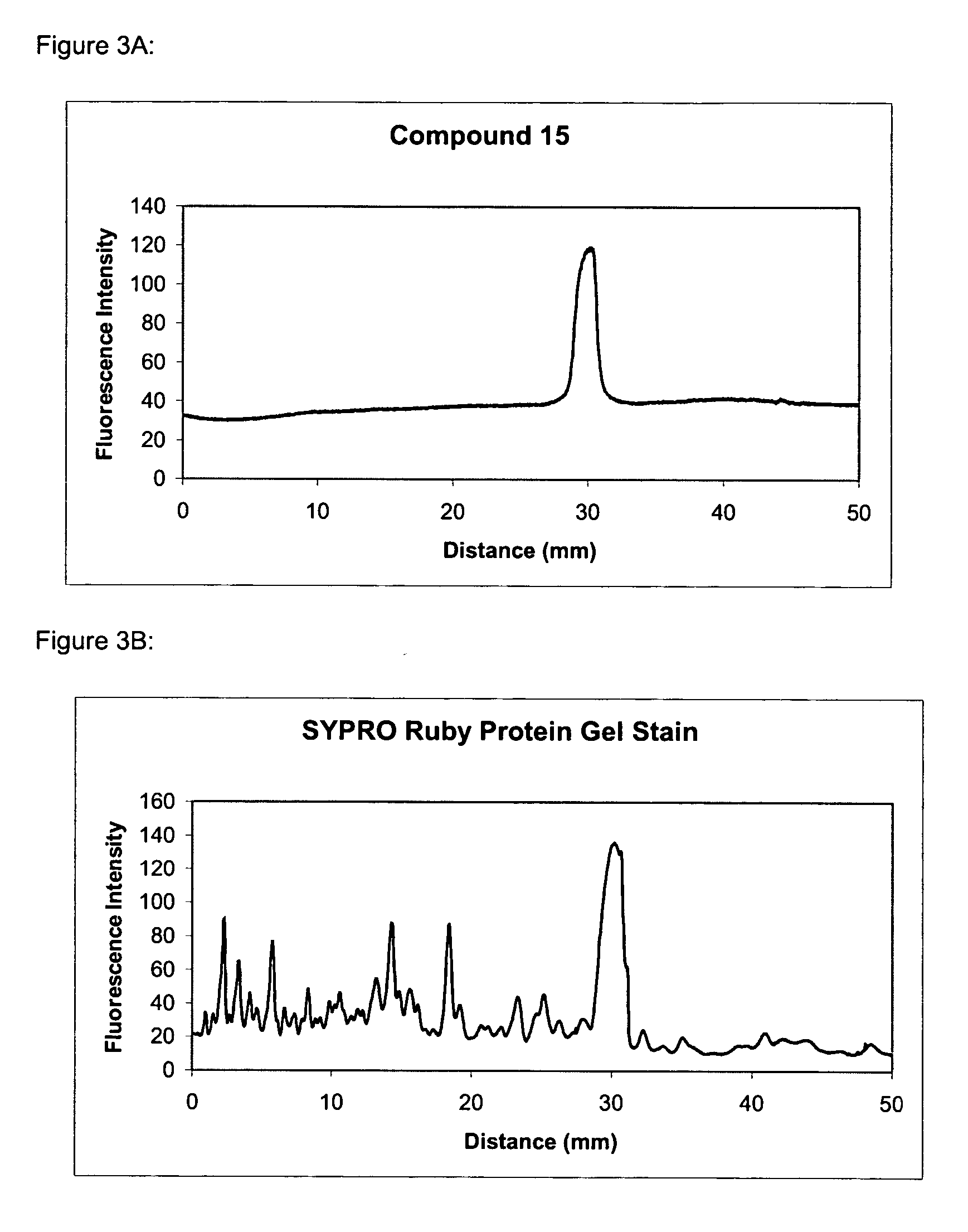
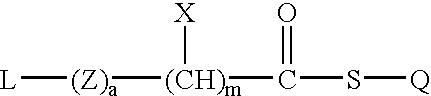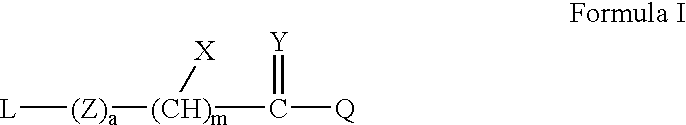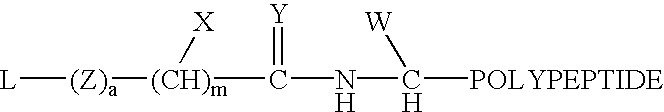Patents
Literature
103 results about "Histidine residue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
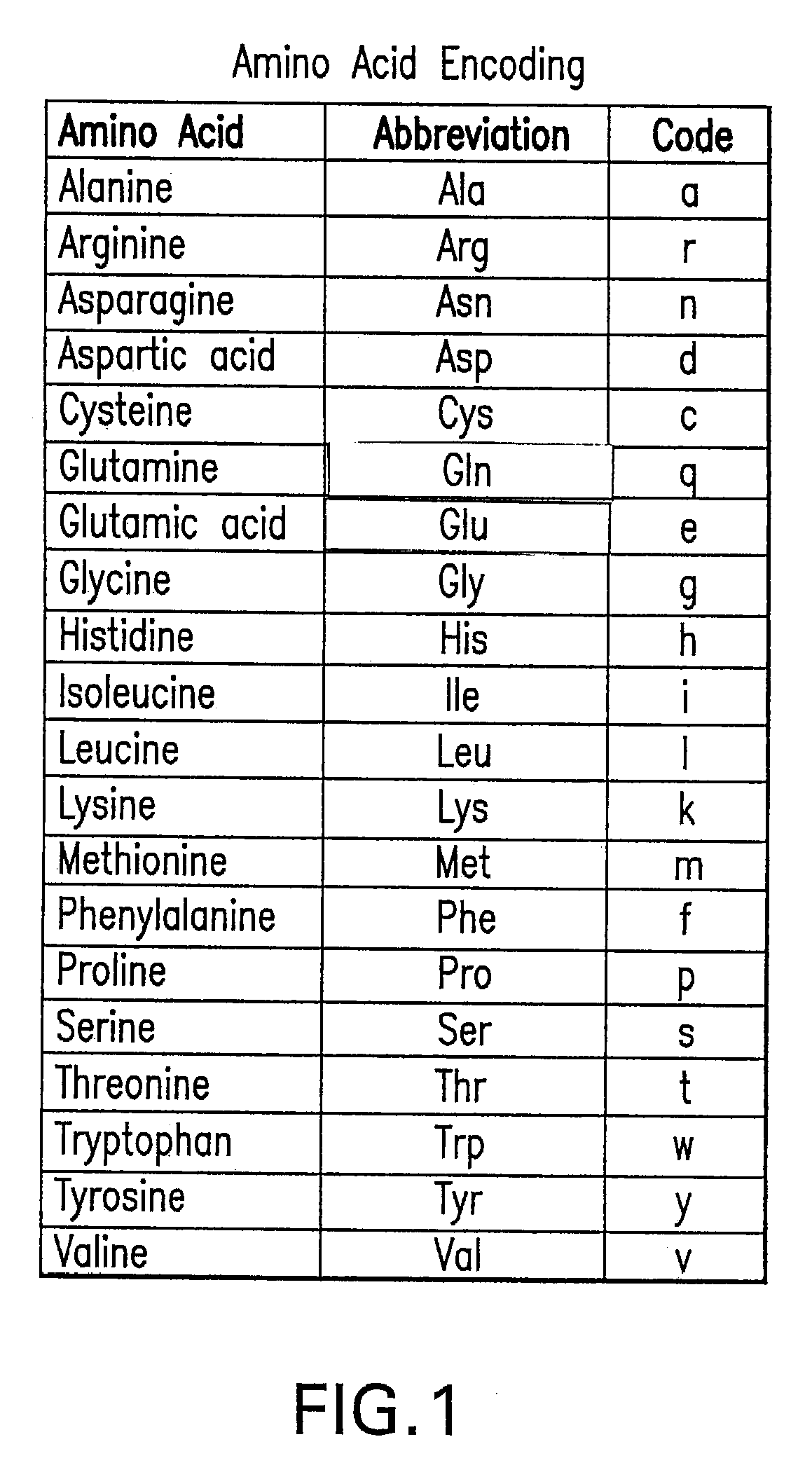
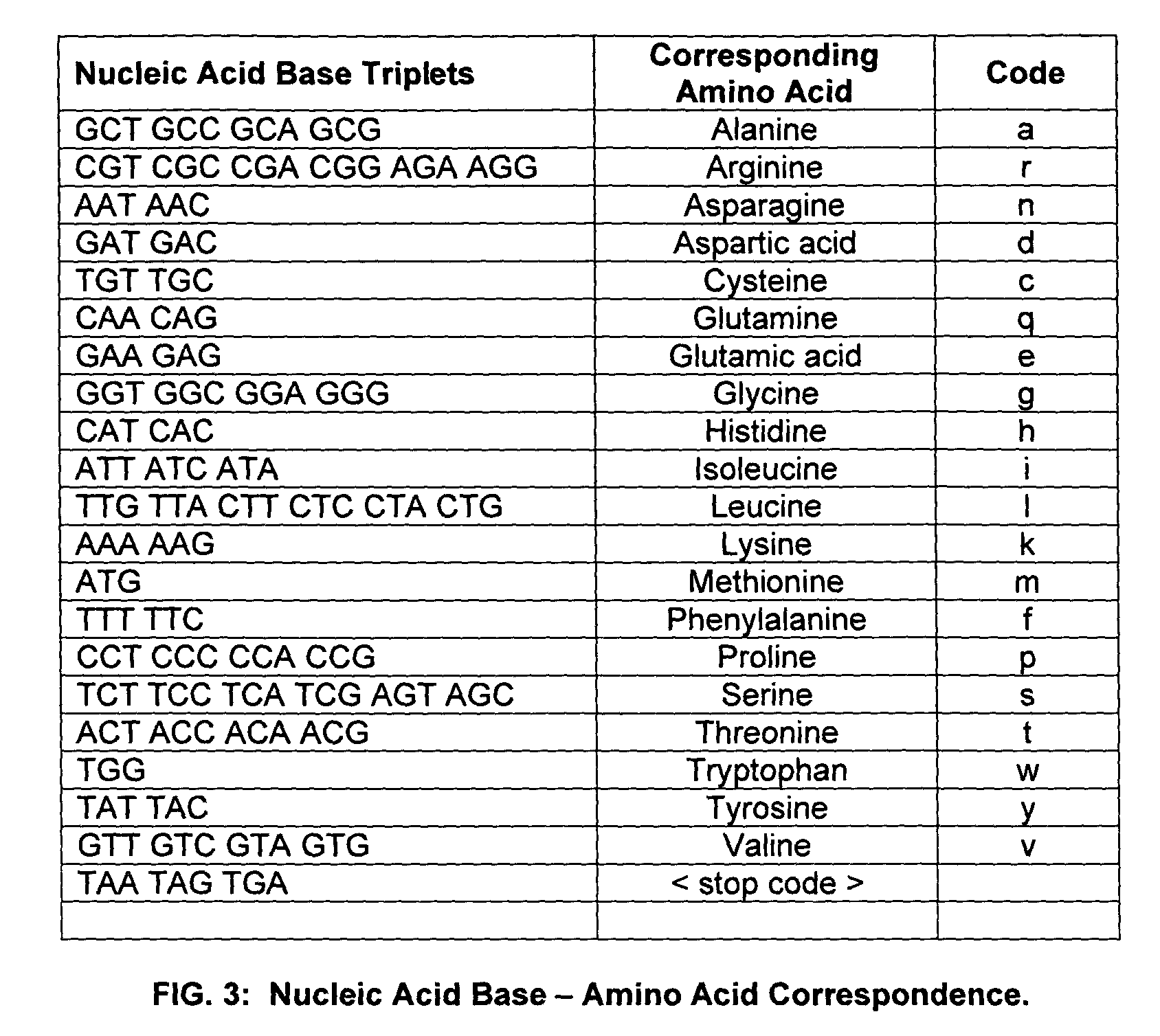
A polyhistidine-tag is an amino acid motif in proteins that typically consists of at least six histidine (His) residues, often at the N- or C-terminus of the protein. It is also known as hexa histidine-tag, 6xHis-tag, His6 tag, by the US trademarked name HIS TAG (US Trademark serial number 74242707), and most commonly as His-Tag.
Nucleic acid encoding poly-zinc finger proteins with improved linkers
InactiveUS7153949B2Enhanced affinity and specificityImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainNucleotide
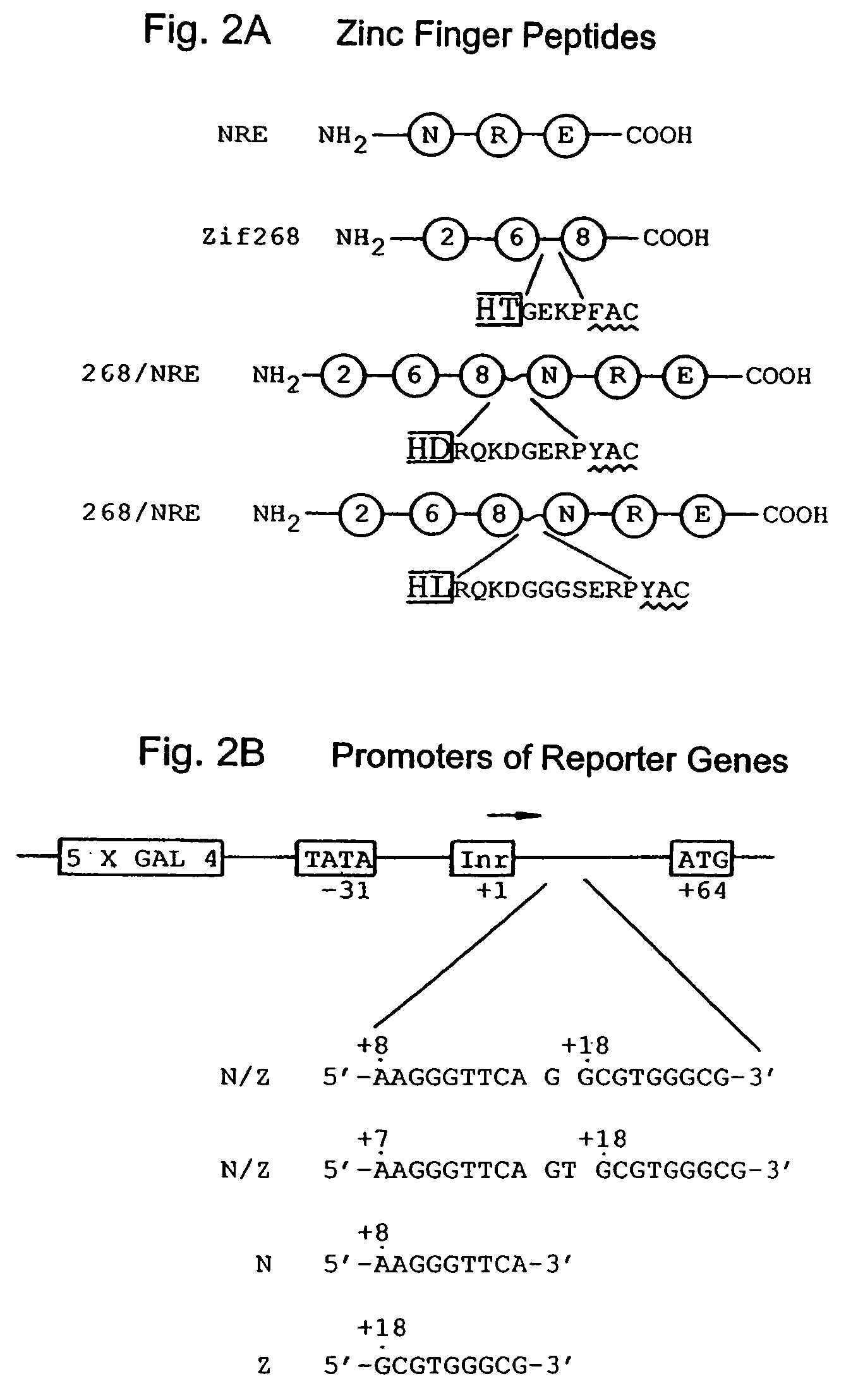
Polynucleotides encoding chimeric proteins, and methods for their production and use are disclosed. The chimeric proteins comprise a flexible linker between two zinc finger DNA-binding domains, wherein the linker contains eight or more amino acids between the second conserved histidine residue of the carboxy-terminal zinc finger of the first domain and the first conserved cysteine residue of the amino-terminal zinc finger of the second domain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
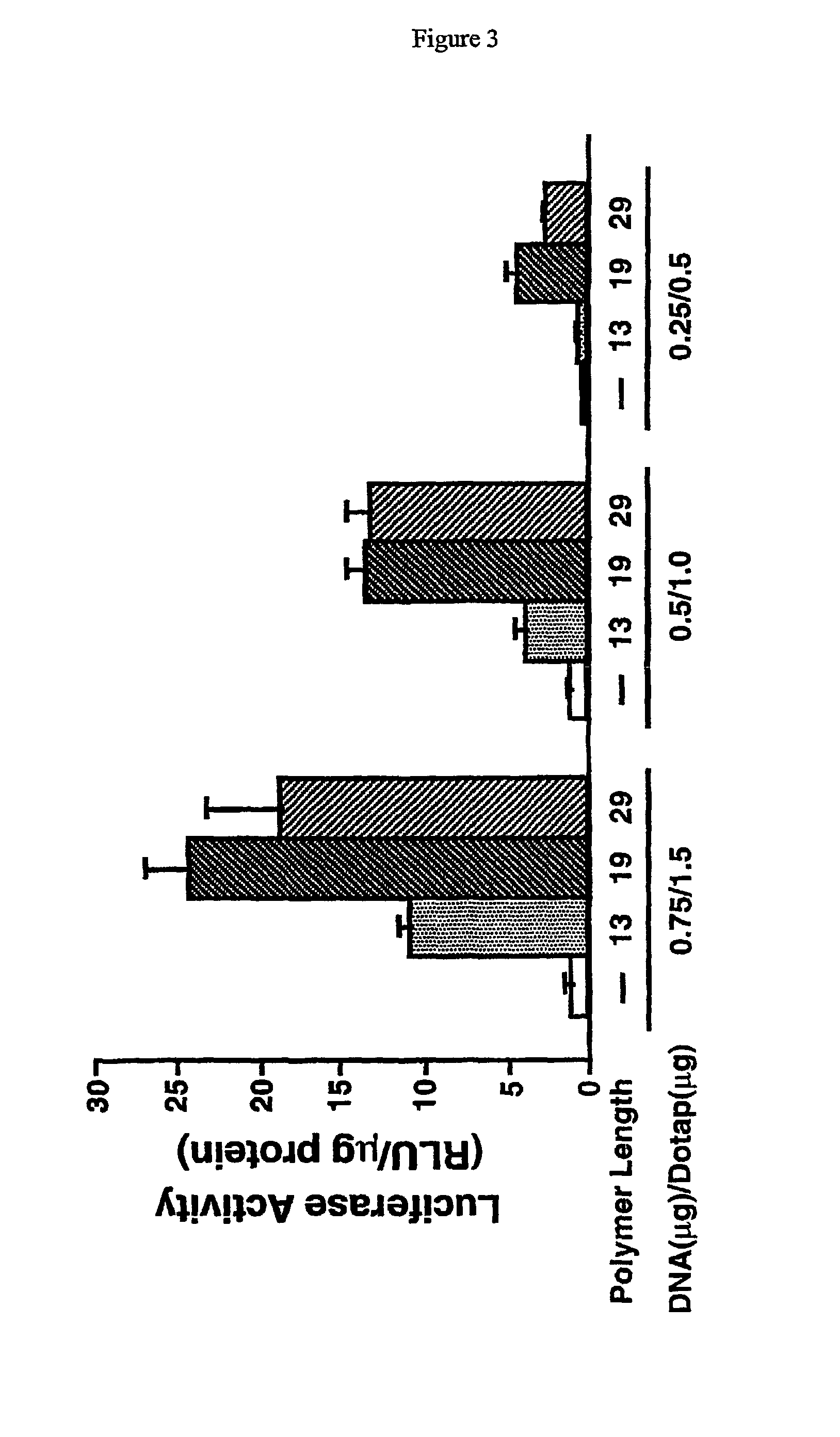
Histidine copolymer and methods for using same
InactiveUS7163695B2Prolong half-life in vivoEnhanced transfectionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsHistidine residueCopolymer
The invention provides a pharmaceutical agent delivery composition comprising: (i) a transport polymer comprising a linear or branched peptide having from about 10 to about 300 amino acid residues, having from about 5 to 100% histidine residues, and optionally having from 0 to about 95% non-histidine amino acid residues; (ii) at least one pharmaceutical agent; and optionally (iii) one or more intracellular delivery components in association with the transport polymer. The invention also provides methods for using such composition to deliver the pharmaceutical agent to the interior of cells.
