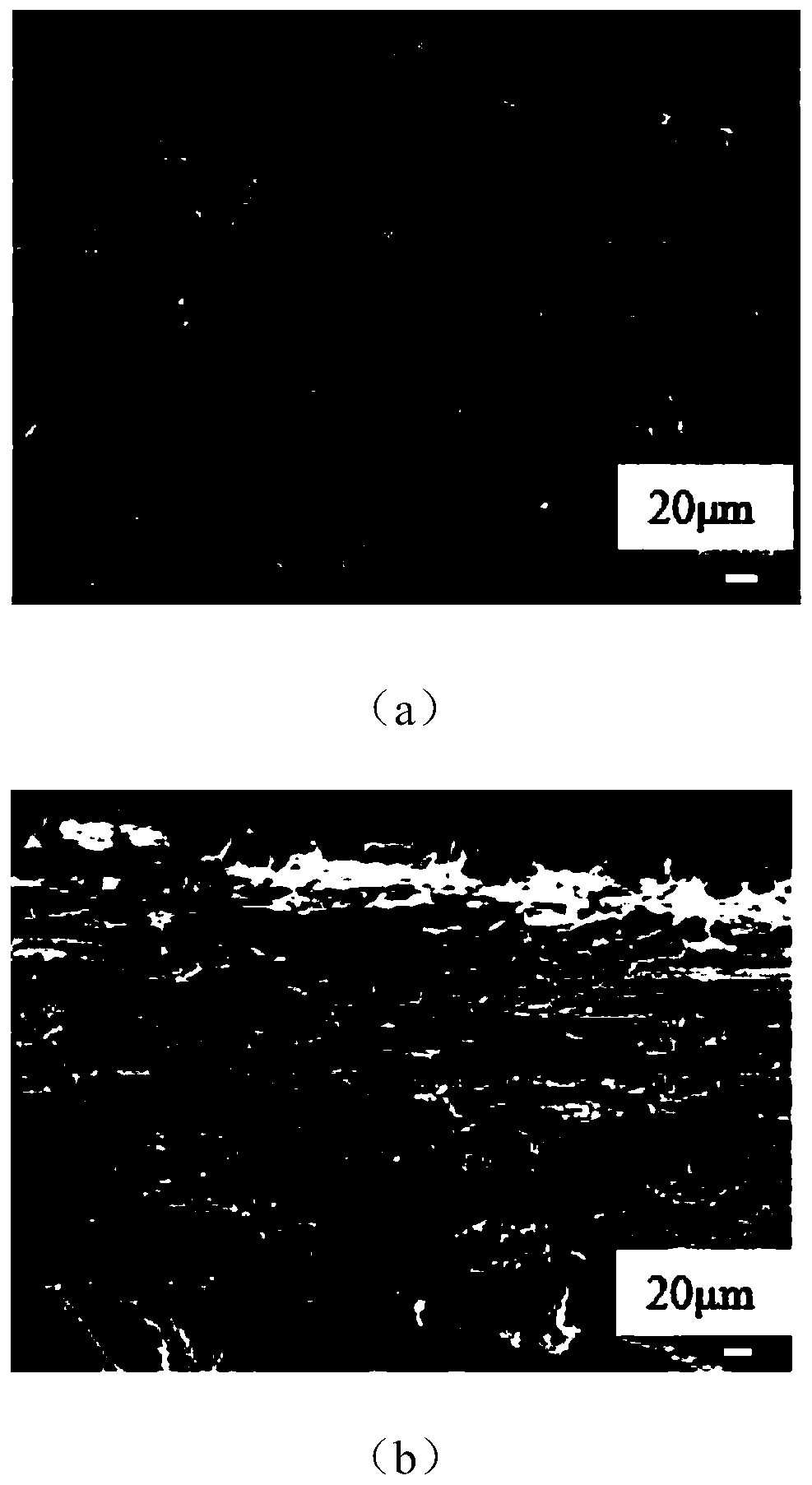
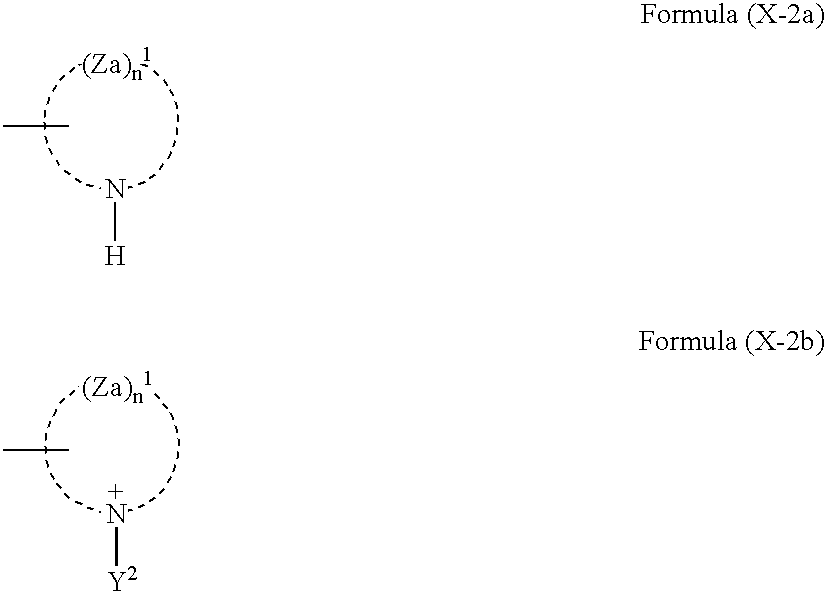
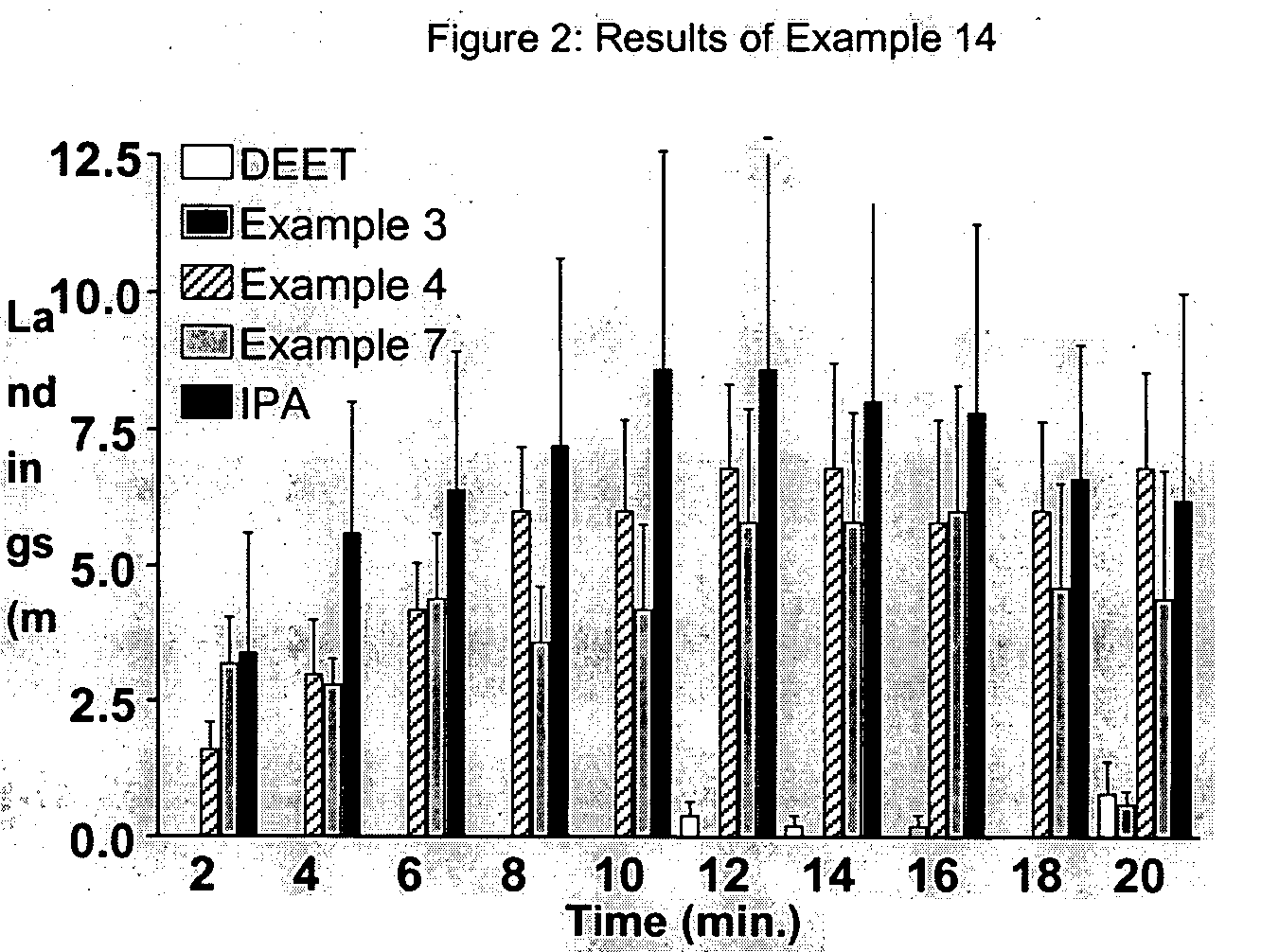
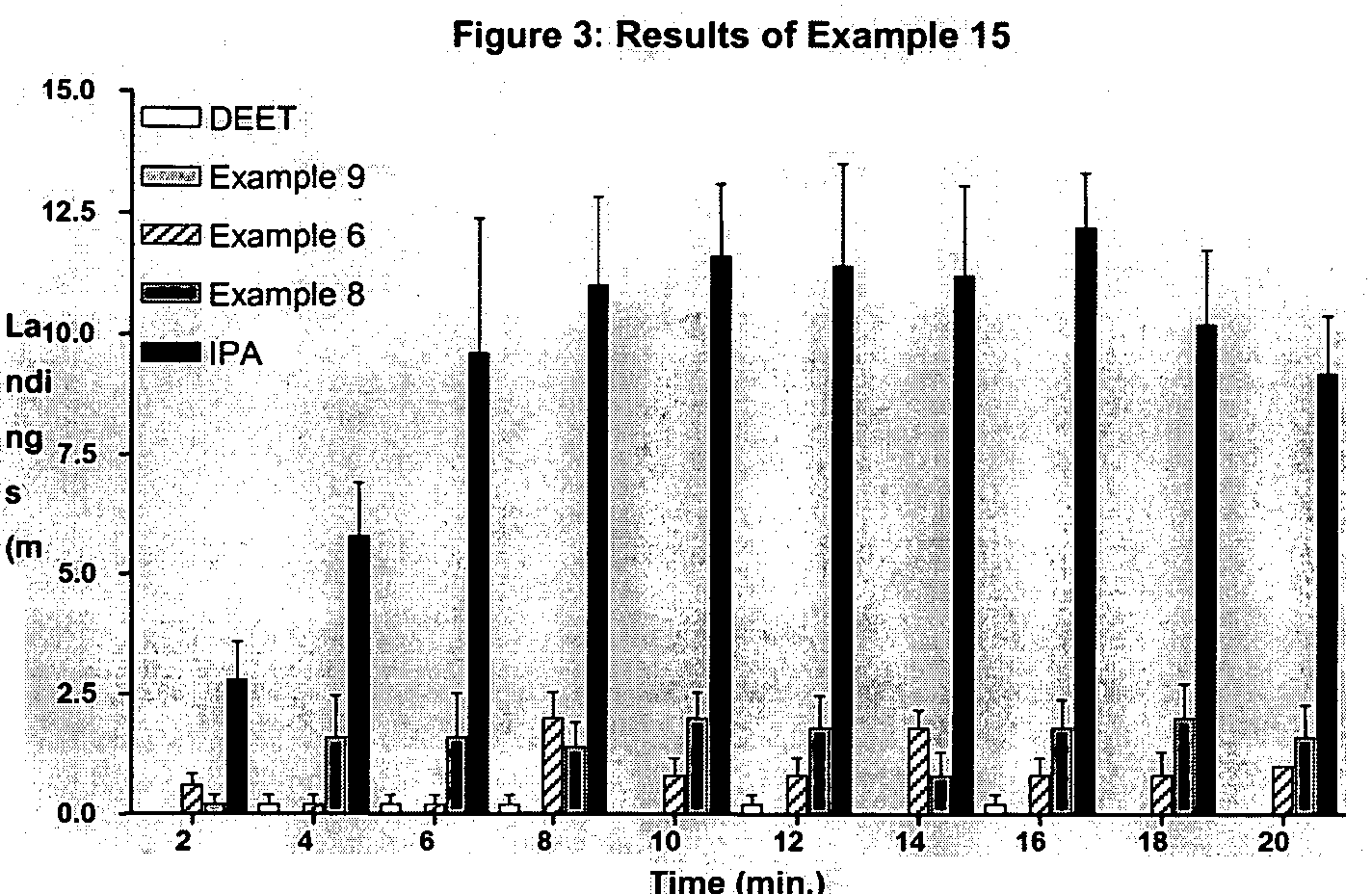
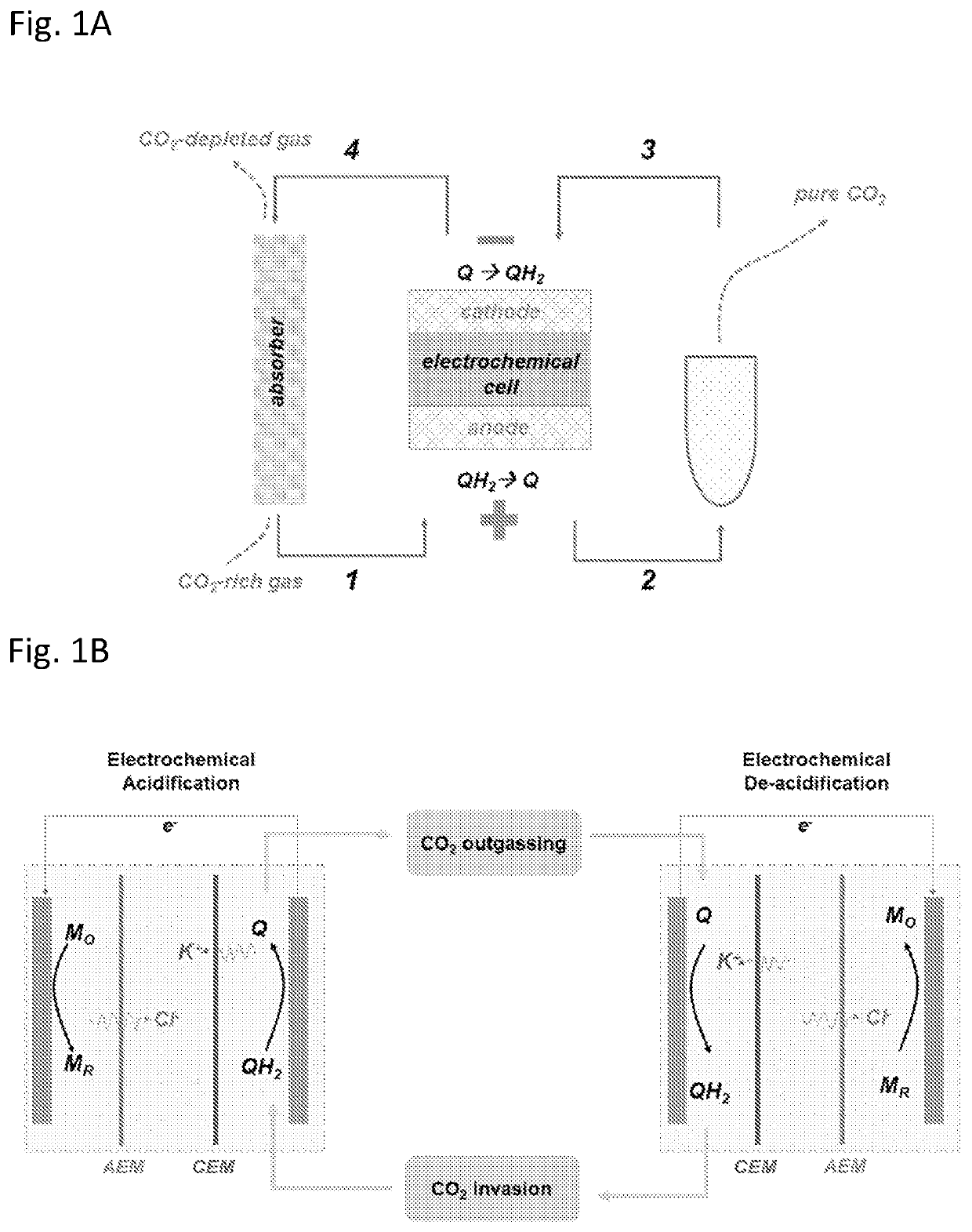
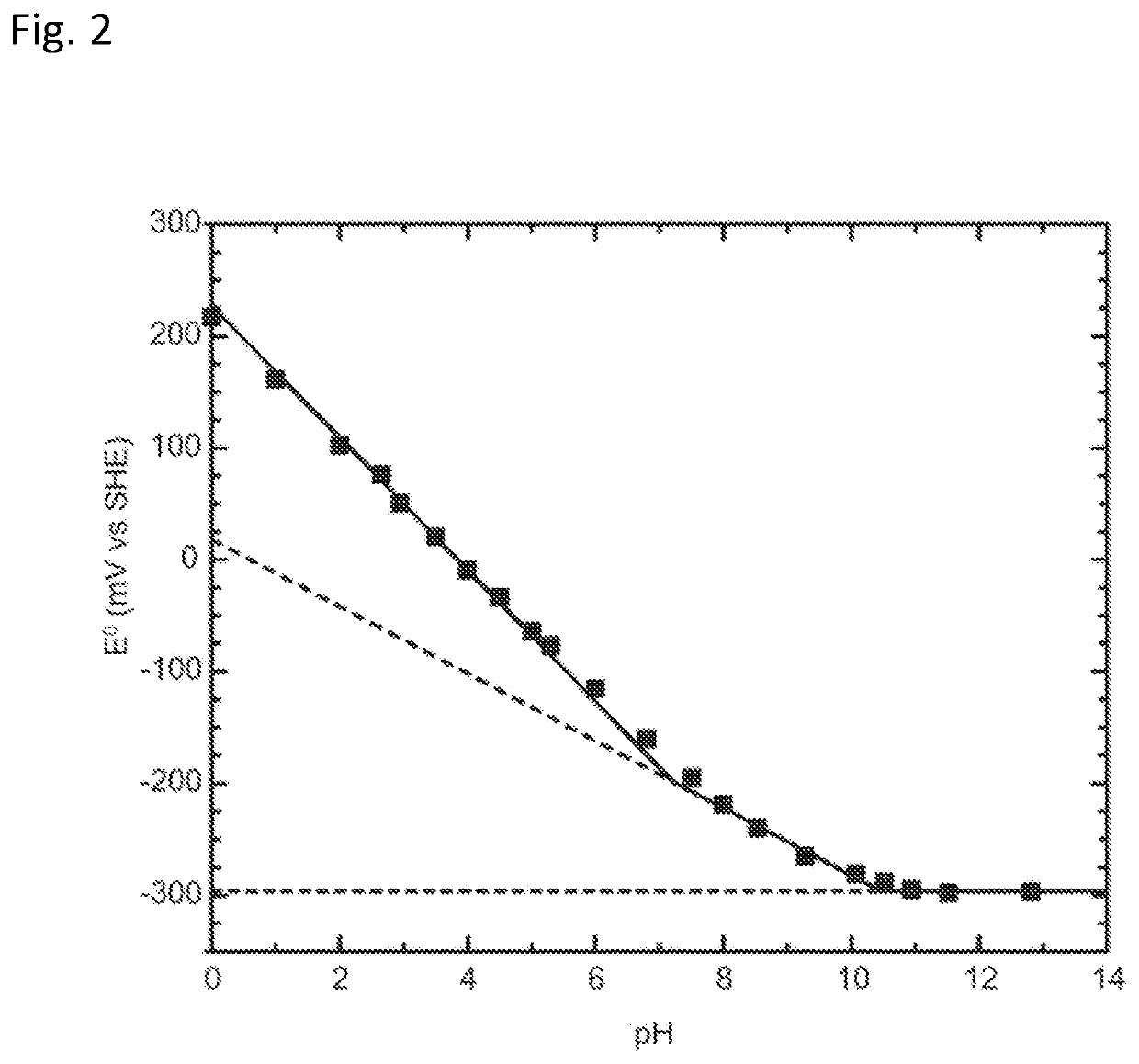
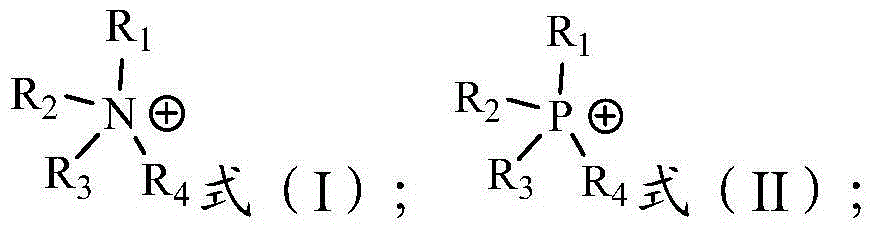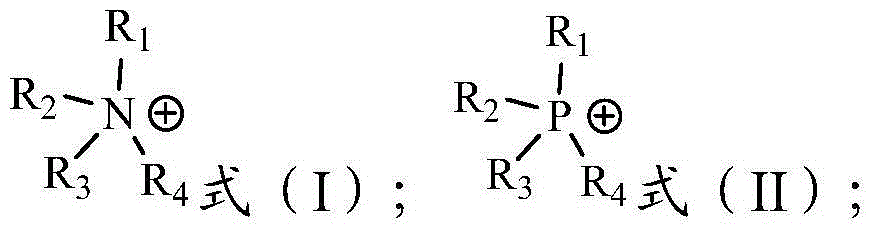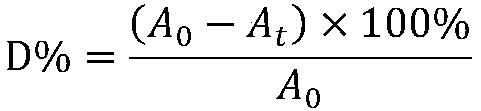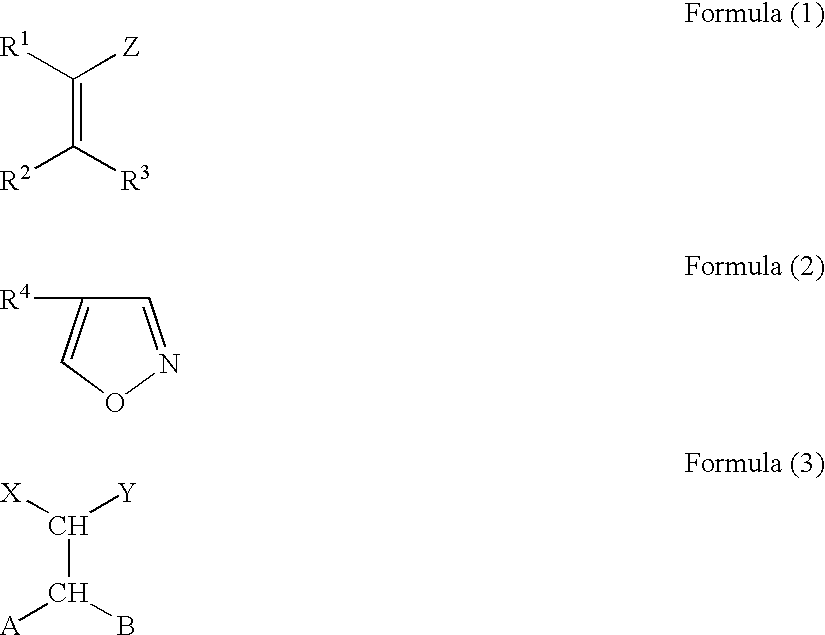Patents
Literature
