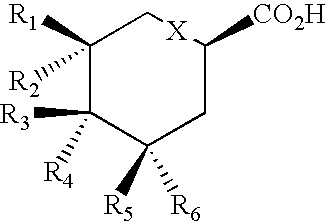
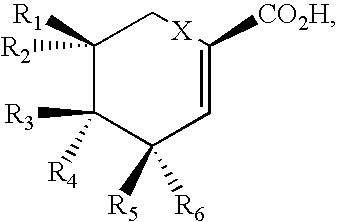
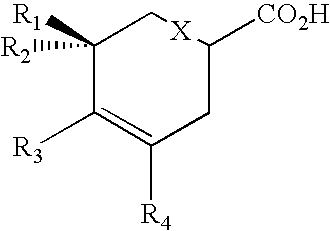
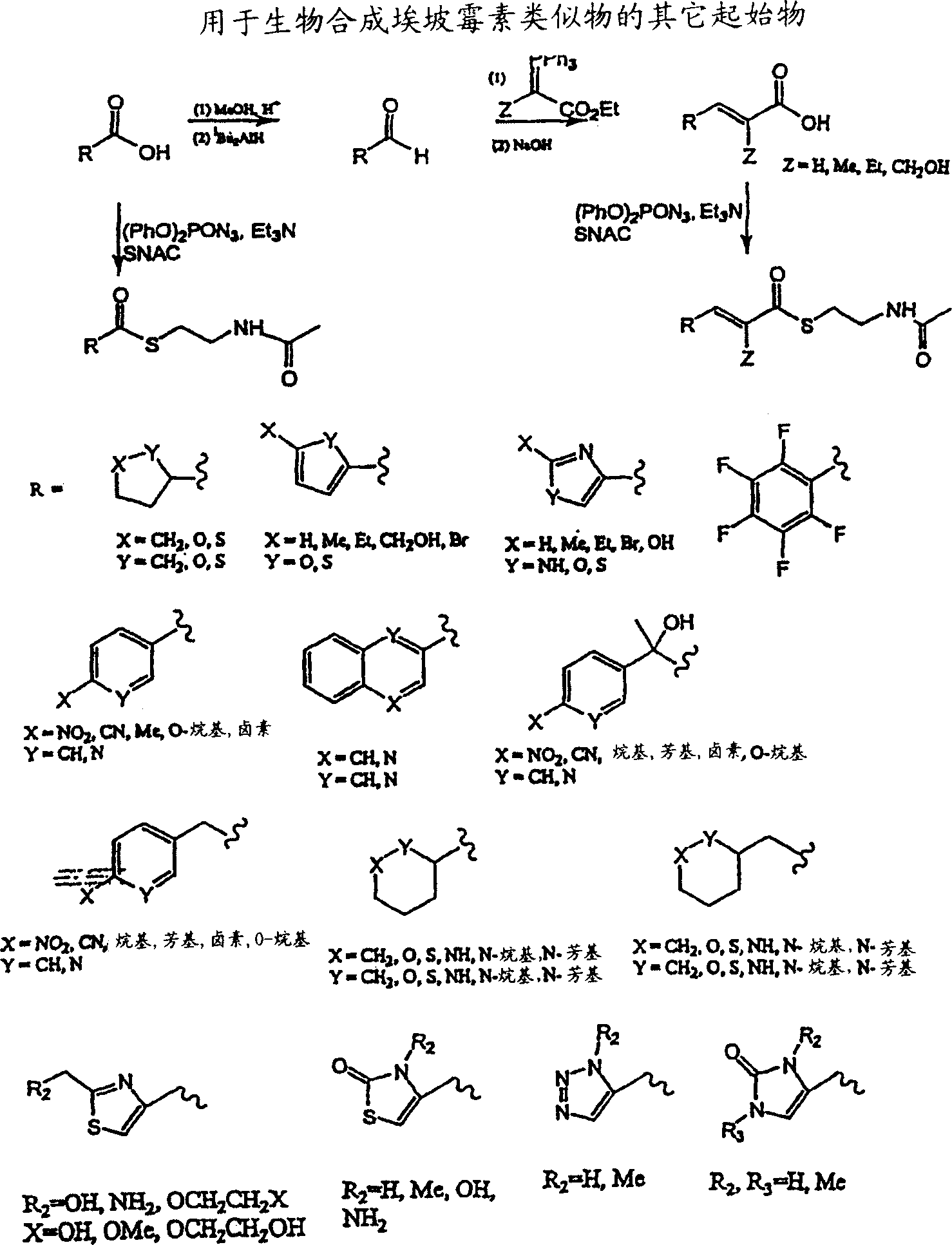
Patents
Literature
104 results about "Polyketide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
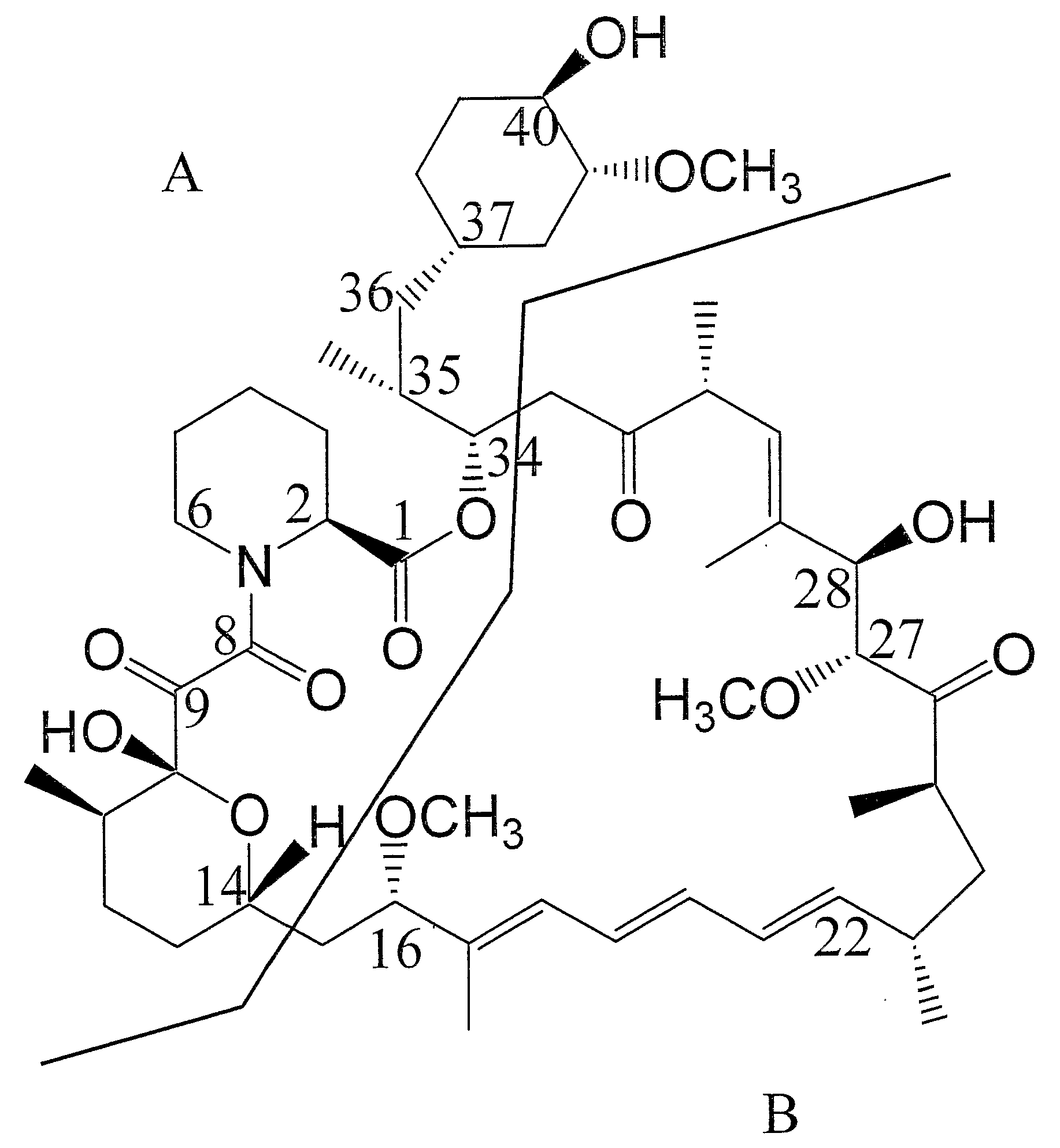
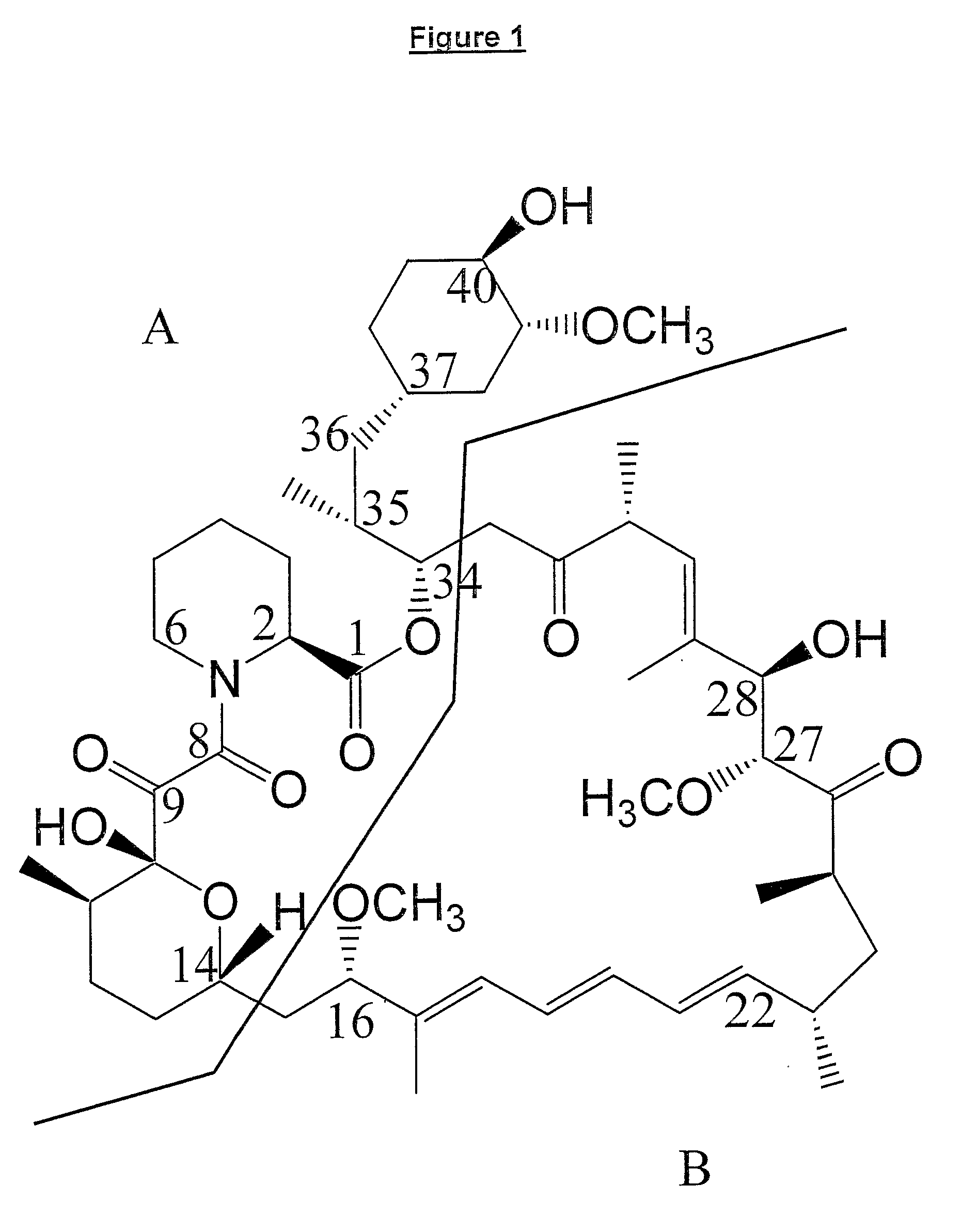
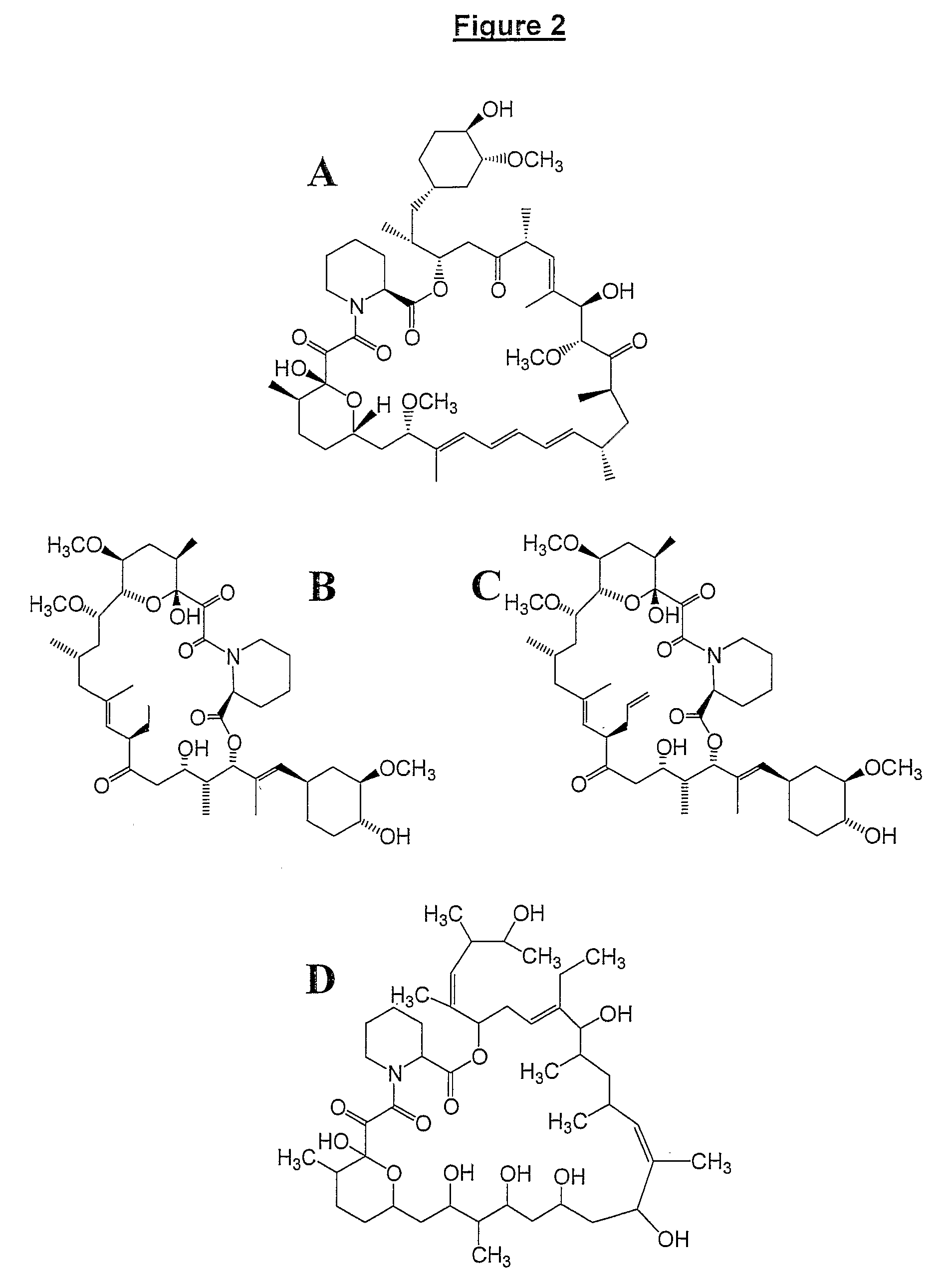
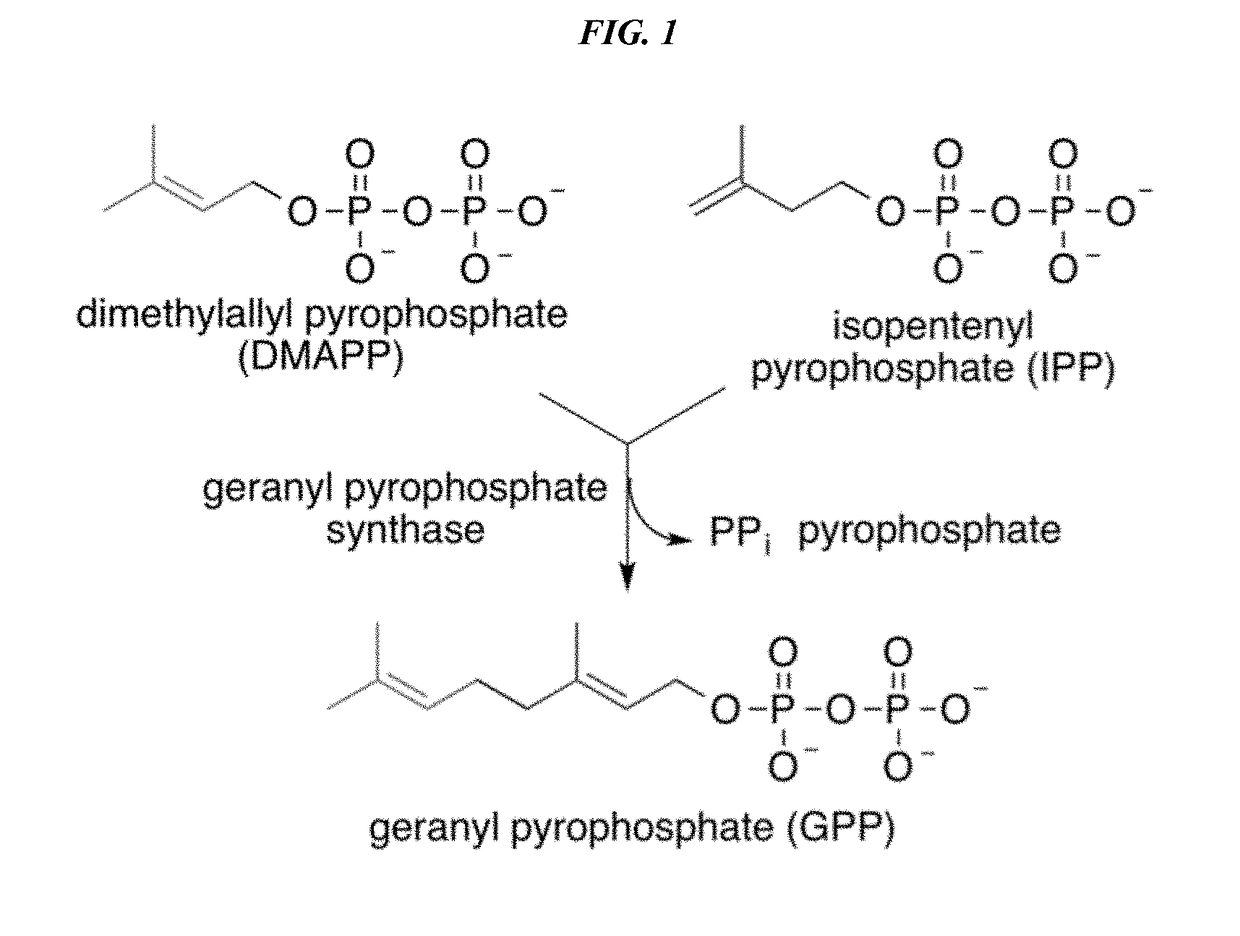
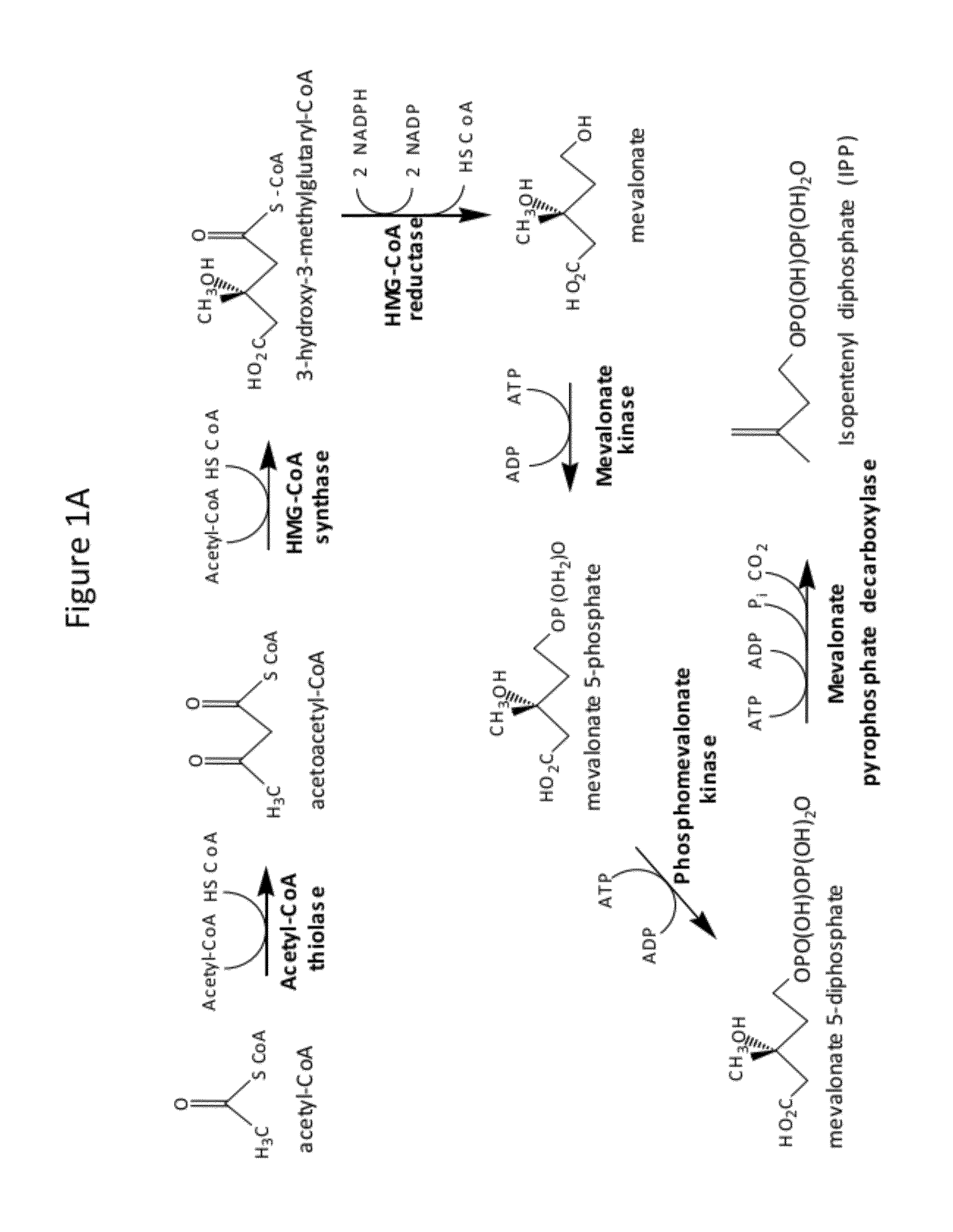
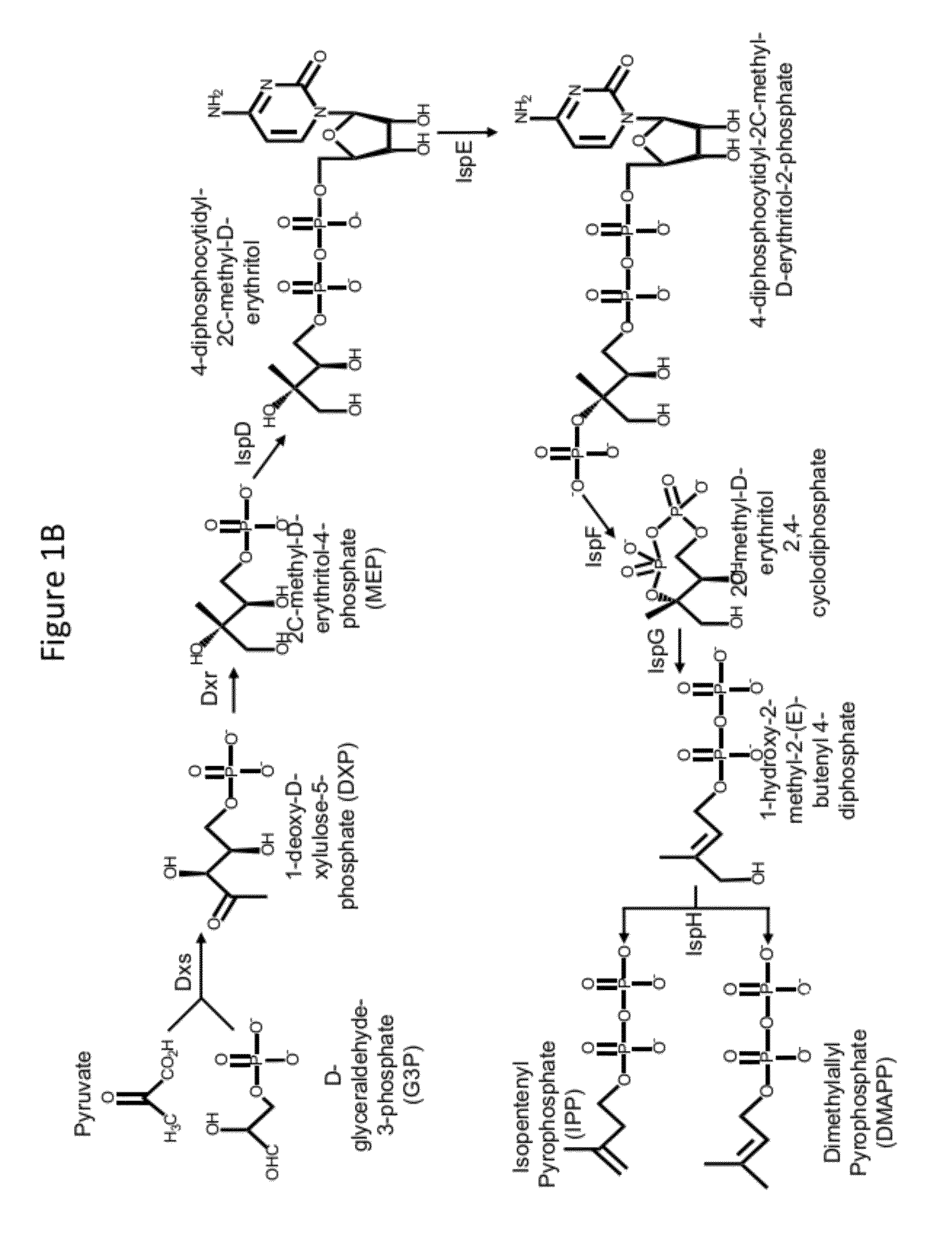
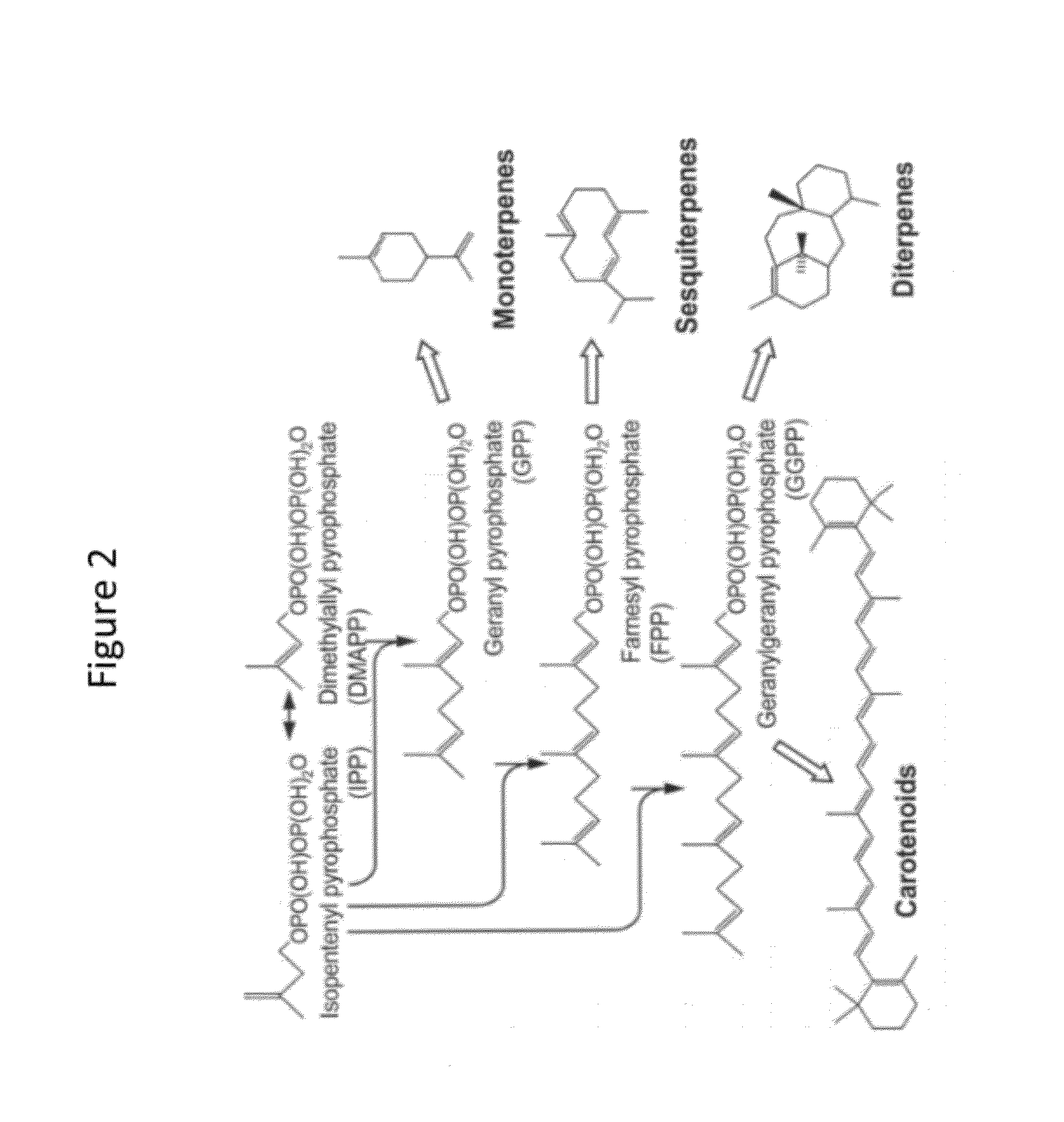
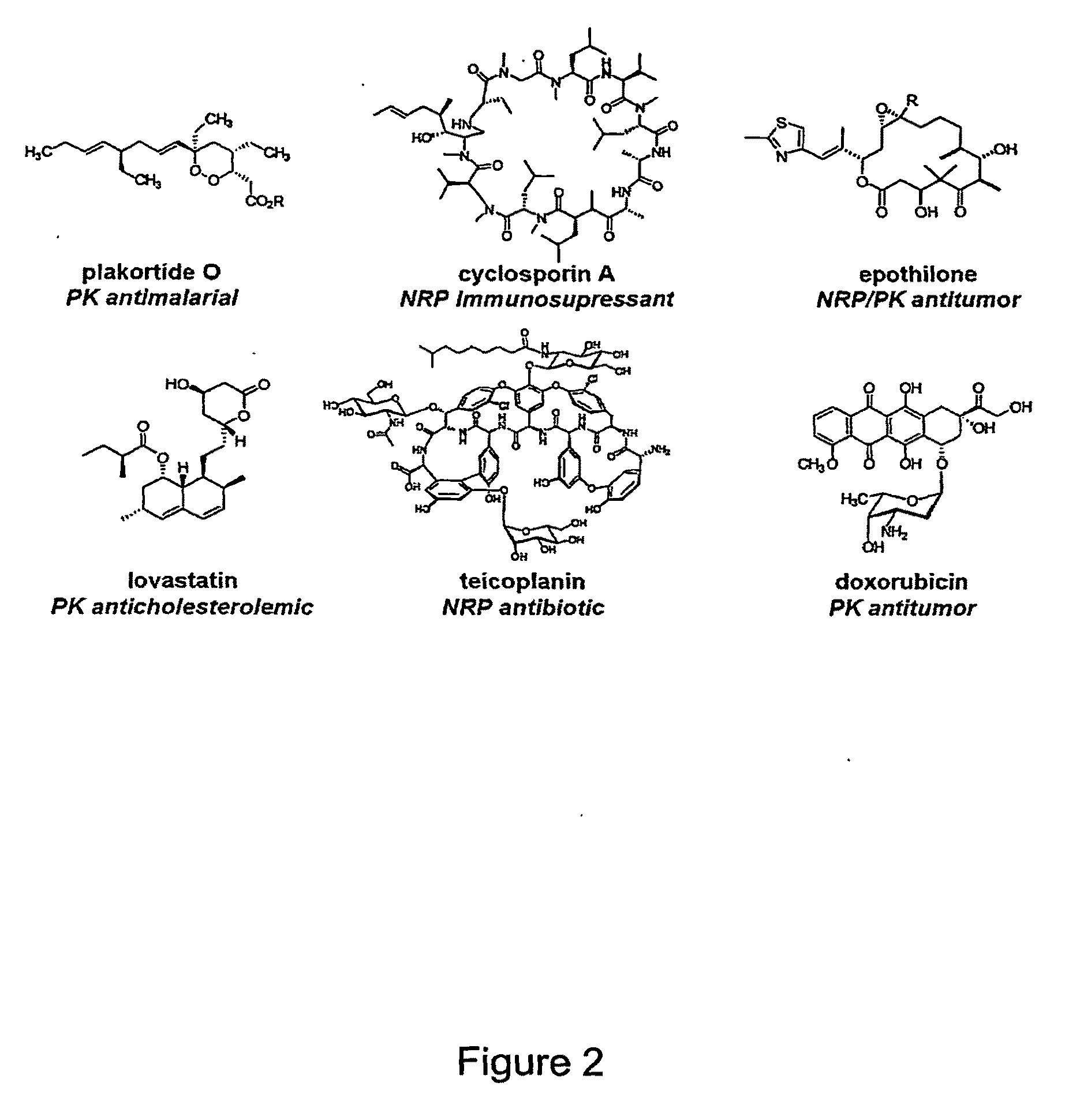
Polyketides are a large group of secondary metabolites which either contain alternating carbonyl and methylene groups (-CO-CH2-), or are derived from precursors which contain such alternating groups. Many polyketides have antimicrobial and immunosuppressive properties. Many mycotoxins produced by fungi are polyketides.
