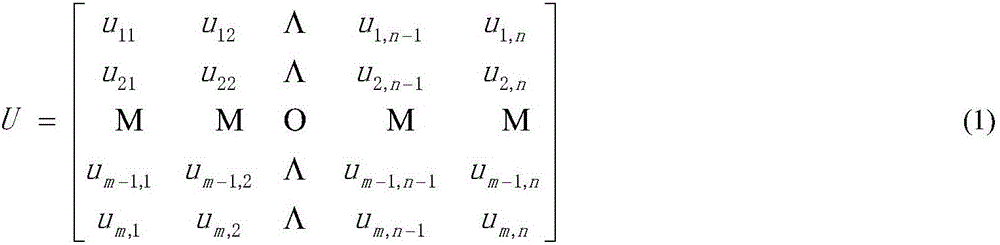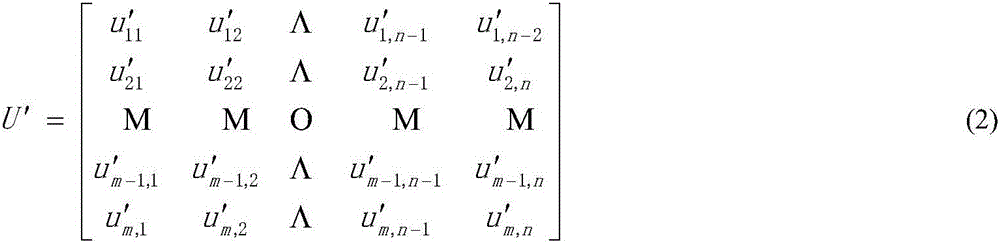Patents
Literature
330 results about "Human liver" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The liver is a vital organ normally present in humans, in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. The liver has a wide range of functions, including detoxification of various metabolites, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. The liver is necessary for survival, and there is currently no way to compensate for the absence of liver function in the long term, although liver dialysis techniques can be used in the short term. The liver is a gland and plays a major role in metabolism with numerous functions in the human body, including regulation of glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, plasma protein synthesis, hormone production, and detoxification. The liver lies below the diaphragm in the abdominal-pelvic region of the abdomen. It produces bile, an alkaline compound which aids in digestion via the emulsification of lipids. The liver's highly specialized tissue consisting of mostly hepatocytes regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex molecules, many of which are necessary for normal vital functions.
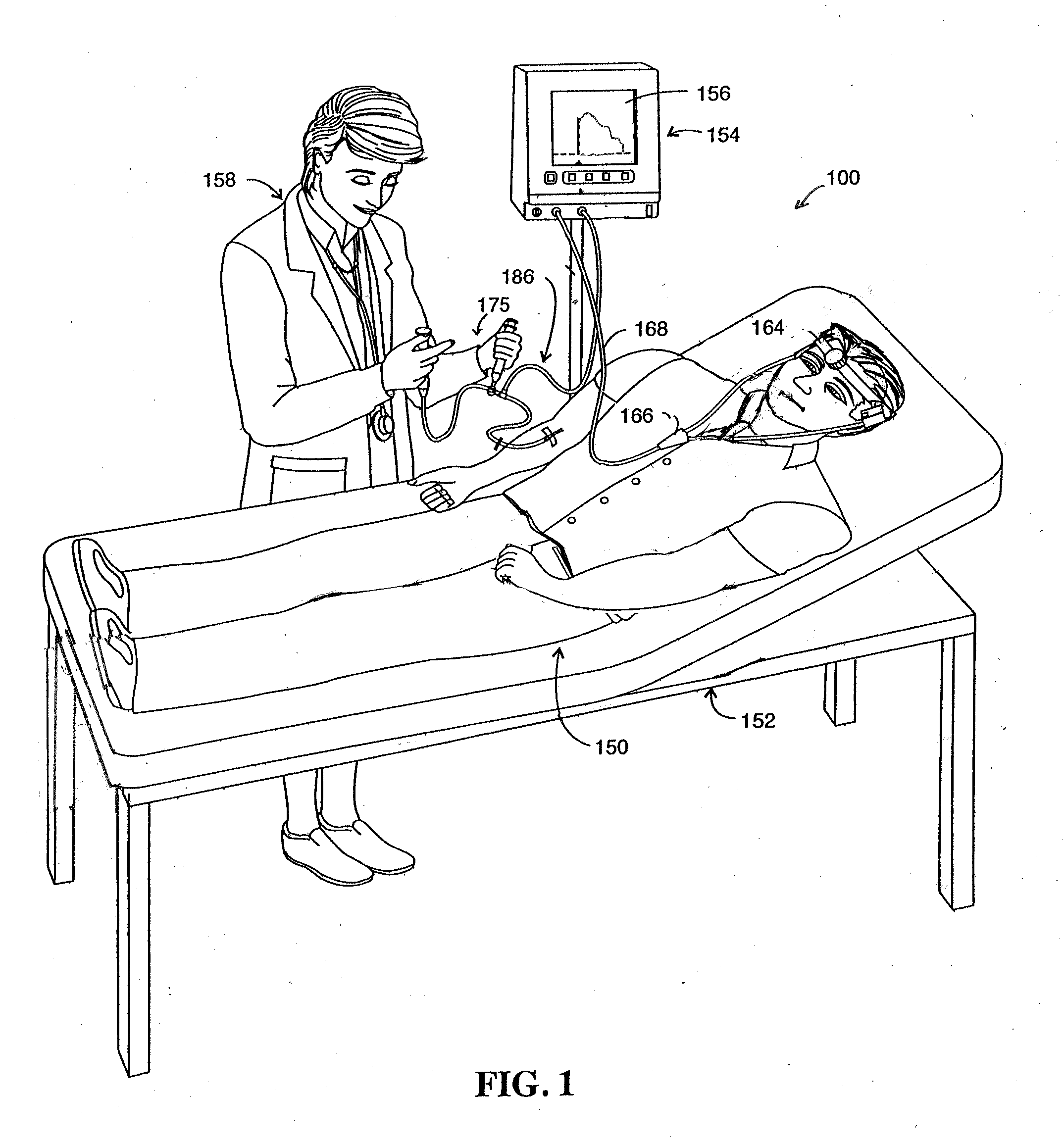
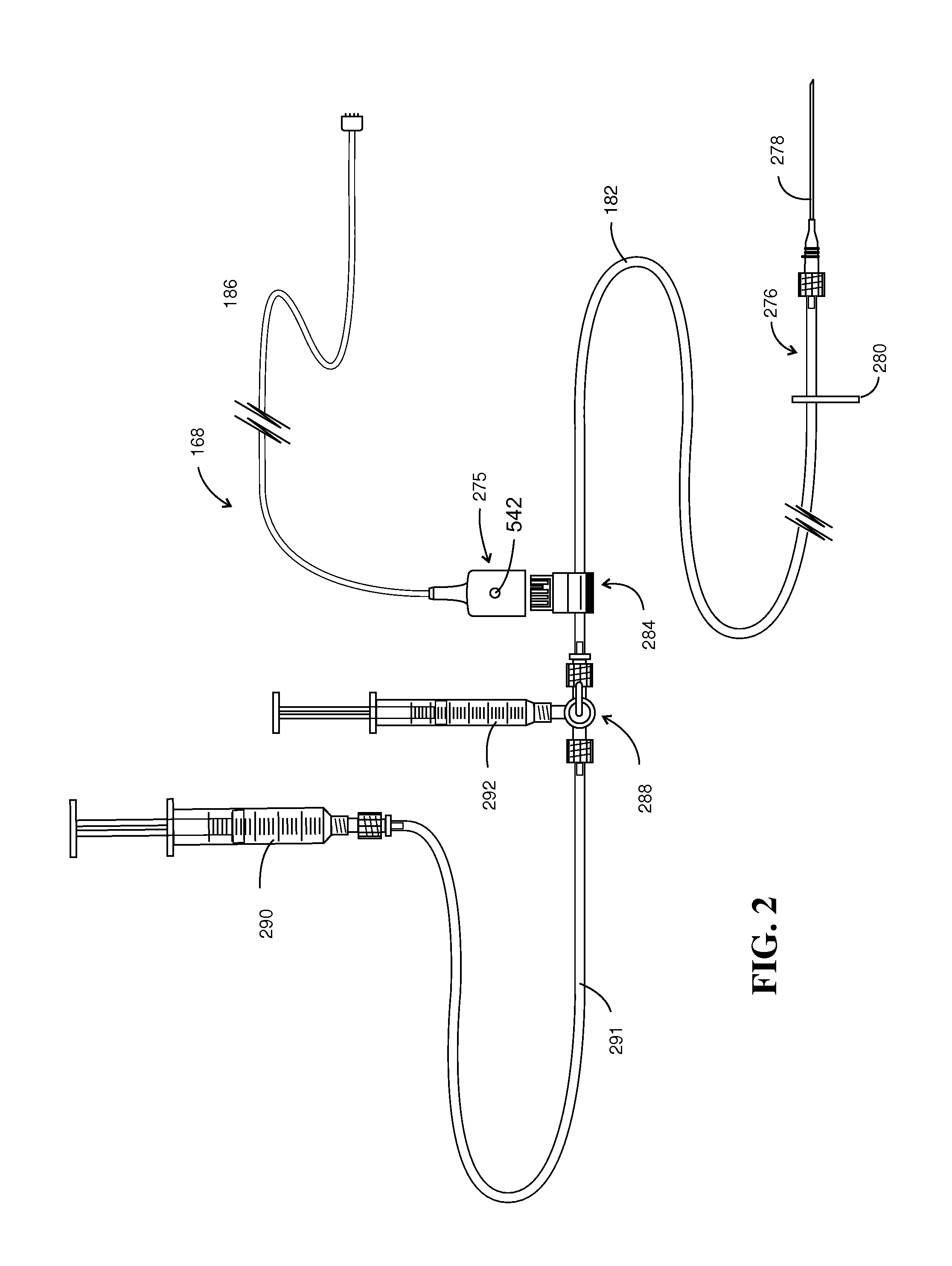
Simplified water-bag technique for magnetic susceptibility measurements on the human body and other specimens
InactiveUS7047059B2Less-expensive fabricationLess-expensive useMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesHuman bodyMagnetic susceptibility
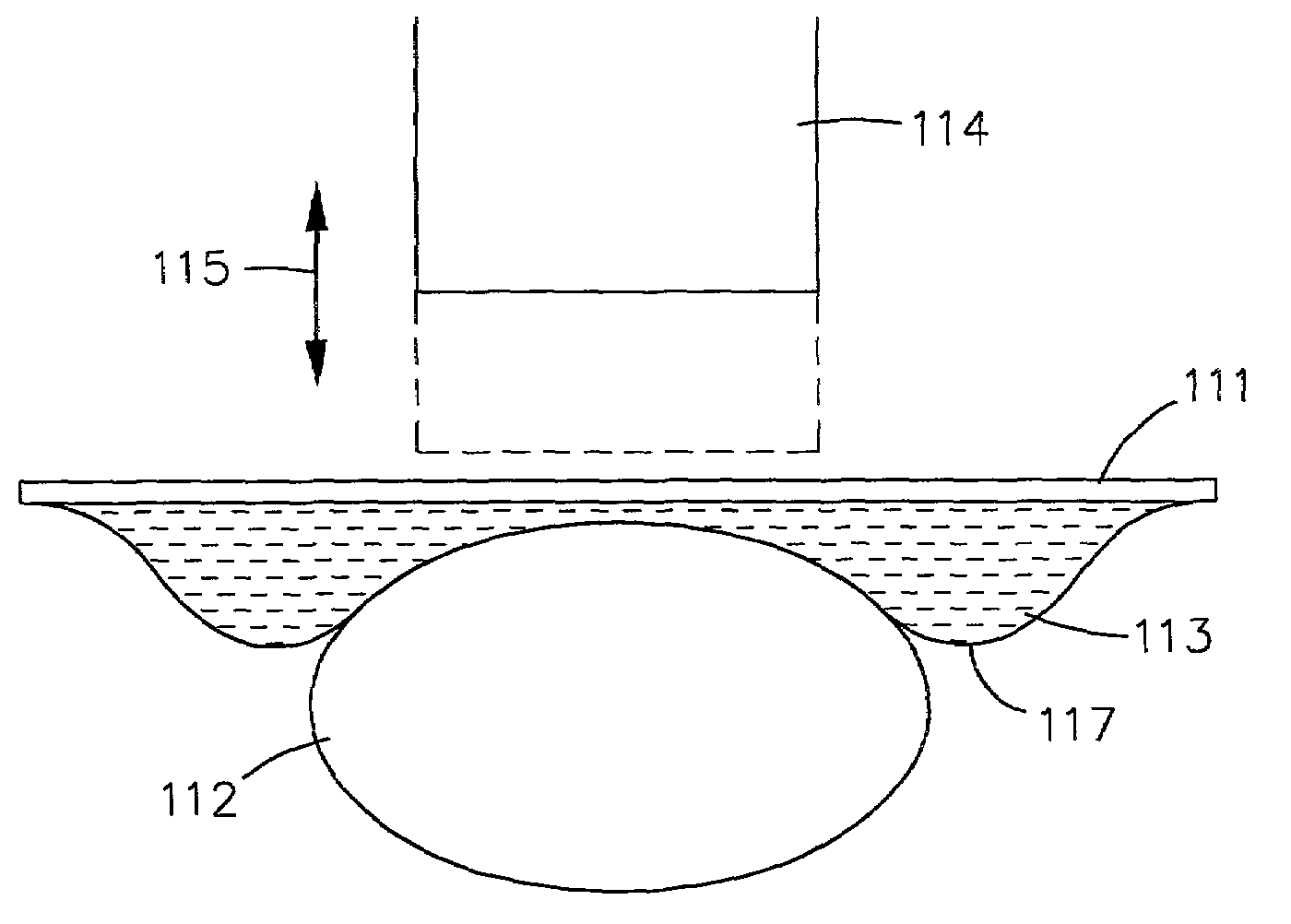
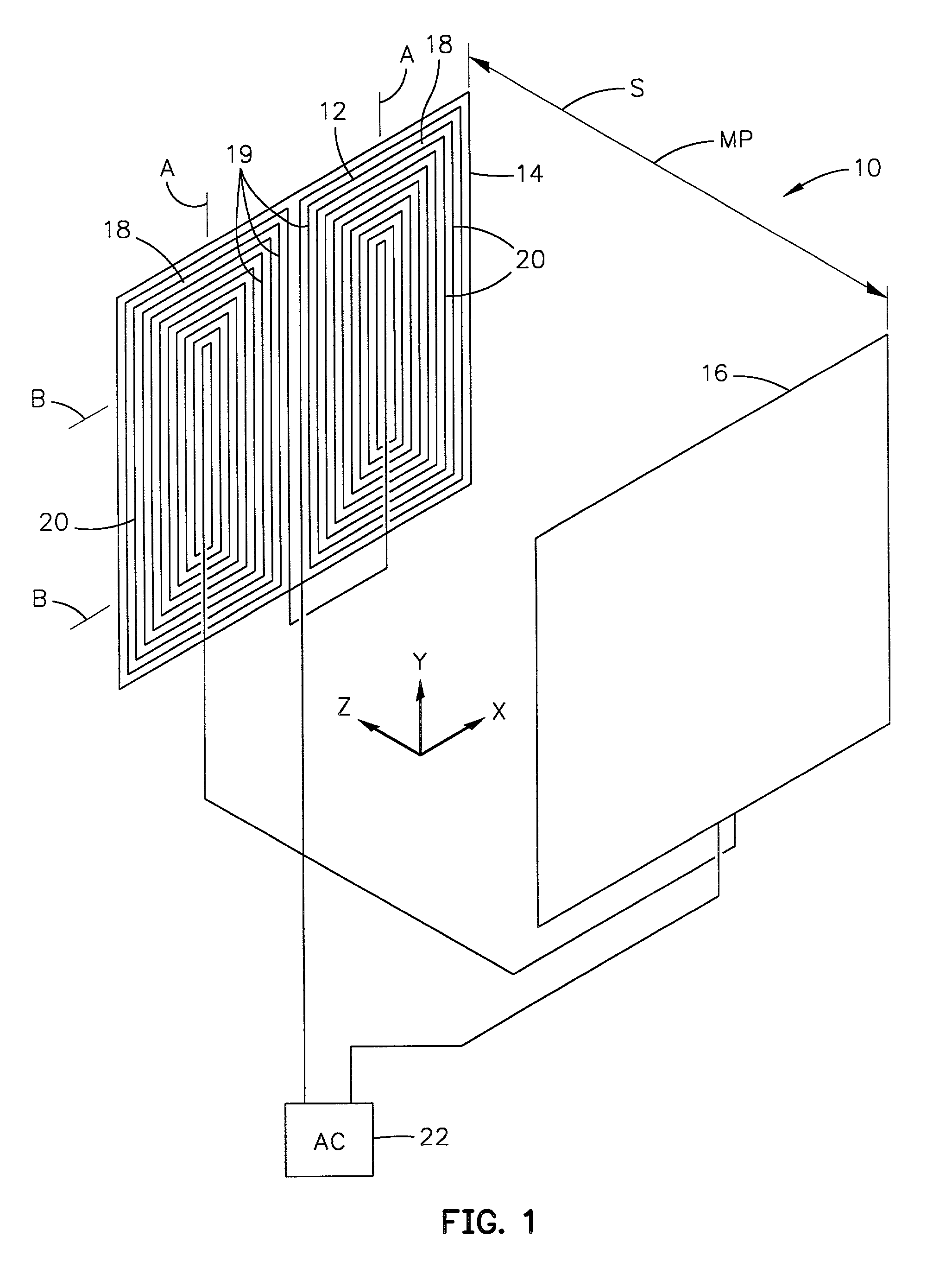
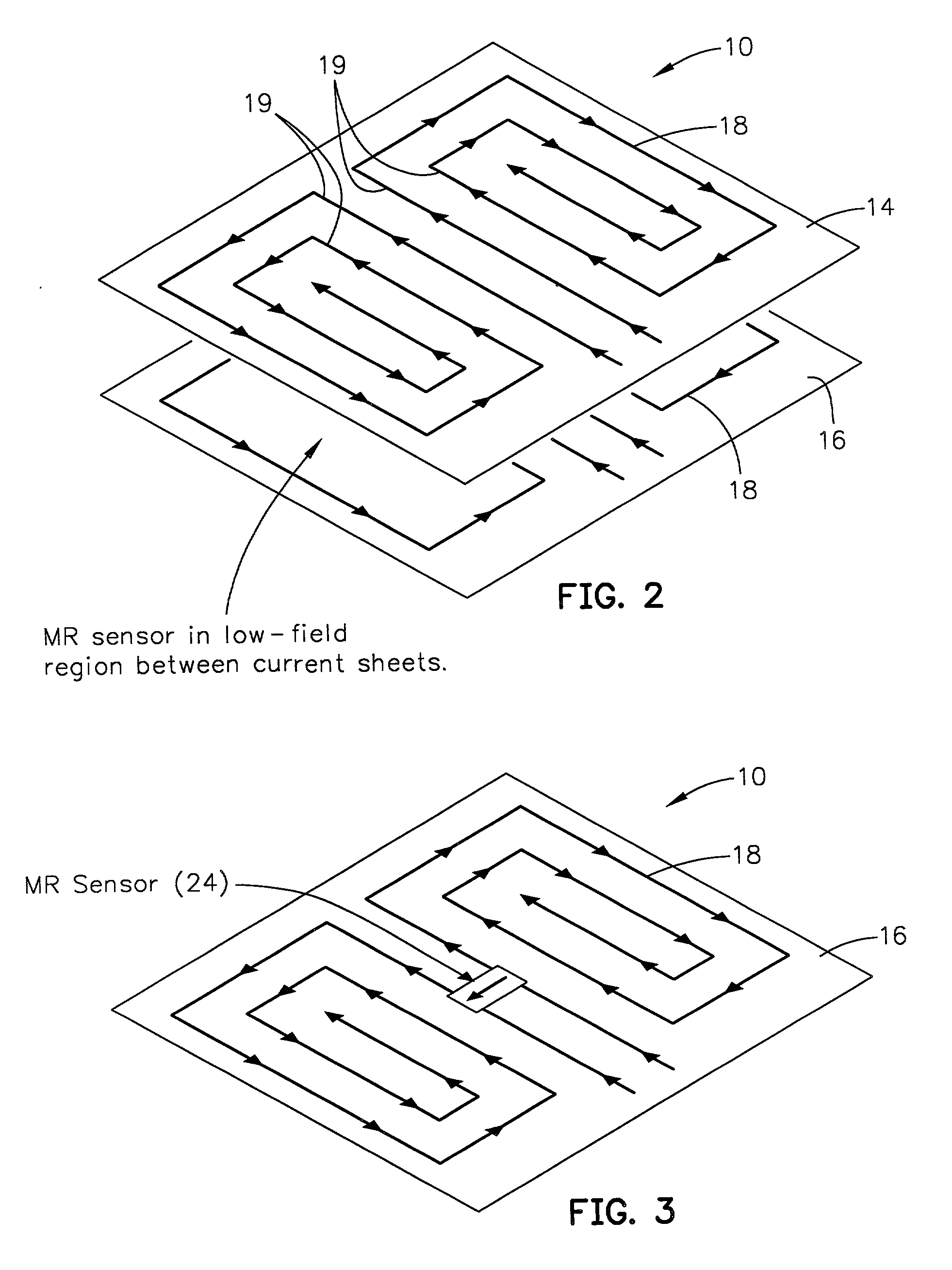
A probe instrument using room-temperature sensor(s) that can measure variations in magnetic susceptibilities. The instrument has sufficient resolution to monitor paramagnetic materials in a human body, such as iron in a human liver, by noninvasively examining patients with iron-overload diseases. The instrument includes room temperature magnetic sensors, and detects the sample, that is, the tissue response to an alternating current field applied by an applied field coil. The applied field coil dimensions are chosen so that the applied field is optimized for maximum response from the liver while minimizing the effects due to the overlying abdominal tissue and at the same time not unduly increasing the sensitivity of the instrument to the lung. To overcome variations in the sensor output due to fluctuations in the applied field, change in the ambient temperature and mechanical relaxation of the instrument, the sensor-sample distance is modulated. The detector assembly is oscillated while the examined patient remains stationary. An improved water-bag technique is employed to eliminate background tissue response. The detector assembly forms part of a probe instrument for performing noninvasively the paramagnetic concentration of a patient.
