Patents
Literature
90 results about "Ribosomal protein E-L30" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
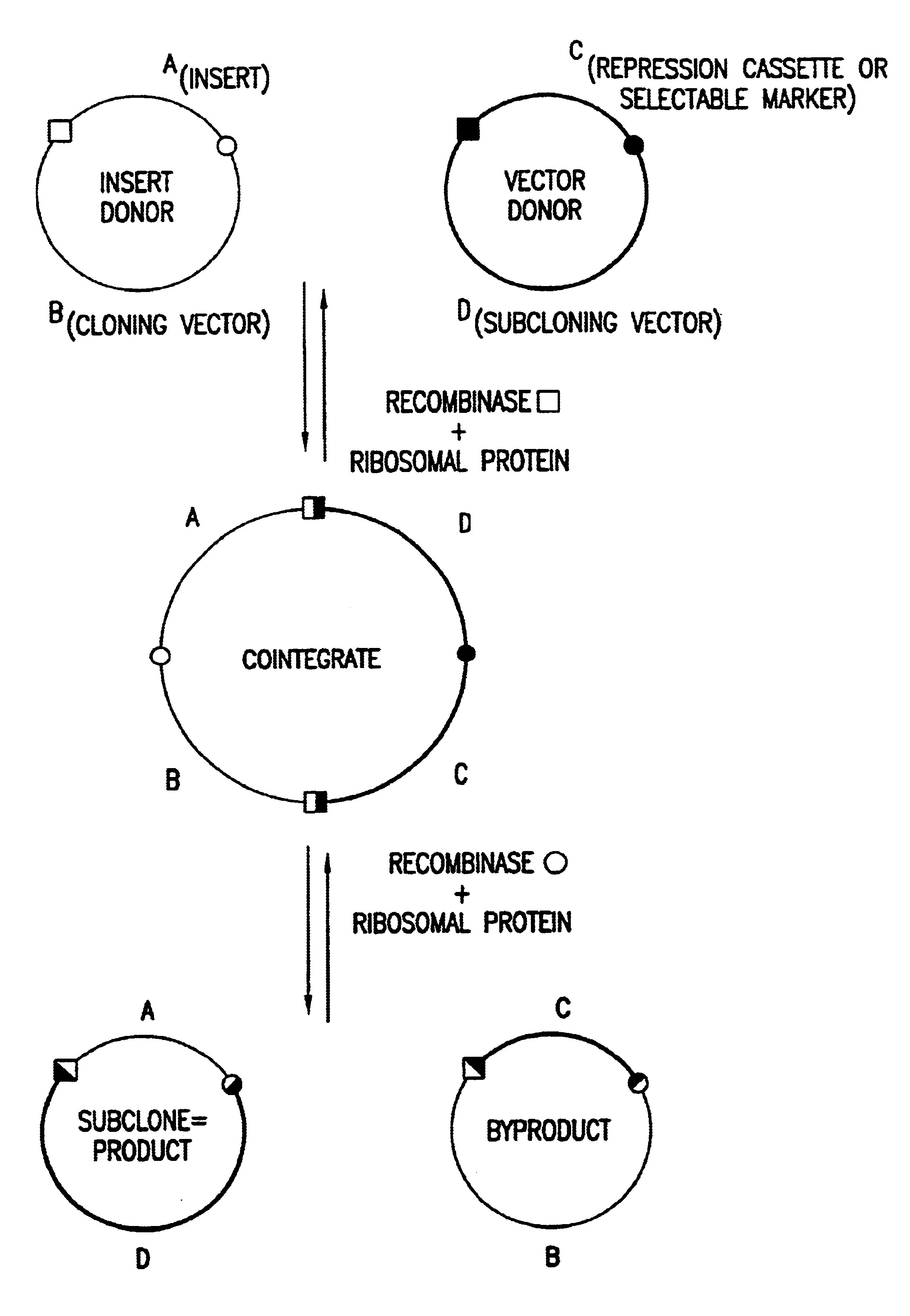
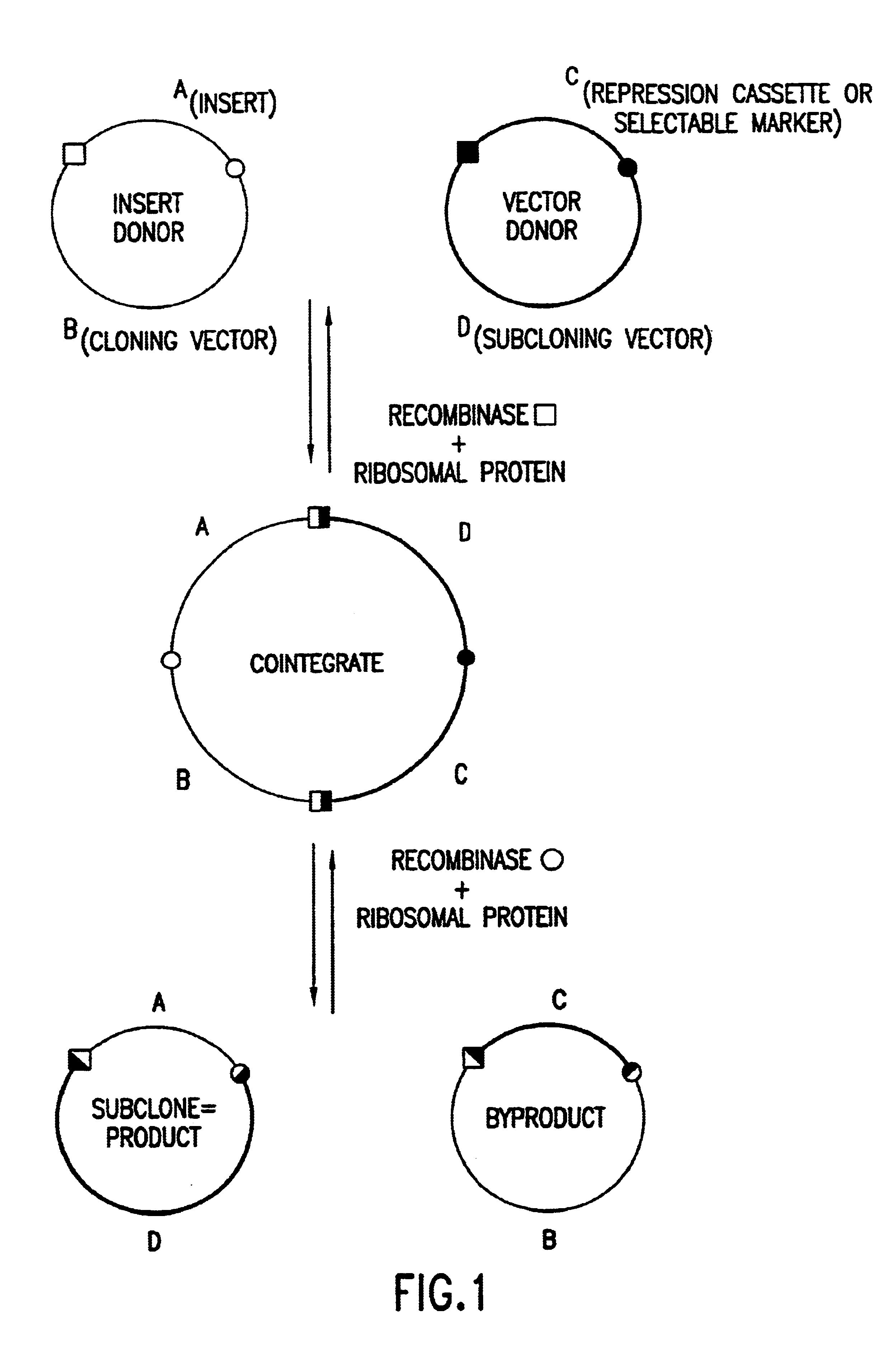
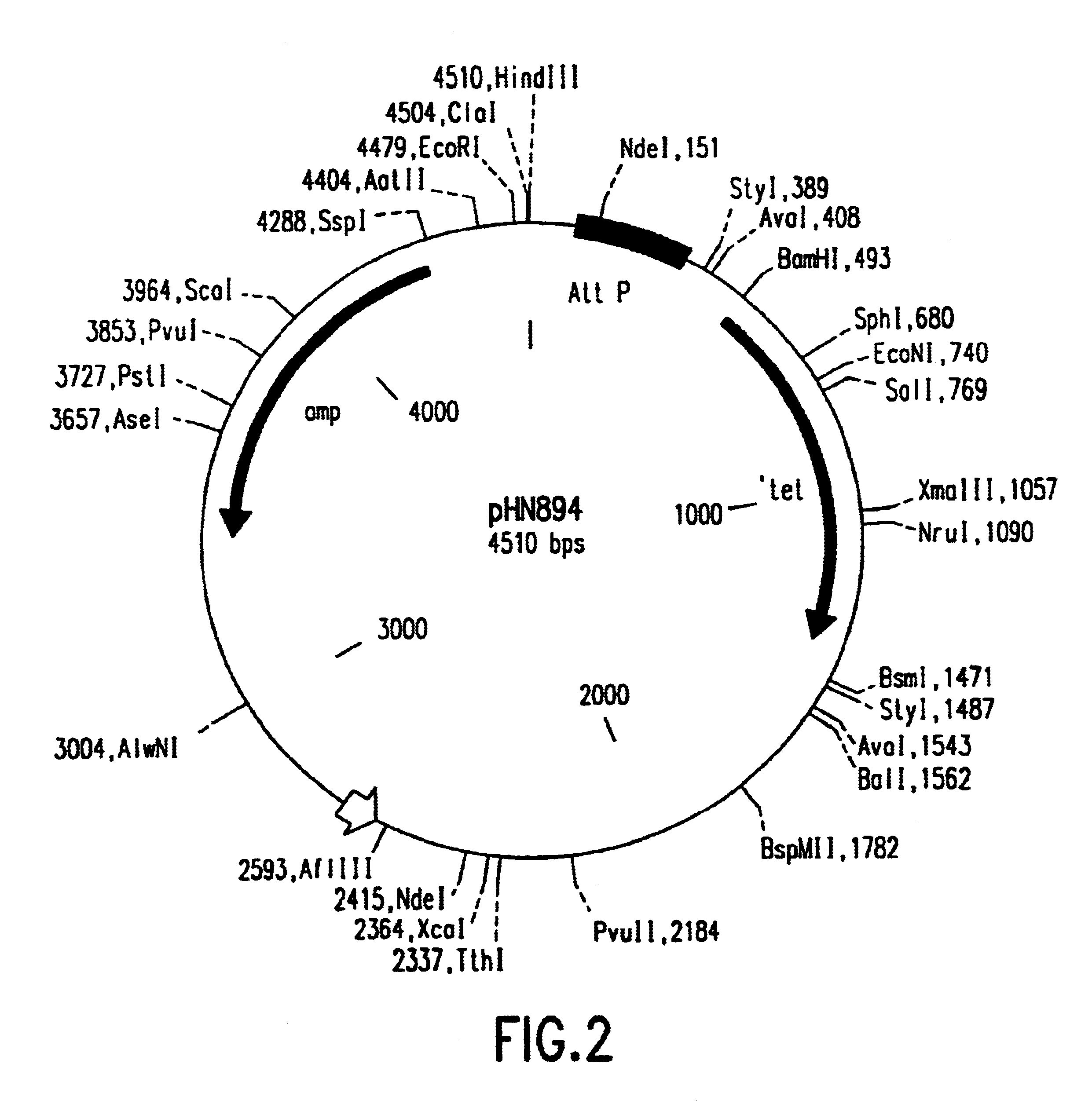
Enhanced in vitro recombinational cloning of using ribosomal proteins
InactiveUS6964861B1Strong specificityIncrease speedBacteriaSugar derivativesRibosomal protein E-L30Escherichia coli
The present invention relates generally to compositions and methods for enhancing recombinational cloning of nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the invention relates to compositions comprising one or more ribosomal proteins and one or more additional protein components required for recombinational cloning. More particularly, the invention relates to such compositions wherein the ribosomal proteins are one or more E. coli ribosomal proteins, still more particularly wherein the ribosomal proteins are selected from the group of E. coli ribosomal proteins consisting of S10, S14, S15, S16, S17, S18, S19, S20, S21, L20, L21, and L23 through L34, and most particularly S20, L27, and S15. The invention also relates to the use of these compositions in methods for recombinational cloning of nucleic acids, in vitro and in vivo, to provide chimeric DNA molecules that have particular characteristics and / or DNA segments. The invention also relates to isolated nucleic acid molecules produced by the methods of the invention, to vectors comprising such nucleic acid molecules, and to host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules and vectors.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for isolating cell-type specific mrnas
ActiveUS20050009028A1Maximum protein expressionImprove translation efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRibosomal protein E-L30Ribosomal protein
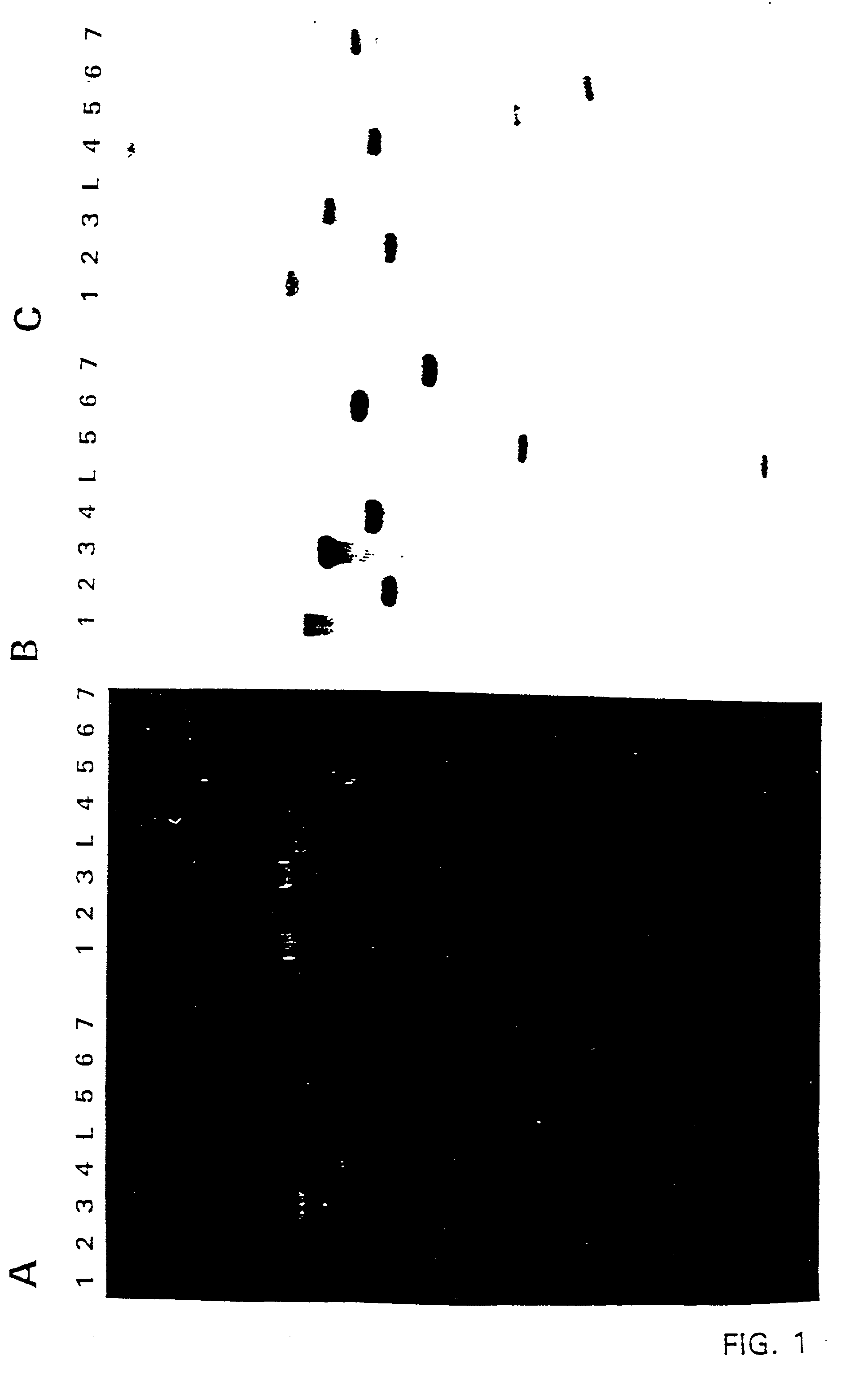
The invention provides methods for isolating cell-type specific mRNAs by selectively isolating ribosomes or proteins that bind mRNA in a cell type specific manner, and, thereby, the mRNA bound to the ribosomes or proteins that bind mRNA. Ribosomes, which are riboprotein complexes, bind mRNA that is being actively translated in cells. According to the methods of the invention, cells are engineered to express a molecularly tagged ribosomal protein or protein that binds mRNA by introducing into the cell a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a ribosomal protein or protein that binds mRNA fused to a nucleotide sequence encoding a peptide tag. The tagged ribosome or mRNA binding protein can then be isolated, along with the mRNA bound to the tagged ribosome or mRNA binding protein, and the mRNA isolated and further used for gene expression analysis. The methods of the invention facilitate the analysis and quantification of gene expression in the selected cell type present within a heterogeneous cell mixture, without the need to isolate the cells of that cell type as a preliminary step.
