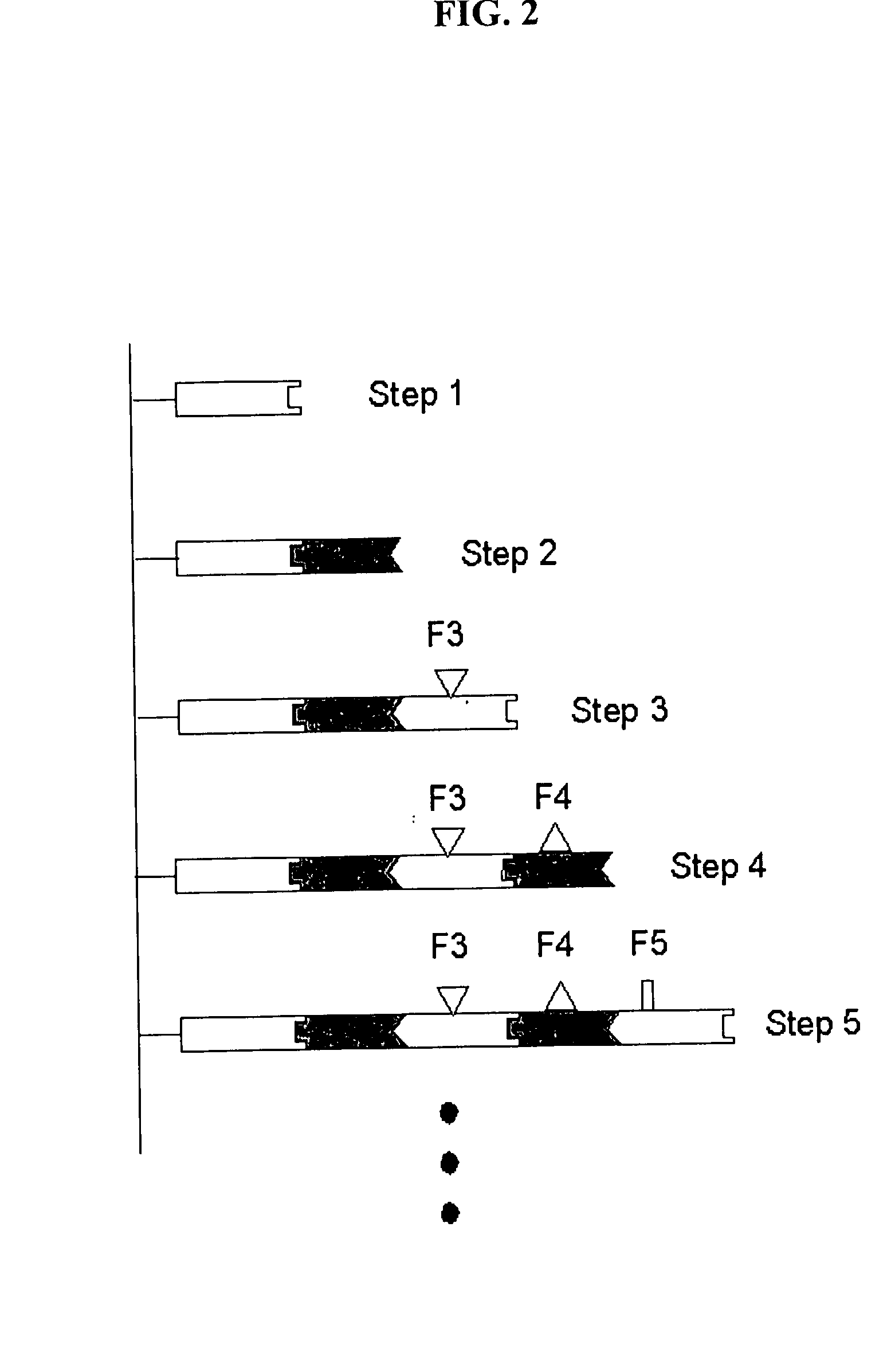
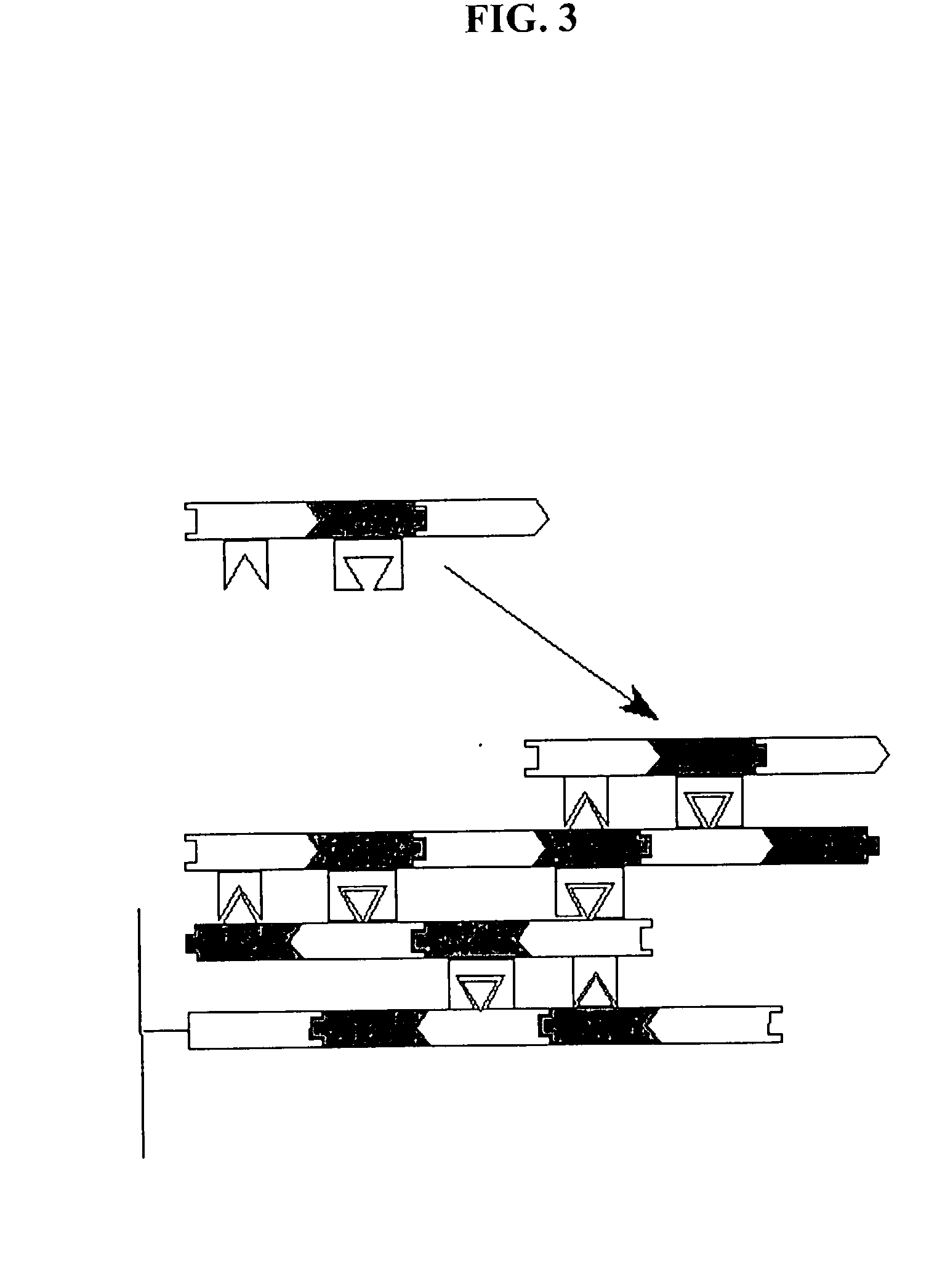
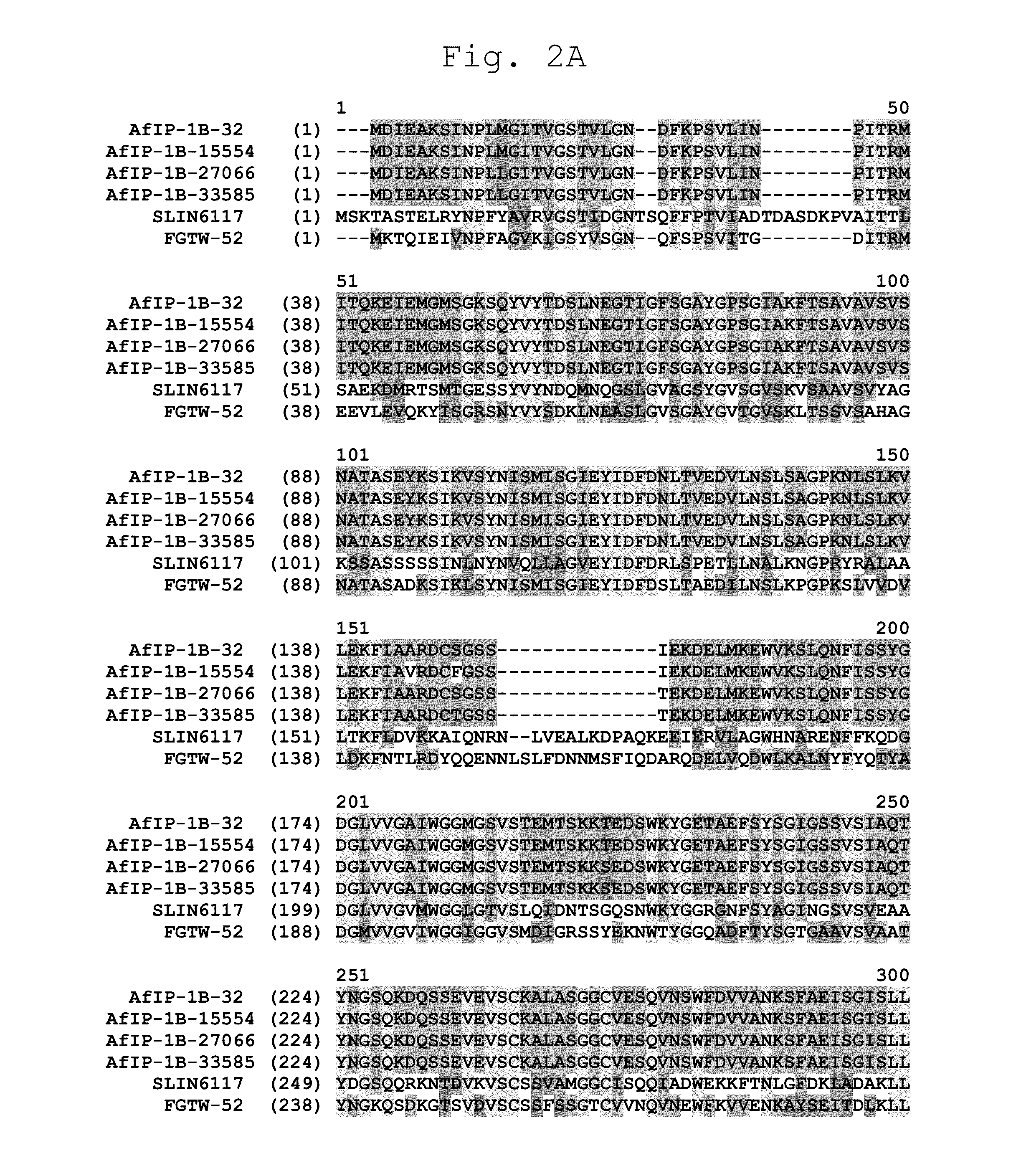
Patents
Literature
3199results about "Bacteria peptides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
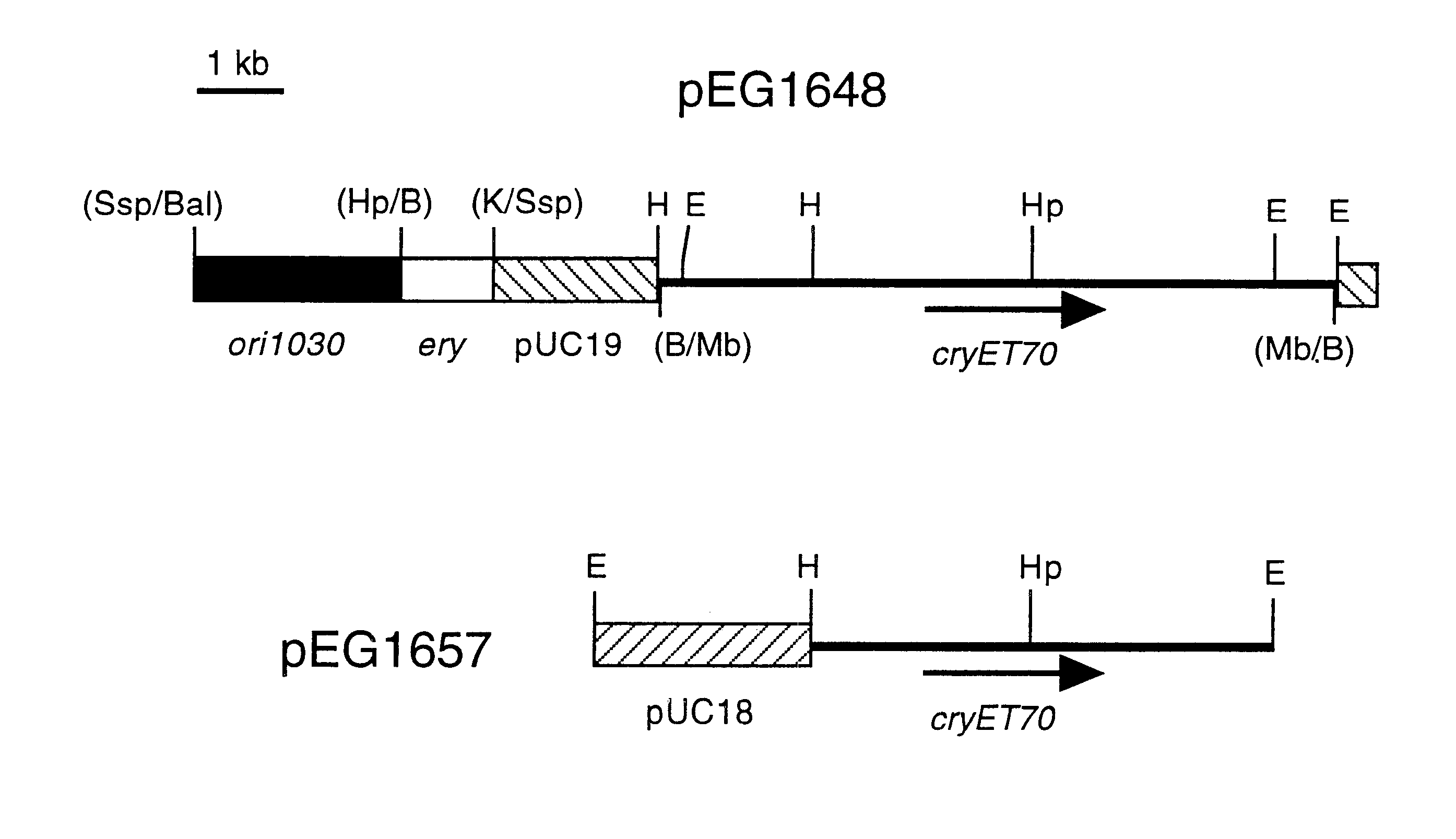
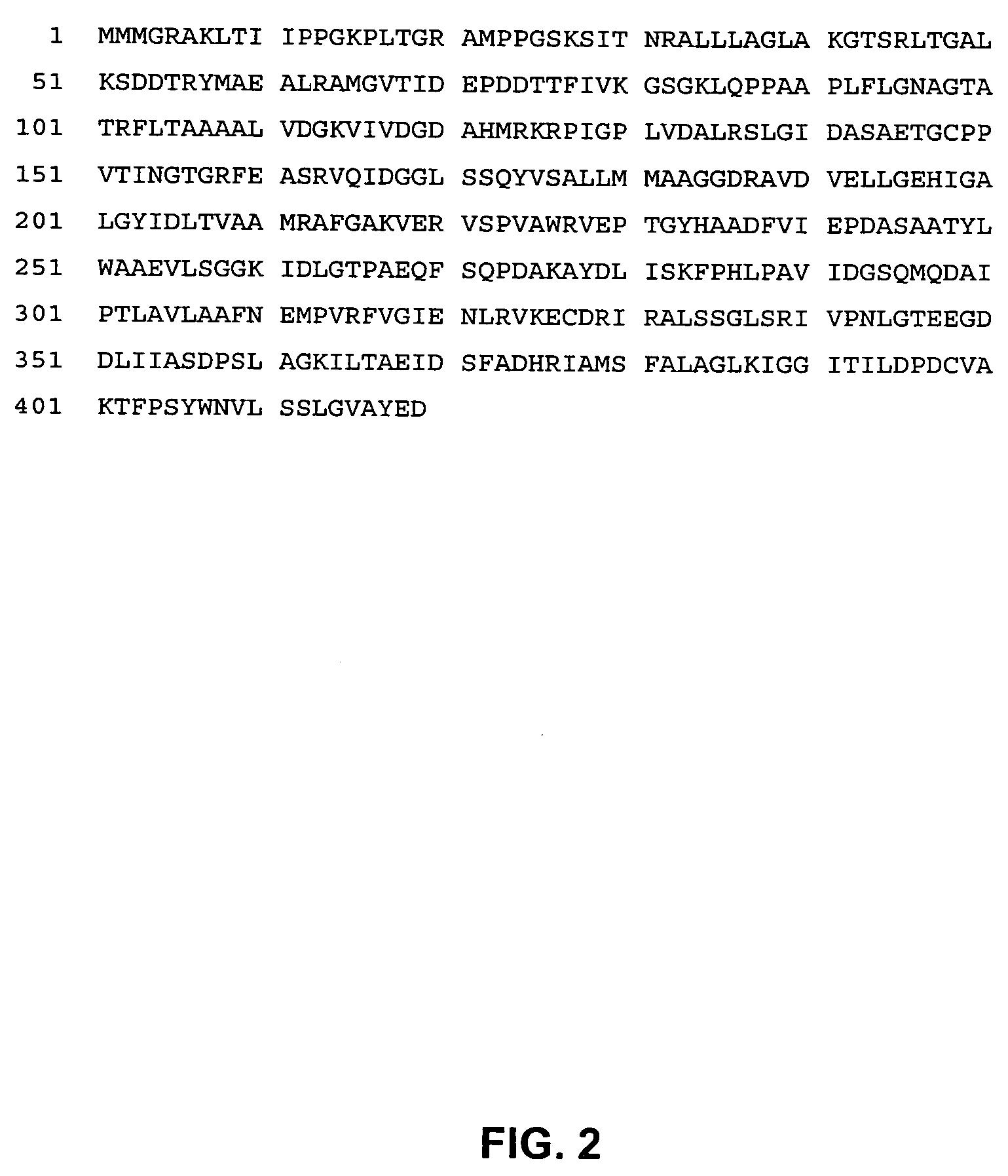
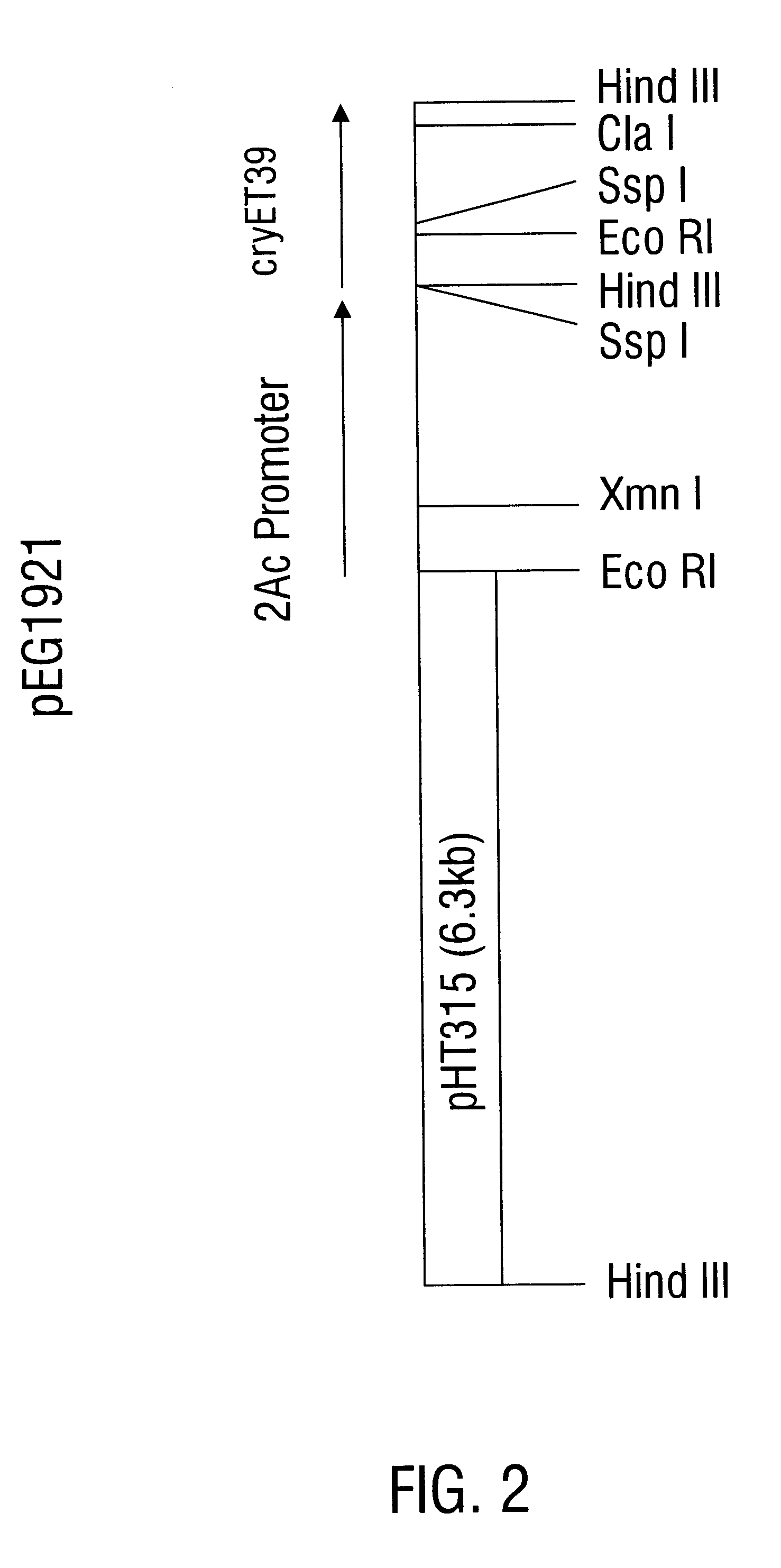
Polypeptide compositions toxic to diabrotic insects, and methods of use
InactiveUS6468523B1Easy to storeInhibit microbial growthBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDelta endotoxinPolynucleotide
Disclosed is a novel Lepidopteran- and Coleopteran-active delta-endotoxin polypeptide, and compositions comprising the polypeptide, peptide fragments thereof, and antibodies specific therefor. Also disclosed are vectors, transformed host cells, and transgenic plants that comprise nucleic acid segments encoding the polypeptide. Also disclosed are methods of identifying related polypeptides and polynucleotides, methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel sequences of the invention, as well as methods for controlling an insect population, such as the Western Corn Rootworm and Colorado potato beetle, and for conferring to a plant population resistance to the target insect species.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Polypeptide compositions toxic to coleopteran insects
InactiveUS6063597AHigh expressionStably occupyBiocideSugar derivativesBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed are Coleopteran-toxic B. thuringiensis delta -endotoxins, nucleic acid sequences, and transgenic plants expressing these genes. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Broad-spectrum delta-endotoxins