Owner:QUANTUM MAGNETICS
Glycosylation variants of iduronate 2-sulfatase
The present invention provides a highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme comprising an iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide with at least 5 kilodalton (kDa) more sugar than iduronate-2-sulfatase purified from a natural source, e.g. human liver. The present invention also provides an enzymatically active polypeptide fragment or variant of such a highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase. The present invention further provides an isolated nucleic acid encoding iduronate-2-sulfatase, as well as an expression vector, a host cell and a method for producing the present highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme. In one embodiment the present invention is directed to a method for producing a glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme which comprises culturing a host cell containing a nucleic acid encoding an enzymatically active iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide wherein the host cell glycosylates the polypeptide to a greater degree than a native iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide expressed by a natural human liver cell.
Owner:WOMENS & CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Liver cell membrane bionic liposome drug carrier as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106109417AIncrease the number ofEnhanced generation abilityOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsCell membraneIn vivo
The invention relates to a liver cell membrane bionic liposome drug carrier, a preparation method of the liver cell membrane bionic liposome drug carrier, and application of the liver cell membrane bionic liposome drug carrier. The liver cell membrane bionic liposome drug carrier is characterized in that (1) the liposome drug carrier has a cell membrane protein component; (2) the liposome drug carrier is capable of loading drug in vitro, and is used for cell targeting fusion release; (3) the cell membrane protein component of the liposome comes from immortalized human liver cells, and is used for conveying targeted shear plasmids of a hepatitis virus genome; (4) the cell membrane protein component of the liposome comes from an immortalized liver tumor cell line, and is used for targeted drug delivery of liver tumor. The liver cell membrane bionic liposome drug carrier can be used for in vivo targeted hepatic cell transmission and drug delivery of CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat) gene targeting plasmids.
