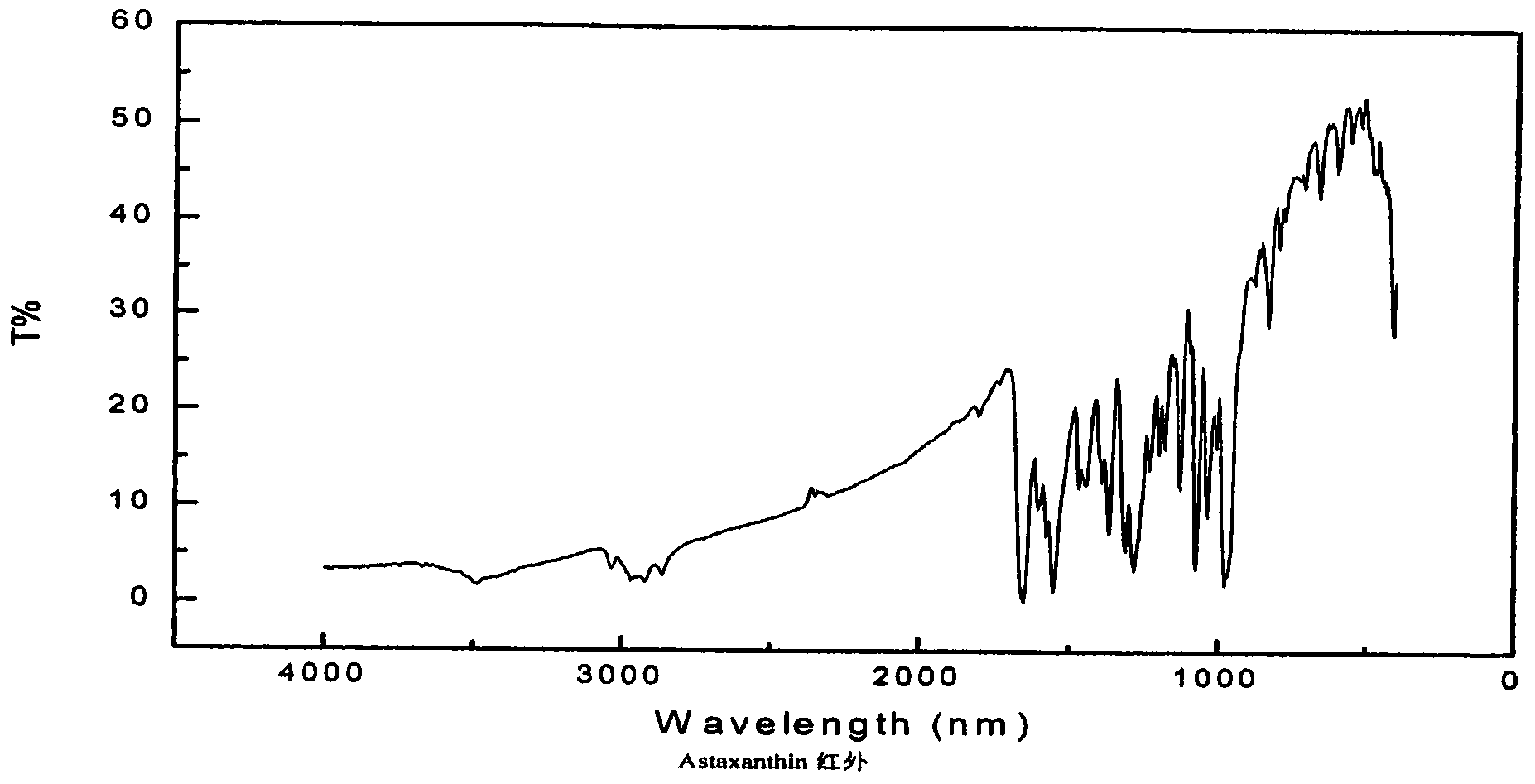
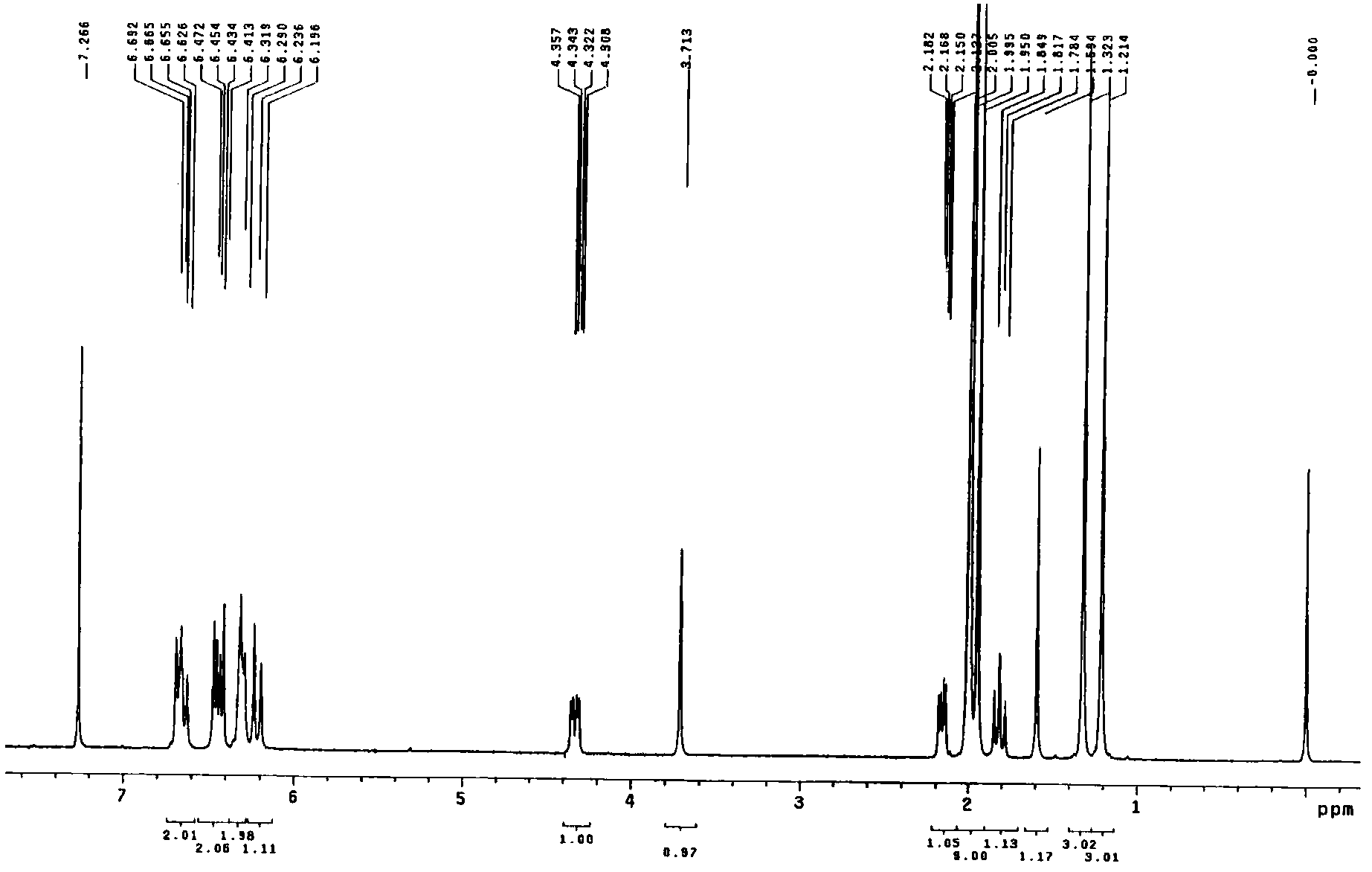
Patents
Literature
164 results about "Phaffia rhodozyma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
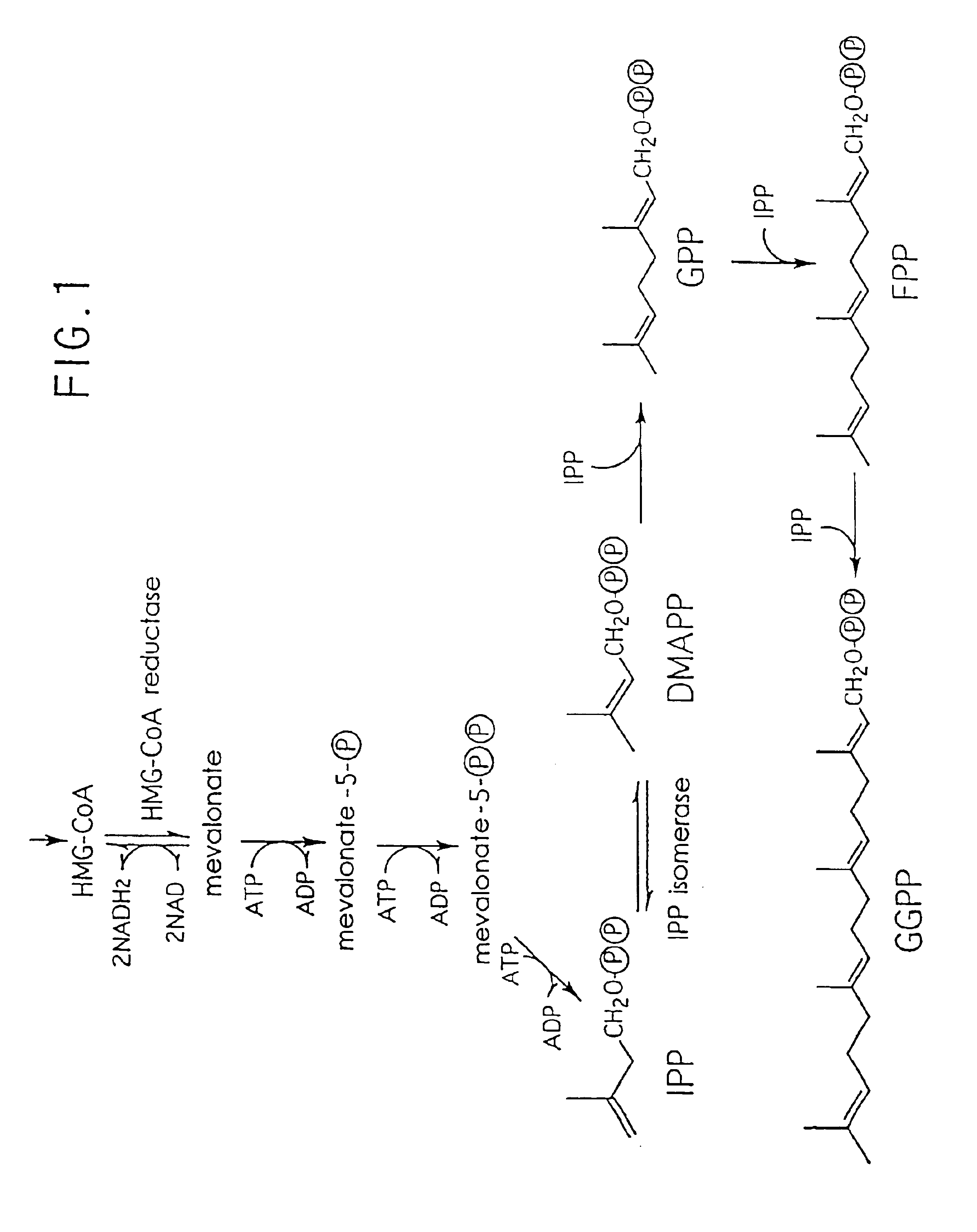
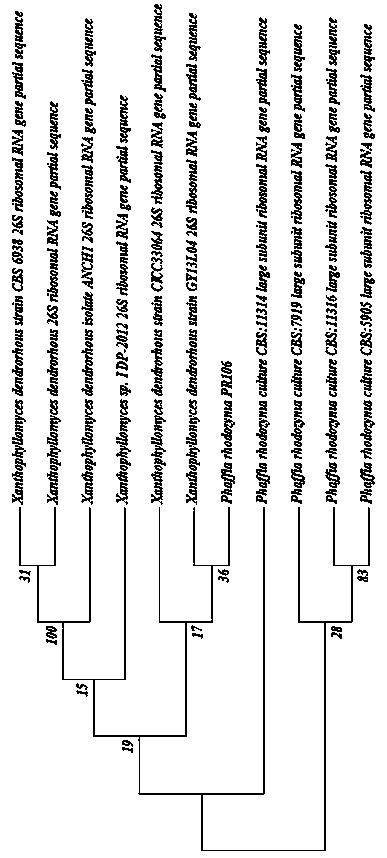
Phaffia rhodozyma was isolated by Herman Phaff in the 1960s, during his pioneering studies of yeast ecology. Initially, the yeast was isolated from limited geographical regions, but isolates were subsequently obtained from Russia, Chile, Finland, and the United States.
Recombinant yeast strain, and building method and application thereof
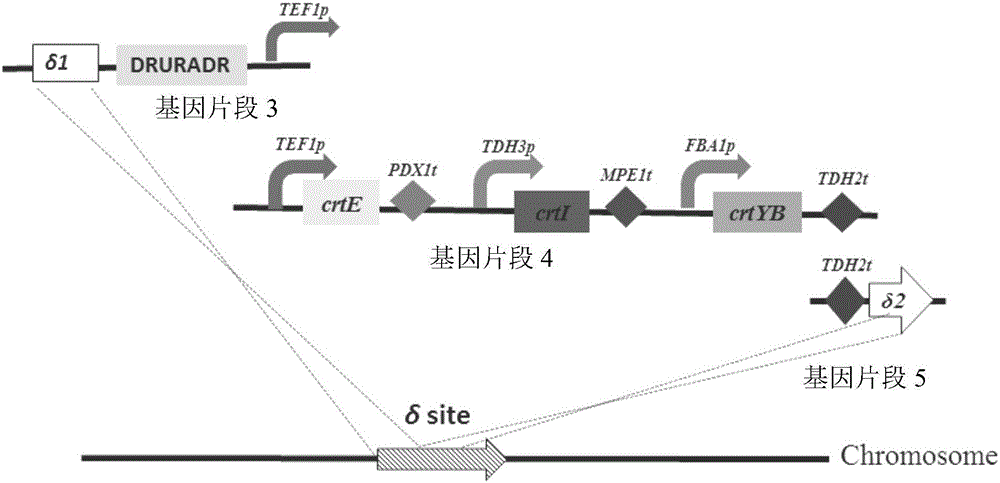
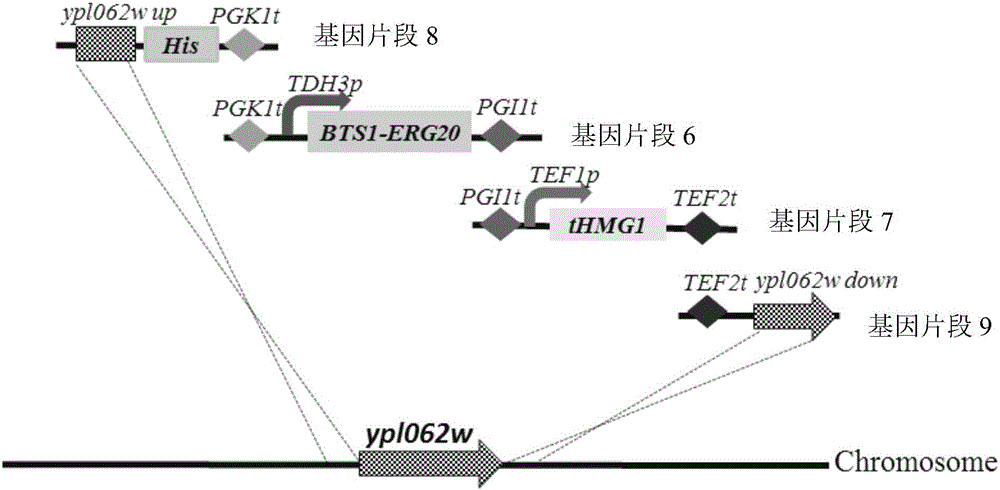
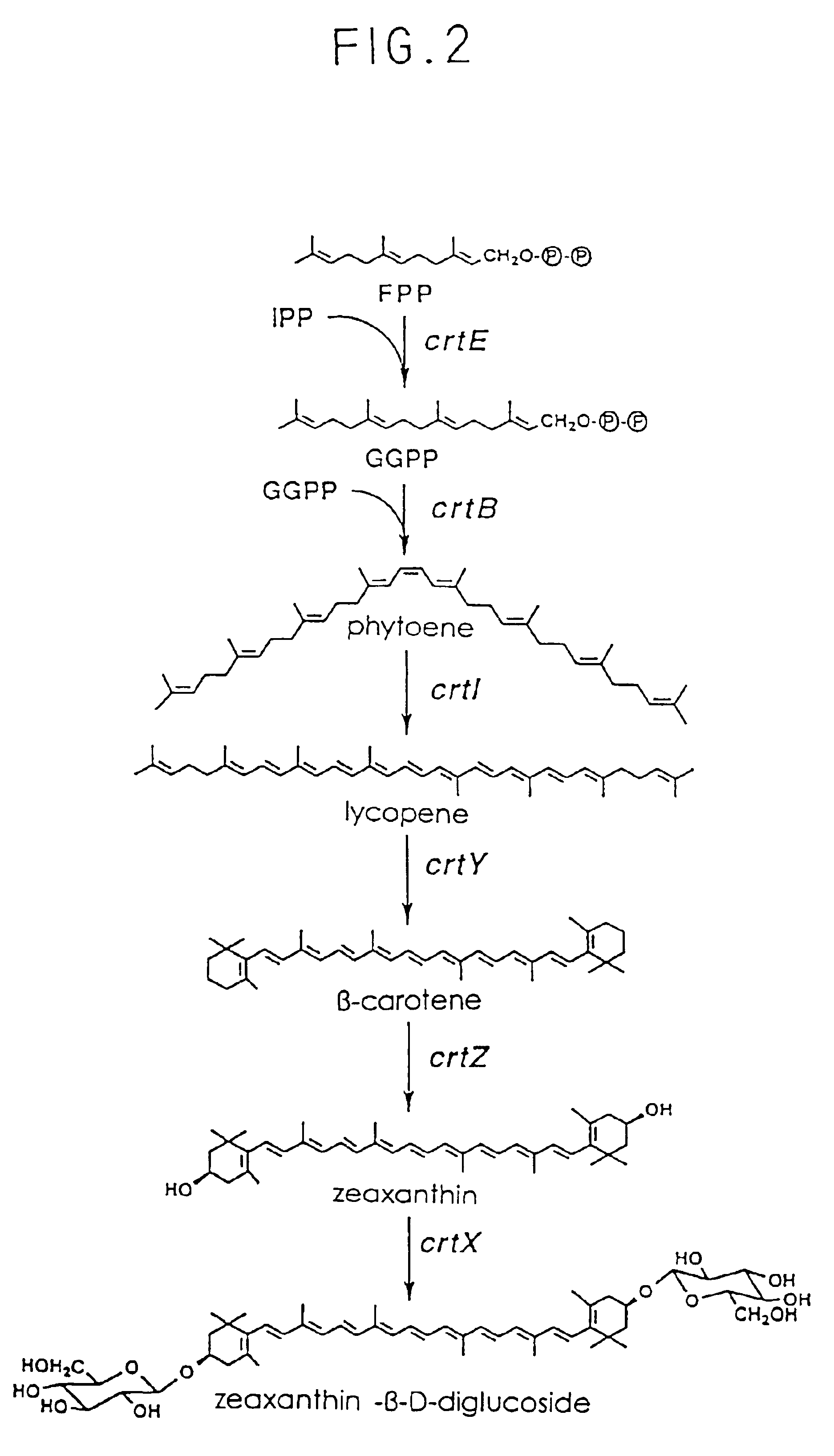
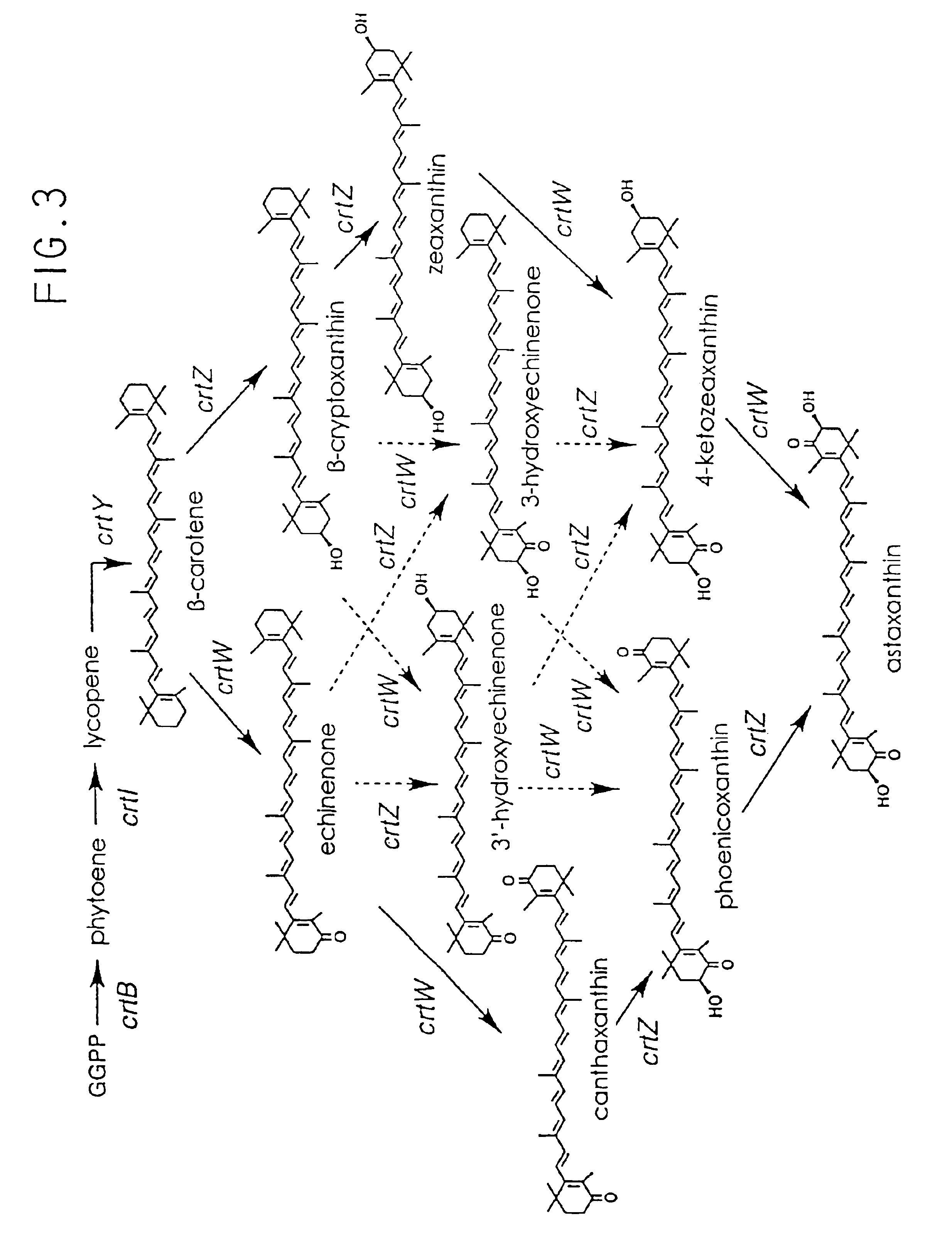
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, and a building method and application thereof. The recombinant yeast strain includes two specific gene segments recombined and integrated onto a genome in a homologous way through yeast. By selecting the specific group for forming a promoter combination and matching phaffia rhodozyma sourced phytoene synthetase and lycopene cyclase dual-function enzyme gene CrtYB, GGPP synthase CrtE, phytoene desaturase CrtI and specific yeast endogenous gene and the like, the substances are integrated onto the yeast strain genome through modular design; the yp1062w gene is knocked away through homologous recombination; one strain of fire-new recombinant yeast without an inducing agent is obtained; the high yield of the beta-renieratene is ensured.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Composite nutrition enhancer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101810246AImprove survival rateImprove disease resistanceAnimal feeding stuffOrder copepodaPhaffia rhodozyma
The invention relates to a composite nutrition enhancer and a preparation method thereof, relating to a feed additive. The invention provides the composite nutrition enhancer, which not only contains large amount of DHA, ARA and natural yeast astaxanthin, but also contains multiple Omega 3 unsaturated fatty acids, multiple amino acids and trace elements. The composite nutrition enhancer is formedby composition of fission chytrid microalgae and phaffia rhodozyma with the weight