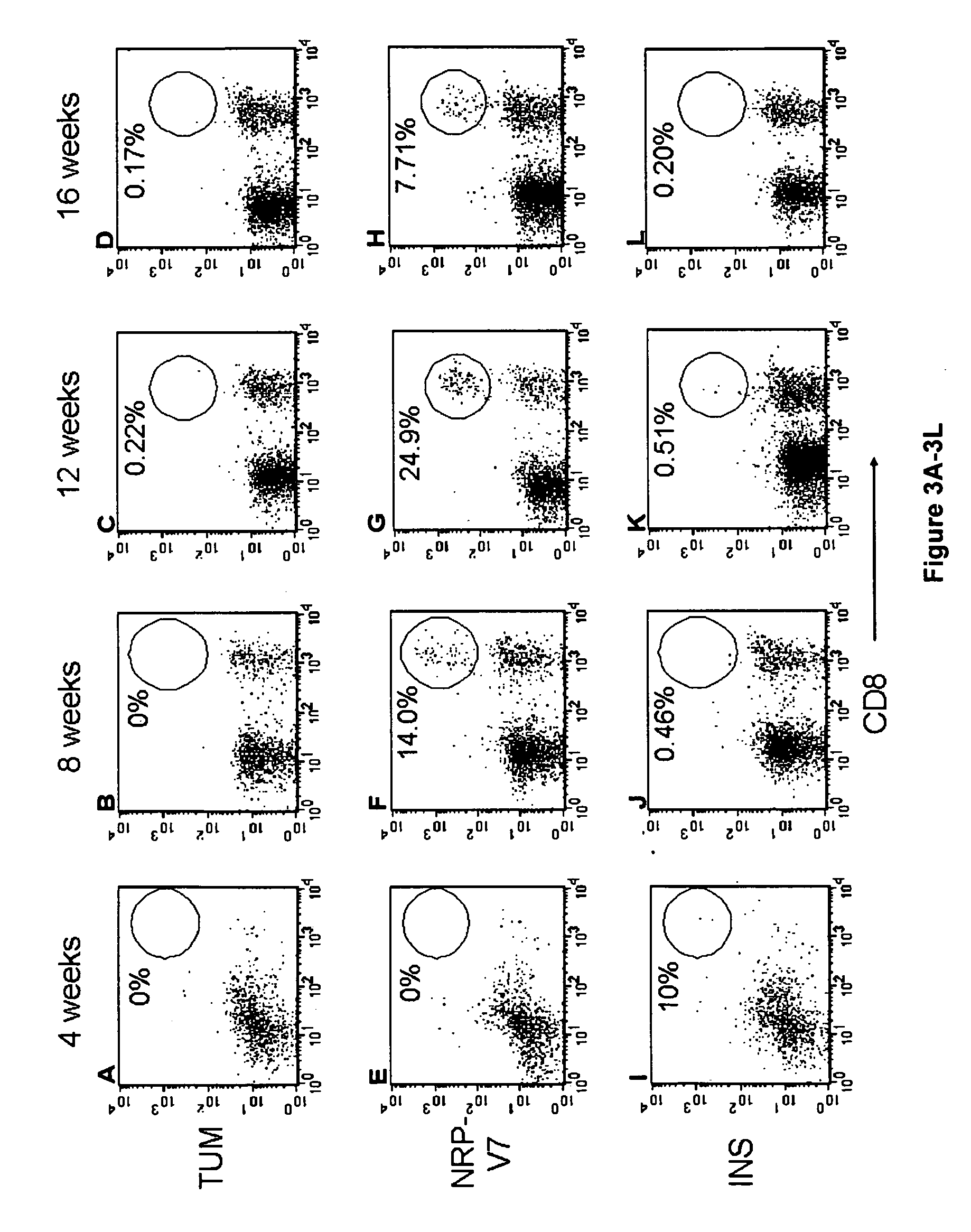
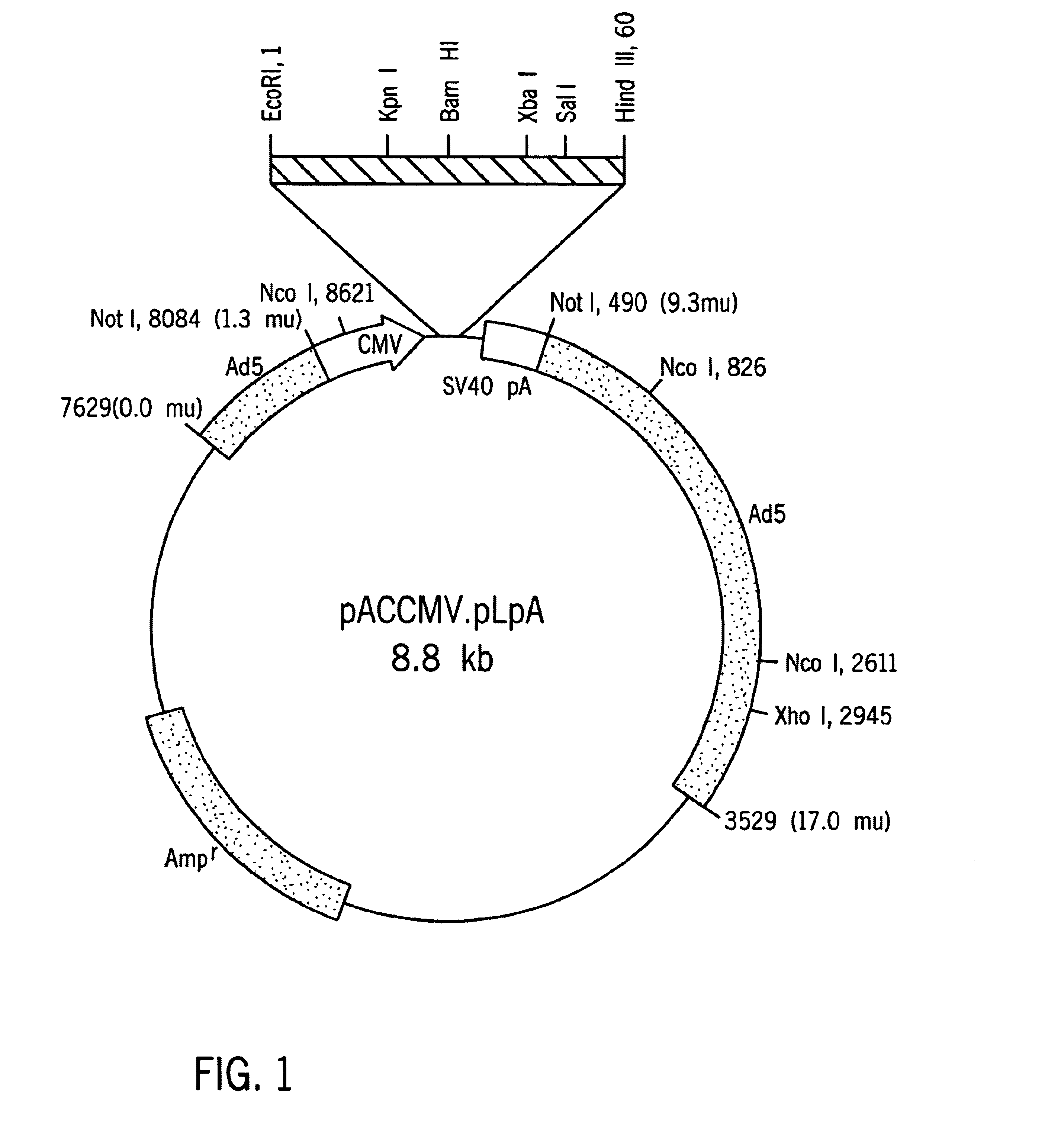
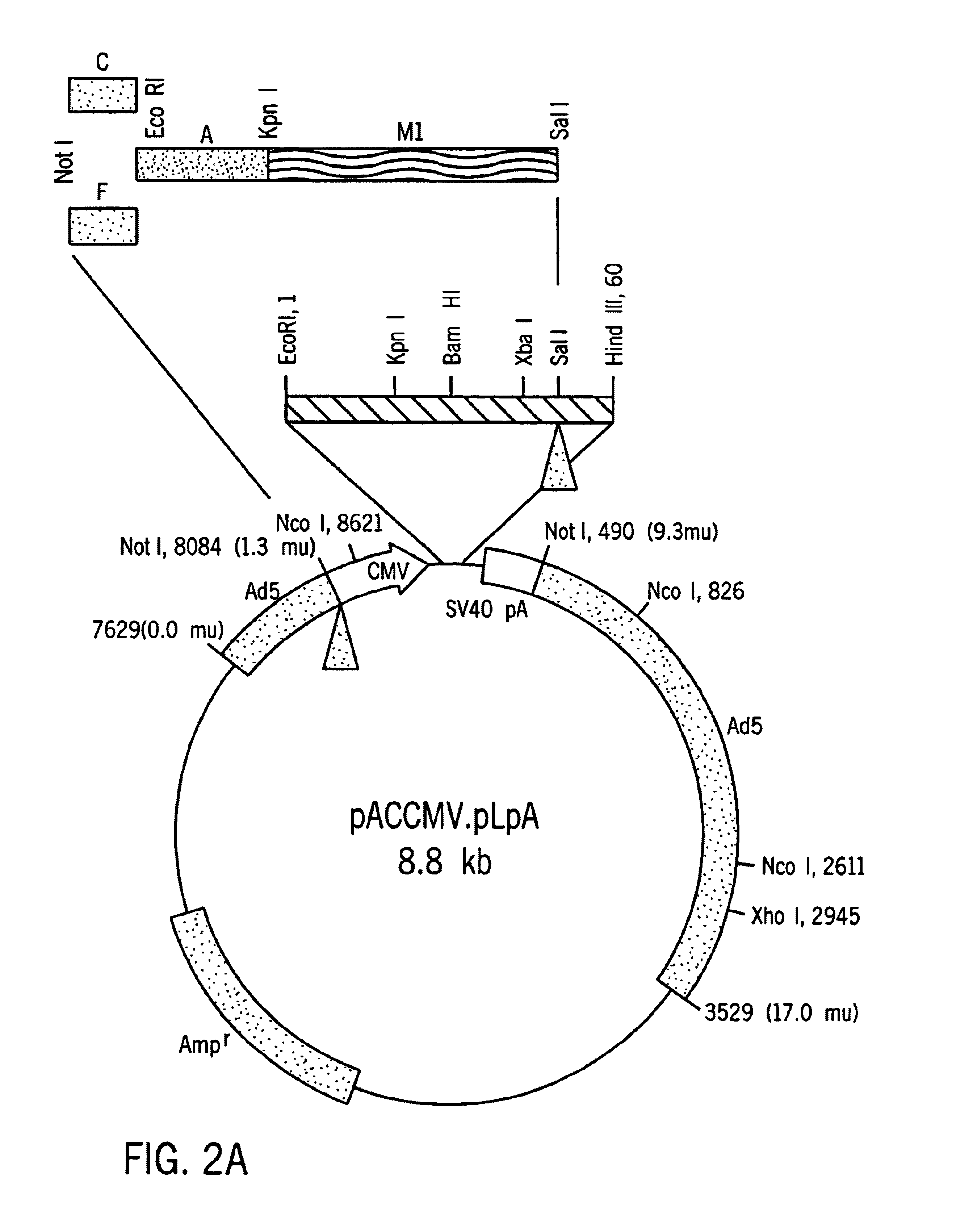
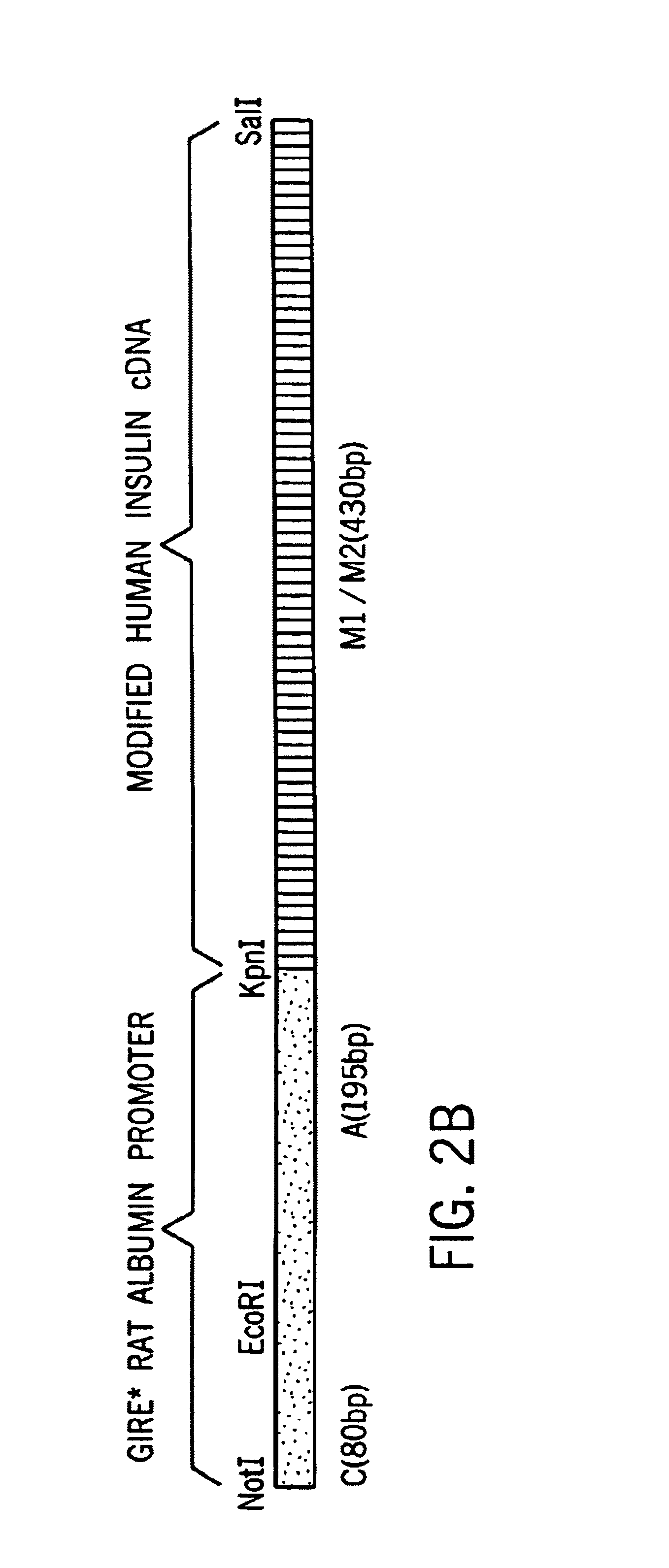
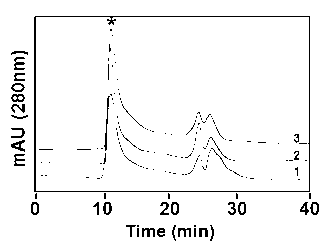
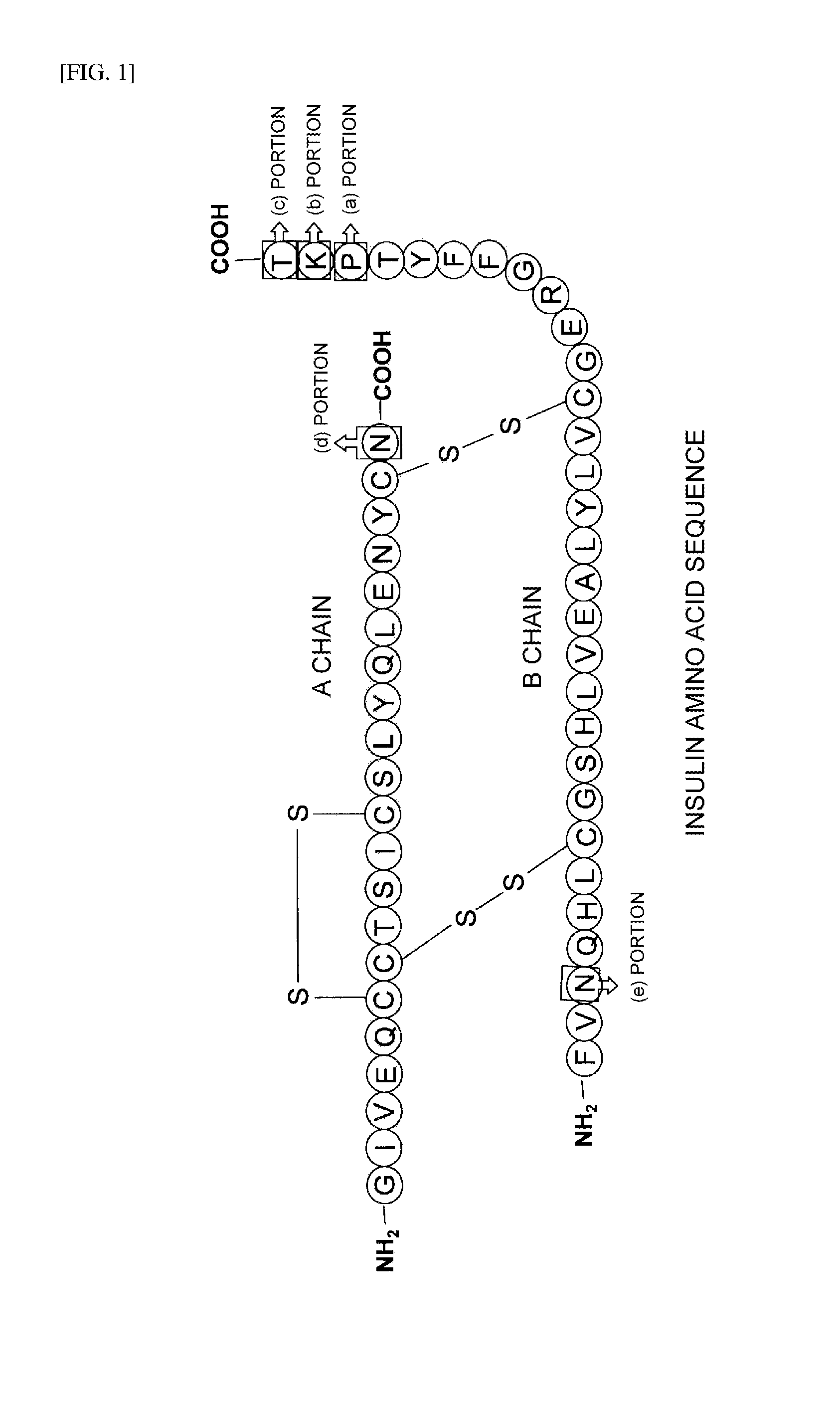
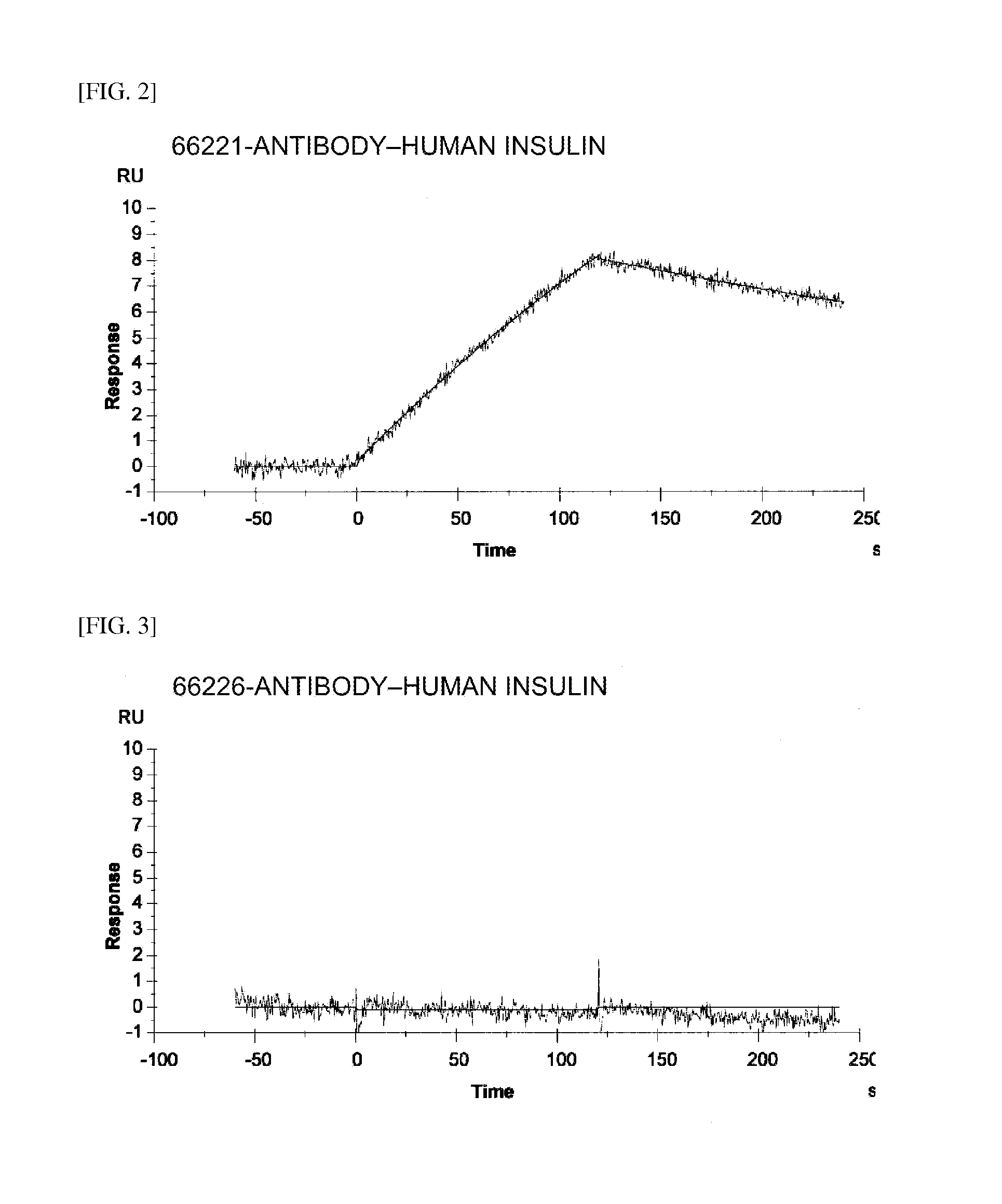
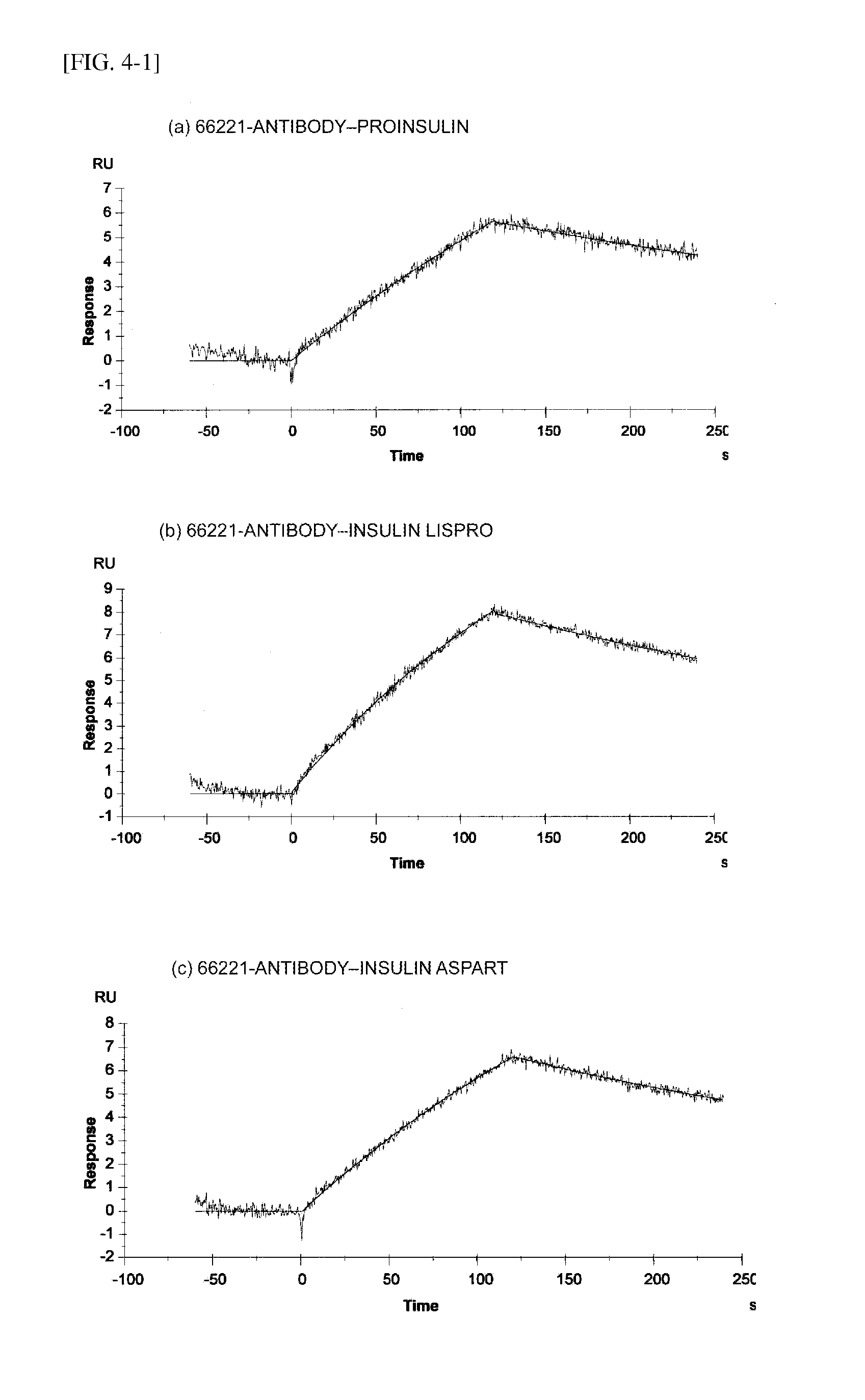
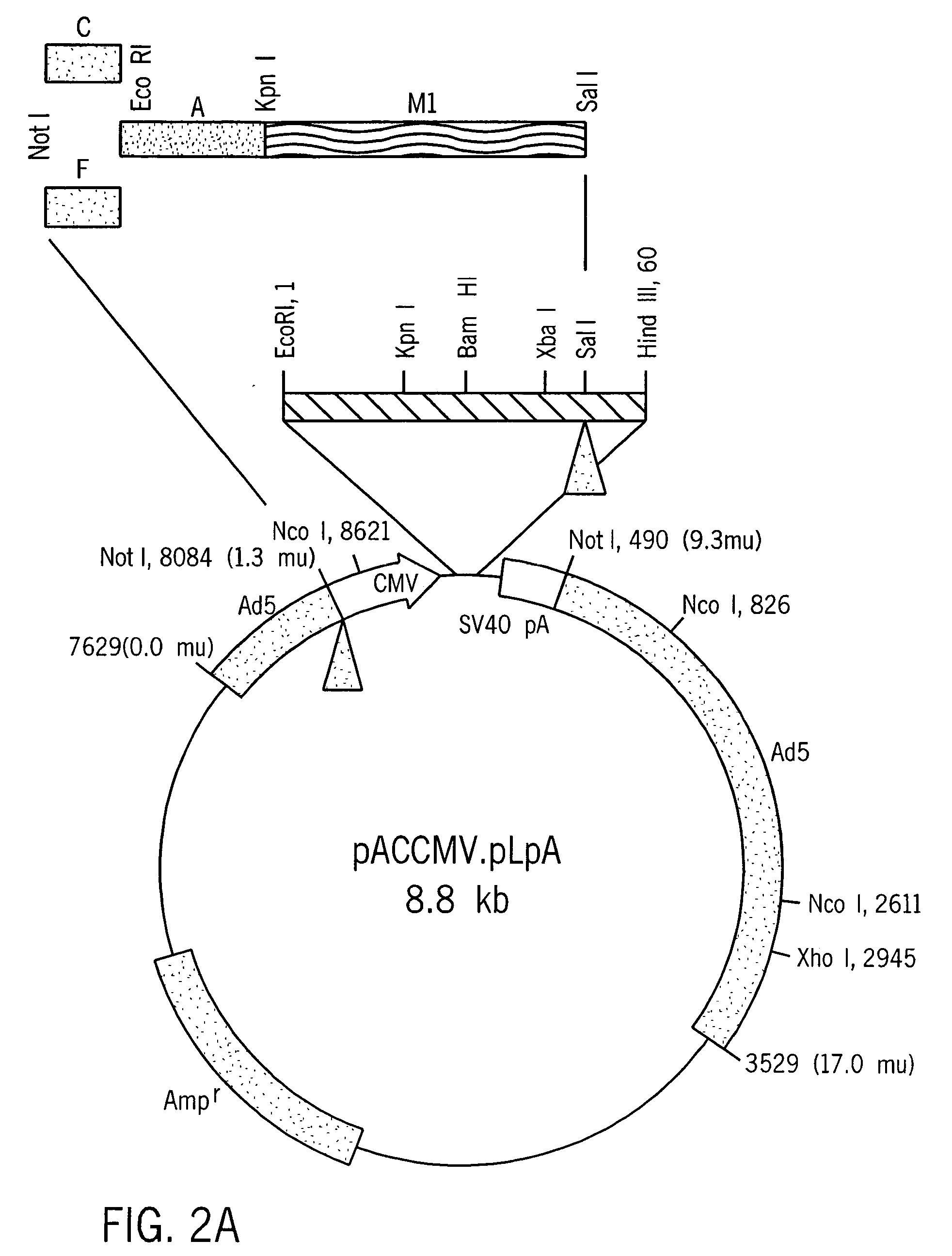
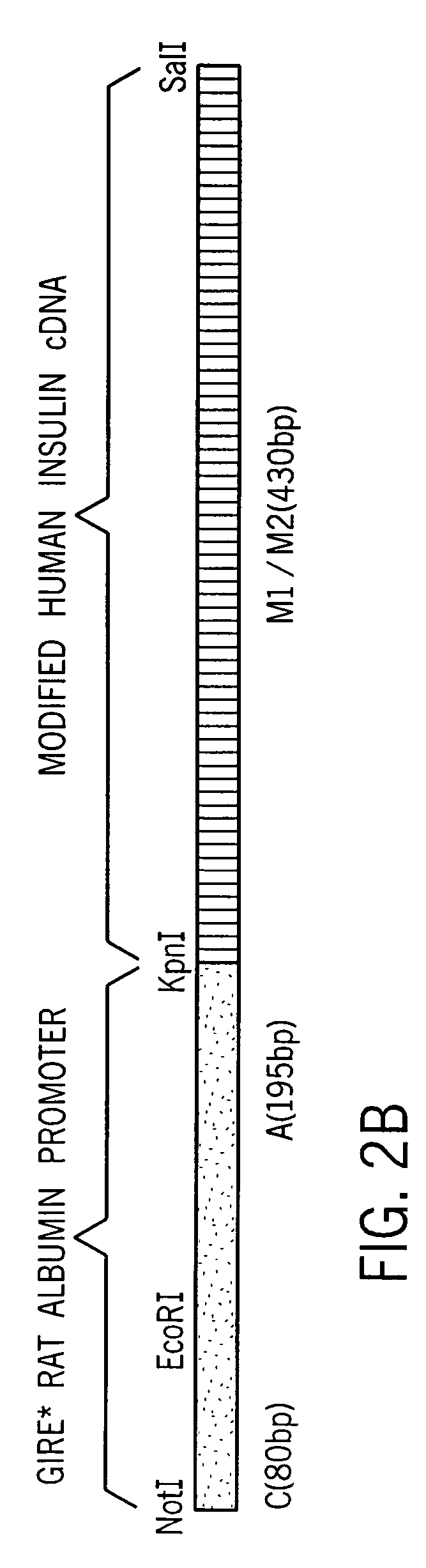
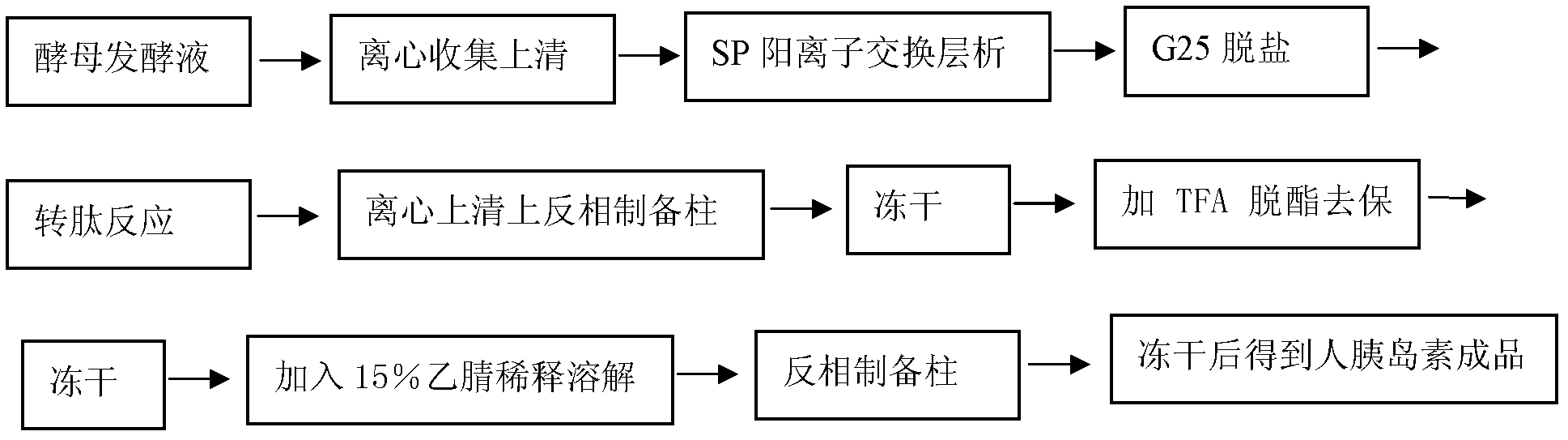
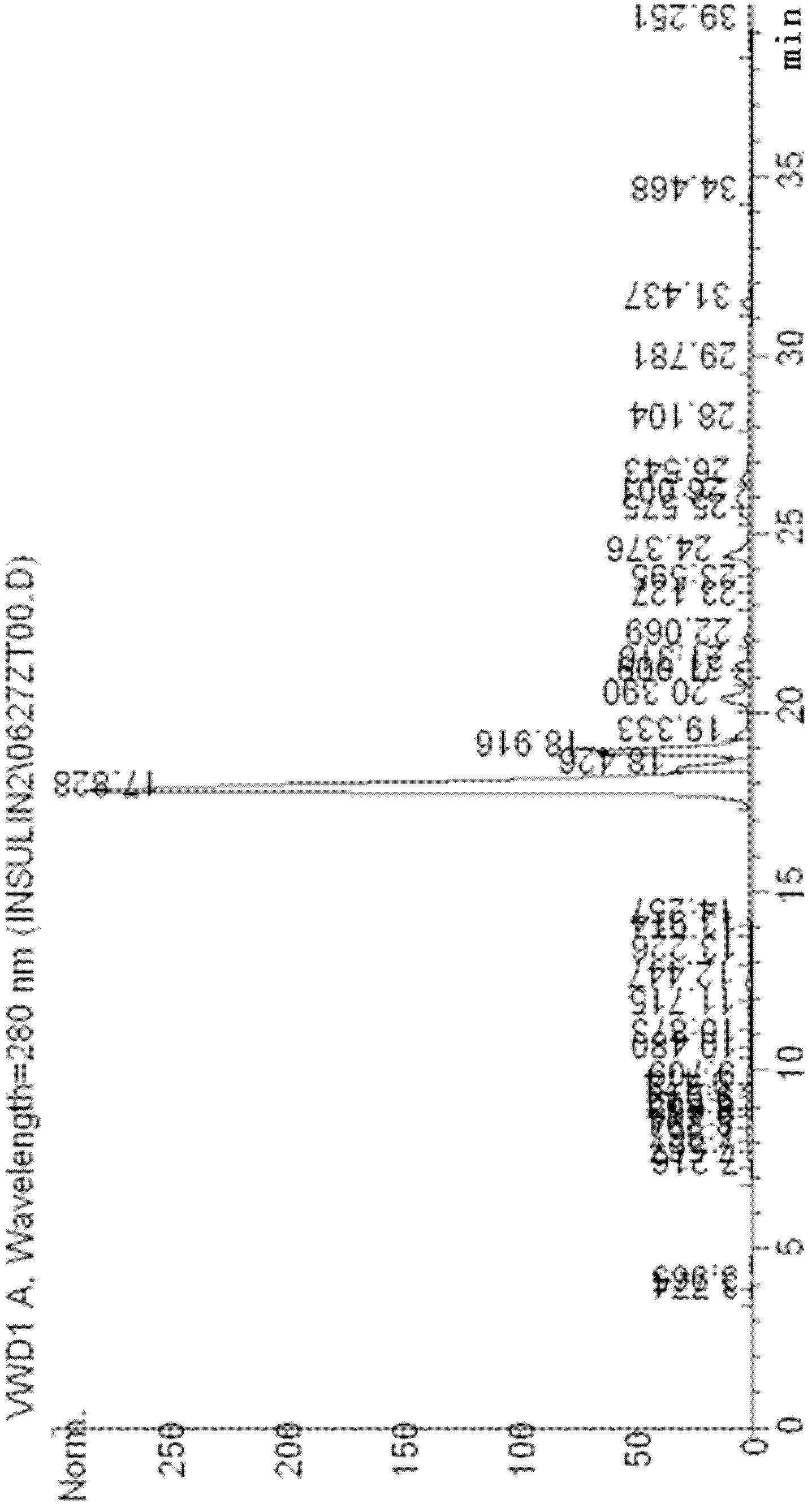
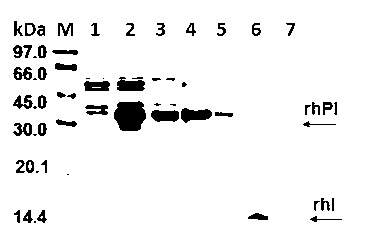Patents
Literature
121 results about "Proinsulin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
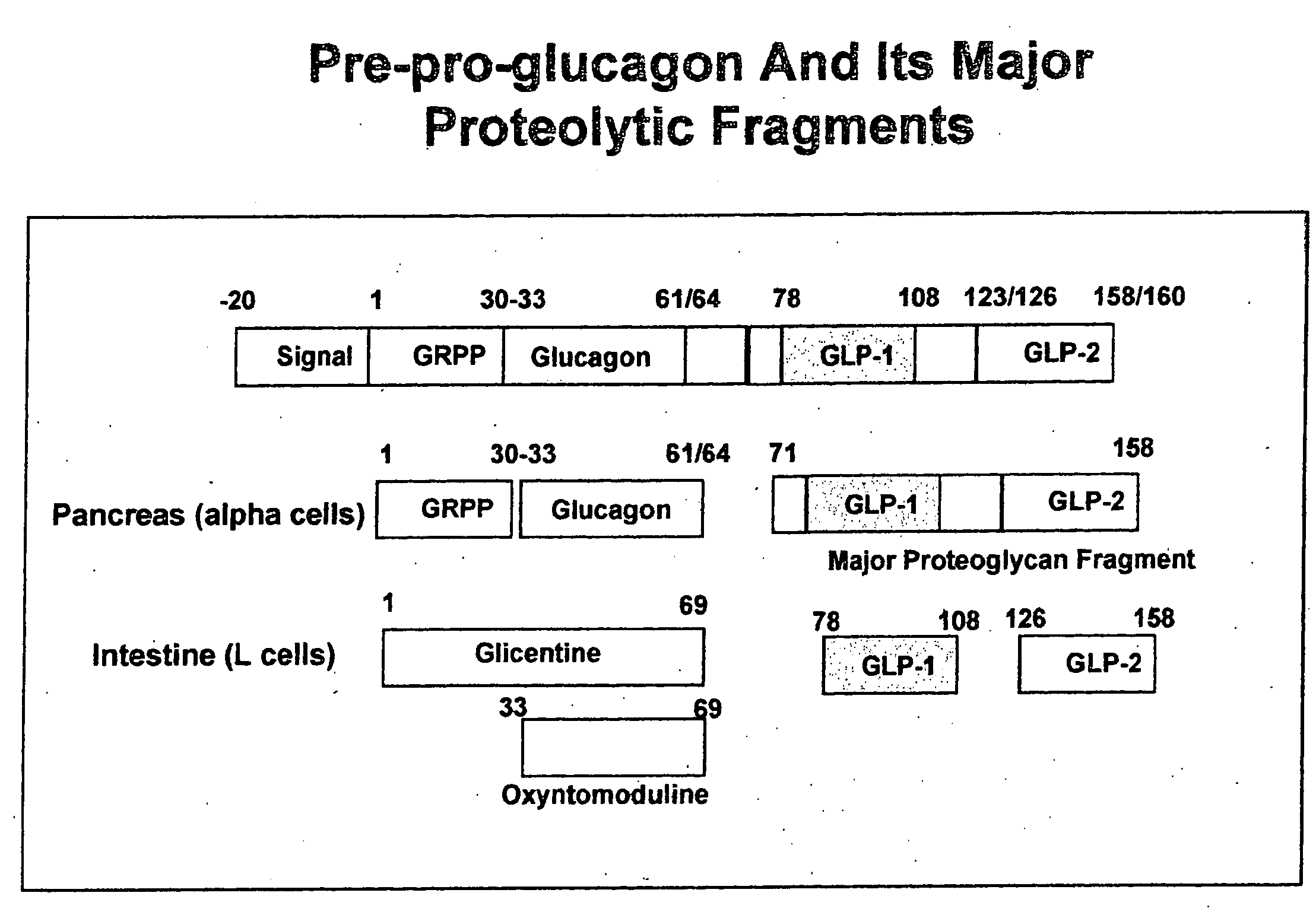
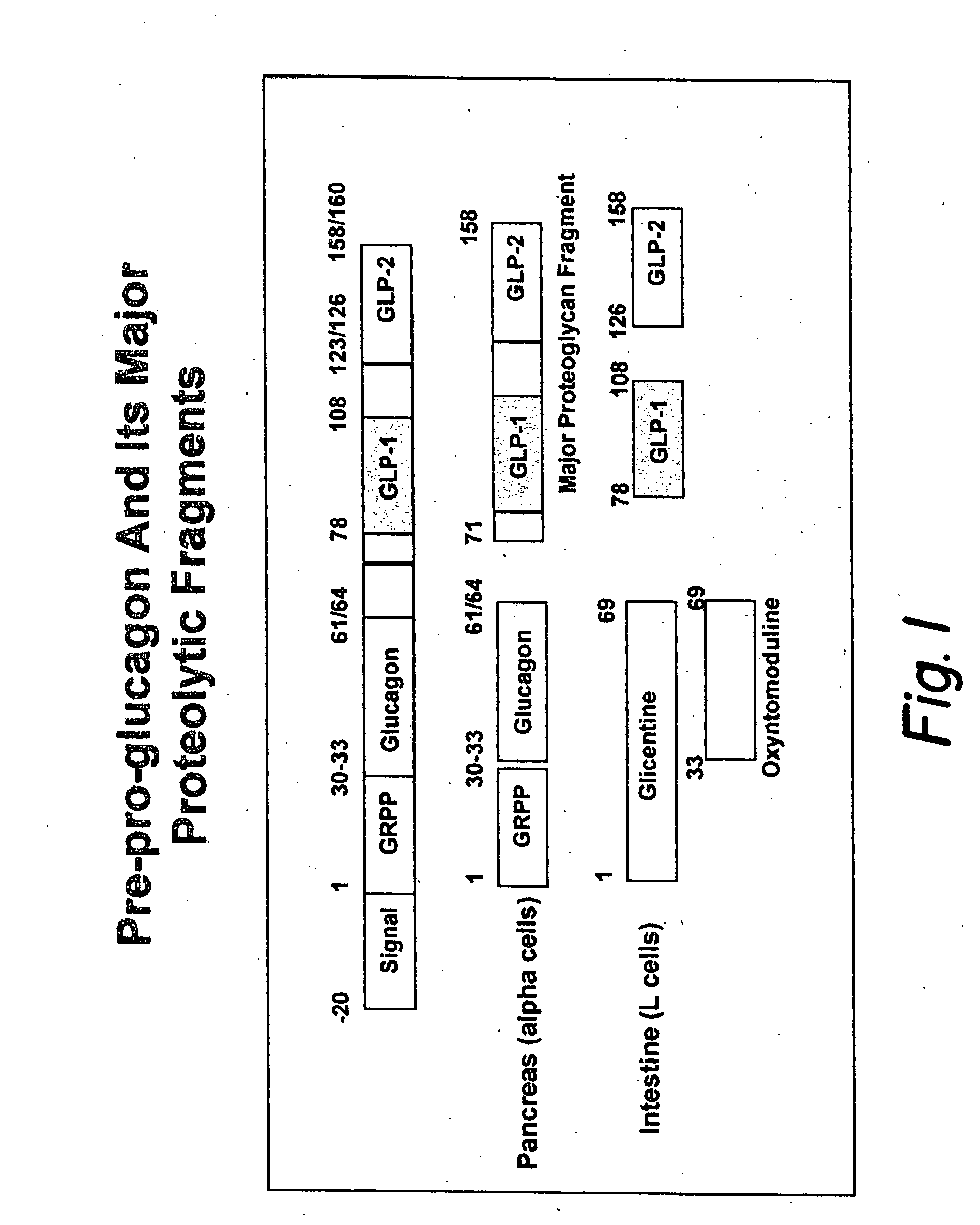
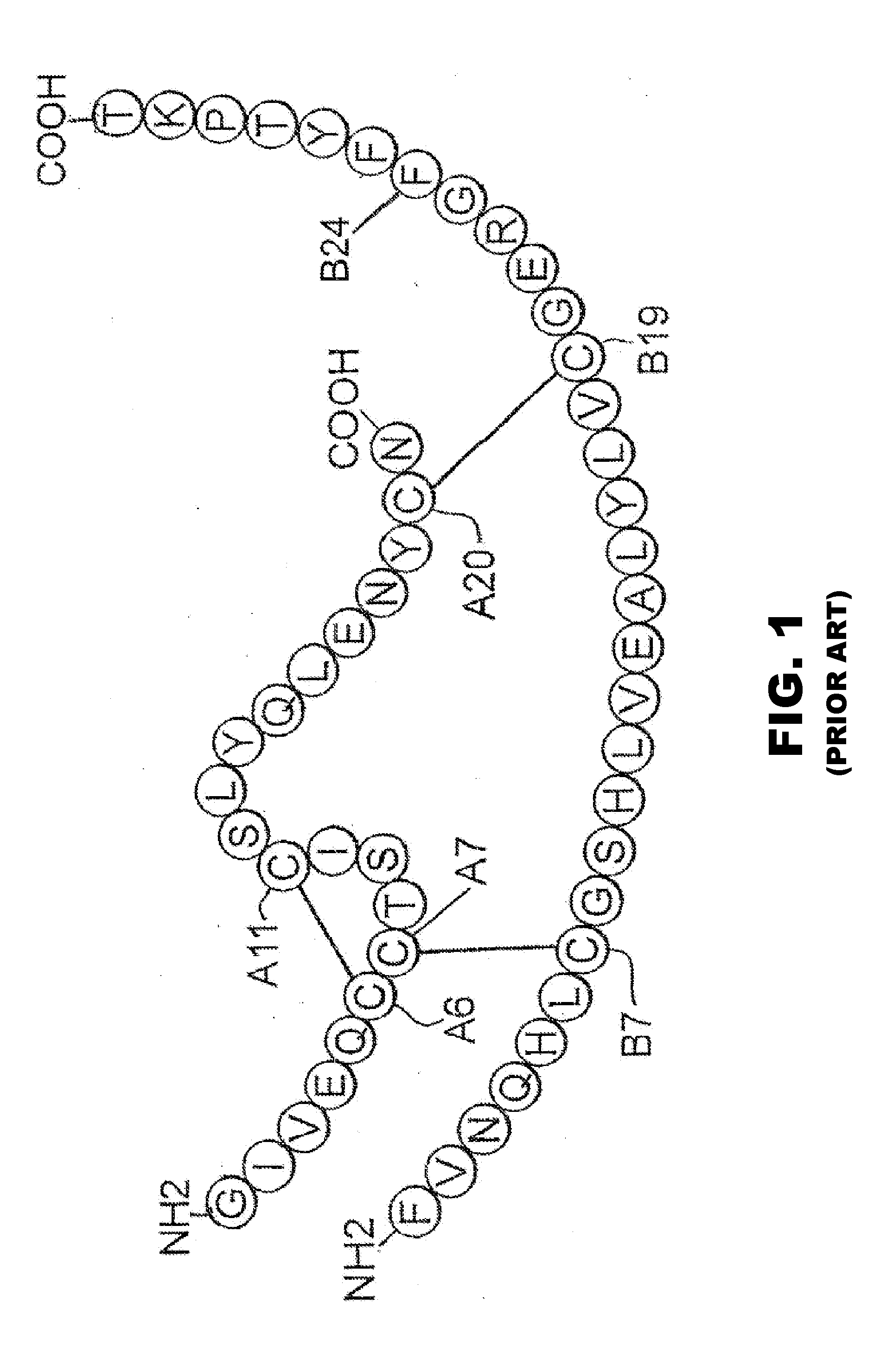
Proinsulin is the prohormone precursor to insulin made in the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans, specialized regions of the pancreas. In humans, proinsulin is encoded by the INS gene. The islets of Langerhans only secrete between 1% and 3% of proinsulin intact. However, because proinsulin has a longer half life than insulin, it can account for anywhere from 5–30% of the insulin-like structures circulating in the blood. There are higher concentrations of proinsulin after meals and lower levels when a person is fasting. Additionally, while proinsulin and insulin have structural differences, proinsulin does demonstrate some affinity for the insulin receptor. Due to the relative similarities in structure, proinsulin can produce between 5% and 10% of the metabolic activity similarly induced by insulin.
Use of diazoxide for the treatment of metabolic syndrome and diabetes complications
InactiveUS6197765B1Reduce releaseReduce weightHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsHyperinsulinemiaSecondary hyperlipidemia
The present invention discloses a treatment for syndrome-X, and resulting complications, that include hyperlipidemia, hypertension, central obesity, hyperinsulinemia and impaired glucose intolerance. Diabetic complications include excess proinsulin levels.
Owner:VARDI PNINA +1
Method of reducing serum proinsulin levels in type 2 diabetics
InactiveUS20050153874A1Lower Level RequirementsLow serum levelsPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin responseLevel insulin
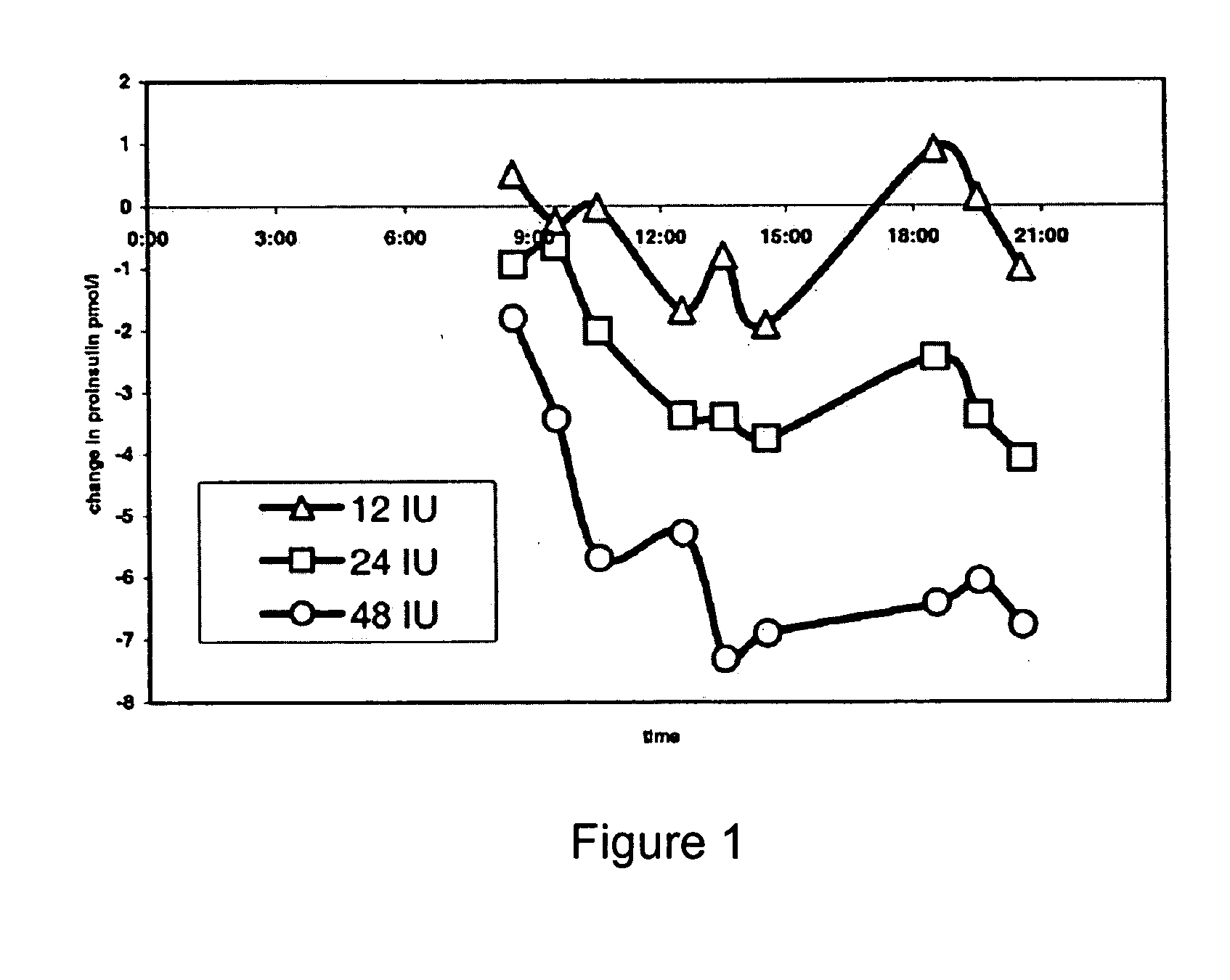
