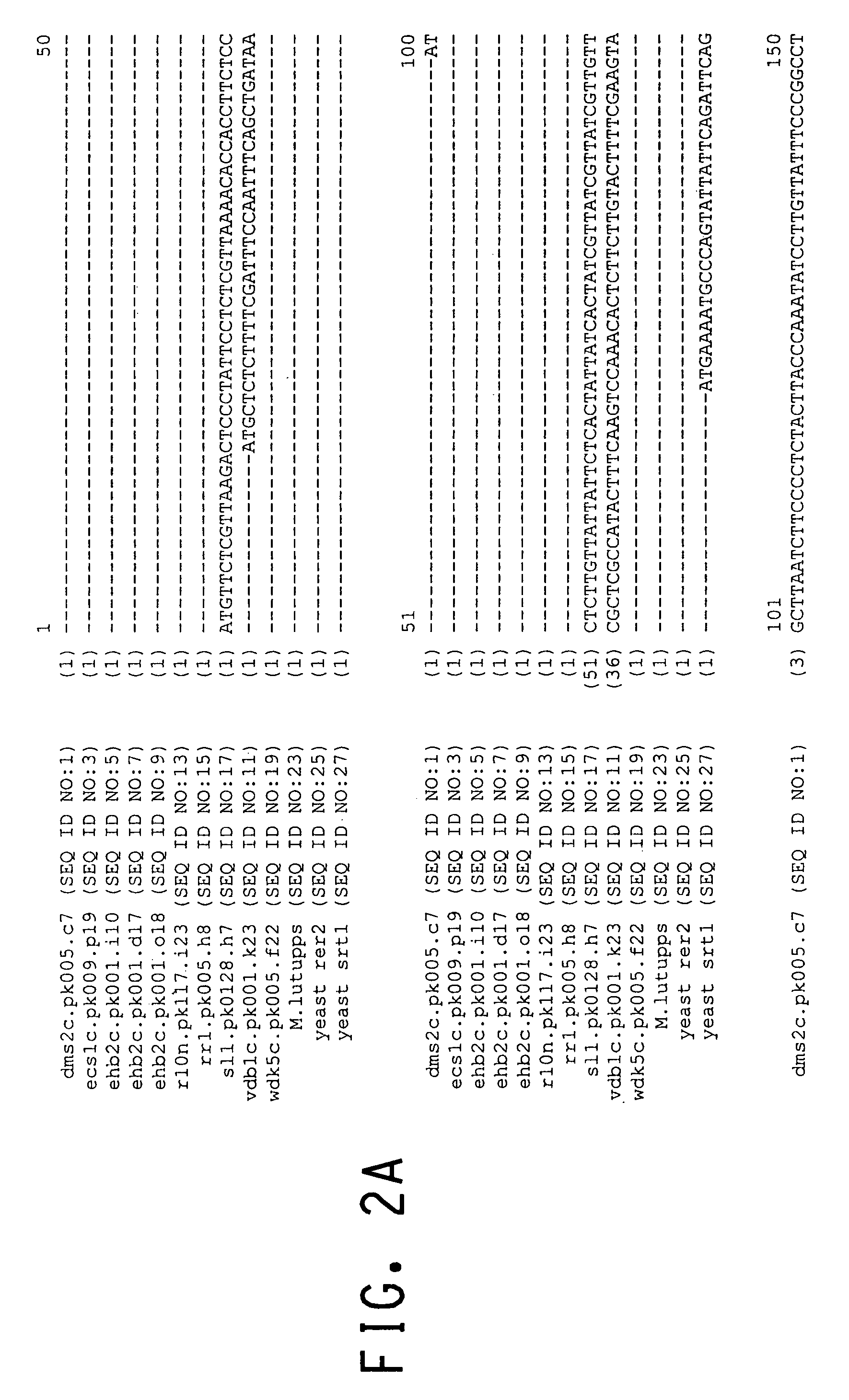
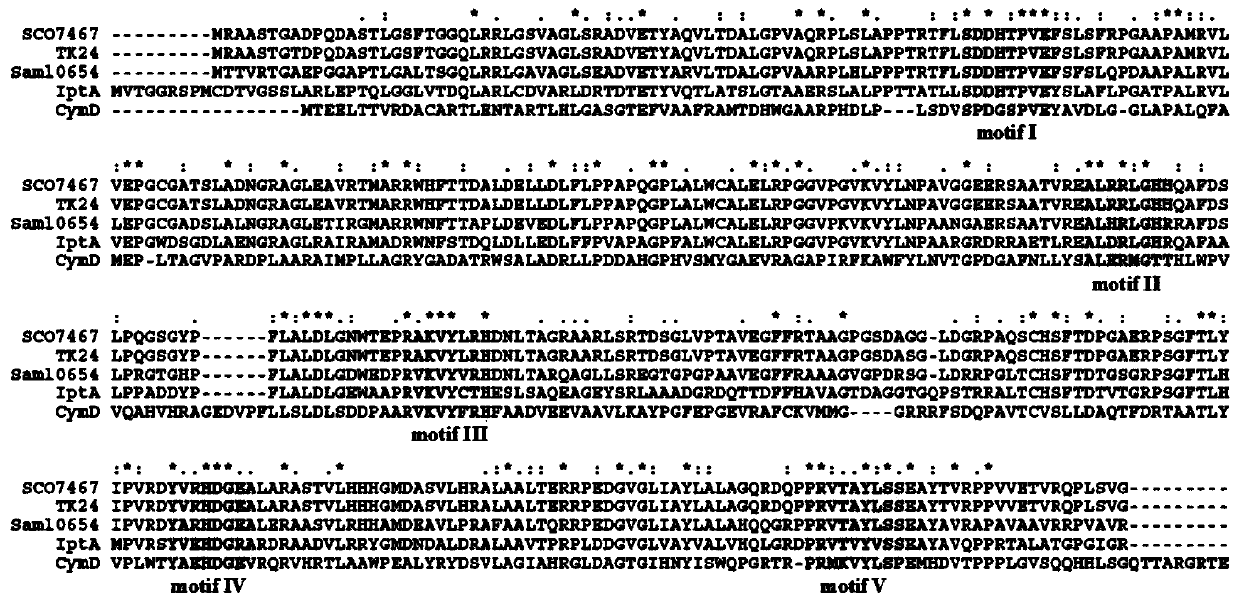
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Prenyltransferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
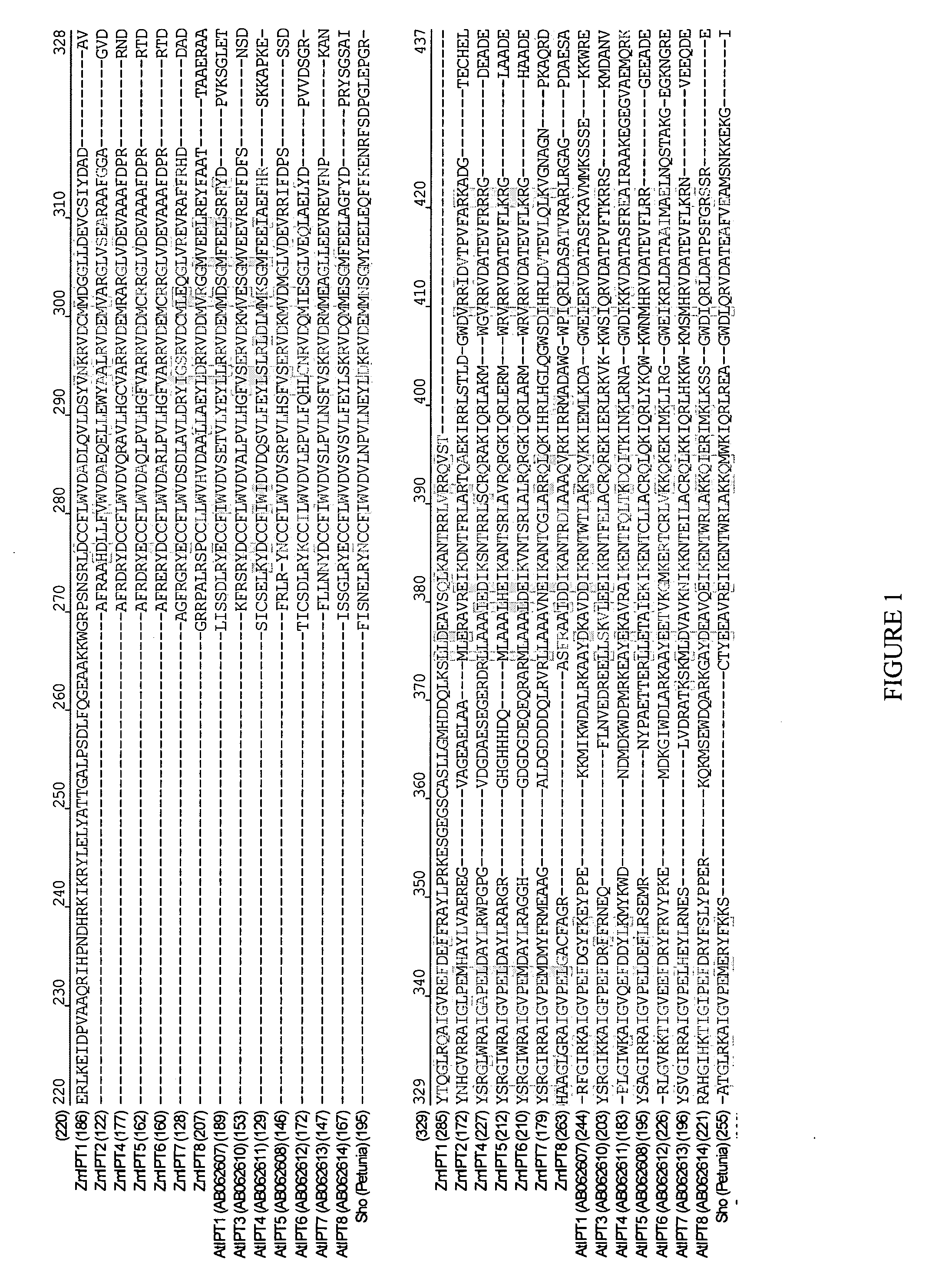
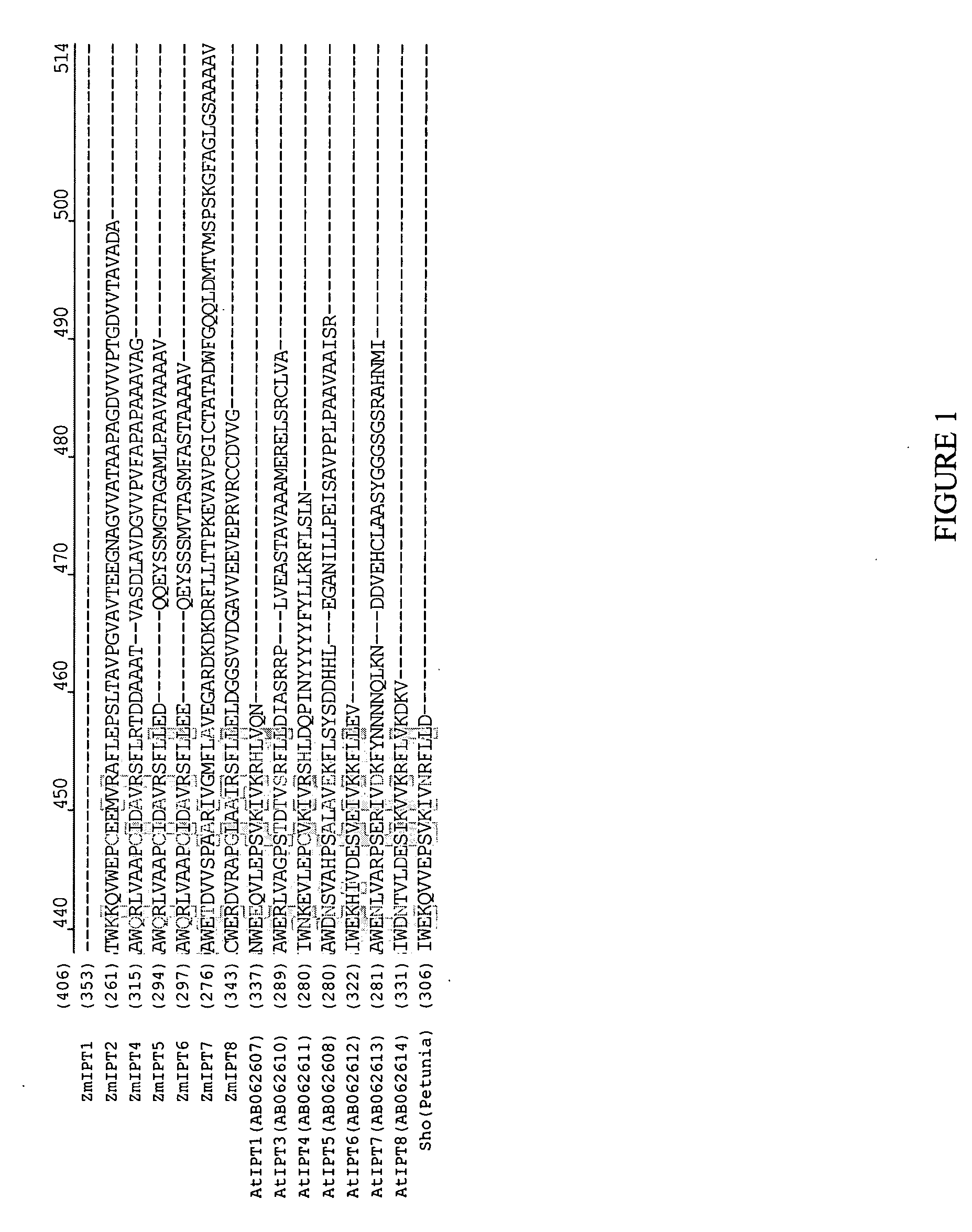
Prenyltransferases are a class of enzymes that transfer allylic prenyl groups to acceptor molecules. Prenyl transferases commonly refer to prenyl diphosphate synthases. Prenyltransferases are commonly divided into two classes, cis (or Z) and trans (or E), depending upon the stereochemistry of the resulting products. Examples of trans-prenyltranferases include dimethylallyltranstransferase, and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase. Cis-prenyltransferases include dehydrodolichol diphosphate synthase (involved in the production of a precursor to dolichol).
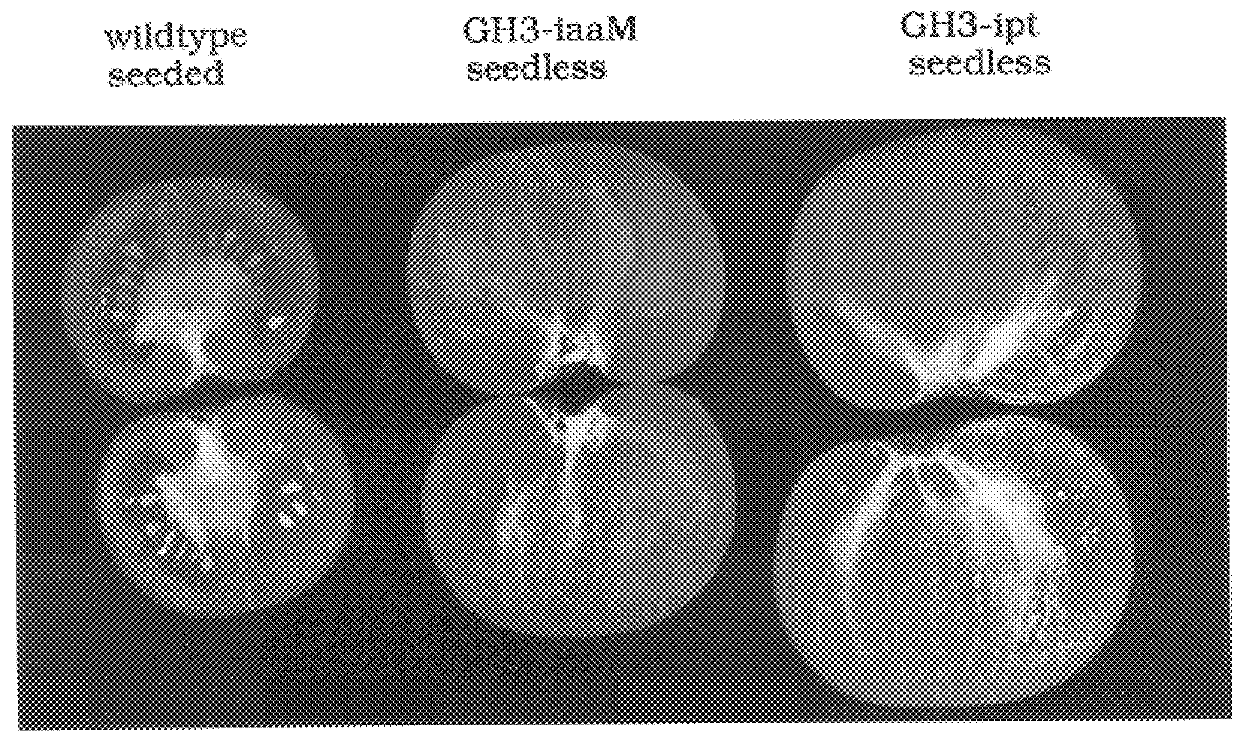
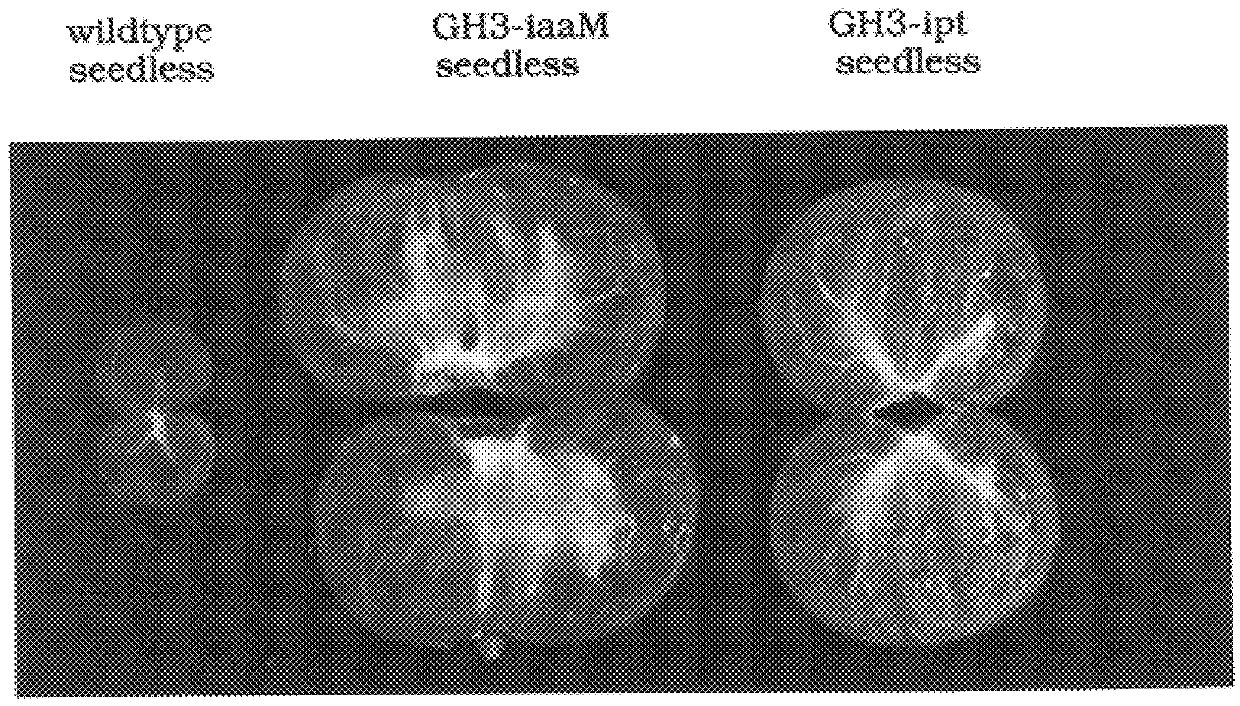
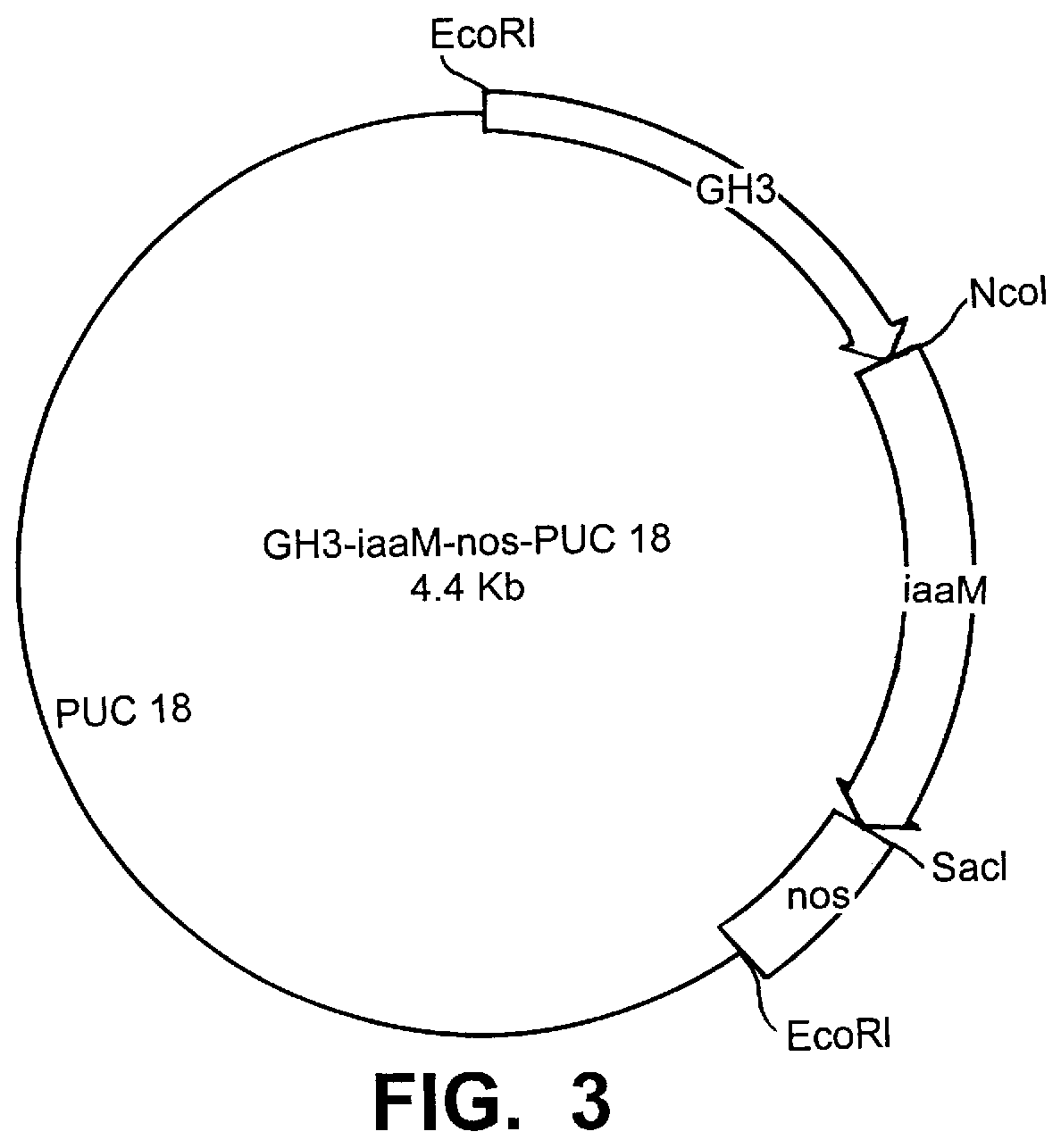
Transgenic seedless fruit comprising AGL or GH3 promoter operably linked to isopentenyl transferase or tryptophan monooxygenase coding DNA
InactiveUS6268552B1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesBiosynthetic genesDNA construct
The present invention provides methods and DNA constructs for the genetic engineering of plant cells to produce plants which produce substantially seedless fruit in the absence of exogenous growth factors (auxins or cytokinins) and in the absence of pollination. The substantially seedless fruits produced by the methods described herein are about the size of wildtype seeded fruit (or somewhat larger) and these fruits are equal to or superior to the wildtype seeded fruit with respect to solid content and flavor. The seedless fruits of the present invention are produced in transgenic plants which contain and express auxin or cytokinin biosynthetic genes, e.g., tryptophan oxygenase or isopentenyl transferase coding sequences expressed under the regulatory control of GH3 or AGL promoter sequences directing preferential or tissue specific expression of a downstream gene in the ovaries or developing fruit.
