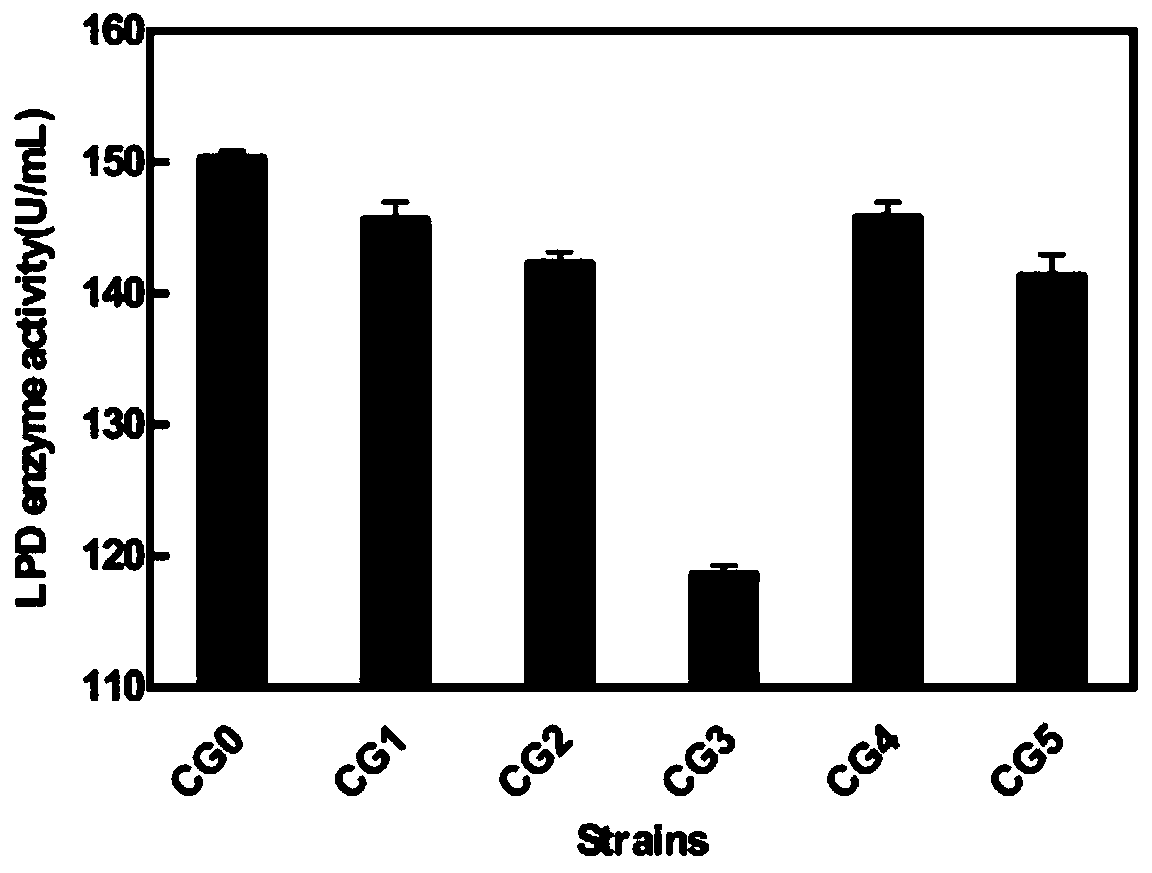
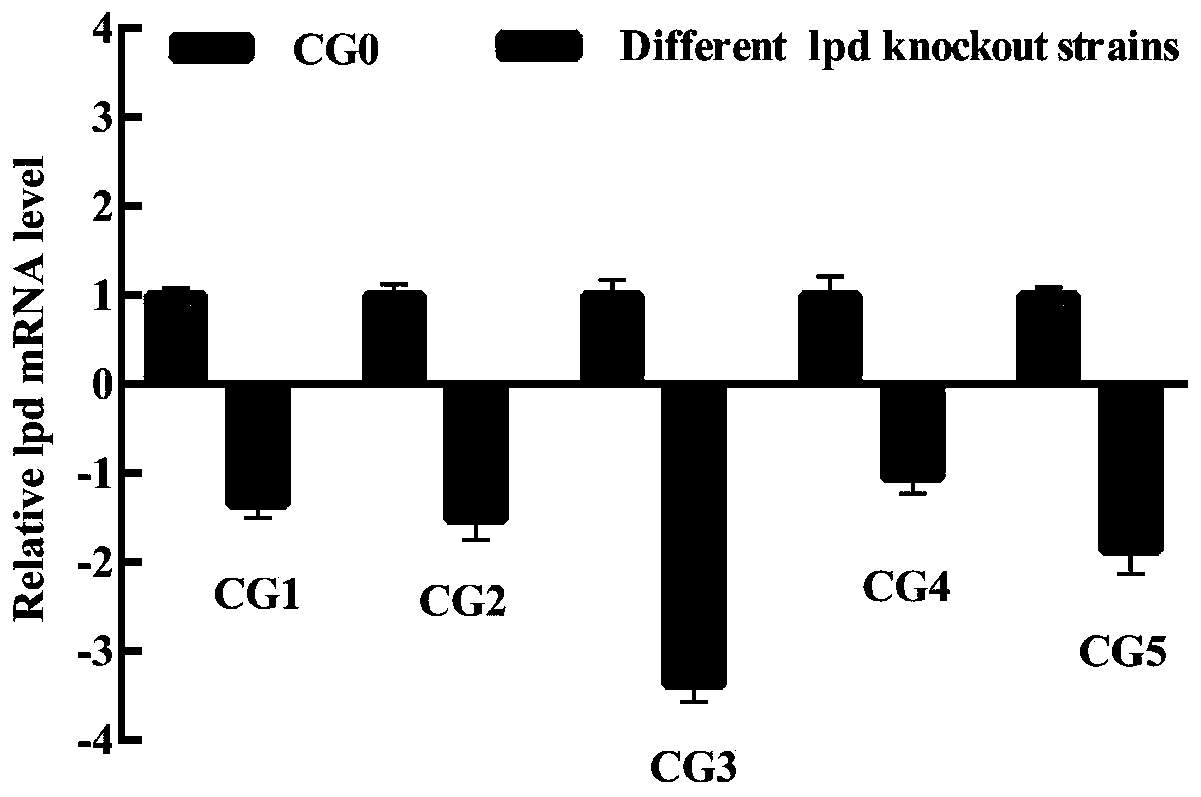
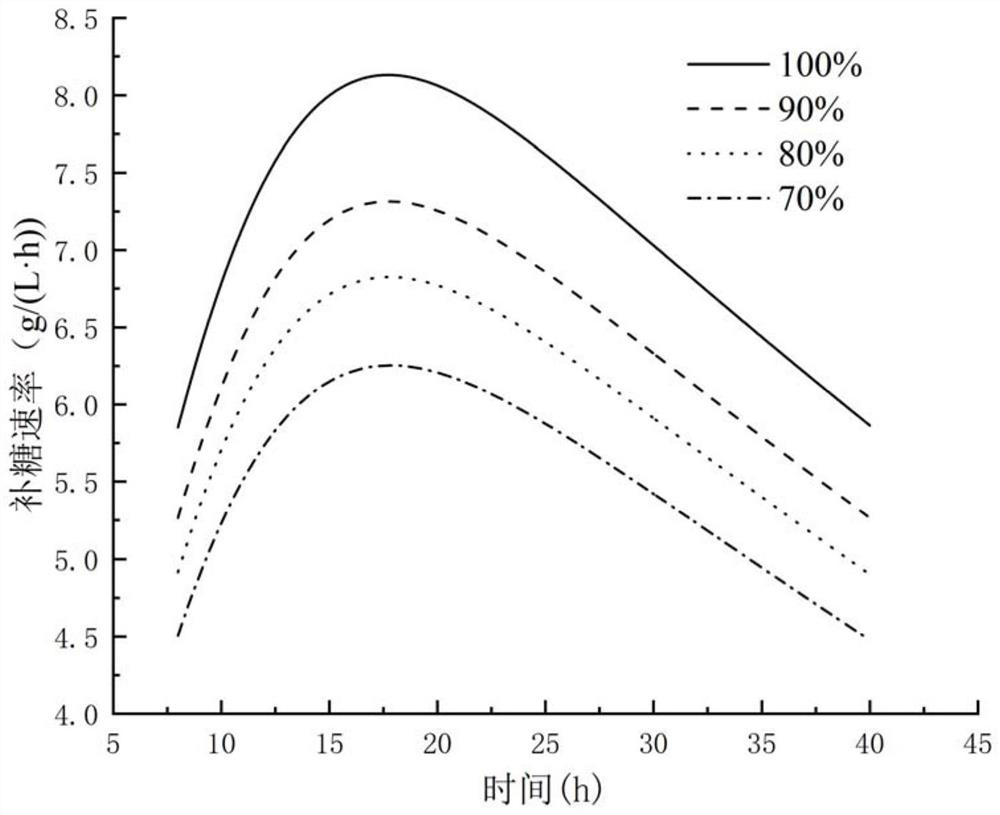
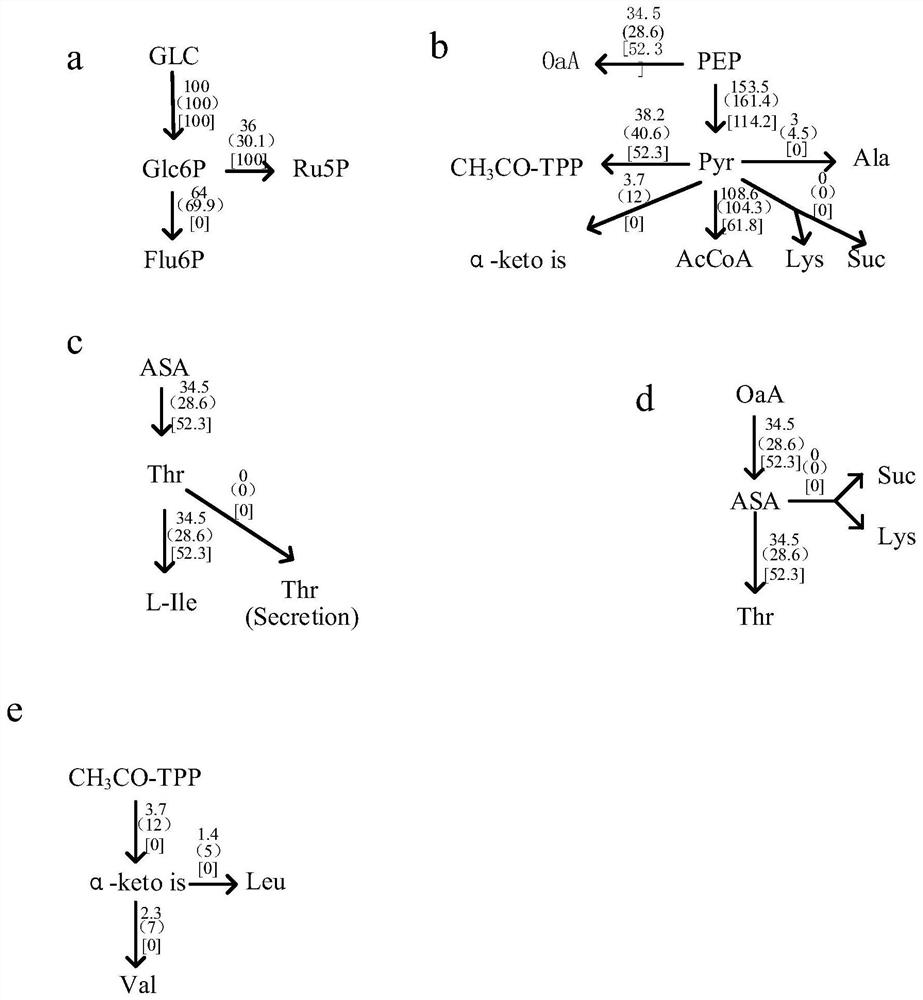
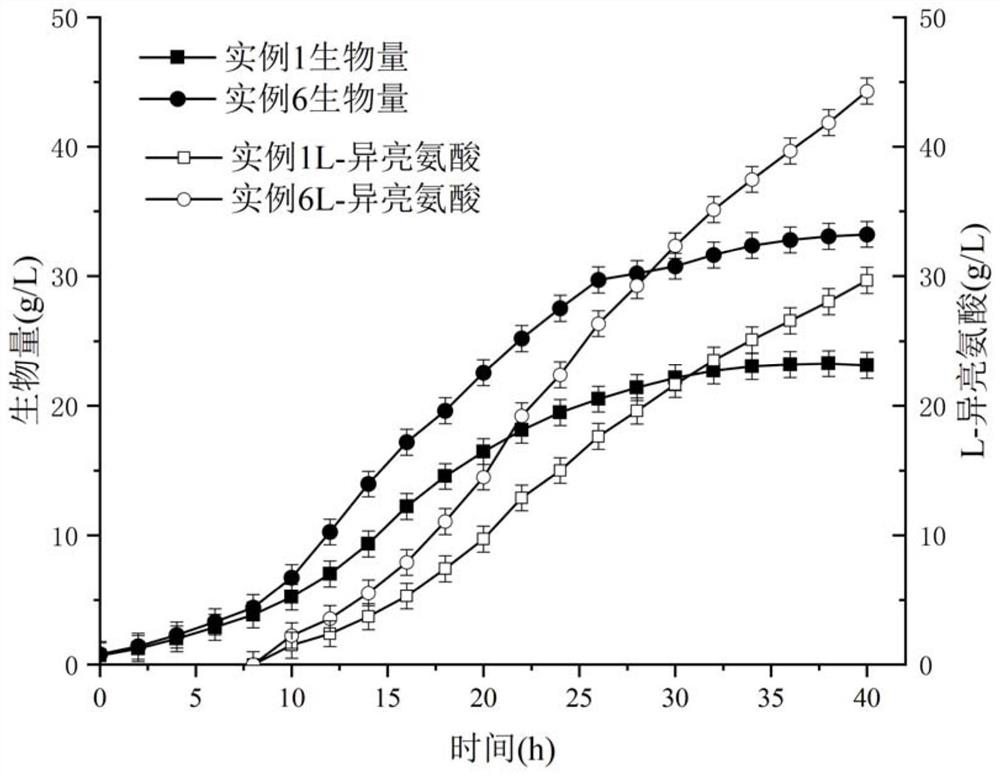
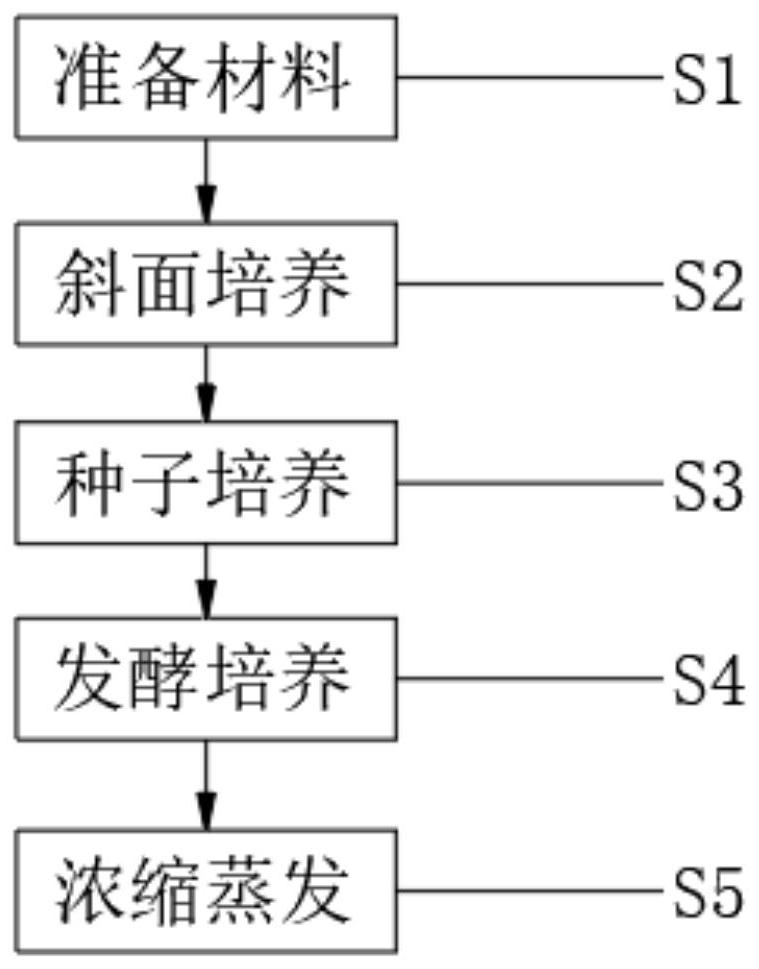
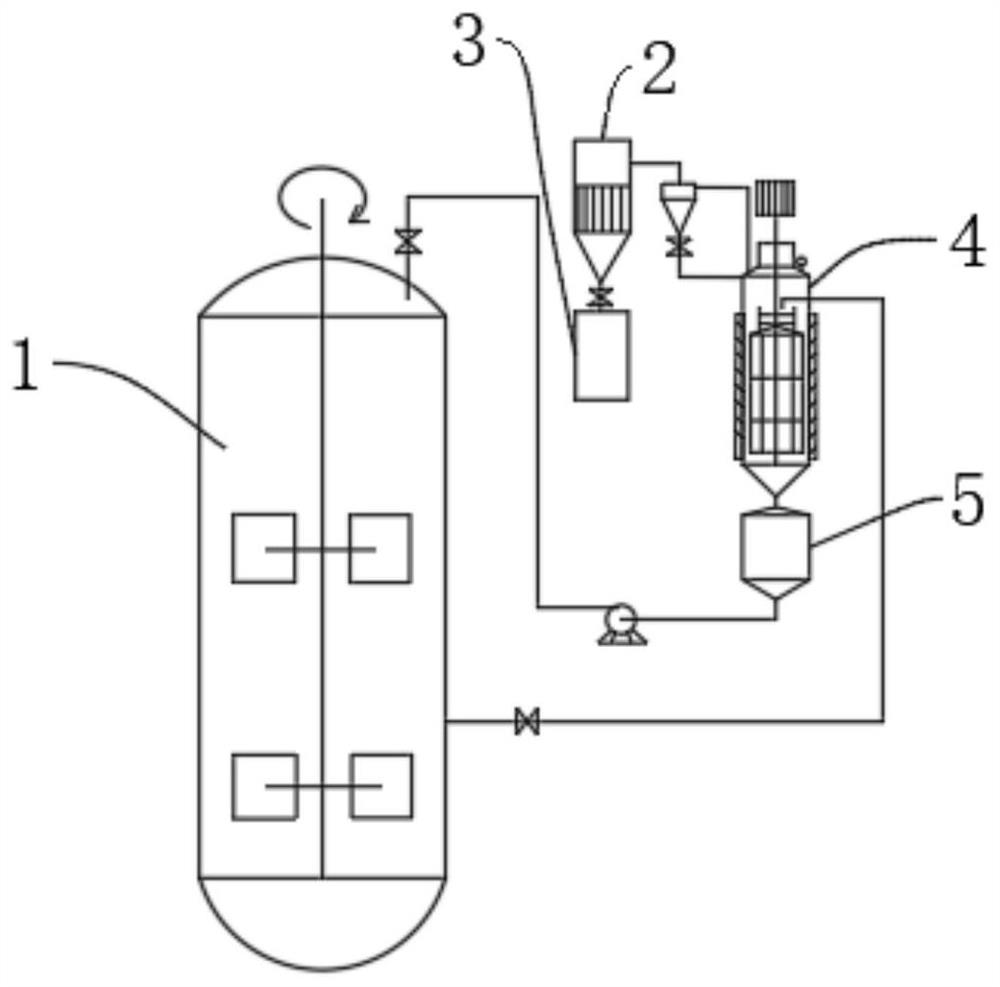
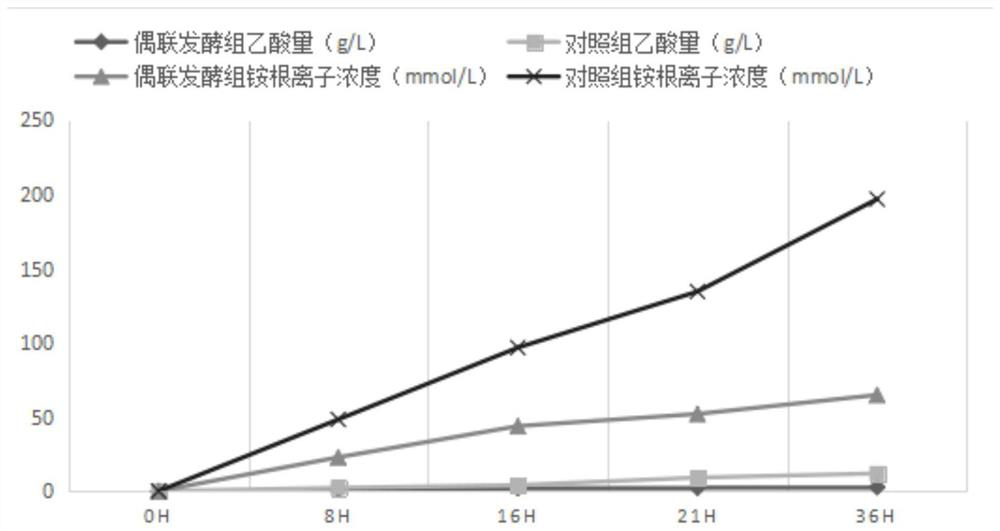
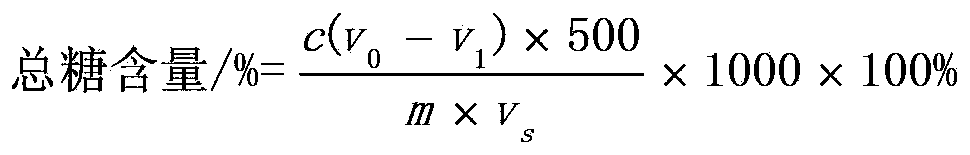Patents
Literature
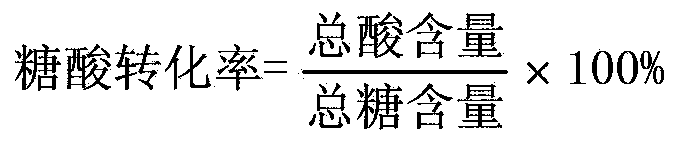
65results about How to "Improve sugar-acid conversion rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
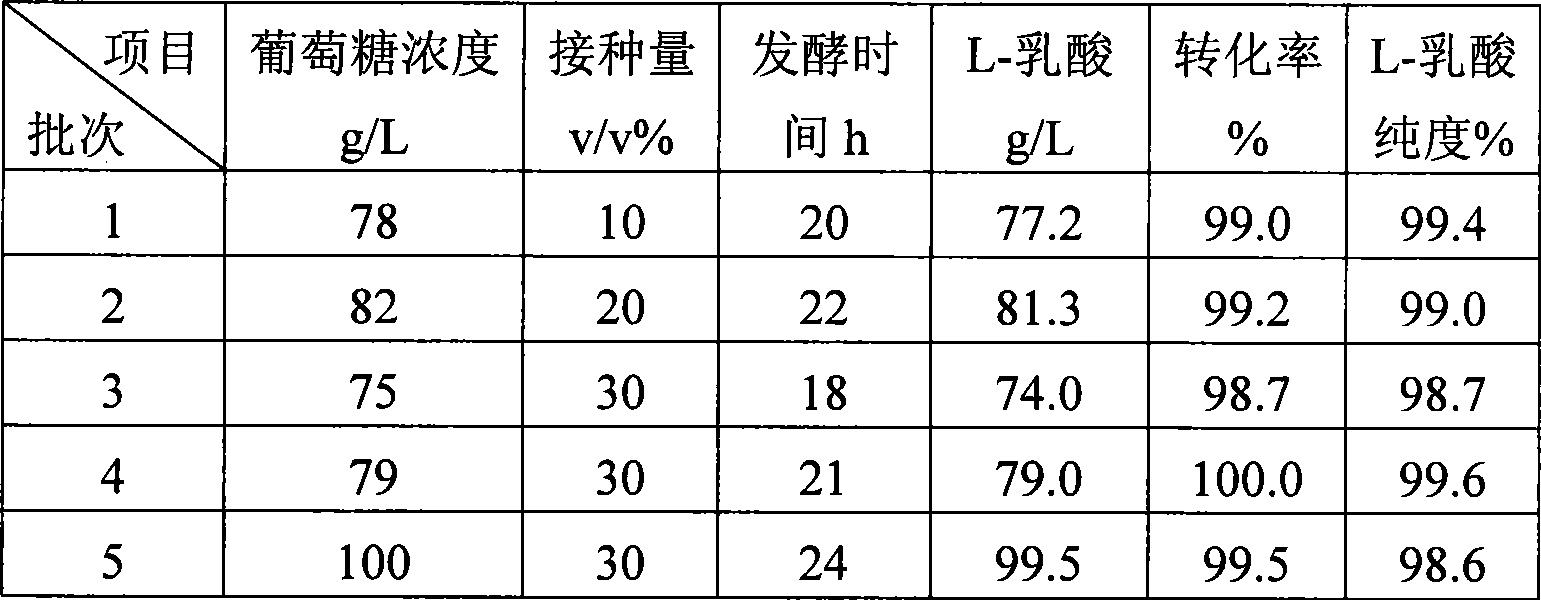
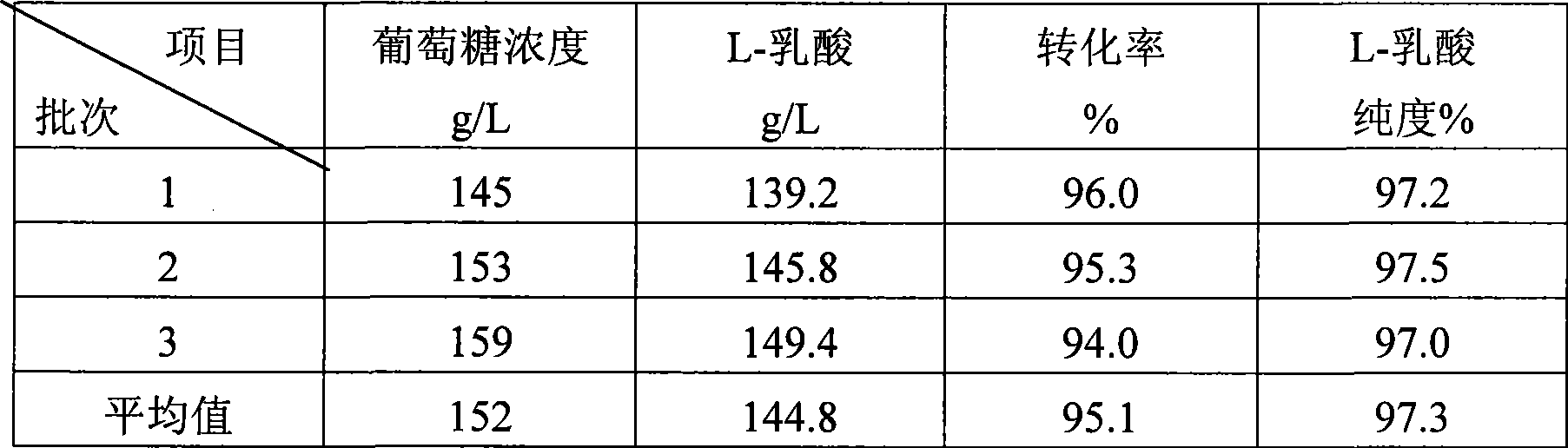
Method for producing L-lactic acid by Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.2602