Owner:MIXSON A JAMES
CATIONIC PEPTIDES FOR siRNA INTRACELLULAR DELIVERY
What is described is a composition for delivery of a RNA molecule to a cell, comprising: a double stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecule of about 15 to about 40 base pairs; and a polynucleotide delivery-enhancing peptide, comprising a region of alternating lysine and histidine residues, or of alternating D and L forms of arginine.
Owner:NASTECH PHARMA
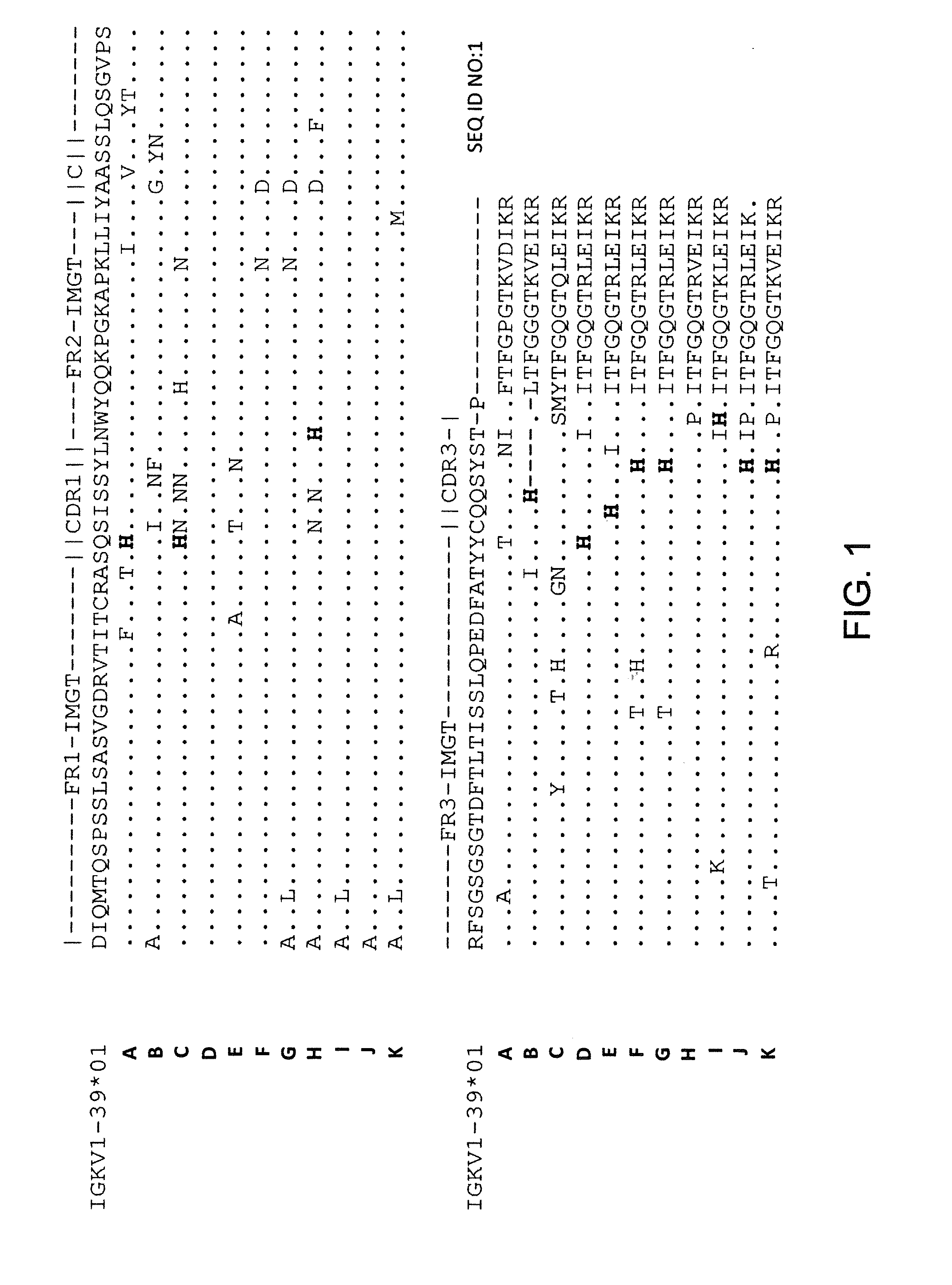
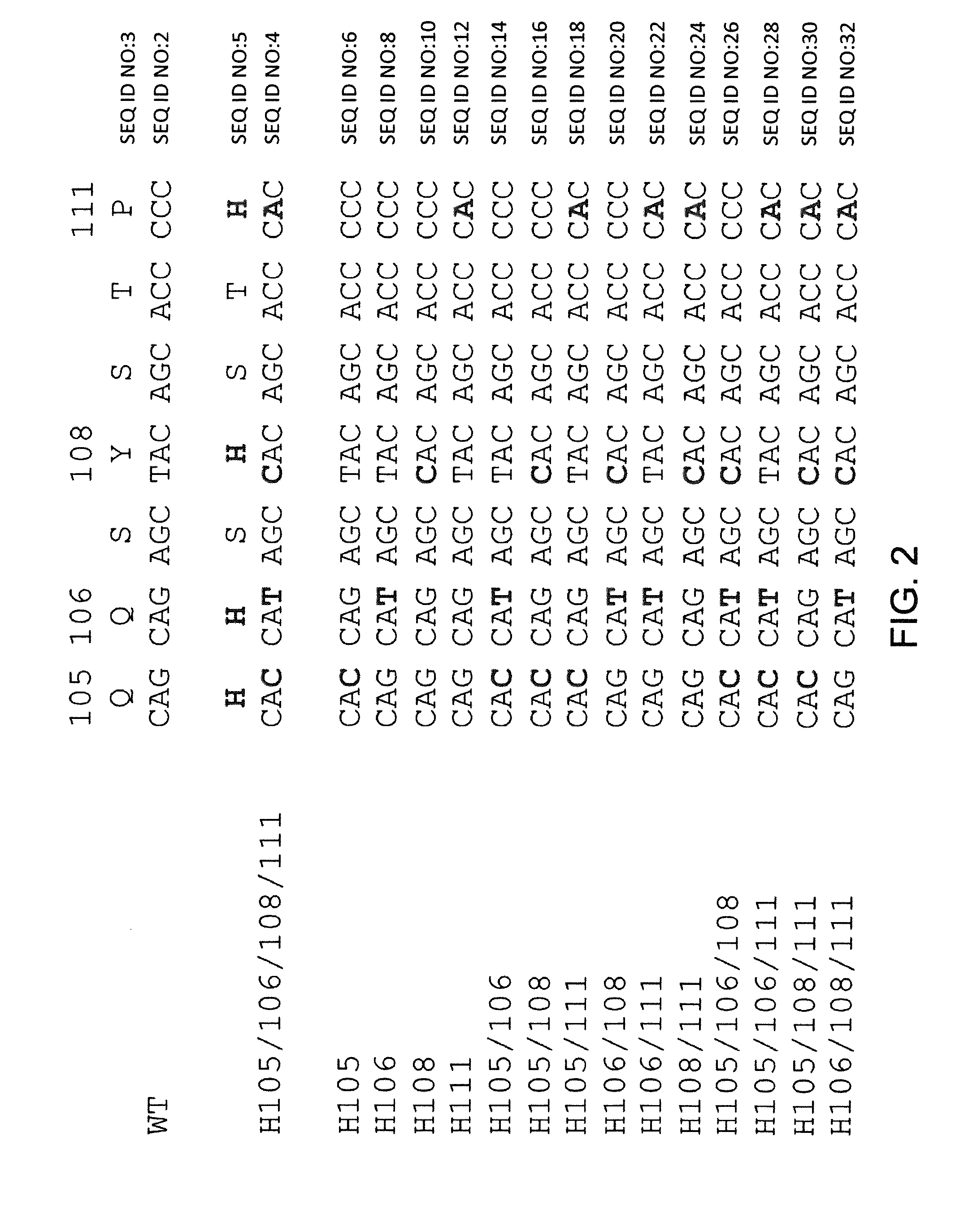
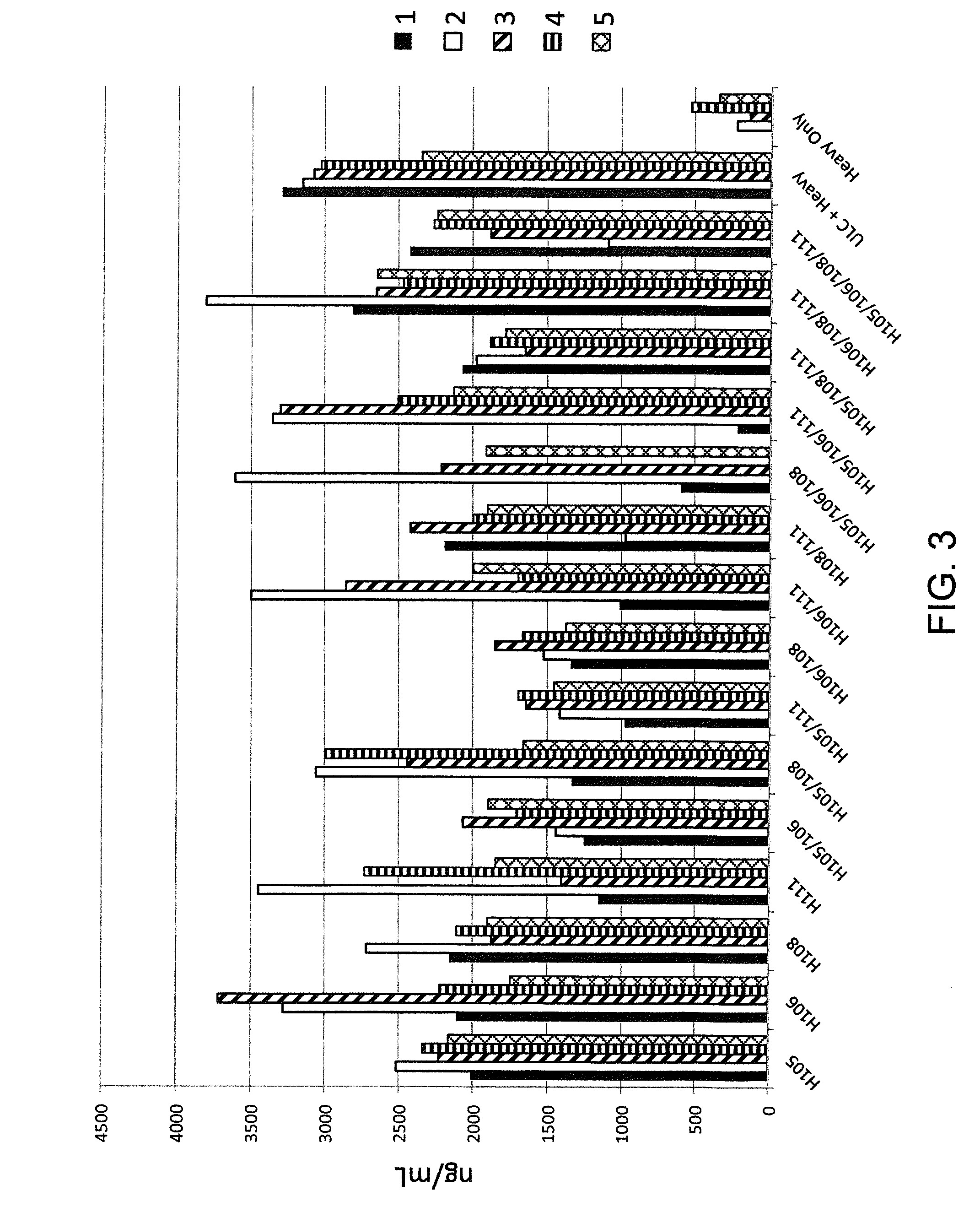
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
InactiveUS20140013456A1Reduce the binding forceNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsNucleotideGenetically modified crops
A genetically modified non-human animal is provided, wherein the non-human animal expresses an antibody repertoire capable of pH dependent binding to antigens upon immunization. A genetically modified non-human animal is provided that expresses human immunoglobulin light chain variable domains derived from a limited repertoire of human immunoglobulin light chain variable gene segments that comprise histidine modifications in their germline sequence. Methods of making non-human animals that express antibodies comprising histidine residues encoded by histidine codons introduced into immunoglobulin light chain nucleotide sequences are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
System and method for identifying complex patterns of amino acids
A method and system are disclosed for identifying and / or locating complex patterns in an amino acid sequence stored in a computer file or database. According to an aspect of the present invention, techniques are provided to facilitate queries of protein databases. For protein descriptions received in response to the queries, embodiments of the present invention may scan the received protein descriptions to identify and locate Replikin patterns. A Replikin pattern is defined to be a sequence of 7 to about 50 amino acids that include the following three (3) characteristics, each of which may be recognized by an embodiment of the present invention: (1) the sequence has at least one lysine residue located six to ten amino acid residues from a second lysine residue; (2) the sequence has at least one histidine residue; and (3) at least 6% of the amino acids in the sequence are lysine residues.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +3
Mutant-type lipases and applications thereof
The present invention provides mutant-type lipases which demonstrate superior lipolytic and esterific activities. The mutant-type lipases are characterized by an amino acid alteration at the residue immediately followed either the serine residue or the histidine residue or both residues of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. The Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad is known to be the three residues, although occur far apart in the amino acid sequence of a lipase, that contribute to the hydrolytic activity in the active site of the lipase. The amino acid residue that follows the serine residue of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad is alanine. The amino acid residue that follows the histidine residue of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad is isoleucine. The wild-type lipase is preferably originated from Staphylococcus, particularly Staphylococcus epidermindis. The present invention also relates to a method for preparing the mutant-type lipases by site-directed mutagenesis using PCR and a method for utilizing the mutant-type lipase to catalyze synthesis of flavor esters to be used in food industry.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
