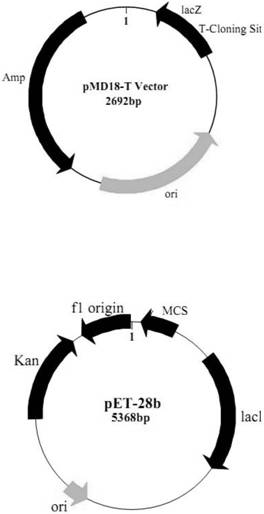
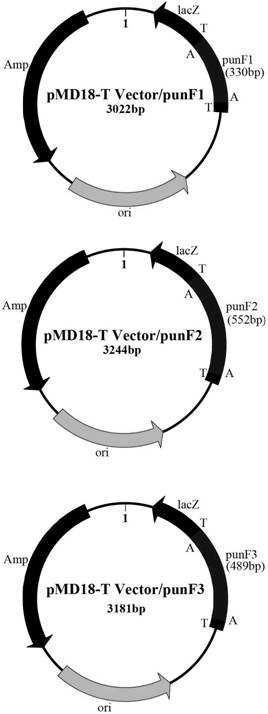
Patents
Literature
349 results about "Biosynthetic genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
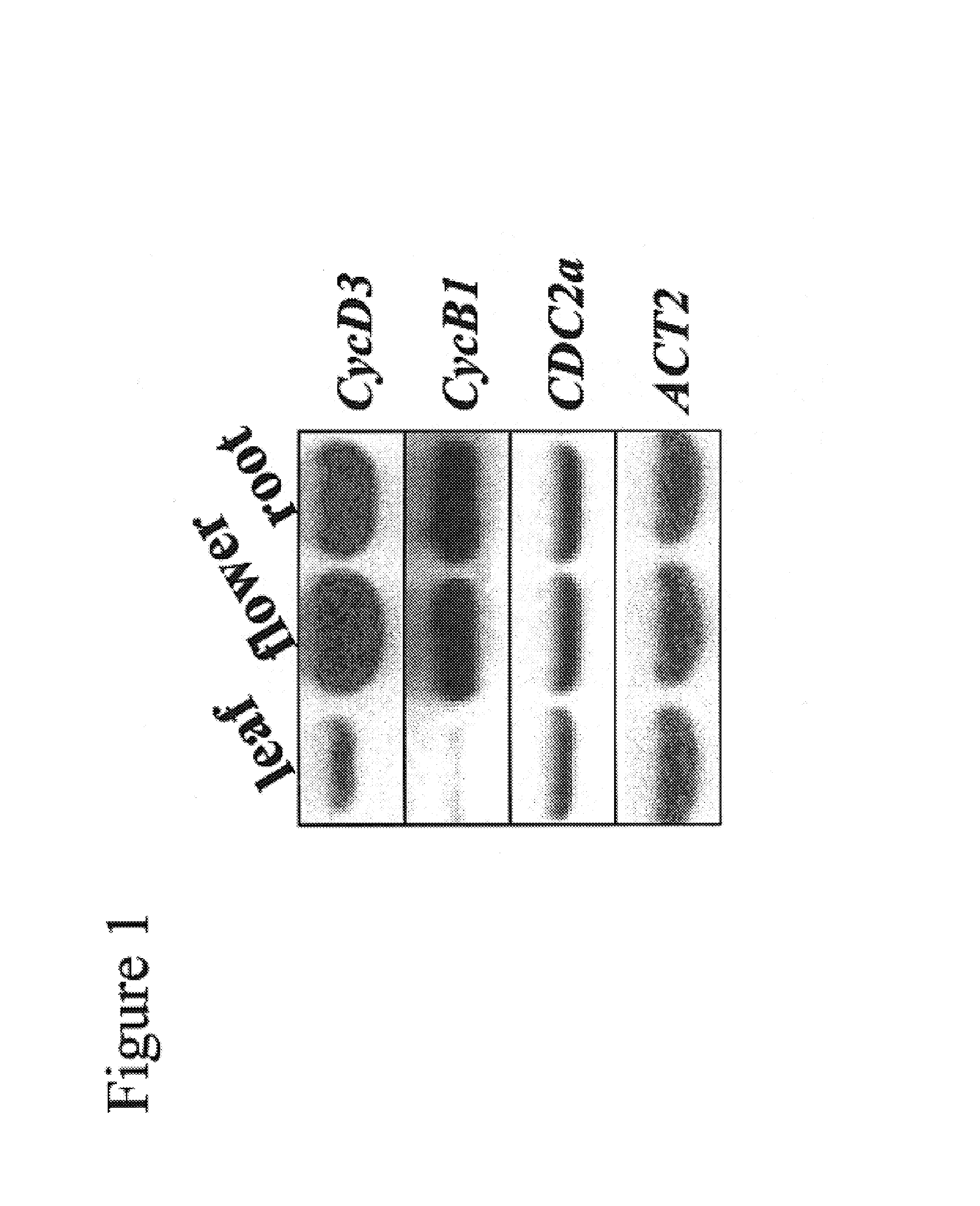
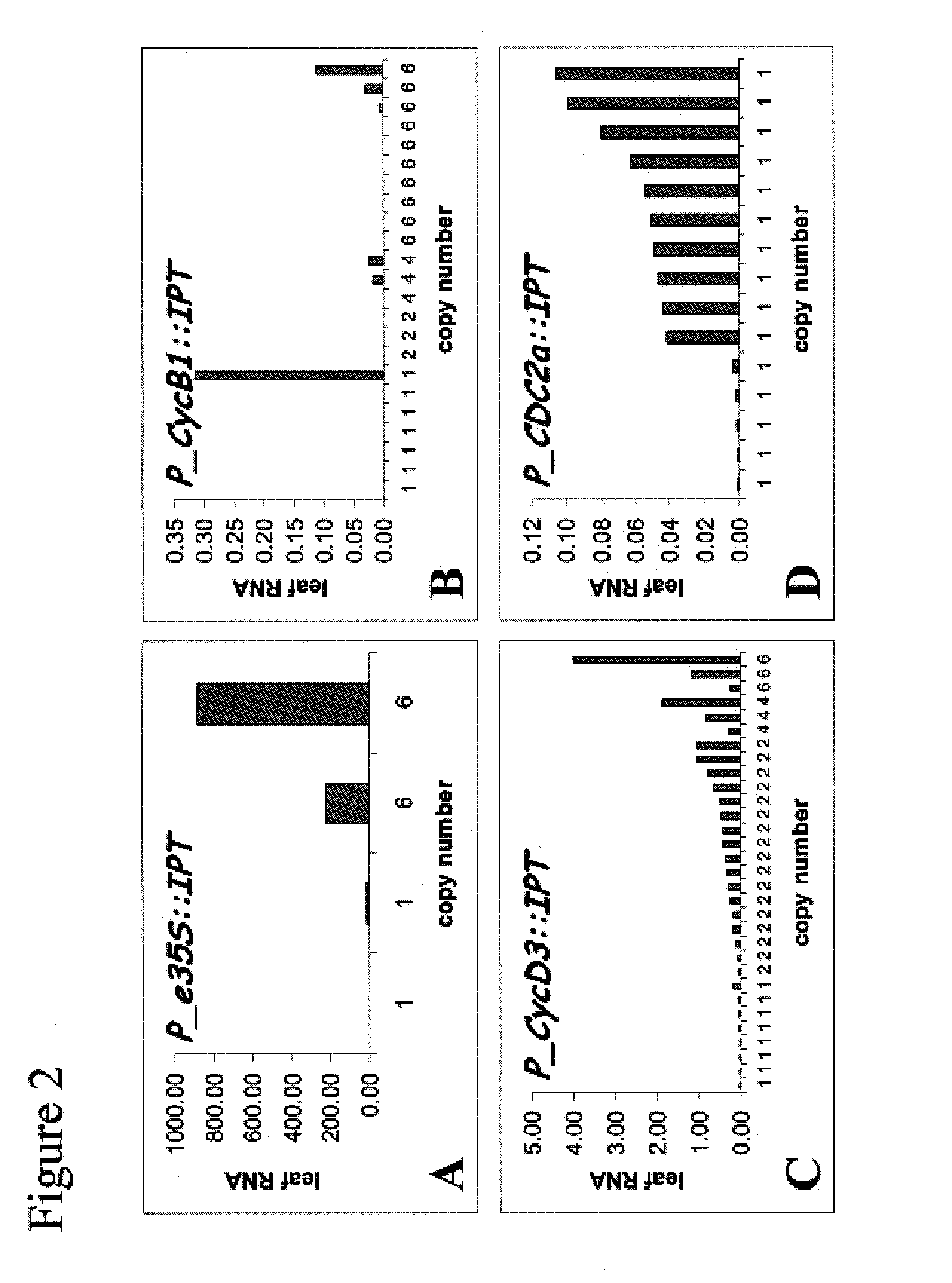
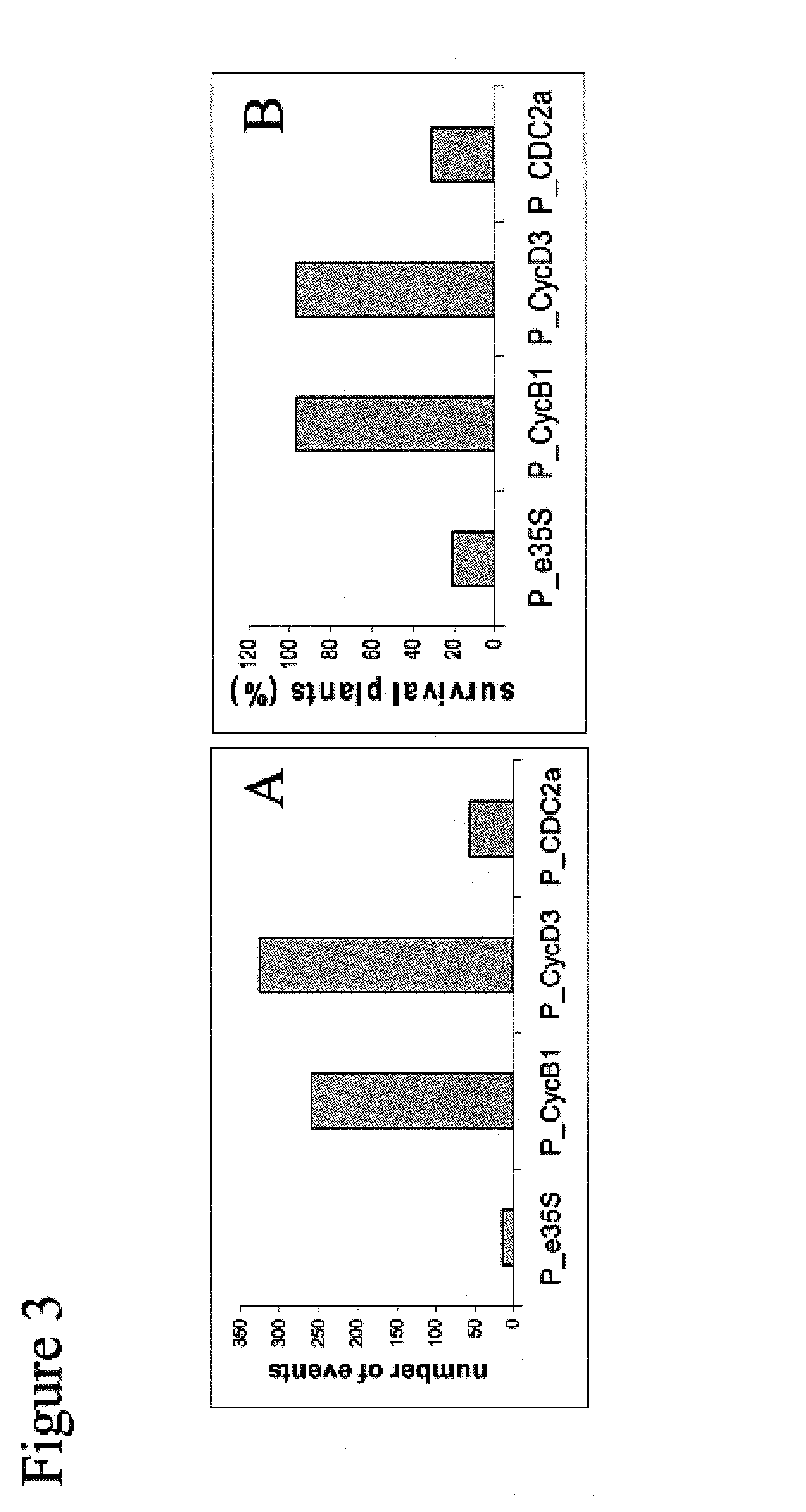
DFR, LDOX/ANS and UFGTs are the major LBGs (downstream structural genes) of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway. DFR (dihydroflavonol-4-reductase) catalyzes the first committed reaction to generate anthocyanins. In A. thaliana, the gene AtDFR is known to encode a functional DFR [24].
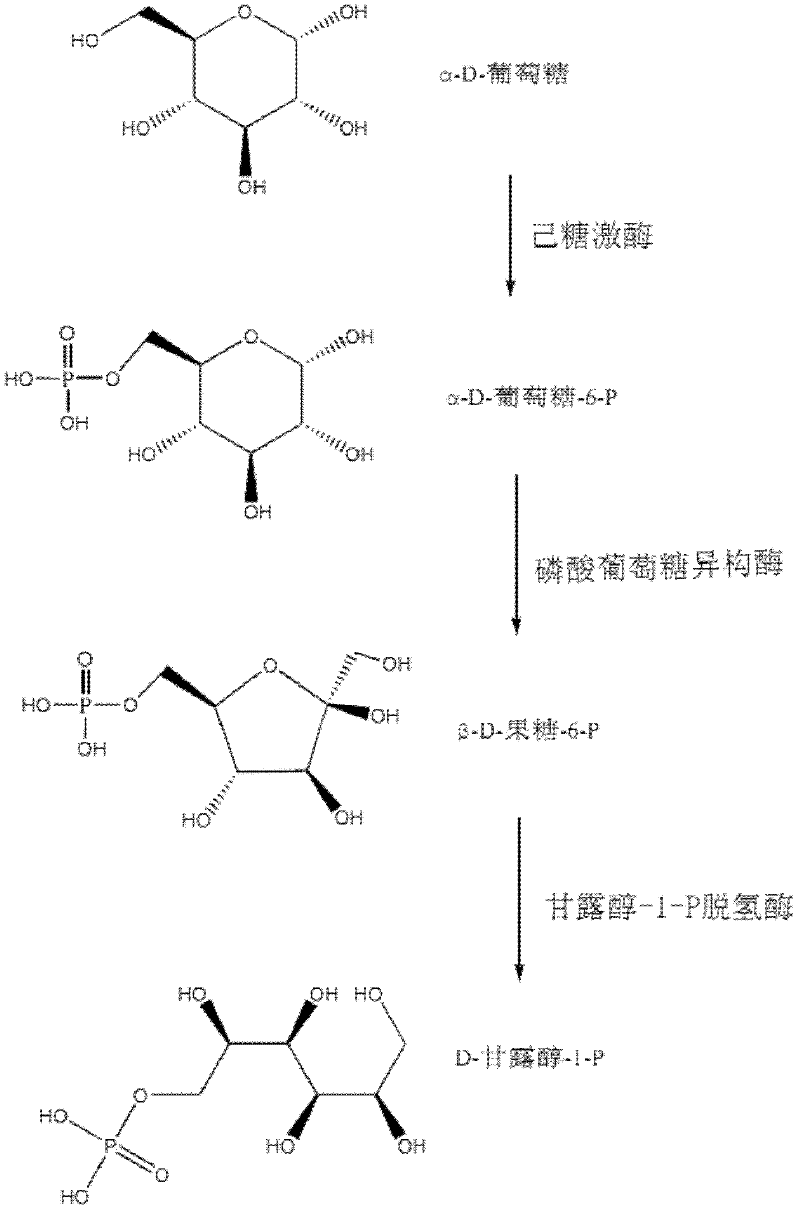
Relevant enzymes for preparing mannitol by performing anabolism on Chinese caterpillar fungus and hirsutella sinensis, gene and application thereof
The invention provides a group of relevant enzymes for preparing mannitol by performing anabolism on Chinese caterpillar fungus serving as a multifunctional production fungus and hirsutella sinensis based on glucose, a gene for encoding these enzymes and application thereof. The relevant enzymes include (1) hexokinase: manA1-A6 proteins of which the sequences are SEQ ID No.1-6, (2) phosphoglucoisomerase: manB1-B3 proteins of which the sequences are SEQ ID No.7-9, and (3) mannitol-1-P dehydrogenase: manC protein of which the sequence is SEQ ID No.10. In the invention, detailed researches are performed on the metabolic pathway of mannitol synthesized by using Chinese caterpillar fungus serving as a multifunctional production fungus, hirsutella sinensis and glucose on the aspect of principle, cloned DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) comprising a nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transferred into engineering bacteria with transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer methods, and host mannitol is endowed with high expression by regulating the expression of a biosynthetic gene of the mannitol.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
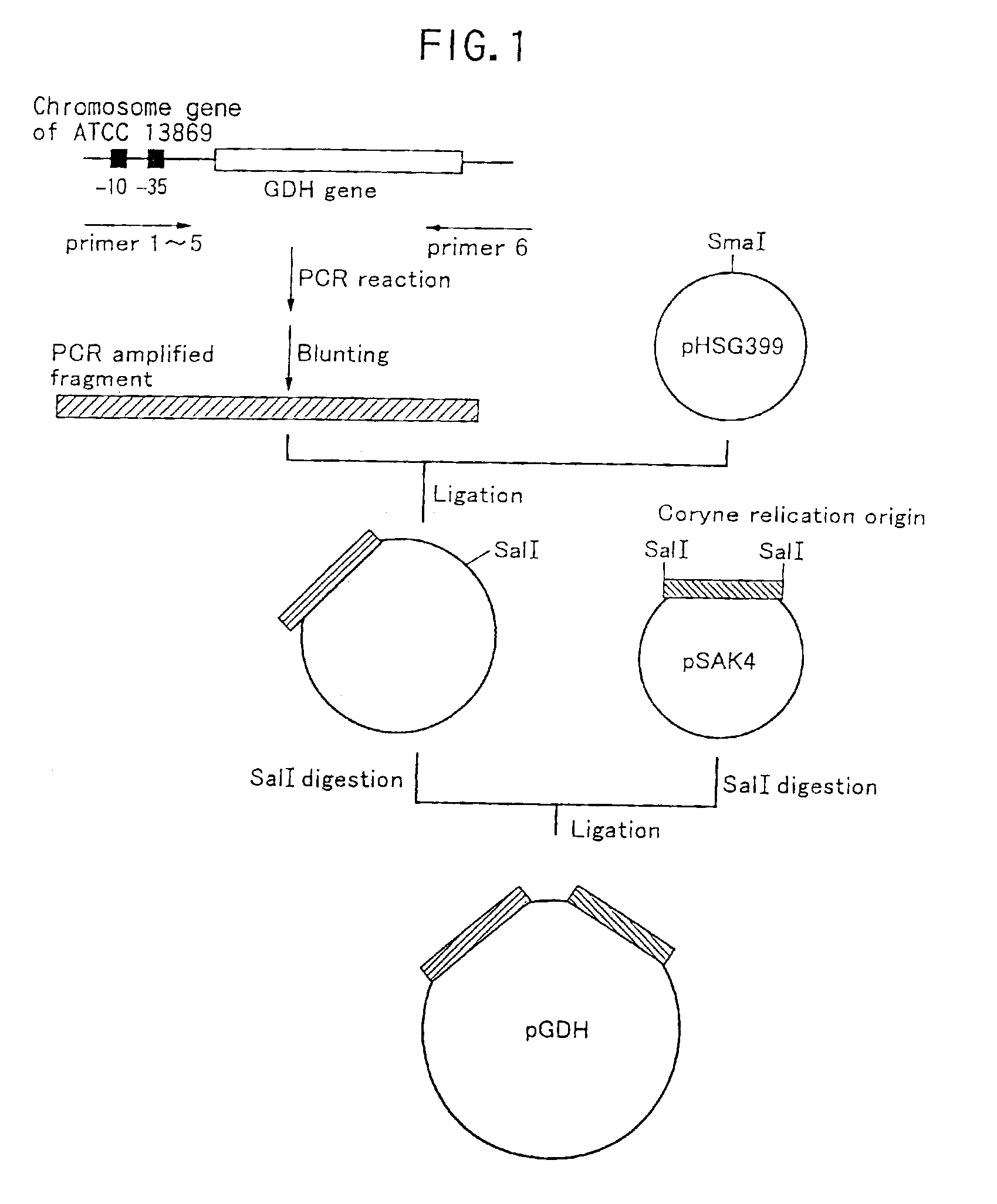
Method of constructing amino acid producing bacterial strains, and method of preparing amino acids by fermentation with the constructed amino acid producing bacterial strains
A method of producing coryneform bacteria having improved amino acid or nucleic acid productivity comprising the steps of introducing a mutation in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium to make it close to a consensus sequence, or introducing a change in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium by gene recombination to make it close to a consensus sequence, to obtain mutants of the coryneform amino acid- or nucleic acid-producing microorganism, culturing the mutants and selecting a mutant capable of producing the intended amino acid or nucleic acid in a large amount. This method allows the construction of a mutant capable of enriching or controlling the expression of an intended gene without using a plasmid and to promote production of amino acids in a high yield by recombination or mutation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