ActiveCN101544993AReduce fermentation costsSimple nutritional requirementsMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismGlucose polymers
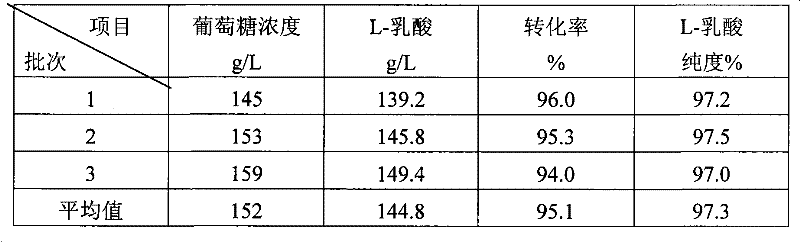
A method for producing L-lactic acid by Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.2602 belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. In the invention, Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.2602 is adopted, and under the condition of no oxygen supply, starchiness hydrolyzed sugar or dextrose is fermented by a semicontinuous intermittent fermentation way or an inter-sugar-compensating fermentation way to generate L-lactic acid with high optical purity. The invention has the advantages that the gemma property of the Bacillus coagulans is stable, and the L-lactic acid obtained by inoculating and fermenting the starchiness hydrolyzed sugar has high optical purity and rate of conversion of sugar and acid and short fermentation period; in addition, the semicontinuous intermittent fermentation way saves the time for preparing seeds by a continuous reladling and subculturing method, shortens the fermentation period, enhances the fermentation strength and obtains the L-lactic acid with both relatively high rate of conversion of sugar and acid and purity.
