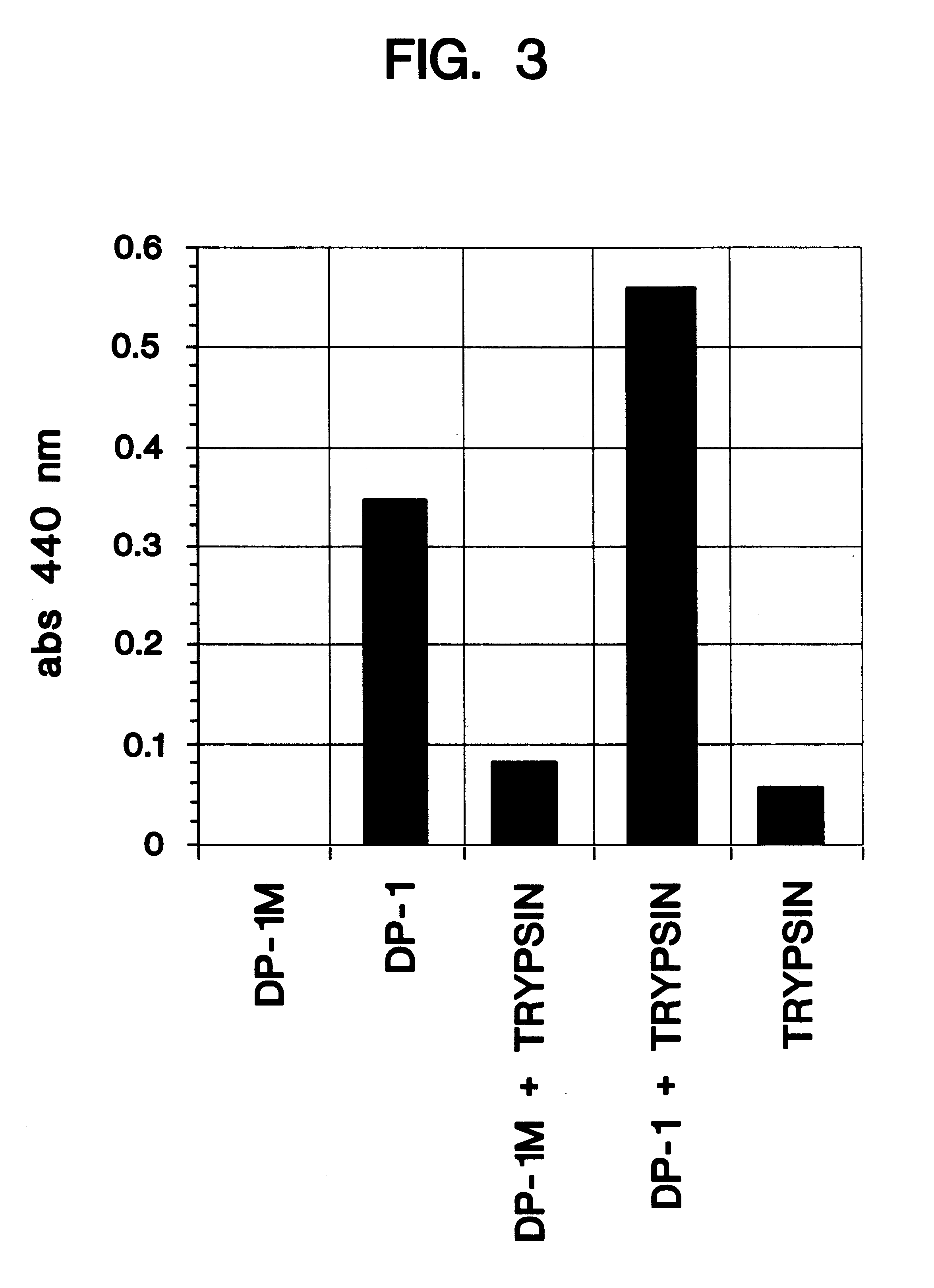
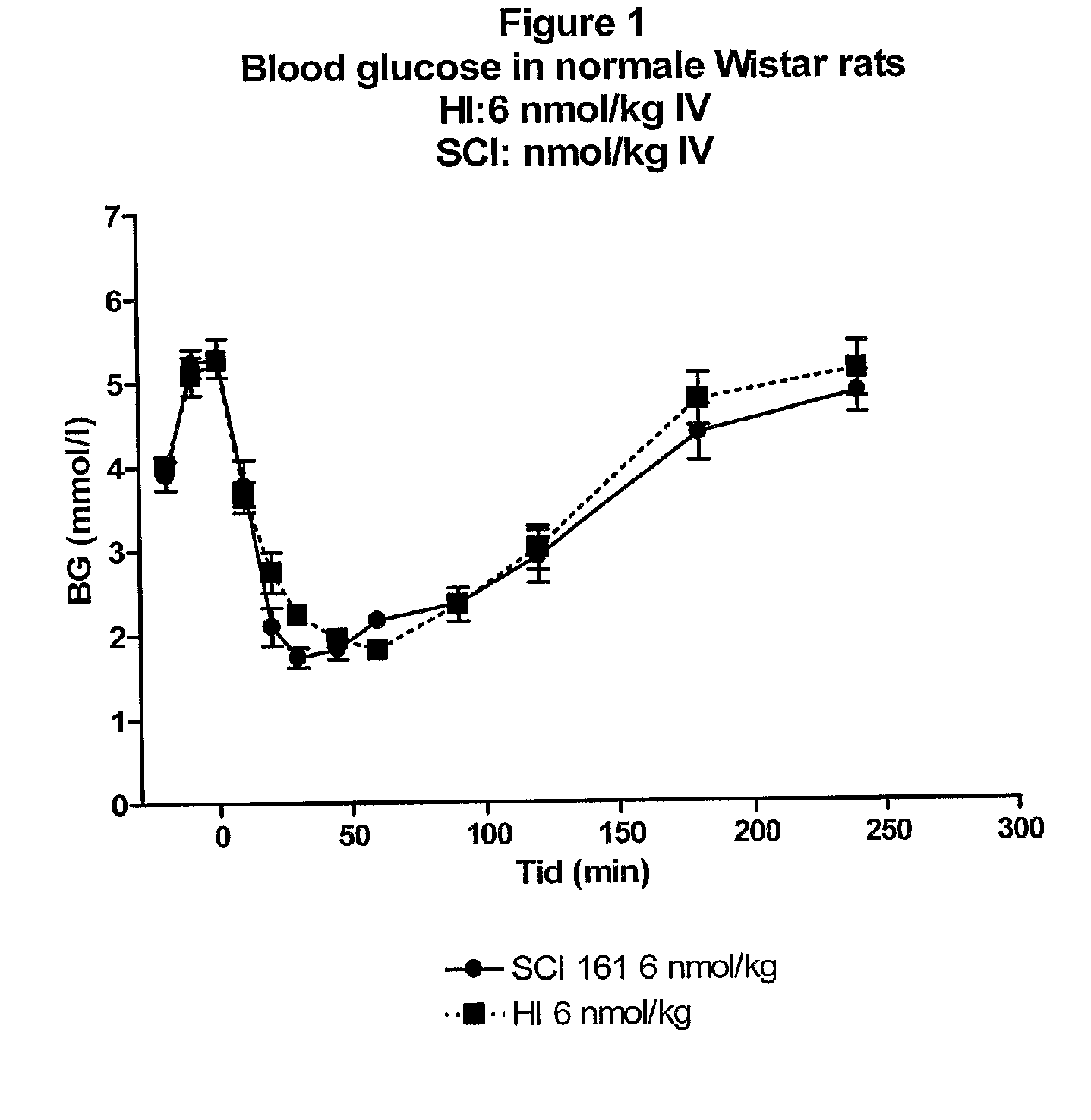
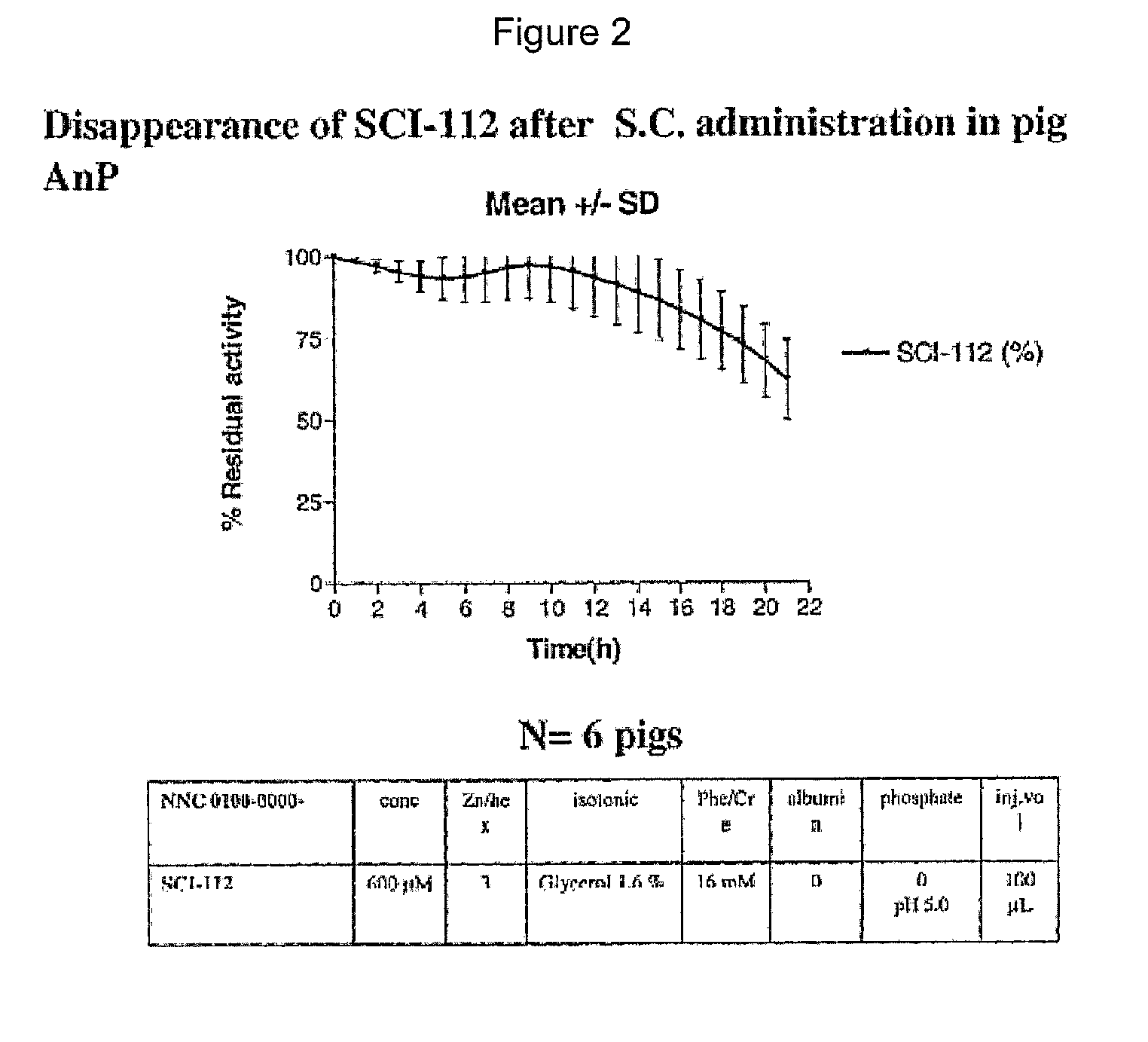
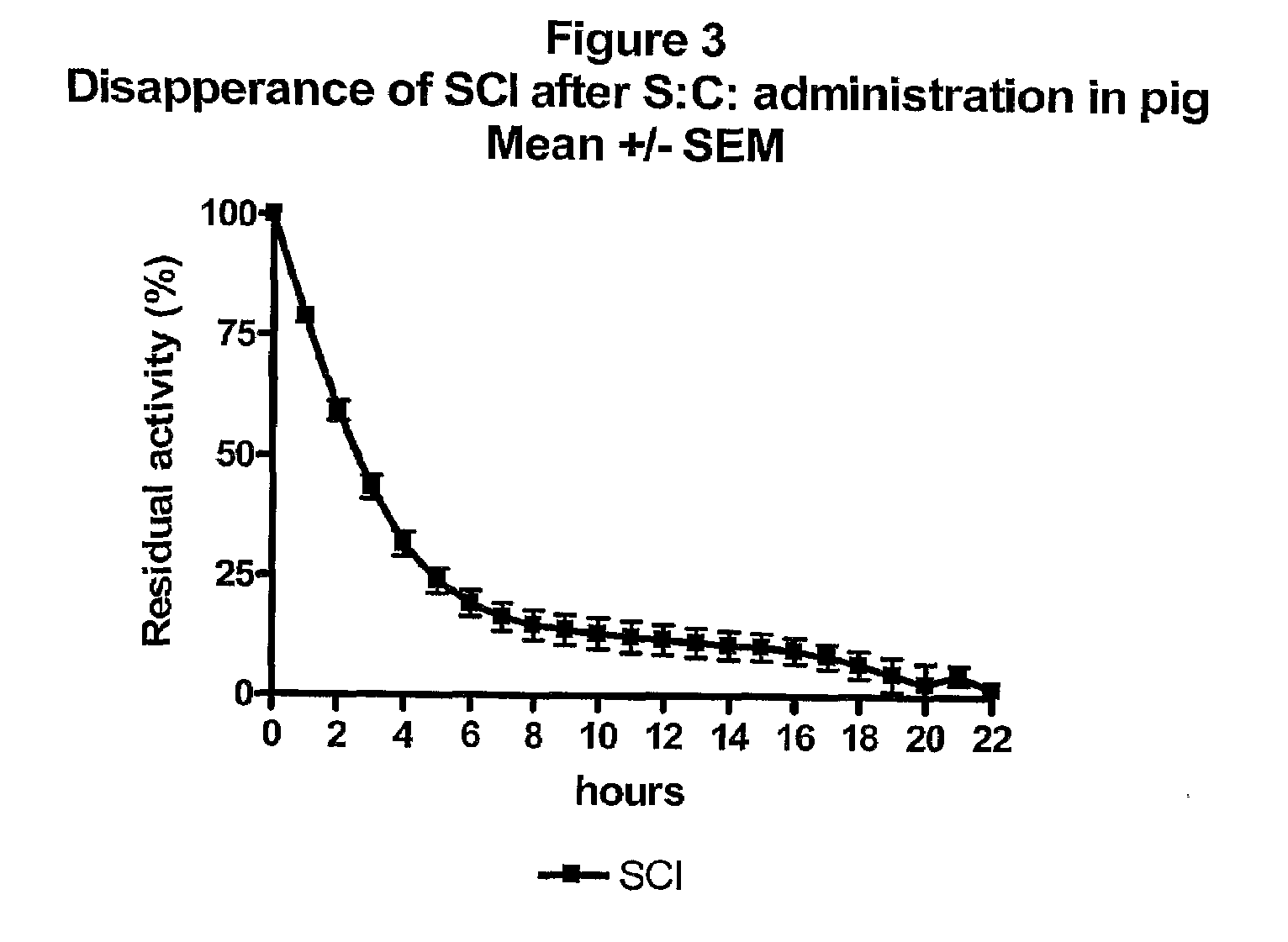
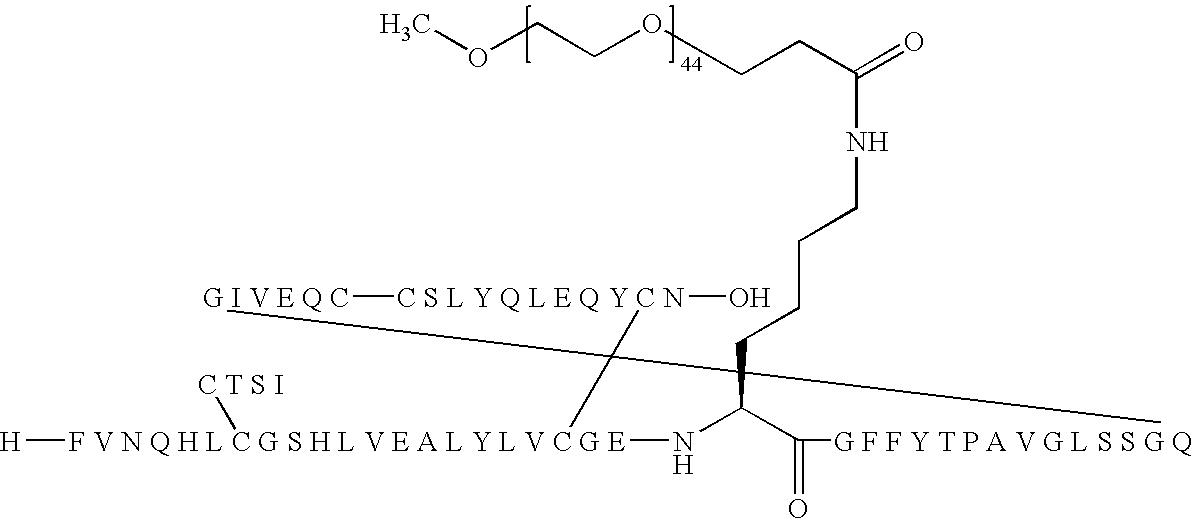
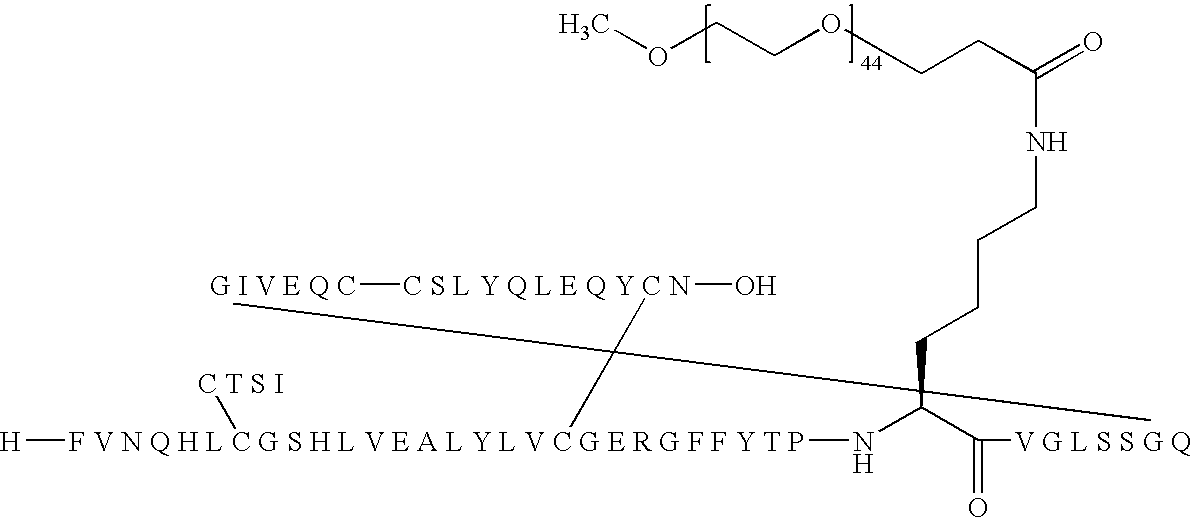
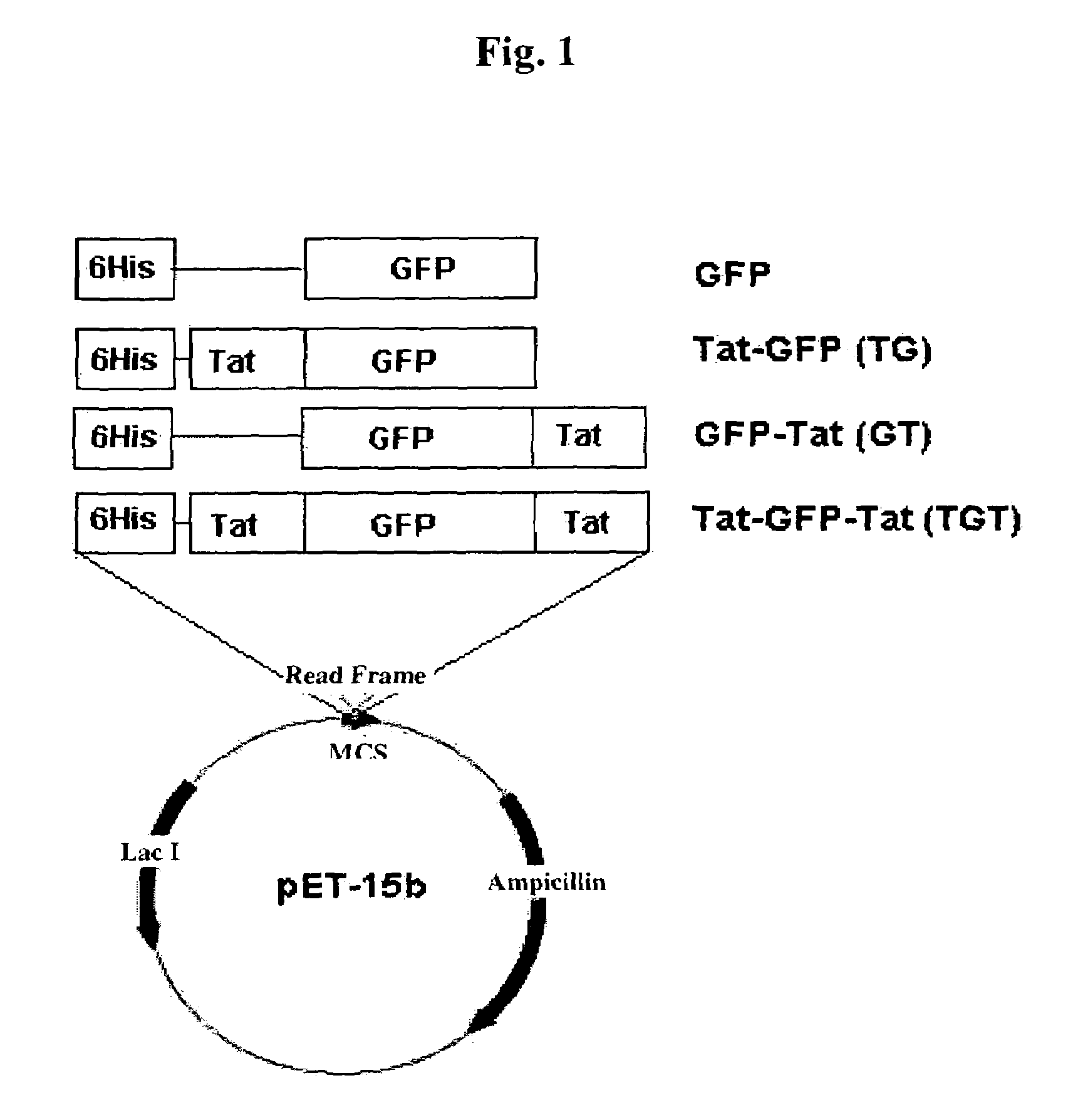
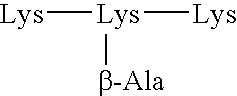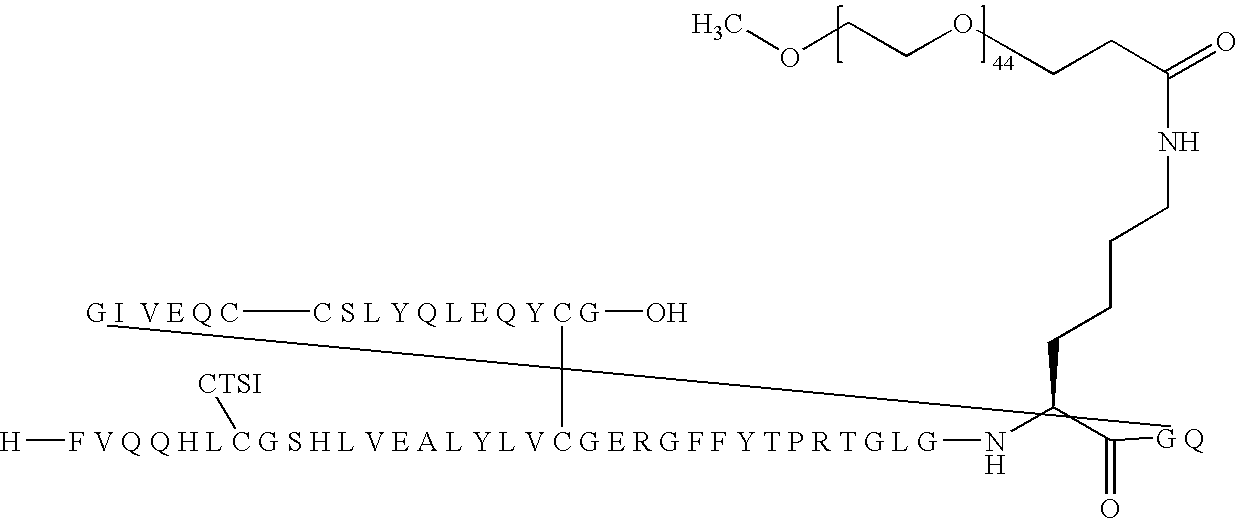Patents
Literature
251 results about "Lysine residue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
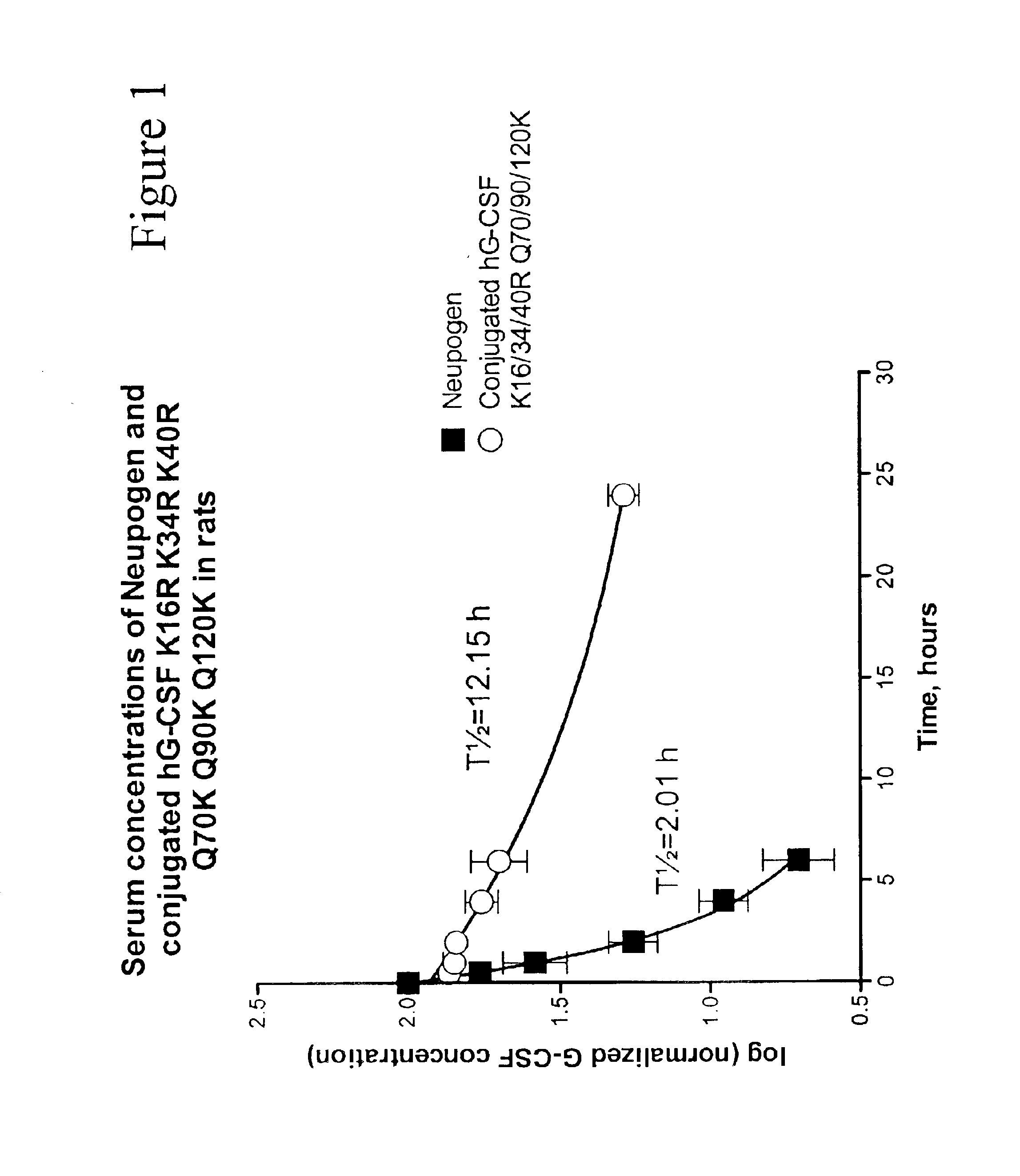
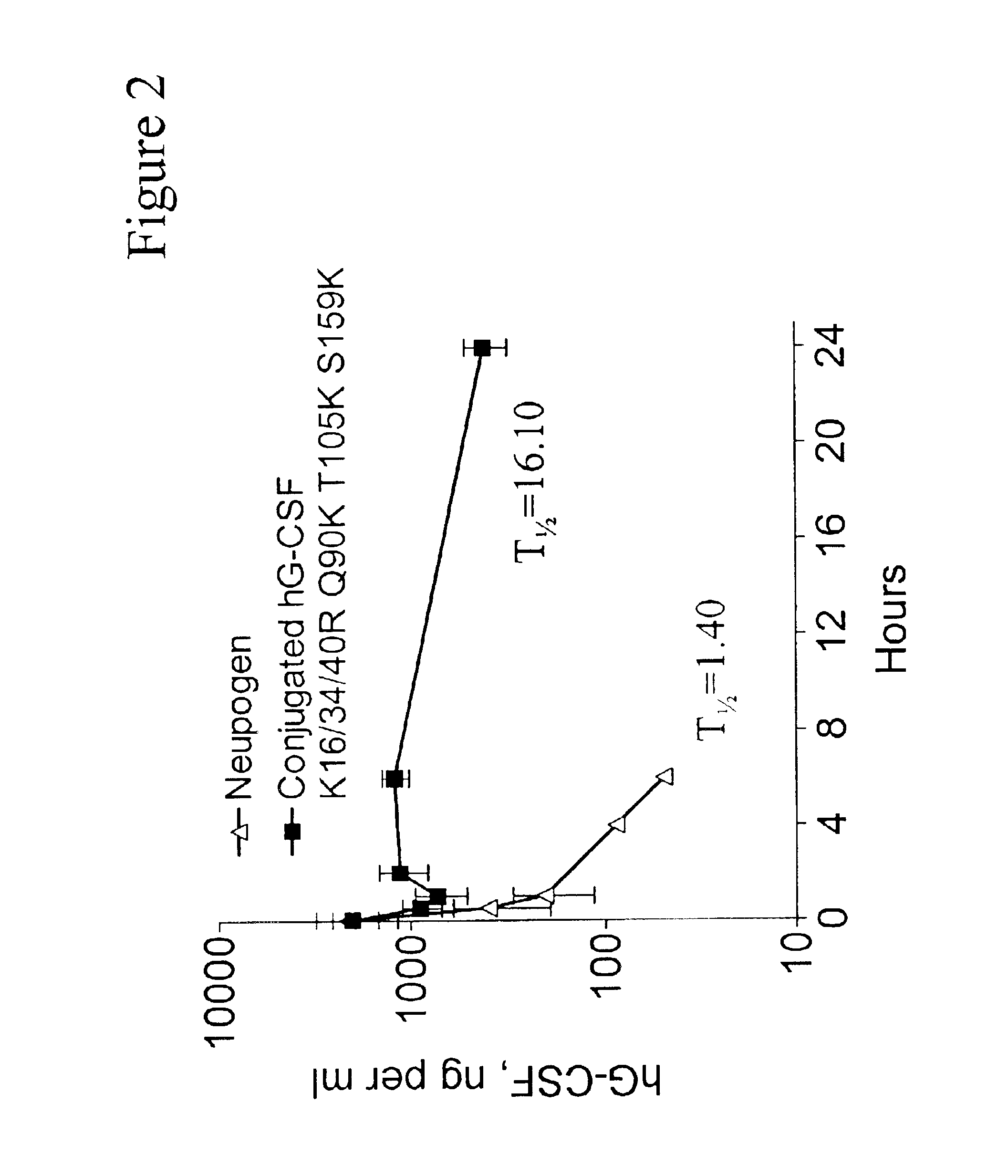
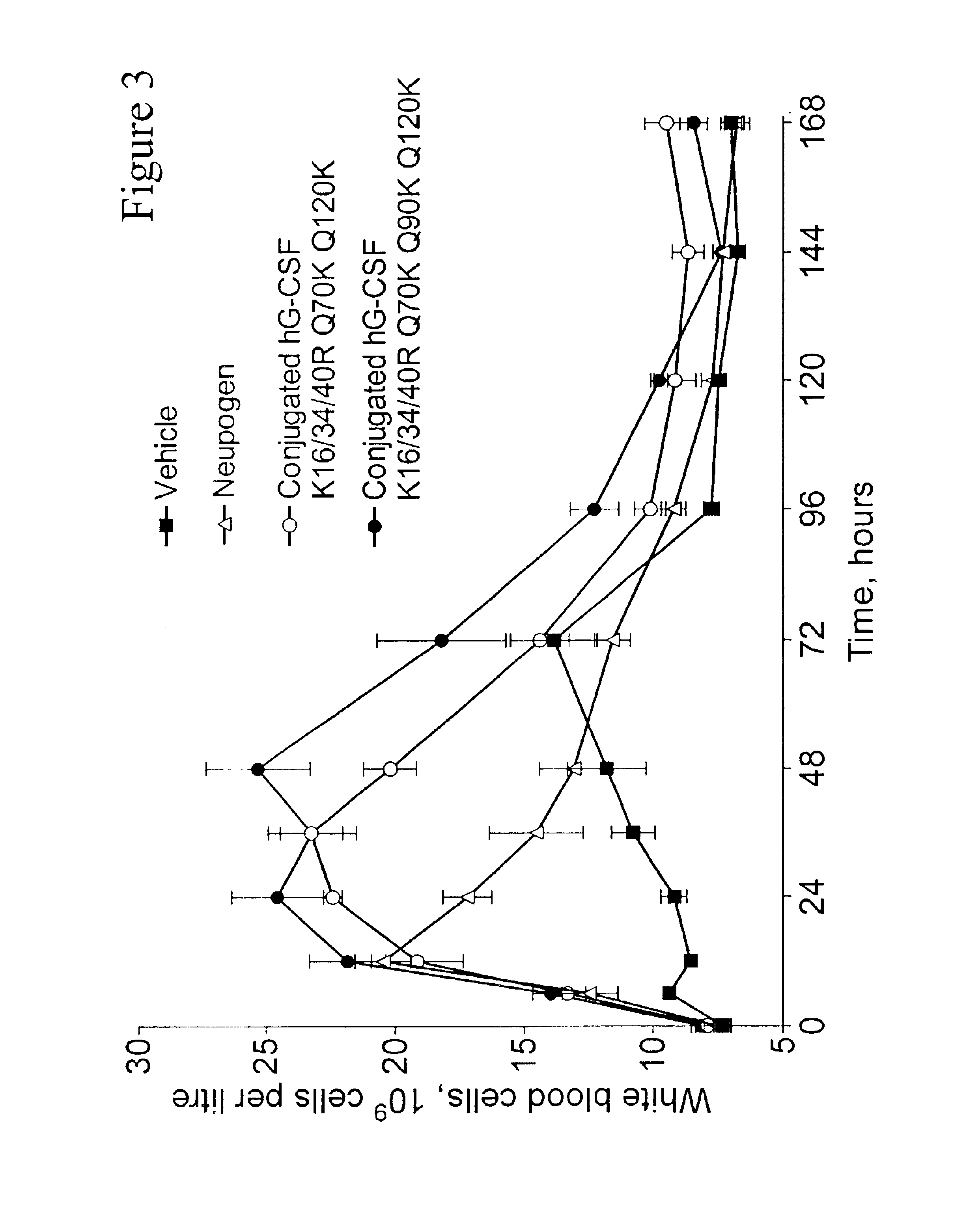
G-CSF conjugates
InactiveUS6831158B2Improved propertyDecrease of bioactivityPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWhite blood cellHalf-life
Owner:MAXYGEN
Protein Hydrolysate Compositions Having Improved Sensory Characteristics and Physical Properties
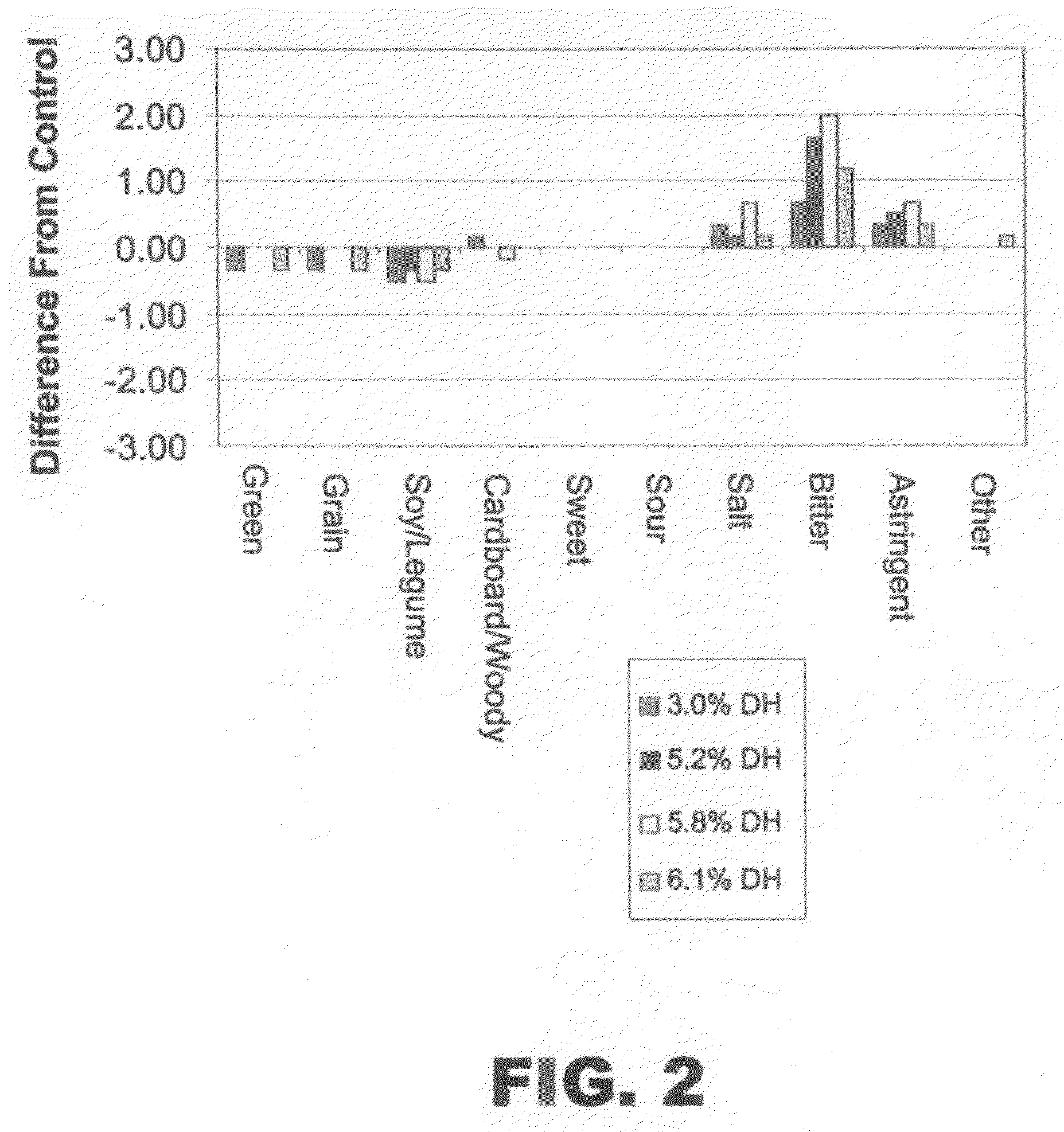
InactiveUS20080305212A1Fatty substance preservation using additivesCocoaArginineProtein hydrolysates
The present invention provides protein hydrolysate compositions, processes for making protein hydrolysate compositions, and food products comprising protein hydrolysate compositions. The protein hydrolysate compositions generally comprise polypeptide fragments having primarily either an arginine residue or a lysine residue at each carboxyl terminus.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
System and method for identifying complex patterns of amino acids
A method and system are disclosed for identifying and / or locating complex patterns in an amino acid sequence stored in a computer file or database. According to an aspect of the present invention, techniques are provided to facilitate queries of protein databases. For protein descriptions received in response to the