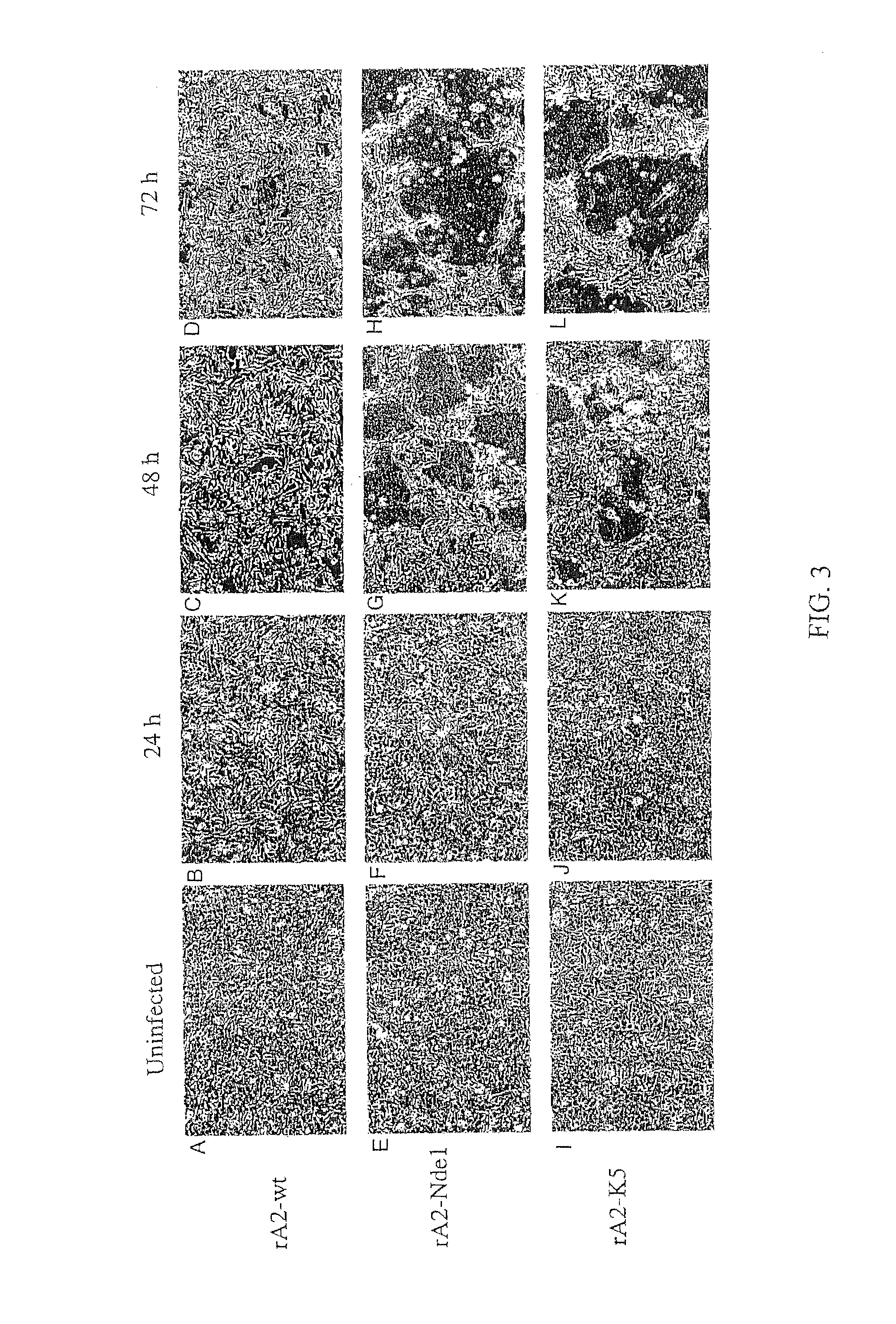
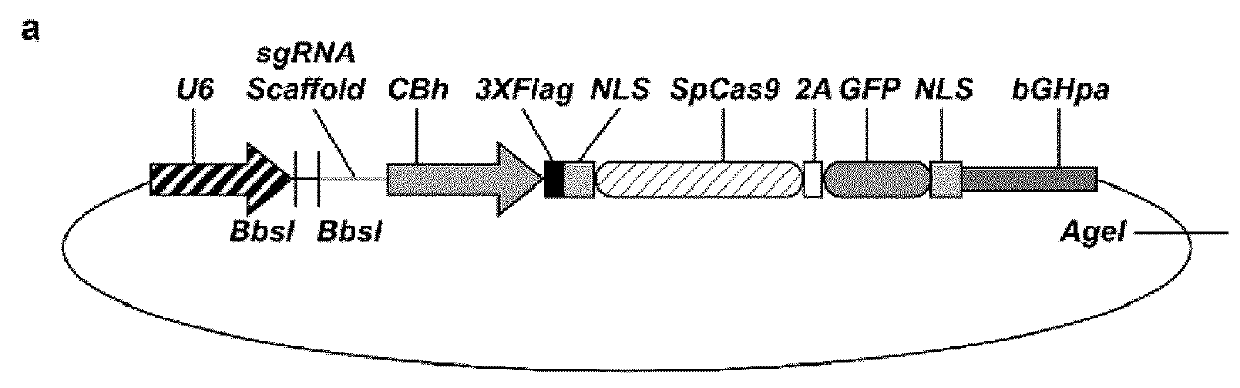
Patents
Literature
111 results about "Frameshift mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.
Method of increasing content of resistant starch in rice through genome editing and sgRNA special for same
ActiveCN106086028AAddressing the lack of low-glycemic foodsAvoid problemsNucleic acid vectorPlant peptidesBiotechnologyAmylase
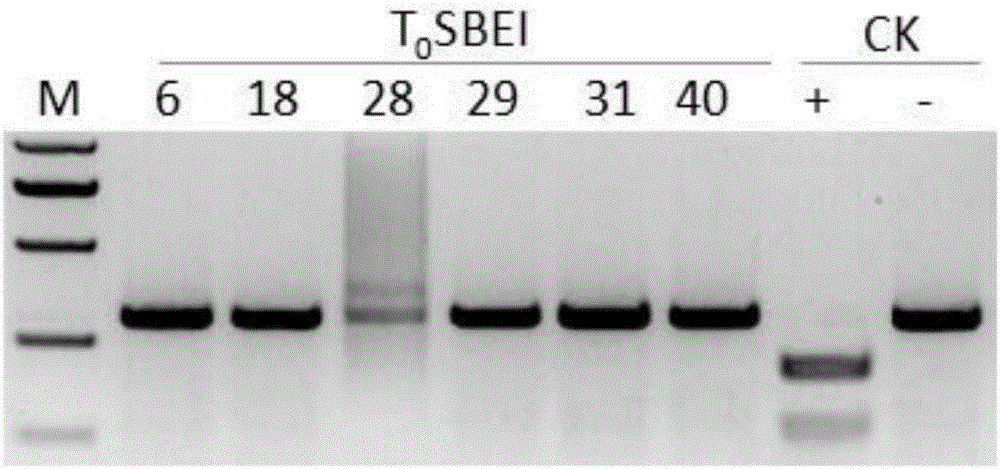
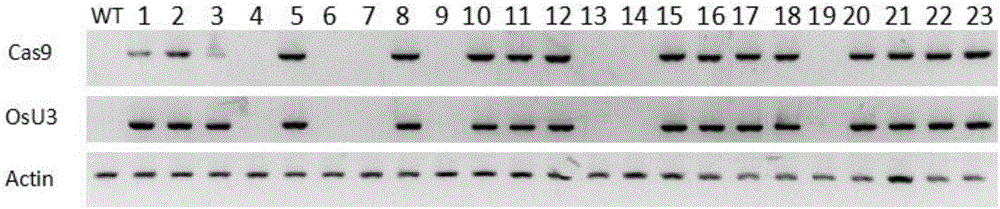
The invention discloses a method of increasing the content of resistant starch in rice through genome editing and sgRNA special for the same. The method provides a method of increasing the content of resistant starch and / or amylase in rice seeds. The method includes the following steps that expression of SBEIIb genes in the rice is inhibited; the SBEIIb genes are genes of encoding SBEIIb protein. The invention further provides a method of increasing the content of resistant starch in rice and includes the step of inhibiting the activity of the SBEIIb protein in the rice. By using the CRISPR / Cas9 technology, the rice SBEIIb genes are edited at fixed points, the rice SBEIIb genes are knocked off by causing frameshift mutation, and the new generation of new rice germplasm with the content of amylase and resistant starch obviously increased is obtained.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR/Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)/-CRISPR-associated protein 9) vector and application thereof
ActiveCN105316327AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionTriticeaeGenetically modified wheat
The invention provides a wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / -CRISPR-associated protein 9) vector and application thereof and belongs to the field of crop molecular biology. The wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 vector and the application thereof have the advantages that gRNA of a third exon of specificity-targeted TaAGO4a is provided firstly, a DNA sequence of the gRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the gRNA contains an enzyme cutting site XmnI; subsequently, the CRISPR / Cas9 vector containing the gRNA is provided, and through co-transformation of Cas9 and the specific gRNA into a wheat protoplast as well as enzyme cutting and sequencing technologies, the condition that the gRNA can guide the Cas9 to cut three copies positioned on a chromosome 3A, a chromosome 3B and a chromosome 3D of the TaAGO4a respectively can be detected successfully so as to cause frameshift mutation of the gene and result in afunction or excalation of the gene; the wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 vector can be used for preparing TaAGO4a gene-deleted transgenic wheat.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods and materials for detecting frameshift mutations
The invention relates to methods and materials for detecting in a biological sample the presence or absence of a target protein having a frameshift mutation that results in missense amino acid sequence downstream of the frameshift mutation, comprising combining with the biological sample a binding ligand that is capable of specifically binding the missense amino acid sequence, and then determining whether the binding ligand binds to the missense amino acid sequence. Binding of the ligand to the missense amino acid sequence is indicative of the presence of the frameshift mutation.
