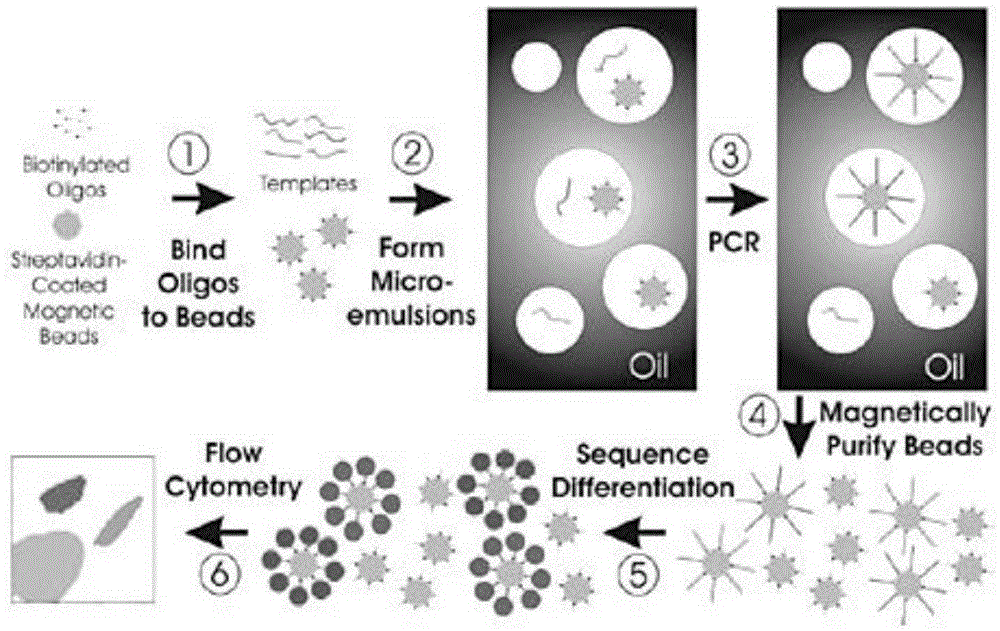
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Dna breakage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
However, to trade genetic information — through a process called recombination — the DNA molecules must break at points along the chromosomes, risking permanent damage and loss of genomic integrity. In humans, errors during recombination can lead to infertility, fetal loss, and birth defects.
Analysis of fragmentation patterns of cell-free DNA
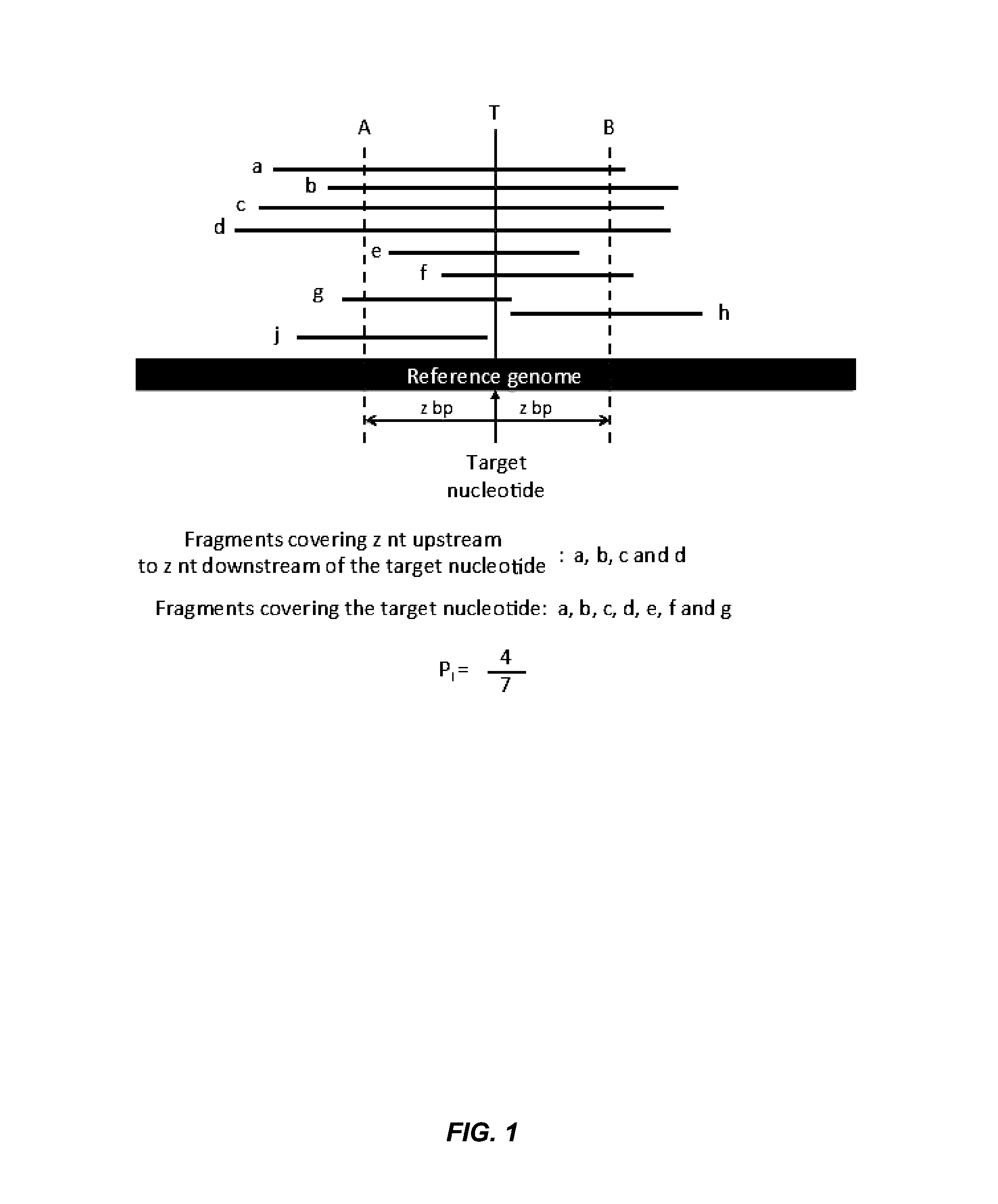
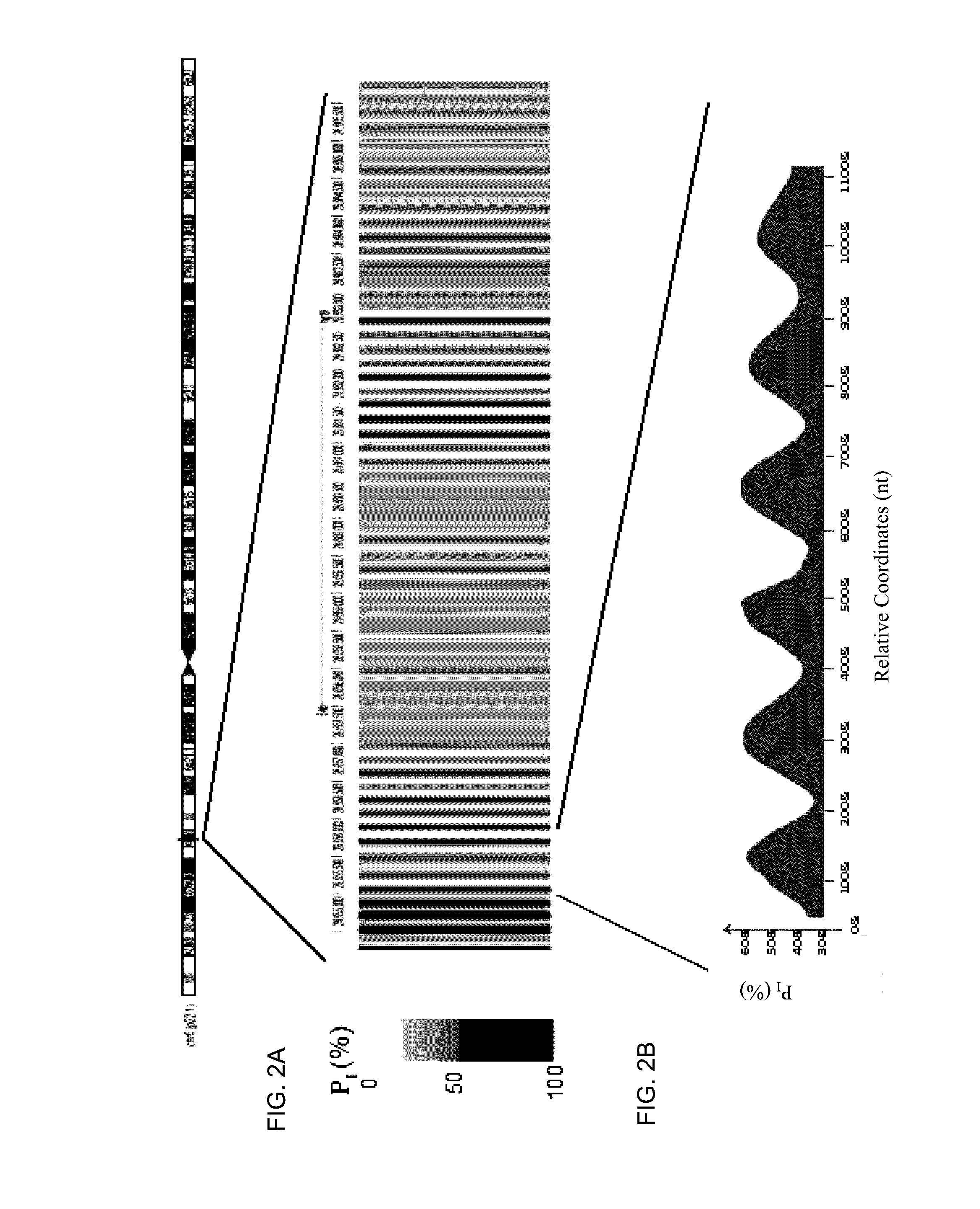
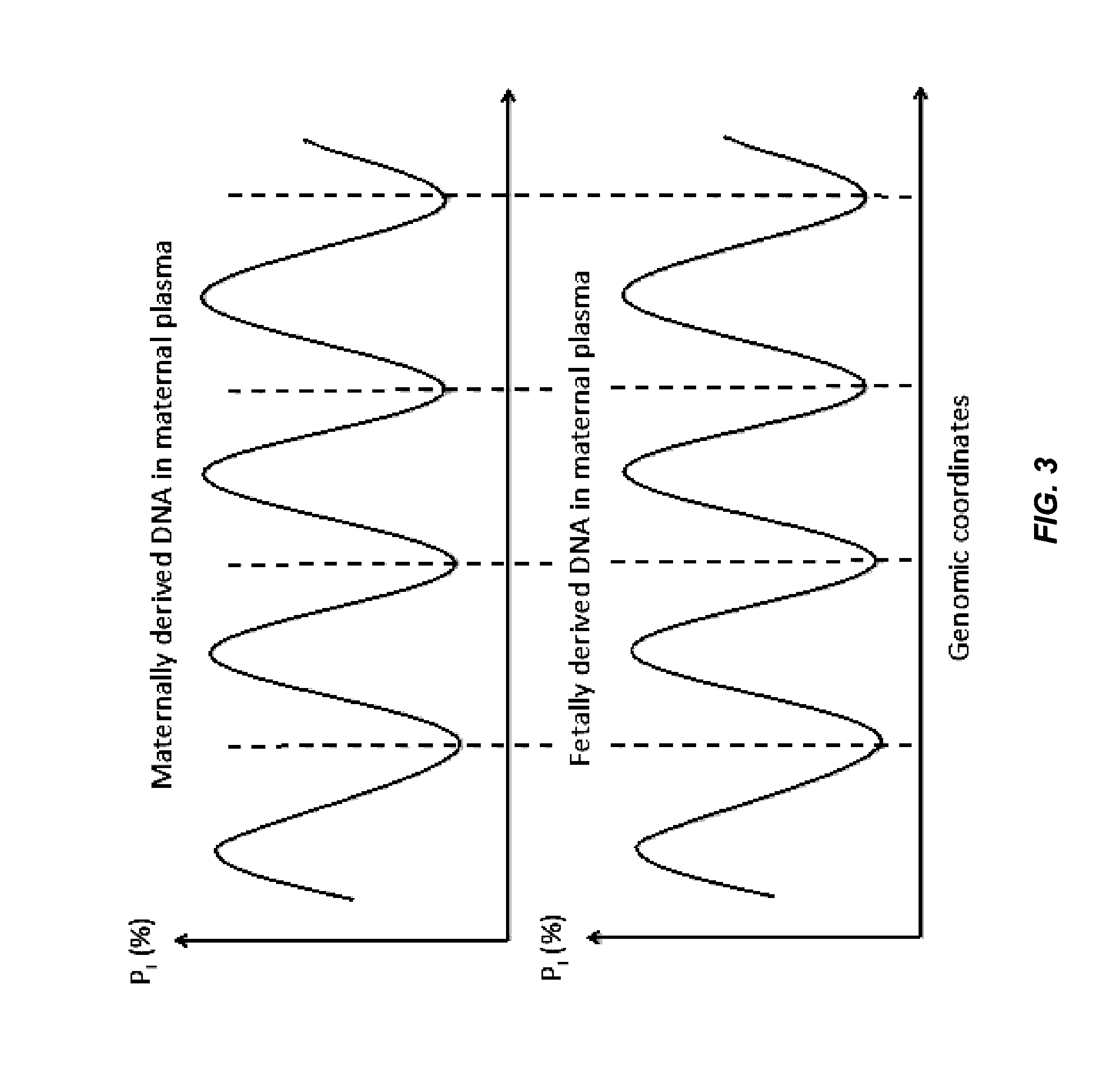
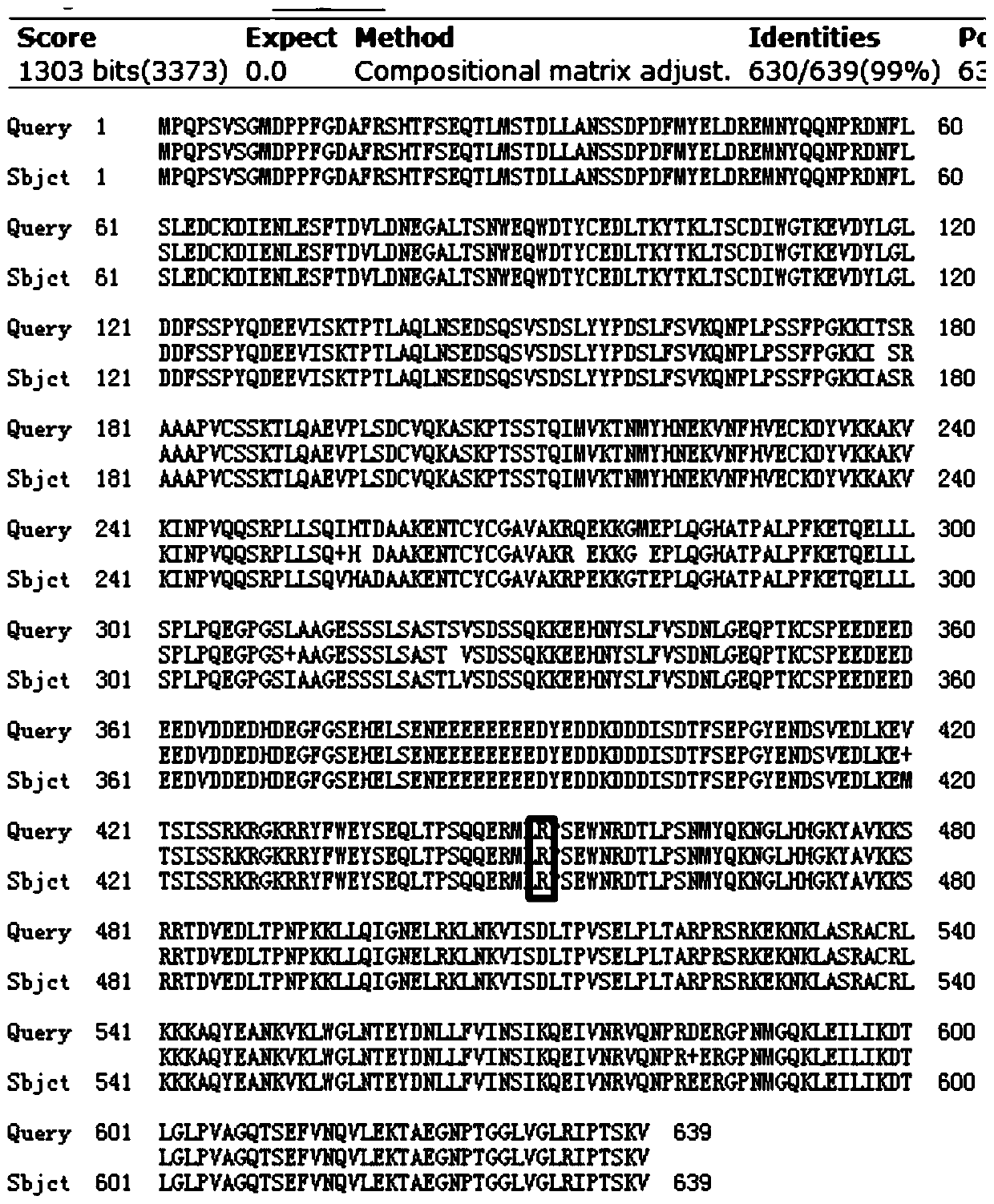
Factors affecting the fragmentation pattern of cell-free DNA (e.g., plasma DNA) and the applications, including those in molecular diagnostics, of the analysis of cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns are described. Various applications can use a property of a fragmentation pattern to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type, to determine a genotype of a particular tissue type (e.g., fetal tissue in a maternal sample or tumor tissue in a sample from a cancer patient), and / or to identify preferred ending positions for a particular tissue type, which may then be used to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Traceless modification method of bacillus subtilis genome
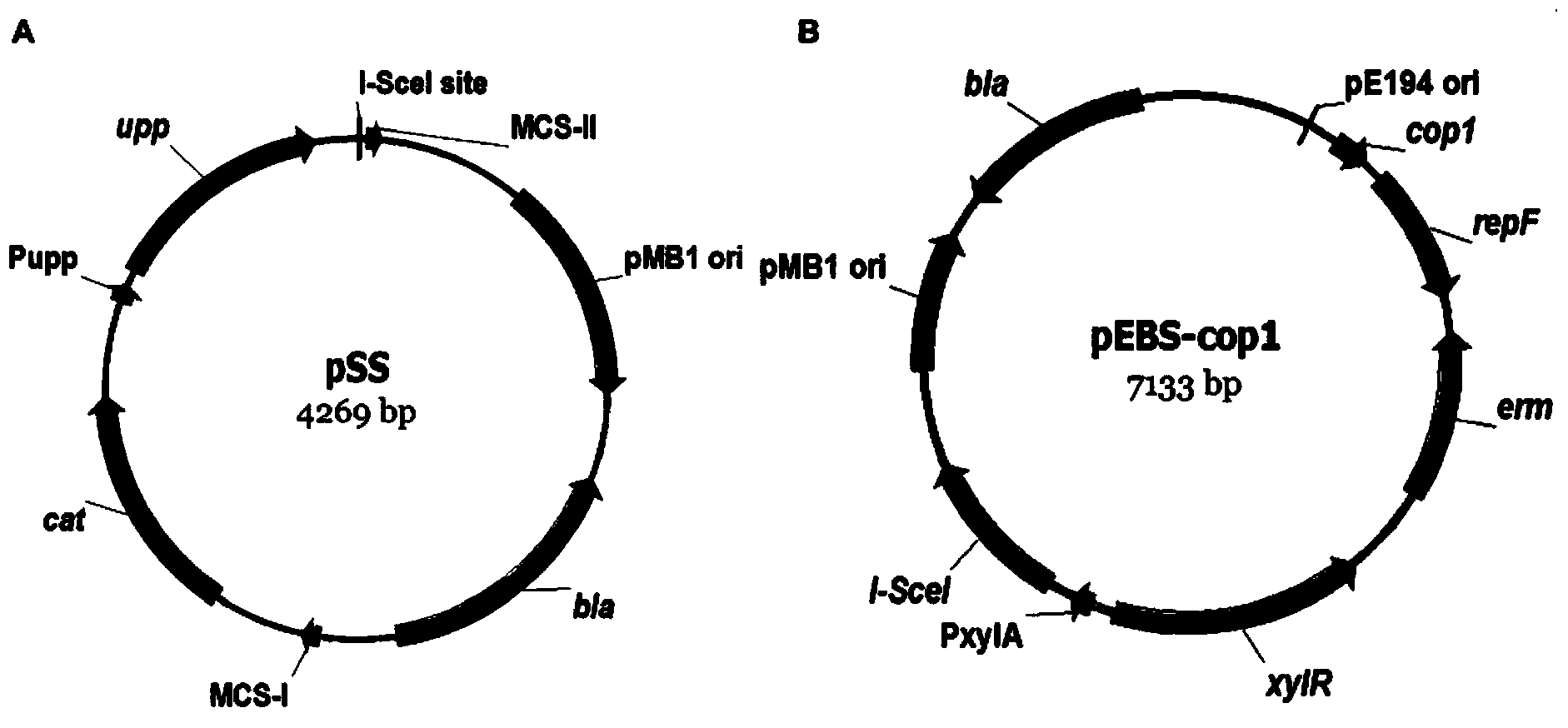
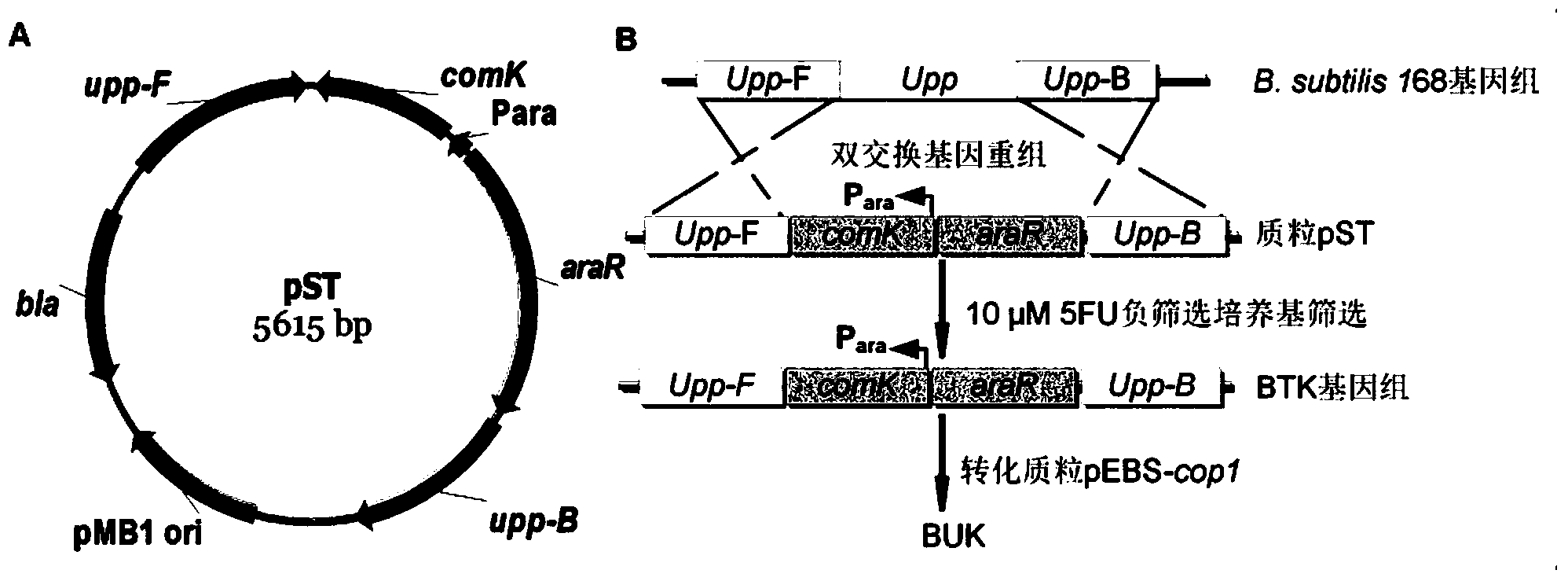
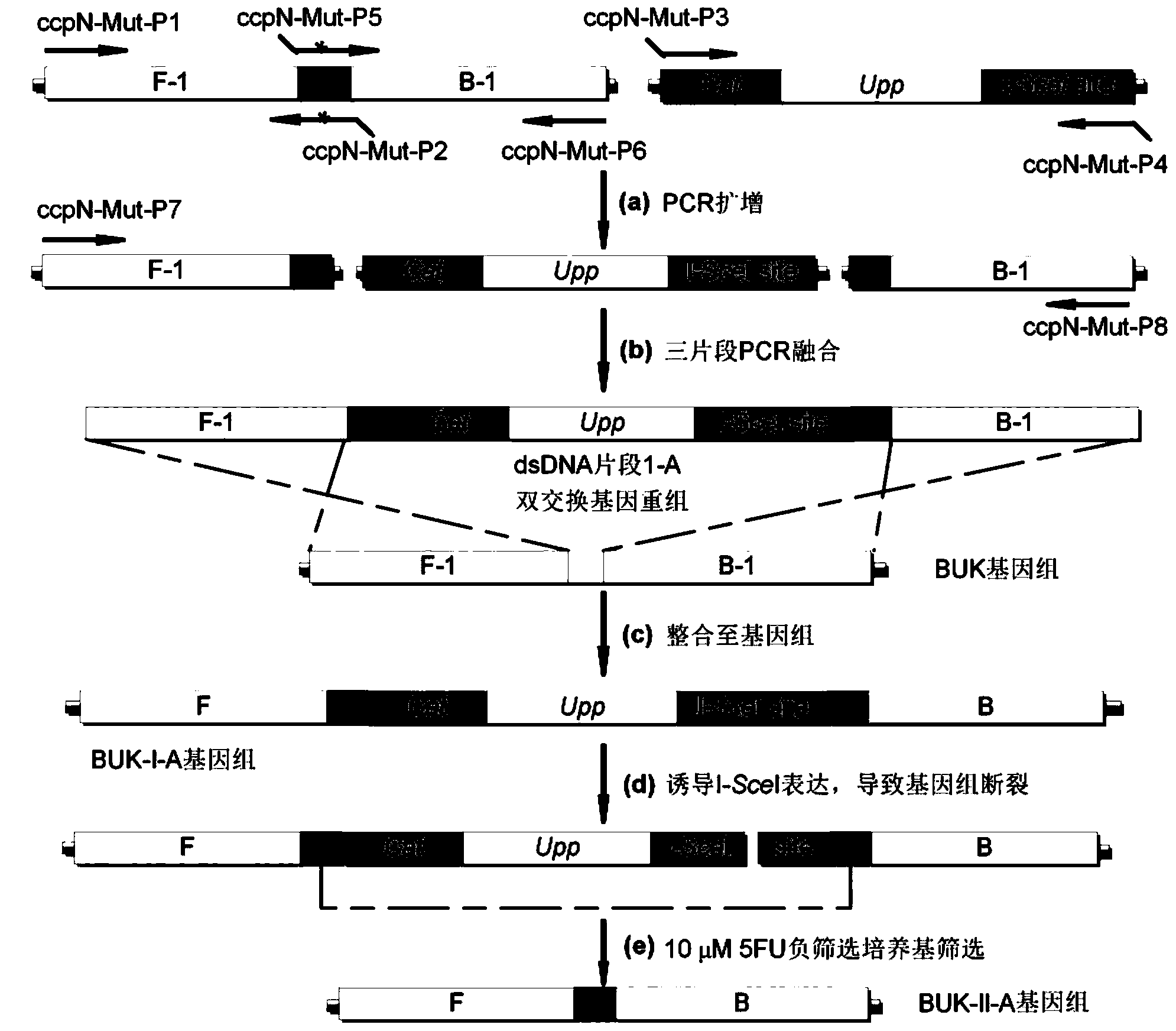
ActiveCN103451224AReduce the preparation processImprove recombination efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideLarge fragment
The invention discloses a traceless modification method of bacillus subtilis genome. The method disclosed by the invention is used for carrying out traceless modification on the bacillus subtilis genome by utilizing an upp positive-negative selection system. The method disclosed by the invention utilizes a ComK expression system, so that the bacillus subtilis has an excellent dsDNA (double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid) conversion efficiency which can be up to 3-5*10<3>cfu / microgram dsDNA. Meanwhile, an exogenous endonuclease I-SceI expression system is utilized to bring double-stranded DNA breakage into the genome, so that the genetic recombination efficiency in negative selection molecules is obviously improved and can be up to 8*10<-4>. According to the method disclosed by the invention, iterative modification can be performed on a plurality of target nucleotide sequences in the bacillus subtilis genome, and the steps of introducing gene mutation to the genome, knocking out target gene sequences from the genome, deleting a large fragment of genomic sequences and the like are included.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Somatic human cell line mutations
ActiveUS20170009256A1Even mixtureDifferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAGenomic mutationDna breakage
The invention provides for a method of producing a mutant somatic human cell line of cells comprising a genomic mutation of interest (MOI) at a predefined genomic site of interest (GOI) in close proximity to a genomic target site, which comprises: a) providing a guide RNA (gRNA) comprising a tracrRNA in conjunction with crRNA including an oligonucleotide sequence that hybridizes with the target site; b) providing an RNA-guided endonuclease which catalyzes the DNA break at the target site upon hybridizing with the gRNA; c) introducing the gRNA into the cells in the presence of the endonuclease to obtain a repertoire of cells comprising a variety of genomic mutations at the target site; d) selecting a cell from said repertoire which comprises a MOI; wherein the cell is haploid for the genomic locus of the target site; and e) expanding the cell to obtain the mutant cell line. The invention further provides for a mutant human somatic cell line obtainable by such method; and libraries of mutant human somatic cell lines of isogenic cells with a variety of genomic mutations at different predefined genomic target sites.