Owner:LI YI
Isopentenyl transferase sequences and methods of use
InactiveUS20060064786A1Reduced activityDecreases level of cytokininClimate change adaptationTransferasesPlant cellPolynucleotide
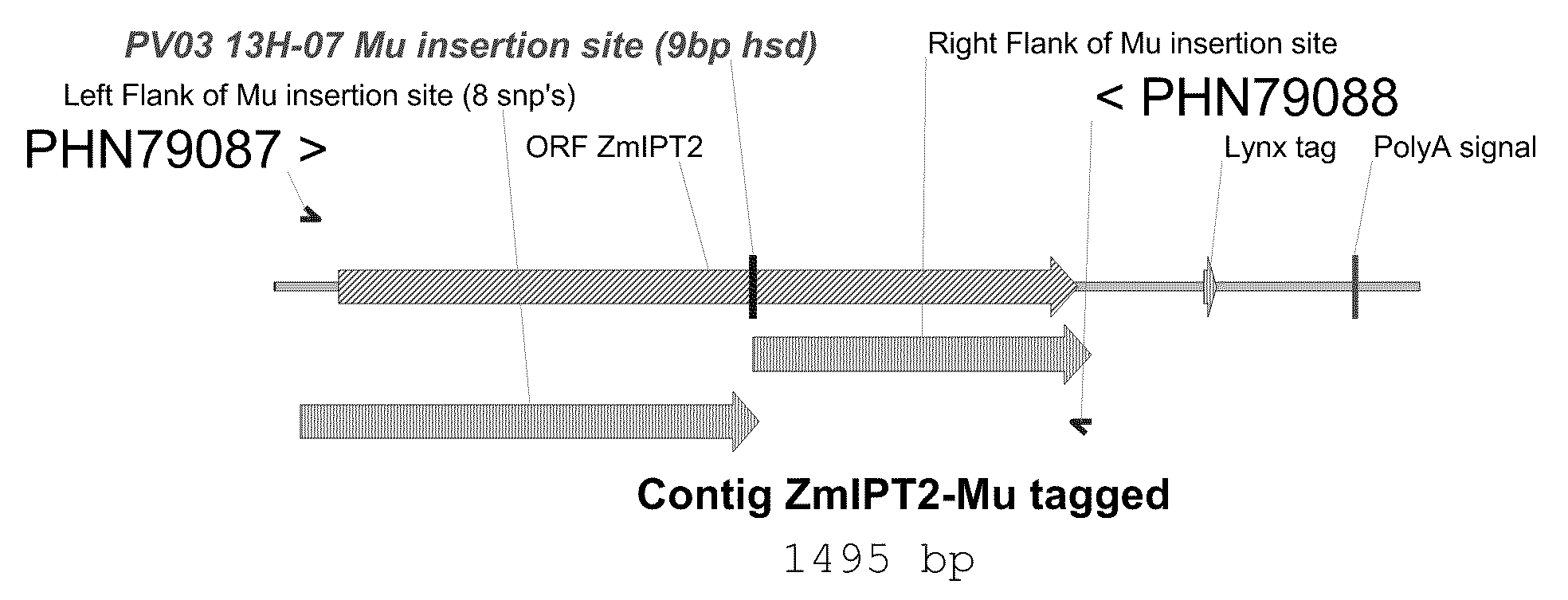
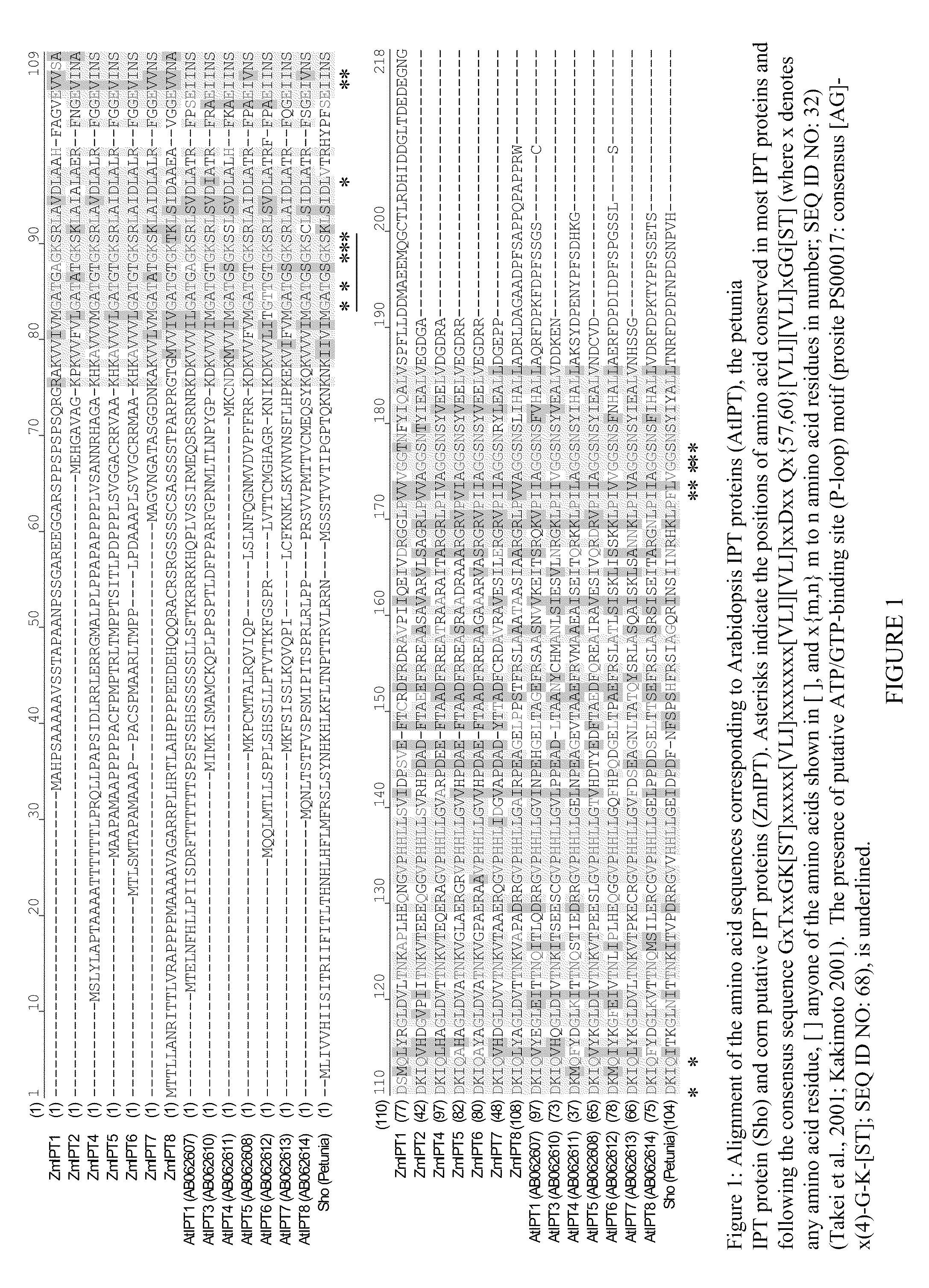
Methods and compositions for modulating plant development are provided. Polynucleotide sequences and amino acid sequences encoding isopentenyl transferase (IPT) polypeptides are provided. The sequences can be used in a variety of methods including modulating root development, modulating floral development, modulating leaf and / or shoot development, modulating senescence, modulating seed size and / or weight, and modulating tolerance of plants to abiotic stress. Polynucleotides comprising an IPT promoter are also provided. The promoter can be used to regulate expression of a sequence of interest. Transformed plants, plant cell, tissues, and seed are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
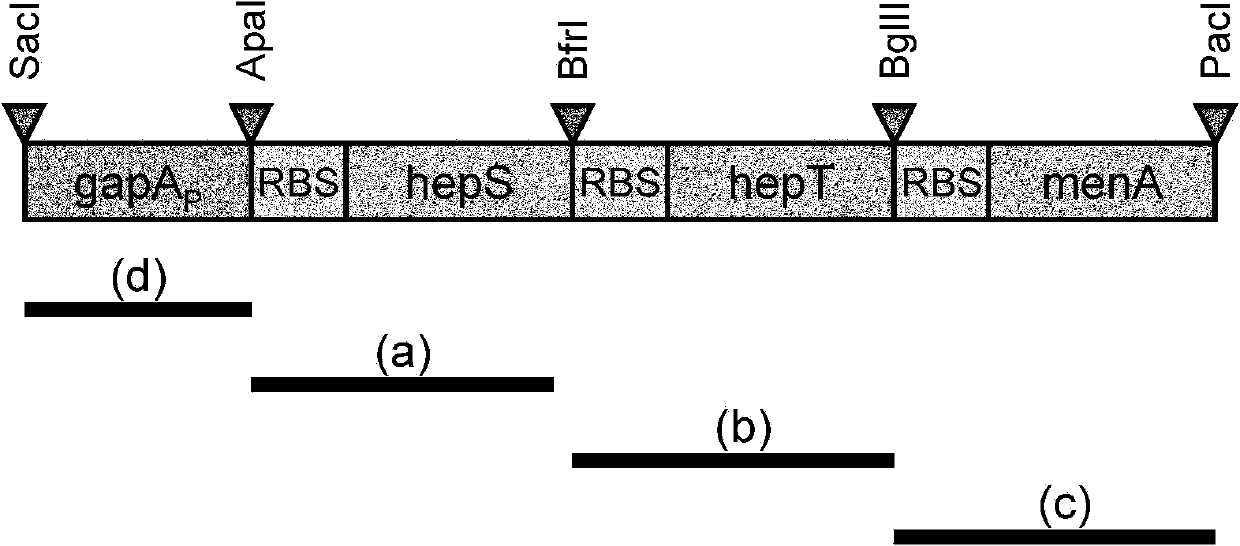
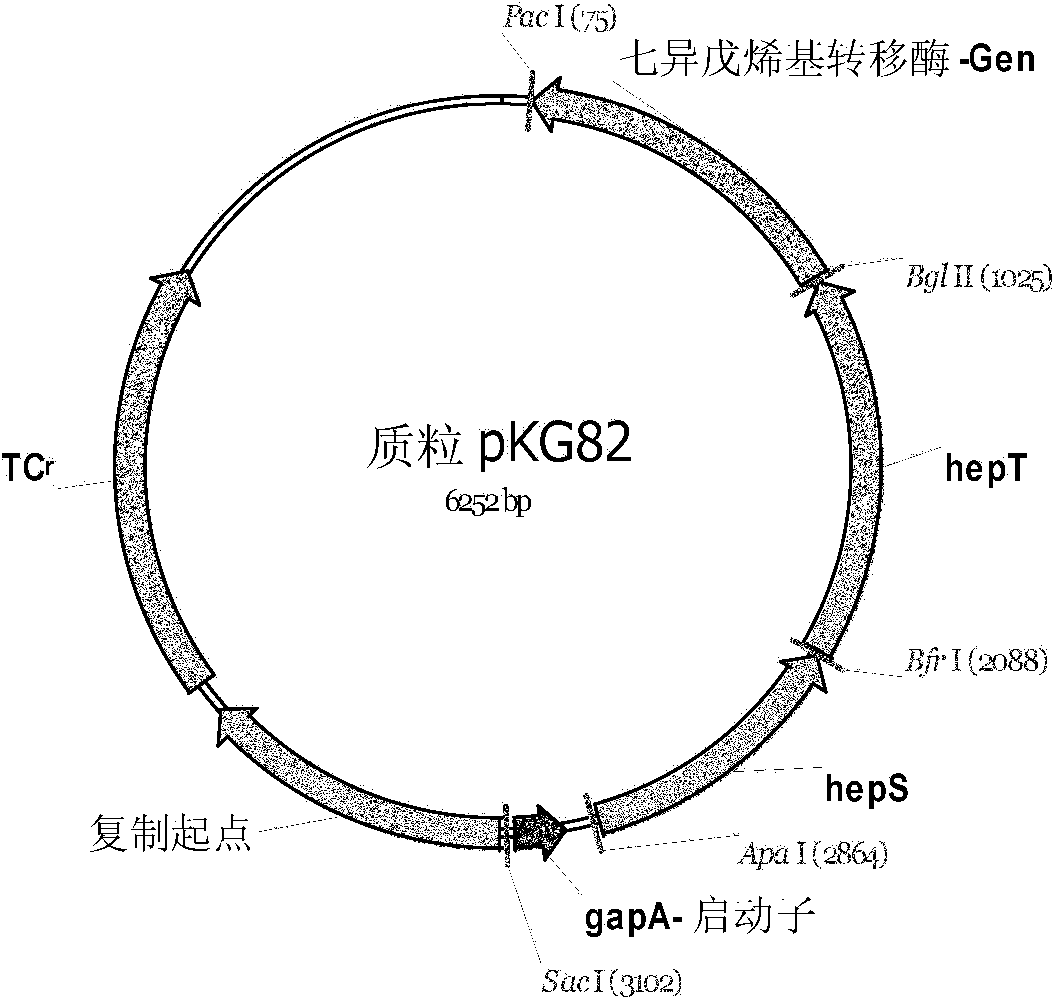
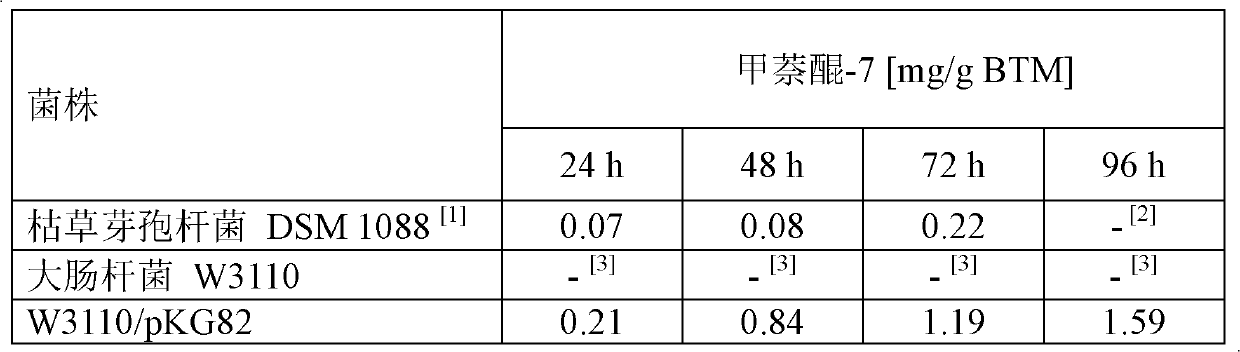
Method for fermentative production of menaquinone-7 using escherichia coli
InactiveCN102168116ASuitable for productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention relates to a method of producing menaquinone-7, characterized in that cells of an E. coli strain comprising the B. subtilis DSM 1088 hepS gene, the B. subtilis DSM 1088 hepT gene and the putative B. subtilis DSM 1088 heptaprenyl transferase gene are fermented in a fermentation medium, with menaquinone-7 being accumulated in the cells of the fermented E. coli strain.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Plant bivalent anti-reverse gene bielement expression carrier
InactiveCN1757740AIncrease resistanceAnti agingVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationPlant genetic engineeringGenetic engineering
A binary expression carrier of Agrobacterium for culturing the seeds of plant by genetic engineering contains the closely linked corm ubiquitin promoter Pubi regulated Arabidopsisí» cold response gene transcription activation factor gene cbf1 and the Arabidopsis specific senescence gene promote SAG12 regulated iso-pentenyl transferase ipt geneí»s two-valence stress-resistant gene. Its preparing process includes such steps as inserting the T-Nos of sag12-ipt fusion gene into a binary carrier, inserting ubi-cbf1 fusion gene and inserting sag12-ipt fusion gene.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
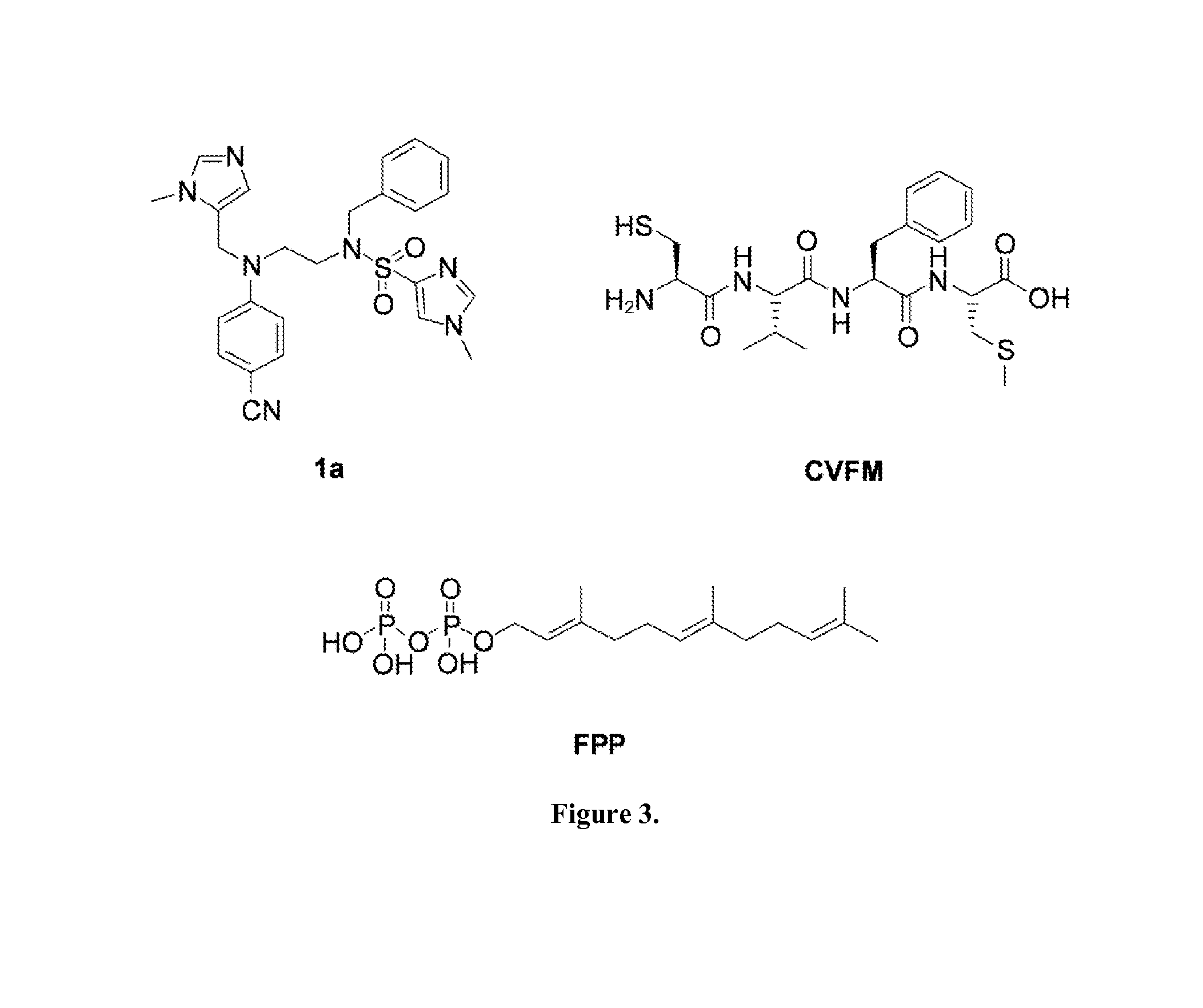
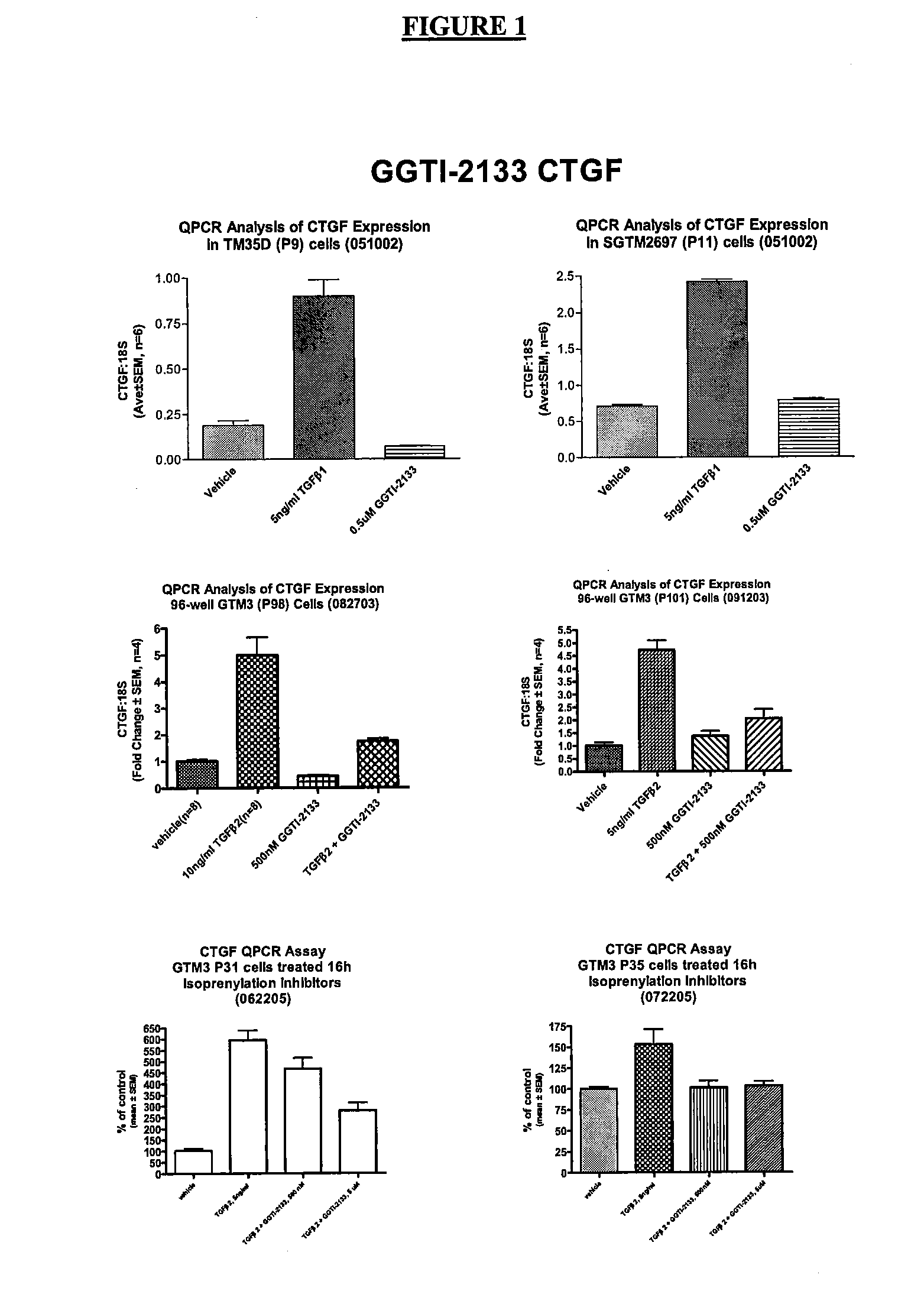
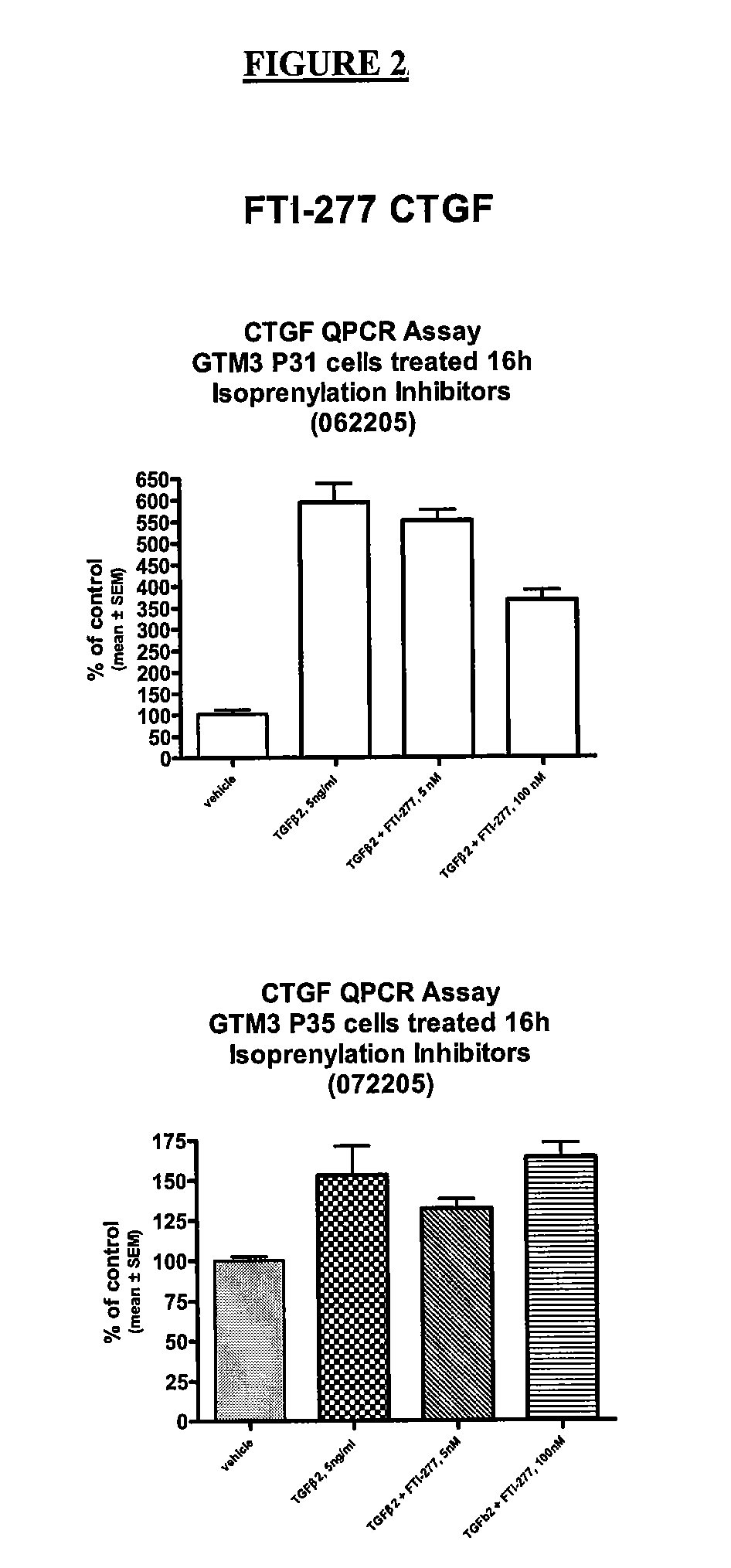
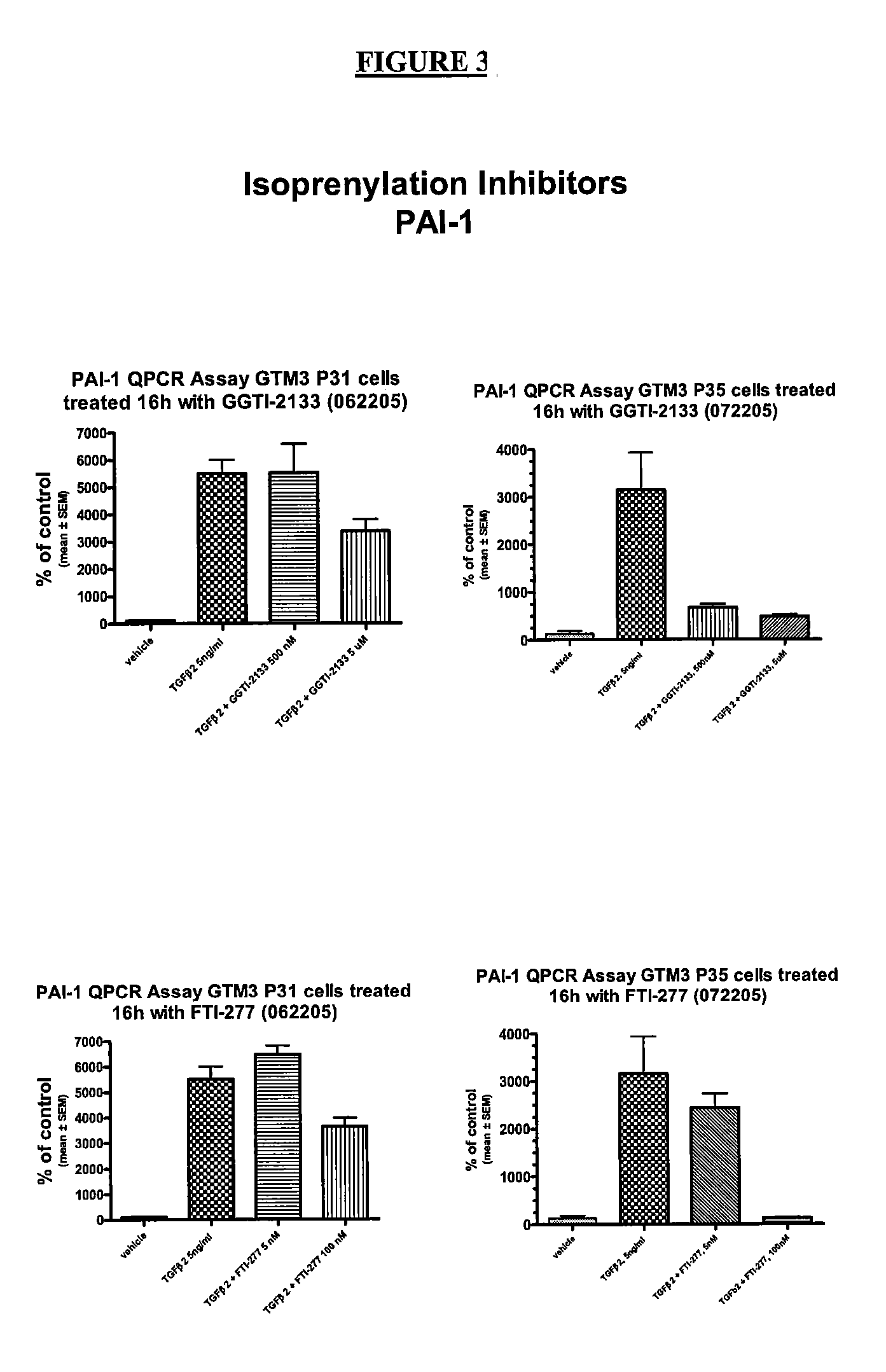
Dual inhibitors of farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I
ActiveUS9040563B2Easy to derivatizeExtensive structure-activity relationship (SAR) studyBiocideOrganic chemistryEthylenediamineAnticarcinogen
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Plant expression vector without antibiotic marker gene and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102181474AAvoid potential risksImprove securityVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsXmaI restriction endonucleaseCulture mediums
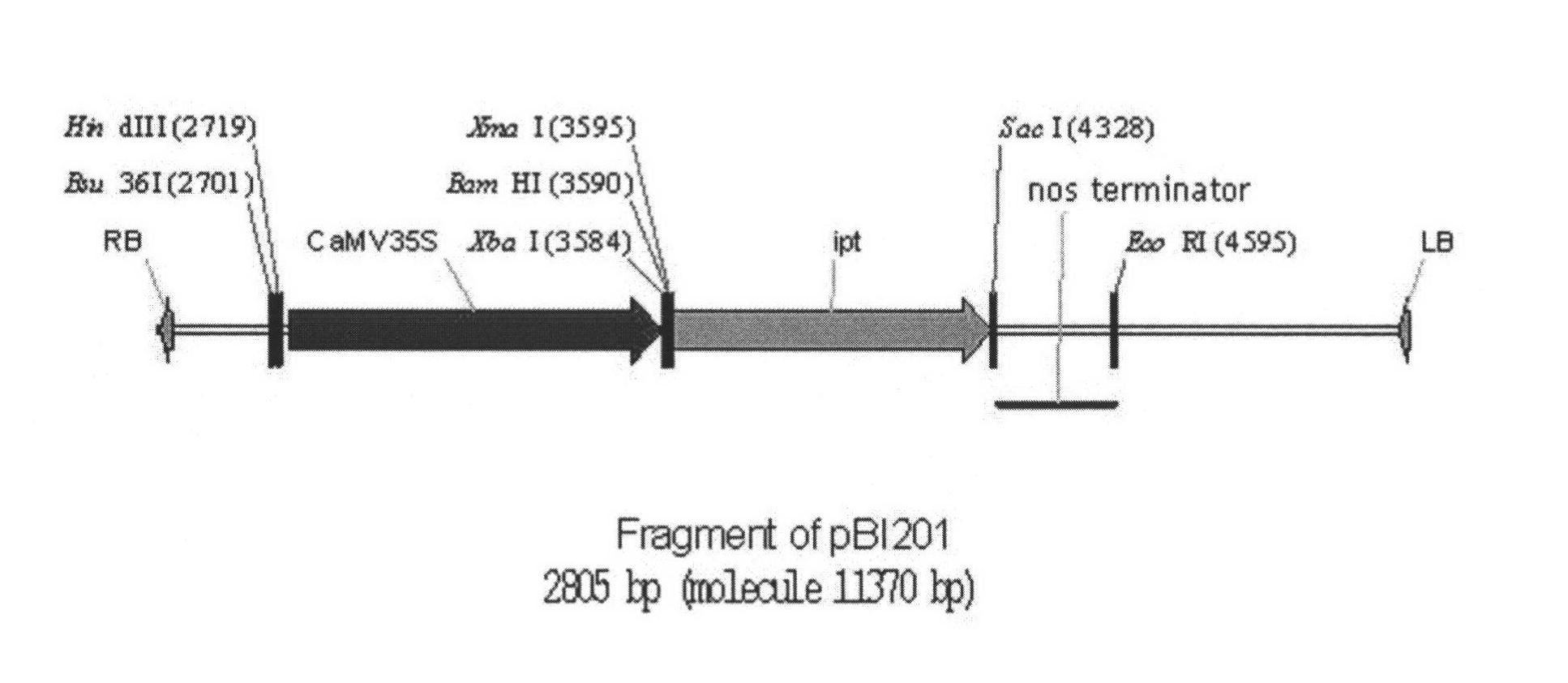
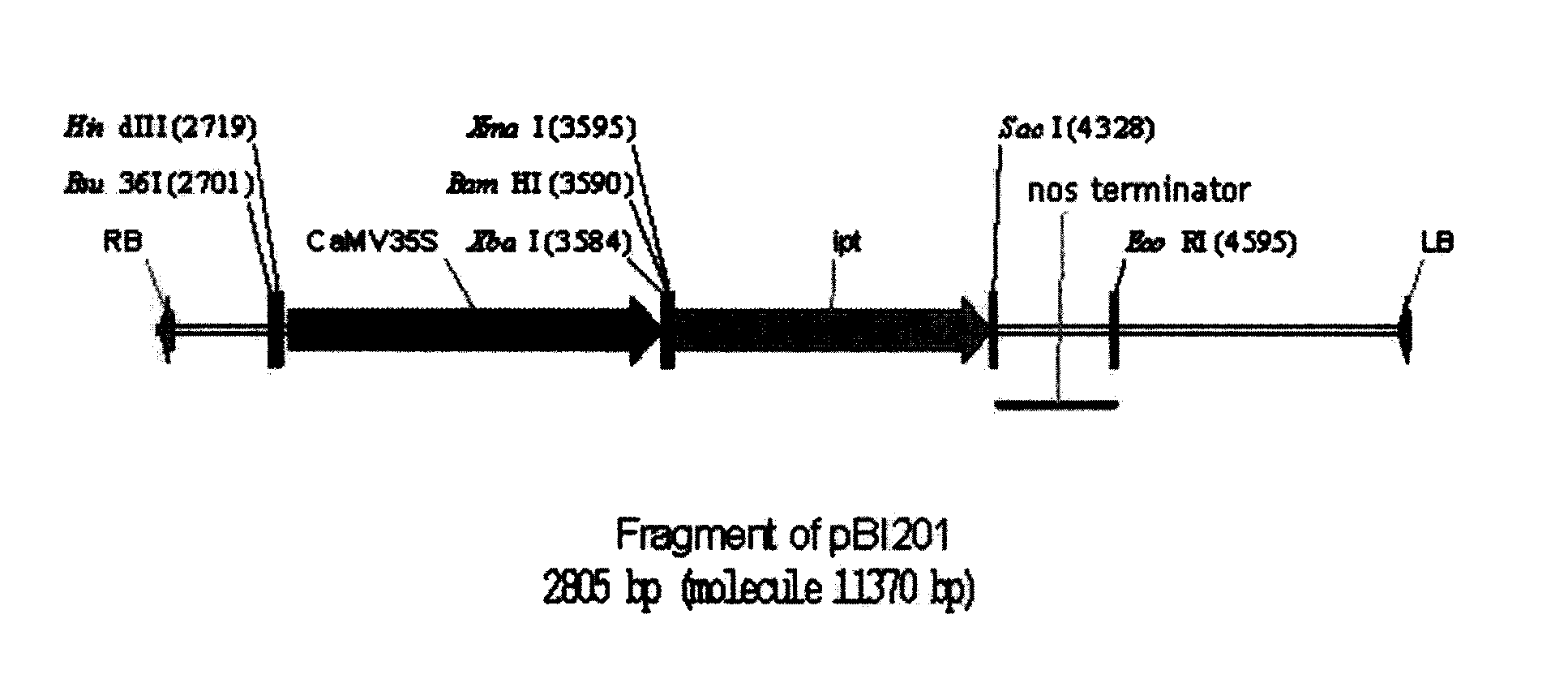
The invention discloses a plant expression vector without antibiotic marker genes and a construction method thereof. The T-DNA region of the vector contains a gene cassette which comprises CaMV 35S promoter, Xba I, Bam HI and XmaI restriction endonuclease enzyme sites, isopentenyl transferase (ipt) gene and nos terminator sequence. The construction method of the vector includes: using a binary vector pBI121 as a base, replacing gus gene with ipt gene, deleting npt II gene through Bsu 36 I and Xba I enzyme sites, reconnecting the CaMV 35S promoter to the T-DNA region. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, transgenic plants can be induced and regenerated on a culture medium with a proper amount of low-concentration cytokinin growth regulators, and the obtained transgenic plants are the transgenic plants expressed by the target genes, which can reduce steps for identifying whether the target gene is expressed, and can avoid potential risks of antibiotic marker genes.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Recombinant pichia pastoris, construction method and application of recombinant pichia pastoris