queries, embodiments of the present invention may scan the received protein descriptions to identify and locate Replikin patterns. A Replikin pattern is defined to be a sequence of 7 to about 50 amino acids that include the following three (3) characteristics, each of which may be recognized by an embodiment of the present invention: (1) the sequence has at least one lysine residue located six to ten amino acid residues from a second lysine residue; (2) the sequence has at least one histidine residue; and (3) at least 6% of the amino acids in the sequence are lysine residues.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +3
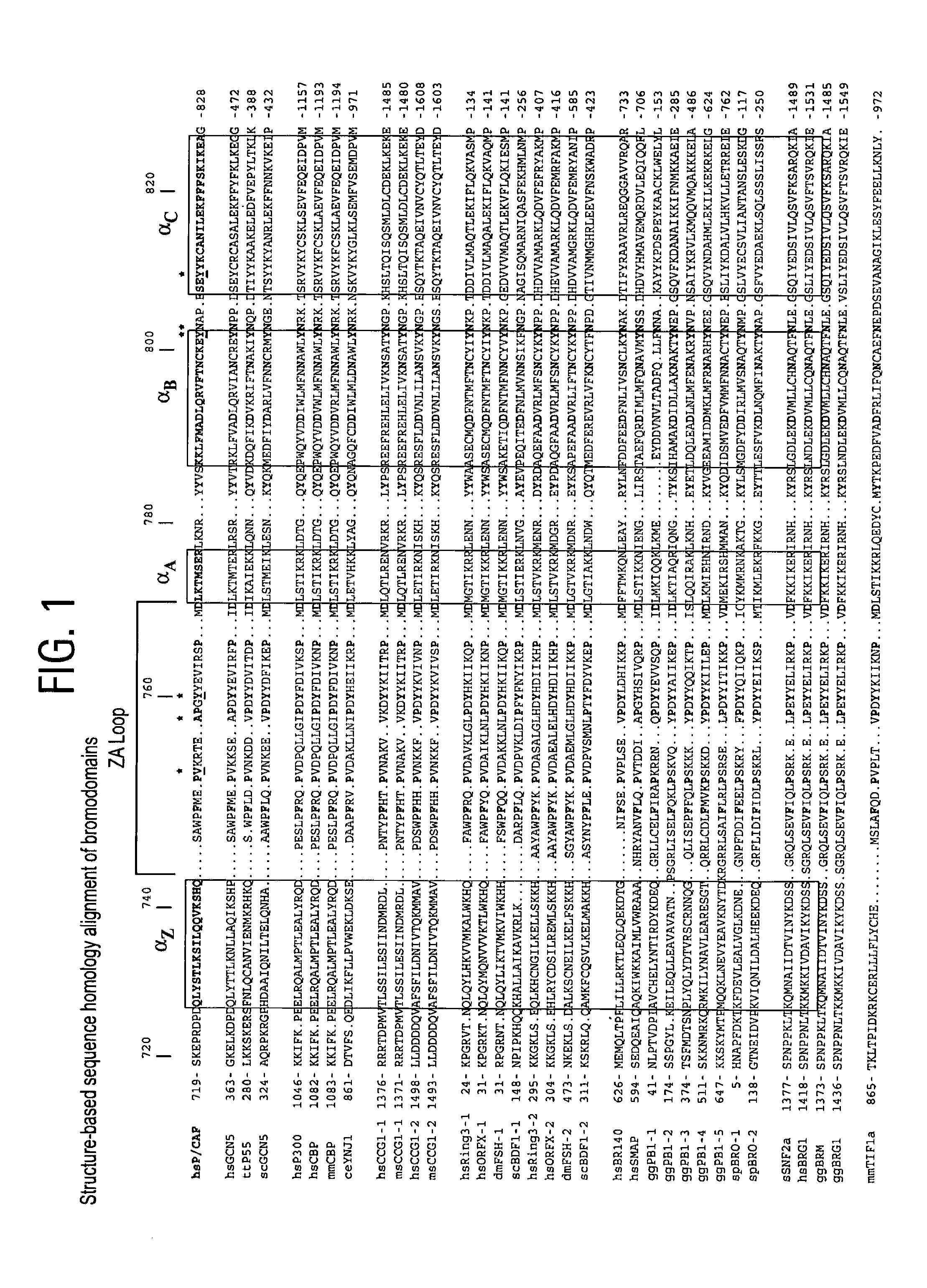
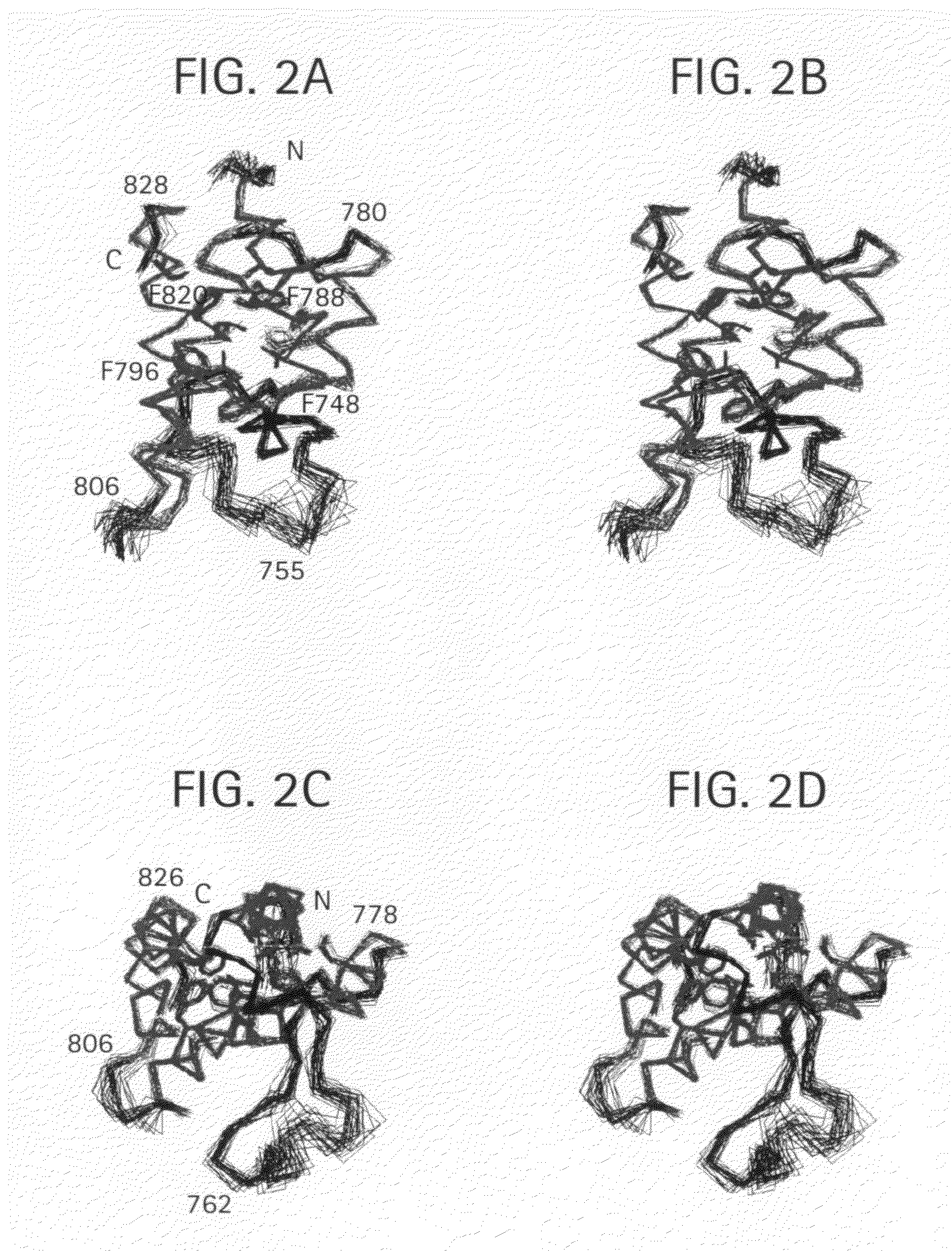
Methods of modulating bromodomains
InactiveUS20120028912A1Inhibit binding/formationInhibit bindingBiocideDispersion deliveryDiseaseBromodomain
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS +1
Non-naturally occurring synthetic lytic peptides
InactiveUS6559281B1Improve the immunityImprove stabilityPeptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsLytic peptideCrystallography
Non-naturally occurring lytic peptides which contain a phenylalanine residue and one or more alanine, valine and lysine residues, and optionally contain chemically masked cysteine or serine residues possess an amphipathic structure which allows them to promote cell lysis in certain pathologic organisms, and particularly in prokaryotes. Peptides having a beta-pleated sheet secondary structure and lacking cysteine residues form one embodiment of these lytic peptides.
Owner:DEMEGEN
Single-Chain Insulin
InactiveUS20090170750A1Lower blood sugar levelsSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin activityPhysical stability