199 results about "Deprotonation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
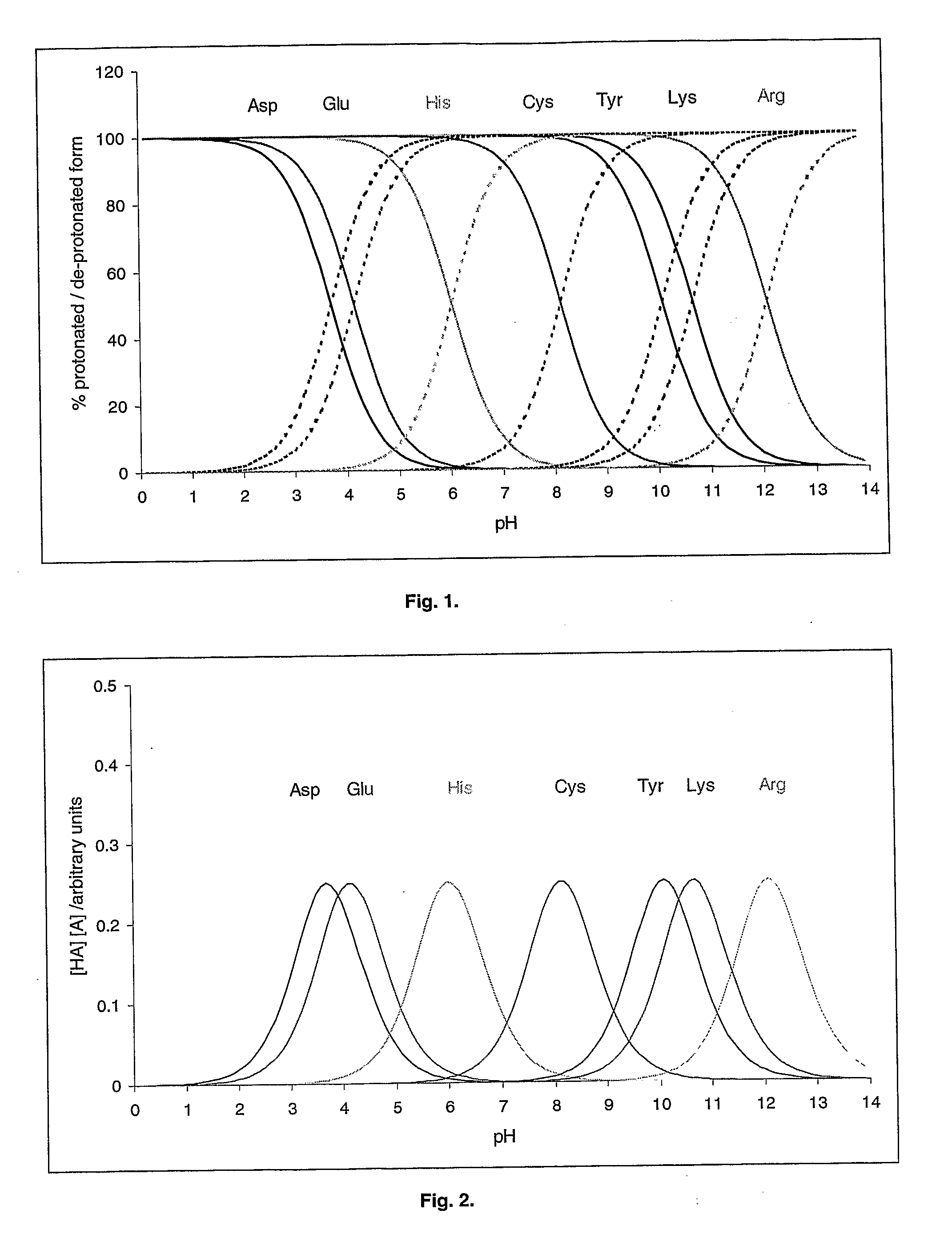
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H⁺) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid-base reaction. The species formed is the conjugate base of that acid. The complementary process, when a proton is added (transferred) to a Brønsted–Lowry base, is protonation (or hydronation). The species formed is the conjugate acid of that base.