InactiveCN106047738ALow substrate specificityHigh catalytic activityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisPrenylation
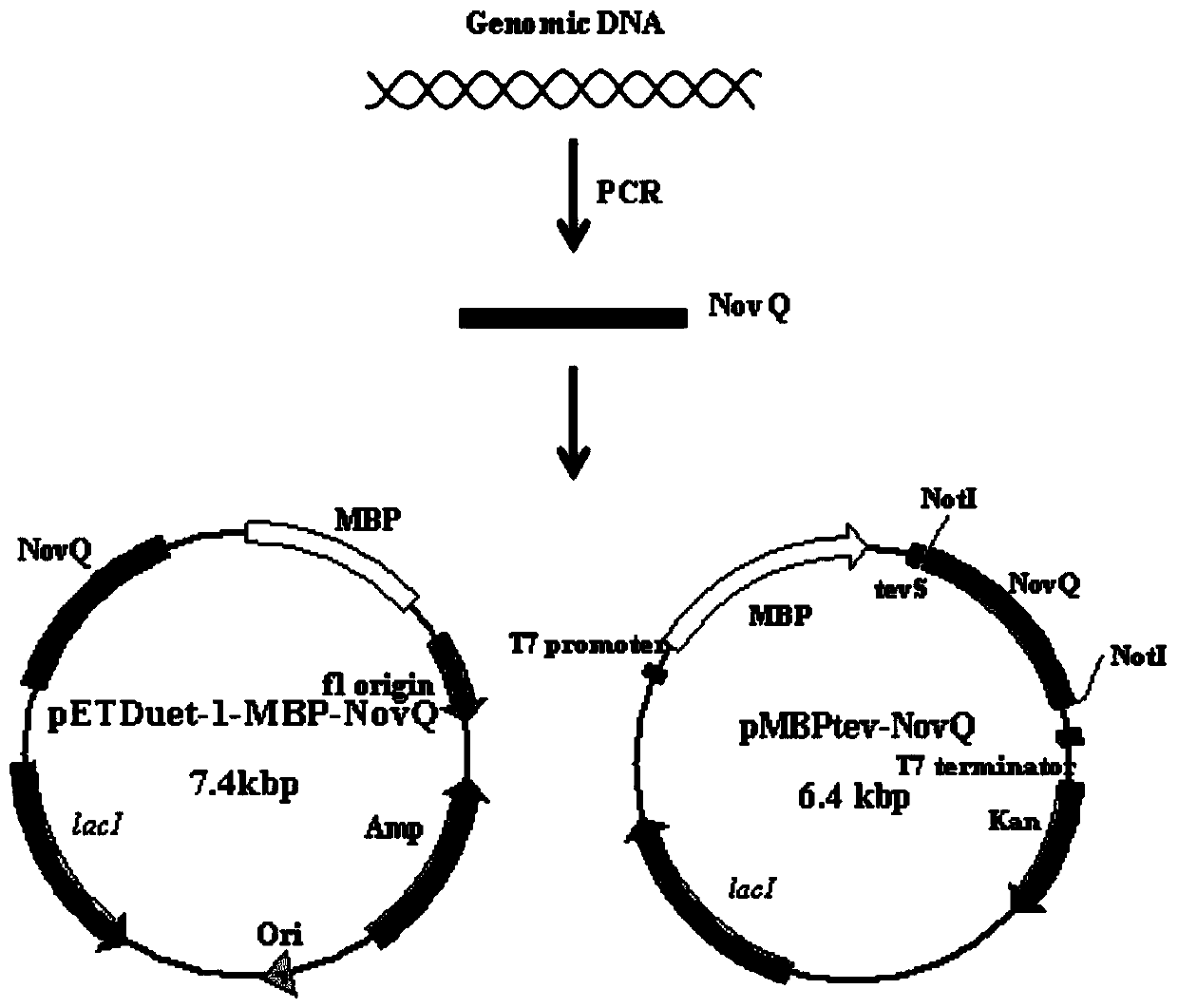
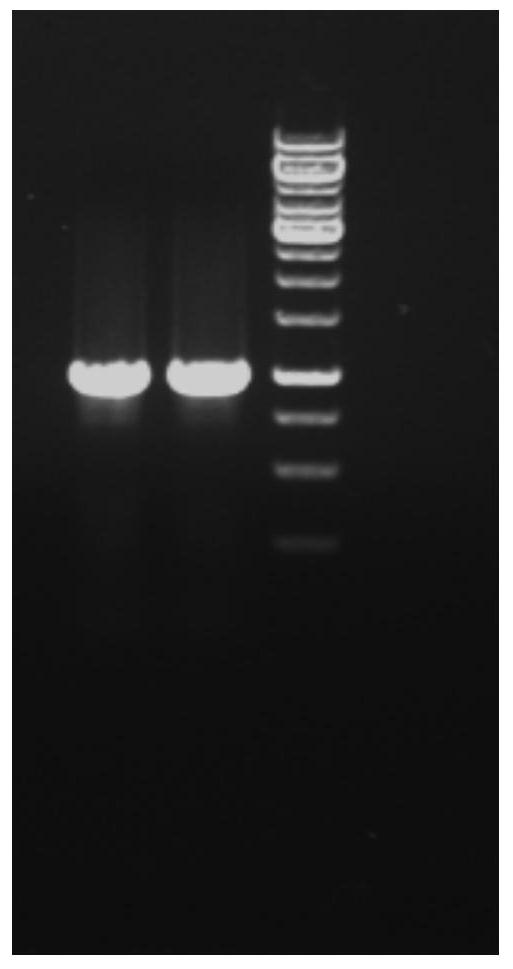
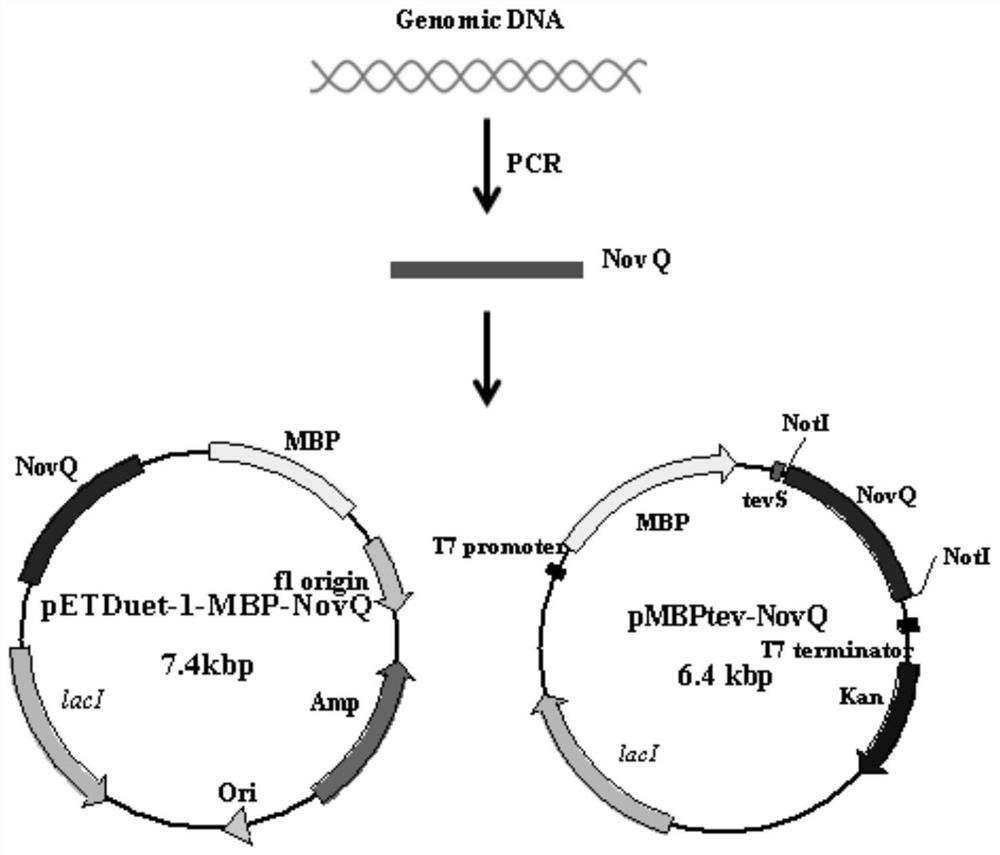
The invention discloses recombinant pichia pastoris (GS115-ppic9-novQ) preserved in CCTCC (China center for type culture collection) on March 11, 2016 with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2016105. The invention further discloses a construction method of the recombinant pichia pastoris and an application in production of aromatic prenyltransferase. By means of induction culture of the engineering bacterium, soluble recombinant aromatic prenyltransferase NovQ with biological activity can be directly obtained in supernatant of a fermentation liquid, and processes such as cell collection, cell disruption and the like are omitted, accordingly, the production process is simplified. Compared with enzymes from other sources, the aromatic prenyltransferase has the advantages that the activity does not depend on structures such as a living cell or a biological membrane, the substrate specificity is low, prenylation of multiple substrates can be catalyzed, the catalytic activity is high and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Isopentenyl transferase sequences and methods of use
ActiveUS20090165177A1Modulated (increased or decreased) cytokinin levelsModulated floral developmentSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationPlant cellPolynucleotide
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Process for production of lactic acid
InactiveCN101300351AImprove productivityBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyMicroorganism4-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyltransferase
A microorganism having the reduction or loss of a 4-hydroxybenzoate-polyprenyltransferase activity or a 2-octapernylphenol 2-octaprenyl-6-methoxyphenol;flavin reductase activity and capable of producing lactic acid, particularly a microorganism having chromosomal DNA having the deletion of a part or the entirety of a gene encoding a protein having a 4-hydroxybenzoate-polyprenyltransferase activity or a protein having a 2-octapernylphenol 2-octaprenyl-6-methoxyphenol;flavin reductase activity; and a process for production of lactic acid using the microorganism.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
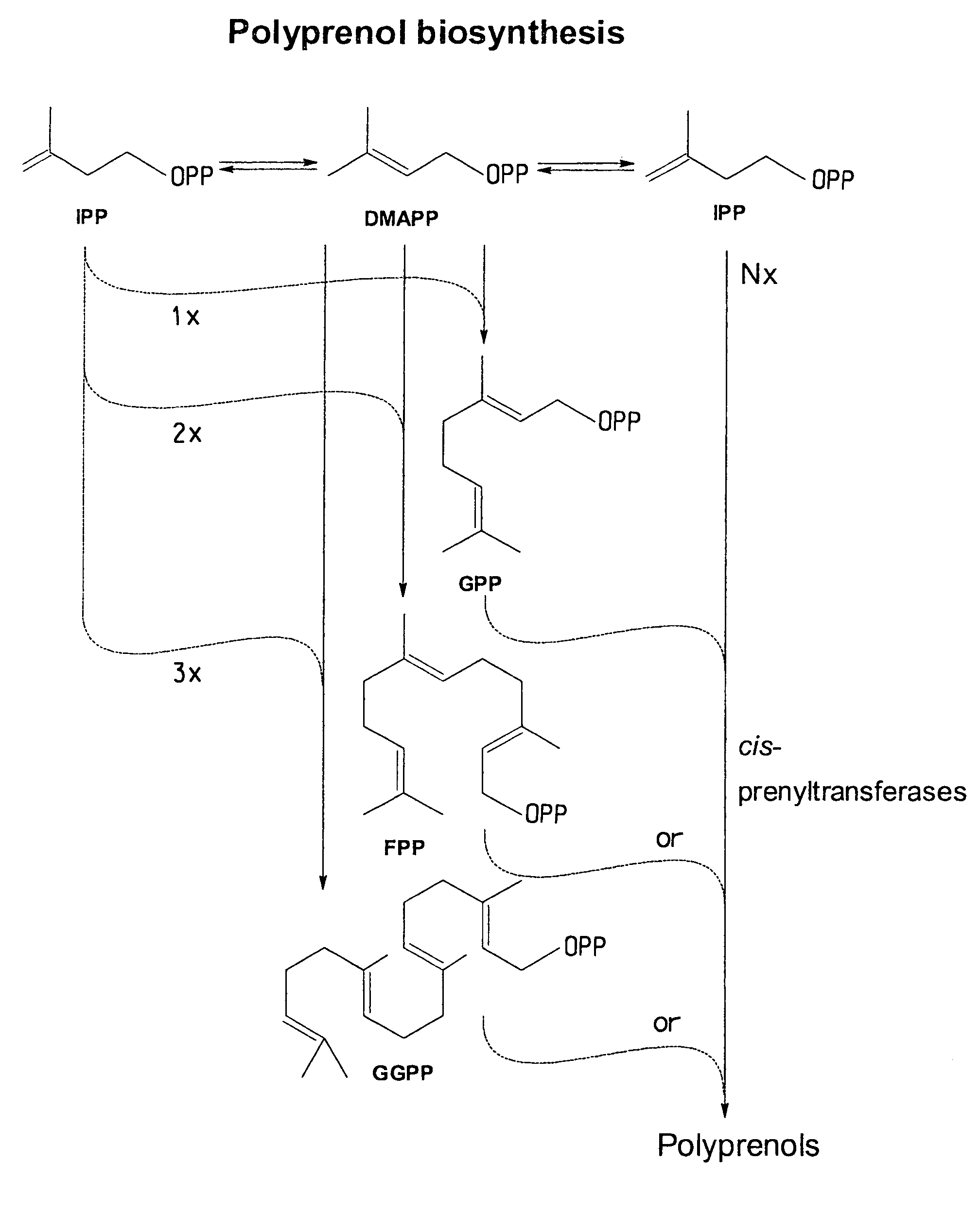
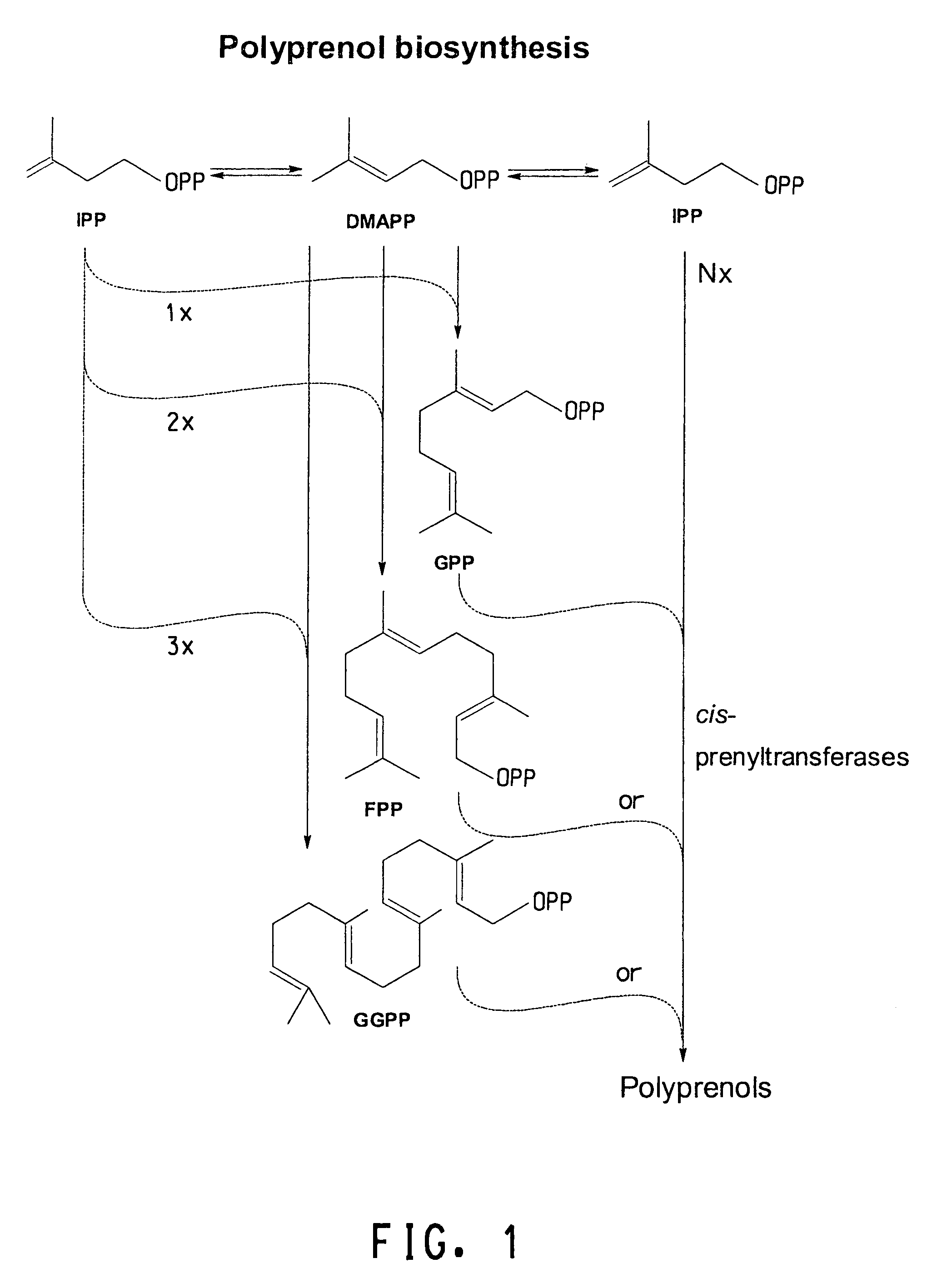
Cis-prenyltransferases from plants
This invention pertains to nucleic acid fragments encoding plant proteins that are homologs to the cis-prenyltransferases UPP synthase from the bacterium Micrococcus luteus or Dedol-PP synthase from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. More specifically, this invention pertains to cis-prenyltransferase homologs from wheat, grape, soybean, rice, African daisy, rubber tree latex and pot marigold.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Biosynthetic Systems Producing Fungal Indole Alkaloids
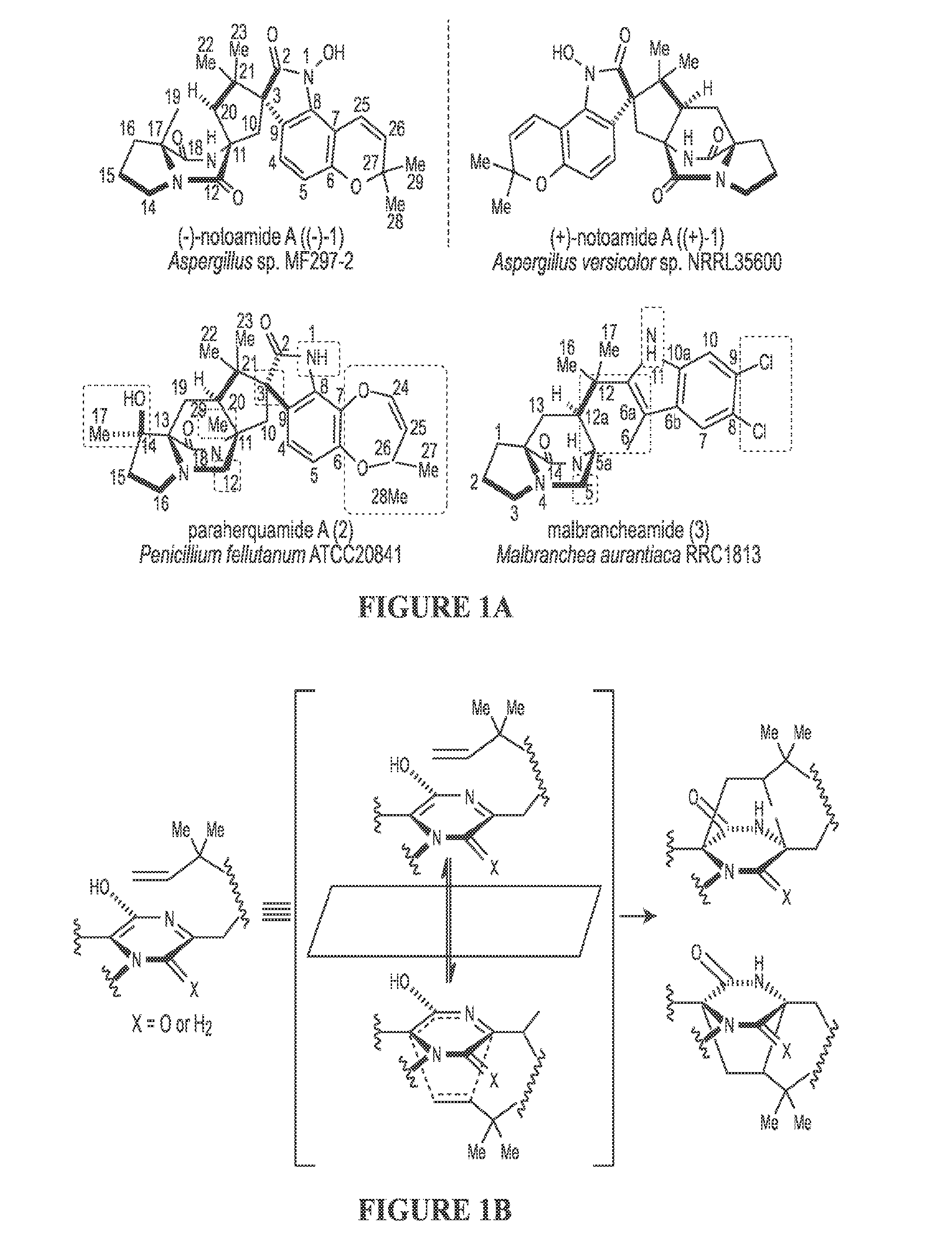
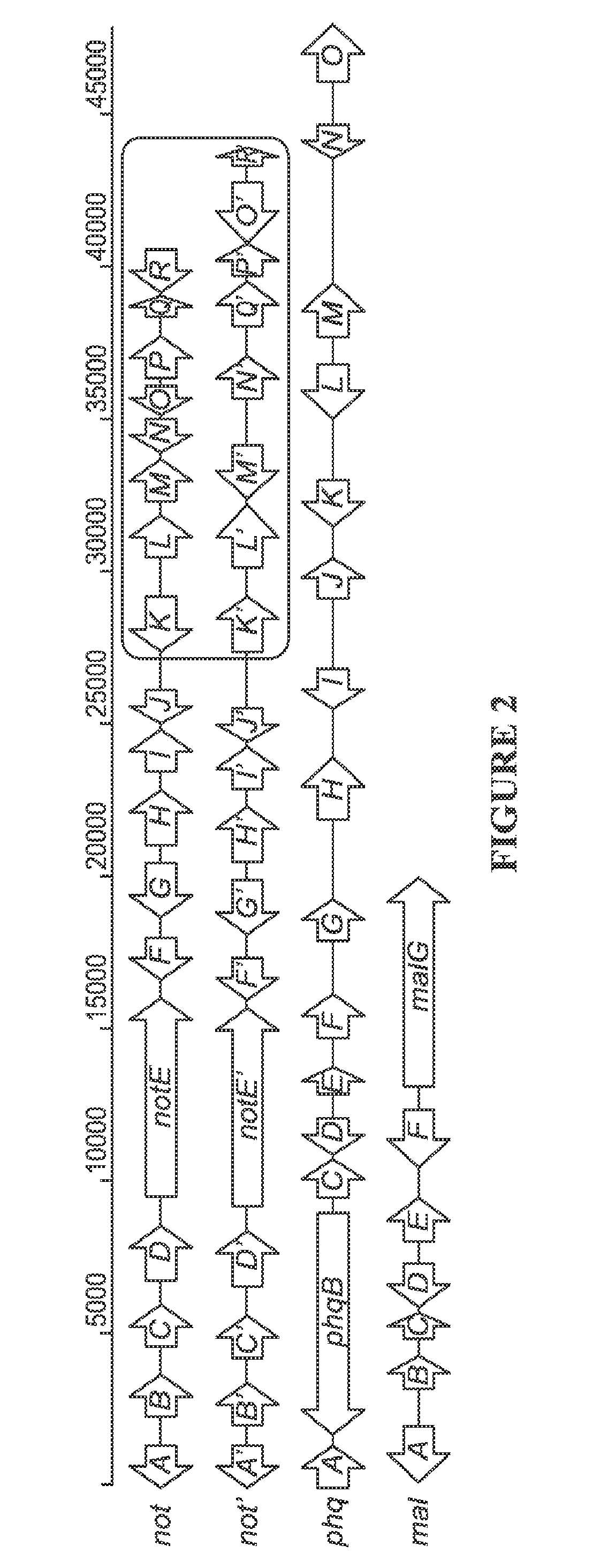
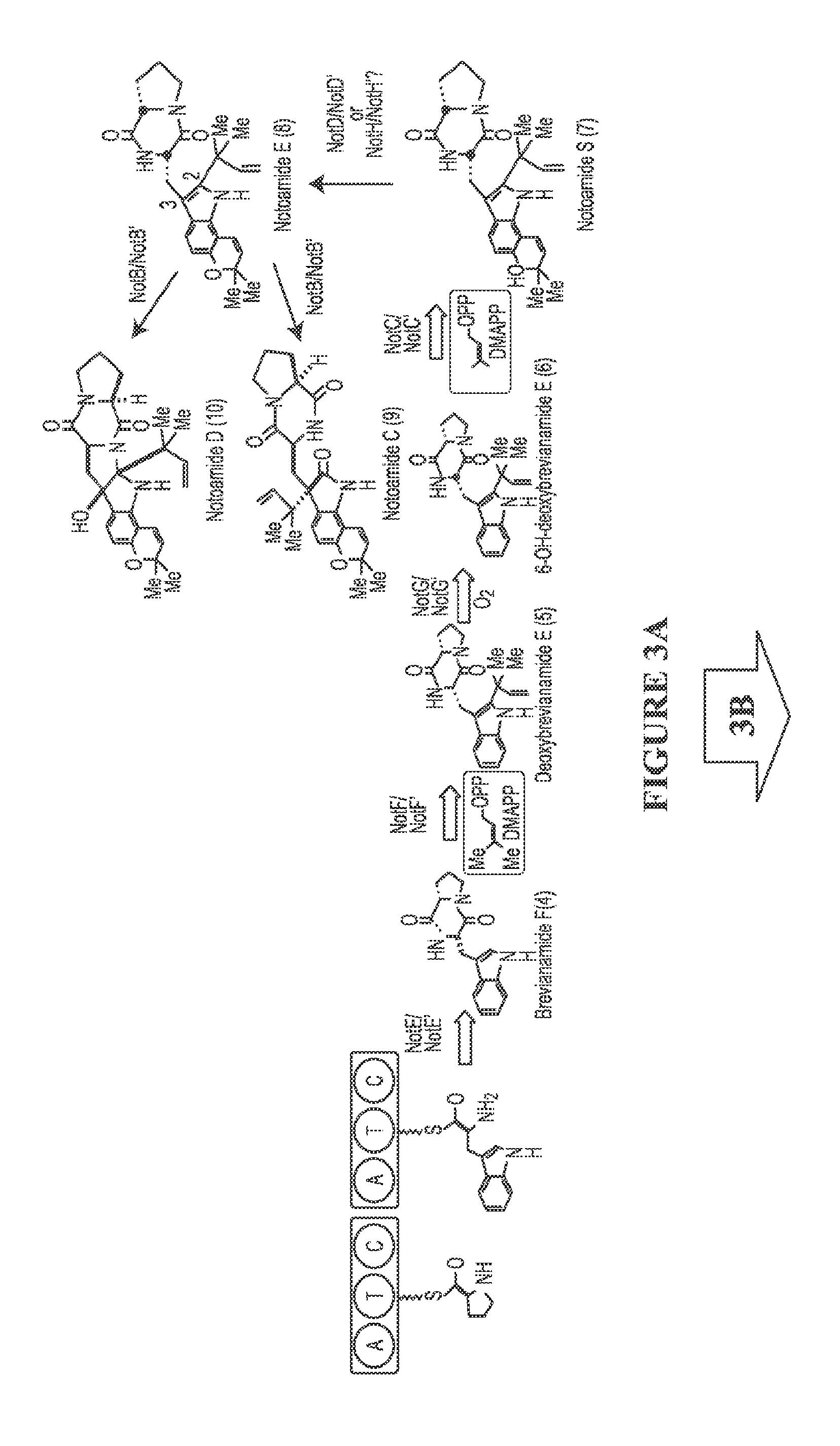
The biosynthesis of fungal bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane indole alkaloids with a wide spectrum of biological activities have attracted increasing interest. Their intriguing mode of assembly has long been proposed to feature a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase, a presumed intramolecular Diels-Alderase, a variant number of prenyltransferases, and a series of oxidases responsible for the diverse tailoring modifications of their cyclodipeptide-based structural core. Until recently, the details of these biosynthetic pathways have remained largely unknown due to lack of information on the fungal derived biosynthetic gene clusters. Herein, we report a comparative analysis of four natural product metabolic systems of a select group of bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane indole alkaloids including (+) / (−)-notoamide, paraherquamide and malbrancheamide, in which we propose an enzyme for each step in the biosynthetic pathway based on deep annotation and on-going biochemical studies.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
