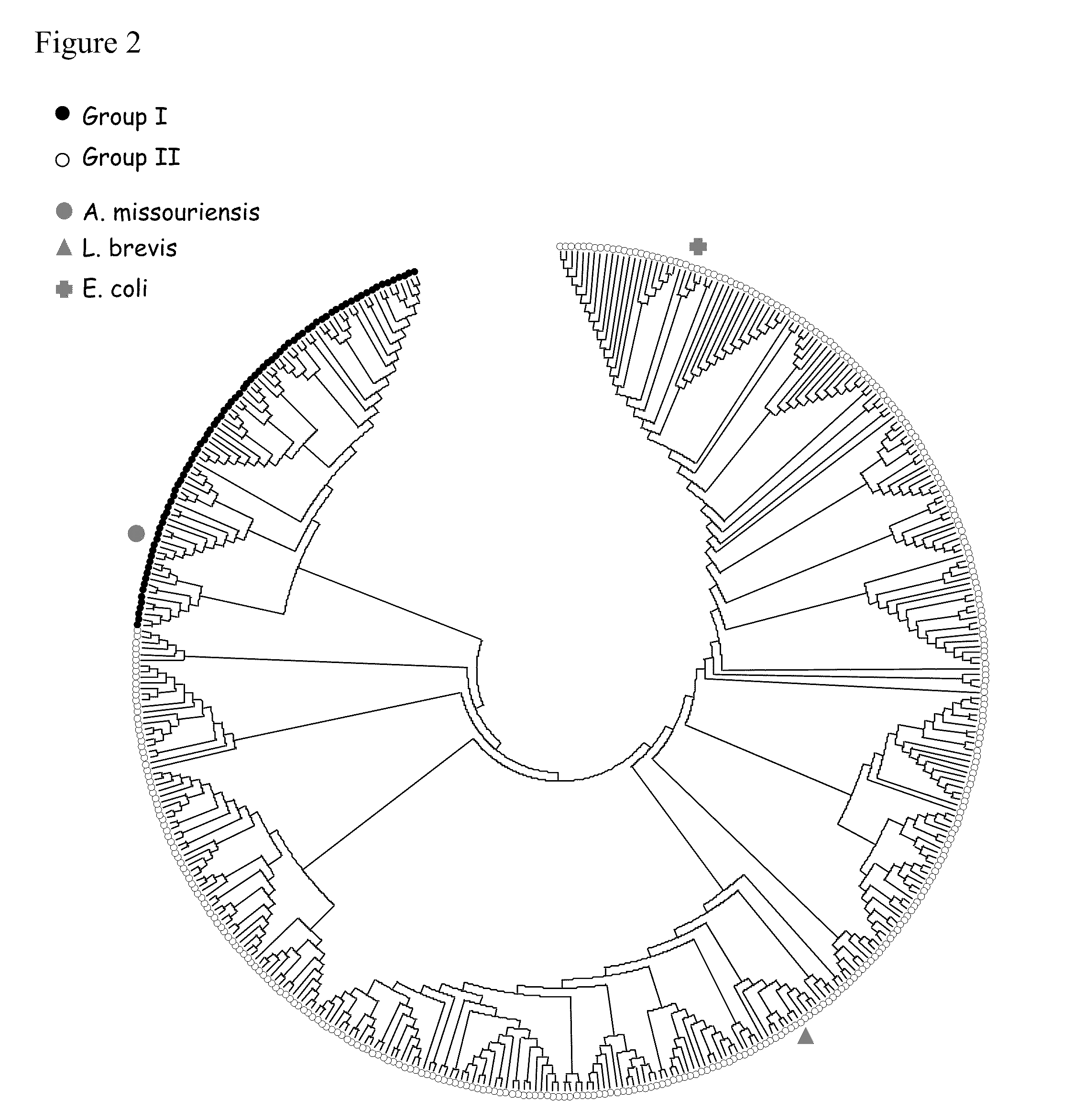
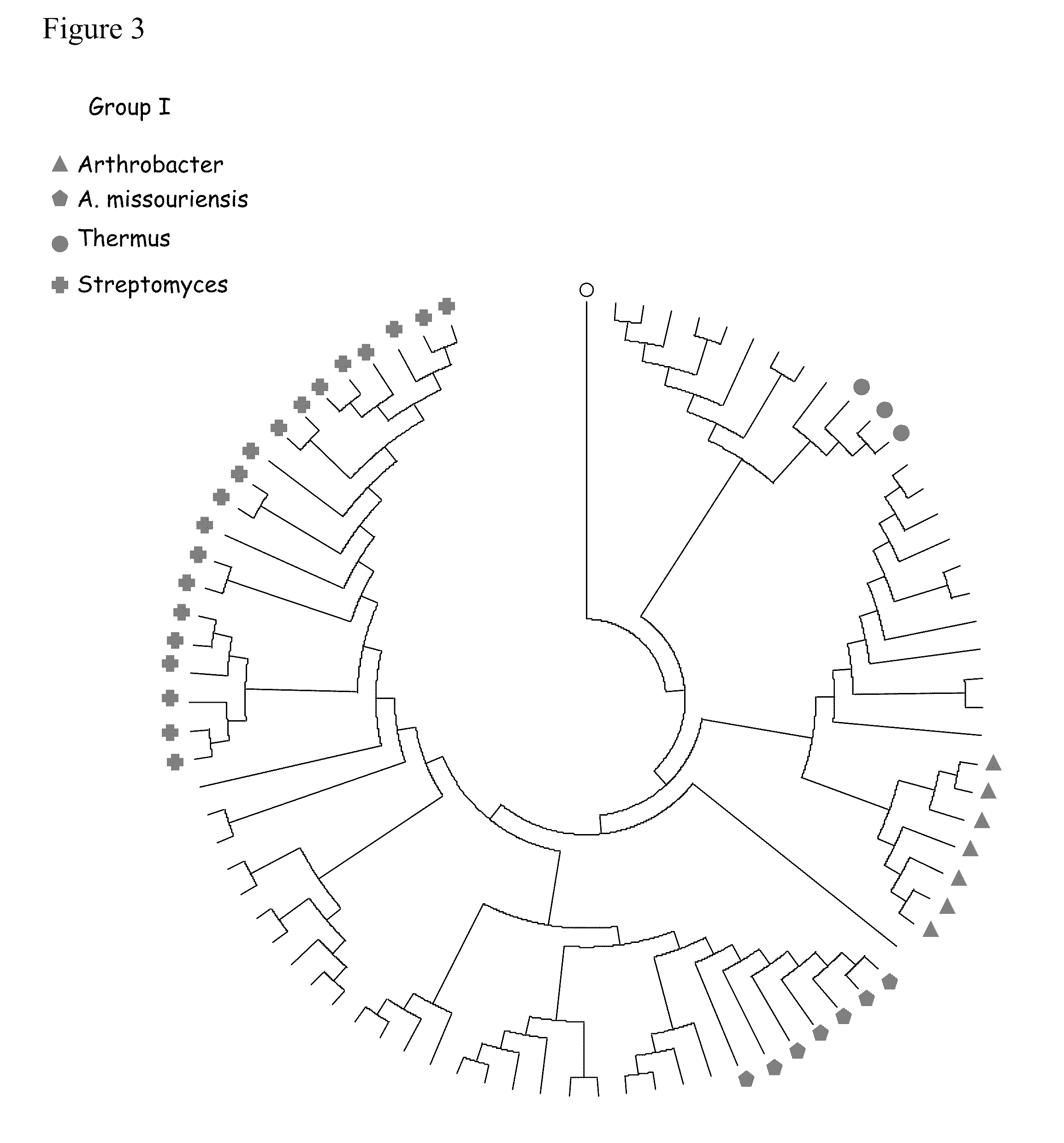
Xylose utilization in recombinant zymomonas
ActiveUS20110318801A1Increase productionImprove utilizationBacteriaBiofuelsHide markov modelMolecular phylogenetics
Zymomonas expressing xylose isomerase from A. missouriensis was found to have improved xylose utilization, growth, and ethanol production when grown in media containing xylose. Xylose isomerases related to that of A. missouriensis were identified structurally through molecular phylogenetic and Profile Hidden Markov Model analyses, providing xylose isomerases that may be used to improve xylose utilization.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
High expression Zymomonas promoters
Identified are mutants of the promoter of the Z. mobilis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, which direct improved expression levels of operably linked heterologous nucleic acids. These are high expression promoters useful for expression of chimeric genes in Zymomonas, Zymobacter, and other related bacteria.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization in stress conditions
ActiveUS20110014670A1Improved xylose utilizationBacteriaUnicellular algaeAcetic acidStress conditions
Strains of xylose utilizing Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization and ethanol production during fermentation in stress conditions were obtained using an adaptation method. The adaptation involved continuously growing xylose utilizing Zymomonas in media containing high sugars, acetic acid, ammonia, and ethanol.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Ethanol production using xylitol synthesis mutant of xylose-utilizing zymomonas
InactiveUS20080187973A1Speed up the conversion processReduces glucose-fructose oxidoreductase activityBacteriaBiofuelsMutantZymomonas
Production of ethanol using a strain of xylose-utilizing Zymomonas with a genetic modification of the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene was found to be improved due to greatly reduced production of xylitol, a detrimental by-product of xylose metabolism synthesized during fermentation.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization in stress conditions
Strains of xylose utilizing Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization and ethanol production during fermentation in stress conditions were obtained using an adaptation method. The adaptation involved continuously growing xylose utilizing Zymomonas in media containing high sugars, acetic acid, ammonia, and ethanol.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