Owner:GREAT BASIN SCI
Method for reducing rice amylose content through gene editing and special sgRNA
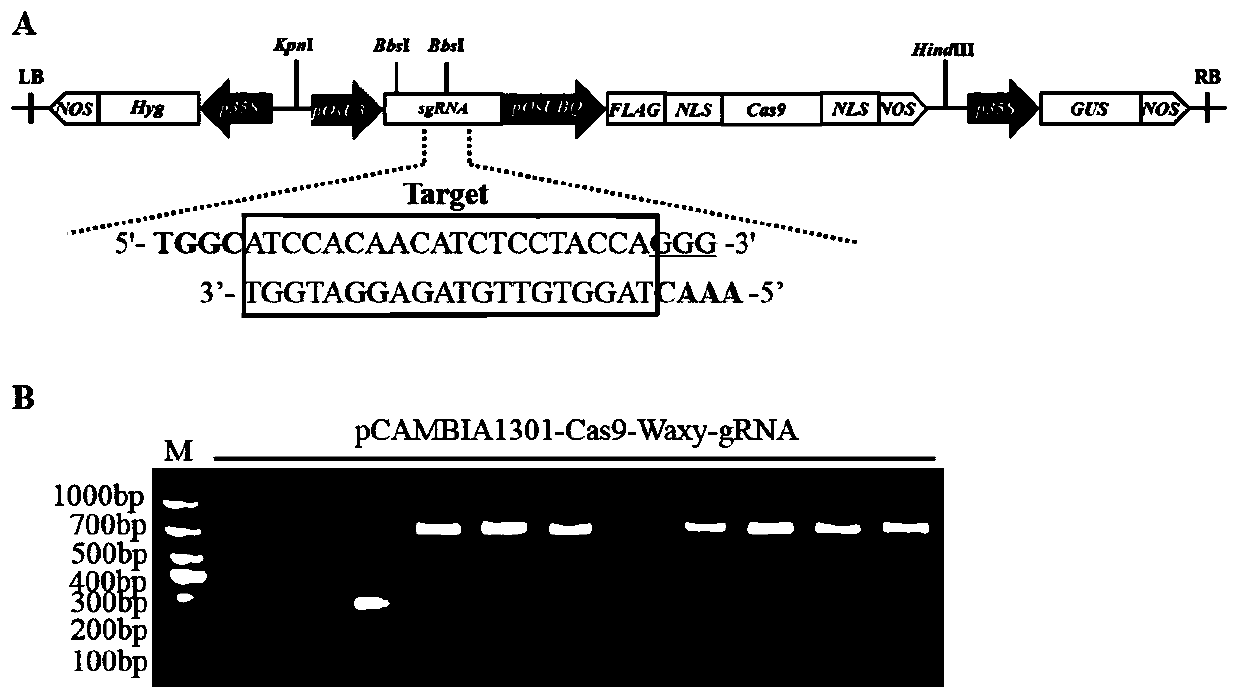
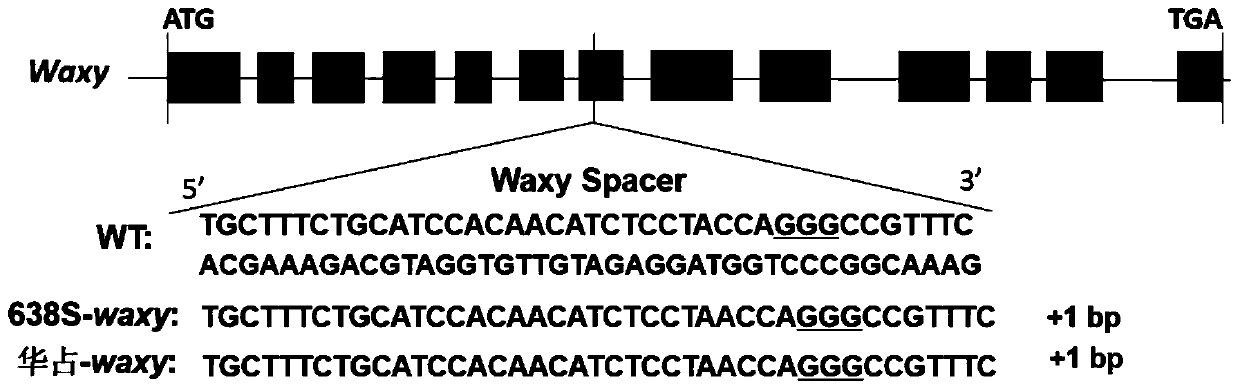
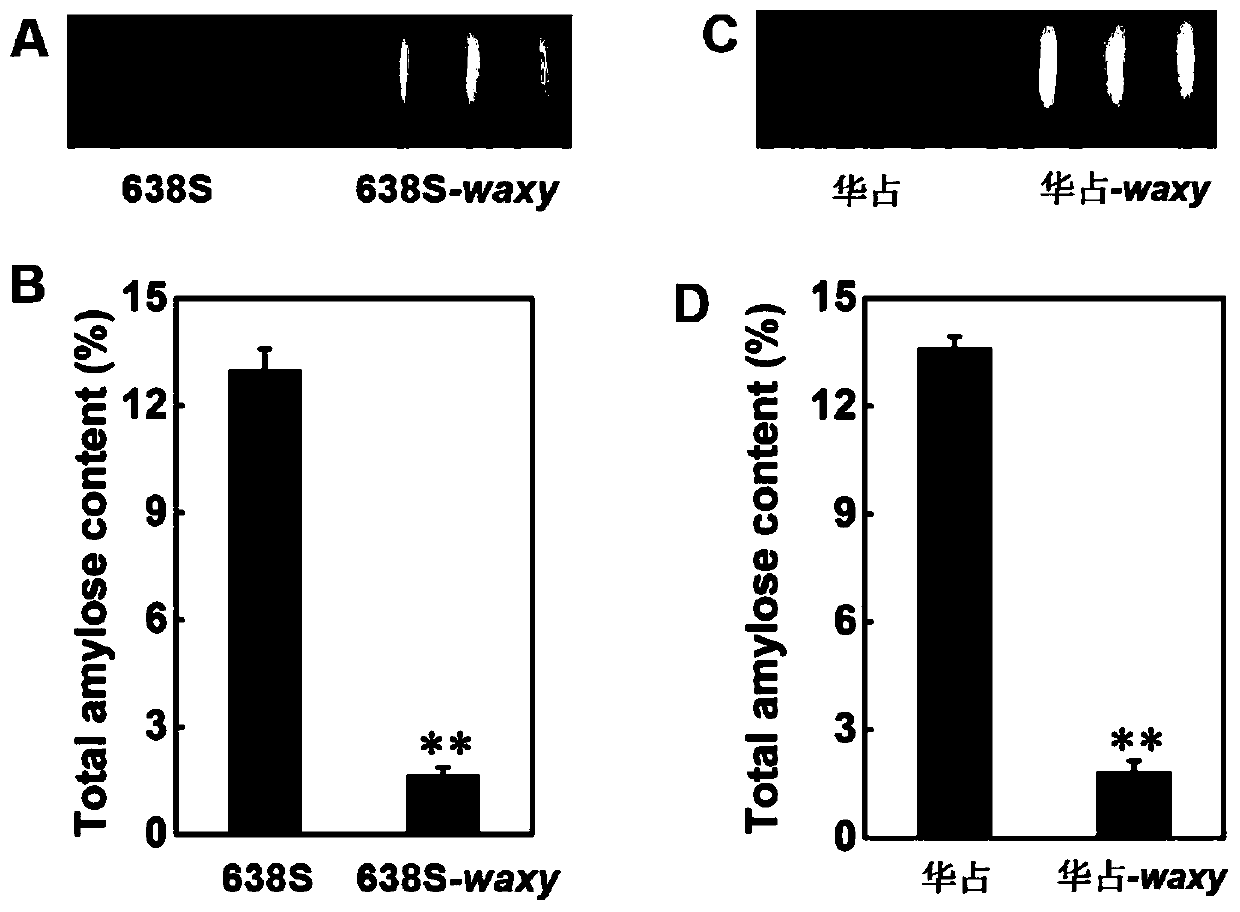
The present invention discloses a method for reducing rice amylose content through gene editing and a special sgRNA, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: expression of a Waxy gene in rice is inhibited; and the Waxy gene is the gene encoding Waxy protein. A CRISPR / Cas9 technology is utilized to edit the rice Waxy gene on site. By causing frameshift mutations and knocking out the rice Waxy gene, a new generation of rice germplasm with significantly reduced amylose content is obtained. Compared with a wild type, the obtained Waxy site-edited strainis significantly lowered in amylose content.
Owner:YUAN LONGPING HIGH TECH AGRI CO LTD +2
Product for diagnosing congenital scoliosis and application of product
ActiveCN104328169AEarly intervention time is goodMicrobiological testing/measurementFrameshift mutationHaplotype
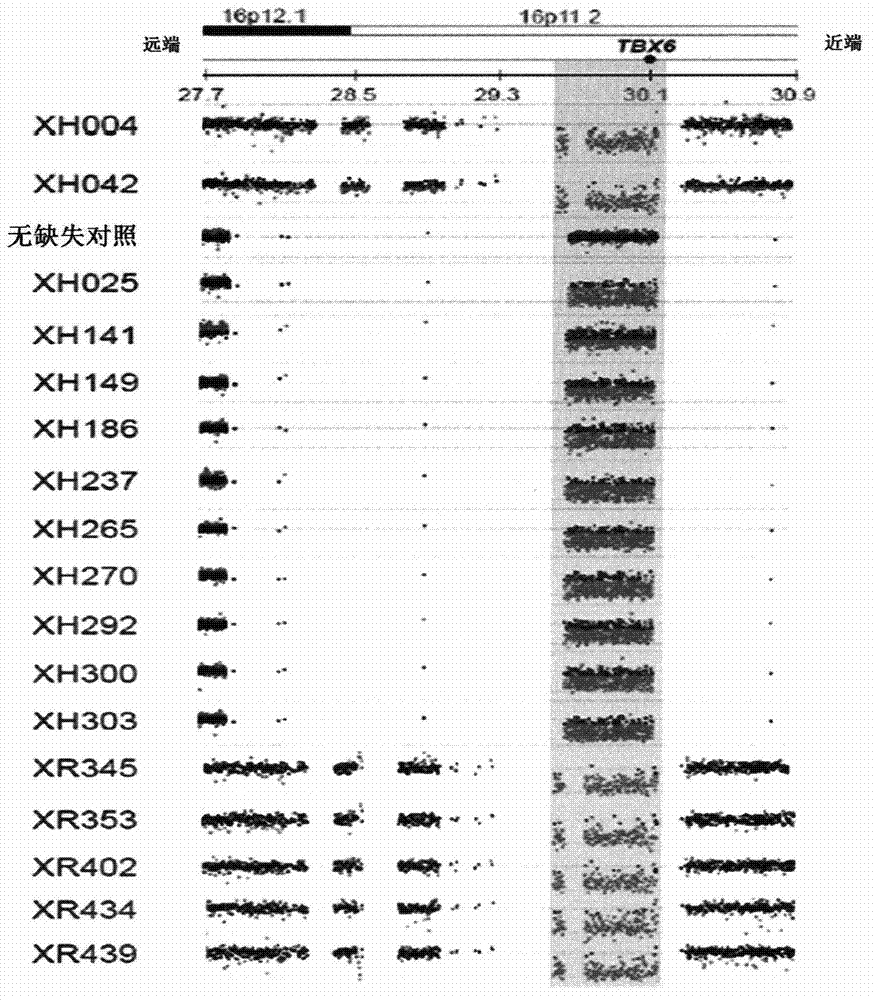
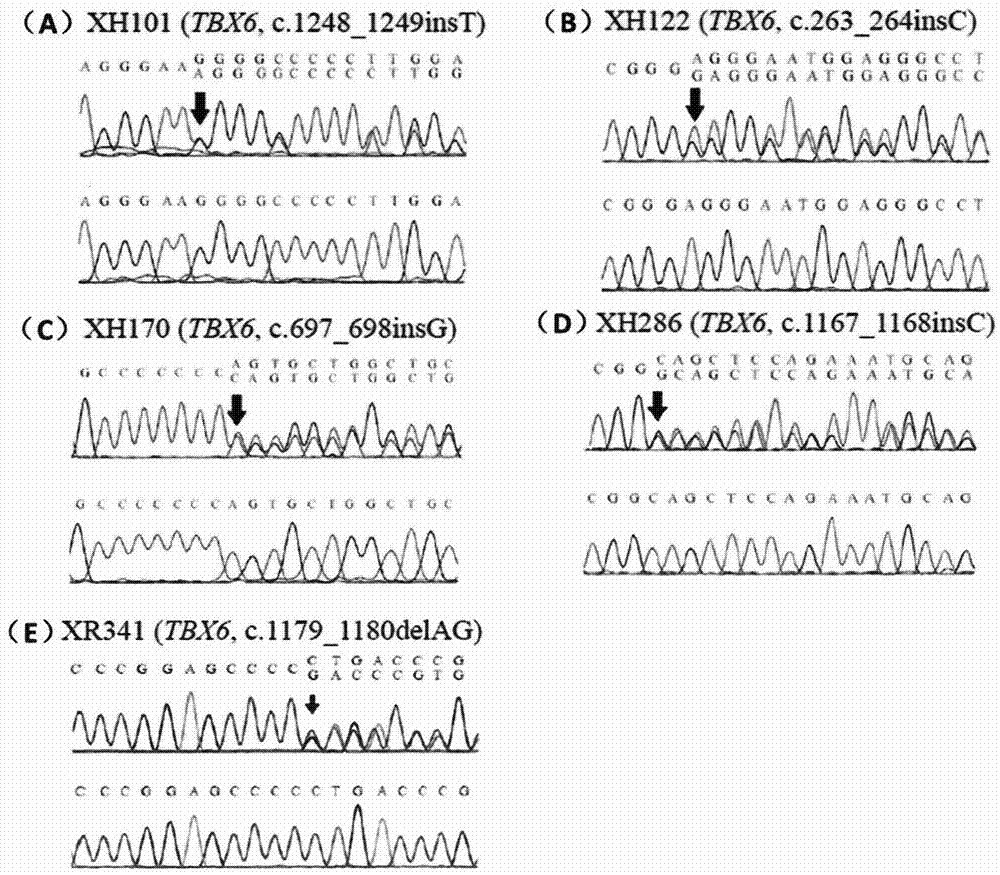
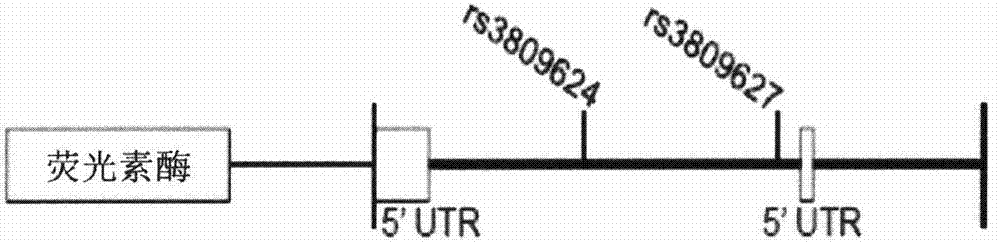
The invention discloses a product for diagnosing congenital scoliosis. According to the product, the judgment is carried by detecting whether a chromosome 16p11.2 is micro-deleted or the TBX6 gene frameshift mutation exists and according to the haplotypes of two SNP sites of rs3809624-rs3809627 in a TBX6 gene on another homologous chromosome. The diagnostic kit is sensitive and can be used for diagnosing the congenital scoliosis in early stage.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Modification of the dystrophin gene and uses thereof
InactiveUS20180265859A1Restoring correct reading frameAvoid large deletionsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMuscular dystrophyFrameshift mutation
Methods of modifying a dystrophin gene are disclosed, for restoring dystrophin expression within a cell having an endogenous frameshift mutation within the dystrophin gene. The methods comprising introducing a first cut within an exon of the dystrophin gene creating a first exon end, wherein said first cut is located upstream of the endogenous frameshift mutation; and introducing a second cut within an exon of the dystrophin gene creating a second exon end, wherein said second cut is located downstream of the frameshift mutation. Upon joining / ligation of said first and second exon ends dystrophin expression is restored, as the correct reading frame is restored. Reagents and uses of the method are also disclosed, for example to treat a subject suffering from muscular dystrophy.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
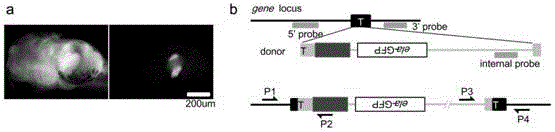
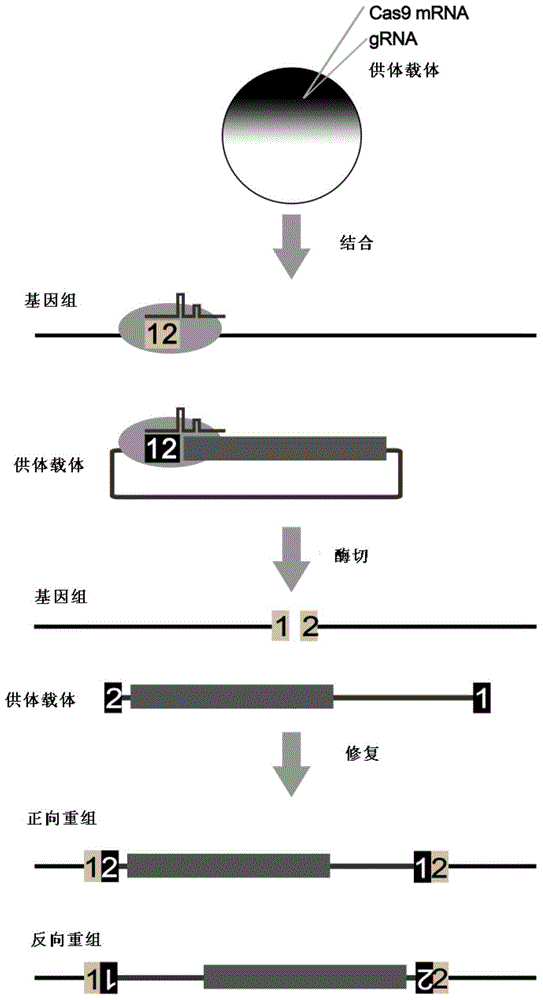
Carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as method and application for gene fixe-point knock-in in Xenopus laevis genome
InactiveCN104611368ARealize fixed-point insertionGenetic stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryA-DNAEmbryo
The invention provides a carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as a method and an application for gene fixe-point knock-in in a Xenopus laevis genome. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), guide RNA (ribonucleic acid), Cas9 nuclease and a donor carrier with a pancreas ela-fluorescent screening label and a Cas9 target fragment are contained in a fertilized egg of Xenopus laevis; (2) under the joint action of guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease, a target gene in the Xenopus laevis genome and the double-chain Cas9 target fragment on the donor carrier are shorn; (3), gene fixed-point knock-in of the Xenopus laevis genome is realized through a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) recovery function of Xenopus laevis cells; (4), G0-generation embryos are screened through the pancreas ela-fluorescent screening label, and F1 is subjected to southern blot identification. The carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as the method and the application for gene fixe-point knock-in in the Xenopus laevis genome lay a foundation for research of genetics and human diseases with Xenopus laevis as a model animal.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single-guide RNA (sgRNA) fragment and application thereof
ActiveCN103820452AShorten the timeLow costVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationReconstruction methodA-DNA
The invention discloses a sgRNA fragment. The DNA sequence of the sgRNA fragment comprises a length of a fixed sequence and a length of a DNA recognition sequence. The sgRNA can recognize different target sites on double strands of a target gene, bond with nuclease and guide nuclease to bond with the target sites of the target gene through recognition of PAM sequences at the target sites and to start random shearing; then nuclease falls off from a shearing opening, thereby forming a DSB gap; then cells repair the double strands of the target gene through a non-homologous end joining repair mechanism, which leads to frameshift mutation; and finally, the target gene is knocked out. The invention further discloses a gene fixed-point reconstruction method and a gene targeting kit. The invention elaborates a series of sgRNAs applicable to the mouse Myod1 gene, and the sgRNAs have high targeting efficiency, short construction time and low cost and can be highly efficiently used for mouse Myod1 gene targeting.
