Patents
Literature
230 results about "Glucagon-like peptide-1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
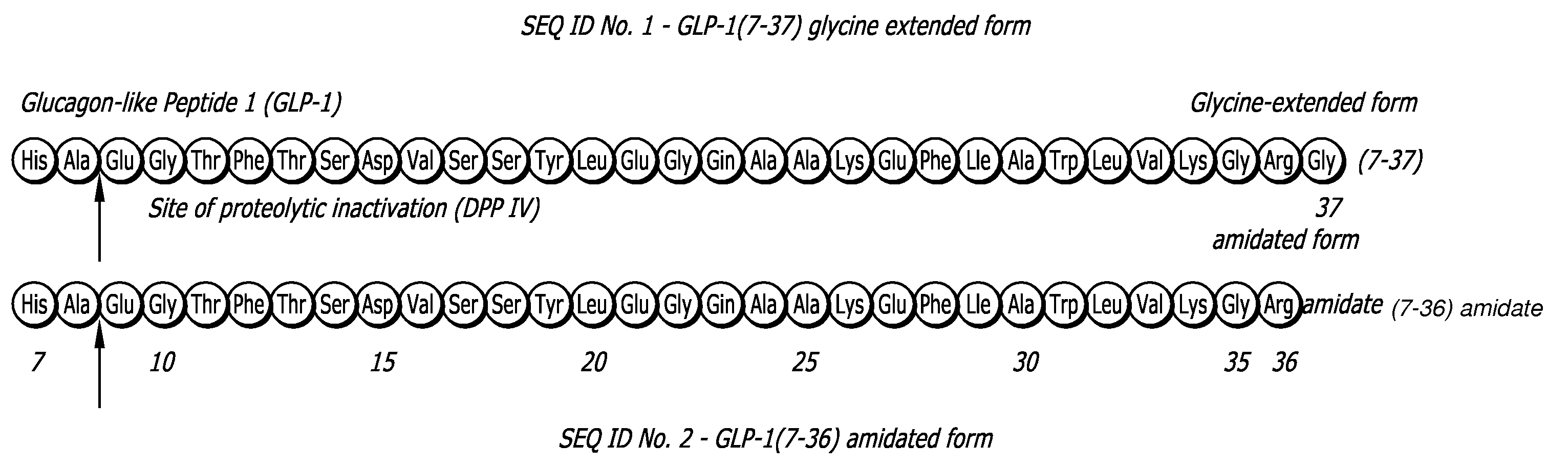
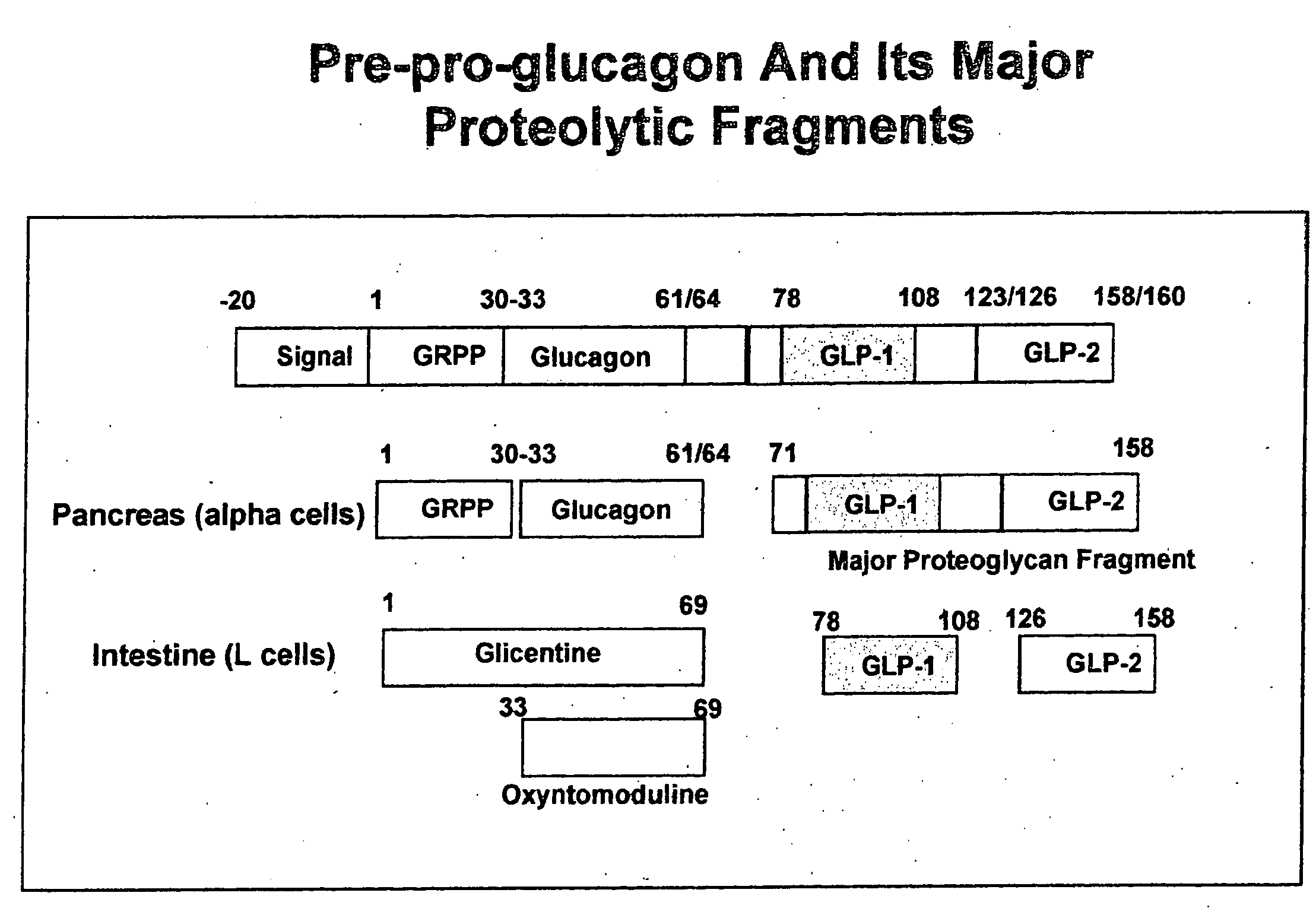
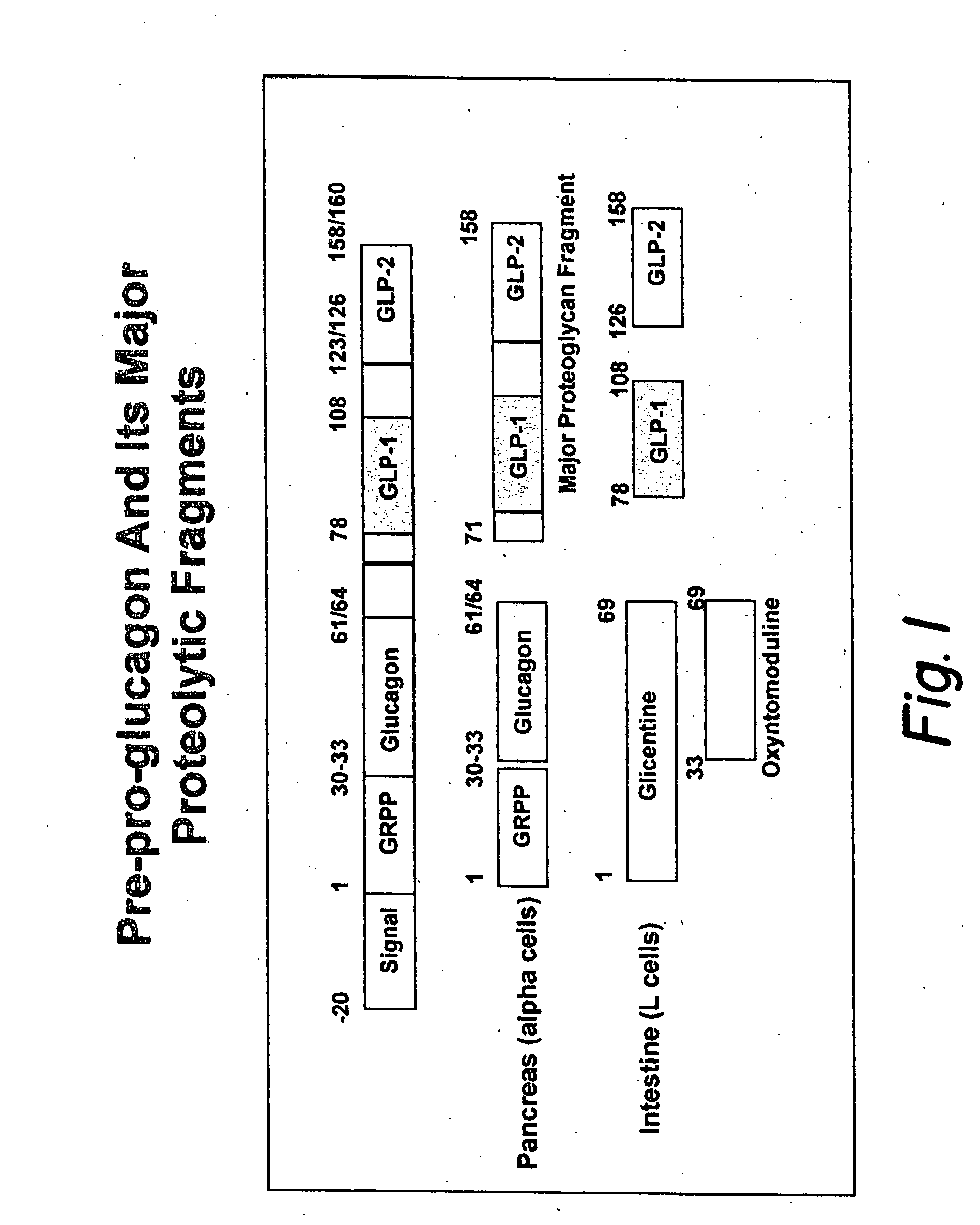
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30 or 31 amino acid long peptide hormone deriving from the tissue-specific posttranslational processing of the proglucagon peptide. It is produced and secreted by intestinal enteroendocrine L-cells and certain neurons within the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem upon food consumption. The initial product GLP-1 (1–37) is susceptible to amidation and proteolytic cleavage which gives rise to the two truncated and equipotent biologically active forms, GLP-1 (7–36) amide and GLP-1 (7–37). Active GLP-1 composes two α-helices from amino acid position 13–20 and 24–35 separated by a linker region.
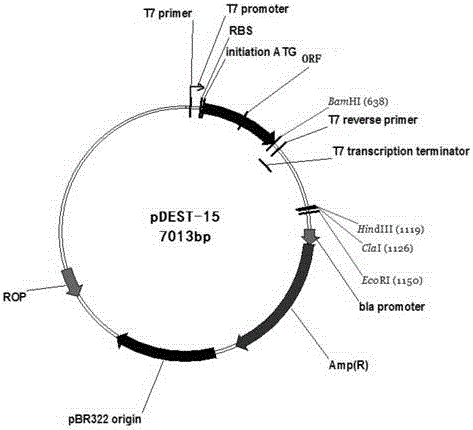
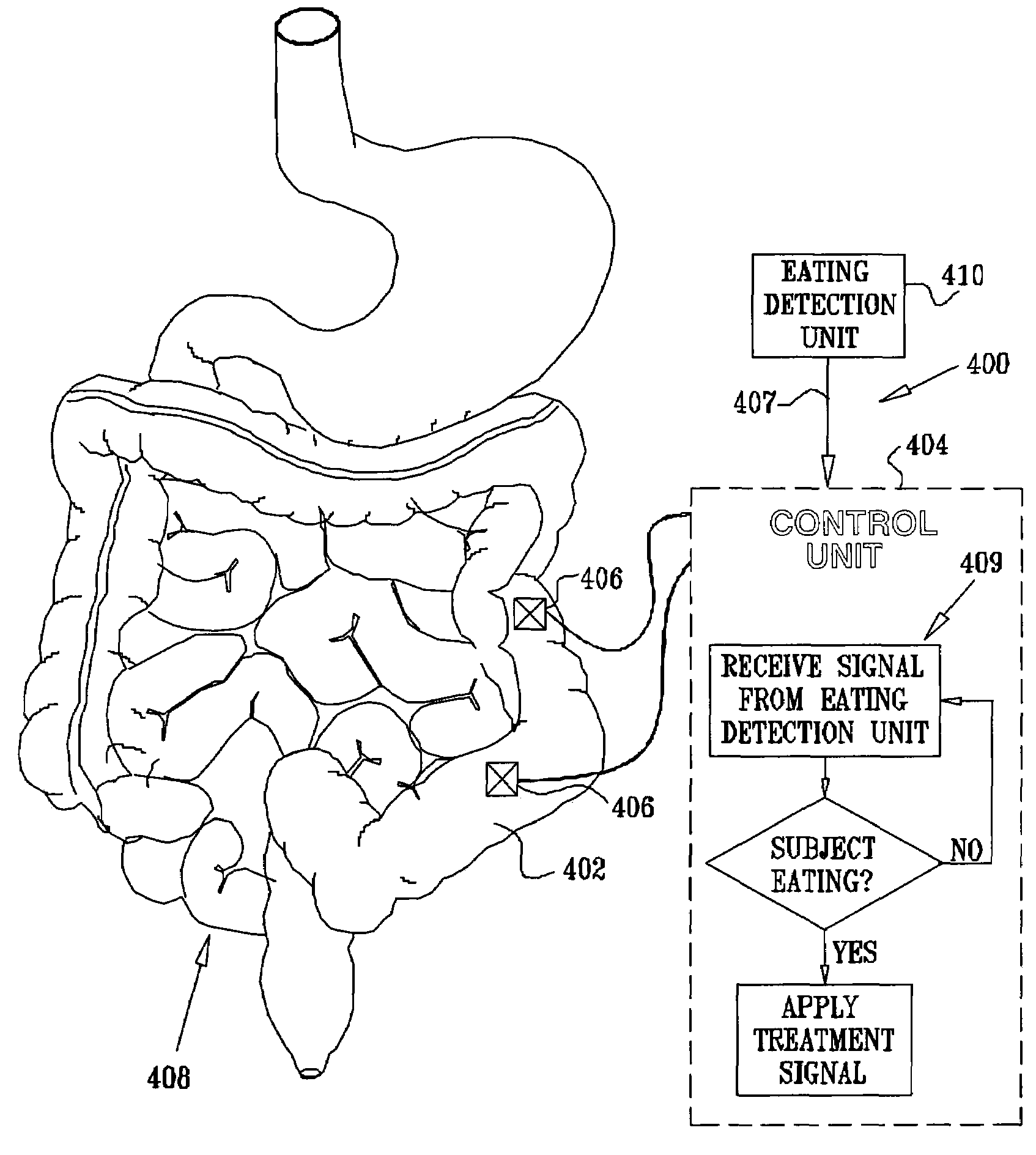
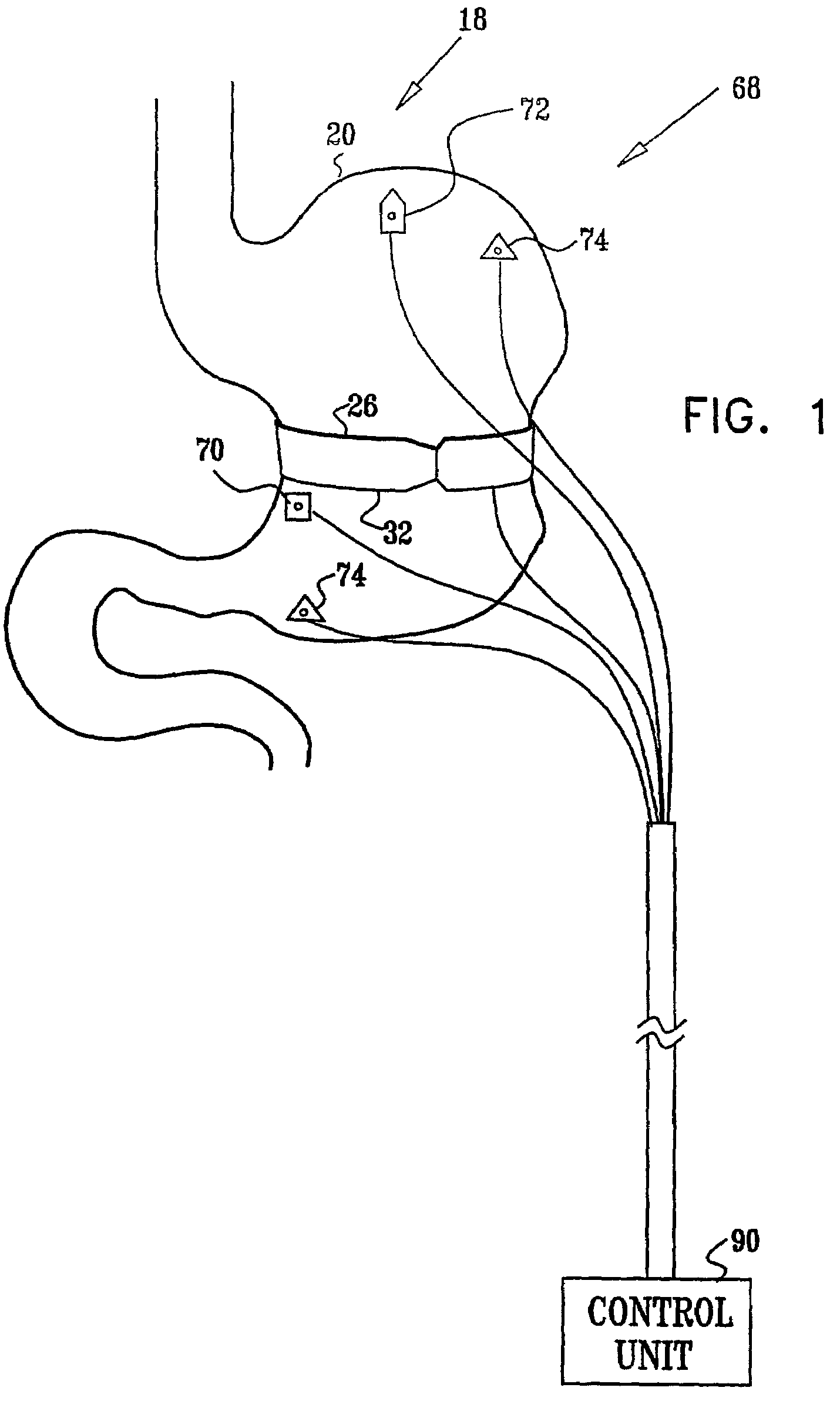
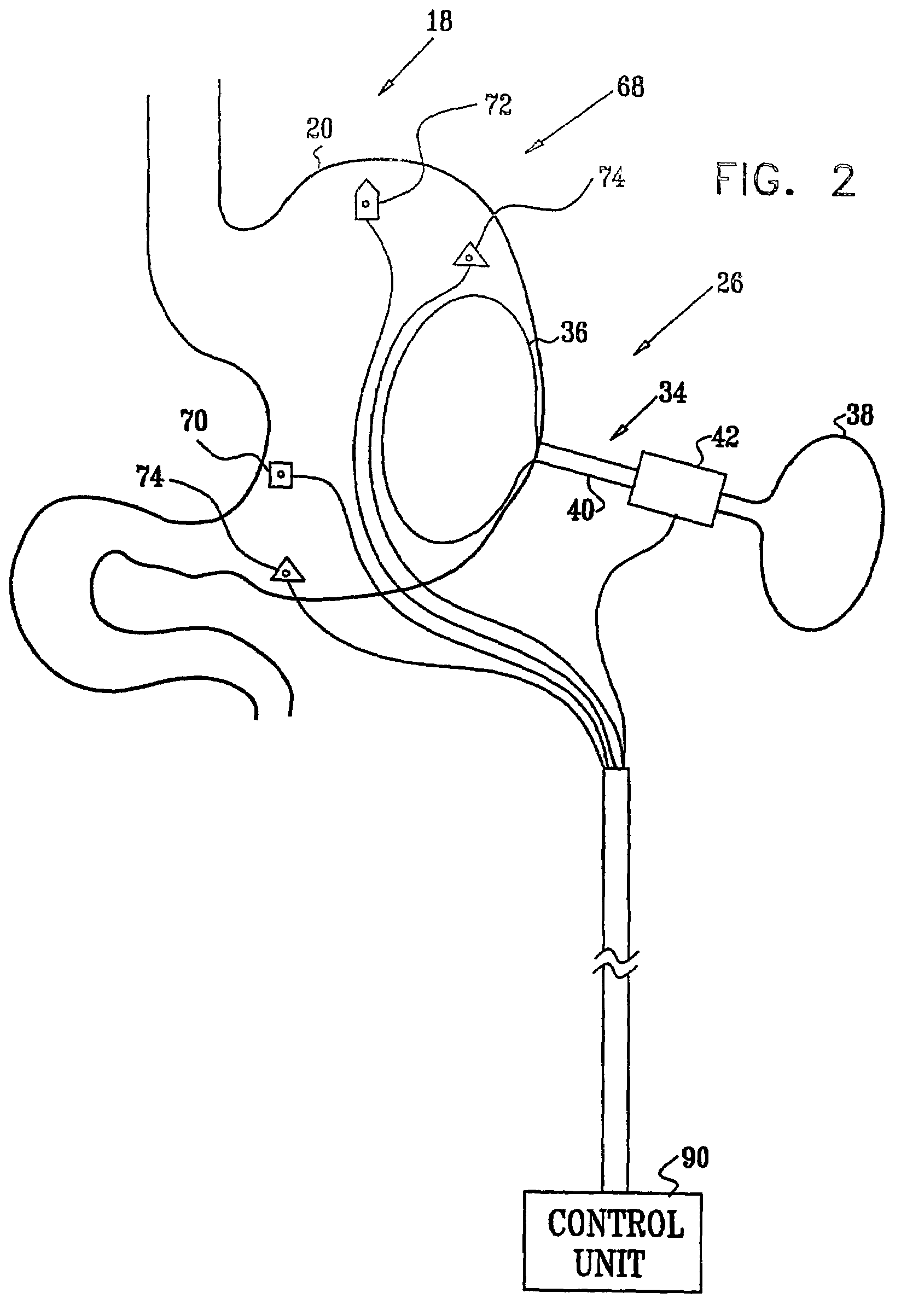
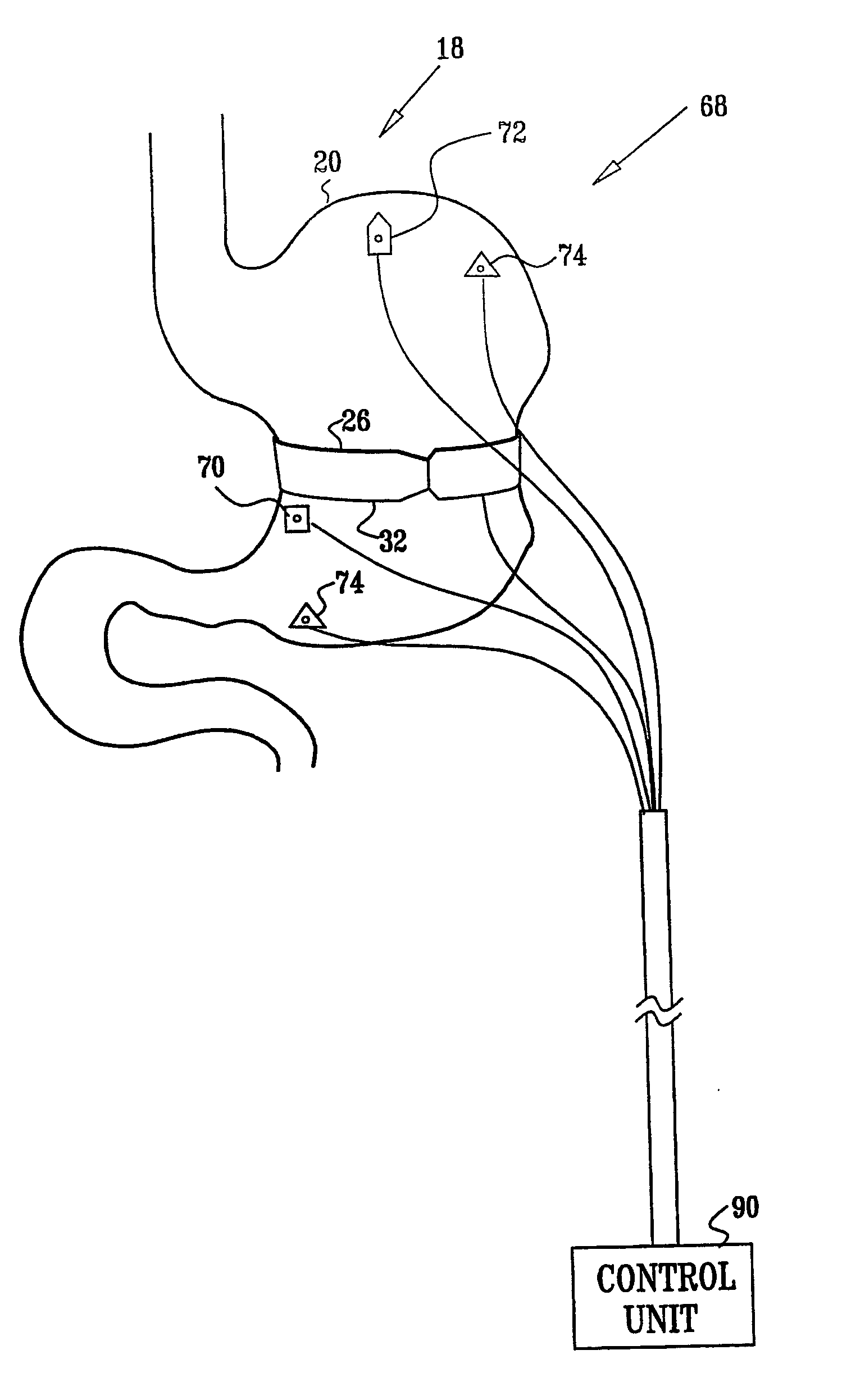
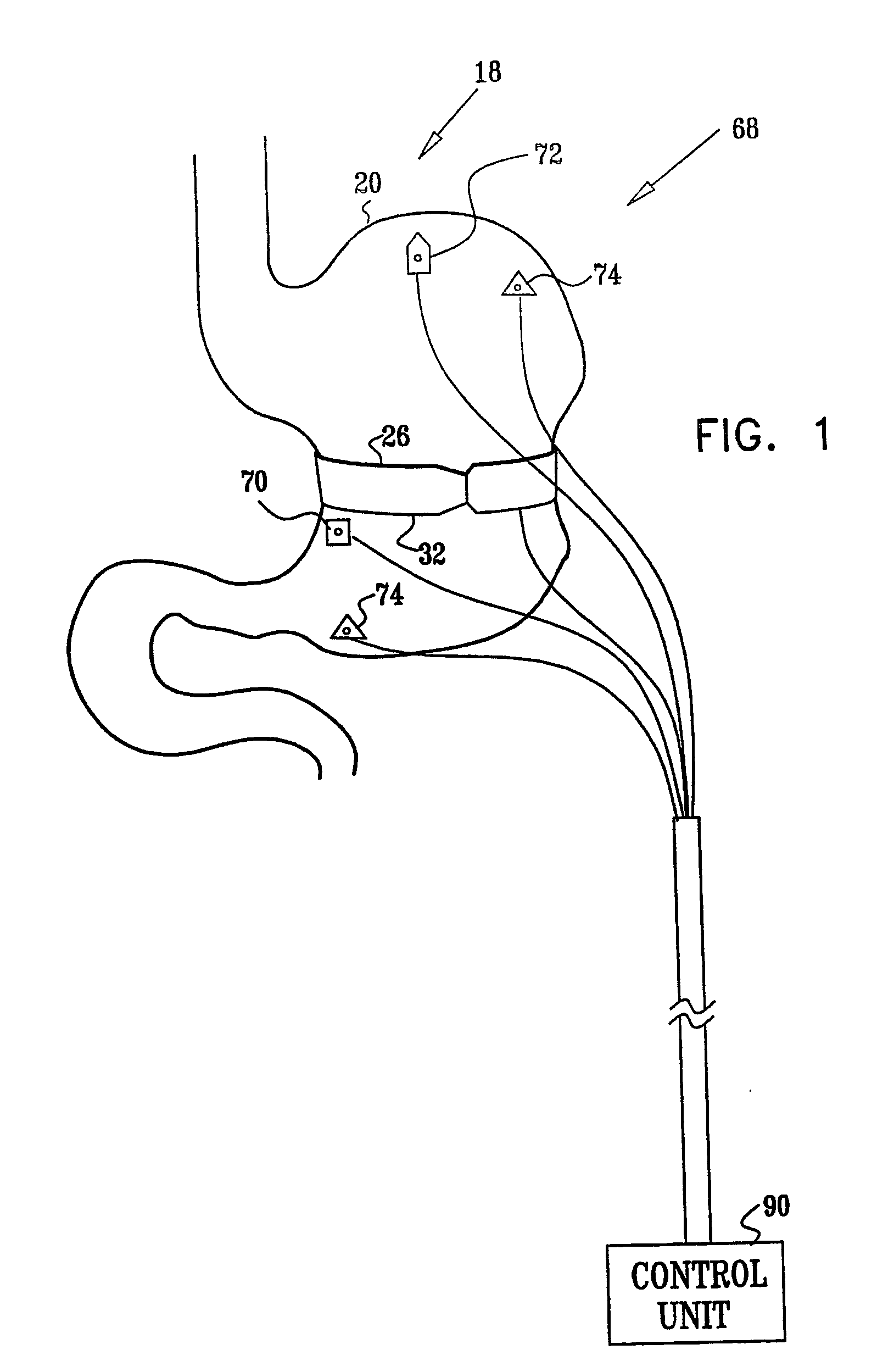
Gastrointestinal methods and apparatus for use in treating disorders
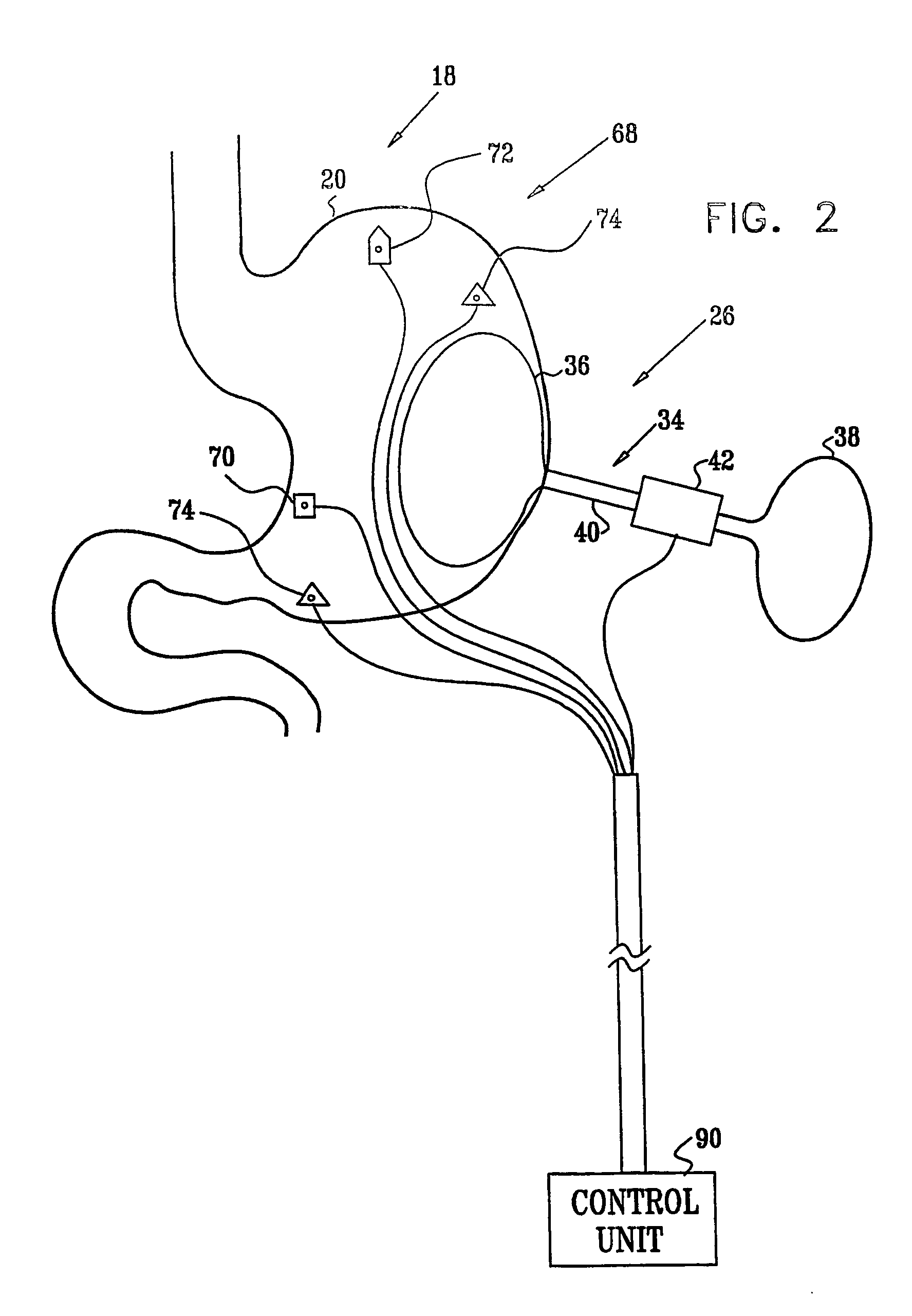
InactiveUS7502649B2Reduce volumeCause a sensation of satiety felt by the patientElectrotherapyMetabolism disorderElectrical resistance and conductanceDisease
A method is provided for detecting a change in posture of a subject. An electrical impedance is measured between two or more sites on a stomach (20) of the subject, and an impedance signal is generated responsive thereto. The change in posture is detected by performing a posture analysis of the impedance signal. A method is also provided for treating a subject. The method includes applying an electrical signal to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a