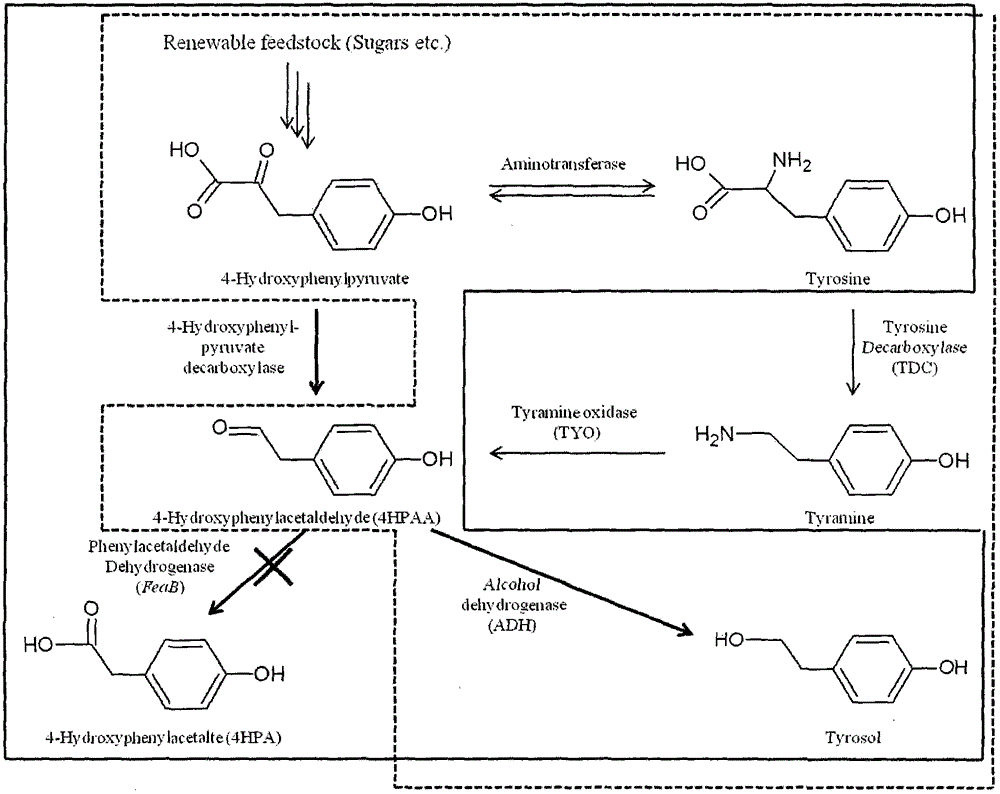
Method for biosynthesis of tyrosol in Escherichia coli and application of tyrosol
ActiveCN104099379ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhenylacetaldehyde dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a method for biosynthesis of tyrosol in Escherichia coli and application of tyrosol, which belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. According to the method for biosynthesis of tyrosol in Escherichia coli, tyrosine or glucose is used as a substrate, (4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvic acid is produced under the catalysis of ammonialyase coded by Escherichia coli; (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde is produced under the action of the microzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate decarboxylase; (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde is catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase so as to produce tyrosol; and a phenylacetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli is knocked out at the same time so as to block the transformation channel for (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde into (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid and promote accumulation of (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde and transformation of (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde into tyrosol. The invention provides a novel production approach for tyrosol; and the method lays a foundation for large-scale industrial production of tyrosol and has important economic values and social benefits.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Zymomonas with improved ethanol production in medium containing concentrated sugars and acetate
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Process for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation for production of ethanol
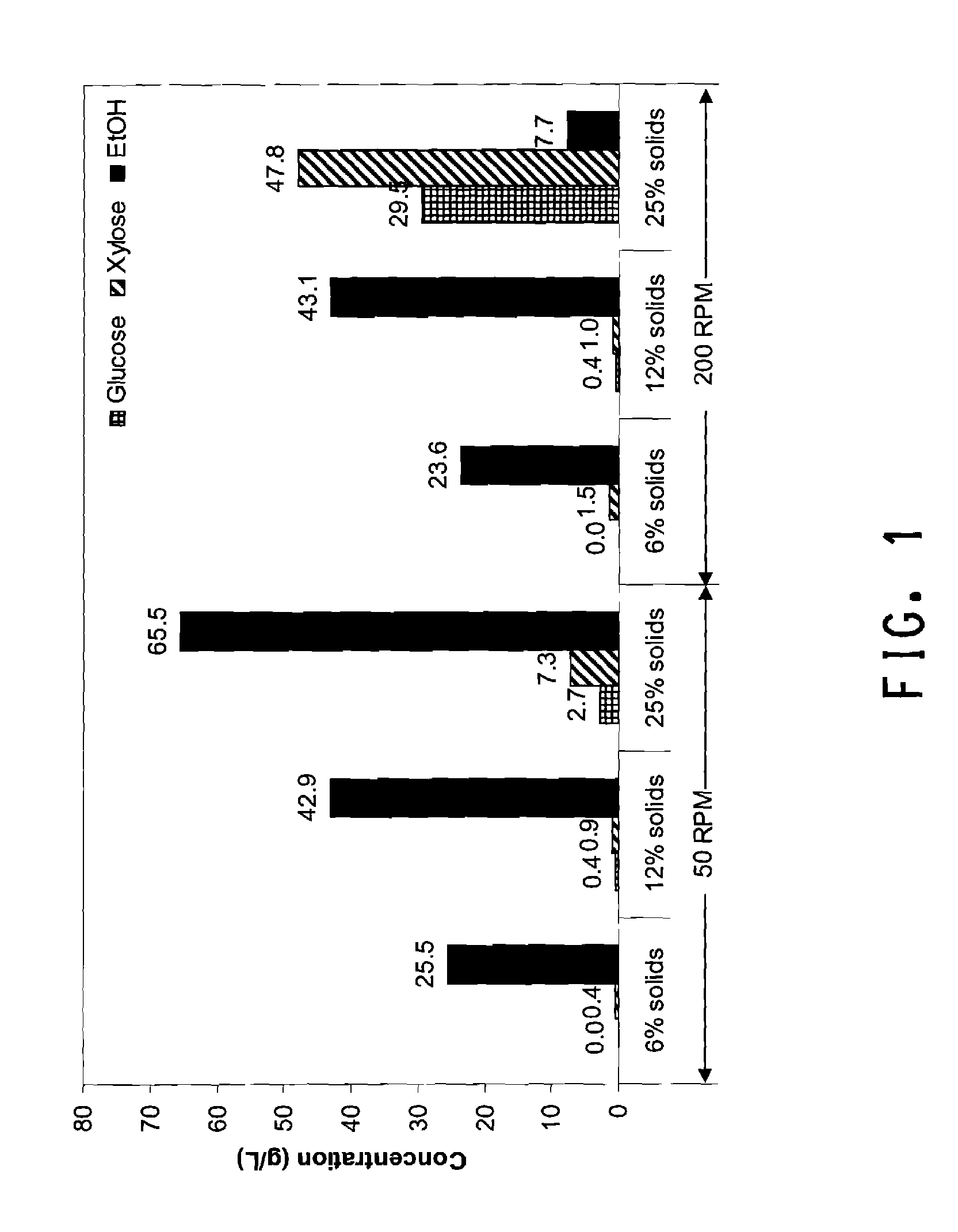
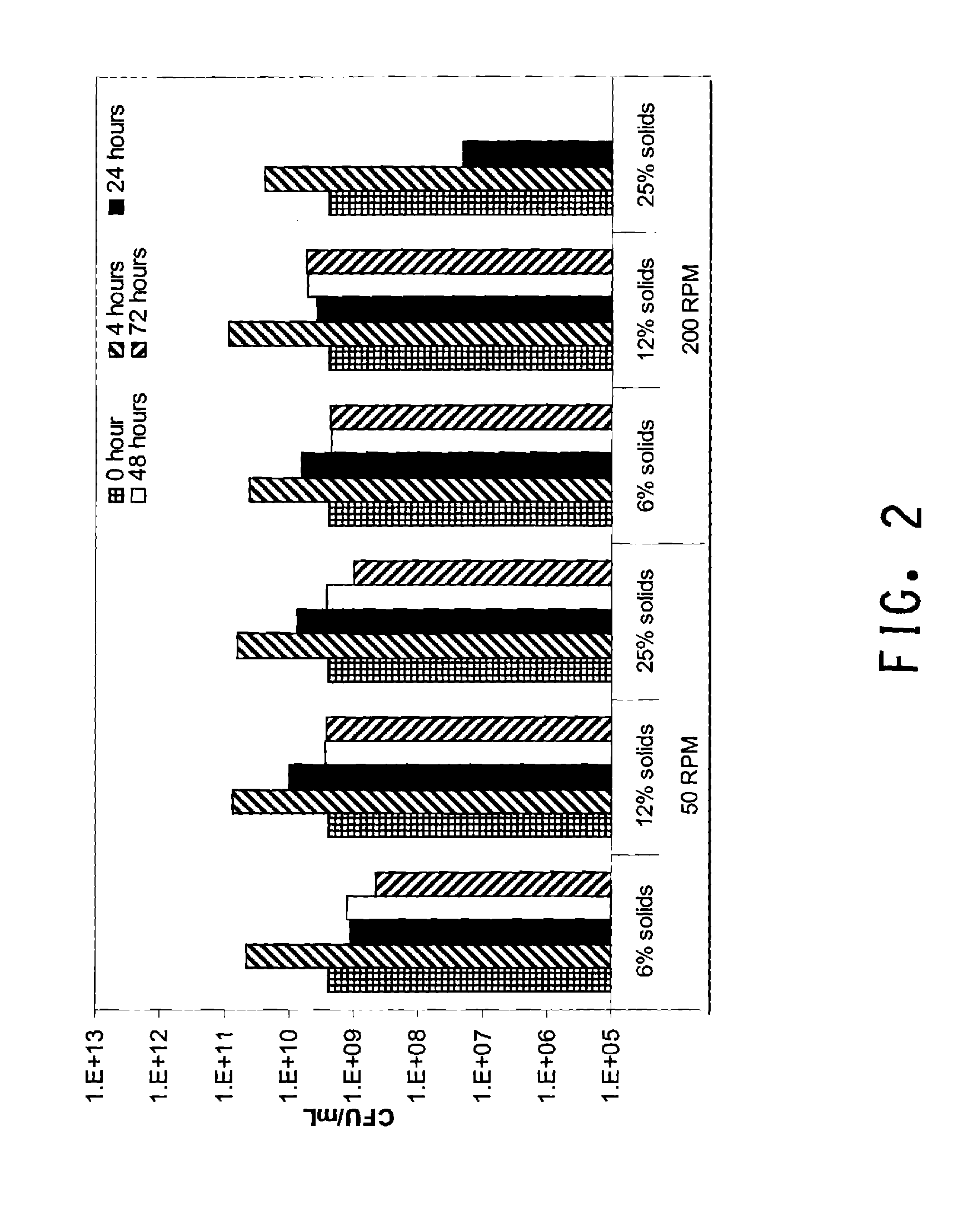
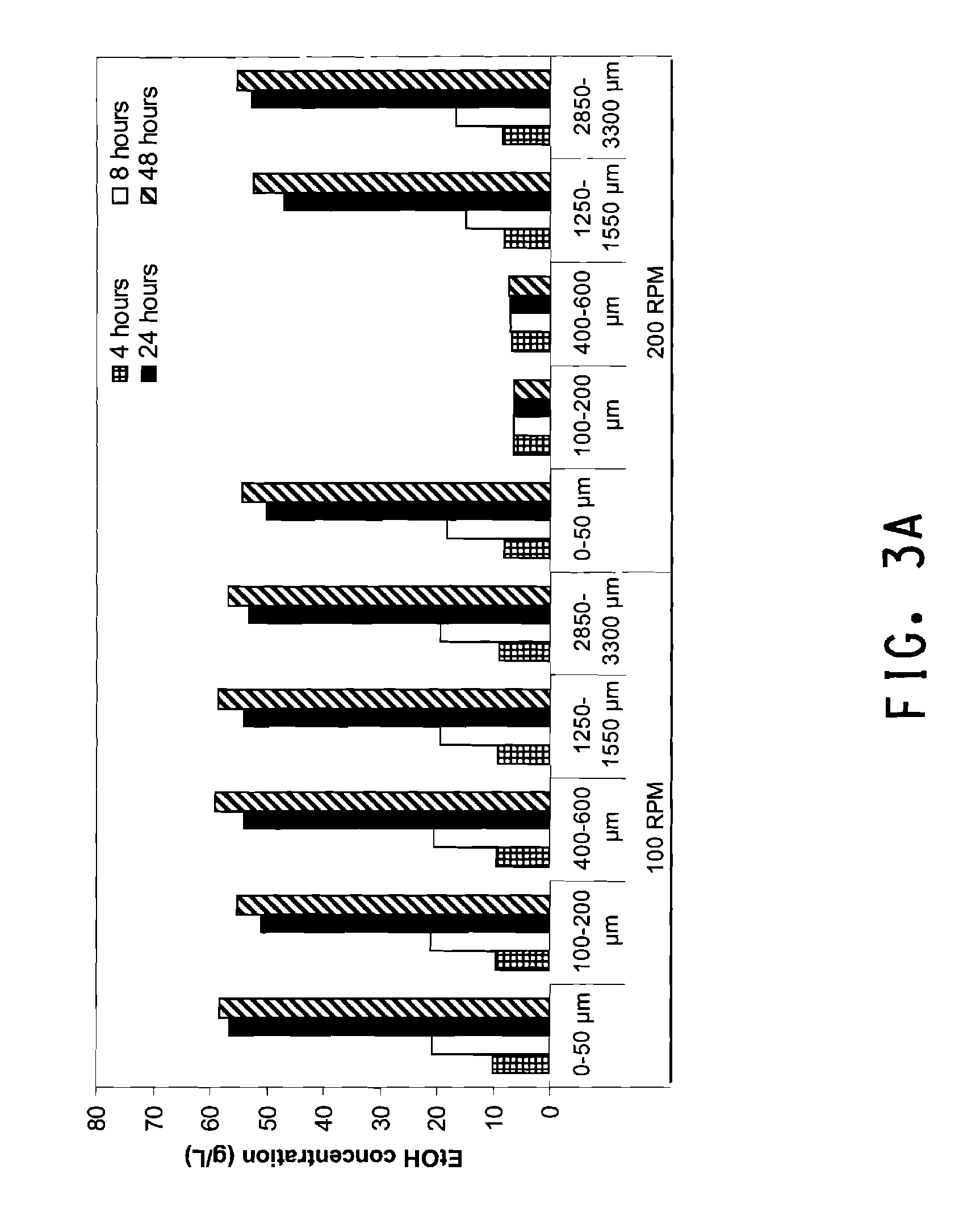
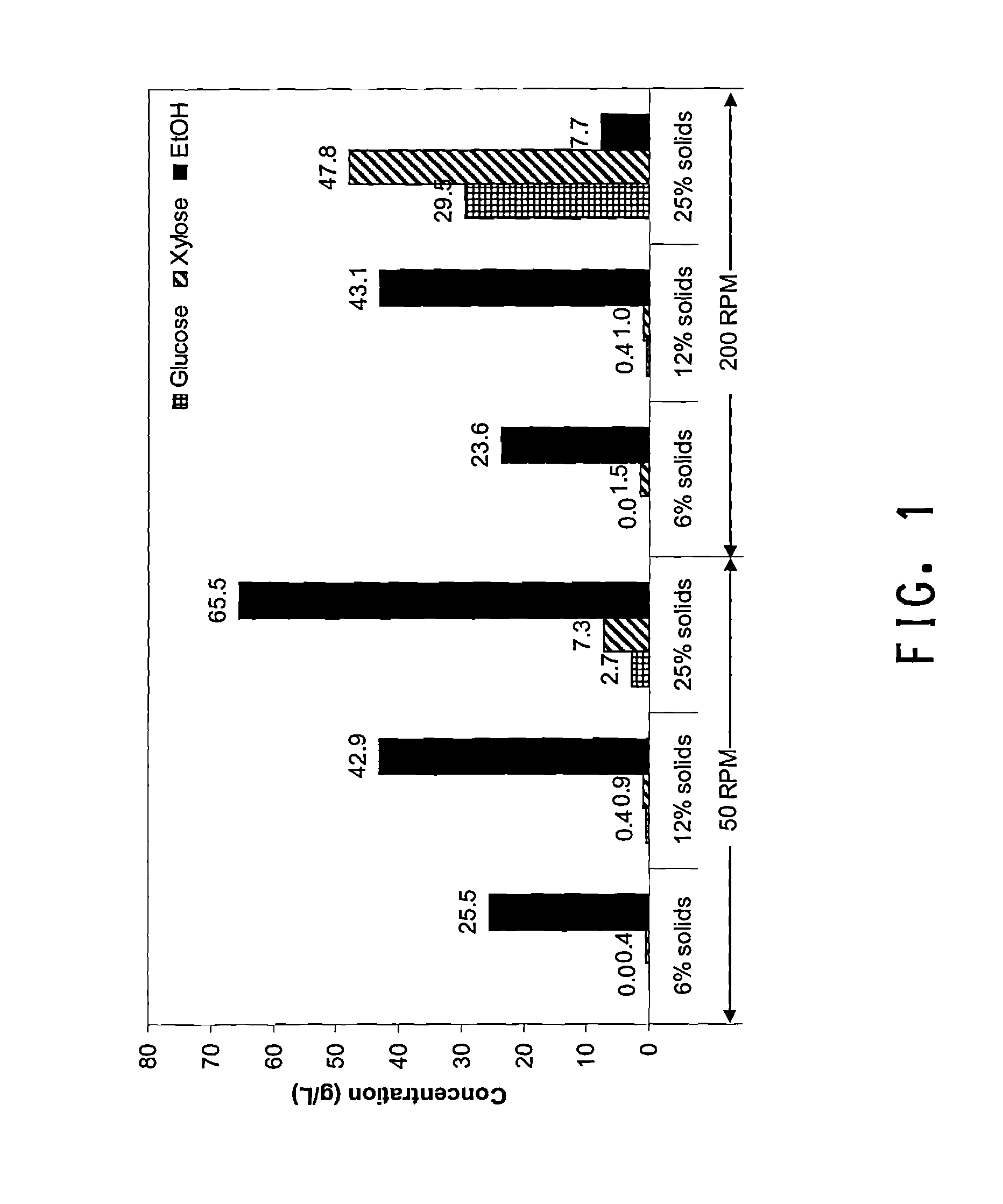
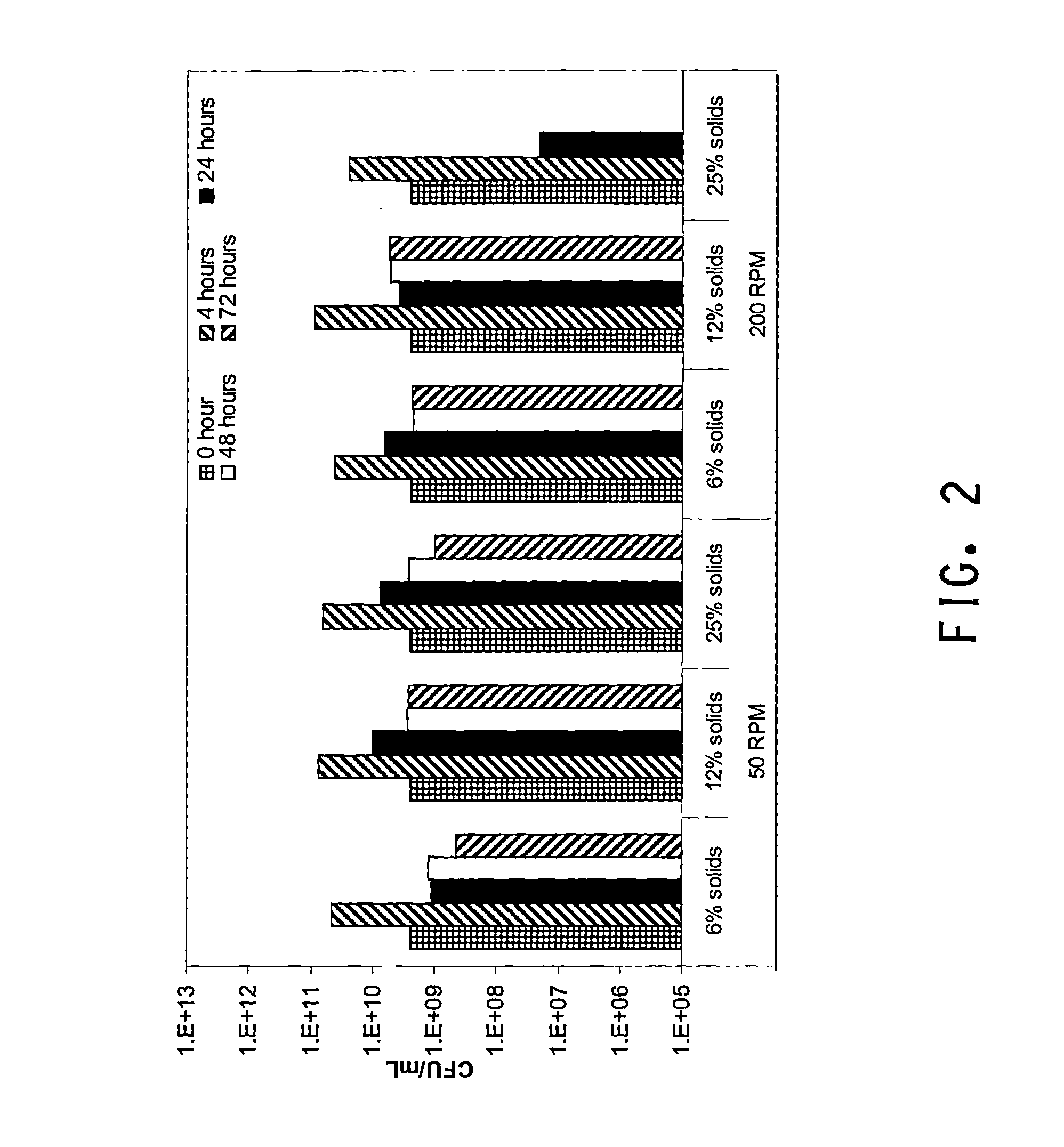
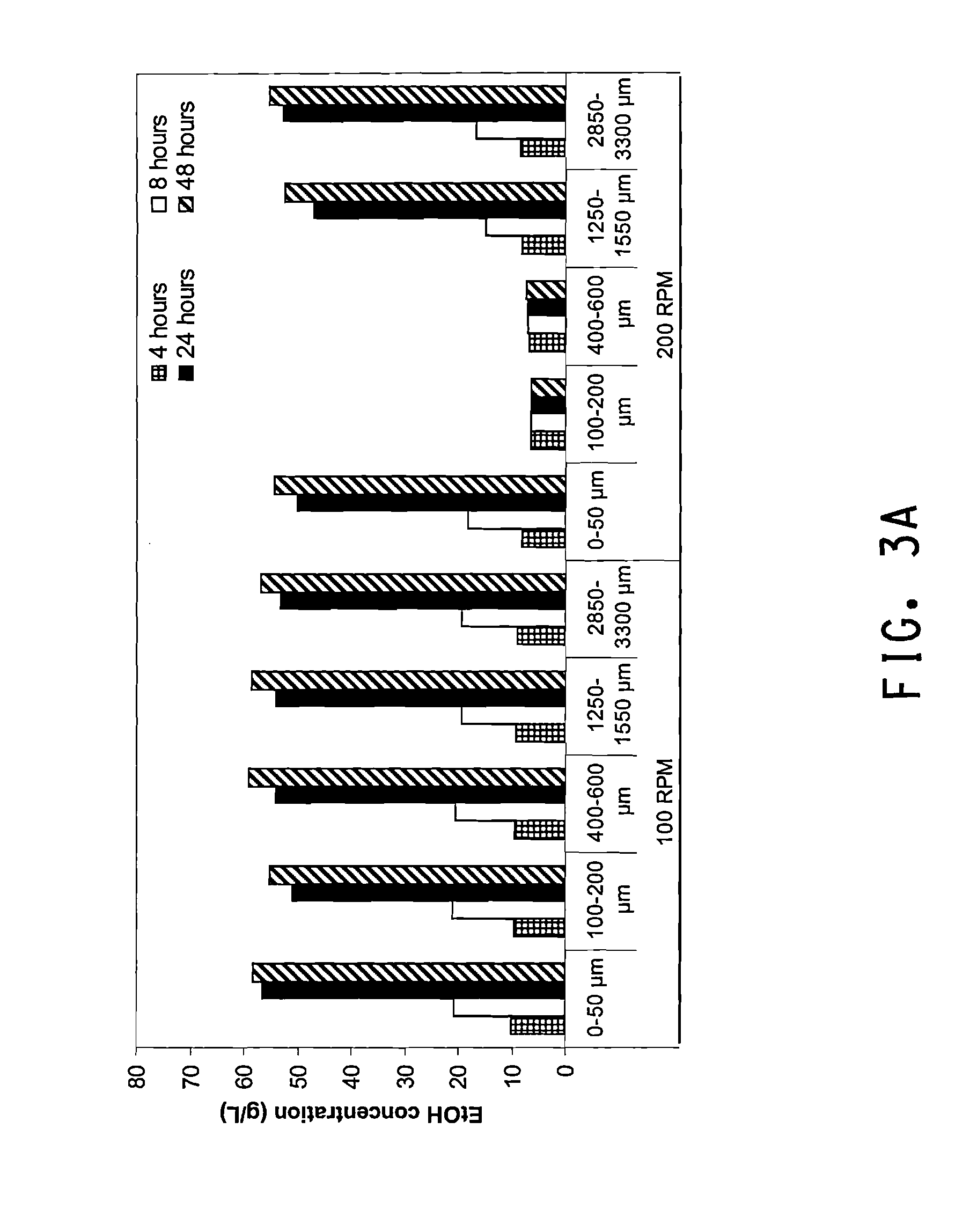
Methods are disclosed for the production of high concentrations of ethanol from biomass using Zymomonas as the ethanologen. Zymomonas is grown under conditions of low impeller agitation with high concentration of insoluble solids in a saccharification-fermentation mixture during a simultaneous saccharification and fermentation reaction for the production of high concentrations of ethanol.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