InactiveUS6713063B1Improved insecticidal activity and broader host-range activityImproving immunogenicityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity and broader insect host range against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Insect-resistant transgenic plants
The invention provides transgenic plants and transformed host cells which express modified cry 3B genes with enhanced toxicity to Coleopteran insects. Also disclosed are methods of making and using these transgenic plants, methods of making recombinant host cells expressing these delta -endotoxins, and methods of killing insects such as Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata howardi Barber) and western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Coleopteran-resistant transgenic plants and methods of their production using modified Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Bb nucleic acids
Disclosed are nucleic acid segments comprising synthetically-modified genes encoding modified Coleopteran-toxic B. thuringiensis Cry 3Bb* delta-endotoxins. Also disclosed are methods of using these genes for preparing a Coleopteran-resistant transgenic plant and reducing insect in restations, and plants thereby produced.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
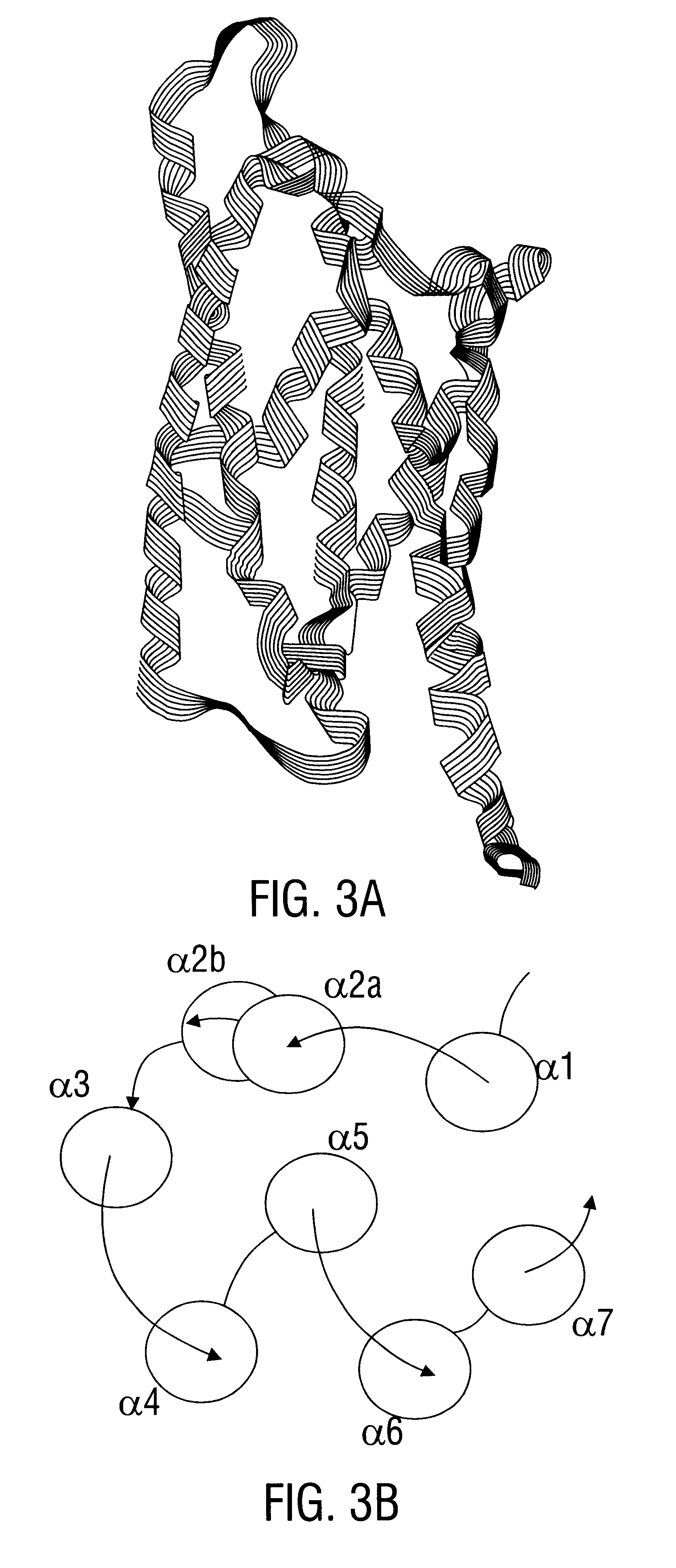
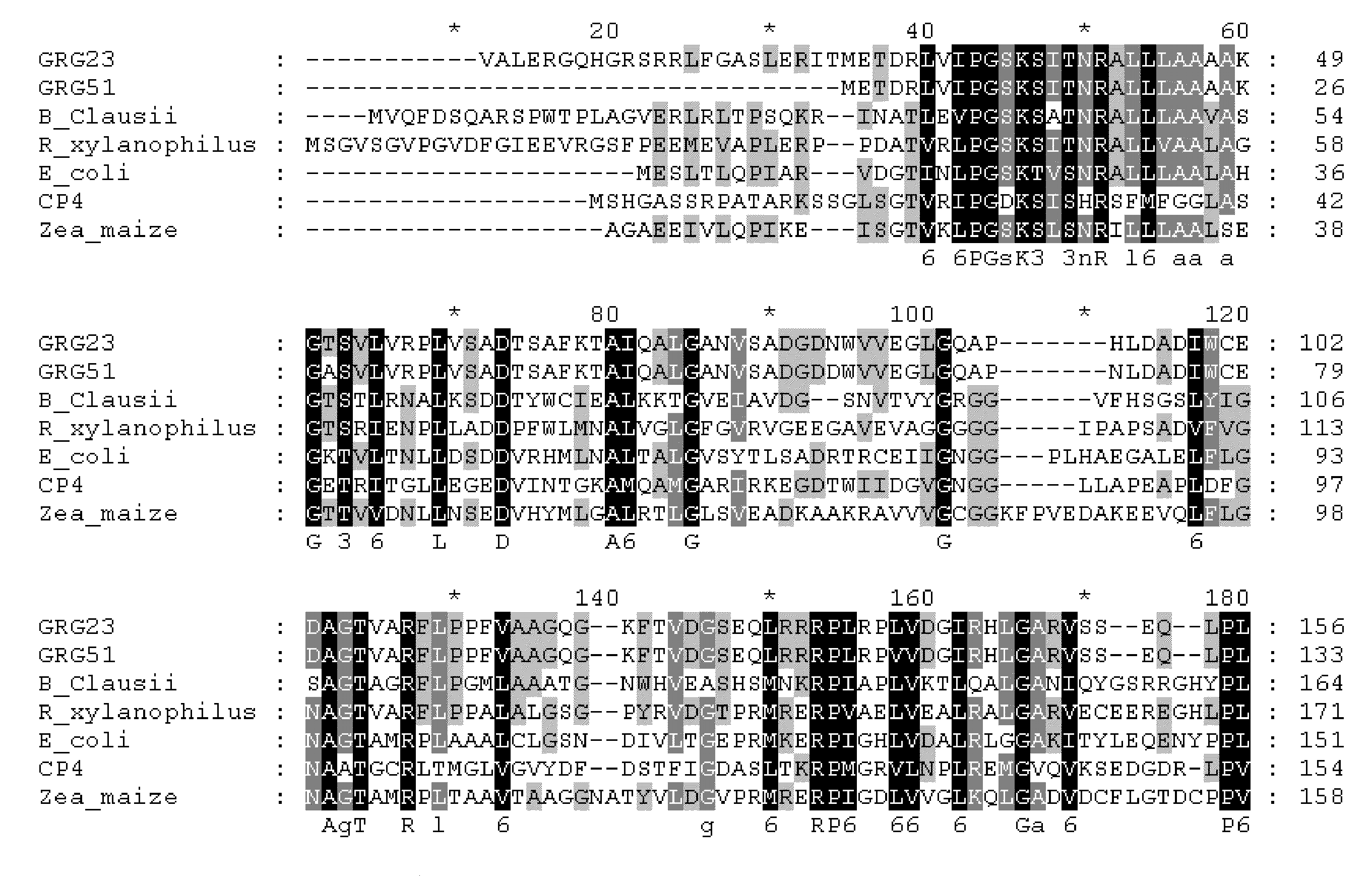
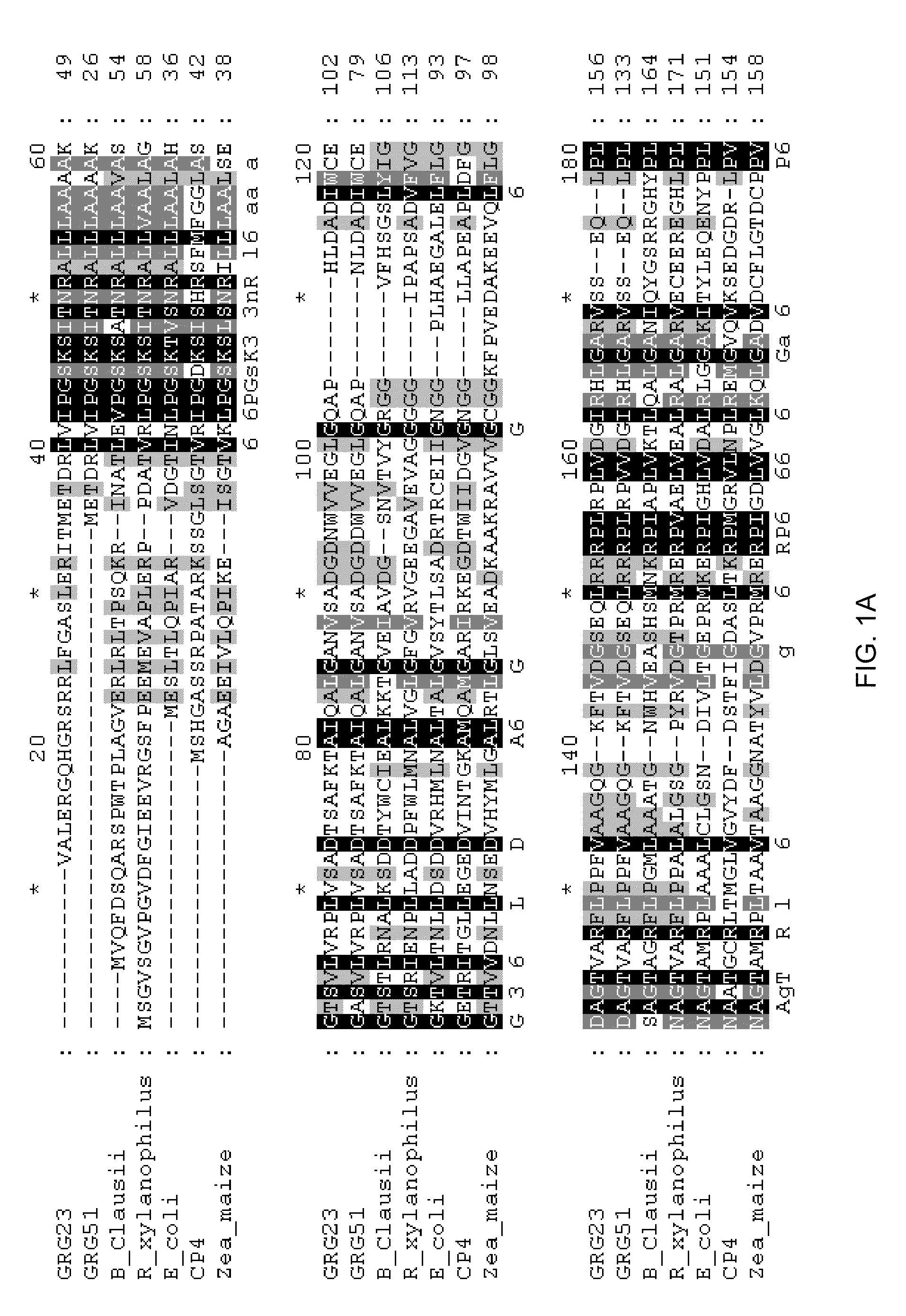
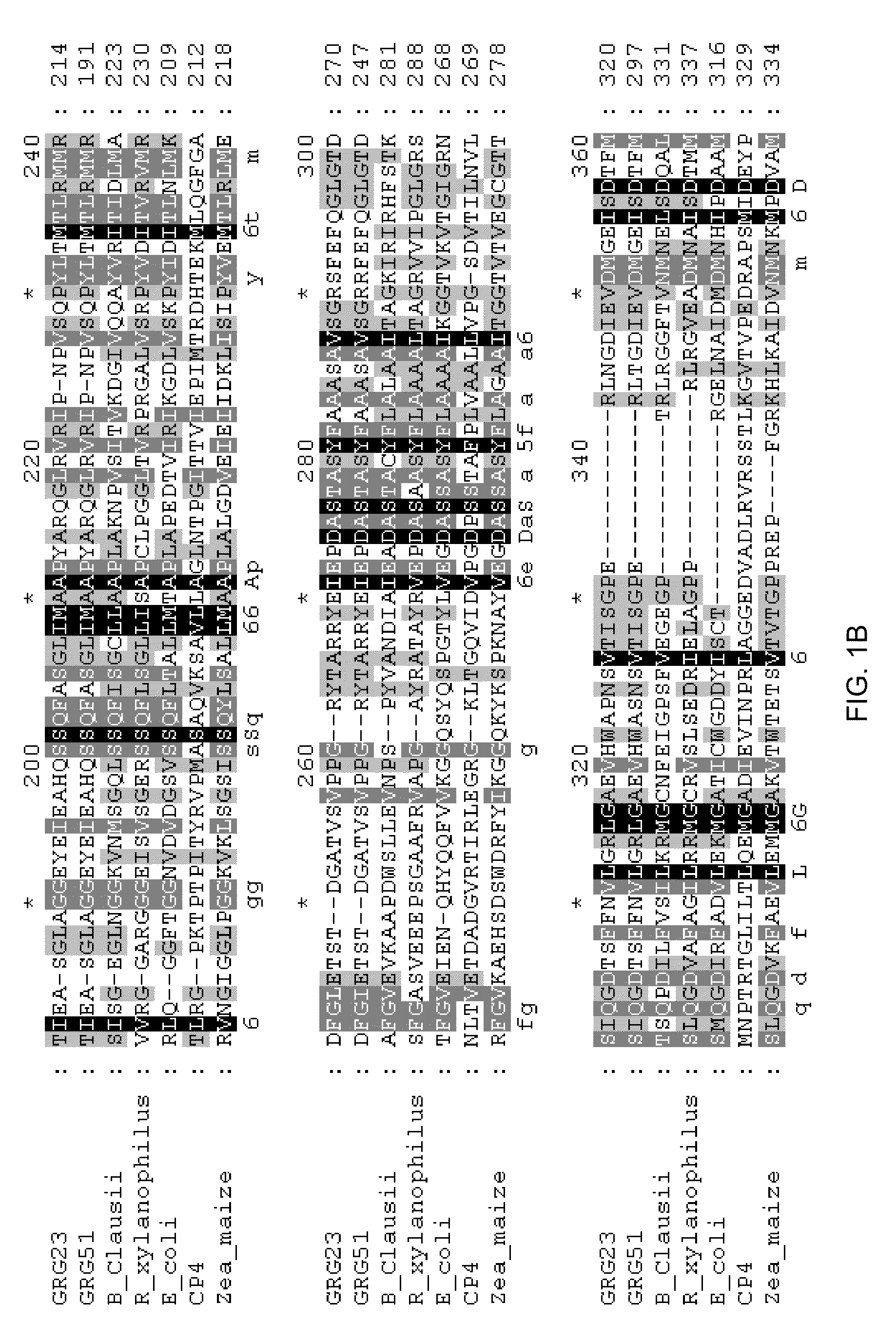
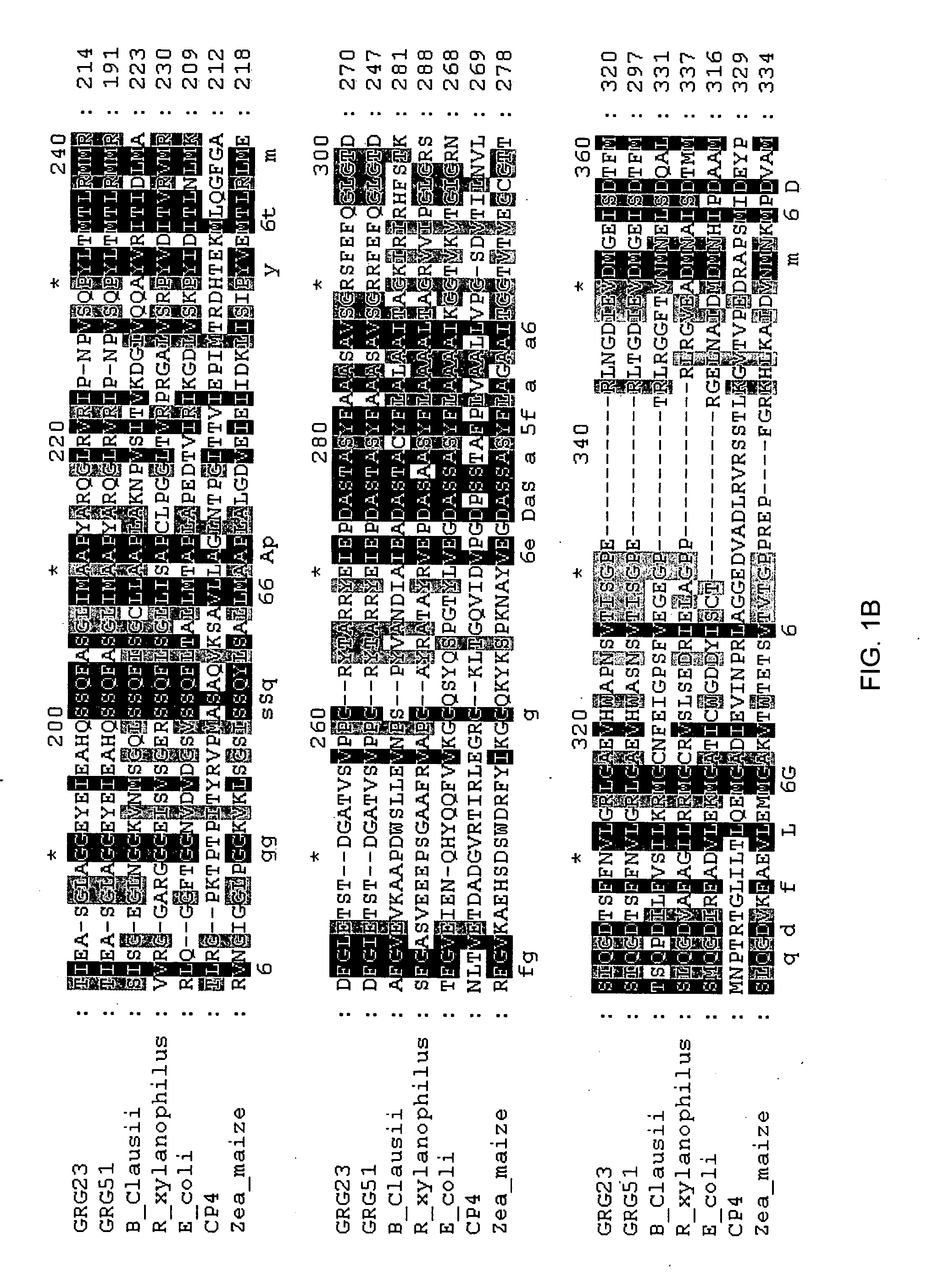
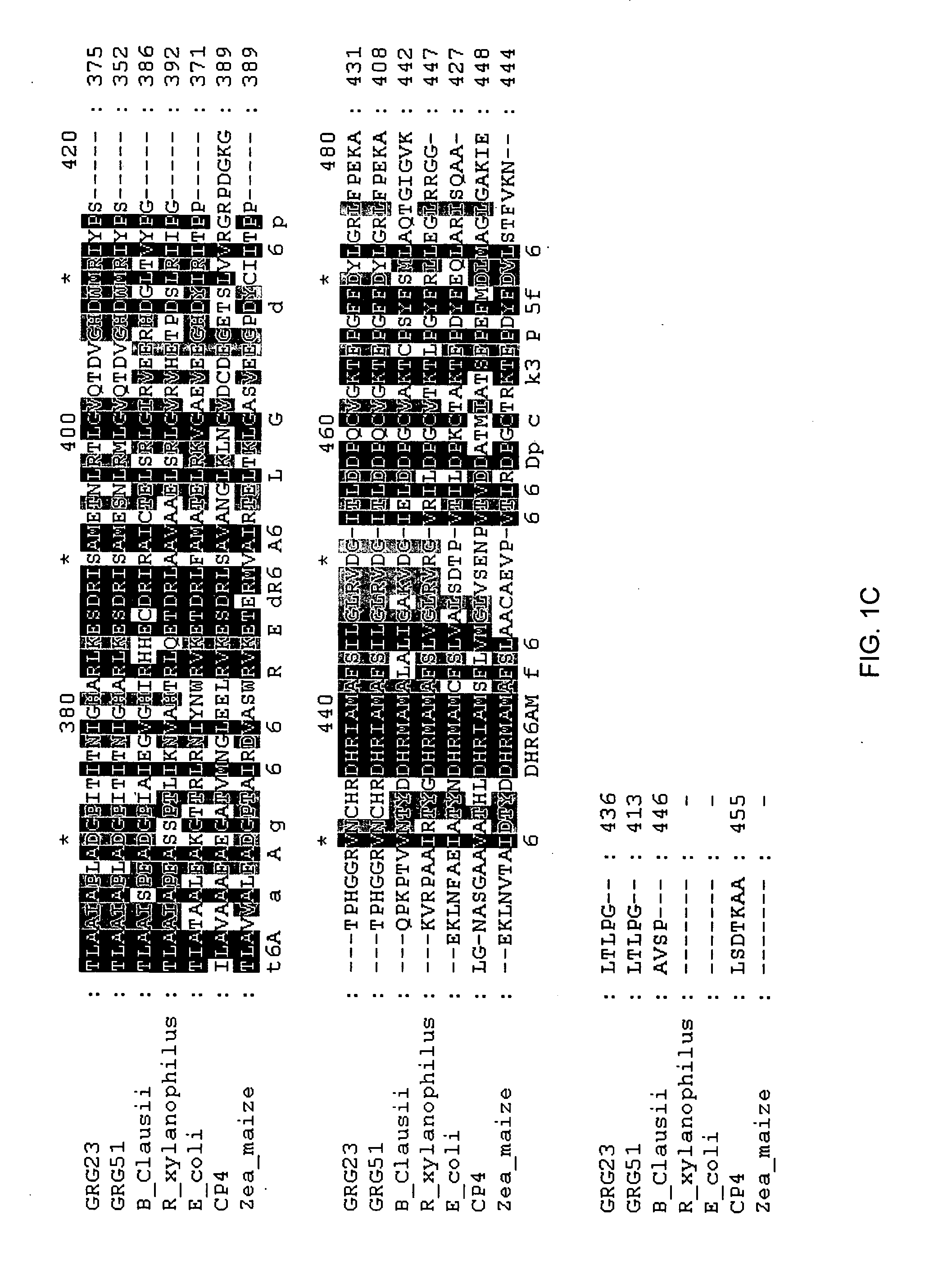
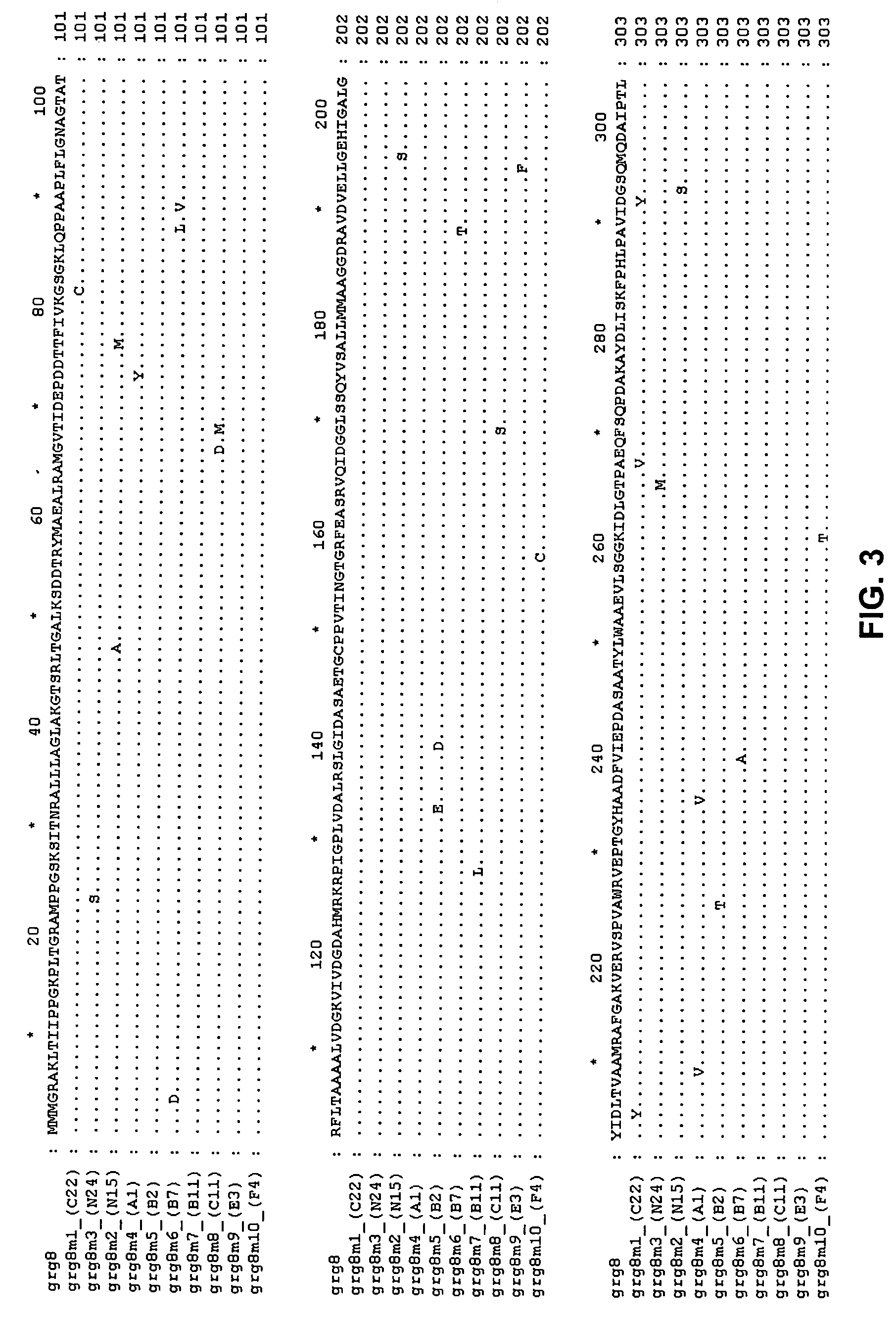
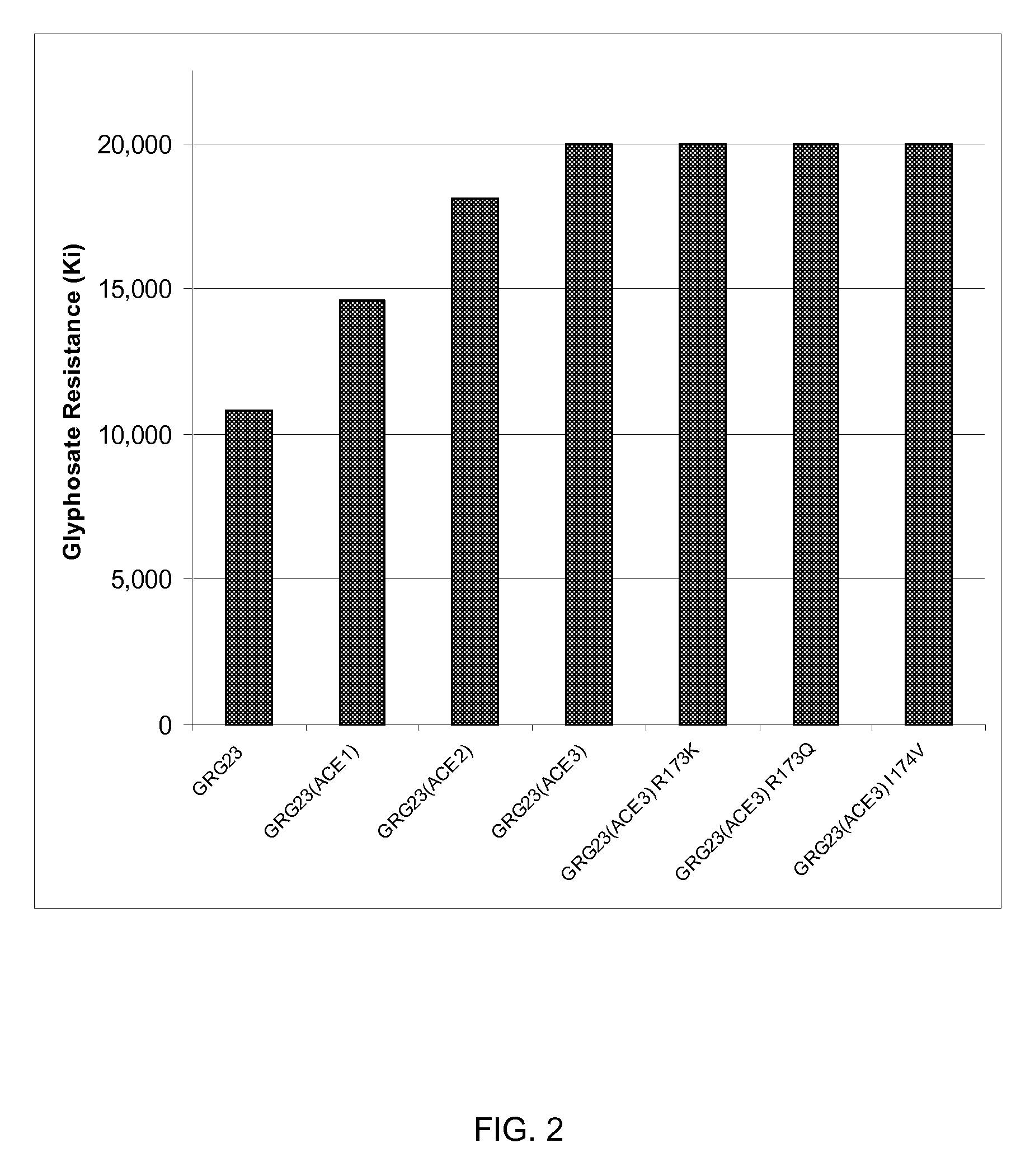
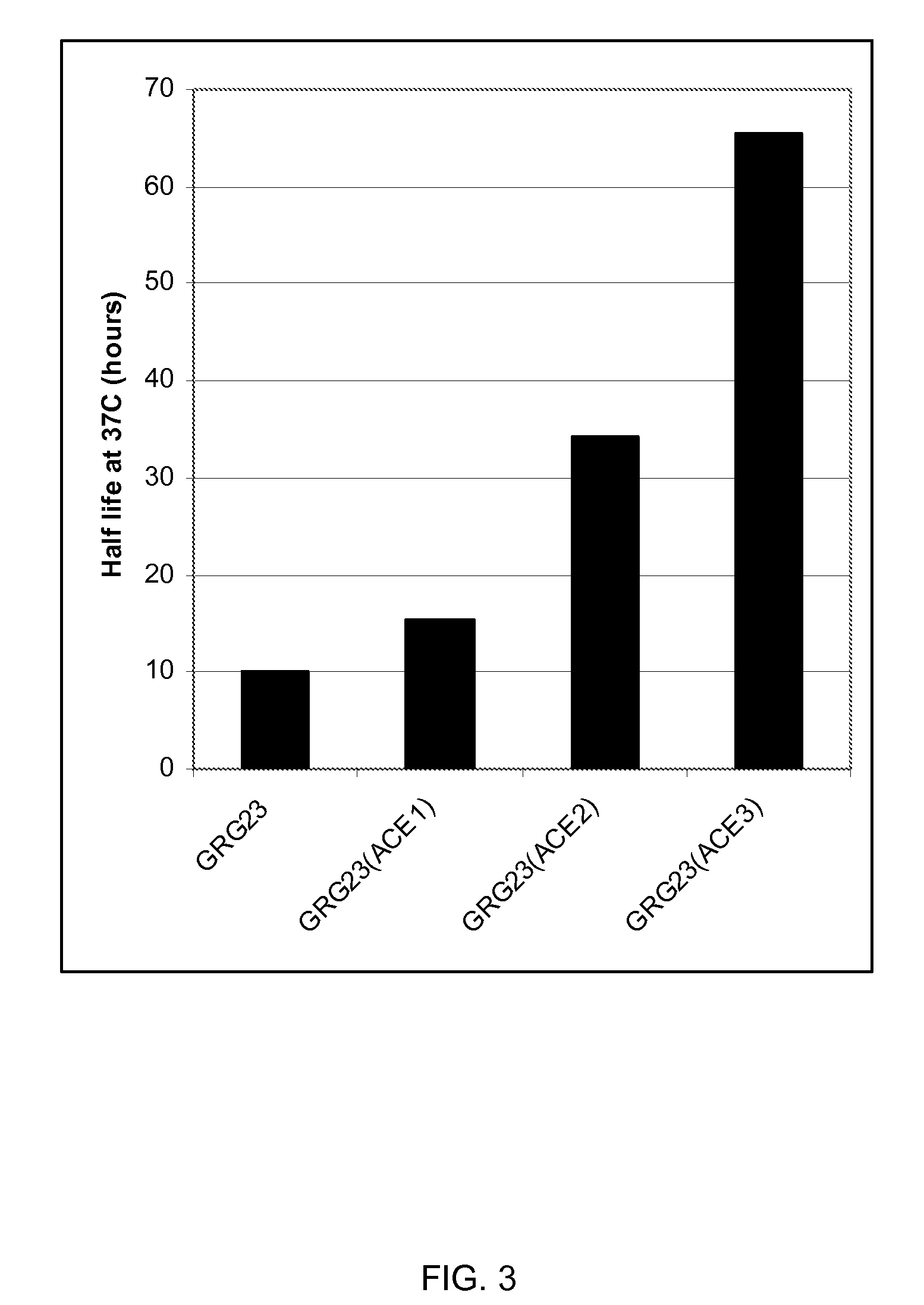
Grg23 and grg51 genes conferring herbicide resistance
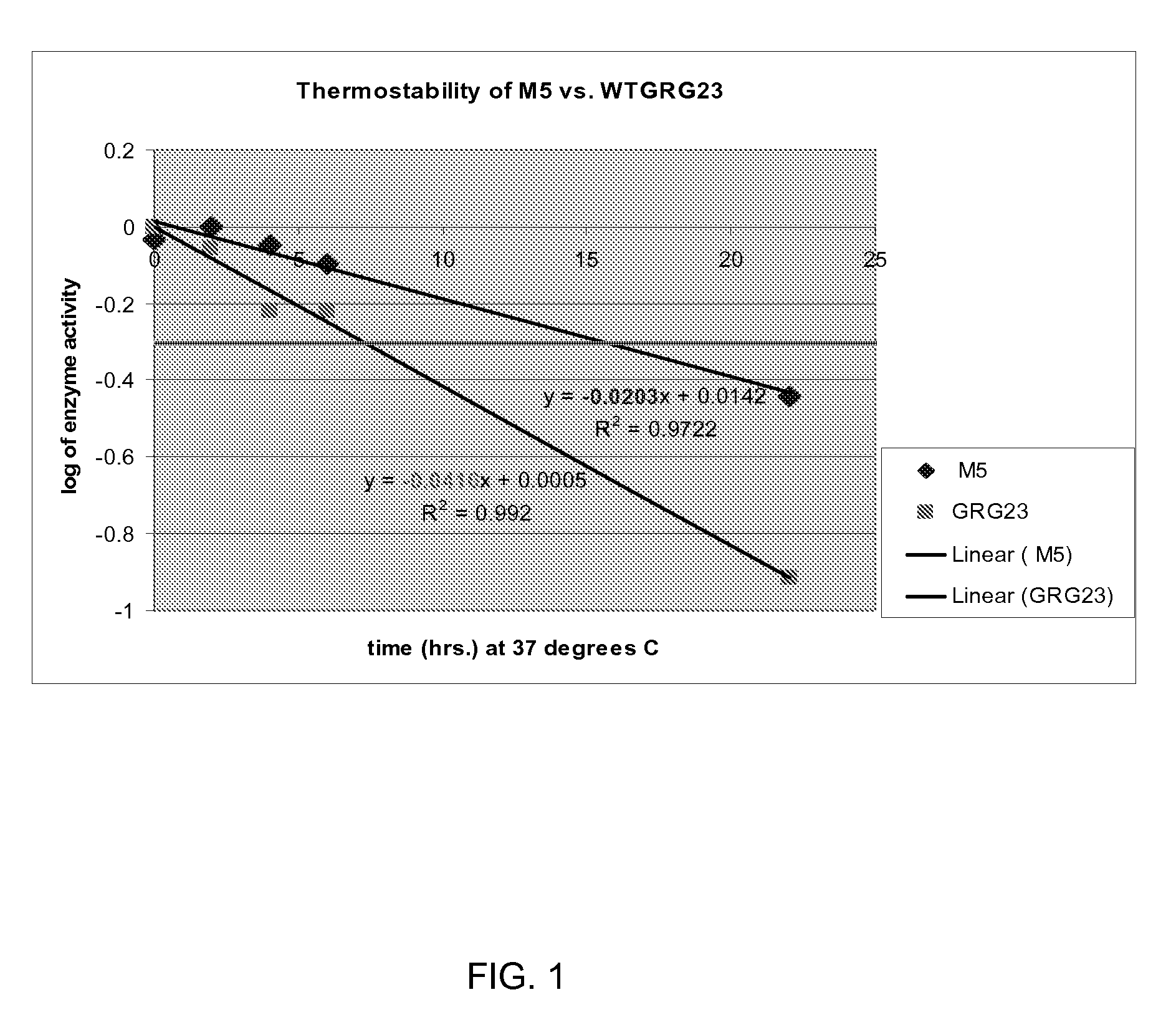
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, or 6, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, or 5. The present invention additionally provides a method to measure enzyme kinetic activity using fluorogenic substrates.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