Owner:TAKEDA SAN DIEGO
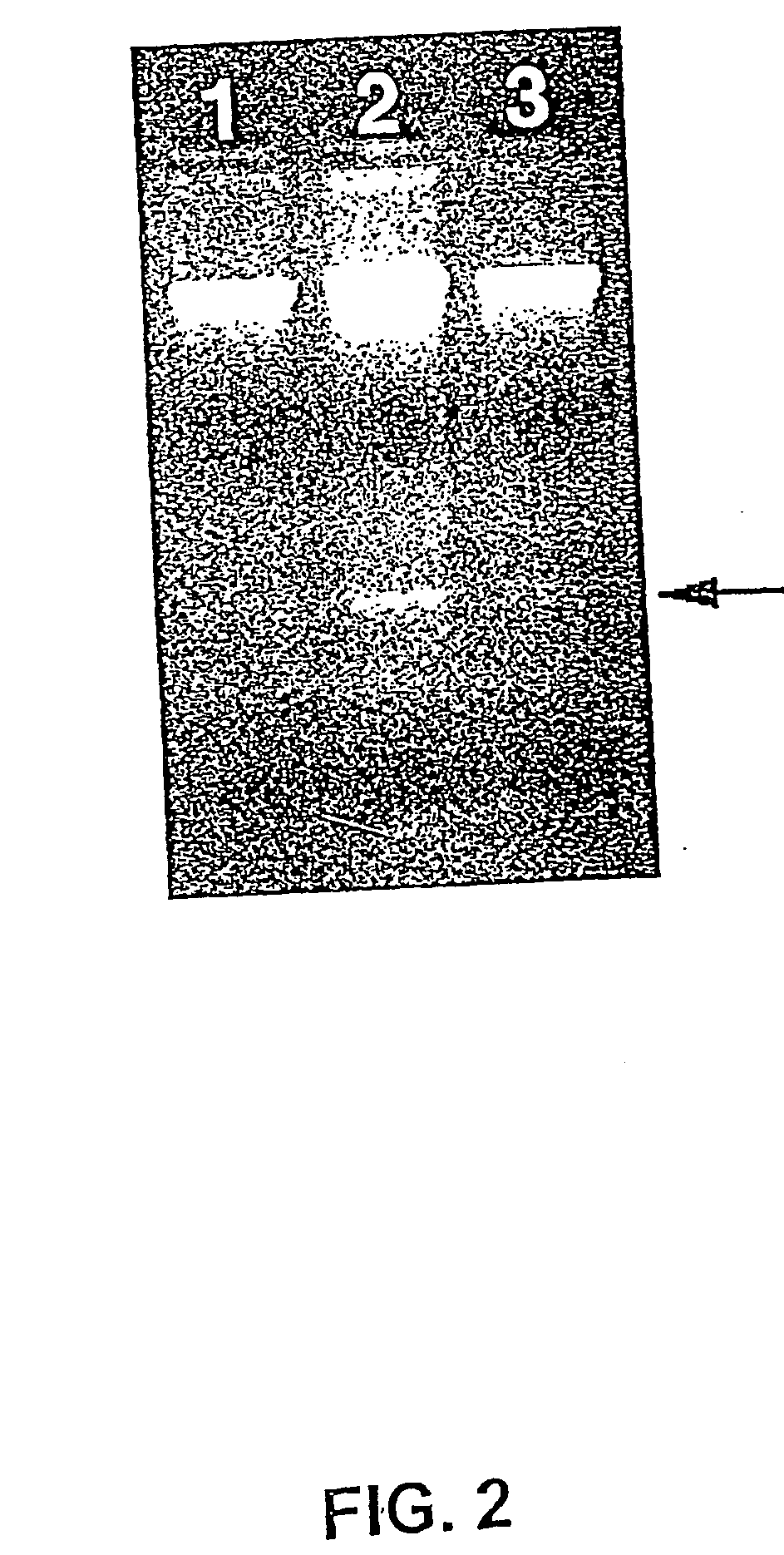
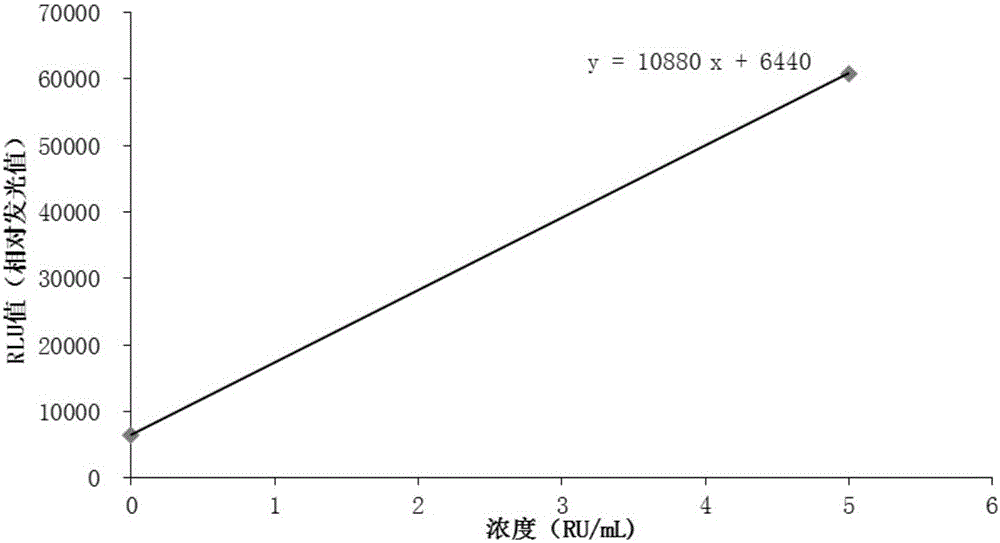
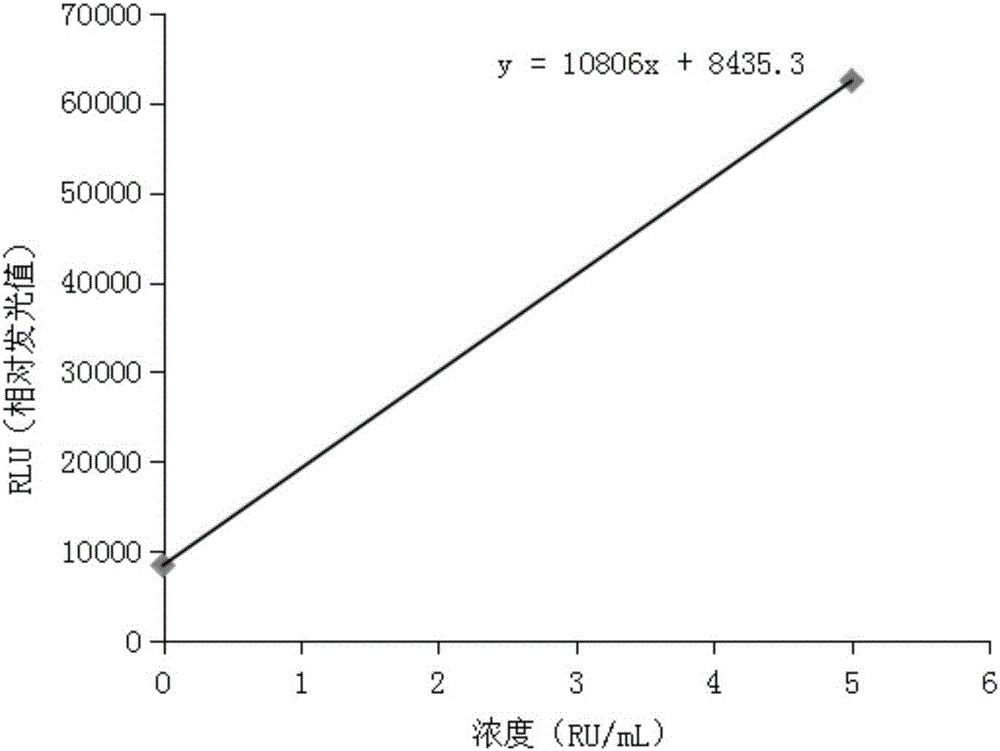
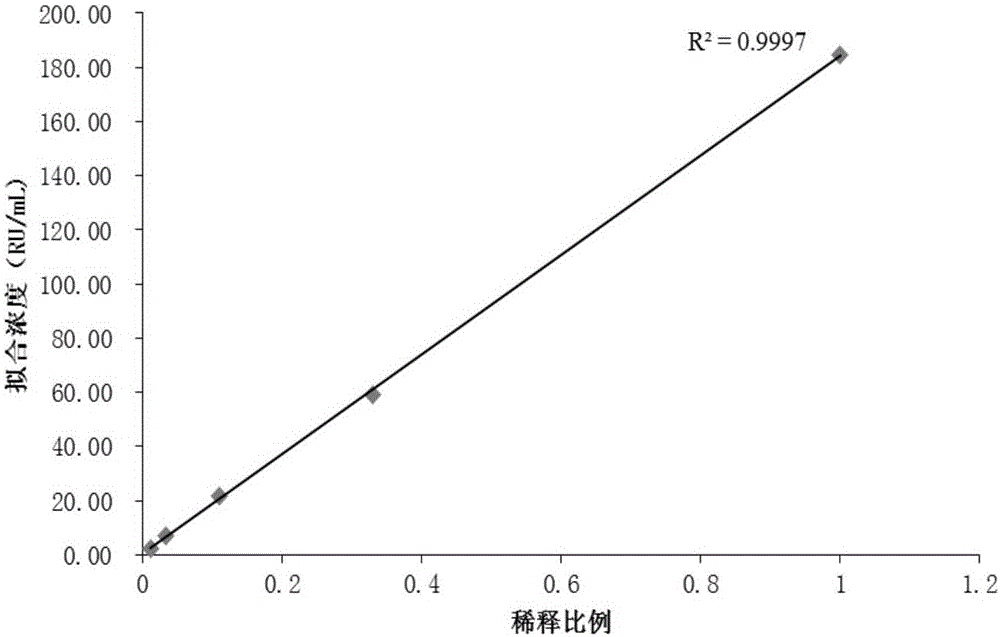
Magnetic particle-based quantitative chemiluminescent assay kit for anti-ribosome P protein antibody IgG, and preparation and detection methods thereof
InactiveCN105954266AEasy to useGuaranteed detection effectChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePolyclonal antibodiesBovine serum albumin
The invention discloses a magnetic particle chemiluminescence quantitative assay kit for anti-ribosomal P protein antibody IgG. The kit includes: anti-ribosomal P protein antibody IgG calibrator; Ribosomal P protein antigen and bovine serum albumin-labeled Tris buffer; alkaline phosphatase-labeled goat anti-human polyclonal antibody and bovine serum albumin in Tris buffer; streptavidin-labeled magnetic particles and bovine serum albumin Serum albumin in Tris buffer; wash solution. Based on the traditional membrane strip immunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, the detection method of the kit increases the sensitivity and linear range by 3-5 orders of magnitude, and realizes quantitative detection in a real sense, with rapid response, reliable results, and It can be used in conjunction with a fully automatic chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer to realize fully automatic use, and has irreplaceable important value for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:北京贝尔医疗设备有限公司
Recombinant materials for carotenoid production
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the amino acid sequences depicted in any one of SEQIDNOs: 24 to 50. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided, preferably wherein said enzyme has an activity selected from isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase activity, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase activity, phytoene synthase activity, phytoene desaturase activity and lycopene cyclase activity, still more preferably those coding for an enzyme having an amino acid sequence selected from the one represented by SEQIDNO: 13, SEQIDNO: 15, SEQIDNO: 17, SEQIDNO: 19, SEQIDNO: 21 or SEQIDNO: 23. Further embodiments concern vectors, transformed host organisms, methods for making proteins and / or carotenoids, such as astaxanthin, and methods for isolating highly expressed promoters from Phaffa.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Polysome-mediated cell type-, tissue type- or condition-enhanced transcript profiling
InactiveUS20100071086A1BryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesRibosomal protein E-L30Rna profiling
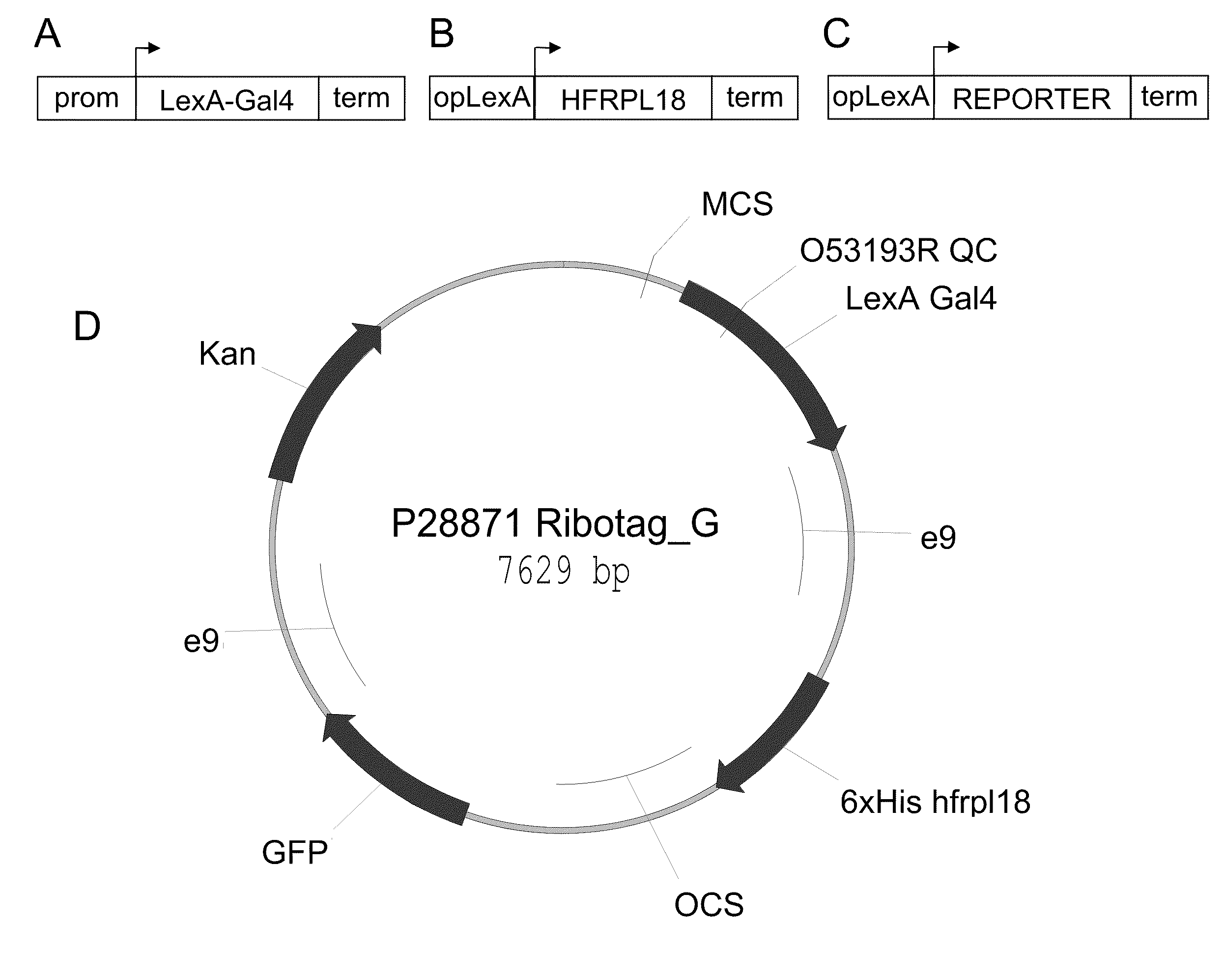
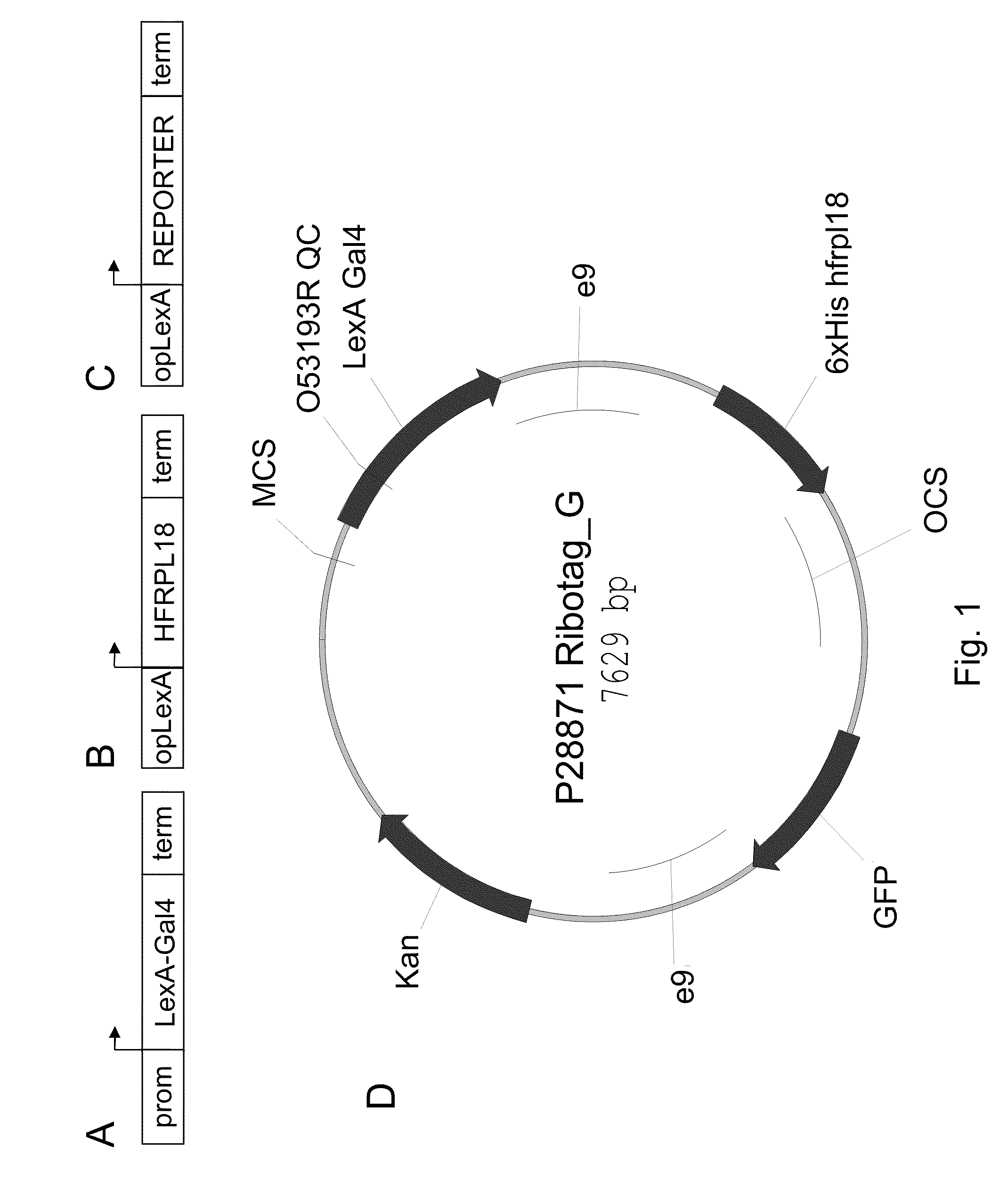
In this invention, a method is described that allows for the efficient creation and identification of validated biological materials that greatly enhance the ability to perform polysome-mediated RNA profiling, such as constitutive, cell type-, tissue type-, or condition-enhanced RNA profiling. The method relies on the use of a tri-partite plant binary expression vector comprised of the following components: a) a DNA promoter element that drives expression of a sequence specific transcription activator protein such as a LexA:Gal4 fusion protein in a unique desired pattern, b) a DNA promoter element comprising a target site for the transcriptional activator protein, such as opLexA, fused to a nucleotide encoding an epitope tagged ribosomal component protein and c) a DNA promoter element comprising a target site for the transcriptional activator protein, such as opLexA, fused to a nucleotide encoding an in vivo reporter protein. By visualization of the co-regulated reporter, this method allows for in planta confirmation that the promoter element is driving expression, such as constitutive, cell type-, tissue type-, or condition-enhanced expression, of the tagged ribosomal protein in the desired cell or tissue types.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Construction method and use of Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria
ActiveCN102146414AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRibosomal protein E-L30
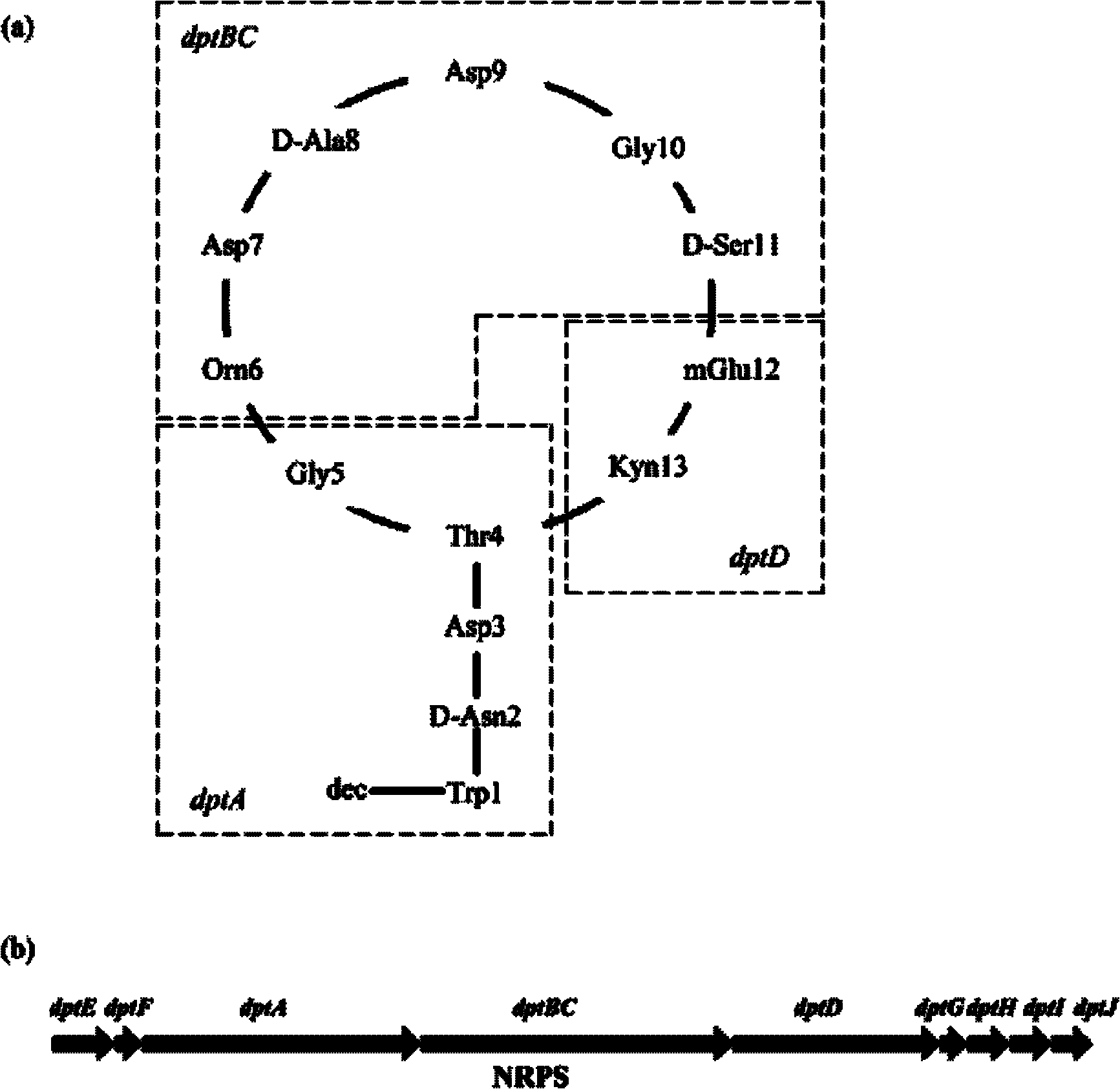
The invention provides a construction method and use of Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria. The construction method comprises: cloning upstream and downstream accessory key genes dptE, dptF, dptG, dptH, dptI and dptJ of a nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) gene in a daptomycin gene cluster; and constructing recombinant plasmids by using an Escherichia coli-Streptomyces shuttle expression vector. The recombinant plasmids are transferred into Escherichia coli ET12567 to culture the ET12567 and the Streptomyces roseosporus together, the Streptomyces roseosporus is transformed by a combined transfer method, a transformant is screened by brulamycin resistance and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is performed for further confirmation. The Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria constructed by the invention can be directly used in the industrial production of daptomycin and can improve yield and reduce cost.