High expression zymomonas promoters
ActiveUS20090246876A1High activityImprove scalabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesHeterologous
Identified are mutants of the promoter of the Z. mobilis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, which direct improved expression levels of operably linked heterologous nucleic acids. These are high expression promoters useful for expression of chimeric genes in Zymomonas, Zymobacter, and other related bacteria.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Complex bacteria for preprocessing of restaurant garbage, preparation method and application thereof
The present invention relates to a composite microbial agent, a preparation method thereof and an application in the preprocessing of kitchen garbage. The active ingredients of the composite microbial agent include 15 percent to 30 percent of bacillus stearothermophilus, 10 percent to 25 percent of bacillus licheniformis, 10 percent to 25 percent of zymomonas, 10 percent to 25 percent of agrobacterium, 15 percent to 30 percent of saccharomyces cerevisiae and 10 percent to 25 percent of candida, which are blended together. The composite microbial agent is prepared according to the following method: (1) the strains, which are preserved under the temperature of 4 DEG C, are respectively inoculated in ordinary broth media, the inoculation amount is 0.1 percent (v / v), and under the temperature between 28 DEG C and 37 DEG C, activating culture lasts for 8 to 18 hours; (2) the strains are then respectively transinoculated into ordinary broth media to be cultured for 8 to 18 hours under the temperature between 28 DEG C and 34 DEG C, the inoculation amount is between 0.1 percent (v / v) and 0.5 percent (v / v), and after culturing, microbial liquids are blended according to the proportion. The composite microbial agent can be used to preprocess kitchen garbage, inhibit the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms in the kitchen garbage and reduce the deterioration and stink of the kitchen garbage, so that the kitchen garbage can be conveniently processed later, so the application prospect of the composite microbial agent is wide.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDENWAY BIO TECH
Method for preparing bio-ethanol by taking seaweed processing waste as raw material