Owner:江苏省苏微微生物研究有限公司
Genetically engineered bacterium for high-yielding L-valine and method for producing L-valine by fermentation
ActiveCN110607268AEasy to synthesizeReduce synthesisBacteriaHydrolasesLactate dehydrogenaseSaccharic acid
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for high-yielding L-valine. A construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium comprises the steps that starting from an escherichia coli W3110, an acetolactate synthase gene alsS of a bacillus subtilis is integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and subjected to high expression; an escherichia coli ppGpp 3'-pyrophosphoric acid hydrolytic enzyme mutant R290E / K292D gene spoT is integrated on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and subjected to high expression; genes of frdA, frdB, frdC and frdD of four subunits of a lactic dehydrogenase gene ldhA, a pyruvate formate lyase I gene pflB and fumaric reductase on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 are knocked out; a branched chain amino acid transaminasegene ilvE of the escherichia coli is replaced with leucine dehydrogenase gene bcd of the bacillus subtilis; and an acetyl-hydroxyl acid isomerized reductase gene ilvC of the escherichia coli is replaced with an encoding gene of a mutant L67E / R68F / K75E. According to the genetically engineered bacterium for the high-yielding L-valine, an L-valine fermentation method is further modified. Double-phasedissolved oxygen control is adopted, and the L-valine yield and the saccharic acid conversion rate are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant dna, bacterial strain and method for fermentative production of l-valine
InactiveCN102286505AHigh activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
The invention relates to a recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), strain and method for producing L-valine by fermentation. The recombinant DNA comprises DNA sequence for coding acetohydroxy acid synthetase free of feedback inhibition of three branched-chain amino acids to acetohydroxy acid synthetase, DNA sequence for coding dihydroxy reduction isomerase, and DNA sequence for coding branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase. The strain is corynebacterium or brevibacterium transformed by introducing the recombinant DNA. The method is implemented by culturing the strain to produce the L-valine. In the invention, the expression L-valine is used for producing the bacterium L-valine biosynthetic gene, so the yield of the L-valine can be greatly increased; and the fermentation model, especially the high-temperature short-time fermentation model, is constructed according to the optimum temperature of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme, so that the metabolism intensity of the strain is enhanced, the activity of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme is enhanced, and the yield of the L-valine and the conversion rate of the sugar acid can be further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant strain, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105734004AImprove sugar-acid conversion rateBroad industrial application prospectsBacteriaTransferasesGenetic engineeringChemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, in particular to a recombinant strain, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. By constructed L-lysine genetically engineered bacteria, effective accumulation of L-lysine in a fermentation process can be implemented, and a higher glucose acid conversion rate is achieved. A genetically engineered strain constructed from the beginning is favorable for achieving high acid yield and high conversion rate, and has broad industrial application prospect, and side effects caused by random mutation are avoided.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Method for producing 2-keto-l-gulonic acid
ActiveCN101736071ASolve the shortcomings of slow growth and slow acid productionOptimizing Growth CorrelationsMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismAnimal science
The invention provides a method for producing 2-keto-l-gulonic acid, including the following steps of: feeding nitrogen source nutrient solution from the 20th to the 26th hour in the fermentation process to compensate nutritional demands of microorganism growth in the fermentation process, finishing feeding solution in the 40th to the 45th hour, wherein the dissolved oxygen is controlled to be 30-50% in the nutrient solution feeding process. The invention utilizes a method of feeding nutrient solution at middle and later stages of fermentation, overcomes disadvantage that biomass grows and generates acid slowly, combines control of factors of temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, low initial glucose, fed-batch glucose compensation and the like, and optimizes the growth relations of biomasses with different sizes in microbial mixed fermentation. The gulonic acid content of the invention is 105-115mg / ml, and the glucose acid convert ratio is 92-95%.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and method for producing L-threonine by using escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106867952AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
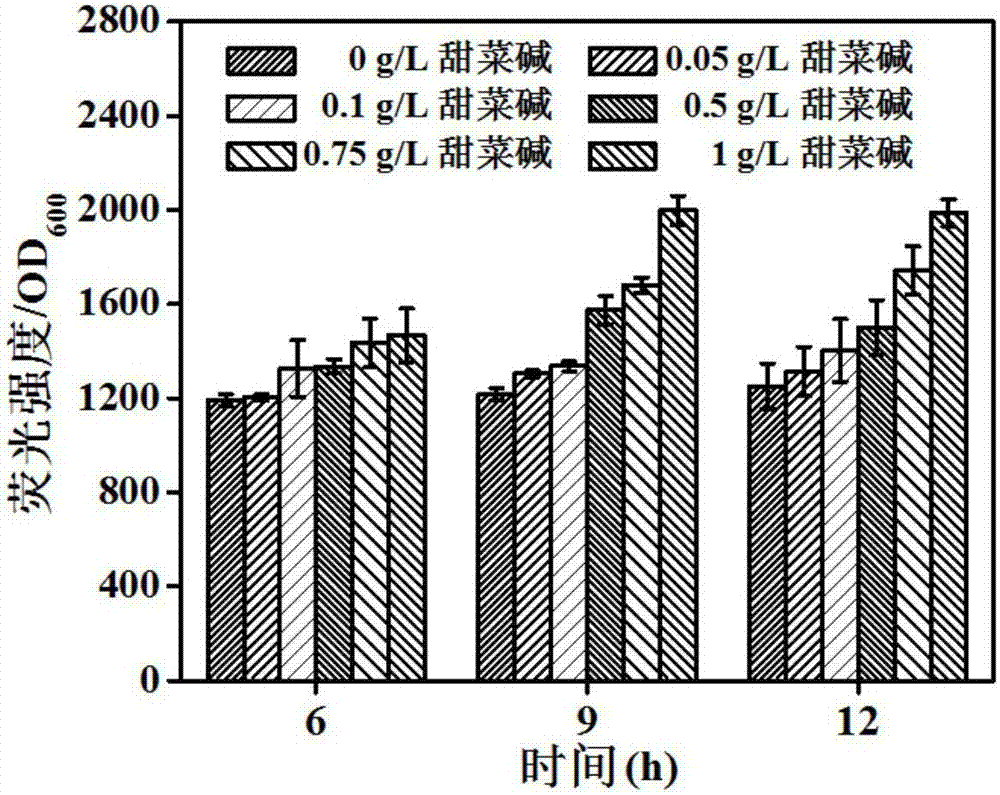
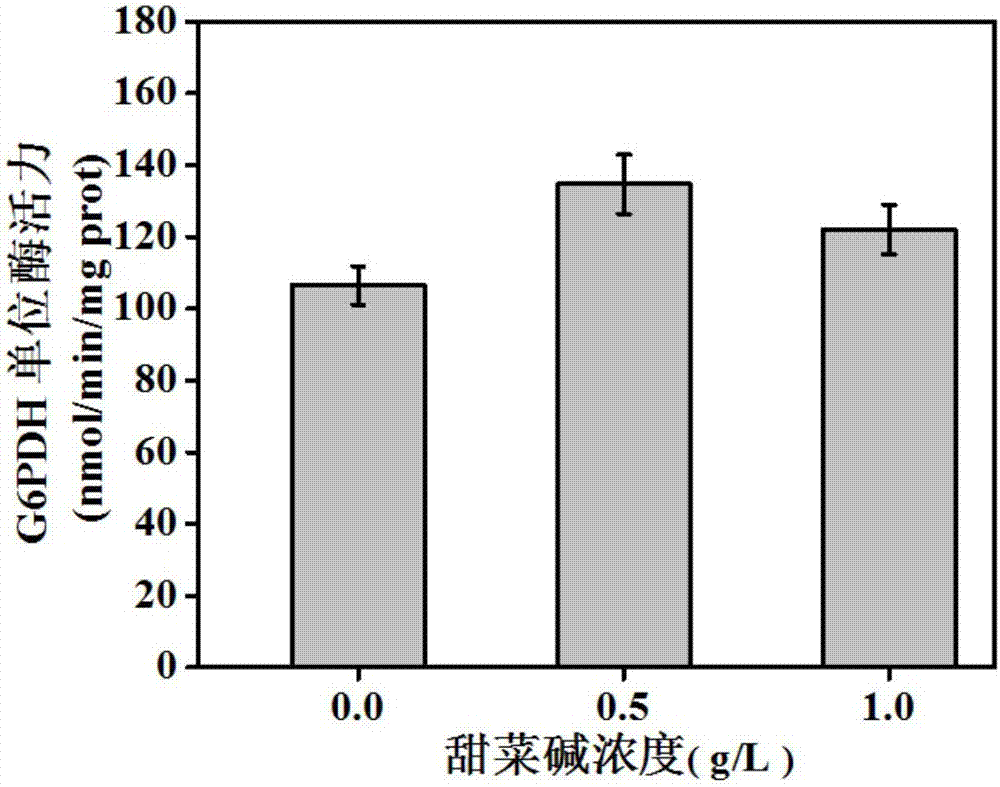
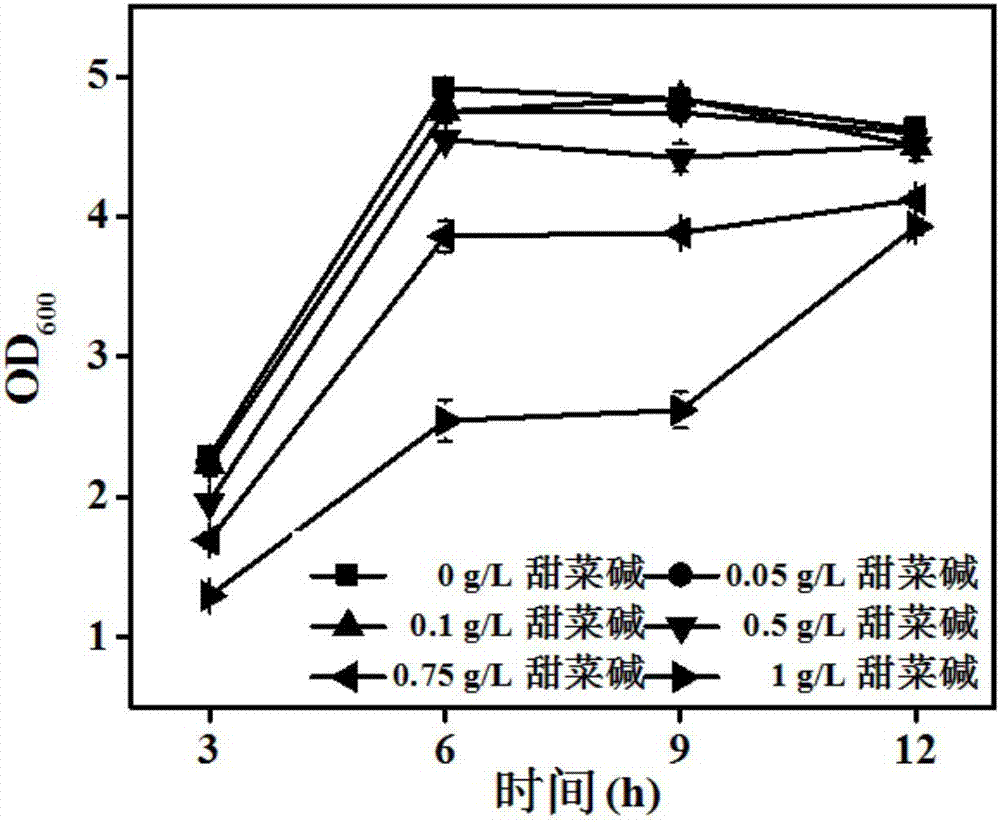
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to an escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and a method for producing L-threonine by using the escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium. The gene engineering bacterium is characterized in that a promoter P<ppc> of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) of an initial strain is replaced into a promoter P<zwf> of 6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (zwf), so that the goal of regulating the L-threonine production capacity by glycine betaine is achieved. In the fermentation process, the glycine betaine is added, so that the L-threonine yield through shaking flask fermentation can reach 50 to 55g / L; the 5L fermentation tank yield reaches 120 to 150g / L; the saccharic acid conversion rate reaches 59 to 61 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lactobacillus casei and application thereof to produce L-lactic acid by fermentation
InactiveCN102653724AImprove sugar-acid conversion rateSignificant social significance and economic valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacilliCorn flour
The invention discloses lactobacillus casei LC-N235 with collection number CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) No: M2012157. According to the invention, the original strain of lactobacillus casei LC-5 is mutated by low-energy nitrogen ion injection; the strain which resists high glucose, adopts EMP path reinforcement and utilizes lactic acid without decomposition can be screened by a high-glucose plate, a succinic acid plate and a pure-lactic acid plate; through fermentation re-screening, the L-lactic acid high-yield strain is screened and used as the original strain for next mutation; and the steps are repeated until the target strain lactobacillus casei LC-N235 is screened. The strain can effectively utilize the cheap corn flour saccharifying liquid to produce L-lactic acid by fermentation, and the saccharic acid conversion rate is high. In a 5L fermentation tank, the output of L-lactic acid reaches 173g / L, which is improved by 46.6% as compared with that of the L-lactic acid produced by fermenting the original strain; and the lactobacillus casei and the application thereof to produce L-lactic acid by fermentation provided by the invention have tremendous social significance and economic values.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
L-valine-producing brevibacterium flavum and method for producing L-valine by using brevibacterium flavum
ActiveCN110643547APromote reproductionReduce consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The present invention belongs to the field of bioengineering technology and particularly relates to L-valine-producing brevibacterium flavum. The brevibacterium flavum is preserved in China Center forType Culture Collection on July 01, 2019, a preservation number is CCTCC M2019496 and a preservation address is Luojia Hill, Bayi Road, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province. The present invention also relates to a method for producing L-valine by using the brevibacterium flavum, the brevibacterium flavum strain is subjected to activation culture and seed liquid culture, and obtained seedliquid is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium for fermentation culture, and the fermentation culture process is firstly aerobic fermentation and then anaerobic fermentation. L-valine production is carried out by using the preserved strain and the production method, yield is high, sugar-acid conversion rate is high, besides, fermentation process takes a short time, and production efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BAYANNUR HUAHENG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Method for producing L-glutamic acid by fermentation in staged gradient oxygen supply manner
InactiveCN103215323AEasy to zoom inRealize industrialized mass productionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBatch fermentationD-Glucose
The invention discloses a method for producing an L-glutamic acid by fermentation in a staged gradient oxygen supply manner. The L-glutamic acid is obtained by inoculating a glutamic acid producing strain into a fermentation medium for fermentation and controlling the concentration of dissolved oxygen in a fermented liquid in a staged gradient oxygen supply manner. According to the method, the yield of the L-glutamic acid achieves over 155g / L and the glucose-acid conversion rate is raised to over 64% by means of respectively controlling different concentrations of dissolved oxygen at an inhibition stage, a logarithmic stage, a transformation stage and an acid production stage of the glutamic acid producing strain and through fed-batch fermentation; and the byproduct, namely lactic acid, during fermentation is reduced greatly.
