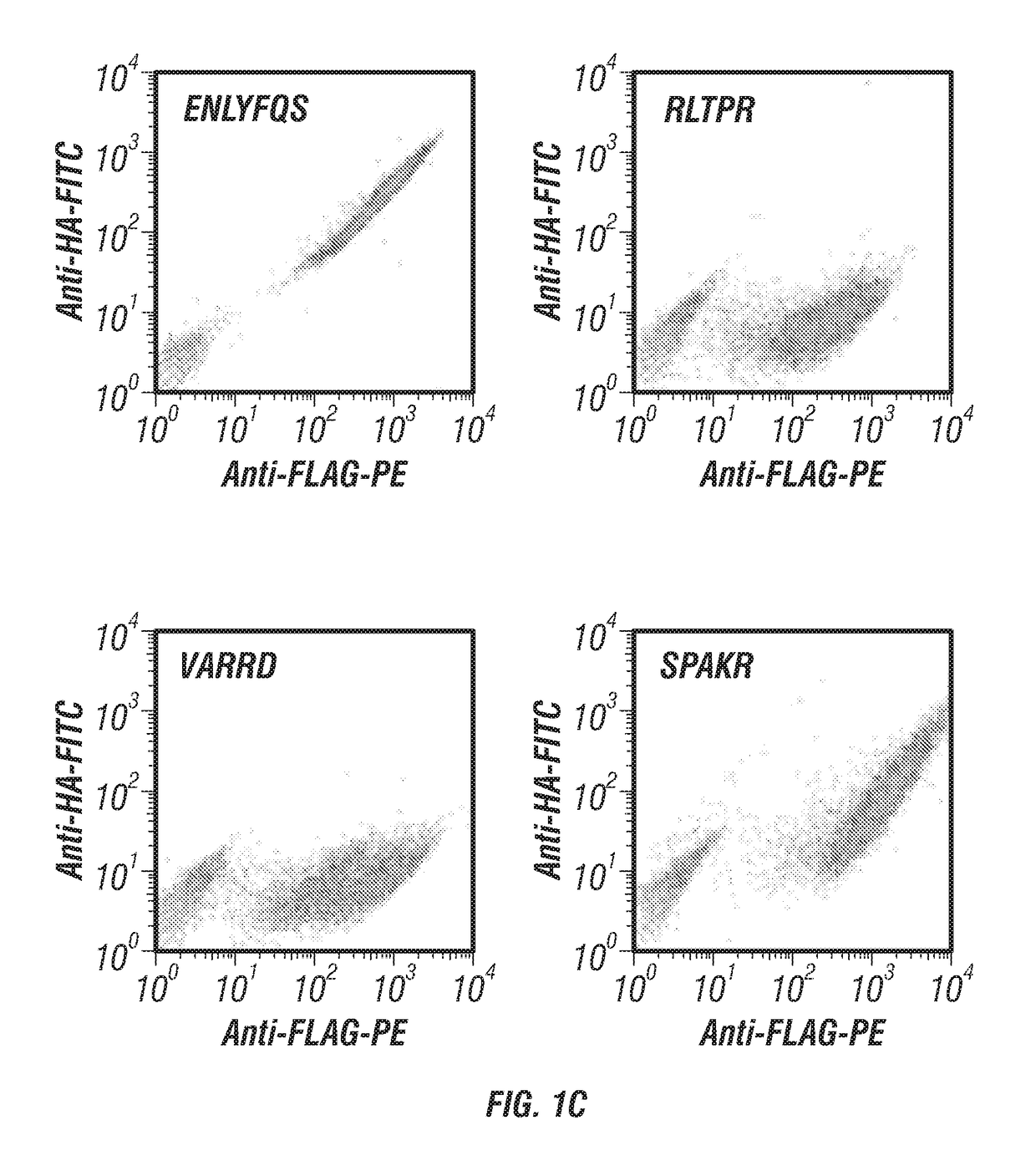
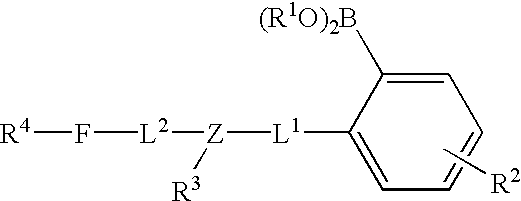Patents
Literature
54 results about "Substrate recognition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A model for enzyme-substrate recognition is presented in which substrates are depicted by continuous functions f, analogous to charge or mass distributions.
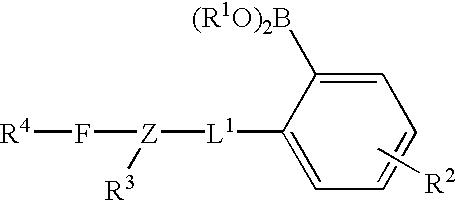
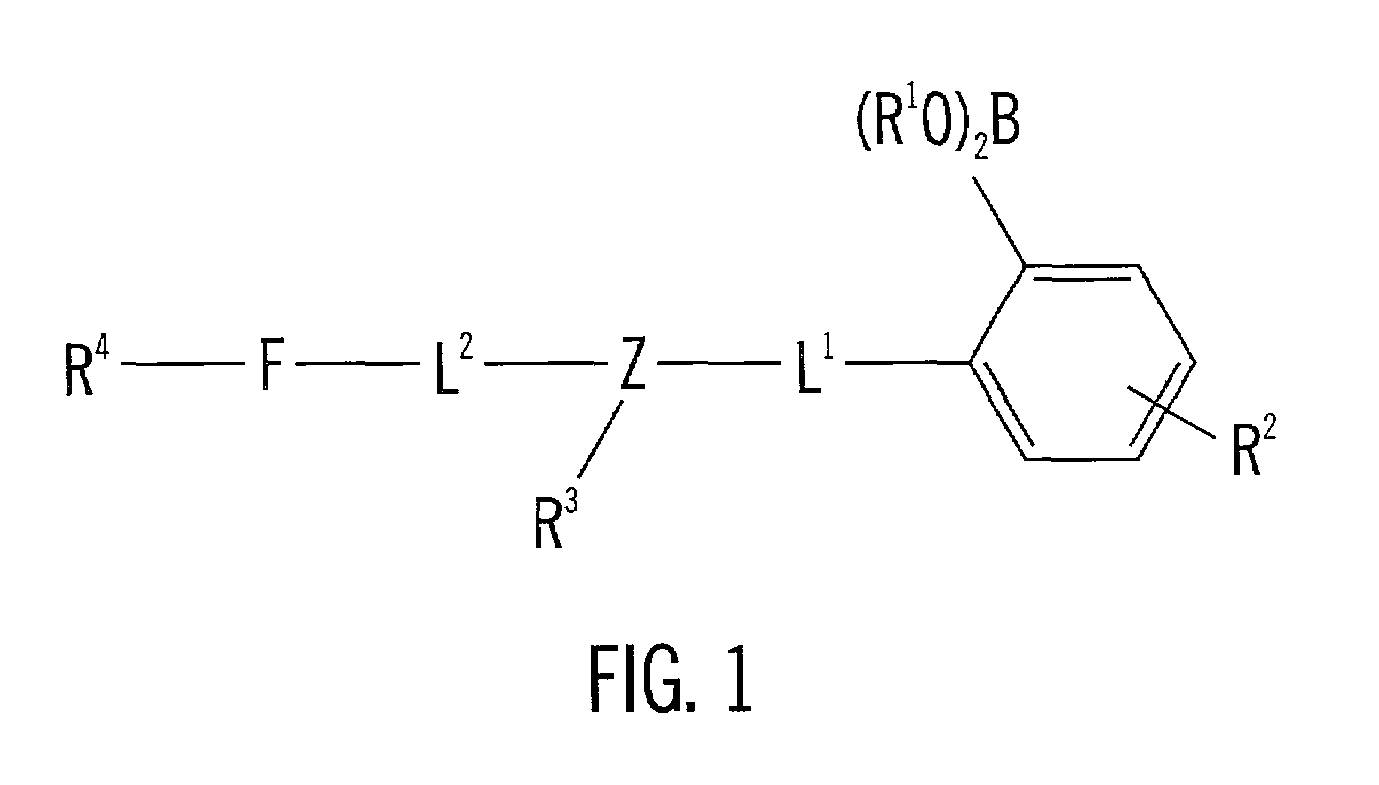
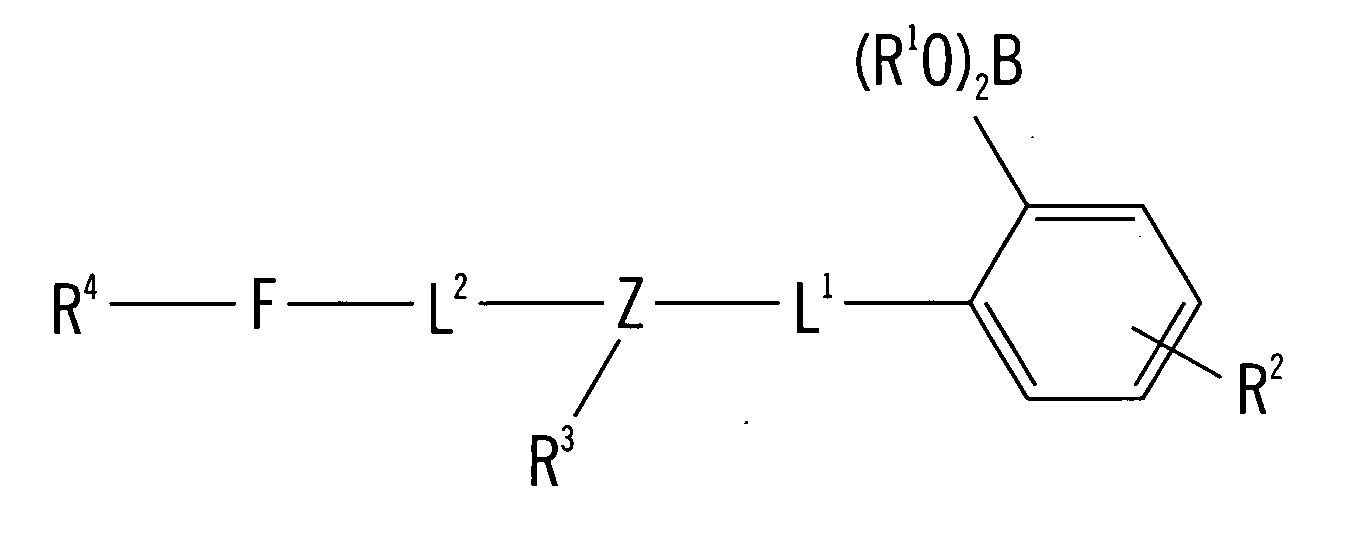
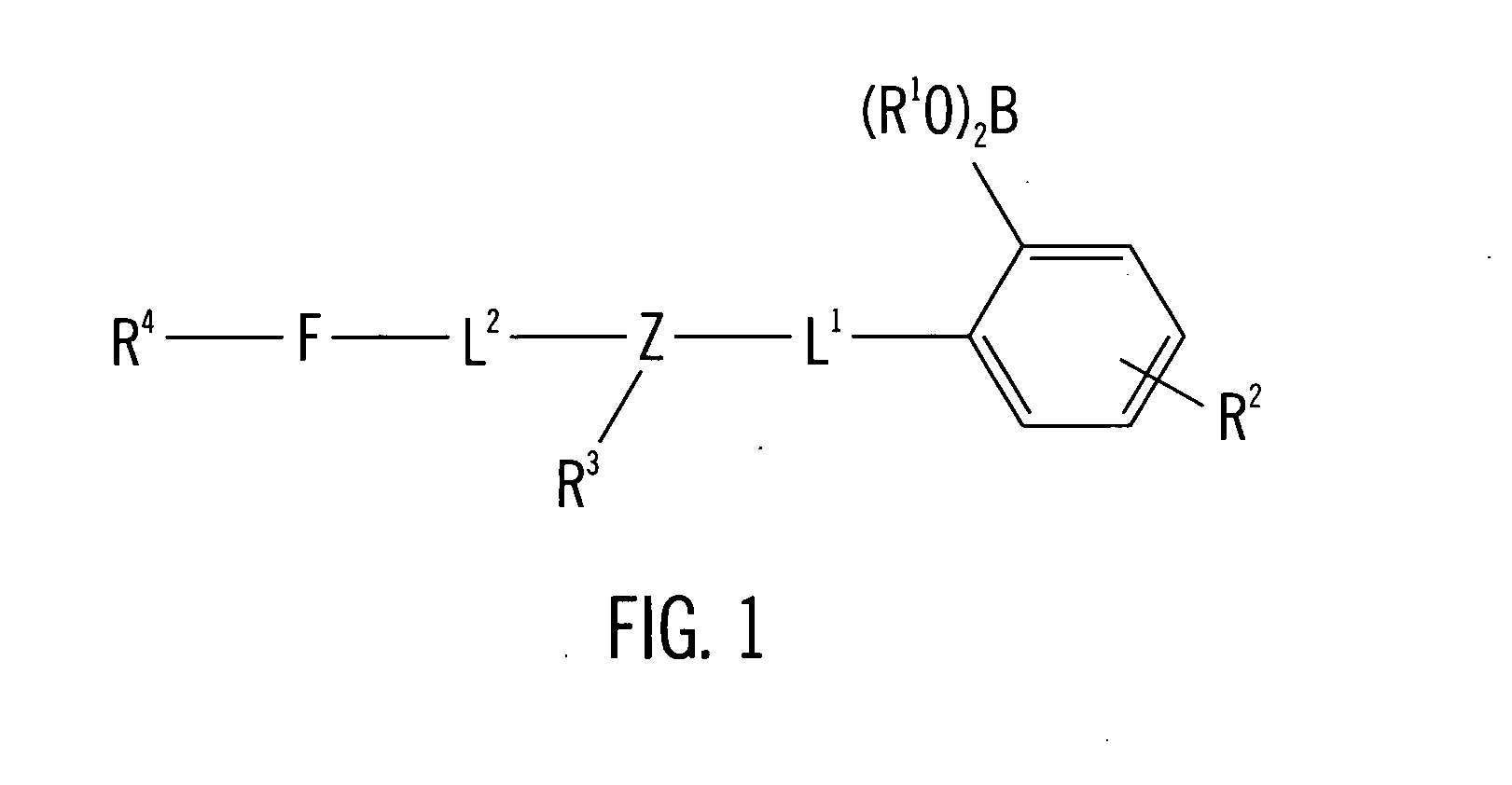
Long wave fluorophore sensor compounds and other fluorescent sensor compounds in polymers
InactiveUS6766183B2Improve sensor sensitivityReduction in the tissue autofluorescence backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceConcentrations glucoseFluorophore
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC +1
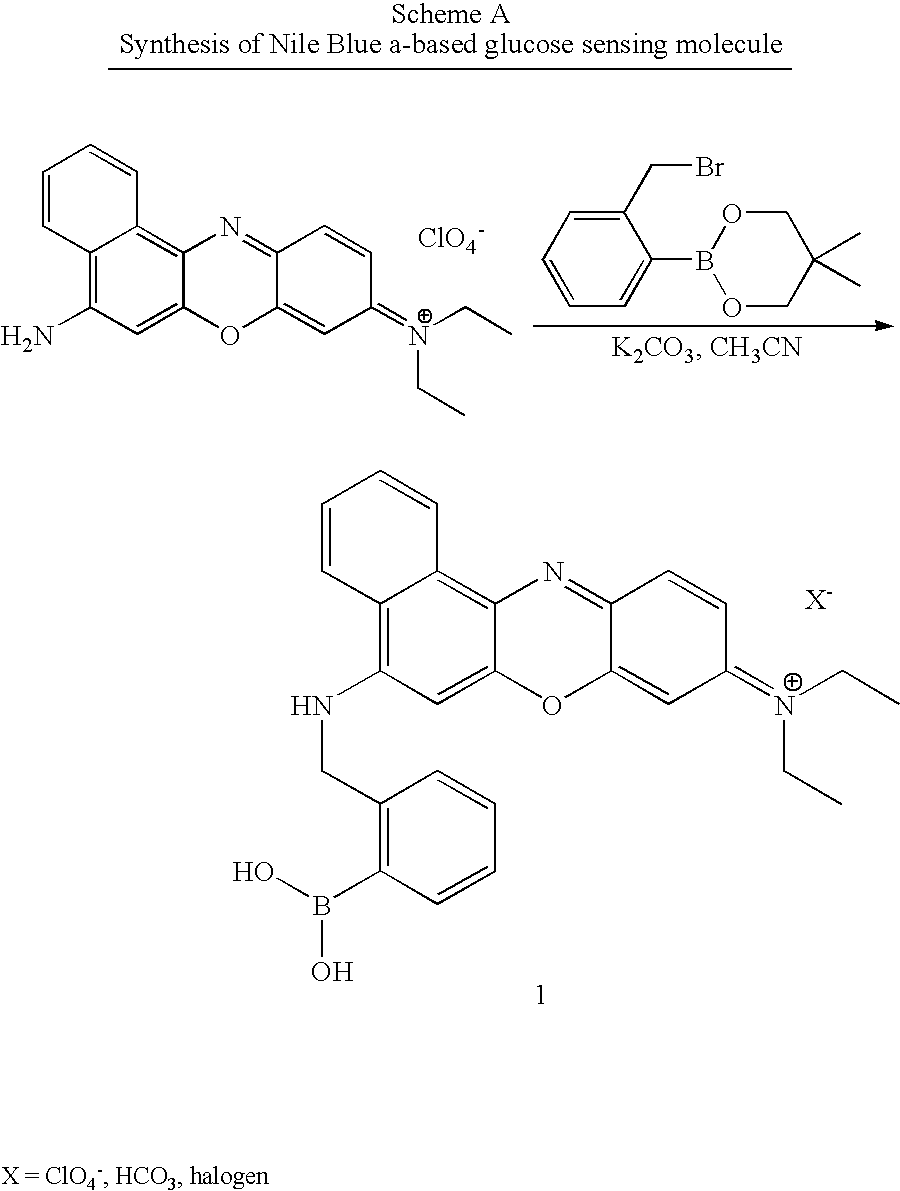
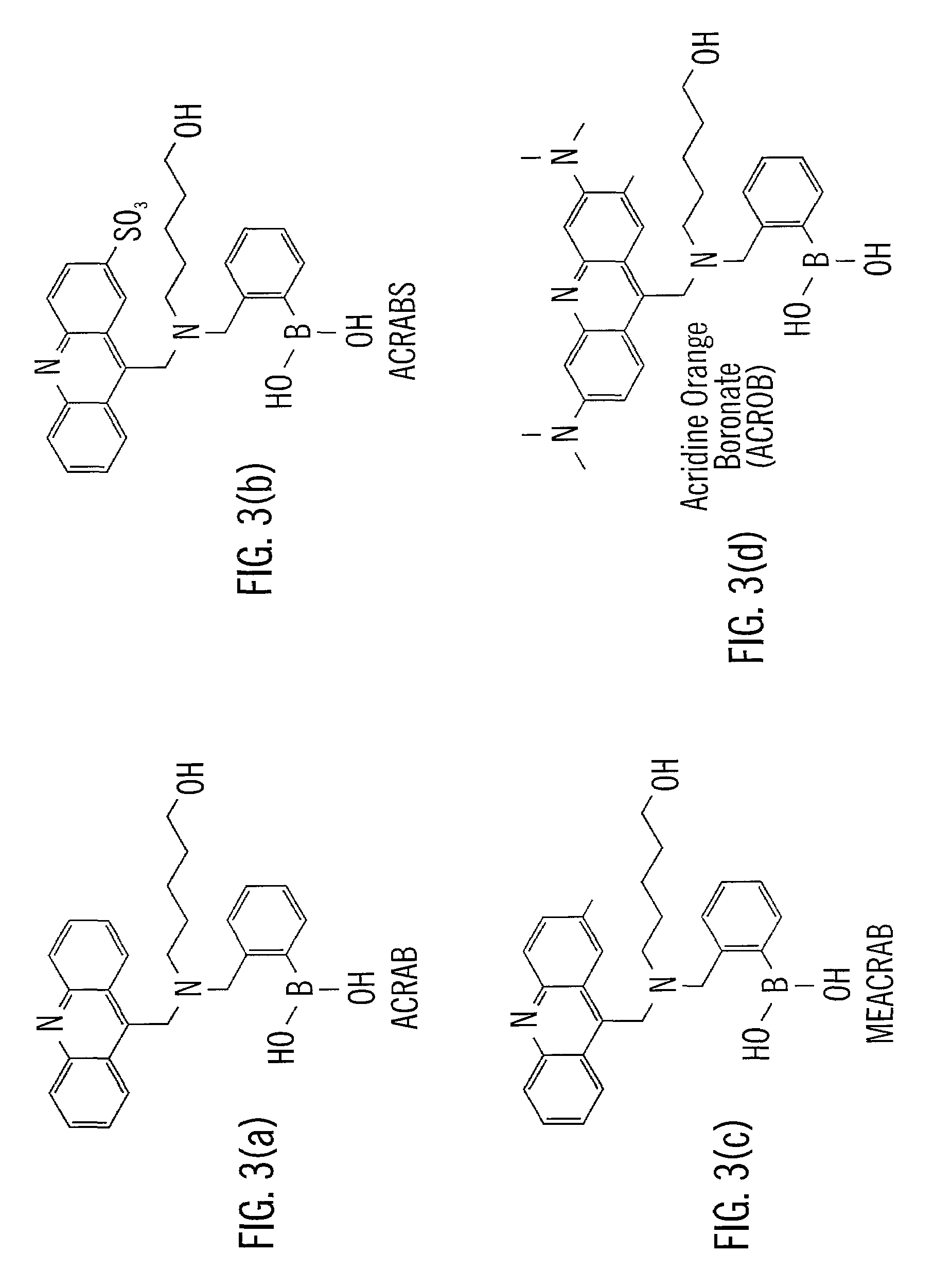
Analyte sensing via acridine-based boronate biosensors
InactiveUS7045361B2Improve sensor sensitivityIncrease overall biocompatibility and functioningMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceConcentrations glucoseFluorophore
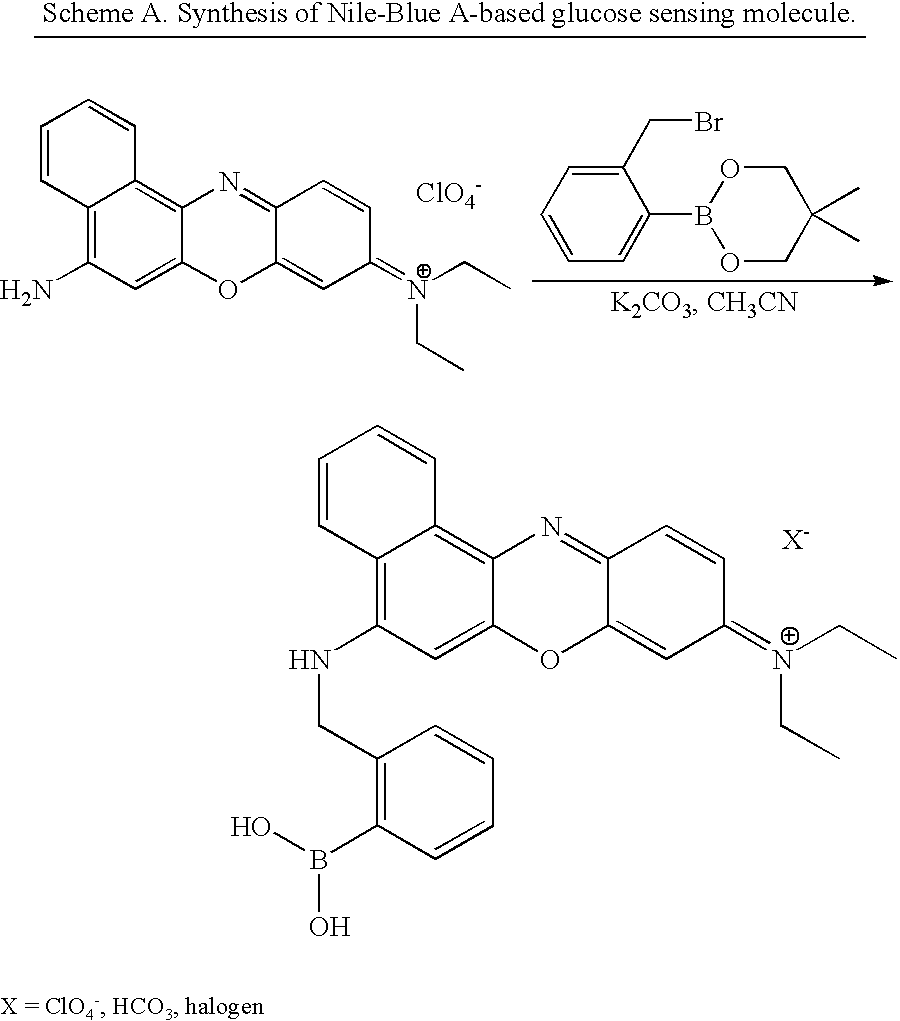
Fluorescent biosensor molecules, fluorescent biosensors and systems, as well as methods of making and using these biosensor molecules and systems are described. These biosensor molecules address the problem of obtaining fluorescence emission at wavelengths greater than about 500 nm. Biosensor molecules generally include an (1) an acridine-based fluorophore, (2) a linker moiety and (3) a boronate substrate recognition / binding moiety, which binds polyhydroxylate analytes, such as glucose. These biosensor molecules further include a “switch” element that is drawn from the electronic interactions among these submolecular components. This fluorescent switch is generally “off” in the absence of bound polyhydroxylate analyte and is generally “on” in the presence of bound polyhydroxylate analyte. Thus, the reversible binding of a polyhydroxylate analyte essentially turns the fluorescent switch “on” and “off”. This property of the biosensor molecules, as well as their ability to emit fluorescent light at greater than about 500 nm, renders these biosensor molecules particularly well-suited for detecting and measuring in-vivo glucose concentrations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Long wave fluorophore sensor compounds and other fluorescent sensor compounds in polymers