InactiveCN101701225AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyOpportunity for facilitationMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberCellulose compounds
The invention relates to a method for preparing bio-ethanol by taking seaweed processing waste as raw material, which is characterized by comprising the steps: selecting the seaweed processing waste, and pretreating the raw material by sulfuric acid or hydrogen peroxide; then, adding cellulase or cellobiase for cellulose compound enzymolysis, and filtering enzymolysis liquid to remove insoluble components; and finally, supplementing inorganic salt, inoculating saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and carrying out alcoholic fermentation under the anaerobic condition. The original structure of algae cellulose is changed by the pretreatment process, and the action probability between the cellulose and degrading enzyme can be promoted, so that the enzymolysis efficiency of the cellulose is improved; furthermore, after the cellulose is treated by the compound enzymolysis of the cellulase and the cellobiase, the feedback inhibition of the cellobiose for the cellulose can be effectively eliminated, the content of glycolysis sugar of yeast can be improved, and the yield of alcoholic fermentation is further improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
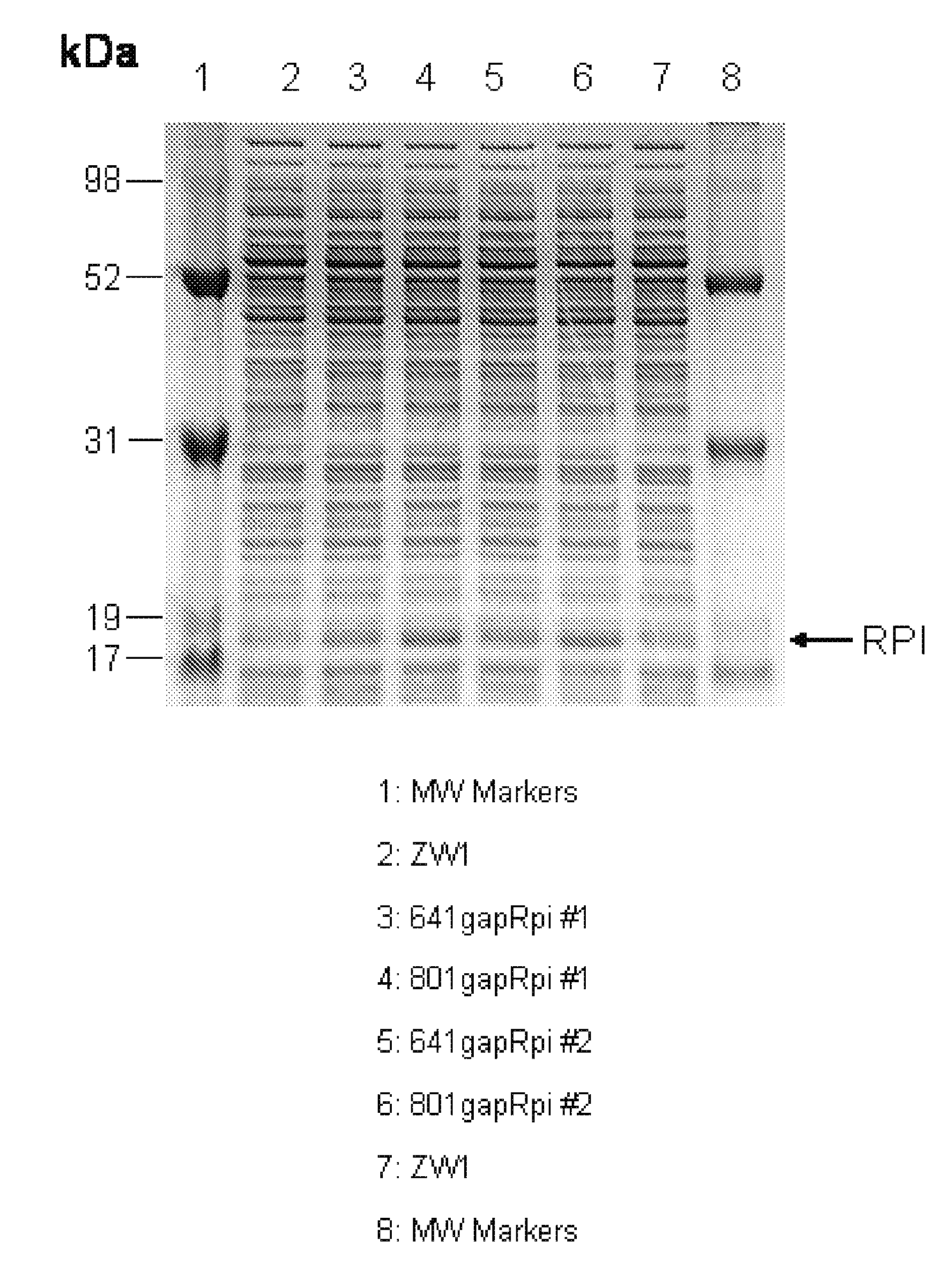
Pnp gene modification for improved xylose utilization in zymomonas
InactiveUS20130157331A1High activityNon-limiting xylose isomerase activityBacteriaTransferasesRibose-5-phosphate isomeraseZymomonas
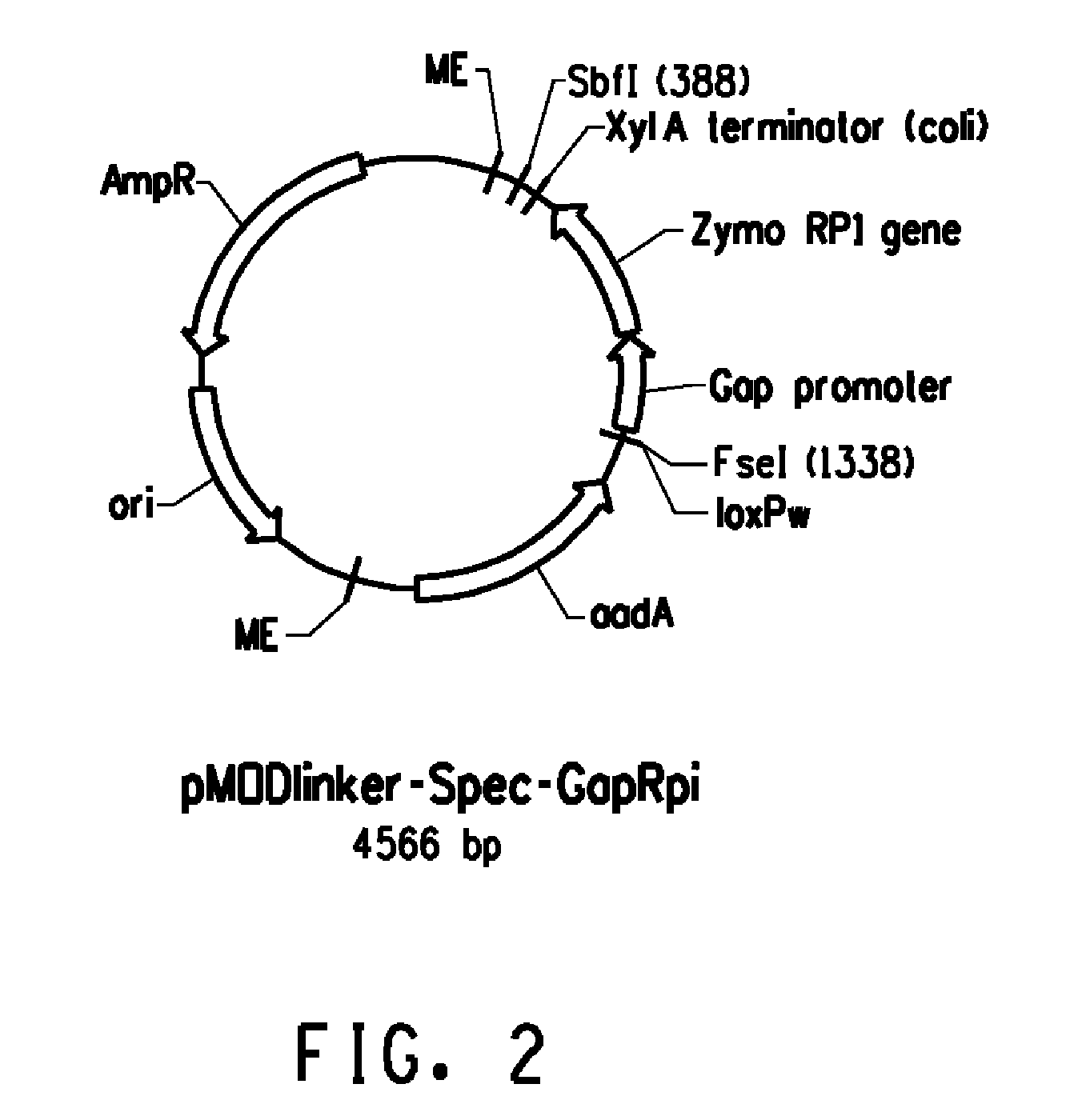
The endogenous pnp gene encoding polynucleotide phosphorylase in the Zymomonas genome was identified as a target for modification to provide improved xylose utilizing cells for ethanol production. The cells are in addition genetically modified to have increased expression of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (RPI) activity, as compared to cells without this genetic modification, and are not limited in xylose isomerase activity in the absence of the pnp modification.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
Process for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation for production of ethanol
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
Formula and preparation method of yeast liquid biocontrol bactericide
InactiveCN103583576AReduce incidenceImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideFungicidesSucrosePhosphate
The invention discloses a formula and a preparation method of a yeast liquid biocontrol bactericide. The formula comprises yeasts, sucrose, trehalose, galactose, ascorbic acid and a 0.05 mol / L phosphate buffer solution. The method comprises the following steps: activating a yeast strain 4-4A by an NYDB (nutrient yeast dextrose broth) liquid culture medium and inoculating two rings into 50 ml of a seed culture medium; putting a cultured yeast fermentation solution into 50 ml of a centrifugal pipe for conducting a centrifuging process at a speed of 4000 r / min for 15 minutes, dumping supernatant liquor, washing by aseptic water for two times, and adding obtained sediments into the 0.05 mol / L phosphate buffer solution to prepare a bacterial suspension solution; selecting the sucrose, the galactose and the trehalose as protecting agents for preparing a solution by the phosphate buffer solution; adding 21.6 ml of the solution into 2.4 ml of a yeast mother solution with 109 CFU / ml (colony forming unit / ml) of the yeasts, fully and uniformly mixing, and sub-packaging a mixture into 1.5 ml of the centrifugal pipe; measuring the number of living yeasts in a yeast preparation. According to the yeast liquid biocontrol bactericide, the occurrence rate of anthracnose after mangoes are harvested is effectively reduced, the yeast liquid biocontrol bactericide is applied for 4-6 times from an early flowering period to a harvest period to prevent and control mango anthracnose, the morbidity and the severity are reduced by 64%-67% and 89%-90% respectively, and the disease prevention and control effect is improved.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for Fermentation and Culture, Fermented Plant Extract, Fermented Plant Extract Composition, Method for Producing Lipopolysaccharide and Lipopolysaccharide
ActiveUS20090162344A1Safe and reliable and inexpensiveCosmetic preparationsBacteriaBiotechnologyEnterobacter
In order to provide a method for culturing an immunopotentiator-containing organism having the experience of being eaten, inexpensively without requiring usage of a component derived from an animal, Acetobacter, Gluconobacter, Xanthomonas, Zymomonas or Enterobacter which is an edible gram-negative bacterium having an immunopotentiation function is cultured using a culture solution composed mainly of wheat or bean curd refuse. Thereby, Acetobacter can be obtained inexpensively and safely, and also a low molecular weight lipopolysaccharide which is the immunopotentiator can be obtained inexpensively and safely. Furthermore, no impurity derived from animal components is mixed.