Owner:CYAGEN BIOSCI INC
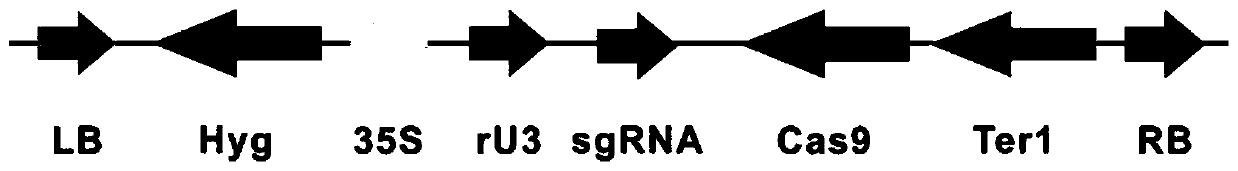
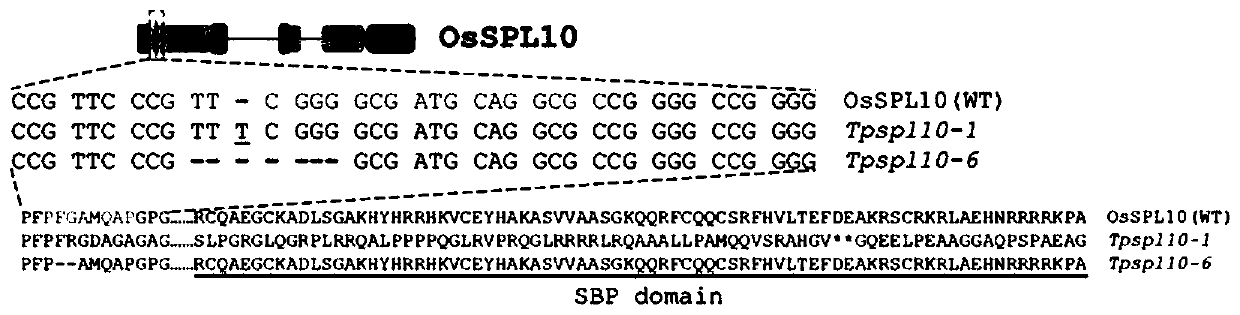
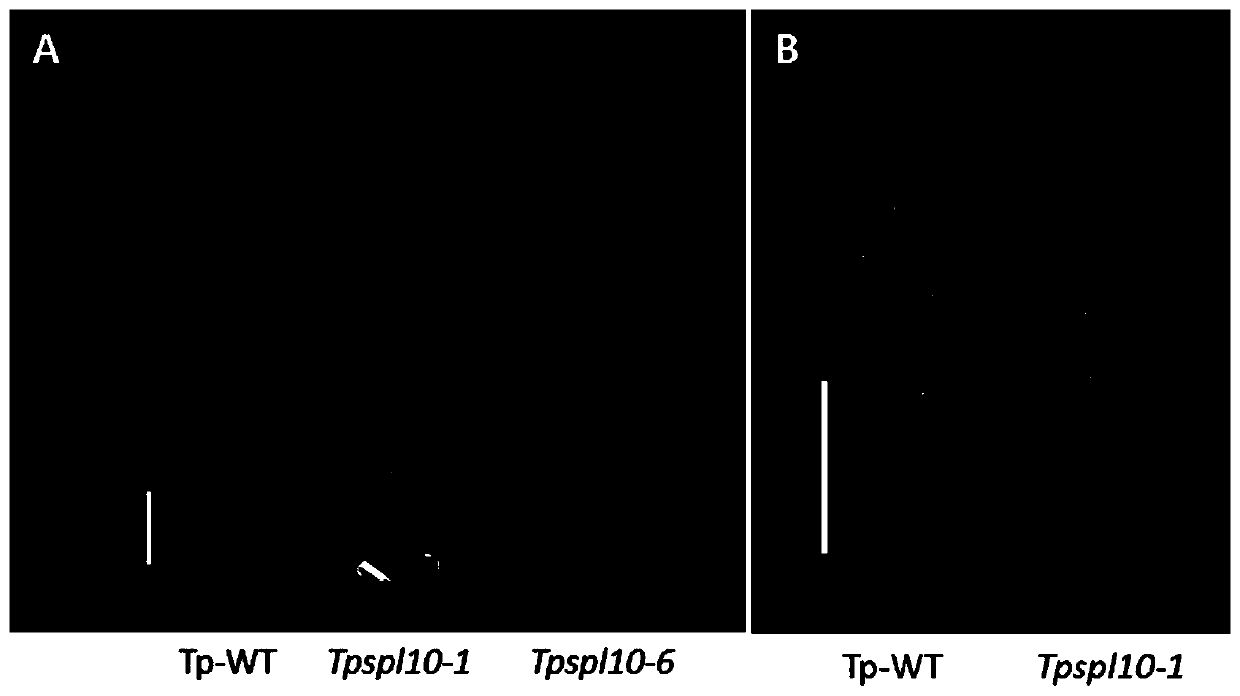
Transcription factor gene Osspl10 of Oryza sativa and application of transcription factor gene Osspl10
InactiveCN110527687AEasy to breedGreat application potentialBacteriaPlant peptidesFrameshift mutationPanicle
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a transcription factor gene Osspl10 of oryza sativa and an application of the transcription factor gene Osspl10. The invention discloses a nucleotide sequence of the gene Osspl10 of oryza sativa and a nucleotide sequence of an SPL family transcription factor coded with the gene Ospl10. A knockoutmutant oryza sativa plant with gene Osspl10 frameshift mutation and loss mutation shows notable reduction of stem length, tiller number and panicle type size. These results indicate that the gene Osspl10 can notably influence yield and correlated character of the oryza sativa, and can have important value in the field of oryza sativa character improvement.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
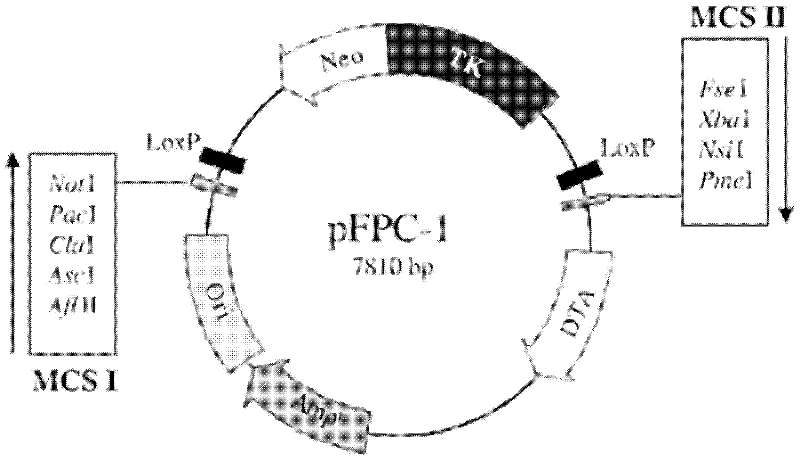
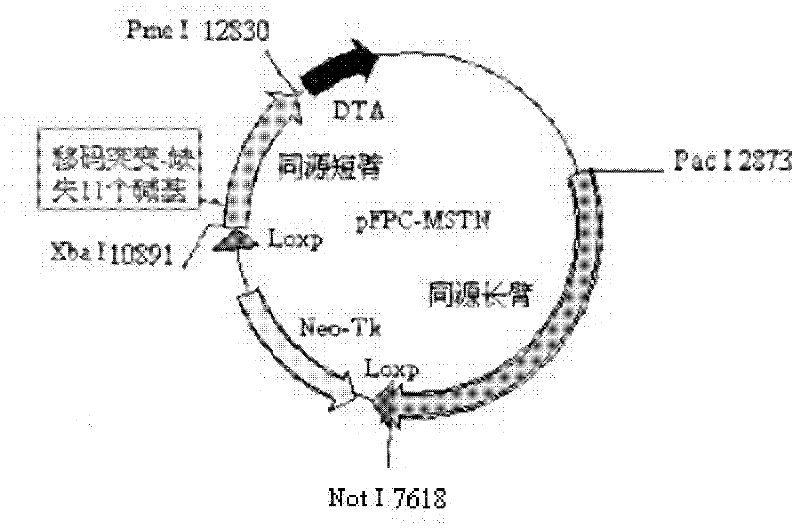
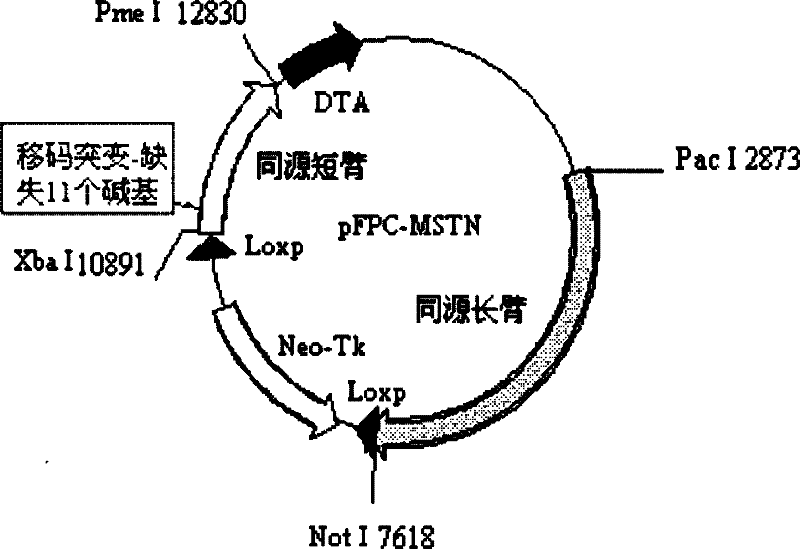
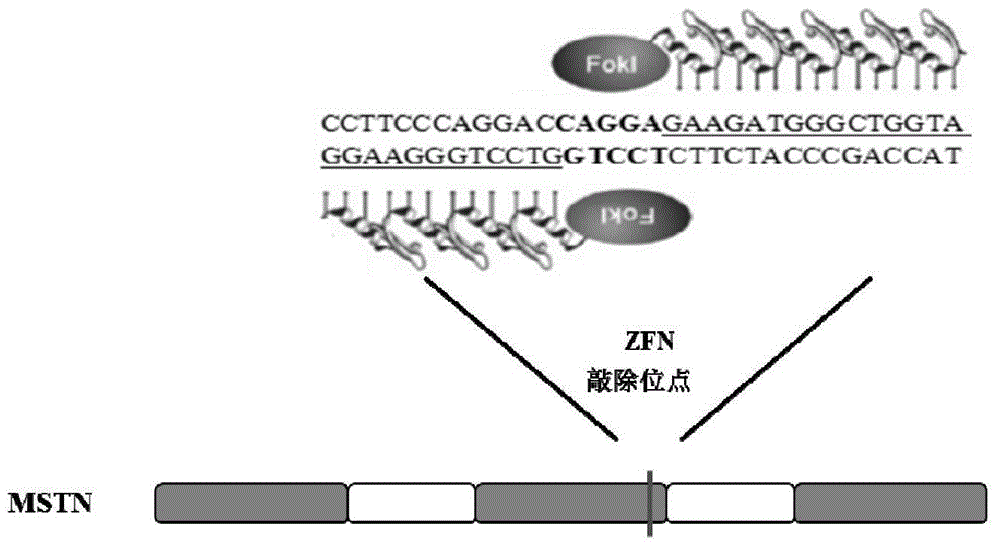
Method for introducing frame-shift mutation in MSTN (myostatin) genes of cattle
InactiveCN102653764AMuscular developmentReduce subcutaneous fatFermentationPlant genotype modificationMyostatinLong arm
The invention discloses a method for introducing frame-shift mutation in bovine MSTN (myostatin) genes. According to the method, a targeting vector for the frame-shift mutation of the bovine MSTN genes is established, and the frame-shift mutation is introduced into the third exon of the bovine MSTN genes by virtue of homologous recombination. The method comprises the following steps of: synthesizing a homologous short arm containing the frame-shift mutation of MSTN, and allowing the homologous short arm to be short of 11bp on the third exon to form the frame-shift mutation; synthesizing a homologous long arm of the MSTN, and inserting a vector pFPC-1 by virtue of a restriction enzyme cutting site to establish the targeting vector pFPC-MSTN of the frame-shift mutation in the bovine MSTN genes; and transfecting bovine somatic cells after the linearization of the targeting vector, and introducing the frame-shift mutation in the bovine MSTN genes by virtue of the homologous recombination. Transgenic cattle with the frame-shift mutation of the MSTN genes can be obtained in the production by virtue of the cells, thereby improving beef production traits of the cattle and improving the quality and yield of beef.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE +1
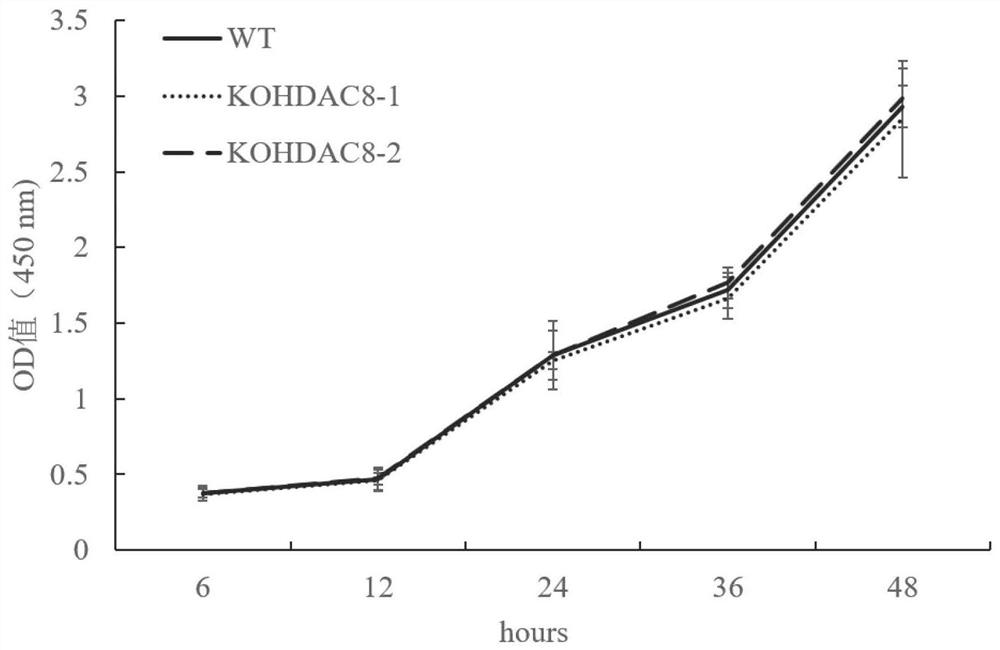
HDAC8 gene knockout BHK-21 cell line as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN112980878ANo significant effect on growth rateHigh titerSsRNA viruses positive-senseHydrolasesVaccine ProductionCell growth rate
The invention discloses a construction method of an HDAC8 gene knockout BHK-21 cell line, which comprises the following steps: carrying out gene knockout on HDAC8 in a cell line BHK-21 for foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 technology, transfecting BHK-21 cells by utilizing CRISPR plasmids for knocking out the HDAC8, and performing separation to obtain a plurality of cell clones by utilizing antibiotic screening in combination with gradient dilution and a cloning ring method. After genome DNA is extracted, PCR amplification and sequencing are carried out, and cell clones of which two HDAC8 genes are subjected to homozygous frameshift mutation are successfully identified. In the HDAC8 knockout BHK-21 cell line, the replication rate of foot-and-mouth disease virus is obviously accelerated, the final virus titer is obviously improved, and the HDAC8 knockout has no obvious influence on the cell growth rate, which shows that the HDAC8 knockout BHK-21 cell line has the prospect of being used for foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production. A foundation is laid for further knocking out HDAC8 from suspension culture type BHK-21 cells and directly applying HDAC8 to production of foot-and-mouth disease vaccines.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Production of attenuated respiratory syncytial virus vaccines involving modification of M2 ORF2
InactiveUS7485440B2Slow kineticsIncrease synthesisSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesOpen reading frameADAMTS Proteins