Owner:NANTONG YIKAI MEDICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Construction method of enramycin high-yielding strain and related gene
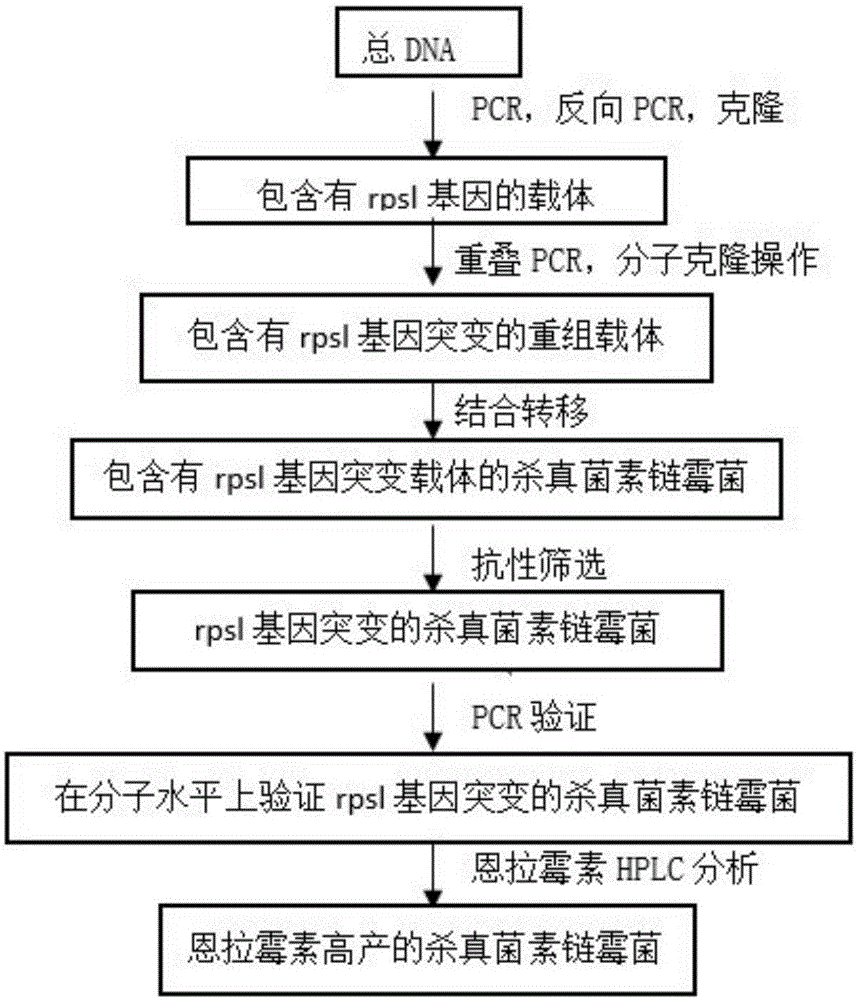
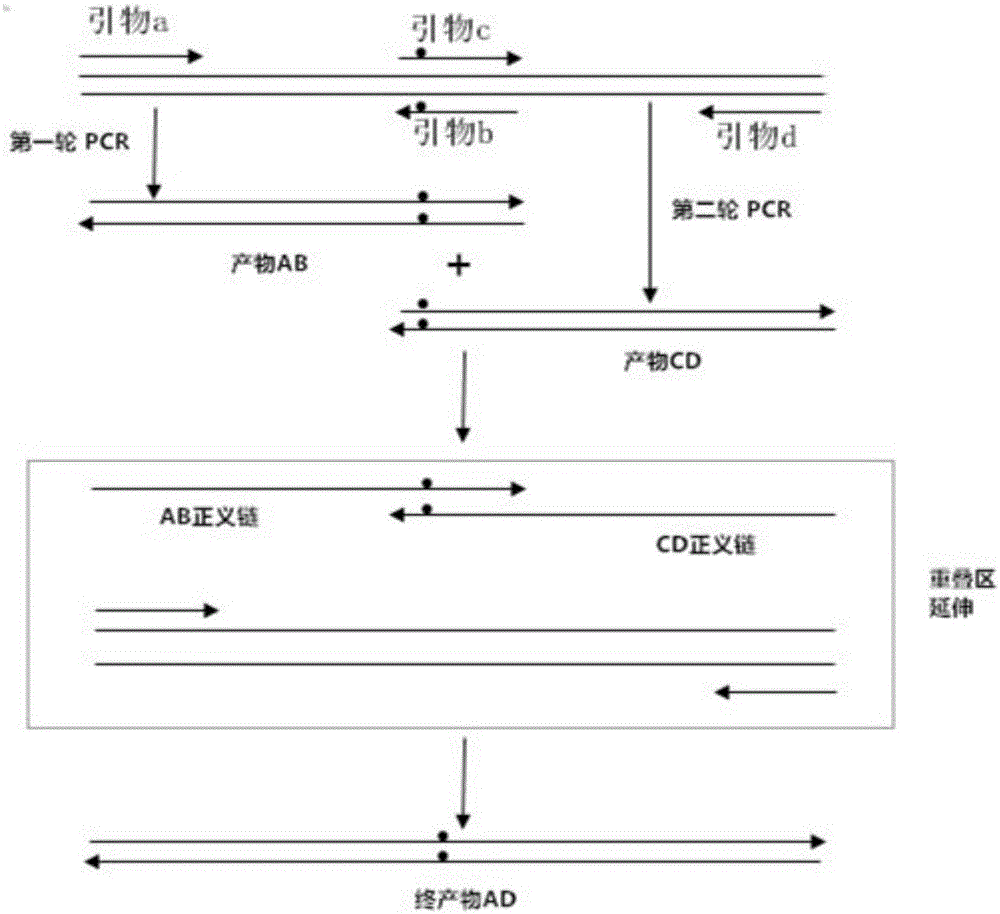
ActiveCN105039382AConvenient and quick genetic manipulation methodOvercoming eye-cultivationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRibosomal protein E-L30Bacterial strain
The invention relates to a gene and a bacterial strain with good streptomyces fungicidicus enramycin resistance and high yield. The sequence is as shown in a sequence 1. Meanwhile, the invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium containing the gene with good streptomyces fungicidicus enramycin resistance and high yield according to claims. A convenient and fast genetic operation method for streptomyces fungicidicus is built; the physical and chemical mutagenesis blindness and the screening work with a huge project are overcome; coding expression of a ribosome S12 protein gene in streptomyces is changed by a site-specific mutagenesis method; the yield of the bacterial strain produced by enramycin is improved; the resistance capability of the mutated bacterial strain is further detected; and compared with an original bacterial strain, the resistance of the mutant strain on streptomycin is improved by at least 10 times.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
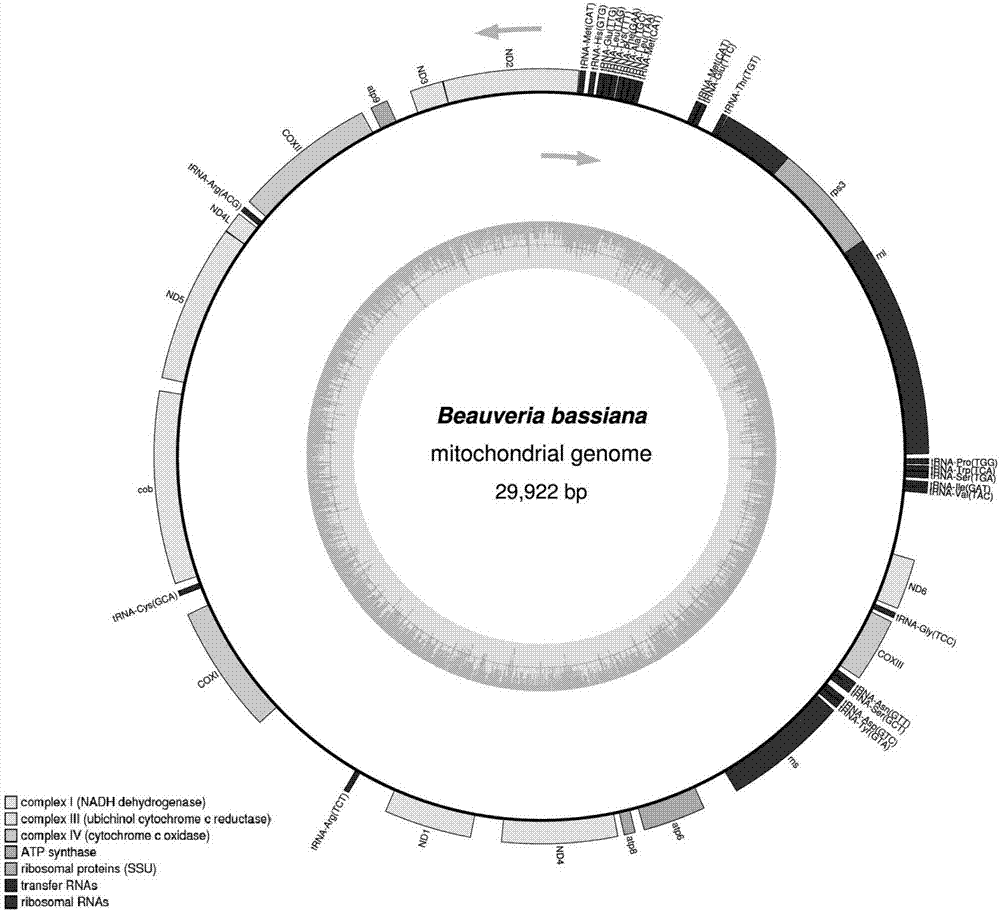
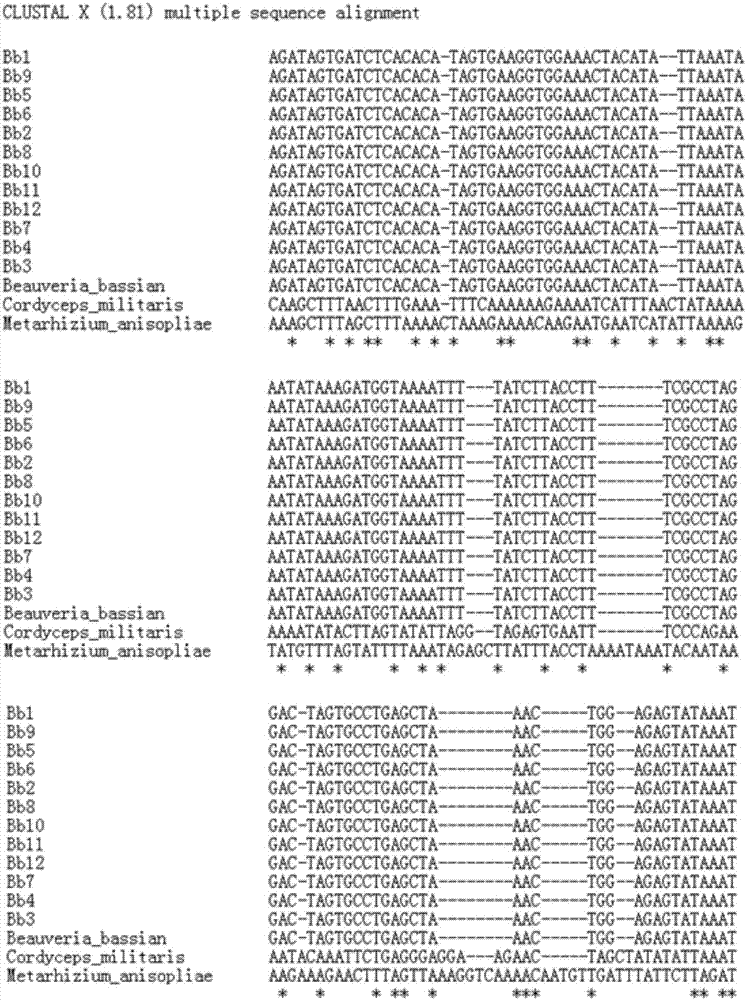
Molecular identifying method for quickly identifying truth of beauveria bassiana in Chinese herbal medicine stiff silkworm
ActiveCN107164471AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesRibosomal protein E-L30Biotechnology
The invention discloses a primer set for quickly identifying truth of beauveria bassiana in Chinese herbal medicine stiff silkworm and a molecular identifying method. The sequence of the primer set is respectively shown as SEQ ID NO.1-2. According to the invention, on the basis of the completion of high-throughput sequencing of complete genome of Guangdong beauveria bassiana mitochondria and bioinformatic comparative analysis of mitochondria complete genome of multiple cordyceps species, the difference of the beauveria bassiana mitochondria gene sequences at the aspect of geographical species is compared and obvious variation of ribosomal protein gene of beauveria bassiana is founded; a pair of primers for specifically detecting beauveria bassiana are screened on the basis of the design; the molecular identifying method for quickly and efficiently identifying truth of beauveria bassiana in Chinese herbal medicine stiff silkworm is established; the method is simple, convenient and quick, has high specificity, high sensitivity and wide application scope and can realize the identification for the truth of the beauveria bassiana from different producing places; a technical support is supplied for quality standardization and normalization and clinic drug safety of the Chinese herbal medicine stiff silkworm.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods for transforming Phaffia strains, transformed Phaffia strains so obtained and recombinant DNA in said methods
InactiveUS6329141B1High expressionSuitable for productionFungiBacteriaRibosomal protein E-L30Open reading frame
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the disclosed amino acid sequences. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV +1
Molecular marker associated with colorectal carcinoma metastasis and prognosis as well as application of molecular marker
InactiveCN107099584AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisRibosomal protein E-L30Lymphatic Spread
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Balsm-pear-seed ribosome inactivated protein and its coding gene and use
InactiveCN101070342AImprove securityExpression conditions are simplePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsRibosomal protein E-L30Ribosomal protein
This invention relates to a balsam pear seed ribosome inactivating protein(RIP) and its encode gene and application. This protein has one of the undermentioned amino acid residue sequence: (1) SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence table; (2) carry out substitution, deficiency or addition of protein that possess activity of inhibiting ribosomal protein synthesis to one to ten amino acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 1 amino acid residue sequence in sequence table. This protein possess hereinafter point: (1) notable effect of resisting tumour and virus infection; (2) high security; (3) simple protein expression condition, easy purification. low cost.