Owner:SOMA +1
Method for producing alcohol by using dry plate of banana dasheen as raw material
InactiveCN1696295AImprove and improve the way of addingReduce manufacturing costBiofuelsFermentationAlcoholDigestion
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Method for increasing phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin
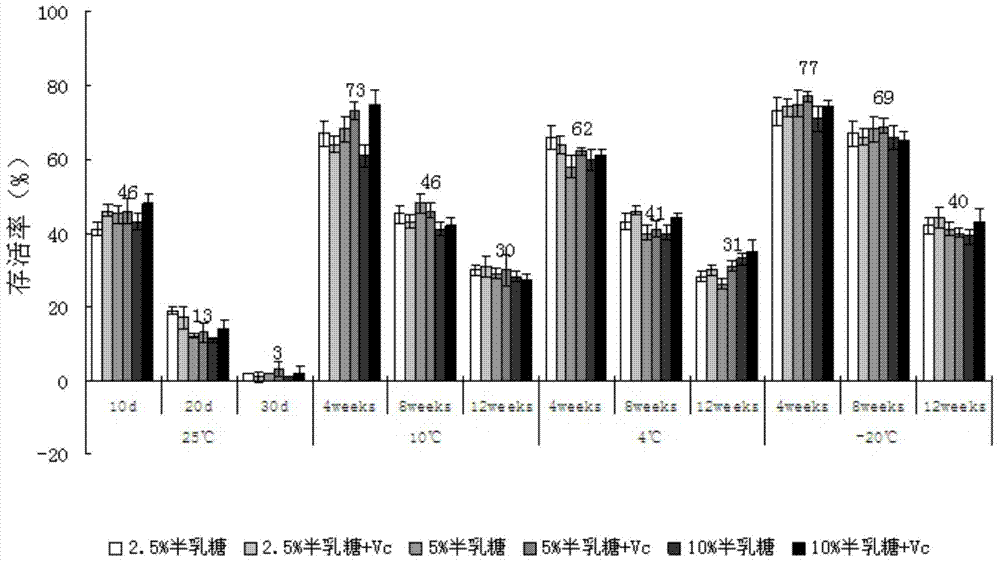
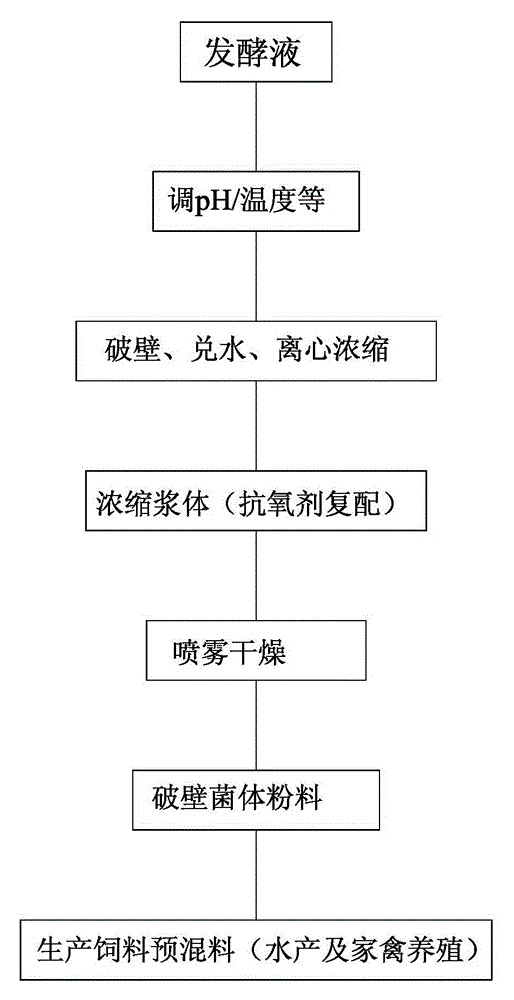
The invention discloses a method for increasing phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin, which comprises the following steps: adjusting pH value of a phaffia rhodozyma broth to 9.0-11.5, controlling the temperature at 35-60 DEG C, stirring for 80-150r / min, breaking wall for 1.0-5.0; neutralizing the pH value to 6.0-7.5, mixing with water having 0.5-1 times of volume, centrifuging and concentrating to obtain the concentrated wall breaking phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin slurry; then uniformly mixing with a proper amount of complex formulation anti-oxidant and performing spray drying, wherein the air intake temperature is 170-185 DEG C, air-out temperature is 70-85 DEG C, and obtaining the astaxanthin dry powder, wherein the moisture of the dry powder is less than 8%, and spray loss amount is less than 4.0%. According to the invention, the method is simple and practical, total pigment can be increased by 10-12%, wall breaking time is short, cost is low, and the method is suitable for industrial production, shelf time of the produced astaxanthin dry powder is longer, taste is fragrant and unique, the phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin has good palatability, and the dry powder can be widely used in animal feed industry.
Owner:XIAMEN HUISON BIOTECH
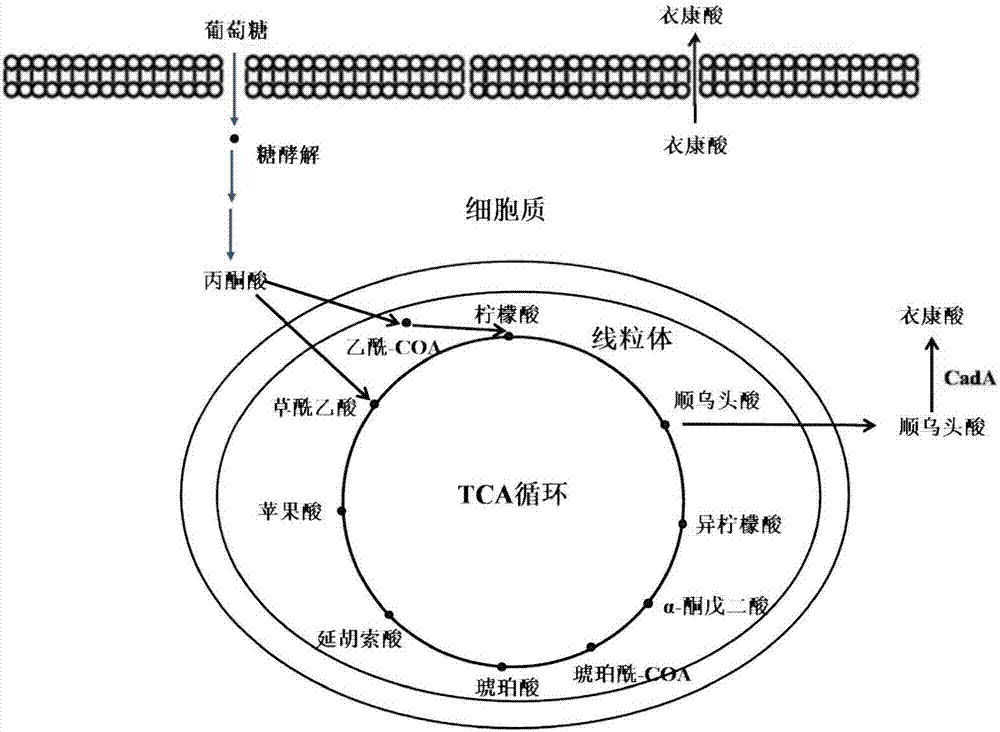
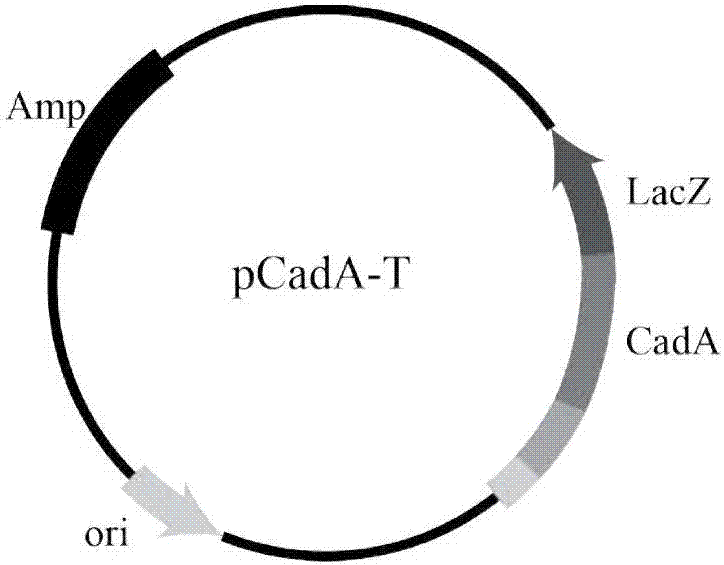
Recombinant yeast strain for generating itaconic acid, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN107058144AStrong toleranceStrong application valueFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
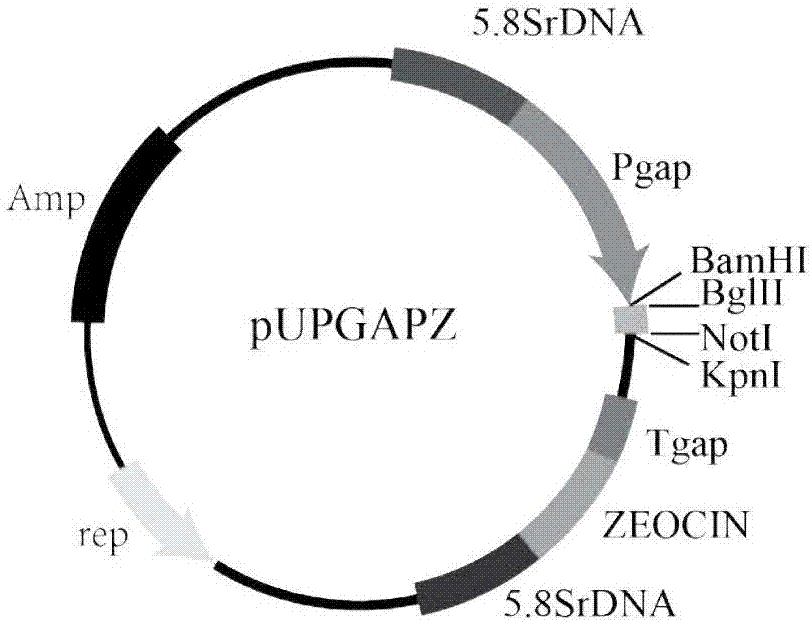
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast strain for generating itaconic acid, and a construction method and application thereof. The recombinant yeast strain is acquired in the manner of taking C. glycerolgenesis as an original strain and inserting aconitate decarboxylase gene into the C. glycerolgenesis gene. The recombinant plasmid of a genetic expression box containing aconitate decarboxylase gene Pgap-CadA-Tgap-zeocin is constructed through genetic engineering reformation, the recombinant plasmid is linearized and then is inserted into a C. glycerolgenesis genome for expressing aconitate decarboxylase and catalyzing aconitate, and then the itaconic acid can be acquired. The recombinant yeast strain provided by the invention can synthesize itaconic acid, and a new thought is provided for producing itaconic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fuel ethanol, and preparation method
InactiveCN101003818ALess investmentShort fermentation cycleBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesYeastDistillation
This invention discloses transparent liquid fuel ethanol with purity higher than 99%. This invention also discloses a method for preparing the fuel ethanol. The method comprises: washing sweet broomcorn straw, juicing, adding 0.2% ammonium sulfate and 10% activated ethanol yeast into the juice, fermenting at 30 deg.C for 48 h, and dehydrating by distillation to obtain fuel ethanol; or cutting sweet broomcorn straw into 2 cm segments, adding 10% activated ethanol yeast, adding 0.2% ammonium sulfate, sealing and fermenting at 32-34 deg.C for 72h, and dehydrating by distillation to obtain fuel ethanol. The method has such advantages as low cost, simple process, low apparatus investment, and easy operation.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Recombinant l-asparaginase from zymomonas
InactiveUS20160348085A1Low costHigh outputHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseZymomonas mobilis
The present invention relates to the construction and optimization of synthetic genes from the Zymomonas mobilis L-asparaginase gene, the method for cloning same and expression thereof in Escherichia coli. The purpose of the production of said enzyme is for producing high levels of a novel L-asparaginase that can be used in L-asparaginase-based pharmaceutical compositions for treating cancer, tumours and diseases involving cell proliferation, as well as for other medical applications.