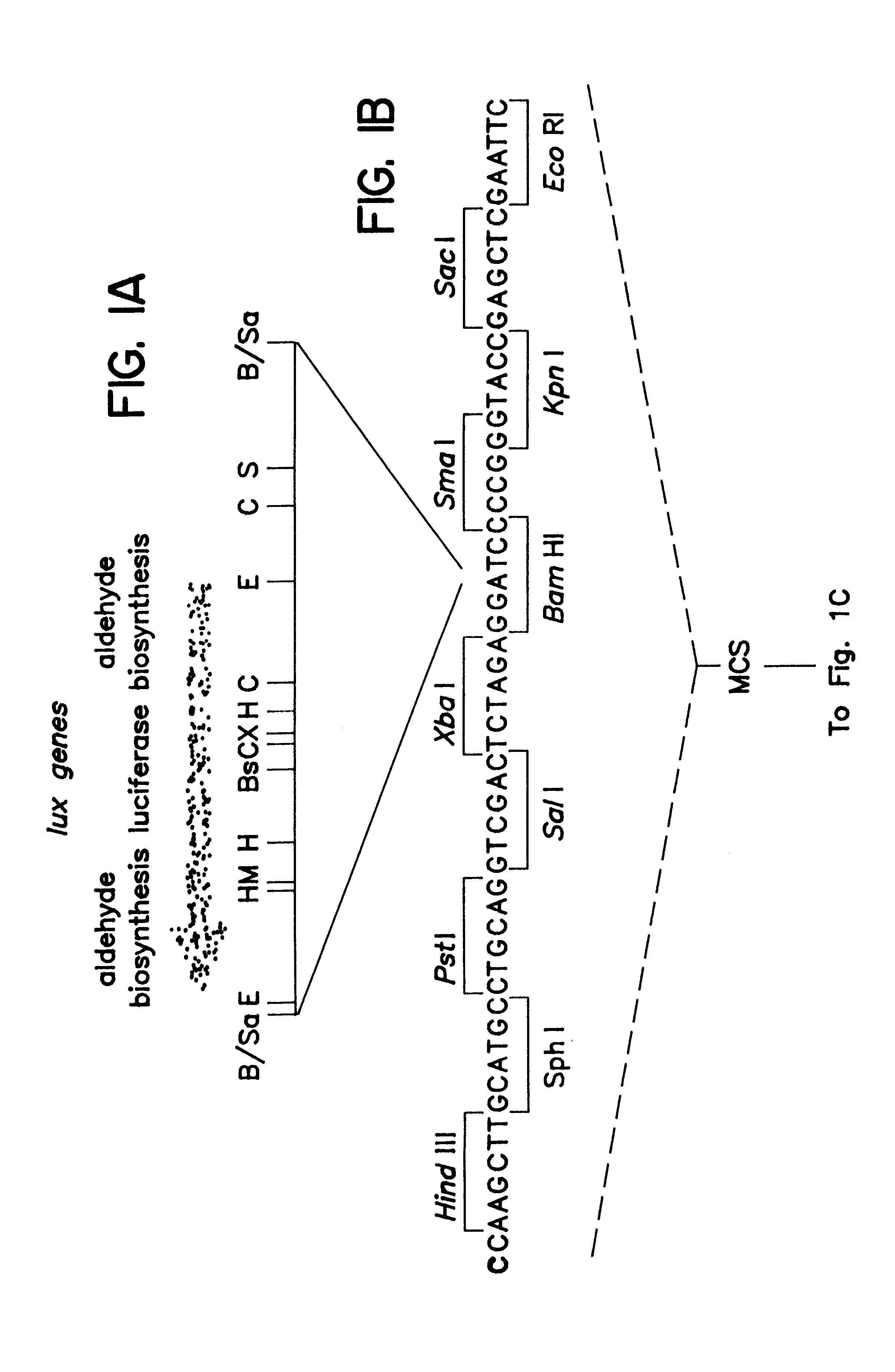
Non-invasive localization of a light-emitting conjugate in a mammal
InactiveUS6217847B1Accurate measurementEvenly distributedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBacteriaMammalNon invasive
Methods and compositions for detecting and localizing light originating from a mammal are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for tracking light emission to selected regions, as well as for tracking entities within the mammal. In addition, animal models for disease states are disclosed, as are methods for localizing and tracking the progression of disease or a pathogen within the animal, and for screening putative therapeutic compounds effective to inhibit the disease or pathogen.
Owner:LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV OF THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES THE
CRY1C polypeptides having improved toxicity to lepidopteran insects
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis nucleic acid segments encoding delta -endotoxins having insecticidal activity against lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are synthetic crystal proteins encoded by these novel nucleic acid sequences. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention. Also disclosed are methods for modifying, altering, and mutagenizing specific loop regions between the alpha helices in domain 1 of these crystal proteins, including Cry1C, to produce genetically-engineered recombinant cry* genes, and the proteins they encode which have improved insecticidal activity. In preferred embodiments, novel Cry1C* amino acid segments and the modified cry1C* nucleic acid sequences which encode them are disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