Production Of Polyketides And Other Natural Products
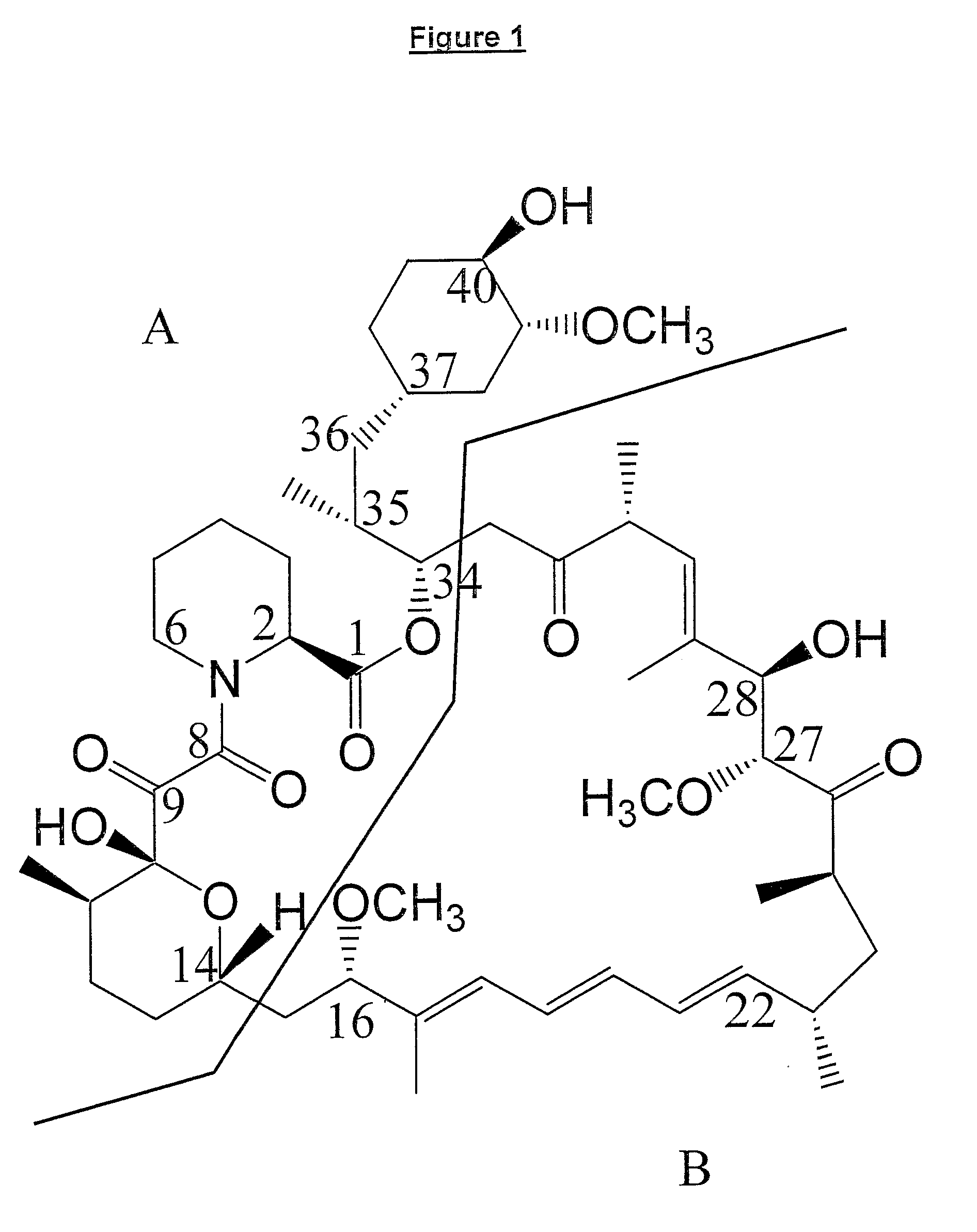
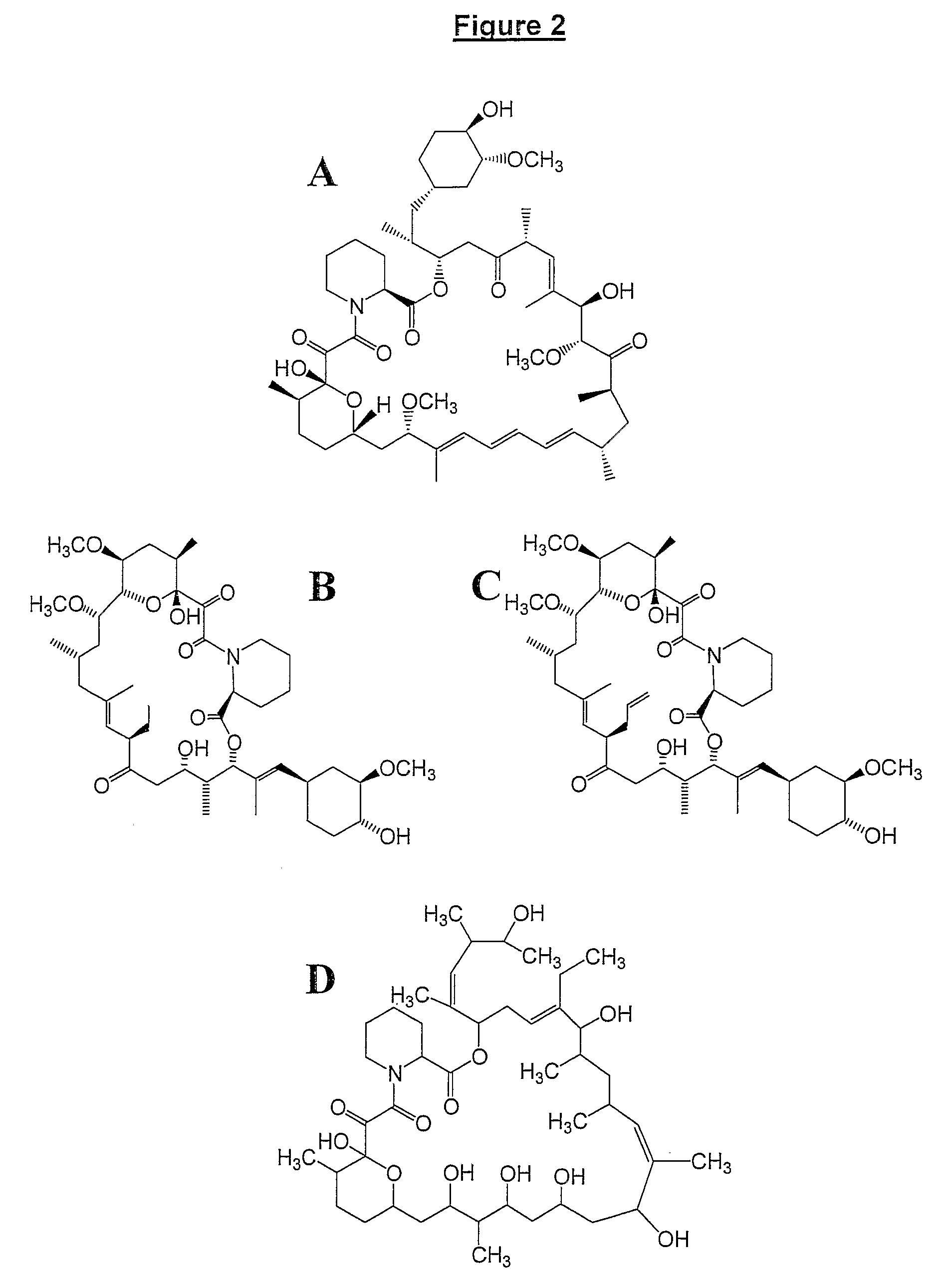
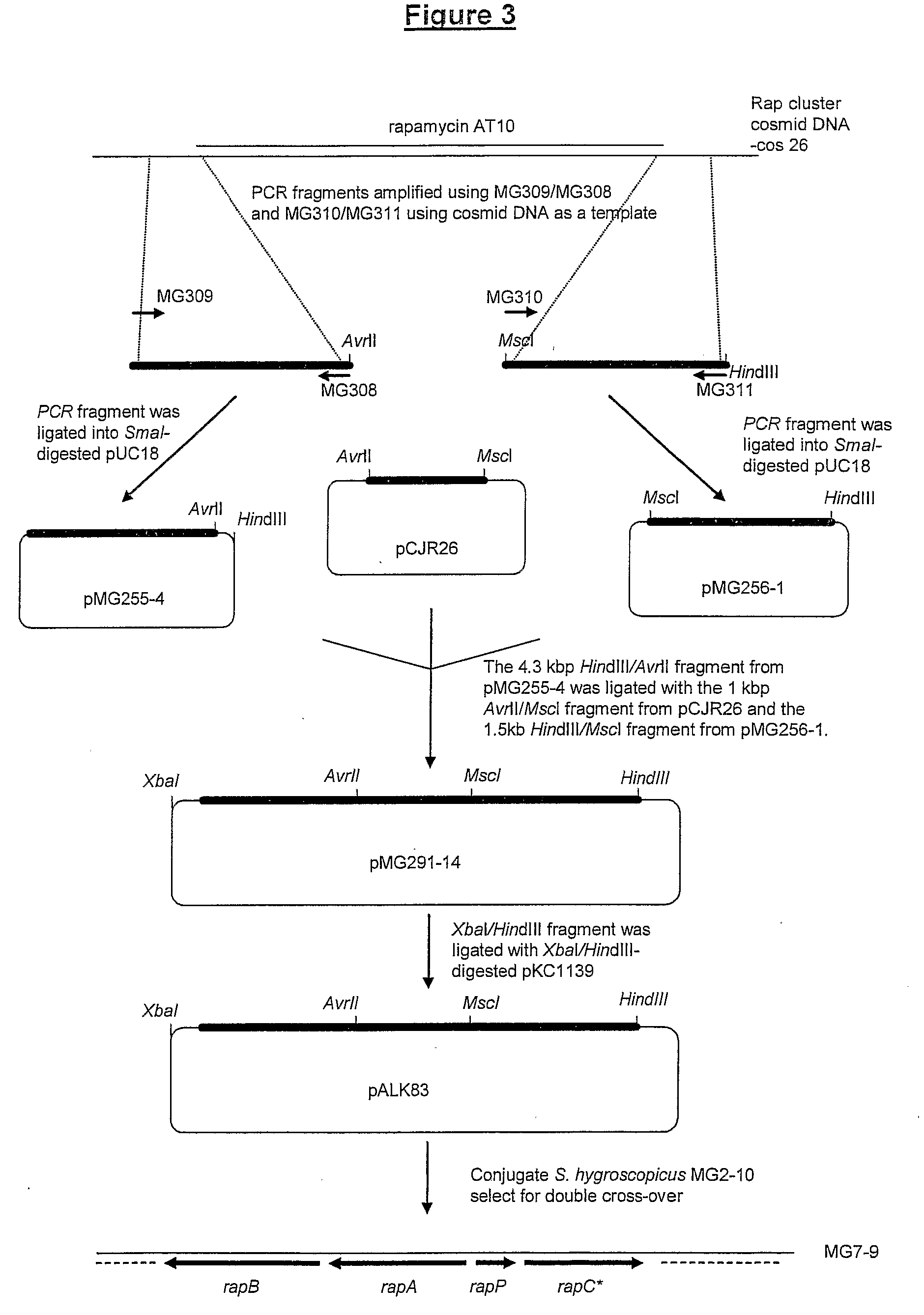
The present invention relates to production of polyketides and other natural products and to libraries of compounds and individual novel compounds. Therefore in aspect the present invention provides 17-desmethylrapamycin and analogues thereof, methods for their production, including recombinant strains, and isolation and uses of the compounds of the invention. In a further aspect the present invention provides for the use of 17-desmethylrapamycin and analogues thereof in the induction or maintenance of immunosuppression, the stimulation of neuronal regeneration or the treatment of cancer, B-cell malignancies, fungal infections, transplantation rejection, graft vs. host disease, autoimmune disorders, diseases of inflammation vascular disease and fibrotic diseases, and in the regulation of wound healing.
Owner:BIOTICA TECH
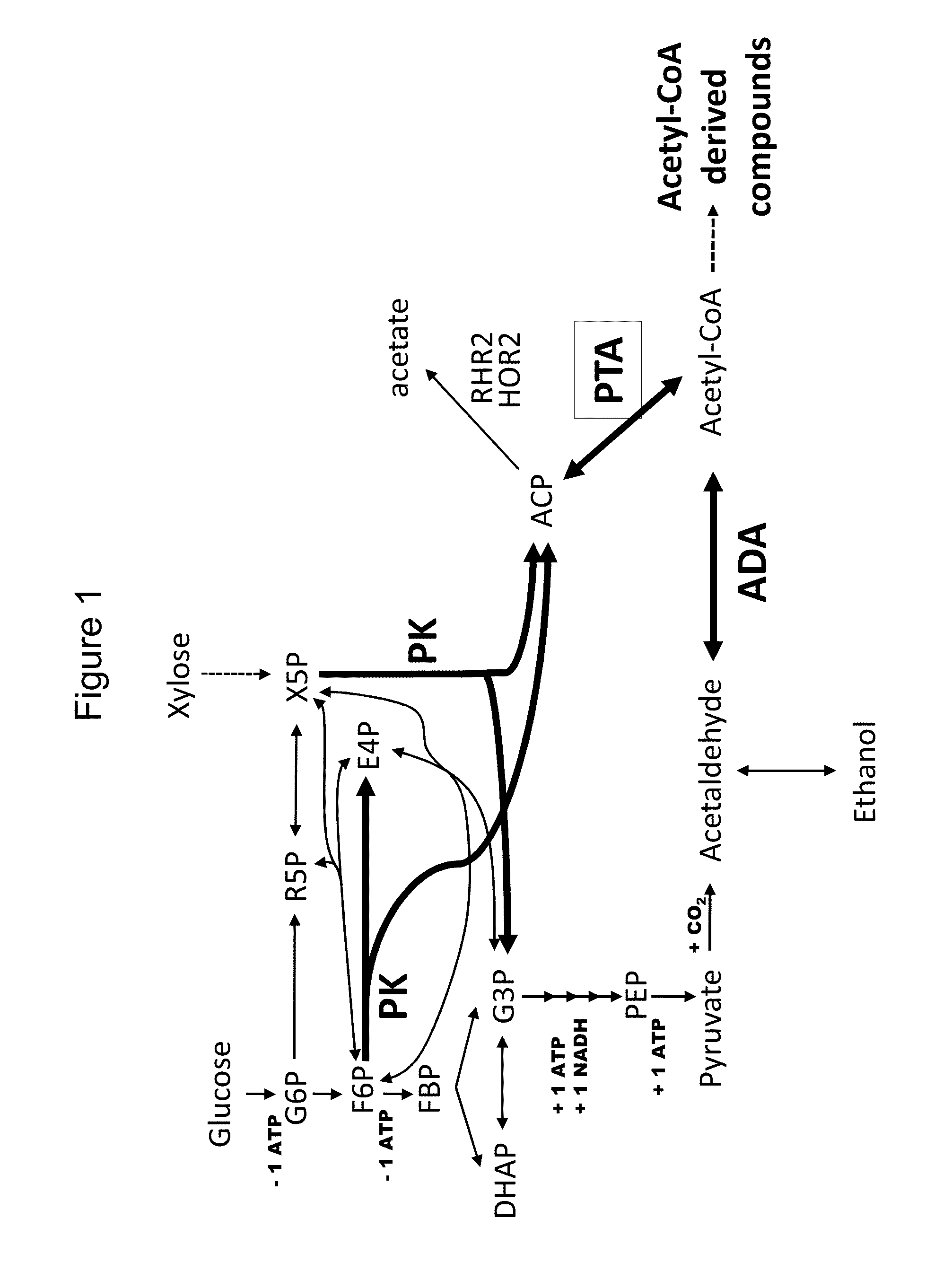
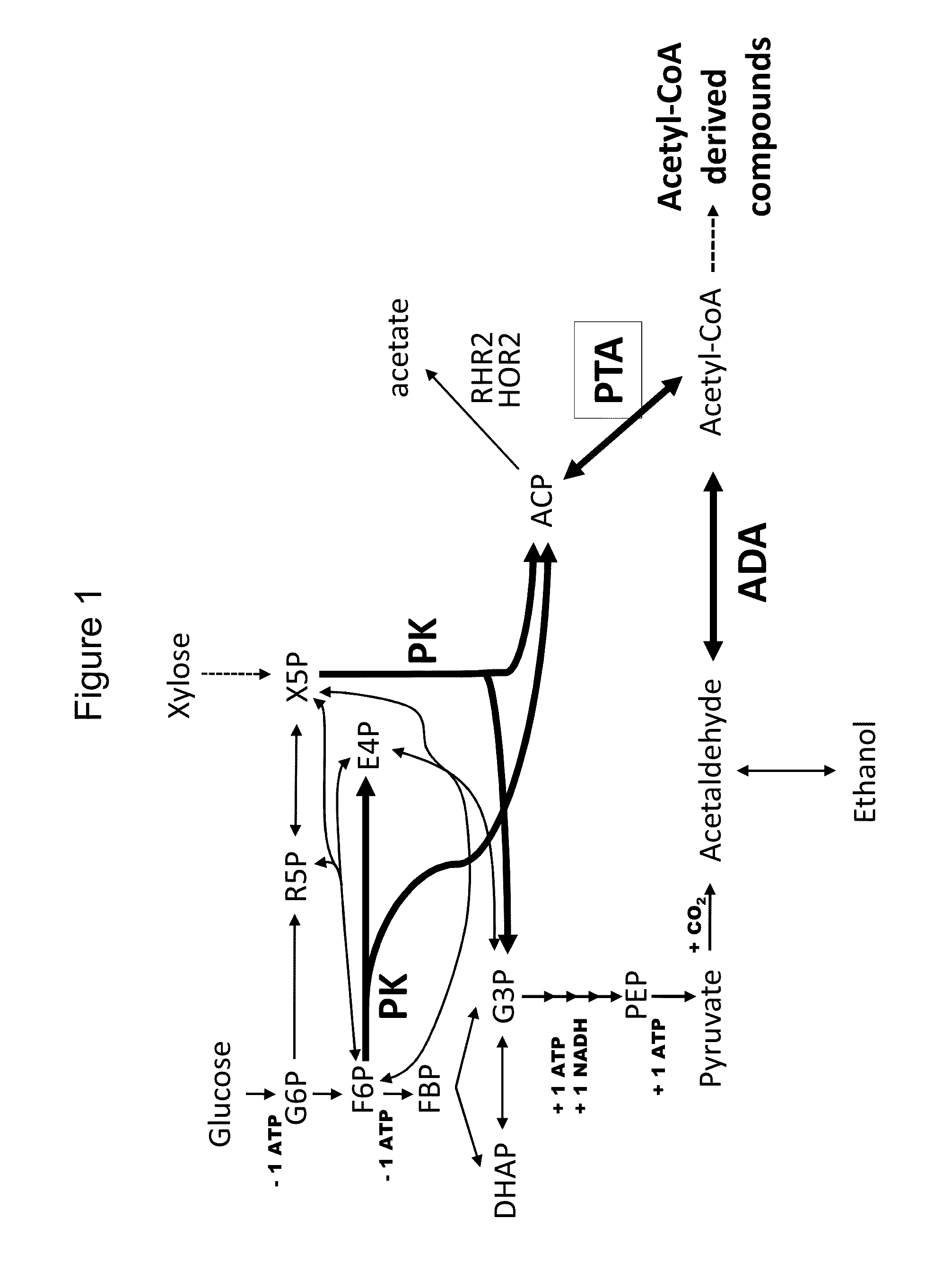
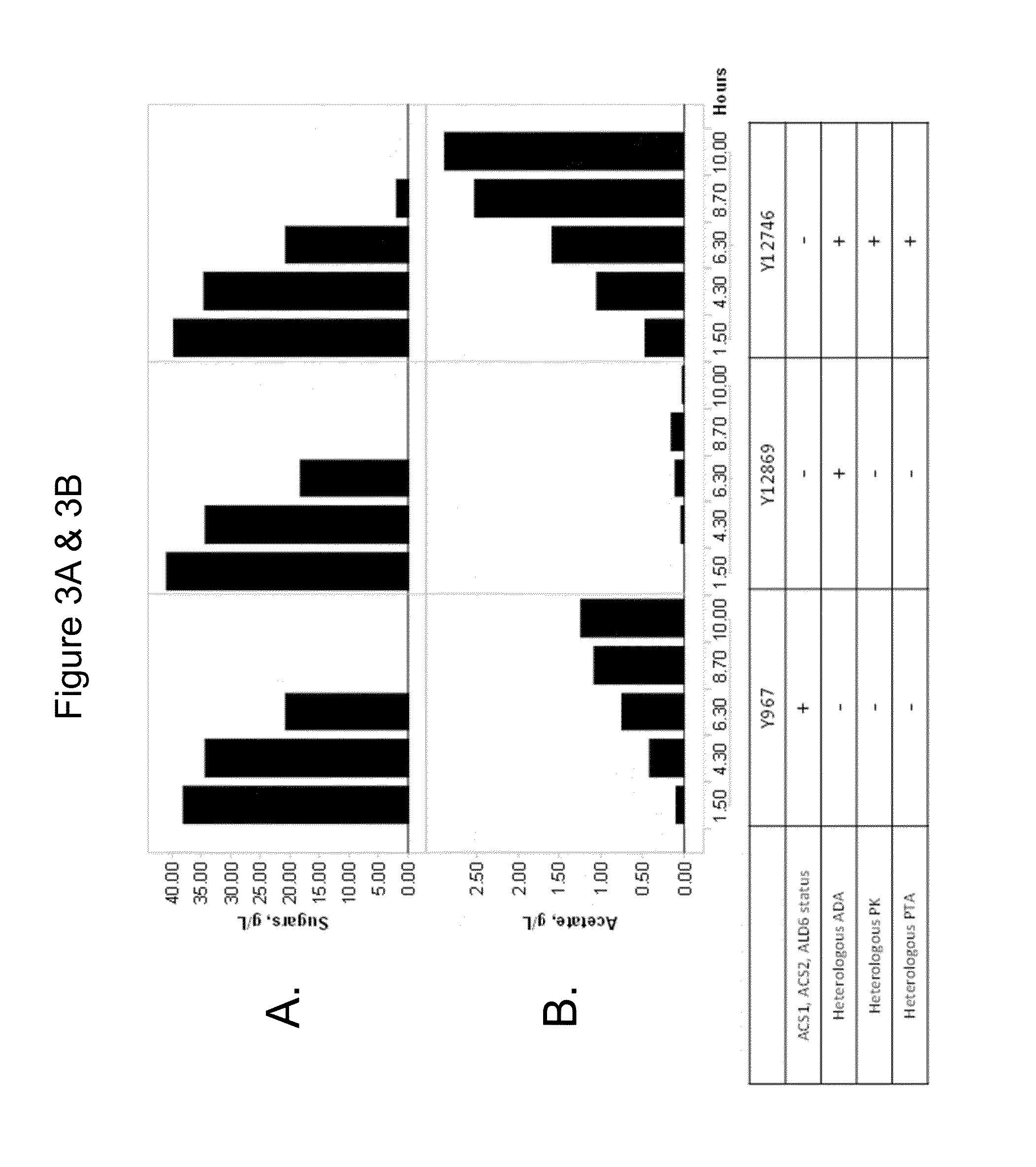
Use of phosphoketolase and phosphotransacetylase for production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived compounds
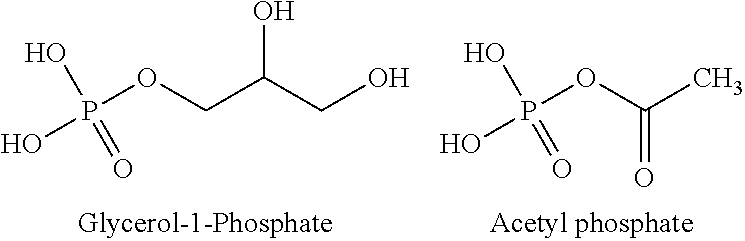
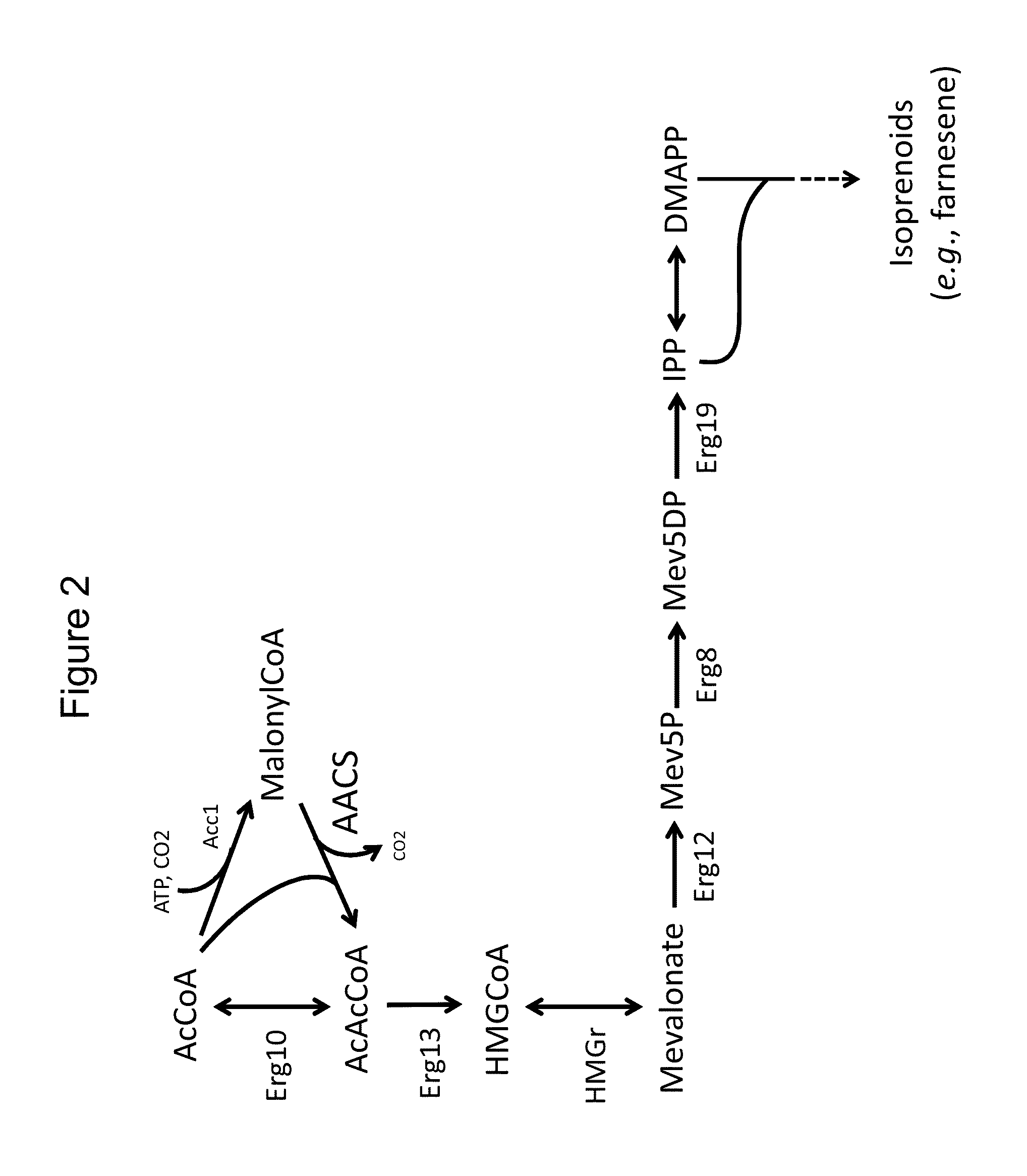
Provided herein are compositions and methods for improved production of acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA derived compounds in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphoketolase (PK), and a functional disruption of an endogenous enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate. In some embodiments, the host cell further comprises a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphotransacetylase (PTA). In some embodiments, the enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate is a glycerol-1-phosphatase. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP1 / RHR2. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP2 / HOR2. The compositions and methods described herein provide an efficient route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived compounds, including but not limited to, isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
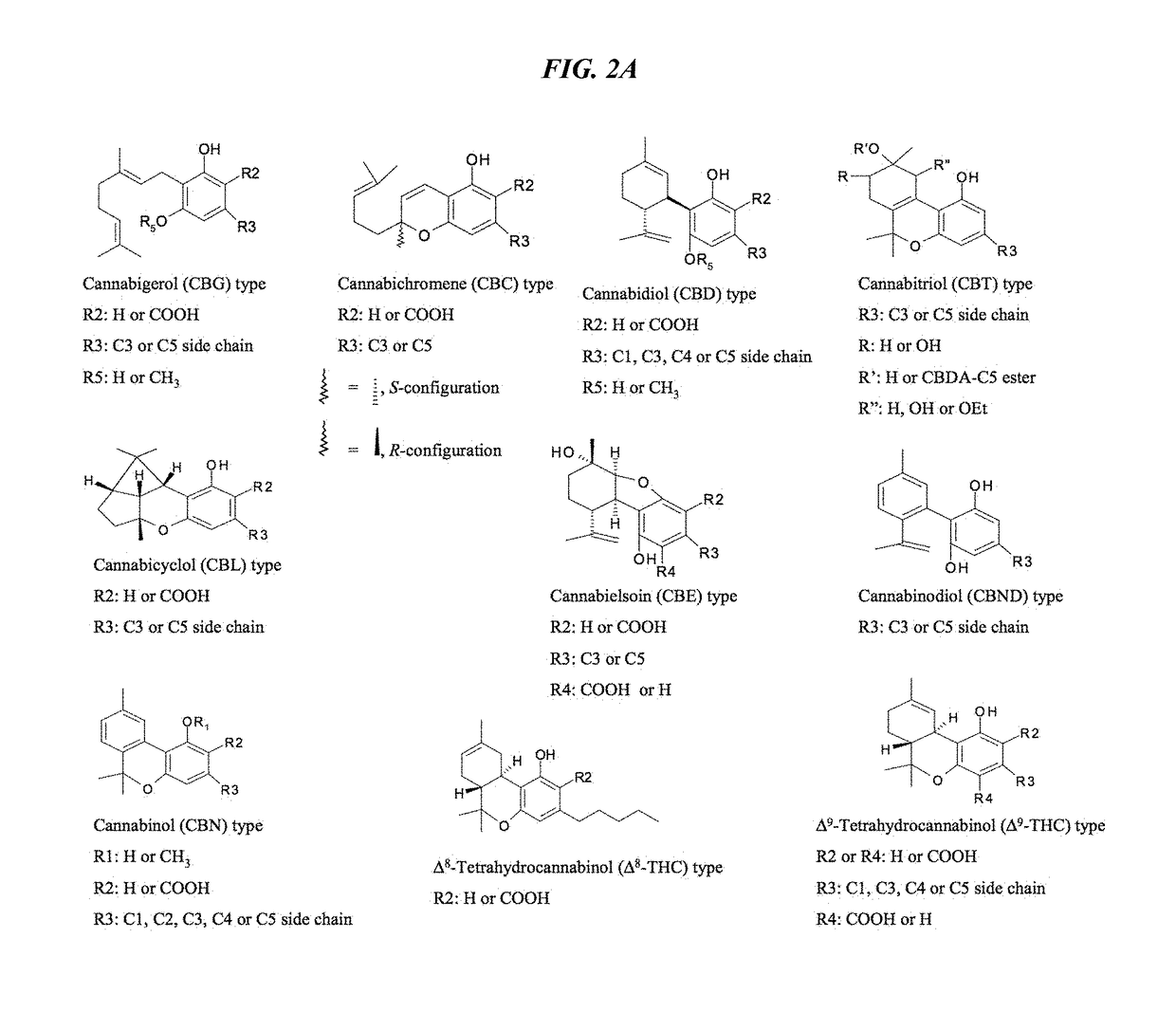
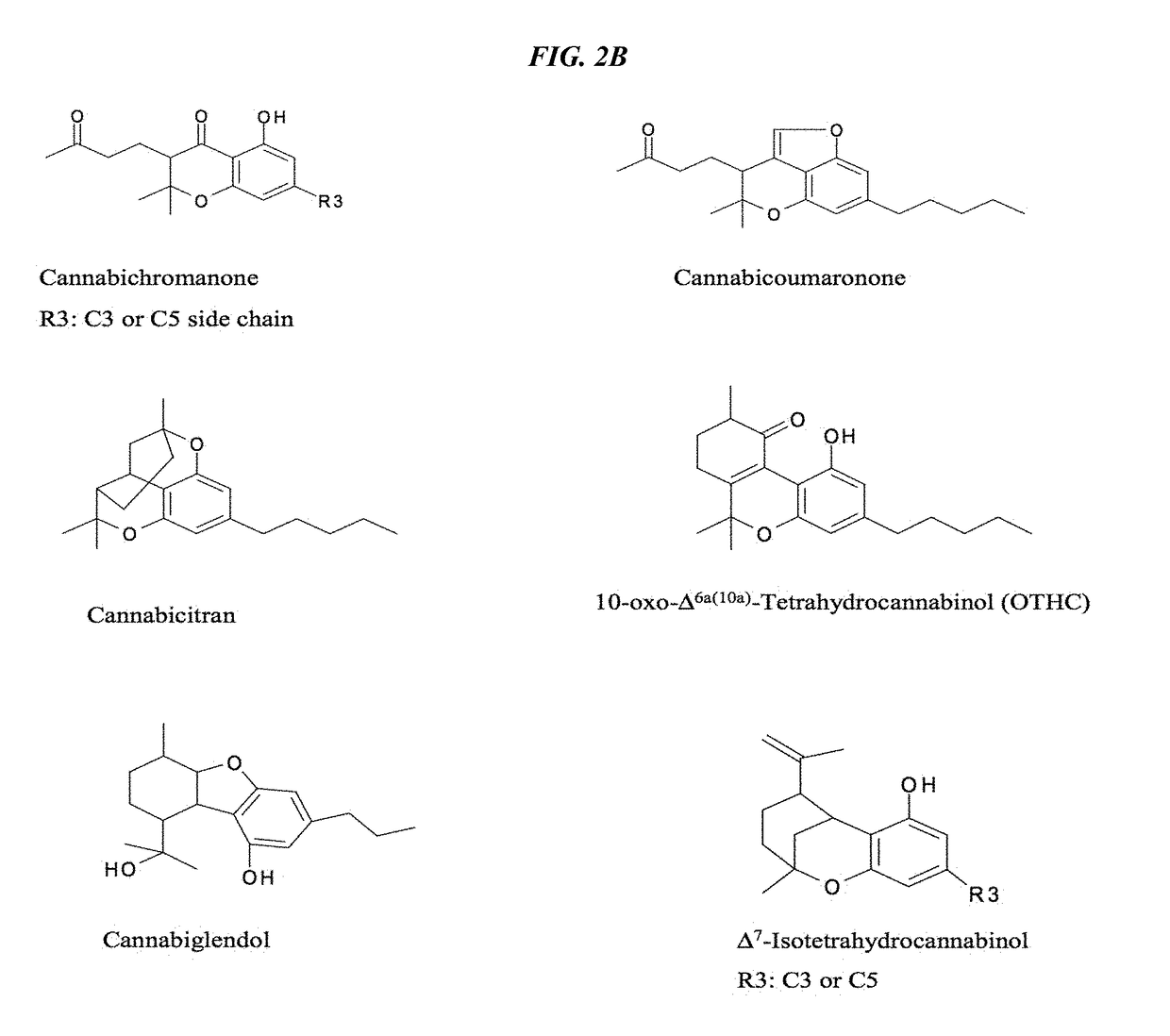
Recombinant production systems for prenylated polyketides of the cannabinoid family
The present invention relates generally to production methods, enzymes and recombinant yeast strains for the biosynthesis of clinically important prenylated polyketides of the cannabinoid family. Using readily available starting materials, heterologous enzymes are used to direct cannabinoid biosynthesis in yeast.
Owner:BAYMEDICA INC
Bacillus velezensis L1-21 and application thereof in preventing Huanglongbing
The invention relates to the technical field of biological prevention and control, in particular to bacillus velezensis L1-21 and application thereof in preventing Huanglongbing. The bacillus velezensis L1-21 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.15726, and the category is named as bacillus velezensis L1-21. The bacillus velezensis L1-21 of the invention has the advantages of high stress resistance, simple nutrition, high reproduction speed, large effective live bacteria number, stable performance and long storage period. The bacillus velezensis L1-21 can prevent the plant disease due to the fact that the bacillus velezensis L1-21 can produce various antibacterial substances, which comprise various compoundssuch as lipopeptides, polyketides and the like, and the antibacterial substances can inhibit the normal growth of pathogenic fungus and bacteria, can kill the pathogenic fungus and bacteria and can play an effect of preventing and controlling the Huanglongbing.
Owner:MICROBIAL FERMENTATION ENG RES CENT CO LTD OF YUNNAN PROVINCE +1