Methods are provided for reducing serum proinsulin levels, lessening post-prandial pancreatic stress, and reducing risk factors for atherosclerosis in subjects with diabetes mellitus, type 2. The method includes administration of insulin in a manner that mimics the meal-related first phase insulin response, using a dose sufficient to reduce serum levels of proinsulin. In some embodiments of the method insulin administration is commenced early in the course of the disease. Mimicking first phase kinetics, peak serum insulin levels can be reached within about 18 minutes of administration. In increasingly preferred embodiments peak serum insulin levels can be reached within about 15, 12, or 10 minutes of administration. Serum insulin levels return to baseline within about two hours of administration.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Insoluble compositions for controlling blood glucose
InactiveUS6531448B1Easy to controlReduce rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineDivalent metal
The present invention relates to insoluble compositions comprising a protein selected from the group consisting of insulin, insulin analogs, and proinsulins; a derivatized protein selected from the group consisting of derivatized insulin, derivatized insulin analog, and derivatized proinsulin; a complexing compound; a hexamer-stabilizing compound; and a divalent metal cation. Formulations of the insoluble composition are suitable for both parenteral and non-parenteral delivery for treating hyperglycemia and diabetes. Microcrystal forms of the insoluble precipitate are pharmaceutically analogous to the neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin crystal form. Surprisingly, it has been discovered that suspension formulations of such insoluble compositions possess unique and controllable dissolution properties that provide therapeutically advantageous glucodynamics compared with insulin NPH formulations.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
C-peptide specific assay procedure
InactiveUS6929924B2Highly accurate C-peptideStrong specificityAnimal cellsBiological material analysisC-peptideProinsulin
The present invention relates to a specific C-peptide assay method which can eliminate all interference due to proinsulin and its intermediates, in particular des-31,32-proinsulin and / or des-64,65-proinsulin. It also relates to antibodies for carrying out this assay.
Owner:BIO RAD EURO GMBH
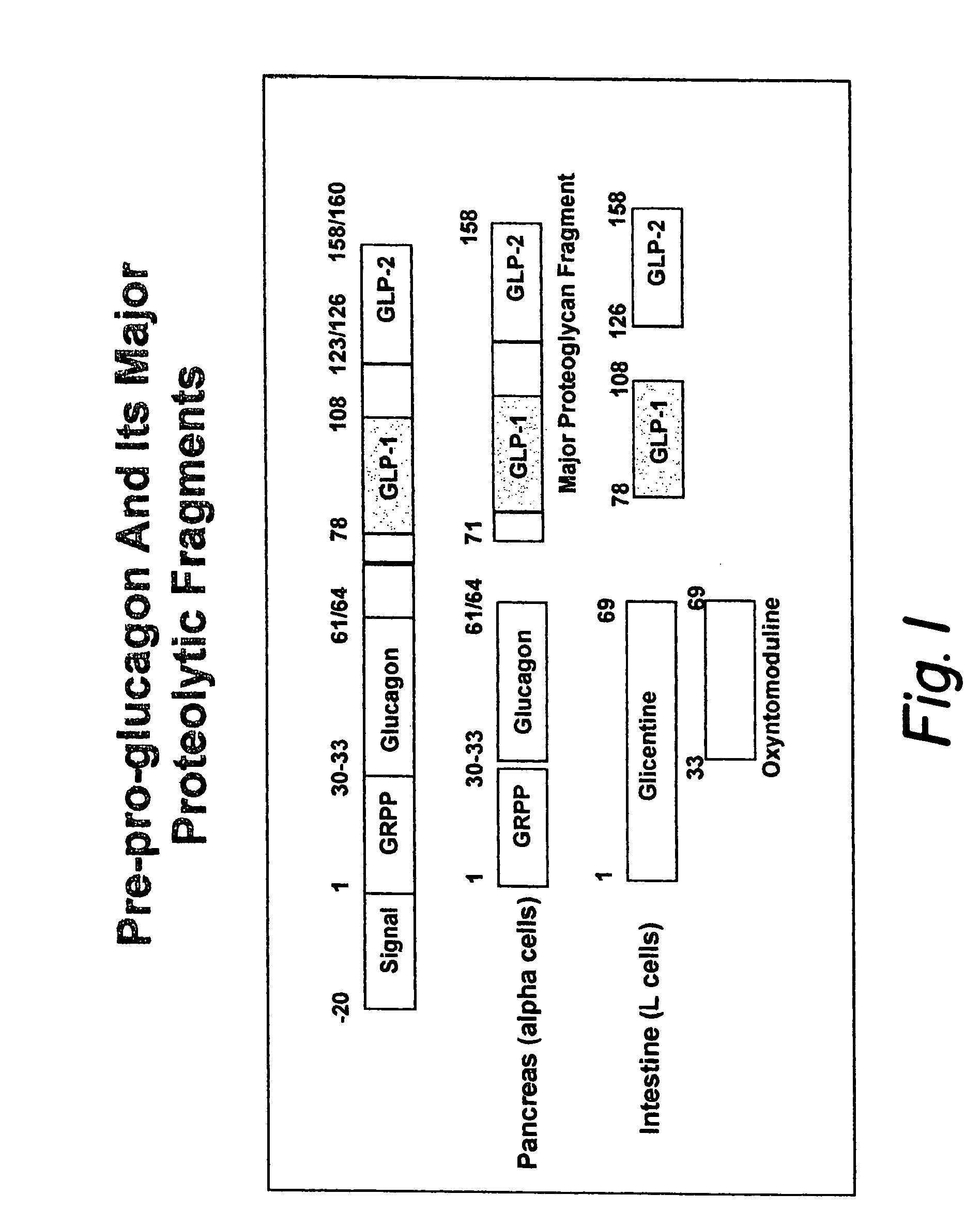
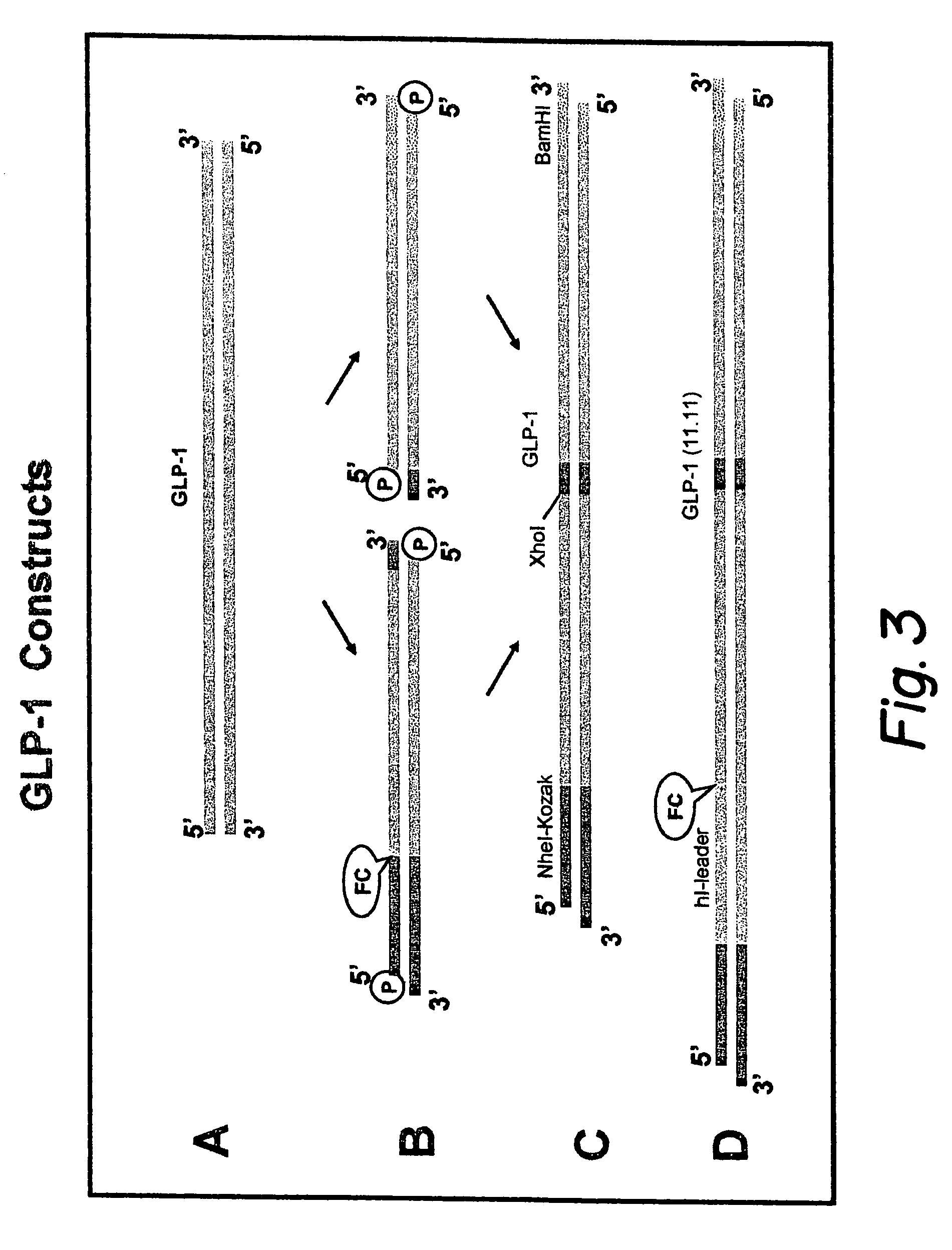
Modified nucleotide sequence encoding glucagon-like peptide-1 (glp-1), nucleic acid construct comprising same for production of glucagon-like peptide-1 (glp-1), human cells comprising said construct and insulin-producing constructs, and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20080299096A1Reduce weightPromote productionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaNucleotide
An isolated chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequence encoding a human pro-insulin leader, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and a furin cleavable site between the human pro-insulin leader sequence and the GLP-1 is provided. Also provided is an isolated modified chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequence encoding a human pro-insulin leader, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and a furin cleavable site between the human pro-insulin leader sequence and the GLP-1. Recombinant expression vectors comprising the chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequences, which produce GLP-1 constitutively are provided, as are human cells transfected with such an expression vector in combination with an expression vector comprising a proinsulin nucleic acid sequence and an expression vector comprising a furin and a glucose-regulatable TGF-alpha promoter. Methods of producing human GLP-1 constitutively are provided as are method of producing GLP-1 and insulin or in a glucose-dependent manner using such transfected cells. Methods of treating a subject having Type II diabetes and methods of treating a subject prone to hyperglycemia or suffering from hyperglycemia are provided in which transfected cells produce human GLP-1 and insulin in a glucose-dependent manner. Also provided are methods of reducing weight in a subject by implanting into the subject transfected cells which produce human GLP-1 and insulin in a glucose-dependent manner.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Insoluble compositions for controlling blood glucose
InactiveUS20030144181A1Easy to controlReduce ratePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineDivalent metal
The present invention relates to insoluble compositions comprising a protein selected from the group consisting of insulin, insulin analogs, and proinsulins; a derivatized protein selected from the group consisting of derivatized insulin, derivatized insulin analog, and derivatized proinsulin; a complexing compound; a hexamer-stabilizing compound; and a divalent metal cation. Formulations of the insoluble composition are suitable for both parenteral and non-parenteral delivery for treating hyperglycemia and diabetes. Microcrystal forms of the insoluble precipitate are pharmaceutically analogous to the neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin crystal form. Surprisingly, it has been discovered that suspension formulations of such insoluble compositions possess unique and controllable dissolution properties that provide therapeutically advantageous glucodynamics compared with insulin NPH formulations.