GRG23 and GRG 51 genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, or 6, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, or 5. The present invention additionally provides a method to measure enzyme kinetic activity using fluorogenic substrates.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Broad-spectrum insect resistant transgenic plants
InactiveUS6281016B1Improve insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityBiocideNanotechAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and tansgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a polypeptide that confers resistance or tolerance to glyphosate herbicides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules corresponding to glyphosate resistant nucleic acid sequences are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:3 or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 or 2.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Broad-spectrum delta -endotoxins
InactiveUS6110464AImprove insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityNanotechBacteriaAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
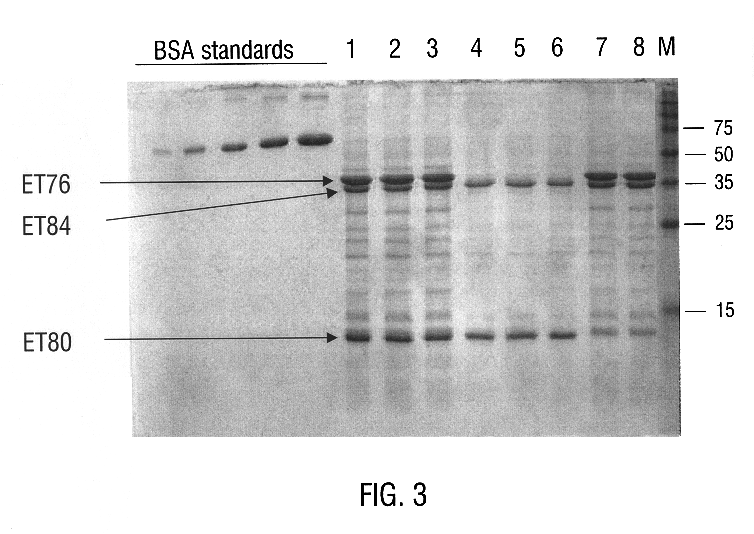
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6093695ARemarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaBacillus thuringiensisCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta -endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against colcopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneur). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Grg23 epsp synthases: compositions and methods of use
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides containing nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, or 35, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, or 34.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Methods for transforming plants to express Cry2Ab delta-endotoxins targeted to the plastids