E. coli and Streptomyces host cells that contain MatBC genes or E. coli host cells that contain pcc genes useful for enhanced polyketide production
InactiveUS6939691B1Increase productionImprove the level ofBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPolyketide
The use of enzymes that catalyze the production of starter and extender units for polyketides in E. coli and Streptomyces is described; these enzymes include malonyl CoA decarboxylase (MatA), malonyl CoA synthetase (MatB), and a malonate transporter (MatC) as well as proprionyl CoA carboxylase (pcc). The matBC gene from Streptomyces coelicolor, the matABC genes from Rhizobium trifoli, and the pccB and accA2 from Streptomyces coelicolor are useful in specific embodiments of the claimed invention. These enzymes may be used to enhance the yield of polyketides that are natively produced or polyketides that are rationally designed. By using these techniques, the synthesis of a complete polyketide has been achieved in E. coli in the presence of a phosphopantetheinyl transferase, such as sfp from Bacillus subtilis. This achievement permits a host organism with desirable characteristics to be used in the production of such polyketides and to assess the results of gene shuffling.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Composition
InactiveUS20150045288A1Avoid contaminationAvoid utilizationAntibacterial agentsBiocidePlantazolicinAnticapsin
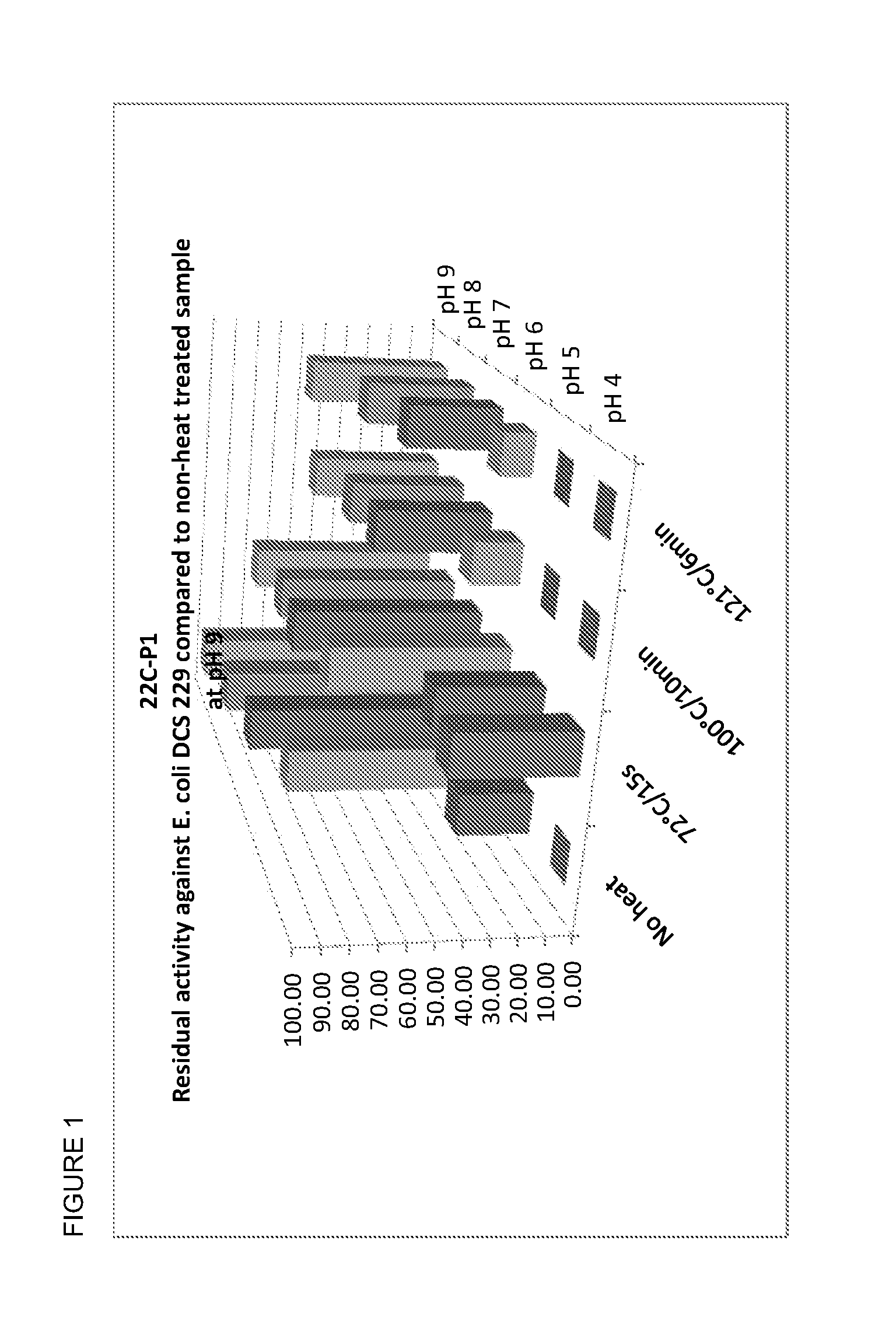
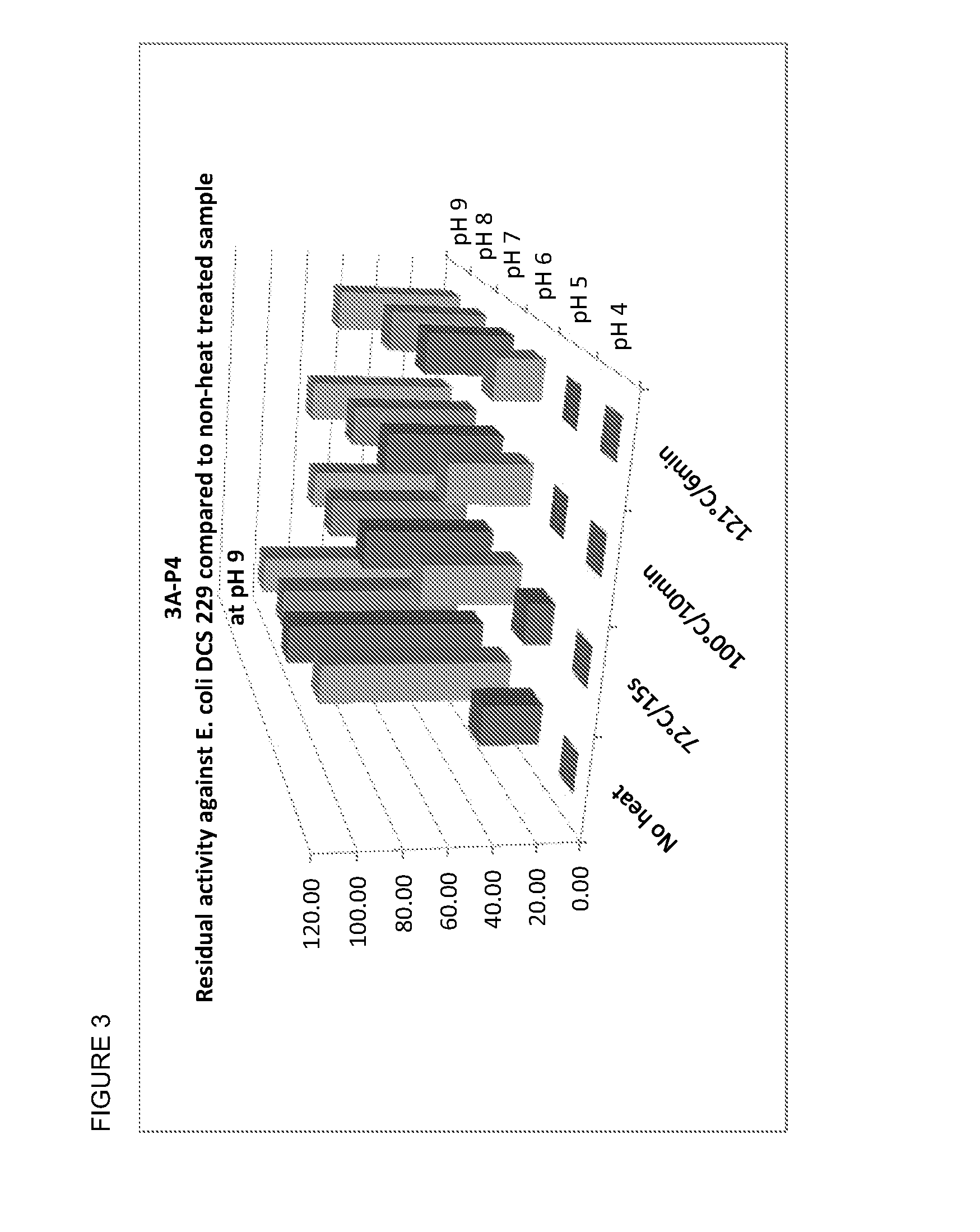
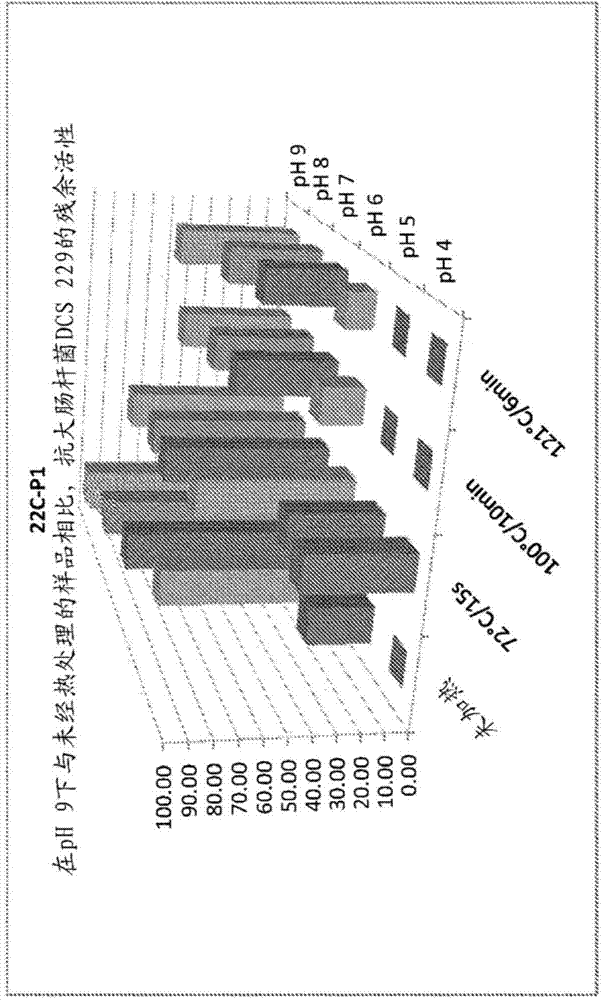
The present invention relates to anti-contaminant composition comprising a cell-free fermentation product of one or more Bacillus subtilis strains (e.g., selected from the group consisting of: 22C-P1, 15A-P4, 3A-P4, LSSA01, ABP278, BS 2084 and BS 18); wherein said fermentation product comprises one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of: a lipopeptide, a polyketide, a bacillibactin, a bacilysin, an anticapsin, a plantazolicin, a LCI, a homologue of a plantazolicin and a homologue of a LCI. In addition, the present invention further relates to methods of preparing the compositions, methods of using the composition, products comprising the composition and uses thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
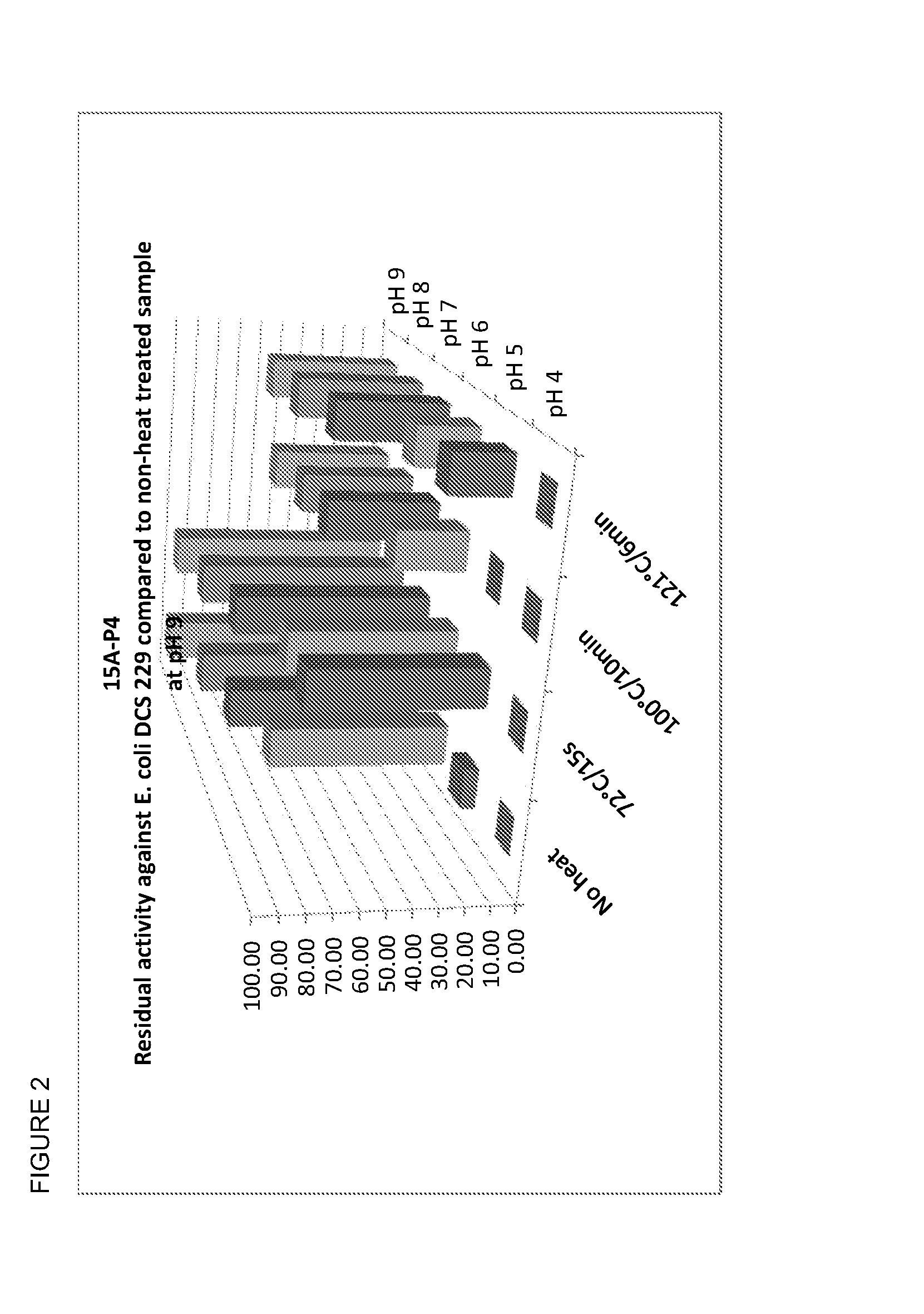
Composition comprising fermentation products from bacillus subtilis
The present invention relates to anti-contaminant composition comprising a cell-free fermentation product of one or more Bacillus subtilis strains (e.g., selected from the group consisting of: 22C-P1, 15A-P4, 3A-P4, LSSA01, ABP278, BS 2084 and BS18); wherein said fermentation product comprises one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of: a lipopeptide, a polyketide, a bacillibactin, a bacilysin, an anticapsin, a plantazolicin, a LCI, a homologue of a plantazolicin and a homologue of a LCI. In addition, the present invention further relates to methods of preparing the compositions, methods of using the composition, products comprising the composition and uses thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Production of polyketides and other natural products
ActiveUS20050272132A1Rapid and parallel generationEasy to assembleBiocideAntimycoticsNatural productPolyketide
The present invention relates to production of polyketides and other natural products and to libraries of compounds and individual novel compounds. One important area is the isolation and potential use of novel FKBP-ligand analogues and host cells that produce these compounds. The invention is particularly concerned with methods for the efficient transformation of strains that produce FKBP analogues and recombinant cells in which cloned genes or gene cassettes are expressed to generate novel compounds such as polyketide (especially rapamycin) FKBP-ligand analogues, and to processes for their,preparation, and to means employed therein (e.g. nucleic acids, vectors, gene cassettes and genetically modified strains).