ratio of 50 percent to 80 percent and 20 percent to 50 percent. All the components are weighed and mixed according to matching ratio after being crushed, mixed evenly, powder-sieved till the particle size is 8-25mum, inspected, weighed and packaged. The invention is especially applicable to feeding of live eels fryand shrimp postlarvae, artificial seawater seedling enhanced artemia salina sinnaeus, rotifer and cladocera (micrura), copepods and the like and various egg-laying poultries.
Owner:XIAMEN HUISON BIOTECH
High-yield natural astaxanthin fermentation method
ActiveCN103820520AHigh yieldLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyAquaculture industry
The invention discloses a high-yield natural astaxanthin fermentation method, which comprises the steps as follows: activating phaffia rhodozyma CGMCC6355 bacterial strains and preparing a seed liquid; inoculating the seed liquid to a fermentation culture medium to perform fermentation culture, and extracting astaxanthin after the end of the fermentation culture, wherein before the fermentation culture, adding an oxygen vector with a volume ratio of 0.5-6 percent to the fermentation culture medium; during the fermentation culture, adding a sugar source to enable the concentration of reducing sugar in a fermentation liquid to reach 2-3 percent when the concentration of the reducing sugar in the fermentation liquid is consumed to below 2 percent, and adding an astaxanthin precursor substance to the fermentation liquid every other 8-24 hours. The astaxanthin produced by adopting the method can be applied to high-grade feed additives for the aquaculture industry and the like, and has the effects on improving the egg laying rate of aquatic animals, boosting the growth, and resisting and preventing diseases. The high-yield natural astaxanthin fermentation method is low in cost, high in the utilization ratio of raw materials, simple to operate, and easy to achieve large-scale industrial production.
Owner:浙江皇冠科技有限公司
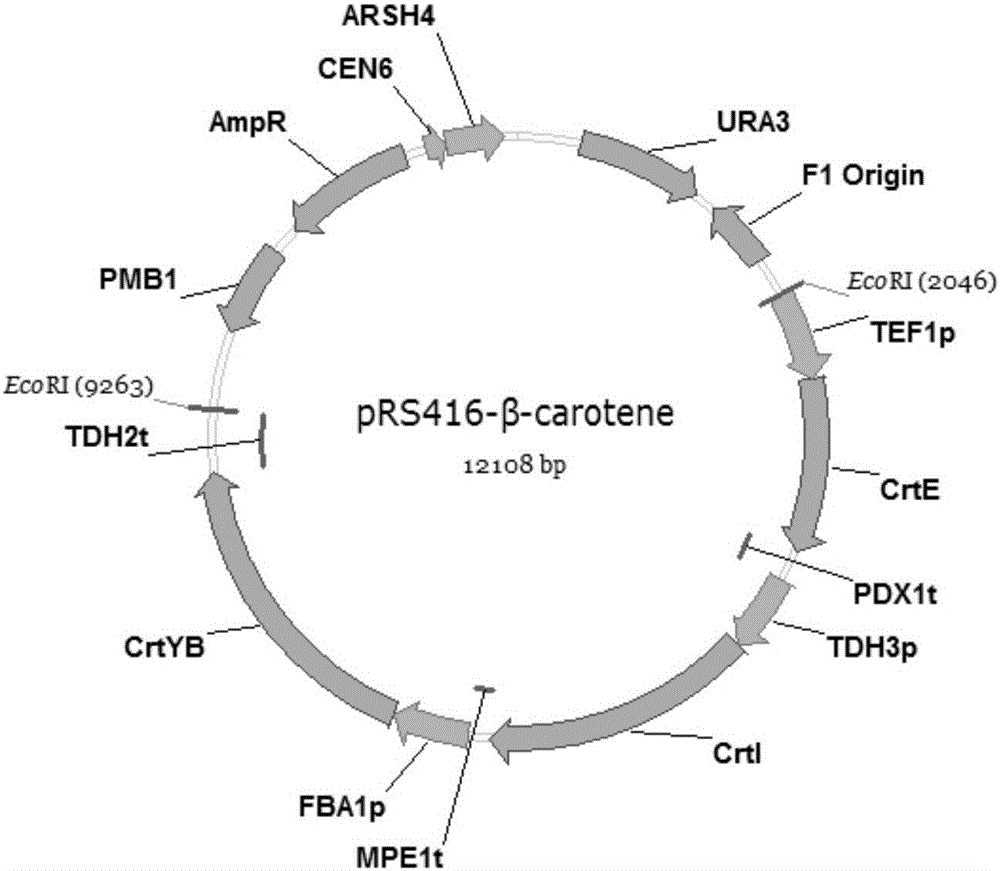
Recombinant materials for carotenoid production