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are provided in which expression of the second translational open reading frame encoded by the M2 gene (M2ORF2) is reduced or ablated to yield novel RSV vaccine candidates. Expression of M2 ORF2 is reduced or ablated by modifying a recombinant RSV genome or antigenome to incorporate a frame shift mutation, or one or more stop codons in M2 ORF2. Alternatively, M2 ORF2 is deleted in whole or in part to render the M2-2 protein partially or entirely non-functional or to disrupt its expression altogether. M2 ORF2 deletion and knock out mutants possess highly desirable phenotypic characteristics for vaccine development. These changes specify one or more desired phenotypic changes in the resulting virus or subviral particle. Vaccine candidates are generated that show a change in mRNA transcription, genomic or antigenomic RNA replication, viral growth characteristics, viral antigen expression, viral plaque size, and / or a change in cytopathogenicity. In addition, M2-2 knock out or deletion virus exhibits increased levels of synthesis of viral proteins in cell culture, providing an enriched source of viral antigen or protein for purification and use as a noninfectious subunit vaccine.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
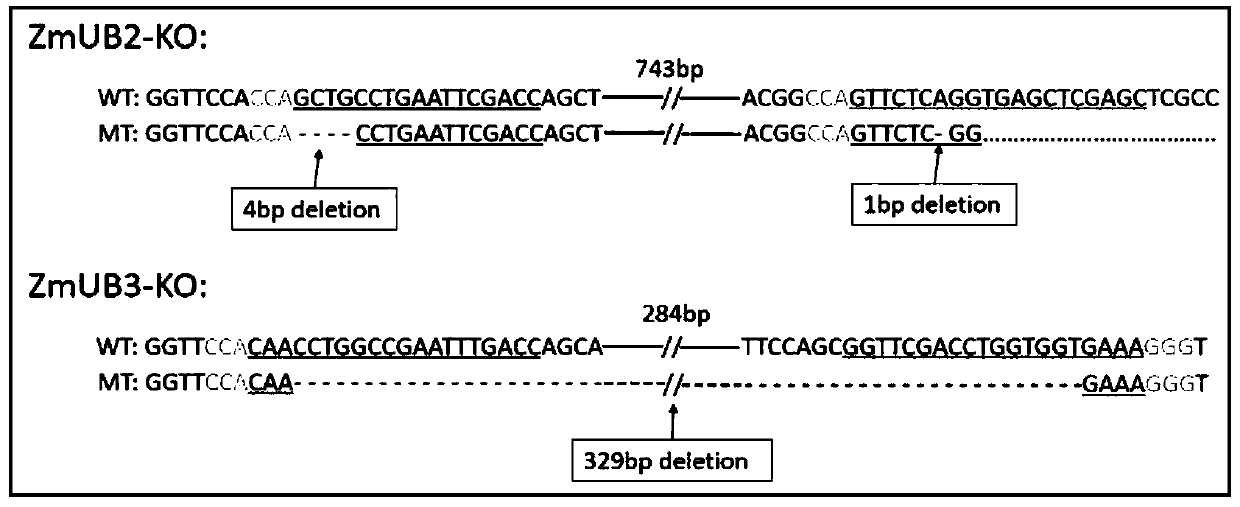
Application of UB2/UB3 gene in regulation and control of corn multi-spike development
ActiveCN110577964ADecreased number of tassel branchesReduce the number of branchesPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyDouble mutation
The invention discloses application of a UB2 / UB3 gene in regulation and control of corn multi-spike development, and particularly relates to application of UB2 and UB3 gene double mutation in regulation and control of corn multi-spike development. According to the invention, gene editing is carried out on two targets UB2 and UB3 in corn by using a CRISPR / Cas9 transgenic technology, so that the target site of the UB2 gene has deletion of a basic group to cause frameshift mutation and deletion of large fragments of the UB3 gene. Results show that the tassel branch number of UB2 and UB3 double mutant plants is reduced, the increase of the spike number of the UB2 and UB3 double mutants is observed for the first time, new female spikes grow on spike stalks of main spikes, the multi-spike property is shown, auxiliary meristem at the lower part is also derepressed to be developed into female spikes, and phenotypes with increased aerial roots are accompanied; and it shows that after the UB2 gene and the UB3 gene are knocked out, a corn mutant plant can show a multi-spike phenotype. The invention provides a theoretical basis for genetic improvement of the corn multi-spike property has a large application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
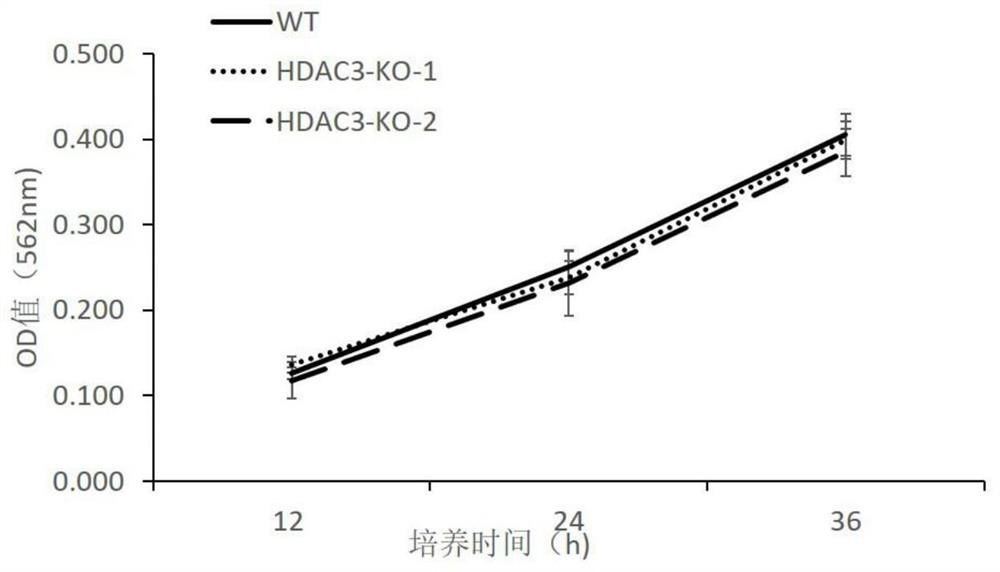
HDAC3 gene knockout BHK-21 cell line as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN112852745ANo significant effect on growth rateHigh titerHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementVaccine ProductionCell growth rate
The invention discloses a construction method of an HDAC3 gene knockout BHK-21 cell line, which comprises the following steps: carrying out gene knockout on HDAC3 in a cell line BHK-21 for foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 technology, transfecting BHK-21 cells by utilizing CRISPR plasmids for knocking out the HDAC3, and separating the cells to obtain a plurality of cell clones by utilizing antibiotic screening in combination with gradient dilution and a cloning ring method; extracting the genome DNA, performing PCR amplification and sequencing, and successfully identifying the cell clones of which two HDAC3 genes are subjected to homozygous frameshift mutation. In the HDAC3 knockout BHK-21 cell line, the replication rate of foot-and-mouth disease virus is obviously accelerated, the final virus titer is obviously improved, and the HDAC3 knockout has no obvious influence on the cell growth rate, so that the HDAC3 knockout BHK-21 cell line has the prospect of being used for foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production. Therefore, the foundation is laid for further knocking out HDAC3 from suspension culture type BHK-21 cells and directly applying HDAC3 to foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
HCBP 6 (Hepatitis C Virus Core-Binding Protein 6) gene knockout cell line and construction method thereof
The invention discloses an HCBP 6 (Hepatitis C Virus Core-Binding Protein 6) gene knockout cell line and a construction method thereof. The construction method for the HCBP 6 gene knockout cell line is characterized in that a CRISPER / Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9) technology is adopted to construct the HCBP 6 gene knockout cell line, a fragment which conforms to a 5'-N[X]-NGG-3' or 5'-CNN-N[X]-3' sequence arrangement rule in the coding sequence of HCPB6 protein is taken as a target sequence, wherein N presents any one of A, G, C and T, X is greater than or equal to 14 or less than or equalto 30, in addition, X is an integer, and N[X] presents X continuous deoxyribonucleotide. The construction method lays a foundation for HCV (hepatitis C virus) infection mechanism research. The HCBP 6gene knockout constructed by the invention forms frameshift mutation on a genome level, the gene can be transferred to the next generation along with the division and the proliferation of cells, anda stable HCBP 6 gene knockout cell line is formed.