Owner:INST ALBERTO LUIZ COIMBRA DE POS GRADUACAO E PESQUISA DE ENGENHARIA COPPE UFRJ
A Method Of Producing High Amount Of Ethanol At High Temperature By Modified Yeast Strain Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
ActiveUS20180327709A1Low input costImprove downstream processingFungiCulture processFlocculationYeast strain
The present invention relates to a modified yeast strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae having MCC accession number 0069 with osmo-tolerant, thermo-tolerant, ethanol tolerant and self-flocculation properties. Further, the present invention relates to a method for obtaining modified yeast strain. The present invention also relates to a method of production of ethanol at high temperature using said yeast strain. The ethanol produced by the method disclosed in the present invention is used as fuel.
Owner:SURANA RAJENDRA
Method for producing ethanol by virtue of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of starch-based biomass
InactiveCN103898165AReduce dosageIncrease glycationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrolysateAlpha-amylase
The invention provides a method for producing ethanol by virtue of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of a starch-based biomass. The method comprises the steps of saccharifying the starch-based biomass by using an alpha-amylase and a saccharifying enzyme in a saccharification kettle; collecting accharified liquor after enzymolysis; and fermenting the saccharified liquor by using a yeast culture medium in a fermentation kettle to obtain a fermentation liquor containing ethanol. The method is characterized in that one part of the saccharified liquor is collected from the saccharification kettle and conveyed to a filtering device during the saccharification process, a solid phase obtained after filtering returns to the saccharification kettle, a liquid phase obtained after filtering is conveyed to the fermentation kettle, and meanwhile, the fermentation liquor of the same volume circularly returns to the saccharification kettle. The invention also provides a device for producing ethanol by virtue of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of the starch-based biomass. The method and the device have the advantages that the inhibition effect on the alpha-amylase and the saccharifying enzyme due to the accumulation of glucose in a hydrolysate in a step-by-step saccharification and fermentation process is avoided, the dosage of the enzymes is reduced and the cost is reduced.
Owner:JILIN DESIGNING INST OF CNPC NORTHEAST REFINING & CHEM ENG
Preparation method of cellulosic ethanol
InactiveCN106967757AGuaranteed outputReduce pollutionBiofuelsFermentationXylose fermentationResource utilization
The invention discloses a preparation method of cellulosic ethanol. The method includes the steps of firstly, performing explosion pretreatment on a cellulose raw material to obtain a preliminarily degraded material suitable for biomass conversion; secondly, mixing molasses with the material obtained in the first step, regulating pH to 3.5-4.5, and performing enzymolysis to obtain fermenting mash; regulating the pH of the fermenting mash obtained in the second step to 4-5, adding yeast which can use xylose fermentation to obtain ethanol to perform fermentation, adding Trichoderma reesei when the fermentation is performed for 6-10 hours, adding saccharomyces cerevisiae when the fermentation is performed for 10-16 hours, continuing fermenting for 30-48 hours to obtain a material containing the cellulosic ethanol, and separating ethanol from the material. The preparation method has the advantages that the ethanol is prepared by the effective resource utilization of the cellulose and the molasses, pentose utilization degree is increased, raw material use amount is lowered, and production cost and environment pollution can be lowered evidently.
Owner:广西轻工业科学技术研究院有限公司 +1