InactiveUS20020193672A1Improve accuracyEliminate errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceConcentrations glucoseFluorophore
Fluorescent biosensor molecules, fluorescent biosensors and systems, as well as methods of making and using these biosensor molecules and systems are described. Embodiments of these biosensor molecules exhibit fluorescence emission at wavelengths greater than about 650 nm. Typical biosensor molecules include a fluorophore that includes an iminium ion, a linker moiety that includes a group that is an anilinic type of relationship to the fluorophore and a boronate substrate recognition / binding moiety, which binds glucose. The fluorescence molecules modulated by the presence or absence of polyhydroxylated analytes such as glucose. This property of these molecules of the invention, as well as their ability to emit fluorescent light at greater than about 650 nm, renders these biosensor molecules particularly well-suited for detecting and measuring in-vivo glucose concentrations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC +1
Substrate recognition by differentiable human mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS20060128012A1Effective therapyPulse automatic controlFilament/thread formingFiberNanofiber
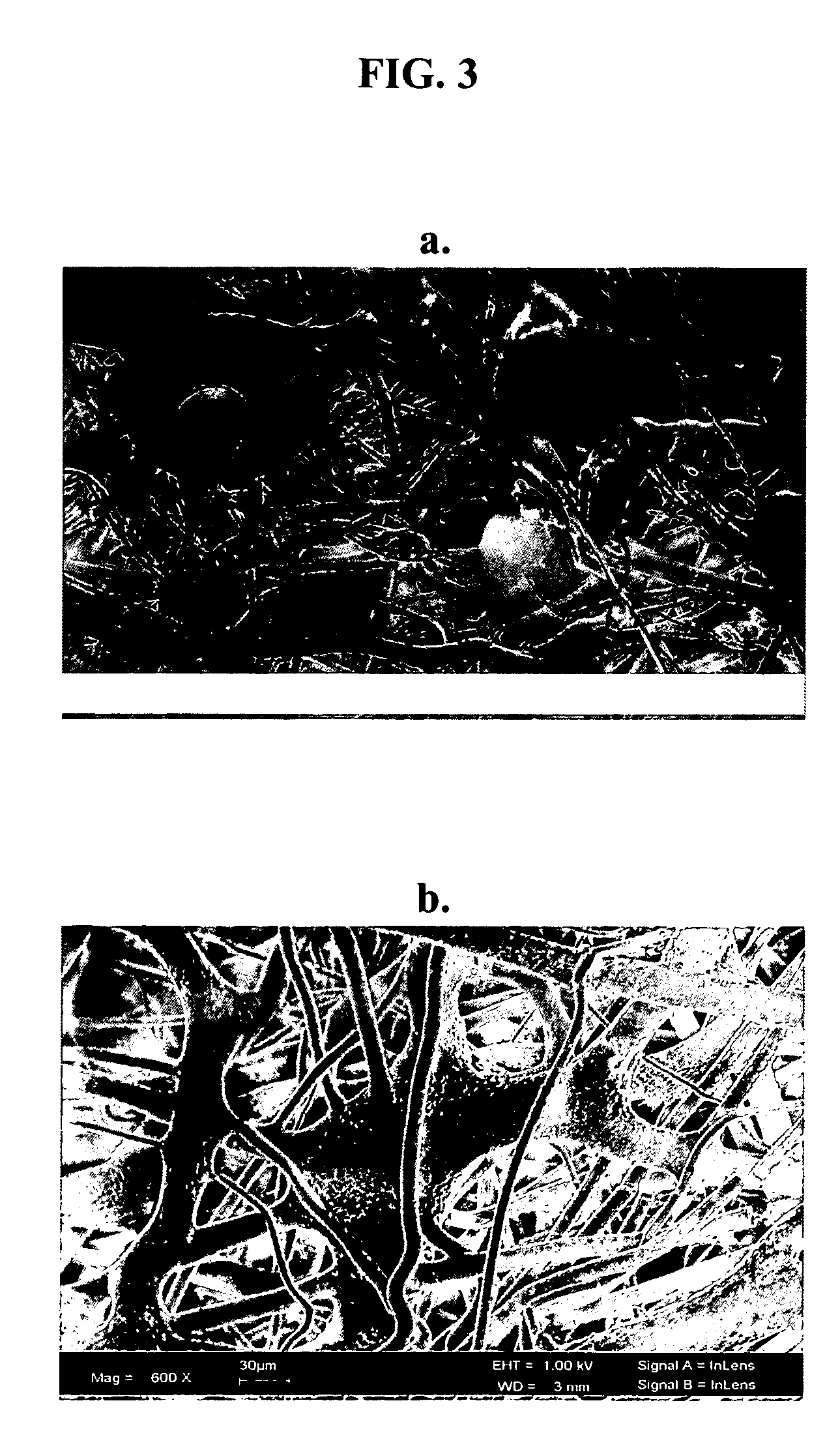
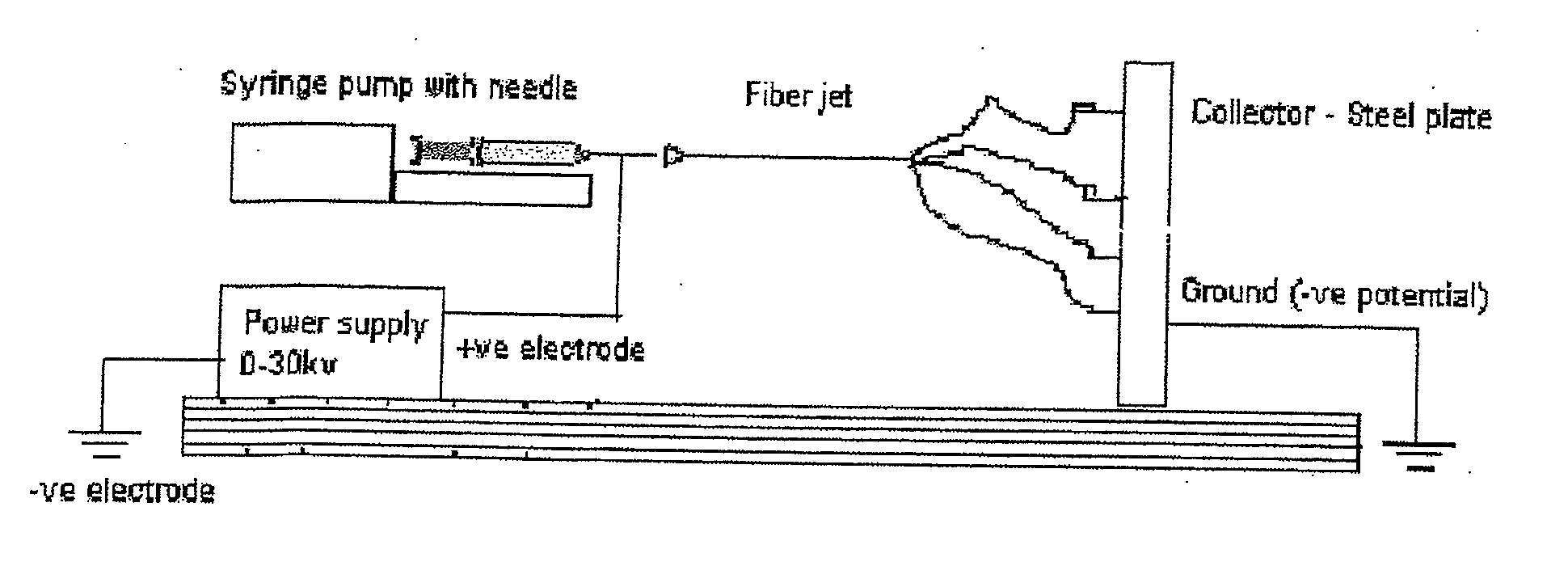
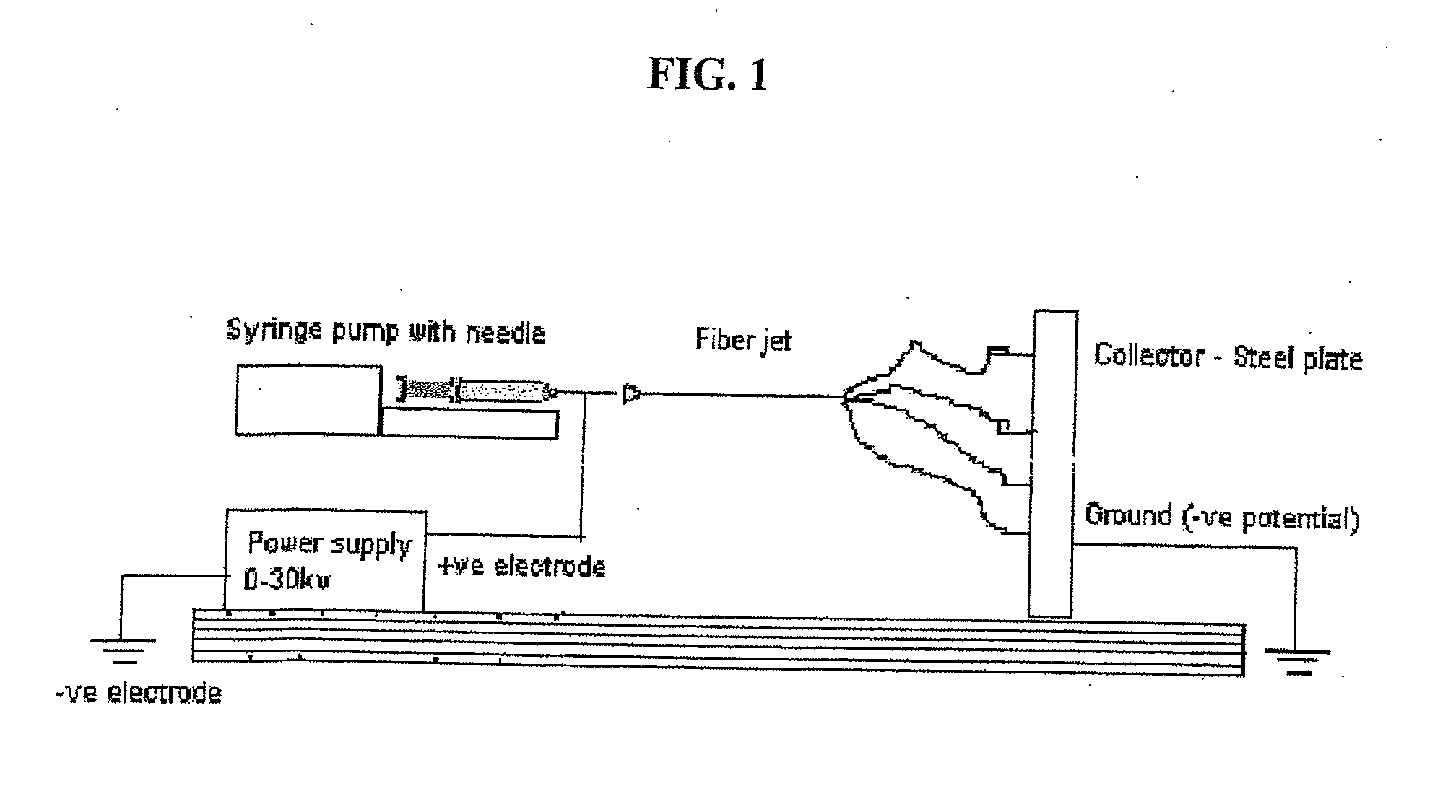
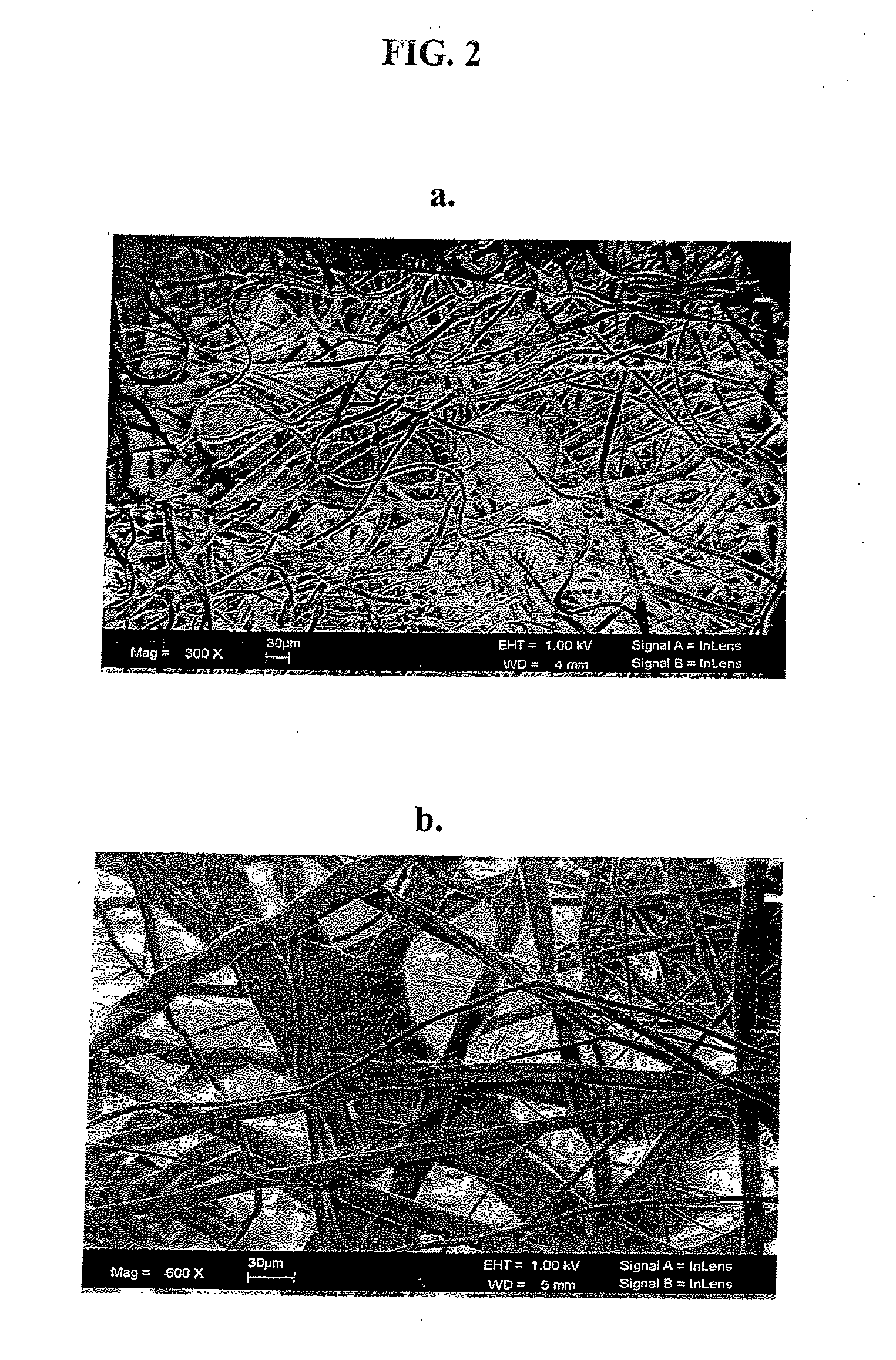
The invention described herein provides a structure for growing isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, which includes a three-dimensional matrix of fibers. The matrix serves as an implantable scaffolding for delivery of differentiable human mesenchymal cells in tissue engineering. The invention further provides compositions that contain the three-dimensional matrix of fibers seeded with isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, wherein the matrix forms a supporting scaffold for growing the isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, and wherein the differentiable human mesenchymal cells differentiate into a mature cell phenotype. The invention further provides methods of preparing the implantable nanofiber matrix scaffolding seeded with differentiable human mesenchymal cells for use in tissue engineering.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Selective inhibitors for protein kinases and pharmaceutical composition and use thereof