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the amino acid sequences depicted in any one of SEQIDNOs: 24 to 50. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided, preferably wherein said enzyme has an activity selected from isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase activity, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase activity, phytoene synthase activity, phytoene desaturase activity and lycopene cyclase activity, still more preferably those coding for an enzyme having an amino acid sequence selected from the one represented by SEQIDNO: 13, SEQIDNO: 15, SEQIDNO: 17, SEQIDNO: 19, SEQIDNO: 21 or SEQIDNO: 23. Further embodiments concern vectors, transformed host organisms, methods for making proteins and / or carotenoids, such as astaxanthin, and methods for isolating highly expressed promoters from Phaffa.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method for preparing astaxanthin by adopting lignocellulose
ActiveCN108977493AReduce manufacturing costSolve the use problemMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismDry weight
The invention provides a technology for producing astaxanthin through efficient saccharifying of lignocellulose type agricultural and forest wastes, aiming at the problems in the aspects of producingthe astaxanthin by fermenting through phaffia rhodozyma and carrying out enzymolysis on lignocellulose. The technology comprises the steps of pre-treating, saccharifying, carrying out phaffia rhodozyma fermentation, extracting the astaxanthin and the like. According to the technology provided by the invention, a lignocellulose biomass is used as a raw material, so that on one hand, the enzyme utilization cost of a saccharifying phase and a production cost of microorganism fermentation are remarkably improved; on the other hand, the comprehensive utilization problems of the agricultural and forest wastes are also solved. By combining biological saccharifying of the lignocellulose and a high-density fermentation phase of the phaffia rhodozyma, ash obtained by saccharifying can be further used as a solid matrix of yeast fermentation and the fermentation density is improved. In the technology provided by the invention, the ratio of the astaxanthin to the dry weight of thalli can reach 2.6percent and the biomass of yeast thalli can reach 65g / L. The purity of the obtained refined astaxanthin is greater than 90 percent through technologies including molecular distillation and the like.