Owner:THE FIFTH MEDICAL CENT OF CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
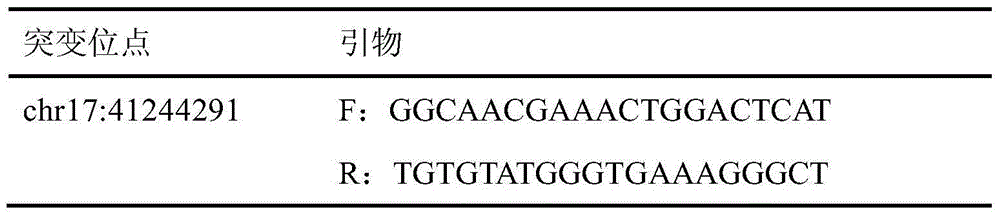
BRCA1 gene g.41244291delT mutation and application in breast cancer auxiliary diagnosis
ActiveCN104946751AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBrca1 geneGene engineering
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and medical oncology and discloses BRCA1 gene g.41244291delT mutation and its application in breast cancer auxiliary diagnosis. The mutation BRCA1 gene sequence has a g.41244291delT site frame-shift mutation in comparison with BRCA1 normal gene sequence. The invention provides a new breast cancer-causing mutation site, and the mutation site can be used in early diagnosis of breast cancer.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
G RNA sequence used for knocking out human BTF gene and knocking-out method thereof
InactiveCN105112412AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionFrameshift mutationRNA Sequence
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to an sgRNA sequence used for knocking out a human BTF (Bcl-2-associated transcription factor 1) gene. The gRNA in a cell can be specifically combined with 251-269bp of a human BTF coding sequence and form a compound with Cas, the BTF gene nucleotide sequence is specifically cut, a cell non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repairing mechanism is used for causing BTF gene frameshift mutation, and then the cell with the BTF gene knocked out is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
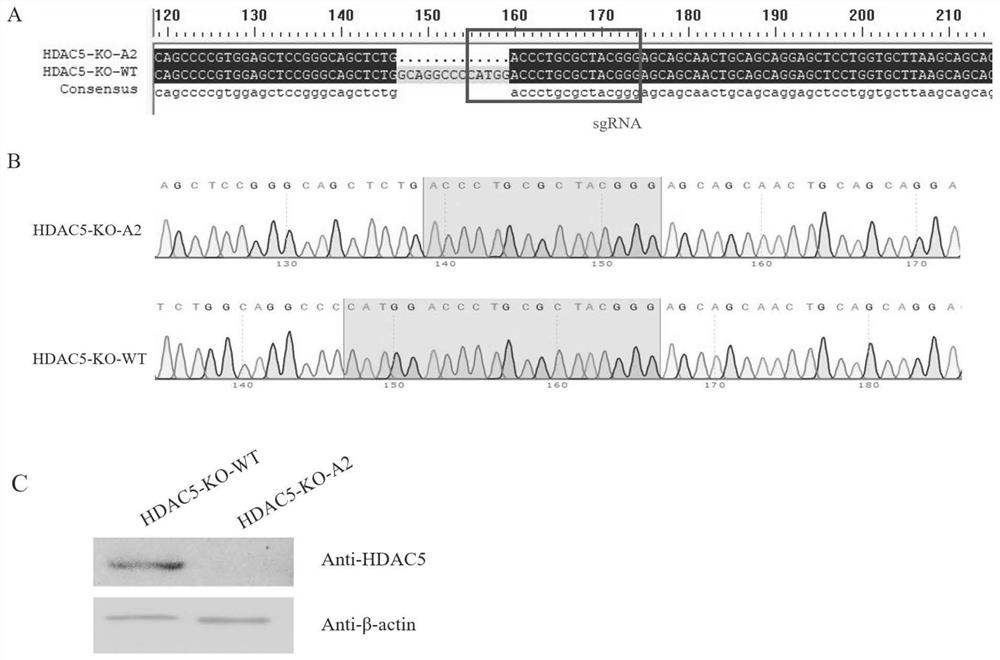
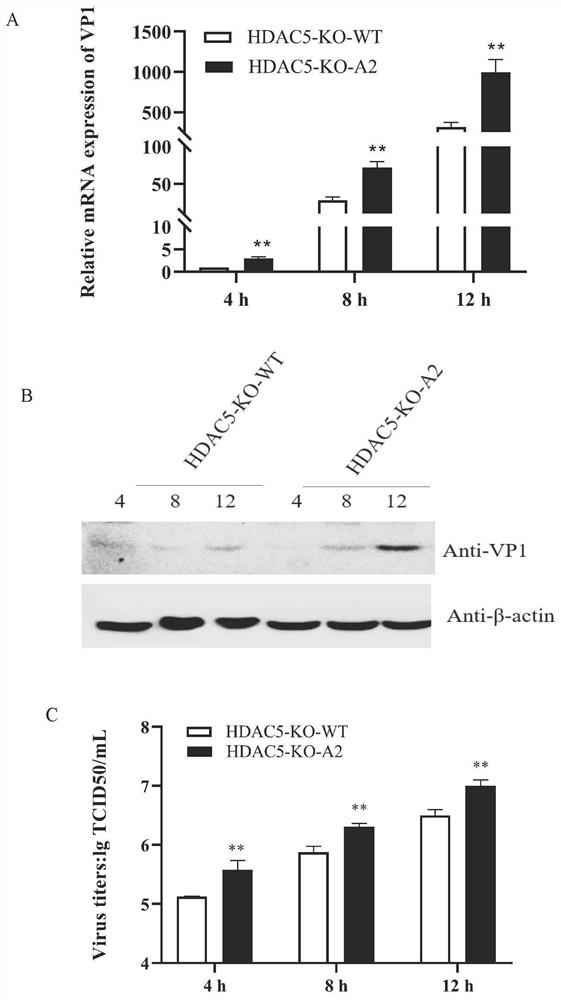
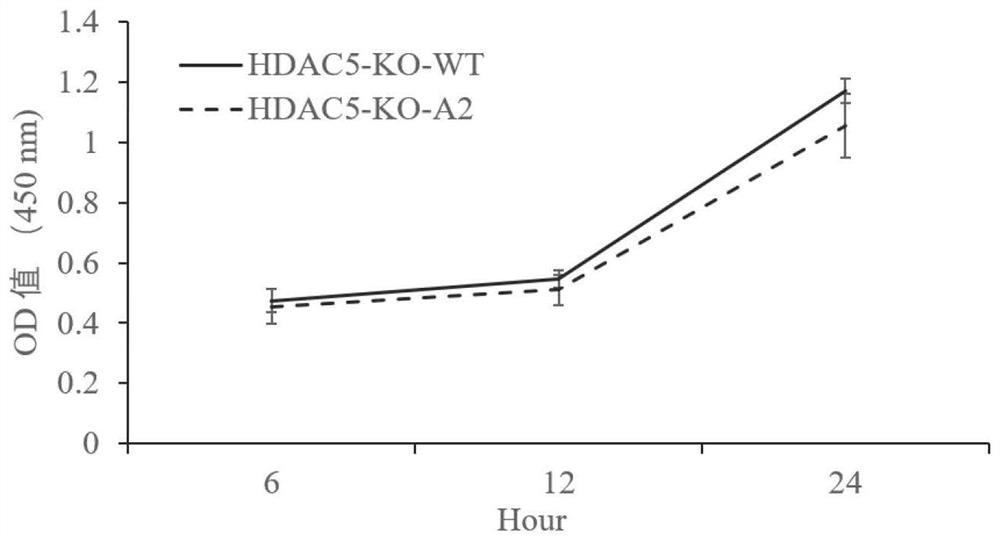
HDAC5 gene knockout BHK-21 cell line as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN112852874ANo significant effect on growth rateHigh titerSsRNA viruses positive-senseHydrolasesVaccine ProductionCell growth rate
The invention discloses a construction method of an HDAC5 gene knockout BHK-21 cell line, which comprises the following steps: carrying out gene knockout on HDAC5 in a cell line BHK-21 for foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 technology, transfecting BHK-21 cells by utilizing CRISPR plasmids for knocking out the HDAC5, and separating the cells to obtain a plurality of cell clones by utilizing antibiotic screening in combination with gradient dilution and a cloning ring method; extracting the genome DNA, performing PCR amplification and sequencing and successfully identifying the cell cloning of which one HDAC5 gene is subjected to homozygous frameshift mutation, wherein the HDAC5-KO-A2 has deletion of 13 basic groups at a Cas9 predetermined cutting position. In the HDAC5 knockout BHK-21 cell line, the replication rate of foot-and-mouth disease virus is obviously accelerated, the final virus titer is obviously improved, and the HDAC5 knockout has no obvious influence on the cell growth rate, so that the HDAC5 knockout BHK-21 cell line has the prospect of being used for foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production. Therefore, the foundation is laid for further knocking out HDAC5 from suspension culture type BHK-21 cells and directly applying HDAC5 to production of foot-and-mouth disease vaccines.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
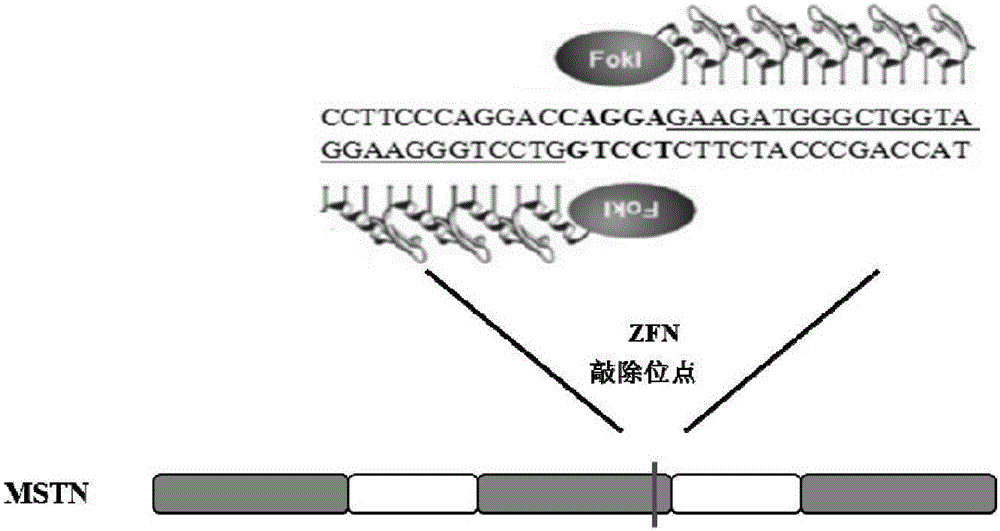
Zinc finger nuclease-mediated porcine MSTN (myostatin) gene mutation sequence and application thereof
ActiveCN105063023APronounced bimuscular phenotypeIncrease muscle massMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryMyostatinZinc finger nuclease
The invention discloses a zinc finger nuclease-mediated porcine MSTN (myostatin) gene mutation sequence and application thereof. By mediating the porcine MSTN gene by the zinc finger nuclease technique, base deletion is enabled, frameshift mutation is resulted in, early termination of translation is caused, an MSTN functional protein is unable to be formed, and the MSTN gene mutation sequence with 3782th to 3796th nucleotides deleted and 3800th nucleotide molecules mutated from T to G is acquired. Experiments show that a pig with the MSTN gene having the 3782th to 3796th nucleotides deleted and the 3800th nucleotide molecules mutated from T to G has evident double-muscled phenotype, both muscle content and lean percentage are evidently increased, and fat content is evidently lowered.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for cultivating new variety of normal-development intermuscular-bone-free fish
ActiveCN112772468AGenetic stabilitySolve small, hard-to-find, hard-to-kick puzzlesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaZooidMating
The invention relates to a method for cultivating a new variety of normal-development intermuscular-bone-free fish, and relates to a method for cultivating a new variety of intermuscular-bone-free fish. The invention provides the method for removing intermuscular bones under the condition that normal growth of fishes is not influenced. The method for cultivating the new variety of the normal-development intermuscular-bone-free fish comprises the following steps of 1, knocking out a bmp6 gene in a fertilized egg of an original fish variety to obtain an F0-generation individual; 2, performing mutant screening on the F0 generation, and matching to obtain an F1 generation population; 3, performing mutant screening on the F1 generation population, selecting individuals with the same frameshift mutation for mating, constructing an F2 generation, and screening out homozygous mutation individuals in the F2 generation; and 4, propagating the F2-generation homozygous mutation individuals to obtain the new variety of the intermuscular-bone-free fish. According to the method, a strain with intermuscular bones deleted can be obtained, growth is not affected, stable inheritance can be achieved, and the problems that the intermuscular bones are small, difficult to find and difficult to remove in production can be solved.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
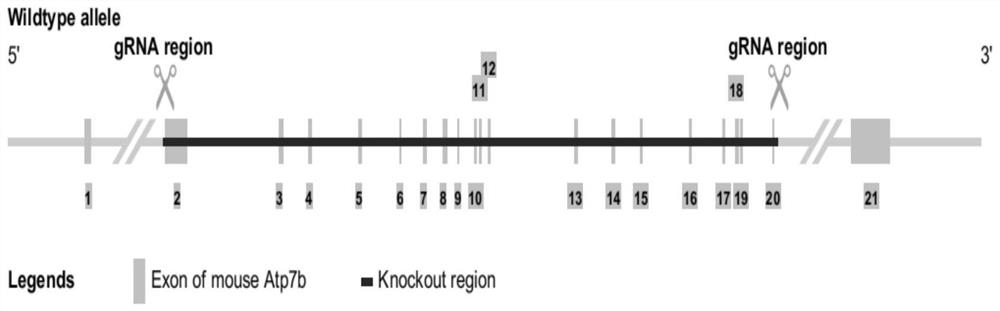
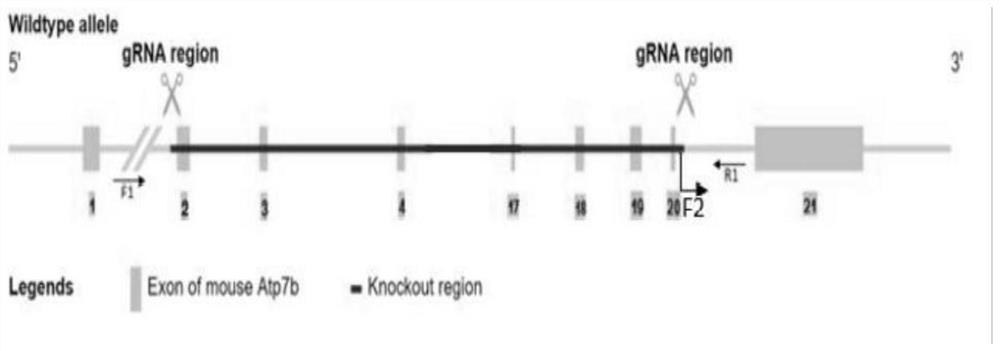
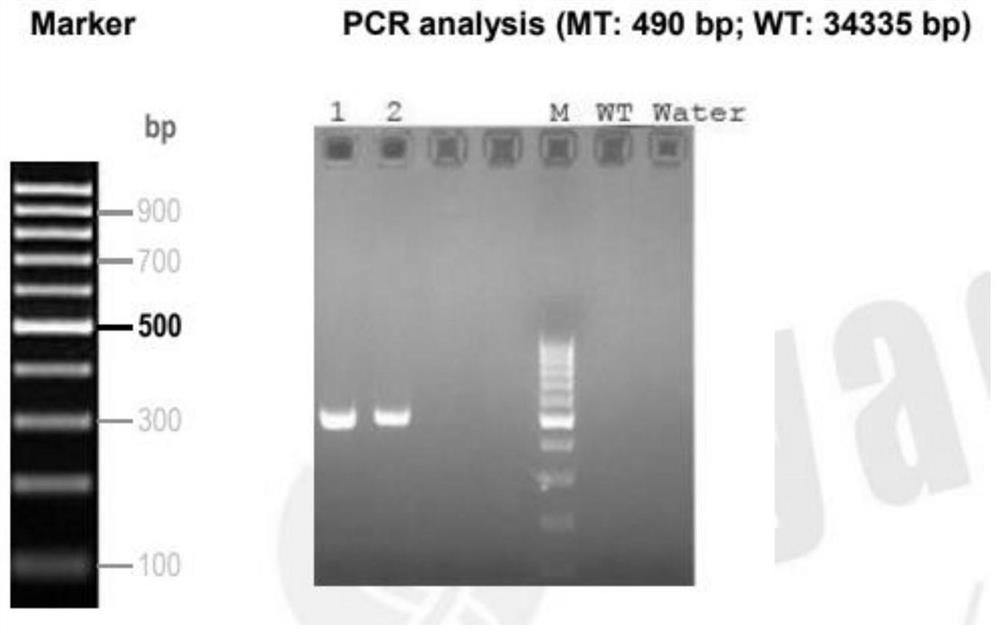
gRNA targeting mouse Atp7b gene and method for constructing Wilson disease mouse model
PendingCN113736787AAchieve the purpose of knockoutFully study the pathogenic mechanismHydrolasesMicroinjection basedDiseaseKnockout animal
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and particularly discloses a group of gRNA targeting a mouse Atp7b gene and a method for constructing a Wilson disease mouse model. Three gRNAs specifically targeted to the Atp7b gene are designed, Exon2-Exon20 of the Atp7b gene is knocked out by utilizing cas9 protein, the sequence of a knocked region is not 3 times, frameshift mutation is caused, and the knocked-out region contains 91.91% of a coding region of the gene, so that the aim of knocking out the gene is fulfilled; and the method for constructing the Atp7b gene knockout mouse model by using the CRISPR / Cas9 system is simple and easy to implement, short in period and high in probability of obtaining positive mice, the pathogenesis of the disease can be fully researched by utilizing the mouse model, and service is provided for further developing a treatment mode aiming at the disease.
