Patents
Literature
81 results about "Xenopus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Xenopus (/ˈzɛnəpəs/) (Gk., ξενος, xenos=strange, πους, pous=foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known species of this genus are Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis, which are commonly studied as model organisms for developmental biology, cell biology, toxicology, neuroscience and for modelling human disease and birth defects.
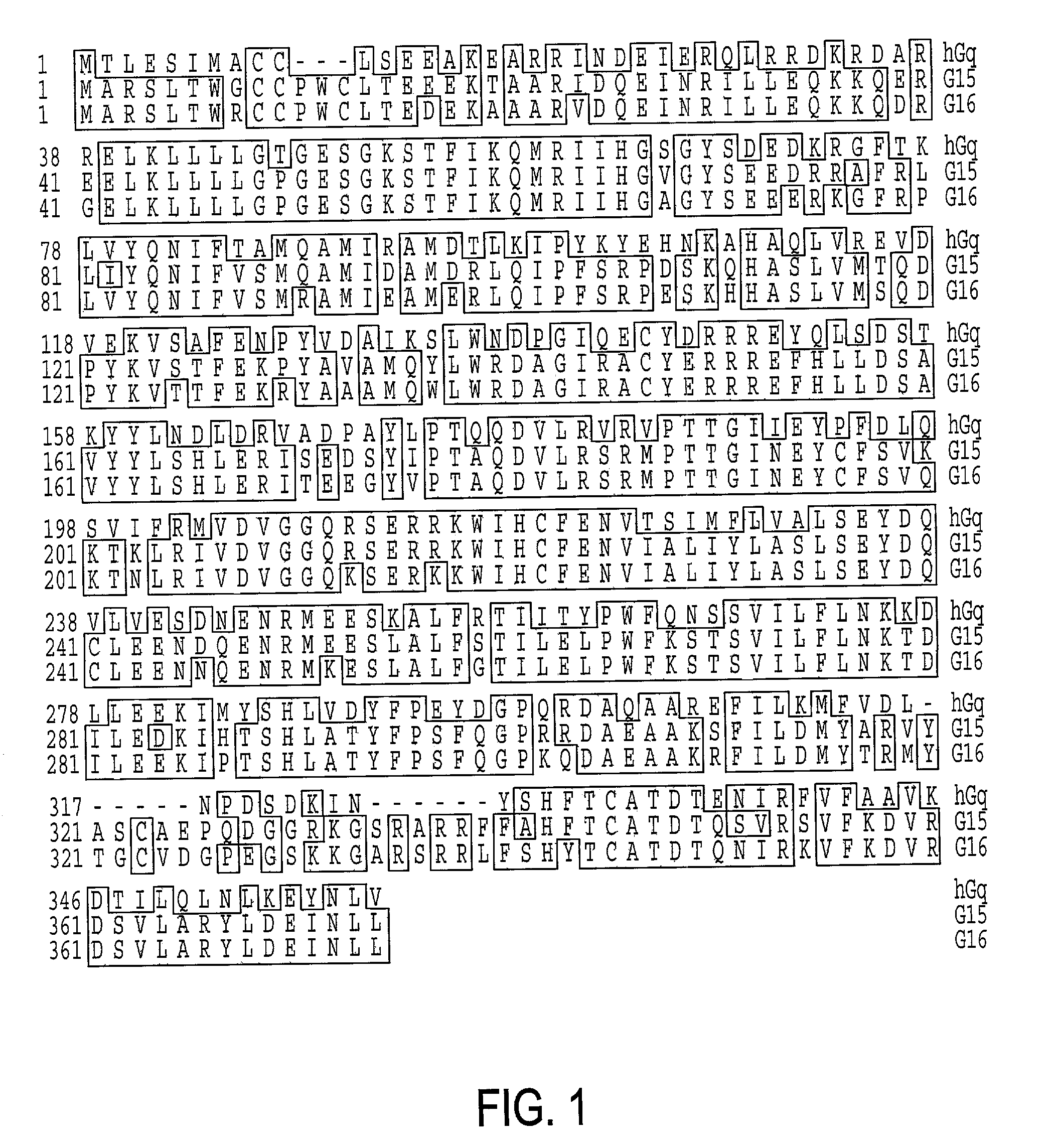
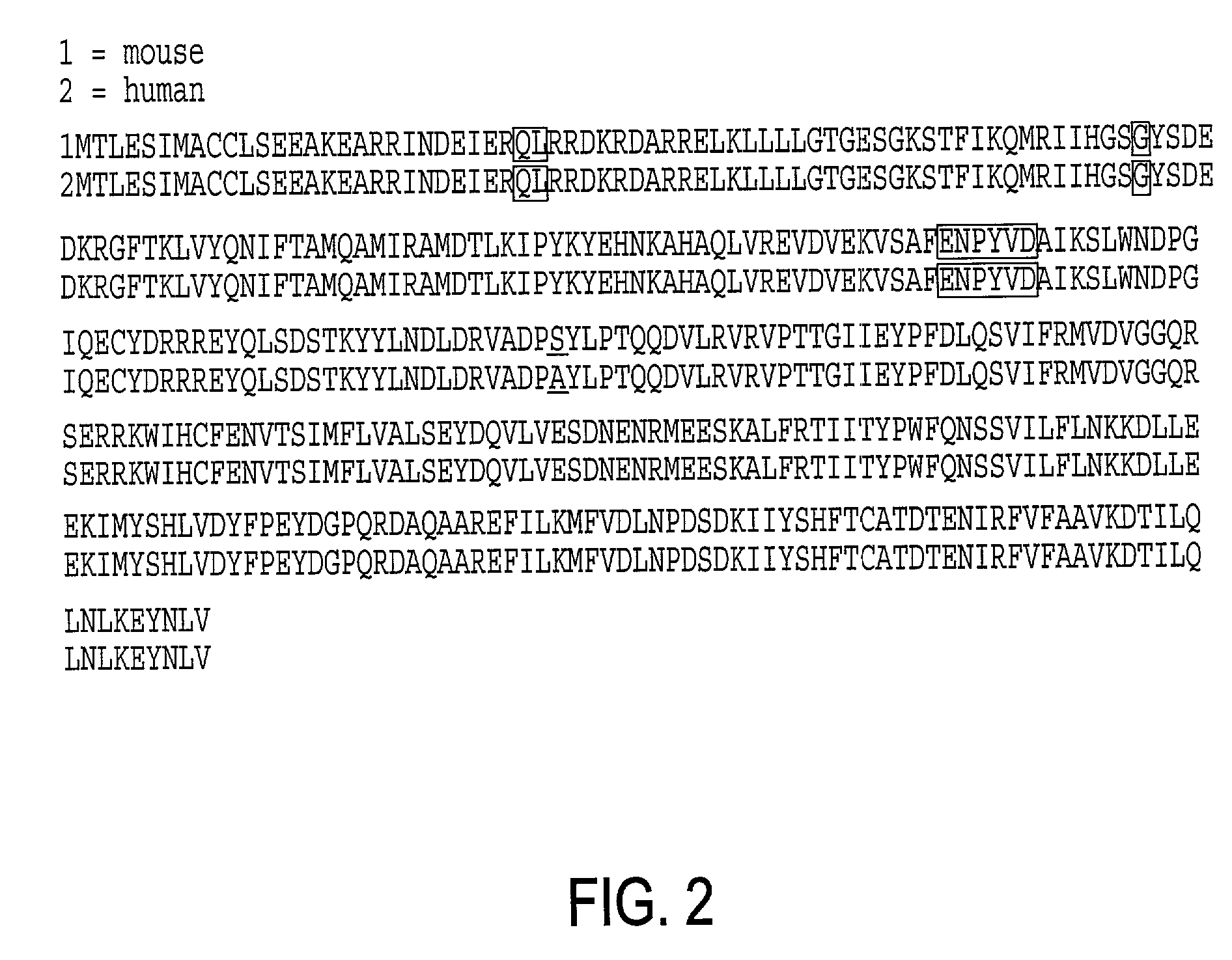
Gaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
ActiveUS20020143151A1Improved functional couplingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureSensory cellFluorescence
The invention provides a series of Galphaq protein variants that functionally couple to sensory cell receptors such as taste GPCRs (TRs) and olfactory GPCRs (ORs) in an overly promiscuous manner. According to the invention, the functional coupling can be determined, for example, by measuring changes in intracellular IP3, or calcium. In a particular embodiment, the Galphaq protein variants can be expressed in mammalian cell lines or Xenopus oocytes, and then evaluated using calcium fluorescence imaging and electrophysiological recording.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Ferroportin1 nucleic acids and proteins
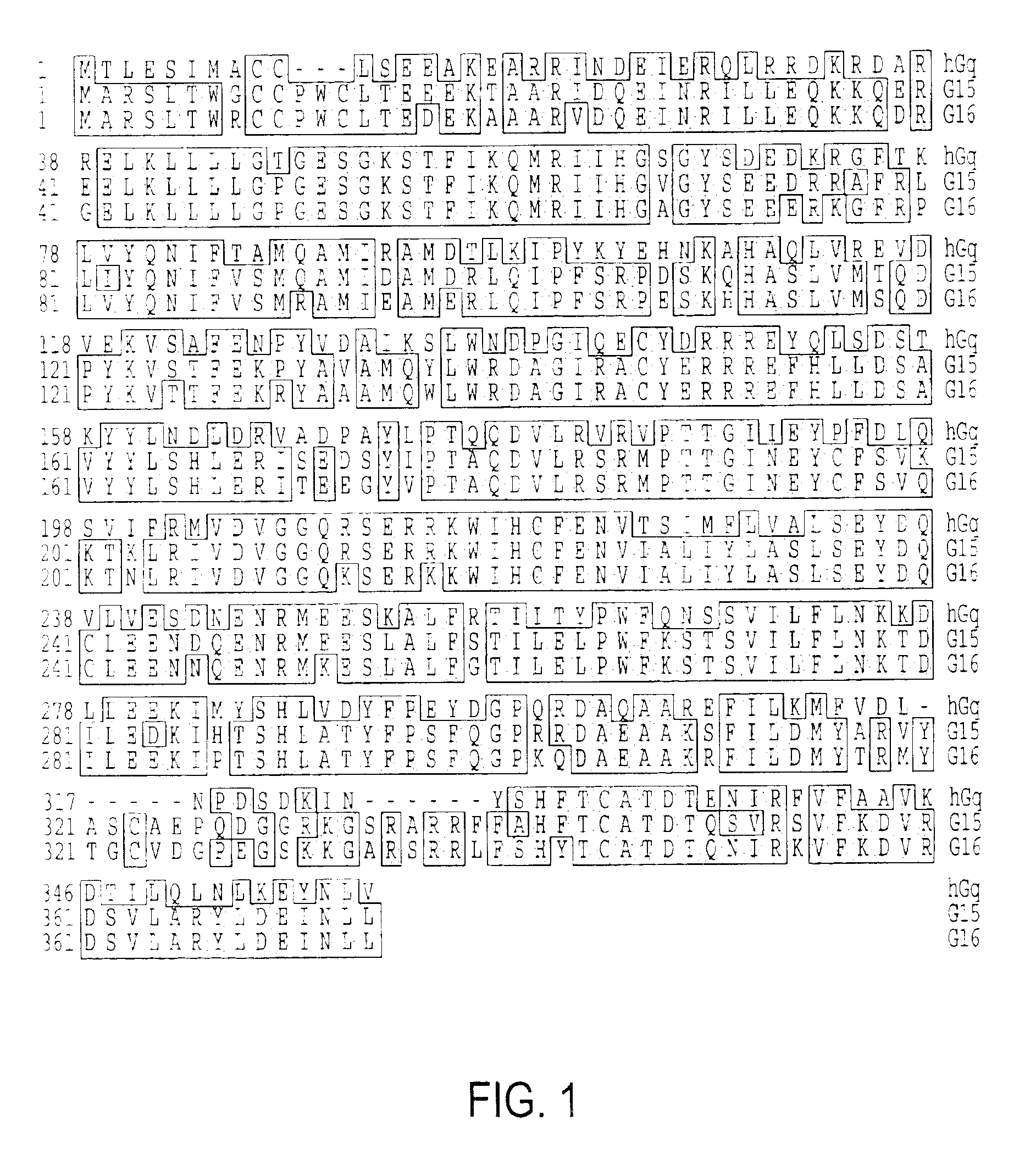
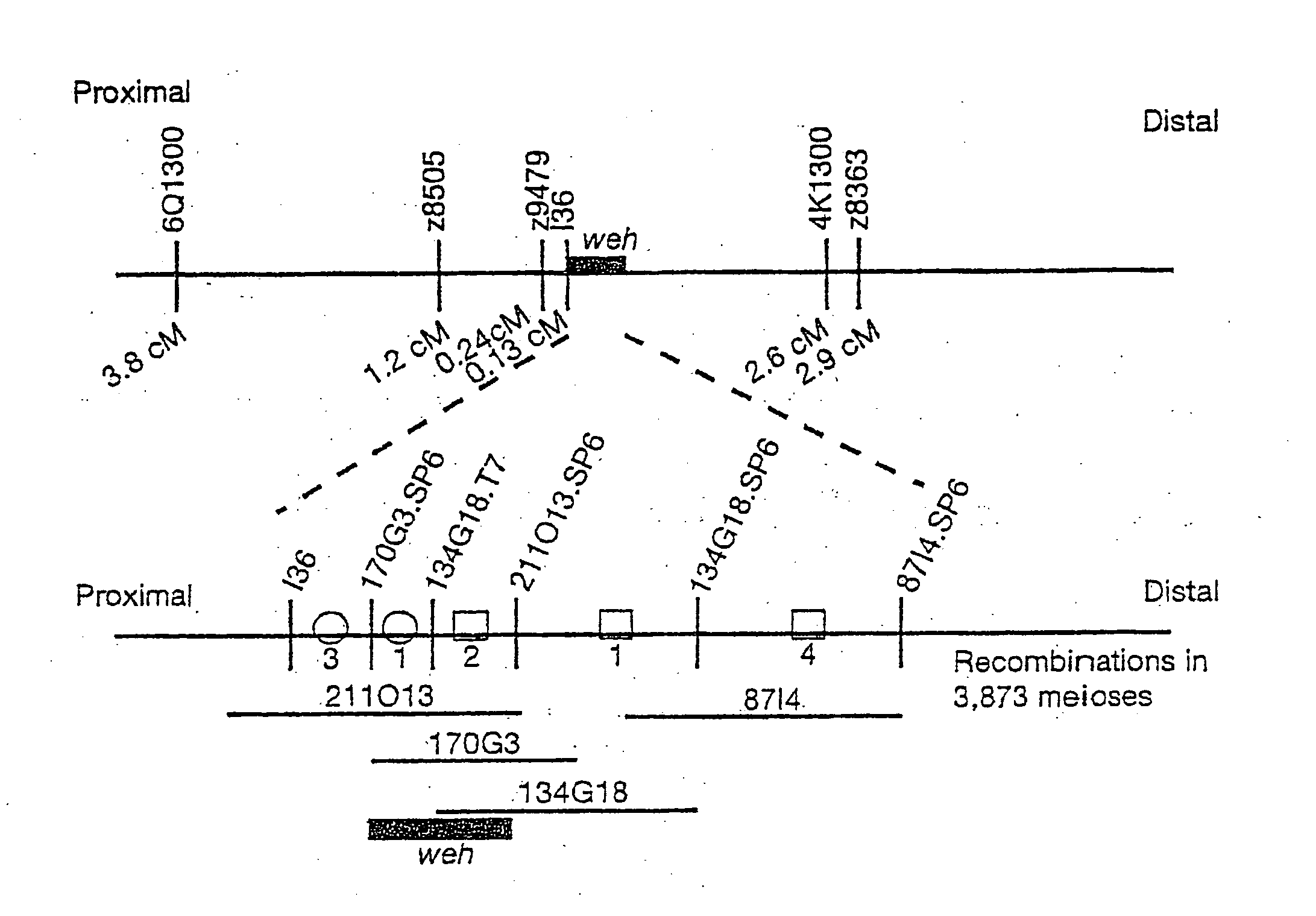
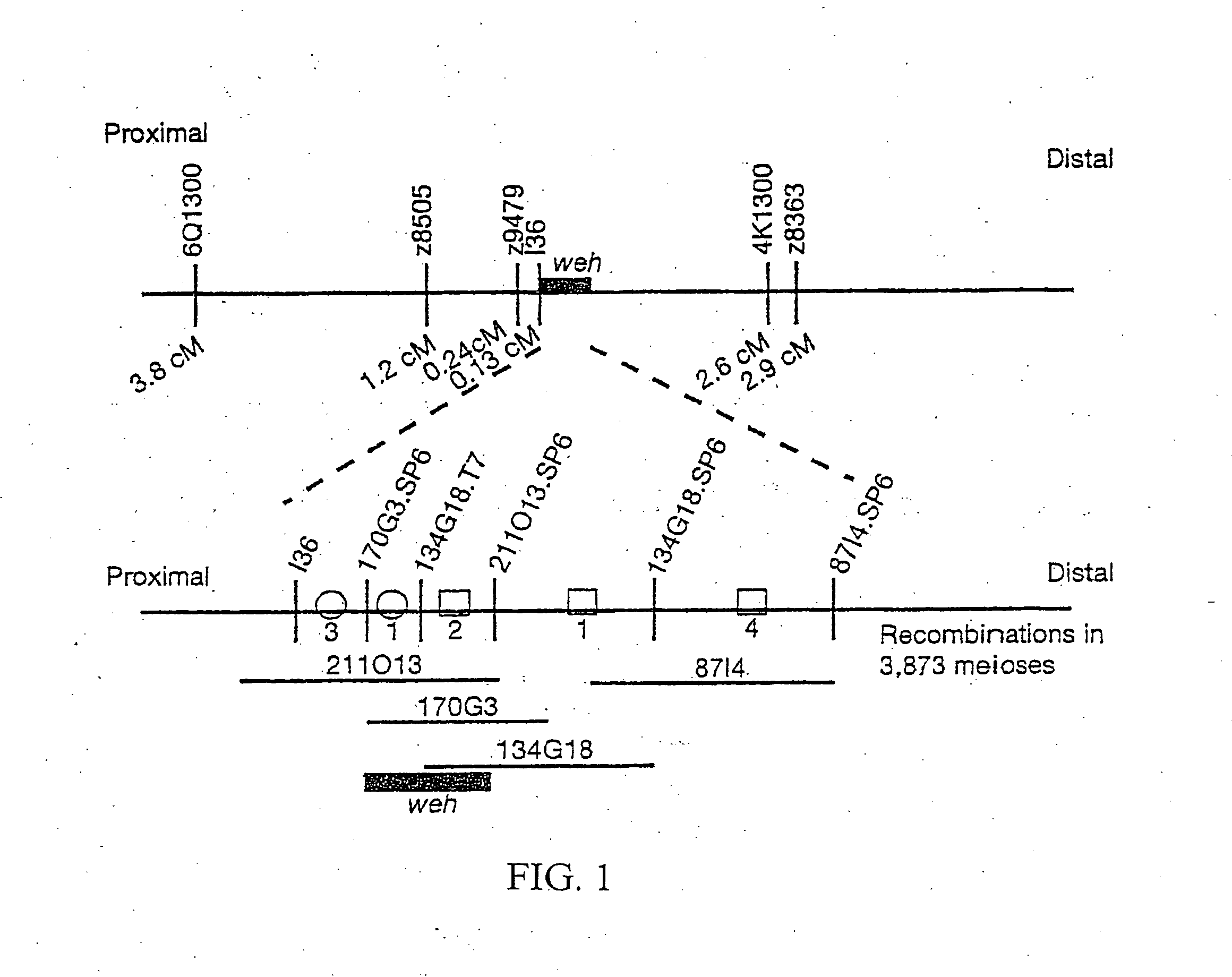
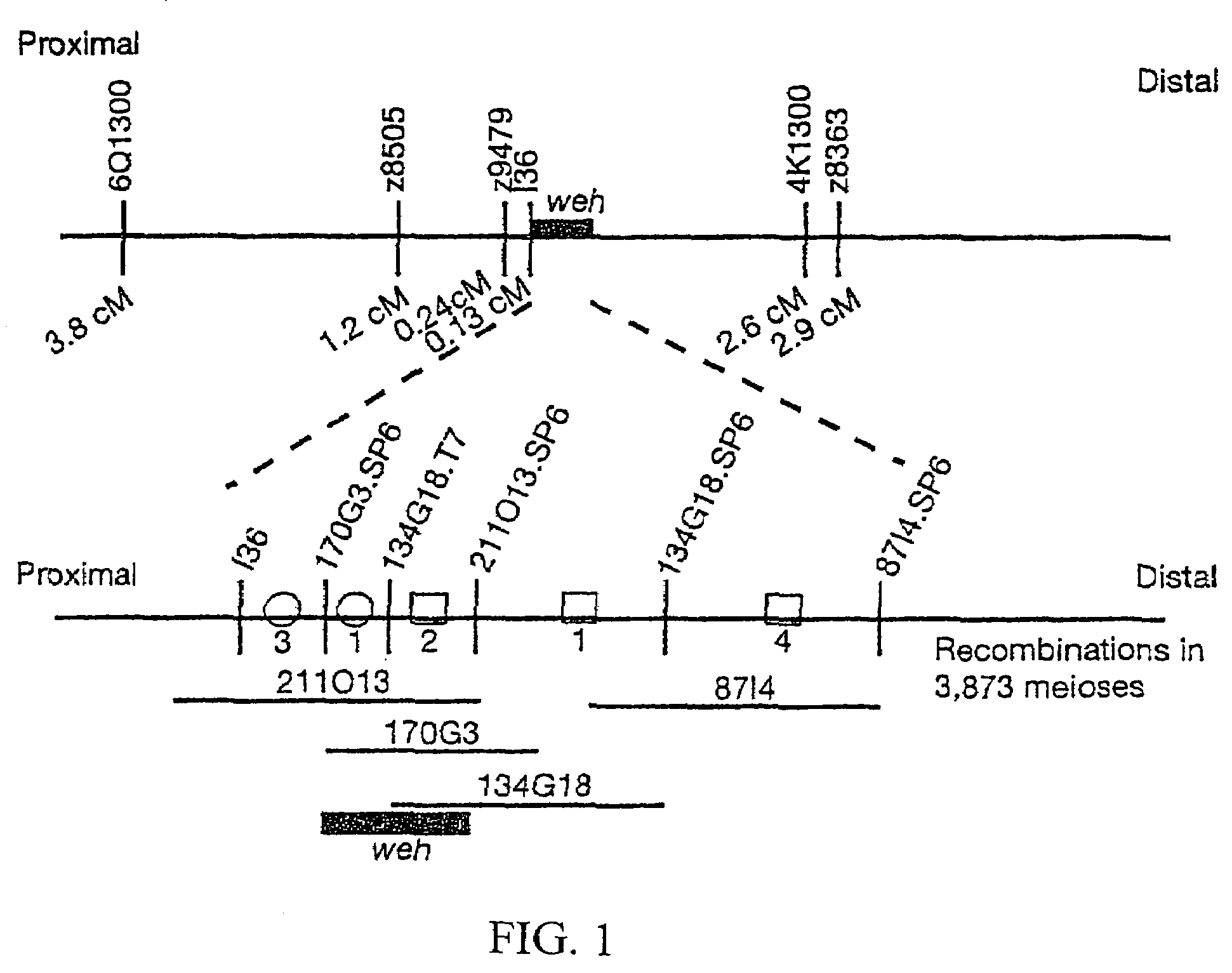
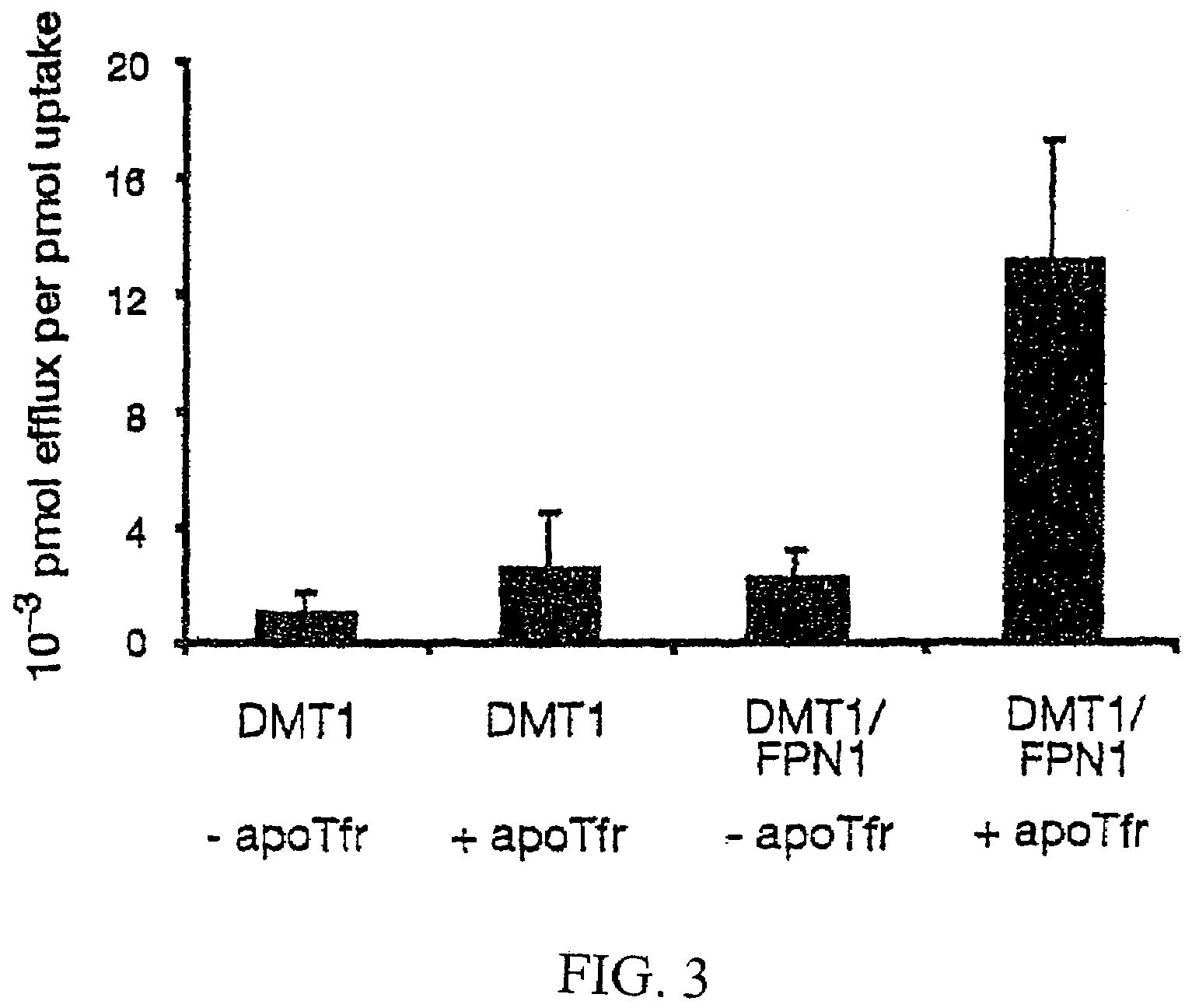
Positional cloning has been carried out to identify the gene responsible for the hypochromic anemia of the zebrafish mutant weissherbst. The gene, ferroportin1, encodes a novel multiple-transmembrane domain protein, expressed in the yolk sac. Zebrafish ferroportin1 is required for the transport of iron from maternally-derived yolk stores to the circulation, and functions as an iron exporter when expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Human and mouse homologs of the ferroportin1 gene have been identified. The invention includes isolated polynucleotides, vectors and host cells comprising nucleotide sequences encoding Ferroportin1 proteins and variants thereof, including those having iron transport function. The invention also includes polypeptides encoded by ferroportin1 genes and variants of such polypeptides, and fusion polypeptides comprising a Ferroportin1 or a portion thereof. Methods to produce a Ferroportin1, methods to produce antibodies to a Ferroportin1 and methods to identify agents binding to a Ferroportin1, which can be inhibitors or enhancers of Ferroportin1 iron transport activity, are also described. Inhibitors of Ferroportin1 activity can be used in a therapy for hemochromatosis.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Ferroportin1 nucleic acids and proteins
Positional cloning has been carried out to identify the gene responsible for the hypochromic anemia of the zebrafish mutant weissherbst. The gene, ferroportin1, encodes a novel multiple-transmembrane domain protein, expressed in the yolk sac. Zebrafish ferroportin1 is required for the transport of iron from maternally-derived yolk stores to the circulation, and functions as an iron exporter when expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Human and mouse homologs of the ferroportin1 gene have been identified. The invention includes isolated polynucleotides, vectors and host cells comprising nucleotide sequences encoding Ferroportin1 proteins and variants thereof, including those having iron transport function. The invention also includes polypeptides encoded by ferroportin1 genes and variants of such polypeptides, and fusion polypeptides comprising a Ferroportin1 or a portion thereof. Methods to produce a Ferroportin1, methods to produce antibodies to a Ferroportin1 and methods to identify agents binding to a Ferroportin1, which can be inhibitors or enhancers of Ferroportin1 iron transport activity, are also described. Inhibitors of Ferroportin1 activity can be used in a therapy for hemochromatosis.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Transgenic non-human mammals producing a cholinesterase in their milk
InactiveUS6987211B1Increased neuromuscular transmissionGreat muscular strengthHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganophosphorous compoundsPhysiology
The present invention relates to novel alternative forms of human acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and nucleotide sequences encoding the same. The genes encoding the novel forms of human AChE have been identified in various malignant tumor cells. In a further aspect, the invention relates to a transgenic animal assay system for evaluating efficacy of drugs against cholinergic proteins, prior to or in the course of therapeutic treatment. Transgenic animals, preferably developing tadpole of Xenopus or mice which express human AChE, are used. The transgenic animal assay system is also useful for evaluating the toxicity of substances which potentially block human AChE (e.g. organophosphorous compounds).