Owner:李因传
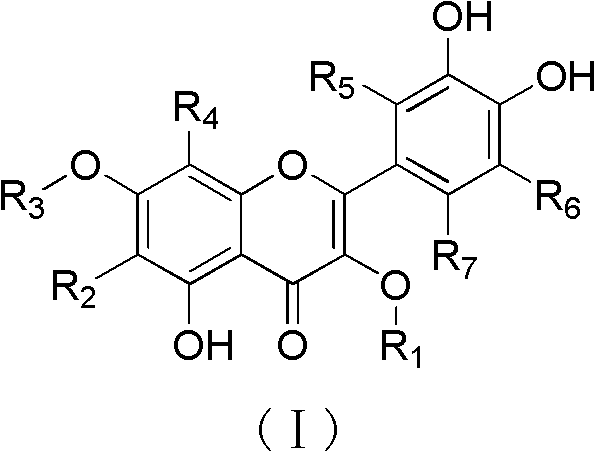
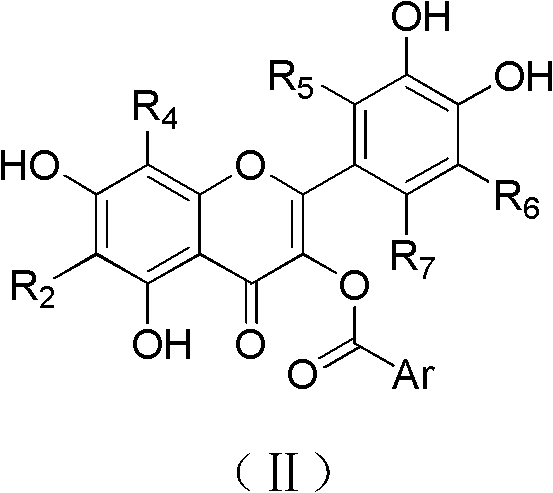
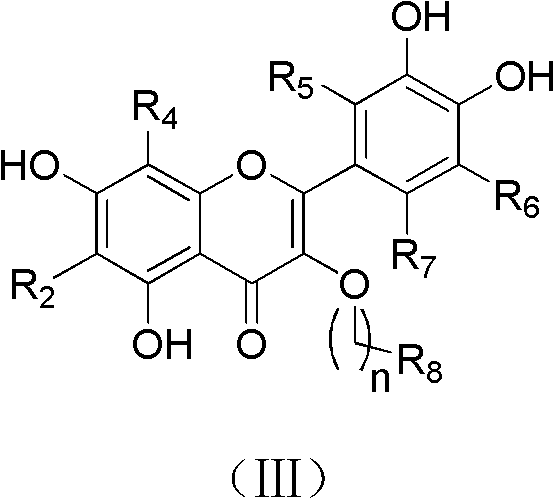
Quercetin derivatives or analogs thereof, and application thereof
InactiveCN102993148AHas anti-HCV effectGood anti-HCV activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseHepatic tumor
The invention belongs to the field of the pharmaceutical chemistry, and relates to quercetin derivatives having a structure represented by formula (I), or analogs thereof, and a use of the quercetin derivatives or the analogs in the inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication. The above compounds or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof can inhibit the replication of hepatitis C viruses in human liver tumor cells, and can be used to prepare medicines for preventing or treating hepatitis C virus related diseases as hepatitis C virus inhibitors, wherein the hepatitis C virus related diseases comprise hepatitis C, and hepatic cirrhosis and hepatic tumors caused by the hepatitis C viruses.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
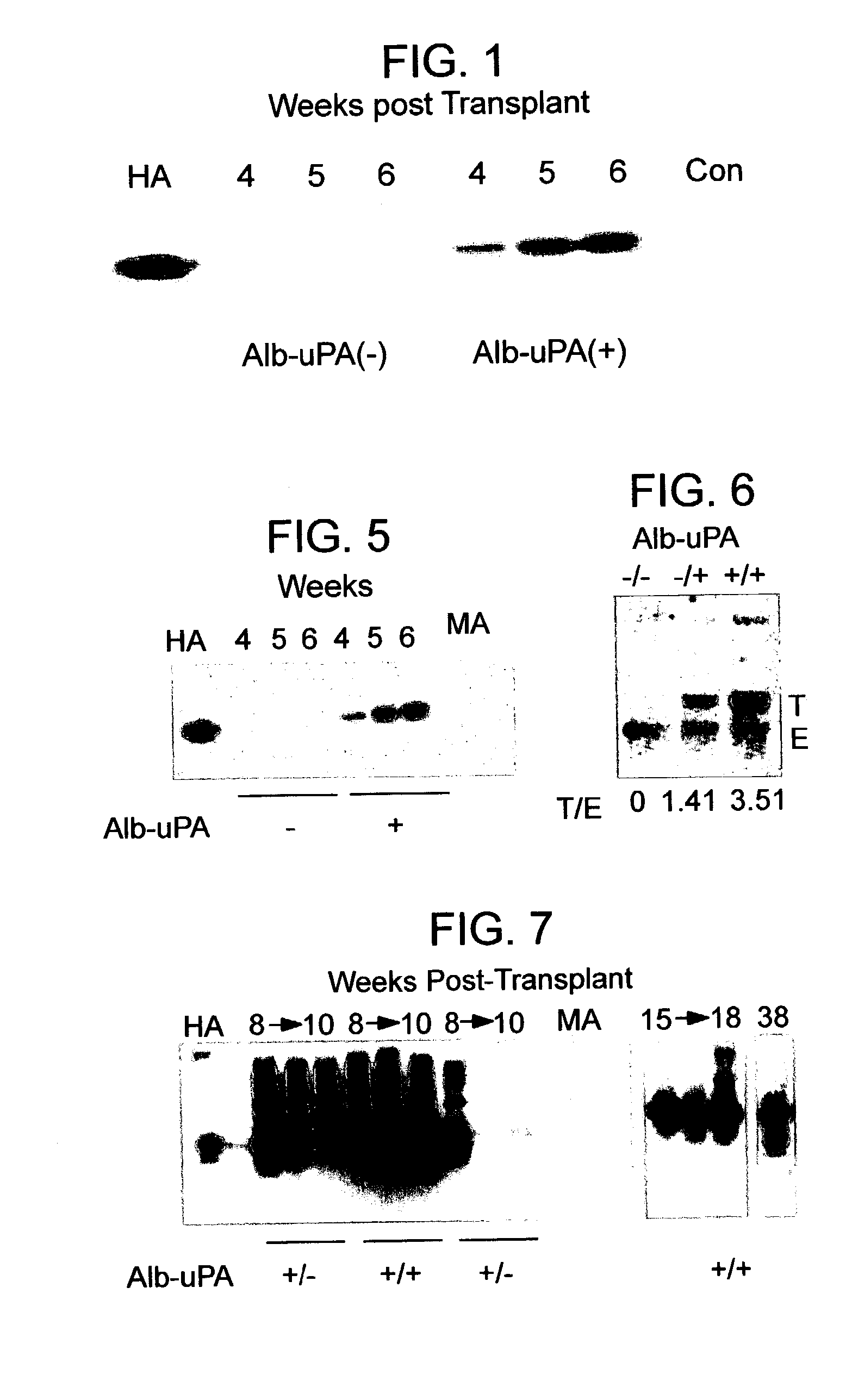
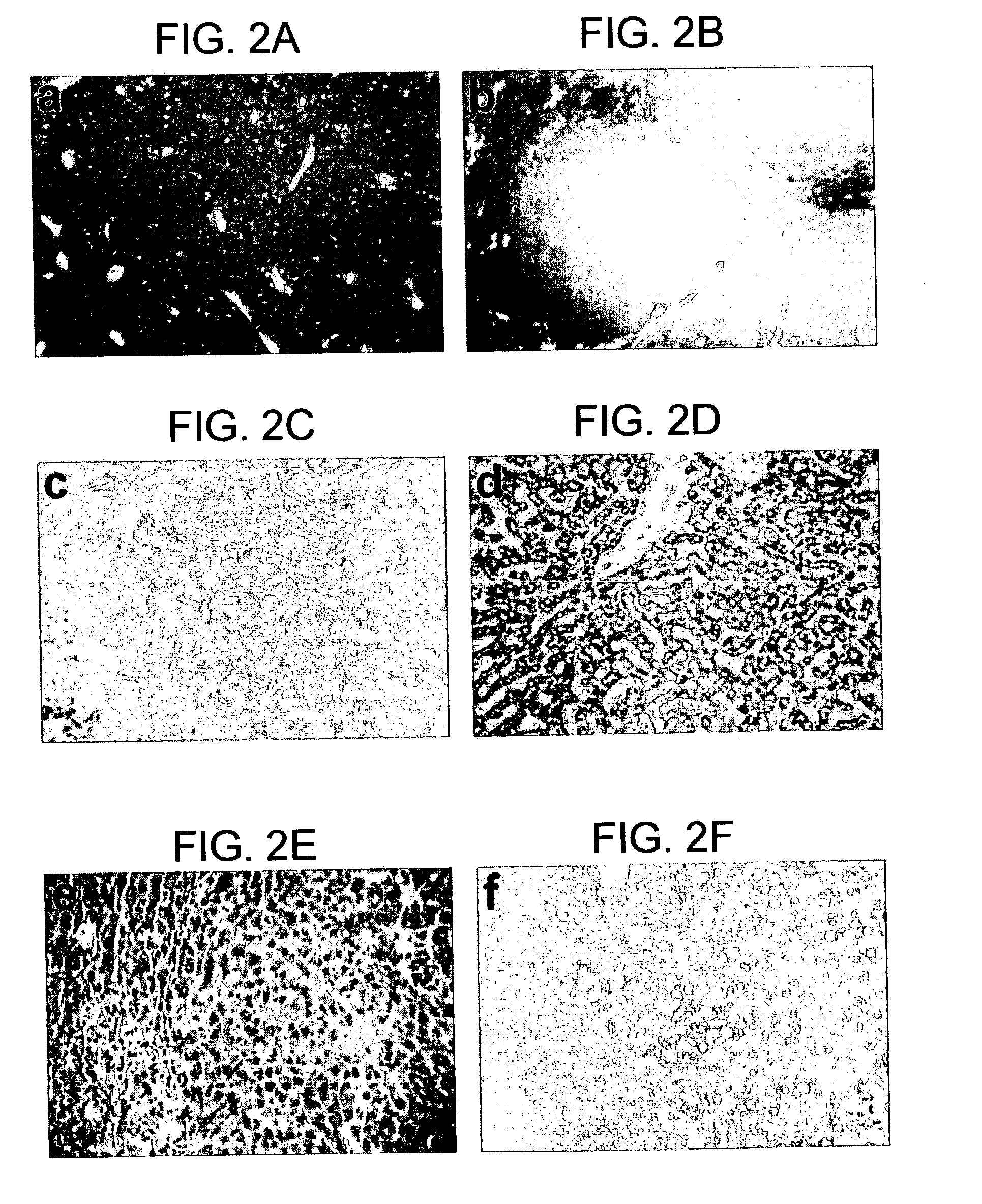
Animal model having a chimeric human liver
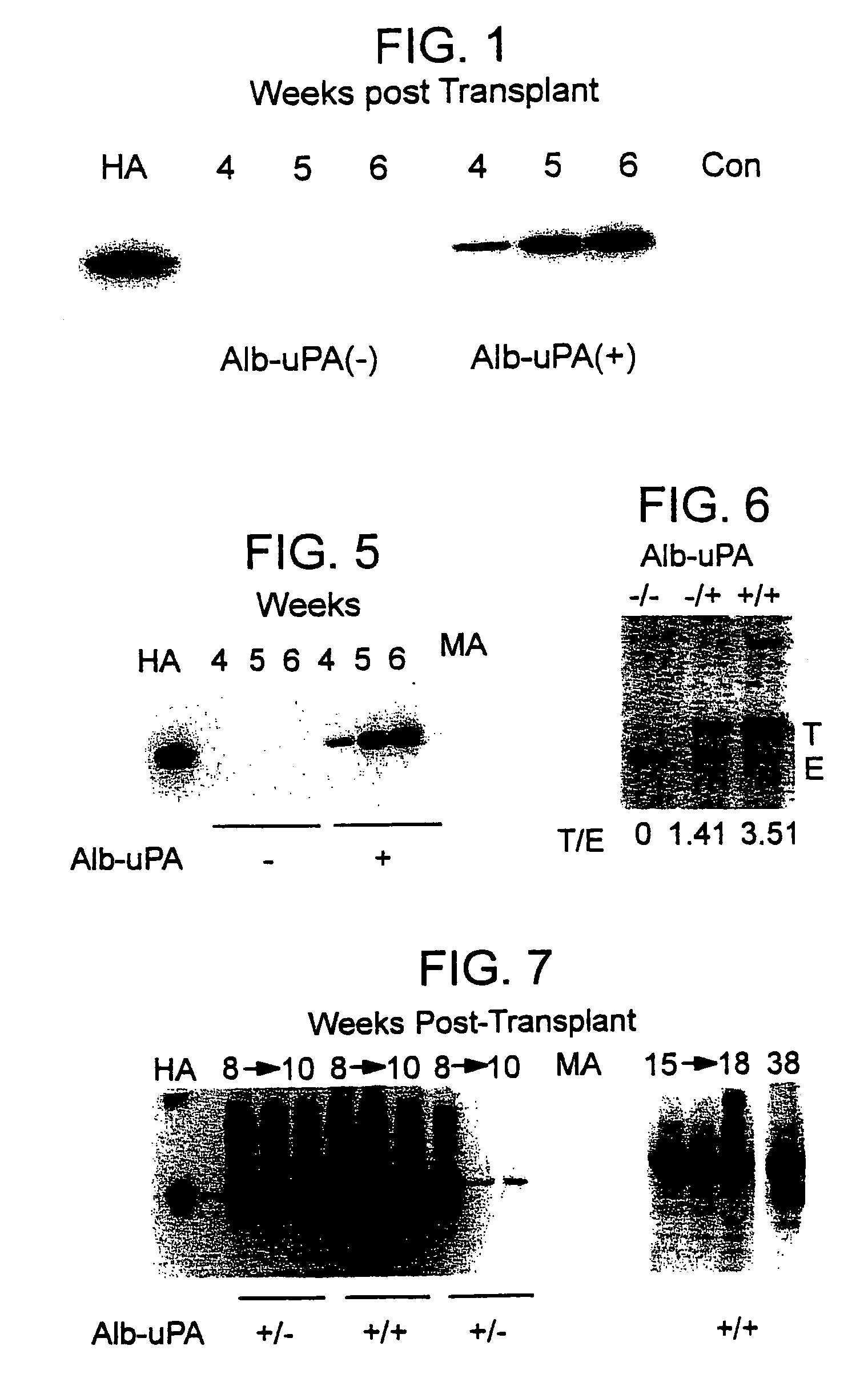
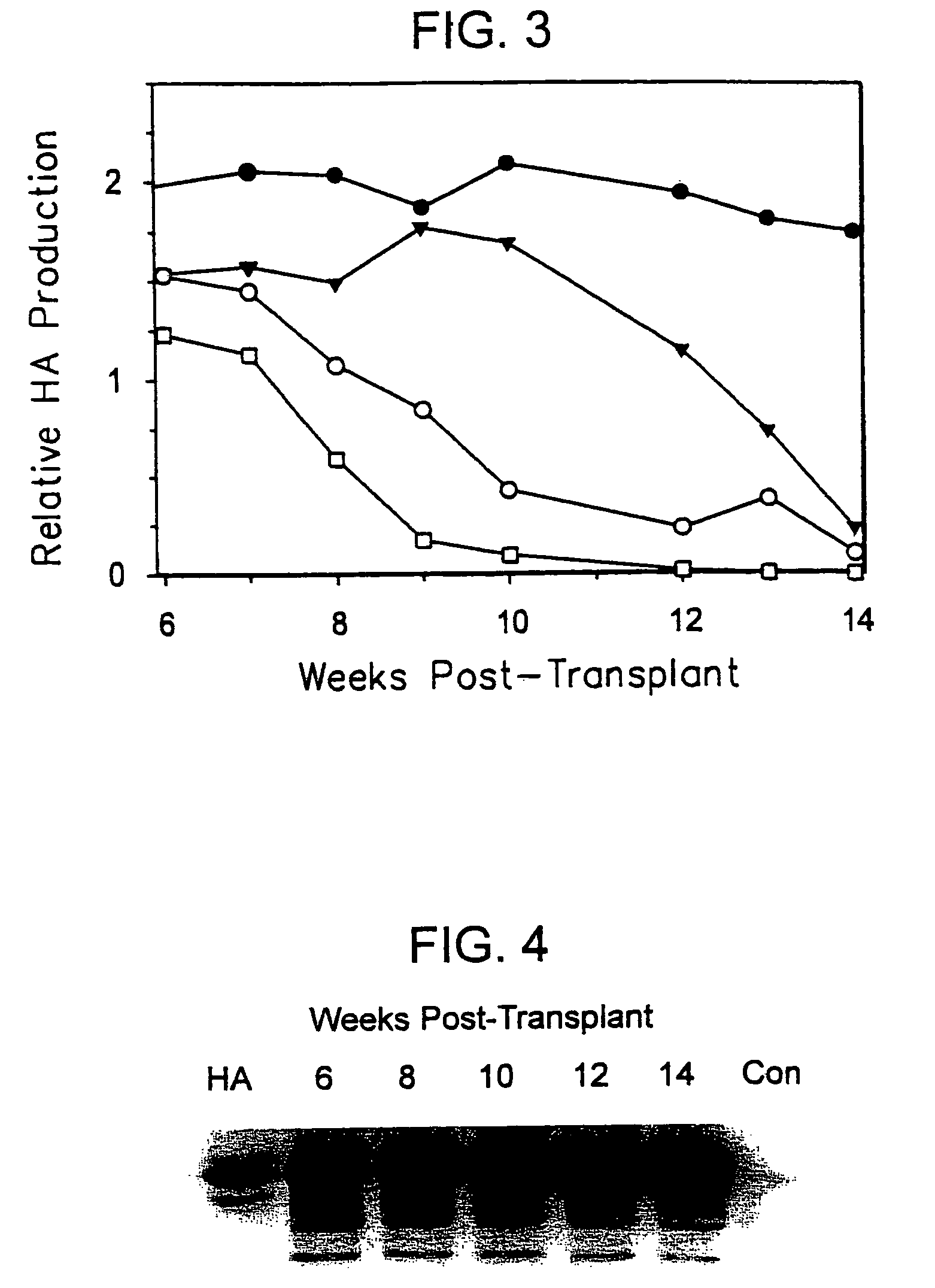
The present invention features a non-human animal model that is susceptible to infection by human hepatotrophic pathogens, particularly human hepatitis C virus (HCV). The model is based on a non-human, immunocompromised transgenic animal having a human-mouse chimeric liver, where the transgene provides for expression of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the liver. The invention also features methods for identifying candidate therapeutic agents, e.g., agents having antiviral activity against HCV infection. The animals of the invention are also useful in assessing toxicity of various agents, as well as the activity of agents in decreasing blood lipids.