Owner:HORIZON DISCOVERY
Inhibitors of endo-exonuclease activity for treating cancer
InactiveUS7115665B1Increase concentrationPrevent proliferationBiocideNitro compound active ingredientsDna breakageSerum ige
The present invention relates to the treatment of cancer with compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease. Endo-exonuclease has been shown to be necessary for the repair of damaged DNA. Compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have been shown to be particularly effective for treating cancer when used in combination with drugs that induce DNA breaks such as cisplatin and mitomycin C. These compounds have a synergistic effect when used in combination for inhibiting tumour growth. The invention includes pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting tumour growth comprising a compound that inhibits endo-exonuclease activity. These pharmaceutical compositions preferably include compounds that induce DNA breaks. The invention includes methods of treating cancer with these pharmaceutical compositions and uses of these compositions to treat cancer. The preferred compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have low toxicity. One such compound is pentamidine. The invention also includes a method for diagnosing cancer and monitoring its progression. This aspect of the invention involves isolating serum from a patient; measuring the concentration of endo-exonuclease in said serum and determining whether said concentration is above a predetermined mean.
Owner:ONCOZYME PHARMA
High-temperature combined method for extracting genomic DNA of fish enteric microorganisms
ActiveCN105483120AStrong specificityTruly reflect the composition structureDNA preparationWater bathsDecomposition
The invention discloses a high-temperature combined method for extracting genomic DNA of fish enteric microorganisms. The high-temperature combined method includes the steps that firstly, the walls of various fish enteric microorganisms are properly broken through a lysozyme method and an ultrasonic method at the same time, wherein the ultrasonic physical wall breaking condition ranges from 150 w to 250 w, ultrasonic treatment is carried out for 2-3 s and then carried out again after an interval of 5 s, and the process is repeated 50-60 times; secondly, the sample obtained after ultrasonic treatment and lysozyme are jointly incubated for 30 min in a water-bath constant-temperature oscillator at the temperature of 55-65 DEG C, and the mixture and RNase A are jointly incubated at the temperature of 27-32 DEG C. According to the method, the walls of the various microorganisms are properly broken under the proper and mild ultrasonic condition, and the genomic DNA is prevented from being broken and degraded. As the specific temperature range for incubating the lysozyme and the sample and the specific temperature range for incubating the RNase A and the sample are set, the splitting decomposition effect of the lysozyme can be improved, and it can be avoided that the genomic DNA is degraded by DNA enzymes in tissues and cells. Operation is easy, the extracted genomic DNA is complete and low in degradation rate, and the fish enteric microorganism structure can be truly reflected by the types of the microorganisms identified according to the extracted DNA.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Methods, compositions and kits for increasing genome editing efficiency
Methods of editing a target genomic region(s), methods of repairing of a DNA break via a HDR pathway, methods of inhibiting or suppressing repair of a DNA break via a NHEJ pathway, and methods of modifying expression of a gene(s) or protein(s) comprise administering to one or more cells that include one or more target genomic regions, a genome editing system and a DNA protein-kinase (DNAPK) inhibitor disclosed herein. Kits and compositions for editing a target gene comprise a genome editing system and a DNAPK inhibitor disclosed herein.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Method for increasing production of plant biomass
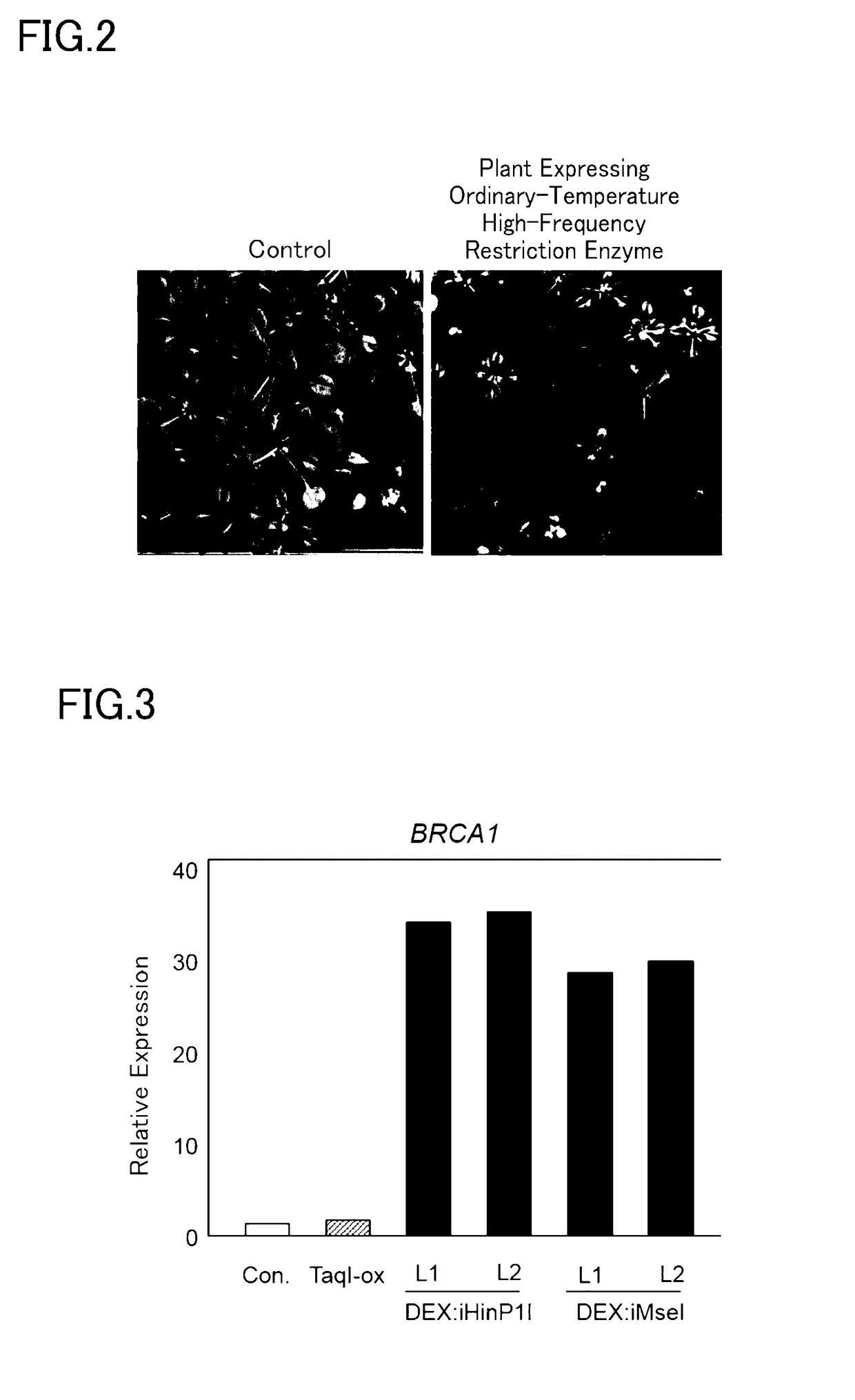
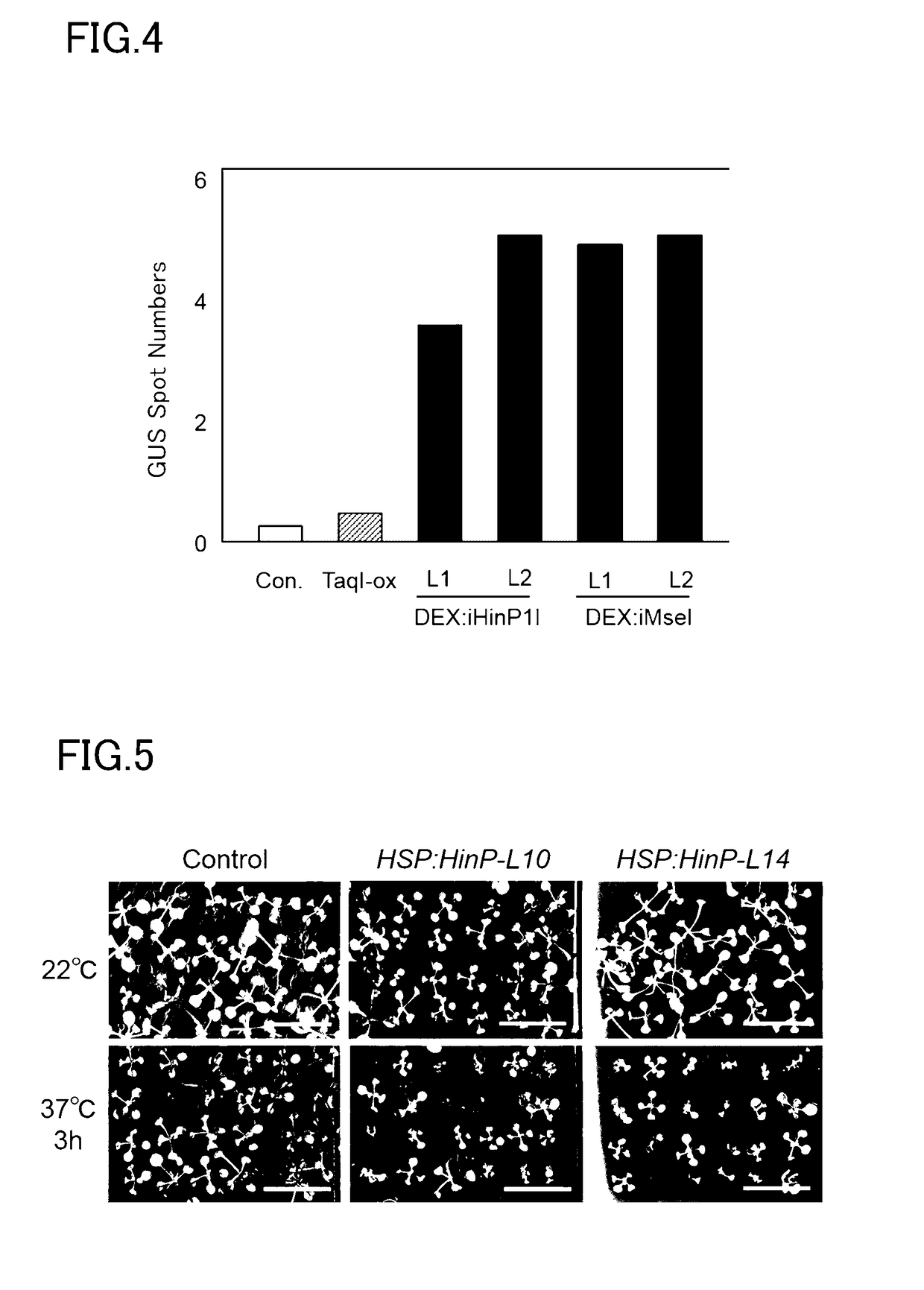
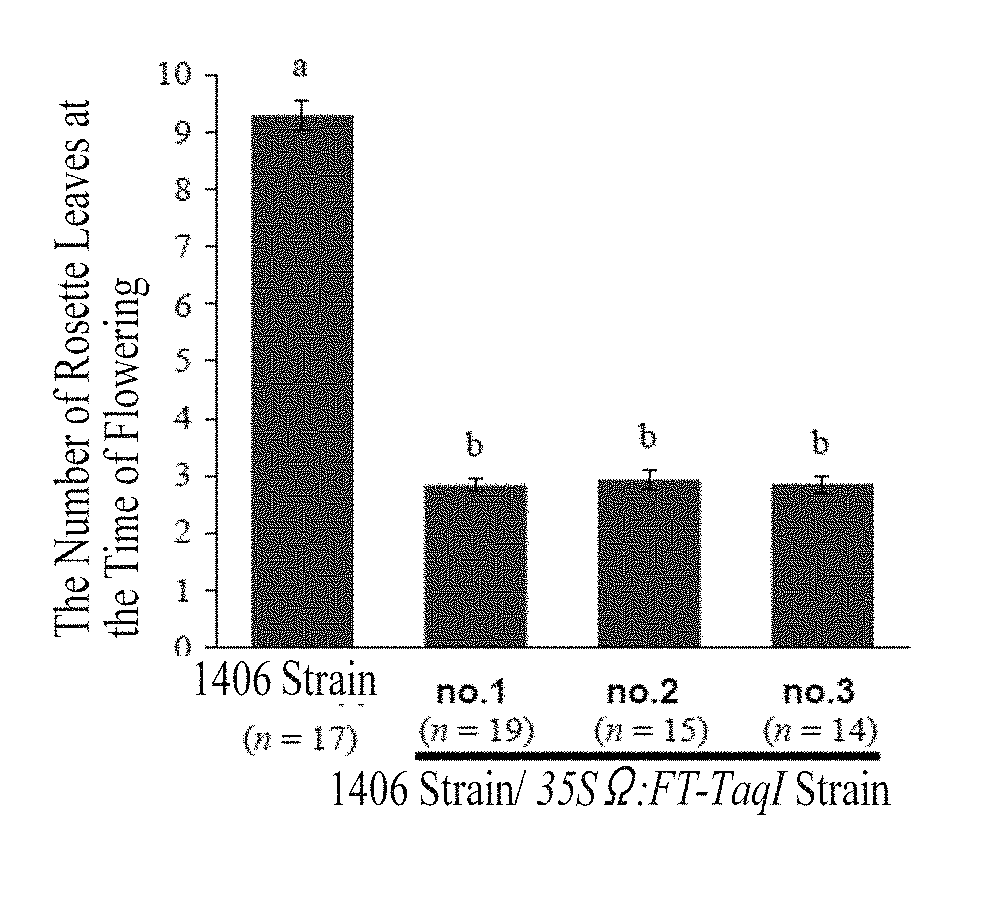
ActiveUS20140273126A1Promotes double-stranded DNA breakageIncreased ploidyHydrolasesClimate change adaptationGrowth plantDna breakage