colon (402) of the subject, and a distal small intestine (408) of the subject. The signal is configured to stimulate cells of the subject to increase secretion of glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) or PYY, or to decrease secretion of ghrelin, in order to treat the subject.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (glp-1) pharmaceutical formulations
InactiveUS20080260838A1Improved GLP- pharmacokinetic profileIncreased GLP- half-lifePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseDiabetes mellitus
A composition is disclosed comprising glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) particles in combination with diketopiperazine (DKP) that is stable both in vitro and in vivo. The composition has utility as a pharmaceutical formulation for treating diseases such as diabetes, cancers, and obesity but is not limited to such diseases or conditions. In particularly, the composition has utility as a pharmaceutical formulation for pulmonary delivery.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Modified transferrin fusion proteins
InactiveUS7176278B2Increased serum half-lifeImprove bioavailabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesDiseaseSerum ige
The present invention discloses fusion proteins comprising transferrin, lactoferrin or melanotransferrin fused to glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). In one embodiment of the invention, the fusion protein displays increased serum half-life as compared to a GLP-1 peptide in an unfused state. The invention includes a pharmaceutical composition comprising the GLP-1 fusion protein of the invention and a carrier. The fusion protein of the invention can be administered to a subject for treatment of diseases or conditions treatable by GLP-1, including, but not limited to, diabetes, obesity, congestive heart failure and inflammatory bowel syndrome.