Owner:BIOTICA TECH
Production of polyketides
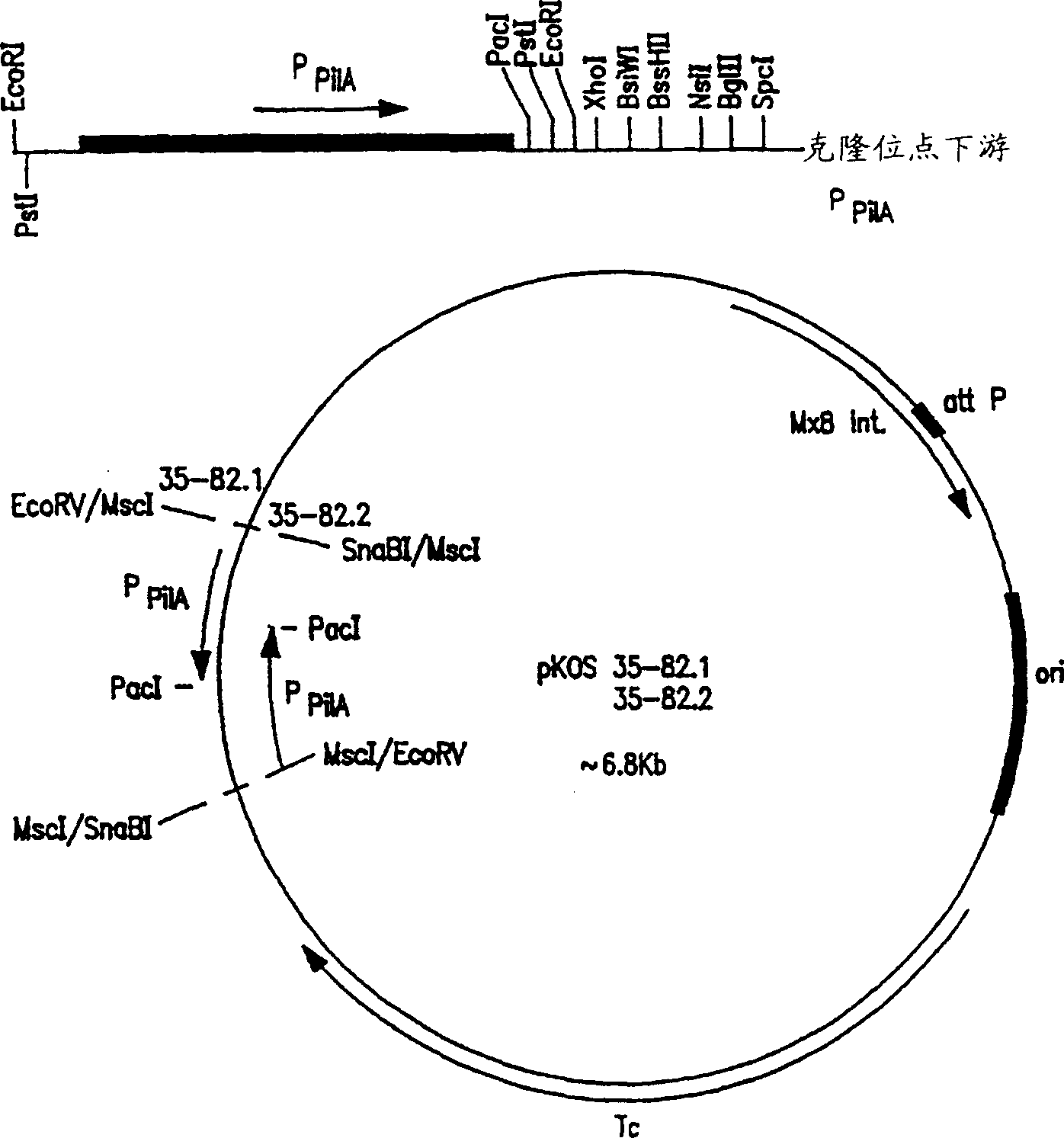
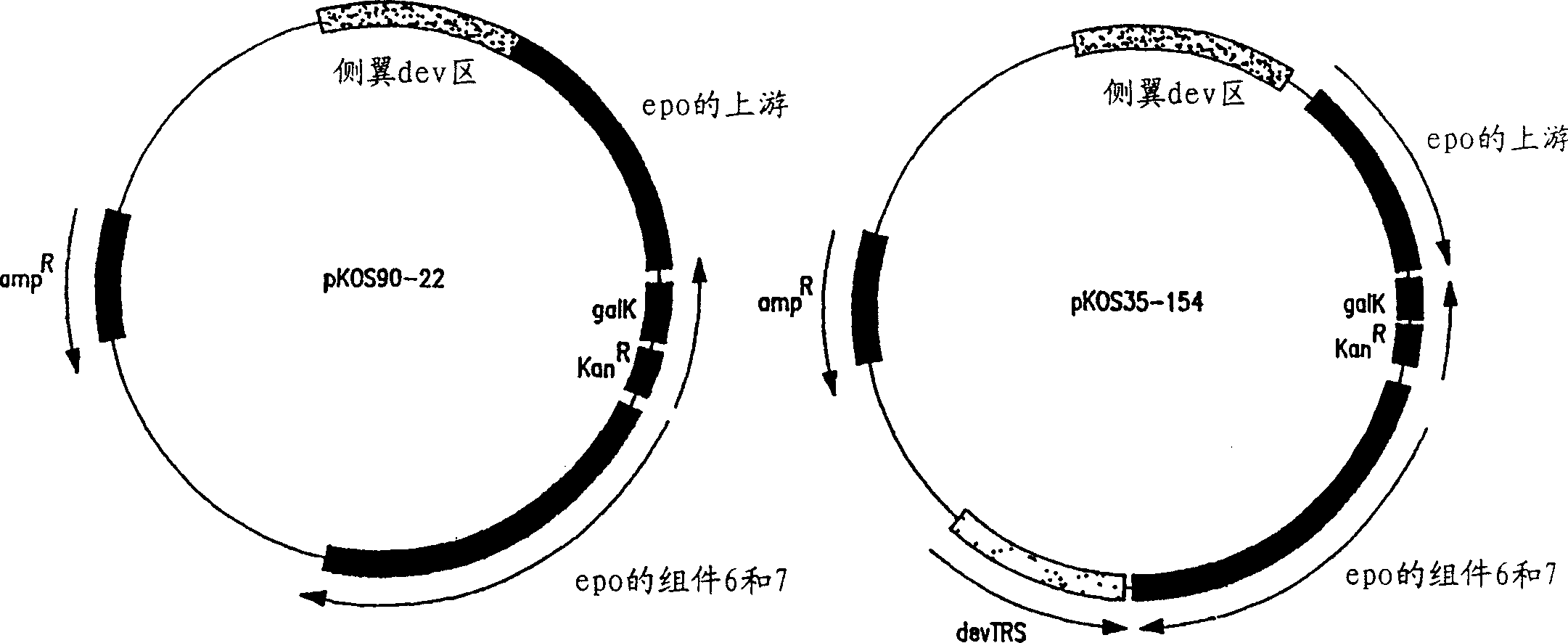
Recombinant Myxococcus host cells can be used to produce polyketides, including epothilone and epothilone analogs that can be purified from the fermentation broth and crystallized.
Owner:KOSAN BIOSCI
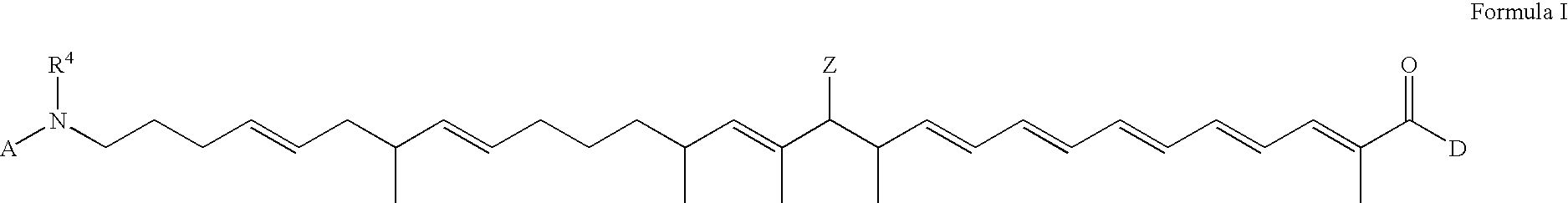
Polyketide with quaternized side chain and preparation method thereof as well as anion-exchange membrane
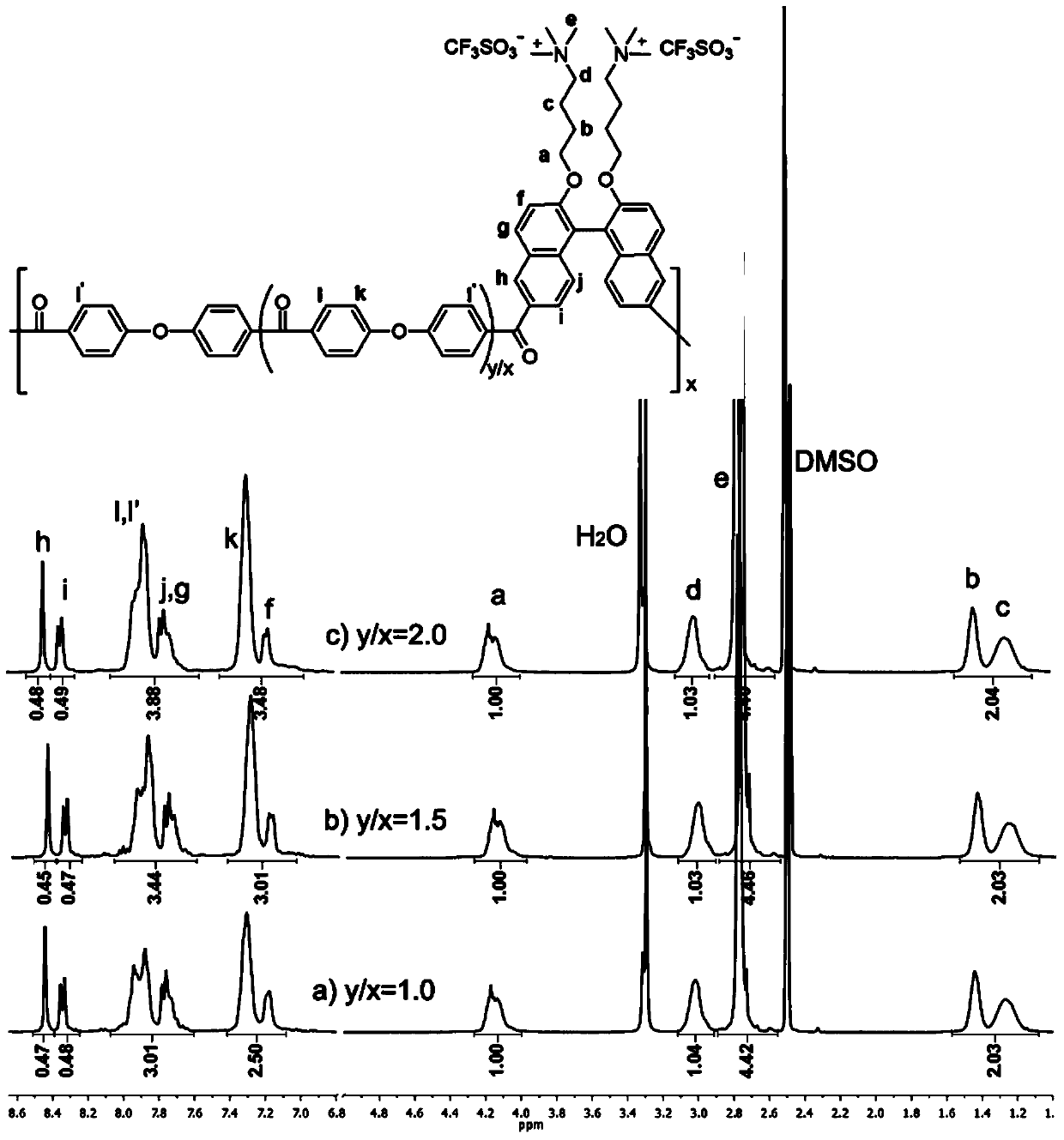
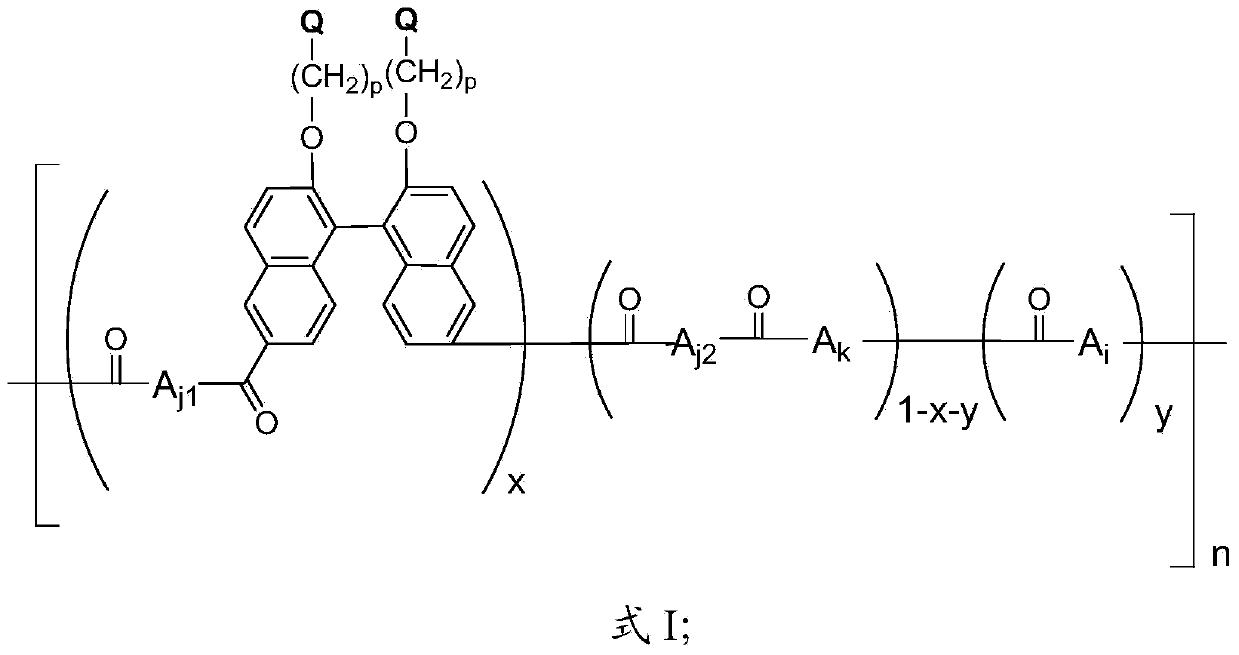
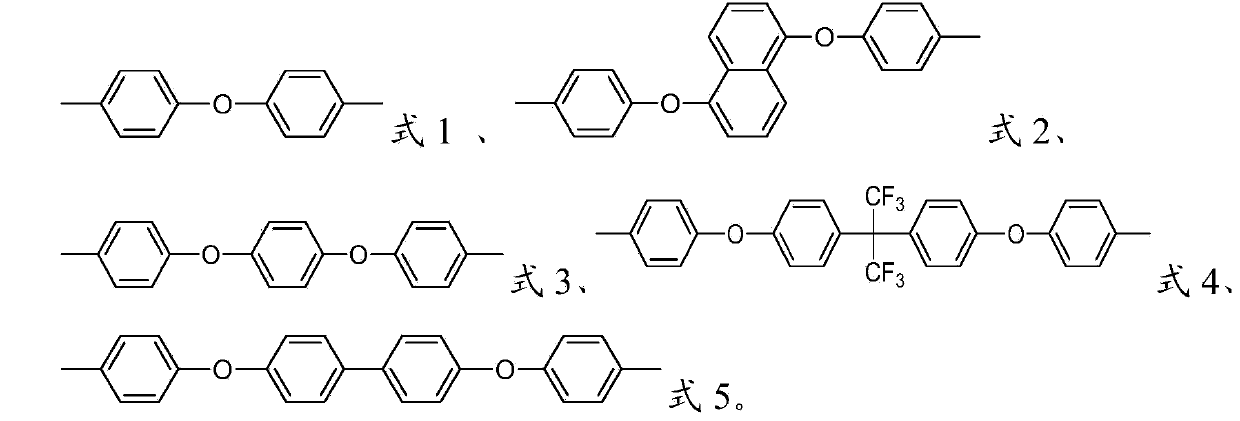
The invention provides polyketide with a quaternized side chain and a preparation method thereof as well as an anion-exchange membrane. The polyketide with the quaternized side chain is as shown in a formula I described in the specification. Compared with the prior art, the polyketide with the quaternized side chain has the advantages that firstly a main chain of the polyketide contains a rigid and hydrophobe naphtyl naphthalene structure, so that when the anion-exchange membrane prepared from the polyketide has relatively high ion exchange capacity, the relatively low swelling ratio still can be maintained; secondly, the anion-exchange membrane prepared from the polyketide with the quaternized side chain as shown in the formula I contains more quaternary ammonium groups, so that the electric conductivity of the anion-exchange membrane is improved; thirdly, the polyketide with the quaternized side chain as shown in the formula I contains more naphthalene nucleuses and ether bonds, therefore, the molecular weight of the polyketide is relatively high, and the prepared anion-exchange membrane has relatively good mechanical property.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Production of polyketides
InactiveUS20070281343A9Useful in treatmentProduce epothilonesOrganic chemistryBacteriaPolyketideMyxococcus
Recombinant Myxococcus host cells can be used to produce polyketides, including epothilone and epothilone analogs that can be purified from the fermentation broth and crystallized.
Owner:KOSAN BIOSCI
Gel-encapsulated microcolony screening
InactiveUS20120196770A1High yieldImprove durabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningIsoprenePolyketide
Provided herein are methods and compositions useful for detecting the production of industrially useful compounds (e.g., isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids) in a cell, for example, a microbial cell genetically modified to produce one or more such compounds. In some embodiments, the methods comprise encapsulating the cell in a hydrogel particle, and detecting the compound within the hydrogel particle.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
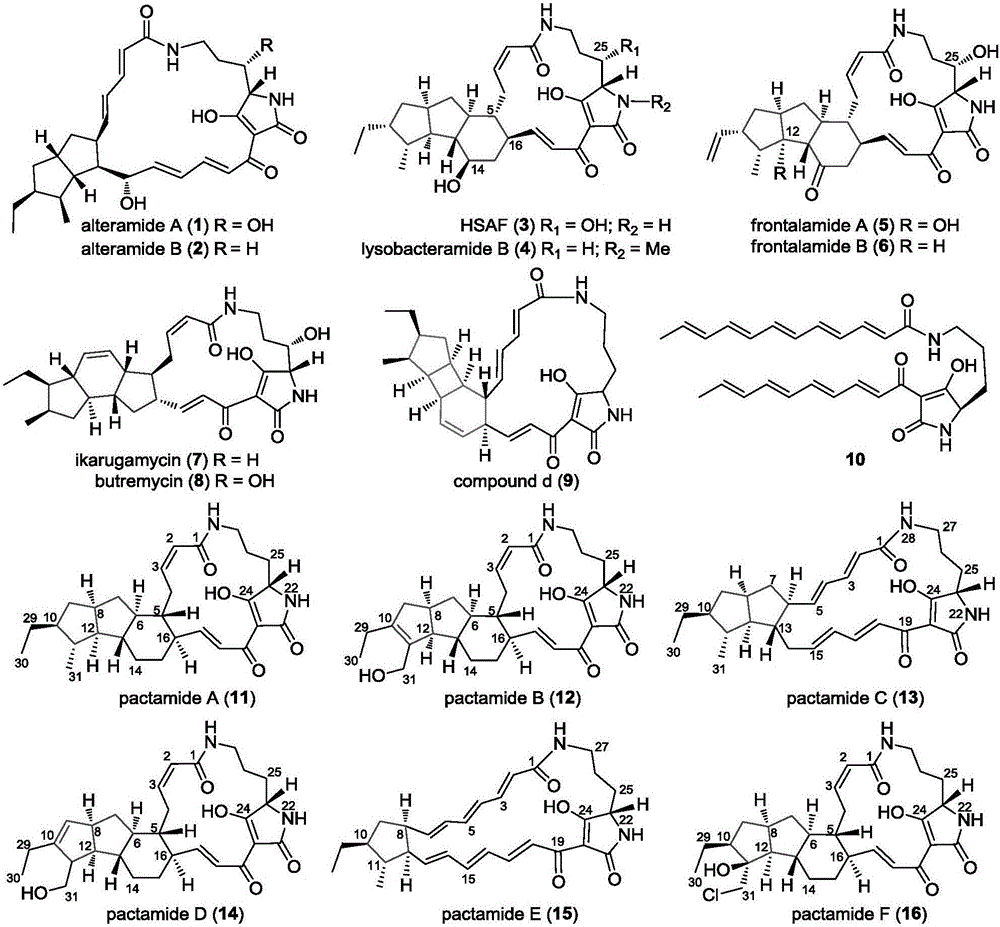
Biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and application thereof
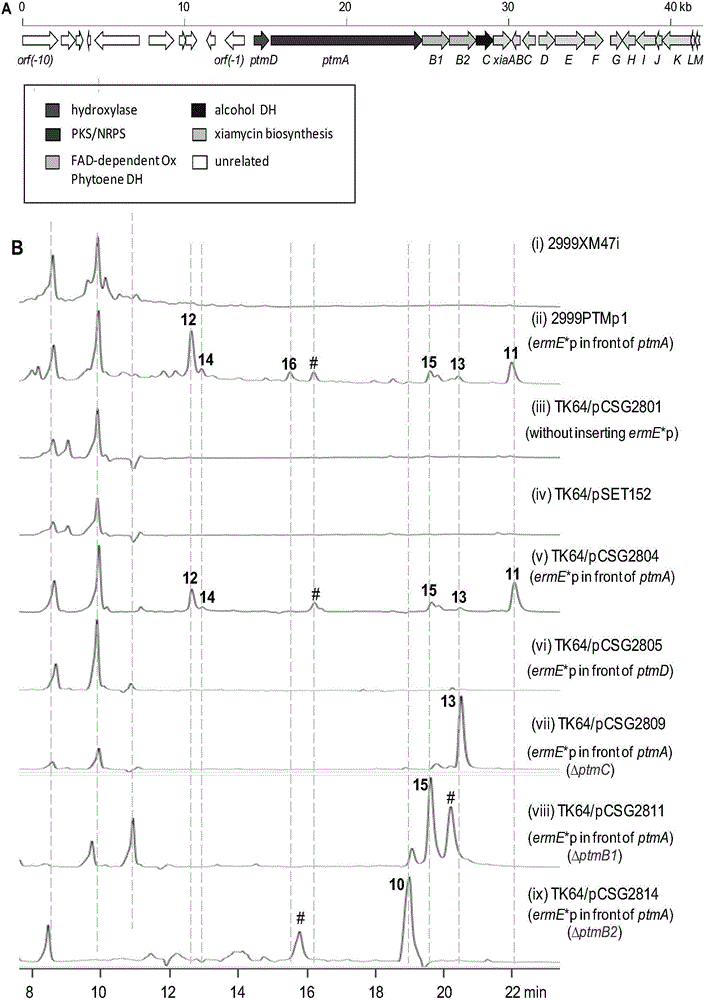
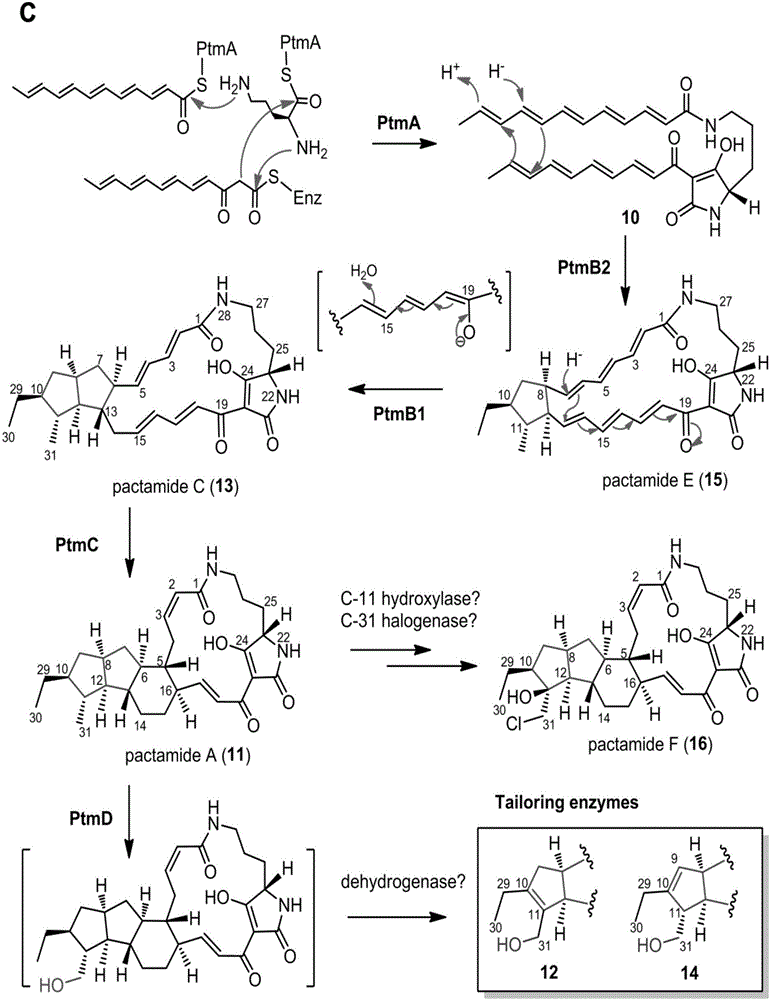
ActiveCN106434702ABiosynthetic gene cluster activationHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclasePolyketide
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant methods and materials for producing epothilone and epothilone derivatives
Recombinant nucleic acids that encode all or a portion of the epothilone polyketide synthase (PKS) are used to express recombinant PKS genes in host cells for the production of epothilones, epothilone derivatives, and polyketides that are useful as cancer chemotherapeutics, fungicides, and immunosuppressants.