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
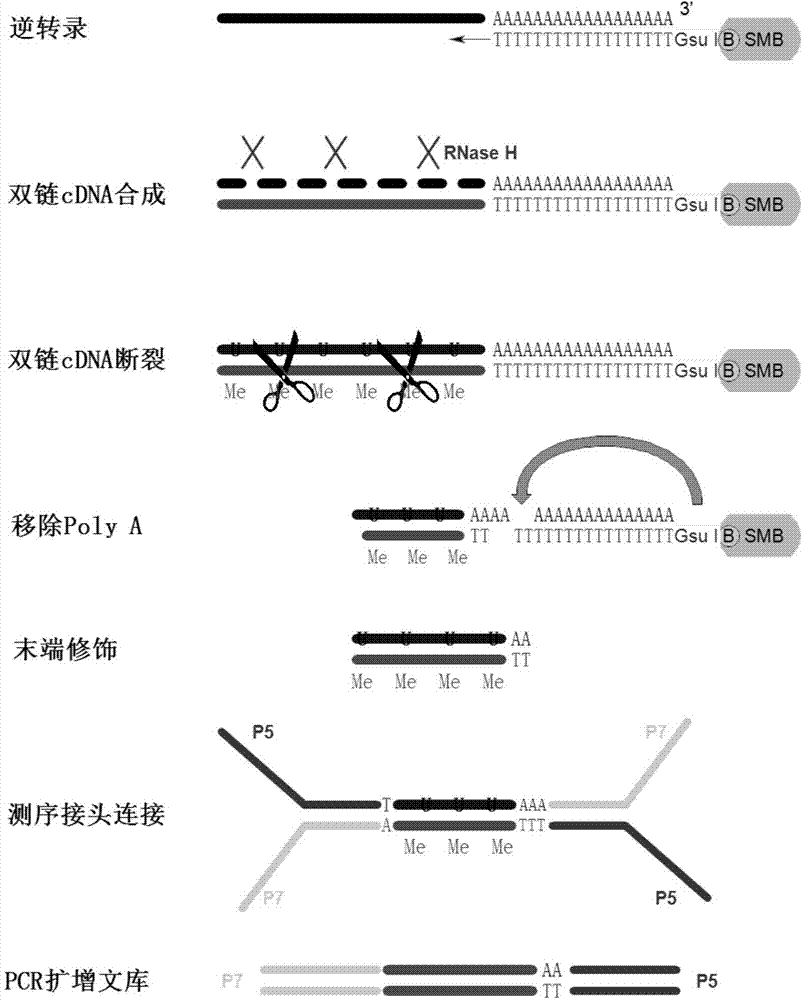
Method for analyzing APA (Alternative Polyadenylation) based on 3T-seq (TT-mRNA Terminal Sequencing) within whole-genome range
InactiveCN103911449AAvoid damageHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexPoly-A RNA
The invention relates to a method for detecting a PAS (Poly A Site) of an RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid), and provides a method for analyzing APA (Alternative Polyadenylation) based on 3T-seq (TT-mRNA Terminal Sequencing) within a whole-genome range. The method for analyzing APA comprises the following steps: preparing magnetic beads containing oligo dT, i.e., mixing an oligo dT primer modified by 5' end biotin and the magnetic beads with streptavidin; mixing the magnetic beads with total RNA and screening RNA containing Poly A; performing reverse transcription, synthesizing the second strand of a double-stranded cDNA and breaking the double-stranded cDNA; removing the Poly A structure; after terminal modification, connecting a sequencing linker; and recovering libraries. According to the method for analyzing APA, RNA horizontal operation is reduced, a Poly A sequence is horizontally removed from the DNA, and the influence of the Poly structure on sequencing is eliminated; double-stranded DNA breaking enzyme is selected for treatment, and on the premise that the quality of the libraries is not affected, the DNA is broken horizontally; the experiment process is simplified, the experiment difficulty and cost are lowered and the method for analyzing APA is wide in application range.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
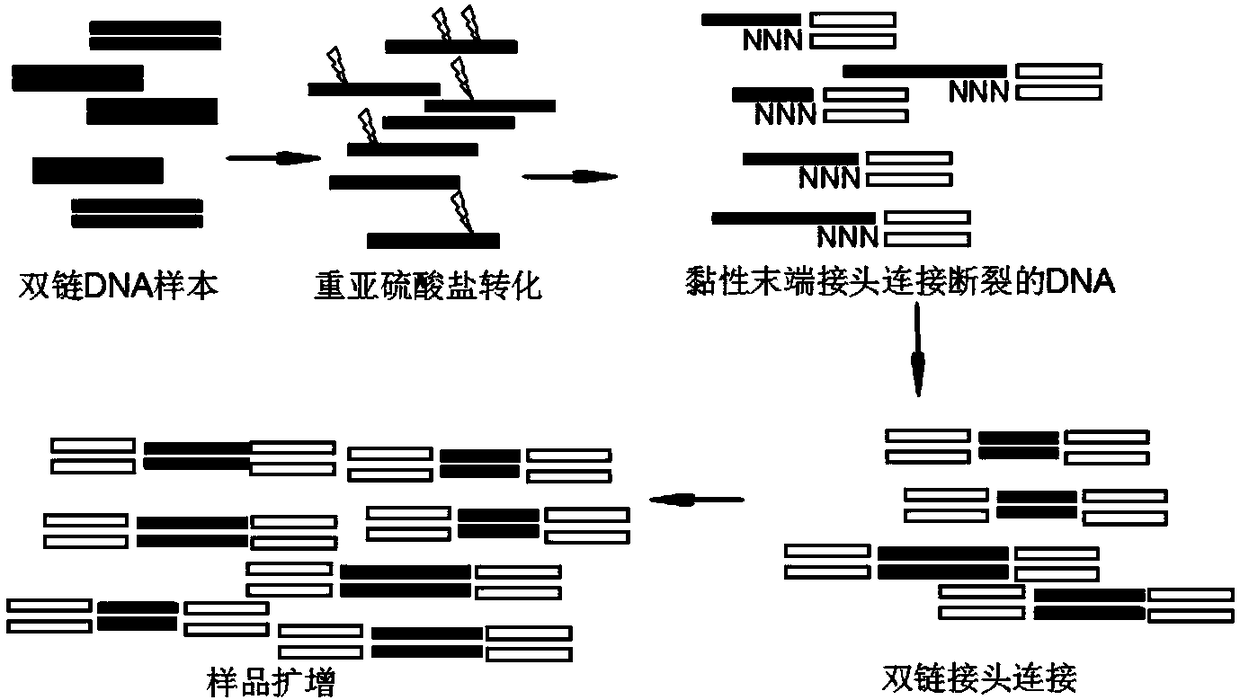
Novel methylation library-establishing kit and application thereof
InactiveCN107904667AReduce lossesImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationDna breakageA-DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology and particularly relates to a novel methylation library-establishing kit and an application thereof. The novel methylation library-establishing kit at least comprises a bisulfate conversion reagent, a sticky end joint, ligase, a DNA extending reagent and a DNA amplifying reagent. The novel methylation library-establishing kit can beapplied to a sample with a low initial mass (as low as 6pg) and suitable for genome DNA with relatively poor mass extracted from FFPE samples and the like, so that the loss of sample information caused by DNA breakage during drug treatment is greatly reduced; and a double-chain DNA joint with a sticky end can be directly introduced by virtue of relatively economic and practical common ligase, sothat the accuracy of data can be improved, the diversity of samples can be preserved to a great extent, and the library deviation property caused by human factors can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
Method for screening and evaluating genetic toxicity of industrial wastewater with complex ingredients
InactiveCN103134844AAccurate evaluationPromote degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCross-linkAdditive ingredient
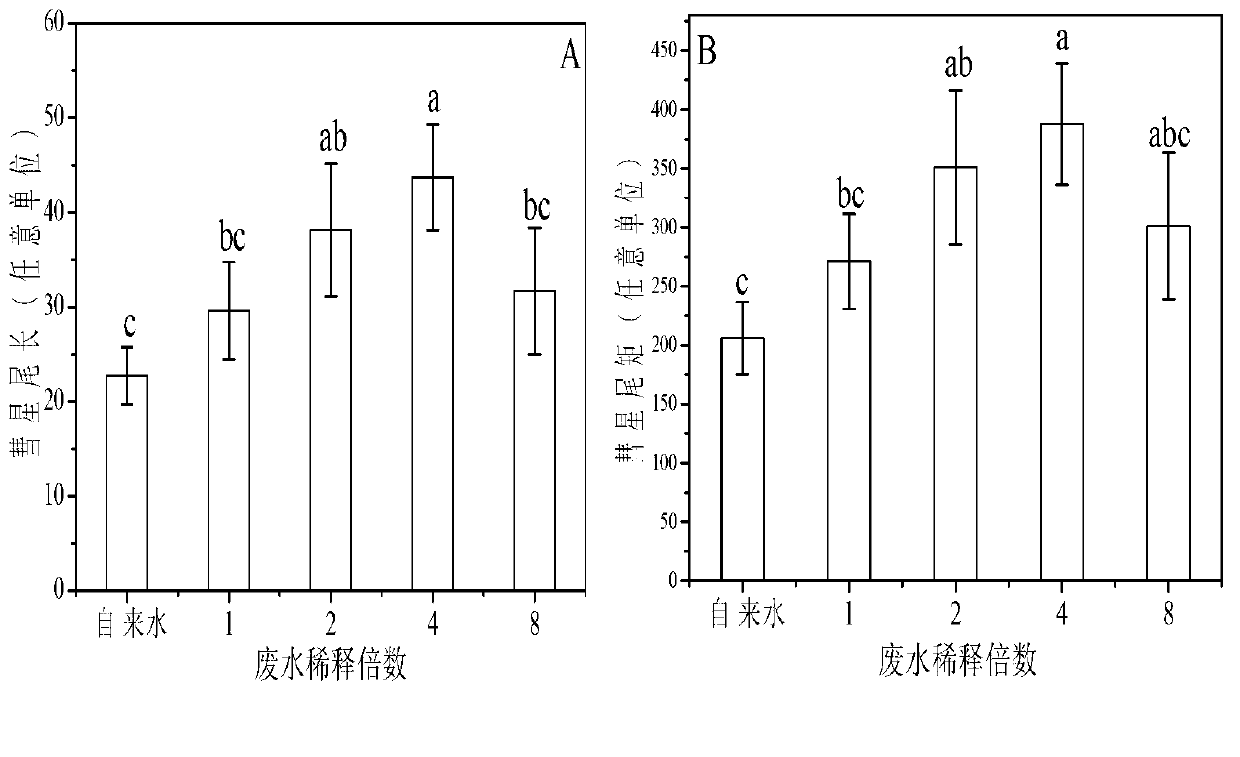
The invention relates to a method for screening and evaluating genetic toxicity of industrial wastewater with complex ingredients. Gemmiparous broad bean seeds are cultivated in a suspension manner in to-be-detected wastewater solution prepared with tap water by means of gradient dilution; after two weeks, root tips are cut down and placed in proteinase K solution, and vacuumizing is carried out. Root tip cell nucleuses are separated, and the single-cell gel electrophoresis (SCGE) technique is used for separating DNA fragments. A fluorescence microscope is used for shooting comet pictures. A cometscore image-analysis system is used for measuring the tail length and the tail moment of the comet. Then, an SPASS program is used for statistic analysis. The method promotes proteinase K to penetrate into root tip meristem cell nucleuses by means of vacuumizing, accelerates degradation of DNA crosslinked protein, thus removes retardation of DNA-protein cross-linking on DNA fragments, and facilitates revelation and accurate evaluation of the true level of NDA breakage and damage inducted by the to-be-detected wastewater.