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
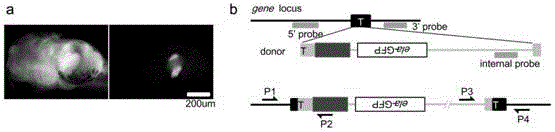
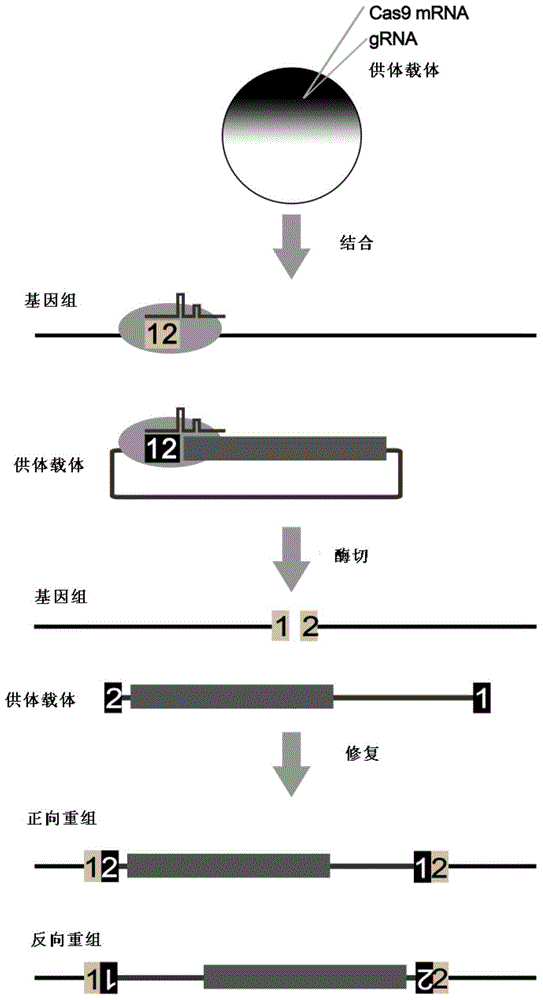
Carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as method and application for gene fixe-point knock-in in Xenopus laevis genome
InactiveCN104611368ARealize fixed-point insertionGenetic stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryA-DNAEmbryo
The invention provides a carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as a method and an application for gene fixe-point knock-in in a Xenopus laevis genome. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), guide RNA (ribonucleic acid), Cas9 nuclease and a donor carrier with a pancreas ela-fluorescent screening label and a Cas9 target fragment are contained in a fertilized egg of Xenopus laevis; (2) under the joint action of guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease, a target gene in the Xenopus laevis genome and the double-chain Cas9 target fragment on the donor carrier are shorn; (3), gene fixed-point knock-in of the Xenopus laevis genome is realized through a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) recovery function of Xenopus laevis cells; (4), G0-generation embryos are screened through the pancreas ela-fluorescent screening label, and F1 is subjected to southern blot identification. The carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as the method and the application for gene fixe-point knock-in in the Xenopus laevis genome lay a foundation for research of genetics and human diseases with Xenopus laevis as a model animal.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
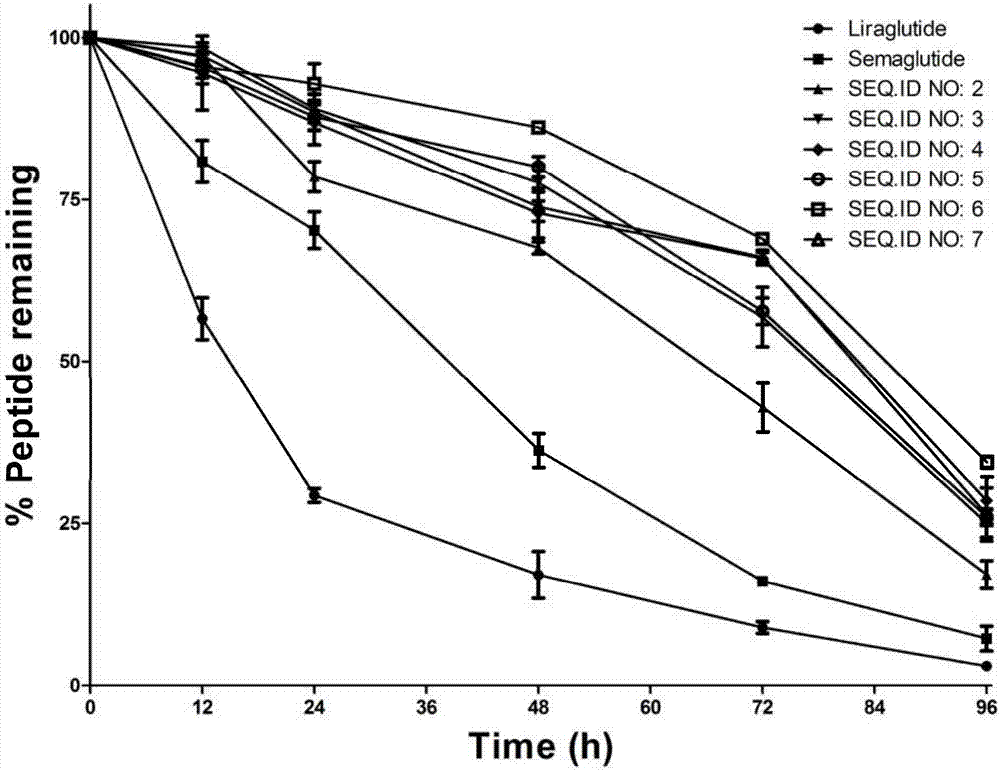
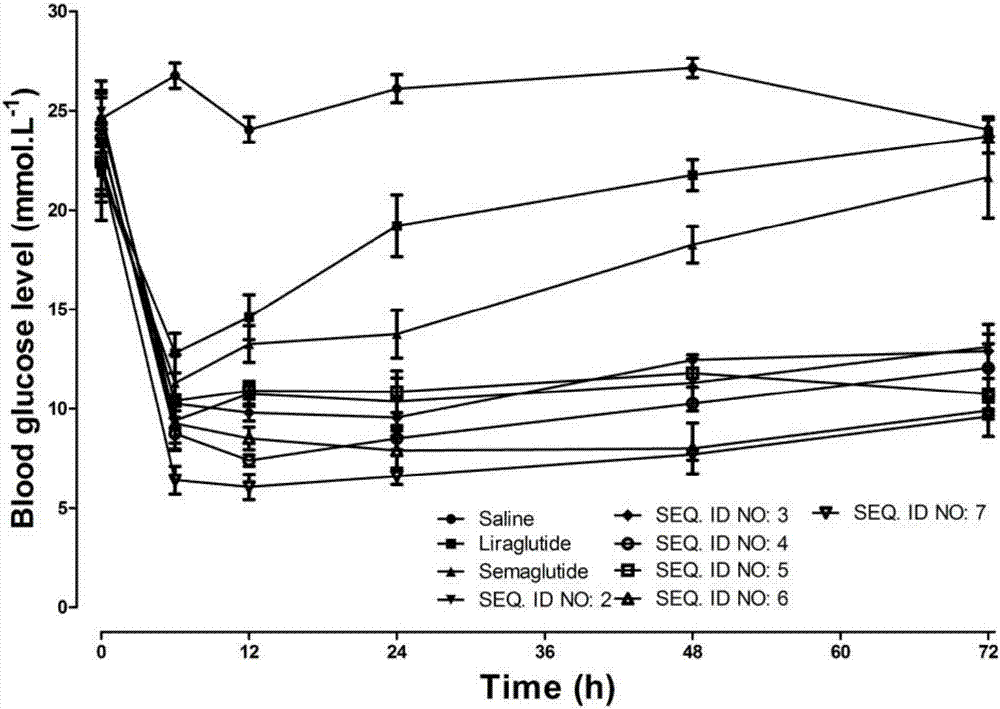
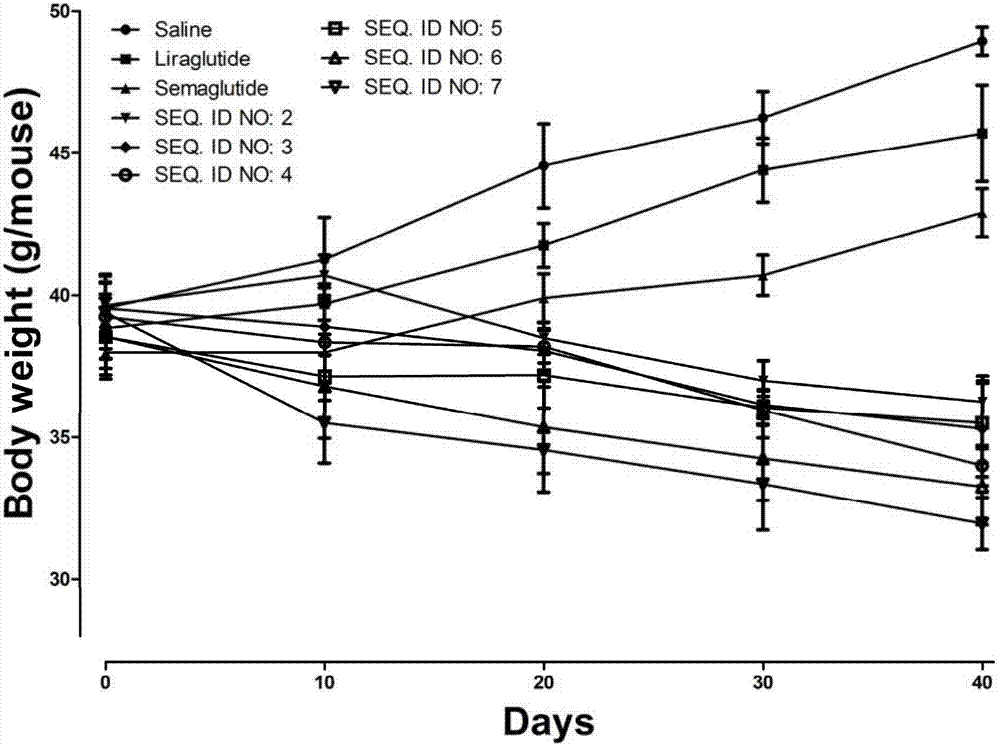
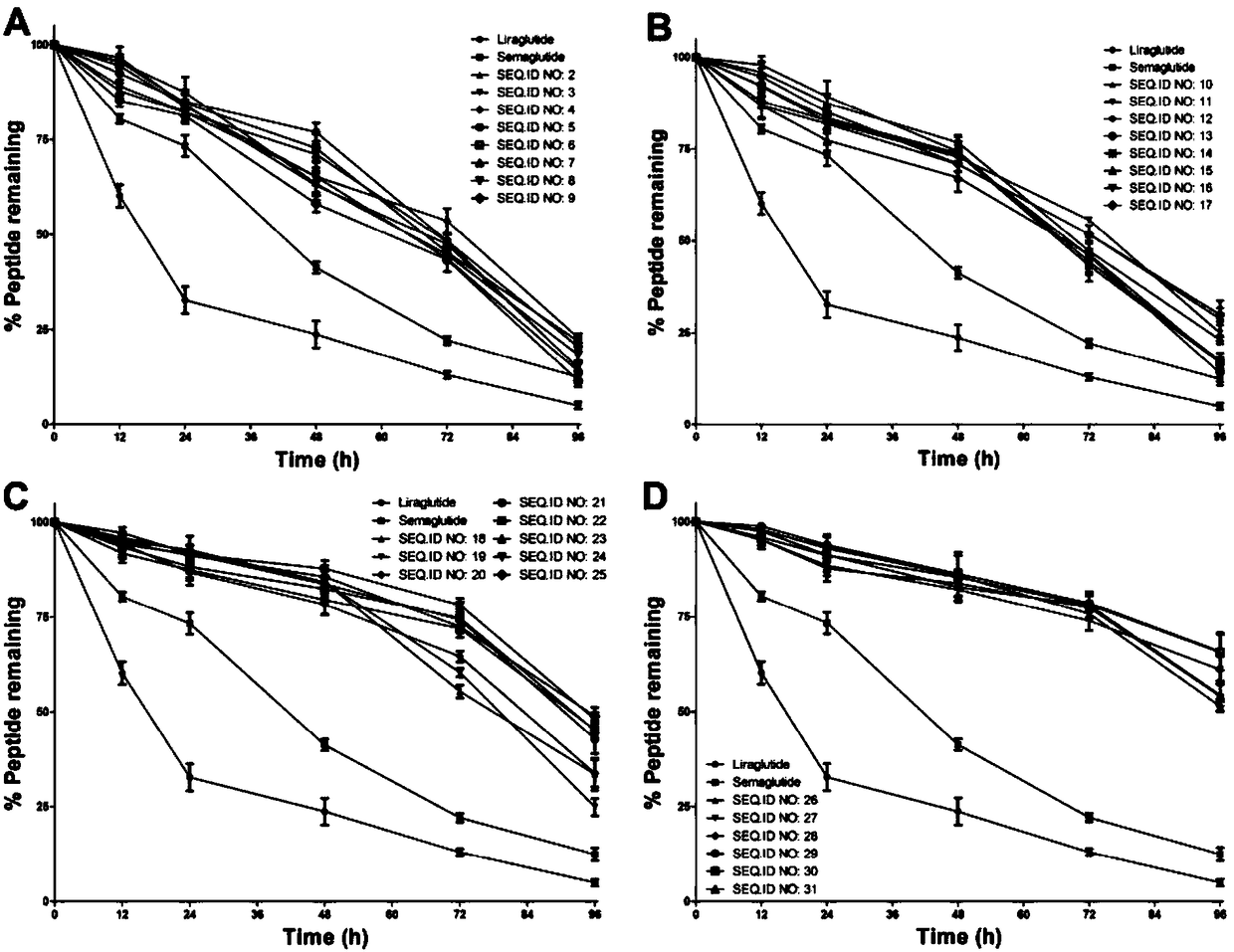
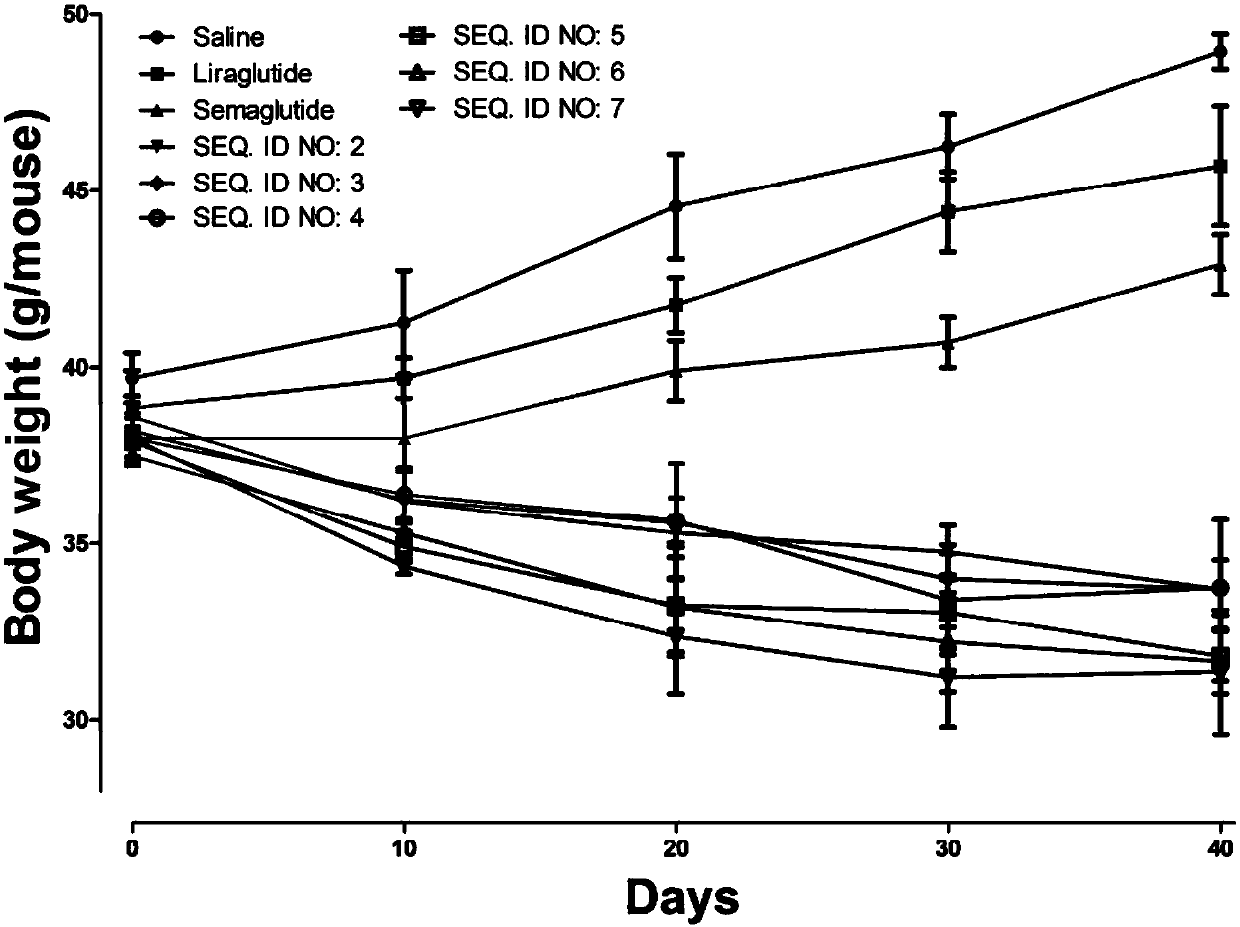
Mycophenolic acid-xenopus laevis glucagon like peptide-1 conjugated peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN107987152AExtensive treatmentImprove in vivo stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide chainGlucagon-like peptide-1
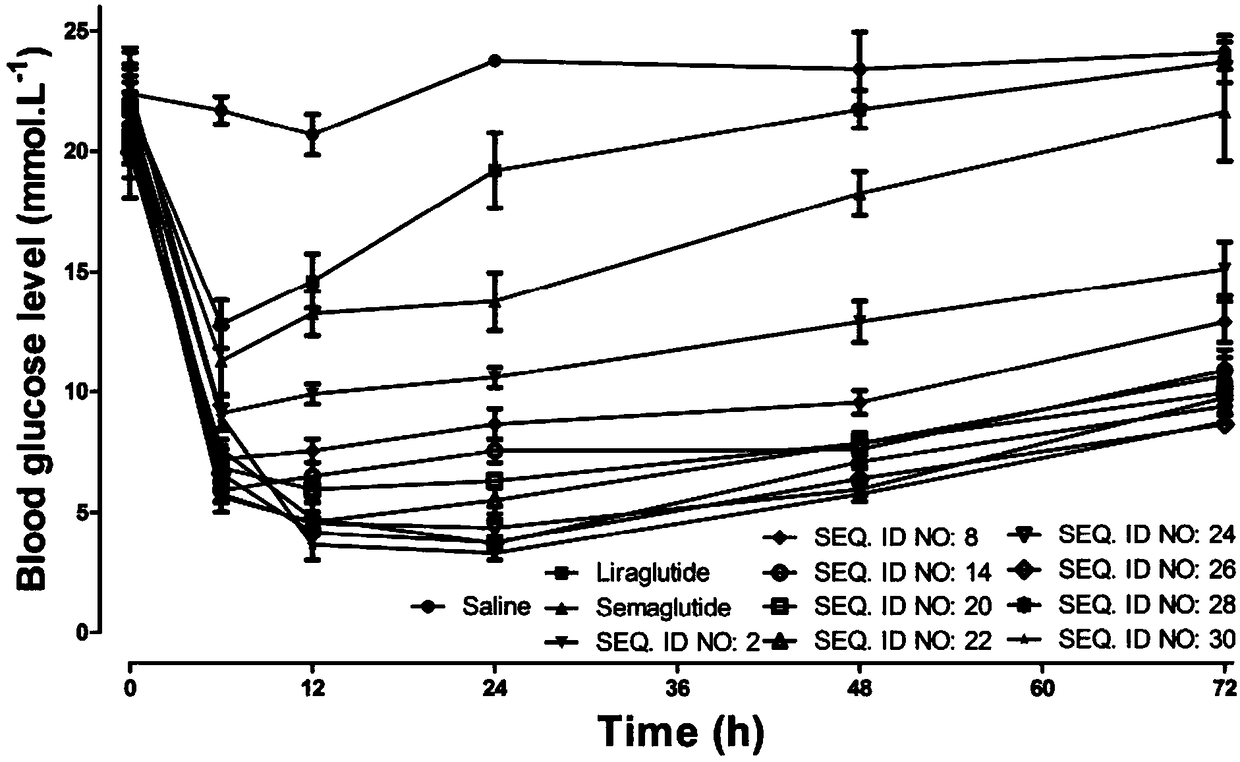
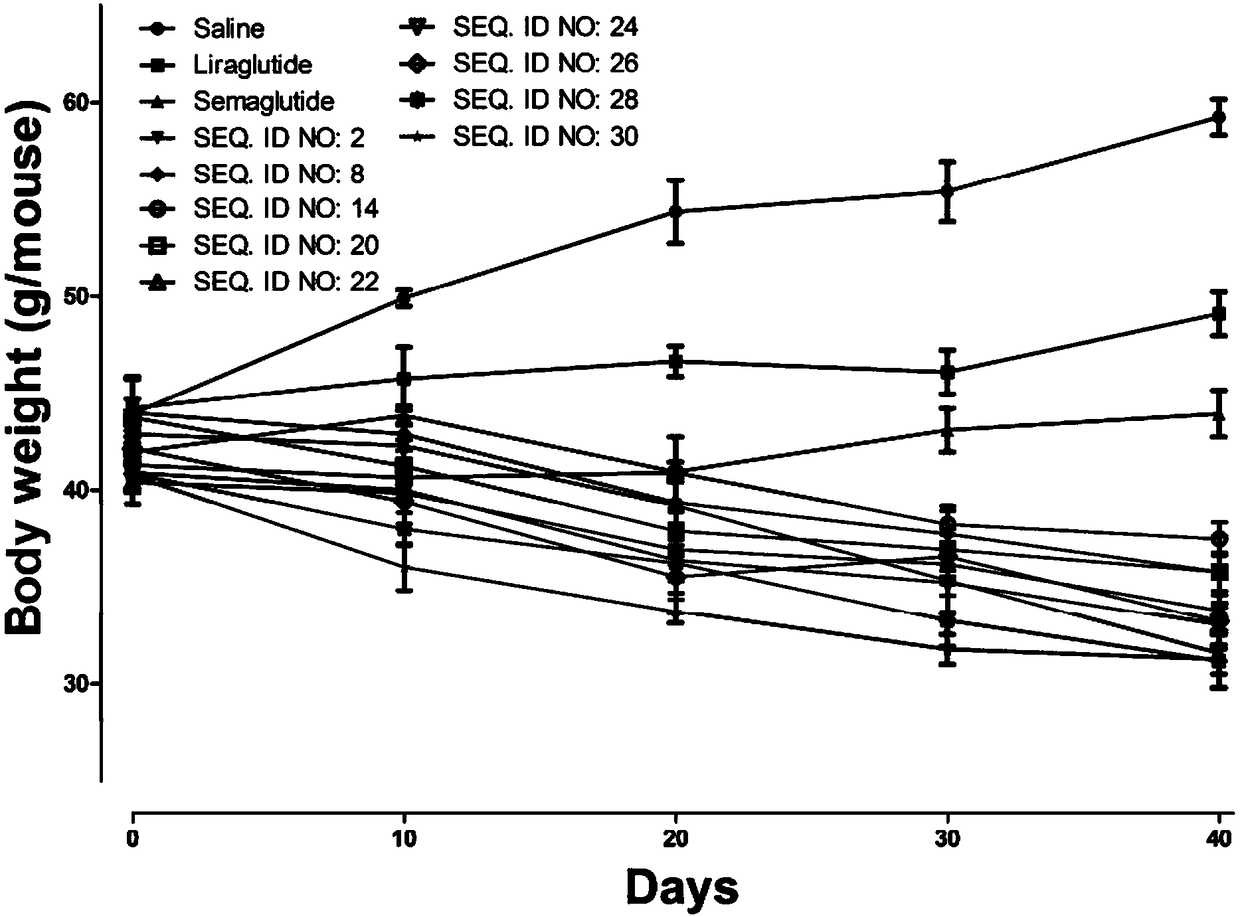
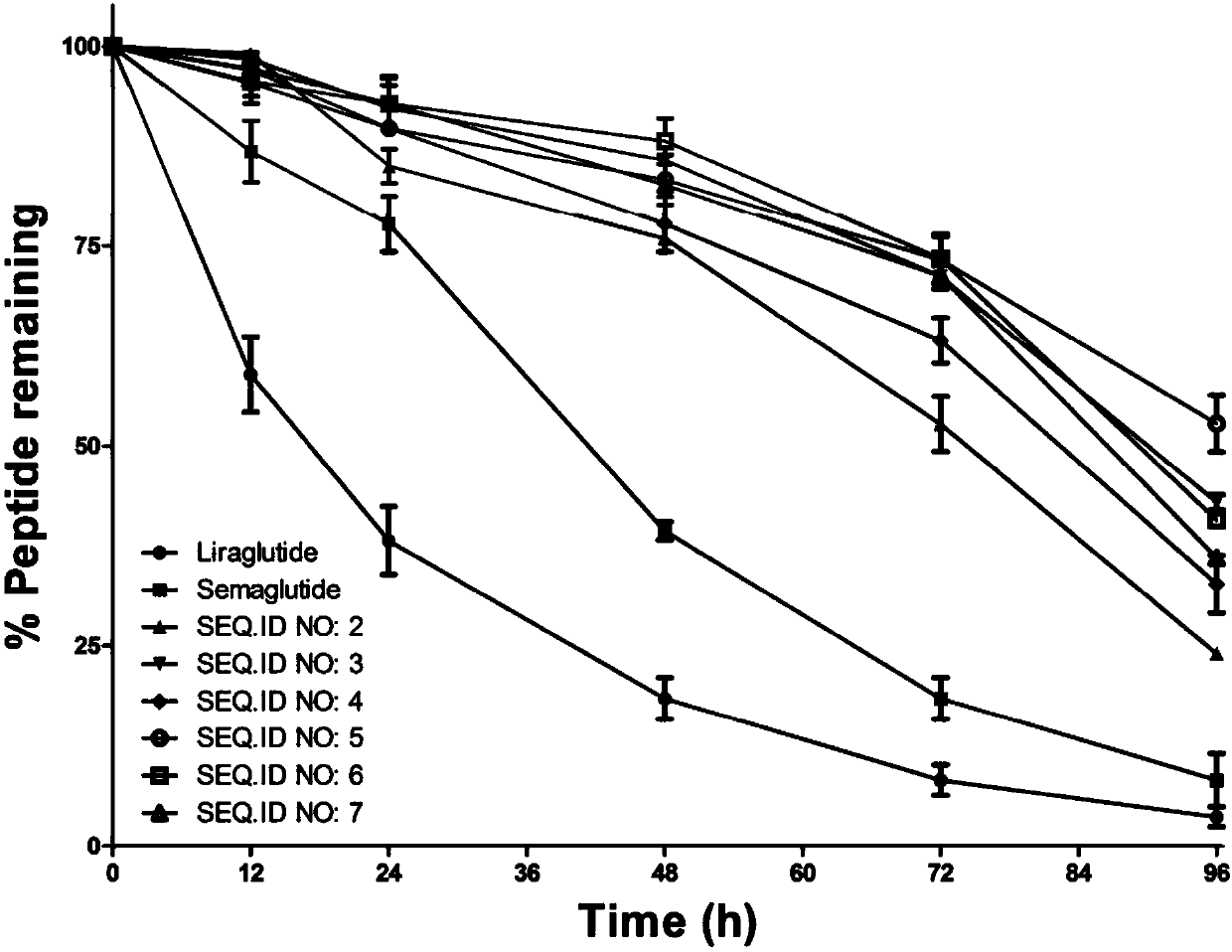
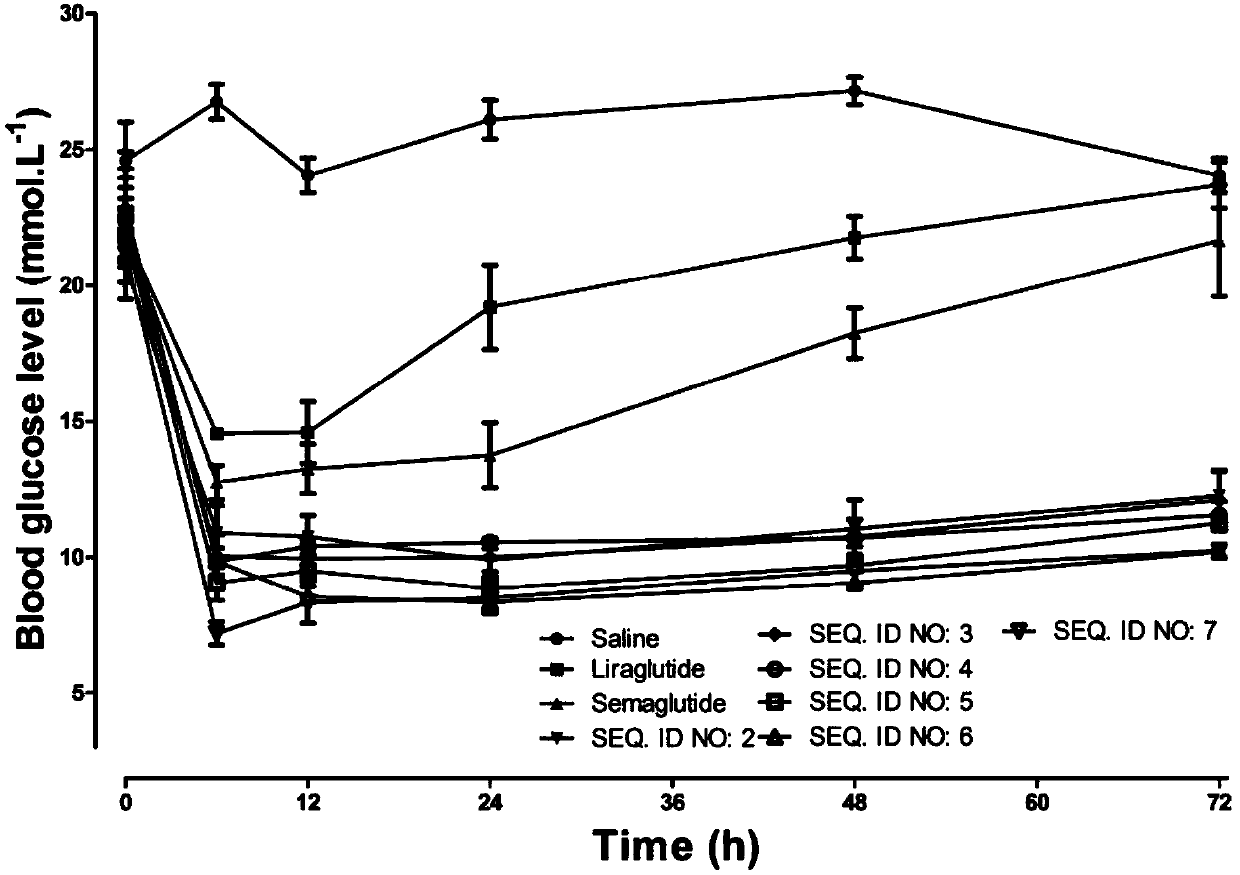