Owner:SHANXI KANGBAO BIOLOGICAL PROD +2
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of peptide beta-lactones and beta-hydroxy acids
ActiveUS10655153B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRibosomal protein E-L30Ribosomal protein
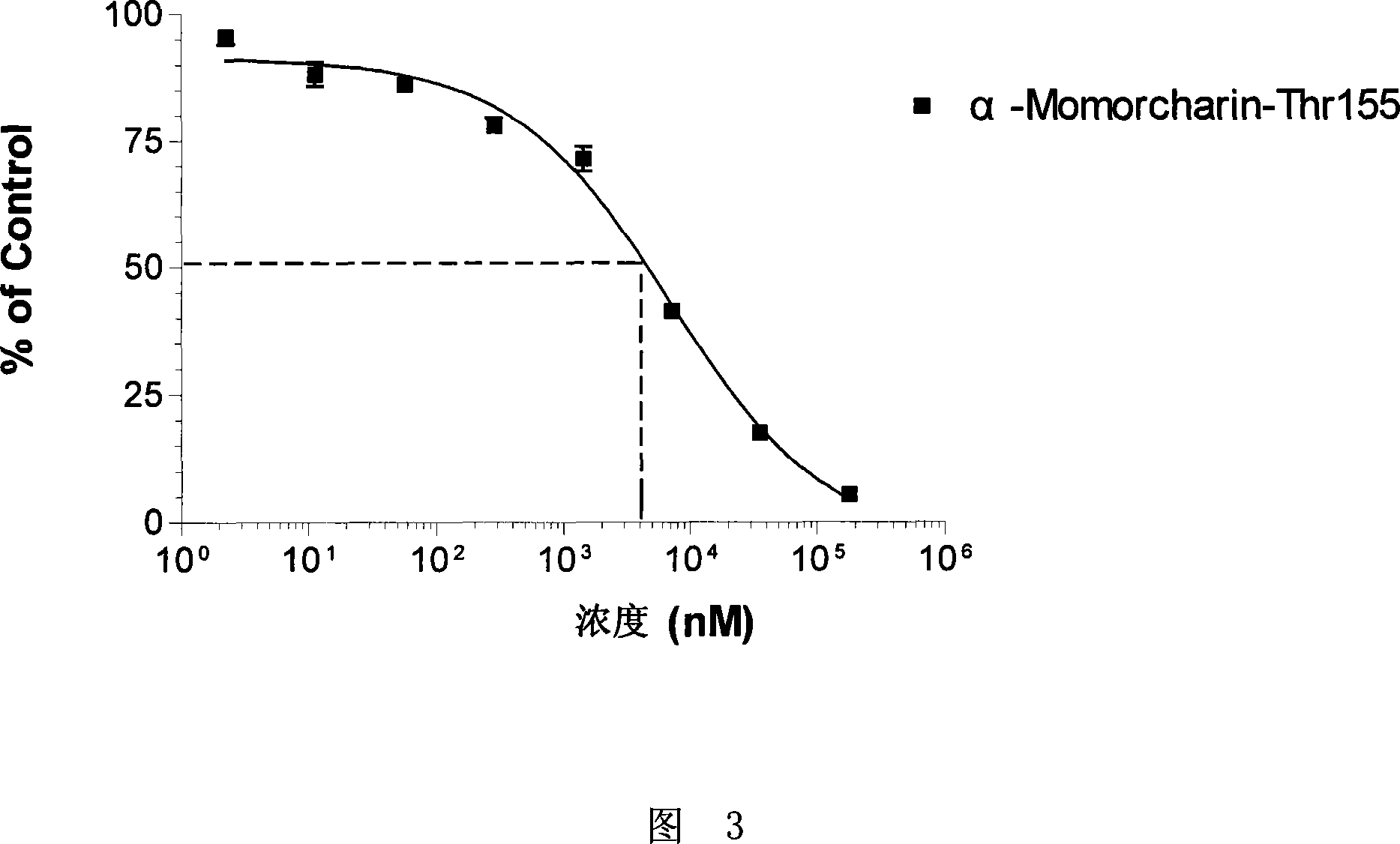
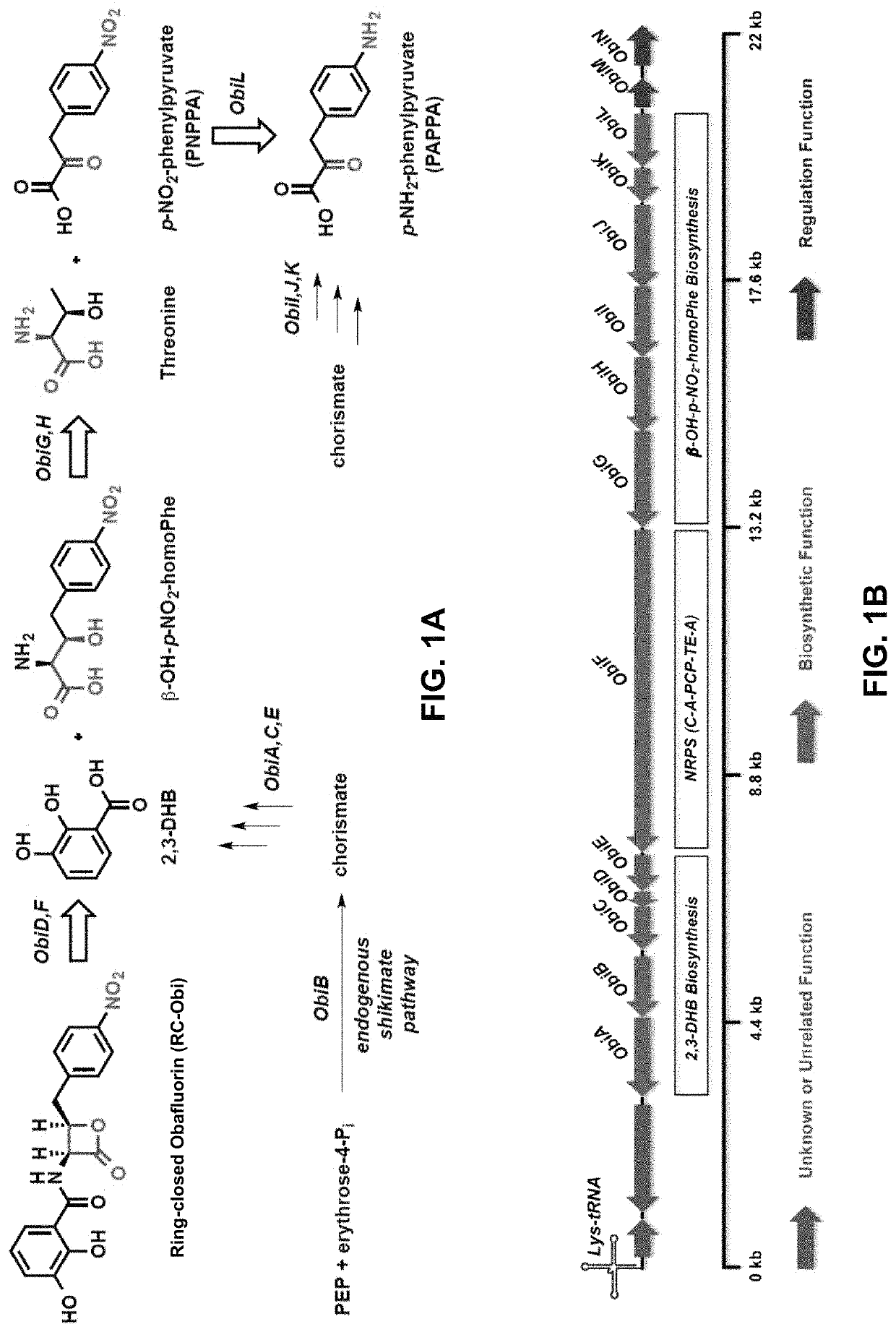
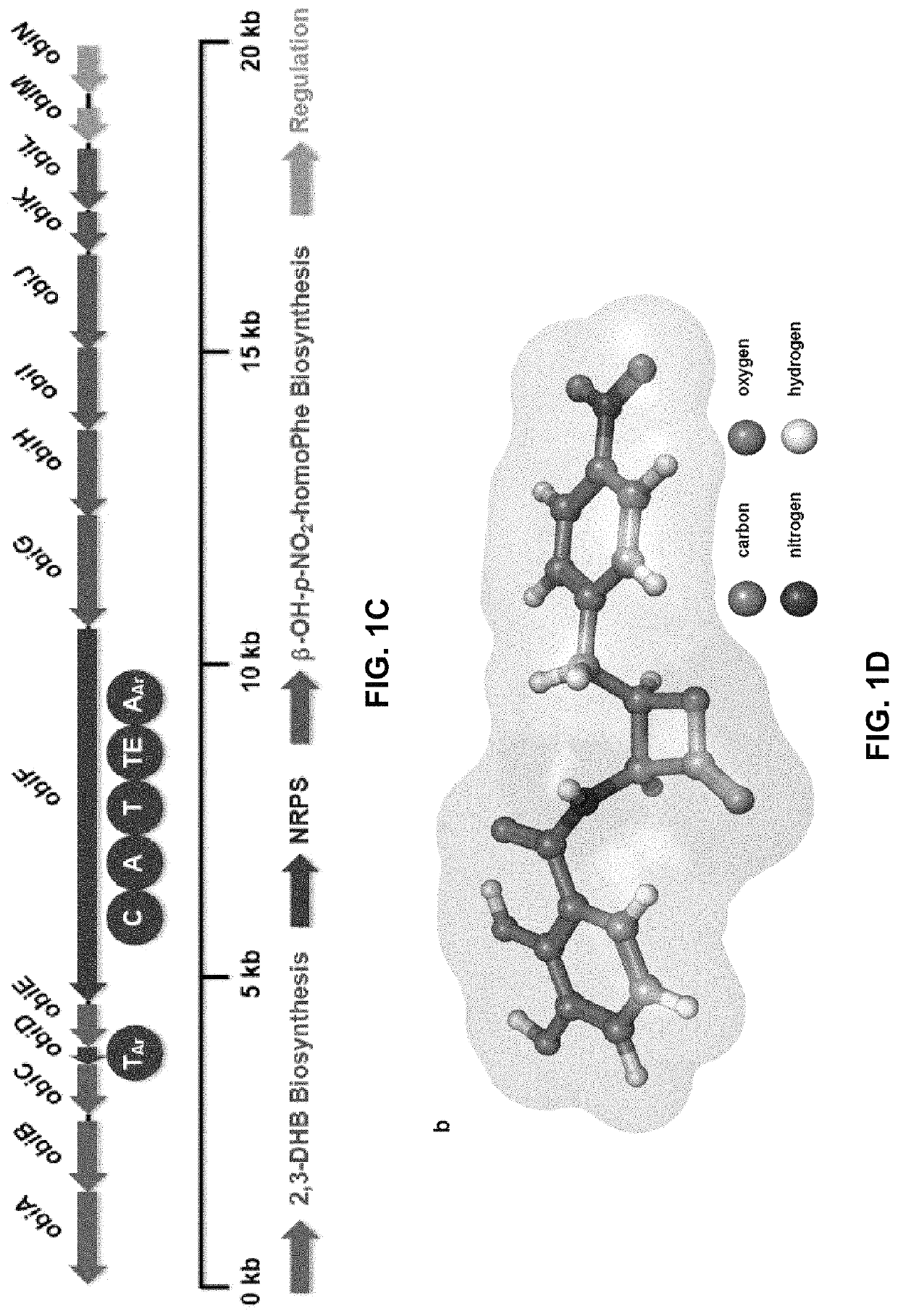
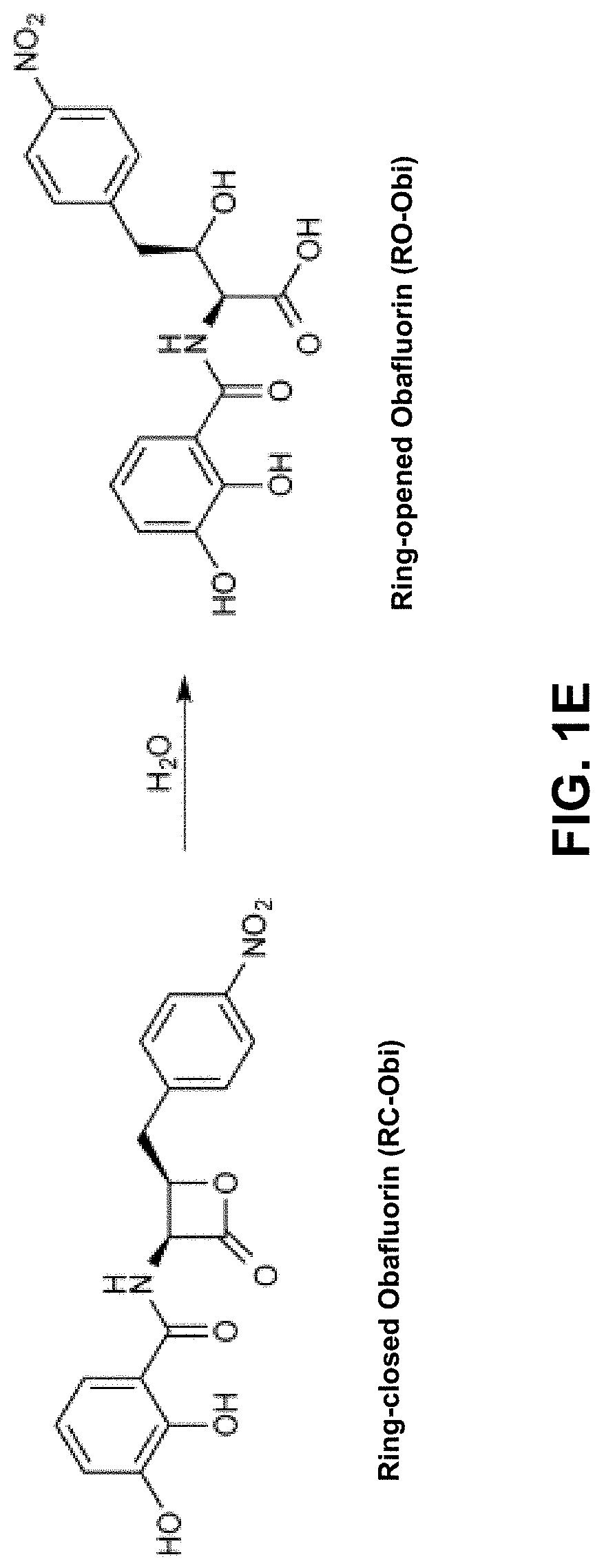
Methods of producing peptide beta-lactones and beta-hydroxy acids are disclosed that include contacting a beta-hydroxy-alpha-amino acid, an aryl carrier protein (ObiD), and ATP with a non-ribosomal protein synthetase. A continuous flow reactor is disclosed that includes an elongate conduit with at least one region that includes a first region with a non-ribosomal protein synthetase immobilized to a substrate. The non-ribosomal protein synthetase of the continuous flow reactor is configured to contact a flow of a reaction mixture that includes a beta-hydroxy-alpha-amino acid and an aryl carrier protein. The non-ribosomal protein synthetase is further configured to release a peptide beta-lactone into the flow of the reaction mixture.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Medical application of three carboxyl substituted aromatic compounds in treating pyrazinamide-resistance tuberculosis and tuberculosis
InactiveCN106109467AInhibit Mycobacterium tuberculosisInhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRibosomal protein E-L30Carboxyl radical
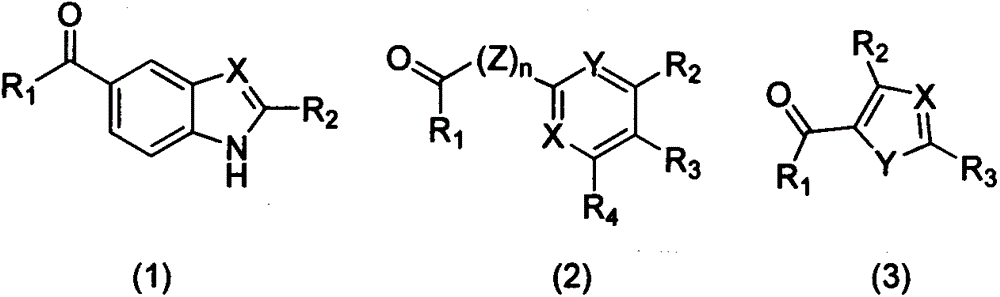
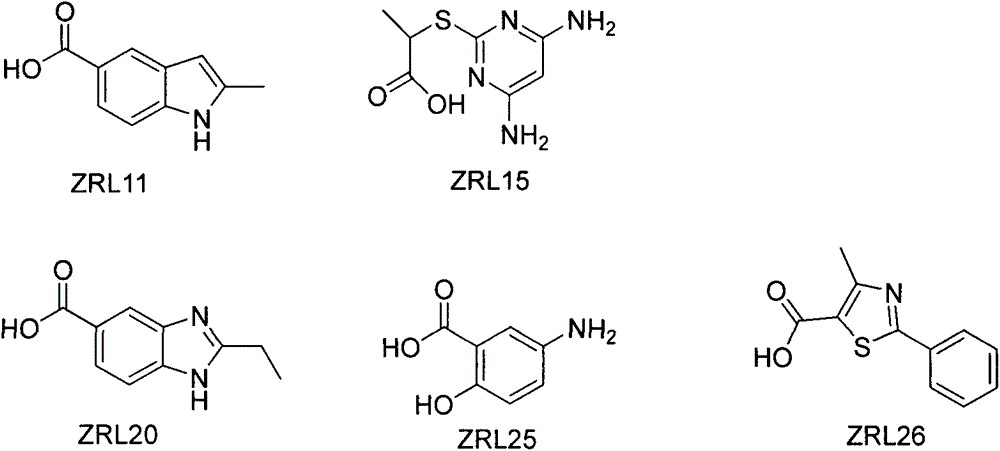
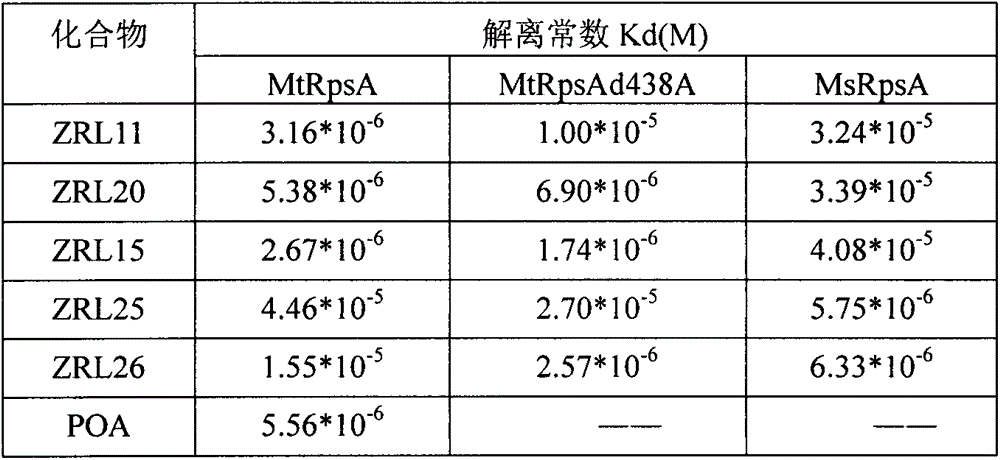
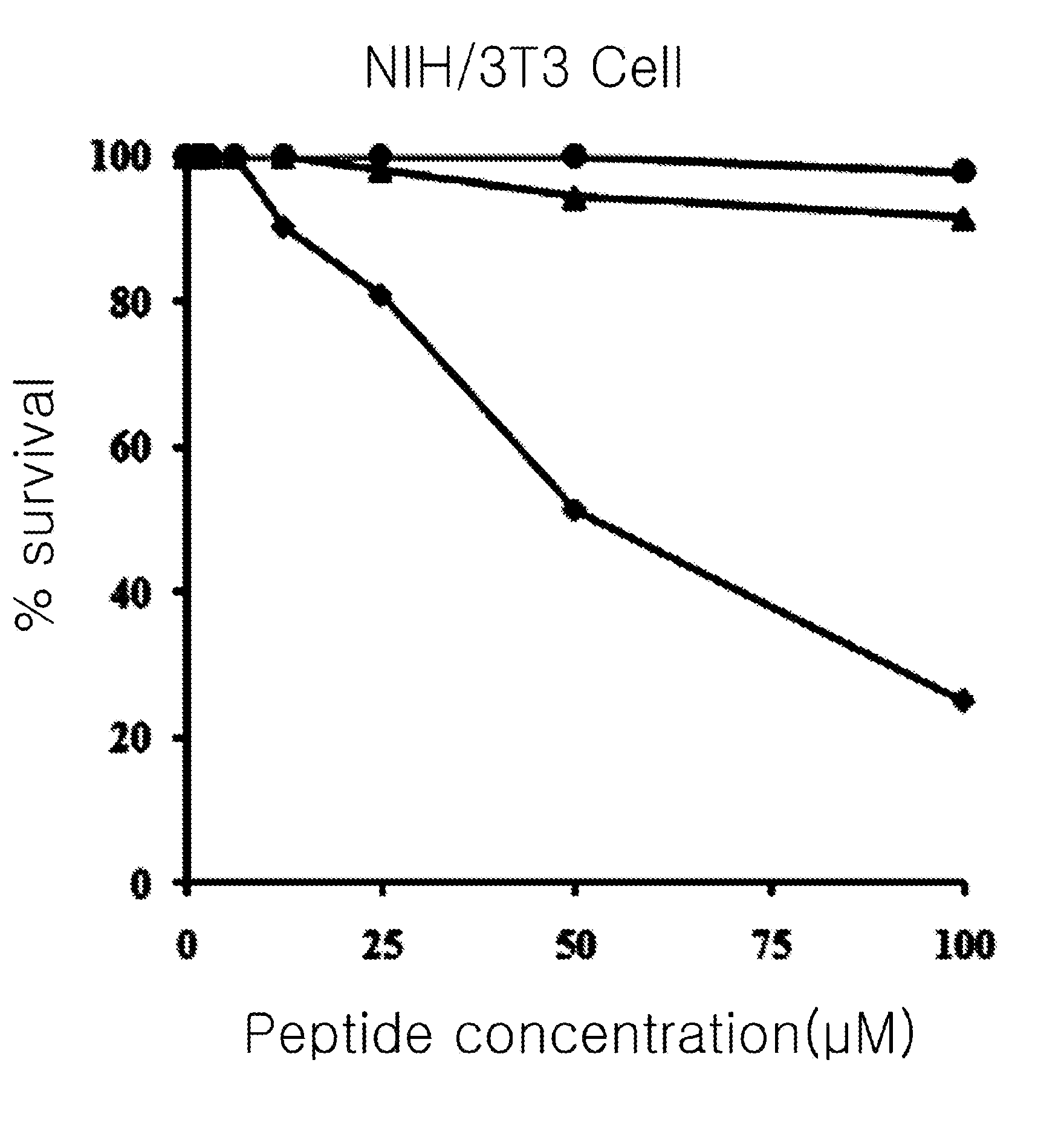
The invention discloses three carboxyl substituted aromatic compounds (shown as Formulas (1-3)), which can antagonize ribosome proteins S1 (RpsA) of a ribosome 30S small subunit, effectively inhibit the growth of mycobacterium tuberculosis and pyrazinamide-resistance mycobacterium tuberculosis and can be used for preparing drugs for treating pyrazinamide-resistance tuberculosis and tuberculosis (as shown in Description).