Owner:HUAINAN NORMAL UNIV
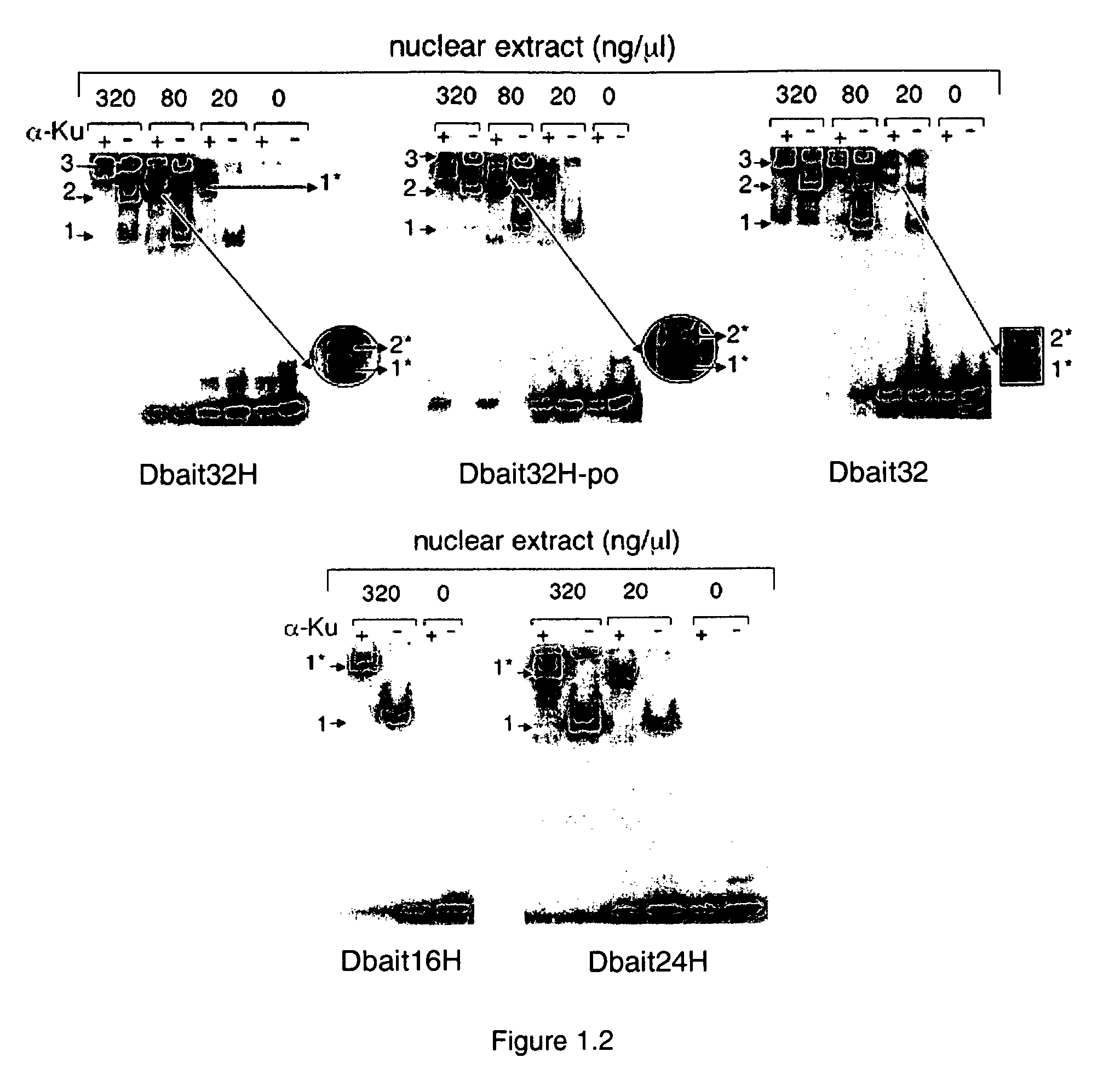
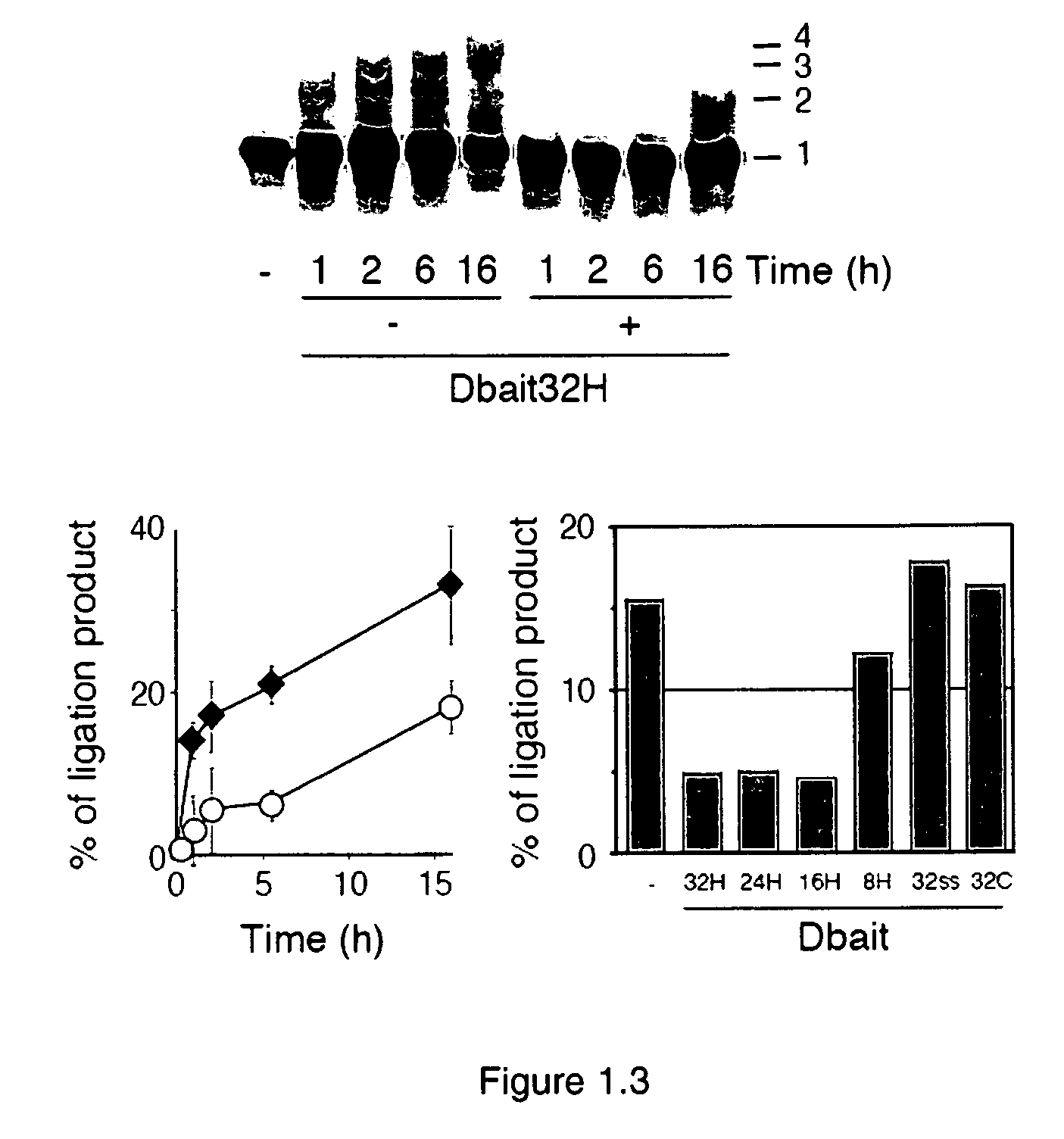
Dbait and uses thereof
The invention relates to compositions and methods for interfering with the DNA repair of double strand breaks (DSBs). The invention discloses novel double-stranded nucleic acid molecules that act as baits and hijack the holocomplex of enzymes responsible of DNA DSB sensing, signaling and / or repair pathways, in particular the non homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DSB repair. The invention discloses the use of these molecules as adjuvant compositions to be used in association with a DNA breaking treatment, particularly radiotherapy or chemotherapy, in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, in an efficient amount to be introduced in the tumor cell nuclei in order to neutralize transiently their DNA repair capacity and trigger their death.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +3
Novel methylation library construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN108166069AReduce lossesImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationDna breakageA-DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology and in particular relates to a novel methylation library construction method and an application thereof. The novel methylation libraryconstruction method provided by the invention is suitable for single-strand connection, amplification or library construction of a DNA sample treated by using bisulfite. Due to the adoption of a method for bisulfite treatment and then adhesive end joint connection, sample information loss caused by DNA breakage resulted from drug treatment is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
SgRNA, CREBRF point mutation-type Bama miniature pig constructed by sgRNA and application
ActiveCN110862988ASpecific bindingPromote homologous recombination repairMetabolism disorderPeptidesBiotechnologySingle strand
The invention provides sgRNA, a CREBRF point mutation-type Bama miniature pig constructed by the sgRNA, and application. The sgRNA comprises a nucleic acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ IDNO: 2. According to the invention, a scheme of combining CRISPR / Cas9 with homologous recombination is adopted, point mutation of CREBRF gene is carried out, the designed gRNA has specific binding property on a target site near the 1370th site of the CEREBRF gene, the CRISPR / Cas9 can be guided to carry out specific recognition cutting near the target site, double-stranded DNA breakage is formed, homologous recombination repair with exogenous single-stranded DNA as a template is promoted, and therefore the point mutation is introduced. The mutant Bama miniature pig prepared by the method has a typical obesity phenotype and can be used as a model organism to be applied to the field of research and development of medicines for treating obesity and diabetes.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pseudobagrus sperm preservation solution and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of fish sperm preservation solutions, in particular to a pseudobagrus sperm preservation solution for solving the problem of pseudobagrus large scale reproduction and a preparation method of the pseudobagrus sperm preservation solution. The sperm preservation solution is prepared from sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, glucose and penicillin and is prepared by weighing the raw materials, adding the raw materials in a plastic bottle or a glass bottle, and preparing into a solution with distilled water. The prepared sperm preservation solution is subjected to sperm chromatin detection with a flow cytometer, spermatids are circled on an FSC / SSC graph, and a door is set on an FL1(FITC) / FL3(ECD) scatter diagram for analysis; and a DNA fragment index at is calculated through a formula to evaluate sperm DNA quality. The sperm preservation solution provided by the invention can be preserved for 10 days in a refrigeration tank at the temperature of 4 DEG C, 98 percent or more of sperms keep exuberant vigor and can still be taken as sperms for semination, and the fertilization rate is 95 percent orabove.
Owner:河南省水产科学研究院
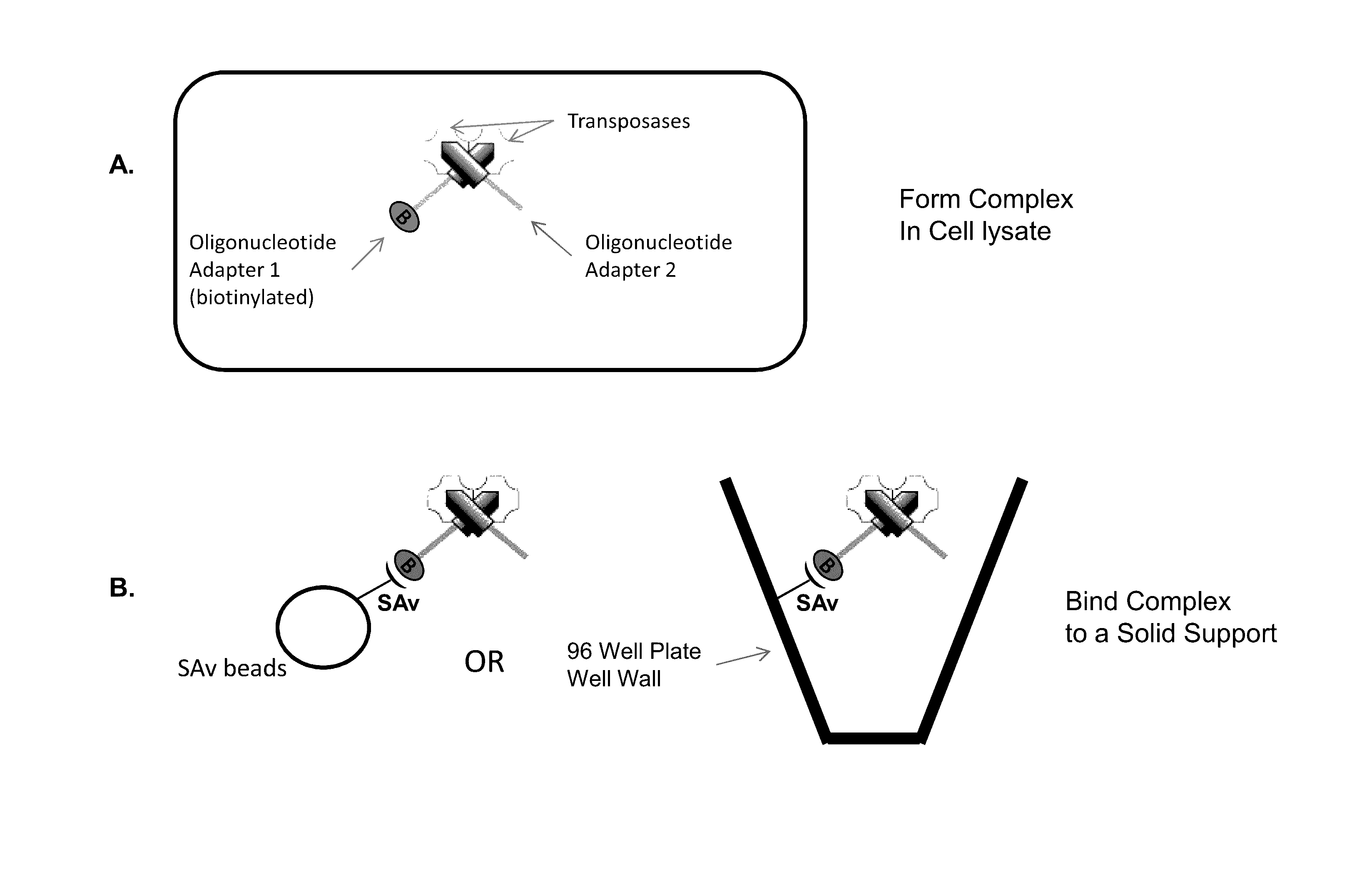
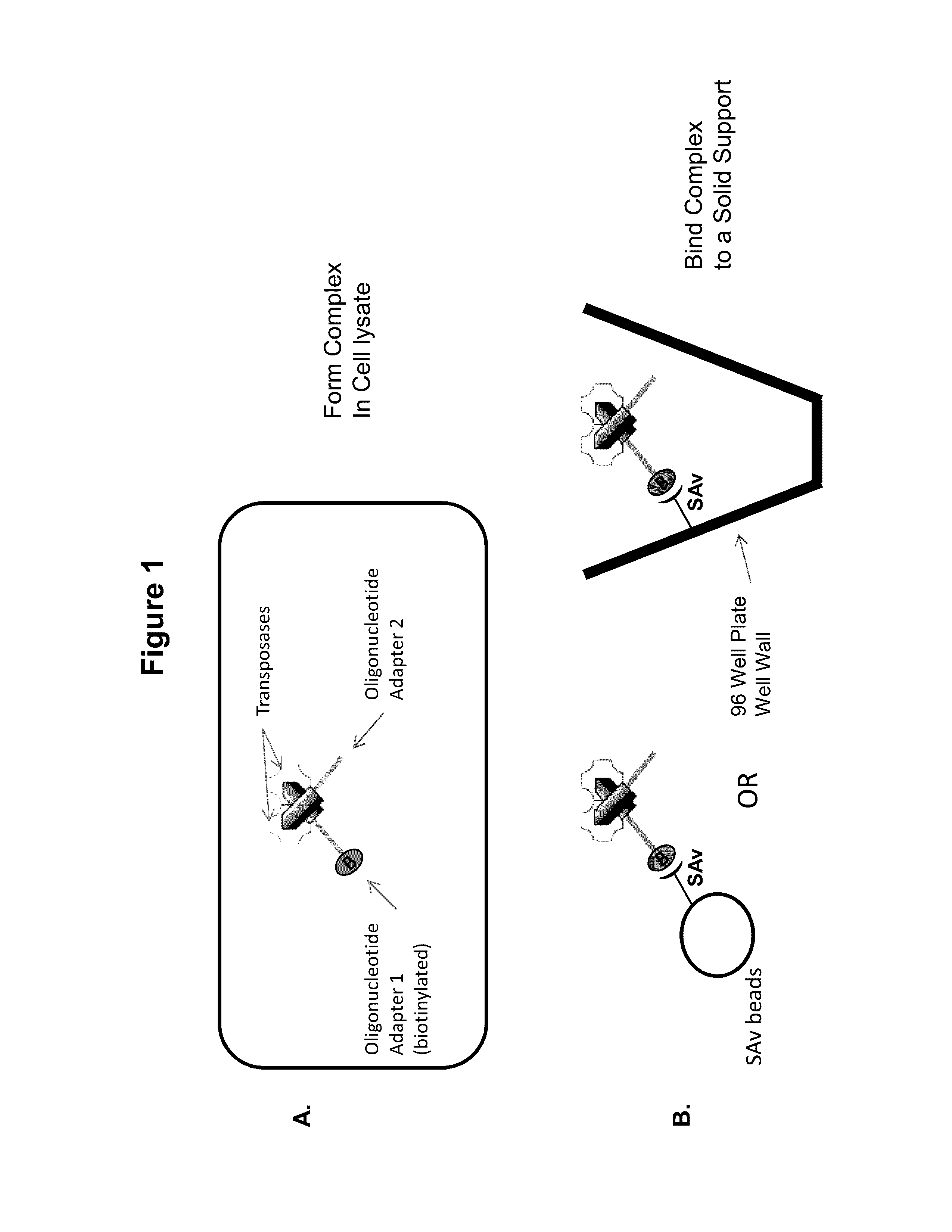
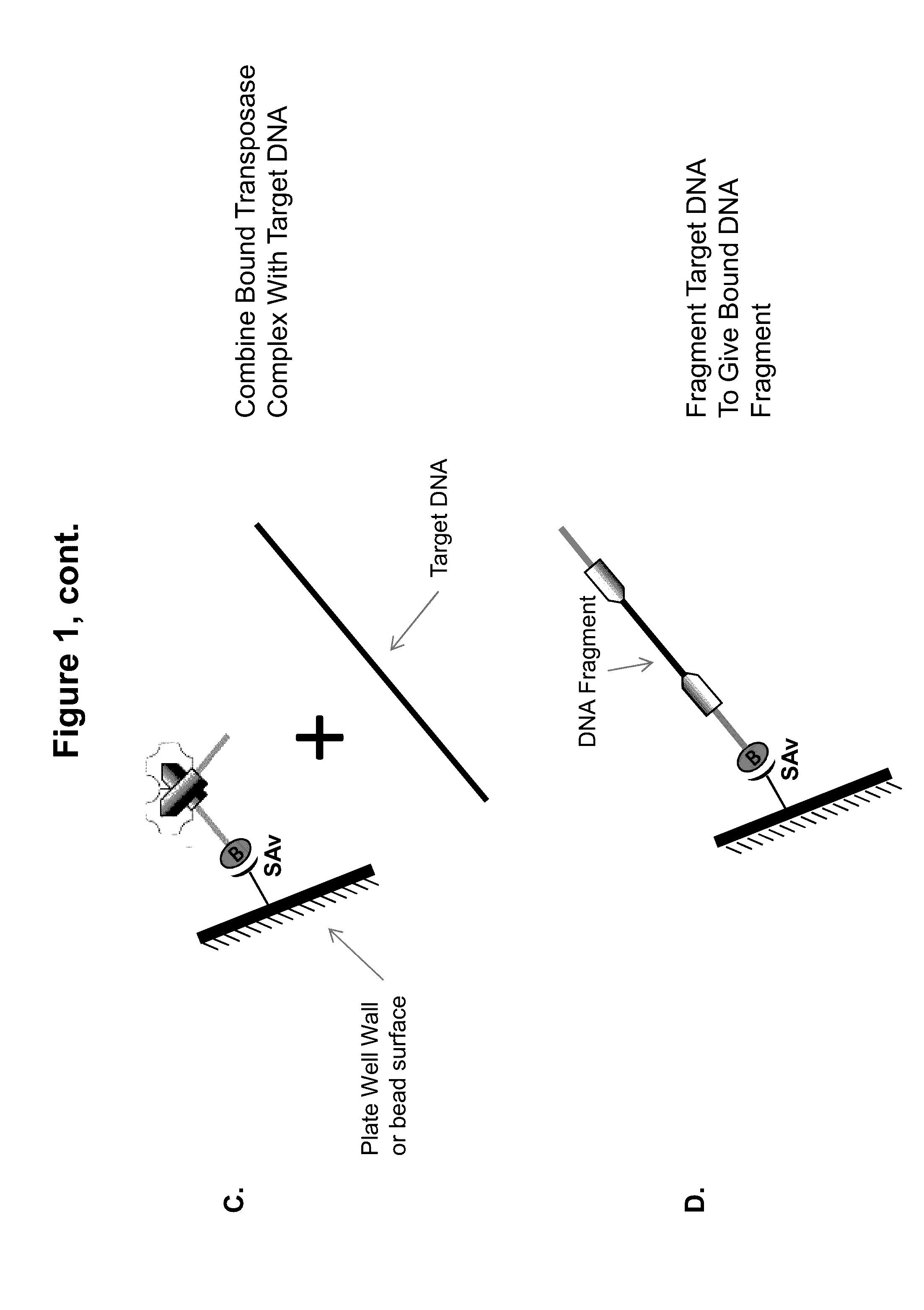
Immobilized Transposase Complexes For DNA Fragmentation And Tagging
ActiveUS20170058326A1Superior property and characteristicHigh activityHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDna breakageDNA fragmentation
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Cell-responsive ruthenium complex anticancer drug and preparation method thereof
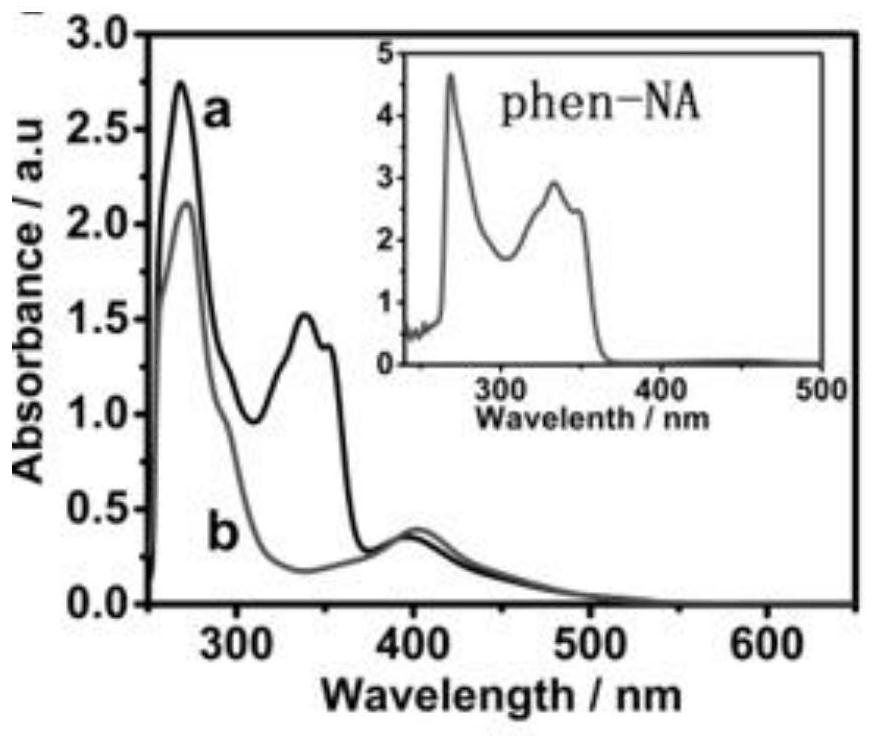
ActiveCN110028529AImprove bindingGood antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsRuthenium organic compoundsDna breakageRuthenium