Owner:青岛中科潮生生物技术有限公司
Phaffia rhodozyma strain with high yield of natural astaxanthin as well as breeding method and application thereof
The invention discloses a phaffia rhodozyma strain with high yield of natural astaxanthin as well as a breeding method and application thereof. The strain is named phaffia rhodozyma CZ10, and is collected with the collection number CGMCC No.6355. The breeding method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting parent strains, classifying the parent strains into two groups, performing LiCl-ultraviolet compound mutation and 60Co-gamma ray mutation respectively, and screening to obtain a plurality of mutated strains I and a plurality of mutated strains II; (2) performing protoplast fusion, regeneration and screening on the mutated strains I and the mutated strains II to obtain a plurality of fusion strains with higher yield of the natural astaxanthin than the mutated strains I and the mutated strains II; and (3) performing recursive protoplast fusion on the obtained fusion strains obtained in the step (2) at least five times to obtain the phaffia rhodozyma strain. The strain disclosedby the invention is applied to industrial production of astaxanthin; and the astaxanthin yield is up to 68mg / L, which is increased by 14.3 times than that of the parent strains before breeding.
Owner:浙江皇冠科技有限公司
Method of separating and purifying astaxanthin from Phaffia rhodozyma
The invention discloses a method of separating and purifying astaxanthin from Phaffia rhodozyma. The method comprises the following steps: dilapidating walls of Phaffia rhodozyma thalli; coarsely extracting astaxanthin by use of acetone; degreasing to remove low-polarity carotenoid; removing dimethyl sulfoxide; crystallizing and the like. The purpose of quickly separating astaxanthin is realized by combining efficient extraction by an organic solvent and simple separation and purification step. The prepared astaxanthin is high in purity and fewer in impurity. The conventional column chromatography step is avoided, and the active functional groups of astaxanthin can be effectively maintained so as to maintain the stability of product quality of astaxanthin in the separation and purification step.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Nutrition enhancer compounding schizochytrium aggregatum powder and phaffia rhodozyma powder, and application thereof on cultivation
The invention discloses a nutrition enhancer compounding schizochytrium aggregatum powder and phaffia rhodozyma powder which is prepared by mixing 80-99.5 percent of schizochytrium aggregatum powder and 0.5-20 percent of phaffia rhodozyma powder. The nutrition enhancer is efficient and safe, when being applied on seedling cultivation, the nutrition enhancer can improve survival rate, immunity, premunition and stress resistance capability of spouts; when being applied on aquaculture, the nutrition enhancer can improve sexual maturity of parent strain, and increase egging laying amount, quality of eggs and hatching rate; when being used as feed additive of eggs, the nutrition enhancer can enrich the DHA and astaxanthin in yolk, reduce the cholesterol content and increase nutrition values of eggs; when being used as feed additive of dairy cow and milch goats, the nutrition enhancer can enrich DHA in milk to produce dairy products with high and stable DHA content; and when being used as the feed additives, the nutrition enhancer can improve the meat quality and mouthfeeling of cultivated varieties, increase the brightness of body color of the cultivated varieties, is not easy to be oxidized, wide in range of application and more obvious in effect.
Owner:XIAMEN HUISON BIOTECH
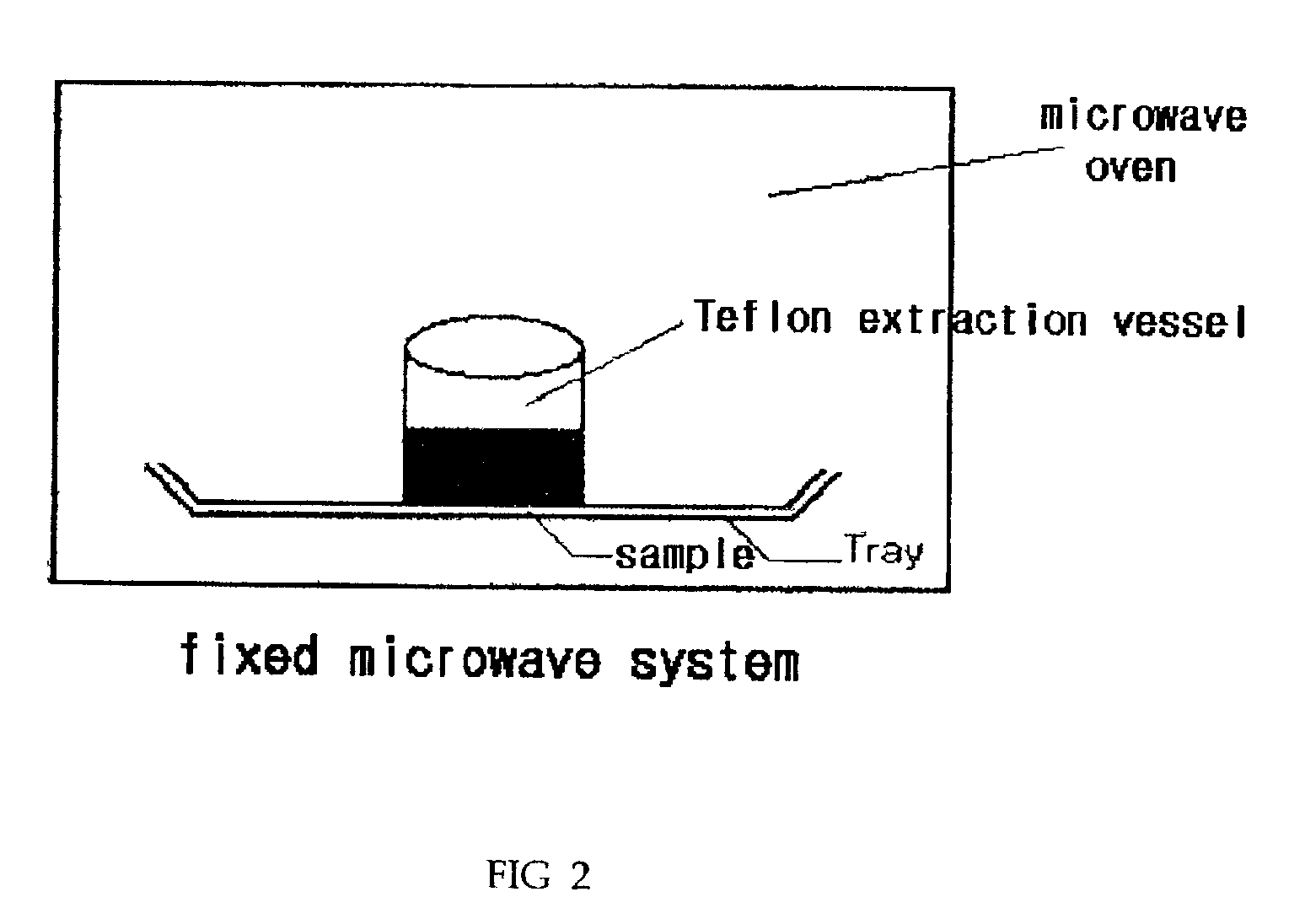
Technology for preparing astaxanthin using microwave-assisted dimethyl sulfoxide method
InactiveCN101607933AHigh yieldSimple processOrganic chemistryEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesOrganic solventBetaxanthins
The invention provides a technology for preparing astaxanthin using a microwave-assisted dimethyl sulfoxide method, which comprises the following steps: adding dimethyl sulfoxide after phaffia rhodozyma yeast fermentation liquor is centrifuged; placing the mixture in microwave to assist to crack walls, adding an organic solvent, keeping temperature and lixiviating, turning the astaxanthin from the inside of cells to the outside of the cells and dissolving the astaxanthin into the organic solvent, and centrifuging the mixed solution to undergo low temperature vacuum concentration to obtain an astaxanthin concentrated solution. The invention successfully combines the microwave wall-cracking technology with dimethyl sulfoxide wall-cracking, thereby reducing the cost, improving the efficiency, saving the extraction time, effectively preventing the astaxanthin structure from destroying and improving the extraction effect of the astaxanthin in the phaffia rhodozyma yeast.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving Phaffia rhodozyma strain high-yield astaxanthin
PendingCN106701880AEasy to synthesizeHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyBetaxanthins
The invention provides a method for improving Phaffia rhodozyma strain high-yield astaxanthin. The method comprises the steps of multiplication culture and fermentation and separation, wherein a fermentation culture medium is prepared from, by weight, 75-85 parts of an agricultural and sideline product pretreatment solution, 20-30 parts of soybean meal, 8-14 parts of glucose, 4-8 parts of peptone, 4-8 parts of concentrated yeast extract powder, 0.2-0.4 part of CaCl2.2H2O, 1-4 parts of MgSO4.7H2O, 1-2 parts of KH2PO4, 1-5 parts of (NH4)2SO4, 1-3 parts of ethanol and 0.01-1 part of triethanolamine. According to the method, while the strain is stimulated to produce the astaxanthin, synthesis of the astaxanthin is promoted in the fermentation process, and therefore the astaxanthin yield is obviously increased, the fermentation cost is lowered, resources are fully utilized, triethanolamine promotes synthesis of the astaxanthin, and then the yield is obviously increased.