Owner:BRADER MARK LAURENCE
Method for preparing recombinant human insulin and analogs of recombinant human insulin
InactiveCN101519446AHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesInsulin activityEscherichia coli
The invention provides a molecule (Preproinsulin) of human proinsulin with a novel N-terminal expressed peptide sequence or analogs of the human proinsulin, a method for producing human insulin by using the molecule, and processes for building related expression vectors and engineering cells and expressing and purifying human proinsulin. The DNA sequence of the human proinsulin coded by the N-terminal expressed peptide sequence or the analogs of the human proinsulin is first introduced into a prokaryotic expression vector and then transferred into an escherichia coli to express the molecule in form of an inclusion body. The invention has the advantages that: the product has high expression amount and is easy to purify; the preparation method avoids the use of CNBr; and the process for processing the recombinant insulin is simple.
Owner:AMTEK PHARMA
Insulin epitopes for the treatment of type 1 diabetes
InactiveUS20070129307A1Loss rateReduce in quantityHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeAmyloid
The invention provides compounds and methods useful for the diagnosis, prediction, therapy, or prophylaxis of type 1 diabetes. The compounds of the invention include peptides derived from IAPP (islet amyloid polypeptide) precursor, proinsulin, insulin, IGRP, IA-1 or phogrin peptides.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Treatment of diabetes with synthetic beta cells
InactiveUS6933133B2Reduce formationReduce expressionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGlucose polymersActrapid insulin
Disclosed is a method for obtaining glucose-regulated expression of active insulin in the cells of a mammalian subject. The method involves delivering into the subject a genetic construct comprising a coding sequence for a human proinsulin operably connected a promoter functional in the host cells. The construct includes a glucose responsive regulatory module having at least one glucose inducible regulatory element comprising a pair of CACGTG motifs linked by a five base nucleotide sequence, which confers glucose inducible expression of the proinsulin coding sequence. To ensure proper processing of the proinsulin to active insulin, the coding sequence was modified to direct the synthesis of a mutant proinsulin polypeptide having amino acid sequences that can be cleaved to mature insulin in suitable host cells, such as hepatocytes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
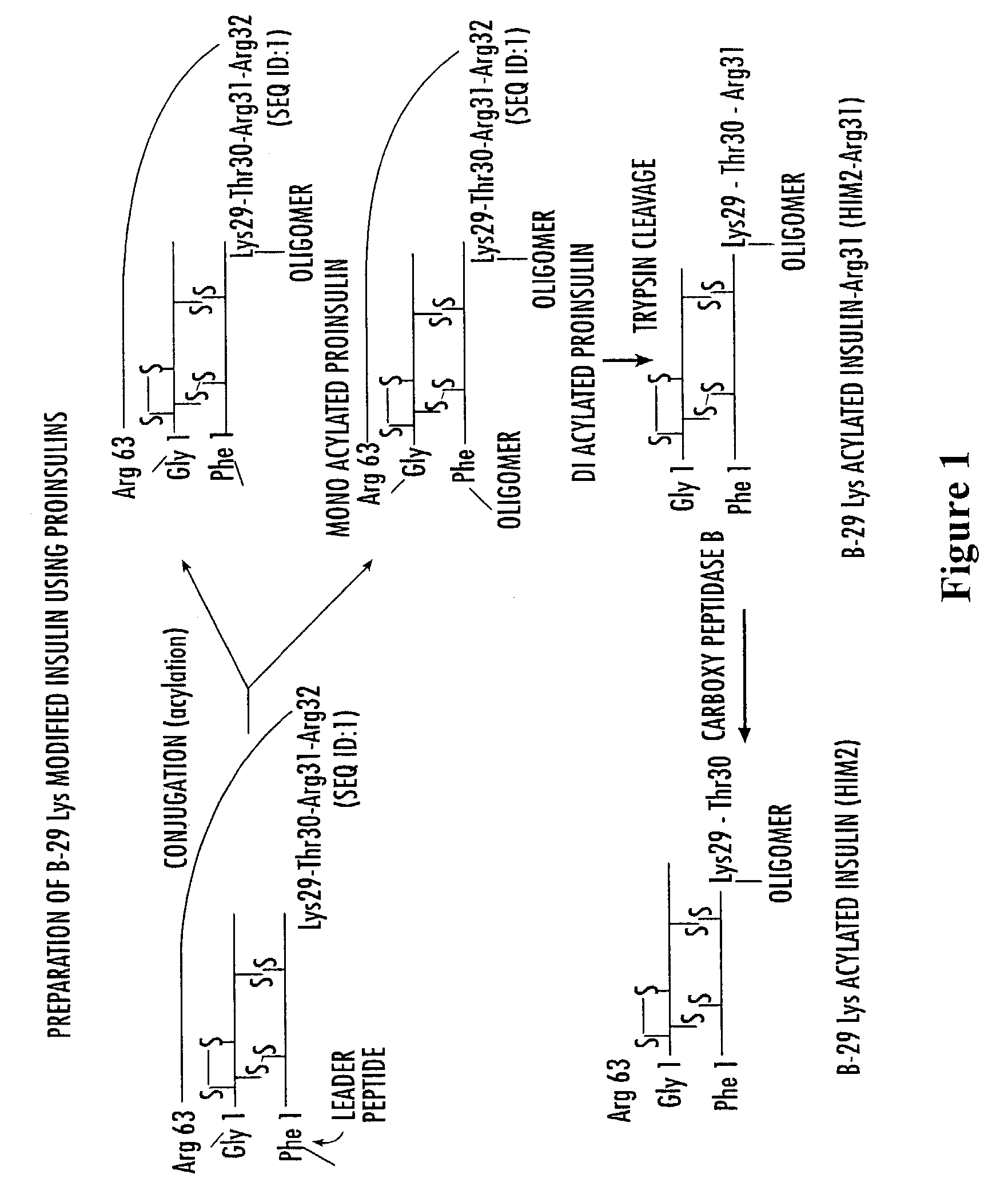
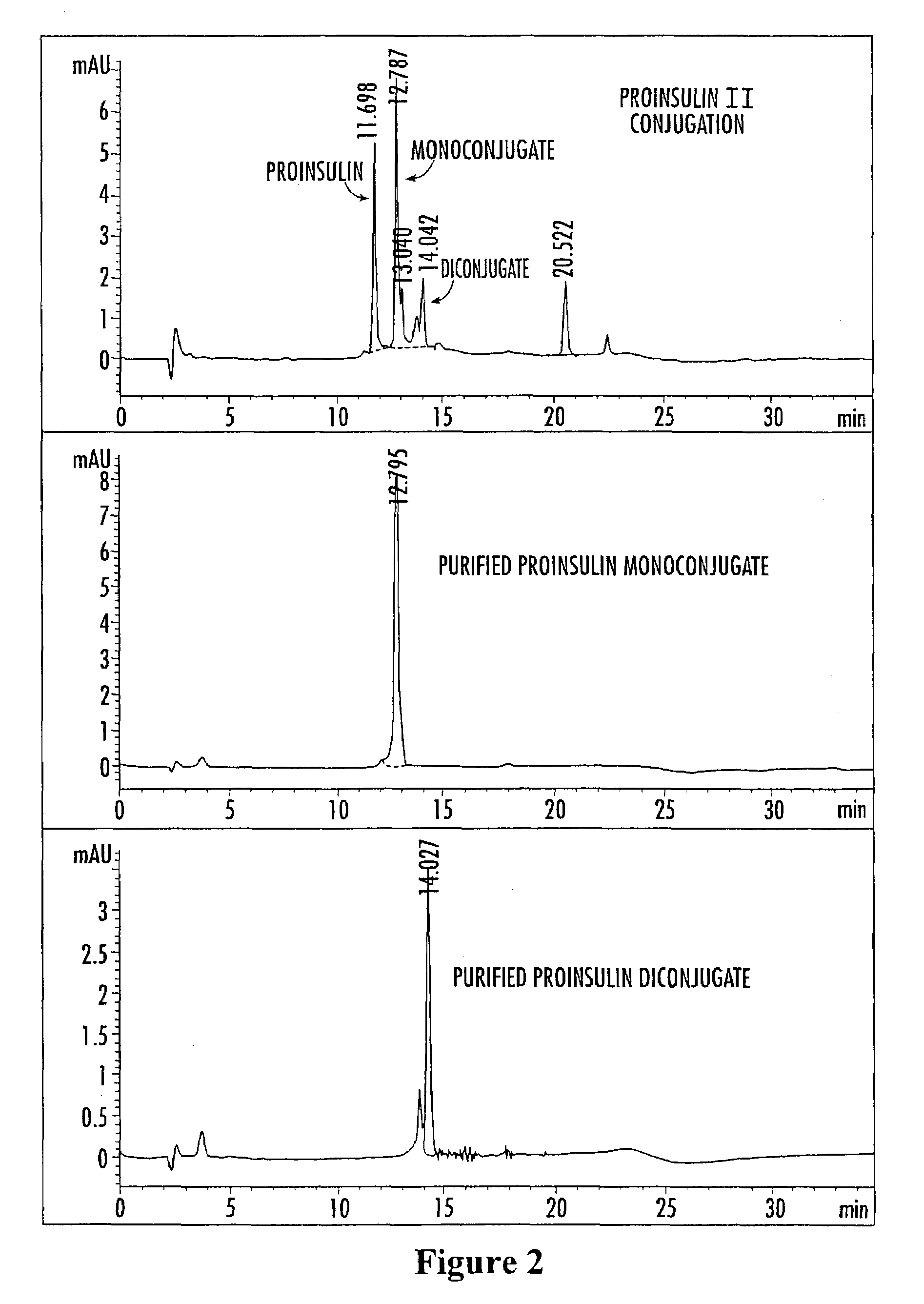
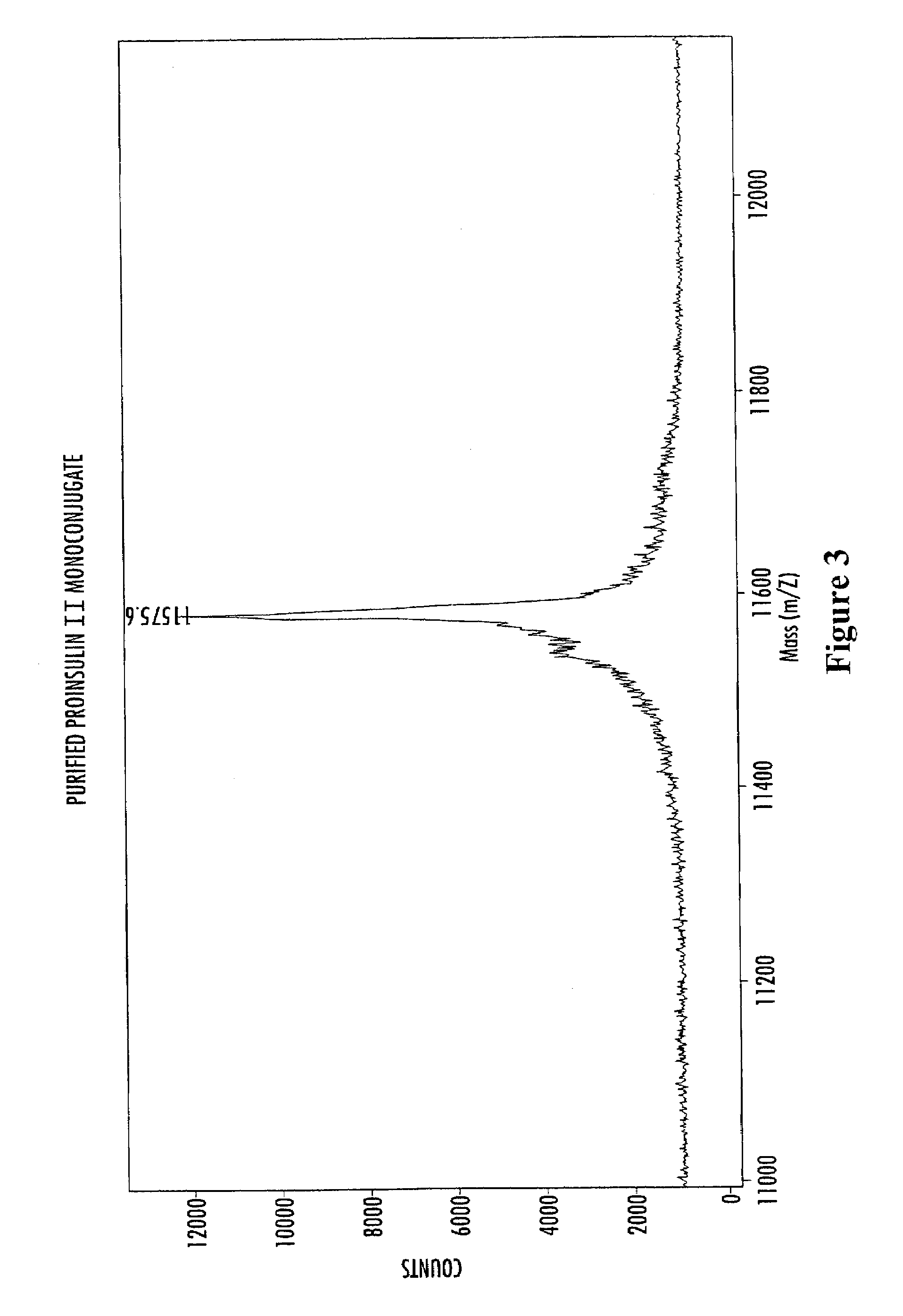
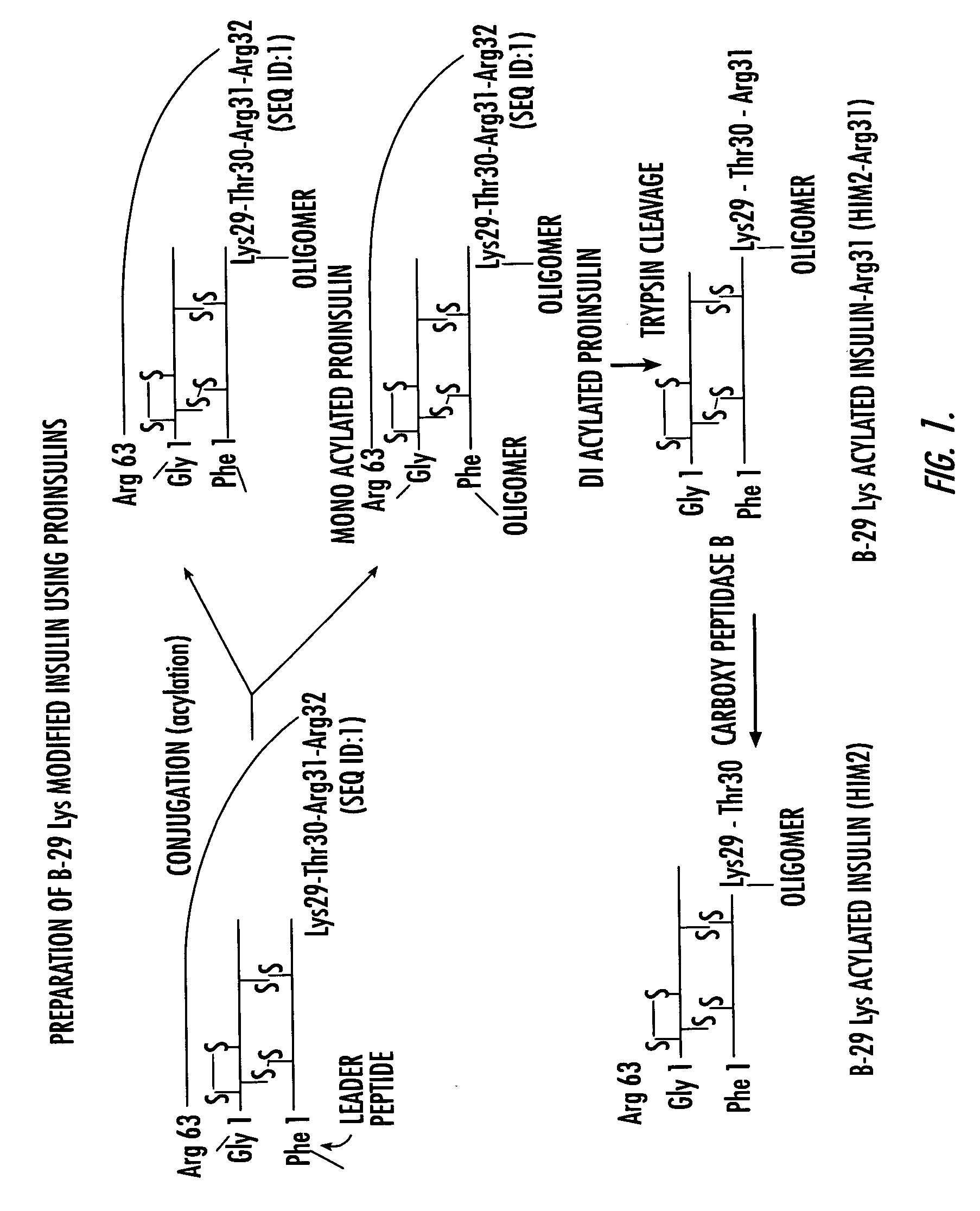
Methods of synthesizing insulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates, and proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates and methods of synthesizing same
InactiveUS6913903B2Less expensiveHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesOligomerProinsulin
Methods for synthesizing proinsulin polypeptides are described that include a contacting a proinsulin polypeptide including an insulin polypeptide coupled to one or more peptides by peptide bond(s) capable of being cleaved to yield the insulin polypeptide with an oligomer under conditions sufficient to couple the oligomer to the insulin polypeptide portion of the proinsulin polypeptide and provide a proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate, and cleaving the one or more peptides from the proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate to provide the insulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate. Methods of synthesizing proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates are also described as are proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates. Methods of synthesizing C-peptide polypeptide-oligomer conjugates are also described.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Method for producing recombined insulin human
ActiveCN101173006ASimple processReduce manufacturing costPeptide preparation methodsInsulinsEscherichia coliInsulin activity
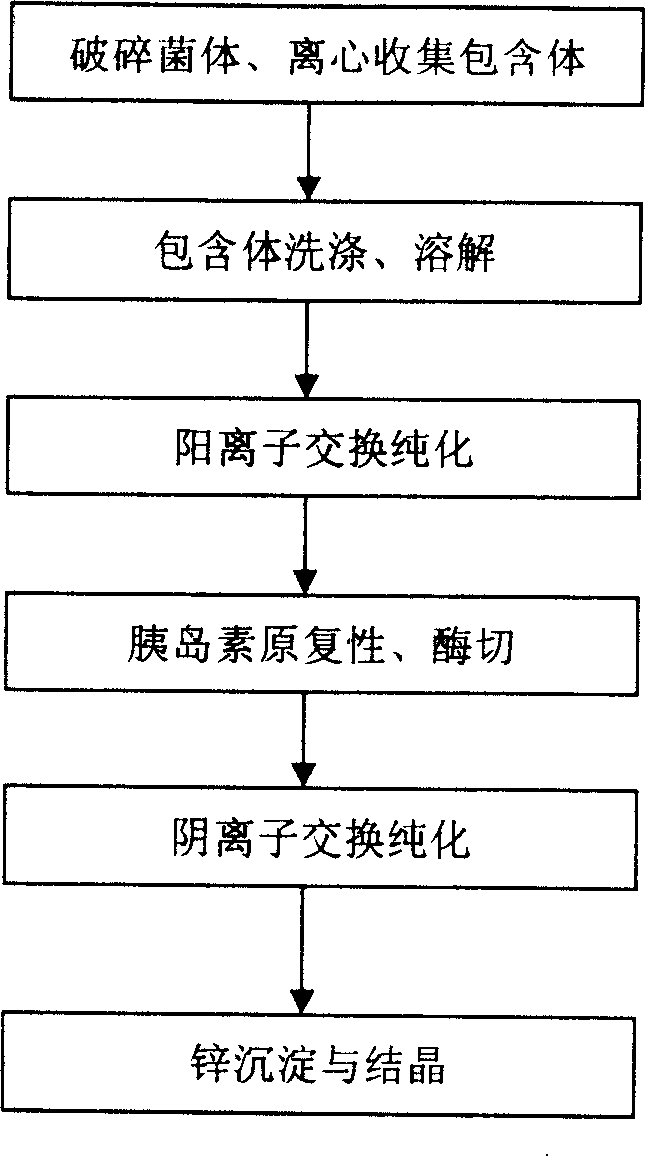
The invention discloses a preparation method of recombinant human insulin, which relates to the protein polypeptide type medicine field. The technical problem needed to be solved by the invention aims at providing a preparation method for Escherichia coli to express the recombinant human insulin in order to overcome the technical disadvantages in the prior art of using the poisonous and harmful substance CNBr and having a complex production process. The preparation method for the recombinant human insulin of the invention comprises the steps of: thallus crashing, inclusion body dissolving, proinsulin sulfonating, purifying proinsulin, and proinsulin renaturation, enzyme cutting transmission, etc., and the preparation method is characterized in that during the inclusion body dissolving process, the -SH of proinsulin is transformed into -SSO3<->, and then human insulin is obtained through purifying the sulfonated proinsulin, reduction renaturation and enzyme cutting transmission by positive ion, and then through the negative ion exchange layer purification. The preparation method of the recombinant human insulin of the invention does not use the CNBr and has simple technique with high human insulin yield coefficient and purity.