The invention relates to the technical field of anticancer drugs, in particular to a ruthenium complex anticancer drug and a preparation method thereof. The ruthenium complex anticancer drug is activated through redox, inserted into tumor cell DNA, and coordinated with DNA to undergo a crosslinking reaction, so as to prevent DNA replication and DNA breakage. Due to the introduction of a planar structure ligand, namely, 1,8-naphthalic anhydride, the binding capacity of the drug to DNA is enhanced by 14.17 times, and the stability and anti-tumor activity of the anticancer drug are greatly improved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
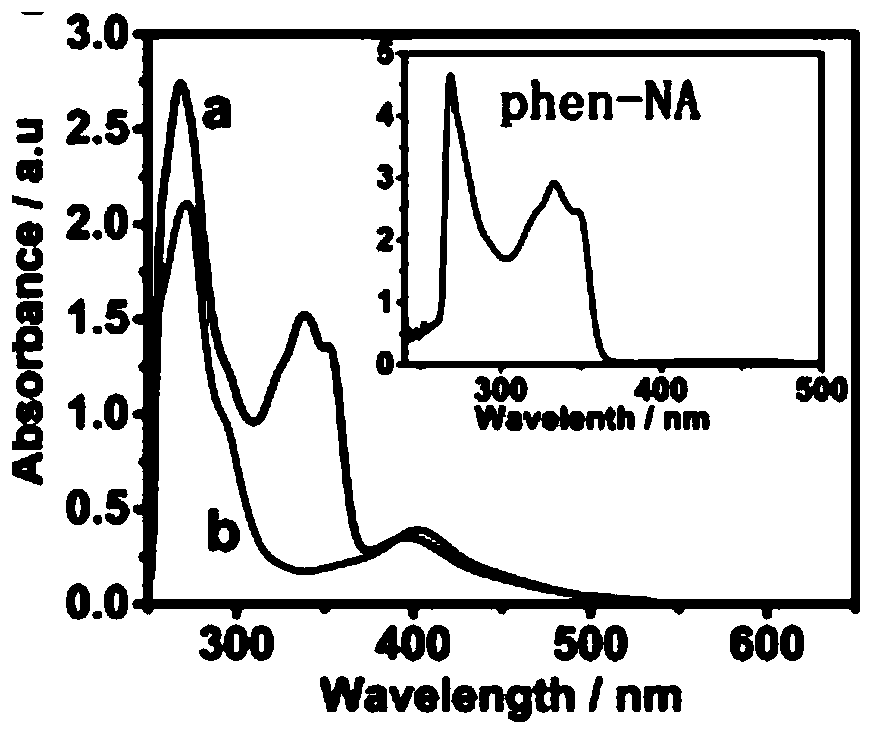
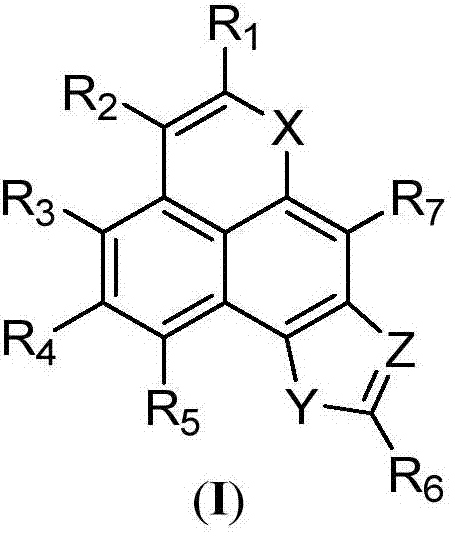
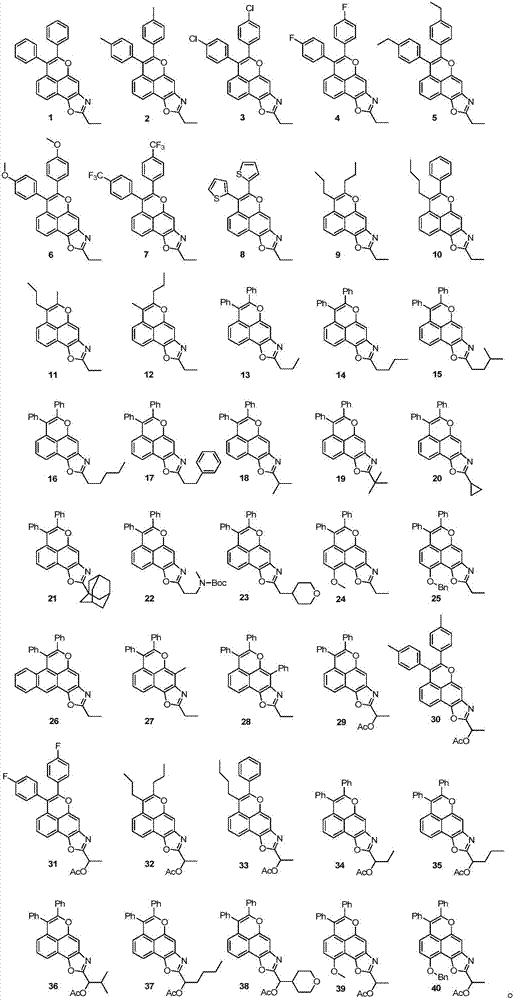
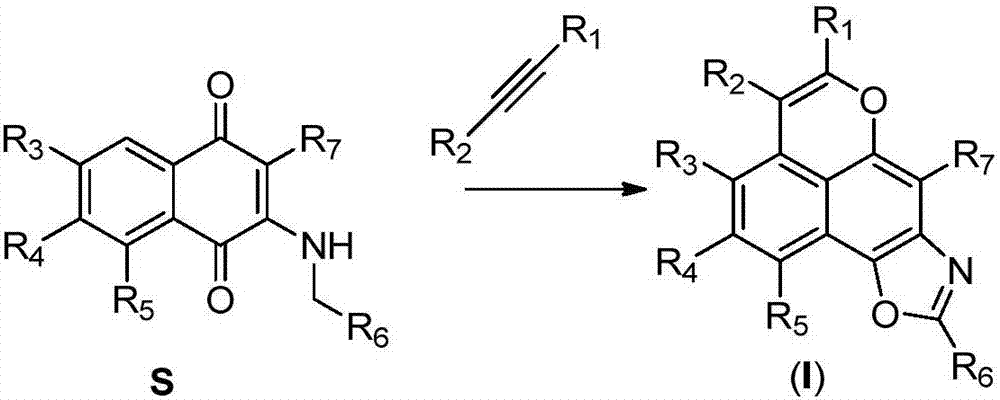
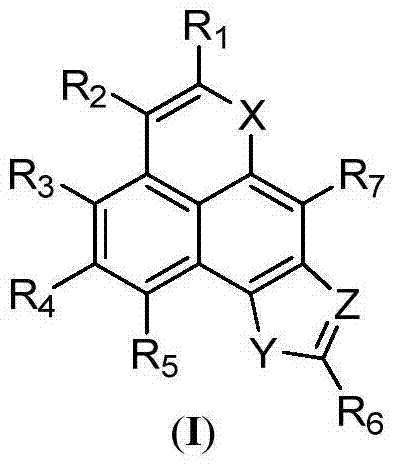
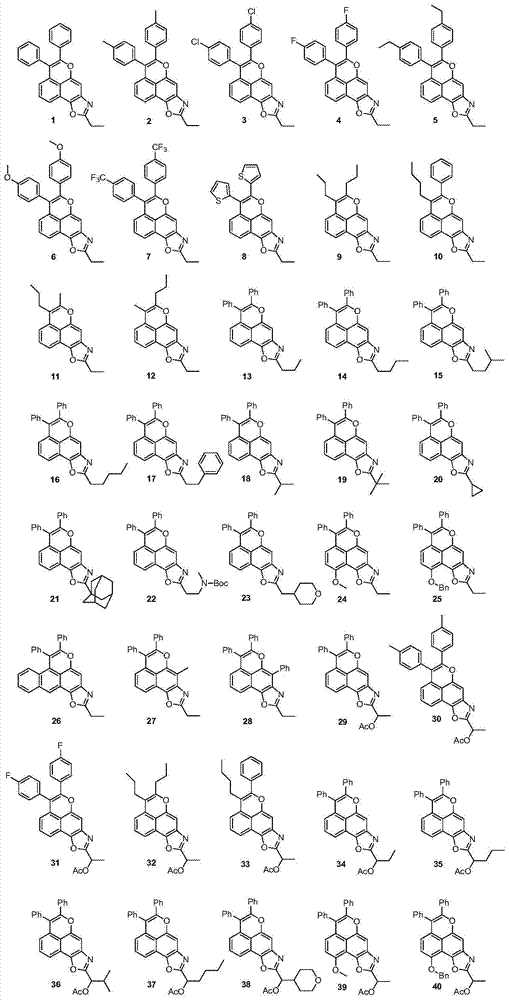
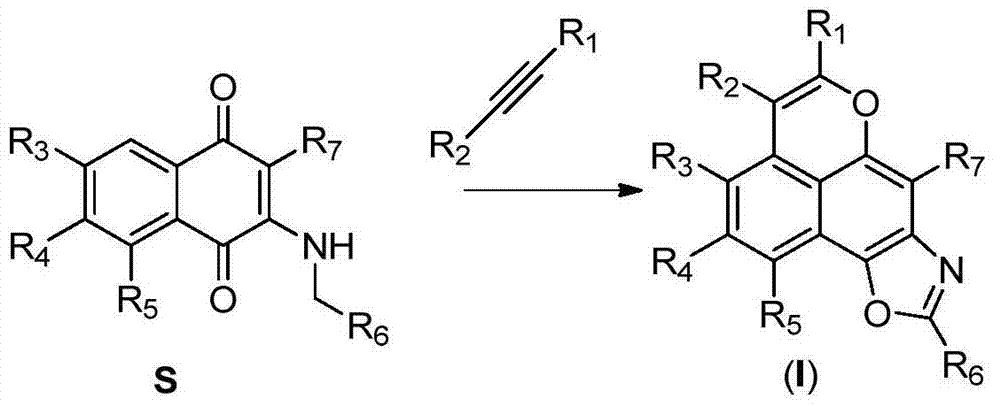
A class of tetracyclic naphthoxazole derivatives and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104761568BInhibit proliferation and growthCascade reaction is simple and easyAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsGrowth retardantQuinone
The invention discloses a novel tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative. The structure of the novel tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative is represented by general formula (I) shown in the specification. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative. The method allows the tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative to be innovatively synthesized through using a carbon hydrogen activation serial reaction with amino substituted quinone as a reaction substrate. The method has the advantages of simplicity, easy implementation and high efficiency. The synthetic tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative has a similar structure with a traditional DNA clastogen, can inhibit cell proliferation and growth, and has antibacterial, antifungal, anti-HIV and antitumor bioactivity. The invention also discloses an application of above compounds as a cell proliferation and growth inhibitor, and an application of the compounds in the preparation of antitumor medicines.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104761568AInhibit proliferation and growthCascade reaction is simple and easyAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsGrowth retardantQuinone
The invention discloses a novel tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative. The structure of the novel tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative is represented by general formula (I) shown in the specification. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative. The method allows the tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative to be innovatively synthesized through using a carbon hydrogen activation serial reaction with amino substituted quinone as a reaction substrate. The method has the advantages of simplicity, easy implementation and high efficiency. The synthetic tetracyclonaphthooxazole derivative has a similar structure with a traditional DNA clastogen, can inhibit cell proliferation and growth, and has antibacterial, antifungal, anti-HIV and antitumor bioactivity. The invention also discloses an application of above compounds as a cell proliferation and growth inhibitor, and an application of the compounds in the preparation of antitumor medicines.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
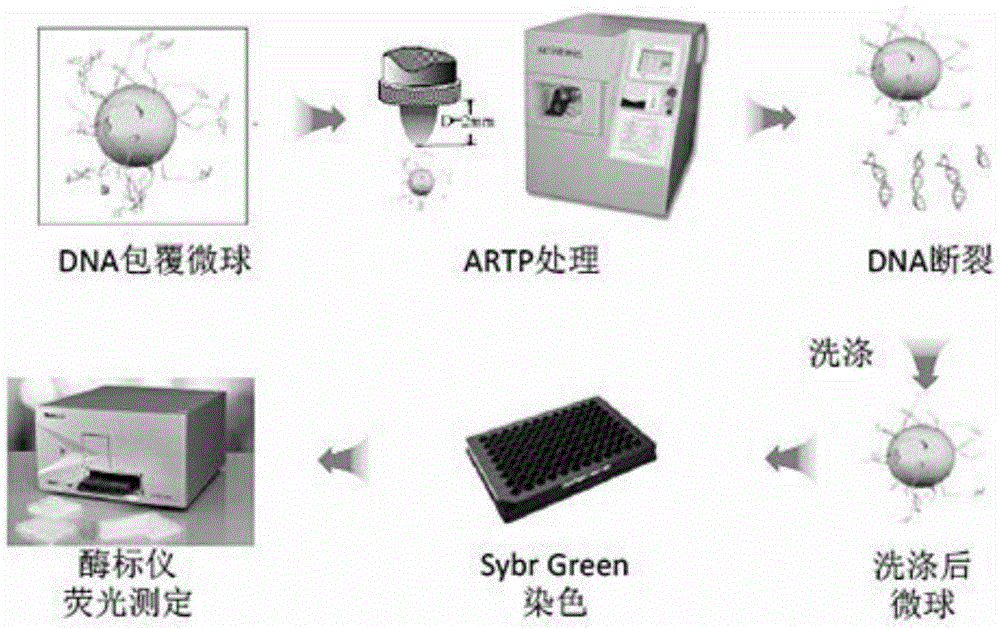
Method for rapid detection of in vitro DNA break damage strength by plasma
The invention relates to a method for rapid detection of in vitro DNA break damage strength by plasma, and the method is used for determining the damage strength of plasma mutagenesis methods including atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) on DNA. The method includes the steps of: 1) treating DNA coated microspheres by plasma mutagenesis method, and setting a control group without plasma treatment; 2) performing washing, and then dyeing the DNA coated microspheres with a dye; 3) determining the fluorescence value of the dyed DNA coated microspheres by a fluorescence detector; and 4) calculating the DNA relative content of the control group and the plasma mutagenesis treated microspheres according to the fluorescence value, and judging the gene damage strength of plasma. The invention utilizes DNA coated microspheres to establish a rapid detection method for in vitro DNA damage strength so as to realize direct and effective evaluation of plasma caused damage strength to DNA.
Owner:WUXI TMAXTREE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Bacterial genome multi-editing method based on double-stranded DNA recombinant engineering and application thereof
PendingCN114085831AEfficiently mediates editingLow cost of substrate preparationNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionDna breakageCompetent cell
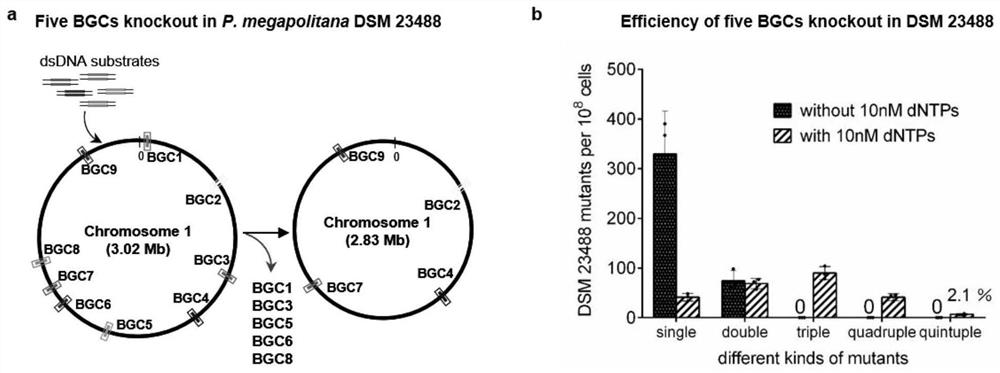
