Patents
Literature
88 results about "Human cell line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Background Information. AC16 Human Cardiomyocyte Cell Line is a proliferating cell line that was derived from the fusion of primary cells from adult human ventricular heart tissues with SV40 transformed, uridine auxotroph human fibroblasts, devoid of mitochondrial DNA (1, 2).
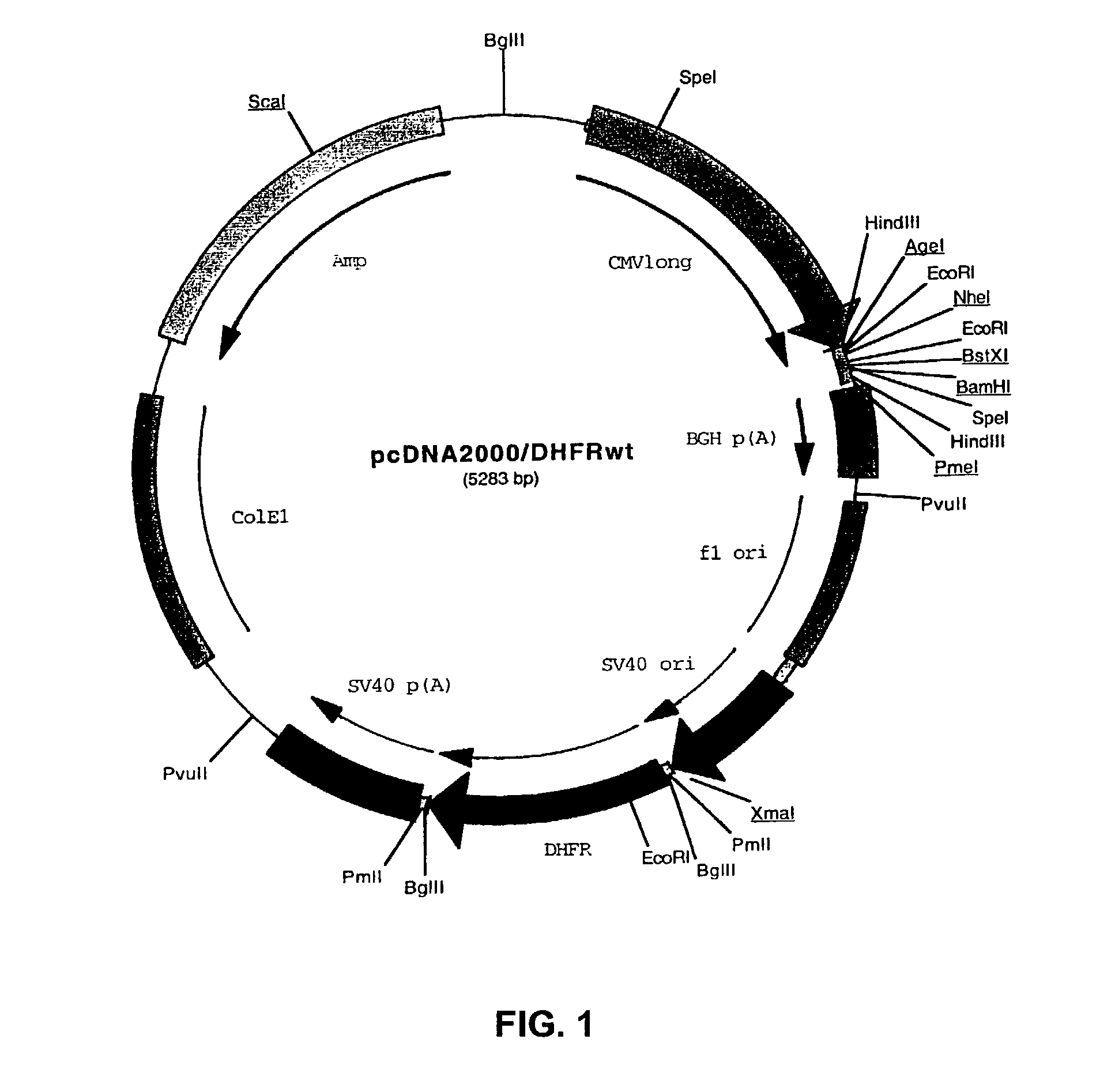
Recombinant protein production in a human cell
InactiveUS6855544B1Easy to handleLarge-scale (continuous) productionSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesHamsterHuman cell
Methods and compositions for the production of recombinant proteins in a human cell line. The methods and positions are particularly useful for generating stable expression of human recombinant proteins of interest that are modified post-translationally, for example, by glycosylation. Such proteins may have advantageous properties in comparison with their counterparts produced in non-human systems such as Chinese Hamster Ovary cells.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
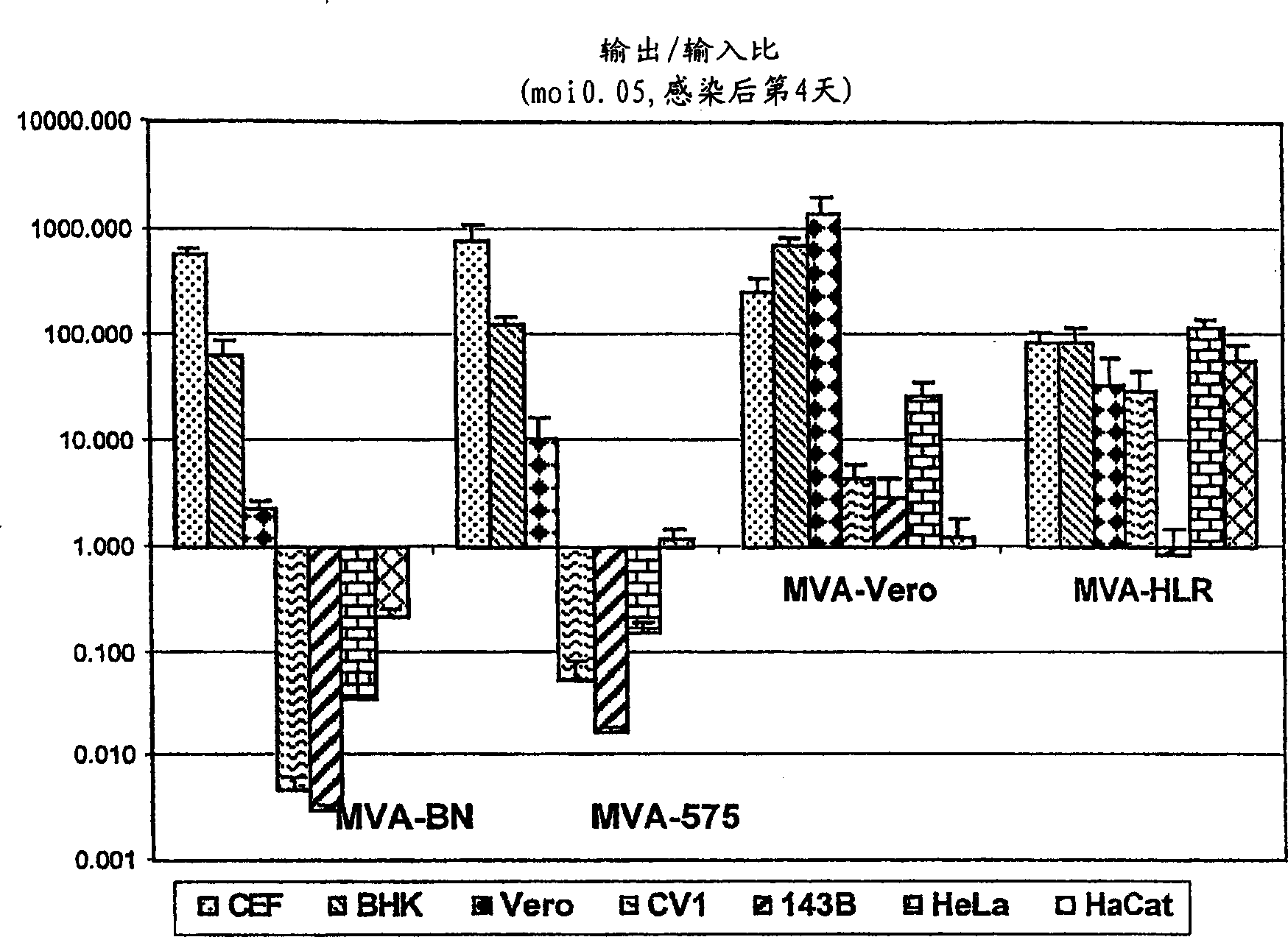
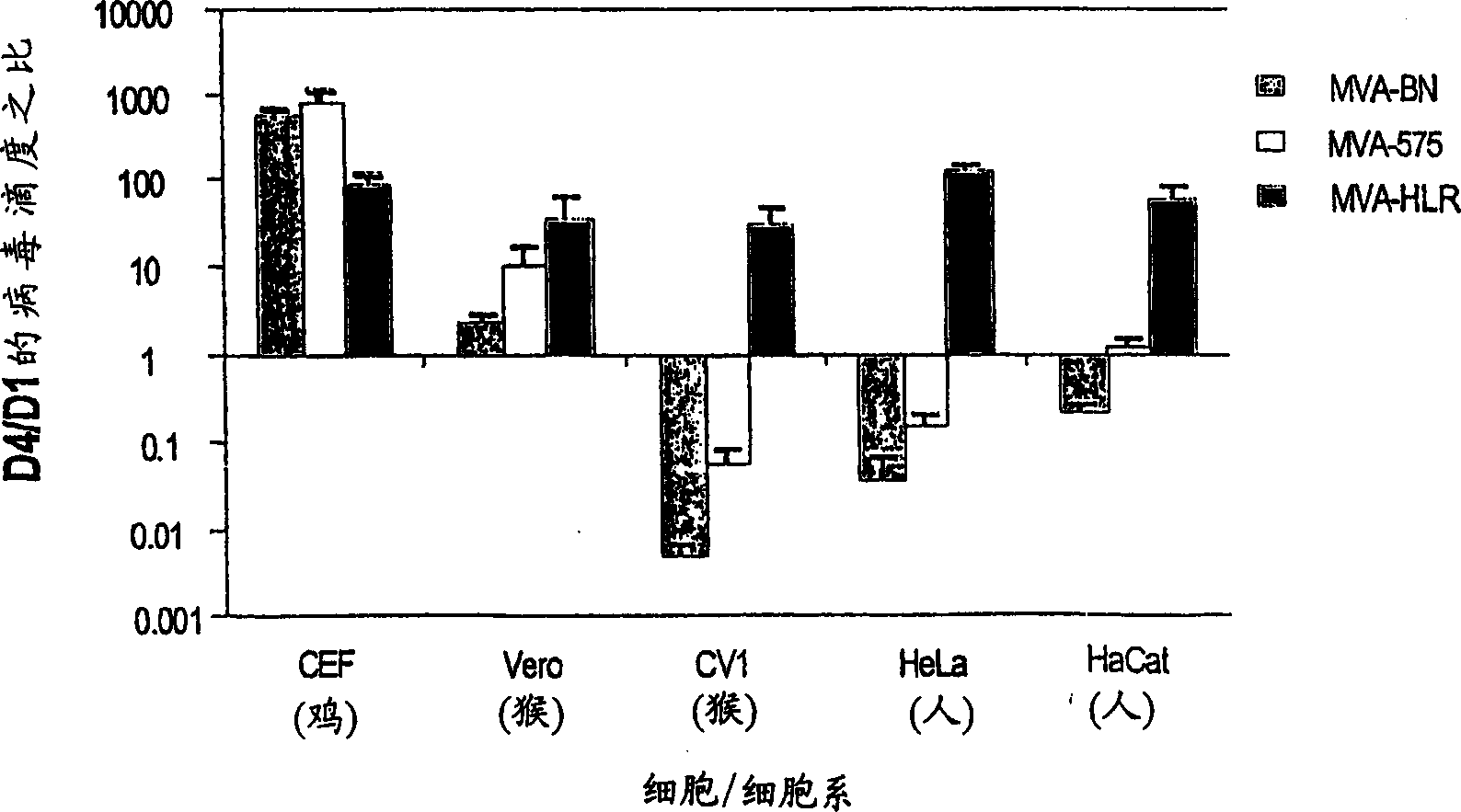
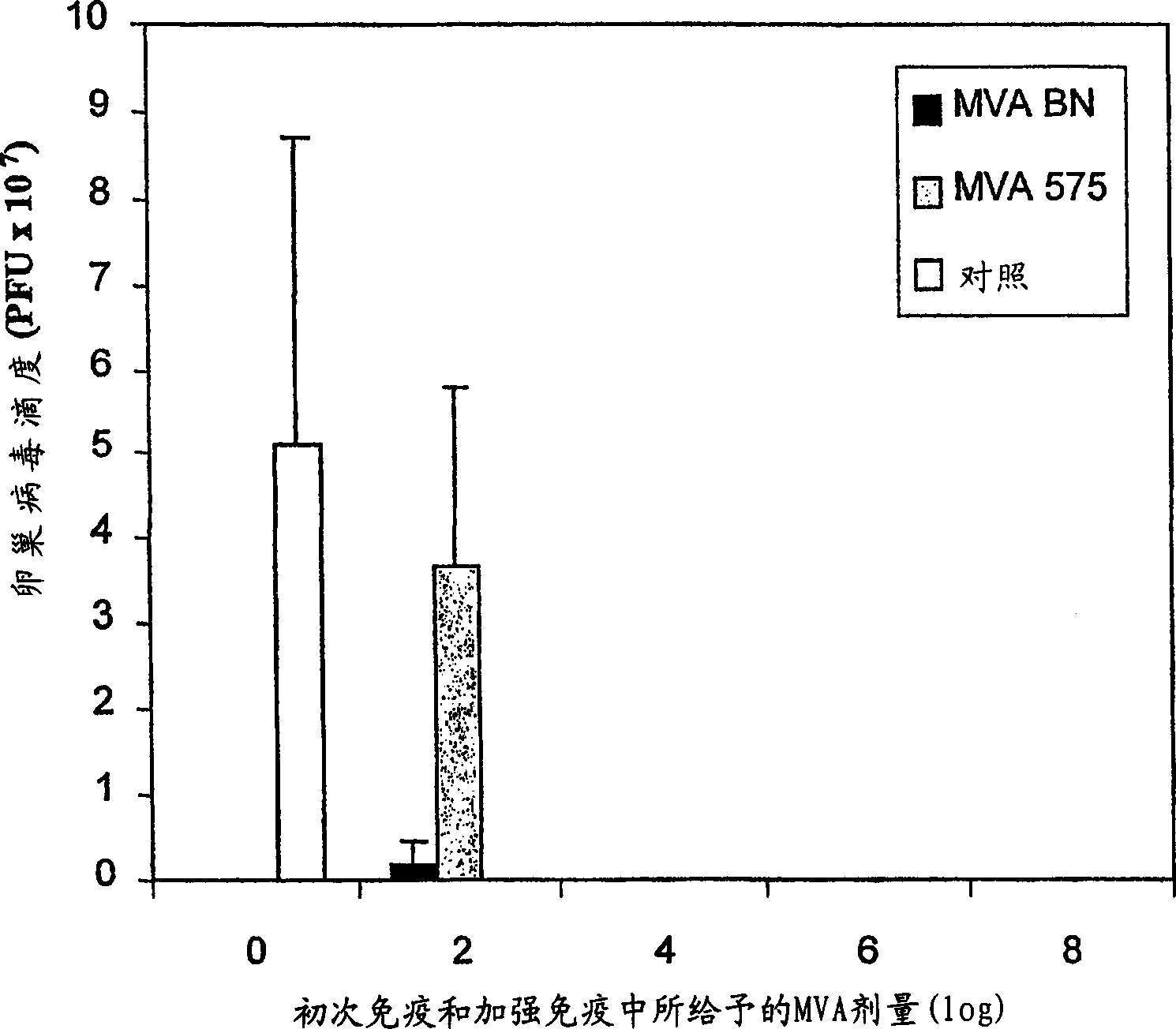
Modified Vaccinia Ankara virus variant and cultivation method
InactiveUS7445924B2Reduce riskGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesSerum free mediaModified vaccinia Ankara
The present invention provides an attenuated virus, which is derived from Modified Vaccinia Ankara virus and characterized by the loss of its capability to reproductively replicate in human cell lines. It further describes recombinant viruses derived from this virus and the use of the virus, or its recombinants, as a medicament or vaccine. A method is provided for inducing an immune response in individuals who may be immune-compromised, receiving antiviral therapy, or have a pre-existing immunity to the vaccine virus. In addition, a method is provided for the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of the virus, or its recombinants, in a vaccinia virus prime / vaccinia virus boost innoculation regimen. The present invention relates to a method of virus amplification in primary cells which are cultivated in a serum free medium. Viruses produced by this method are advantageously free of any infectious agents comprised in animal sera.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Modified vaccinia ankara virus variant and cultivation method
