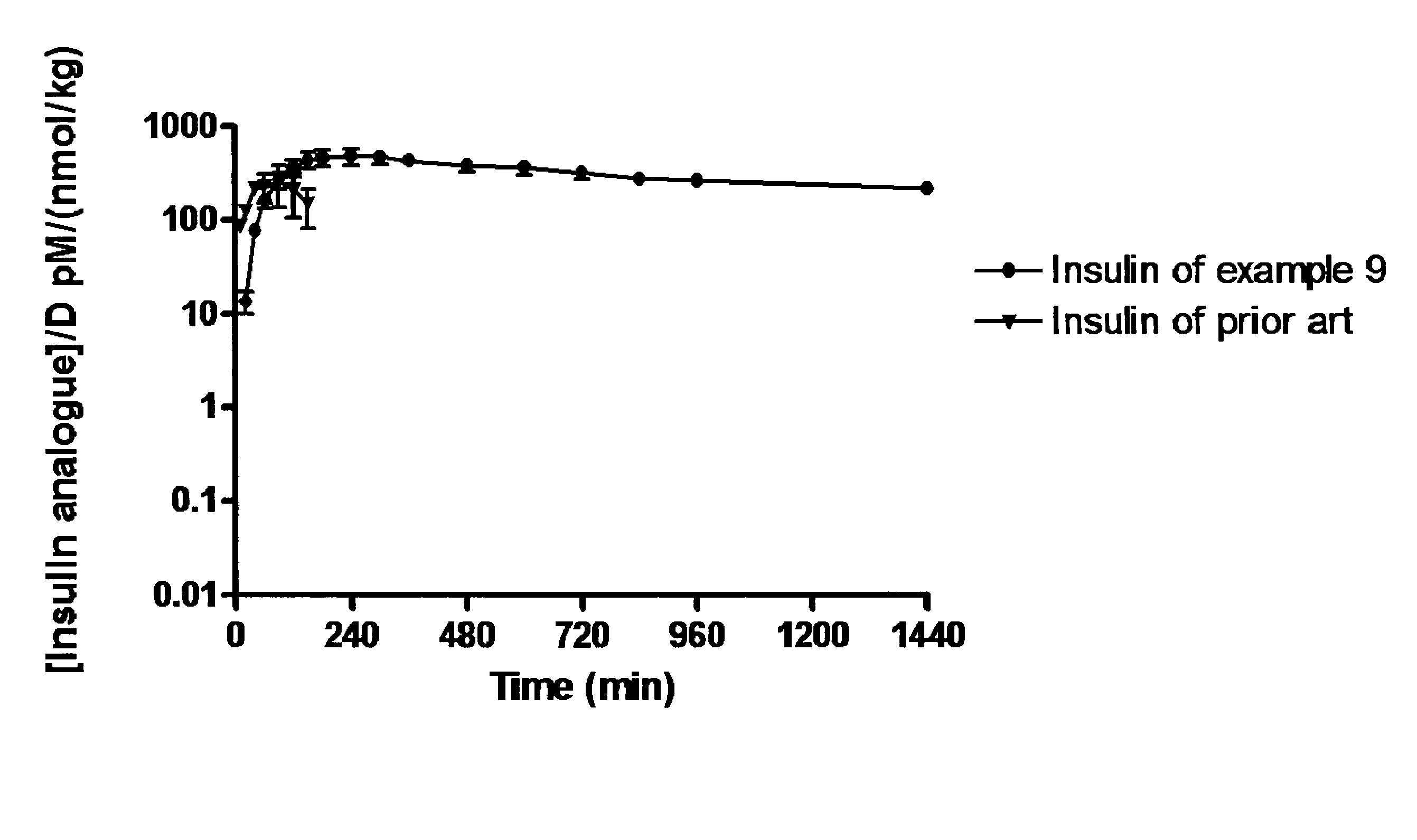
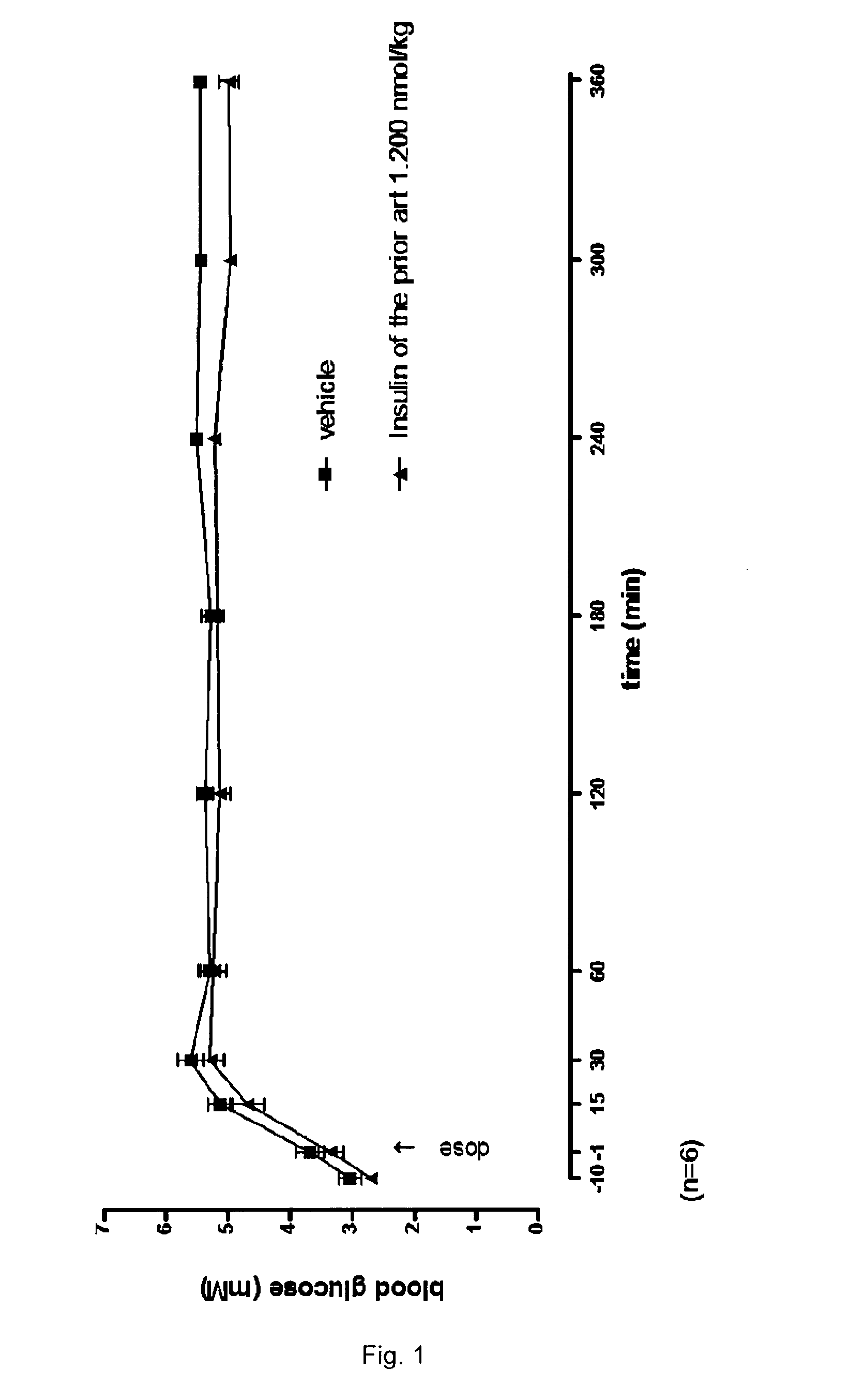
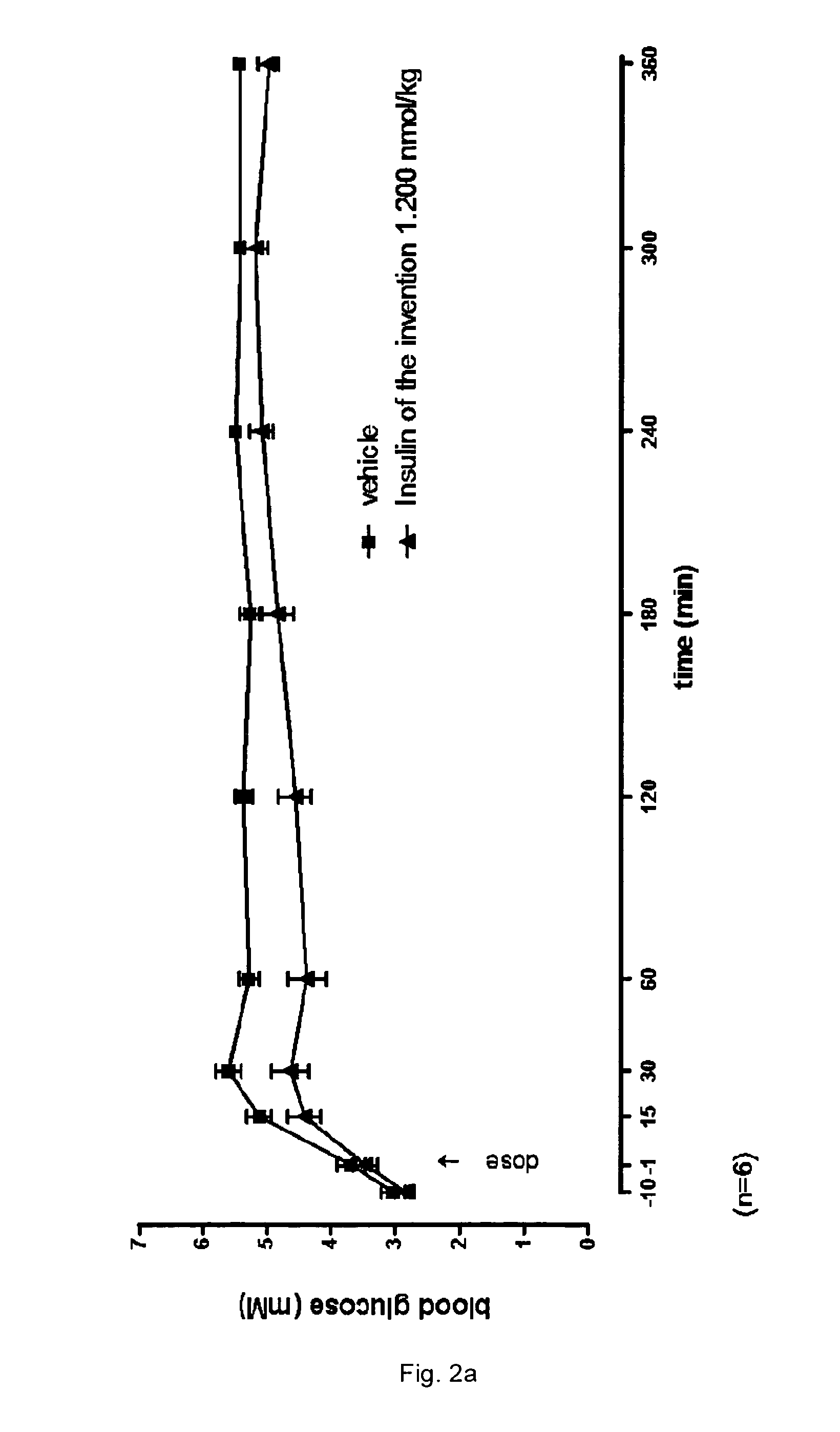
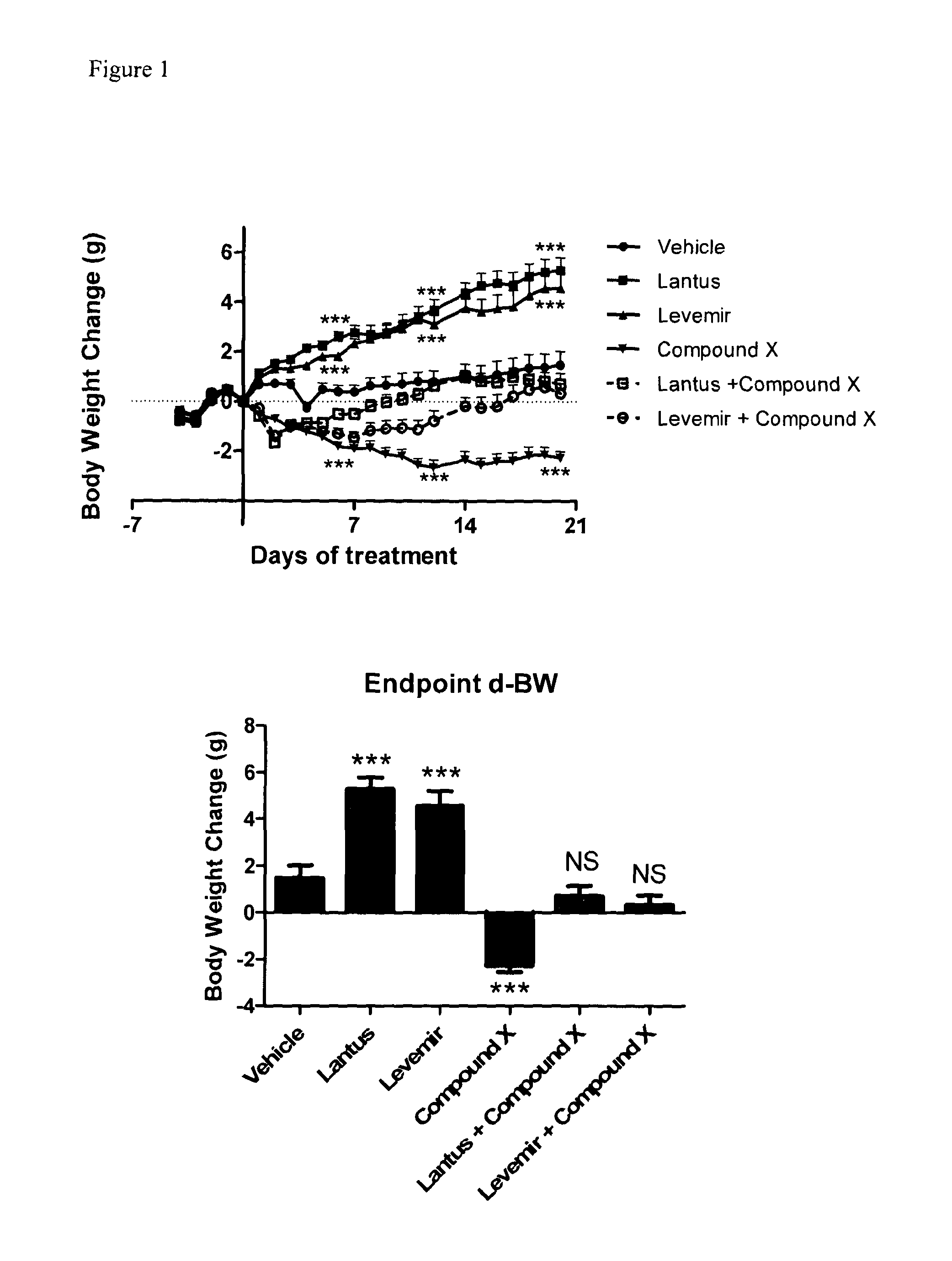
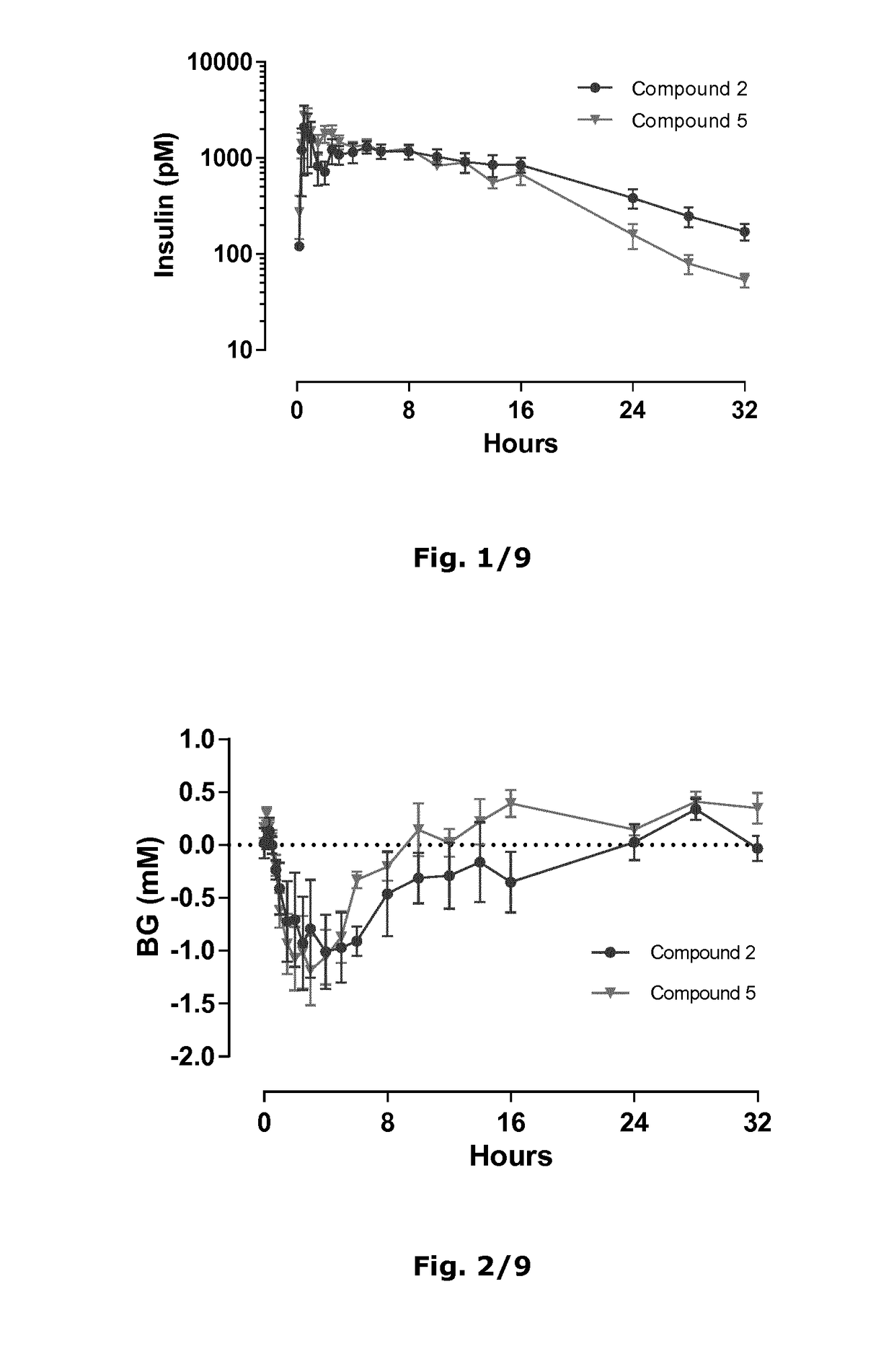
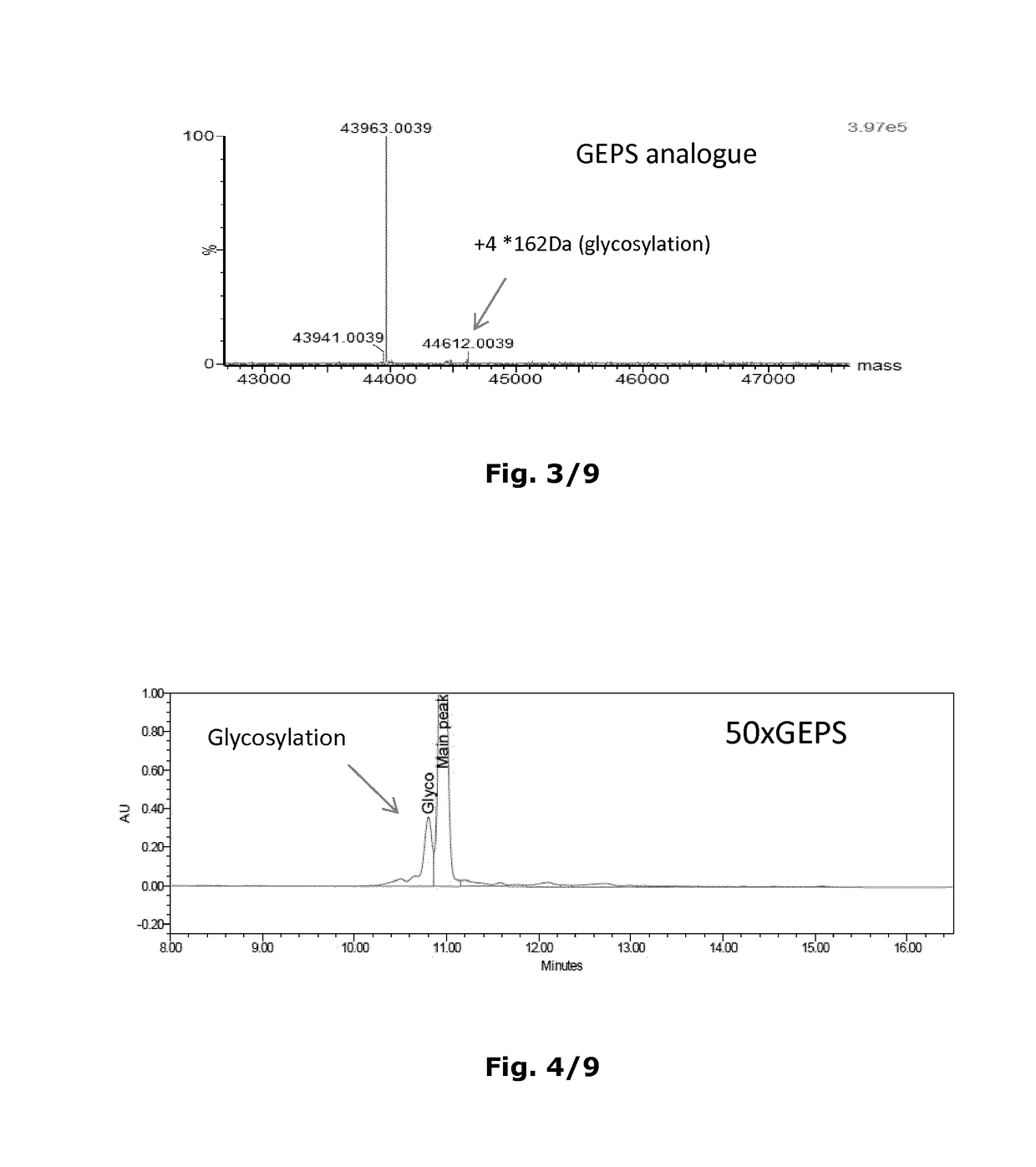
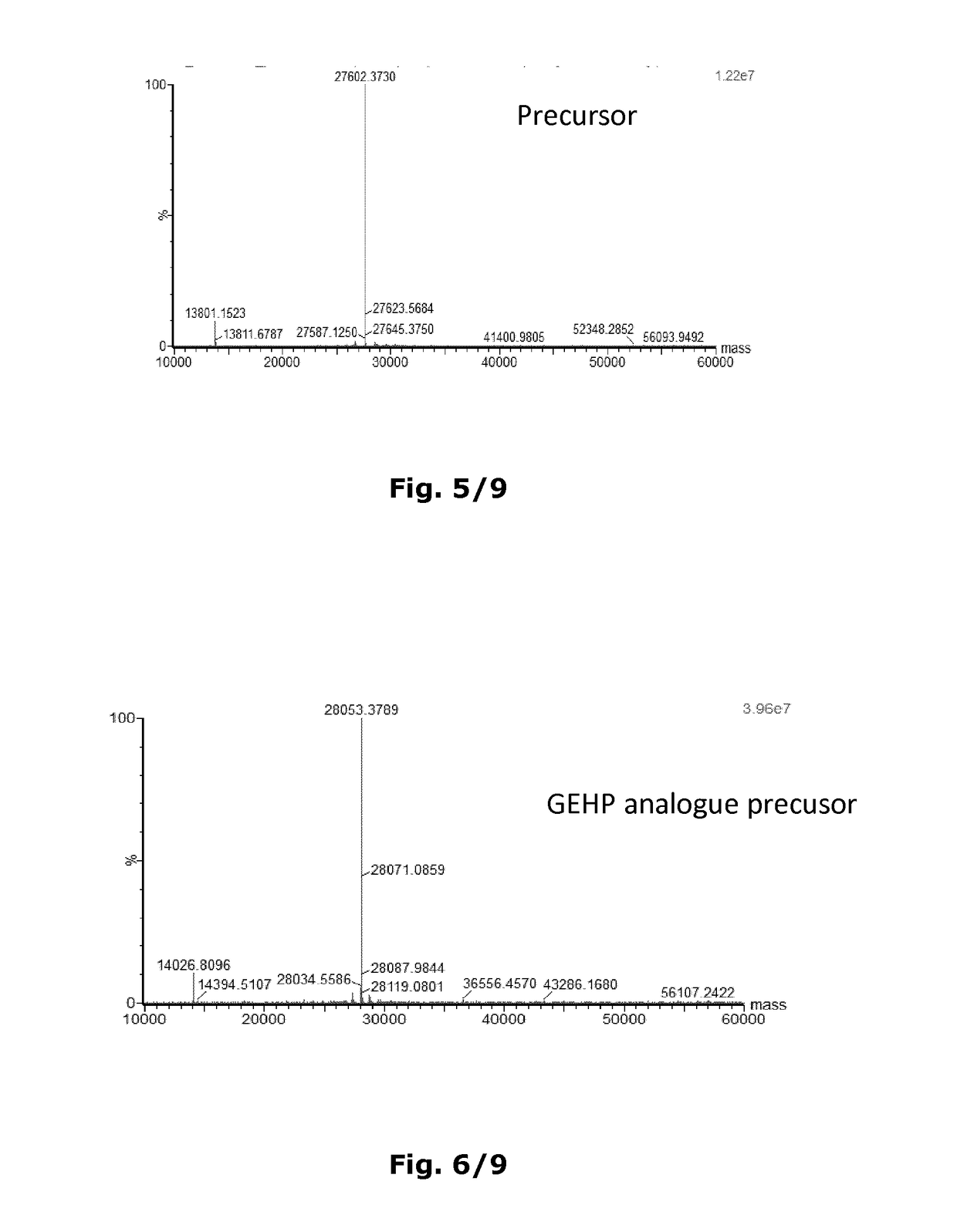
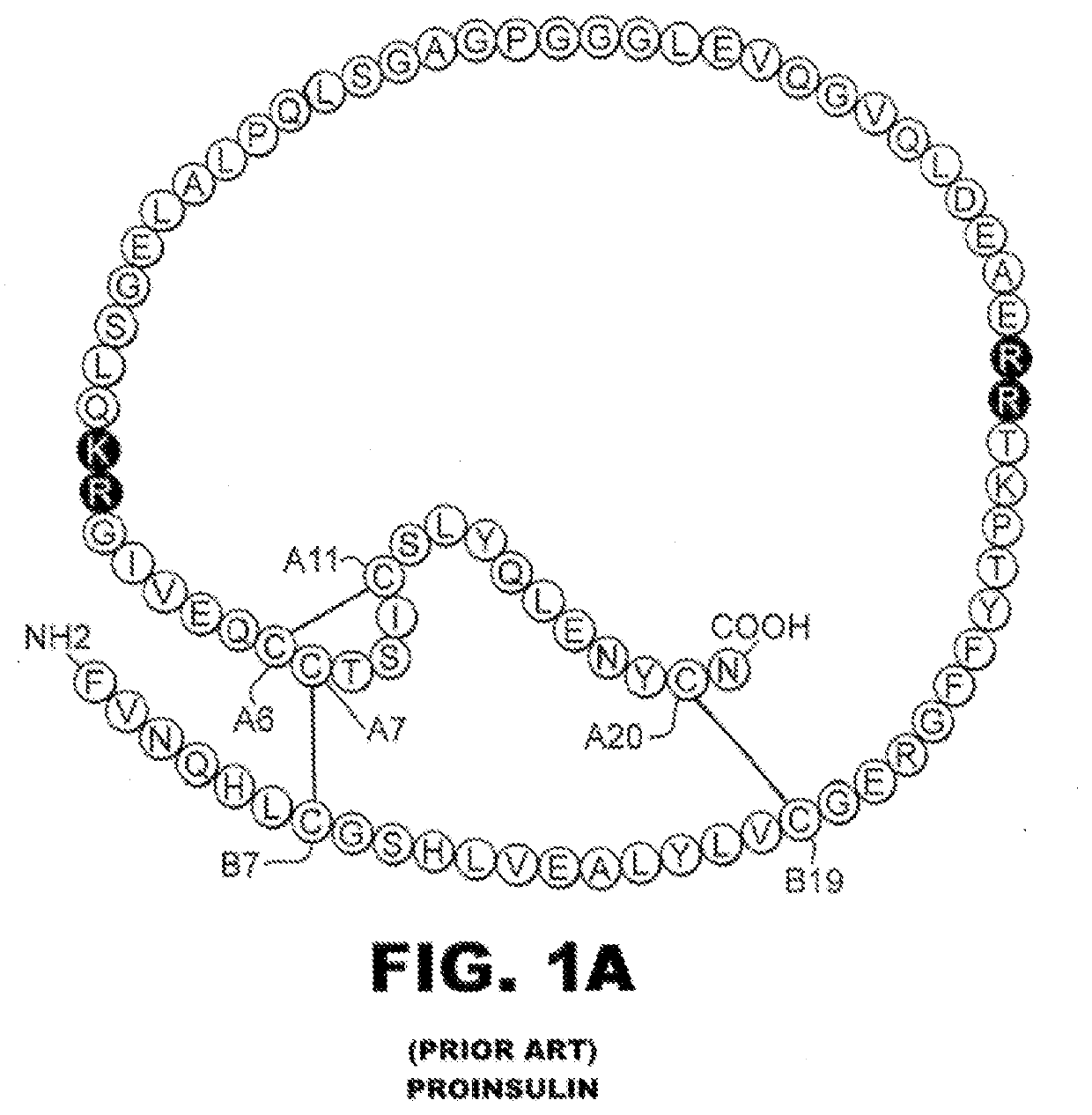
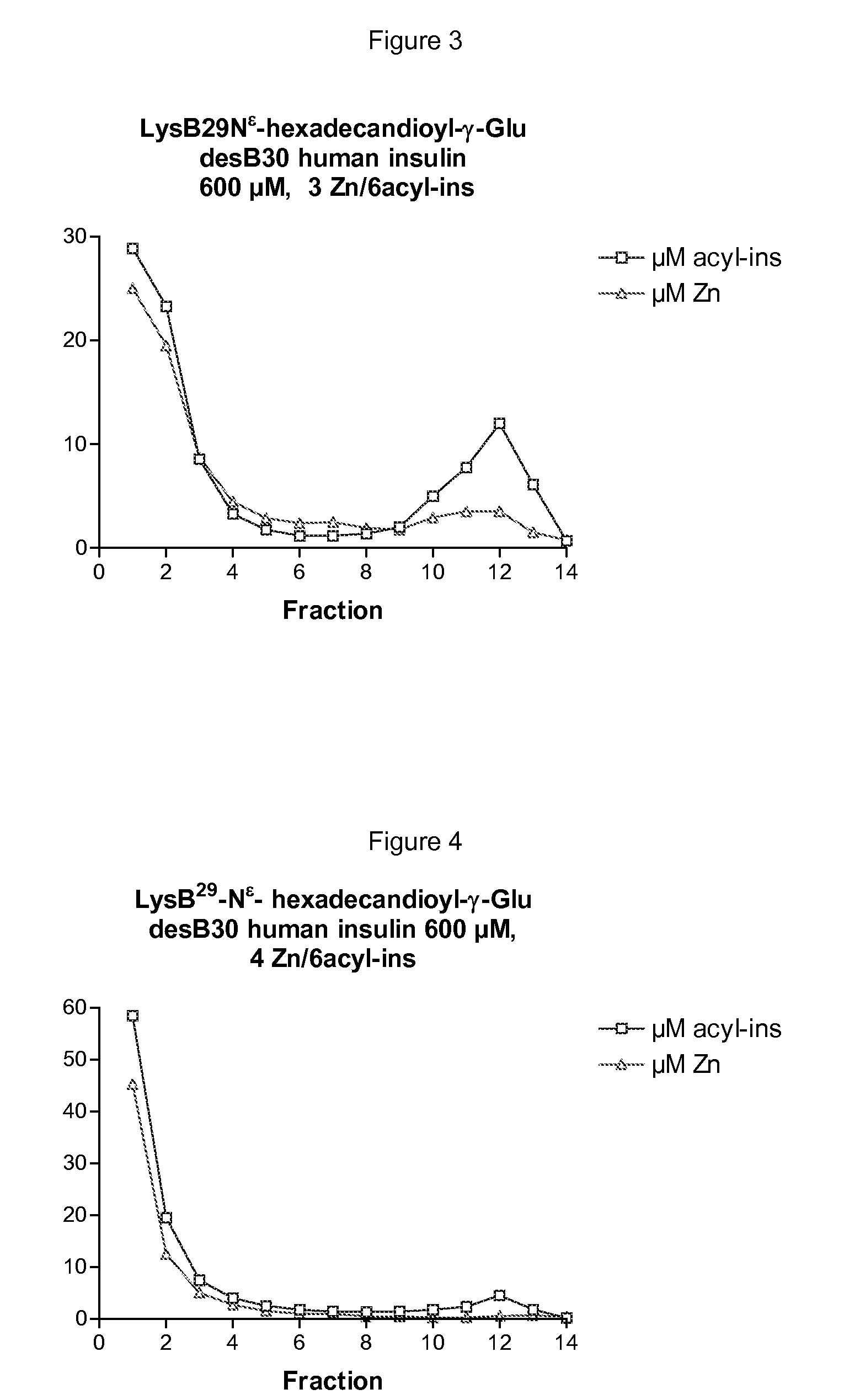
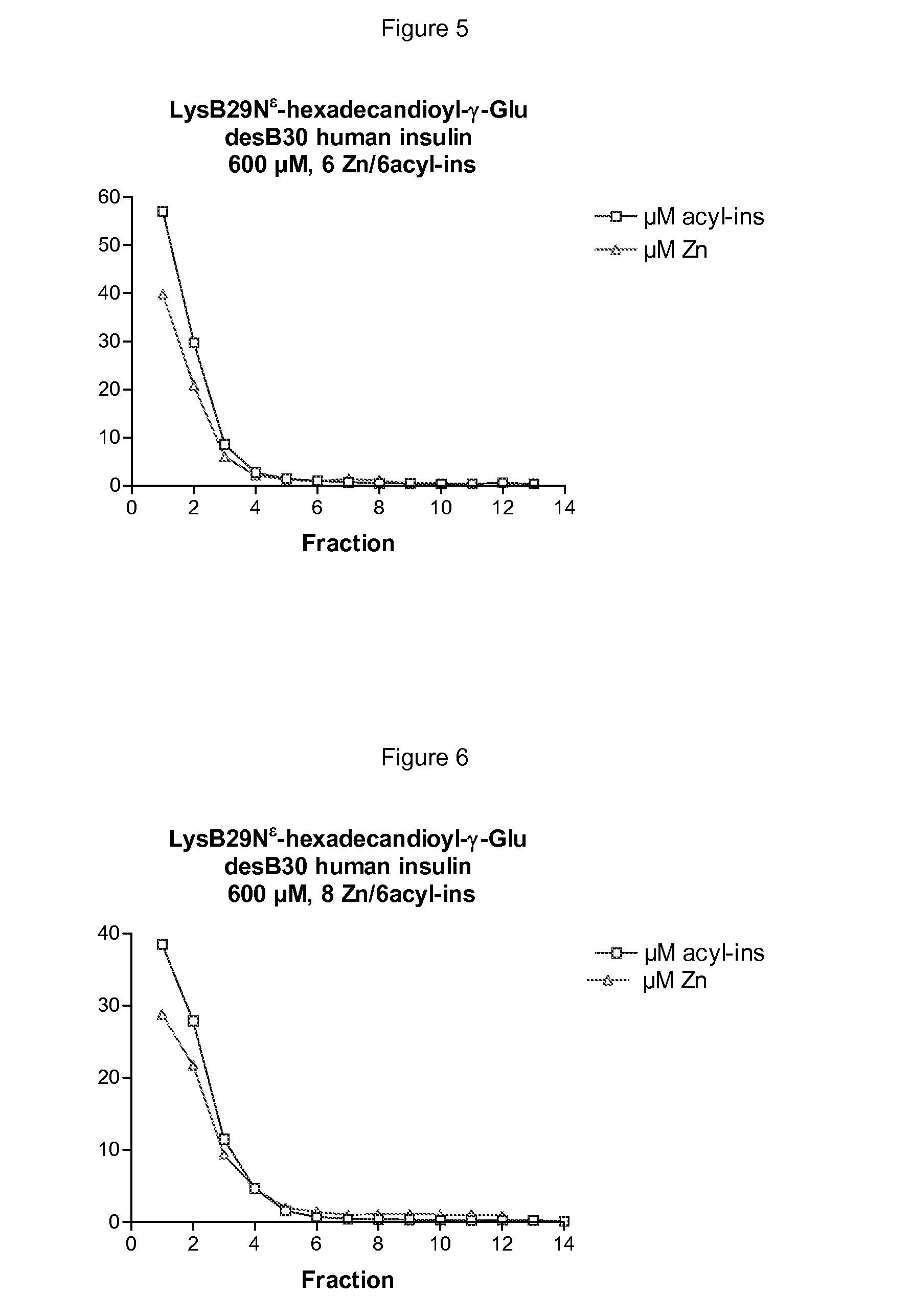
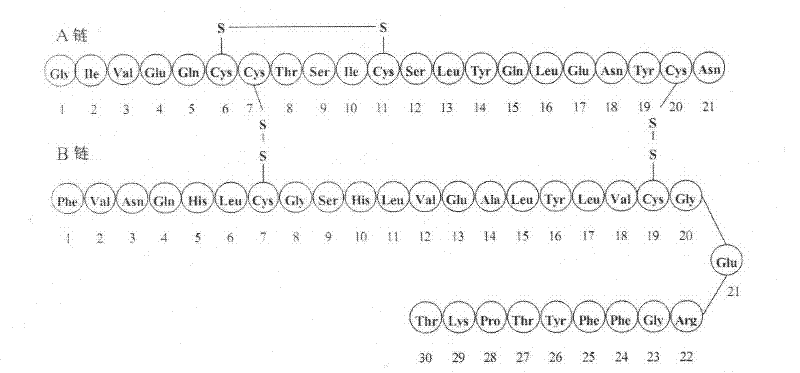