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Organ transplant rejection and associated conditions
The application discloses markers associated with organ transplant rejection and associated conditions, and in particular provides materials and methods for the diagnosis, prognosis or treatment of chronic rejection of transplanted organ such as heart and kidney. Examples of the markers include ribosomal protein L7, β-transducin, 1-TRAF (also known as TANK) or lysyl-tRNA synthetase, or antibodies against these antigens.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Novel antibiotic peptide derived from ribosomal protein l1 of helicobacter pylori and use thereof
The present invention relates to a new antibiotic peptide and a usage thereof, which are derived from ribosomal protein L1, RPL1 of Helicobacter pylori. Specifically, the antibiotic peptide comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ. ID. NO:1 derived from ribosomal protein L1, RPL1 of Helicobacter pylori is substituted with a Phenylalanine, which is situated at the first and the eighth position from the antibiotic peptide, or in addition an Asparagine, which is situated at the thirteenth position of the antibiotic peptide, is substituted with lysine, wherein the produced peptides have maintained more decreased cytotoxicity when comparing to the existing antibiotic peptides and can be used as a safe antibiotics by showing more antibacterial activity.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
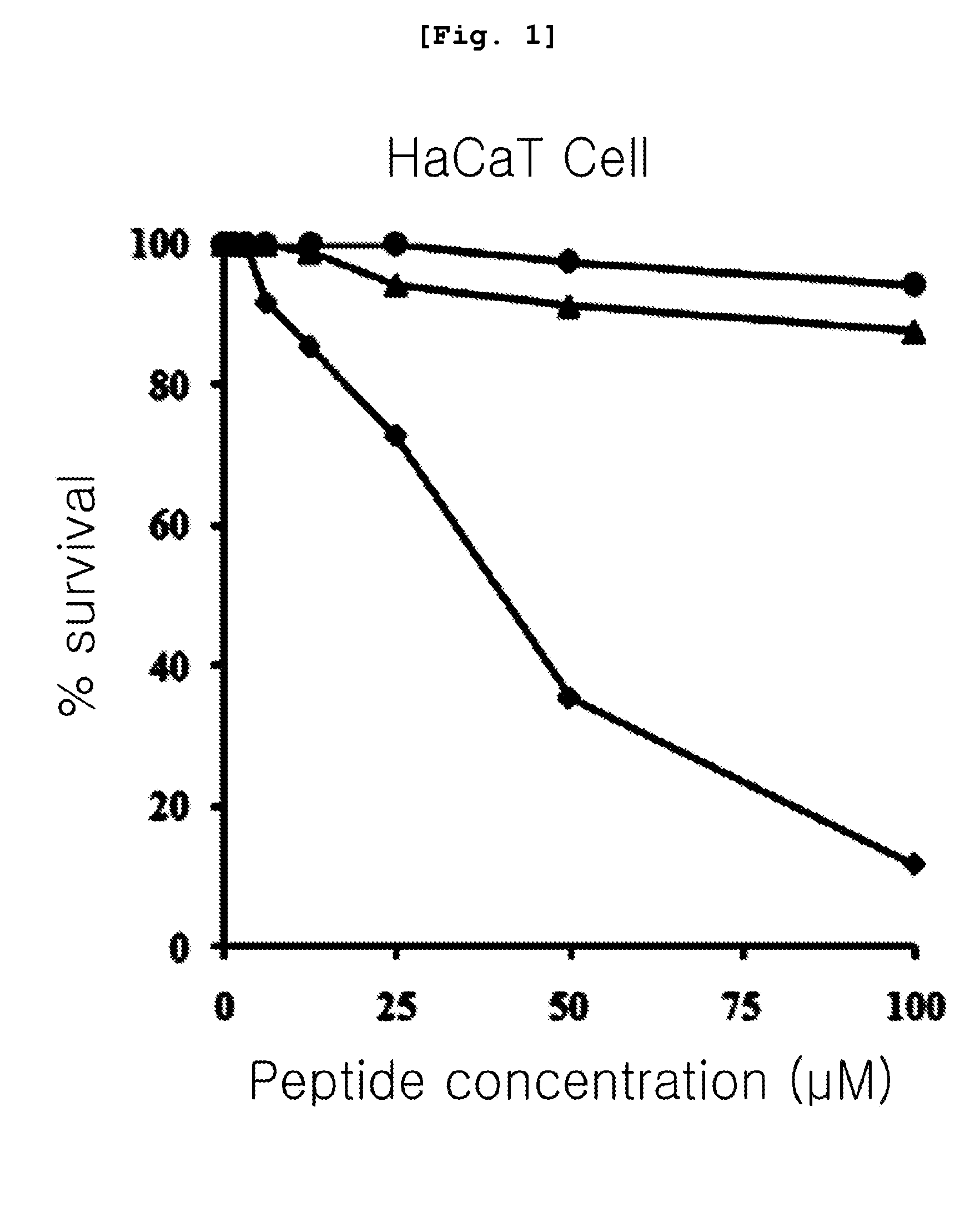
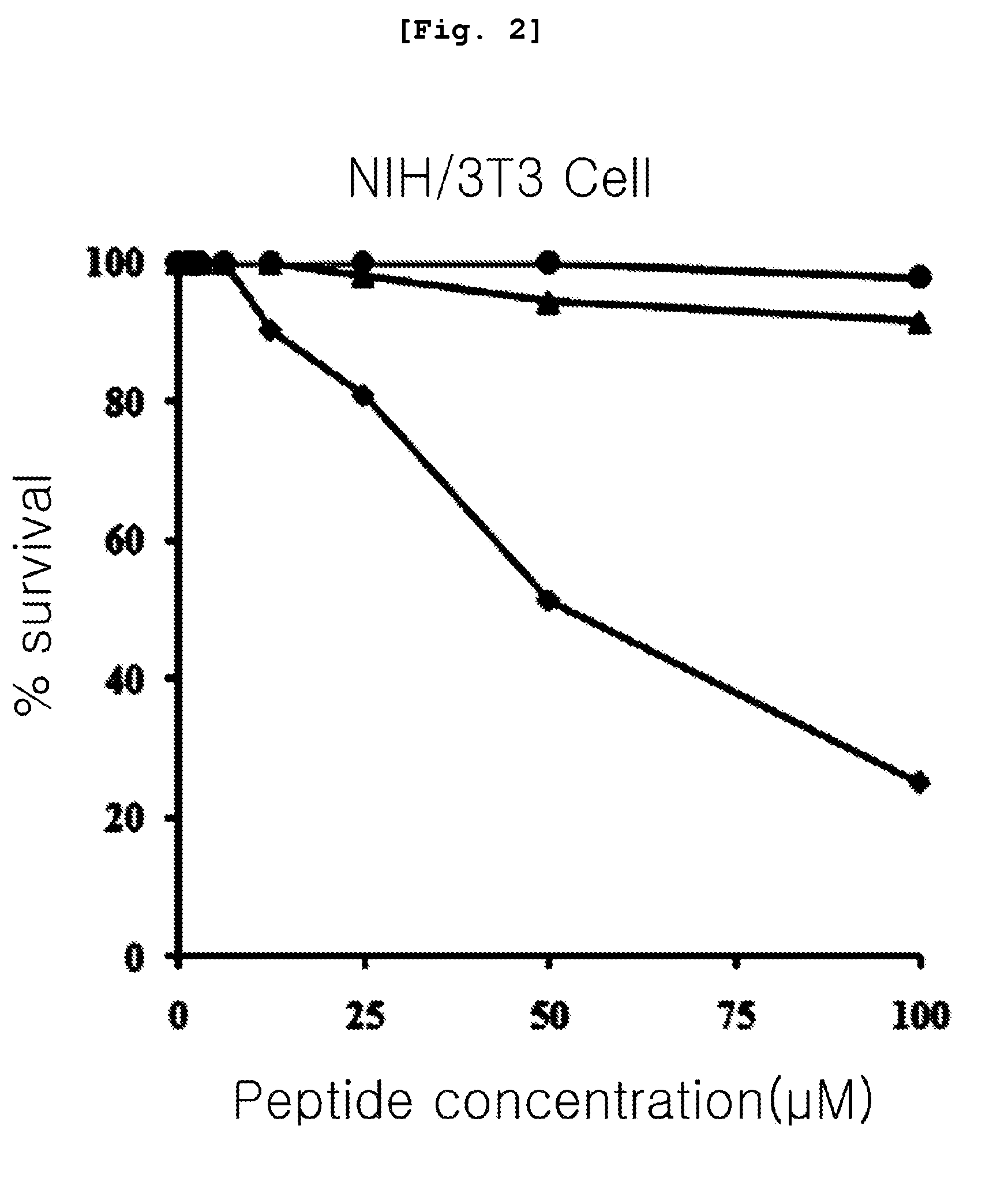
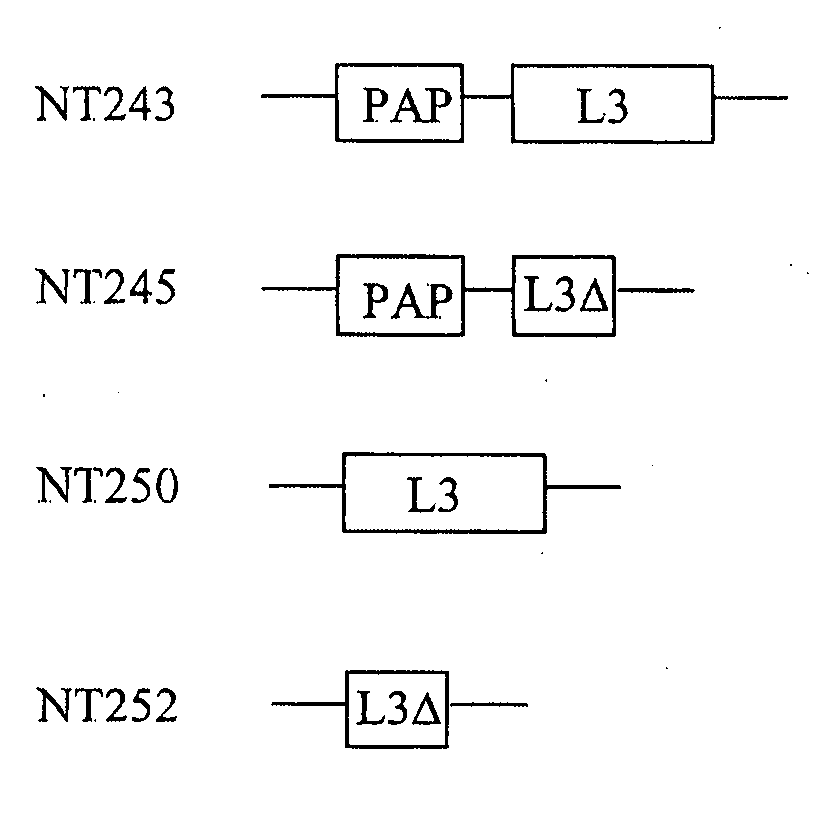
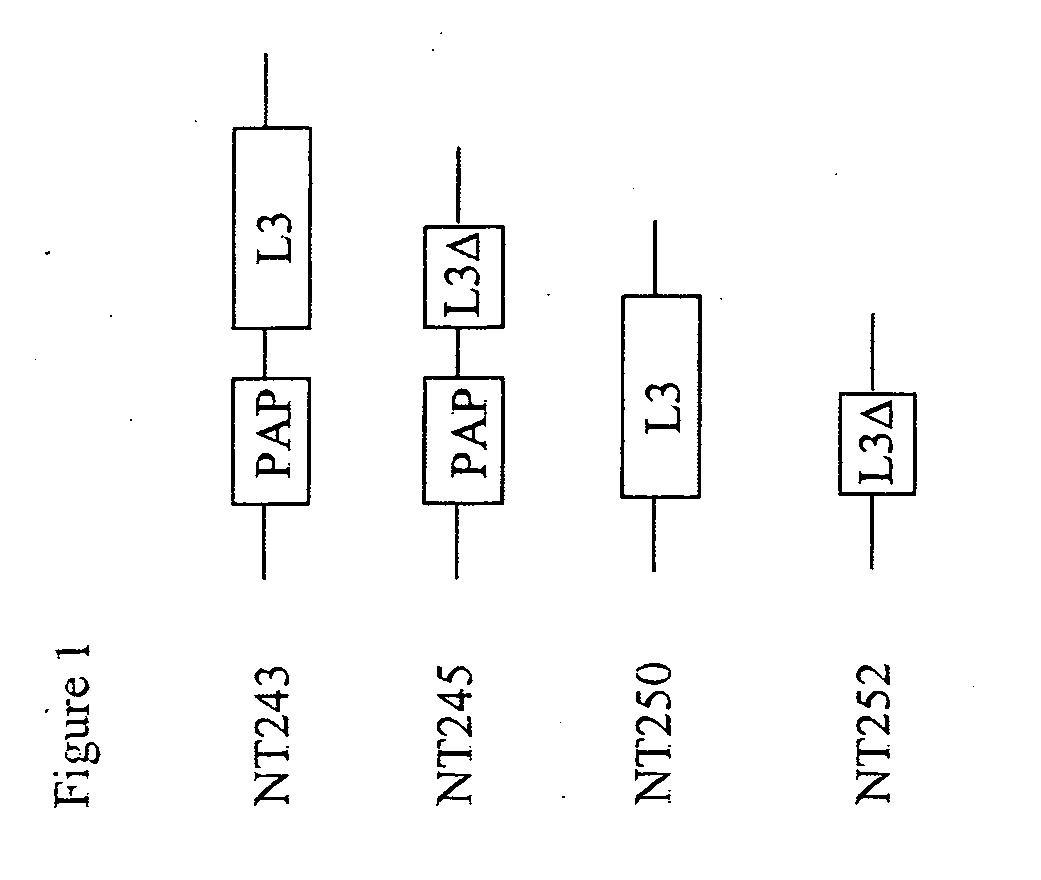
Transgenic plants expressing L3 delta proteins are resistant to trichothecene fungal toxins
InactiveUS20060005271A1Low toxicityImprove the immunityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationRibosomal protein E-L30Fungal toxin
Disclosed are specific mutants of L3 and transgenic plants that produce them. The plants exhibit increased resistance to fungal toxins that target ribosomal L3 protein. Also disclosed are transgenic plants that co-produce L3 mutant and an RIP protein, and exhibit increased resistance to various fungal toxins and viruses, while reducing toxicity normally associated with production of the RIP. Uses of the L3 mutants in animals are further disclosed.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method for rapidly identifying strain-level pathogenic bacteria in food through double adsorption
InactiveCN108020674AHigh-resolutionStrengthen the effect of microwave wall breakingBiological testingProtein DatabasesRibosomal protein E-L30
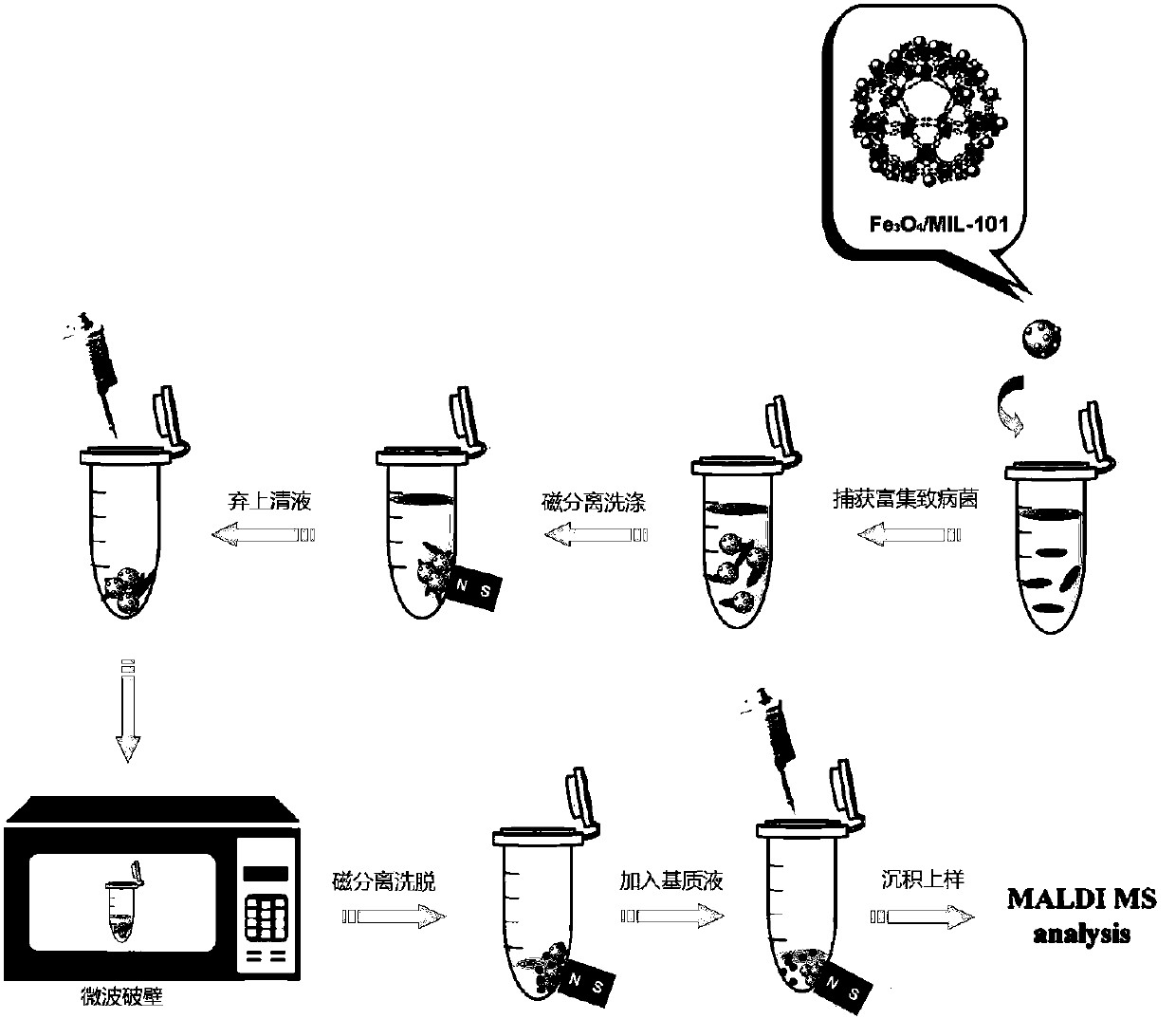
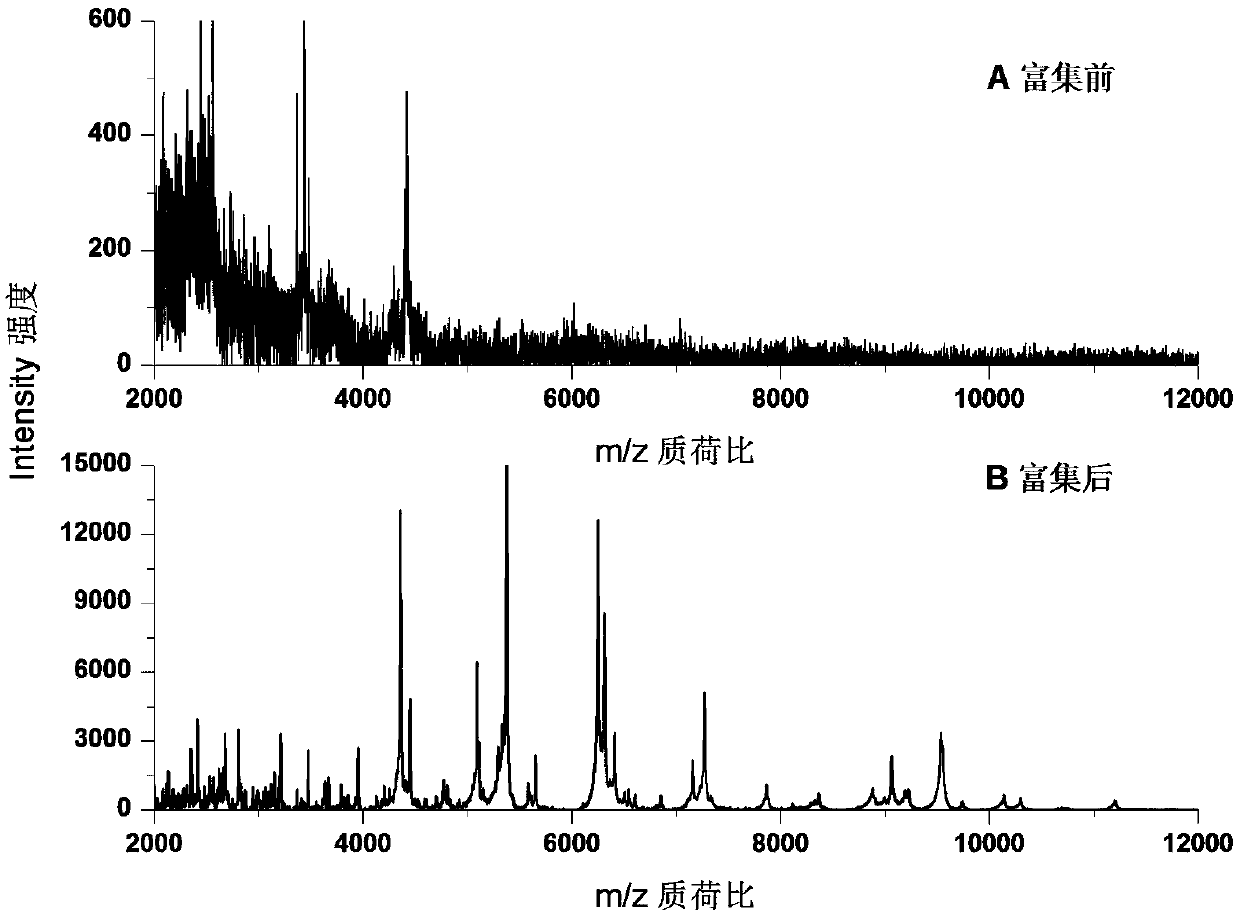
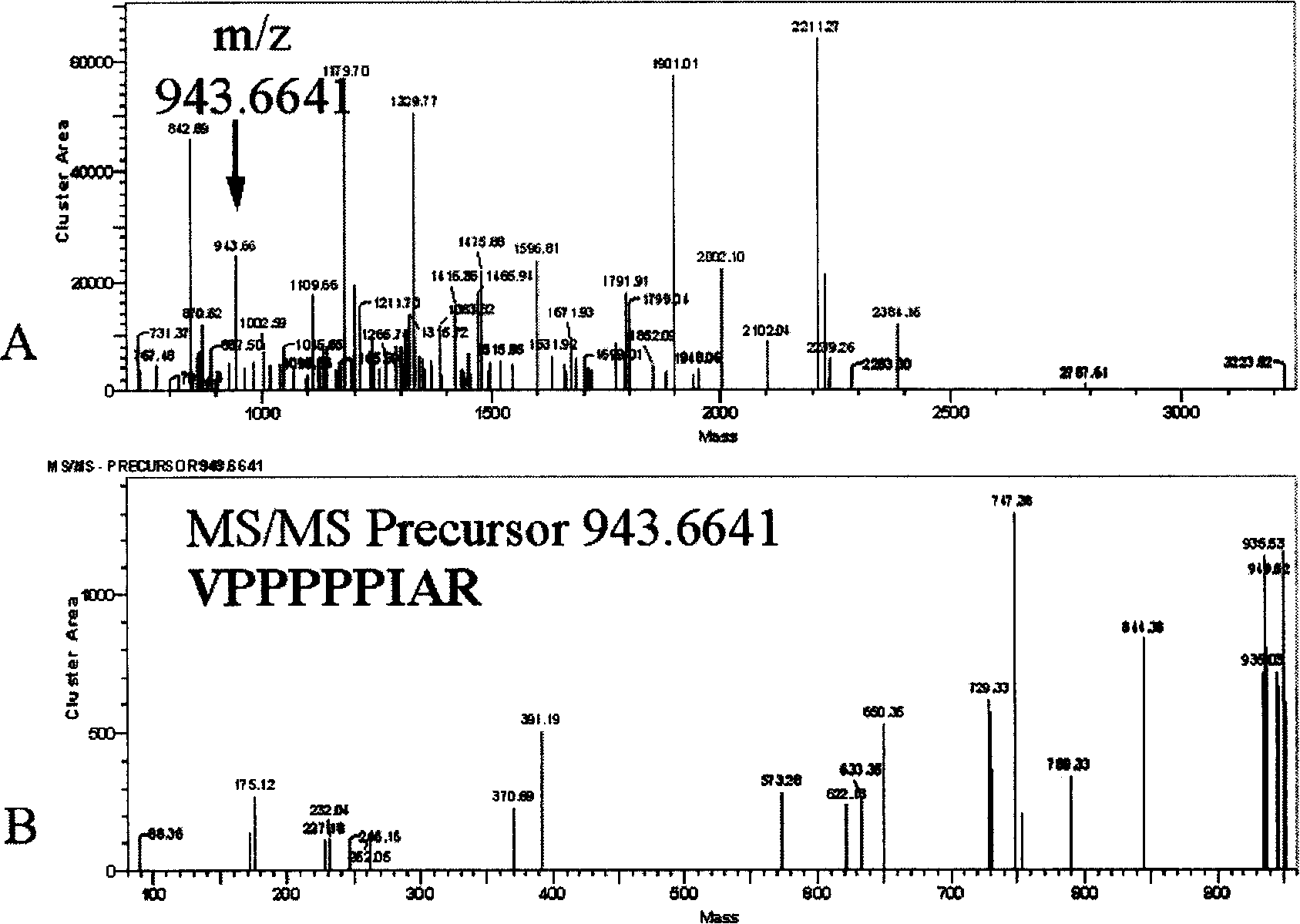
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying strain-level pathogenic bacteria in food through double adsorption. The method comprises main steps as follows: a) strain-level pathogenic bacteria in liquid food are adsorbed by MIL-101 magnetic particles, and wall breaking is performed under microwave assistance; after wall breaking, to-be-identified pathogenic bacterium protein is rapidlyenriched through the MIL-101 magnetic particles; b) a mass spectrum graph of the pathogenic bacterium protein is collected through MALDI / TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization / time of flight mass spectrometry); c) a Tagident search tool is used for performing protein database searching on mass spectrum peak, and ribosomal protein is selected; d) a rapid microorganism identification database is sought by use of ribosomal protein obtained through searching, and the attributes of the strain-level pathogenic bacteria are determined. The method has the advantages of simplicity and rapidness. Enrichment of pathogenic bacteria, wall breaking and mycoprotein enrichment are integrated, finally, a ribosomal protein database is used for rapidly identifying the pathogenic bacteria, and the strain level of pathogenic bacteria in the liquid food is rapidly identified.