The invention relates to a mycophenolic acid-xenopus laevis glucagon like peptide-1 (XenGLP-1) conjugated peptide and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing structural modification on side chains of XenGLP-1, and introducing mycophenolic acid small-molecule derivatives with a high binding rate of serum protein, thereby obtaining the XenGLP-1 conjugated peptide with high hypoglycemic activity and long pharmacological action time. The XenGLP-1 conjugated peptide disclosed by the invention has the effect of obviously improving the biological activity, and has excellent effects of reducing blood glucose and losing weight for a long time.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
ActiveUS7041457B2Increase promiscuityHigh activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureSensory cellFluorescence
The invention provides a series of Galphaq protein variants that functionally couple to sensory cell receptors such as taste GPCRs (TRs) and olfactory GPCRs (ORs) in an overly promiscuous manner. According to the invention, the functional coupling can be determined, for example, by measuring changes in intracellular IP3, or calcium. In a particular embodiment, the Galphaq protein variants can be expressed in mammalian cell lines or Xenopus oocytes, and then evaluated using calcium fluorescence imaging and electrophysiological recording.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
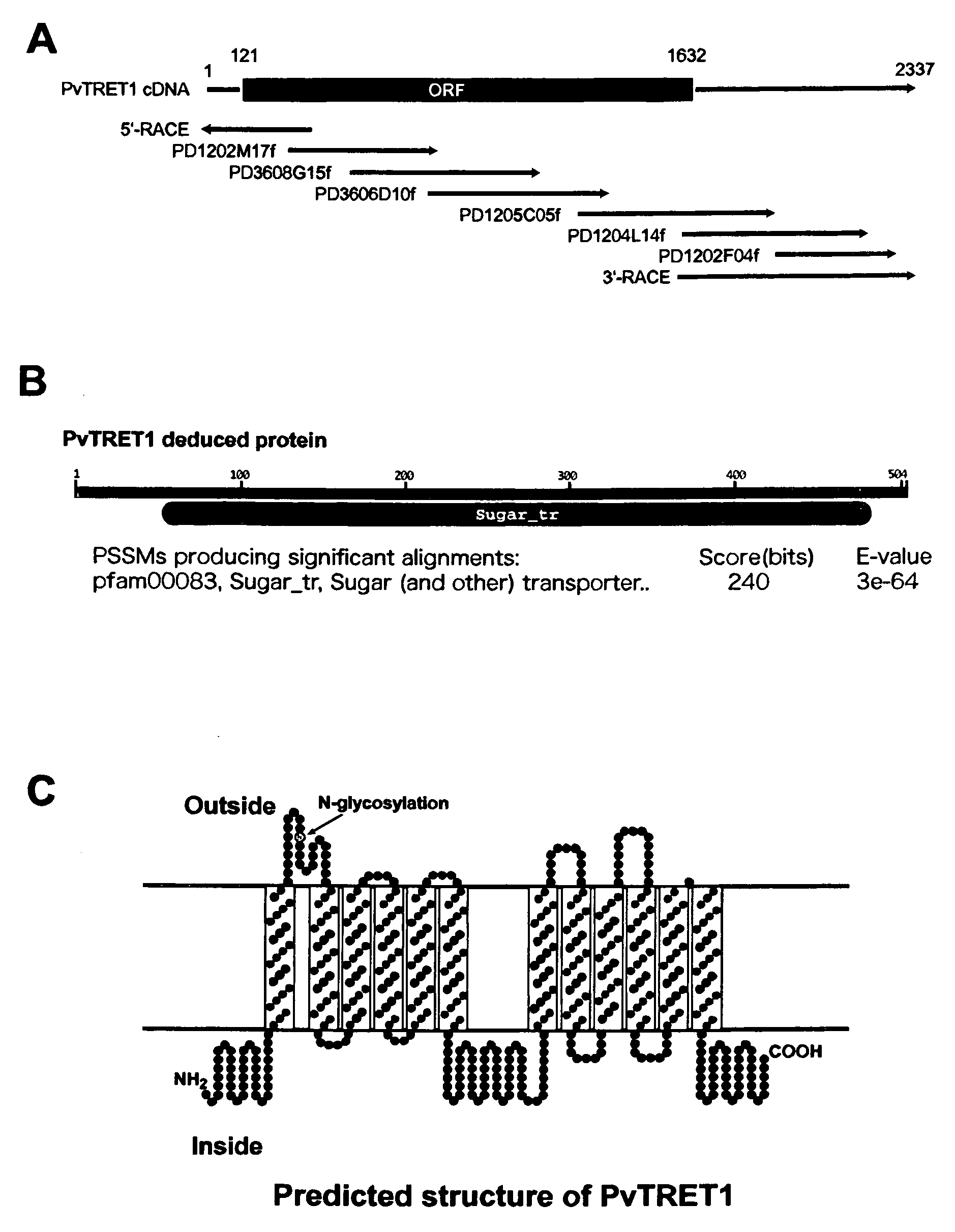
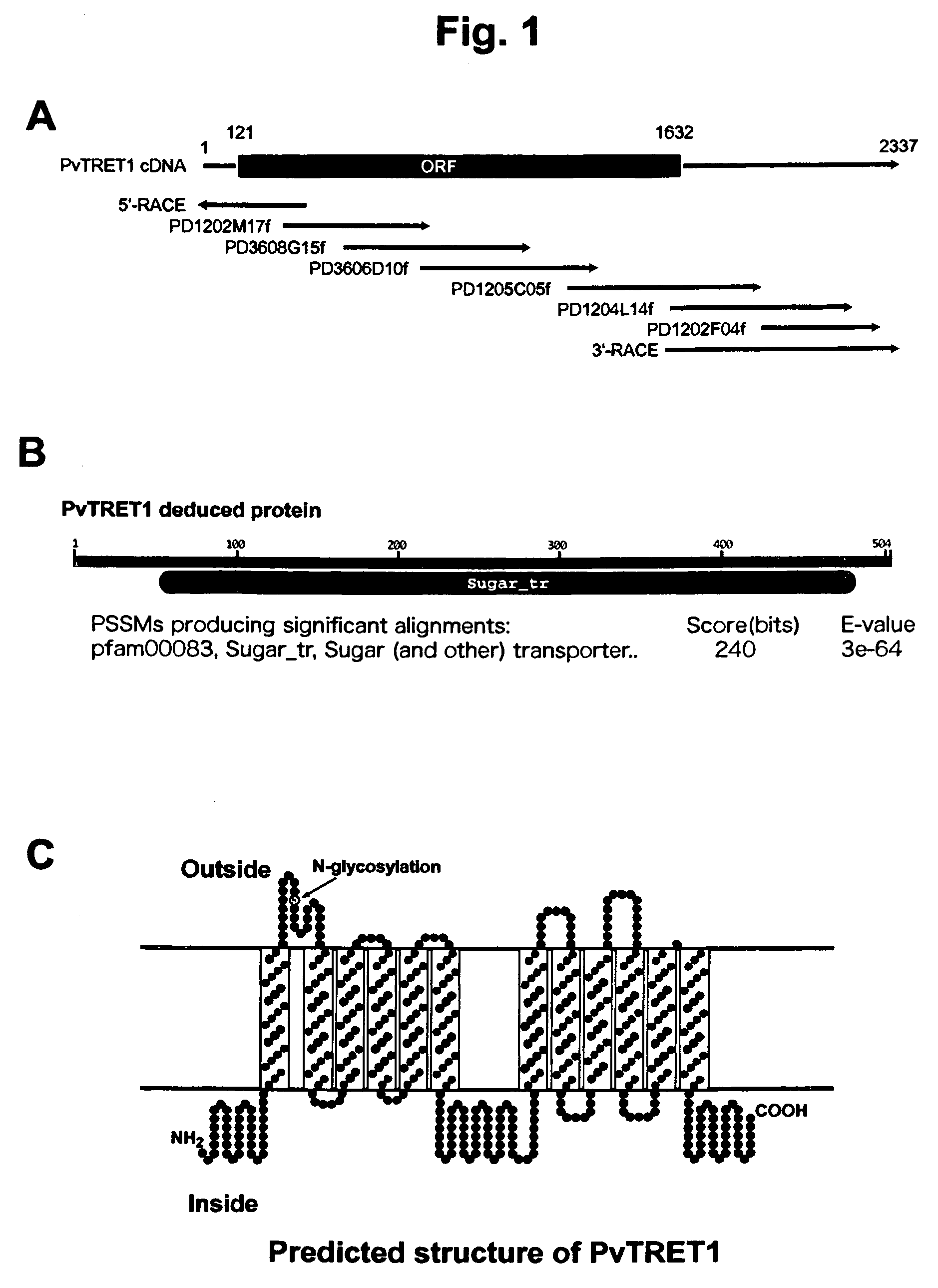
Trehalose transporter gene and method of introducing trehalose into cells
InactiveUS20090111176A1Allows trehalose uptake easily into cellsSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsConcentration gradientMembrane potential
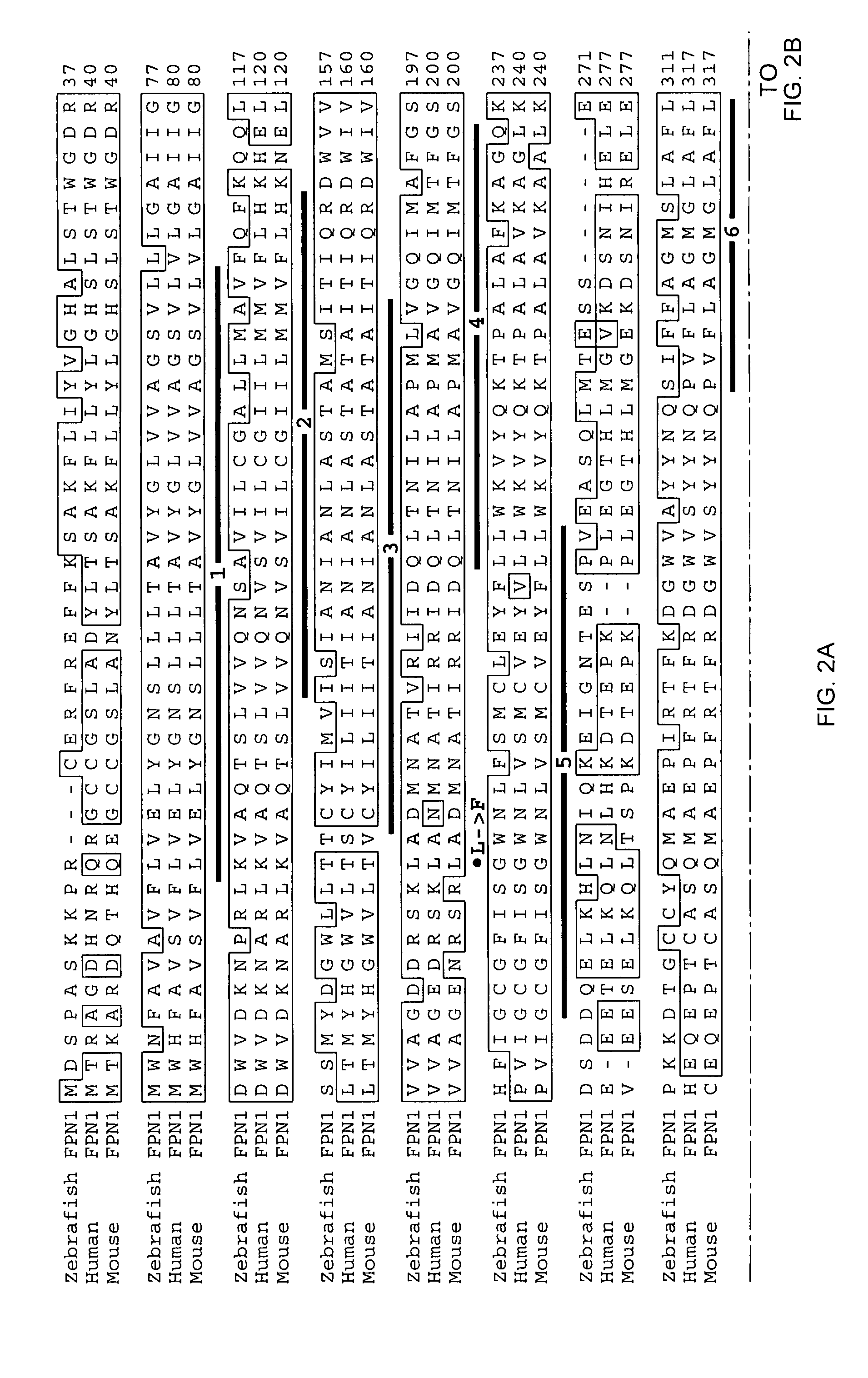
There are provided trehalose transporter gene and a method of introducing trehalose into cells by using the gene. Candidates for the trehalose transporter genes were searched in P. vanderplanki EST, resulting in being obtained cDNA designated as Tret1. Tret1 encodes a 504 amino acid protein with 12 trans-membrane structures. Tret1 expression was induced by desiccation stress and predominant in the fat body. Functional expression of TRET1 in Xenopus oocytes showed that transport activity was specific for trehalose and independent of extracellular pH and electrochemical membrane potential. The direction of transport of TRET1 was reversible depending on the concentration gradient of trehalose. Apparent Km and Vmax of TRET1 for trehalose were extraordinarily high values. These results indicate that TRET1 is a facilitated, high-capacity trehalose-specific transporter. Tret1 is widespread in insects. Furthermore, TRET1 conferred trehalose permeability upon cells including those of vertebrates as well as insects.