InactiveUS20050214323A1Reduce riskViral antigen ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSerum free mediaModified vaccinia Ankara
The present invention provides an attenuated virus, which is derived from Modified Vaccinia Ankara virus and characterized by the loss of its capability to reproductively replicate in human cell lines. It further describes recombinant viruses derived from this virus and the use of the virus, or its recombinants, as a medicament or vaccine. A method is provided for inducing an immune response in individuals who may be immune-compromised, receiving antiviral therapy, or have a pre-existing immunity to the vaccine virus. In addition, a method is provided for the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of the virus, or its recombinants, in a vaccinia virus prime / vaccinia virus boost innoculation regimen. The present invention relates to a method of virus amplification in primary cells which are cultivated in a serum free medium. Viruses produced by this method are advantageously free of any infectious agents comprised in animal sera.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
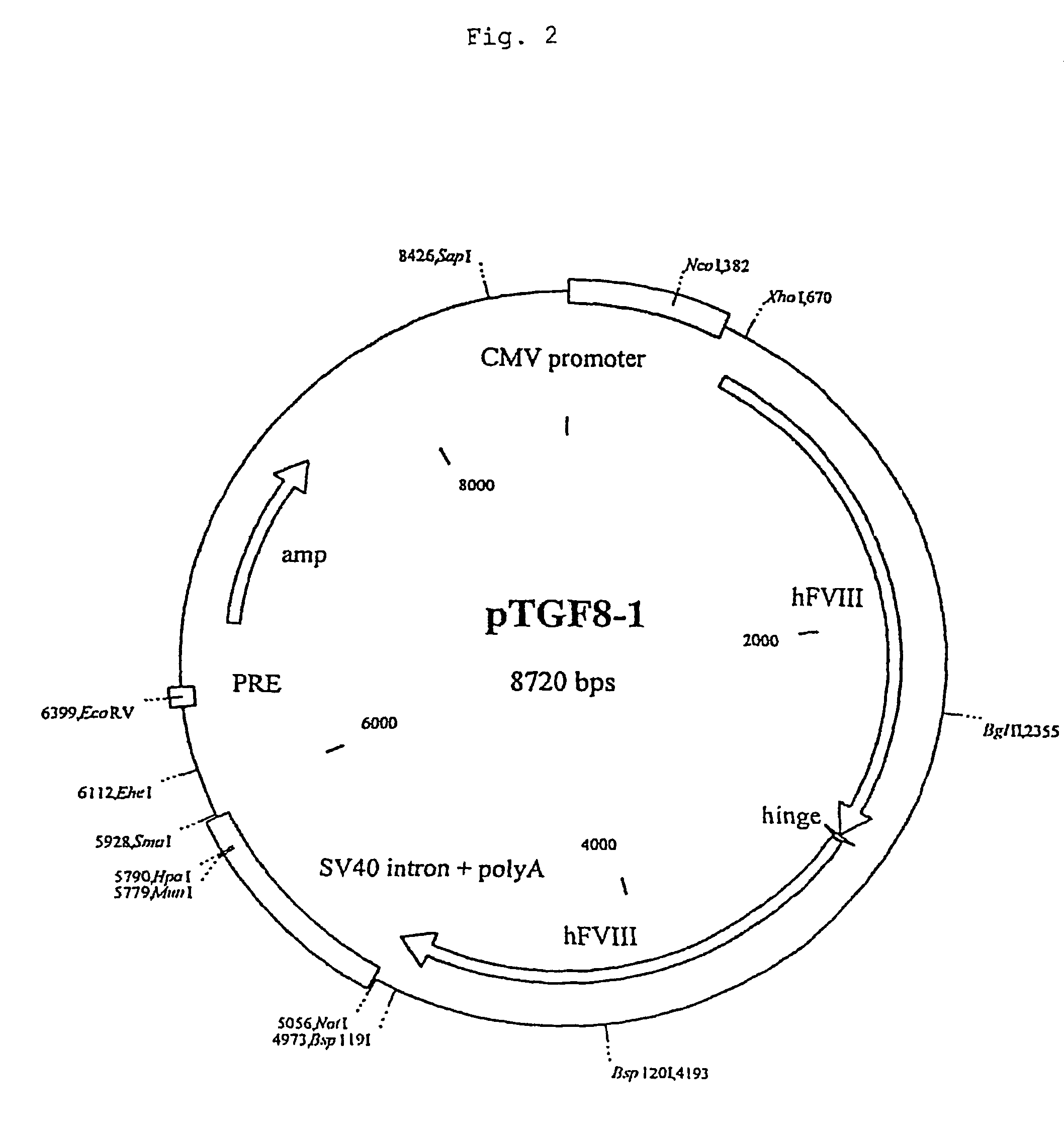
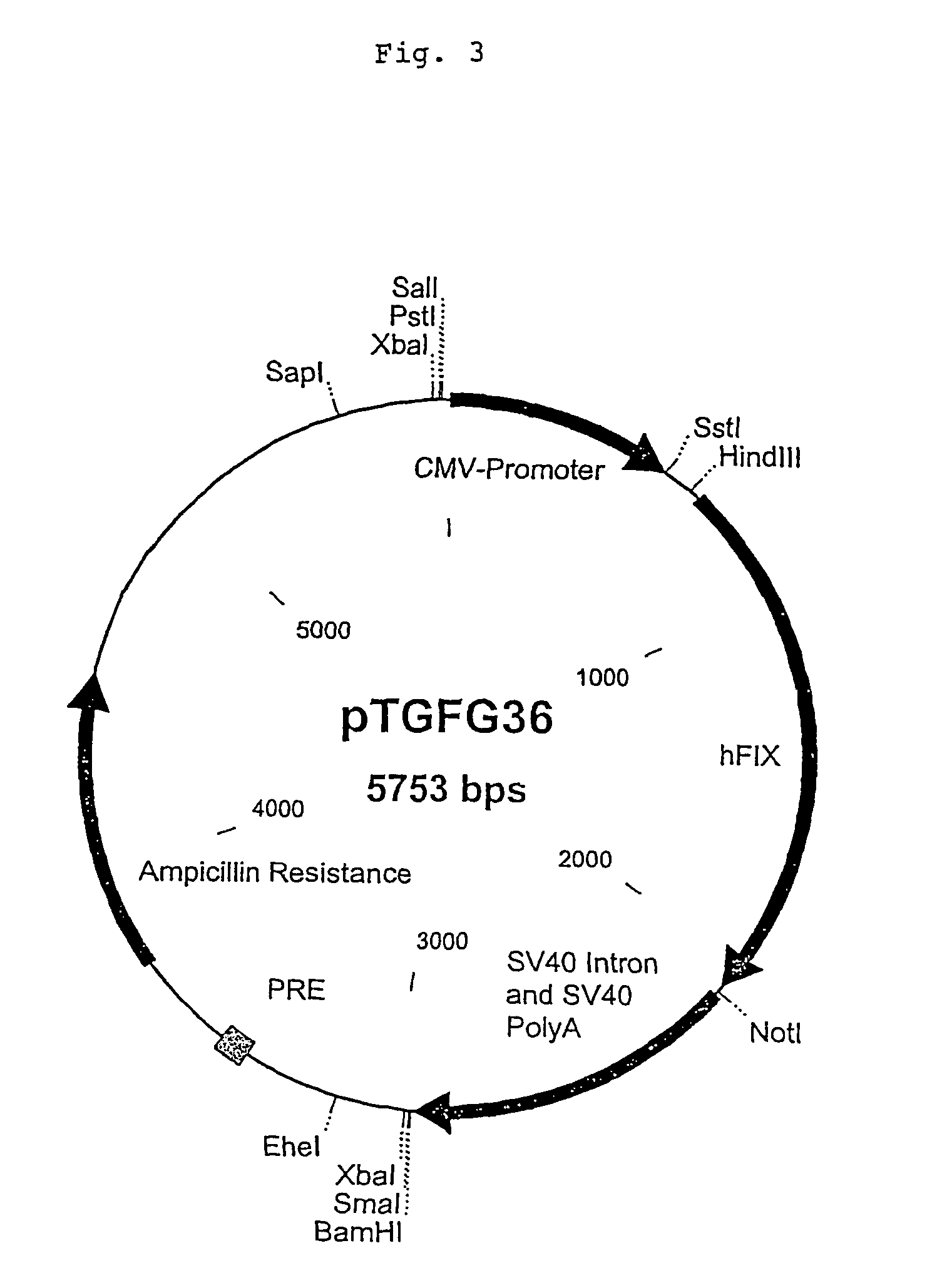
Recombinant blood clotting factors
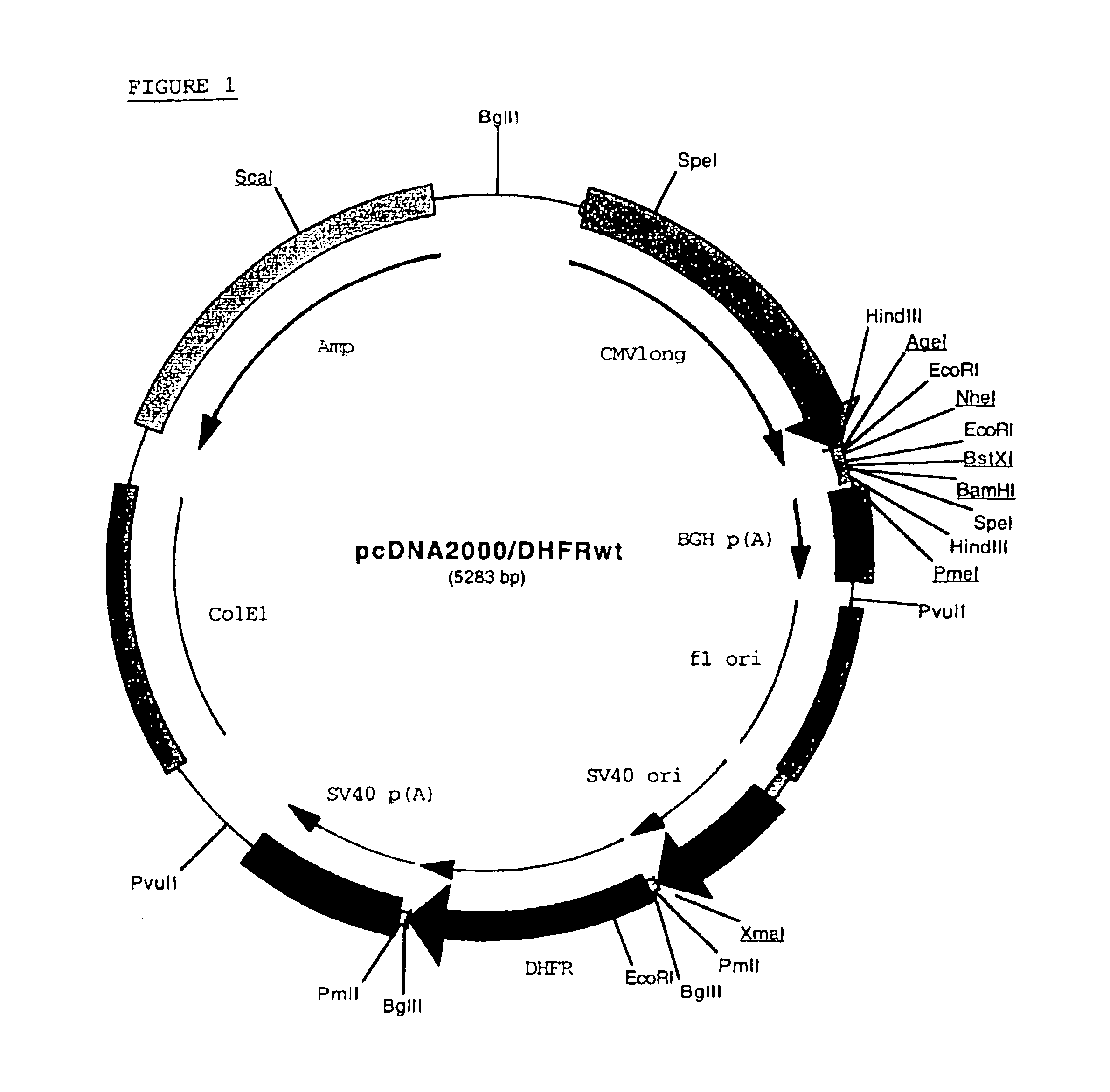
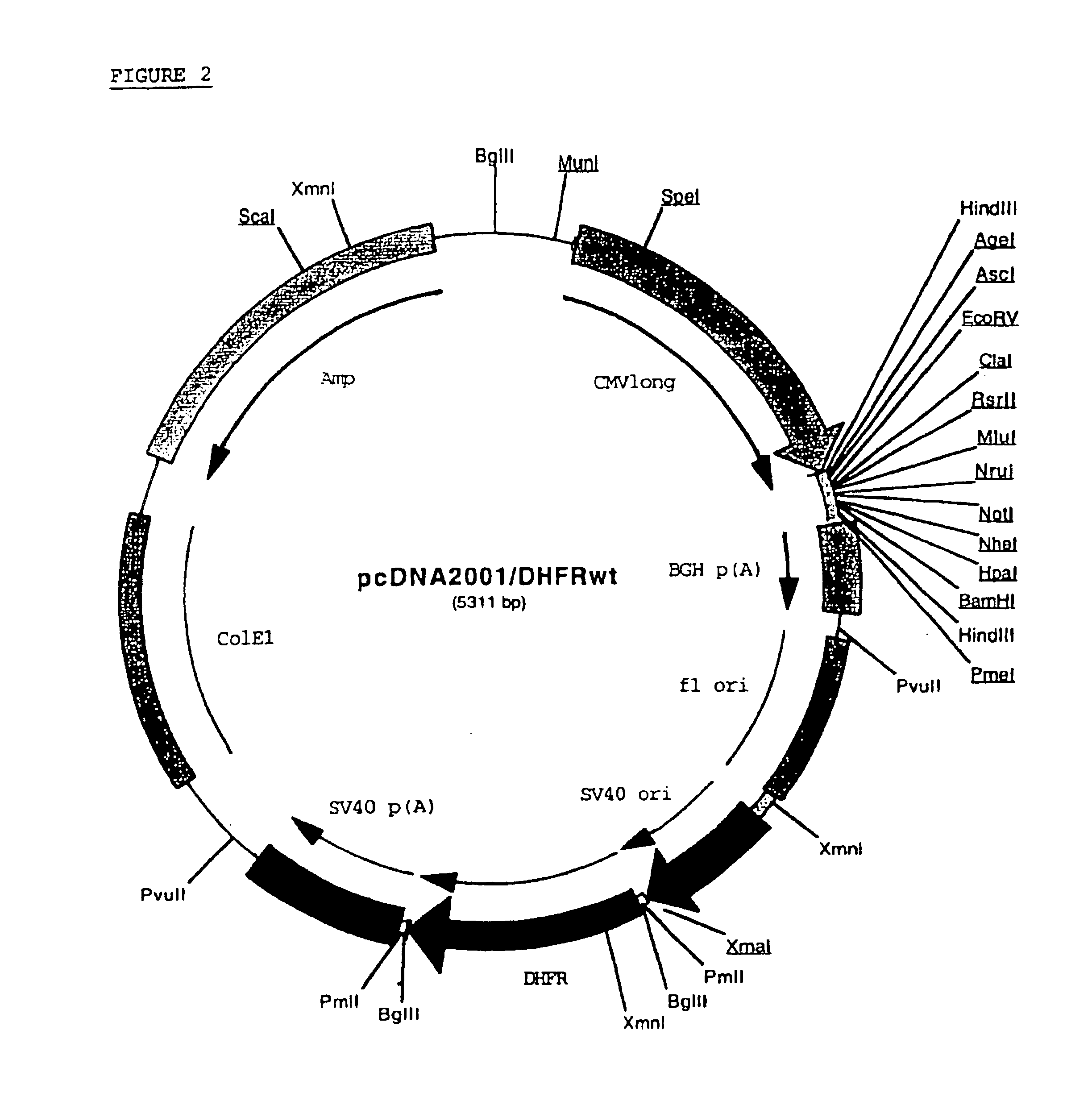
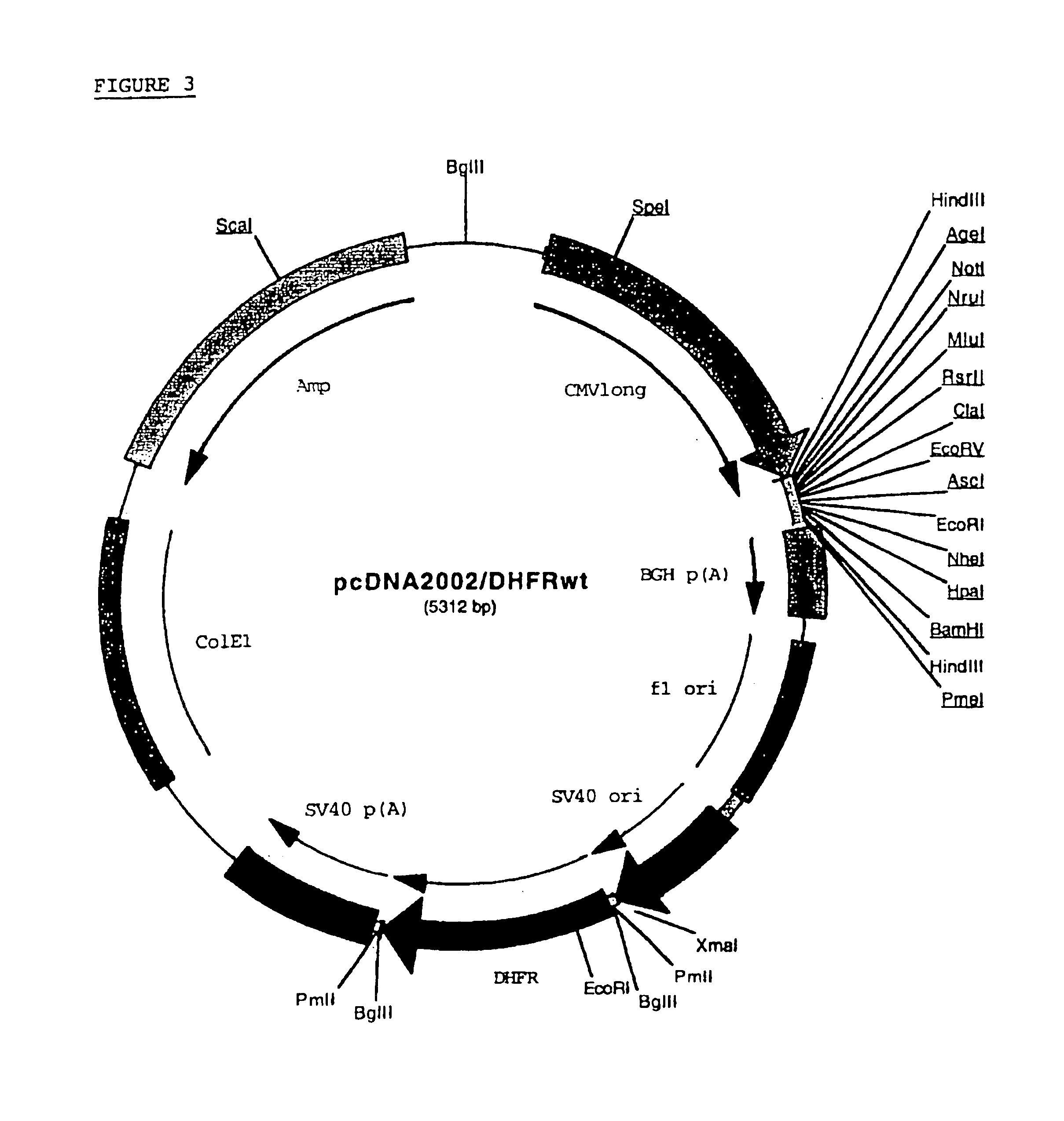
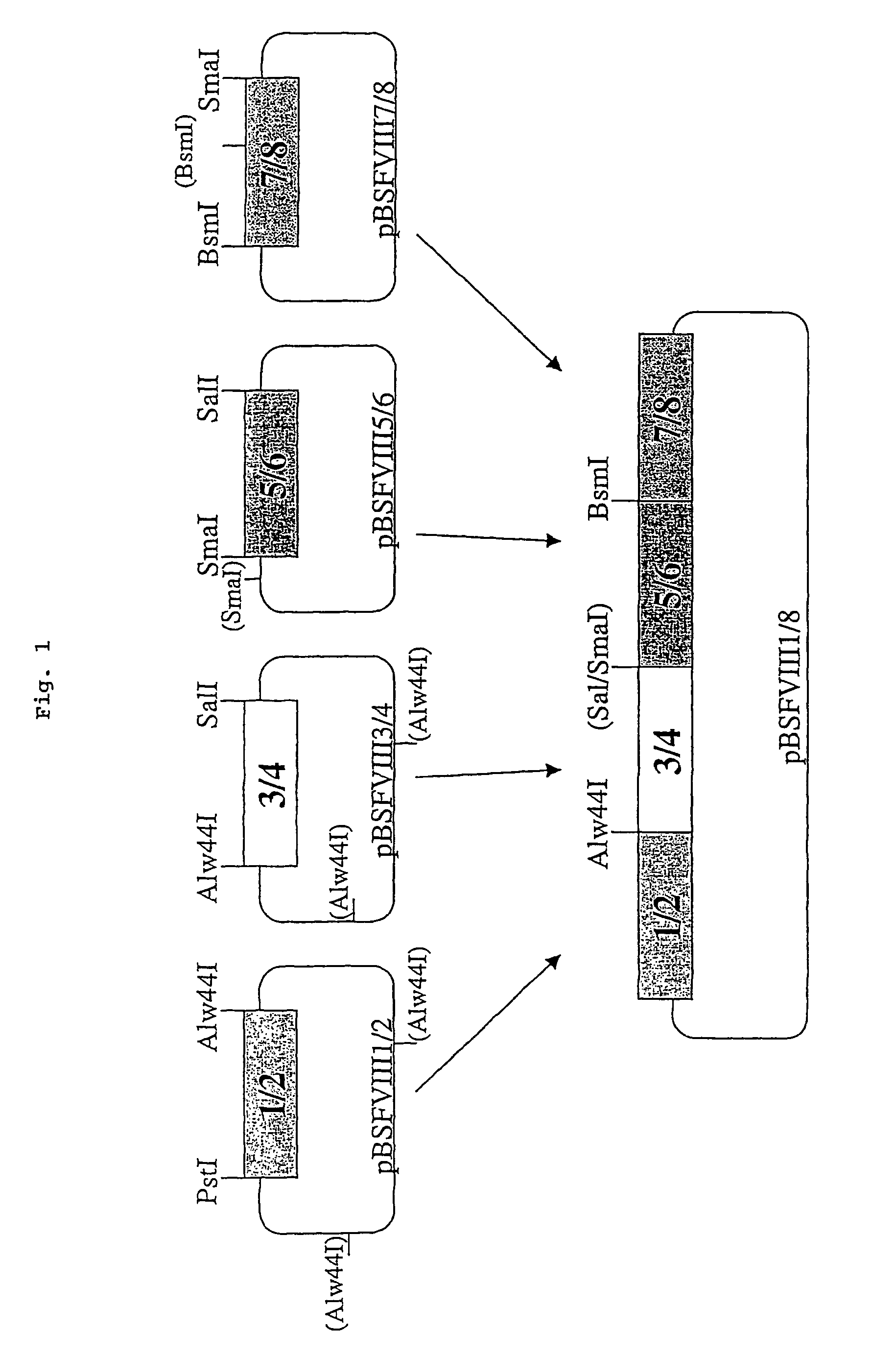
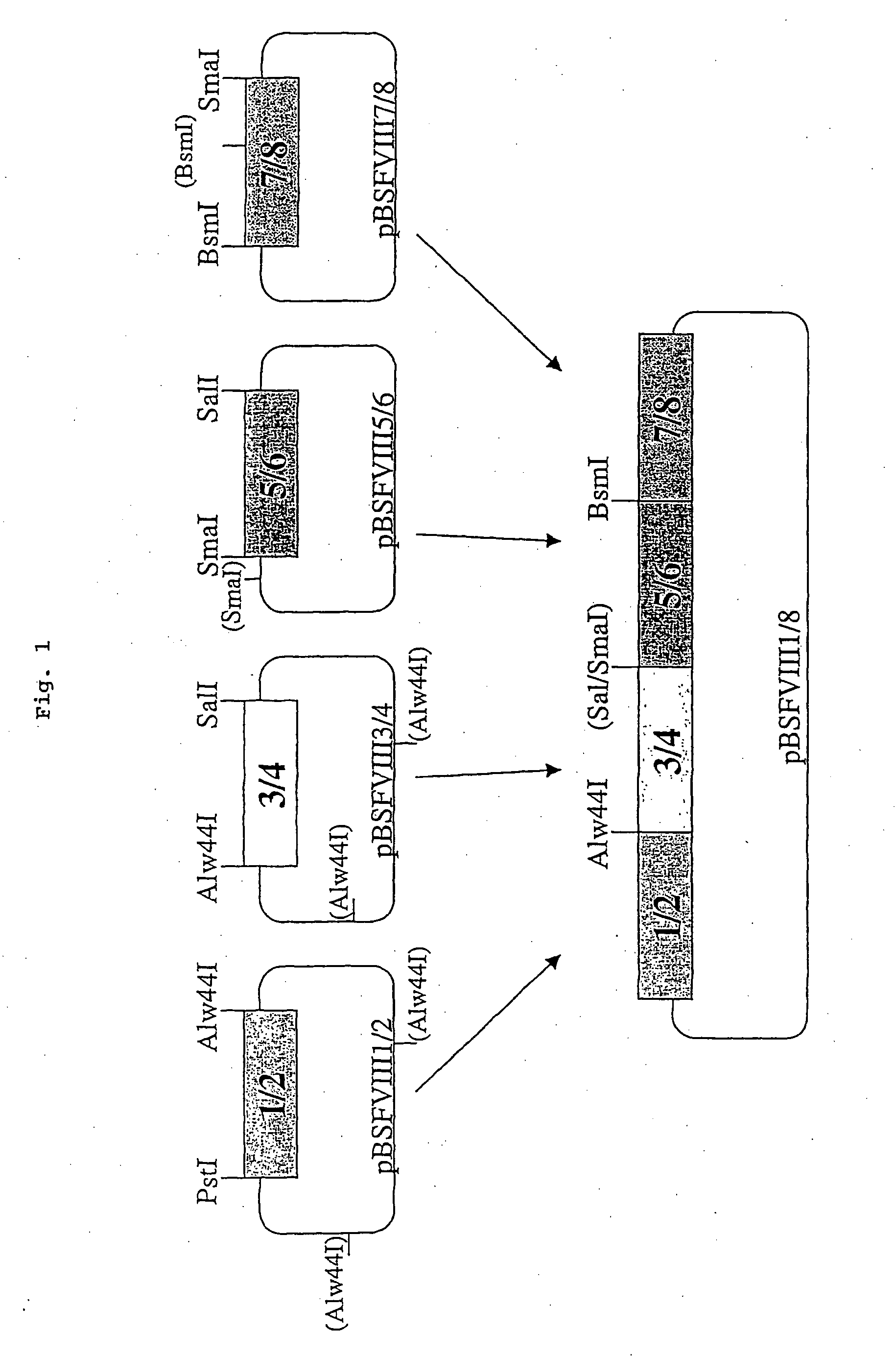
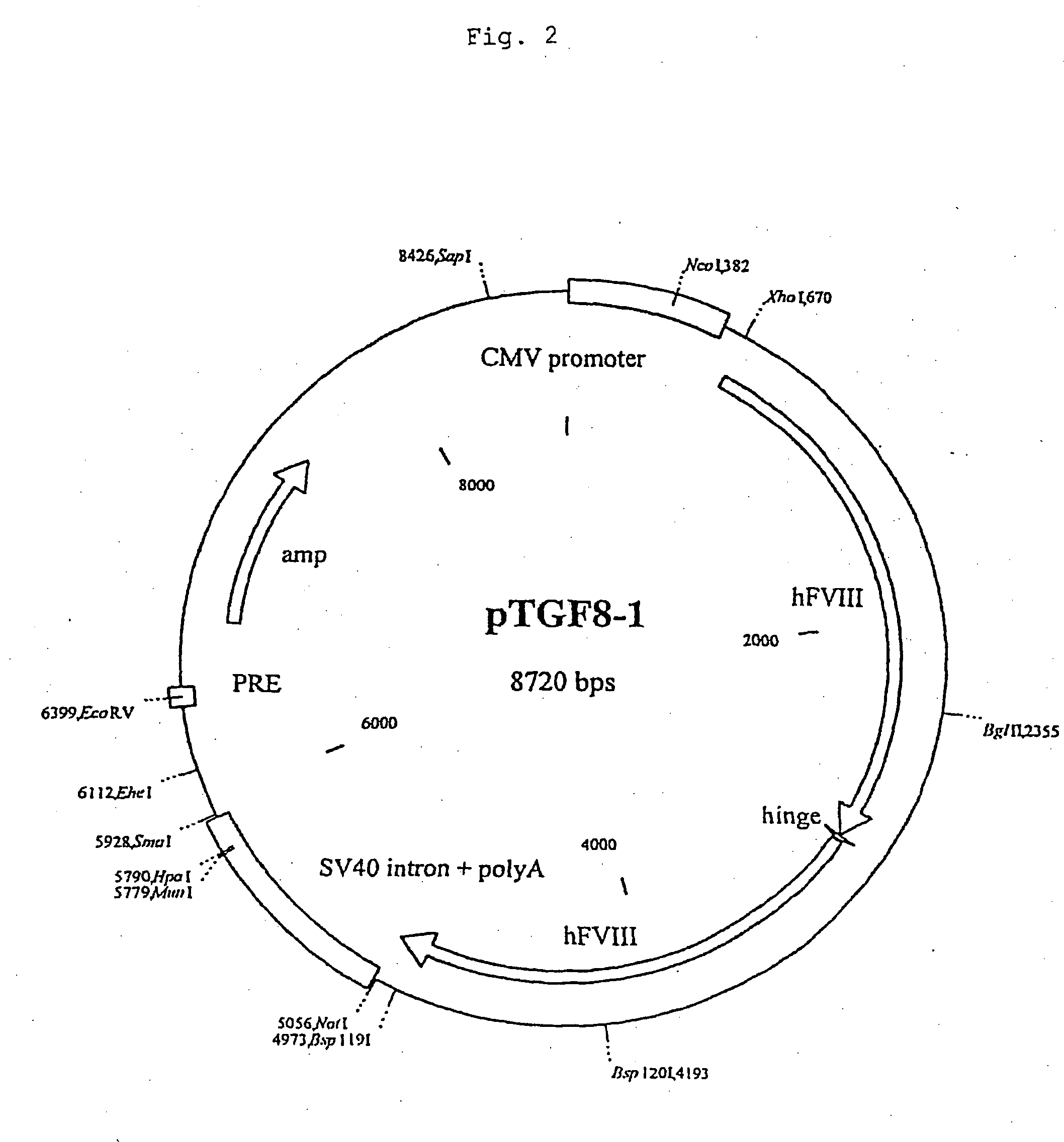
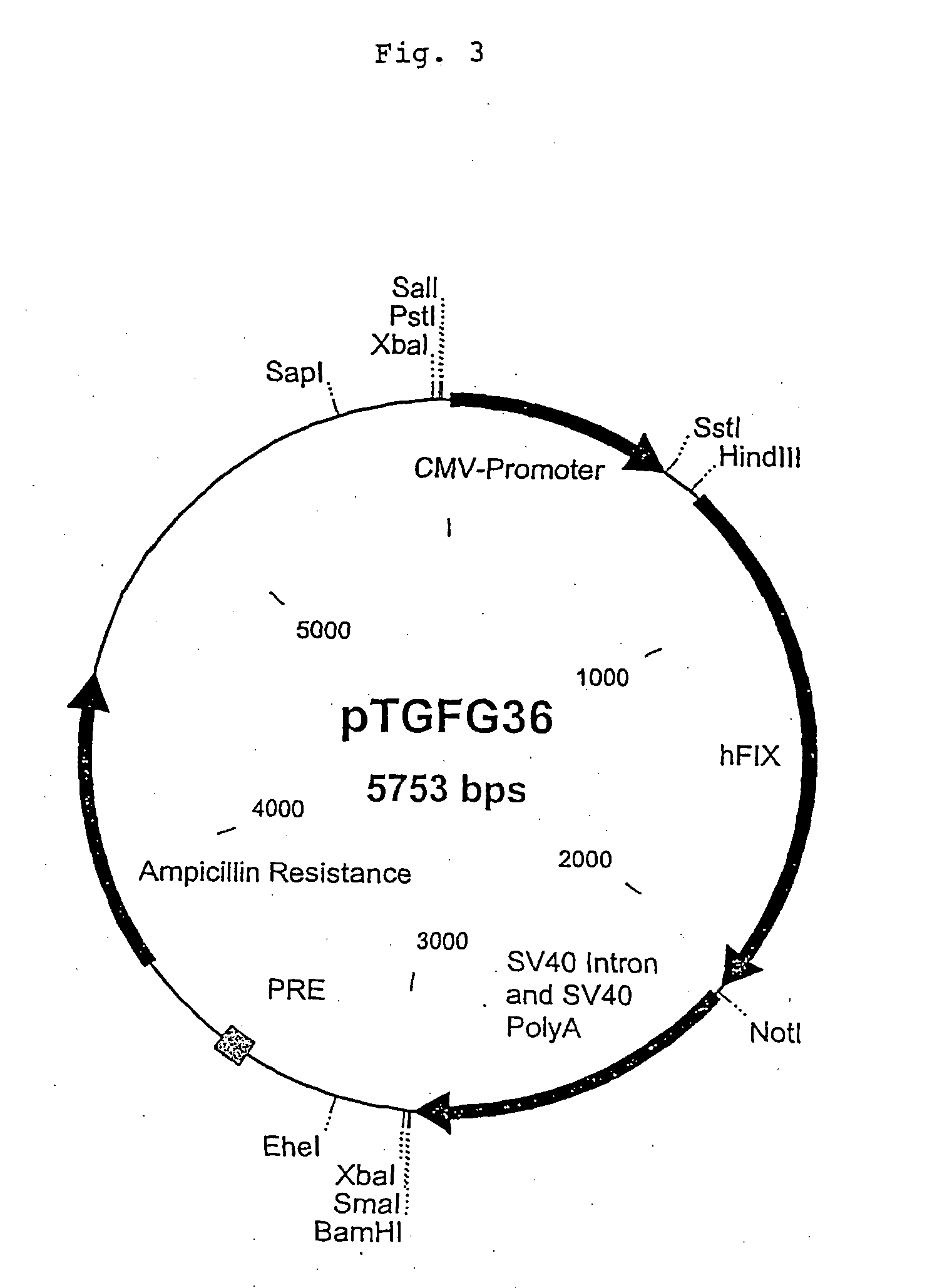
The present invention relates to an improved method for the production of recombinant human blood clotting factors, in particular of factor VIII and factor IX. An immortalized human cell line can be used to stably express viral transcription activator proteins and carrying a vector having a promoter functionally linked to a DNA sequence coding for a blood coagulating factor, provided that said promoter is not a viral promoter which is stimulated by said viral transcription activator proteins. The invention further relates to an immortalized human cell line carrying said vector, factor VIII muteins particularly suitable for the above production method; pharmaceutical compositions comprising such factor VIII muteins, and the use of such factor VIII muteins for preparing a medicament for treating hemophilia.
