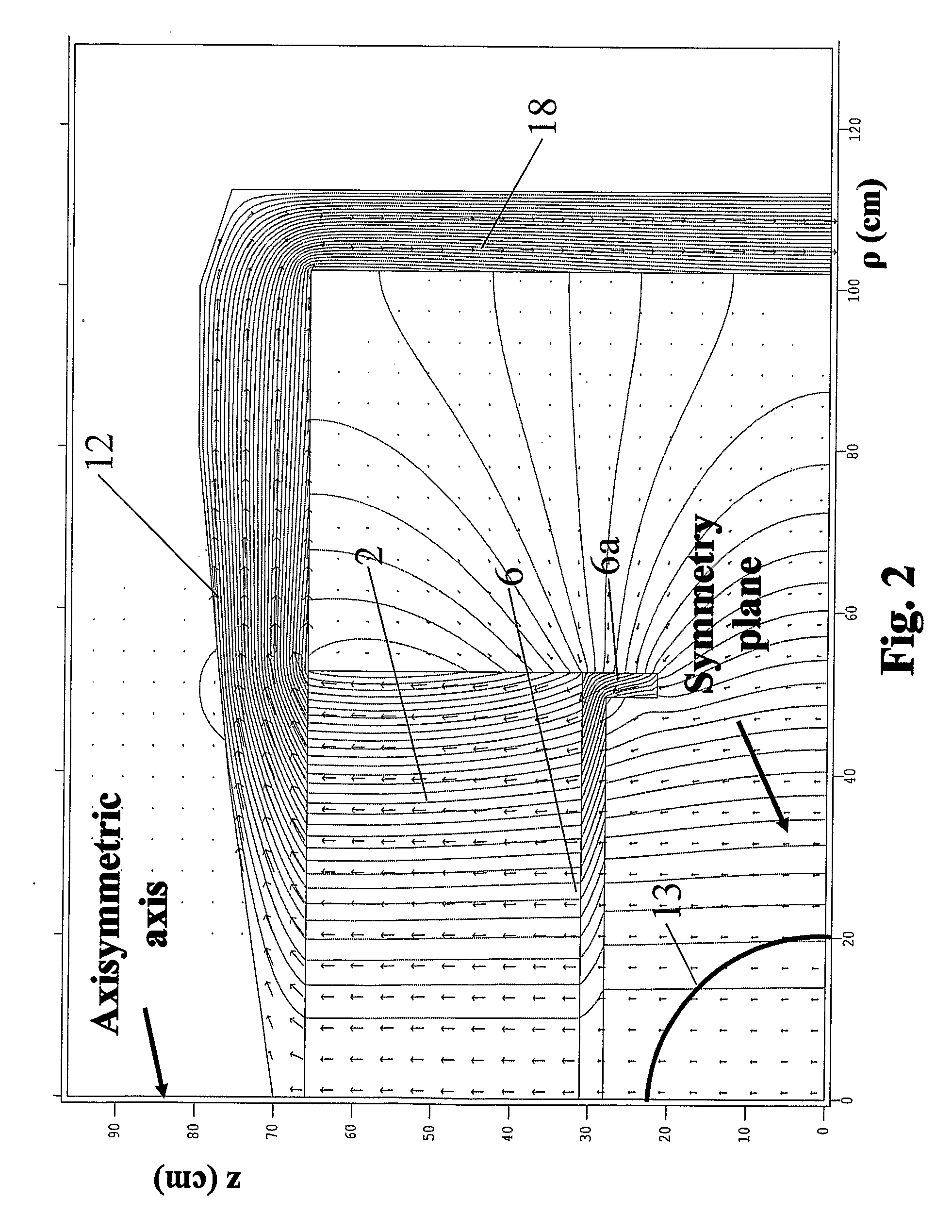
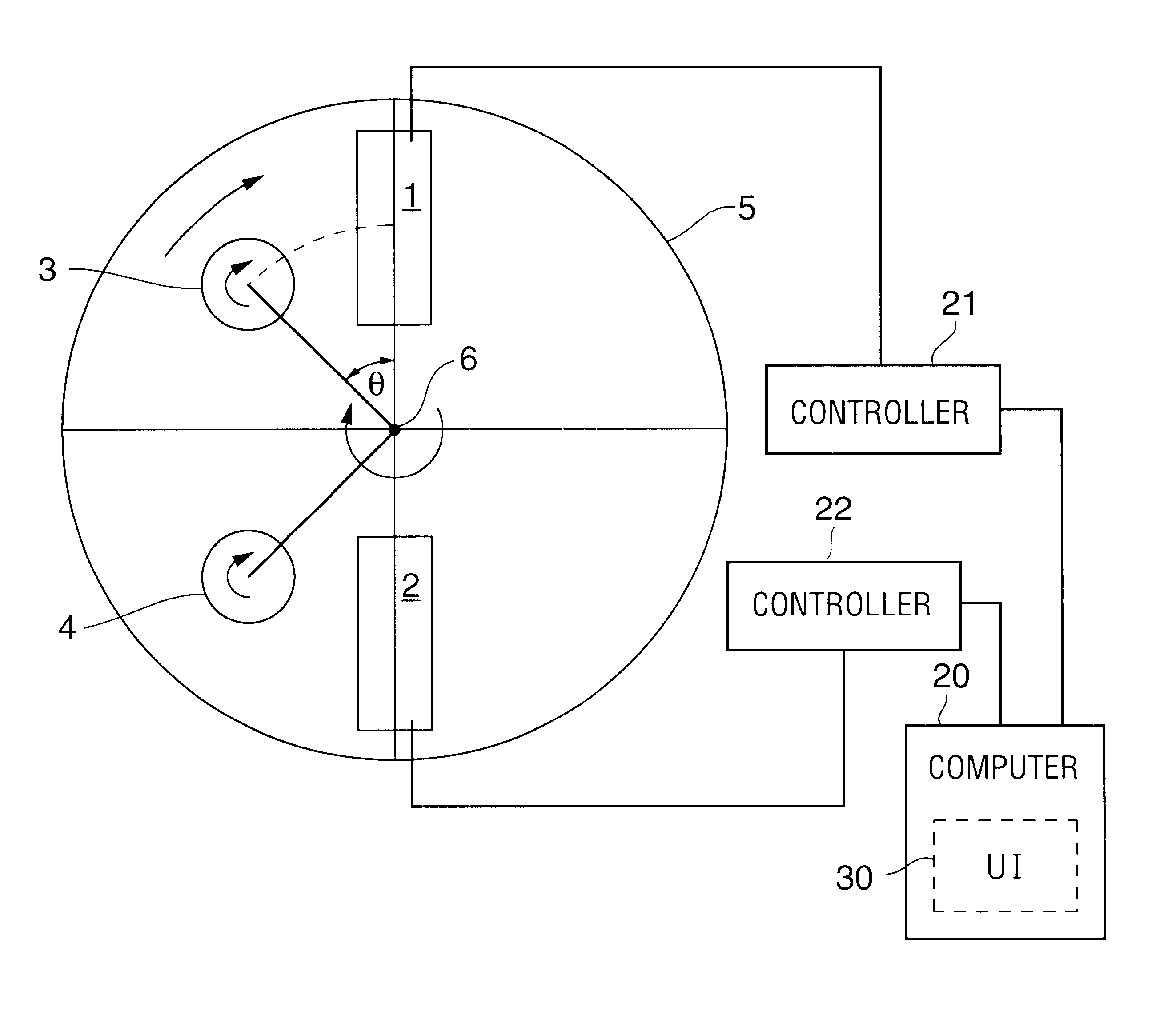
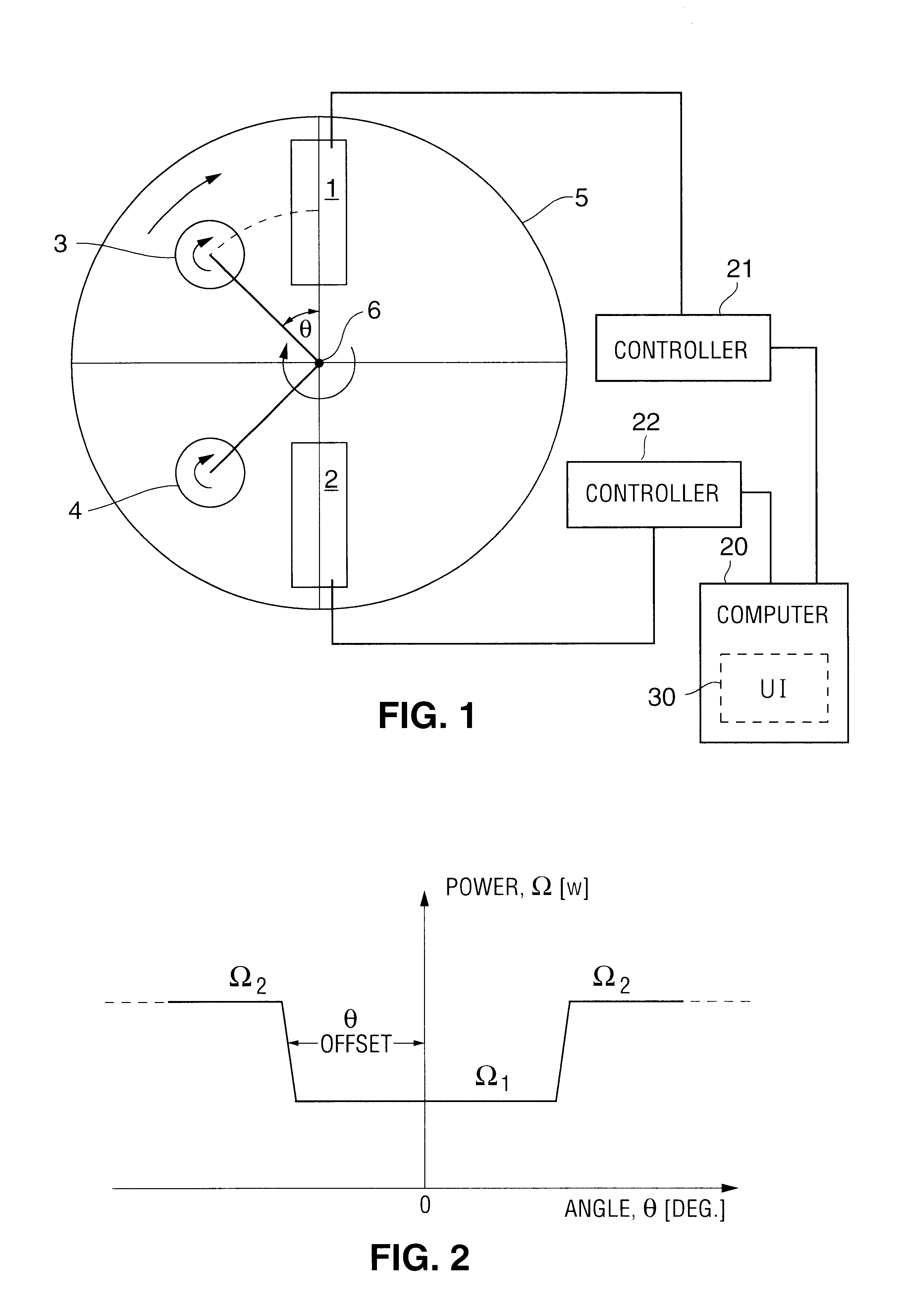
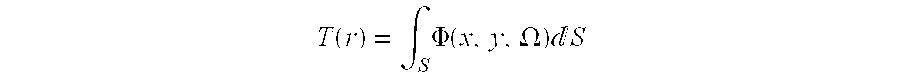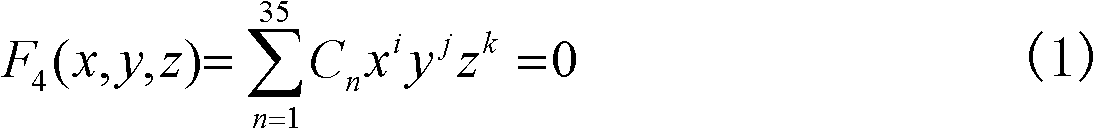Patents
Literature
119 results about "Flux distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
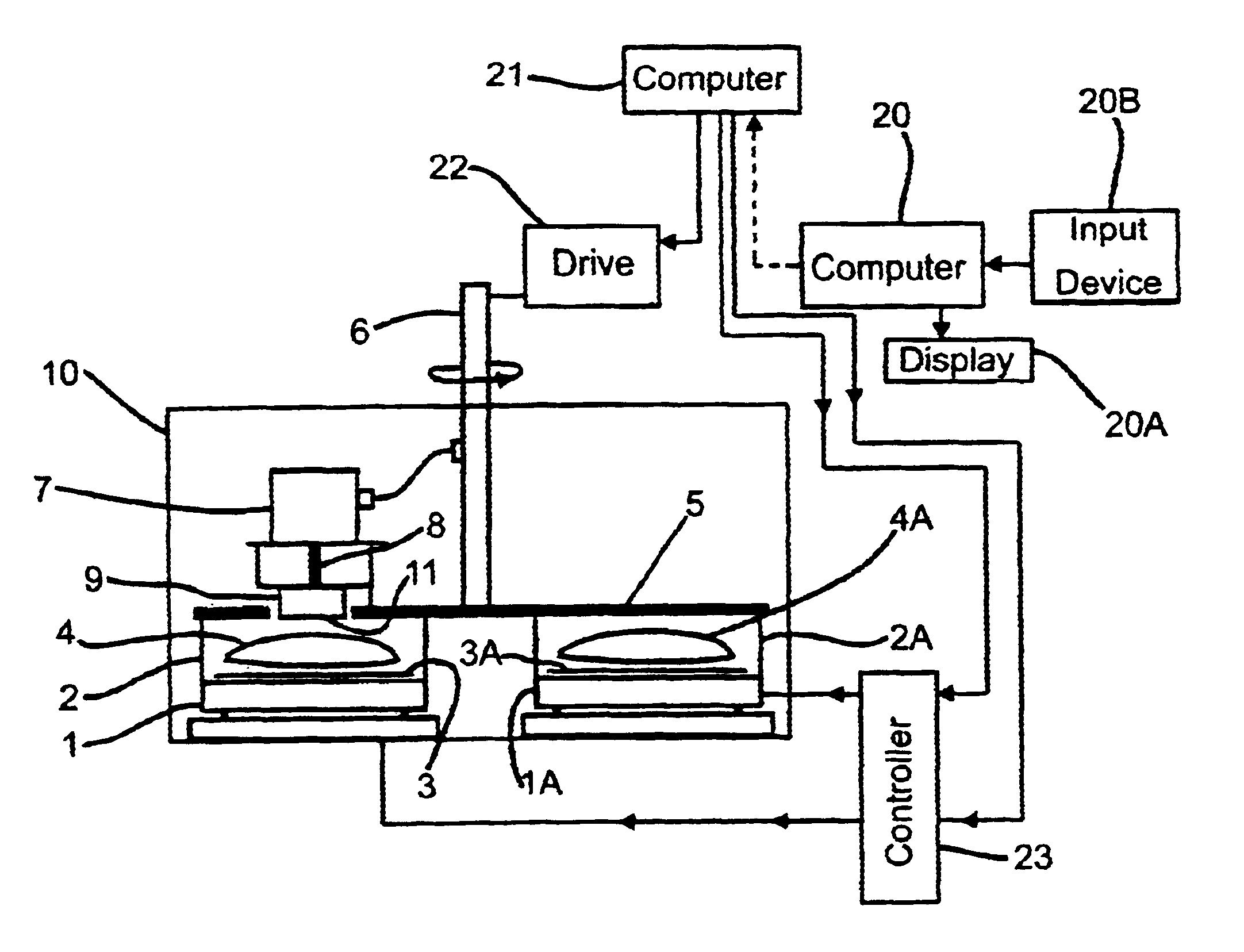
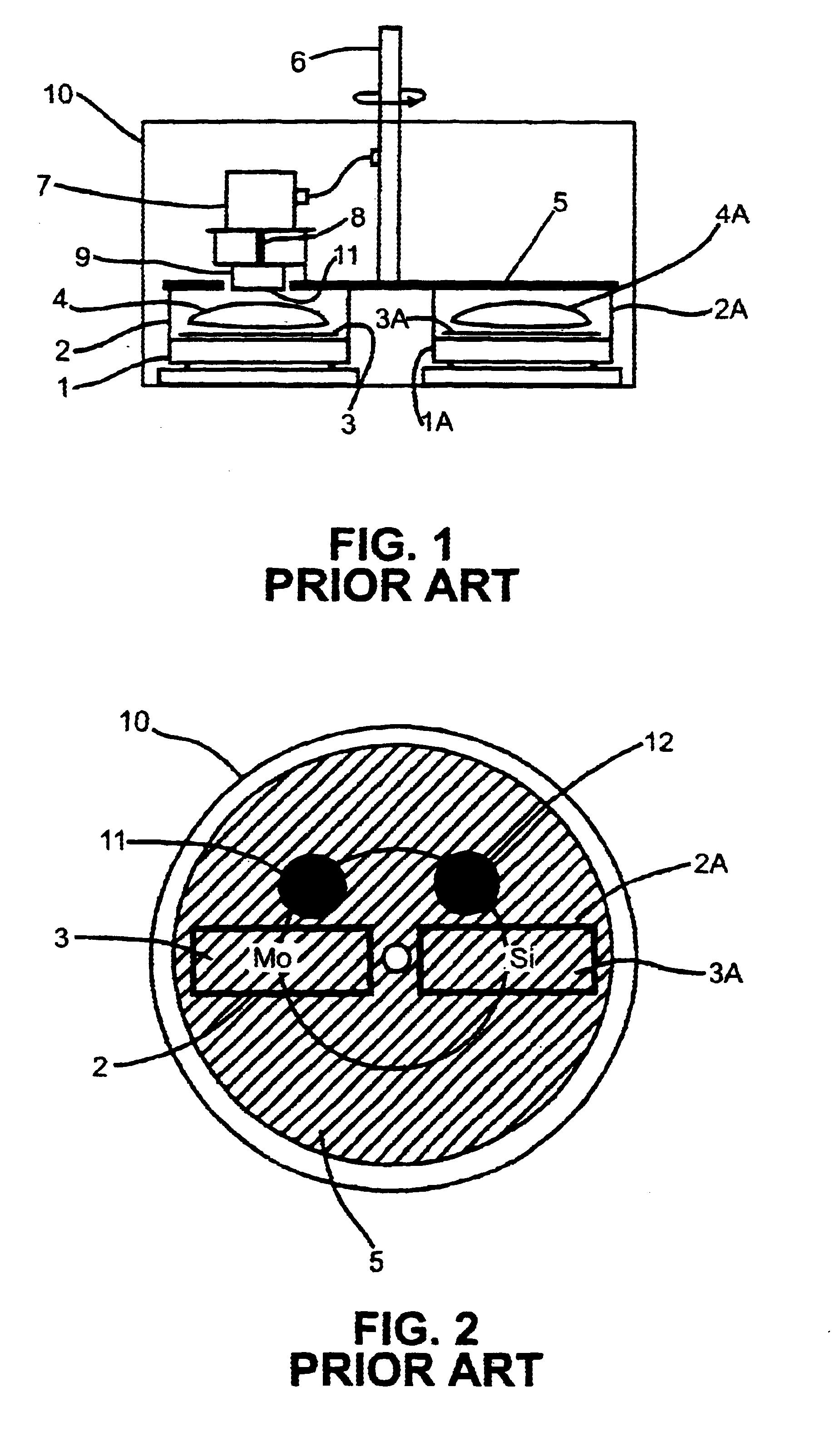
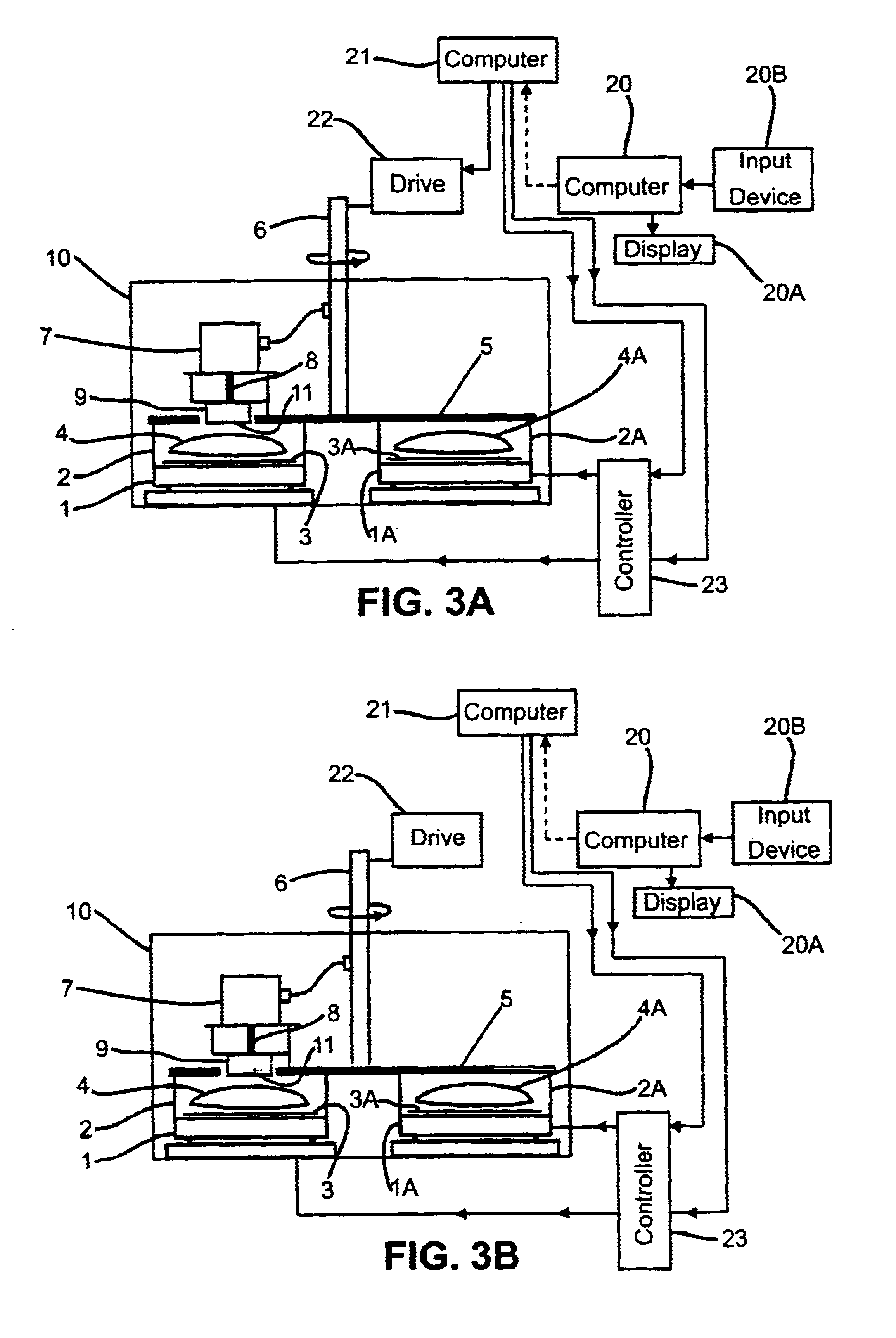
Linear illumination lens with Fresnel facets
ActiveUS7559672B1Large amount of processingImprove efficacyMechanical apparatusFurnace componentsCamera lensFresnel lens
A linear Fresnel lens for LED illumination is configured initially by using a meridional flux-assignment method and is then corrected by assessing the three-dimensional flux distribution of individual facets. The facet angles are slightly altered as required to produce uniformity. A variety of specialized lens shapes are generated, such as for illuminating shelves in commercial refrigerator food-display cases. The lens shapes are suitably thin for economical production by extrusion.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
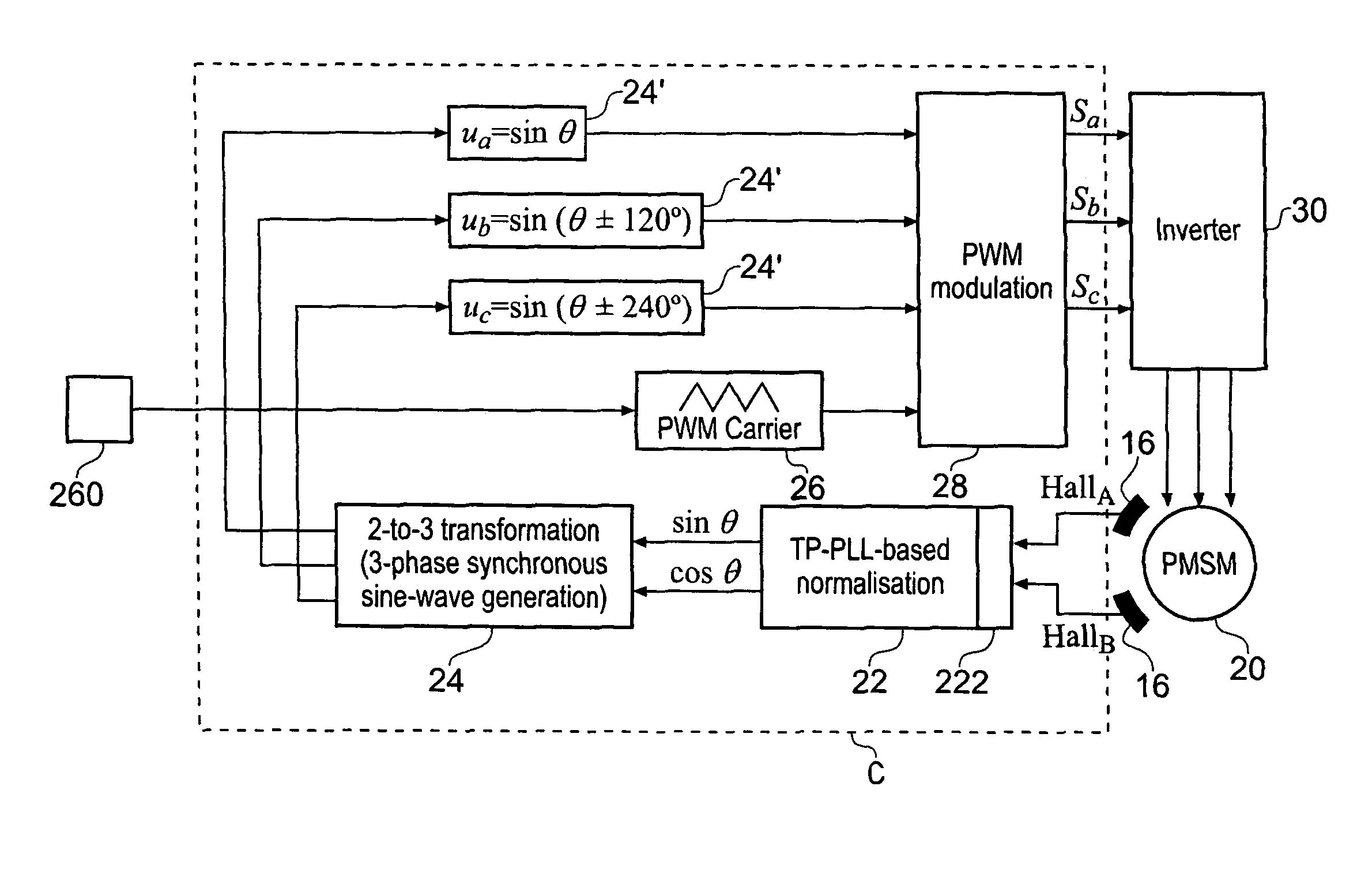
Permanent magnet synchronous motor and controller therefor
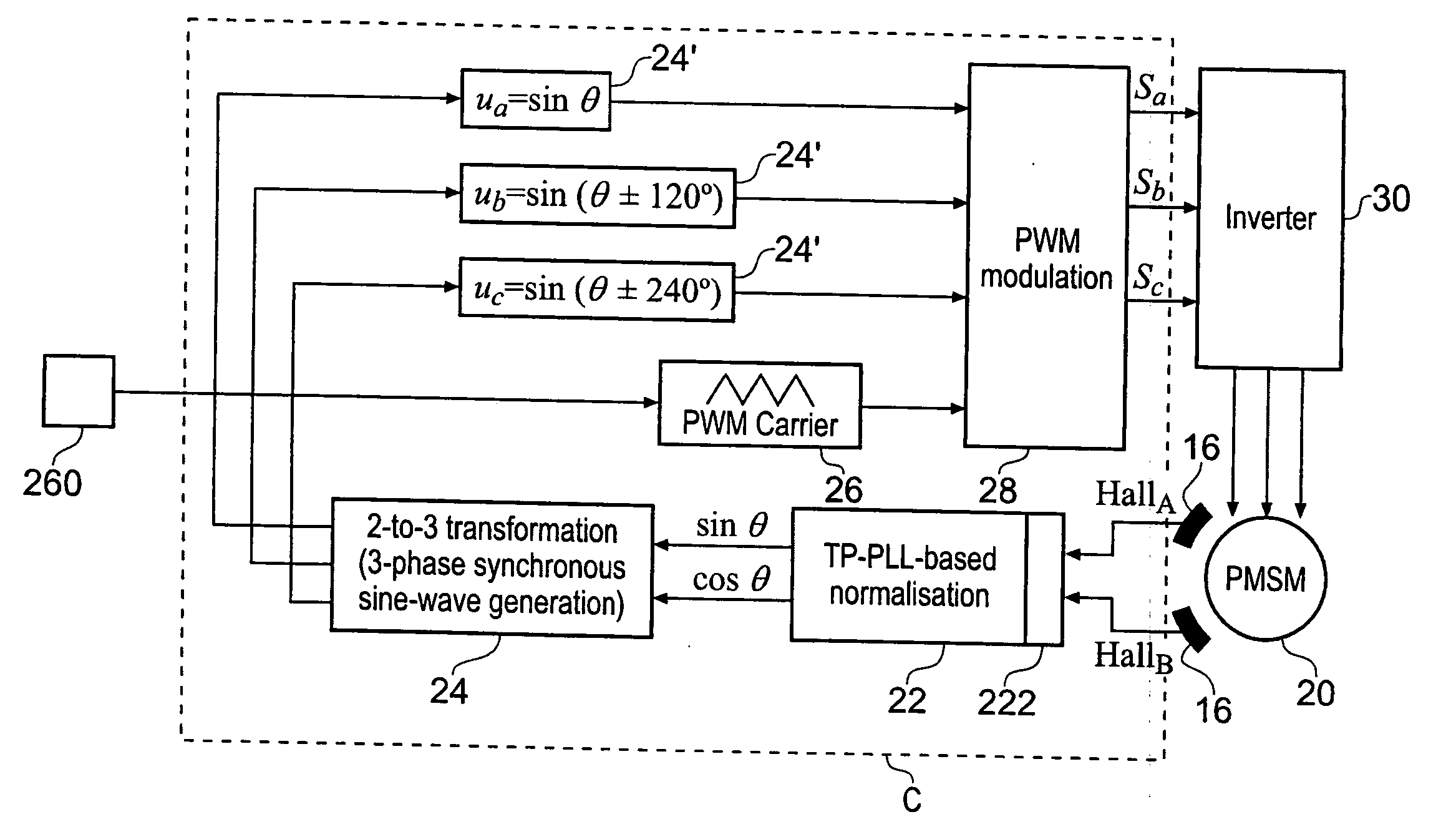
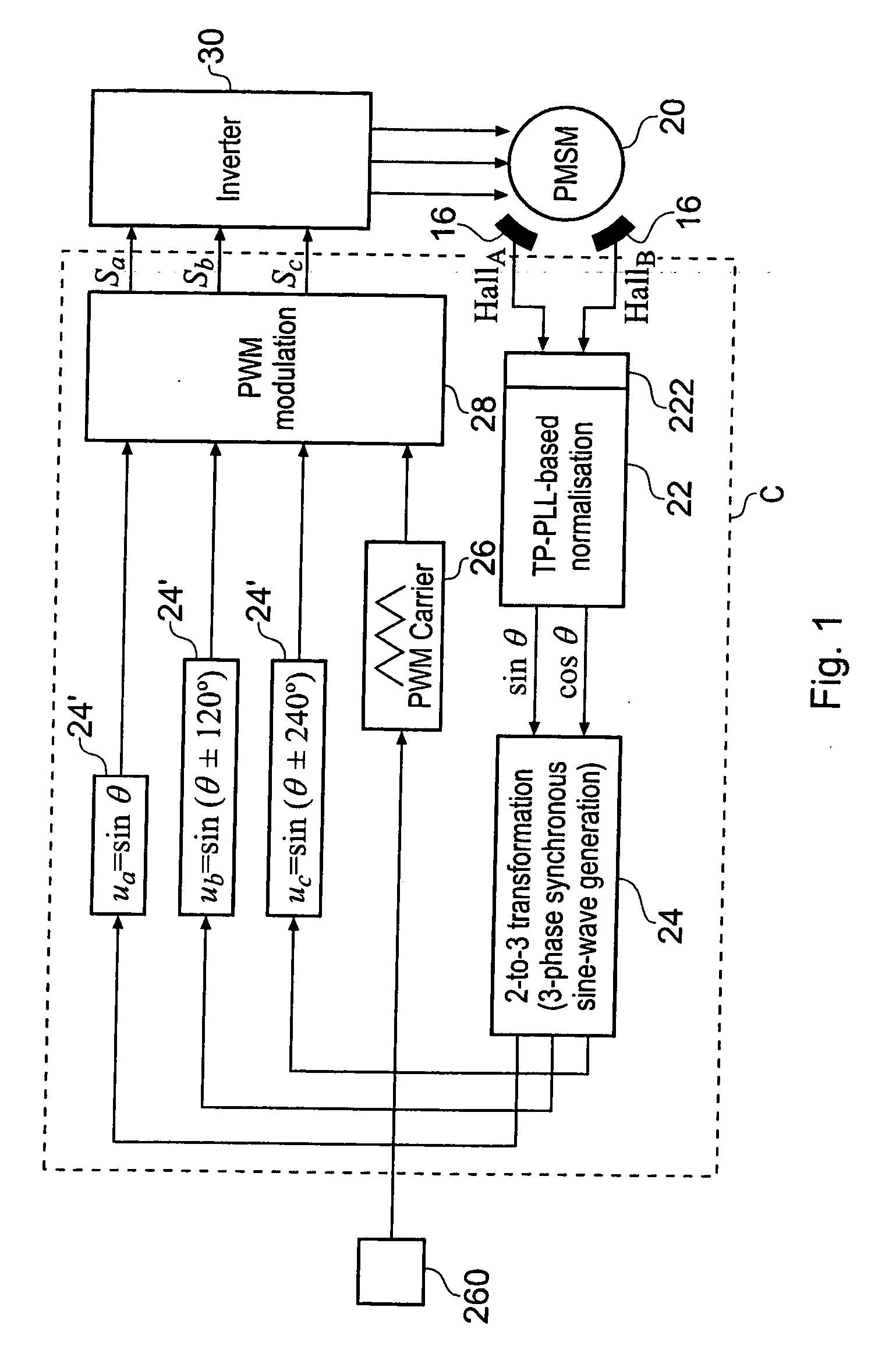
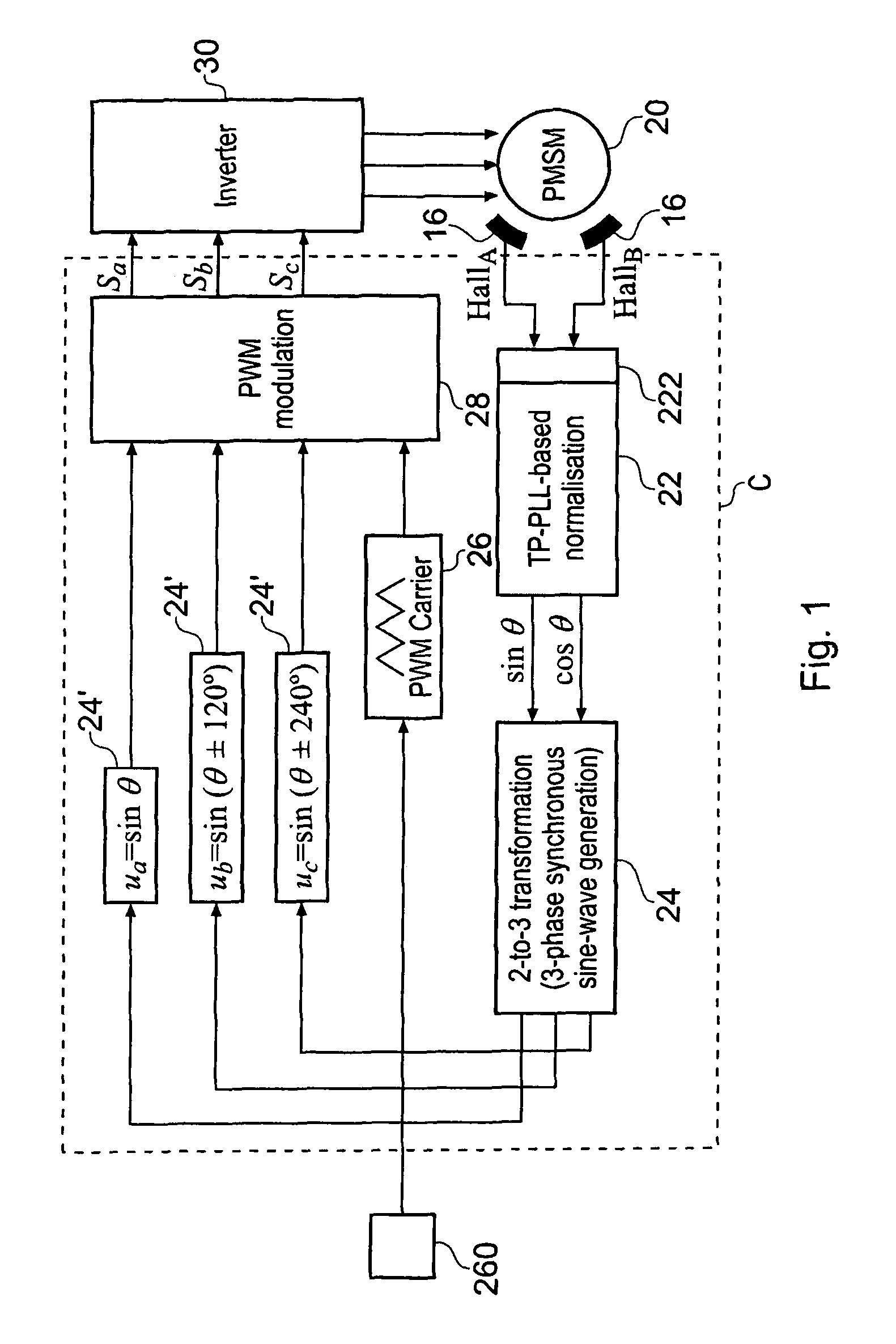
InactiveUS20050248306A1Low costReduce impactTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsLoop control
A low-cost sine-wave drive for a 3-phase permanent magnet synchronous AC machines (PMSM) in open-loop control is based on the measurements of two linear Hall sensors. The two Hall sensors are excited by a magnetic ring with the same pole number as the PMSM rotor magnet and sinusoidal flux