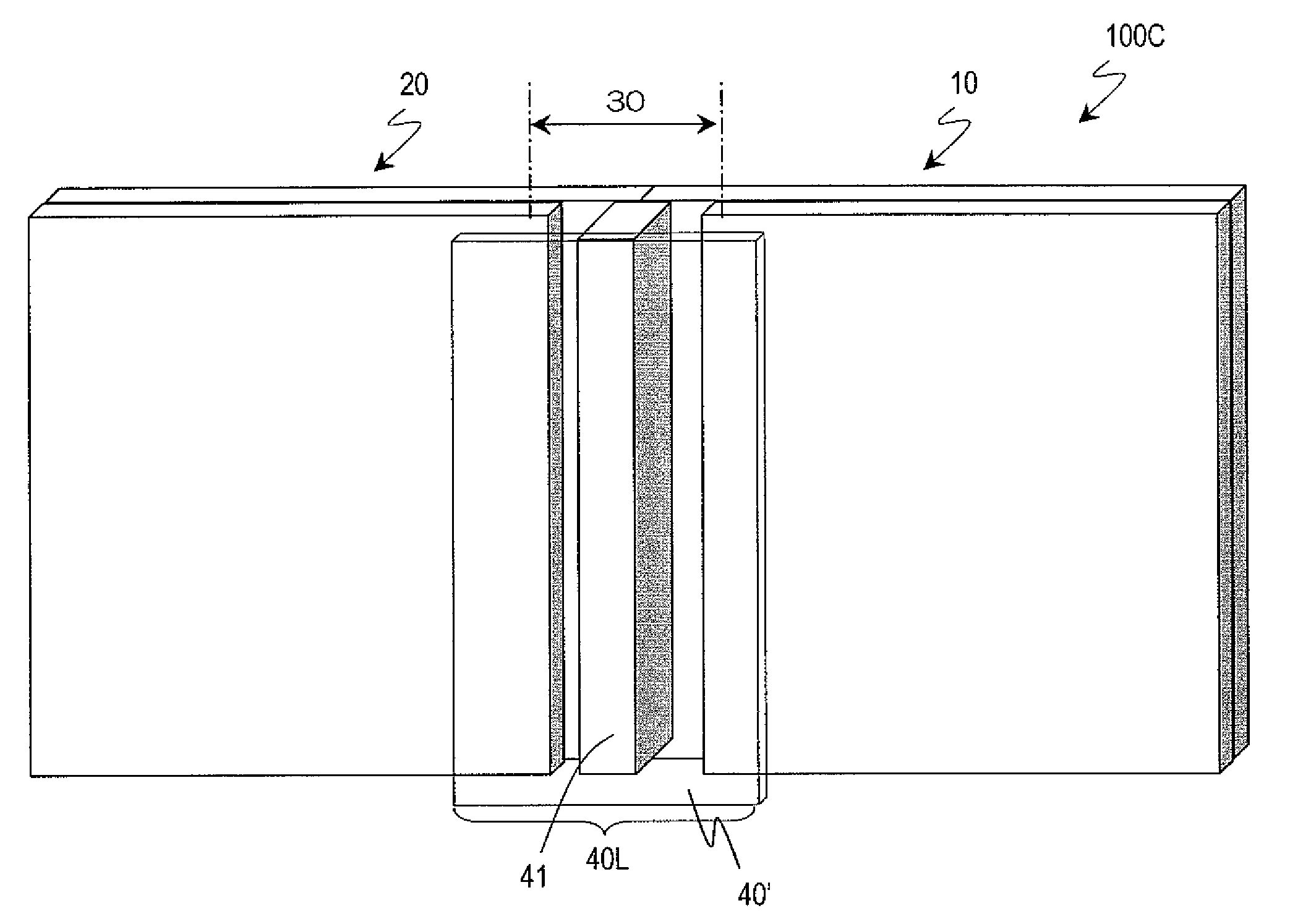
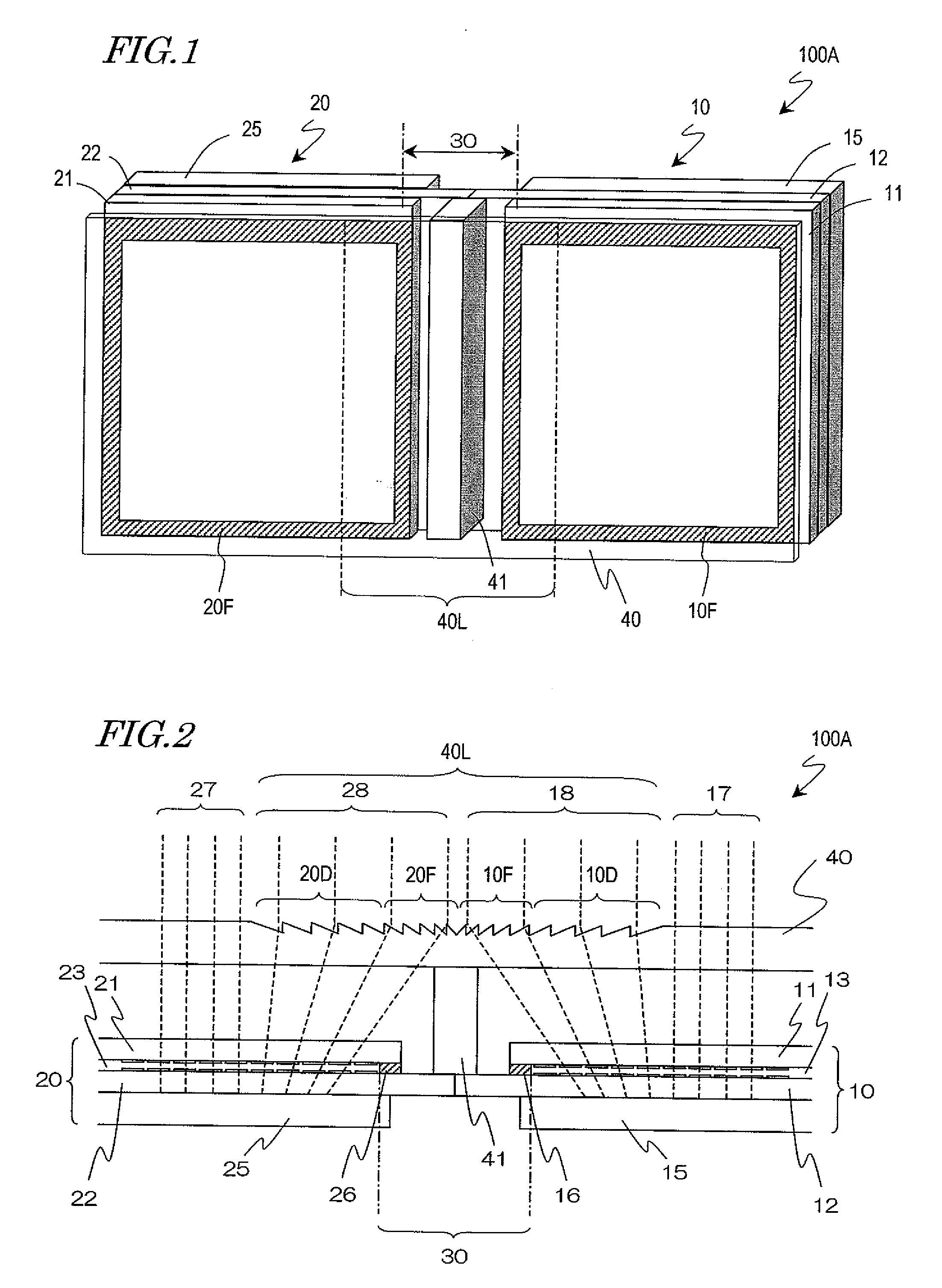
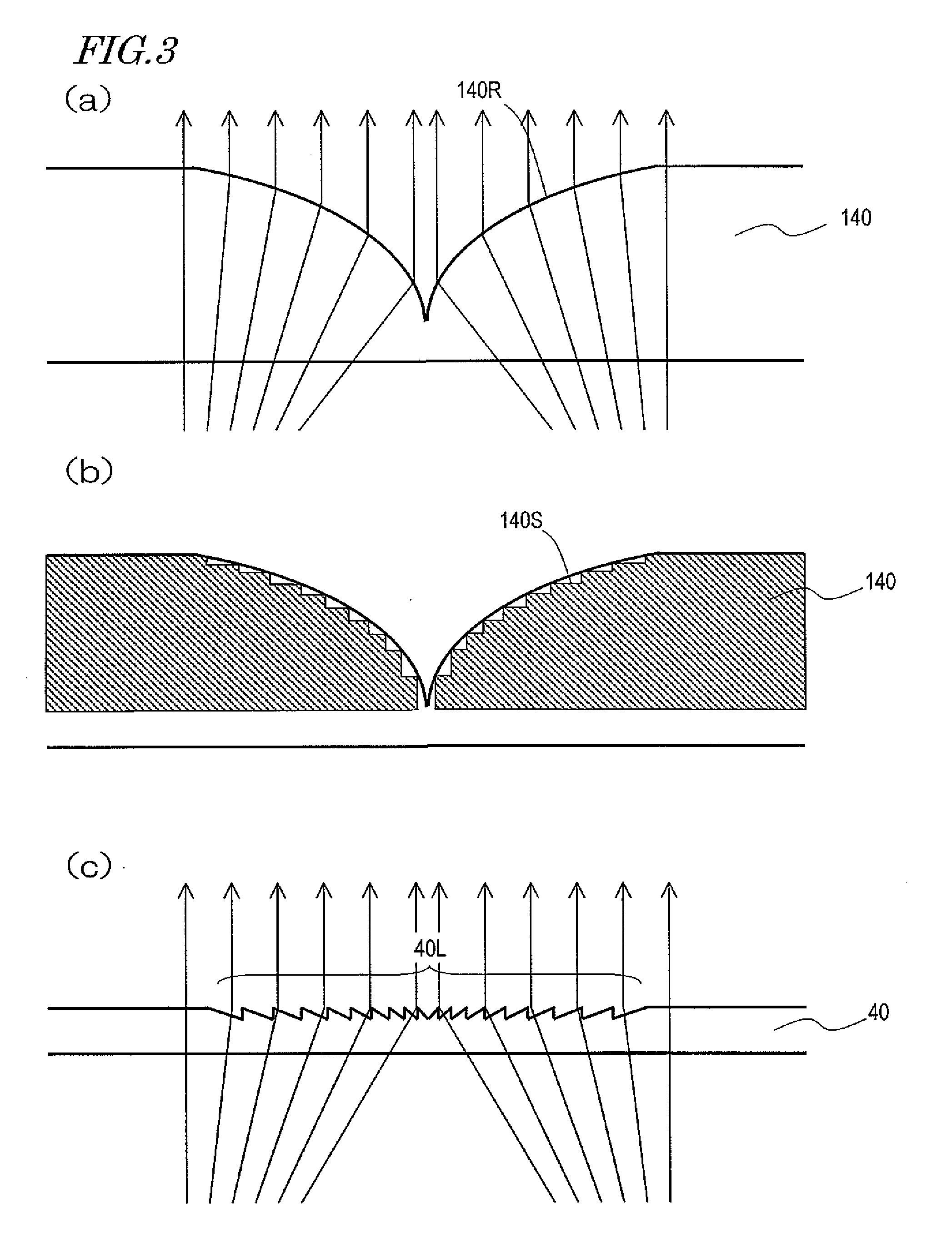
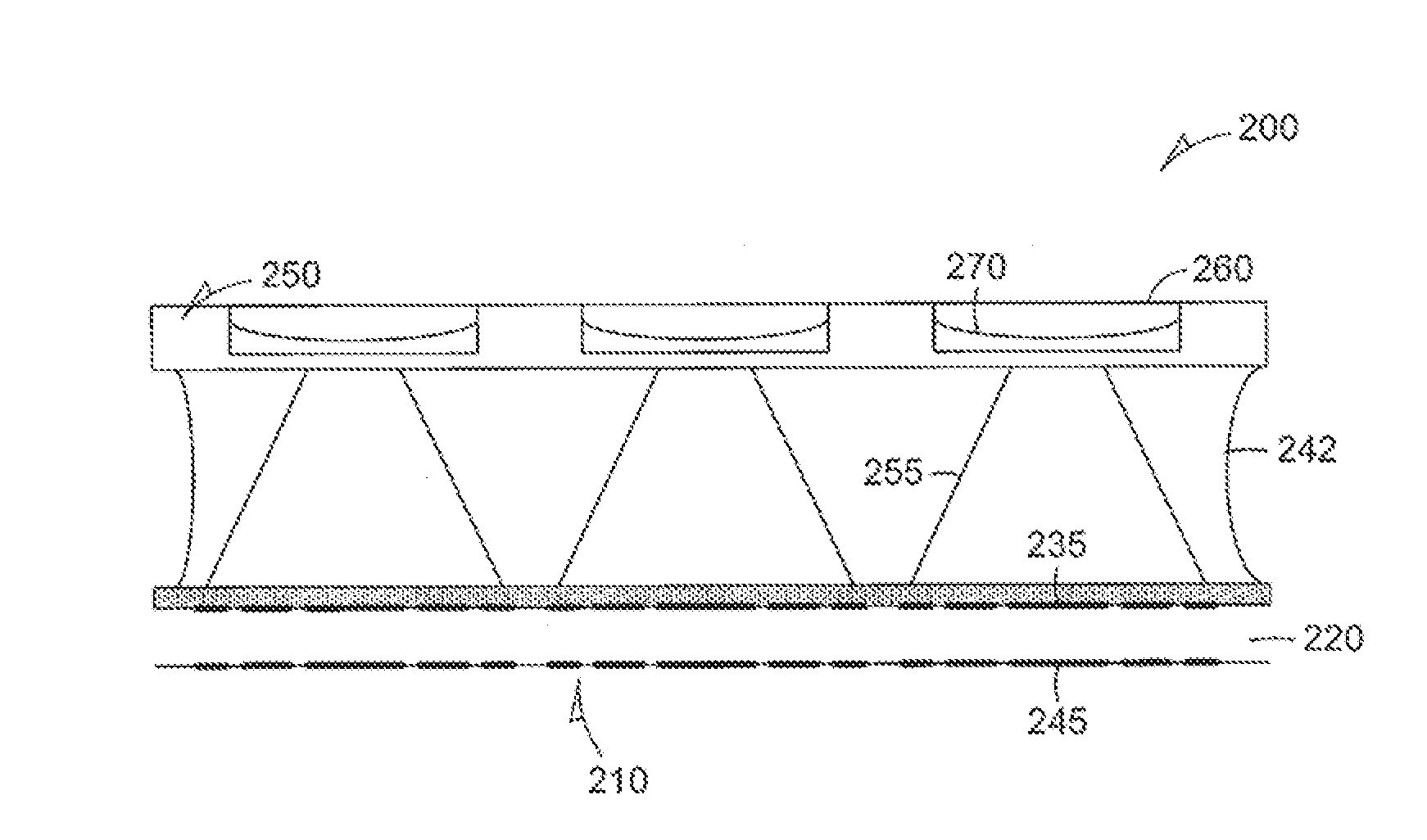
Patents
Literature
2504 results about "Fresnel lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Fresnel lens (/ˈfreɪn-, ˈfrɛn.ɛl, -əl/ FRAYN-, FREN-el, -əl, /freɪˈnɛl/ fray-NEL or /ˈfrɛznəl/ FREZ-nəl) is a type of composite compact lens originally developed by French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel for lighthouses. It has been called "the invention that saved a million ships."