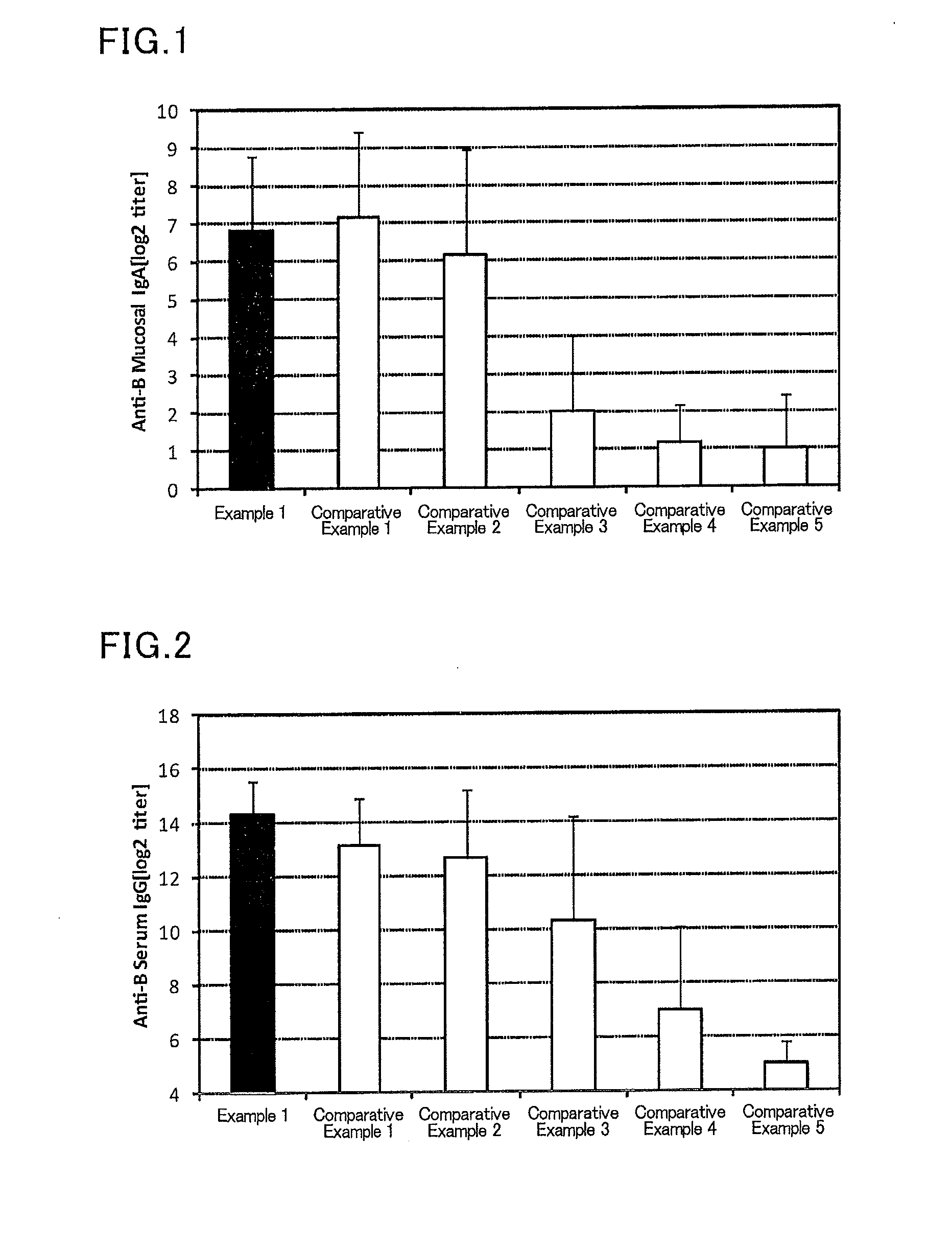
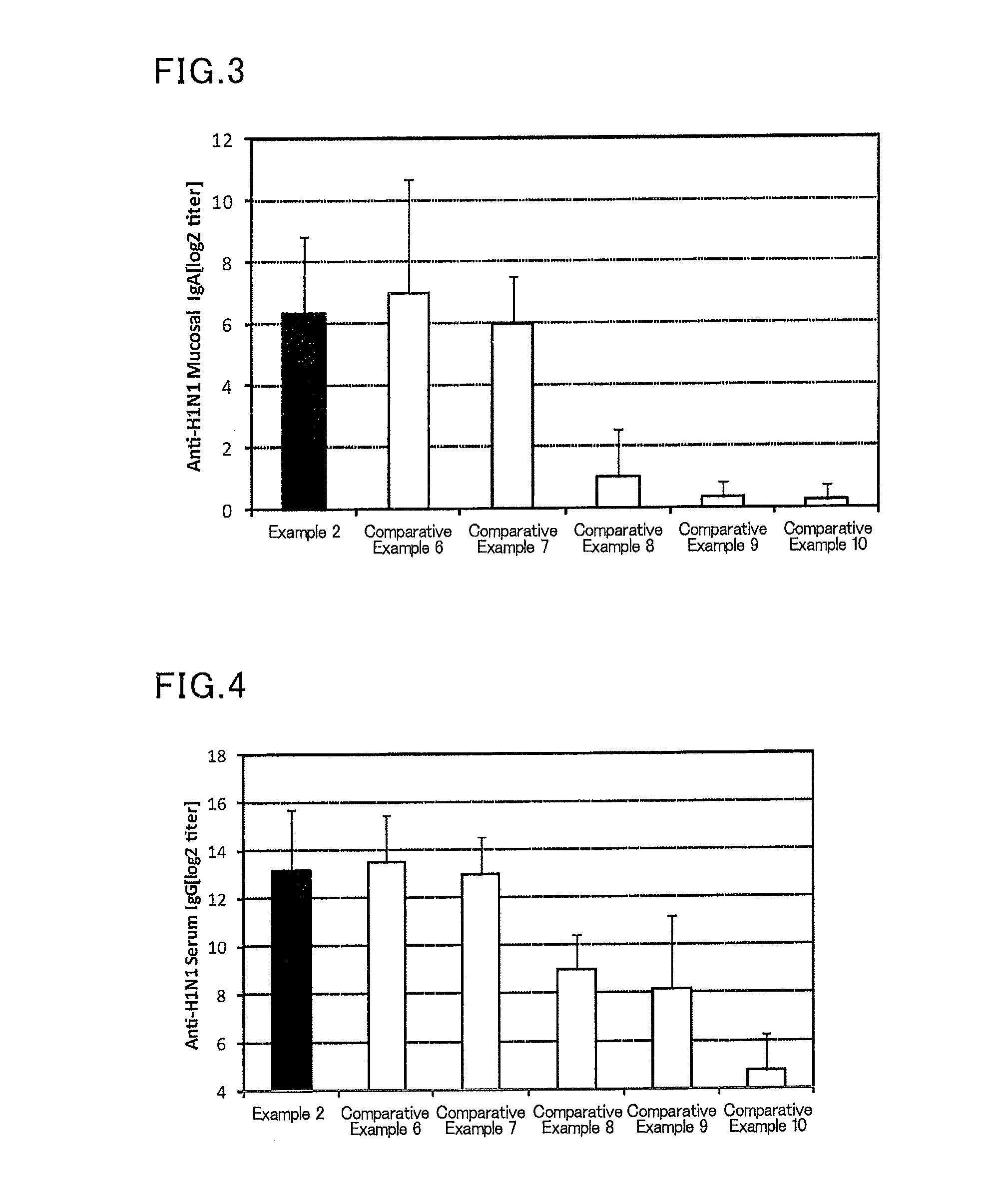
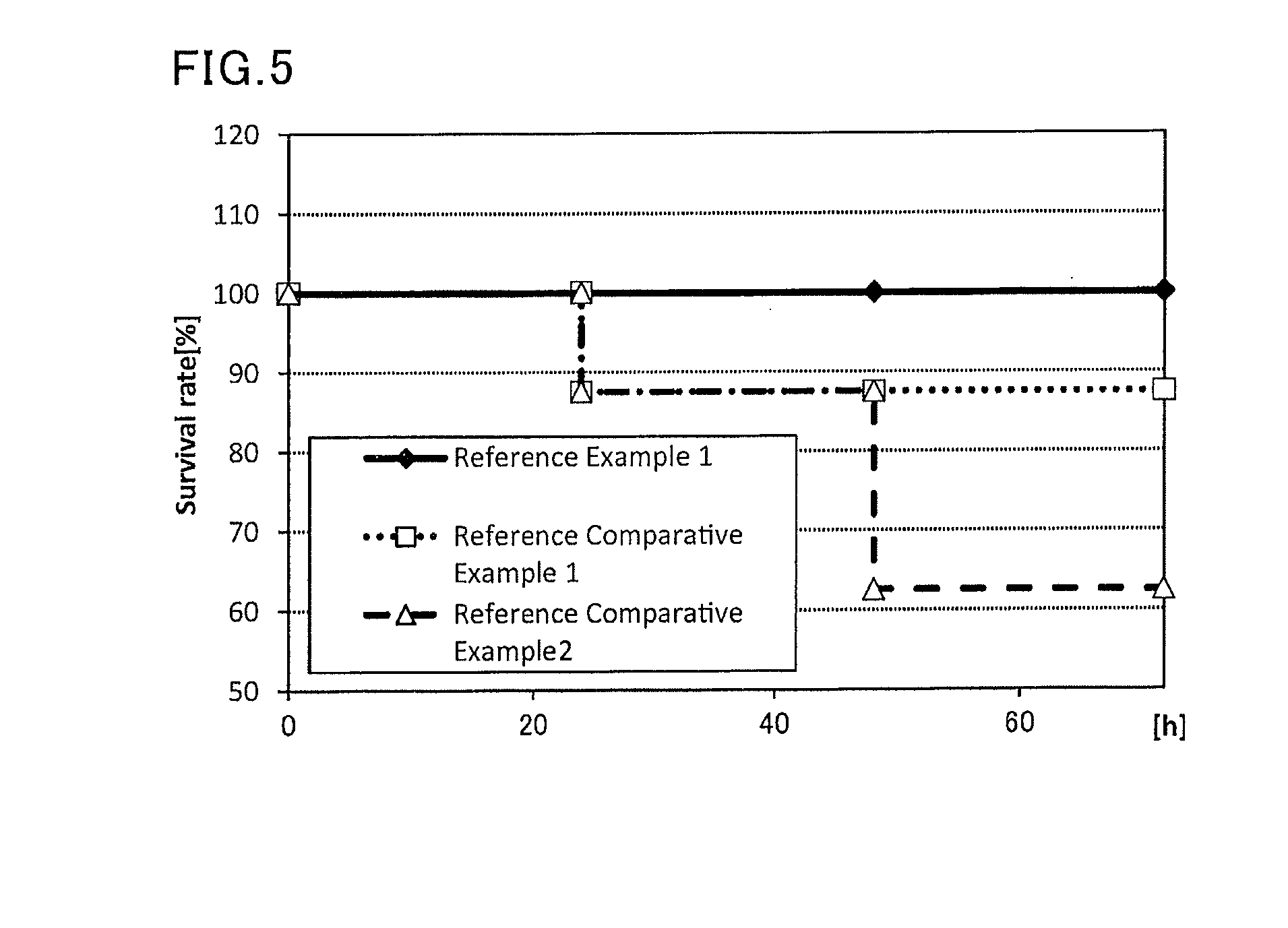
Mucosal vaccine composition
ActiveUS20160193327A1Safe and effectiveSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsMucosal Immune ResponsesXanthomonas
The present invention aims at providing a mucosal vaccine composition that can be administered to an intraoral mucous membrane, ocular mucous membrane, ear mucous membrane, genital mucous membrane, pharyngeal mucous membrane, respiratory tract mucous membrane, bronchial mucous membrane, pulmonary mucous membrane, gastric mucous membrane, enteric mucous membrane, or rectal mucous membrane, that is useful as a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for infectious diseases or cancers, and is capable of safely and effectively inducing the systemic immune response and mucosal immune response. The present invention provides a mucosal vaccine composition to be administered to at least one mucous membrane selected from the group consisting of a human or animal intraoral mucous membrane, ocular mucous membrane, ear mucous membrane, genital mucous membrane, pharyngeal mucous membrane, respiratory tract mucous membrane, bronchial mucous membrane, pulmonary mucous membrane, gastric mucous membrane, enteric mucous membrane, and rectal mucous membrane, containing: at least one antigen; and as an adjuvant, a lipopolysaccharide derived from at least one gram-negative bacterium selected from the group consisting of Serratia, Leclercia, Rahnella, Acidicaldus, Acidiphilium, Acidisphaera, Acidocella, Acidomonas, Asaia, Belnapia, Craurococcus, Gluconacetobacter, Gluconobacter, Kozakia, Leahibacter, Muricoccus, Neoasaia, Oleomonas, Paracraurococcus, Rhodopila, Roseococcus, Rubritepida, Saccharibacter, Stella, Swaminathania, Teichococcus, Zavarzinia, Pseudomonas, Achromobacter, Bacillus, Methanoculleus, Methanosarcina, Clostridium, Micrococcus, Flavobacterium, Pantoea, Acetobacter, Zymomonas, Xanthomonas, and Enterobacter, or a salt thereof.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Engineering bacteria with motor fermented monad fructosan sucrase gene mutation construction and use thereof
InactiveCN1746311ATetracycline resistantIncreased conversion efficiency to ethanolBacteriaHydrolasesSaccharumSaccharophagus degradans
An engineering bacterium with levansucrase gene of kinesthetic zymomonas mutation, its construction and use are disclosed. The engineering bacterium is prepared by inserting tetracin resistance gene into levansucrase gene of kinesthetic zymomonas, inducing the obtained recombinant plasmid into kinesthetic zymomonas, screening mutant strain with tetracin resistance and obtaining target engineering bacterium. It has tetracin resistance and higher alcohol conversion rate.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing batroxobin through fermentation of recombinant methanol yeast
InactiveCN102242101AHigh activityHigh specific activityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesYeastArginine
The invention aims to provide a method for preparing batroxobin through fermentation of recombinant methanol yeast. The method comprises batch fermentation and fed-batch fermentation of yeast, and methanol induced expression of the batroxobin, wherein the yeast is recombinant site-directed mutated batroxobin that the 45-position arginine of natural batroxobin is mutated into lysine. The method is characterized in that: a carbon source for the batch fermentation and fed-batch fermentation of the yeast is glycerol, and the pH is 5.0-5.5; and the pH in the methanol induced expression of the batroxobin is 6.8-7.0, the temperature is 25DEG C and the methanol concentration is 0.5 percent. Research results indicate that: by the method, the fermentation efficiency can be greatly improved, and the expression level of a target product is obviously improved.
Owner:辽宁远大诺康医药有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com