Owner:JIANGSU WANBANG BIOPHARMLS +1
Preparation method for insulin aspart through recombinant expression by using yeast
ActiveCN105087724AImprove digestion efficiencyLow miscut rateMicroorganism based processesInsulinsEnzyme digestionThreonine
The invention discloses a preparation method for insulin aspart through recombinant expression by using yeast, and concretely relates to a preparation method for insulin aspart through recombinant expression by using pichia yeast. Concretely, the method comprises the following technological process: effectively secreting and expressing human aspart proinsulin, performing lysyl endopeptidase single enzyme digestion to obtain insulin aspart deleting B30, coupling with a threoninate, and performing deprotection, anti-phase purification and crystallization. The method is relatively suitable for industrialized preparation of recombinant insulin aspart.
Owner:CHONGQING PEG BIO BIOTECH CO LTD
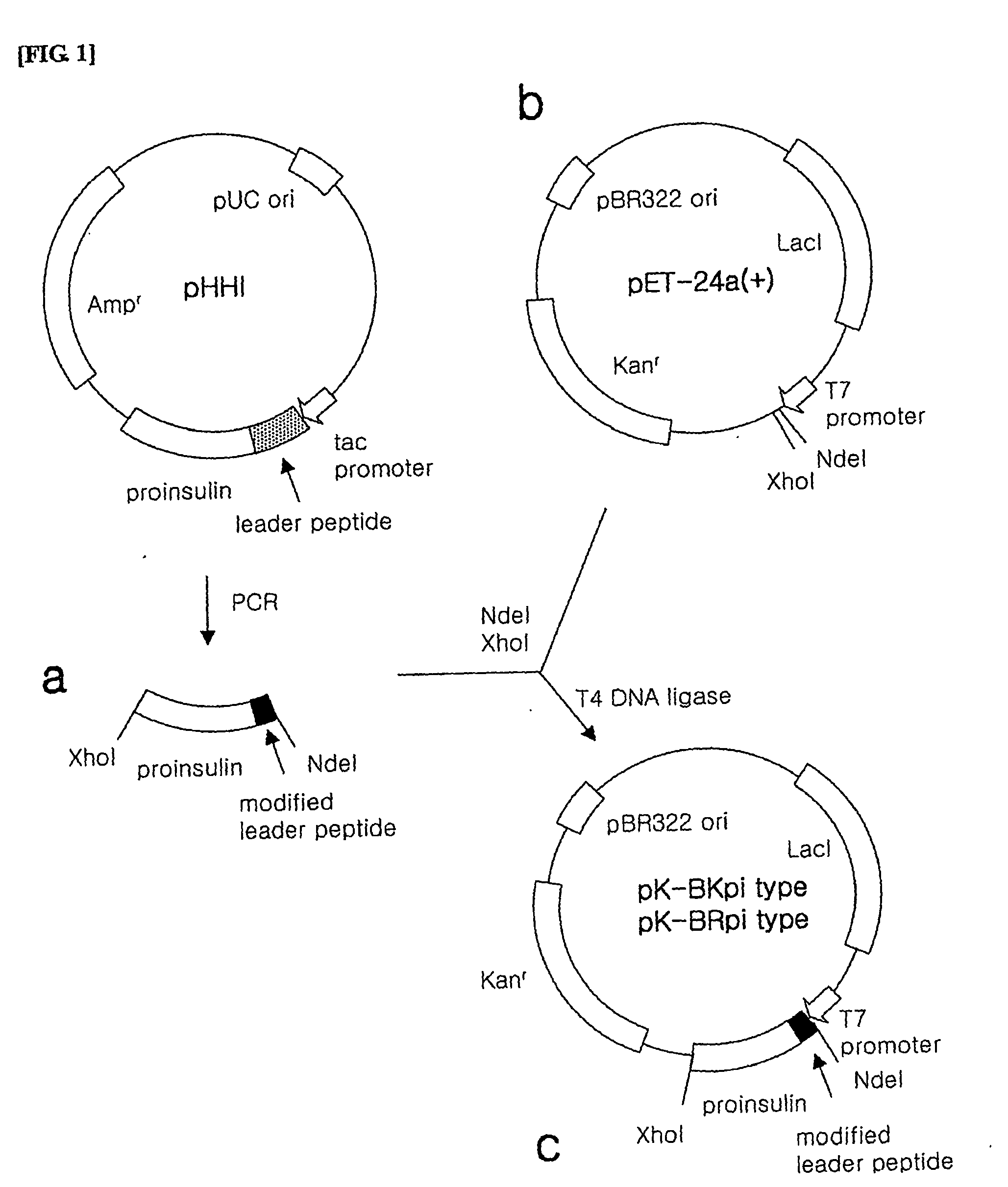
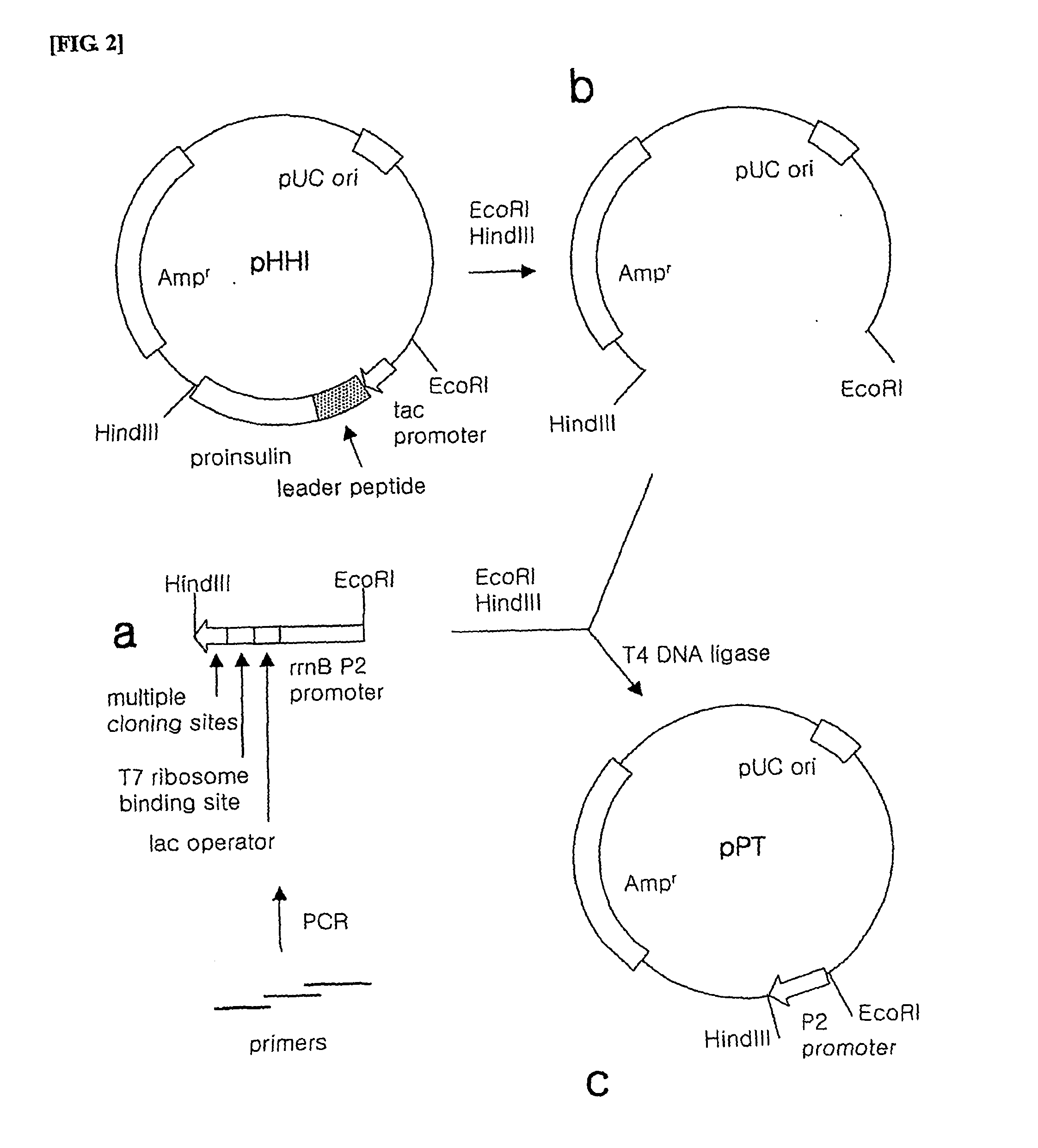
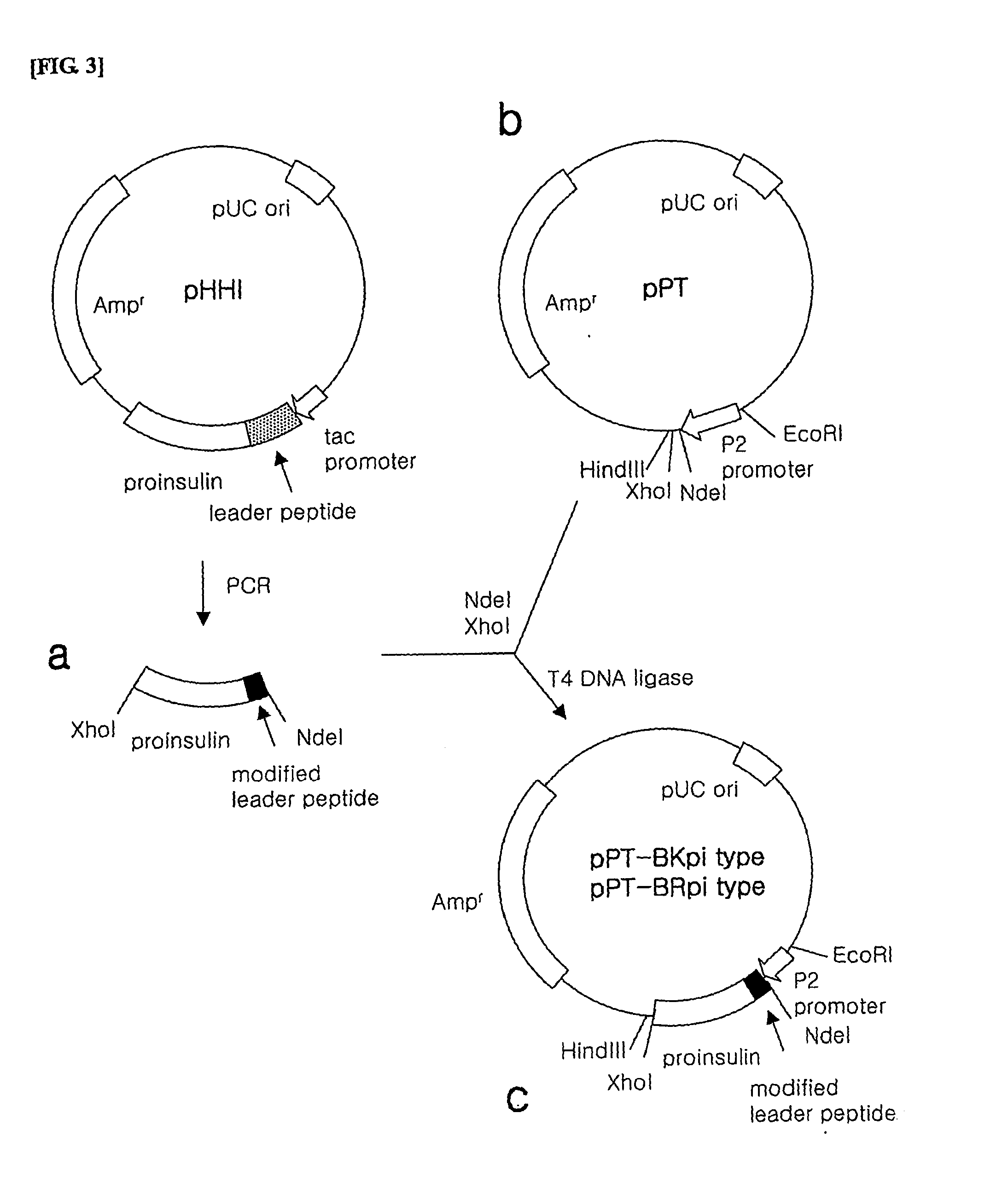
Method for producing recombined human proinsulin
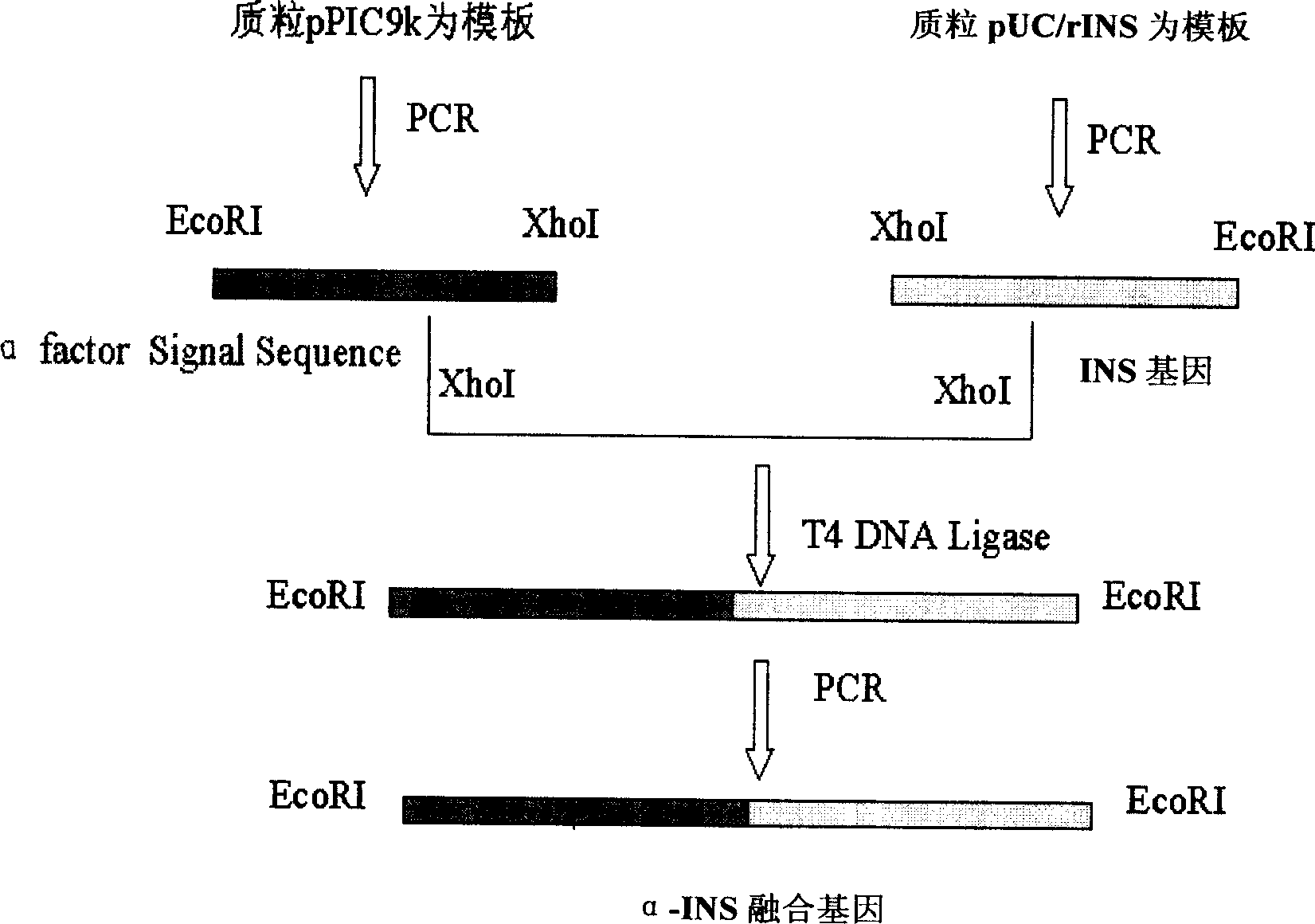
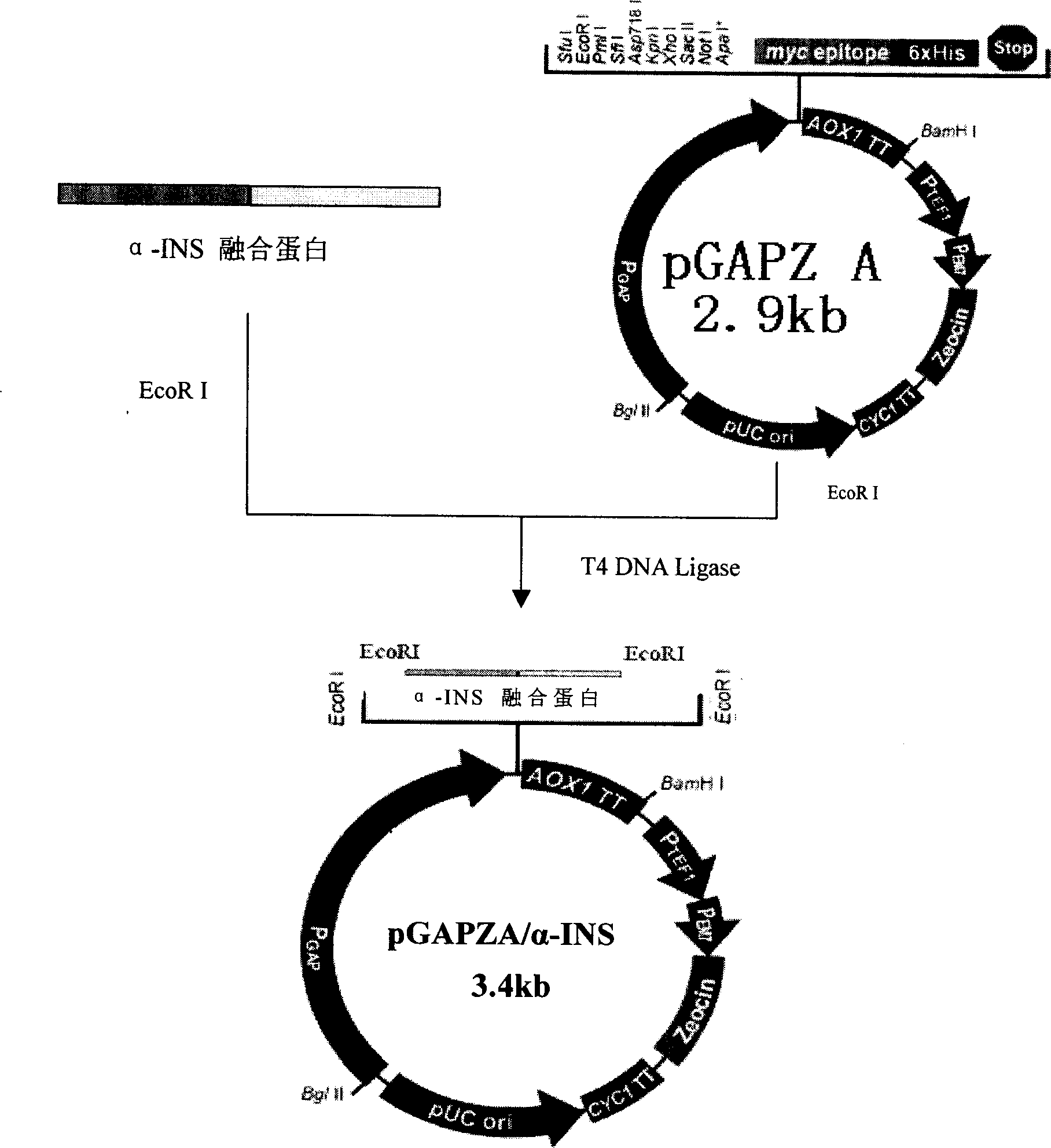
This invention provides a method for producing recombinant human proinsulin from N-end leader peptide, and relevant expression vector. The method comprises: (1) fusing yeast alpha-factor leader peptide sequence and the human proinsulin N-end leader peptide, and introducing into a yeast constitutive expression vector; (2) transferring into Pichia pastoris cells to realize constitutive and secretory expression; (3) fermenting and purifying. The recombinant human proinsulin has such advantages as high stability, high activity and simple production. The method has such advantages as high expression level, high purification yield, and high efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEWSUMMIT BIOPHARMA