Owner:BIOREXIS TECH INC
Human appetite control by glucagon-like peptide receptor binding compounds
InactiveUS6998387B1Appetite suppressantReducing spontaneous food intakePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCompound aGlucagon-like peptide-1
A composition including a compound which binds to a receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1 and a pharmaceutical carrier. The amount of the compound present is effective to control appetite in a human. Also disclosed is a method for controlling appetite and for reducing food intake in a human by administering to the human a composition comprising a compound which binds to a receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1 and a pharmaceutical carrier.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Gastrointestinal methods and apparatus for use in treating disorders
InactiveUS20070179556A1Increase signal strengthReduce spacingElectrotherapyMetabolism disorderElectrical resistance and conductanceDisease
A method is provided for detecting a change in posture of a subject. An electrical impedance is measured between two or more sites on a stomach (20) of the subject, and an impedance signal is generated responsive thereto. The change in posture is detected by performing a posture analysis of the impedance signal. A method is also provided for treating a subject. The method includes applying an electrical signal to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a colon (402) of the subject, and a distal small intestine (408) of the subject. The signal is configured to stimulate cells of the subject to increase secretion of glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) or PYY, or to decrease secretion of ghrelin, in order to treat the subject.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Human glucagon-like peptide-1 mimics and their use in the treatment of diabetes and related conditions
InactiveUS20070287670A1Improve the level ofSenses disorderNervous disorderGlucagon-like peptide-1Drug biological activity
The present invention provides novel human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) peptide mimics that mimic the biological activity of the native GLP-1 peptide and thus are useful for the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with GLP activity. Further, the present invention provides novel, chemically modified peptides that not only stimulate insulin secretion in type II diabetics, but also produce other beneficial insulinotropic responses. These synthetic peptide GLP-1 mimics exhibit increased stability to proteolytic cleavage making them ideal therapeutic candidates for oral or parenteral administration.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
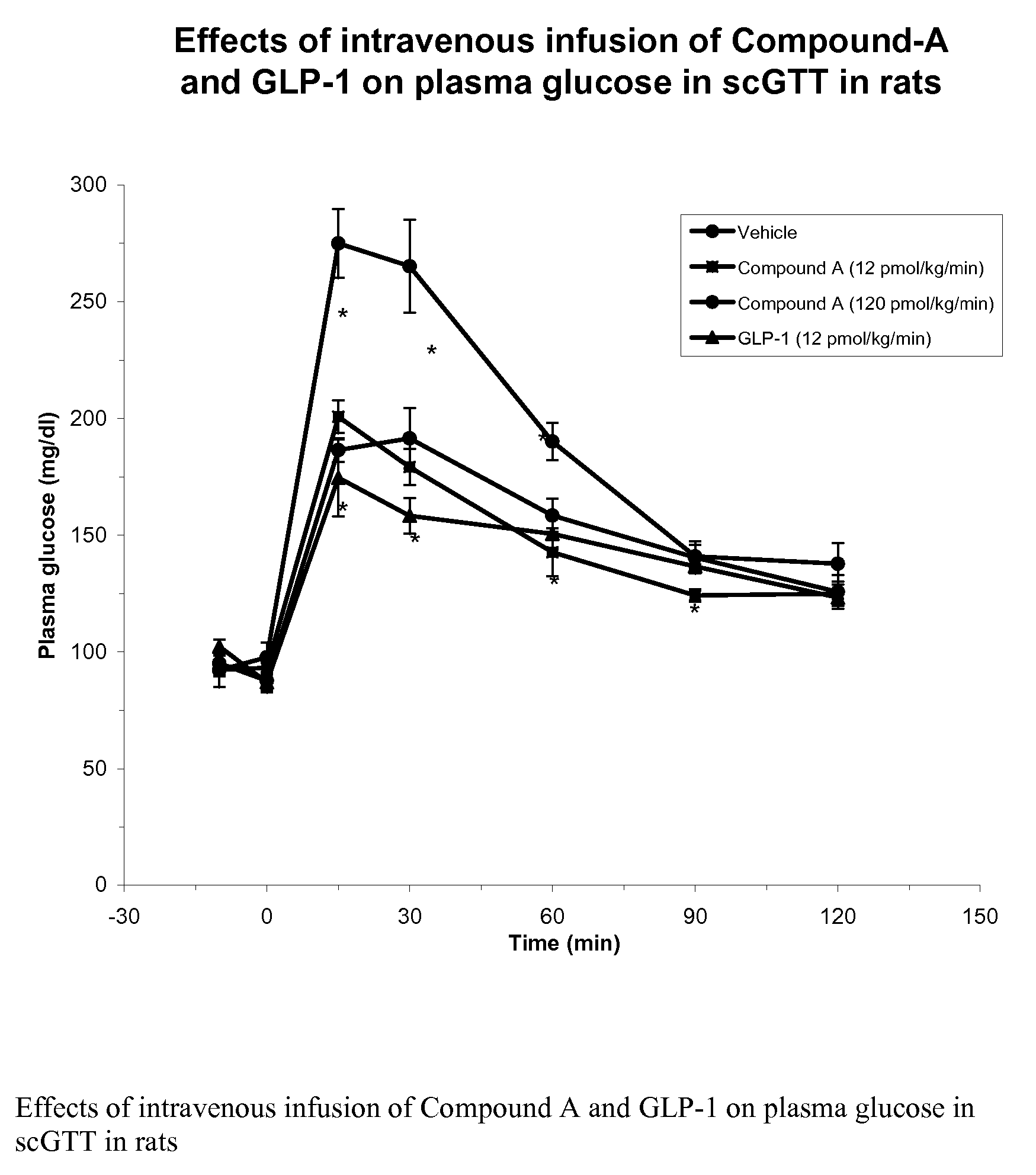
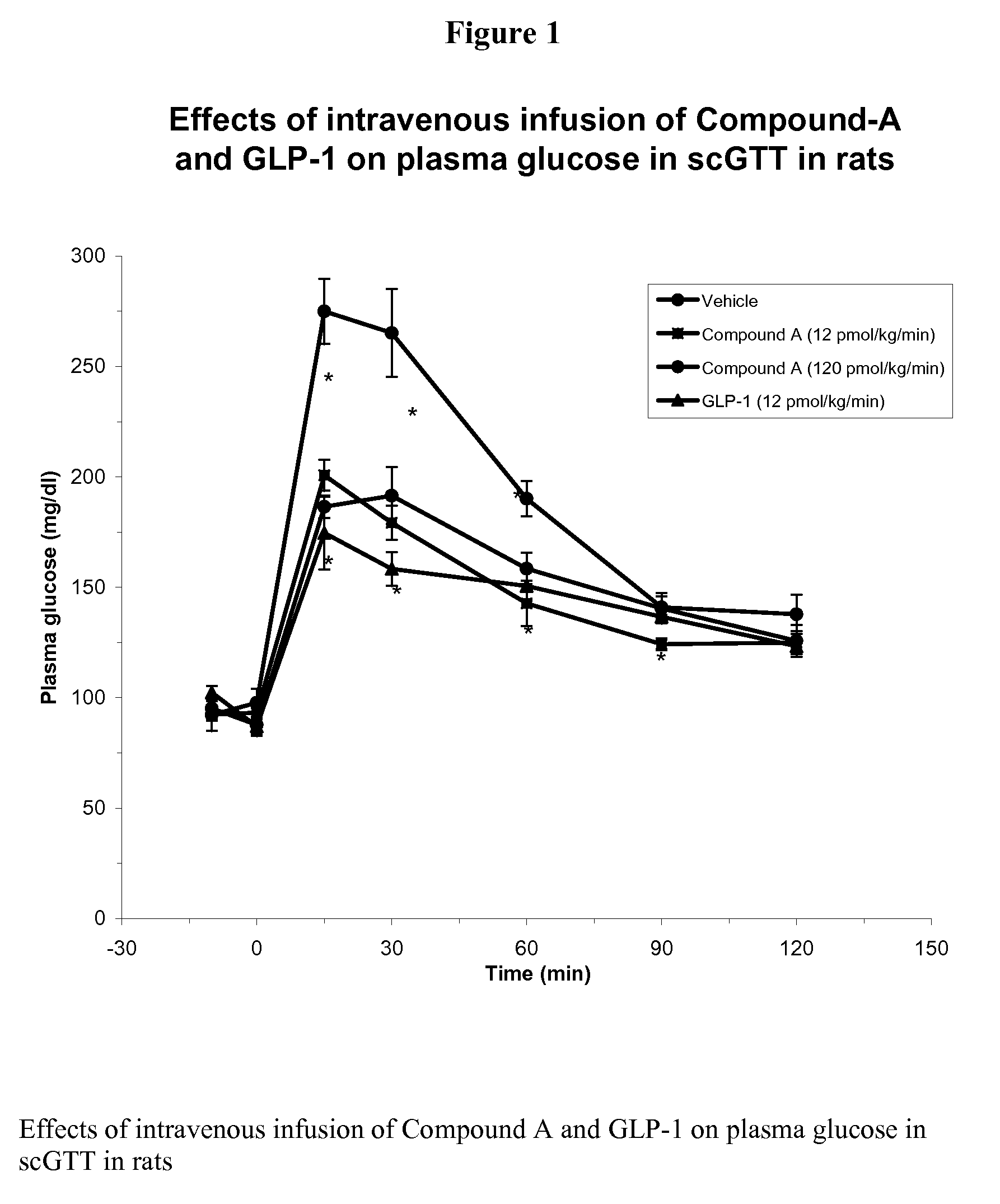
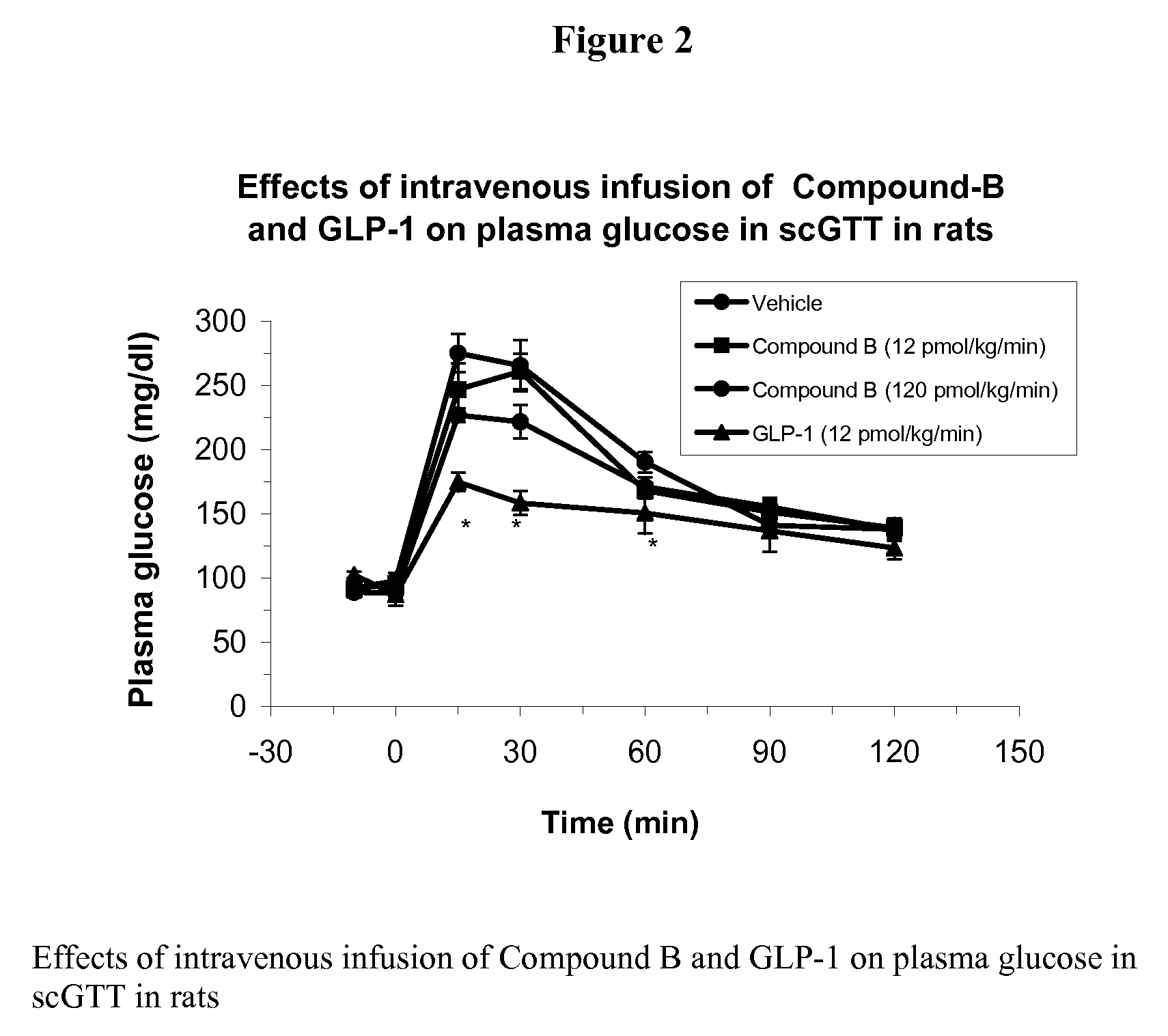
Synergistic use of thiazolidinediones with glucagon-like peptide-1 and agonists thereof to treat metabolic instability associated with non-insulin dependent diabetes
InactiveUS7223728B2Lower blood sugar levelsIncrease secretionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin dependent diabetesSide effect
Thiazolidinedione (TZD) and its pharmacologically active derivatives can be used, in combination with agonists of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), to treat non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, optionally with other therapies, by improving glycemic control while minimizing side effects, such as heart hypertrophy and elevated fed-state plasma glucose, which are associate with both TZD and GLP-1 monotherapies. Thus, the co-administration of TZD and GLP-1 helps regulate glucose homeostasis in Type II diabetic patients.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Methods and compositions for treating polycystic ovary syndrome
InactiveUS7105489B2Reduce insulin resistanceIncrease insulin sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsPhysiologyGlucagon-like peptide-1
The present invention relates to methods of treating polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) comprising administering glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) to subjects suffering therefrom.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Treatment of diabetes
InactiveUS6899883B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusGlucagon-like peptide-1
Owner:LONDON HEALTH SCI CENT RES
Treating diabetes with glucagon-like peptide-1 secretagogues
InactiveUS20070032420A1Increase basal GLP- levelDecrease DPP-IV activityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaDipeptidyl peptidase