Owner:浙江皇冠科技有限公司
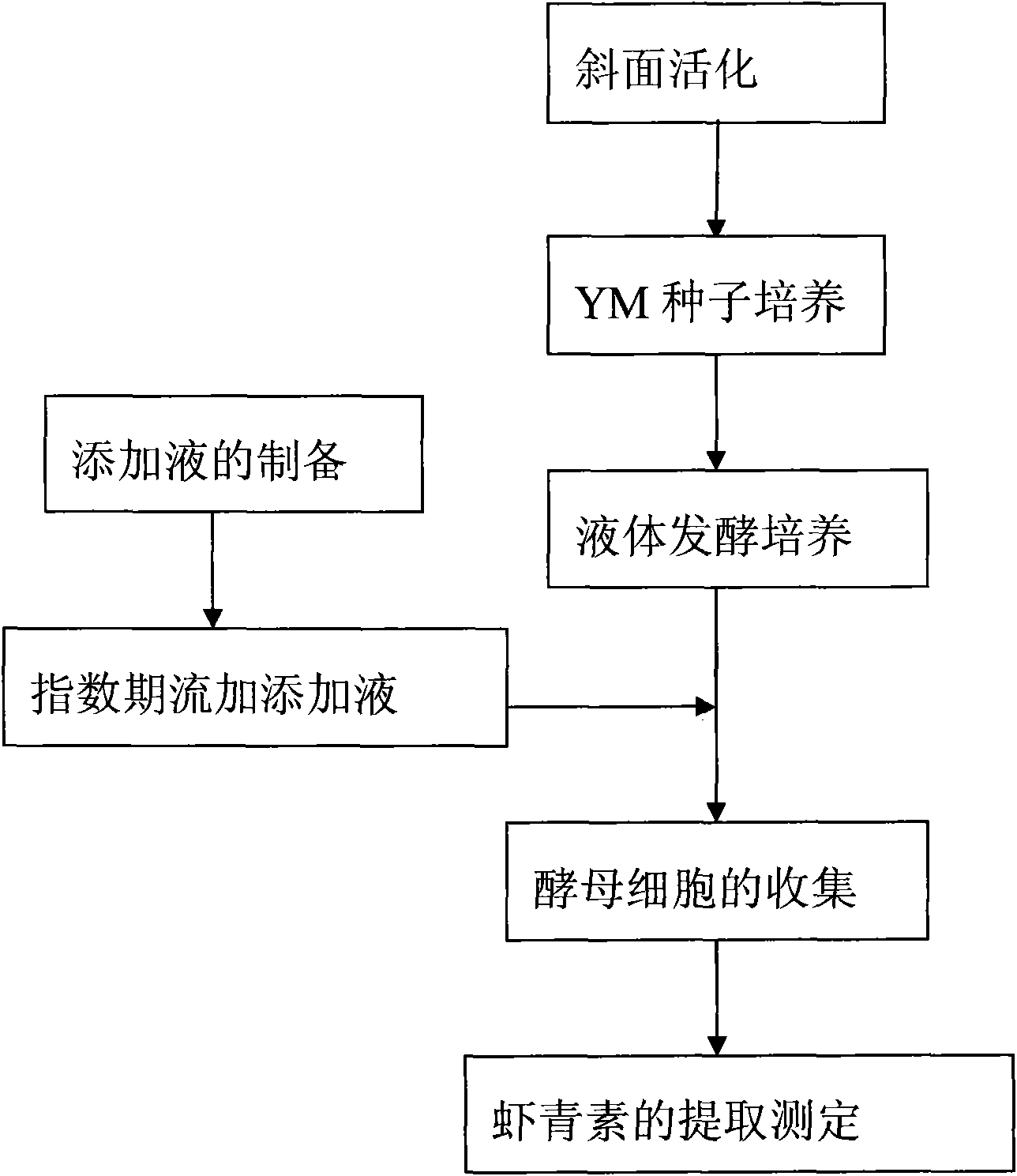
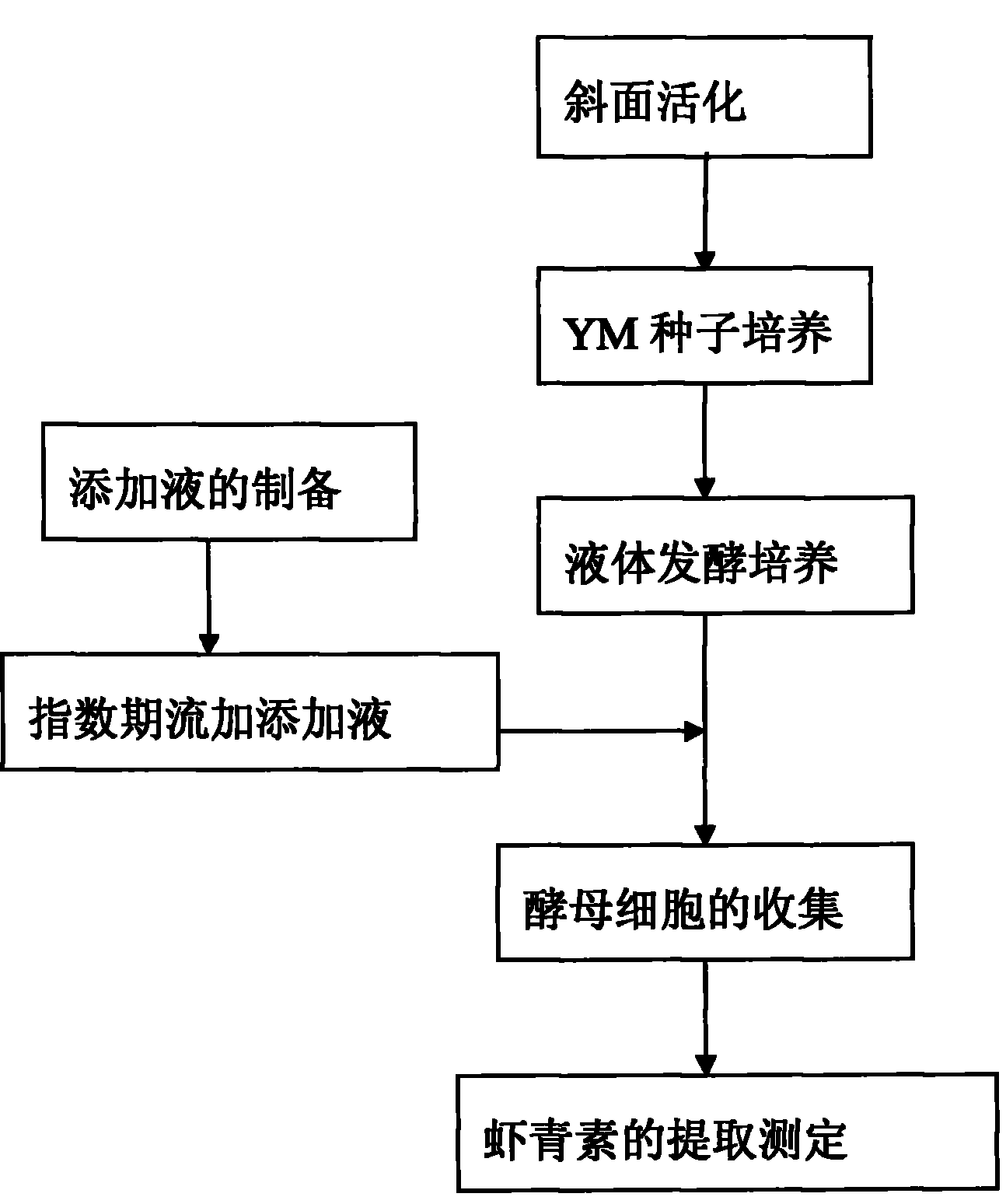
Method for biosynthesizing astaxanthin by using exponential intermittent feed supplement mode
InactiveCN101985645AIncrease productionAvoid inhibitionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBetaxanthinsPhaffia rhodozyma
The invention relates to a method for biosynthesizing astaxanthin by using an exponential intermittent feed supplement mode. The method comprises the following steps: S1, taking subsidiary agricultural products rich in synthetic precursors of the astaxanthin to prepare an adding fluid and sterilizing the adding fluid for 15-30 minutes at the temperature of 115-121 DEG C; S2, taking and cultivating Phaffia rhodozyma in a liquid fermentation medium, feeding 0.5-5% the adding fluid in a batch mode at intervals of 3-12 hours after the exponential phase, and after carrying out fed-batch for 1-4 times, continuing to carry out cultivation 12-48 hours; and S3, extracting the astaxanthin. In the method of the invention, a small amount of astaxanthin synthetic accelerator is added in the exponential phase of the fermentation, thus avoiding premature addition of the astaxanthin synthetic accelerator from inhibiting yeast plant growth and greatly improving the yield of the astaxanthin at the same time, wherein the yield of the astaxanthin is improved by 20-95% compared with a control group. The extracted astaxanthin can be used as feed additives in high-grade aquatic products industry, fish breeding and poultry raising industry and the like. The invention has the advantages that the raw material price is low, the operation is simple and the popularization and application value is high.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
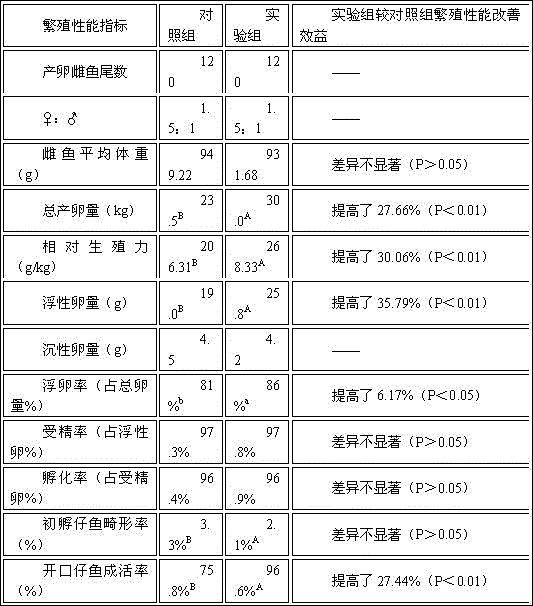
Larimichthys crocea parent fish compound feed
InactiveCN106213067ANutritional balanceMeeting nutritional needsFodderClimate change adaptationFish oilMonocalcium phosphate
The invention discloses a larimichthys crocea parent fish compound feed which is composed of the following raw material components in parts by weight: 1000 parts of brown fishmeal, 600-800 parts of white fish meal, 150-200 parts of puffed soybean meal, 60-80 parts of green gram starch, 150-200 parts of beer yeast powder, 30-50 parts of phaffia rhodozyma powder, 140-150 parts of liver powder, 80-100 parts of squid meal, 500-600 parts of high gluten flour, 100-200 parts of kelp powder, 40-60 parts of soya bean lecithin powder, 40-60 parts of fish oil, 10-15 parts of choline, 5-15 parts