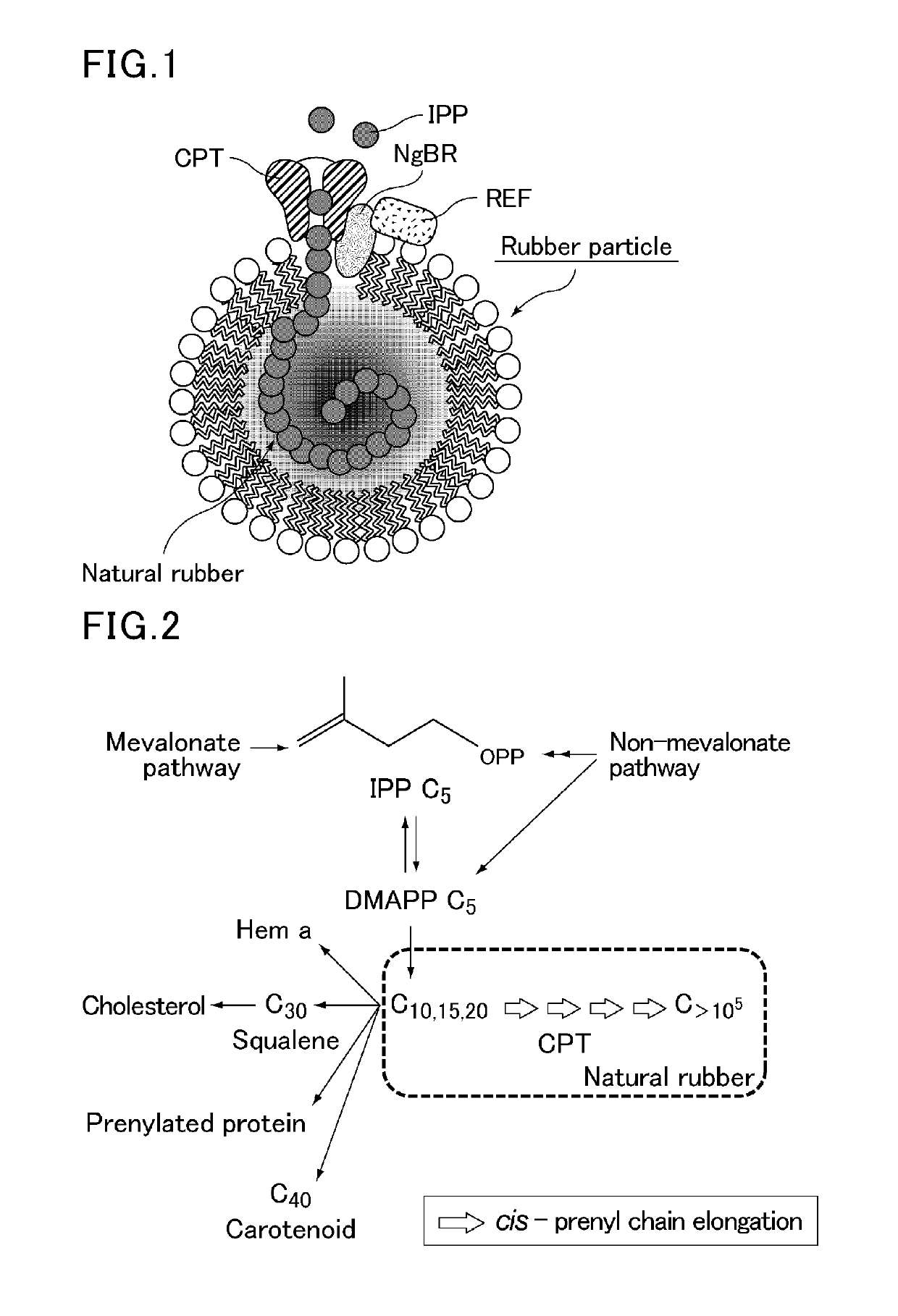
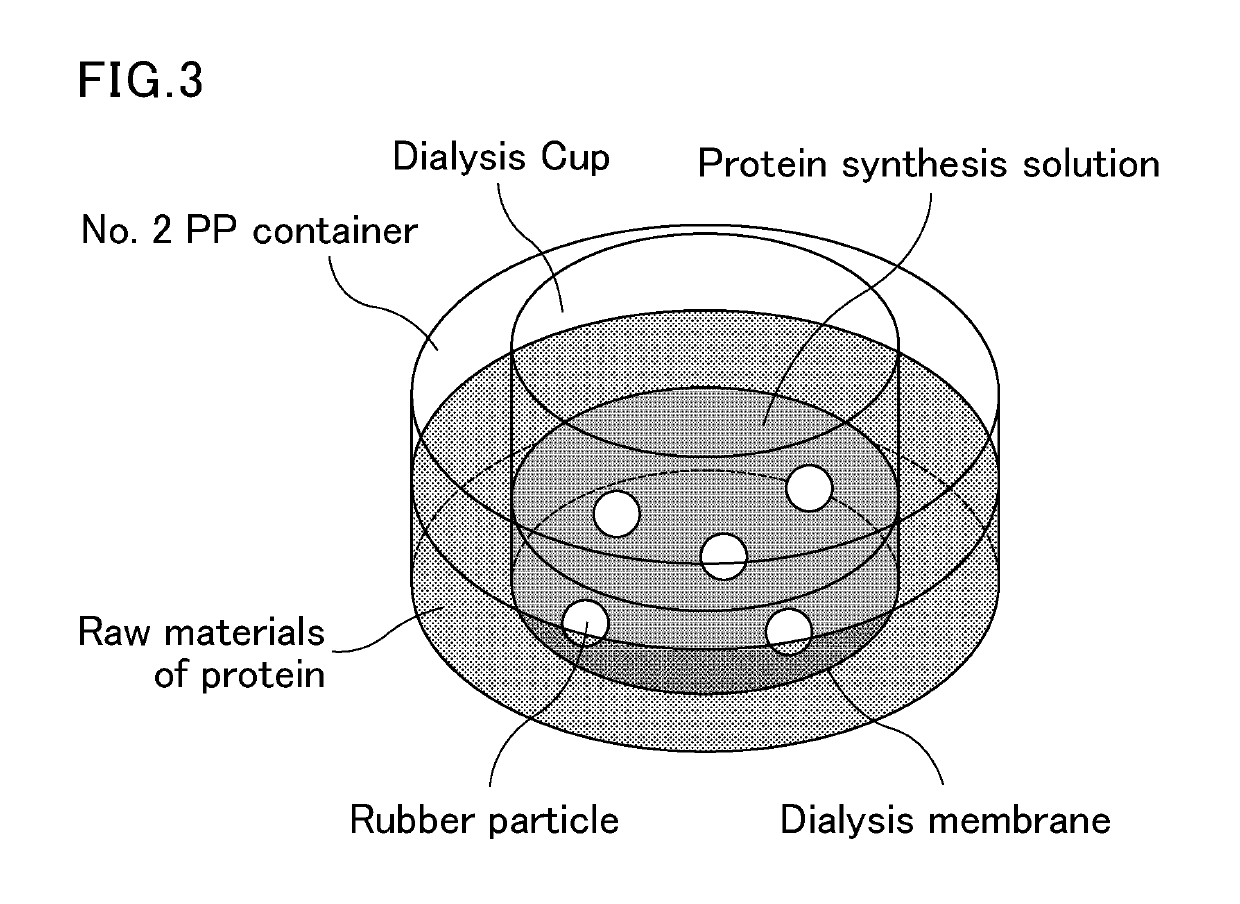
Production method for polyisoprenoid, vector, transgenic plant, production method for pneumatic tire, and production method for rubber product
ActiveUS20180171364A1High activityEfficient productionTransferasesSpecial tyresBiotechnologyPromoter activity
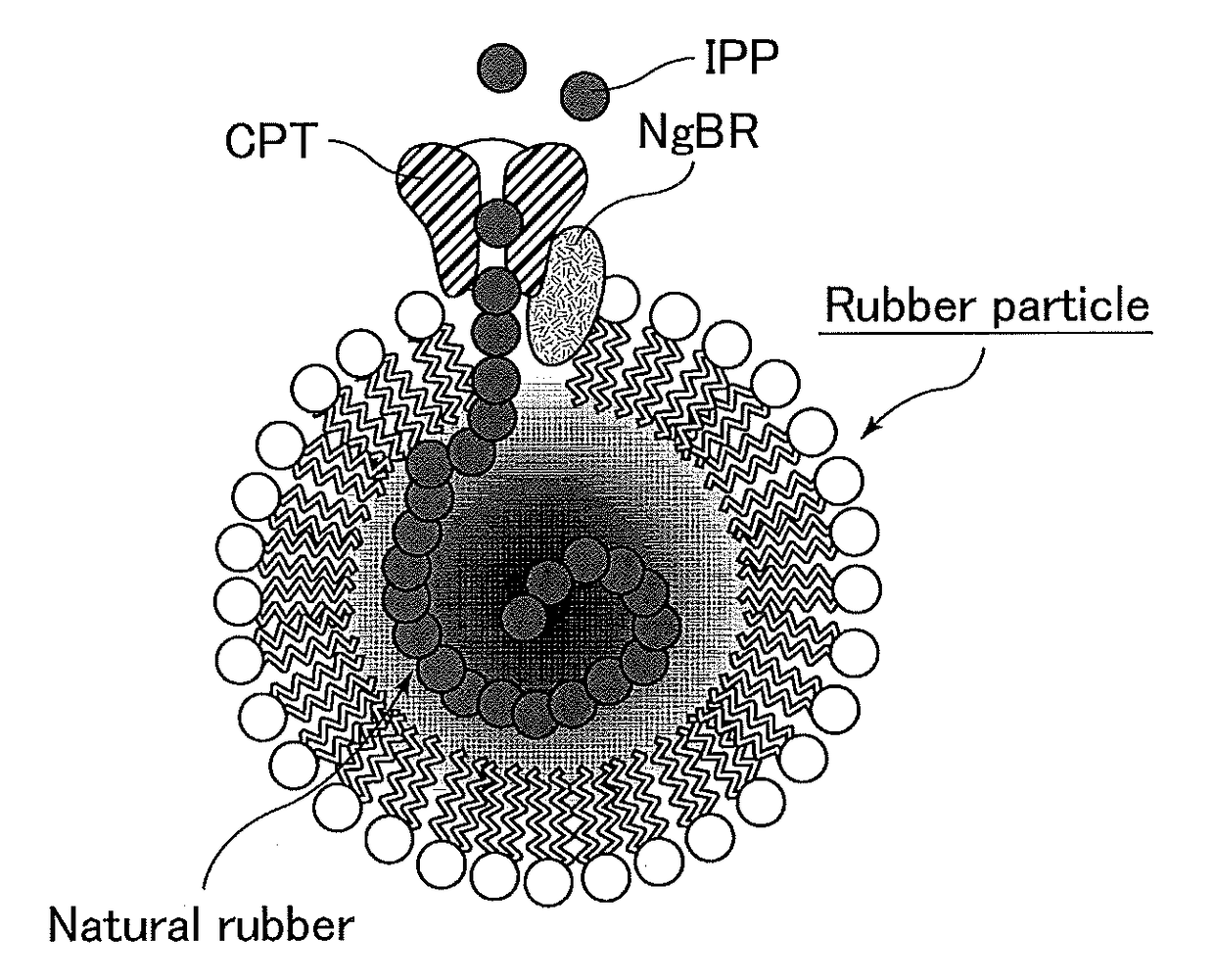
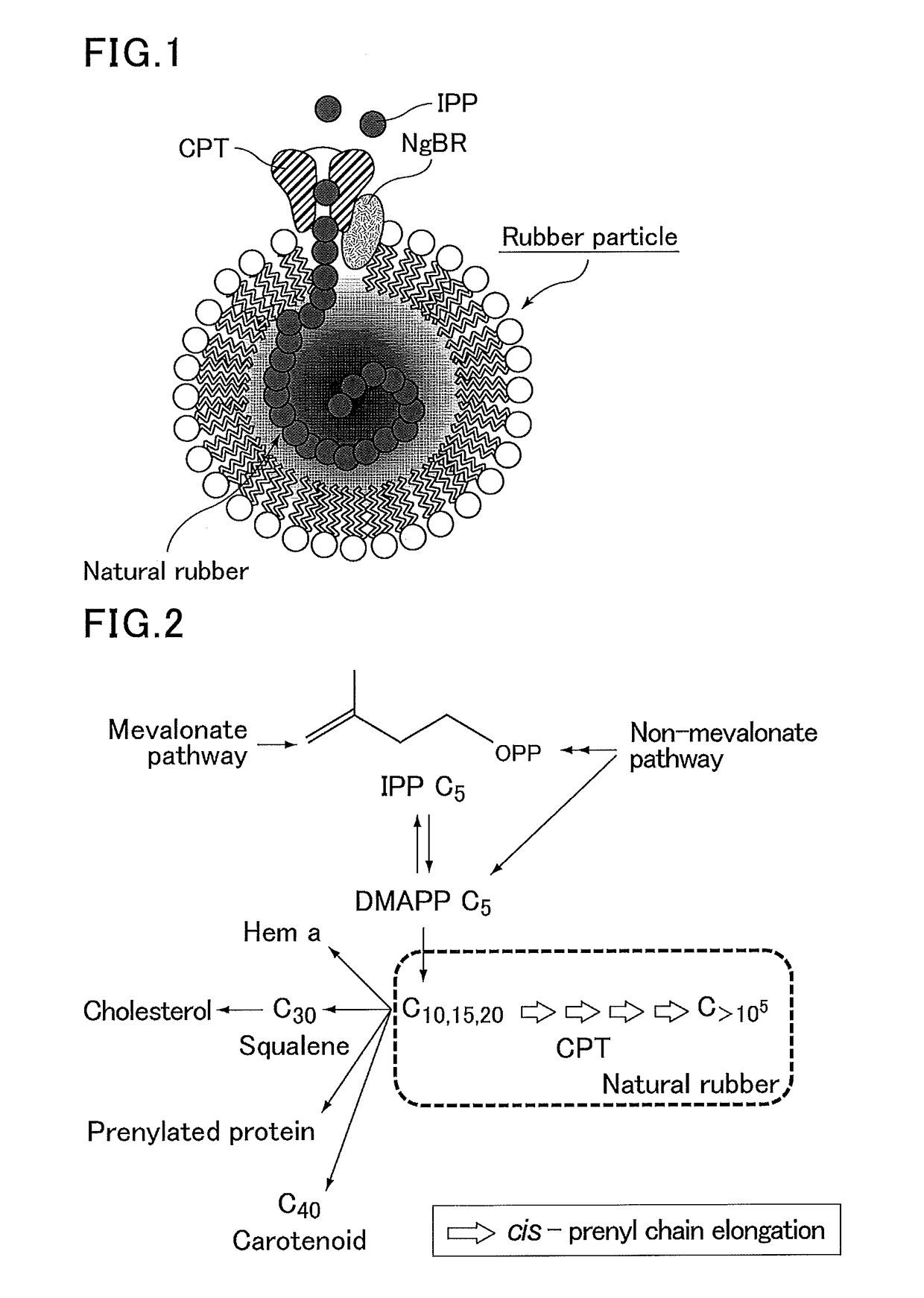
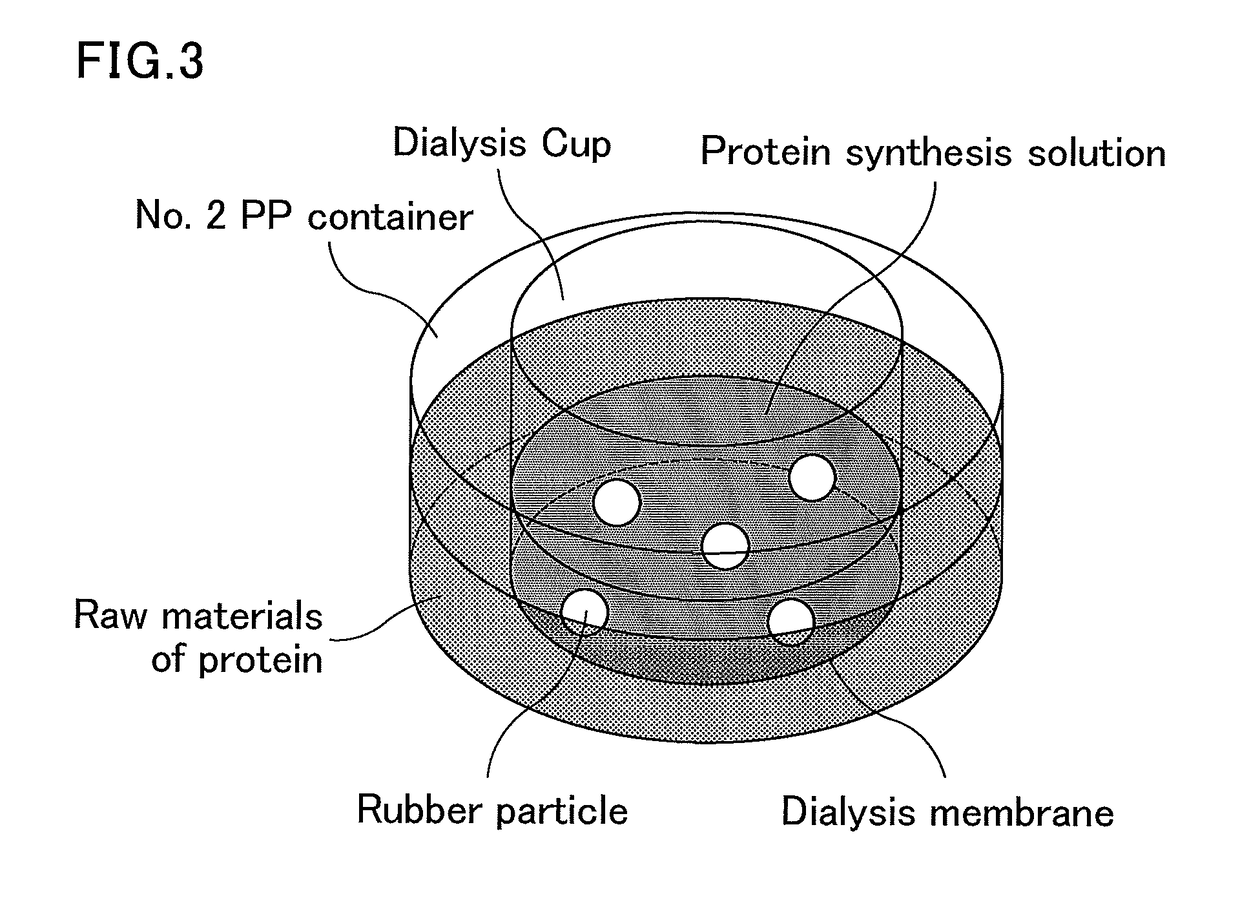
The present invention provides a method for producing a polyisoprenoid with which it is possible to enhance the rubber synthesis activity of rubber particles to increase natural rubber production. The present invention relates to a method for producing a polyisoprenoid in vitro, which involves the use of a gene coding for a cis-prenyltransferase (CPT) family protein and a gene coding for a Nogo-B receptor (NgBR) family protein, and further involves the use of rubber particles bound to proteins encoded by these genes; or a method for producing a polyisoprenoid, which includes introducing into a plant a vector in which a promoter having a promoter activity that drives laticifer-specific gene expression is linked to a gene coding for a CPT family protein and a gene coding for a NgBR family protein, to express proteins encoded by the genes specifically in laticifers.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD +1
Transformant for expressing cis-prenyltranferase and Nogo B receptor
ActiveUS10000774B2Activity can be stabilized and enhancedIncrease productionCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesGenePolyprenol
Provided are a transformant produced by introducing a gene coding for a cis-prenyltransferase and a gene coding for a Nogo-B receptor, which are considered to be involved in polyisoprenoid biosynthesis, into a host to allow the host to express the cis-prenyltransferase and the Nogo-B receptor, and a method for producing a polyisoprenoid using the transformant. The present invention relates to a transformant produced by introducing a gene coding for a cis-prenyltransferase and a gene coding for a Nogo-B receptor into a host to allow the host to express the cis-prenyltransferase and the Nogo-B receptor.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Method for producing polyisoprenoid, transformed plant, method for producing pneumatic tire and method for producing rubber product
ActiveUS10385362B2High activityEnhance the activity of the CPT family proteinTransferasesTyresElongation factorIn vivo
Provided is a method for producing a polyisoprenoid, which can increase natural rubber production by enhancing the rubber synthesis activity of rubber particles. The present invention provides methods for producing a polyisoprenoid using a gene coding for a cis-prenyltransferase (CPT) family protein, a gene coding for a Nogo-B receptor (NgBR) family protein and a gene coding for a rubber elongation factor (REF) family protein, specifically a method for producing a polyisoprenoid in vitro using rubber particles bound to proteins coded for by these genes, and a method for producing a polyisoprenoid in vivo using a recombinant organism (plant) having these genes introduced therein.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD +1
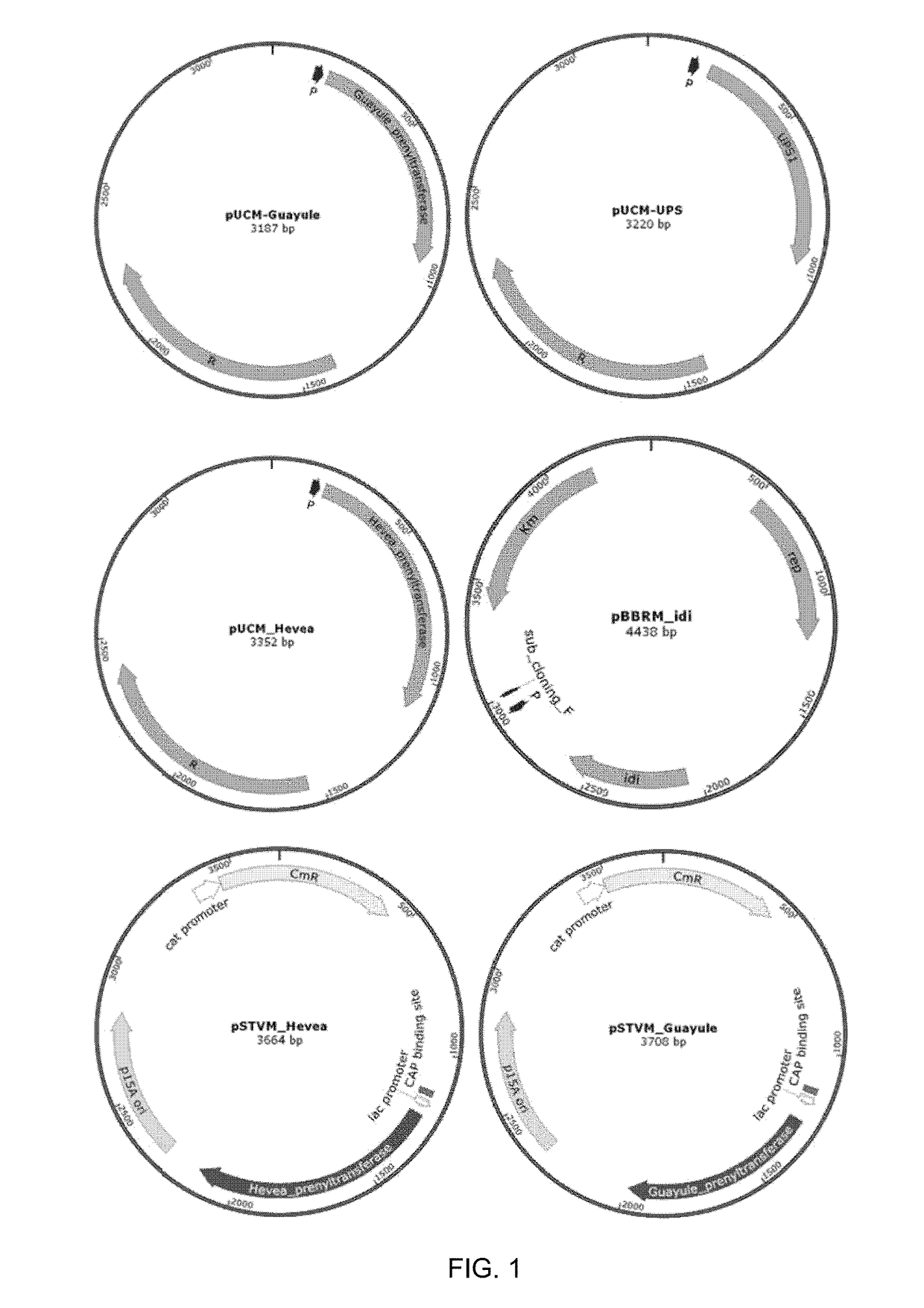
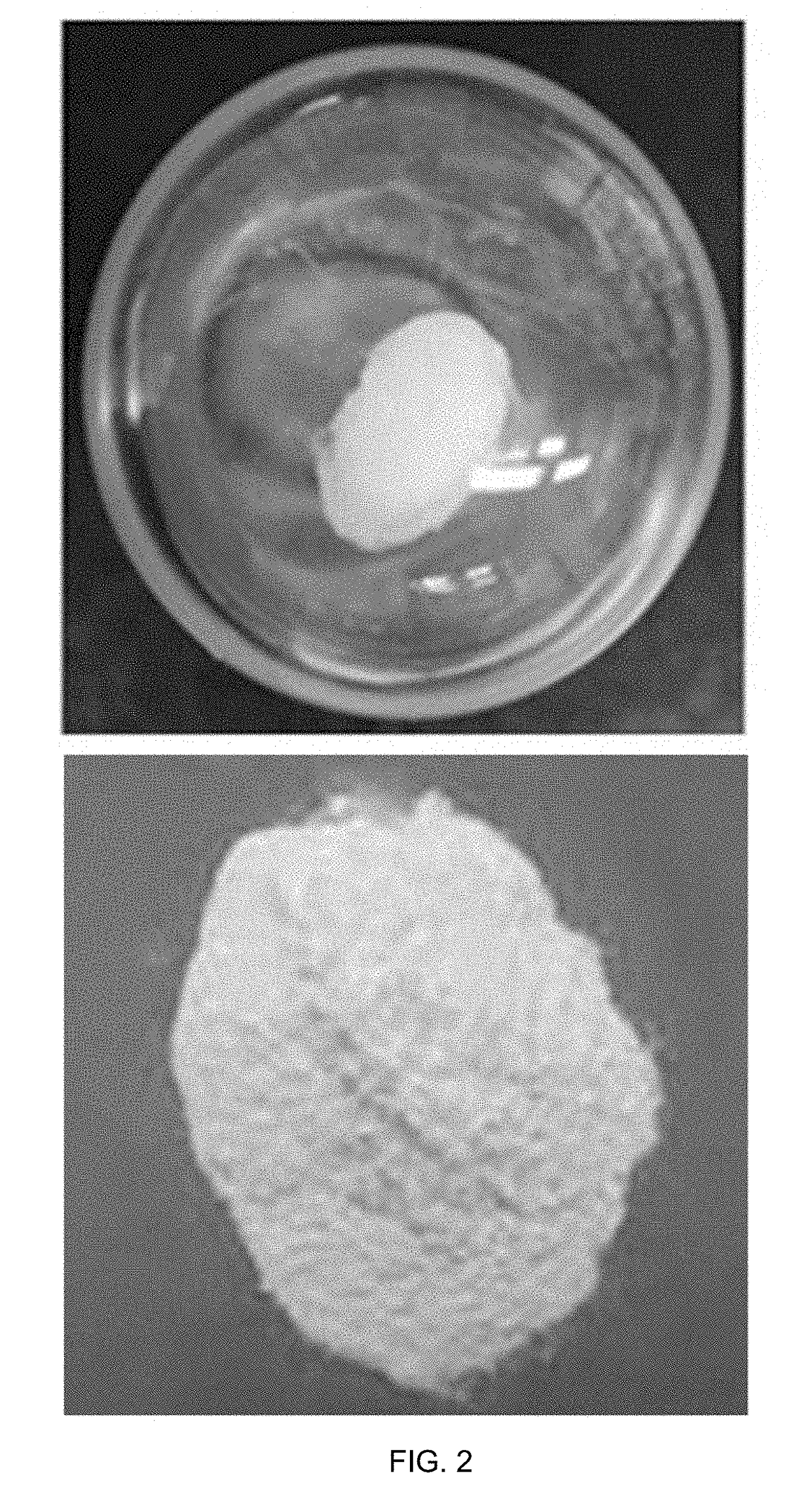
Method for producing natural rubber by using recombinant microorganism
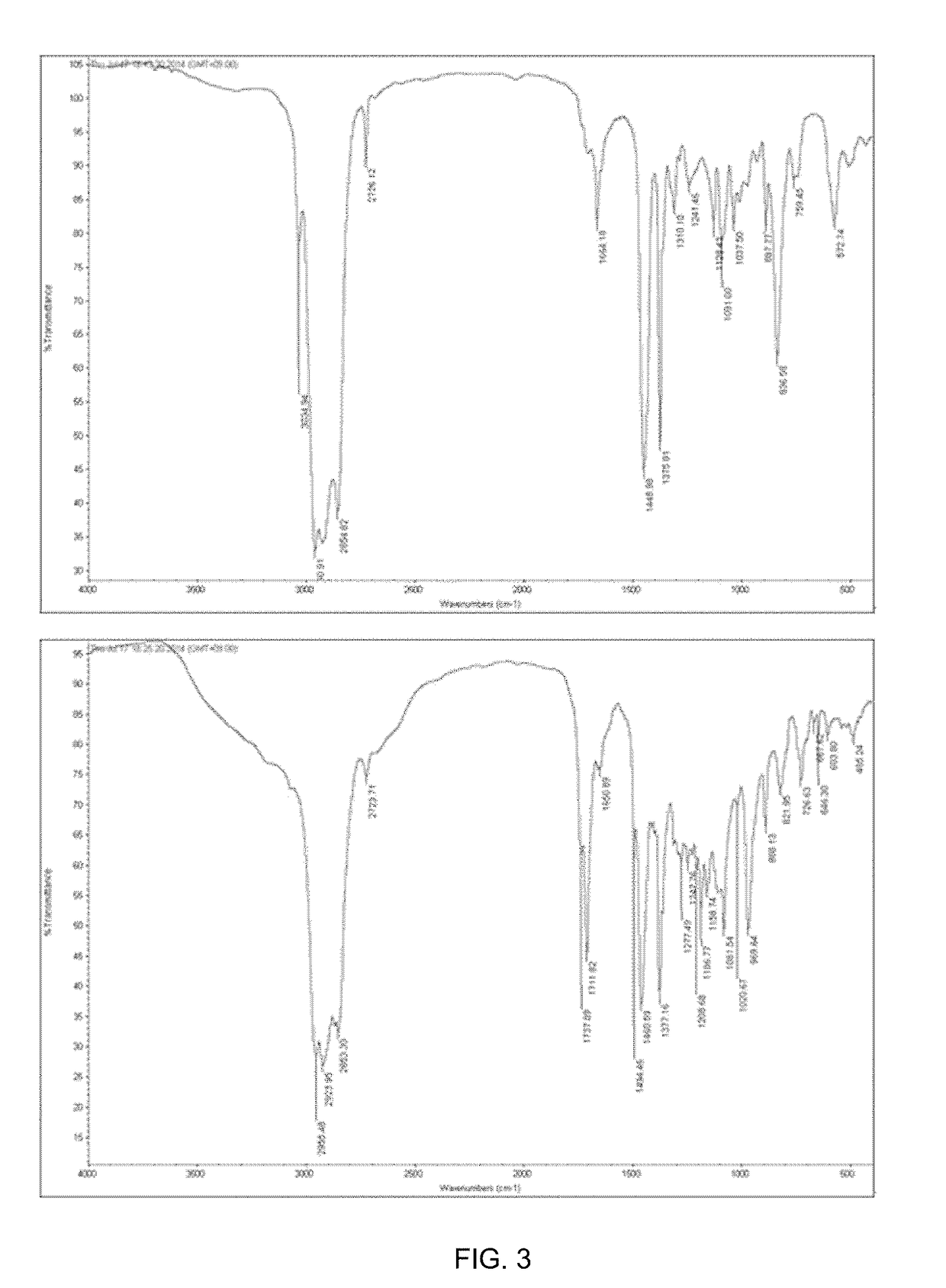
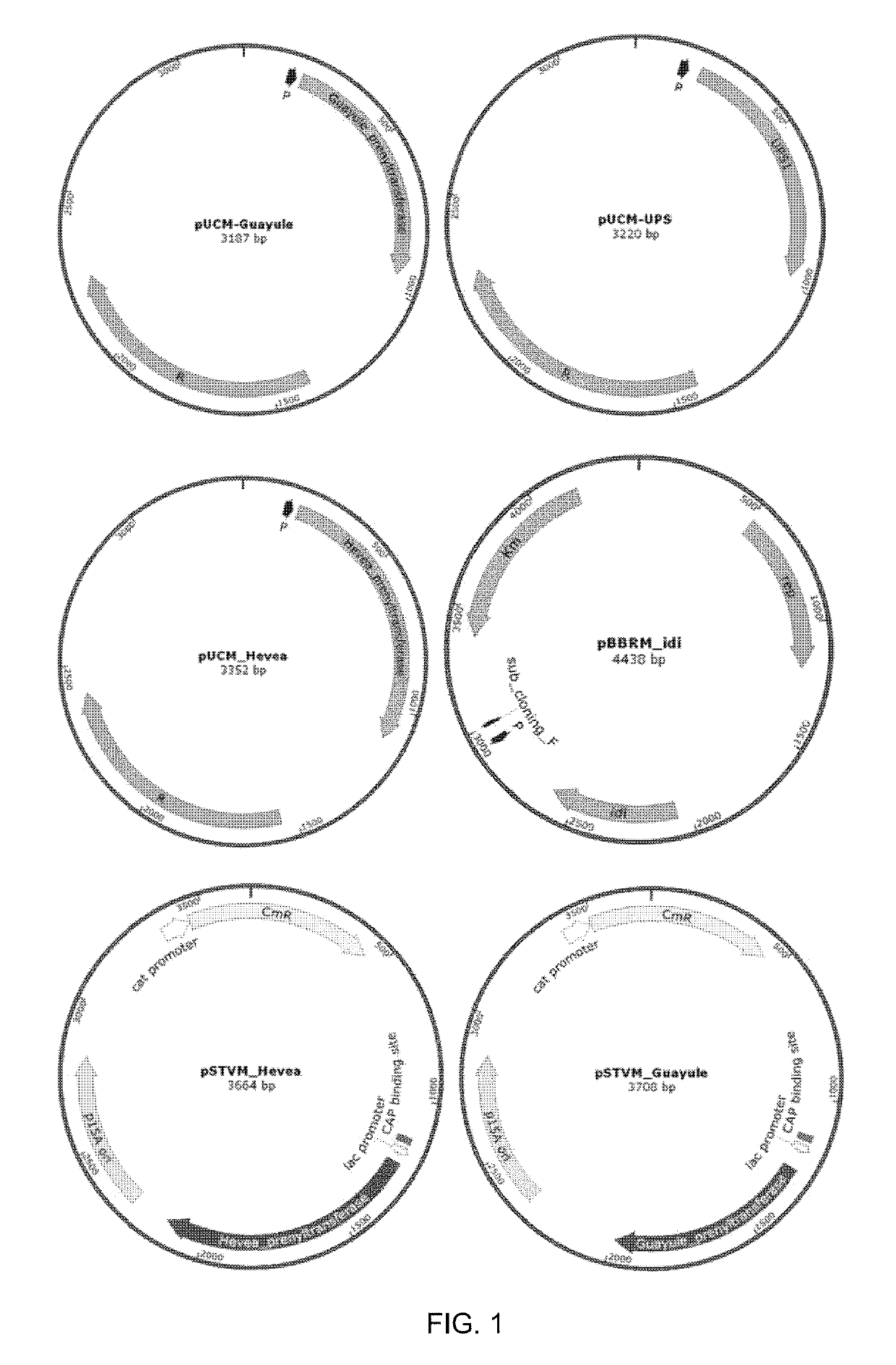
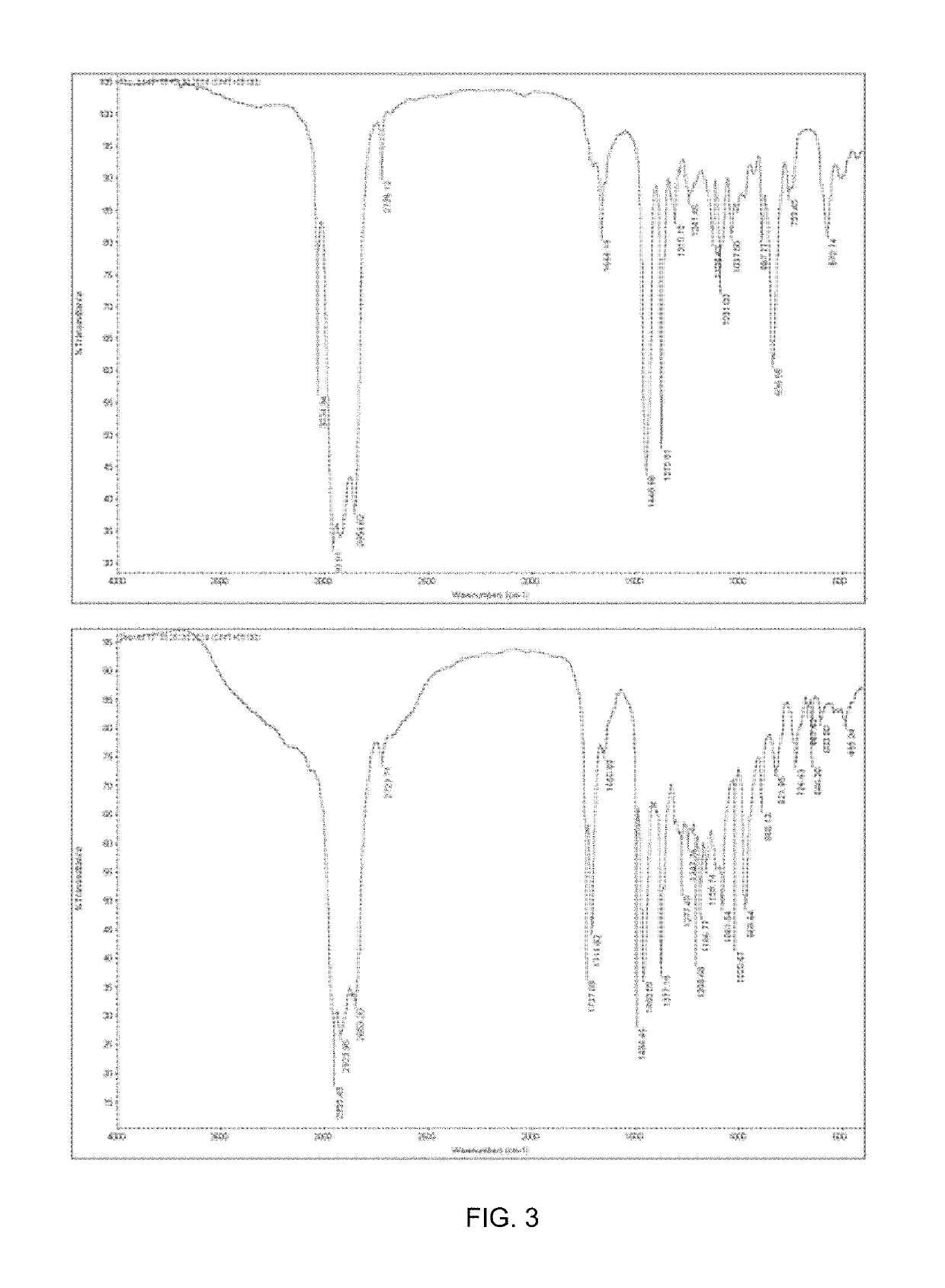