In general this invention can be viewed as encompassing novel methods of treating diabetes and insulin resistance. The inventors have made the discovery that increasing secretion of endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in combination with inhibiting the activity of dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPP-IV) can have a significant impact on hyperglycemia and insulin secretion in subjects suffering from diabetes and / or insulin resistance. Further the invention encompasses methods of identifying subjects having elevated secretion of GLP-1, methods of assessing sensitivity to a GLP-1 secretagogue, and methods of treating diabetes in these subjects by administering a GLP-1 secretagogue to alleviate at least one symptom of diabetes.
Owner:ENTELOS INC
Compositions and methods for treating peripheral vascular disease
The present invention relates to methods of treating intermittent claudication comprising administering glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) molecules to subjects suffering therefrom.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Compositions and methods for treating peripheral vascular disease
InactiveUS20060030528A1Improve skeletal muscle performancePromote oxidationBiocideDipeptide ingredientsVascular diseaseGlucagon-like peptide-1
The present invention relates to methods of treating intermittent claudication comprising administering glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) molecules to subjects suffering therefrom.
Owner:AMYLIN PHARMA INC
Exendin improves β-cell response in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance
InactiveUS7265087B1Restore responseLowering plasma insulin levelPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCell sensitivityGlucagon-like peptide-1
A composition for the treatment of impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) including a compound which binds to a receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1, and a pharmaceutical carrier. The amount of the compound present is an effective amount to improve pancreatic β-cell sensitivity to blood glucose levels in a human with IGT. Also, a method for improving the pattern of insulin secretory responses in a human with IGT by administering to the human a composition comprising a compound which binds to a receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1 and a pharmaceutical carrier.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Human glucagon-like-peptide-1 modulators and their use in the treatment of diabetes related conditions
InactiveUS20070238669A1Improve the level ofNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsGlucagon-like peptide-1Drug biological activity
The present invention provides novel human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)-receptor modulators that have biological activity similar or superior to native GLP-1 peptide and thus are useful for the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with GLP activity. Further, the present invention provides novel, chemically modified compounds that not only stimulate insulin secretion in type II diabetics, but also produce other beneficial insulinotropic responses. These synthetic peptide GLP-1 receptor modulators exhibit increased stability to proteolytic cleavage making them ideal therapeutic candidates for oral or parenteral administration. The compounds of this invention show desirable pharmacokinetic properties and desirable potency in efficacy models of diabetes.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
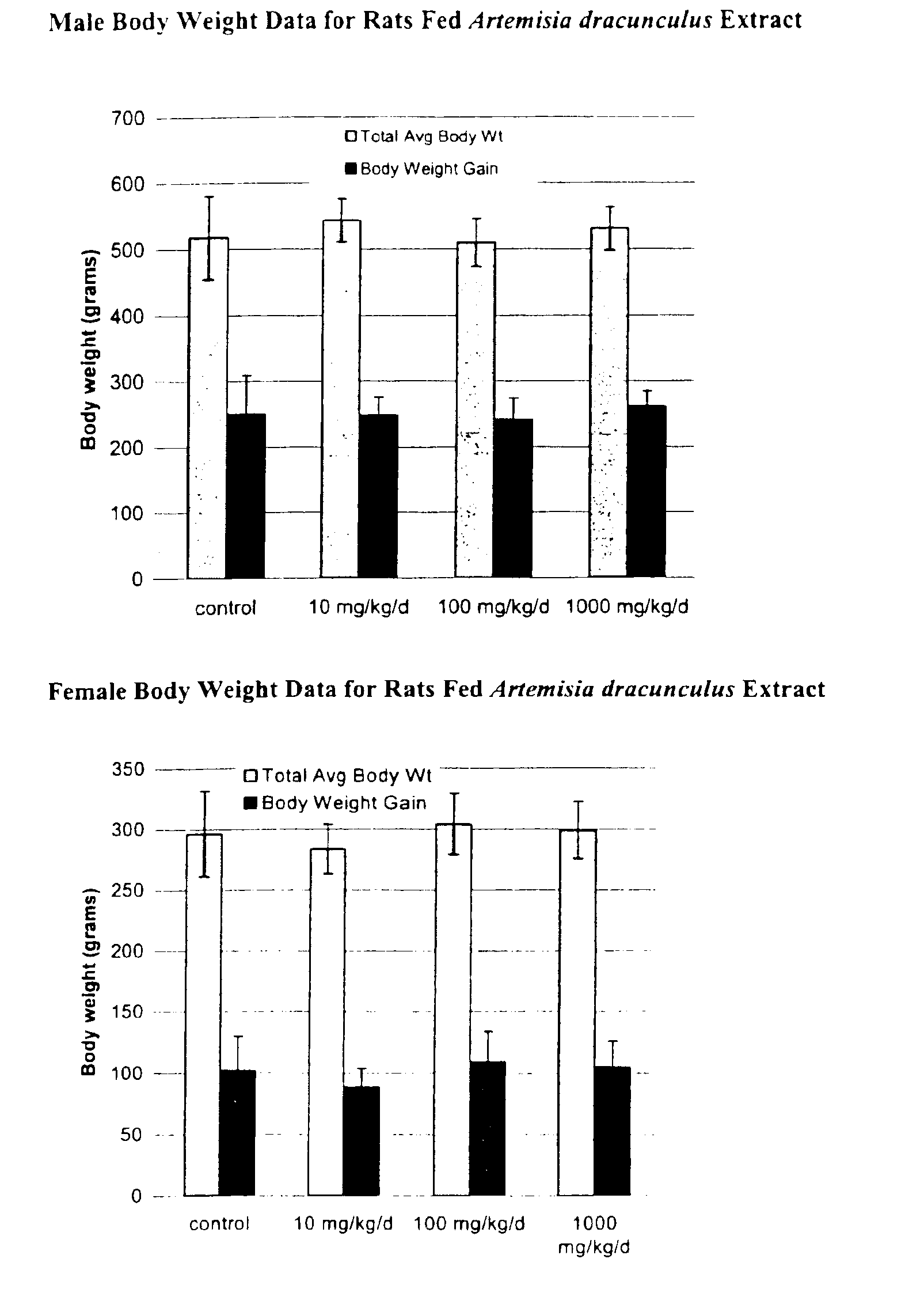
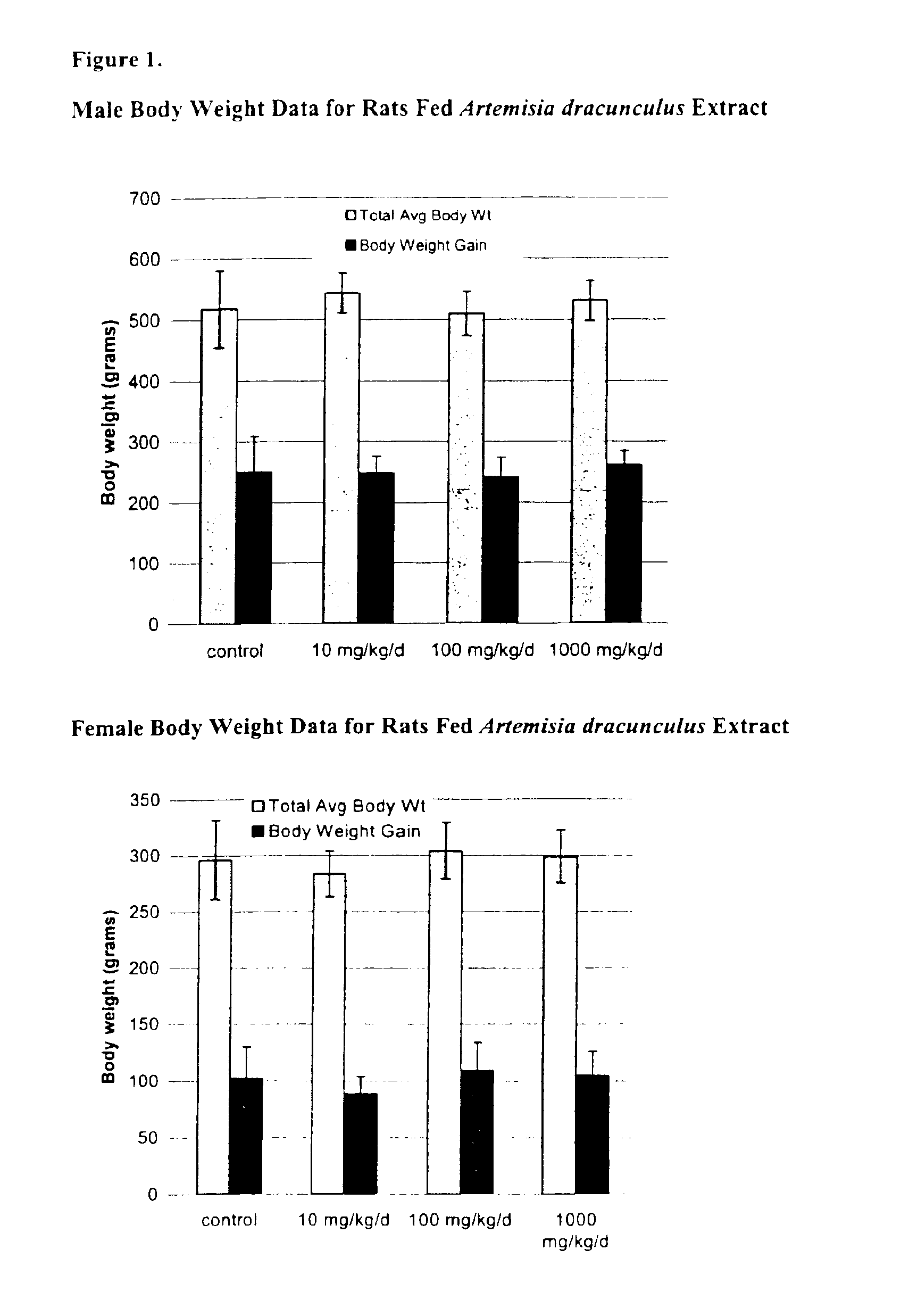
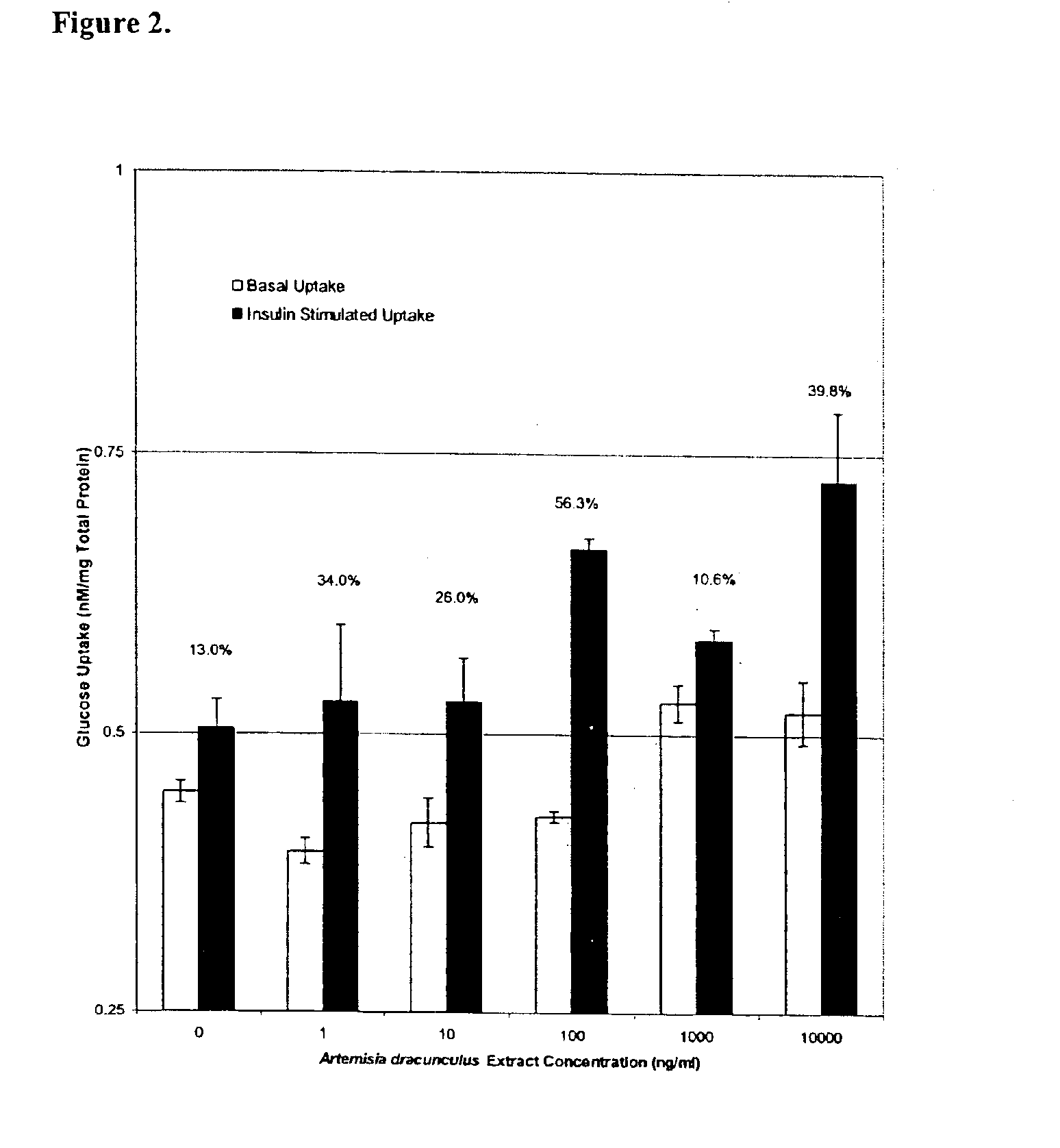
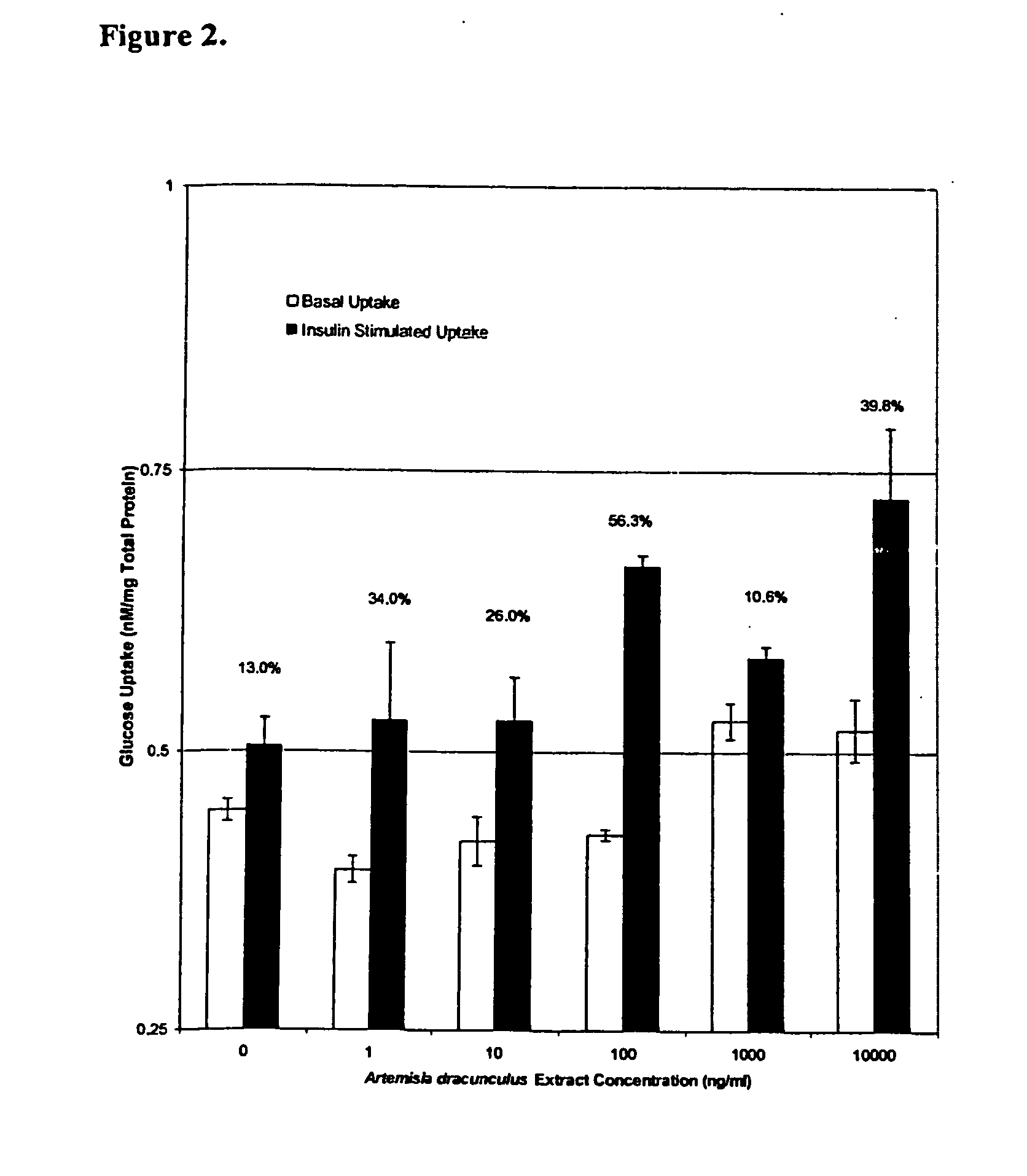
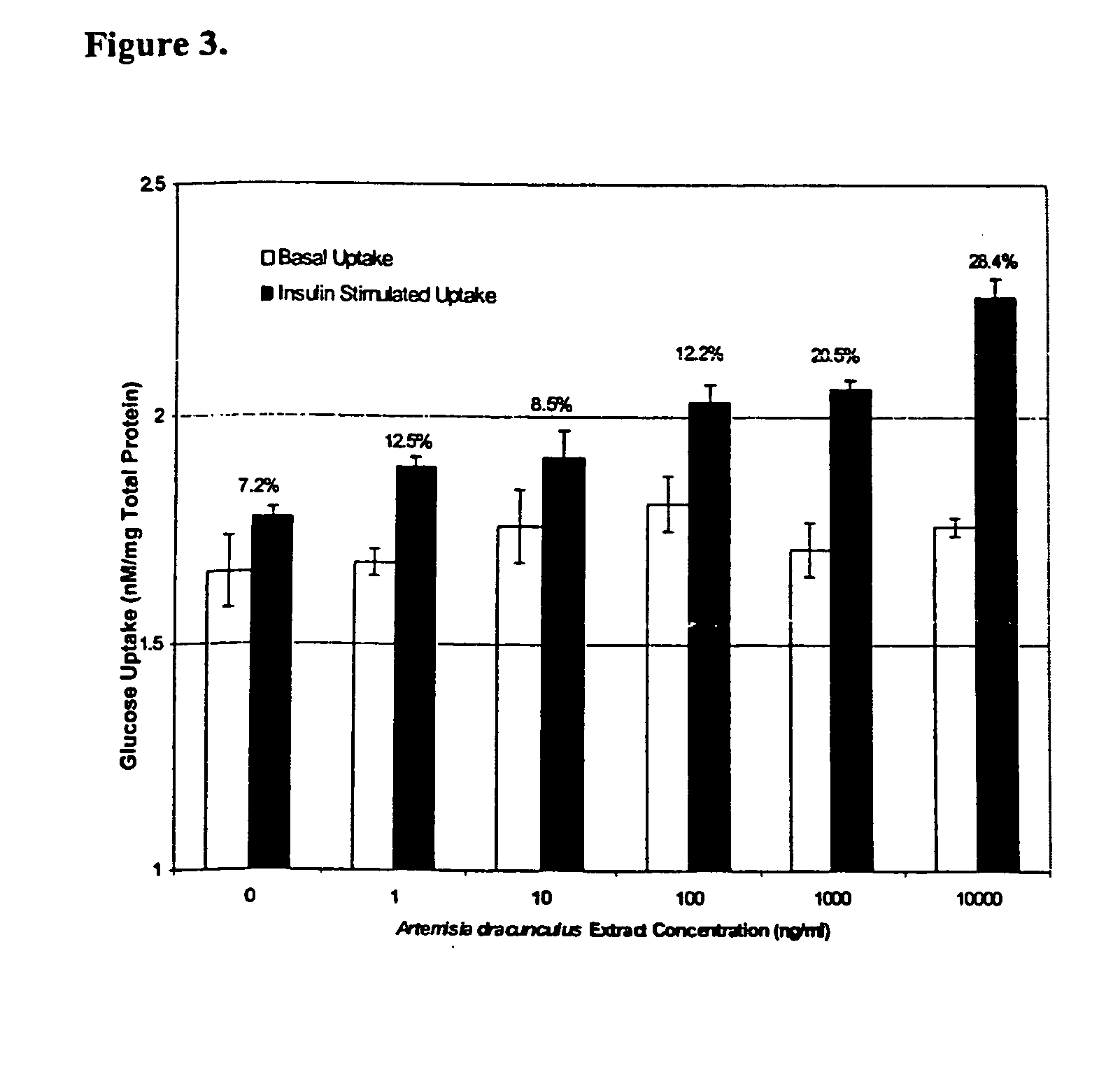
Methods for treating disorders using plant extracts
InactiveUS20050069598A1High affinityInhibit gastric emptyingAntibacterial agentsBiocideMammalFractionation
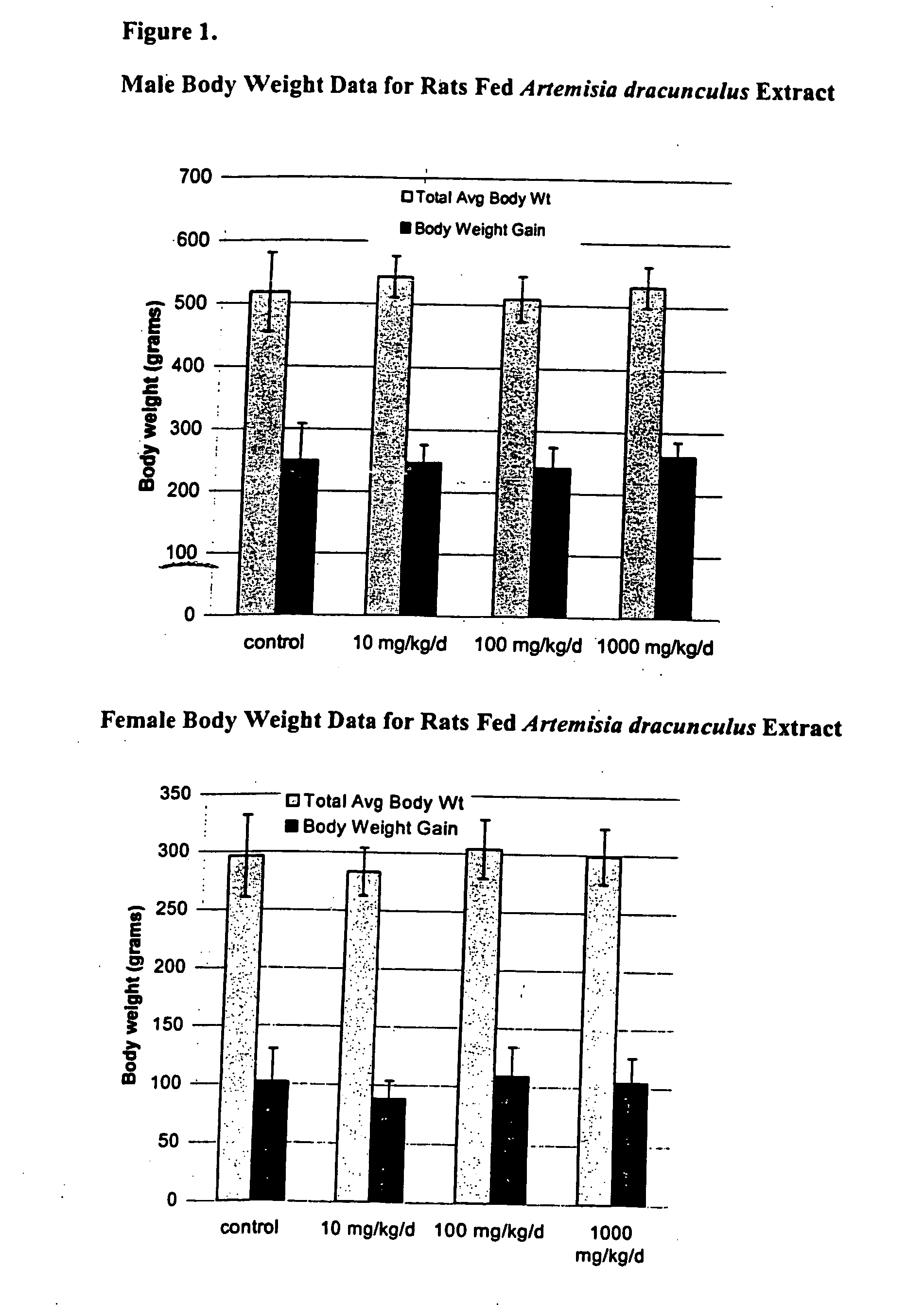
The present invention provides materials and methods relating to mildly polar fluid extracts of plant materials, such as Artemisia plant species, useful in methods for treating diabetes and methods for modulating the activity of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and in methods for modulating phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) activity in a diabetes-specific manner. The extracts are generally non-toxic and non-mutagenic and may be administered to diabetics with beneficial effect on blood glucose levels. The extracts may also be administered to non-diabetics without deleterious effect. The plants are easily grown with a minimum of time, labor, and cost. Extracts are inexpensively and quickly prepared without the need for fractionation to remove potentially deleterious compounds, and the extracts may be administered to mammals such as humans through various routes, in a variety of forms, and at convenient concentrations.