of taurine, 3-9 parts of VC, 1-3 parts of VE, 0.5-1 part of inositol, 20-40 parts of bone meal, 5-10 parts of monocalcium phosphate, 20-40 parts of salt, 10-20 parts of vitamin premix and 20-30 parts of mineral substance premix. According to the invention, the egg laying amount, spawning rate, fertility rate and hatching rate of larimichthys crocea parent fish and the survival rate of larimichthys crocea fries can be obviously improved, and the abnormality rate of the fries is reduced.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
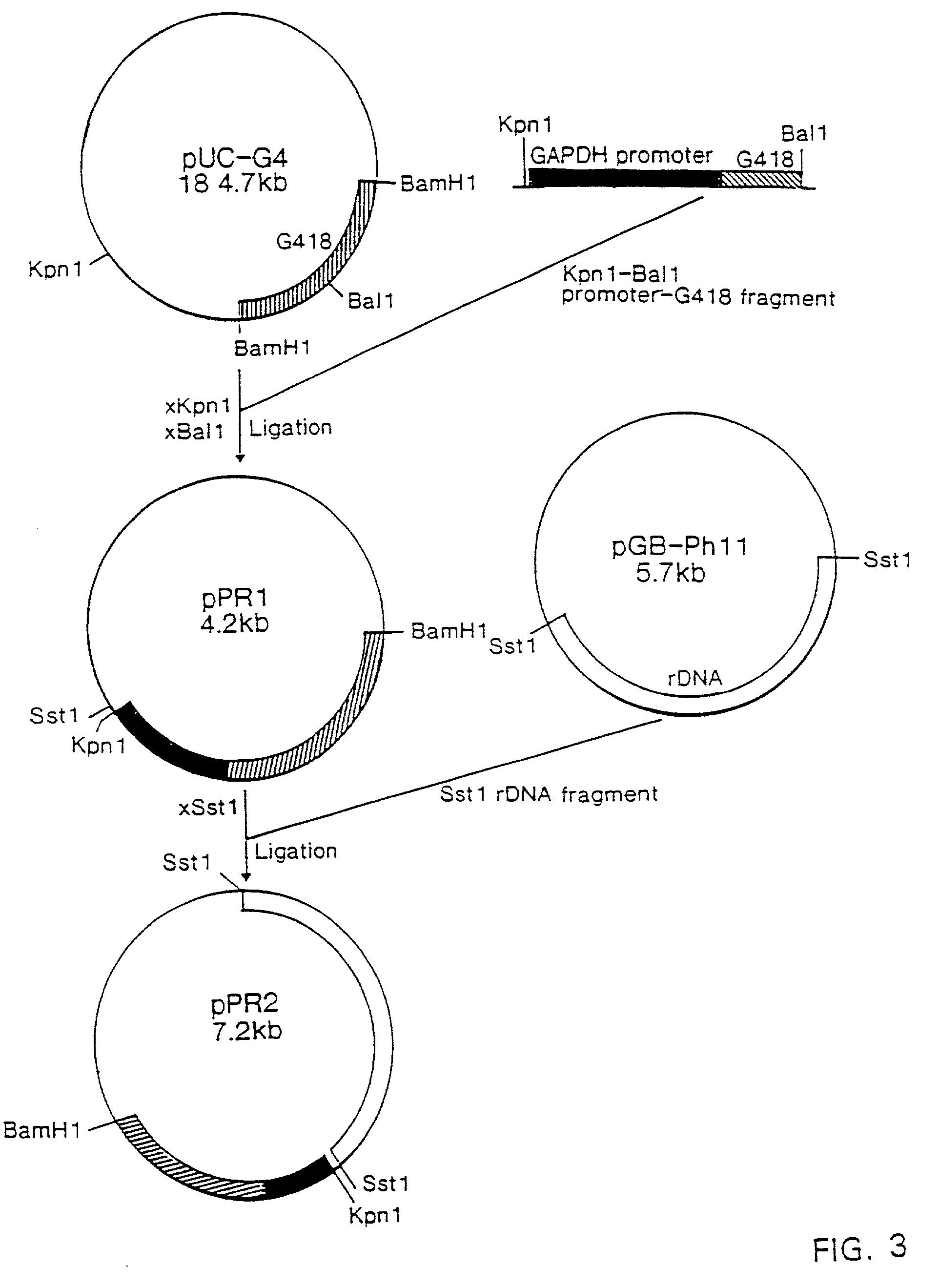
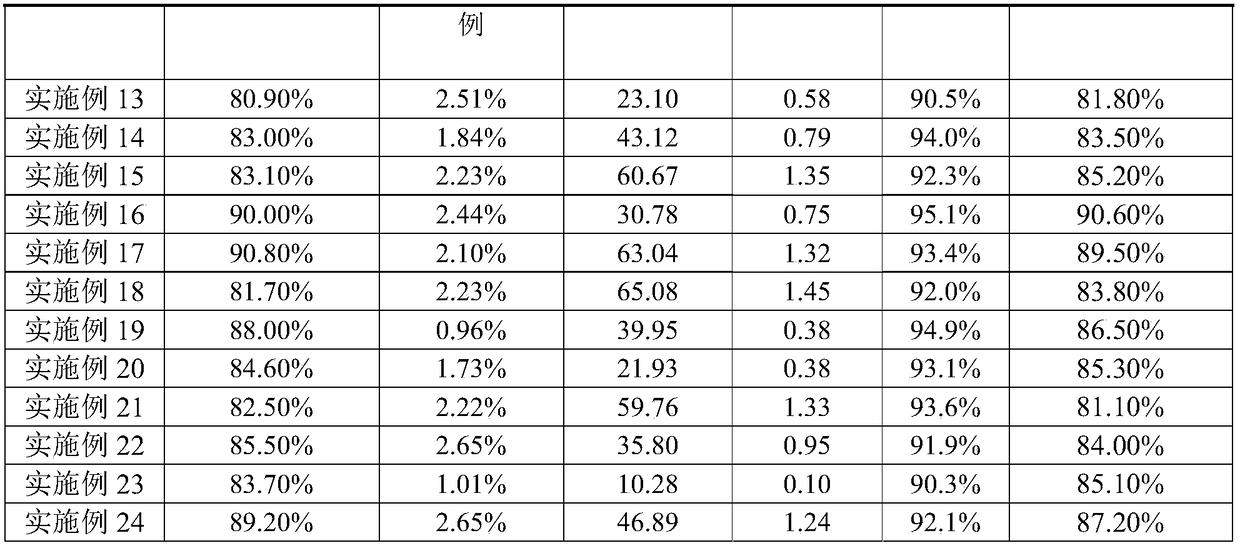
Methods for transforming Phaffia strains, transformed Phaffia strains so obtained and recombinant DNA in said methods
InactiveUS6329141B1High expressionSuitable for productionFungiBacteriaRibosomal protein E-L30Open reading frame
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the disclosed amino acid sequences. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV +1
Probiotic fermented fodder for improving egg quality and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107373038AEasy to processReduce energy consumptionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffYolkDisease
The invention provides probiotic fermented fodder for improving the egg quality and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that lactobacillus plantarum, bacillus subtillis and phaffia rhodozyma are inoculated into corresponding fluid nutrient medium and are cultured for 18 to 24 hours at the constant temperature of 37 DEG C; then bacteria solutions are inoculated in proportion into a solid state fermented nutrient medium with potato dregs, bean dregs and the like as the main raw materials, and fermentation is performed for 48 to 72 hours at the temperature of 28 to 32 DEG C; and cryodrying at the temperature of 50 to 55 DEG C is performed, and then pulverization is conducted to obtain the probiotic fermented fodder. By adopting the probiotic fermented fodder, the laying rate of laying hens and the fodder conversion rate can be increased, the immunologic functions of the laying hens are regulated, the disease resistance is improved, the fodder antibiotics are replaced, the egg quality and the yolk color are improved, and the cholesterol content in an egg is decreased. A production process provided by the invention has the advantages of being low in investment, low in energy consumption, free of waste liquid pollution and the like, and meanwhile, a new approach is developed for utilization of agricultural by-products.