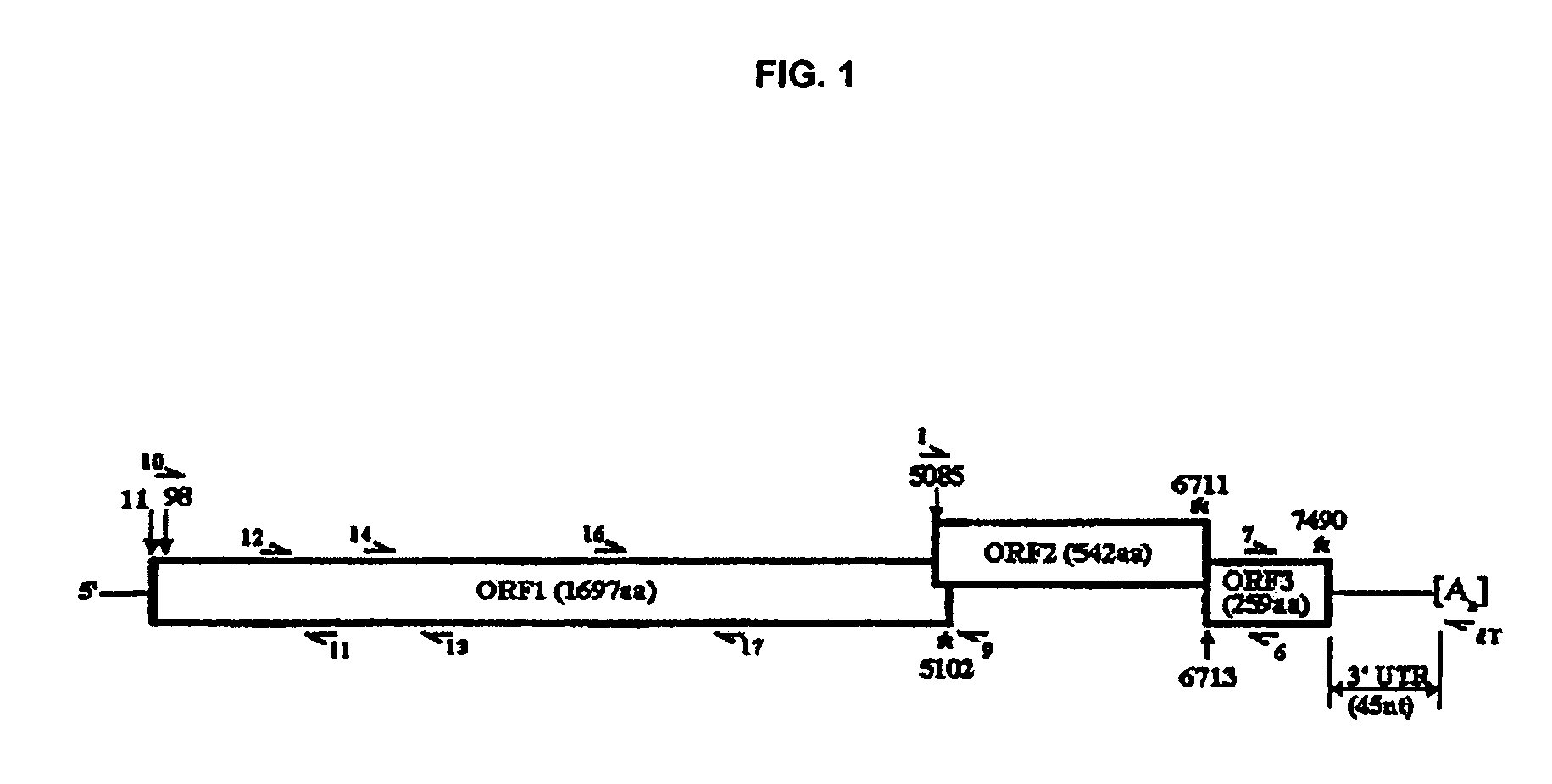
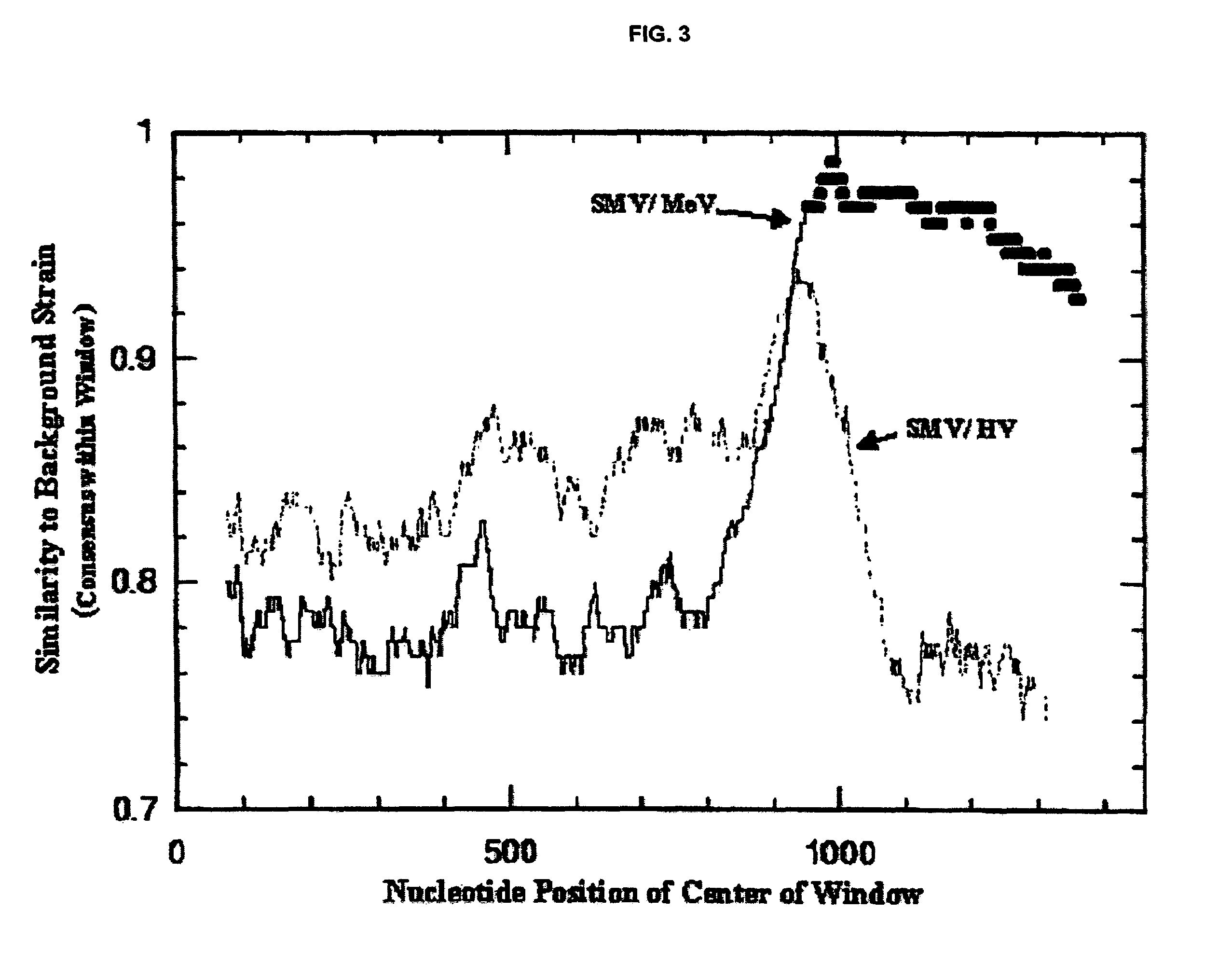
Snow mountain virus genome sequence, virus-like particles and methods of use
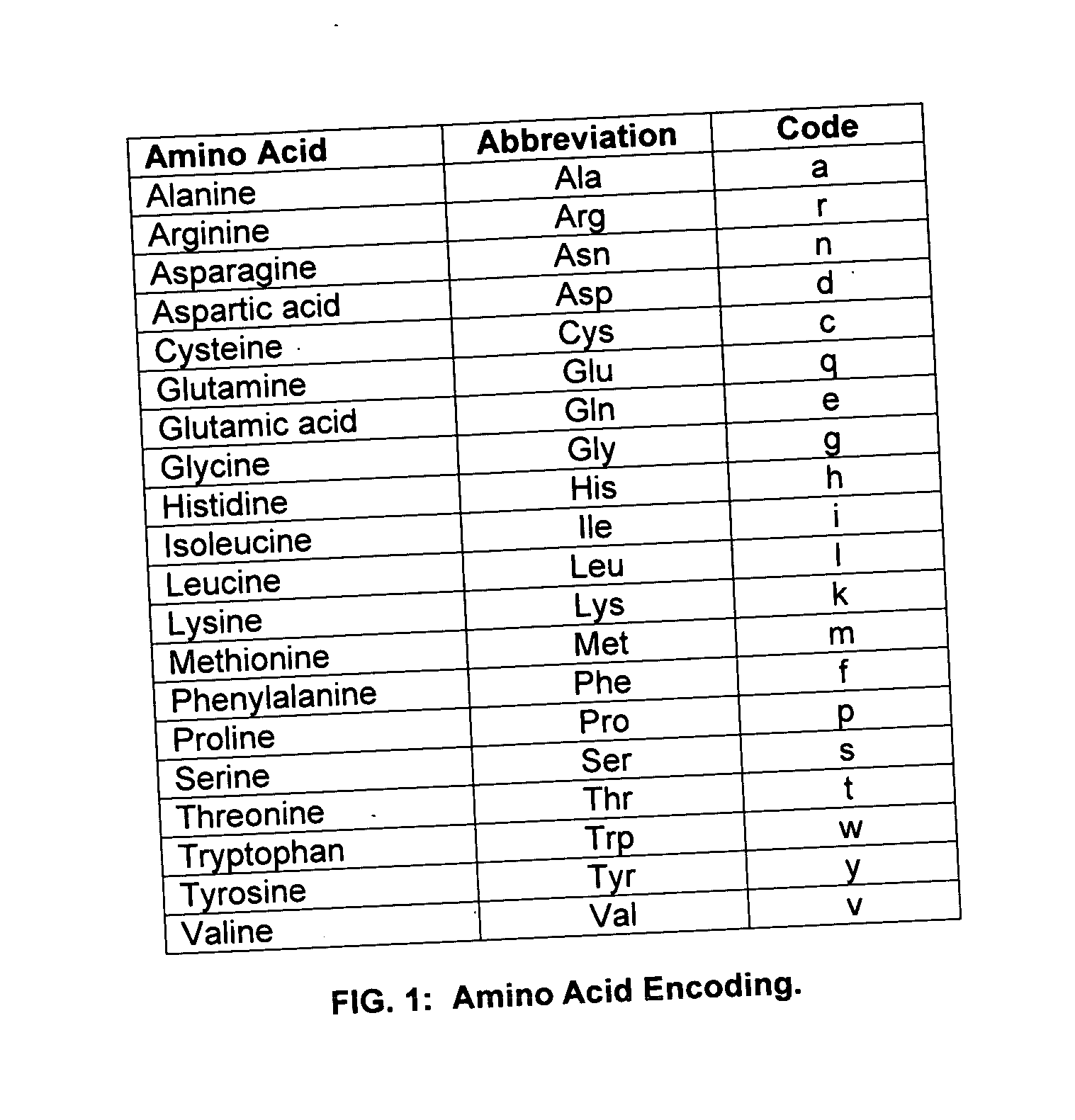
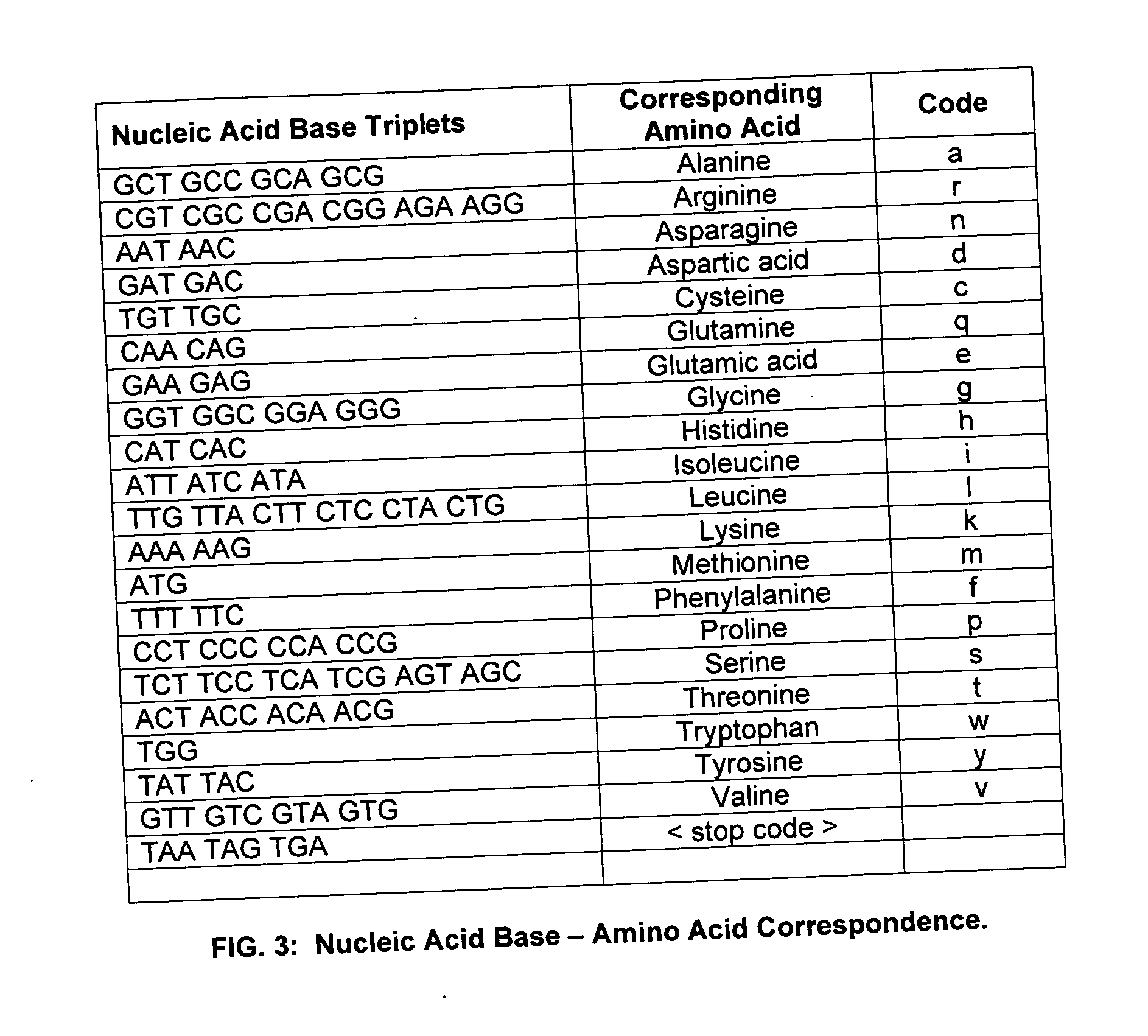
Snow Mountain Virus (SMV) belongs to the Norovirus genus of the Caliciviridae family. SMV is a genogroup II (GII) reference strain of human enteric caliciviruses associated with epidemic gastroenteritis. The positive sense RNA genome sequence of SMV was determined to be 7,537 nucleotides in length excluding the 3′ polyadenylated tract. The genome is organized into three open reading frames. Pairwise sequence alignments showed SMV ORF1 is highly conserved with other GII noroviruses, and most closely related to GII strains Melksham and Hawaii viruses. Comparative sequence analyses showed the SMV is a recombinant norovirus. VP1 / NP2 proteins assembled into virus-like particles (VLPs) when expressed in insect cells by a recombinant baculovirus. Characterization of one clone that expressed VP1 but failed to assemble into VLPs, identified histidine residue 91 as important for particle assembly.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
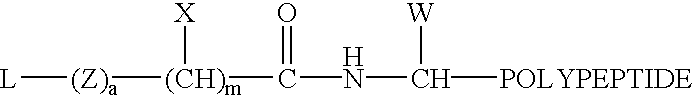
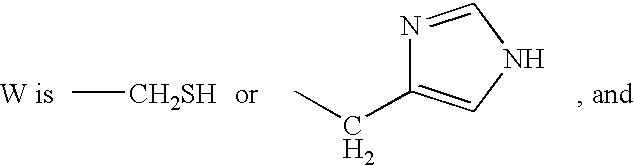
Thioester polymer derivatives and method of modifying the N-terminus of a polypeptide therewith
InactiveUS6908963B2High yieldPeptide preparation methodsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCrystallographyHistidine residue
The invention provides reagents and methods for conjugating polymers specifically to the α-amine of polypeptides in high yield. The invention provides monofunctional, bifunctional, and multifunctional PEGs and related polymers having a thioester moiety capable of specifically conjugating to the α-amine of a polypeptide having a cysteine or histidine at the N-terminus. The invention provides active thioester derivatives of PEG that have suitable reactivity with an N-terminal cysteine or histidine residue of a polypeptide to produce an amide bond between the PEG and polypeptide. Use of these active esters to prepare PEG-proteins and PEG-peptides is described.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
System and method for identifying complex patterns of amino acids
InactiveUS7774144B2SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DatabasesHistidine residue
A method and system are disclosed for identifying and / or locating complex patterns in an amino acid sequence stored in a computer file or database. According to an aspect of the present invention, techniques are provided to facilitate queries of protein databases. For protein descriptions received in response to the queries, embodiments of the present invention may scan the received protein descriptions to identify and locate Replikin patterns. A Replikin pattern is defined to be a sequence of 7 to about 50 amino acids that include the following three (3) characteristics, each of which may be recognized by an embodiment of the present invention: (1) the sequence has at least one lysine residue located six to ten amino acid residues from a second lysine residue; (2) the sequence has at least one histidine residue; and (3) at least 6% of the amino acids in the sequence are lysine residues.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +3
Thioester-terminated water soluble polymers and method of modifying the N-terminus of a polypeptide therewith
InactiveUS7078496B2Avoid crosslinkingDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsWater solubleHistidine residue