The present invention is related to single-chain insulin having insulin activity comprising a B- and an A-chain or a modified B- and A-chain connected by a connecting peptide of from 6-11 amino acids. The single-chain insulins will have biological insulin activity and an IGF-1 receptor affinity similar to or lower than that of human insulin and a high physical stability. The single-chain insulin may contain at least one basic amino acid residues in the connecting peptide. The single-chain insulins may also be acylated in one or more Lys residues.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
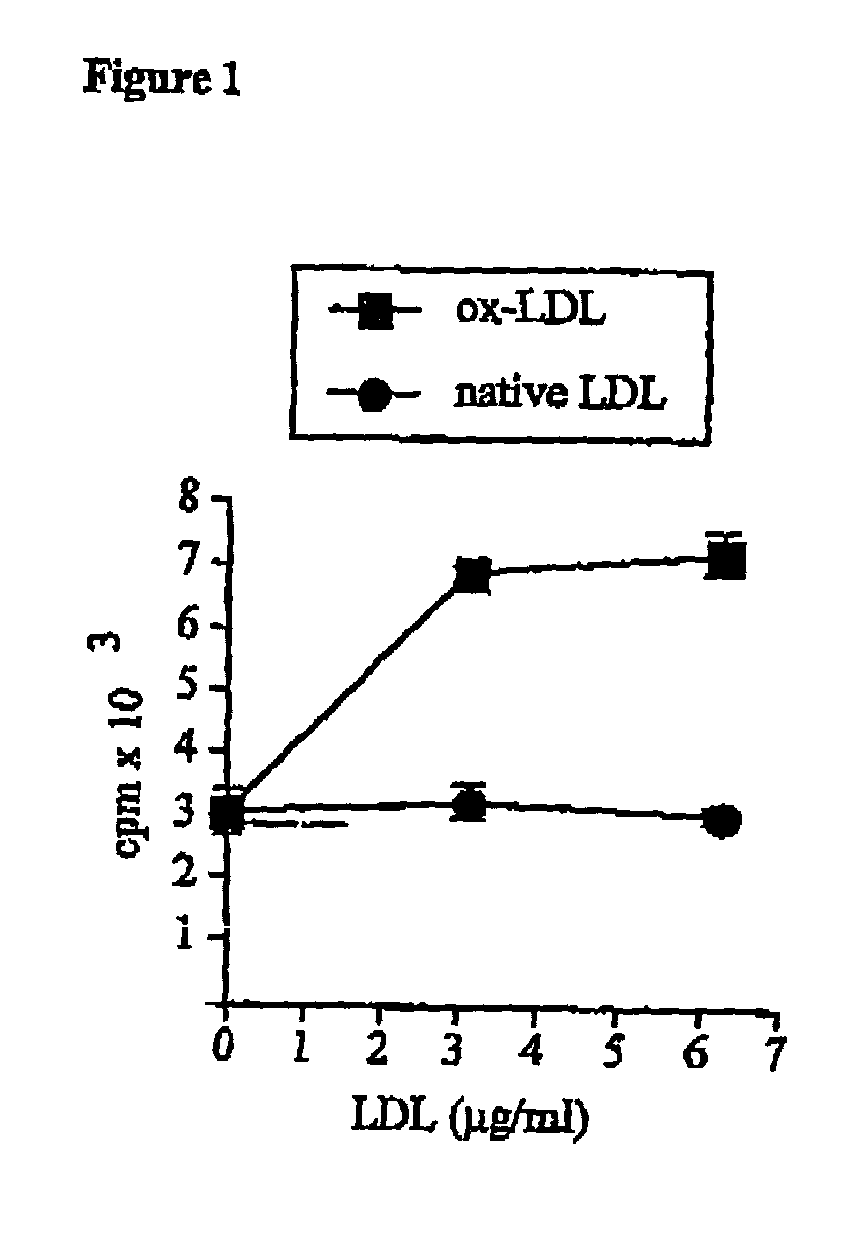
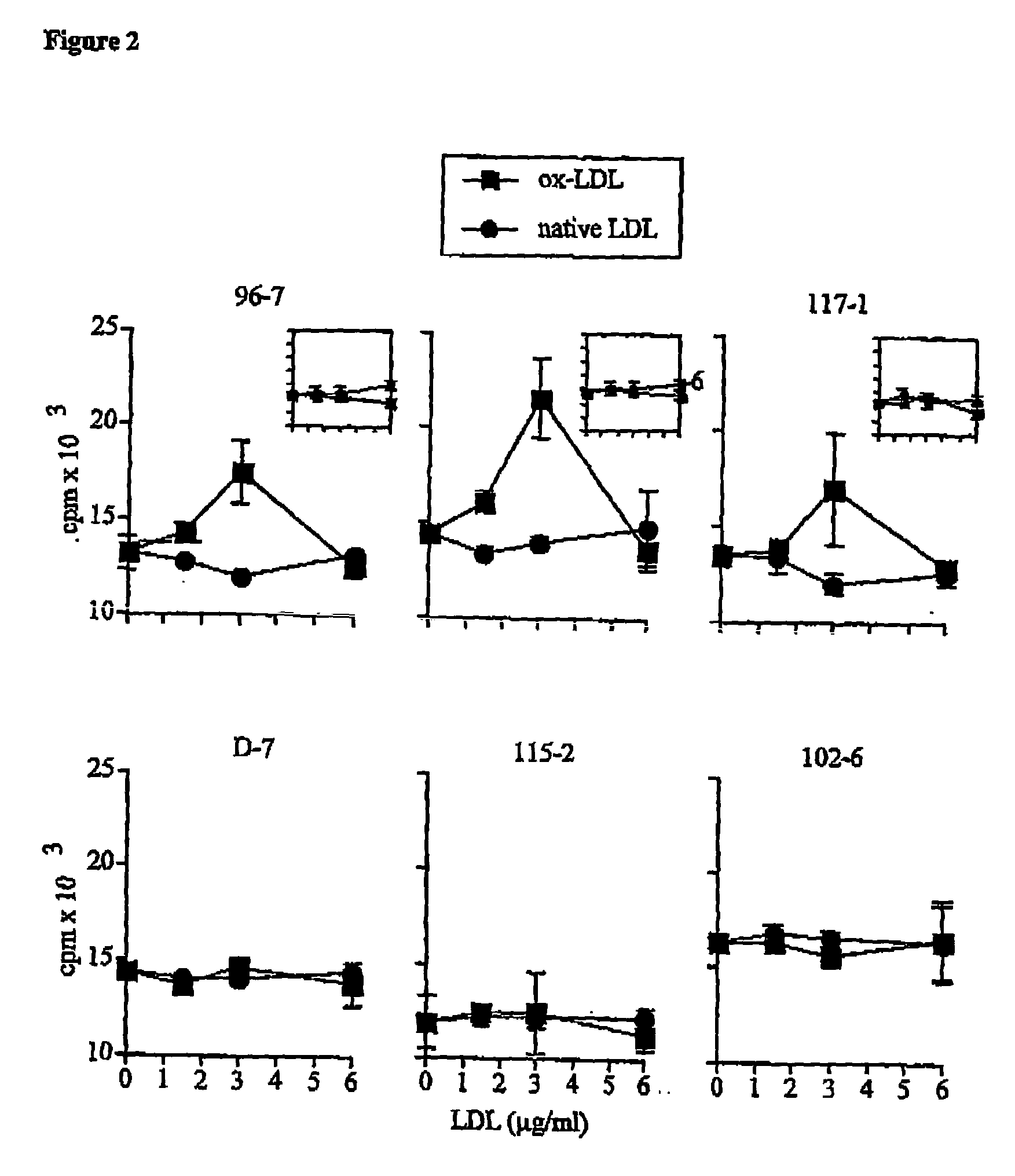
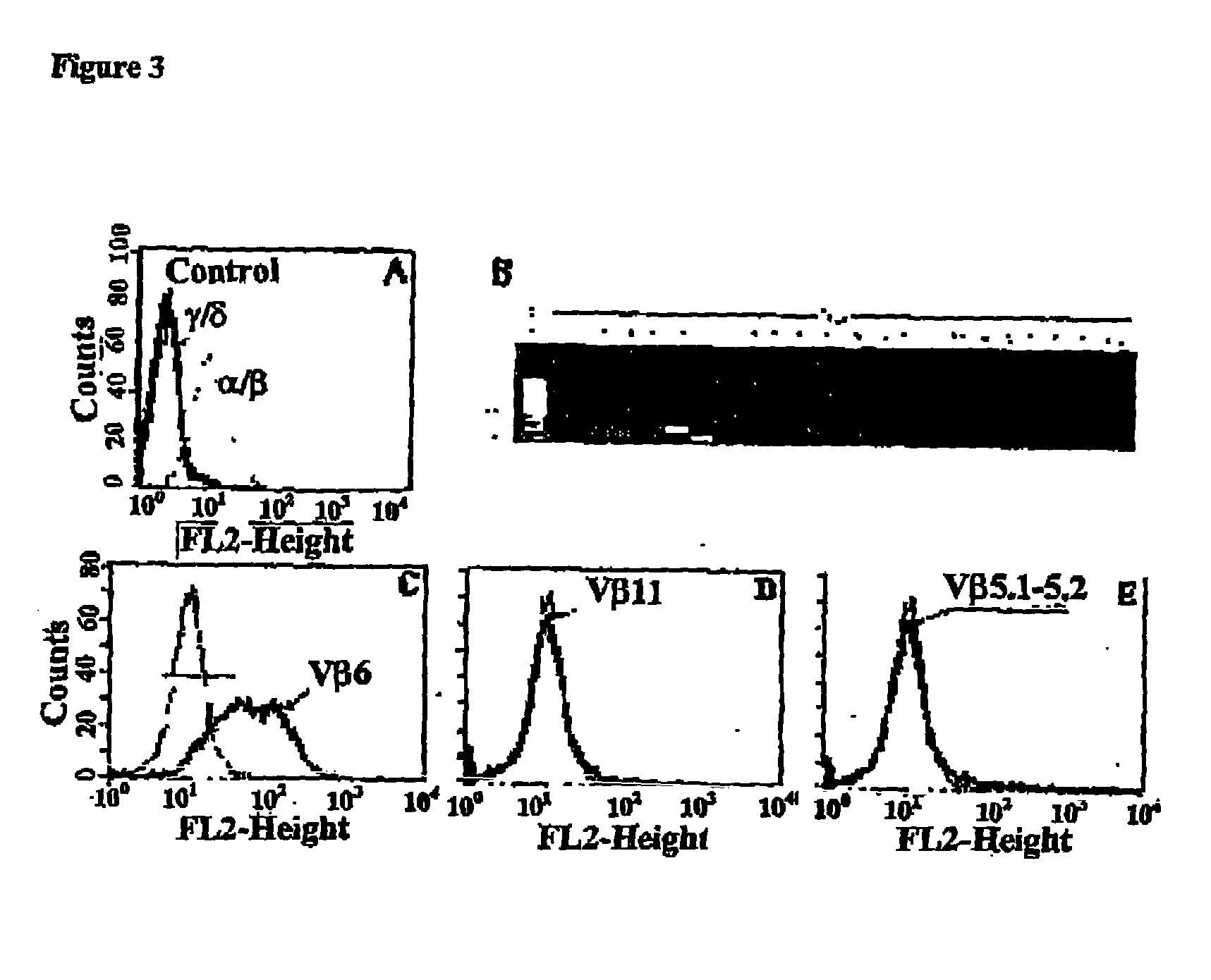
Atherosclerosis vaccine
InactiveUS20040002111A1Peptide preparation methodsLipid/lipoprotein ingredientsAntigenComplementarity determining region
The present invention relates to an antigenic composition capable of eliciting antibodies by interacting with alphabeta chains of a T cell receptor (TcR), which composition is comprised of a peptide-aldehyde conjugate. The aldehyde portion may be a dialdehyde, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), or a monoaldehyde, such as 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), while the peptide portion preferably comprises at least one lysine residue. The antigenic composition according to the invention is capable of recognizing and interacting with a TcR having a complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) of alpha10 and beta6 chains that comprises a cluster of charged and polar amino acids. The invention also relates to a method of producing a vaccine against atherosclerosis by screening of a library of candidate compounds for their ability to bind to a conjugate of oxidized LDL and a dialdehyde as well as to such a vaccine as such.