distributions. The output signals of the Hall sensors are unified through a two-phase-type phase-lock-loop in order to reduce the impact of the sensor mounting non-uniformity during mass production. The peak torque and speed of motor is simply controlled by adjusting the amplitude of pulse-width-modulation carrier. Smooth torque control is achieved due to sinusoidal 3-phase currents. Such a simple sine-wave drive can be achieved with or without the assistance of a micro-controller unit (MCU). No current sensor is required for the motor phase current detection. This motor can be used in industrial applications where there is no strict requirement on torque response and constant speed control of PMSM machines.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Apparatus for Treating Solutions of High Osmotic Strength
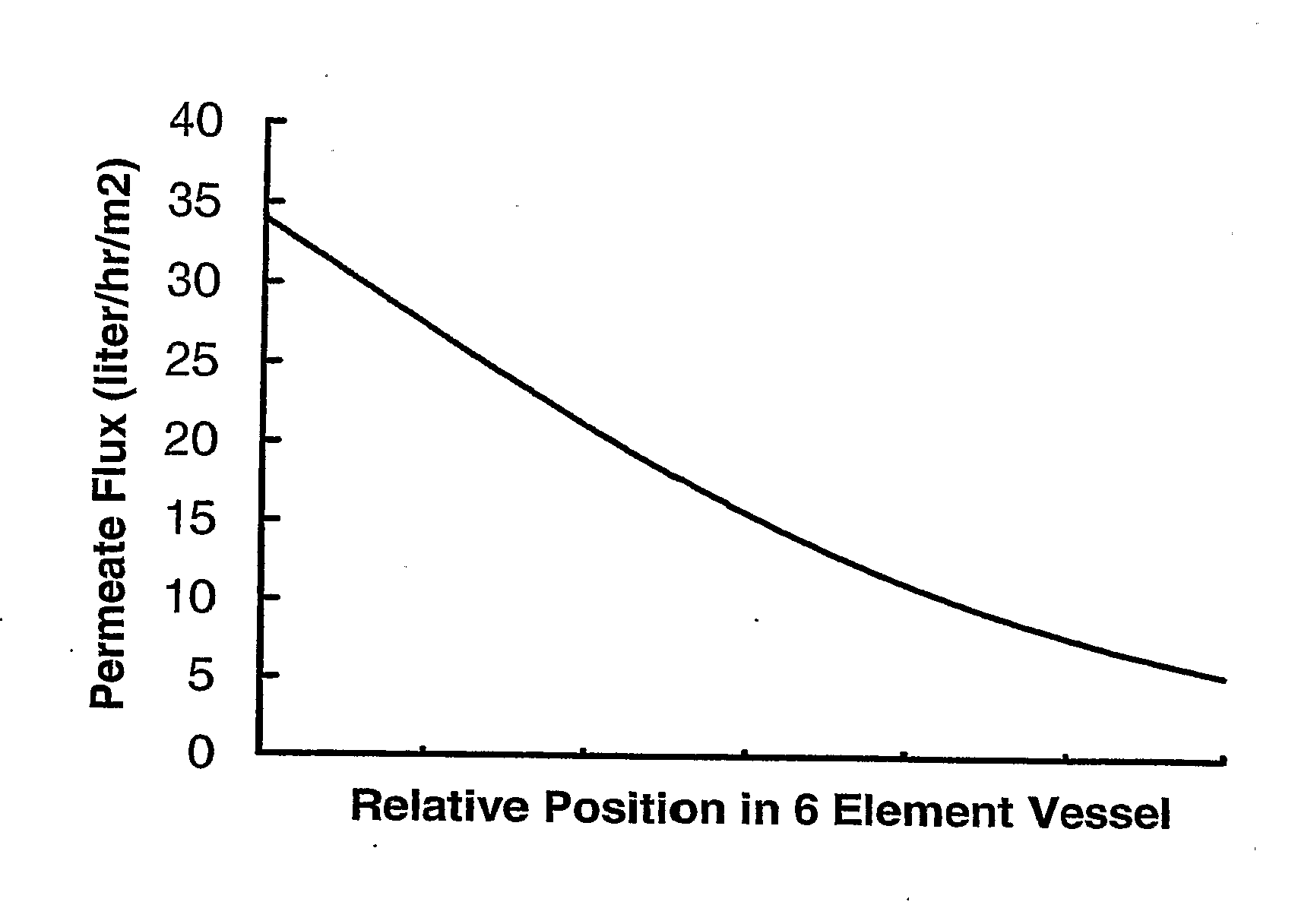
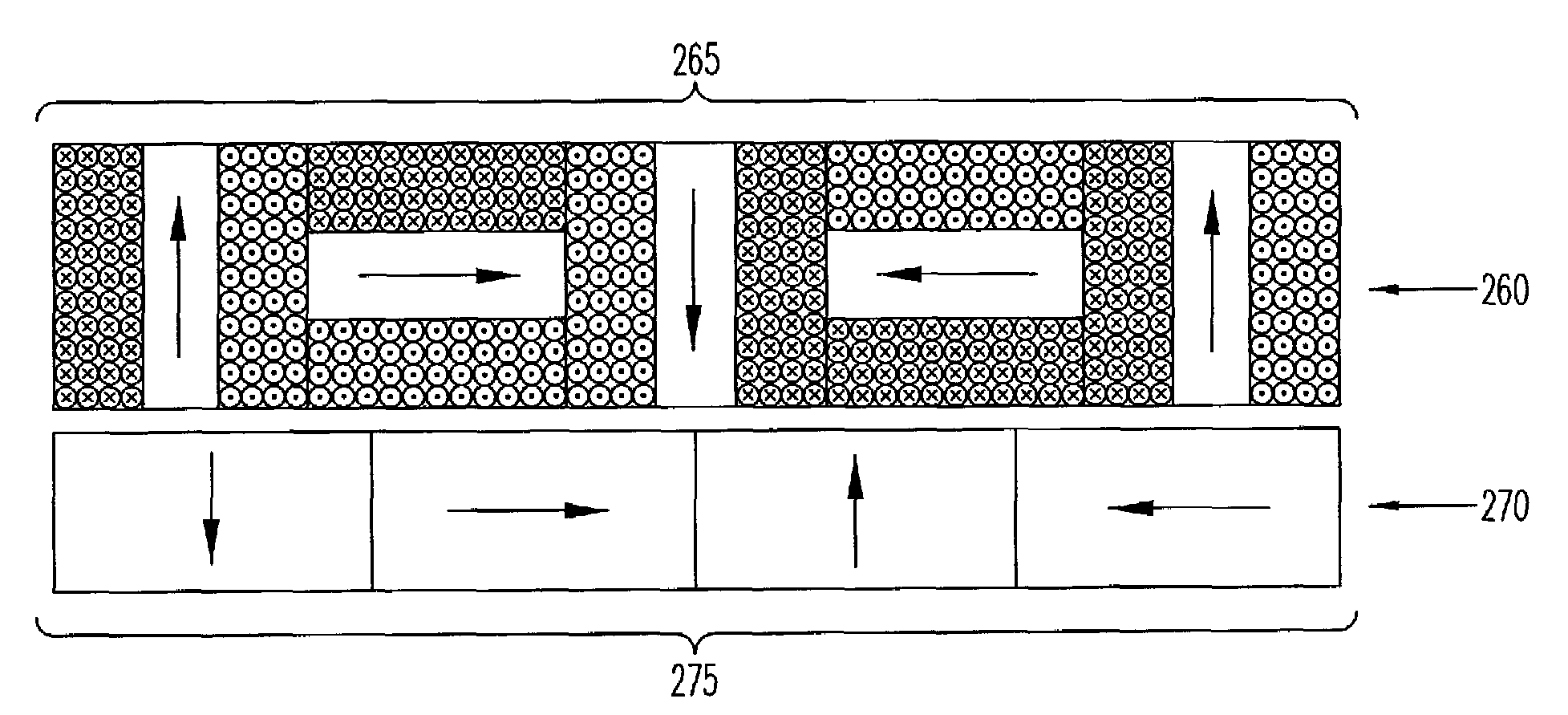
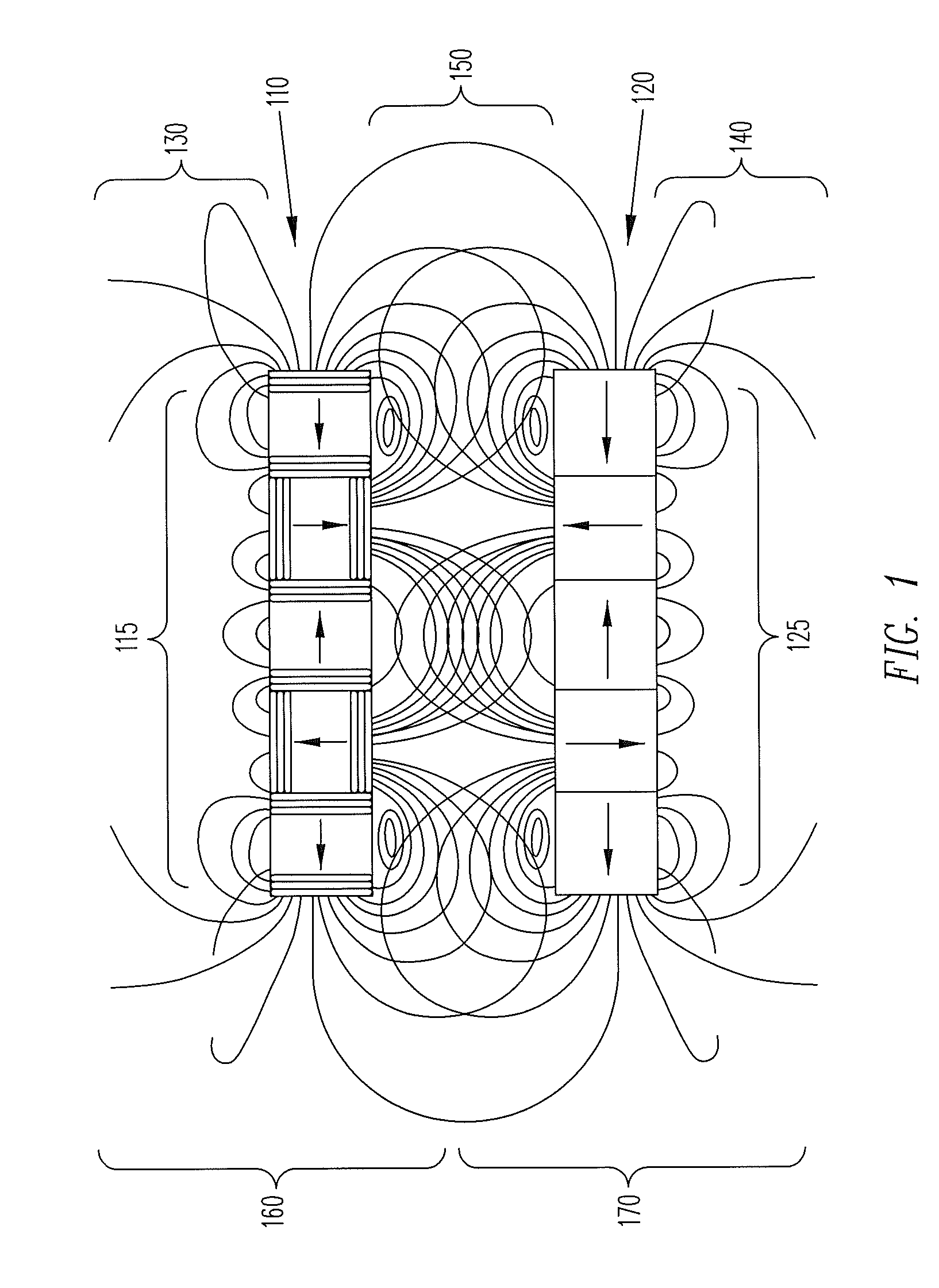
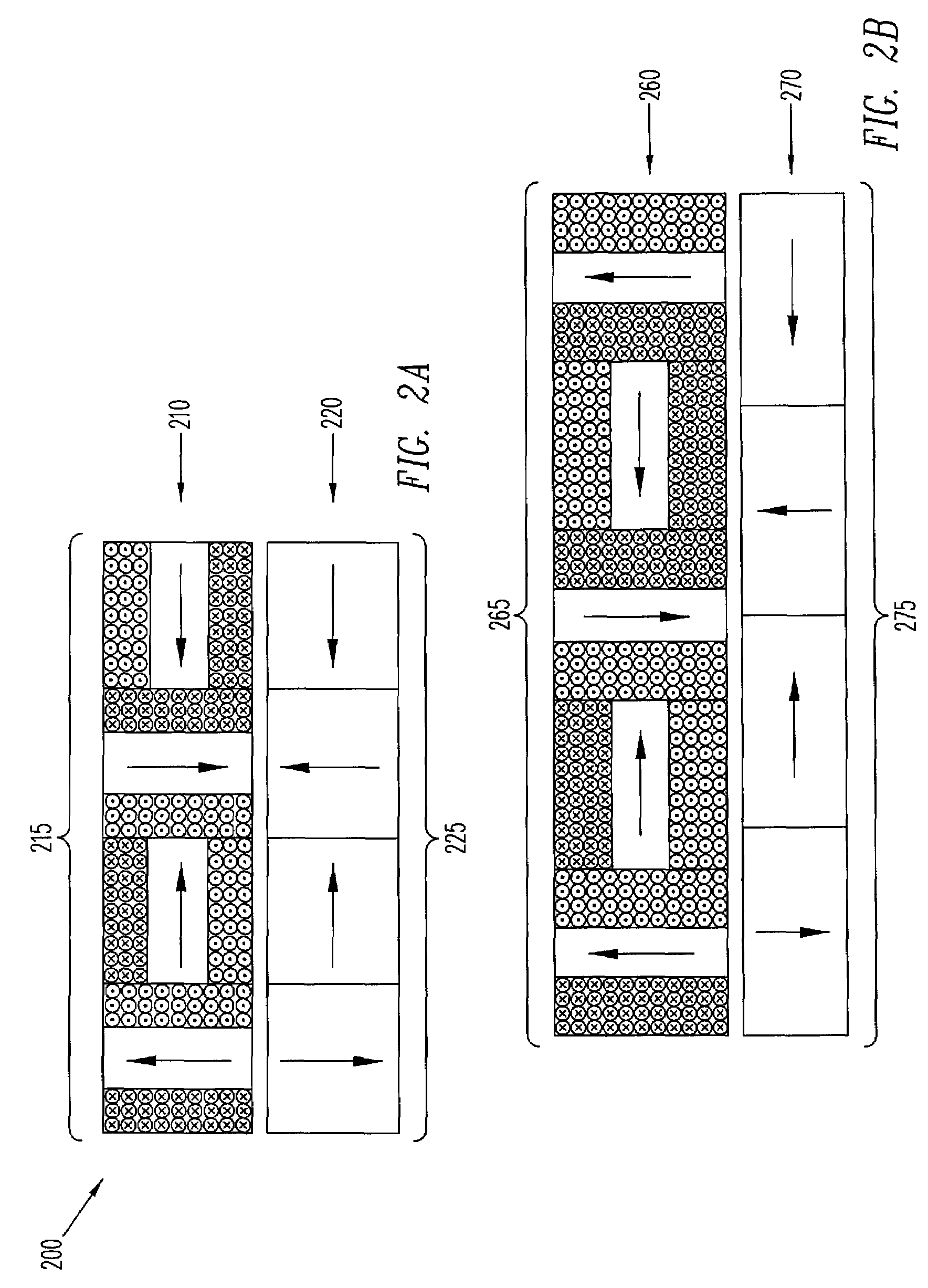
InactiveUS20070272628A1Improves pressure vesselUniform flux distributionGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentFiltrationReverse osmosis
The present invention pertains to an apparatus and method for treating a solution of high osmotic strength, especially seawater and solutions of greater than 20 bar osmotic pressure, by passing the solution through a vessel containing spiral wound reverse osmosis or nanofiltration elements. The vessel contains at least three elements in series and at least two of these elements have standard specific fluxed that differ by at least 50%. The invention allows a more even flux distribution within a filtration system to be obtained, and it may advantageously be combined with variations en element construction and feed spacers.