The invention provides reagents and methods for conjugating a polymer specifically to the α-amine of a polypeptide. The invention provides monofunctional, bifunctional, and multifunctional PEGs and related polymers having a terminal thioester moiety capable of specifically conjugating to the α-amine of a polypeptide having a cysteine or histidine residue at the N-terminus. The invention provides reactive thioester-terminated PEG polymers that have suitable reactivity with an N-terminal cysteine or histidine residue of a polypeptide to produce an amide bond between the PEG molecule and the polypeptide.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Formulation strategies in stabilizing peptides in organic solvents and in dried states
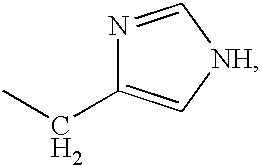
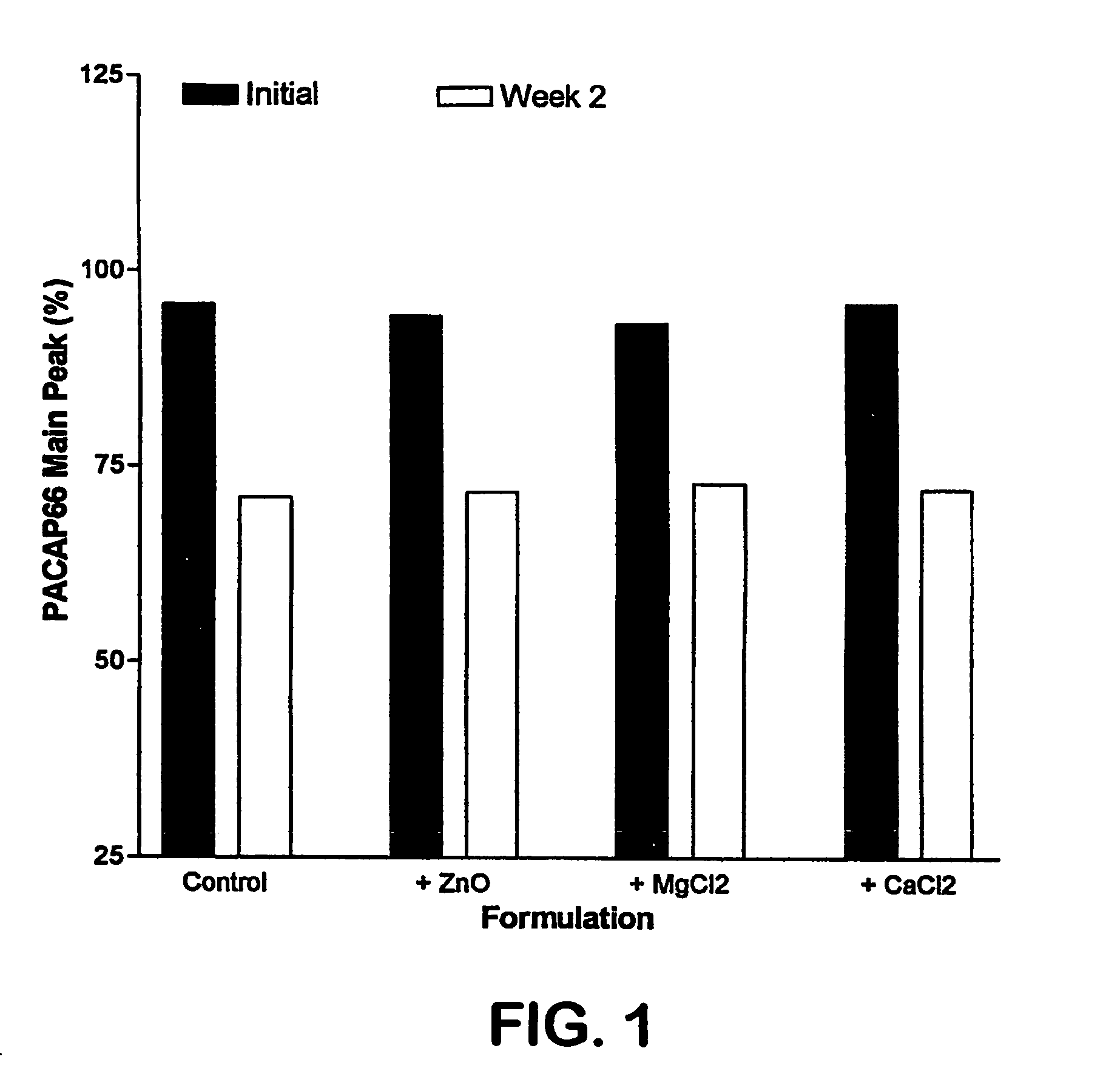
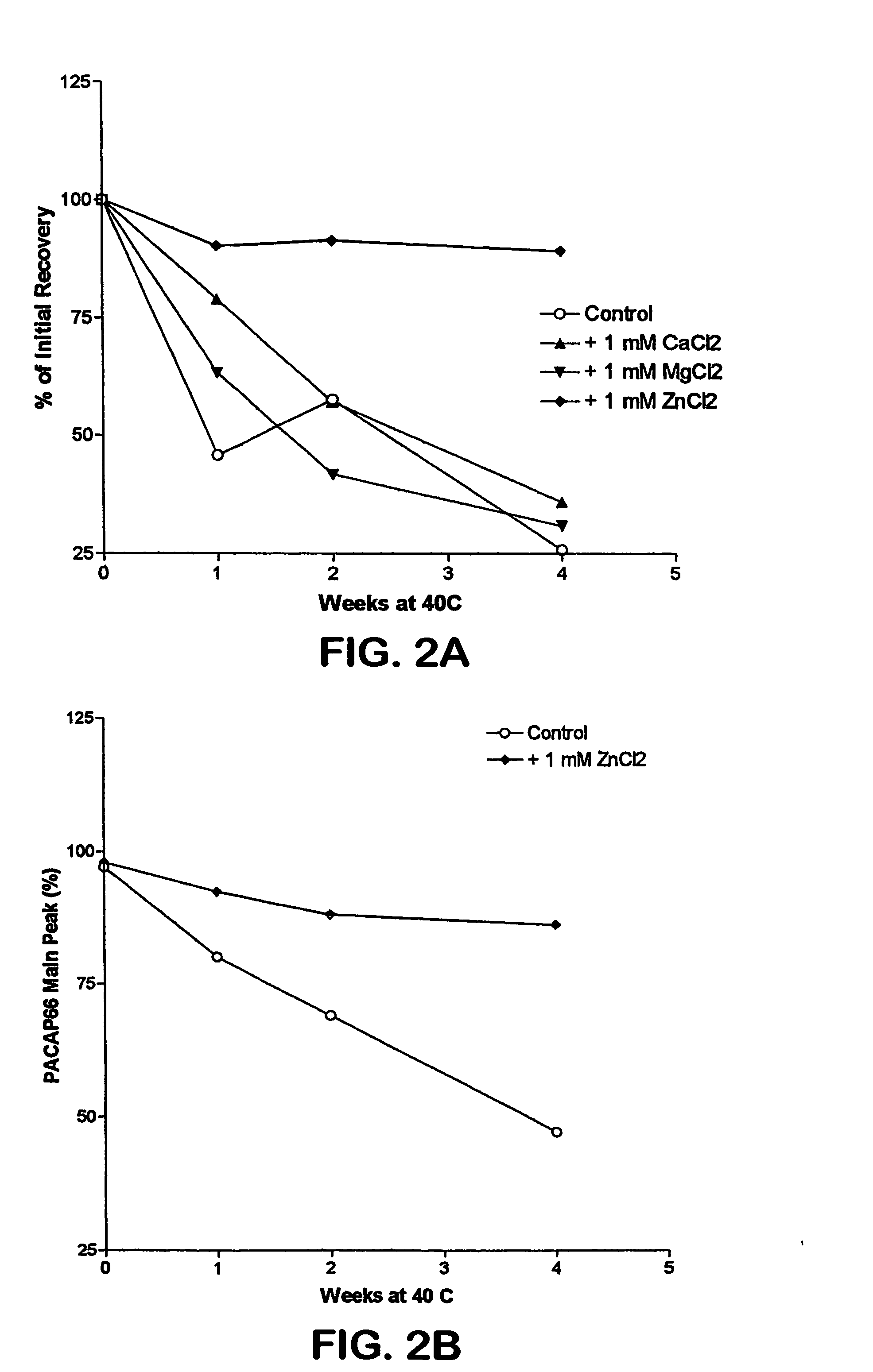
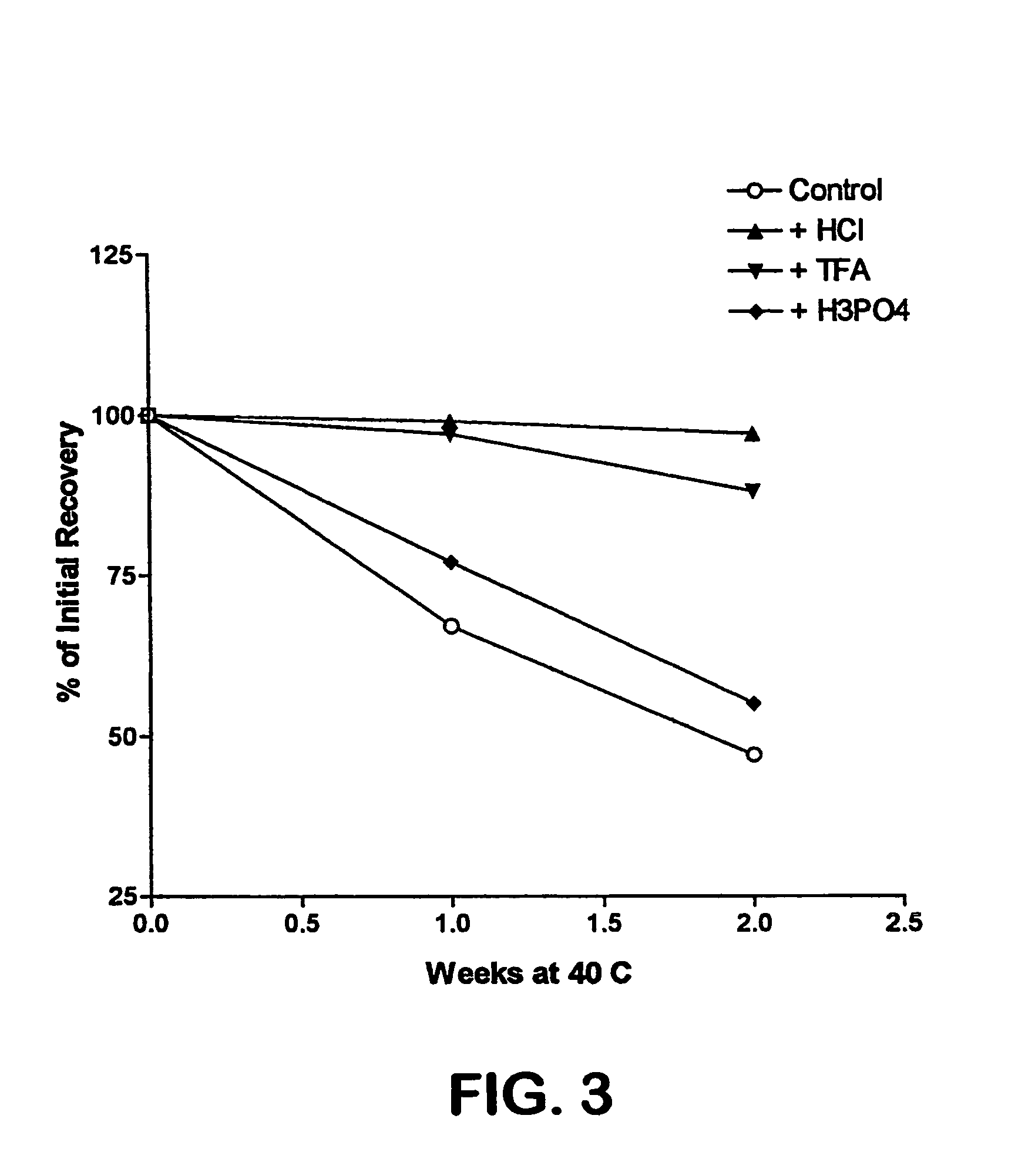
The invention relates to stabilized formulations of therapeutically active peptides, particularly PACAP 66. Formulations of the invention include a peptide containing at least one histidine residue, a transition metal salt and an organic solvent. The above formulations may contain peptides that have at least one asparagine residue and are acidified and dried (such as spray-dried or freeze-dried) before formulation preparation. Other formulations of the invention relate to stabilized formulations of PACAP 66 or peptides containing an asparagine residue, which are acidified and dried (such as spray-died or freeze-dried) with or without a transition metal salt.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Genetic recombinant human-like collagen
ActiveCN103102407AAvoid immune rejectionAvoid Biosafety HazardsCosmetic preparationsFungiCollagenanHistidine residue
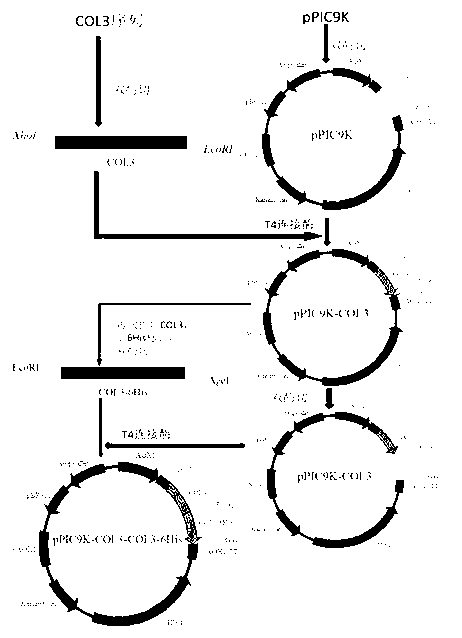
The invention discloses humanized genetic recombinant human-like collagen produced by eukaryotic bacteria. The humanized genetic recombinant human-like collagen has amino acid with the total length of 474, and is formed by connecting two sections of completely-identical human III-type collagen sections in series; the end C is connected with six histidine residue groups serving as specificity affinity purification markers. The performance of the genetic recombination human-like collagen is superior to animal collagens and original nuclear engineering bacteria recombinant collagens; and with the specificity affinity purification markers, the high-purity product is easily acquired.
Owner:JIANGSU TRAUTEC MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Synthesis and application of exenatide joined with polyethylene glycol
InactiveCN102532303AImprove in vivo stabilityExtended half-lifeHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical SubstancesHistidine residue
The invention relates to exenatide joined with polyethylene glycol. The structural general formula of exenatide is (I), mPEG represents residue of methoxy polyethylene glycol, the selected value of n is 0-3, R represents an exenatide molecule from which an amino is removed, the amino is of lysine residue or of N-end histidine residue in the exenatide molecule, and the molecular weight of the exenatide joined with polyethylene glycol is 9,800-110,000. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the compound and application of the compound in preparing medicines for curing type 2 diabetes mellitus. The exenatide joined with polyethylene glycol has the advantages of being long in half-life period and good in stability and hypoglycemic effect.
Owner:CHEMFUTURE PHARMATECH JIANGSU
Fibrillation resistant proteins
ActiveUS20090304814A1Improve the immunityIncreased susceptibilityBiocideFungiFibrillationHistidine residue
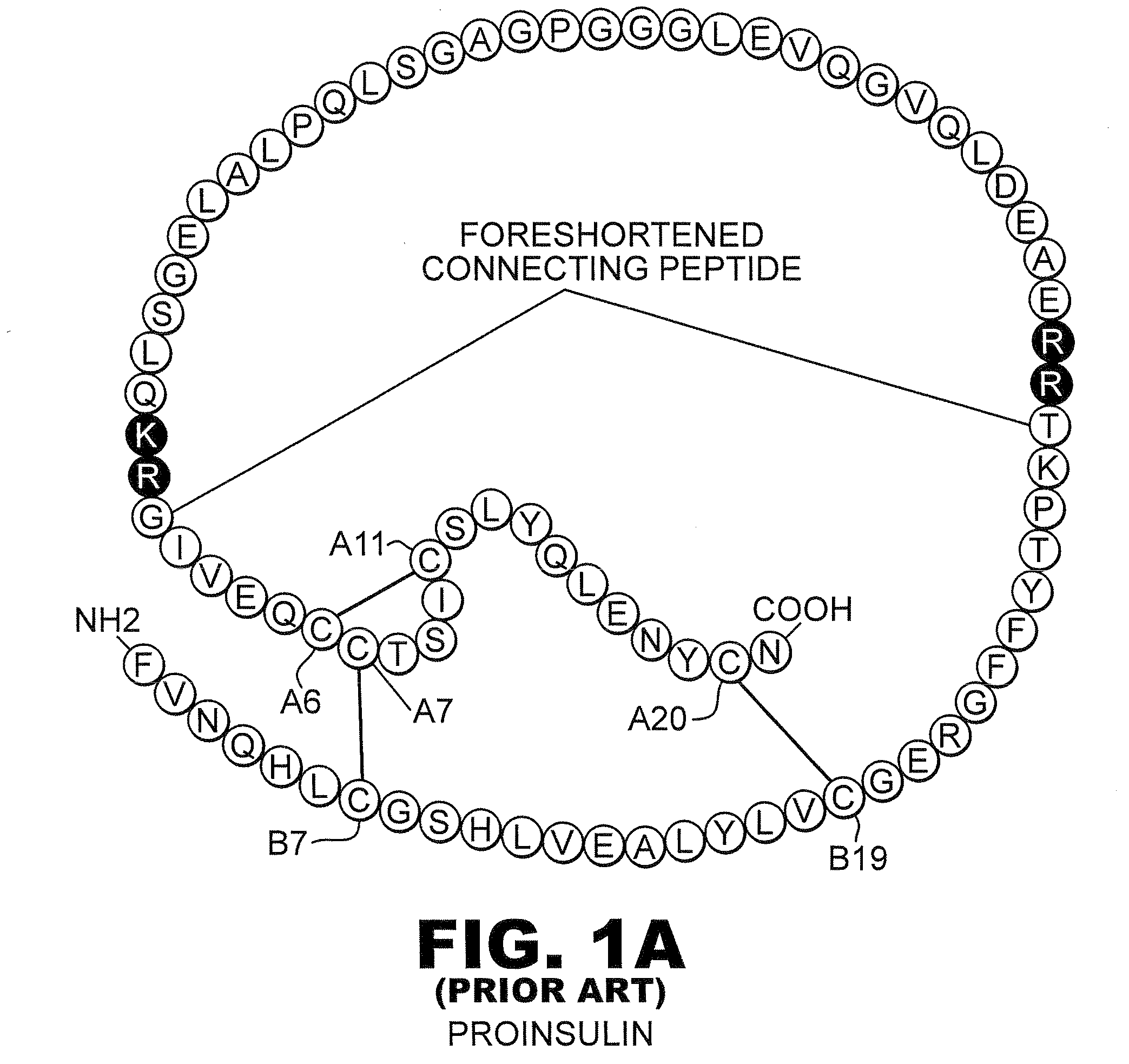
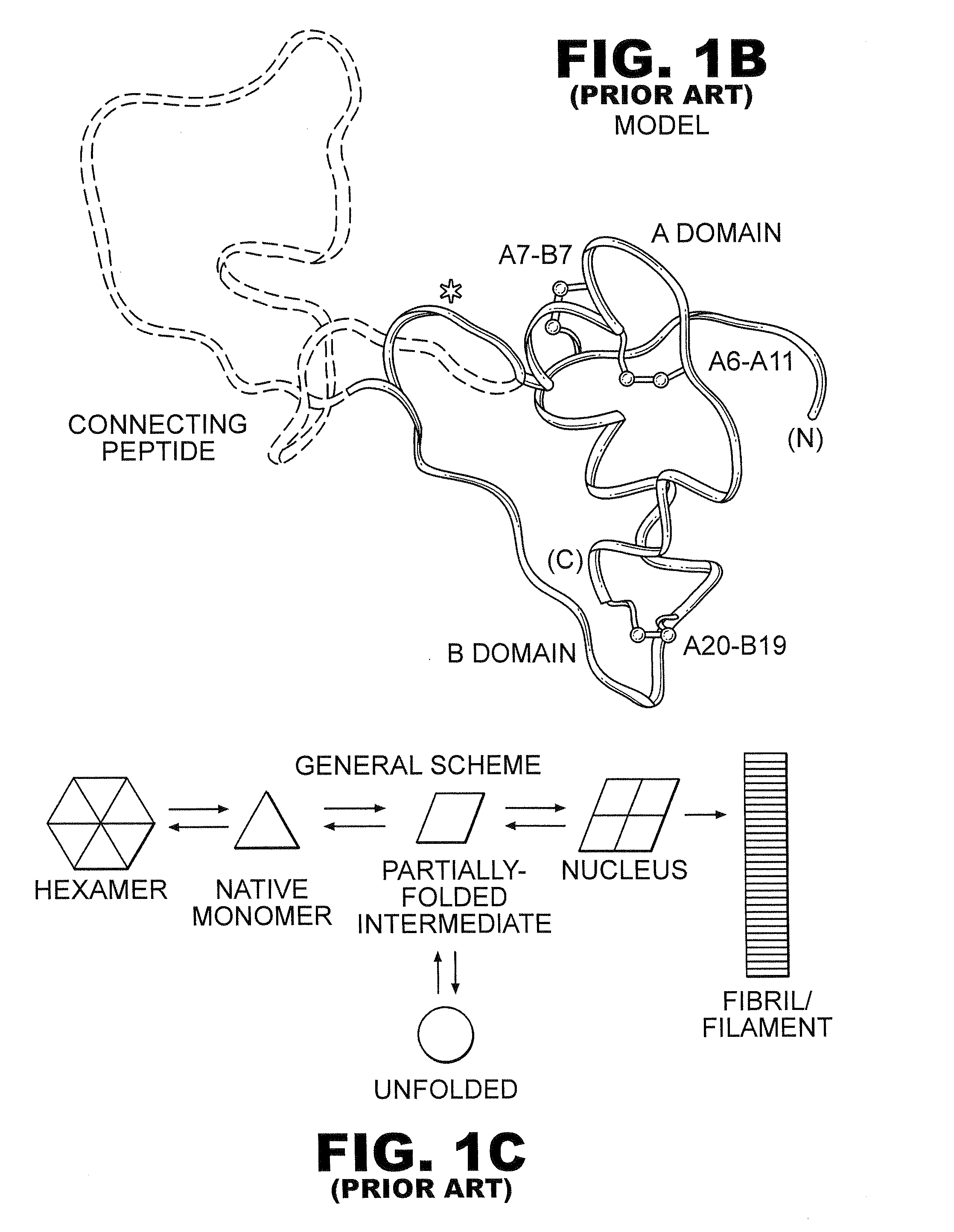
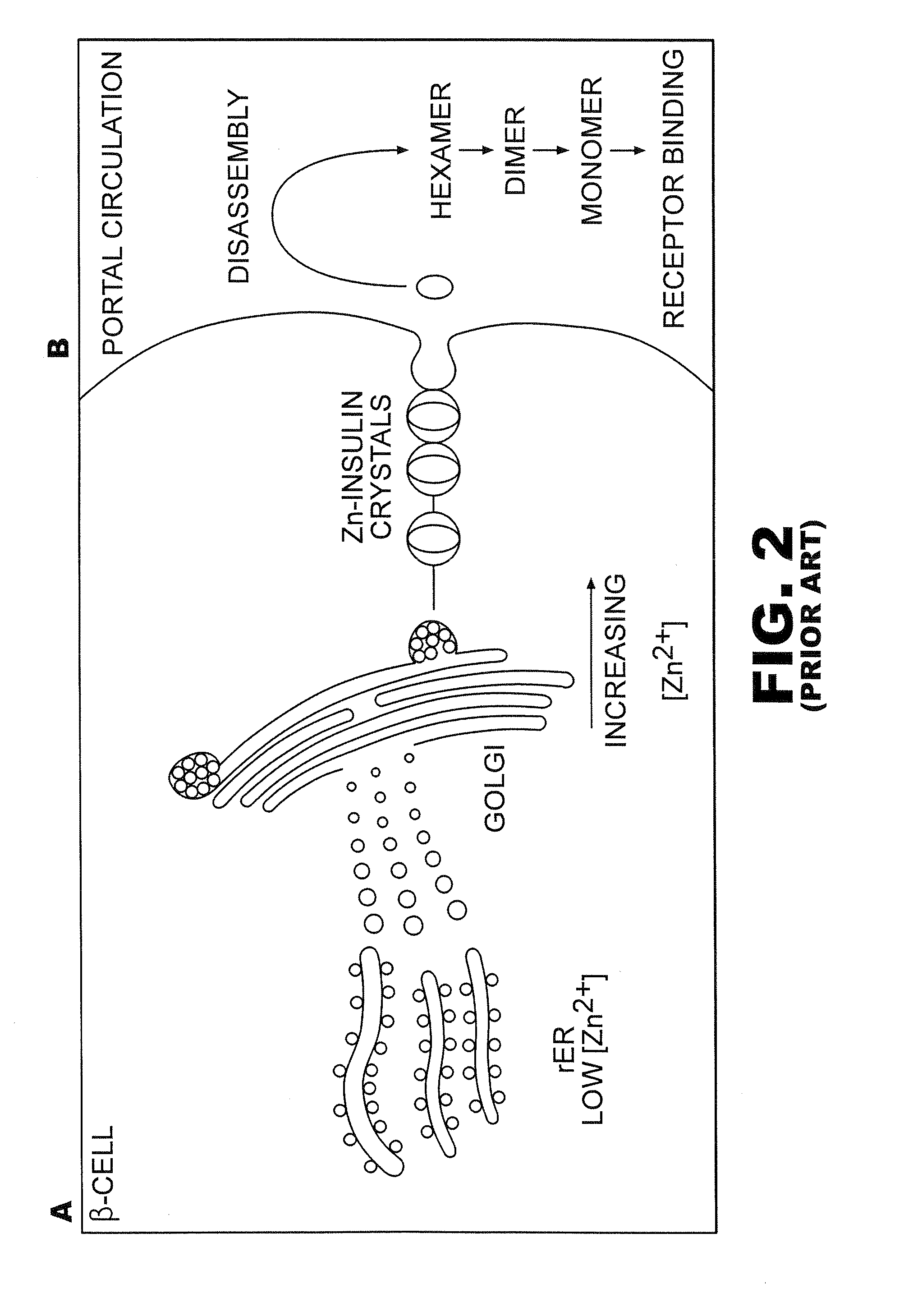