Owner:永州市掌望生态农业有限公司
Process for extracting astaxanthin pigment from yeast and extracted pigment thereof
InactiveUS20030087335A1Easily diffused into the cellsAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsYeastBetaxanthins
The present invention relates to a process for extracting astaxanthin pigment from the yeast cells of Phaffia rhodozyma comprising the steps of i) cultivating the yeast, ii) treating yeast culture suspension with microwave to destroy the cell walls and microbodies, iii) drying it or extracting astaxanthin pigment using the solvent selected from the group consisting of ethanol, methanol, acetone and mixture of them. Further, the present invention also relates to the astaxanthin extracted by above method.
Owner:HAITAI FOODS PROD
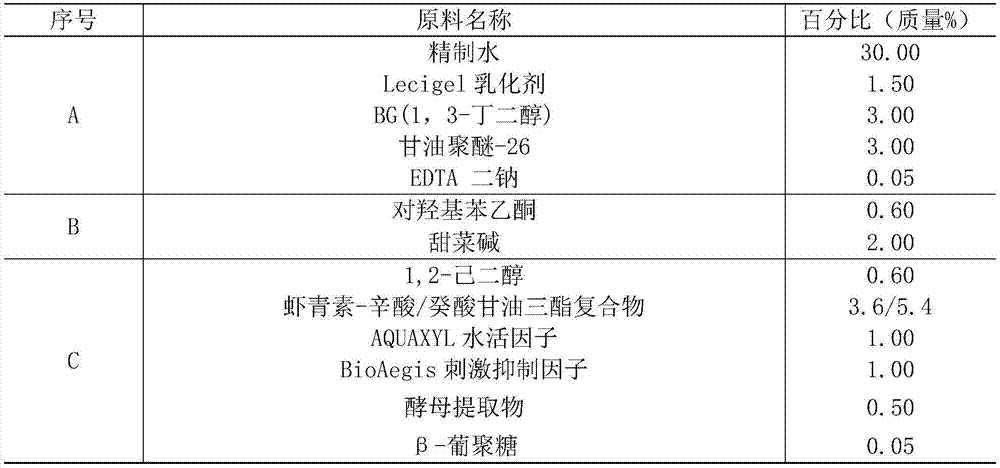
Cosmetics based on phaffia rhodozyma raw materials and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105434319AImprove securityStrong free radical scavenging abilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPhaffia rhodozymaYeast cell extract
The invention discloses cosmetics based on phaffia rhodozyma raw materials and a preparation method thereof. The cosmetics contain astaxanthin coming from phaffia rhodozyma, or contain astaxanthin coming from phaffia rhodozyma, glucan coming from phaffia rhodozyma and yeast extract coming from phaffia rhodozyma. The raw materials used for the cosmetics come from phaffia rhodozyma, and the safety is high. Moreover, the astaxanthin, glucan and yeast extract which come from phaffia rhodozyma are matched to be used, so that the free radical scavenging capacity of the cosmetics can be further enhanced. The cosmetics are deep development and utilization of phaffia rhodozyma and are favorable for improving economic application value of phaffia rhodozyma.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for increasing yield of haematococcaceae astaxanthin with saccharose as carbon source through co-culture
The invention provides a method for increasing the yield of haematococcaceae astaxanthin with saccharose as a carbon source through co-culture. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, saccharose or a saccharose substitute is added in a conventional microalgae culture medium, and sterilization is carried out; secondly, cells of microalgae capable of generating astaxanthin in the ogarithmic growth period are selected and collected, and the cells of the microalgae and phaffia rhodozyma are mixed at the proportion of 20:1-1:1, inoculated into the microalgae culture medium and cultured under the ventilation condition; thirdly, in the late culture stage, an induction strategy is adopted for induction, and a mixture of microalgae bodies and phaffia rhodozyma thalli is collected and used for extracting astaxanthin. By means of the method, the haematococcaceae which can accumulate astaxanthin but is poor in saccharose utilization capability and the phaffia rhodozyma which has the extracellular sucrase secretion capability and can accumulate astaxanthin are co-cultured, the haematococcaceae can normally grow in the culture medium with saccharose as the carbon source and accumulate astaxanthin together with the phaffia rhodozyma, the problem that saccharose cannot be used by algae for producing astaxanthin is effectively solved, and the culture cost of astaxanthin is reduced.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Phaffia rhodozyma strain rich in astaxanthin and screening method and application of Phaffia rhodozyma strain
InactiveCN105861342AImprove fermentation yieldMeet the needs of industrial productionFungiMicroorganism based processesFood additiveDry weight
The invention belongs to the field of biological fermentation engineering, and provides a Phaffia rhodozyma strain rich in astaxanthin and a screening method and application of the Phaffia rhodozyma strain in order to industrially produce astaxanthin through Phaffia rhodozyma. The Phaffia rhodozyma strain is named as Phaffia rhodozyma XM-1601 which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 3rd, 2016, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 12413. The fermentation biomass dry weight of Phaffia rhodozyma reaches 65 g / L, the astaxanthin fermentation yield reaches 320 mg / L, and the astaxanthin content is about 4.92 mg / g. The Phaffia rhodozyma strain XM-1601 is widely applied to the fields of animal feed additives, food additives, healthcare products and the like.
Owner:吉林省希玛生物科技有限公司
Preparation method and application of fermented Chinese herb biological fodder for ruminant animals
ActiveCN109315586AImprove efficacyPromote digestionAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a fermented Chinese herb biological fodder for ruminant animals. The Chinese herb biological fodder is prepared from the following raw materials of 21 to 29 parts of radix astragali seu hedysari, 18 to 32 parts of poria cocos, 22 to 28 parts of radix codonopsis, 9 to 18 parts of wormwood and 10 to 20 parts of liquorice root; aspergillus oryzae, bacillus natto and phaffia rhodozyma are inoculated for aerobic fermentation, and then enterococcus faecium and pediococcus pentosaceus are inoculated for anaerobic fermentation to obtain the fermented Chinese herb biological fodder. According to the fermented Chinese herb biological fodder disclosed by the invention, Chinese herb raw material compatibility is reasonable; by means of step-by-step fermentation of beneficial microorganisms, pharmaceutical functions of the Chinese herbs are obviously improved; meanwhile, a lot of metabolite is generated, the rumen environment of the ruminant animals is improved, the fodder utilization rate is improved, diseases are reduced, the fodder cost is reduced, and the economical benefits are improved.
Owner:湖北华大瑞尔科技有限公司
Method for extracting phaffia rhodozyma intracellular astaxanthin
The invention discloses a method for extracting astaxanthin from Phaffia rhodozyma cells. Firstly, the fermented liquid of Phaffia rhodozyme is concentrated to obtain bacteria sludge; Astaxanthin is extracted with a mixed solution of acetic acid, and then back-extracted with oil. The mixed phase is shaken and mixed at a constant temperature. After centrifugal separation, the upper oil phase is collected to obtain an astaxanthin oil product rich in astaxanthin. The method has simple process, is easy to operate and control, and is suitable for industrial production of astaxanthin.
Owner:XIAMEN HUISON BIOTECH
Method for preparing astaxanthin feed additive by using bear spent grains
The invention discloses a method for preparing an astaxanthin feed additive by using bear spent grains, which comprises the steps of pretreatment of the bear spent grains, enzymolysis of the bear spent grains, sterilization, preparation of a seed liquid of phaffia rhodozyma, fermentation culture of the phaffia rhodozyma, drying and the like. The method has the characteristics of high utilization ratio, good product quality and easy industrialization, realizes the production of the astaxanthin feed additive by industrial wastes, namely the bear spent grains, and achieves the aims of resource utilization and high value of the wastes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Sesame seed blend oil and making method thereof
The invention provides sesame seed blend oil, and relates to the technical field of food processing. The sesame seed blend oil comprises the following components of 50-100 parts of sesame seeds, 5-10parts of linseed oil, 5-10 parts of walnut oil, 1-5 parts of olive oil, 1-5 parts of perilla seed oil, 1-5 parts of corn oil, 1-5 parts of sea buckthorn oil, 1-5 parts of soybean oil, 1-5 parts of rapeseed oil, 1-5 parts of hemp oil, 1-5 parts of siritch, 1-3 parts of an additive and 1-3 parts of traditional Chinese medicine liquid, wherein the additive is prepared by mixing phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin with a vitamin additive in the mass ratio of the phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin to the vitamin additive being 1 to 1, the traditional Chinese medicine liquid comprises the following componentsof 18-26 parts of foxtail millet sprouts, 7-14 parts of rice grain sprouts, 15-22 parts of medicated leaven, 13-19 parts of endothelium corneum gigeriae galli and 20-29 parts of malt, and the vitaminadditive is one or more of vitamin E, vitamin C and beta-carotene. The sesame seed blend oil has the benefits of being simple in technology, reasonable in formula and high in nutrient value, and has popularization prospects.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Medium temperature type astaxanthin producing bacterial strain and its culture process
InactiveCN1986773ASimple nutritional requirementsIncrease production capacityFungiFermentationBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The present invention provides Phaffia rhodozyma A-1 CGMCC No.1837 as one kind of medium temperature type astaxanthin producing bacterium. The present invention provides also the culture process of the medium temperature type astaxanthin producing bacterium. The medium temperature type astaxanthin producing bacterium has simple nutrient requirement for production and industrial production power consumption lower than that for low temperature type astaxanthin producing bacterium. The culture process of the medium temperature type astaxanthin producing bacterium is simple, short in culture period, high in astaxanthin yield and favorable to industrial production.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Composite microecological preparation and application thereof
The invention discloses a composite microecological preparation and an application thereof. The composite microecological preparation comprises saccharomycetes, acid-producing bacteria and bacillus, wherein the viable count ratio of the saccharomycetes to the acid-producing bacteria to the bacillus is (1-3): (1-4): (1-2), the effective viable count of each gram of the composite microecological preparation is greater than or equal to 1010 CFU / g, the saccharomycetes are selected from at least one of saccharomyces cerevisiae, phaffia rhodozyma, rhodotorula mucilaginosa and candida utilis, the acid-producing bacteria are selected from at least one of lactobacillus plantarum, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, clostridium butyricum and lactobacillus rhamnosus, and the bacillus is selected from at least one of bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus coagulans, bacillus amyloliquefaciens and bacillus megatherium. According to the composite microecological preparation and the application thereof, the intestinal health level of animals can be improved, the growth of the animals can be promoted, the anti-stress capability of the animals can be improved, the immune system of the animals can be activated, and diseases can be reduced.