Owner:KIKAWADA TAKAHIRO +5
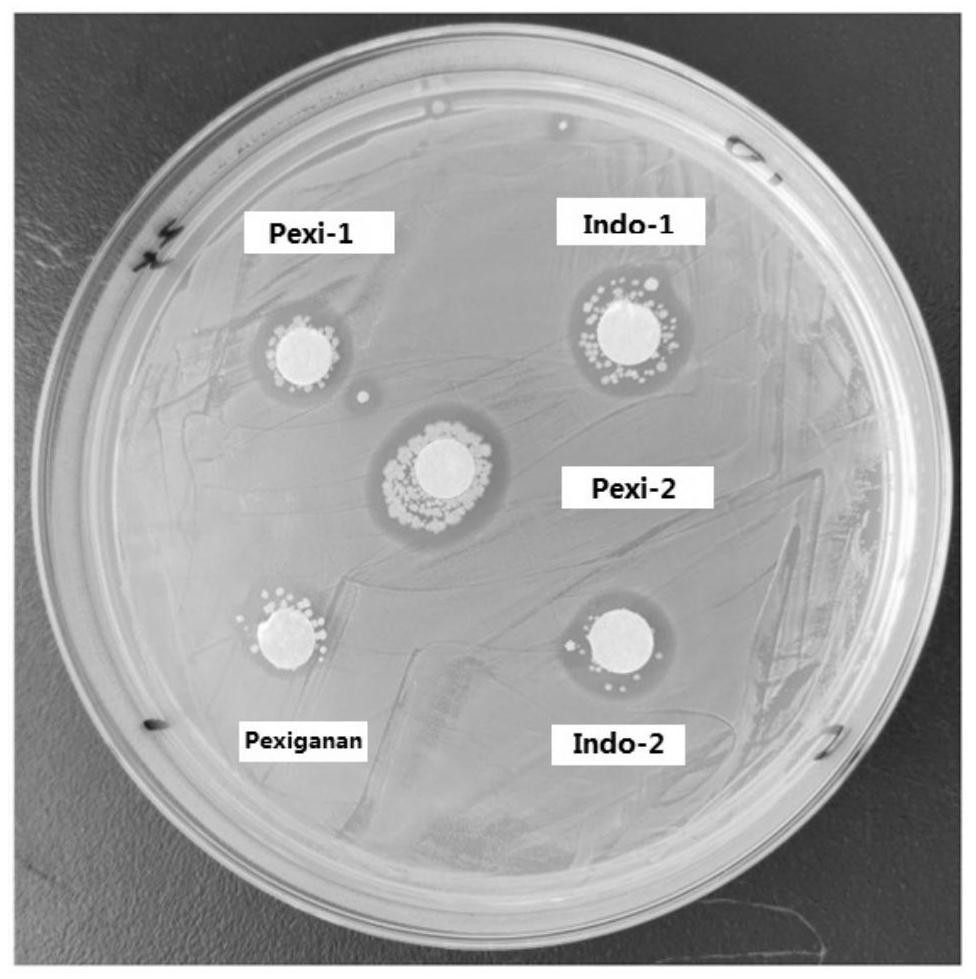
Antibacterial peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN111925430AImprove structural propertiesGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsHemolysisCytotoxicity
The invention provides an antibacterial peptide and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The antibacterial peptide is designed and obtained through a rational moleculardesign method on the basis of family analogues Pexiganan of the antibacterial peptide magainin derived from the epithelium of xenopus laevis. The antibacterial peptide is an antibacterial peptide Pexi-1 with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 or an antibacterial peptide Pexi-2 with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The antibacterial peptide provided by the invention hasgood structural characteristics, can significantly improve the antibacterial effect on staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and aspergillus flavus, effectively reduces the hemolysis rate and cytotoxicity of chicken erythrocytes, and can be effectively used in animal-related production activities.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Reprogramming normal and cancerous human cell lines into human induced poluripotent stem cells by co-electroporation with living xenopus laevis frog oocytes
InactiveUS20110143415A1Rapid reprogrammingCell differentiationArtificial cell constructsColony morphologyGene delivery
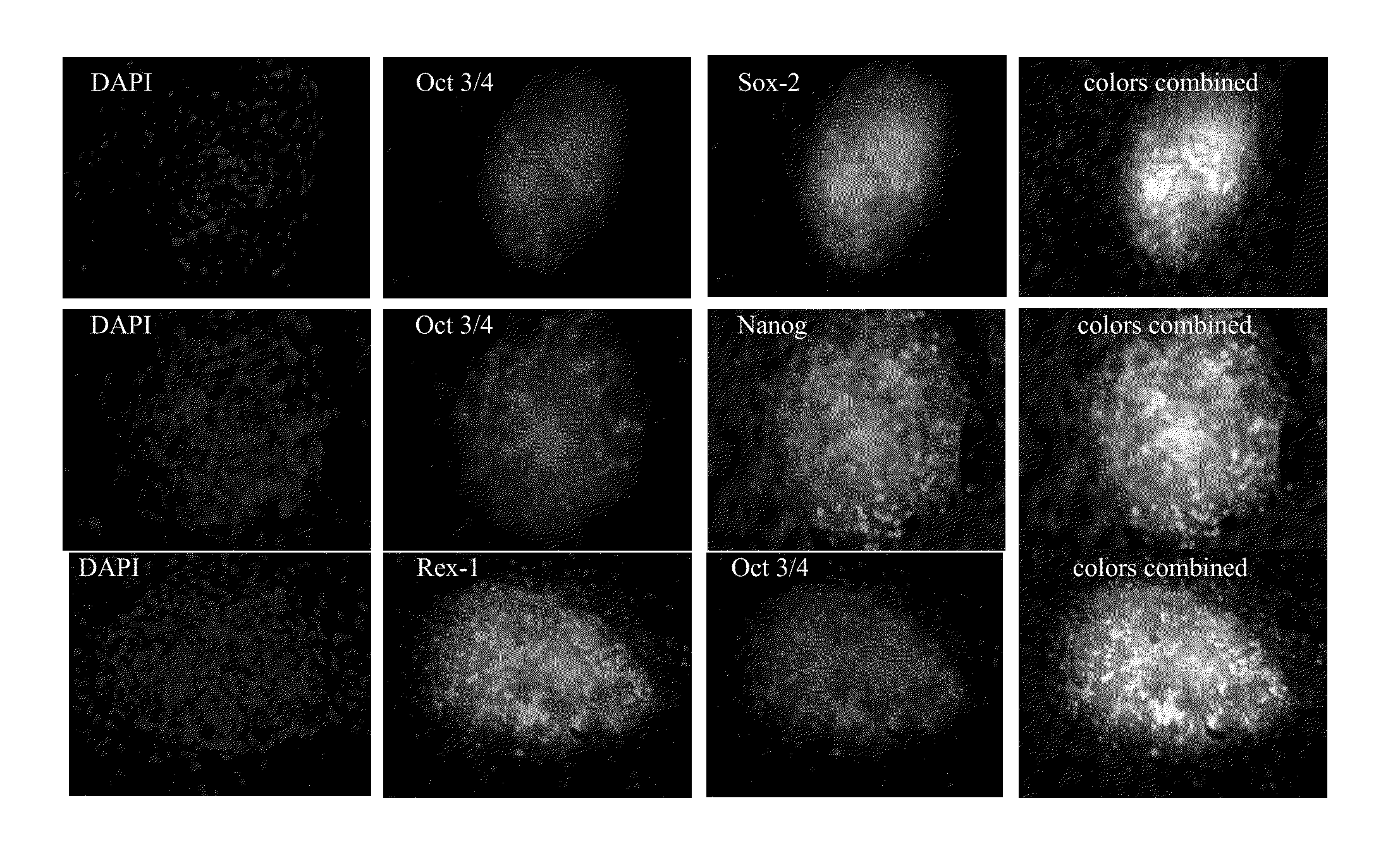
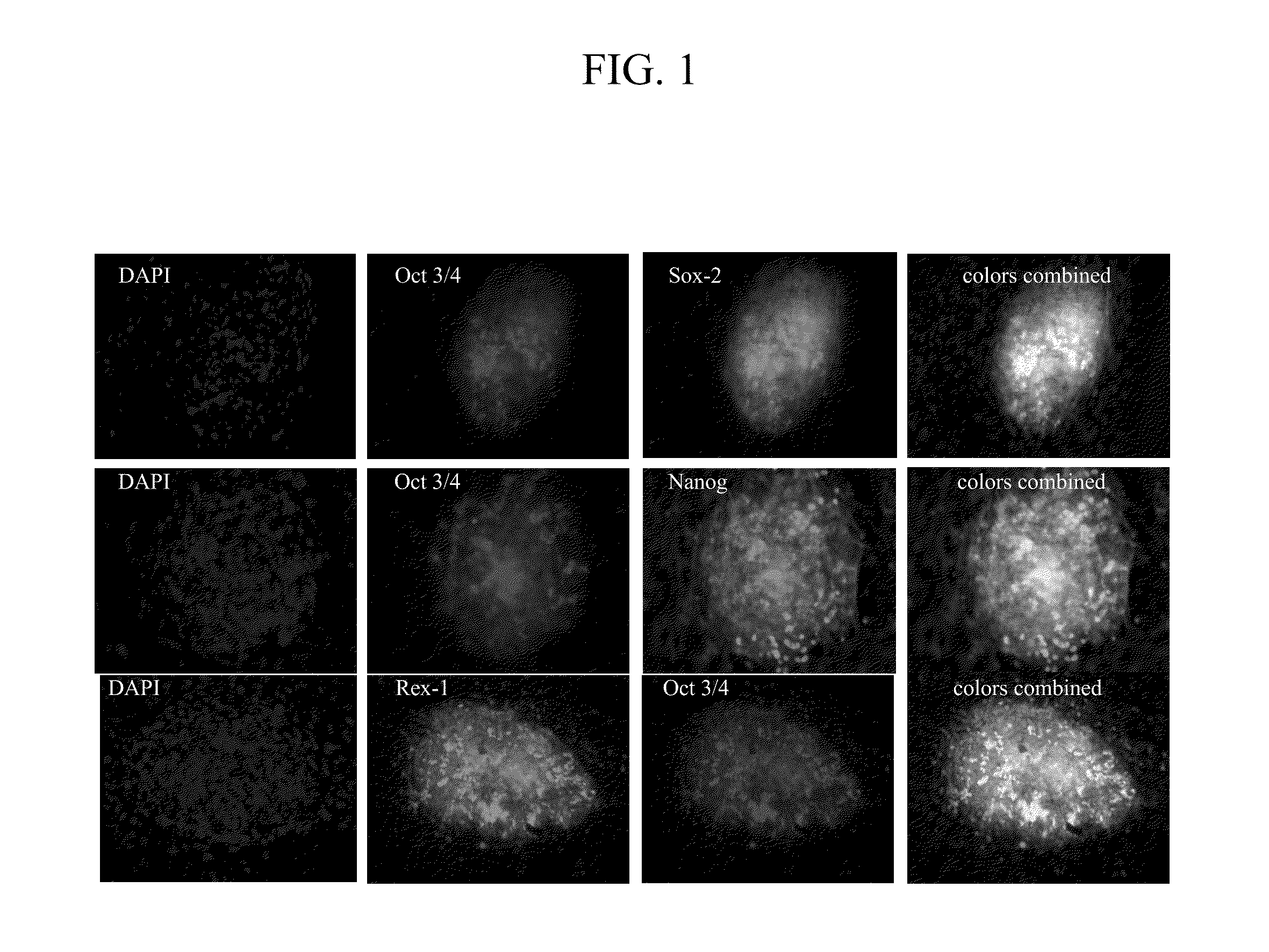
Using electroporation, it is possible to activate the natural reprogramming potential of living Xenopus laevis oocytes and pass it on to donor cells placed with eggs in one electroporation chamber. We demonstrated that co-electroporation at 150 v / cm / 25 μF of mature oocytes with ˜105 cells / ml of suspension of various normal and cancerous human cell lines, such as bone marrow stromal cells, foreskin fibroblasts, pre-adipocytes, CD4+ T-lymphocytes, cheek cells, cervical carcinoma (HeLa) cells and breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) cells, reprograms donor cells into iPSc-like cells, which form colonies on irradiated MEF feeders. The iPSc-like cells generated by this study resemble human embryonic stem cells in colony morphology and expression of stem cell-associated transcription factors, including Oct3 / 4, Nanog, SOX-2, Rex-1, TRA-1-60 and SSEA-1. New method obviates the use of retroviral or lentiviral gene delivery vectors and other “non-parental” reprogramming approaches.