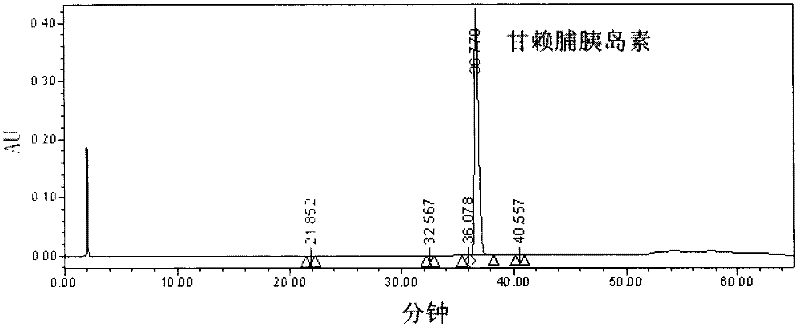
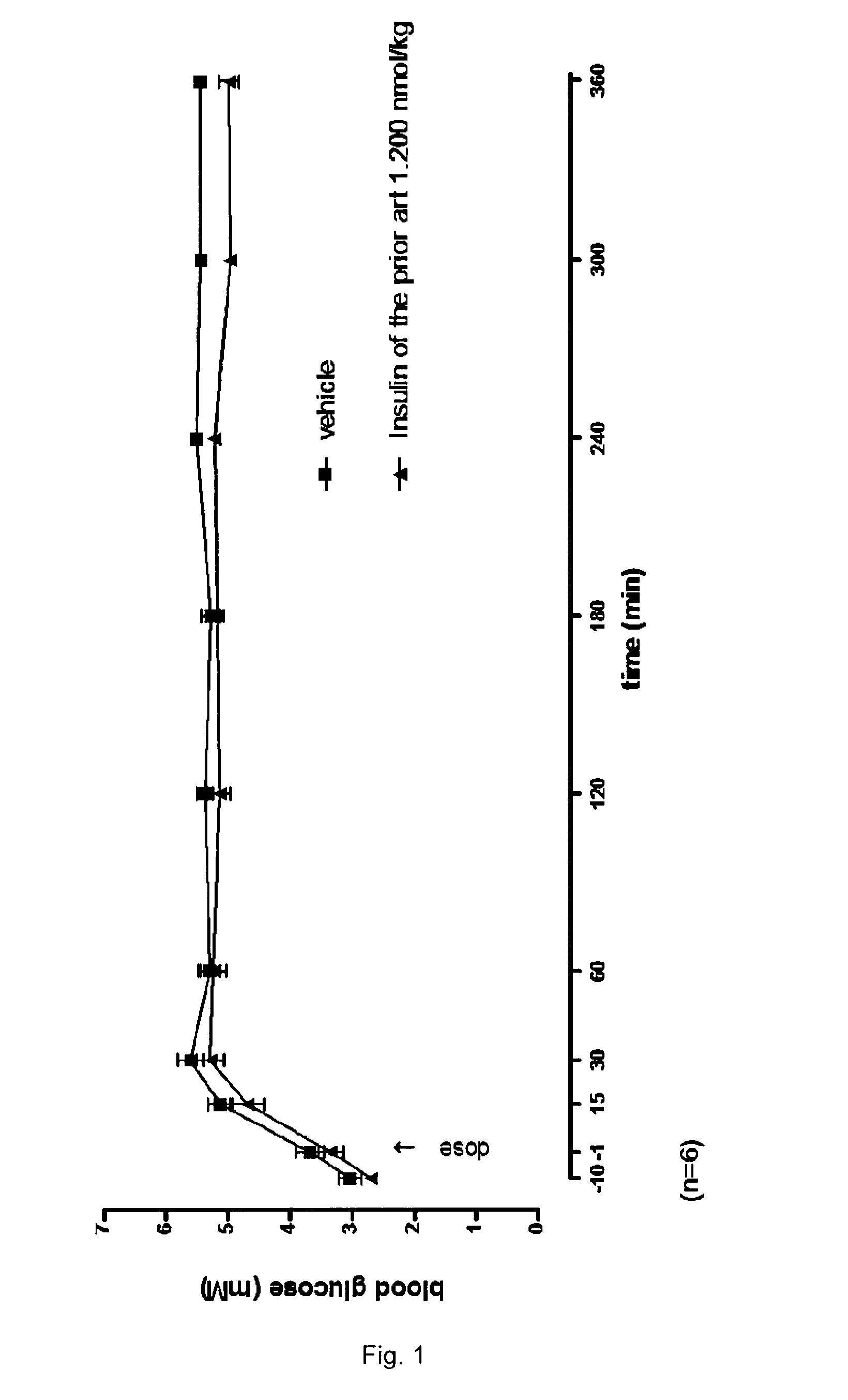
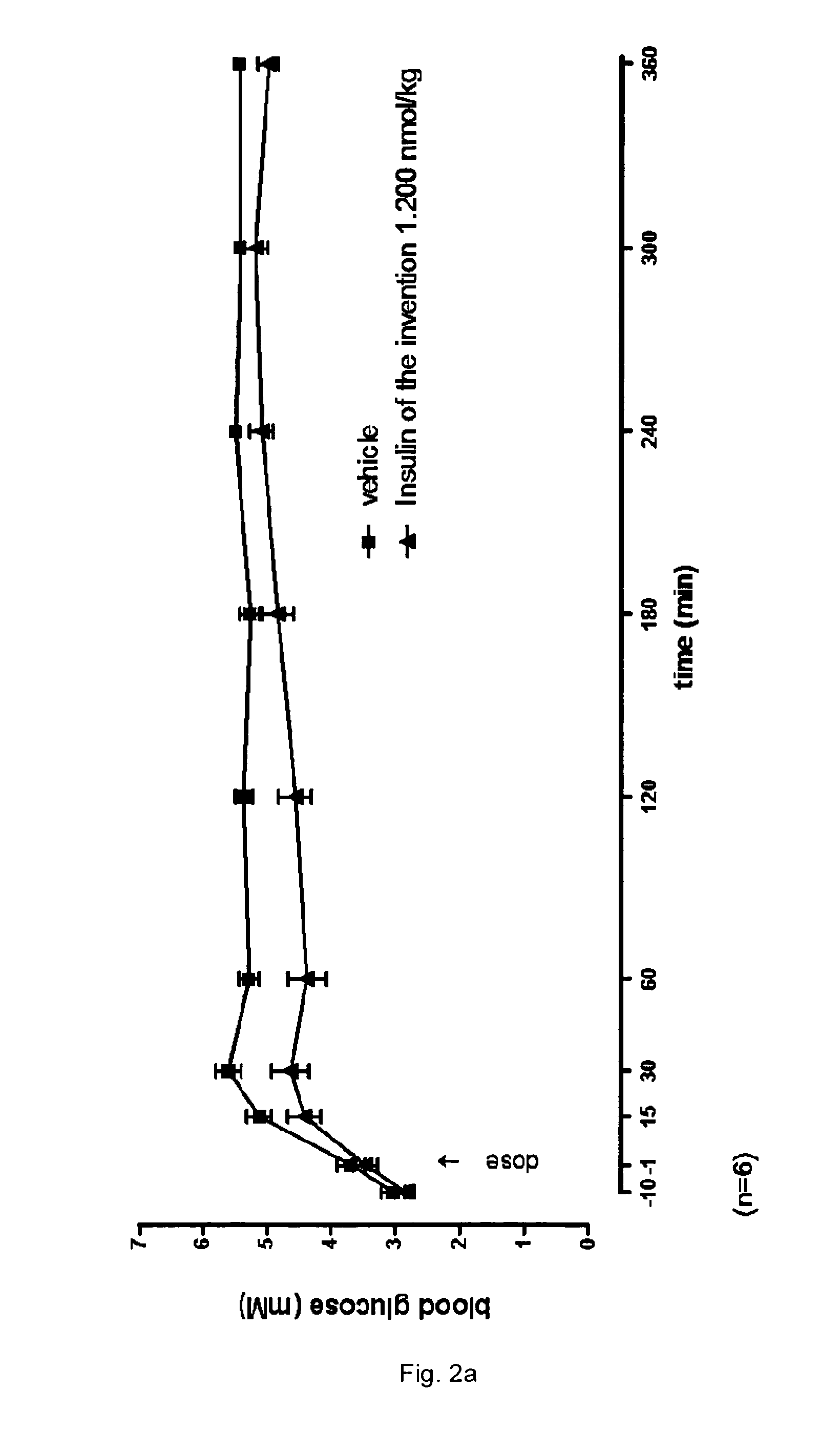
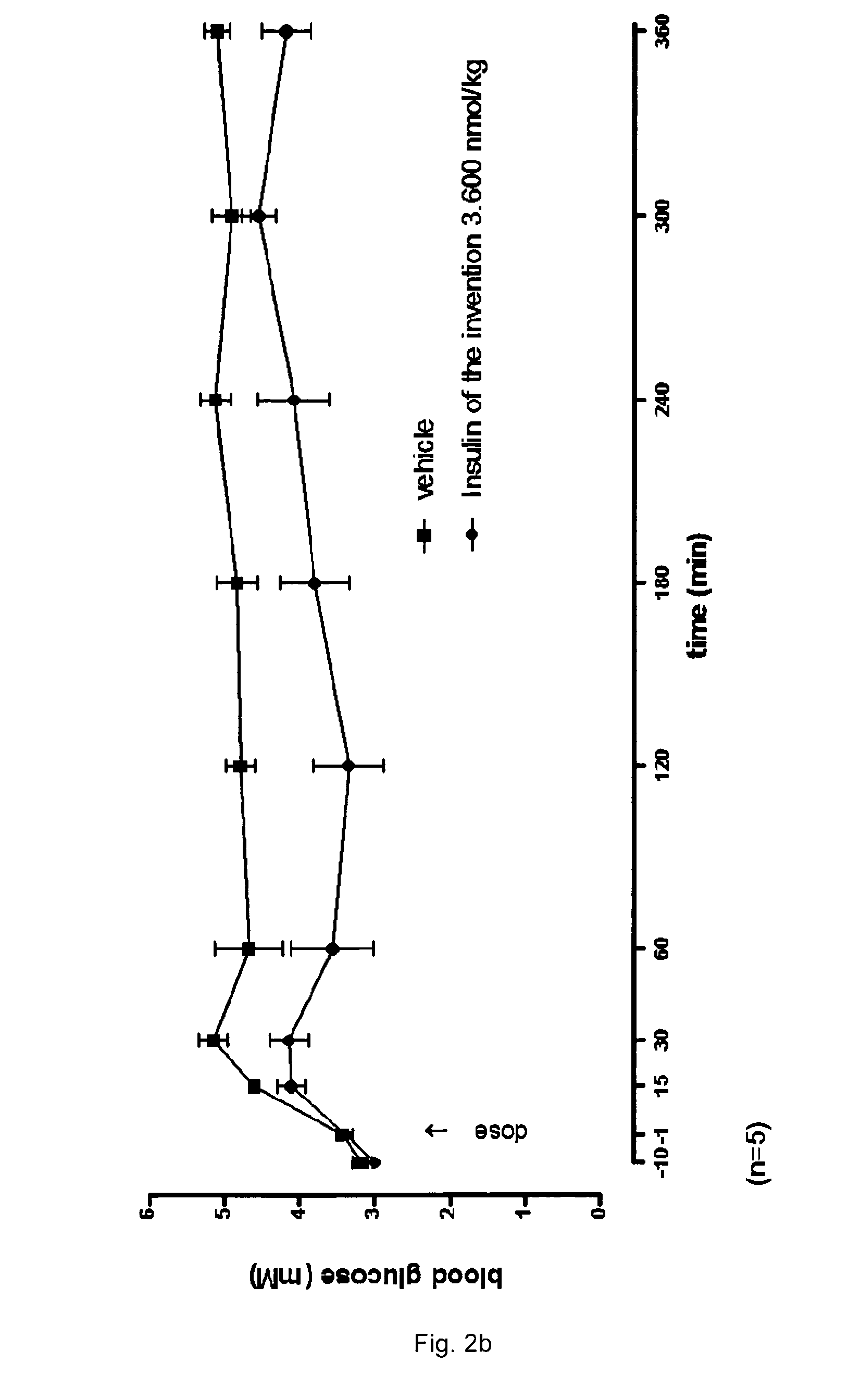
Patents
Literature
164 results about "Insulin Analogue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
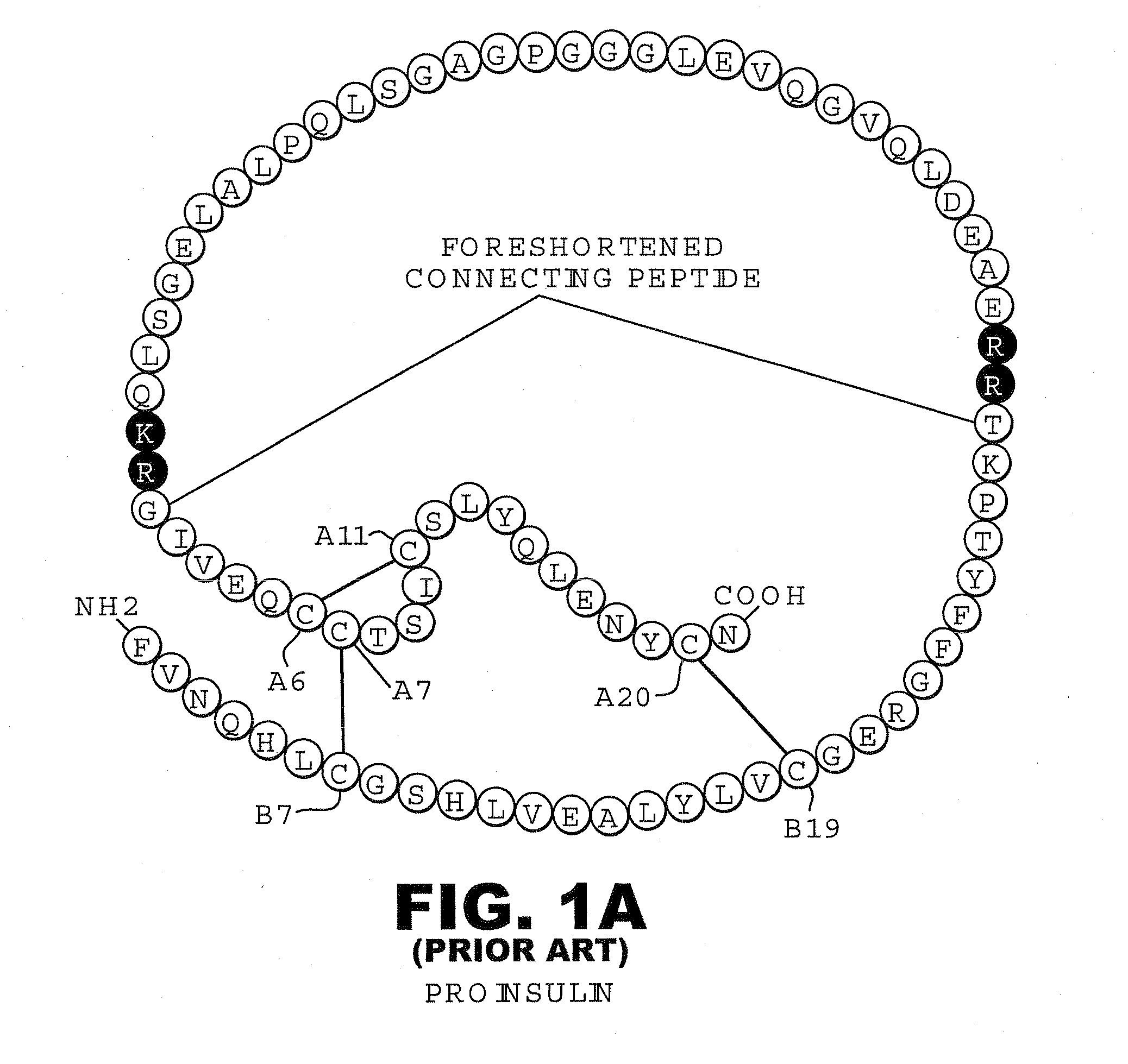
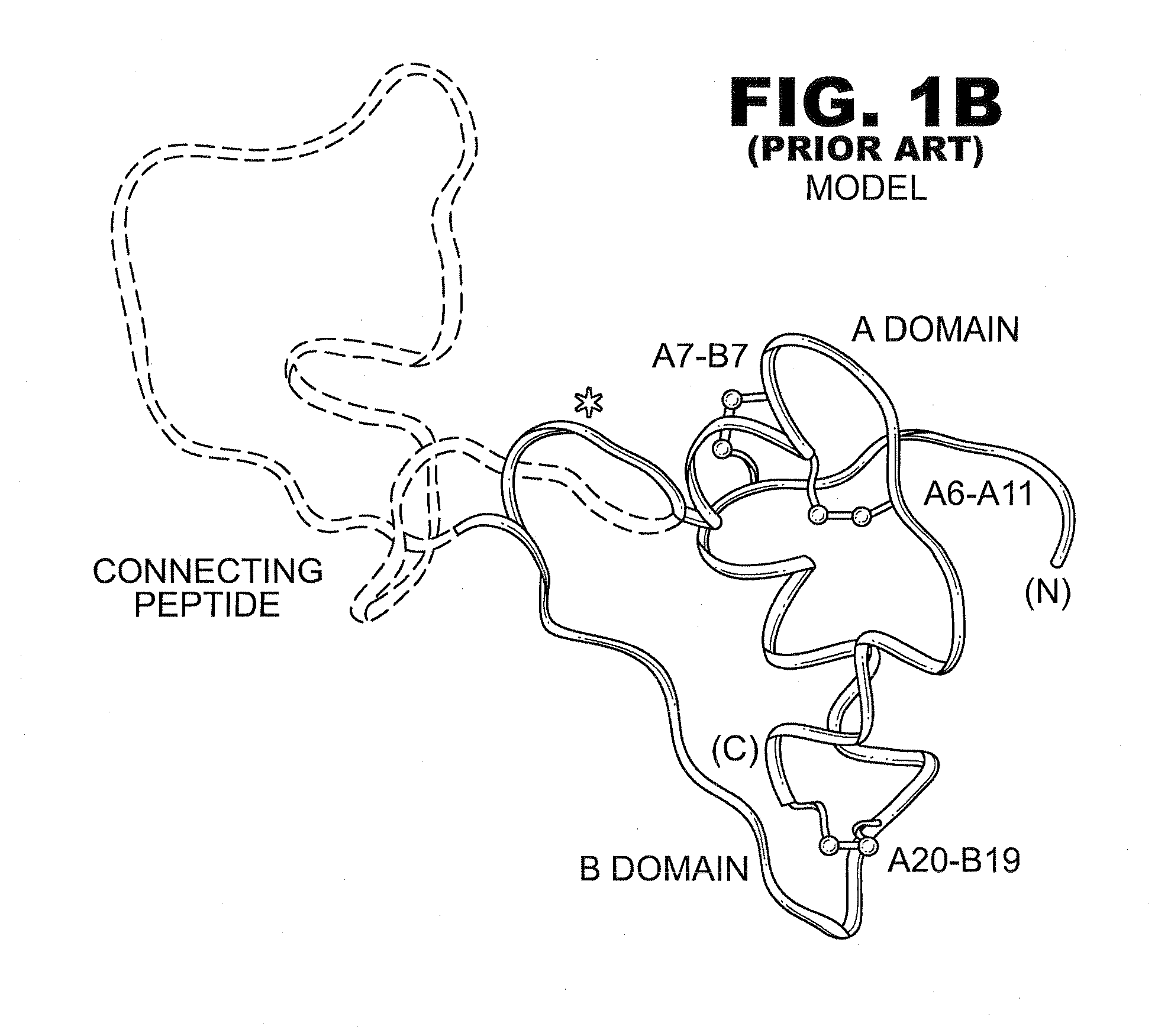
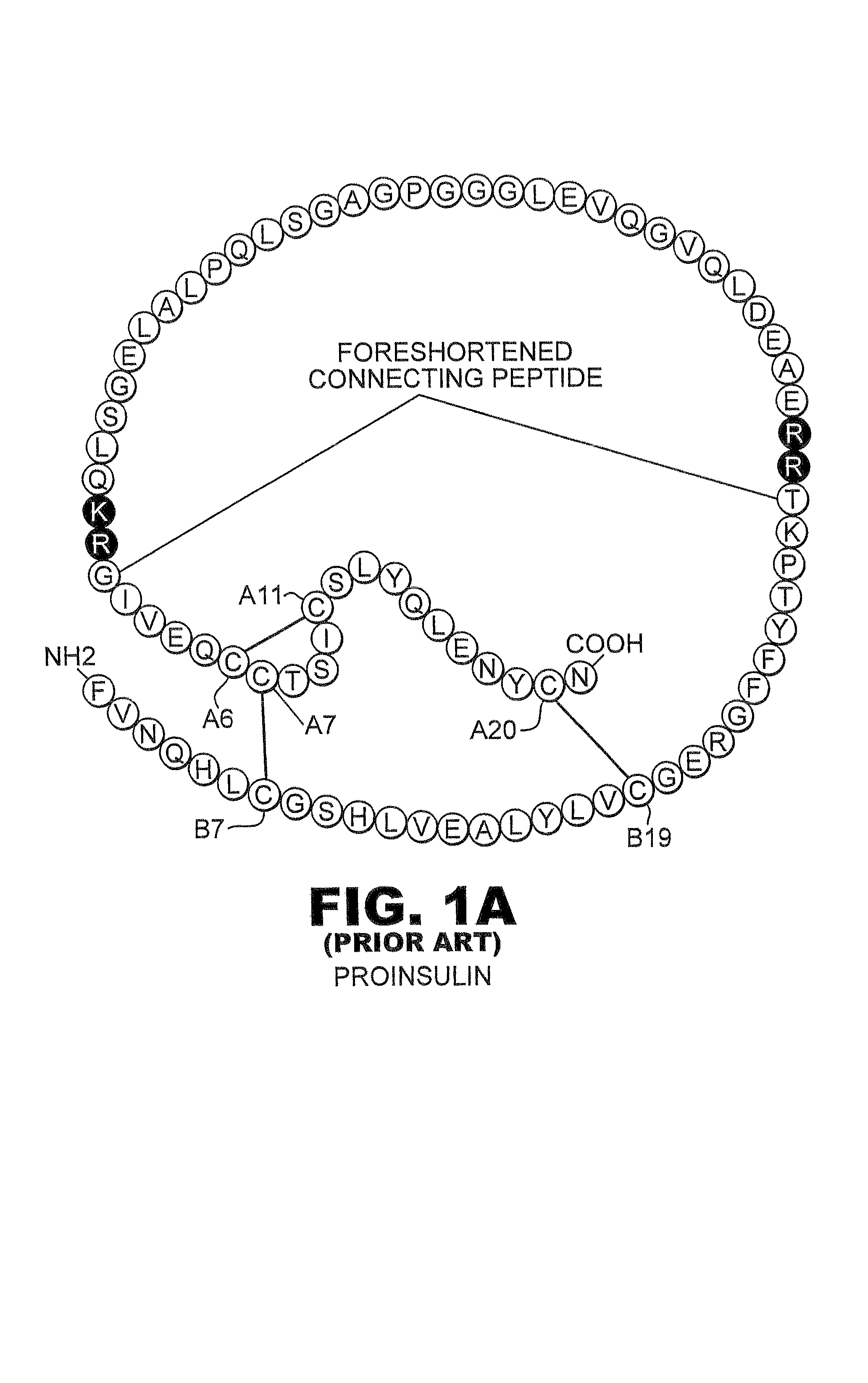
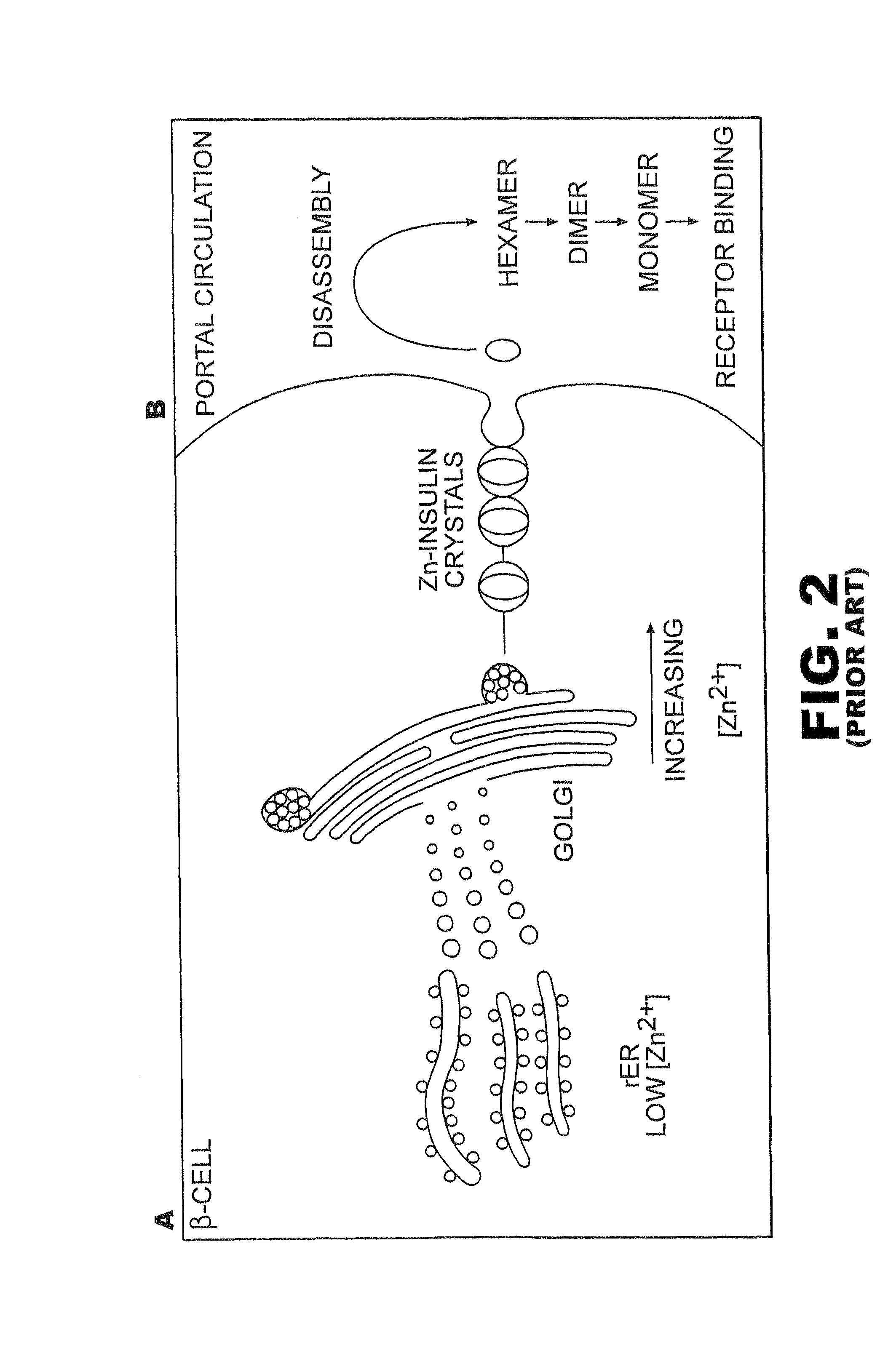
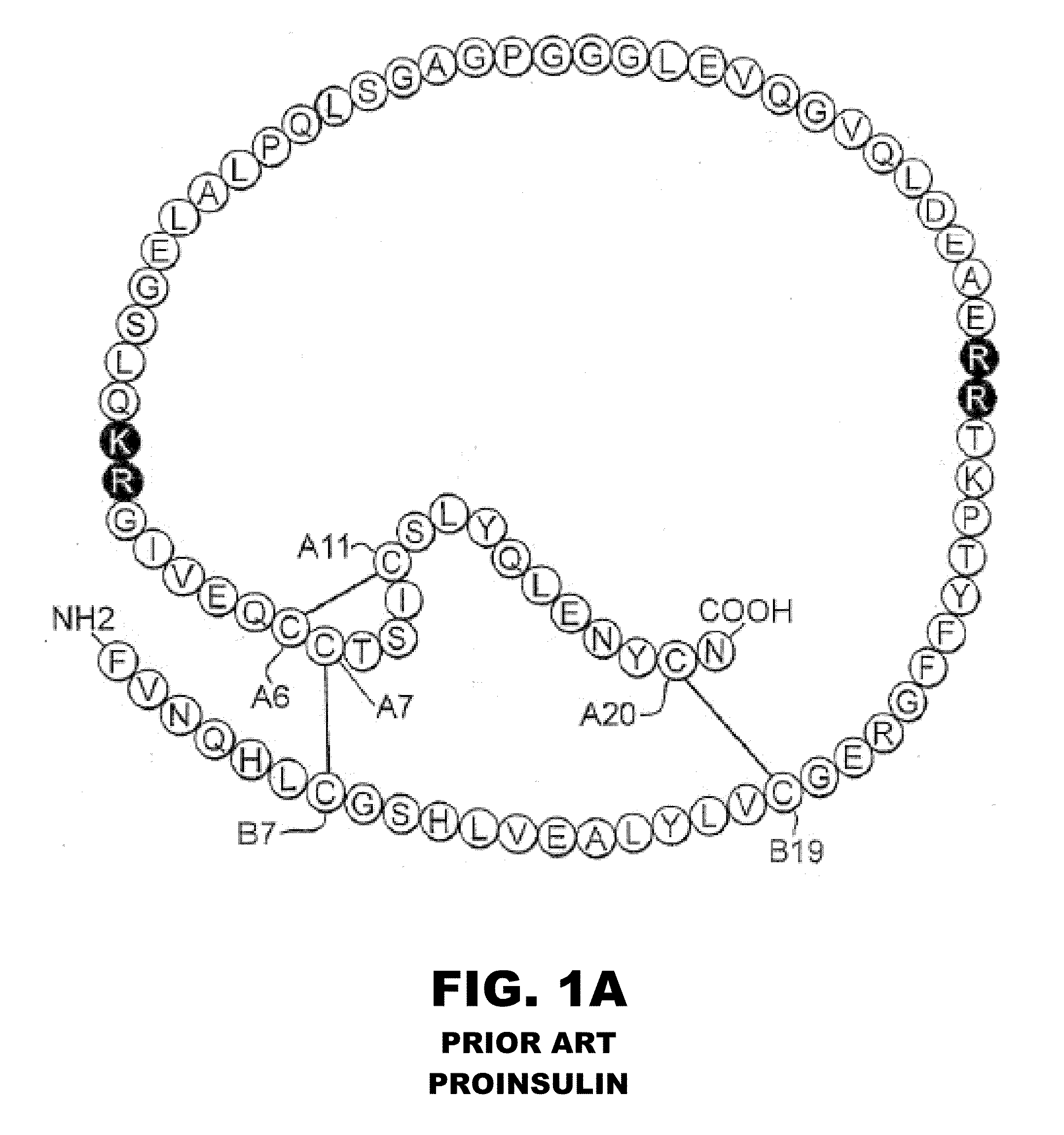