Ruthenium(II) catalysts for use in stereoselective cyclopropanations
ActiveUS7754902B2High stereoselectivityHigh yieldRuthenium organic compoundsCobalt organic compoundsProtonationSalen ligand
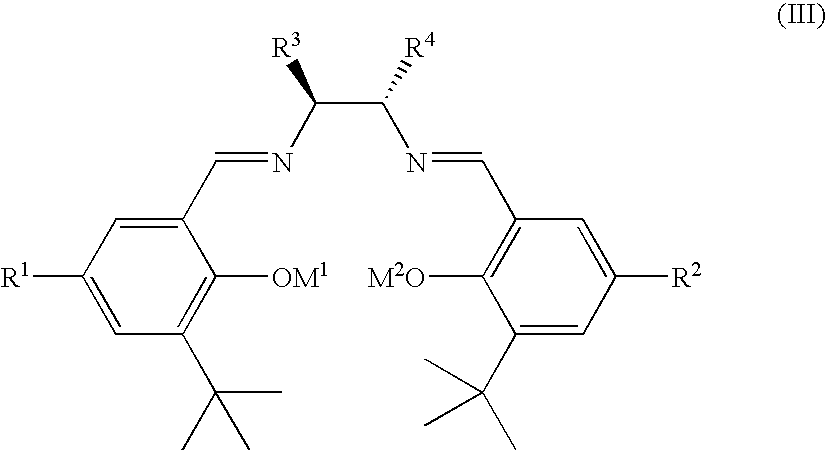
Chiral ruthenium catalysts comprising salen and alkenyl ligands are provided for stereoselective cyclopropanation, and methods of cyclopropanation are provided. The chiral ruthenium catalyst is prepared in situ by combining an alkenyl ligand, a deprotonated chiral salen ligand, and a ruthenium (II) metal. A preferred catalyst is prepared in situ by combining 2,3-dihydro-4-venylbenzofuran, deprotonated 1,2-cyclohexanediamino-N,N′-bis(3,5-di-t-butyl-salicylidene) and RuCl2(p-cymene)]2.
Owner:VANDA PHARMA INC
Fluid system having controllable reversible viscosity
ActiveUS7119050B2Improve solubilityPreventing potential phase separationFluid removalFlushingProtonationBetaine
This Invention relates to methods of treating a subterranean hydrocarbons reservoir comprising contacting the formation with a treating fluid comprising an aqueous solution, an acid, a surfactant acting as gelling agent essentially consisting of erucylamidopropyl betaine (or a protonated / deprotonated homolog or salt thereof). The treating fluid may further comprise a lower n-alcohol for improved temperature stability.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Organic lithium salt electrolytes having enhanced safety for rechargeable batteries and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20060068295A1Improve propertiesImprove thermal stabilityAlkaline accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsProtonationCarboxylic salt
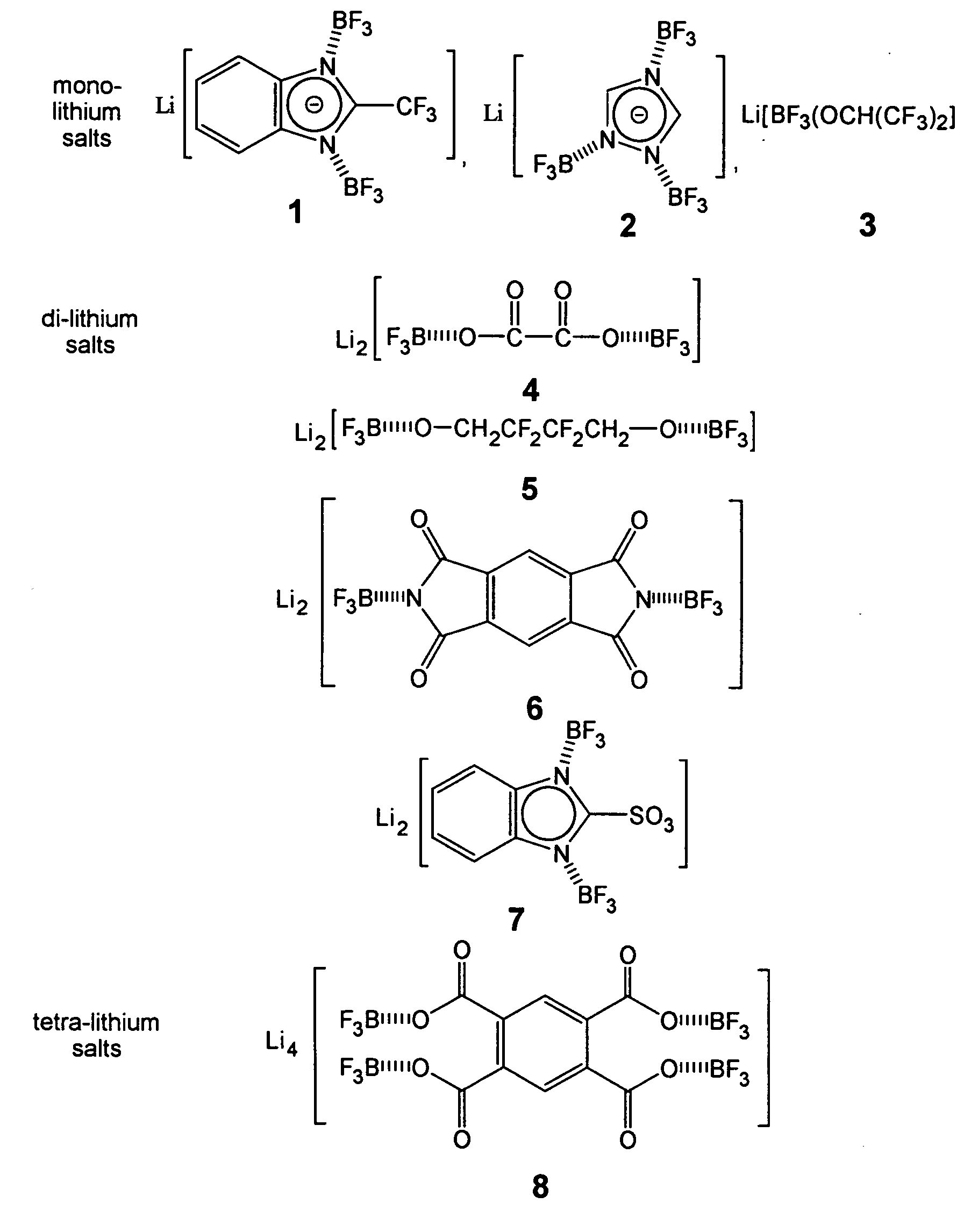
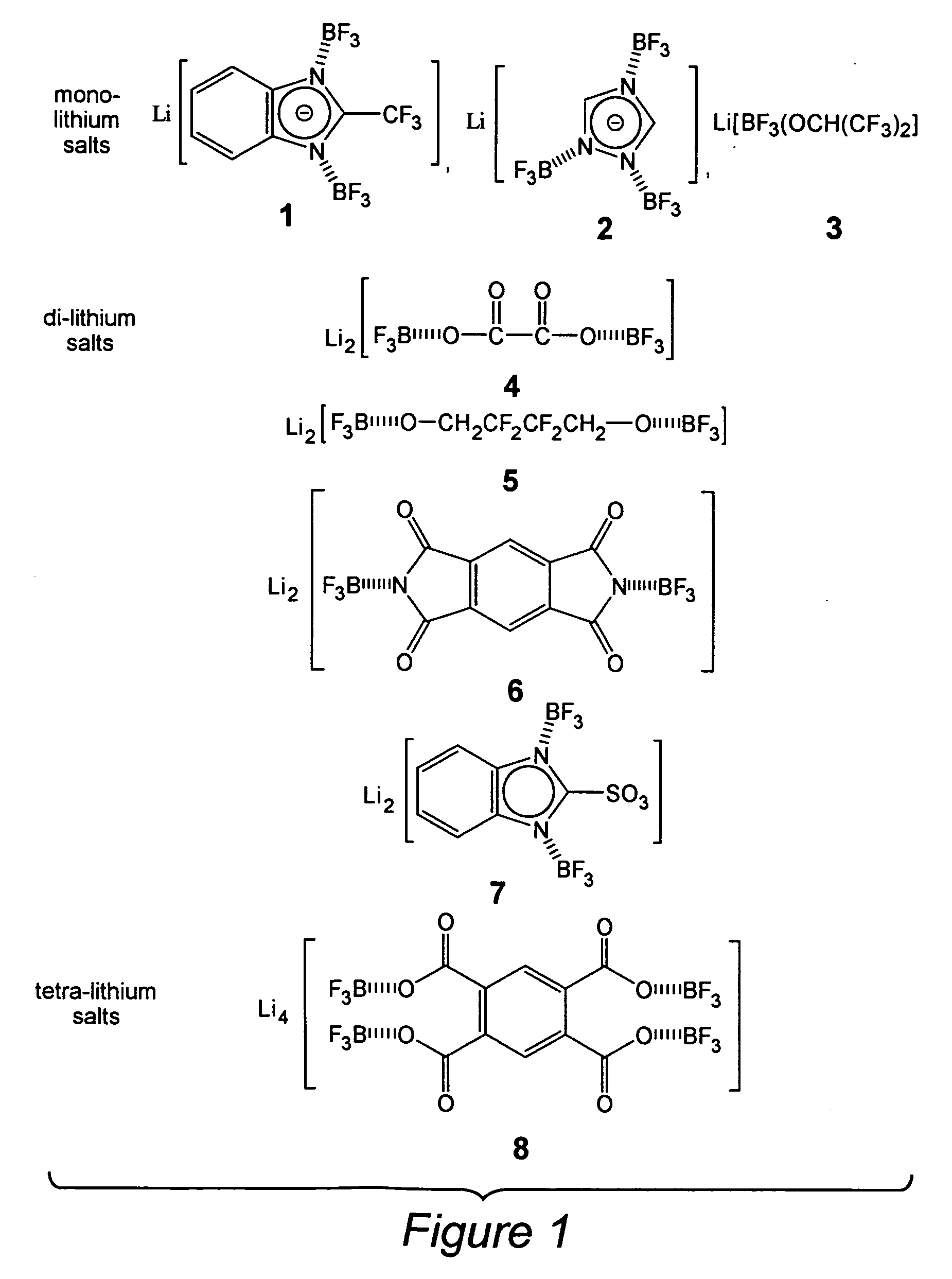
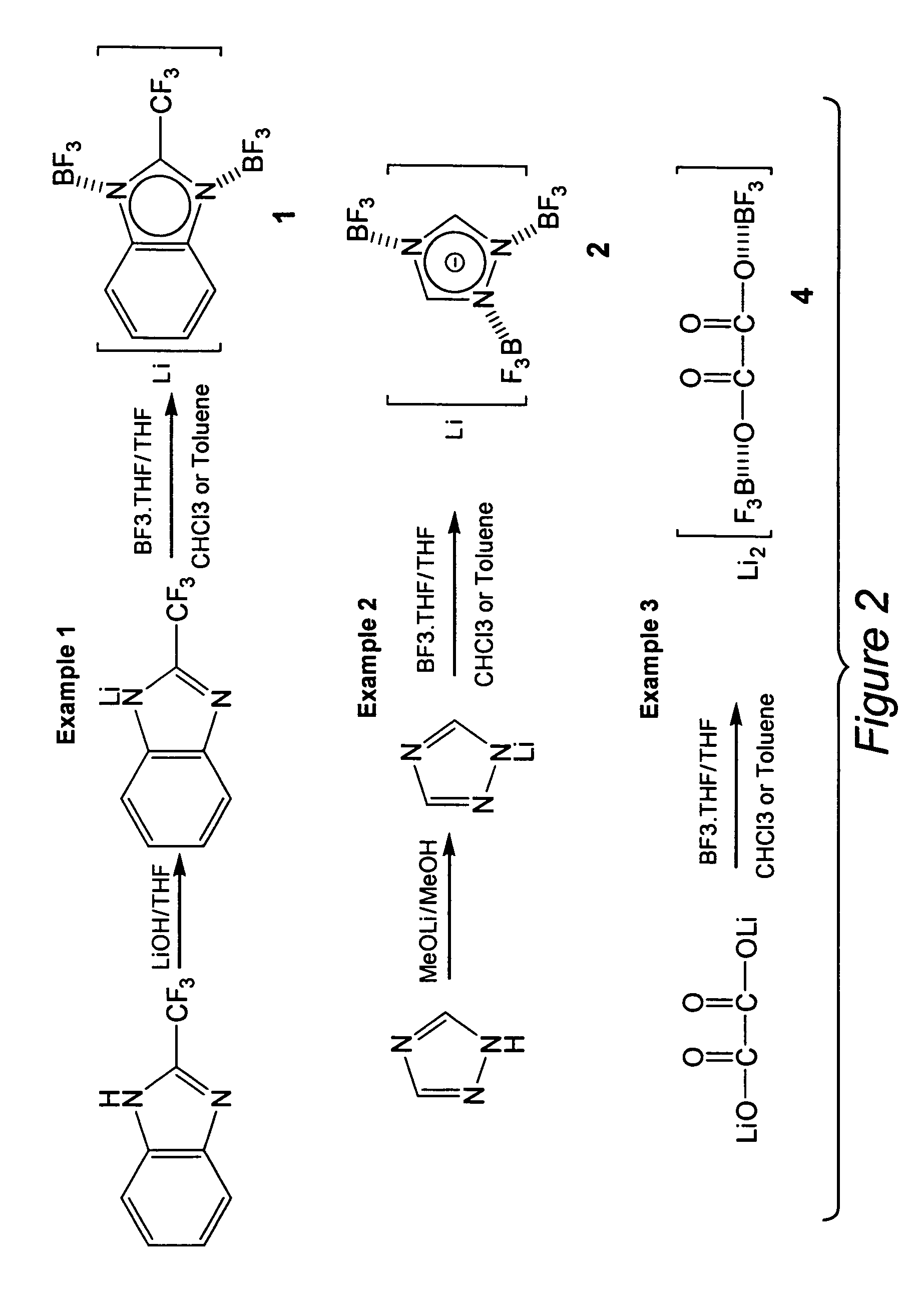
Organic lithium salts suitable for use in electrolytes for primary or secondary rechargeable batteries include de-localized bulky anions over Lewis acid fragments, typically BF3, and organic moieties. The organic moieties may be, for example, anions derived from fused nitrogen heterocycles (e.g. benzeneimidate, benzitriazolate and the like); multi carboxylates (e.g. oxalate, 1,2,4,5-benzenetetracarboxylate and the like), and pyromellitic diimidate. The organic lithium salts of the invention have the general formula: Liq[Org(MXn)m], in which Org represents the organic moieties and MXn represents an organic or inorganic boron, aluminum or phosphorous containing Lewis acid. The organic lithium salts are conveniently prepared by reacting an organic compound having at least one de-protonation group selected from NH, OH, SH or COOH with an inorganic or organic lithium compound to generate an organic lithium processor salt, and thereafter bringing the organic lithium processor salt into contact with an inorganic or organic Lewis acid to obtain the organic lithium product salt.