InactiveUS6489542B1Reduce in quantityHigh expressionSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationDelta endotoxinBacillus e
Disclosed is a means of controlling plant pests by a novel method of expressing Cry2Ab B. thuringiensis delta-endotoxins in plants, targeted to the plastids. The invention comprises novel nucleic acid segments encoding proteins comprising Cry2Ab B. thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. The nucleic acid segments are disclosed, as are transformation vectors containing the nucleic acid segments, plants transformed with the claimed segments, methods for transforming plants, and methods of controlling plant infestation by pests.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
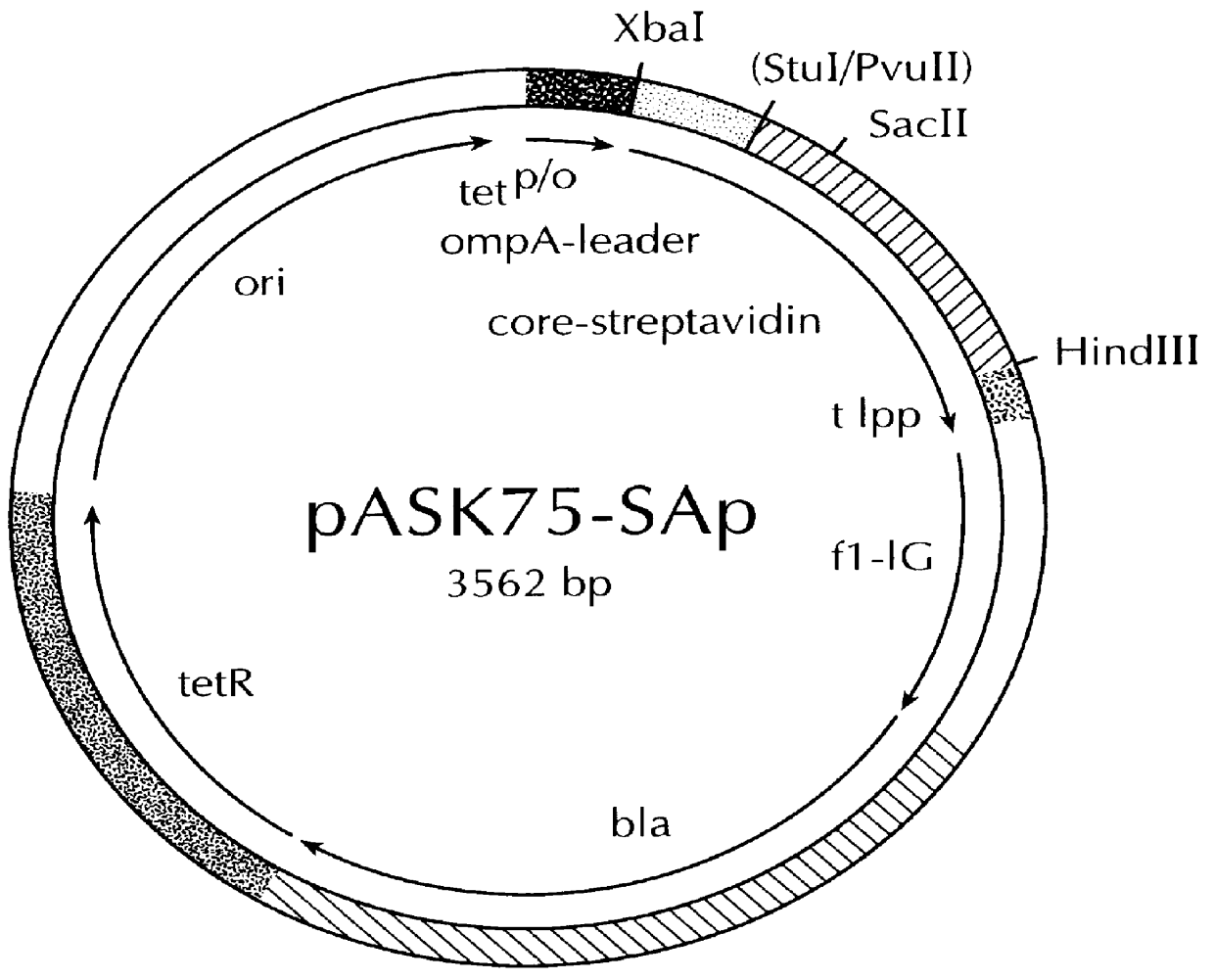
Streptavidin muteins
InactiveUS6103493AHigh affinityElution can be checked visuallyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide ligandSubject matter
The invention concerns a polypeptide selected from muteins of streptavidin which is characterized in that it (a) contains at least one mutation in the region of the amino acid positions 44 to 53 with reference to wild type-(wt)-streptavidin and (b) has a higher binding affinity than wt-streptavidin for peptide ligands comprising the amino acid sequence Trp-X-His-Pro-Gln-Phe-Y-Z in which X represents an arbitrary amino acid and Y and Z either both denote Gly or Y denotes Glu and Z denotes Arg or Lys. In addition nucleic acids coding for the polypeptide, a vector containing this nucleic acid, a cell transfected with the vector as well as the use of a polypeptide in a method for the isolation, purification or determination of proteins are disclosed. Yet a further subject matter is a reagent kit containing the polypeptide.