ActiveUS9738660B2High selectivityIncreased selective inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryArylPTK Inhibitors
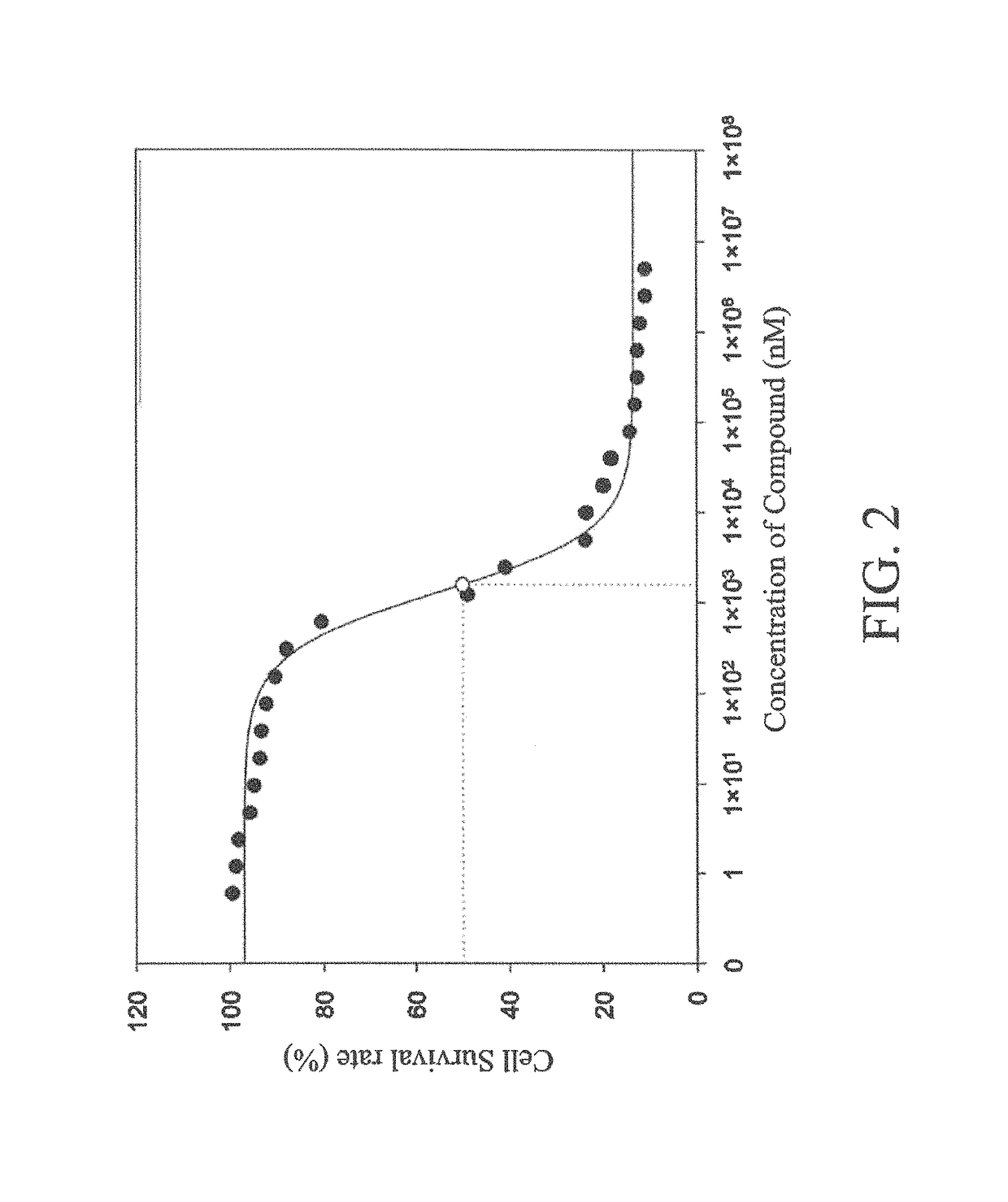
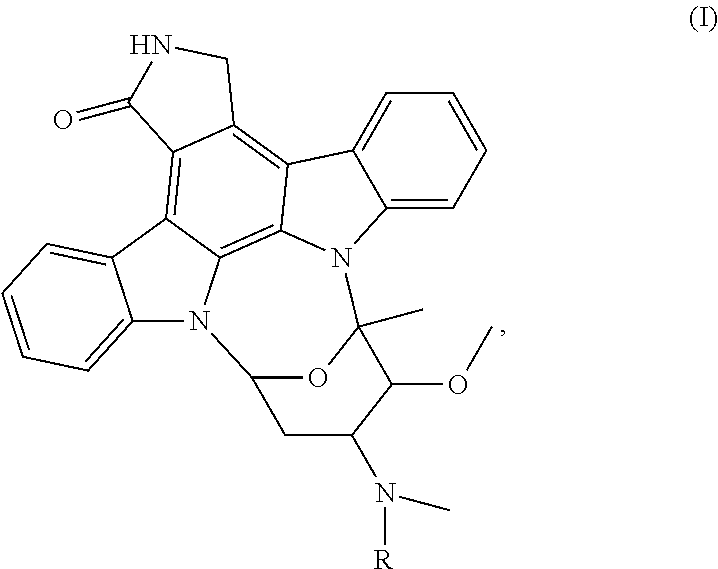
The present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or the salt thereof:wherein R is at least one selected from the group consisting of unsubstituted C1-4 alkyl, C1-4 alkyl substituted by C6-18 aryl or —OR1, and —C(═O)Z. The compound is a type-S protein kinase inhibitor, which binds to an ATP-binding site and a substrate-recognition site of a protein kinase simultaneously. The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition, which includes a compound of formula (I) or a salt and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier thereof. The present invention further provides a use of a compound of formula (I) or a salt thereof, which is for the manufacture of a protein kinase inhibitor as a drug.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
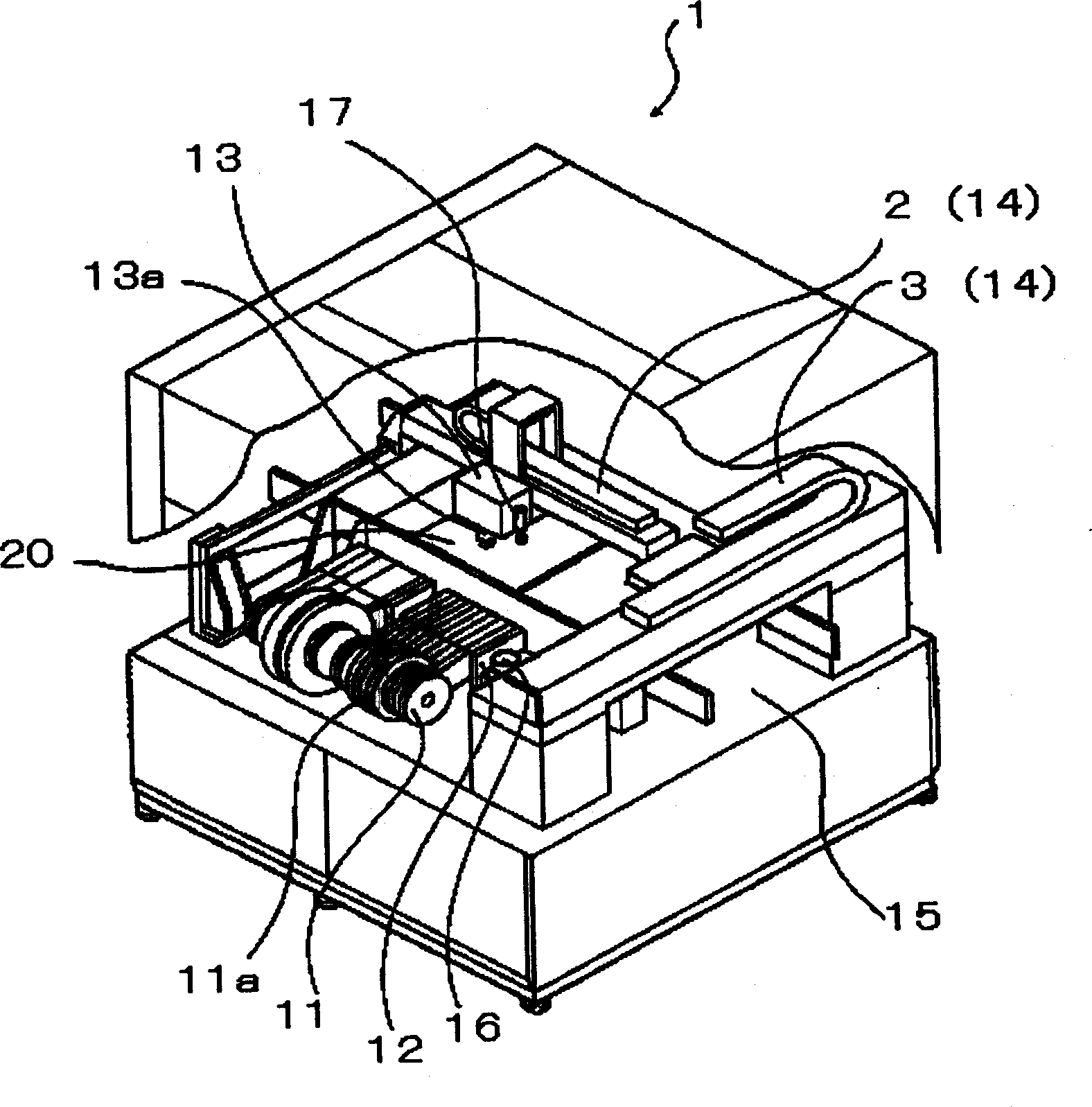
Position matching method and screen printer
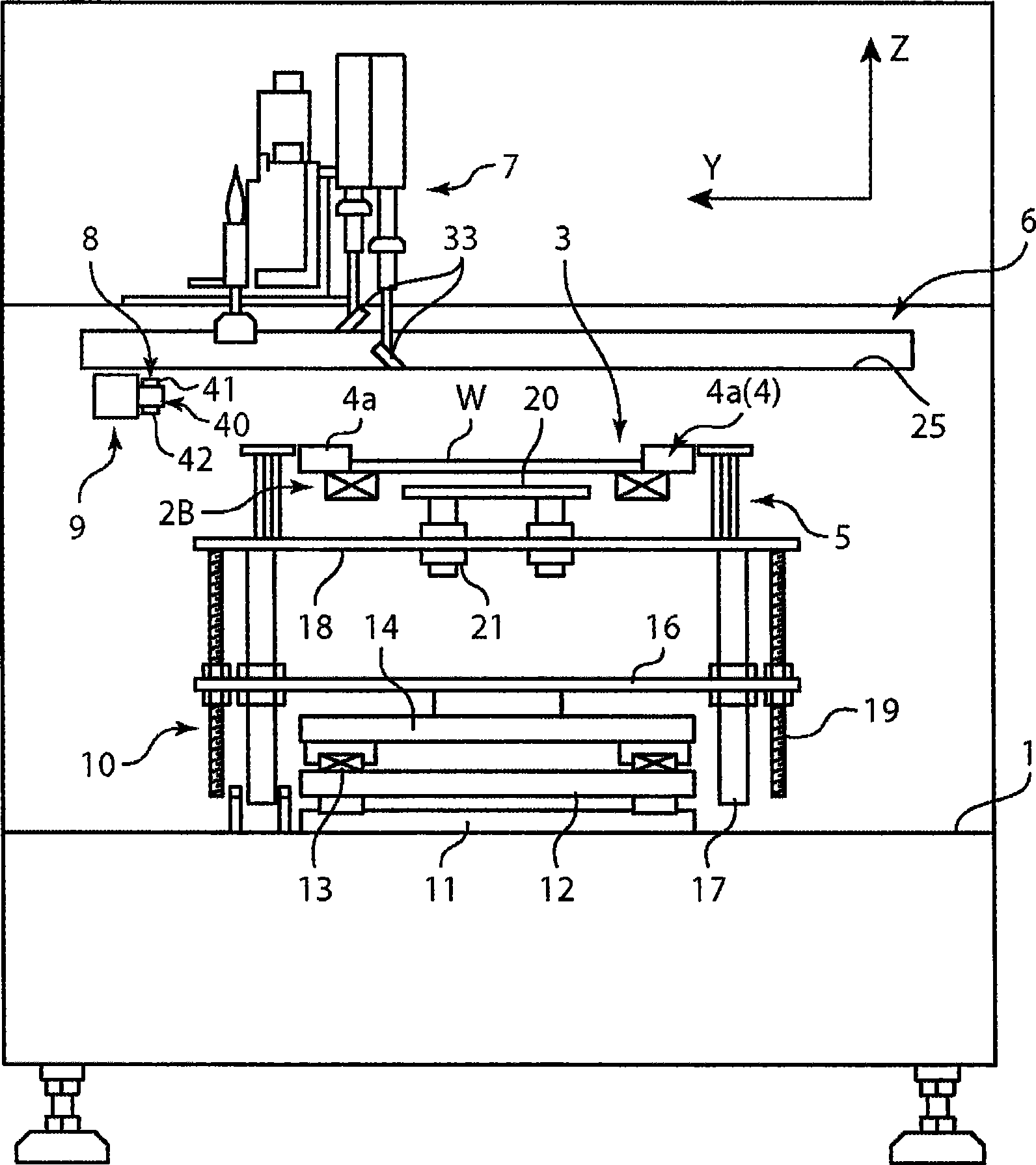
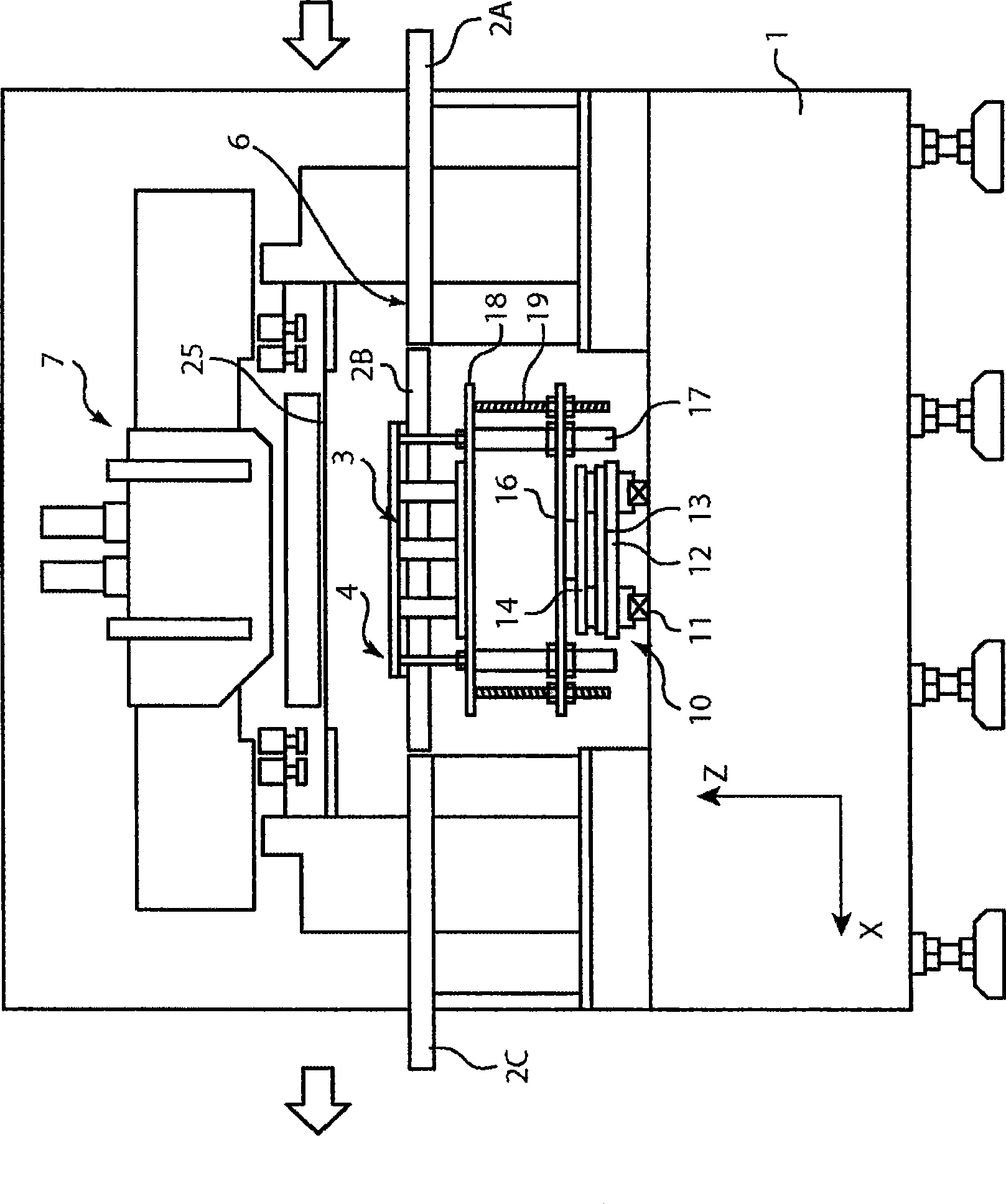
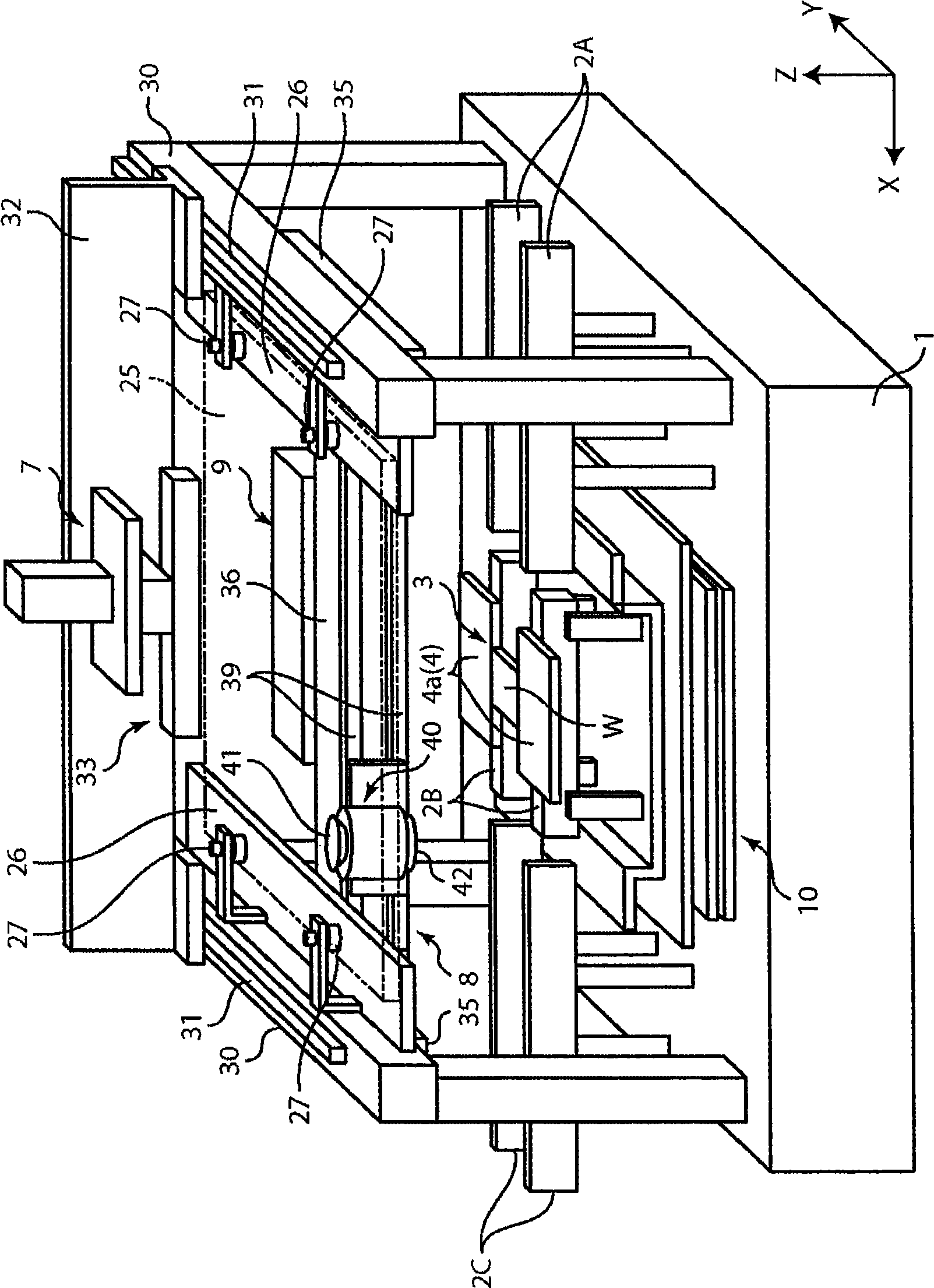
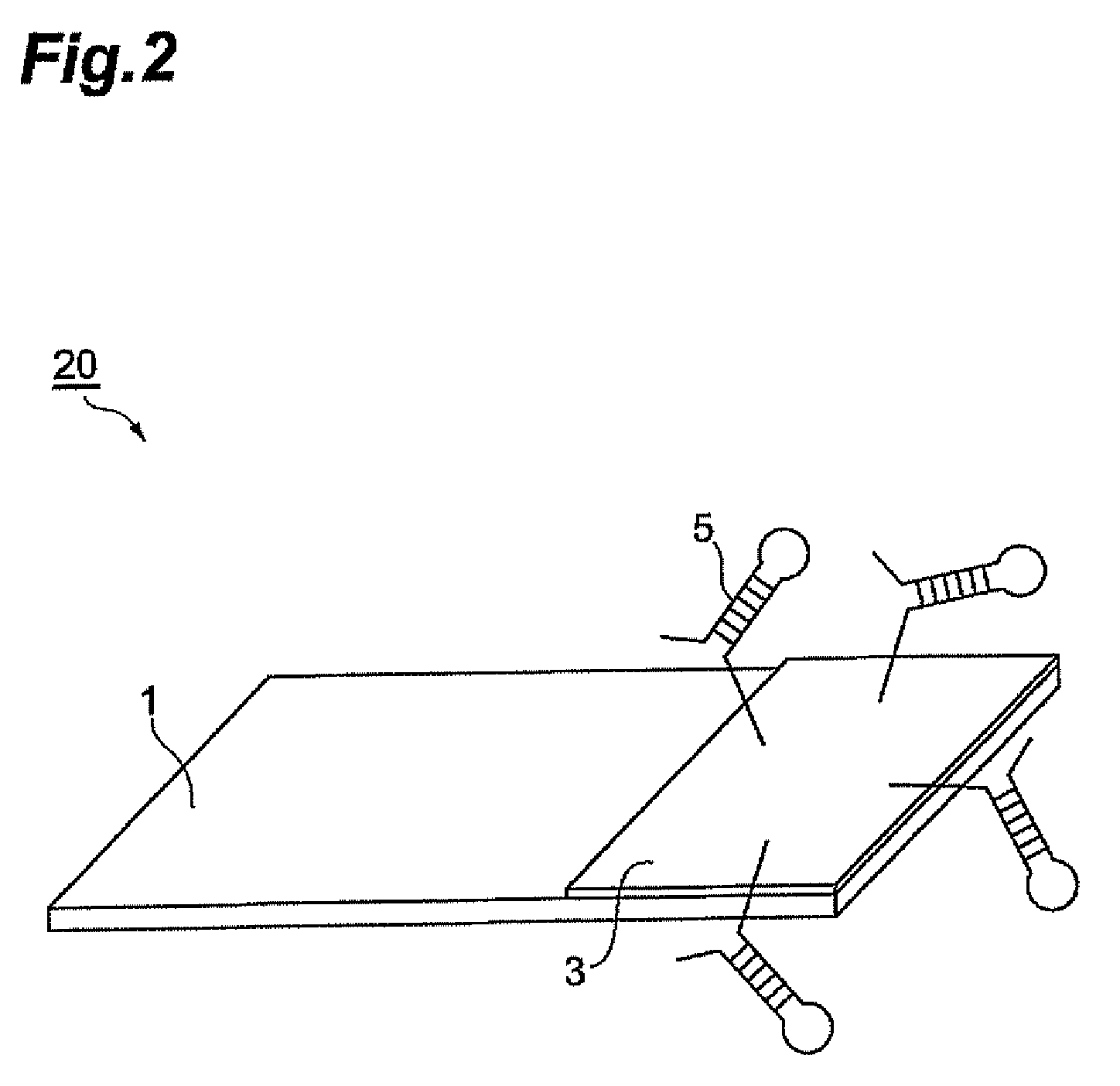
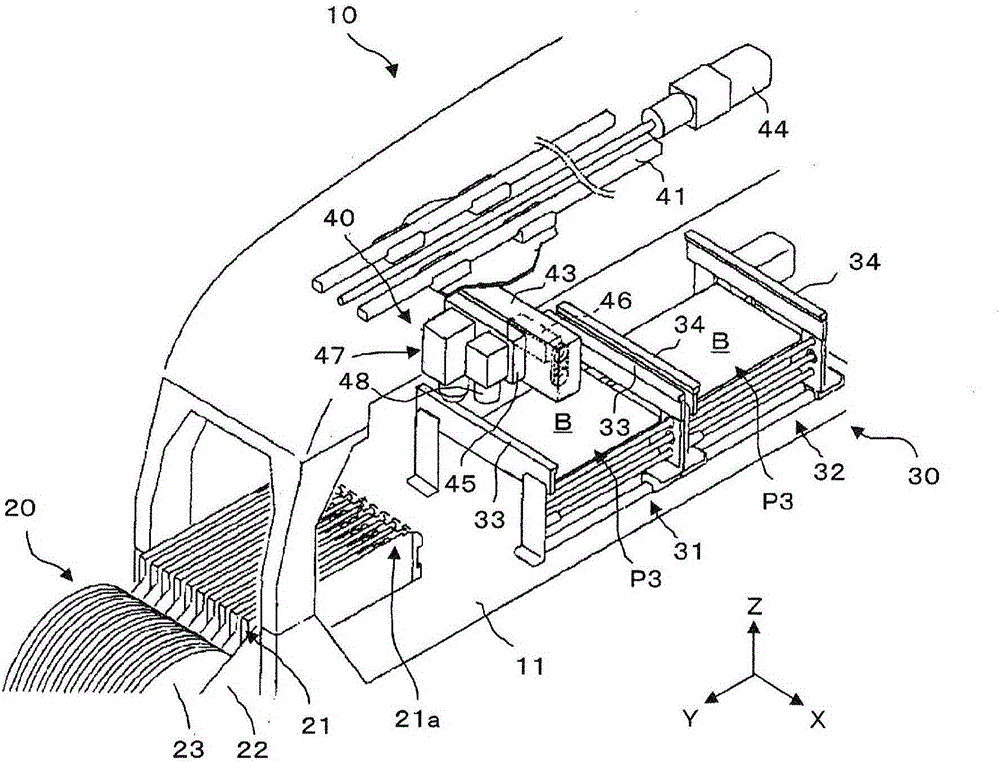
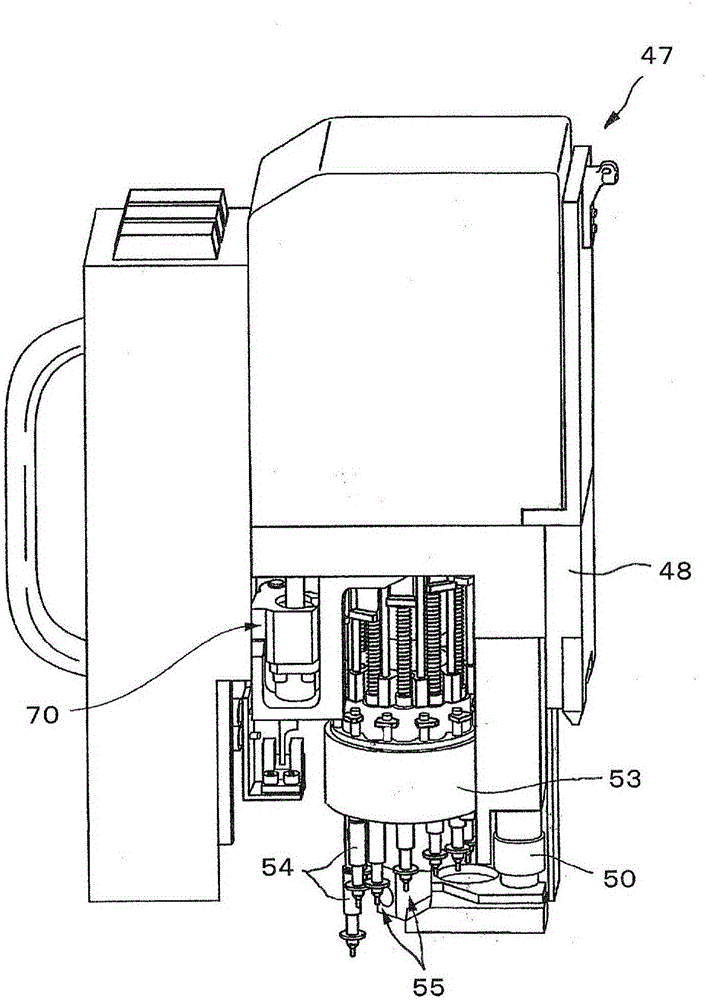
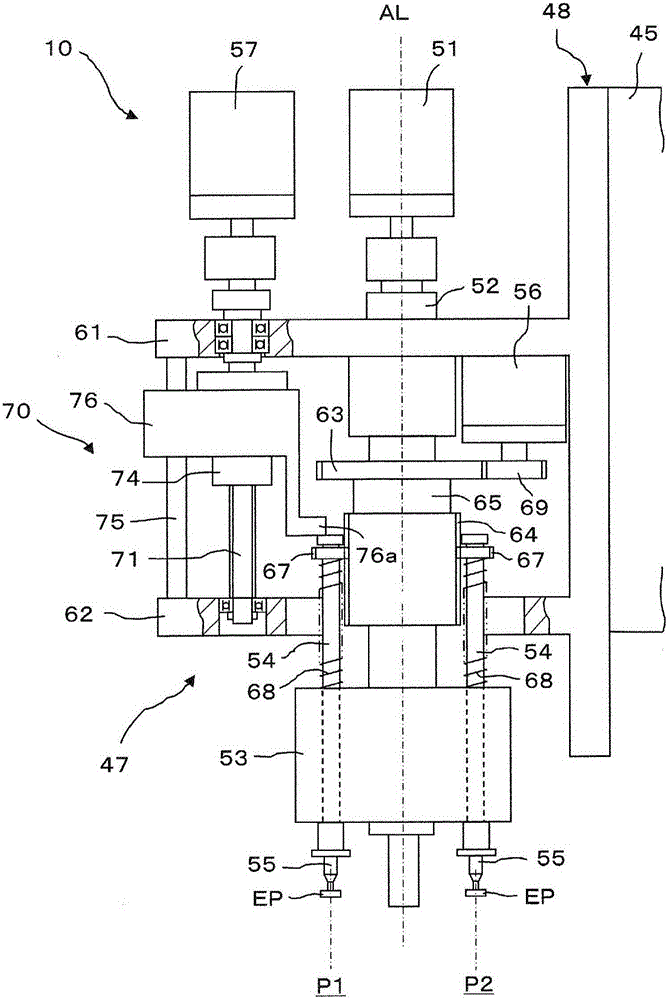
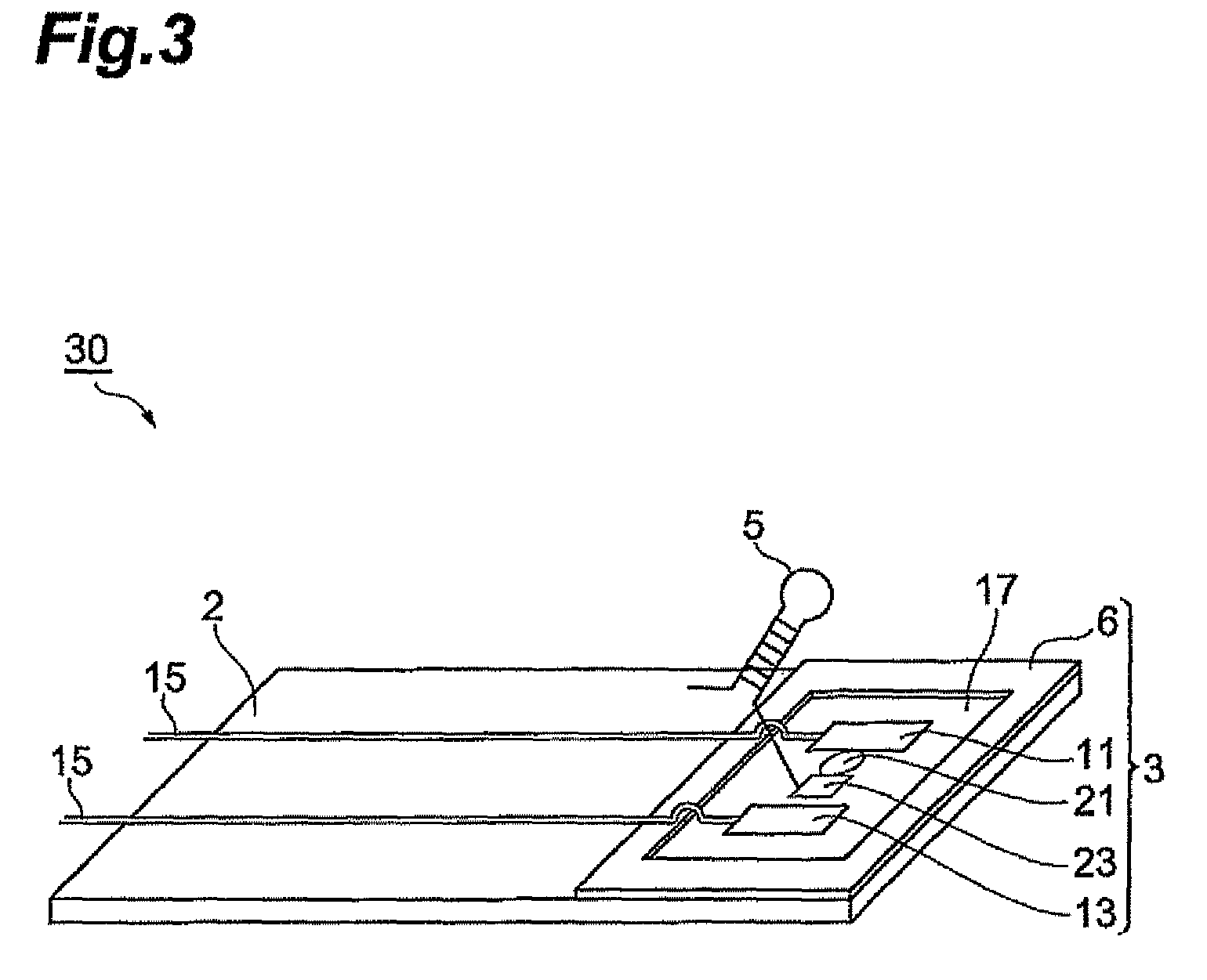
The invention relates to a position matching method for a screen printing device and a screen printing device. The screen pringting device includes a mask sheet (25), a movable printing stage (3), a camera head (40) having a mask recognition camera (41) and a substrate recognition camera (42), and a controller for controlling them. The controller executes mark recognition of the substrate (W) by using the substrate recognition camera (42). The camera head (40) is driven / controlled so as to execute mask recognition of the mask sheet (25) periodically by using the recognition camera (41) while the same mask sheet is used. Moreover, according to the latest mask position information acquired by the mark recognition of the mask sheet (25) and the substrate position information, the controller obtains a correction amount based on the position shift between the mask sheet (25) and the substrate (W) and drives / controls the printing state (3) according to the correction amount so as to mount the substrate (W) on the mask sheet (25).