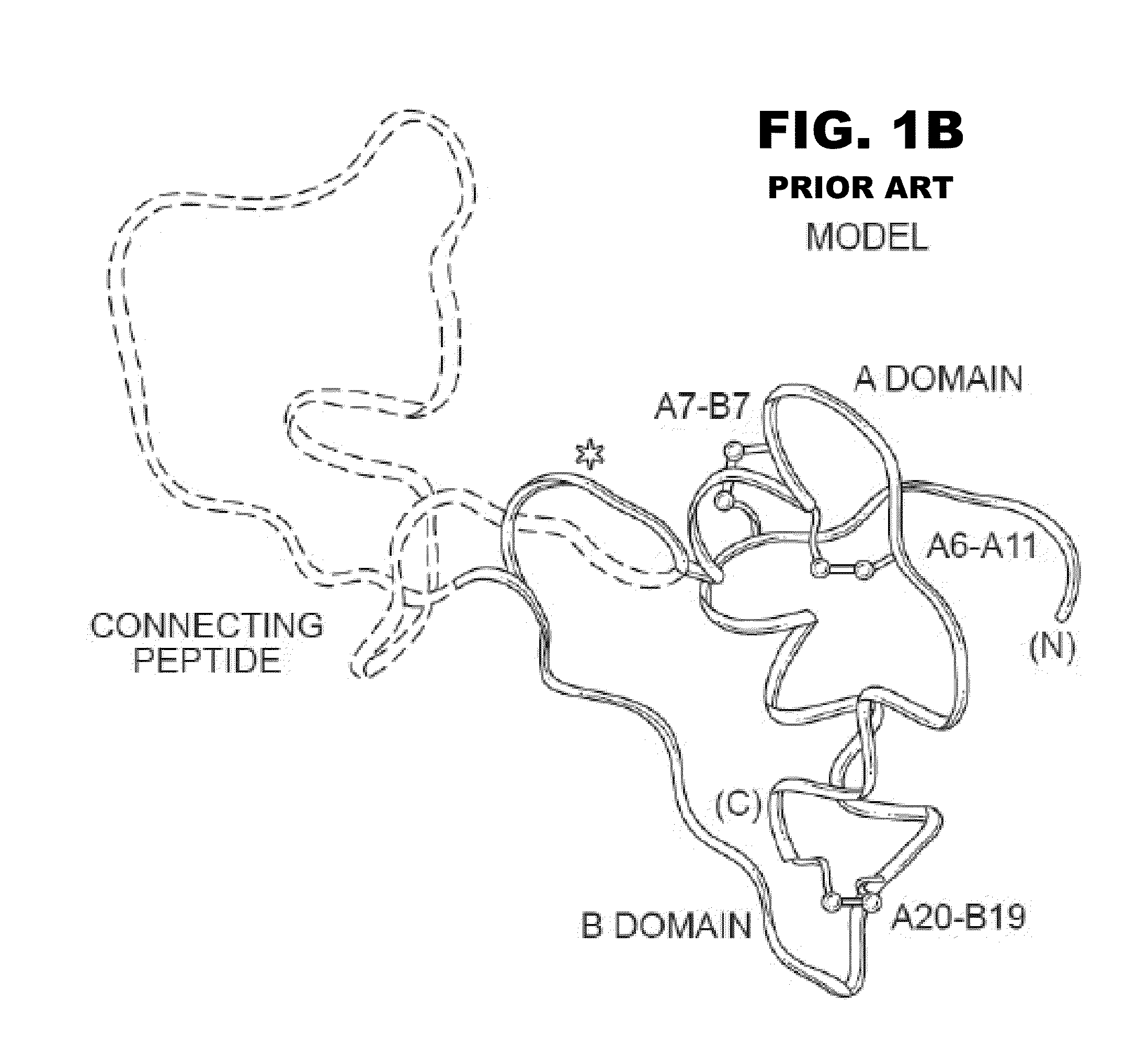
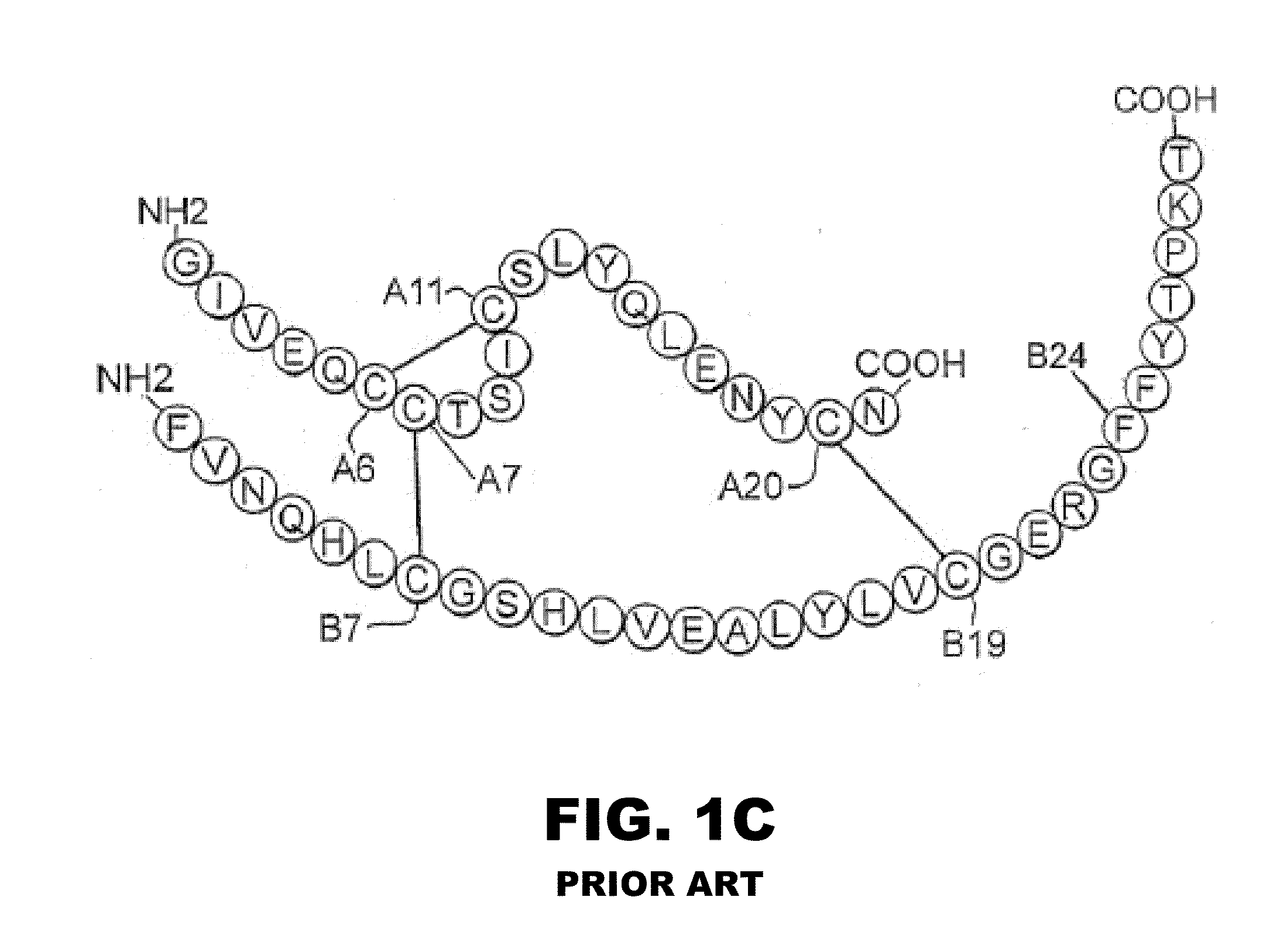
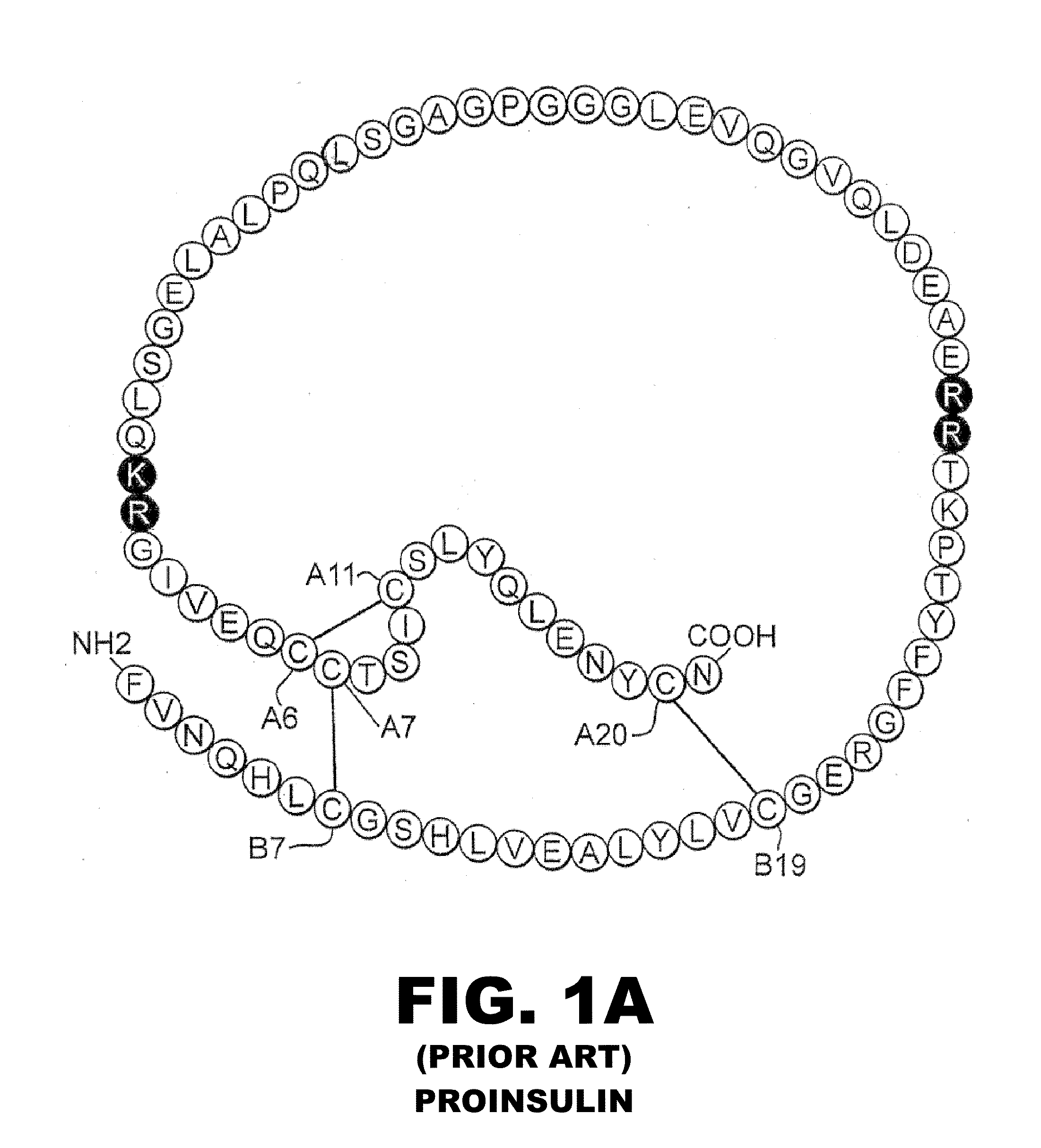
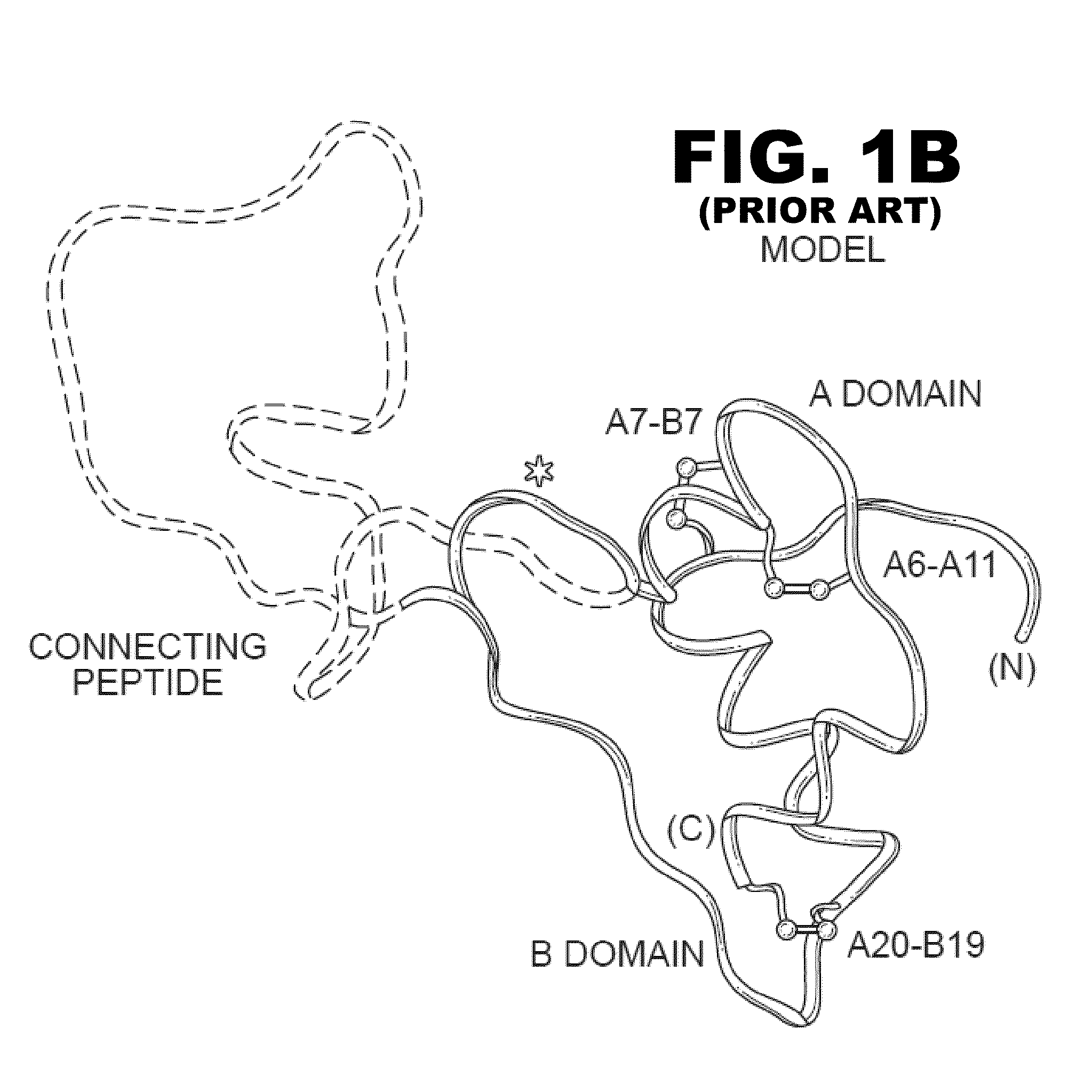
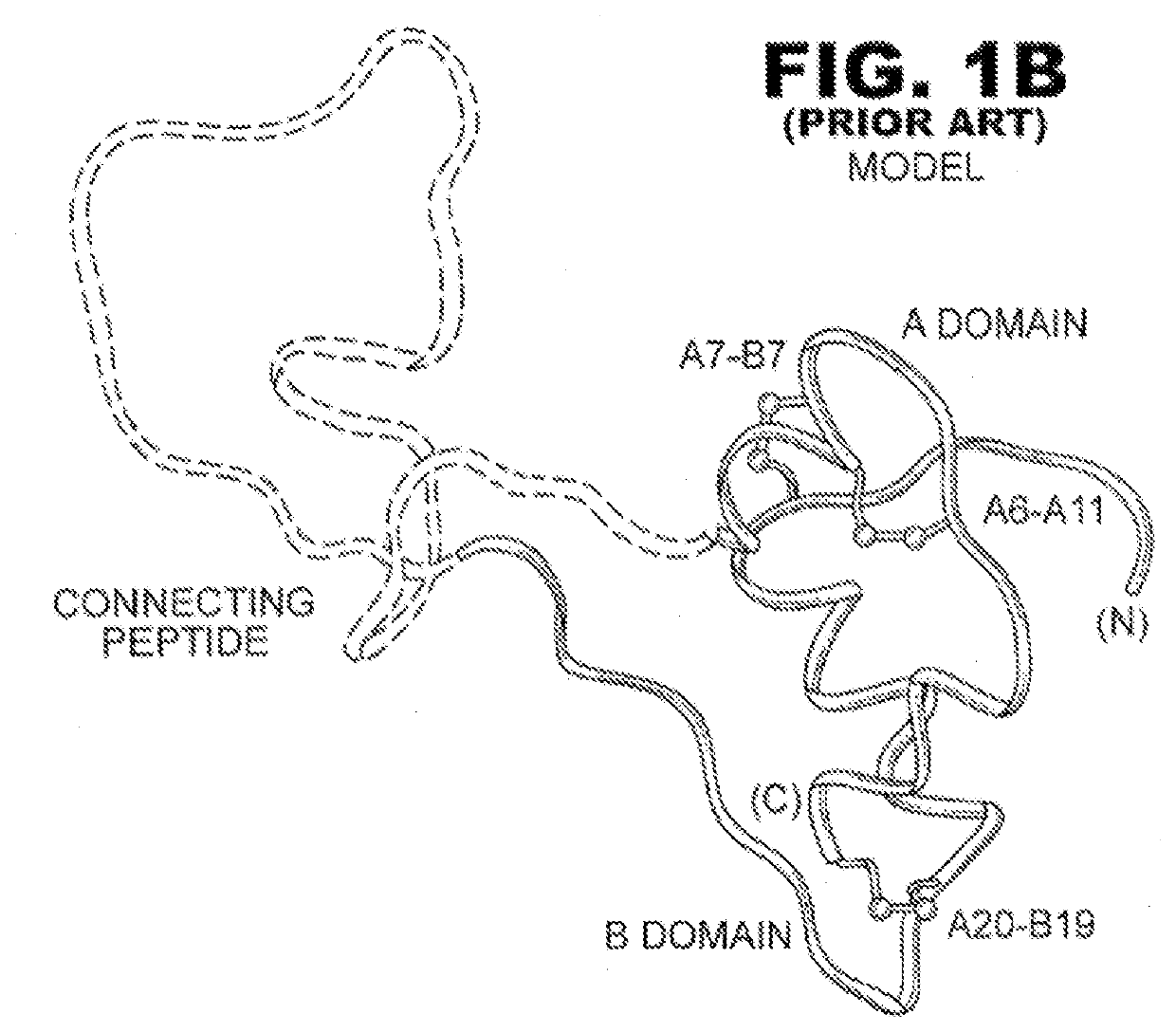
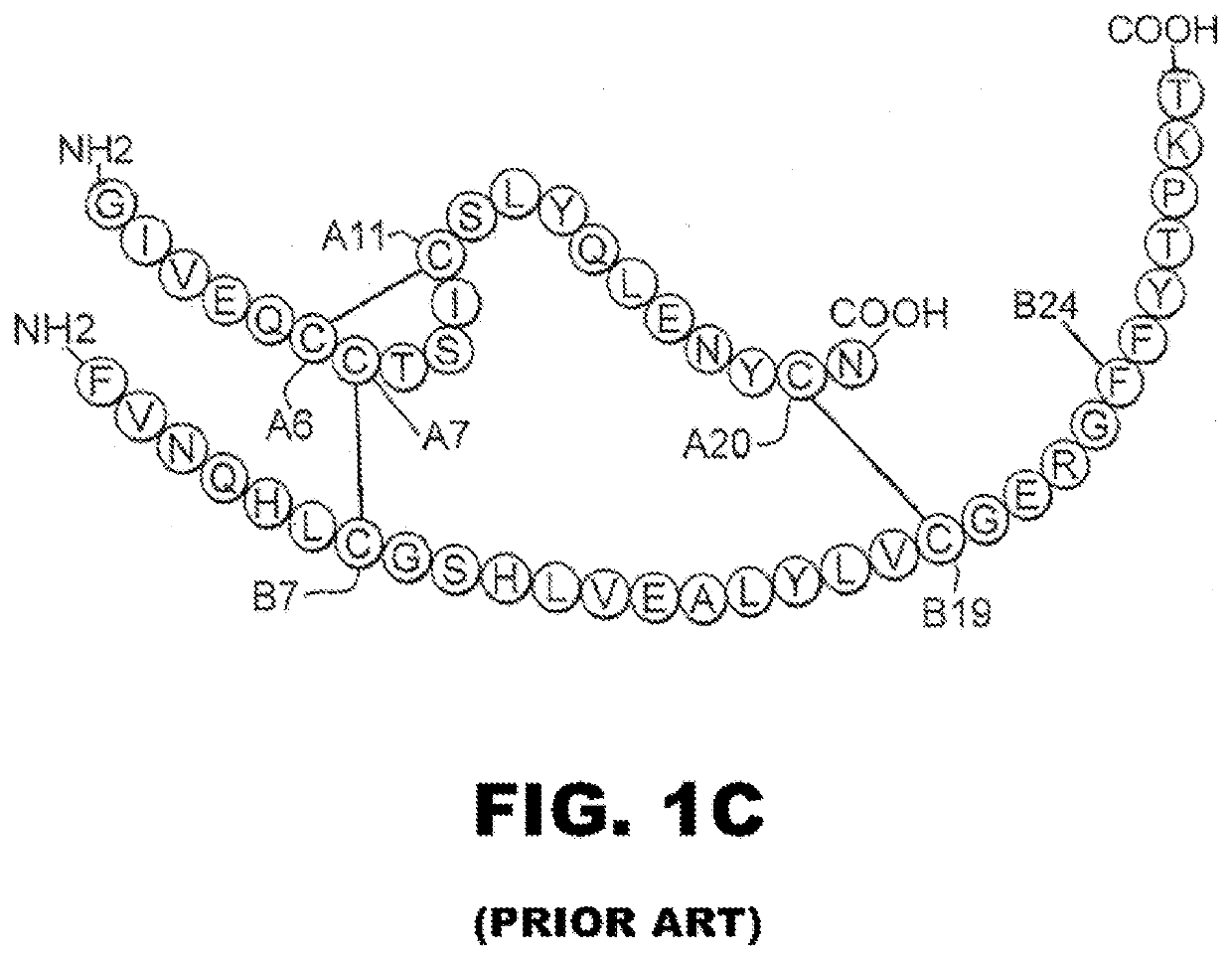
Analogue insulin is a sub-group of human insulin. Analogue insulin is laboratory grown but genetically altered to create either a more rapid acting or more uniformly acting form of the insulin.