Owner:KOSAN BIOSCI
Production of polyketides and other natural products
The present invention relates to production of polyketides and other natural products and to libraries of compounds and individual novel compounds. Therefore in aspect the present invention provides 17-desmethylrapamycin and analogues thereof, methods for their production, including recombinant strains, and isolation and uses of the compounds of the invention. In a further aspect the present invention provides for the use of 17-desmethylrapamycin and analogues thereof in the induction or maintenance of immunosuppression, the stimulation of neuronal regeneration or the treatment of cancer, B-cell malignancies, fungal infections, transplantation rejection, graft vs. host disease, autoimmune disorders, diseases of inflammation vascular disease and fibrotic diseases, and in the regulation of wound healing.
Owner:BIOTICA TECH
Polyketides and antibiotics
InactiveUS7022825B2Increase synthesisImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesPolyketideSide chain
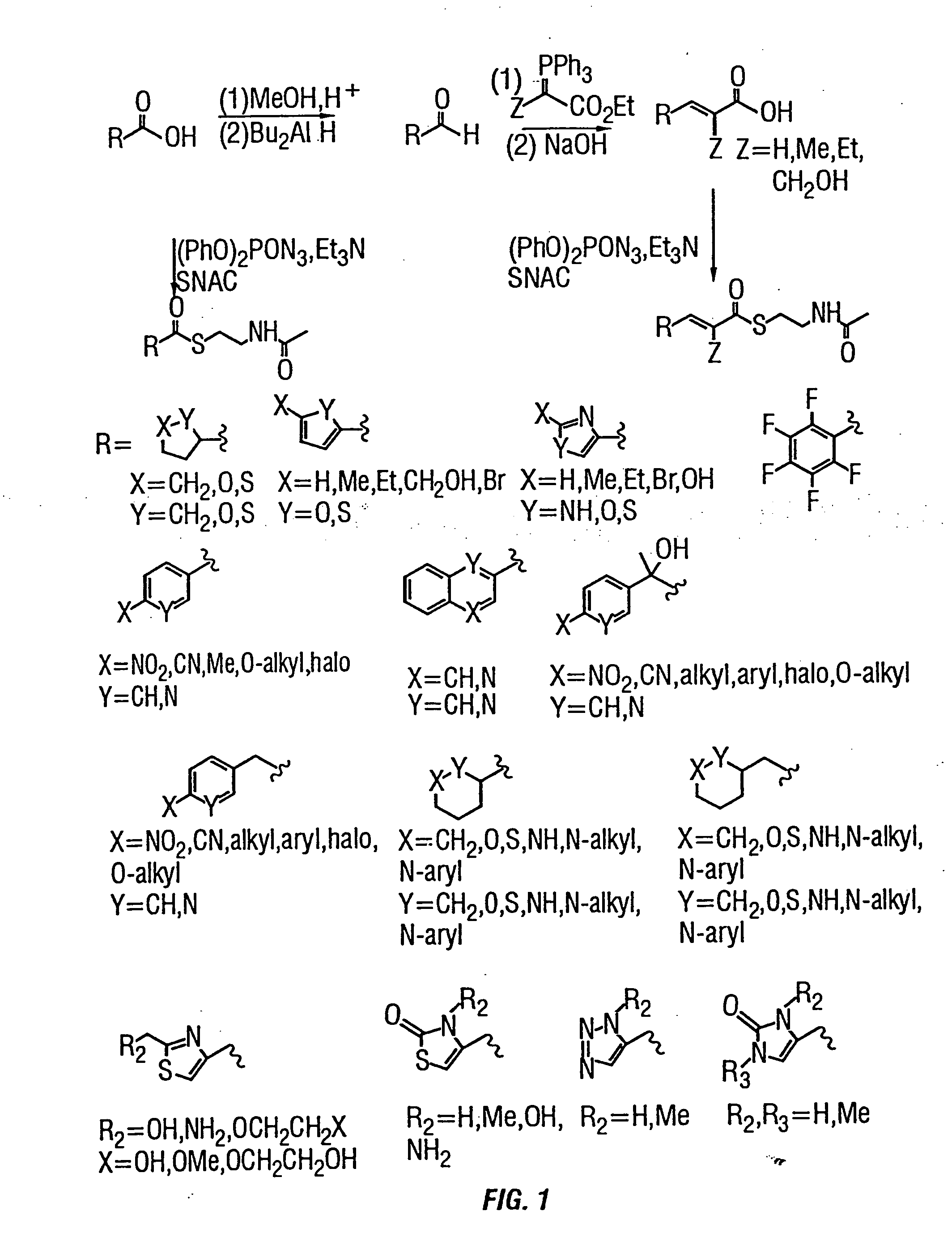
Facile methods for preparing diketide and triketide thioesters are disclosed. The resulting thioesters may be used as intermediates in the synthesis of desired polyketides, and may contain functional groups which ultimately reside in side chains on the resulting polyketide and thus can be used further to manipulate the polyketide so as form derivatives. The polyketides produced may also be tailored by glycosylation, hydroxylation and the like. New polyketides and their derivatives and tailored forms are thereby produced.
Owner:KOSAN BIOSCI
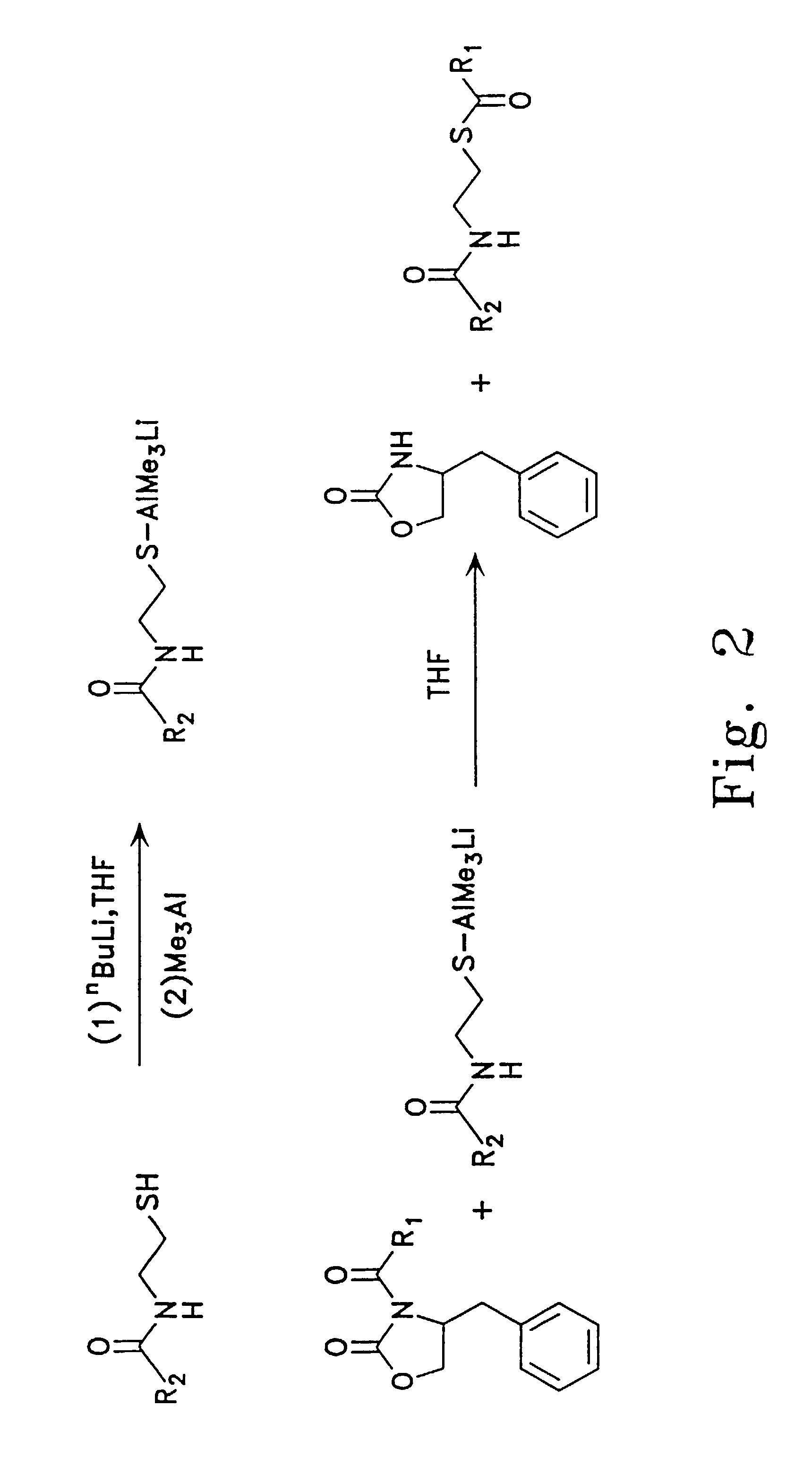
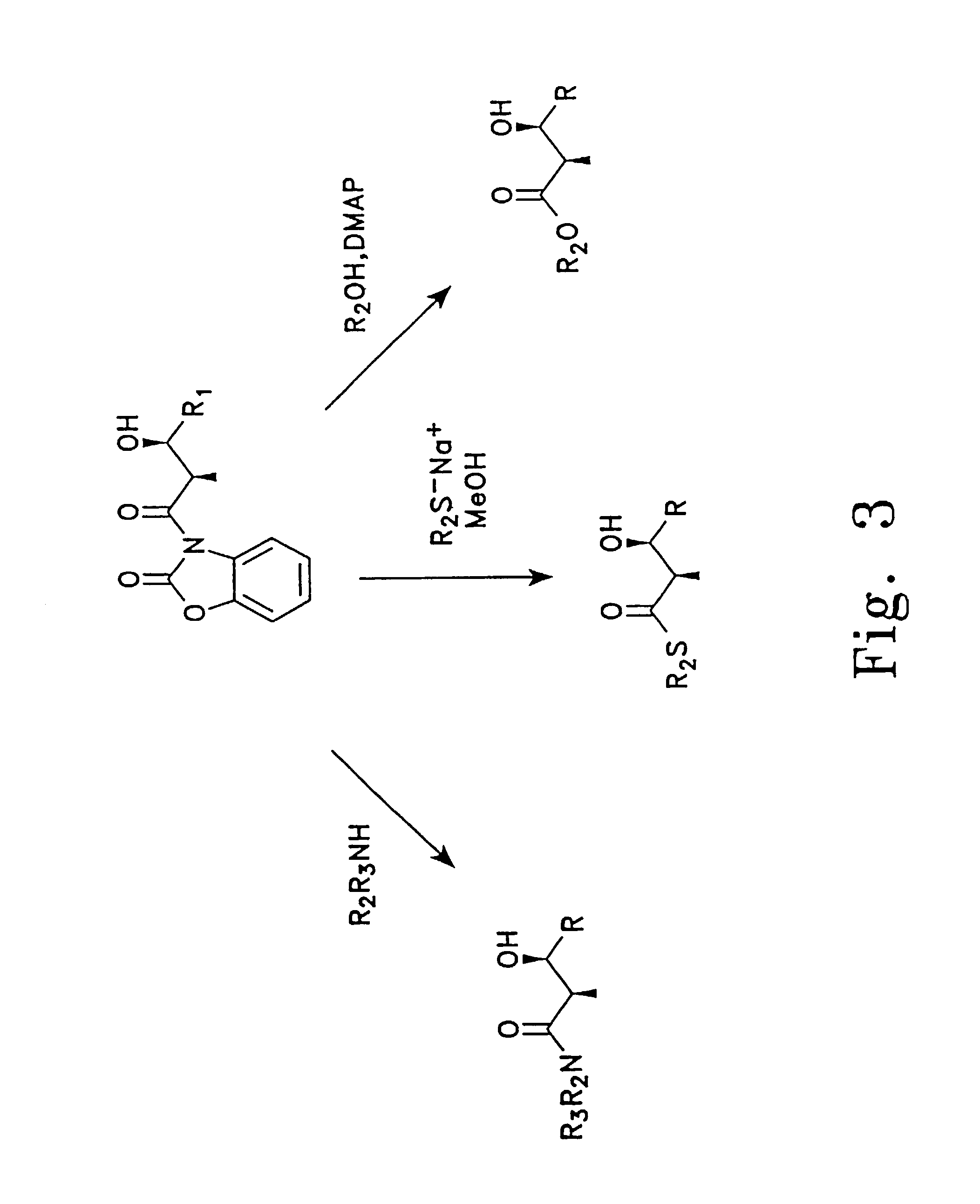
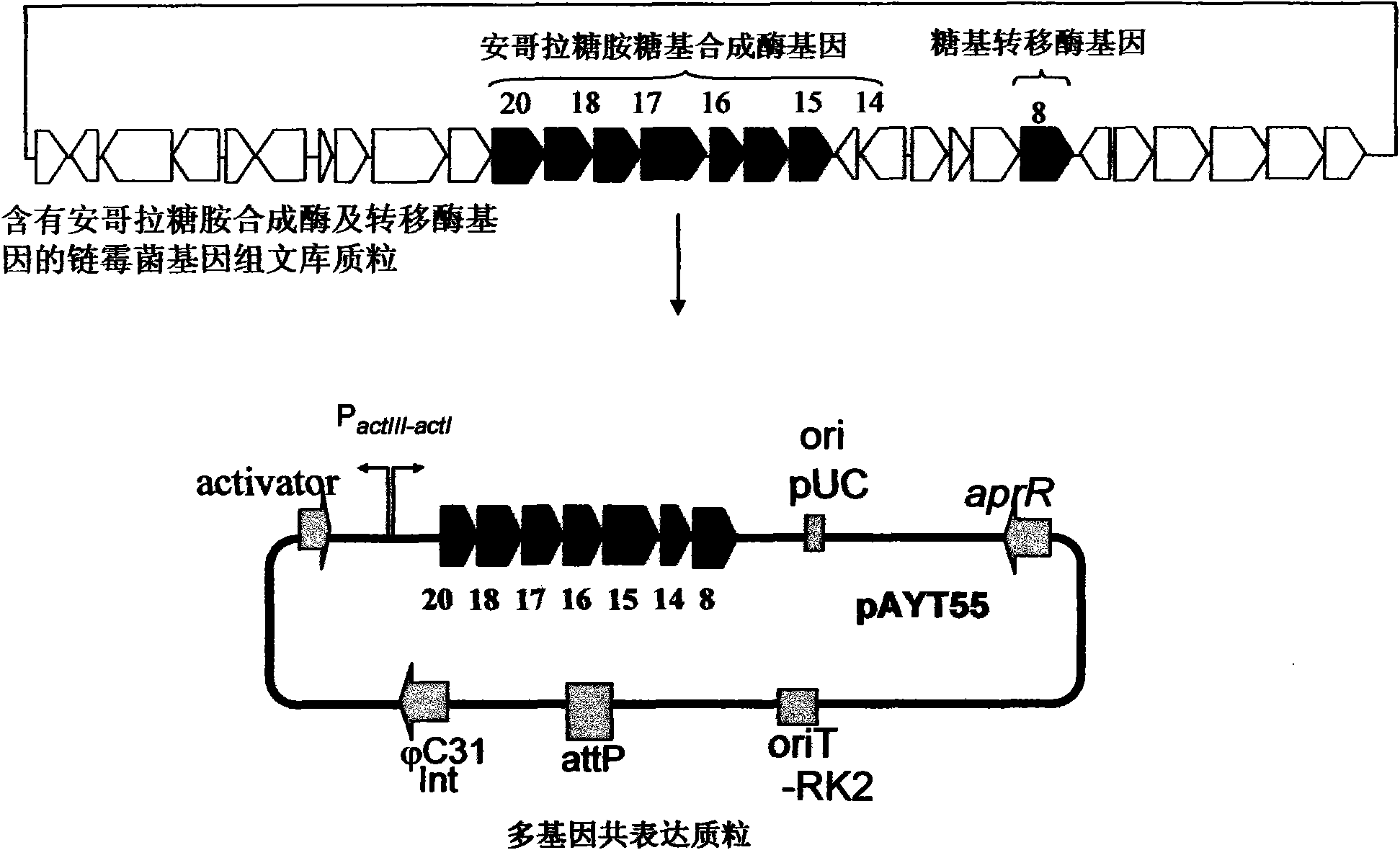
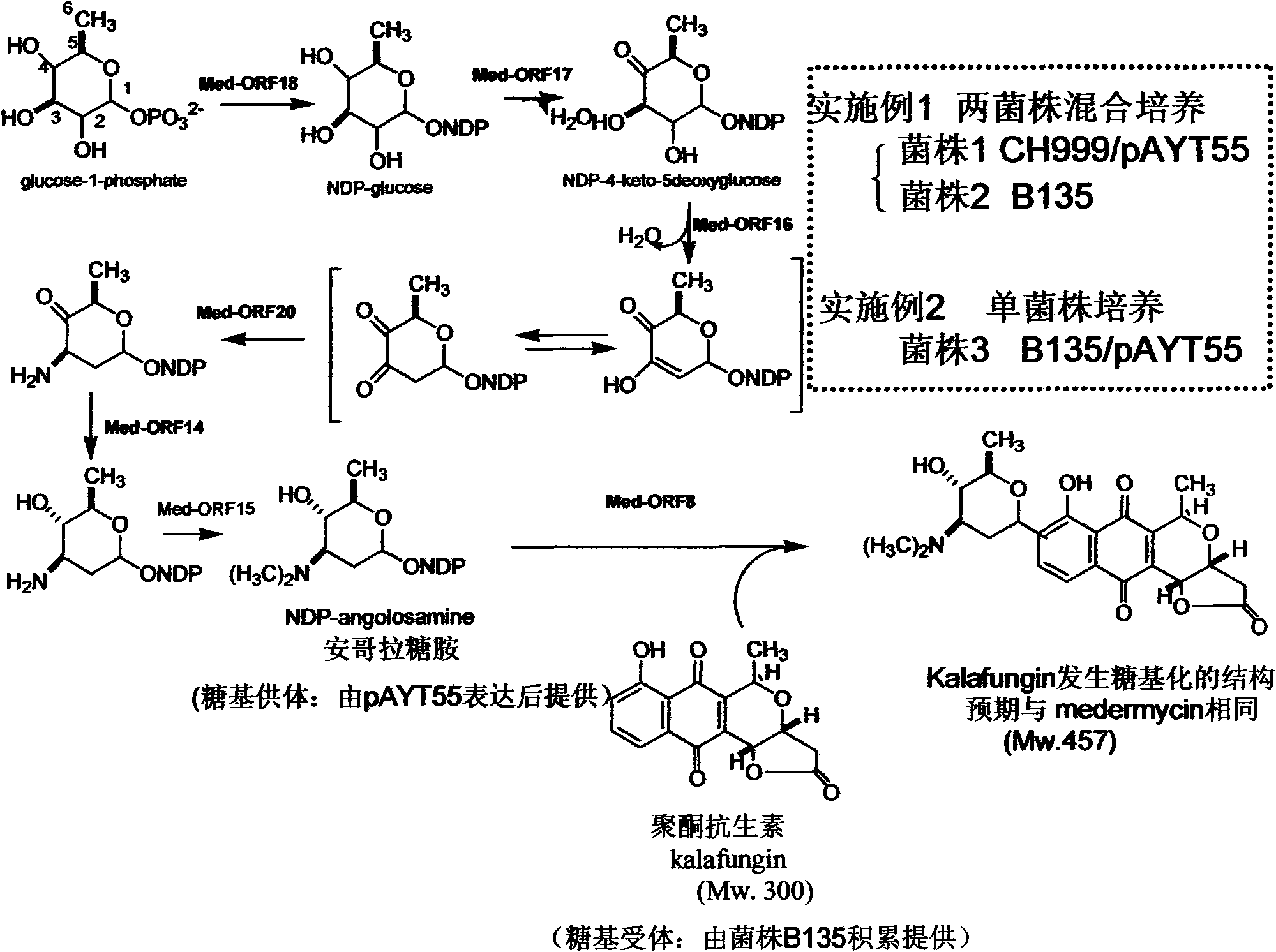
Construction and application of multiple gene coexpression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase
InactiveCN101613711ASimplify the screening processGuaranteed normal expressionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolyketideGene coexpression
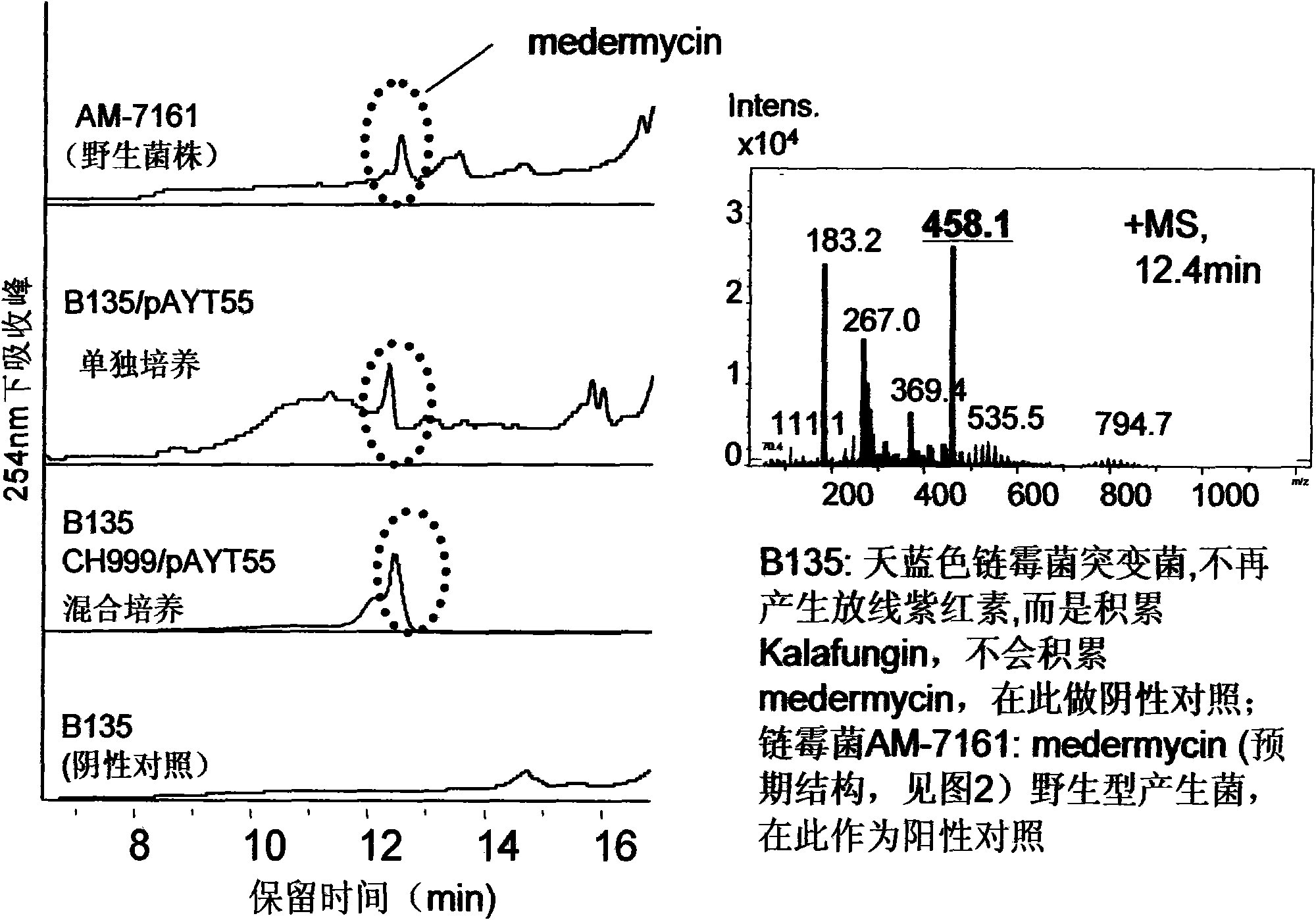
The invention provides construction and application of a multiple gene co-expression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase. The invention is characterized by taking a streptomyces genome bank plasmid as a template; amplifying six angolosamine synthetase genes and a glycosyltransferase gene through PCR and connecting the genes in sequence and placing the genes in the lower reaches of a streptomyces promoter PactIII-actI to form a transcription unit; transferring the transcription unit to a streptomyces plasmid carrier pSET152, thus constructing a streptomyces expression plasmid pAYT55 co-expressed by multiple genes; leading the pAYT55 into a host cell streptomyces coelicolor CH999, mixedly culturing obtained engineering bacteria and streptomyces B135 of accumulated polyketide kalafungin, thus realizing bioconversion of kalafungin into a novel antibiotic with angolosamine; or directly leading pAYT55 into the streptomyces B135 and carrying out single culture to realize glycosylation of kalafungin. Therefore, by adopting the system, rare angolosamine can be synthesized in the cell and angolosamine modification can be carried out on polyketide by adopting the low substrate recognition specificity of antibiotic glycosyltransferases.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Application of polycyclic polyketides in preparation of anti-HV (herpes virus) drug
The invention discloses an application of polycyclic polyketides in preparation of an anti-HV (herpes virus) drug. It is found that the polyketides can inhibit diseases caused by infection of four HVs including HSV-1 (herpes simplex virus-1), HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus-2), VZV (varicella zoster virus) and CMV (cytomegalo virus). The compounds show equivalent activity but have different acting mechanisms as compared with commercial drugs such as acyclovir and can overcome drug resistance of existing commercial drugs. Therefore, the compounds have good application prospects in treatment of related diseases caused by infection of HVs including HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV and CMV.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Genetic engineering bacterium capable of promoting biological synthesis of medermycin and application thereof