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Analyte sensing via acridine-based boronate biosensors
InactiveUS20050191761A1Good biocompatibilityFunction increaseMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceConcentrations glucoseFluorophore
Fluorescent biosensor molecules, fluorescent biosensors and systems, as well as methods of making and using these biosensor molecules and systems are described. These biosensor molecules address the problem of obtaining fluorescence emission at wavelengths greater than about 500 nm. Biosensor molecules generally include an (1) an acridine-based fluorophore, (2) a linker moiety and (3) a boronate substrate recognition / binding moiety, which binds polyhydroxylate analytes, such as glucose. These biosensor molecules further include a “switch” element that is drawn from the electronic interactions among these submolecular components. This fluorescent switch is generally “off” in the absence of bound polyhydroxylate analyte and is generally “on” in the presence of bound polyhydroxylate analyte. Thus, the reversible binding of a polyhydroxylate analyte essentially turns the fluorescent switch “on” and “off”. This property of the biosensor molecules, as well as their ability to emit fluorescent light at greater than about 500 nm, renders these biosensor molecules particularly well-suited for detecting and measuring in-vivo glucose concentrations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Novel aromatic prenyltransferases, nucleic acids encoding same and uses therefor
ActiveUS20060183211A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenyltransferase activityIsoprene
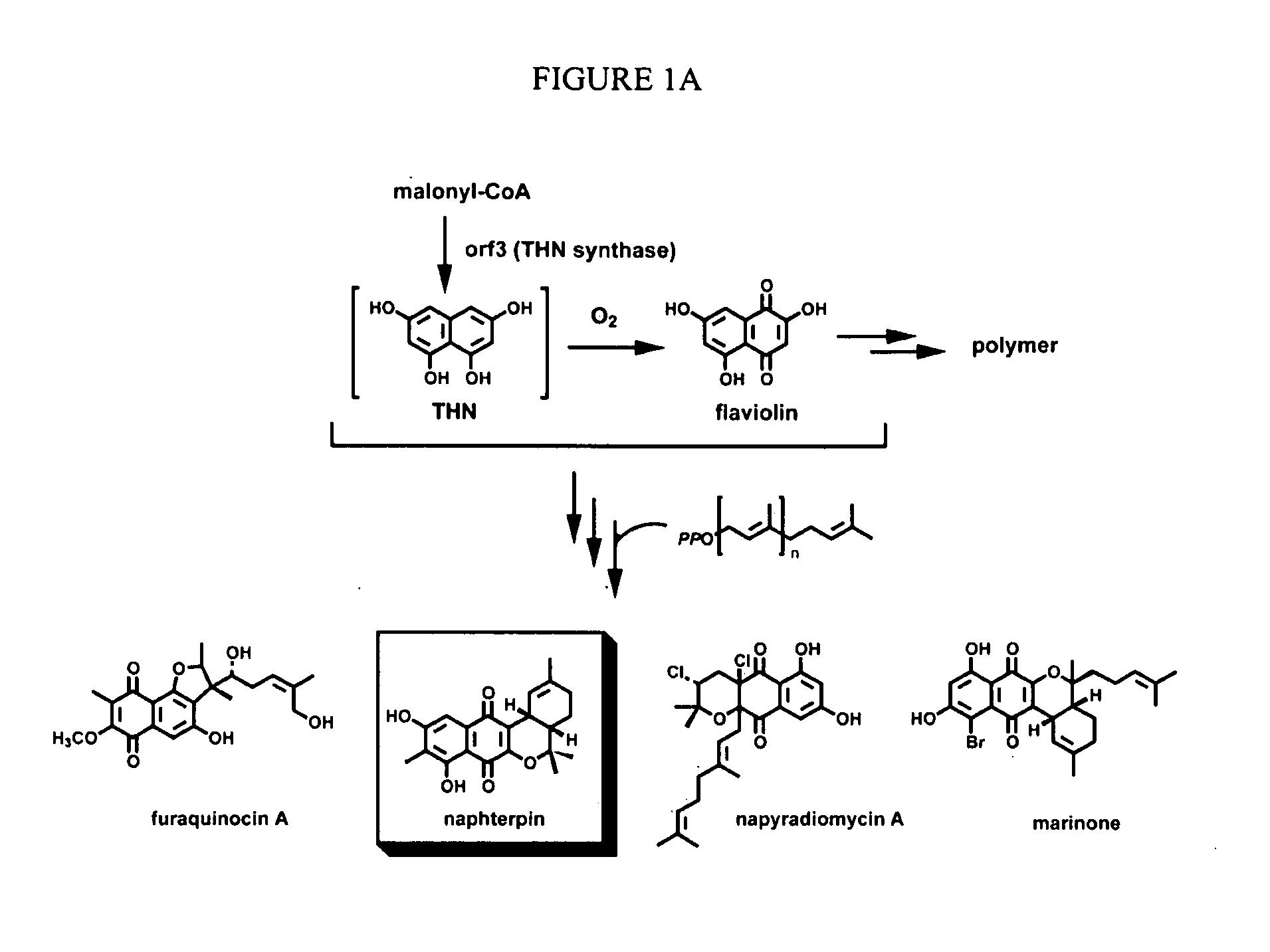
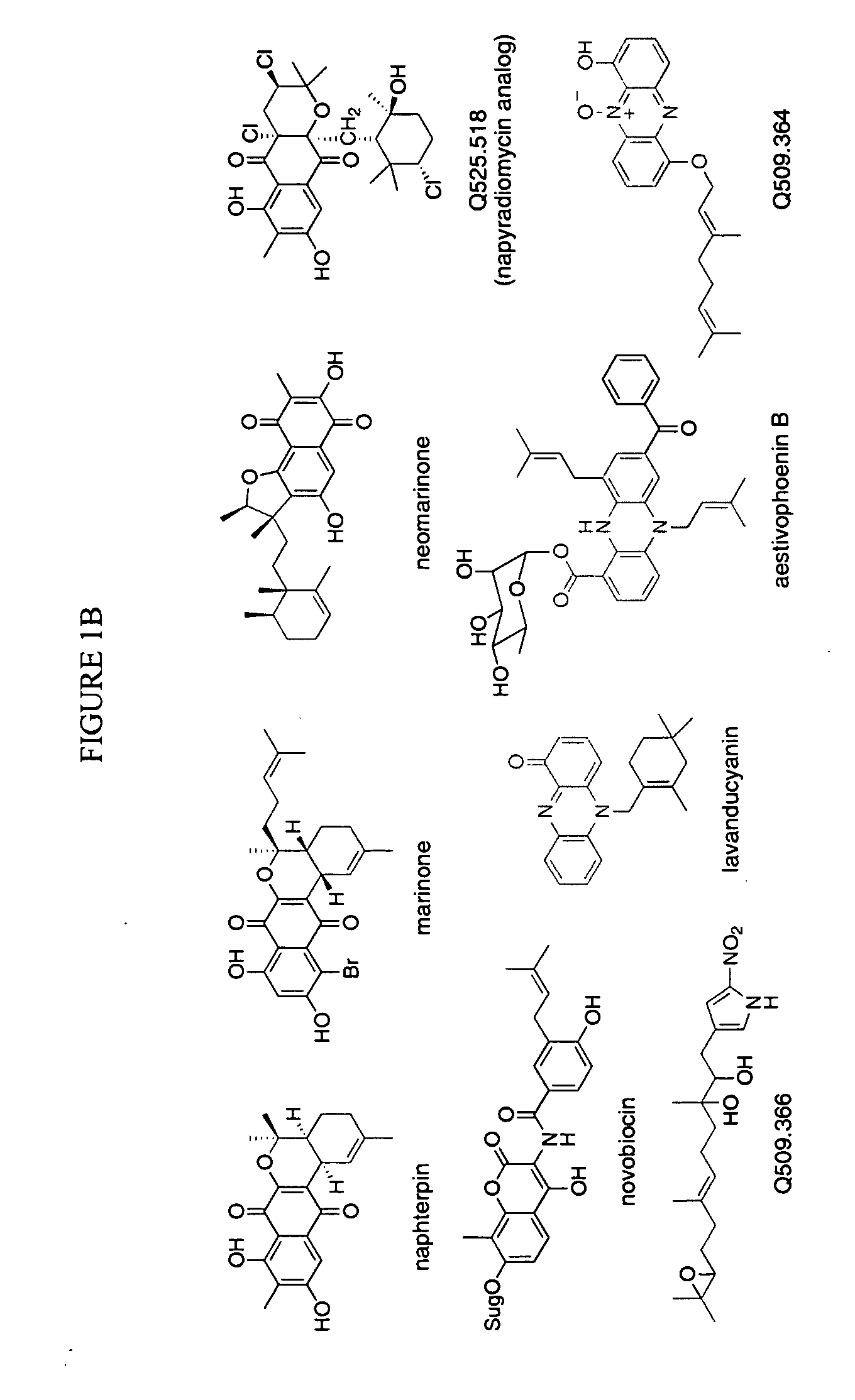
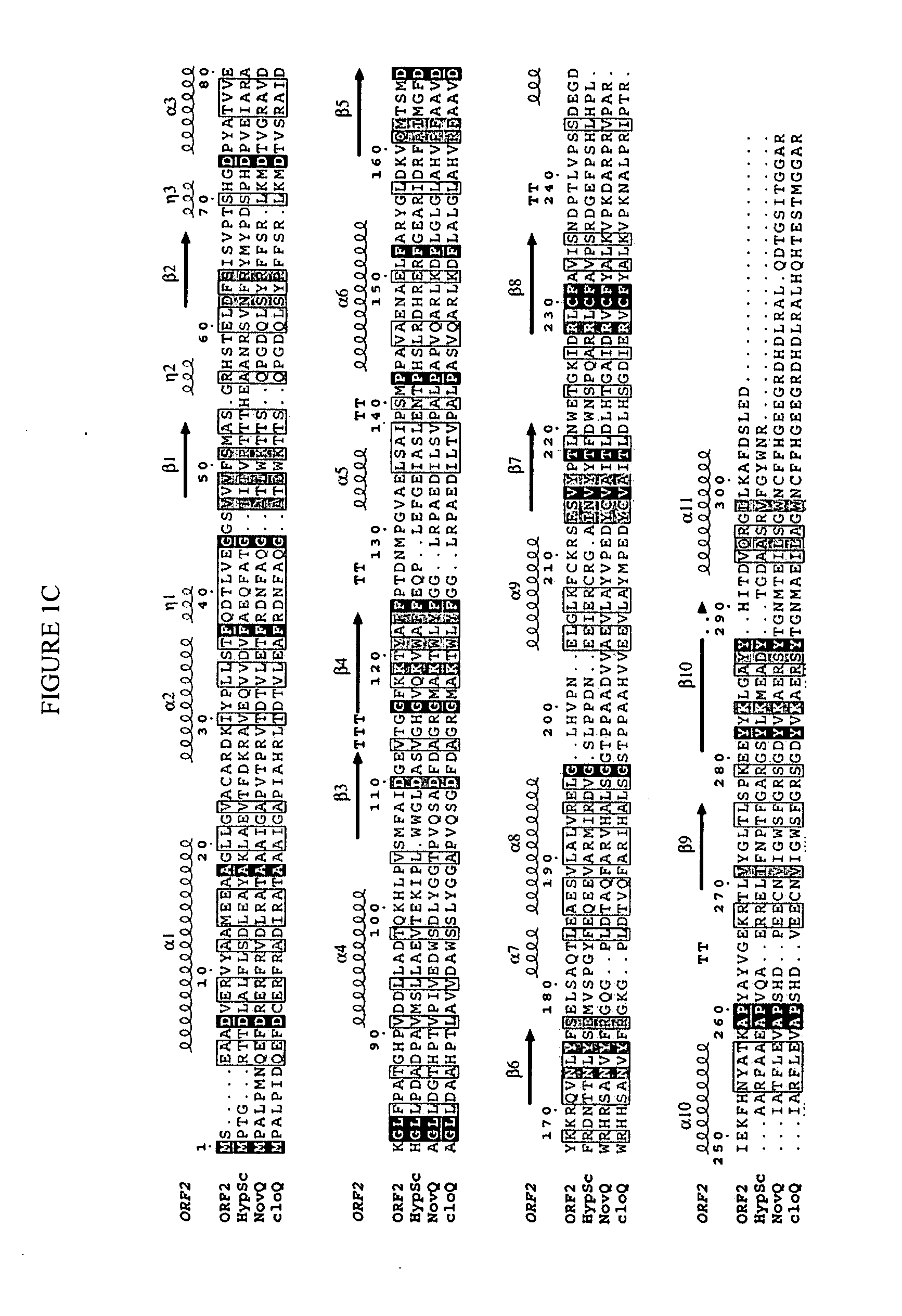
In accordance with the present invention, a novel aromatic prenyltransferase, Orf2 from Streptomyces sp. strain CL190, involved in naphterpin biosynthesis has been identified and the structure thereof elucidated. This prenyltransferase catalyzes the formation of a C—C bond between a prenyl group and a compound containing an aromatic nucleus, and also displays C—O bond formation activity. Numerous crystallographic structures of the prenyltransferase have been solved and refined, e.g., (1) prenyltransferase complexed with a buffer molecule (TAPS), (2) prenyltransferase as a binary complex with geranyl diphosphate (GPP) and Mg2+, and prenyltransferase as ternary complexes with a non-hydrolyzable substrate analogue, geranyl S-thiolodiphosphate (GSPP) and either (3) 1,6-dihydroxynaphthalene (1,6-DHN), or (4) flaviolin (i.e., 2,5,7-trihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, which is the oxidized product of 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene (THN)). These structures have been solved and refined to 1.5 Å, 2.25 Å, 1.95 Å and 2.02 Å, respectively. This first structure of an aromatic prenyltransferase displays an unexpected and non-canonical (β / α)-barrel architecture. The complexes with both aromatic substrates and prenyl containing substrates and analogs delineate the active site and are consistent with a proposed electrophilic mechanism of prenyl group transfer. These structures also provide a mechanistic basis for understanding prenyl chain length determination and aromatic co-substrate recognition in this structurally unique family of aromatic prenyltransferases. This structural information is useful for predicting the aromatic prenyltransferase activity of proteins.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Substrate Recognition By Differentiable Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
InactiveUS20100233807A1Effective therapyPulse automatic controlFilament/thread formingFiberThree dimensional matrix
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
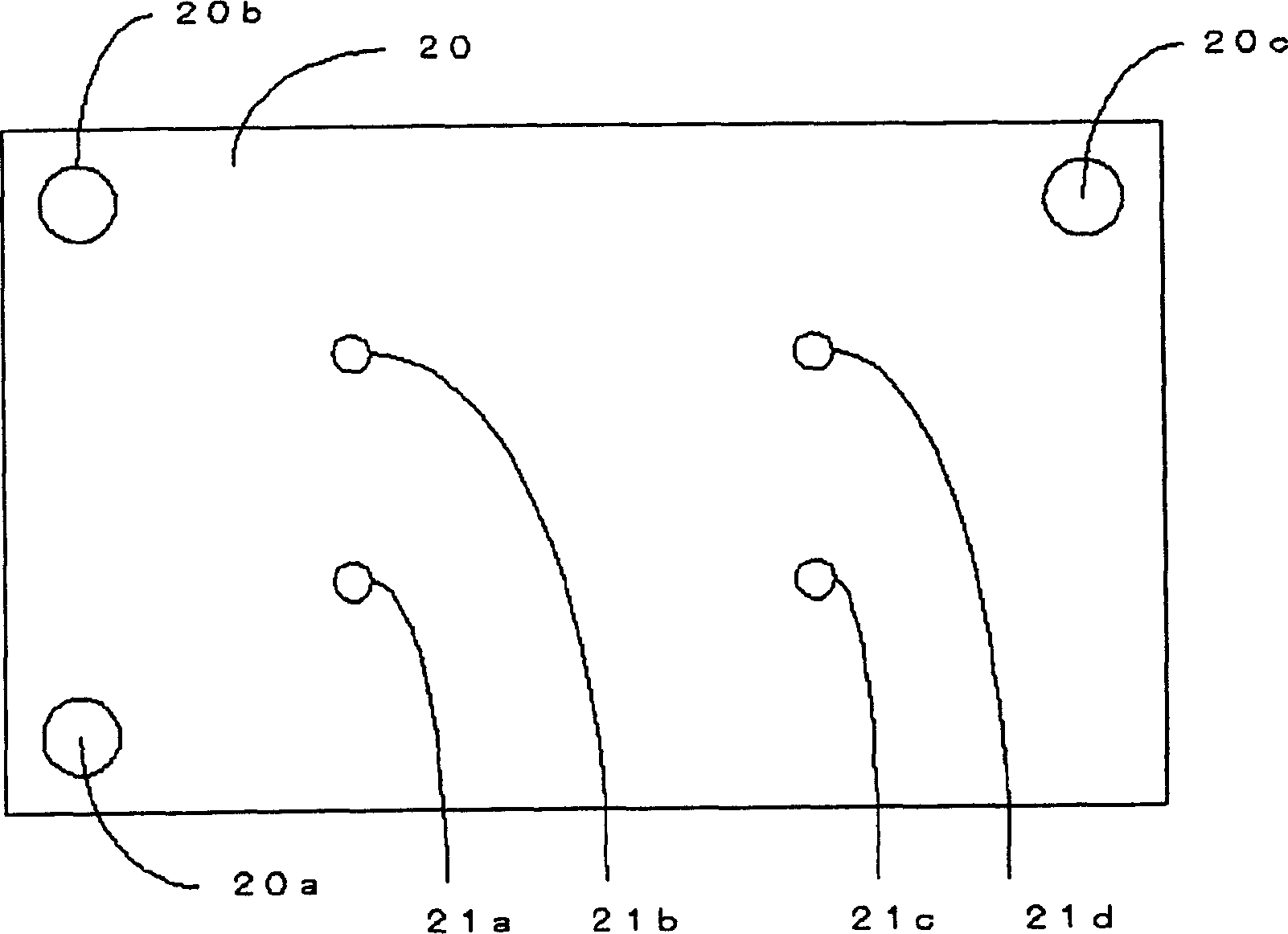
Electronic component mounting apparatus and electronic component mounting method
An electronic component mounting device and an electronic component mounting method. The position recognition of the printed wiring board is carried out before and after the chip component is mounted, and when the front and rear deviation is outside a certain range, the printed wiring board is treated as a defective product. CPU (61) compares the recognition position after installation and the recognition position before installation of each positioning mark M attached to the printed circuit board (6) that is photographed by the substrate recognition camera (70) and recognized and processed by the recognition processing device (68) , the CPU (61) judges whether the difference is within a certain range stored in the RAM (62) in any direction of the XY direction, that is, within plus or minus 0.100mm (millimeter), and when it is judged as outside the range, the CPU (61) Abnormal stop of the control electronics mounting unit.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH INSTR CO LTD
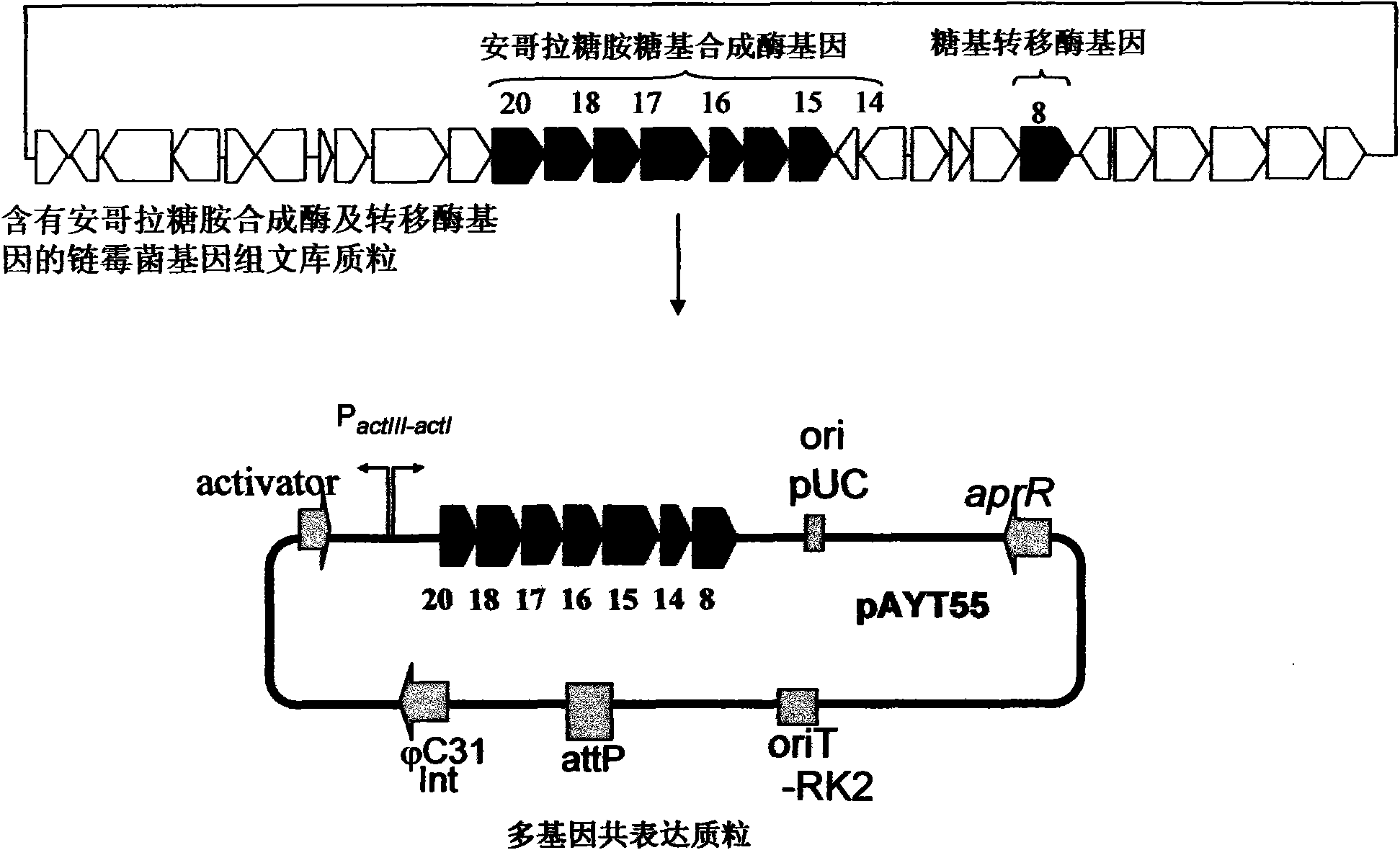
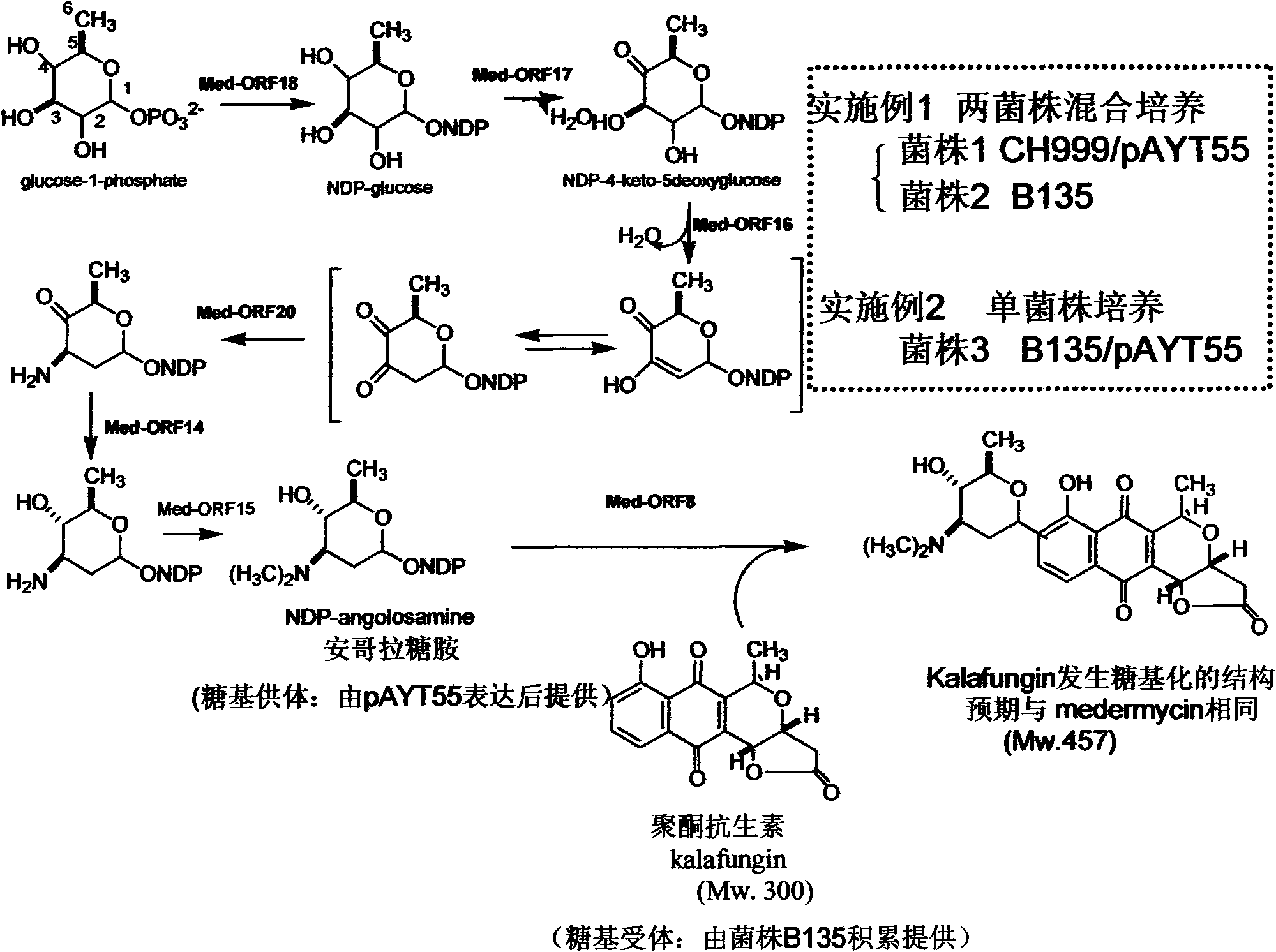
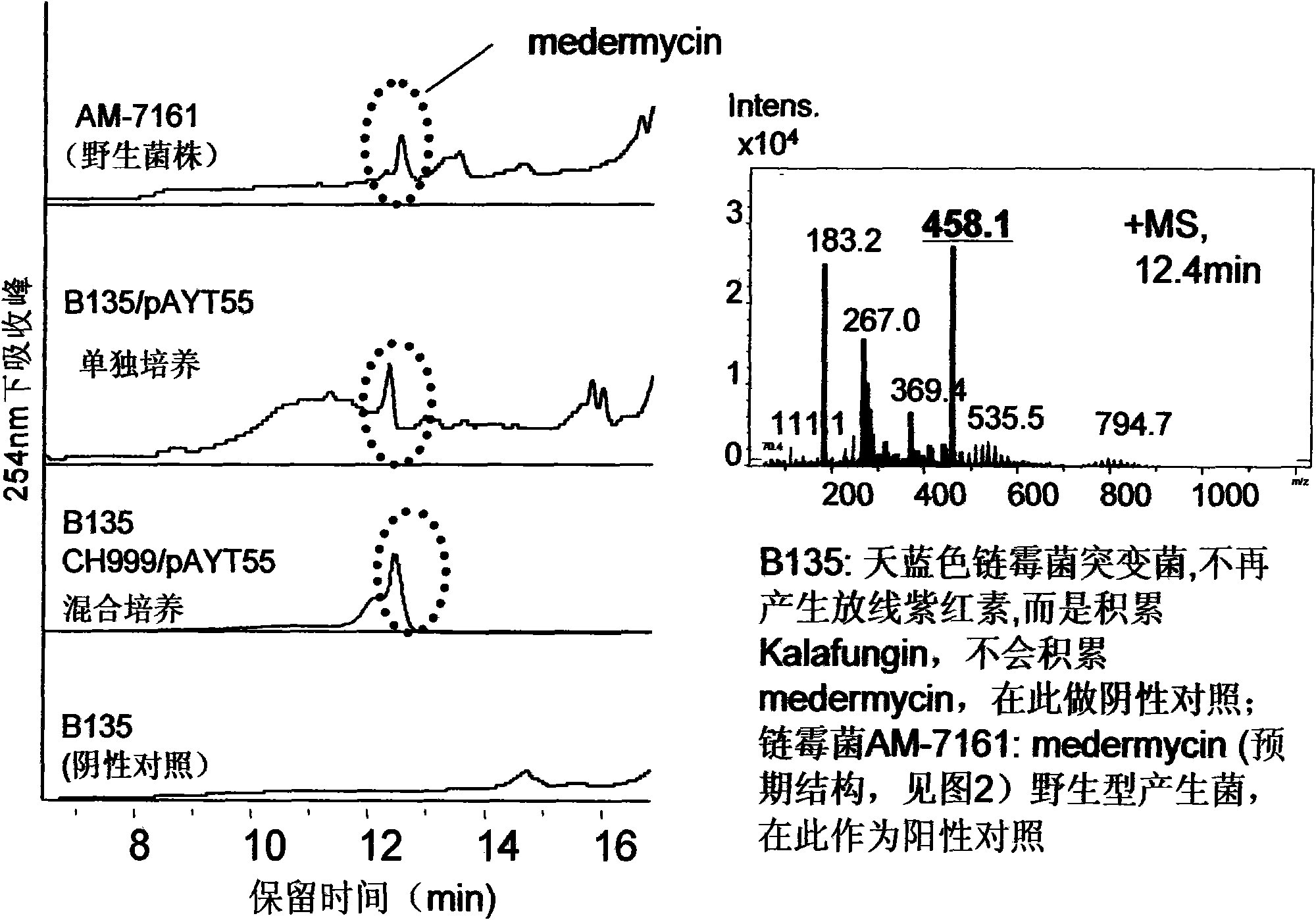
Construction and application of multiple gene coexpression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase
InactiveCN101613711ASimplify the screening processGuaranteed normal expressionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolyketideGene coexpression
The invention provides construction and application of a multiple gene co-expression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase. The invention is characterized by taking a streptomyces genome bank plasmid as a template; amplifying six angolosamine synthetase genes and a glycosyltransferase gene through PCR and connecting the genes in sequence and placing the genes in the lower reaches of a streptomyces promoter PactIII-actI to form a transcription unit; transferring the transcription unit to a streptomyces plasmid carrier pSET152, thus constructing a streptomyces expression plasmid pAYT55 co-expressed by multiple genes; leading the pAYT55 into a host cell streptomyces coelicolor CH999, mixedly culturing obtained engineering bacteria and streptomyces B135 of accumulated polyketide kalafungin, thus realizing bioconversion of kalafungin into a novel antibiotic with angolosamine; or directly leading pAYT55 into the streptomyces B135 and carrying out single culture to realize glycosylation of kalafungin. Therefore, by adopting the system, rare angolosamine can be synthesized in the cell and angolosamine modification can be carried out on polyketide by adopting the low substrate recognition specificity of antibiotic glycosyltransferases.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Correcting method for electronic part mounting device and device for using said method
InactiveCN1532520ASimple and Quick CalibrationMeasurement devicesPrintersComputer visionSubstrate recognition
To provide a method for calibrating the position of a camera by which a deviation between the mutual coordinate system of the part recognition camera and coordinate system of the substrate recognition camera can be calibrated simply and rapidly.In the method for calibrating the deviation of the places of the cameras, a fixture part 30 enabled by both recognition methods is used. The method has an image pick-up process in which the part 30 is image-picked up by the part recognition camera first, the image pick-up process in which a fixture substrate is image-picked up by the substrate recognition camera 17, a mounting process in which the fixture part 30 is mounted, a computing process in which the center of the part is obtained by the substrate recognition camera 17 and the quantities of displacements obtained respectively with the place of the recognition center of the camera 17 are computed in the mark of the fixture part 30 after the mounting, and a calibrating process in which the coordinate systems of the camera 17 or the camera 16 are calibrated on the basis of the quantities of the displacements. (C)2005,JPO&NCIPI.