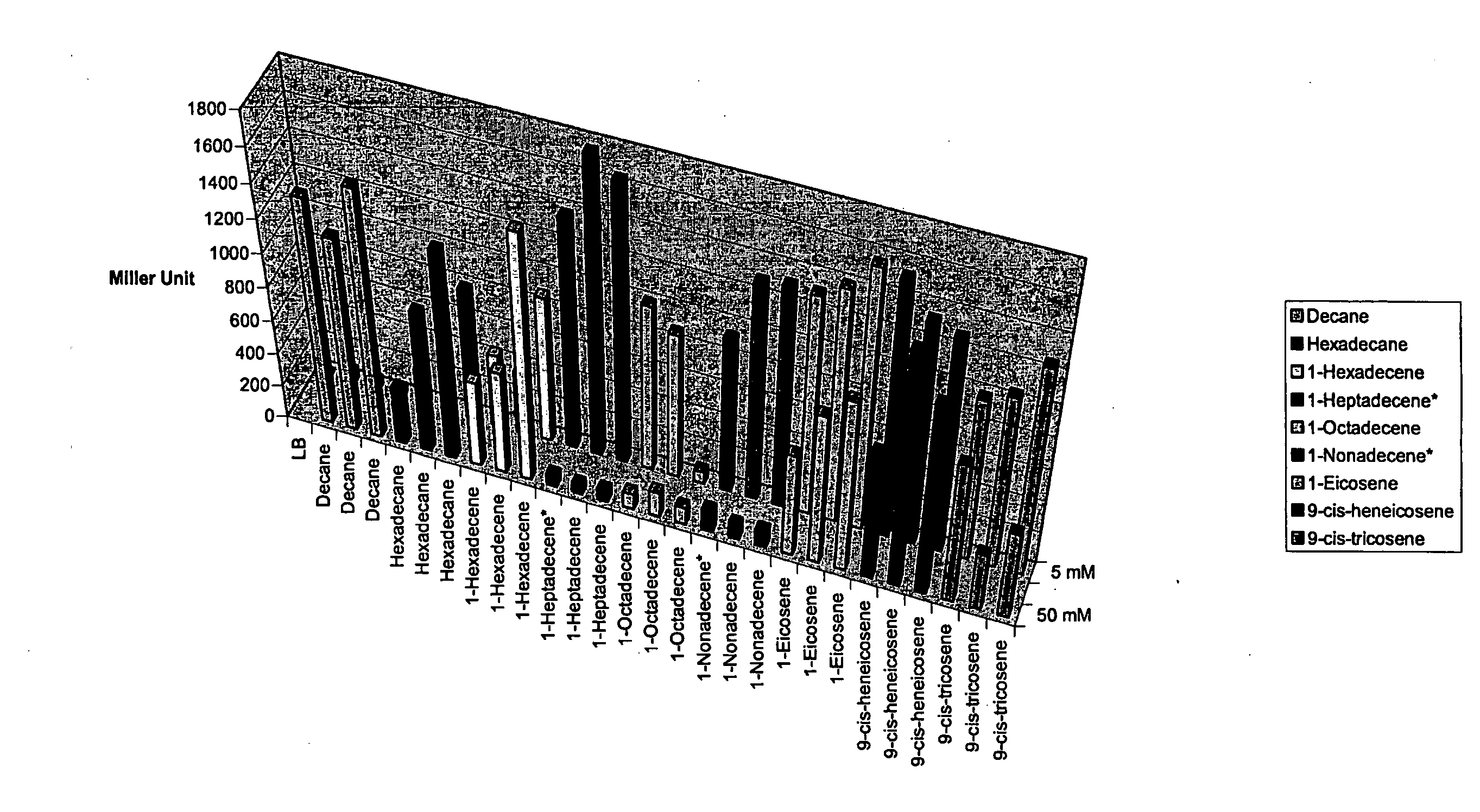
Methods and Compositions for Identification of Hydrocarbon Response, Transport and Biosynthesis Genes
InactiveUS20080293060A1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiosynthetic genesResponse element
Disclosed is a method using an alkane response element (ARE) from, e.g., Acinetobacter spp. to (i) identify and clone hydrocarbon biosynthesis genes, (ii) identify and clone hydrocarbon transporter genes (iii) identify and clone hydrocarbon response genes. Screening cells were developed that expressed a transcriptional activator, e.g., alkR, and included a reporter gene, e.g., GFP operatively linked to an ARE promoter, e.g., the alkM promoter. The cells were transformed with libraries from organisms capable of hydrocarbon biosynthesis. Transformed cells that expressed the reporter gene harbored library-derived genes involved in one or more of the above-mentioned processes; and these genes were isolated from the cells using standard molecular biology techniques. Additional systems were designed wherein screening cells also expressed a gene identified in the original screen, e.g., an additional hydrocarbon pathway gene, e.g., an enhancer.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
Transgenic systems for the manufacture of poly (3-hydroxy-butyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)
InactiveUS7455999B2Efficient PHA synthesisHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBiosynthetic genes
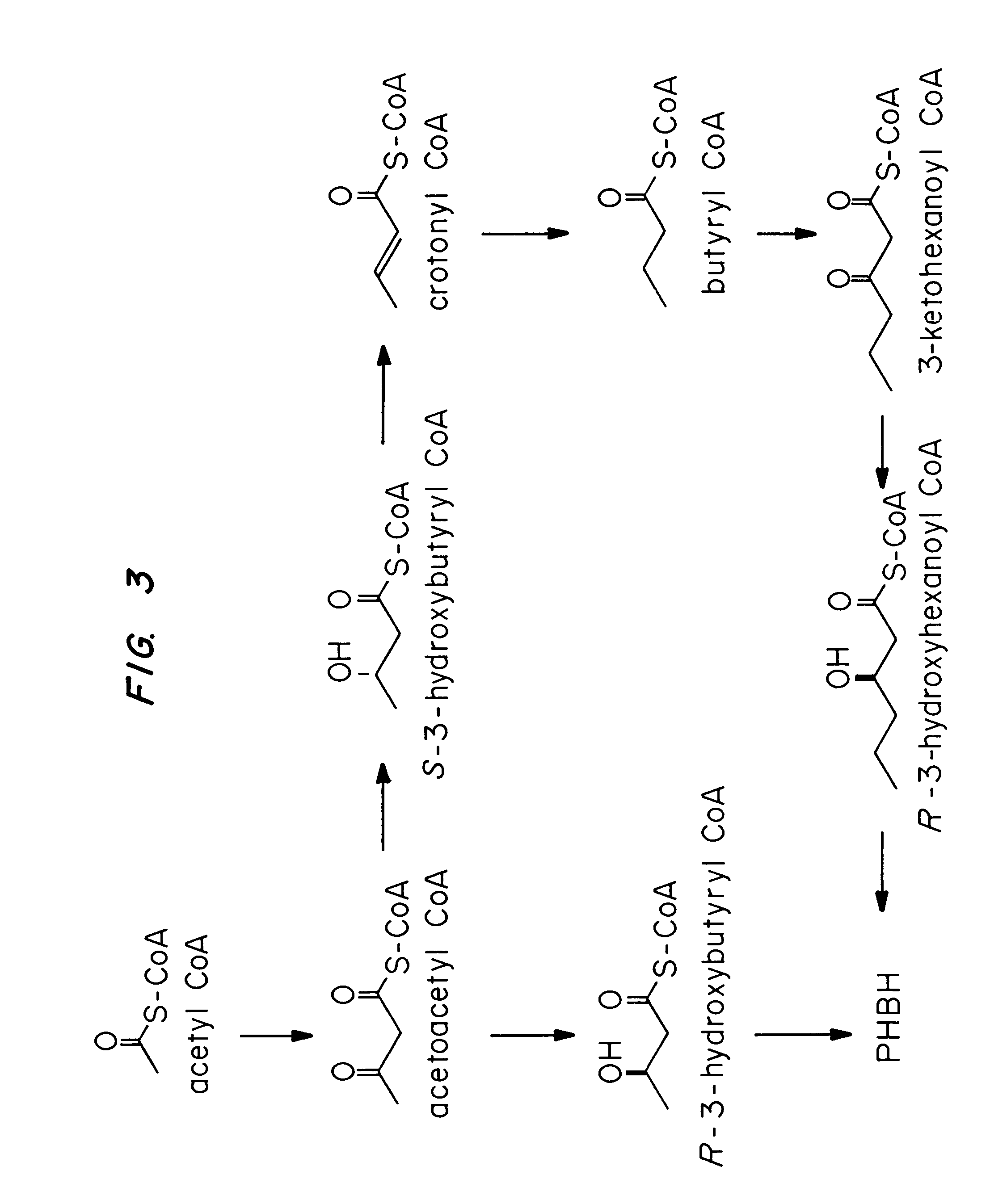
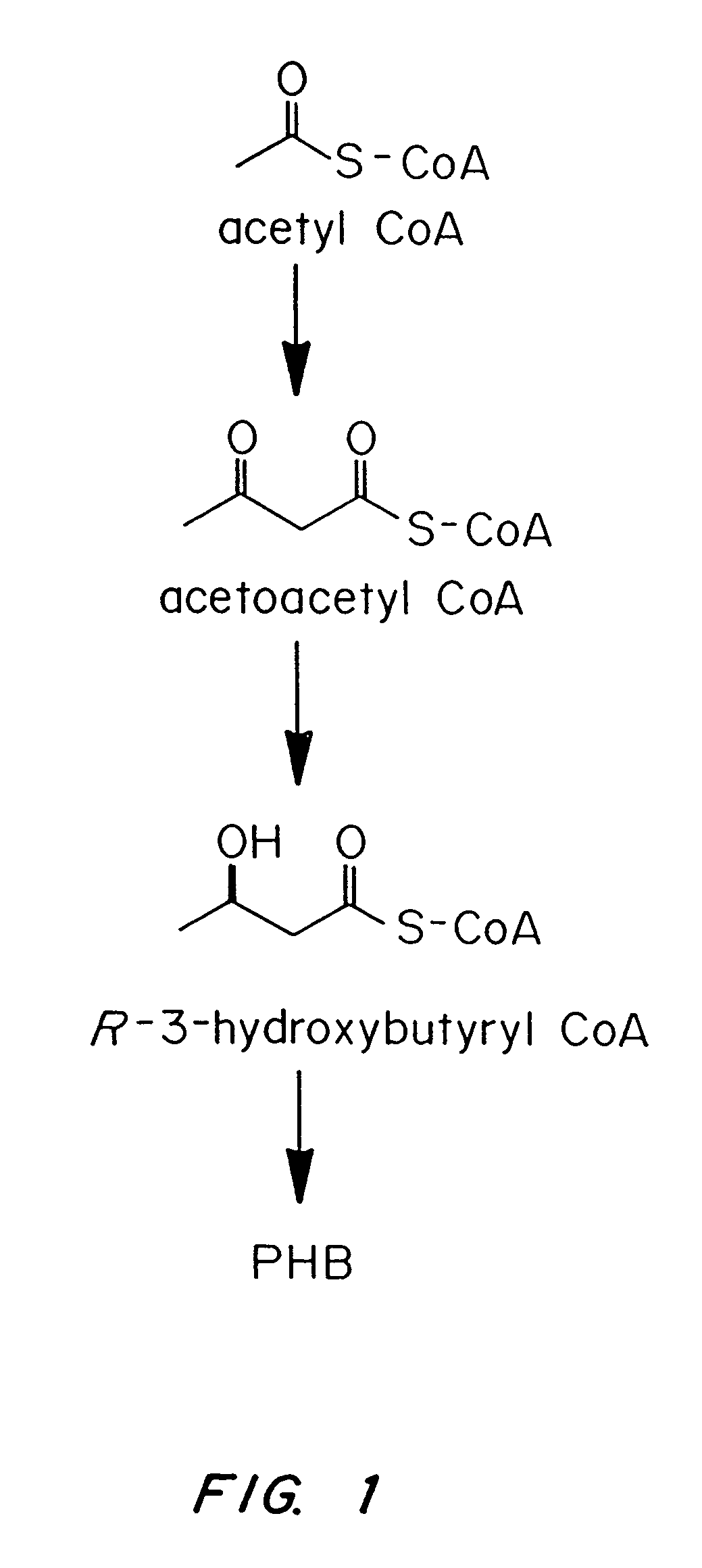
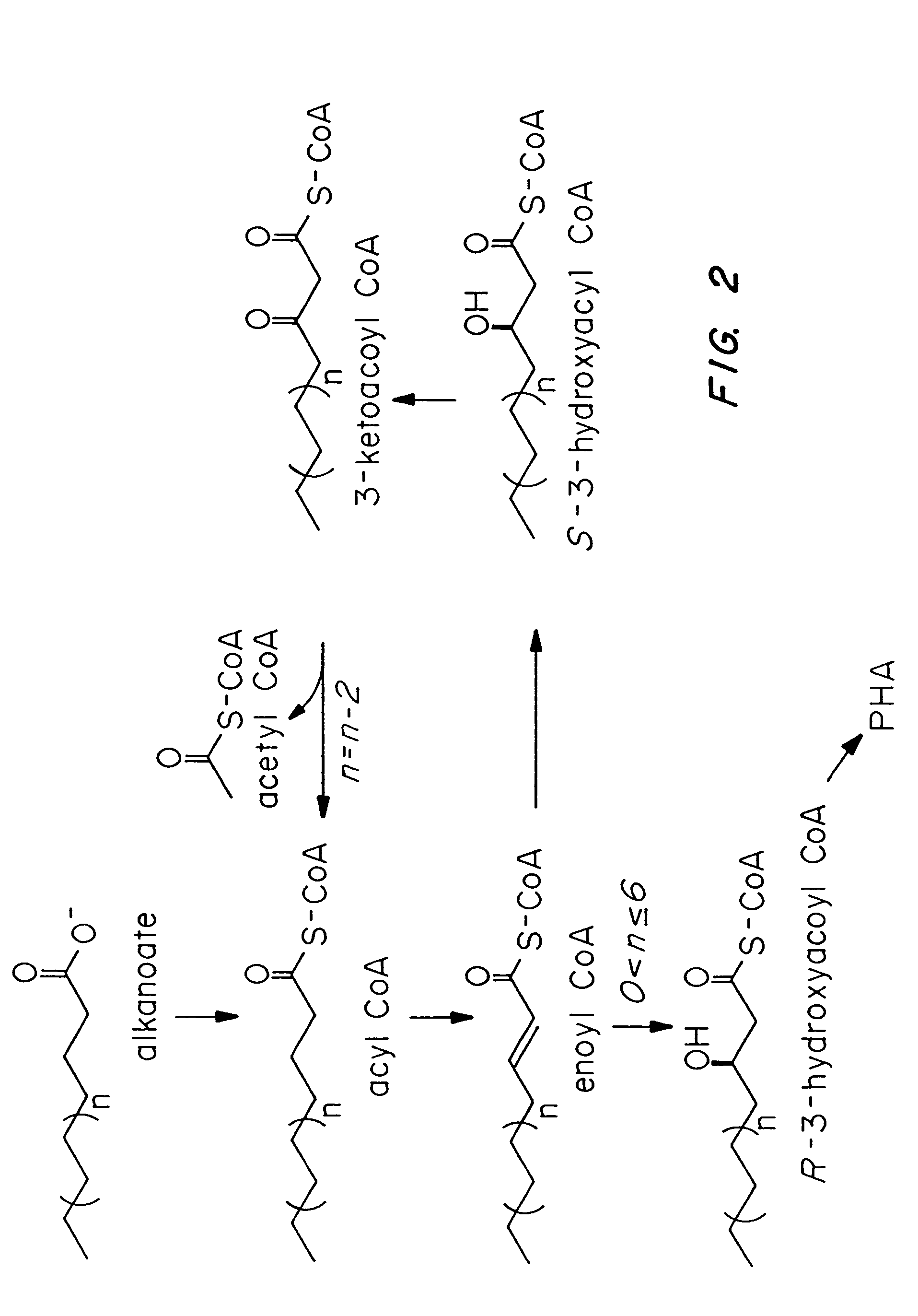
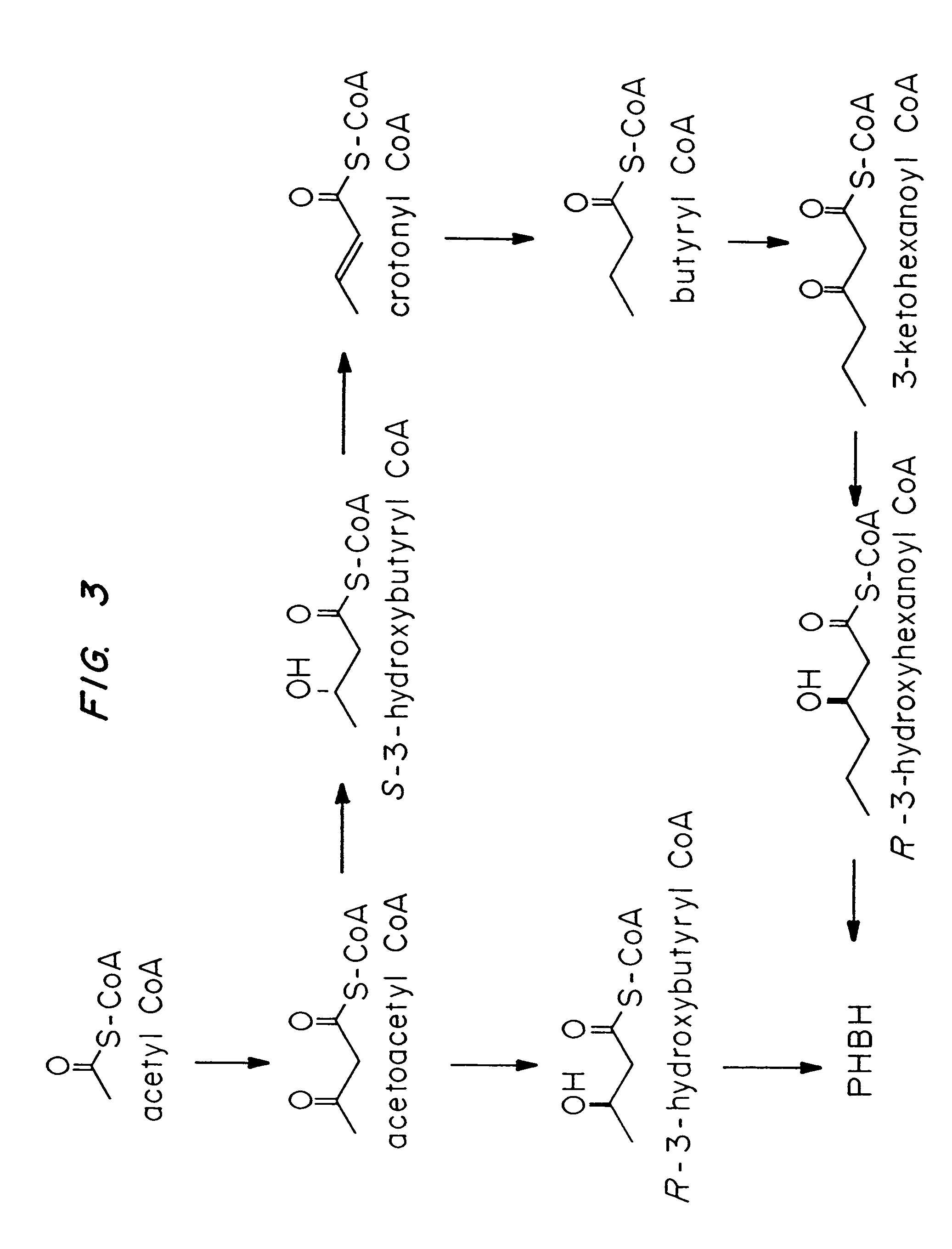
Methods for engineering transgenic organisms that synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) containing 3-hydroxyhexanoate as comonomer have been developed. These processes are based on genetically engineered bacteria such as Escherichia coli or in plant crops as production systems which include PHA biosynthetic genes from PHA producers. In a preferred embodiment of the method, additional genes are introduced in wild type or transgenic polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) producers, thereby creating new strains that synthesize 3HH monomers which are incorporated into PHAs. The 3HH monomer preferably is derived in microbial systems using butanol or butyrate as feedstocks, which are precursors of 3-hydroxyhexanoyl-CoA. Pathways for in vivo production of butyrol-CoA specifically encompassing butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity are provided.