Owner:TIANJIN MODERN VOCATIONAL TECH COLLEGE
Method and reagent kit for detecting two proteins expressed in human liver organization
The invention relates to a detection method for testing a protein HOP and a heterogeneous ribosome protein C1 / C2 which are both expressed in human liver tissue, as well as reagent box used in the method. The method is characterized in that: by means of the fluorescence differential two-dimensional electrophoresis method -MALDI-TOF / TOF, the inventor manages to identify the overexpression of the two proteins on human liver cell carcinoma tumor tissue, and carries out immune histochemistry validations of Western bolt and large amount of samples over the expression levels in the human liver cell carcinoma tissue. The detection method for proteins and the reagent box can be used in the detections for clinical or research purposes.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
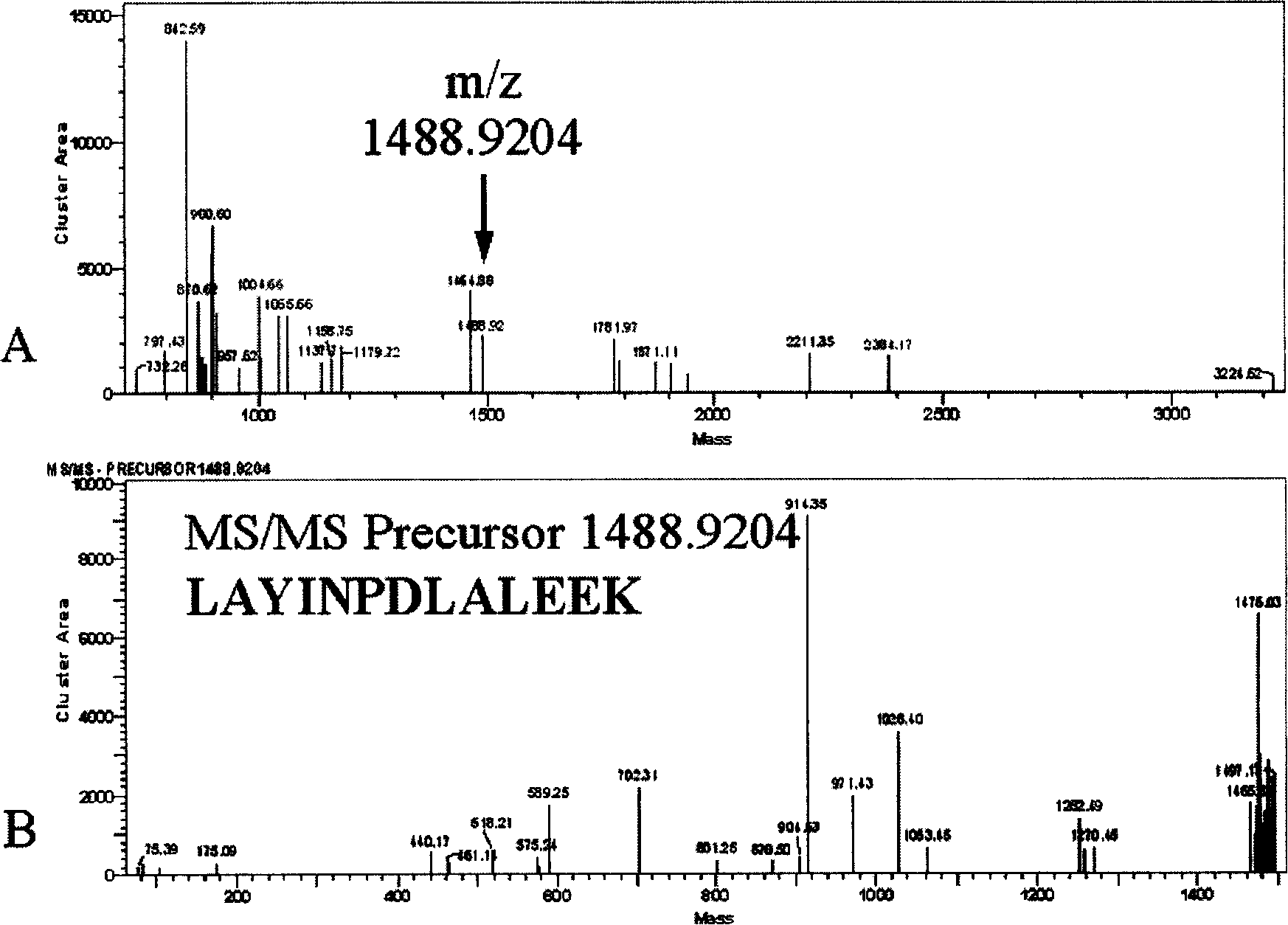
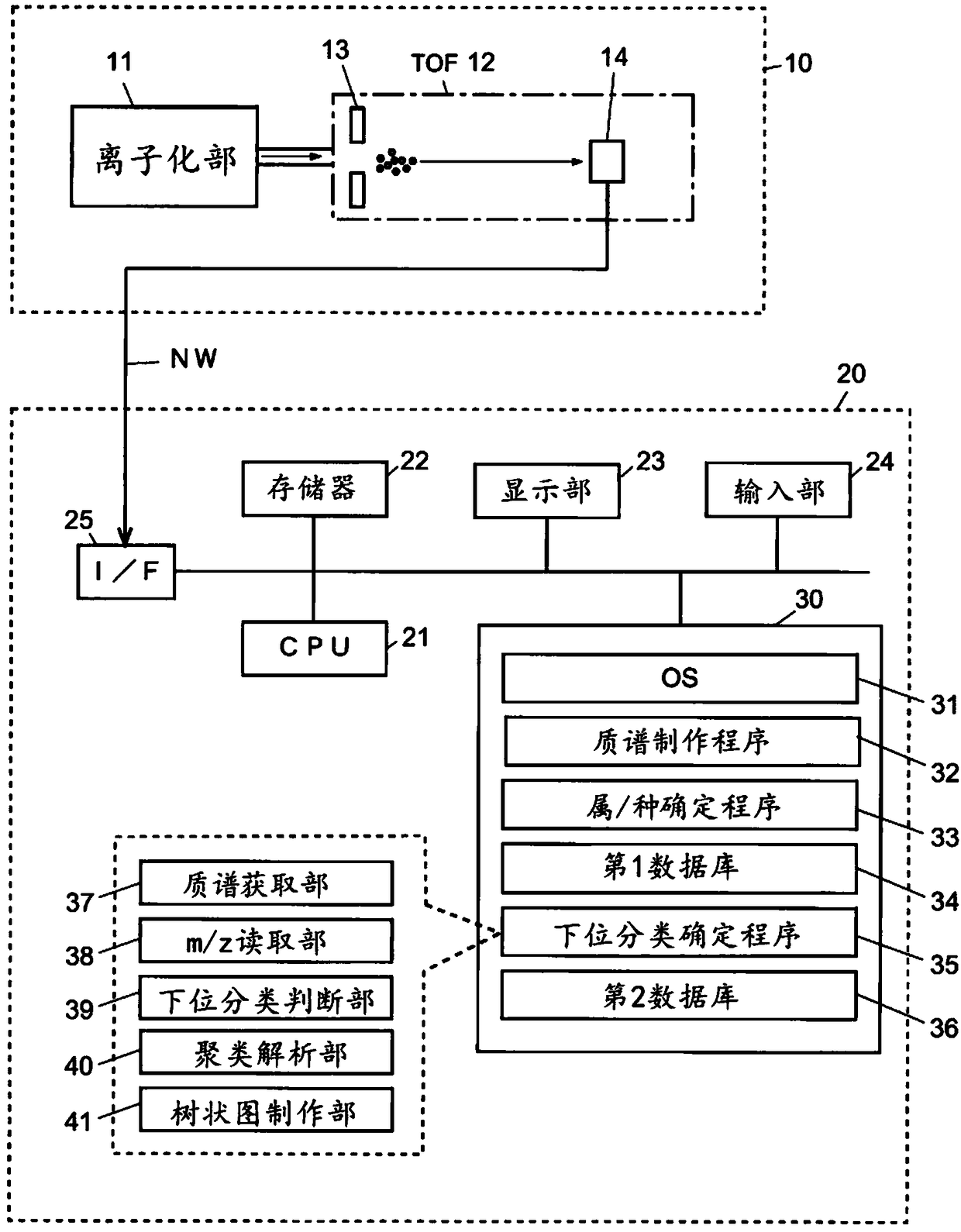
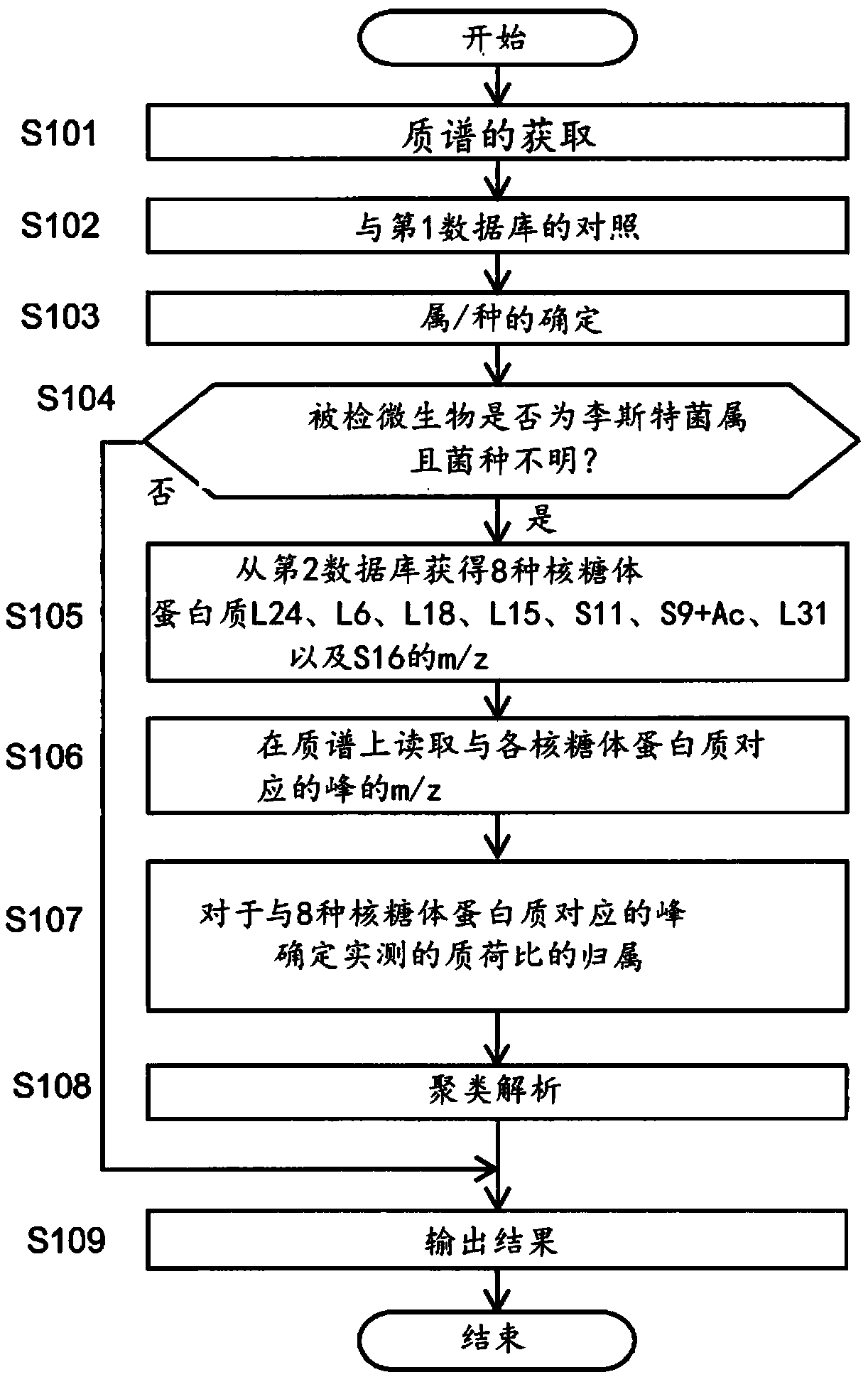
Microorganism identification method
PendingCN109154018AGood reproducibilityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisRibosomal protein E-L30Microorganism
Provided is a microorganism identification method involving the selection and use of a marker protein that makes it possible to quickly identify bacterial species of the genus Listeria with good reproducibility. The microorganism identification method comprises: a step in which a sample containing microorganisms is subjected to mass spectrometry and a mass spectrum is obtained; a reading step in which the mass-to-charge ratio m / z of peaks derived from a marker protein is read from the mass spectrum; and an identification step in which the mass-to-charge ratio m / z is used as a basis to identifywhether the microorganisms included in the sample include any bacterial species of the genus Listeria. The microorganism identification method is characterized in that one or more of the following seventeen types of ribosomal proteins is used as the marker protein: L3; L4; L23; L2; L24; L6; L18; S5; L15; S13; S11; L10; L21; L13; S9; L31; and S16. The microorganism identification method is also characterized in that among the seventeen types of ribosomal proteins, particularly one or more of the following eight types of ribosomal proteins is used: L24; L6; L18; L15; S9; L31; and S16.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD +1
Surface based translation system
Translationally competent ribosomes are bound to a solid substrate through a specific attachment site. A spatial array of such immobilized ribosomes may be produced on a planar substrate, microbeads, on fiber optics. One or more components of the ribosome complex are preferably labeled, e.g. with a fluorescent dye. Ribosomal RNAs, including mRNA and tRNA; and / or ribosomal proteins may be labeled at specific positions, and arrays of immobilized ribosomes may comprise a panel of different labels and positions of labels. Fluorescence detection can then be used to monitor conformational dynamics and translation rates.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Giant panda ribosomal subunit gene RPL23a recombinant protein and application thereof in preparing anti-cancer drugs
InactiveCN102558333AAnti-cancer function revealedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsRibosomal protein E-L30Amino acid
The invention discloses a giant panda ribosomal subunit gene RPL23a recombinant protein and application thereof in preparing anti-cancer drugs. The amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein is defined by SEQ ID NO: 7. The inhibitory effect of giant panda ribosomal subunit gene RPL23a recombinant protein on growth of Hep-2 cells is observed by acting the giant panda ribosomal subunit gene RPL23a recombinant protein on the Hep-2 cells, which reveals the anticancer function of the giant panda ribosomal subunit gene RPL23a recombinant protein and provides scientific basis and resources for developing anti-cancer protein drugs and studying on anti-cancer mechanism.