Owner:北京轻发生物技术中心 +1
Actinobacillus succinogenes capable of producing succinic acid
ActiveCN102533622AReduce manufacturing costIncrease production intensityBacteriaMutant preparationSaccharic acidD-Glucaric Acid
The invention discloses actinobacillus succionogenes capable of producing succinic acid with high yield and a method for screening and producing the succinic acid by a fermentation method. The actinobacillus succinogenes takes CGMCC1593 as the original strain and is obtained by blending a plurality of turns of protoplast in a progressive way through a method of '96-pore plate culture, HPLC concentration detection and then anaerobic bottle re-screening'. The actinobacillus succinogenes has already been preserved on February 26, 2012 in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the preservation number CCTCCNO: M2012036. The actinobacillus succinogenes adopts fed-batch culture in a 5 to 15 L fermentation tank, 95.6 g / L succinic acid is produced in 48 hours, the production intensity is 1.99 g / (L.h), and the saccharic acid transformation rate is 0.71 g / g. Compared with other bacterial strains at home and abroad, the actinobacillus succinogenes has the advantages of high yield and lowerproduction cost.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving saccharic acid conversion rate in L-tryptophan fermentation process
InactiveCN103409477AImprove sugar-acid conversion rateIncrease biomassMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologySaccharic acid
The invention relates to an improved method for preparing L-tryptophan through a fermentation process, and concretely relates to a method for improving the saccharic acid conversion rate in an L-tryptophan fermentation process. In the invention, the content of acetic acid in the fermentation process is substantially reduced by controlling the dissolved oxygen level, the initial glucose concentration, the glucose limited feeding, the specific thallus growth rate and the like according to a cellar metabolic flux distribution regulating principle, so the thallus biomass, the L-tryptophan output and the saccharic acid conversion rate are substantially improved. The method effectively increases the conversion rate in the L-tryptophan fermentation process and substantially improves the L-tryptophan output without adding extra apparatuses or manpower investment, and is suitable for the industrialized production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
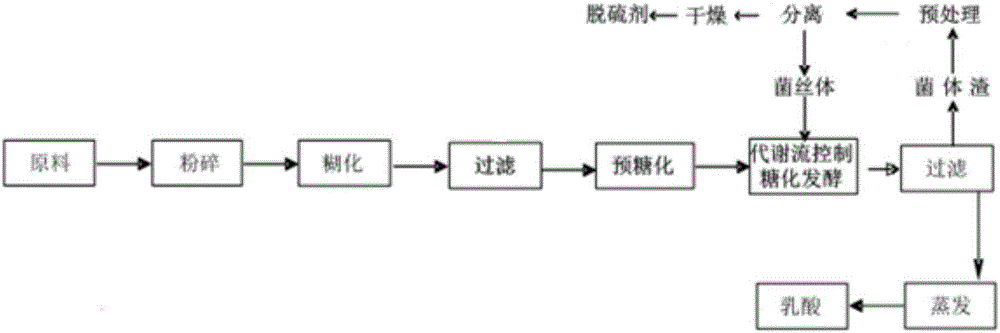
Method for lactic acid fermentation thallus residue pretreatment and method for circulation fermentation production of lactic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of lactic acid fermentation, and particularly relates to a method for lactic acid fermentation thallus residue pretreatment and application of the method for circulation fermentation production of lactic acid. The method for pretreatment comprises the steps that thallus residues obtained through filtering and separation of a lactic acid fermentation solution are pretreated through a composite medium; the pretreated thallus residues are filtered and separated to obtain soluble nutrient substances and insoluble impurities; the composite medium is prepared from ammonium sulfate, ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt, sodium dodecyl sulfate and sodium citrate. According to the method for lactic acid fermentation thallus residue pretreatment, soluble nutrient substances, including thallus and unconsumed nutrients, obtained after treatment of the composite medium can continue to participate in fermentation, the separated thallus is adopted as a nutrition nitrogen source to be returned to a fermentation working procedure, the consumption of nutrient substances in the fermentation culture medium can be reduced, the problem of fermentation waste residue outlet is solved, consumption of raw and auxiliary materials is lowered, the composite medium can be recycled, and resource recycling is achieved.
Owner:河南金丹乳酸科技股份有限公司
Biomembrane-electrodialysis coupling continuous production technology of L-lactic acid
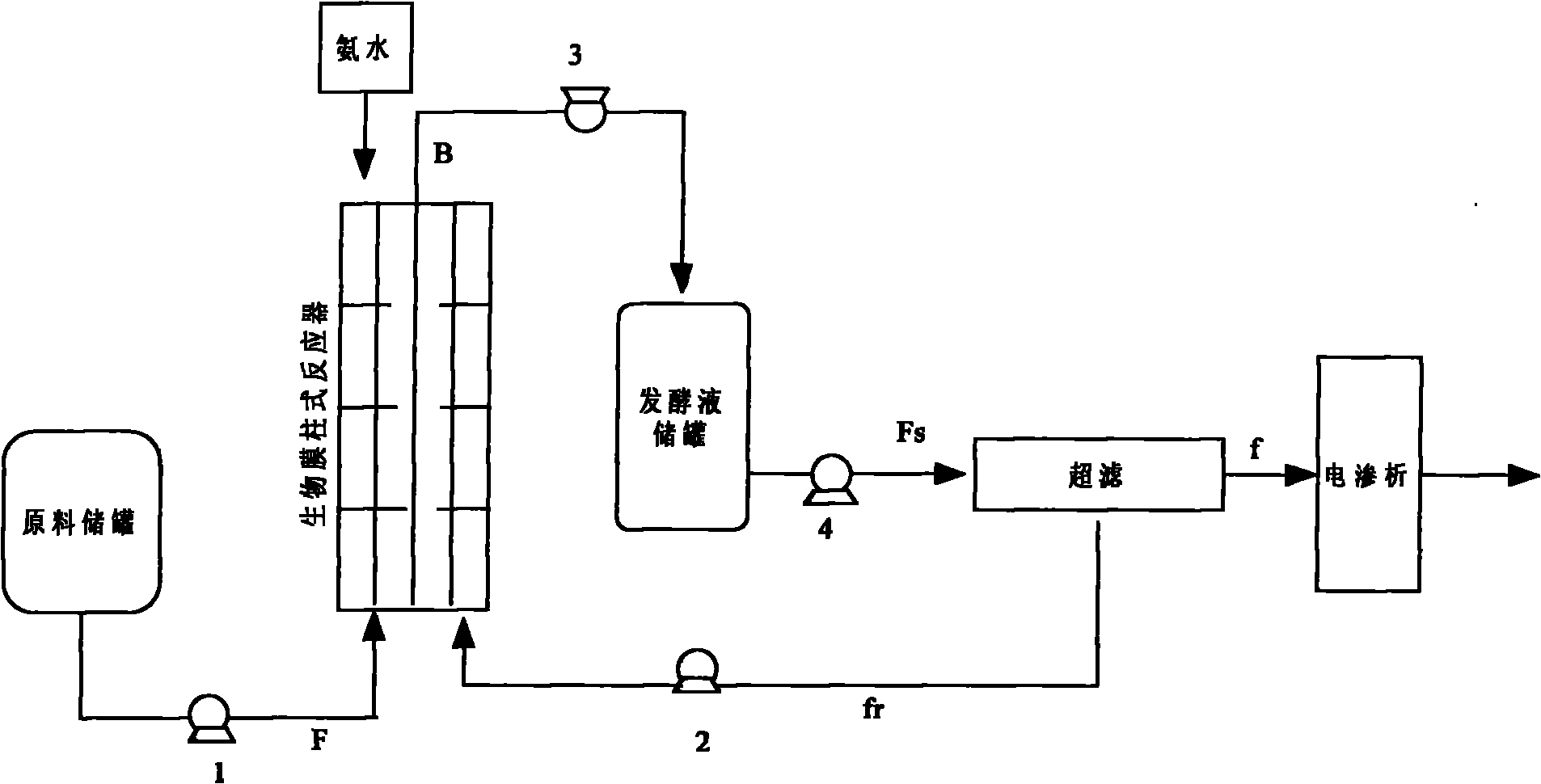
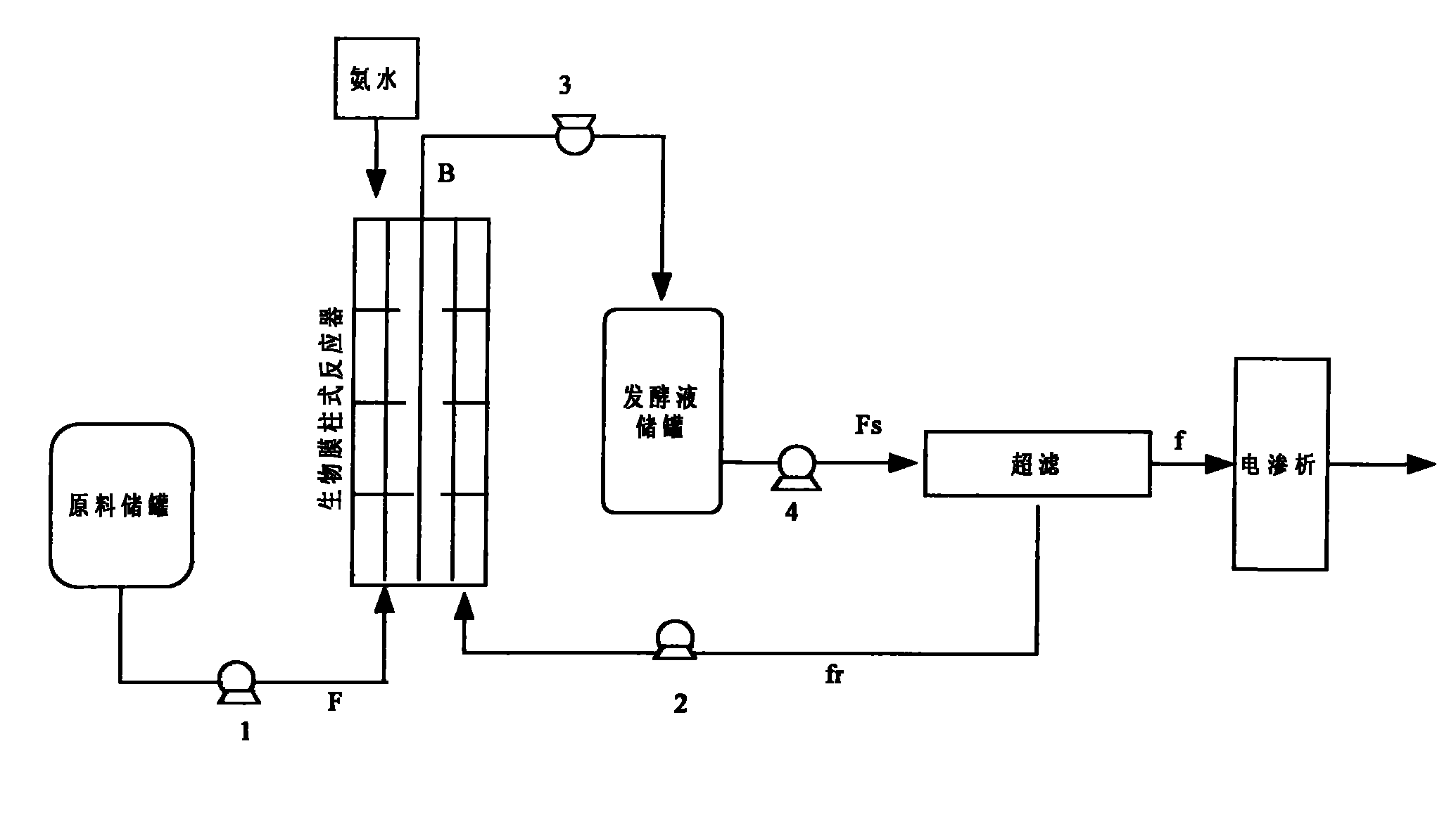
ActiveCN102041279ATake advantage ofReduce pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationUltrafiltrationGlucose polymers
The invention provides a biomembrane-electrodialysis coupling continuous production technology of L-lactic acid. The production technology comprises the following steps: a clear liquid biomembrane column reactor is used to perform continuous anaerobic fermentation, the lactic acid producing strains are adsorbed by combined perforated ring filler, an ultrafiltration membrane is used to filter the fermentation liquor, thalli are blocked by the ultrafiltration membrane, the blocked thalli and liquid are sent back to the biomembrane column reactor, and L-lactic acid is separated through electrodialysis. The method provided by the invention uses the biomembrane column reactor to adsorb lactic acid producing strains on the membrane and uses the ultrafiltration membrane to block lactic acid bacteria, thus the thalli concentration and sugar utilization rate can be effectively increased, and the lactic acid concentration, the acid producing rate and the conversation rate from glucose to lacticacid can be increased greatly.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Technology for preparation of succinic acid finished product by bioconversion of cassava raw material
ActiveCN103361385ALow priceHigh in starchMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiltrationIon exchange
Provided is a technology for preparation of succinic acid finished product by bioconversion of cassava raw material. The technology comprises the following steps: A, crushing of cassava pieces; B, liquification of cassava; C, saccharification of cassava; D, disinfection of fermentation tanks and material supplementing tanks; E, preparation of fermentation medium; F, disinfection of the fermentation medium; G, inoculated fermentation of the medium; H, filtration and decoloration of the fermentation solution; I, ion exchange of the fermentation liquor after decoloration; J, evaporation and concentration of succinic acid solution; K, crystallization of the succinic acid concentrated solution; and L, desiccation of the succinic acid crystals. The technology takes reasonable technology steps, pretreats non-grain crop cassava, selects specific strains, ferments the cassava raw material solution and obtains succinic acid. During the preparation process, the conversion rate of sugar to acid is extremely high and cassava is used fully.
Owner:山东兰典生物科技股份有限公司
Method for improving fermentation-production citric acid yield through use of two-stage dissolved oxygen control technology
ActiveCN103352007AIncrease productionImprove sugar-acid conversion rateFungiMicroorganism based processesOrganic acidProcess optimization
The invention discloses a method for improving fermentation-production citric acid yield through use of two-stage dissolved oxygen control technology, and belongs to the field of fermentation process optimization. In the first stage of fermentation (28-32 h), dissolved oxygen is controlled between 45% and 55%, and in the second stage of the fermentation (37-50 h), the dissolved oxygen is controlled between 35% and 45%. Through use of the two-stage dissolved oxygen control technology, the citric acid yield is significantly improved, and the highest sugar-acid conversion rate is 99%, whereas the sugar-acid conversion rate of a contrast embodiment is 86%. The two-stage dissolved oxygen control fermentation technology is simple and efficient, has important industrial application value, and at the same time has a certain guidance and enlightenment significance on fermentation production of other organic acids.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
L-homoserine production bacterial strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109666617AIncrease productionFermentation results are stableBacteriaTransferasesL-threonineMicrobiology
The invention provides an L-homoserine production bacterial strain. The L-homoserine production bacterial strain is characterized by containing a single and stable chromosome and not containing DNA carrier plasmids or other free DNA carriers, one or more genes related to L-threonine synthesis on the chromosome DNA of the bacterial strain are subjected to knockout or weakening, and / or the genes aresubjected to mutation for enhancement, and / or one or more genes related to the L-homoserine metabolic pathway are integrated and copied on the chromosome DNA of the bacterial strain.