Owner:INST FUR BIOANALYTIC
Lepidopteran-active Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6593293B1Low steady state levelGreat and less stabilityBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinAureobasidium sp.
Disclosed are Bacillus thuringiensis strains comprising novel crystal proteins which exhibit insecticidal activity against lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are novel B. thuringiensis genes and their encoded crystal proteins, as well as methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel nucleic acid sequences of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
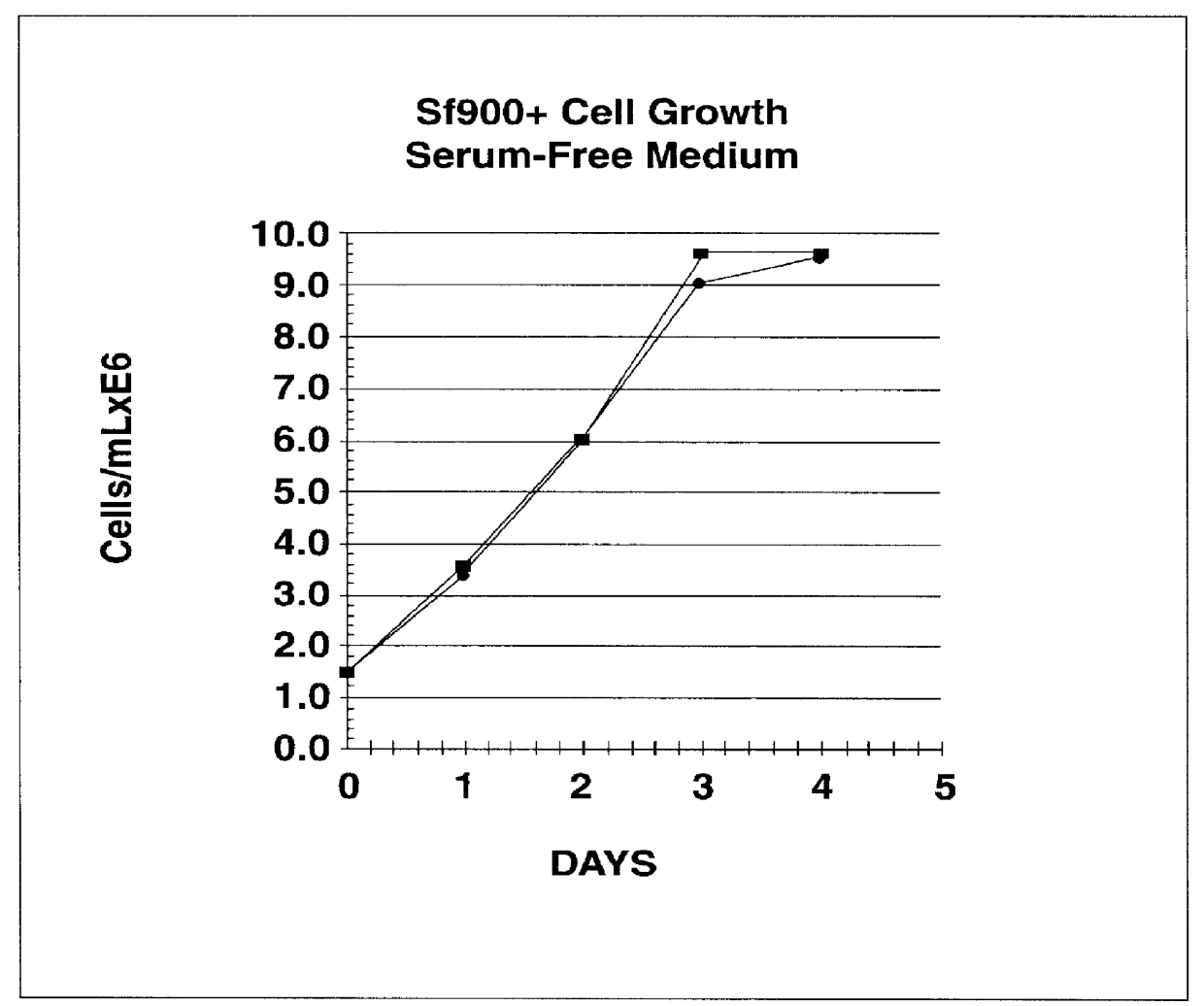
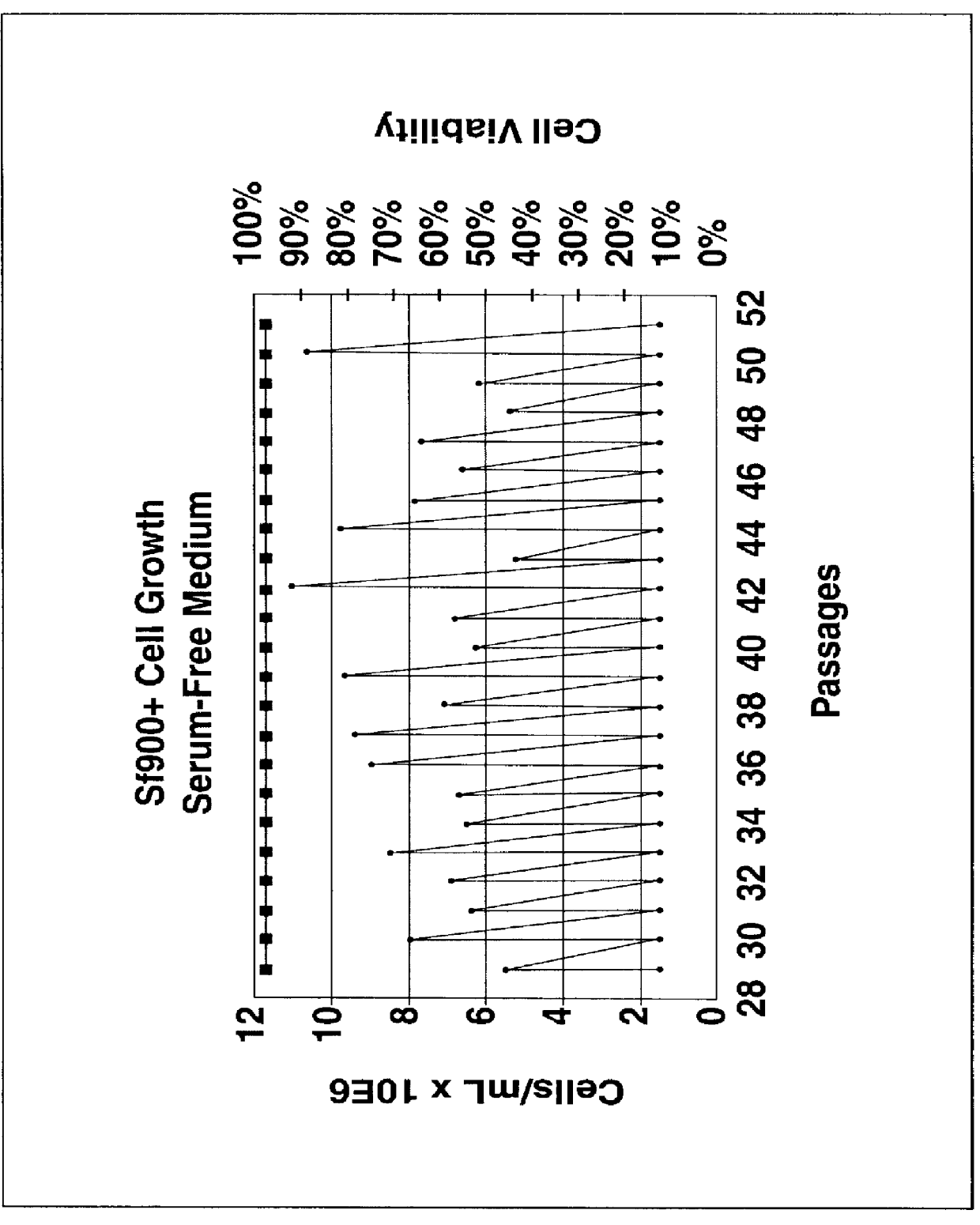
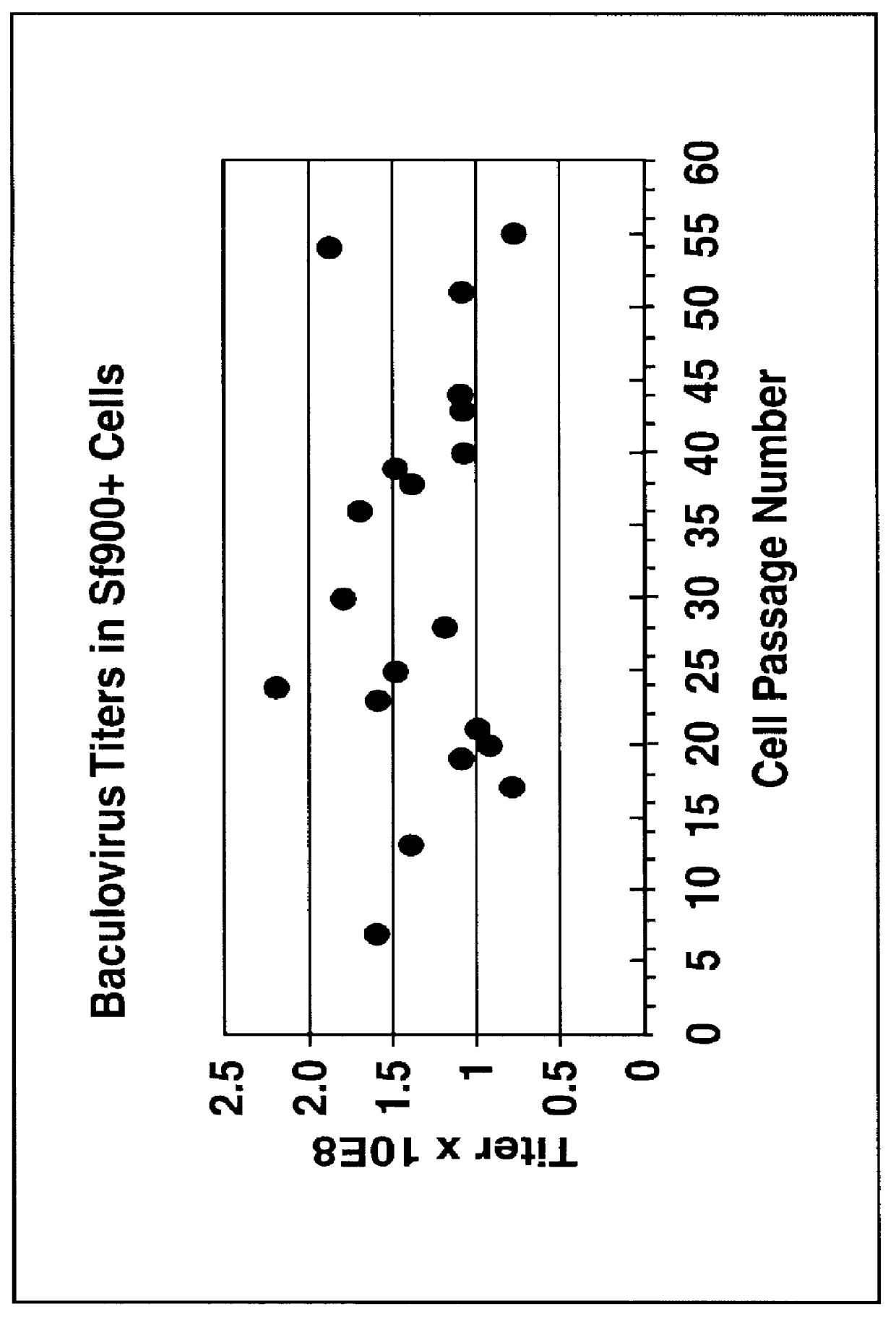
Spodoptera frugiperda single cell suspension cell line in serum-free media, methods of producing and using
InactiveUS6103526AAvoid infectionHigh densityConnective tissue peptidesInvertebrate cellsSerum free mediaAdjuvant
Disclosed and claimed is a new insect cell line, Sf900+, ATCC CRL-12579. The insect cell line was established from Lepidoptera, Noctuidae, Spodoptera frugiperda Sf-9 (ATCC CRL-1711) through multiple rounds of limiting dilution and selection in a serum-free insect medium supplemented with added human insulin. The insect cell line is useful in BEVS or as an adjuvant and has many characteristics and advantages. Also disclosed and claimed are recombinant proteins from recombinant baculovirus expression in insect cells such as Sf900+ cells, for instance, HA, NA, EPO, CD4, CEA, and thrombospondin.