Modified nucleotide sequence encoding glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), nucleic acid construct comprising same for production of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), human cells comprising said construct and insulin-producing constructs, and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7829664B2Reduce weightPromote productionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaNucleotide
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
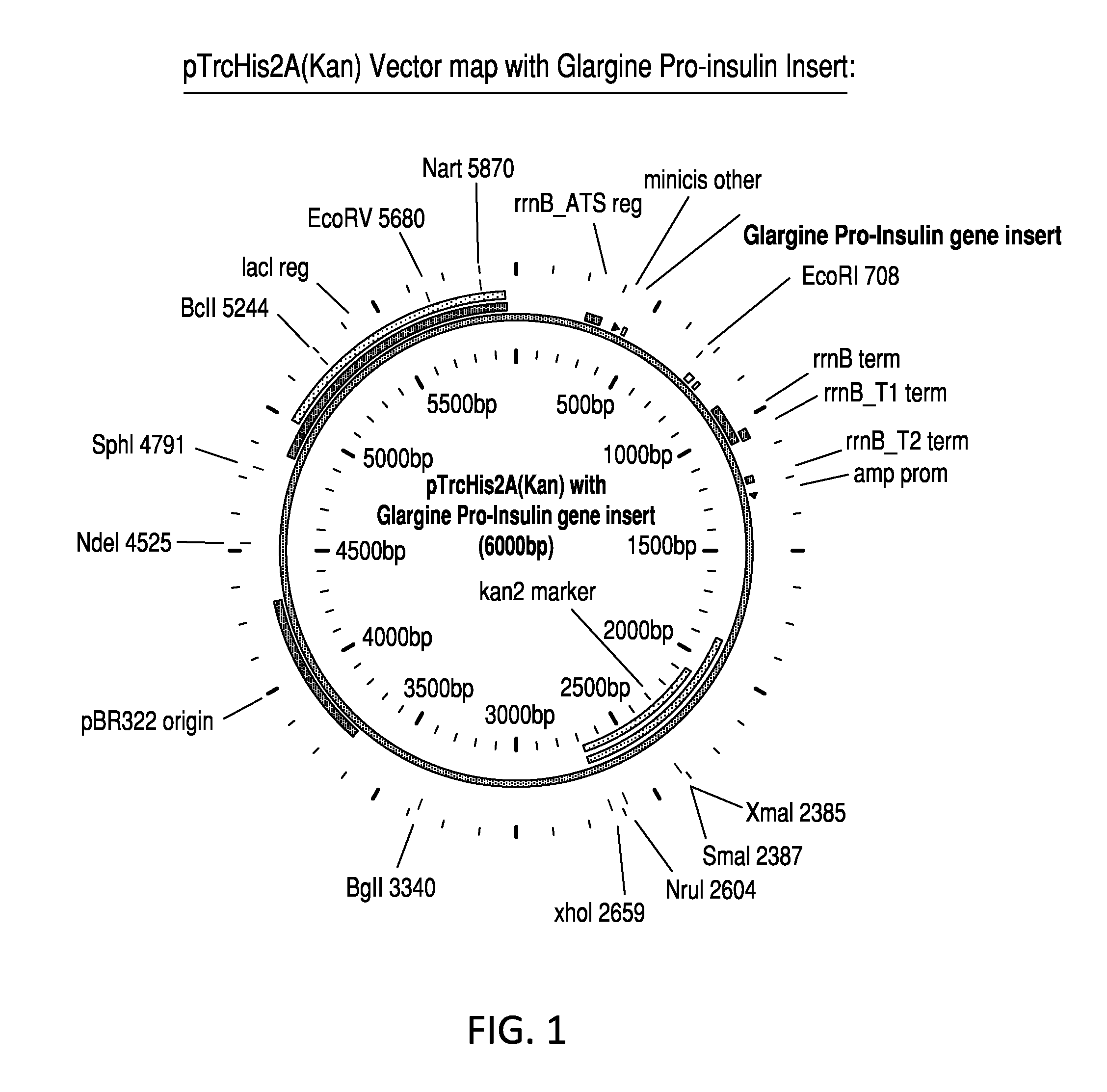
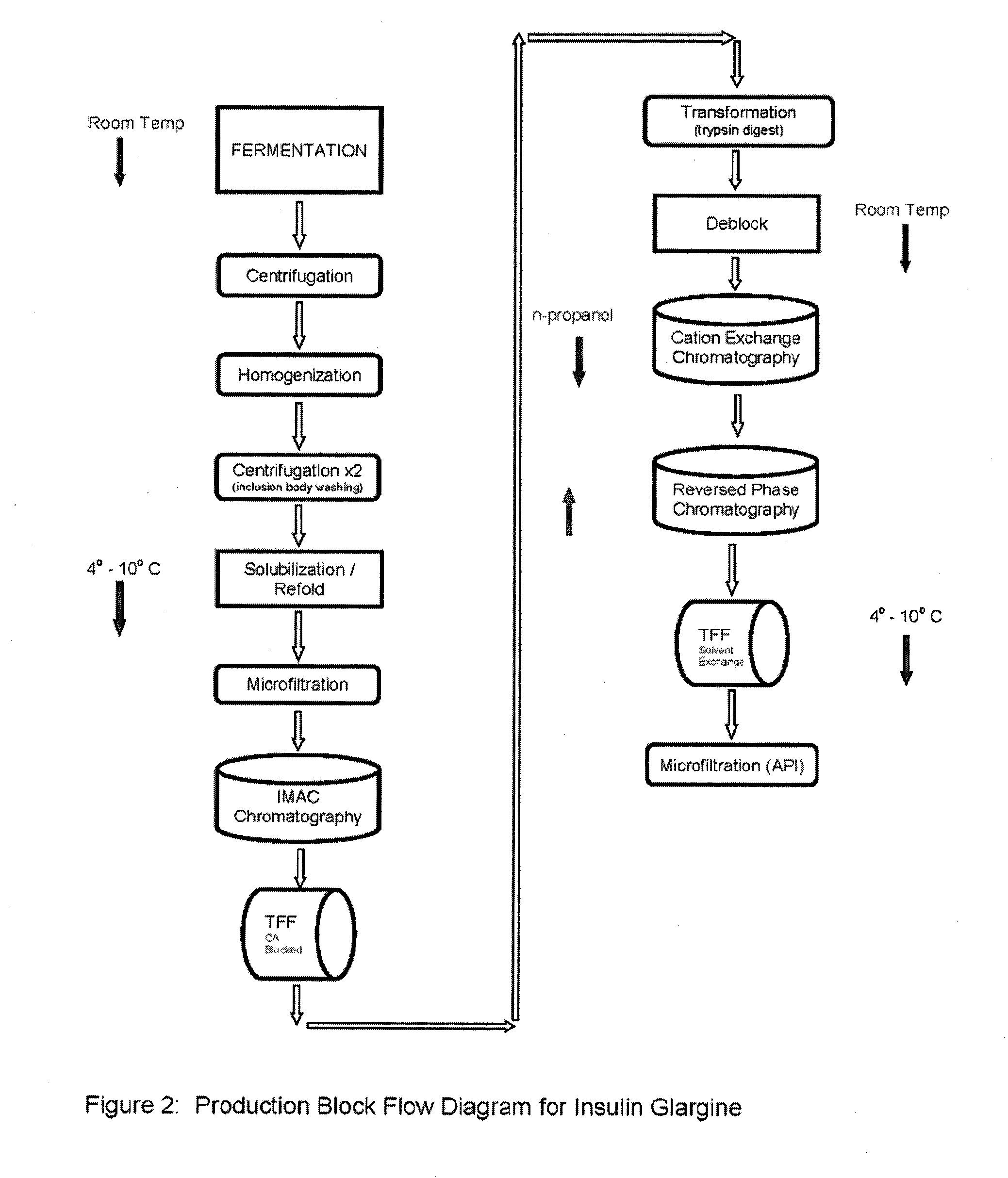
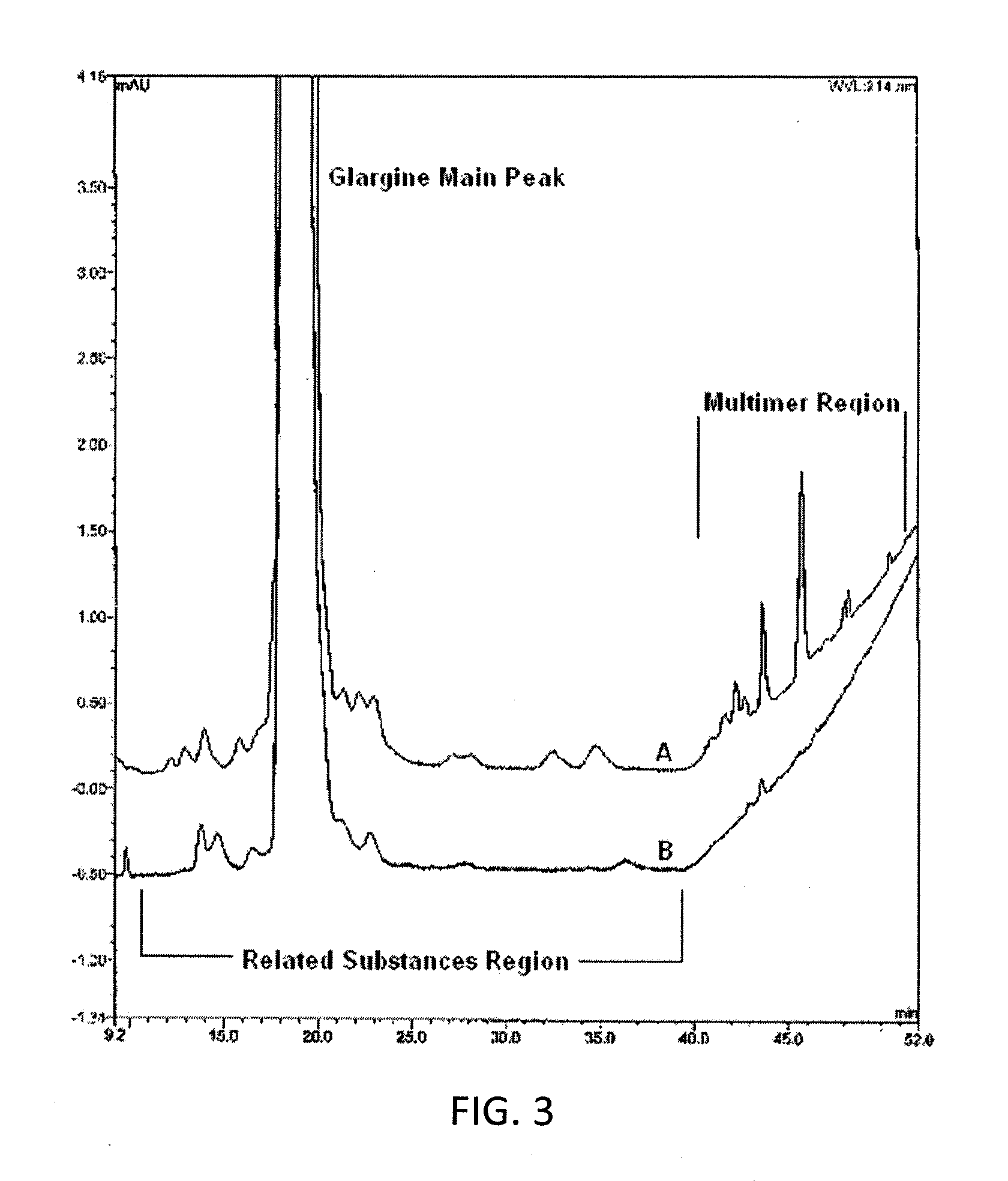
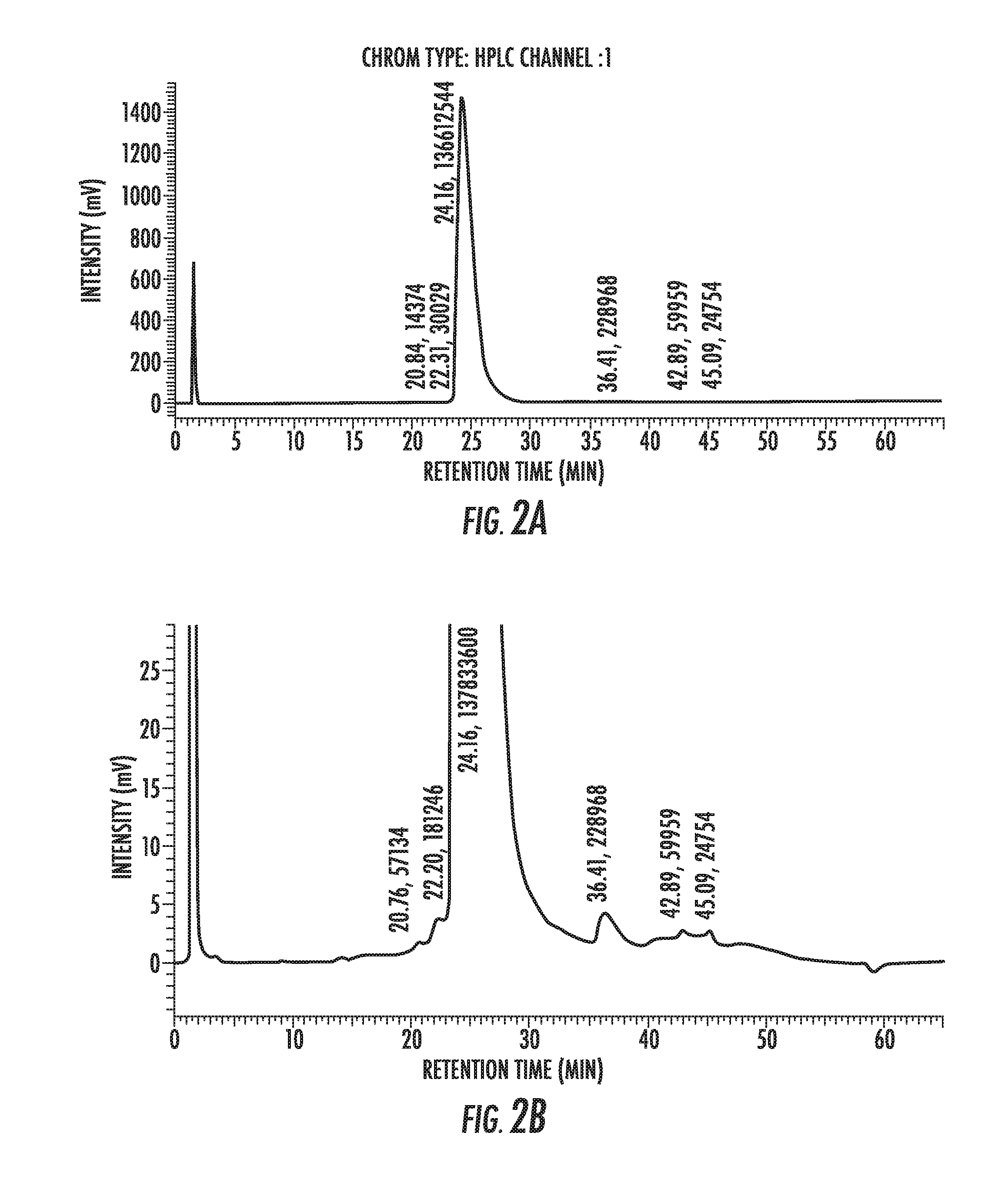
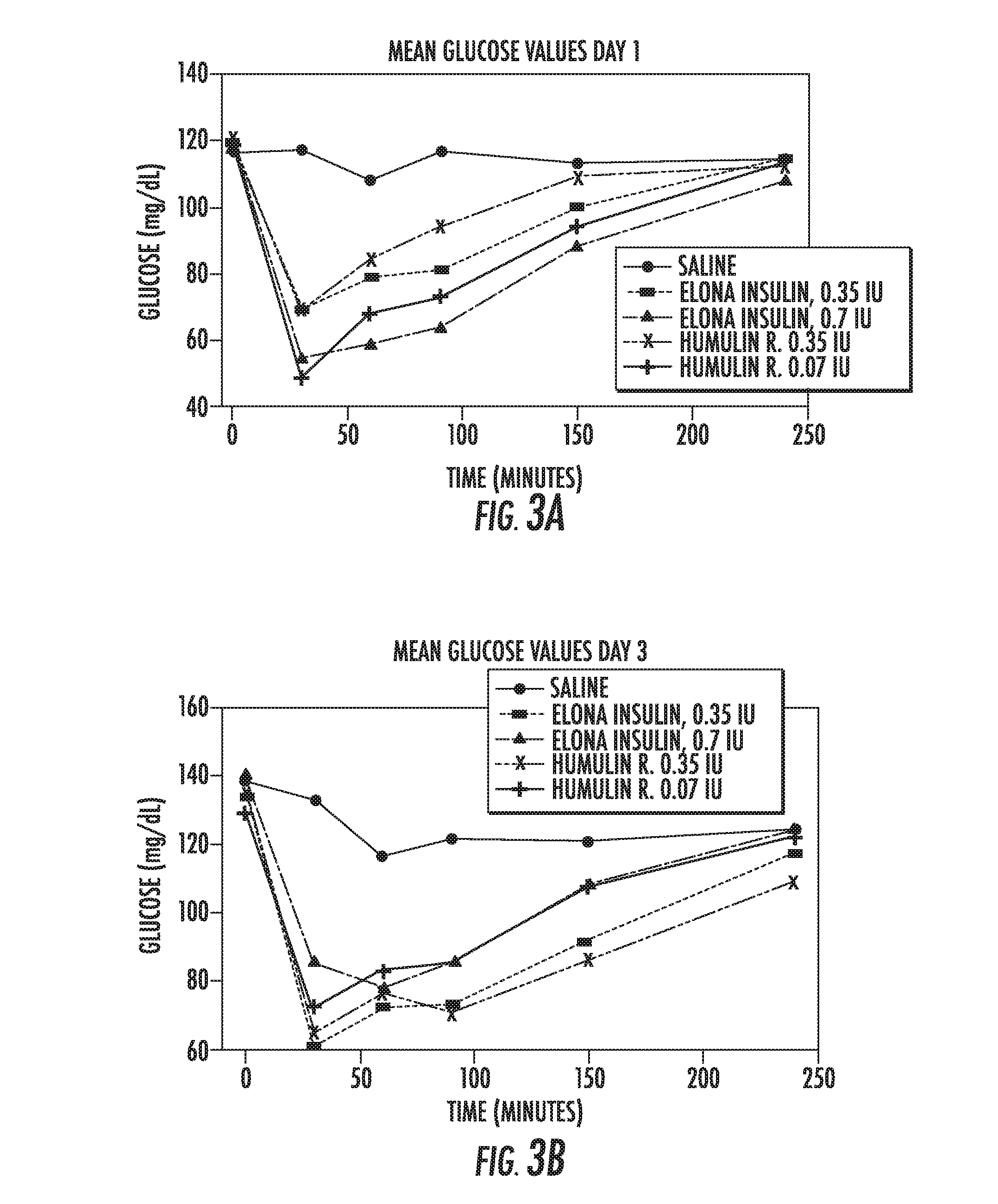
Glargine proinsulin and methods of producing glargine insulin analogs therefrom
Glargine proinsulin sconstructs that have a modified C-peptide amino acid and / or nucleic acid sequence for producing glargine insulin analogs are provided. Highly efficient processes for preparing the glargine insulin analogs and improved preparations containing the glargine insulin analogs prepared according to the methods described herein are also provided.
Owner:ELONA BIOTECH
Chemiluminescence immunoassay kit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103513037AHigh detection sensitivityImprove detection accuracyChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological material analysisBiotinProinsulin
The invention provides a human proinsulin chemiluminescence immunoassay kit and a preparation method thereof. The kit provided by the invention comprises an anti-proinsulin reagent 1, an anti-proinsulin reagent 2, a magnetic separation reagent, a proinsulin calibrator, a chemiluminescence substrate, and a washing liquid. The invention also provides a preparation method of the kit. The preparation method comprises the following steps: coupling antibody and biotin, preparing the anti-proinsulin reagent 1, coupling enzyme and antibody, preparing the anti-proinsulin reagent 2, preparing the magnetic separation reagent, preparing the proinsulin correction sample, and preparing the chemiluminescence substrate. Compared to the proinsulin kit existing in the present market, the kit provided by the invention has the characteristics of high detection sensitivity, good repeatability, and low cost.