Owner:OCTAPHARMA +1
Cancer immunotherapy with a viral antigen-defined, immunomodulator-secreting cell vaccine
A human cell line, which lacks major histocompatibility class I (MHC-I) antigens and major histocompatibility class II (MHC-II) antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express (i) a nucleotide sequence encoding an immunomodulator and (ii) a nucleotide sequence encoding a viral antigen, and a method of inducing or stimulating an immune response in a human to a viral-associated disease or cancer comprising administering to the human (i) the aforementioned human cell line in an amount sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral associated disease or cancer, (ii) a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-11 antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an immunomodulator, and a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-II antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an antigen of EBV, simultaneously or sequentially in either order, by the same or different routes, in amounts sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral-associated disease or cancer, or (iii) an immunomodulator and a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-II antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an antigen of EBV, simultaneously or sequentially in either order, by the same or different routes, in amounts sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral associated disease or cancer.
Owner:JOHNS HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
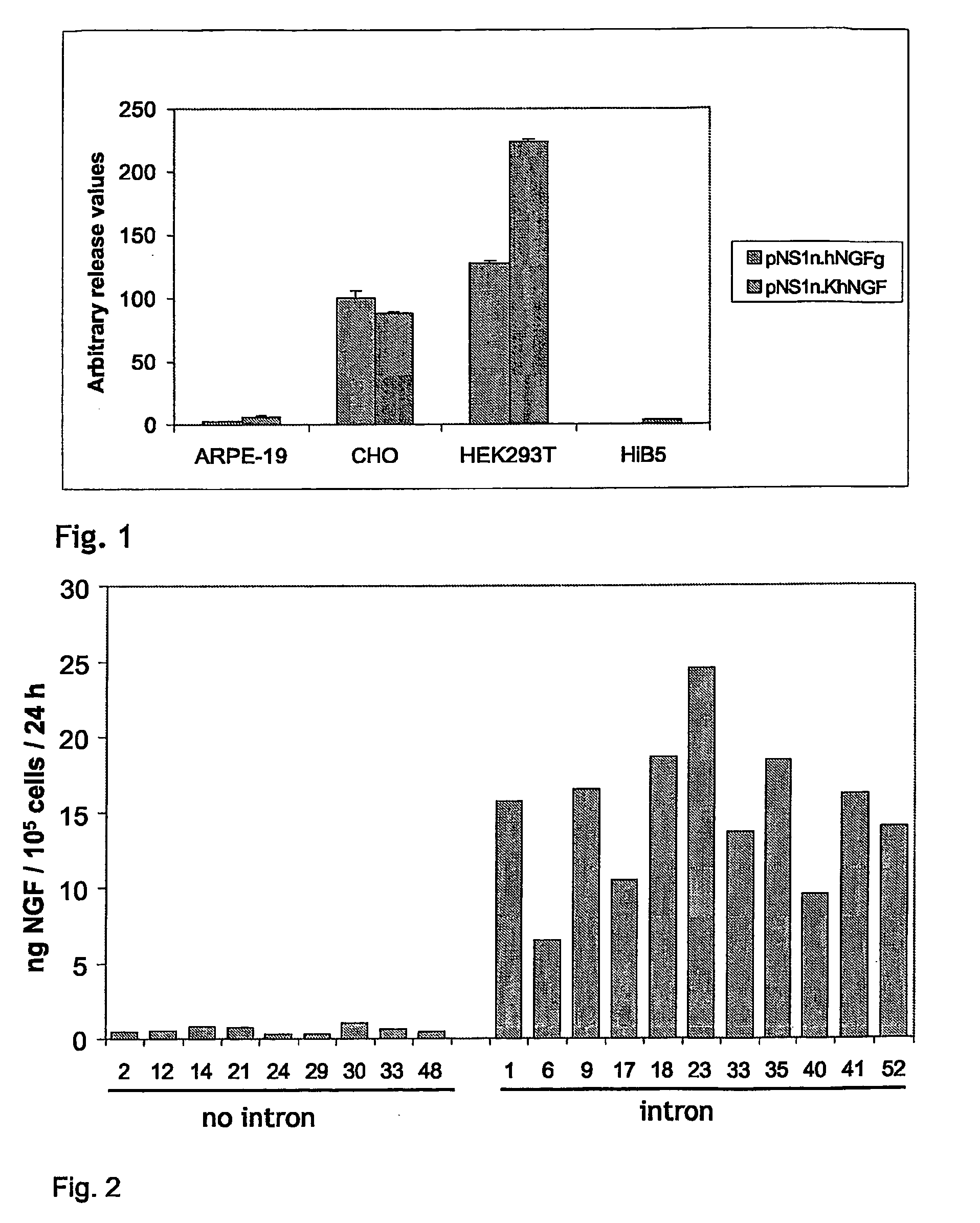
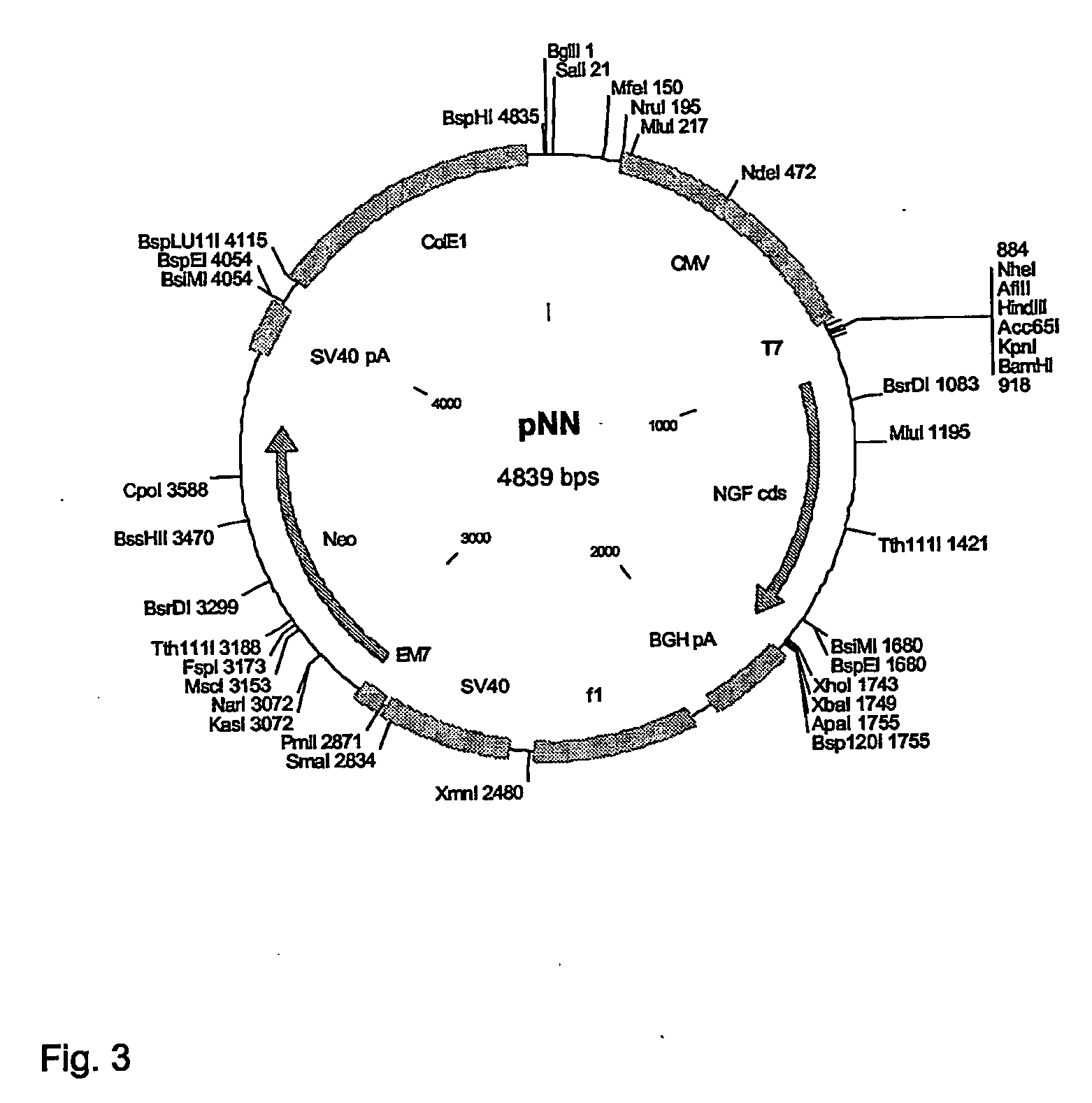
Human Therapeutic Cells Secreting Nerve Growth Factor
InactiveUS20080286323A1Safe cellularSafe capsular deliveryPowder deliveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHuman cellPeripheral neuron
The present invention relates to human cell lines genetically modified to overexpress bioactive NGF. In another aspect the present invention relates to encapsulated human cell lines genetically modified to overexpress bioactive NGF, which can be used in therapy of Alzheimer's disease, peripheral neuropathy and other neurological disorders amenable to local and prolonged NGF therapy.