Owner:PROTEIN SCI
Clostridial toxin derivatives able to modify peripheral sensory afferent functions
InactiveUS6395513B1Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsClostridial toxinProjection neuron
The invention relates to an agent specific for peripheral sensory afferents. The agent may inhibit the transmission of signals between a primary sensory afferent and a projection neuron by controlling the release of at least one neurotransmitter or neuromodulator from the primary sensory afferent. The agent may be used in or as a pharmaceutical for the treatment of pain, particularly chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and Ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6537756B1Remarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta-endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against coleopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Coleopteran-toxic polypeptide compositions and insect-resistant transgenic plants
InactiveUS6555655B1Easy to storeInhibit microbial growthBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinPolynucleotide
Disclosed are novel insecticidal polypeptides, and compositions comprising these polypeptides, peptide fragments thereof, and antibodies specific therefor. Also disclosed are vectors, transformed host cells, and transgenic plants that contain nucleic acid segments that encode the disclosed delta-endotoxin polypeptides. Also disclosed are methods of identifying related polypeptides and polynucleotides, methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising these polynucleotide sequences, as well as methods for controlling an insect population, such as Colorado potato beetle, southern corn rootworm and western corn rootworm, and for conferring to a plant resistance to a target insect species.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
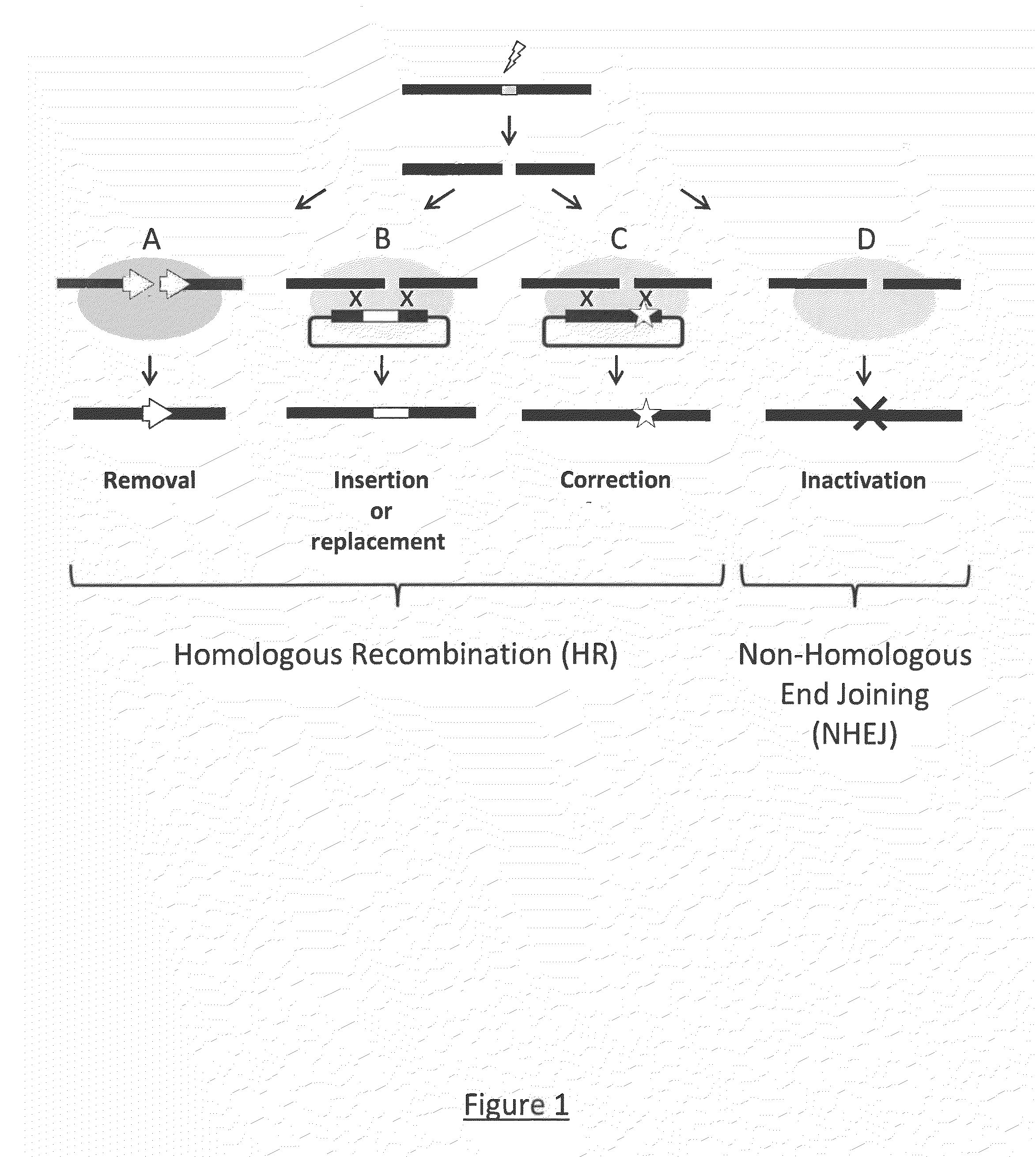
Method for the generation of compact tale-nucleases and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130117869A1Simple processSimple and efficient vectorizationFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesDNA-binding domainNuclease
The present invention relates to a method for the generation of compact Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs) that can efficiently target and process double-stranded DNA. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for the creation of TALENs that consist of a single TALE DNA binding domain fused to at least one catalytic domain such that the active entity is composed of a single polypeptide chain for simple and efficient vectorization and does not require dimerization to target a specific single double-stranded DNA target sequence of interest and process DNA nearby said DNA target sequence. The present invention also relates to compact TALENs, vectors, compositions and kits used to implement the method.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Staged assembly of nanostructures
The present invention provides methods and assembly units for the construction of nanostructures. Assembly of nanostructures proceeds by sequential, non-covalent, vectorial addition of an assembly unit to an initiator or nanostructure intermediate during an assembly cycle, a process termed "staged assembly." Attachment of each assembly unit is mediated by specific, non-covalent binding of a single pre-determined joining element of one assembly unit to a complementary joining element on a target initiator or nanostructure intermediate. Each interaction of a joining element is designed such that the joining element does not interact with any other joining element of the assembly unit. Self-association of the assembly unit is therefore obviated: only one assembly unit can be added at a time to a target initiator or nanostructure intermediate.
Owner:NANOFRAMES
Novel Insecticidal Proteins and Methods for Their Use
ActiveUS20140033361A1Improve pest resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyOrder Lepidoptera
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest including plants, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The pesticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, Dipteran, fungal, Hemipteran and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
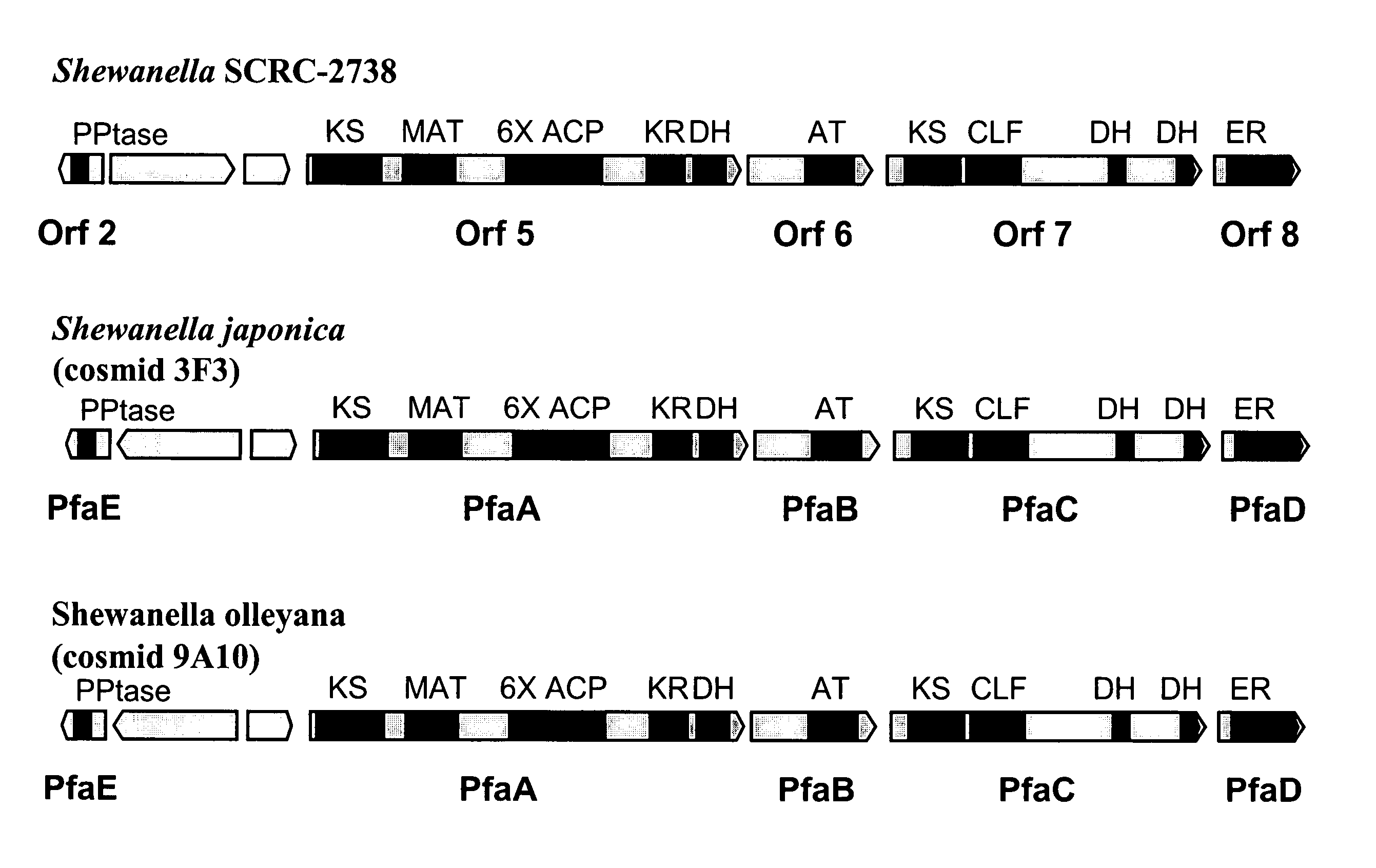
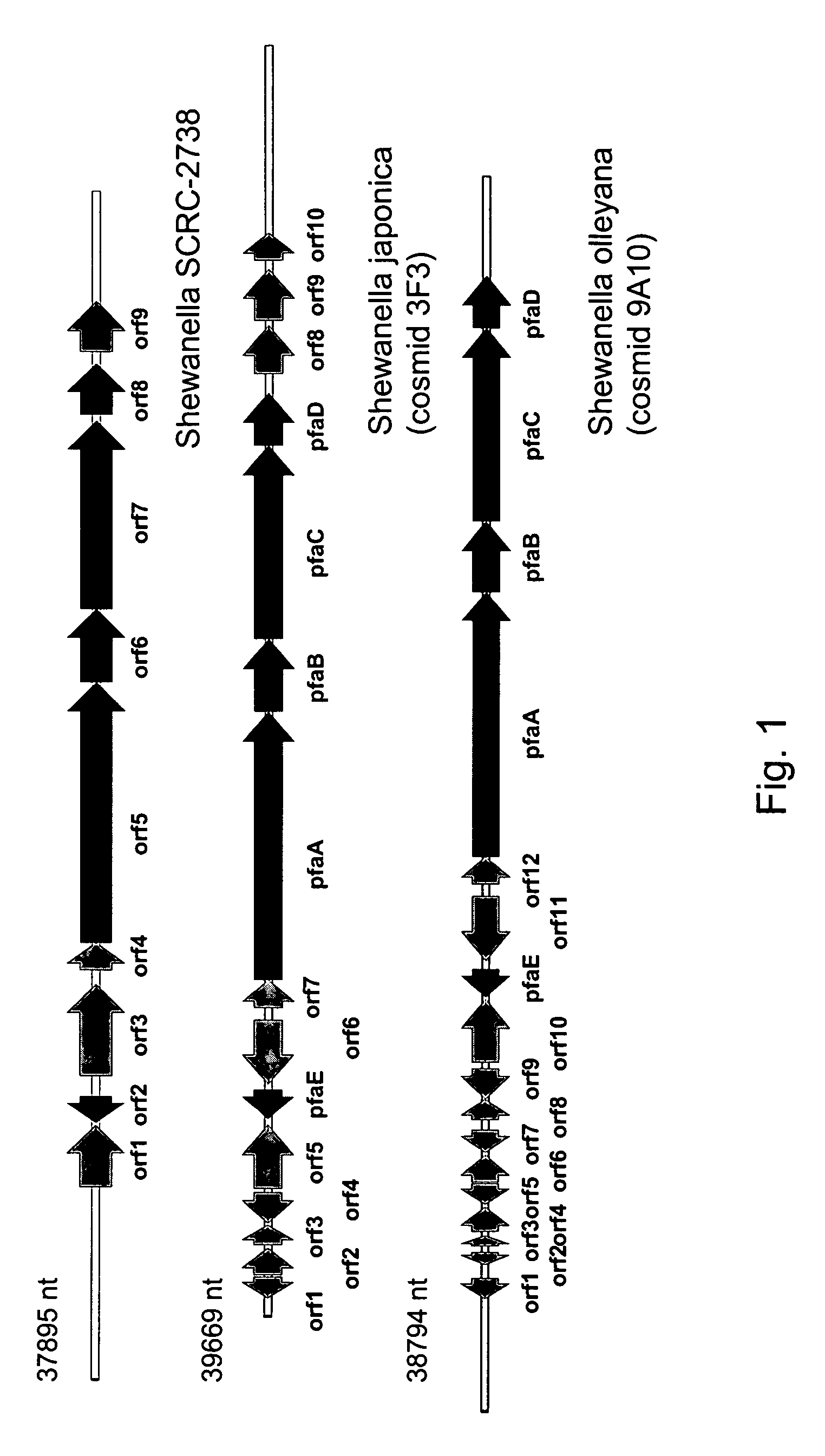
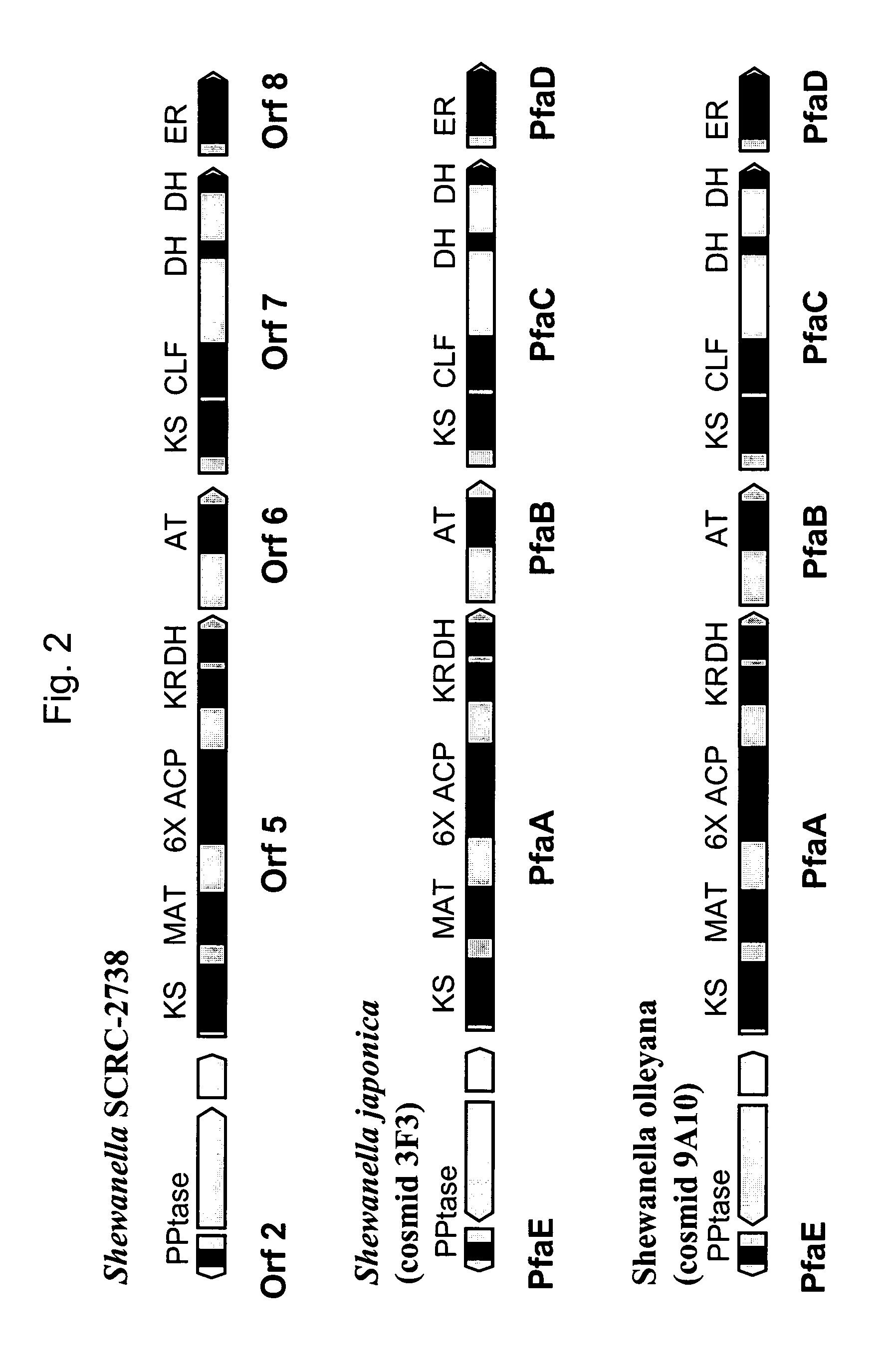
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from the bacterial microorganisms Shewanella japonica and Shewanella olleyana, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Nucleic acid segments encoding modified bacillus thuringiensis coleopteran-toxic crystal proteins
InactiveUS6060594AHigh expressionStably occupyNanotechSugar derivativesBacillus thuringiensisAureobasidium sp.