Owner:PAYLIAN SERGEI
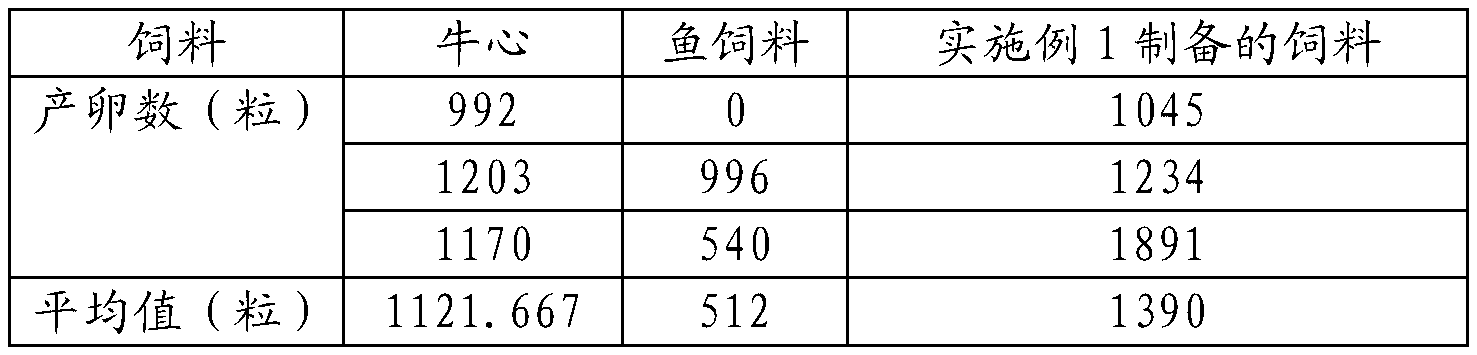
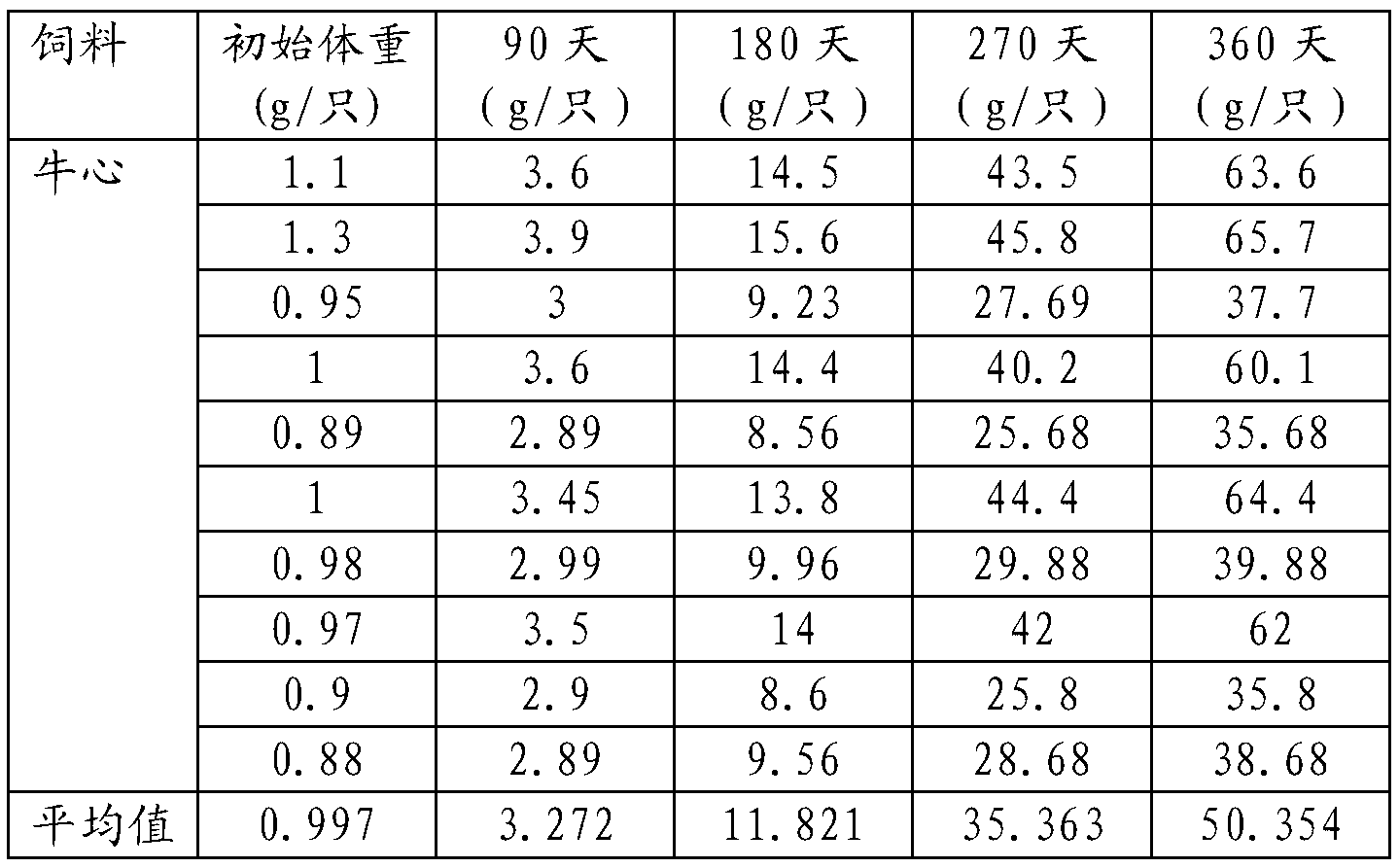
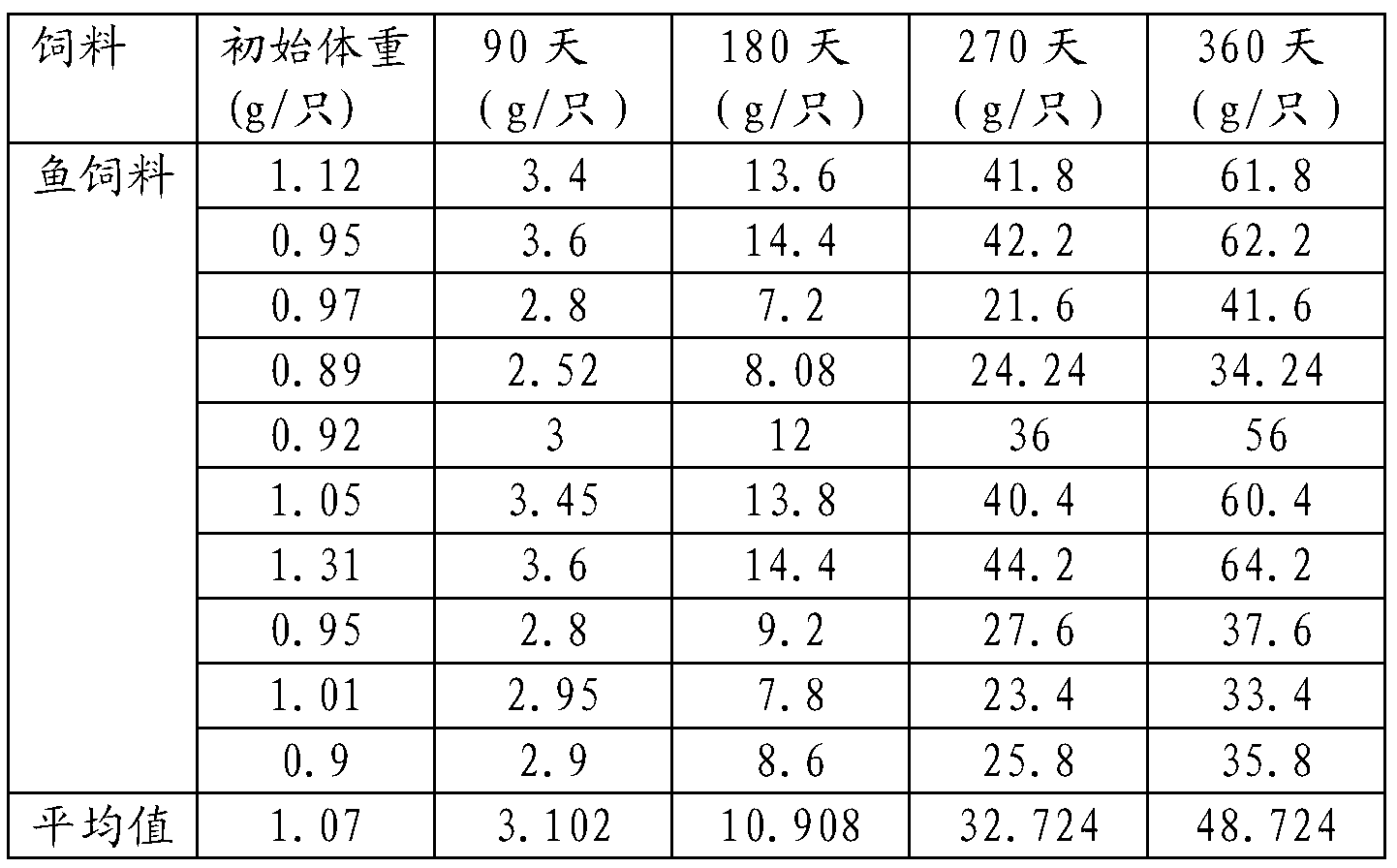
Xenopus laevis feed
The invention relates to a xenopus laevis feed. The feed comprises the following raw materials based on percentage composition of total material weight: 40-55% of fish meal, 8-12% of shrimp med, 0-10% of bran, 8-12% of wheat flour, 8-12% of peanut meal, 3-7% of saccharomyces cerevisiae and 0-25% of algae powder. The xenopus laevis feed provided by the invention is convenient to store, low in cost, balanced in nutrition, prepared according to the required nutrition of xenopus laevis in different growth stages of tadpole, froglet and adult frogs, and conductive to the healthy and fast growth and development of the xenopus laevis.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Xenopus laevis GLP-1 analogue and uses thereof
InactiveCN108359005AExtensive treatmentImprove in vivo stabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSynthesis methodsSide chain
The invention relates to an Xenopus laevis GLP-1 analogue, a synthesis method and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the side chain and the C terminal of Xenopus laevis GLP-1 are subjected to structure modification to obtain the Xenopus laevis GLP-1 analogue with advantages of high blood glucose lowering activity and long pharmacological action time; and the Xenopus laevis GLP-1 analogue has significantly improved biological activity, and further has effects of strong long-acting blood glucose lowering and strong weight reducing.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Artificial method for inducing natural spawning and incubation of xenopus laevis
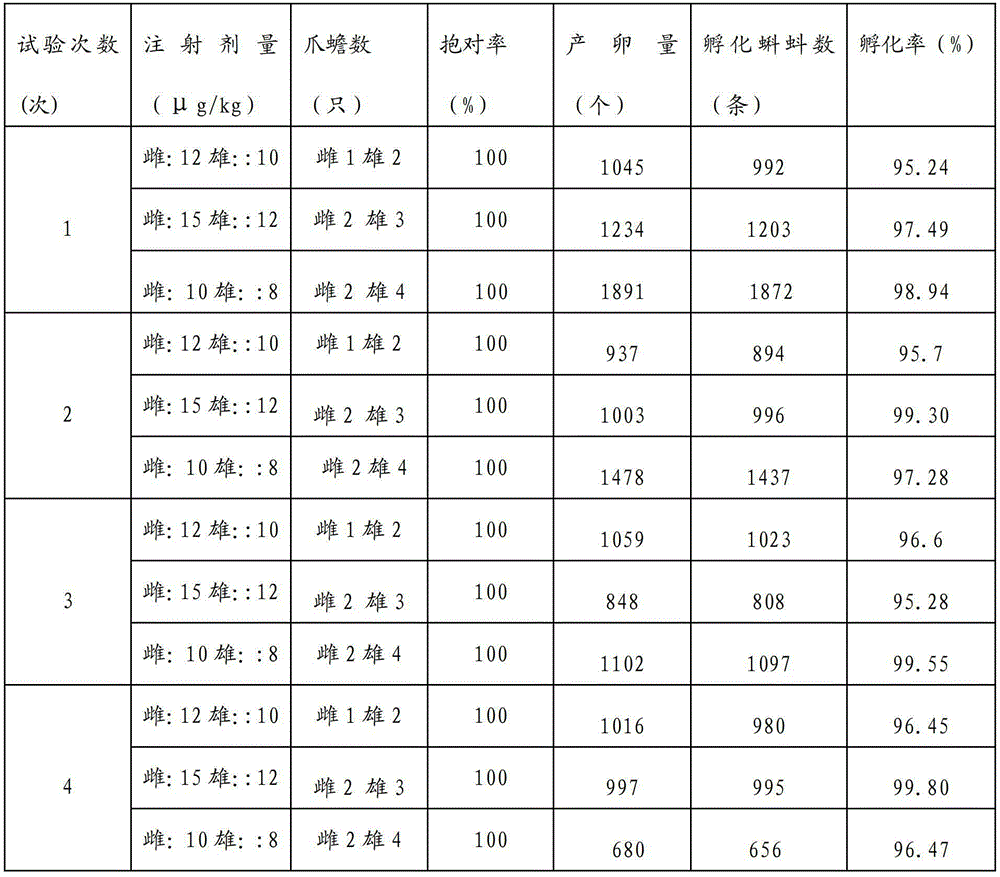
The invention relates to an artificial method for inducing natural spawning and incubation of xenopus laevis. The method comprises the following steps: selecting sexually mature female xenopus laevis which do not lay eggs within 3 months and sexually mature male xenopus laevis which do not discharge sperms within 3 months; subcutaneously injecting hormone in the female xenopus laevis and male xenopus laevis; placing the xenopus laevis into a spawning pond according to the method of two male and one female or three male and two female or four male and two female; and after the female xenopus laevis lay eggs, taking out the oosperms and placing the oosperms into an incubator to incubate, wherein the oosperms are changed into little tadpoles after incubating for 24 to 72 hours. The method promotes natural spawning of the xenopus laevis, is simple to operate, convenient to popularize, low in cost and low in technical difficulty, fills the gap of quick spawning of the xenopus laevis in China, can provide sufficient tadpoles for mass breeding, and is applicable to test in the scientific research institutions and commercial breeding of the xenopus laevis.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
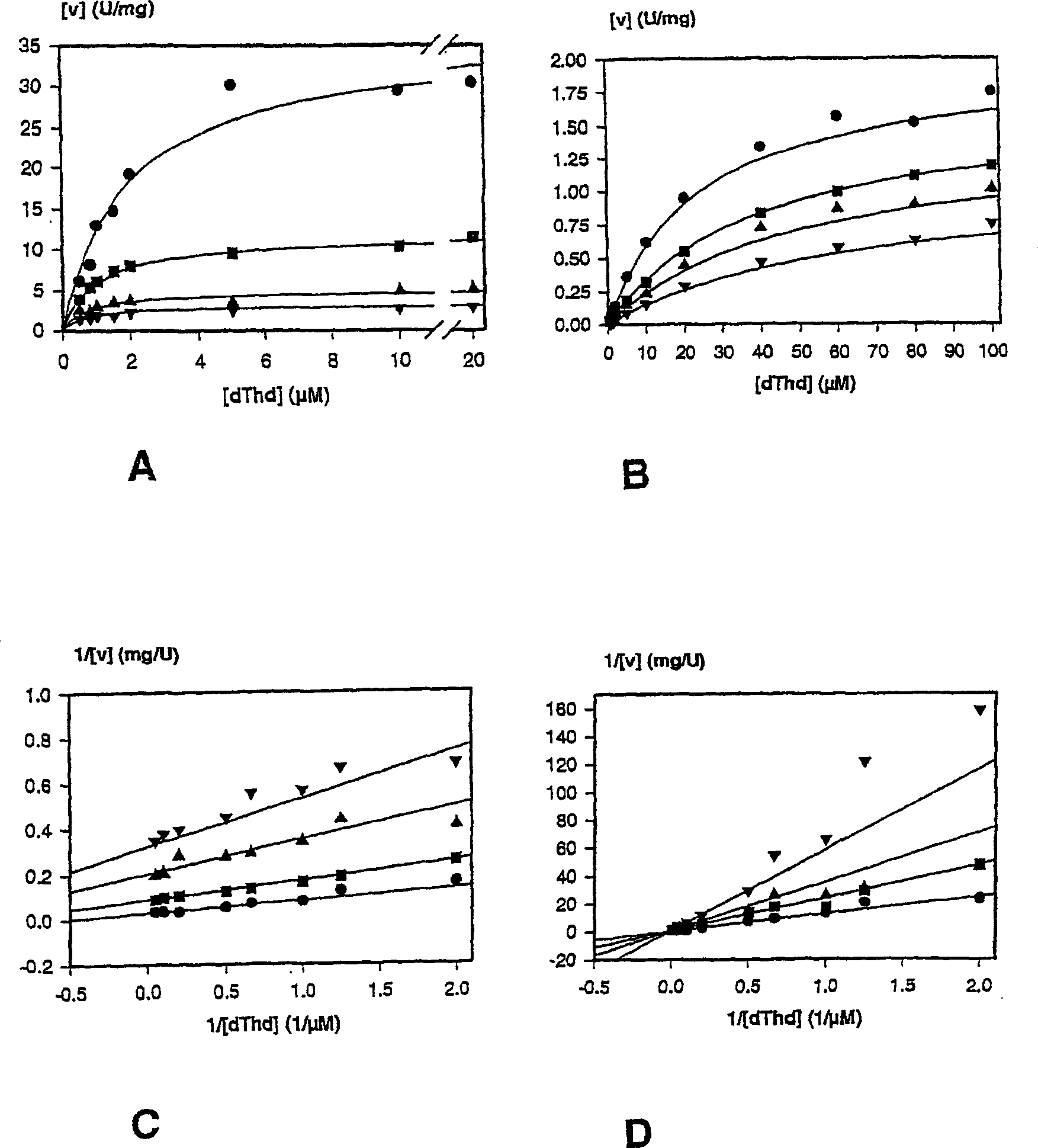
Novel deoxyribonucleside kinase enzyme multi-substrate variants
This invention relates to novel multi-substrate deoxyribonucleoside kinase variants. More specifically the invention provides novel deoxyribonucleoside kinase variants derived from insects or lower vertebrates, in particular from Drosophila melanogaster, from Bombyx mori, or from Xenopus laevis, novel polynucleotides encoding multi-substrate nucleoside kinase variants, vector constructs comprising the polynucleotide, host cells carrying the polynucleotide or vector, methods of sensitising cells to prodrugs, method of inhibiting pathogenic agents in warm-blooded animals, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising deoxyribonucleoside kinase variants of the invention.
Owner:沃尔夫冈・肯特 +2
Pharmaceutical composition containing beta-galactosylation azo ene glycol and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103007253AExtended release timeGood tissue specificityEsterified saccharide compoundsAntibacterial agentsAlcoholRelease time
The invention relates to the technical field of medical pharmaceutical engineering, relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing an NO donor and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a pharmaceutical composition containing beta-galactosylation azo ene glycol and a preparation method thereof. The pharmaceutical composition containing beta-galactosylation azo ene glycol provided by the invention comprises NO donor medicine containing beta-galactosylation azo ene glycol, sperm of xenopus laevis, montmorillonite and moisture-proofing agent; and the preparation method of the pharmaceutical composition comprises the following steps of: dissolving sperm of xenopus laevis in alcoholic solution, adding montmorllonite, fully stirring, filtering the montmorillonite, and drying; dissolving the NO donor medicine containing beta-galactosylation azo ene glycol in alcohol, then adding the montmorllonite, fully stirring, filtering the montmorillonite, volatilizing the alcohol and then adding the moisture-proofing agent, and mixing evenly, thus the pharmaceutical composition containing beta-galactosylation azo ene glycol is obtained. The pharmaceutical composition containing beta-galactosylation azo ene glycol provided by the invention is waterproof and antiacid, release time of the NO donor can be prolonged, and stable and controllable aims are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Apparatus and method for electrophysiological testing
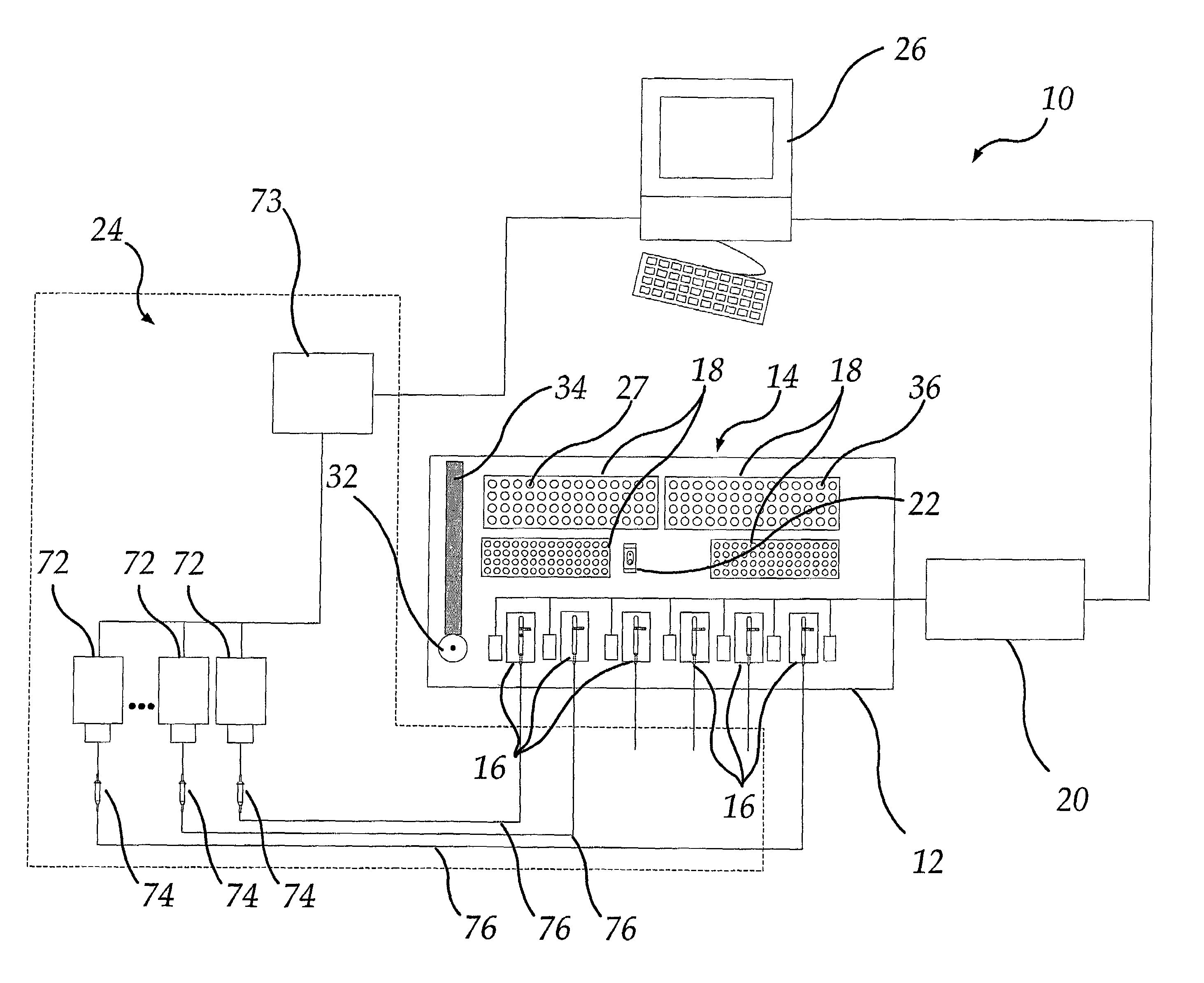
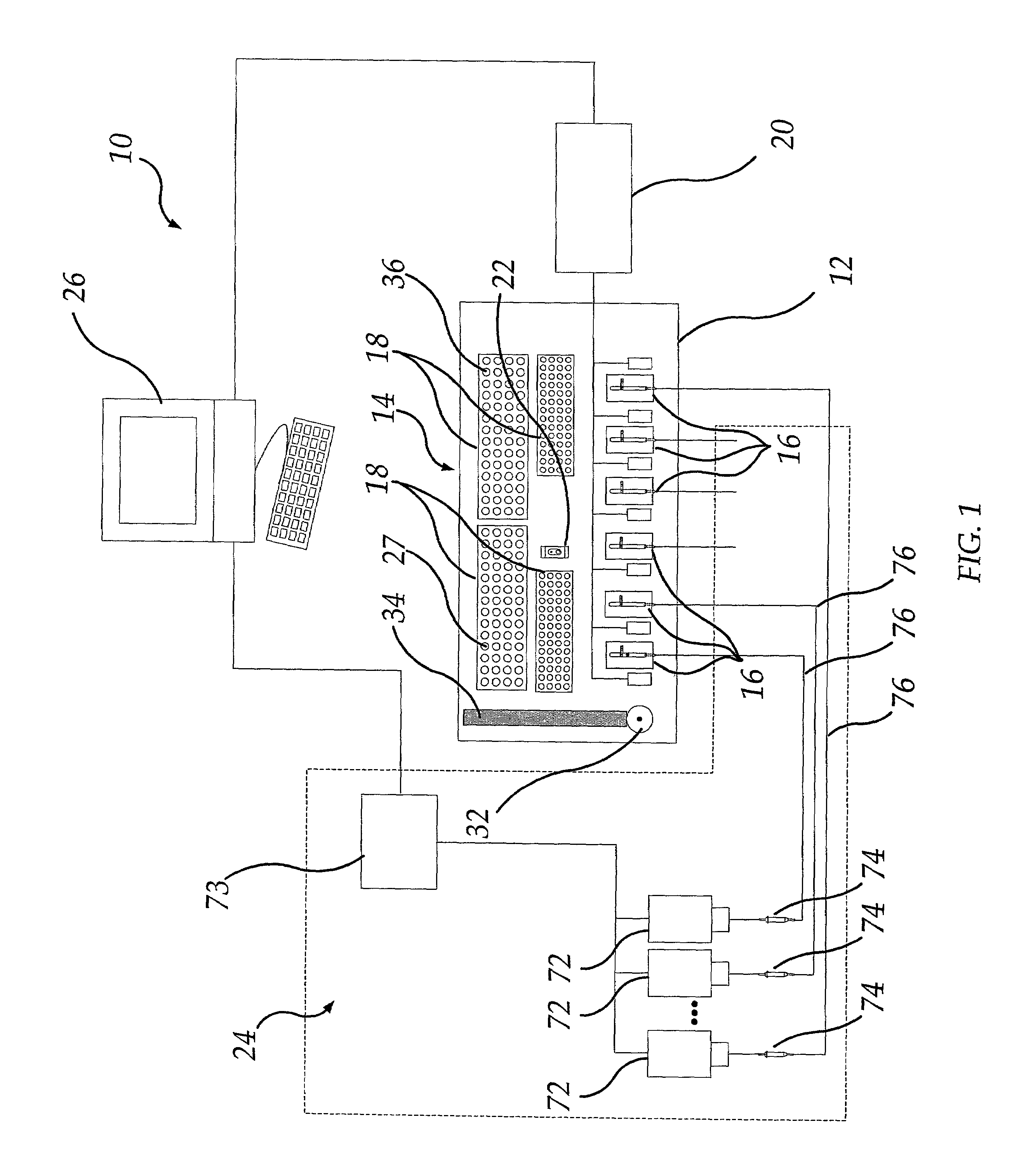
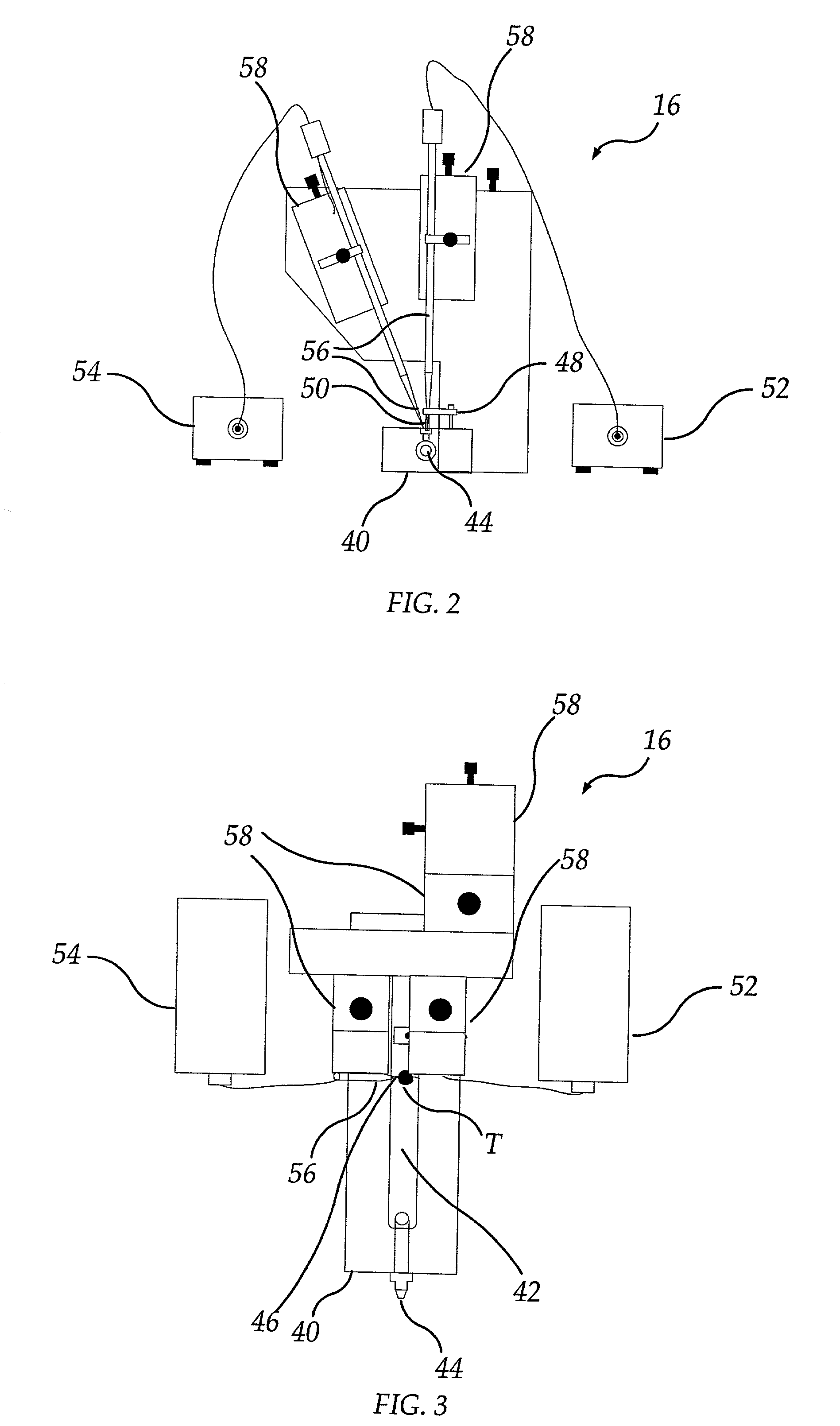
InactiveUS7011939B2Reduce consumptionImprove productivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWorkstationData treatment