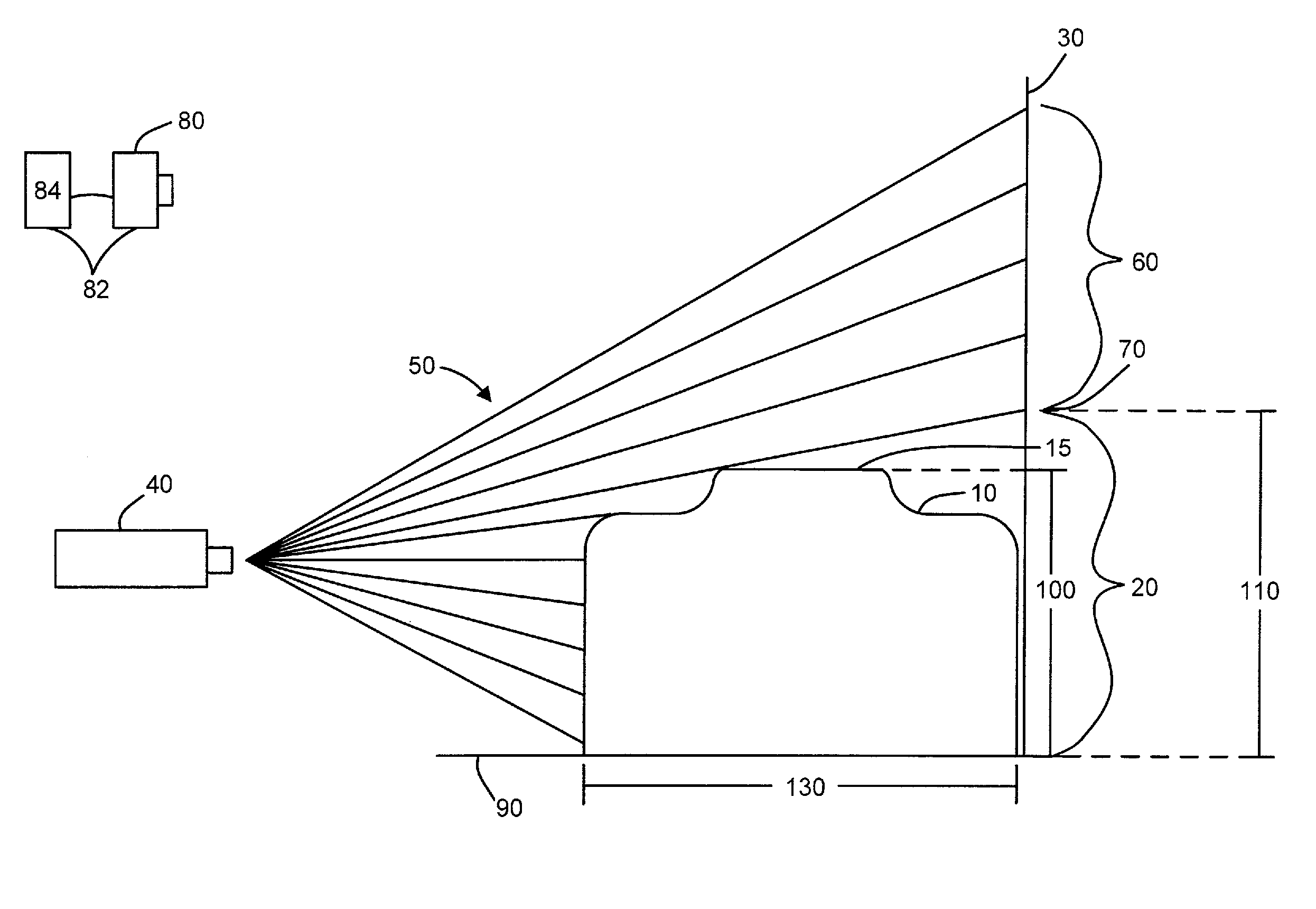
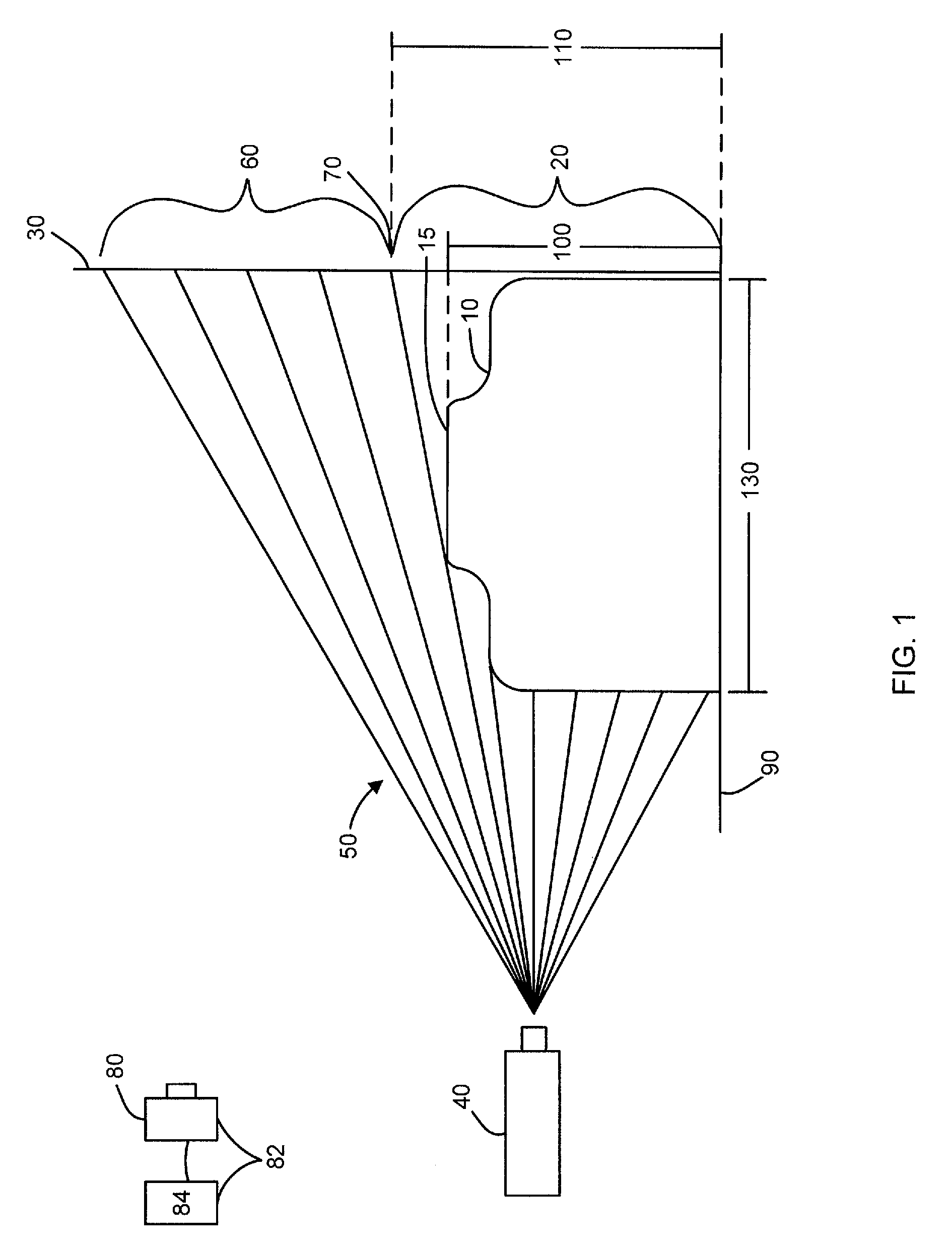
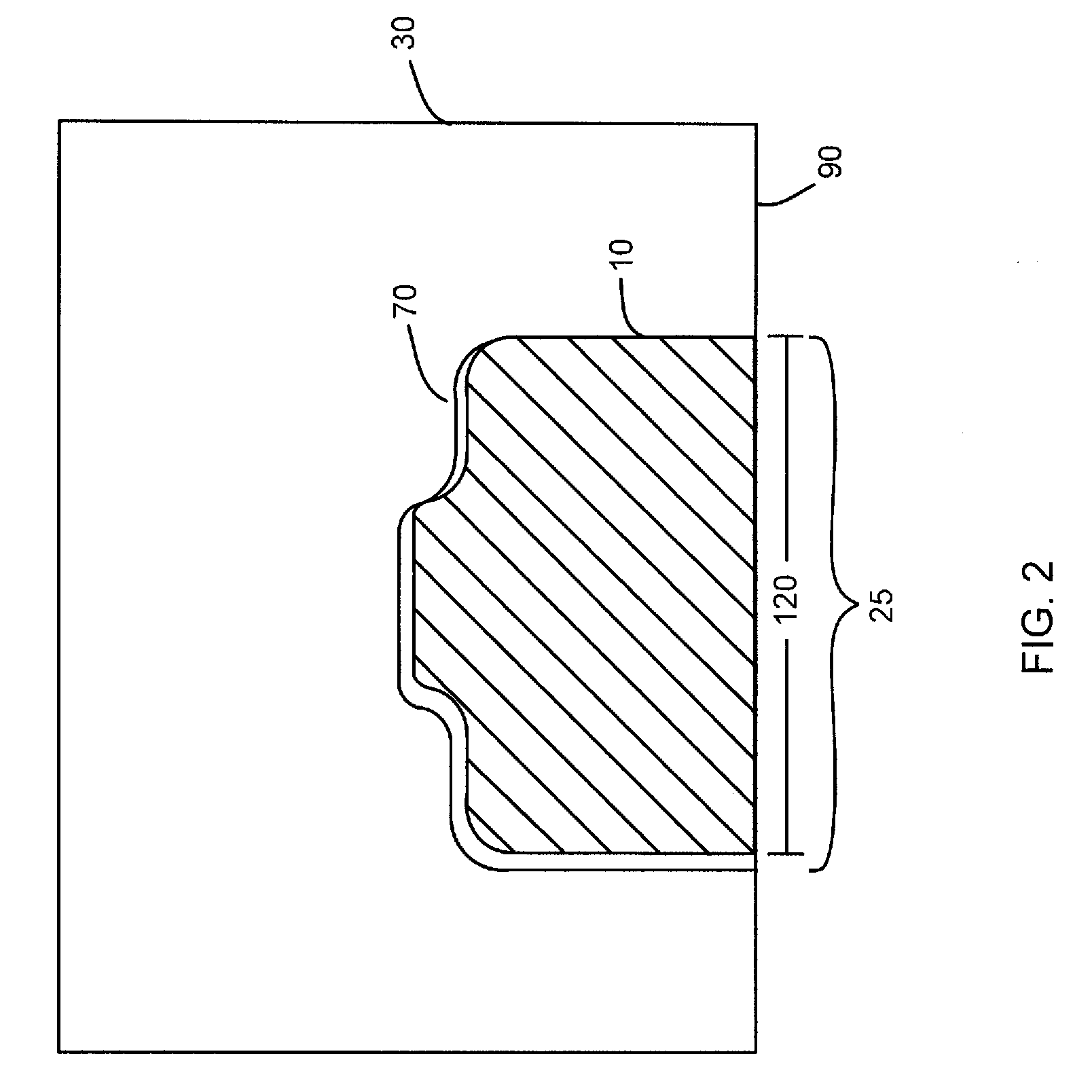
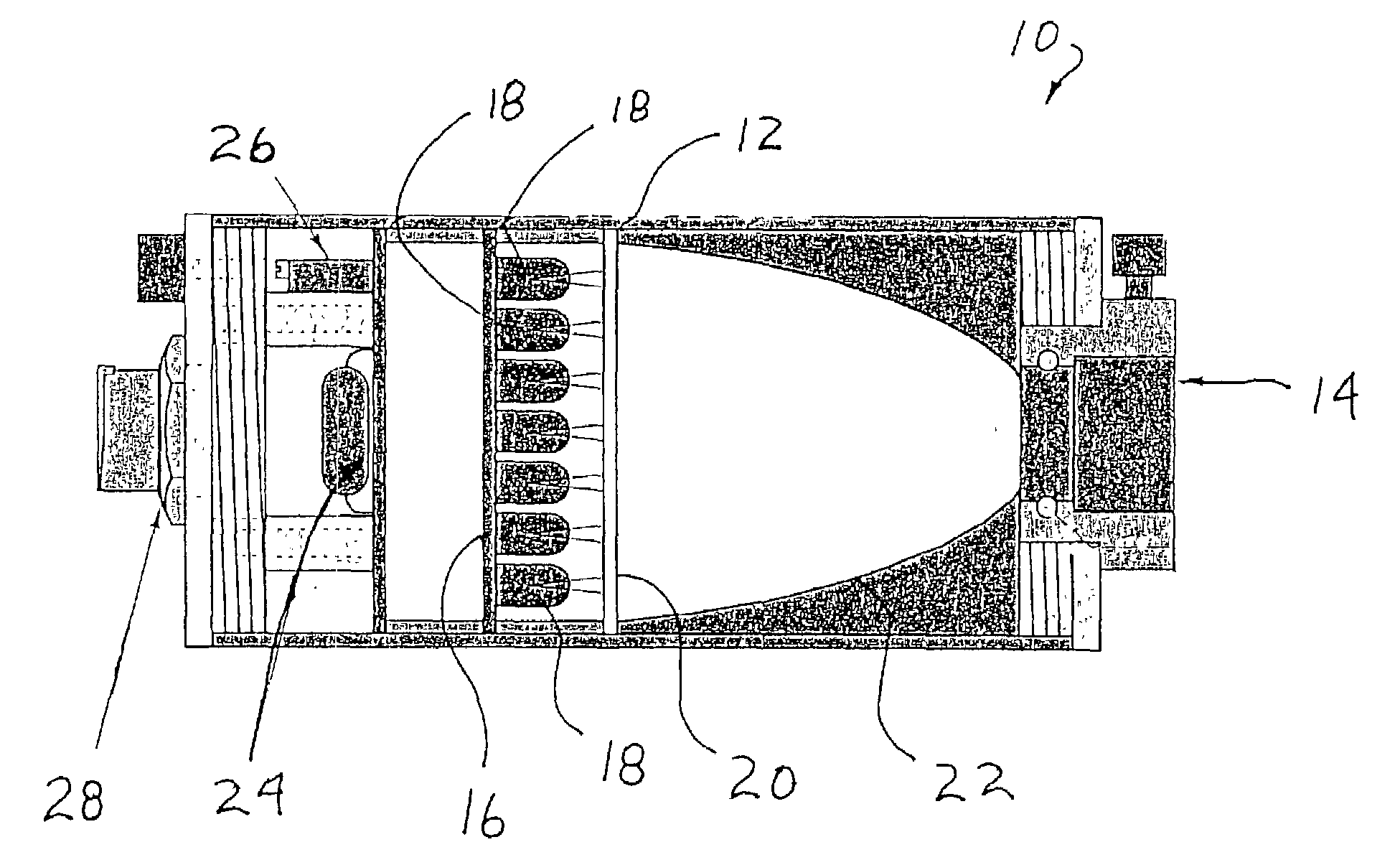
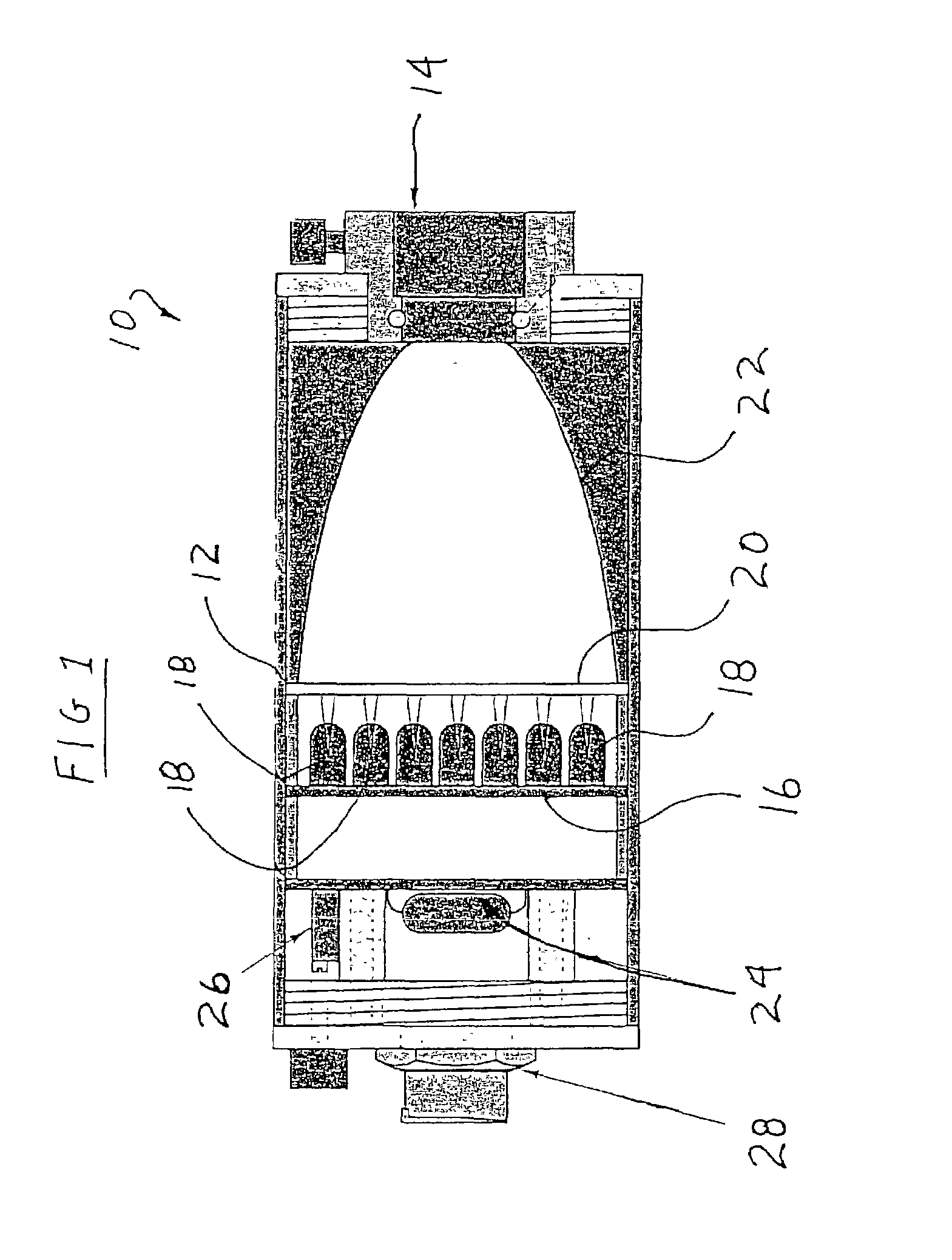
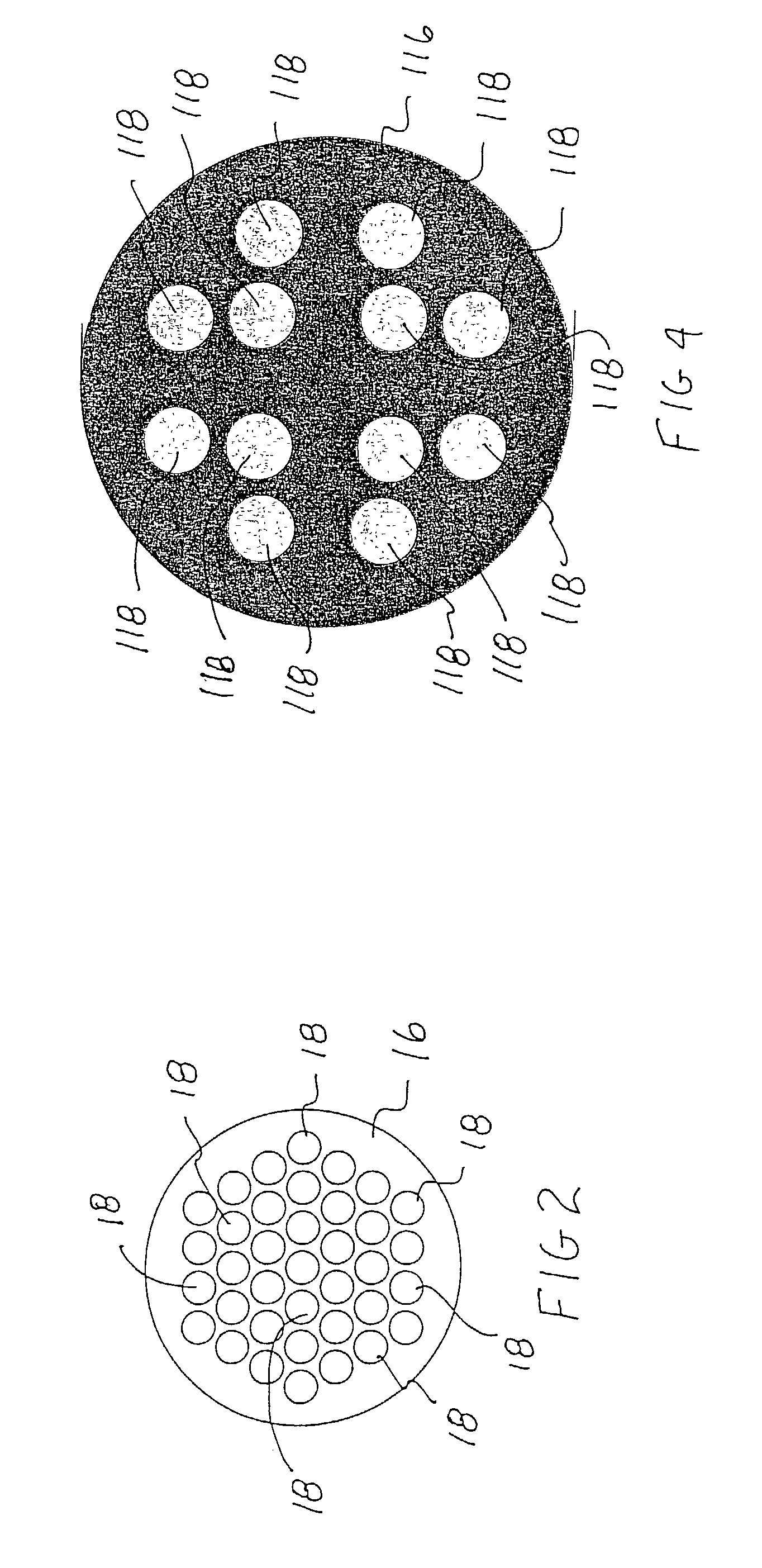
System and method for measuring irregular objects with a single camera
ActiveUS8643717B2Rapid and efficient mannerAccurate chargesCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsFresnel lensSize measurement
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
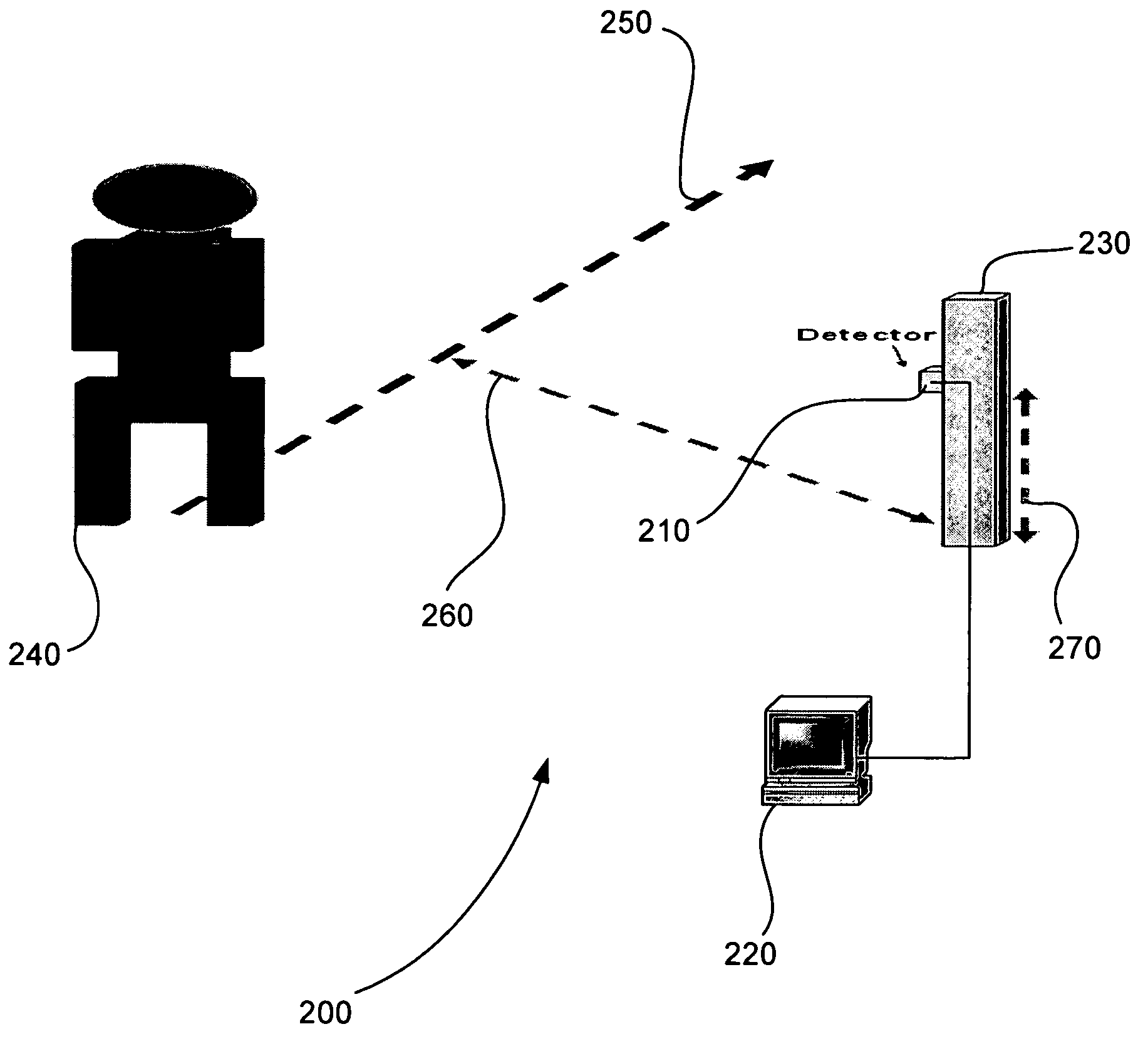
Sensor system for identifying and tracking movements of multiple sources
ActiveUS7351975B2Improves collection efficiency and spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansSensing radiation from moving bodiesVisibilityFresnel lens
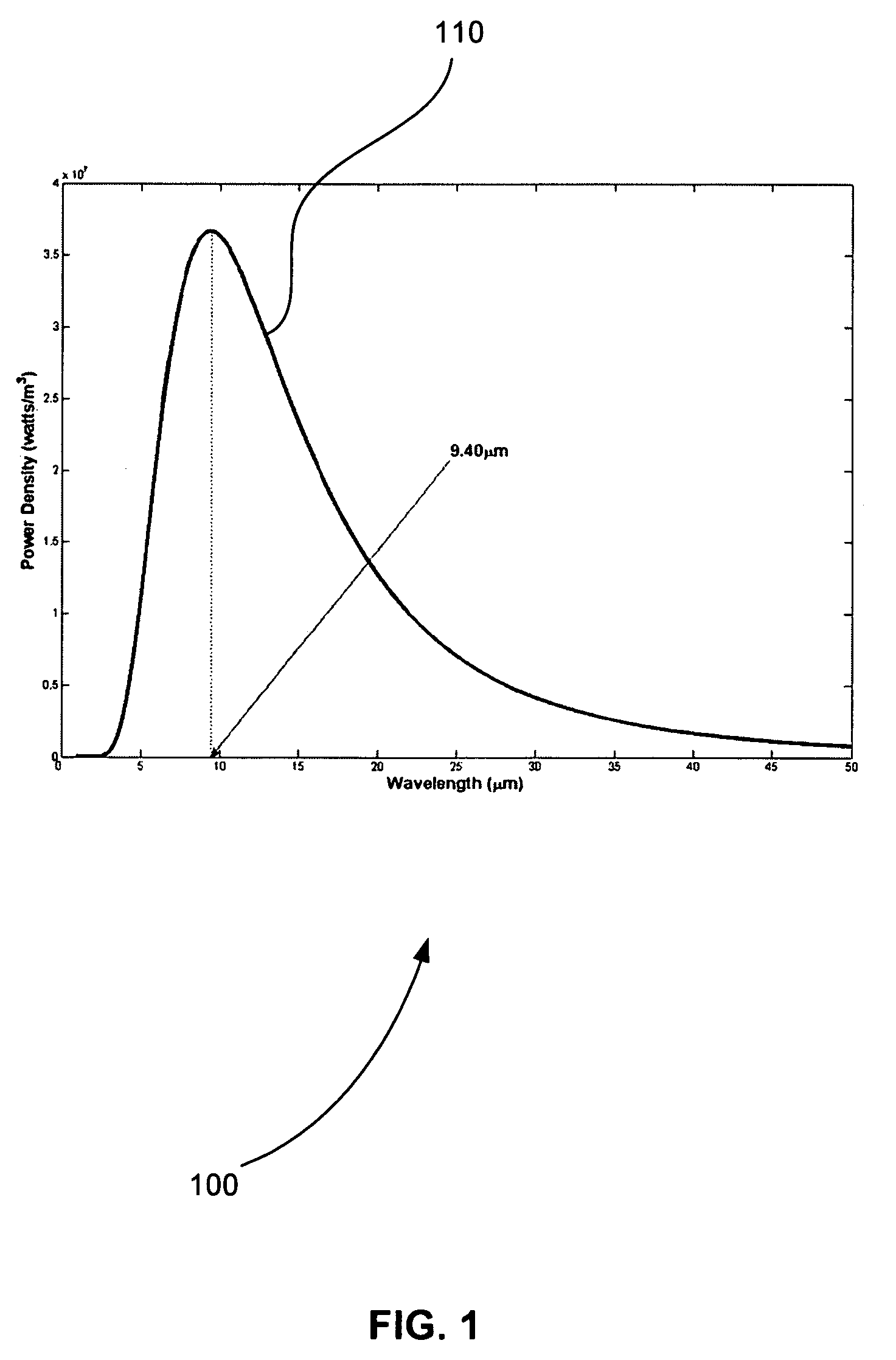
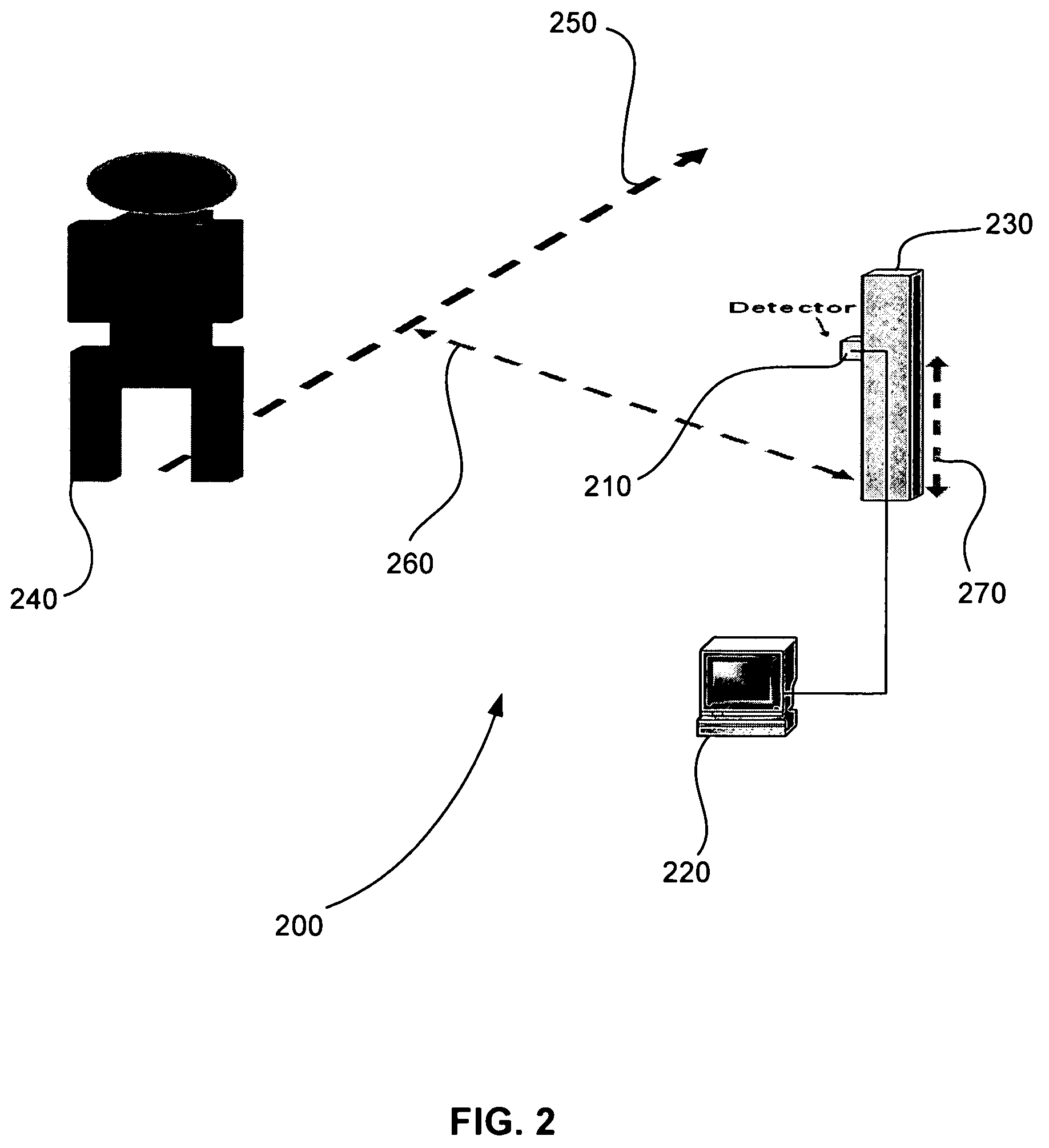
A system identifies a human being from the movement of the human being. The system includes a dual element pyroeleetric detector, a Fresnel lens array, and a processor. The dual element pyroelectric detector detects radiation from the human being as the human being moves over time. The Fresnel lens array is located between the dual element pyroelectric detector and the human being. The Fresnel lens array improves collection efficiency and spatial resolution of the dual element pyroelectric detector. The Fresnel lens array includes a mask. The mask provides at least one zone of visibility. The processor is coupled to the dual element pyroelectric detector, the processor converts the detected radiation to a spectral radiation signature. The processor compares the spectral radiation signature to at least a second spectral radiation signature to identify the human being.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Linear illumination lens with Fresnel facets
ActiveUS7559672B1Large amount of processingImprove efficacyMechanical apparatusFurnace componentsCamera lensFresnel lens
A linear Fresnel lens for LED illumination is configured initially by using a meridional flux-assignment method and is then corrected by assessing the three-dimensional flux distribution of individual facets. The facet angles are slightly altered as required to produce uniformity. A variety of specialized lens shapes are generated, such as for illuminating shelves in commercial refrigerator food-display cases. The lens shapes are suitably thin for economical production by extrusion.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Forming an optical element on the surface of a light emitting device for improved light extraction
InactiveUS6987613B2Easy to integrateMaximize production efficiencyDiffraction gratingsSemiconductor devicesWafer bondingAlternative methods