Owner:NSGENE AS
Human liver cell line
In this application is described the establishment and maintanence of a normal human hepatocyte cell line able to support complete development of malaria parasite development in vitro. Advantages and uses of the cell line are also described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
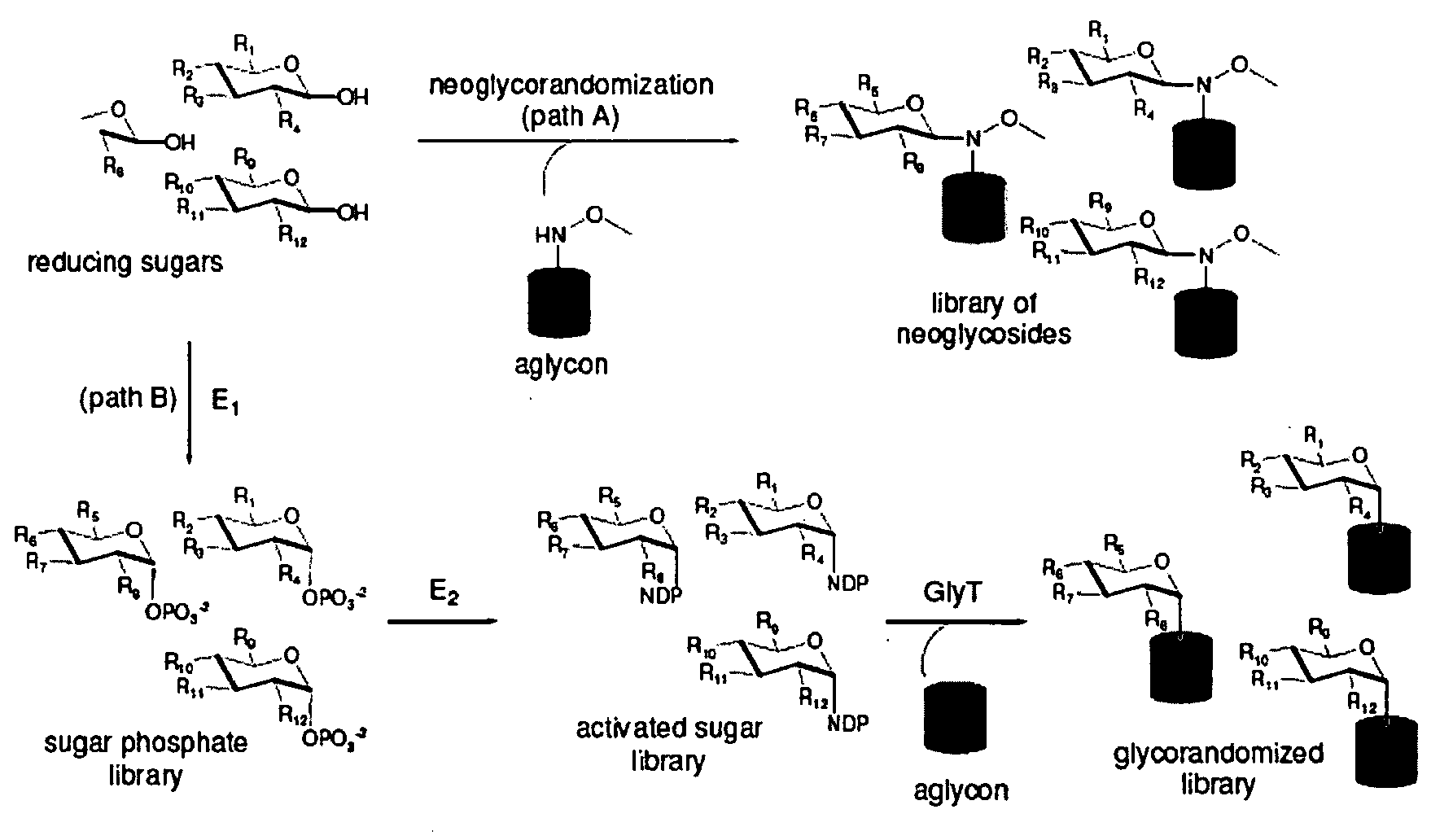
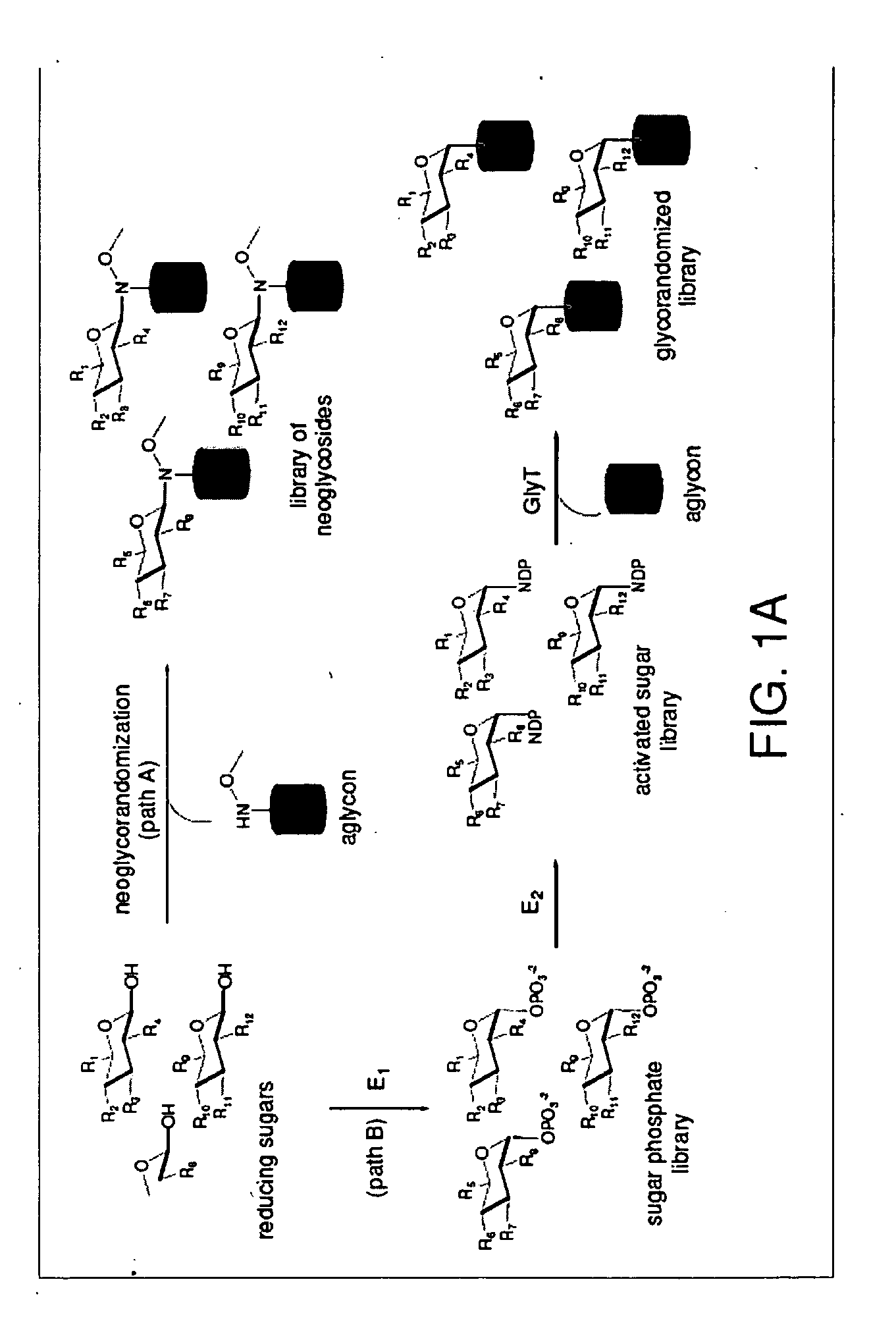
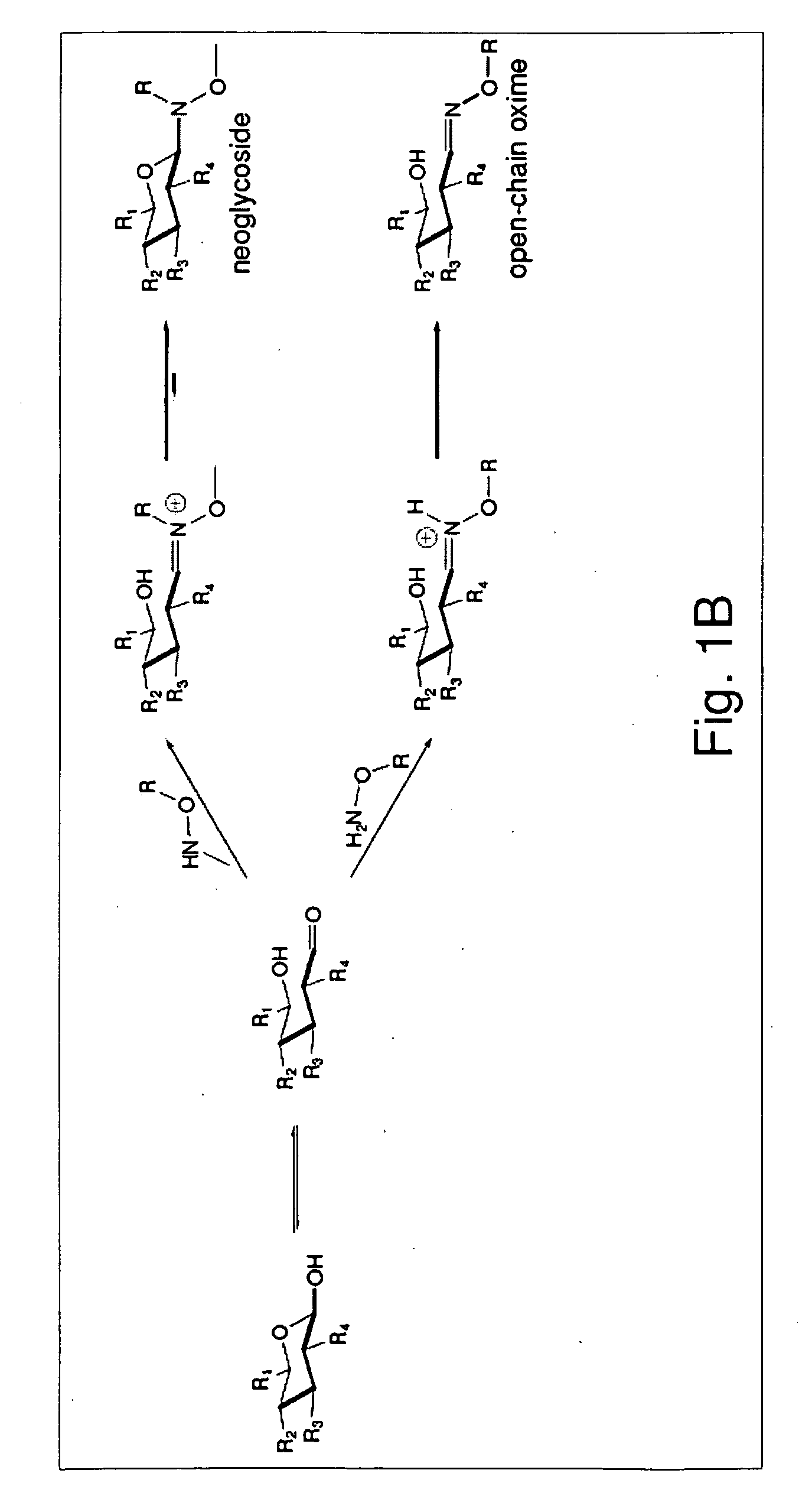
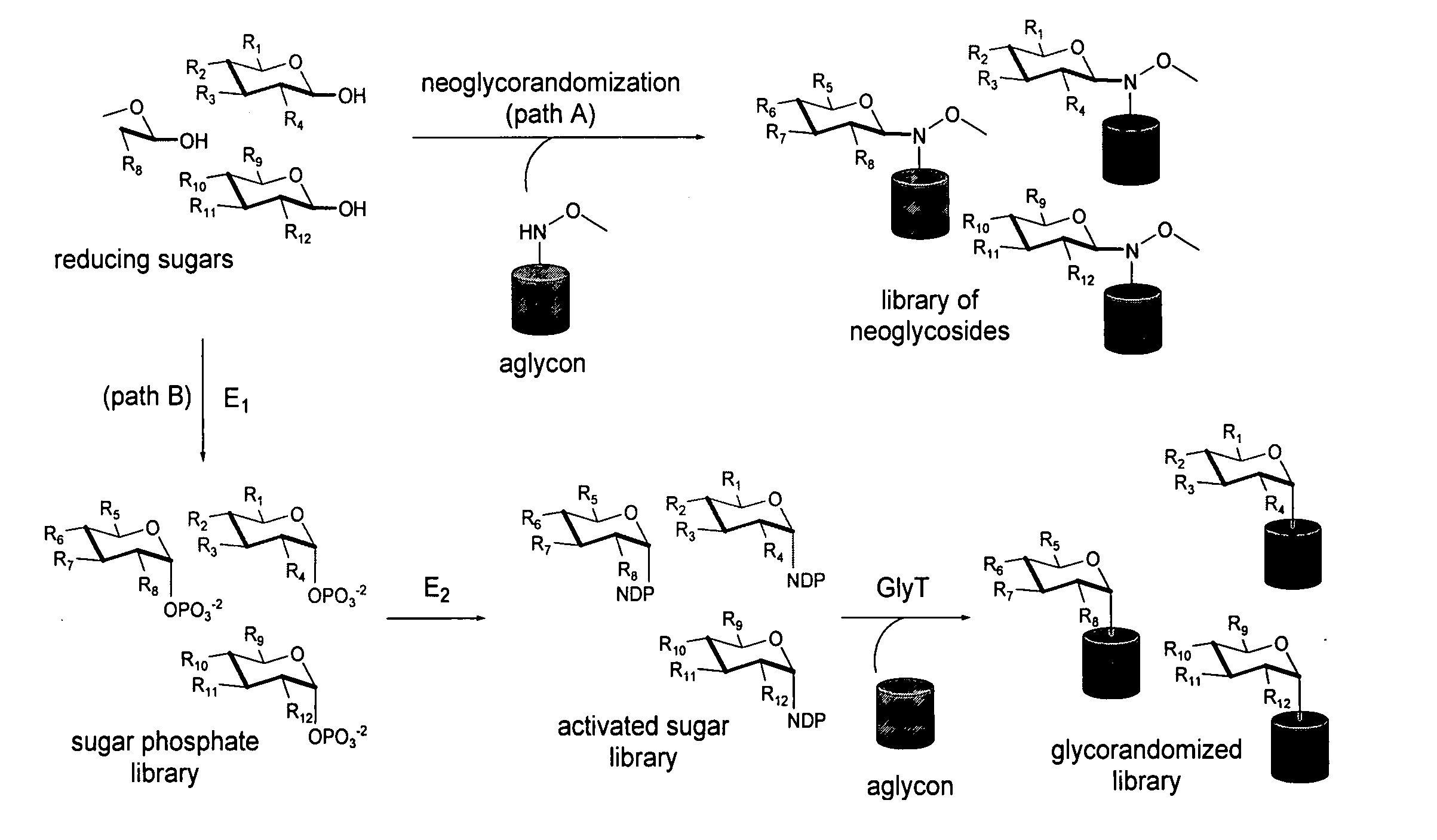
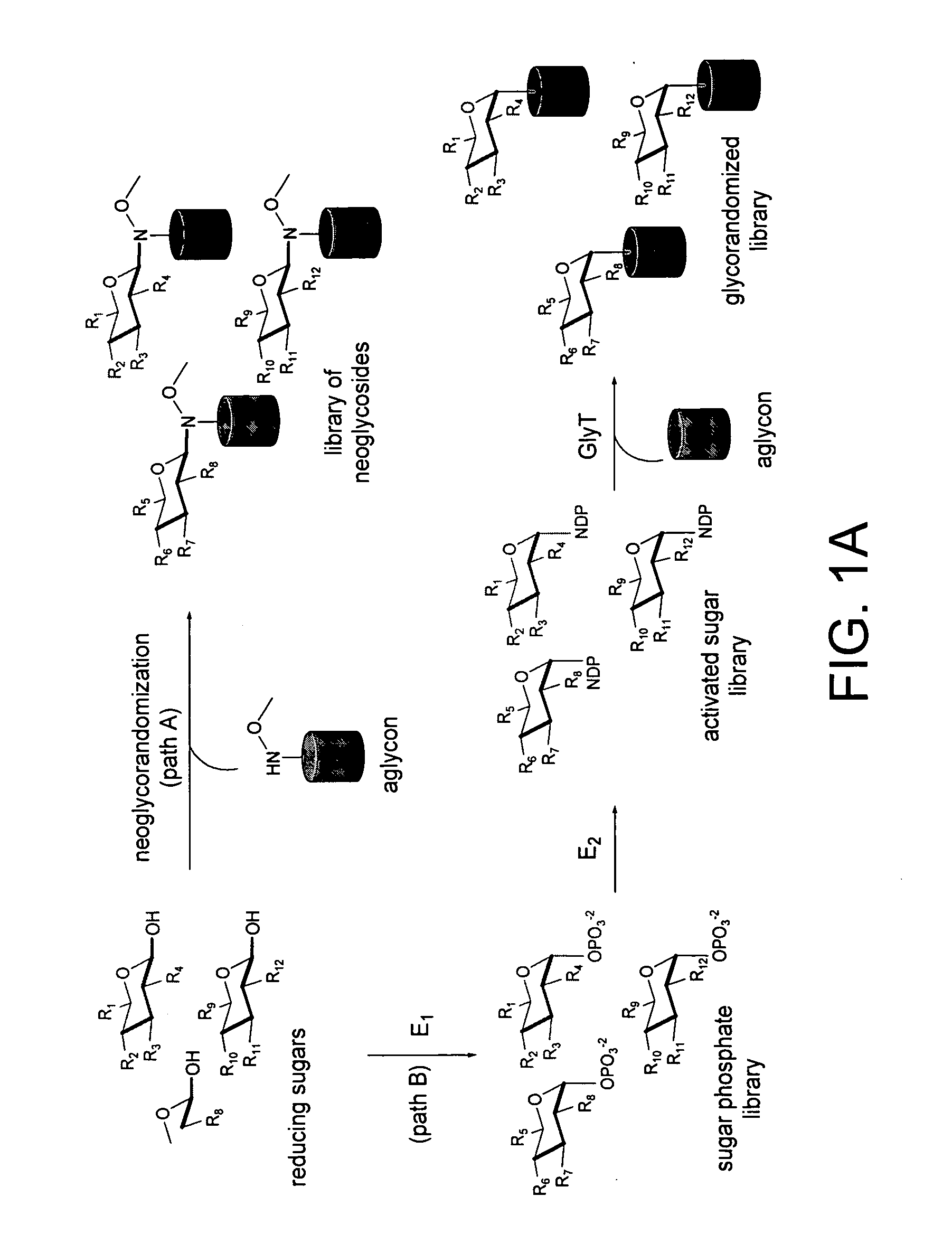
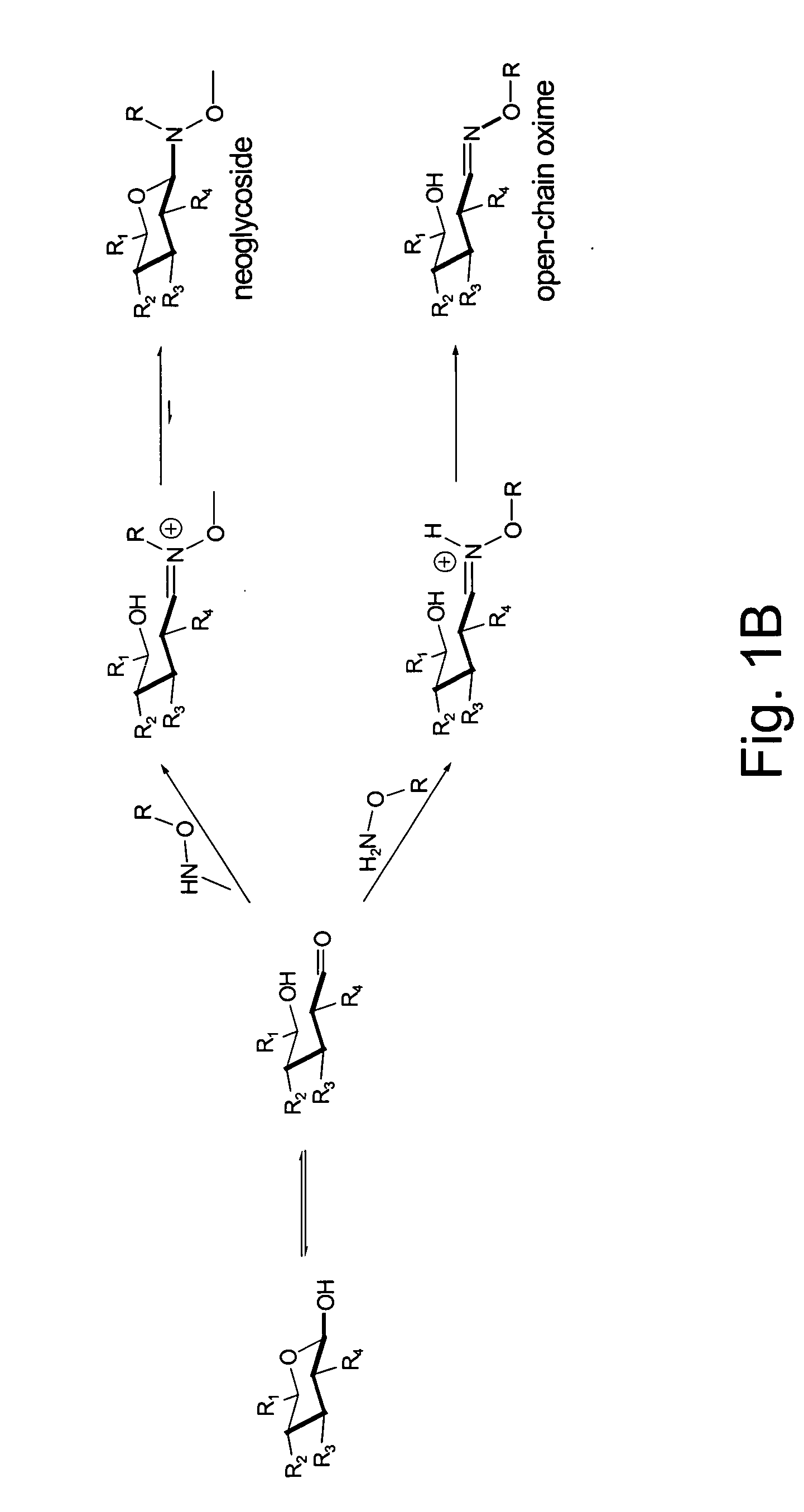
Neoglycorandomization and digitoxin analogs
ActiveUS20090075842A1Enhance desirable propertyEliminate side effectsBiocideSugar derivativesATPaseSide effect
The present invention provides methods of producing libraries of compounds with enhanced desirable properties and diminished side effects as well as the compounds produced by the methods. In preferred embodiments, methods of the present invention use a universal chemical glycosylation method that employs reducing sugars and requires no protection or activation. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a library of neoglycoside digitoxin analogs that includes compounds with significantly enhanced cytotoxic potency toward human cancer cells and tumor-specificity, but are less potent Na+ / K+-ATPase inhibitors in a human cell line than digitoxin.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Osf2/Cbfa1 nucleic acids and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS6518063B1Improving immunogenicityIncrease stability and selectivityOrganic active ingredientsNanotechHeterologousNucleotide
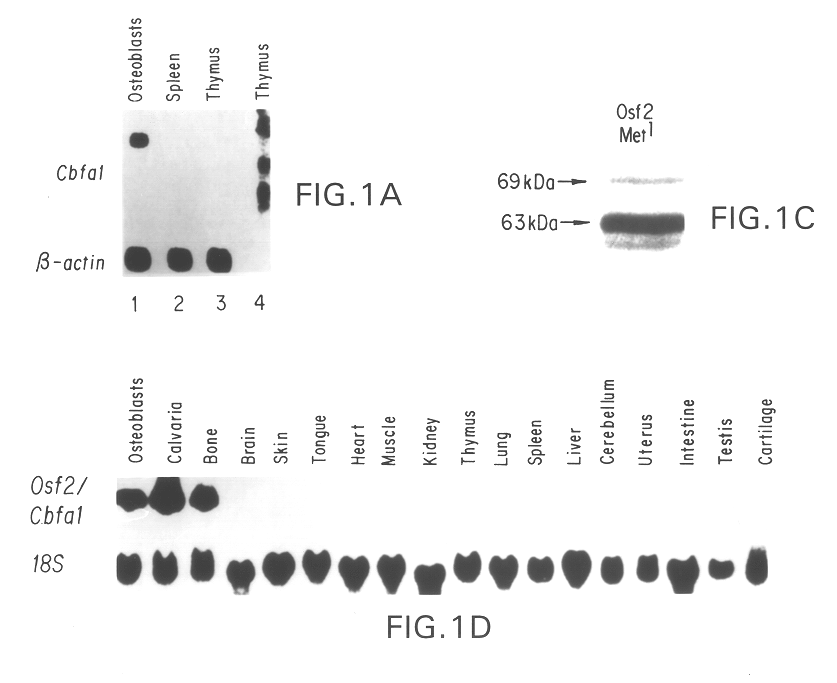
Disclosed are methods and compositions comprising a novel osteoblast-specific transcription factor designated Osf2 / Cbfa1. Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding this polypeptide derived from human cell lines, and the use of these polynucleotides in a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Methods, compositions, kits, and devices are also provided for identifying compounds which are inhibitors of osteoblast differentiation, and identifying Osf2 / Cbfa1 polynucleotides and polypeptides in a sample. Also disclosed are nucleic acid compositions comprising an Osf2 promoter, and the use of the promoter in heterologous and homologous gene transcription and protein production.