A method and apparatus for running a plurality of tests concurrently to obtain data relating to the electrophysiological properties of receptors and channels in biological membranes of test subjects, such as, for example, Xenopus oocytes. The invention further provides software for controlling, acquiring, and recording data relating to electrophysiological properties of receptors and channels in biological membranes of test subjects, such as, for example, oocytes. This invention increases the throughput rate for experiments and assays employing receptors and ion channels expressed in biological membranes of test subjects, such as, for example, oocytes. In the case of an oocyte, these receptors and channels may be natively expressed (endogenous), may be placed into the oocyte (exogenous), or may be expressed from other RNA or DNA previously placed into the oocyte (exogenous).The invention provides a means for a sole researcher to operate a plurality of electrophysiological test stations in the time and space conventionally required by a single electrophysiological test station. The invention automates these stations and provides a means for a sole individual to perform large sets of experiments that would be physically and mentally exhausting in the absence of this invention. In addition, this invention provides efficient database and data analysis software integrated with the data acquisition software, thereby increasing the user's data-handling productivity to keep pace with the augmented data generation capacity.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
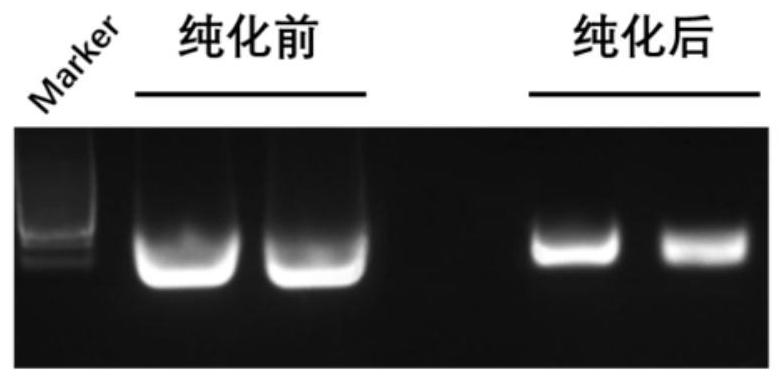
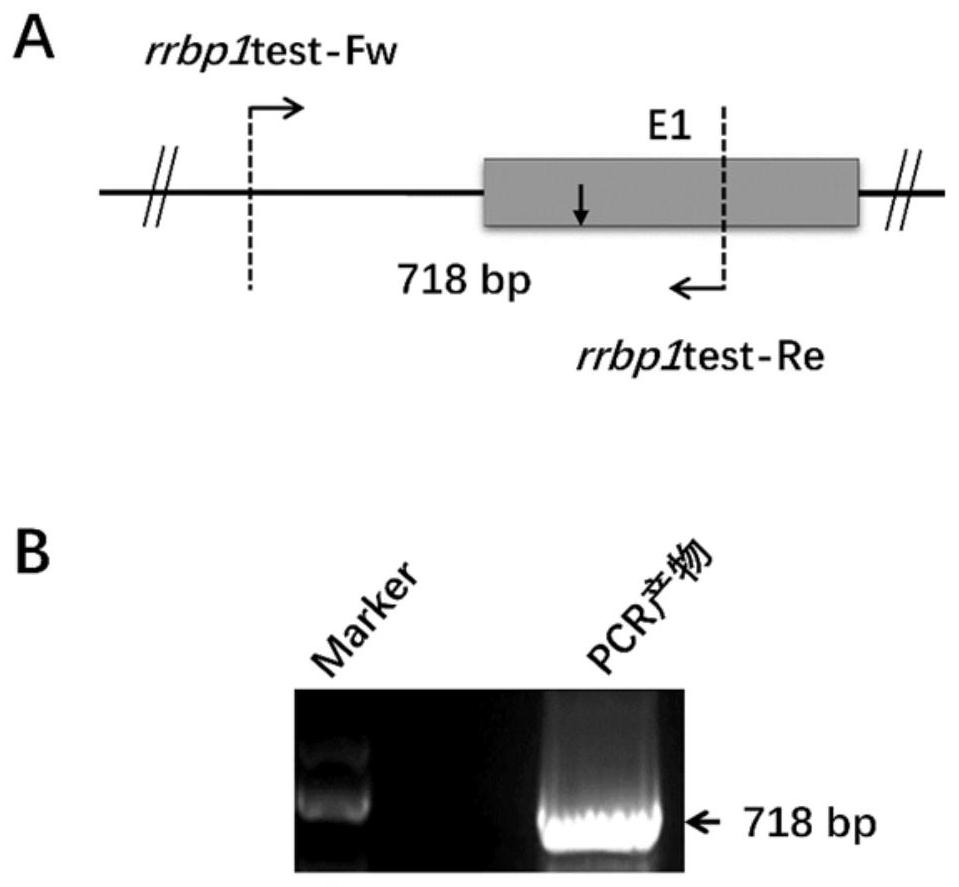
Preparation method of rrbp1 gene knock-out xenopus tropicalis model, and application
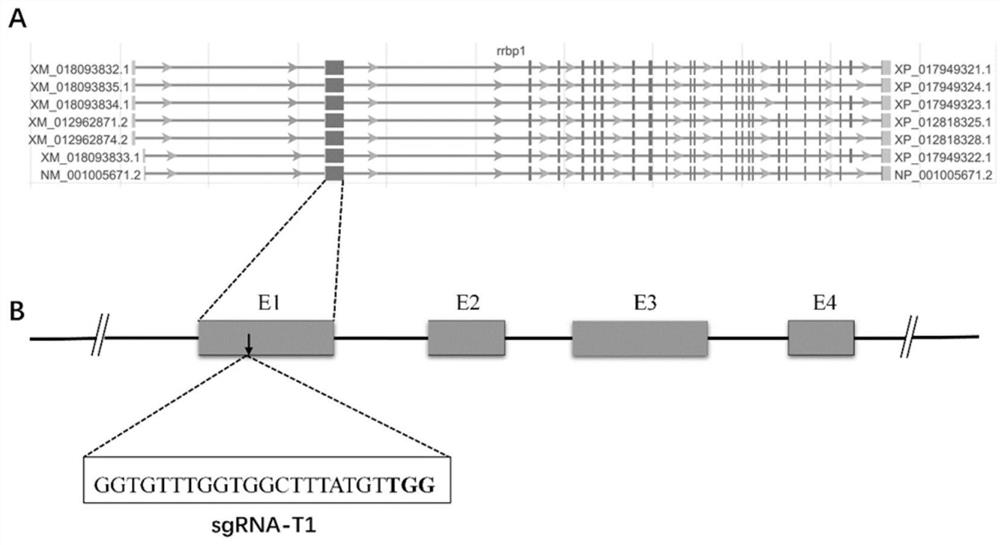
ActiveCN111718933AHigh knockout efficiencyReliable genetic modificationMicroinjection basedStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention relates to a preparation method of a rrbp1 gene knock-out xenopus tropicalis model, and an application. The preparation method comprises the steps of selecting a rrbp1 gene knock-out target point, designing sgRNA, synthetizing a double-stranded DNA fragment, constructing a sgRNA expression vector, performing in vitro transcription to obtain the sgRNA, mixing the sgRNA with Cas9 proteins, performing microinjection into fertilized eggs, and performing screening so as to obtain the rrbp1 gene knock-out xenopus tropicalis model. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, a reliable genetic modification animal model is provided for clarifying the functions of a rrbp1 gene in xenopus tropicalis, and a powerful research tool is provided for further studying tumor and cardiovascular diseases related to the rrbp1 gene based on the model; and besides, the method disclosed by the invention provides technical support for innovation of xenopus tropicalis mode animal germplasm resources.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for inducing fetal bovine fibroblast to reprogram
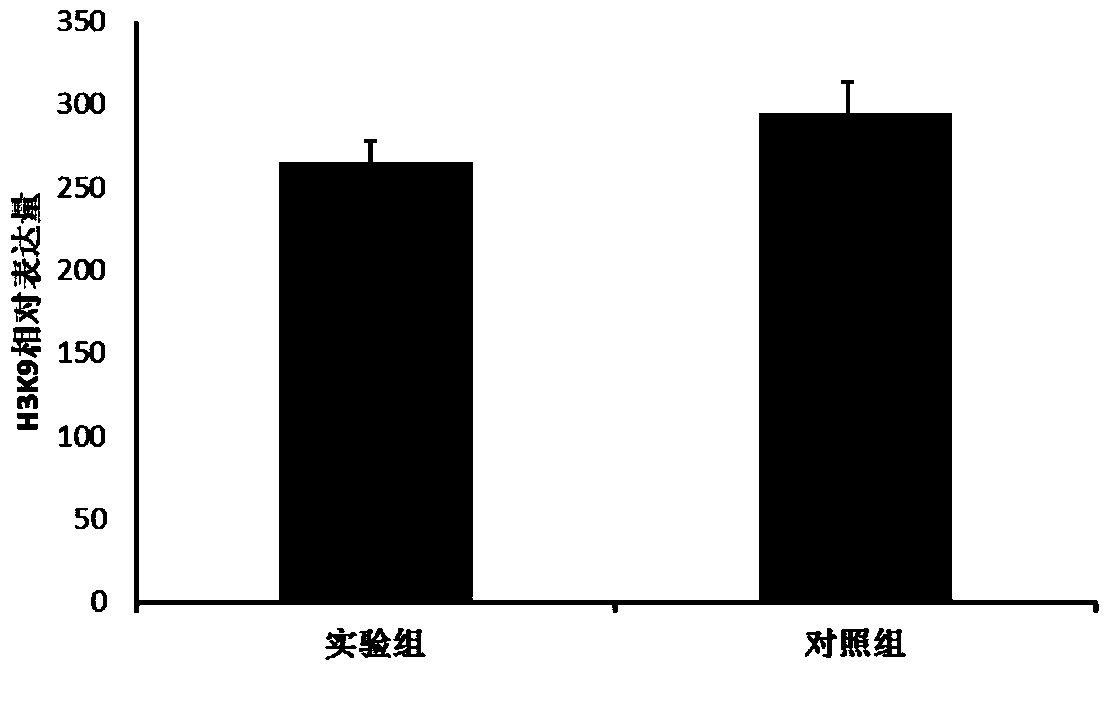
InactiveCN103667179AEfficient methodMethod stableEmbryonic cellsAlkaline phosphatase stainingReprogramming
The invention belongs to the field of cells, and discloses a method for inducing fetal bovine fibroblast to reprogram. According to the invention, the fetal bovine fibroblast is subject to permeabilized treatment by a digitonin solution, and is subject to co-incubation with xenopus oocytes extract; whole medium containing 2mMcaCl2 is adopted to block reversible pores in the cell membrane, extract treated medium is adopted to cultivate and induce the fetal bovine fibroblast to reprogram to obtain fetal bovine fibroblast pluripotent stem cells. The method discloses by the invention is efficient, stable, and safe; the alkaline phosphatase staining of the fetal bovine fibroblast pluripotent stem cells disclosed by the invention shows a positive result; the acetylation degree of histone H3K9 is lowered; Oct-4 protein and pluripotent marker gene Oct-4, Nanog are expressed; therefore the fetal bovine fibroblast undergoes reprogramming, the gene expression mode of cells is changed to show characteristics of stem cell, partial growing totipotent is restored, and the fetal bovine fibroblast can be used as nuclear donor cells to prepare clone embryo for body cell clone.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Use of Xenopus laevis oocytes a microincubators
The present invention concerns methods for de-differentiation and stabilize cells, such as progenitor cells, by introducing the cells into the cytoplasm of host oocytes, such as Xenopus laevis oocytes. Advantageously, this method obviates the need for any nuclear transfer procedure, which is known to disrupt the chromosomal architecture of donor and recipient cells. The present invention also concerns host oocytes encapsulating cells that have been introduced into their cytoplasm. The present invention also concerns cells that have been removed from the host oocytes.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Novel gene Xsynuclein for xenopus laevis GRK family
InactiveCN101186921AHelp in developmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseHigh level expression
The invention discloses the total length cloning of the cDNA of the new gene Xsynuclein of the GRK family of African laevis. The total length of the cDNA is 1040bp, which includes a complete and opening reading frame and can code the protein containing 129 amino acids. The invention also discloses two TR-PCR primers of the gene, TR-PCR method and technique of whole-mount in situ hybridization. The new gene Xsynuclein of the GRK family of African laevis has high level expression in the central nervous system in the period of embryo and adult. The new gene Xsynuclein can take part in the process of forming the forebrain of the embryo and has close relations to neurodegenerative diseases, breast cancer, ovarian cancer and the like. The new gene Xsynuclein of the GRK family of African laevis and the coding protein thereof will hopefully make breakthrough in curing neurodegenerative diseases, breast cancer, ovarian cancer and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method of modulating tissue growth using Frzb Protein
InactiveUS6924367B2High activityReduced activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFrzbADAMTS Proteins
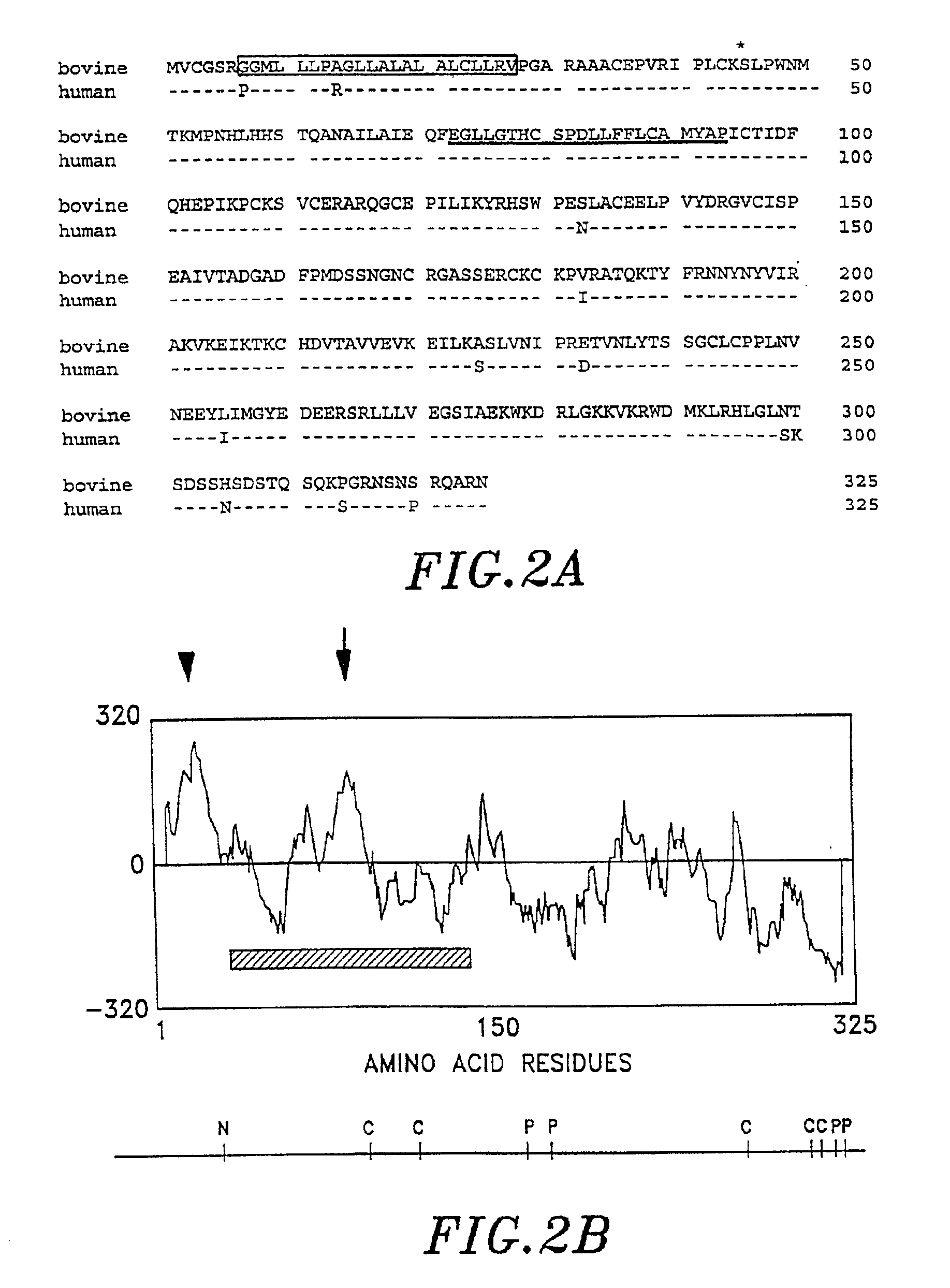
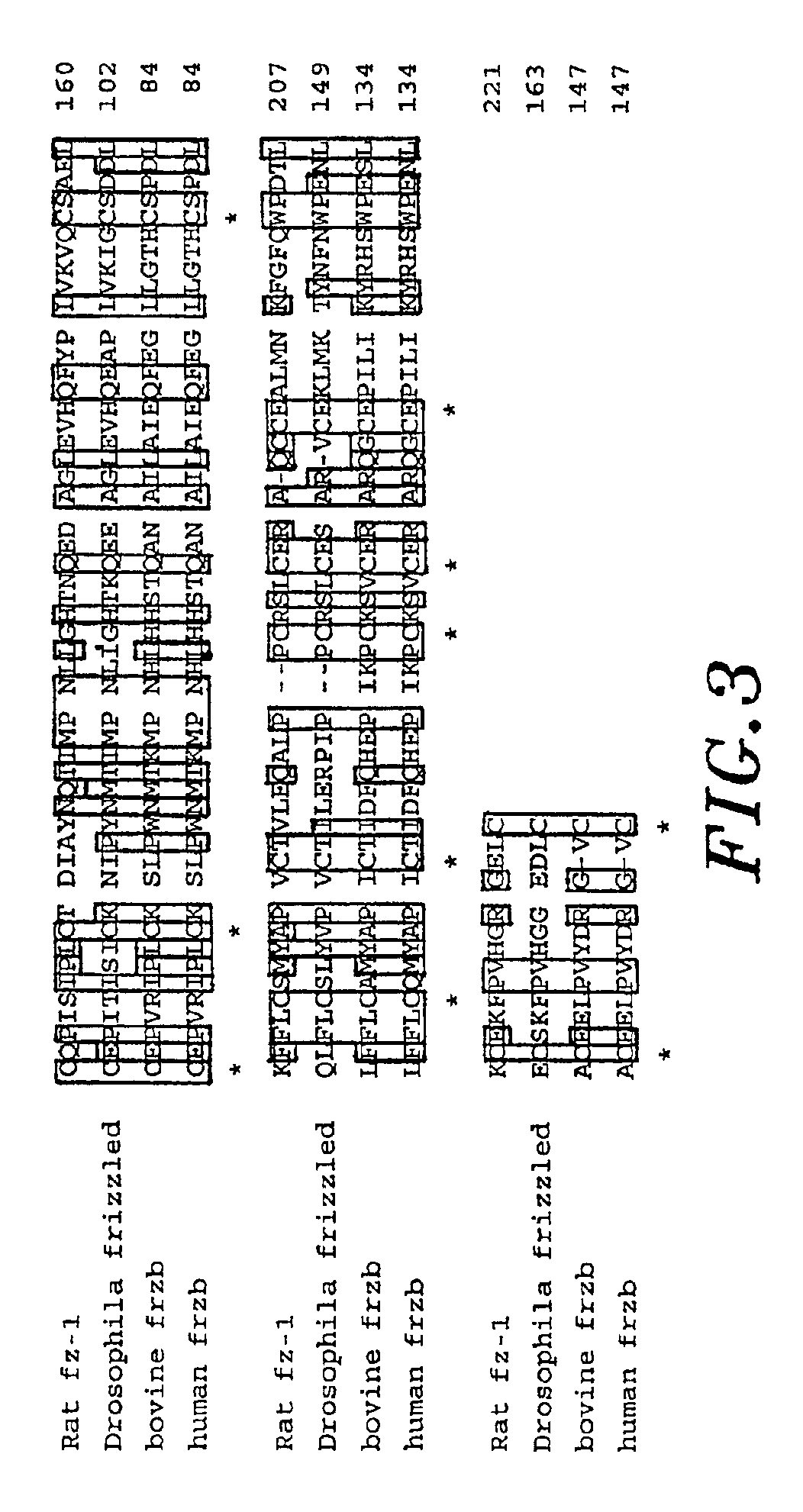
An isolated cDNA encoding a growth-inducing protein, Frzb, capable of stimulating bone, cartilage, muscle, and nerve tissue formation. Frzb binds to and modulates the activity of Wnt growth factors which play a role in various developmental and neoplastic processes. The cDNA and protein sequences of human, bovine and Xenopus Frzb are provided. Production and purification of recombinant Frzb are also described.