Owner:CHINA WEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
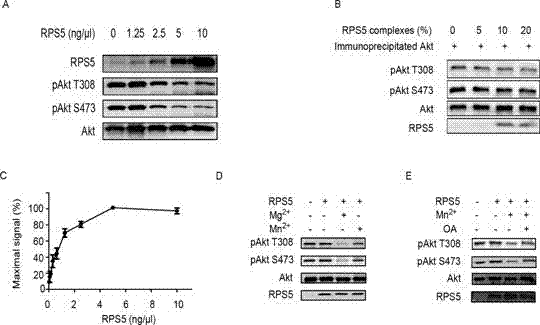
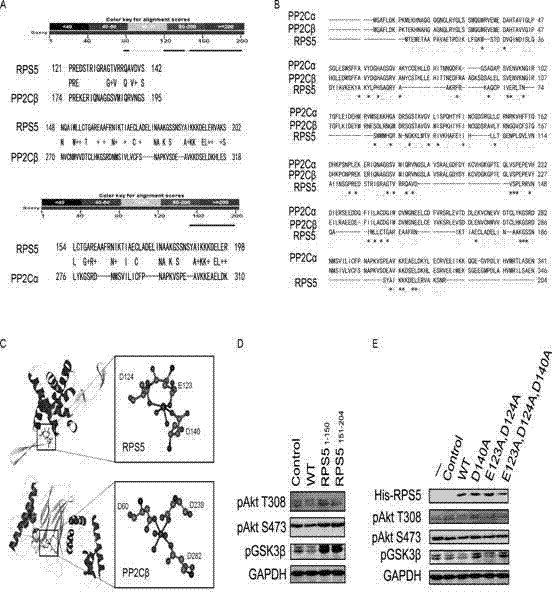
Purpose of ribosomal protein S5 in catalyzing of protein molecules for generatation of dephosphorylation reaction
InactiveCN103160557AInhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRibosomal protein E-L30Disease
The invention provides a purpose of ribosomal protein S5 (RPS5) in catalyzing of protein molecules for generation of dephosphorylation reaction, the ribosomal protein S5 serves as PP2C sampling protein phosphatase, provides purposes of RPS5 or agonist or inhibitor of the RPS5, the RPS5 or the agonist or the inhibitor of the RPS5 is used for preparing compounds for treating diseases or a pathological process which an Akt and MAPK access participates in, and further provides a detection method of the RPS5 protein phosphatase activity and a method for screening the agonist or the inhibitor of the RPS5. The invention has the advantages that the RPS5 is demonstrated to be the PP2C sampling protein phosphatase for the first time, the Akt and MAPK access is regulated and controlled, and therefore the RPS5 self can be used as the protein phosphatase, can be used for preparing the compounds for treating the diseases or the pathological process which the Akt and MAPK access participates in or screening substances restraining or activating the RPS5, and is used for treating the diseases or the pathological process which the Akt and MAPK access participates in.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
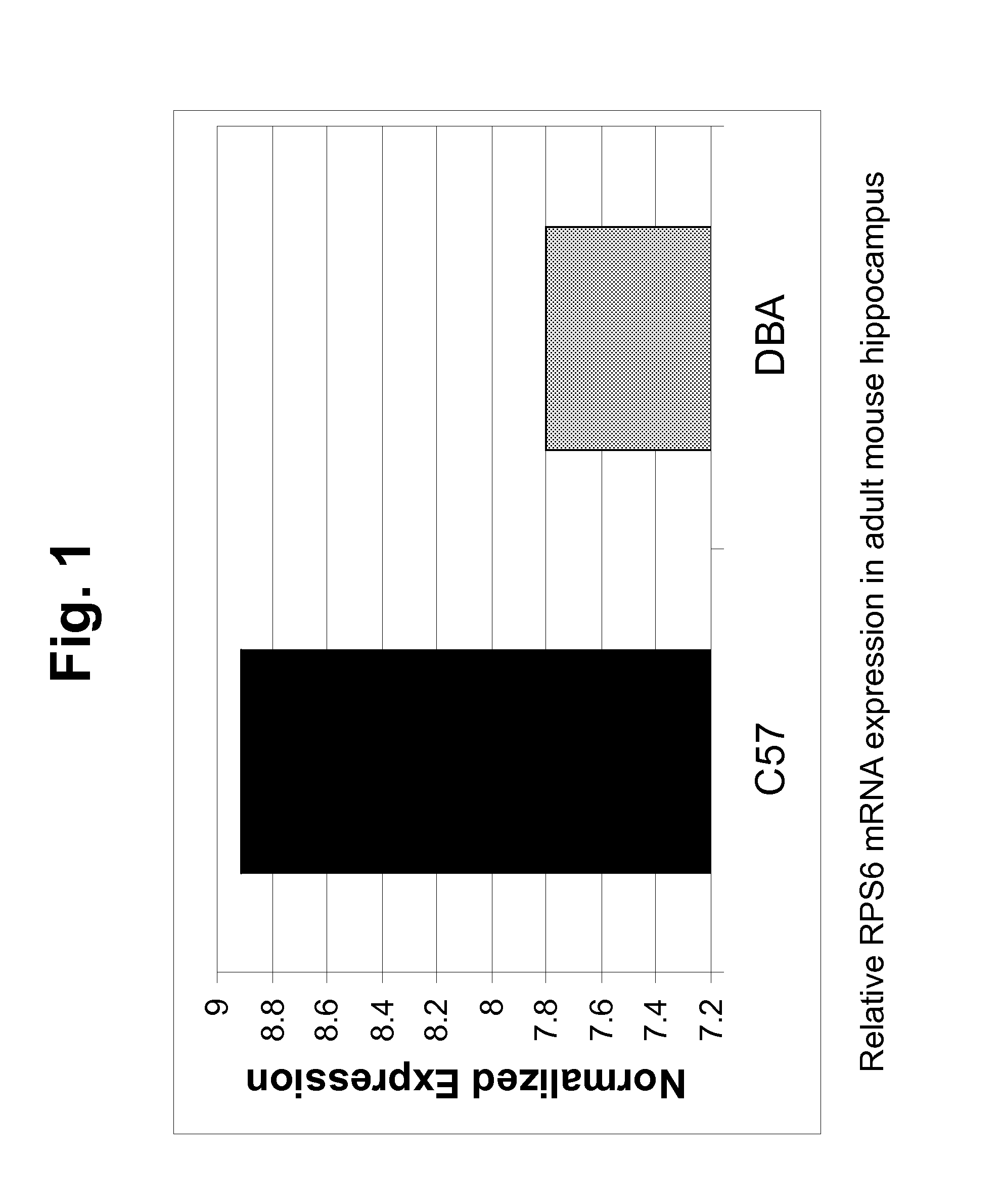
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of depression and anxiety
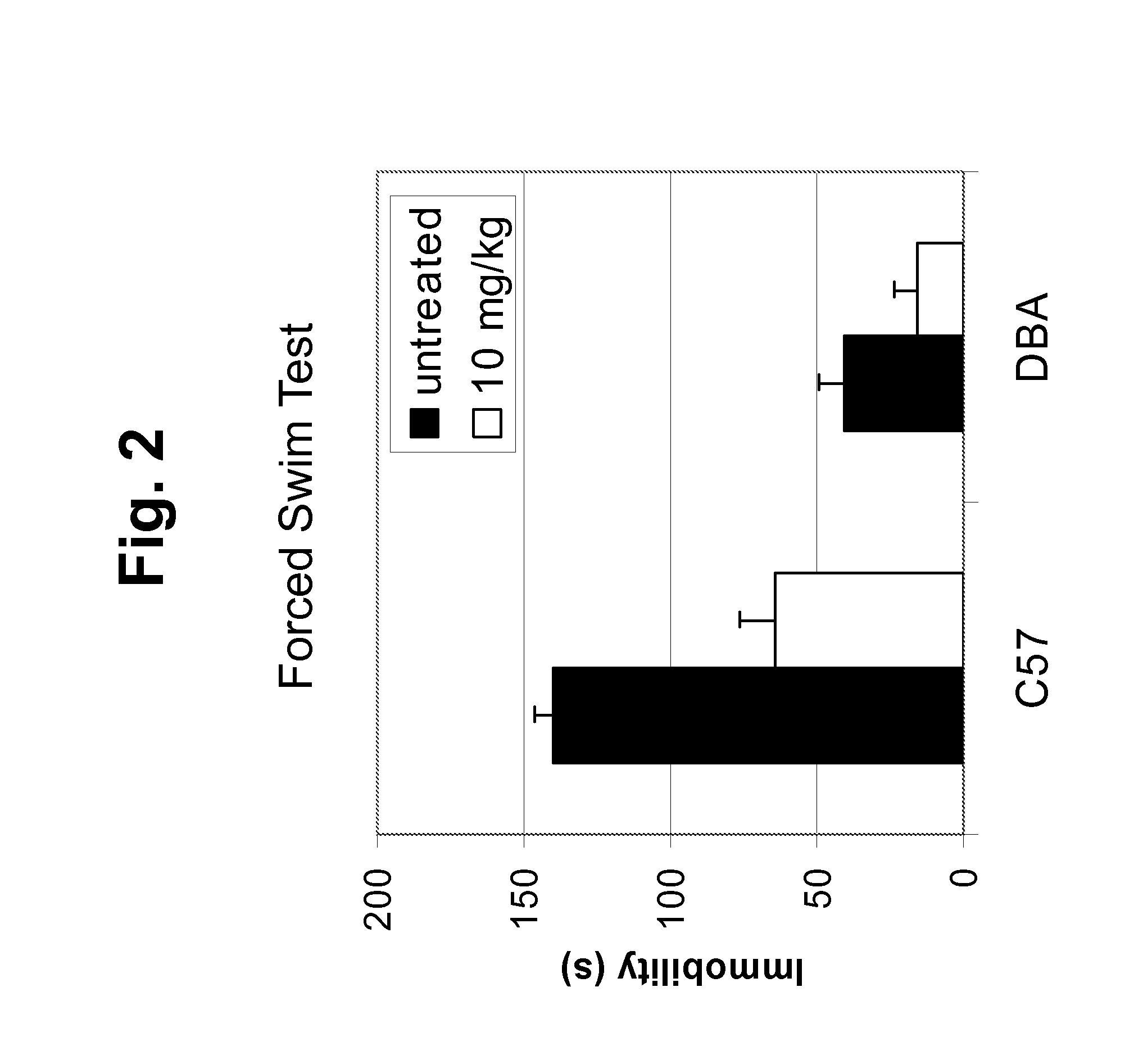
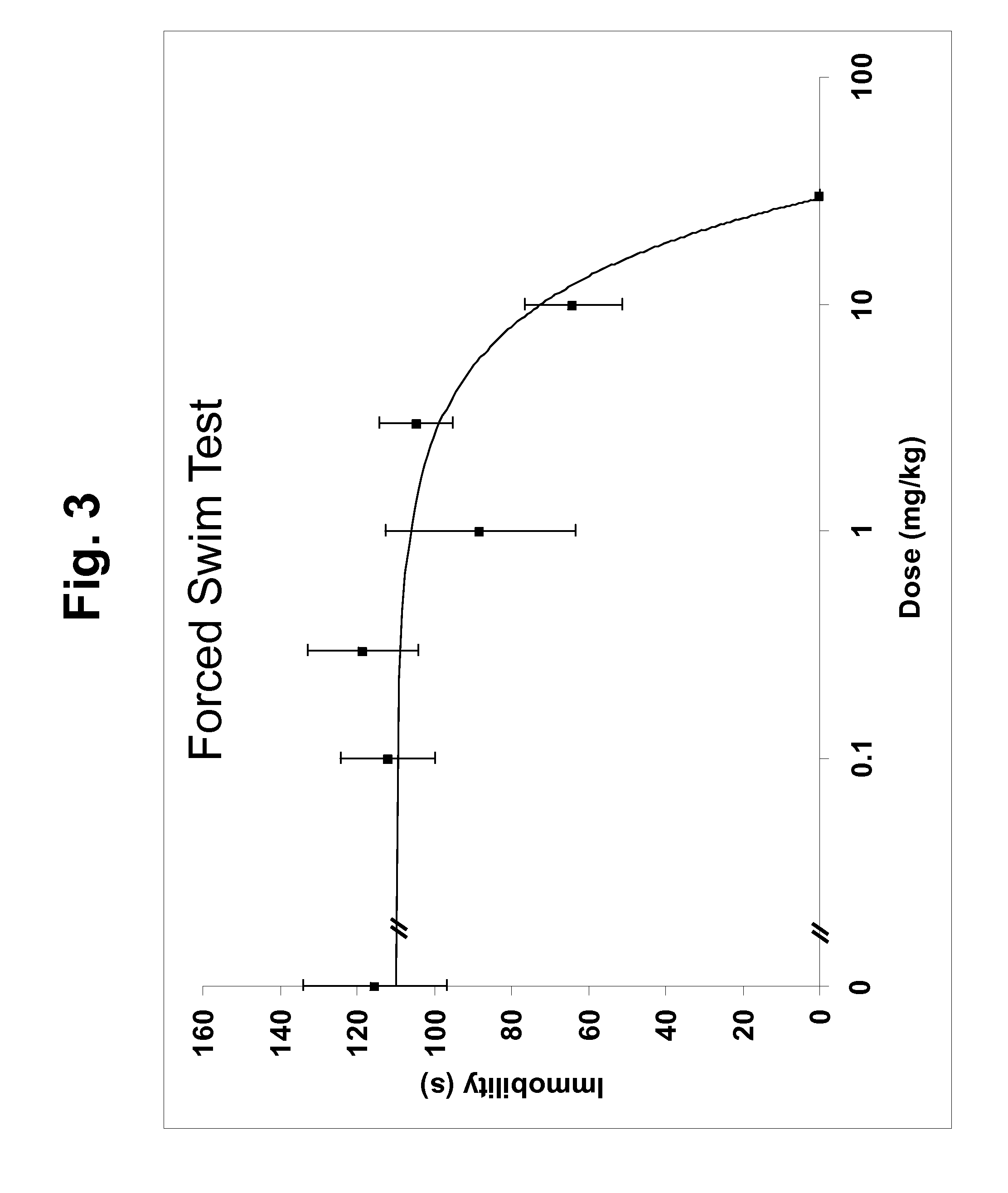
The present invention relates to identification of cellular components, genotypes and gene expression profiles associated with mood disorders. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to the correlation between ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6) and depression and / or anxiety. Embodiments of the present invention further relate to regulation of the activity of RPS6, e.g., by p90 Ribosomal S6 protein kinase. Embodiments of the present invention provide methods and compositions for, e.g., diagnosing, treating, and monitoring depression and / or anxiety, or risk thereof, and for selecting, monitoring, and tailoring treatments for depression and / or anxiety.