Owner:CARDIOVAX
System and method for identifying complex patterns of amino acids
InactiveUS7774144B2SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DatabasesHistidine residue
A method and system are disclosed for identifying and / or locating complex patterns in an amino acid sequence stored in a computer file or database. According to an aspect of the present invention, techniques are provided to facilitate queries of protein databases. For protein descriptions received in response to the queries, embodiments of the present invention may scan the received protein descriptions to identify and locate Replikin patterns. A Replikin pattern is defined to be a sequence of 7 to about 50 amino acids that include the following three (3) characteristics, each of which may be recognized by an embodiment of the present invention: (1) the sequence has at least one lysine residue located six to ten amino acid residues from a second lysine residue; (2) the sequence has at least one histidine residue; and (3) at least 6% of the amino acids in the sequence are lysine residues.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +3
Protein appropriate for orientation-controlled immobilization and immobilization carrier on which the proteins are immobilized
InactiveUS20090299035A1Prepared efficiently and rapidlyFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAcidic amino acidsIsoelectric point
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel protein having the following amino acid sequence altered for specifically and efficiently binding a protein to an immobilization carrier via the carboxy terminus. The protein is used for immobilizing a portion represented by R1-R2 on an immobilization carrier, comprising the amino acid sequence represented by the general formula R1-R2-R3-R4-R5 [wherein:the sequences are oriented from the amino terminal side to the carboxy terminal side;the sequence of the R1 portion is the sequence of a subject protein to be immobilized and contains neither a lysine residue nor a cysteine residue;the sequence of the R2 portion may be absent, but when the sequence of the R2 portion is present, the sequence of the R2 portion is a spacer sequence composed of amino acid residues other than lysine and cysteine residues;the sequence of the R3 portion is composed of two residues of amino acid represented by cysteine-X (where X denotes an amino acid residue other than lysine or cysteine);the sequence of the R4 portion may be absent, but when the sequence of the R4 portion is present, the sequence of the R4 portion contains neither a lysine residue nor a cysteine residue, but contains an acidic amino acid residue capable of acidifying the isoelectric point of the entire protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by the general formula R1-R2-R3-R4-R5; andthe sequence of an R5 portion is an affinity tag sequence for protein purification.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Synthesis and application of exenatide joined with polyethylene glycol
InactiveCN102532303AImprove in vivo stabilityExtended half-lifeHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical SubstancesHistidine residue
The invention relates to exenatide joined with polyethylene glycol. The structural general formula of exenatide is (I), mPEG represents residue of methoxy polyethylene glycol, the selected value of n is 0-3, R represents an exenatide molecule from which an amino is removed, the amino is of lysine residue or of N-end histidine residue in the exenatide molecule, and the molecular weight of the exenatide joined with polyethylene glycol is 9,800-110,000. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the compound and application of the compound in preparing medicines for curing type 2 diabetes mellitus. The exenatide joined with polyethylene glycol has the advantages of being long in half-life period and good in stability and hypoglycemic effect.
Owner:CHEMFUTURE PHARMATECH JIANGSU
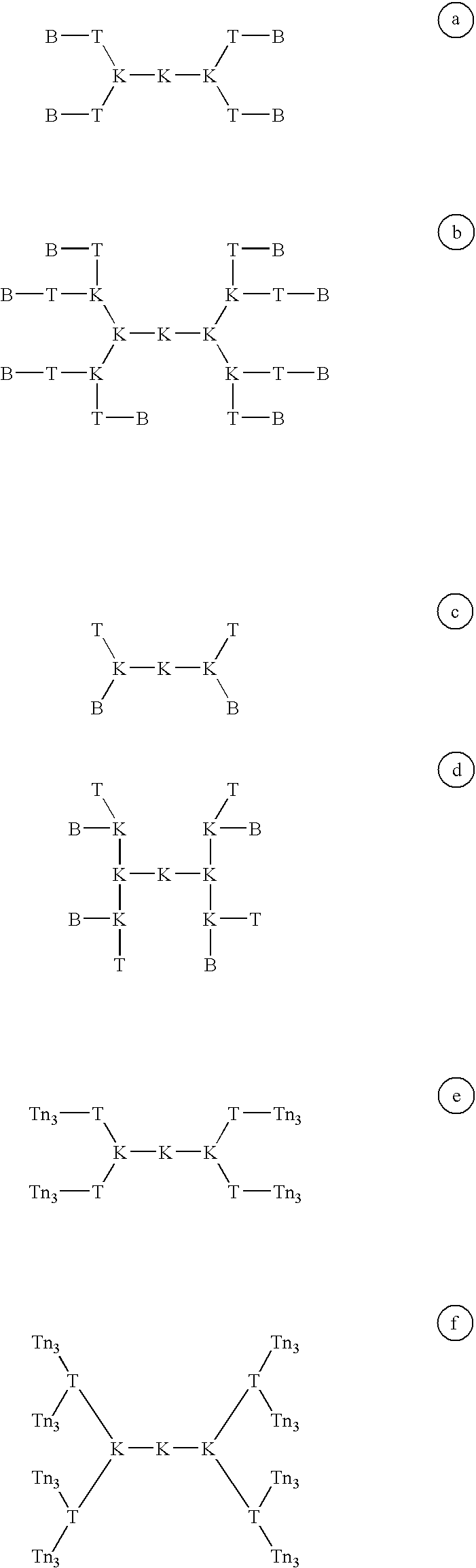
Multiple antigen glycopeptide carbohydrate vaccine comprising the same and use thereof
InactiveUS6676946B2Enhance antibody responseEfficient T cell helpPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteria peptidesT epitopeGlycopeptide
A carbohydrate peptide conjugate containing:(i) a carrier containing a dendrimeric poly-lysine enabling multiple epitopes to be covalently attached thereto,(ii) at least one peptide containing one T epitope or several identical or different T-epitopes,(iii) at least one carbohydrate moiety which is tumor antigen, or a derivative thereof, containing a B epitope, provided it is not a sialoside, or several identical or different epitopes, wherein said conjugate containing at least 3-lysines and up to 15 lysine covalently linked to one another, and wherein:(a) to the NH2 and of at least two lysine residues is bound at least one carbohydrate residue being not a sialoside, optionally substituted and containing an epitope and wherein the peptide containing one T epitope is covalently bound to the end of said carbohydrate which induces immune responses.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
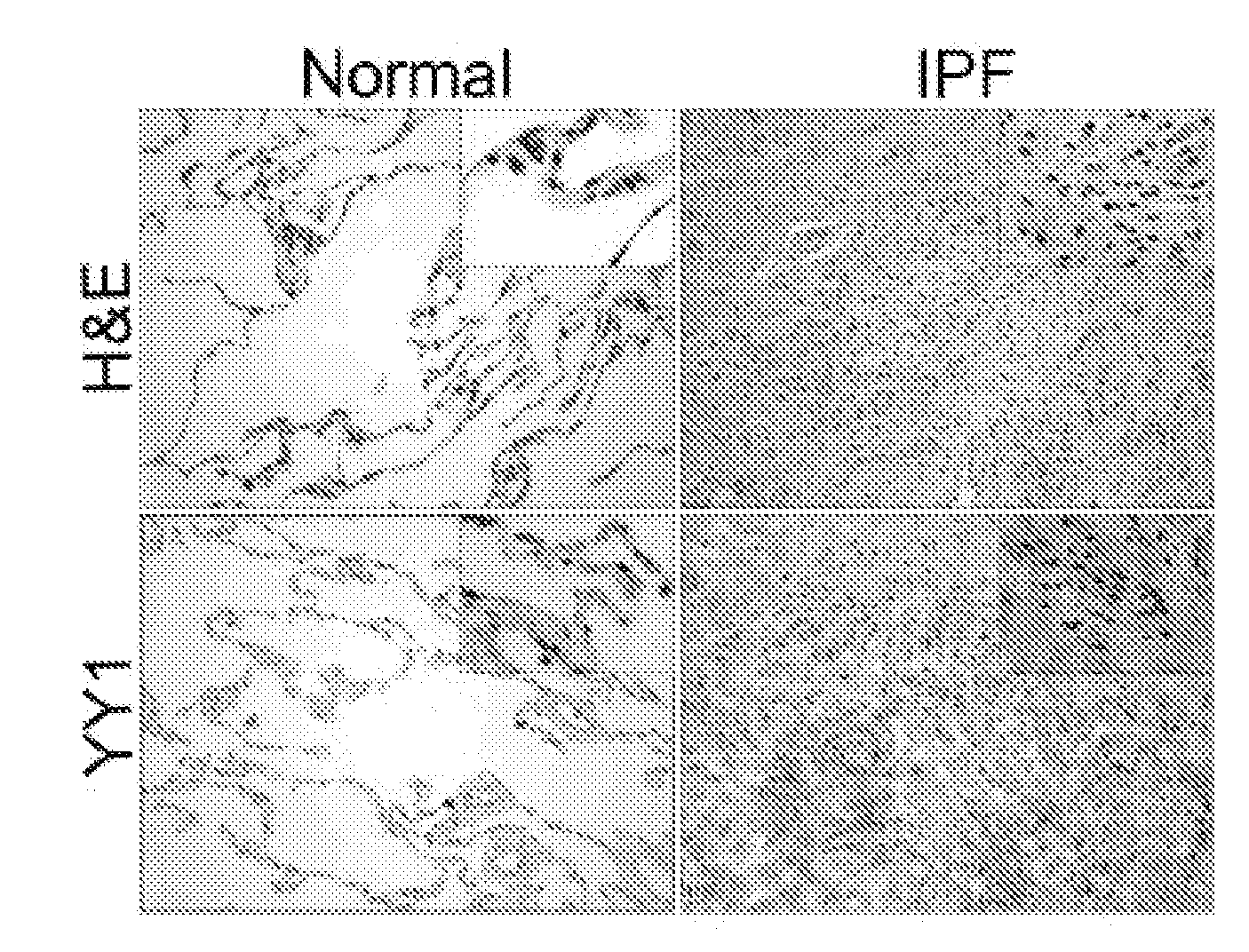
Methods of diagnosing and treating fibrosis
InactiveUS20110286990A1Improve developmentPrevent and reduce disease progressionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEZH2Fibrosis
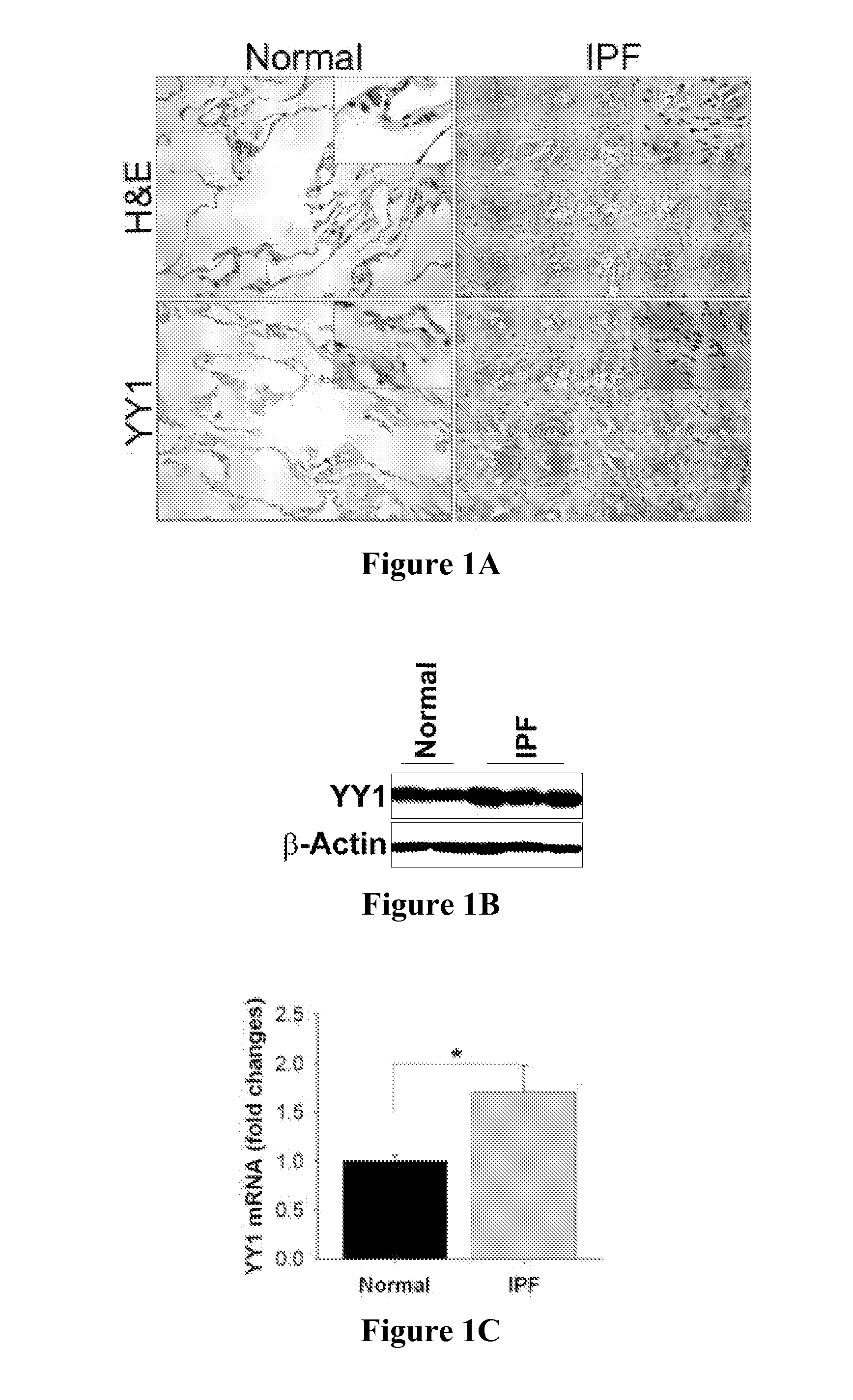
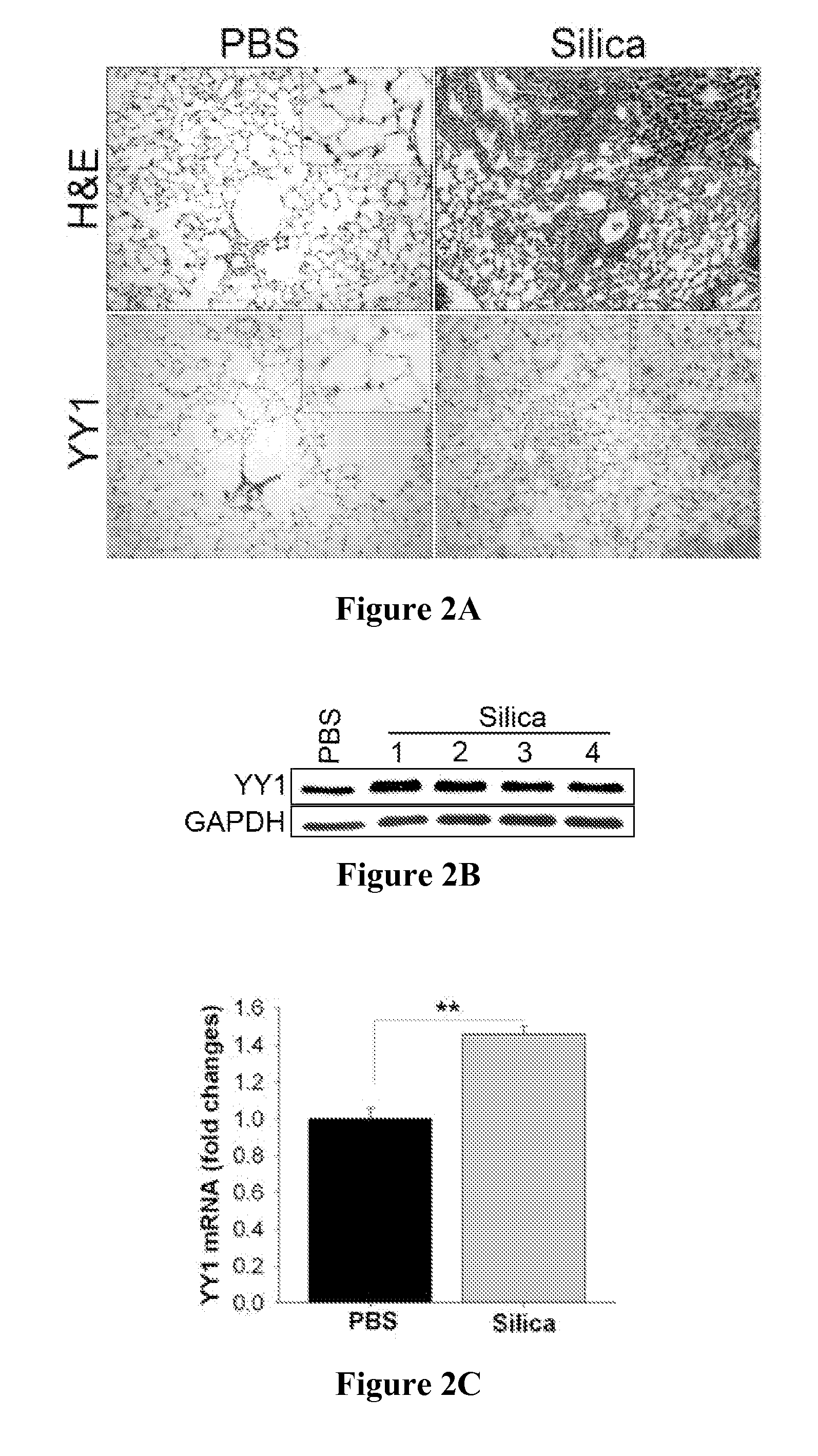
The present invention is directed to methods of diagnosing and treating a fibrotic condition in a mammalian subject. These methods involve measuring the levels of trimethylation at lysine residue 27 of histone-3 and / or measuring the expression levels of EZH2 or YY-1. Agents useful for treating fibrosis or a fibrotic condition are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Laying hen feed
ActiveCN103099064AEgg shell quality advantageFeed-to-egg ratio advantageAnimal feeding stuffTrace elementFodder
The invention discloses laying hen feed. The laying hen feed consists of the following components in parts by weight: 10-50 parts of calcium hydrogen phosphate, 30-70 parts of stone powder, 20-30 parts of salt, 10-20 parts of sodium sulfate, 6-10 parts of choline, 18-20 parts of compound trace elements, 4-5 parts of compound vitamin, 10-25 parts of lysine, 10-15 parts of methionine, 100-150 parts of bone meal, 350-400 parts of cottonseed meal, 50-100 parts of blood cell protein powder, 100-200 parts of corn protein powder, 50-100 parts of lysine residue and 10-15 parts of additive. In application, complete feed can be prepared by mixing the laying hen feed with conventional basal feed. The invention relates to the laying hen feed which is applicable to laying hens in an egg producing period to meet the needs for exact effect, lasting egg production peak and high feed-gain ratio of the laying hen feed.