Owner:HON HAI RECISTION IND
Cholic acid-XenGLP-1 (xenopus glucagon-like peptide-1) conjugated peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN107698677AExcellent timeExcellent weight loss effectNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCholic acidBinding ratio
The invention relates to a cholic acid-XenGLP-1 (xenopus glucagon-like peptide-1) conjugated peptide and an application thereof. Side chains of XenGLP-1 are subjected to structural modification, a cholic acid micromolecular derivative with a high serum protein binding ratio is introduced, and the XenGLP-1 conjugated peptide with higher hypoglycemic activity and longer pharmacological action time is obtained. The XenGLP-1 conjugated peptide has significantly improved bioactivity and high long-term hypoglycemic and weight losing functions.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
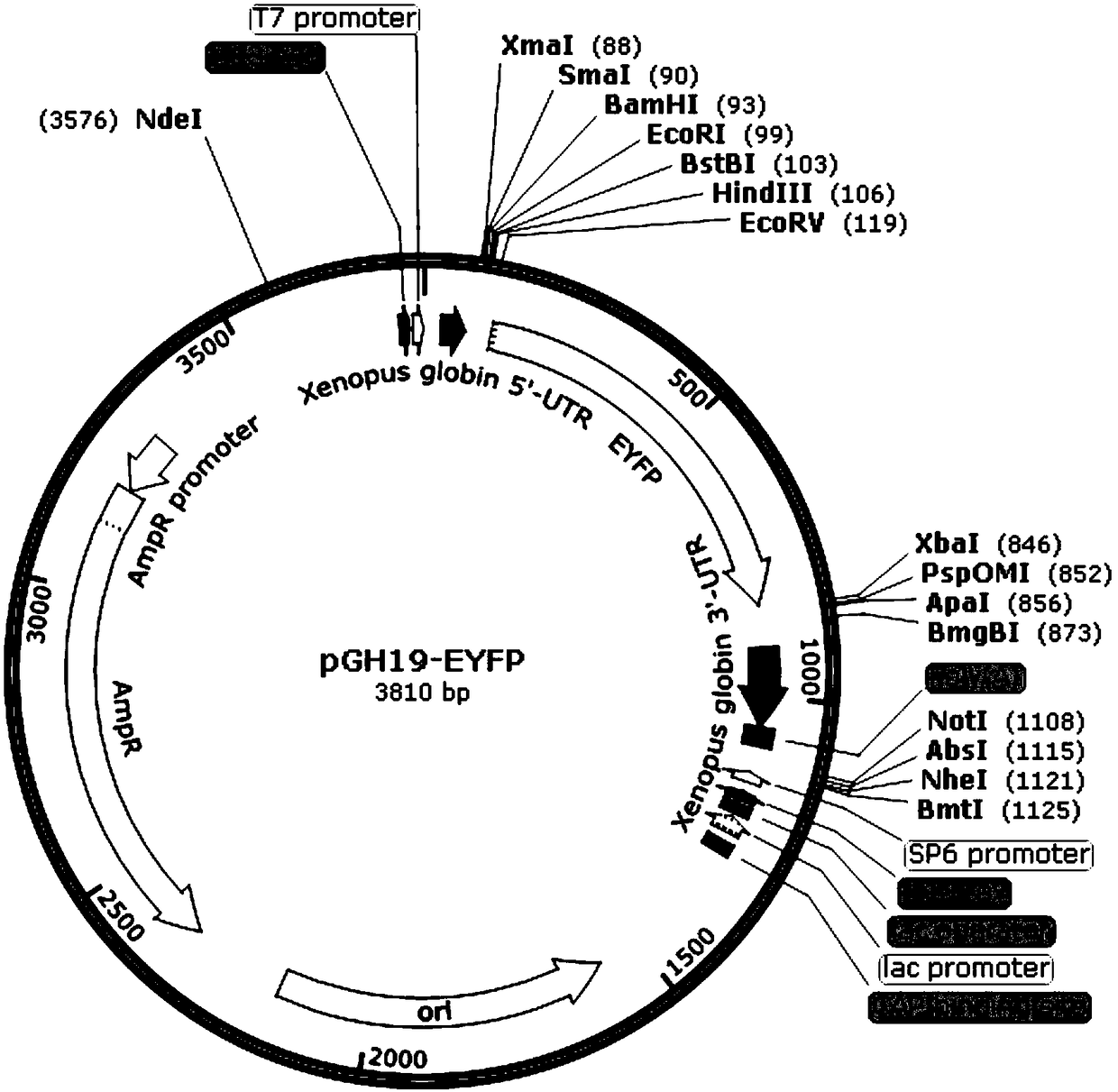
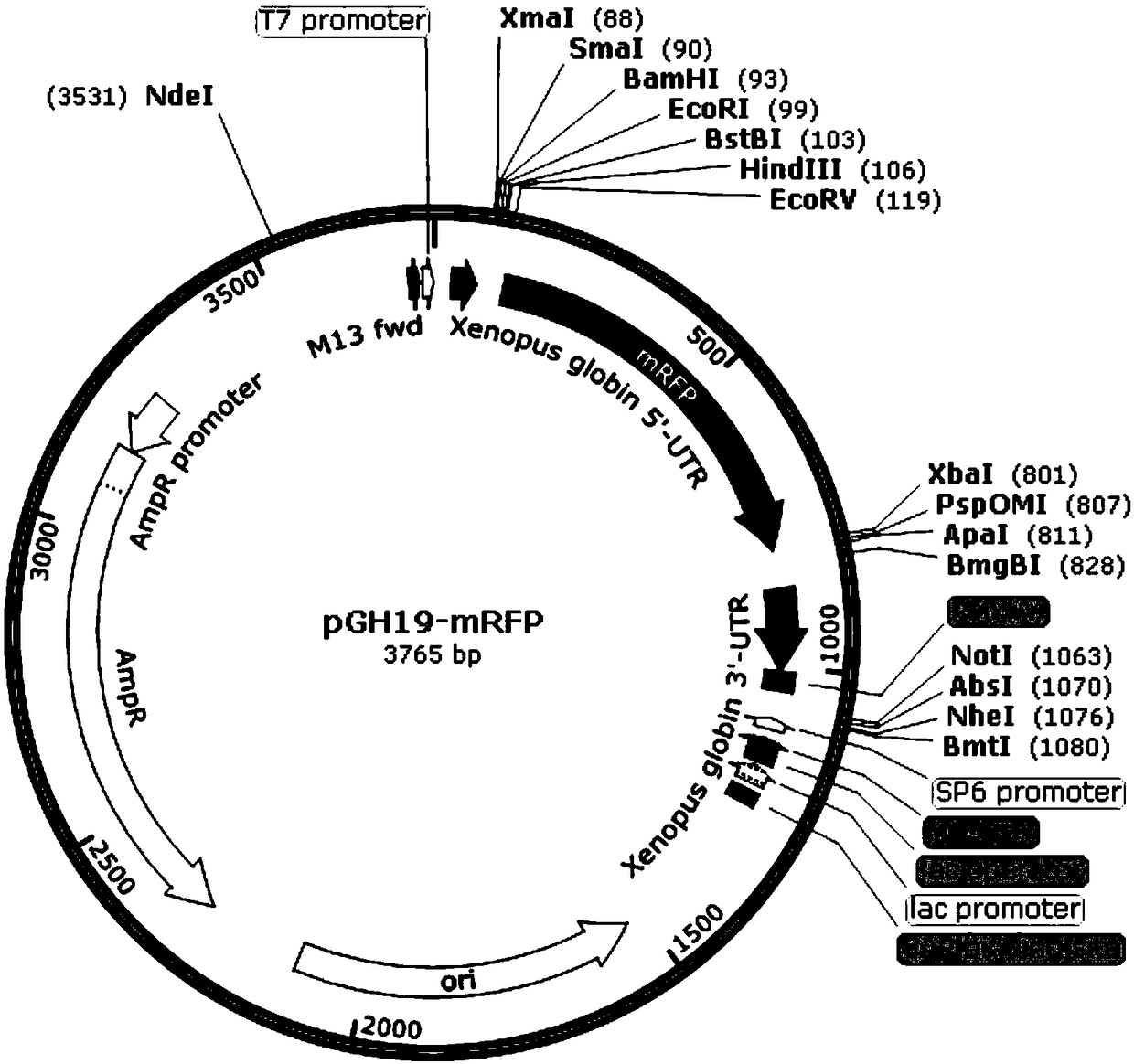
Xenopus laevis oocyte expression carrier with yellow or red fluorescence protein label and application
ActiveCN109055425APrecise positioningEasy extractionNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a xenopus laevis oocyte expression carrier with a yellow or red fluorescence protein label and application. pGH19 plasmid is modified through a molecular biology means, and isspecifically developed to be a carrier pGH19-EYFP or pGH19-mRFP which is suitable for expression of the xenopus laevis oocyte and contains the enhanced yellow or monomer red fluorescence protein label. The carrier can normally express the target gene, and can detect the distribution situation and the expression mode of the target protein with the yellow or red fluorescence label through a fluorescence microscope or a confocal microscope, and thus a more visual and simpler detection method can be provided for the protein situation of xenopus laevis oocyte expression. The spatiotemporal dynamicsof the protein expression can be observed in real time. The expression situation of the target protein can be detected only by using an universal antibody as for the following extraction, purification, identification and functional analysis of the target protein, the experimental process is greatly simplified, and the experimental time is saved and economic cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for screening uric acid-lowering small molecule compounds
ActiveCN110487877AHigh transfection efficiencyRealize screeningMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsIsotope
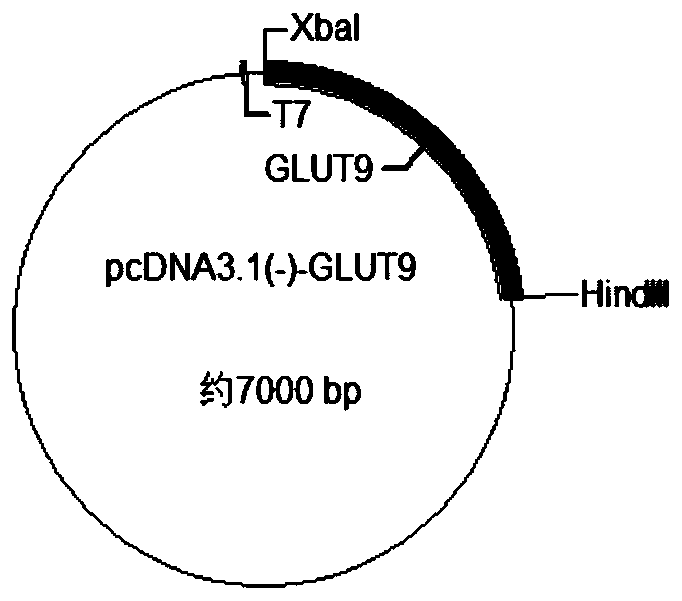
The invention discloses a method for screening uric acid-lowering small molecule compounds for promoting uric acid excretion based on a patch clamp technology. The method comprises the following stepsof: constructing recombinant plasmids for expressing a GLUT9 gene; instantaneously transfecting the recombinant plasmids to an HEK293T cell; after 18-24 hours, recording the change of a current whenthe GLUT9 cells are expressed to transport uric acid by utilizing a patch clamp technology; and verifying the reliability of the model through positive drugs, namely benzbromarone and probenecid, andnegative drugs, namely RDEA3170 and allopurinol. The method is simple, convenient and rapid to operate; the result is stable, reliable and good in reproducibility; compared with an existing method fordetecting isotope uptake by using xenopus oocytes, the method has the advantages that the consumed time is shorter, the cost is lower, and high-throughput screening of the GLUT9 inhibitor can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
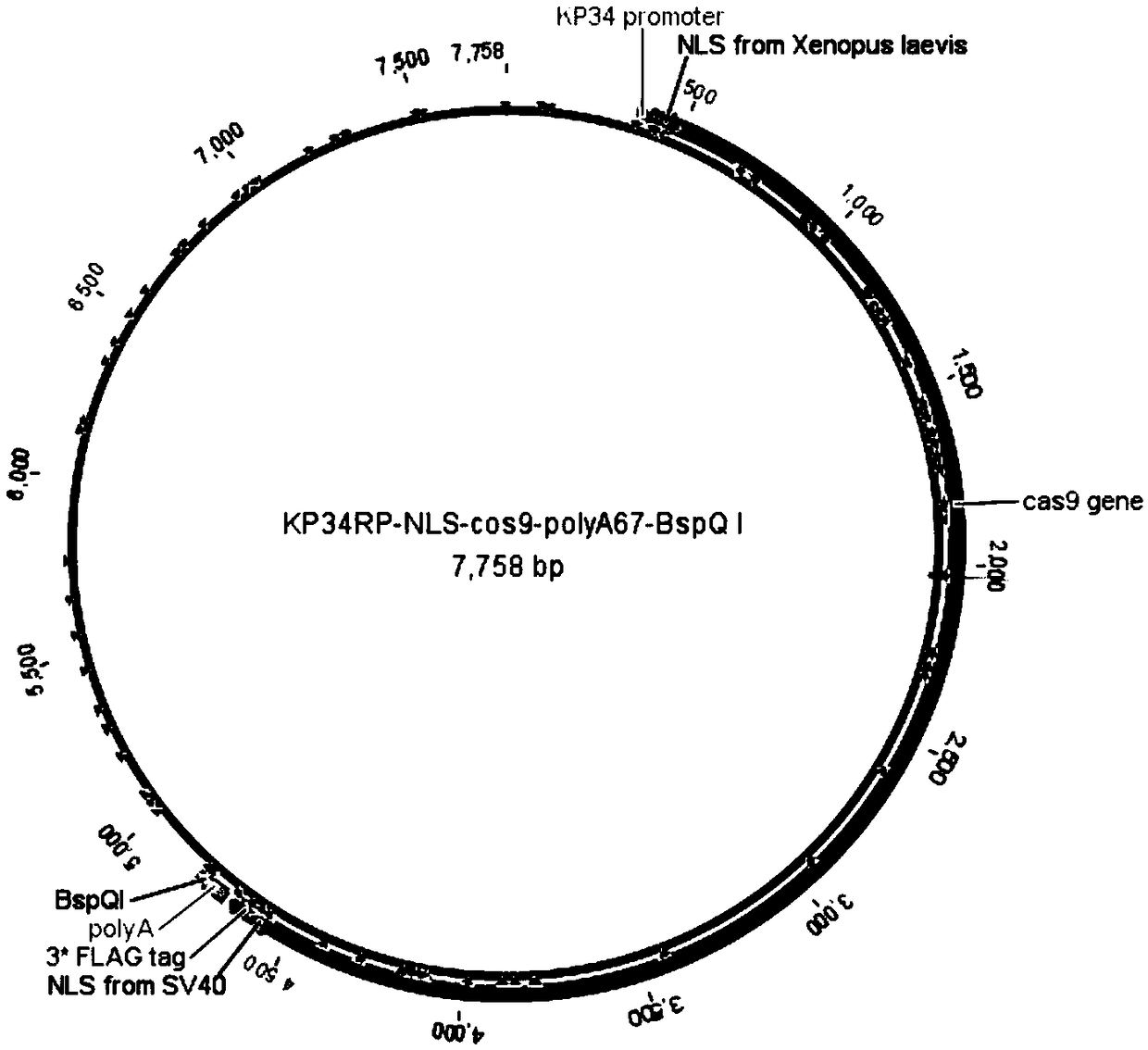
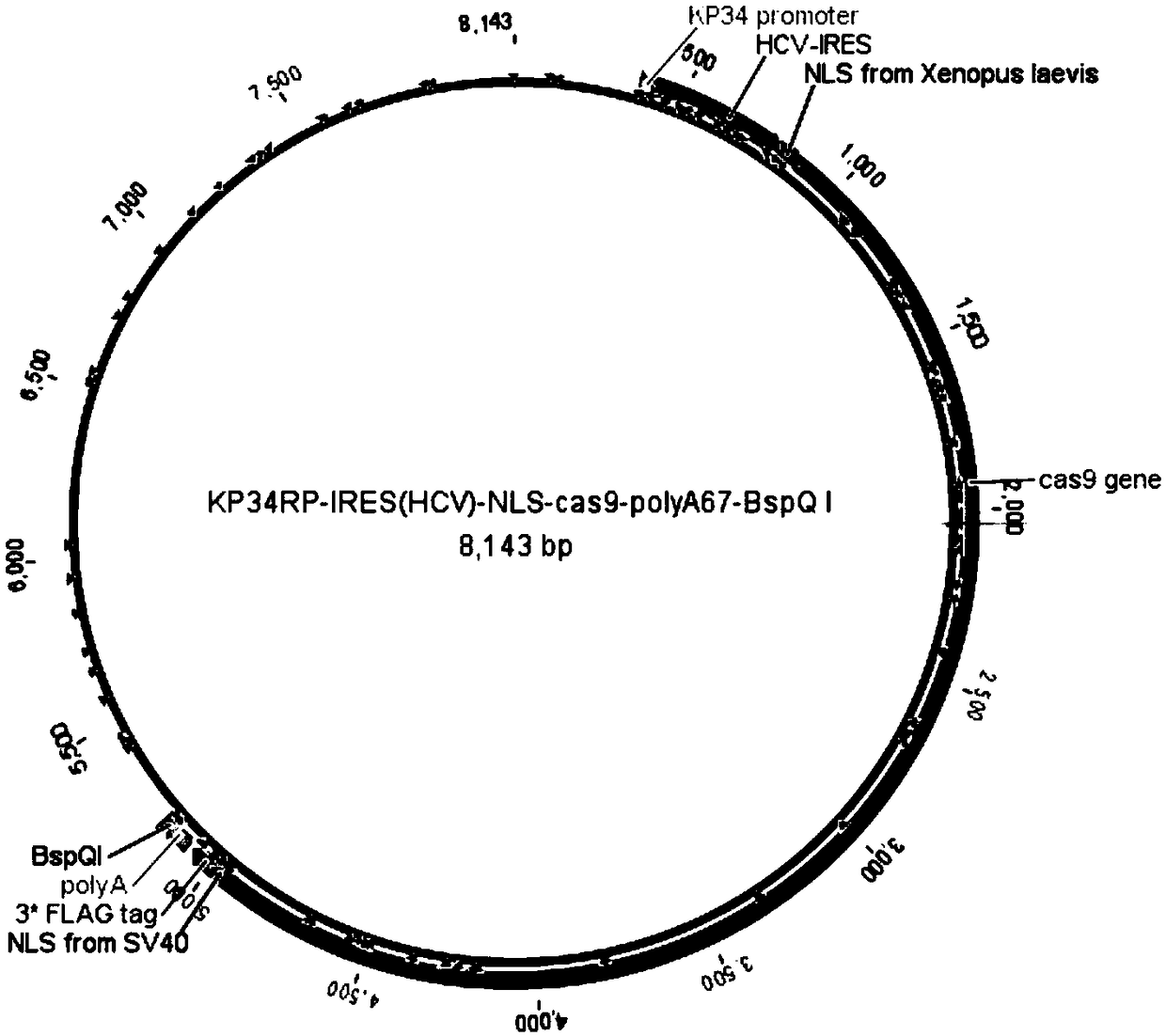
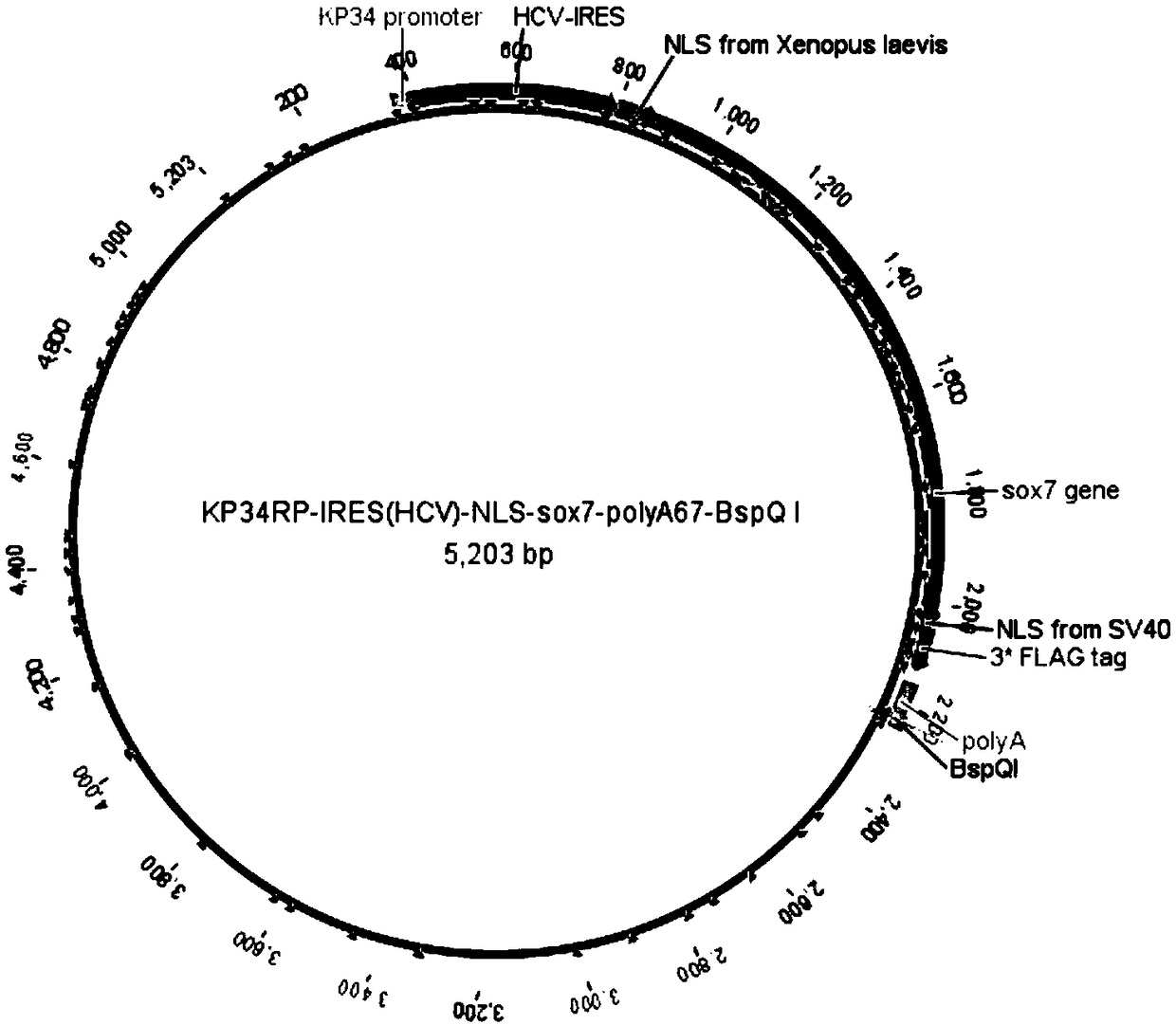
Production application of mono-subunit RNA polymerase KP34RP in long-chain mRNA synthesis
The invention discloses a production application of mono-subunit RNA polymerase KP34RP in long-chain mRNA synthesis. The mono-subunit RNA polymerase is bacteriophago-like particle mono-subunit RNA polymerase (a formula is as shown in the description). The KP34RP is used for preparing long-chain cap-cas9mRNA which is as show in a sequence list SEQ ID NO.4, IRES-cas9mRNA which is as show in a sequence list SEQ ID NO.5, and IRES-sox7mRNA which is as show in a sequence list SEQ ID NO.6, wherein cas9 is extensively applied to gene editing, and sox7 plays an important role in embryonic development.While three types of mRNA transcription template plasmids are constructed, at the gene sequence 5'-terminal and 3'-terminal, sequence elements of a nucleoplasmin positioning signal sequence NLS derived from xenopus laevis which is as shown in a sequence list SEQ ID NO.1, an internal ribosome entry site sequence IRES from hepatitis C virus which is as shown in a sequence list SEQ ID NO.2 and poly(A)+BspQI which is as shown in a sequence list SEQ ID NO.3 are added. It is guaranteed that the in-vitro synthesized mRNA can be efficiently translated to a function protein with activity in a cell. Theproduction application is uniform in product, high in purity, reaches a milligram level in average, and is capable of completely meeting market requirements to mRNA research and application.