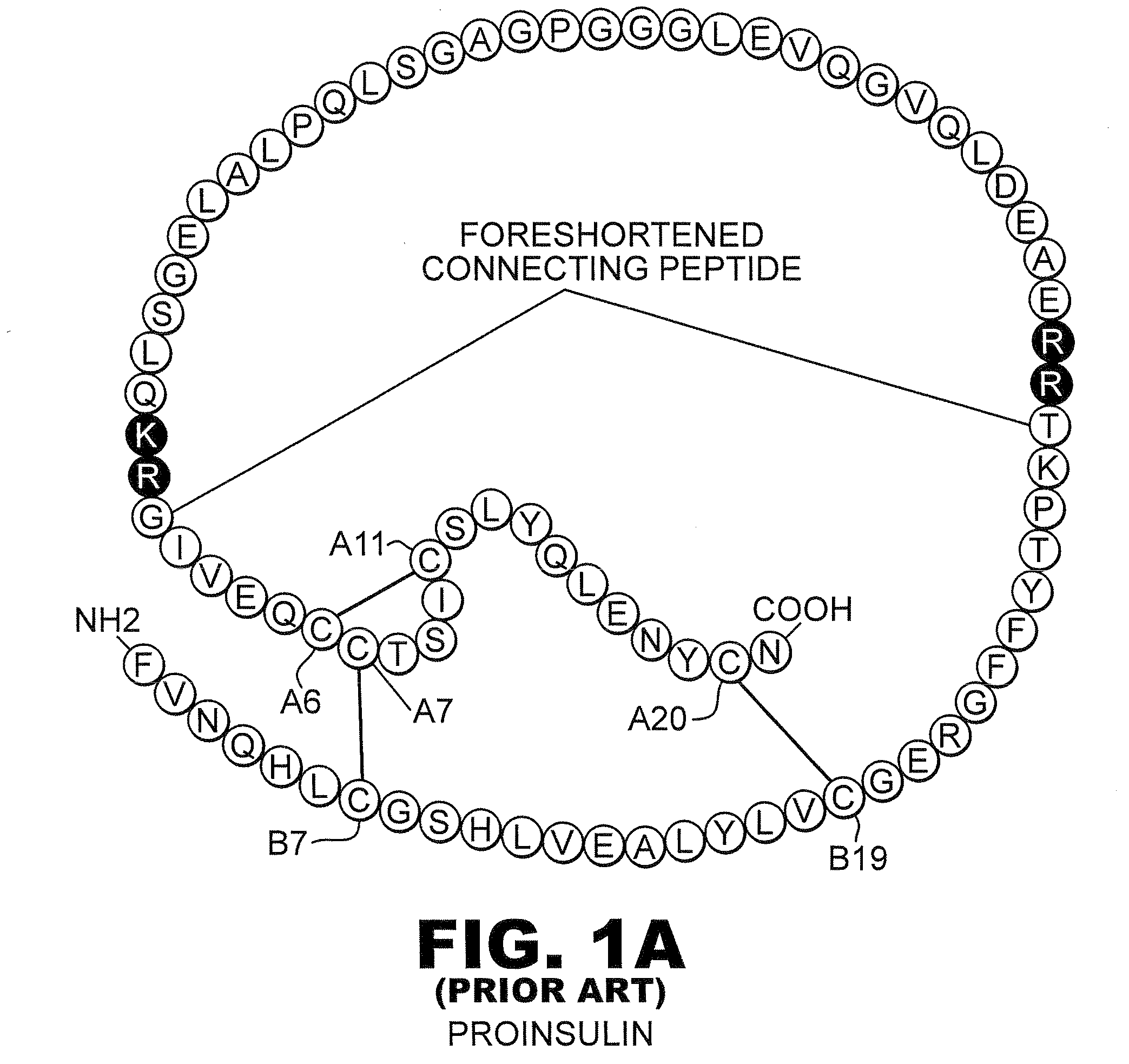
Isoform-specific insulin analogues
InactiveUS20110195896A1Improve stabilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNormal insulinInsulin Analogue
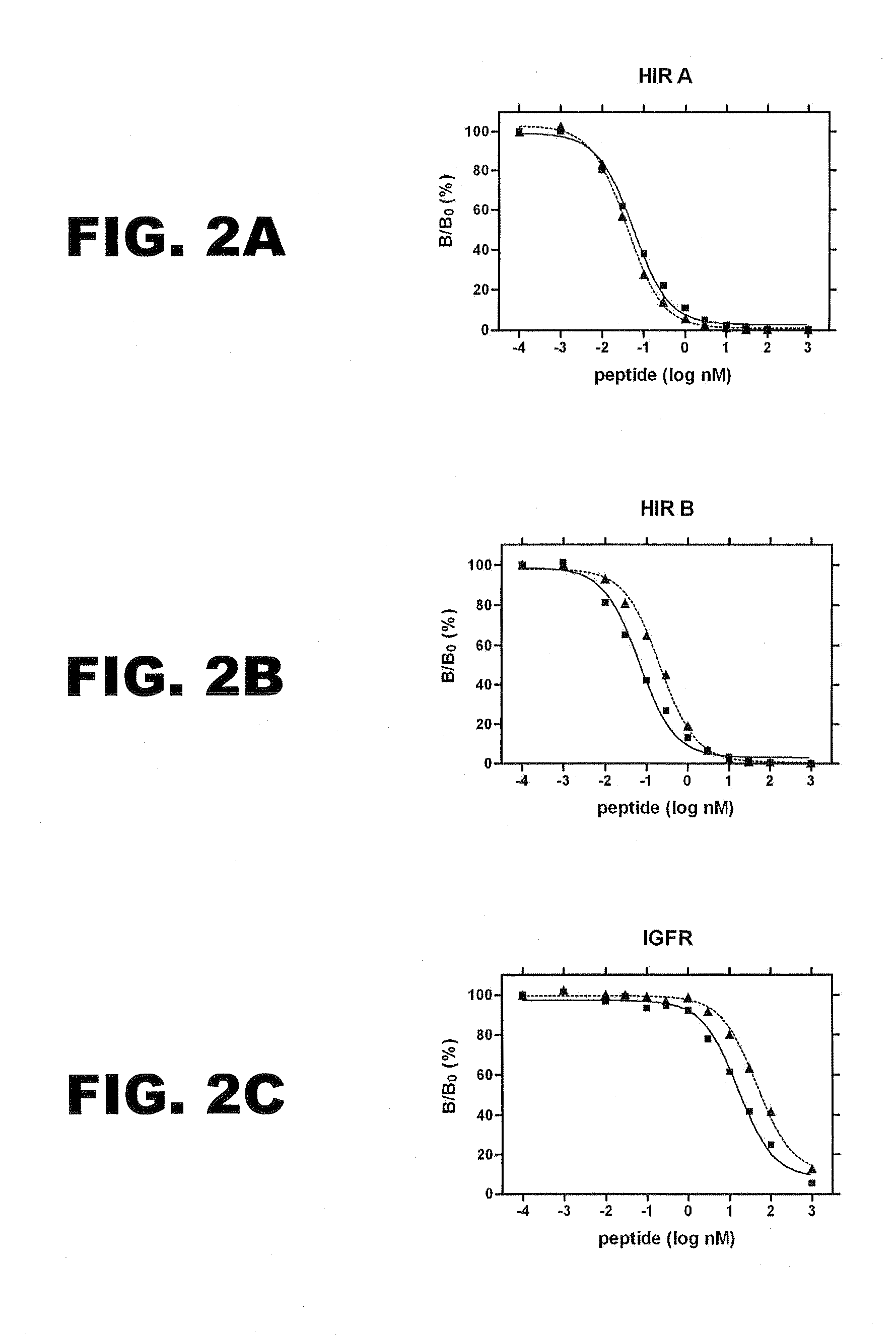
A method treating a mammal by administering a physiologically effective amount of an insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof where the insulin analogue displays more than twofold greater binding affinity to insulin receptor isoform A (IR-A) than insulin receptor isoform B (IR-B). The insulin analogue may be a single-chain insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, containing an insulin A-chain sequence or an analogue thereof and an insulin B-chain sequence or an analogue thereof connected by a polypeptide of 4-13 amino acids. A single-chain insulin analogue may display greater in vitro insulin receptor binding to IR-A but lower binding to IR-B than normal insulin while displaying less than or equal binding to IGFR than normal insulin.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
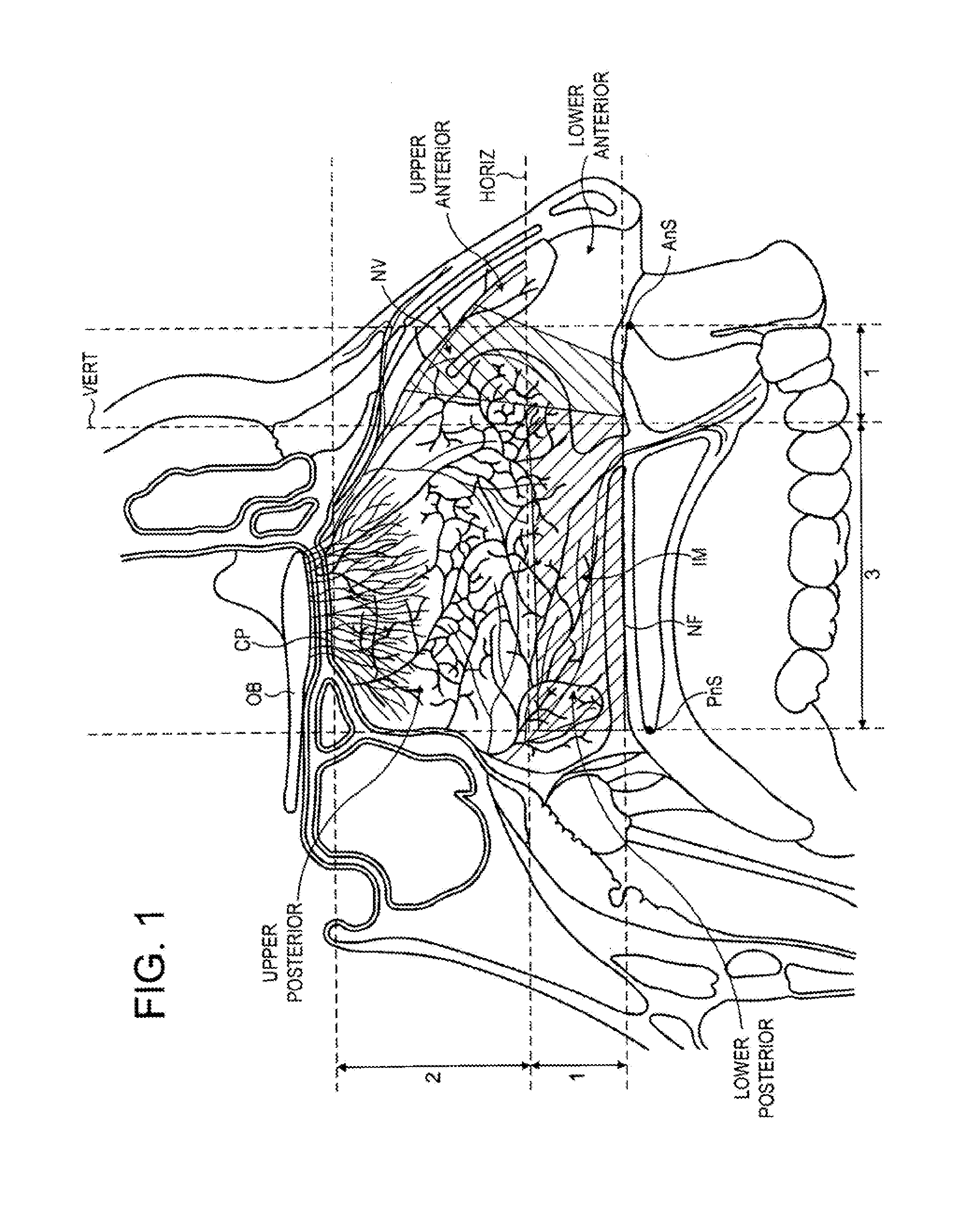
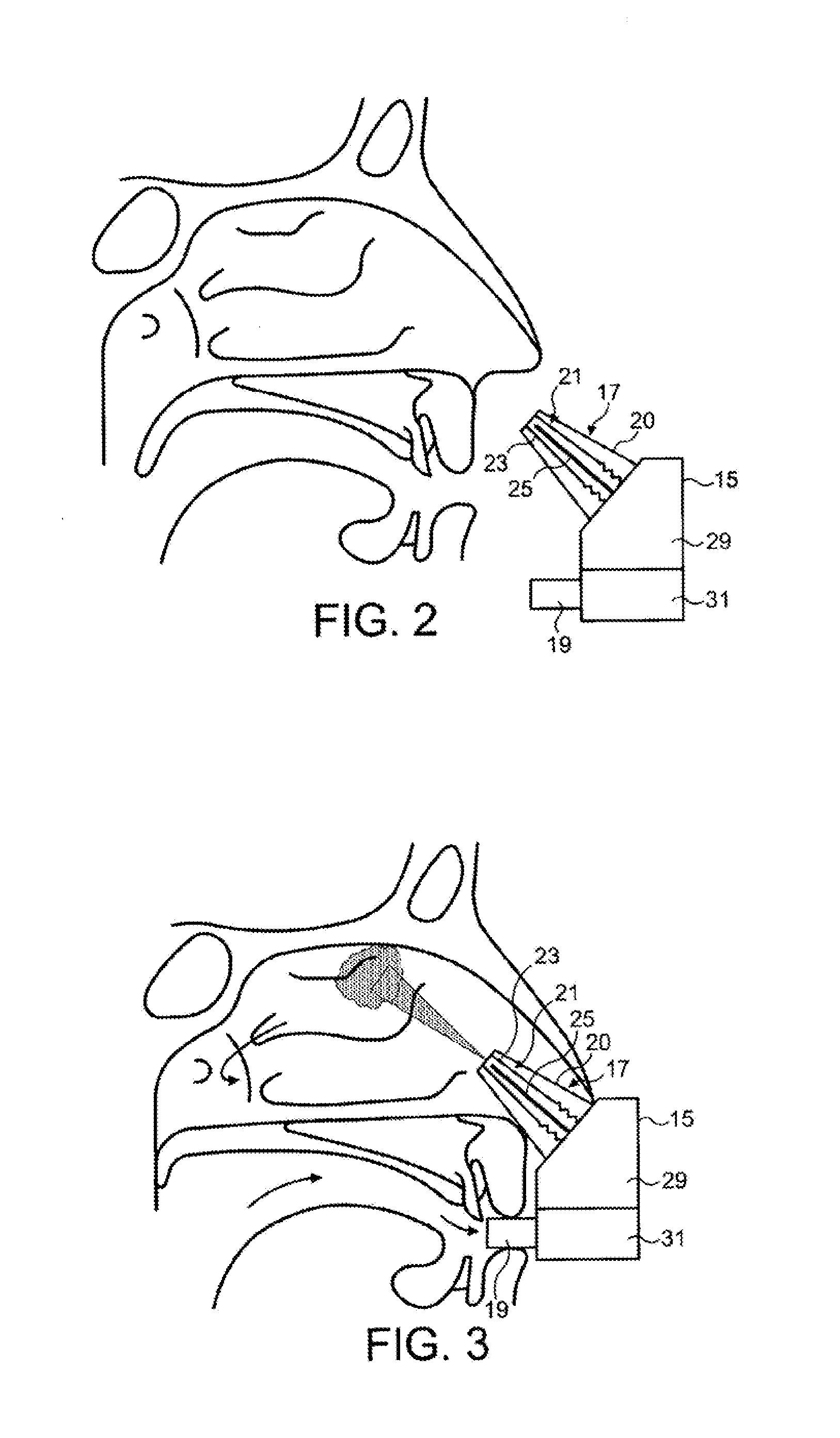
Intranasal administration
ActiveUS20150165139A1Minimizes deliveryAvoid accumulationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNasal cavityPosterior region
Intranasal administration of proteins, such as insulin and insulin analogues, in particular immunogenic proteins to the upper posterior region of a nasal cavity of a subject, and in particular the olfactory bulb region.