Owner:南通和美华科技饲料有限公司
PEG-conjugated erythropoietin
InactiveUS20060276634A1Optimization rangeLong retentionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsMedicinePolyethylene glycol
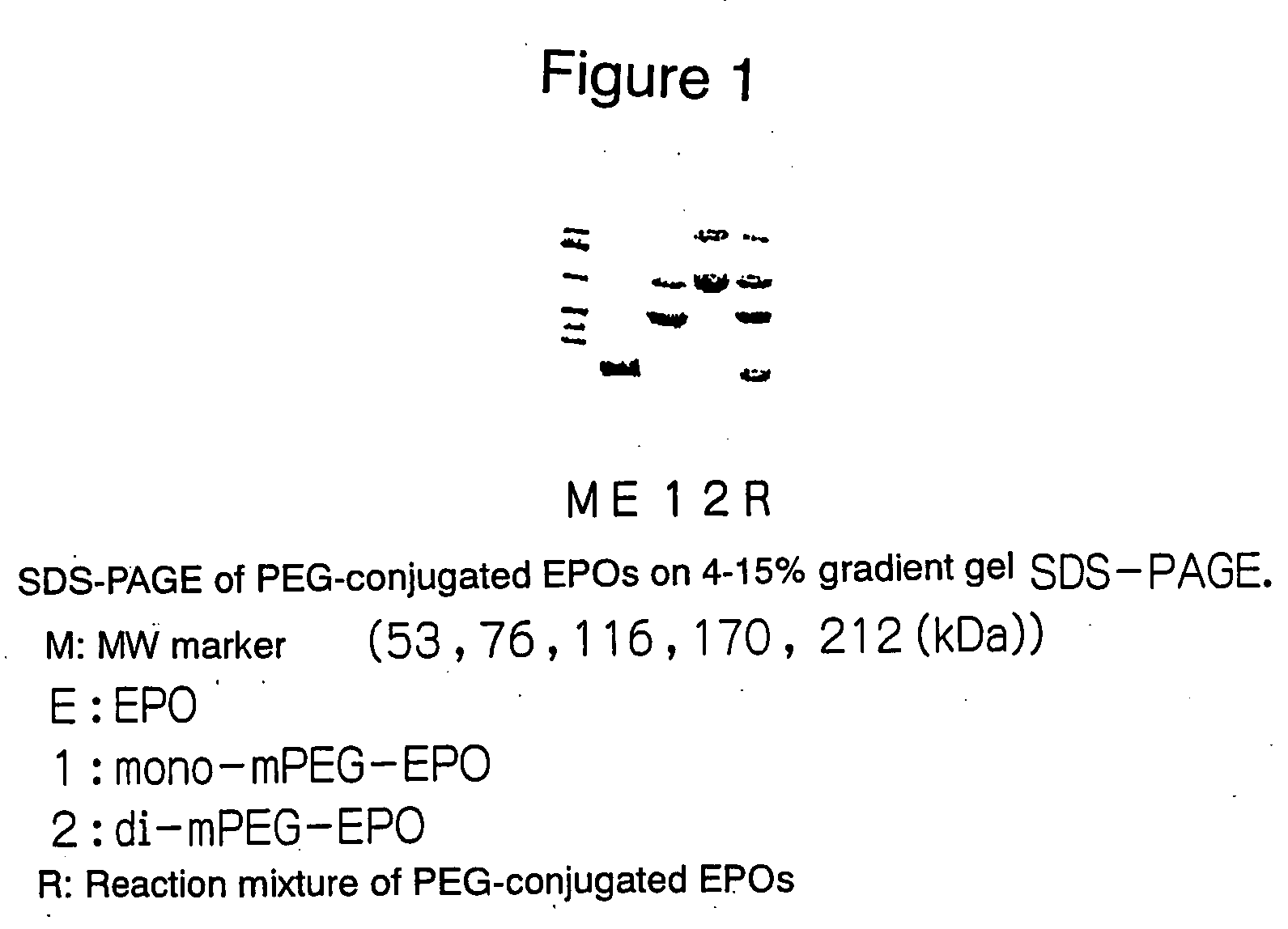
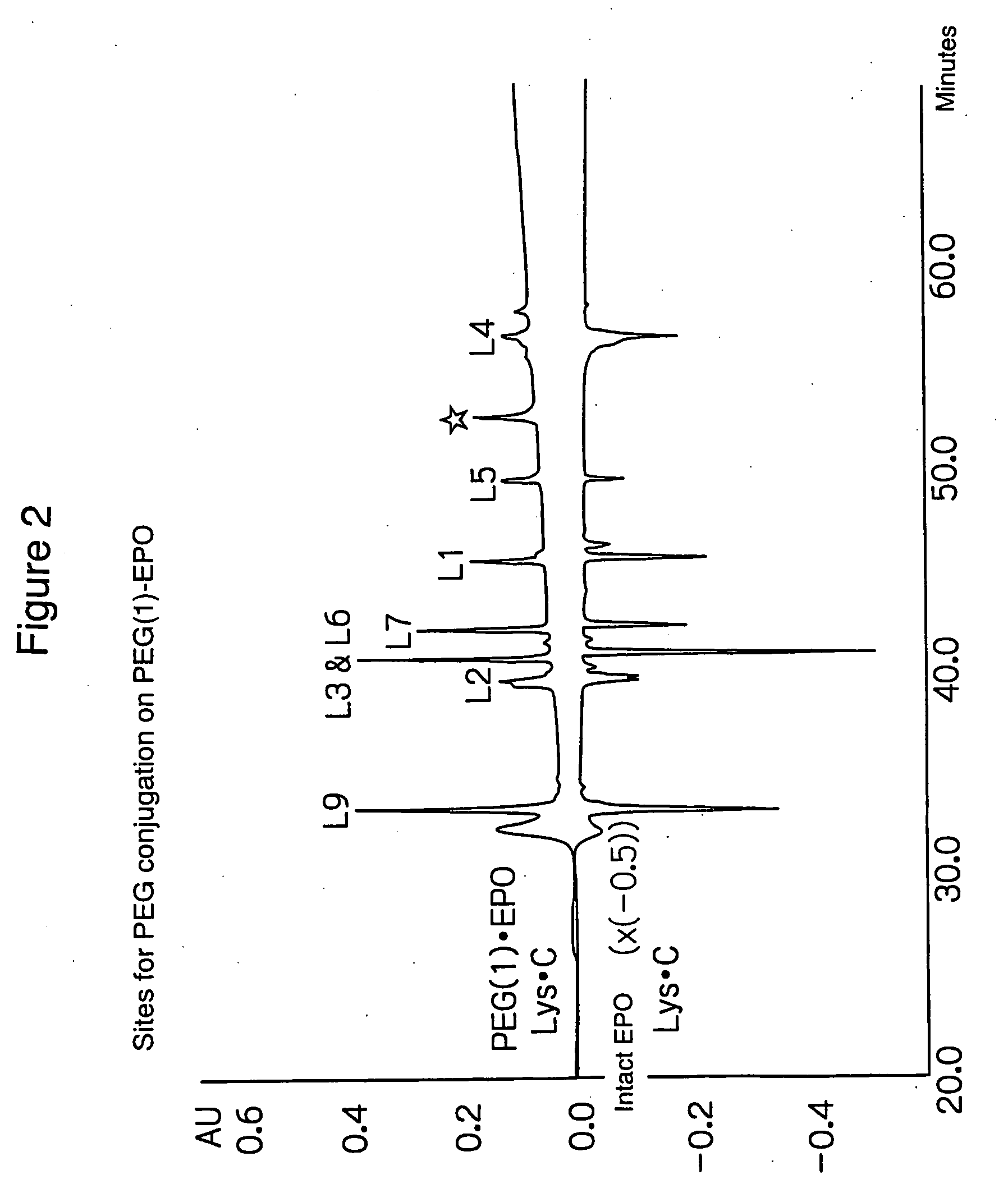
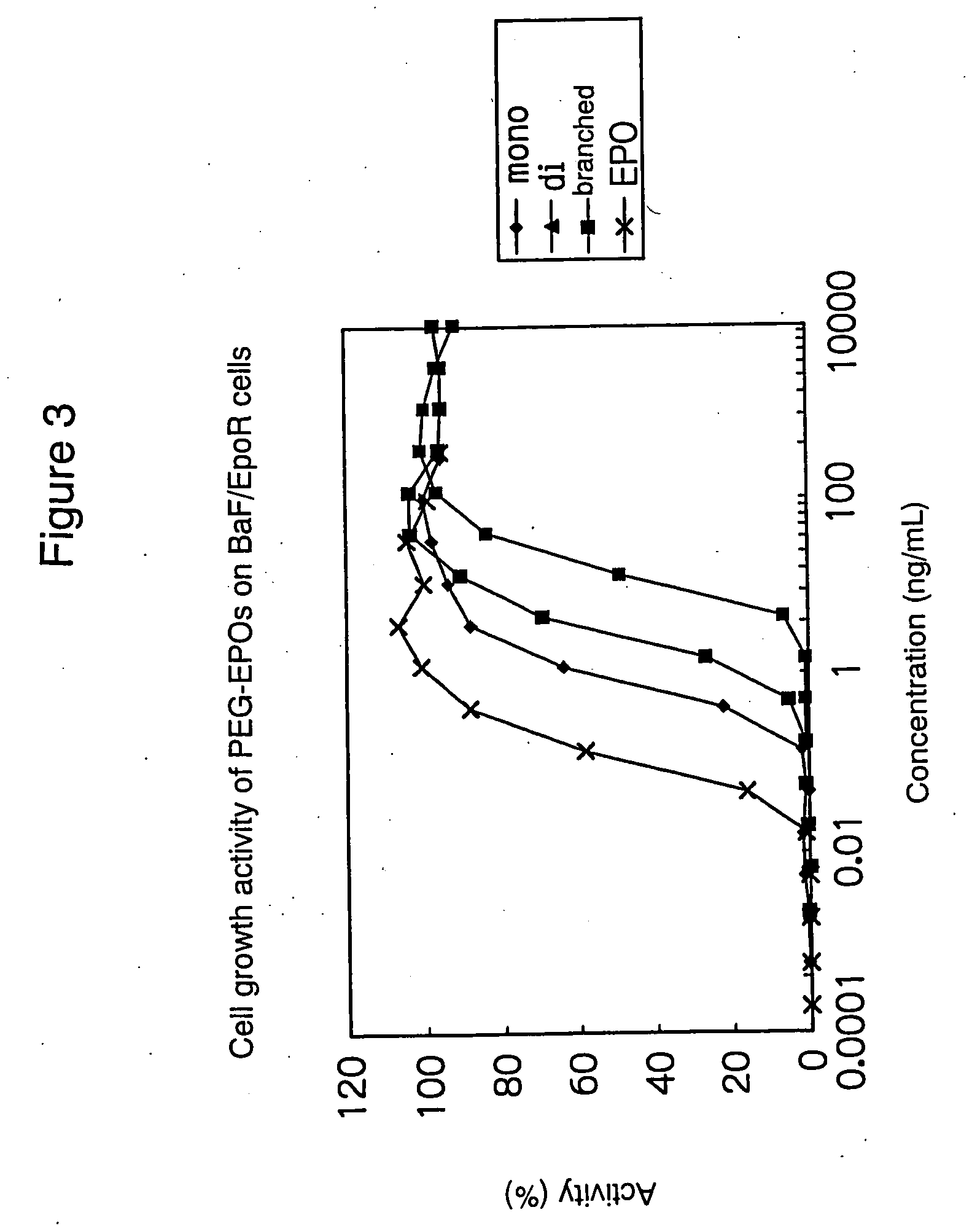
The present invention provides a polyethylene glycol-conjugated erythropoietin (PEG-conjugated EPO) prepared by PEG conjugation on the lysine residue at position 52 of native erythropoietin (native EPO). In order to achieve more sustained efficacy without losing physiological activities of native EPO, a glycoprotein rich in sugar chains, there has been a need to develop a PEG-conjugated EPO with significantly sustained efficacy by introducing a controlled number of PEG molecules at controlled positions. This PEG-conjugated EPO addresses such a need and provides more sustained efficacy.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Method for the linkage of bifunctional chelating agents and (radioactive) transition metal complexes to proteins and peptides
InactiveUS20070184537A1Avoiding misfolding and denaturationIn-vivo radioactive preparationsFermentationPeptideLysine residue
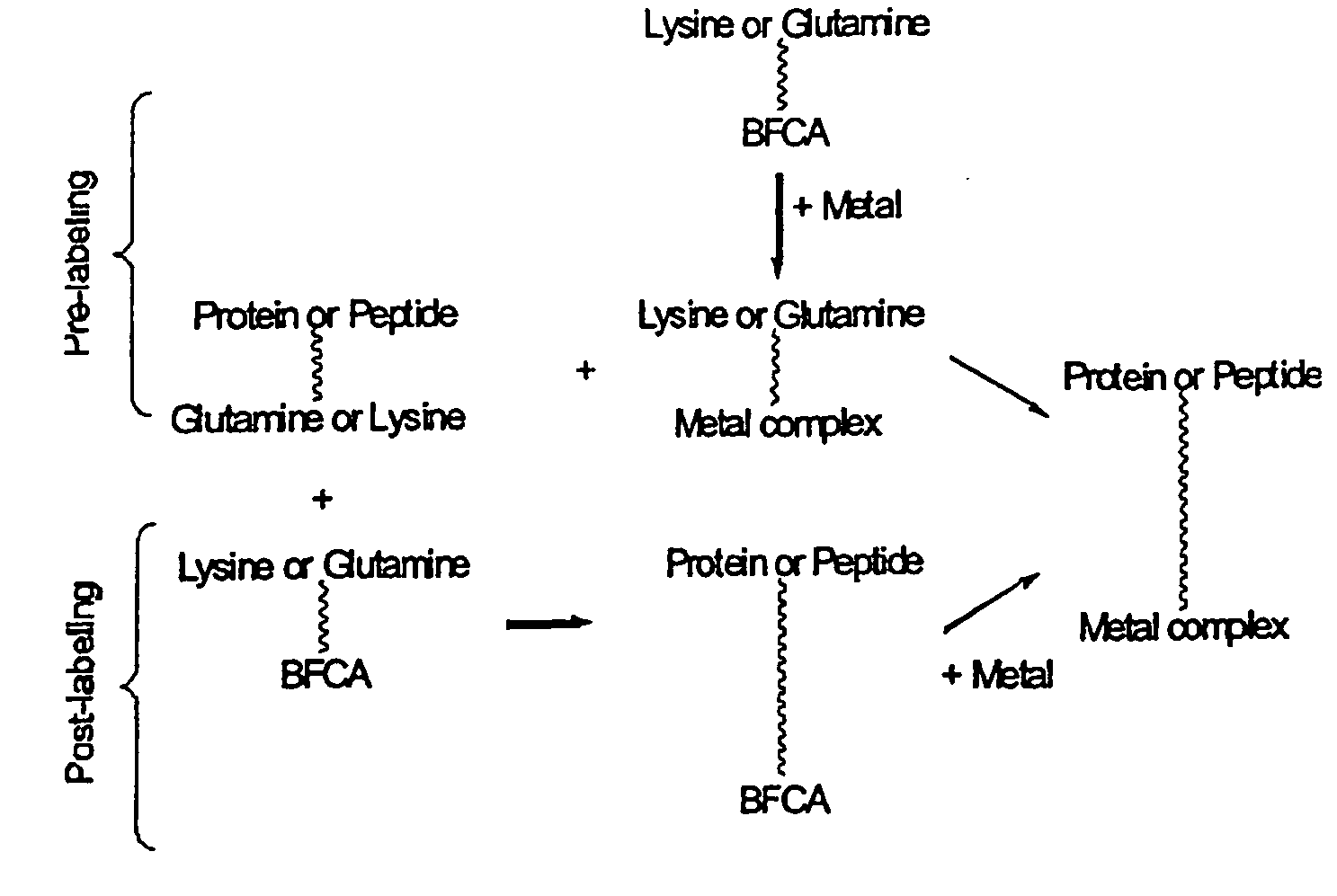
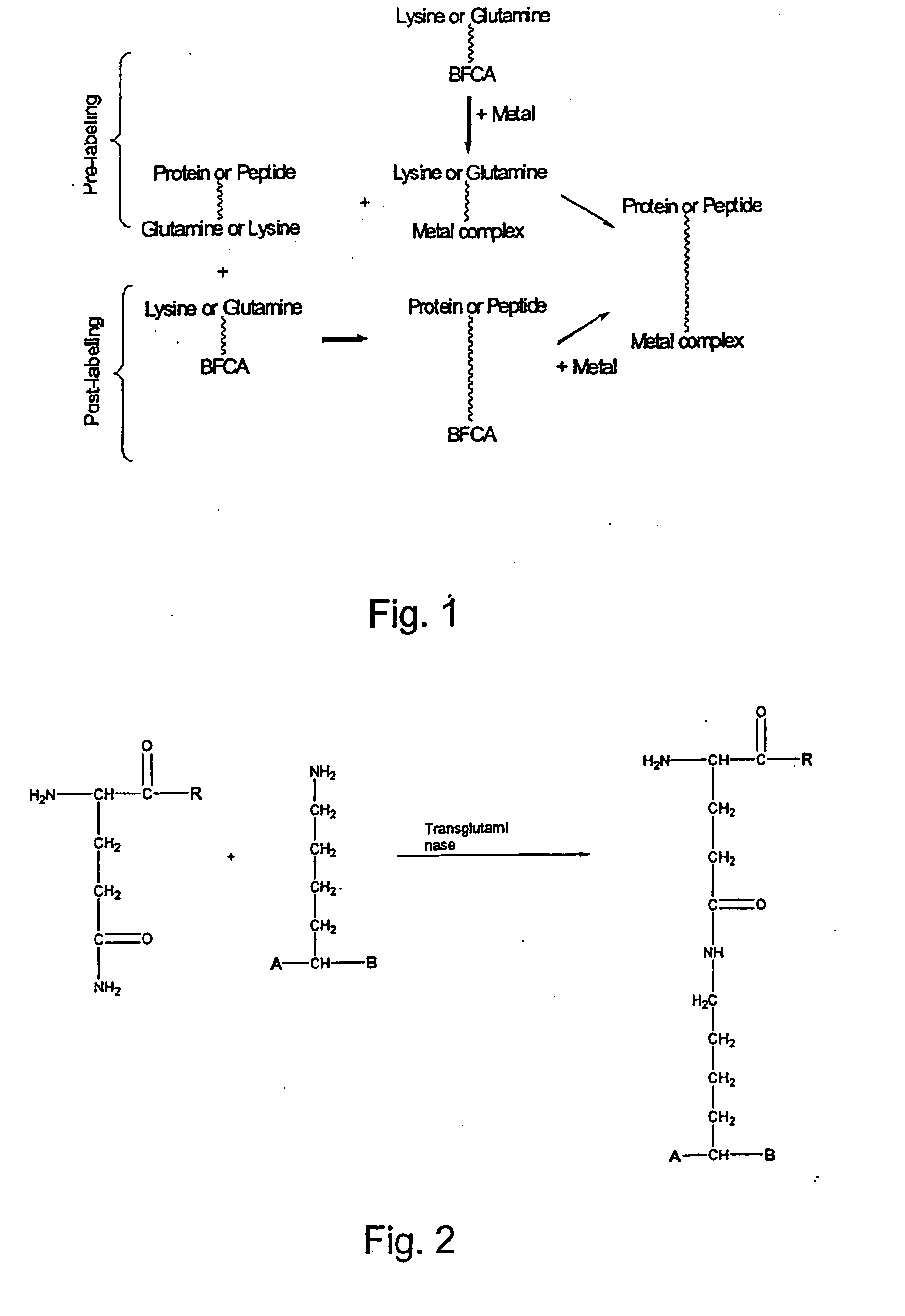
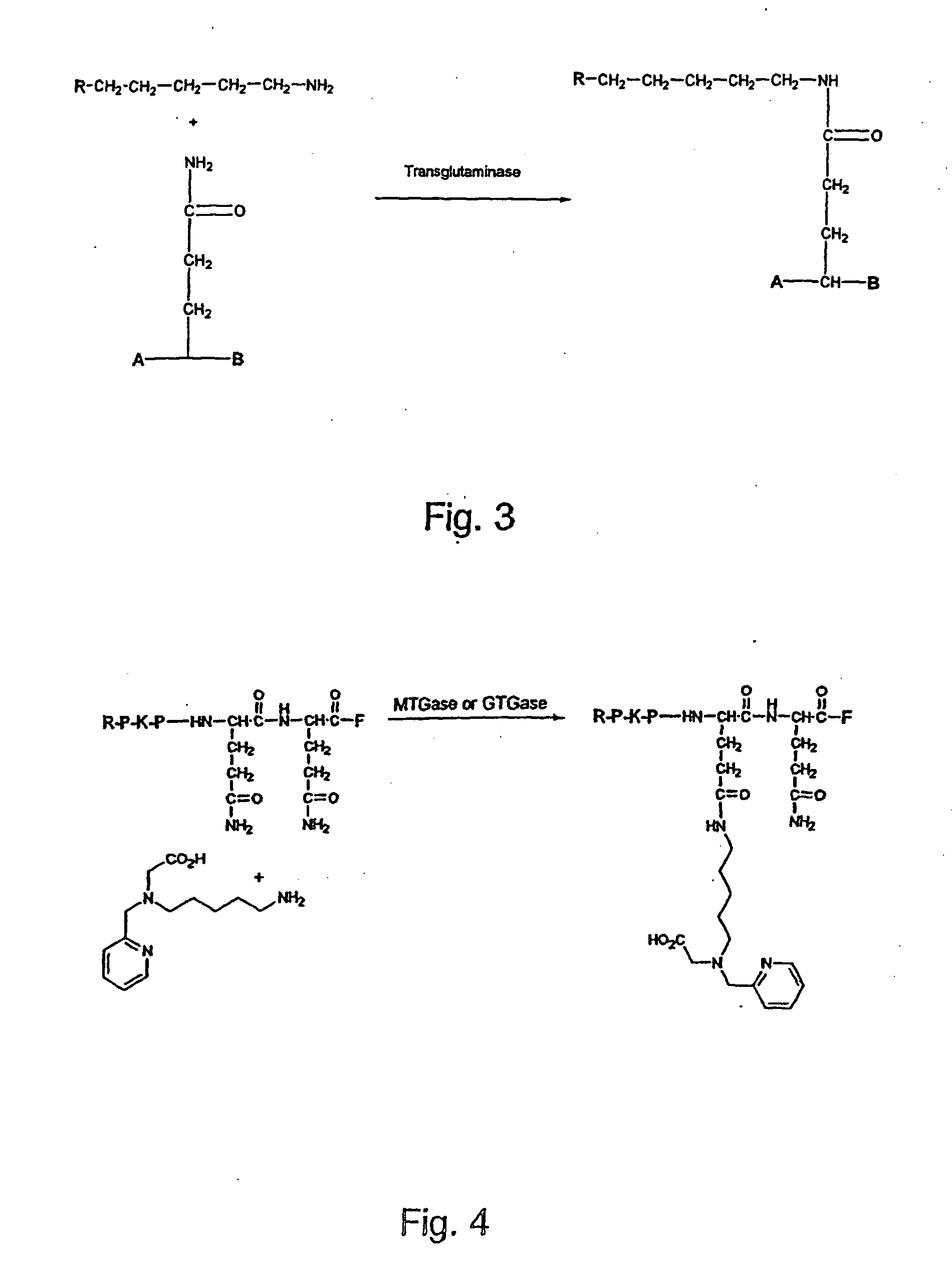
The present invention relates to a method for radioactive labeling of a protein or peptide, by providing a protein or peptide having at least one glutamine or lysine residue; adding a metal chelating agent having at least one lysine or glutamine residue, respectively, which metal chelating agent is optionally complexed with a radioactive or paramagnetic metal; reacting the protein or peptide and metal chelating agent in the presence of a transglutaminase to obtain a protein or peptide with a metal chelating group covalently bound thereto, and optionally complexing the metal chelating group with a radioactive or paramagnetic metal. The invention also relates to proteins and peptides thus labeled and to proteins and peptides that have been coupled to a metal chelating agent but not yet labeled.