Owner:RIBNICKY DAVID M +1
Modified nucleotide sequence encoding glucagon-like peptide-1 (glp-1), nucleic acid construct comprising same for production of glucagon-like peptide-1 (glp-1), human cells comprising said construct and insulin-producing constructs, and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20080299096A1Reduce weightPromote productionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaNucleotide
An isolated chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequence encoding a human pro-insulin leader, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and a furin cleavable site between the human pro-insulin leader sequence and the GLP-1 is provided. Also provided is an isolated modified chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequence encoding a human pro-insulin leader, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and a furin cleavable site between the human pro-insulin leader sequence and the GLP-1. Recombinant expression vectors comprising the chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequences, which produce GLP-1 constitutively are provided, as are human cells transfected with such an expression vector in combination with an expression vector comprising a proinsulin nucleic acid sequence and an expression vector comprising a furin and a glucose-regulatable TGF-alpha promoter. Methods of producing human GLP-1 constitutively are provided as are method of producing GLP-1 and insulin or in a glucose-dependent manner using such transfected cells. Methods of treating a subject having Type II diabetes and methods of treating a subject prone to hyperglycemia or suffering from hyperglycemia are provided in which transfected cells produce human GLP-1 and insulin in a glucose-dependent manner. Also provided are methods of reducing weight in a subject by implanting into the subject transfected cells which produce human GLP-1 and insulin in a glucose-dependent manner.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
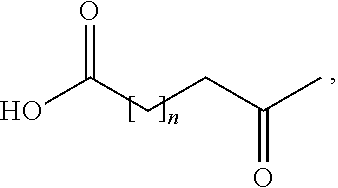
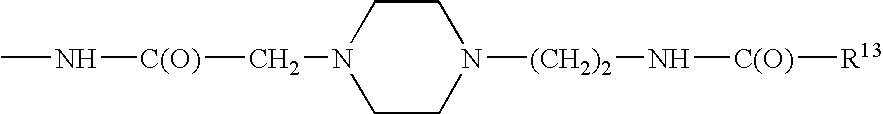
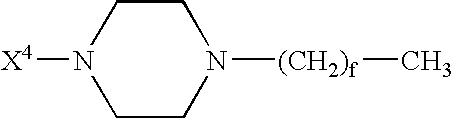
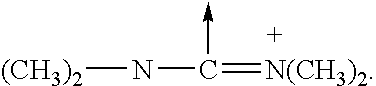
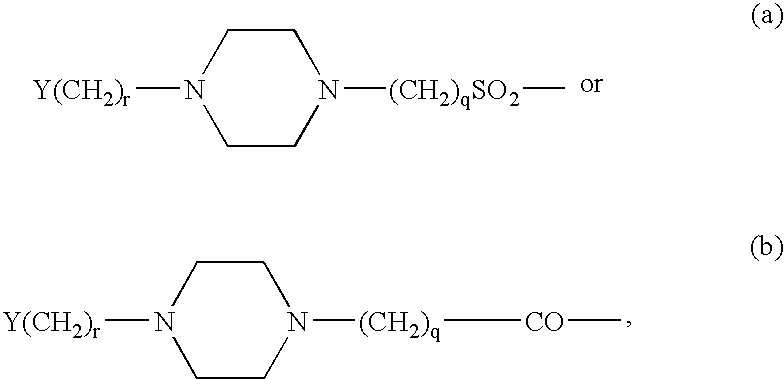
Branched peg remodeling and glycosylation of glucagon-like peptide-1 [glp-1]
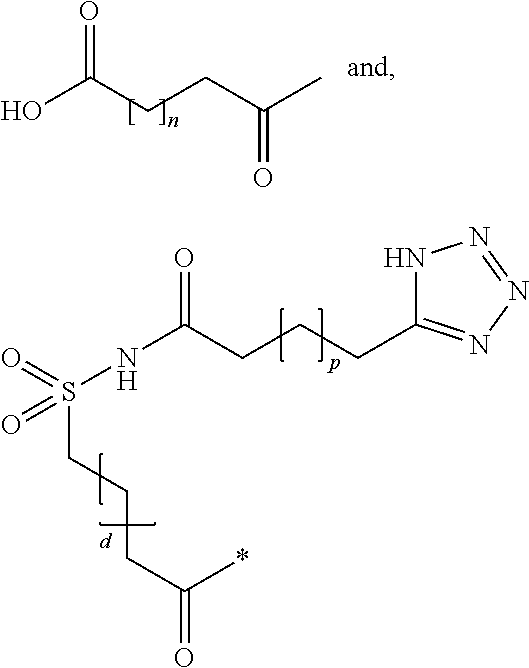
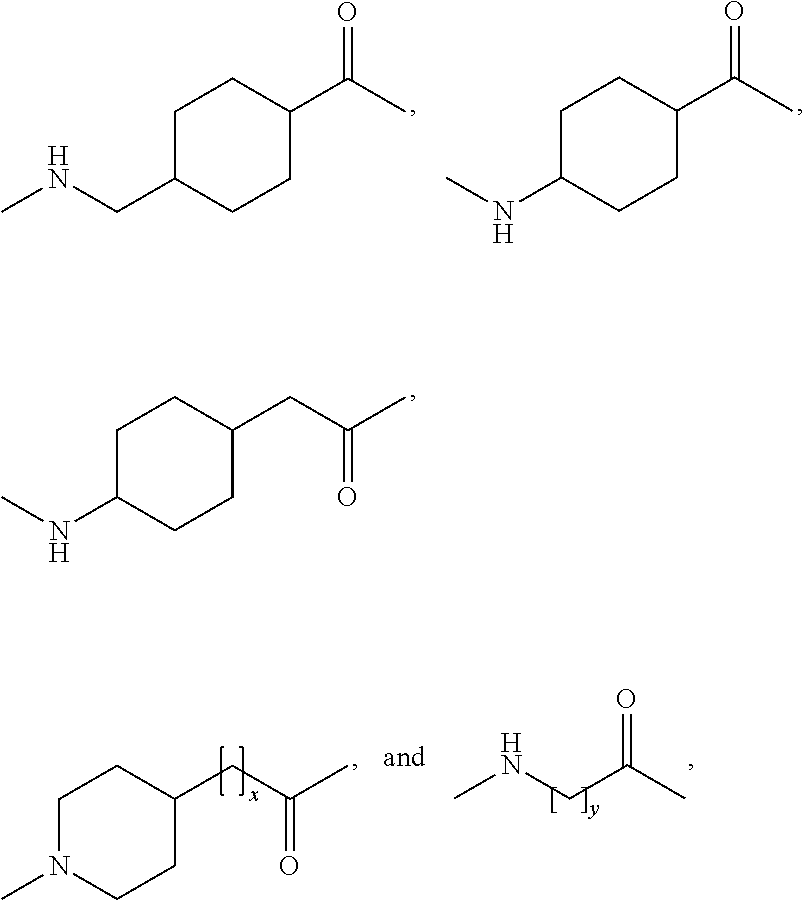
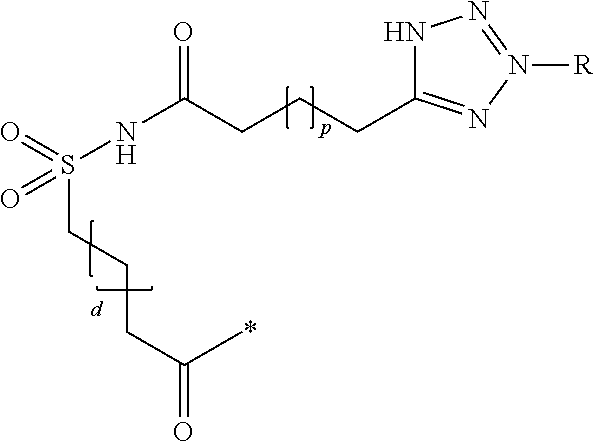
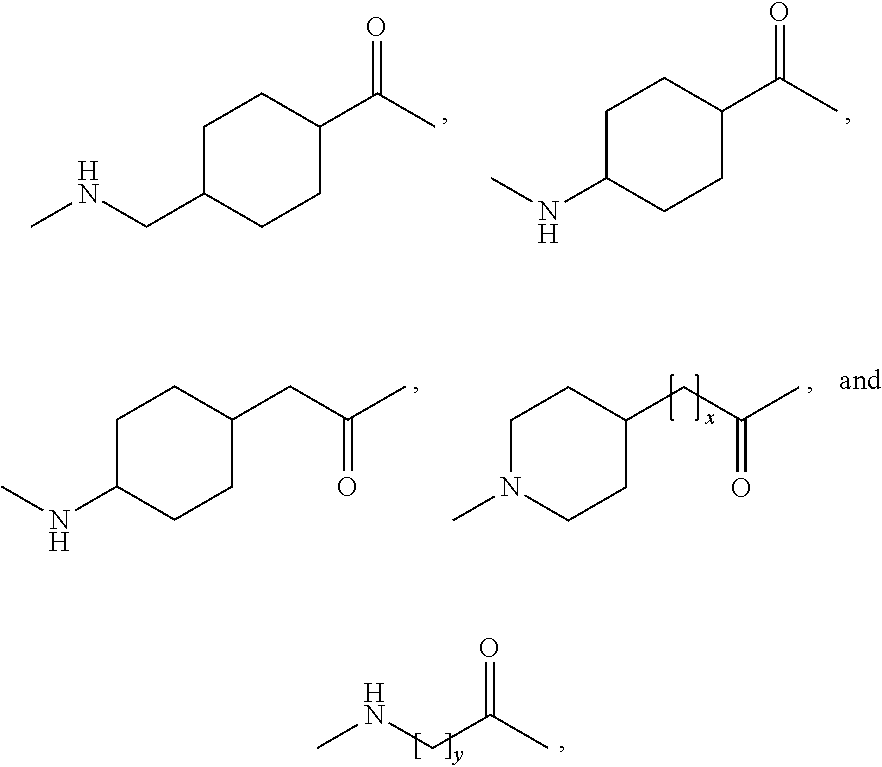
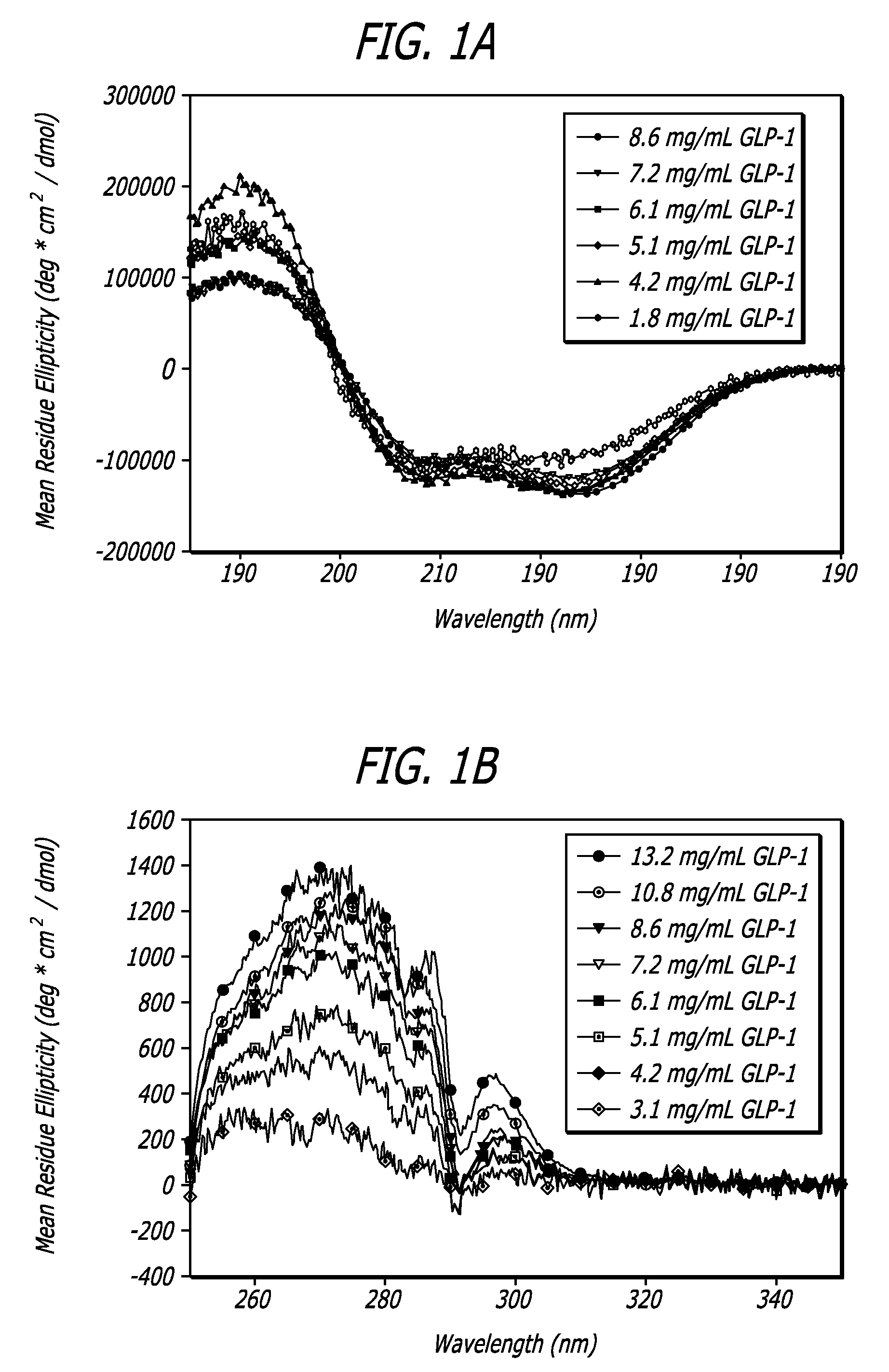
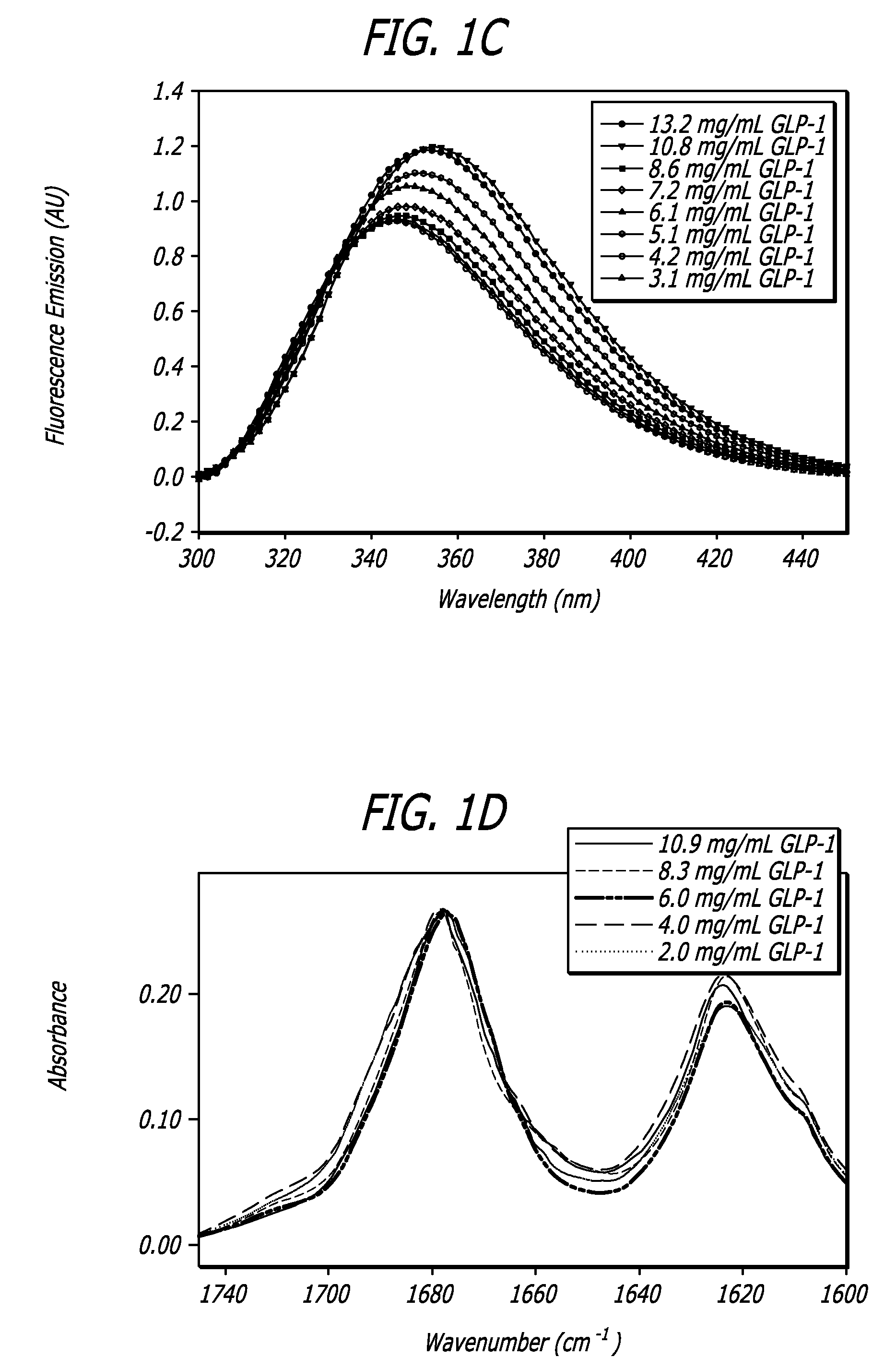
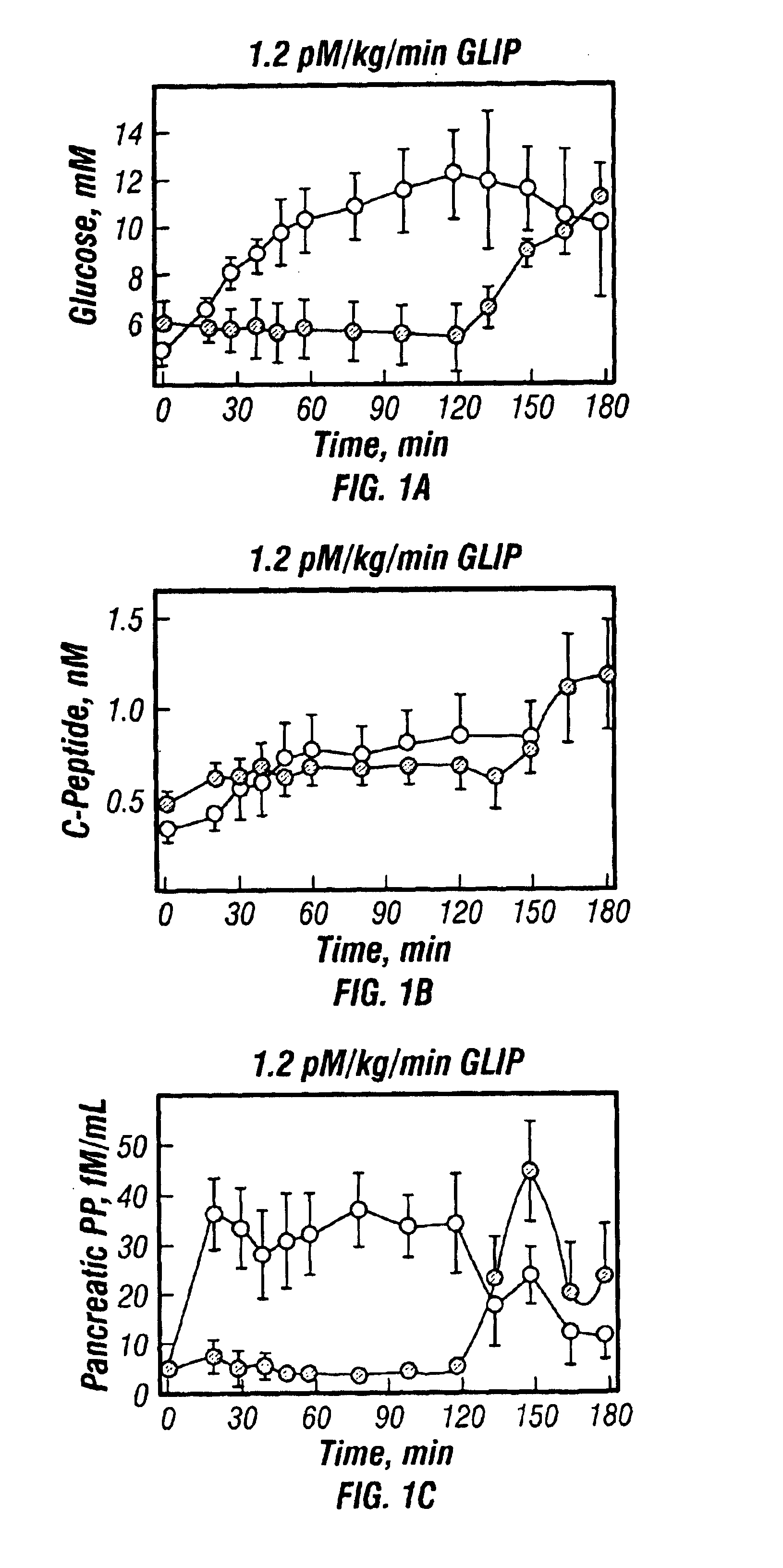
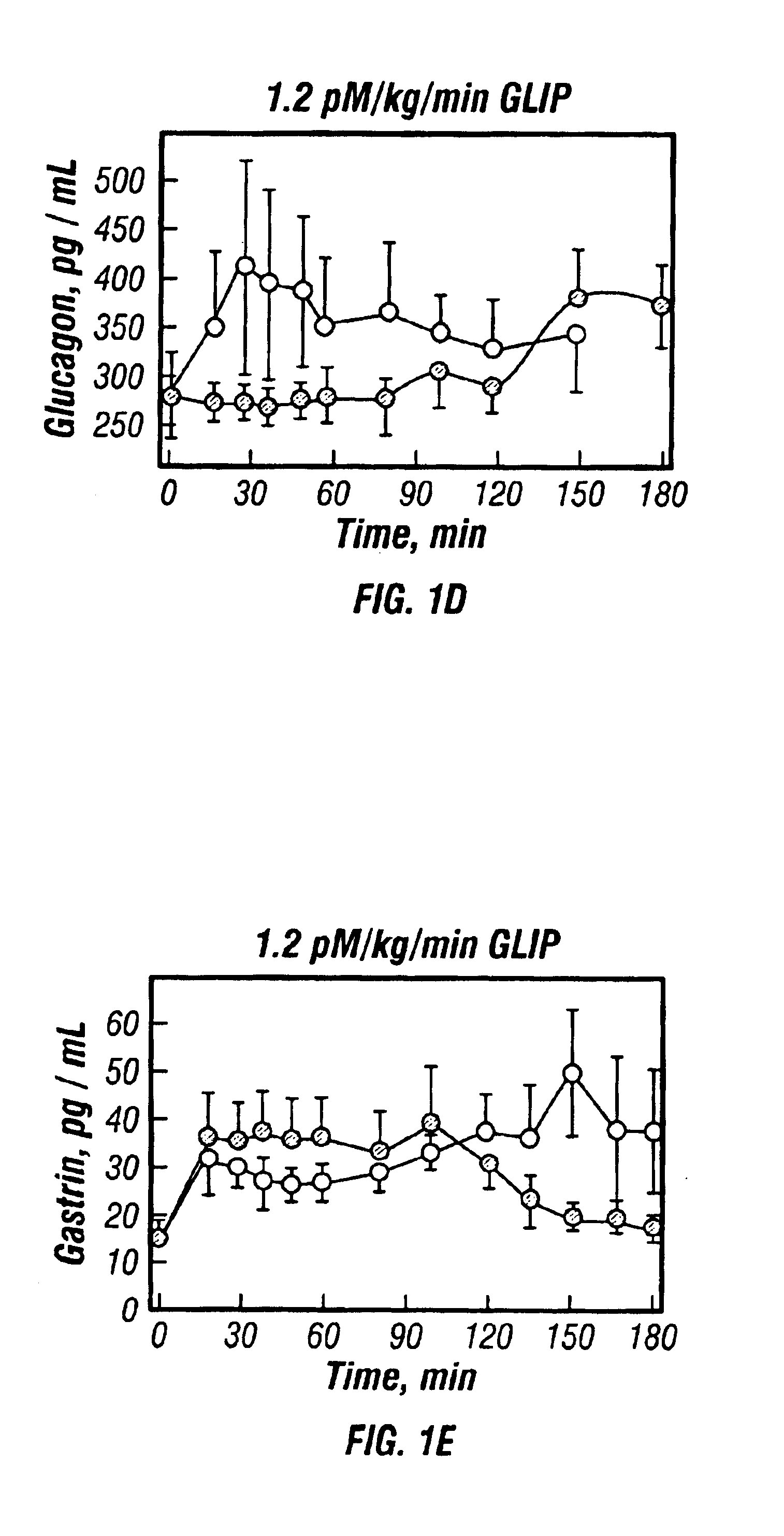
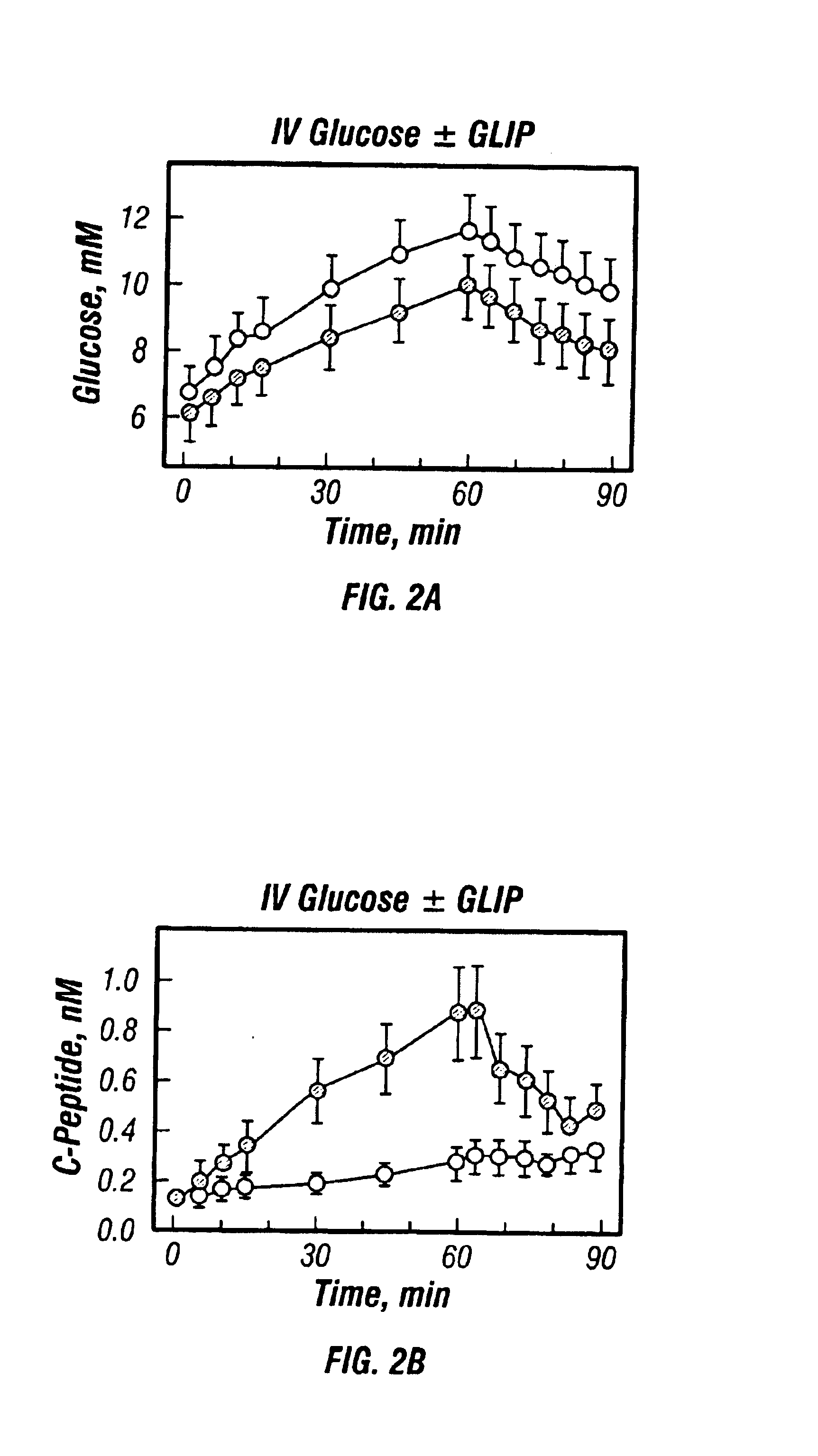
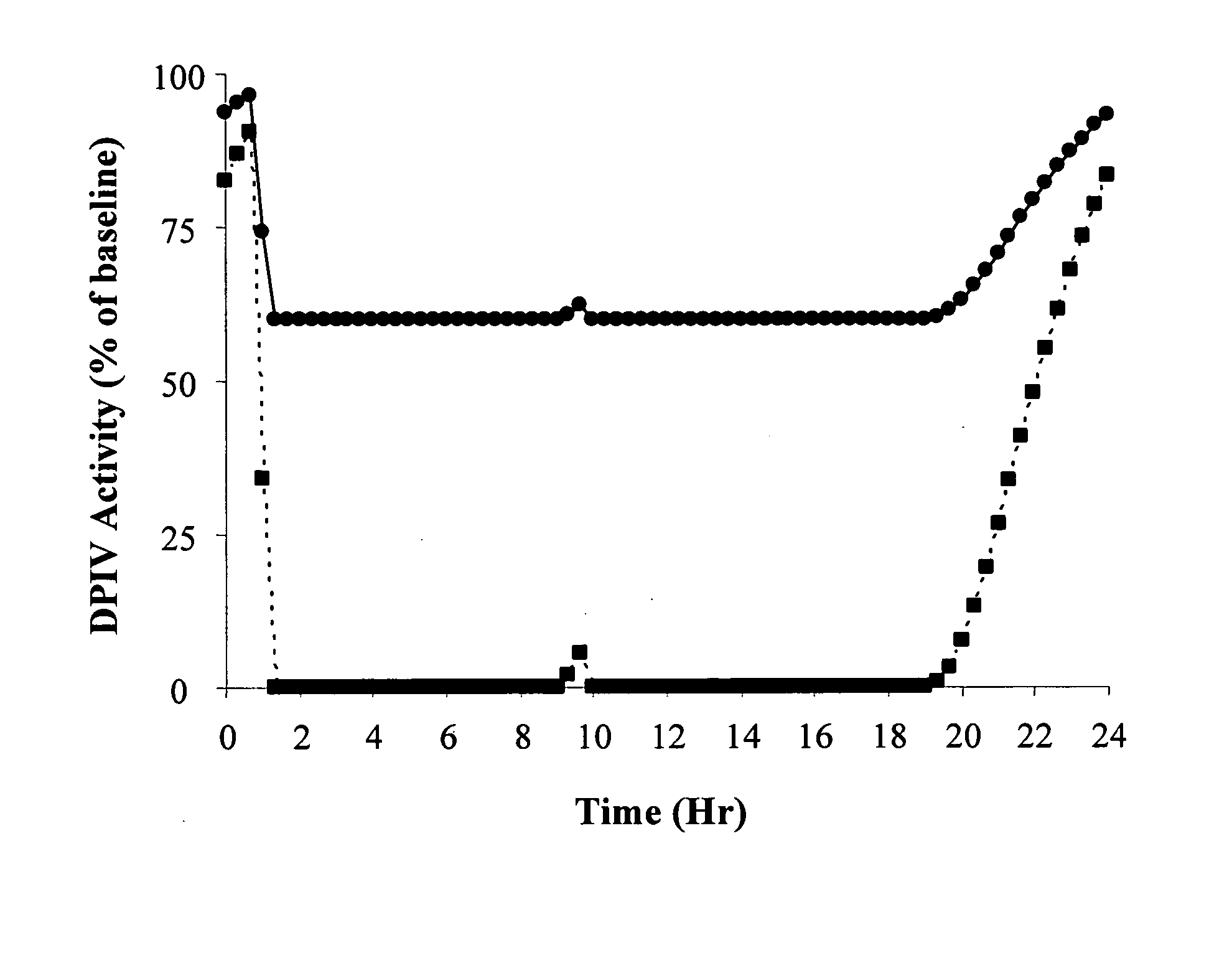