Owner:TEXAS SYST UNIV OF BOARD OF REGENTS THE
Method and cell composition for screening compounds for anti-inflammatory activity
InactiveUS20050208474A1Lower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug screeningDna encodingCytokine
A method and cell line for screening test compounds for antiinflammatory activity are disclosed. The cell line is a human cell line capable of producing a selected cytokine associated with an inflammatory response in humans, and transfected with (i) a vector containing DNA encoding a cytokine regulatory factor under the control of a first promoter, and (ii) a vector containing DNA encoding a detectable-marker protein, under the control of a second promoter which is responsive to cytokine induction. In the screening method, the cells are cultured under conditions of cytokine regulatory factor overexpression and cytokine induction. Addition of test compound that results in a diminution of the detectable-marker protein is evidence of anti-inflammatory activity.
Owner:GENETROL BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Somatic human cell line mutations
ActiveUS20170009256A1Even mixtureDifferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAGenomic mutationDna breakage
The invention provides for a method of producing a mutant somatic human cell line of cells comprising a genomic mutation of interest (MOI) at a predefined genomic site of interest (GOI) in close proximity to a genomic target site, which comprises: a) providing a guide RNA (gRNA) comprising a tracrRNA in conjunction with crRNA including an oligonucleotide sequence that hybridizes with the target site; b) providing an RNA-guided endonuclease which catalyzes the DNA break at the target site upon hybridizing with the gRNA; c) introducing the gRNA into the cells in the presence of the endonuclease to obtain a repertoire of cells comprising a variety of genomic mutations at the target site; d) selecting a cell from said repertoire which comprises a MOI; wherein the cell is haploid for the genomic locus of the target site; and e) expanding the cell to obtain the mutant cell line. The invention further provides for a mutant human somatic cell line obtainable by such method; and libraries of mutant human somatic cell lines of isogenic cells with a variety of genomic mutations at different predefined genomic target sites.
Owner:HORIZON DISCOVERY
Screening method of safety and efficacy of skin antioxidants through use of a plurality of normal human skin cells
InactiveCN103320490AStrong ability to divide and proliferateHigh degree of standardizationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntioxidantUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a screening method of safety and efficacy of skin antioxidants through use of a plurality of normal human skin cells. The screening method includes the following steps: (1) separation, culture and identification of normal human primary cells; (2) toxicity test of substances for testing; (3) preparation of the substances for testing and concentration determination of the substances for testing; (4) determination of ultraviolet-light induced radiation dose; and (5) verification of antioxidant effects of the substances for testing. The normal human skin cells are prepared through standardized culture in vitro, so that the normal human skin cells has strong division propagation capability, high degree of standardization, less difference among batches, and the same activity and functions as that in vivo. Results which are obtained through use of the normal healthy human skin cells are more reliable than the results obtained through use of animal or human cell lines. Through use of the screening method, toxic effects and antioxidant efficacy of the substances for testing can be evaluated in two aspects including a qualitative aspect and a quantitative aspect. The method, through replacement of the living animal and human skin, can be directly used for toxicity and efficacy tests of antioxidant substances in products including chemicals, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and the like.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUADAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Recombinant protein production in a human cell
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Neoglycorandomization and digitoxin analogs
The present invention provides methods of producing libraries of compounds with enhanced desirable properties and diminished side effects as well as the compounds produced by the methods. In preferred embodiments, methods of the present invention use a universal chemical glycosylation method that employs reducing sugars and requires no protection or activation. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a library of neoglycoside digitoxin analogs that includes compounds with significantly enhanced cytotoxic potency toward human cancer cells and tumor-specificity, but are less potent Na+ / K+-ATPase inhibitors in a human cell line than digitoxin.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
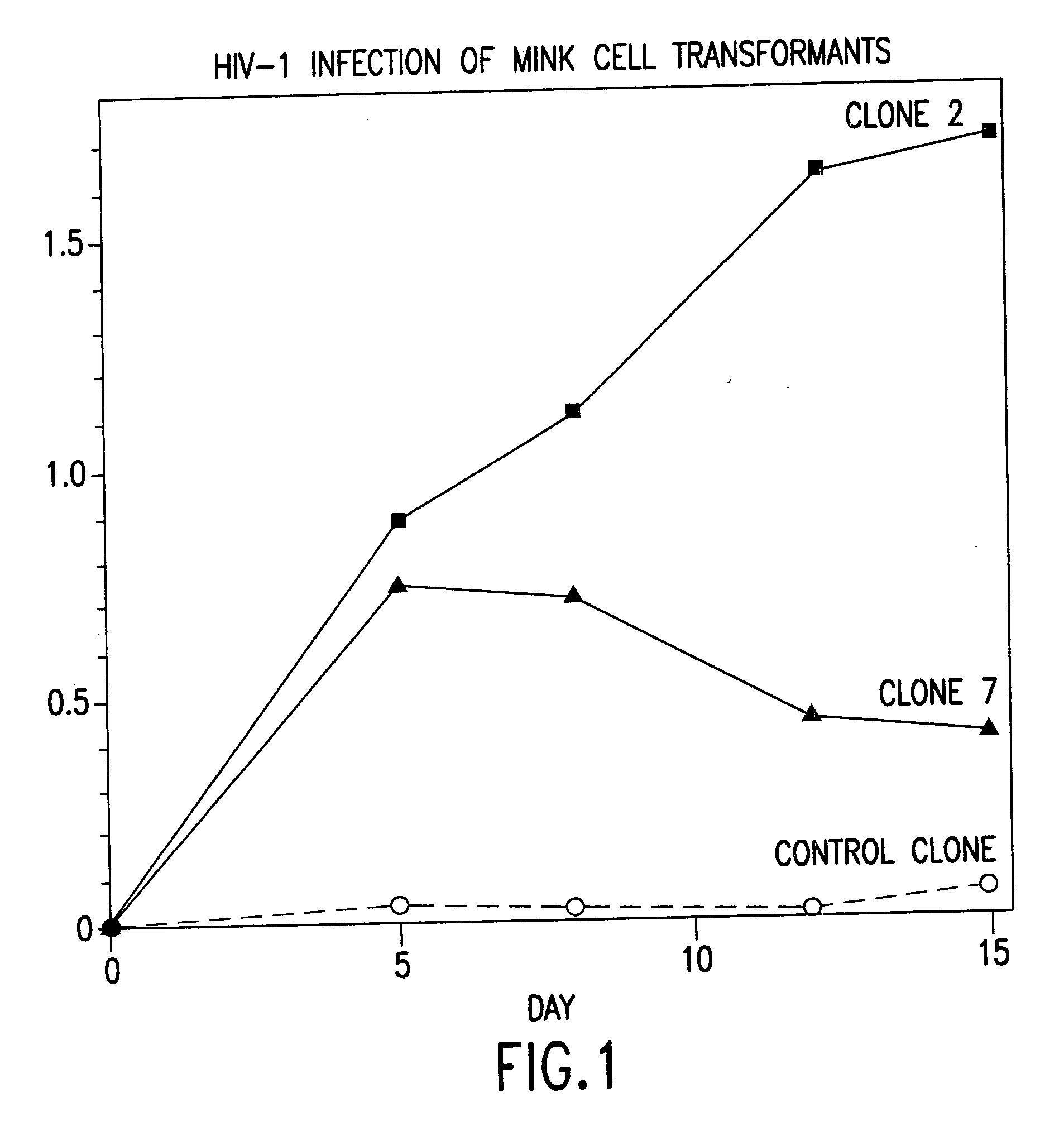
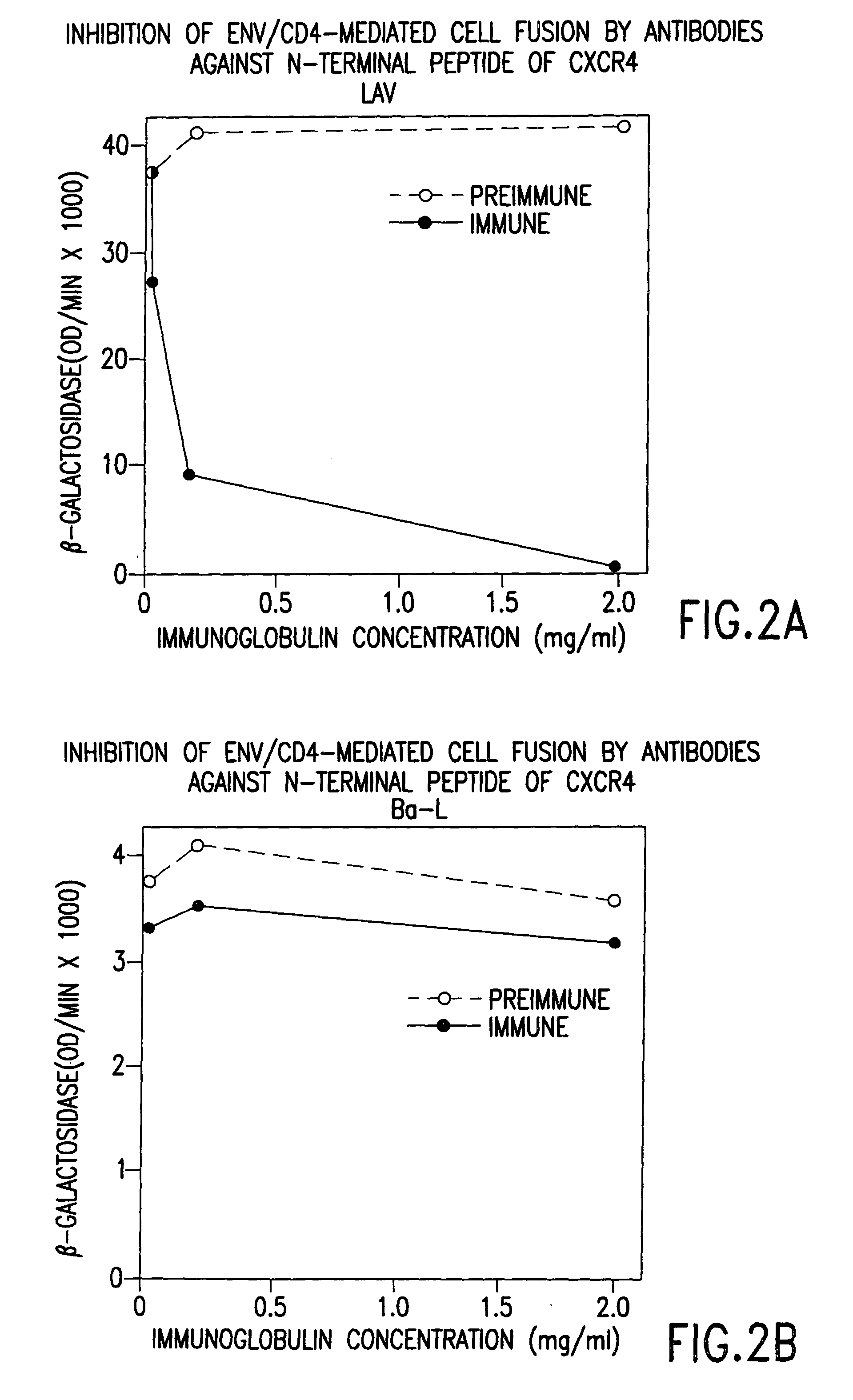
Cells expressing both human CD4 and a human fusion accessory factor associated with HIV infection
The susceptibility to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection depends on the cell surface expression of the human CD4 molecule and a human fusion accessory factor associated with HIV infection (CXCR4). CXCR4 is a member of the 7-transmembrane segment superfamily of G-protein-coupled cell surface molecules. CXCR4 plays an essential role in the membrane fusion step of HIV infection. The establishment of stable, nonhuman cell lines and transgenic mammals having cells that coexpress human CD4 and CXCR4 provides valuable tools for the continuing research of HIV infection and the development of more effective anti-HIV therapeutics. In addition, antibodies against CXCR4, isolated and purified peptide fragments of CXCR4, and CXCR4-binding biologic agents, capable of blocking membrane fusion between HIV and target cells represent potential anti-HIV therapeutics.
Owner:BERGER EDWARD +3
Production of recombinant blood clotting factors in human cell lines
ActiveUS20040023333A1Increased activationStable against proteolytic inactivationFactor VIIFungiHuman cellA-DNA
The present invention relates to an improved method for the production of recombinant human blood clotting factors, in particular of factor VIII and factor IX, utilizing an immortalized human cell line stably expressing viral transcription activator proteins and carrying a vector having a promoter functionally linked to a DNA sequence coding for a blood coagulating factor, provided that said promoter is not a viral promoter which is stimulated by said viral transcription activator proteins; an immortalized human cell line carrying said vector, factor VIII muteins particularly suitable for the above production method; pharmaceutical compositions comprising such factor VIII muteins and the use of such factor VIII muteins for preparing a medicament for treating hemophilia.
Owner:OCTAPHARMA +1
Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Expressing human Antisense Gene Cyp2j2 and Its Preparation Methods
ActiveUS20080131403A1Inhibit migrationPromote apoptosisBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHuman tumorLymphatic Spread
A recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing antisense human CYP2J2 gene and preparation method thereof are provided, the recombinant adeno-associated virus is prepared through cloning human CYP2J2 cDNA (1509 bp, which encode the protein containing 503 amino acids) from human leucocyte DNA by PCR, cotransfecting three plasmids by the calcium phosphate precipitation technique to pack and prepare the recombinant adeno-associated virus containing the antisense target gene, and purifying. The recombinant adeno-associated virus obtained from the above method can be transfected into different kinds of human tumor cell lines, inhibiting the proliferation and migration of tumor cells, promoting the apoptosis of tumor cells and suppressing the growth and metastases of tumor. Therefore, it can prove that the selective inhibitor of CYP2J2 and the recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing antisense human CYP2J2 gene are the potential medicine for treating tumor.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Modified vaccinia ankara virus variant and cultivation method
InactiveUS20080317778A1Reduce riskBiocideGenetic material ingredientsSerum free mediaModified vaccinia Ankara
The present invention provides an attenuated virus, which is derived from Modified Vaccinia Ankara virus and characterized by the loss of its capability to reproductively replicate in human cell lines. It further describes recombinant viruses derived from this virus and the use of the virus, or its recombinants, as a medicament or vaccine. A method is provided for inducing an immune response in individuals who may be immune-compromised, receiving antiviral therapy, or have a pre-existing immunity to the vaccine virus. In addition, a method is provided for the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of the virus, or its recombinants, in a vaccinia virus prime / vaccinia virus boost inoculation regimen. The present invention relates to a method of virus amplification in primary cells which are cultivated in a serum free medium. Viruses produced by this method are advantageously free of any infectious agents comprised in animal sera.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
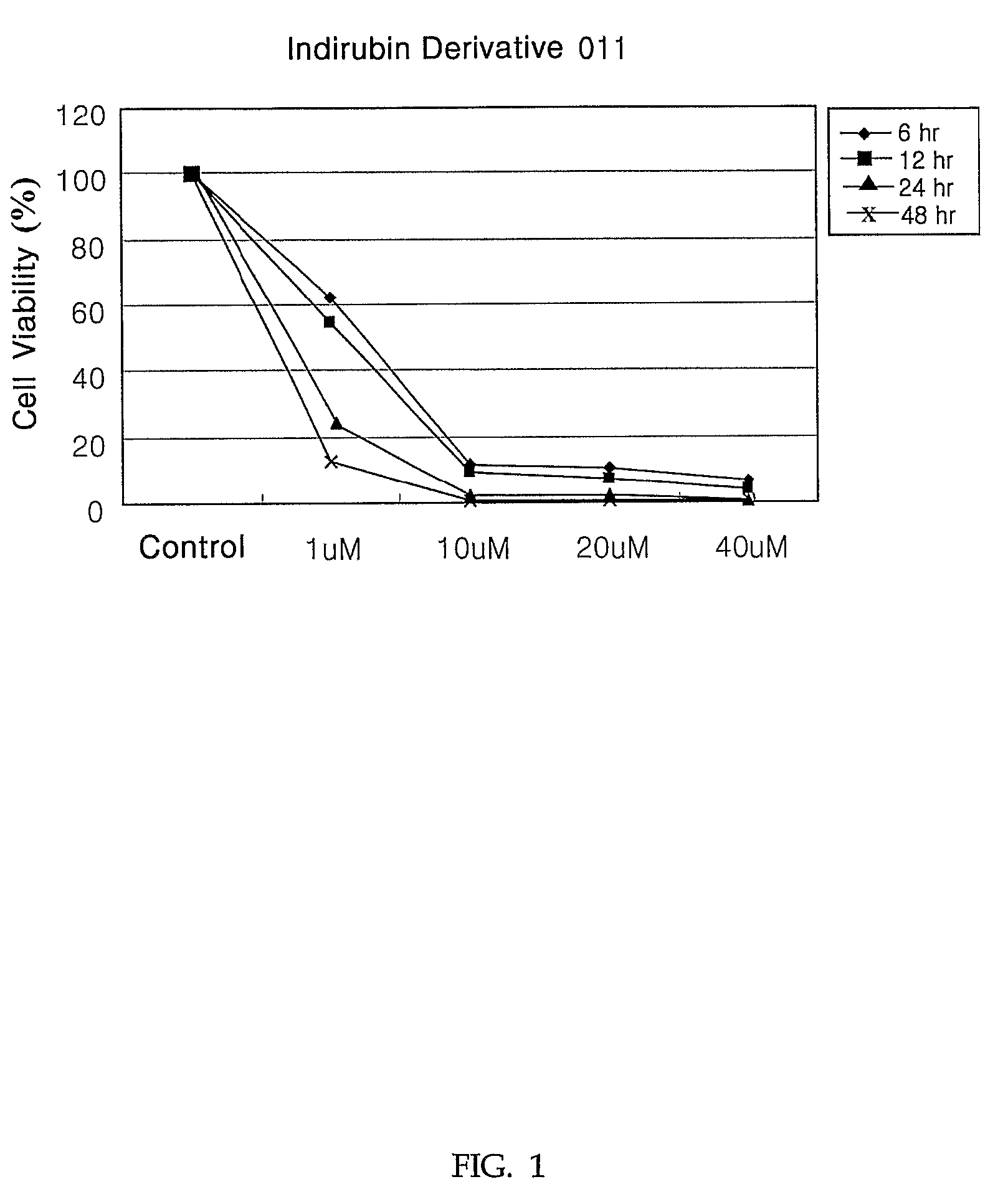
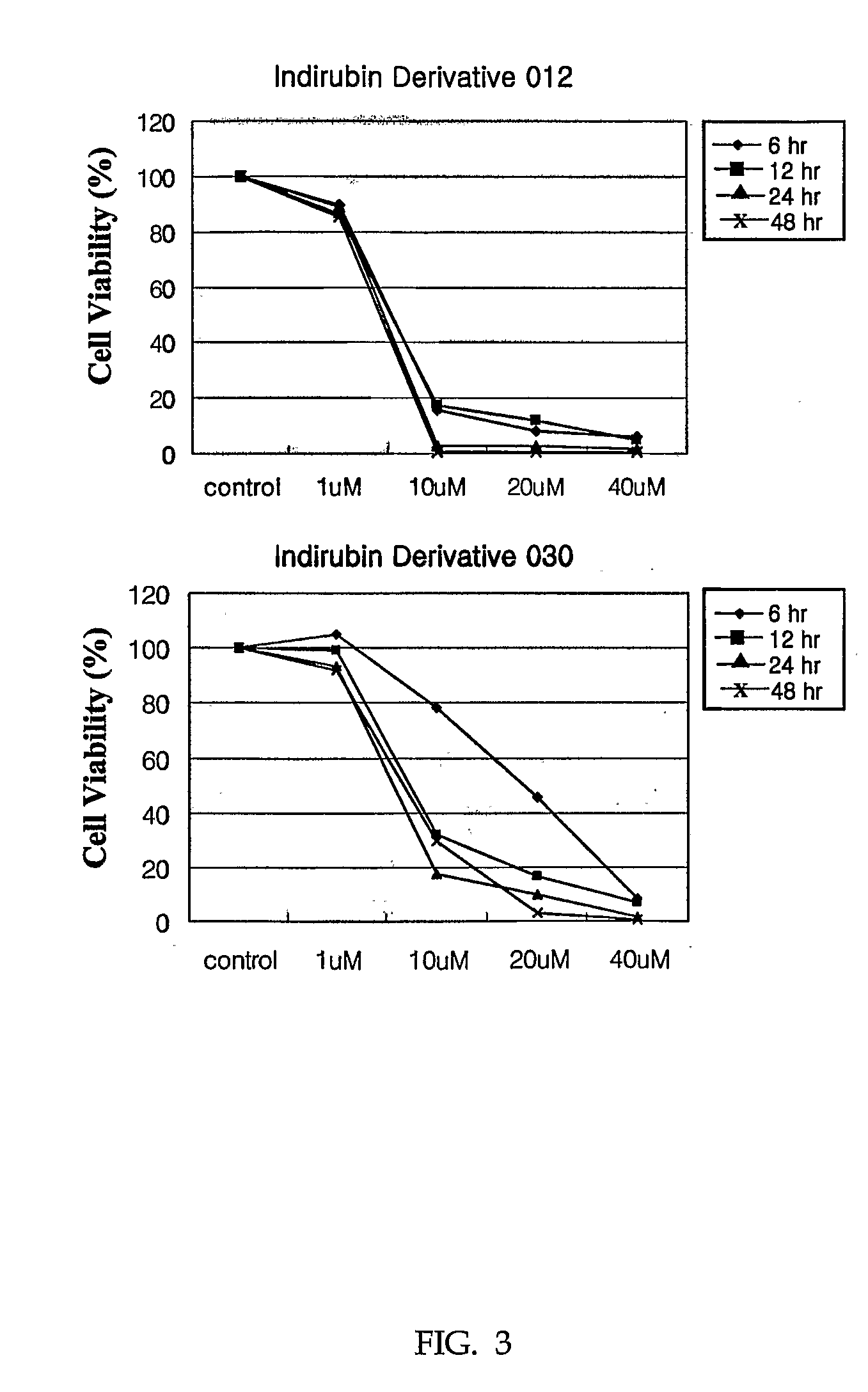
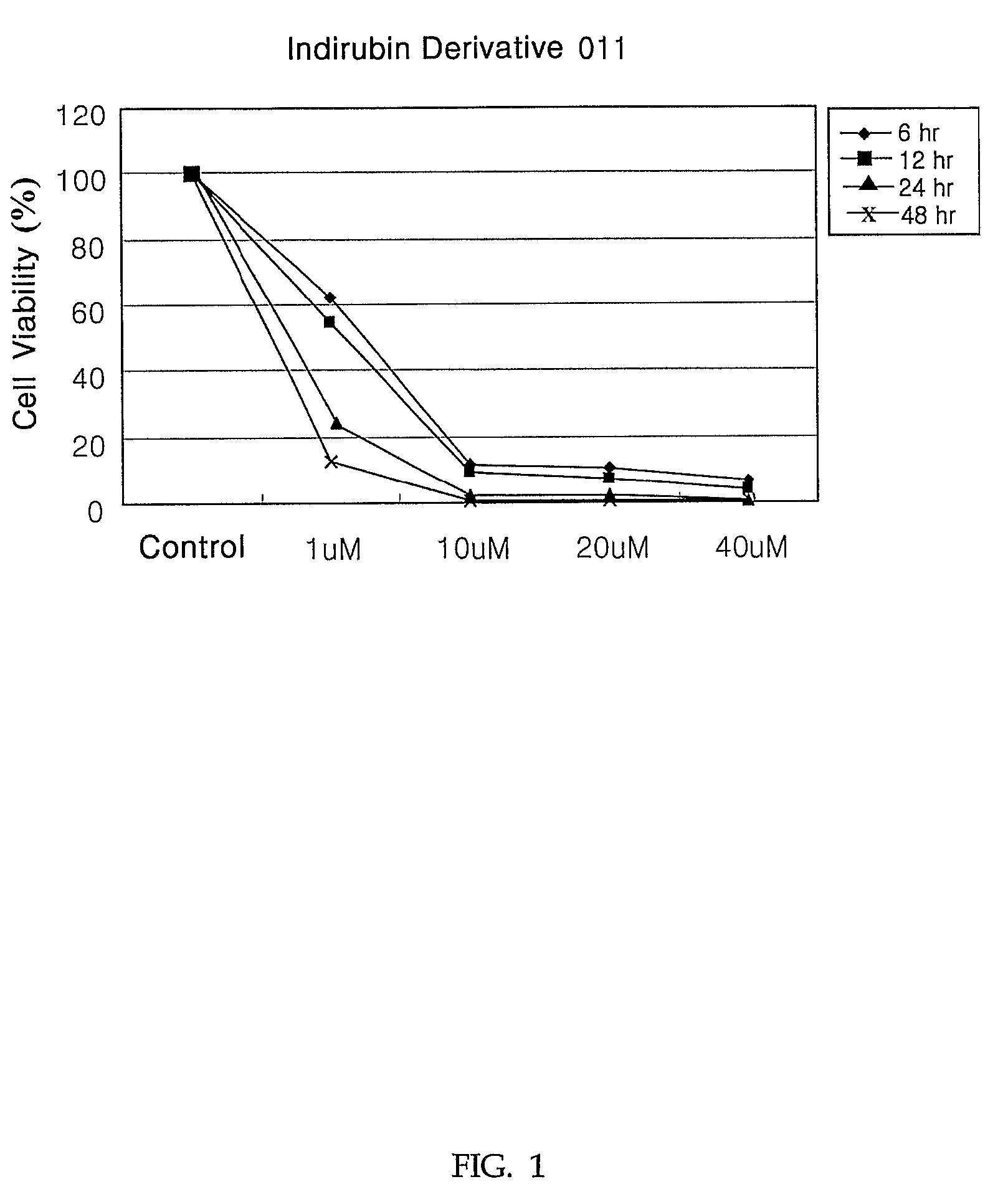
Indirubin derivatives having anticancer property against human cancer cell line
The present invention relates to an indirubin derivative having anticancer property by inhibiting cell proliferation as to human cancer cell line. More particularly, this invention provides the synthesis of indirubin derivative known as CDK(Cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor. Further, inhibition activity of proliferation as to human cancer cell line and apoptosis against induced-differentiation of said indirubin derivative are researched to develop a novel indirubin derivative having efficacious anticancer properties as to various human cell lines.