Owner:MICKOLS WILLIAM EDWARD +4
Electric motor with Halbach arrays
Electric motor configurations are provided with Halbach arrays. In one example, an electric motor includes a first plurality of magnets arranged in a first Halbach array. The first plurality of magnets is configured to provide a first magnetic field that substantially exhibits a first Halbach flux distribution. A first plurality of electromagnets comprising a first plurality of coils are arranged in a second Halbach array. A controller is adapted to selectively direct current through the first plurality of coils to induce a second magnetic field to interact with the first magnetic field. The second magnetic field substantially exhibits a second Halbach flux distribution.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
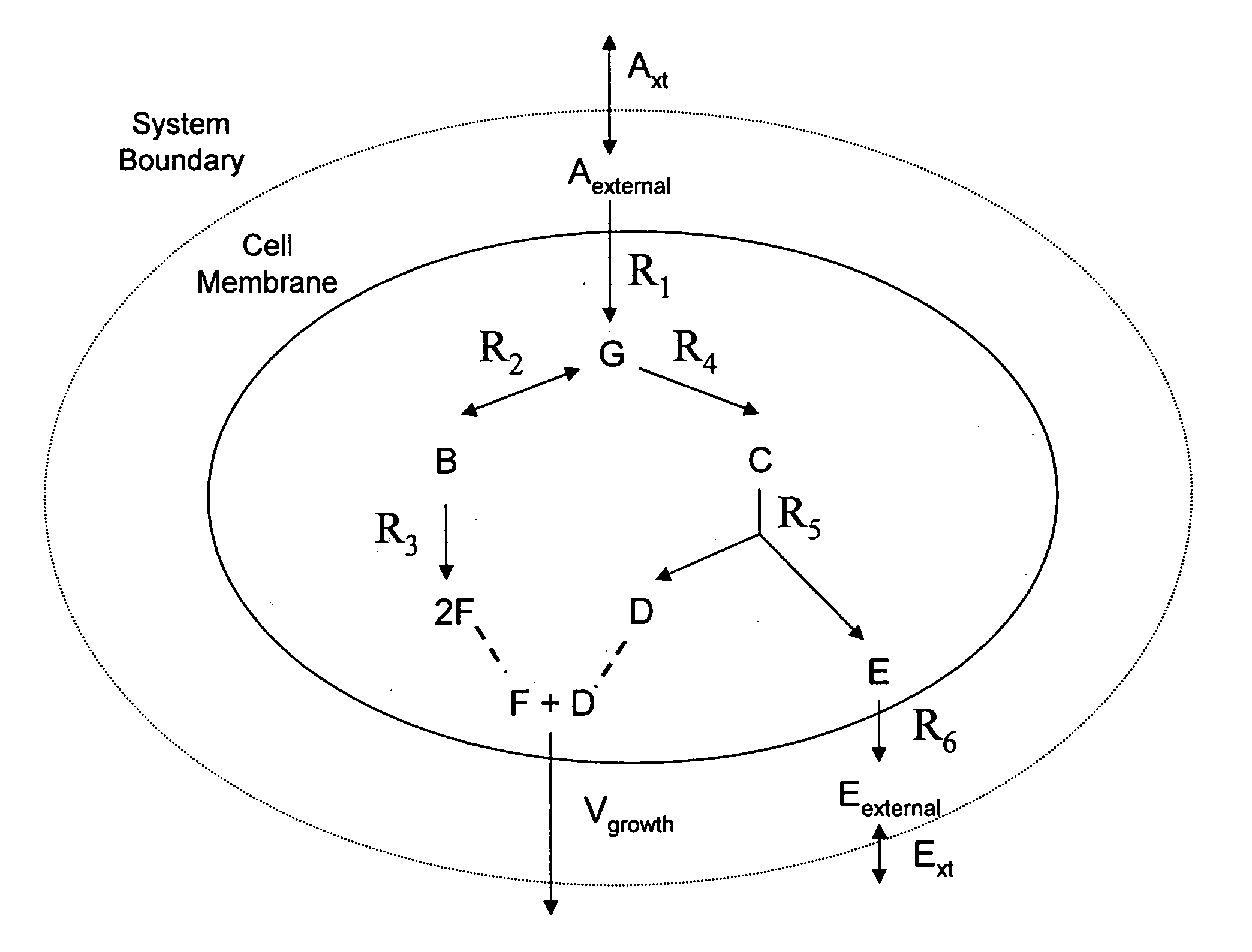
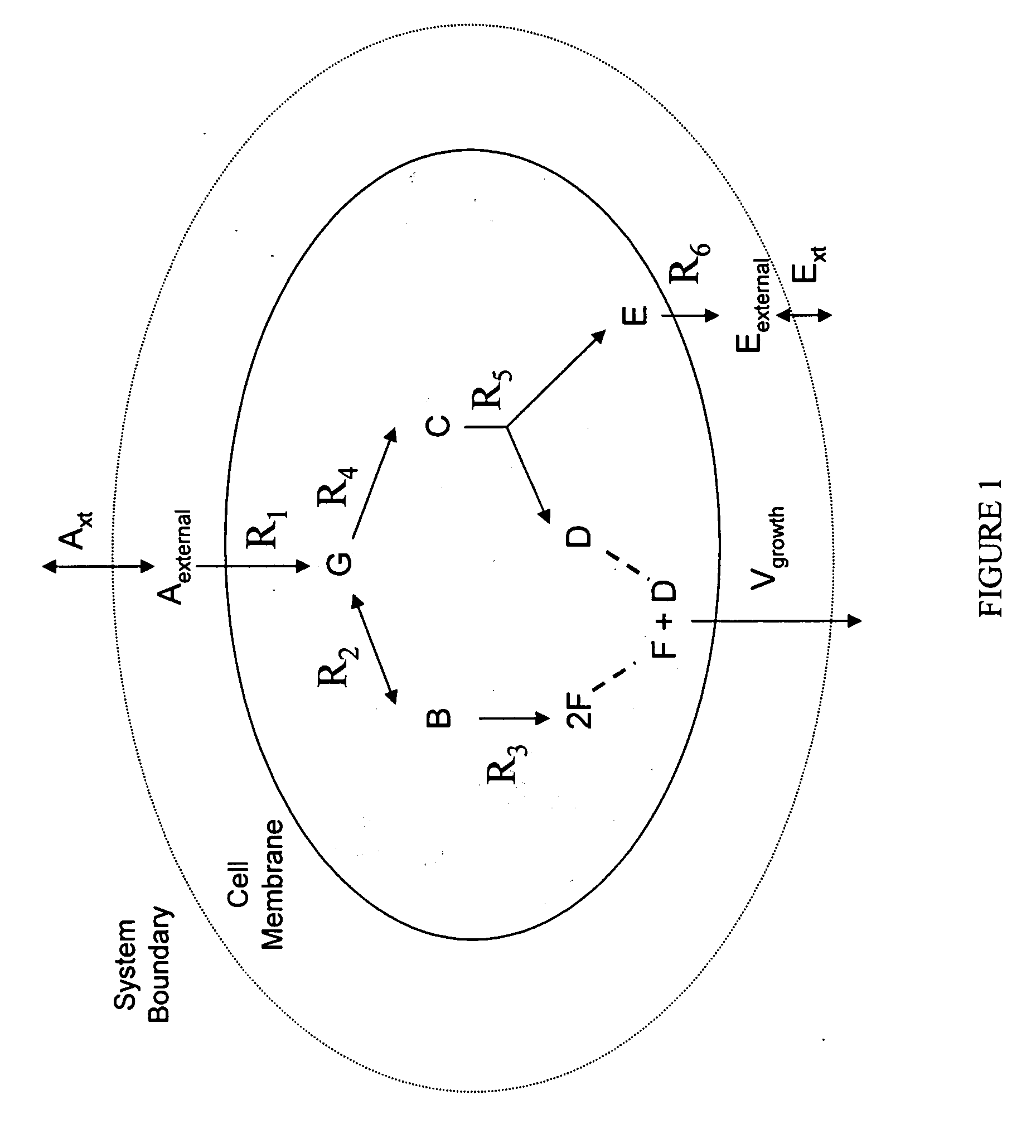
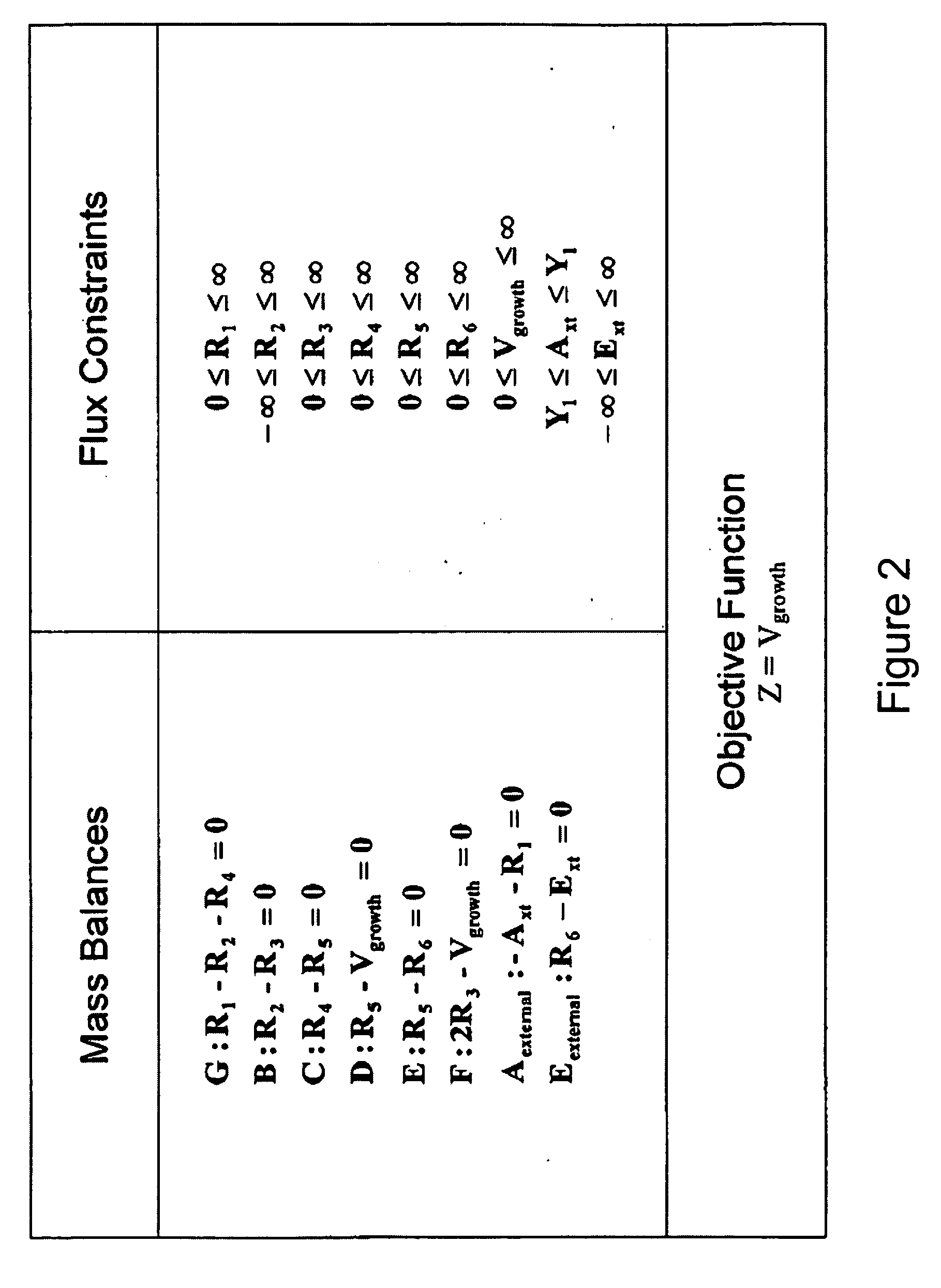
Multicellular metabolic models and methods
ActiveUS20060147899A1Chemical property predictionCompound screeningMulticellular organismMetabolic Model
The invention provides a computer readable medium or media, having: (a) a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures, and (e) commands for determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells. The first, second and third data structures also can include a plurality of data structures. Additionally provided is a method for predicting a physiological function of a multicellular organism. The method includes: (a) providing a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) providing a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) providing a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) providing a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures; (e) providing an objective function, and (f) determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Permanent magnet synchronous motor and controller therefor
InactiveUS7714529B2Reduce impactStable controlTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsLoop control
A low-cost sine-wave drive for a 3-phase permanent magnet synchronous AC machines (PMSM) in open-loop control is based on the measurements of two linear Hall sensors. The two Hall sensors are excited by a magnetic ring with the same pole number as the PMSM rotor magnet and sinusoidal flux distributions. The output signals of the Hall sensors are unified through a two-phase-type phase-lock-loop in order to reduce the impact of the sensor mounting non-uniformity during mass production. The peak torque and speed of motor is simply controlled by adjusting the amplitude of pulse-width-modulation carrier. Smooth torque control is achieved due to sinusoidal 3-phase currents. Such a simple sine-wave drive can be achieved with or without the assistance of a micro-controller unit (MCU). No current sensor is required for the motor phase current detection. This motor can be used in industrial applications where there is no strict requirement on torque response and constant speed control of PMSM machines.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