Owner:MODGENE
Human ribosomal protein molecules hRrp15p and preparation method and application thereof
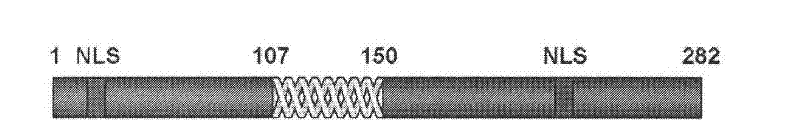
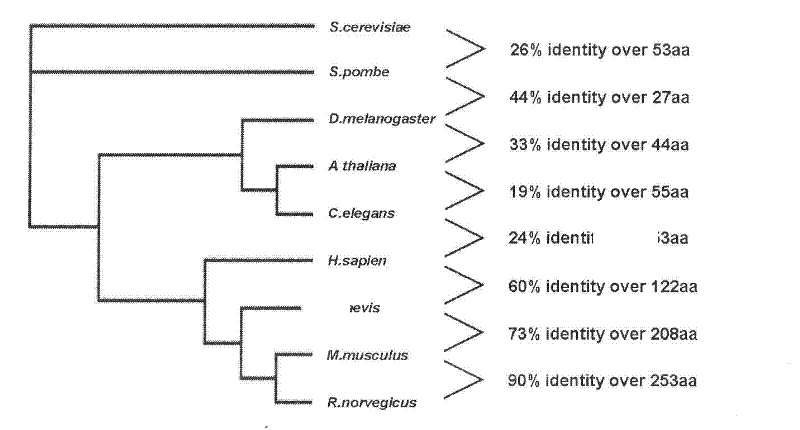
The invention discloses specific nucleotide of human ribosomal protein molecules hRrp15p. The nucleotide comprises a) a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 or a complementary DNA sequence thereof, and b) a nucleotide sequence formed by deletion, substitution or insertion of one or more bases in the a) and still having nucleotide function, wherein the full length of the nucleotide shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 is 849 bases. The amino acid sequence such as SEQ ID NO: 2 corresponding to the nucleotide sequence has 282 amino acids. Polyclonal antibodies of hRrp15p are prepared, and multiple mutants of the protein molecules are constructed; and intracellular expression of the hRrp15p, sub-cellular positioning and influence of the protein molecules on nucleolin nucleolus positioning are deeply researched. Therefore, the problem hollow to position the nucleolin in a nucleolus structure is solved, the formation of the nucleolus structure is promoted, and morphological basis is laid for exertion of functions of the nucleoli in cells.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for purifying egg yolk antibody by using affinity immune medium
ActiveCN111888797AImprove extraction efficiencyHigh extraction purityEgg immunoglobulinsSolid sorbent liquid separationBiotechnologyRibosomal protein E-L30
The invention discloses a method for purifying an egg yolk antibody by utilizing an affinity immune medium and belongs to the technical field of foods. According to the method of the invention, a novel antibody affinity immunopurification method is developed by using a diatomite affinity protein label. According to the affinity purification technology, a cheap diatomite filter aid is adopted as acarrier, an antigen protein with a ribosomal protein L2 label is adopted as a coupling ligand, the specific adsorption effect of the ribosomal protein L2 on diatomite is utilized to construct the affinity immune purification method which is low in cost and high in efficiency. The development of the efficient and low-cost specific yolk antibody affinity purification technology can effectively improve the separation and extraction efficiency of specific yolk immunoglobulin, improve the additional value of the egg yolk antibody, and expand the application field of the egg yolk antibody, so that the efficient and low-cost specific yolk antibody affinity purification technology has important significance on improving the competitiveness of the specific egg yolk immunoglobulin in the high-end biological antibody market.
Owner:YOULIKANG (JIANGSU) BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
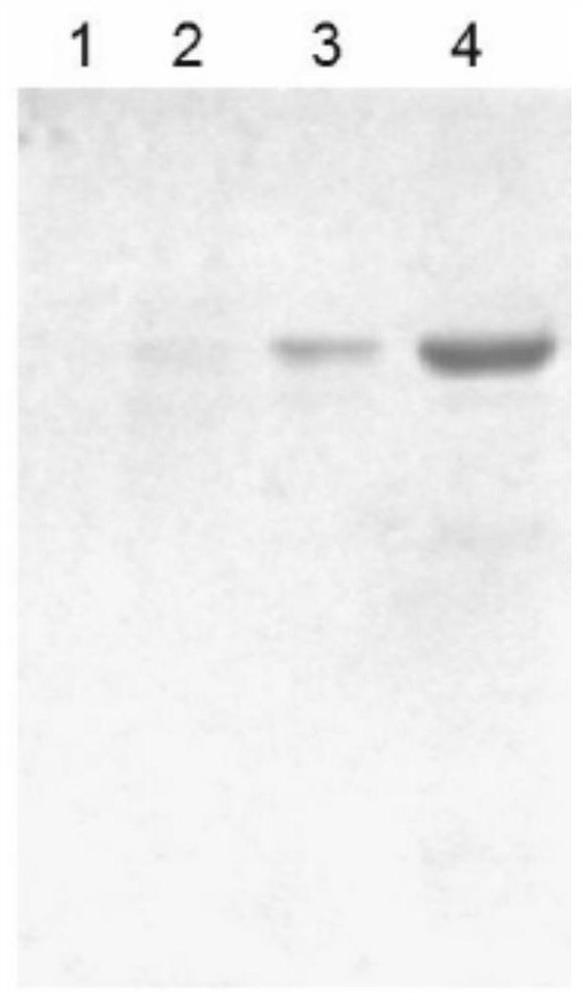
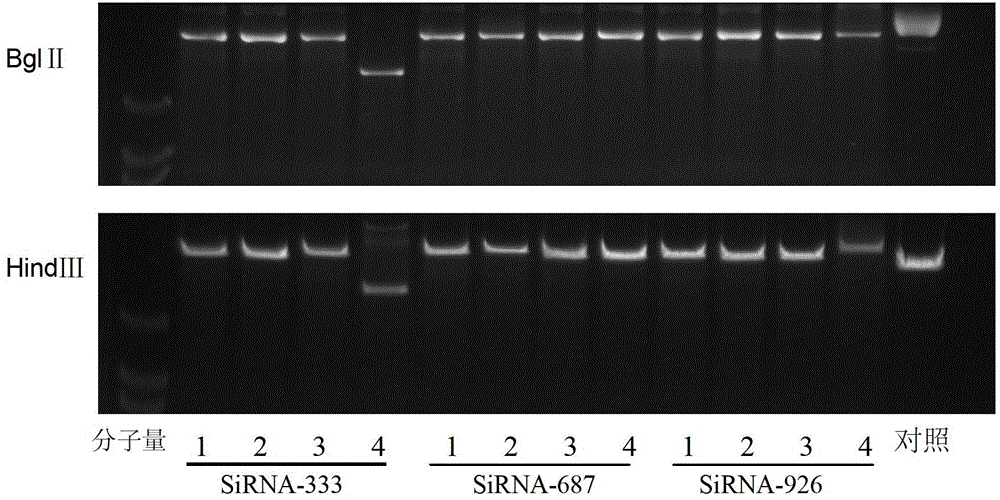
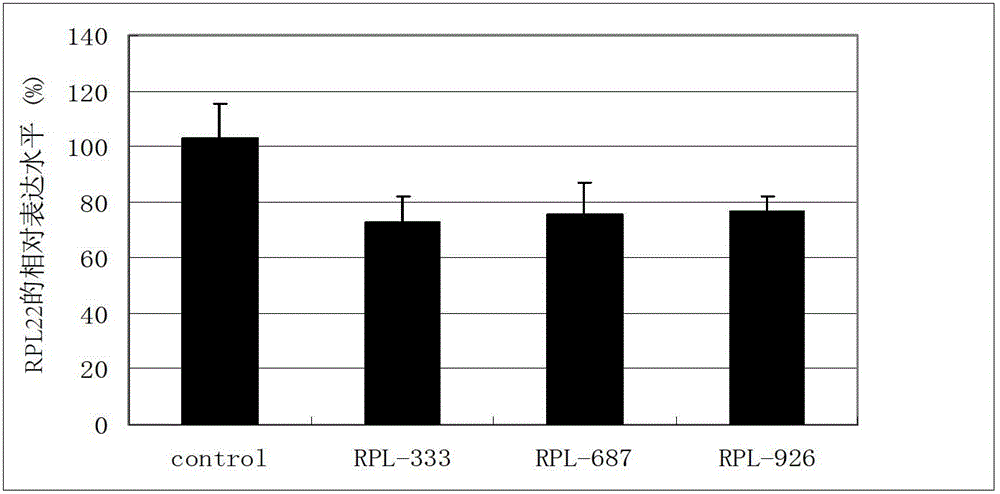
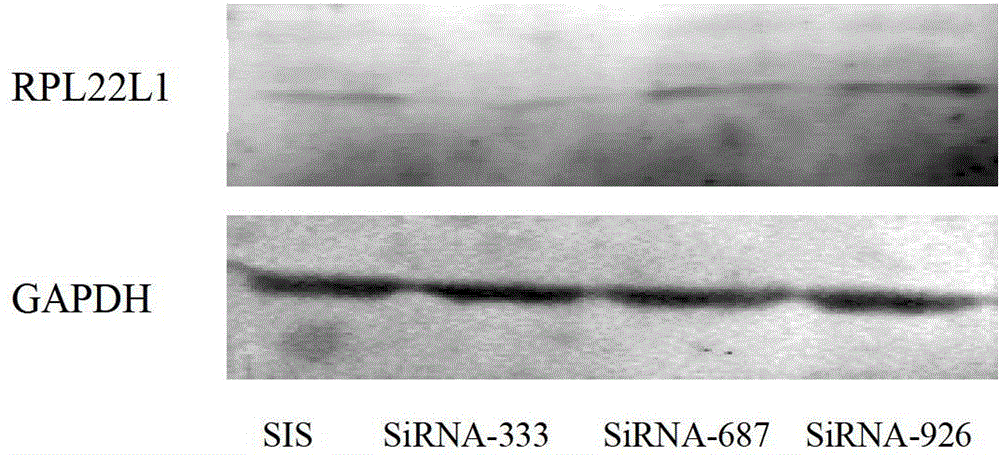
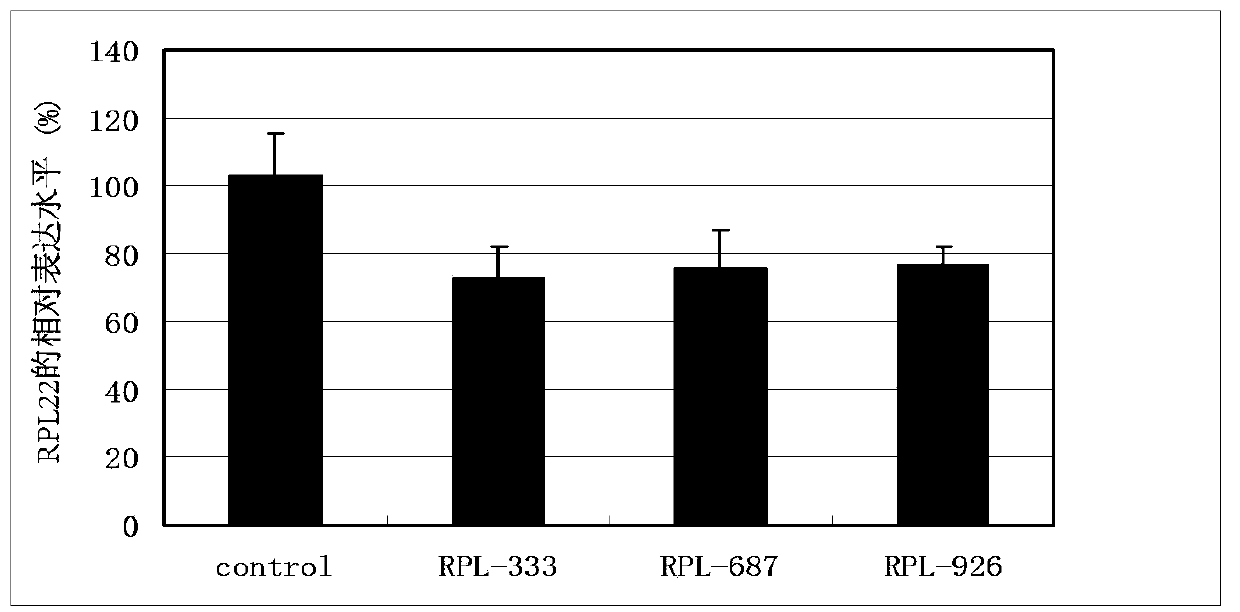
Application of antisense nucleotide sequences of ribosomal protein analogues RPL22L1 in preparing medicines capable of suppressing growth of ovarian cancer cells
ActiveCN103417985BGrowth inhibitionReduce the degree of malignancyGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsRibosomal protein E-L30Cancer cell
The invention discloses an application of antisense nucleotide sequences of ribosomal protein analogues RPL22L1 in preparing medicines capable of suppressing growth of ovarian cancer cells. The application is characterized in that the antisense nucleotide sequences of three pairs of ribosomal protein analogues RPL22L1 are synthesized and are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2 or SEQ ID NO.3. According to the invention, aiming to the high-amplification ovarian cancer cells of RPL22L1, the antisense nucleotide sequences of the RPL22L1 are utilized, and the expression of the RPL22L1 is reduced through adopting an RNAi interference method. According to the study, the nucleotide sequences can effectively suppress the growth of the ovarian cancer cells to reduce the malignity degree. When the antisense nucleotide sequences of the RPL22L1 are applied to the preparation of the medicines capable of suppressing growth of ovarian cancer cells, novel medicine selection and targeted therapies can be provided for biological treatment of the ovarian cancer, thereby improving the therapeutic specificity.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Sheep brucella M5 strain ribosome protein L7/L12 gene, encoding protein and uses thereof
InactiveCN101177684AEfficient detectionEffective preventionBacterial antigen ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsMicroRNAGene silencing
The invention provides a gene of strain ribosome protein L7 / L12 of brucellosis M5 of sheep type and encoded protein and application thereof. The encoded protein of the gene of the invention has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2. The gene of the invention can be used for preparing gene vaccine. For example, the siRNA or shRNA or microRNA can be synthesized and used for gene silencing by the sequence of the invention. By preparing the expression protein of the gene of the invention, the recombinant protein vaccine can be researched, or a test kit can be developed, which provides an effective solving way for the brucellosis.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Expression purification, crystal structure and application of mycobacterium tuberculosis ribosomal protein S7
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and specifically relates to expression purification, a crystal structure and an application of a mycobacterium tuberculosis ribosomal protein S7. The protein S7 contains 156 amino acids, has the molecular weight of about 17.6 kDa, and has the isoelectric point of about 10.56; the protein S7 has high soluble expression in an expression strain escherichia coli rosetta (DE3), and has good purity and homogeneity. A three-dimensional structure of the ribosomal protein S7 is obtained by an X-ray diffraction method; the resolution ratio reaches up to 1.80 Angstroms; the space group is P2[1]2[1]2[1]. The structure is integrally composed of 6 alpha spirals and 2 beta spirals, wherein an alpha spiral beam structure composed of alpha spiral 1, alpha spiral 2, alpha spiral 3, alpha spiral 4 and alpha spiral 5 has interaction with other proteins on other ribosomes; a beta hairpin structure connected between alpha 3 and alpha 4 has an RNA recognition function. The three-dimensional structure of the ribosomal protein S7 has broad application prospects in screening of novel anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Application of antisense nucleotide sequences of ribosomal protein analogues RPL22L1 in preparing medicines capable of suppressing growth of ovarian cancer cells
ActiveCN103417985AGrowth inhibitionReduce the degree of malignancyGenetic material ingredientsSexual disorderRibosomal protein E-L30Cancer cell
The invention discloses an application of antisense nucleotide sequences of ribosomal protein analogues RPL22L1 in preparing medicines capable of suppressing growth of ovarian cancer cells. The application is characterized in that the antisense nucleotide sequences of three pairs of ribosomal protein analogues RPL22L1 are synthesized and are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2 or SEQ ID NO.3. According to the invention, aiming to the high-amplification ovarian cancer cells of RPL22L1, the antisense nucleotide sequences of the RPL22L1 are utilized, and the expression of the RPL22L1 is reduced through adopting an RNAi interference method. According to the study, the nucleotide sequences can effectively suppress the growth of the ovarian cancer cells to reduce the malignity degree. When the antisense nucleotide sequences of the RPL22L1 are applied to the preparation of the medicines capable of suppressing growth of ovarian cancer cells, novel medicine selection and targeted therapies can be provided for biological treatment of the ovarian cancer, thereby improving the therapeutic specificity.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
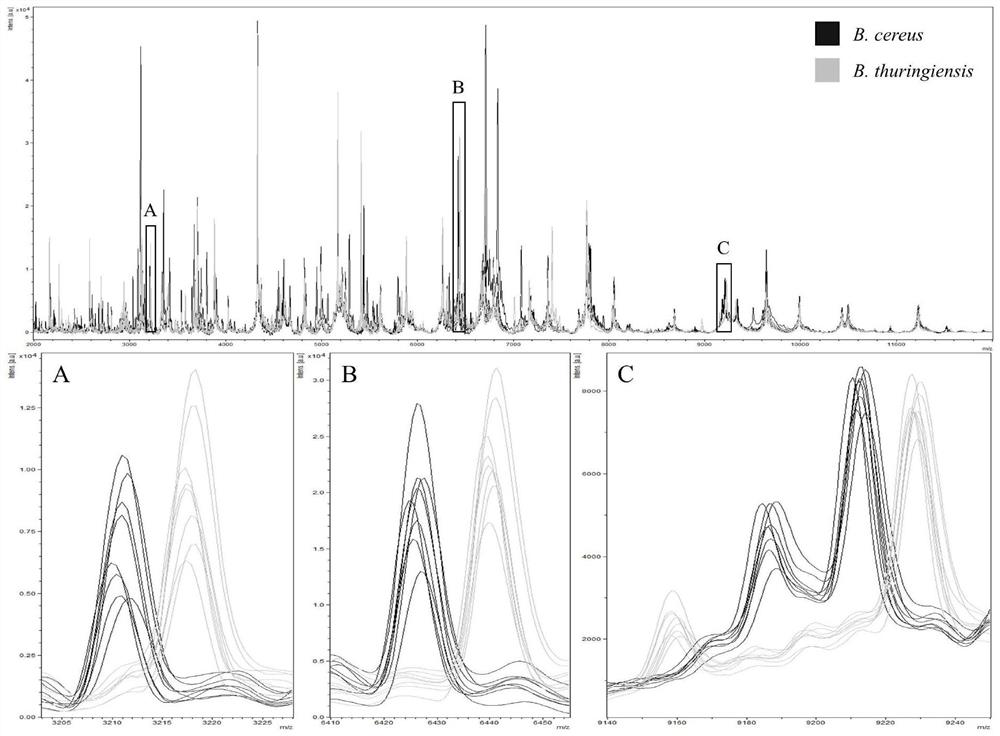
Method for rapidly identifying bacillus cereus and bacillus thuringiensis based on MALDI-TOFMS
InactiveCN113219115AAccurate distinctionReliable resultsComponent separationRibosomal protein E-L30Bacillus thuringiensis
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying bacillus cereus and bacillus thuringiensis based on MALDI-TOFMS. According to the invention, a 50S ribosomal protein L30, a 50S ribosomal protein L31 type B and a 30S ribosomal protein S20 are used as characteristic proteins. According to the method, whole genome sequencing information of the bacillus cereus and the bacillus thuringiensis is used for guiding screening and identification of the MALDI-TOFMS characteristic peaks, the MALDI-TOFMS characteristic peaks capable of accurately distinguishing the bacillus cereus and the bacillus thuringiensis are obtained, the result is accurate and reliable, and a thought is provided for distinguishing related species through the MALDI-TOFMS.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com