Owner:KMT HEPATECH
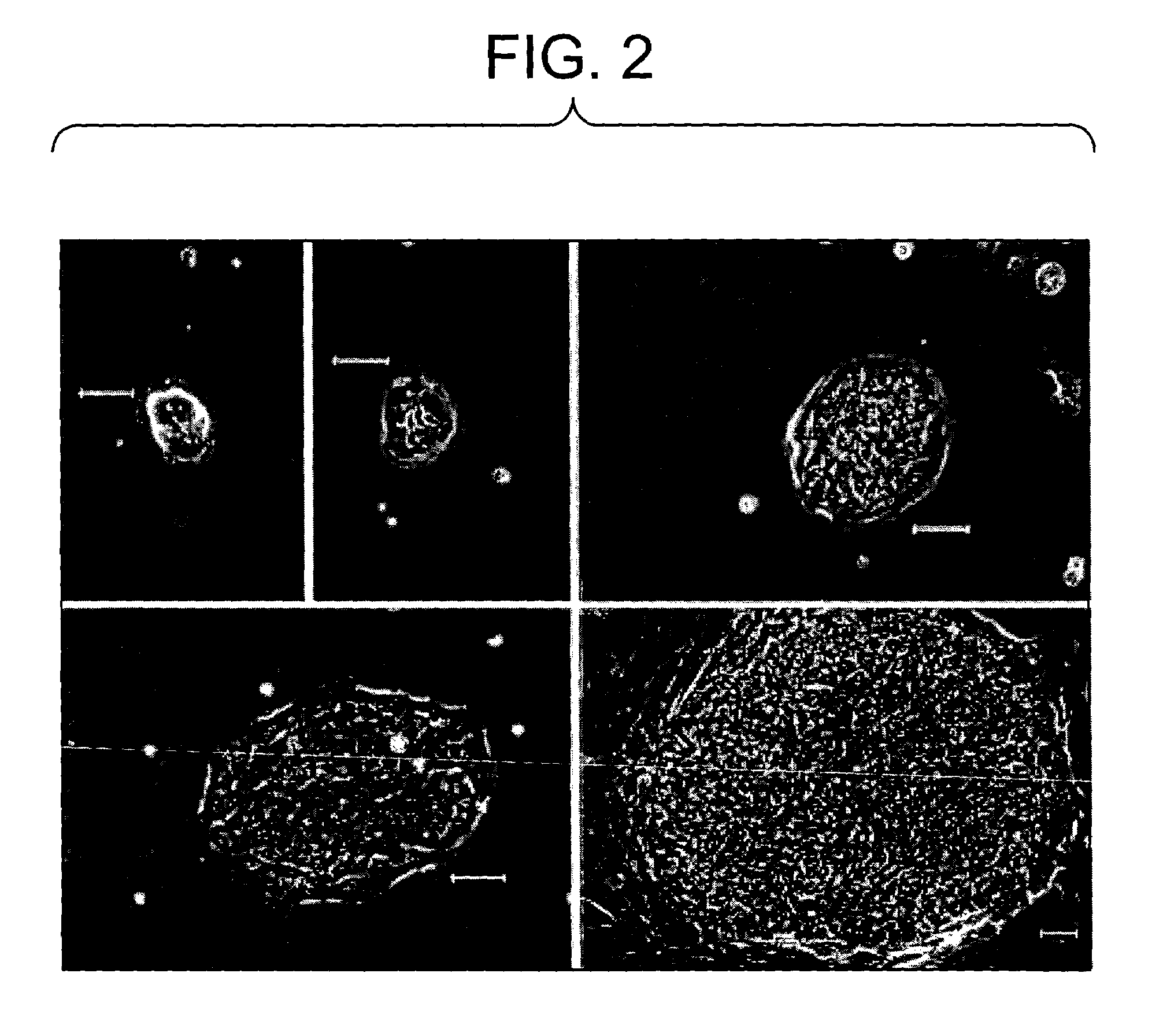
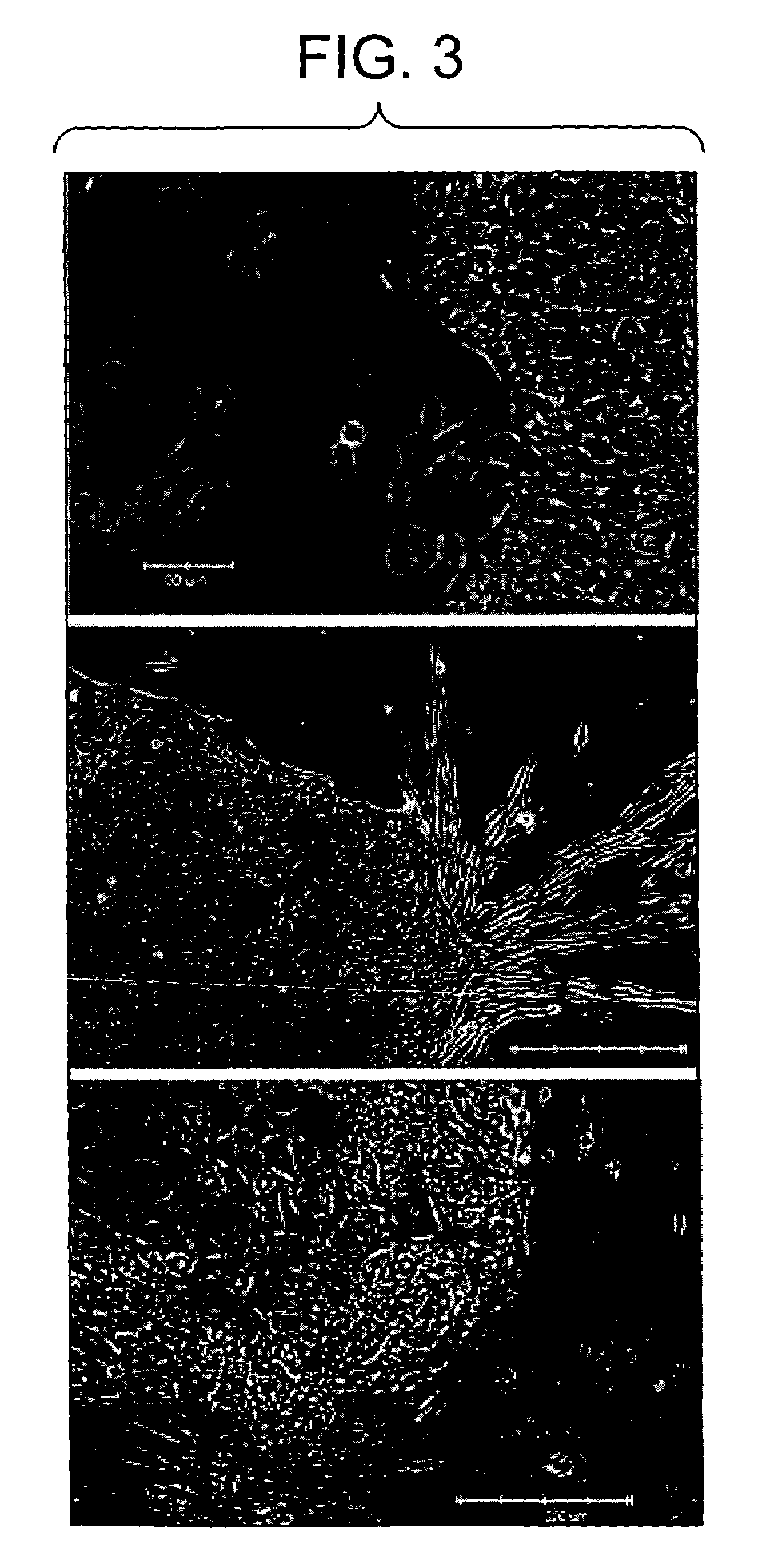
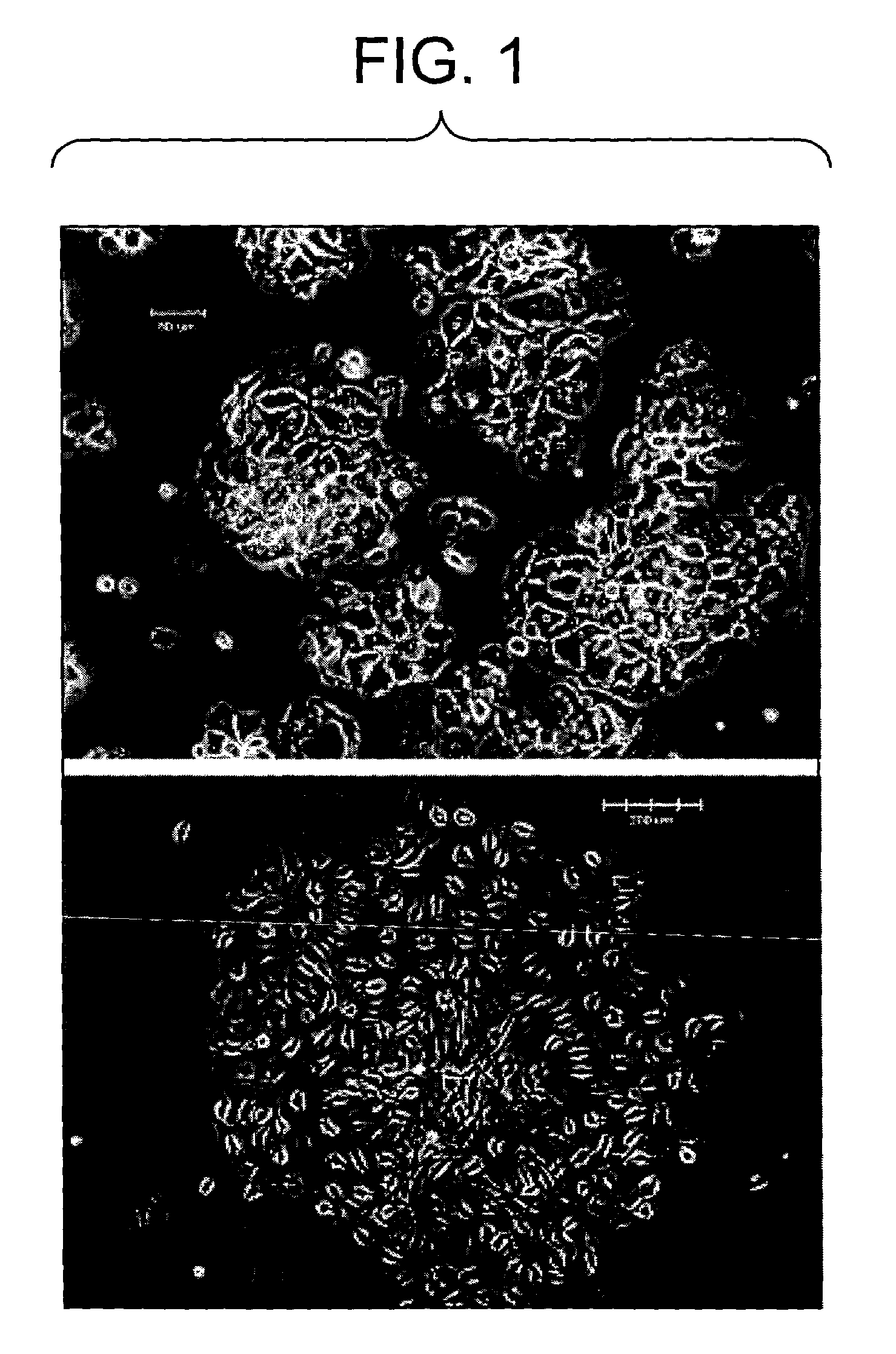
Construction method and application of in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue
InactiveCN106916781AFast printingImprove efficiencyHepatocytesDrug screeningDrug developmentAqueous solution
The invention relates to a construction method for in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing a solution of seed cells with an aqueous solution of biological ink so as to obtain a cell printing solution; (2) under the control of a computer, uniformly extruding the cell printing solution with a cell printer at a set speed according to a designed path and allowing the cell printing solution to rapidly coagulate at a certain temperature so as to form gel microfilaments, and repeating the above operations so as to finish construction of a multilayer cell structure in a layer-upon-layer scanning manner; (3) subjecting the multilayer cell structure to secondary crosslinking and culturing the multilayer cell structure with a cell culture solution so as to obtain a stable multilayer cell structure; and (4) culturing the stable multilayer cell structure with an induction medium so as to obtain the in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue. The method provided by the invention can construct in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue with good functionality, and the constructed in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue is applicable to fields like treatment of hepatopathy, medicinal development, medicine screening, etc.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Peony flower tea with whole flower or whole petal and its preparation method
InactiveCN101185472AWith freshVisualTea substituesFood preparationAdditive ingredientFunctional activity
The invention discloses a peony tea with a whole flower or a whole petals and a preparation method thereof and relates to a preparation method of edible or medicinal dry peony. The invention comprises the steps of flowers picking, flowers cleaning, dry-proof ingredient spraying, drying and sterilization, sorting, directly packaging or packaging by adding other Chinese herbal medicine for storage; according to the weight percentage per kilogram based on the total amount of the peony tea, the healthy peony tea consists of 18-22 percent of whole flowers of dry peony or peony petals, 0-10 percent of candy sugar, 10-14 percent of dry chrysanthemums, 14-20 percent of dry jujube, 8-10 percent of medlar, 16-20 percent of hawthorn, 12-16 percent of canyon straw, 4-6 percent of orange peel. The peony tea is fresh and natural and can regulate menstruation and alleviate pain; the peony is natural in neutral in nature and is beneficial to the human liver and spleen and can regulate functional activities of vital energy, harmonize the liver meridian, activate the spleen, dissipate hygrosis and replenish qi and blood of the source of vital function, thus having the effects of regulating menstruation and alleviating algomenorrhea for women, preventing cancer, benefiting vital energy, strengthening the middle warmer, alleviating pain and detoxifying, etc.
