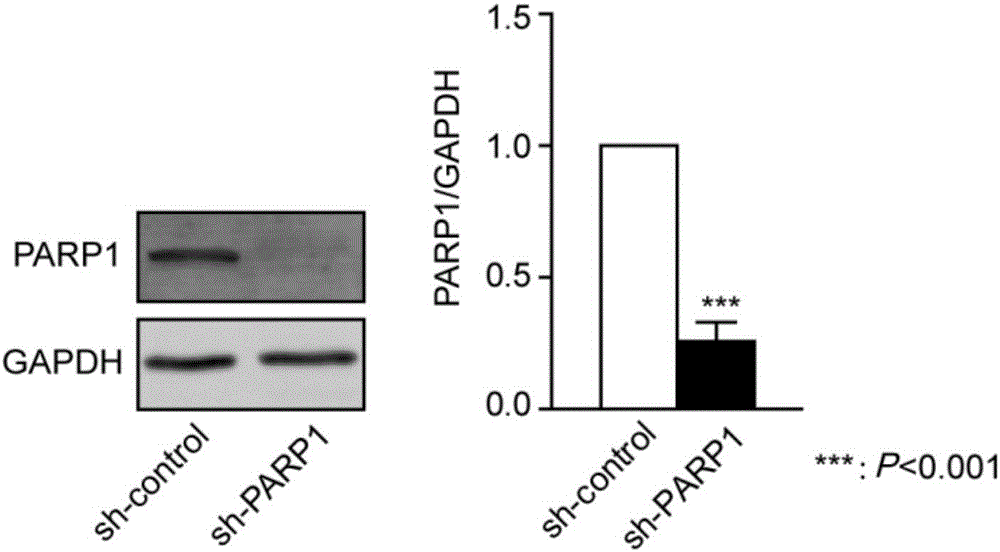
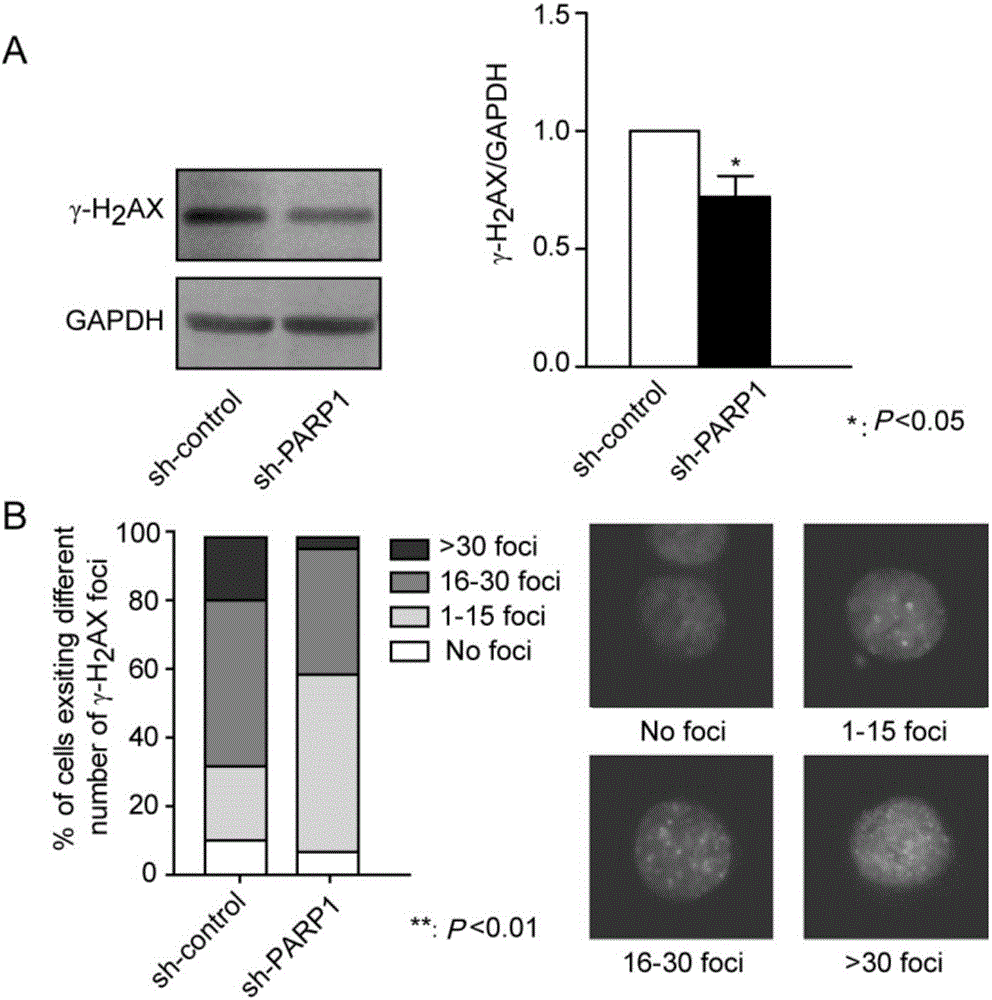
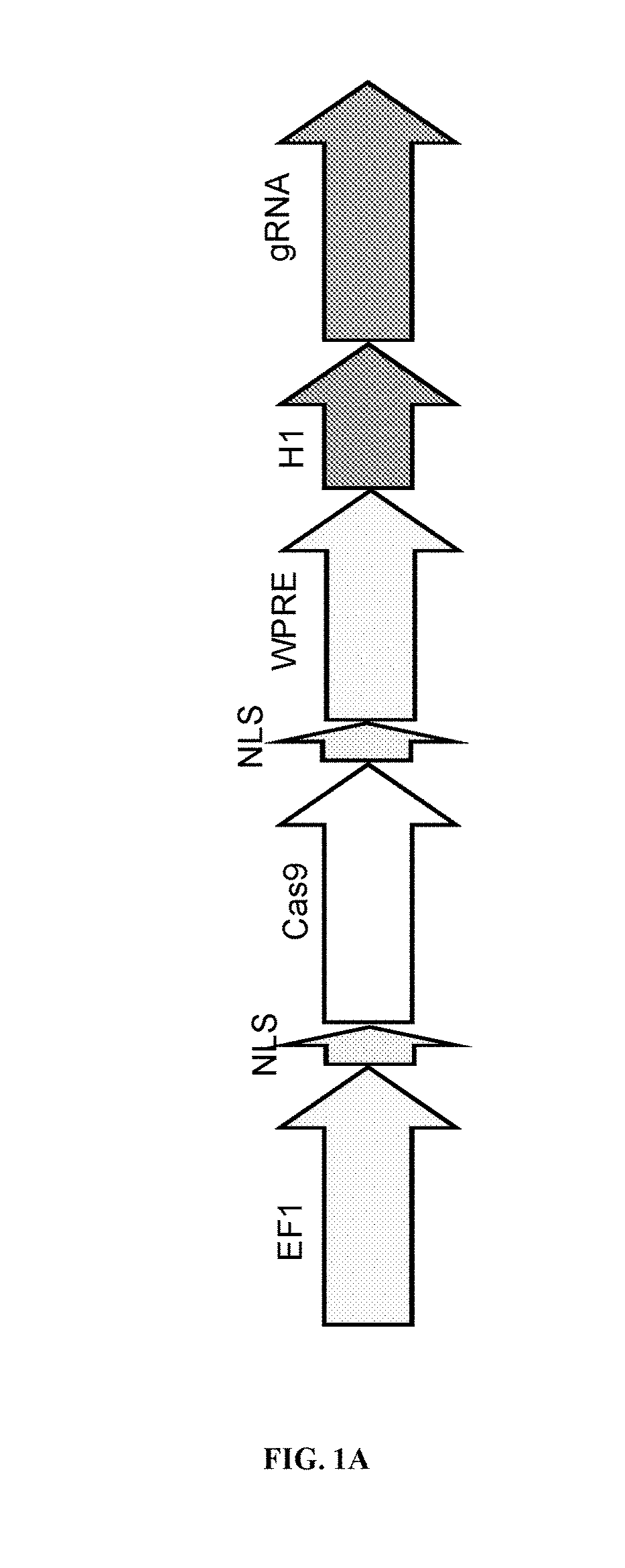
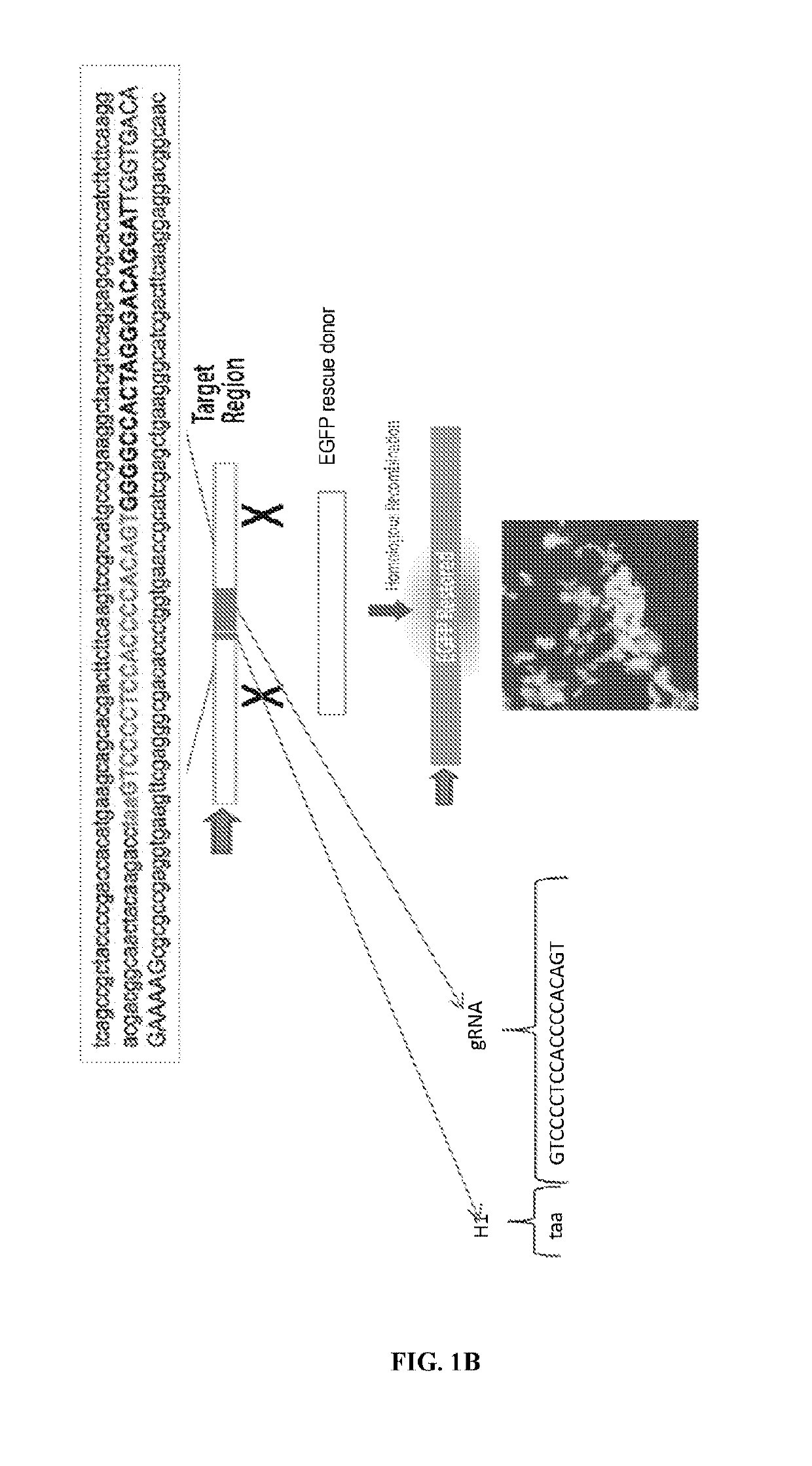
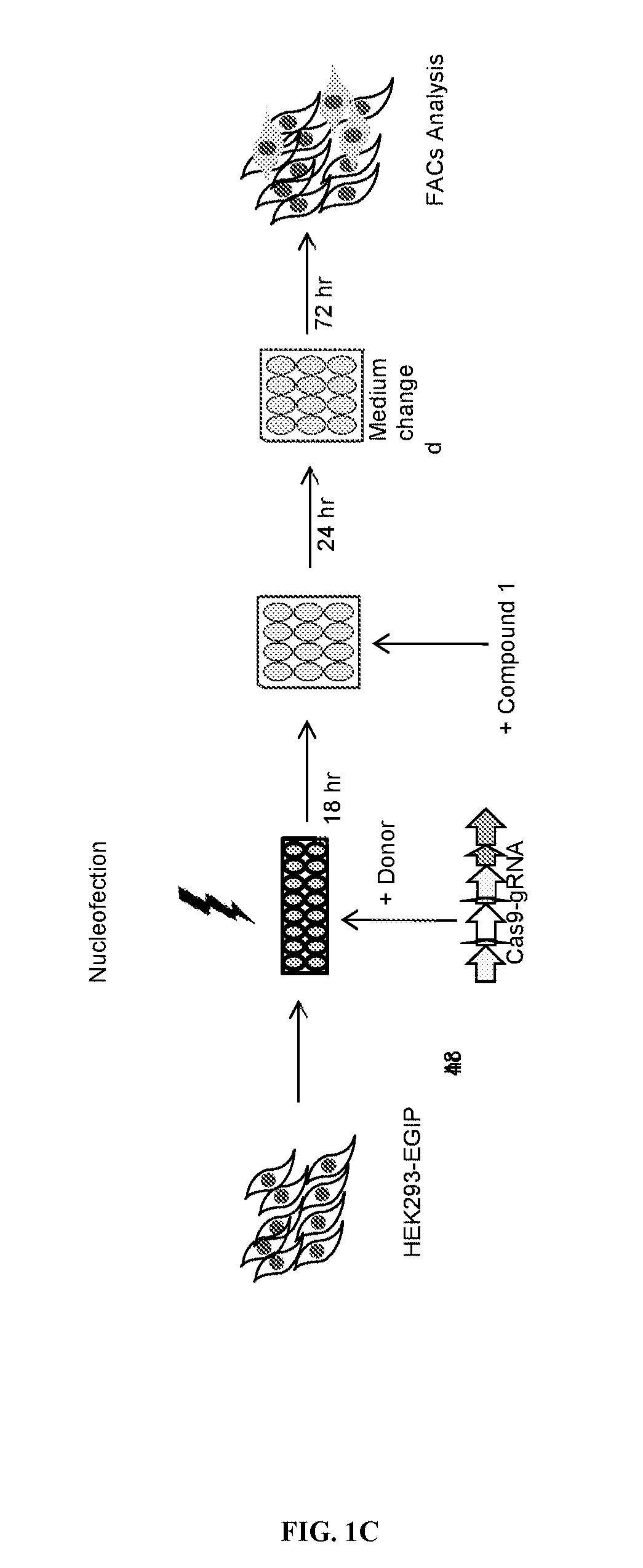
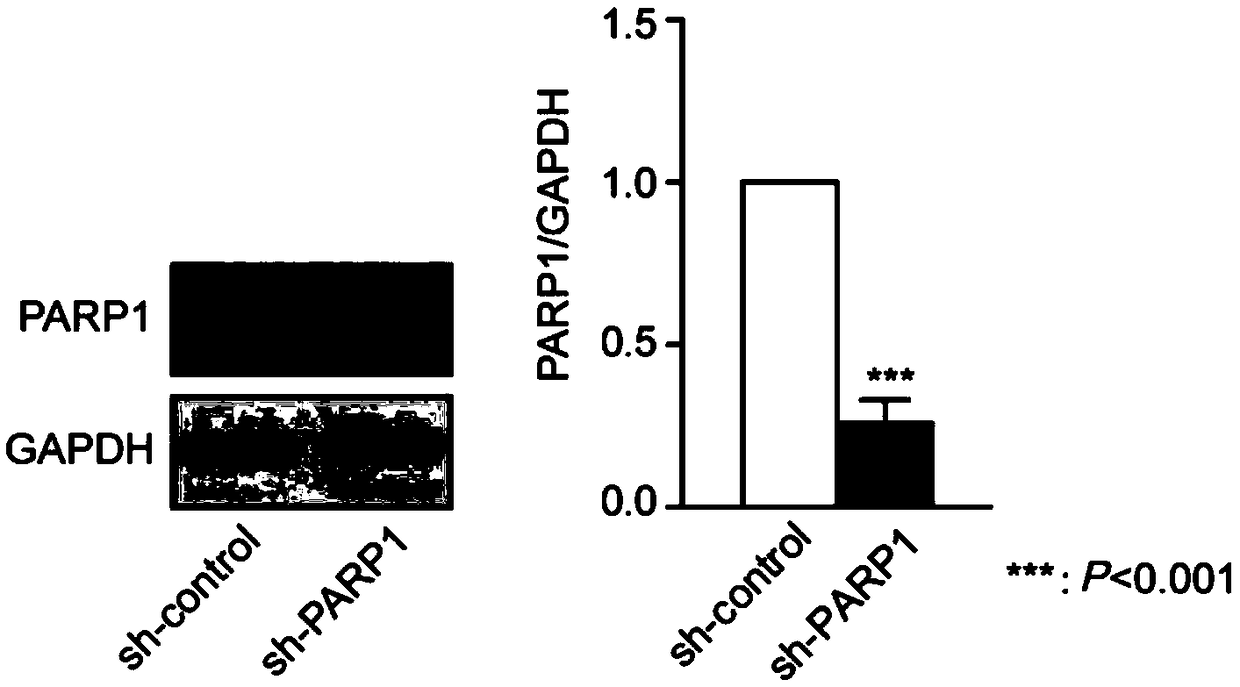
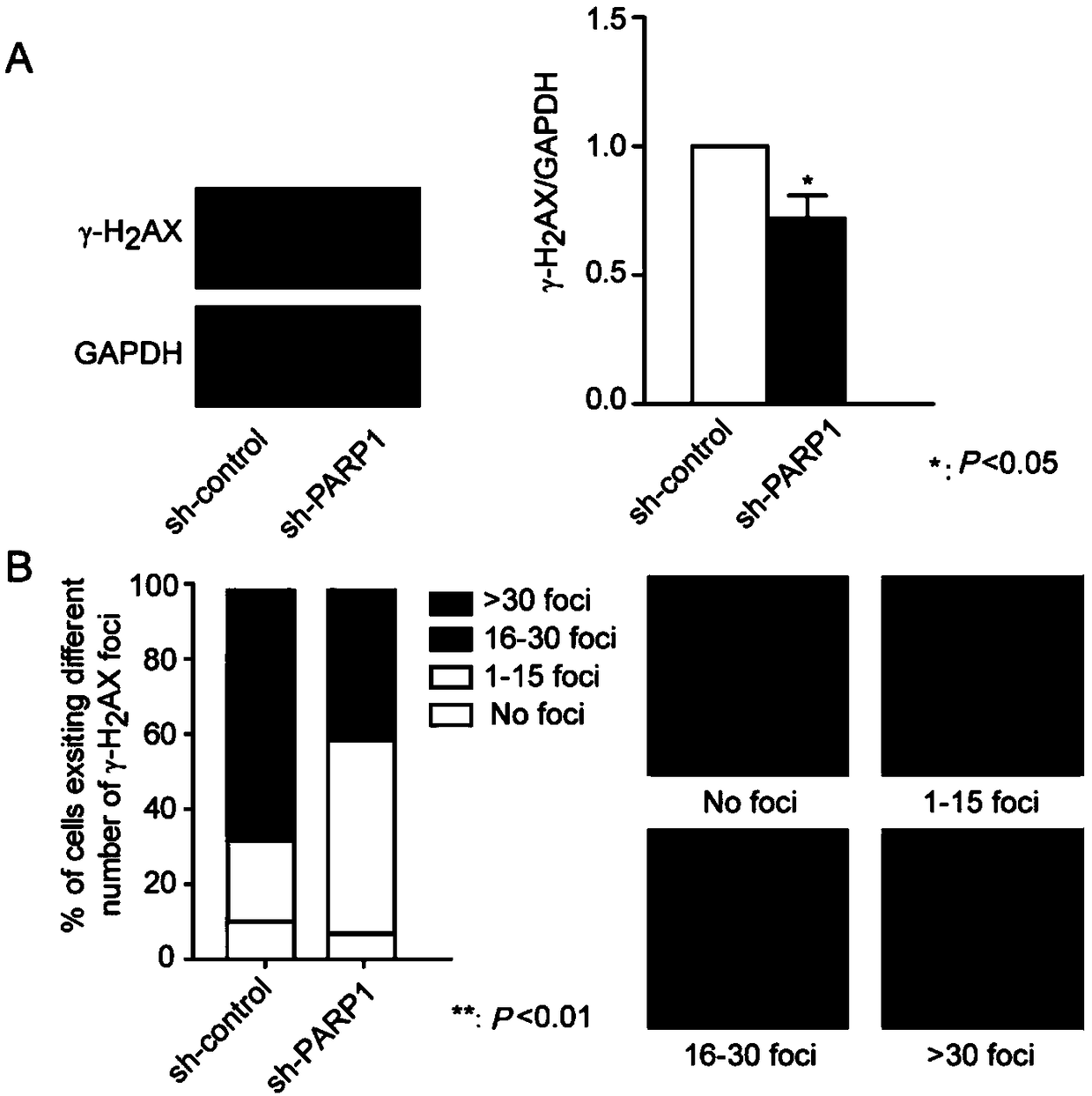
Patents
Literature
43 results about "NHEJ Pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
When the NHEJ pathway is inactivated, double-strand breaks can be repaired by a more error-prone pathway called microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ). In this pathway, end resection reveals short microhomologies on either side of the break, which are then aligned to guide repair.
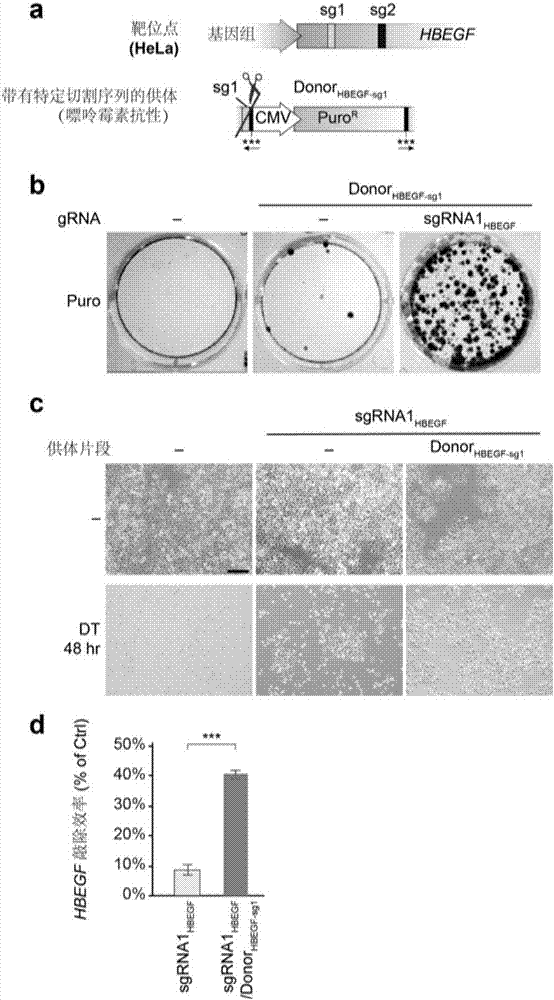
Method for improving efficiency of CRISPR mediated homologous recombination
InactiveCN106399367ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionSignalling pathwaysBiology
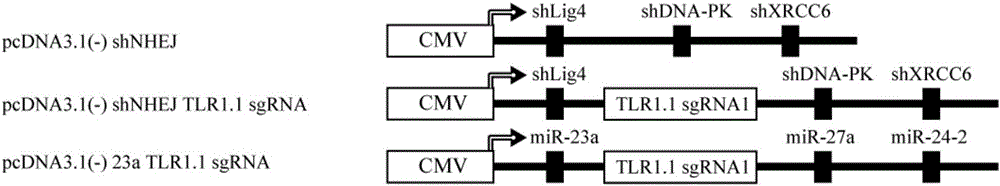
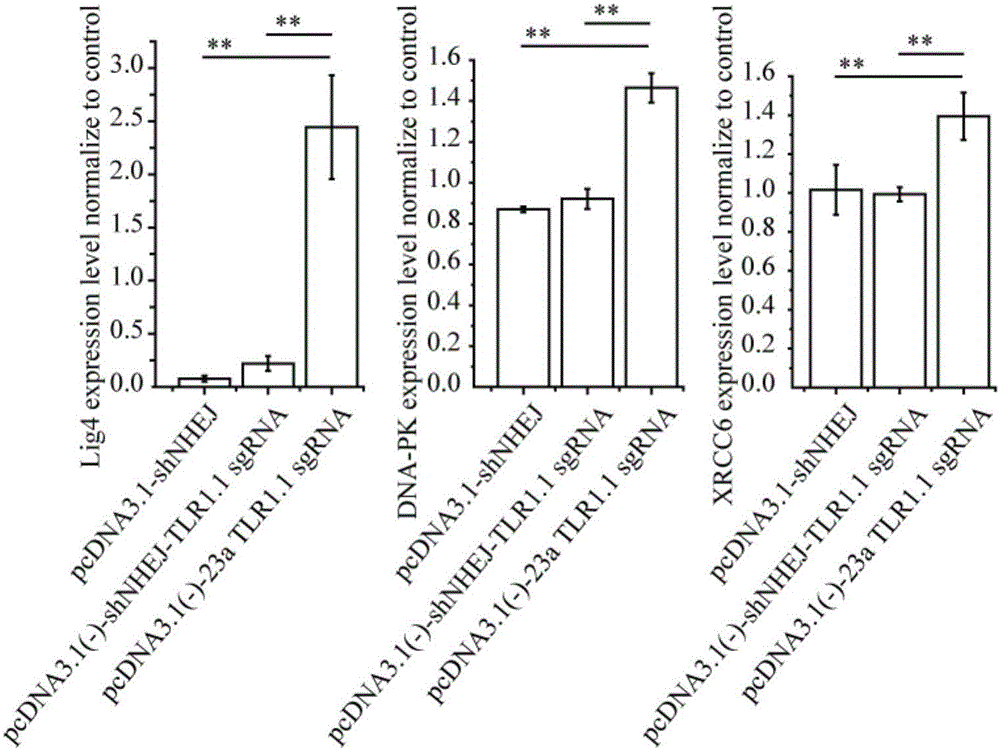
The invention discloses a method for improving the efficiency of CRISPR mediated homologous recombination. The method includes the steps of: inhibiting the expression of Lig4, DNA-PK and XRCC6 by shRNA so as to inhibit the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair pathway; conducting fusion expression on sgRNA and shRNA at targeting genome specific positions to form shRNA-sgRNA polycistron; and placing the polycistron at the RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III promoter downstream. The carrier constructed by the method provided by the invention has a concise structure and is