Owner:SKC POWER TECH
Light-emitting diode device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109935708AImprove luminous efficiencyAvoid deprotonation of the methylammonium cationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExcited stateCharge carrier
The invention belongs to the field of quantum dots, and specifically relates to a light-emitting diode device and a preparation method thereof. The light-emitting diode comprises an anode, a compositelight-emitting layer, an electron transport layer and a cathode which are arranged in a stacked manner, wherein the composite light-emitting layer includes a perovskite quantum dot material and a non-perovskite quantum dot material, and the electron transport layer includes an electron transport material grafted with a defective passivating agent. The light-emitting diode not only can promote thecarrier transport performance, but also can effectively avoid methyl ammonium cation deprotonation between a defective group and the perovskite quantum dot material in the composite light-emitting layer, thereby optimizing the application effect of the perovskite quantum dot material in the light-emitting diode device, promoting the synergistic effect of the perovskite quantum dot material and the non-perovskite quantum dot material to produce excited-state complex electroluminescence, and improving the light-emitting efficiency of the light-emitting diode and the stability of the device.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
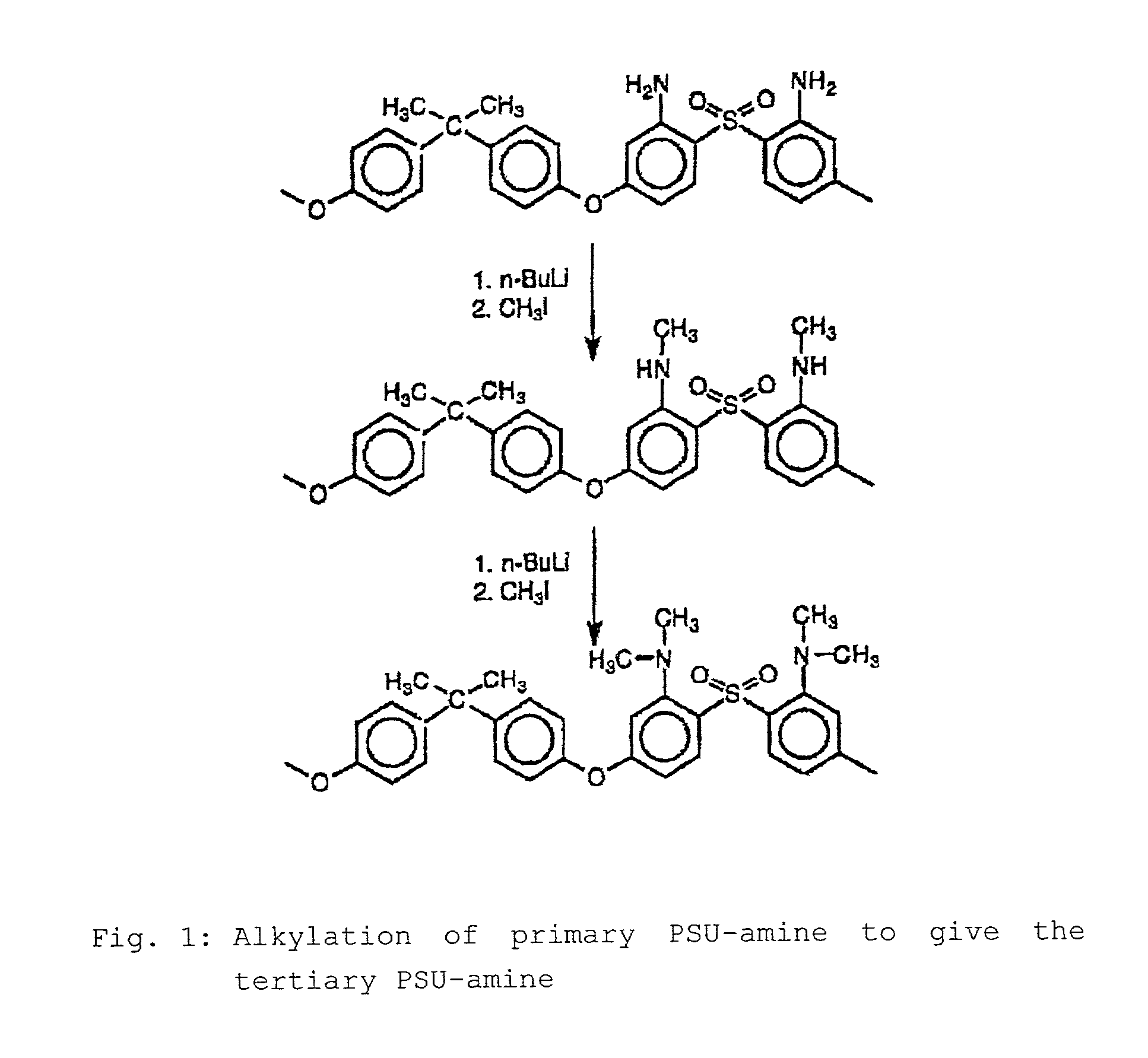
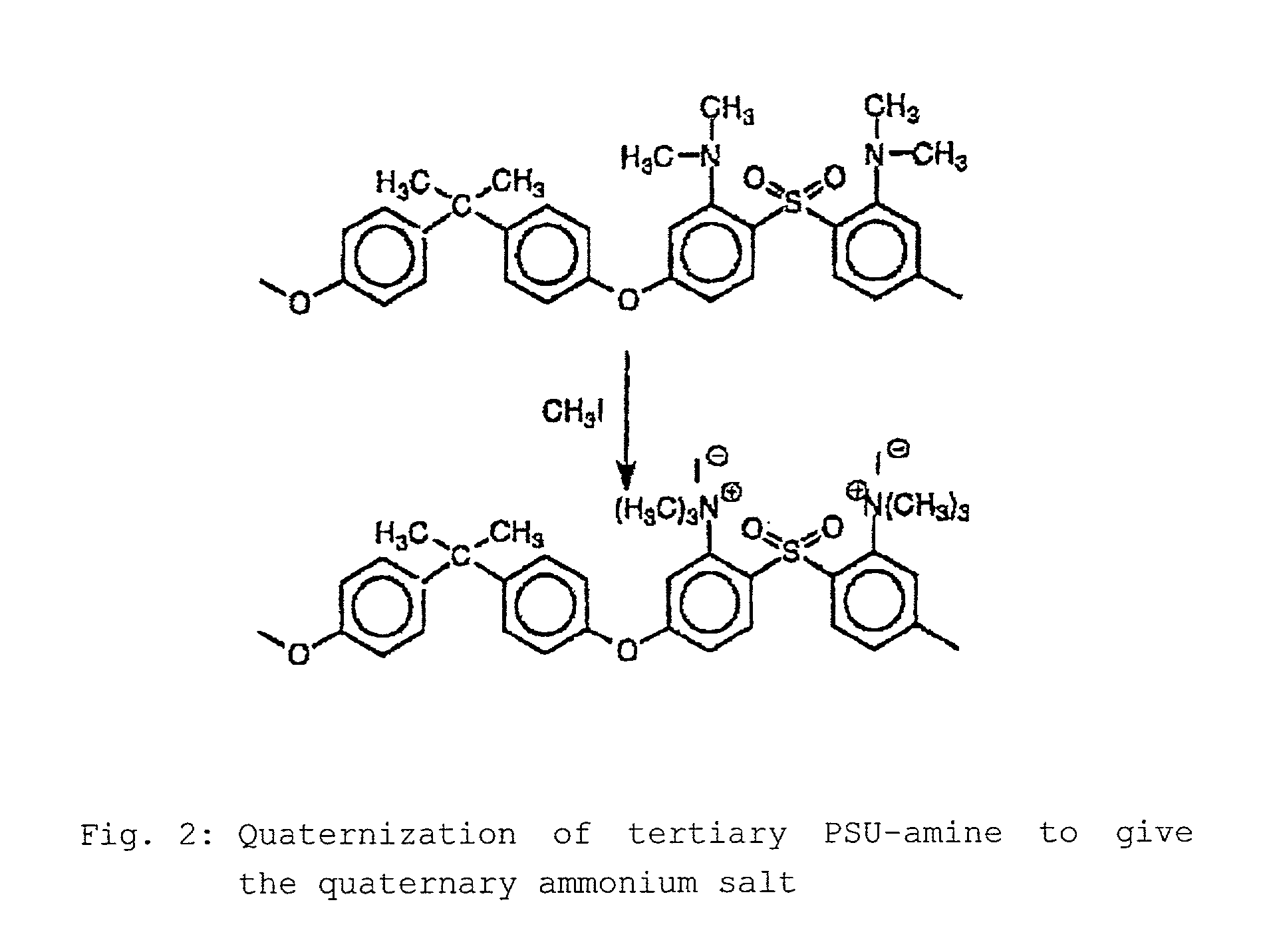
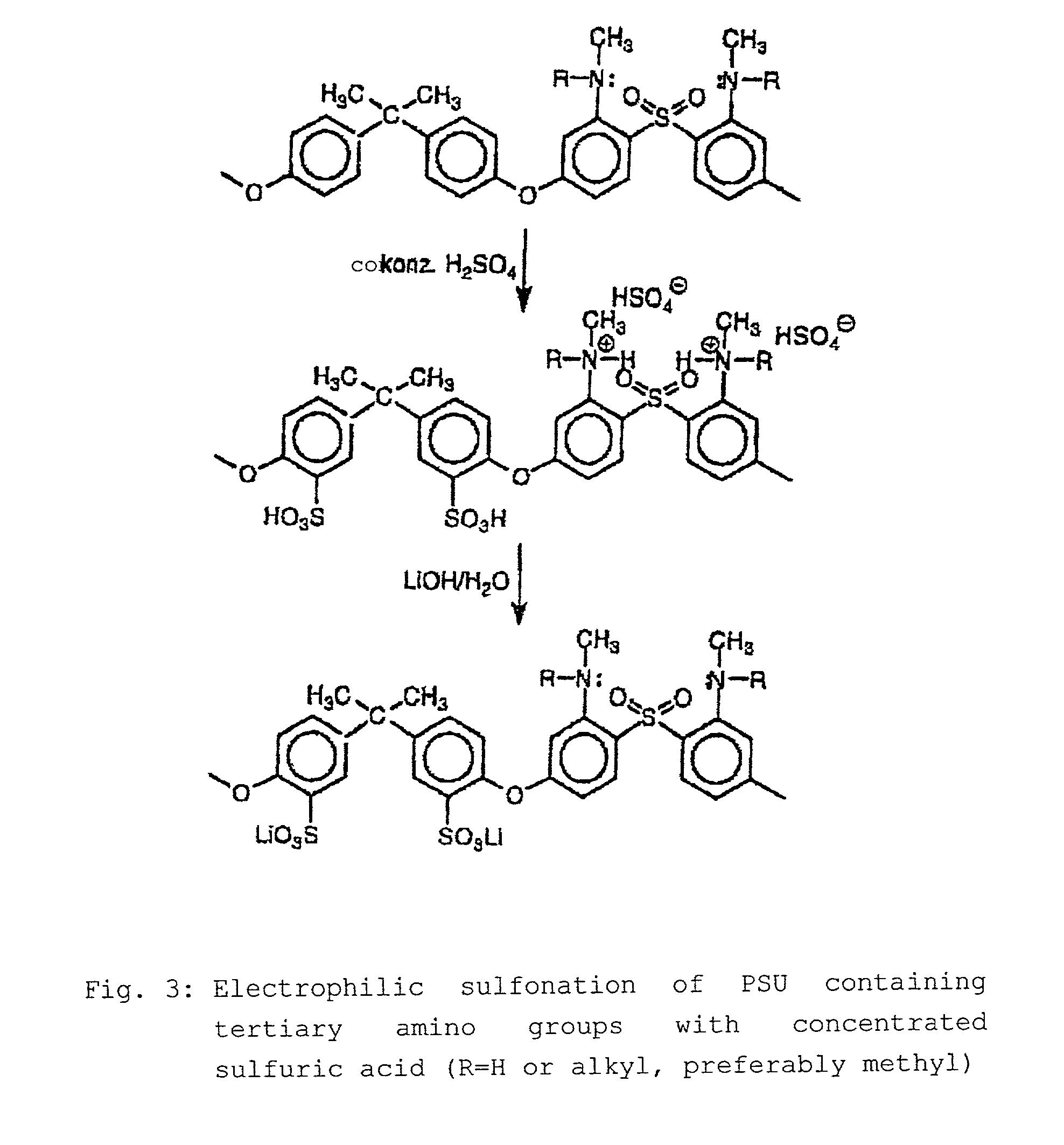
Step-by-step alkylation of polymeric amines
InactiveUS7132496B2Ion-exchange process apparatusNon-metal conductorsHydrophilic polymersOrganic base
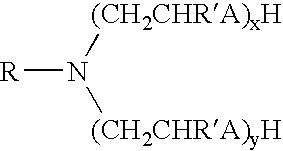
The invention relates to the following: a method for step-by-step alkylation of primary polymeric amines by step-by-step deprotonation with a metallo-organic base and a subsequent reaction with an alkyl halide; a method for modifying tertiary polymeric amines with other functional groups; polymers with secondary / tertiary amino groups and with quaternary ammonium groups; polymers with secondary / tertiary amino groups and other functional groups, especially cation exchanger groupings; membranes consisting of the above polymers, either non-crosslinked or ionically or covalently cross-linked; acid-base-blends / membranes, and a method for producing same, consisting of basic polymers with polymers containing sulphonic acid, phosphonic acid or carboxyl groups; the use of ion exchanger polymers as membranes in membrane processes, e.g., polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells, direct methanol fuel cells, redox batteries, or electrodialysis; the use of the inventive hydrophilic polymers as membranes in dialysis and reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, diffusion dialysis, gas permeation, pervaporation and perstraction.