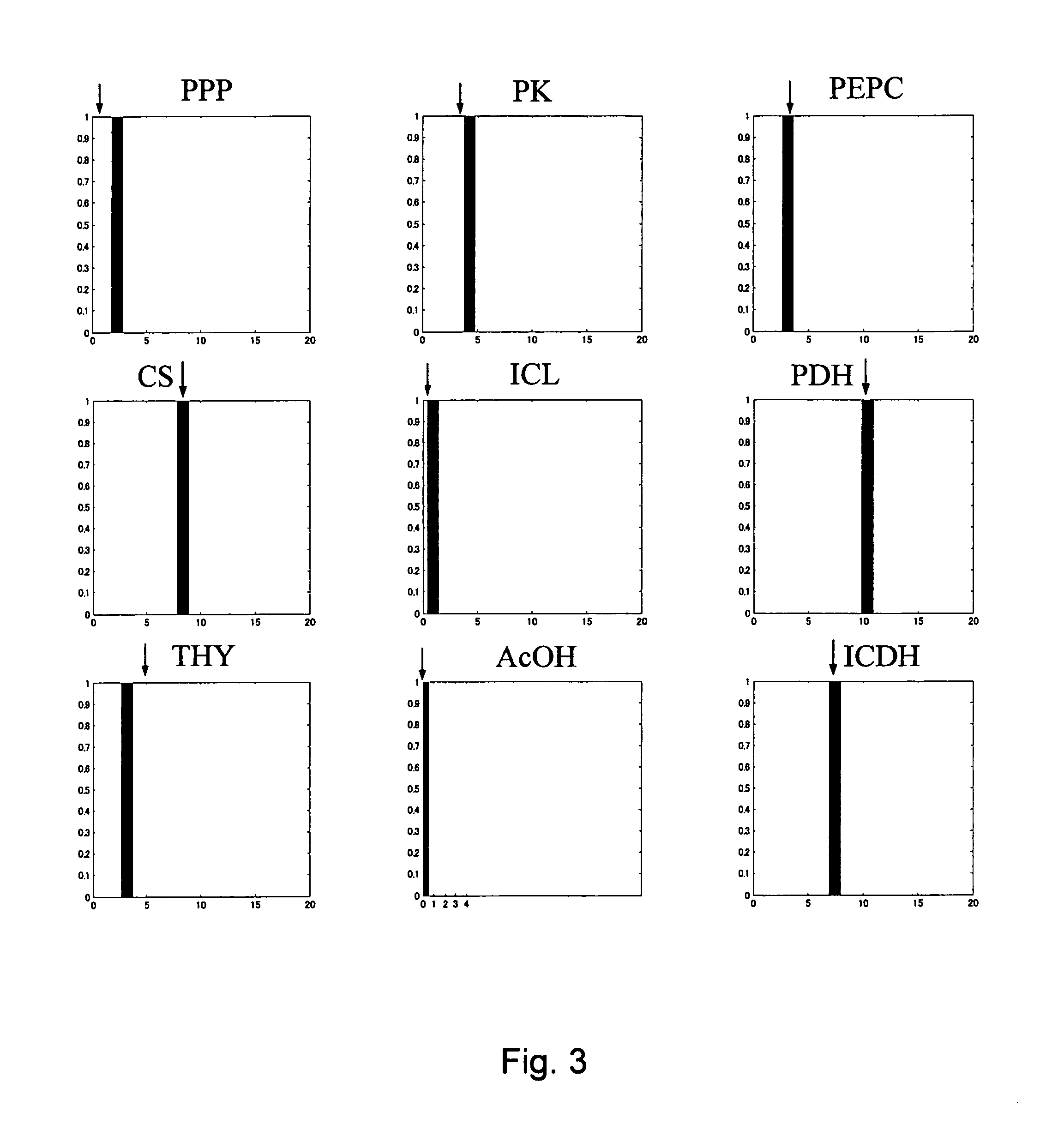
Method for determining metabolic flux
InactiveUS20050221278A1High yieldIncrease productivityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementAlgorithmVector element
A method for determining metabolic flux distribution of a cell, which comprises the steps of: 1) creating a stoichiometric matrix based on formulas of biochemical reactions from a substrate to a product, 2) computing a set of vectors of solutions existing in a solution space which the stoichiometric matrix may have, 3) selecting, from the computed set of vectors of solutions, maximum vectors whose vector elements corresponding to respective substances for which input values can be obtained are maximum, and 4) performing linear combination for the selected vectors in accordance with the following equations to obtain a vector representing metabolic flux distribution: Sflux=∑i=1nai·pi·S(i)+∑i=1nbi·qi·A(i)(I)∑i=1nai+∑i=1nbi=1(II)Sflux: Vector representing metabolic flux distribution to be determined, S(i): Vector selected for substance for which inputted value can be obtained, A(i): Adjustment vector, a, b: Coefficients for linear combination (b may be 0), p: Coefficient for obtaining consistency with input value as numerical value, q: Coefficient of adjustment vector.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
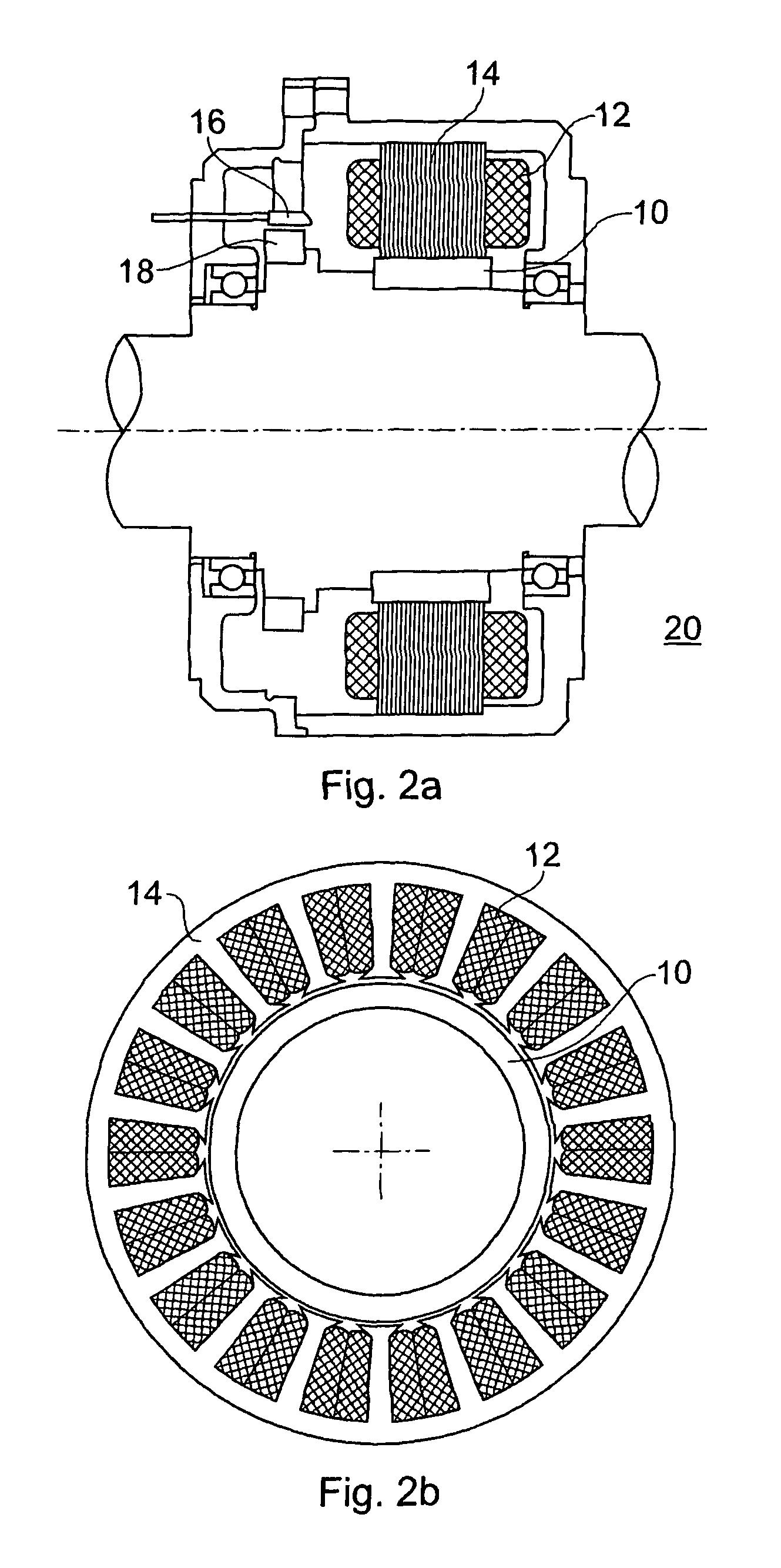
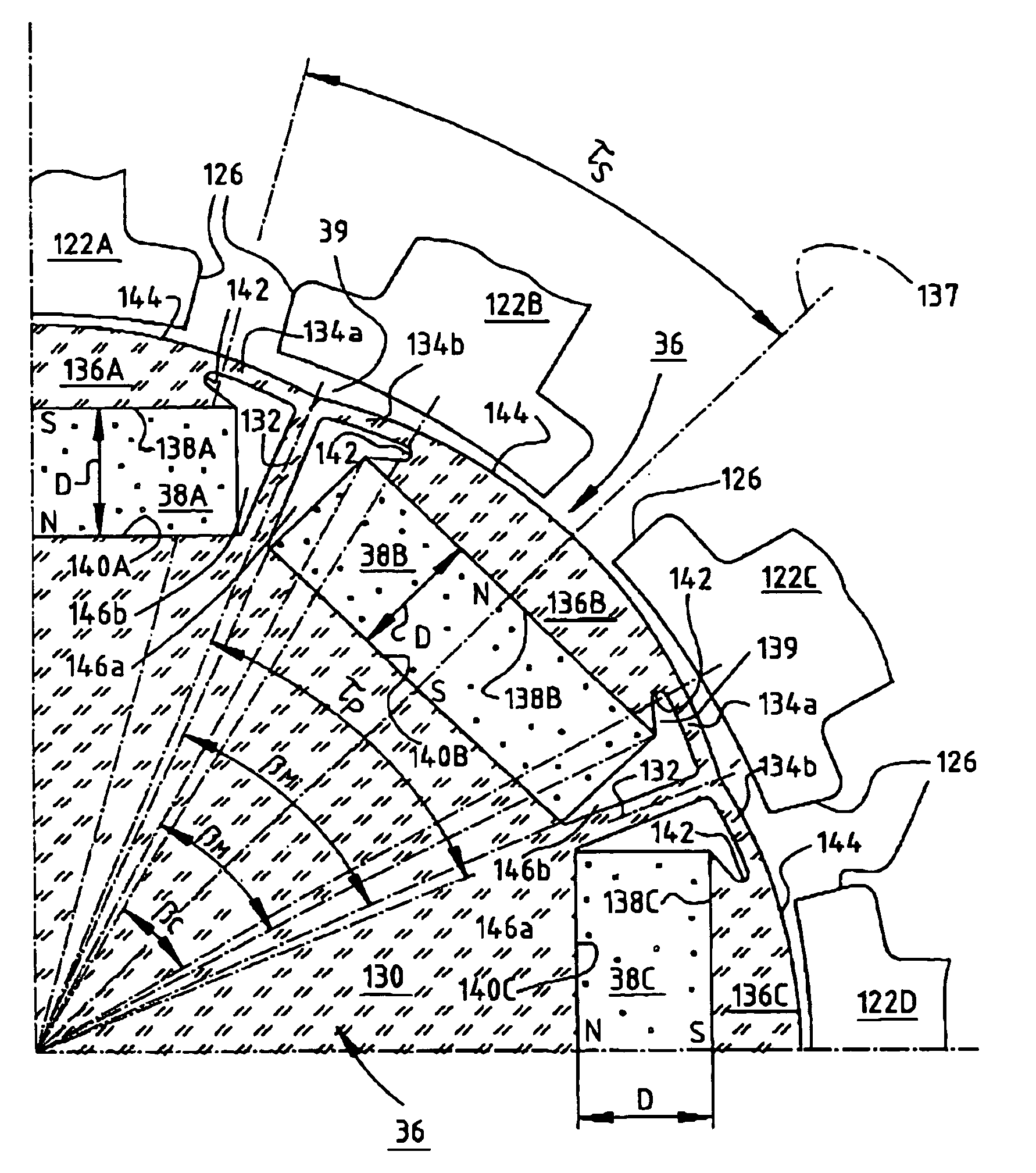
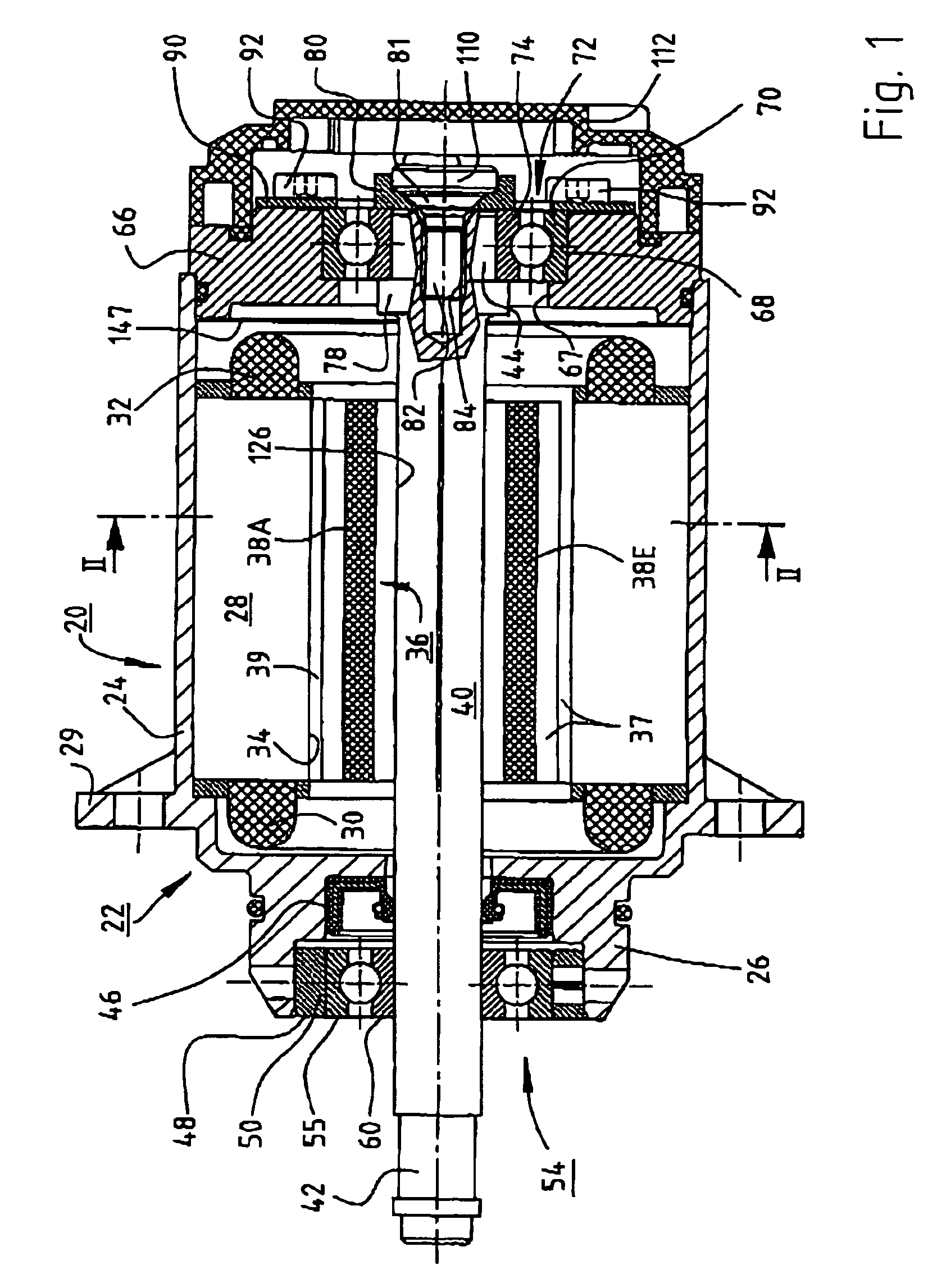
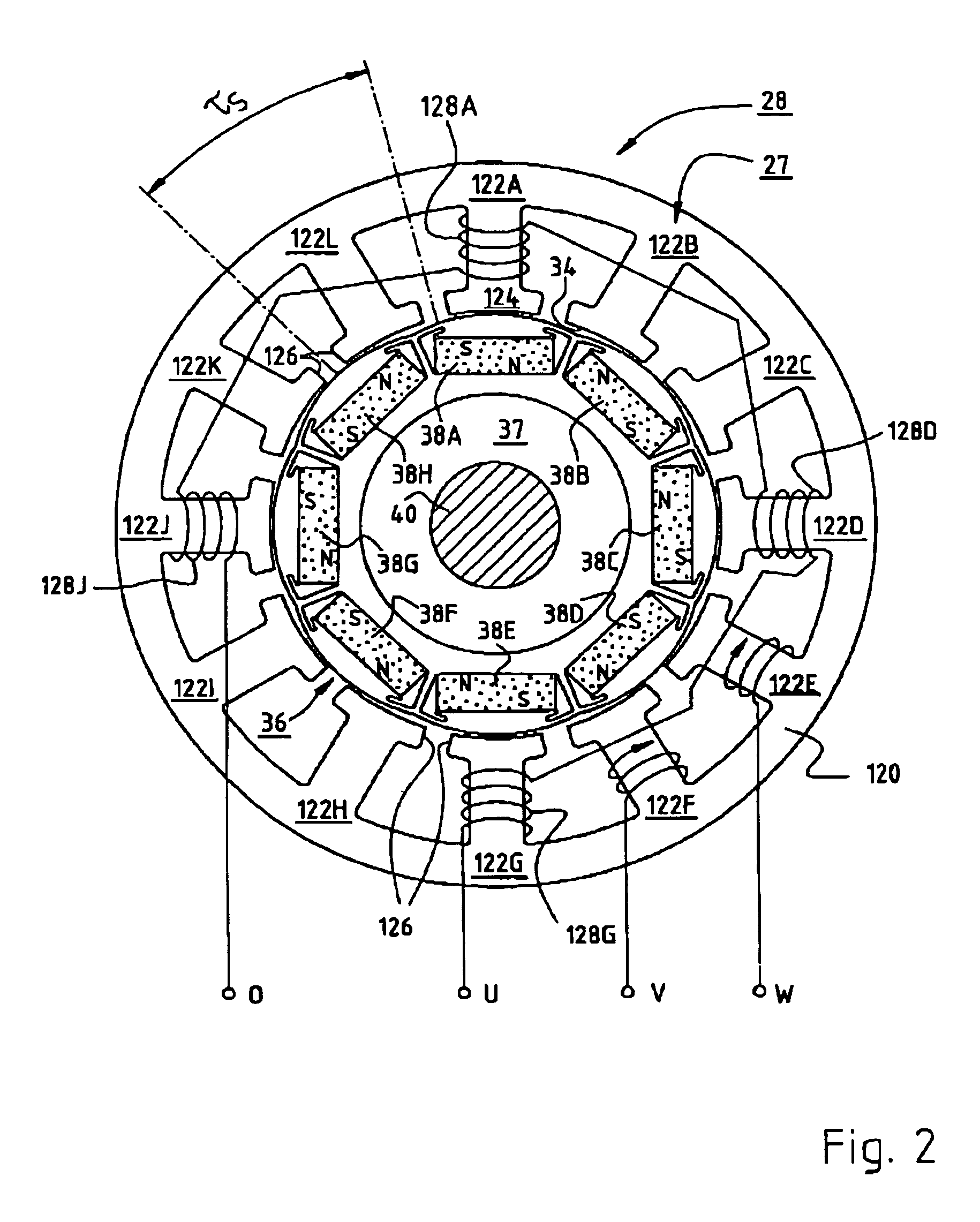
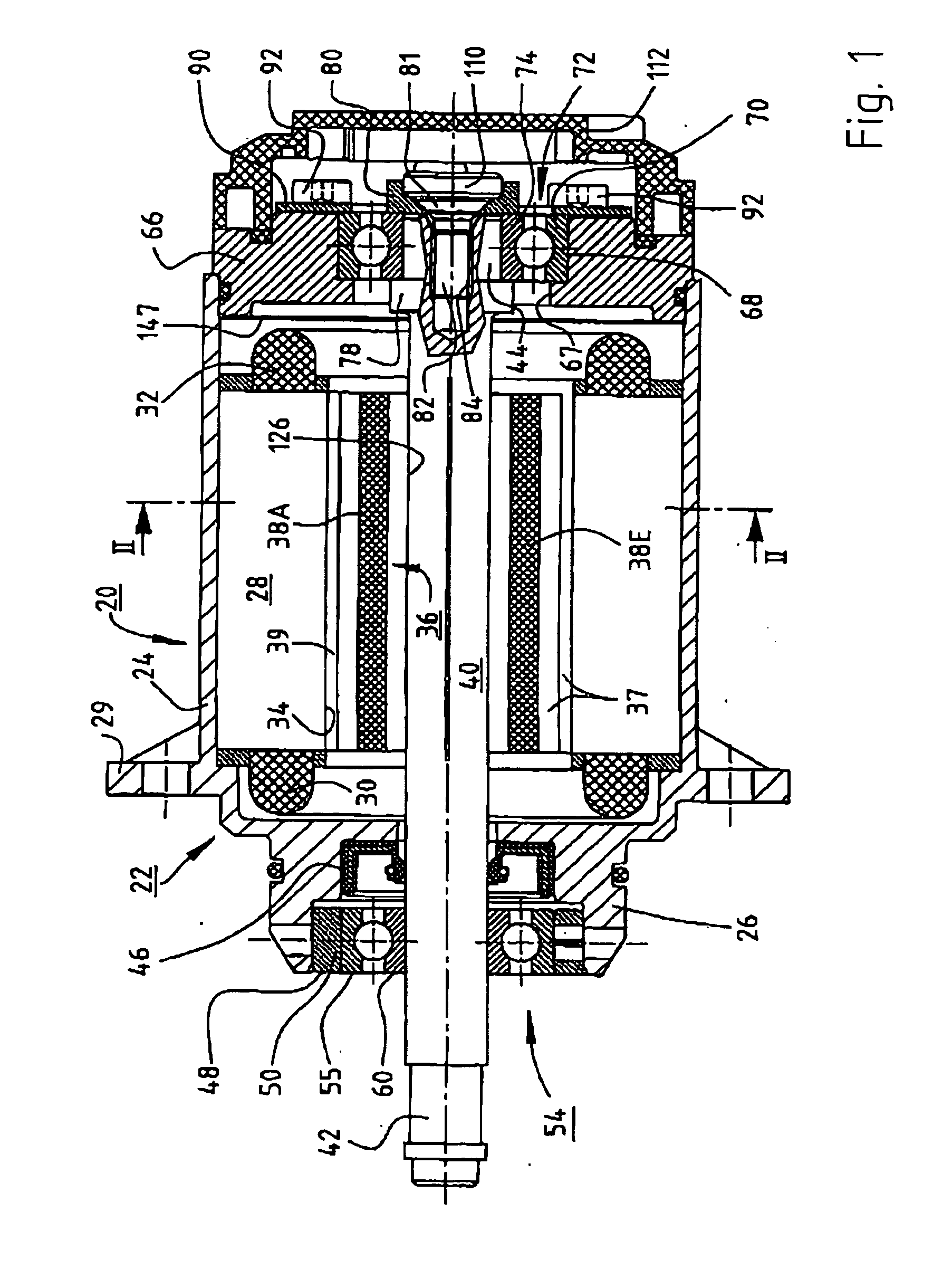
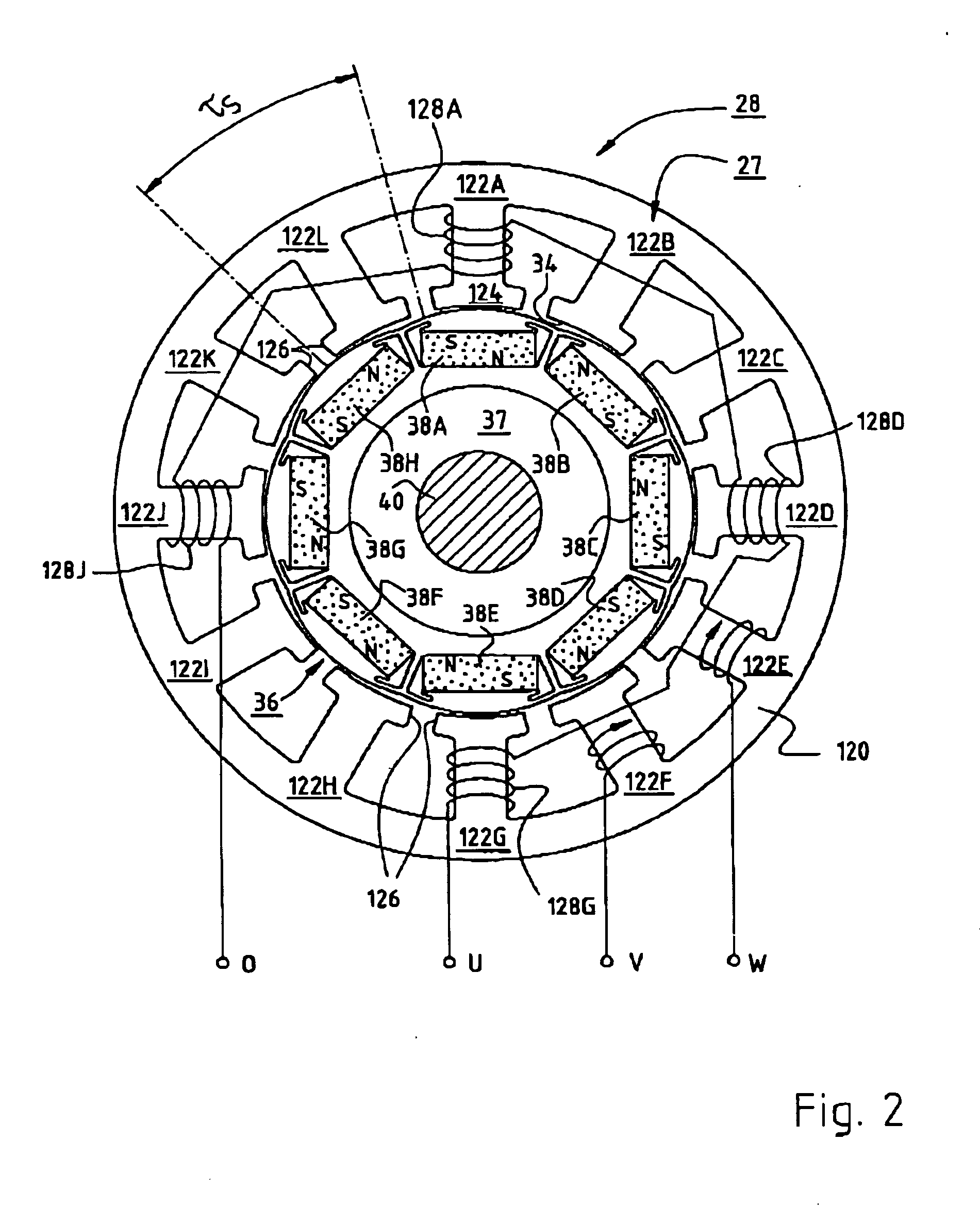
Electric motor with poles shaped to minimize cogging torque
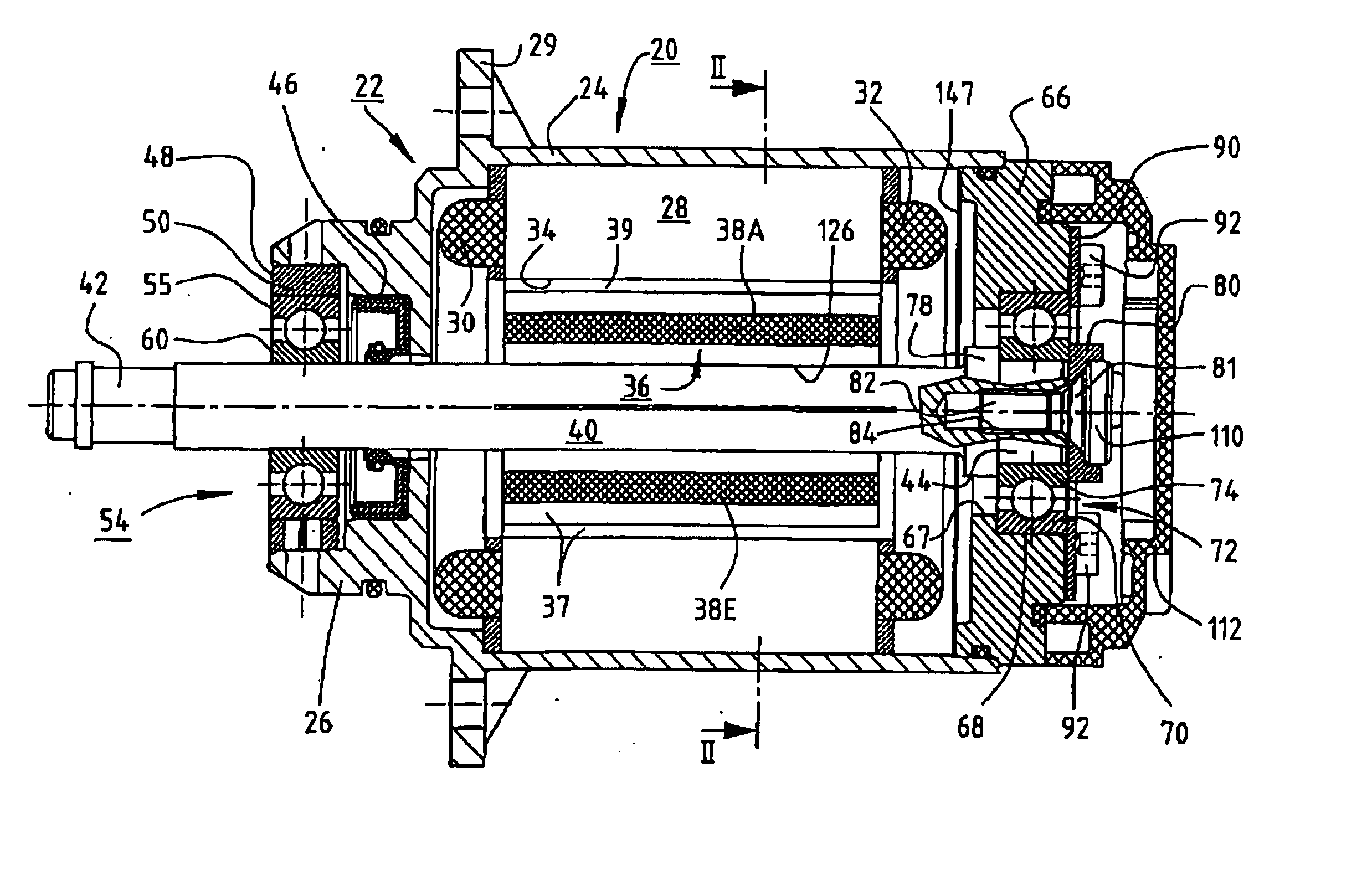
InactiveUS7230359B2Minimized cogging torqueGood sinusoidal formMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesEngineering
An electric motor has a rotor (36) and a stator (28) having a lamination stack formed with slots (126). The slots have a predetermined slot pitch (τs), and a multi-phase stator winding is arranged in them. The rotor (36) has salient poles having pole shoes (136) and a magnetic return path (130). Between the return path (130) and each pole shoe (136), a recess (138, 140) is formed for receiving a permanent magnet (38). On each side of such a permanent magnet (38), a region (146a, 146b) of poor magnetic conductivity is arranged, in order to make the flux distribution in the air gap more sinusoidal. Measuring in a circumferential direction, the width (β) of a pole shoe (136) decreases with increasing distance from an interface (138) between said return path and said permanent magnet (38), and, at a place of lowest width, the pole shoe has an angular extent (βc) which has, with respect to the slot pitch (τs) between said stator slots (126), the following relationship:βc=n*τs*(1−0.02) . . . n*τs*(1−0.2),where n=1, 2, 3 . . . andβc and τs are measured in mechanical degrees.