Provided is a light emitting device including a Fresnel lens and / or a holographic diffuser formed on a surface of a semiconductor light emitter for improved light extraction, and a method for forming such light emitting device. Also provided is a light emitting device including an optical element stamped on a surface for improved light extraction and the stamping method used to form such device. An optical element formed on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter reduces reflective loss and loss due to total internal reflection, thereby improving light extraction efficiency. A Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be formed on a surface by wet chemical etching or dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching, reactive ion etching, and chemically-assisted ion beam etching, optionally in conjunction with a lithographic technique. In addition, a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be milled, scribed, or ablated into the surface. Stamping, an alternative method for forming an optical element, can also be used to form a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter. Stamping includes pressing a stamping block against the surface of a light emitting diode. The stamping block has a shape and pattern that are the inverse of the desired optical element. Optionally, stamping can be done before, after, or concurrently with wafer-bonding. Alternatively, a material can be stamped and later bonded to the semiconductor light emitter.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Forming an optical element on the surface of a light emitting device for improved light extraction
Provided is a light emitting device including a Fresnel lens and / or a holographic diffuser formed on a surface of a semiconductor light emitter for improved light extraction, and a method for forming such light emitting device. Also provided is a light emitting device including an optical element stamped on a surface for improved light extraction and the stamping method used to form such device. An optical element formed on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter reduces reflective loss and loss due to total internal reflection, thereby improving light extraction efficiency. A Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be formed on a surface by wet chemical etching or dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching, reactive ion etching, and chemically-assisted ion beam etching, optionally in conjunction with a lithographic technique. In addition, a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be milled, scribed, or ablated into the surface. Stamping, an alternative method for forming an optical element, can also be used to form a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter. Stamping includes pressing a stamping block against the surface of a light emitting diode. The stamping block has a shape and pattern that are the inverse of the desired optical element. Optionally, stamping can be done before, after, or concurrently with wafer-bonding. Alternatively, a material can be stamped and later bonded to the semiconductor light emitter.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Light emitting diode system packages