Disclosed are nucleic acid segments comprising synthetically-modified genes encoding Coleopteran-toxic B. thuringiensis delta -endotoxins. Also disclosed are methods of using these genes for the recombinant expression of polypeptides, the preparation of vectors containing the genes, and methods for transforming suitable host cells.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Collagen binding protein compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6288214B1Prevent and lessen adhesionReduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsCarrier protein
Disclosed are the cna gene and cna-derived nucleic acid segments from Staphylococcus aureus, and DNA segments encoding cna from related bacteria. Also disclosed are Col binding protein (CBP) compositions and methods of use. The CBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to Col. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(Col binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of bacterial colonization in an animal such as a human. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of S. aureus infection.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
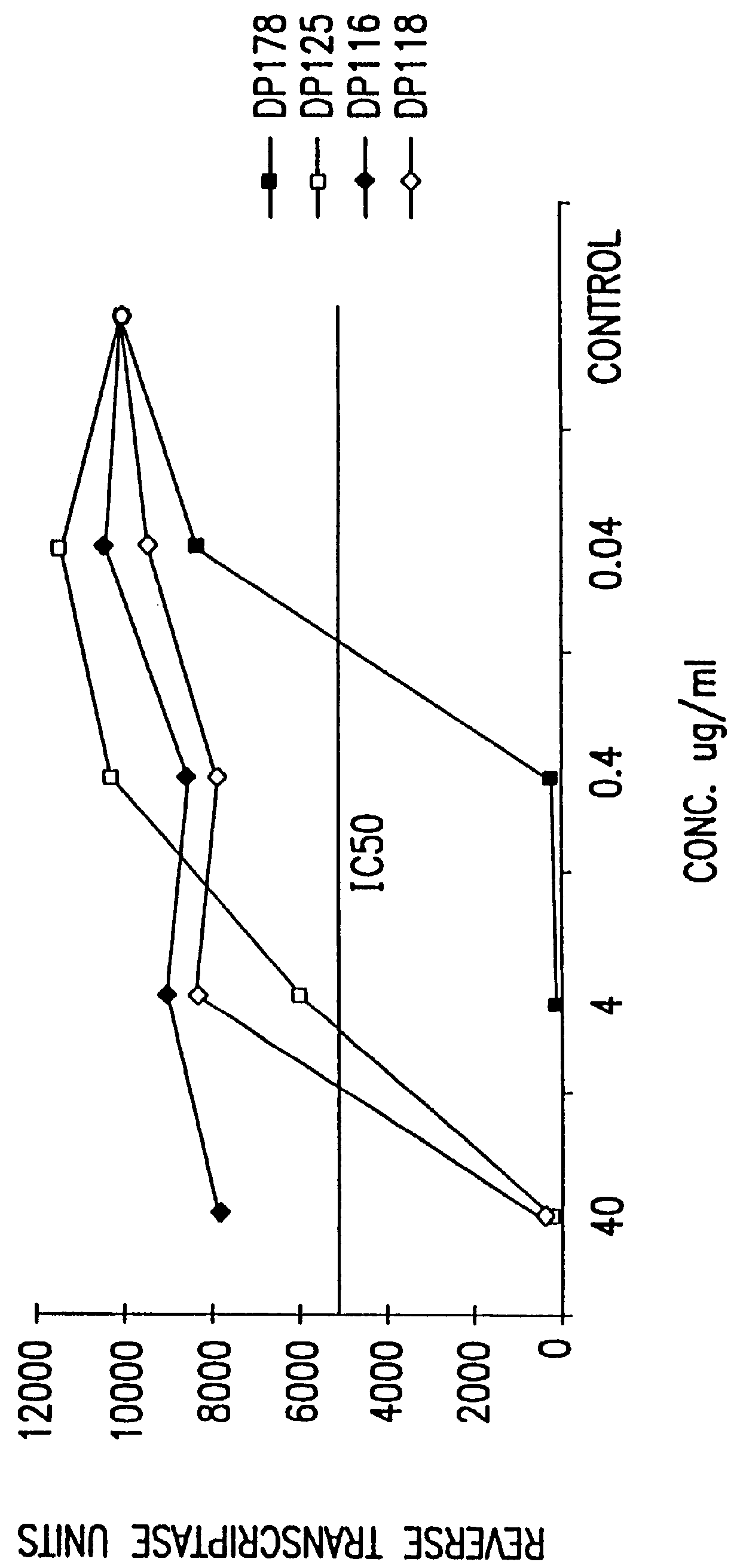
Simian immunodeficiency virus peptides with antifusogenic and antiviral activities
InactiveUS6017536ASsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsSimian immunodeficiency viruses SIVDefective virus
The present invention relates to peptides which exhibit antifusogenic and antiviral activities. The peptides of the invention consist of a 16 to 39 amino acid region of a simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) protein. These regions were identified through computer algorithms capable of recognizing the ALLMOTI5, 107x178x4, or PLZIP amino acid motifs. These motifs are associated with the antifusogenic and antiviral activities of the claimed peptides.
Owner:TRIMERIS +1
Mixing and matching TC proteins for pest control
InactiveUS7491698B2High activityEffective control of widerBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousToxin protein
The subject invention relates to the surprising discovery that toxin complex (TC) proteins, obtainable from Xenorhabdus, Photorhabdus, and Paenibacillus, can be used interchangeably with each other. In particularly preferred embodiments of the subject invention, the toxicity of a “stand-alone” TC protein (from Photorhabdus, Xenorhabdus, or Paenibacillus, for example) is enhanced by one or more TC protein “potentiators” derived from a source organism of a different genus from which the toxin was derived. As one skilled in the art will recognize with the benefit of this disclosure, this has broad implications and expands the range of utility that individual types of TC proteins will now be recognized to have. Among the most important advantages is that one skilled in the art will now be able to use a single set of potentiators to enhance the activity of a stand-alone Xenorhabdus protein toxin as well as a stand-alone Photorhabdus protein toxin. (As one skilled in the art knows, Xenorhabdus toxin proteins tend to be more desirable for controlling lepidopterans while Photorhabdus toxin proteins tend to be more desirable for controlling coleopterans.) This reduces the number of genes, and transformation events, needed to be expressed by a transgenic plant to achieve effective control of a wider spectrum of target pests. Certain preferred combinations of heterologous TC proteins are also disclosed herein. Other objects, advantages, and features of the subject invention will be apparent to one skilled in the art having the benefit of the subject disclosure.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Base-detecting pore
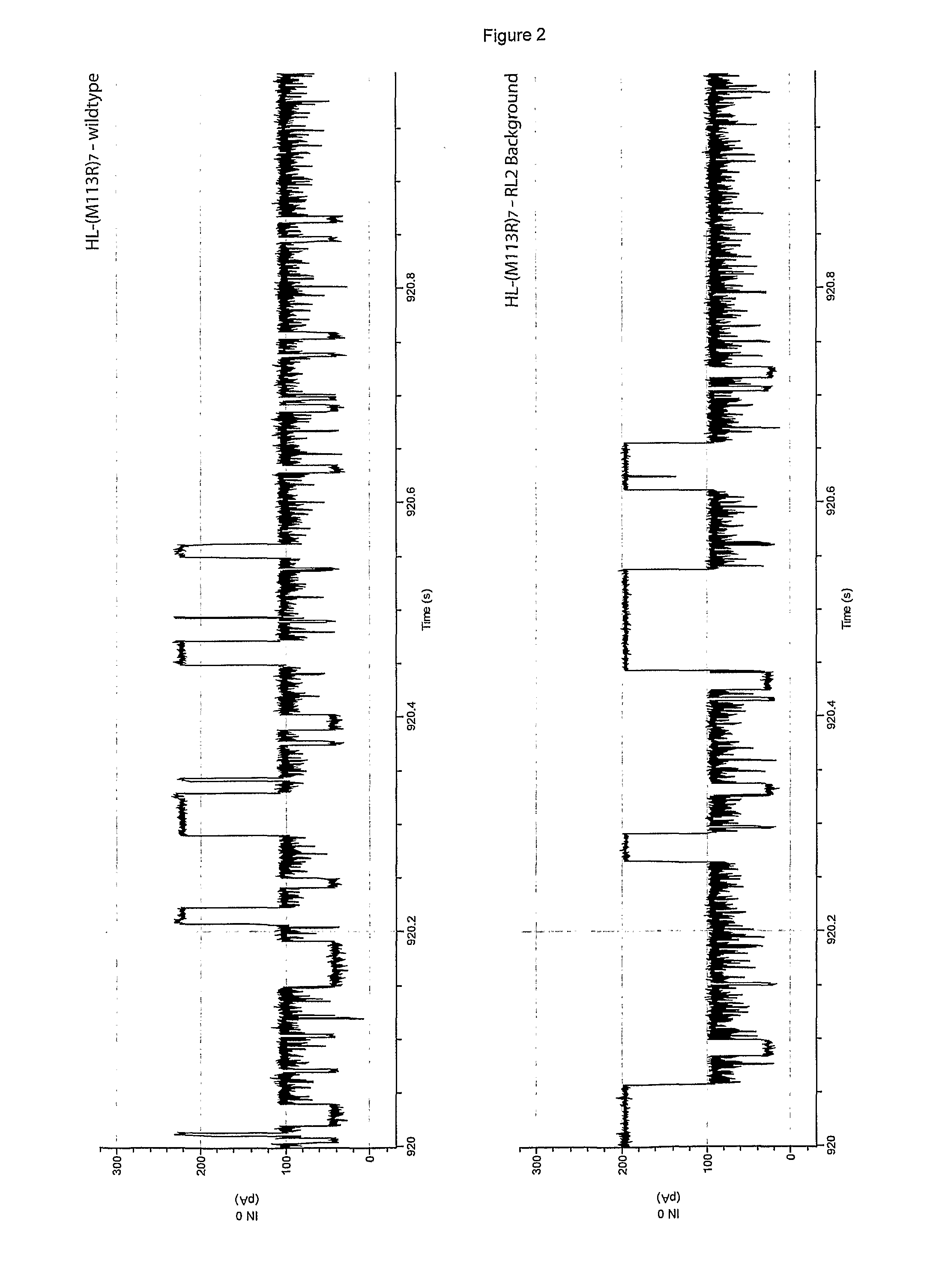
ActiveUS20110177498A1Enhanced interactionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHemolysinDNA
The invention relates to a mutant α-hemolysin (α-HL) pore which is useful for detecting one or more nucleotides by stochastic sensing. The pore is particularly useful for sequencing DNA or RNA. A molecular adaptor that allows detection of the nucleotide(s) is covalently attached to the pore. The pore is specifically modified to facilitate positioning of the adaptor and may be modified to facilitate covalent attachment.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com