Owner:HARING THOMAS
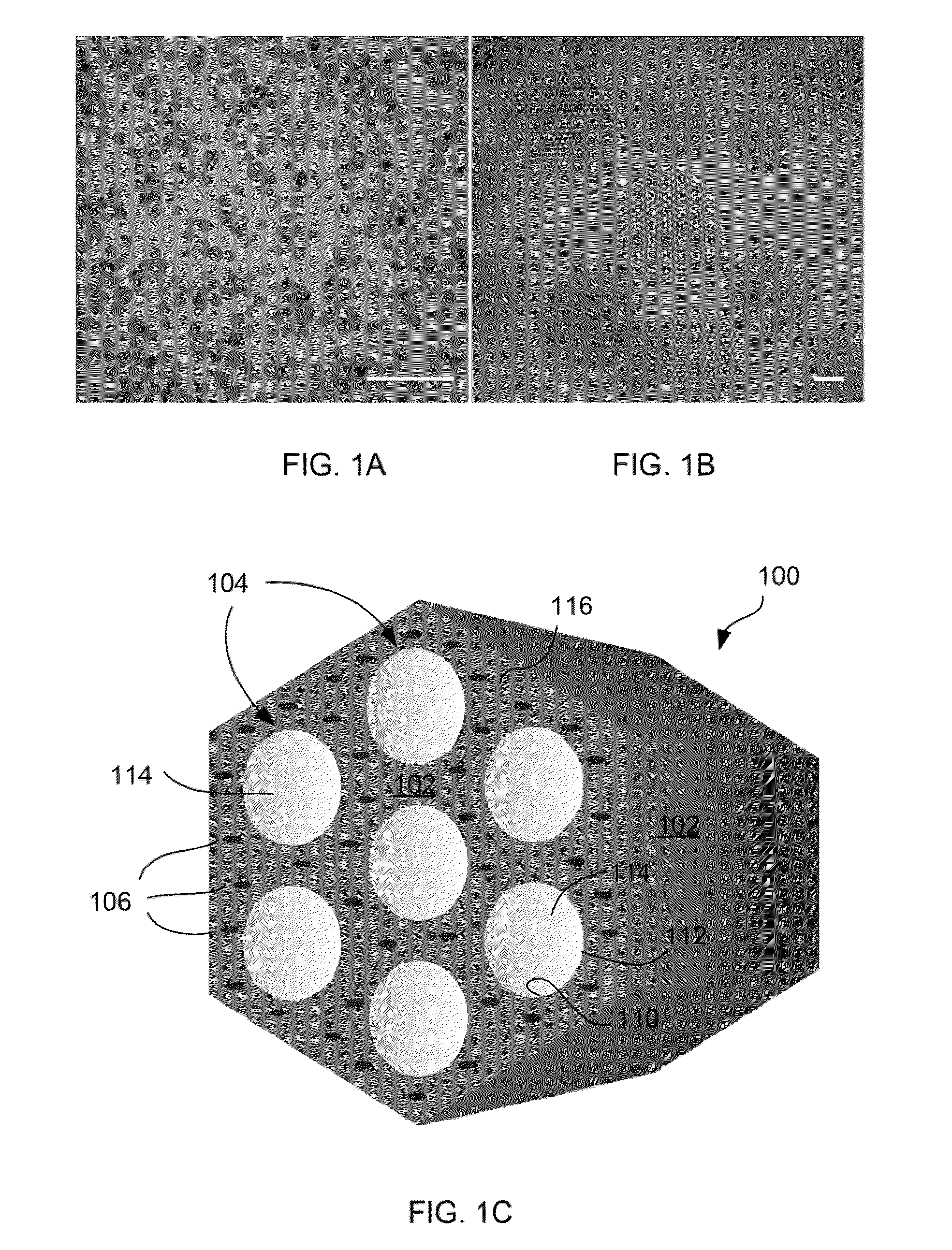
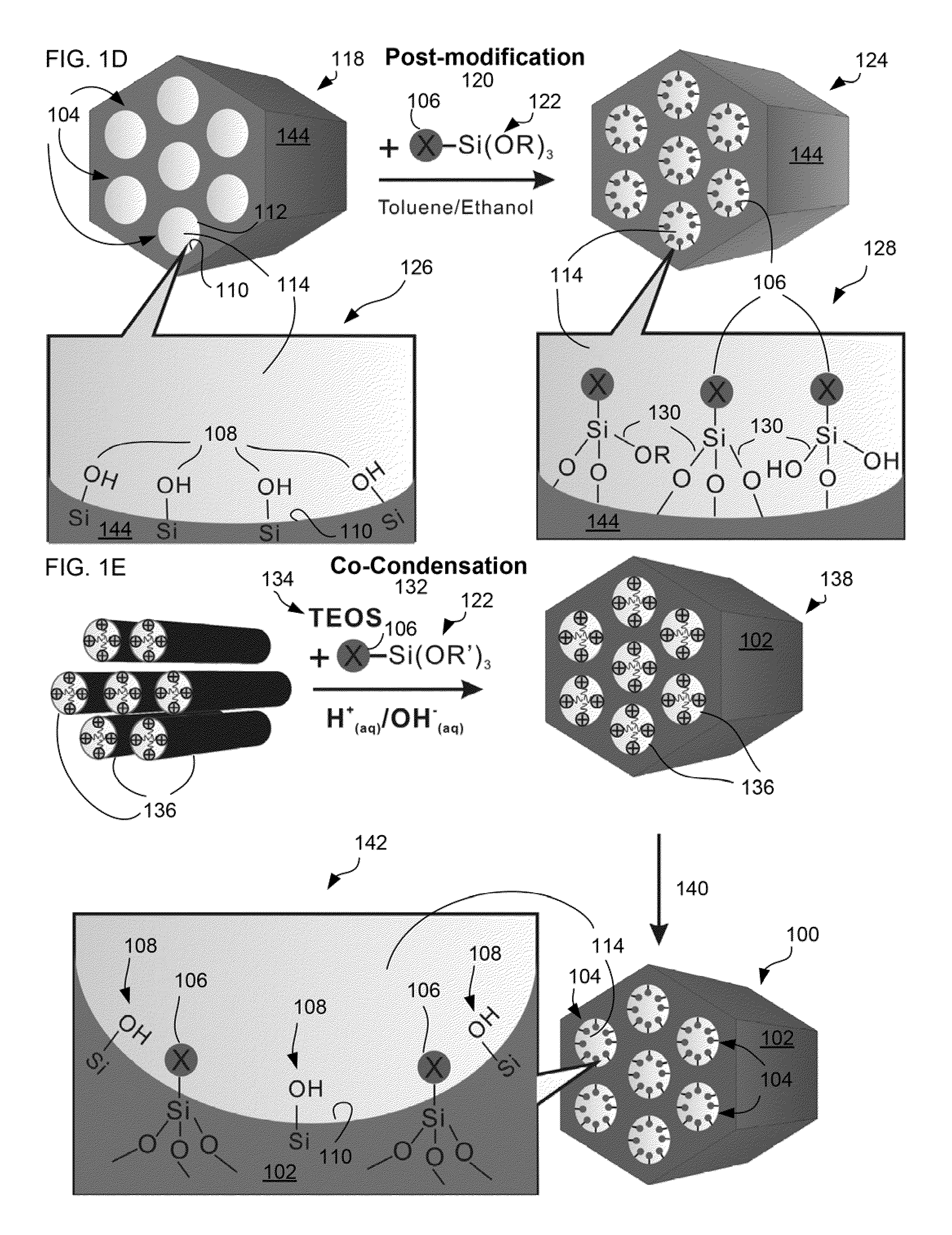
Charged mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based drug delivery system for controlled release and enhanced bioavailability
A charged mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN)-based drug delivery system for controlled release and enhanced bioavailability is disclosed. The system comprises a positively charged MSN, which has a silica matrix and an array of pores and / or nanochannels in the matrix. The entire substance of the matrix, all the surfaces and the pores and / or nanochannels comprise a plurality of silanol (Si—OH) and quaternary ammonium functional groups. The bioavailability of a negatively charged bioactive compound can be increased by loading it into the pores and / or nanochannels. The silanol (Si—OH) functional groups on the surfaces lining the walls of the pores and / or nanochannels are free to deprotonate in a fluid having pH above the pI of the positively charged MSN and lead to a sustained release of the negatively charged drug from the pores and / or nanochannels, and thereby enhance the bioavailability of the drug.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Methods for using reversible phase oil-based drilling fluid
Invert emulsion compositions including an oleaginous, a non-oleaginous and an amine surfactant that are useful in the oil and gas well drilling art are disclosed. The amine surfactant is selected so that the invert emulsion can be converted form a water-in-oil type emulsion to a oil-in-water type emulsion upon the protonation of the amine surfactant. Deprotonation of the amine surfactant reverses the conversion. This solution also permits the conversion of oil-wet solids in the fluid into water-wet solids.
Owner:MI
Rare earth extraction and separation method
ActiveCN104087750AImprove extraction efficiencySignificant synergistic extraction effectProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementPhosphonium
The invention provides a rare earth extraction and separation method which comprises the following step of extracting a rare earth-containing solution through an organic phase containing an extraction agent and a diluent, wherein two extraction agents are selected from ionic liquid, positive ions in the ionic liquid are selected from quaternary ammonium positive ions or quaternary phosphonium positive ions, and negative ions in the ionic liquid are selected from negative ions obtained by performing deprotonation on an acidic phosphine extraction agent. When rare earth elements are extracted by taking two kinds of compounded different bifunctional ionic liquid as the extraction agents, the method has an obvious synergistic extraction effect and is high in rare earth extraction efficiency and good in separation effect. The experimental result proves that the synergistic extraction coefficients of La<3+>, Nd<3+>, Eu<3+>, Dy<3+> and Er<3+> can be 6, 100, 400, 300 and 450, the synergistic extraction coefficients of Ce<3+>, Pr<3+>, Sm<3+>, Ho<3+> and Lu<3+> are respectively 3, 9, 15, 25 and 30, and the method has an obvious synergistic effect.