InactiveUS20060044806A1High densityEfficient couplingPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceFresnel lensTotal internal reflection
Light emitting diode systems disclosed include semiconductor diodes arranged in cooperation with electrical contacts, mounting provisions, and optical couplings; where the optical couplings include at least a Fresnel lens. A Fresnel lens is further coupled to additional optical elements such as a concave or ‘negative’ lens and still further to a reflector operating via principles of total internal reflection. Both the concave lens and the reflector are aspherical in preferred versions. A cover element of single piece plastic may be formed in a molding process whereby all three of these optical elements, i.e. the Fresnel lens, the negative lens and the reflector, are formed into the single plastic piece. Further, the plastic piece may be arranged to also accommodate auxiliary systems such as alignment indexing and fastening means as well as interlocking peripheral configurations.
Owner:ABRAMOV VLADIMIR SEMENOVICH +4
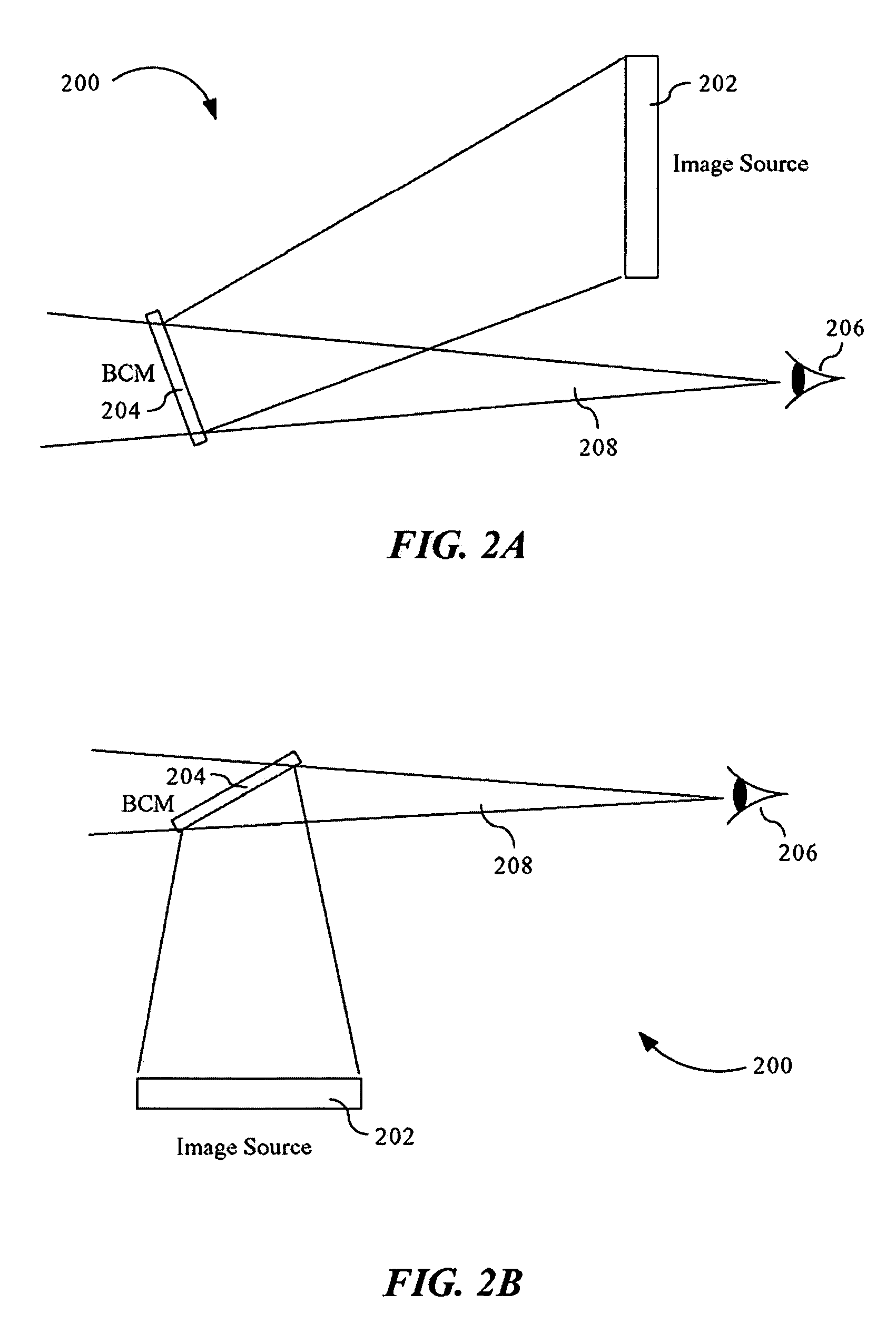
Advanced compact head up display
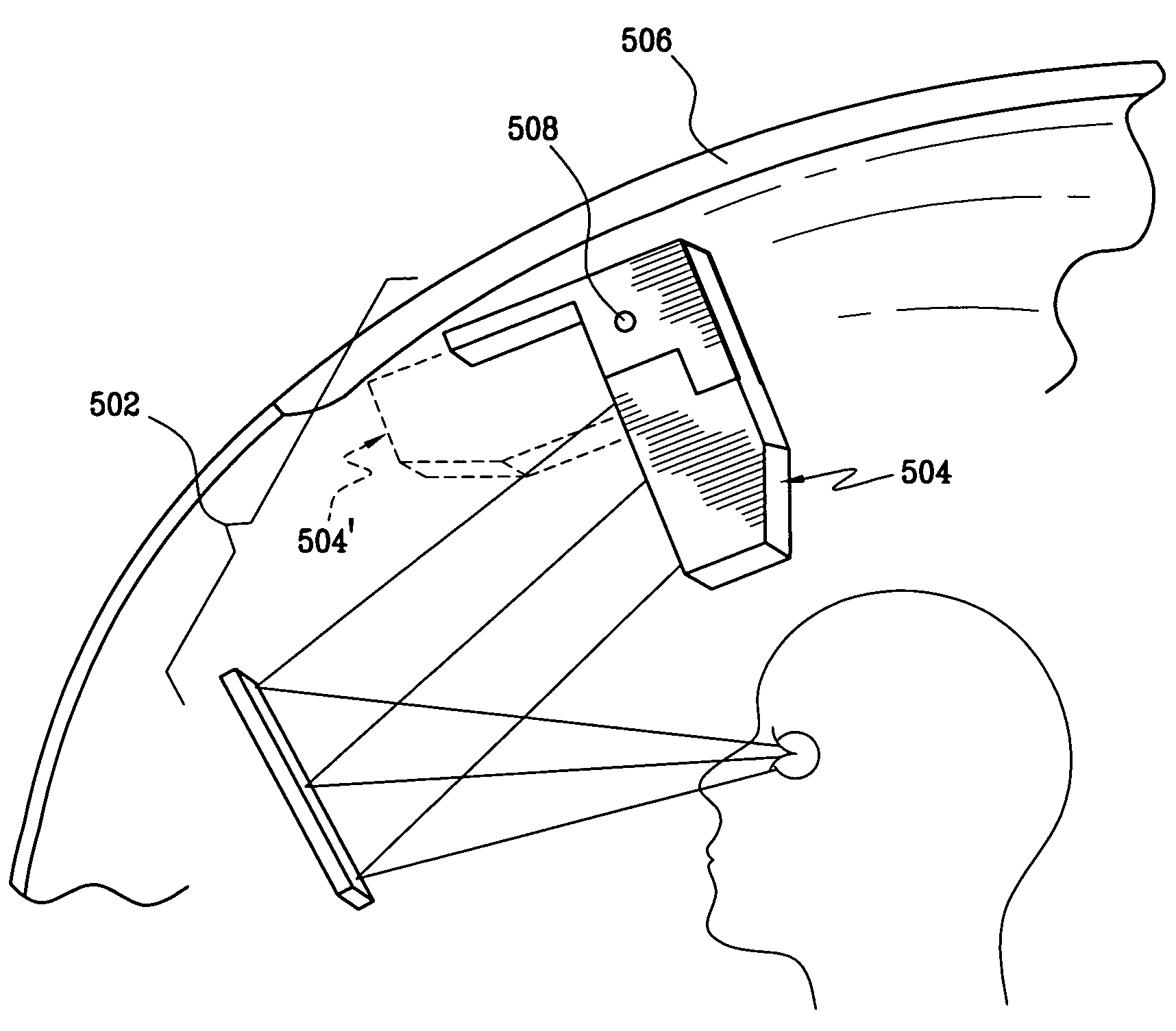
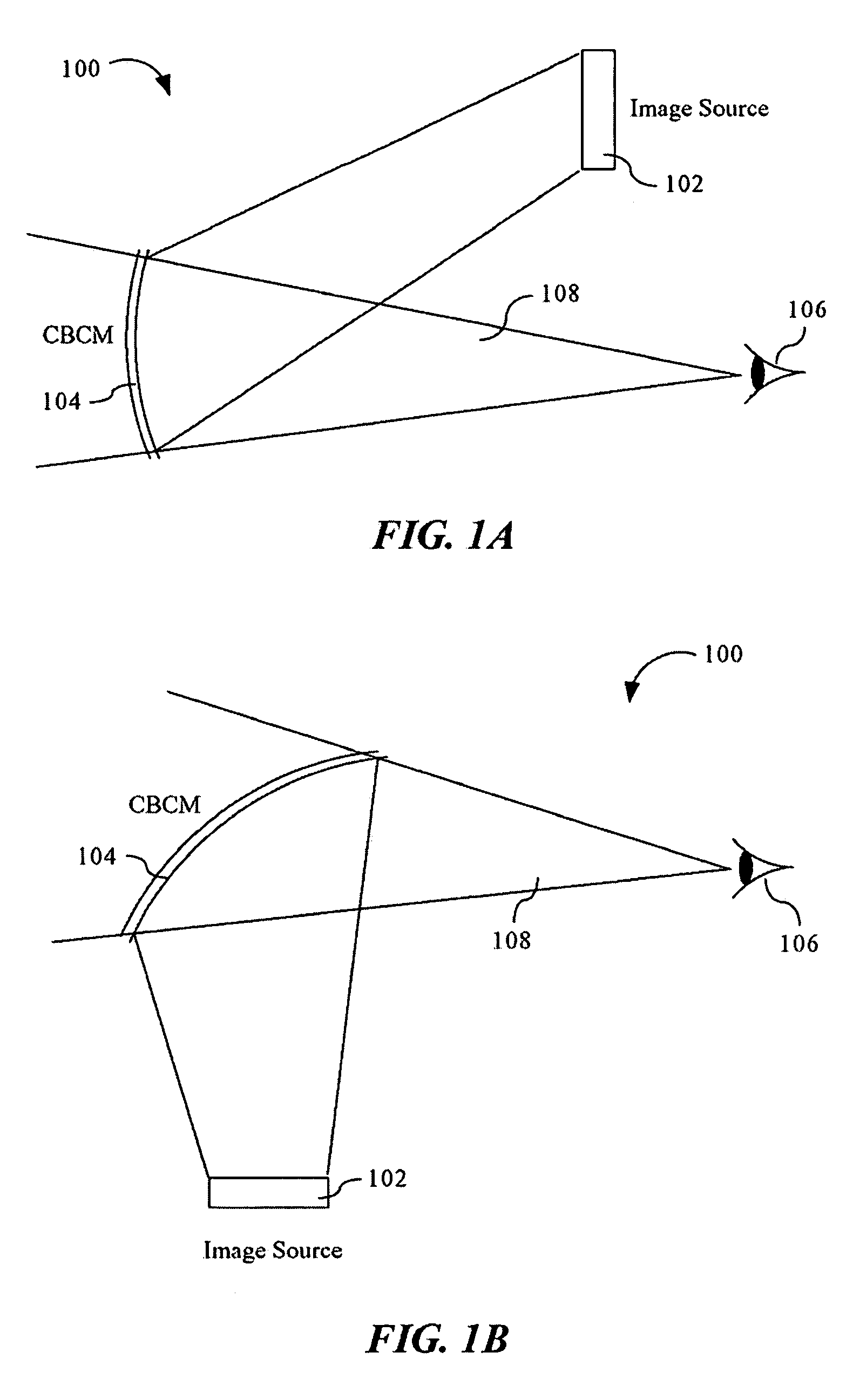
ActiveUS7095562B1Simplifies optical systemMinimize aberrationLighting support devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsHead-up displayDashboard
A head up display system for a vehicle that includes a compact image source for projecting an image. The compact image source may be foldable up toward or into a cockpit ceiling of the vehicle, be positioned within a dashboard of the vehicle, or located at another suitable position. A combiner reflects the projected image with optical power toward an observer for observation. The combiner is positioned so that the observer, in a line of sight, may see a visual exterior view of an outside scene through the combiner and the projected image in the combiner. In a preferred embodiment, the image source includes an illumination system that includes a high power light emitting diode (LED) array assembly. A Fresnel lens array is operatively associated with the LED array assembly for receiving light produced by the LED and providing a nearly collimated light output. A spatial light modulator receives the nearly collimated light output. The preferred combiner is a meniscus combiner that includes a meniscus lens; a multi-layer dichroic coating formed on a first surface of the meniscus lens; and, an anti-reflection coating formed on a second, opposite surface of the meniscus lens. The meniscus combiner preferably utilizes a non-symmetric aspheric meniscus lens.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Optical member, light source apparatus, display apparatus, and terminal apparatus