Owner:RNASYN BIOTECH CO LTD
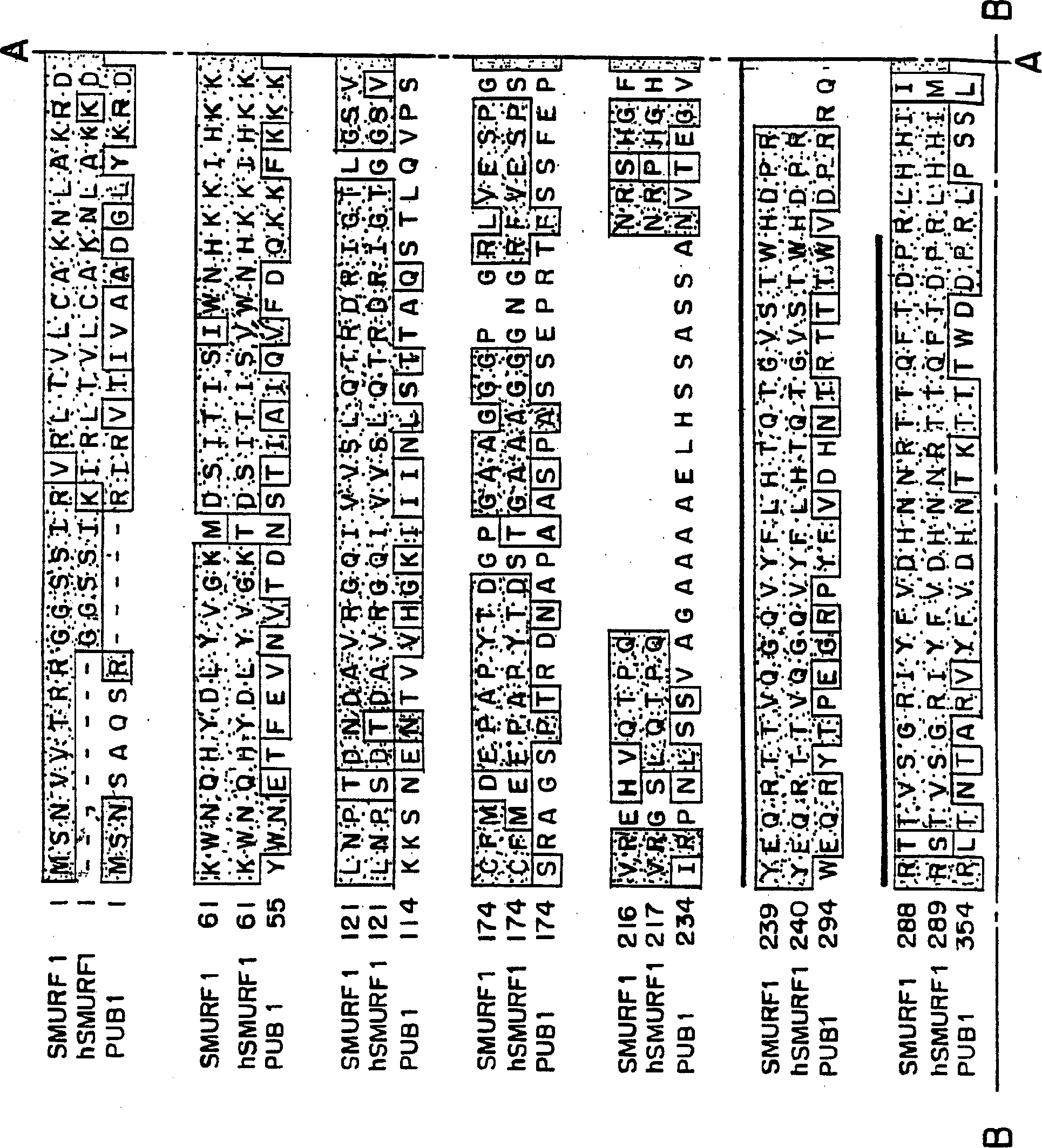
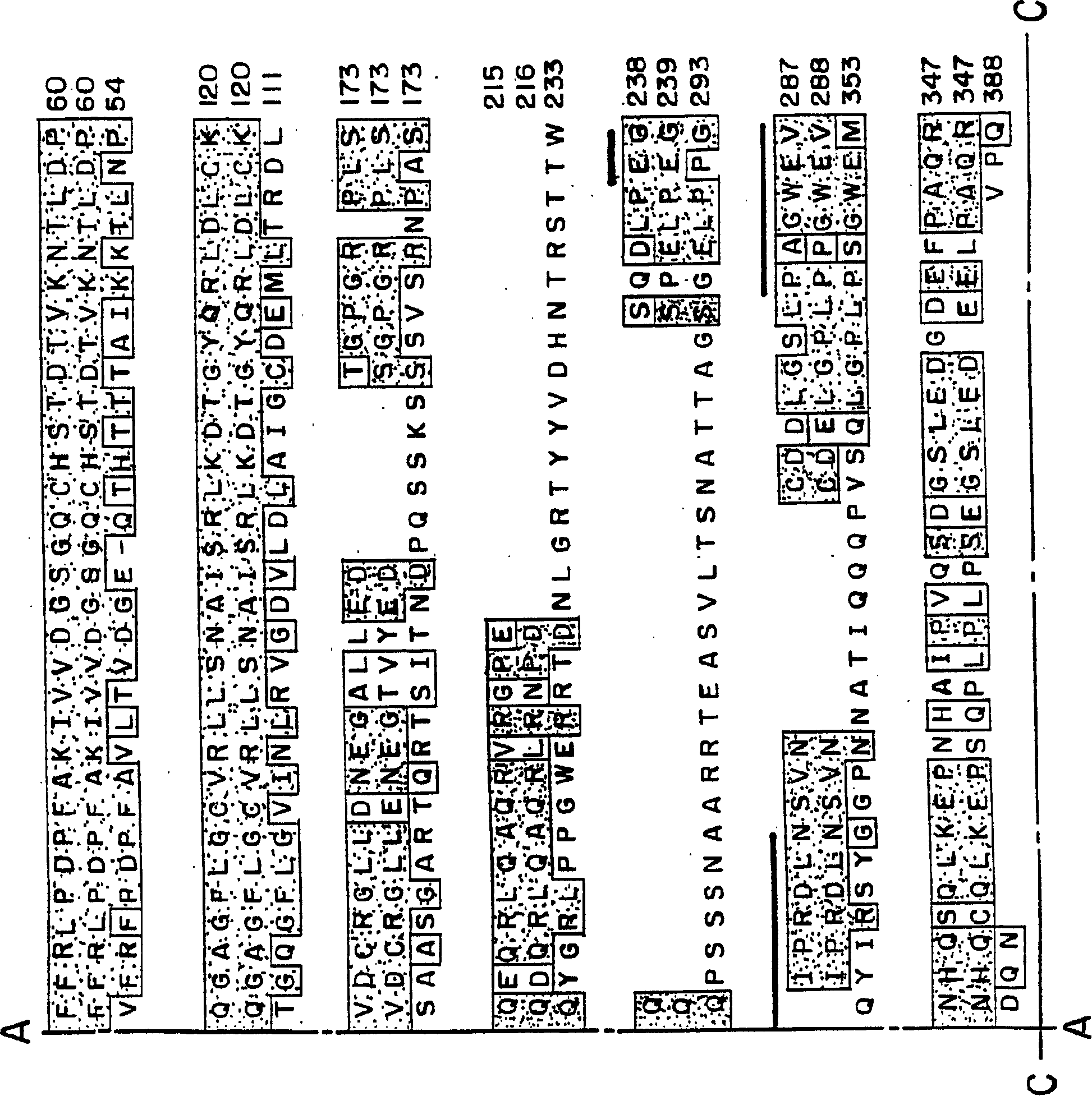
Antagonists of BMP and TGF beta signalling pathway
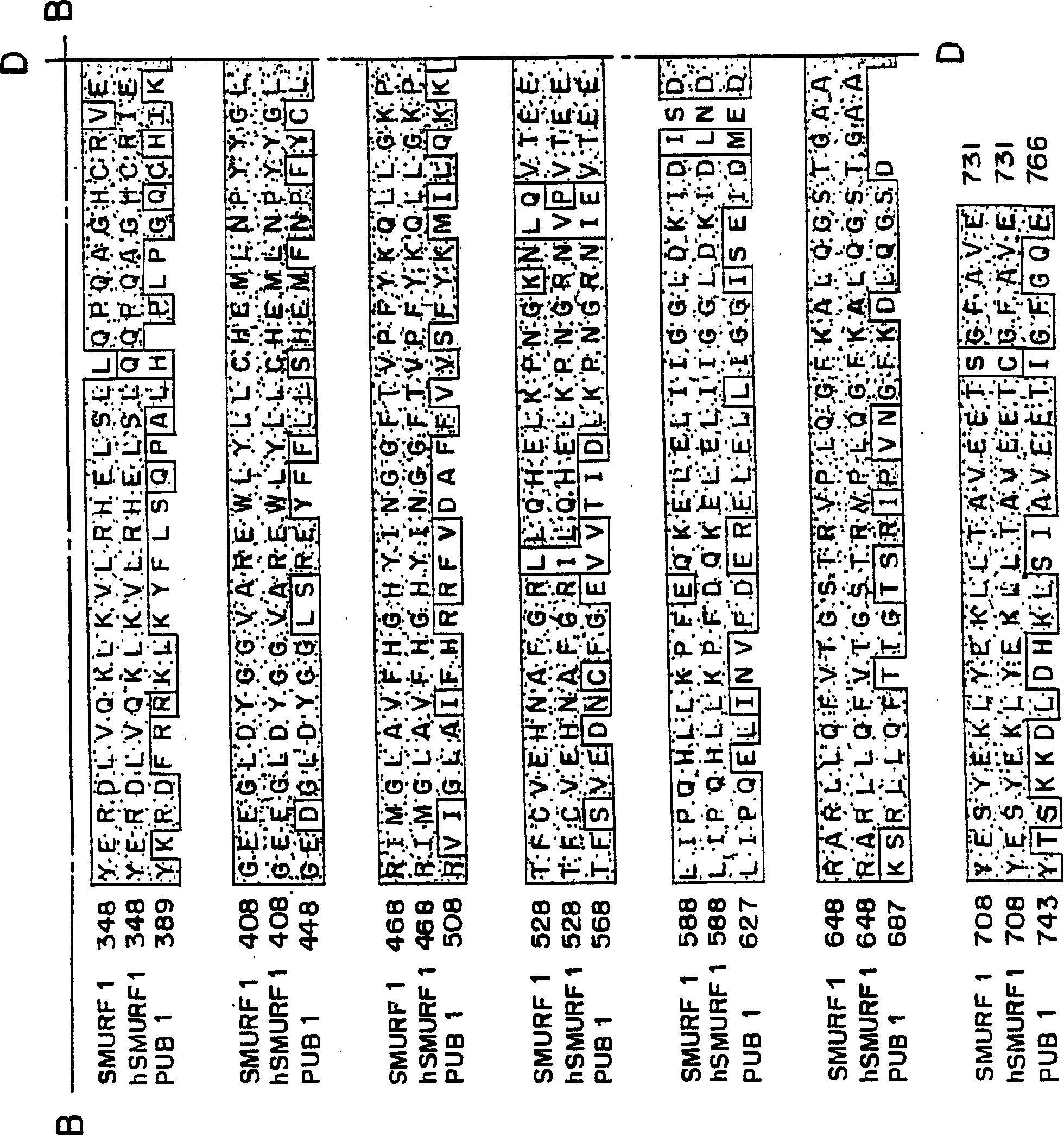
This invention provides unique members of the Hect family of ubiquitin ligases that specifically target BMP and TGF beta / activin pathway-specific Smads. The novel ligases have been named Smurf1 and Smurf2. They directly interact with Smads1 and 5 and Smad7, respectively, and regulate the ubiquitination, turnover and activity of Smads and other proteins of these pathways. Smurf1 interferes with biological responses to BMP, but not activin signalling. In amphibian embryos Smurf1 inhibits endogenous BMP signals, resulting in altered pattern formation and cell fate specification in the mesoderm and ectoderm. The present invention provides a unique regulatory link between the ubiquitination pathway and the control of cell fate determination by the TGF beta superfamily during embryonic development. Thus, Smurf1 is a negative regulator of Smad1 signal transduction, by targeting Smad1, Smurf1 blocks BMP signalling. In mammalian cells, Smurf2 suppresses TGF beta signalling, and in Xenopus, blocks formation of dorsal mesoderm and causes anterior truncation of the embryos. Smurf2 forms a stable complex with Smad7, which induces degradation and downregulation of TGF beta / activin signalling.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Device and Method for Sorting Biological Entities
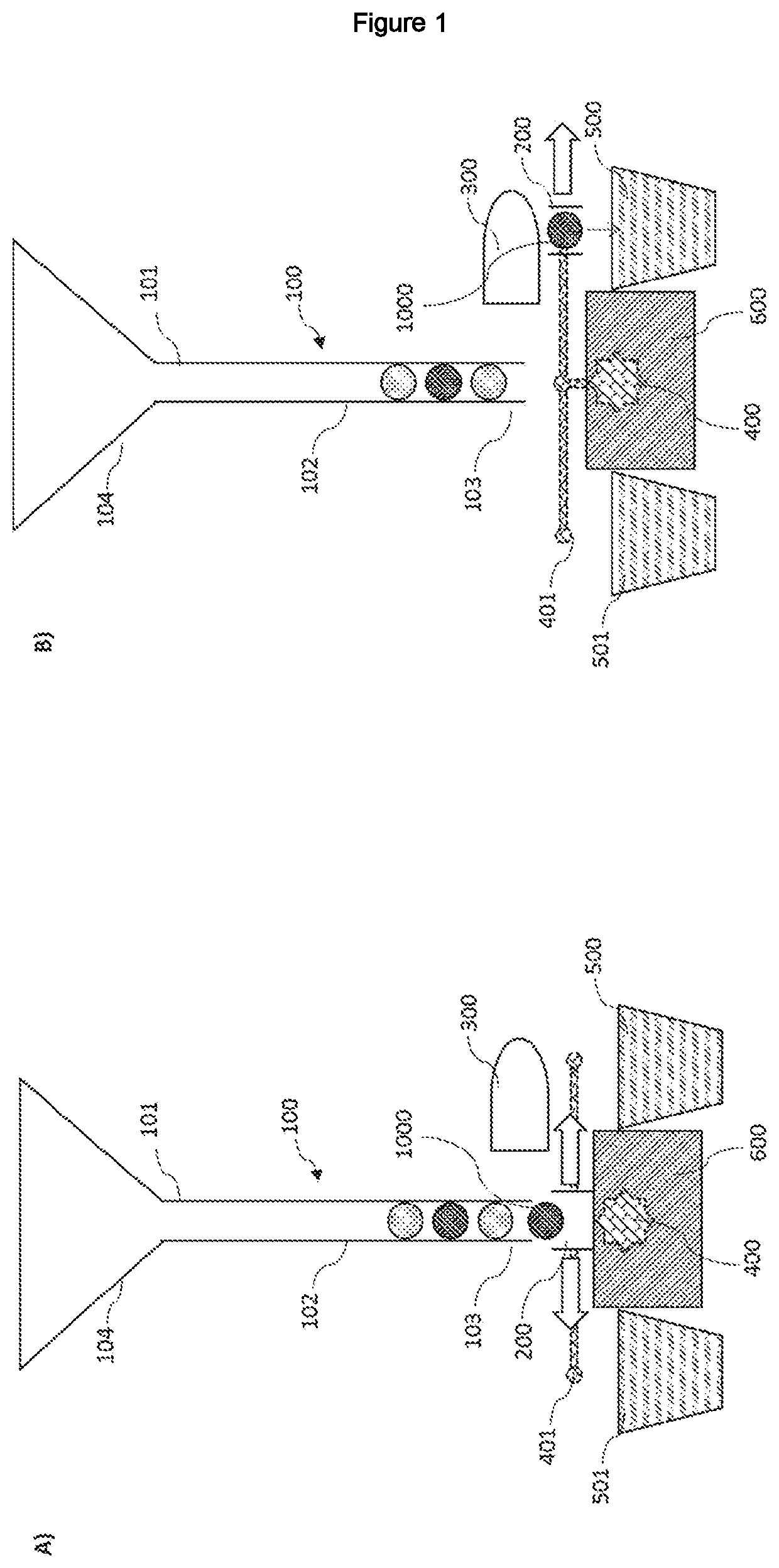
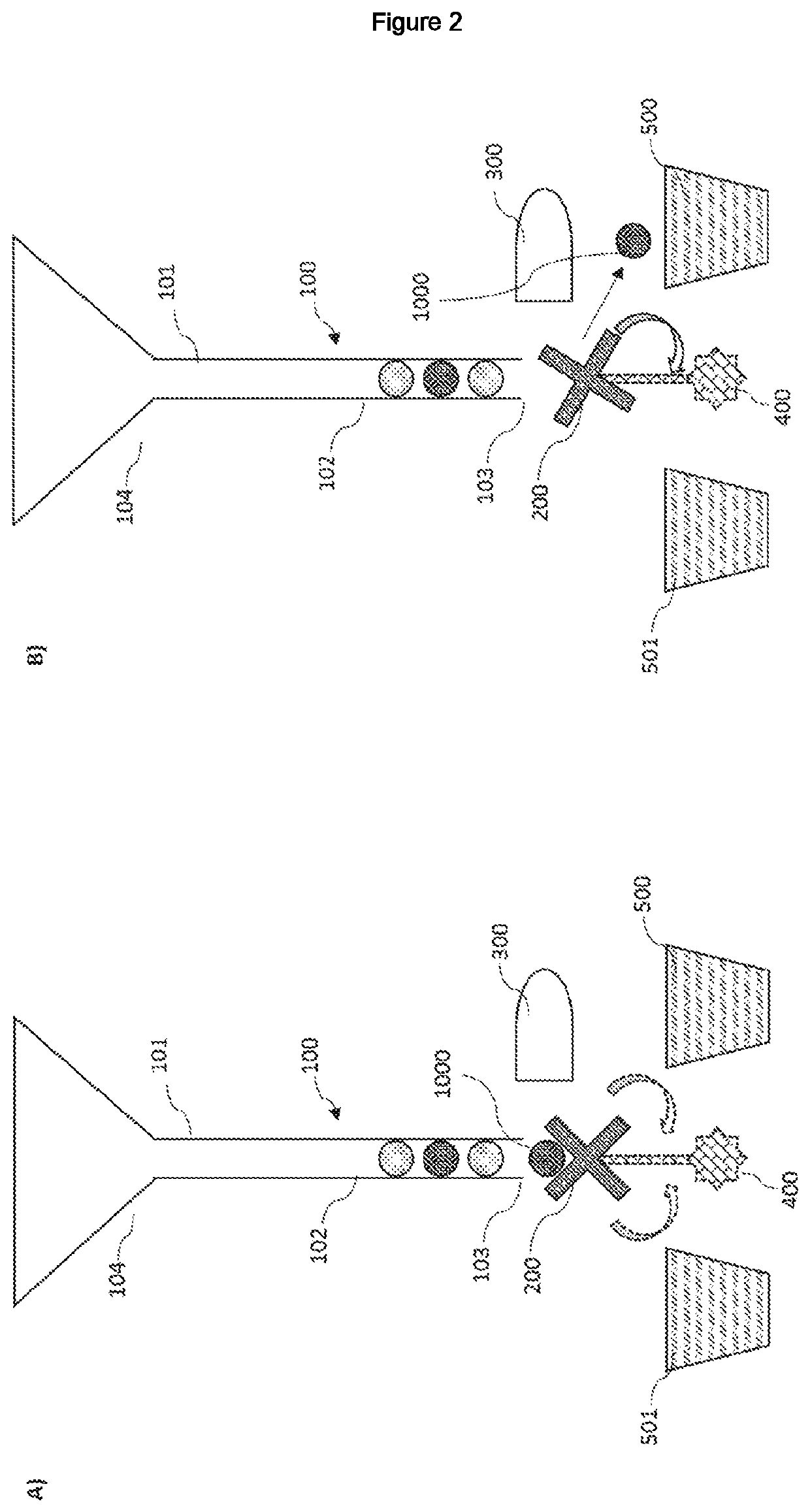
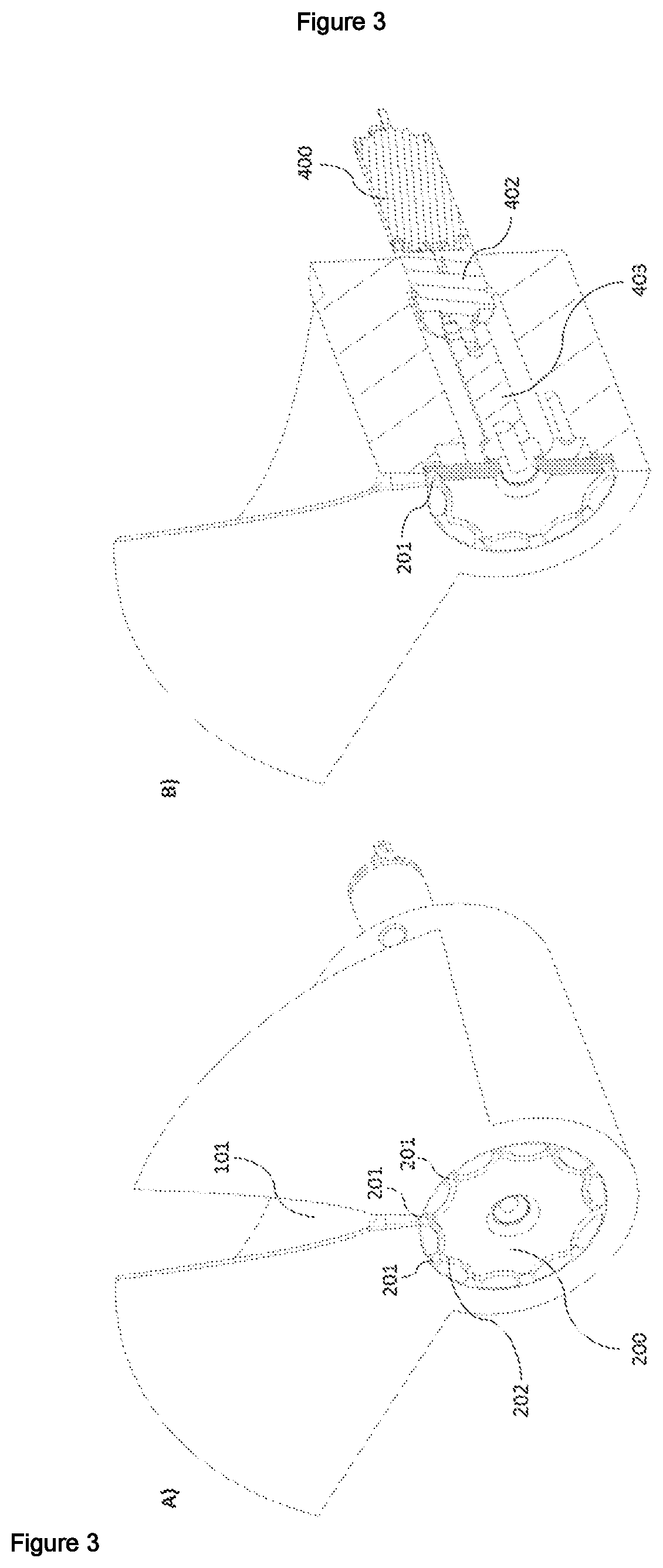
ActiveUS20210072142A1Ease and precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological particle analysisBiotechnologyZoology
A device for sorting biological entities is disclosed. The device comprises a channel to canalize the biological entities and a selector having slots to accommodate said entities. Means for detecting and analysing an optical parameter of the biological entities is coupled with the selector. The selector can switch from a rest position to a sorting position, or at least two sorting positions, based on the detected and analysed optical parameter, so that biological entities can be sorted on the basis of their optical properties. The device is particularly intended for sorting egg cells, zygotes, embryos, or larvae of an insect, an amphibian or a fish such as Xenopus laevis, C. elegans or zebfrafish Danio rerio.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Fast method of testing interfering substance of thyroid gland-tail absorption test of African xenopus leavis
The present invention provides a method for quickly detecting thyroid interferent. It uses the tail of xanopus tadpole of 53-55 stage as test material, and uses thyroid hormone to induce it to be absorbed and shortened, at the same time it makes the testing method undergo the process of exposure treatment, and utilizes the comparison of difference of shortened condition of tail of testing material exposure group and contrast to evaluate the thyroid interference activity.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com