Owner:SICHUAN LIER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
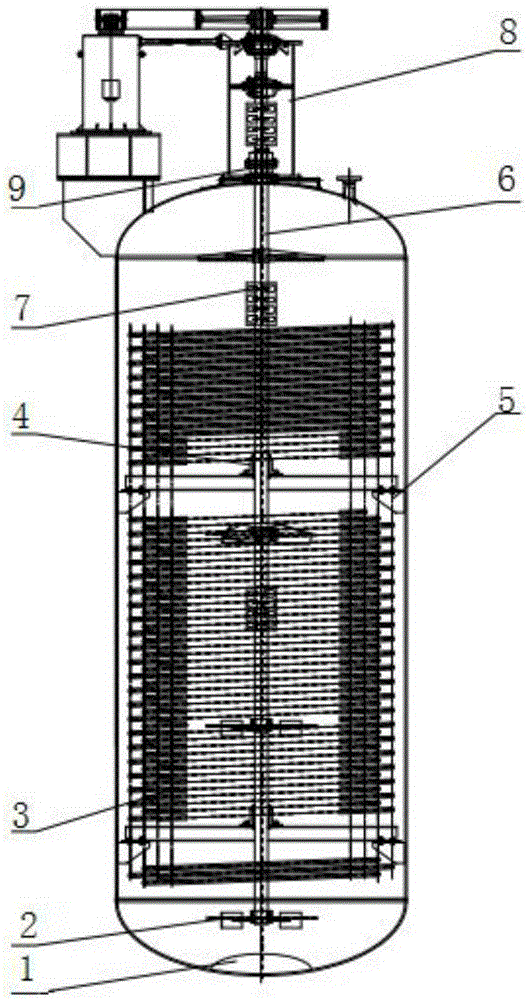
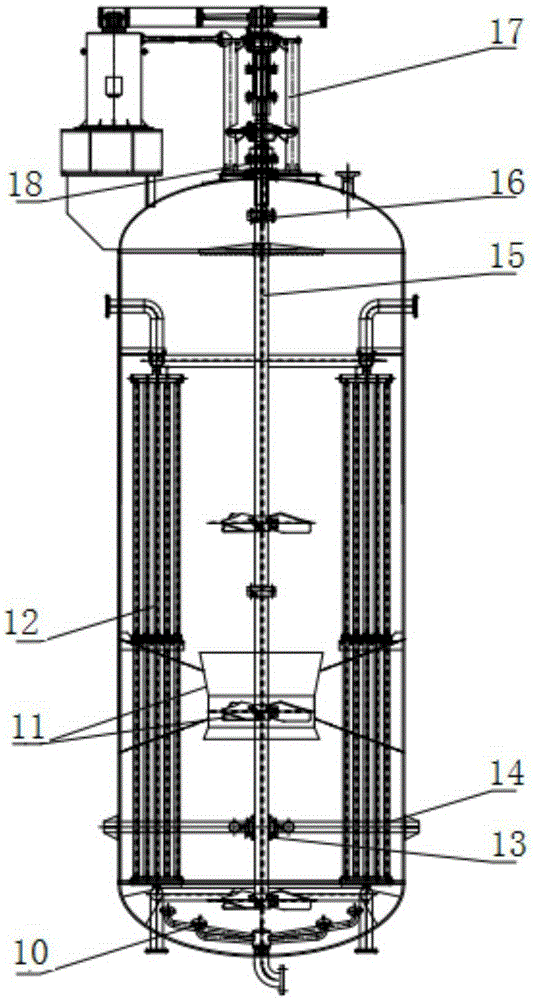
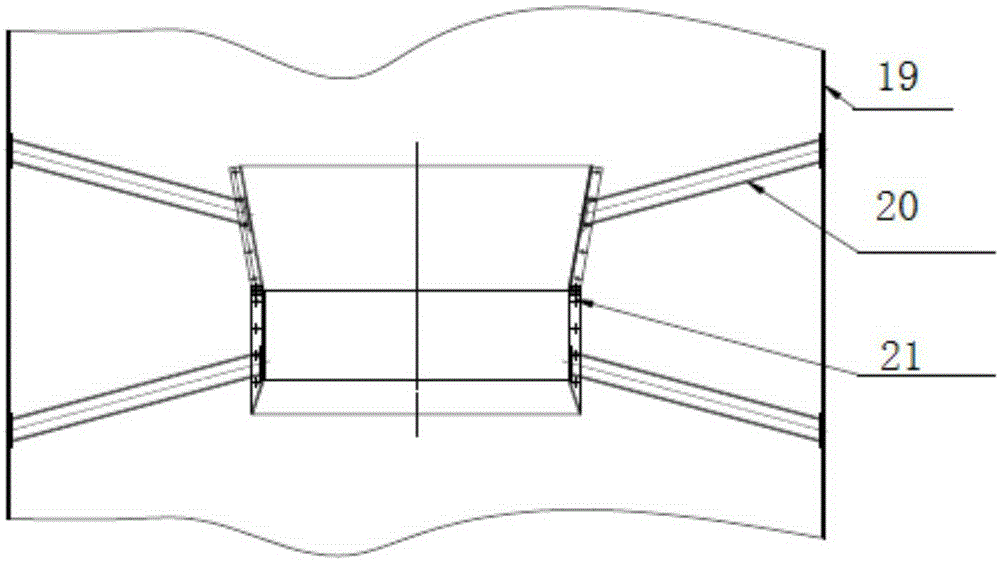
High-steady-state, high-effect, and large-volume fermenting tank
ActiveCN106566769AImprove dissolved oxygen effectAirtightBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringOperational stability
The invention discloses a high-steady-state, high-effect, and large-volume fermenting tank. The fermenting tank comprises a tank body, wherein a hollow stirring shaft is perpendicularly arranged in the center of the interior of the tank body; a plurality of stirrers for performing axial flowing of a fermenting liquid in the tank body are uniformly distributed on the hollow stirring shaft; the lower part of the hollow stirring shaft is connected with a middle bearing bracket through a middle bearing; multiple groups of vertical type column pipe coolers are distributed, in the axial direction of the tank body, in the interior of the tank body; a multi-bubble-cap air distributing apparatus is arranged at the bottom of the tank body; the multi-bubble-cap air distributing apparatus comprises a main air pipe; and the main air pipe is connected to the exterior of the tank body. By virtue of the mechanical units, comprising an external transmission rack, a tank top mechanical sealing part, the stirring shafts, a coupler, the middle bearing bracket and a wear-resisting bearing bush, for constituting the fermenting tank structure, the operational stability of the fermenting tank is greatly improved; full guarantee is provided for energy-saving, consumption-reducing and high-efficient production; and obvious economic benefits and a demonstration effect are achieved.
Owner:ZIBO SANTIAN CHEM EQUIP CO LTD
L-ammonium lactate tolerant bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN103305437AImprove sugar-acid conversion rateRelease product inhibitionBacteriaMutant preparationBacilliChemistry
The invention discloses an L-ammonium lactate tolerant bacterial strain and an application thereof in producing L-ammonium lactate through fermentation. According to the invention, low-energy nitrogen ions are injected in mutant original strains, and then the strains are screened by using a high-sugar tablet, a succinic acid tablet and an ammonium lactate tablet so as to obtain high-sugar-resistant and EMP approach reinforced strains which do not decompose and use a lactic acid. In a 3L fermentation tank, the strains are subjected to cultivation and acclimatization in a culture medium filled with critical-concentration ammonium lactate, and a bacteria liquid subjected to acclimatization of 72 hours is used as an original bacteria liquid of the next mutagenesis and acclimatization. The process is repeated until a target strain (Lactobacilluscasei) LC-An226 is screened. The strain has the characteristics of good ammonium lactate tolerance and high saccharic acid conversion rate. In a 5L fermentation tank, the output of L-ammonium lactate in the fermentation liquor reaches 206 g / L, and increased by 58.46% compared with the production of L-ammonium lactate by using original strains through fermentation, therefore, the strain has great social significance and economic values.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof in producing L-glutamic acid
ActiveCN111206011AIncrease productionImprove sugar-acid conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFermentation brothBiological organism
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof in producing L-glutamic acid and belongs to the technical field of biologics. The invention provides the recombinant C.glutamicum DL01 / pDXW-10-ppc capable of producing L-glutamic acid with a high yield, the recombinant C.glutamicum DL01 / pDXW-10-ppc is inoculated into a 5-L fermentation tank for fermentation for48 hours, then the yield of the L-glutamic acid in a fermentation broth can be as high as 136.09+ / -5.53g / L, the sugar acid conversion rate is as high as 58.9%, and the yield and the sugar acid conversion rate are respectively increased by 45.5% and 13.7% when being compared with those of wild Corynebacterium glutamicum G01.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Lactobacillus casei and application thereof to produce L-lactic acid by fermentation
InactiveCN102653724BImprove sugar-acid conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySaccharic acid
The invention discloses lactobacillus casei LC-N235 with collection number CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) No: M2012157. According to the invention, the original strain of lactobacillus casei LC-5 is mutated by low-energy nitrogen ion injection; the strain which resists high glucose, adopts EMP path reinforcement and utilizes lactic acid without decomposition can be screened by a high-glucose plate, a succinic acid plate and a pure-lactic acid plate; through fermentation re-screening, the L-lactic acid high-yield strain is screened and used as the original strain for next mutation; and the steps are repeated until the target strain lactobacillus casei LC-N235 is screened. The strain can effectively utilize the cheap corn flour saccharifying liquid to produce L-lactic acid by fermentation, and the saccharic acid conversion rate is high. In a 5L fermentation tank, the output of L-lactic acid reaches 173g / L, which is improved by 46.6% as compared with that of the L-lactic acid produced by fermenting the original strain; and the lactobacillus casei and the application thereof to produce L-lactic acid by fermentation provided by the invention have tremendous social significance and economic values.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Method for producing D-lactic acid through fermentation
ActiveCN111378698AIncrease profitImprove sugar-acid conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationBacilliChemistry
The invention relates to the field of microbial fermentation, and particularly discloses a method for producing D-lactic acid through fermentation. The method comprises the following step: inoculatinga fermentation culture medium with at least part of a carbon source provided by saccharification liquid against Lactobacillus plantarum with a preservation number of CGMCC No.16835. A production method of the saccharification liquid comprises the steps of mixing a slurry containing a starchy raw material and amylase for spray liquefaction, then conducting flash evaporation, cooling and heat preservation, and then mixing liquefaction liquid and a saccharifying enzyme for saccharification; the dosage of the saccharification liquid makes a content of carbon in the fermentation culture medium equal to 60-80 g / L; and conditions of lactic acid fermentation comprise a temperature of 37-45 DEG C, a pH value of 5.3-6.5, the time of 40-60 h, and the rotating speed of stirring of 50-150 rpm, and theinoculation quantity of the Lactobacillus plantarum makes Lactobacillus plantarum OD600 in a lactic acid fermentation system after inoculation is conducted range from 0.3 to 1. According to the method for producing the D-lactic acid through fermentation, the adopted raw materials have the characters of being wide in source and low in cost, by means of the provided method, production can be conducted in a wide pH value range and a wide temperature range, the workload of raw material pre-treatment is reduced, and the method for producing the D-lactic acid through fermentation has the charactersof being high in sugar utilization rate and conversion rate and short in production cycle.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
Glucose control process for increasing yield of L-isoleucine
InactiveCN112029683AIncrease profitReduce accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySaccharic acid
The invention provides a glucose control process for increasing the yield of L-isoleucine. The glucose control process is a glucose sub-moderate sugar supplementing process; thalli are divided into four stages, namely an adaptation stage, a thalli expanding culture stage, an acid production peak stage and a decay stage; the thalli are Corynebacterium glutamate, have lysine defect types, and are fermented by adopting a base material high initial sugar; namely, 80-120 g / L of glucose is added to a base material at a time, a low-sugar feeding process is adopted in the middle and later periods, namely the feeding acceleration rate ranges from 5.20 g / (L.h) to 7.47 g / (L.h); and the thallus fermentation condition is dynamically and accurately regulated and controlled, and fermentation conversion of thalli is achieved, According to the method, the problems that the thallus adaptation period is long, the acid production peak period is short, the thallus enters the decay period in advance and thelike are solved, the glucose utilization rate is optimized, the saccharic acid conversion rate is increased, accumulation of by-products is reduced, and the heteroacid content is greatly reduced on the premise that the biomass and the acid production amount are not reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Continuous cultivation method of Aspergillus niger citrate seeds based on mycelium ball dispersion technology
ActiveCN104099253BReduce step-by-step expansion of cultivation processShort training periodFungiMicroorganism based processesFermentationAspergillus niger
A citric acid aspergillus niger seed continuous culture method based on a mycelium pellet dispersion technology comprises the steps as follows: (1), an aspergillus niger spore solution is inoculated to a seed culture medium and cultured and prepared into a mature seed solution; (2), the mature seed solution is treated by a disperser to obtain a dispersed mycelium seed solution; (3), part of the dispersed mycelium seed solution obtained in the step (2) is transferred to a fermentation medium for fermentation with 5%-15% of inoculum concentration, and the fermentation is finished when the reducing sugar concentration of the fermentation medium is lower than 0.5%; and (4), part of the dispersed mycelium seed solution obtained in the step (2) is inoculated to a seed culture medium with 5%-15% of inoculum concentration to be cultured and prepared into a next level of mature seed solution, and then the operation returns to the step (2), so that the continuous culture for aspergillus niger seeds is realized. According to the aspergillus niger seed continuous culture method provided by the invention, the tedious culture process of aspergillus niger spores can be directly reduced, simultaneously, the culture time of mature seeds can be effectively shortened, and the utilization rate of raw materials is increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for optimizing amino acid fermentation
PendingCN110129386AHigh activityReduce volumeFermentationAmino acid fermentationIndustrial fermentation
The invention discloses a method for optimizing amino acid fermentation, and relates to the technical field of amino acid fermentation. Aiming at the technical problem of low sugar acid conversion rate in the prior fermentation process, the invention provides a method for improving the sugar acid conversion rate of amino acid fermentation. When amino acid is produced by strain fermentation, when the volume of a fermentation liquid reaches 65%-75% of the liquid level of a fermentation tank, the fermentation liquid is continuously put, the continuous put volume is 5-10% of the volume of the fermentation tank, sugar liquid is continuously added for culture after continuous put, and the fermentation liquid is collected and prepared to obtain amino acid. The method is suitable for industrial fermentation to produce an amino acid product.