Owner:CYAGEN BIOSCI INC
Method for creating red rice strain by targeting Rc gene by using gene edition technique
ActiveCN108823235AAchieving beige improvementEfficient breedingVectorsPlant peptidesBiotechnologyGenome editing
The invention discloses a method for creating a red rice strain by targeting a Rc gene by using a gene edition technique. The method comprises the following steps: editing sequences of a rc gene frameshift mutation point by using a gene edition technique, screening and collecting an RC genotype with function recovery, and successfully improving rice colors of two materials, namely nonglutinous rice Gangyou 8518 and japonica rice Xiushui 134. By adopting the method, an efficient breeding mode is provided for creating red rice germplasm resources and culturing excellent red rice varieties.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Zinc finger nuclease mediated MSTN gene mutation sequence and application thereof
PendingCN105063057APronounced bimuscular phenotypeIncrease muscle massMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMyostatinZinc finger nuclease
The invention discloses a zinc finger nuclease mediated MSTN gene mutation sequence and application thereof. Base deletion is promoted by mediating porcine MSTN (myostatin) gene by virtue of a zinc finger nuclease technology to cause frameshift mutation, and as a result, MSTN functional protein is not formed since translation is terminated in advance; and meanwhile, a mutation sequence of the MSTN gene that nucleotides on 3781st-3791st sites are deleted is obtained. Tests prove that pigs of nucleotide deletion on 3781st-3791st sites in the MSTN gene have marked double-muscled phenotype as well as significant increase in both muscle content and lean percentage.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
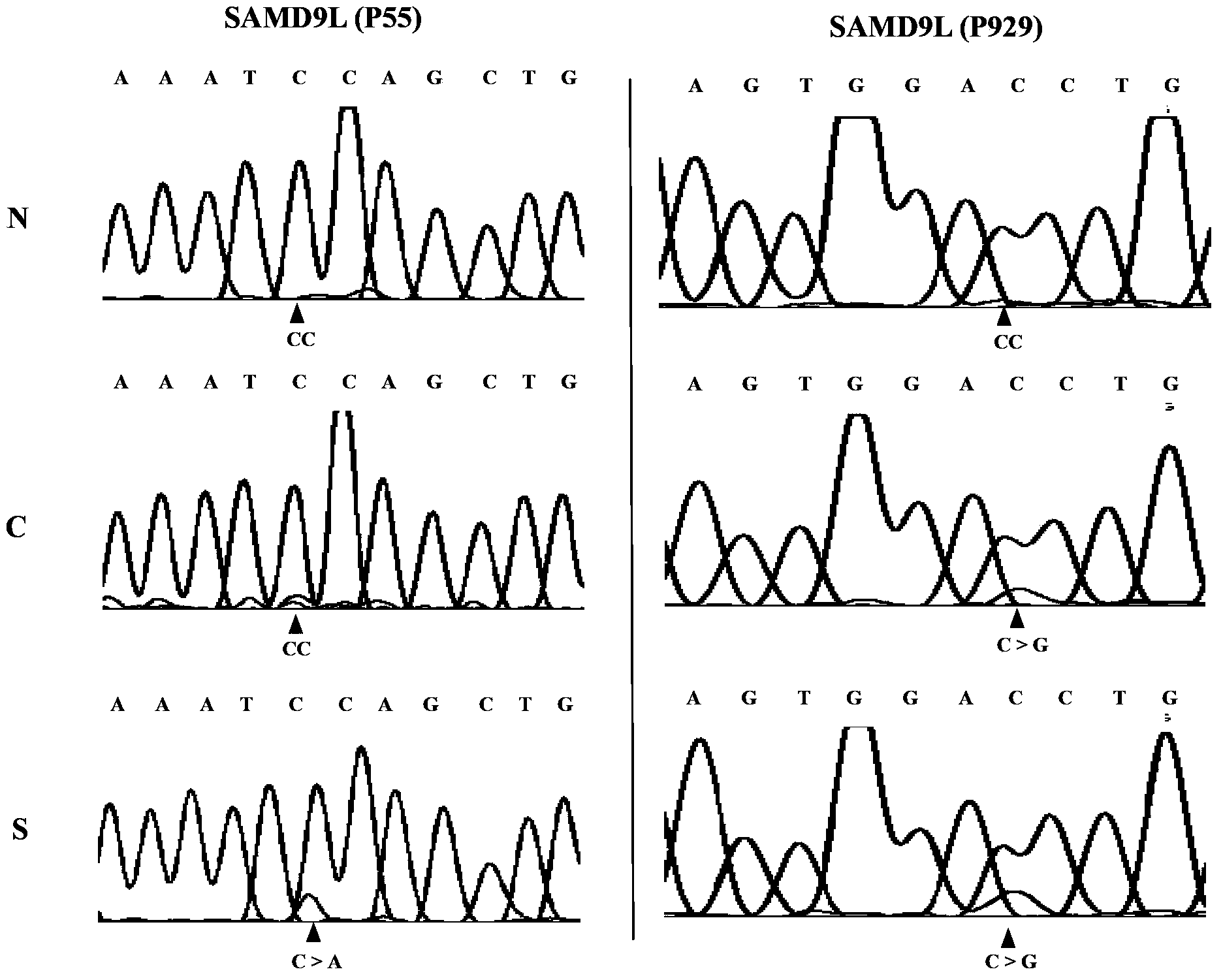
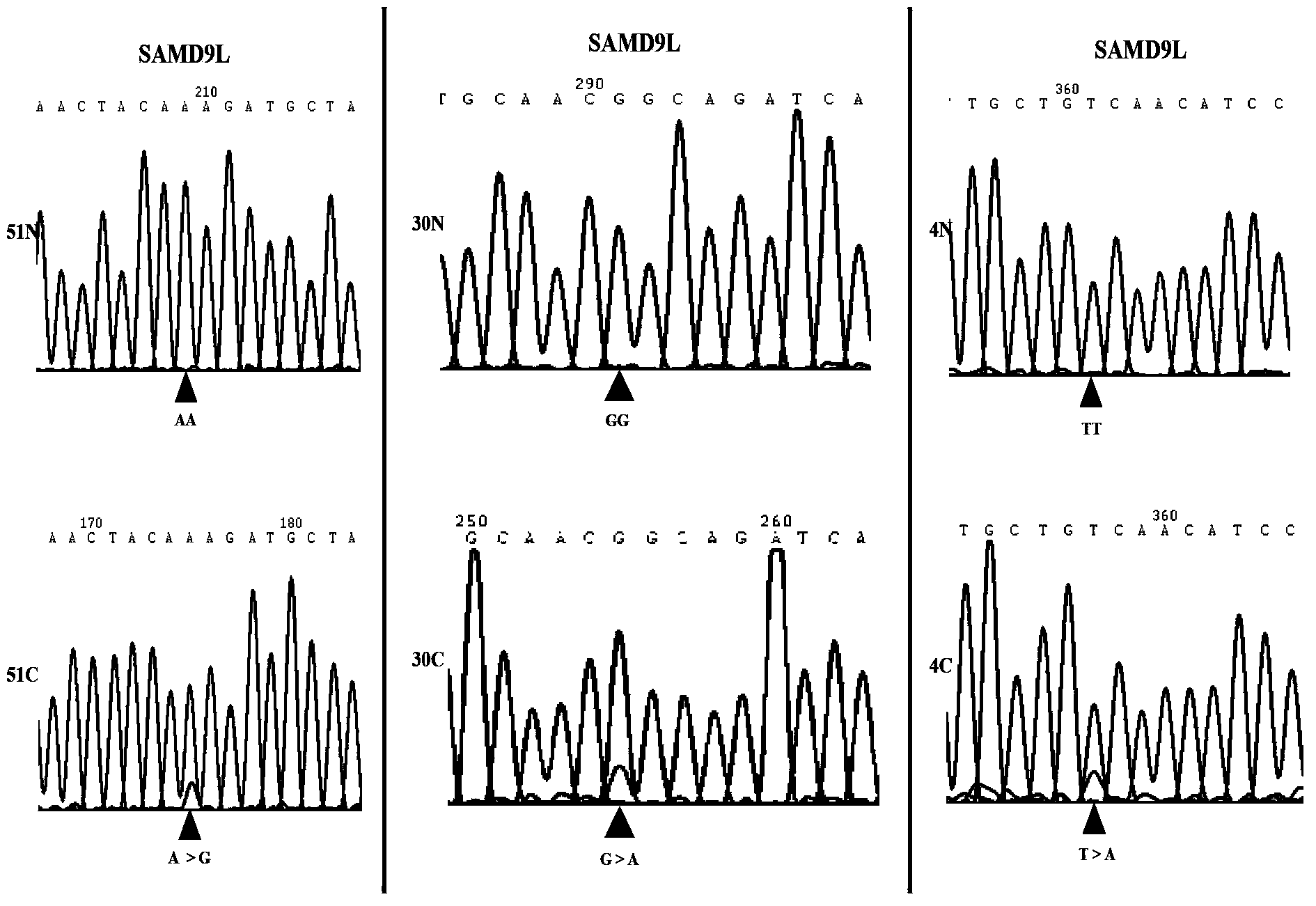
Applications of human SAMD9L gene and protein product encoded by human SAMD9L gene
InactiveCN103571927AAccurate diagnosisRapid diagnosisPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameLymphatic Spread
The present invention discloses applications of human SAMD9L gene and a protein product encoded by the human SAMD9L gene, wherein the SAMD9L gene sequence, especially the open reading frame sequence of the protein encoded by the human SAMD9L gene, generates missense mutation, nonsense mutation, frameshift mutation and other gene structure variations with different forms in tumors so as to be adopted as the specific marker gene for liver cancer diagnosis, such that liver cancer diagnosis is accurate and rapid. According to the present invention, the human SAMD9L protein can be applied on tumor patients so as to treat or alleviate related diseases caused by SAMD9L protein deletion, nonfunction or abnormality; and the human SAMD9L gene can be over-expressed in cancer cells through the transgenic technology, or the SAMD9L protein can be supplied through the in vitro supply manner to control cancer cell proliferation and metastasis so as to achieve the tumor treatment purpose.