convenient to use, also enhances the homologous recombination efficiency by dozens of times, greatly expands the function and application of the CRISPR carrier, and is a good tool for functional gene and signal pathway research, medical research, and recombinant protein expression.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEIGUANG BIOLOGICAL PROD
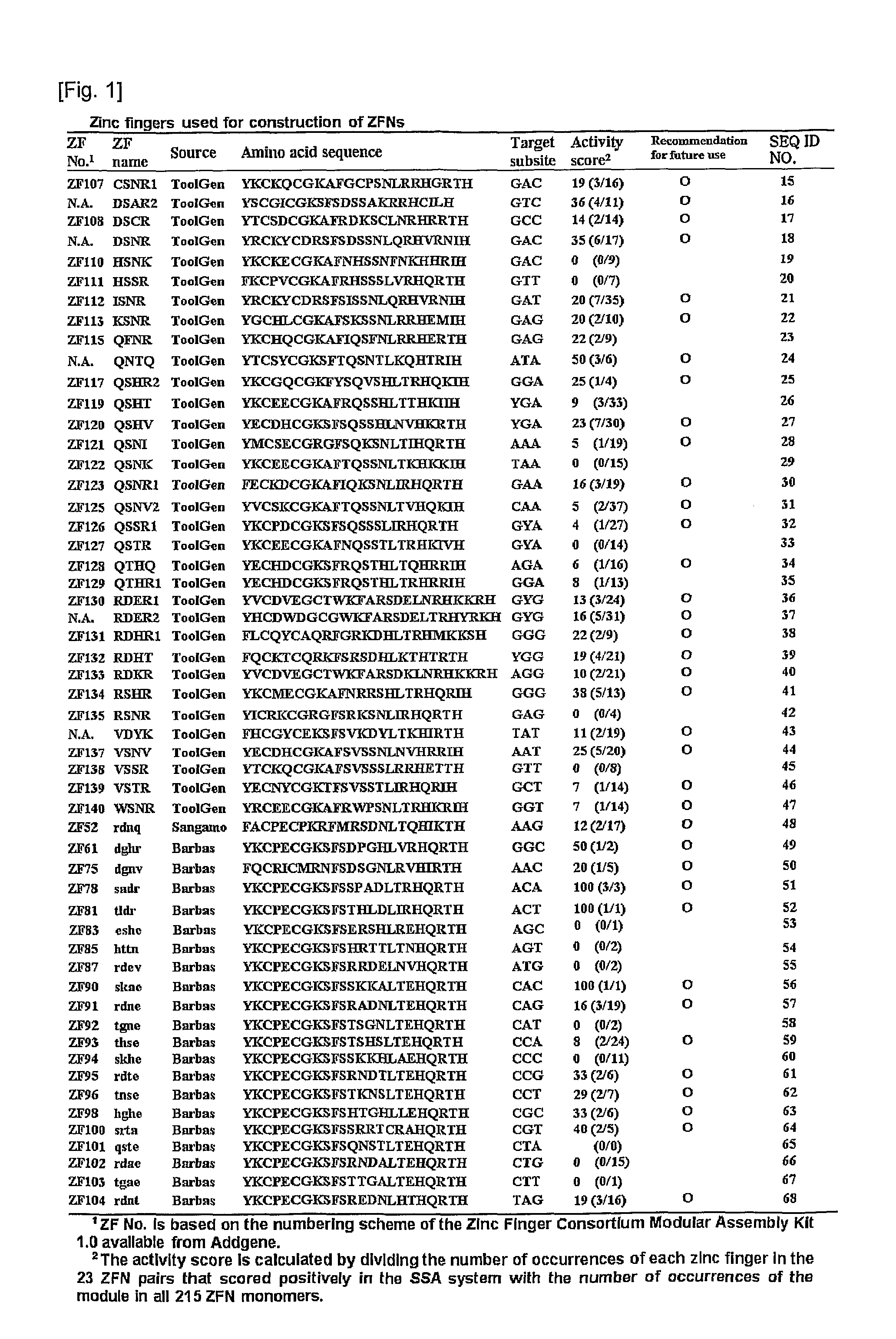
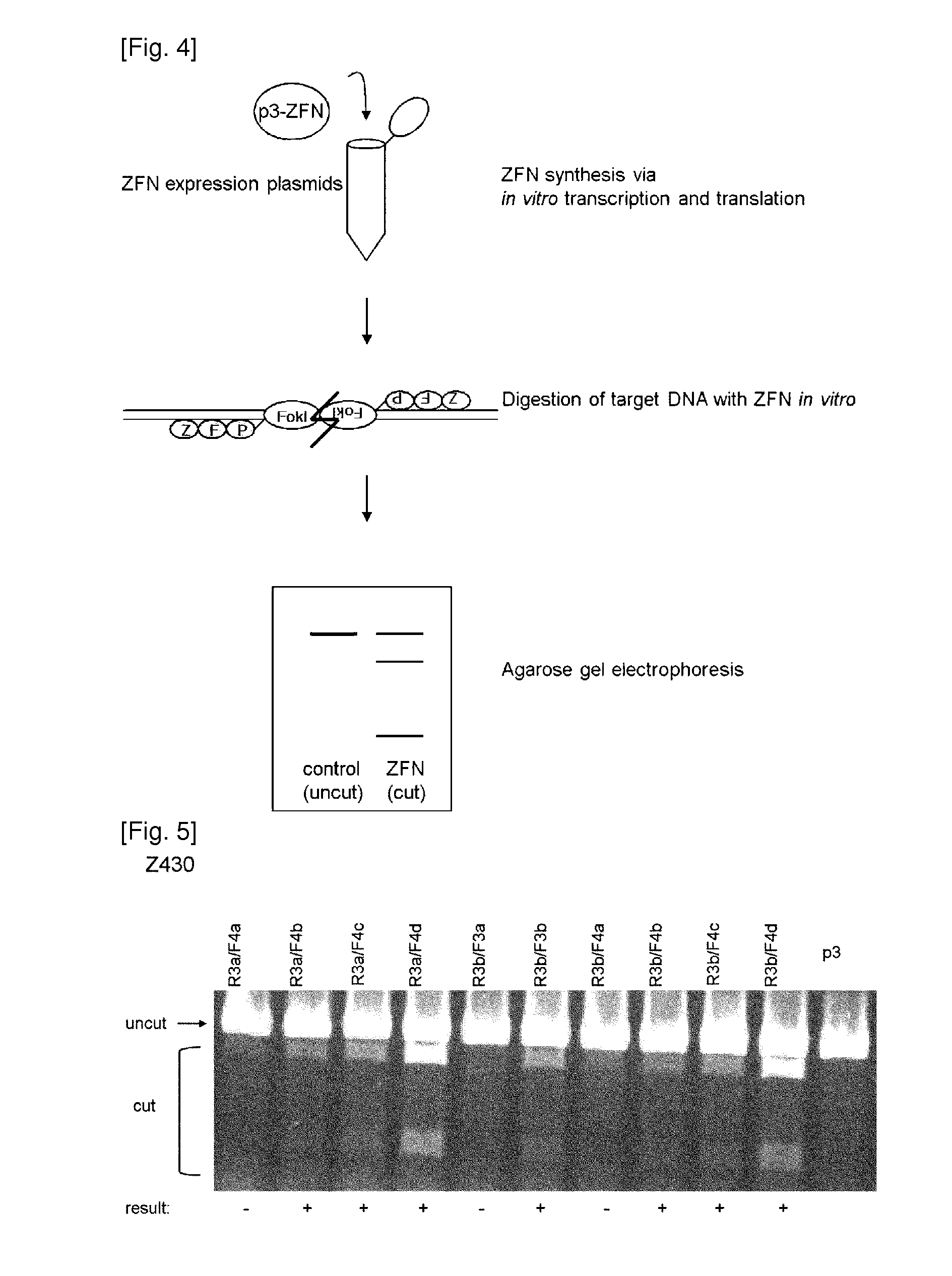
Novel Zinc Finger Nuclease and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20110281306A1Easy to produceModification for usingFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesZinc finger nucleasePolynucleotide
The present invention relates to methods and compositions useful for targeted cleavage and alteration of a genomic sequence, targeted cleavage followed by homologous recombination between an exogenous polynucleotide and a genomic sequence, or targeted cleavage followed by non-homologous end joining.
Owner:TOOLGEN INC
Method for increasing non-homologous end joining efficiency of CRIPSR/Cas9 target knock-out genes
InactiveCN106906242AImprove accuracyVectorsOther foreign material introduction processesCancer researchBiomedical technology
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and biomedicine, and relates to a method for increasing the efficiency of CRIPSR / Cas9 target knock-out genes NHEJ. According to the method for increasing the efficiency of CRIPSR / Cas9 target knock-out gene NHEJ, small molecule interference RNA that efficiently interferes with expression of PTEN genes is screened out; by using CRISPR / Cas9 