InactiveUS20130059780A1Controlled more and lessImprove blood sugar controlFungiBacteriaWild typeGlucagon-like peptide-1
The present invention provides polypeptides that include an O-linked glycoconjugate in which a species such as a water-soluble polymer, a therapeutic agent of a biomolecule is covalently linked through an intact O-linked glycosyl residue to the polypeptide. The polypeptides of the invention include wild-type peptides and mutant peptides that include an O-linked glycosylation site that is not present in the wild-type peptide. Also provided are methods of making the peptides of the invention and methods, pharmaceutical compositions containing the peptides and methods of treating, ameliorating or preventing diseased in mammals by administering an amount of a peptide of the invention sufficient to achieve the desired response.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Methods and compositions for treating polycystic ovary syndrome
The present invention relates to methods of treating polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) comprising administering glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), exendin, and analogs and agonists thereof, to subjects suffering therefrom.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Method for biosynthesis preparation of human GLP-1 polypeptide or analogue thereof
InactiveCN106434717AEasy to separateHigh expressionNucleic acid vectorFusion with protease siteEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
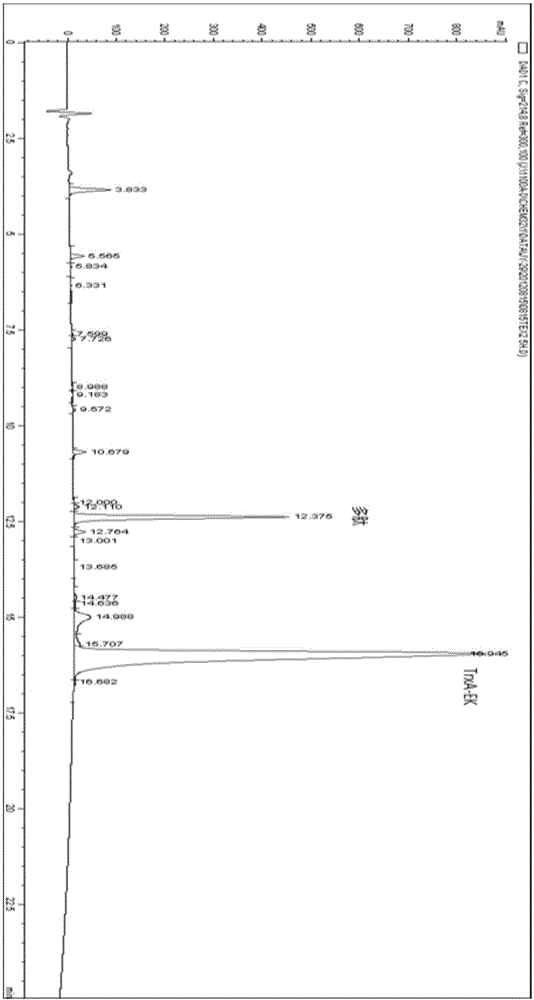
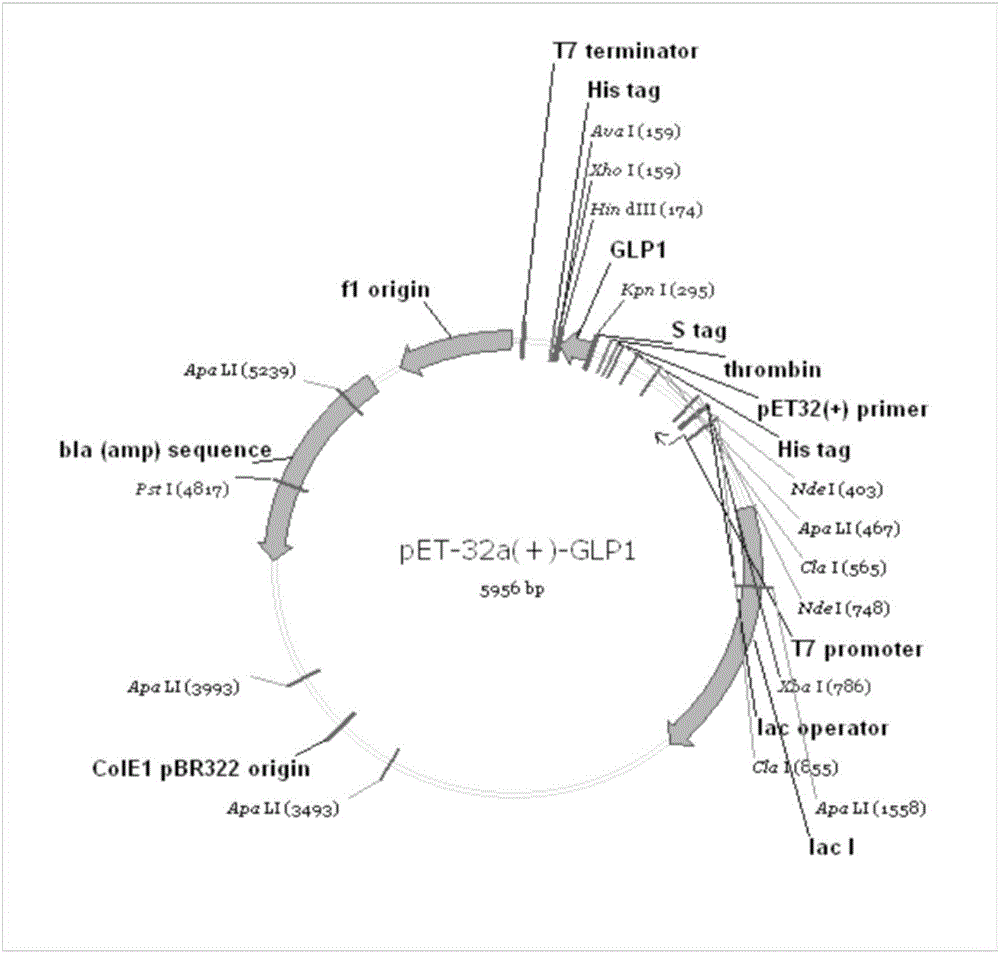
The invention relates to a method for biosynthesis preparation of human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and an analogue thereof. With adopting of a gene engineering technology, a recombinant escherichia coli expressed GLP-1 fusion protein is constructed, and a protein enzyme digestion site is designed in the fusion protein; a fusion gene has a gene sequence with a form of A-B-C structure, wherein A is a chaperonin gene, B is a nucleotide sequence encoding a connection peptide containing the enzyme digestion site, and C is a gene encoding the GLP-1 or the analogue thereof. After recombinant engineering bacteria is subjected to induced expression, the fusion protein is purified and subjected to enzyme digestion, and then the GLP-1 and the analogue thereof are obtained and are detected to have biological activity. The preparation method of the GLP-1 and the analogue thereof provided by the invention is simple and quick, the production conditions are mild, the product is convenient to separate and extract, the process is simple, and the industrialization prospect is good.