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Method for on-line monitoring neutron flux distribution of nuclear reactor core
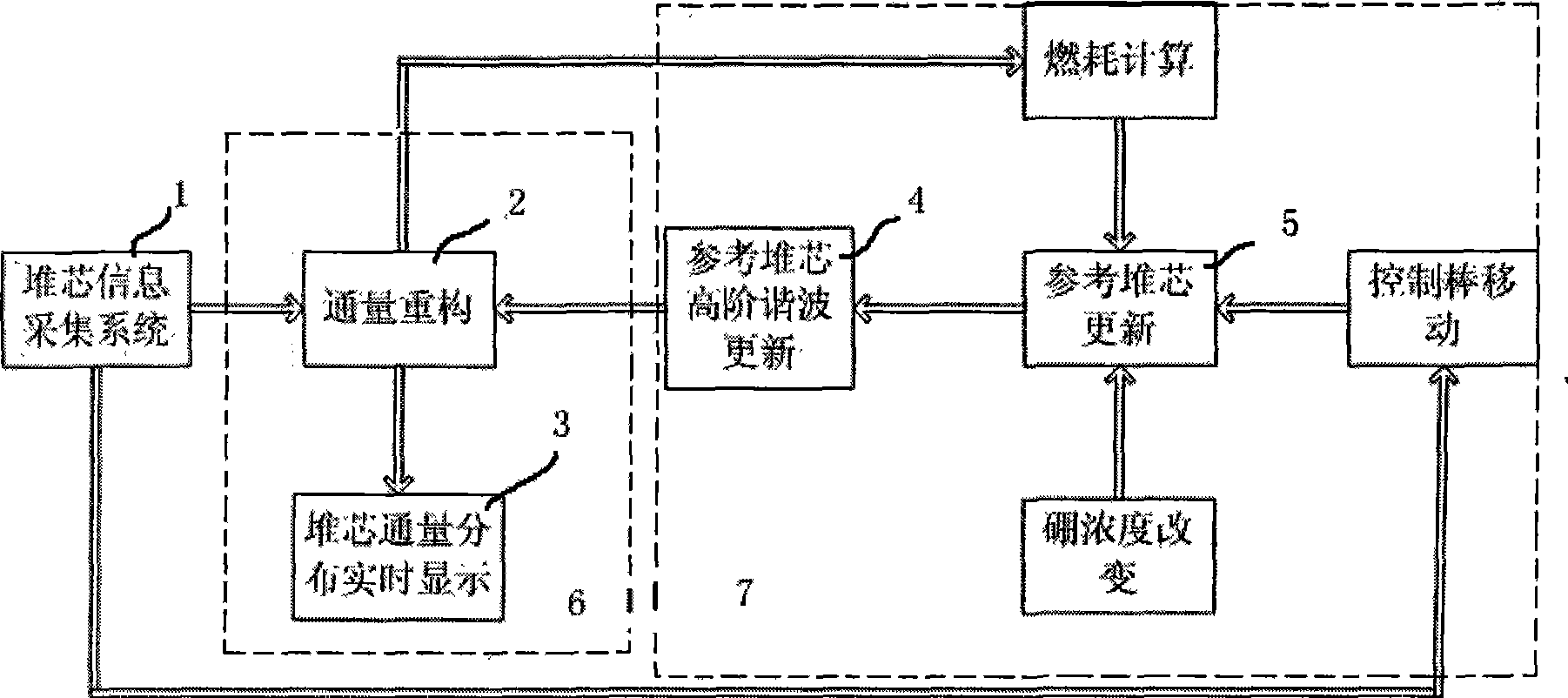
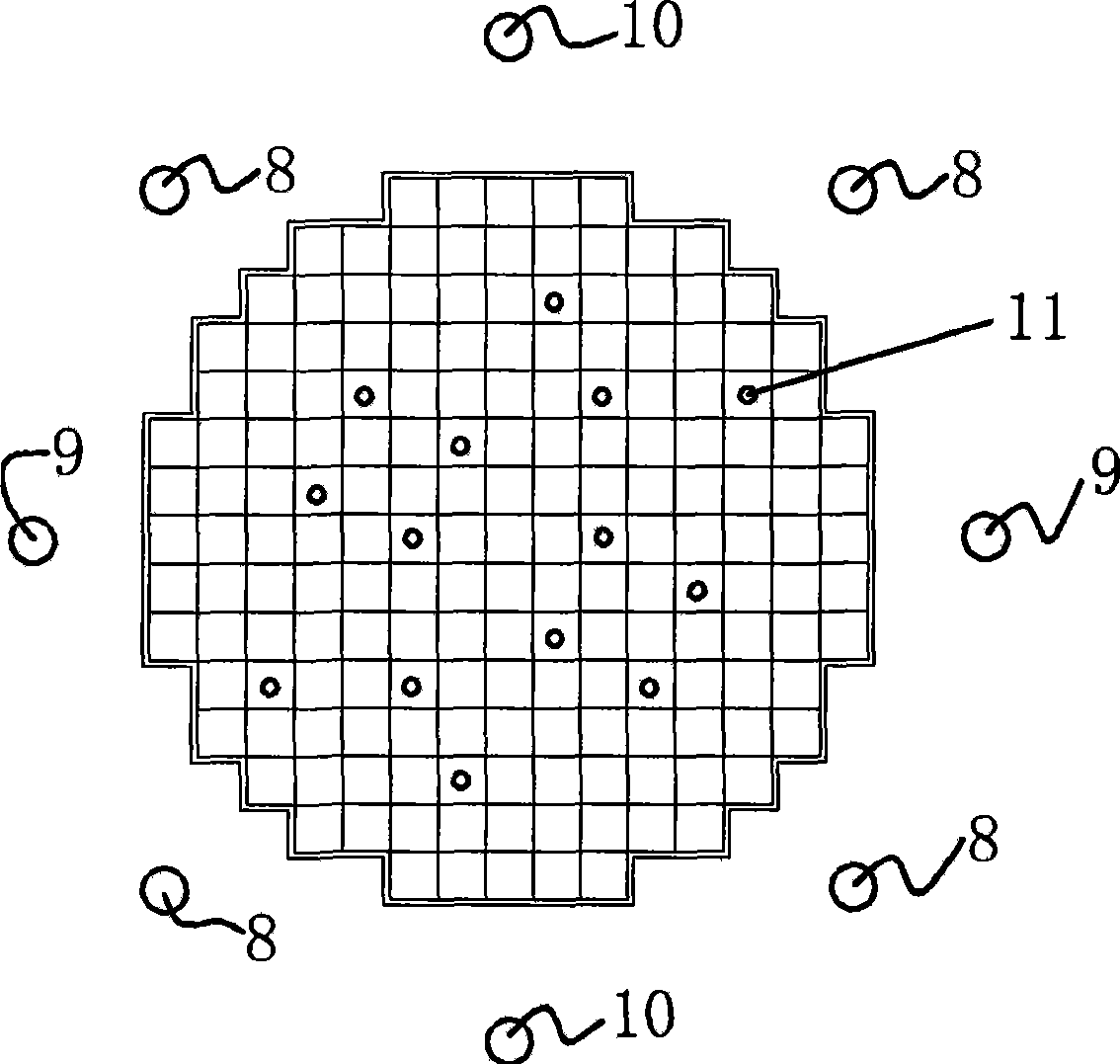
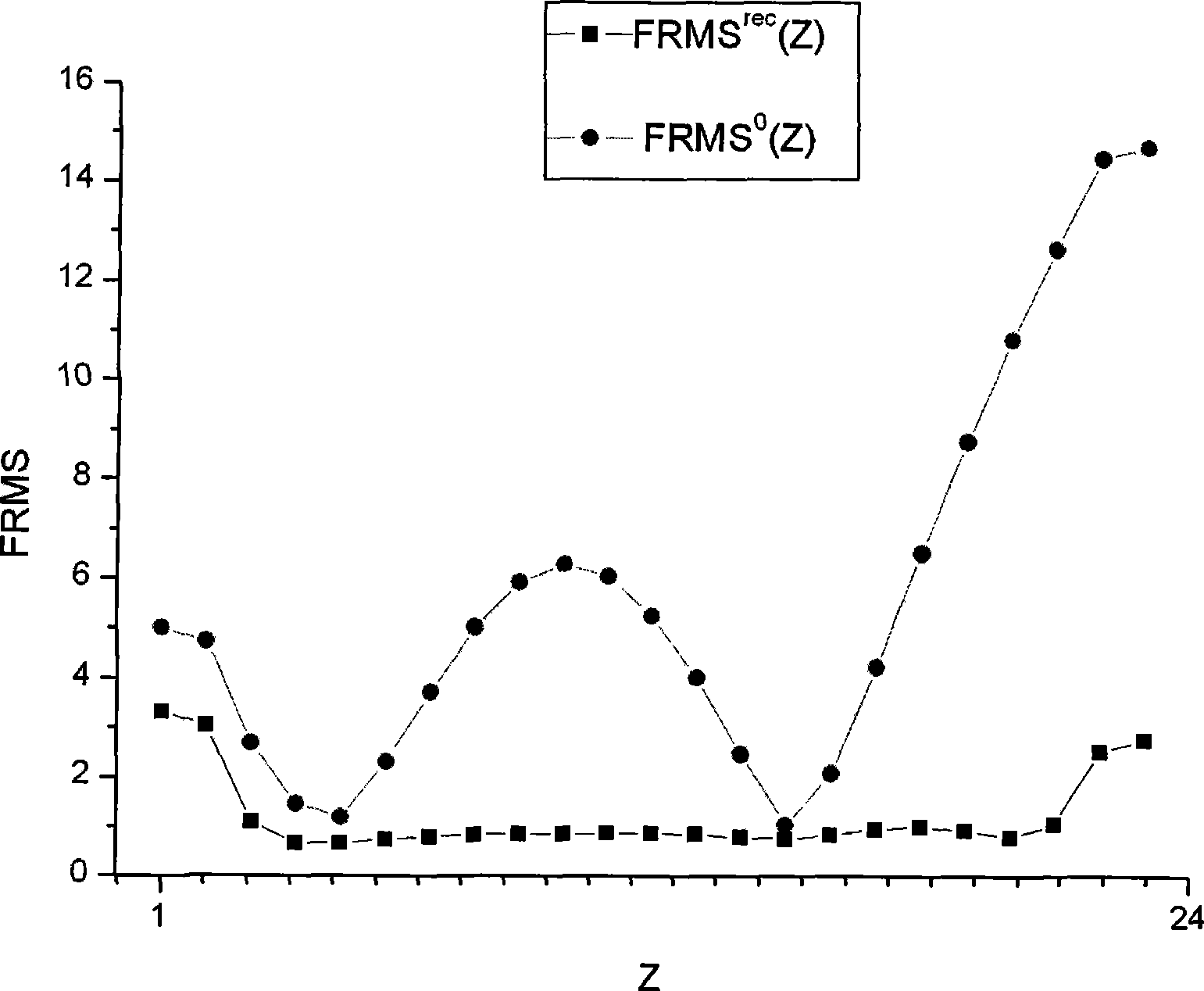
InactiveCN101399091AEasy to implementLow costNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention relates to the nuclear reactor core power monitoring field and discloses a method for online monitoring the neutron flux distribution of the reactor core. The method bases on M1 internal neutron detectors and M2 external neutron detectors which are arranged on the reactor. According to a reference reactor core model of a renewal reactor that MPhi is equal to (1 / k) FPhi, higher order harmonics are solved. Then, reading data of the internal neutron detectors and the external neutron detectors are combined. The neutron flux distribution in the core of a real reactor is reconstructed online.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Electric motor with poles shaped to minimize cogging torque
InactiveUS20050062354A1Minimized cogging torqueGood sinusoidal formMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsEngineeringFlux distribution
An electric motor has a rotor (36) and a stator (28) having a lamination stack formed with slots (126). The slots have a predetermined slot pitch (τS), and a multi-phase stator winding is arranged in them. The rotor (36) has salient poles having pole shoes (136) and a magnetic return path (130). Between the return path (130) and each pole shoe (136), a recess (138, 140) is formed for receiving a permanent magnet (38). On each side of such a permanent magnet (38), a region (146a, 146b) of poor magnetic conductivity is arranged, in order to make the flux distribution in the air gap more sinusoidal. Measuring in a circumferential direction, the width (β) of a pole shoe (136) decreases with increasing distance from an interface (138) between said return path and said permanent magnet (38), and, at a place of lowest width, the pole shoe has an angular extent (βC)which has, with respect to the slot pitch (τS) between said stator slots (126), the following relationship: βC=n*τS*(1−0.02) . . . n*τS*(1−0.2), where n=1, 2, 3 . . . and βC and τS are measured in mechanical degrees.
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
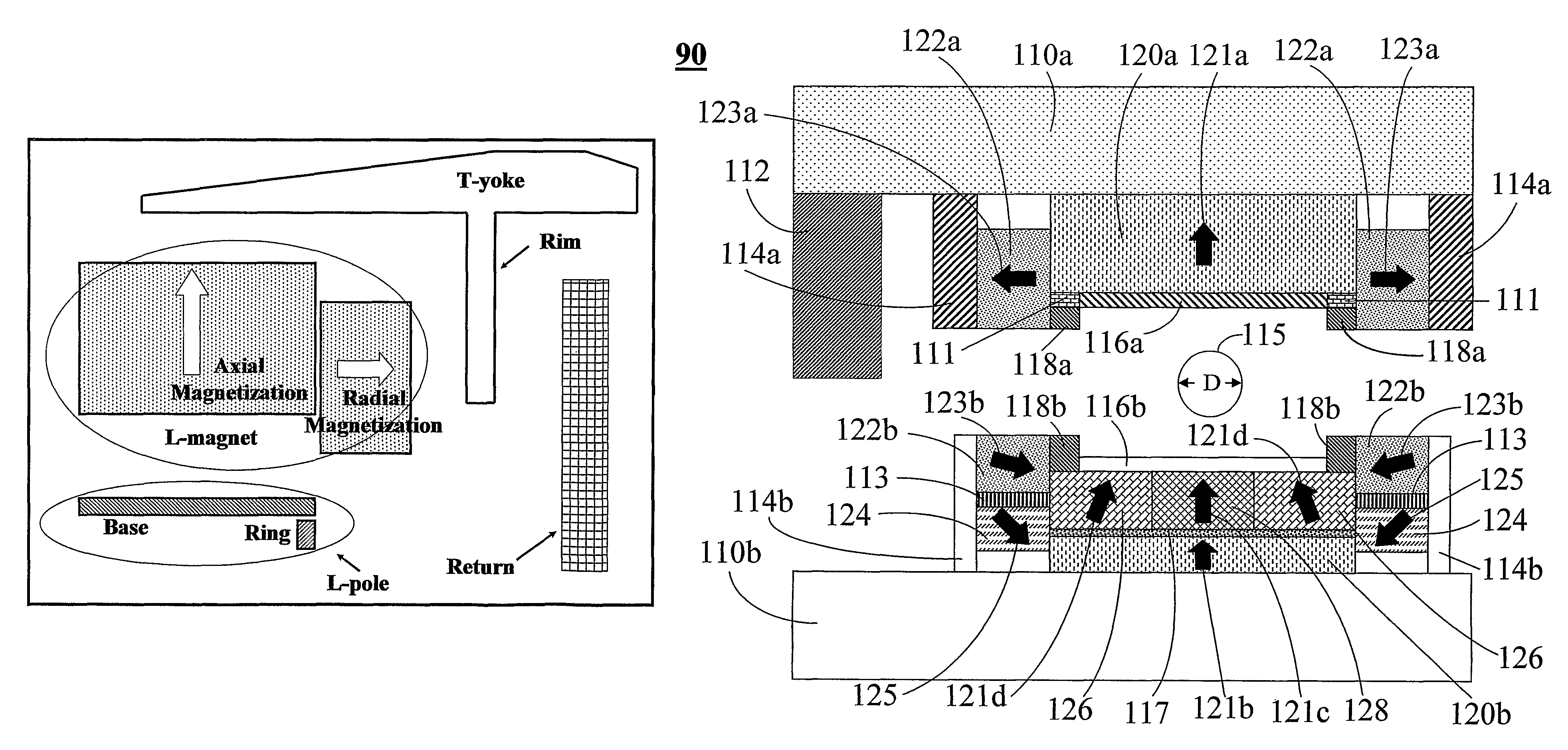
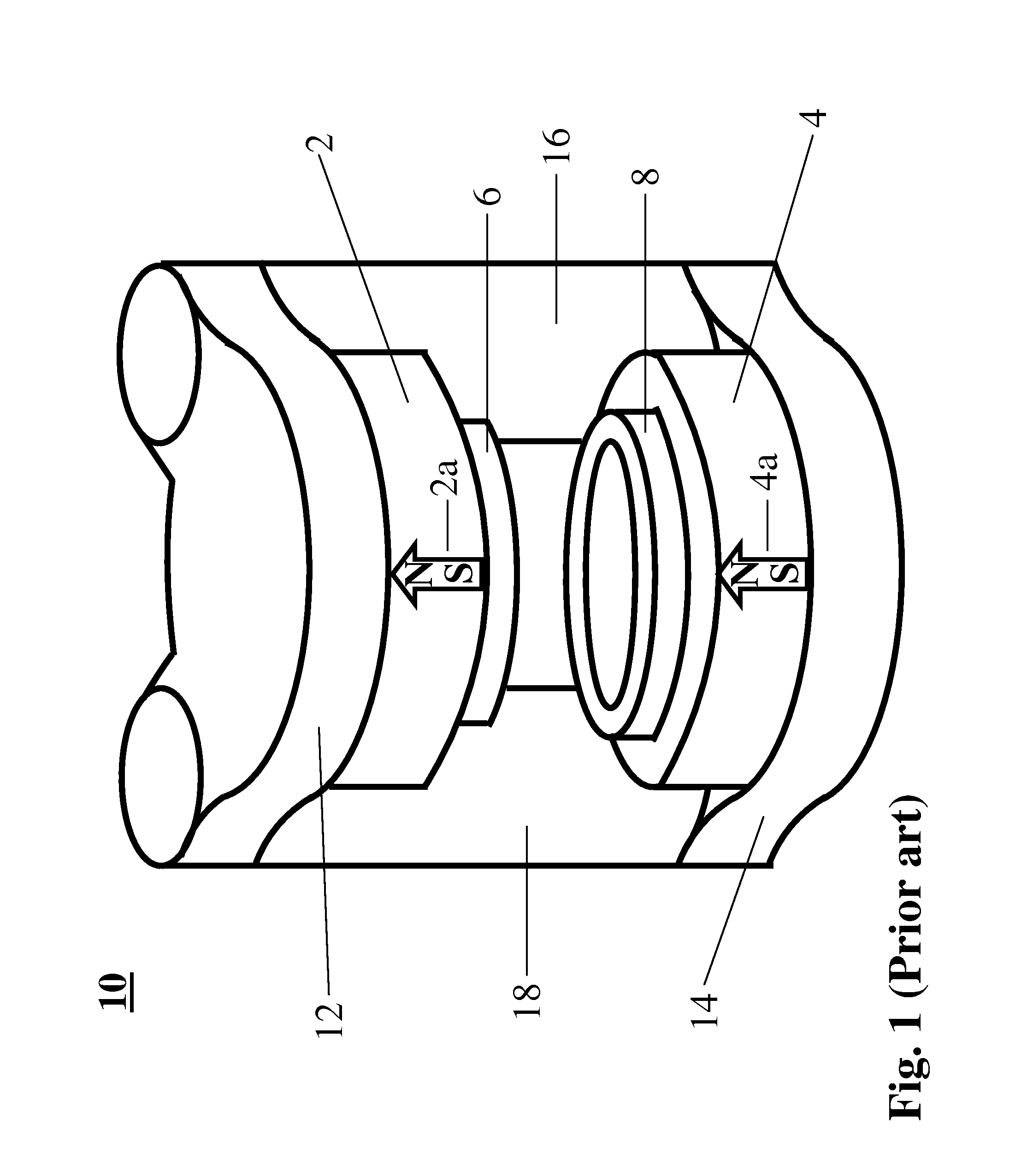
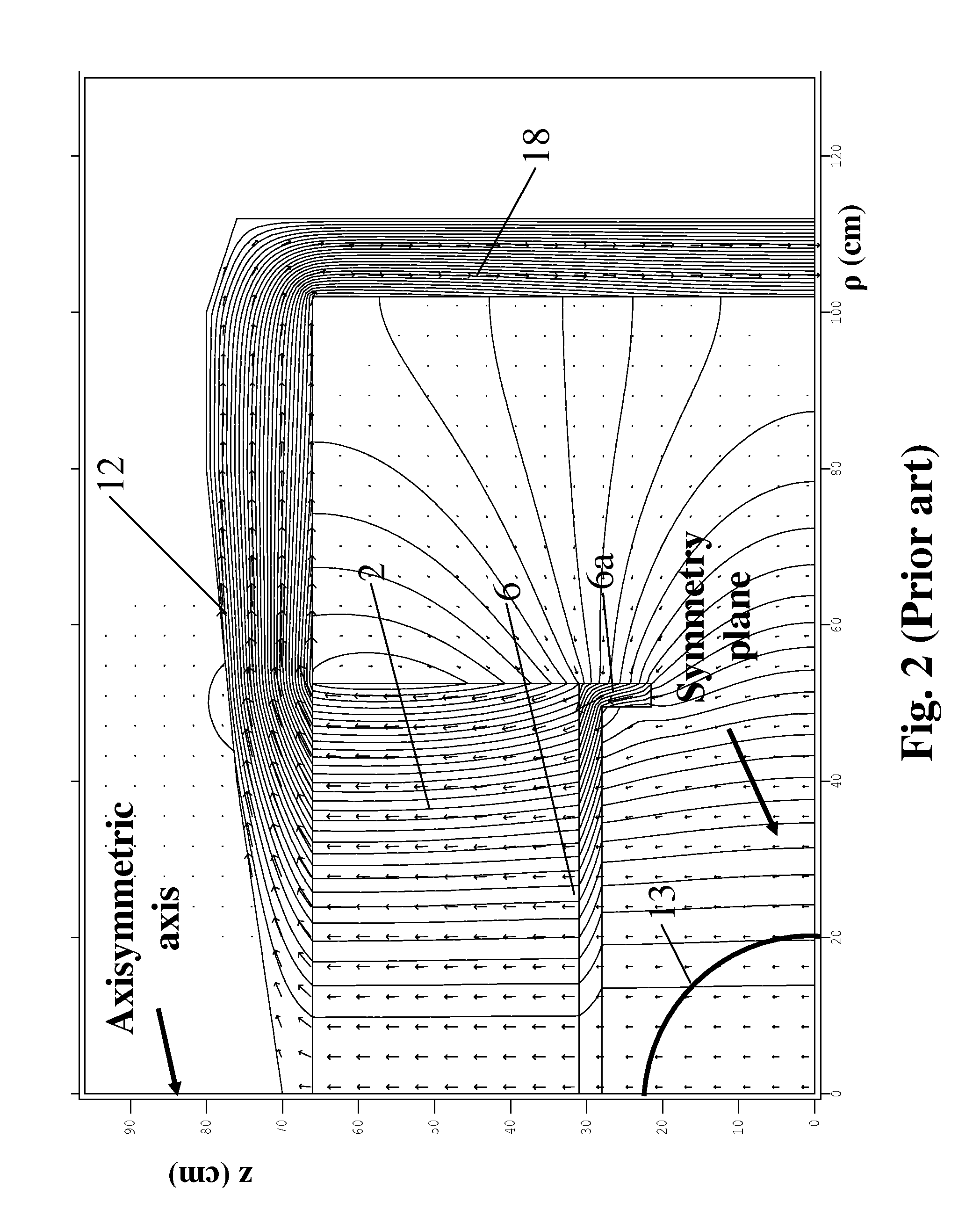
Open MRI Magnetic Field Generator
ActiveUS20090085700A1Reducing fringe field generationEfficient yokeMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsWhole bodyFlux loop
A magnet primarily for use in MRI applications comprises a pair of poles oriented about a plane of symmetry parallel to each therebetween defining an air gap region, magnetic field sources secured on the surfaces of the poles opposite the air gap that have yokes disposed on them, the yokes connected to each other by returns so that the entire magnet assembly can form a closed magnetic flux circuit to substantially confine the magnetic fields generated by the apparatus in the air gap where an imaging region is formed to place subjects for the purposes of examination. The main assembly being cylindrical in geometry has permanent magnets for magnetic field sources that are composed of two regions, a central disk-like portion magnetized substantially along the axial direction and an outer ring-like region magnetized substantially along the radial direction extending axially to form part of the pole together producing a very efficient and even flux distribution throughout the entire magnet assembly with minimal flux leakage. A further means of reducing flux leakage is incorporated in the yokes which have two sections, a disk-like region and an ring-like section to enclose the permanent magnets. The poles are made of multiple sections with a central disk-like region and an outer ring-like region that is a combination of permanent magnets and high permeability materials. This magnet assembly can achieve 1.0 Tesla or greater magnetic fields for whole-body scanning without saturating the magnet pole and other structures.
