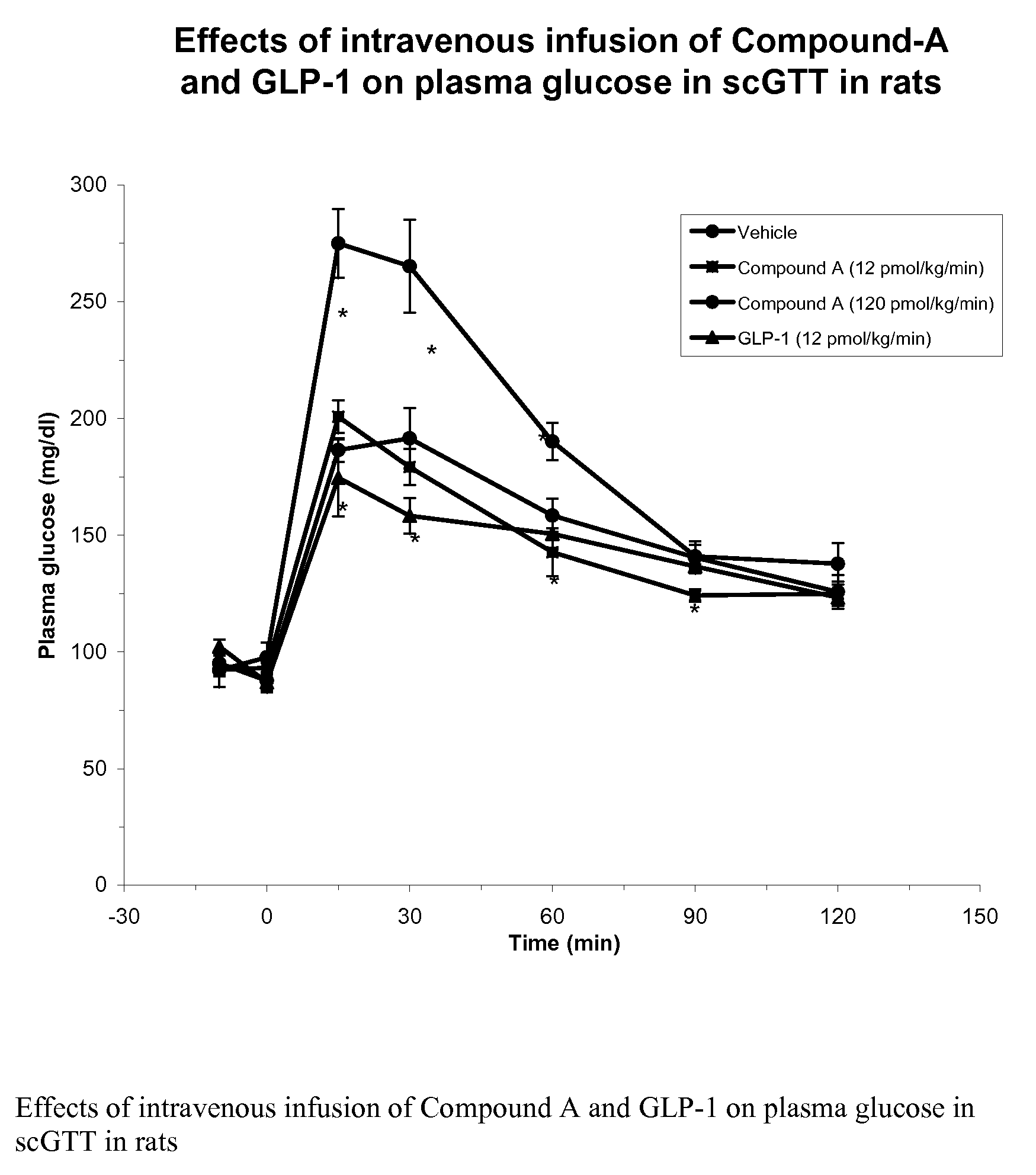
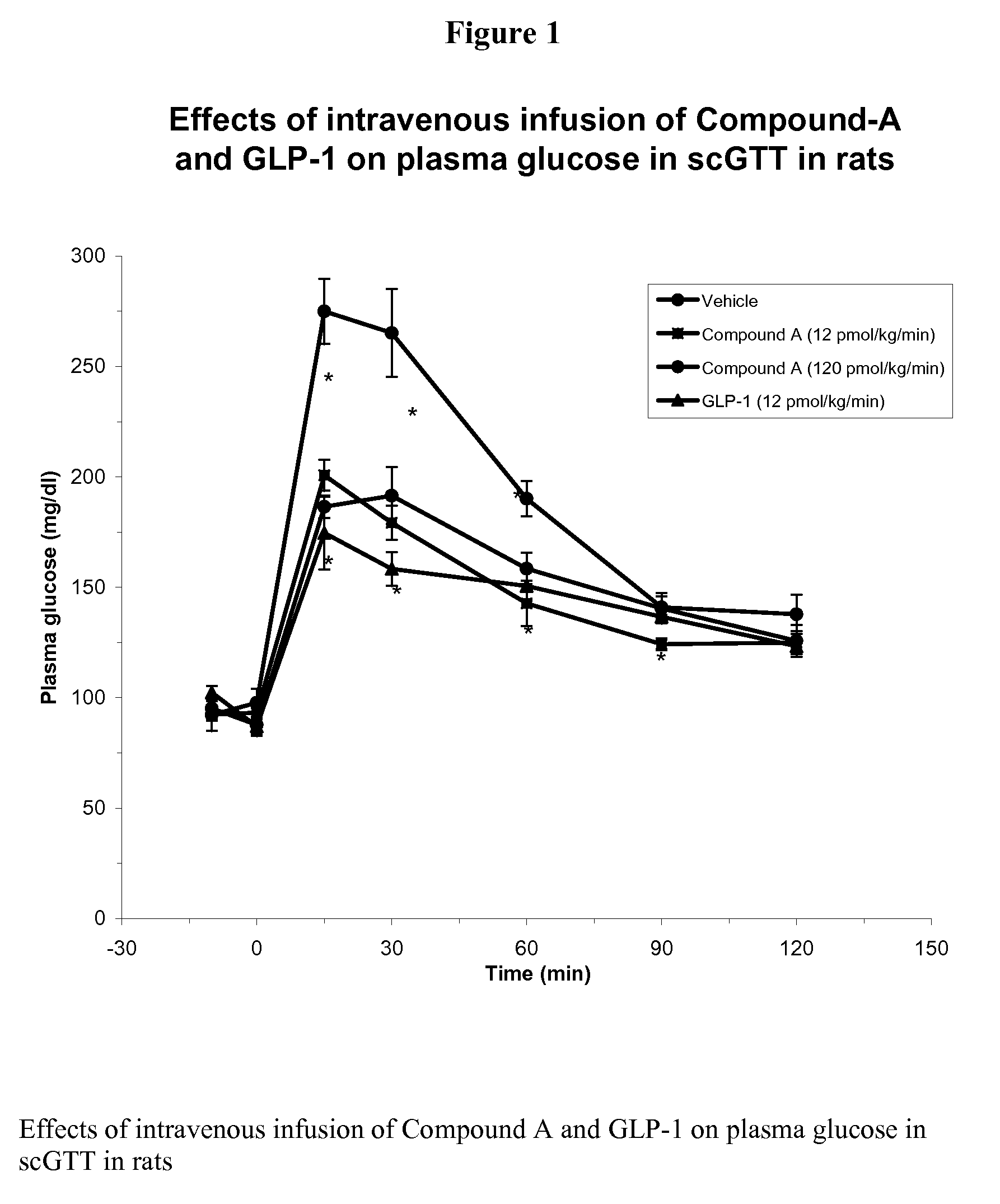
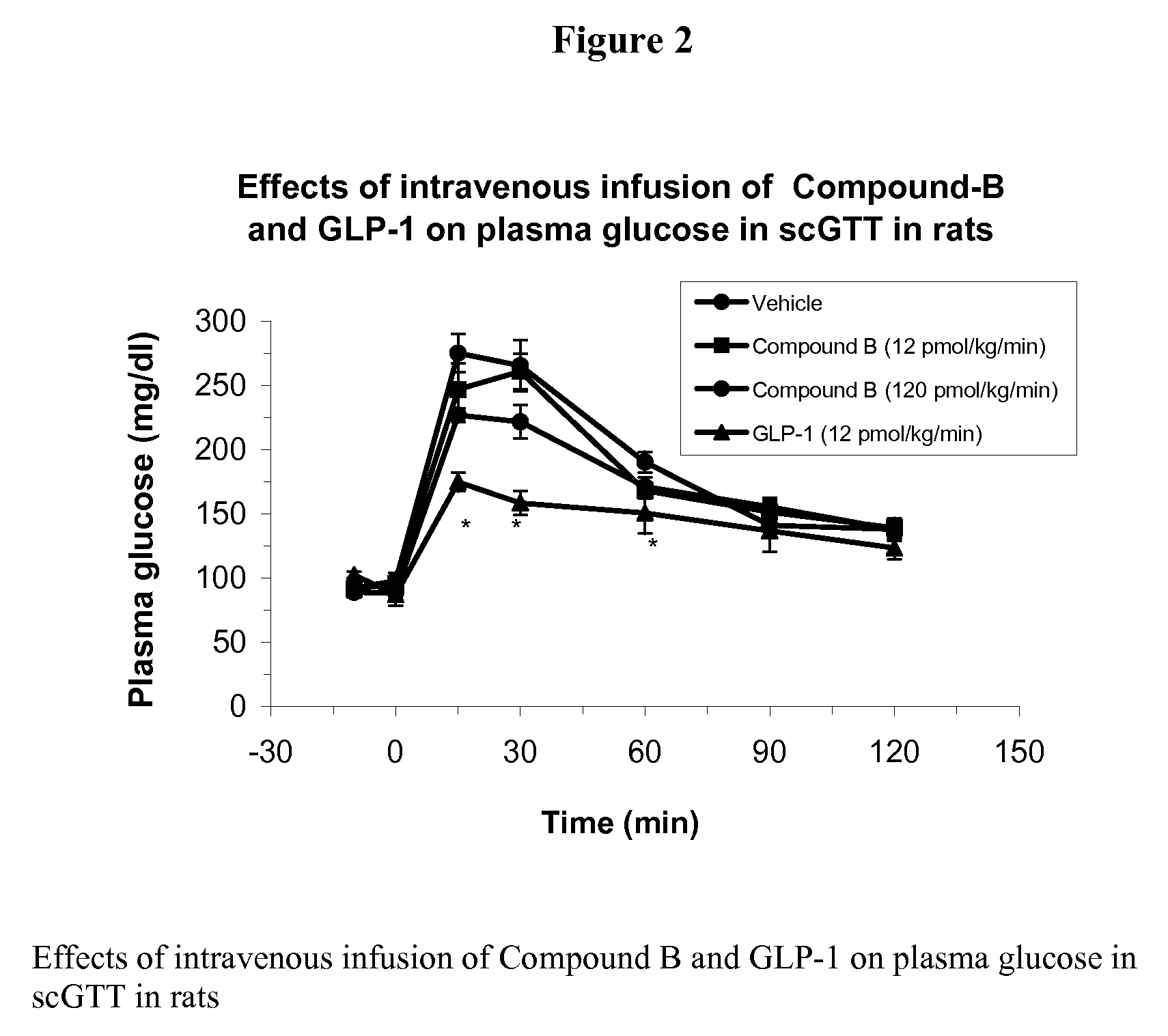
Human glucagon-like peptide-1 mimics and their use in the treatment of diabetes and related conditions
a technology of glucagon-like peptides and mimics, which is applied in the field of human glucagon-like peptides and their use in the treatment of diabetes and related conditions, can solve the problems of short serum half-life of such peptides and the significant problem of therapy involving the use of glp-1-type molecules, and achieve the effect of increasing high density lipoprotein levels and elevating blood levels of fatty acids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Simultaneous Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis of GLP-1 11-Mer Peptide Mimics
[0103] Dipeptidyl resin, containing non-natural non-commercial amino acid residues at positions 10 and 11, was prepared using the following manual procedure in a batch-wise mode before continuing peptide chain elongation utilizing the automated simultaneous synthesis protocol on the MPS-396 peptide synthesizer. The synthesis of the Nα-Fmoc-protected biphenylalanine derivatives used in the manual couplings is described in Examples 8-10.