Owner:OPTINOSE INC
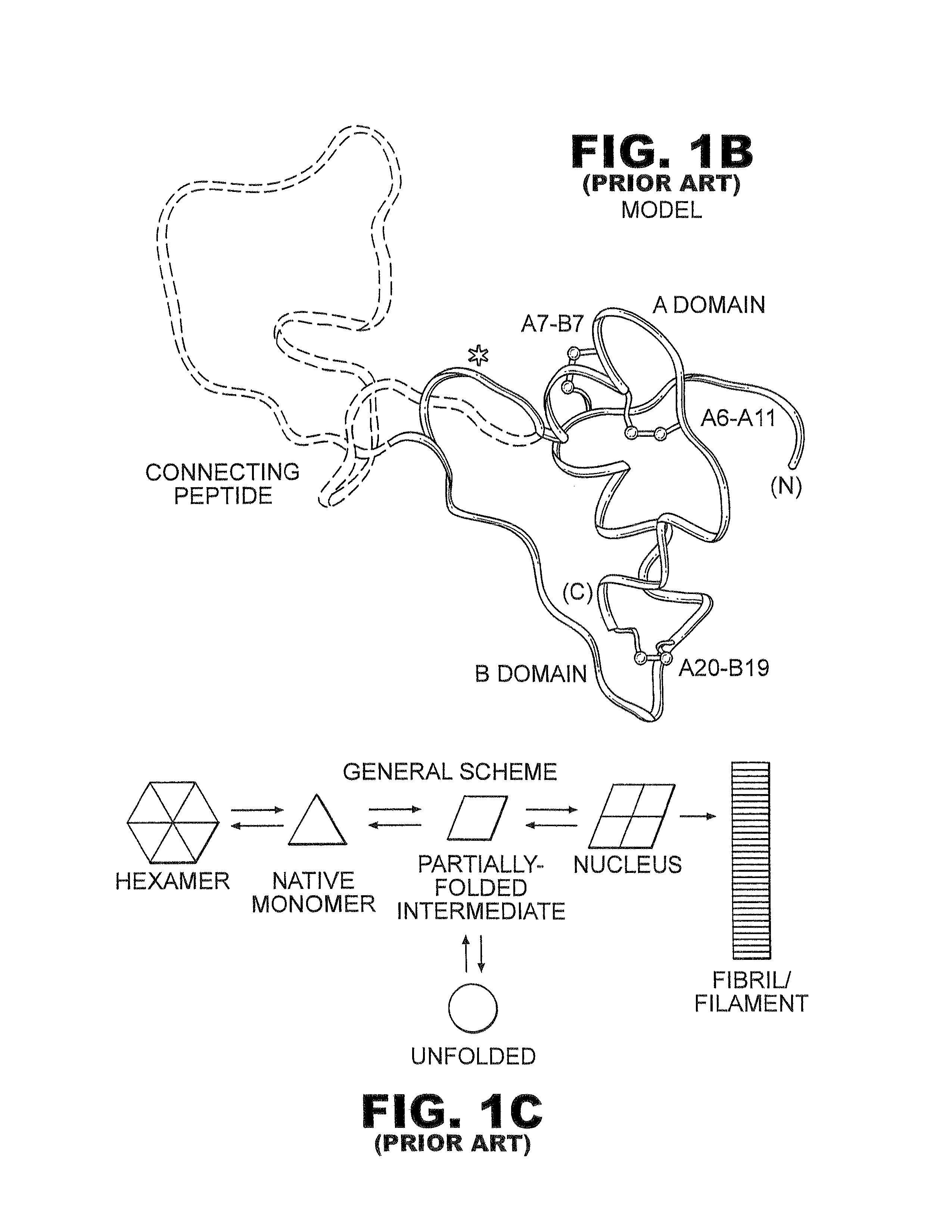
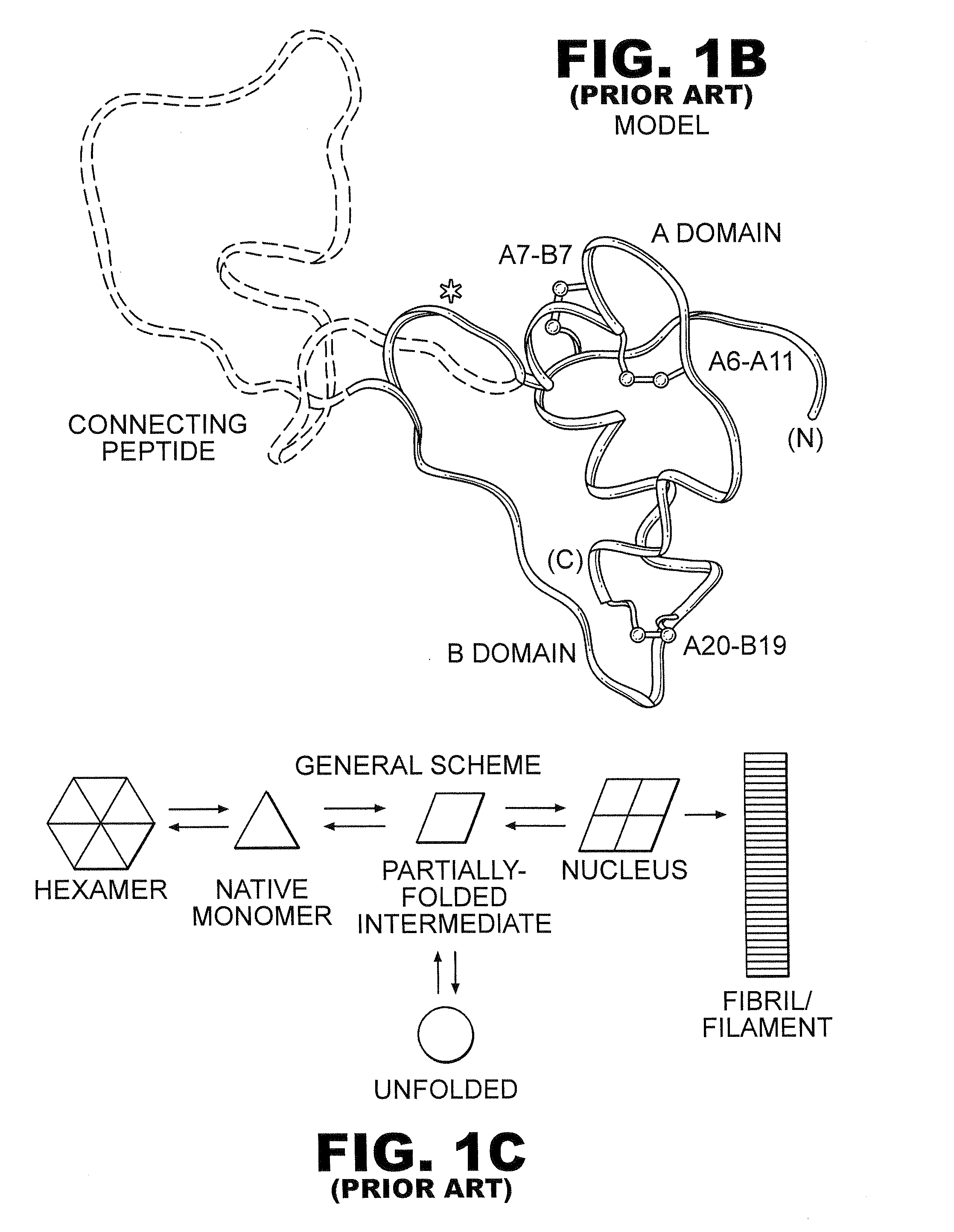
Fibrillation-resistant insulin and insulin analogues
InactiveUS8192957B2High thermodynamic stabilityMaintain biological activityBacteriaSugar derivativesInsulin A ChainNormal insulin
A fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may be a single-chain insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, containing an insulin A chain sequence or an analogue thereof and an insulin B chain sequence or an analogue thereof connected by a polypeptide of 4-10 amino acids. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue preferably displays less than 1 percent fibrillation with incubation at 37° C. for at least 21 days. A single-chain insulin analogue displays greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying less than or equal binding to IGFR than normal insulin. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its greater fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Halogen-stabilized insulin
An insulin analogue comprises a B-chain polypeptide incorporating a halogenated phenylalanine at position B24, B25 or B26. The halogenated phenylalanine may be ortho-monofluoro-phenylalanine, ortho-monobromo-phenylalanine, ortho-monochloro-phenylalanine, or para-monochloro-phenylalanine. The analogue may be of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A nucleic acid encodes such an insulin analogue. The halogenated insulin analogues retain significant activity. A method of treating a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to a patient. Halogen substitution-based stabilization of insulin may enhance the treatment of diabetes mellitus in regions of the developing world lacking refrigeration.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
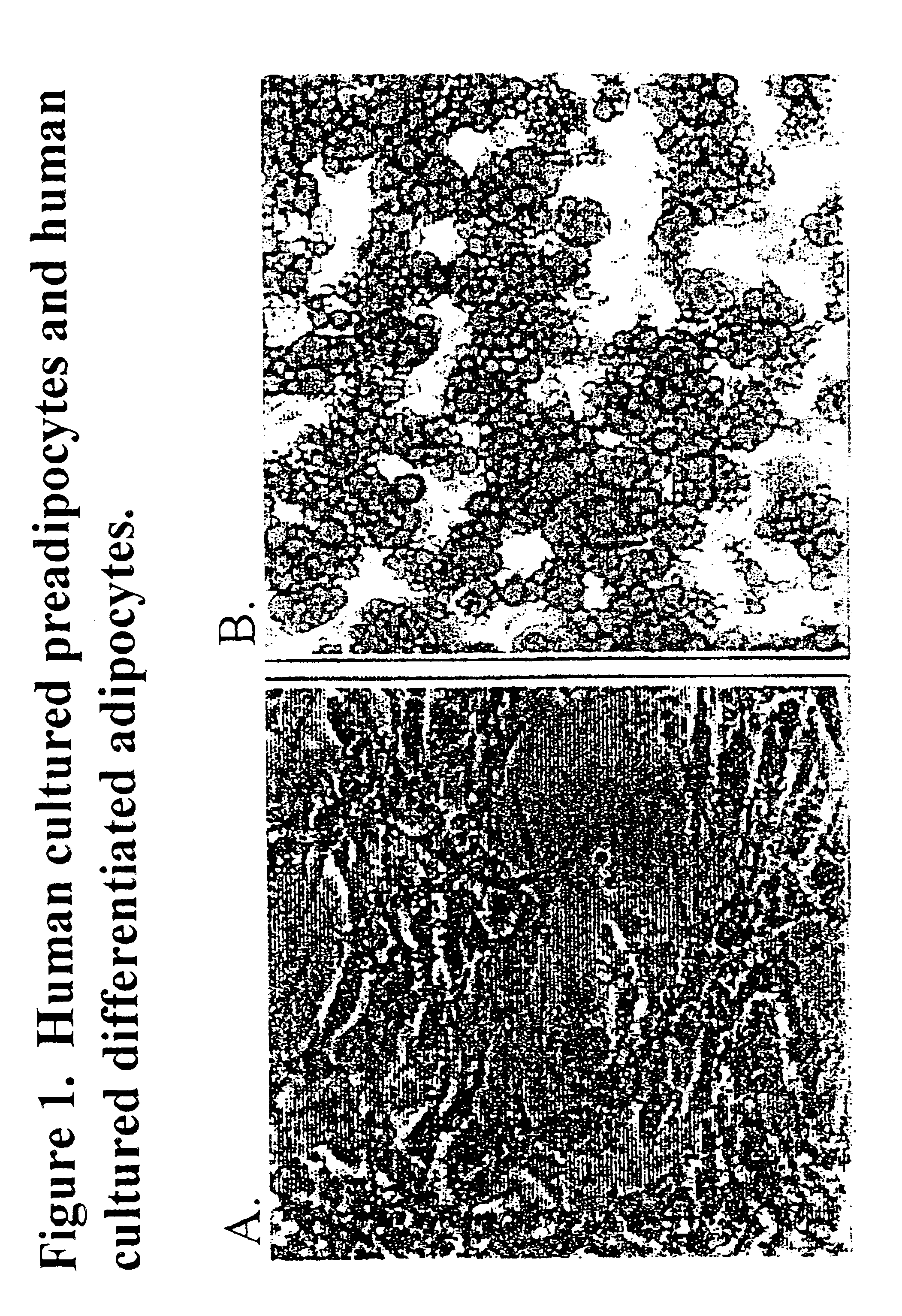
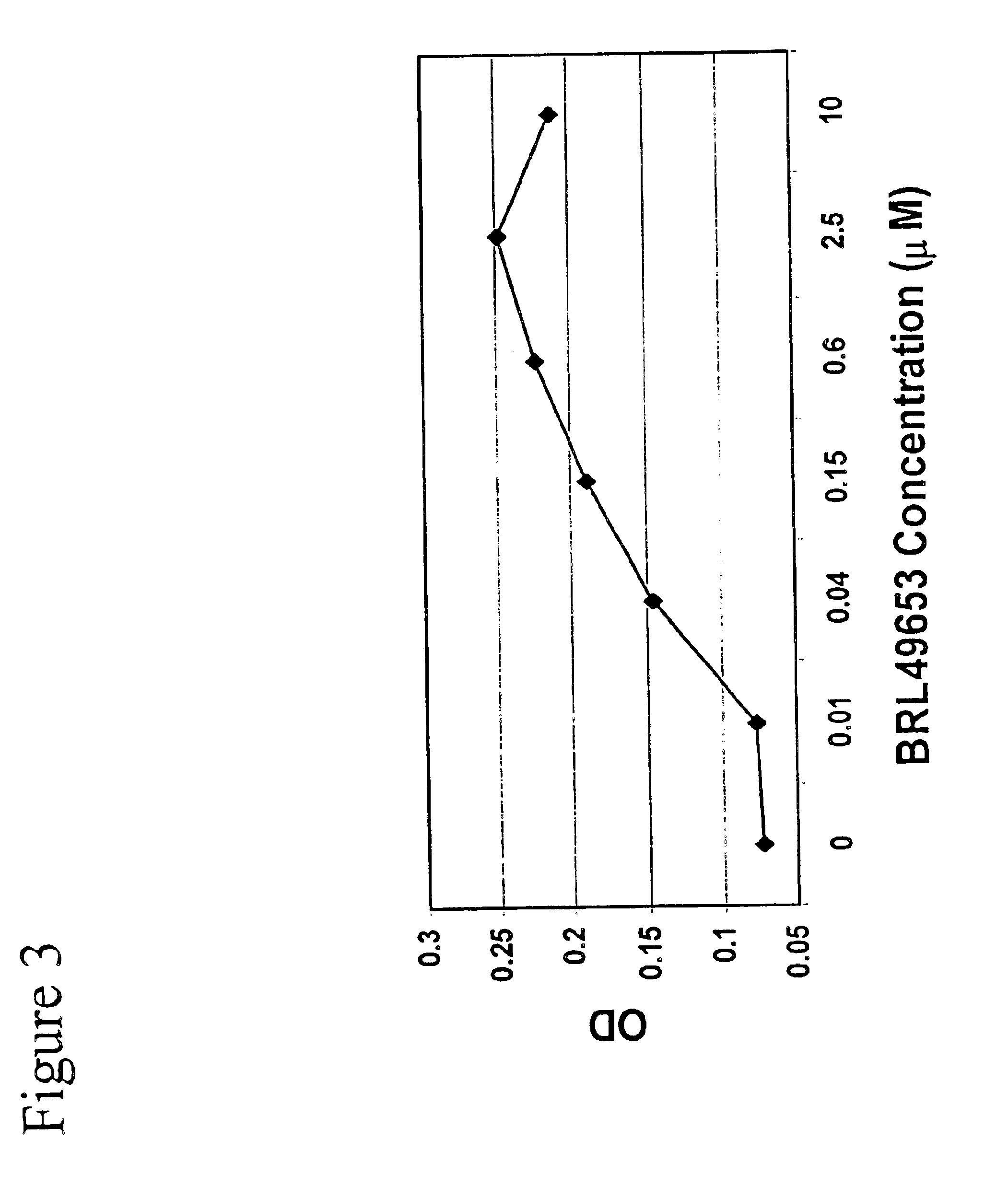
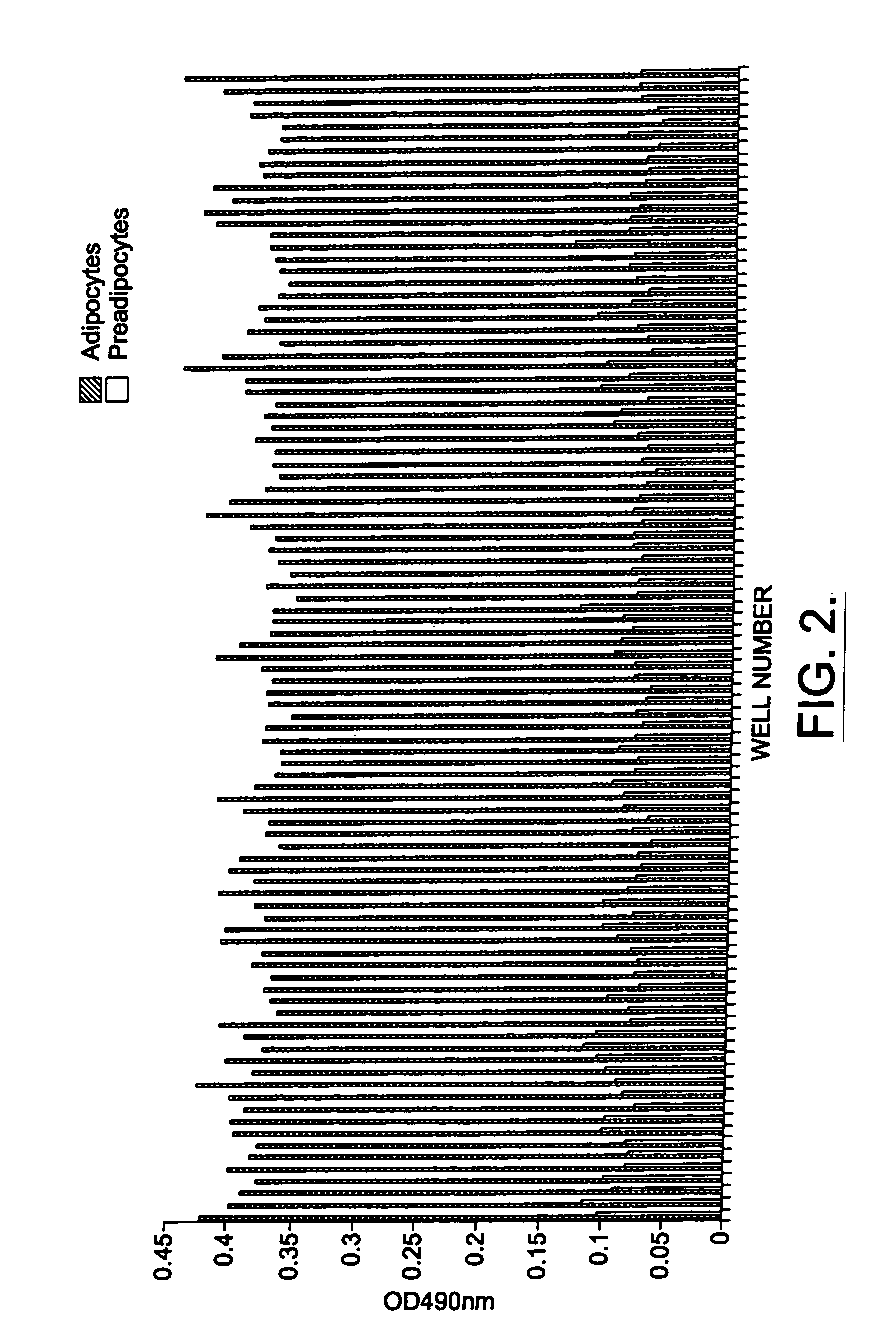
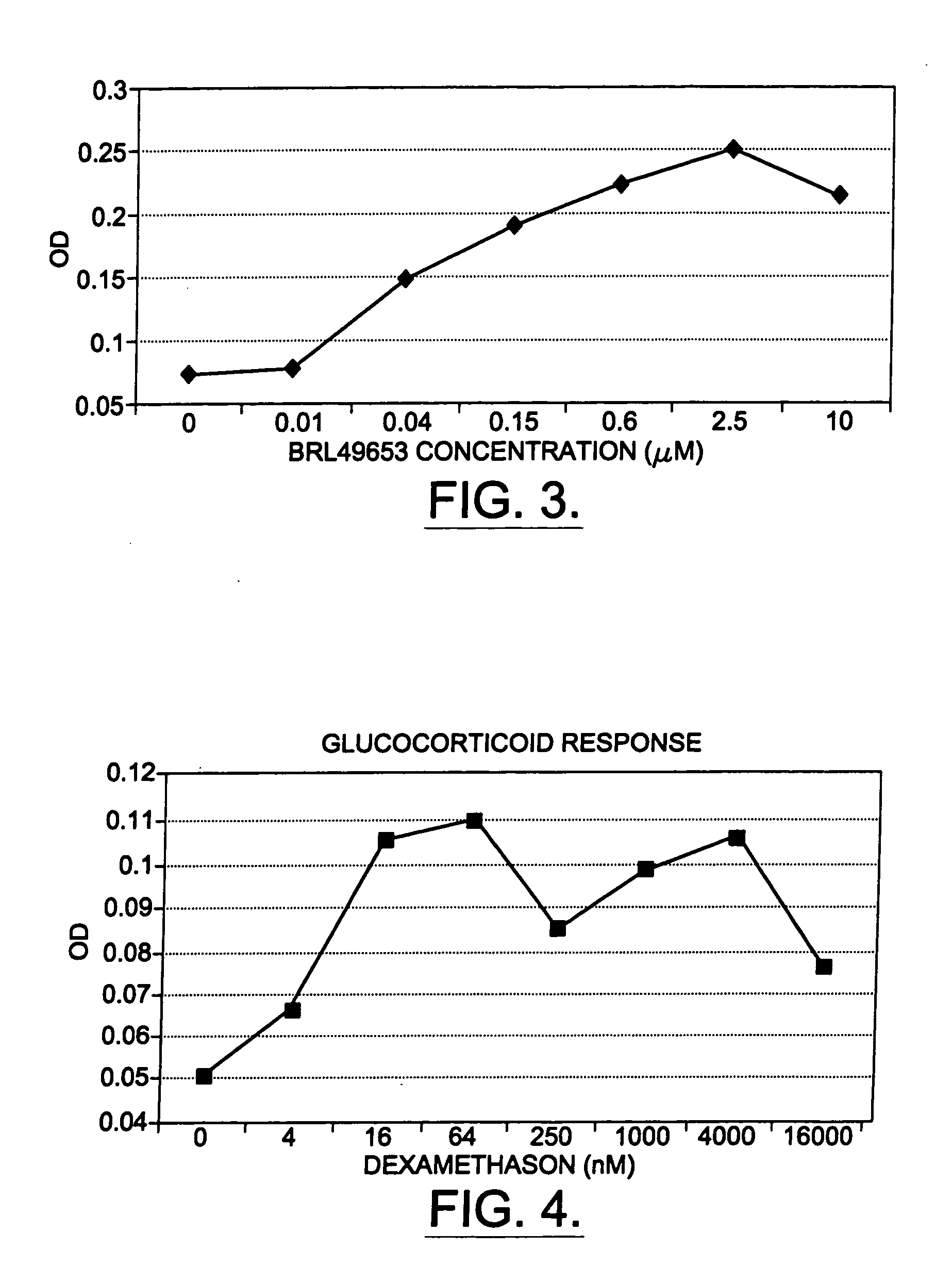
Methods and compositions for the differentiation of human preadipocytes into adipocytes
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the consistent and quantitative differentiation of human preadipocytes isolated from adipose tissue into adipocytes bearing biochemical, genetic, and physiological characteristics similar to that observed in isolated primary adipocytes. The methods of the invention comprise incubating isolated human preadipocytes, plated at least about 25,000 cells / cm2, in a medium containing, glucose, a cyclic AMP inducer such as isobutylmethylxanthine or forskolin, a glucocorticoid or glucocorticoid analogue, insulin or an insulin analogue and a PPARγ agonist or a RXR agonist. The compositions of the invention include media for the differentiation of human preadipocytes, human adipocytes differentiated by the methods of the invention and transfected adipocytes.The present invention also provides methods for determining the ability of a compound to affect the differentiation of human preadipocytes to adipocytes, for determining the ability of a compound to act as a PPARγ antagonist. a glucocorticoid, a glucocoticoid analogue, or an insulin analogue, for transfecting cultured human adipocytes, and as a means to identify novel polypeptides secreted from human adipocytes into the conditioned medium. The methods and compositions have use in the drug discovery of compounds having relevance to the disease states of diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease and in the studies of these diseases.
Owner:SEED INTPROP LAW GRP
Fibrillation resistant proteins
ActiveUS20090304814A1Improve the immunityIncreased susceptibilityBiocideFungiFibrillationHistidine residue
Protection of proteins against fibrillation may be afforded by introduction of certain histidine substitutions into the protein, such that a pair of histidines are present with sufficient spacing as to allow the histidines to coordinate with zinc. In the case of insulin, introduction of histidine residue substitutions at residues A4 and A8 together or a histidine residue substitution at residue B1, provides increased resistance to fibrillation while maintaining at least a majority of the activity of the insulin analogue. Introduction of a histidine residue substitution at residue A8 restores at least a portion of fibrillation resistance that may have been harmed by substitutions present on the B-chain such as those present in fast-acting insulins. Proteins protected by such histidine substitutions may be used to provide a pharmaceutical composition. A method of treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
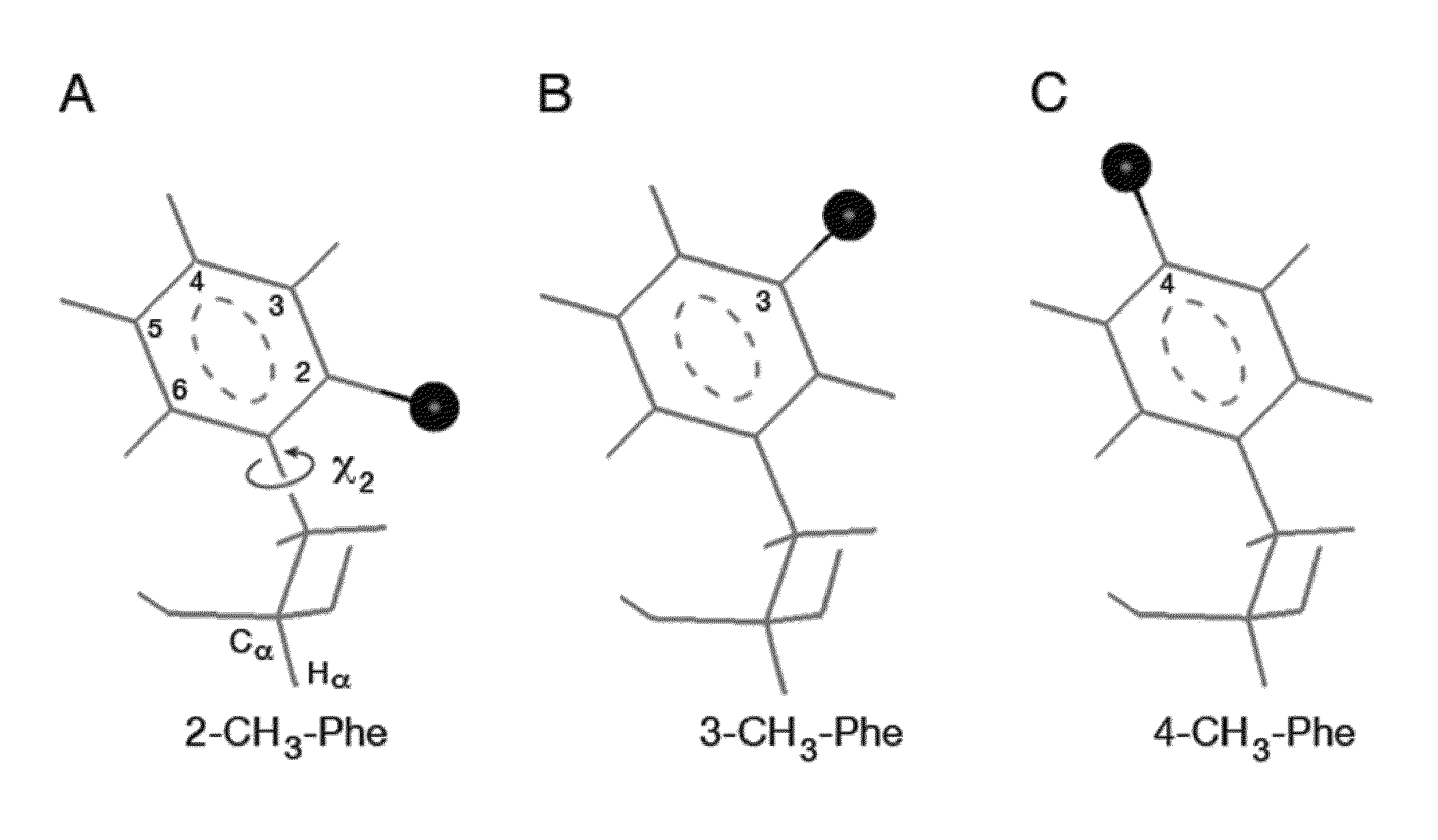
Non-standard insulin analogues
ActiveUS20110077196A1Improve stabilityHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsPhenylalanineAspartic acid
An insulin analogue comprises a B-chain polypeptide containing at least one alteration selected from a methylated phenylalanine substitution at position B24 and an addition of two amino acids to the carboxyl end of the B-chain polypeptide. A first amino acid at position B31 is selected from glutamate and aspartate, and a second amino acid at position B32 is selected from glutamate, alanine and aspartate. The methylated phenylalanine may be ortho-monofluoro-phenylalanine, meta-monobromo-phenylalanine or para-monochloro-phenylalanine. The analogue may be an analogue of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A nucleic acid encoding such an insulin analogue is also provided. A method of treating a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to a patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