ActiveUS20060291243A1Strong light directivityHigh light utilization ratioLighting elementsOptical light guidesFresnel lensOptoelectronics
A planar light source, Fresnel lens sheet, and louver are disposed in the stated order in a light source apparatus. The Fresnel lens sheet deflects and focuses in one dimension light that has entered from the planar light source. The louver is disposed in the optical path of the light emitted from the Fresnel lens sheet, and the directivity of the light can be increased by restricting the traveling direction of the light to the focal direction of the Fresnel lens sheet. The light utilization ratio can thereby be increased, the directivity of planarly emitted light can be increased, and the brightness can be made uniform at the point of observation.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
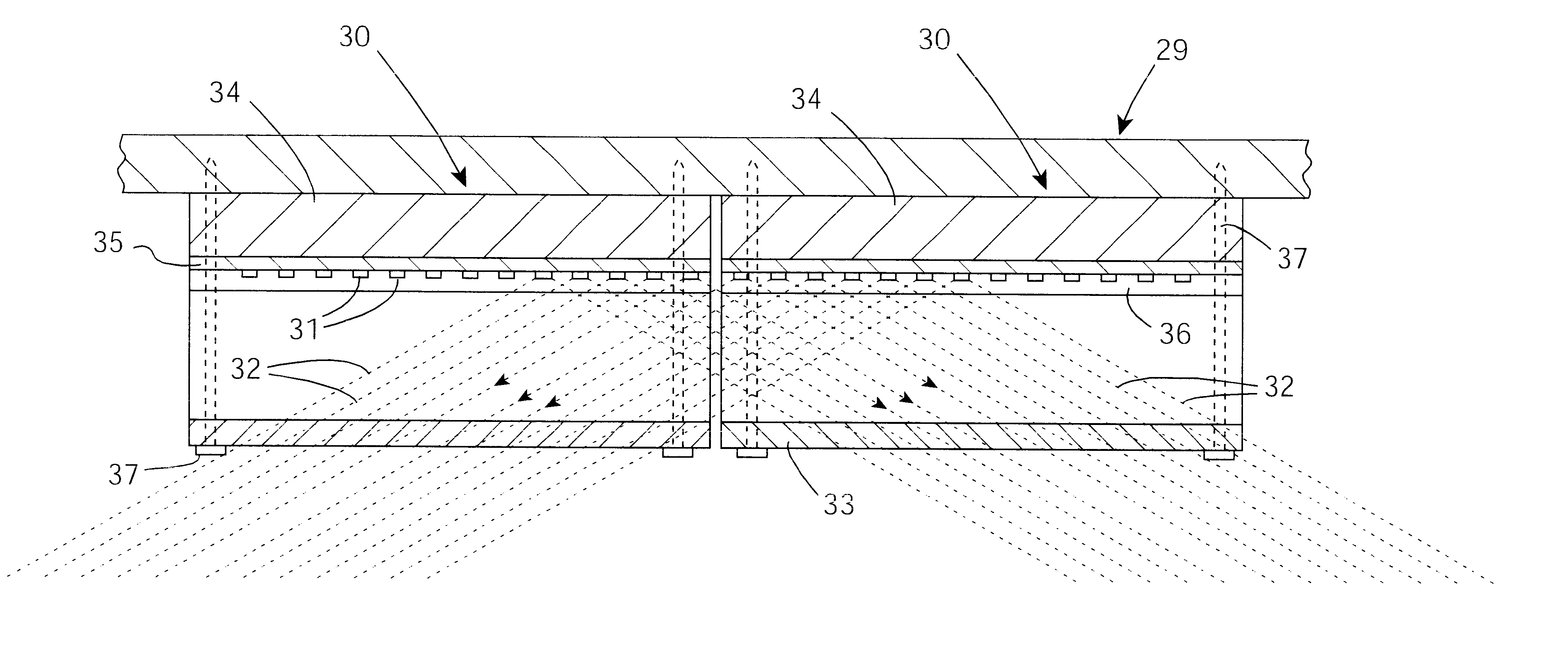
Optical sensor device for detecting wetting
InactiveUS7751054B2Small thicknessIncrease the areaScattering properties measurementsPhotoelectric discharge tubesFresnel lensElectrical conductor
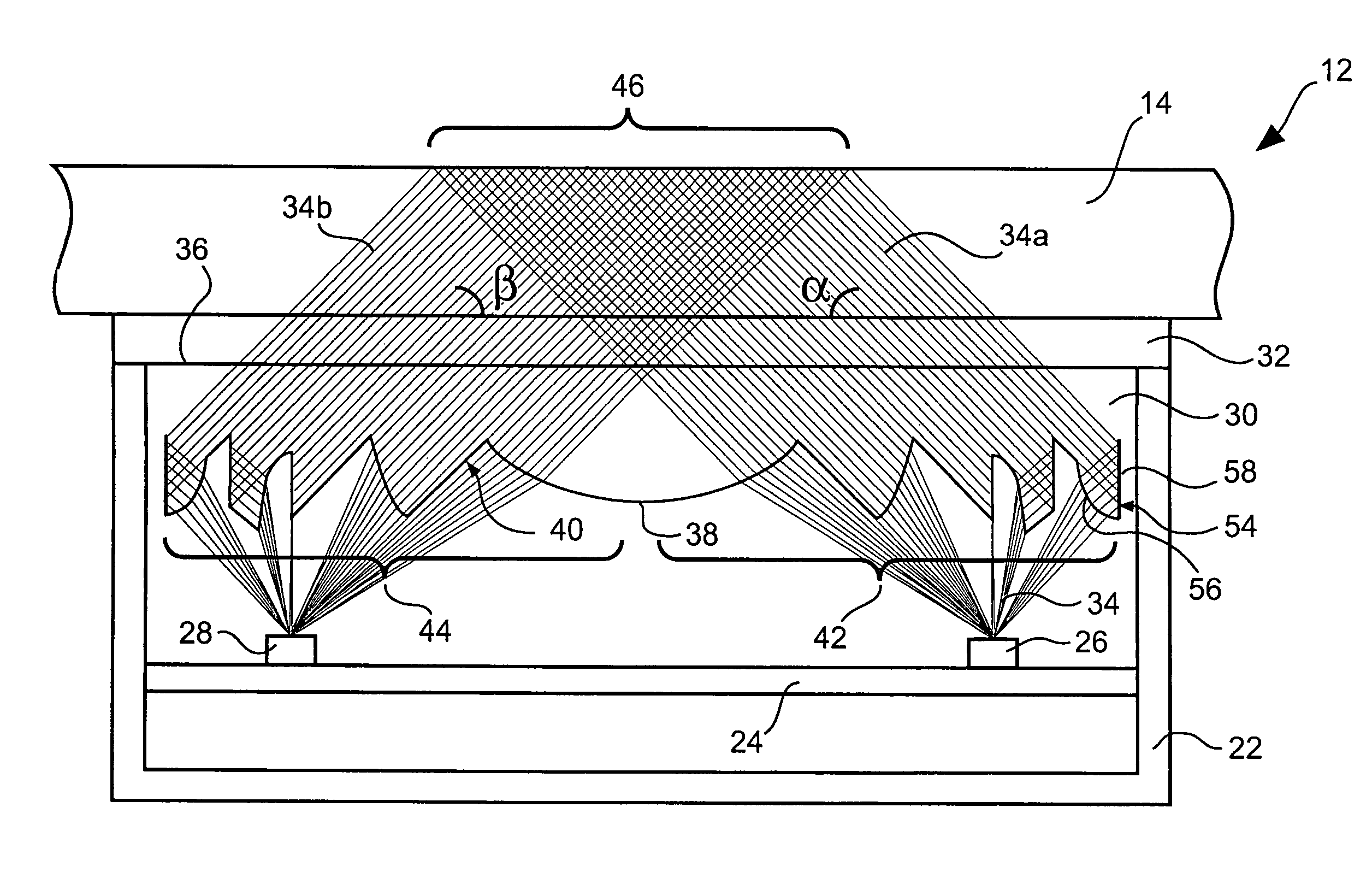
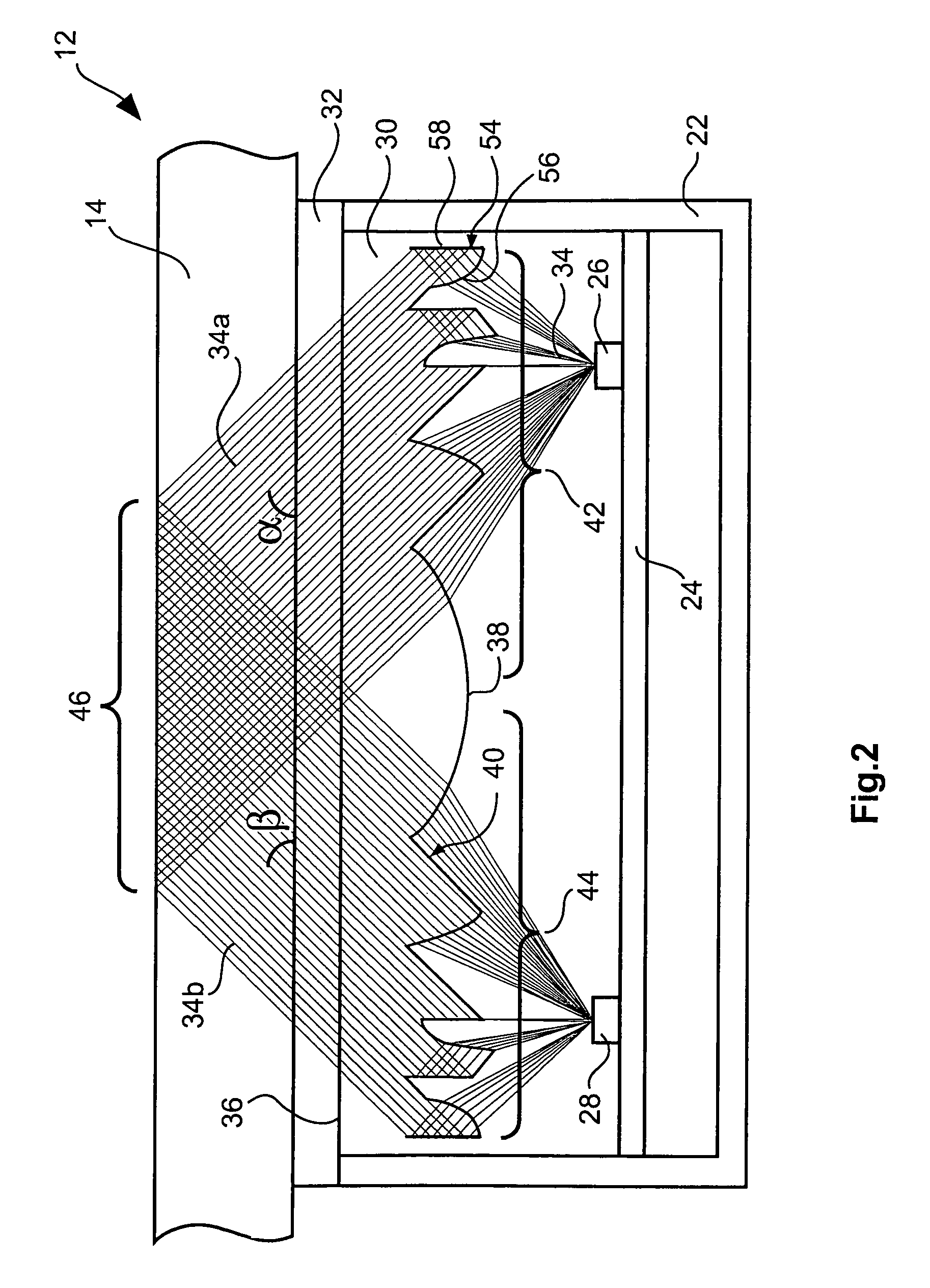
An optical sensor device (10) is able to be coupled to a window (14), in particular to a windscreen of a motor vehicle. The optical sensor device (10) comprises a sensor unit (12), which includes a emitter (26), a receiver (28) and a light conductor unit (30). By the light conductor unit (30), a light beam (34) emitted by the emitter (26) is coupled into the window (14), coupled out of the window (14) and directed onto the receiver (28). The light conductor unit (30) includes Fresnel lens regions and associated reflecting regions.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS & COMPONENTS GMBH & CO KG
Illuminating apparatus
InactiveUS6974236B2Efficient ConcentrationImprove propertiesMachines/enginesEngine cooling apparatusPhysicsFresnel lens
This specification discloses an illuminating apparatus having a light source and an optical unit disposed forwardly on the object side of the light source, the optical unit being provided with an incidence surface on which light from the light source is incident, a light emergence surface provided with a Fresnel lens, and a side reflecting surface for totally reflecting the light incident on the incidence surface toward the Fresnel lens, wherein the light totally reflected by the side reflecting surface is refracted by the Fresnel lens and efficiently irradiates the object.