Owner:HANGZHOU JIUYUAN GENE ENG +1
Method for treating type 2 diabetes with an extract of Artemisia
InactiveUS6893627B2Increasing glucose uptakeMethod securityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMammalFractionation
The present invention provides materials and methods relating to mildly polar fluid extracts of plant materials, such as Artemisia plant species, useful in methods for treating diabetes and methods for modulating the activity of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and in methods for modulating phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) activity in a diabetes-specific manner. The extracts are generally non-toxic and non-mutagenic and may be administered to diabetics with beneficial effect on blood glucose levels. The extracts may also be administered to non-diabetics without deleterious effect. The plants are easily grown with a minimum of time, labor, and cost. Extracts are inexpensively and quickly prepared without the need for fractionation to remove potentially deleterious compounds, and the extracts may be administered to mammals such as humans through various routes, in a variety of forms, and at convenient concentrations.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE OF UNIVESITY OF NEW JERSEY
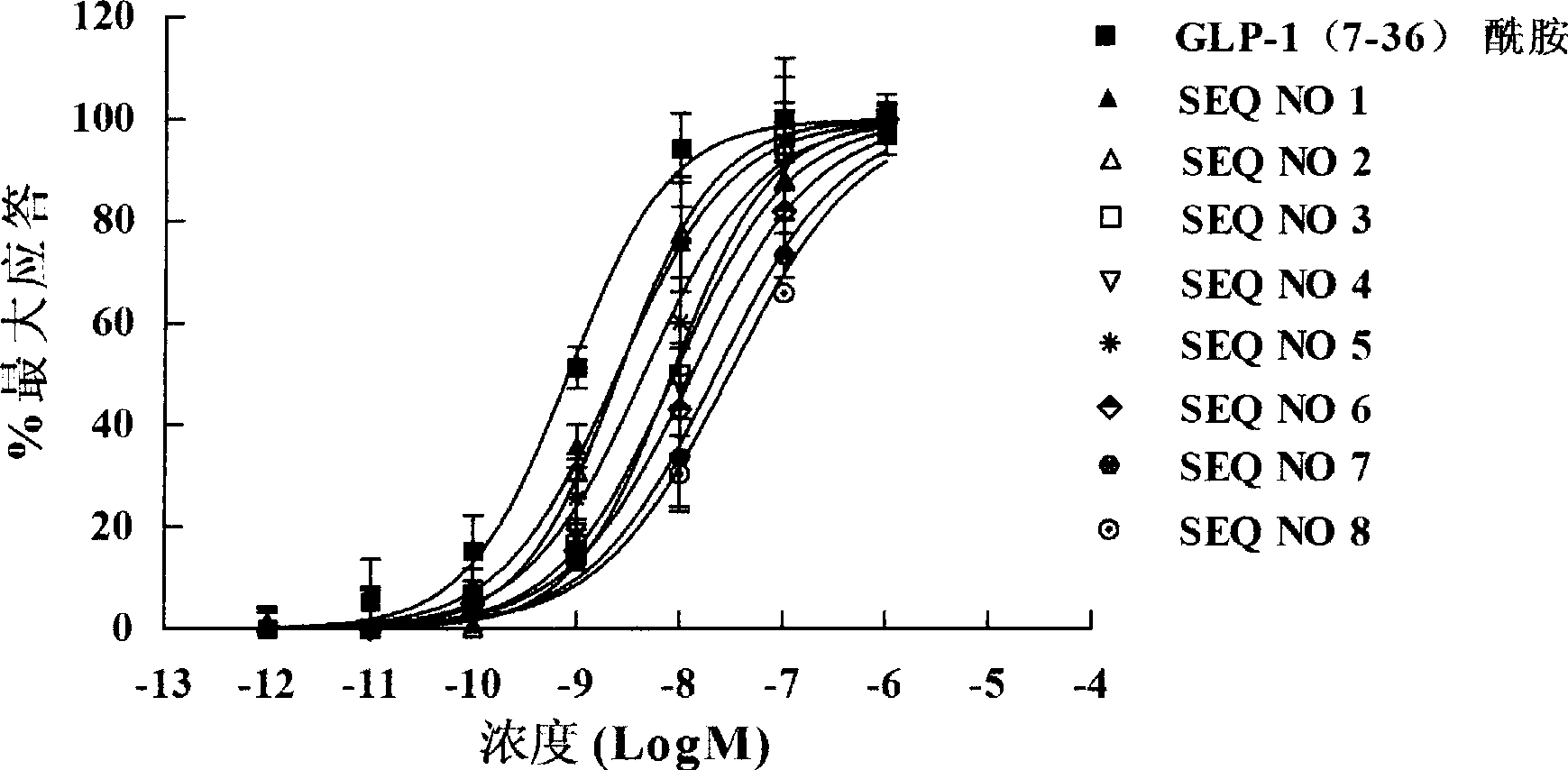
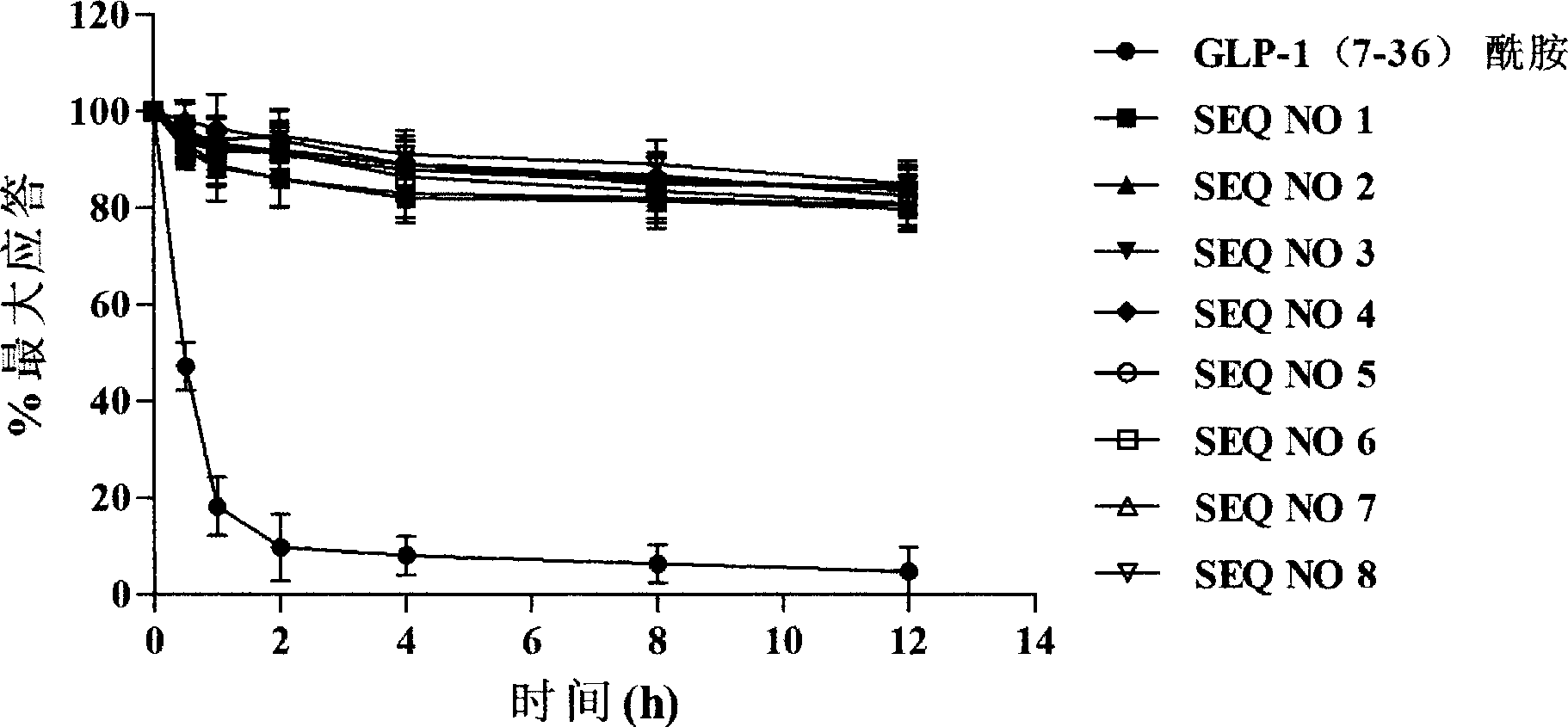
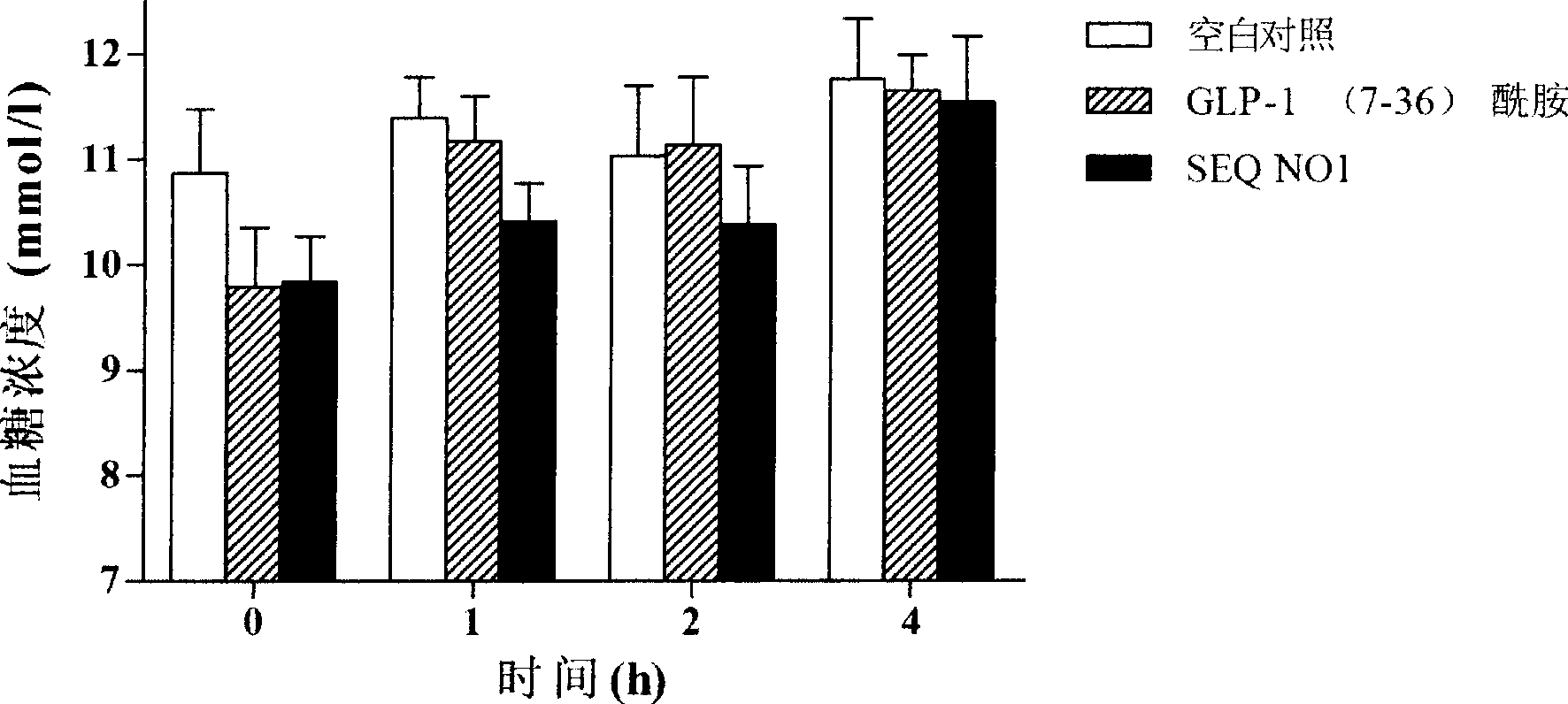
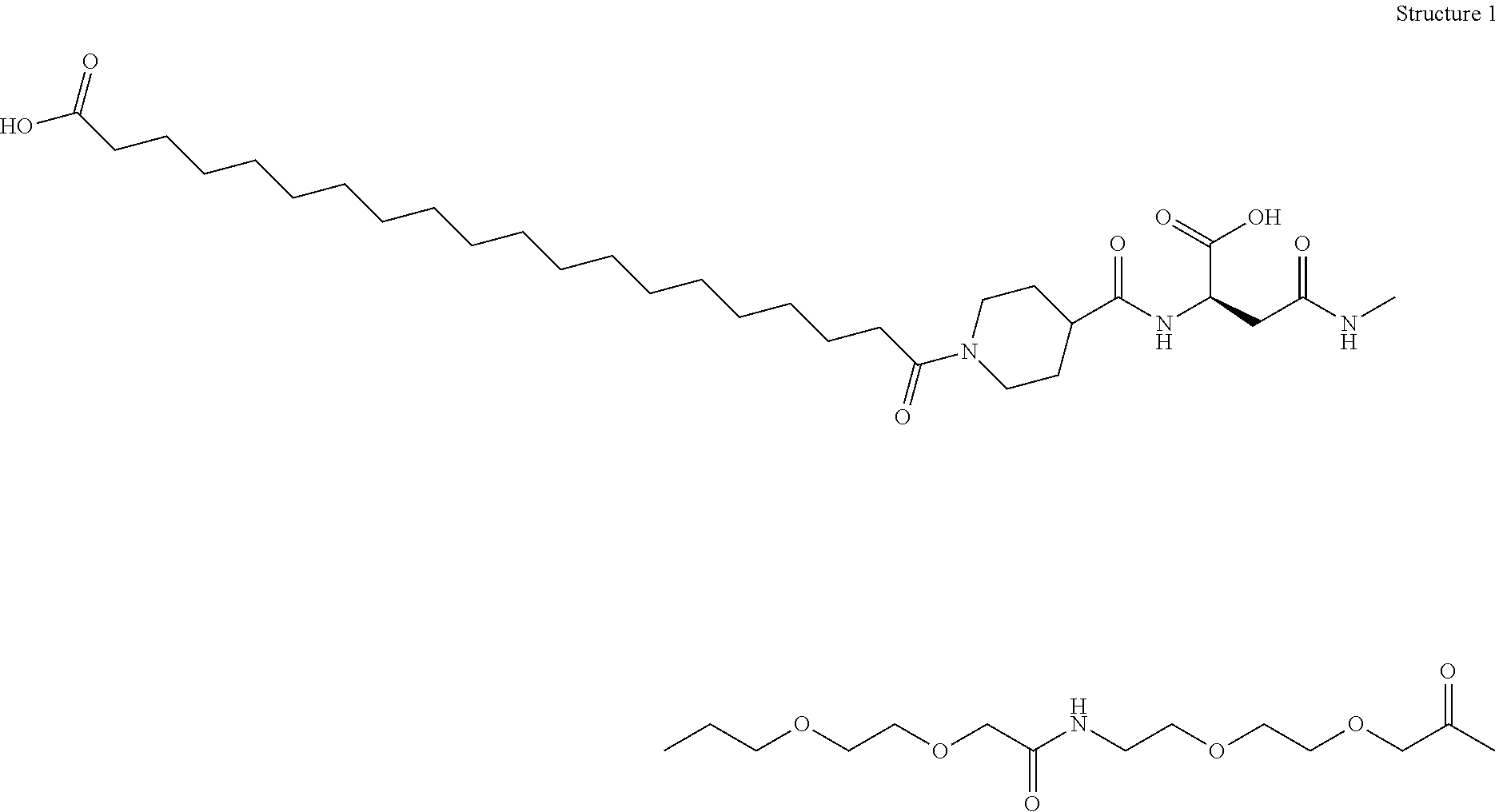
Novel glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1) analogues and use thereof
ActiveCN101337989AImprove stabilityProlong the action timePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderChemical synthesisMicrowave
The invention relates to a novel GLP-1 analog and the application thereof. The GLP-1 analog with higher stability and higher hypoglycemic activity is obtained by reconstructing 8, 22 amino acid residue sites of natural GLP-1. The chemical synthesis is achieved at high efficiency and high speed by using microwave to promote solid phase synthesis, and the crude product is purified by a preparative grade HPLC and lyophilized to obtain the GLP-1 analog.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Novel glp-1 receptor stabilizers and modulators
Compounds that bind the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor, methods of their synthesis, methods of their therapeutic and / or prophylactic use, and methods of their use in stabilizing GLP-1 receptor in vitro for crystallization of the GLP-1 receptor are provided. Certain compounds may have activity as modulators or potentiators with respect to glucagon receptor, GIP receptor, GLP-1 and GLP-2 receptors, and PTH receptor on their own or in the presence of receptor ligands such as GIP (1-42), PTH (1-34), Glucagon (1-29), GLP-2 (1-33), GLP-1 (7-36), GLP-1 (9-36), oxyntomodulin and exendin variants.