Protection of proteins against fibrillation may be afforded by introduction of certain histidine substitutions into the protein, such that a pair of histidines are present with sufficient spacing as to allow the histidines to coordinate with zinc. In the case of insulin, introduction of histidine residue substitutions at residues A4 and A8 together or a histidine residue substitution at residue B1, provides increased resistance to fibrillation while maintaining at least a majority of the activity of the insulin analogue. Introduction of a histidine residue substitution at residue A8 restores at least a portion of fibrillation resistance that may have been harmed by substitutions present on the B-chain such as those present in fast-acting insulins. Proteins protected by such histidine substitutions may be used to provide a pharmaceutical composition. A method of treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
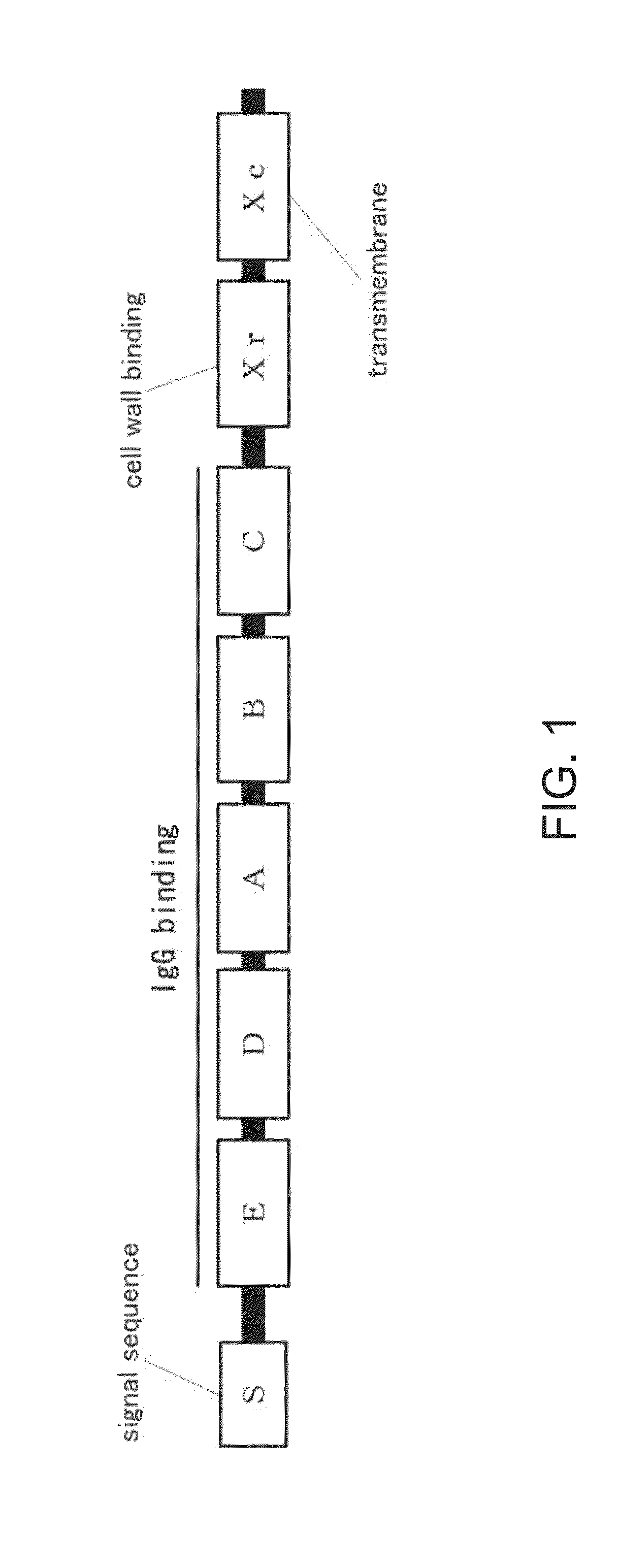
Novel process for producing antibody enzyme, novel antibody enzyme and utilization thereof
InactiveUS20060030015A1Reduce developmentInhibition of disease progressionAnimal cellsFungiStructure analysisHelicobacter pylori
A process for producing an antibody enzyme which involves an antibody structure analysis step of confirming the presence of a catalyst triplet residue structure wherein a serine residue, an aspartate residue and a histidine residue or a glutamate residue are located stereostructurally close to each other in the stereostructure of an antibldy anticipated based on its amino acid sequence. Since the above-described catalyst triplet residue structure is a structure specific to an antibody enzyme, an antibody enzyme can be efficiently screened by using the same. Examples of the antibody enzyme as described above include an antibody enzyme against Helicobacter pylori urease and an antibody enzyme against chemokine receptor CCR-5.
Owner:TOWA KAGAKU CO LTD
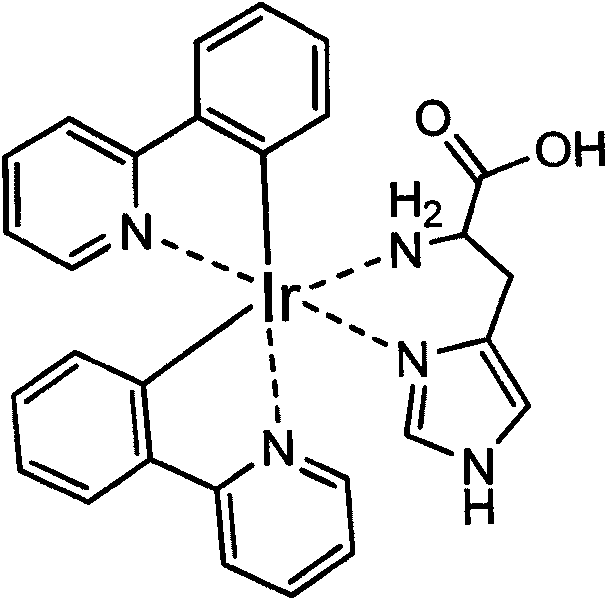
Method for labeling antibody by fluorophore generated by combination of iridium coordination compound and histidine
InactiveCN101750486AEasy to operateChanges in luminous propertiesImmunoglobulinsMaterial analysisIridiumSolvent molecule
The invention discloses a novel biomolecule labeling method, i.e. taking cyclic iridium coordination compound containing solvent molecules to combine with histidine residue in protein or polypeptide to generate a fluorophore. The method can label polypeptide and bioactive molecules of protein including antibody and the like, and can be further applied to the application field of bioinstrumentation, cell and tissue labeling, biomolecule tracing and the like. Since the fluorescence color of the compound is rich, and the labeling reaction can be completed in normal-temperature and normal butter solution in one step, thus having advantage compared with the commonly-used labeled compound and the labeling method in market, and having wide application prospect.
Owner:苏州纳凯科技有限公司
Phage Display By Novel Filamentous Bacteriophage
InactiveUS20090105090A1Loss in growthLoss in infectionPeptide librariesBacteriaPeptide ConformationHistidine residue
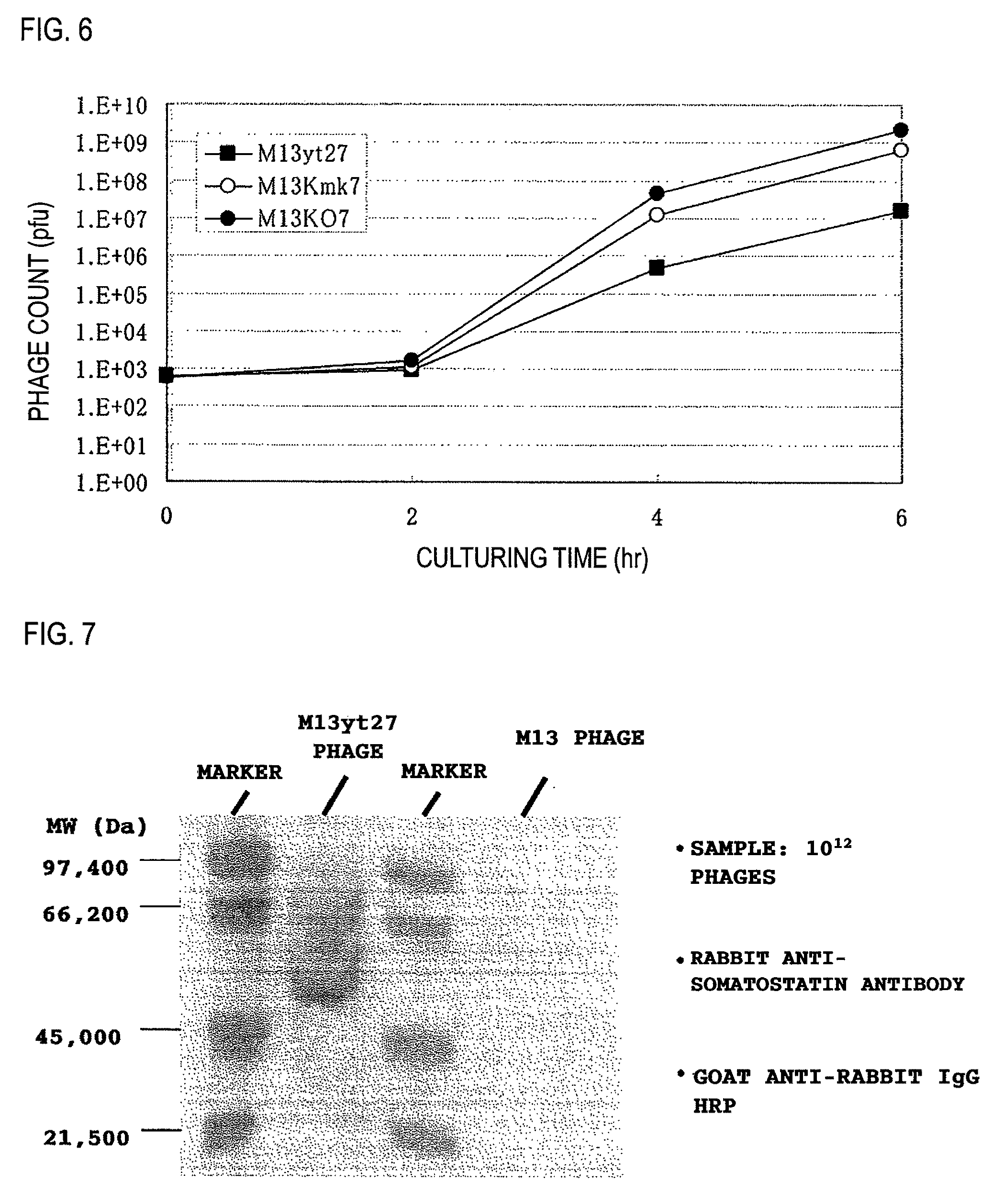
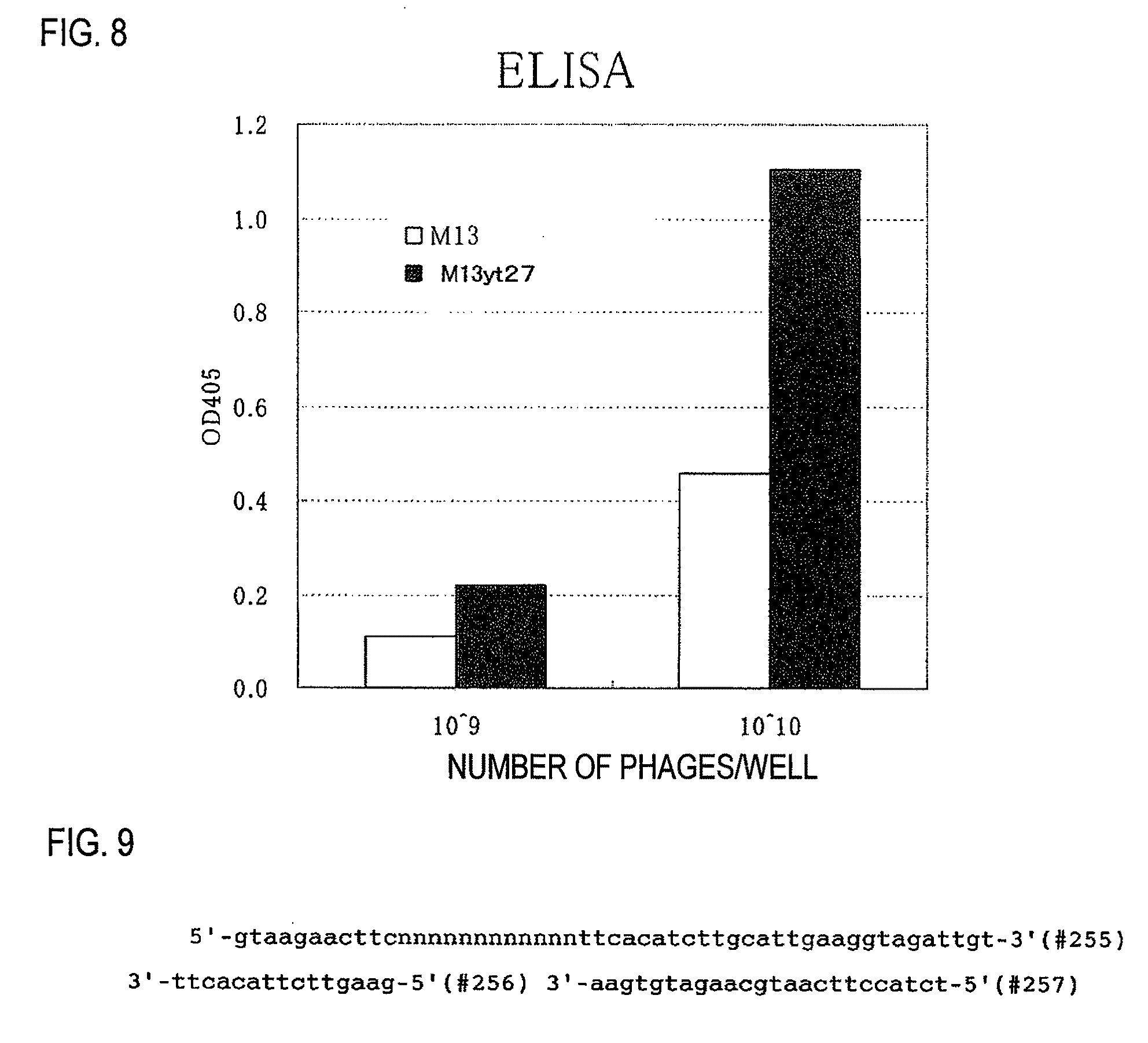
[Problems] To provide a phage display vector which can be fused in the inside of pIII and a phage display method using the vector.[Means for Solving Problems] Disclosed is a phage display method which is characterized by using a mutant pIII protein having an amino acid residue inserted between a proline residue at position 11 and a histidine residue at position 12 in an M13 phage pIII protein as depicted in SEQ ID NO:1. The method enables to produce a random peptide with high efficiency and to provide a novel source in peptide conformation.