Owner:顾明
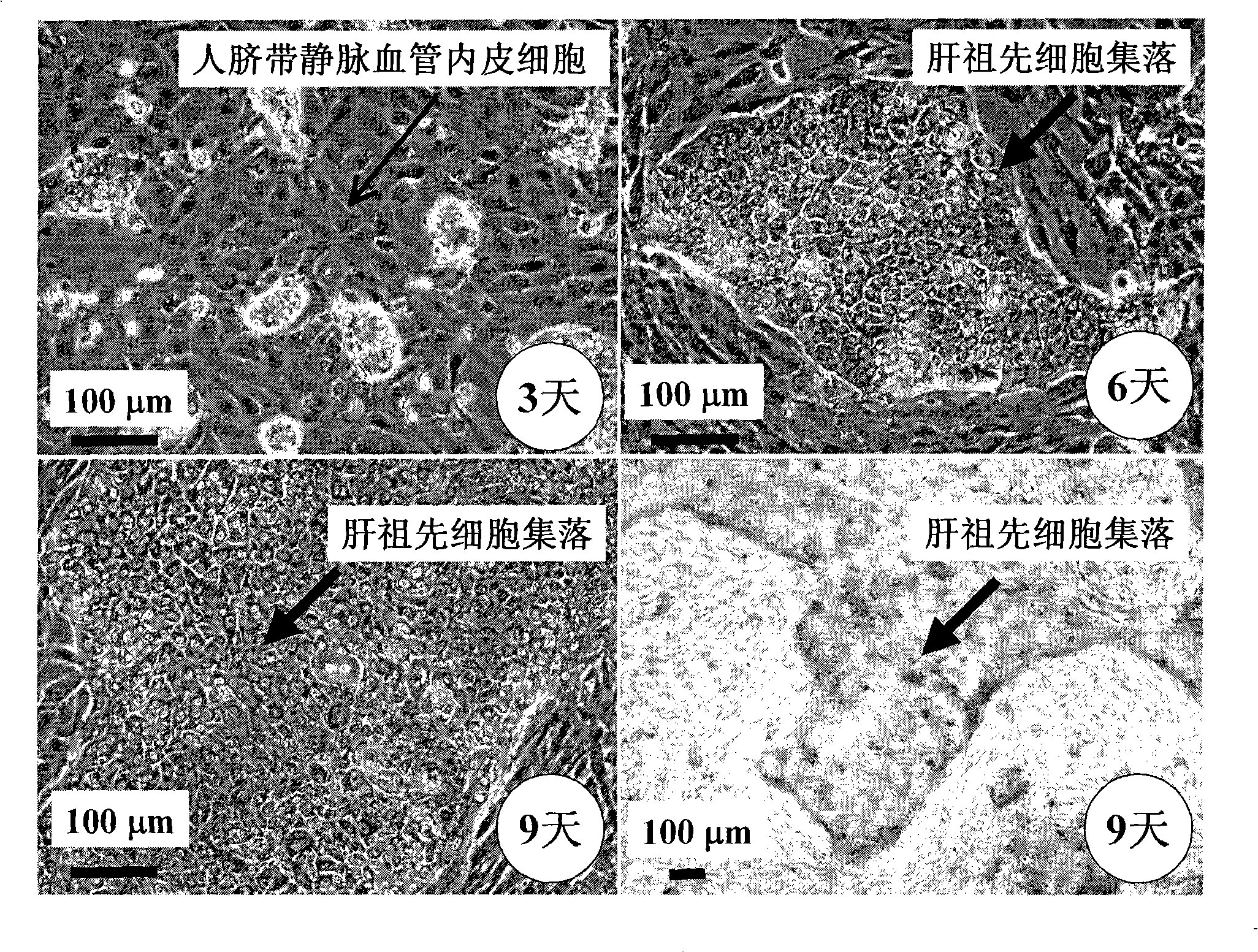
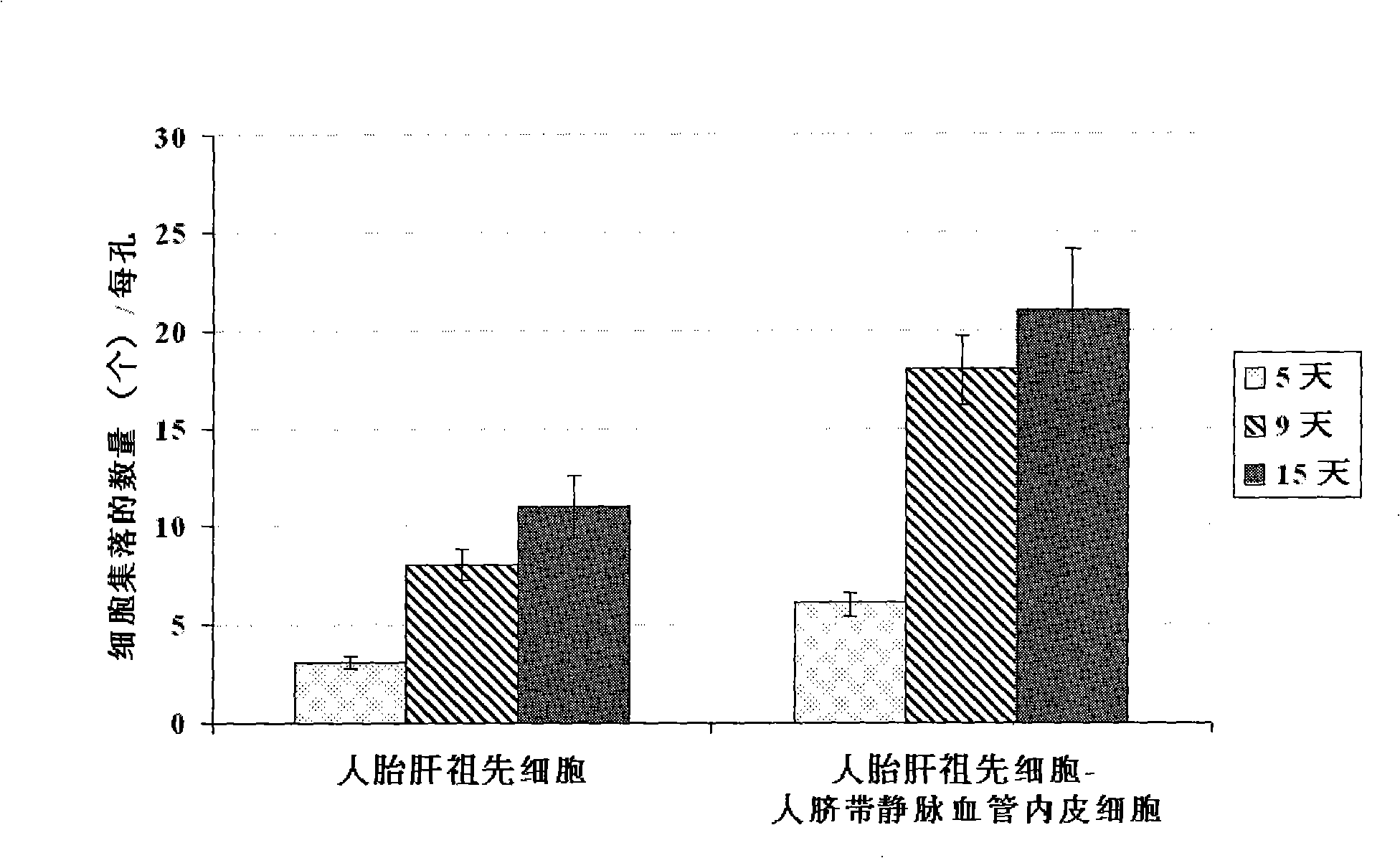
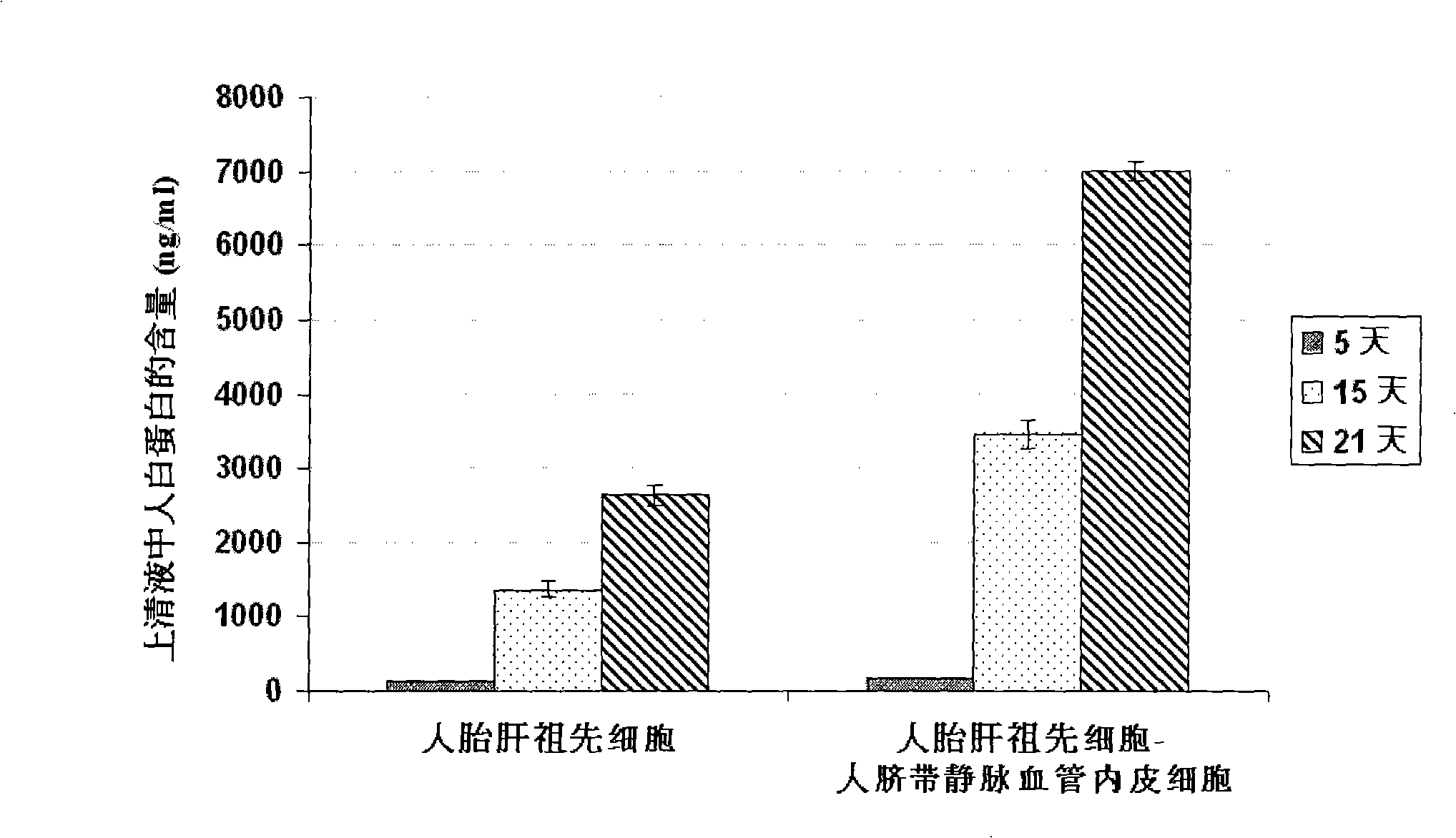
In vitro culture-amplified human liver progenitor cell and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101275121AAccelerate self-renewalConvenient sourceArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The present invention provides a preparing method of a human hepatic progenitor cell which is amplified and cultivated in vitro, including: a. separating the human hepatic progenitor cell; b. co-cultivating a feeder cell and the human hepatic progenitor cell separated from the step a by a medium having no serum on an extracellular matrix containing human fibrin sealant or other analogues, obtaining a human hepatic progenitor cell colony by amplification. The human hepatic progenitor cell colony is easy to separate from the surface of human fibrin sealant by the simple gelatinolytic band process, purified or / and subcultured by further single cell preparation technology process such as enzymatic degradation etc. The human hepatic progenitor cell prepared by the method is hepatic progenitor cell treatment, including a cell transplantation and a bioartificial liver support system, providing excellent human hepatocyte source for cytotoxicity test platform in the drug screening, virus infection and drug screening platform etc.