Owner:ANYGEN
Somatic haploid human cell line
ActiveUS20170002380A1Speed up the conversion processEven mixtureMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAGenomic mutationChromosomal region
The invention provides for a somatic fully haploid, karyotypically stable human cell line, e.g. obtainable by targeted deletion of one or more disomic chromosomal regions of a somatic near-haploid human parental cell, a method of producing the same, as well as the use of the cell line for producing isogenic cell variants, comprising genomic mutations at different genomic target sites, and a library of such cell variants.
Owner:HORIZON DISCOVERY
Composition to detoxify formaldehyde in gaseous state, in aqueous solutions, and to protect human cell lines against formaldehyde
A chemical compound is disclosed herein for performing a complex enzymatic neutralization and fixation of formaldehyde, providing a method for instantaneous neutralization of formaldehyde vapors and offering a complete and rapid control of incidental releases, and a complete protection of workers against airborne formaldehyde during the course of their work. The compound includes alkanolamine, for instantaneous reaction with formaldehyde, and for absorbing hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide from the air, and a human protein, which reacts with airborne formaldehyde and forms the major enzyme involved in formaldehyde oxidation in oral mucosa. The compound also contains cyclodextrins for inclusion complexation of all the components of spent and / or unused aqueous formaldehyde solutions.
Owner:FARKAS GABRIEL J
Reprogramming normal and cancerous human cell lines into human induced poluripotent stem cells by co-electroporation with living xenopus laevis frog oocytes
InactiveUS20110143415A1Rapid reprogrammingCell differentiationArtificial cell constructsColony morphologyGene delivery
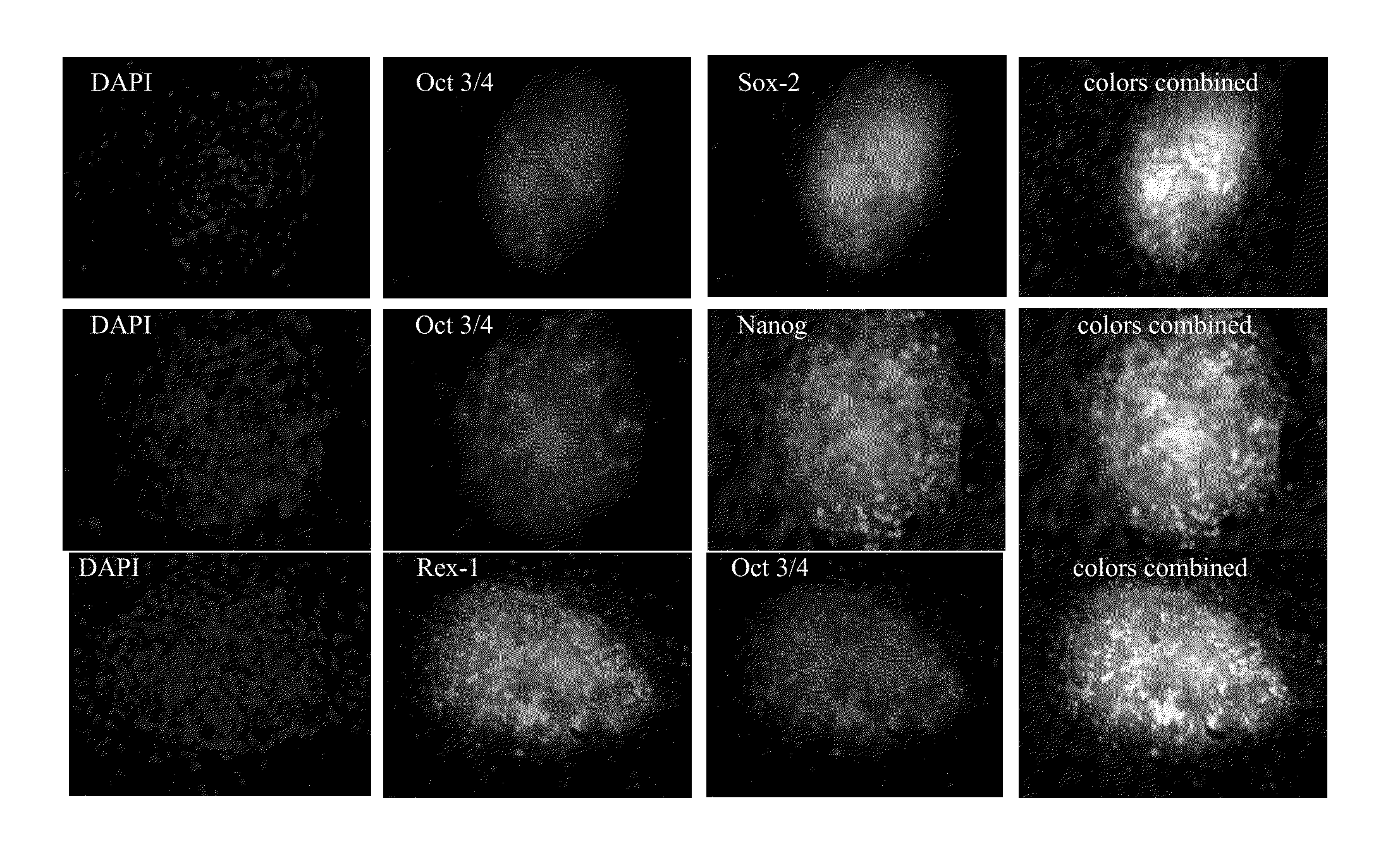
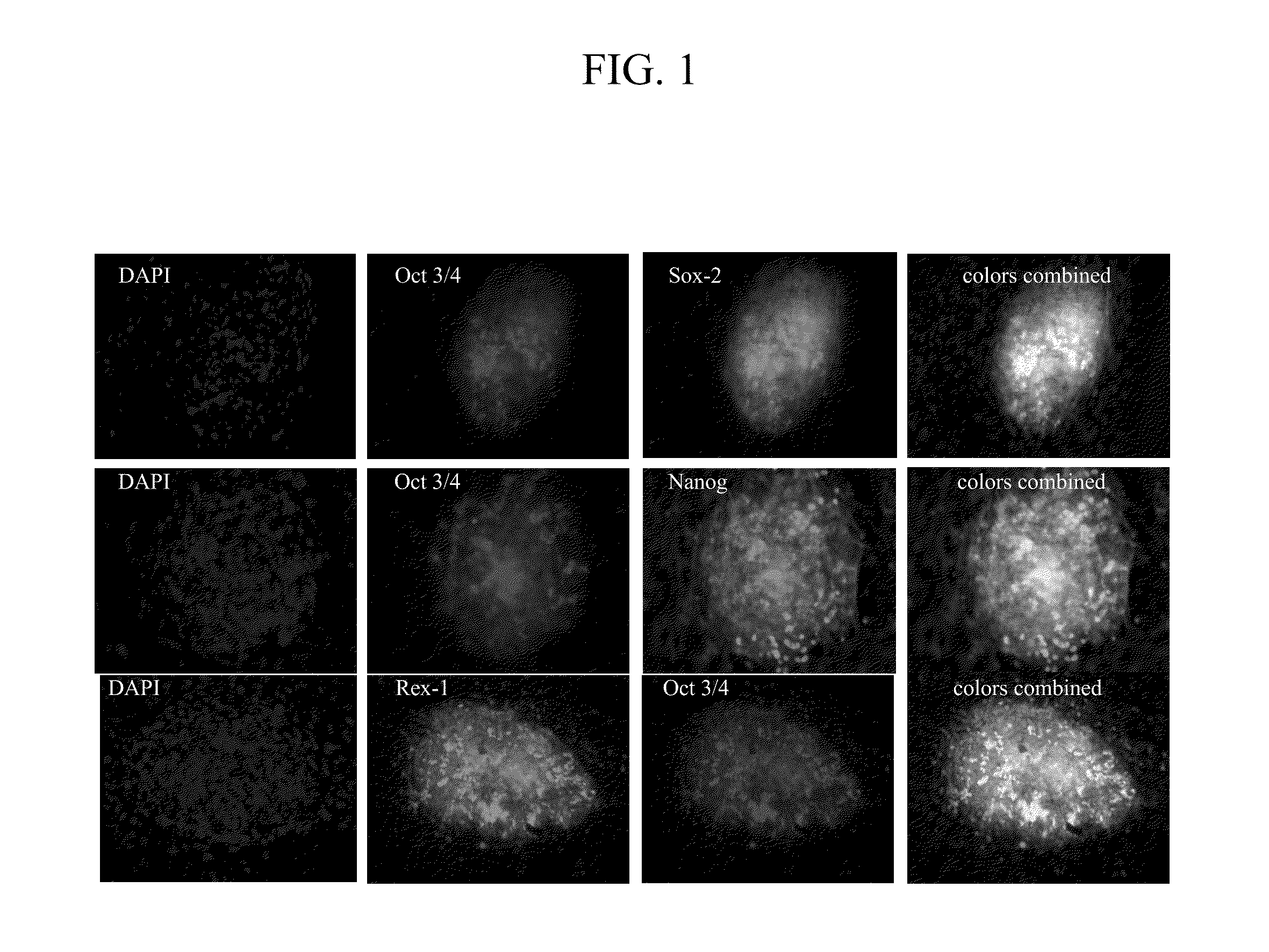
Using electroporation, it is possible to activate the natural reprogramming potential of living Xenopus laevis oocytes and pass it on to donor cells placed with eggs in one electroporation chamber. We demonstrated that co-electroporation at 150 v / cm / 25 μF of mature oocytes with ˜105 cells / ml of suspension of various normal and cancerous human cell lines, such as bone marrow stromal cells, foreskin fibroblasts, pre-adipocytes, CD4+ T-lymphocytes, cheek cells, cervical carcinoma (HeLa) cells and breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) cells, reprograms donor cells into iPSc-like cells, which form colonies on irradiated MEF feeders. The iPSc-like cells generated by this study resemble human embryonic stem cells in colony morphology and expression of stem cell-associated transcription factors, including Oct3 / 4, Nanog, SOX-2, Rex-1, TRA-1-60 and SSEA-1. New method obviates the use of retroviral or lentiviral gene delivery vectors and other “non-parental” reprogramming approaches.
Owner:PAYLIAN SERGEI
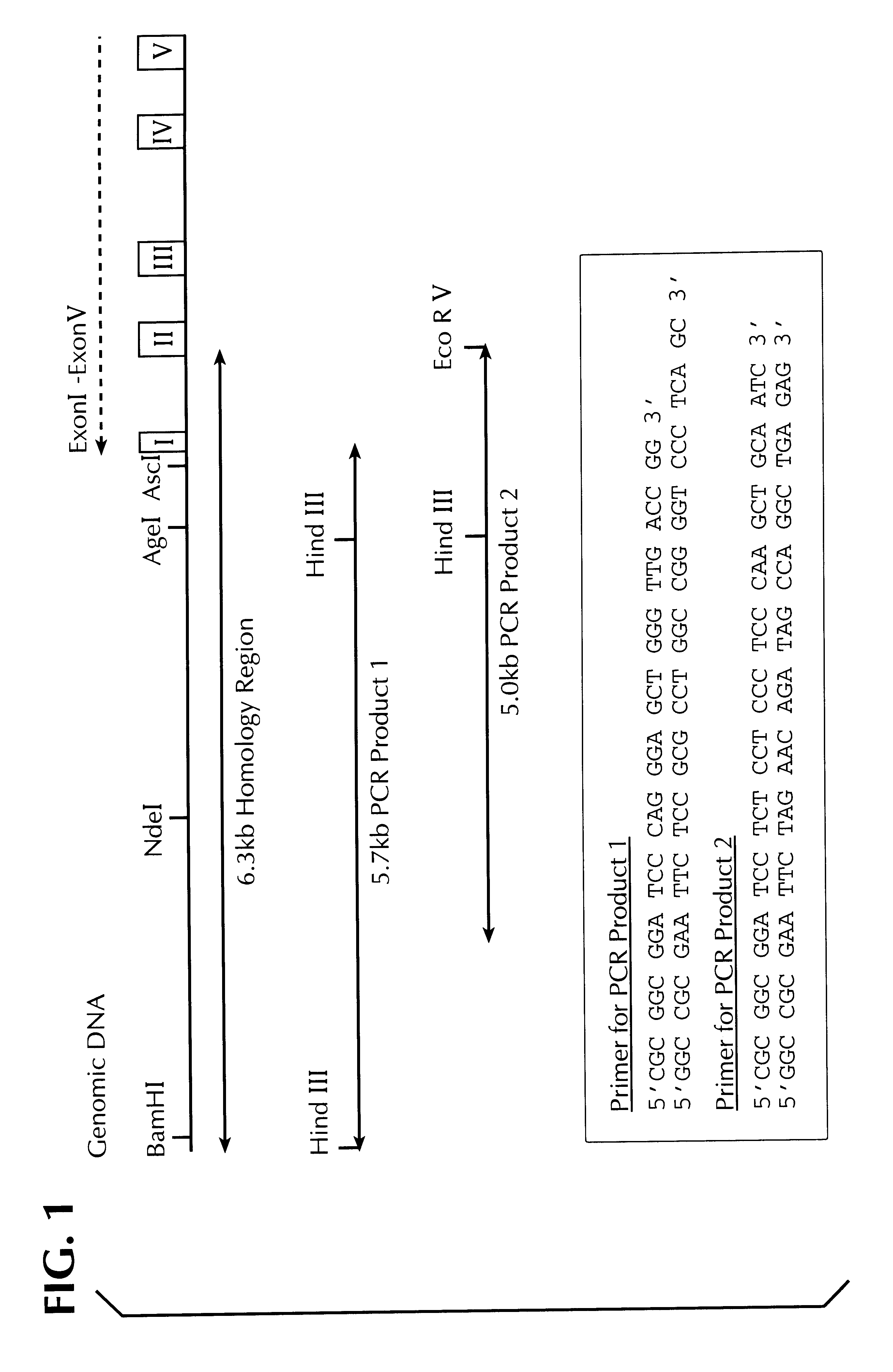
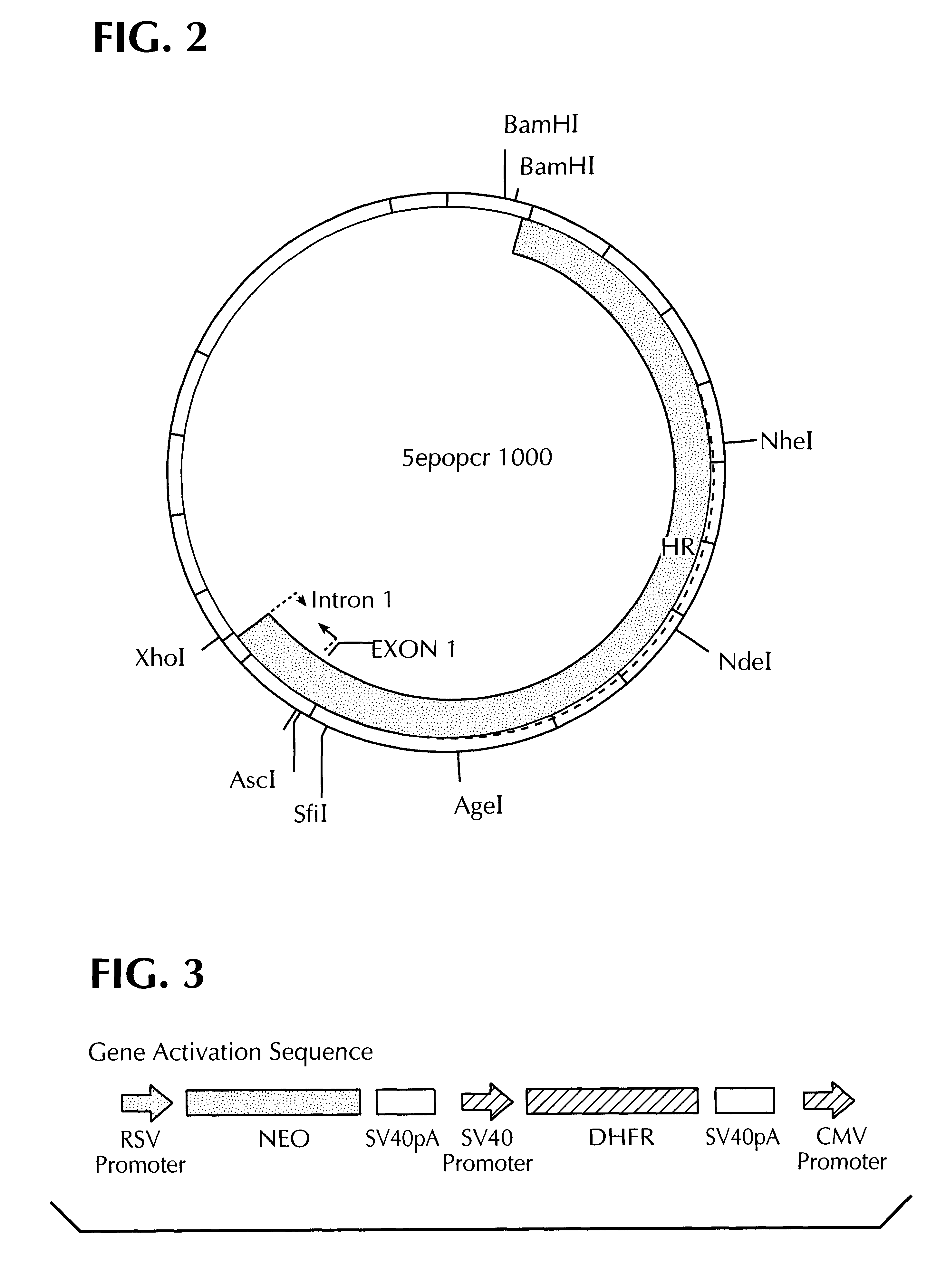
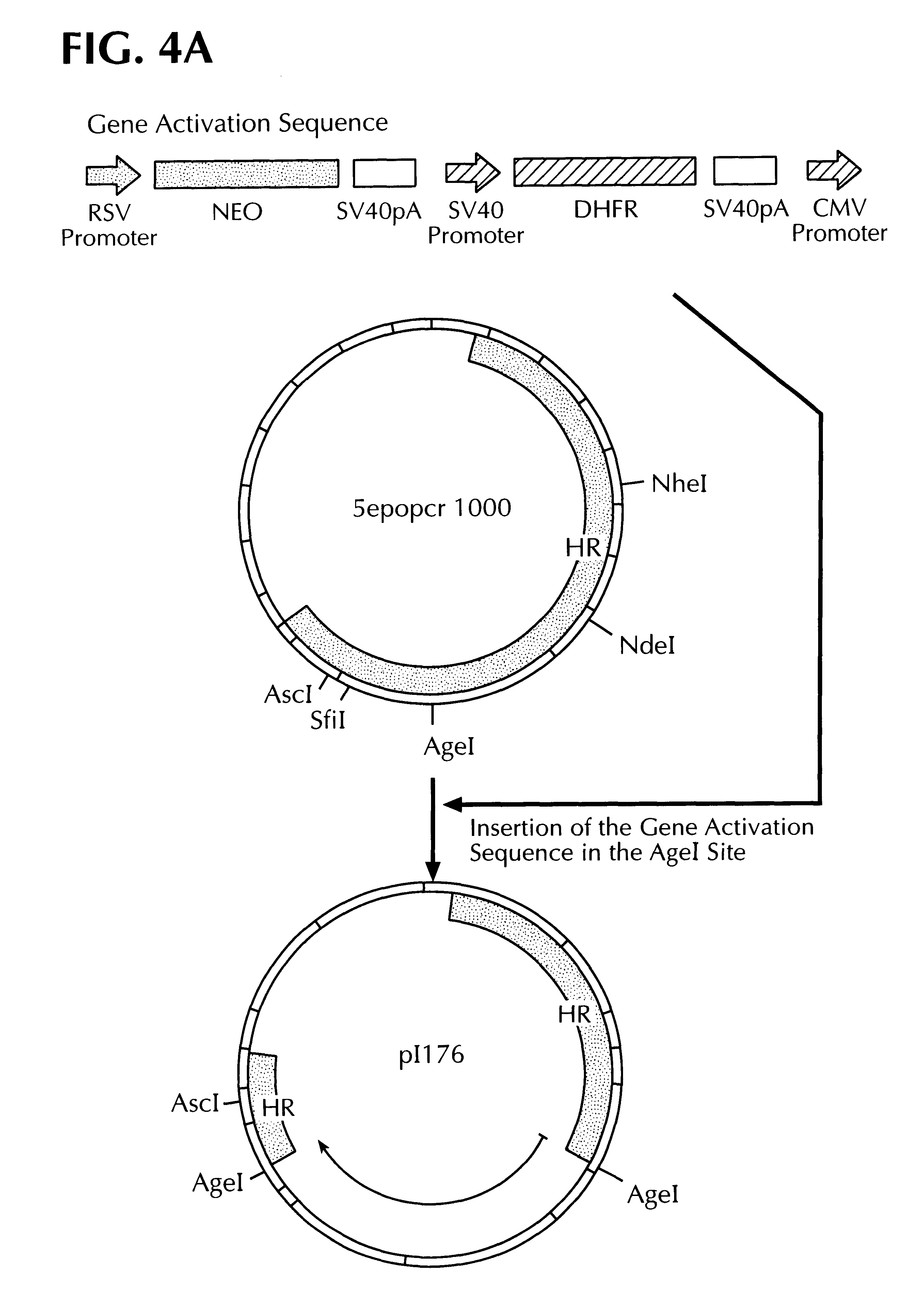
Methods for identifying human cell lines useful for endogenous gene activation, isolated human lines identified thereby, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6548296B1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA constructHuman cell
The invention concerns human cells which, due to an activation of the endogenous human EPO gene, are able to produce EPO in an adequate quantity and purity to enable a cost-effective production of human EPO as a pharmaceutical preparation. Furthermore the invention concerns a process for the production of such human EPO-producing cells, DNA constructs for the activation of the endogenous EPO gene in human cells as well as a process for the large-scale production of EPO in human cells.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Indirubin derivatives having anticancer property against human cancer cell line
The present invention relates to an indirubin derivative having anticancer property by inhibiting cell proliferation as to human cancer cell line. More particularly, this invention provides the synthesis of indirubin derivative known as CDK(Cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor. Further, inhibition activity of proliferation as to human cancer cell line and apoptosis against induced-differentiation of said indirubin derivative are researched to develop a novel indirubin derivative having efficacious anticancer properties as to various human cell lines.