Owner:UCHIYAMA FUMIAKI
Site-specific labeling of affinity tags in fusion proteins
InactiveUS20060141554A1Fast dynamicsRapid time periodPreparing sample for investigationNickel organic compoundsAcetic acidChemical Moiety
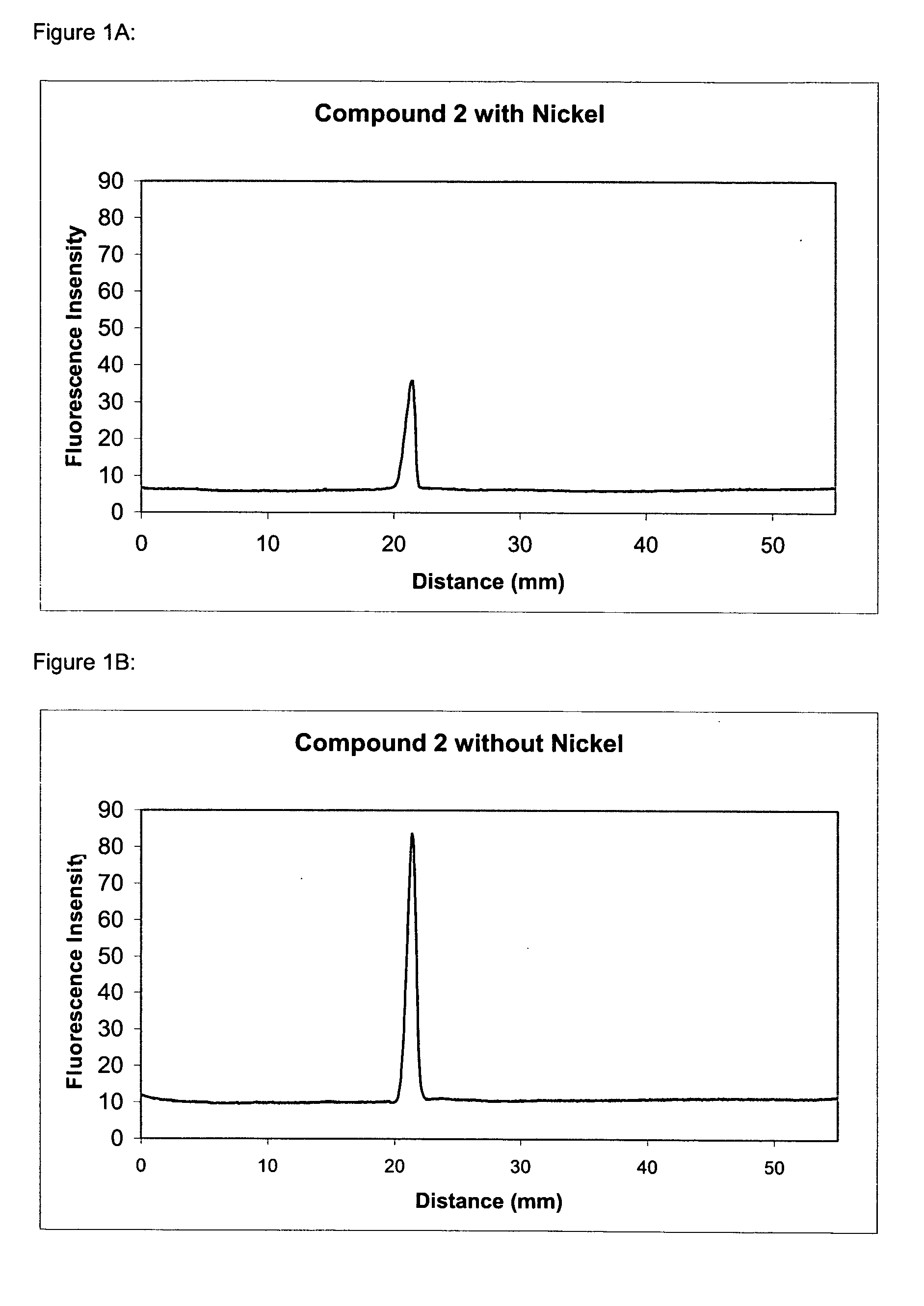
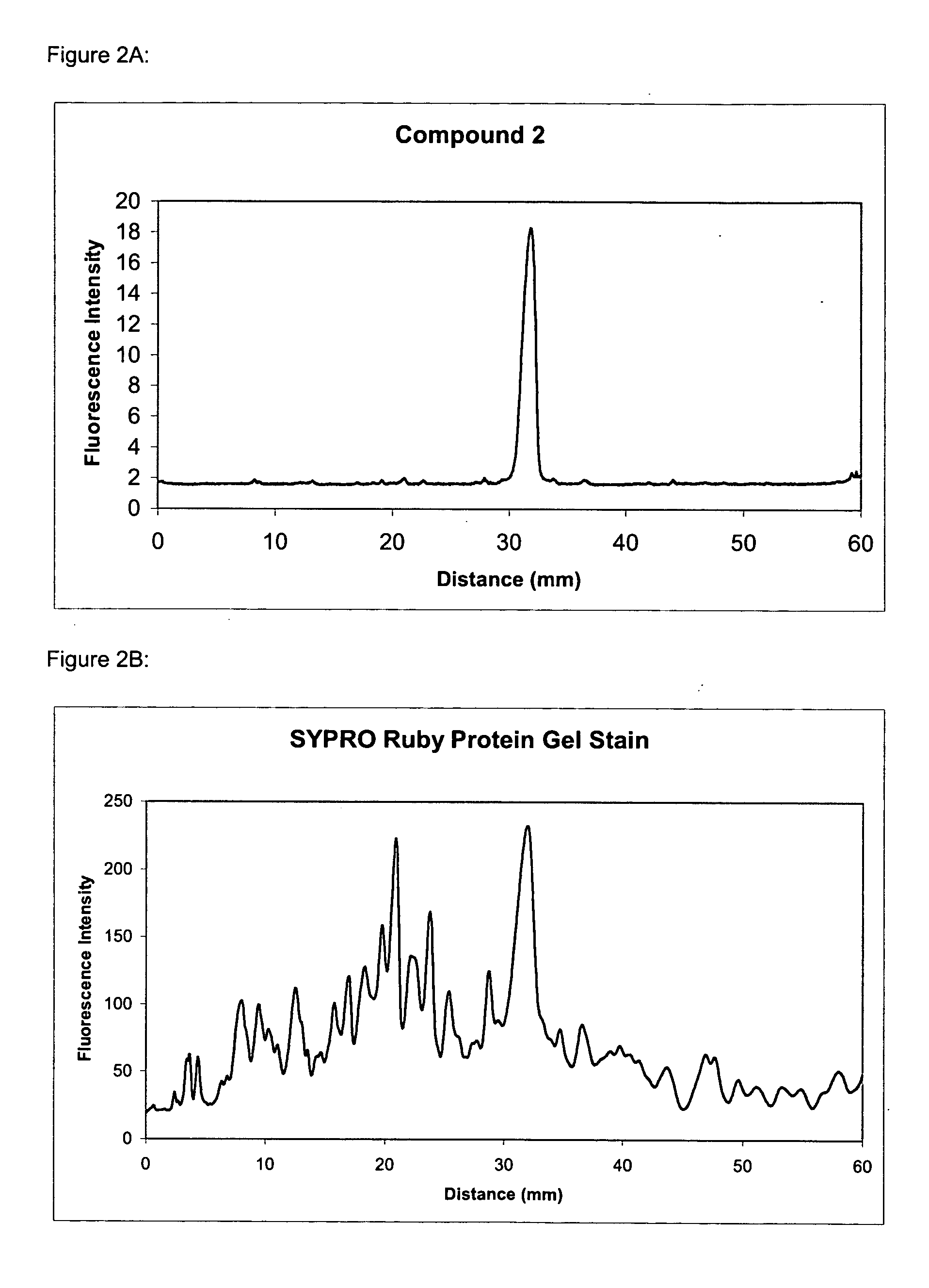
The present invention provides methods and fluorescent compounds that facilitate detecting and labeling of a fusion protein by being capable of selectively binding to an affinity tag. The fluorescent compounds have the general formula A(B)n, wherein A is a fluorophore, B is a binding domain that is a charged chemical moiety, a protein or fragment thereof and n is an integer from 1-6 with the proviso that the protein or fragment thereof not be an antibody or generated from an antibody. The present invention provides specific fluorescent compounds and methods used to detect and label fusion proteins that contain a poly-histidine affinity tag. These compounds have the general formula A(L)m(B)n wherein A is a fluorophore, L is a linker, B is an acetic acid binding domain, m is an integer from 1 to 4 and n is an integer from 1 to 6. The acetic acid groups interact directly with the positively charged histidine residues of the affinity tag to effectively label and detect a fusion protein containing such an affinity tag when present in an acidic or neutral environment.
Owner:INVITROGEN
Igg-binding peptide and method for detecting and purifying igg using same
ActiveCN103890174AHigh selectivityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsComponent separationCysteine thiolateArginine
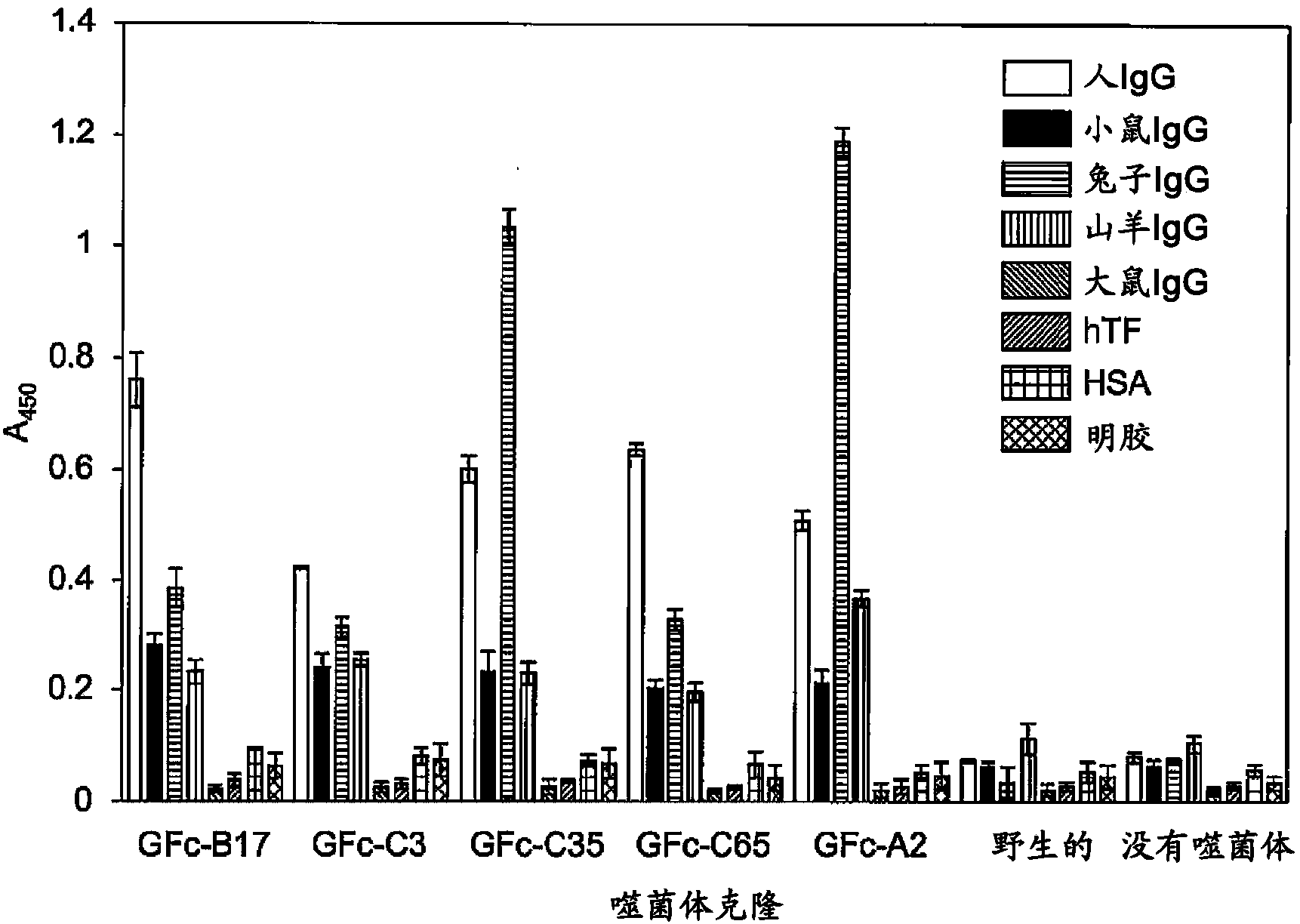
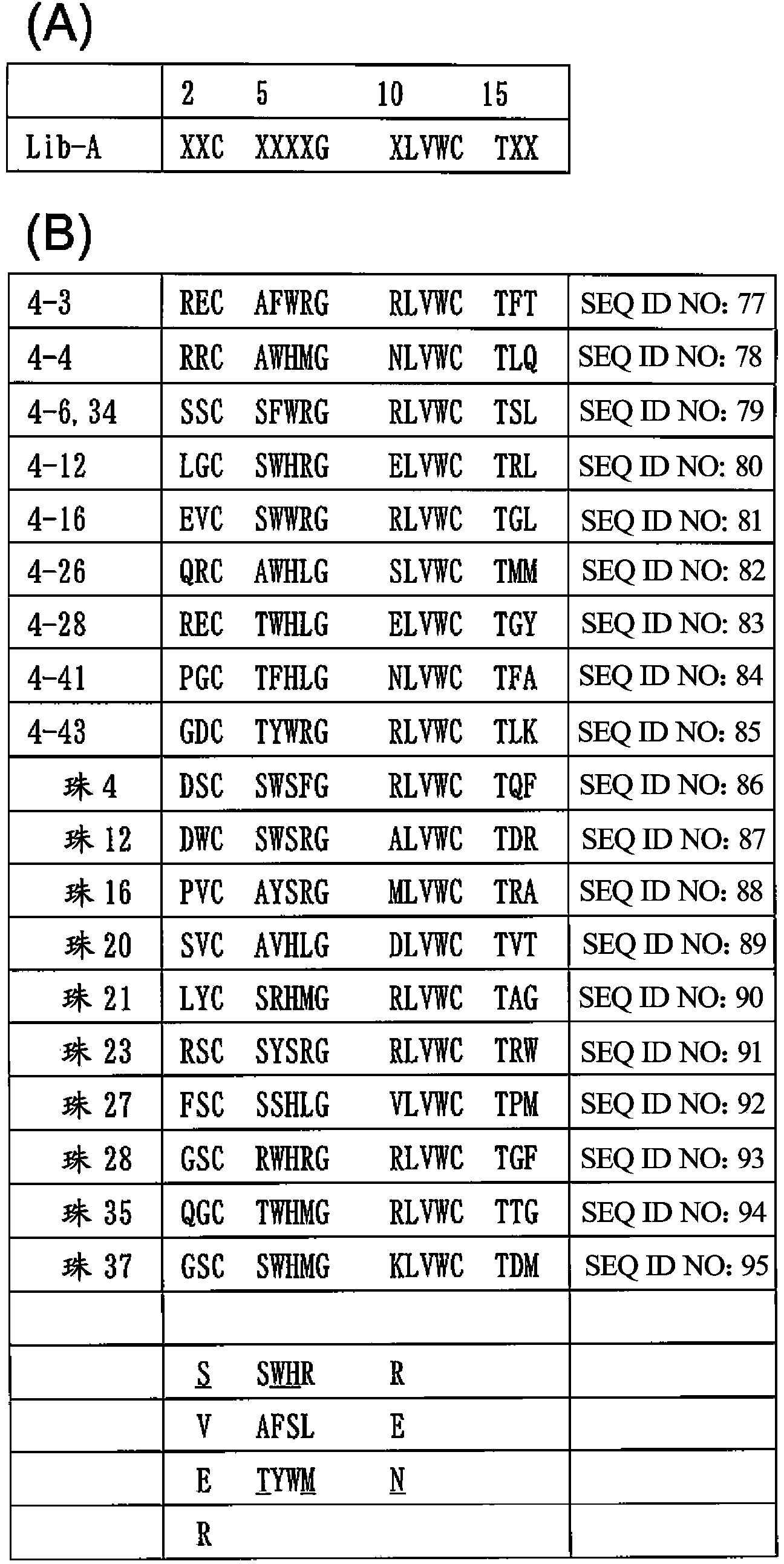
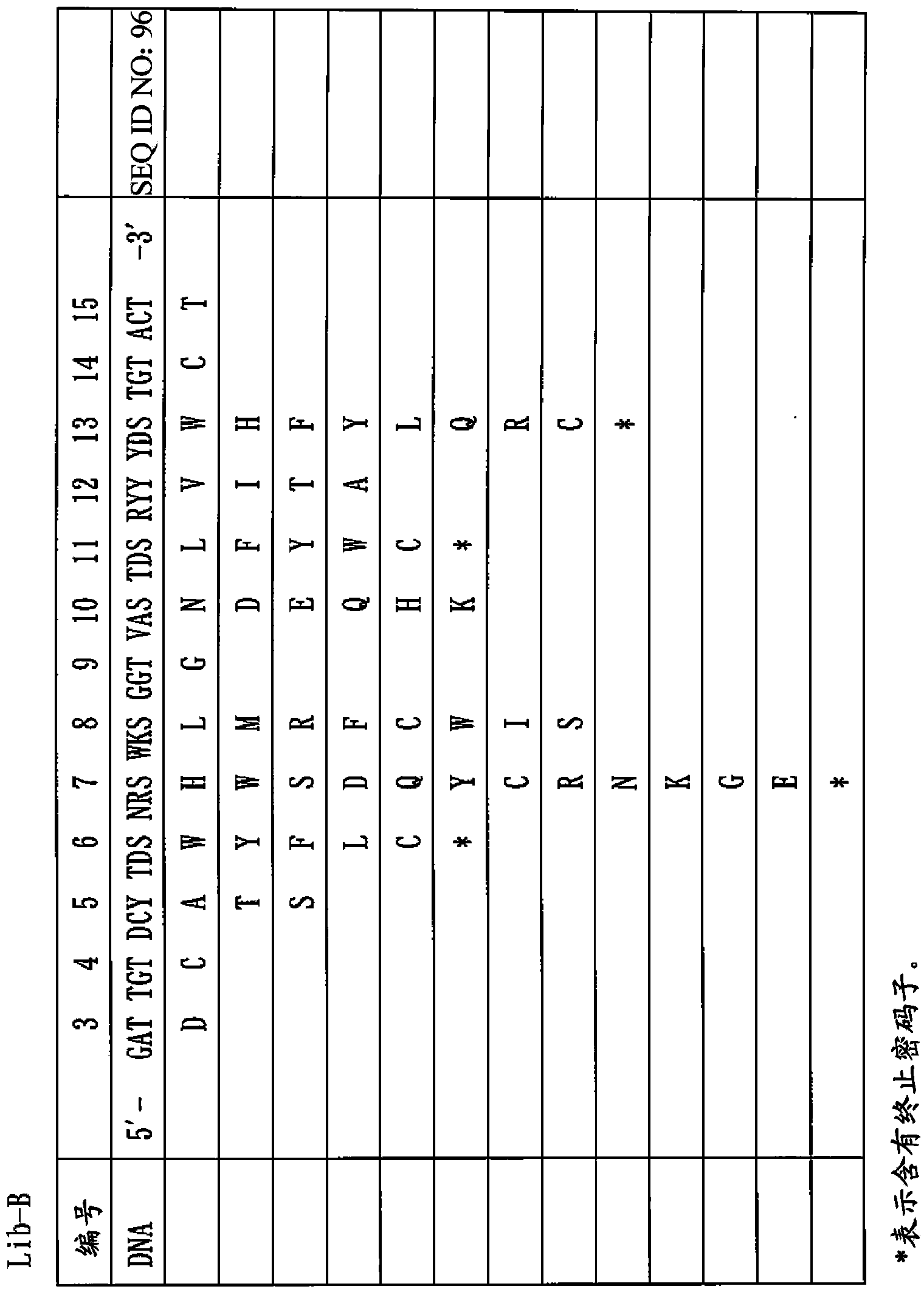
Provided is a peptide capable of binding to human IgG specifically or selectively. A peptide characterized by comprising an amino acid sequence represented by formula (I): (X1-3)-C-(X2)-H-R-G-(Xaa1)-L-V-W-C-(X1-3) (wherein Xs independently represent an arbitrary amino acid residue other than a cysteine residue; C represents a cysteine residue; H represents a histidine residue; R represents an arginine residue; G represents a glycine residue; Xaa1 represents a glutamic acid residue or an asparagine residue; L represents a leucine residue; V represents a valine residue; and W represents a tryptophan residue) and composed of 13-17 amino acid residues, and also characterized by being capable of binding to human IgG.