InactiveCN102660488AEfficient expressionEfficient importBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRibosome Recycling FactorPolyketide
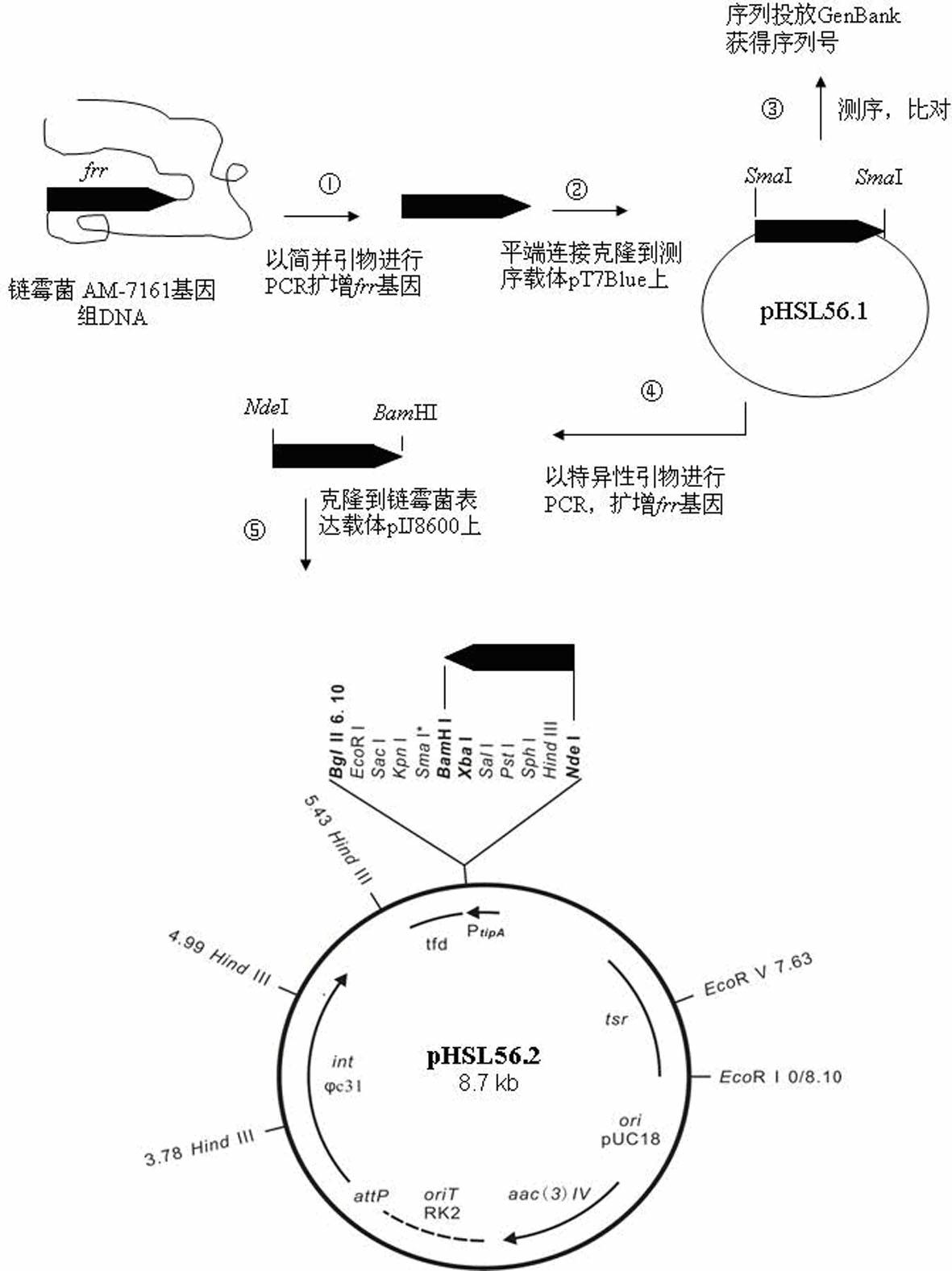
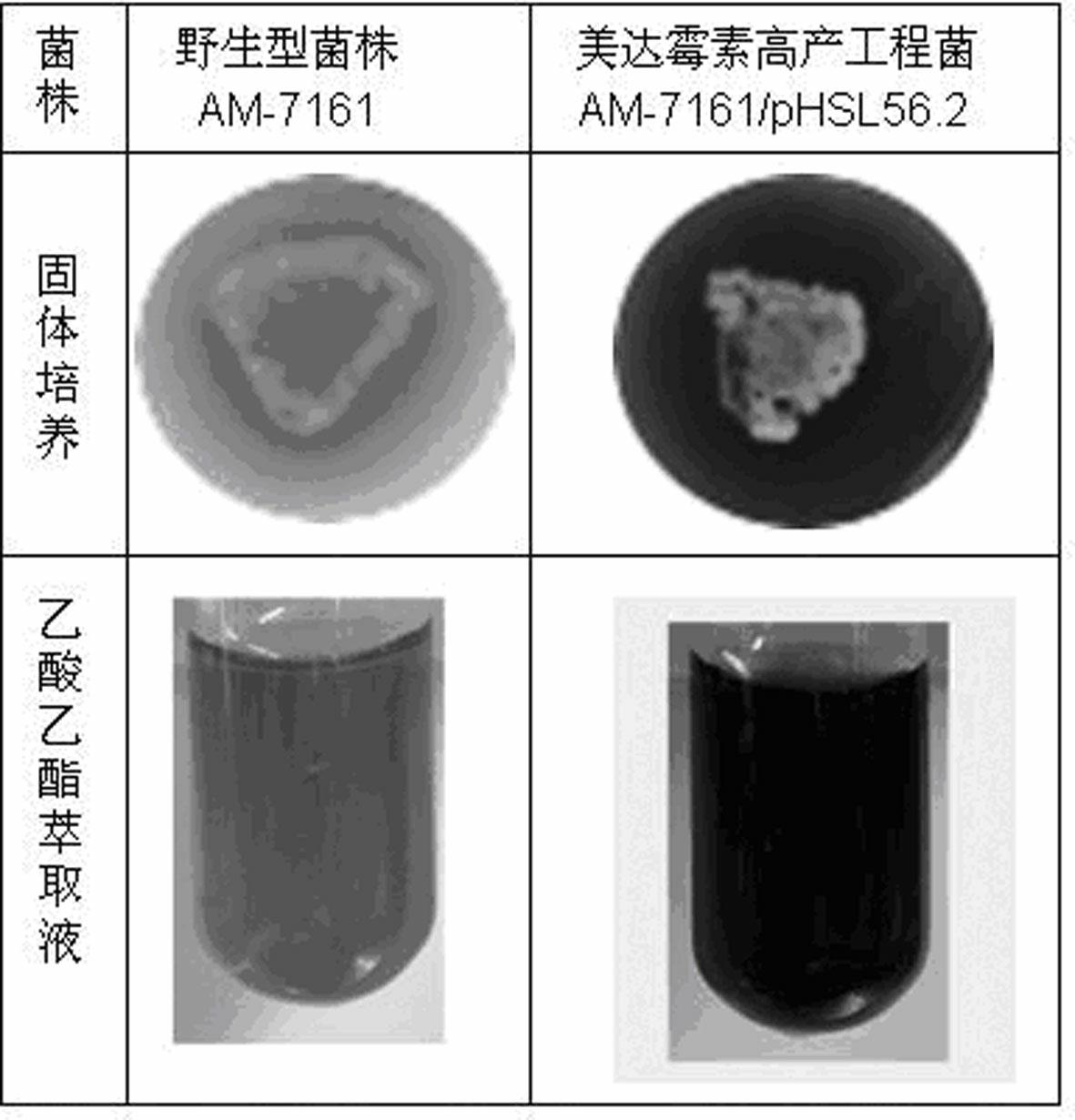
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium capable of promoting the synthesis of antibiotic medermycin and a method for producing the medermycin by using the same. The method comprises the steps that by taking deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a genome of Streptomyces nashvillensis AM-7161 as a formwork and utilizing degenerate primers to conduct polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, a new complete sequence of genes of ribosome recycling factors (RRFs) of the Streptomyces is obtained; the genes are downstream placed on an efficient promoter PtipA of the Streptomyces, so that a plasmid pHSL56.2 capable of efficently expressed in the Streptomyces is constructed; the pHSL56.2 is led into the host cell Streptomyces AM71-61, and then an engineering bacterium AM71-61 / pHSL56.2 (with a preservation number of CCTCCNo:M2012093) is obtained; and when the engineering bacterium AM71-61 / pHSL56.2 is used to conduct solid fermentation and liquid fermentation, the accumulation of the antibiotic medermycin can be effectively promoted. The efficient expression plasmid pHSL56.2 of the genetic engineering bacterium can also be directly led into a Streptomyces strain cell for producing other antibiotics of a benzoisochromanequinones family or other aromatic polyketide antibiotics, so as to obtain corresponding antibiotic high-yield engineering bacteria. By utilizing the method, the antibiotic high-yield bacteria can be genetically bred, so that the synthetic capability of the antibiotics is enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Gel-encapsulated microcolony screening
Provided herein are methods and compositions useful for detecting the production of industrially useful compounds (e.g., isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids) in a cell, for example, a microbial cell genetically modified to produce one or more such compounds. In some embodiments, the methods comprise encapsulating the cell in a hydrogel particle, and detecting the compound within the hydrogel particle.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Production of monascus-like azaphilone pigment
InactiveUS20110250656A1Improve photostabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolyketideFood item
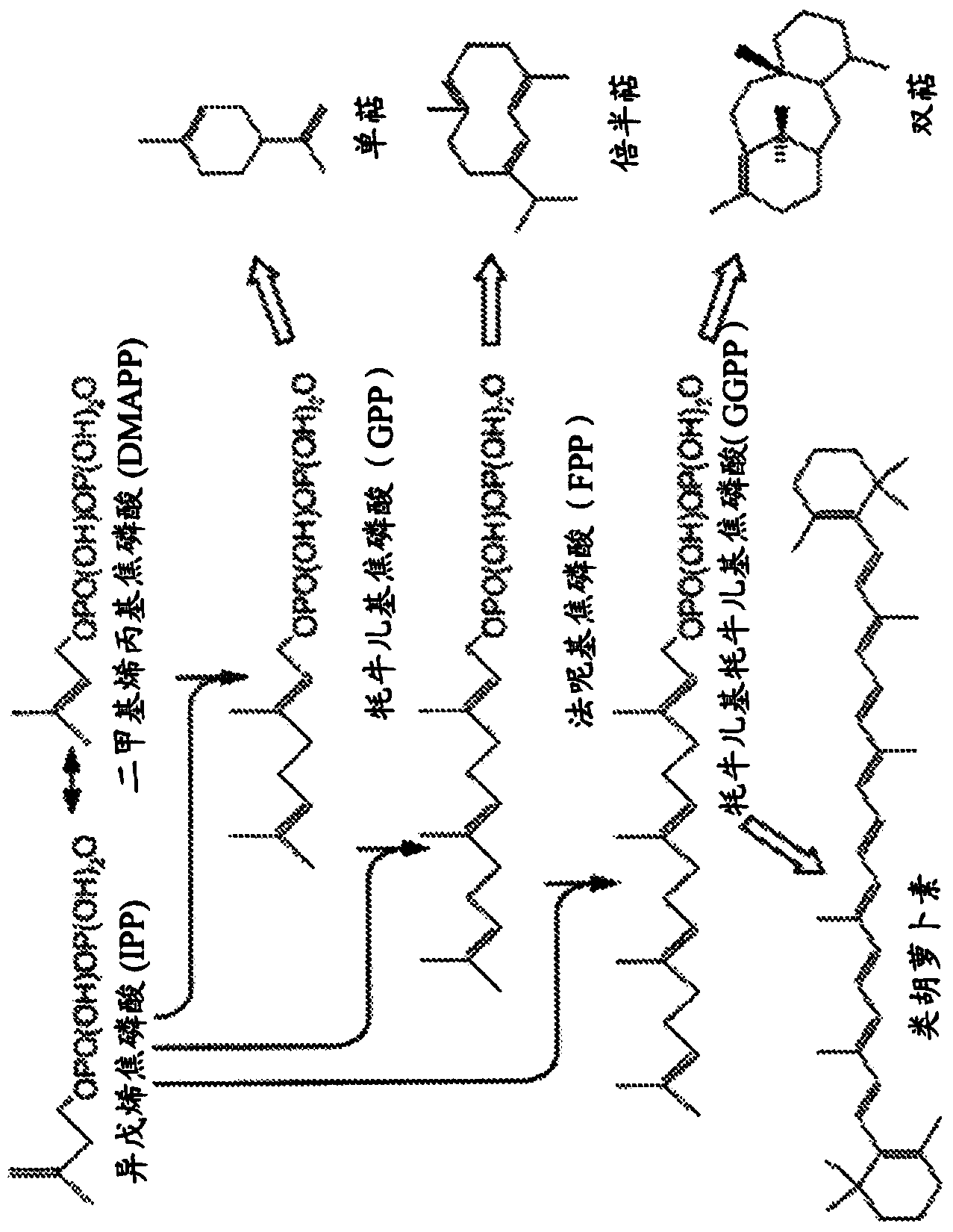
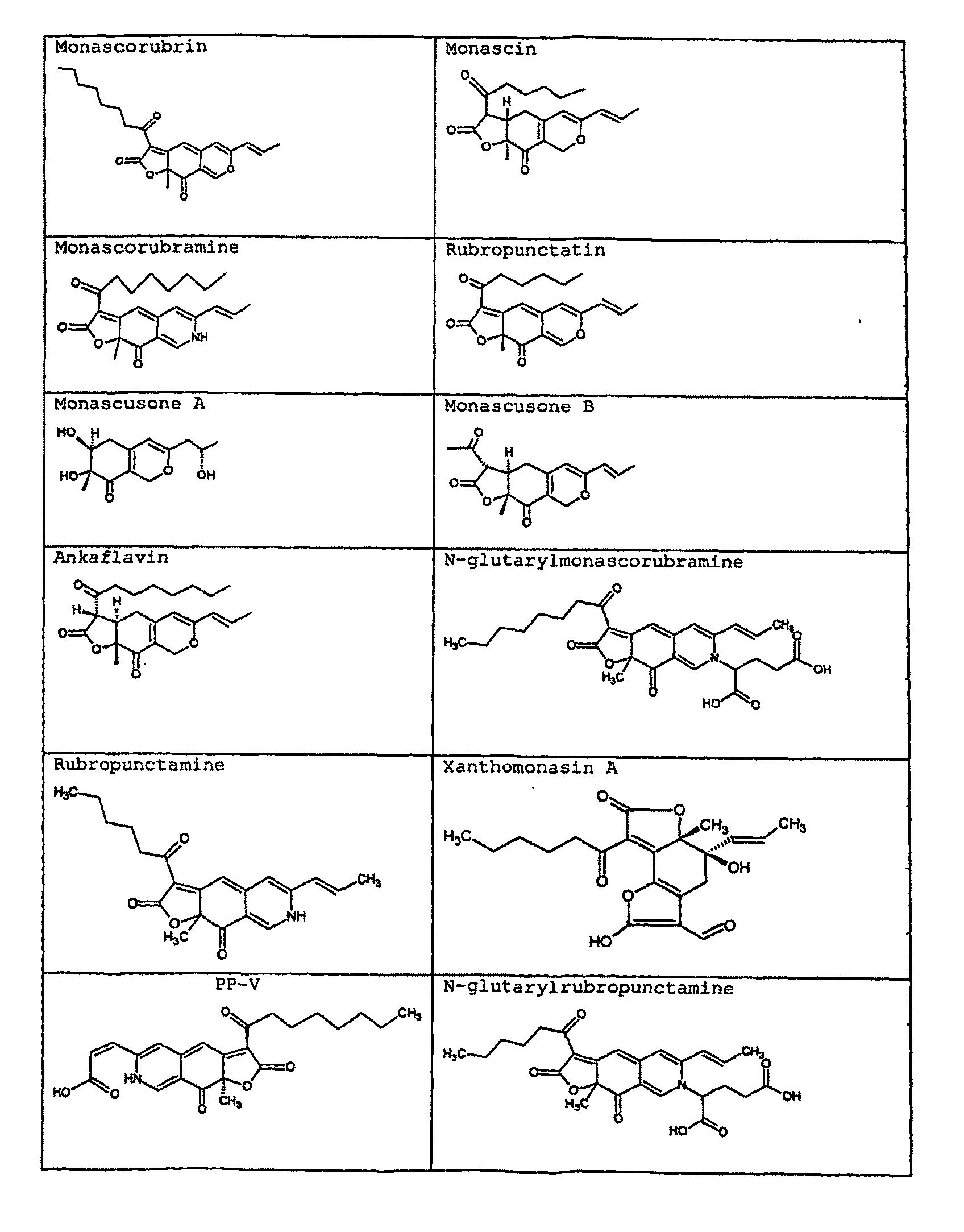
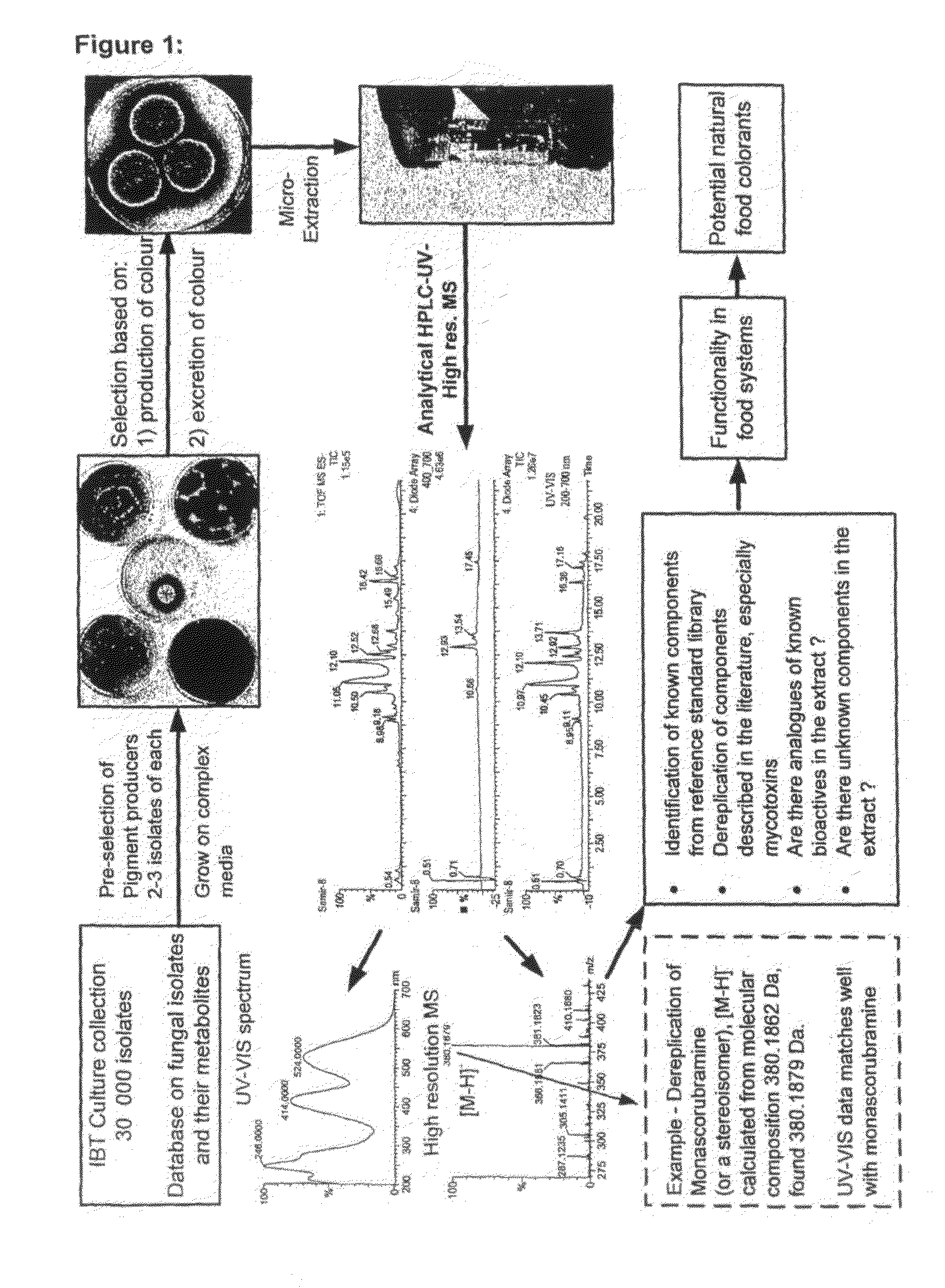
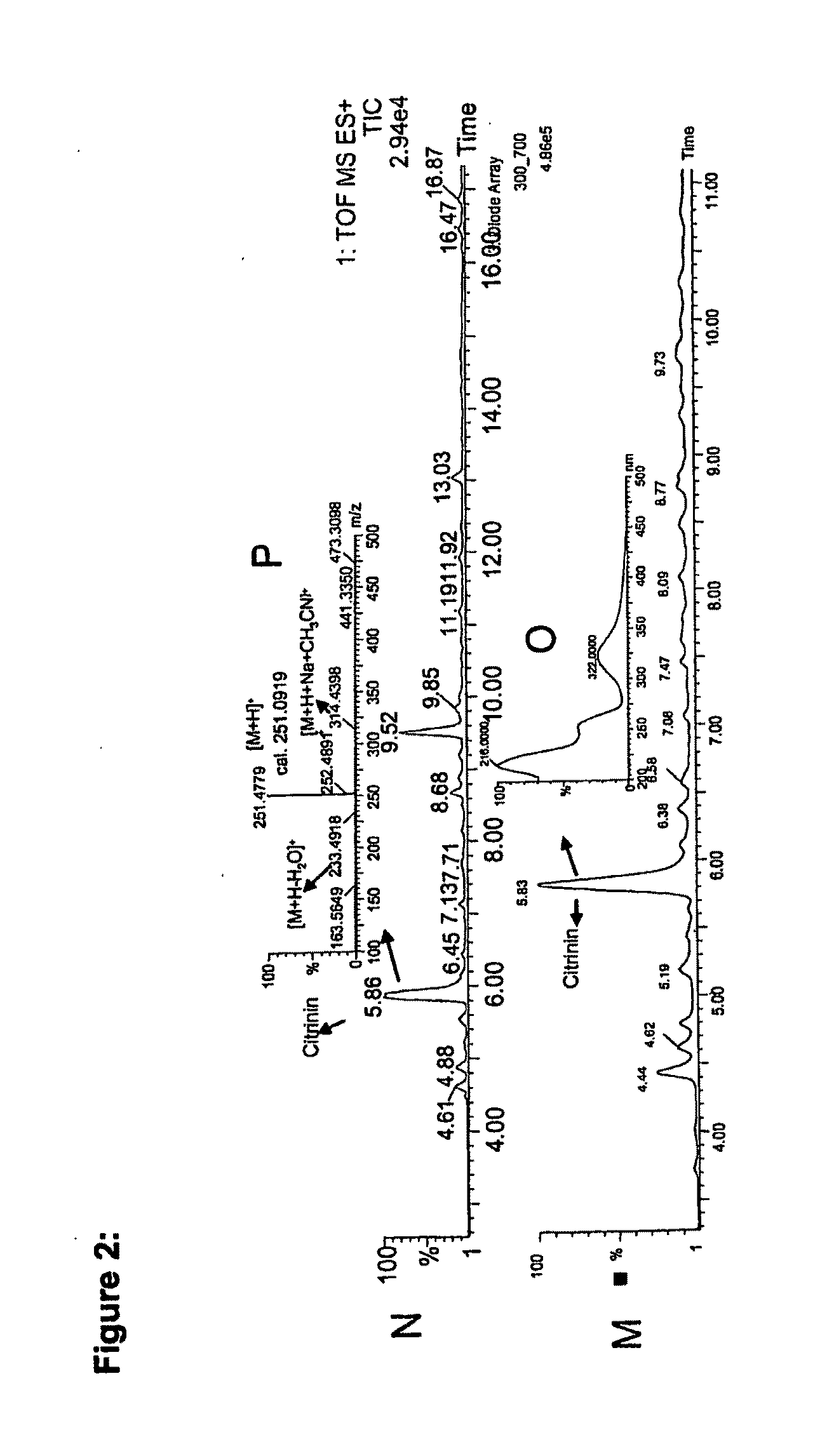
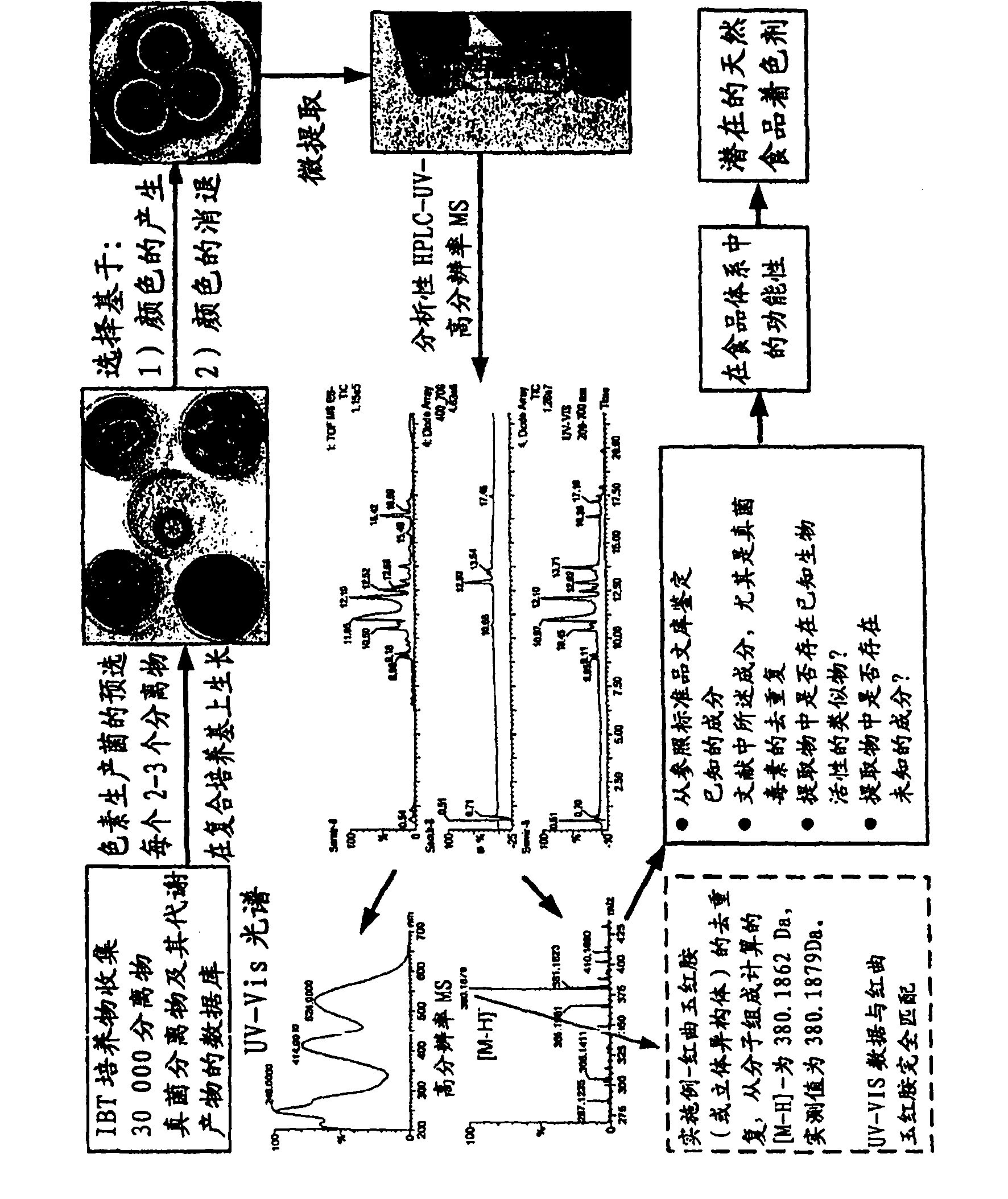
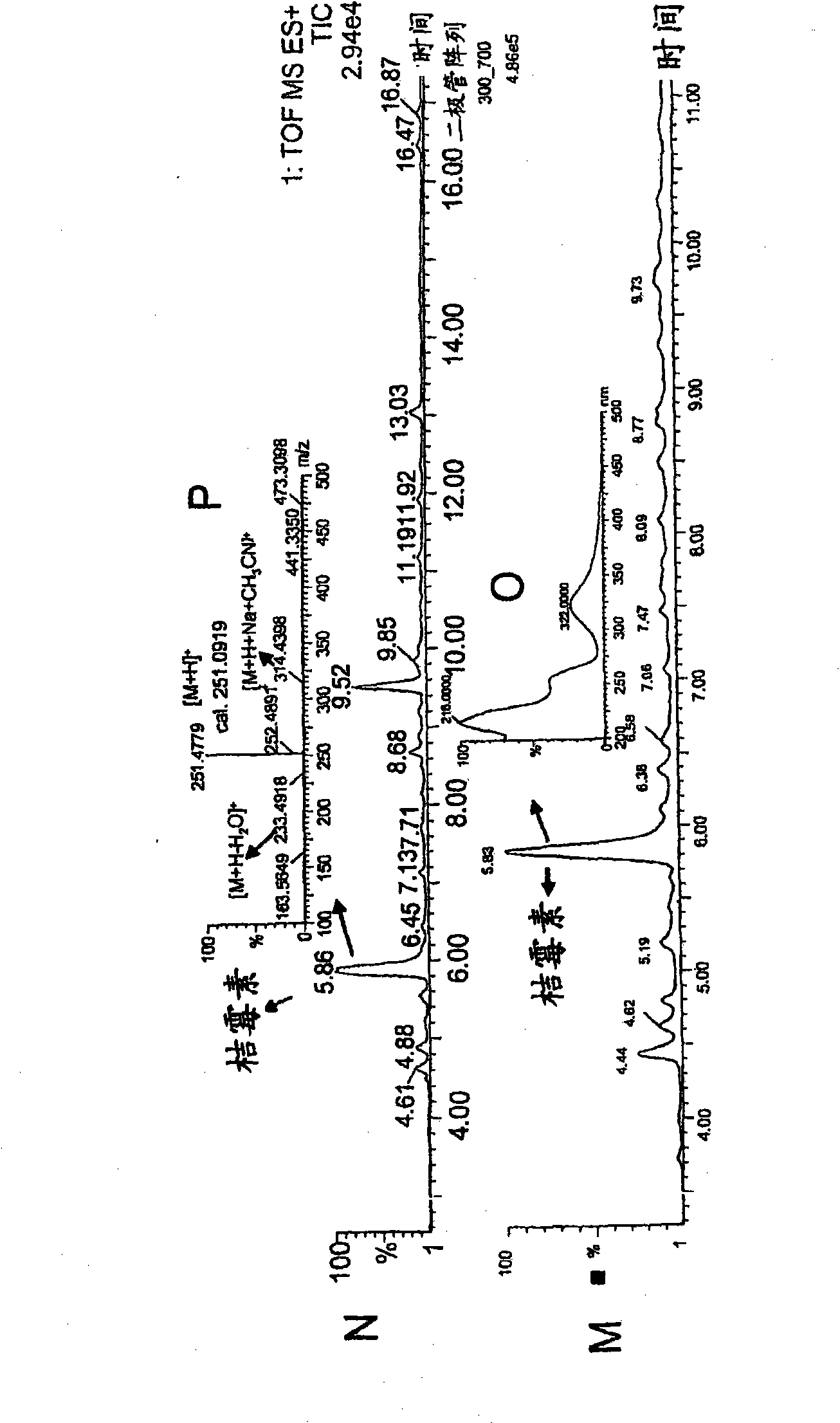
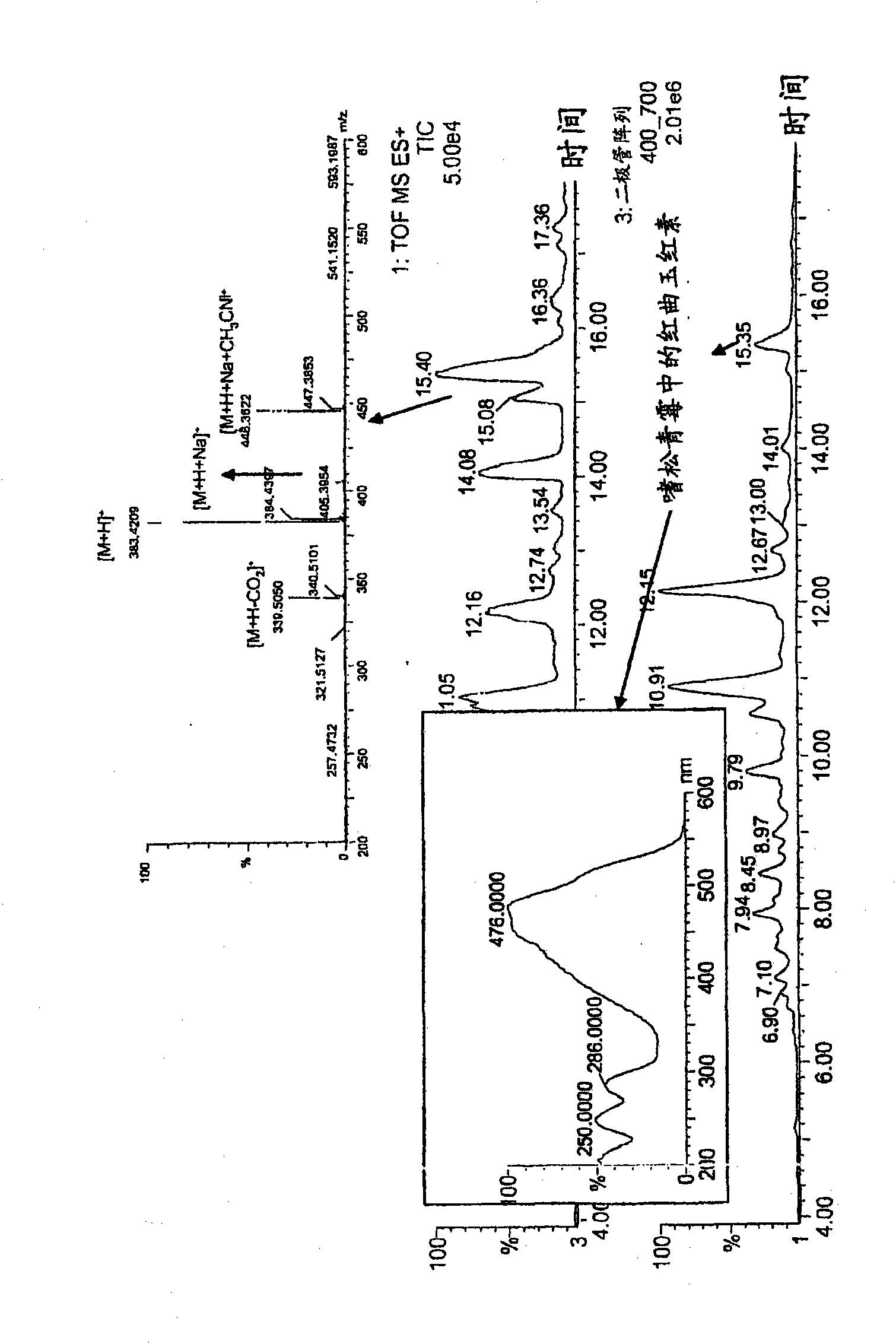
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnological production of polyketide based colorants from filamentous fungi, in particular a method for preparing a biomass comprising a Monascus-like pigment composition from a nontoxigenic and non-pathogenic fungal source. The present invention further relates to use of the Monascus-like pigment composition as a colouring agent for food items and / or non-food items, and a cosmetic composition comprising the Monascus-like pigment composition.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Selective enrichment media and uses thereof
ActiveUS9029118B1Preventing undesirable false positive responseBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementSulfur drugAminocoumarins
Selective enrichment media and methods for selectively growing and detecting Salmonella spp. The media comprise a carbon and nitrogen source, an inorganic salt, a fermentable sugar, one or more selective agents, and an efflux pump inhibitor. Various selective agents include sulfa drugs, surfactants, aminocoumarins, cycloheximide, supravital stains, ascorbic acid, bromobenzoic acid, myricetin, rifamycins, polyketides, and oxazolidinones. Various efflux pump inhibitors include arylpiperazines, such as 1-(1-naphthylmethyl)piperazine, and quinoline derivatives, such as 4-chloroquinoline. The selective agents and efflux pump inhibitors are provided in the media in combinations and amounts that inhibit growth of non-Salmonella microorganisms without substantially affecting growth and metabolism of Salmonella species. Methods of selectively growing and detecting Salmonella species are provided.