A method for producing natural rubber by using a recombinant microorganism is disclosed, the method comprising: (a) manufacturing an expression vector capable of expressing a gene encoding a cis-prenyltransferase, which is a guayule-derived natural rubber synthetase represented by the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 or a Hevea brasiliensis-derived natural rubber synthetase represented by the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 6, and an expression vector capable of expressing a gene coding for a natural rubber precursor synthetase; (b) transforming a host microorganism with the expression vector; (c) culturing the transformed host microorganism; and (d) separating natural rubber from the cultured transformed host microorganism. The natural rubber obtained by the method has a white powder form identical to that of natural rubber, and shows an FT-IR spectrum pattern extremely similar to that of natural rubber.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
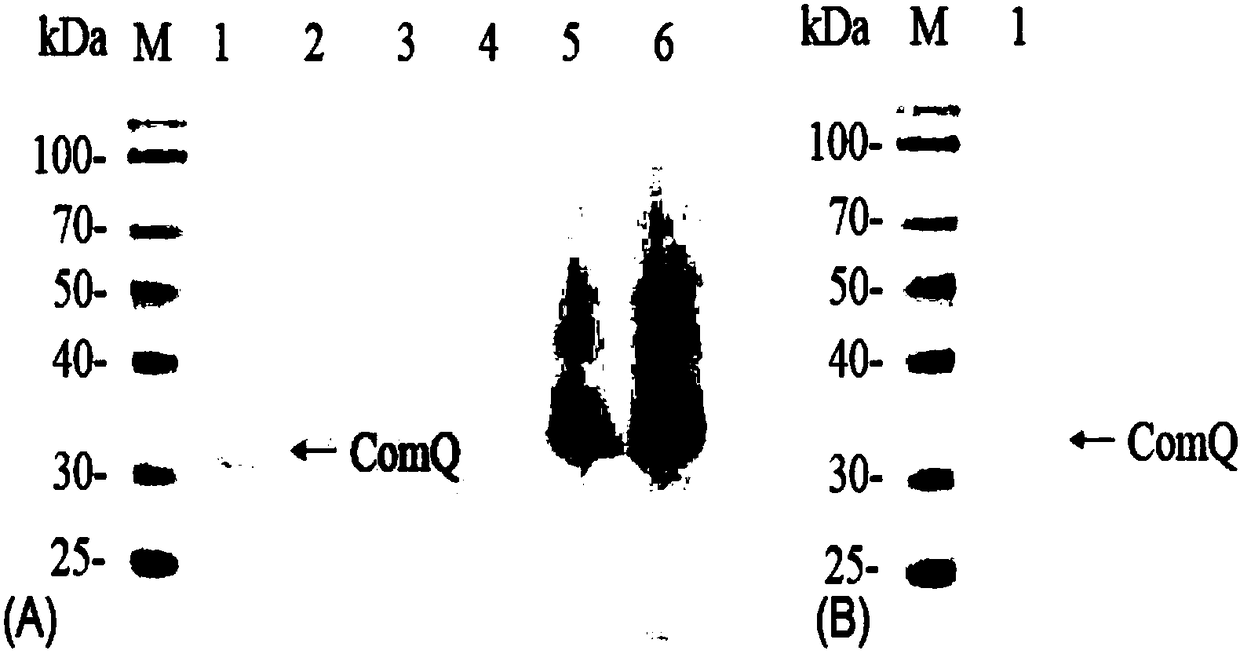
Construction method and application of genetically-engineered bacterium for expressing prenyltransferase ComQ
InactiveCN108486142ATransferasesMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionChemical transformation
The invention relates to a construction method and application of a genetically-engineered bacterium for expressing prenyltransferase ComQ, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and protein engineering. The method is mainly characterized by including the steps of designing a primer of the prenyltransferase ComQ, amplifying target genes of the prenyltransferase ComQ, constructing recombinant plasmid through an enzyme digestion and enzyme linking method, identifying the recombinant plasmid and constructing a genetically-engineered bacterial strain through chemical transformation. By means of the method, the genetically-engineered bacterial strain for expressing the prenyltransferase is constructed for biosynthesis of various aromatic compounds with the pharmacological activity and isopentenylated peptides compounds by means of the prenyltransferase, and the genetically-engineered bacteria are used for heavily expressing, separating and purifying the prenyltransferase; bymeans of the prenyltransferase which is obtained through separation and purification, isopentenylated treatment can be conducted on aromatic radicals in peptide compounds so that the method can be used for isopentenylated treatment of the aromatic compounds.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Gene encoding prenyltransferase and recombinant plasmid carrying the same
Owner:OCEAN UNTVERSITY OF CHINA
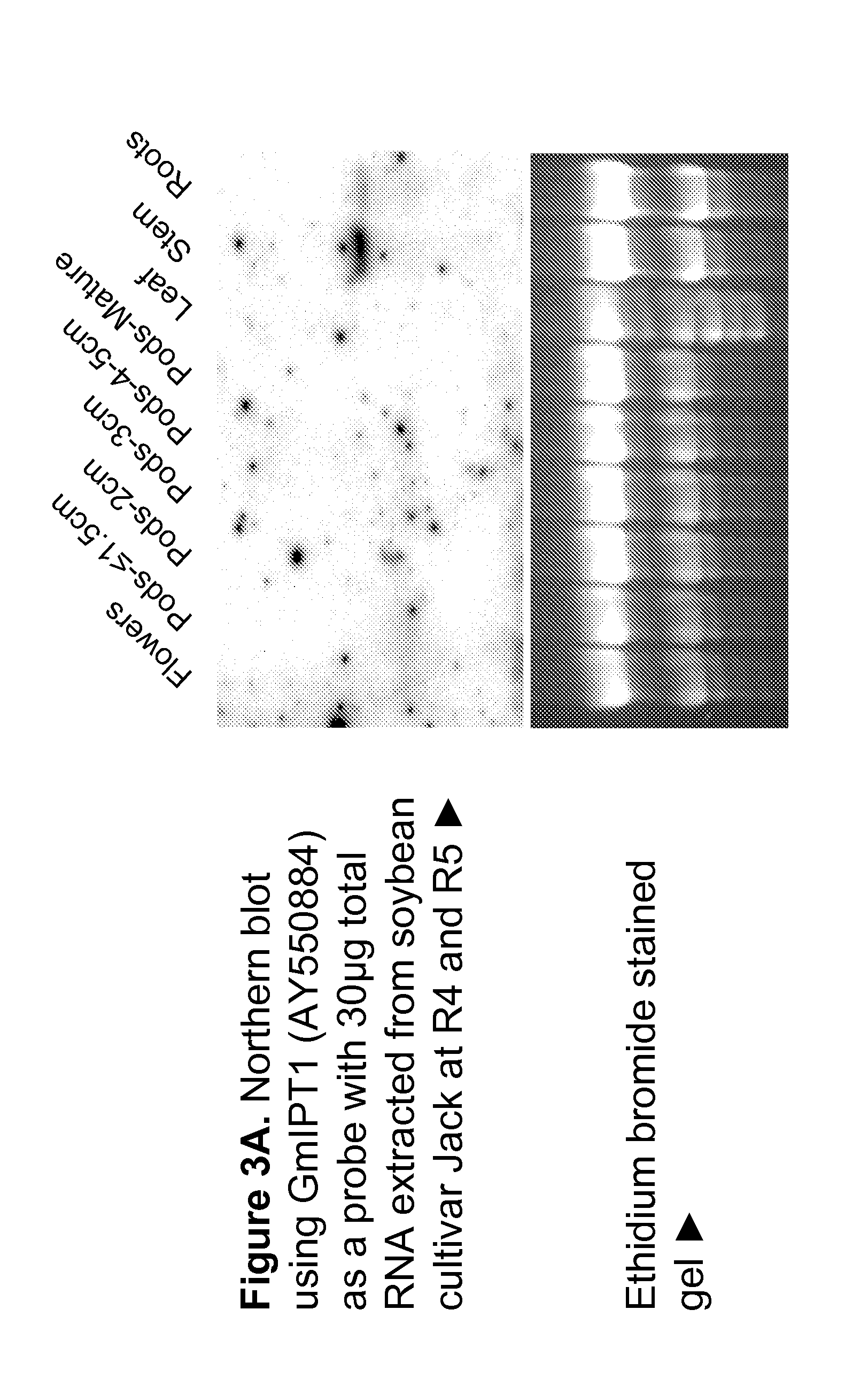
Soybean isopentenyl transferase genes and methods of use
InactiveUS7553951B2Modulated (increased or decreased) cytokinin levelsModulated floral developmentFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellPolynucleotide
Methods and compositions for modulating plant development are provided. Polynucleotide sequences encoding isopentenyl transferase (IPT) polypeptides are provided, as are the amino acid sequences of the encoded polypeptides. The sequences can be used in a variety of methods including modulating root development, modulating floral development, modulating leaf and / or shoot development, modulating senescence, modulating seed size and / or weight, and modulating tolerance of plants to abiotic stress. Transformed plants, plant cells, tissues, and seed are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Microorganisms and Methods for the Fermentation of Cannabinoids
PendingUS20210348137A1Improve efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsCarbon-sulfur lyasesCyclaseBeta oxidation
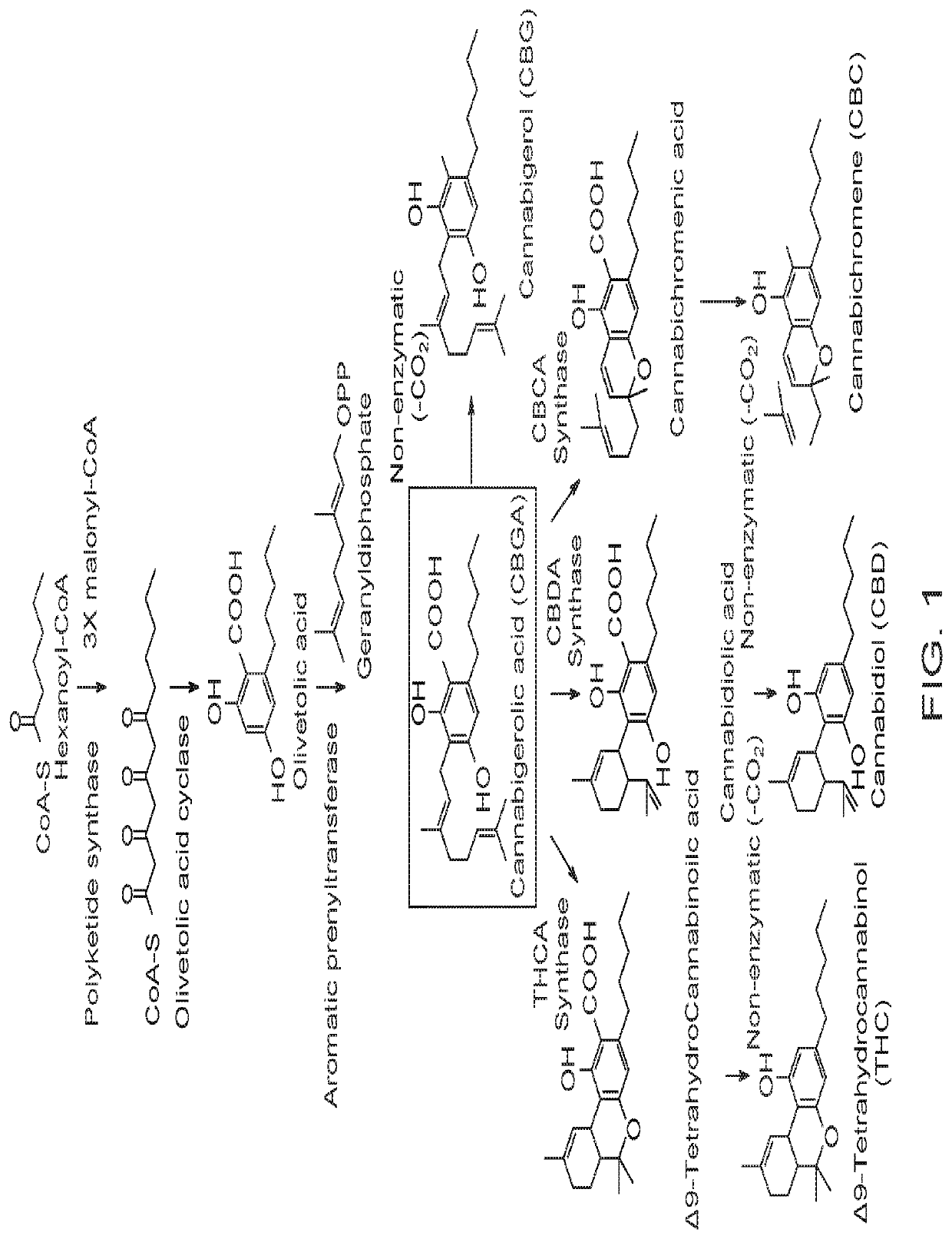
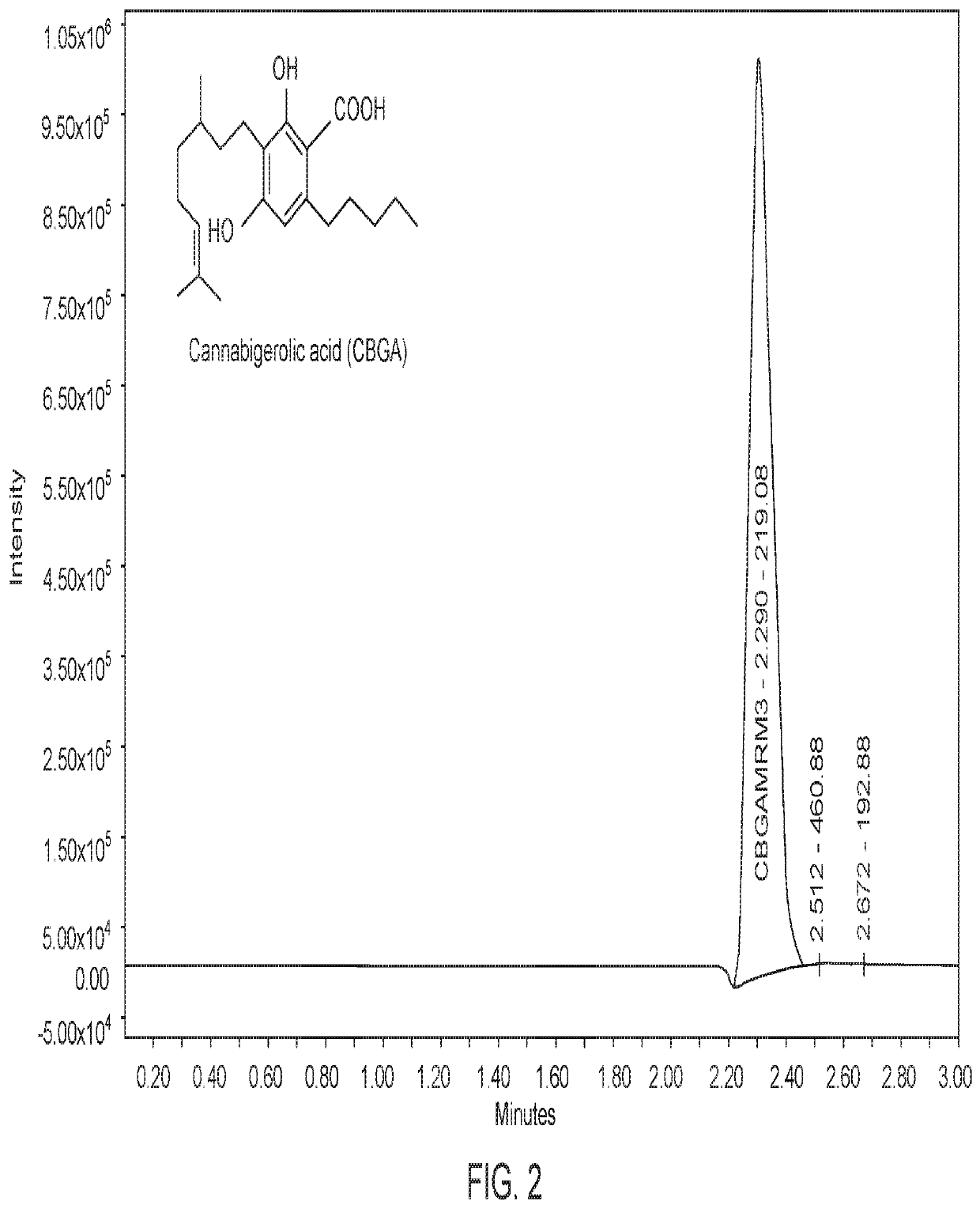
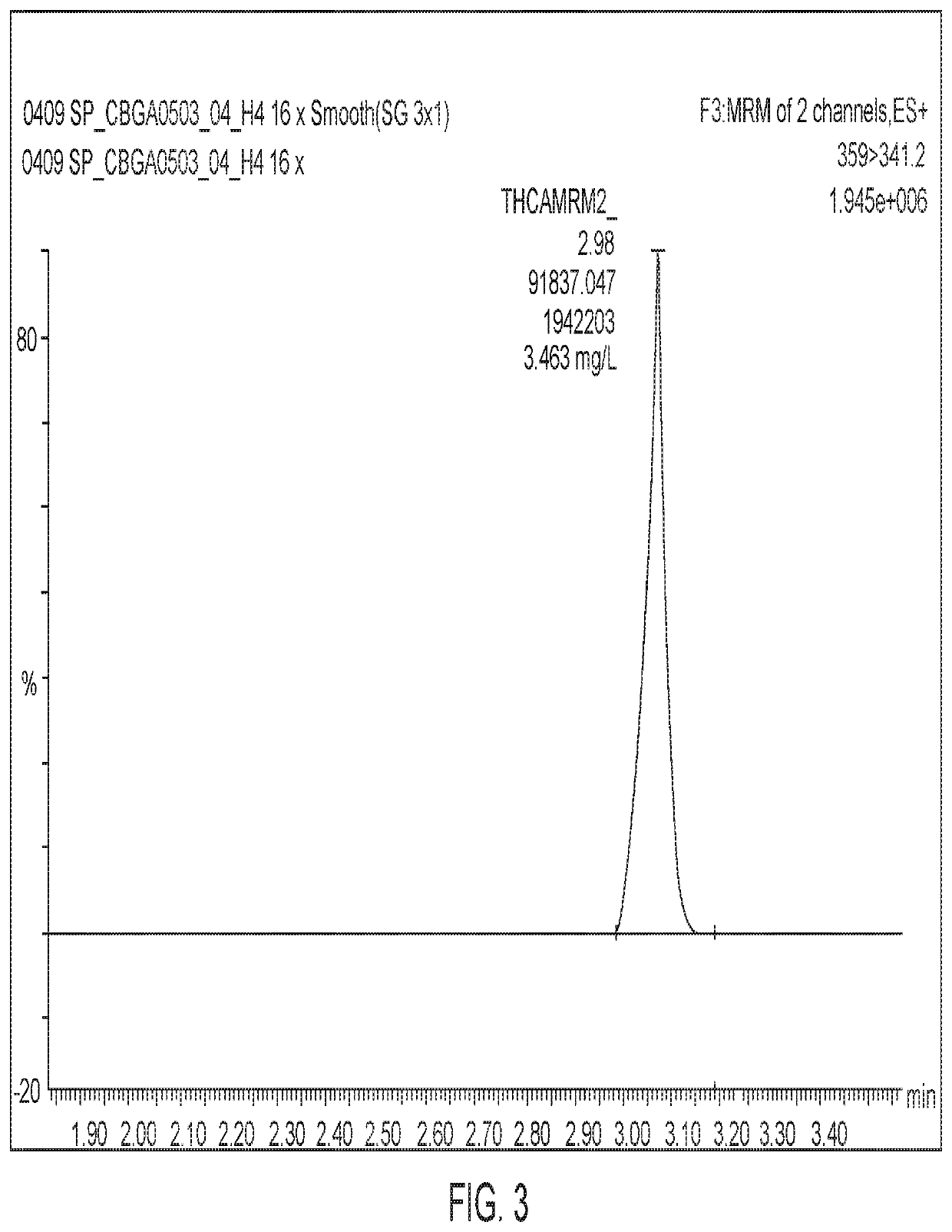
Disclosed herein are microorganism and methods that can be used for the synthesis of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) and cannabinoids. The methods disclosed can be used to produce CBGA, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabichromenic acid (CBCA), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC). Enzymes useful for the synthesis of CBGA and cannabinoids, include but are not limited to acyl activating enzyme (AAE1), polyketide synthase (PKS), olivetolic acid cyclase (OAC), prenyltransferase (PT), THCA synthase (THCAS), CBDA synthase (CBDAS), CBCA synthase (CBCAS), HMG-Co reductase (HMG1), and / or farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase (ERG20). The microorganisms can also have one or more genes disrupted, such as gene that that controls beta oxidation of long chain fatty acids.