Owner:JUKI CORP
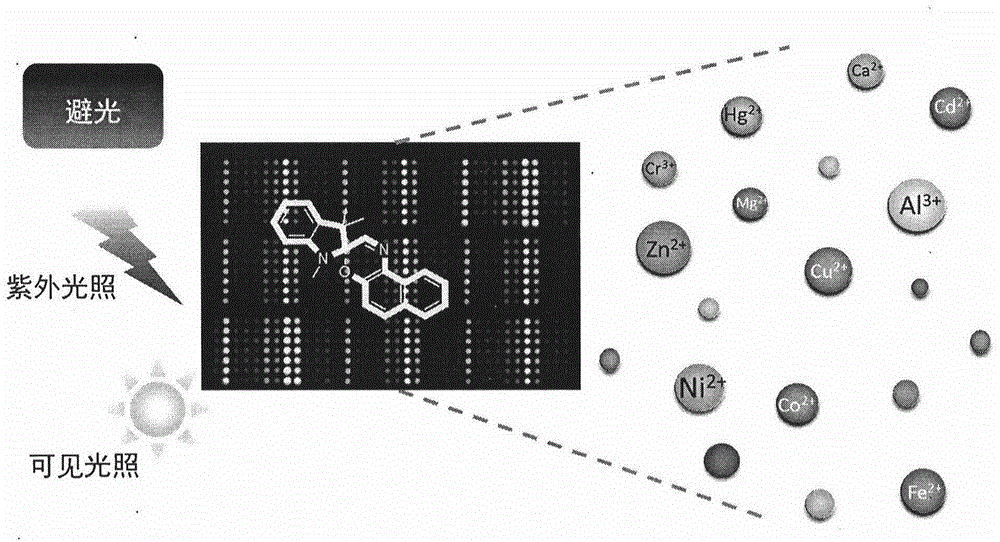
Photochromic dynamic multi-substrate detection microchip and polymorphism analysis method
InactiveCN104437688ARich chemical informationAvoid multipleLaboratory glasswaresFluorescence/phosphorescenceSensor arrayFluorescence
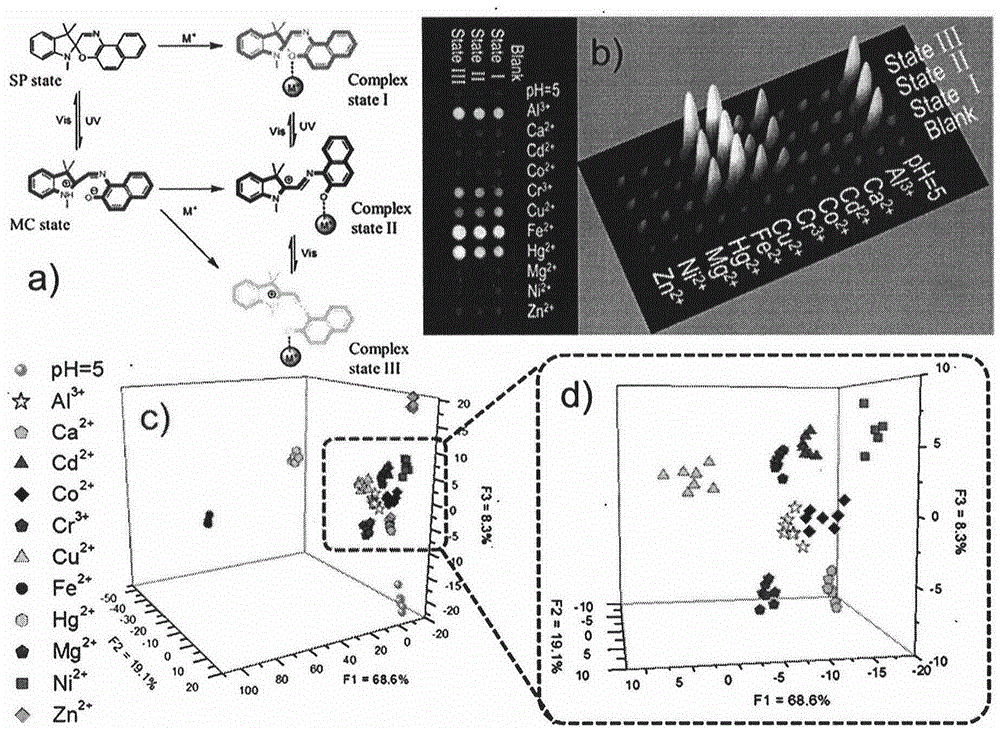
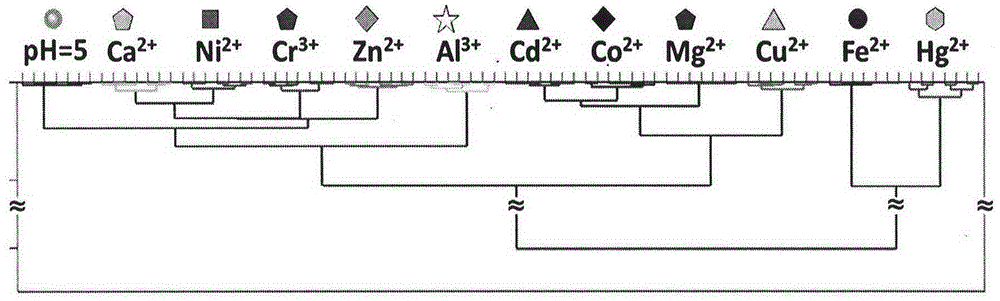
The invention belongs to the field of photochromic material and multi-substrate analysis. Photochromic molecules are introduced into a sensor array so as to prepare an efficient universal multi-substrate detection analysis microchip. According to the invention, photochromic molecules, namely spiropyrane / spirooxazine, are utilized, the response optical difference of the microchip to various metal cations under different photostimulation conditions (light resistance, ultraviolet light illumination and visible light illumination) is analyzed comprehensively, and an array chip consisting of a single spiropyrane or spirooxazine compound is designed. Fluorescence and absorption chemical information is recorded via a plurality of channels, and difference analysis and identification can be carried out on different kinds of metal cations as multiple as possible by utilizing high-flux statistics methods such as principal component analysis (PCA), hierarchic classification analysis (HCA) and linear difference analysis (LDA) and the like. According to the invention, the single chemical sensor is used for detecting and analyzing multiple substrates by constructing the photochromic dynamic multi-substrate detection microchip, and the product has broad-spectrum universality and great operability for multi-substrate recognition and detection at various complex environments.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for generating engineered enzymes
ActiveUS20170233781A1Accurate identificationPrevent unwanted cleavageMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesYeastProteinase activity
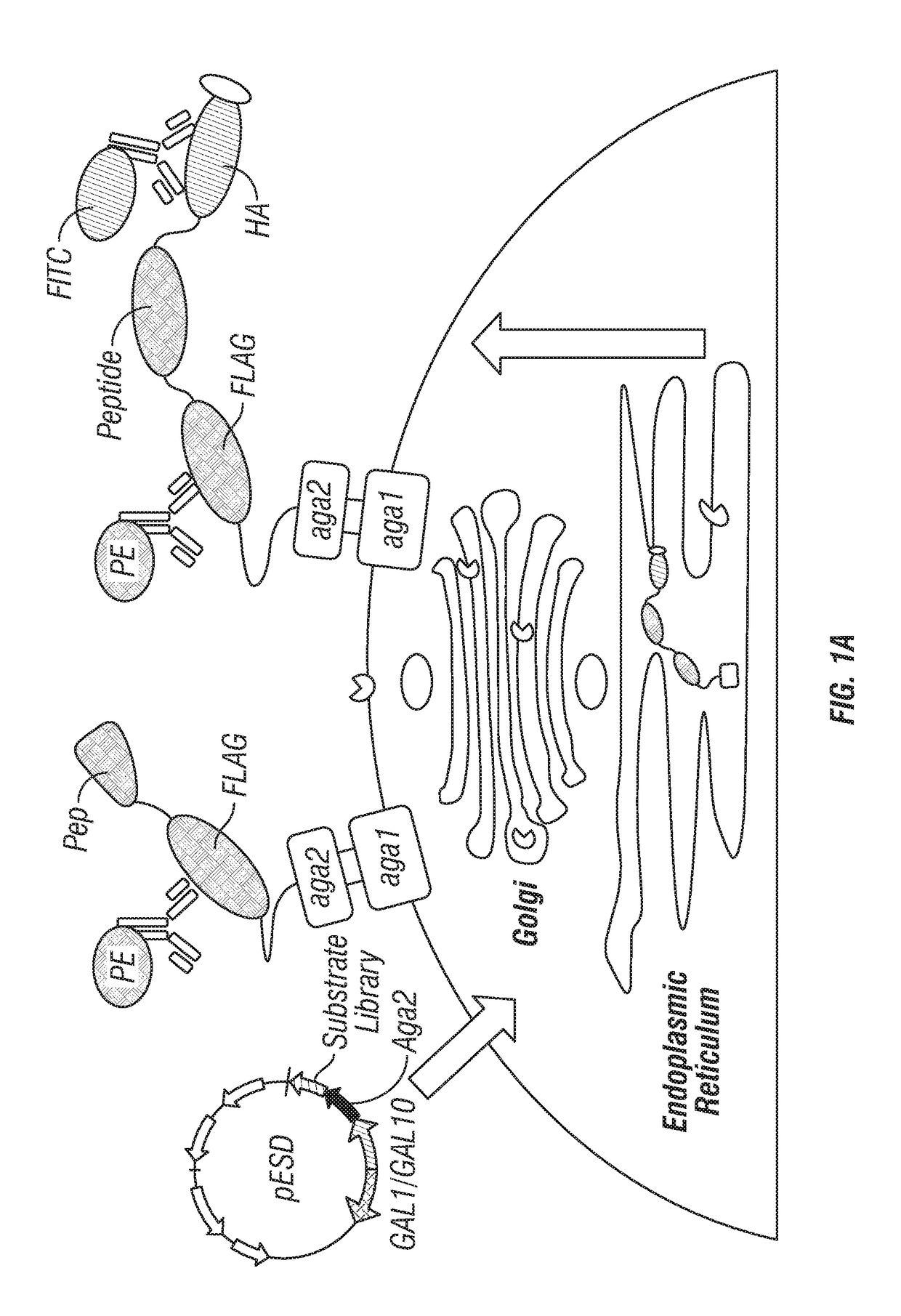
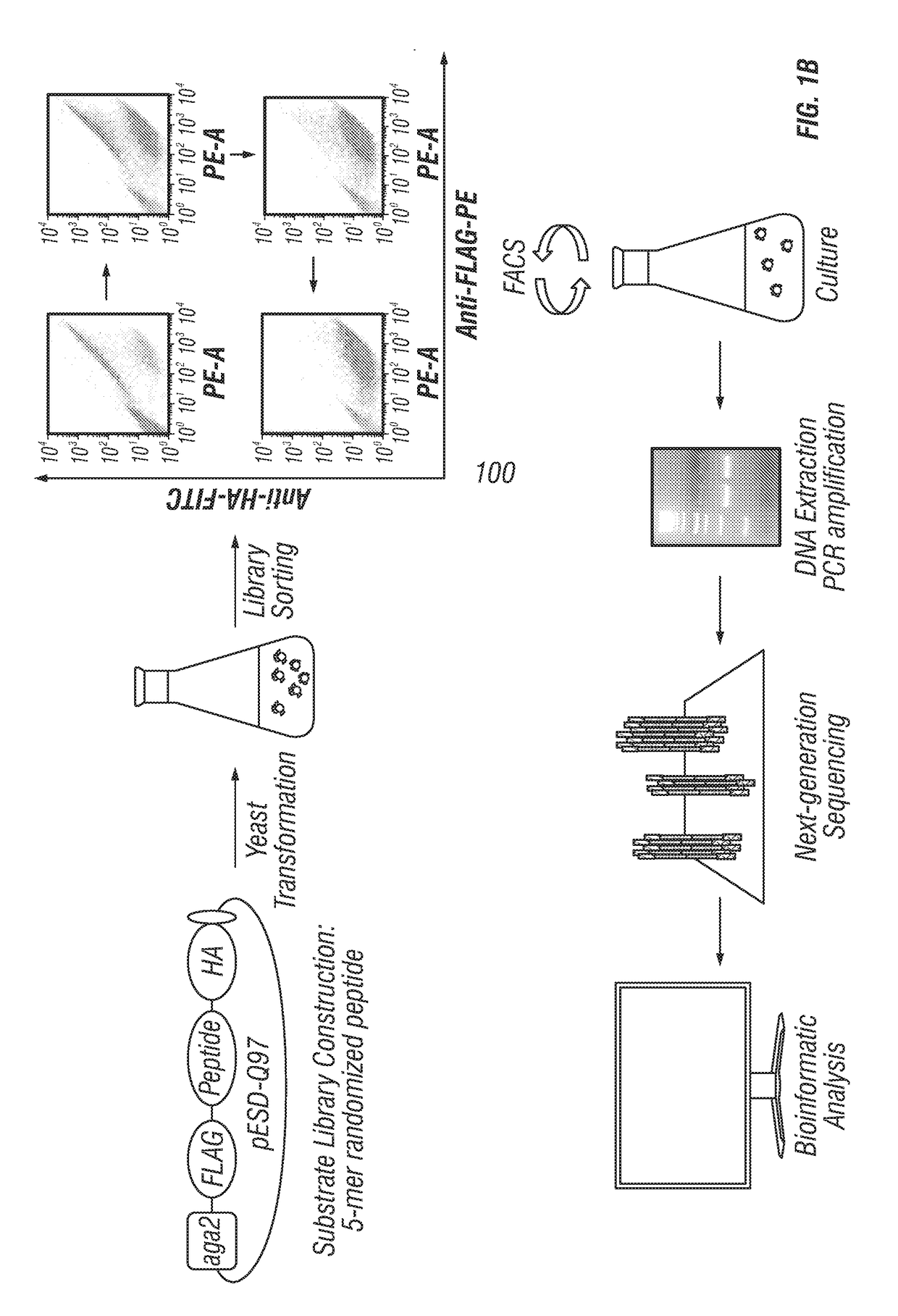
Provided are improved methods for identifying the substrate recognition specificity or activity of a protease, convertase (sortase), or kinase. In some embodiments, methods are provided for identifying the endogenous protease or convertase cleaving patterns (e.g., “cleaveOme”) inside the secretory pathway of a living cell. Select embodiments involve aspects of yeast endoplasmic reticulum sequestration screening and next generation sequencing. Methods of producing polypeptides in Kex2 knockout yeast are also provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
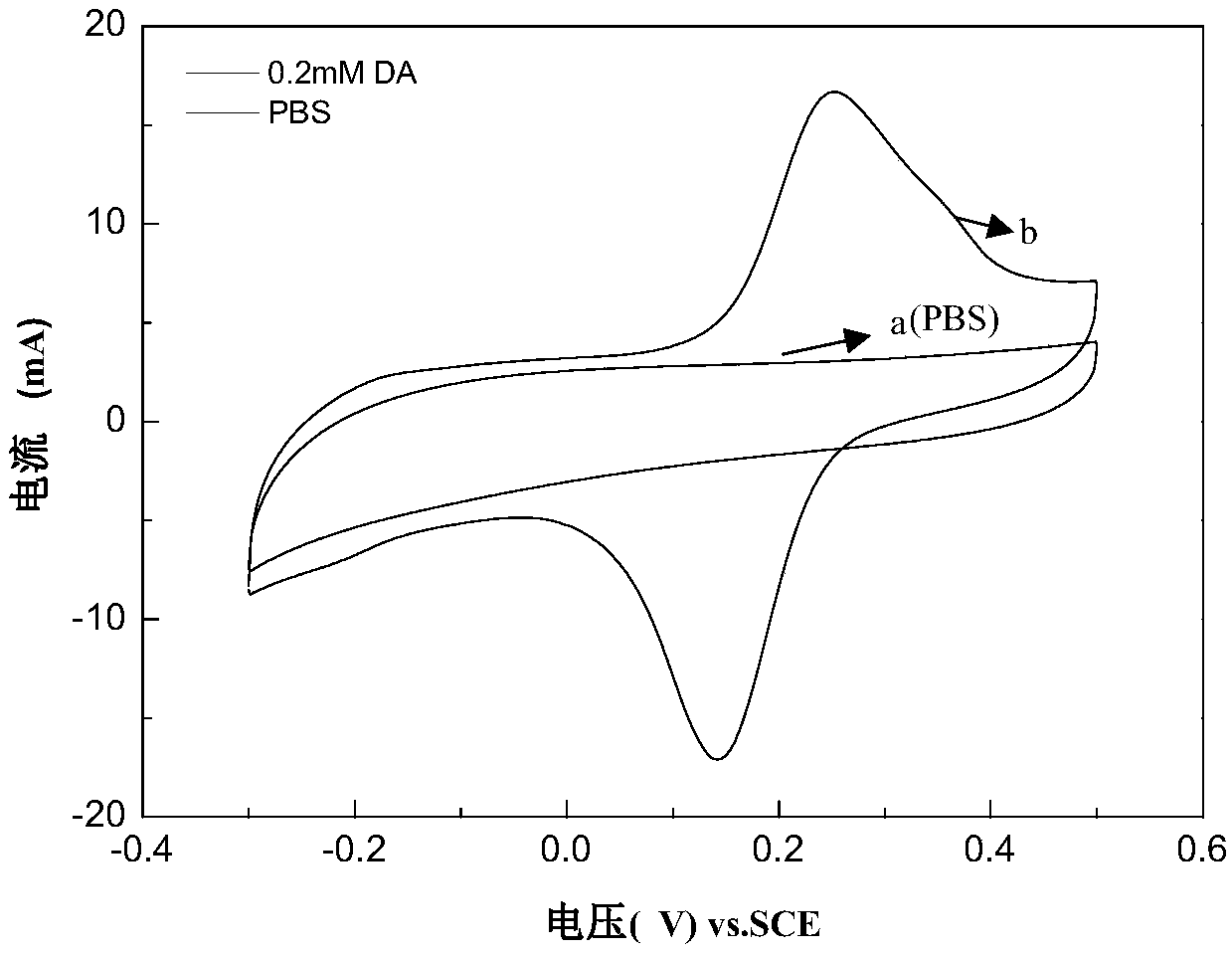
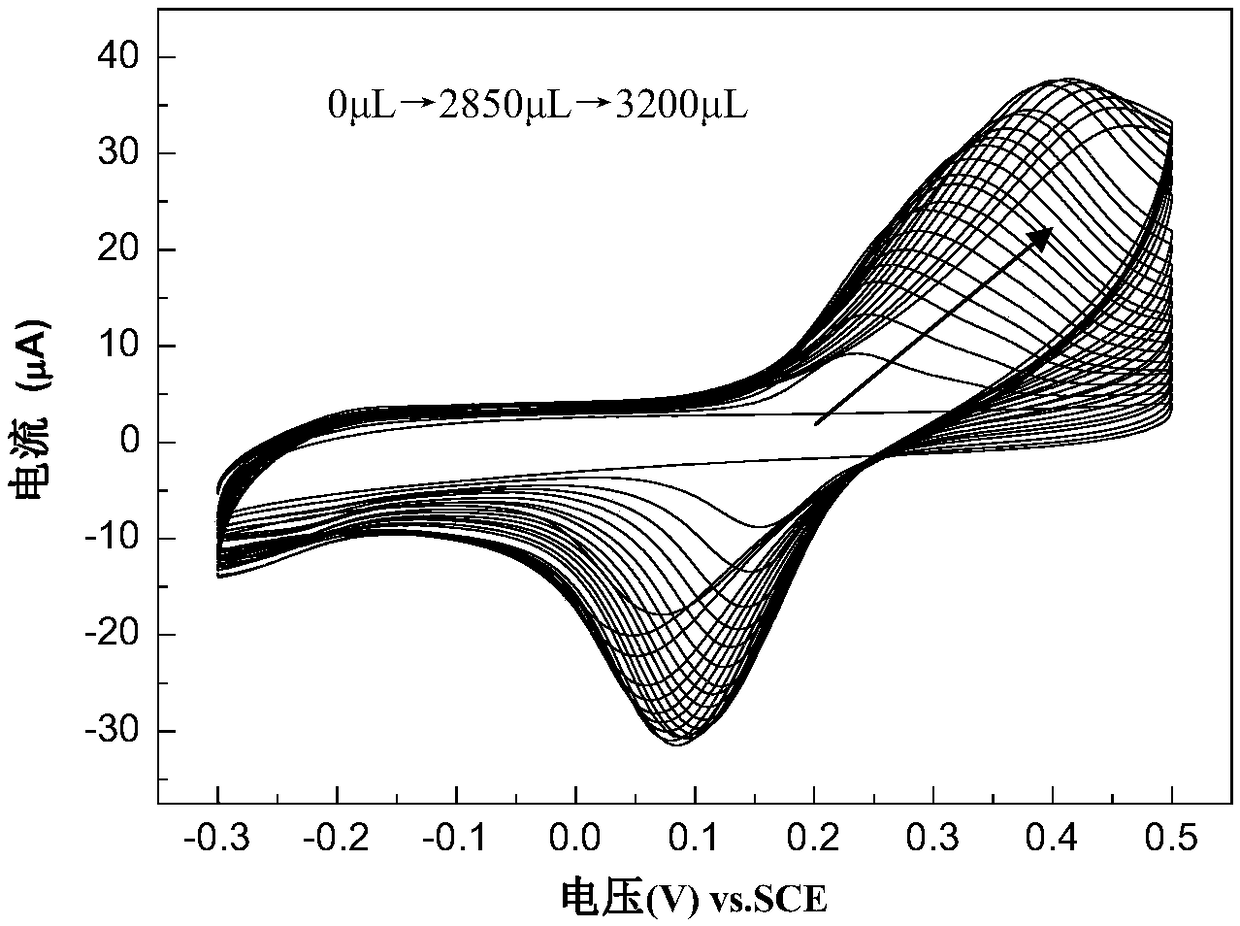
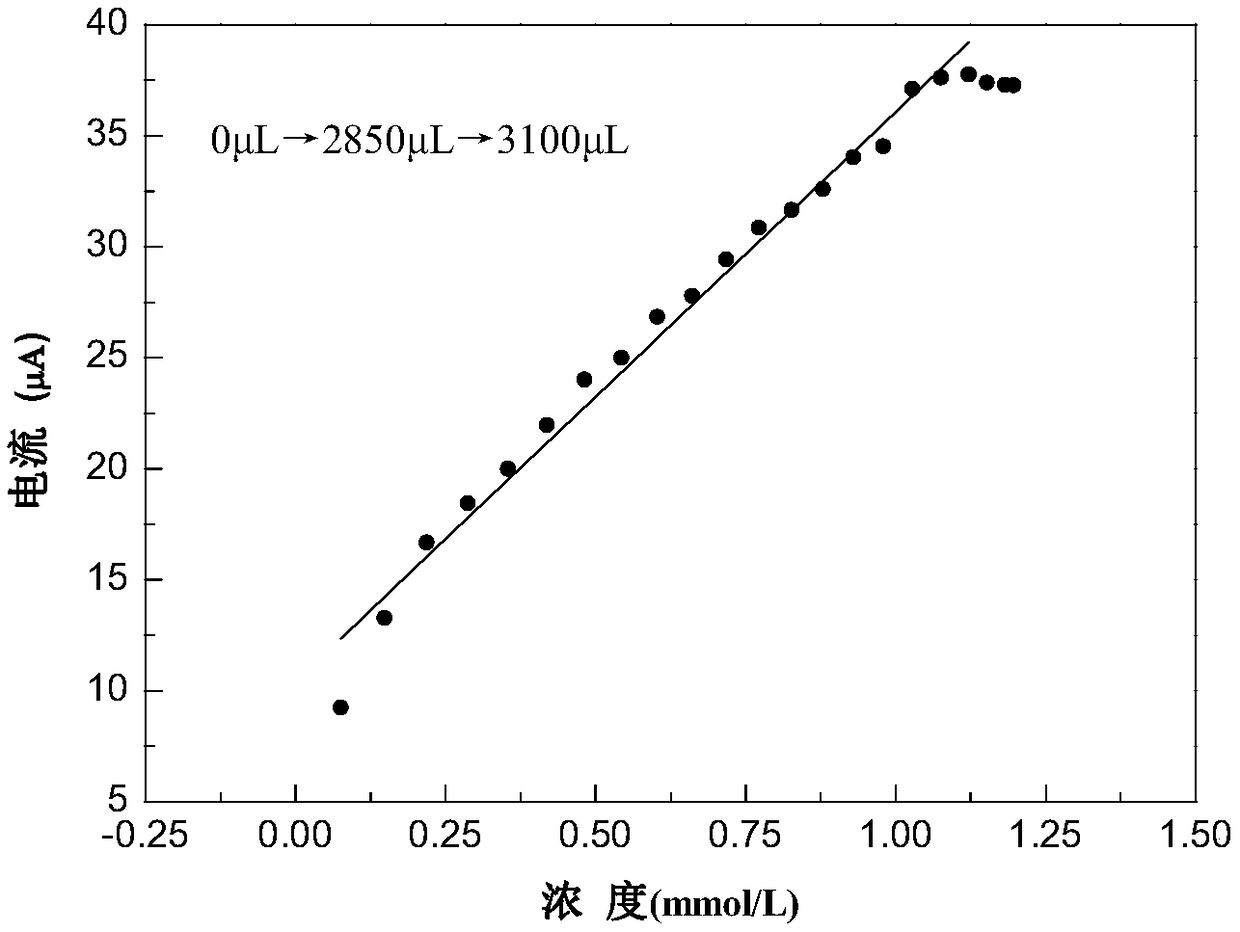
Dopamine sensor based on nitrogen doped graphene as well as preparation and application thereof
PendingCN108872343AQuick checkAccurate detectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNitrogenNitrogen doped graphene
The invention belongs to the technical field of an electrochemical sensor, and discloses a dopamine sensor based on nitrogen doped graphene as well as preparation and application thereof. The sensor consists of a reference electrode, a counter electrode and a modified work electrode, wherein the modified work electrode consists of a work electrode and a substrate recognition membrane cured at thesurface of the work electrode; the substrate recognition membrane is mainly prepared from nitrogen doped graphene composite materials and perfluorinated sulfonic acid resin. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the sensor. The sensor has high selectivity, reproducibility and stability; the dopamine can be accurately detected; the antijamming capability is high; meanwhile, the detection range is wider; the detection limit is lower. The method is simple; the cost is low. The prepared sensor is used for detecting the dopamine.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
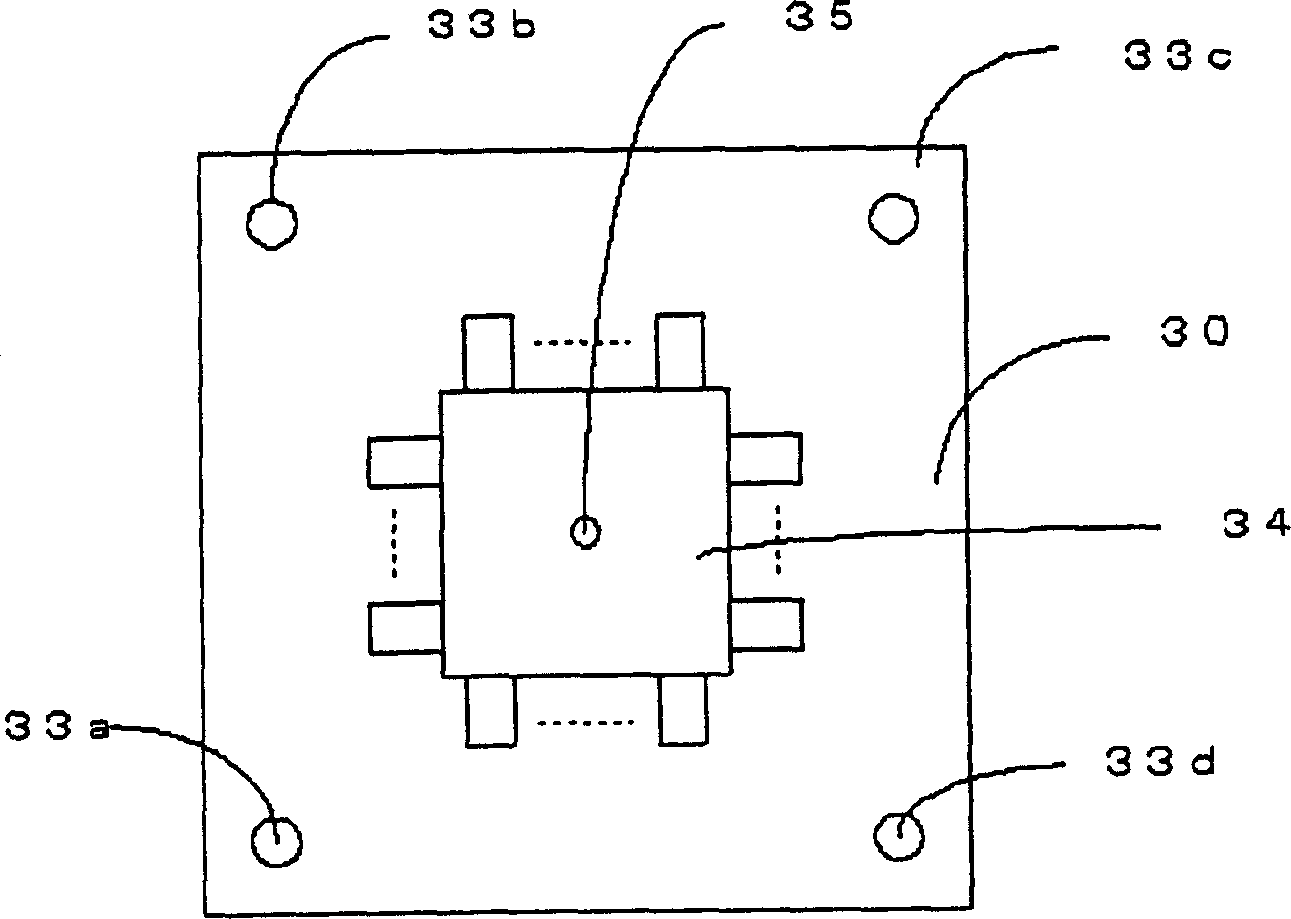
Glass substrate recognition chip and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveCN1632648AImprove overall utilizationStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiochemical engineeringProtection layer
This invention provides a glass base plate identification chip, which is processed by the following steps: to divide multiple independent metal blocks on the base plate as one identification part or multiple test parts, wherein, each test part is connected with one test line; to cover one protection layer above the metal block to fill the gap between metal blocks; to form multiple air holes bare to the test part surface in the protection layer; to form transparent electrode above the protection layer and at the relative area of the test part full of air holes.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Method for synthetizing D-phenyllactic acid through recombinant Escherichia coli