Owner:LIAN JIANYU +2
Method and system using power modulation for maskless vapor deposition of spatially graded thin film and multilayer coatings with atomic-level precision and accuracy
A method and system for producing a film (preferably a thin film with highly uniform or highly accurate custom graded thickness) on a flat or graded substrate (such as concave or convex optics), by sweeping the substrate across a vapor deposition source operated with time-varying flux distribution. In preferred embodiments, the source is operated with time-varying power applied thereto during each sweep of the substrate to achieve the time-varying flux distribution as a function of time. A user selects a source flux modulation recipe for achieving a predetermined desired thickness profile of the deposited film. The method relies on precise modulation of the deposition flux to which a substrate is exposed to provide a desired coating thickness distribution.
Owner:EUV
Method for establishing measurement data-based simple and convenient irradiation source model of medical linear accelerator
InactiveCN102921115AAvoid dependenceAvoid Heavy Computing TasksSpecial data processing applicationsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorIrradiation
The invention discloses a method for establishing a measurement data-based simple and convenient irradiation source model of a medical linear accelerator. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: supposing that an irradiation source of the medical linear accelerator is on the part of the bottommost end of an MLC (Multi-leaf Collimator); measuring a flux pattern of data inversion from the accelerator through adjustment; and realizing simulation of the irradiation source of the medical linear accelerator by using a method of combining weight of outgoing particles and flux strength by combining the position of the outgaining particles with the flux distribution. Dose distribution in a template is obtained by using geometric description of a particle transport model of classic monte carlo program EGSnrc and a model of DOSXYZnrc. The method is established based on measurement data of the medical linear accelerator, so that the dependence of the conventional full accelerator simulation on the technical detail of the structure of the accelerator and heavy calculation task brought by need of sectional re-simulation in each modification process of the simulation parameter are avoided. The model can be used as an irradiation source model for an accurate monte carlo dosage calculation tool in a human body and can also be used for providing a source model for a dosage verification tool in a treatment planning system and an analytical dosage calculation tool of a treatment scheme optimization algorithm.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for optimizing gas-solid two-phase flow field and ammonia spraying of selective catalytic reduction denitration device
ActiveCN103927420AIn line with the actual situation of the projectGood practice guideDispersed particle separationSpecial data processing applicationsGas solidGrating
The invention provides a method for optimizing a gas-solid two-phase flow field and ammonia spraying of a selective catalytic reduction denitration device. The method includes the steps of obtaining the gas-solid two-phase flow characteristics of smoke and fly ash particles in an SCR denitration device by means of a non-uniform inlet boundary condition and by simulating the gas-solid two-phase flowing process of the SCR denitration device with the help of the Fluent software, processing the numerical calculation result through postprocessing software, analyzing the flow field uniformity problem existing in the SCR denitration device, optimizing the gas-solid two-phase flow field of the SCR denitration device by taking measures of changing the shape and the arrangement method of a diversion plate in a connection flue, changing the shape and the position of a rectification component on a ceiling of a reactor, changing the distances between rectification grating blades and the heights of the rectification grating blades and changing the structure of the SCR reactor, and other measures, calculating the NOx flux distribution of the area according to the smoke speed analysis and the concentration distribution of the ammonia spraying positions in the connection flue, and controlling the ammonia spraying amount matched with the NOx flux distribution in the area according to the optical ammonia nitrogen ratio.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Uninterruptible power supply
ActiveUS20130015704A1Suppress surge currentEffectively impactSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc source parallel operationOperation modeThree-phase
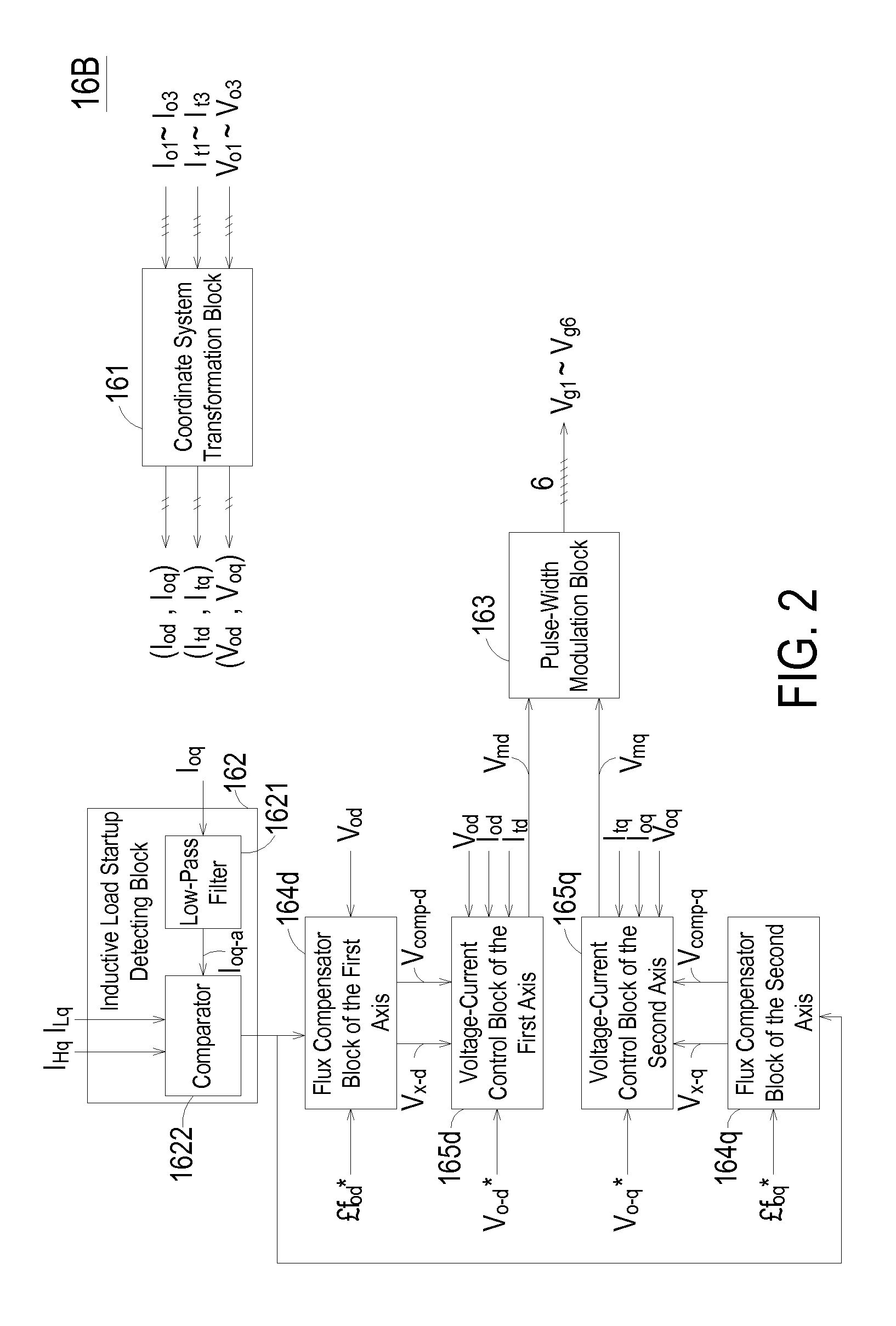
Disclosed is an uninterruptible power supply, including a rectifier for generating a DC voltage; an energy storage unit; an inverter for converting the DC voltage into a three-phase modulating voltage; a filter; a bypass switch circuit for selectively outputting a three-phase AC voltage or the three-phase modulating voltage as a three-phase load voltage; and a control circuit for controlling the operation of the uninterruptible power supply. The control circuit may use a flux compensation block with different operating modes to adjust the three-phase load voltage at the startup phase of a second inductive load and at the stable phase of the second inductive load, thereby compensating or correcting the flux of the second inductive load to prevent the flux distribution of the second inductive load from being saturated.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC +1
Open MRI magnetic field generator
ActiveUS8077002B2Reduce leakageImprove efficiencyMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsWhole bodyFlux distribution
A magnet primarily for use in MRI applications comprises a pair of poles oriented about a plane of symmetry parallel to each therebetween defining an air gap region, magnetic field sources secured on the surfaces of the poles opposite the air gap that have yokes disposed on them, the yokes connected to each other by returns so that the entire magnet assembly can form a closed magnetic flux circuit to substantially confine the magnetic fields generated by the apparatus in the air gap where an imaging region is formed to place subjects for the purposes of examination. The main assembly being cylindrical in geometry has permanent magnets for magnetic field sources that are composed of two regions, a central disk-like portion magnetized substantially along the axial direction and an outer ring-like region magnetized substantially along the radial direction extending axially to form part of the pole together producing a very efficient and even flux distribution throughout the entire magnet assembly with minimal flux leakage. A further means of reducing flux leakage is incorporated in the yokes which have two sections, a disk-like region and an ring-like section to enclose the permanent magnets. The poles are made of multiple sections with a central disk-like region and an outer ring-like region that is a combination of permanent magnets and high permeability materials. This magnet assembly can achieve 1.0 Tesla or greater magnetic fields for whole-body scanning without saturating the magnet pole and other structures.
Owner:LIAN JIANYU +2
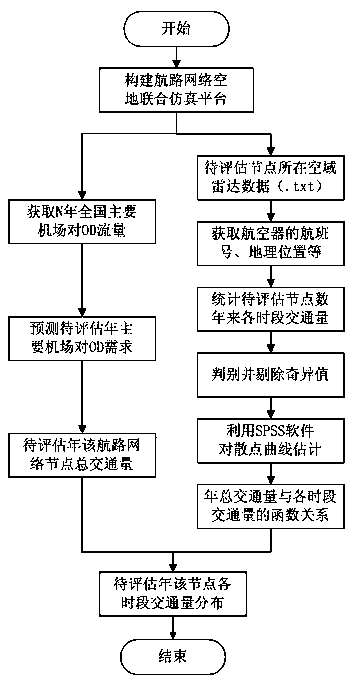
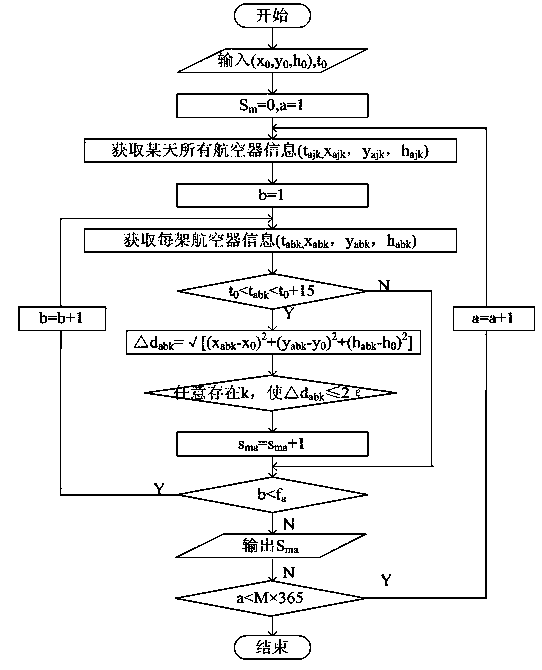
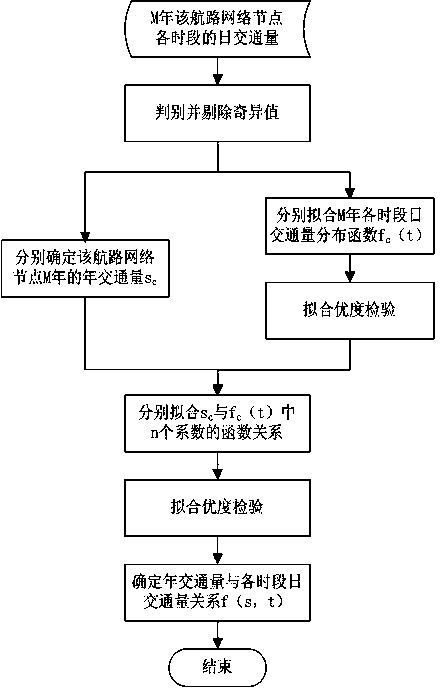
Calculating method of space-time flow of air route network nodes
The invention discloses a calculating method of space-time flow of air route network nodes. The method comprises the steps that firstly, M-year radar data of airspace where the air route network nodes to be assessed are located are obtained, and specific information of an aircraft is analyzed; secondly, the traffic volume of time frames of the air route network nodes to be assessed in M years is determined, singular values are removed, and a function relation between the annual traffic volume and the number of flights passing in each time frame of the air route network nodes to be assessed is determined in a fitting mode; thirdly, OD flow in many years of main airports in the whole country is obtained, OD requirements of the main airports, needing to be forecast, in the whole country in the year are forecast, and annular traffic volume of the air route network nodes to be assessed is calculated in the year needing forecast ; finally, traffic volume distribution of each time frame of the air route network nodes to be assessed in the year needing forecast is calculated. The calculating method provides data support for forecast of flow of each time frame, flight conflict can be handled in advance, a traffic jam is reduced, the air route network using rate is increased, and the work amount of a controller is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
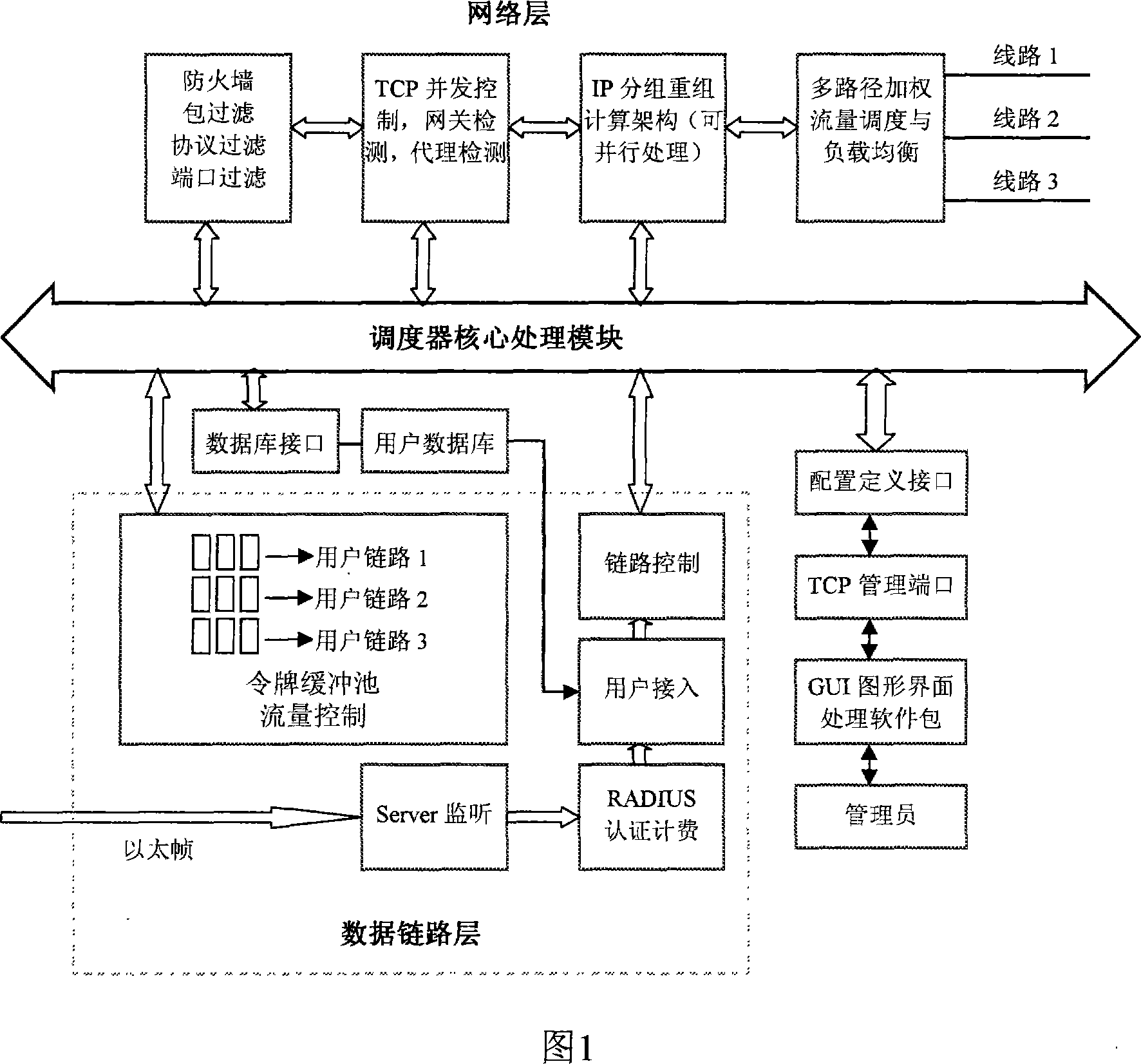
Wideband network access and flow management scheduling system
InactiveCN101098305AUniform flowEfficient conversionData switching by path configurationNetwork address translationNetwork address
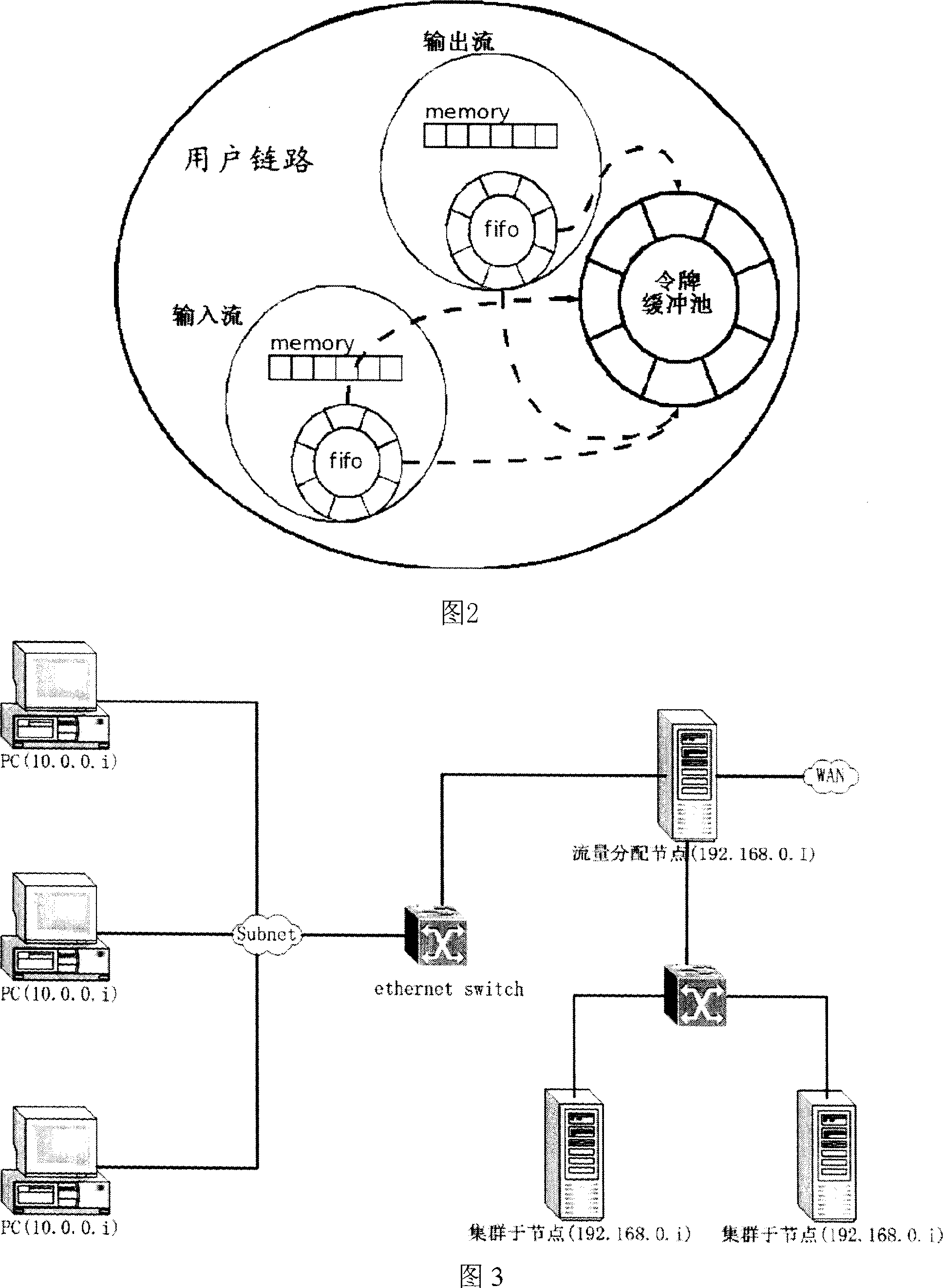
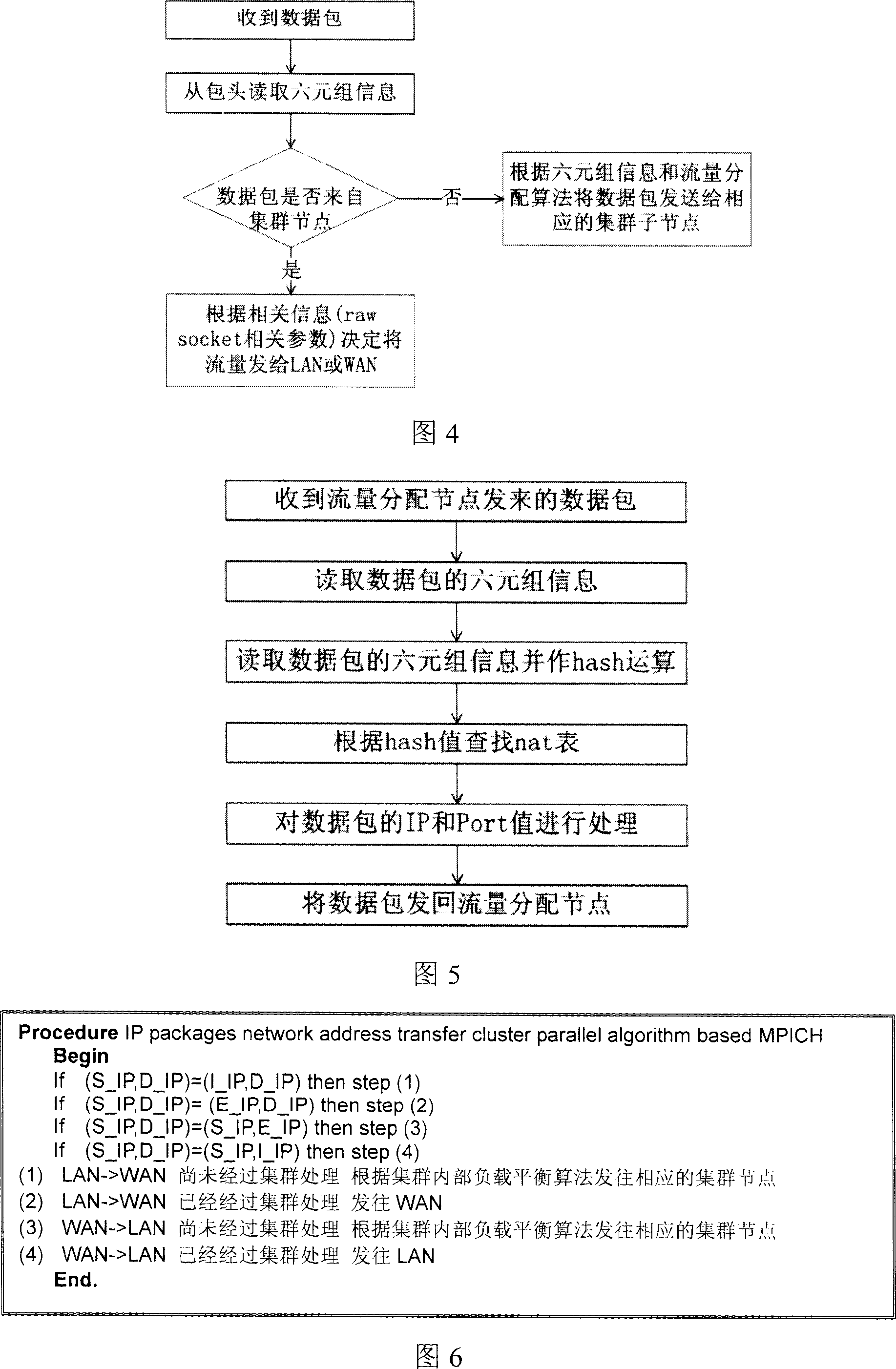
The invention provides a wideband network access and flux management distribution system, which comprises a core processor, a data chain layer processor, a network layer processor, and a managing module. The invention uses multistage parallel treatment of IP pack head recombination to convert network address, to realize parallel sending connection control of multiple users and wideband distribution based on angles, therefore, the flux load accessed between multiple chain outlets of server can be balanced. The inventive integrates flux balance, charge identification, network access, and fireproof wall, particularly for the network access and flux distribution of wideband region of high school and different charge strategies.