system to target knockout genes, the small molecule RNA is cotransfected into the target gene, thus the NHEJ efficiency of target genes is effectively improved and the NHEJ of target gene in cell multiple targets is significantly improved. The method has the advantages of low cost, simple operation and high efficiency, and has a good promoting effect on the efficiency and application of CRISPR / Cas9 technology.
Owner:重庆高圣生物医药有限责任公司
Products and methods for enhanced transgene expression and processing
InactiveUS20120231449A1Increase volumeHigh activityAnimal cellsVectorsADAMTS ProteinsSecreted substance
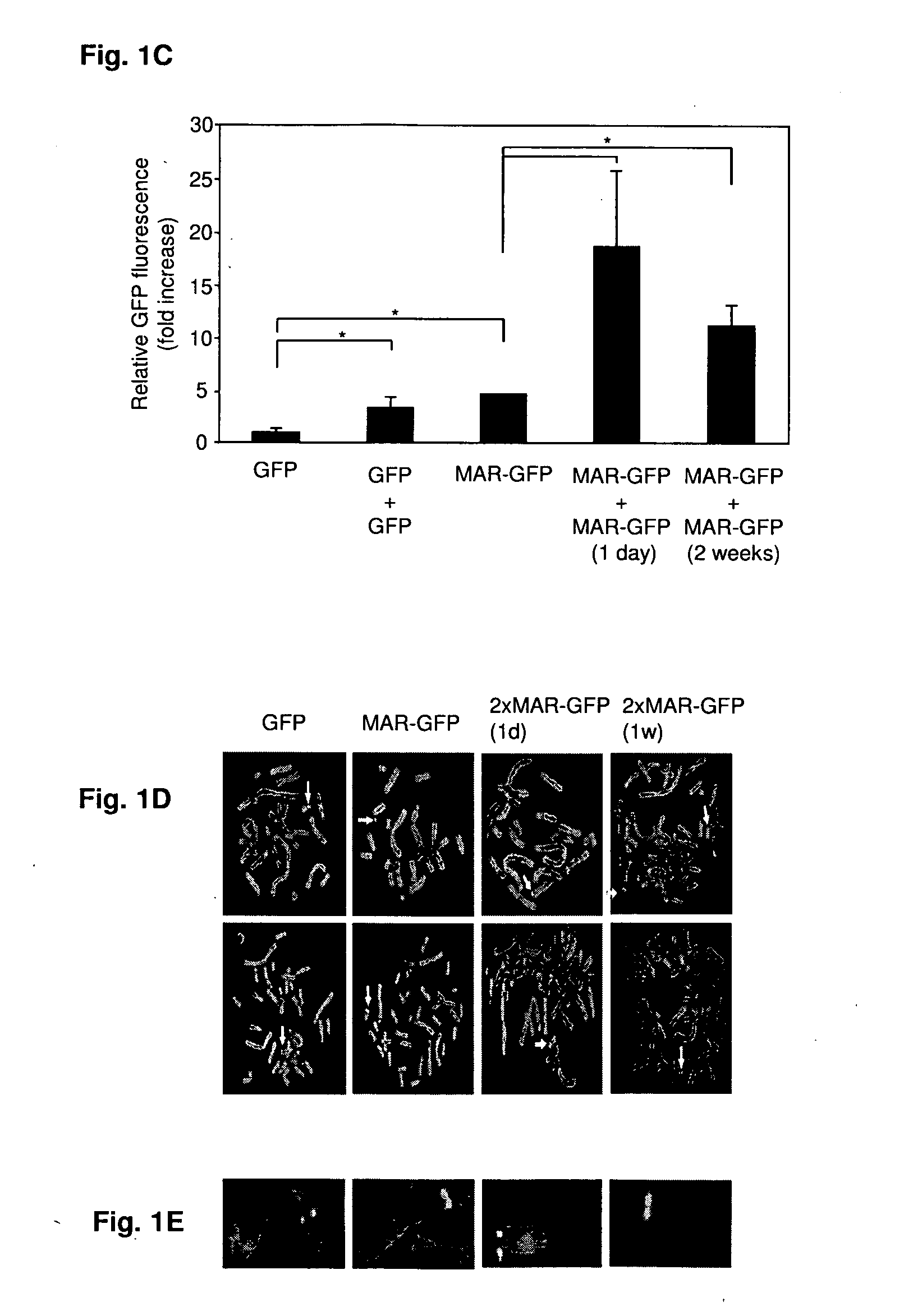
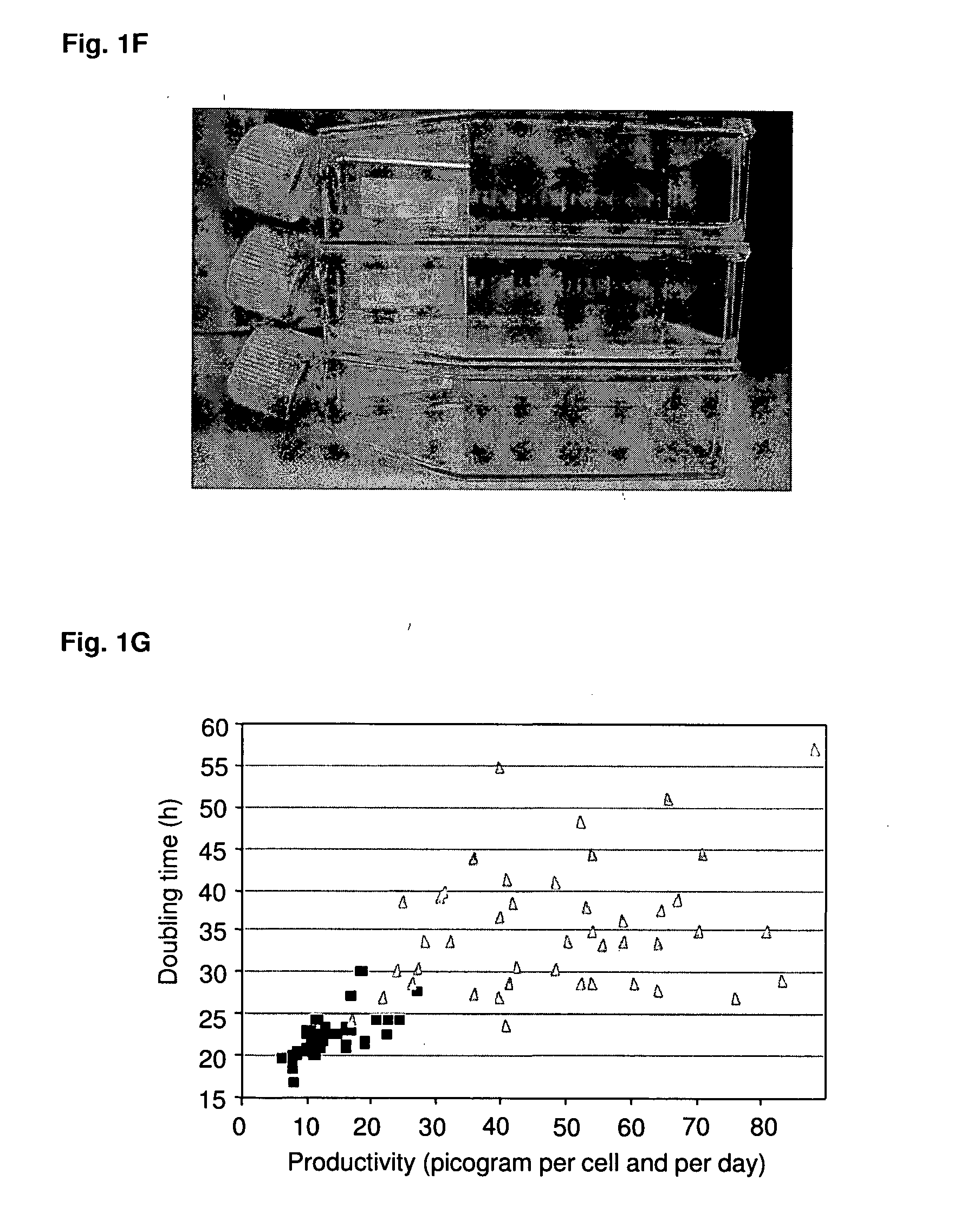
Disclosed are methods and eukaryotic host cells for transgene expression. The cells may be treated and / or modified to increase homologous recombination (HR), decrease non homologous end joining (NHEJ) and / or to enhance a HR / NHEJ ratio in said cell. Such cells can be transfected with vectors comprising the transgene, which advantageously integrates into the genome of the cell to form a concatemeric structure which may comprise more than 200 transgene copies. Certain expression enhancing elements such as MARs are advantageously provided to further enhance and / or facilitate transgene expression. Disclosed is also a recombinant eukaryotic host cell, in particular a non-primate host cell, comprising a transgenic sequence encoding a protein and / or a RNA, in particular a primate protein and / or RNA, involved in translocation across the ER membrane and / or secretion across the cytoplasmic membrane.