Owner:PARADIGM DIAGNOSTICS
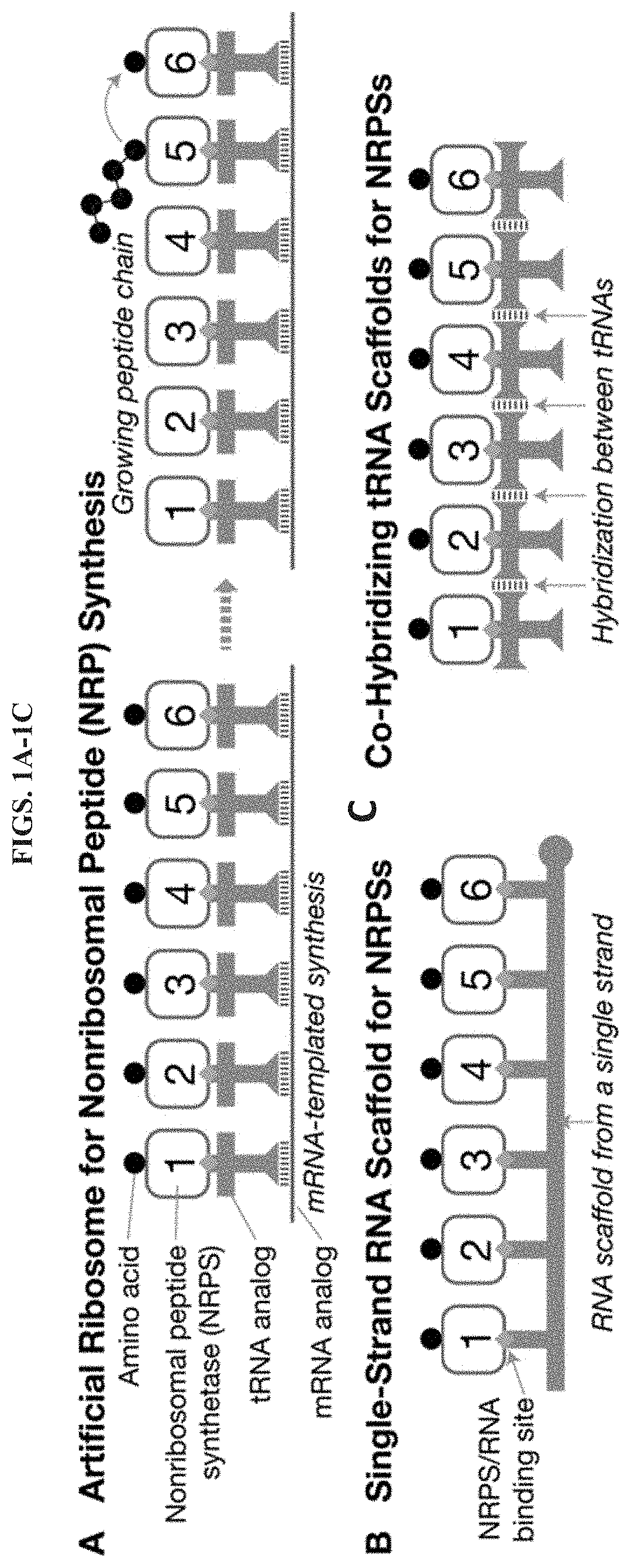
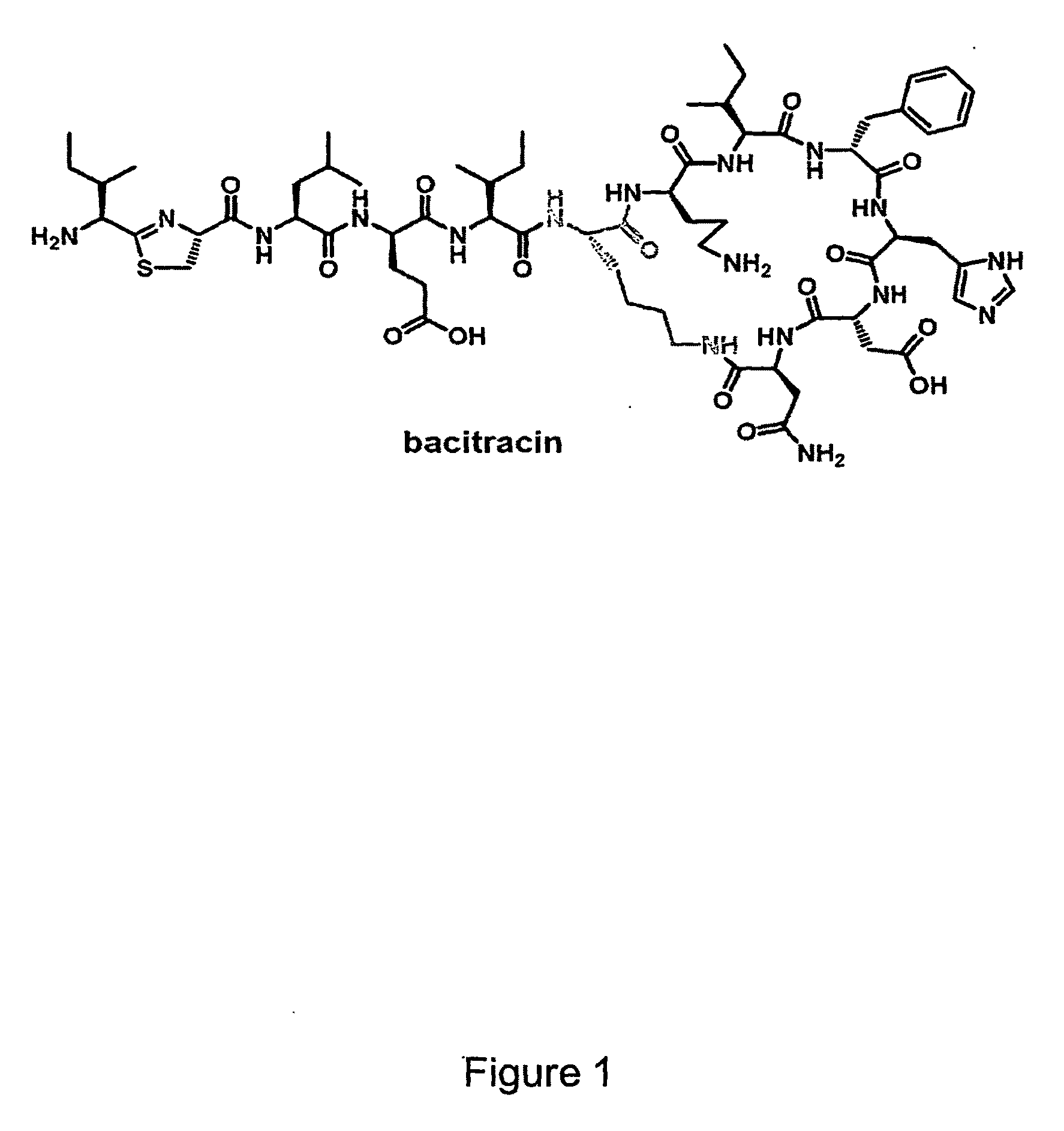
Artificial Ribosomes for Fully Programmable Synthesis of Nonribosomal Peptides
Provided herein, in some embodiments, are artificial ribosomes that synthesize nonribosomal peptides, polyketides, and fatty acids with full control over peptide sequence. Also provided herein are methods for programmed synthesis of nonribosomal peptides, polyketides, and fatty acids. In particular, provided herein are methods for scalable synthesis of a wide range of antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and anticancer compounds.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
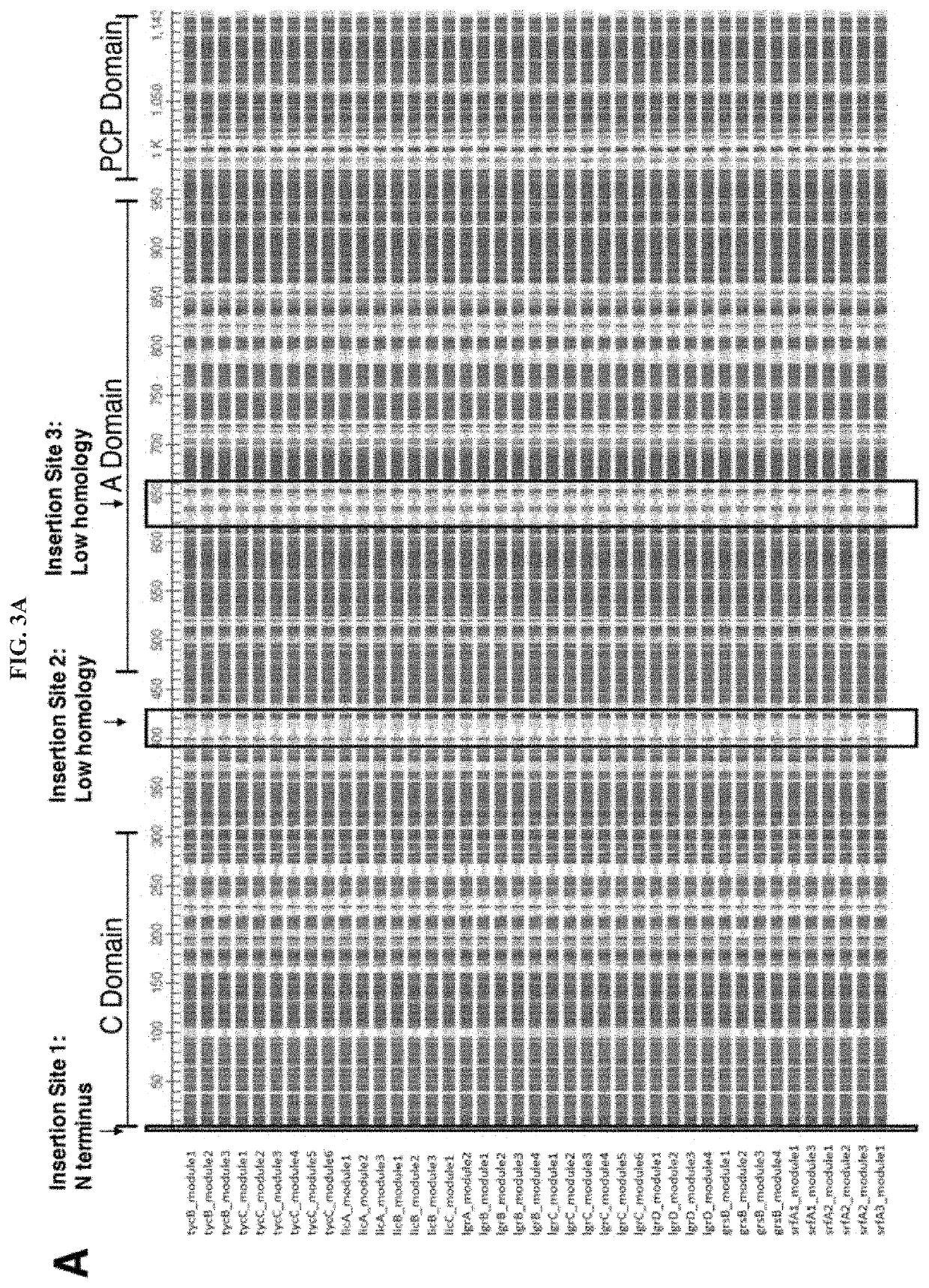
Methods of Producing Modified Assembly Lines and Related Compositions
The present invention provides a method producing a modified assembly line, such as those that produce non-ribosomal peptides and polyketides. The modified assembly lines of the invention can be used to produce novel compounds with therapeutic activities. The invention also provides organisms containing modified assembly lines and libraries of modified assembly lines.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Use of phosphoketolase and phosphotransacetylase for production of acetyl-coenzyme A derived compounds
Provided herein are compositions and methods for improved production of acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA derived compounds in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphoketolase (PK), and a functional disruption of an endogenous enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate. In some embodiments, the host cell further comprises a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphotransacetylase (PTA). In some embodiments, the enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate is a glycerol-1-phosphatase. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP1 / RHR2. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP2 / HOR2. The compositions and methods described herein provide an efficient route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived compounds, including but not limited to, isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
Production of monascus-like azaphilone pigment
InactiveCN101970580ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolyketideBiomass
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnological production of polyketide based colorants from filamentous fungi, in particular a method for preparing a biomass comprising a Monascus-like pigment composition from a nontoxigenic and non-pathogenic fungal source. The present invention further relates to use of the Monascus-like pigment composition as a colouring agent for food items and / or non-food items, and a cosmetic composition comprising the Monascus-like pigment composition.