Owner:XIAMEN INST OF RARE EARTH MATERIALS
Micro-channel chemical preparation method of porous metal-organic framework material
InactiveCN104892404AIncrease surface areaUniform particle sizeGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic compound preparationLiquid mediumMixed materials
The purpose of the invention is providing a micro-channel chemical preparation method of porous metal-organic framework material. The method comprises the following steps: respectively injecting a liquid medium containing one or more organic compounds with at least one unidentate ligand, a liquid medium containing one or more metal ions, a liquid medium containing a deprotonation assistant and an inert gas into a micro-channel reactor through different inlets, carrying out a coordination reaction on the above obtained mixed material liquid in the micro-channel at a certain temperature under a certain pressure to form a coordination compound, crystallizing, filtering, washing, and drying to prepare the porous metal-organic framework material, wherein the micro-channel reactor has at least two inlets and one outlet; the addition amount of the deprotonation assistant is 0-50% of the mole number of all metal ions; a ratio of the volume velocity of inert gas added into the micro-channel reactor to the bulk volume velocity of the liquid phase is 0-100:1; and the crystallization process can be omitted. The method has the characteristics of simple and safe operation, high efficiency, large throughput and easy amplification.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stable Aqueous Systems Comprising Proteins
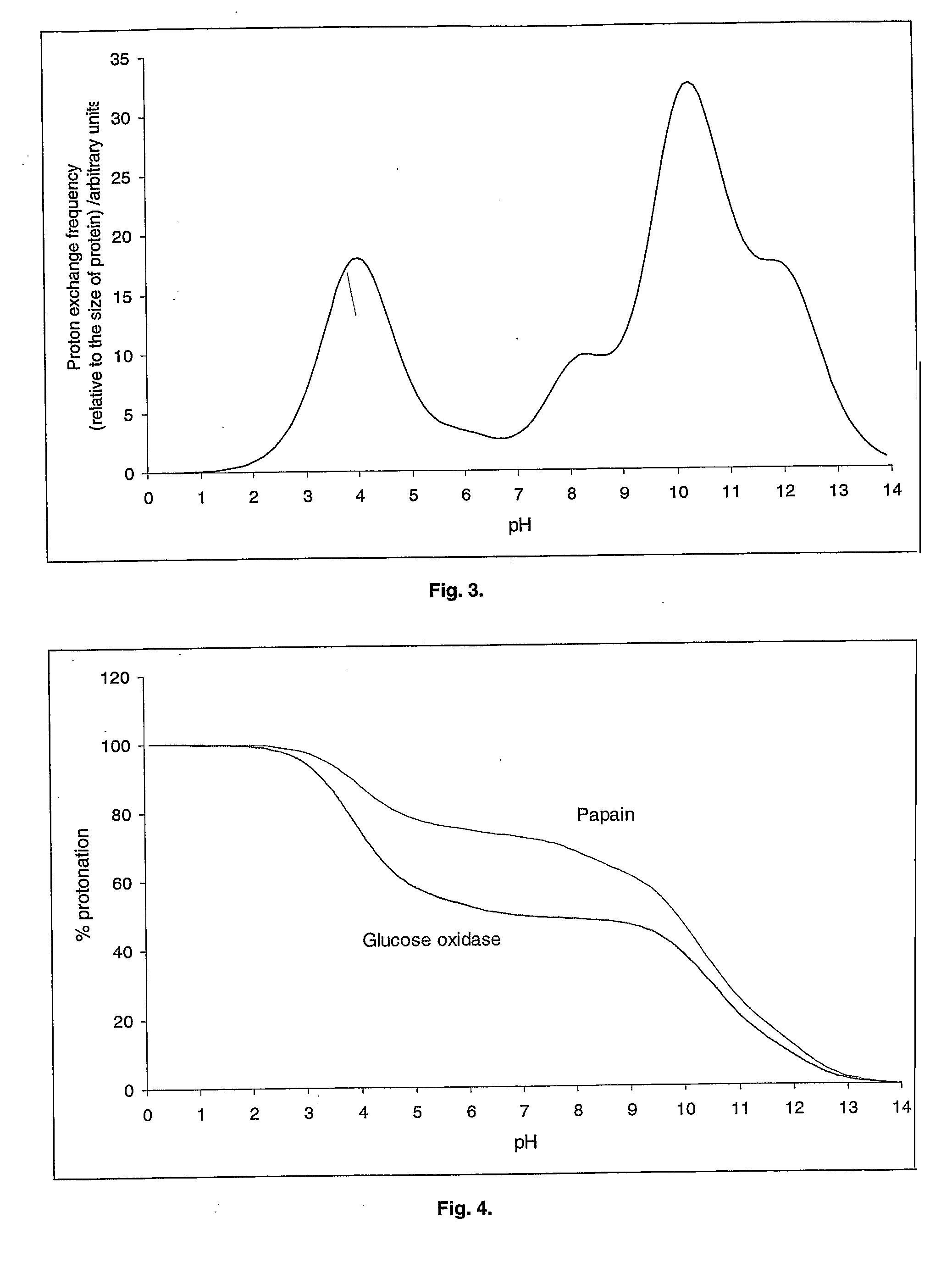
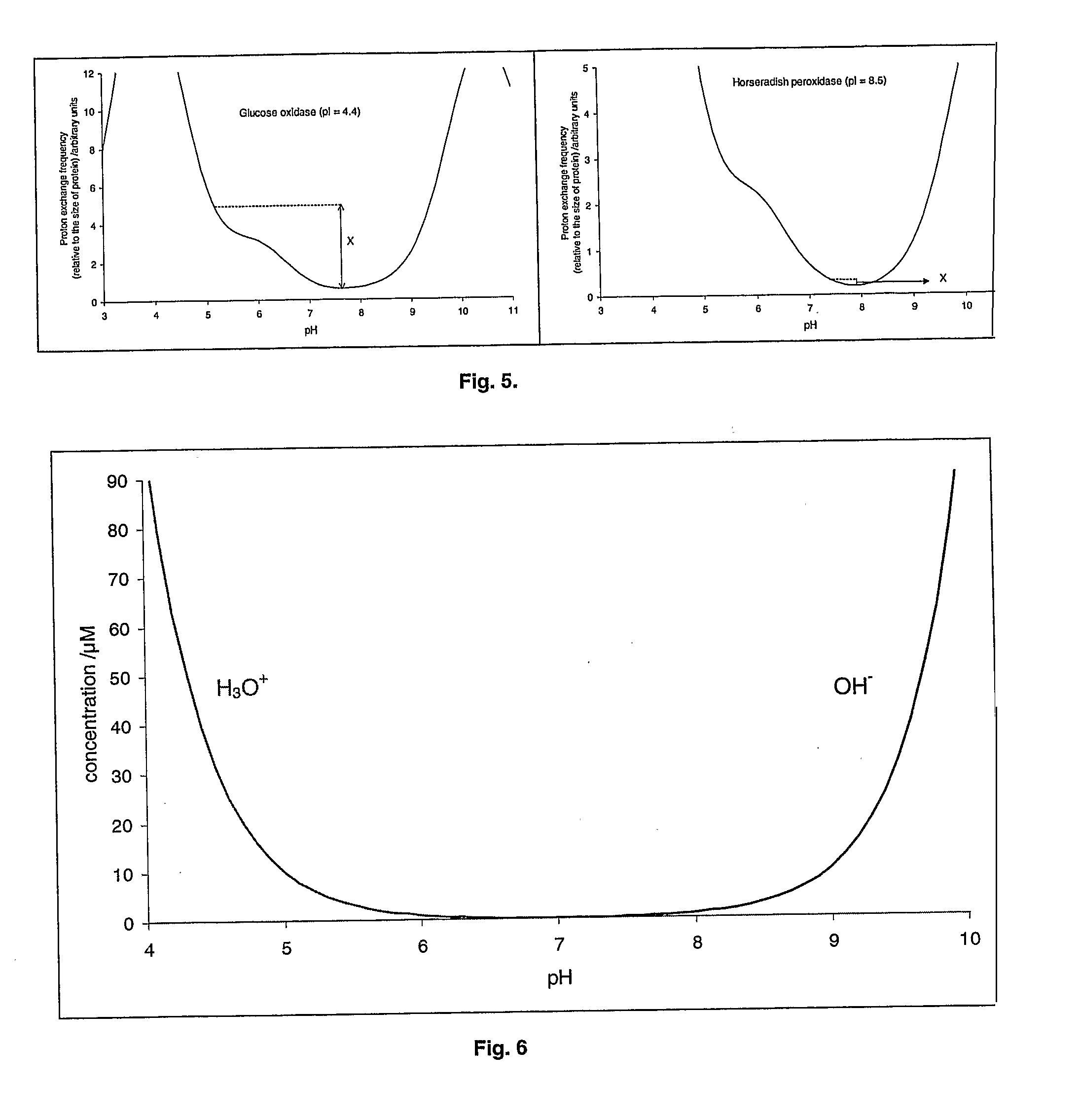
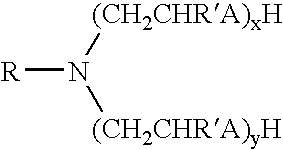
An aqueous system comprises a protein and one or more stabilising agents, characterised in that (i) the one or more stabilising agents have ionisable groups capable of exchanging protons with the protein and with the ionised products of water dissociation; (ii) the ionisable groups include first groups that are positively charged when protonated and uncharged when deprotonated, and second groups that are uncharged when protonated and negatively charged when deprotonated; and (v) the pH of the composition is within a range of protein stability that is at least 50% of the maximum stability of the protein with respect to pH.
Owner:ARECOR LTD
Method for using reversible phase oil-based drilling fluid
Invert emulsion compositions including an oleaginous, a non-oleaginous and an amine surfactant that are useful in the oil and gas well drilling art are disclosed. The amine surfactant is selected so that the invert emulsion can be converted form a water-in-oil type emulsion to a oil-in-water type emulsion upon the protonation of the amine surfactant. Deprotonation of the amine surfactant reverses the conversion. This solution also permits the conversion of oil-wet solids in the fluid into water-wet solids.
Owner:MI
Wetness sensor for use in an absorbent article
A wetness sensor for an absorbent article that is formed from an ink is provided. The ink includes a proton-accepting chromogen and a proton-donating agent (or color developer). Prior to use, the ink is generally dry and in a protonated form so that it has a visible color. However, upon contact with bodily fluids (e.g., urine, fecal matter, mucus, menses, vaginal fluid, etc.), water in the fluid can lead to deprotonation of the chromogen, thereby resulting in a shift of the absorption maxima of the chromogen towards either the red (“bathochromic shift”) or blue end of the spectrum (“hypsochromic shift”). To increase the rate of the color change during use, the proton-donating agent is an aliphatic carboxylic acid that is highly soluble in the bodily fluid (e.g., urine), and therefore results in a color change that is very rapid and may be detected within a relatively short period of time.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Ruthenium(II) catalysts for use in stereoselective cyclopropanations
ActiveUS20070270593A1High stereoselectivityHigh yieldRuthenium organic compoundsCobalt organic compoundsProtonationSalen ligand
Chiral ruthenium catalysts comprising salen and alkenyl ligands are provided for stereoselective cyclopropanation, and methods of cyclopropanation are provided. The chiral ruthenium catalyst is prepared in situ by combining an alkenyl ligand, a deprotonated chiral salen ligand, and a ruthenium (II) metal. A preferred catalyst is prepared in situ by combining 2,3-dihydro-4-venylbenzofuran, deprotonated 1,2-cyclohexanediamino-N,N′-bis(3,5-di-t-butyl-salicylidene) and RuCl2(p-cymene)]2.