Owner:ELESZTO GENETIKA INC
Method for catalytically synthesizing vitamin K2 through NovQ aromatic isopentenyl transferase
ActiveCN105861582ASimple production processReduce manufacturing costFermentationVitamin K2Vitamin K3
The invention discloses a method for catalytically synthesizing vitamin K2 through NovQ aromatic isopentenyl transferase. The method comprises the steps that 1, vitamin K3 is dissolved in an ethanol aqueous solution, NaBH4 is added, under the protection of N2, the temperature is controlled to be not more than 50 DEG C, stirring reaction is conducted till the system becomes light green transparent liquid, after neutralization is conducted till the pH is 4.0, extraction is conducted on a product with ethyl acetate, after concentration is conducted, freezing crystallization is conducted, clean liquid is filtered, and vitamin K3 hydroquinone is obtained; 2, vitamin K3 hydroquinone and DMAPP are added into an enzymatic reaction system, reaction is conducted under the closed and N2 protection conditions, after the reaction is completed, Fe<3+> is added, N2 protection is removed, after adequate oxidation is conducted, extraction is conducted with ethyl acetate, and the product is obtained. According to the method for catalytically synthesizing the vitamin K2 through the NovQ aromatic isopentenyl transferase, the core link adopts a biological enzyme catalytic engineering technology, and the cheap vitamin K3 is utilized for catalytically synthesizing high-value vitamin K2; the production technology is simple, the production cost is low, and the production process is green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
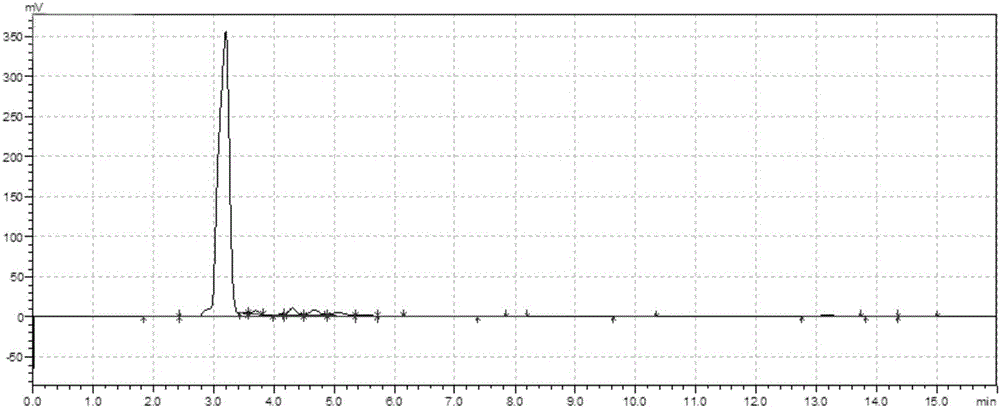
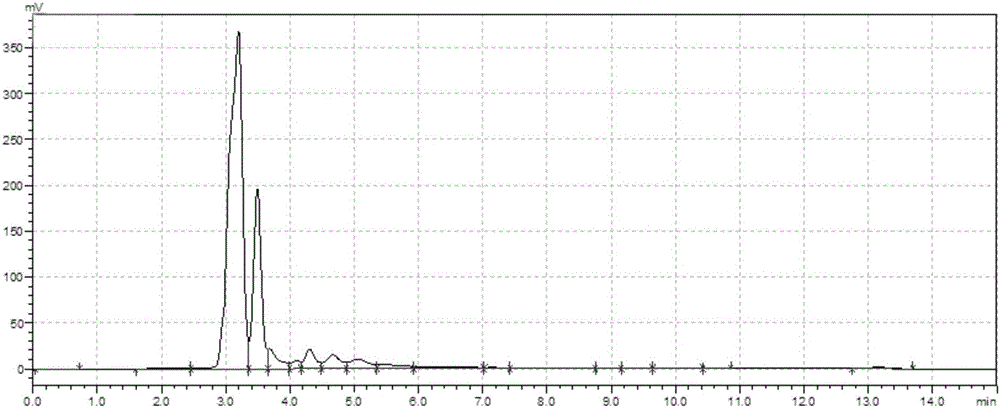
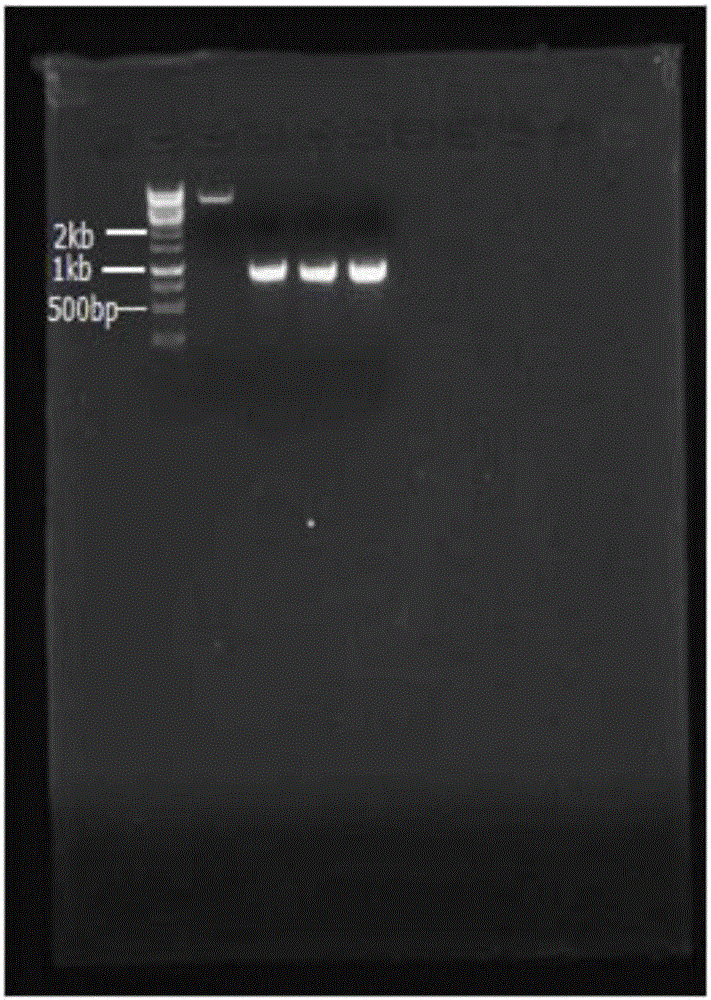
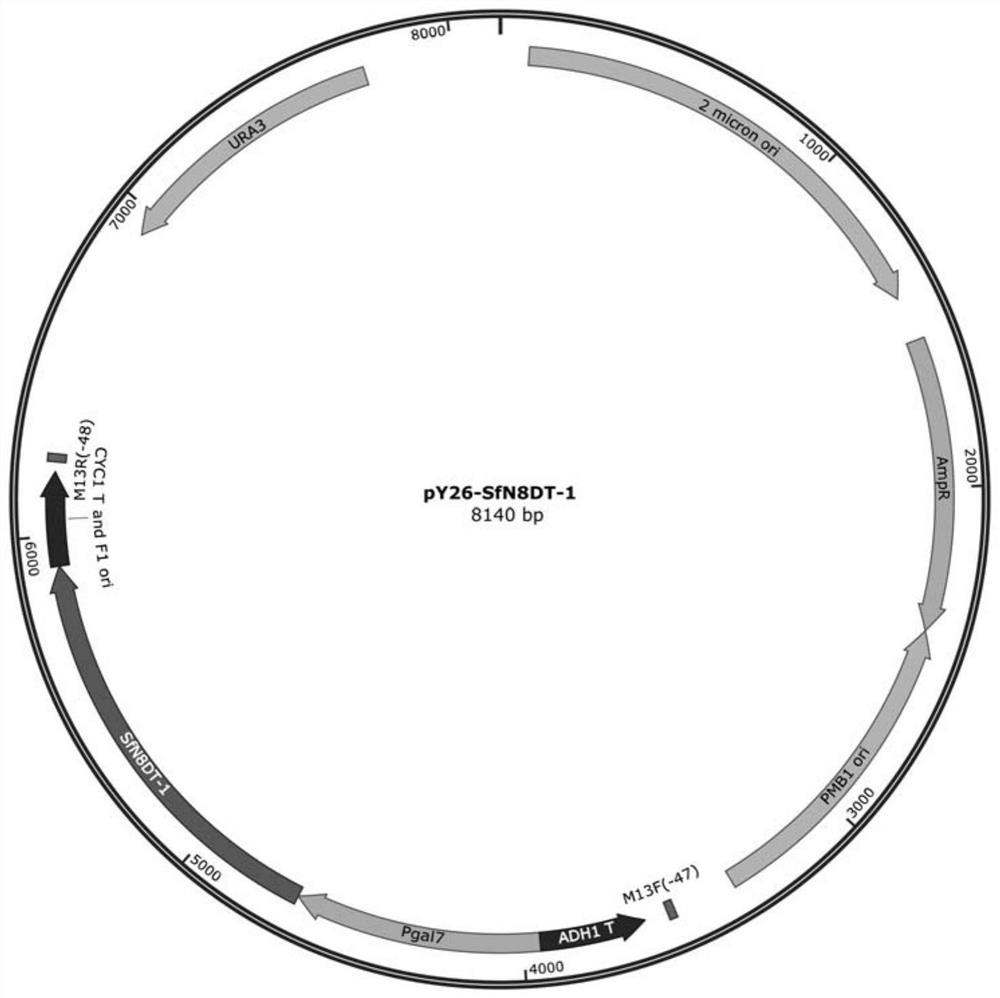
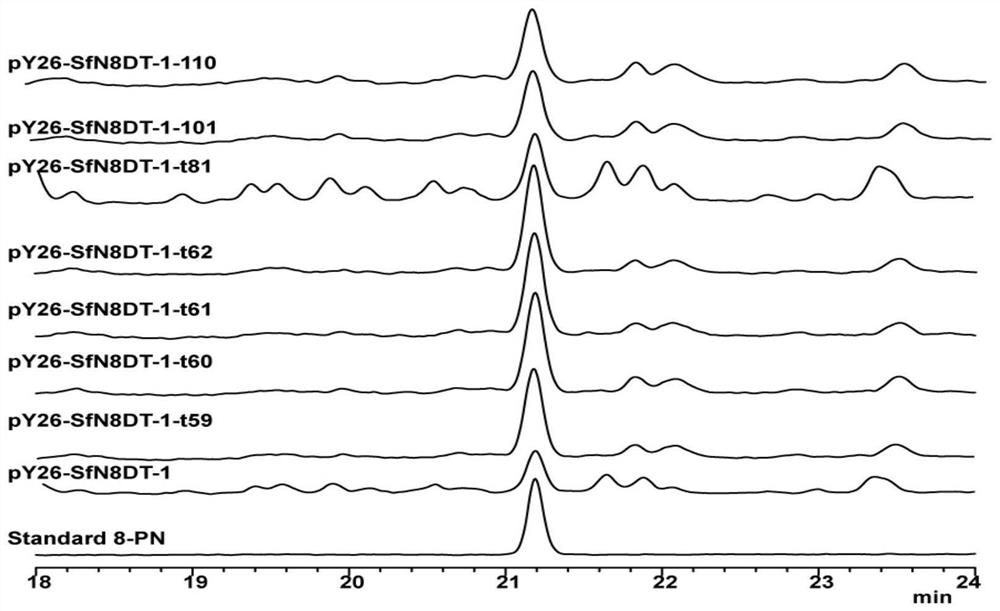
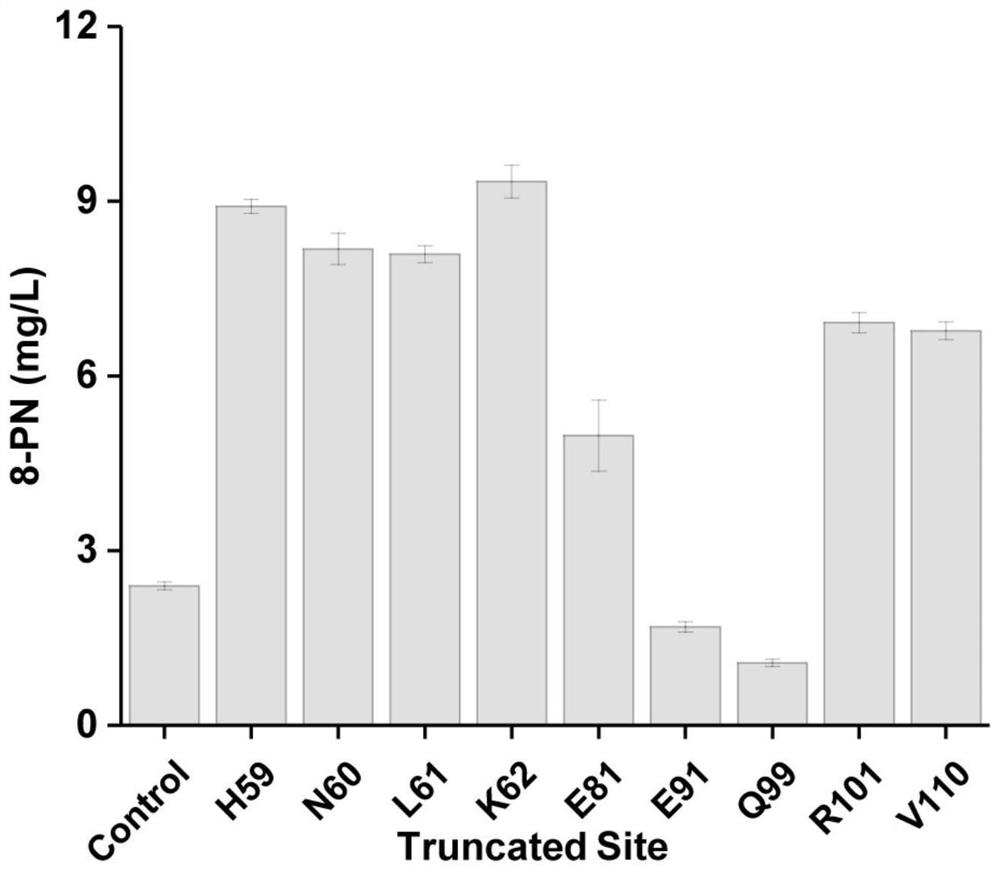
Truncated sophora flavescens isopentenyl transferase and application thereof
The invention discloses truncated sophora flavescens isopentenyl transferase and application thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. On the basis of isopentenyl transferase SfN8DT-1 from sophora flavescens, truncation of different sites is respectively carried out on an N terminal, and a recombinant plasmid pY26-SfN8DT-1 and seven truncated isopentenyl transferase mutant plasmids are constructed. The recombinant plasmid is transferred into saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for denovo synthesis of 8-isopentenyl naringenin. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae can produce 9.33 mg / L of the 8-isopentenyl naringenin at most after being fermented in a YPD culture medium for 120 hours, the yield is improved by 290.10% compared with that of a control strain PN01-pY26-SfN8DT-1, and the yield of the 8-isopentenyl naringenin is the highest among currently reported yields of biosynthesized 8-isopentenyl naringenin. The strategy lays a foundation for producing the 8-isopentenyl naringenin by transforming the saccharomyces cerevisiae through metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fermentation and one-step purifying method for obtaining aromatic isoprenyl transferase
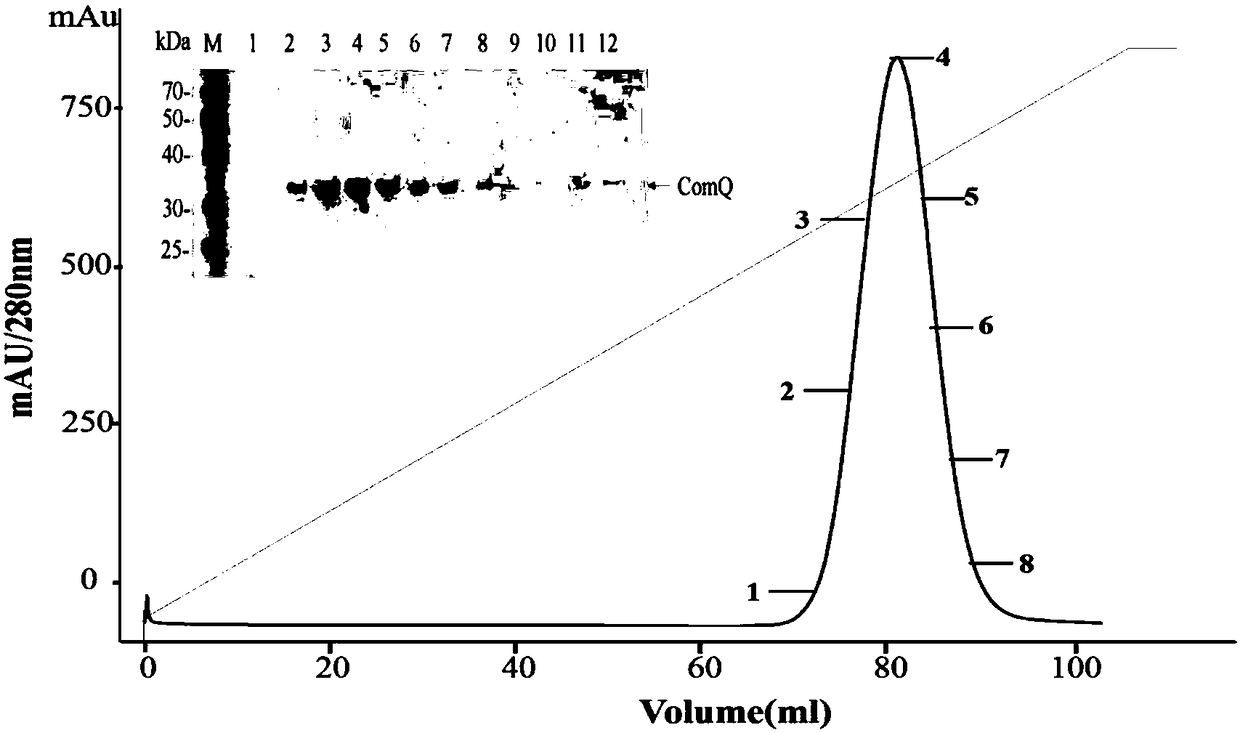
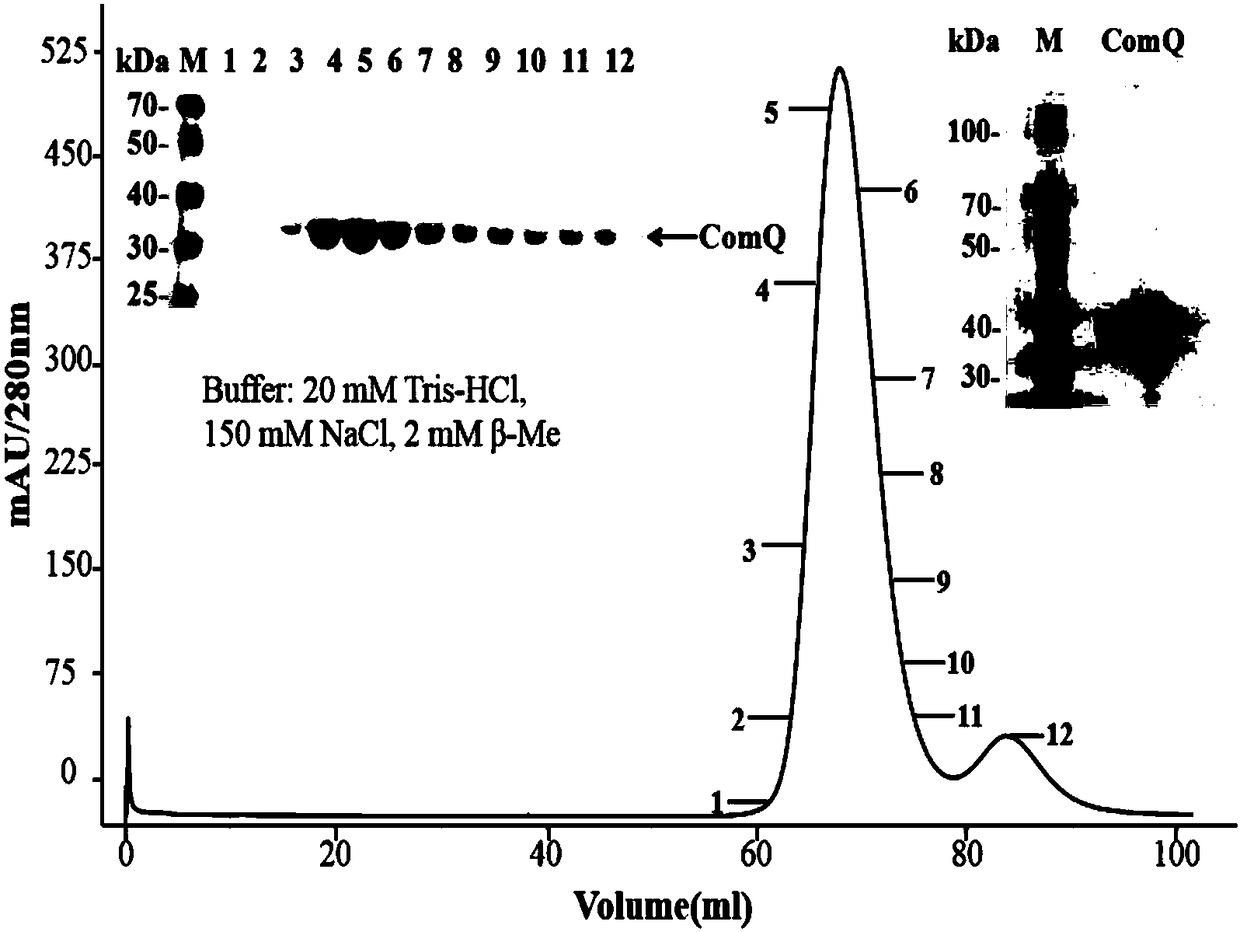
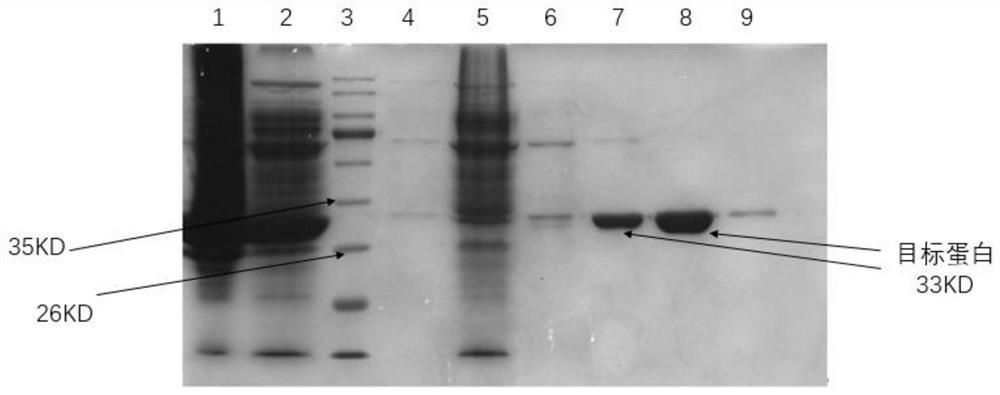
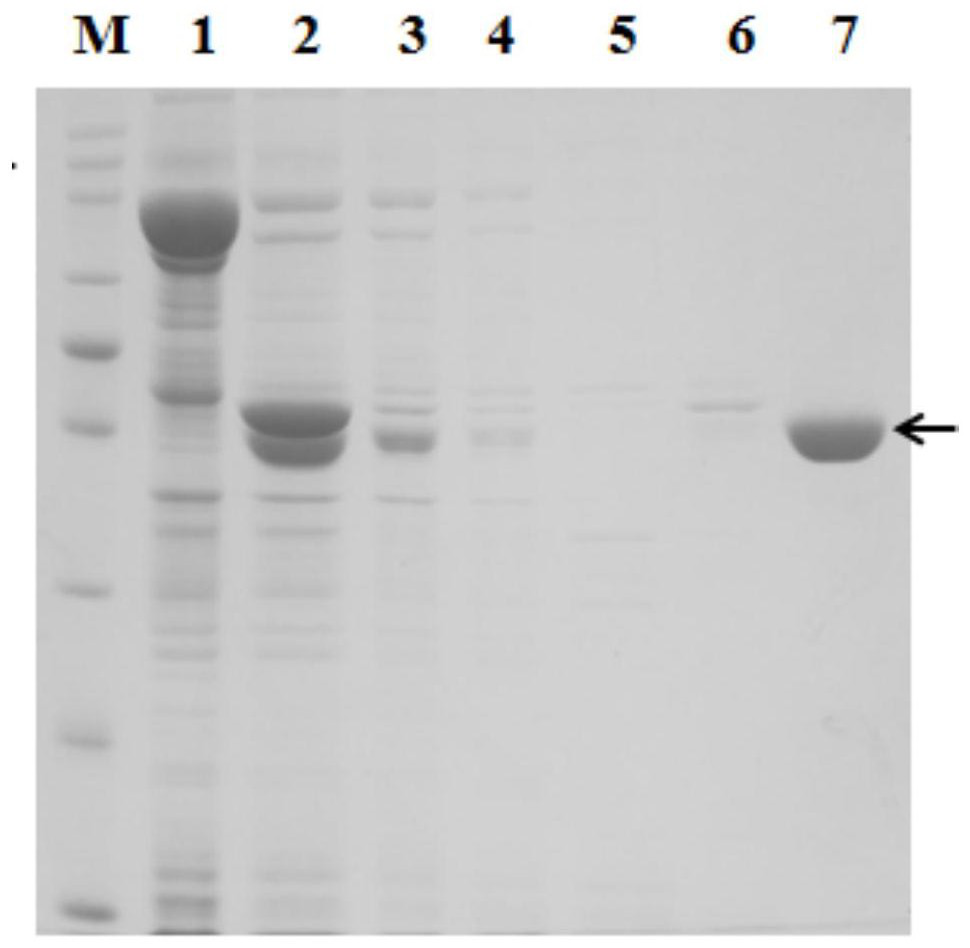
ActiveCN109762834ASimple processIncrease vitalityTransferasesFermentationCytosolPurification methods