Owner:METABOLIX
Transgenic systems for the manufacture of poly(2-hydroxy-butyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)
InactiveUS7504556B2ProductionHigh speedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacteroides
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Live bacterial vaccines resistant to carbon dioxide (CO2), acidic ph and/or osmolarity for viral infection prophylaxis or treatment
InactiveUS20100136048A1Enhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseBacteroides
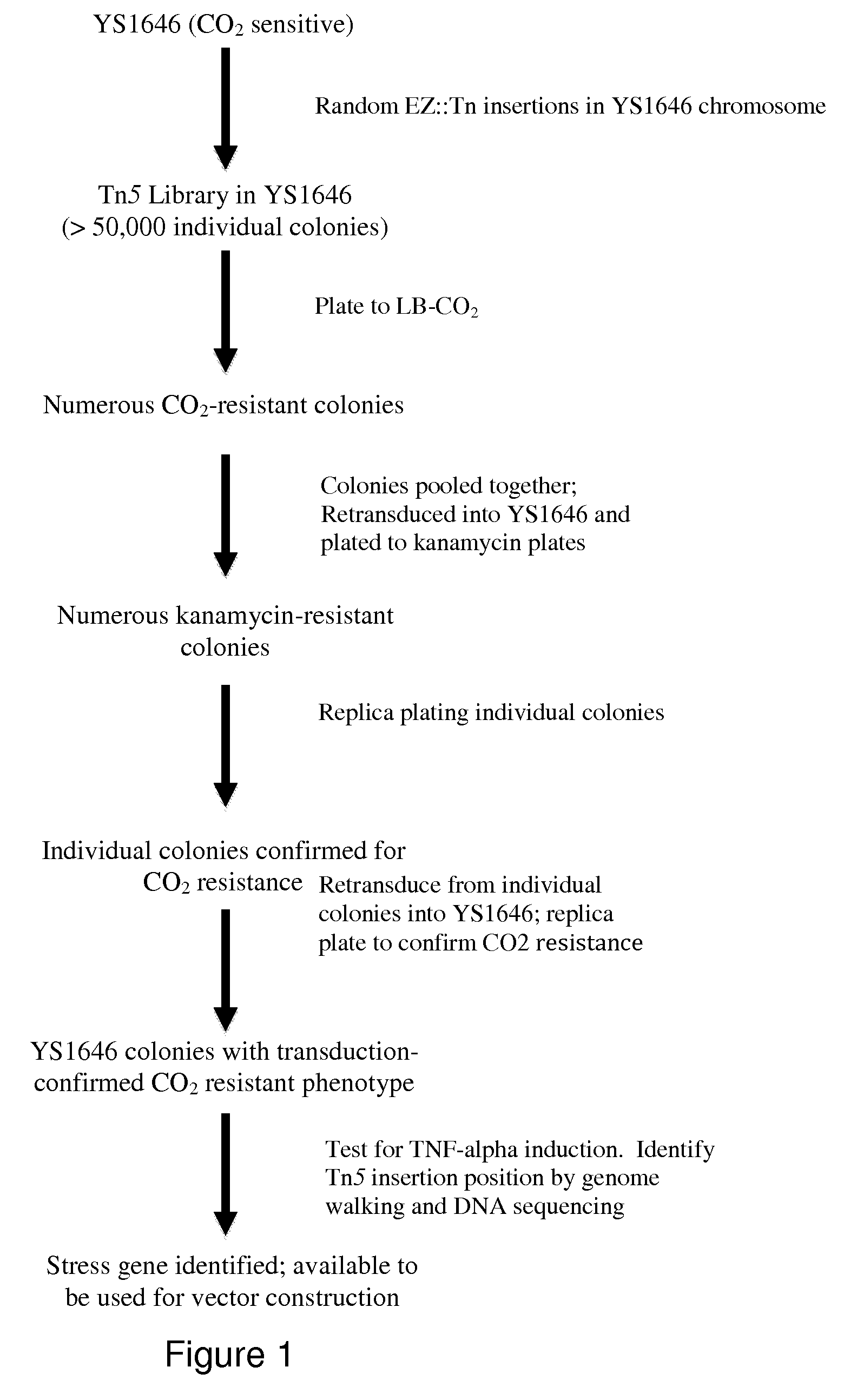
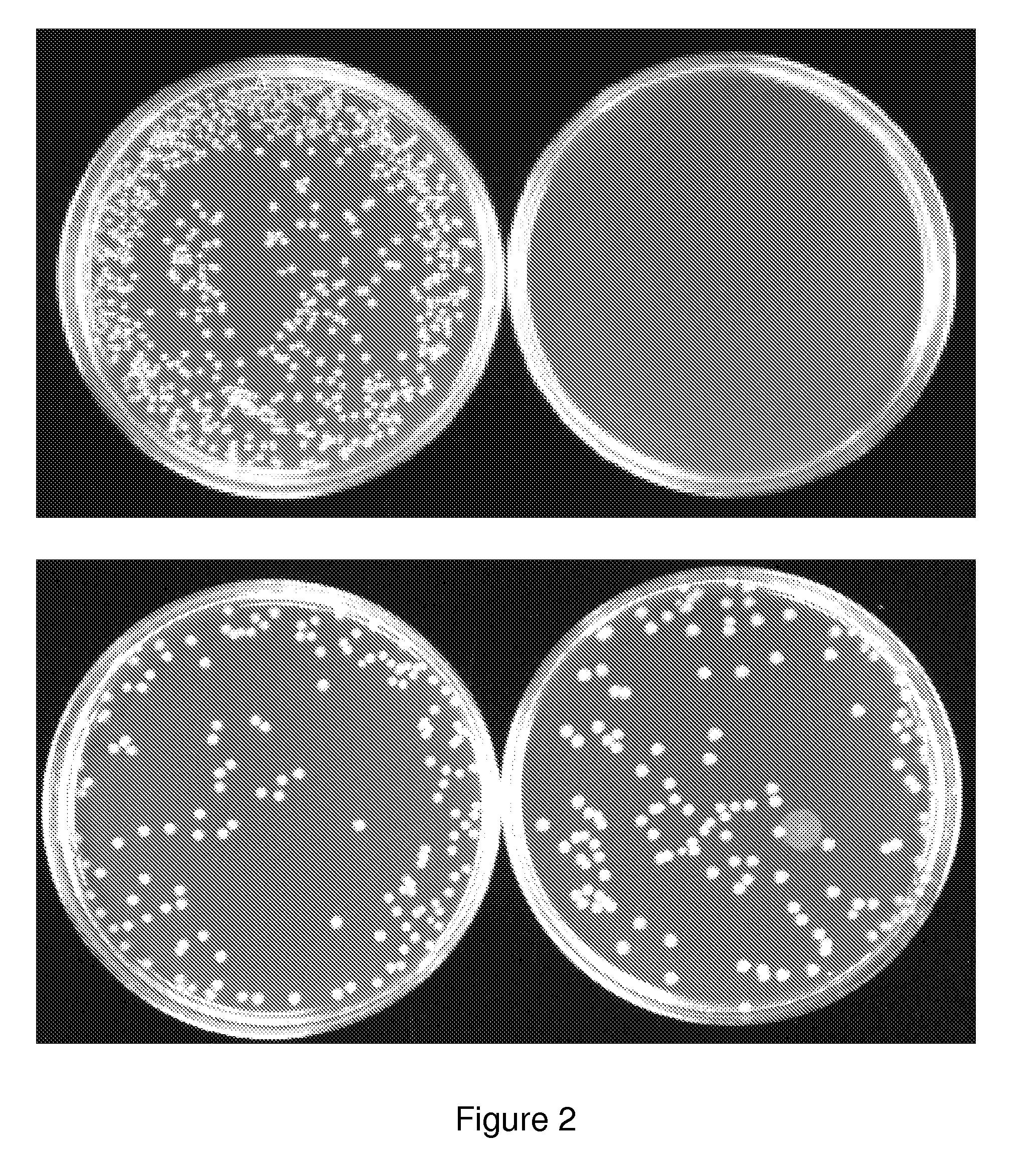
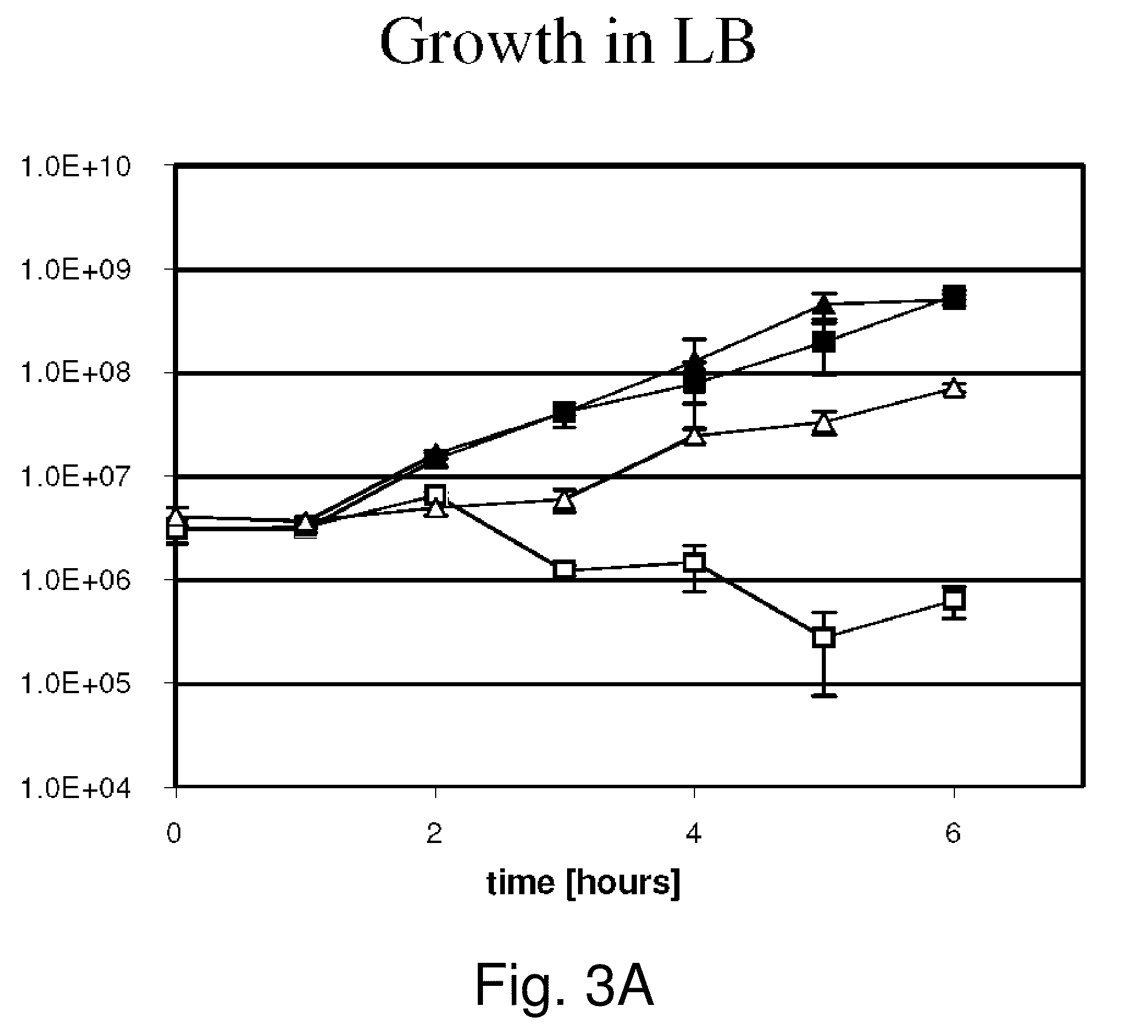
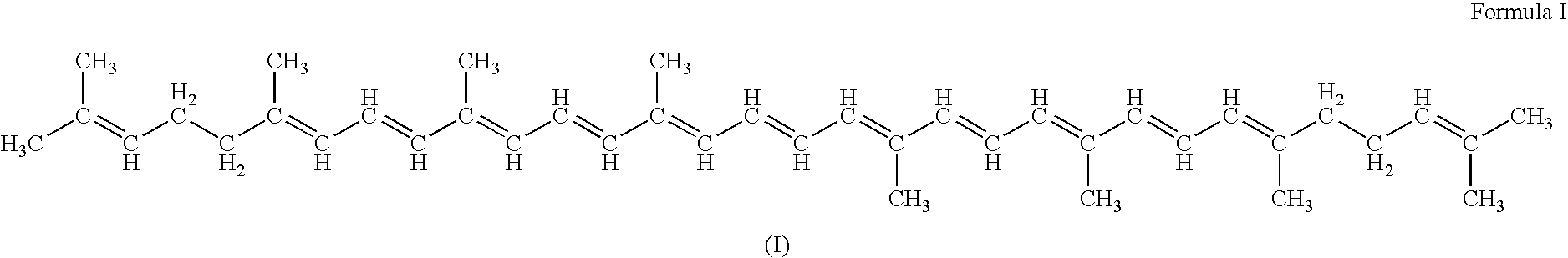
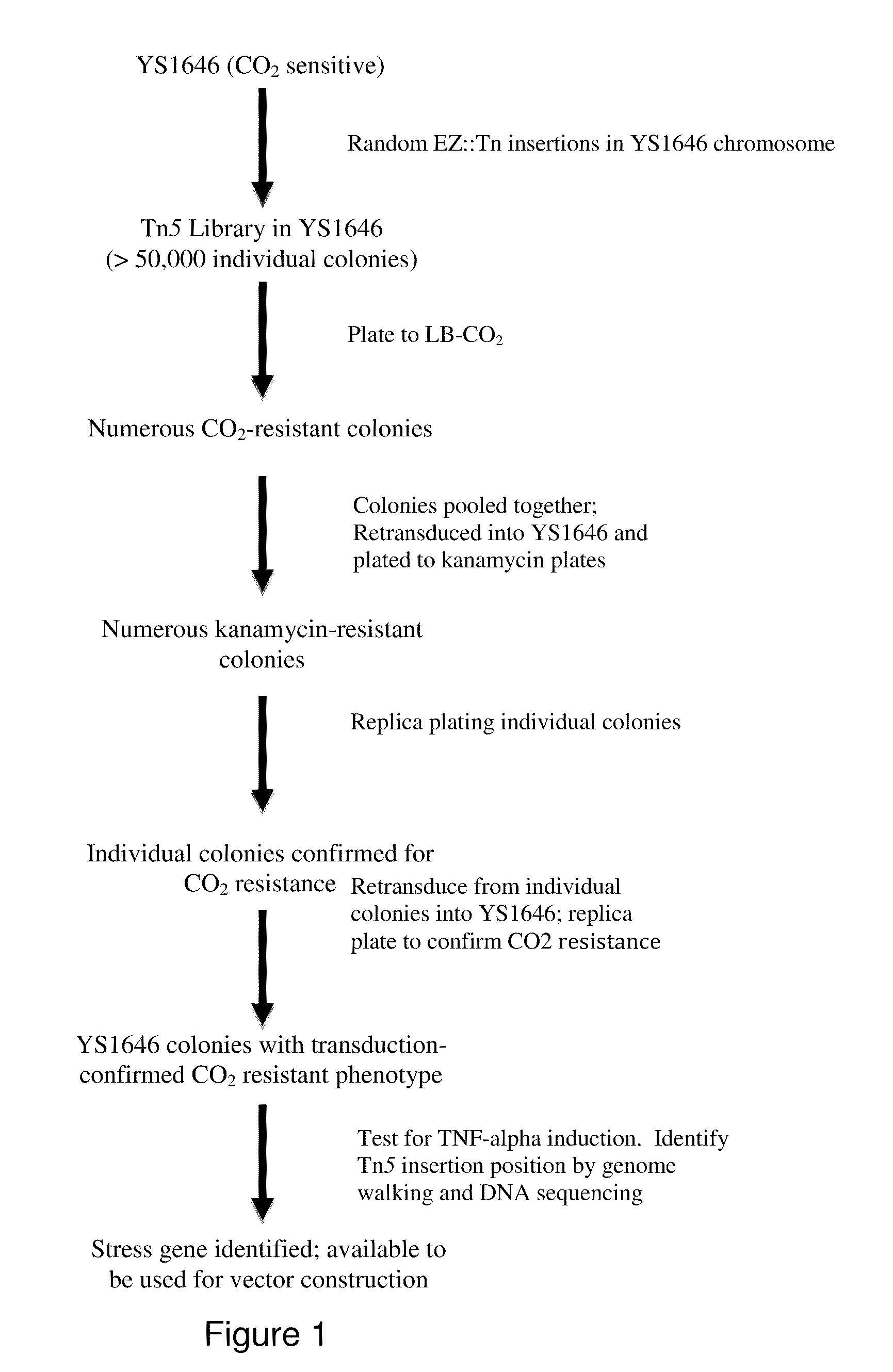
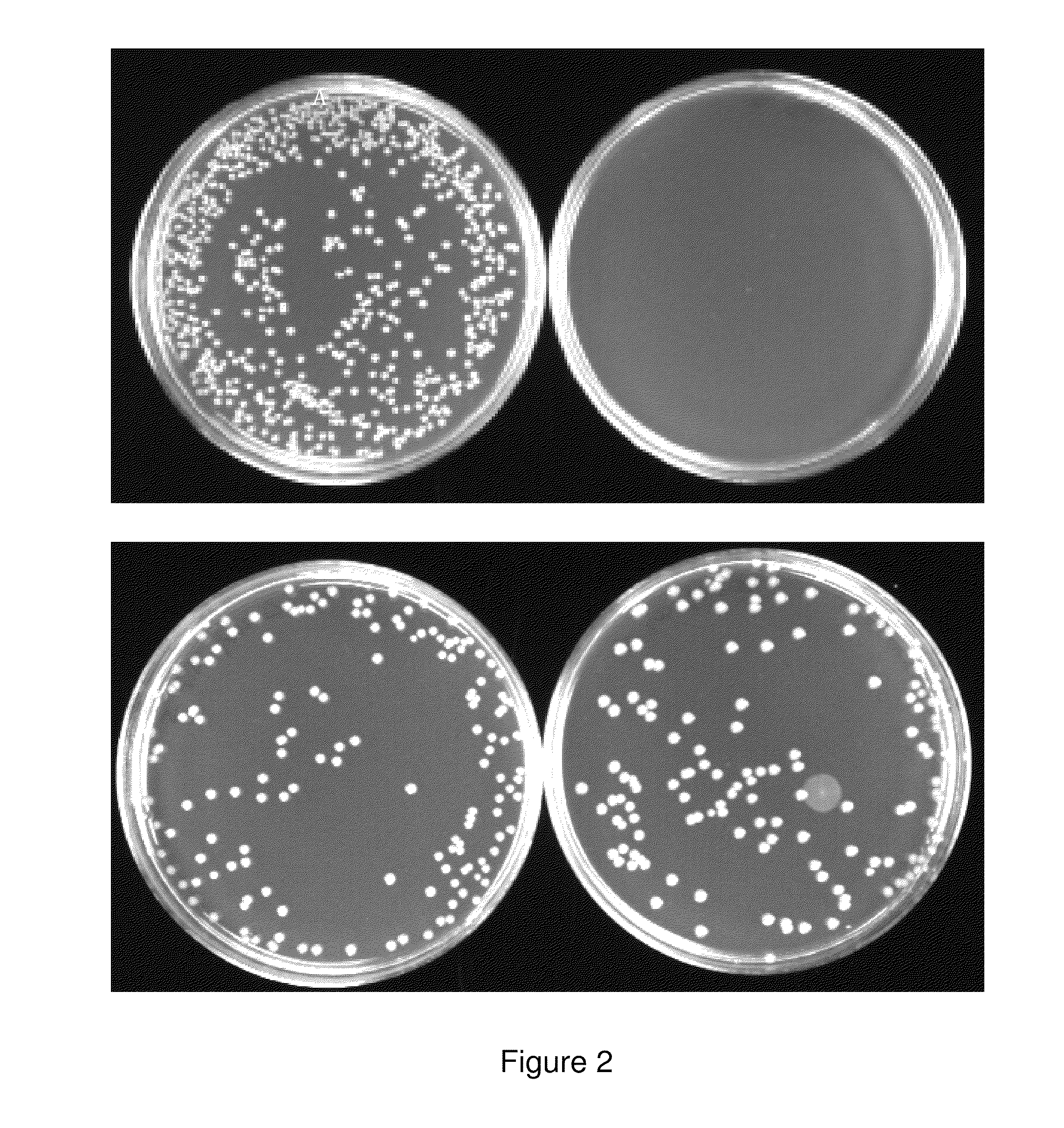
The present invention relates to gram-negative bacterial mutants resistant to one or more stress conditions, including, but not limited to, CO2, acid pH, and high osmolarity. The present invention also relates more particularly to gram-negative bacterial mutants with reduced TNF-α induction having a mutation in one or more lipid biosynthesis genes, including, but not limited to msbB, that are rendered stress-resistant by a mutation in the zwf gene. The present invention provides compositions comprising one or more stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants, preferably attenuated stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for prophylaxis or treatment of a virally induced disease in a subject comprising administering to said subject one or more stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants, preferably attenuated stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants. The present invention further relates to methods for prophylaxis or treatment of a virally induced disease in a subject comprising administering to said subject one or more stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants as vectors for the delivery of one or more therapeutic molecules. The methods of the invention provide more efficient delivery of therapeutic molecules by stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants engineered to express said therapeutic molecules.
Owner:AVIEX TECH
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
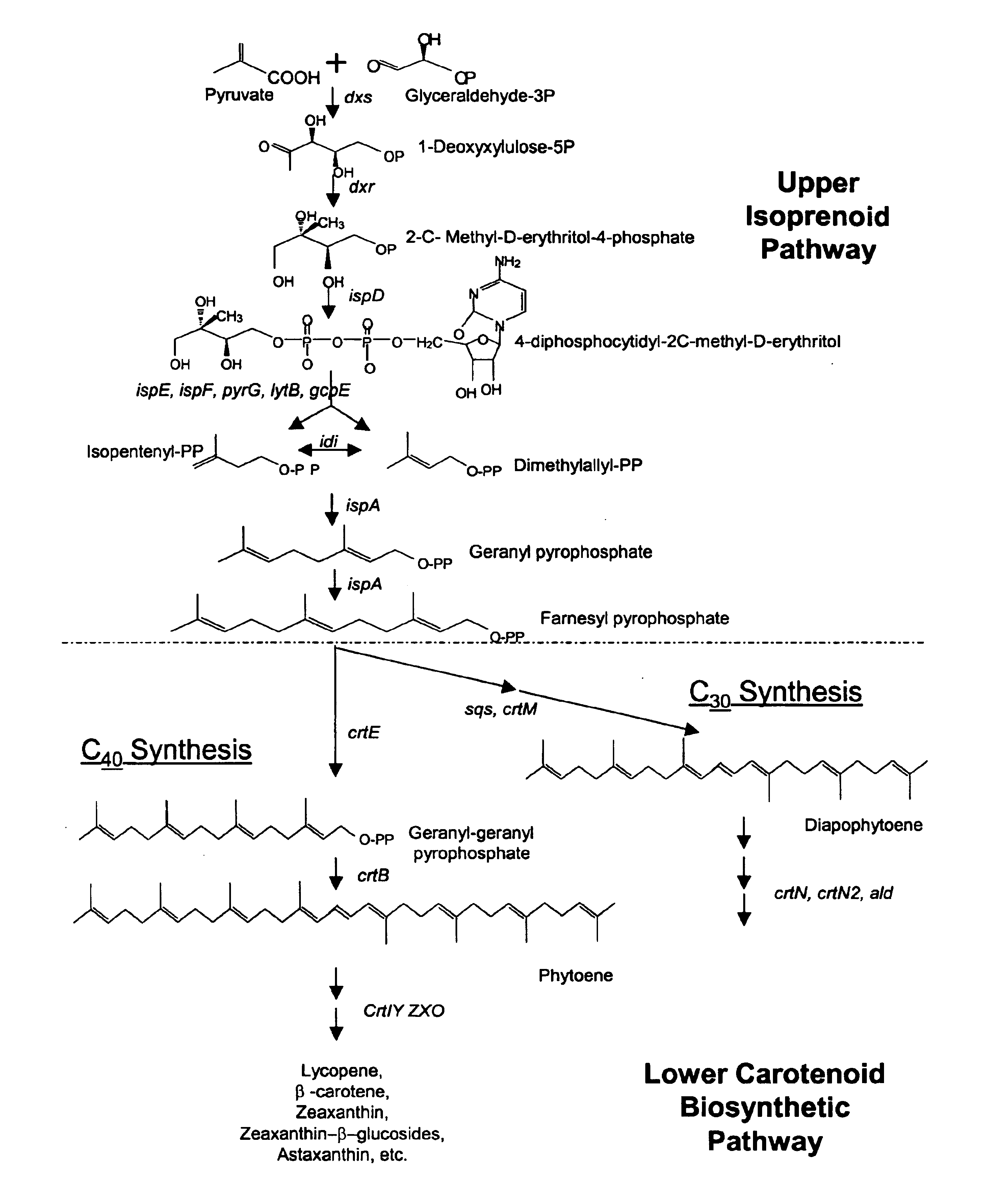
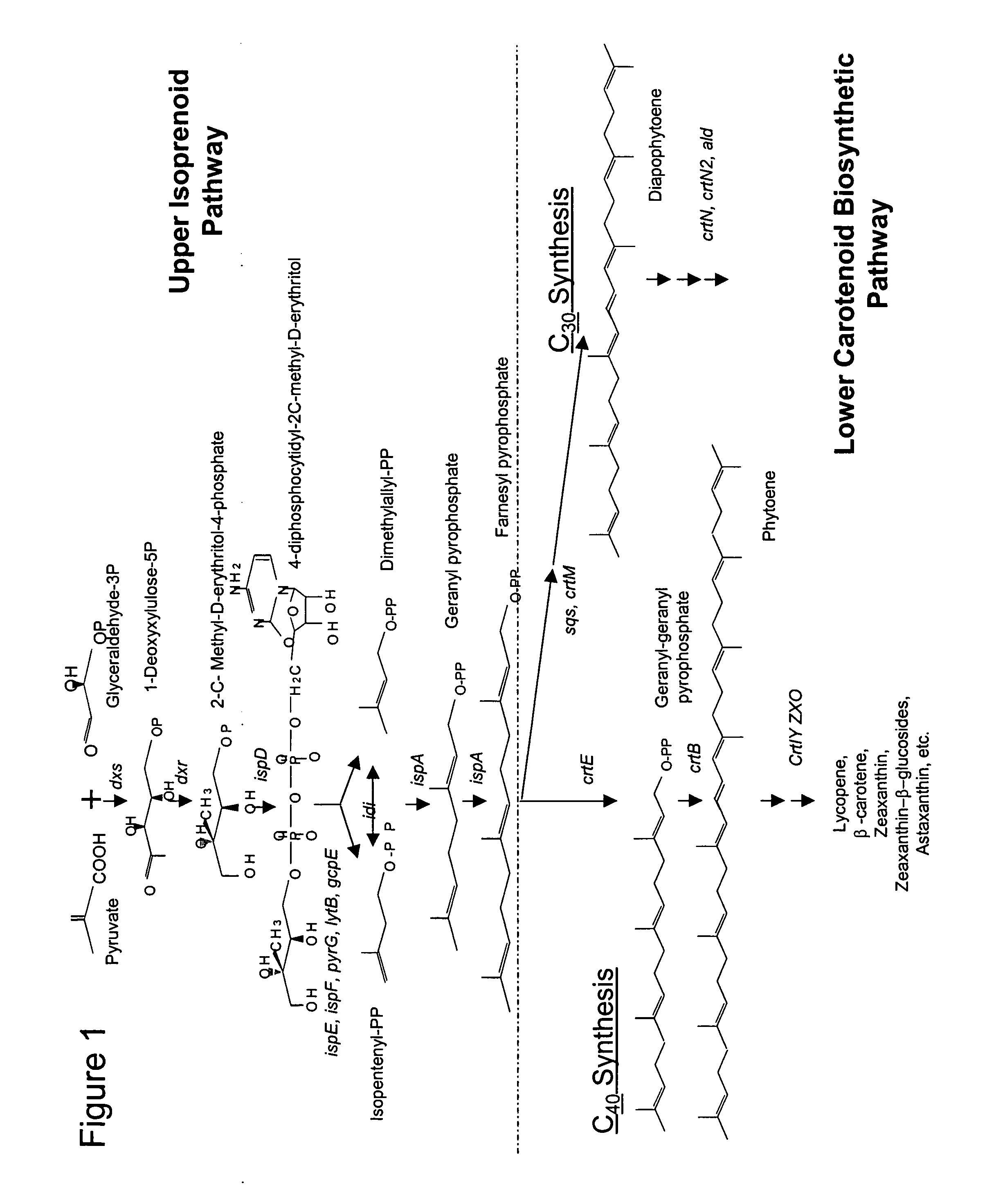
A unique carotenogenic biosynthetic gene cluster has been isolated from Panteoa agglomerans strain DC404, wherein the genetic organization of the cluster is crtE-idi-crtY-crtI-crtB-crtZ. The genes contained within this cluster encode geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase (Idi), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), phytoene synthase (CrtB), and β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ). The gene cluster, genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Live bacterial vaccines resistant to carbon dioxide (CO2), acidic ph and/or osmolarity for viral infection prophylaxis or treatment
The present invention relates to gram-negative bacterial mutants resistant to one or more stress conditions, including, but not limited to, CO2, acid pH, and high osmolarity. The present invention also relates more particularly to gram-negative bacterial mutants with reduced TNF-α induction having a mutation in one or more lipid biosynthesis genes, including, but not limited to msbB, that are rendered stress-resistant by a mutation in the zwf gene. The present invention provides compositions comprising one or more stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants, preferably attenuated stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for prophylaxis or treatment of a virally induced disease in a subject comprising administering to said subject one or more stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants, preferably attenuated stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants. The present invention further relates to methods for prophylaxis or treatment of a virally induced disease in a subject comprising administering to said subject one or more stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants as vectors for the delivery of one or more therapeutic molecules. The methods of the invention provide more efficient delivery of therapeutic molecules by stress-resistant gram-negative bacterial mutants engineered to express said therapeutic molecules.