Owner:秦勇
Delivering a short Arc lamp light for eye imaging
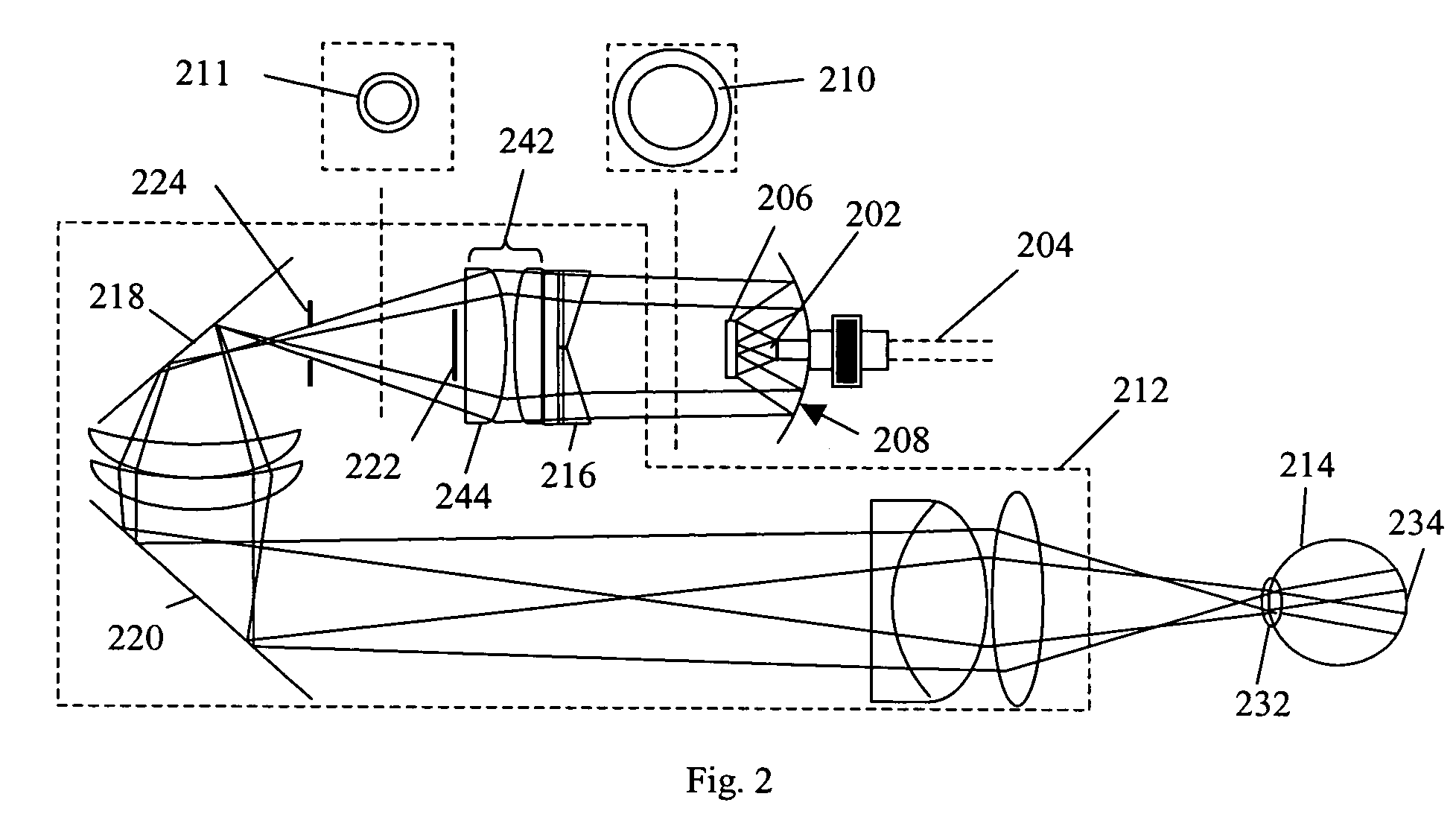
A light delivery technique includes optical configurations as well as the associated methods that generate a ring beam from a linear light source. In one embodiment, a remote light source module delivers illumination light to a fundus camera and / or slit lamp. In another embodiment, an arrangement combines the use of a light pipe homogenizer and a ring beam transformer for efficiently collecting light from a substantially axially linear light source, homogenizing the collected light that lacks low angle flux relative to the optical axis, and transforming the light into a ring beam with a substantially improved low angle flux distribution. In still another embodiment, light emitted from a substantially axially linear light source is directly collected by a curved surface mirror and spatially filtered into a ring beam. The ring illumination beam can be co-axially projected on a sample such as the pupil of a human eye and at the same time the light beam also has a large enough relatively uniform angular flux distribution so that a wide area on the retina of the eye can be uniformly illuminated.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
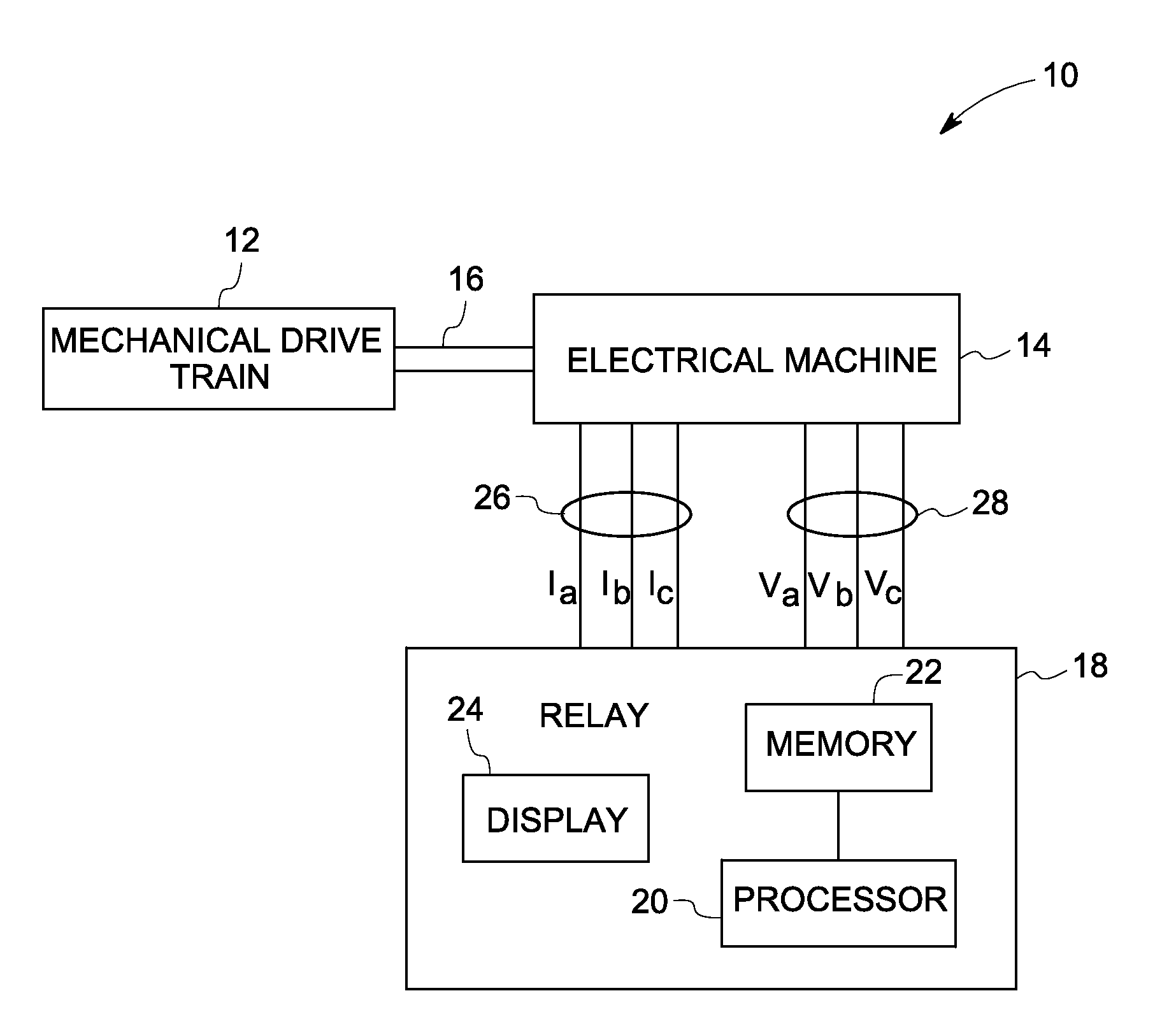
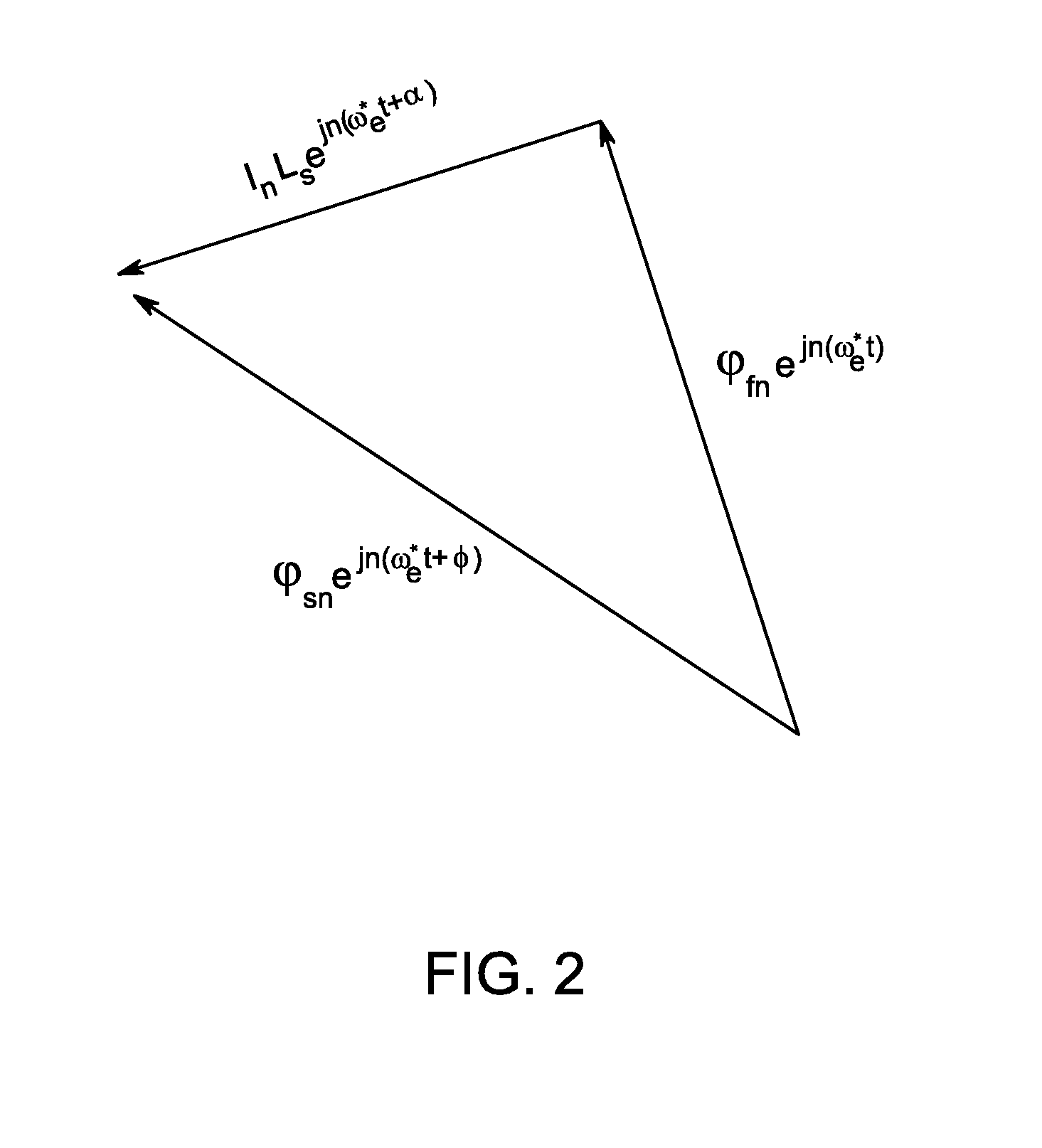
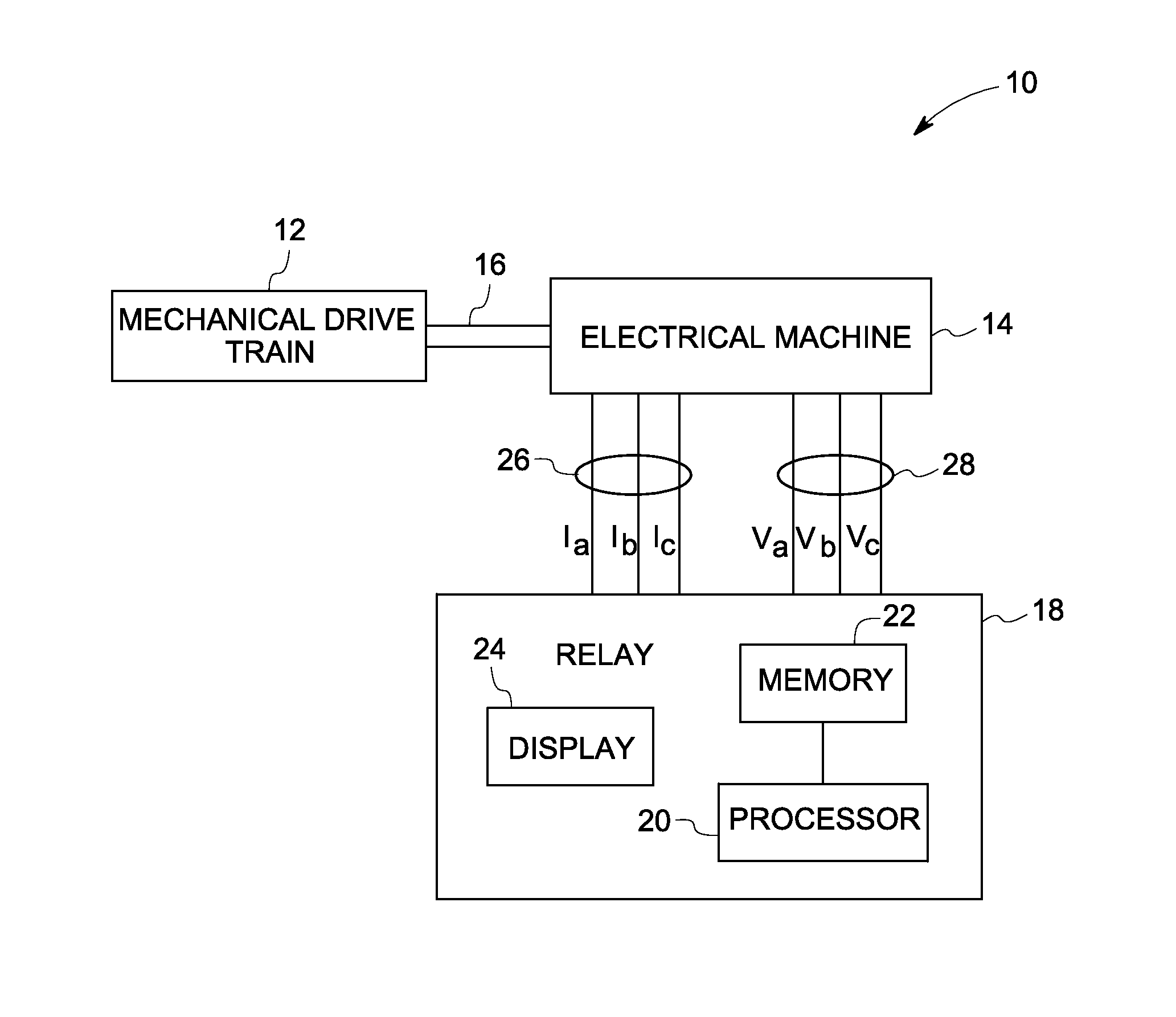
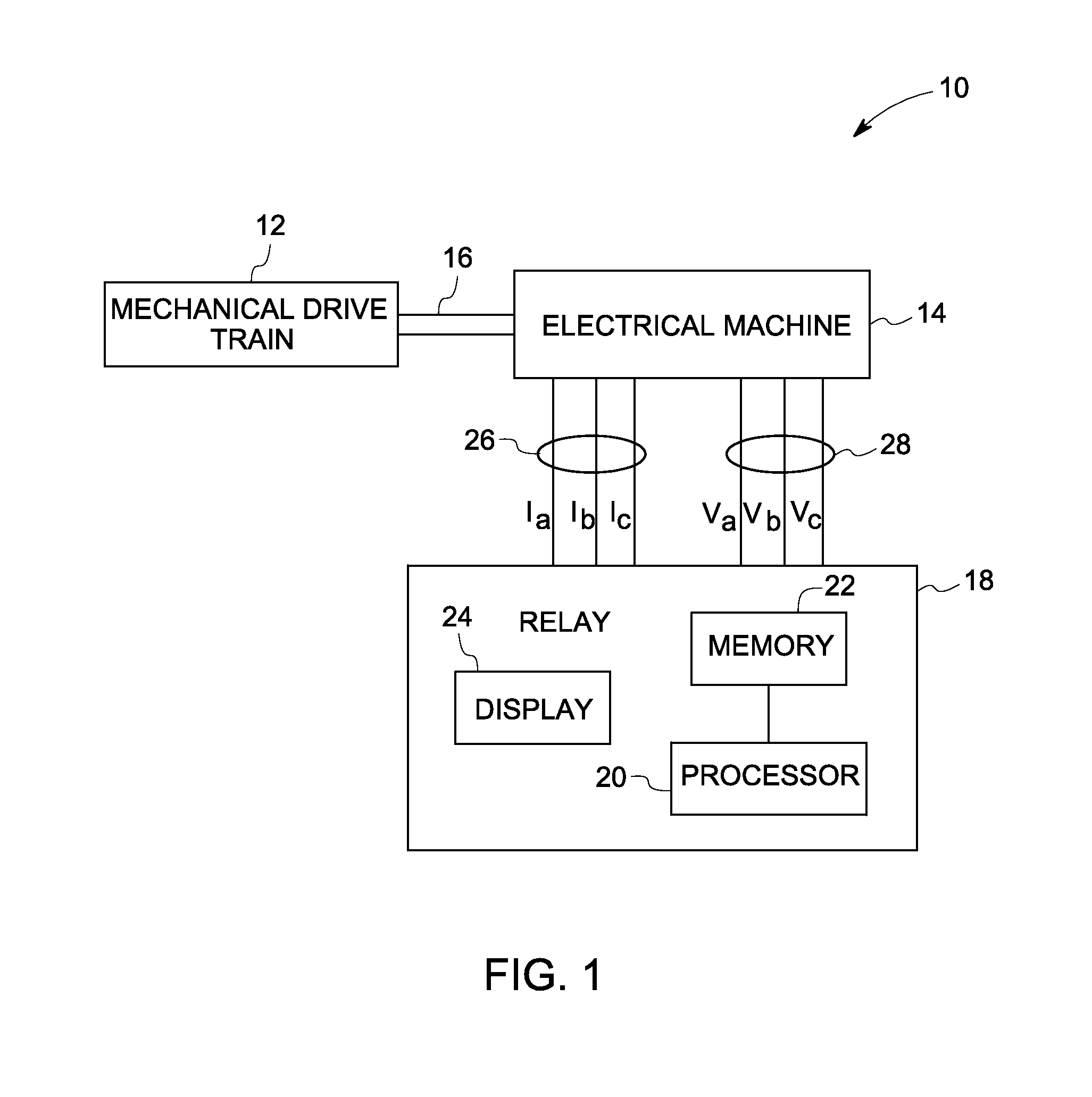
Condition monitoring of mechanical drive train coupled with electrical machines
A method of monitoring health of a mechanical drive train is provided. The method includes obtaining voltage and current signals from at least one phase of an electrical machine coupled with the mechanical drive train. The method also includes representing the electrical machine having a non-sinusoidal flux distribution as a combination of a plurality of harmonic order sinusoidally distributed virtual electrical machines based on the obtained voltage and current signals. The method further includes determining a torque profile associated with one or more combinations of the sinusoidally distributed virtual electrical machines. Finally, the method includes detecting the presence of an anomaly in the mechanical drive train based on the torque profile or spectrum.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Bipolar plate of fuel cell
InactiveCN1692515ALow flow resistanceEven flow distributionFuel cell auxillariesCollectors/separatorsFuel cellsEngineering
In a bipolar plate of a fuel cell including a plate having a certain area and thickness; inflow and outflow buffer grooves respectively formed at both sides of the plate so as to have a certain area and depth; plural channels for connecting the inflow buffer groove and the outflow buffer groove; plural buffer protrusions formed in the inflow and outflow buffer grooves so as to have a certain height; an inflow path formed on the plate so as to be connected to the inflow buffer groove; and an outflow path formed on the plate so as to be connected to the outflow buffer groove, it is possible to uniformize flux distribution and reduce flow resistance of fuel and air respectively flowing into a fuel electrode and an air electrode of a fuel cell.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for producing 1,3-propylene of using glycerol anaerobic fermentation
ActiveCN1955304AIdeal flux distributionEfficient fermentation productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismGlycerol
This invention provides a promoting cell synthesizing trimethylene glycol method by adding organic intermediary metabolism molecule, and it belongs to trimethylene glycol biosynthesize technology field. Aim at the problem of low transformation efficiency of single cell using glycerine anaerobic fermentation in present technology, this invention realizes ideal flux distribution of substrate and product during the process of trimethylene glycol fermentation, which makes high effect trimethylene glycol fermentation into reality. The invention breaks through the bottleneck of low trimethylene glycol transformation efficiency using glycerine biosynthesis, which improves the transformation efficiency of substrate, shortens fermenting time and cuts down the cost.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
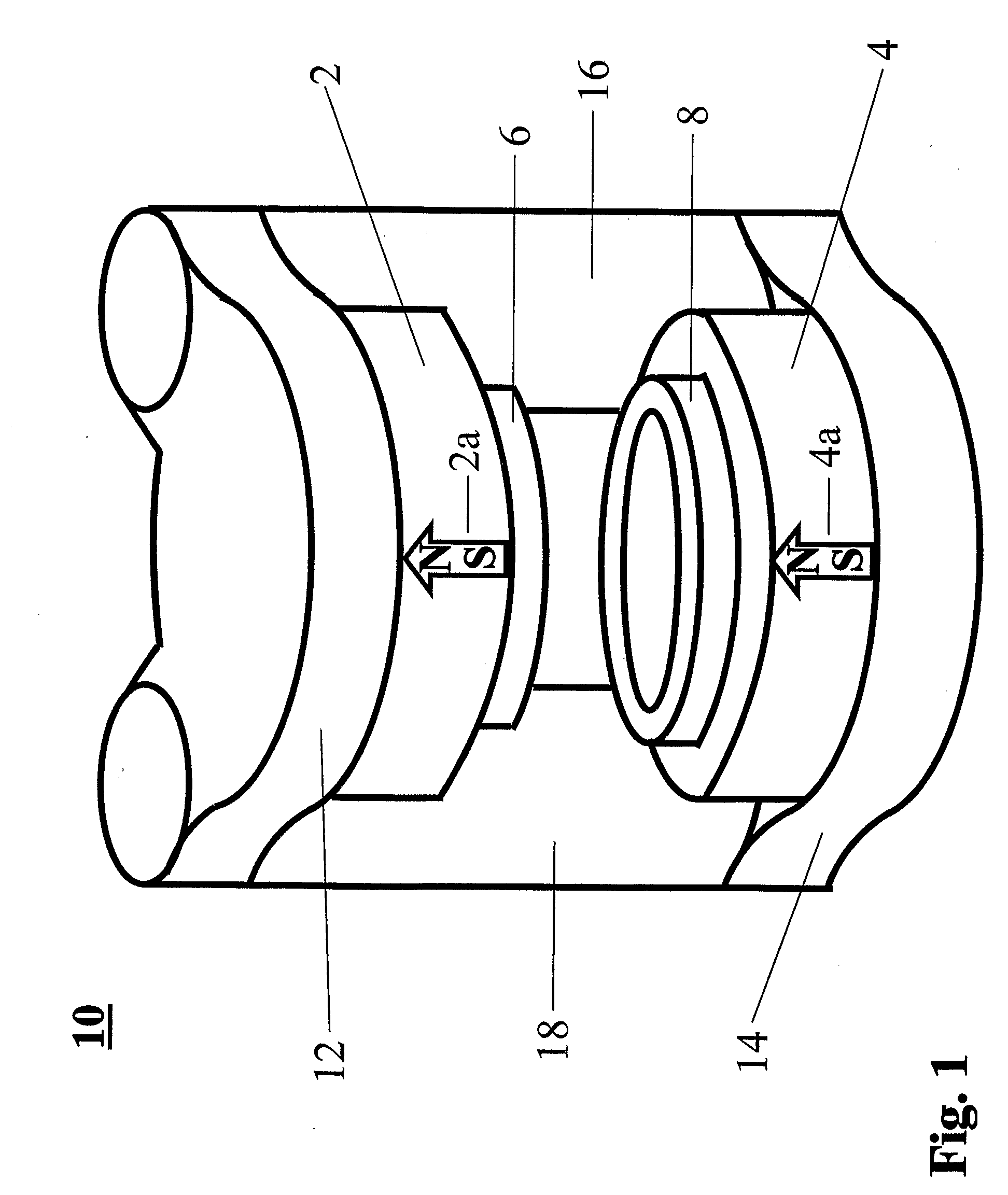
Axial flux permanent magnet generator/motor
InactiveUS20050029886A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotational axisMagnetic poles
The present invention is related to a permanent magnet electrical generator / motor comprising a stator, a rotor, a rotational axis and an air gap between stator and rotor so that the magnetic flux across said air gap is essentially oriented along said rotational axis, said rotor preferably comprising a plurality of permanent magnets to form rotor poles, said generator / motor being characterised in that said stator comprises a disc (1), and a plurality of magnetic cores (2), said cores (2) being attached to said disc (1) by attachment means, said cores comprising coils (6) wound round the legs of said cores. Furthermore, said machine comprises means for distributing the flux across the air gap between rotor and stator. Preferably, this takes on the form of flux distribution plates (28,29), placed between rotor and stator.