Owner:SELEXIS SA
Gene knockout method
The invention relates to a donor structure and a gene knockout method, system and kit. The gene knockout method comprises inserting a marker gene in the donor structure into a cell genome at a double-stranded cleavage site through non-homologous end joining. Through expressive cells without marker-enriched genes, the efficiency of gene knockout based on a sequence-specific nuclease is improved.
Owner:艾博抗有限公司
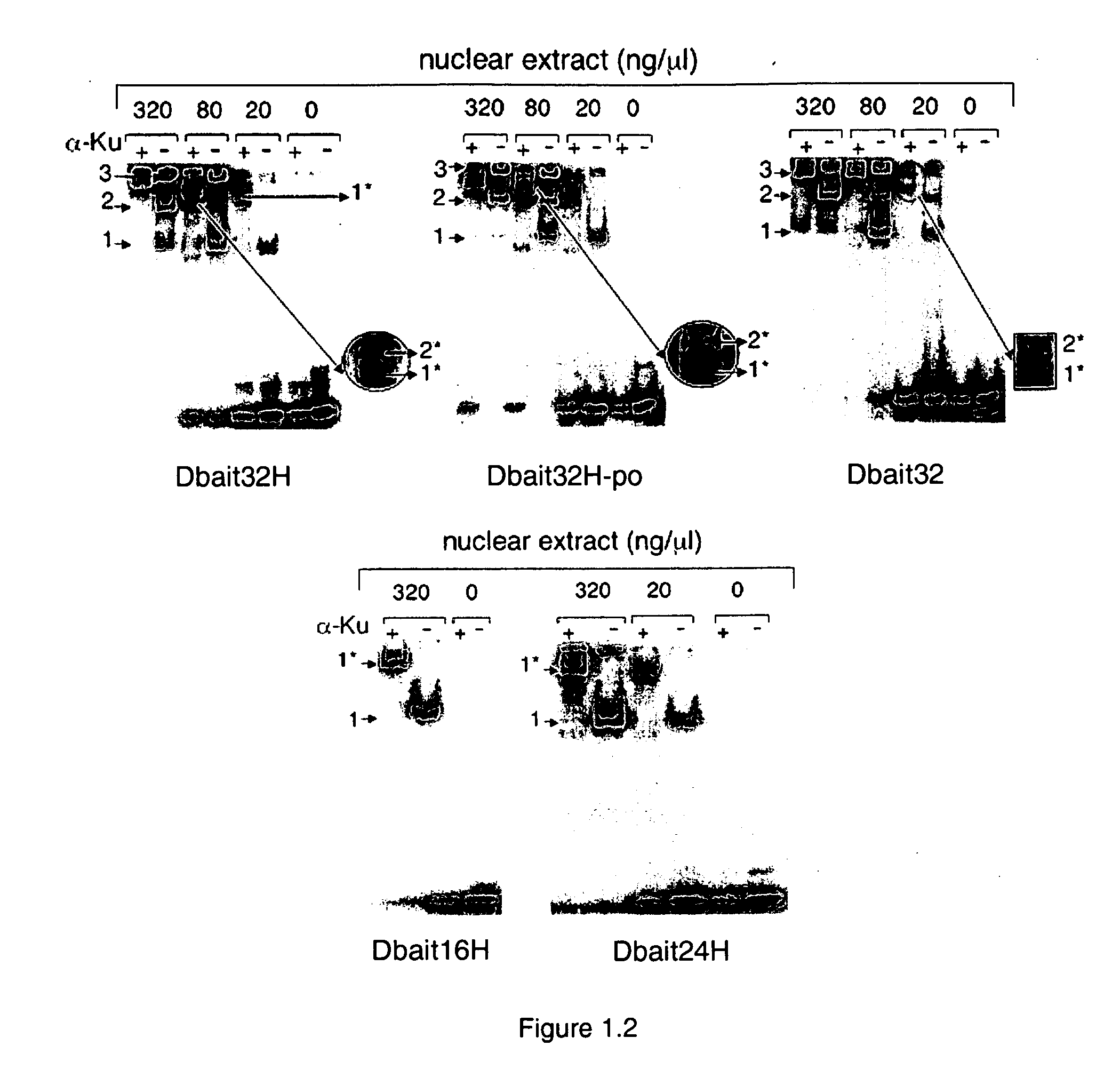
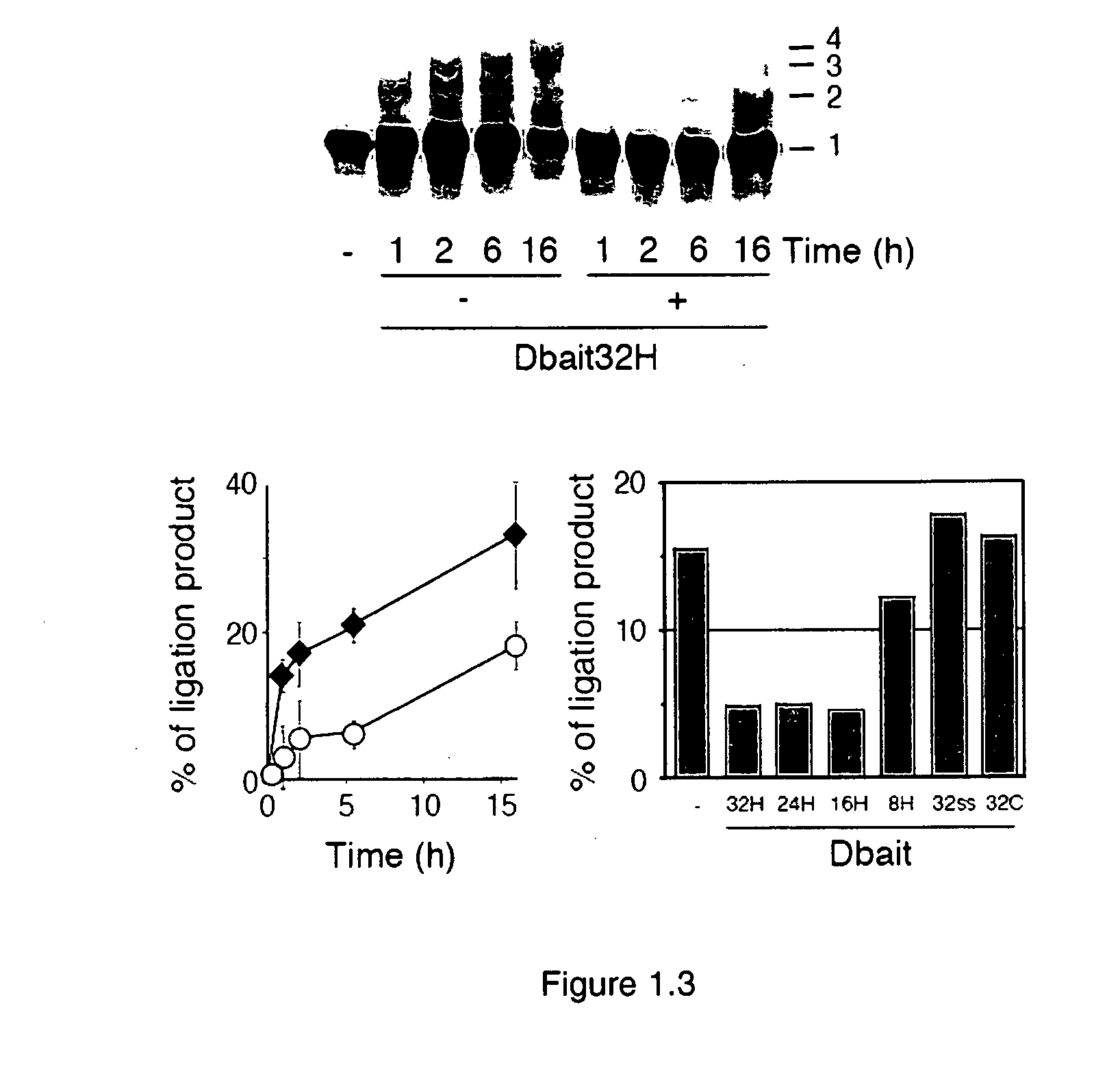
Dbait and uses thereof
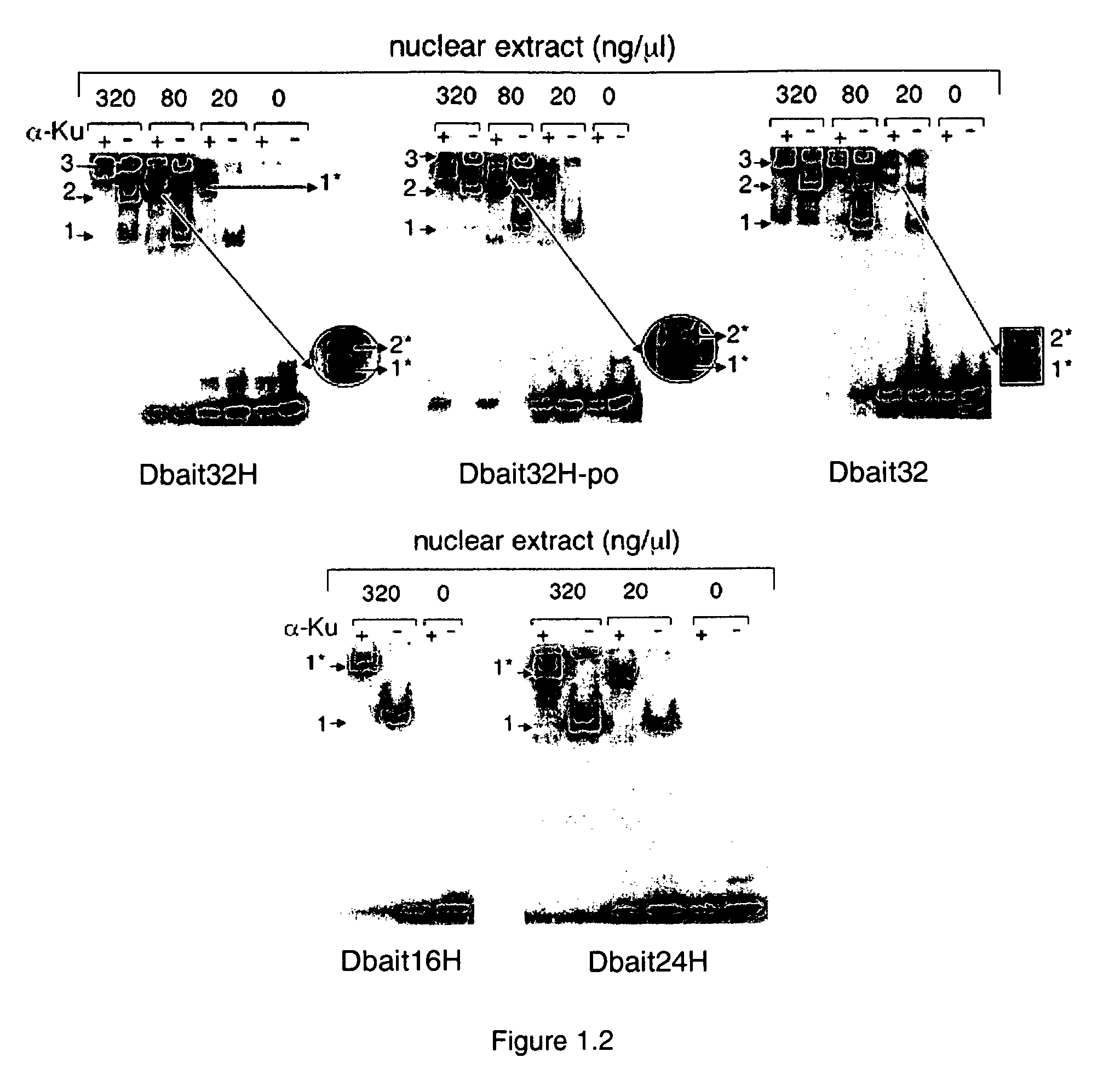
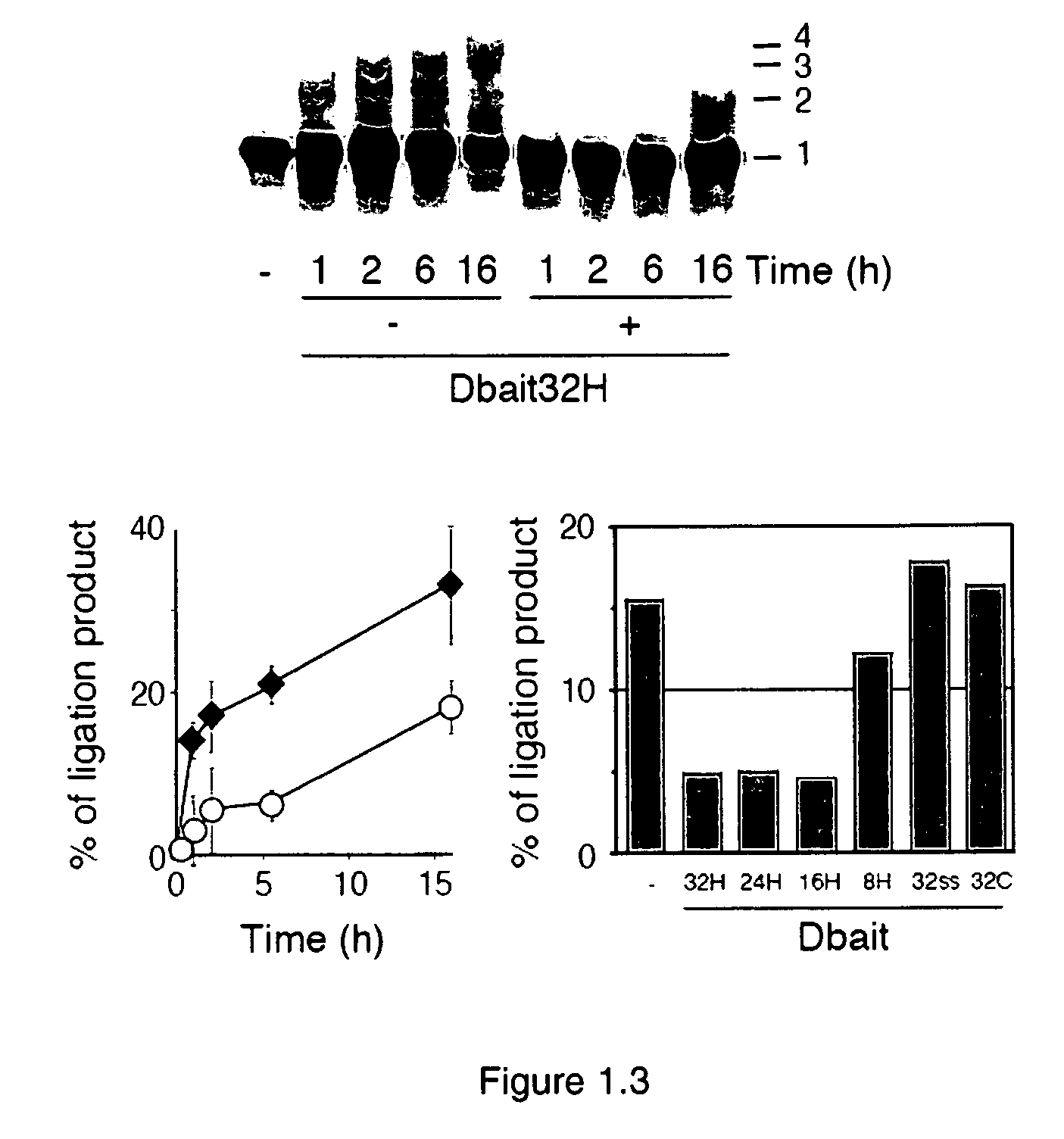
The invention relates to compositions and methods for interfering with the DNA repair of double strand breaks (DSBs). The invention discloses novel double-stranded nucleic acid molecules. that act as baits and hijack the holocomplex of enzymes responsible of DNA DSB sensing, signaling and / or repair pathways, in particular the non homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DSB repair. The invention discloses the use of these molecules as adjuvant compositions to be used in association with a DNA breaking treatment, particularly radiotherapy or chemotherapy, in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, in an efficient amount to be introduced in the tumor cell nuclei in order to neutralize transiently their DNA repair capacity and trigger their death.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +3
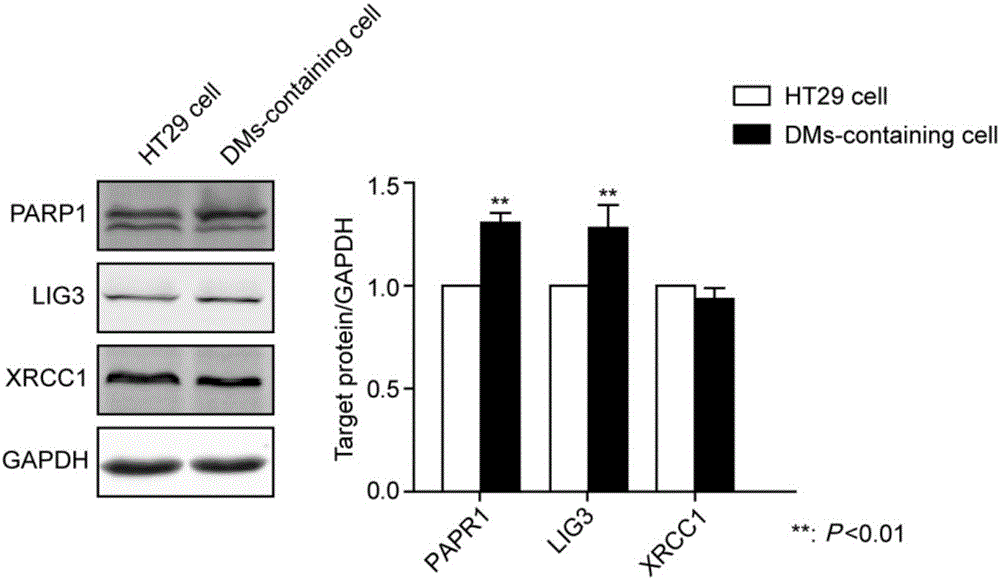
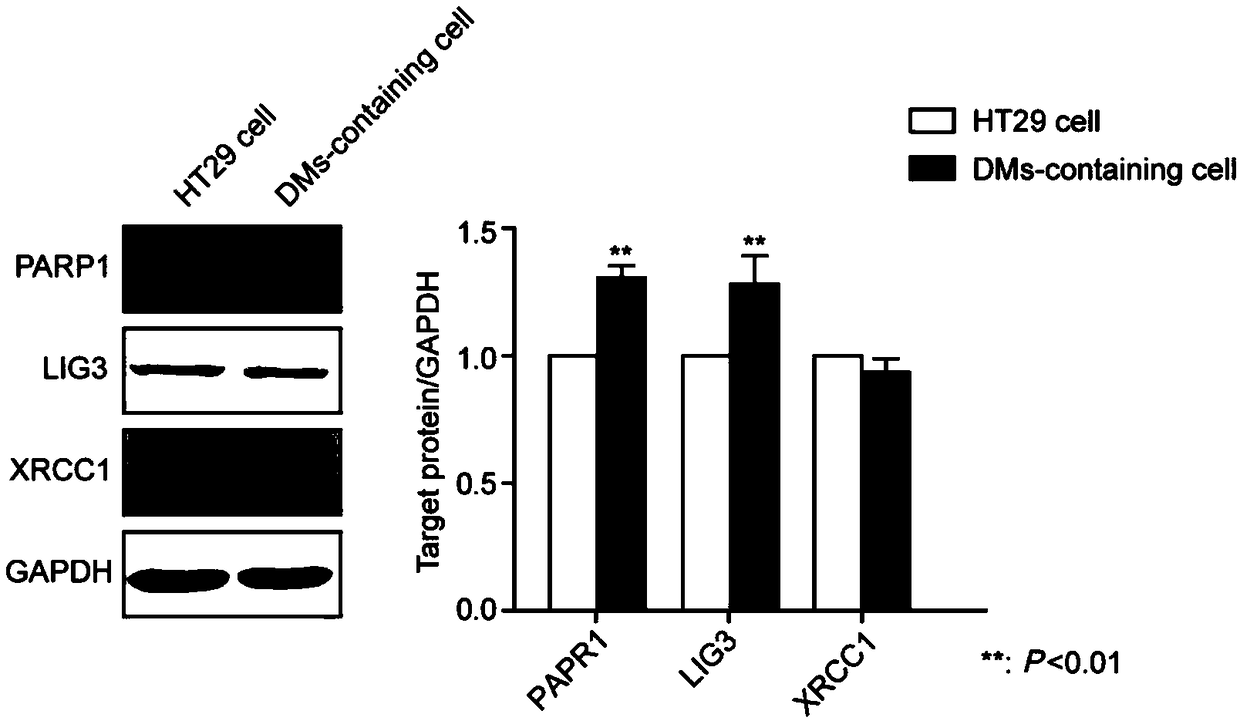
Application of PARP1 inhibitor in preparation of medicine for reversing drug resistance of tumor cells to amethopterin
ActiveCN106492217AOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsIndividualized treatmentTumor therapy
The invention discloses application of a PARP1 inhibitor in the preparation of a medicine for reversing drug resistance of tumor cells to amethopterin and belongs to the technical field of tumour biotherapy. It is found by the inventor through researches that as for malignant cells with MTX resistance and DHFR gene high-amplification, by specifically inhibiting the key protein RARP1 of A-NHEJ pathway, DHFR gene copy number can be reduce and DMs in cells can be decreased so as to reverse drug resistance of tumors and enhance efficiency of tumor therapy. Therefore, on the basis of the above researches, the invention brings forward the application of the PARP1 inhibitor in the preparation of a medicine for reversing the drug resistance of tumor cells to MTX by reducing DHFR gene copy number. The invention provides a new targeting therapeutic scheme for the MTX as the main therapeutic drug and for the biotherapy of malignant tumors which are easy to resist drugs and also provides a scientific basis for effectively fighting against MTX drug resistance. In addition, the invention is also of great positive significance for deeply understanding the nature of chemotherapy resistance and finding resistance target for individualized treatment.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Single-guide RNA (sgRNA) fragment and application thereof
ActiveCN103820452AShorten the timeLow costVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationReconstruction methodA-DNA
The invention discloses a sgRNA fragment. The DNA sequence of the sgRNA fragment comprises a length of a fixed sequence and a length of a DNA recognition sequence. The sgRNA can recognize different target sites on double strands of a target gene, bond with nuclease and guide nuclease to bond with the target sites of the target gene through recognition of PAM sequences at the target sites and to start random shearing; then nuclease falls off from a shearing opening, thereby forming a DSB gap; then cells repair the double strands of the target gene through a non-homologous end joining repair mechanism, which leads to frameshift mutation; and finally, the target gene is knocked out. The invention further discloses a gene fixed-point reconstruction method and a gene targeting kit. The invention elaborates a series of sgRNAs applicable to the mouse Myod1 gene, and the sgRNAs have high targeting efficiency, short construction time and low cost and can be highly efficiently used for mouse Myod1 gene targeting.
Owner:CYAGEN BIOSCI INC
Methods, compositions and kits for increasing genome editing efficiency
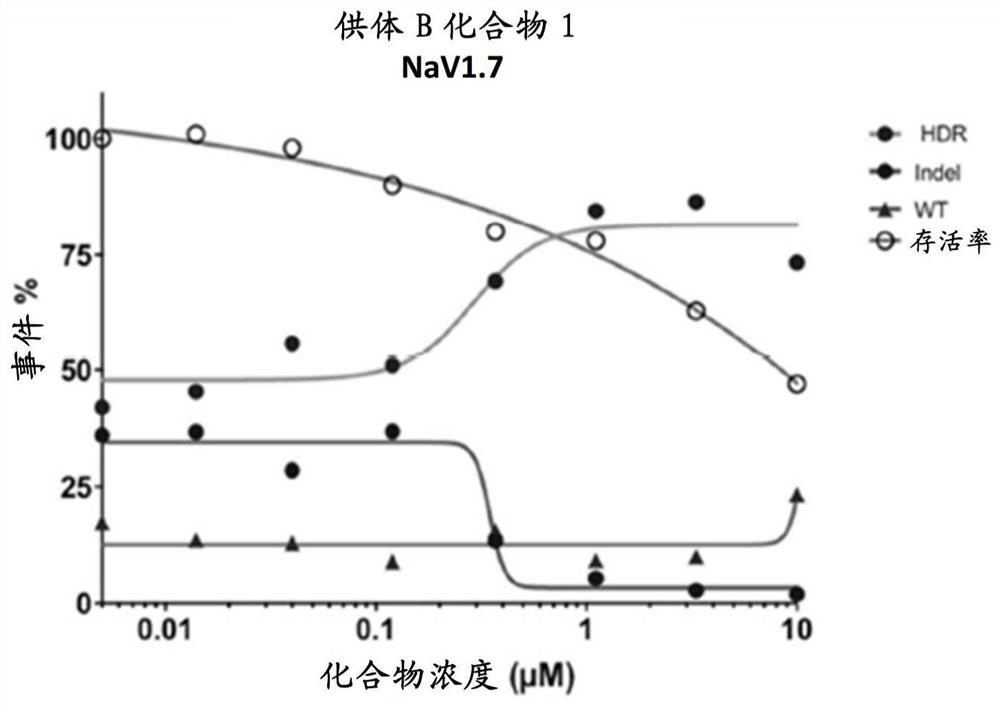
Methods of editing a target genomic region(s), methods of repairing of a DNA break via a HDR pathway, methods of inhibiting or suppressing repair of a DNA break via a NHEJ pathway, and methods of modifying expression of a gene(s) or protein(s) comprise administering to one or more cells that include one or more target genomic regions, a genome editing system and a DNA protein-kinase (DNAPK) inhibitor disclosed herein. Kits and compositions for editing a target gene comprise a genome editing system and a DNAPK inhibitor disclosed herein.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Use of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 inhibitor in lung cancer treatment
InactiveCN103720689AChange cycle distributionPromote growthOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsWilms' tumorTgf beta1