Owner:CHINESE NAT HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI
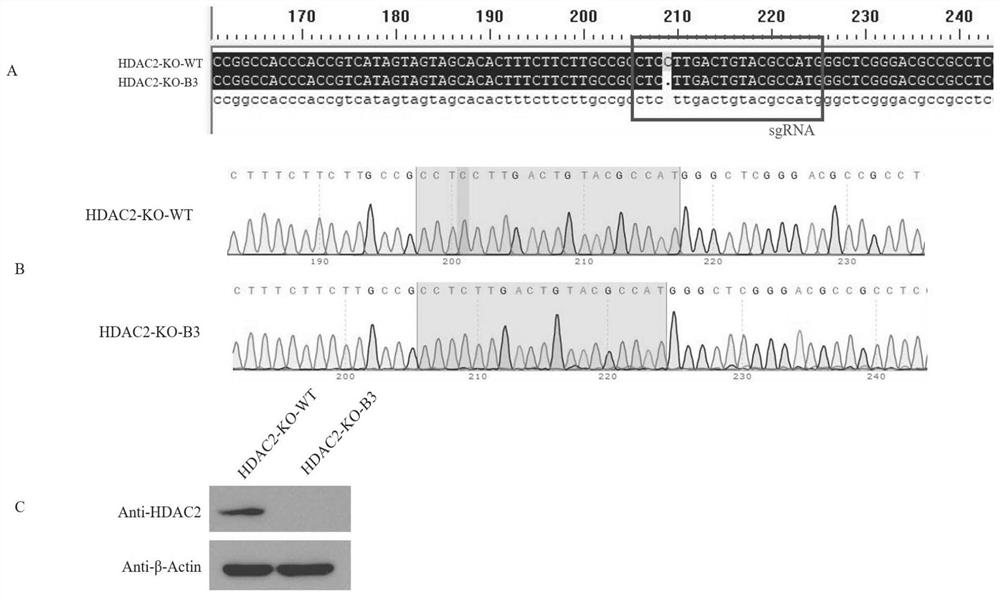
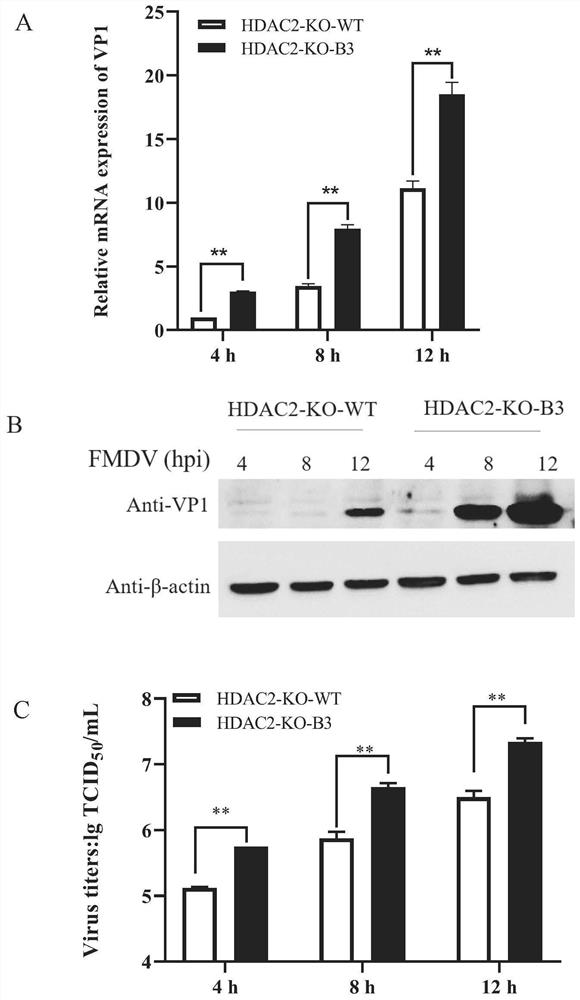
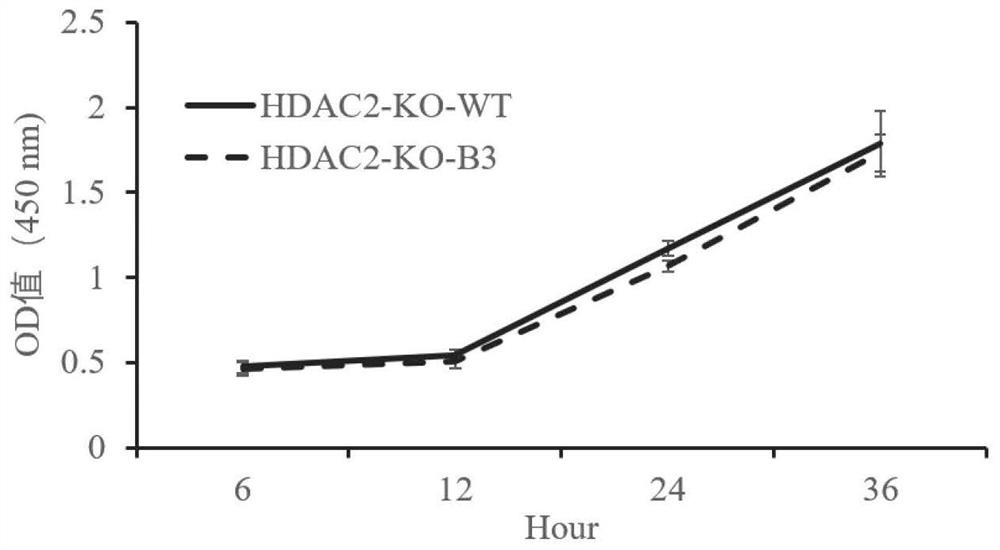
HDAC2 gene knockout BHK-21 cell line as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN112877275ANo significant effect on growth rateHigh titerSsRNA viruses positive-senseHydrolasesVaccine ProductionCell growth rate
The invention discloses a construction method of an HDAC2 gene knockout BHK-21 cell line. The construction method comprises the following steps: carrying out gene knockout on HDAC2 in a cell line BHK-21 for foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 technology; the inventor transfects BHK-21 cells with CRISPR plasmids for knocking out HDAC2, and then separates a plurality of cell clones by using a cloning ring method by combining antibiotic screening with gradient dilution; after genome DNA is extracted, PCR amplification and sequencing are carried out, and cell cloning of which one HDAC2 gene is subjected to homozygous frameshift mutation is successfully recognized; wherein the HDAC2-KO-B3 has the deletion of one basic group at the predetermined cutting position of the Cas9. In the BHK-21 cell line with HDAC2 knockout, the replication rate of foot-and-mouth disease virus is obviously accelerated, the final virus titer is obviously improved, and the cell growth rate is not obviously influenced after HDAC2 knockout, so that the HDAC2 knockout BHK-21 cell line has the prospect of being used for foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production. A foundation is laid for further knocking out HDAC2 from suspension culture type BHK-21 cells and directly applying HDAC2 to production of foot-and-mouth disease vaccines.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting cutting efficiency of gene editing target
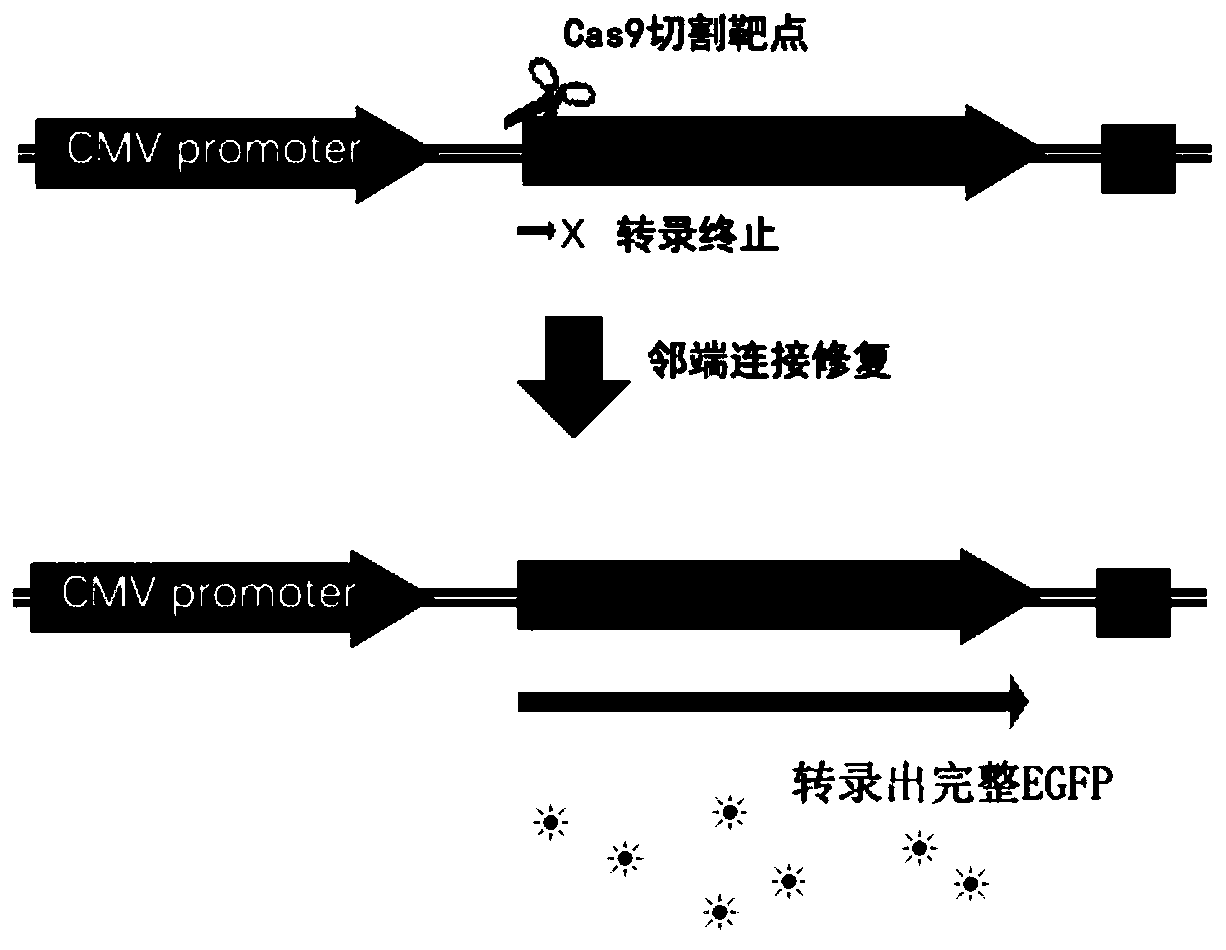
PendingCN111471744ASensitive detectionEasy to detectHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementIntracellularFrameshift mutation
The invention discloses a method for detecting the cutting efficiency of a gene editing target. The method comprises the following steps of constructing a target detection vector containing a frame shift mutation reporter gene; inserting a gene editing target sequence into an N end of the target detection vector containing the frame shift mutation reporter gene to obtain a detection vector; and transferring the detection vector into animal cells, repairing the mutation reporter gene by the cells when endonuclease successfully cuts the target, and detecting the activity of the reporter gene toobtain the target cutting efficiency. The method is sensitive and visual in detection and can be quantified; and target cutting occurs in the cells, which is extremely similar to actual gene editing reaction conditions, and can reflect the target cutting effect in actual gene editing.