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
Pegylated Single-Chain Insulin
InactiveUS20100216690A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderOrganic chemistryLysine residue
The present invention is related to a single-chain insulin comprising the B- and the A-chain of human insulin or analogues thereof connected by a connecting peptide having from 3-35 amino acid residues, wherein the single-chain insulin comprises at least one PEG group attached to at least one lysine residue in the single-chain insulin molecule and / or to the B1 N terminal amino acid residue. The PEGylated single-chain insulins may comprise up to 4 PEG groups which may be the same or different.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Immobilized protein that is immobilized only at its amino terminus in orientation-controlled manner
InactiveUS20100130721A1Maximize functionalityFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesCysteine thiolateLysine residue
This invention provides an immobilized protein bound to an immobilization carrier at a protein amino terminus via the sole α-amino group of the protein comprising an amino acid sequence containing neither lysine residues nor cysteine residues represented by the general formula S1-R1-R2, wherein: the sequences are oriented from the amino terminal side to the carboxy terminal side; the sequence of the S1 portion may be absent, but when the sequence of the S1 portion is present, the sequence of the S1 portion is a spacer sequence composed of amino acid residues other than lysine and cysteine residues; the sequence of the R1 portion is the sequence of a subject protein to be immobilized and contains neither lysine residues nor cysteine residues; and the sequence of the R2 portion may be absent, but when the sequence of the R2 portion is present, the sequence of the R2 portion is a spacer sequence composed of amino acid residues other than lysine and cysteine residues.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
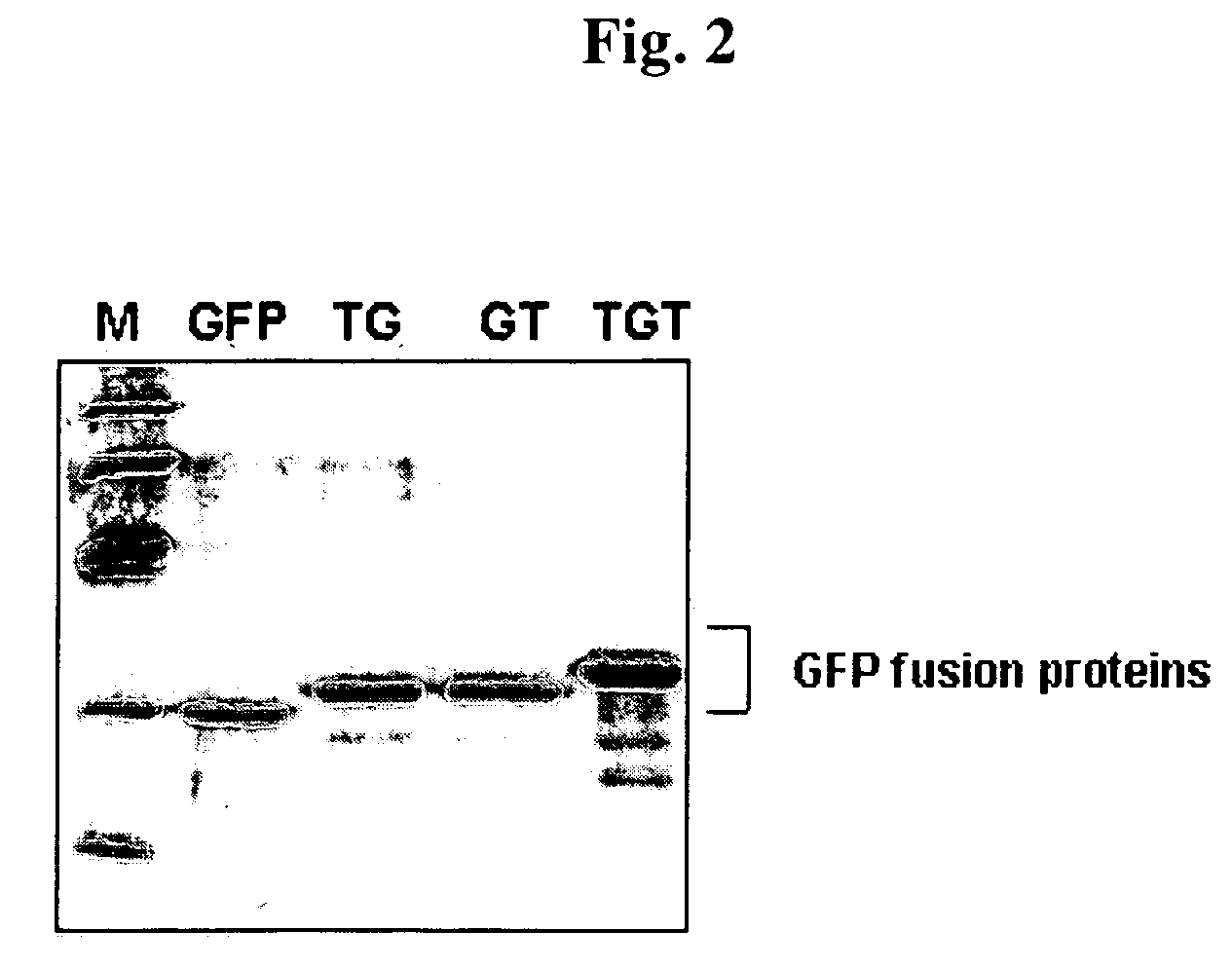
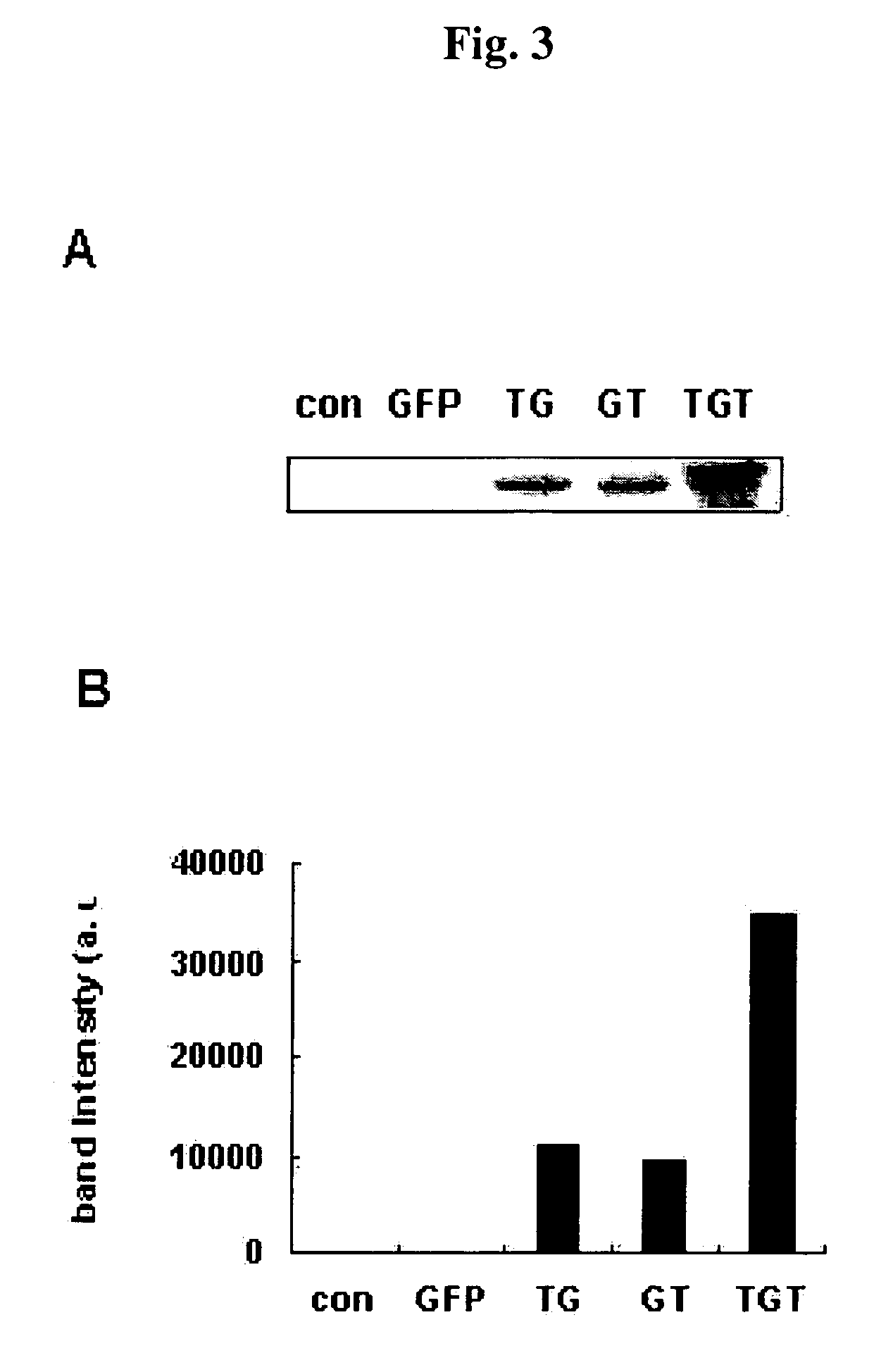
Advanced cell-transducing transport domain-target protein-transport domain fusion protein and uses thereof
ActiveUS7306944B2Improve efficiencyGood removal effectCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein targetSuperoxide
The present invention provides a fusion protein which delivers a functional protein or peptide into a cell at enhanced efficiency. The fusion protein of the present invention is a transduction domain-target protein-transduction domain fusion protein, wherein the transduction domain, which comprises 6-12 amino acid residues whose more than ¾ consist of arginine or lysine residues, is covalently bonded to each of the amino- and carboxyl-terminal ends of the target protein. Green fluorescence protein and Cu / Zn-superoxide dismutate (SOD) are used as the target protein.
Owner:BIOCELTRAN
Protein analysis
InactiveUS20050176070A1High densityShorten the timeAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningBiotin-streptavidin complexAntigen
A method of forming an array of proteins selected from antigens or antibodies; said method comprising the steps of (i) expressing in a recombinant cell, a fusion protein which comprises either (a) an antigen or (b) an antibody binding protein, fused to a peptide having up to 50 amino acids, which peptide comprises amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO 1 LX1X2IX3X4X5X6KX7X8X9X10 (SEQ ID NO 1) where X1 is a naturally occurring amino acid, X2 is any naturally occurring amino acid other than leucine, valine, isoleucine, tryptophan, phenylalanine or tyrosine, X3 is phenylalanine or leucine, X4 is glutamine or asparagine, X5 is alanine, glycine, serine or threonine, X6 is glycine or methionine, X7 is isoleucine, methionine or valine, X8 is glutamine, leucine, valine, tyrosine or isoleucine, X9 is tryptophan, tyrosine, valine, phenylalanine, leucine or isoleucine and X10 is any naturally occurring amino acid other than asparagine or glutamine; where said peptide is capable of being biotinylated by a biotin ligase at the lysine residue adjacent to X6; (ii) biotinylating said peptide of the fusion protein at the lysine residue adjacent X6; (iii) isolating the biotinylated fusion protein; (iv) applying the biotinylated fusion protein to an avidin or streptavidin coated non-porous support; (v) forming an array of at least three different proteins on the support by either (a) where the fusion protein comprises an antigen, carrying out steps (i) to (iv) the desired number of times to form an antigen array; or (b) where the fusion protein comprises an antibody binding protein, applying to said protein, either prior to or after step (iv) a plurality of different antibodies or binding fragments thereof.
Owner:NEXTGEN SCI
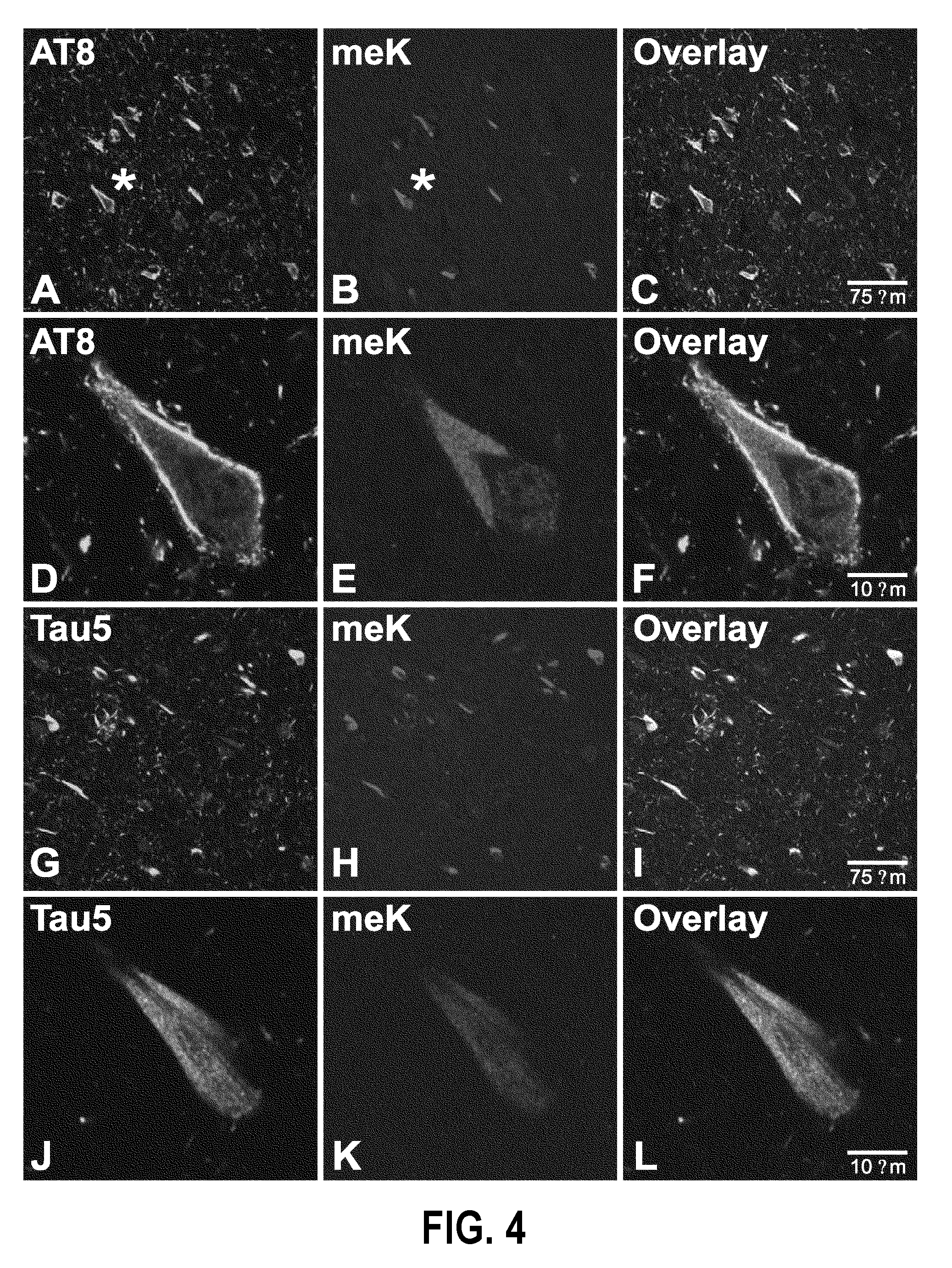
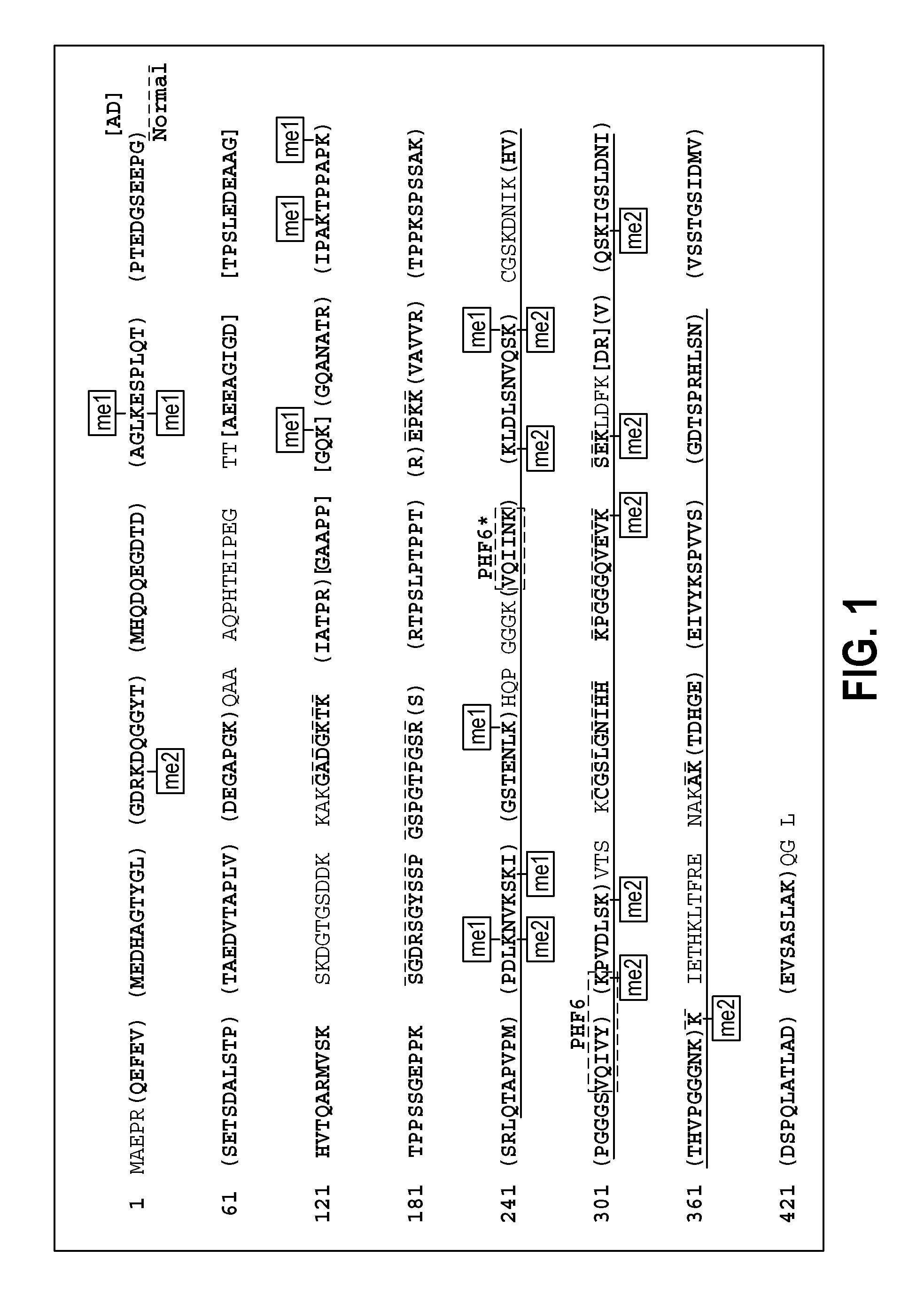