Owner:AVIEX TECH
Transgenic seedless fruit comprising AGL or GH3 promoter operably linked to isopentenyl transferase or tryptophan monooxygenase coding DNA
InactiveUS6268552B1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesBiosynthetic genesDNA construct
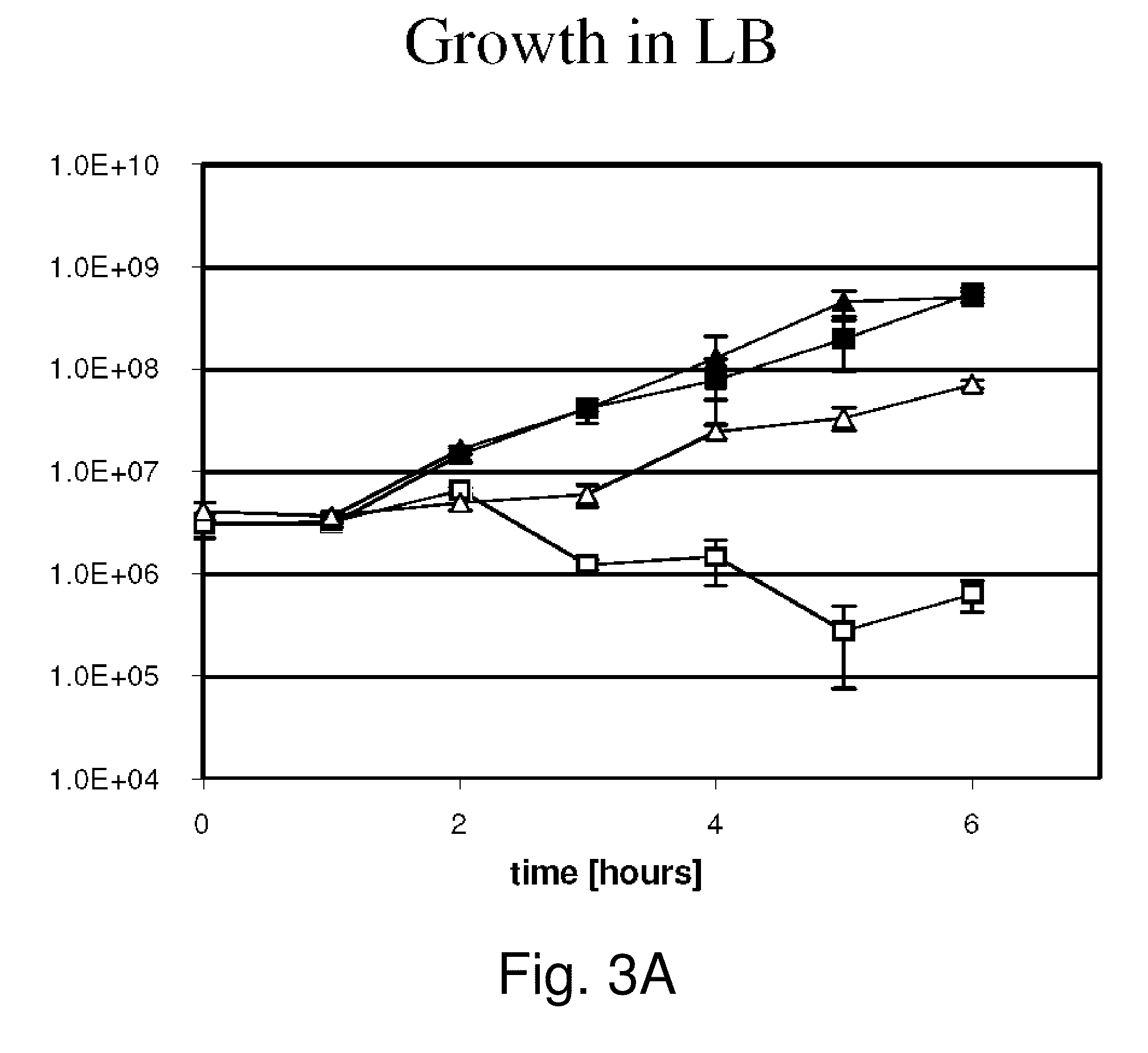
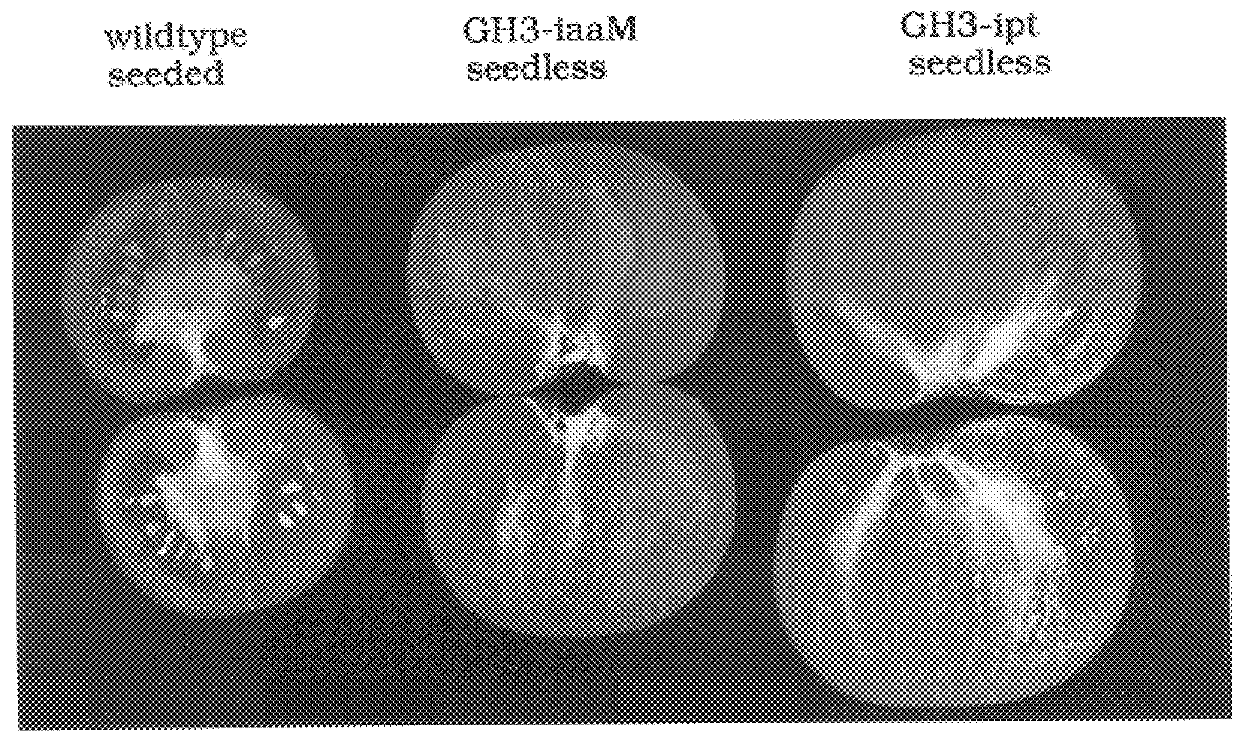
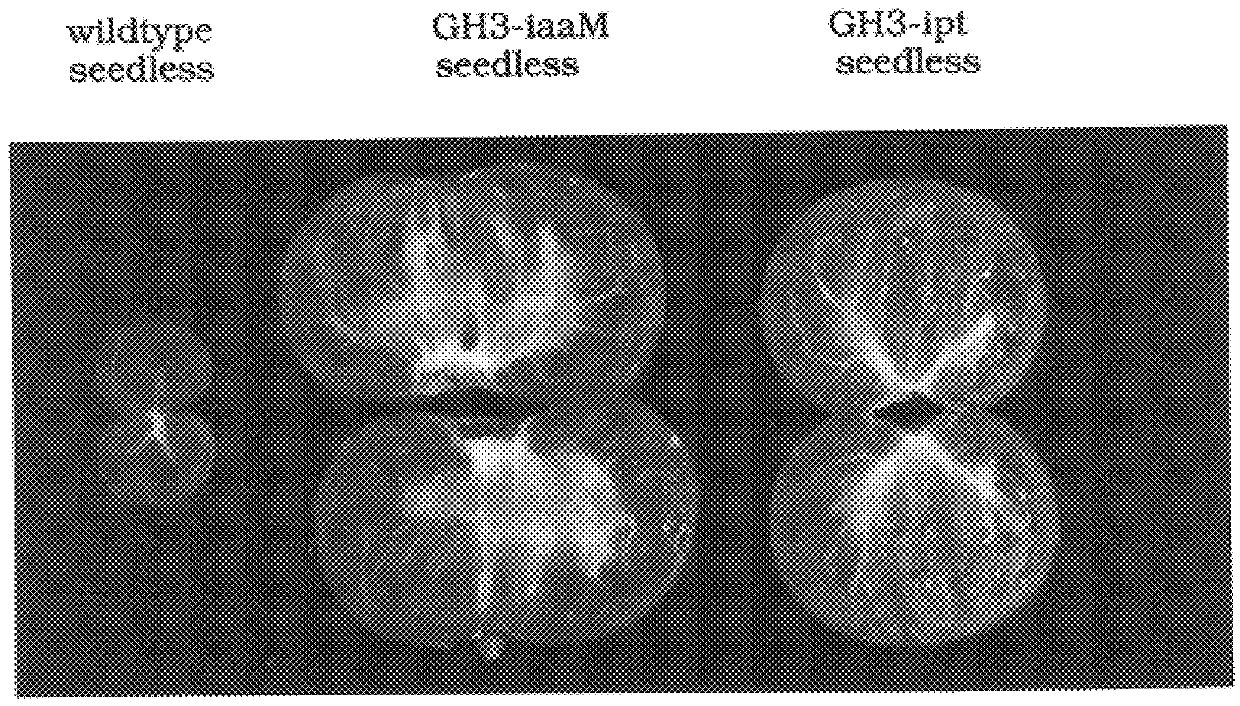
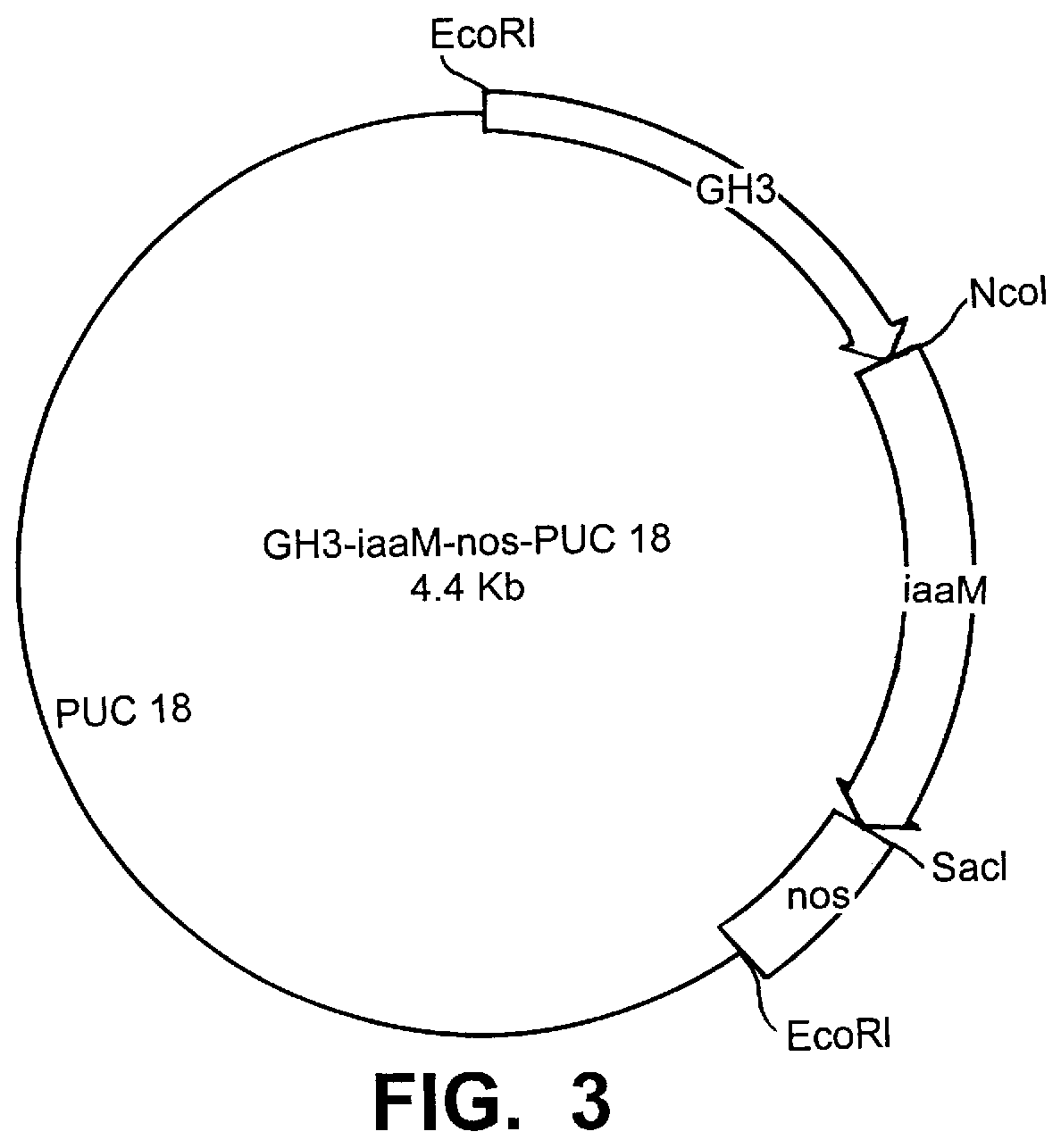
The present invention provides methods and DNA constructs for the genetic engineering of plant cells to produce plants which produce substantially seedless fruit in the absence of exogenous growth factors (auxins or cytokinins) and in the absence of pollination. The substantially seedless fruits produced by the methods described herein are about the size of wildtype seeded fruit (or somewhat larger) and these fruits are equal to or superior to the wildtype seeded fruit with respect to solid content and flavor. The seedless fruits of the present invention are produced in transgenic plants which contain and express auxin or cytokinin biosynthetic genes, e.g., tryptophan oxygenase or isopentenyl transferase coding sequences expressed under the regulatory control of GH3 or AGL promoter sequences directing preferential or tissue specific expression of a downstream gene in the ovaries or developing fruit.
Owner:LI YI
Recombinant dna, bacterial strain and method for fermentative production of l-valine
InactiveCN102286505AHigh activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
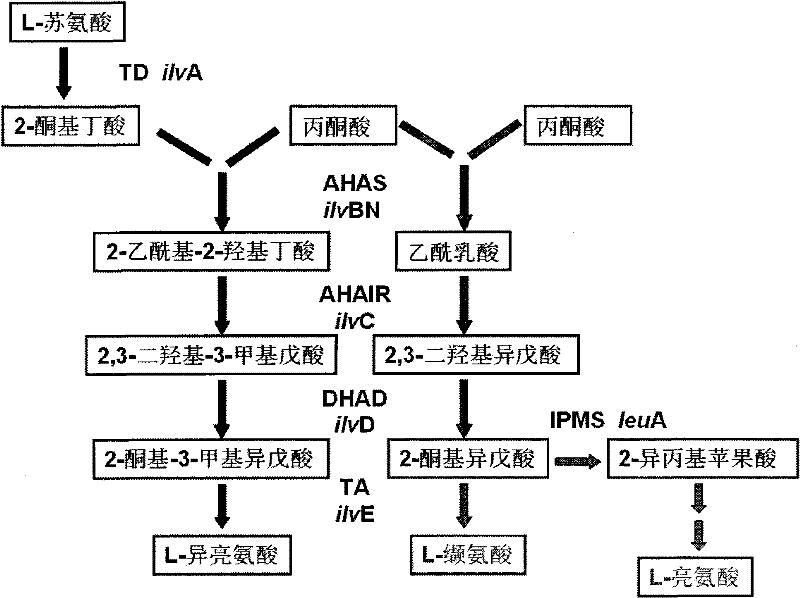
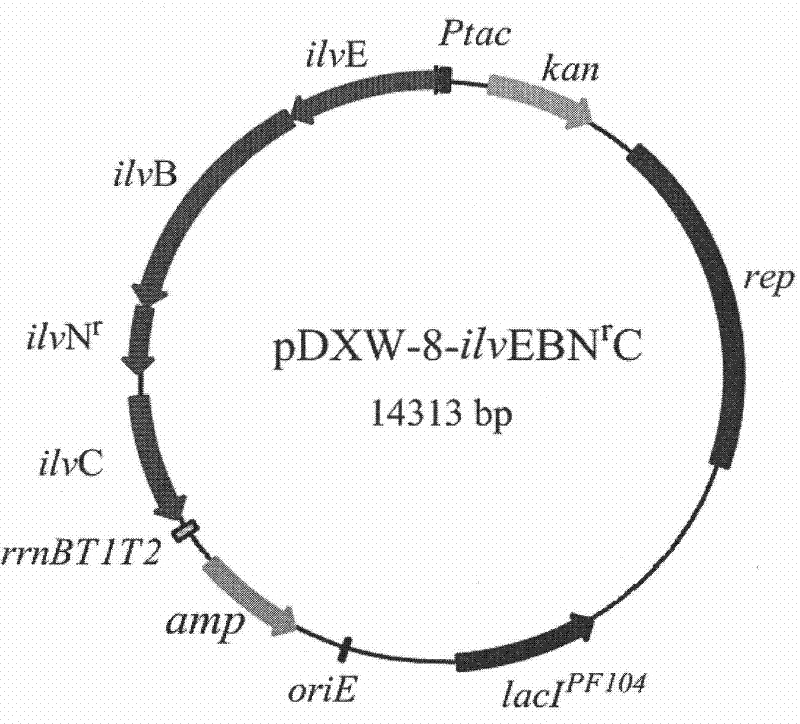
The invention relates to a recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), strain and method for producing L-valine by fermentation. The recombinant DNA comprises DNA sequence for coding acetohydroxy acid synthetase free of feedback inhibition of three branched-chain amino acids to acetohydroxy acid synthetase, DNA sequence for coding dihydroxy reduction isomerase, and DNA sequence for coding branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase. The strain is corynebacterium or brevibacterium transformed by introducing the recombinant DNA. The method is implemented by culturing the strain to produce the L-valine. In the invention, the expression L-valine is used for producing the bacterium L-valine biosynthetic gene, so the yield of the L-valine can be greatly increased; and the fermentation model, especially the high-temperature short-time fermentation model, is constructed according to the optimum temperature of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme, so that the metabolism intensity of the strain is enhanced, the activity of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme is enhanced, and the yield of the L-valine and the conversion rate of the sugar acid can be further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
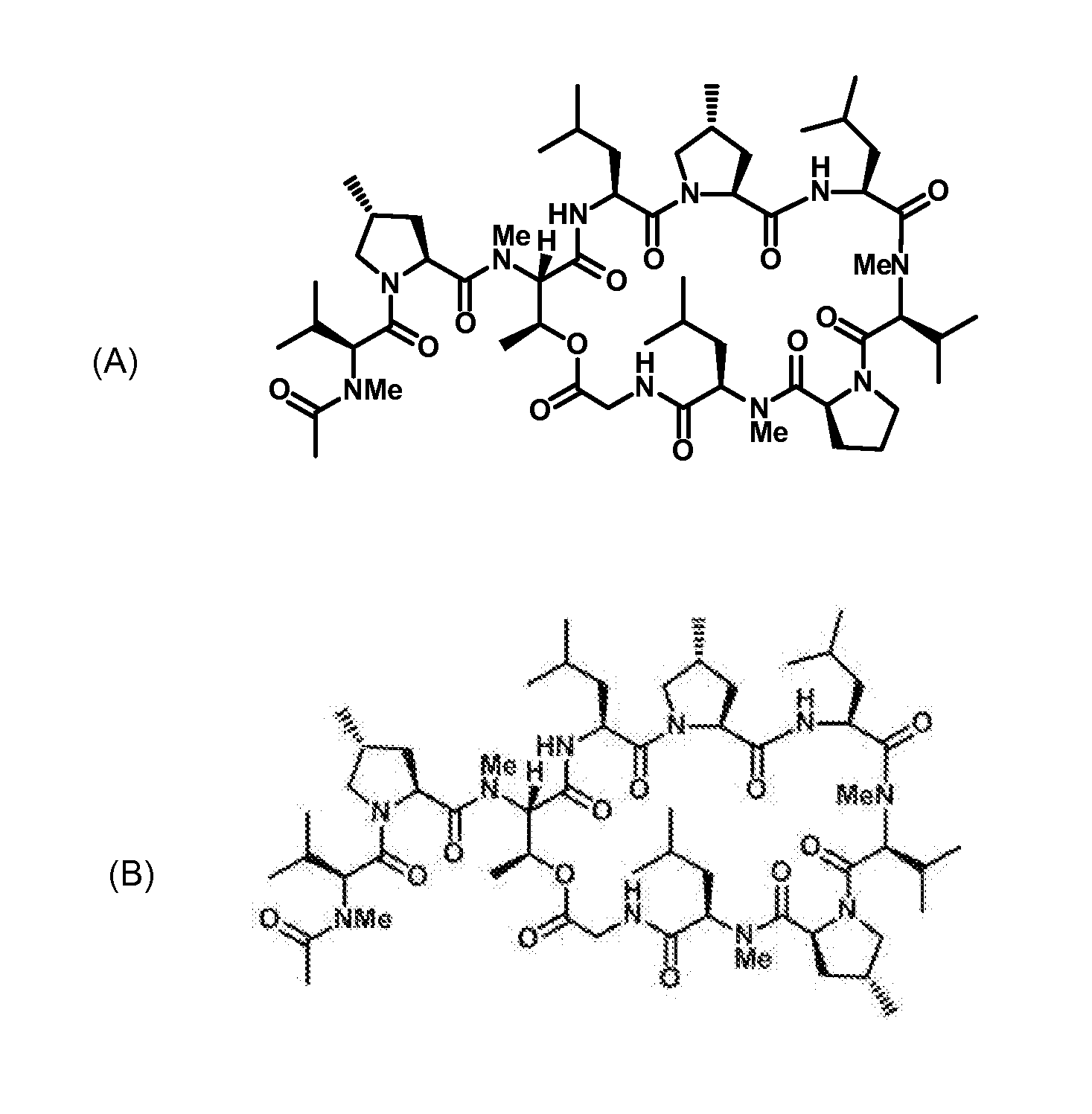
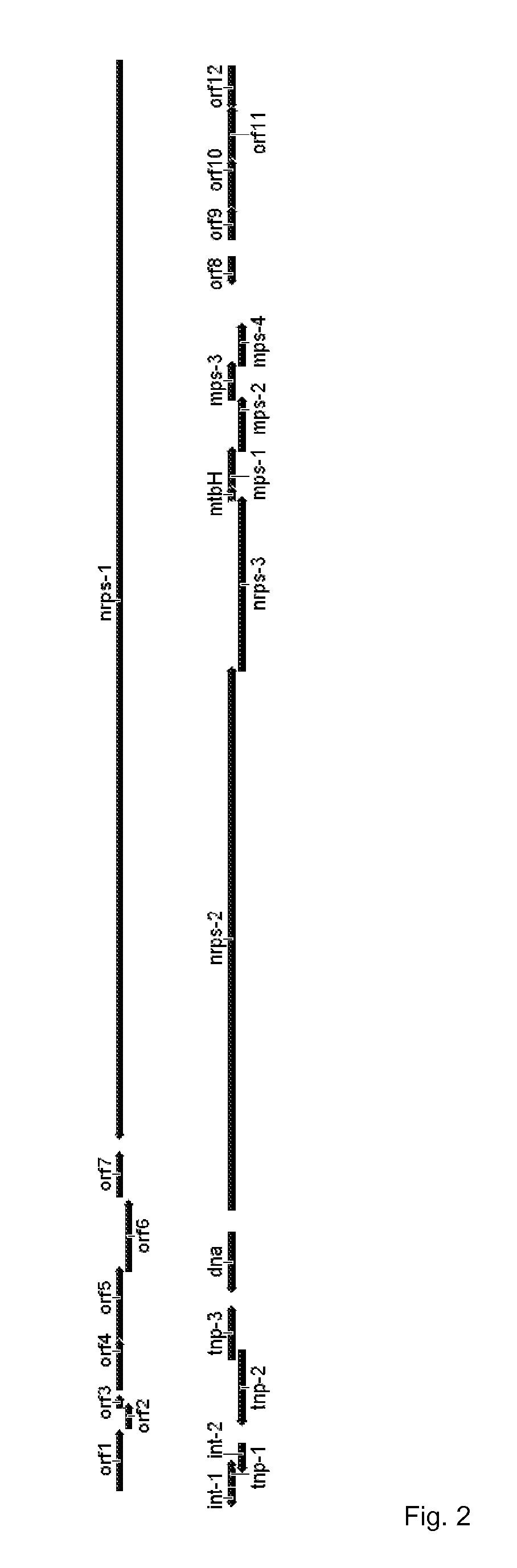
Gene cluster for biosynthesis of griselimycin and methylgriselimycin
ActiveUS20140295457A1Increase productionEasy to produceBacteriaHydrolasesAntibiotic AgentsGene cluster
The present invention refers to the gene cluster and genes comprised by the gene cluster which are involved in the biosynthesis of griselimycin and methylgriselimycin and to the use of the gene cluster, genes comprised thereby and proteins encoded thereby for the production of antibiotic agents.