Owner:芦银雪
System for Non-Invasive Assay of Liver Function
InactiveUS20120330116A1Enhance selective passageControl incidenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSensor arrayDisplay device
A system, method and apparatus are disclosed for using a transcutaneous detection system to measure the quantity of a circulating organ activity detection analyte in the blood, and thereby assay the activity of an organ. A preferred organ for assay is the human liver and a preferred indicator is indocyanine green (ICG) dye The procedure is under the control of a monitor / controller having a visual display and capable of providing cues to the operator. A sensor array apparatus for use in conjunction with the system monitor / controller is configured for increased sensitivity of assaying organ function.
Owner:CARDOX
Human liver cell line
In this application is described the establishment and maintanence of a normal human hepatocyte cell line able to support complete development of malaria parasite development in vitro. Advantages and uses of the cell line are also described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
HAb18GC2 monoclonal antibody and its light and heavy chain variable area genes, coding polypeptide and use
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibody HAb18GC2 and its variable area gene of its heavy chain and light chain and polypeptide, and their uses in preparing therapeutic agent for reversing hepatic fibrosis etc. matrix deposition disease. The present monoclonal antibody HAb18GC2 can bind specificly with antibody HAb18G / CD147 highly expressed in human liver fibrosis tissue and with liver astrocyte and possesses function of facilitating MMPs secretion and reducing the extracellular matrix. The antibody light, heavy chain variable area genes are successfully cloned in the present invention and small molecule gene engineered antibodies of all kinds are constructed and expressed based on the gene for preparing drug for reversing liver fibrosis matrix deposition-related disease. The polypeptide coded by the present gene can crosslink with multiple effector molecule and prepare drug for reversing liver fibrosis matrix deposition-related disease.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
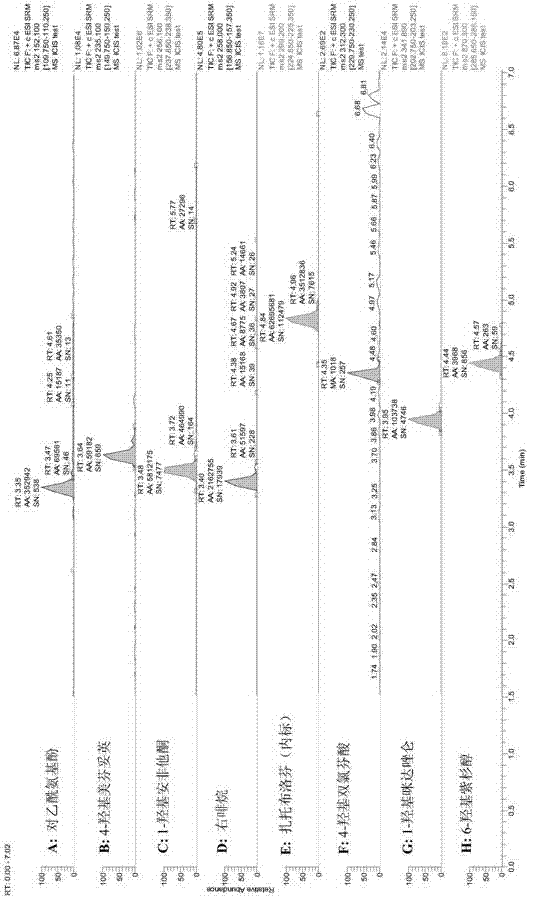
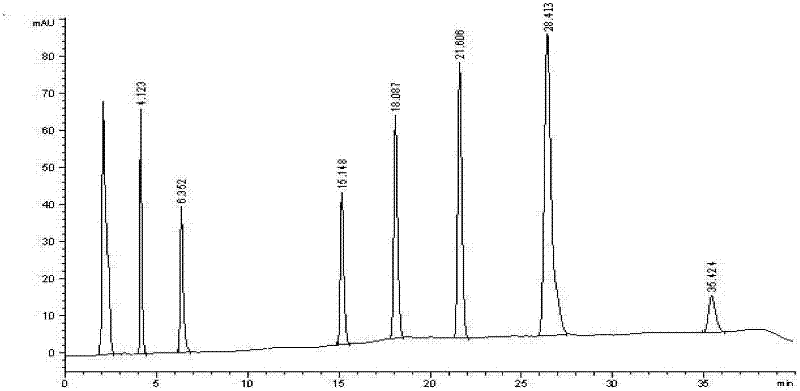
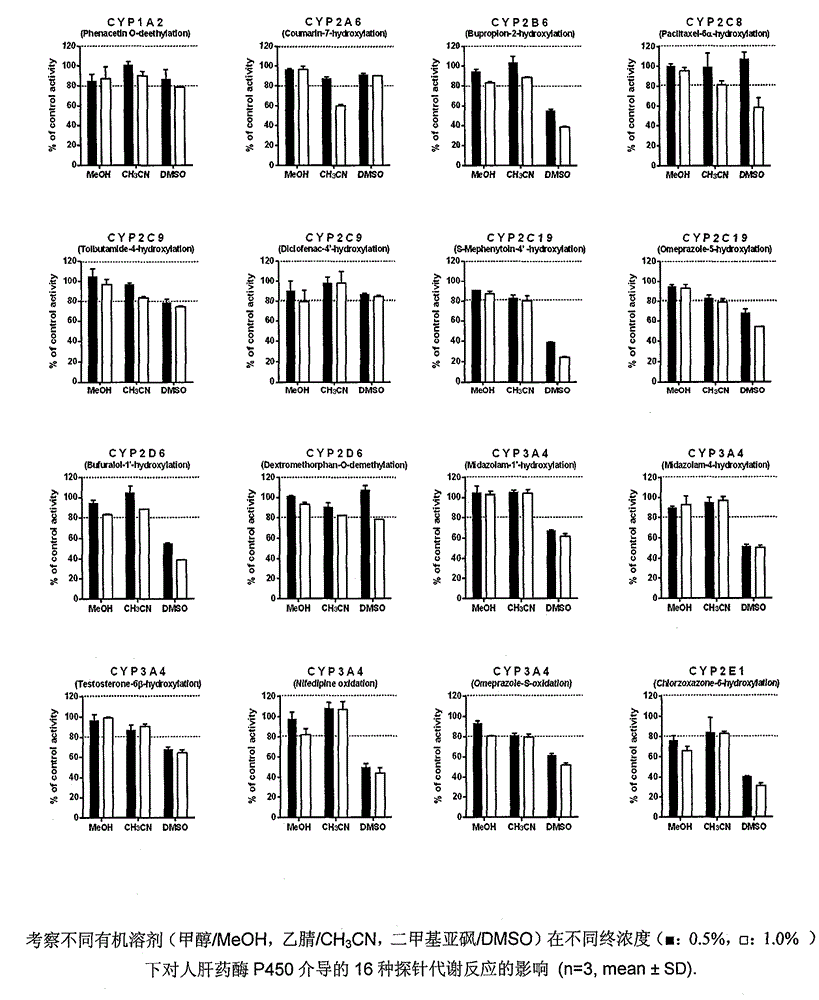
Detection method for simultaneously determining metabolic products of seven CYP450 enzyme probe substrates in human liver microsomes
InactiveCN104849371AThe pretreatment method is simpleSuitable for routine testingComponent separationMetaboliteHepatica
The invention relates to a detection method for simultaneously determining the metabolic products of seven CYP450 enzyme probe substrate in human liver microsomes, and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The detection method comprises the following steps: performing incubation on specificity probe substrates of CYP450 enzyme and the human liver microsomes for different periods of reaction time to generate corresponding metabolic products, using Zaltoprofen as an interior label, adopting a high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after protein precipitation pretreatment, and thus simultaneously detecting the concentrations of the metabolic products of seven probe substrates. The method disclosed by the invention is high in specificity, high in sensitivity and simple and convenient in operation, and has already successfully been applied to the research of baicalin on CYP450 enzyme inhibiting action of the human liver microsomes.
Owner:WUXI PEOPLES HOSPITAL
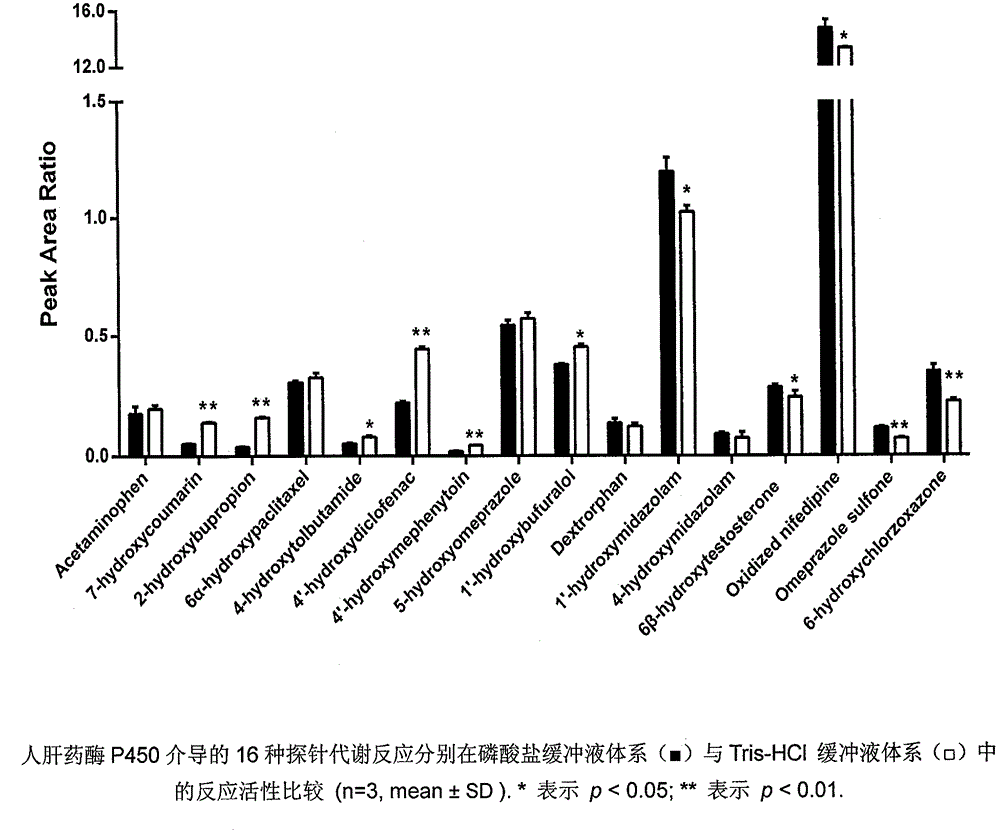
Preparation method, detection method and application of probe drug composition for determination of metabolic activity of cytochrome P450
InactiveCN102650620AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityComponent separationIn-vivo testing preparationsDrugs solutionMicroparticle
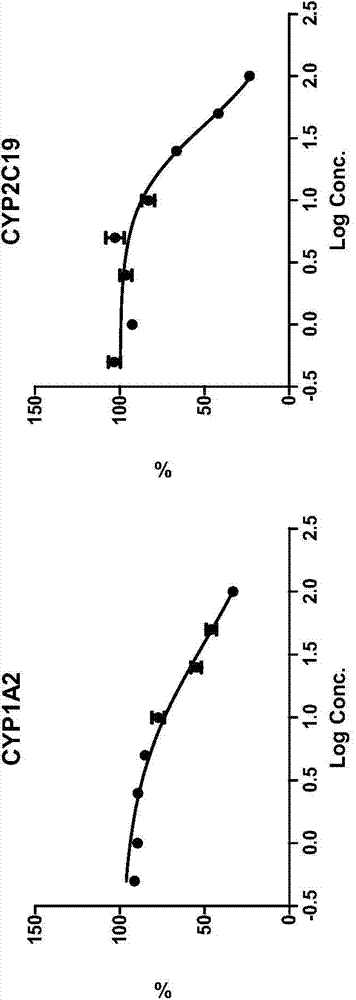
The invention relates to a preparation method, a detection method and application of a probe drug composition for determination of metabolic activity of cytochrome P450. The composition mainly comprises a preparation made with a specific probe with major isoforms of CYP450, i.e. CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4, as an active component. Cocktail probe drug solution is prepared, the probe drug composition is injected into an animal or liver microsomes for in vitro co-incubation, and the concentration of each probe drug is determined to assess the metabolic activity of the CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4. In the early stage of research and development of new drugs, the effects of the drugs on the activity of each isoform of the cytochrome P450 are screened in a high-throughput way, and the interactions of the drugs can be predicted. In the stage of clinical research, the testing can be performed with the probe drug composition in an in-vivo probe method, and the effects of the drugs on the in-vivo metabolic activity of different isoforms of the human liver CYP450 can be examined.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
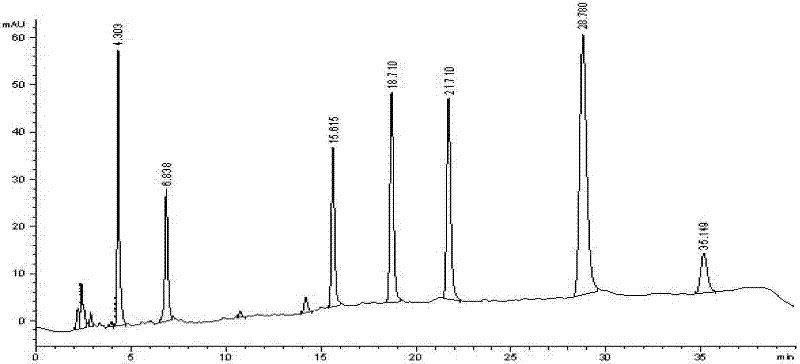
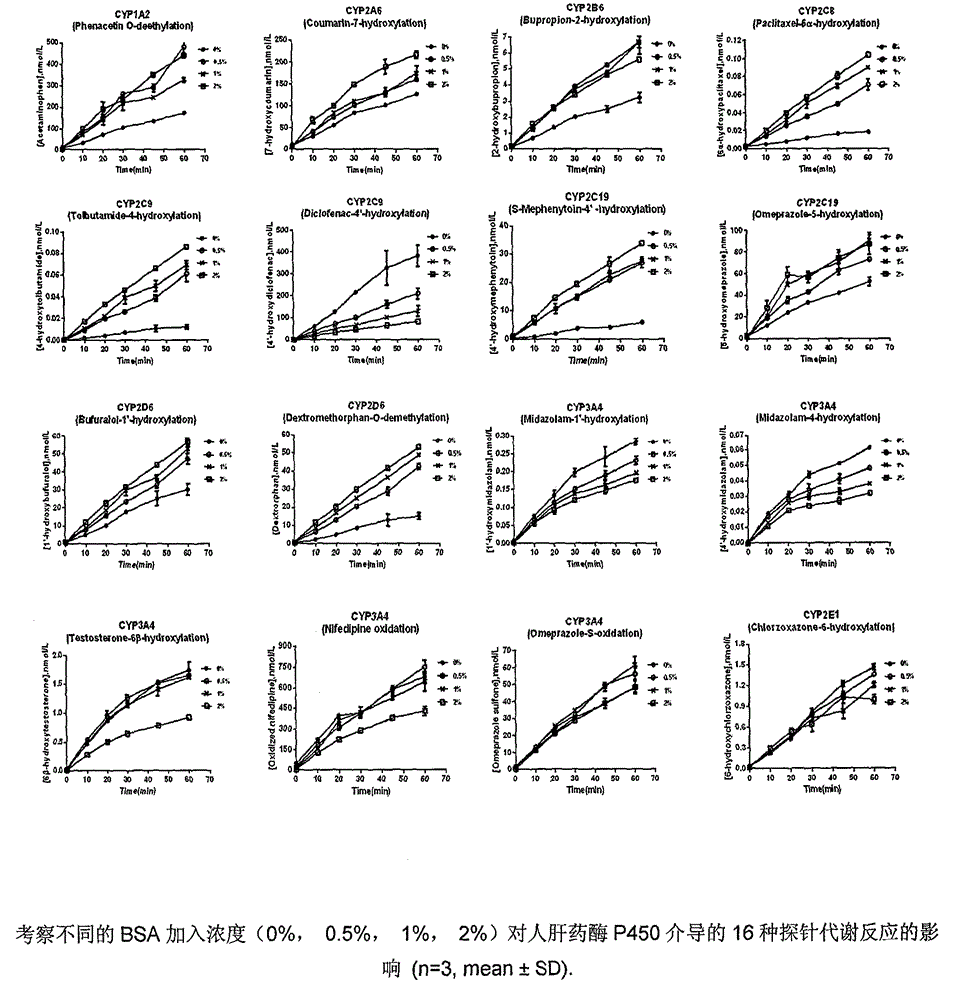
Method for rapidly screening in-vitro inhibitory effect of nine human liver CYP450 enzymes
ActiveCN104928350AImprove accuracyReduce the incidence of false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