Owner:DTU丹麦科技大学
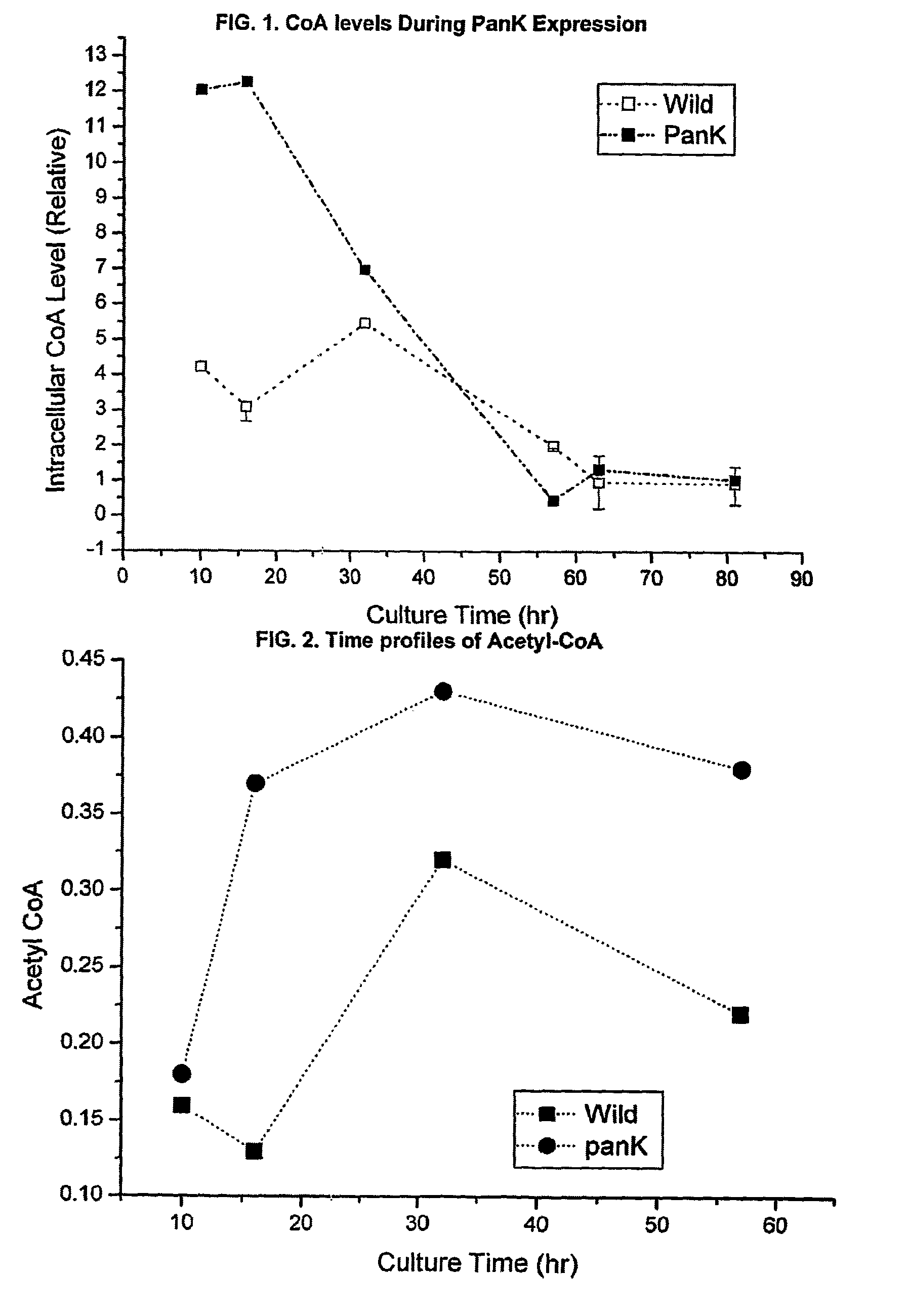
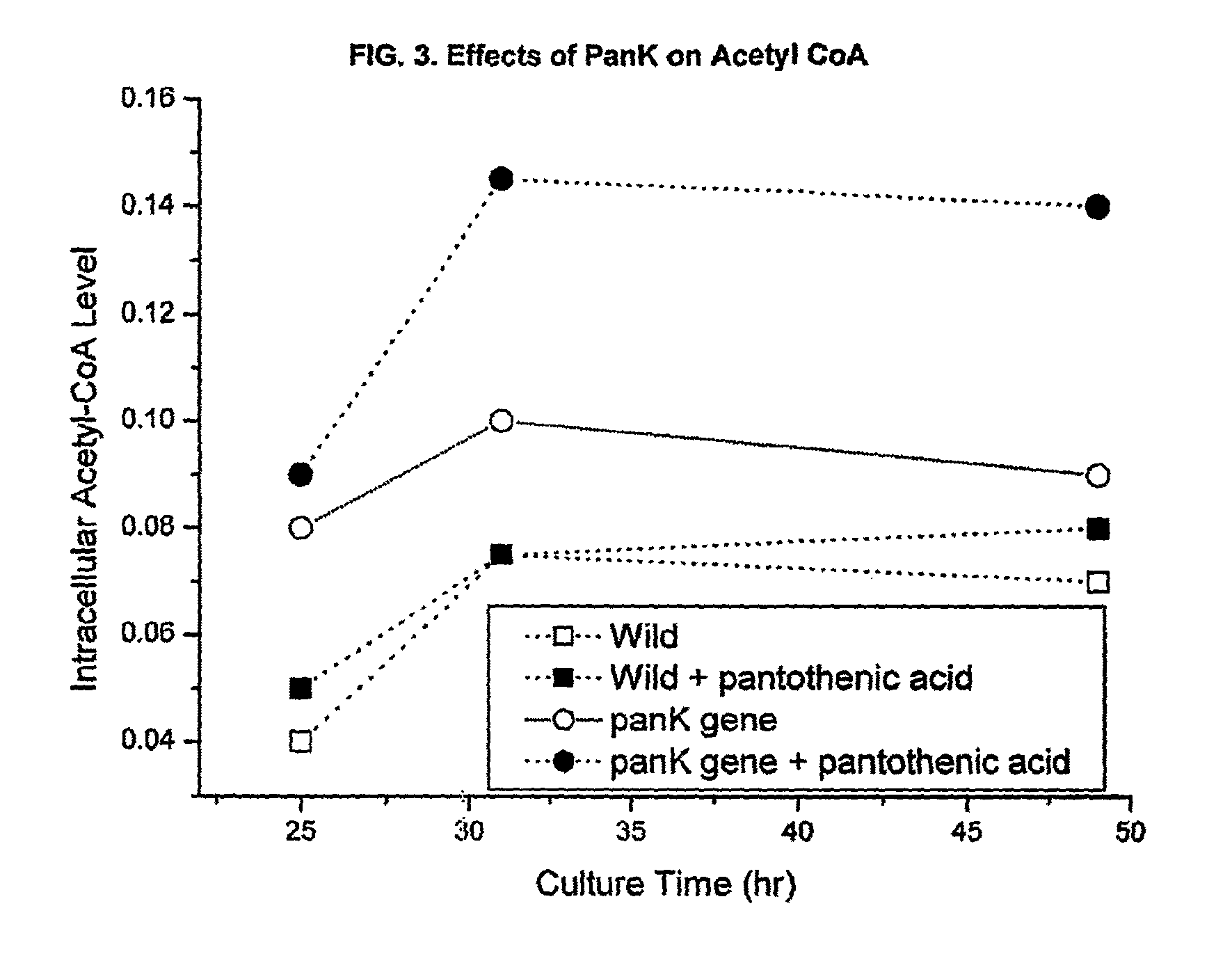
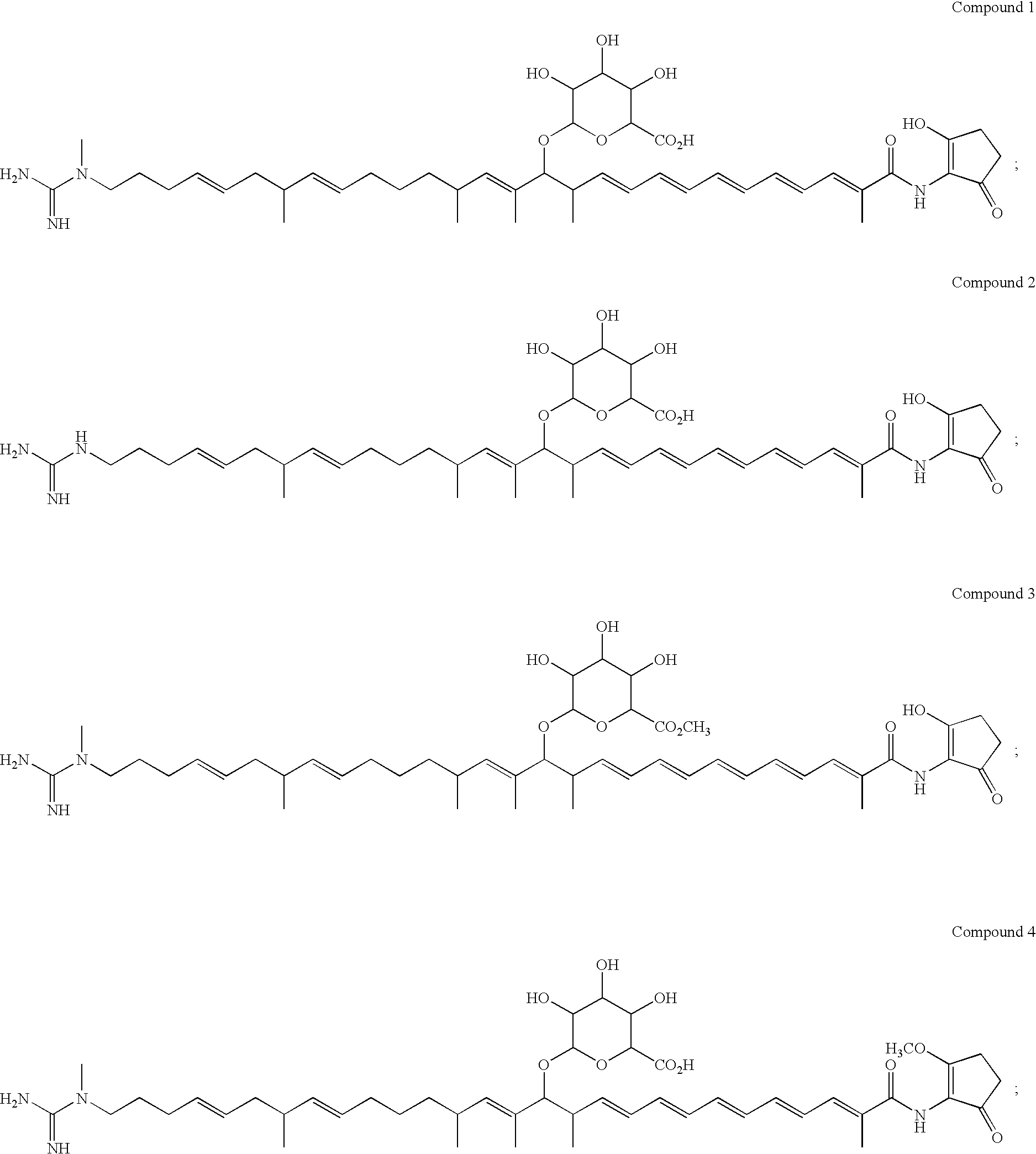
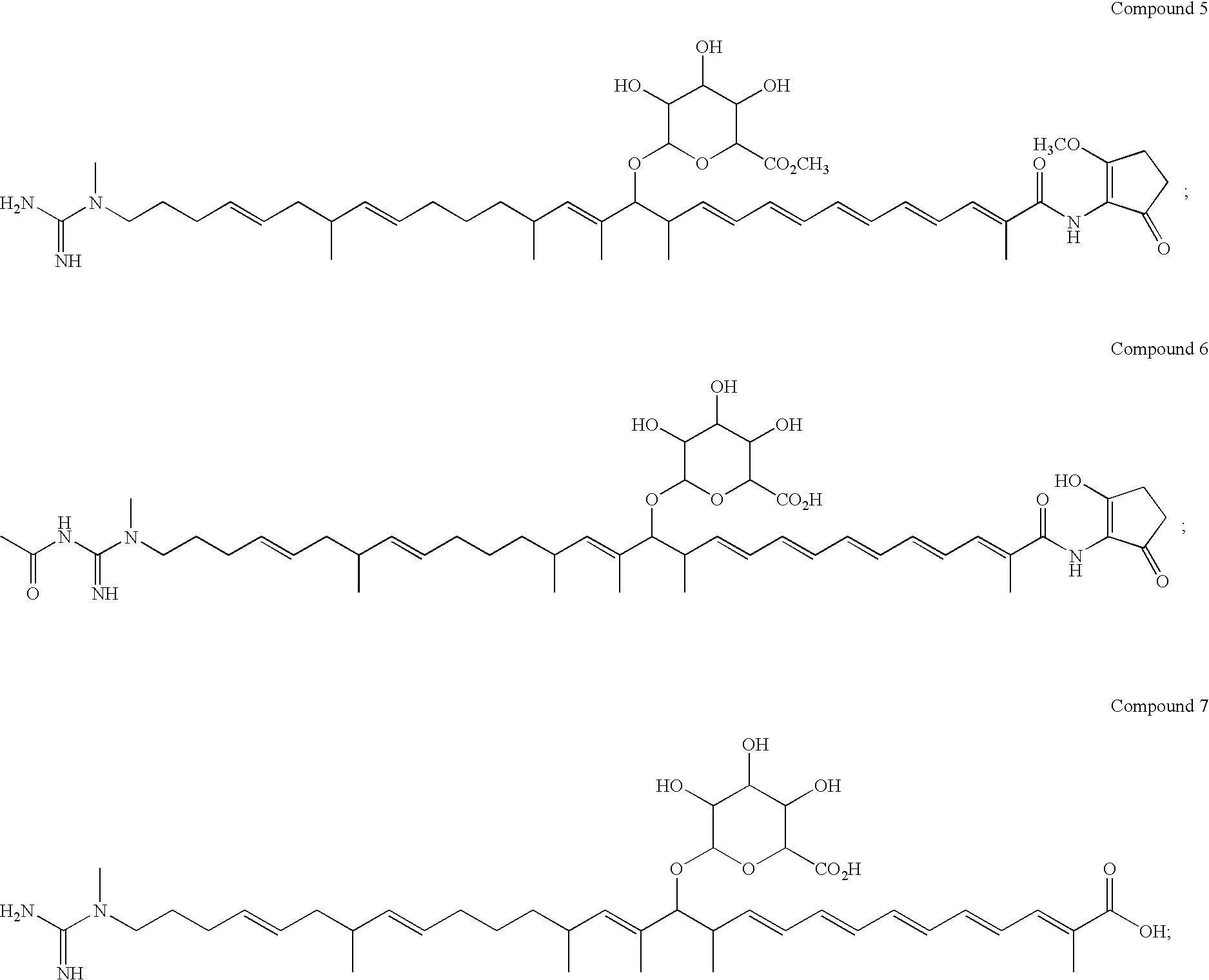
Pantothenate kinase overexpression and pantothenic acid supplementation in actinomycetes
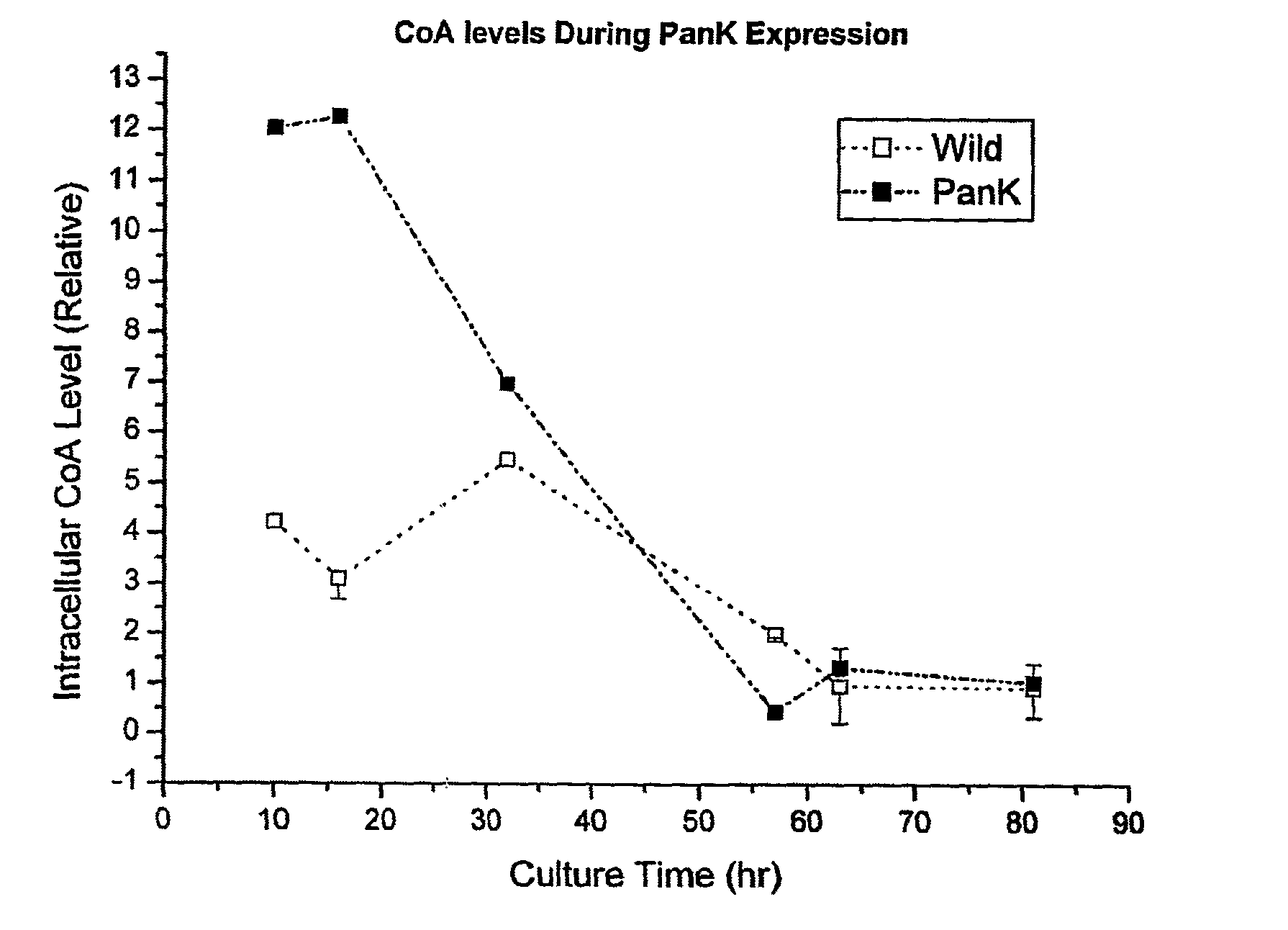
InactiveUS8143035B2Promote biosynthesisImprove the level ofOrganic chemistryBacteriaPolyketideSecondary metabolite
The invention relates to the synthesis of polyketides in Actinomycetes by overexpression of pantothenate kinase and supplementation with pantothenic acid. This results in increasing in vivo CoA production and thereby drives increased production of secondary metabolites, such as polyketides.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Polyene polyketides and methods of production
Novel polyene polyketides, their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs and derivatives have been found to have antibiotic activity. One method for obtaining the compounds is by cultivation of Amycolatopsis orientalis ATCC™ 43491 or a mutant or variant such as the strain IDAC-220604-1. Another method for obtaining the compounds is post-biosynthesis chemical modification of the compounds obtained by cultivation. Novel polynucleotide sequences and encoded proteins for the biosynthesis of the polyene polyketides are also presented.
Owner:THALLION PHARMA
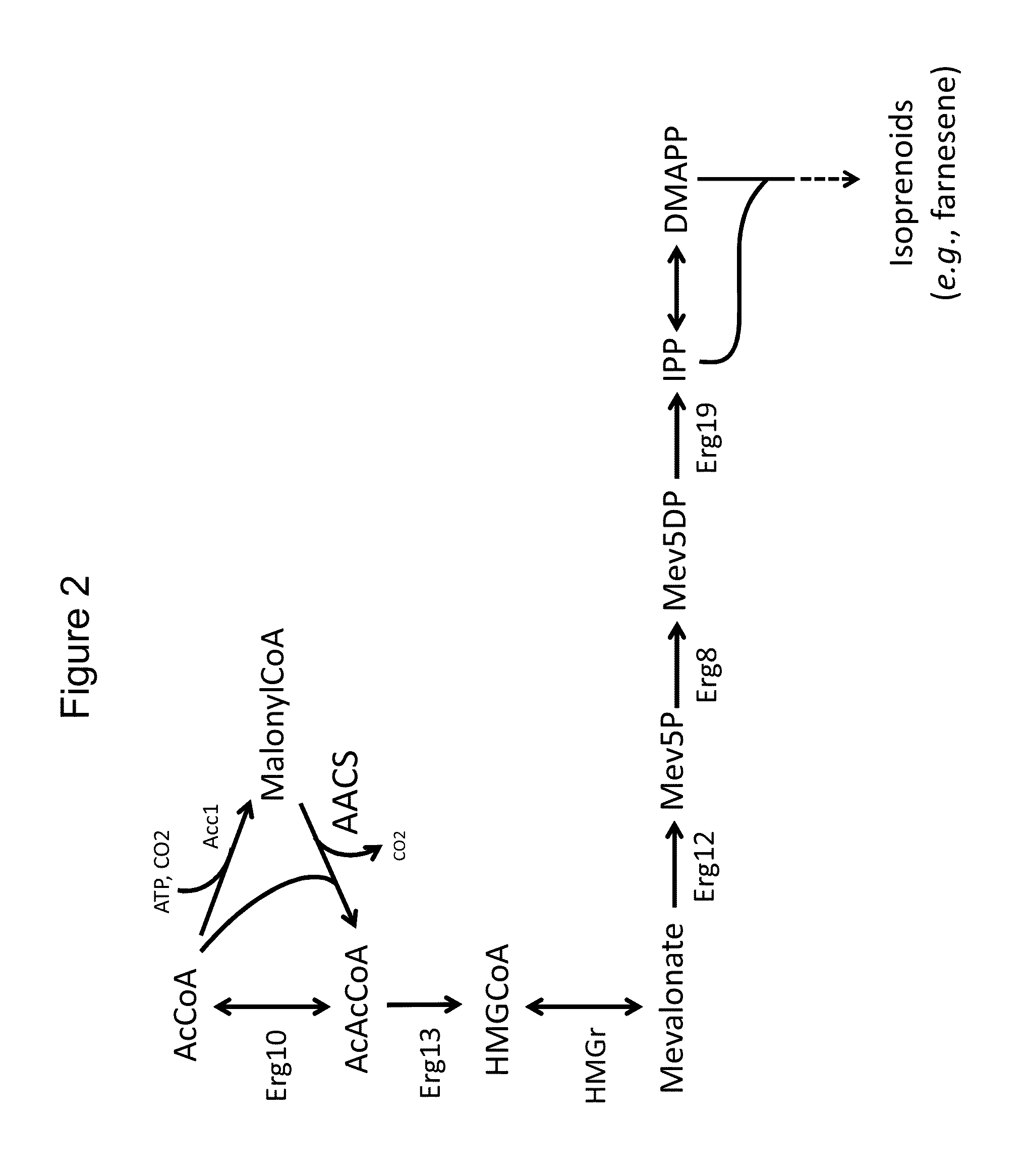
Microorganism production of high-valve chemical products, and related compositions, methods and systems
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganism strains, such as bacterial strains, in which there is an increased utilization of malonyl-CoA for production of a chemical product, which includes polyketides and 3-hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH +1
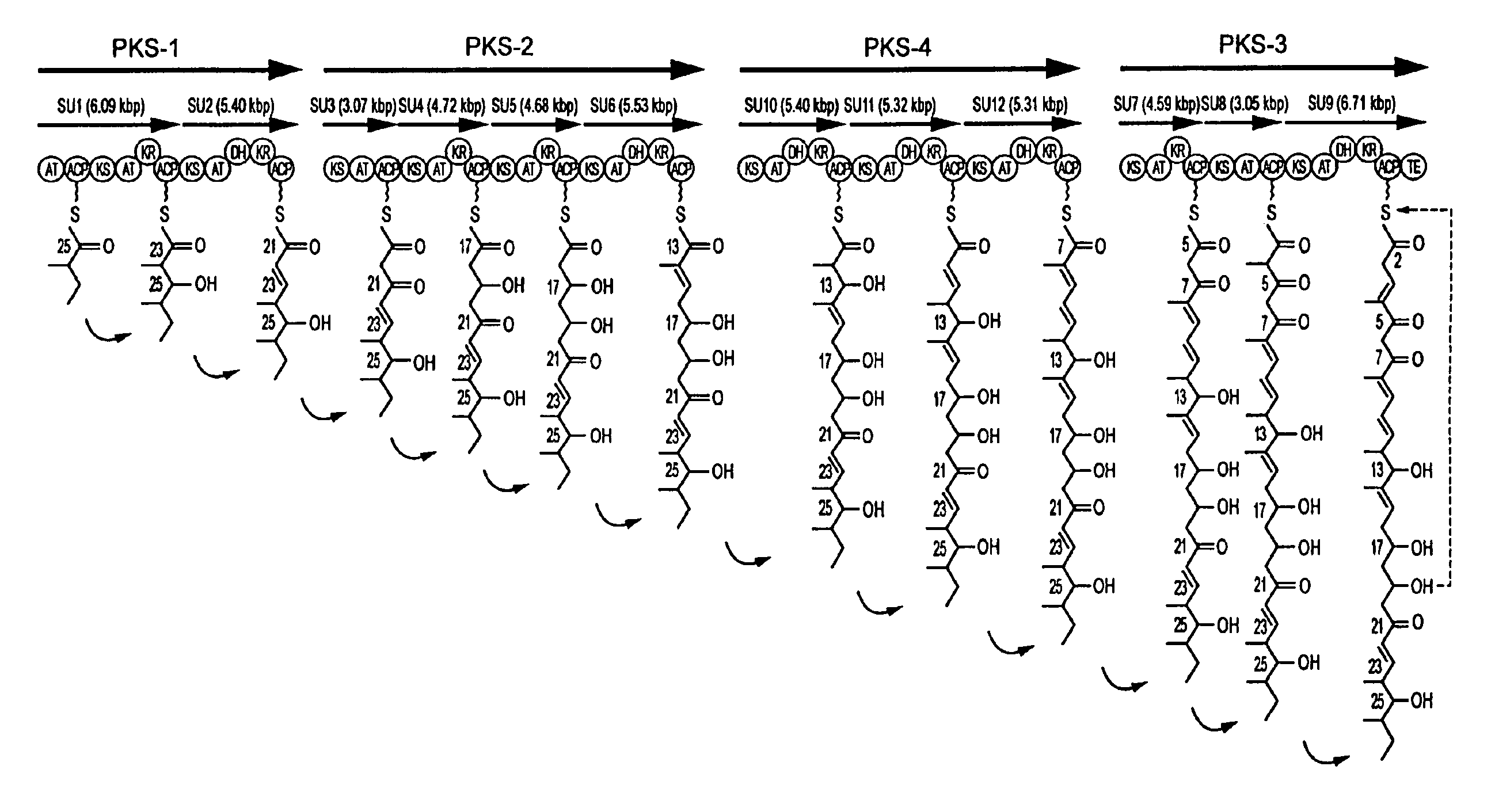
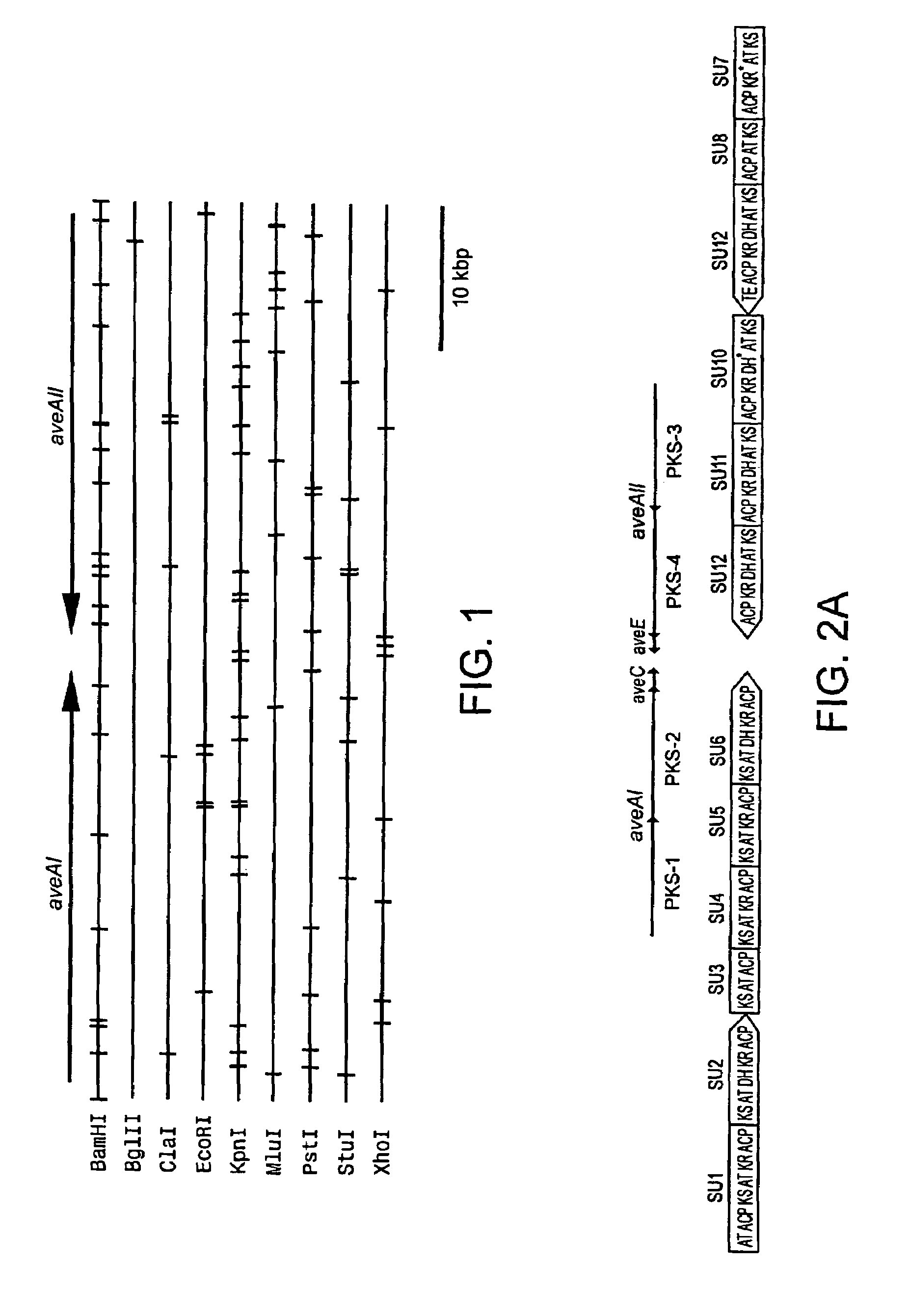
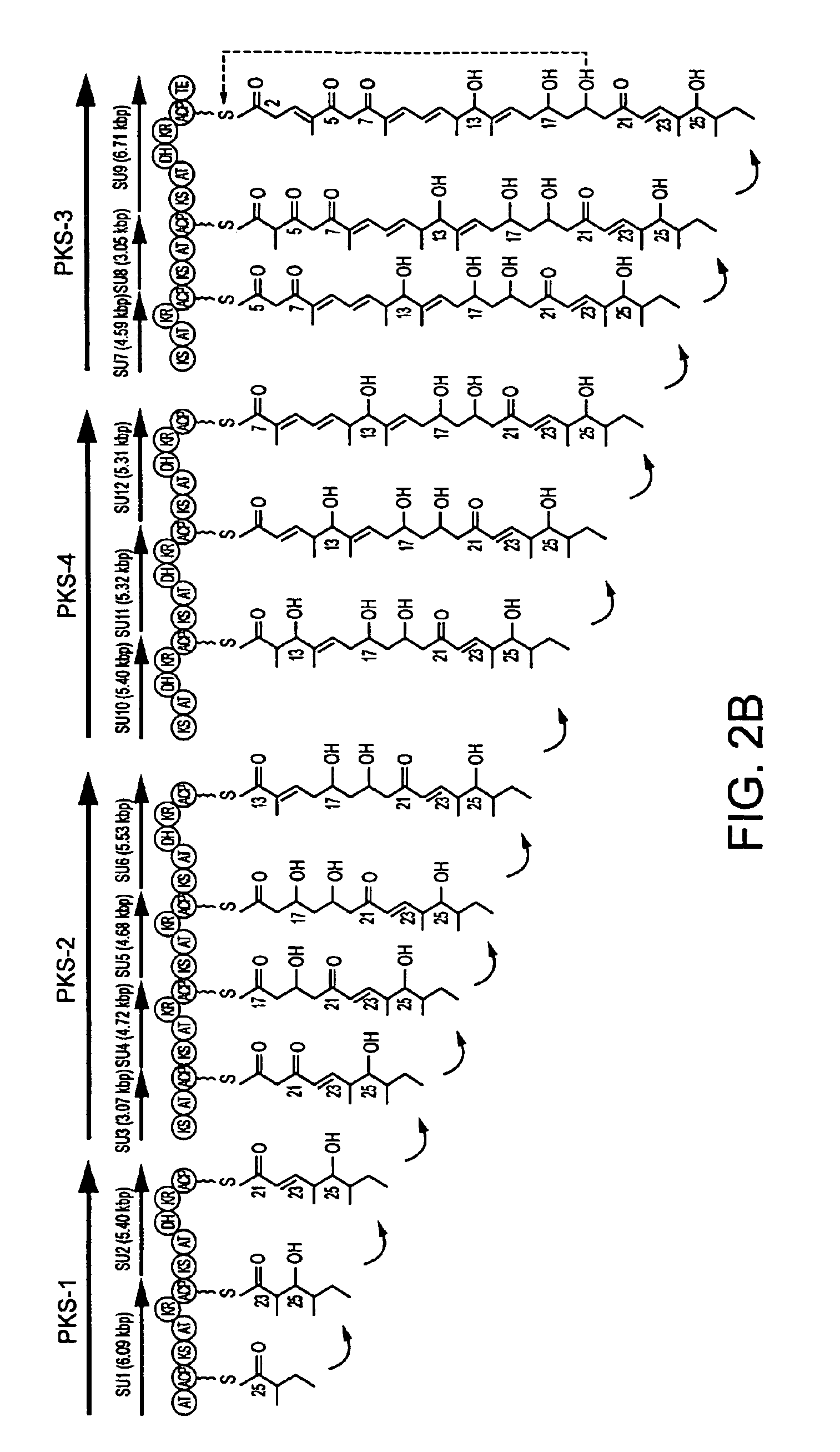
Avermectin aglycon synthase genes
The present invention relates to an isolated DNA which comprises a DNA sequence encoding avermectin aglycon synthase domains that corresponds to multifunctional enzyme proteins involved in the biosynthesis of a polyketide compound, or its mutants having avermectin aglycon synthase activity, particularly functional modules and submodules in the DNA sequence derived from Streptomyces avermitilis, a polypeptide or mutants thereof encoded by the DNA or the mutants, a vector containing the DNA or the mutants, a host cell transformed with the DNA, the mutants thereof, or the vector, and a method for producing avermectin.
Owner:THE KITASATO INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com