Owner:RECEPTOS LLC
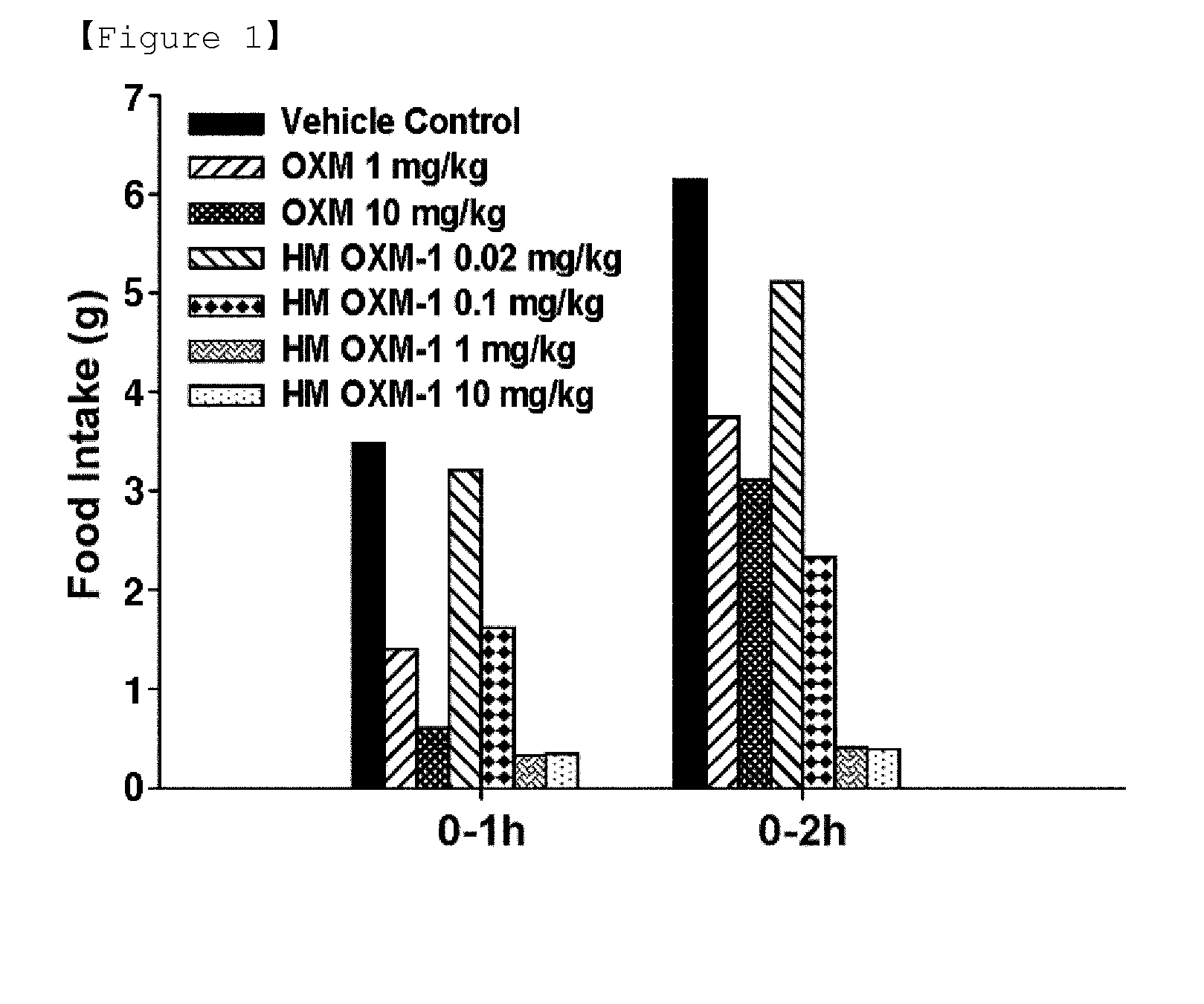
Novel oxyntomodulin derivatives and pharmaceutical composition for treating obesity comprising the same
ActiveUS20140128318A1Reduces food intakeSuppresses gastric emptyingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesSide effectReceptor activation
The present invention relates to a novel peptide showing more excellent activities on a glucagon like peptide-1 receptor and a glucagon receptor than native oxyntomodulin, and a composition for the prevention or treatment of obesity comprising the peptide as an active ingredient. Unlike native oxyntomodulin, the novel peptide of the present invention reduces food intake, suppresses gastric emptying, and facilitates lipolysis with reduced side-effects, and also shows excellent receptor-activating effects. Thus, it can be widely used in the treatment of obesity with safety and efficacy.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Human appetite control by glucagon-like peptide receptor binding compounds
InactiveUS20060128627A1Appetite suppressantReducing spontaneous food intakePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCompound aCompound (substance)
A composition including a compound which binds to a receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1 and a pharmaceutical carrier. The amount of the compound present is effective to control appetite in a human. Also disclosed is a method for controlling appetite and for reducing food intake in a human by administering to the human a composition comprising a compound which binds to a receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1 and a pharmaceutical carrier.
Owner:AMYLIN PHARMA INC
Modified glucagon sample peptide-1analogue and modifying matter, and uses thereof
InactiveCN101367873AGood biological propertiesImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAmino acid substitutionGlucagon-like peptide-1
The present invention relates to a mutant polypeptide of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and a modified compound thereof. In particular, a lysine is added in front of the end N of the glucagon-like peptide-1 to form the mutant polypeptide, and the glucagon-like peptide-1 includes natural GLP-1(7-36)amide or GLP-1(7-37) and a partial amino acid-subsituted derivative. Not only do the GLP-1 mutant polypeptide and the modified compound thereof show the effects of promoting insulin secretion and lowering blood sugar, but also, compared with the natural GLP-1, the stability and internal action time of the GLP-1 mutant polypeptide and the modified compound thereof are notably increased in respect to proteolytic enzyme, and the GLP-1 mutant polypeptide and the modified compound thereof can be used for the preparation of drugs treating diabetes or adiposity.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
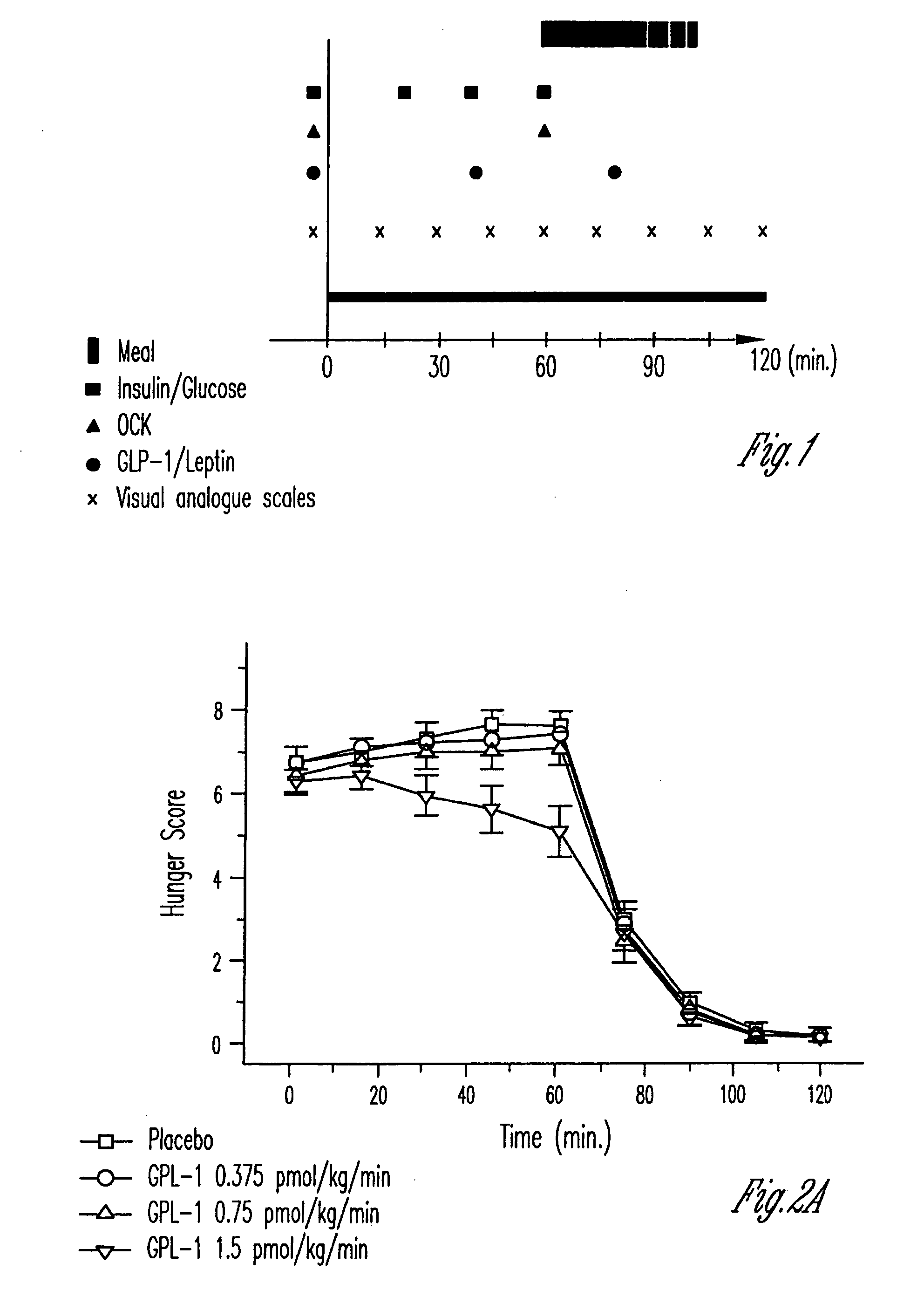
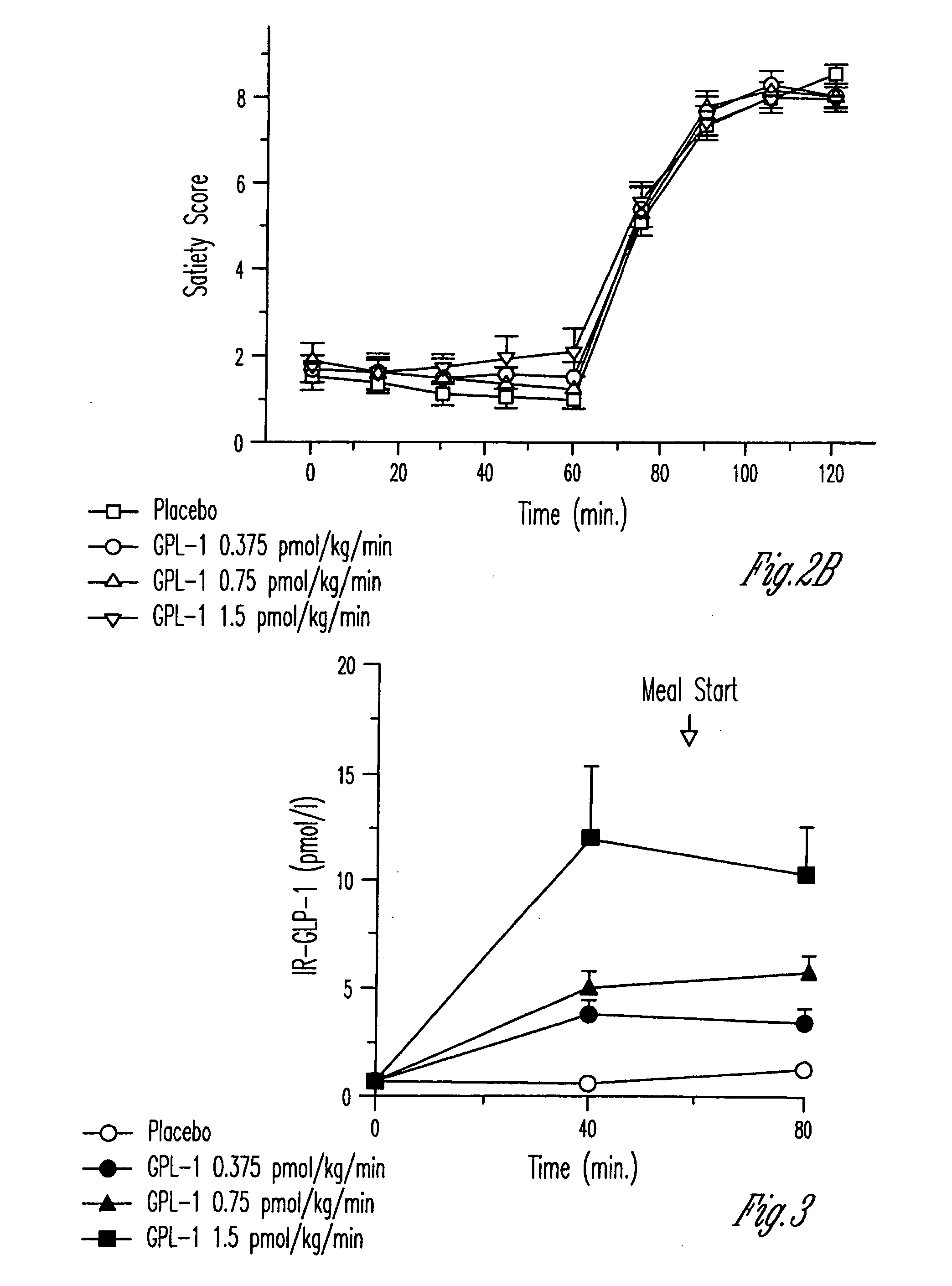
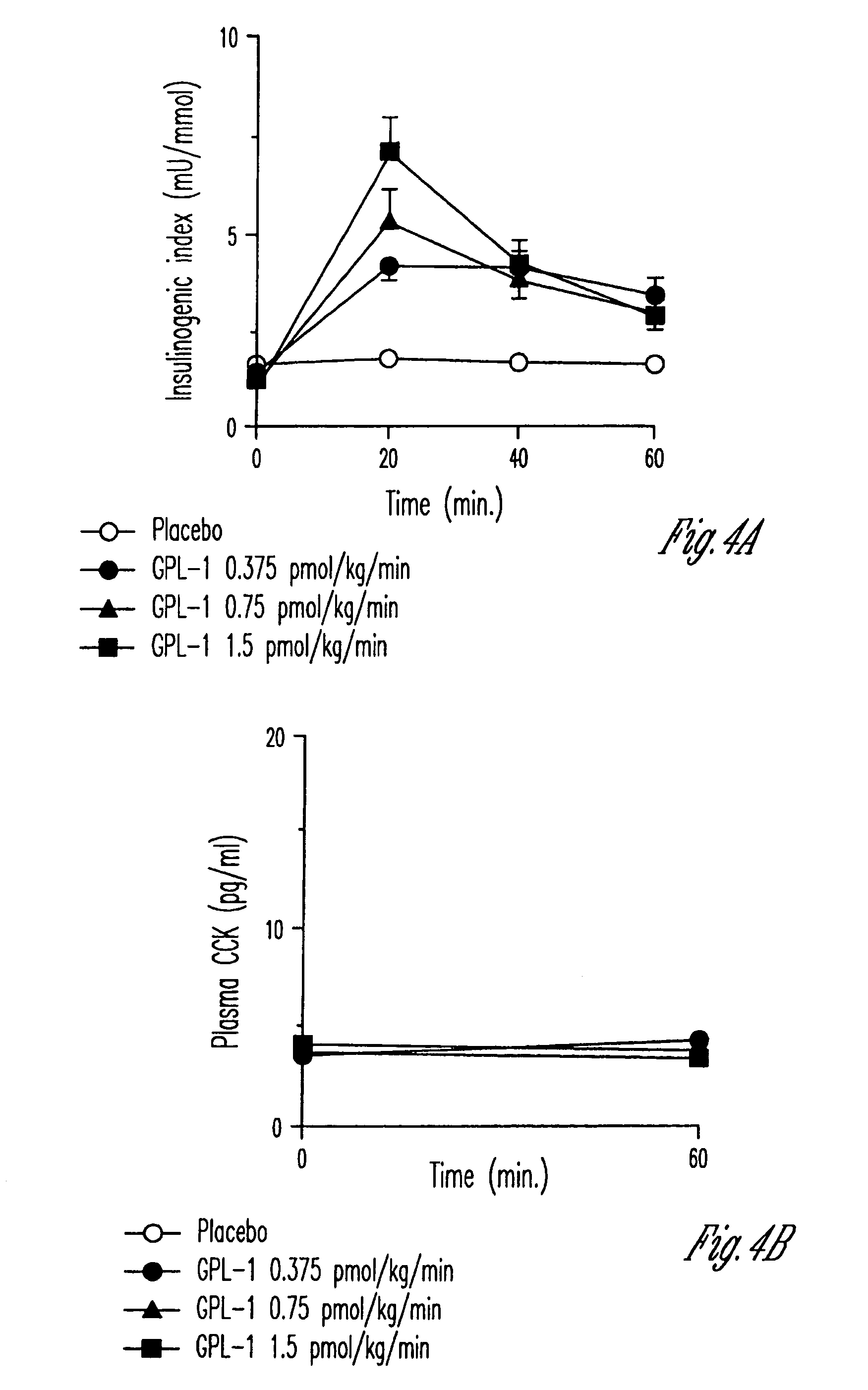
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 derivatives and their pharmaceutical use
The invention relates to protracted Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) derivatives and therapeutic uses thereof. The GLP-1 derivative of the invention comprises a modified GLP-1(7-37) sequence having a total of 2-12 amino acid modifications, including Glu22 and Arg26, and being derivatised with an albumin binding residue or pegylated in position 18, 20, 23, 30, 31, 34, 36, 37, or 39. These compounds are useful in the treatment or prevention of diabetes type 2 and related diseases. The compounds are potent, stable, have long half-lives, a high affinity of binding to albumin, and / or a high affinity of binding to the extracellular domain of the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R), all of which is of potential relevance for the overall aim of achieving long-acting, stable and active GLP-1 derivatives with a potential for once weekly administration.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Peptides Derivatized with A-B-C-D- and their Therapeutical Use
The invention relates to protracted peptide derivatives such as Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1), exendin-4, and analogues thereof, as well as therapeutic uses thereof. The peptide derivative of the invention comprises a peptide wherein at least one amino acid residue is derivatized with A-B—C—, or A-B—C-D-. These compounds are useful in the treatment or prevention of diabetes type 2 and related diseases. The compounds are potent, have a low ratio of binding affinity to the GLP-1 receptor in the presence of high / low albumin concentrations, have long half-lives, and have a high affinity of binding to albumin, all of which is of potential relevance for the overall aim of achieving long-acting, stable and active GLP-1 derivatives with a potential for once weekly administration.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


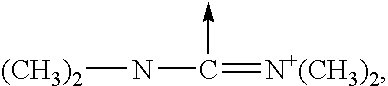

![Branched peg remodeling and glycosylation of glucagon-like peptide-1 [glp-1] Branched peg remodeling and glycosylation of glucagon-like peptide-1 [glp-1]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9633ebd4-315e-420d-b033-e313e2785e9a/US20130059780A1-20130307-D00001.png)
![Branched peg remodeling and glycosylation of glucagon-like peptide-1 [glp-1] Branched peg remodeling and glycosylation of glucagon-like peptide-1 [glp-1]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9633ebd4-315e-420d-b033-e313e2785e9a/US20130059780A1-20130307-C00001.png)
![Branched peg remodeling and glycosylation of glucagon-like peptide-1 [glp-1] Branched peg remodeling and glycosylation of glucagon-like peptide-1 [glp-1]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9633ebd4-315e-420d-b033-e313e2785e9a/US20130059780A1-20130307-C00002.png)