The invention discloses use of a transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 inhibitor in lung cancer treatment. The TGF-beta1 inhibitor inhibits a TGF-beta1 channel to increase the radiosensitivity of lung cancer cells. Through the manner, according to the use of the TGF-beta1 inhibitor in lung cancer treatment, the sensitivity enhancement effect of the TGF-beta1 inhibitor on the lung cancer cells is caused by inhibition on non-homologous end joining repair of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) double-strand break, change of cycle distribution of the lung cancer cells after irradiation, and obvious reduction of tumor growth by the TGF-beta1 inhibitor combined with X-ray treatment of 5Gy. The DNA repair capacity can be reduced by inhibition on the TGF-beta1 channel of tumor cells before irradiation, the cell cycle distribution is changed, the cell cloning ability is reduced, the tumor growth is delayed, and effective auxiliary means are provided by inhibiting the TGF-beta1 channel as radiotherapy of a patient with a lung cancer.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for increasing HR (Homologous Recombination) repairing frequency of ovine embryo fibroblasts after gene editing
InactiveCN105671045AIncrease the frequency of repairsHigh target shooting efficiencyNucleic acid vectorOther foreign material introduction processesEmbryoLIG4
The invention discloses a method for increasing HR (Homologous Recombination) repairing frequency of ovine embryo fibroblasts after gene editing. The method provides application of a substance for restraining the expression of an Lig4 gene in in-vitro ovine embryo fibroblasts containing gene editing DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) fragments in preparation of products for promoting HR repairing of the in-vitro ovine embryo fibroblasts containing the gene editing DNA fragments. An experiment of the invention shows that siRNA (Small Interfering Ribose nucleic Acid) which restrains the expression of the ovine Lig4 gene is screened, the expression of the ovine Lig4 gene is restrained through the siRNA, an intracellular HR repairing path is stimulated by restraining an NHEJ (Non-homologous End Joining) repairing path of the ovine embryo fibroblasts, the frequency of adopting HR repairing by cells is increased, and a basis is provided for increasing gene targeting efficiency of the ovine embryo fibroblasts and researching accurate editing of an ovine genome.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
Gene knockout method
The invention relates to a universal donor construct, and a gene knockout method, system and kit. According to the gene knockout method in the invention, a marker gene included in the universal donorconstruct is inserted to a double-strand break position in a cell genome by non-homologous end joining, and cells in which genes are knocked out are enriched by an expressed marker, so the efficiencyof gene knockout via sequence-specific nucleases is improved. The universal donor construct of the invention comprises a universal linear donor DNA which contains a universal target sequence cleavableby the sequence-specific nucleases; the universal target sequence does not exist in the genome of a cell to undergo gene knockout; therefore, when performing gene knockout, it is not necessary to specifically construct a matching linear donor DNA, and a general linear donor DNA and a gRNA targeting to the universal linear donor DNA can be directly used.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Methods and materials for assessing responsiveness to parp inhibitors and platinating agents
This document provides methods and materials involved in assessing responsiveness to PARP inhibitors and platinating agents. For example, methods and materials for using levels of non-homologous end-joining pathway members (e.g., artemis mRNA or polypeptide levels, Ku80 mRNA or polypeptide levels, or DNA-PKcs mRNA or polypeptide levels) to determine if cancer cells that are homologous recombination-deficient are likely to be susceptible or resistant to PARP inhibitors and platinating agents are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Combination drug composition for treating liver cancer
InactiveCN109512822APrevent proliferationLow growth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsA-DNAOncology
The invention relates to a combination drug composition for treating liver cancer. The combination drug composition is prepared from a PARP1 protein inhibitor Olaparib and a DNA-PKcs protein inhibitorNU7441. A DNA double strand breakage repair passage in a liver cancer cell is highly activated by protein inhibited by the combination drug composition, and accordingly an effective target spot is provided for treating liver cancer. Compared with the prior art, the micromolecular drug Olaparib can interdict homologous recombination repairing and selective non-homologous end joining repairing in liver cancer tissue, while NU7441 can interdict the non-homologous end jointing repairing, so that a combination of the two drugs can completely interdict the DNA double strand breakage repairing passage and thereby effectively inhibit proliferation of liver cancer, and the tumor increasing inhibition rate is as lowest as 62.3%, and as highest as 83.9%.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
In-fusion cloning method for recombinant baculovirus
The invention discloses an in-fusion cloning method for recombinant baculovirus. The method employs two main constitution members: a linearizable replication-deficient baculovirus vector and a rescued recombination DNA fragment, the above two members are directly subjected to recombination in an insect cell for generating recombinant baculovirus. DNA recombination of the linearizable replication-deficient baculovirus vector and the rescued recombinant DNA fragment in the insect cell relates to homologous recombination and / or non-homologous end joining of 10-50 bp homologous arms. The method is applicable to high-flux construction of recombinant virus and one-step cloning of multiple genes for multiple expression.