Owner:SANOFI SA
DNA encoding SPNF of the spinosyn cluster
InactiveUS7015001B2Altered spinosyn synthesisInhibit productionFungiSugar derivativesMicroorganismBiotechnology
Spinosyn biosynthetic genes from Saccharopolyspora spinosa, spinosyn producing microorganisms transformed with the biosynthetic genes, methods using the biosynthetic genes to increase production of spinosyn insecticidal macrolides, and methods using the genes or fragments thereof to change the products produced by spinosyn-producing microorganisms are provided.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Transgenic plants expressing cytokinin biosynthetic genes and methods of use therefor
ActiveUS20060010515A1Improved yield related characteristicHigh expressionOther foreign material introduction processesEnzymesHeterologousBiosynthetic genes
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Platensimycin biosynthetic gene cluster of streptomyces platensis
The present invention relates to the cloning and sequence of a biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces platensis that produces platensimycin and platencin. Also provided are engineered micro-organisms for the production of these compounds, and analogs thereto, as well as methods of screening for compounds with anti-bacterial activity.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Biological synthesis gene cluster for Azintamide
InactiveCN101275141AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationPlant genotype modificationHeterologousEnzyme Gene
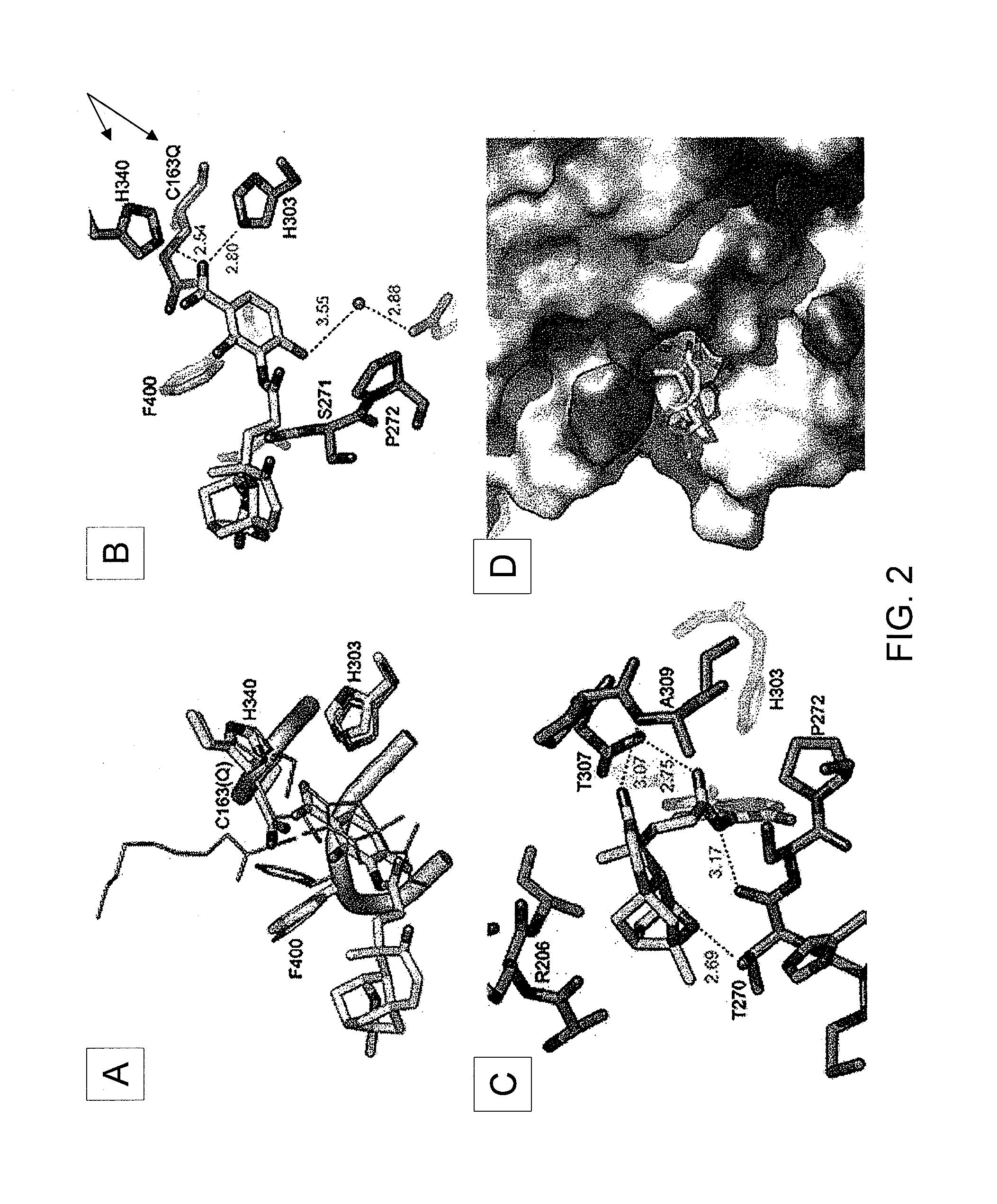
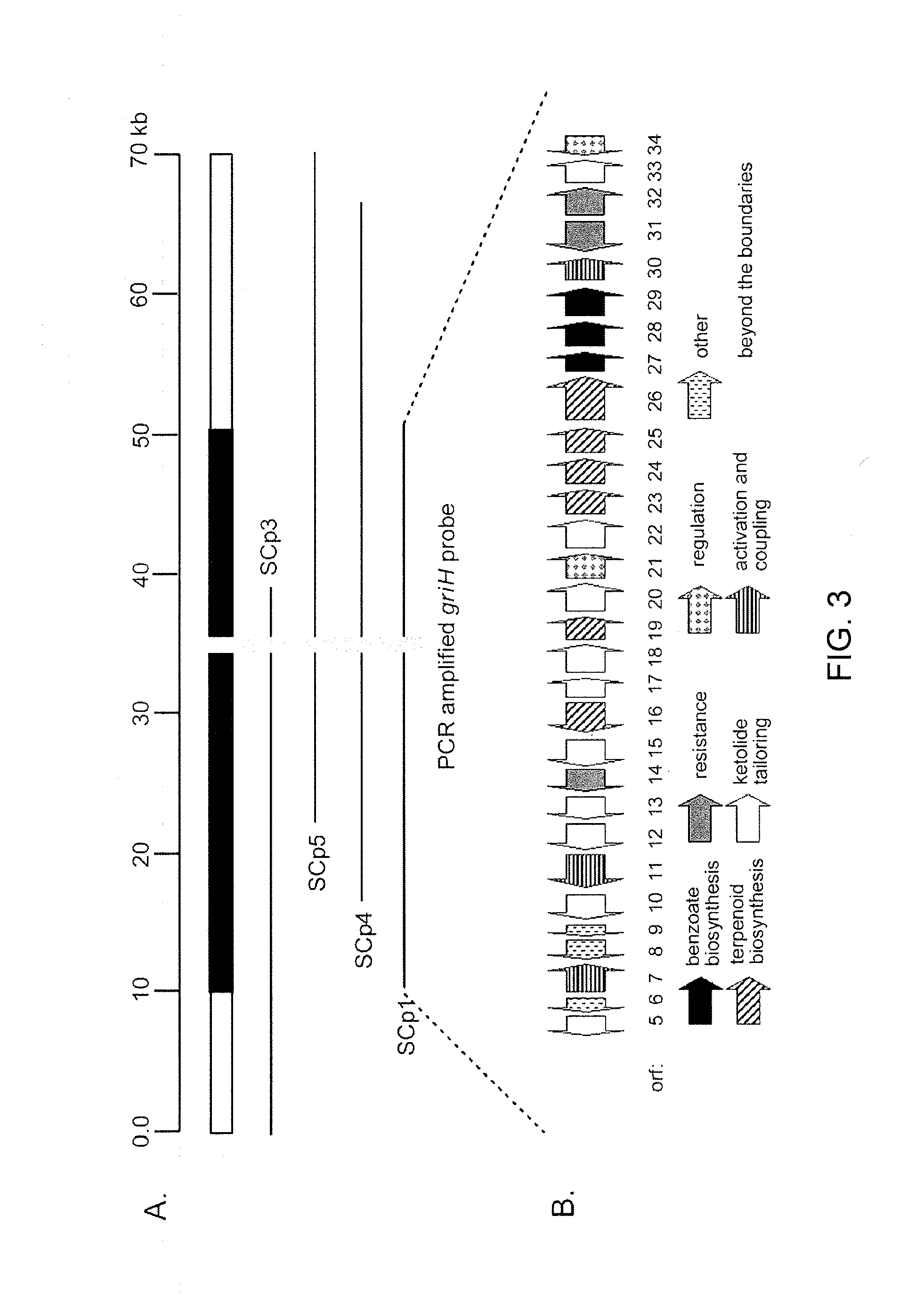
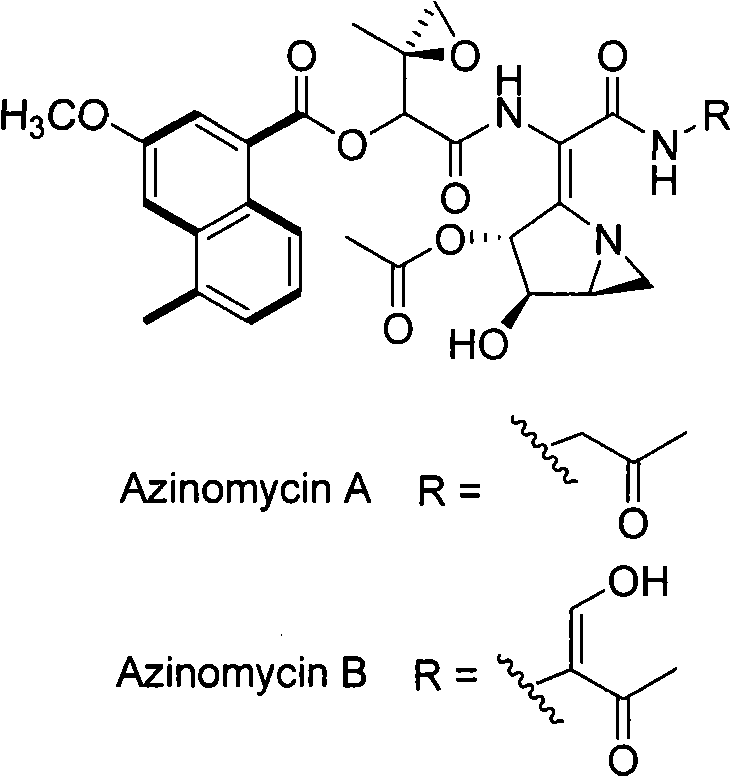
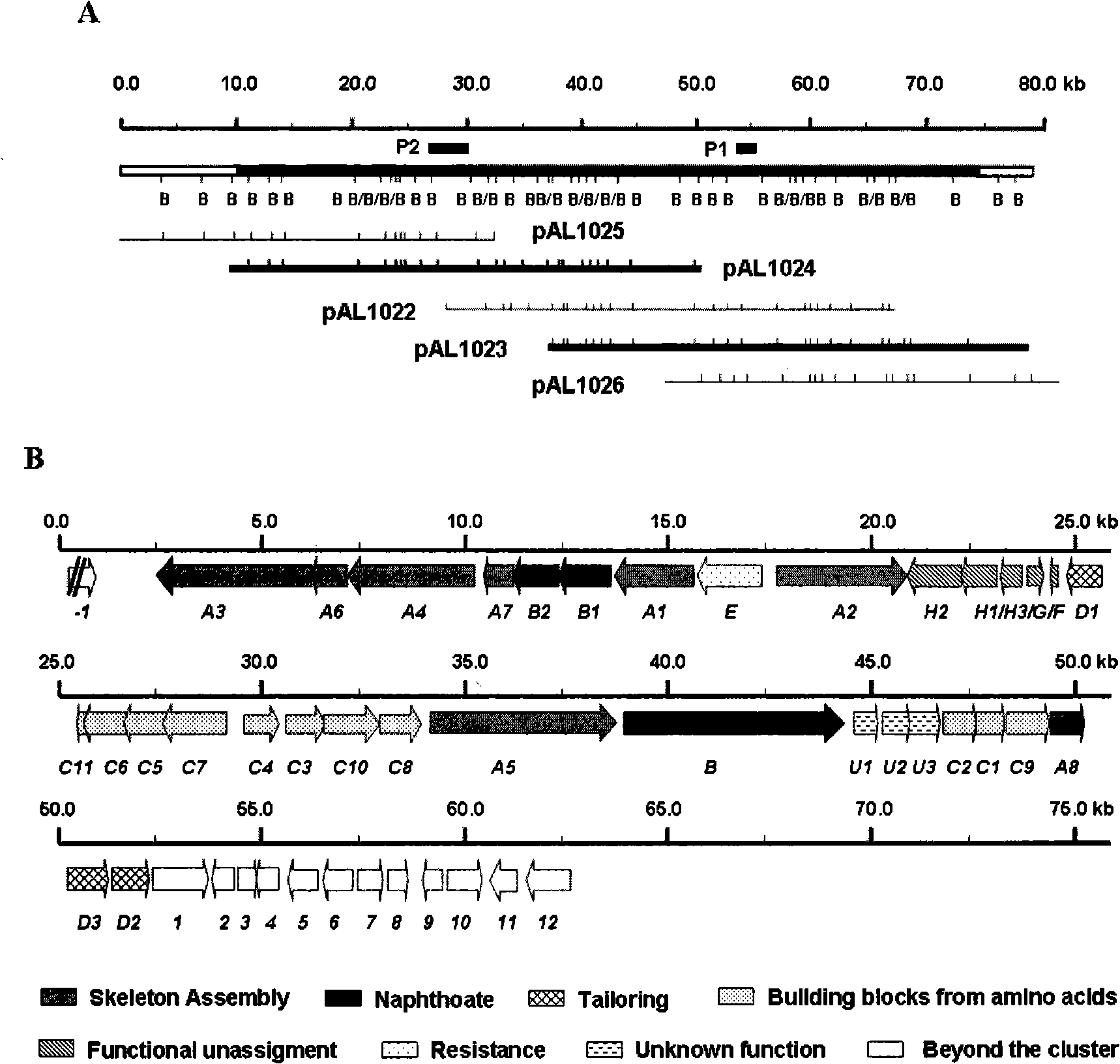
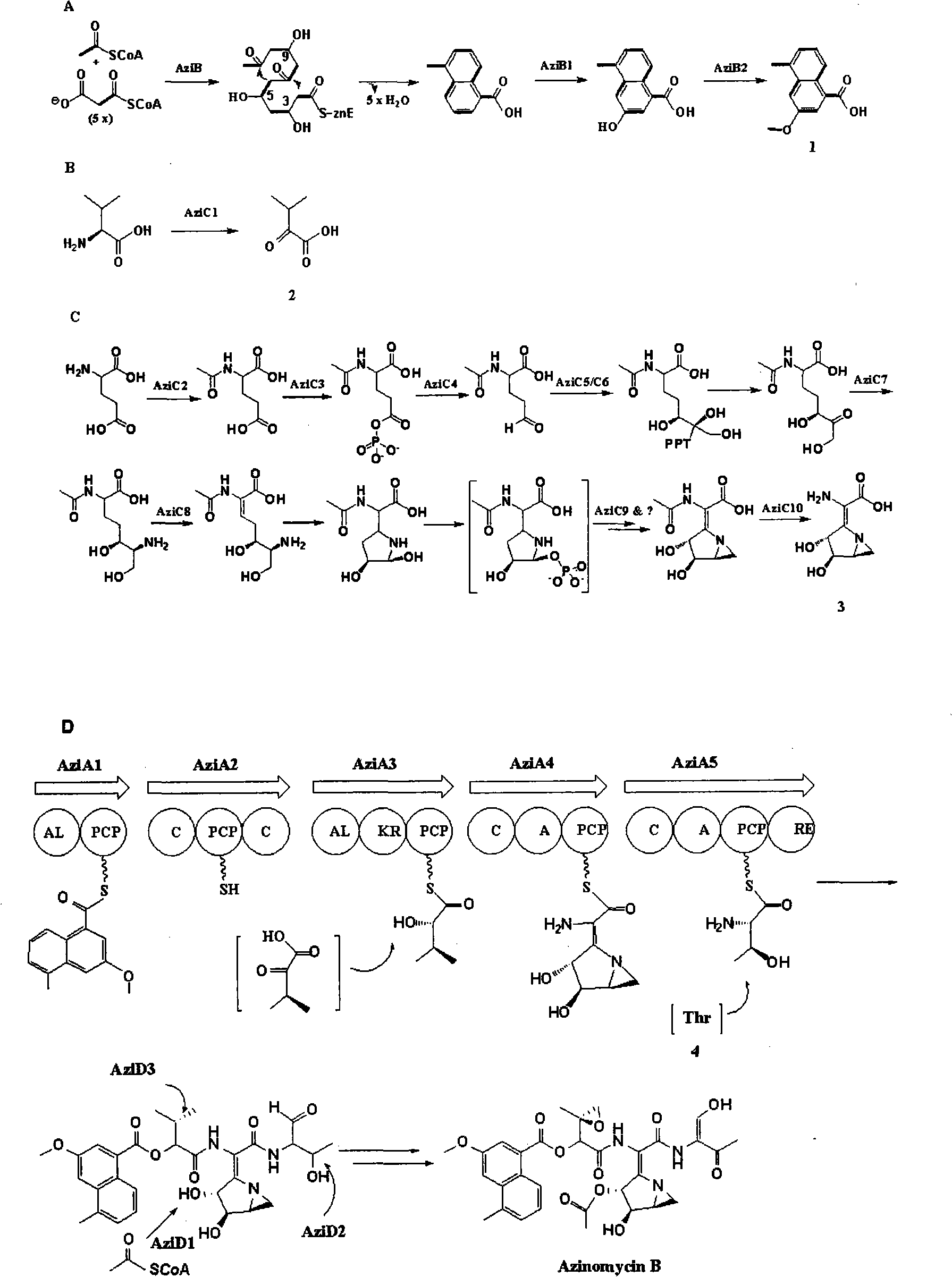
The present invention provides cloning sequencing, analyzing, function research of a biosynthesis gene cluster of an antibiotic-Azinomycin B having antitumor activity produced by streptomyces, and its application. The whole gene cluster includes 34 genes: one repeatedly using I type polyketide synthase gene; two naphthalene ring modification enzyme genes; 8 non-ribosomal polypeptide skeleton synthesis and modification enzyme genes; 11 non-natural amino acid structure unit synthase genes; 1 resistance gene; 3 post modification enzyme genes and 8 genes which functions are not determined. The genetic operation of the biosynthesis gene breaks the synthesis of Azinomycin B; the precursor compound is produced by the heterologous expression of synthesis gene and modification gene of naphthalene ring. The gene of the invention and the protein can be used for searching and finding compound or gene, protein applied in medical, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
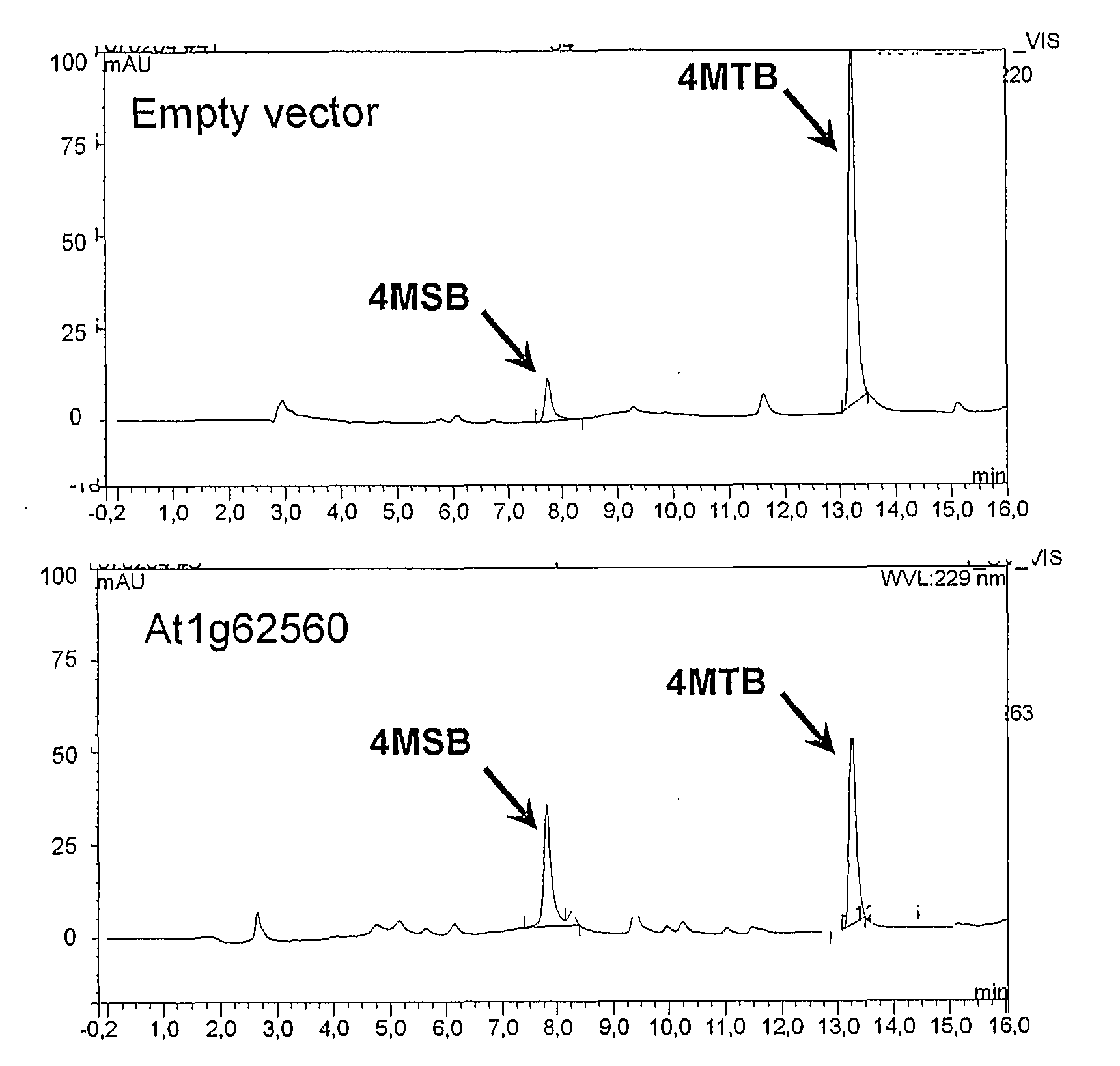
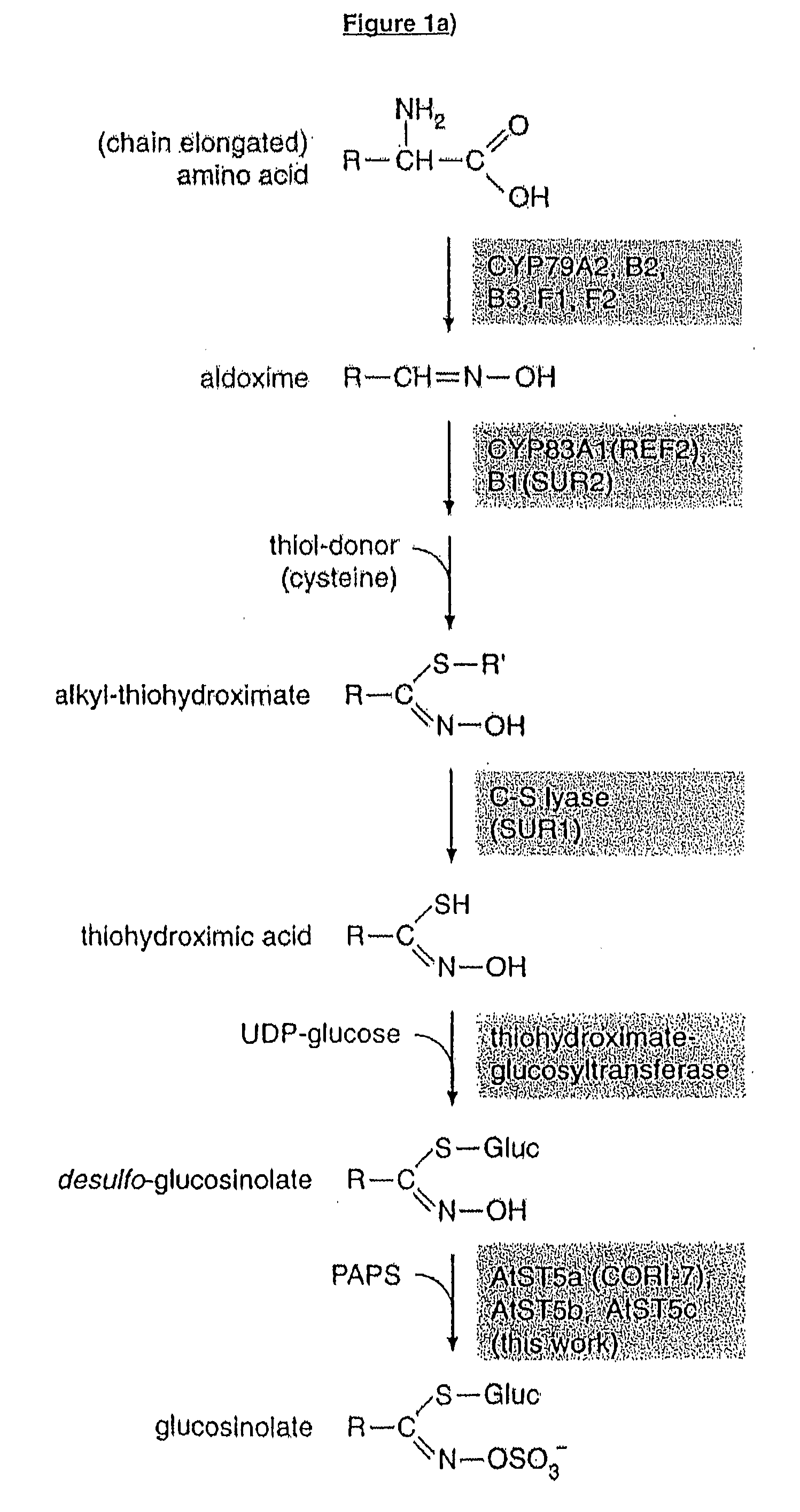
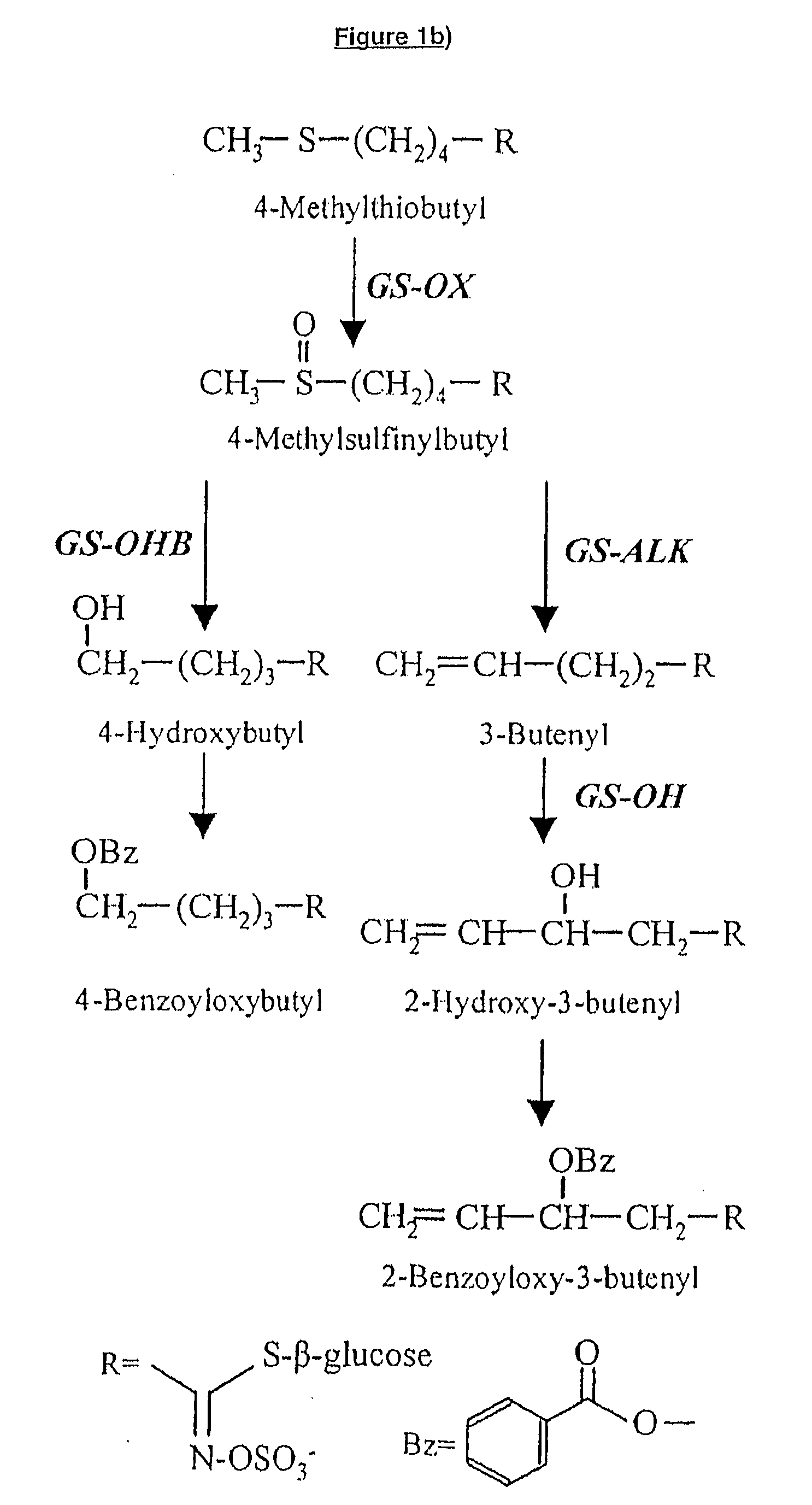
Flavin monooxygenases and transcription factors involved in glucosinolate biosynthesis
InactiveUS20100011462A1Add flavorImprove seed qualitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiosynthetic genesTranscriptional regulation
The invention provides methods and materials relating generally to plant derived flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMOs) capable of catalysing oxidation of a thio- to a sulphinyl-group during glucosinolate biosynthesis. It further relates to plant derived MYB factors capable of transcriptional regulation of biosynthetic genes. These have utility in the modification of glucosinolate biosynthesis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
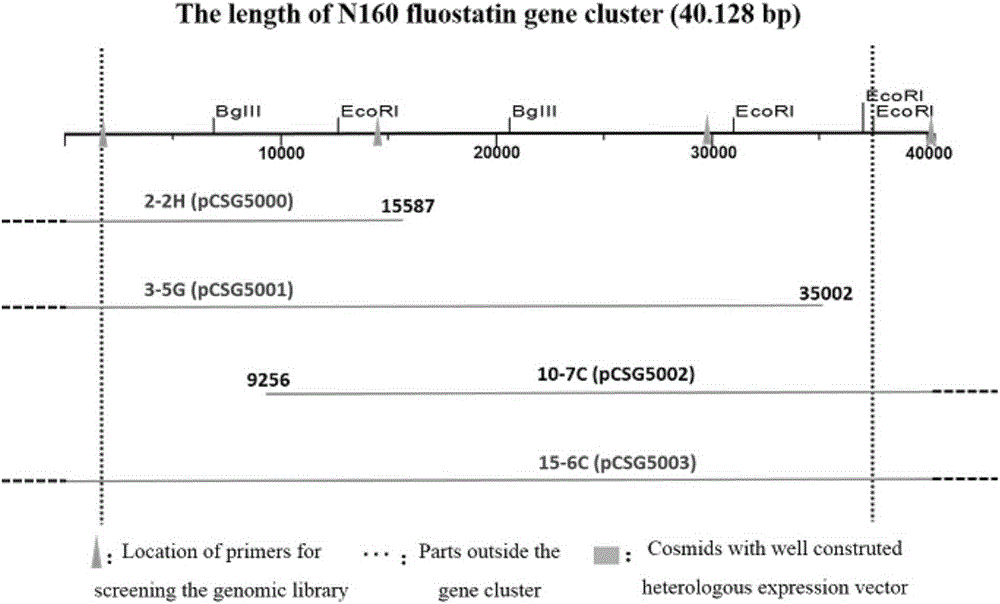
Biosynthetic gene cluster of romatic-polyketide atypical fluostatins and applications of biosynthetic gene cluster
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of romatic-polyketide atypical fluostatins and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the biosynthetic gene cluster of fluostatins derived from micromonospora rosaria SCSIO N160 (preservation No: CCTCC NO: M2012392) is shown in the 1st-40128th base sequences in SEQ ID NO. 1, and contains 32 genes. Genes and proteins thereof provided by the invention can be used for seeking and finding compounds or genes and proteins for medicine, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids, novel biosynthesis genes, and novel plant expression constructs