Owner:ANYGEN
Modified vaccinia ankara virus variant
InactiveCN1476483AAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsModified vaccinia AnkaraHuman cell line
The present invention provides an attenuated virus derived from a modified vaccinia Ankara virus characterized by loss of the ability to replicate repeatedly in human cell lines. The present invention further describes recombinant viruses derived from the virus and the use of the virus or recombinants thereof as drugs or vaccines. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method of inducing an immune response even in immunocompromised patients, patients who are already immune to vaccine viruses, or patients who are receiving antiviral therapy.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
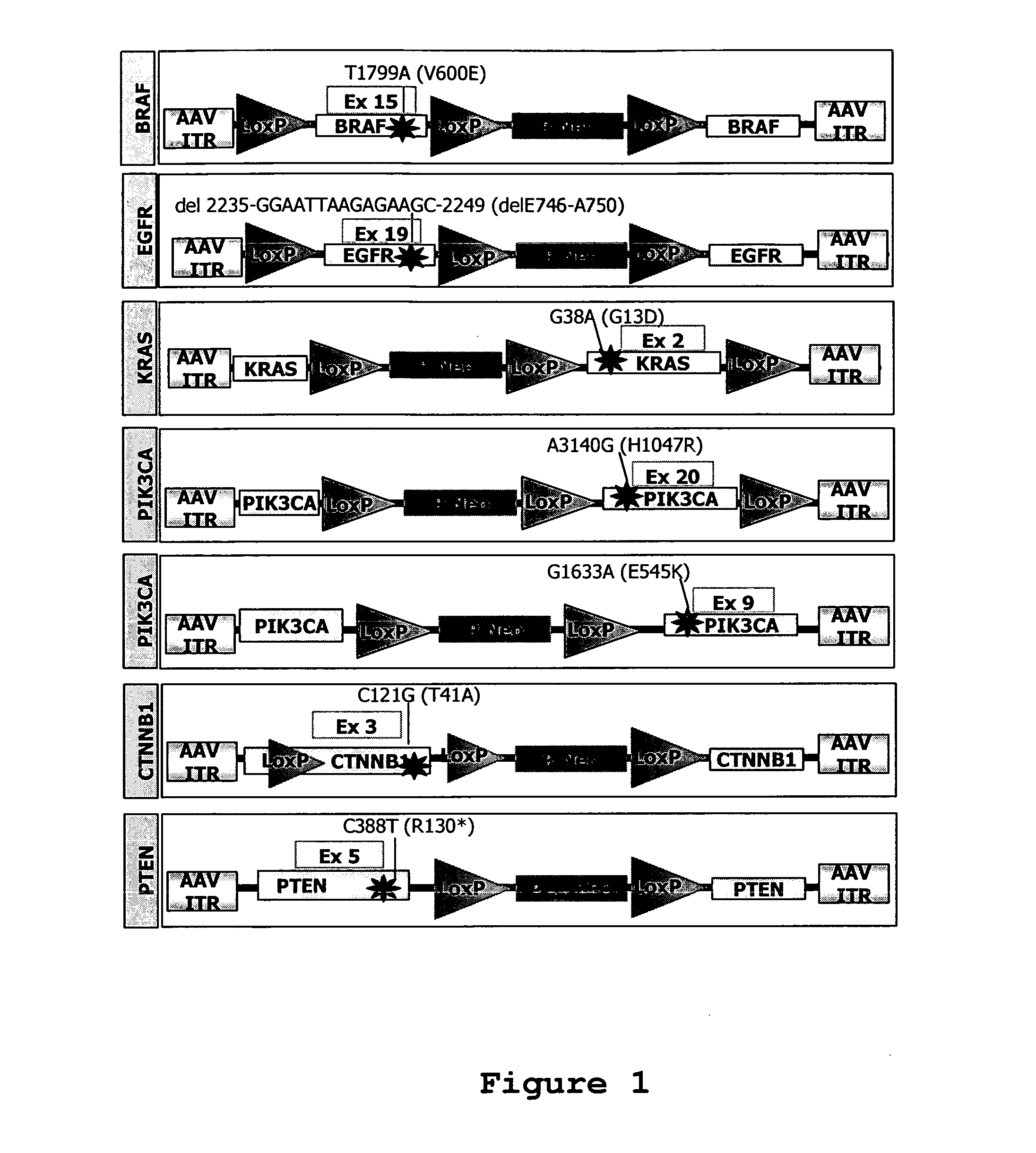
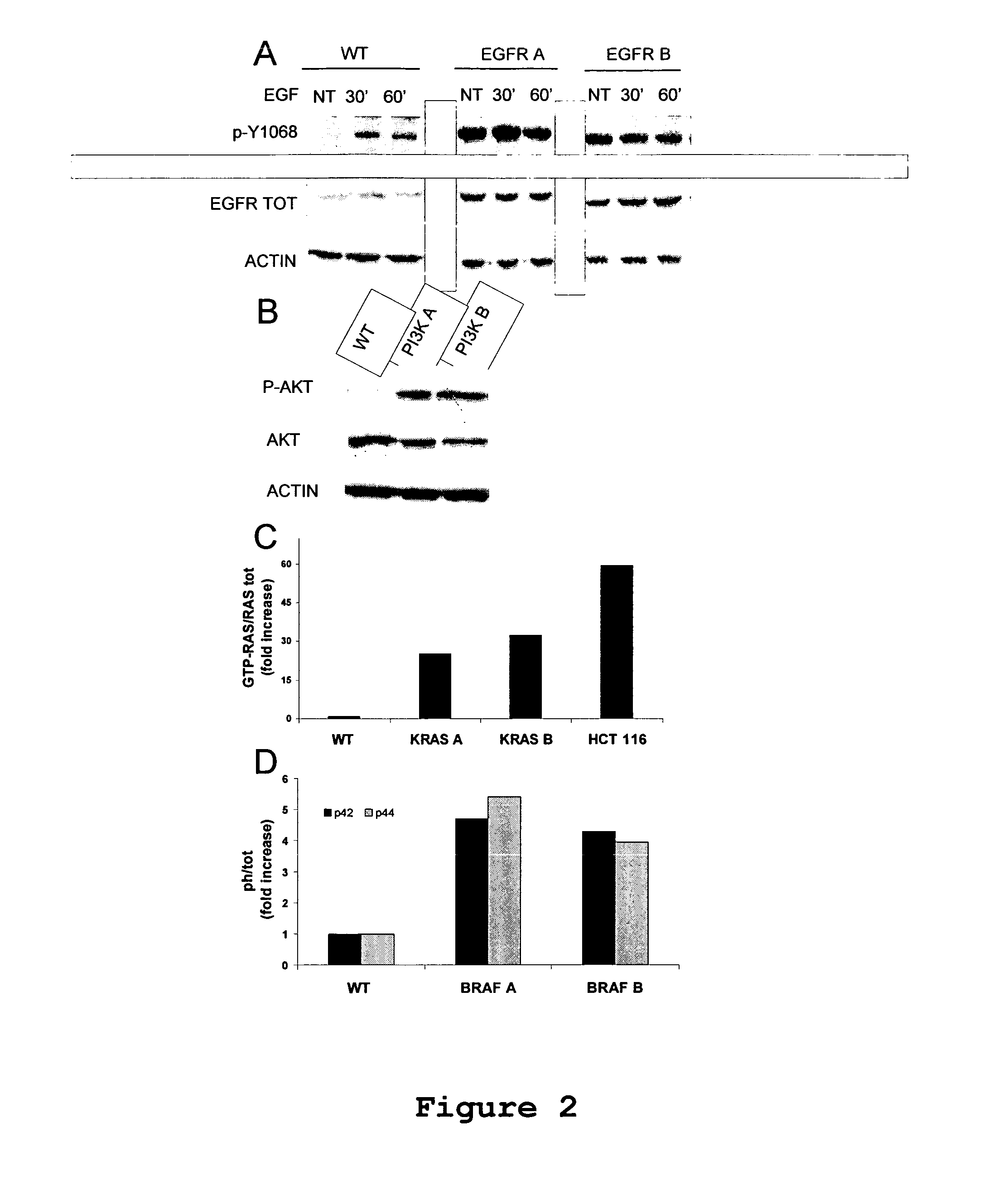
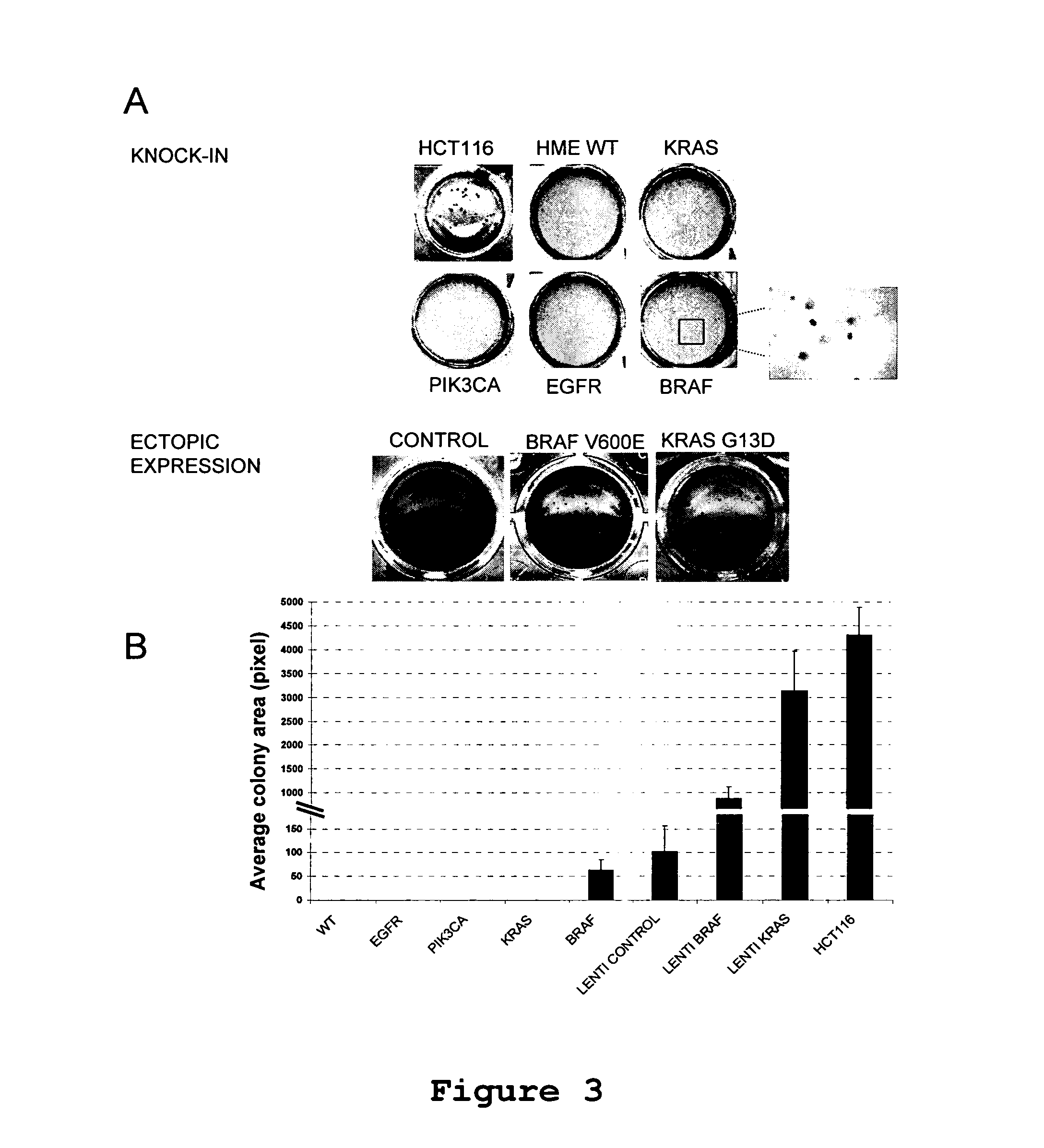
Isogenic human cell lines comprising mutated cancer alleles and process using the cell lines
Isogenic human cell lines comprising at least one mutated cancer allele under the control of the cell line endogenous promoter, which corresponds to the wild-type cancer allele promoter are disclosed, as well as an in vitro process for determining sensitivity / resistance of a patient suffering from a tumor to a pharmacological agent comprising the following steps: a) identifying at least one mutated cancer allele in a tissue affected by a tumor of said patient; b) providing an isogenic human cell line representative of the tissue, wherein the cell line comprises at least the identified mutated cancer allele, which is under the control of the cell line endogenous promoter corresponding to the wild-type cancer allele promoter; c) putting in contact said cell line with the pharmacological agent; d) determining a variation of proliferation, apoptosis or cytotoxicity of the cell line in presence of the pharmacological agent; wherein the variation of proliferation, apoptosis car cytotoxicity indicative of the sensitivity / resistance of the patient tumor to the pharmacological agent.
Owner:BARDELLI ALBERTO +2
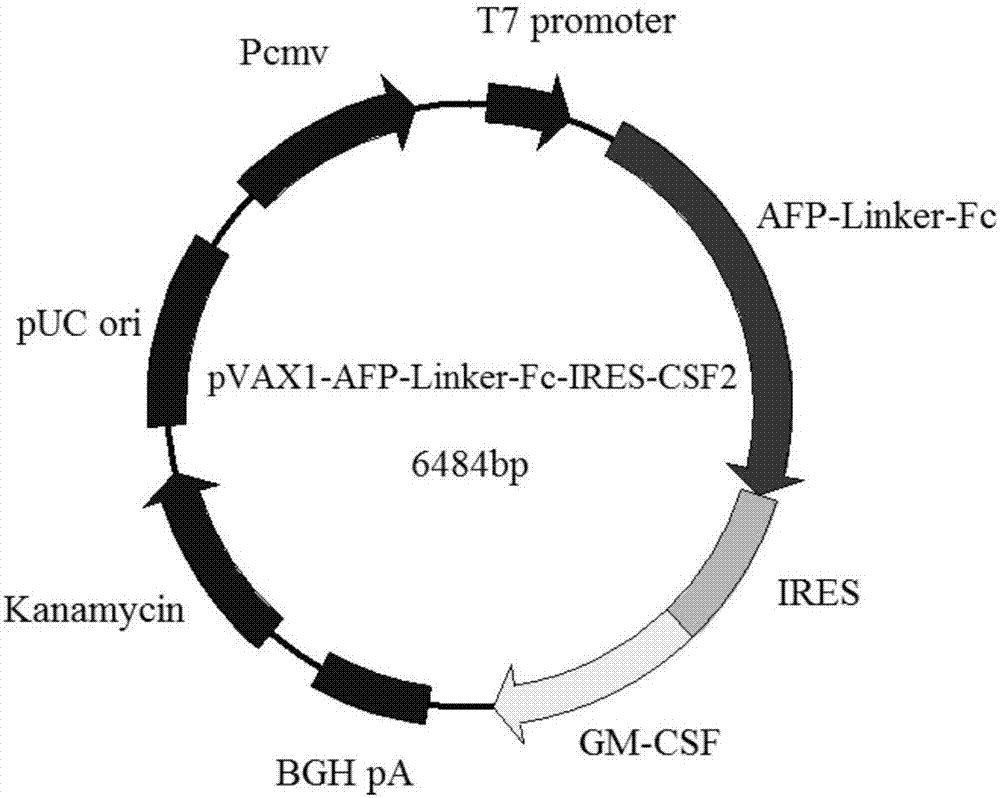
Gene vaccine for preventing and treating tumors and preparation method and application of gene vaccine
ActiveCN107281475AExtended half-lifeImprove stabilityNucleic acid vectorCancer antigen ingredientsSpecific immunityWilms' tumor
The invention discloses a gene vaccine for preventing and treating tumors. The gene vaccine comprises a recombinant gene eukaryotic expression vector carrying a human AFP gene, a human IgG1 Fc fragment gene and a human CSF2 gene at the same time. The gene vaccine can be applied to gene immunotherapy and prevention of diseases, such as a liver cancer, and is capable of developing the immunomodulatory effect of cytokines and generating a specific immune response through targeting to the diseases, such as the liver cancer; and the number of components of the vaccine is also reduced by adopting a dual-gene co-expression strategy. The test result shows that the vaccine is capable of normally expressing a target gene in an in-vitro human cell line and capable of significantly inhibiting division and proliferation of liver cancer cells under an in-vitro condition.