Owner:杭州洪晟生物技术股份有限公司
Quinoxalinone compounds, compositions, methods, and kits for increasing genome editing efficiency
PendingUS20200361877A1Improve HDR efficiencyImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryQuinoxalineGenome editing
Compounds, methods of editing a target genomic region(s), methods of repairing of a DNA break via a HDR pathway, methods of inhibiting or suppressing repair of a DNA break via a NHEJ pathway, and methods of modifying expression of a gene(s) or protein(s) comprise administering to one or more cells that include one or more target genomic regions, a genome editing system and a DNA protein-kinase (DNA-PK) inhibitor disclosed herein. Kits and compositions for editing a target gene comprise a genome editing system and a DNA-PK inhibitor disclosed herein.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Quinoxalinone compounds, compositions, methods, and kits for increasing genome editing efficiency
Compounds, methods of editing a target genomic region(s), methods of repairing of a DNA break via a HDR pathway, methods of inhibiting or suppressing repair of a DNA break via a NHEJ pathway, and methods of modifying expression of a gene(s) or protein(s) comprise administering to one or more cells that include one or more target genomic regions, a genome editing system and a DNA protein-kinase (DNA-PK) inhibitor disclosed herein. Kits and compositions for editing a target gene comprise a genome editing system and a DNA-PK inhibitor disclosed herein.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Dbait and uses thereof
The invention relates to compositions and methods for interfering with the DNA repair of double strand breaks (DSBs). The invention discloses novel double-stranded nucleic acid molecules that act as baits and hijack the holocomplex of enzymes responsible of DNA DSB sensing, signaling and / or repair pathways, in particular the non homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DSB repair. The invention discloses the use of these molecules as adjuvant compositions to be used in association with a DNA breaking treatment, particularly radiotherapy or chemotherapy, in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, in an efficient amount to be introduced in the tumor cell nuclei in order to neutralize transiently their DNA repair capacity and trigger their death.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +3
Methods of nuclease-based genetic engineering
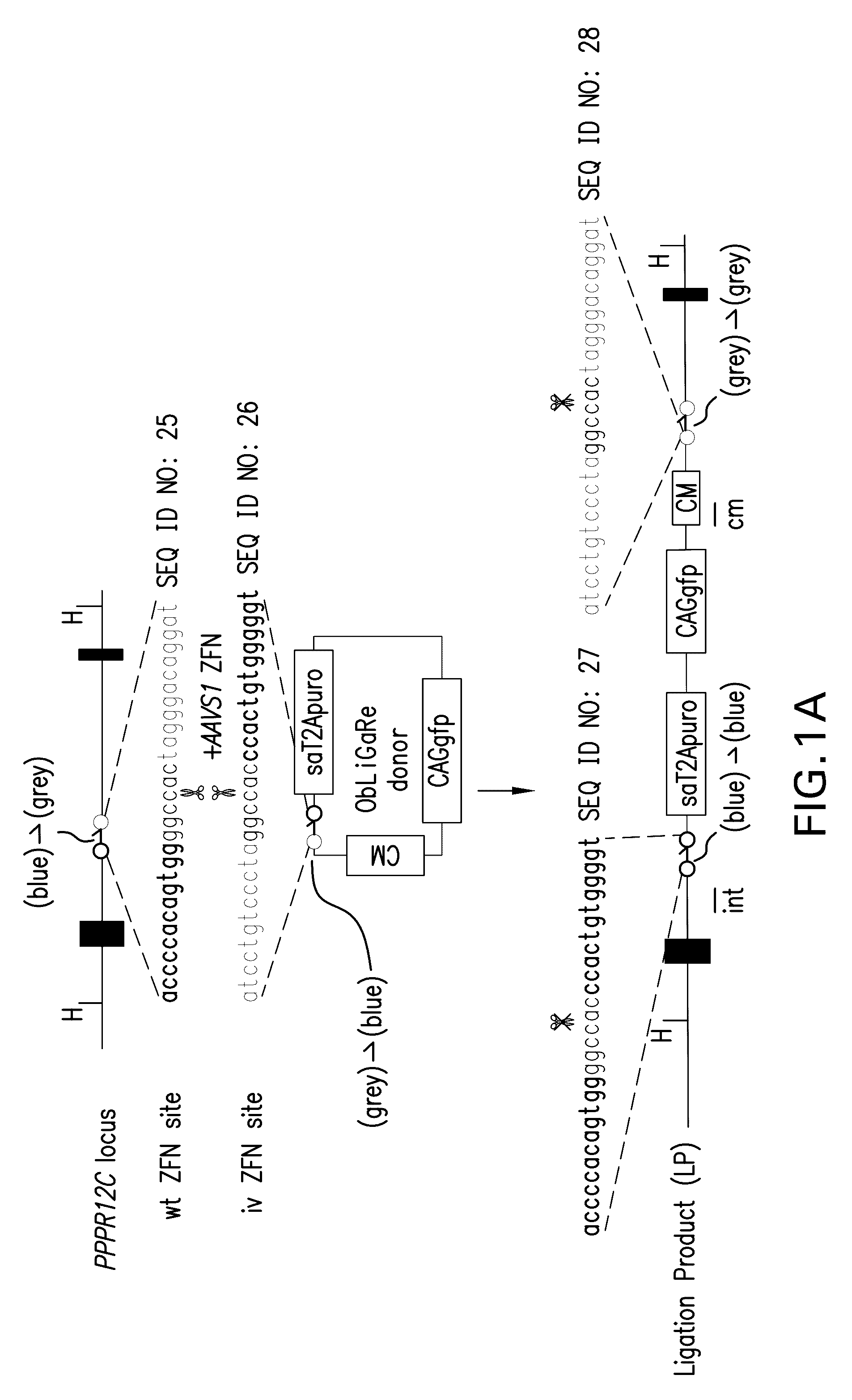
The present invention relates to genetic techniques employing the direct ligatation of an external DNA fragment generated in situ by the same ZFNs that target the genome. ObLiGaRe, i.e., the obligated ligation-gated recombination, is a new method for genetic engineering using custom designed nucleases, and a strategy of site-specific gene insertion utilizing the NHEJ pathway. It applies a similar logic to the one used in unidirectional loxP sites (Oberdoerffer et al., 2003) but maintains all the advantages and flexibility of CDNs.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Methods and materials for assessing responsiveness to PARP inhibitors and platinating agents
This document provides methods and materials involved in assessing responsiveness to PARP inhibitors and platinating agents. For example, methods and materials for using levels of non-homologous end-joining pathway members (e.g., artemis mRNA or polypeptide levels, Ku80 mRNA or polypeptide levels, or DNA-PKcs mRNA or polypeptide levels) to determine if cancer cells that are homologous recombination-deficient are likely to be susceptible or resistant to PARP inhibitors and platinating agents are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Application of up-regulating agent of HR or NHEJ pathway in preparation of medicament for treating diabetes mellitus and preventing diabetic individual tumorigenesis
ActiveCN110870915ACompounds screening/testingNervous disorderDiabetes Mellitus ComplicationsVascular endothelium
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method for Determining the Repair Activity of Non-Homologous End Joining
ActiveUS20170254799A1High sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesActivity levelPlasmid transfection
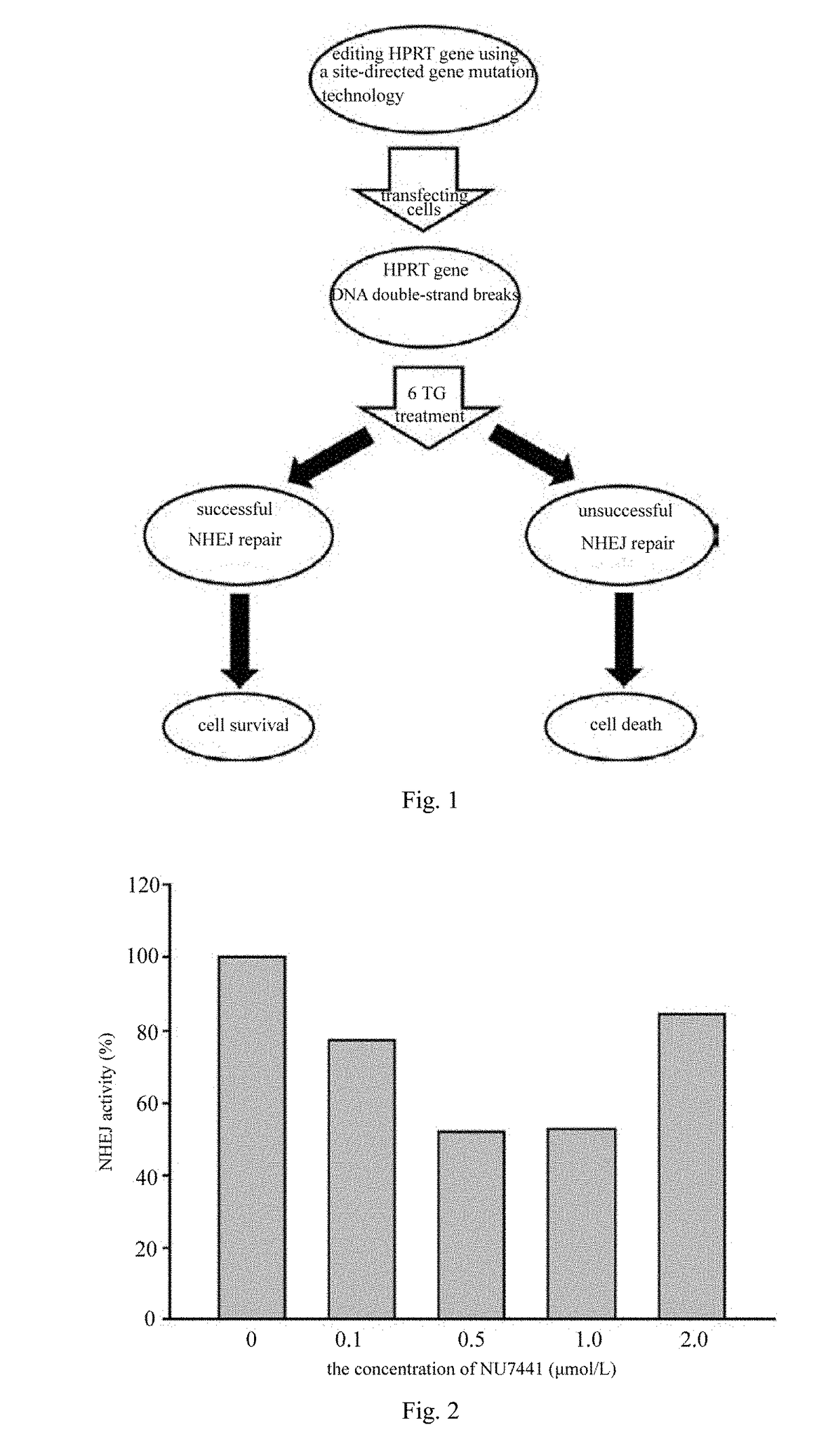
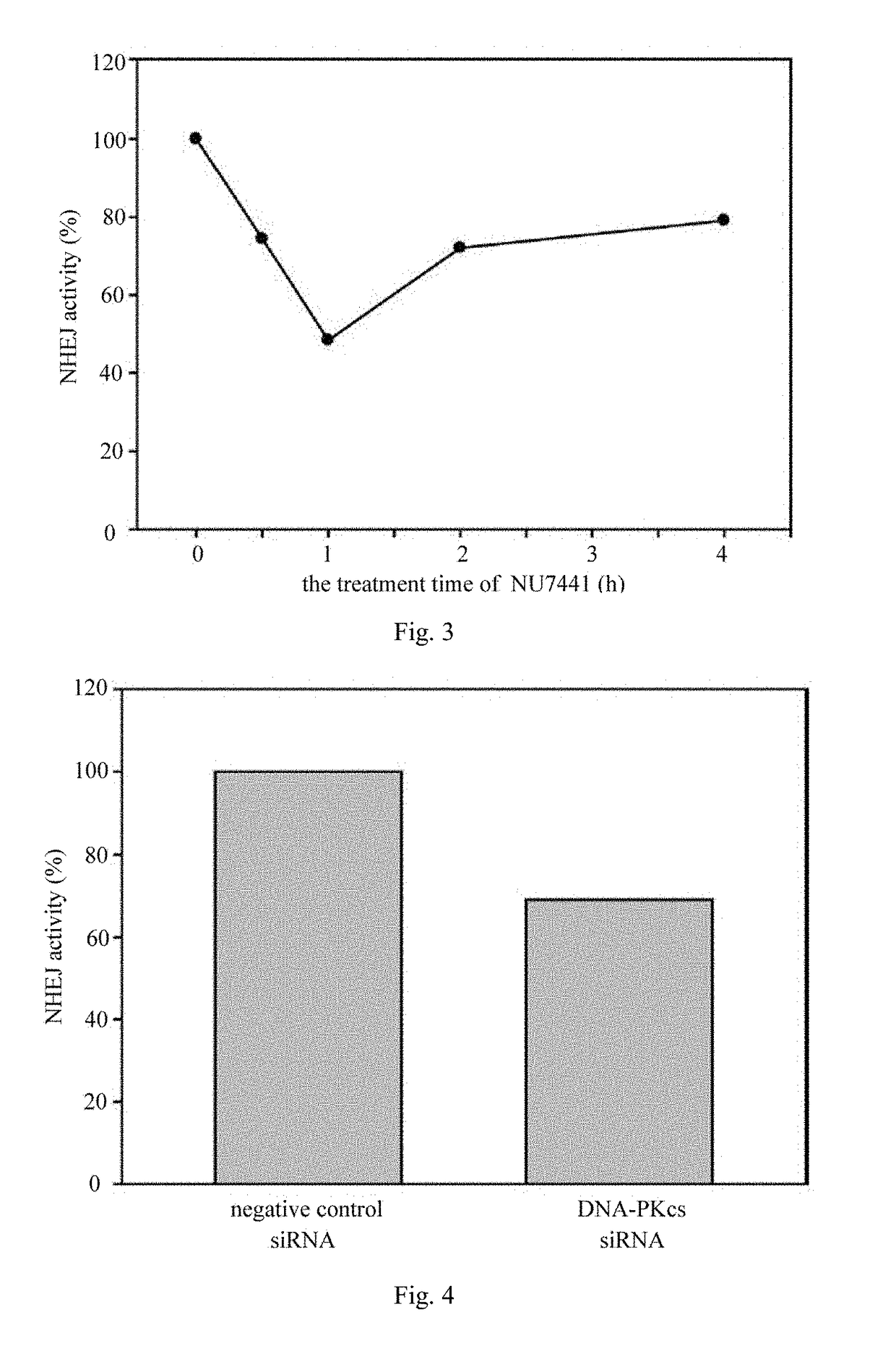
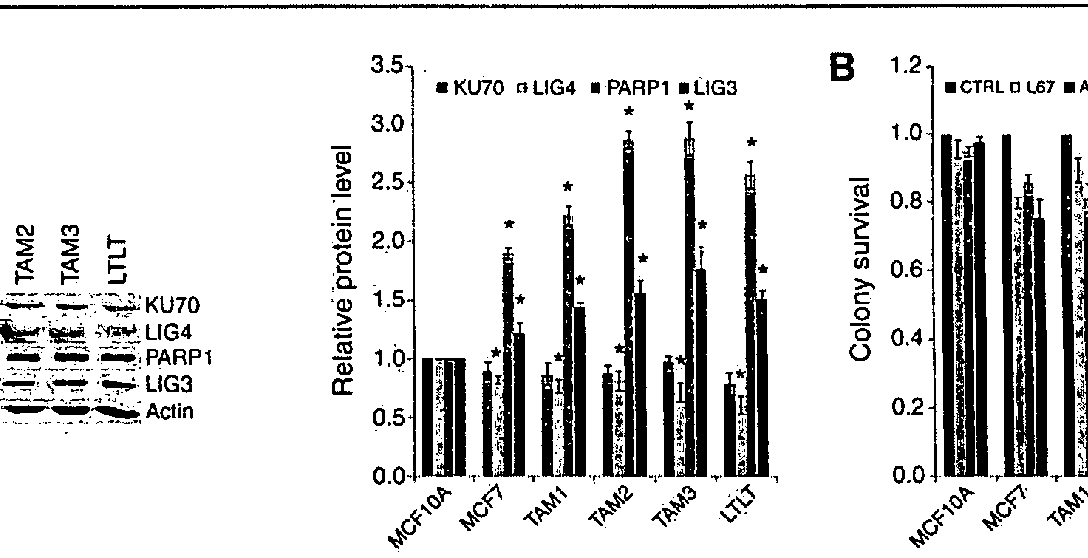
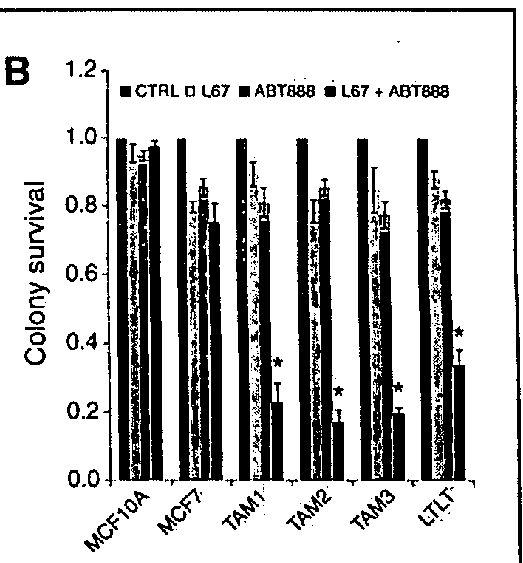
