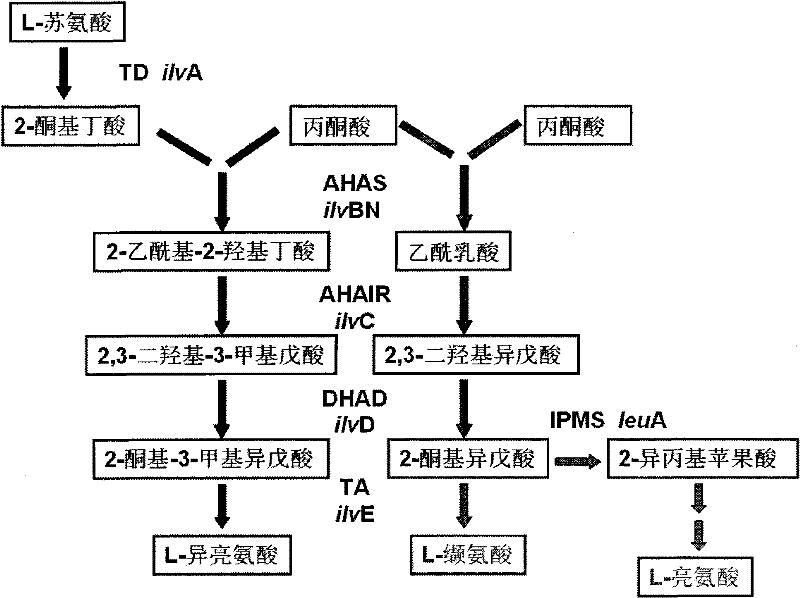
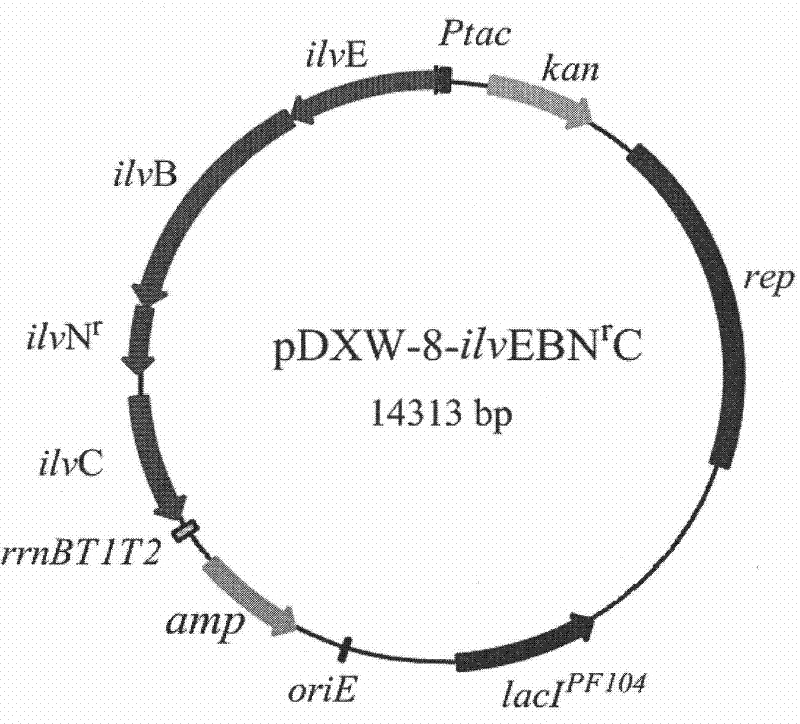
Recombinant dna, bacterial strain and method for fermentative production of l-valine
A valine, DNA sequence technology, applied in the field of microbial engineering, to achieve the effects of improving metabolic intensity, activity, yield and sugar-acid conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1 Construction of expression plasmid pDXW-8-ilvEBN r C
[0084] a) Cloning of ilvBNC operon and ilvE gene: Brevibacterium flavum B. flavum NV128 genome as a template, SEQ ID NO: 1 (including SD sequence) and SEQ ID NO: 2 as primers, PCR to obtain ilvBNC operon, ilvBNC operon Connected with T vector to form pUCm-T-ilvBNC; B. flavum NV128 genome as template, SEQ ID NO: 5 (including SD sequence) and SEQ ID NO: 6 as primers, PCR to obtain ilvE gene, connected with ilvE gene T vector to form pUCm -T-ilvE.
[0085] b) ilvN site-directed mutation relieves the feedback inhibition of three branched-chain amino acids on acetolactate synthase: using pUCm-T-ilvBNC as a template, SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4 as primers, PCR to obtain mutants, DpnI method Screen mutants. The mutant was verified by sequencing, and the mutant was named pUCm-T-ilvBN r c. Ensure that Gly-Ile-Ile at positions 20-22 of the regulatory subunit of acetolactate synthase is mutated to Asp-Asp-Phe....
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2 Construction of Escherichia coli JM109 / pDXW-8-ilvEBNC and JM109 / pDXW-8-ilvEBN r C
[0090] (1) Competent preparation of Escherichia coli JM109
[0091] a) LB medium JM109 was cultured to an OD value of 0.3-0.5.
[0092] b) 3,000g (or 6,000r / min) at 4°C for 5min. Discard the supernatant and harvest the bacteria.
[0093] c) Resuspend in TSB which is 1 / 10 of the original culture volume.
[0094] e) Place on ice for 10 minutes, aliquot on ice, 60 μL per tube, and store at -70°C.
[0095] TSB formula (requires high pressure), LB (pH6.1) contains: 10% PEG 3350 or 4000, 5% DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), 10mmol / L MgCl 2 , 10mmol / L MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 10% glycerin.
[0096] 5×KCM solution formula: 0.5mol / L KCl, 0.15mol / L CaCl 2 , 0.25mol / L MgCl 2 .
[0097] (2) Conversion:
[0098] a) Plasmids pDXW-8-ilvEBNC and pDXW-8-ilvEBN r C respectively 5 ~ 10 μ L, 5 × KCM solution 10 μ L, double distilled water 30 μ L, (total 50 μ L), mix well, put on ice.
[0099] b) Tak...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3 Structural Engineering Bacteria B.flavum ATCC 14067 / pDXW-8-ilvEBN r C
[0106] (1) A single colony was inoculated in 30 mL LBG medium and cultured at 30°C for 16 hours.
[0107] (2) Inoculate in Epo medium to OD 600 =0.3, culture OD at 30℃ 600 = 0.9.
[0108] (3) Cool on ice for 10 minutes, and centrifuge at 4,000 g for 10 minutes at 4°C.
[0109] (4) Wash 4 times with 15 mL 10% glycerol, and resuspend with 0.2 mL 10% glycerol.
[0110] (5) Add appropriate amount of DNA to cool on ice, 0.1cm electric shock cup 1.8kV 10S.
[0111] (6) Add 1 mL of LBHIS medium and incubate at 30°C for 1 hour.
[0112] (7) Coat the LBHIS solid kana plate and incubate for 36 hours.
[0113] The aforementioned Epo medium formula: 10g / L trypton (peptone), 5g / L yeast extract (yeast extract), 10g / L NaCl, 4g / L isonicotinic acid hydrazide (isoniazid), 25g / L glycine (glycine), 0.1% Tween 80.
[0114] The aforementioned LBHIS medium formula: 5g / L trypton (peptone), 5g / L NaCl, 2.5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com