InactiveCN104099350AIncrease productionHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to a recombinant lactate dehydrogenase gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, and tyrosine is mutated into any one of alanine, valine and leucine in the 52 position of the sequence. The invention further relates to recombinant Escherichia coli containing the recombinant lactate dehydrogenase gene and a method for synthetizing D-phenyllactic acid through the recombinant Escherichia coli. According to the method, the tyrosine on a substrate recognition site of D-LDH is replaced by smaller hydrophobic amino acid residue-valine with a site-directed mutagenesis technology, so that the affinity and the catalytic efficiency of the D-LDH to substrate phenylpyruvic acid are improved, after conversion of an expression host, the yield of phenyllactic acid is significantly increased when being compared with that of un-mutated strains, and after whole-cell conversion for 6 h, the yield of the phenyllactic acid is increased from 18 g / L to 24.6 g / L.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Biosensor
InactiveUS20090087867A1Not to damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBacterial antigen ingredientsBody fluidSubstrate recognition
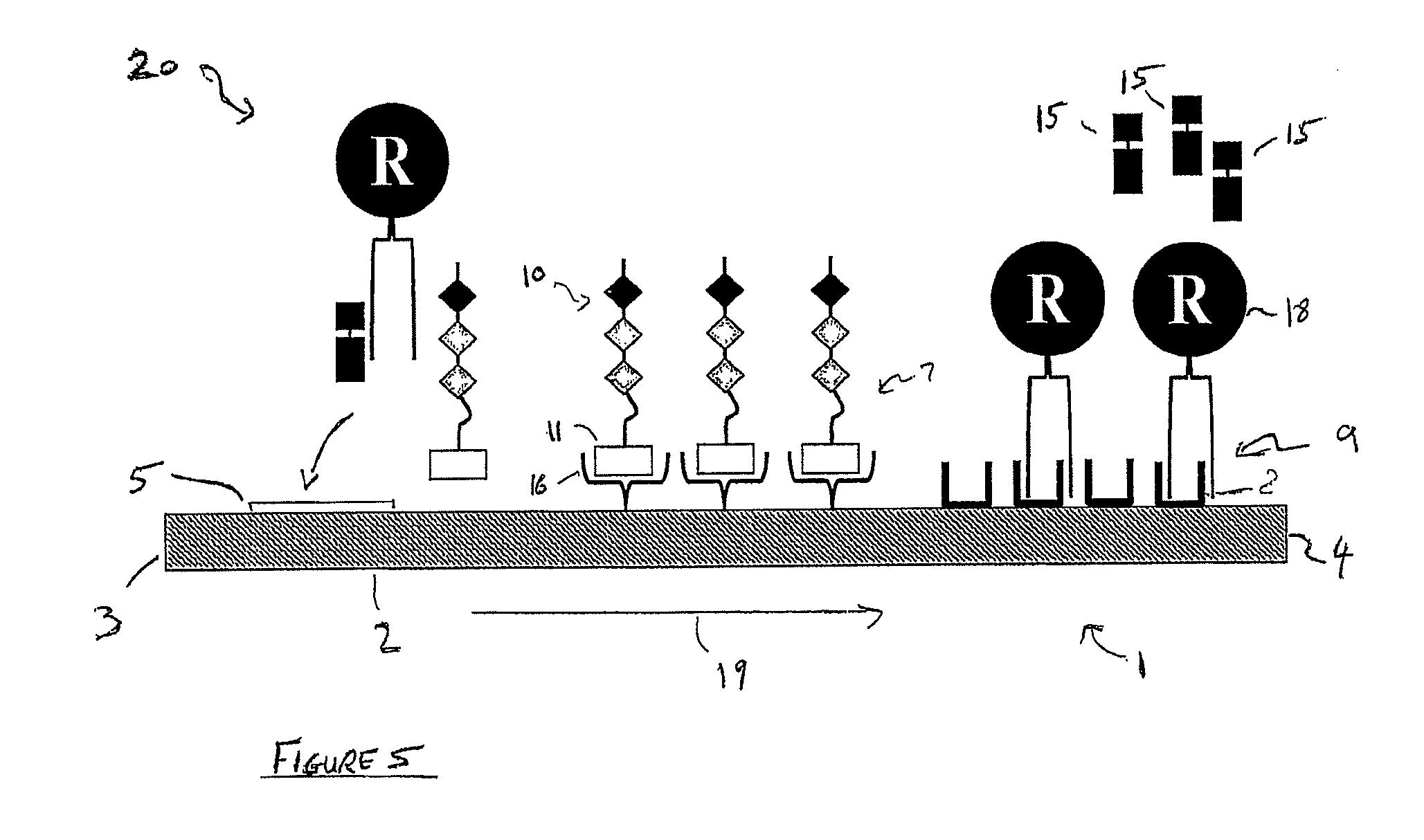
The invention provides a biosensor comprising a microbe-binding aptamer(s) in the substrate recognition element. It is possible to obtain a stabilized biosensor wherein the detection sensitivity for target microbe (target bacterium) is not impaired depending on the storage condition or measuring sample, and target bacterium in a body fluid can be directly measured by insertion of the substrate recognition element of the biosensor.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Component mounting device and method of calibration in component mounting device
The objective of the present invention is to capture a fiducial marker provided at a base side and a fiducial marker provided at a mounting head side with one recognition camera. In the present invention, a substrate recognition optical path (81) for recognizing a substrate marker (BM) provided on a substrate (B) from above and a component recognition optical path (82) for recognizing a component picked up by a pickup nozzle (55) from below are separately provided for the optical axis of the recognition camera (50), a first fiducial marker (91) to be captured via the substrate recognition optical path is disposed at a predetermined position on the base side, a second fiducial marker (93) to be captured via the component recognition optical path is disposed at a predetermined position on the mounting head (47) side, and a calculation means is provided for calculating the positional relationship of the first and second fiducial markers relative to the optical axis of the recognition camera by capturing the first fiducial marker and the second fiducial marker with the recognition camera.
Owner:FUJI KK
Component-mounting method and component-mounting apparatus
ActiveUS7020322B2Improve recognition efficiencyReduce in quantitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVisual field lossPattern recognition
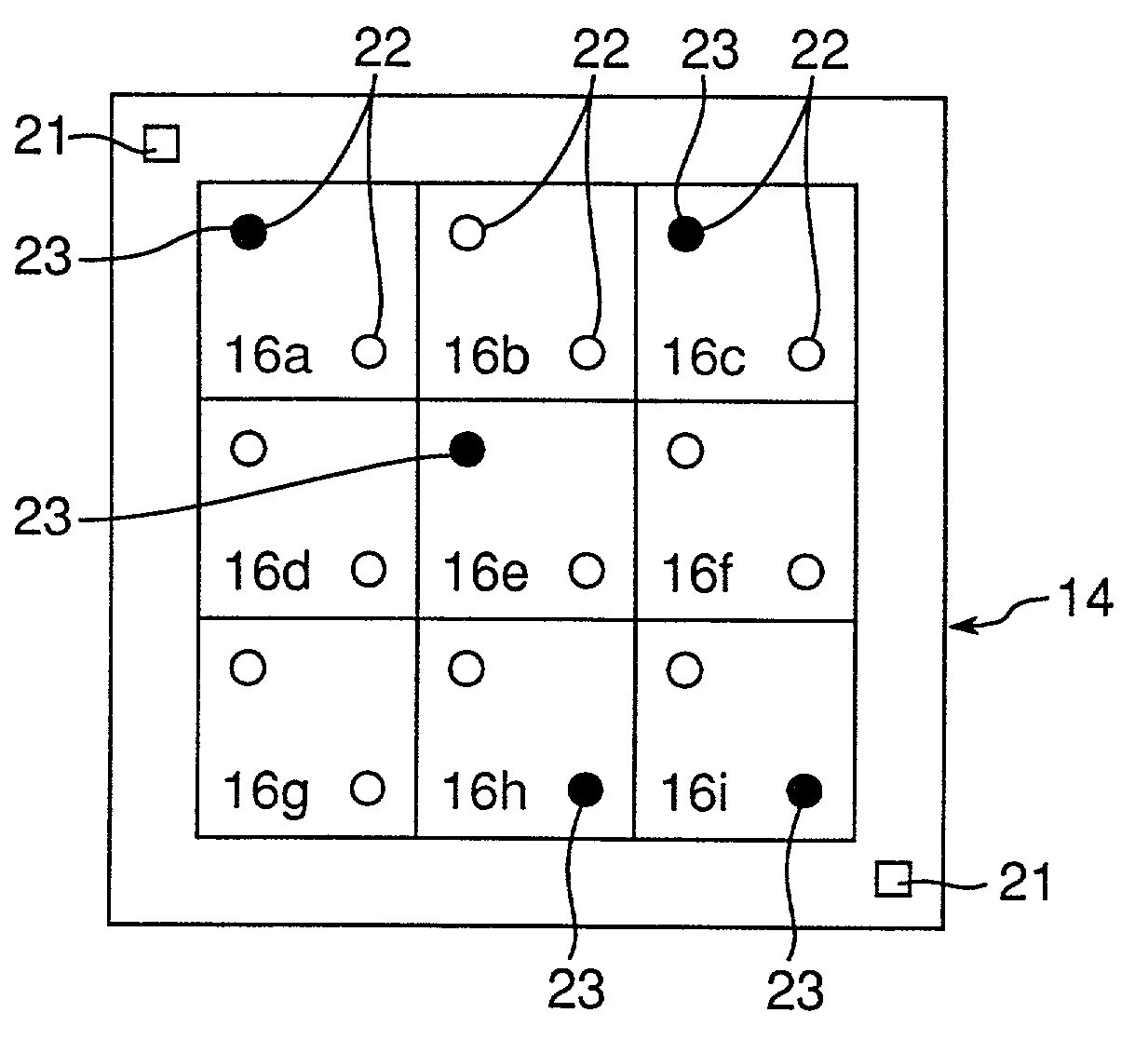
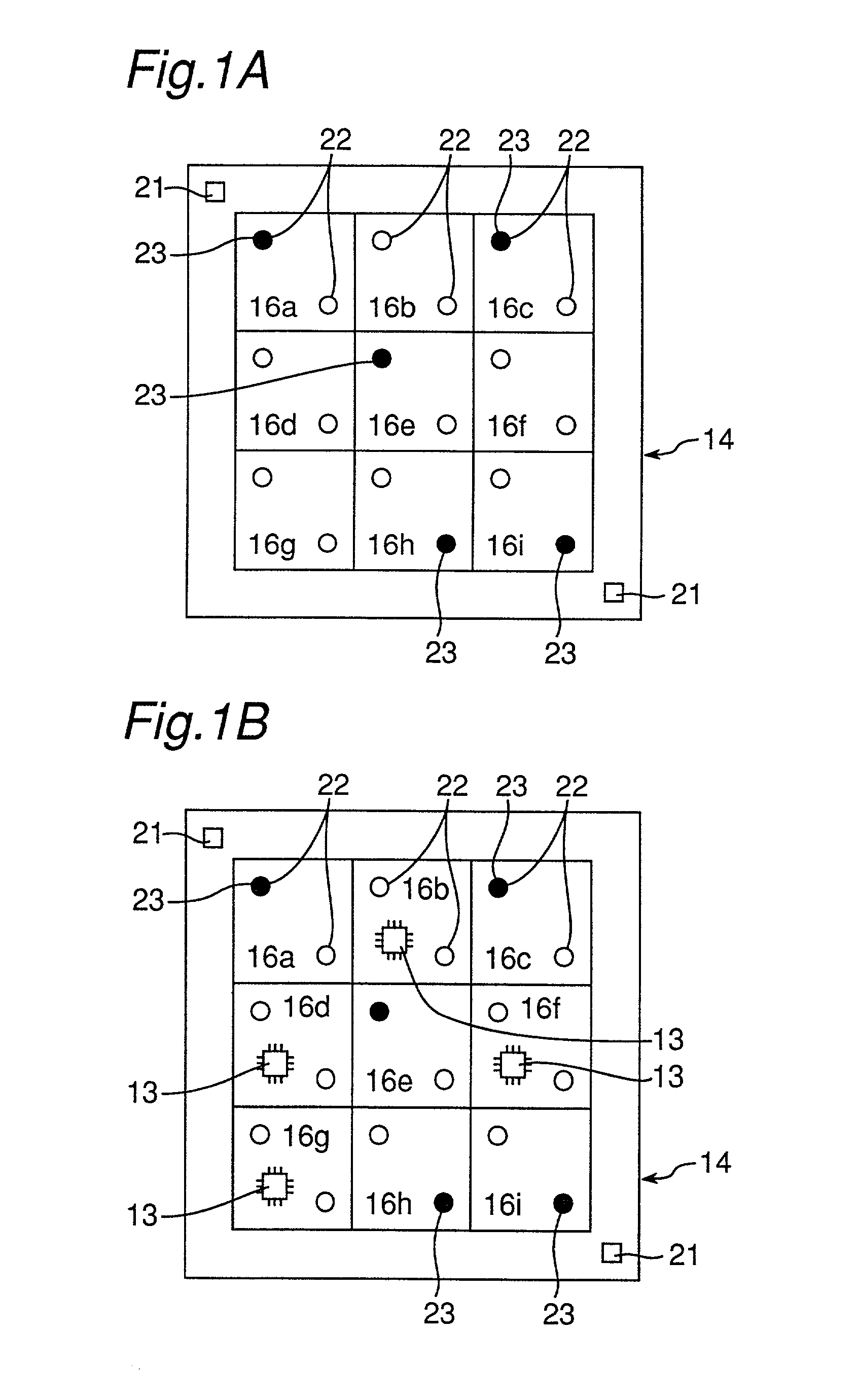
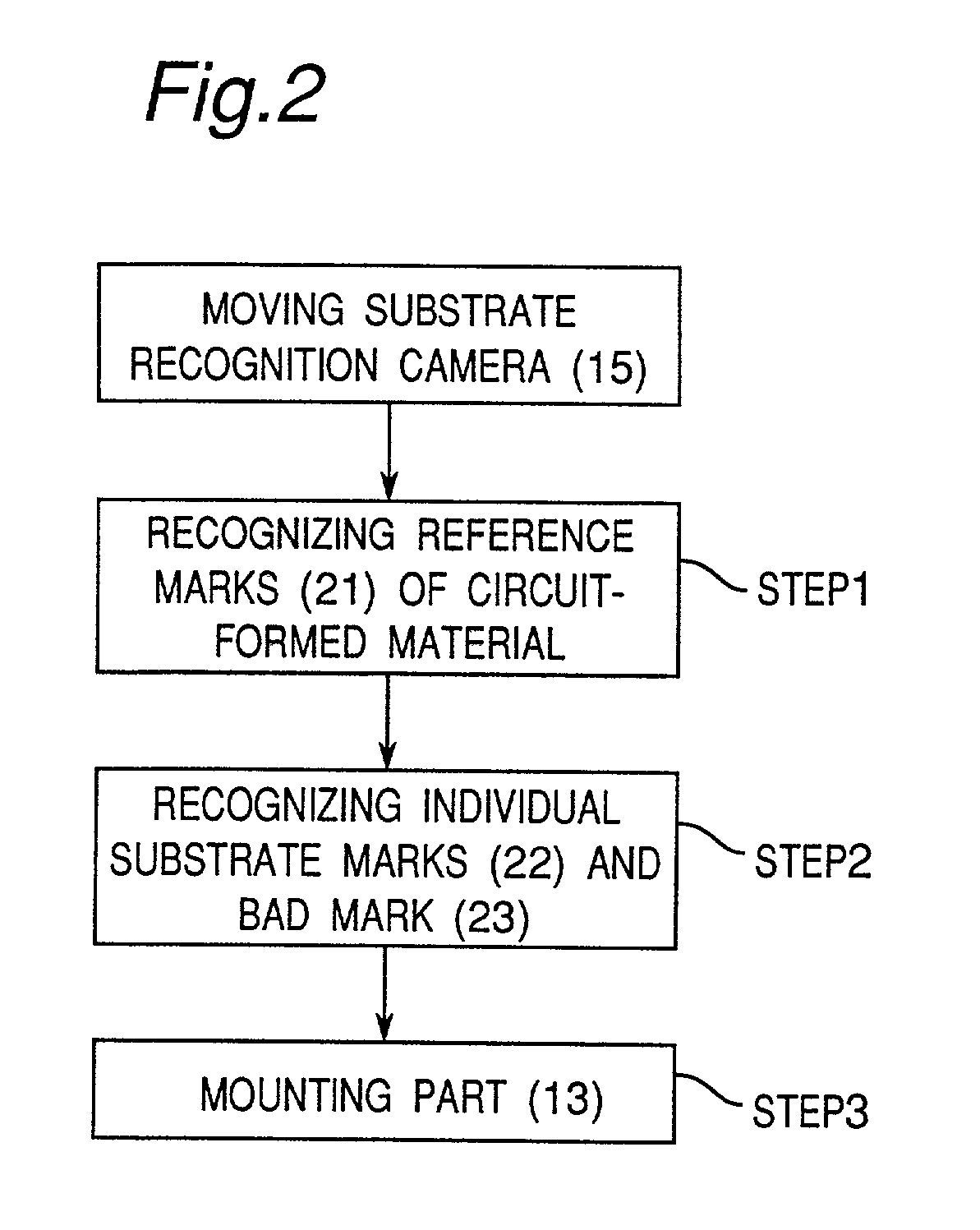
A number of recognition operations for a circuit-formed substrate as a whole is reduced by concurrently recognizing a bad mark and an individual substrate mark in the course of a recognition process of a single or a plurality of individual substrate(s) provided by sectioning the circuit-formed substrate. Results of the recognition of an inclination and dislocation of the circuit-formed substrate are used to control a position of a substrate-recognition camera which recognizes the individual substrate, thereby reducing a rate of occurrence of recognition errors. When a component of recognition marks or the individual substrate mark is captured within a visual field of the substrate-recognition camera, a position of a corresponding one of these recognized marks is specified, and such a mark is again recognized, and thus, the occurrence of a recognition error can be inhibited.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Enzyme detection device
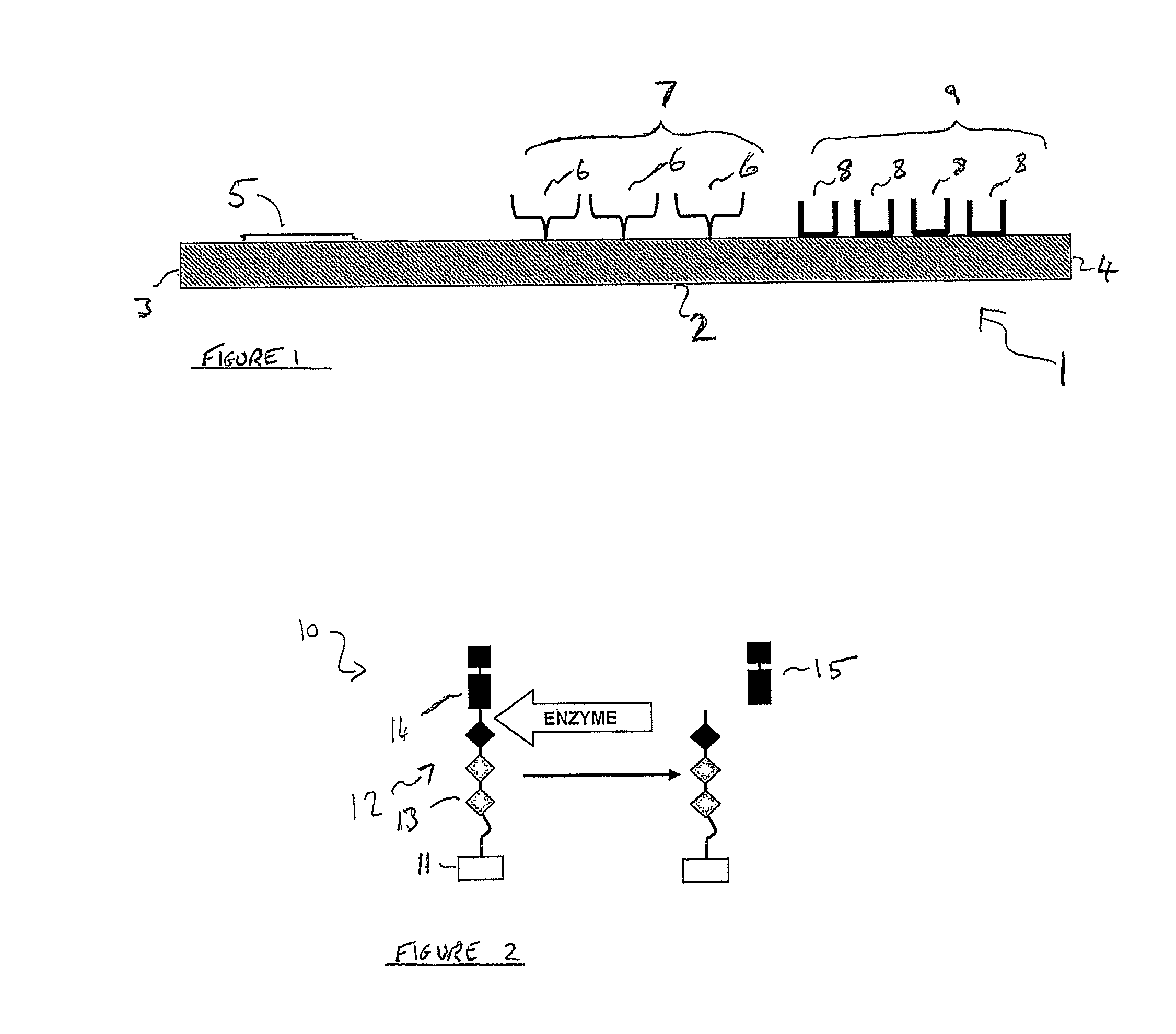
ActiveUS8592167B2Low dissociation rateIncrease dissociation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMolecular bindingSubstrate recognition
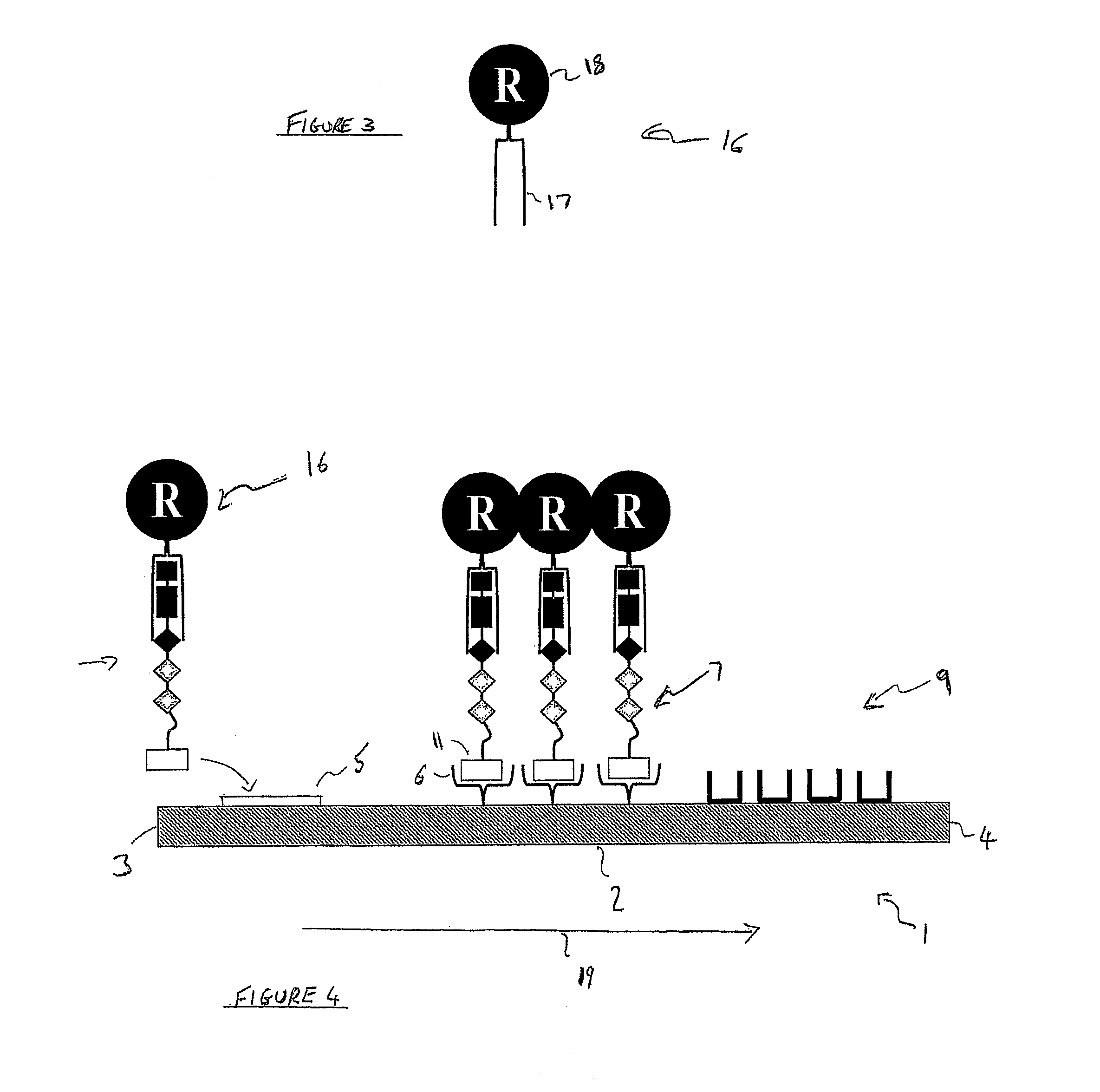
An enzyme detection device (1) for detecting the presence, in a sample, of an enzyme capable of modifying a provided substrate (10). The device (1) comprises a substrate which has a modification region (14) that is sensitive to modification by the enzyme from an unmodified state to a modified state. The device (1) further comprises a substrate recognition molecule (16) which binds the modification region (14) in either the modified or the unmodified state. The modification region 14 of the substrate is preferentially bound by the substrate recognition molecule (16) as compared with the enzyme when mixed. The device further comprises a detectable label (18) coupled to the substrate recognition molecule (17).