Owner:北京惠中医疗器械有限公司
Compositions and methods for the treatment of type 1 diabetes
ActiveUS20190022154A1Avoid destructionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesPancreatic hormone
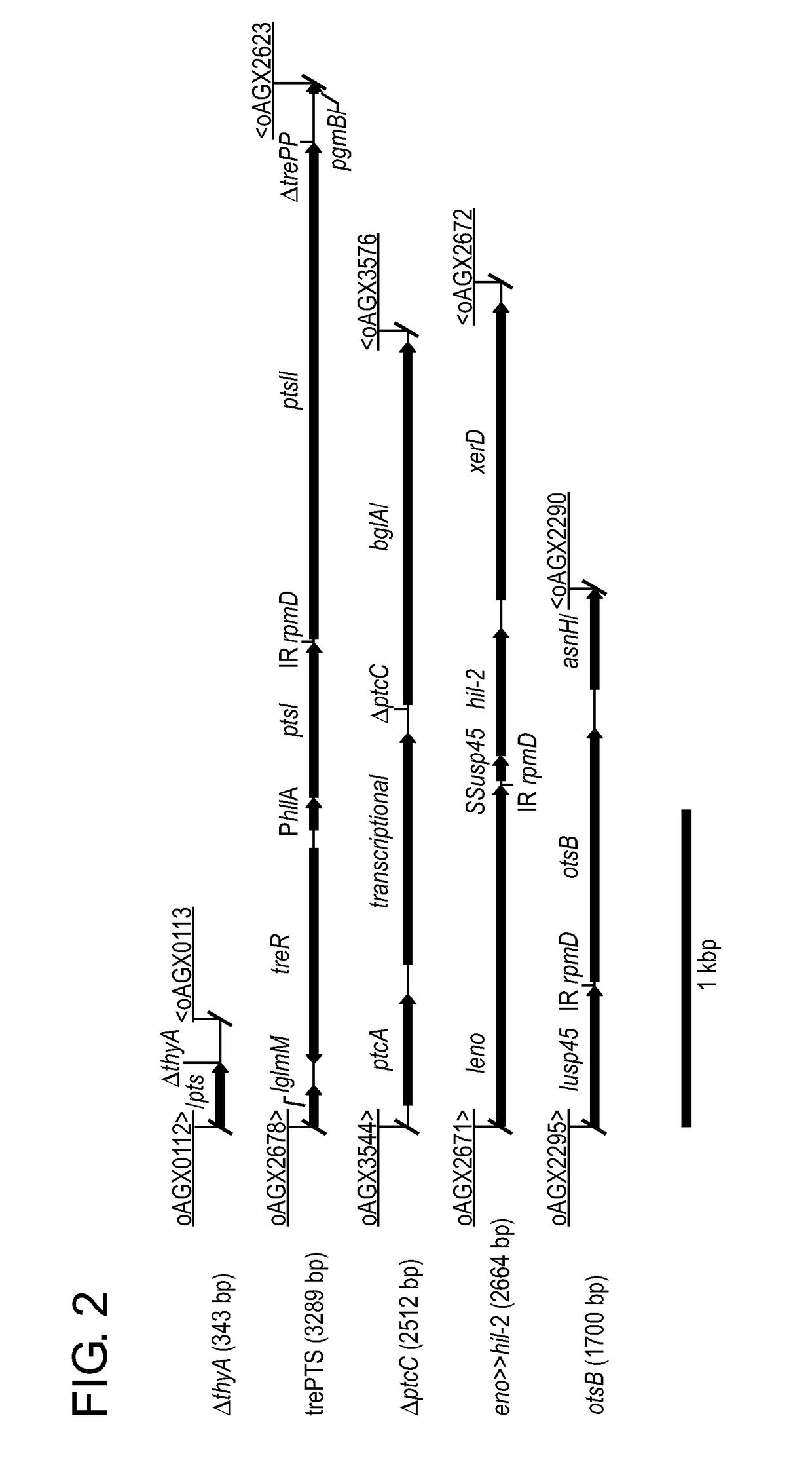
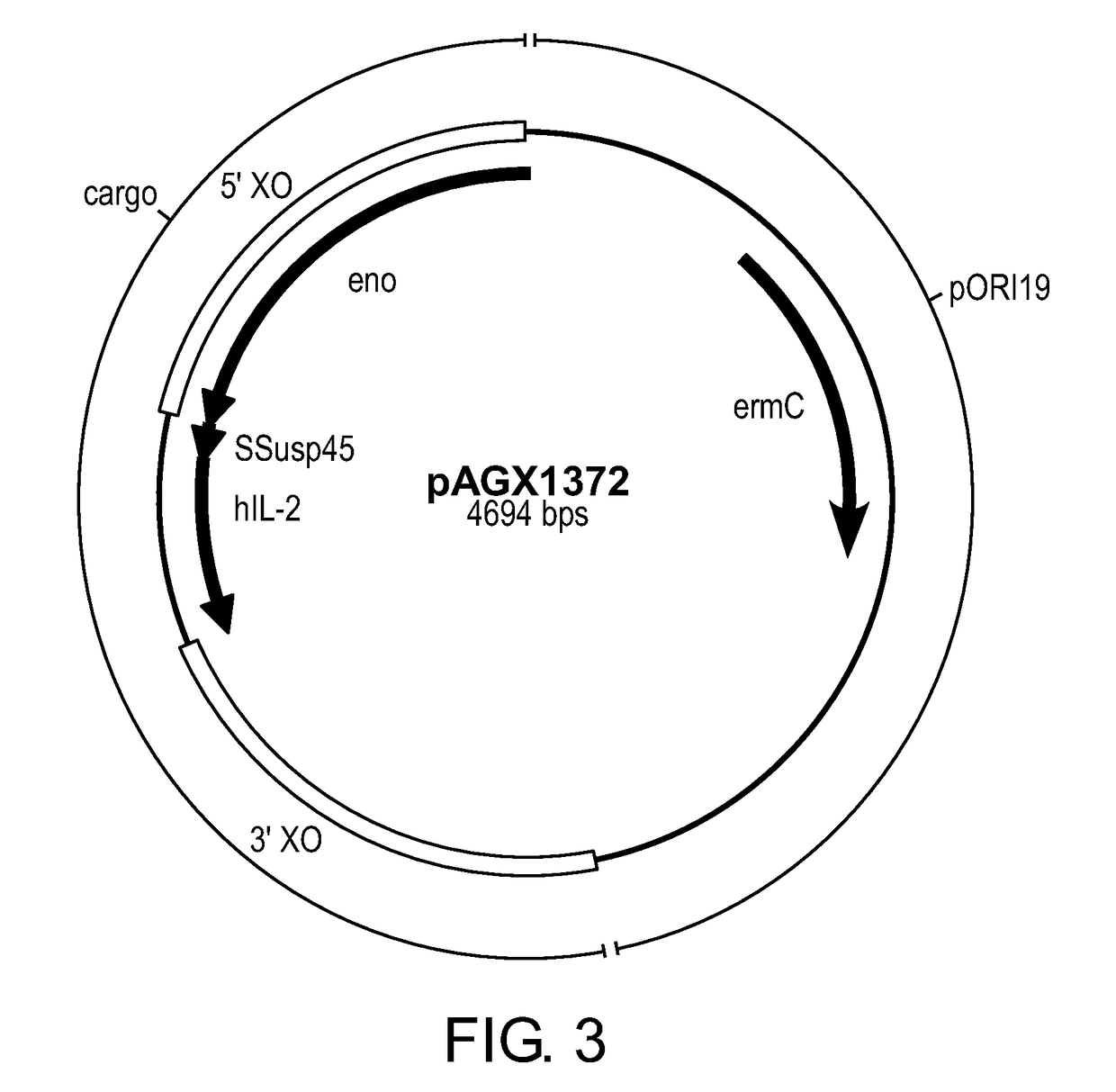
Provided herein are compositions and methods for the treatment of type 1 diabetes (T1D) in mammalian subjects. The compositions include lactic acid fermenting bacteria (LAB) expressing an IL-2 gene and a T1D-specific self-antigen (e.g., proinsulin (PINS)) gene. Exemplary methods include: orally administering to a mammalian subject, a therapeutically effective amount of the composition. The composition can be administered to the subject mucosally, resulting in delivery of the LAB into the gastrointestinal tract, where the LAB is released. Bioactive polypeptides expressed by the LAB are thus administered via mucosal delivery. The LAB may be selected to deliver a low-dose of IL-2 to the subject. The methods may not require concomitant systemic anti-CD3 antibody treatment. The methods may be suited for subjects possessing residual beta-cell function, e.g., those with recent-onset T1D.
Owner:INTREXON ACTOBIOTICS NV
Recombinant human proinsulin renaturation and purification method
InactiveCN103172727ACompact structureLong retention timePeptide preparation methodsInsulinsPurification methodsDigestion
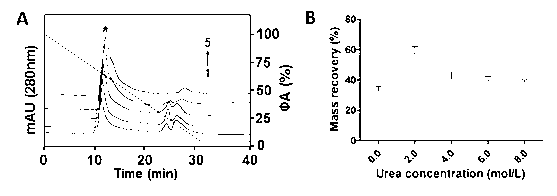
The invention discloses a method for performing high performance size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) and purifying recombinant human proinsulin renaturation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing ultrasonic cell disruption on the proinsulin-containing thallus cell, washing and dissolving the buffer solution in strong denaturant (such as 8mol / L or 6-7 mol / L guanidine hydrochloride) thereby obtaining the recombinant human proinsulin subjected to crude separation; (2) directly feeding the proinsulin-containing denaturated leaching liquor under the optimized chromatographic condition, wherein the purity of target fraction rhPI obtained through one-step chromatography by employing urea concentration linear gradient elute can be over 96 percent, and the mass recovery rate is 56.8 percent; and (3) further desalting the proinsulin-containing original fraction, thereby obtaining the renaturated and purified high-purity and activity fraction. The recombinant human proinsulin obtained by the method can be converted into insulin through digestion on a chromatographic column or digestion in a solution, and the chromatographic process is easy to operate, high in repeatability and easy for large-scale production.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Insulin assay
ActiveUS20110195438A1Sensitively and specifically assayedAccurate monitoringImmunoglobulins against hormonesBiological testingINSULIN USEBiochemistry
The present invention provides an insulin-specific assay and an assay reagent capable of sensitively and specifically assaying insulin using an antibody having a property of reacting with insulin bound to an anti-insulin antibody while not reacting with insulin not bound to an anti-insulin antibody, without being affected by proinsulin and insulin analogs.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
Medicaments and methods to treat autoimmune disease and cancer
InactiveCN101687019ANervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
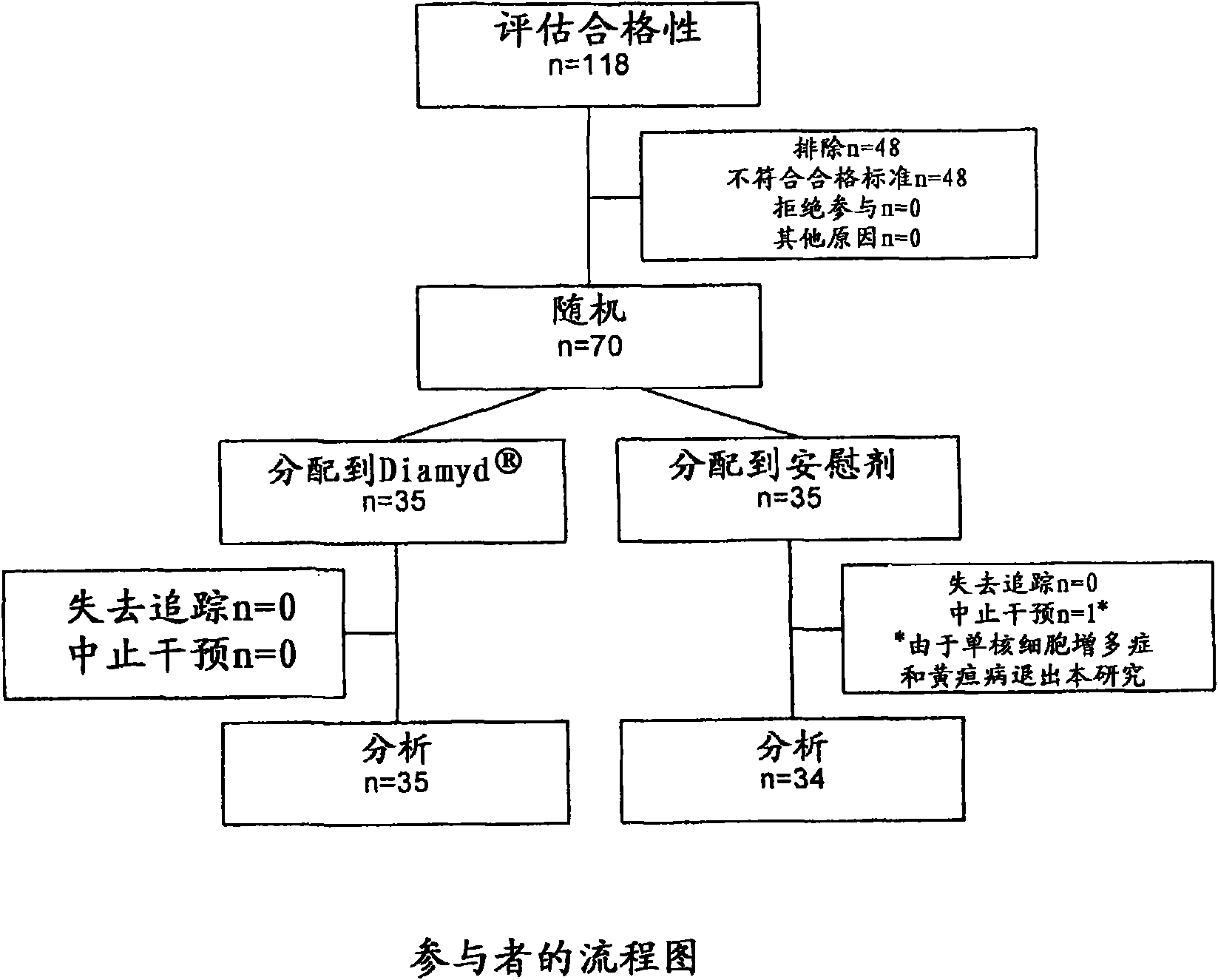
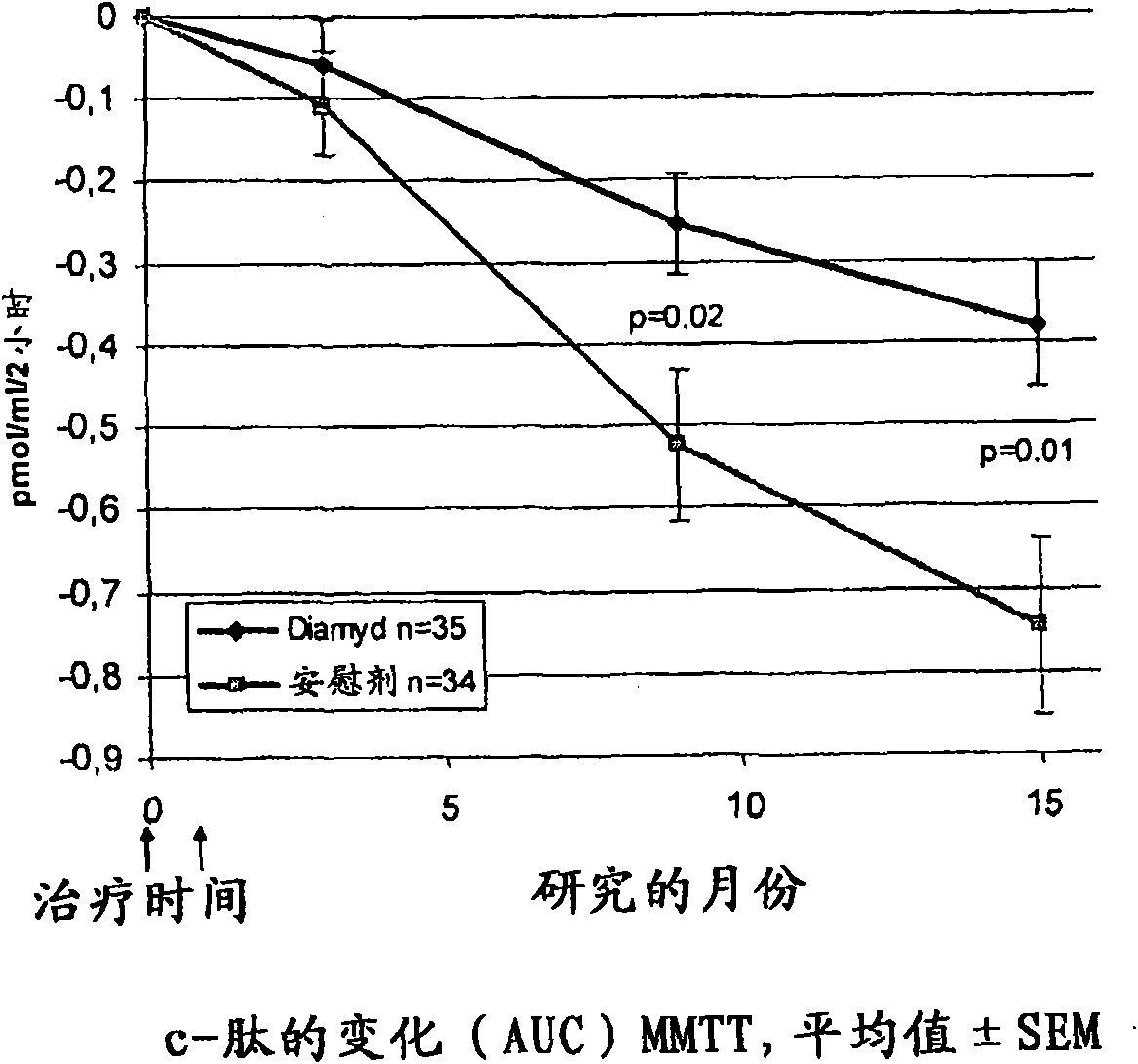
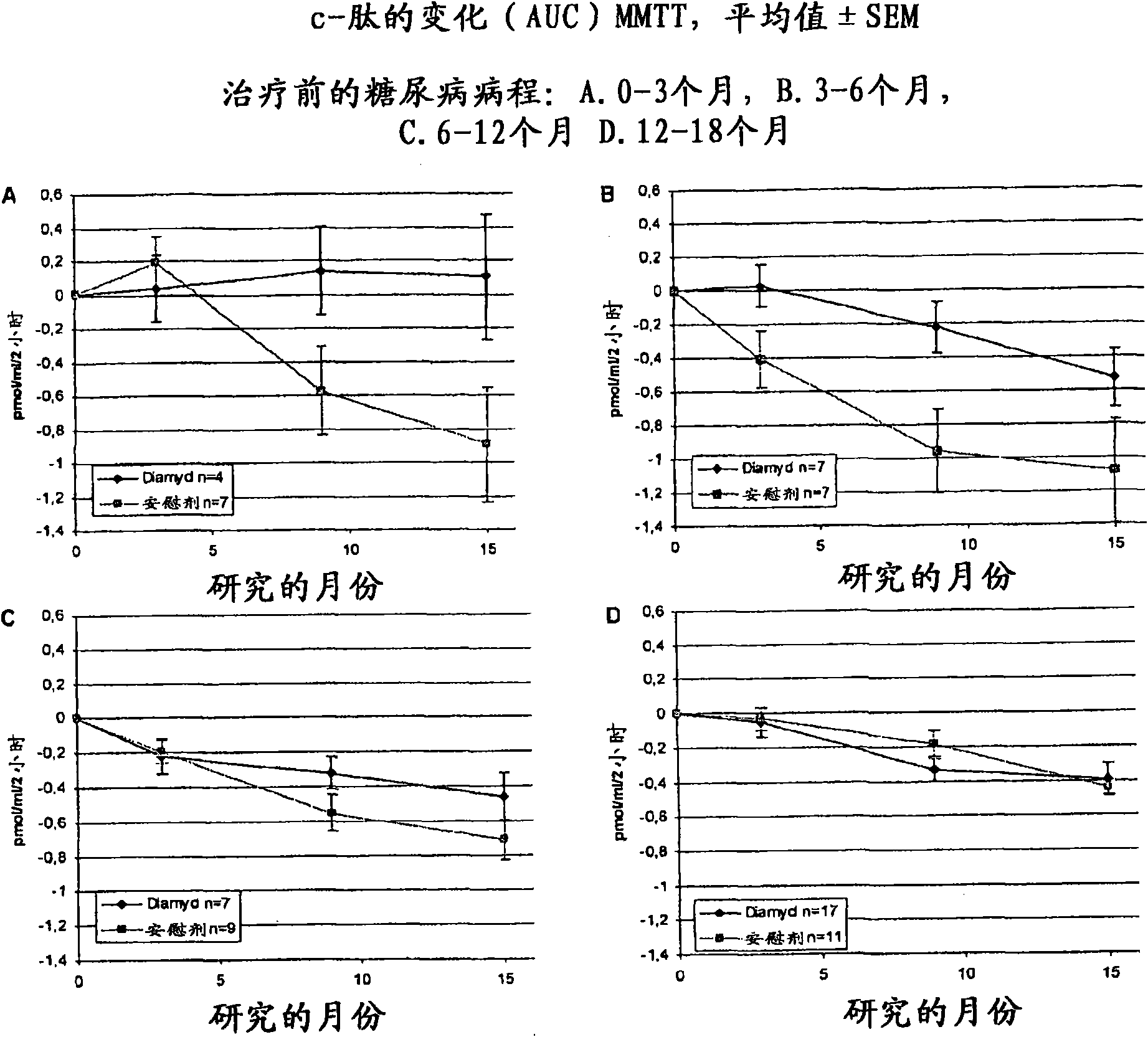
The present invention relates to methods and formulations for GAD- vaccination to evoke a systemic effect rather that a GAD-specific effect. The present invention may therefore be used in the treatment of disease in humans not bearing on a GAD-specific effect. The invention includes a method to treat an autoimmune disease or disorder by administering at least one sequestered autoantigen in a primeand boost regimen for sensitization purposes followed by a boost for treatment purposes. This may be done upon diagnosis. Examples of sequestered autoantigens include: GAD65, GAD67, Pro-Insulin, Basic Myelin Protein, MOG and Chondrotoin II. The present invention relates to medications and methods for treatment of autoimmune disease within six months from diagnosis.