The present invention relates to a method for the production of unsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds. The invention furthermore relates to the use of nucleic acid sequences SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 11 encoding polypeptides having desaturase activity in the method and for generating a transgenic organism, preferably a transgenic plant or a transgenic microorganism, with an increased content of fatty acids, oils or lipids with unsaturated C18-, C20-, or C22-fatty acids, and to their homologs or derivatives, to gene constructs encompassing these genes, and to their use alone or in combination with biosynthesis genes of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The invention also relates to multiexpression cassettes for seed-specific expression, and to vectors or organisms which encompass a desaturase gene alone or in combination with further desaturases and / or elongase genes or homologs using said expression cassettes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Enzyme synthesized by Chinese caterpillar fungus hirsutella sinensis to metabolize guanine nucleotide and genes and application of enzyme
InactiveCN102690796AIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyBiosynthetic genes
The invention relates to IMP (inosine monophosphate) dehydrogenase synthesized by 'Bailing' producing fungus Chinese caterpillar fungus hirsutella sinensis to metabolize guanine nucleotide based on xanthosine monophosphate and coding genes and application of the IMP dehydrogenase. The IMP dehydrogenase comprises proteins shown by SEQ ID No.1, SEQ ID No.2 and SEQ ID No.3, and coding genes of the IMP dehydrogenase correspond to nucleotide sequences shown by SEQ ID No.4, SEQ ID No.5 and SEQ ID No.6. Detailed studies on metabolic pathways of the xanthosine monophosphate synthesizing the guanine nucleotide in principle are carried out and include that cloned DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) in the provided nucleotide sequences can be transferred into engineering bacteria by means of transduction, transformation and transconjunction, and high expressivity is given to the host guanine nucleotide by adjusting expressions of guanine nucleotide biosynthetic genes, so that an effective way for increasing output of the guanine nucleotide is provided, and the IMP dehydrogenase and the coding genes have significant application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Process for expression of foreign genes in methylotrophic bacteria through chromosomal integration
InactiveUS20050287625A1Stable productionImprove the level ofBacteriaEnzymesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
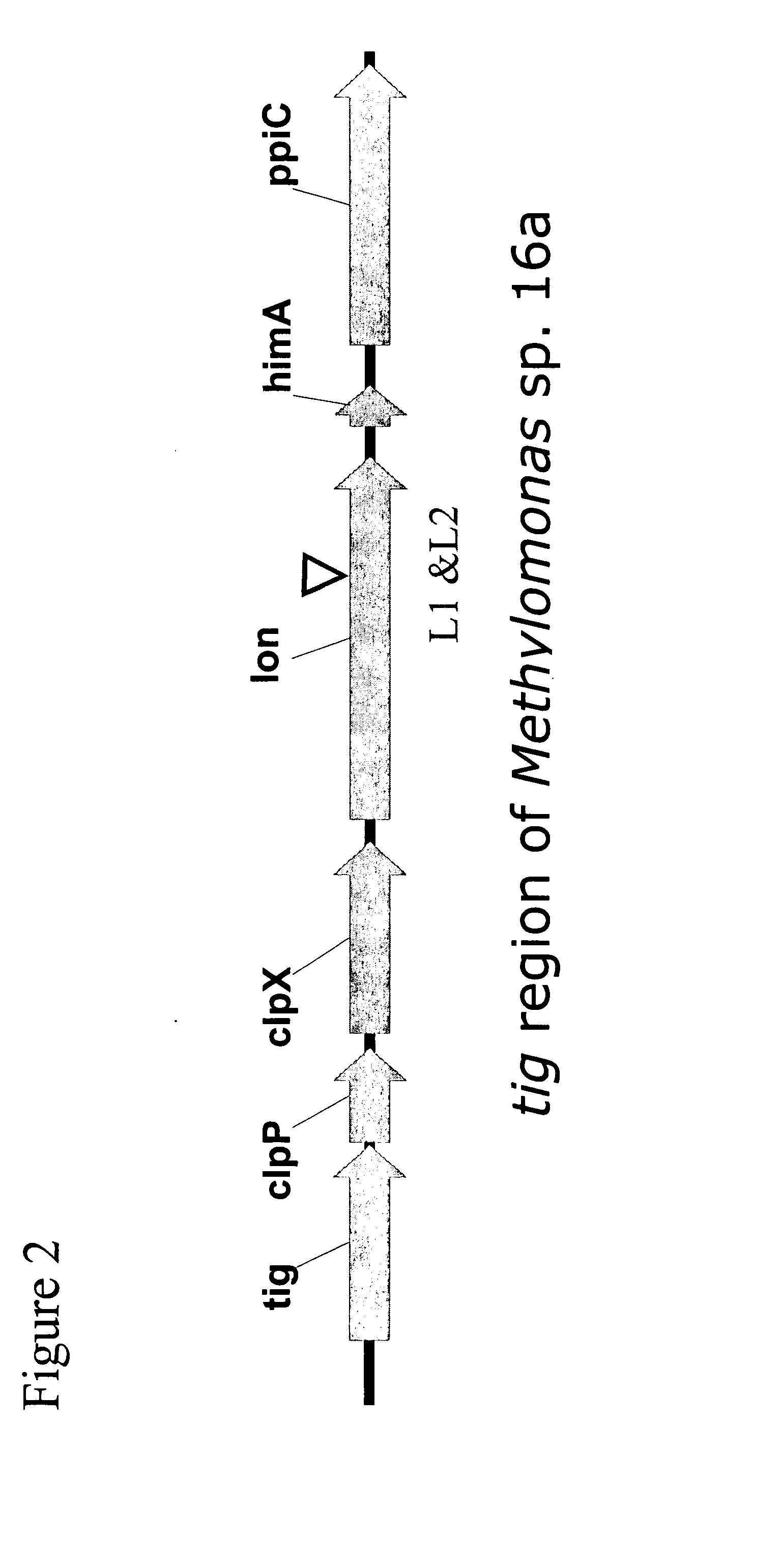
Provided is a method for expressing an introduced gene or genes in a C1 metabolizing microorganism host wherein the gene(s) are integrated into the tig region of the chromosome. This method provides high level expression in a stable manner in which growth rate of the host strain is not highly affected and a selection marker is not required. The use of this method for expressing carotenoid biosynthetic genes and resulting production of canthaxanthin is also described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Biosynthetic gene cluster of grincamycin and P-1894B and application thereof
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of grincamycin and P-1894B and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the biosynthetic gene cluster of grincamycin and P-1894B is shown as the base sequences from 3722-40612 of SEQ ID NO.1. The biosynthesis-associated all gene and protein information containing grincamycin and P-1894B provided by the invention can help people to understand the biosynthetic mechanism of angucycline natural products so as to provide materials and knowledge for further genetic modification. The gene and the protein provided by the invention can be used for seeking for and discovering compounds or genes and proteins which can be applied to medicines, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthetic genes and host cells for the synthesis of polyketide antibiotics and method of use
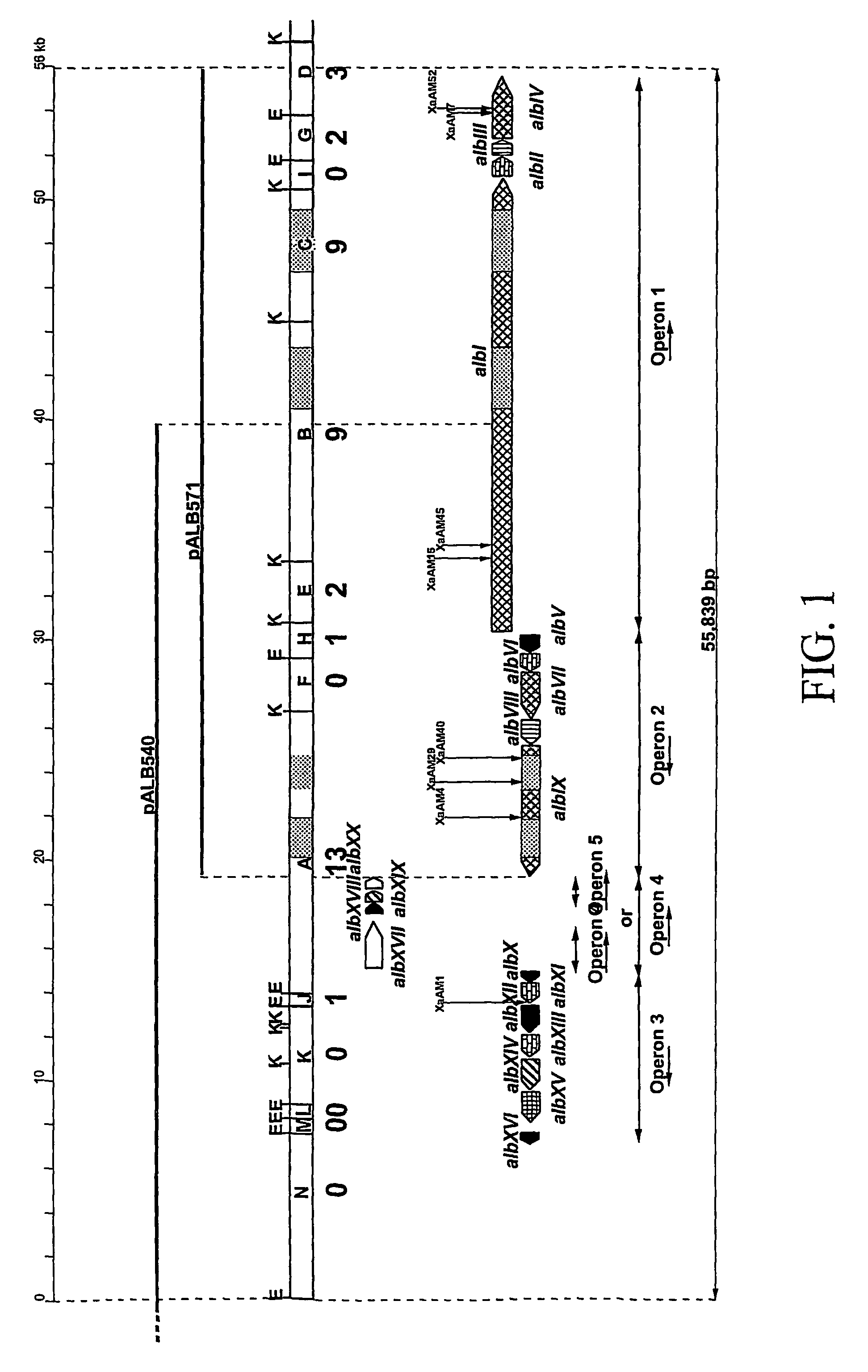
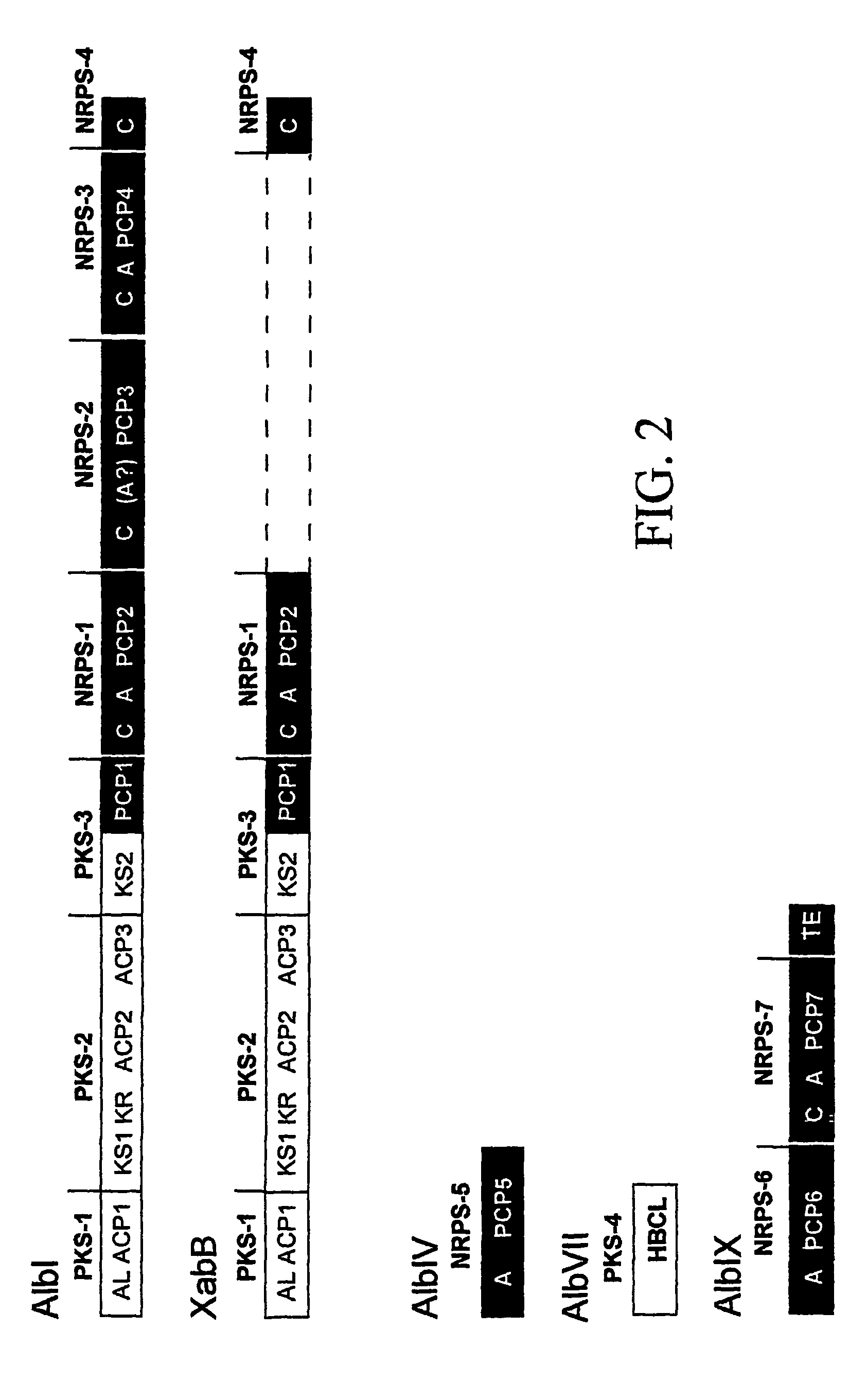
Three gene clusters that together encode albicidin biosynthesis, the complete gene DNA sequences, and the deduced protein sequences for the enzymes and methods for using the DNA sequences are disclosed and discussed as well as methods for plant protection and creating new antibiotics. The novel Albicidin family of antibiotics is disclosed and their structure deduced.