The invention discloses a rapid screening method for comprehensively evaluating the in-vitro inhibitory effect of nine human liver CYP450 metabolic enzymes by utilizing 14 probe substrates and 16 probe reaction. The invention mainly relates to a method for monitoring metabolic activity variation of 9 human liver CYP450 enzymes and rapidly and comprehensively evaluating an inhibitory effect of a tested compound on the metabolic enzyme by adopting an in-vitro mixed probe incubation method and LC / MS / MS. According to the method, the exclusiveness and diversity of the probe substrate, interaction of the probe substrates, influence of different inoculation conditions (by charging organic solvent, buffer solution and BSA) in a warm inoculation system and the enzyme kinetics characteristics of 16 probe reactions under the selected inoculation condition are comprehensively considered, a brand new in-vitro system is established by integrating high-sensitive and high-selective LC-MS / MS technology, so that the inhibitory effect of the tested compounds on the nine human liver main metabolic enzymes can be more accurately and comprehensively predicted in the high-throughput screening of the novel drug development, and the predictability on the interaction of the later metabolism can be improved.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Long-term in-vitro culture and directional differentiation system and method for liver stem cell
ActiveCN104388383AMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemMolecular phenotypeDirected differentiation
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical engineering and particularly relates to a long-term in-vitro culture and directional differentiation system and method for a liver stem cell. The long-term in-vitro culture and directional differentiation system comprises an amplification culture medium with specific chemical components, and a differential medium with specific chemical components, wherein the amplification culture medium is used for carrying out in-vitro culture of a mouse or human liver stem cell, and the differential medium is used for carrying out induced differentiation on the mouse or human liver stem cell to form a matured liver cell. By using the long-term in-vitro culture and directional differentiation system and method, a selectively-amplified liver stem cell in mother cells of the liver can be obtained from a mouse embryonic liver tissue or through human multipotential stem cell differentiation, the liver stem cell can be cultured for more than 20 generations under such a condition, and the stable molecular phenotype of the liver stem cell is maintained. By using the long-term in-vitro culture and directional differentiation system and method, the cultured mouse or human liver stem cell can be further subjected to induced differentiation to form the matured liver cell with functions of secreting albumin, metabolizing urea and the like.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Human hepatocyte-like cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060154235A1Improve efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsCytochrome P450Culture mediums
The present invention provides modified methods of producing human hepatocyte-like cells which exhibit phenotypes more similar to those of human hepatocytes. The present invention also provides the human hepatocyte-like cells and uses thereof. The methods of the present invention comprises a prolonged incubation period and addition of dexamethasone to the culture medium. The methods of the inventors produce human hepatocyte-like cells whose morphology is more similar to that of human hepatocytes, compared with the conventional system. The cells produced have both morphological and functional features of primary culture cells from normal human liver, including cytochrome P450 (CYP), multi-drug resistance-associated protein (MRP), and multi-drug protein (MDR). The use of human hepatocyte-like cells of the present invention enables, without using any animal model, assessment of metabolism and hepatotoxicity of test compounds, which are drug candidates, and screening for therapeutic agents for hepatic diseases, inhibitors to hepatitis virus infection, and therapeutic agents for viral hepatitis.
Owner:EFFECTOR CELL INST
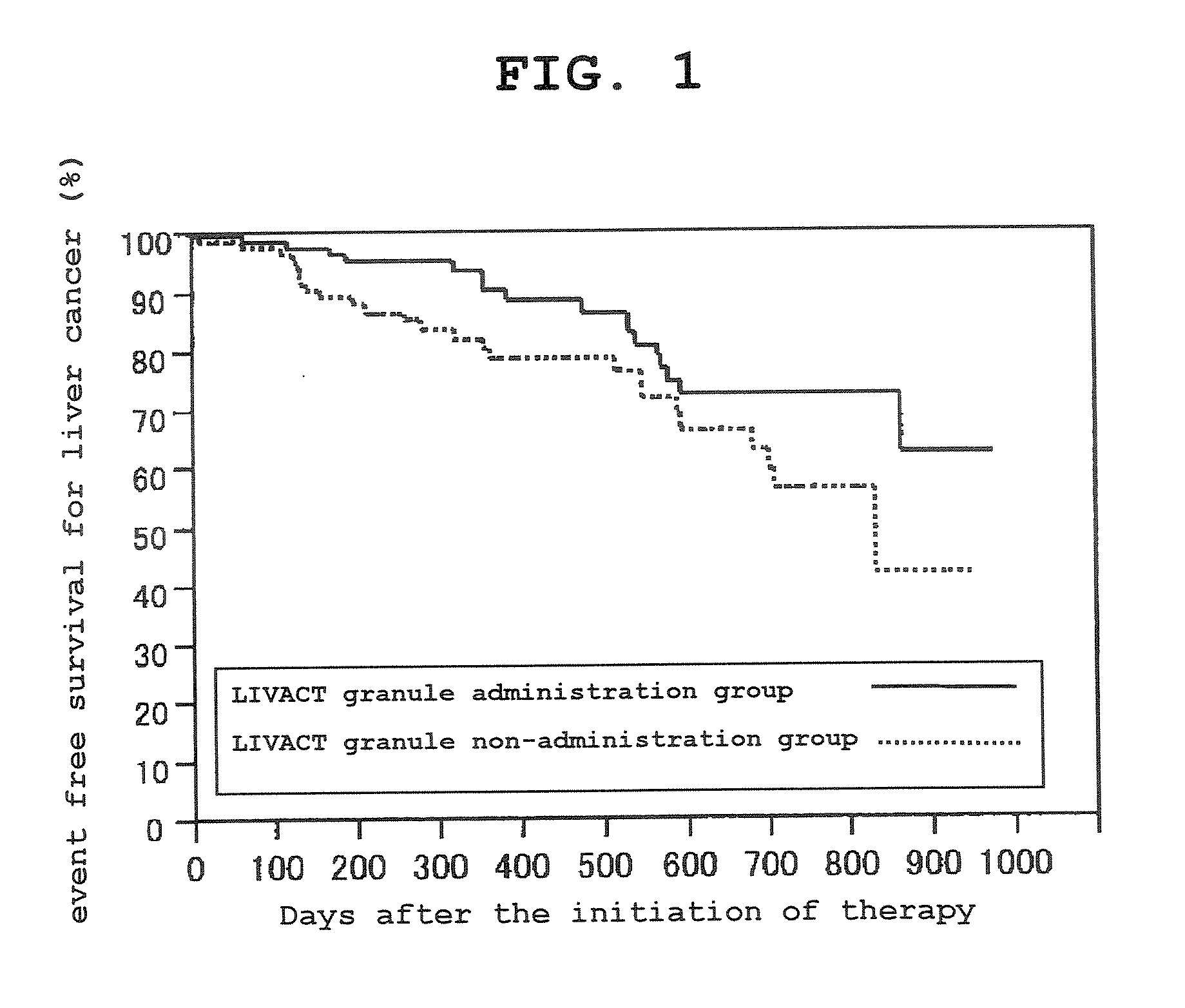
Inhibitor for the onset and progress of liver cancer to be used in hepatitis c virus-positive human liver cirrhosis patients
InactiveUS20070197647A1Avoid developmentInhibit progressBiocideOrganic active ingredientsIsoleucine+LeucineTert-leucine
The present invention provides, as a pharmaceutical agent having an effect to inhibit the development and / or progression of liver cancer in hepatitis C virus-positive human cirrhosis patients, an agent for inhibiting the development and / or progression of liver cancer in hepatitis C virus-positive human cirrhosis patients, which contains three kinds of amino acids of isoleucine, leucine and valine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Marker genes responding to treatment with toxins
InactiveUS20030165854A1Optimize treatment planEfficacy of treatmentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRat liverDisease
The present invention relates to a combination comprising a plurality of cDNAs which are differentially expressed in treated rat liver and in human liver and which may be used in their entirety or in part to diagnose, stage, or treat a liver disorder, to monitor diagnostic and therapeutic applications, to detect metabolic and toxicological responses, and to elucidate drug mechanism of action.