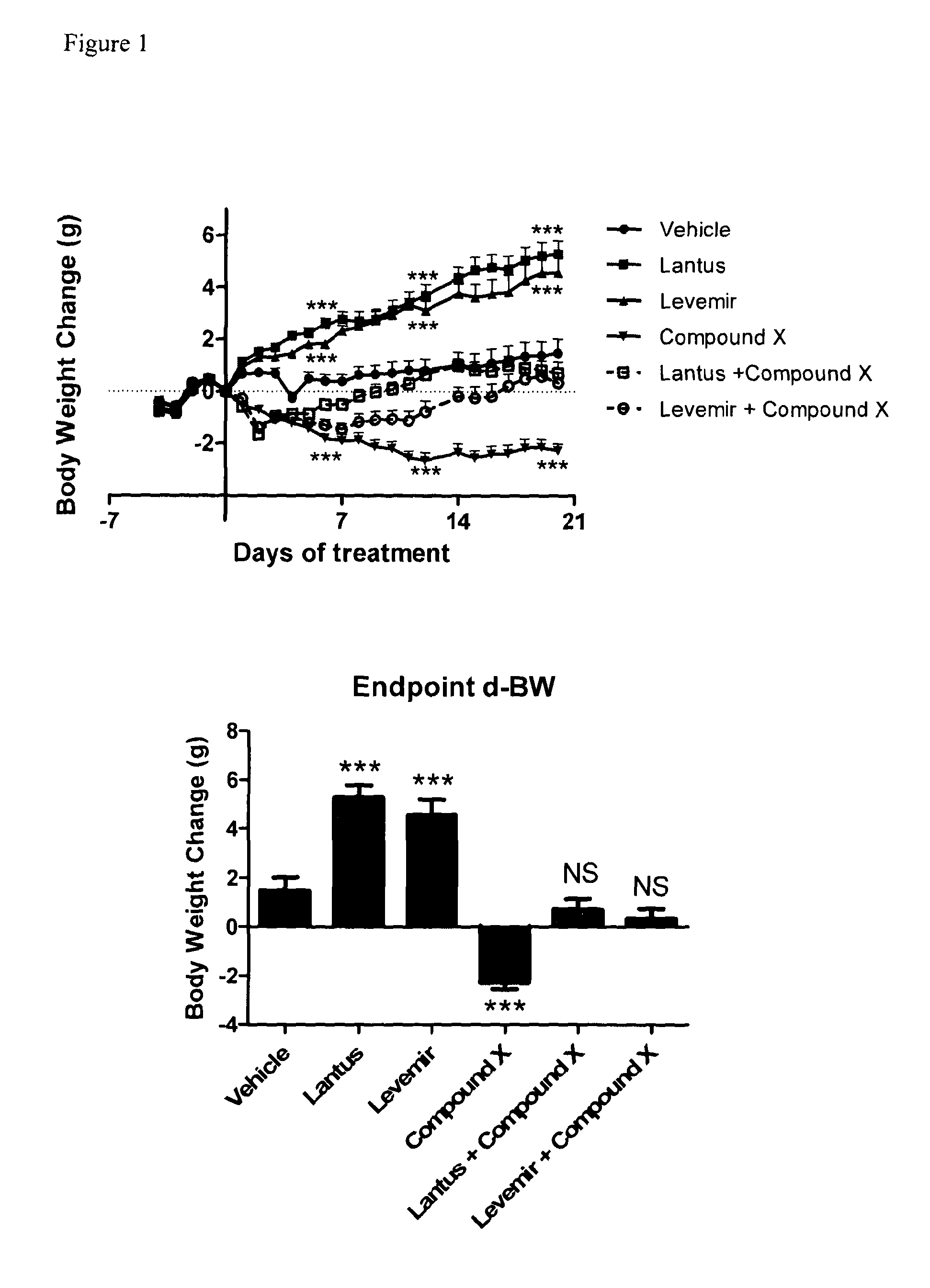
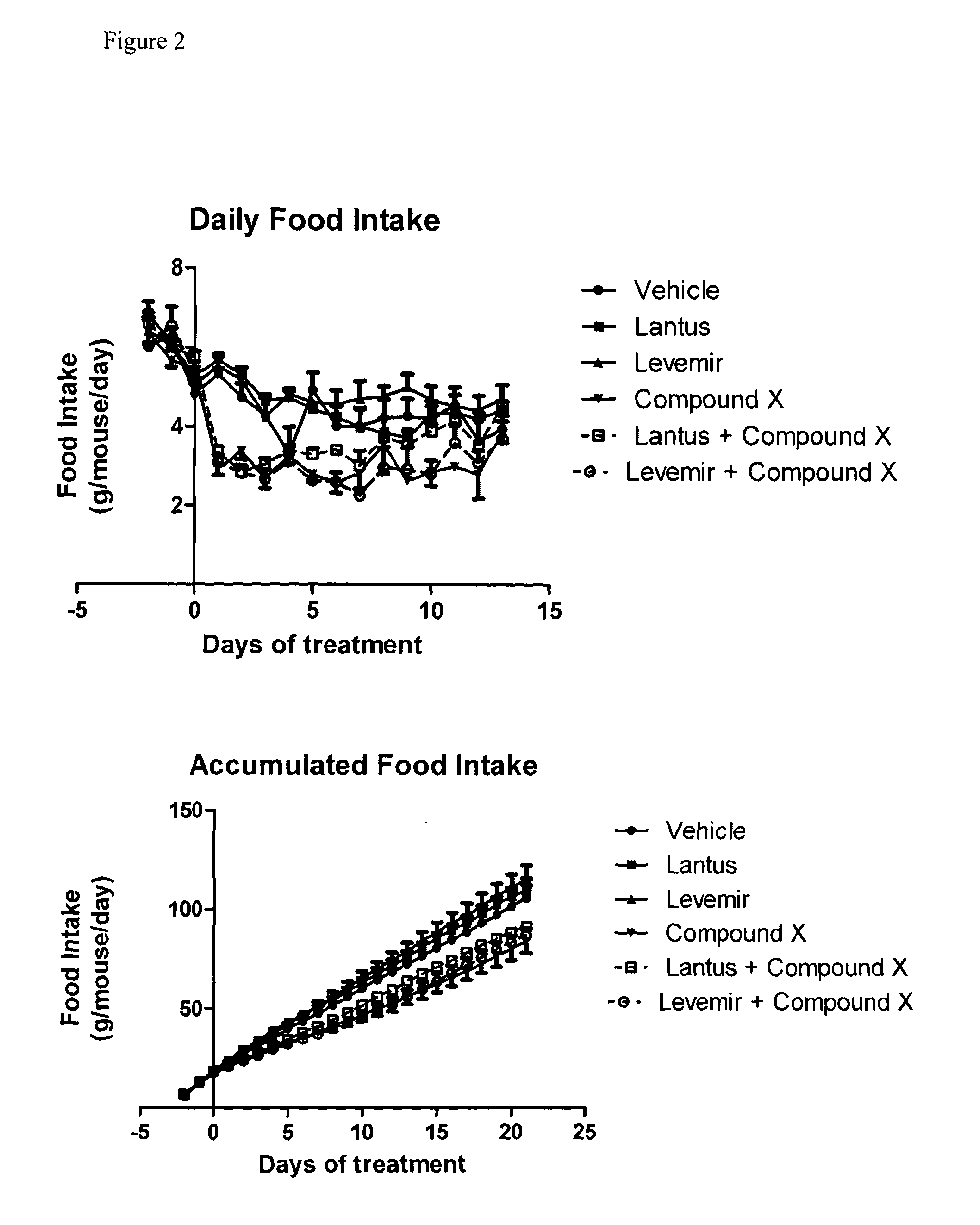
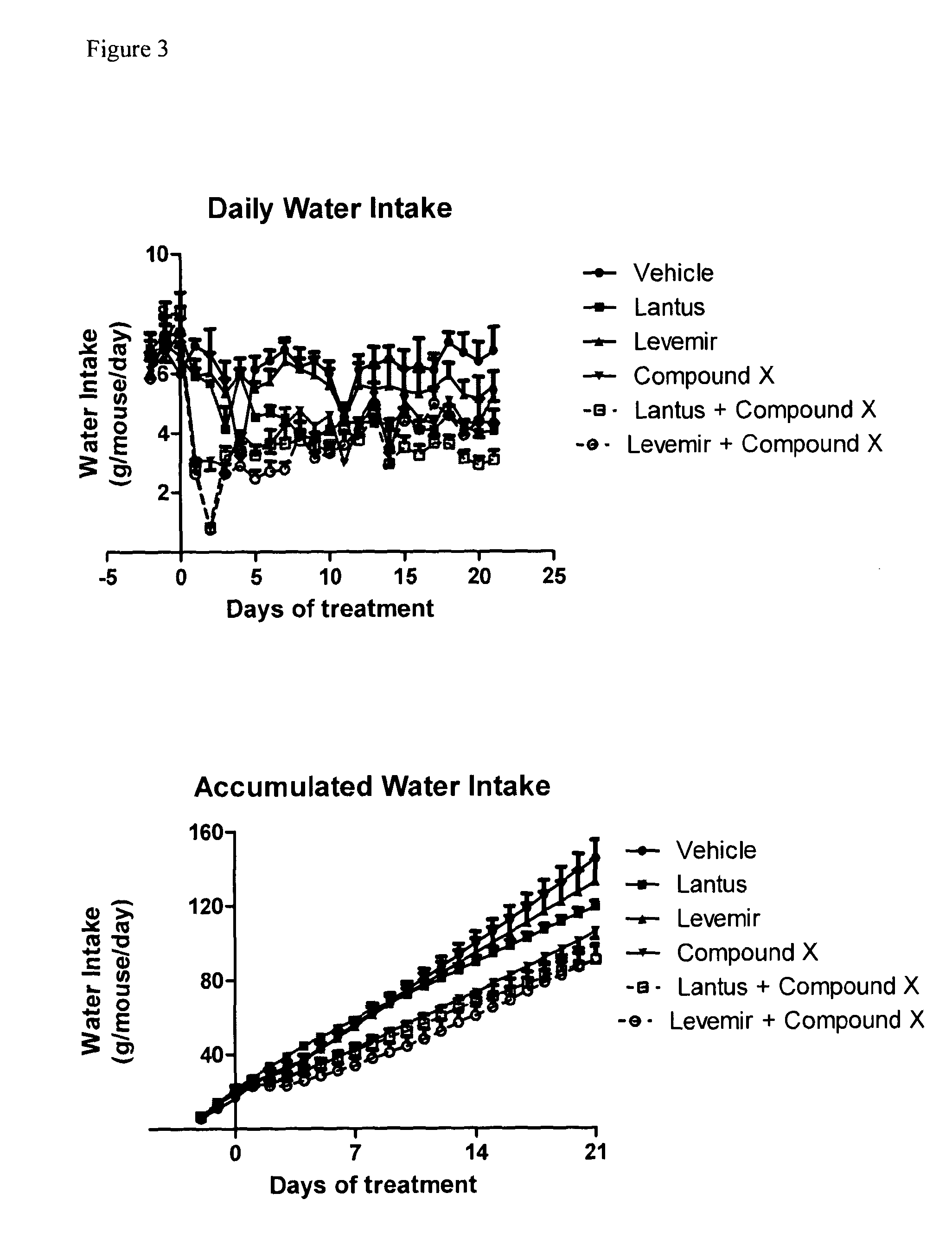
Combination of acylated glucagon analogues with insulin analogues
InactiveUS20140011733A1Prevent and reduce weight gainImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPancreatic hormoneInsulin Analogue
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Protease stabilized, acylated insulin analogues
ActiveUS20110105720A1Satisfactory potencyPeptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityInsulin Analogue
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Combination of acylated glucagon analogues with insulin analogues
InactiveUS20160000883A1Prevent and reduce weight gainImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin AnalogueMetabolic disorder
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Insulin analogues of enhanced receptor-binding specificity
InactiveUS20120184488A1Good physical propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin A ChainArginine
A method of treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of an insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient. The insulin analogue or physiologically acceptable salt thereof contains an insulin A-chain sequence modified at positions selected from the group consisting of A0, A1, A4, A8, and A21. The insulin analogue may exhibit decreased affinity for the IGF receptor in comparison to wild type insulin of the same species and at least 20% of the affinity of wild-type insulin for the insulin receptor of the same species. Position A0 may be arginine. Position A1 may be D-alanine, D-aspartic acid, or D-leucine. Position A8 may be histidine, lysine, or arginine. Optionally, an insulin B-chain analogue sequence comprises a histidine at position B1. A nucleic acid may encode such an insulin polypeptide.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Stabilized Pharmaceutical Formulations of Insulin Analogues and/or Insulin Derivatives
ActiveUS20150216941A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical formulationInsulin Analogue
Owner:SANOFI SA
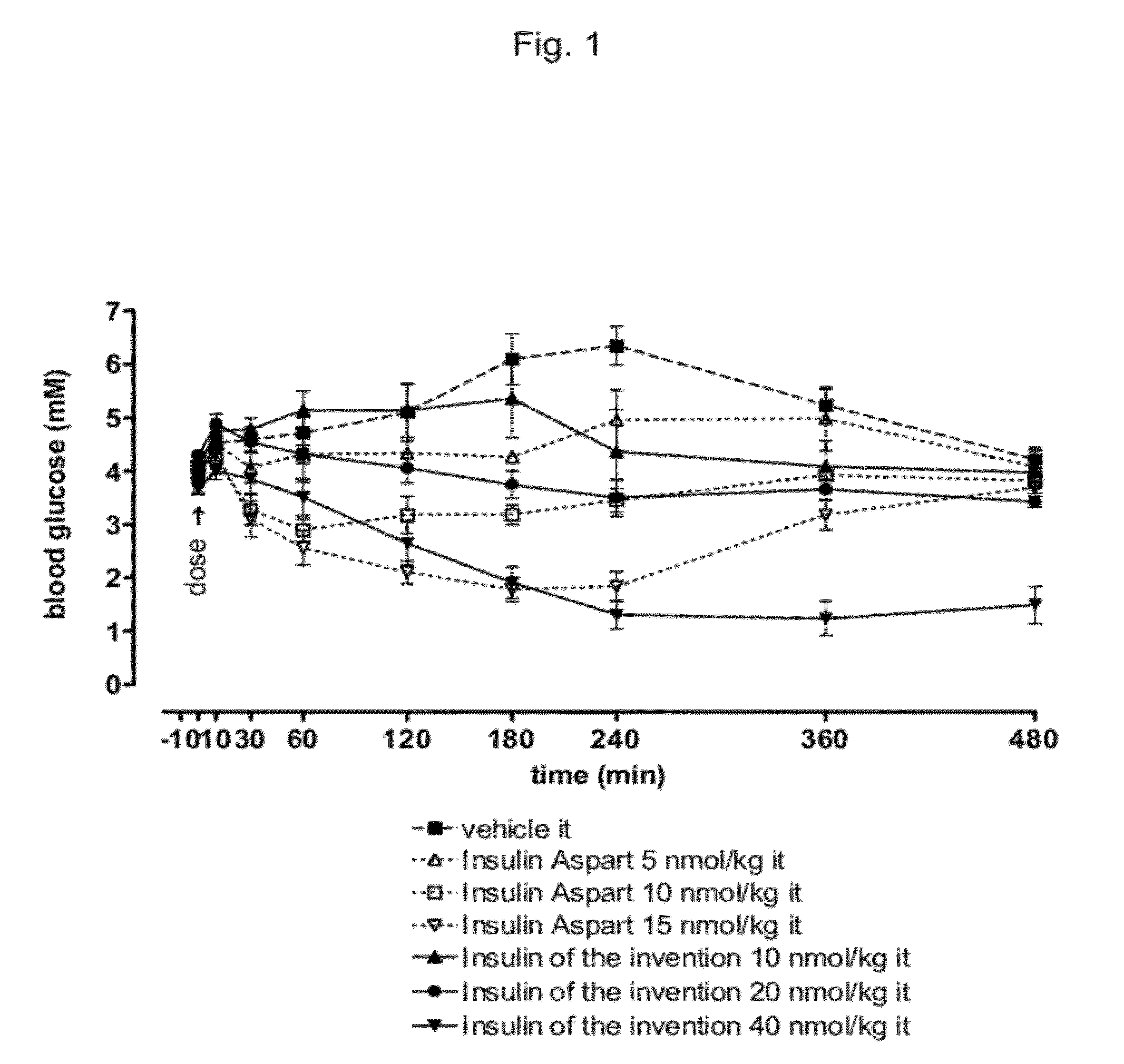
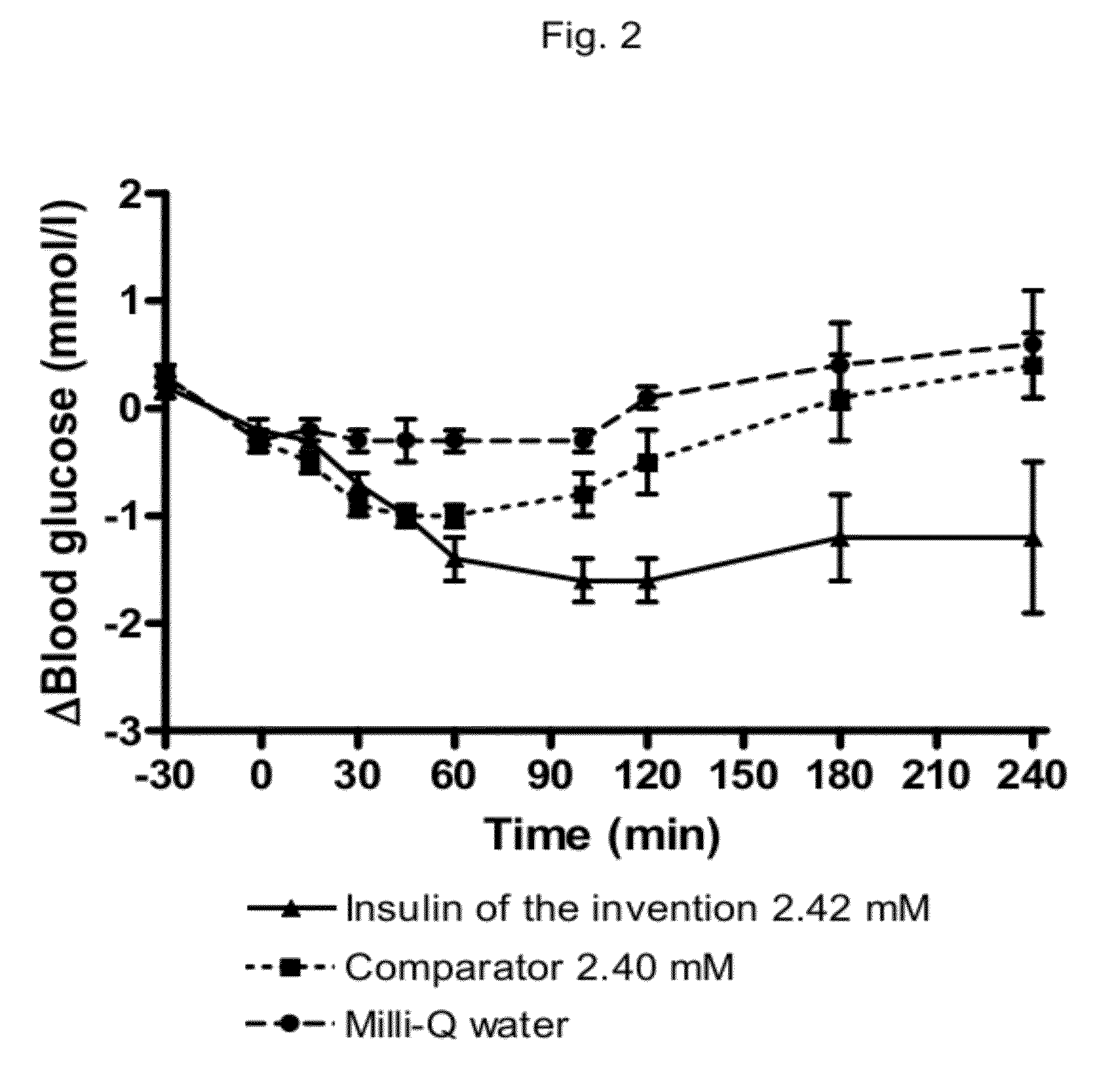
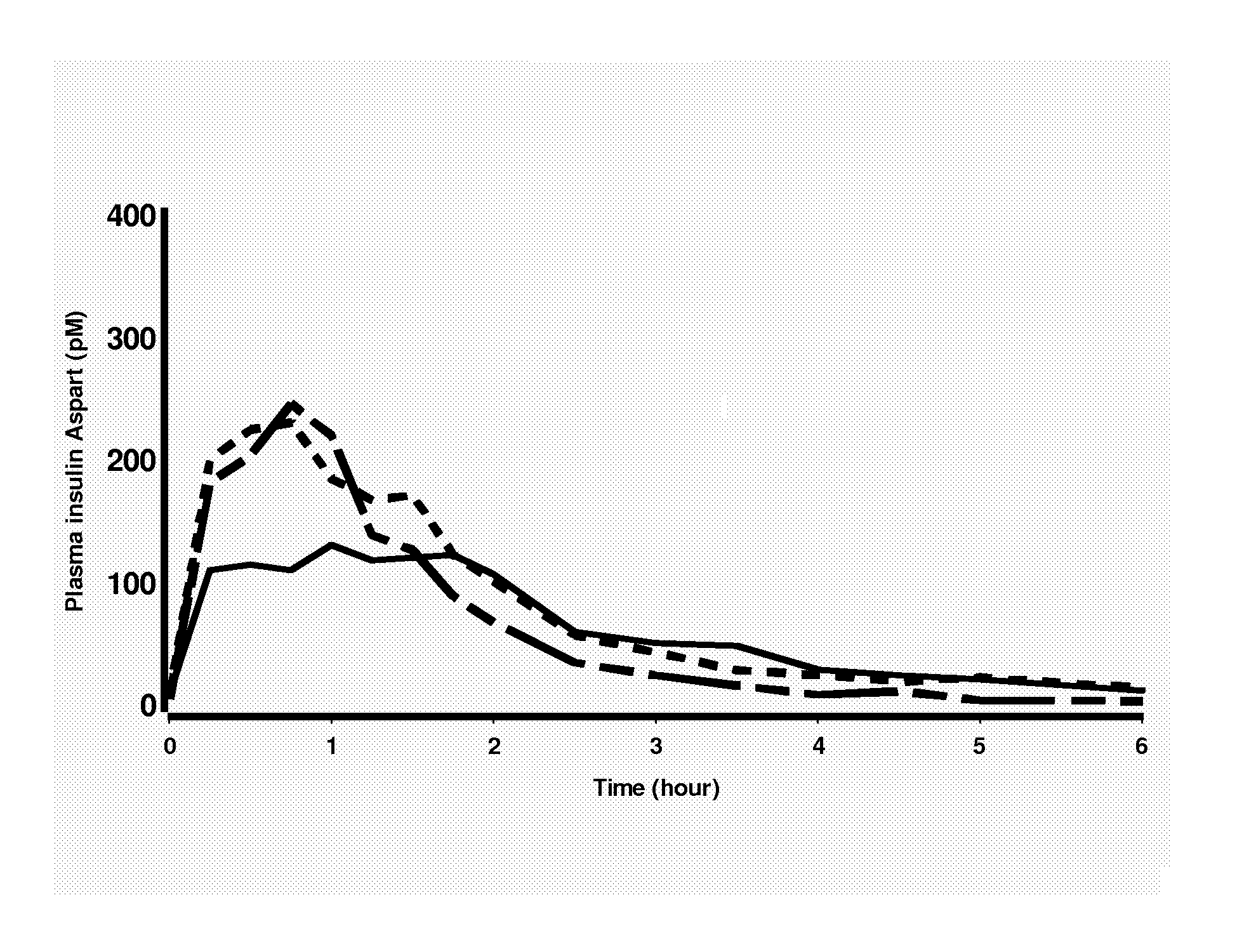
Rapid Acting Insulin Analogues
InactiveUS20110021423A1Promote formationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineInsulin B Chain
The invention is related to fast acting insulin analogues which can form soluble mix-tures (pre-mixed or self-mixed) with long acting insulin analogues. The fast action is achieved through monomerizing substitutions / deletions in the C-terminus of the B-chain of human insulin and the mixability with long acting insulin analogues is achieved through a substitution of the Zn-binding His in position B10 of human insulin with a Gln amino acid residue. In one embodiment the invention is related to fast acting insulin analogues in which at least one of the natural amino acid residues in position B22-B30 in the human B-chain has been substituted with another amino acid residue having the effect of promoting formation of the monomeric form of insulin, the His amino acid residue in position 10 in the B-chain is substituted with a Gln and wherein further one or more of the amino acid residues in position B22-B30 optionally have been deleted.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
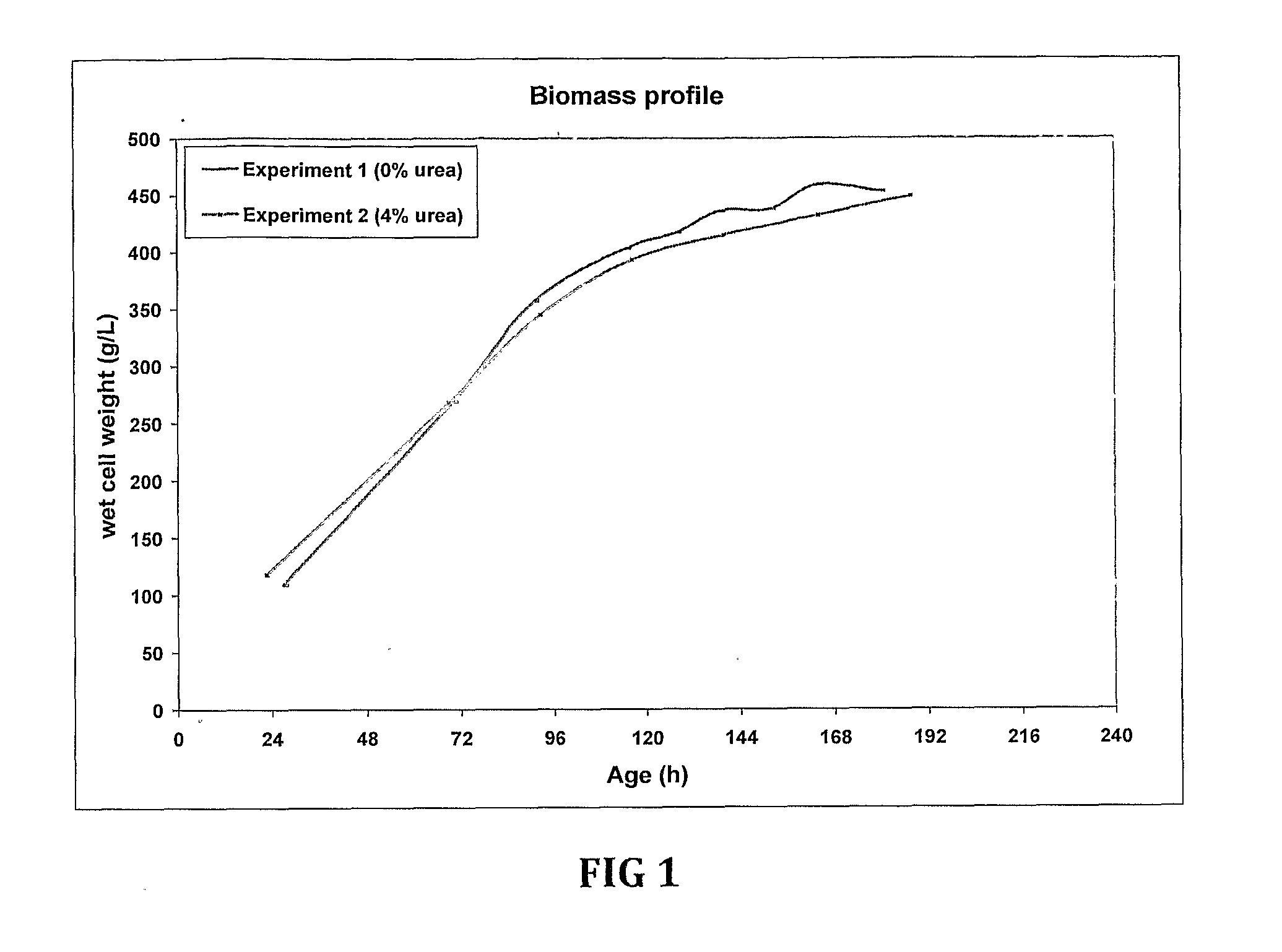
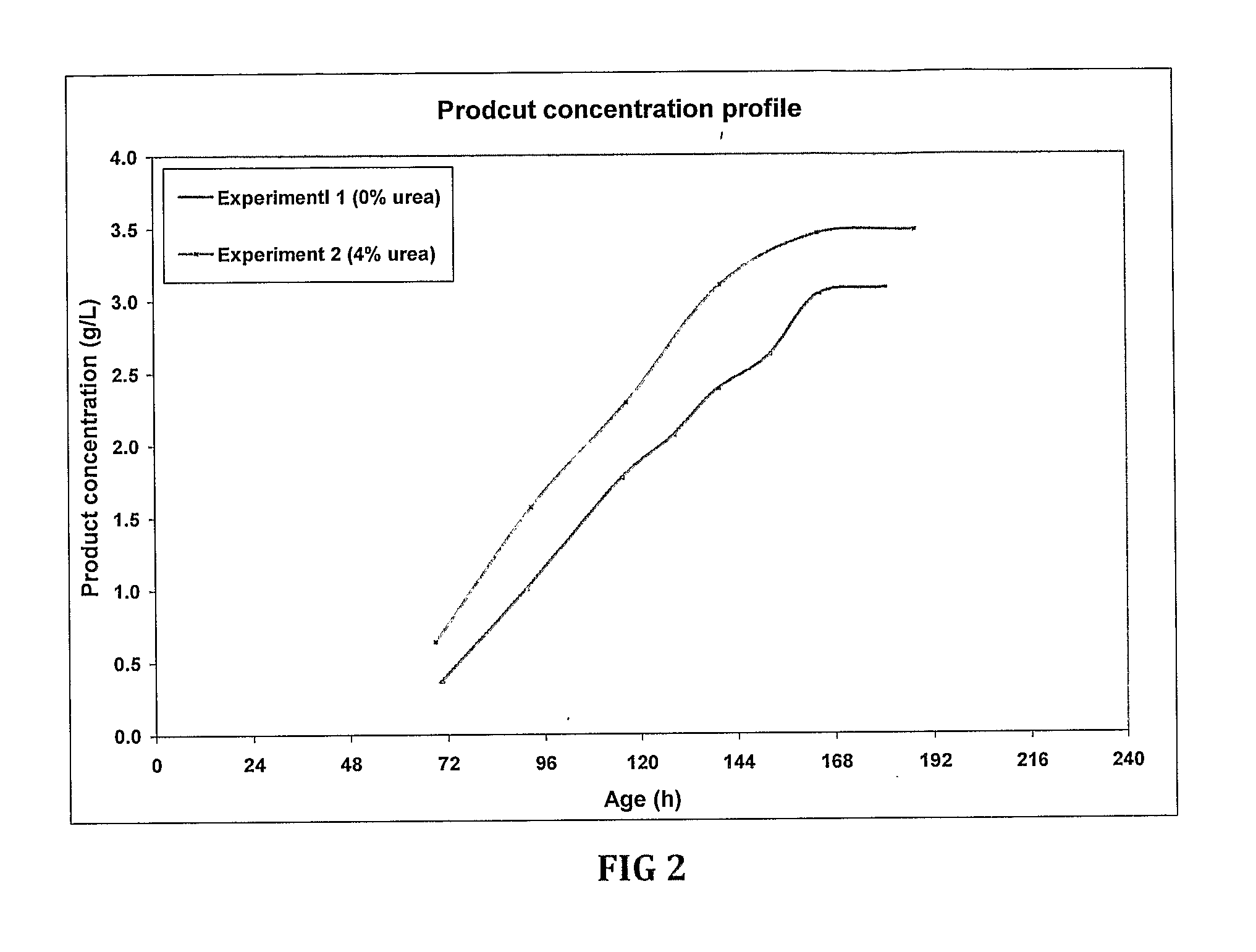
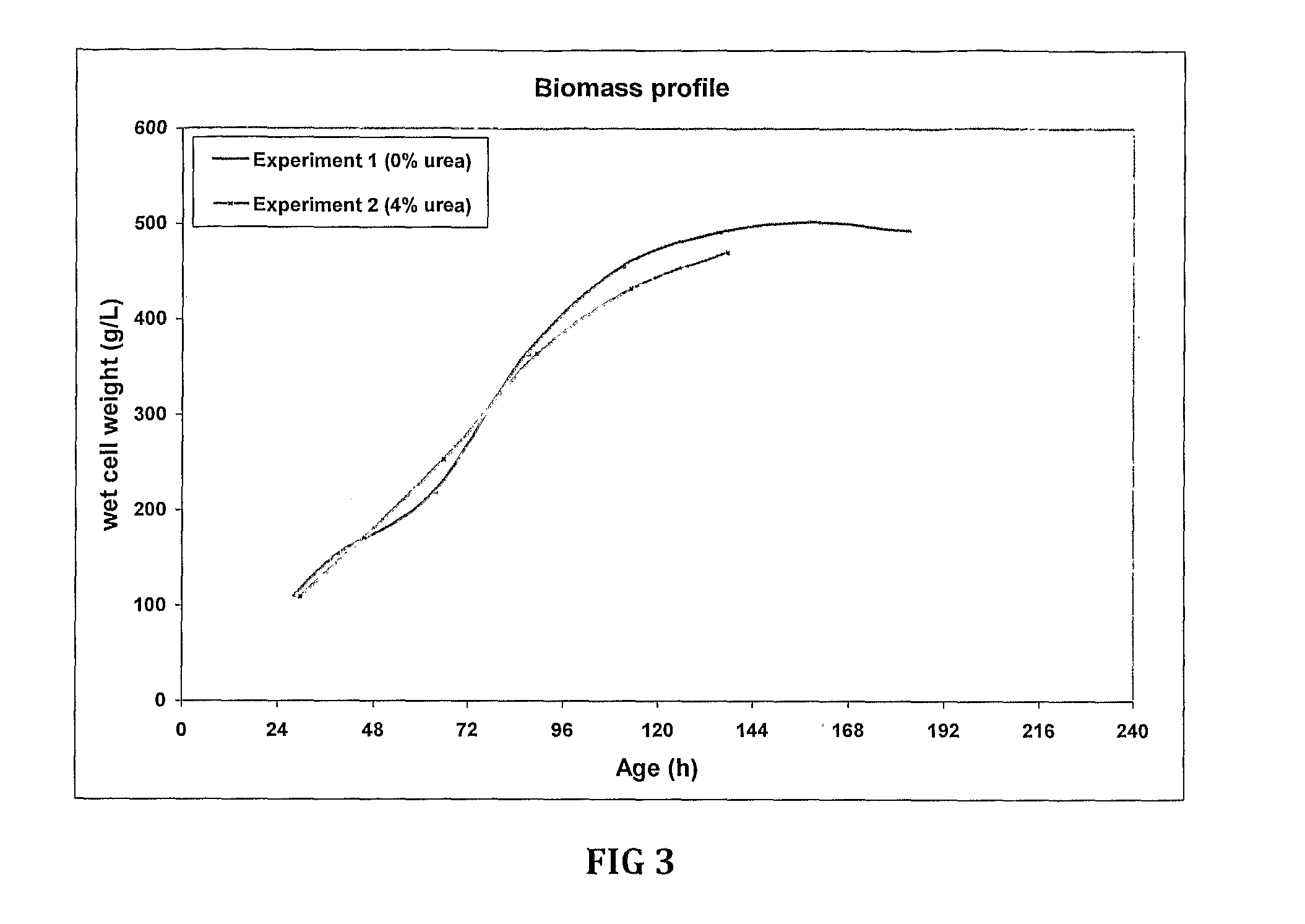
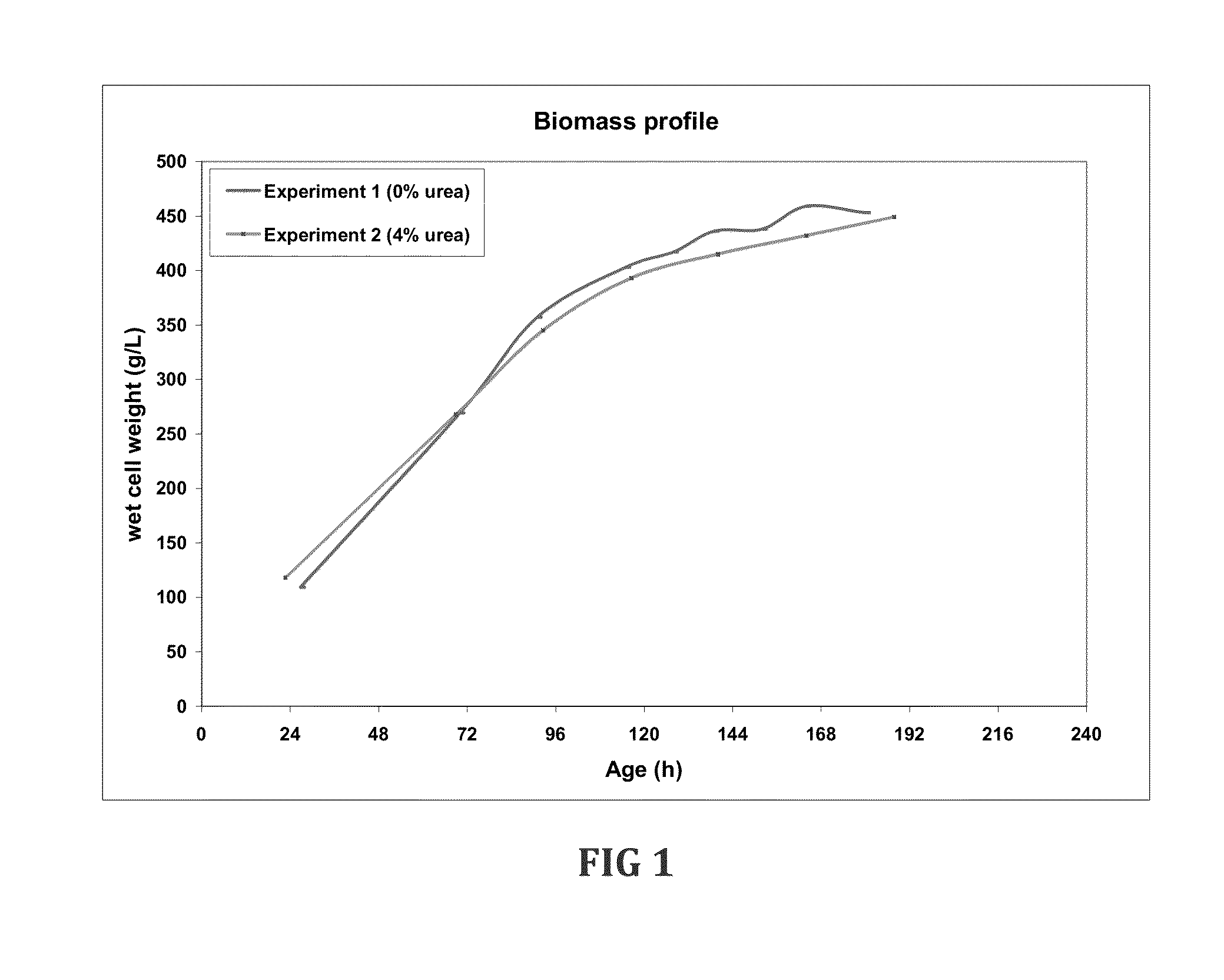
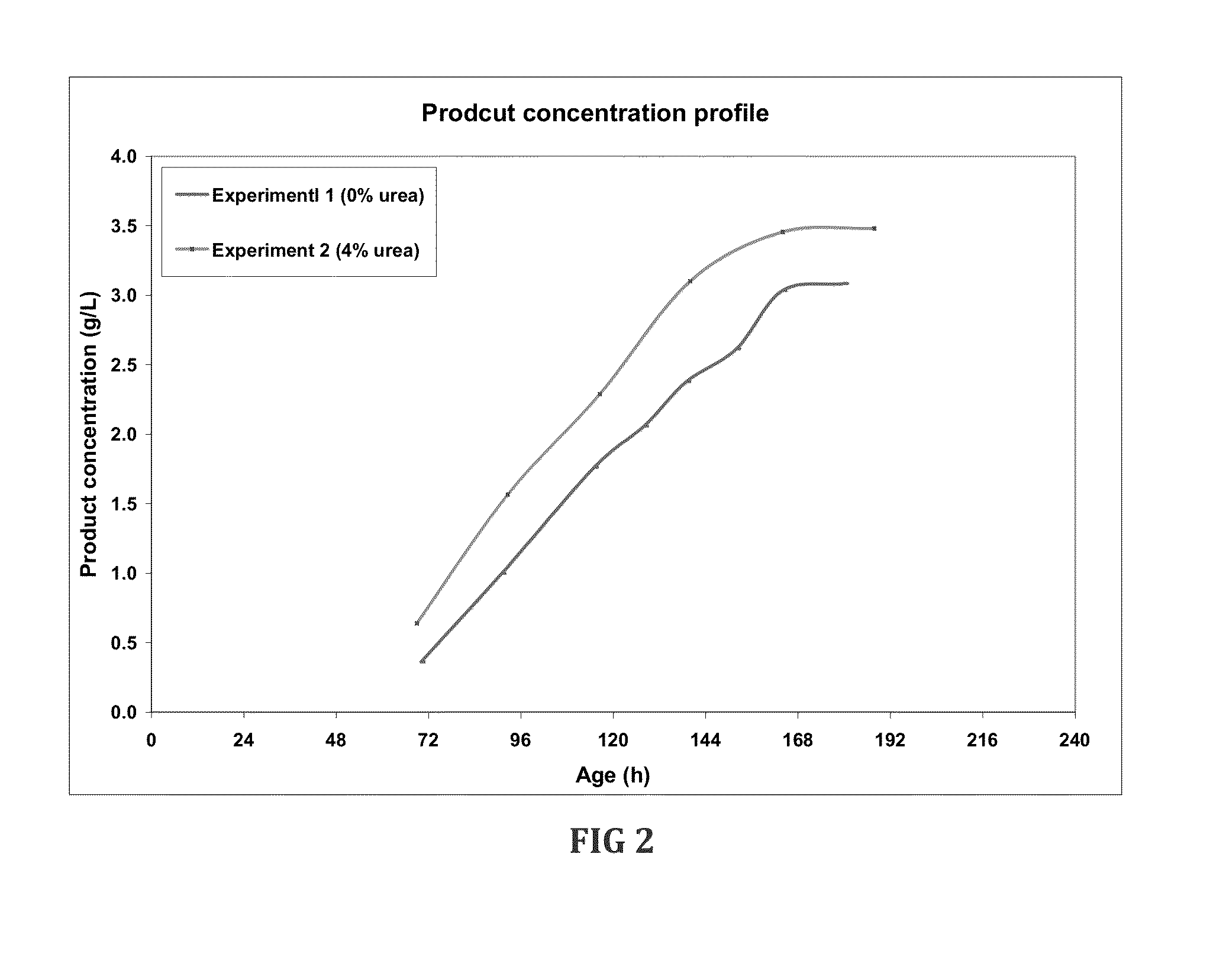
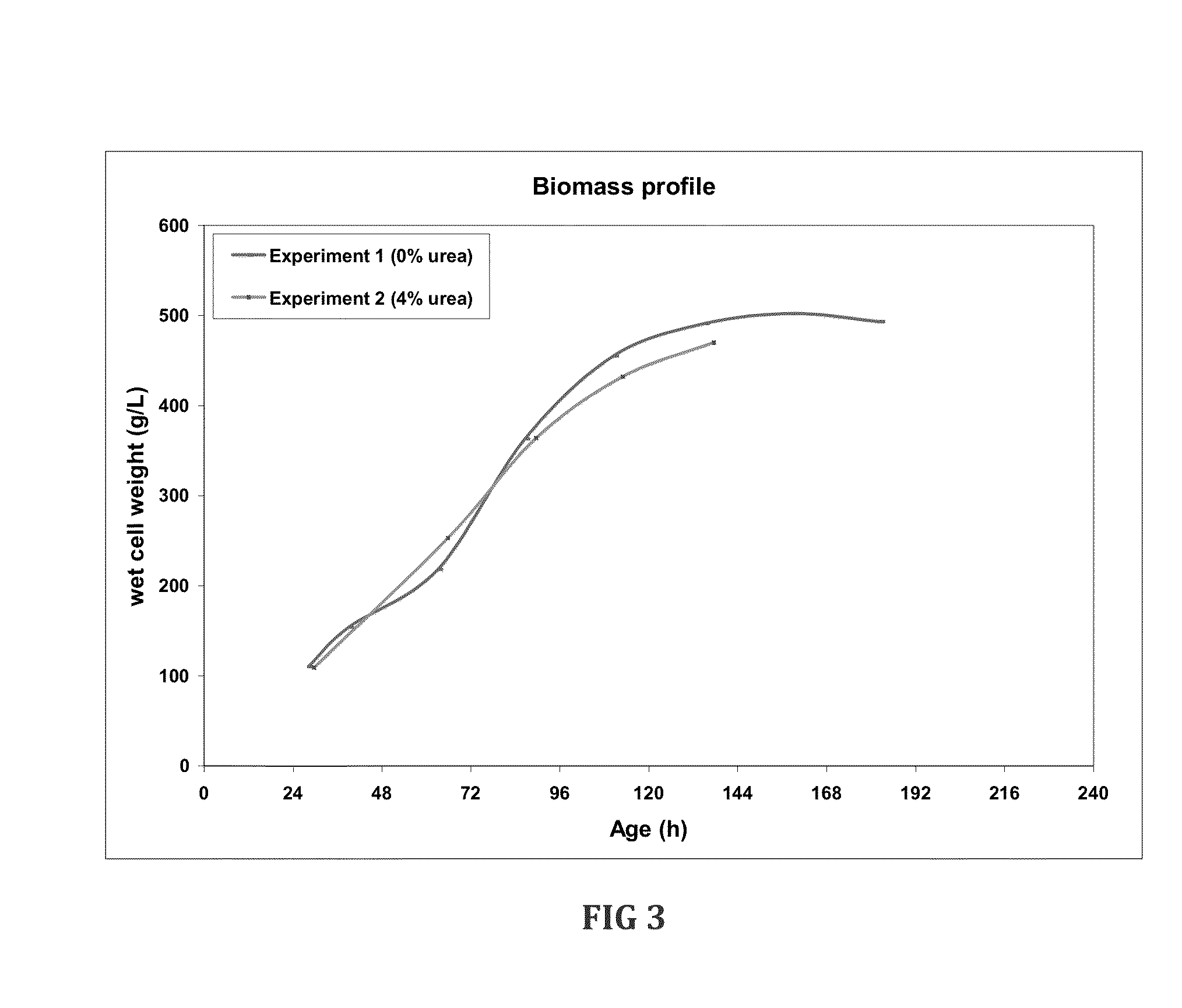
Fermentation medias and processes thereof
The present invention demonstrates the utility of carbonic acid amides such as urea or its derivatives, carbamates, carbodiimides & thiocarbamides as nitrogenous supplements in fermentation media for production of recombinant proteins to achieve enhanced bioconversion rates and peptides like insulin and insulin analogues, exendin and enzymes such as lipase using methanol inducible fungal expression systems such as Pichia.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
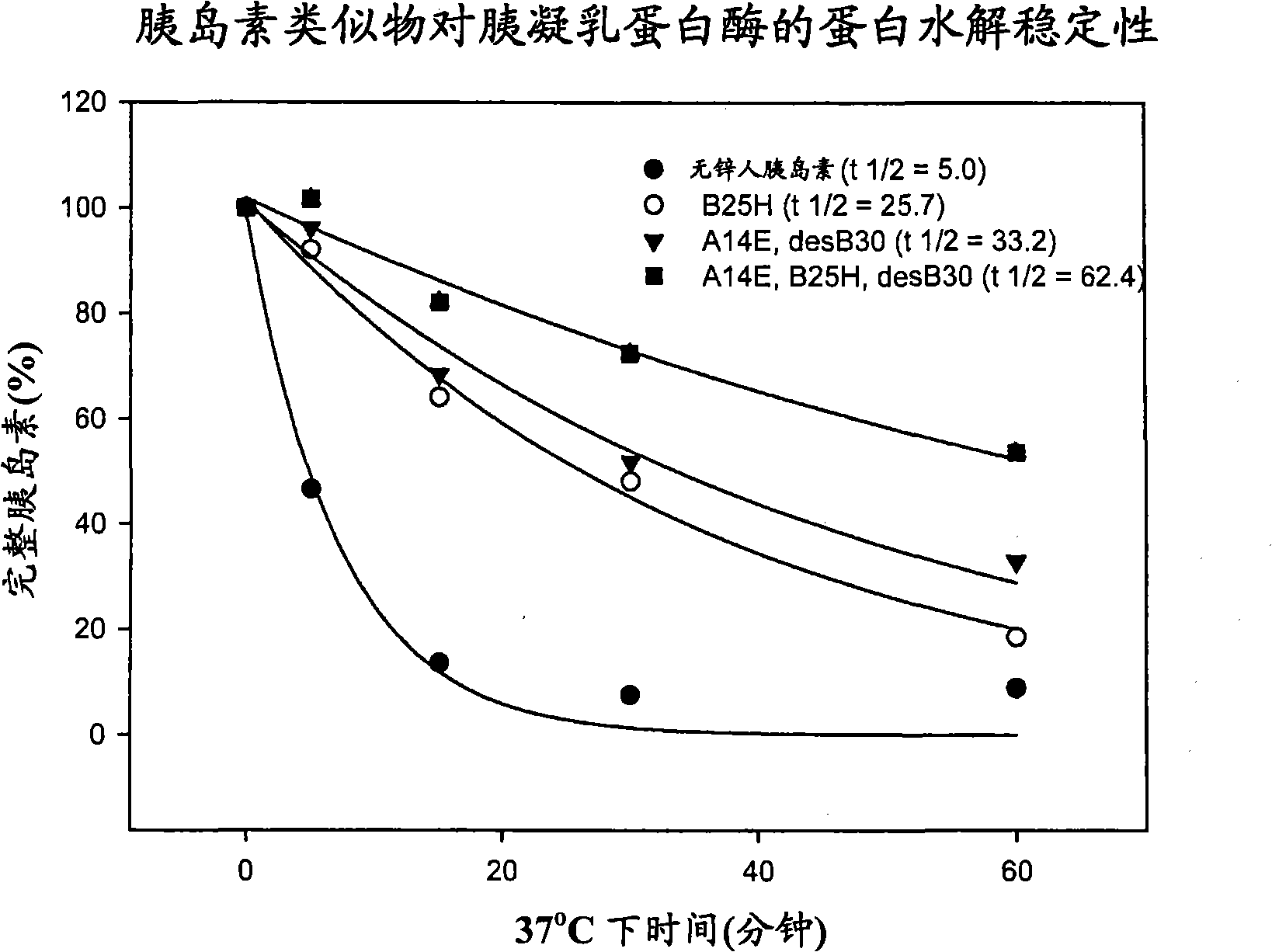
Protease resistant insulin analogues
PendingCN101541830APeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPancreatic hormoneProtease resistant
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
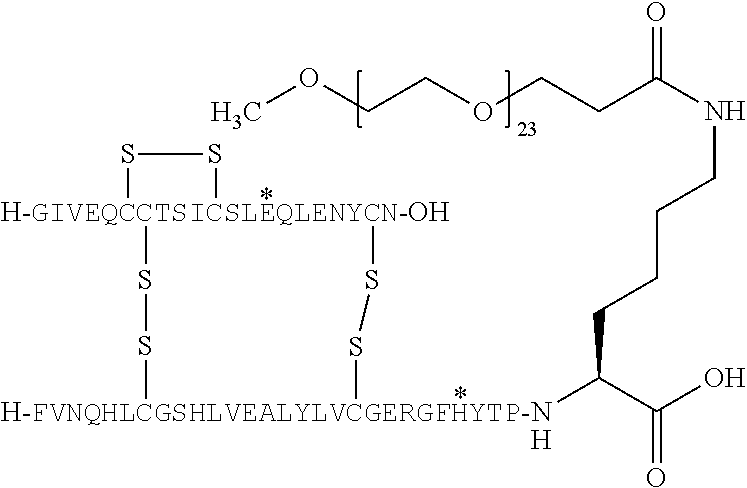
Protease Stabilized, Pegylated Insulin Analogues
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Protease-stabilized insulin analogues
InactiveUS20110092419A1Proteolytic stability is enhancedRetained biological insulin activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsINSULIN PREPARATIONSInsulin Analogue
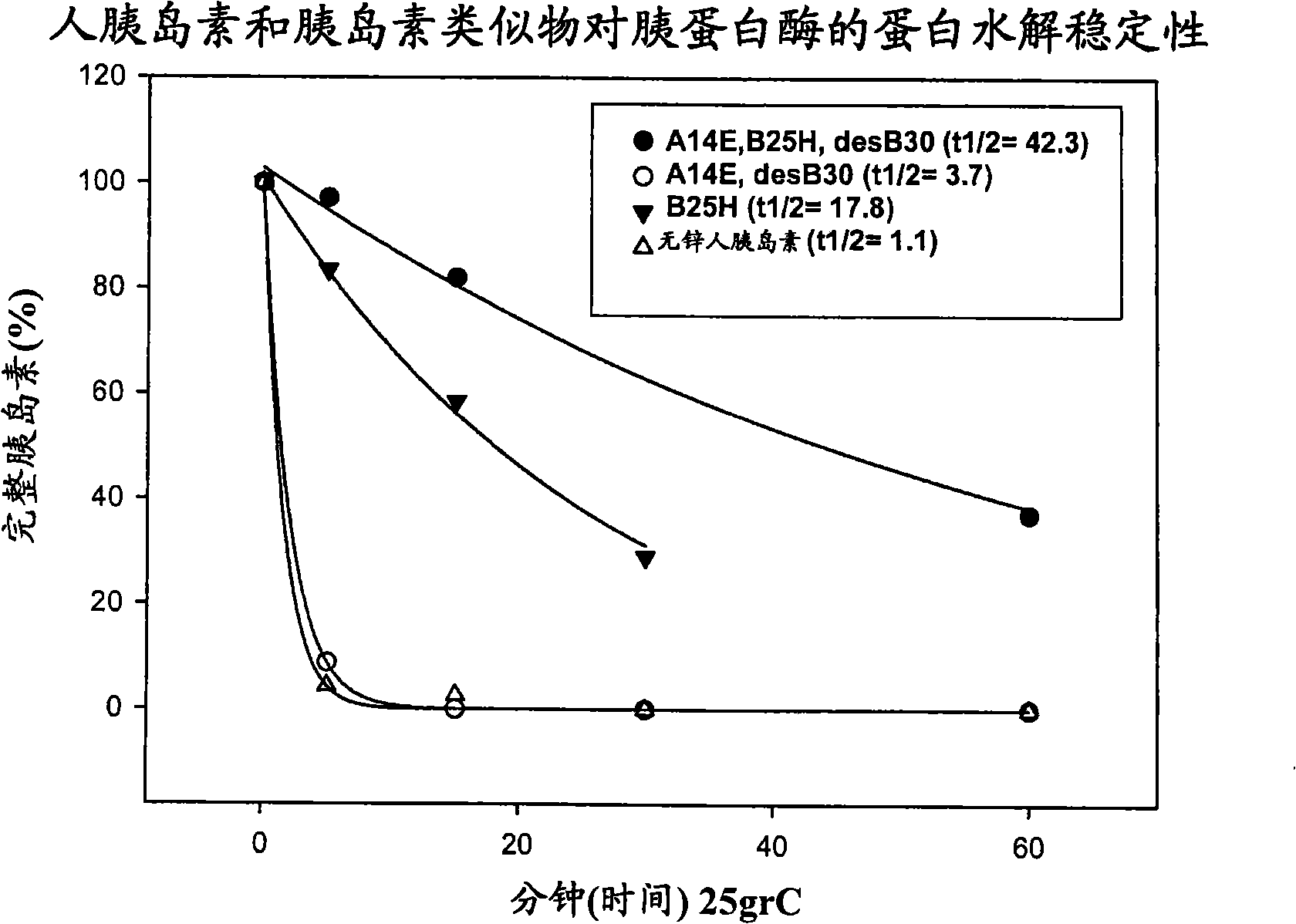
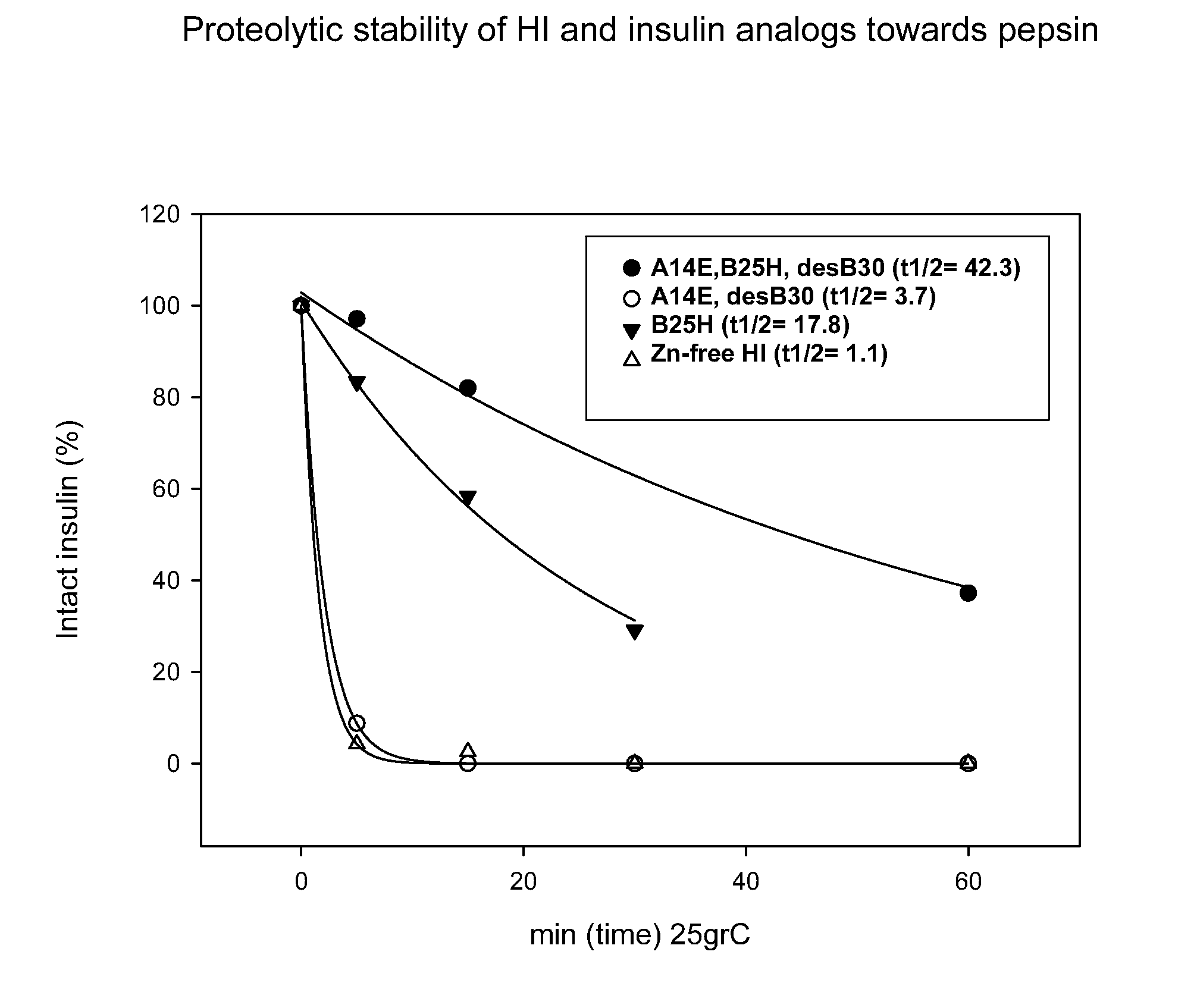
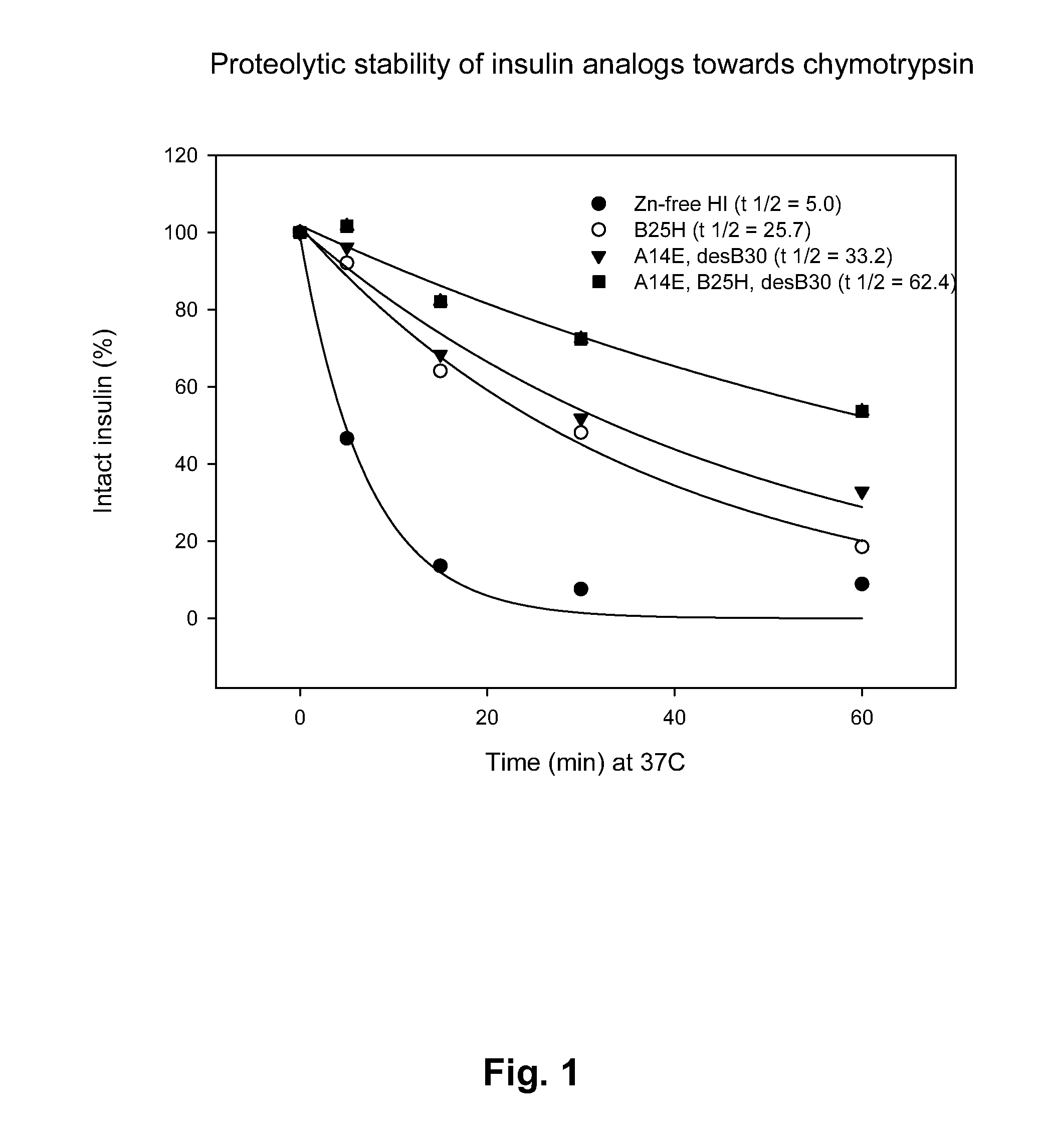
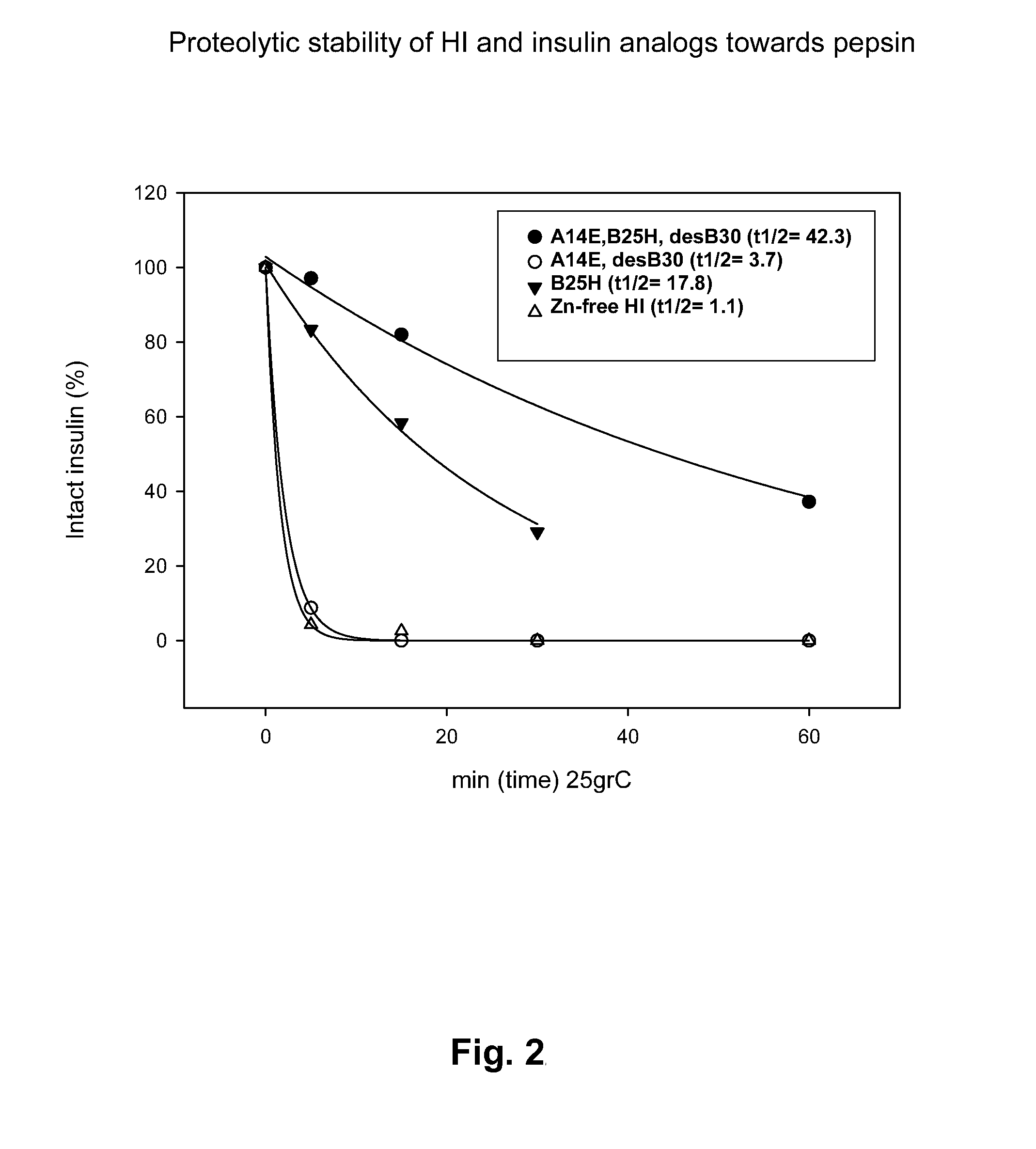