Owner:VANDA PHARMA INC
Wetness Sensor for Use in an Absorbent Article
A wetness sensor for an absorbent article that is formed from an ink is provided. The ink includes a proton-accepting chromogen and a proton-donating agent (or color developer). Prior to use, the ink is generally dry and in a protonated form so that it has a visible color. However, upon contact with bodily fluids (e.g., urine, fecal matter, mucus, menses, vaginal fluid, etc.), water in the fluid can lead to deprotonation of the chromogen, thereby resulting in a shift of the absorption maxima of the chromogen towards either the red (“bathochromic shift”) or blue end of the spectrum (“hypsochromic shift”). To increase the rate of the color change during use, the present inventors have discovered that a specific type of proton-donating agent may be employed. More particularly, the proton-donating agent is an aliphatic carboxylic acid that is highly soluble in the bodily fluid (e.g., urine), and therefore results in a color change that is very rapid and may be detected within a relatively short period of time. The extent of the color change is also generally sufficient to provide a “real-time” indication of wetness on the absorbent article.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Rosin-based CO2/N2 response type polymerizable surfactant, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109868066AImprove stabilityGood dispersionTransportation and packagingMixingProtonationGlycidyl methacrylate
The invention discloses a rosin-based CO2 / N2 response type polymerizable surfactant. Maleopimaric acid reacts with glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) for introducing polymerizable monomers, and then an imidization reaction is carried out with N,N-dimethyl-1,3-propane diamine for introducing tertiary amine groups capable of responding to CO2. The surfactant has a response property on CO2 / N2, and after CO2is introduced, a water solution is weakly acidic, so that tertiary amine is protonated to form a tertiary amine salt and then is positively charged to become a form of a water-soluble cation; and after N2 is introduced to drive CO2, the positively charged tertiary amine salt is deprotonated to be recovered to an original state of a water-insoluble tertiary amine, and good response reversibility is achieved. The invention also discloses emulsification performance and dispersion performance of the surfactant, a Pickering emulsion and carbon nano tube dispersion liquid prepared by using the surfactant also have good responsiveness to the CO2 / N2, and end-group double bonds can be used for preparing a high-molecular surfactant by a polymerization reaction.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
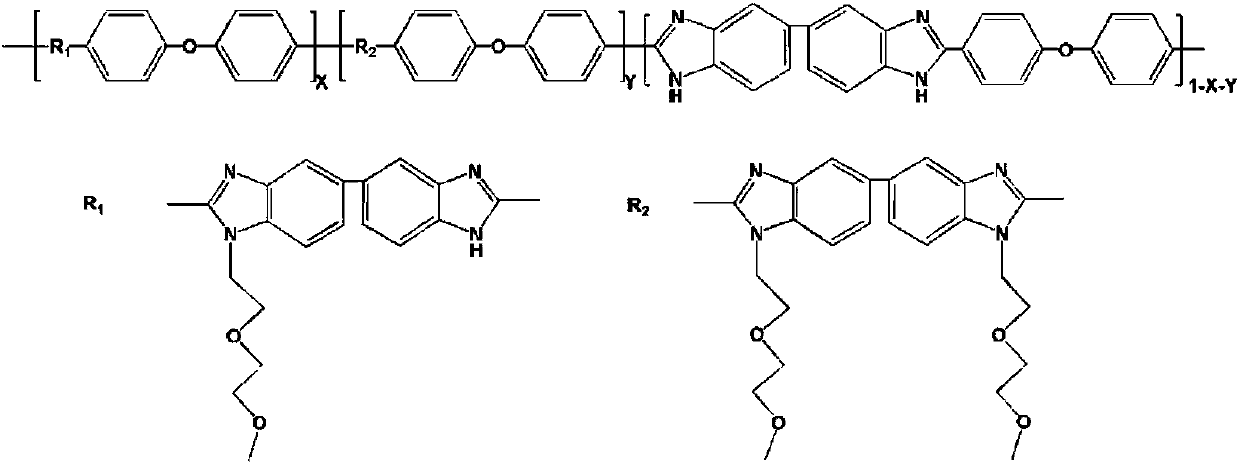
Nonionic hydrophilic side-chain polybenzimidazole membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107674417ALow vanadium ion permeabilityReduce penetrationCell electrodesProtonationSide chain
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
P-aramid nanofiber solution and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a novel method for preparing a p-aramid nanofiber solution, belongs to the field of macromolecules and also belongs to the field of nano-materials. According to the solution, p-aramid nanofibers have the diameter of 20-50nm and the length of about 10 microns. The method comprises the steps: purging a dry three-mouthed bottle with nitrogen gas for 10 minutes under the protection of nitrogen gas, adding a deprotonation reagent (sodium hydride or potassium hydride or lithium hydride) and anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide under the protection of nitrogen gas, mechanically stirring, heating to the temperature of 70 DEG C within 20 minutes, continuously reacting for 40 minutes, and then, cooling to the temperature of 30 DEG C; and then, slowly adding poly-p-phenylene terephthalamide staple fibers, and reacting for 6-72 hours at the temperature of 30 DEG C, thereby obtaining an orange-red solution containing the p-aramid nanofibers, wherein the weight percent of the p-aramid nanofibers is 0.05-3.6%. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and is strong in operability, and a feasible method is provided for the low-cost and large-scale preparation of p-aramid nanofiber materials.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Method for separating tetravalent cerium or tetravalent cerium and fluorine
InactiveCN102409172AReduce pollutionImprove extraction efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementProtonationQuaternary ammonium cation
The invention provides a method for separating tetravalent cerium. The method comprises the following steps: a) providing feed liquor, wherein the feed liquor contains tetravalent cerium ions, trivalent rare earth ions and sulphuric acid and the concentration of sulphuric acid in the feed liquor is 0.06mol / L-0.5mol / L; b) extracting the feed liquor in the step a) with a mixed solution of ionic liquid and a diluent to obtain extract liquor and raffinate, wherein the cations of the ionic liquid are quaternary ammonium cations and the anions of the ionic liquid are anions obtained by deprotonating an acidic phosphine extractant; and c) performing back extraction on the extract liquor obtained in the step b) by using dilute sulphuric acid as the back-extractant to obtain back extraction liquor containing tetravalent cerium. The invention also provides a method for separating tetravalent cerium and fluorine. The method for separating tetravalent cerium and fluorine, provided by the invention, has lower extraction acidity and back-extractant acidity, thus the consumptions of acid and base can be reduced, the production cost can be saved and the environmental pollution can be reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of TiO2/ZIF-8 composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN109499620AImprove catalytic degradation efficiencyUniform and firm loadOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic solventTitanium
The invention relates to a preparation method of a TiO2-loaded composite photocatalyst. The method comprises the following steps: subjecting a mixed solution of a soluble zinc salt, 2-methylimidazoleand a first organic solvent to a heated reaction in an autoclave, subjecting 2-methylimidazole to deprotonation, self-assembling ZIF-8 from 2-methylimidazole and zinc ions, carrying out filtering, washing and drying, and then, carrying out grinding, so as to obtain ZIF-8 powder; subjecting a hydrolyzable titanium source to a hydrolysis reaction with water in a second organic solvent, so as to obtain a nano-titania containing first solution; concentrating the first solution to improve the concentration of nano-titania sol, so as to obtain a second solution; adding the ZIF-8 powder into the second solution, carrying out thorough mixing through ultrasonic oscillation, and carrying out filtering, washing and drying, thereby obtaining the TiO2 / ZIF-8 composite photocatalyst.
Owner:HUAIHUA UNIV
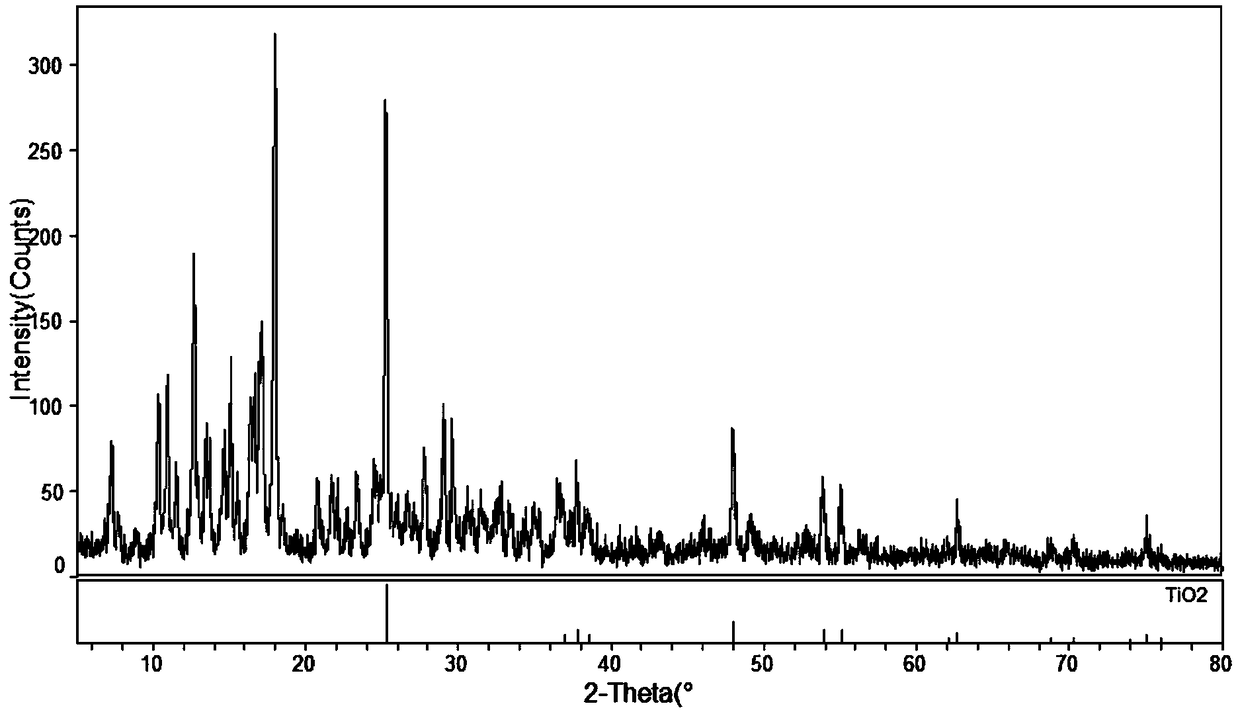
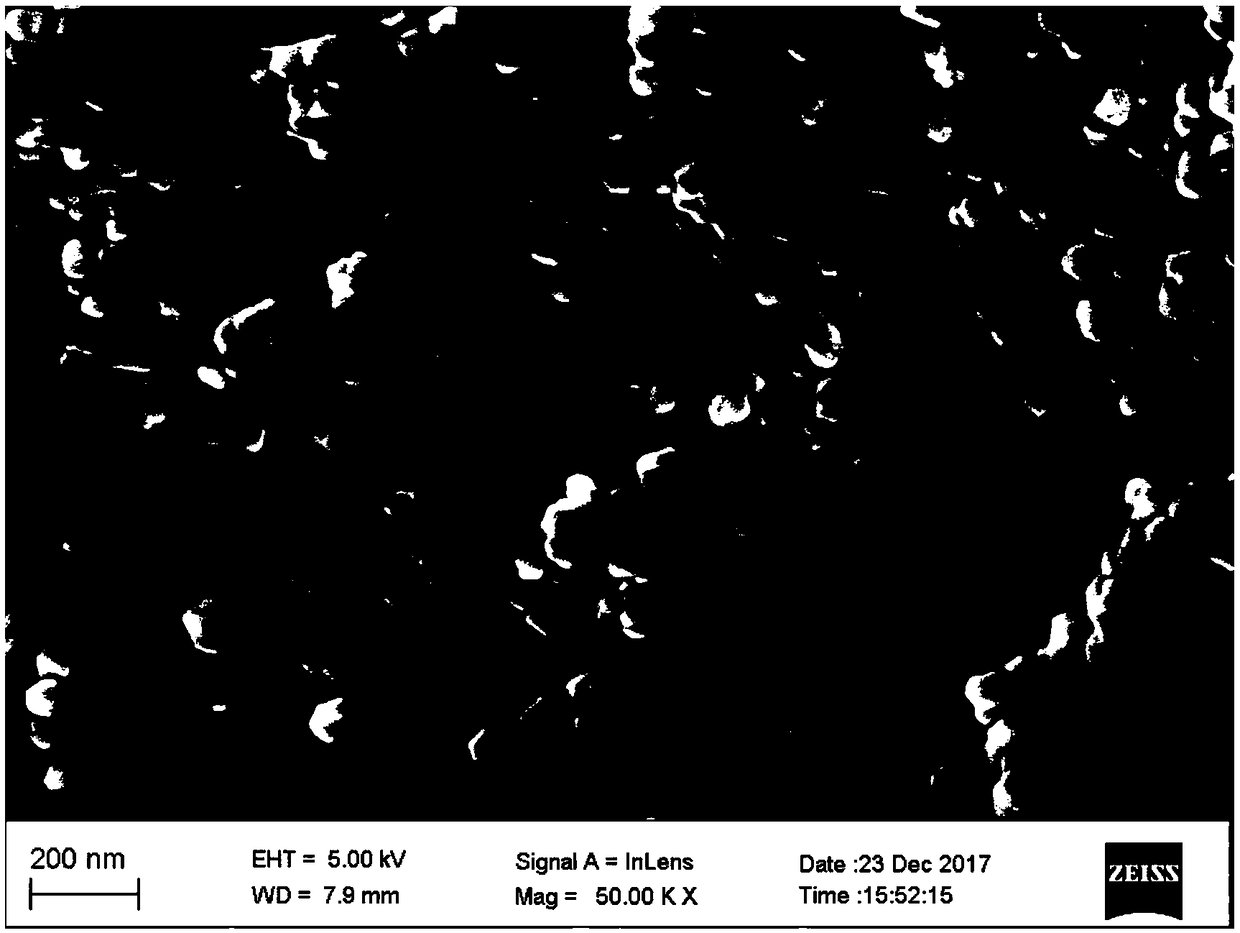
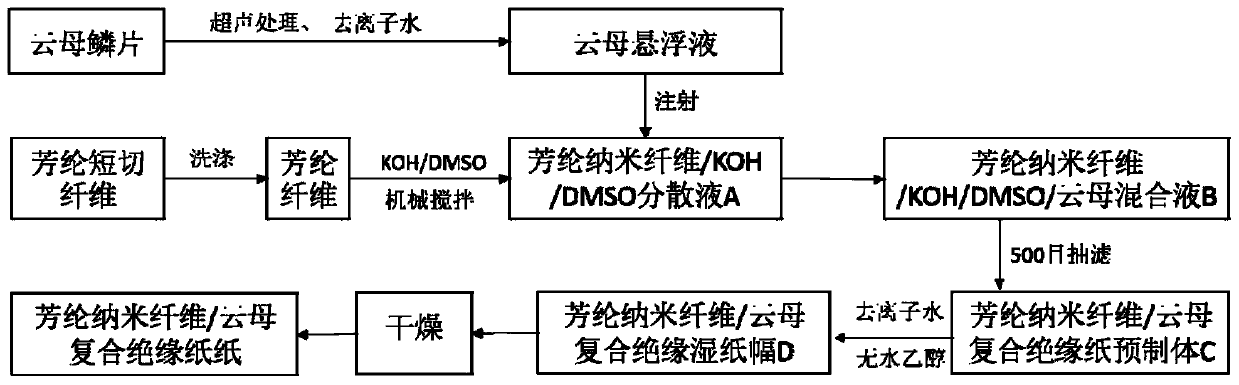
Preparation method of aramid nanofiber/mica composite insulating paper
ActiveCN110106737ALarge specific surface areaMany active sitesPaper/cardboardSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperMotor insulationPapermaking
The invention discloses a preparation method of aramid nanofiber / mica composite insulating paper. The preparation method of the aramid nanofiber / mica composite insulating paper aims at achieving the self-film-forming coating and interface enhancement effects of aramid nanofibers on mica by turning macro aramid fibers into aramid nanofibers through deprotonation and utilizing an in-situ depositionmethod, achieves that the adaptability of the particle diameter of the mica is wide, and the uniformity, mechanical strength and dielectric strength of the aramid nanofiber / mica composite insulating paper are much higher than the properties of common aramid mica insulating paper, solves the problems of existing aramid mica insulating paper during wet papermaking that (1) the particle diameter of the mica is limited by the properties, (2) the mechanical strength is low, (3) due to voids and pore diameters which are generated by free accumulation and distribution of the mica, the dielectric strength is low, (4) the two faces of paper forming have large difference and low uniformity, is simple in operation, has a significant effect, and provides a novel method for the preparation of a motor insulation material with higher performance.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Photothermographic material
The present invention provides a photothermographic material containing a non-photosensitive silver salt of an organic acid, a photosensitive silver halide, a reducing agent for silver ions and a binder on one surface of a support, which comprises at least one compound represented by the following formula (I) and at least one compound producing imagewise a chemical species that can form development initiation points on and in the vicinity of the non-photosensitive silver salt of an organic acid: (X)k-(L)m-(A-B)n wherein X represents a silver halide adsorption group or a light absorption group, L represents a (k+n)-valent bridging group, A represents an electron-donating group, B represents a leaving group or a hydrogen atom, A-B is dissociated or deprotonated after oxidation to generate a radical A', k represents 0-3, m represents 0 or 1, and n represents 1 or 2. Thus, there is provided a photothermographic material that shows low fog and high Dmax (maximum density), has photographic characteristics of high sensitivity and high contrast, and shows little increase of fog even if it is stored for a long period of time after development
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Derivatives of dihydronepetalactone and method for preparation
3-substituted dihydronepetalactone is prepared by deprotonation of nepetalactone and treatment with Grignard reagent to form alkyl and aryl substituted compounds. The compounds so prepared are odorous and have a wide range of utility ranging from insect repellents to fragrance compounds, such as perfumes, among others.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Release on demand corrosion inhibitor composition
ActiveUS20100291307A1Avoid corrosionLow corrosion rateOther chemical processesPretreated surfacesProtonationMetallate
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Methods for Using Reversible Phase Oil-Based Drilling Fluid
Invert emulsion compositions including an oleaginous, a non-oleaginous and an amine surfactant that are useful in the oil and gas well drilling art are disclosed. The amine surfactant is selected so that the invert emulsion can be converted form a water-in-oil type emulsion to a oil-in-water type emulsion upon the protonation of the amine surfactant. Deprotonation of the amine surfactant reverses the conversion. This solution also permits the conversion of oil-wet solids in the fluid into water-wet solids.