[0104] An amount of 4-(2′,4′-dimethoxyphenyl-Fmoc-aminomethyl)-phenoxyacetyl-p-methyl benzhydrylamine resin (Rink amide MBHA resin; loading: 0.5 mmol / g) sufficient to synthesize several 1′-mer analogs, was swelled by washing with DMF (4×10 mL / g, 5 minutes). The Fmoc group was then removed using two treatments, 3 and 18 minutes each respectively, with 20% piperidine in DMF (10 mL / g). The resin was washed with DMF (4×10 mL / g) and NMP (4×10 mL / g). A 0.5 M solution of Fmoc-L-bipheny...
example 2
Synthesis of N-Acylated and N-Alkylated 11-Mer Peptide Analogs
(A) General Procedure for the Synthesis of N-Alkylated 11-Mer Peptide Analogs by Reductive Alkylation
[0119] The synthesis of N-alkylated 11-mer peptide analogs was started from the protected intermediate 11-mer peptidyl-resin (1) (0.025 mmol), which was prepared by the general method described herein. The Fmoc group was removed using the procedure described in that method, to yield the protected resin intermediate 2. This was swollen in DMF, washed 3 times with 1% AcOH / DMF, and then treated with 2-20 eq. of aldehyde or N-Boc-protected aminoaldehyde (see synthesis below), dissolved in 1% AcOH / DMF (or CH2Cl2) (1 M), and the same excess amount of Na(AcO)3BH as that of the aldehyde. After overnight reaction, the resin was drained, washed with DMF and DCM, 3 times each, and dried. The reductively alkylated peptide (4) was cleaved and deprotected by treatment with TFA / tri-isopropylsilane / water (90:5:5, v:v:v; 1-2 mL) for 2 h...
example 3
Synthesis of N-Arylalkyl Amides of 10-Mer Peptide Analogs
[0126] The synthesis of N-arylalkyl amides of 10-mer peptide analogs was started with a reductive alkylation reaction of a relevant arylalkylamine with an alkoxybenzaldehyde resin as in the following example. 2-(3,5-Dimethoxy-4-formylphenoxy)ethoxymethyl polystyrene resin (Novabiochem, 1.12 mmol / gram, 0.025 mmol, 27.3 mg) was washed with 1% Acetic Acid in DCM (5×3 mL). A solution of 2-(2-pentafluorophenyl)ethyl amine (0.125 mmol, 26.4 mg) in DCM (3 mL) was added to the resin. After 5 minutes, solid NaBH(OAc)3 (0.125 mmol, 26.5 mg,) was added and the reaction was vortexed for 16 hours. The resin was rinsed with DMF (5×3 mL) and DCM (5×3 mL).
[0127] A solution of Fmoc-[BIP(2-Et)]-OH (0.05 mmol, 25.3 mg) and HOAt (0.05 mmol, 6.81 mg) in NMP(0.5 mL) was added to the resin followed by DIC (0.05 mmol, 7.82 μL). The reaction was vortexed for 16 hrs. The resin was rinsed with NMP(5×3 mL). The remaining sequence of the desired 10-mer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com