Owner:MOLOGIC LTD
Biosensor
InactiveUS8133720B2Not to damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBacterial antigen ingredientsMicroorganismCell sensitivity
The invention provides a biosensor comprising a microbe-binding aptamer(s) in the substrate recognition element. It is possible to obtain a stabilized biosensor wherein the detection sensitivity for target microbe (target bacterium) is not impaired depending on the storage condition or measuring sample, and target bacterium in a body fluid can be directly measured by insertion of the substrate recognition element of the biosensor.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Locked nucleic acid ribozyme of targeted serine-threonine protein kinase aurora kinase A and application thereof
InactiveCN101914536AGrowth inhibitionEnhanced inhibitory effectGenetic material ingredientsUrinary disorderProstate cancerLocked nucleic acid
The invention relates to locked nucleic acid ribozyme of targeted serine-threonine protein kinase aurora kinase A, wherein the nucleotide sequence thereof is shown as SEQ IDNO:1 in a sequence table, 15 deoxynucleotides positioned at the middle part in the nucleotide sequence form a catalytic structure domain, 8 nucleotides positioned at the left side of the catalytic structure domain form a first substrate recognition structure domain, 8 nucleotides positioned at the right side of the catalytic structure domain form a second substrate recognition structure domain, and both the first substrate recognition structure domain and the second substrate recognition structure domain contain two locked nucleic acids tL. The locked nucleic acid ribozyme of the targeted serine-threonine protein kinase aurora kinase A can be applied to preparing medicines for treating prostatic cancer.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
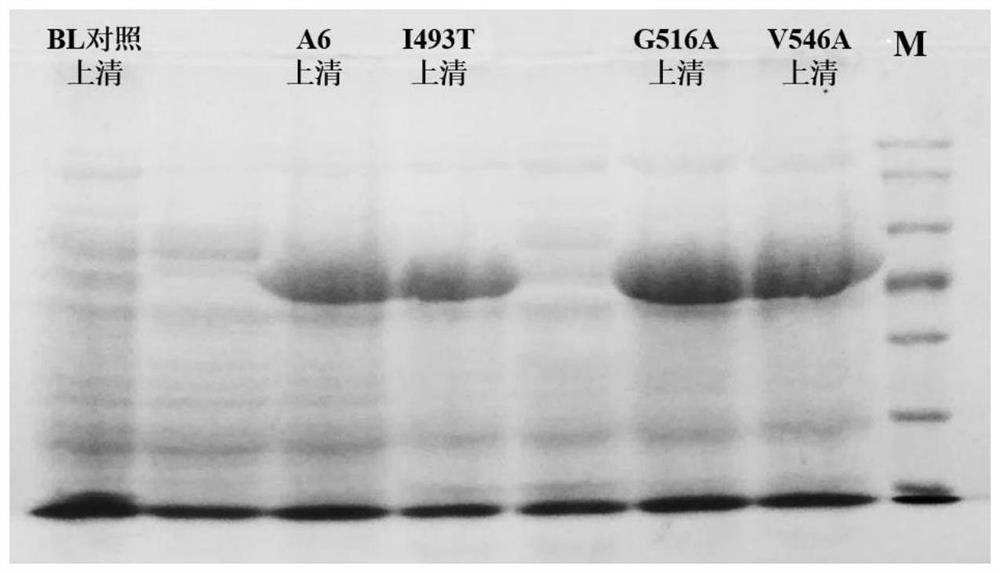
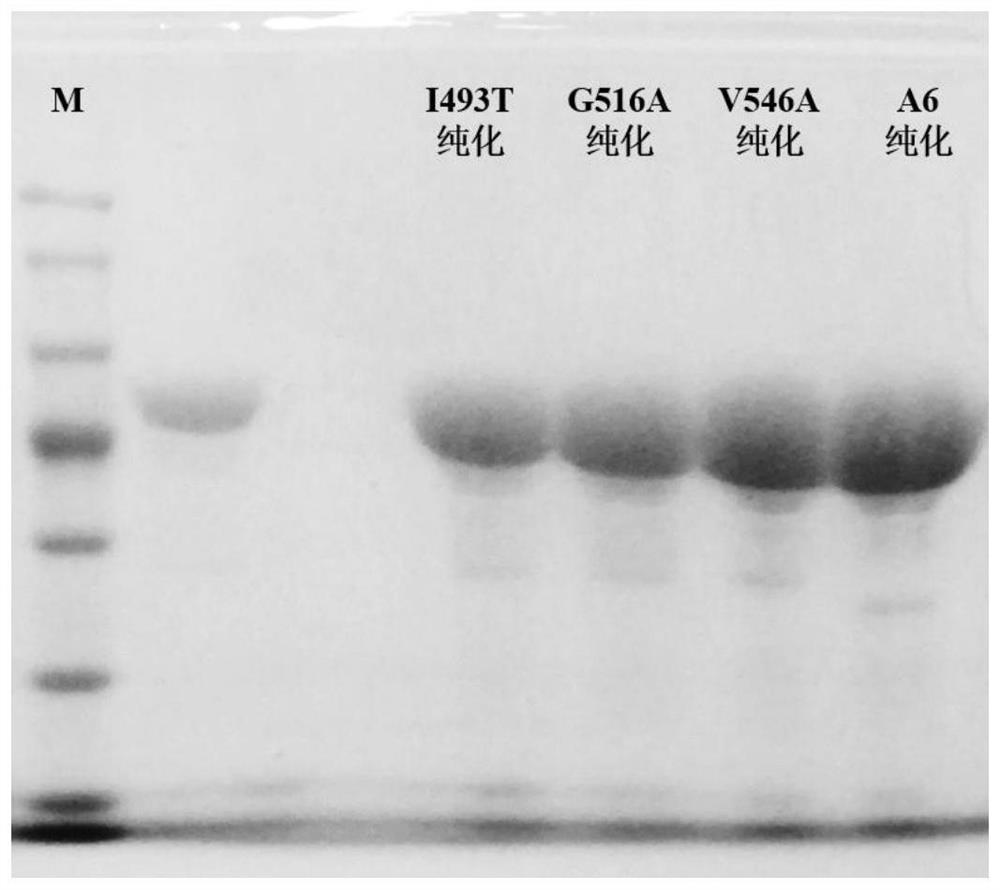
Adenylation protein A6 mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
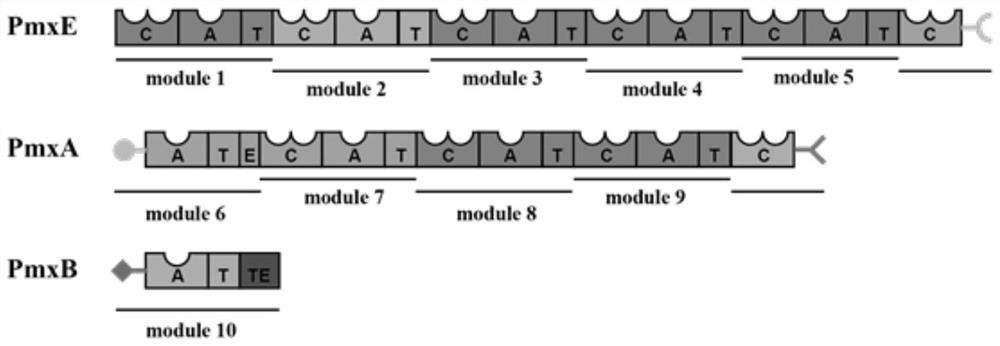
ActiveCN113278601AAltered substrate recognitionHigh activityBacteriaTransferasesEngineered geneticActive site
The invention discloses an adenylation protein A6 mutant as well as a coding gene thereof, and application of the adenylation protein A6 mutant as a key enzyme of an adenylation structural domain in catalytic synthesis of polymyxin. The adenylation protein A6 mutant is obtained by carrying out point mutation on the 516th amino acid of the adenylation protein A6 with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. According to the mutant, gene engineering and enzyme engineering means are adopted to research the active site of the A domain, and the key amino acid residue (A6 516th site residue) related to the substrate specificity of the A domain is determined by constructing the mutant, such that the substrate specificity of the obtained mutant G516A is changed compared with the adenylation protein A6, the activity on L-Ala is substantially improved, an the activity to L-Arg appears, and it is proved that substrate recognition of adenylation protein can be changed by modifying the amino acid residues of the site, and a new way is provided for extension of the structure of polymyxin family compounds.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Electronic component mounting device and electronic component mounting method
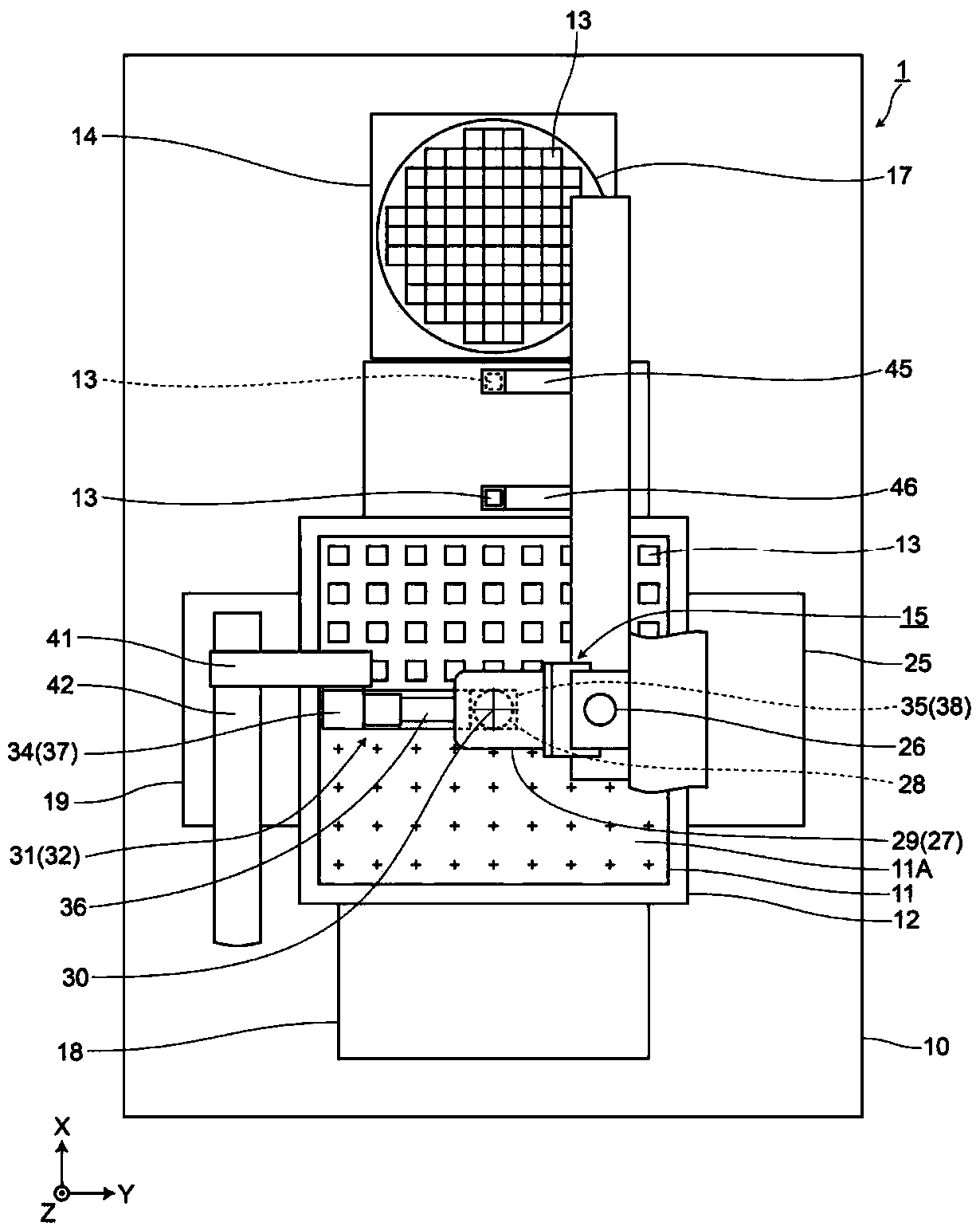
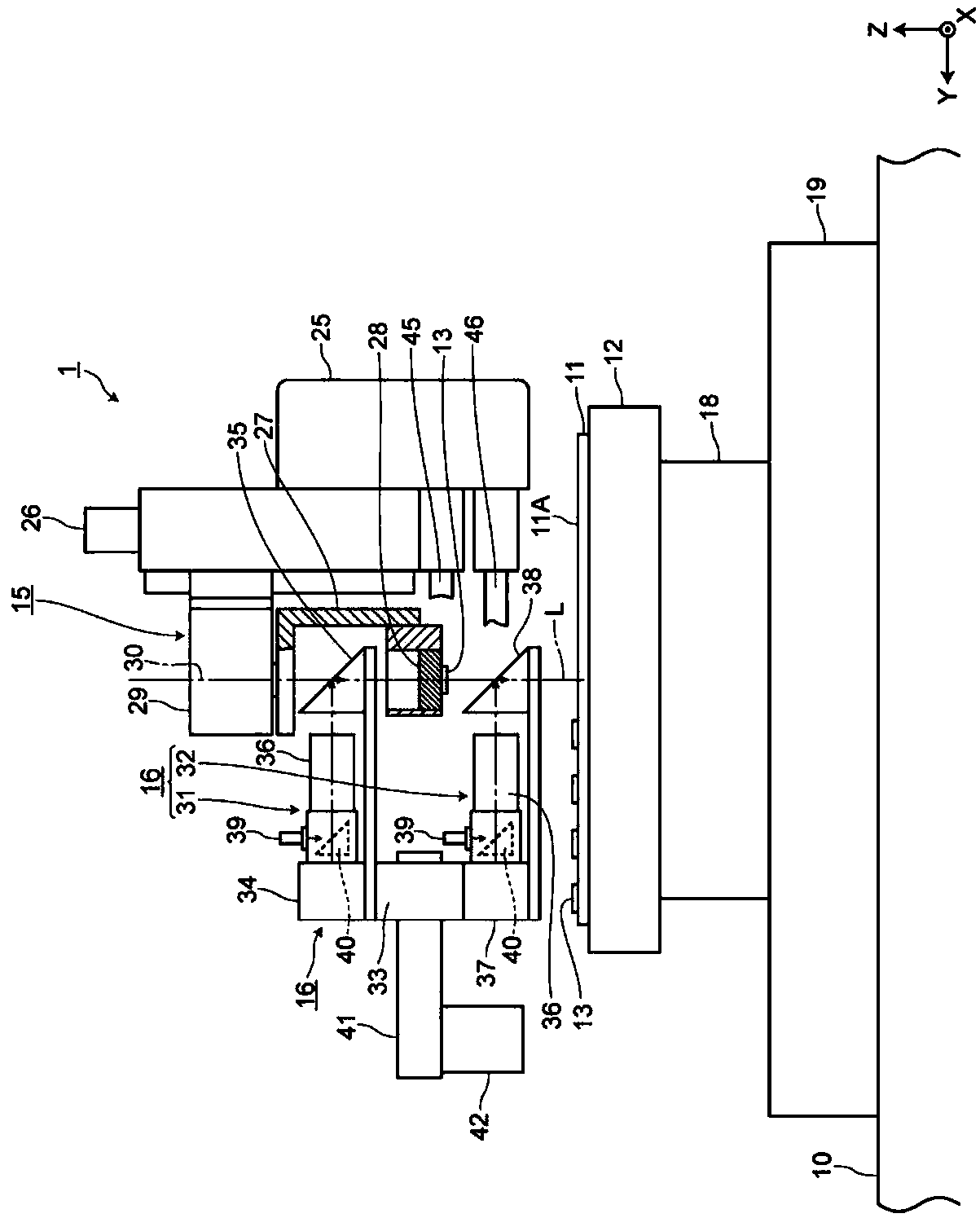
ActiveCN109906029AShort cycle timeSuppression of movement errorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical componentsElectronic componentSubstrate recognition
The purpose of the present invention is to provide an electronic component mounting device and an electronic component mounting method capable of accurately performing position alignment of a chip component and a substrate at a short beat time. The electronic component mounting device (1) and the electronic component mounting method according to the present invention are provided with: a chuck (28) that is formed of a transparent material and holds a chip component (13) attached thereto; a first mirror (35) that is provided on the opposite side of the chip component (13) with respect to the chuck (28) and projects an image of the chip component (13); a chip component recognition camera 34 that recognizes the chip component 13; a second mirror 38 provided between the substrate 11 and the chuck 28 and projecting an image of the substrate 11; and a substrate recognition camera 37 that recognizes the substrate 11, wherein the first mirror (35) and the second mirror (38) integrally move tothe chip component (13) and the substrate (11) at the recognition operation positions A and B, and after the positions of the chip component (13) and the substrate (11) are recognized, the position deviation of the chip component (13) and the substrate (11) is corrected on the basis of the recognition information.