The invention discloses a fermentation and one-step purifying method for obtaining aromatic isoprenyl transferase. The method comprises the steps that a large amount of soluble isoprenyl transferase NovQ can be obtained in cytosol of cells, high-activity proteins can be obtained through one-step purification, and the obtaining efficiency of proteins is improved. According to the method, zymoprotein with higher purity is obtained under the premise that an enzymatic result is not damaged by using the coexpression of a fusion label and the NovQ protein. Compared with other aromatic isoprenyl transferase acquisition methods, the yield is high, the enzymatic purifying and extracting method is simple, and the method has wide application prospects in in vivo and in vitro generating process of terpene.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Isopentenyl transferase mutant and method for producing cannabinoid phenol
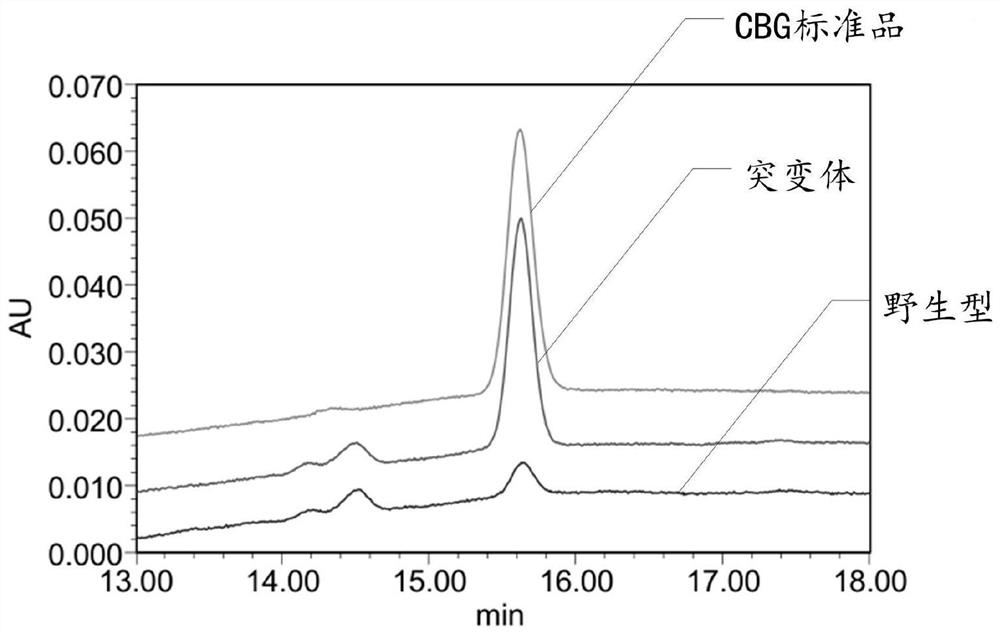
PendingCN114350635AHigh catalytic activityHigh purityBacteriaTransferasesGeranyl pyrophosphateSite-directed mutagenesis
According to the isopentenyl transferase mutant and the method for producing cannabinoid phenol, existing isopentenyl transferase is subjected to site-directed mutagenesis, so that olive alcohol and geranyl pyrophosphate can be helped to catalyze to generate cannabinoid phenol with relatively high catalytic activity and purity, and the isopentenyl transferase mutant has relatively high production and application prospects.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
Transformant for expressing cis-prenyltranferase and nogo b receptor
ActiveUS20170009259A1Increased polyisoprenoid yieldActivity can be stabilized and enhancedCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsTransferasesGenePolyprenol
Provided are a transformant produced by introducing a gene coding for a cis-prenyltransferase and a gene coding for a Nogo-B receptor, which are considered to be involved in polyisoprenoid biosynthesis, into a host to allow the host to express the cis-prenyltransferase and the Nogo-B receptor, and a method for producing a polyisoprenoid using the transformant. The present invention relates to a transformant produced by introducing a gene coding for a cis-prenyltransferase and a gene coding for a Nogo-B receptor into a host to allow the host to express the cis-prenyltransferase and the Nogo-B receptor.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
A degenerate primer and application for identifying heterozygous isoprenoid compound-producing bacteria
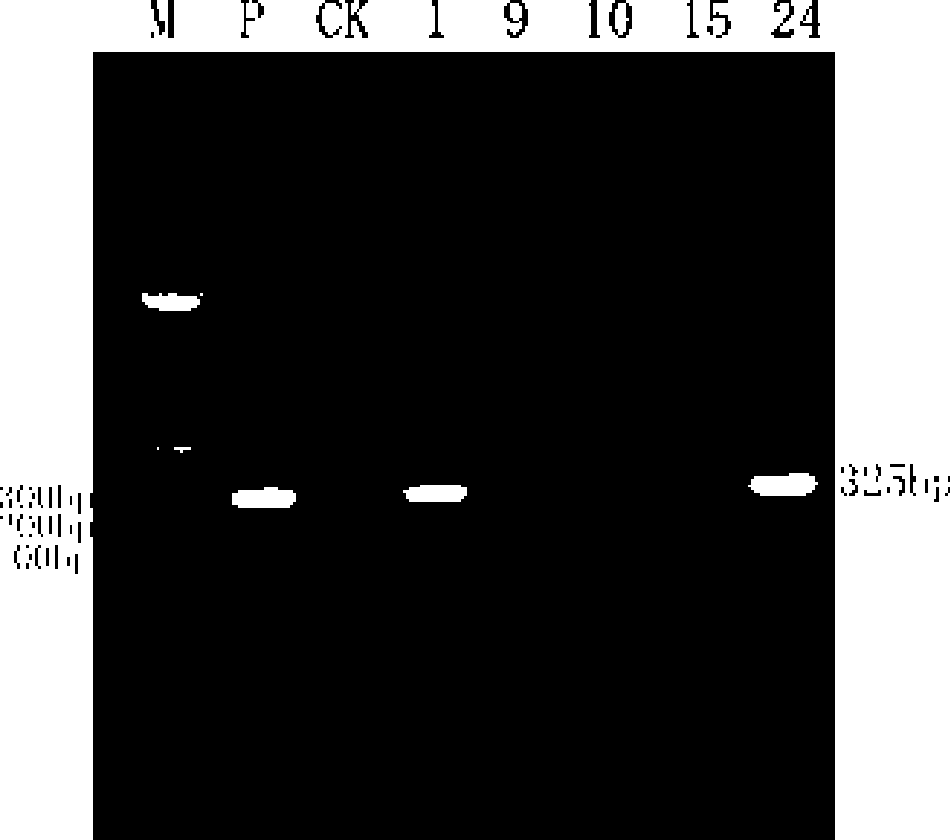
ActiveCN106367508BImprove work efficiencyPurposefulMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismPrenylation
The invention discloses degenerate primers for identifying hybrid isoprenoid-producing bacteria and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biology. The sequences of the degenerate primers are disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also discloses a method for identifying hybrid isoprenoid-producing bacteria by using the degenerate primers. A direct PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method is utilized to identify hybrid isoprenoid-producing bacteria, thereby avoiding the defects of high complexity, time consuming, blindness, high leakage possibility and the like in the strain fermentation, fermentation product purification and identification and other processes in the traditional identification method, greatly enhancing the work efficiency, and having higher purposiveness. The degenerate primers have important meanings in discovering hybrid isoprenoid microbial natural product drugs and exploring novel prenyltransferase.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Plant expression vector without antibiotic marker gene and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102181474BAvoid potential risksImprove securityVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyTransgene
The invention discloses a plant expression vector without antibiotic marker genes and a construction method thereof. The T-DNA region of the vector contains a gene cassette which comprises CaMV 35S promoter, Xba I, Bam HI and XmaI restriction endonuclease enzyme sites, isopentenyl transferase (ipt) gene and nos terminator sequence. The construction method of the vector includes: using a binary vector pBI121 as a base, replacing gus gene with ipt gene, deleting npt II gene through Bsu 36 I and Xba I enzyme sites, reconnecting the CaMV 35S promoter to the T-DNA region. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, transgenic plants can be induced and regenerated on a culture medium with a proper amount of low-concentration cytokinin growth regulators, and the obtained transgenic plants are the transgenic plants expressed by the target genes, which can reduce steps for identifying whether the target gene is expressed, and can avoid potential risks of antibiotic marker genes.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Method for producing natural rubber by using recombinant microorganism