The present invention relates to novel insulin analogues comprising mutations at position A14 in the A chain and at positions B27, B28, B29 and B30 in the B chain and exhibiting resistance towards protease; a method for the preparation of such insulin analogues; insulin preparations containing the insulin analogues of the invention; and, a method of treating diabetes mellitus using these insulin analogues.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Fermentation Medias and Processes Thereof
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Long-acting insulin or insulin analogue conjugate
ActiveUS20180161448A1Increase compliance of administrationEliminate side effectsVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The present invention relates to insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate, and a use thereof, wherein the insulin and / or insulin analogue have improved in vivo durability and stability by linking the same with an Fe region of immunoglobulin. The insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate of the present invention show an in vivo activity similar to that of insulin. In addition, the insulin and / or insulin analogue conjugate of the present invention are long-acting formulations of insulin and / or the analogue thereof, in which serum half-life is remarkably increased, and therefore, the present invention provides remarkable insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate, which do not induce hypoglycemia, a drawback of insulin treatment.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Insulin compositions and method of making a composition
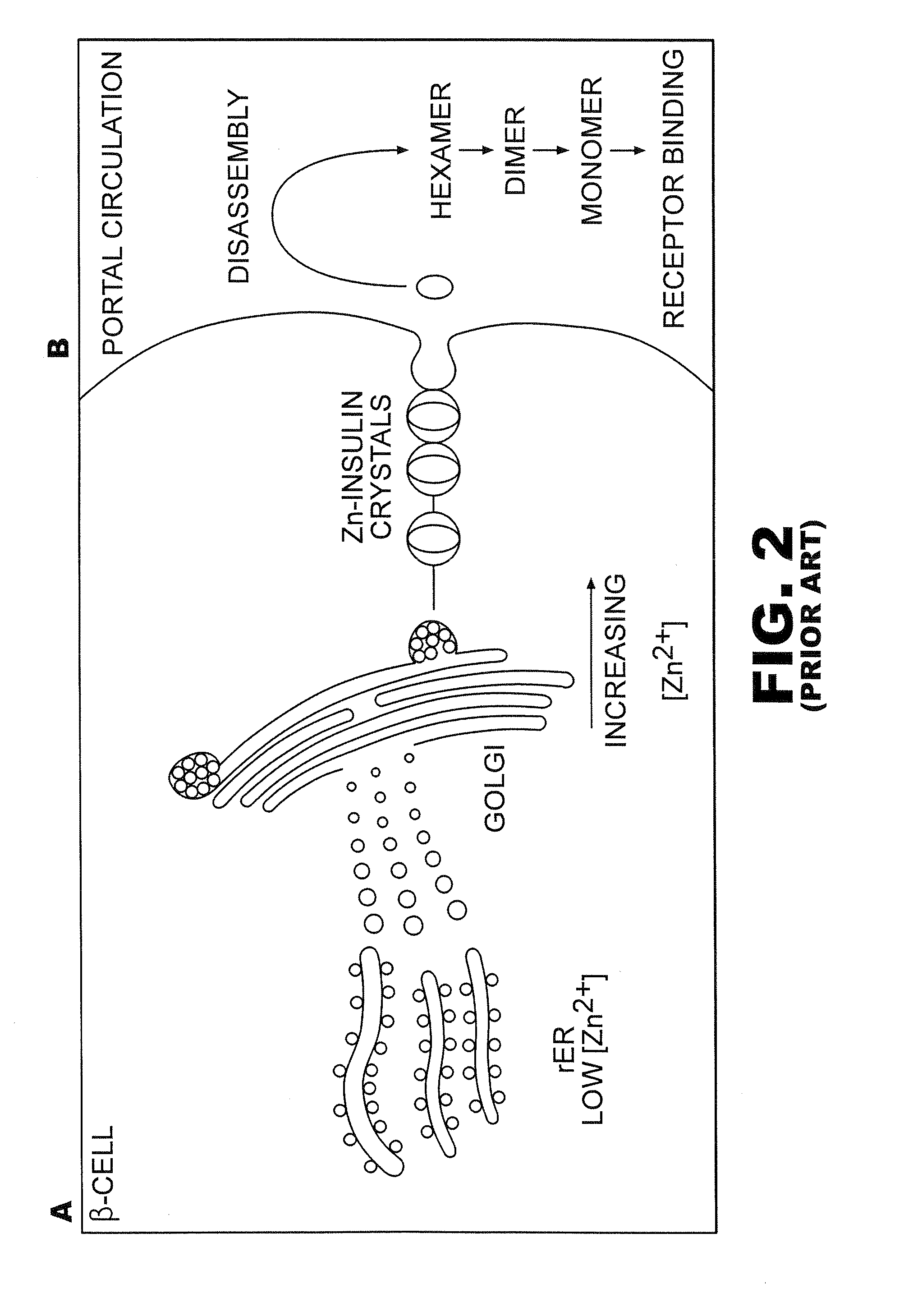
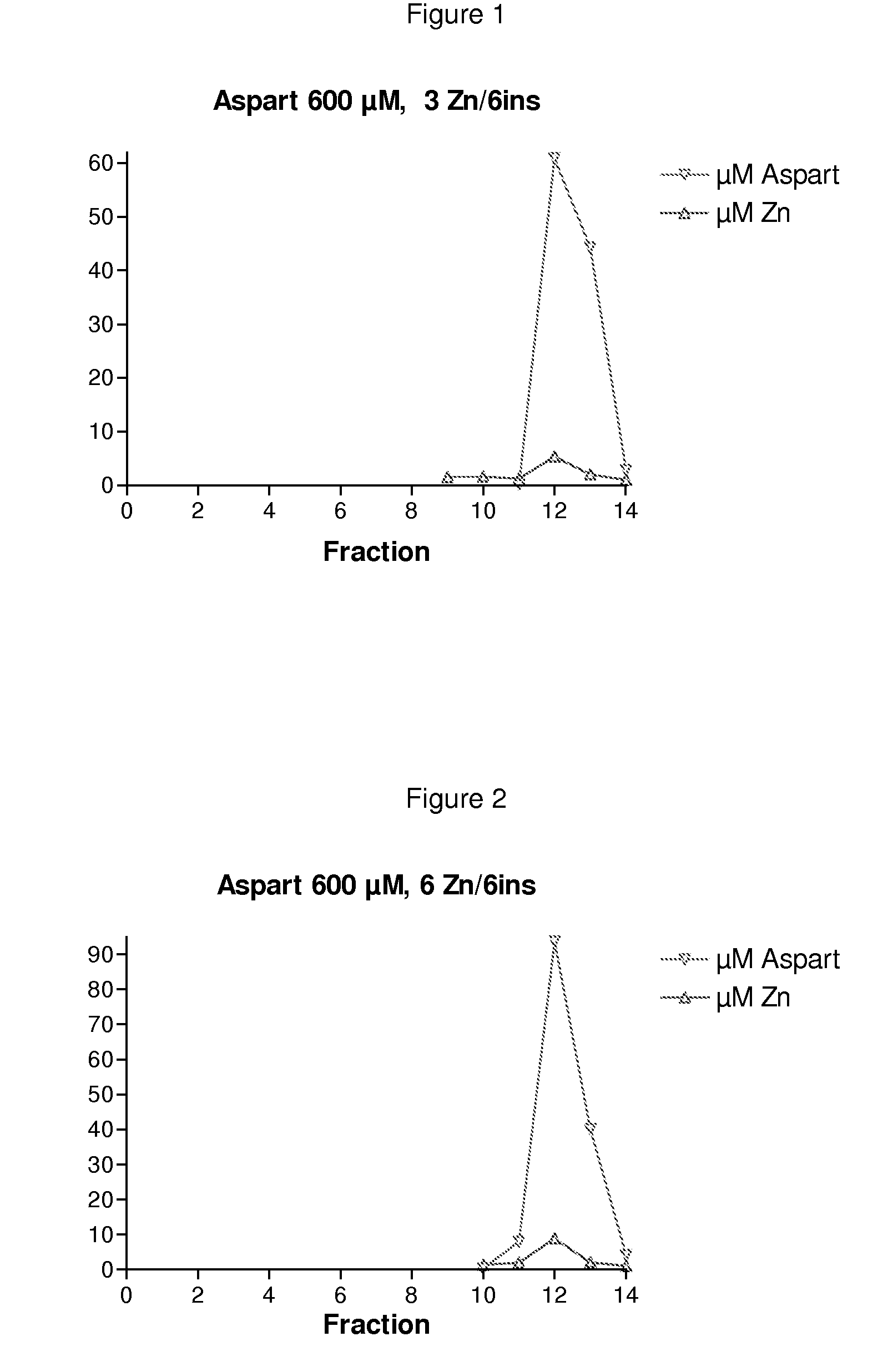
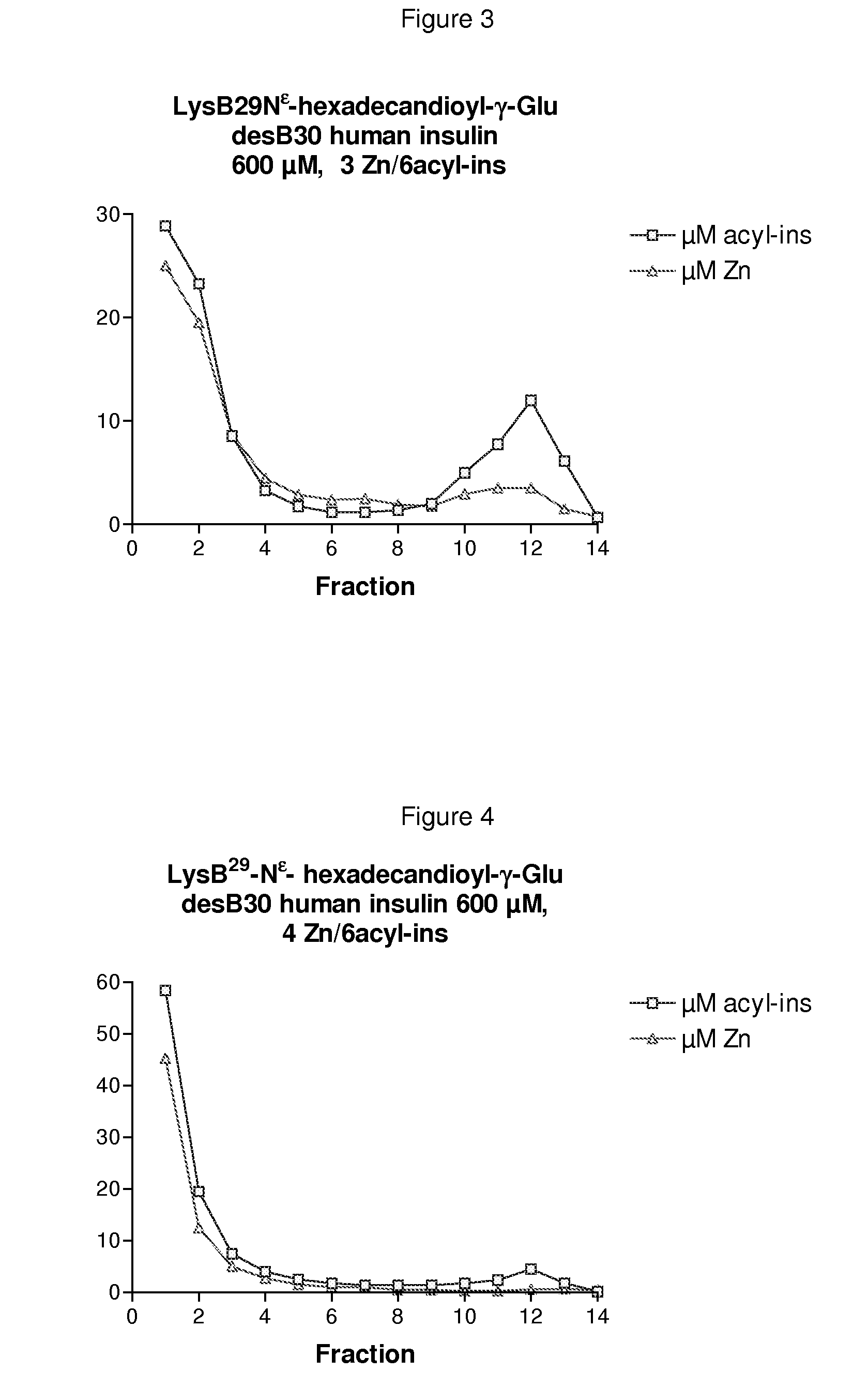
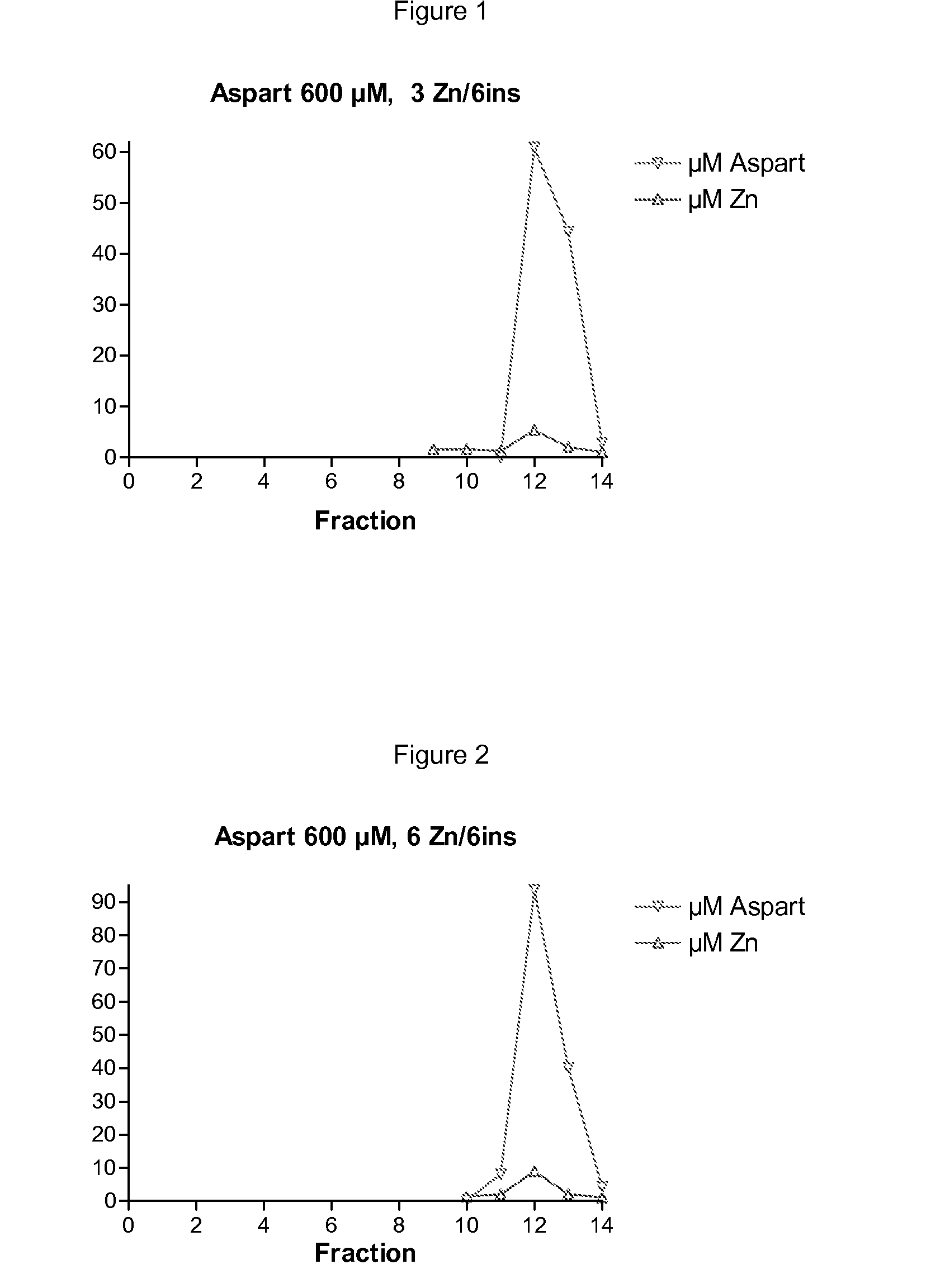
InactiveUS20090074882A1High molecular weightBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsZinc atomInsulin Analogue
The invention is related to insulin compositions with a high content of zinc atoms per six molecules of acylated insulin. The insulin is an acylated insulin and may be mixed with a further insulin analogue such as the rapid acting insulin Asp B28 human insulin.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Insulin analogues with enhanced stability and reduced mitogenicity
ActiveUS10822386B2Impaired self-assembly-andAct quicklyPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulinsDiabetes mellitusDipeptide
A polypeptide comprises an insulin B-chain sequence having the substitutions: Asp at position B10, Ala at position B12, and Glu at position B29, relative to wild type insulin. The polypeptide may additionally comprise a substitution of a halogenated phenylalanine at position B24, such as ortho-fluoro-phenylalanine. Optionally, the polypeptide may additionally comprise a C-terminal dipeptide extension wherein at least one amino acid in the dipeptide contains an acidic side chain, such as Glu-Glu, and / or an N-terminal deletion of one, two or three residues from the B chain. An insulin analogue may comprise any of these polypeptides with an insulin A-chain polypeptide that optionally contains a Glu A8 substitution. The A-chain sequence may be a separate polypeptide or it may be joined to the B-chain polypeptide by a two amino acid linker. The linker may be Trp-Lys or Ala-Lys. The insulin analogue may be used to treat a patient with diabetes mellitus.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Insulins with polar recombinant extensions
ActiveUS20180291076A1Reduce yieldHigh viscosityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusMedicine
The present invention relates to novel insulins or insulins analogues that are extended with predominantly sequences of polar amino acid residues in order to improve the half-life and stability of the drug substance. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising such drug substances, and relates to the use of such drug substances for the treatment or prevention of medical conditions relating to diabetes.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Single-chain insulin analogues stabilized by a fourth disulfide bridge
ActiveUS20200140517A1Unfavorable effectReduces conformational fluctuationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDisulfide bondingDiabetes mellitus
A single-chain insulin analogue comprises a B-chain insulin polypeptide connected to an A-chain insulin polypeptide by a C-domain polypeptide. The B-chain insulin polypeptide contains a Cysteine substitution at position B4. The A-chain insulin polypeptide contains a Cysteine substitution at position A10. The C-domain polypeptide is 4 to 11 amino acids long. The analogue mitigates the unfavorable activity of this 4th disulfide bridge in conventional two-chain insulin analogues resulting in a duration of insulin signaling similar to that of wild-type insulin. A method of treating a patient with diabetes mellitus comprises the administration of a physiologically effective amount of the protein or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to a patient. Use of a single-chain insulin analogue of the present invention in an insulin delivery device (such as a pump or pen) or as part of a high-temperature polymer-melt manufacturing process.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Methods and compositions for the differentiation of human preadipocytes into adipocytes