Owner:ATHLETE FA KK
Substrate recognition method and element assemble mounting system
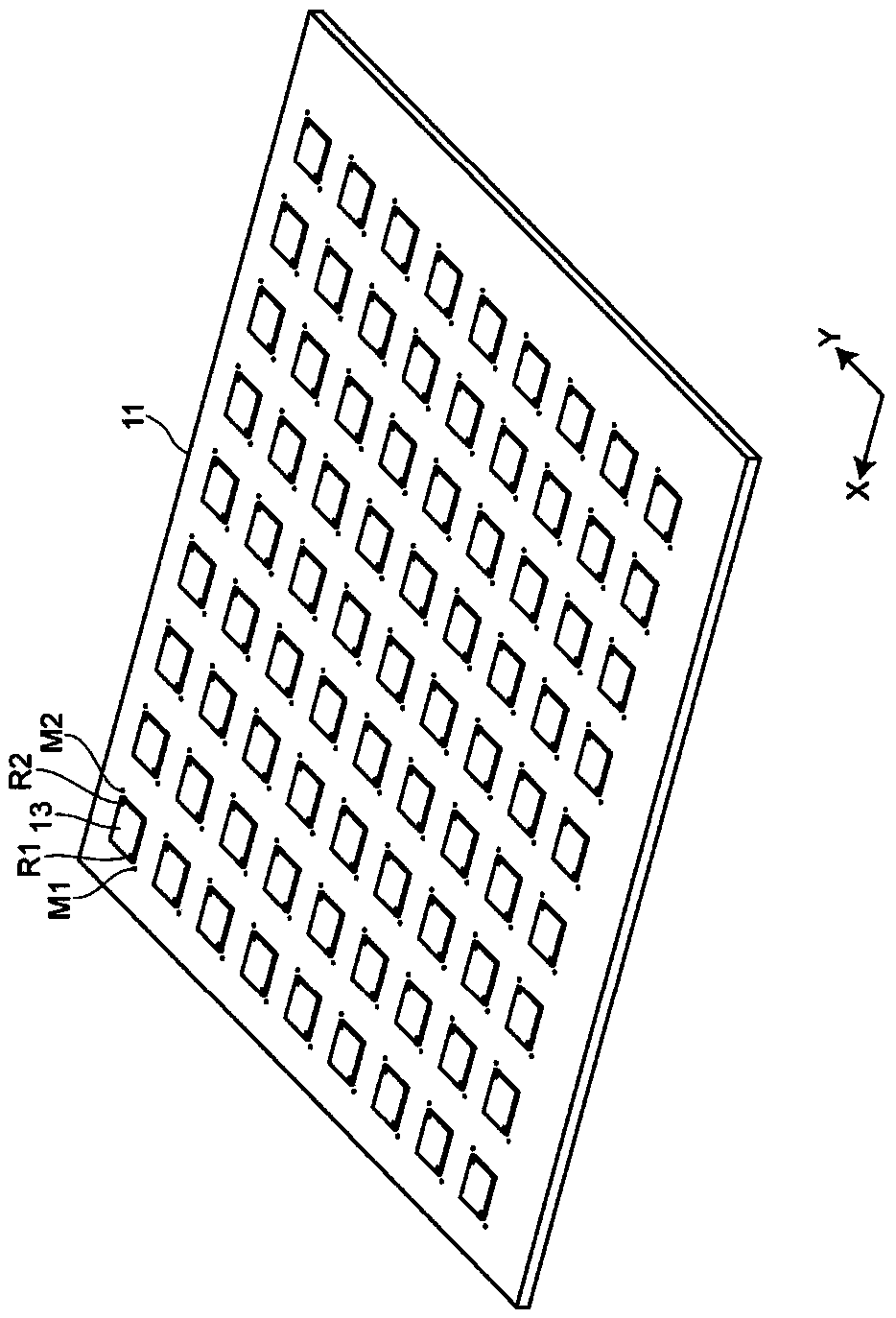
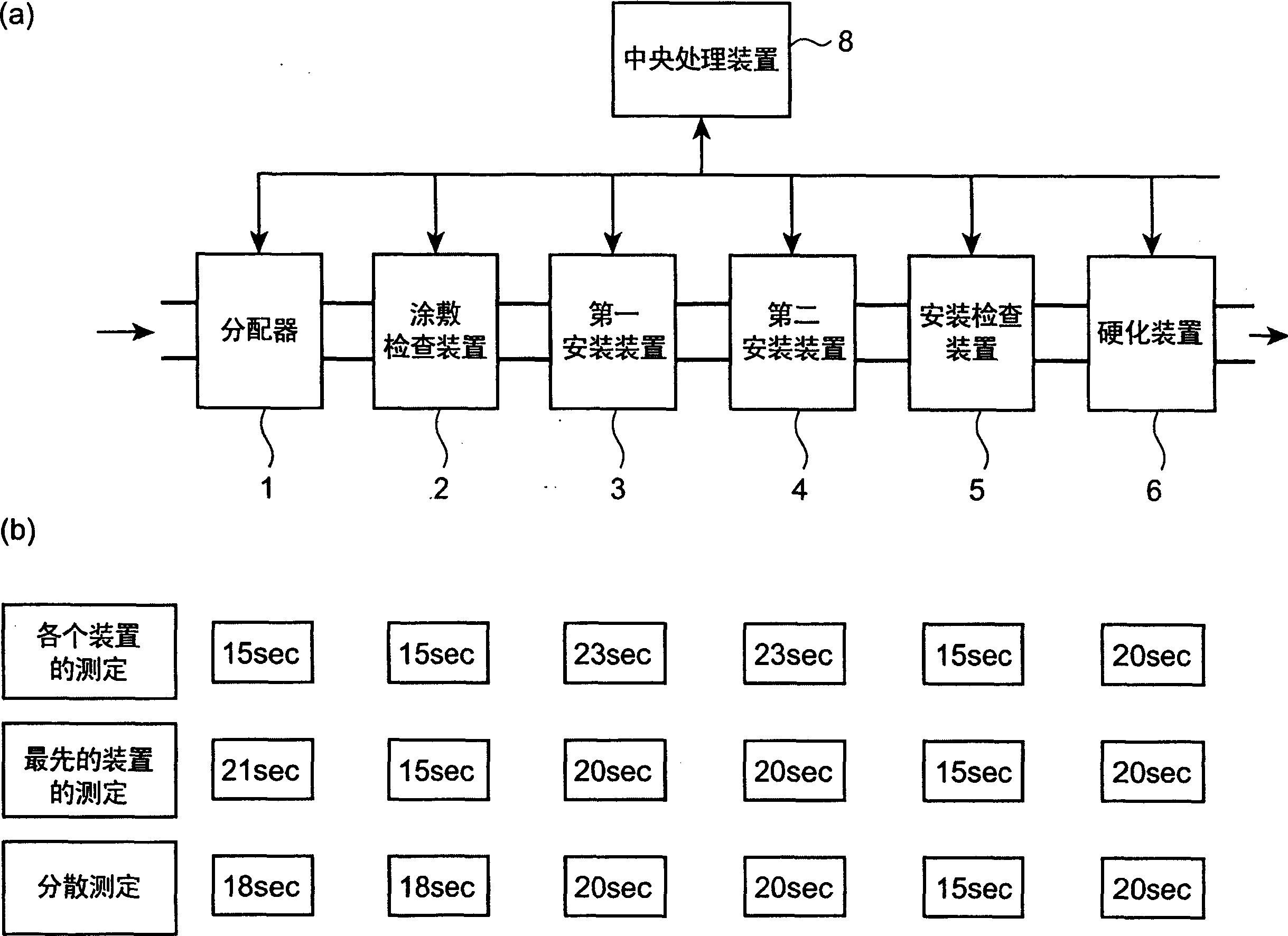
InactiveCN1849058AShorten the pace of productionSmooth production rhythmElectrical componentsProduction lineEngineering
The substrate identification method of the present invention can reasonably perform the substrate identification process of each device included in the component mounting production line, and at the same time can smoothly produce the circuit substrate. For each component mounting line including dispenser (1), coating inspection device (2), first mounting device (3), second mounting device (4), mounting inspection device (5) and hardening device (6) The device compares the production rhythm of each device (1 to 6) and determines the speed of the production rhythm of the production line. When the device is a device that uses a partial mark attached to the substrate, that is, a device that performs image recognition on the mark to generate correction data, the recognition operation of part or all of the mark that needs to be image recognized in the device is assigned to the use The above-mentioned distribution is carried out in one or more devices used in the process preceding the process of the device, and at the same time, the production rhythm of each device is not slower than the production rhythm of the hardening device.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Closed substrate loading and unloading system for coating machine
ActiveCN107539777AReduced Chances of ContaminationAvoid Contaminated SituationsConveyor partsEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention relates to a closed substrate loading and unloading system for a coating machine, which comprises a housing and a substrate transfer mechanism, a clamp transfer mechanism, an unloading mechanism, a loading mechanism, a substrate recognition mechanism, a radius recognition mechanism, a manipulator, a receiving mechanism, a square substrate storage rack, and a circular substrate storage frame inside the housing. The loading mechanism, the substrate recognition mechanism, the square recognition mechanism for recognizing the shape of the clamp, a manipulator for gripping the clamp, the receiving mechanism for loading the clamp, the square substrate storage rack for storing square substrates, and the circular substrate storage rack for storing circular substrates are arranged in order. The substrate transfer mechanism and the clamp transfer mechanism are located above the receiving mechanism. The housing has an inlet and an outlet, the loading mechanism is located at the inlet, and the unloading mechanism is located at the outlet. The closed substrate loading and unloading system can realize the automatic clamping and unloading of the substrates and belongs to the technical field of the loading and unloading of substrates.
Owner:广东腾胜科技创新有限公司
OLED substrate recognition system and method
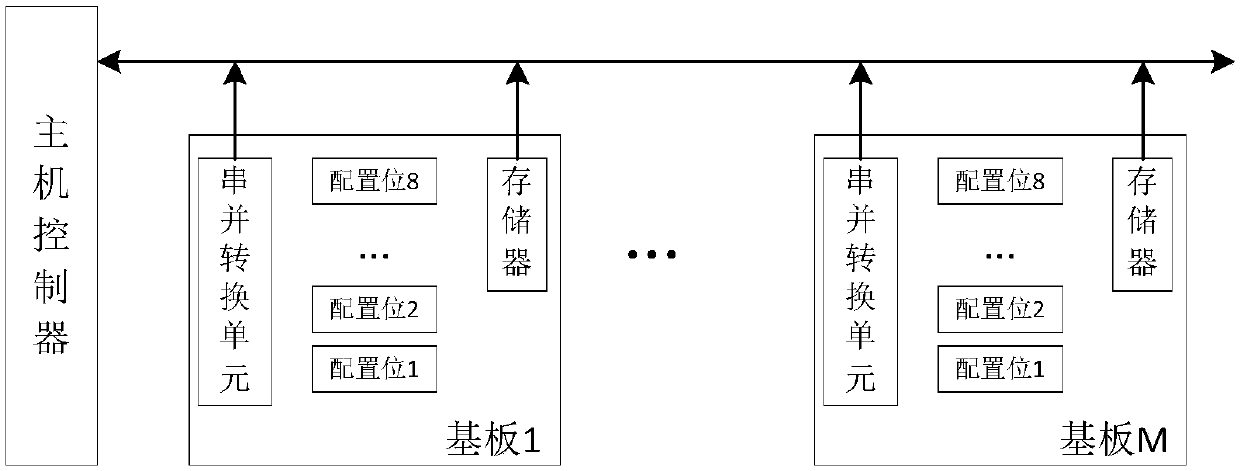
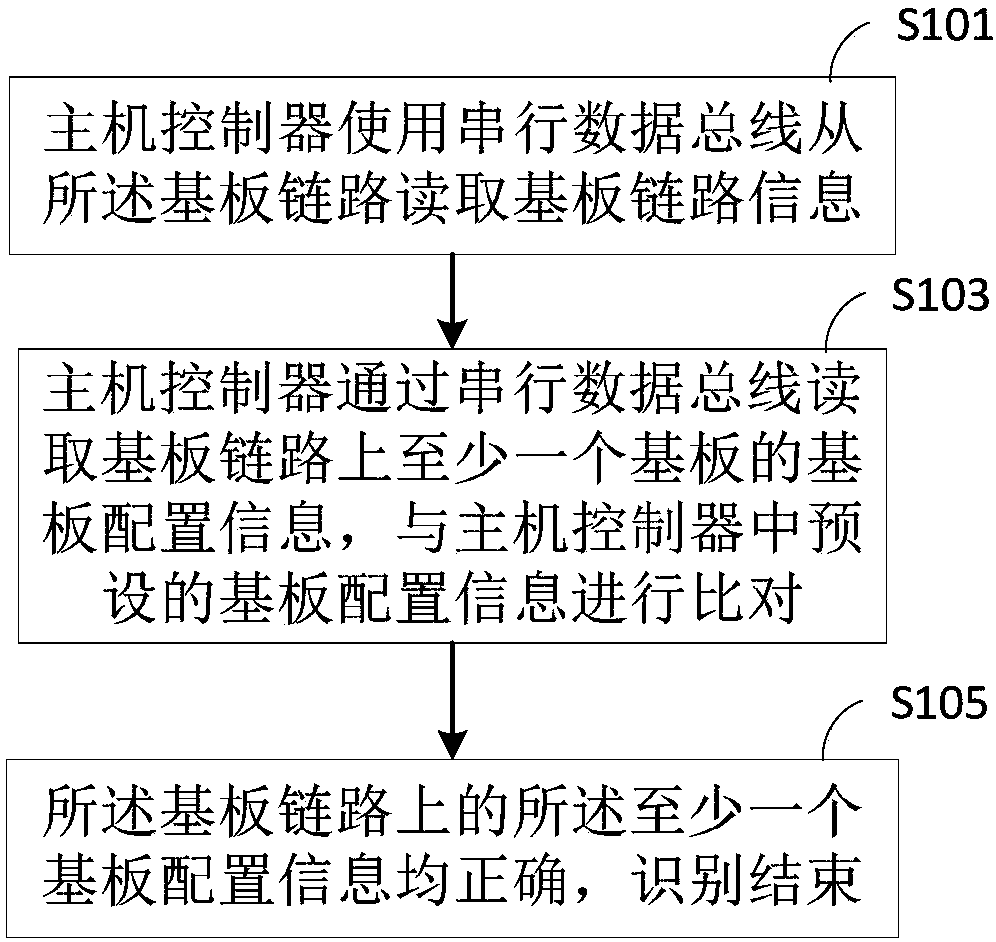
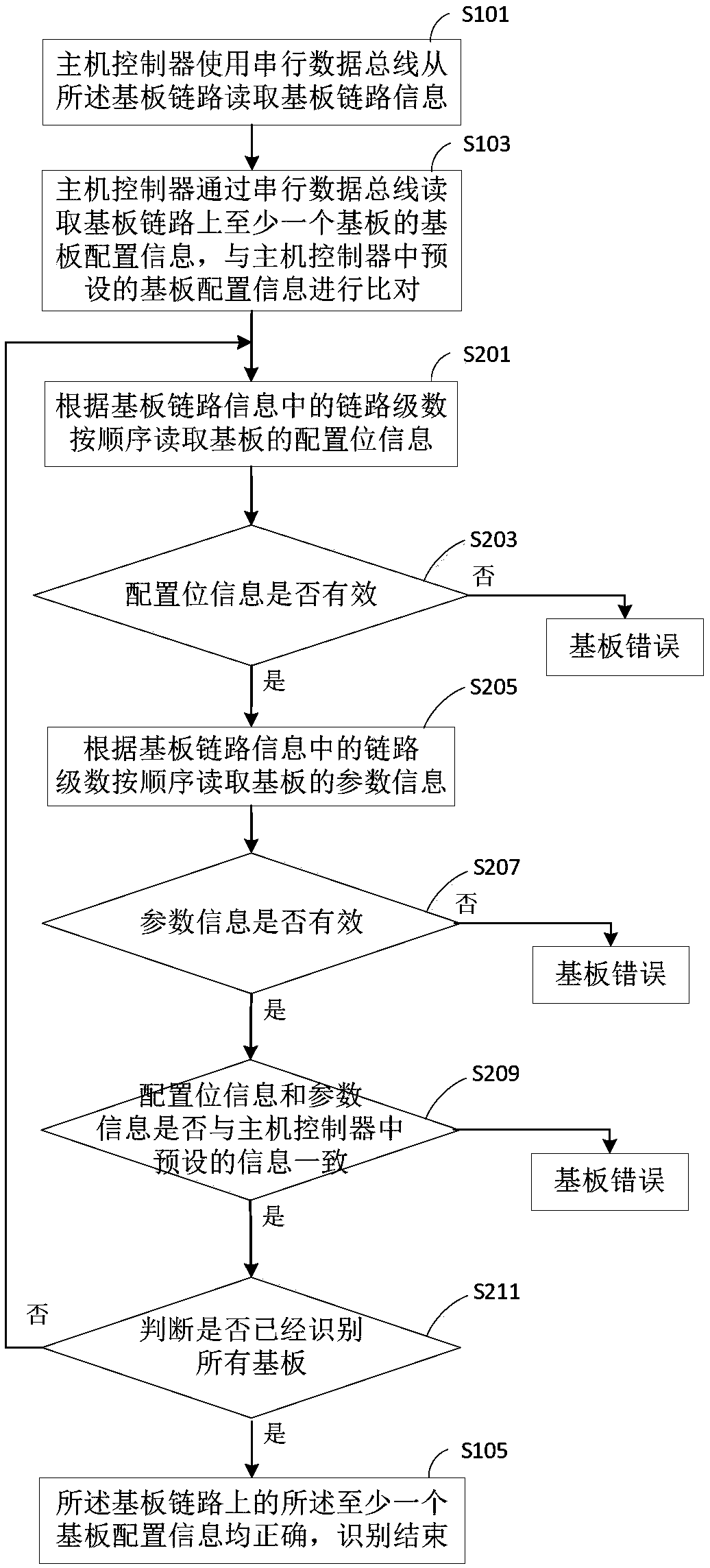
ActiveCN108052462AEliminate damageAccurate connectionElectric digital data processingTest programSubstrate recognition
The invention discloses an OLED substrate recognition system. The system comprises a host controller, a serial data bus and at least one substrate. The host controller, the serial data bus and the atleast one substrate form a substrate link, wherein the The host controller reads substrate link information through the serial data bus and reads substrate configuration information of the at least one substrate on the substrate link through the serial data bus according to the substrate link information, comparing the configuration information of each substrate with the substrate configuration information preset in the host controller, and outputting results. The embodiment of the invention provides the OLED substrate recognition system and method, on-line identification of a link substrate for driving an OLED panel can be achieved, and an invalid test caused by a mismatch between the substrate and a test program during an OLED panel test process and the damage of the substrate or the panel to be tested caused by a false test are avoided, so that panel test efficiency is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU HUAXING YUANCHUANG TECH CO LTD
Plant immunoregulation related protein and application thereof
ActiveCN112961843ADecreased disease resistanceImproves broad-spectrum disease resistanceHydrolasesLigasesBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
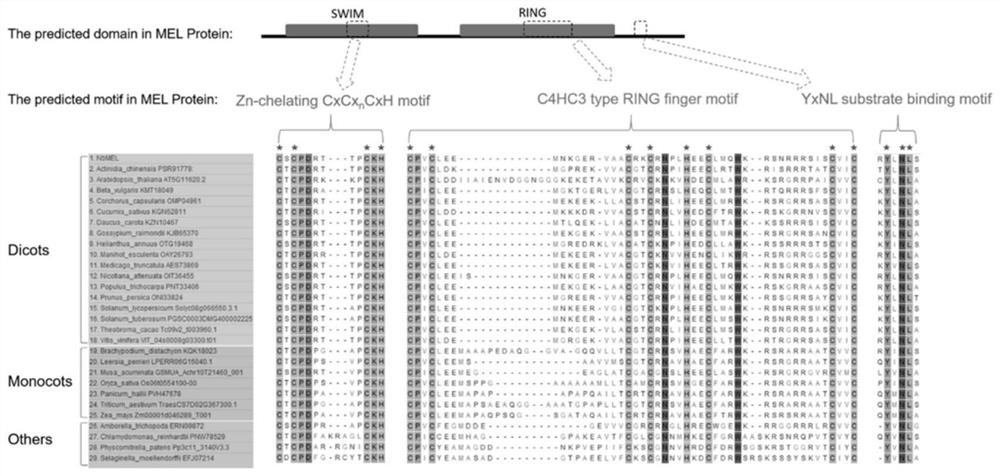
The invention discloses a plant immunoregulation related protein MEL and application thereof, and relates to the field of plant genetic engineering. The invention discloses the related protein MEL for regulating and controlling plant immunity. The protein encodes a conserved SWIM structural domain, a conserved RING structural domain and a conserved substrate recognition sequence Y phi NL. The broad-spectrum disease resistance of the plant to pathogens can be remarkably improved by regulating the expression quantity of MEL in the plant, and a crop disease-resistant gene engineering method is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of cationic starch-based glutathione peroxidase
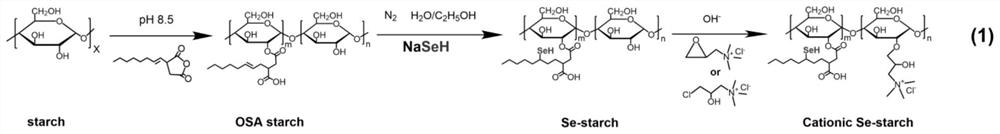
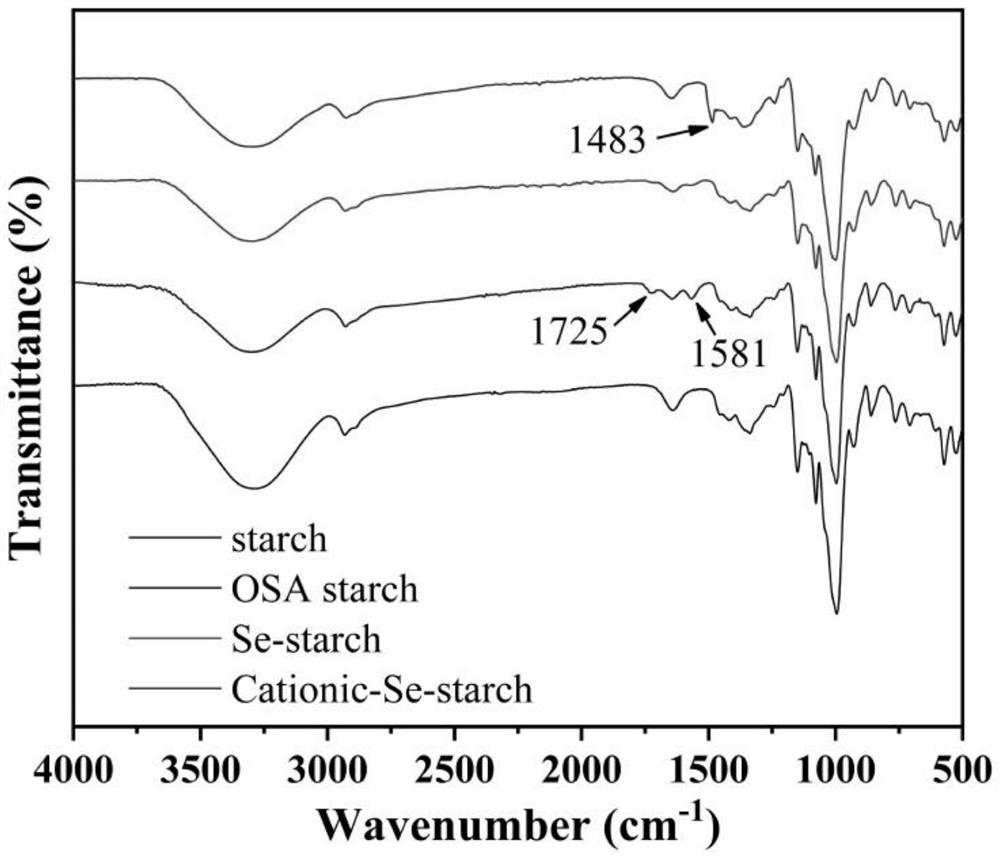
ActiveCN114262389AAccelerate the process of industrializationImprove bindingEnzymesOCTENYLSUCCINIC ACIDSuccinic acid
The invention relates to the technical field of starch modification, in particular to a preparation method of cationic starch-based glutathione peroxidase. The invention relates to a preparation method of cationic starch-based glutathione peroxidase. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing OSA (Octenyl Succinic Acid) starch ester; (2) preparation of selenium starch (Se-Starch); and (3) preparation of the cationic Se-Starch (Cation Se-Starch). The cationic selenized starch can simulate a catalytic center, a hydrophobic microenvironment and a substrate recognition site of natural glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and meanwhile, the effective matching and synergistic effect of three catalytic elements of the catalytic center, the hydrophobic microenvironment and the recognition site plays a positive role in improving the antioxidant catalytic activity of the cationic selenized starch.
Owner:BEIBU GULF UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com