Owner:INCYTE
Human liver progenitors
InactiveUS20050148072A1Low densityReduce in quantityHepatocytesGenetic material ingredientsProgenitorGlycophorin
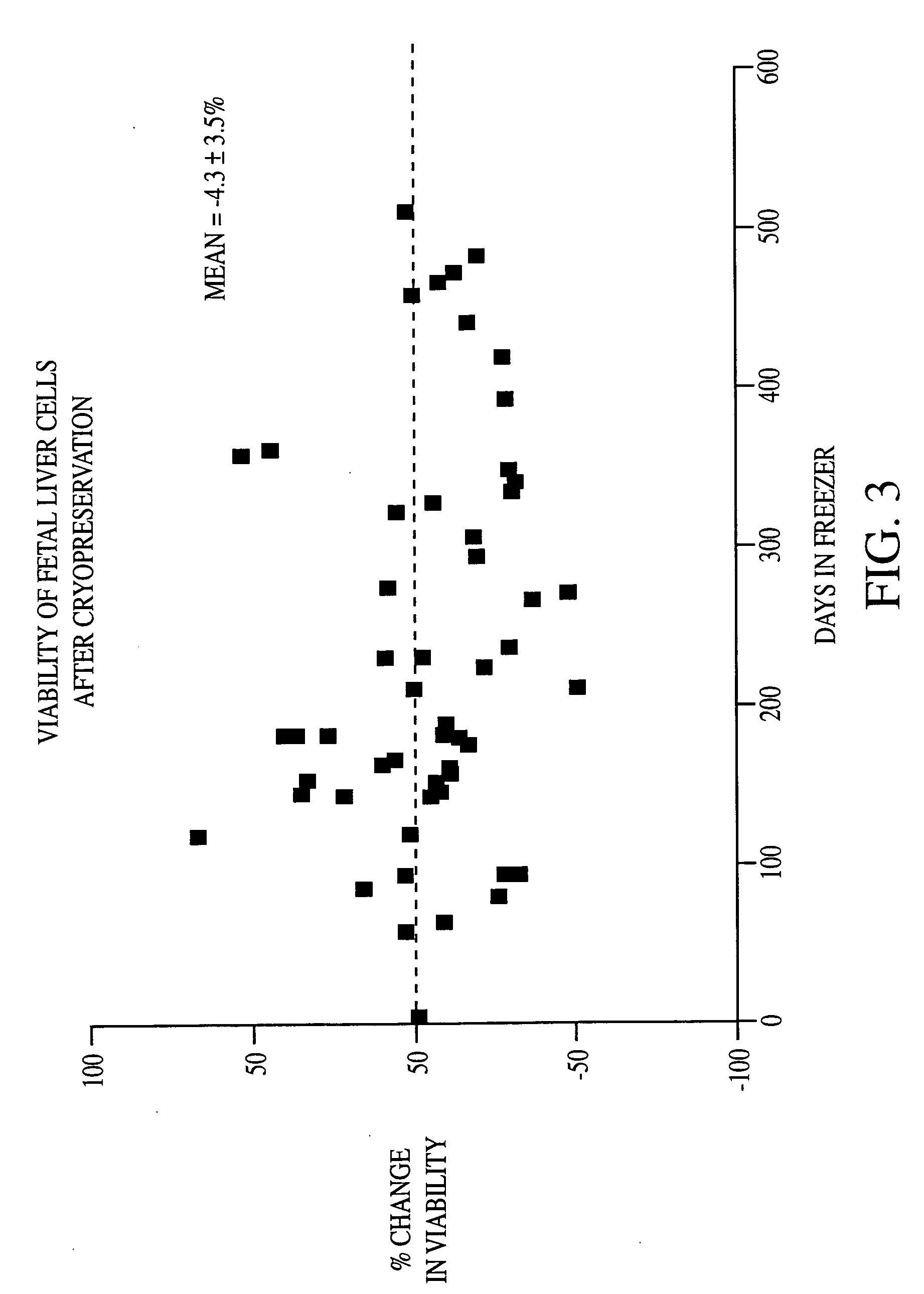
Methods of isolating and cryopreserving progenitors from human liver are disclosed which include processing human liver tissue to provide a substantially single cell suspension comprising progenitors and non-progenitors of one or more cell lineages found in human liver; subjecting the suspension to a debulking step, which reduces substantially the number of non-progenitors in the suspension, and which provides a debulked suspension enriched in progenitors exhibiting one or more markers associated with at least one of the one or more cell lineages; and selecting from said debulked suspension those cells, which themselves, their progeny, or more mature forms thereof express one or more markers associated with at least one of the one or more cell lineages. Among these markers are CD14, CD34, CD38, CD45, and ICAM. Hepatic progenitors are characterized as being 6-15μ in diameter, diploid, glycophorin A−, CD45−, AFP+++, ALB+, ICAM+, and with subpopulations varying in expression of CD14+. CD34++, CD38++, CD117+. These progenitor subpopulations have characteristics expected for cells that are particularly useful in liver cell and gene therapies and for establishing bioartificial organs.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Animal model having a chimeric human liver
The present invention features a non-human animal model that is susceptible to infection by human hepatotrophic pathogens, particularly human hepatitis C virus (HCV). The model is based on a non-human, immunocompromised transgenic animal having a human-mouse chimeric liver, where the transgene provides for expression of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the liver. The invention also features methods for identifying candidate therapeutic agents, e.g., agents having antiviral activity against HCV infection. The animals of the invention are also useful in assessing toxicity of various agents, as well as the activity of agents in decreasing blood lipids.
Owner:KMT HEPATECH
Primitive and proximal hepatic stem cells
InactiveUS20070099297A1Minimize formationExtensive growth potentialHepatocytesMammal material medical ingredientsProgenitorLiver disorder
Hepatic progenitors comprise two populations of human hepatic stem cells, primitive and proximal hepatic stem cells, and two populations of committed progenitors, one for biliary cells and one for hepatocytes. Human primitive hepatic stem cells are a very small fraction of the liver cell population and give rise to proximal hepatic stem cells constituting a much larger fraction of the liver. Human proximal hepatic stem cells give rise to biliary and hepatocyte committed progenitors. Primitive and proximal stem cells are the primary stem cells for the human liver. Human primitive hepatic stem cells may be isolated by immunoselection from human livers or culturing human liver cells under conditions which select for a human primitive hepatic stem cell. Proximal hepatic stem cells may be isolated by immunoselection, or by culturing human liver cells under conditions which include a developmental factor. Proximal hepatic stem cells may also be isolated by culturing colonies comprising a primitive hepatic stem cell under conditions which include a developmental factor. Resulting compositions may be used for treating liver disorders and for producing bioartificial organs.
Owner:VESTA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Immortalized human liver cell line, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101659941AProlong survival timeEnhance detoxification functionMicrobiological testing/measurementDialysis systemsArtificial liverSupporting system
The invention discloses an immortalized human liver cell line, a preparation method and an application thereof. The immortalized human liver cell line has the main function of primarily cultured humanliver cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: transferring SV40T antigen and human telomerase catalyzed subunit gene into primarily cultured separated human normal liver cell by slow virus carrier; and sieving in a cloning way to obtain the immortalized human liver cell line. The immortalized human liver cell line also can be extrinsically amplified in large scales in a microcarrier way. The immortalized human liver cell line can be used for preparing a biological artificial liver support system and preparing the medicament for curing the liver failure.
Owner:苏州瑞徕生物科技有限公司
Special marine dietary food for patients with liver deficiency
InactiveCN102077938ALower fasting blood sugar levelsImprove glucose toleranceFood preparationNutritional statusFood borne
The invention discloses a special marine dietary food for patients with liver deficiency. The dietary food is prepared from the food-borne marine oligopeptides as the main raw materials, and marine bioactive polysaccharide, seaweed powder, nutritional amino acids, oligosaccharides, nutrients, vitamins and minerals by mixing. The special marine dietary food can be made into powder or particles anddissolved by warm water for use. The special marine dietary food can be easily dissolved, and has the greatest biological absorption and maximum bioavailability for human body. The special marine dietary food can provide body with marine protein with high-quality, activity factors and nutrients, and supplement essential vitamins and minerals for human body, and can be helpful to improve the nutritional condition of patients with liver deficiency. Through the coordination of the food-borne marine oligopeptides, the biological active ingredients in the marine bioactive polysaccharides in, the seaweed powder, the nutritional amino acids and other factors together, the special marine dietary food can protect human livers, and improve the immunity to prevent the occurrence of liver disease. The food is suitable for the patients with liver deficiency.
Owner:广州蓝钥匙海洋生物工程有限公司
Differentiated human liver cell cultures and their use in bioartificial liver systems
InactiveUS20120111795A1Function increaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiver failureOrganism
The present invention concerns human hepatocyte cell line cultures and their use in bioartificial liver (BAL) systems. These systems are used to treat subjects suffering from liver failure to temporarily compensate for loss of hepatocellular function and generally comprise a bioreactor loaded with functional liver cells. Until now, it has been problematic to acquire cells with a broad spectrum metabolic functionality, resembling that of freshly isolated human hepatocytes, to the extent that they are in fact suitable for successful clinical BAL application The present inventors have managed to develop human hepatocyte cell line cultures that display broad-spectrum metabolic functionality such as to render them particularly suitable for effective clinical BAL application.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Liver tumor marker sequences
InactiveUS20070042420A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsKidney cancerPreneoplastic foci
Polypeptides whose expression is upregulated in liver tumor cells and cells from liver preneoplastic foci relative to expression in normal liver cells are disclosed as are polynucleotides that encode the polypeptides. In humans, the polynucleotide maps to a region of chromosome 15. The overexpression has also been confirmed in human liver, breast, colon and kidney cancer cell lines. It is believed that the polypeptides are overexpressed in tumor and preneoplastic cells in general.
Owner:FARNHAM PEGGY J +2
Method for preparing pig and human liver cell for biological artificial liver
InactiveCN1632107AIncrease the number ofHigh activityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsArtificial liverEmbryo
Disclosed is method to prepare biological artificial pig for liver and liver cell of human, which includes the two courses of pouring outside the body of separating liver cell and washing the liver cell, uses the four-stepped pouring method on the basis of the one with two steps, and designs the relative agent. The invention has increased the quality, living rate and purity of separating the liver cell, it is suitable for acquiring liver from pig, dog or grown-ups, or liver separation from liver of human embryo by legal artificial labor, and the liver cell prepared can be widely used in research and transplantation of liver cell, biological artificial liver and mixed artificial liver.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mice transplanted with human hepatocytes
Disclosed is a mouse having human hepatocytes transplanted therein. Specifically disclosed is a mouse having human hepatocytes transplanted therein. In the mouse, a foreign thymidine kinase gene or an urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene is retained so that the gene can be expressed specifically in the liver of the mouse, and hepatocytes of the mouse are substituted by human hepatocytes.
Owner:CENT INST FOR EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS +1
Novel recombinant adeno-associated virus capsids resistant to pre-existing human neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20170360962A1Improved profileEnhanced transductionGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemHepaticaTropism
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Primitive and proximal hepatic stem cells
Hepatic progenitors comprise two populations of human hepatic stem cells, primitive and proximal hepatic stem cells, and two populations of committed progenitors, one for biliary cells and one for hepatocytes. Human primitive hepatic stem cells are a very small fraction of the liver cell population and give rise to proximal hepatic stem cells constituting a much larger fraction of the liver. Human proximal hepatic stem cells give rise to biliary and hepatocyte committed progenitors. Primitive and proximal stem cells are the primary stem cells for the human liver. Human primitive hepatic stem cells may be isolated by immunoselection from human livers or culturing human liver cells under conditions which select for a human primitive hepatic stem cell. Proximal hepatic stem cells may be isolated by immunoselection, or by culturing human liver cells under conditions which include a developmental factor. Proximal hepatic stem cells may also be isolated by culturing colonies comprising a primitive hepatic stem cell under conditions which include a developmental factor. Resulting compositions may be used for treating liver disorders and for producing bioartificial organs.
Owner:VESTA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
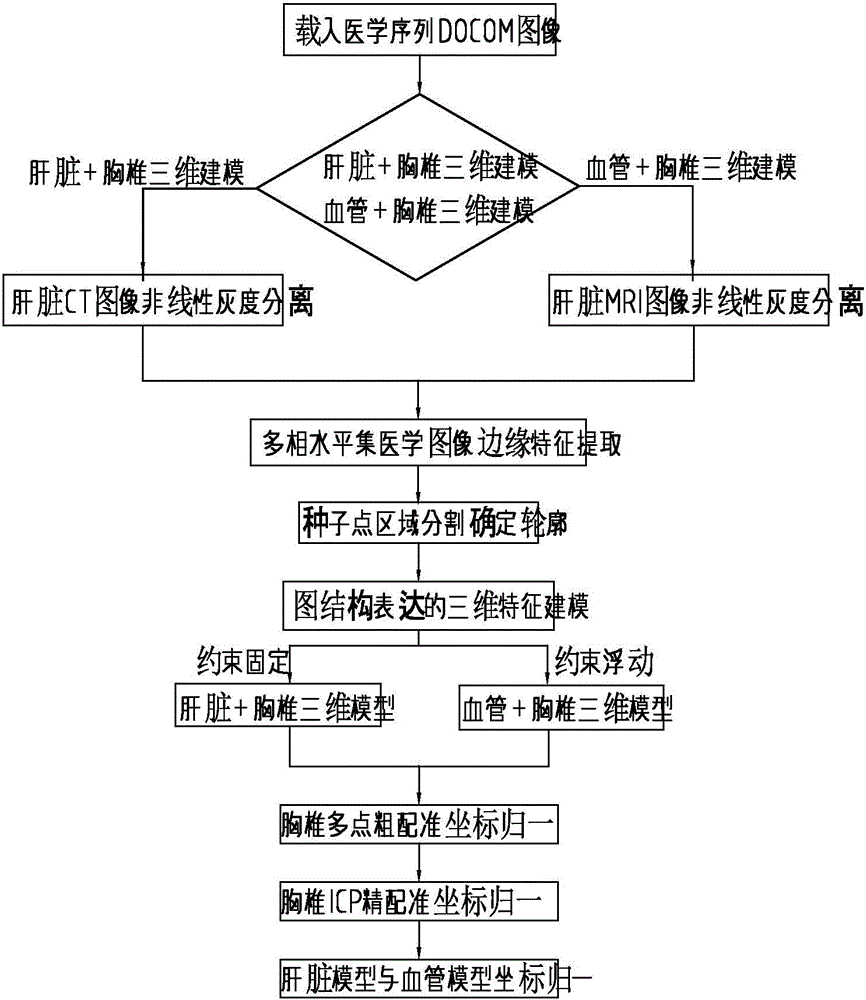
Human liver feature modeling and vascular model space normalization method
InactiveCN106846330ARealize spatial normalizationImprove surgical skillsImage enhancementImage analysisBlood vesselInformation data
The invention discloses a human liver feature modeling and vascular model space normalization method. The method comprises the steps of preprocessing multi-source medical image information data; extracting human liver edge features; performing three-dimensional modeling; and performing multi-source information and different-medium-based human liver and vascular feature coordinate normalization. According to the method, liver medical image feature extraction and three-dimensional model rebuilding are realized through gray level nonlinear transformation and multiphase piecewise smooth level set algorithms for gray level non-uniformity of human liver CT image and MRI image; and for the fact that accurate corresponding references do not exist in three-dimensional spaces of a multi-medium liver vascular model and a liver model, the problem in liver tissue organ coordinate normalization is solved through an external feature registration technology fusing multisource feature information.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com