Owner:MI
Method for preparing aramid nanofibers by using mechanical coupling chemical alkali dissolution method
ActiveCN108316039AIncrease the areaImprove surface activityCellulosic pulp after-treatmentPulping with inorganic basesProtonationDissolution
The invention discloses a method for preparing aramid nanofibers by using a mechanical coupling chemical alkali dissolution method. According to the method provided by the invention, fibrillation treatment is coupled with homogenization treatment, so that the size of aramid fibers is greatly reduced before a deprotonation reaction is performed, the specific surface area and surface activity of thearamid fibers are improved, the sub-micron-sized aramid fibers and a KOH / DMSO system are more easily subjected to a rapid deprotonation process, the reaction time is greatly shortened, the reaction concentration is increased, the reaction efficiency is significantly improved, and industrialized production is facilitated; the method has a simple preparation process, realizes short-process preparation and is easy to control; and the prepared aramid nanofibers have a small diameter, good size homogeneity, a large length-diameter ratio, high strength and excellent heat resistance, can be used asa novel construction enhancement unit of construction of macro composite materials, and has broad application prospects in the fields of composite materials, biology, medicine, electronics, energy sources and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thermally developable photosensitive material
InactiveUS20020197570A1Reduce foggingImprove storabilityX-ray/infra-red processesElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisProtonationLeaving group
The present invention provides a thermally developable photosensitive material including a support, the image-forming layer containing a non-photosensitive organic silver salt, a photosensitive silver halide, a reducing agent, a binder and a compound represented by the following formula (I), wherein after the material is exposed and thermally developed at 121° C. for 24 seconds, at least 90% of the developed silver is in contact with the photosensitive silver halide grains after development;<paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>(X kL mA-B)n Formula (I)< / in-line-formula>wherein: X represents a silver halide-adsorbing group or light-absorbing group; L represents a (k+n)-valent linking group; A represents an electron-donating group, B represents a leaving group or a hydrogen atom, and after oxidized, (A-B) is eliminated or deprotonated to form a radical A'; and k falls between 0 and 3; m represents 0 or 1; n represents 1 or 2, but if k=0 and n=1, then m=0.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Derivatives of dihydronepetalactone and method for preparation
3-substituted dihydronepetalactone is prepared by deprotonation of nepetalactone and treatment with Grignard reagent to form alkyl and aryl substituted compounds. The compounds so prepared are odorous and have a wide range of utility ranging from insect repellents to fragrance compounds, such as perfumes, among others.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
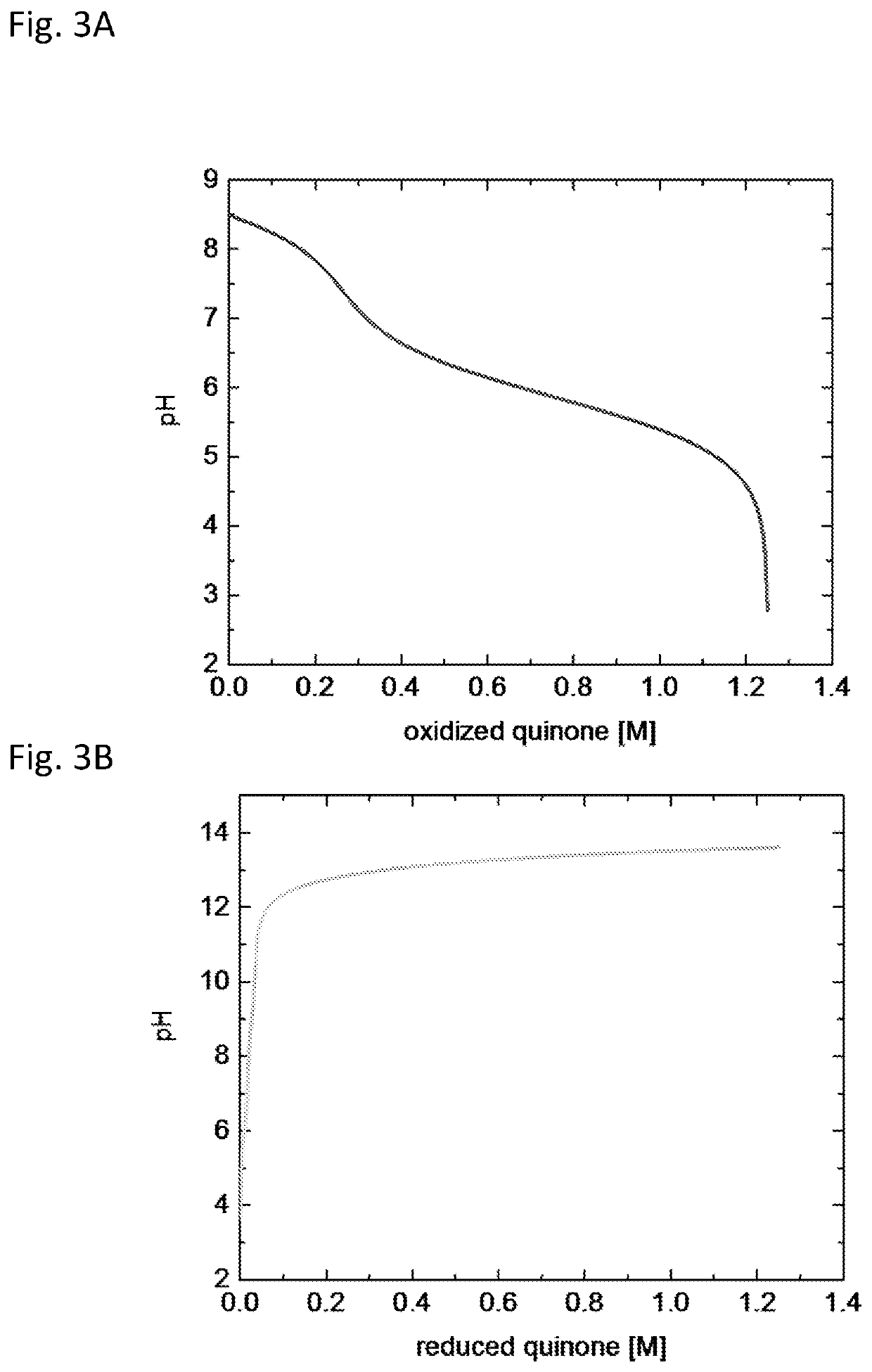
Proton coupled electrochemical co2 capture system
The invention provides an electrochemical CO2 capture device and methods employing proton-coupled redox active species, e.g., a quinone, phenazine, alloxazine, isoalloxazine, or polyoxometalate, whose protonation and deprotonation can be controlled electrochemically to modify the pH of an aqueous solution or aqueous suspension. This change in pH can be used to sequester and release CO2. The CO2 capture device can be used to sequester gaseous CO2 from a point source, such as flue gas, or from ambient air.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
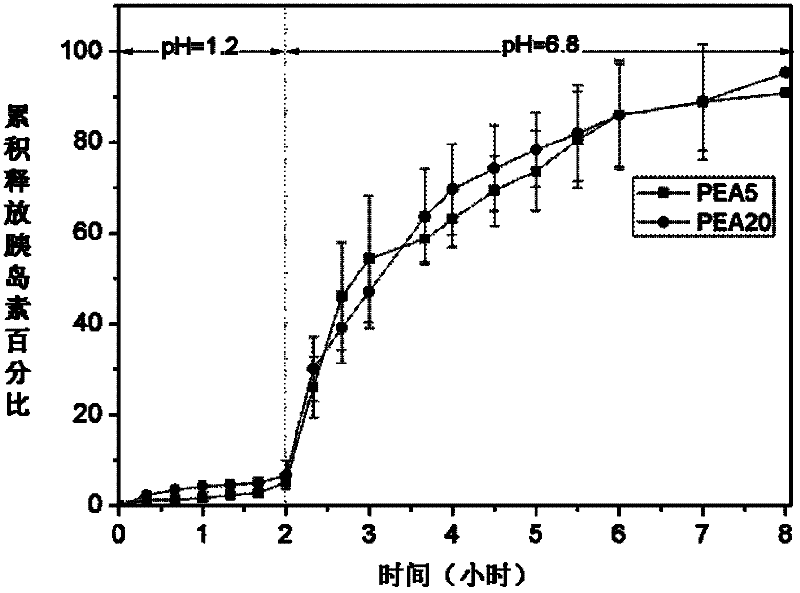
Insulin carrying microsphere and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102397258AImprove bioavailabilityAchieve releasePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineSide chain
The invention discloses an insulin carrying microsphere. A polyesteramide material of which the side chain contains a carboxyl and a hydrophobic isobutyl group at the same time serves as a carrier, wherein the carboxyl endows entericsolubility to the insulin carrying microsphere. Under a strong-acidity environment of gastric juice, because of deprotonation of the carboxyl, the polyesteramide material is not dissolved, the microsphere has certain contractile effect, and then a protein medicament is protected. Under a neutral condition of a small intestine, because of ionization of the carboxyl, the polyesteramide material is gradually dissolved, the microsphere is corroded, and then the wrapped medicament is released. On the other hand, the hydrophobic isobutyl has the effect of regulatingthe pH sensitivity of the material, the hydrophobicity of the insulin carrying microsphere is improved, and the effect with an intestinal cell membrane is enhanced. Therefore, the insulin carrying microsphere has high pH sensitivity, and the releasing and absorption of the insulin in an intestinal tract can be realized.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Reparation method of gradient porous metal organic framework ZIF (Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework)-8
The invention relates to a preparation method of a gradient porous metal organic framework ZIF (Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework)-8. The preparation method comprises the following steps of dissolving anorganic ligand 2-methylimidazole in deionized water, after the 2-methylimidazole is thoroughly dissolved, adding a polydiallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride solution, and uniformly agitating; dissolvinga divalent zinc slat in deionized water, thoroughly dissolving, then mixing with an organic ligand solution, and carrying out an agitation reaction to obtain suspension liquid; filtering or centrifugally separating the suspension liquid to obtain a solid product, washing with deionized water, and then drying, so that a ZIF-8 series material is obtained. Due to the control, to deprotonation balance and the growth process of a crystal, of the positive ions of polydiallyl dimethyl quaternary ammonium, the prepared ZIF-8 series material has microporous and mesoporous structures at the same time,further, is adjustable in mesoporous volume and stable in performance, and is wide in application prospect, and the preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, convenient, easy and feasible, is green and pollution-free and is convenient to industrially operate.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com