Owner:LE CENT DE COOPERATION INT & RES & DEV AGRONOMIQUE POUR LE DEVPEMENT CIRAD +1
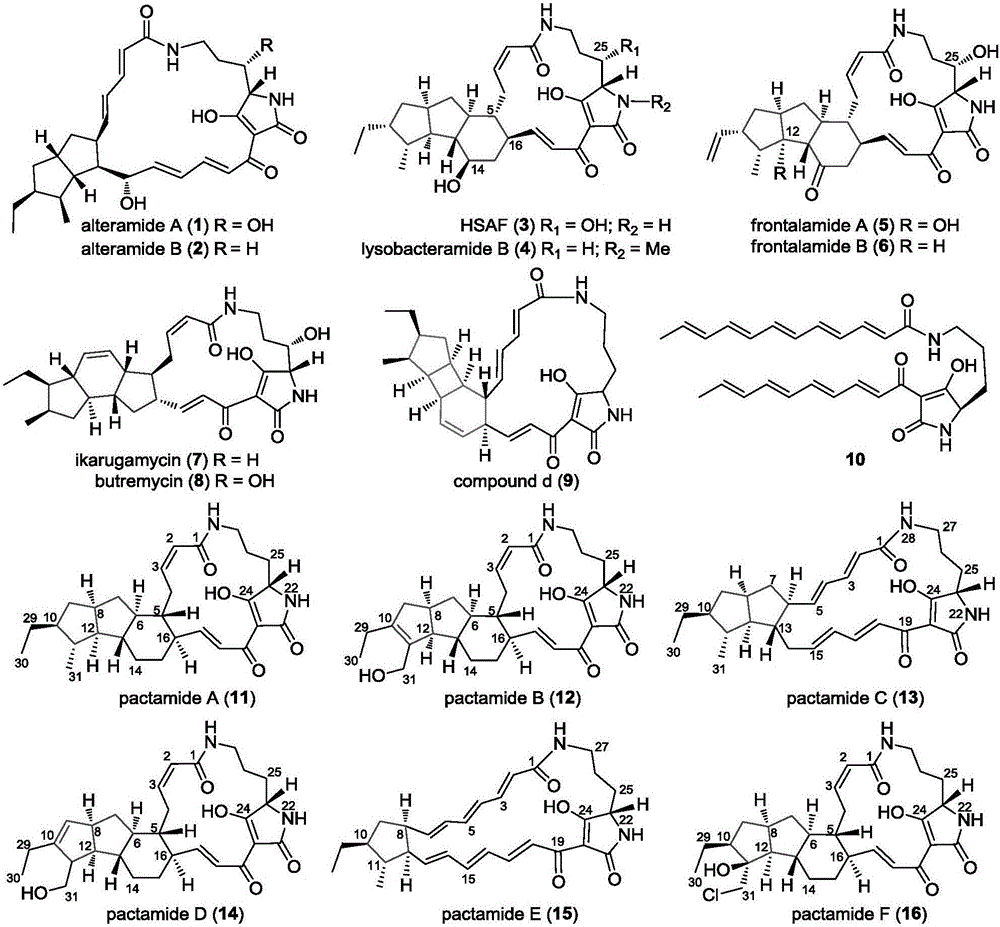
Biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and application thereof
ActiveCN106434702ABiosynthetic gene cluster activationHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclasePolyketide
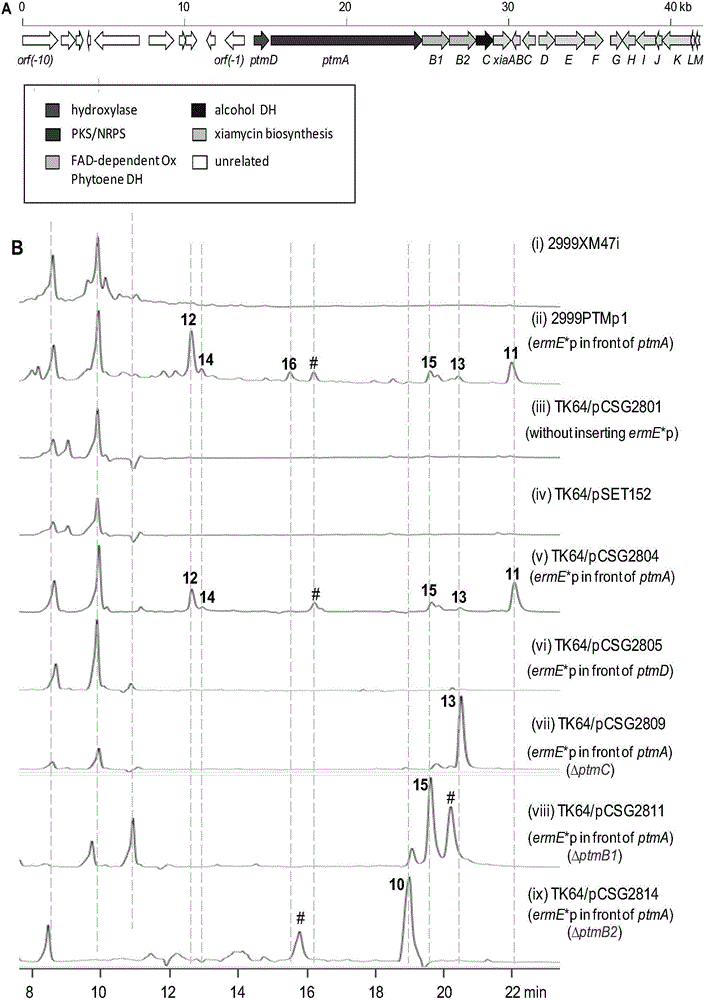
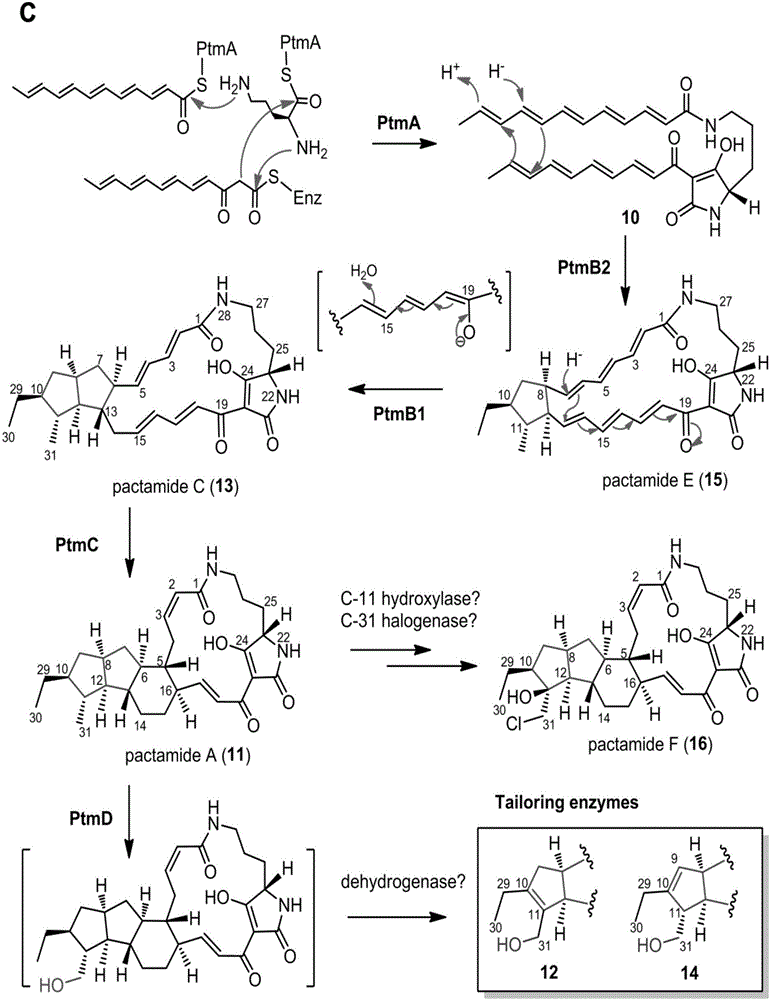
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthesis gene cluster of polyenoid and polyol macrolide compound
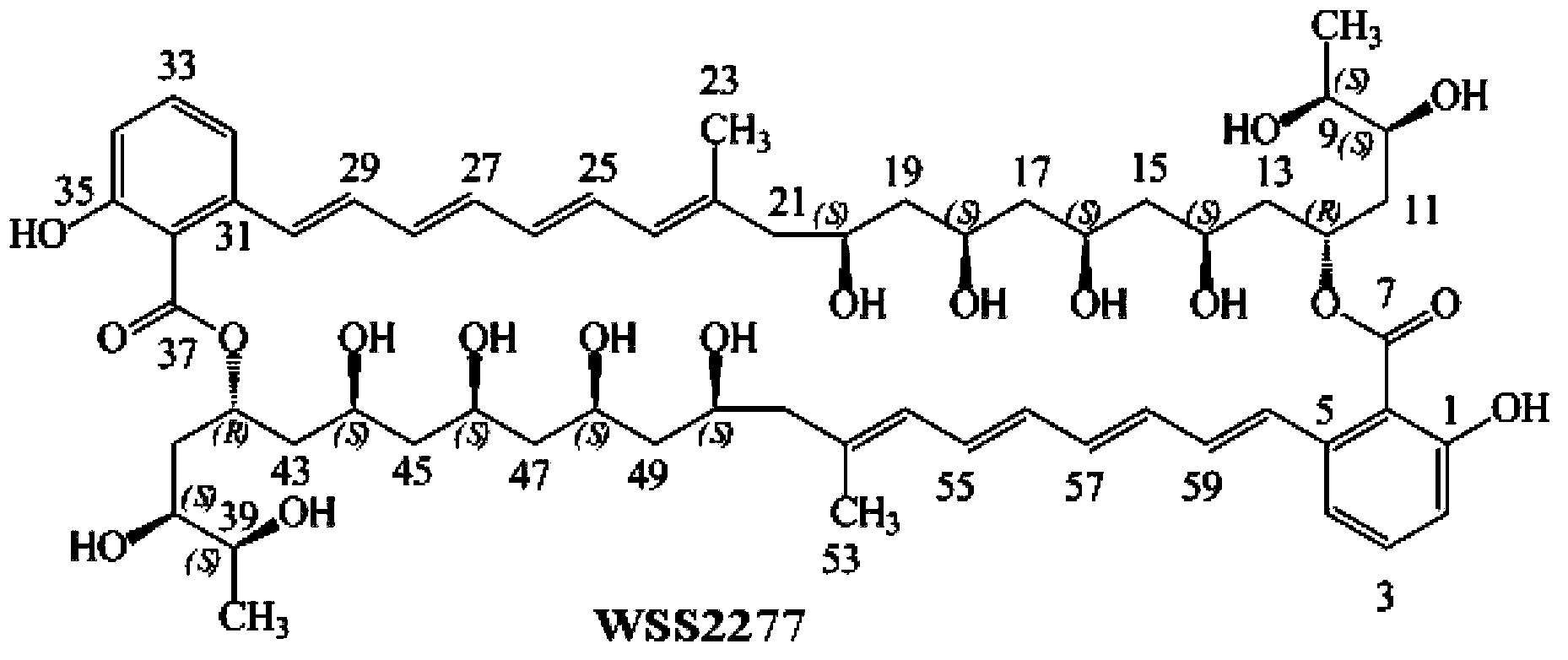
InactiveCN103820474AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiosynthetic genesNucleotide
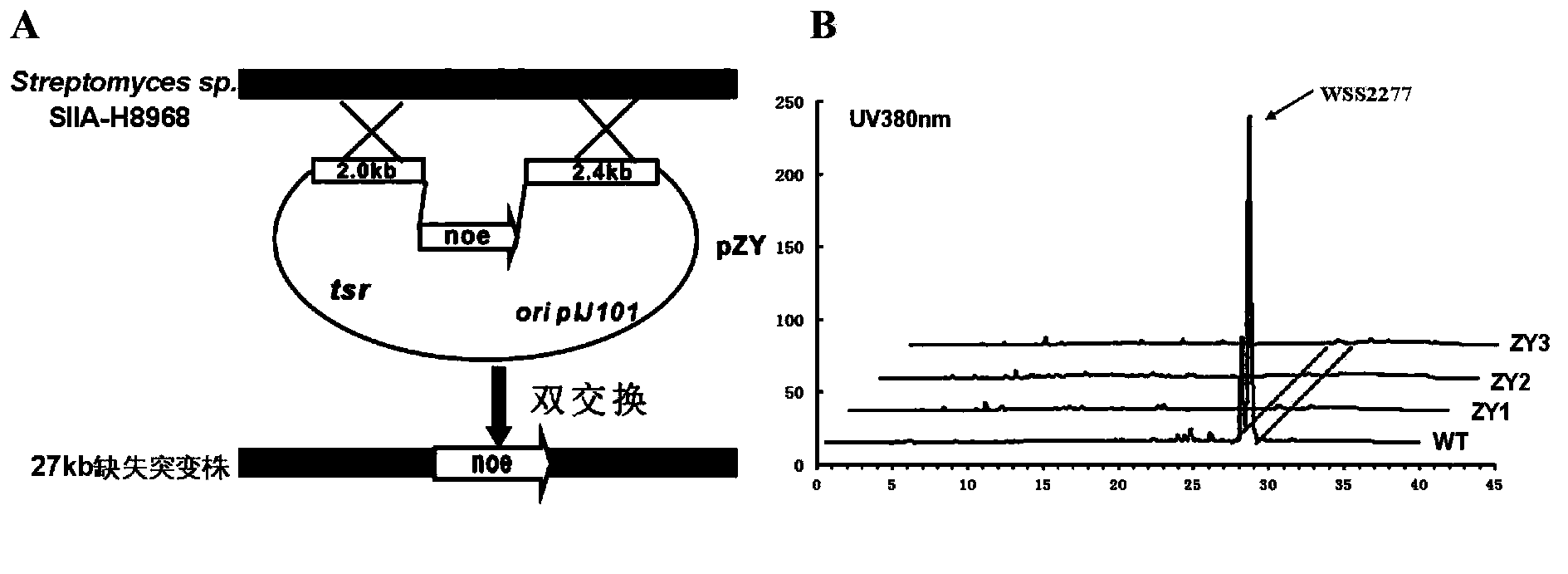
The invention discloses cloning, sequencing, analysis, function study and application of a biosynthesis gene cluster of a novel anti-microbial and anti-tumor compound WSS2277 in the field of biotechnologies. The gene cluster comprises nucleotide sequences of twenty-one genes or complementary sequences which are formed by the sequences 1, wherein the fourteen genes including siaA, siaB1, siaB2, siaC, siaD, siaE, siaF, siaG, siaH, siaI, siaJ, siaK, siaL and siaM are responsible for the synthesis of a carbon skeleton, and the seven genes incluidng siaN, siaO, siaP, siaQ, siaR, siaS and siaT are responsible for regulating biosynthesis. The information of the genes which are related to the biosynthesis of the WSS2277 is provided by the invention, and a foundation is provided for the study and the genetic modification of the biosynthesis of the WSS2277. A novel structural analogue can be generated through the modification of carbon skeleton synthesis genes in the WSS2277, and the yield of the WSS2277 or a derivative thereof can be provided through the interruption or the high replication of regulator genes in the WSS2277. The genes and proteins, which are provided by the invention, can also be used for searching and discovering compounds or genes and proteins, which can be applied to the fields of medicine, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SICHUAN INDAL INST OF ANTIBIOTICS CHINA NAT PHARMA GROUP CORP
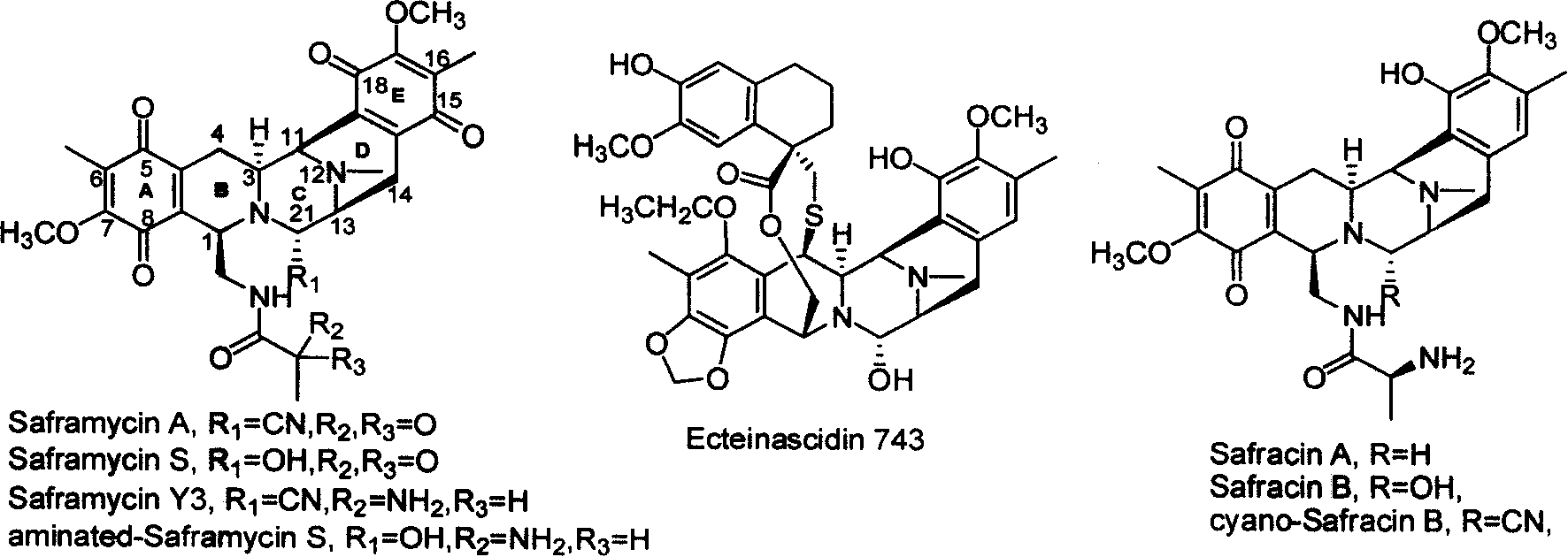
Safraninemycin biological synthesis gene cluster
The invention relates to the cloning, sequencing, analyzing, functional study of biological synthetic gene cluster of erythromycin produced by streptomycete in tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid family which has the antineoplastic activity and application thereof. The whole gene cluster contains 30 genes: 3 nonribosome polypeptide synthetase genes, 4 antecedent molecule synthetic genes of 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-O-methyl-tyrosine, 2 peptid ring skeleton synthetic genes, 7 erythromycin modifying genes, 5 genes related to S-adenosine methionine synthesis, 3 regulation genes, 2 resistance genes and 4 genes with uncertain function. Genetic manipulation of the genes can block the synthesis of erythromycin, change the output and get analogue of erythromycin. The gene cluster can be used for gene engineering, protein expression, enzymic catalytic reaction, etc. of tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid family and finding out compounds or genes being suitable for medicine, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-yield engineering bacterium of nicomycin x component and its application
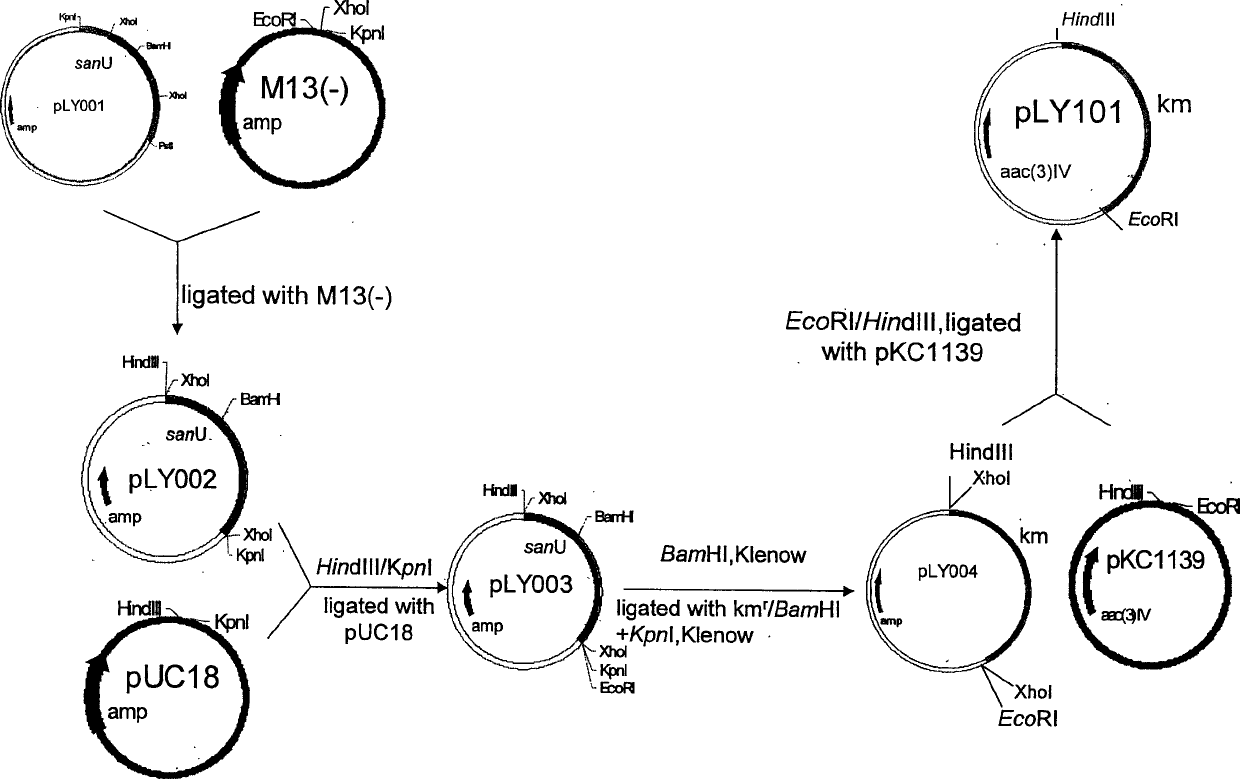
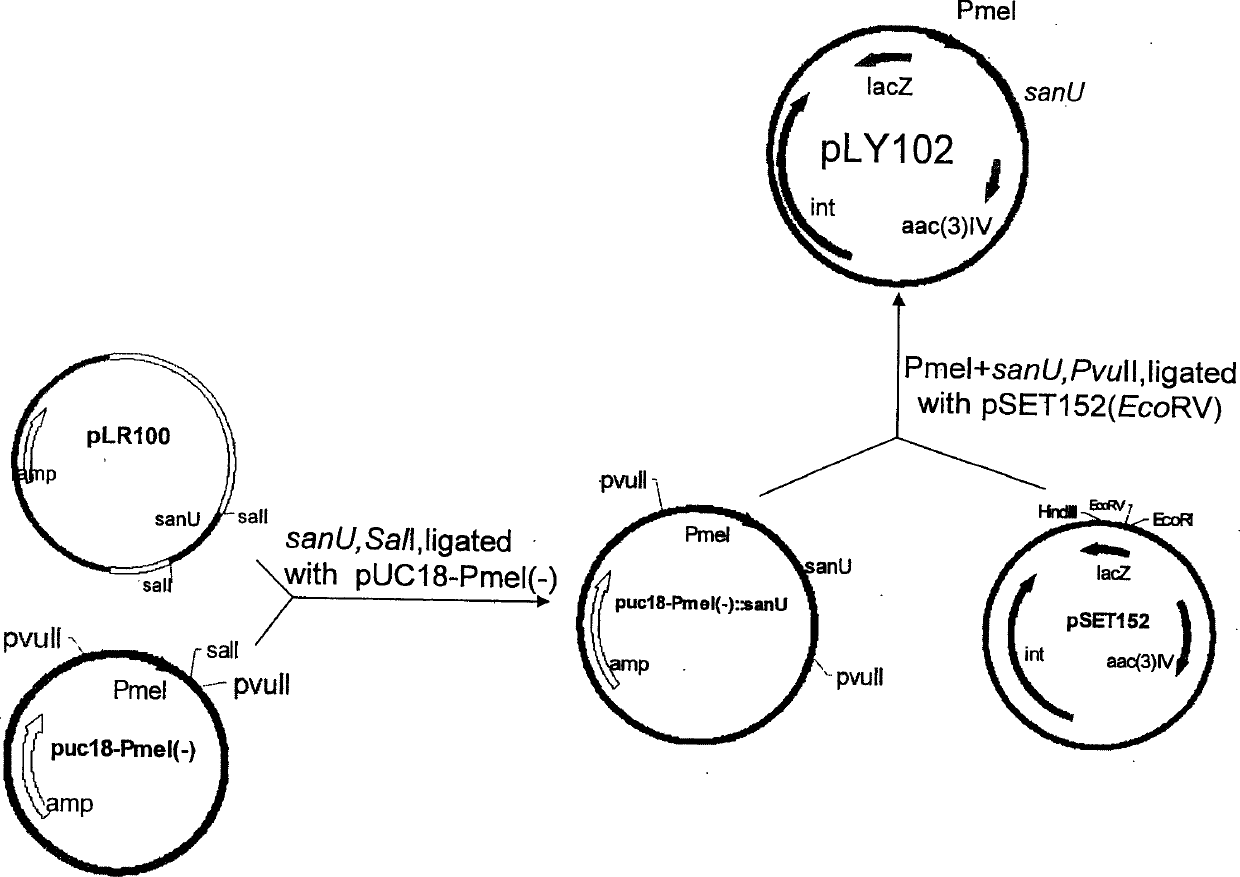
The present invention belongs to the field of antibiotic gene engineering, and is especially the process of cloning nicomycin biological synthetic gene sanU from one strain of Streptomyces ansochromogenes 7100 CGMCC 4.321; connecting the synthetic gene sanU with promoter of melanin biosynthetic structure gene, cloning onto the polycloning site of integrative single-copy plamid, transforming wild Streptomyces ansochromogenes 7100 CGMCC 4.321 protoplast to obtain nicomycin X component of the recombinant engineering bacterium in the yield 2 times higher than wild strain. The high-yield engineering bacterium may be used in preparing antiseptic medicines.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