Owner:VLAAMSE INSTELLING VOOR TECHNOLOGISCH ONDERZOEK NV VITO
Method and system for spatially-resolved 3-dimensional characterization of near-field sprays
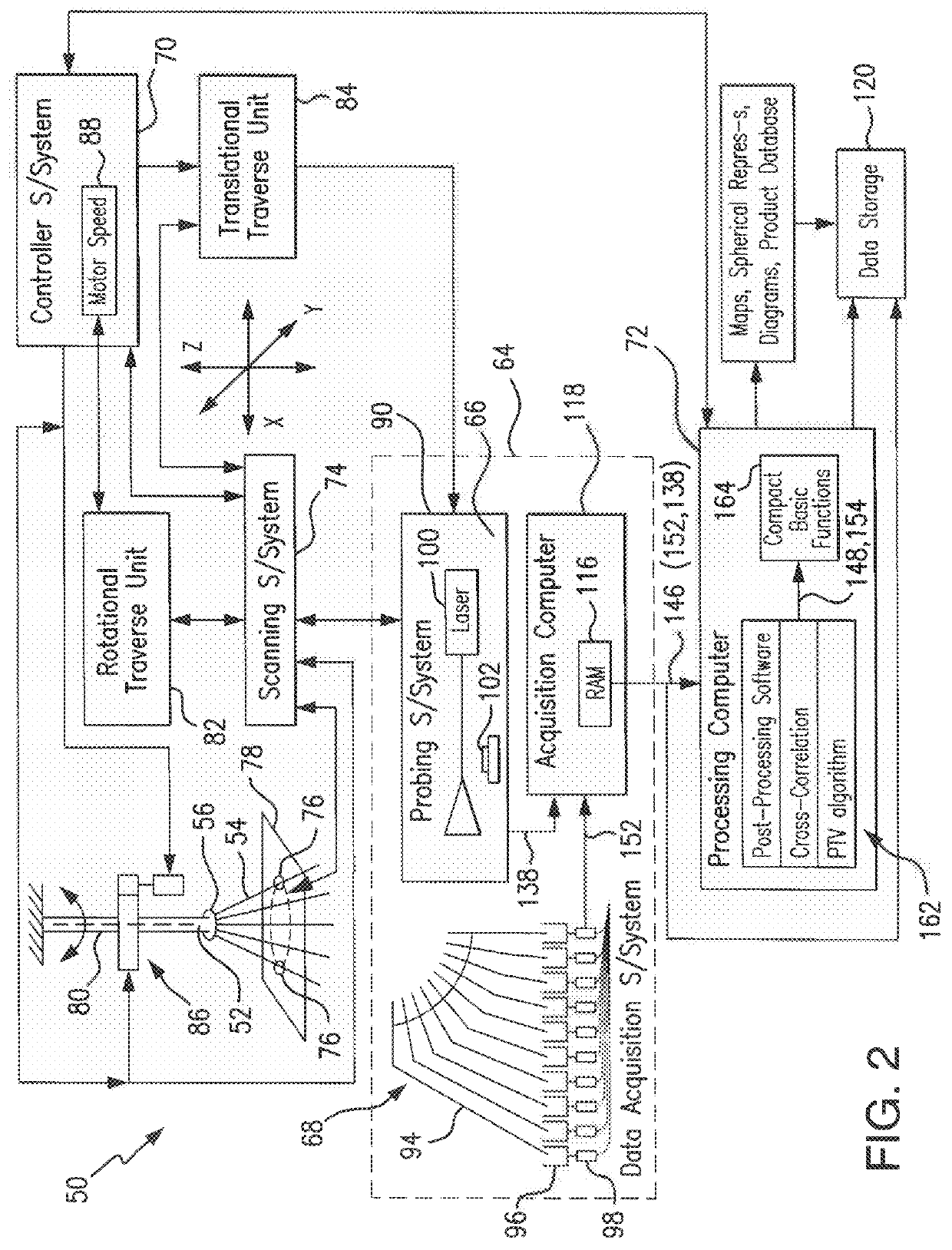
ActiveUS9964495B1Unprecedented accuracyAccurately dispersion performanceImage analysisInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsData compressionMeasurement study
Near-field spray characteristics are established from local measurements which are acquired by data acquisition sub-system capable of complete scanning of the area (volume) of interest in the spray which uses different laser-based probes (shadowgraphy, PIV, diffraction) to obtain drops related measurements. A mechanical patternator measures volume flux distribution of the spray under study. The measurement data are post-processed to obtain spatially-resolved spray characteristics which are mapped in a spherical coordinate system consistent with the kinematics of the spray. A data compression scheme is used to generate compact analytical functions describing the nozzle spray based on the measurement data. These analytical functions may be useful for initiating the nozzle spray in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) based spray dispersion and fire suppression modeling.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
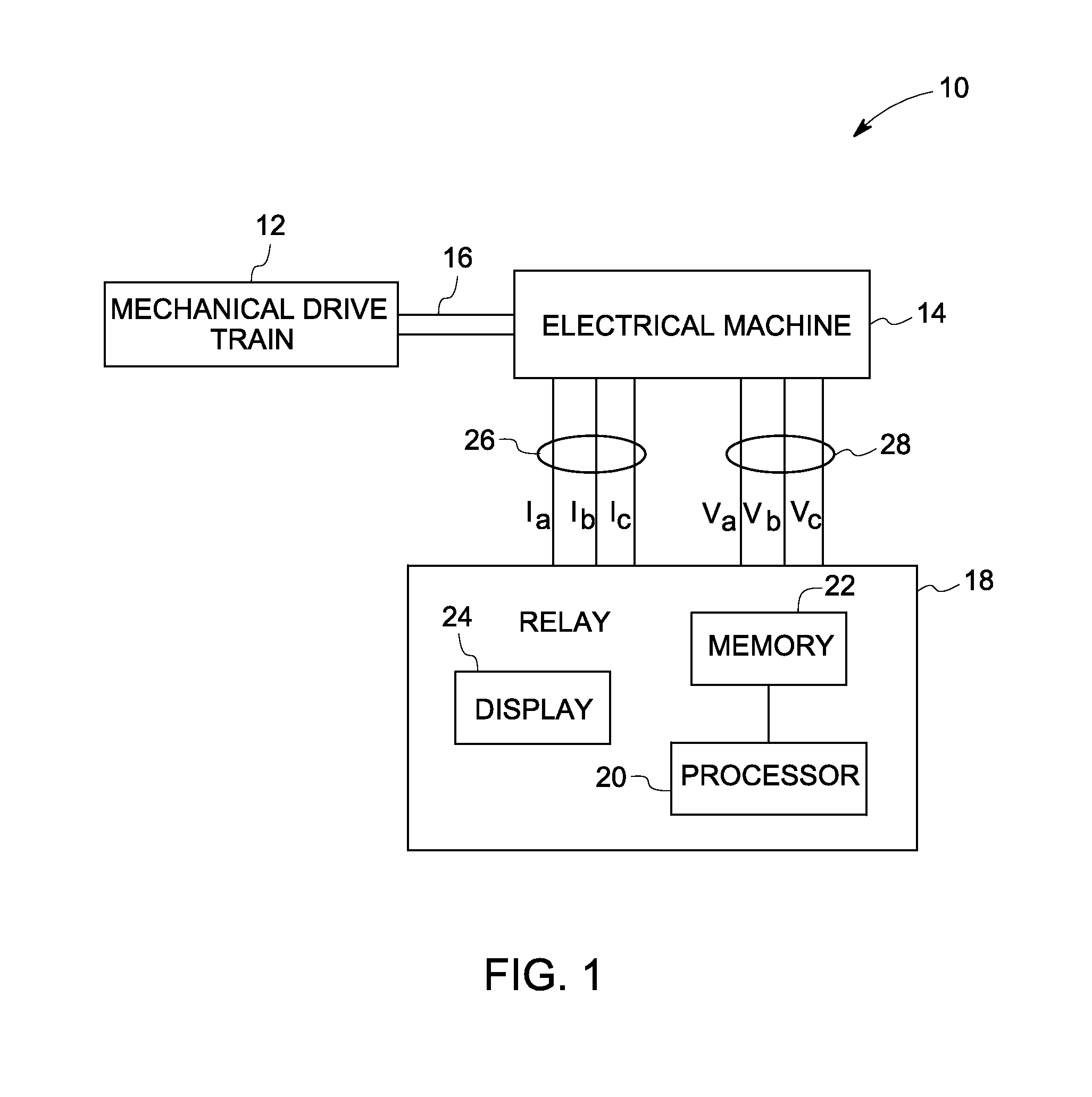
Condition monitoring of mechanical drive train coupled with electrical machines
A method of monitoring health of a mechanical drive train is provided. The method includes obtaining voltage and current signals from at least one phase of an electrical machine coupled with the mechanical drive train. The method also includes representing the electrical machine having a non-sinusoidal flux distribution as a combination of a plurality of harmonic order sinusoidally distributed virtual electrical machines based on the obtained voltage and current signals. The method further includes determining a torque profile associated with one or more combinations of the sinusoidally distributed virtual electrical machines. Finally, the method includes detecting the presence of an anomaly in the mechanical drive train based on the torque profile or spectrum.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Air-conditioning unit for meanwhile refrigerating and heating
ActiveCN101245957ATo achieve the purpose of cooling and heating at the same timeMaximize energy savingCompression machines with reversible cycleAir conditioning systemsFour-way valveEngineering
The invention provides an air conditioner unit which can achieve the refrigeration and heating at the same time. The air conditioner unit comprises an outdoor unit, a refrigerant distributor and an indoor unit. The outdoor unit, the refrigerant distributor and the indoor unit form a complete circulation system by a connecting pipeline; wherein, the refrigerant distributor comprises a high pressure gas / liquid separator, an electronic expansion valve A, an electronic expansion valve B, and a four-way valve which is corresponding to the indoor unit, and the aims of the refrigeration and the heating of the air conditioner unit are achieved at the same time by controlling the flowing direction of each four-way valve. Furthermore, the refrigeration and the heating can be achieved at the same time by precisely controlling the flux distribution when the outdoor temperature ranges from minus 5 DEG C to 30 DEG C; the maximum energy-saving effect can be achieved under the situation of providing refrigeration and heating at the same time.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
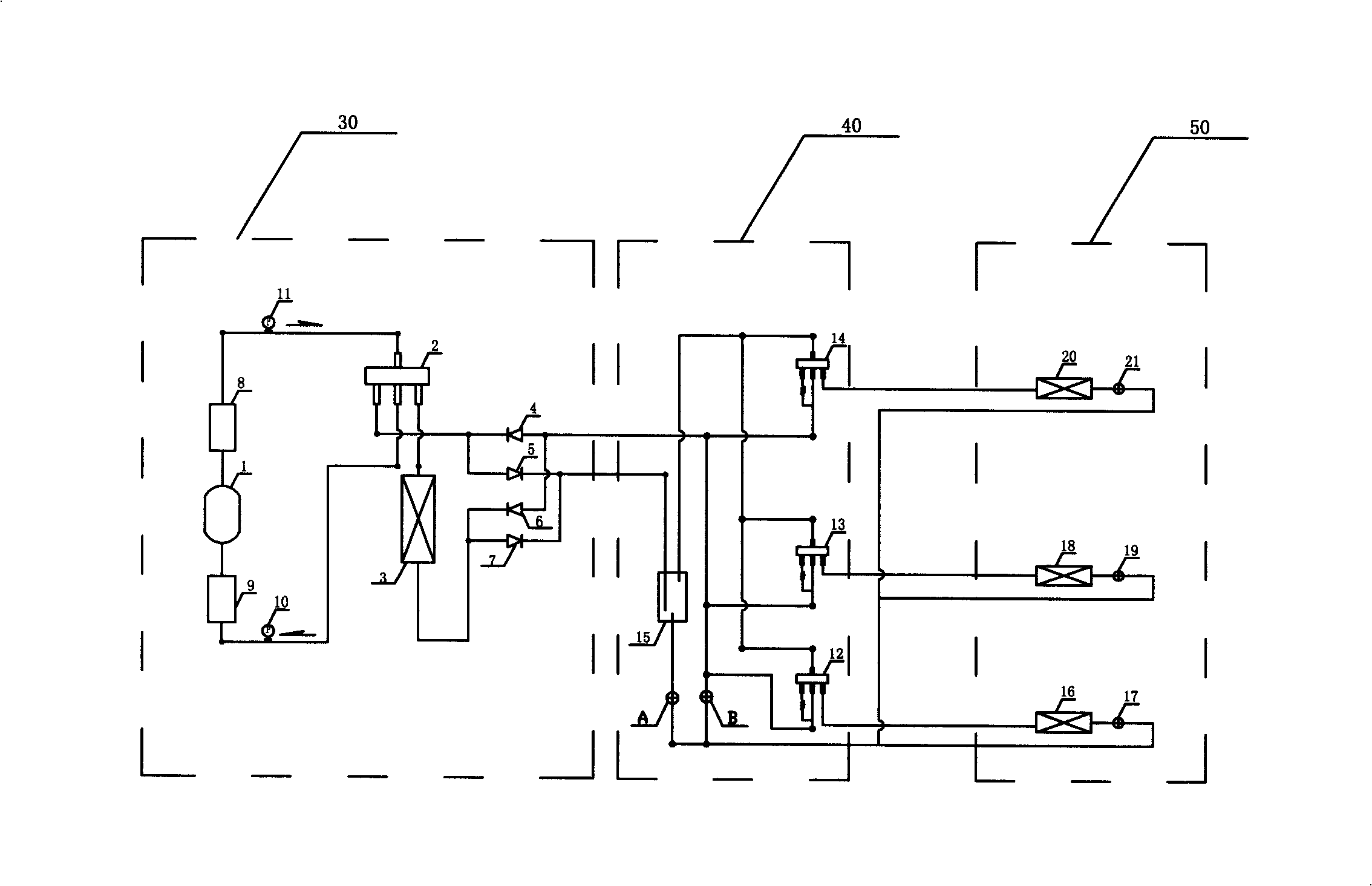
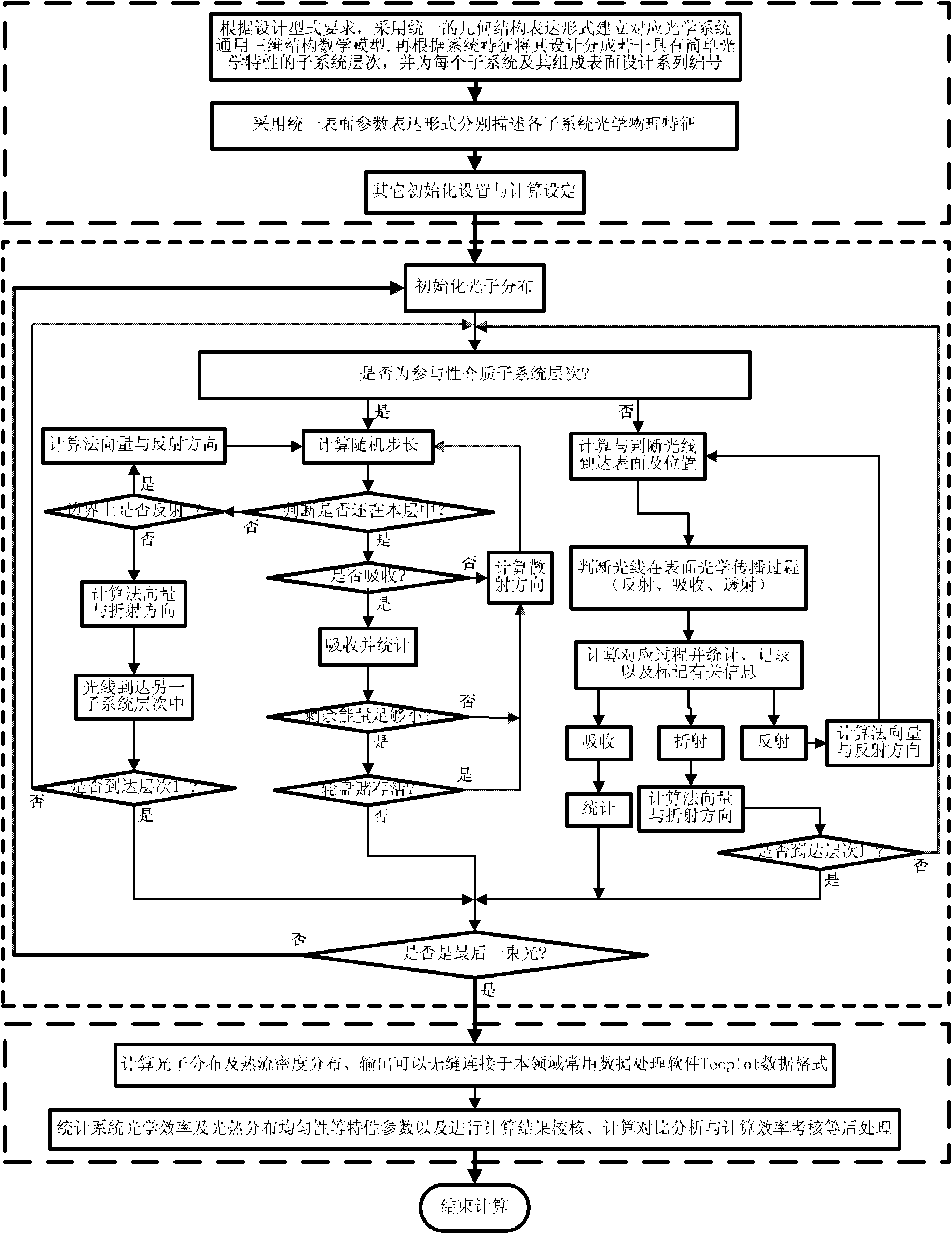
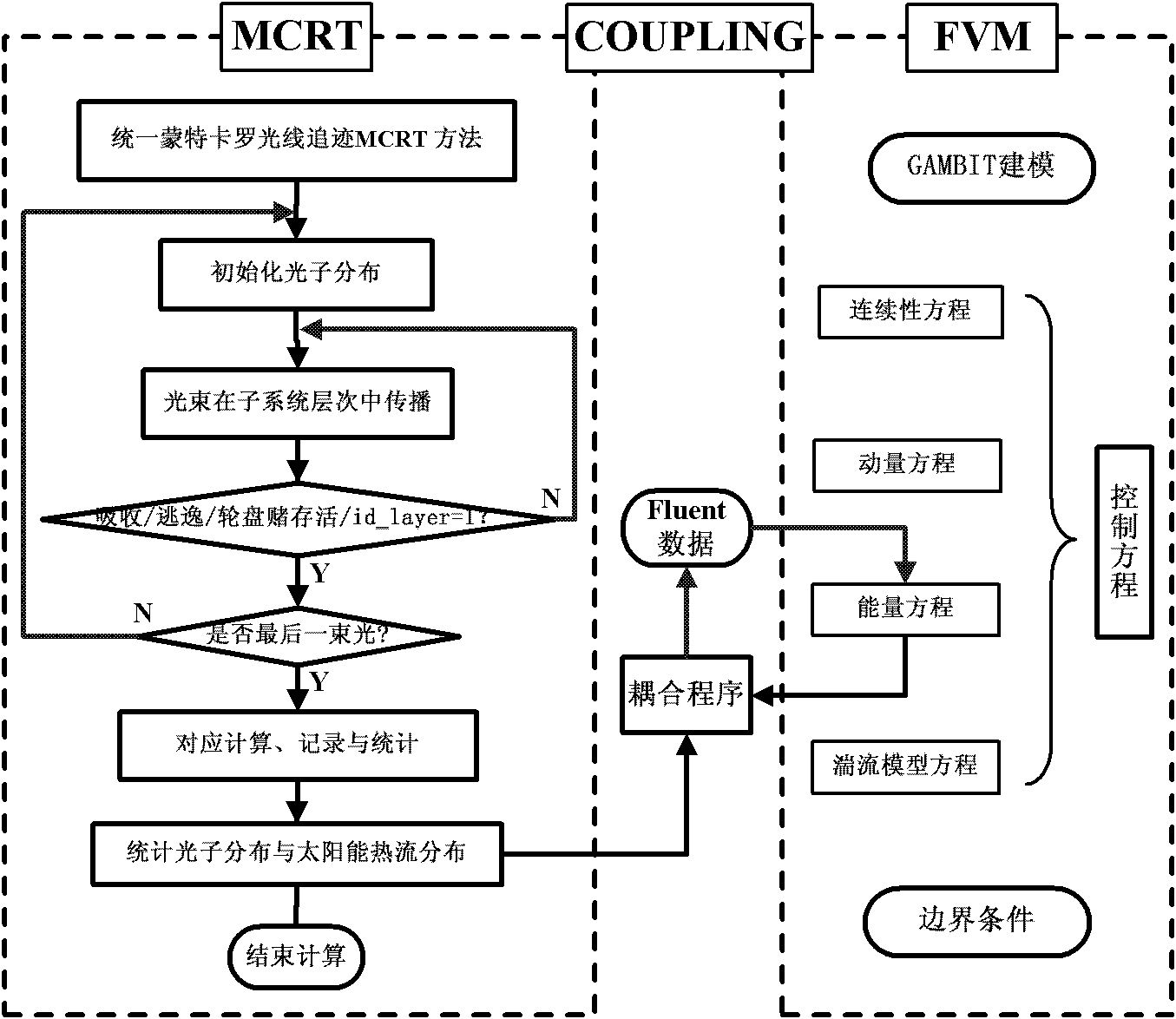
A design method for multi-level multi-surface complex solar energy concentrating heat collection system
InactiveCN102270251AEasy to useHigh degree of intelligenceSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemSystems designFluid coupling
The invention discloses a design method of a multi-level and multi-surface complex solar concentrating heat collection system, comprising the following steps of: firstly, according to requirements on design types, establishing a universal three-dimensional mathematical model corresponding to an optical system; subsequently, performing optical calculation by a uniform Monte Carlo ray tracing method; and then, taking optical efficiency and uniformity of distribution of light and heat as examination basis, until the designed system meets the design requirements on the needed optical efficiency and uniformity of distribution of light and heat; establishing a corresponding numerical calculation module in a universal computational fluid and a heat transfer platform under a required operation condition; coupling a solar heat flux distribution calculated by the Monte Carlo ray tracing method with the numerical calculation model so as to perform light-heat-fluid coupling calculation; and then,further taking the flowing heat transfer performance of a working medium fluid in the system and the system thermal performance as the examination basis, until the designed system completely meets various design requirements on the optical efficiency, the uniformity of distribution of light and heat, the flowing performance of the working medium, the system thermal performance and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Transmission-reflection linear spotlight heat collector
InactiveCN104406312AAvoid the consequences of bending deformation and even structural failureReduce wind resistanceSolar heating energySolar heat devicesFresnel lensHeat flow
The invention discloses a transmission-reflection linear spotlight heat collector. The heat collector comprises a linear focus Fresnel lens, a vacuum heat collecting pipe, and a parabolic groove surface reflection lens; and the heat collector has a single-axis light tracking ability. The vacuum heat collecting pipe is located at the focal line position of the linear focus Fresnel lens and the parabolic groove surface reflection lens; the Fresnel lens focuses the central light of approximately parallel sunlight to the sunward wall of the vacuum heat collecting pipe; the parabolic groove surface reflection lens focuses the bilateral light of approximately parallel sunlight to the bilateral downsun walls of the vacuum heat collecting pipe; the heat conductive medium inside the vacuum heat collecting pipe absorbs the focused solar energy, so as to finish the heat up process. The solar heat collector can be applied to the field of solar energy photo-thermal, and significantly solves the difficulty that the thermal flux distribution on circumference direction of the heat collecting pipe in the conventional groove type heat collector is uneven; the heat collector is excellent in performance and low in cost.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com