Owner:武安市益微益生物科技有限公司
Phaffia rhodozyma YZUXHONG686 and application thereof
InactiveCN101580806ASimple nutritional requirementsLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastBetaxanthins
The invention discloses Phaffia rhodozyma YZUXHONG686CCTCC NO.M 208262 and application thereof. The Phaffia rhodozyma YZUXHONG686CCTCC NO.M 208262 is used for producing astaxanthin, the nutritional condition is simple, medium components are used in industrial production, the process is simple and convenient, the yield of the astaxanthin is high, and the application facilitates the industrial production.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Methods of producing carotenoids using DNA molecules encoding isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase
InactiveUS6821749B1Reduce the amount of solutionIncrease volumeSugar derivativesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
The production of carotenoid is accomplished using a DNA molecule that encodes a polypeptide as obtained from Haematococcus pluvialis, Phaffia rhodozyma, or Saccharomyces cerevisiae, having isopentonyl pyrophosphate (IPP) isomerase activity, or DNA molecule having a nucleotide sequence that hybridizes thereto. In particular, one can introduce such a DNA molecule into a carotenoid-producing microorganism, culture the microorganism thus transformed, and then obtain carotenoids in the culture broth and cells.
Owner:KIRIN HOLDINGS KK
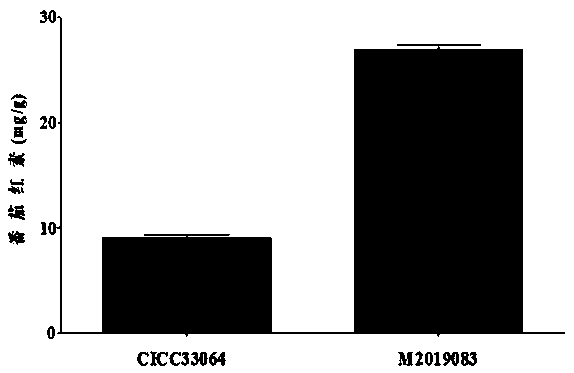
Phaffia rhodozyma with high output of lycopene and production method of lycopene
The invention discloses phaffia rhodozyma. The collection number of the phaffia rhodozyma is CCTCC M 2019083. A production method of the lycopene comprises the following steps of (1) selecting the phaffia rhodozyma, activating, inoculating into a fermenting culture medium, and culturing in a bed shaking way, so as to obtain a fermenting solution; (2) centrifuging the fermenting solution, collecting precipitate to obtain strain, washing by water, centrifuging, removing supernatant, adding 3mol / L of hydrochloric acid solution, uniformly oscillating, soaking, boiling in water bath, cooling, centrifuging, collecting precipitate, washing by water, centrifuging, and removing supernatant, so as to obtain cell fragments; (3) adding acetone, oscillating and extracting under the light shading condition, centrifuging, and collecting supernatant; (4) relieving pressure and evaporating, adding methanol, obtaining a methanol lycopene solution, transferring into a chromatographic column, eluting by methanol, collecting the eluting solution, relieving pressure and evaporating, so as to obtain the lycopene; preparing the dry strain with lycopene content of 30.32mg / g.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
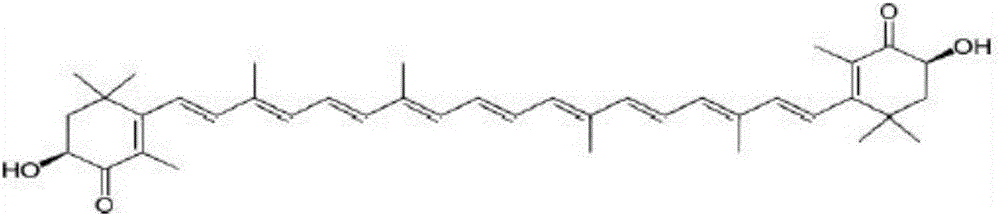
Application of phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin in preparing medicament for preventing and controlling type II diabetes
The invention provides an application of microbial source phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin in preparation of medicines for preventing and curing type II diabetes mellitus. Experiments show that the phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin has good functions of preventing and curing type II diabetes mellitus and can be used to prepare the medicines for preventing and curing type II diabetes mellitus. In particular, the phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin can be used to prepare medicines for reducing individual blood sugar of type II diabetes mellitus, or medicines for preventing individual insulin resistance to type II diabetes mellitus. The application has the advantages that: the invention provides an application of microbial source astaxanthin, namely phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin in the preparation of medicines for preventing and curing type II diabetes mellitus and provides a foundation for development of new drugs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
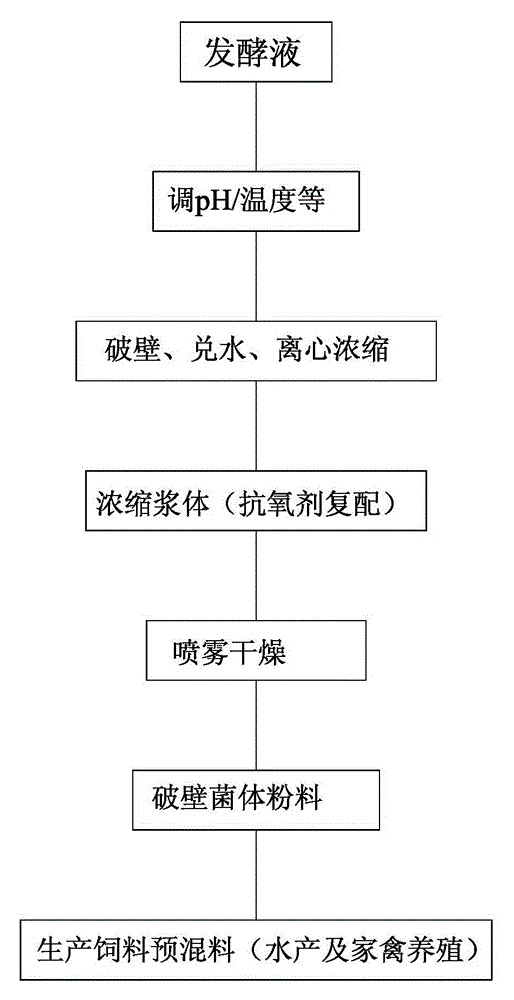
Method for increasing phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin
The invention discloses a method for increasing phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin, which comprises the following steps: adjusting pH value of a phaffia rhodozyma broth to 9.0-11.5, controlling the temperature at 35-60 DEG C, stirring for 80-150r / min, breaking wall for 1.0-5.0; neutralizing the pH value to 6.0-7.5, mixing with water having 0.5-1 times of volume, centrifuging and concentrating to obtain the concentrated wall breaking phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin slurry; then uniformly mixing with a proper amount of complex formulation anti-oxidant and performing spray drying, wherein the air intake temperature is 170-185 DEG C, air-out temperature is 70-85 DEG C, and obtaining the astaxanthin dry powder, wherein the moisture of the dry powder is less than 8%, and spray loss amount is less than 4.0%. According to the invention, the method is simple and practical, total pigment can be increased by 10-12%, wall breaking time is short, cost is low, and the method is suitable for industrial production, shelf time of the produced astaxanthin dry powder is longer, taste is fragrant and unique, the phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin has good palatability, and the dry powder can be widely used in animal feed industry.
Owner:XIAMEN HUISON BIOTECH
Phaffia rhodozyma culture method for improving content of astaxanthin in phaffia rhodozyma cells
InactiveCN101705274APromote biosynthesisPromote accumulationMicroorganism based processesFermentationYeastBetaxanthins
The invention relates to a phaffia rhodozyma culture method for improving the content of astaxanthin in phaffia rhodozyma, which comprises the steps of the preparation of solid seeds of a phaffia rhodozyma wild strain JCM9042, first-grade seed culture, second-grade seed culture, fermentation culture and the determination of the content of the astaxanthin in a fermentation broth. The culture method uses an ergosterol synthesized inhibitor, and can obviously promote the accumulation of the astaxanthin in the phaffia rhodozyma; and compared with a culture method which does not use the ergosterol synthesized inhibitor, the culture method can improve the content of the astaxanthin high up to more than 3 to 8 times. The method is simple and easy, has low costs of the ergosterol synthesized inhibitor and a culture medium, effectively reduces the production cost of the astaxanthin, and is favorable for industrialized culture.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com