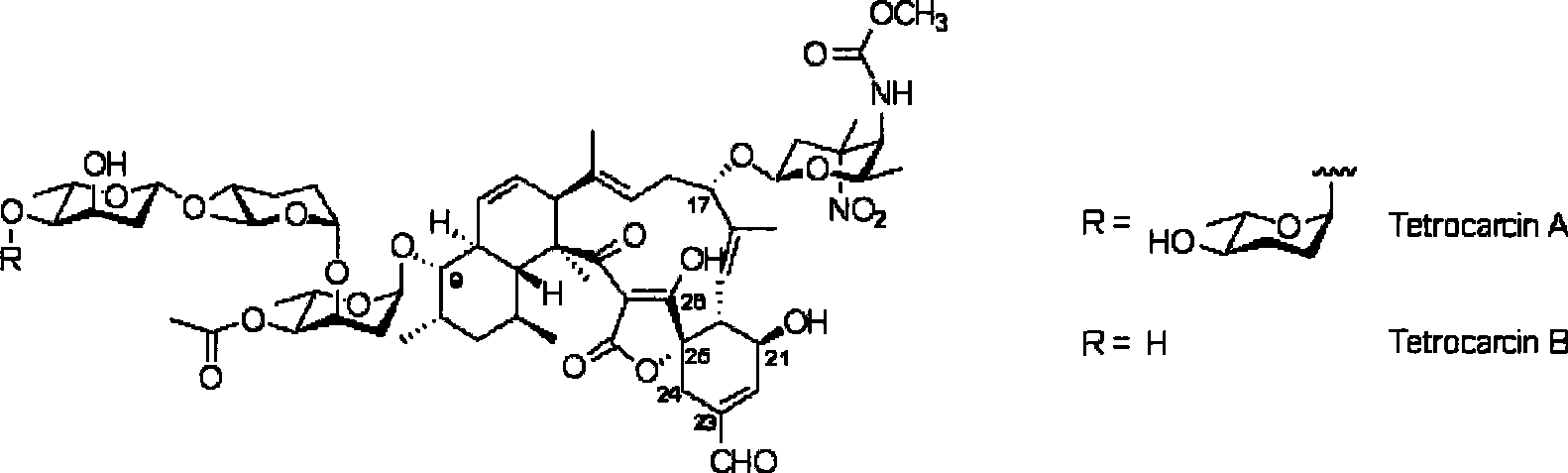
Biological synthesis gene cluster of tetrokacin A and use thereof
The invention relates to a clone, sequencing, analysis and function study of biosynthesis gene cluster of antibiotics-Tectrocarcin A which has anti-tumor activity and is generated by Micromonospora chalcea NRRL11289 and the application thereof. The whole gene cluster contains 36 genes: 5 non-reused I type polyketone synthetase genes; 4 special three-carbon biosynthesis genes; 11 desoxy sugar biosynthesis genes; 9 post modifying genes; 2 regulator genes; 1 resistance gene; and 4 genes with uncertain function. Due to the genetic manipulation of biosynthesis genes, the biosynthesis of Tectrocarcin A can be prevented. The genes and the proteins thereof which are provided by the invention can also be used for searching and discovering the compounds, genes or proteins that can be applies in medicine, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthetic gene cluster of phoslactomycins
InactiveCN102061299AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationDNA/RNA fragmentationEthylmalonic acidBiosynthetic genes
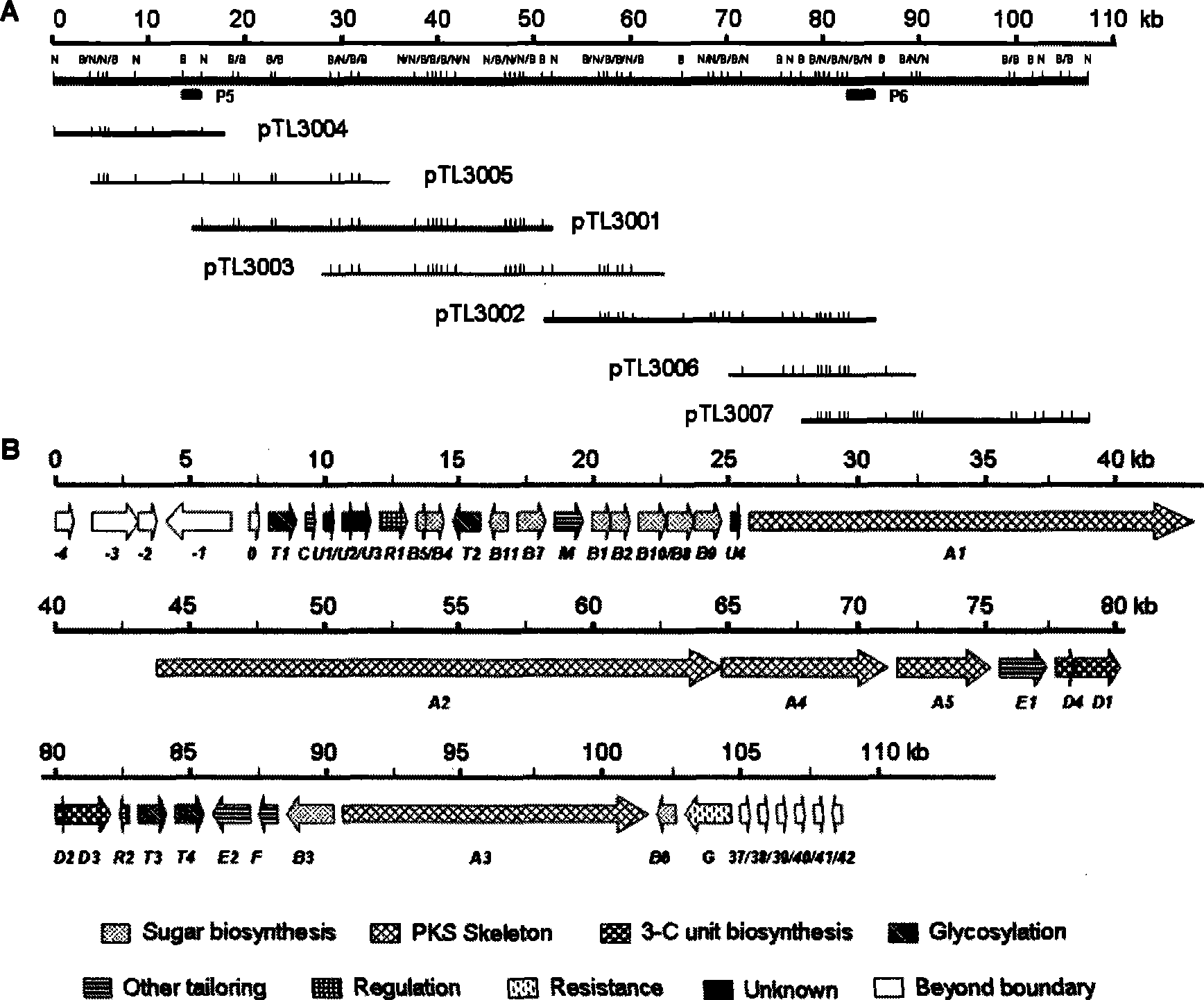
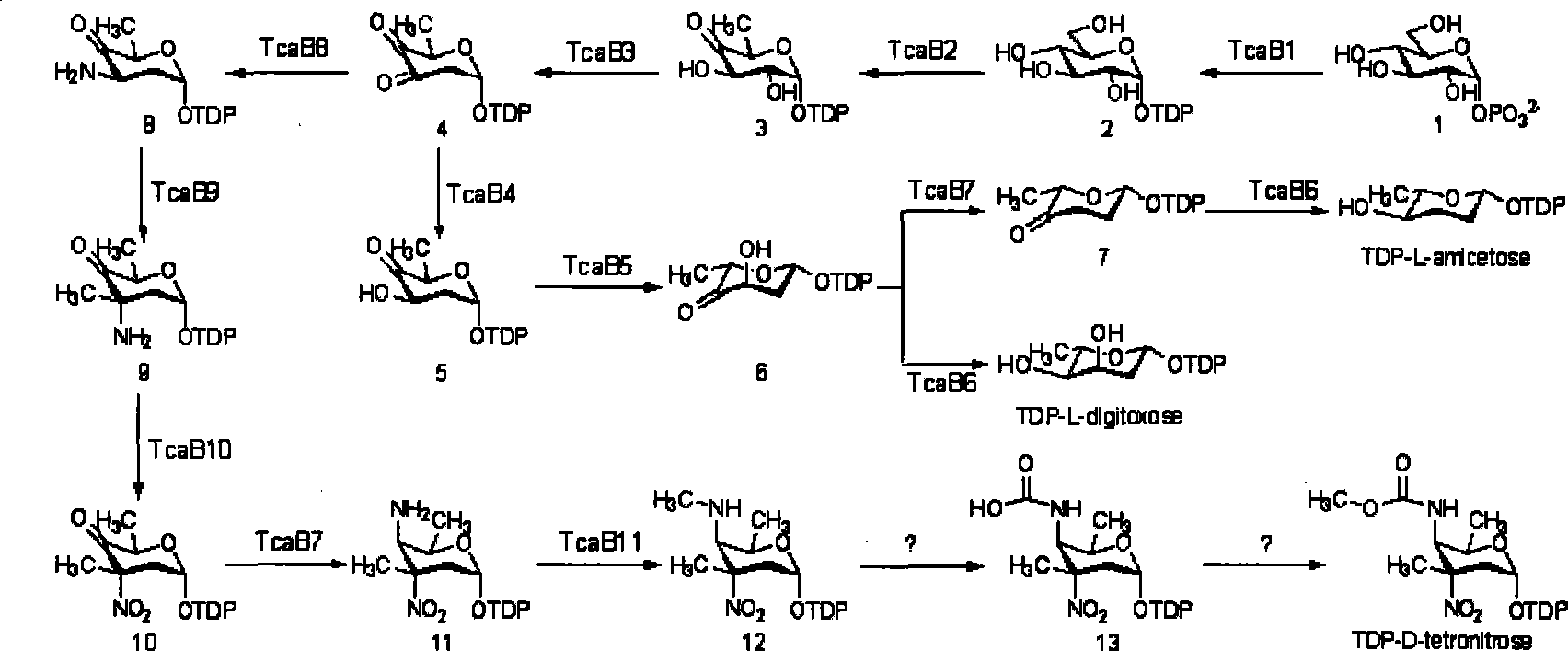
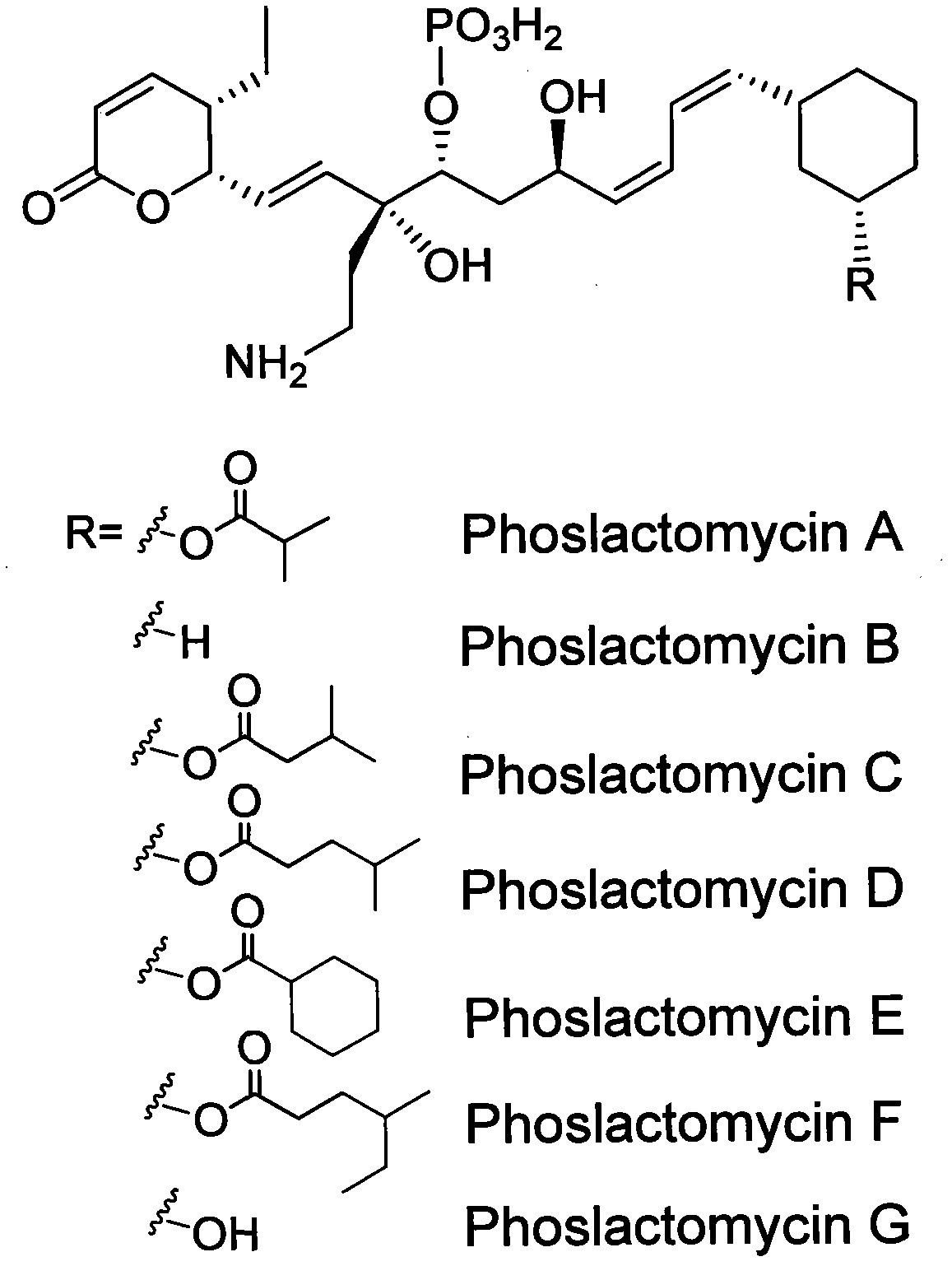
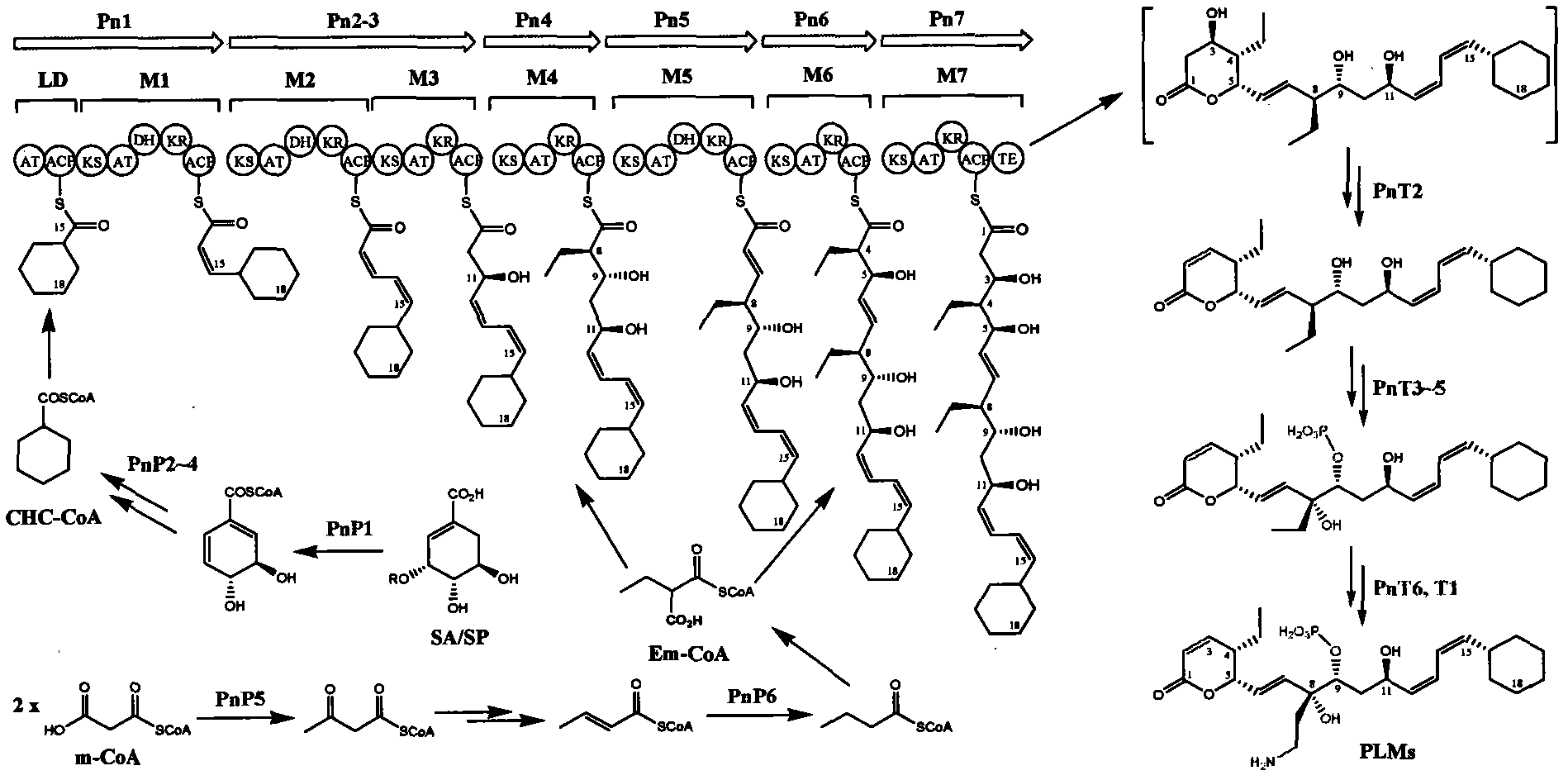
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of phoslactomycins produced by Streptomyces platensis SAM-0654. The whole gene cluster contains twenty twelve genes as follows: seven I-type linear polyketone synthetase (PKS) genes, two ethylmalonyl CoA synthetase genes, four cyclohexylformyl-CoA synthetase genes, six post-modified enzyme genes, two regulation genes and a resistance gene. Through carrying out genetic operation on the biosynthetic gene cluster, the synthesis of the phoslactomycins can be blocked. The gene cluster provided by the invention can be used for output variation of the phoslactomycins, combination generation of polyketone compounds and the like, and also can be used for searching and finding compounds or genes for medicine, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Transgenic plants expressing cytokinin biosynthetic genes and methods of use therefor
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
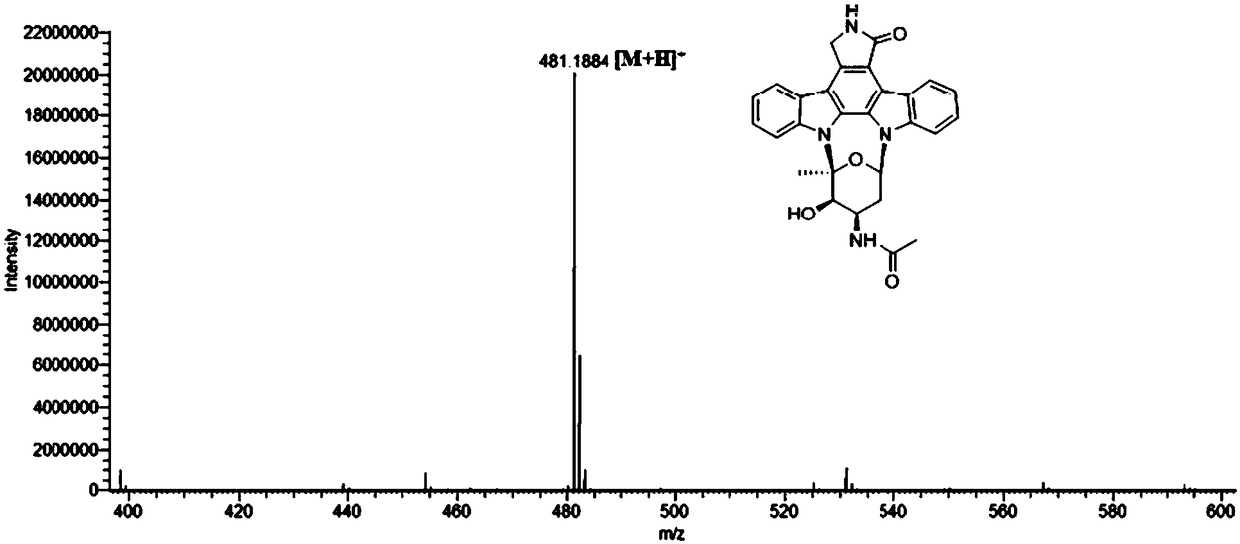
Indolocarbazole alkaloid with cytotoxic activity as well as preparation method and application
ActiveCN108299467AGood inhibitory effectLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseCancer cell
The invention provides indolocarbazole alkaloid with cytotoxic activity as well as a preparation method thereof, aiming at the problems which exist in indolocarbazole alkaloid in the prior art. The new indolocarbazole alkaloid is obtained through a recombination strain constructed by adopting a biotechnological means and directional transformation carried out on an STA biosynthesized gene clusterspc, thereby opening up a new thought for combinatorial biosynthesis research of the indolocarbazole alkaloid. The indolocarbazole alkaloid with the cytotoxic activity has a good inhibiting effect onall cancer cell strains; compared with STA, the toxicity of the indolocarbazole alkaloid to human normal hepatocyte LO2 is greatly reduced, so that the indolocarbazole alkaloid has potential for developing a medicine for treating diseases relevant to protein kinase. In addition, the method provided by the invention is easy to operate and implement, can be used for realizing industrialized mass production, and has a broad application prospect and tremendous commercial value.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com