The invention belongs to the technical field of engineering, and particularly relates to a bacterial genome multi-editing method and application thereof. The bacterial genome multi-editing method based on double-stranded DNA recombinant engineering comprises the following steps: (1) mixing dsDNA substrates targeting different target sequences, and introducing the mixed dsDNA substrates into host competent cells with recombinase plasmids; (2) recovering the competent cells at the temperature lower than the optimum growth temperature; dNTPs with the final concentration of 10 nM is added in the resuscitation process; and (3) screening out a single colony with a marker from the recovered competent cells, and identifying. The method has the advantages that the substrate preparation cost is low, the length of the inserted gene is not limited, the method is not dependent on double-stranded DNA breakage, a plurality of guide RNA expression vectors do not need to be constructed, and a restrictive repair system of host bacteria does not need to be inactivated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods and systems for reducing DNA fragmentation in a population of sperm cells
InactiveCN102666841AReduce breakageIncrease incidenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDna breakageDNA fragmentation
Owner:INGURAN LLC
A method of DNA amplification
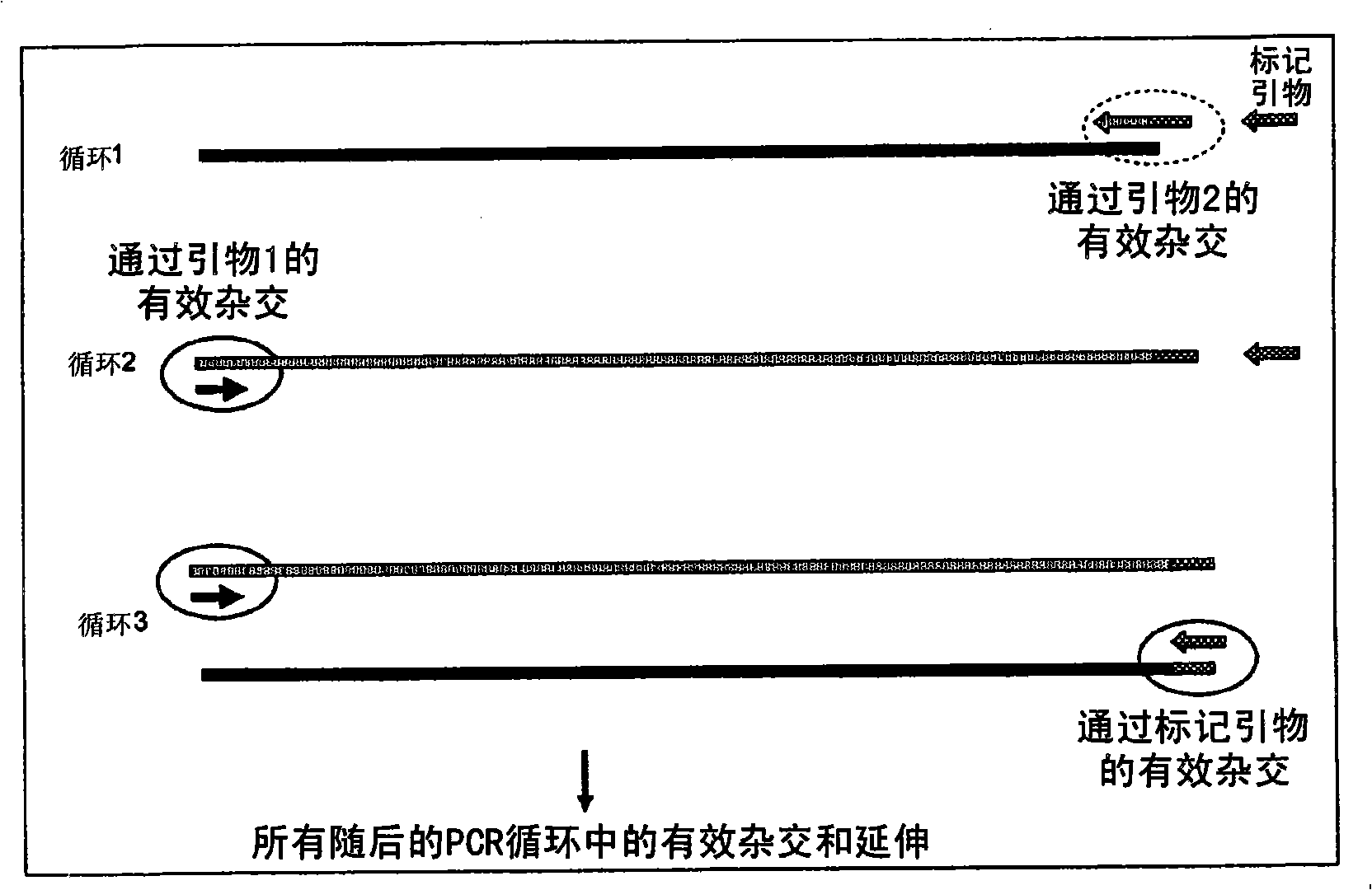
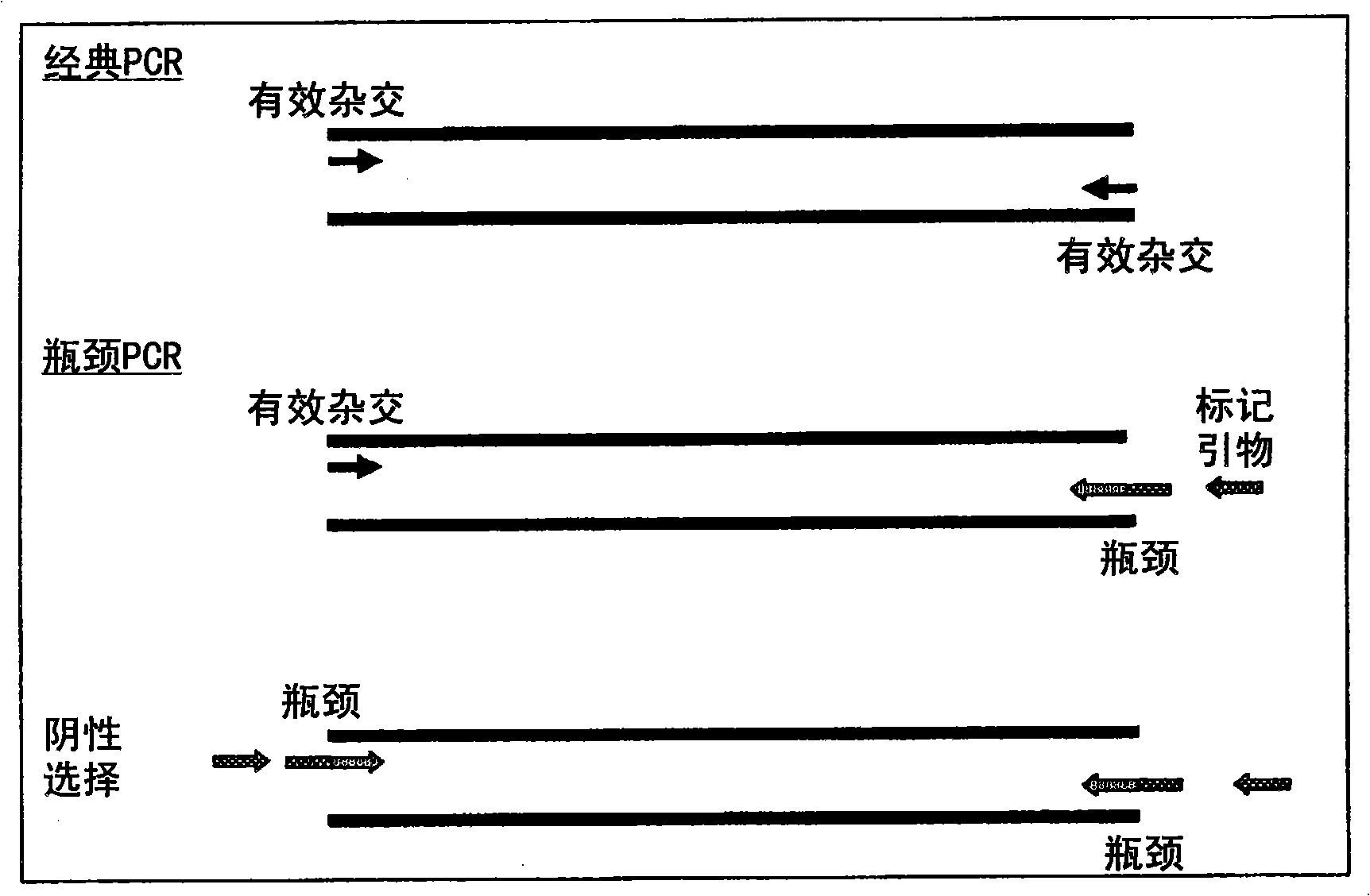
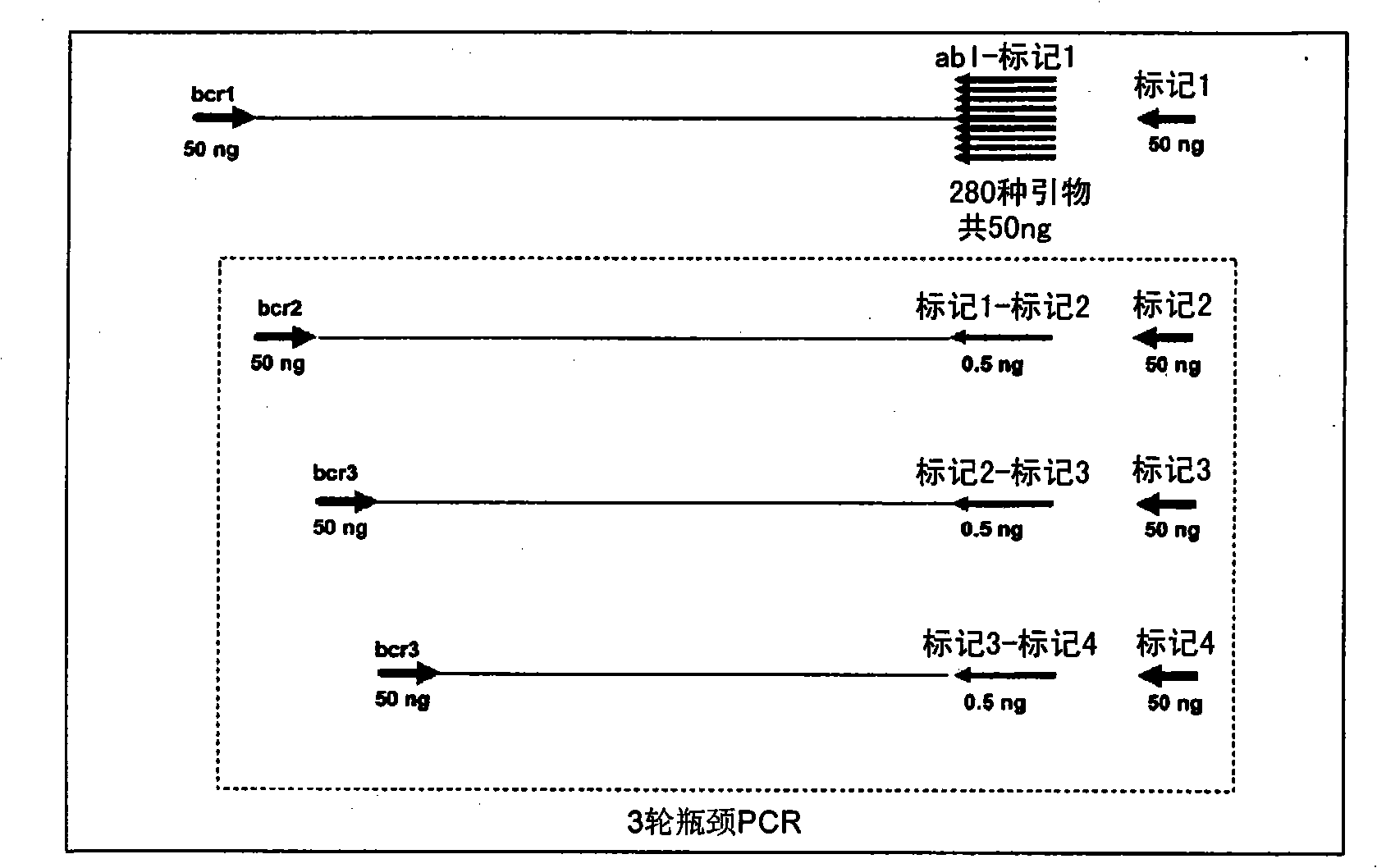
The present invention relates generally to a method of amplifying a nucleic acid region of interest and, more particularly, to a method of amplifying a nucleic acid region of interest using a PCR method designed to minimise the generation of amplicons from primers which have bound to nucleic acid regions other than the specific region of interest. The method of the present invention is based on the determination that by rendering inefficient the functionality of either the forward primer or the reverse primer, the rate of amplification of irrelevant nucleic acid regions can be reduced relative to amplification of the region of interest. The provision of a selective means of amplifying a nucleic acid region of interest is useful in a range of applications including, but not limited to, the diagnosis and / or monitoring of disease conditions which are characterised by specific gene sequences, the characterisation or analysis of gene regions of interest, the identification or characterisation of DNA breakpoint regions and the isolation of gene sequences of interest where only the nucleotide sequence at one end of the gene sequence of interest is known.
Owner:MONOQUANT PTY LTD
Method of modifying genome of organism and use thereof
ActiveUS20180371477A1Effective genomic modificationReduce loadMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant preparationDna breakageBiological body
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +2
Polypeptide for Genome Shuffling in Plants, and Use Therefor
ActiveUS20180305708A1Reduce the impactHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDna breakageGenome shuffling
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Nucleic acid sample treating method, sequencing method and kit
ActiveCN112391442ASave operating timeEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDna breakageEnzyme system
The invention provides a DNA sample treating method, a sequencing method and a kit. The method for treating a DNA sample comprises the following steps: performing fragmentation, terminal repair and dAtail addition on DNA in a first premixed system to obtain a first product, wherein the first premixed system comprises premixed enzyme, and the premixed enzyme comprises DNA fragmentation enzyme, polynucleotide kinase and DNA polymerase. Based on test experiments and an optimized mixed enzyme system, multiple enzymes are mixed in the same reaction system, DNA breakage, terminal repair and dA tailaddition are realized in one step, the convenience and rapidness are achieved, the operation time of sample treatment before loading is saved, and therefore the industrialization is facilitated.
Owner:GENEMIND BIOSCIENCES CO LTD
Genome-wide analysis of APA based on 3t-seq
InactiveCN103911449BAvoid damageHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementPoly-A RNABiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention relates to a method for detecting a PAS (Poly A Site) of an RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid), and provides a method for analyzing APA (Alternative Polyadenylation) based on 3T-seq (TT-mRNA Terminal Sequencing) within a whole-genome range. The method for analyzing APA comprises the following steps: preparing magnetic beads containing oligo dT, i.e., mixing an oligo dT primer modified by 5' end biotin and the magnetic beads with streptavidin; mixing the magnetic beads with total RNA and screening RNA containing Poly A; performing reverse transcription, synthesizing the second strand of a double-stranded cDNA and breaking the double-stranded cDNA; removing the Poly A structure; after terminal modification, connecting a sequencing linker; and recovering libraries. According to the method for analyzing APA, RNA horizontal operation is reduced, a Poly A sequence is horizontally removed from the DNA, and the influence of the Poly structure on sequencing is eliminated; double-stranded DNA breaking enzyme is selected for treatment, and on the premise that the quality of the libraries is not affected, the DNA is broken horizontally; the experiment process is simplified, the experiment difficulty and cost are lowered and the method for analyzing APA is wide in application range.