Owner:OTSUKA CHEM CO LTD +1
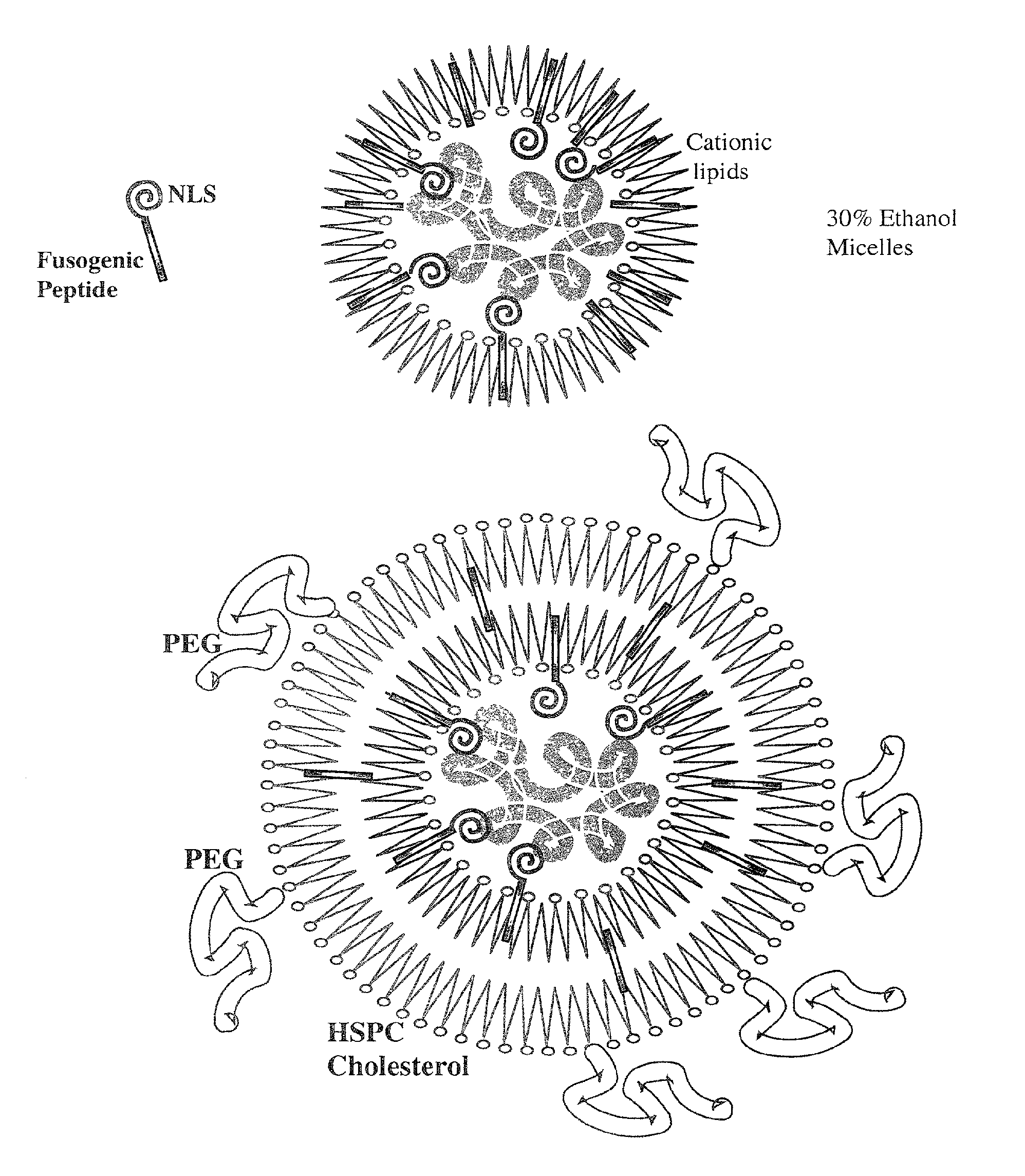
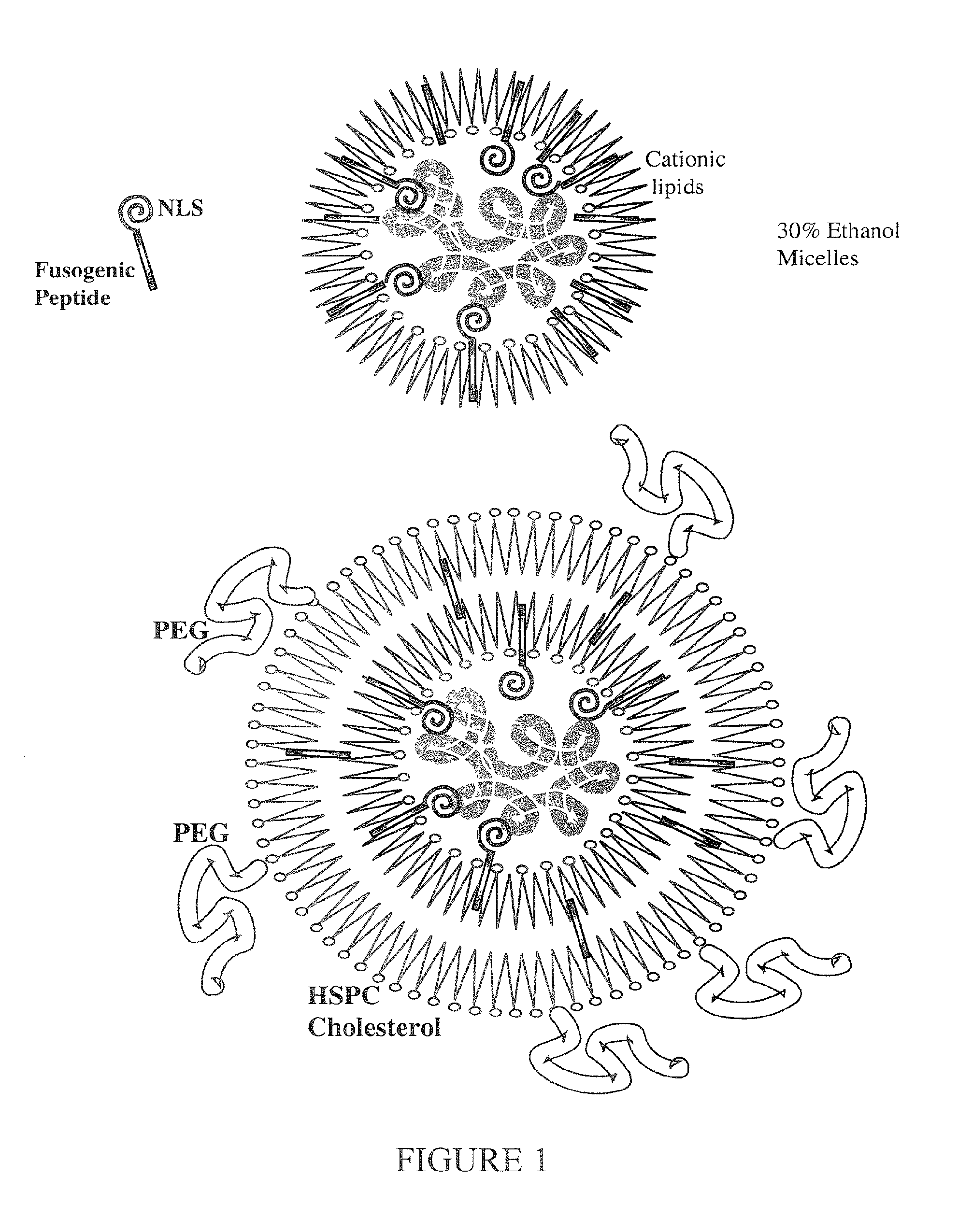
Encapsulation of Plasmid DNA (Lipogenes) and Therapeutic Agents with Nuclear Localization Signal/Fusogenic Peptide Conjugates into Targeted Liposome Complexes
InactiveUS20120183596A1Increase the entranceHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorNucleotide
A method is disclosed for encapsulating plasmids, oligonucleotides or negatively-charged drugs into liposomes having a different lipid composition between their inner and outer membrane bilayers and able to reach primary tumors and their metastases after intravenous injection to animals and humans. The formulation method includes complex formation between DNA with cationic lipid molecules and fusogenic / NLS peptide conjugates composed of a hydrophobic chain of about 10-20 amino acids and also containing four or more histidine residues or NLS at their one end. The encapsulated molecules display therapeutic efficacy in eradicating a variety of solid human tumors including but not limited to breast carcinoma and prostate carcinoma. Combination of the plasmids, oligonucleotides or negatively-charged drugs with other anti-neoplastic drugs (the positively-charged cis-platin, doxorubicin) encapsulated into liposomes are of therapeutic value. Also of therapeutic value in cancer eradication are combinations of encapsulated the plasmids, oligonucleotides or negatively-charged drugs with HSV-tk plus encapsulated ganciclovir.
Owner:REGULON
Mutated protein of protein a having reduced affinity in acidic region and antibody-capturing agent
ActiveUS20140179898A1Reduced ability to bindEasy to eluteBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsMutated proteinProteome
A modified protein of an extracellular domain of protein A, which has the reduced ability to bind to immunoglobulin in an acidic region, compared with the wild-type extracellular domain of protein A, without impairing a selective antibody-binding activity in a neutral region. On the basis of three-dimensional structure coordinate data on a complex of the extracellular domain of protein A bound with the Fc region of immunoglobulin G, the modified protein is obtained by the substitution of amino acid residues that are located within the range of 10 angstroms from the Fc region and have a 20% or more ratio of exposed surface area, by histidine residues. Preferably, the modified protein is obtained by the substitution of amino acid residues at sites identified from the analysis of sequences selected from a library constituted by the protein group, by histidine residues. These substitutions may be combined.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Trivalent iron porphrin and its derivative-short peptide compound and its synthesis
A trivalent iron-porphyrin and its derivative-short peptide compound and its synthesizing process are disclosed. Said compound is composed of heme or subheme and short peptide, and is prepared from heme or subheme and amino acid derivative as raw materials and dimethyl formamide as solvent through swelling, removing protecting, coupling, cyclic removing protecting and coupling, coupling heme or subheme and severing. Its advantages are high antioxidizing activity and the activity of peroxidase, high purity and low toxin.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Application of tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide
InactiveCN102174078AEfficient combinationImprove bindingPeptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsArginineCell selectivity
The invention belongs to the field of the membrane penetrating peptide and particularly relates to a tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide and application thereof. The sequence of the tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide comprises a basic amino acid cluster which is composed of 5 to 12 consecutive arginine residues. The tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide is characterized in that the C or N end of the basic amino acid cluster is connected with three histidine residues. The tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide has cell membrane penetration capacity, can distinguish tumor cells and normal tissue cells and can efficiently penetrate through the tumor cell membrane without penetrating through the normal tissue cell membrane basically.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
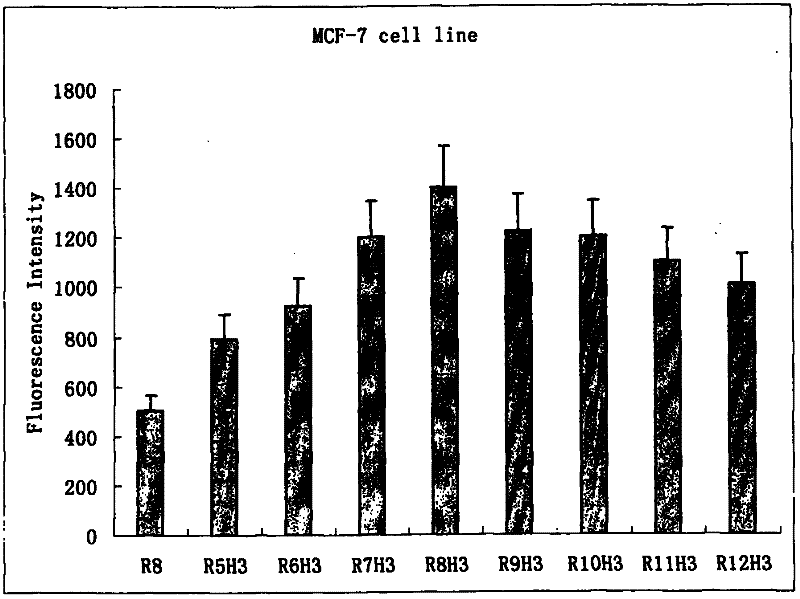
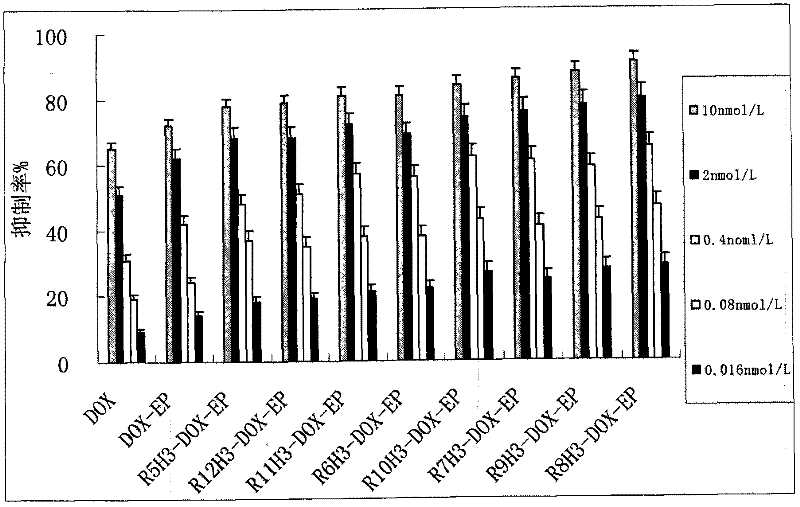
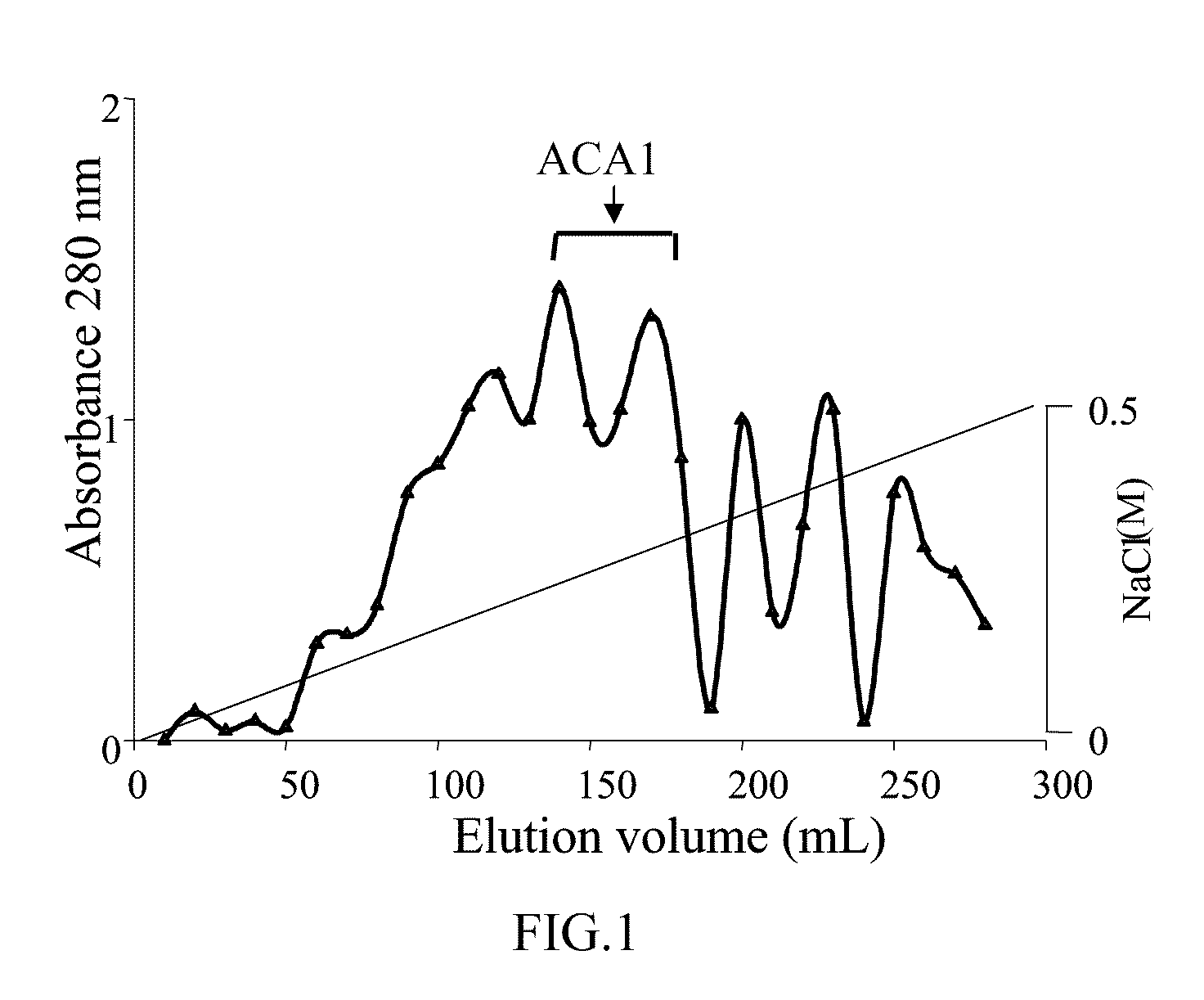
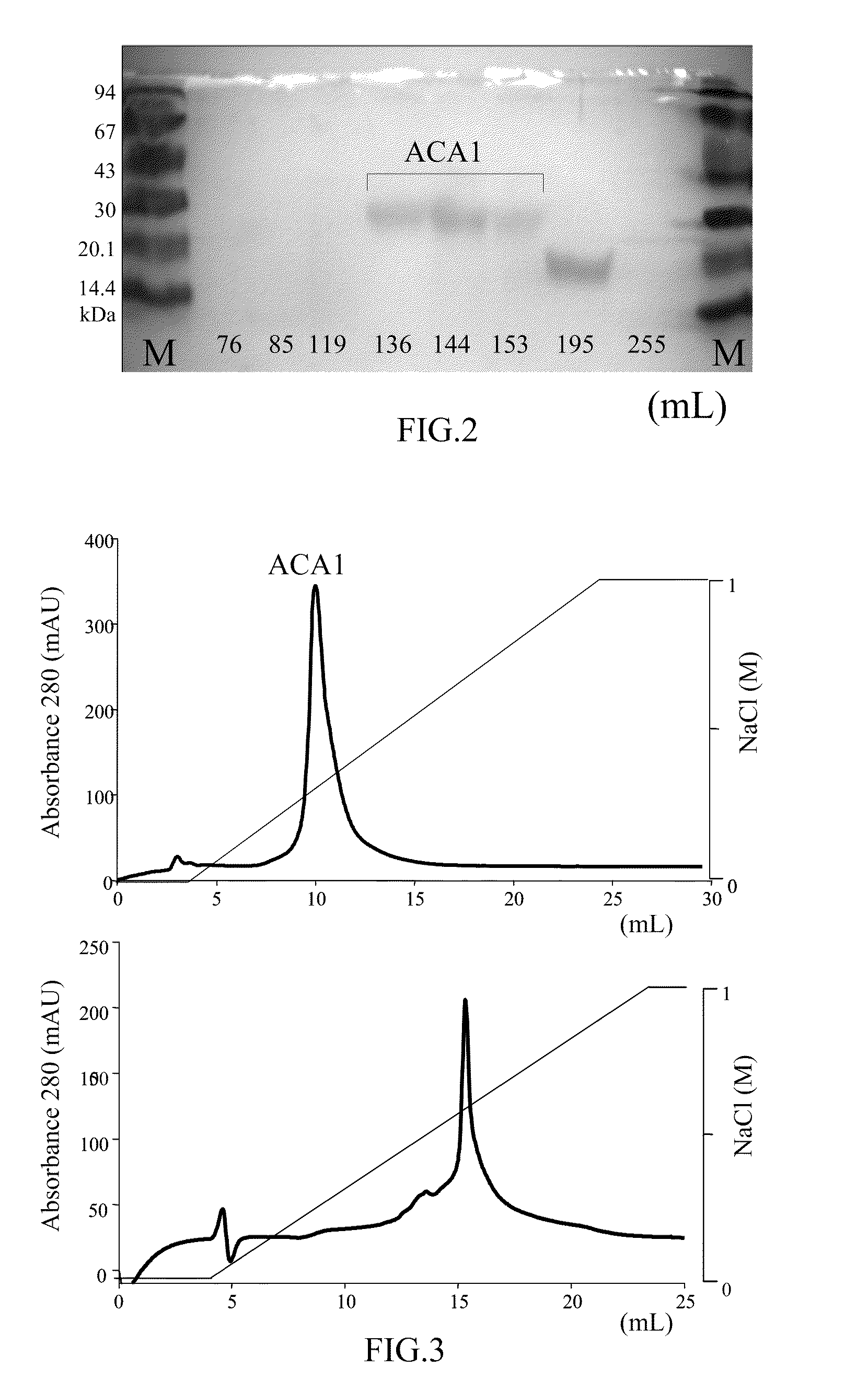
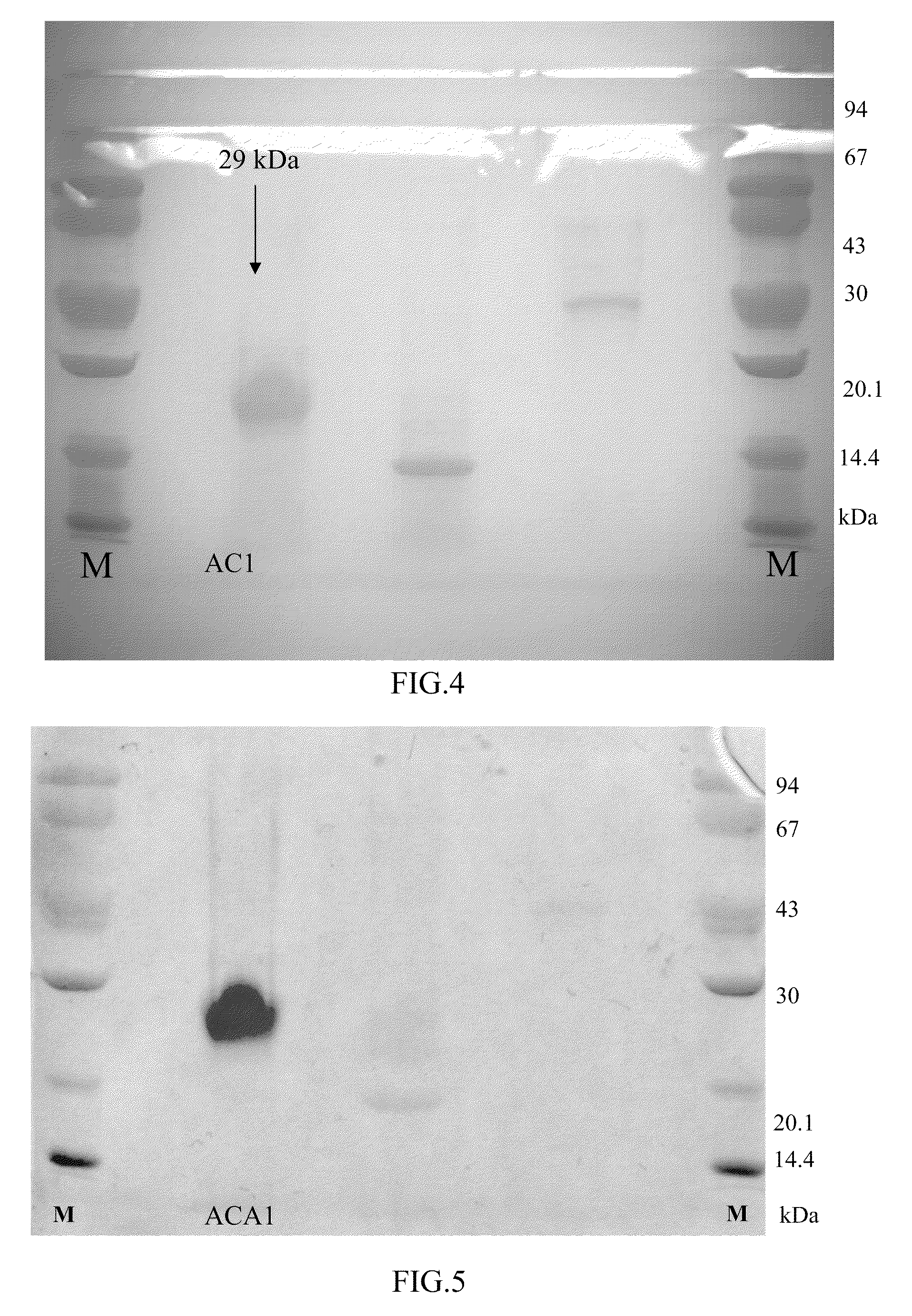
Protein ACA1 of Antrodia camphorata
InactiveUS7531627B2Increase productionInduced proliferationSugar derivativesSaccharide peptide ingredientsRed blood cellTumor necrosis factor alpha
A new protein, named ACA1, has been isolated and purified from the medical fungi Antrodia camphorata using the technique of anion-exchange chromatography. ACA1, a glycoprotein with a molecular mass of 29 kDa, has a pI value of pH 5.3 and contains 118 amino acids in its peptide moiety. In addition, ACA1 contains methionine, half-cystine and histidine residues, which are not existent in FIP-fve and Ling Zhi-8. ACA1 is not able to agglutinate red blood cells from human and mouse. Moreover, ACA1 possesses immunomodulatory activities, which are demonstrated by their stimulatory activity toward RAW 264.7 macrophages and mouse splenocytes. ACA1 can directly enhance the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and nitric oxide by RAW 264.7 macrophages, and induce cell proliferation and interferon-gamma secretion by mouse splenocytes.
Owner:CHIEN PO JUNG
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Novel compounds, use thereof in cosmetic and cosmeceutic applications, and compositions comprising same
ActiveUS20100311667A1Increase productionPreventing, reducing, delaying or treating a skin conditionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycineHydrogen
A compound of the formula I: R-A-Gly-His-B (I) wherein: A and B are independently of each other a L-lysine residue, a D-lysine residue, or a L- or D-lysine residue in which the NH2 group of the side chain comprises a modification, where-in said modification is (i) a replacement with a hydrogen, (ii) an acetylation, (iii) a benzoylation, or (iv) a palmitoylation; GIy is a glycine residue; His is a L- or D-histidine residue; R is CH3—(CH2)n—CO—, wherein n=2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 or 8; R′ is a group of formula (II): N(Z)(Z′) (II) wherein: Z and Z′ is hydrogen, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a phenyl group, an hexyl group, a decyl group or an hexadecyl group; or a racemate, an enantiomer or a diastereomer thereof, or mixtures thereof, or a salt thereof.
Owner:LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS CANADA
Escherichia coli strain secreting human granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)
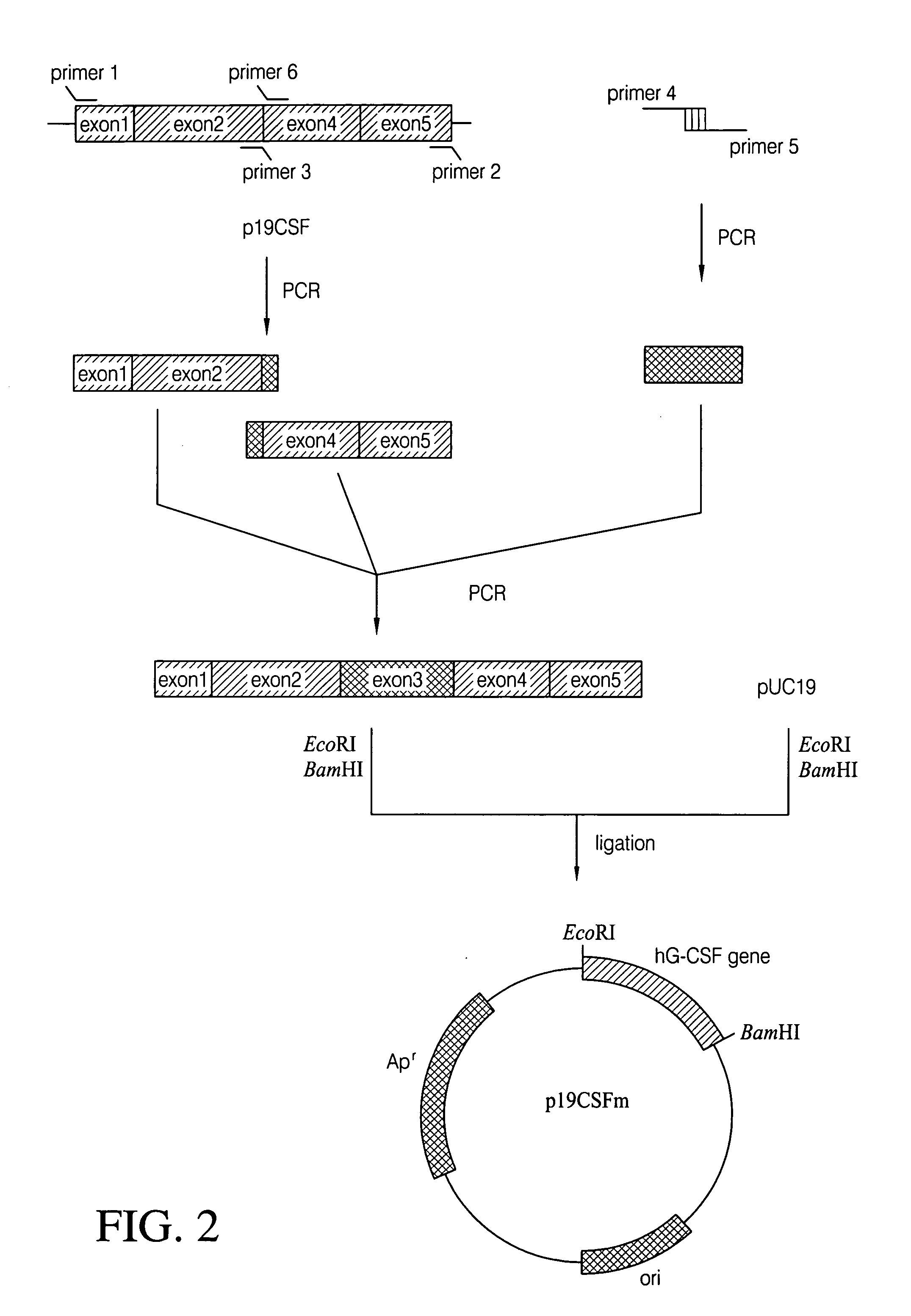
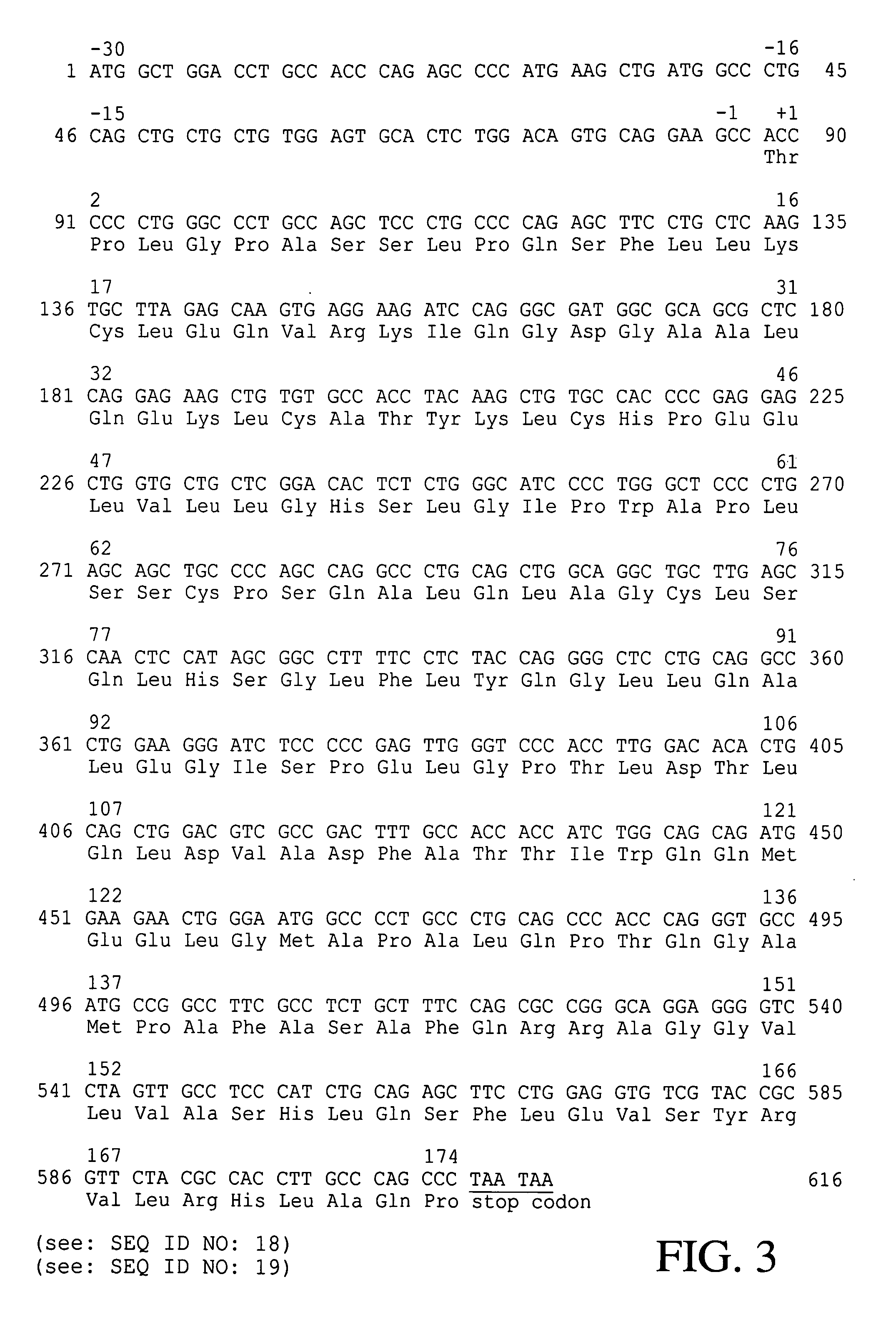
The present invention provides a recombinant plasmid vector comprising a kanamycin resistance gene, a promoter, an endoxylanase signal sequence, a nucleotide sequence coding for an oligopeptide consisting of 13 amino acids including 6 consecutive histidine residues, and a human granulocyte colony stimulating factor(hG-CSF) gene; an E. coli transformed with the said vector; and, a process for producing complete hG-CSF protein with high purity from the protein pool secreted by the said microorganism. In accordance with the invention, the hG-CSF protein can be prepared with high purity through rather simple process facilitating secretion of large amount of hG-CSF fusion protein into the periplasm, which does not require complicated processes such as solubilization and subsequent refolding required for isolation of the hG-CSF protein produced in cytoplasm as insoluble inclusion bodies by conventional techniques, thus, the hG-CSF protein can be widely used as an active ingredient in the development of supplementary agents for anticancer therapy.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Novel peptides, use thereof in cosmetic and cosmeceutic applications, and compositions comprising same
InactiveUS20100310484A1Preventing and delaying and reducing and treating effect of agingCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticEnantiomerSide chain
A peptide of formula I (SEQ ID NO: 1): Lip-A-Gly-His-B-R (I) wherein: Lip is a lipoyl residue of R or S configuration; A is absent or is a lysine residue of configuration L or D; GIy is a glycine residue; His is a histidine residue of configuration L or D; B is a lysine residue of configuration L or D, or a lysine residue of configuration L or D in which the NH2 group of the side chain comprises a modification, wherein said modification is (i) a replacement with a hydrogen or (ii) a modification with a protecting group selected from the group consisting of acetyl, benzoyl, tosyl, sulfonyl benzene, benzyloxycarbonyle and palmitoyl; wherein R is O(Z) or N(Z′)(Z′), and wherein Z, Z′ and Z′ are independently of each other a hydrogen or a protecting group selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, propyl, phenyl, hexyl, decyl and hexadecyl, or a racemate, an enantiomer or a diastereomer thereof, or a mixture thereof, or a salt thereof. A peptide of formula II (SEQ ID NO: 2): Lip-A-His-B-C-Trp-R (II) wherein: Lip is a lipoyl residue of configuration R or S; His is a histidine residue of configuration L; Trp is a tryptophane residue of configuration L; A is absent, is an amino acid residue of configuration L or D selected from the group consisting of a lysine residue, an alanine residue, a glutamic acid residue and a glycine residue, or is a spacer of formula: NH—(CH2)n-CO— wherein n is an integer comprised between 2 and 14; B is an aromatic amino acid residue of configuration D selected from the group consisting of a phenylalanine residue, a homophenylalanine residue, a tryptophane residue, a β-(1-Naphthyl)-alanine residue, a β-(2-Naphthyl)-alanine residue and a phenylglycine residue; C is a basic amino acid residue of configuration L selected from the group consisting of an arginine residue, a lysine residue, an ornithine residue and a homoarginine residue; wherein R is O(Z) or N(Z′)(Z′),
Owner:LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS CANADA
Site-specific labeling of affinity peptides in fusion proteins
InactiveUS20090004641A1Fast dynamicsRapid time periodMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationAcetic acidCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention provides methods and fluorescent compounds that facilitate detecting and labeling of a fusion protein by being capable of selectively binding to an affinity tag. The fluorescent compounds have the general formula A(B)n, wherein A is a fluorophore, B is a binding domain that is a charged chemical moiety, a protein or fragment thereof and n is an integer from 1-6 with the proviso that the protein or fragment thereof not be an antibody or generated from an antibody. The present invention provides specific fluorescent compounds and methods used to detect and label fusion proteins that contain a poly-histidine affinity tag. These compounds have the general formula A(L)m(B)n wherein A is a fluorophore, L is a linker, B is an acetic acid binding domain, m is an integer from 1 to 4 and n is an integer from 1 to 6. The acetic acid groups interact directly with the positively charged histidine residues of the affinity tag to effectively label and detect a fusion protein containing such an affinity tag when present in an acidic or neutral environment.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Compounds, use thereof in cosmetic and cosmeceutic applications, and compositions comprising same
ActiveUS9115176B2Preventing, reducing, delaying or treating a skin conditionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEnantiomerDiastereomer
Owner:LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS CANADA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com