Owner:DIAMYD THERAPEUTICS
Treatment of diabetes with synthetic beta cells
InactiveUS7425443B2Reduce formationReduce expressionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsActrapid insulinGlucose polymers
Disclosed is a method for obtaining glucose-regulated expression of active insulin in the cells of a mammalian subject. The method involves delivering into the subject a genetic construct comprising a coding sequence for a human proinsulin operably connected a promoter functional in the host cells. The construct includes a glucose responsive regulatory module having at least one glucose inducible regulatory element comprising a pair of CACGTG motifs linked by a five base nucleotide sequence, which confers glucose inducible expression of the proinsulin coding sequence. To ensure proper processing of the proinsulin to active insulin, the coding sequence was modified to direct the synthesis of a mutant proinsulin polypeptide having amino acid sequences that can be cleaved to mature insulin in suitable host cells, such as hepatocytes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Recombinant human proinsulin transpeptidation method and application in recombinant human proinsulin downstream purification thereof
InactiveCN102864198ASolve the shortcomings of long reaction time and many by-products in transpeptide conversionReduce generationMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsThreoninePancreatic hormone
The invention provides a recombinant human proinsulin transpeptidation method and an application in recombinant human proinsulin downstream purification thereof. The recombinant human proinsulin transpeptidation method is characterized by carrying out transpeptidation reaction on purified recombinant human proinsulin to obtain recombinant human insulin, wherein the reaction system of the transpeptidation reaction comprises 10-30g / L of recombinant human proinsulin, 100-200ml / L of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), 63-103g / L of o-tert-butyl threonine tert-butyl ester, 600-800ml / L of 1,4-butanediol, 2-6g / L of trypsin, 0.2-100mmol / L of Ca<2+>, 0.2-100mmol / L of Mg<2+>, and water, and the pH value is 6.5-7.0. The reaction conditions of the transpeptidation reaction comprise a temperature of 27-47 DEG C, and a stirring time of 2-10 h. According to the invention, the recombinant human proinsulin transpeptidation method disclosed herein can be applied in downstream purification of recombinant human proinsulin. The recombinant human proinsulin transpeptidation method disclosed herein shortens the time of the transpeptidation reaction, raises the production efficiency, and can reduce by-products.
Owner:上海泰龙生物医药科技有限公司
Insulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates, proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates and methods of synthesizing same
InactiveUS7166571B2Less-expensive and high yieldingStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesOligomerC-peptide
Methods for synthesizing proinsulin polypeptides are described that include contacting a proinsulin polypeptide including an insulin polypeptide coupled to one or more peptides by peptide bond(s) capable of being cleaved to yield the insulin polypeptide with an oligomer under conditions sufficient to couple the oligomer to the insulin polypeptide portion of the proinsulin polypeptide and provide a proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate, and cleaving the one or more peptides from the proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate to provide the insulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate. Methods of synthesizing proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates are also provided as are proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates. Methods of synthesizing C-peptide polypeptide-oligomer conjugates and other pro-polypeptide-oligomer conjugates are also provided.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Methods of synthesizing insulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates, and proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates and methods of synthesizing same
ActiveUS20050080001A1Less expensiveHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesOligomerC-peptide
Methods for synthesizing proinsulin polypeptides are described that include a contacting a proinsulin polypeptide including an insulin polypeptide coupled to one or more peptides by peptide bond(s) capable of being cleaved to yield the insulin polypeptide with an oligomer under conditions sufficient to couple the oligomer to the insulin polypeptide portion of the proinsulin polypeptide and provide a proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate, and cleaving the one or more peptides from the proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate to provide the insulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugate. Methods of synthesizing proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates are also described as are proinsulin polypeptide-oligomer conjugates. Methods of synthesizing C-peptide polypeptide-oligomer conjugates are also described.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Method of insulin production
InactiveUS20180291077A1Improve purification efficiencyLow costCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersHigh concentrationProinsulin
The present invention relates to a method of preparing insulin from proinsulin comprising converting high-concentration proinsulin into insulin by enzymatic cleavage, a method of purifying insulin, and insulin prepared therefrom.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Ultra-concentrated rapid-acting insulin analogue formulations
InactiveUS20140323398A1Good chemical stabilityImprove physical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide chainPharmaceutical formulation
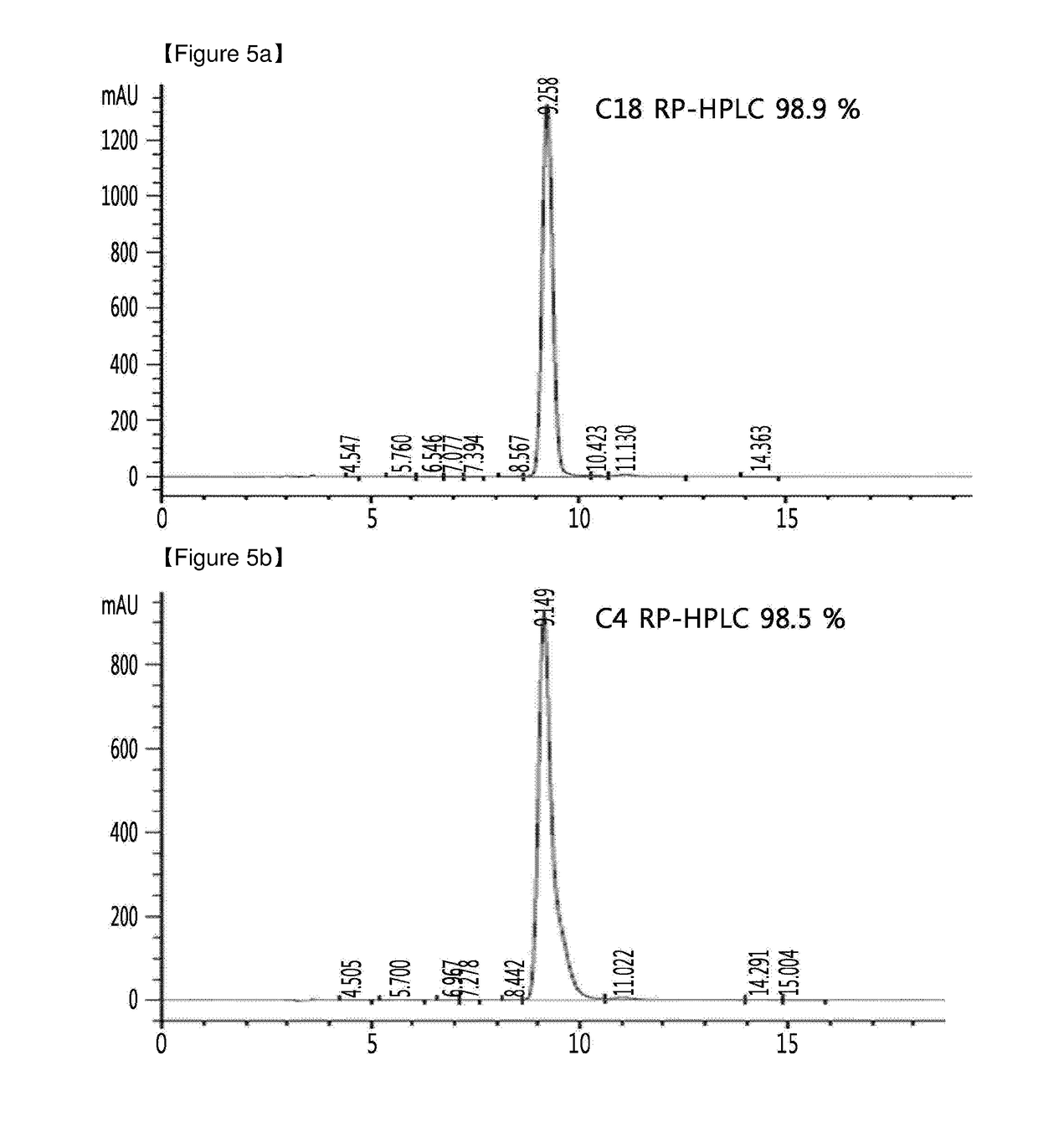
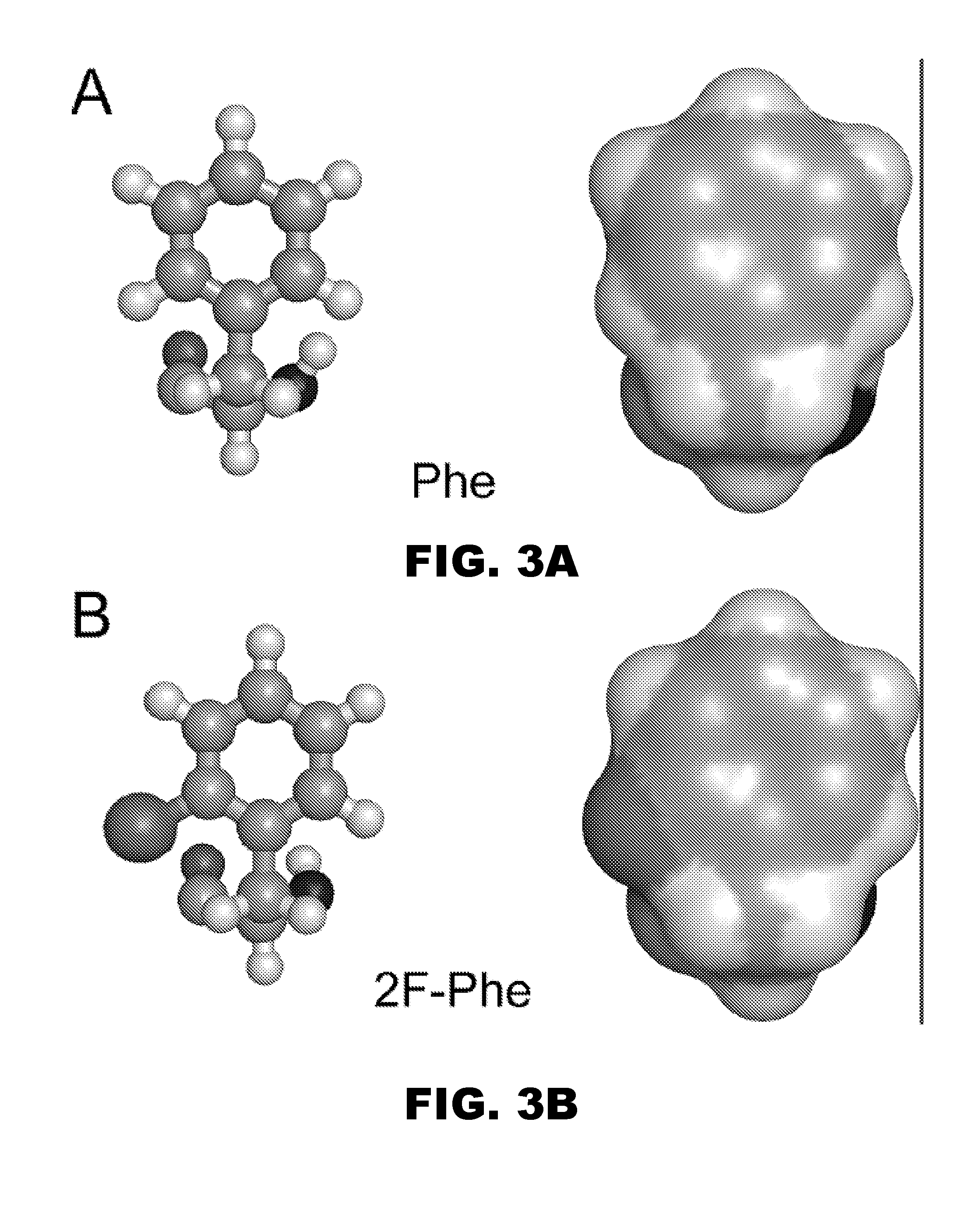
A pharmaceutical formulation comprises insulin having a variant insulin B-chain polypeptide containing an ortho-monofluoro-Phenylalanine substitution at position B24 in combination with a substitution of an amino acid containing an acidic side chain at position B10, allowing the insulin to be present at a concentration of between 0.6 mM and 3.0 mM. The formulation may optionally be devoid of zinc. Amino-acid substitutions at one or more of positions B3, B28, and B29 may additionally be present. The variant B-chain polypeptide may be a portion of a proinsulin analogue or single-chain insulin analogue. The insulin analogue may be an analogue of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A method of lowering the blood sugar of a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Plasmids expressing human insulin and the preparation method for human insuling thereby
InactiveUS20060035316A1Improve isolationMinimizationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsINSULIN USEArginine
The present invention relates to human insulin expression plasmids and a method for producing insulin using the same. The plasmids comprise a sequence encoding a compound of the formula R—B—X-A, in which R is a leader peptide of the formula of Met-Thr-Met-Ile-Thr-Y (SEQ ID NO: 36), in which Y is one selected from lysine, arginine, a peptide containing lysine as an amino acid at its C-terminal, or a peptide containing arginine as an amino acid at its C-terminal; B is human insulin B-chain or analogue thereof; X is a peptide connecting B with A; and A is human insulin A-chain or analogue thereof. The method for preparing insulin using the plasmids according to the present invention converts the proinsulin fusion protein into human insulin in a single enzymatic cleavage process and minimizes the generation of by-products after the enzymatic cleavage, thereby producing insulin at a high yield. Therefore, the plasmids according to the present invention and the method for preparing insulin using the same can be usefully applied to the industrial mass-production of human insulin.
Owner:CHONGKUNDANG BIO
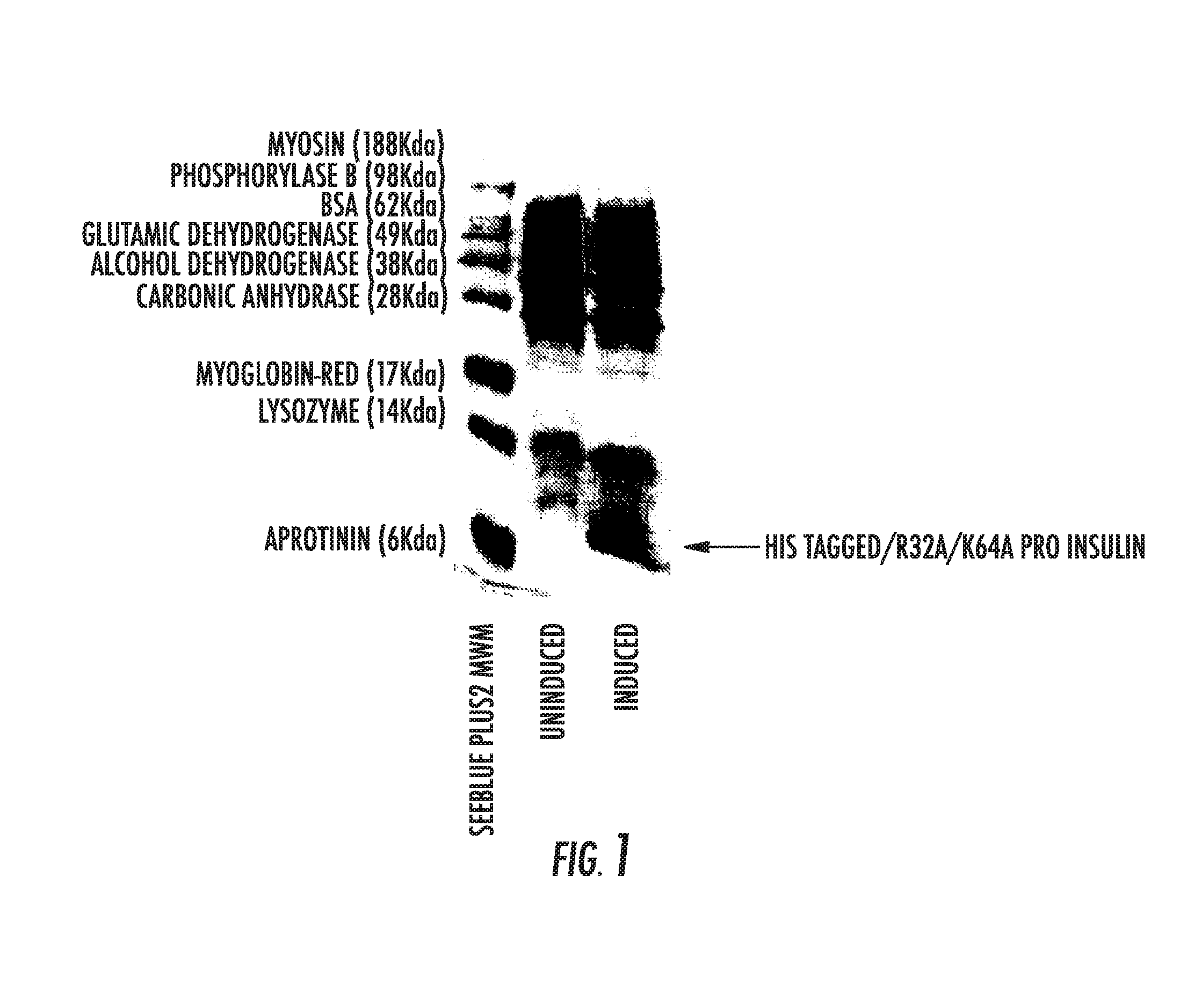
Insulin production methods and proinsulin constructs
InactiveUS20160289291A1Reduce eliminateIncrease heightPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulinsProinsulinImproved method
Novel proinsulins and glargine, aspart and Lis-Pro proinsulin analogs having specific amino acid and / or nucleic acid modifications suitable for improved methods of insulin production, as well as novel and highly efficient processes for preparing the same. The novel proinsulins and proinsulin analogs may be converted into human insulin and insulin analogs, respectively, that are useful in therapeutic preparations.
Owner:AGILA BIOTECH PVT LTD
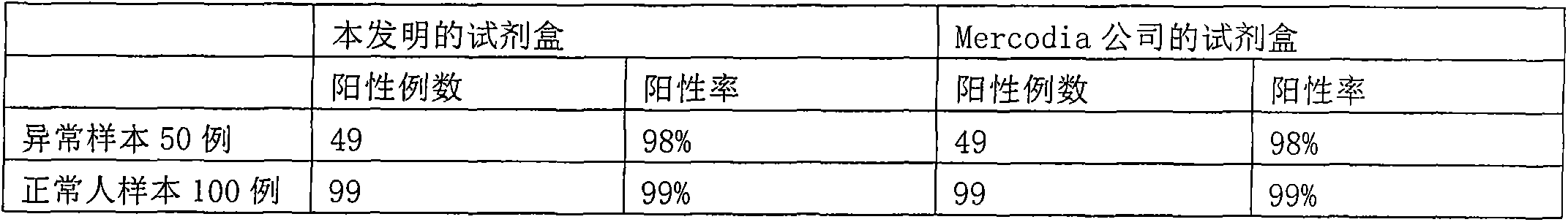
Method For Measuring Proinsulin And C-Peptide And A Kit Therefor
InactiveUS20080138830A1Simpler and more cost-effectiveImprove accuracyBiological material analysisBiological testingEpitopeAnalyte
Methods to determine the concentrations in a sample of proinsulin and of molecules comprising C-peptide are disclosed. The concentrations are determined within the same reaction compartment and using only one capture antibody, specific for an epitope within C-peptide. Kits are disclosed for use in the disclosed methods. Methods to determine the concentrations in a sample of n analytes from a group of N analytes and the total concentration of the N analytes are disclosed. N is 2 or more and n is any integer value from 1 to N. Each of the N analytes has at least one common portion present in each other analyte, and the n analytes have each a distinct portion not present in any other of the N analytes. The concentrations are determined within the same reaction compartment using only one capture antibody which is specific for an epitope within the common portion.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL +1
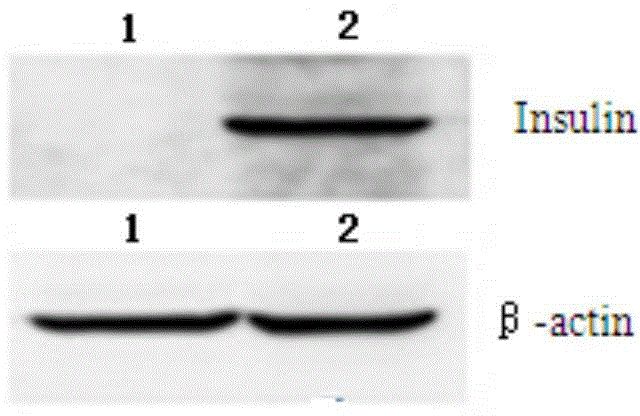
Human hematopoietic stem cell expressing human exogenous proinsulin and application thereof
InactiveCN104313054ALower blood sugarMetabolism disorderMicroorganism based processesEukaryotic plasmidsA-DNA
The invention belongs to the field of medical molecular biology, and particularly relates to a human hematopoietic stem cell expressing a human exogenous proinsulin and a preparation method and an application thereof. The human hematopoietic stem cell expressing the human exogenous proinsulin is obtained by the steps: a DNA recombinant technology is adopted, a human proinsulin gene is cloned into a lentiviral expression vector, a lentiviral expression vector which can express the human proinsulin gene is obtained, the expression vector and a lentiviral packaging plasmid are co-transfected to a 293FT cell, a lentiviral particle is packaged, a cell culture solution supernatant containing a virus is collected, newly-isolated UCB HSCs are infected, and the human hematopoietic stem cell expressing the human exogenous proinsulin is obtained. The human hematopoietic stem cell can be amplified in vitro, and an amplified cell is transplanted by a cell and is capable of normal self renewal and multi-directional differentiation in vivo; the secreted proinsulin can activate an insulin receptor and a downstream target gene, is transplanted to an NOD / SCID / Diabetes I mouse, can significantly reduce blood glucose of the type I diabetic mouse, and improves the survival rate of the mouse.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com