The invention discloses a method for determining the repair activity of NHEJ. In this method, HPRT gene is mutated by using a site-directed gene mutation technology, and plasmid transfection, and 6-TG treatment are performed. By means of the method of the invention, the NHEJ repair activity level of cells can be observed by measuring the cell viability. The method can be used for screening the effects of different drugs and different genes on the NHEJ repair activity.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Targeting abnormal DNA repair in therapy-resistant breast and pancreatic cancers
ActiveUS20160051517A1Reduce decreaseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTherapy resistantAbnormal tissue growth
In one embodiment, the invention provides a method of treating a subject suffering from a breast cancer tumor which is non-responsive or intrinsically resistant to anti-estrogen therapy comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an inhibitor of alternative (ALT) non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) factor to the subject.In another embodiment the invention provides a method of treating a subject who suffers from a pancreatic cancer which is non-responsive to chemotherapy and / or radiation comprising co-administering a therapeutically effective amount of PARP1 inhibitor and a DNA ligase IIIα inhibitor to the subject. Related diagnostic methods, nucleic acid arrays, devices and kits are also provided.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Molecular marker and kit for diagnosing cancer
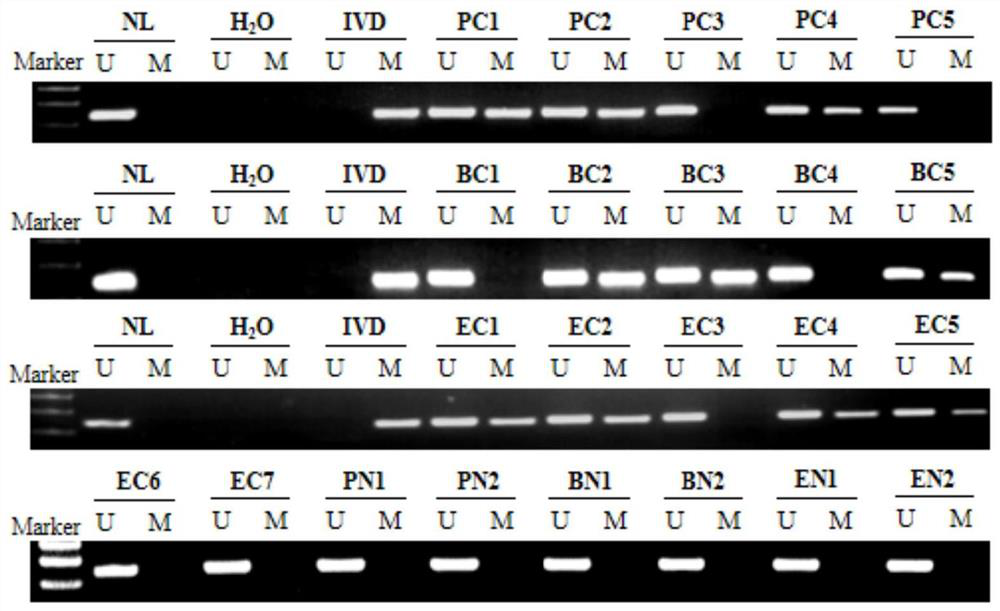
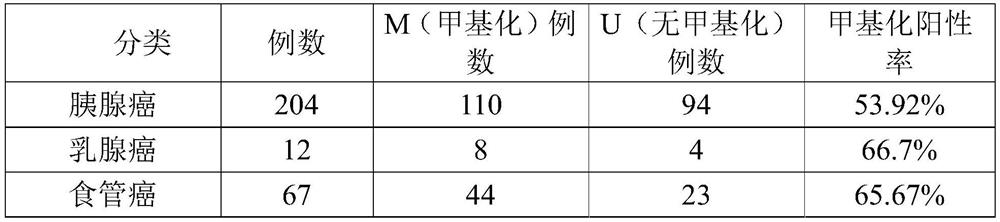
PendingCN114150061ASimple and fast operationImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA methylationPancreas Cancers
The invention discloses a molecular marker and a kit for cancer diagnosis, and particularly relates to application of BEND4 gene promoter region DNA methylation as a molecular marker in preparation of cancer diagnosis products. According to the application disclosed by the invention, frequent high methylation of a BEND4 promoter region in pancreatic cancer, breast cancer and esophageal cancer is found through an MSP method for the first time, BEND4 participates in an NHEJ pathway of DNA damage repair, and BEND4 methylation is a synergistic lethal marker for killing tumor cells by combining an ATM inhibitor with chemotherapeutic drugs such as cis-platinum and the like. The invention also provides a primer and a kit for detecting the methylation state of the promoter region of the BEND4 gene. The application of the primer and the kit to detect the hypermethylation state of the BEND4 gene promoter region can be used as a powerful means for diagnosis, curative effect observation, prognosis judgment, minimal residual disease detection and the like of pancreatic cancer, breast cancer and esophageal cancer, and the primer and the kit are simple and convenient to operate and good in stability and have profound clinical significance and generalization performance.
Owner:THE FIRST MEDICAL CENT CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
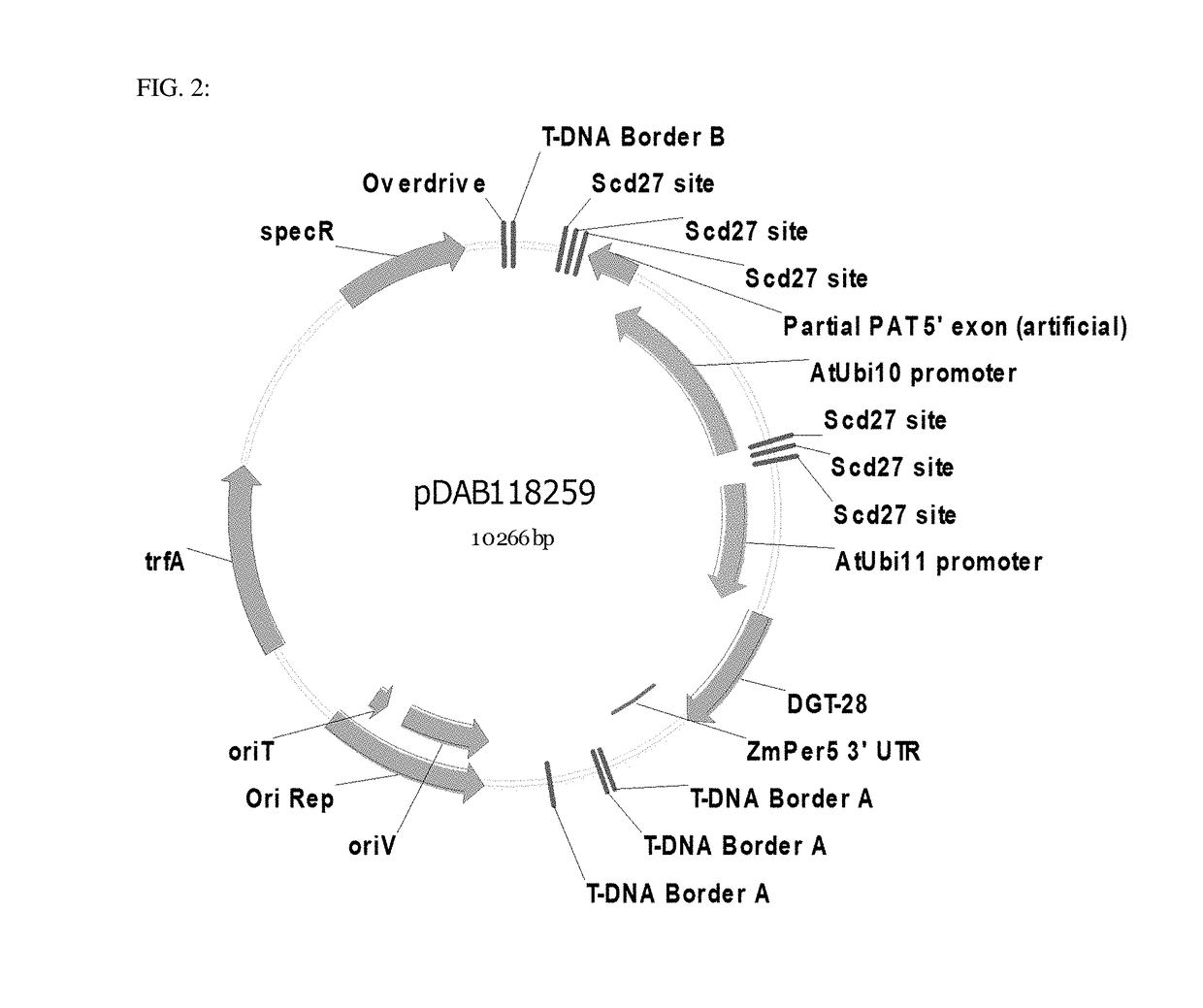
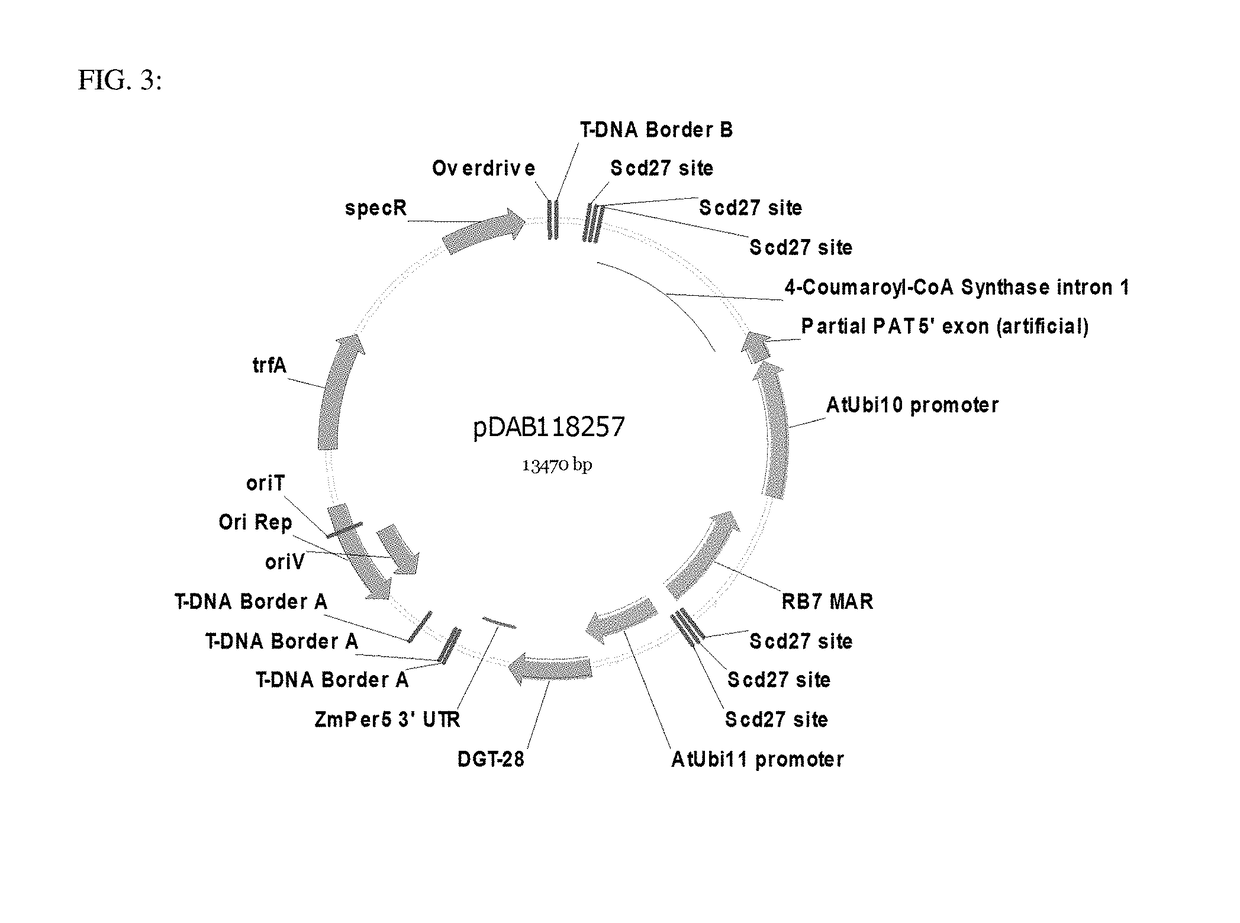
Site specific integration of a transgne using intra-genomic recombination via a non-homologous end joining repair pathway
Compositions and methods to modify at least one target locus in a plant cell are provided, which comprises providing a plant cell, a plant, or a plant part with one or more target loci and one or more donor loci, providing at least one cleaving site specific nuclease to produce a double strand break within the target loci, followed by non-homologous end joining of at least one donor locus within at least one target locus. Target loci, donor loci and nuclease loci used in these methods, and plant cells, plants and plant parts comprising these target loci, donor loci, nuclease loci and / or the recombined loci are also provided.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Combinational strategy for reducing ransom integration events when transfecting plants
The present disclosure provides methods for transfecting plants and for expressing RNA or polypeptide molecules in plants. In particular, plants having reduced expression and / or activity of a component of the classical NHEJ pathway and a component of the POLQ pathway are transfected in order to reduce random integration events. The disclosure further provides transfected plants and plant progeny produced by the methods disclosed herein.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIVERSITY +1