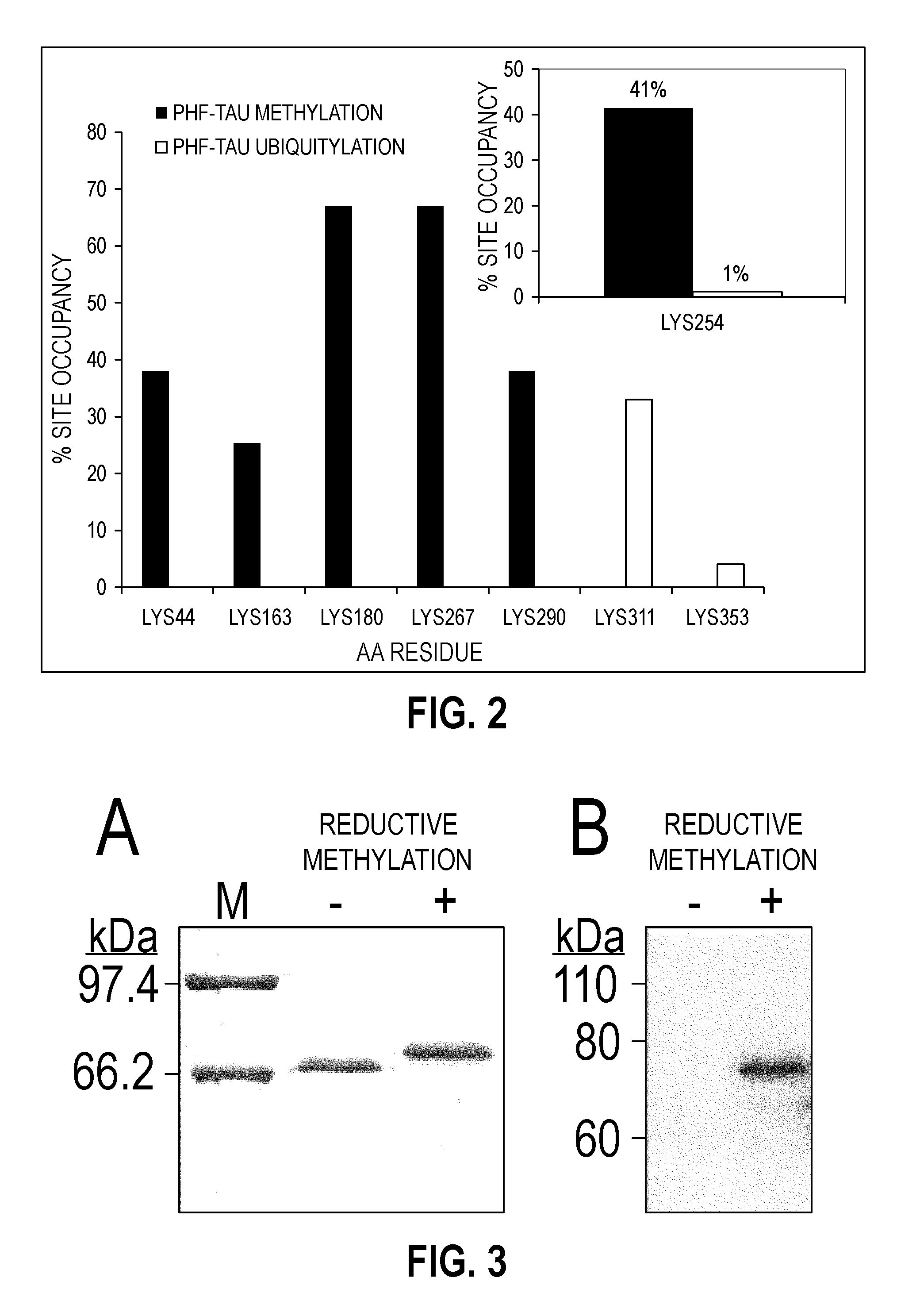
Methylated Peptides Derived from Tau Protein and Their Antibodies for Diagnosis and Therapy of Alzheimer's Disease
ActiveUS20140294839A1Low extensionImprove understandingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenPost translational
In sporadic Alzheimer's disease, neurofibrillary lesion formation is preceded by extensive post-translational modification of the microtubule associated protein tau. Immunoassays have been developed recently that detect tau in biological specimens, thus providing a means for pre-mortem diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, which has remained elusive. These assays have been improved by the analysis of relevant post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, however opportunity for improvement remains. The present invention addresses this issue by disclosing synthetic methylated peptides derived from the tau protein of paired helical filaments and non-diseased control brain. Alzheimer's disease specificity is provided by the presence or absence of methyl moieties on lysine residues and differences between mono-, di-, and tri-methylation. The methylated peptide is useful as an antigen and a binding partner for identifying compounds that interact with the peptide and the methylated tau protein, including antibodies that can distinguish non-diseased brain from that affected by Alzheimer's disease. The resulting antibodies are useful diagnostically and therapeutically. The compounds that specifically bind to methylated tau proteins are useful for eliminating abnormally methylated tau.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE +1
Acylated Single Chain Insulin
InactiveUS20090099065A1Improve propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin A ChainMedicine
The invention is related to an acylated, single-chain insulin comprising the B- and the A-chain of human insulin or an analogue thereof connected by a connecting peptide, wherein a lysine residue being substituted for the natural amino acid residue in one of the positions A12-A23 in the human insulin A-chain has been chemically modified by acylation.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Protein hydrolysate compositions having improved sensory characteristics and physical properties
The present invention provides protein hydrolysate compositions, processes for making protein hydrolysate compositions, and food products comprising protein hydrolysate compositions. The protein hydrolysate compositions generally comprise polypeptide fragments having primarily either an arginine residue or a lysine residue at each carboxyl terminus.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
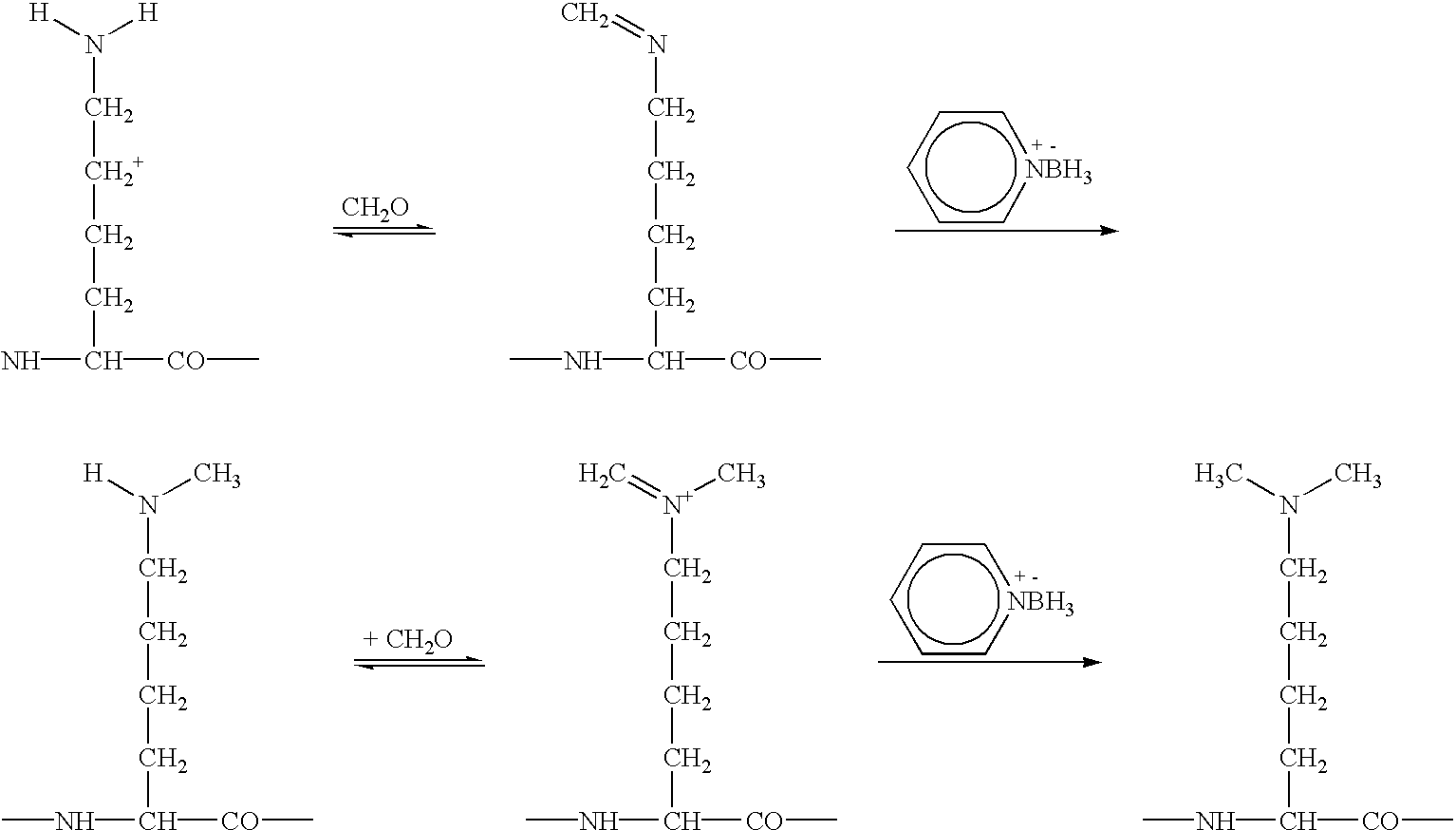
Method of covalently modifying proteins with organic molecules to prevent aggregation
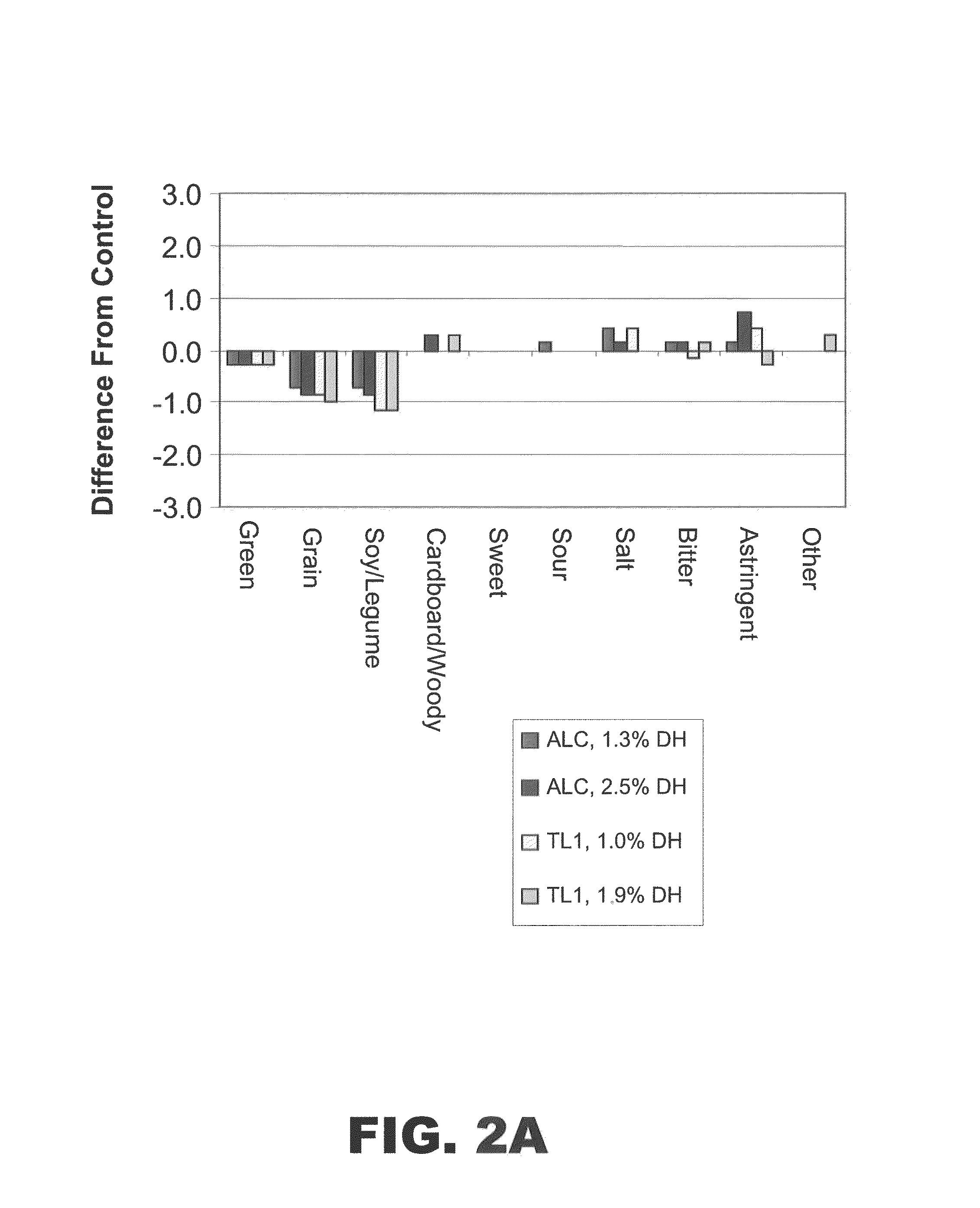
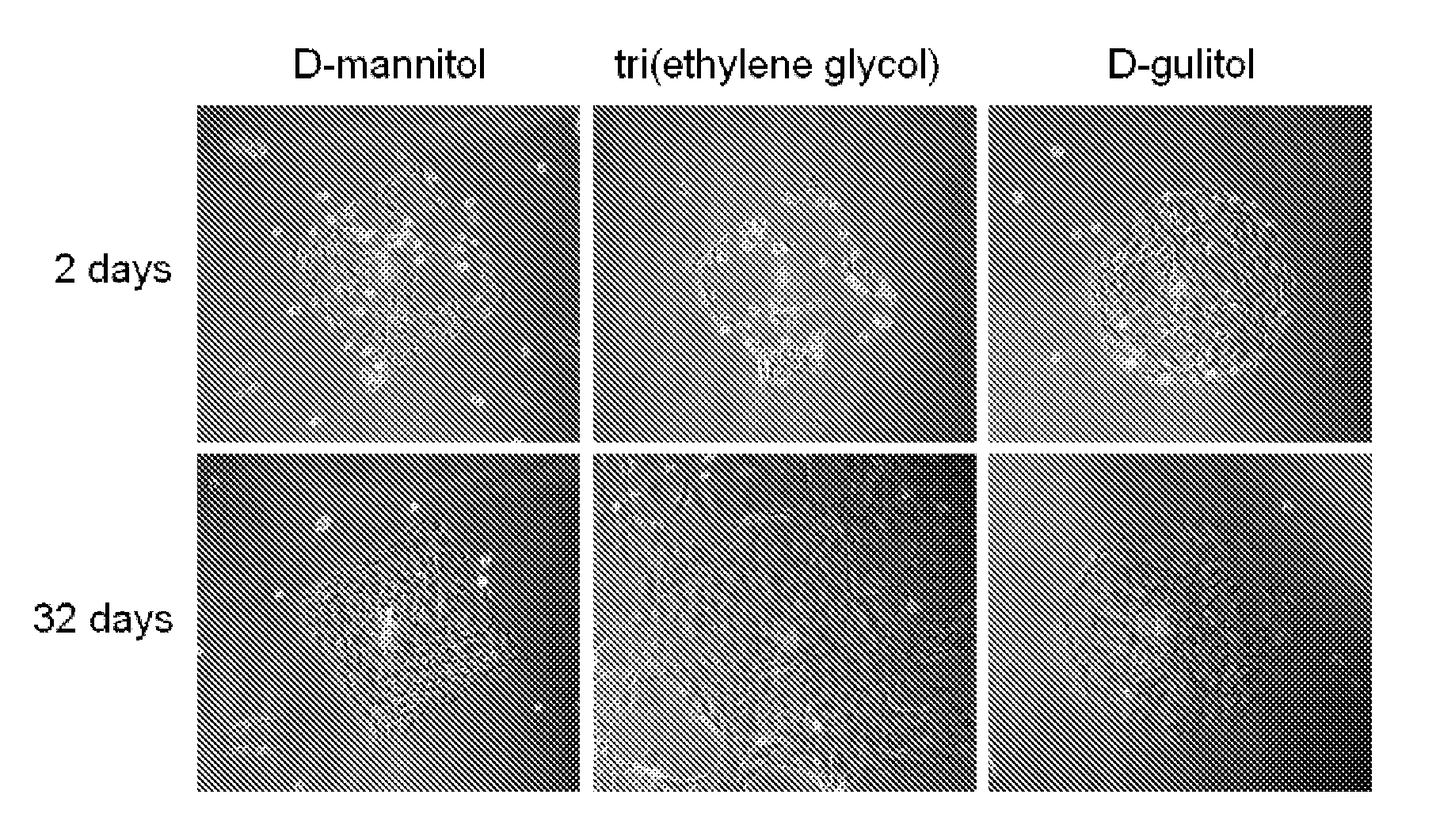
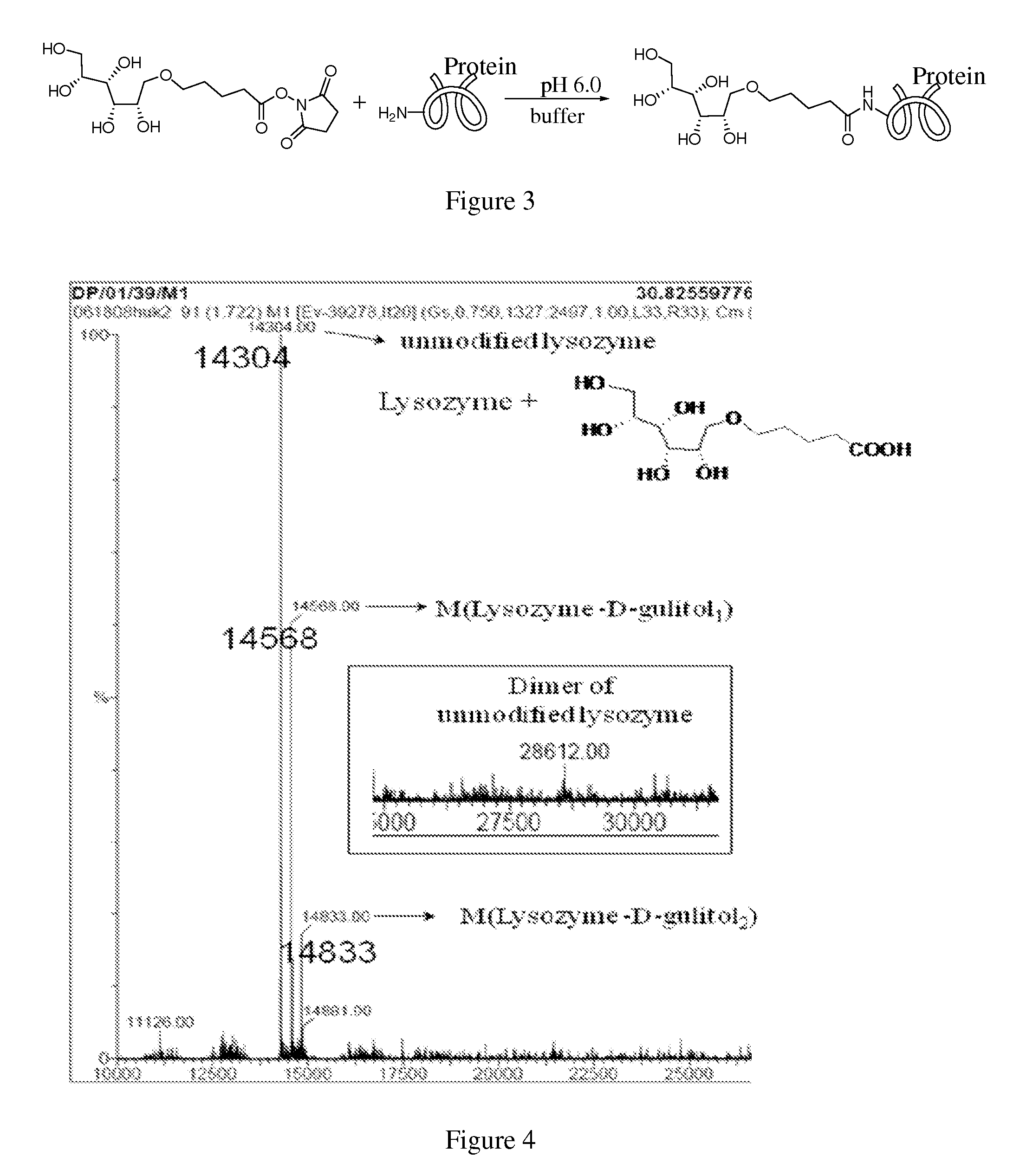
ActiveUS20100273991A1Prevents aggregation of proteinHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsEnergy modified materialsCell AggregationsAlcohol sugars
A system and method for preventing protein aggregation is developed by covalent modification of proteins with organic molecules that can preserve the native protein folding. Proteins are covalently modified with sugar alcohols or cyclodextrins (organic Kosmotropes) or other small molecule drugs by water-driven bioorganic reactions in water. In the water-driven bioorganic reactions, the reagent is stable in water and can modify lysine residues or cysteine residue of a protein at physiological conditions with high yield and fast rate. Proteins and antibodies will be modified by non-natural sugar alcohols. As a result, the efficacy of protein drugs (reduction in aggregation and enzymatic degradation, and increase in blood stream life time) may be improved.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing superoxide dismutase (SOD)-loaded gamma-poly glutamic acid hydrogel
InactiveCN103977447AImprove activity retention performanceEvenly dispersedCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCarboxyl radicalSide chain
The invention discloses a method for preparing superoxide dismutase (SOD)-loaded gamma-poly glutamic acid hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a 1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride / N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDC / NHS) activation system, and forming an SOD-gamma-polyglutamic acid (PGA) immobilized product by using lysine residues and poly glutamic acid side chain carboxyl of SOD; crosslinking the SOD-gamma-PGA obtained by the reaction by using a diamine crosslinking agent cysteamine hydrochloride, so as to form an SOD-gamma-PGA gel system. The gel system can be applied to wound dressing or mask, and can play the antioxidant damage action, and the skin wound is quickly repaired.