InactiveUS20050158706A1Microbiological testing/measurementDrug screeningGlucocorticoidPre adipocytes
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the consistent and quantitative differentiation of human preadipocytes isolated from adipose tissue into adipocytes bearing biochemical, genetic, and physiological characteristics similar to that observed in isolated primary adipocytes. The methods of the invention comprise incubating isolated human preadipocytes, plated at least about 25,000 cells / cm2, in a medium containing, glucose, a cyclic AMP inducer such as isobutylmethylxanthine or forskolin, a glucocorticoid or glucocorticoid analogue, insulin or an insulin analogue and a PPARγ agonist or a RXR agonist. The compositions of the invention include media for the differentiation of human preadipocytes, human adipocytes differentiated by the methods of the invention and transfected adipocytes. The present invention also provides methods for determining the ability of a compound to affect the differentiation of human preadipocytes to adipocytes, for determining the ability of a compound to act as a PPARγ antagonist. a glucocorticoid, a glucocoticoid analogue, or an insulin analogue, for transfecting cultured human adipocytes, and as a means to identify novel polypeptides secreted from human adipocytes into the conditioned medium. The methods and compositions have use in the drug discovery of compounds having relevance to the disease states of diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease and in the studies of these diseases.
Owner:ARTECEL SCIENCE INC
Protease resistant insulin analogues
ActiveUS20100009898A1Improve stabilityRetained biological insulin activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPancreatic hormoneProtease resistant
The present invention relates to novel insulin analogues exhibiting resistance towards protease, wherein at least two amino acids are substituted and / or deleted relative to the parent insulin molecule. A method for the preparation of such insulin analogues, insulin preparations containing the insulin analogues of the invention and a method of treating diabetes mellitus using these insulin analogues is also provided.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Long-acting insulin or insulin analogue conjugate
ActiveUS10894089B2Increase compliance of administrationEliminate side effectsVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsIntravenous gammaglobulinHypoglycemia
The present invention relates to insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate, and a use thereof, wherein the insulin and / or insulin analogue have improved in vivo durability and stability by linking the same with an Fc region of immunoglobulin. The insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate of the present invention show an in vivo activity similar to that of insulin. In addition, the insulin and / or insulin analogue conjugate of the present invention are long-acting formulations of insulin and / or the analogue thereof, in which serum half-life is remarkably increased, and therefore, the present invention provides remarkable insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate, which do not induce hypoglycemia, a drawback of insulin treatment.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Insulin compositions and method of making a composition
The invention is related to insulin compositions with a high content of zinc atoms per six molecules of acylated insulin. The insulin is an acylated insulin and may be mixed with a further insulin analogue such as the rapid acting insulin Asp B28 human insulin.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Insulin analogue having quick response and stability under acidic condition and preparation thereof
ActiveCN102199206AQuick effectProtect capillariesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical formulationInsulin Analogue
The invention relates to an isulin analogue having quick response and stability under acidic condition, and a medicinal composition and a medicinal preparation thereof. Asparagine (Asn) at the A 21 position of the chain A of the isulin analogue is mutated into glycine (Gly), the isulin analogue can be mixed with a long-acting isulin analogue such as insulin glargine to form a premixed preparationwith two functions of quick-acting sugar reduction and stable long-acting sugar reduction, and the problems that the conventional natural insulin (of pigs, cows and human) and quick-acting isulin analogues are unstable in the acidic environment, and the conventional isulin premixed preparation is not clarified and needed to be introduced with a foreign protein (such as protamine) serving as a slow release preparation so as to easily cause immune reaction, and is needed to be injected twice each day, namely in the morning and evening are solved, so that the safety of the preparation is higher.
Owner:GAN&LEE PHARMA
Protease stabilized, acylated insulin analogues
ActiveUS8691759B2Satisfactory potencyPeptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityProtease
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com