Application of parp1 inhibitor in the preparation of drugs for reversing drug resistance of tumor cells to methotrexate
ActiveCN106492217BOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsIndividualized treatmentTumor therapy
The invention discloses application of a PARP1 inhibitor in the preparation of a medicine for reversing drug resistance of tumor cells to amethopterin and belongs to the technical field of tumour biotherapy. It is found by the inventor through researches that as for malignant cells with MTX resistance and DHFR gene high-amplification, by specifically inhibiting the key protein RARP1 of A-NHEJ pathway, DHFR gene copy number can be reduce and DMs in cells can be decreased so as to reverse drug resistance of tumors and enhance efficiency of tumor therapy. Therefore, on the basis of the above researches, the invention brings forward the application of the PARP1 inhibitor in the preparation of a medicine for reversing the drug resistance of tumor cells to MTX by reducing DHFR gene copy number. The invention provides a new targeting therapeutic scheme for the MTX as the main therapeutic drug and for the biotherapy of malignant tumors which are easy to resist drugs and also provides a scientific basis for effectively fighting against MTX drug resistance. In addition, the invention is also of great positive significance for deeply understanding the nature of chemotherapy resistance and finding resistance target for individualized treatment.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
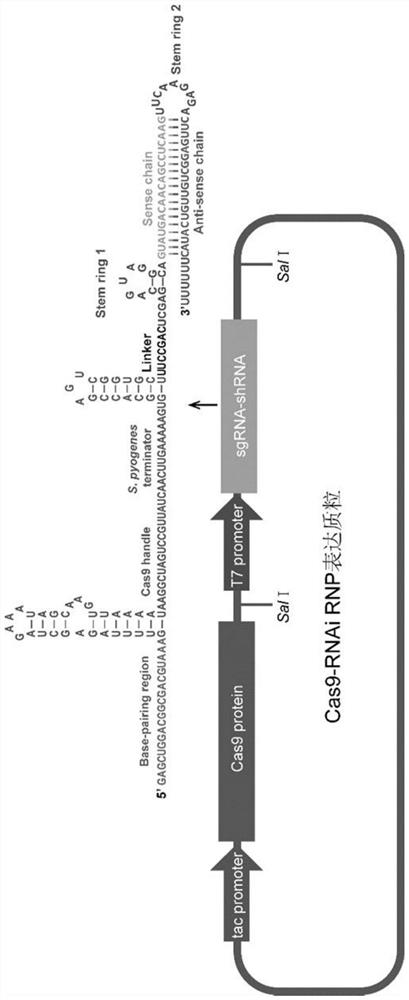
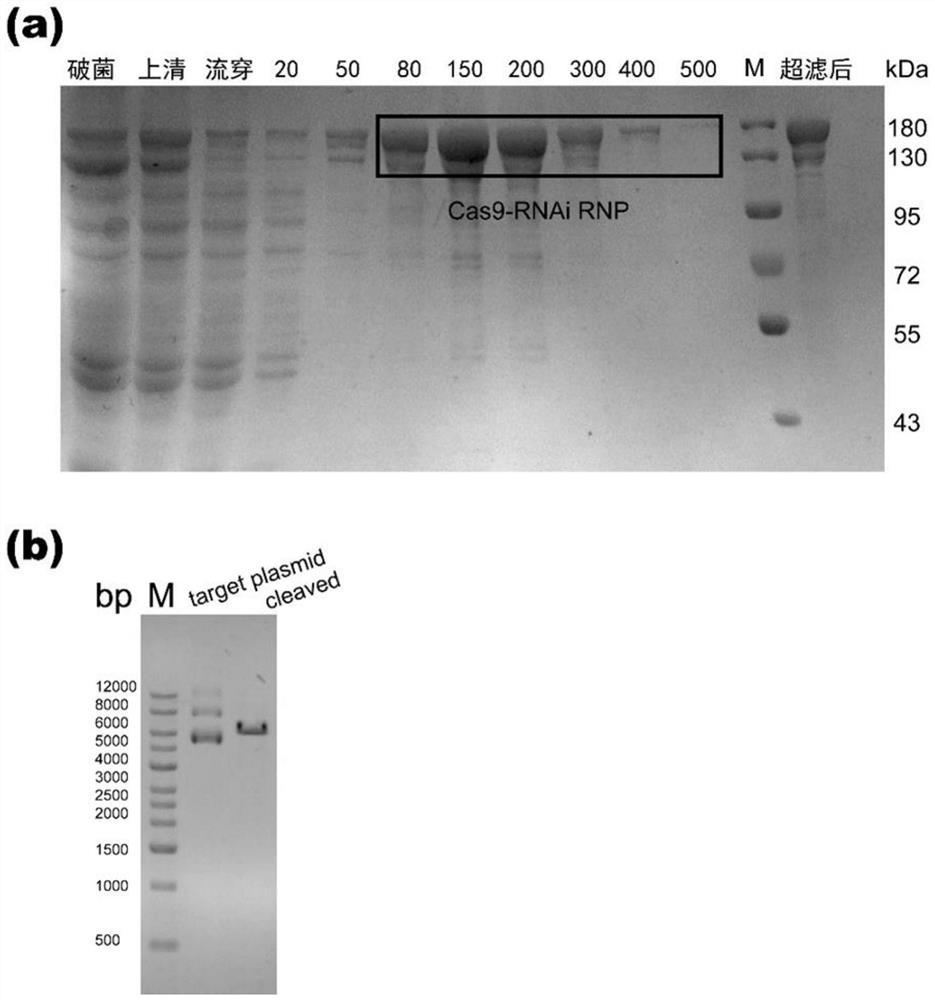
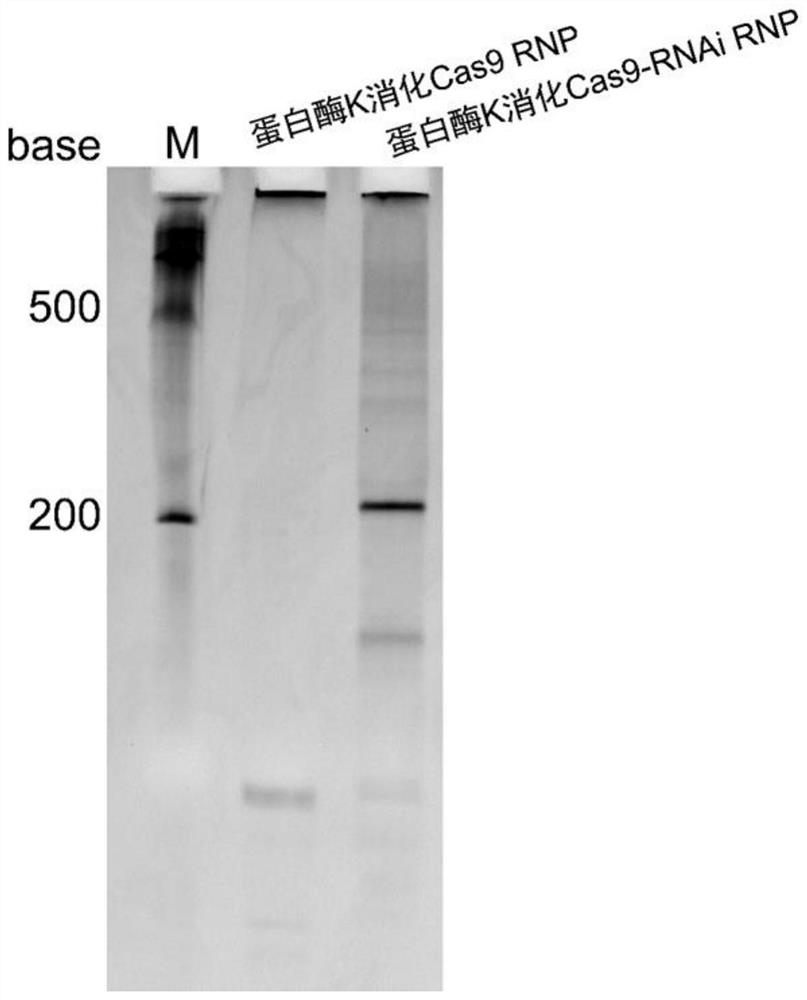
Preparation method and application of Cas9-RNAi RNP with efficient homologous directional repair activity
PendingCN114672504AEfficient repairShort manufacturing timeHydrolasesMicroencapsulation basedBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a preparation method of Cas9-RNAi RNP with efficient homologous directional repair activity, which comprises the following steps: transiently inhibiting key protein Ligase 4 of an NHEJ pathway, constructing a similar structure of shRNA by prolonging the 3'end of gRNA of Cas9RNP, and expressing Cas9RNP by using escherichia coli cells in a one-step method to obtain Cas-RNAi RNP carrying specific sgRNA-shRNA. According to the Cas-RNAi RNP disclosed by the invention, the function combination of gene editing and RNA interference is realized, and the shRNA base sequence aiming at the Ligase 4 gene is designed so as to temporarily inhibit the NHEJ pathway, so that efficient HDR repair is realized.
Owner:BRAVOVAX
Production method for genetically modified plant cells
InactiveCN102639695ADirect induction of mutationsMutant preparationRecombinant DNA-technologyZinc finger nucleasePlant cell
By using a plant cell wherein the functioning of the protein involved in non-homologous end joining repair is artificially inhibited, the transduction-efficiency for mutations is dramatically increased in the non-homologous end joining repair process which is subsequent to the inducement of DNA double-strand breaks by zinc finger nucleases.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Preparation method of cell line with high homologous recombination rate
PendingCN114717263AHigh rate of homologous recombinationEasy to editHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesGenome editingWild type
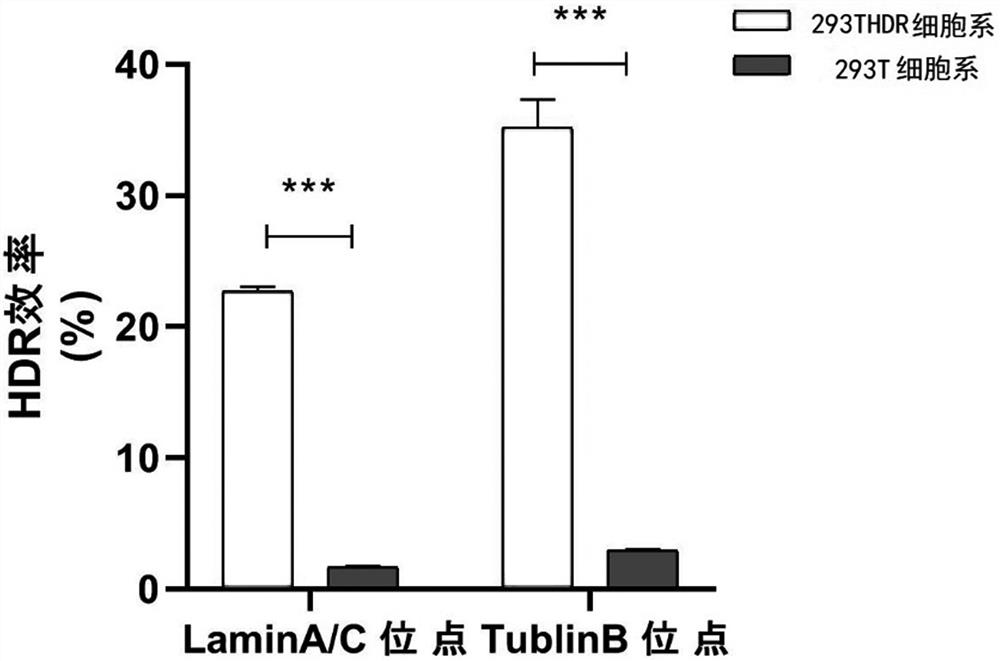
The invention relates to a preparation method of a cell line with a high homologous recombination rate, which comprises the following steps: stably inserting a donor vector into an AAVS1 position by using a siRNA technology and a gene editing technology, knocking down important genes LIG4 and Ku70 in an NHEJ pathway, and simultaneously overexpressing important proteins SWIT5 and SFR1 in a homologous recombination pathway, so that the cell line with the high homologous recombination rate is obtained. And screening by a monoclonal sorting method to obtain the improved 293T cell line with high homologous recombination efficiency. The proliferation effect and transfection effect of the cell line obtained by the method are similar to those of a wild type, and the homologous recombination efficiency is 20 times that of the wild type, so that the subsequent accurate gene editing operation is facilitated, and the scientific research can be more efficiently carried out at low cost.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com