Owner:重庆英茂盛业生物科技有限公司
Pseudorabies virus gene deleted strain, inactivated vaccine for porcine pseudorabies, and preparation method and application of inactivated vaccine
PendingCN110846285AHigh viral titerGreat stress responseViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesRabiesAdjuvant
The invention discloses a pseudorabies virus gene deleted strain, and a preparation method of an inactivated vaccine for porcine pseudorabies. The gene deleted strain is a pseudorabies virus gE gene deleted strain, which is constructed through reading frame frameshift mutation caused by deletion of a plurality of basic groups from a wild-type pseudorabies virus (PRV) strain gE gene sequence. The preparation method includes the following steps: constructing the pseudorabies virus gE gene deleted strain; domesticating a porcine testicular cell and subjecting the same to suspension culture; inoculating the porcine testicular cell with the pseudorabies virus gE gene deleted strain, and harvesting a cell culture when 80-90% of the cell has lesions to obtain cell venom containing supernatant; taking the supernatant to measure the valence, and inactivating the qualified cell venom in a sterilization container; and mixing the inactivated cell venom with an adjuvant to obtain the inactivated vaccine for the porcine pseudorabies. The prepared inactivated vaccine for the porcine pseudorabies has high immunogenicity, long immunization period, and no side effects after immunization, is safe andreliable, and can effectively prevent infections of pseudorabies virus epidemic strains.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Pre-T vector and T vector composed of pre-T vector and application thereof
ActiveCN108588102APitfalls of Avoiding False Positive ClonesAvoid false positivesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionBlue stain
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and relates to a pre-T vector and a T vector composed of the pre-T vector and application thereof. The improved promoter is a recognition site for mutation from a nucleotide sequence from -35 region to -10 region in a promoter region into endonuclease. By the T vector, the problem that the product of transcription or translation of exogenous genes by a strong promoter during blue-white selection of a vector might be toxic to host and cloning will fail can be overcome, blue-white selection of a vector might be toxic to host as a strong promoter starts transcription or translation; the defect that delection of 1-2 bp at enzyme digestion site leads to lacZalpha gene frameshift mutation and false positive clones are generated can be avoided; and the false negative phenomenon that a plate is full of blue stains because exogenous DNA fragment is small and insertion of exogenous DNA does not change a reading frame of lacZalpha gene can beeliminated.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
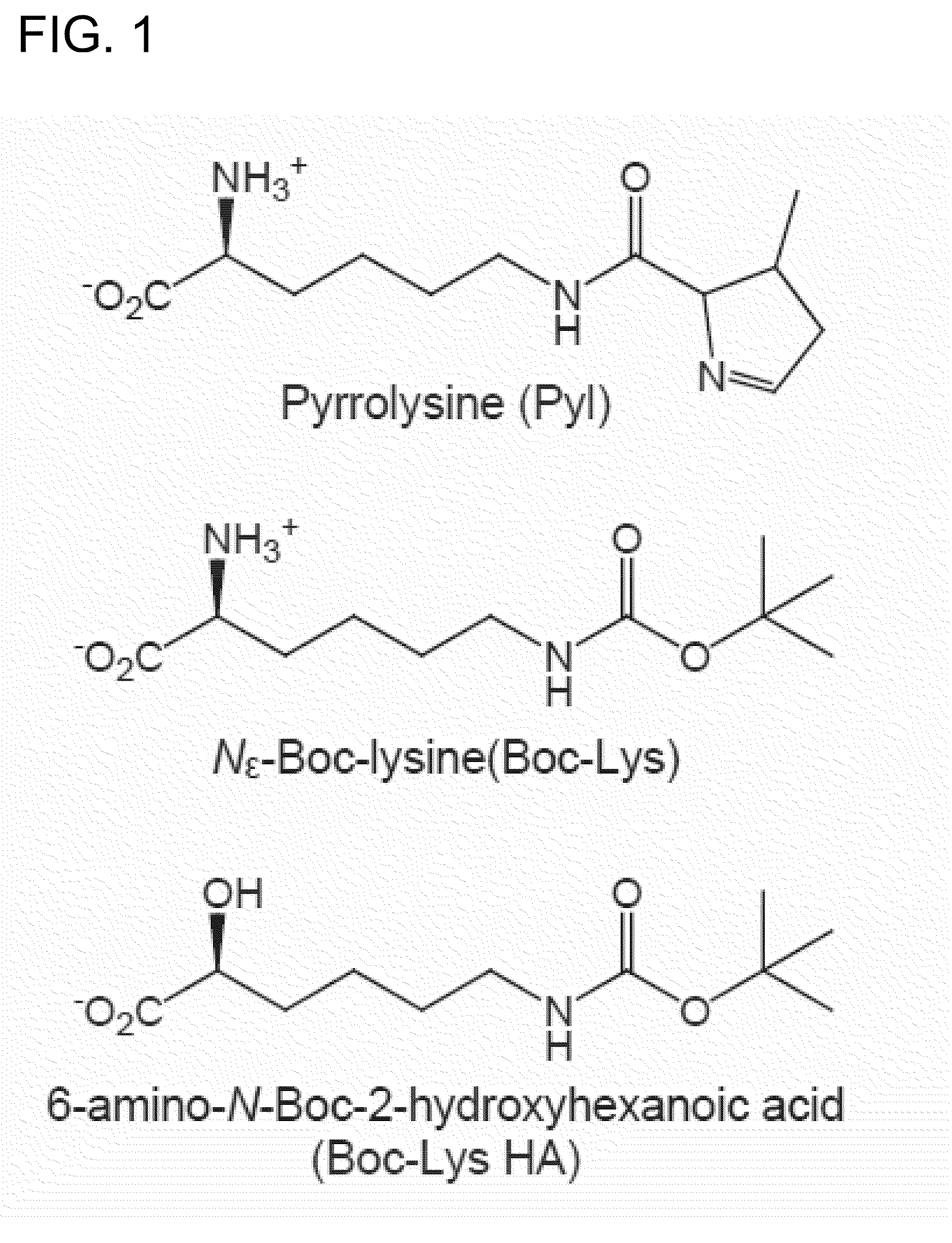
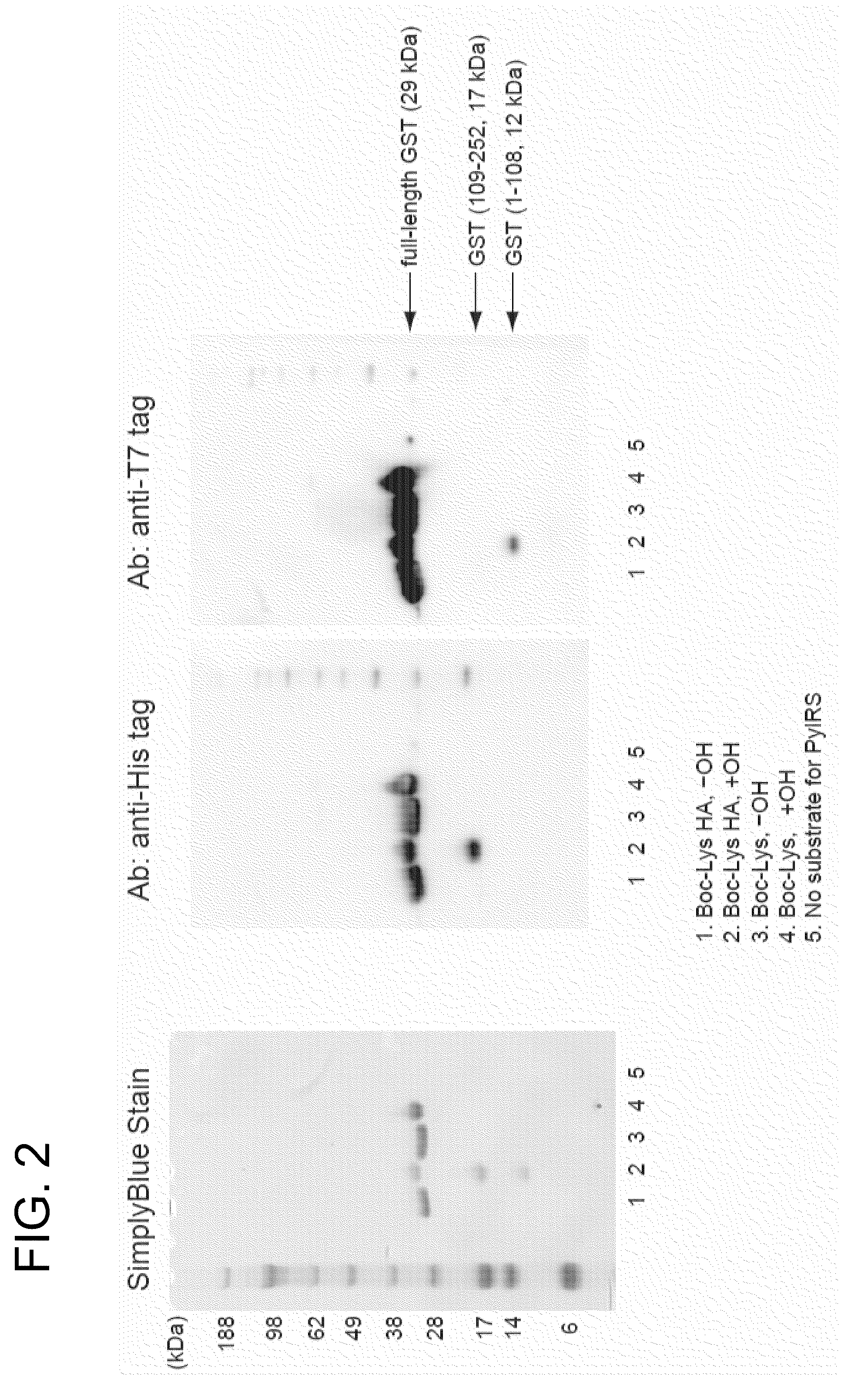
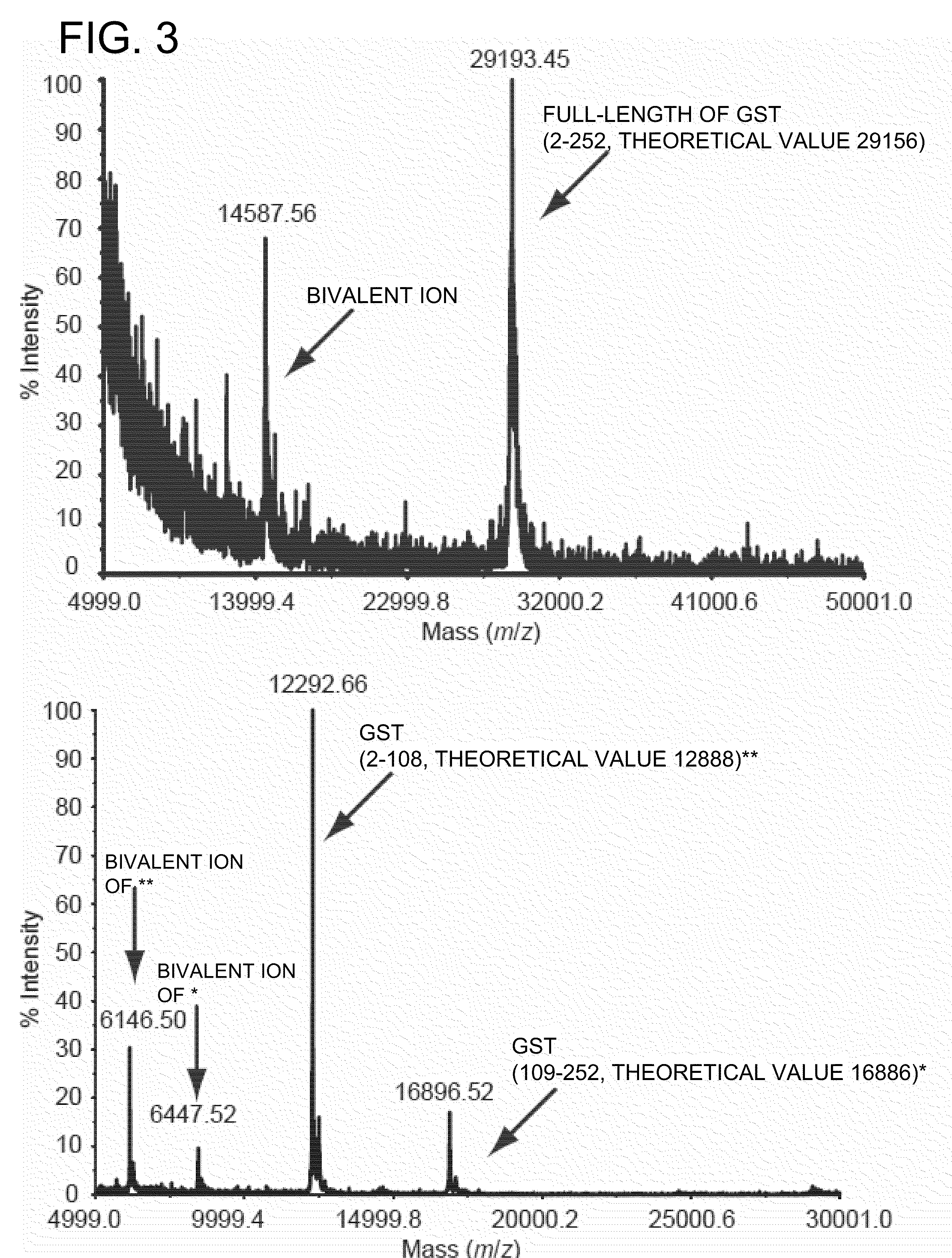
Process for production of non-natural protein having ester bond therein
A non-natural protein having at least one ester bond in its polypeptide main chain is synthesized by using an in vivo translation system in a ribosome. The following components (a) to (c) are expressed in a cell or an cell extraction solution in the presence of an α-hydroxy acid: (a) an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase which can activate the α-hydroxy acid; (b) suppressor tRNA which can bind to the α-hydroxy acid in the presence of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; and (c) a gene encoding a desired protein having a nonsense mutation or a frame-shift mutation at a desired site.
Owner:RIKEN
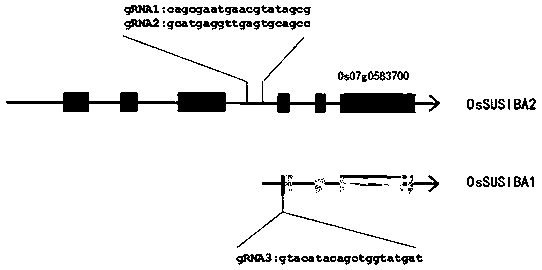
Creation method of low-methane-emission paddy rice variety
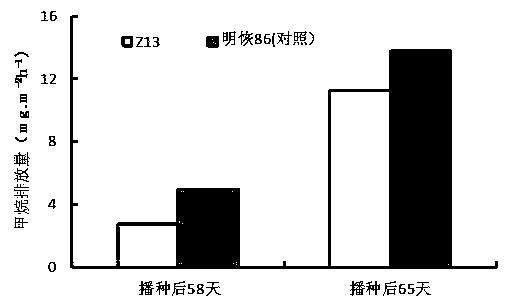
ActiveCN109022481AImplement targeted responsesSolve the emission problemHydrolasesAgriculture gas emission reductionAgricultural scienceFrameshift mutation
The invention provides a creation method of a low-methane-emission paddy rice variety, wherein the susiba-like gene sequence of the rice is represented as the SEQ ID No.1; the ATG initiation site andATG promoter domain position, which encode the susiba-like gene, are subjected to gene edition to obtain a rice mutant with frameshift mutation of the susiba-like gene; when the susiba-like gene is inactivated or is reduced in expression level, the metabolism causing transportation and accumulation of carbohydrates in the paddy rice is initiated, thus reducing the methane emission of a rice field.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com