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
New application of astragalus polysaccharide
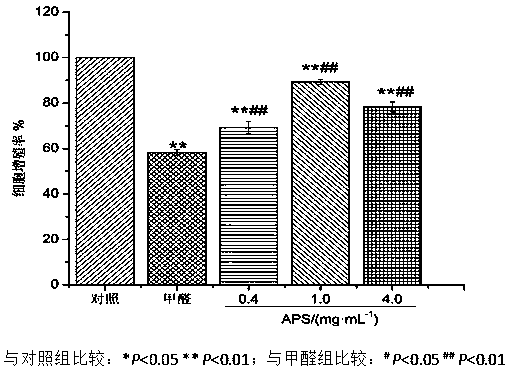
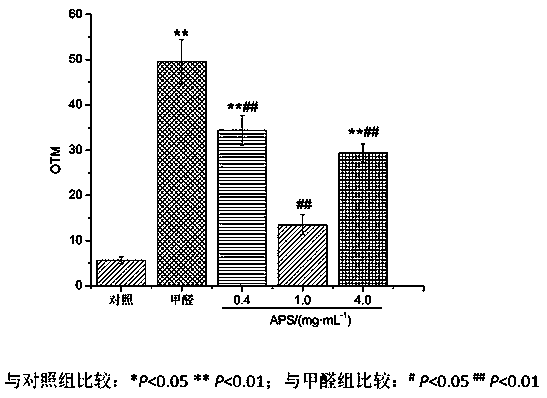
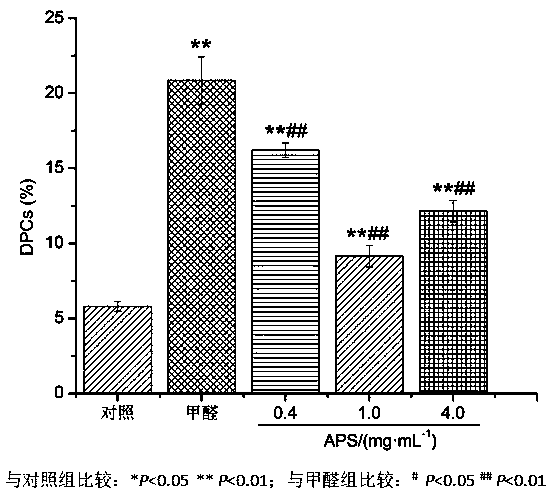
InactiveCN110179813AIncrease proliferative activityReduced DNA Fragmentation EffectsOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsProliferation activityLeukemia
The invention discloses a new application of astragalus polysaccharide, and belongs to the technical field of biology medicine. A basis is provided for preventing and treating myoblastosis through radix astragali. The inventor of the invention finds that the astragalus polysaccharide can obviously reinforce the proliferation activity of human BM-MSCs in formaldehyde environment, and can reduce DNAfragmentation and DPCs formation of human BM-MSCs induced by formaldehyde so as to have good protection effects. The astragalus polysaccharide can promote DNA injury repair factors of XPA, XPC, ERCC1, RPA1 and RPA2 mRNA and protein expression, and improve DNA damage repair capacity. The inventor finds that the astragalus polysaccharide can reinforce the proliferation activity of human BM-MSCs inthe formaldehyde environment for the first time, can reduce the DNA fragmentation effects of the human BM-MSCs in the formaldehyde environment and can reduce the DPCs formation of the human BM-MSCs inthe formaldehyde environment.
Owner:GANSU UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
A high temperature compound method for extracting genomic DNA of fish gut microbes
ActiveCN105483120BStrong specificityTruly reflect the composition structureDNA preparationWater bathsDecomposition
The invention discloses a high-temperature combined method for extracting genomic DNA of fish enteric microorganisms. The high-temperature combined method includes the steps that firstly, the walls of various fish enteric microorganisms are properly broken through a lysozyme method and an ultrasonic method at the same time, wherein the ultrasonic physical wall breaking condition ranges from 150 w to 250 w, ultrasonic treatment is carried out for 2-3 s and then carried out again after an interval of 5 s, and the process is repeated 50-60 times; secondly, the sample obtained after ultrasonic treatment and lysozyme are jointly incubated for 30 min in a water-bath constant-temperature oscillator at the temperature of 55-65 DEG C, and the mixture and RNase A are jointly incubated at the temperature of 27-32 DEG C. According to the method, the walls of the various microorganisms are properly broken under the proper and mild ultrasonic condition, and the genomic DNA is prevented from being broken and degraded. As the specific temperature range for incubating the lysozyme and the sample and the specific temperature range for incubating the RNase A and the sample are set, the splitting decomposition effect of the lysozyme can be improved, and it can be avoided that the genomic DNA is degraded by DNA enzymes in tissues and cells. Operation is easy, the extracted genomic DNA is complete and low in degradation rate, and the fish enteric microorganism structure can be truly reflected by the types of the microorganisms identified according to the extracted DNA.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Intracellular responsive ruthenium complex anticancer drug and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110028529BImprove bindingGood antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsRuthenium organic compoundsDna breakagePharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to the technical field of anticancer drugs, and more specifically to a ruthenium complex anticancer drug and a preparation method thereof. The ruthenium complex anticancer drug is activated by redox, inserted into tumor cell DNA, and at the same time coordinates the DNA to undergo cross-linking reaction, prevent DNA replication, and cause DNA breakage. Due to the introduction of planar structure ligand 1,8‑naphthalene dicarboxylic anhydride, the drug’s ability to bind to DNA has been enhanced by 14.17 times, which greatly improves the stability and anticancer properties of anticancer drugs. tumor activity.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com