A method for producing natural rubber by using a recombinant microorganism is disclosed, the method comprising: (a) manufacturing an expression vector capable of expressing a gene encoding a cis-prenyltransferase, which is a guayule-derived natural rubber synthetase represented by the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 or a Hevea brasiliensis-derived natural rubber synthetase represented by the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 6, and an expression vector capable of expressing a gene coding for a natural rubber precursor synthetase; (b) transforming a host microorganism with the expression vector; (c) culturing the transformed host microorganism; and (d) separating natural rubber from the cultured transformed host microorganism. The natural rubber obtained by the method has a white powder form identical to that of natural rubber, and shows an FT-IR spectrum pattern extremely similar to that of natural rubber.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
A fermentation and one-step purification method for obtaining aromatic prenyltransferase
The invention discloses a fermentation and one-step purification method for obtaining aromatic prenyl transferase. Through plasmid construction and the use of fusion tags, a large amount of soluble prenyltransferase NovQ can be obtained in the cytosol of cells, and then a highly active protein can be obtained after one-step purification, which improves the efficiency of protein acquisition. Co-expression of the fusion tag and the NovQ protein can obtain a high-purity enzyme protein without destroying the enzyme result. Compared with other prenyltransferase acquisition methods, the present invention has the advantages of high yield, simple enzyme extraction and purification methods, etc., and has wide application prospects in the in vitro and in vivo production processes of terpenoids.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing novel lawn grass seeds and products
InactiveCN101461326AExcellent Germplasm ResourcesIncrease chlorophyll contentHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureStainingFiltration
The invention provides a novel formulating method of lawn grass seeds. The invention adopts an agrobacterium-mediated method, through the steps of wound curing induction, staining and filtration, differentiation, radication and transplantation and the like, performs genetic transformation on ryegrass using a binary expression vector pBinAipt-bar, obtains ryegrass transgene plant which fights against senium and herbicide. Compared with the prior art, the invention constructs isopentenyl transferase gene (ipt) with herbicide-resistance gene into fusion gene for switching into ryegrass, obtains transgene plant which fights against herbicide and suspends caducity. The plant is increased in chlorophyl content and number of tillers, thereby providing an excellent lawn seeds resource.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Prenyltransferase inhibitors for ocular hypertension control and the treatment of glaucoma
InactiveUS20070232675A1Reduce connectionsBiocideSenses disorderElevated intraocular pressureOcular hypertension
The invention concerns in one embodiment a method of treating glaucoma or elevated intraocular pressure comprising administering a pharmaceutically effective amount of a composition comprising at least one prenyltransferase inhibitor. In another embodiment, the invention concerns a composition for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure and glaucoma comprising a pharmaceutically effective amount of a prenyltransferase inhibitor.
Owner:ALCON RES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com