Owner:CANON KK
Planar solar concentrator power module
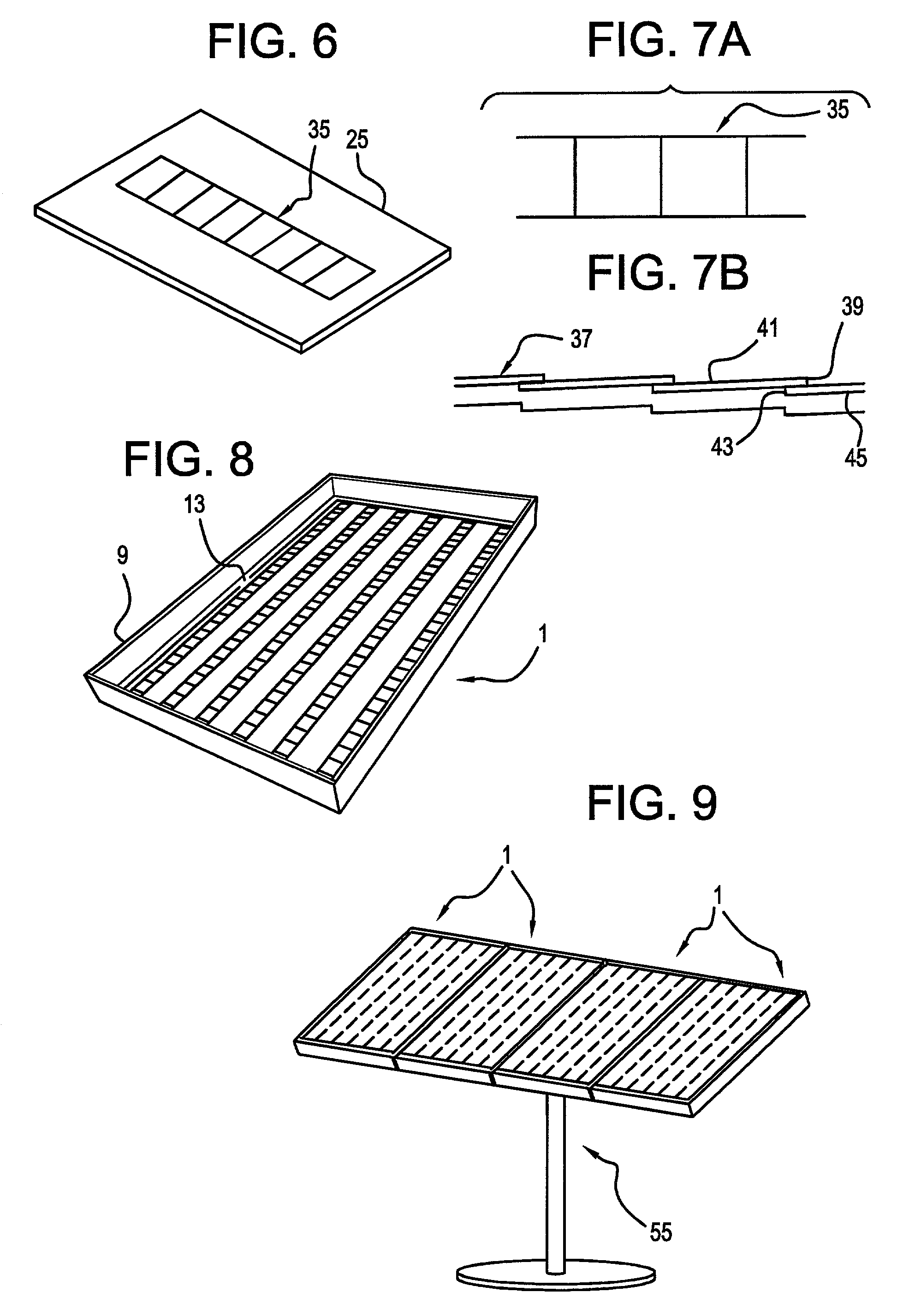
InactiveUS7388146B2Low costEasy customer acceptanceSolar heating energySolar heat devicesElectrical batterySolar power
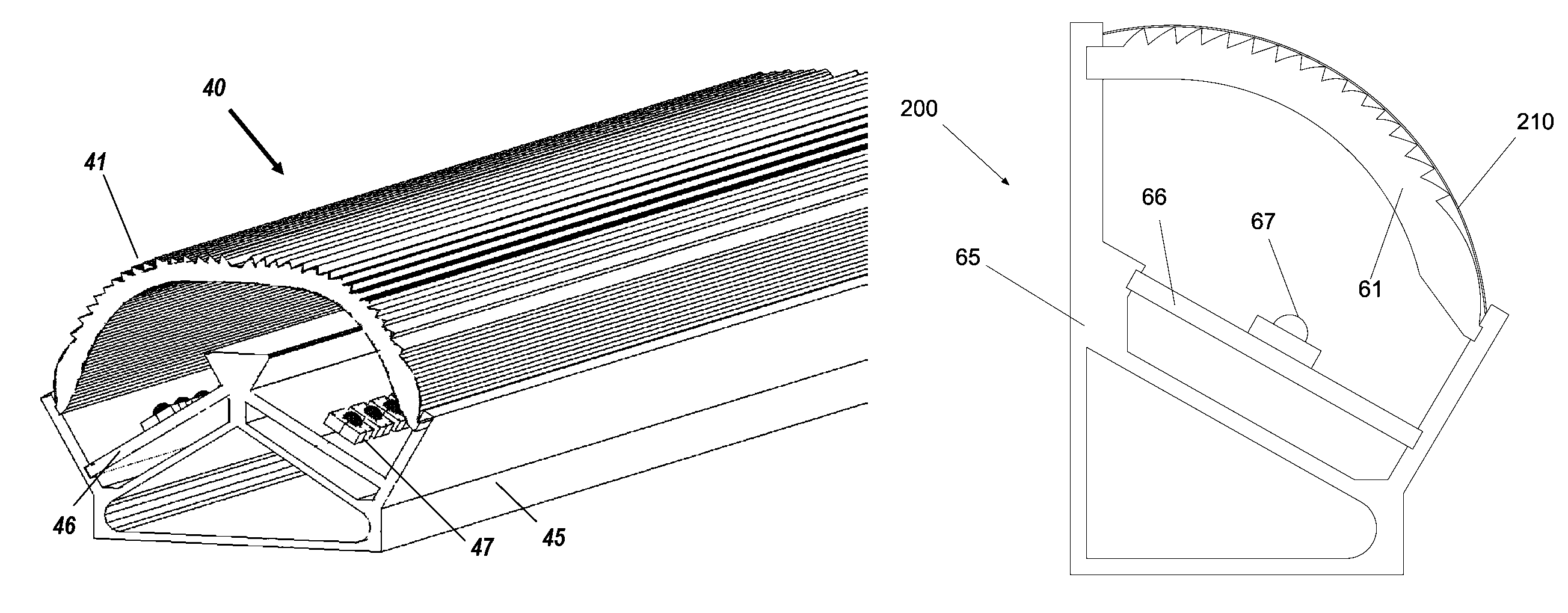
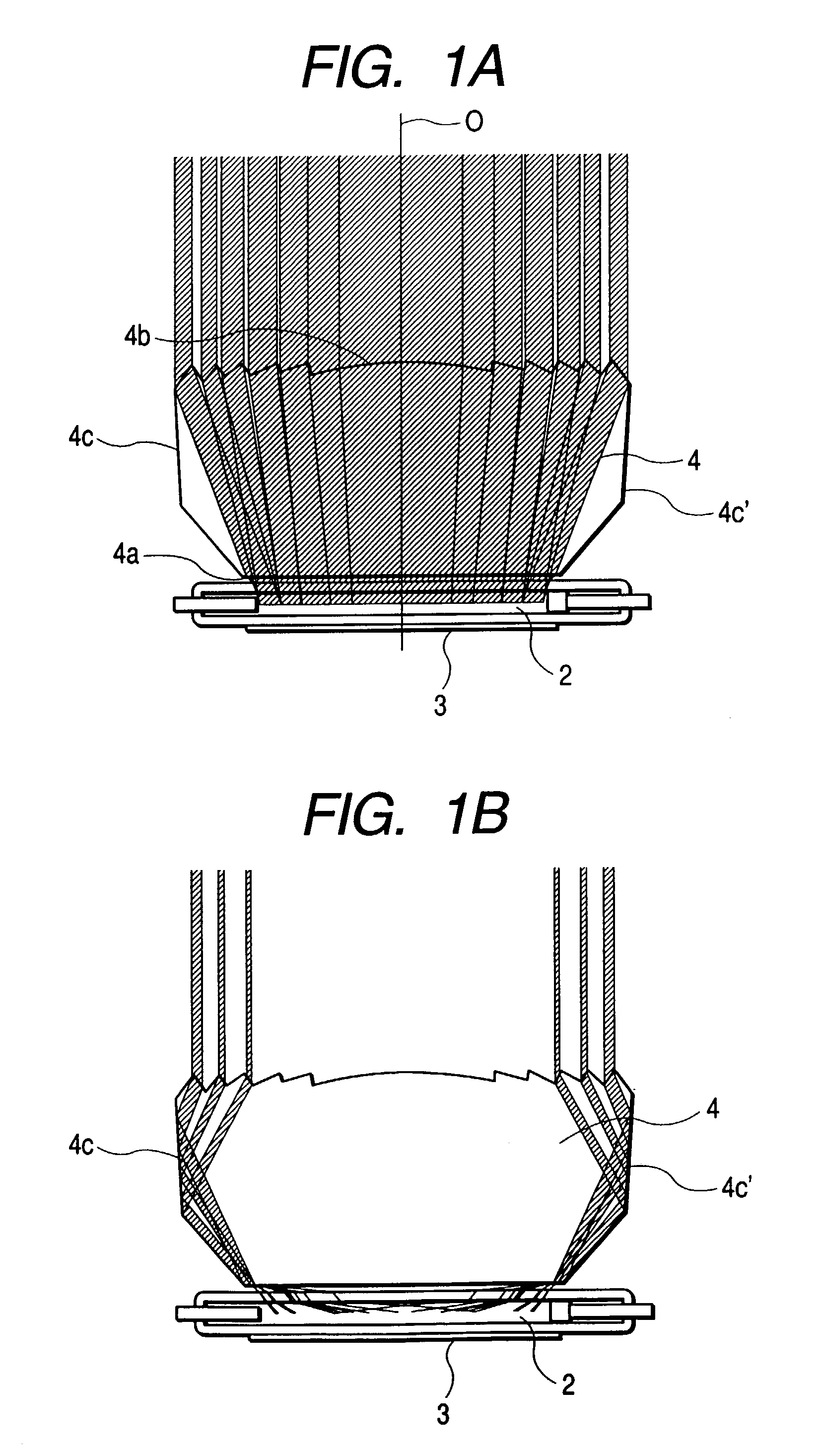
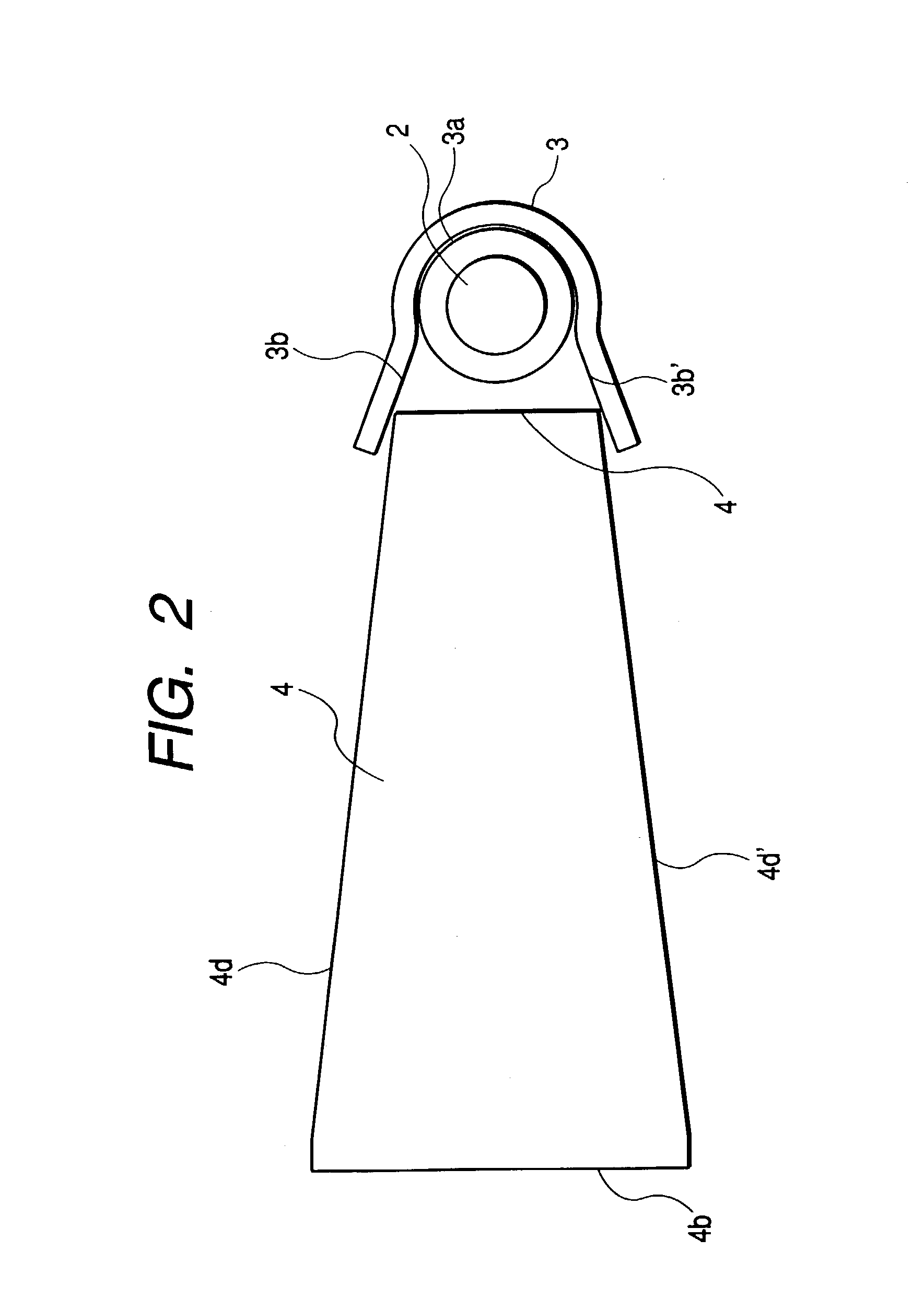
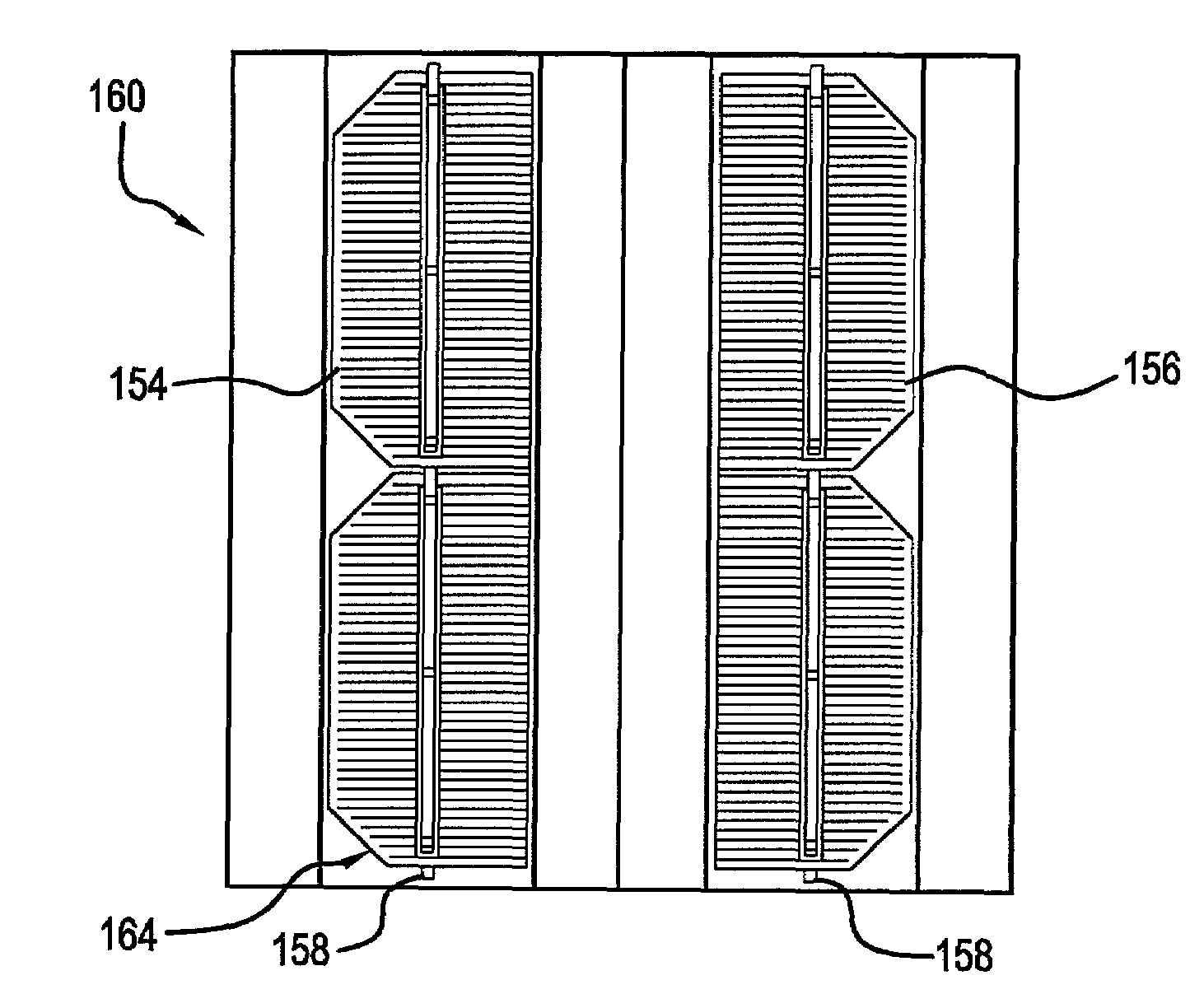
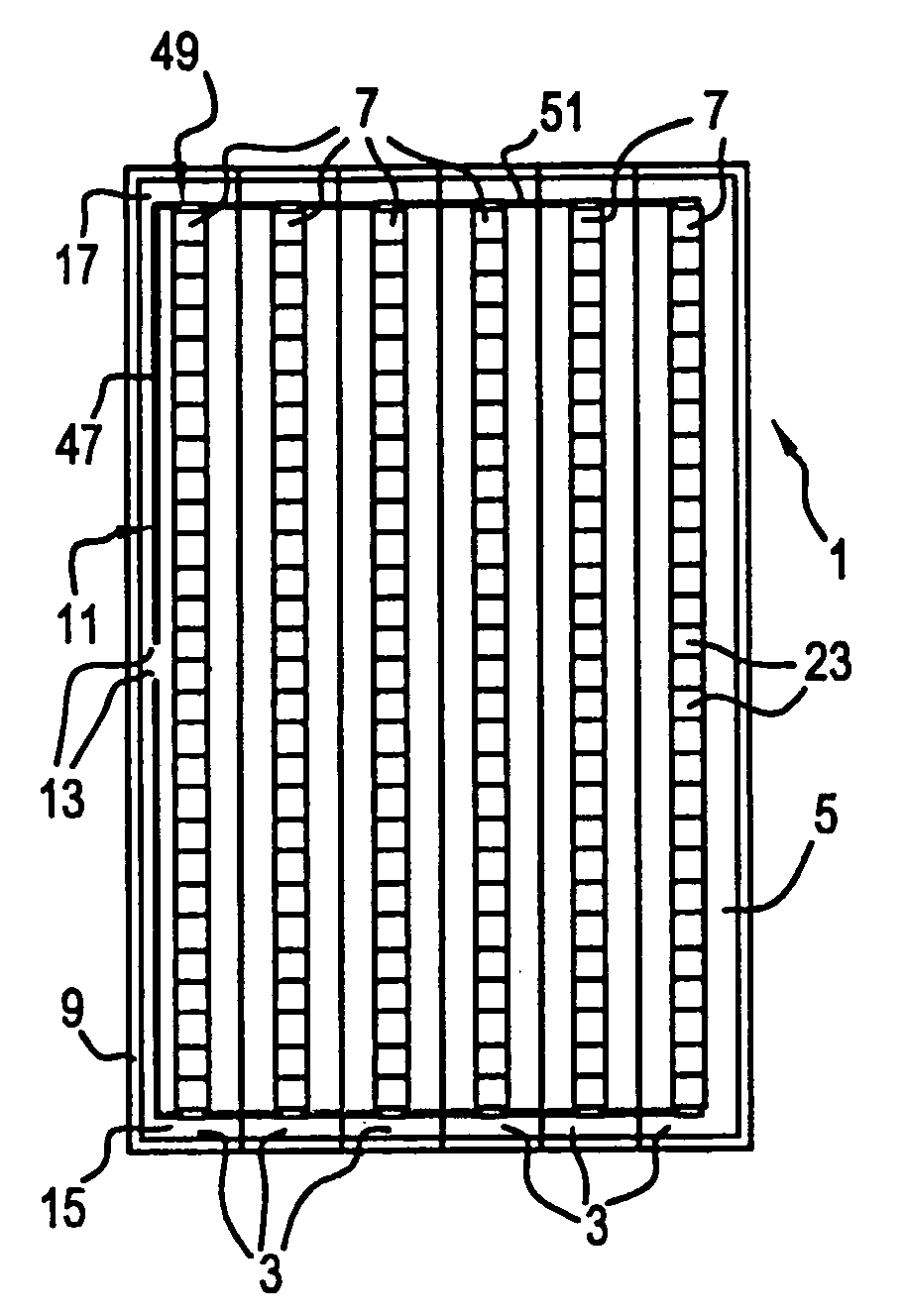
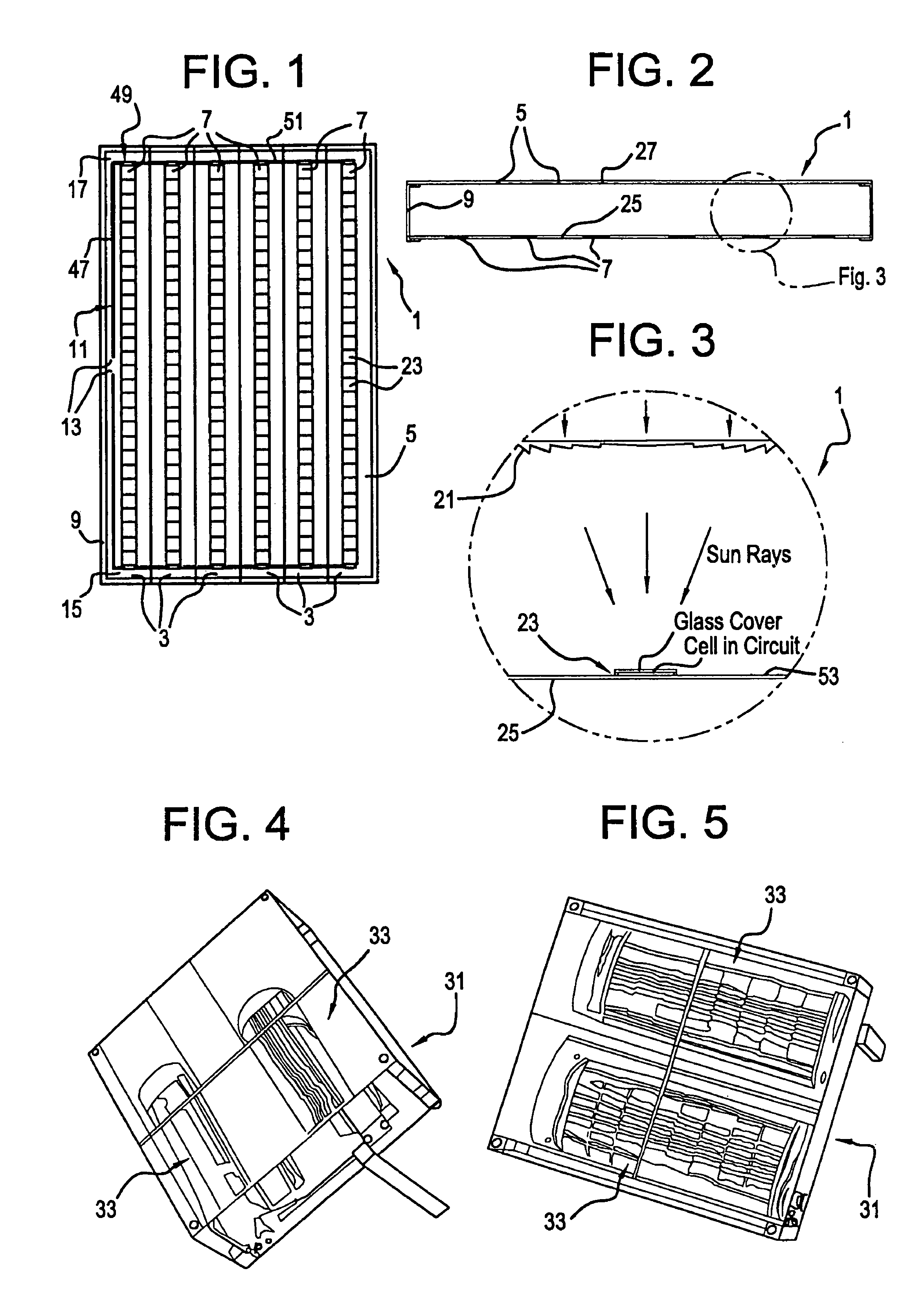
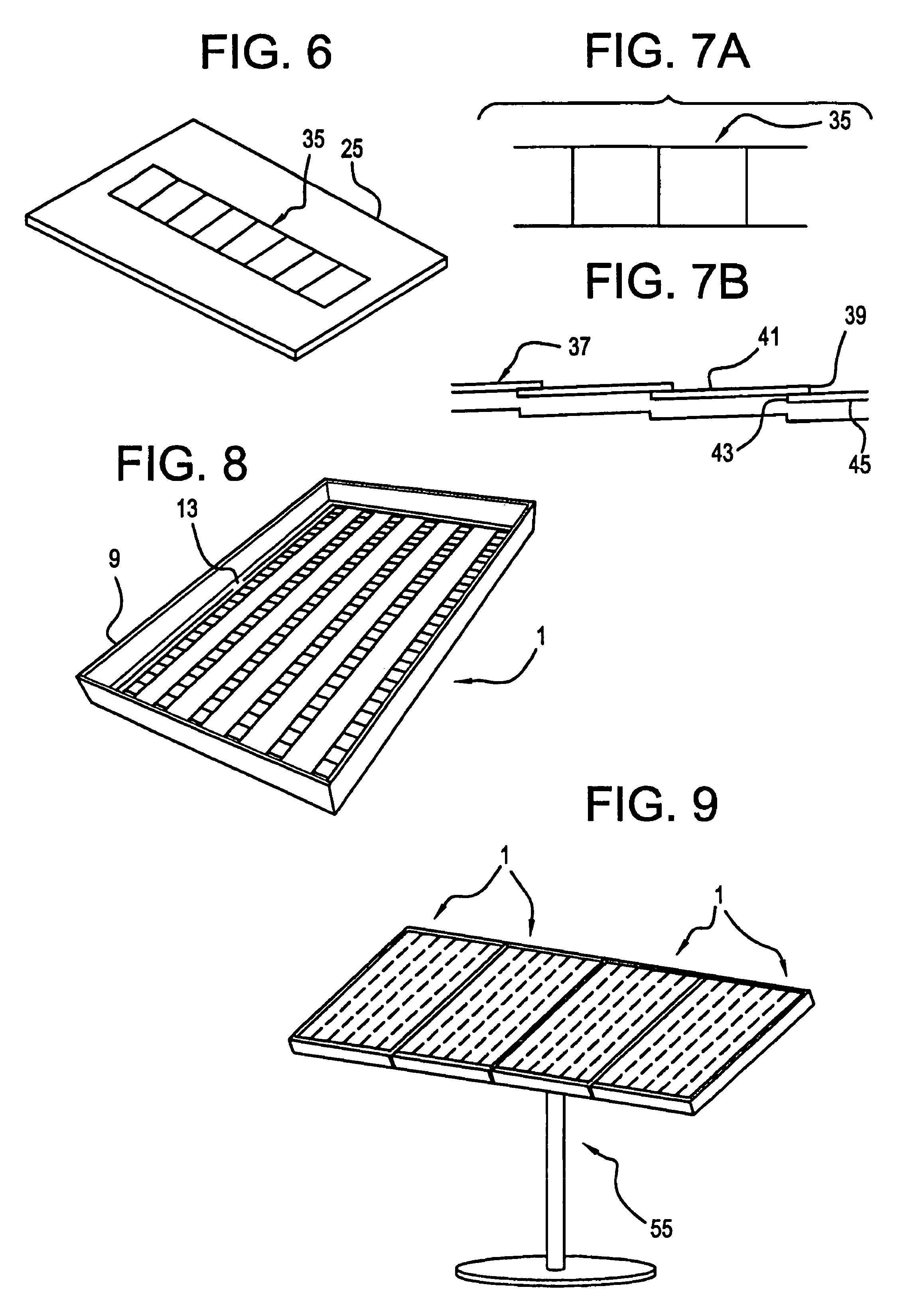
A planar concentrator solar power module has a planar base, an aligned array of linear photovoltaic cell circuits on the base and an array of linear Fresnel lenses or linear mirrors for directing focused solar radiation on the aligned array of linear photovoltaic cell circuits. The cell circuits are mounted on a back panel which may be a metal back plate. The cell circuit area is less than a total area of the module. Each linear lens or linear mirror has a length greater than a length of the adjacent cell circuit. The cell circuit may have cells mounted in shingle fashion to form a shingled-cell circuit. In an alternative module, linear extrusions on the circuit element have faces for mounting the linear mirrors for deflecting sun rays impinging on each mirror onto the shingled-cells. The linear extrusions are side-wall and inner extrusions with triangular cross-sections. The circuit backplate is encapsulated by lamination for weather protection. The planar module is generally rectangular with alternating rows of linear cell circuits and linear lenses or linear mirrors.
Owner:JX CRYSTALS
Autostereoscopic display with fresnel lens element and double sided prism film adjacent a backlight having a light transmission surface with left and right eye light sources at opposing ends modulated at a rate of at least 90 hz
InactiveUS7750982B2Color television detailsPlanar/plate-like light guidesFresnel lensLiquid-crystal display
An autostereoscopic display is described. The autostereoscopic display apparatus includes a backlight having opposing first and second light input surfaces and a light transmission surface extending between the opposing first and second light input surfaces and a right eye light source located to provide light into the first light input side and a left eye light source located to provide light into the second light input side, wherein the left eye light source and the right eye light source are configured to be modulated between the left eye light source and the right eye light source at a rate of at least 90 hertz. A double sided prism film is adjacent to the light transmission surface. The double sided prism film has a plurality of linear prism features on a first major surface and a plurality of lenticular features on a second major surface. The first major surface opposes the second major surface. The double sided prism film is disposed between the light transmission surface and a Fresnel lens element. A liquid crystal display panel is positioned to receive light transmitted through the double sided prism film.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Solid state light source
A light source includes a housing, an LED array of individual LED elements mounted in the housing, and a controller mounted in the housing and coupled to the LED array. The controller sequentially, intermittently pulses the LED elements of the LED array. The controller over drives the LED elements of the LED array with a current in excess of several times the continuous forward rating for the individual LED elements. The housing is a substantially closed, waterproof, tubular member and may include a power source in the housing. The light source may form a portable light source. The light source may include a fiber optic bundle coupling in the housing and a fresnel lens between the LED array and the fiber optic bundle coupling.