Owner:绥化象屿金谷生化科技有限公司
Method for fermentation of L-glutamic acid by cottonseed cake meal hydrolysate
The invention relates to a method for fermentation of L-glutamic acid by a cottonseed cake meal hydrolysate. The method is characterized in that: the cottonseed cake meal hydrolysate is added into an L-glutamic acid fermentation medium, amino nitrogen concentration of the cottonseed cake meal hydrolysate is 0.5-3.0%, the L-glutamic acid fermentation medium is a temperature sensitive L-glutamic acid fermentation medium, and the adding amount of the cottonseed cake meal hydrolysate is 15-25ml / l. By controlling the adding amount of the cottonseed cake meal hydrolysate, smooth L-glutamic acid fermentation can be effectively guaranteed. Utilization of the cottonseed cake meal hydrolysate not only broadens the organic nitrogen source resources, but also decreases the fermentation cost, so that the cottonseed cake meal hydrolysate has broad application prospects in the fermentation industry.
Method for improving fermentation yield and conversion rate of threonine
PendingCN114381476AImprove efficiencyImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention relates to the technical field of threonine fermentation, and discloses a method for improving the fermentation yield and conversion rate of threonine. The method for improving the fermentation yield and conversion rate of threonine comprises the following steps: S1, preparing materials; s2, slant culture; s3, seed culture; s4, fermentation culture; according to the method, fermentation liquid containing high-concentration acetic acid and ammonium ions in the middle and later periods of threonine fermentation enters a feed liquid inlet of the scraper evaporator from the fermentation tank under the dual action of the positive pressure of the fermentation tank and the negative pressure of the scraper evaporator by utilizing a fermentation coupling scraper concentration evaporation technology; acetic acid and ammonium ions enter the condenser through evaporation, concentrated fermentation liquor enters the fermentation tank through the concentrated liquor temporary storage tank for continuous fermentation, the process operation is simple, energy consumption is low, continuous feeding can be achieved, volatile substances such as acetic acid and ammonium ions can be continuously removed, continuous discharging can be achieved, the acetic acid and ammonium ion removal efficiency is high, and the production cost is low. The stability and the automation degree are high.
Owner:江苏元易邦生物科技有限公司
A Strain of L-Ammonium Lactate Resistant Bacteria and Its Application
InactiveCN103305437BImprove sugar-acid conversion rateHigh purityBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologySaccharic acid
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
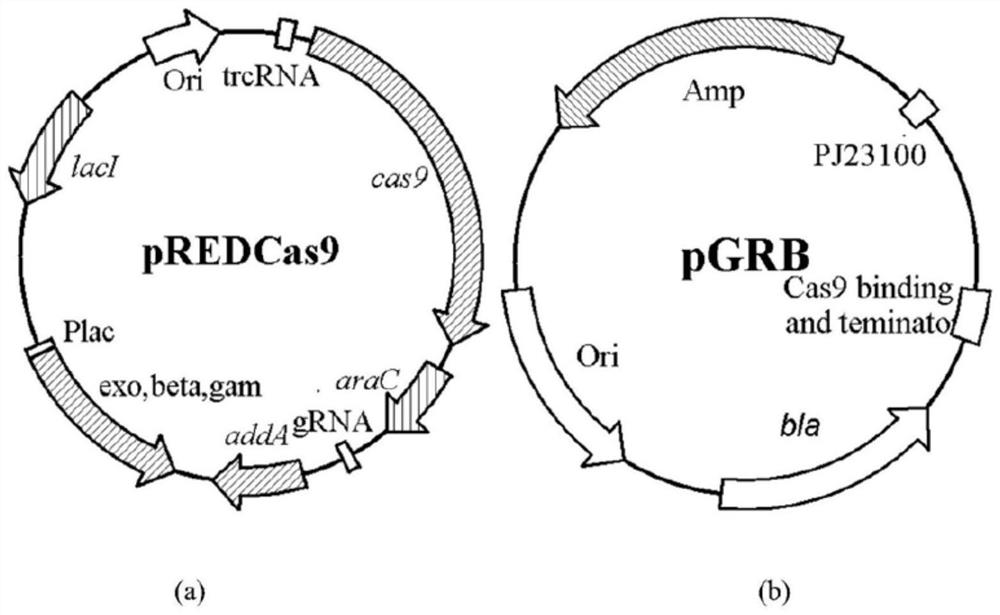
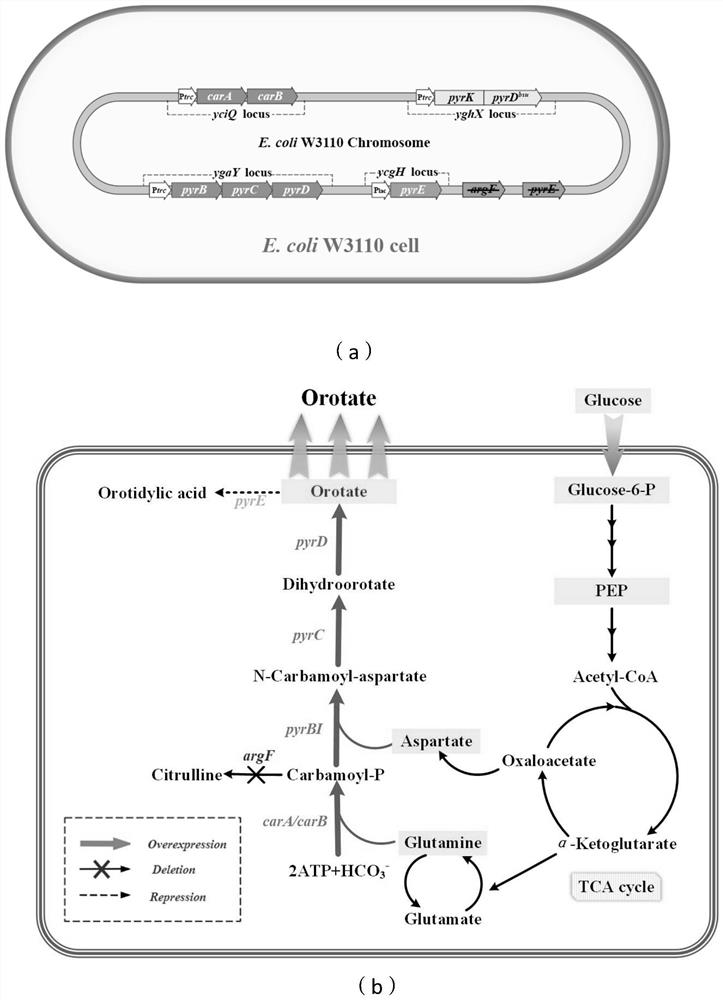
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing orotic acid as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for producing orotic acid and a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium, the genetically engineered bacterium is a genetically engineered bacterium E.coli Ora which does not contain plasmids and is used for synthesizing high-yield orotic acid from the beginning, and compared with an existing orotic acid producing bacterium, the genetically engineered bacterium has the advantages of being good in genetic stability, high in fermentation yield, high in saccharic acid conversion rate and the like, and has a good application prospect. The genetically engineered bacterium takes glucose and other cheap carbon sources as substrates to efficiently synthesize the orotic acid from the beginning, the yield of the orotic acid can reach up to 135.6 g / L, and the genetically engineered bacterium has a good industrial application prospect; the genetically engineered bacterium analyzes and reconstructs metabolic flux related to orotic acid in a pyrimidine nucleotide metabolic network in escherichia coli, and enhances synthesis and accumulation of orotic acid; then, dihydrolactate dehydrogenase in wild type bacillus subtilis pyrimidine nucleoside operon is introduced, so that the synthesis of orotic acid is further enhanced, and the requirement of large-scale industrial production is met.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for producing L-lactic acid by Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.2602
ActiveCN101544993BStrong environmental resistanceEasy to saveMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismGlucose polymers
A method for producing L-lactic acid by Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.2602 belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. In the invention, Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.2602 is adopted, and under the condition of no oxygen supply, starchiness hydrolyzed sugar or dextrose is fermented by a semicontinuous intermittent fermentation way or an inter-sugar-compensating fermentation way to generate L-lactic acid with high optical purity. The invention has the advantages that the gemma property of the Bacillus coagulans is stable, and the L-lactic acid obtained by inoculating and fermenting the starchiness hydrolyzed sugar has high optical purity and rate of conversion of sugar and acid and short fermentation period; in addition, the semicontinuous intermittent fermentation way saves the time forpreparing seeds by a continuous reladling and subculturing method, shortens the fermentation period, enhances the fermentation strength and obtains the L-lactic acid with both relatively high rate ofconversion of sugar and acid and purity.
Owner:江苏省苏微微生物研究有限公司
Method for preparing d-lactic acid by fermentation
ActiveCN111378698BIncrease profitImprove sugar-acid conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyAmylase
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com