Owner:杭州贝罗康生物技术有限公司
Cell penetrating peptide and method for delivering biologically active substance using same
ActiveCN106255699AEfficient deliveryPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsTat peptideGenetic Materials
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: a new cell penetrating peptide; and a composition for delivery of a biologically active substance, a composition for gene therapy, a method for delivery of the biologically active substance, and a method for the gene therapy using the same. The cell penetrating peptide of the present invention can effectively deliver a protein into human cell lines and tissues, can deliver a protein with higher efficiency in comparison with a TAT peptide that is commercially used as a cell penetrating peptide, and can also be usefully used in the delivery of biologically active substances such as proteins, genetic materials, chemical compounds etc. which may be used for therapeutic purposes in a cell.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Ph+ acute B lymphocytic leukemia KQBL-84 cell line and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN109097334AHigh degree of malignancyMolding speed is fastGenetically modified cellsTumor/cancer cellsDiseaseBone marrow cell
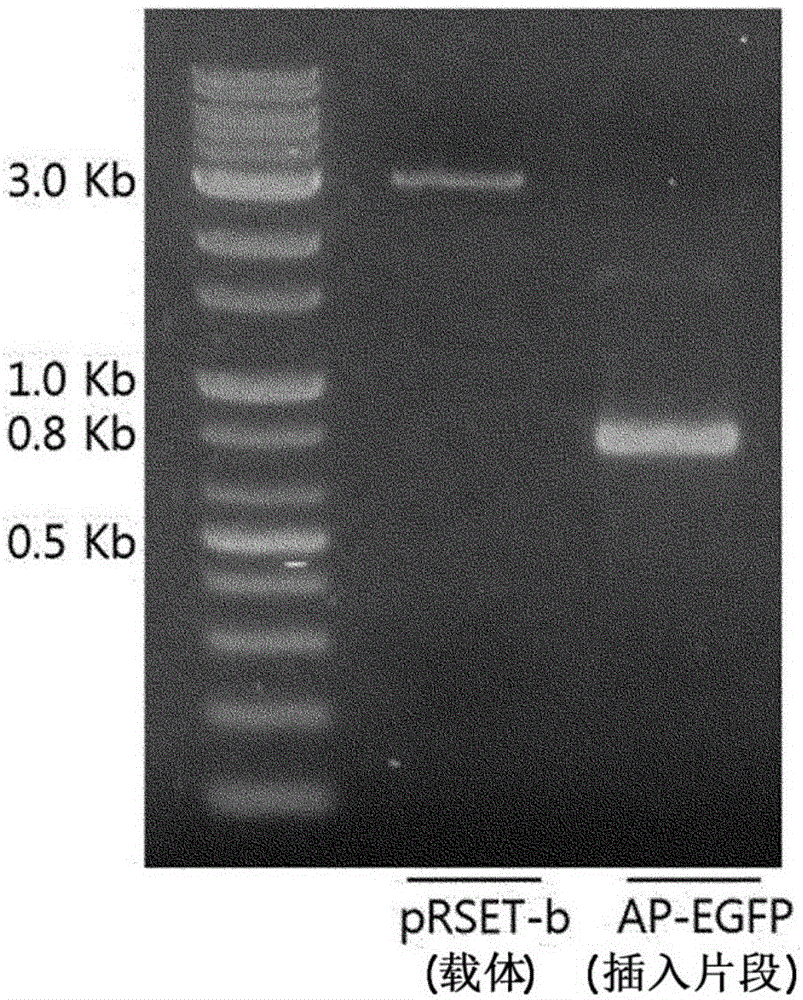
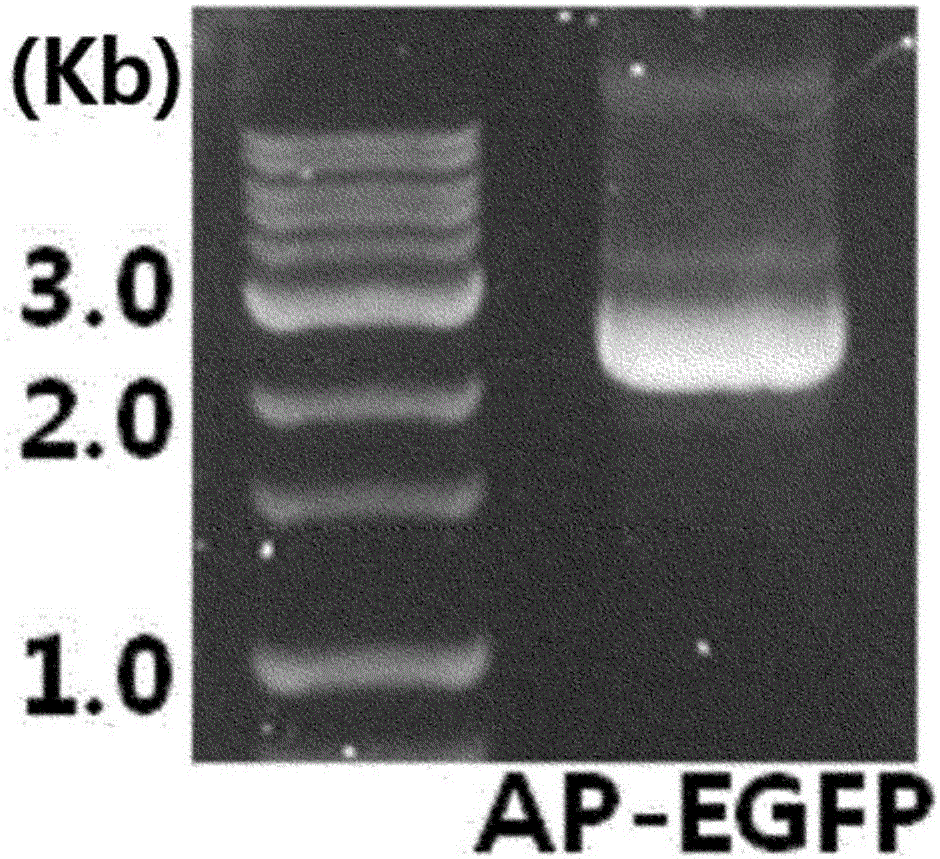
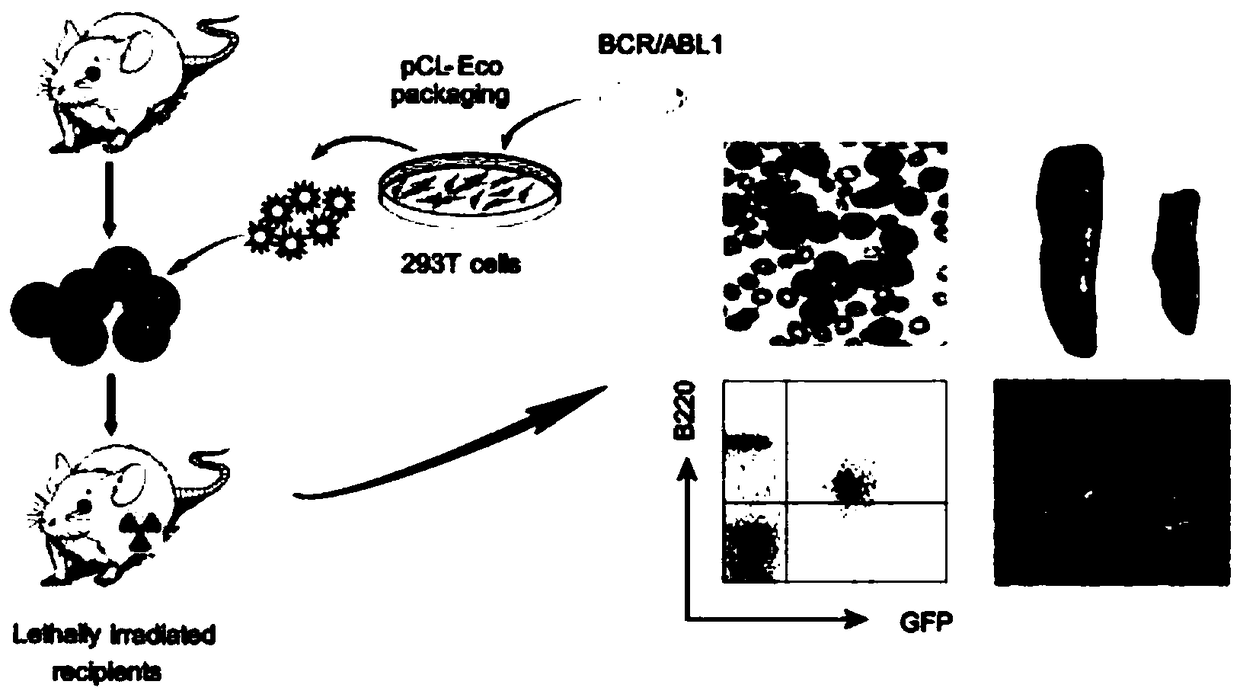
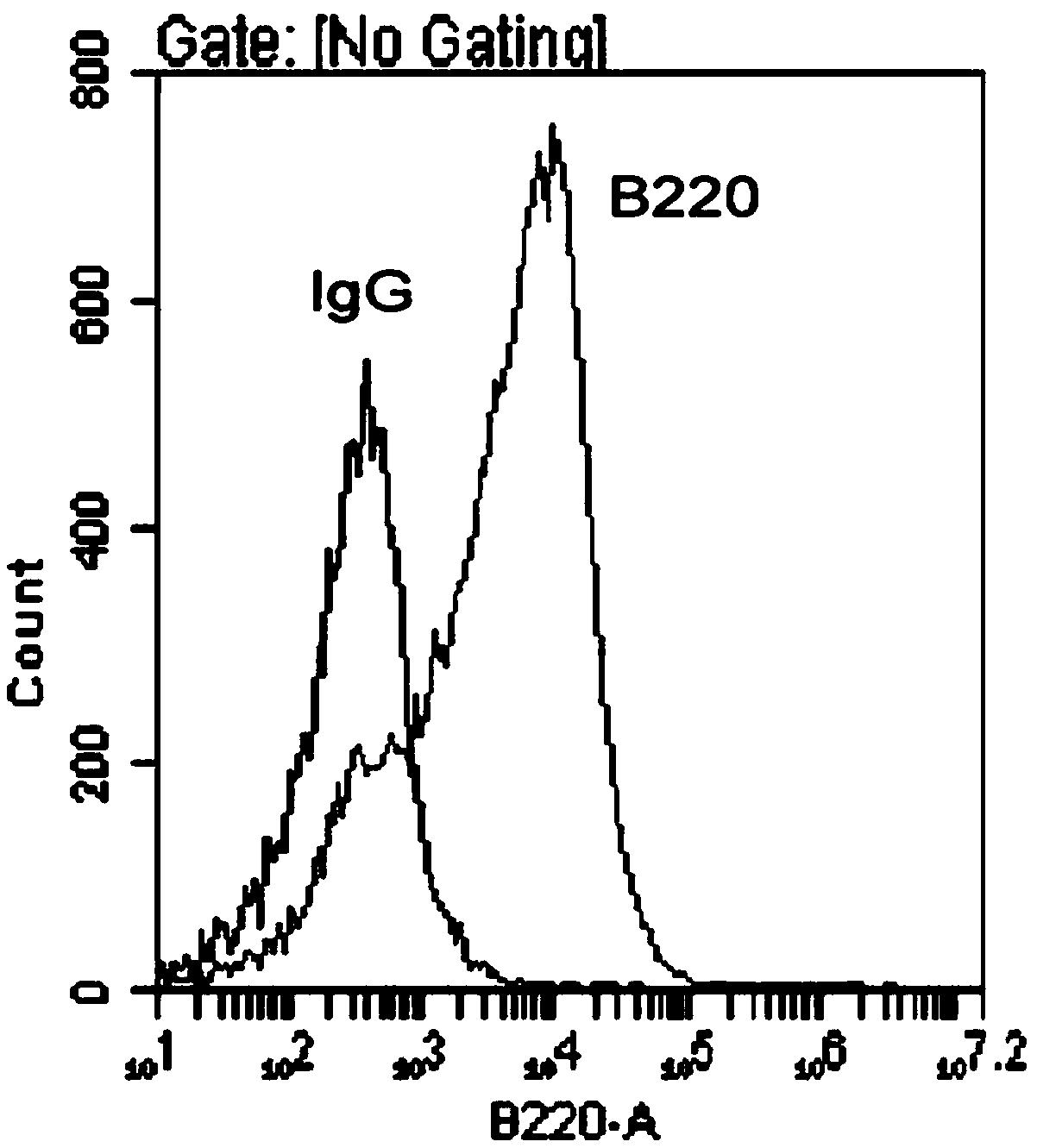
The invention discloses a Ph+ acute B lymphocytic leukemia KQBL-84 cell line and a construction method and an application thereof. The cell line is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on July 25, 2018 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: C2018164. The cell line is characterized in that an MSCV-P210 retrovirus carrying a human fusion gene BCR-ABL infects bone marrow cells ofa C57bl / 6 donor mouse to obtain a primary human cell line stably expressing the BCR-ABL human protooncogene, and screening and culture are then performed to obtain a highly carcinogenic and stably inherited precursor B cell line. Cells of the line established in vitro are injected into a C57bl / 6 homologous receptor mouse. The cell line can be used for efficiently constructing a primary B-ALL mousemodel. The model has higher malignancy, rapid disease modeling and low modeling cost, and is suitable for evaluation of treatment methods of refractory / relapsing B-ALL and pathogenesis study of patients with B-ALL in Philadelphia chromosome positive (Ph+).
Owner:GUIZHOU EDUCATION UNIV
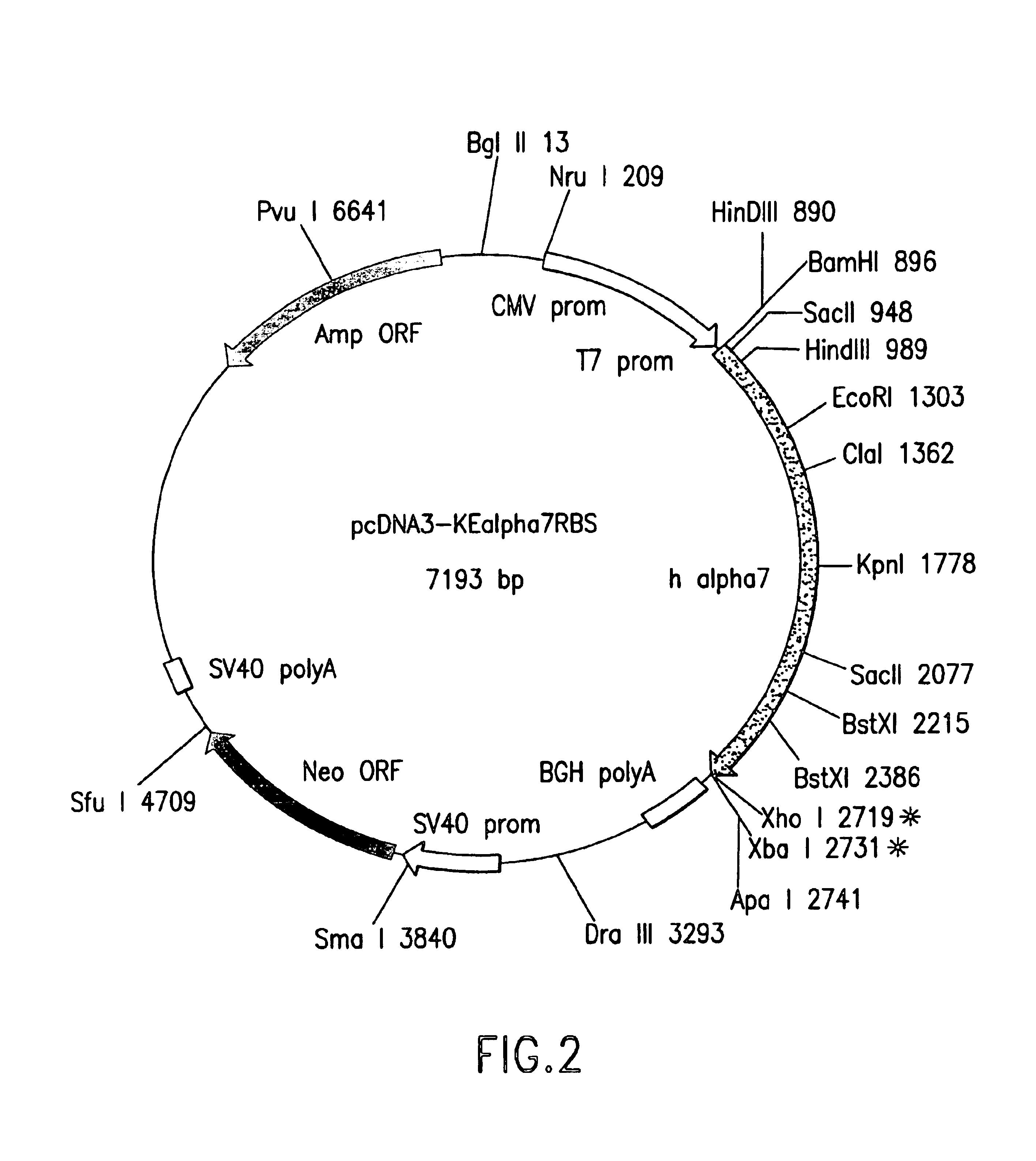
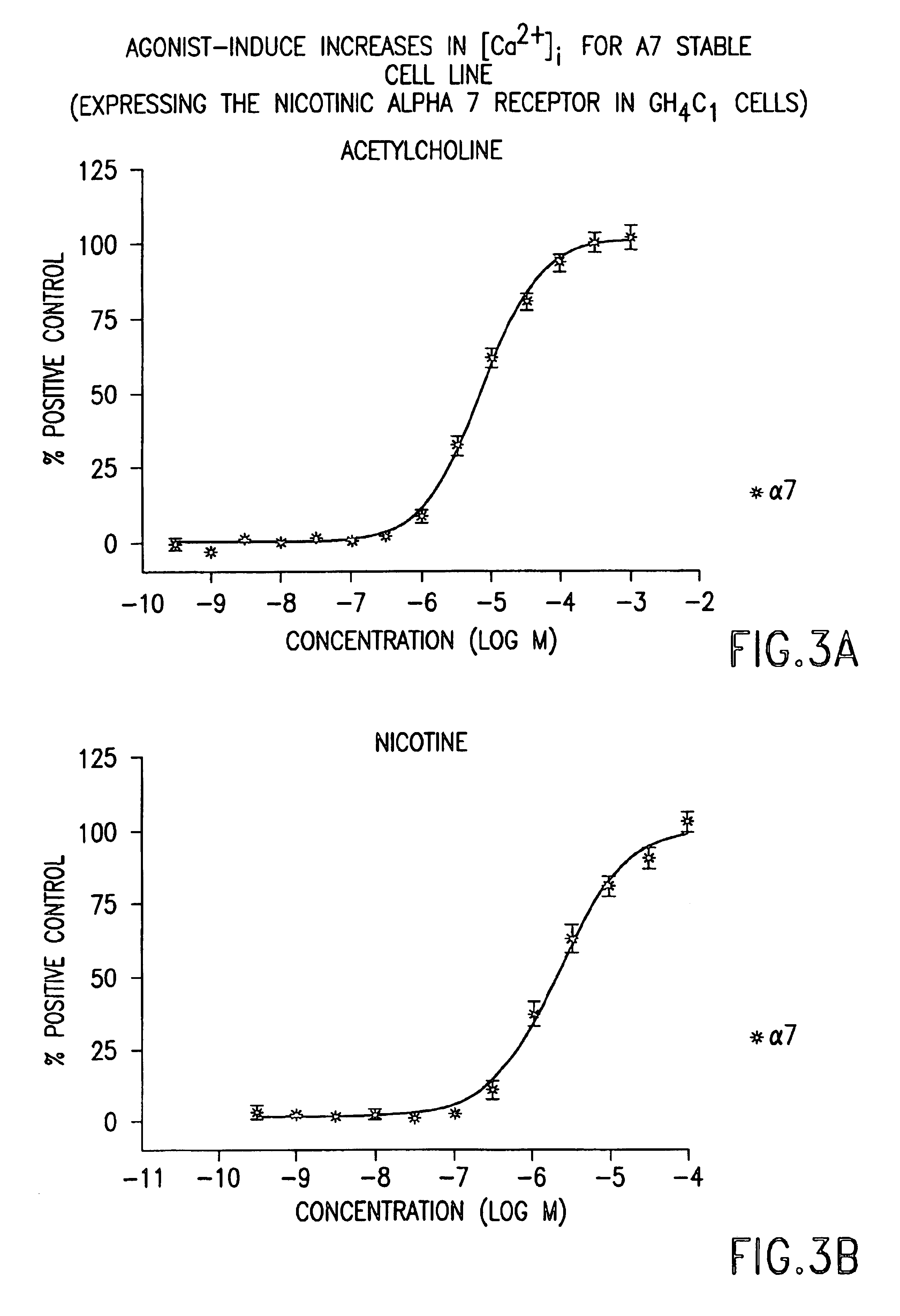
DNA encoding human α and β subunits of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, cells transformed therewith, and recombinant cell line expressing a human α and β subunit of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, i.e., DNA or RNA encoding human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha and beta subunits, mammalian and amphibian cells containing said DNA, methods for producing α and β subunits and recombinant (i.e., isolated or substantially pure) α subunits and β subunits are provided. In addition, cells expressing various multimeric combinations of subunits (i.e., α1, α2 α3 α4 α5 α6 and / or α7 in combination with at least one of an α and β subunit are also provided. A recombinant, non-human cell line expressing the human α7 subunit of nAChR is disclosed.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com