Owner:TIANJIN AROLYN BIOTECH
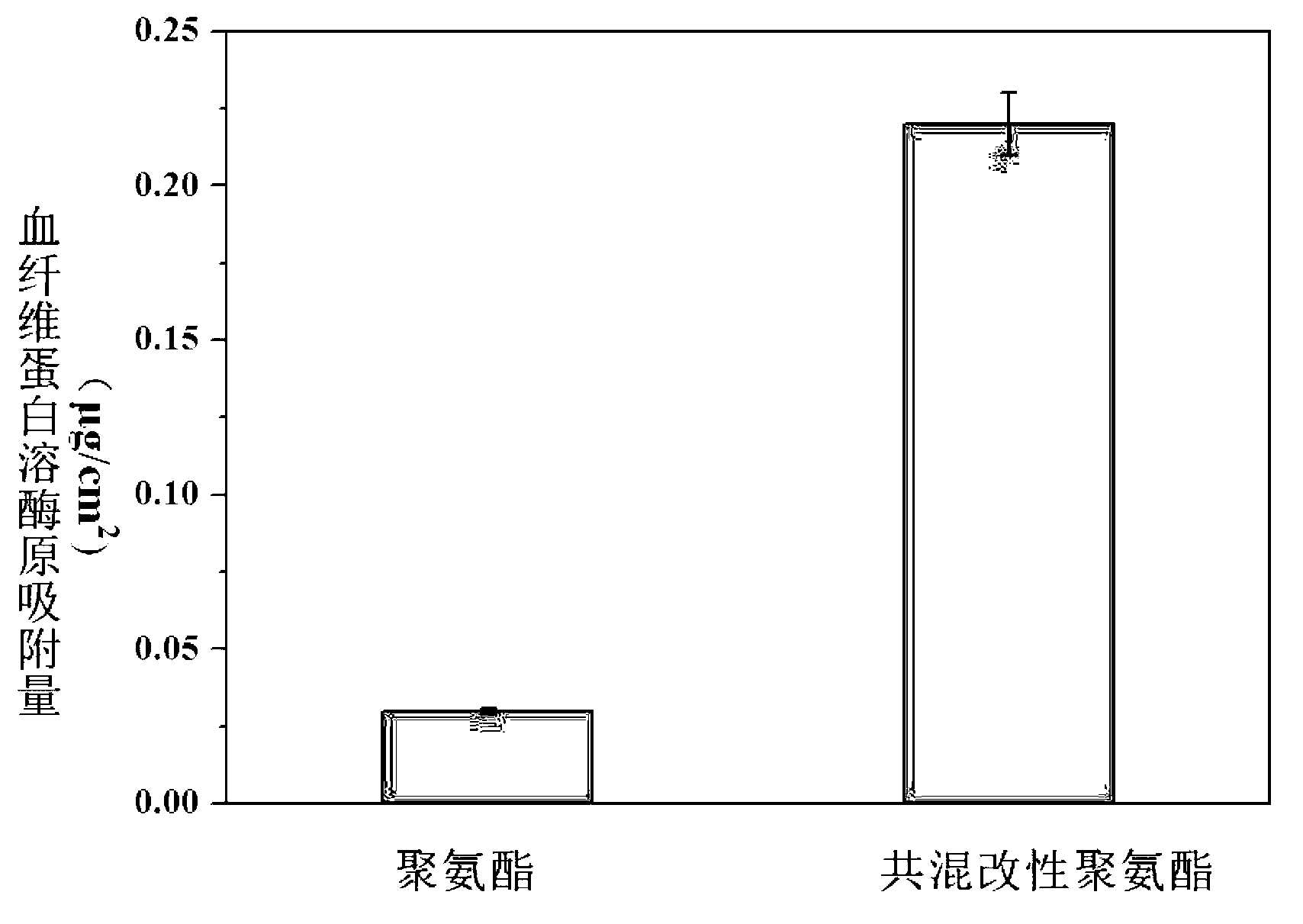
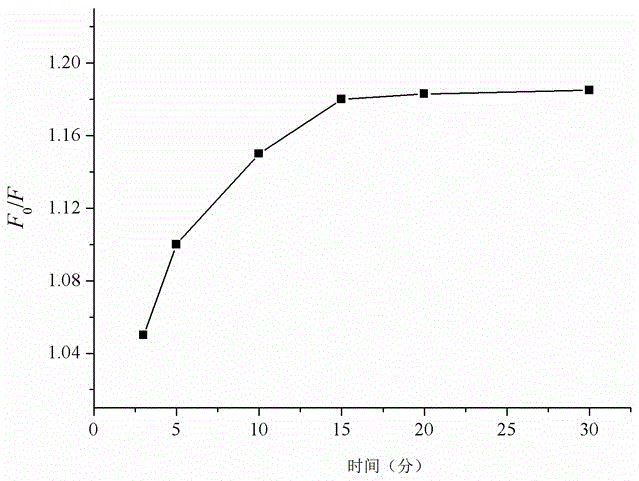
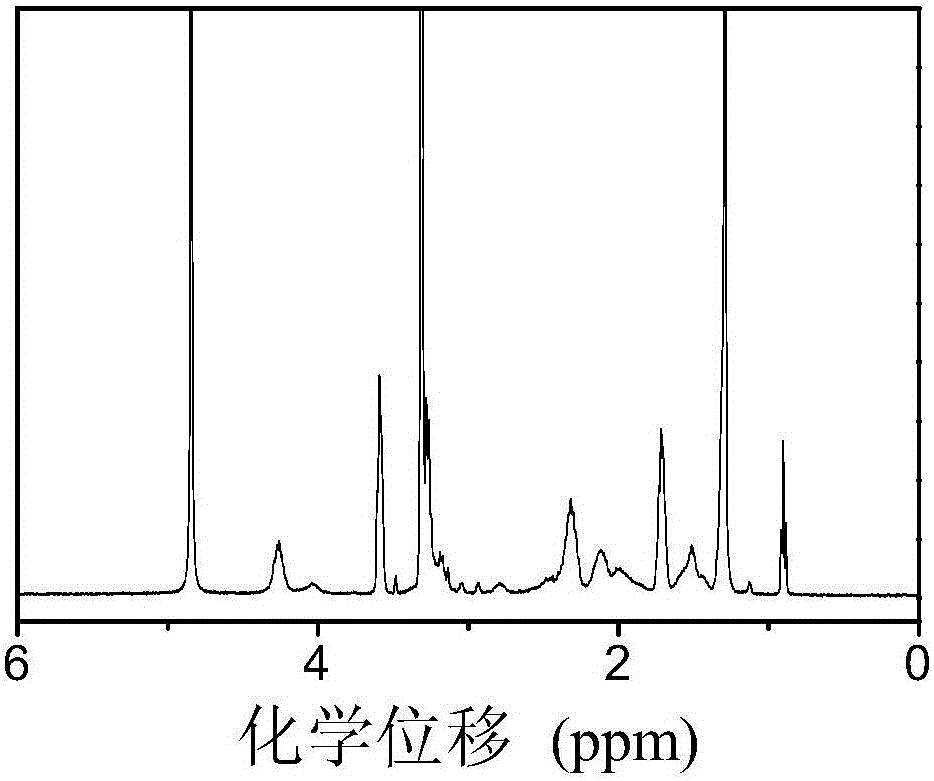
Copolymer containing lysine residue on side chain and preparation method thereof as well as fibrinolytic functional material
ActiveCN103193926AEasy to operateSimple processPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPolymer scienceFunctional monomer
The invention relates to a copolymer containing a lysine residue on a side chain, a preparation method of the copolymer, and a fibrinolytic functional material prepared on the basis of the copolymer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: synthesizing a lysine functional monomer; on the presence of an initiator, preparing the copolymer containing the lysine residue at the side chain by carrying out free radical polymerization on the functional monomer and a vinyl monomer; and blending the prepared copolymer with other commercially available medical polymer materials, and processing and molding to prepare a biological medical functional polymer material of which the surface has a fibrinolytic function. When the obtained material contacts with blood, the fibrinolytic system of a human body can be simulated and nascent thrombus on the surface of a material can be dissolved. The copolymer can be adjusted and controlled directly by changing the charging ratio of the lysine functional monomer to a comonomer, so that the process is simple; the copolymer containing the lysine residue on the side chain can be conveniently blended with various commercially available medical polymer materials, and can be subjected to various processing for molding, so that the construction of a fibrinolytic system on the surface of a material is realized while a biological material in a certain shape is prepared, and the universality is strong.
Owner:JIANGSU BIOSURF BIOTECH CO LTD
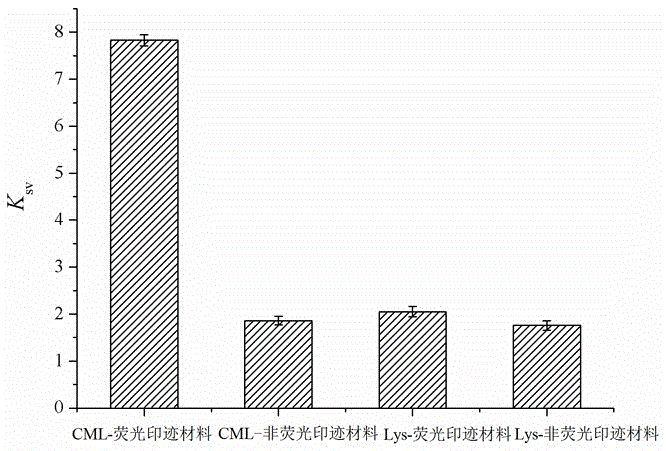
Carboxymethyl lysine fluorescence imprinting material and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105842214AHigh selectivityLarge specific surface areaFluorescence/phosphorescenceFunctional monomerPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a carboxymethyl lysine fluorescence imprinting material and a preparing method and application thereof .According to the preparing method, thin layer nano material graphene is used as a carrier, a fluorescence nano material namely quantum dots excellent in optical performance is used as a response element, a molecularly imprinting polymer high in selectivity and specificity is used as a recognition element, an efficient, portable, fast and sensitive molecularly imprinting fluorescence sensing system is set up, carboxymethyl lysine is used as template molecules, 3-aminopropyl triethoxy silane is used as a functional monomer, tetraethoxy-silicane is used as a crosslinking agent, and ammonia water is used as a catalyst .The surface molecularly imprinting material based on graphene and quantum dots is prepared through a reversed-phase microemulsion synthesis method, and carboxymethyl lysine residues can be detected from food fast and easily .
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Oligo-polyamino acid and sodium alginate combined hybrid antibacterial hydrogel
The invention discloses oligo-polyamino acid and sodium alginate combined hybrid antibacterial hydrogel. The invention provides an amphiphilic molecule based on oligo-polyamino acid as shown by formula I or II and a preparation method of the amphiphilic molecule based on oligo-polyamino acid. In the invention, the hybrid hydrogel prepared by combining the amphiphilic molecule based on polyamino acid with sodium alginate has the characteristics of biocompatibility, biodegradability and the like. A cationic lysine residue is introduced into the polyamino acid segment and experiences static combination with carboxyl on the sodium alginate to generate crosslinking, and the mechanical strength of the hydrogel is improved; and moreover, the cationic lysine has antibacterial activity, and thus the hybrid hydrogel has excellent antibacterial property. Moreover, compared with other types of antibacterial hydrogel materials, the hybrid antibacterial hydrogel has the advantages of low preparation cost, simplicity in preparation method, short preparation cycle, easiness in large-scale production, intrinsic antibacterial activity and the like and has a remarkably broad application prospect in the field of biomedical materials.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel compounds, use thereof in cosmetic and cosmeceutic applications, and compositions comprising same
ActiveUS20100311667A1Increase productionPreventing, reducing, delaying or treating a skin conditionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycineHydrogen
A compound of the formula I: R-A-Gly-His-B (I) wherein: A and B are independently of each other a L-lysine residue, a D-lysine residue, or a L- or D-lysine residue in which the NH2 group of the side chain comprises a modification, where-in said modification is (i) a replacement with a hydrogen, (ii) an acetylation, (iii) a benzoylation, or (iv) a palmitoylation; GIy is a glycine residue; His is a L- or D-histidine residue; R is CH3—(CH2)n—CO—, wherein n=2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 or 8; R′ is a group of formula (II): N(Z)(Z′) (II) wherein: Z and Z′ is hydrogen, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a phenyl group, an hexyl group, a decyl group or an hexadecyl group; or a racemate, an enantiomer or a diastereomer thereof, or mixtures thereof, or a salt thereof.
Owner:LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS CANADA
Labeling reagent and methods of use
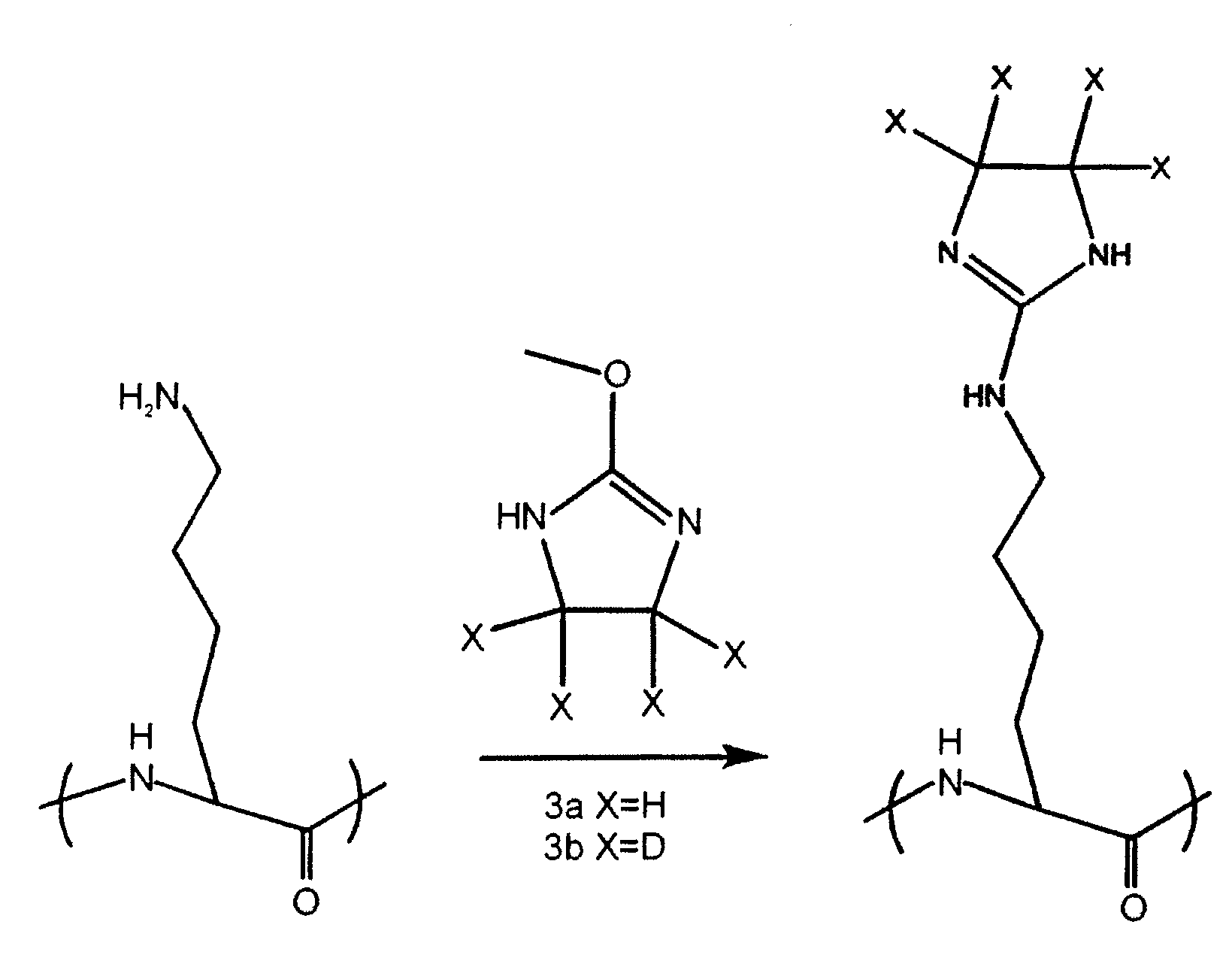
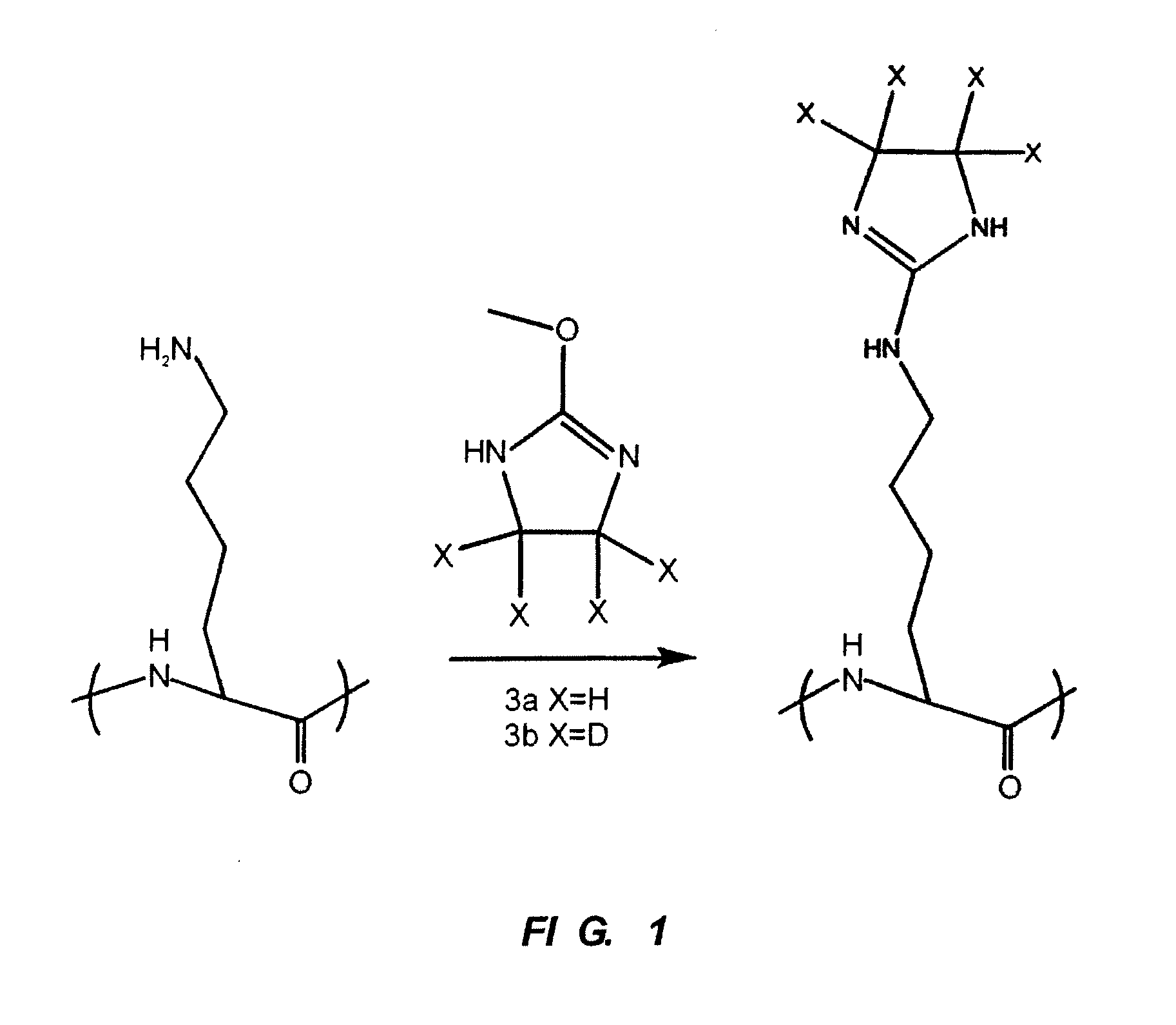
InactiveUS20080242838A1Increase overall sequence coverageEfficient protein identificationParticle separator tubesPeptide/protein ingredientsIonic strengthCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:IRM
Chemical treatment of in vivo tissue to alter charge and net charge density characteristics
InactiveUS20050106270A1High charge densityHigh modulusBiocideInorganic active ingredientsChemical treatmentTissue protein
A method for treating animal tissue with acylation agents to alter the net charge and net charge density of the treated tissue for therapeutic applications is provided. The method involves applying an alkaline solution to the exposed tissue surface area. This results in deprotonation of ε-amino groups of lysine residues on the exposed tissue proteins so that the tissue proteins have a net charge. Then, an acylating agent is applied and the acylating agent reacts with the tissue protein to form a protein complex having an altered net charge. Acylating agents such as sulfonic acids, sulfonyl chlorides, and acid chlorides can be used. The method can be used to treat a wide variety of human tissues including the human cornea for correcting myopia. The method can also be used to treat skin tissue, so that there is an increase in dermal thickness and pliability. The method can be further used to treat articular cartilage.
Owner:DEVORE DALE PAUL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com