Owner:LED PIPE
High Efficiency Concentrating Photovoltaic Module Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20090223555A1Low cost per watt of electricityReduce the amount requiredPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationThermal expansionEngineering
A Concentrating Photovoltaics (CPV) module includes a metal frame, a plurality of Fresnel lenses, a secondary reflective or refractive concentrator, multi-junction solar cells with up to 40% efficiency and a novel heat spreading material. The Fresnel lenses and the secondary concentrator focus the sun over 500 times to maximize the amount of photons collected by the solar cells and converted to electricity. A newly designed soft board material provides coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) matched carrier for the solar cells and an efficient electrical connectivity method. The carrier board is attached to a specially formulated heat spreader made of graphite. At 40% the weight of aluminum and 18% the weight of copper, this specially formulated material offers thermal heat conductivity that is superior to copper. The combination of the above creates CPV modules with the highest efficiency and lowest cost per Watt.
Owner:STALIX
Liquid crystal diffraction lens element and optical head device
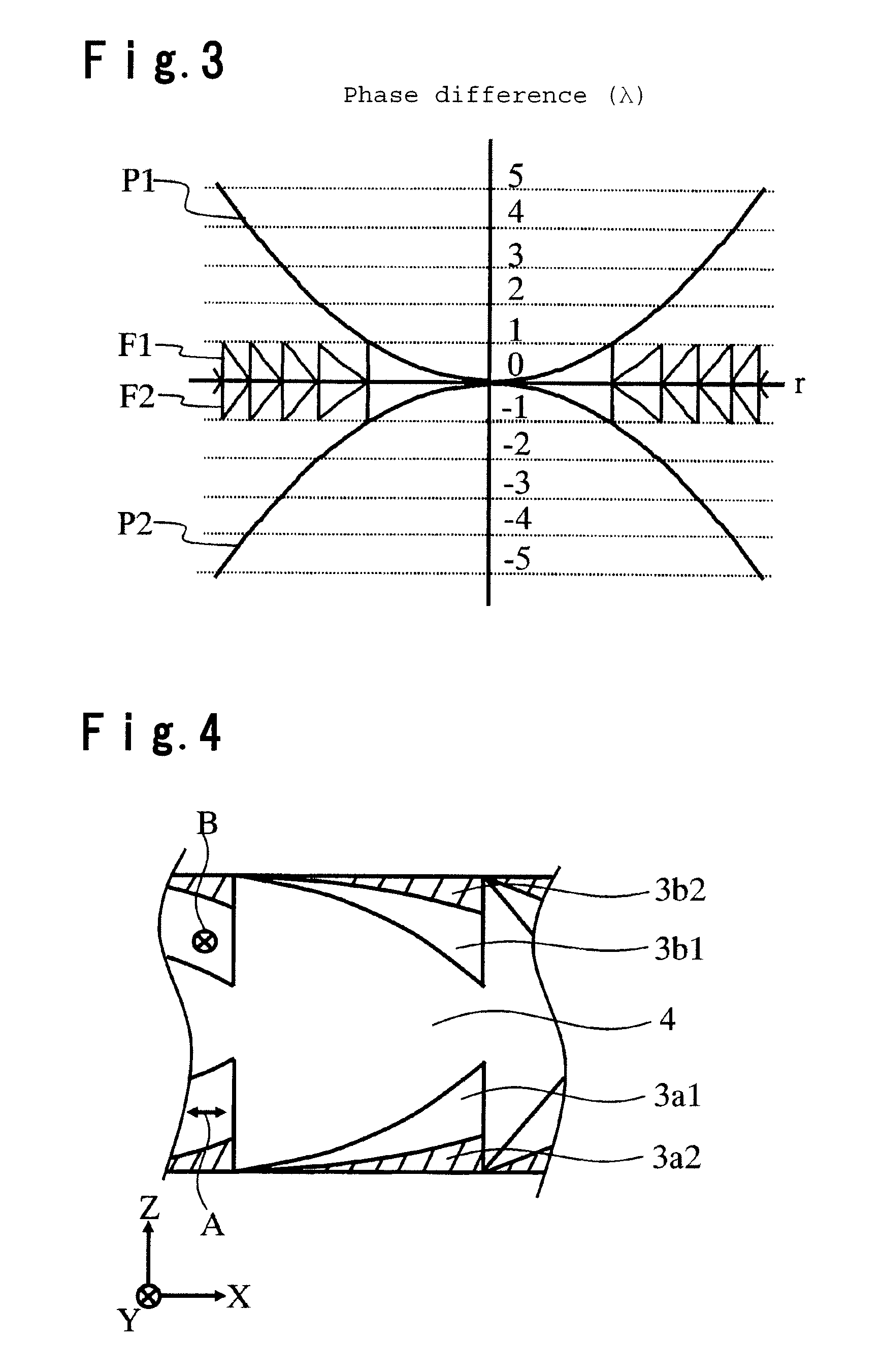
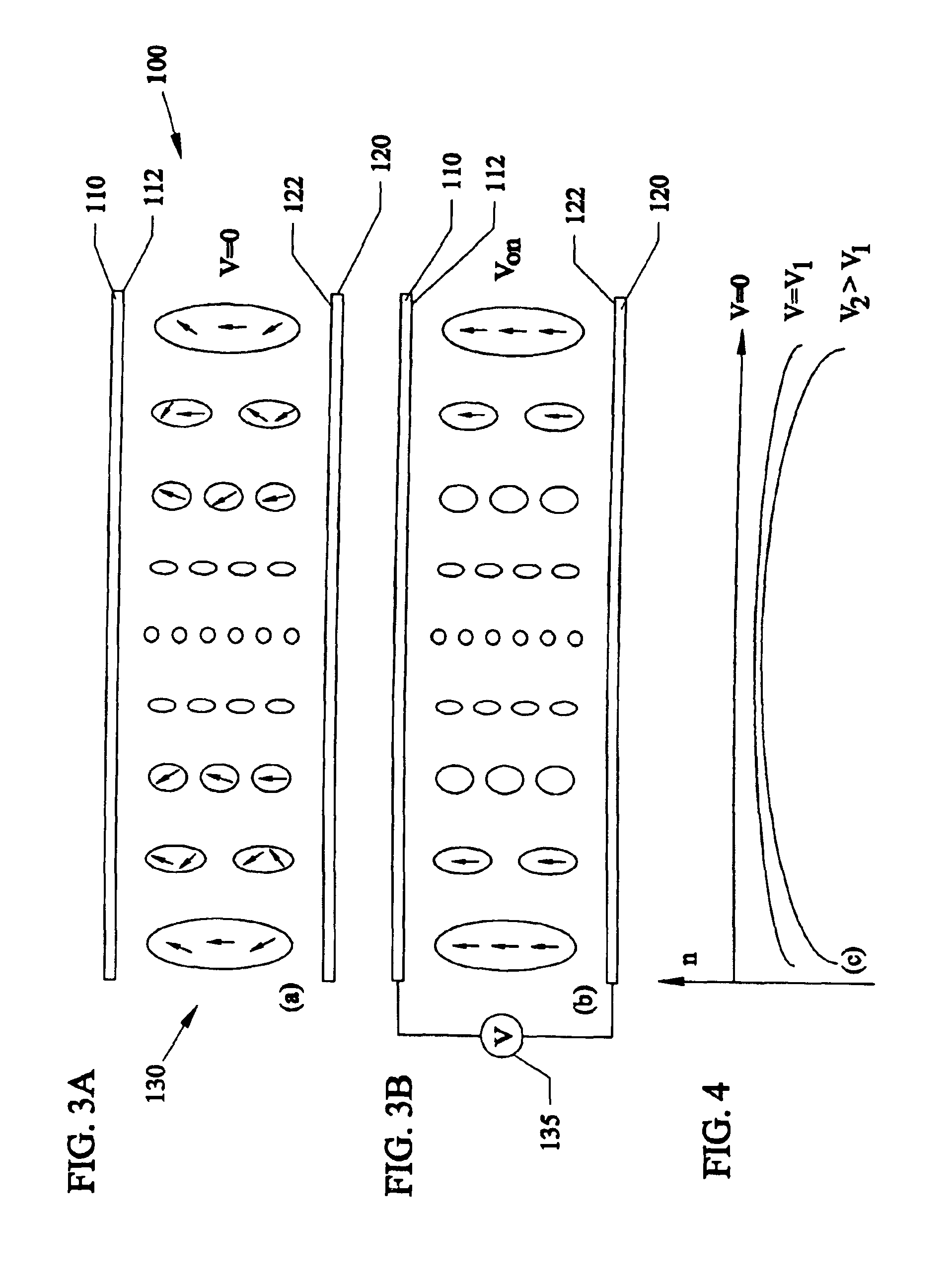
InactiveUS20070182915A1Improve design flexibilityReduce temperature-related change of efficiencyRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansFresnel lensSingle element
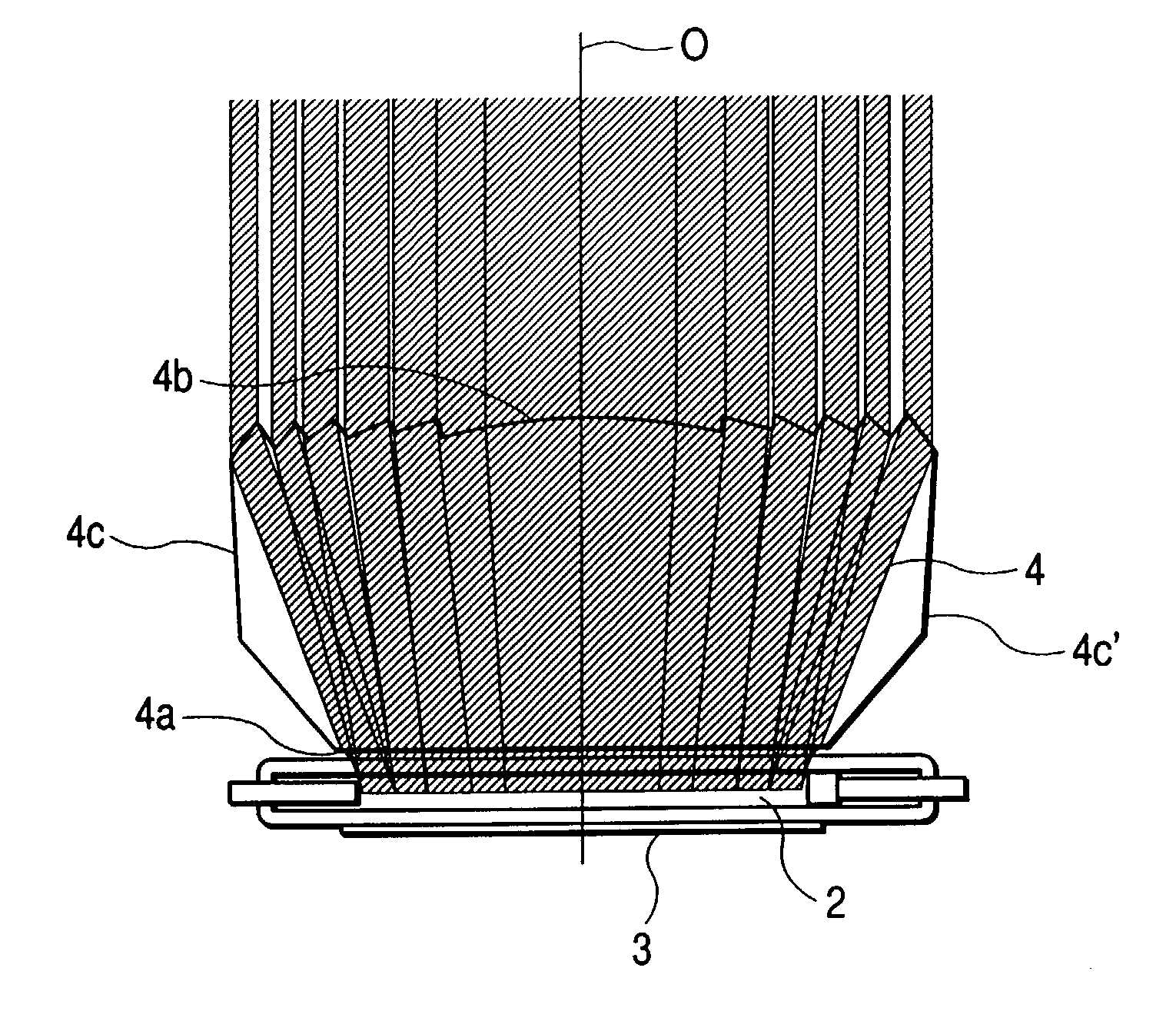
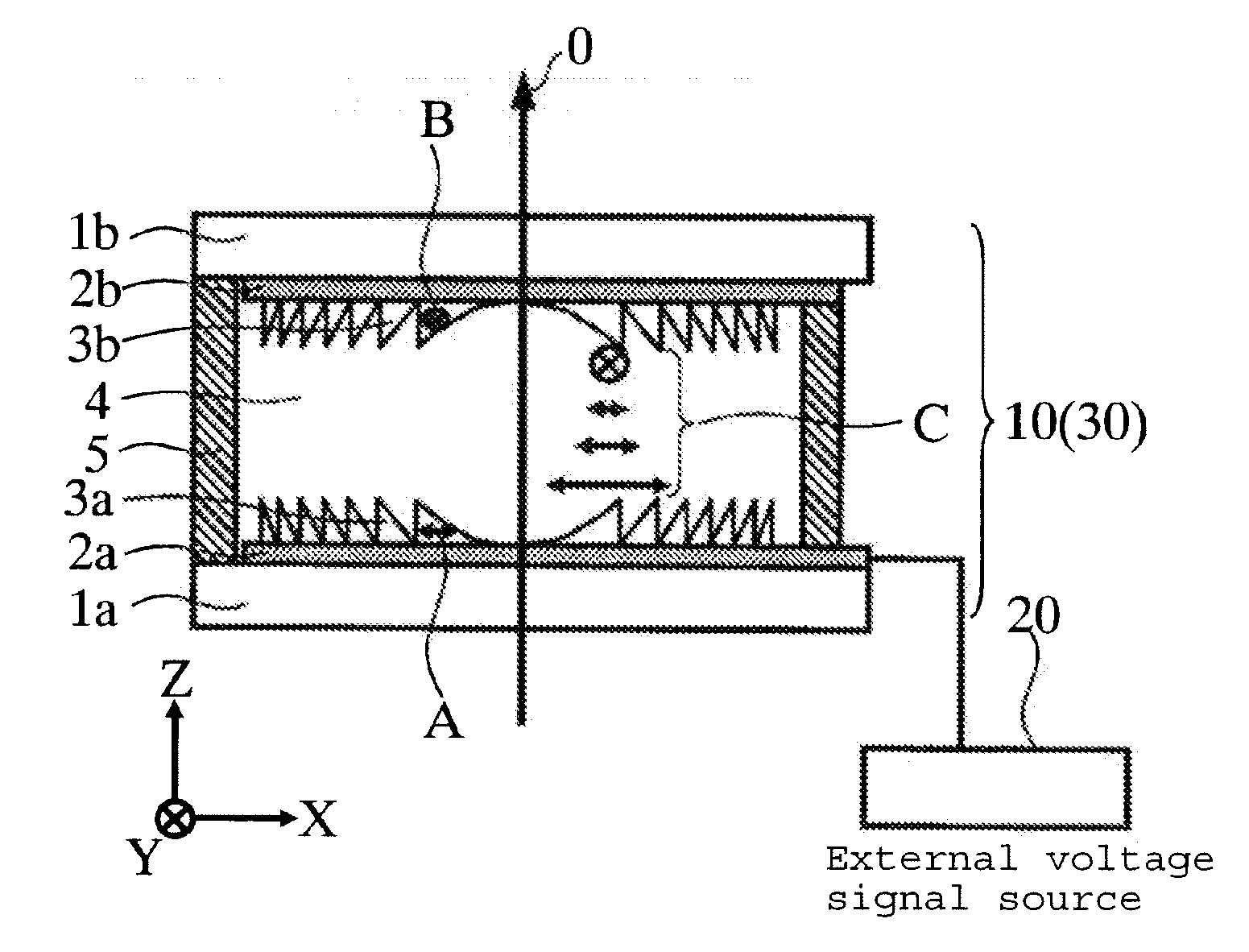
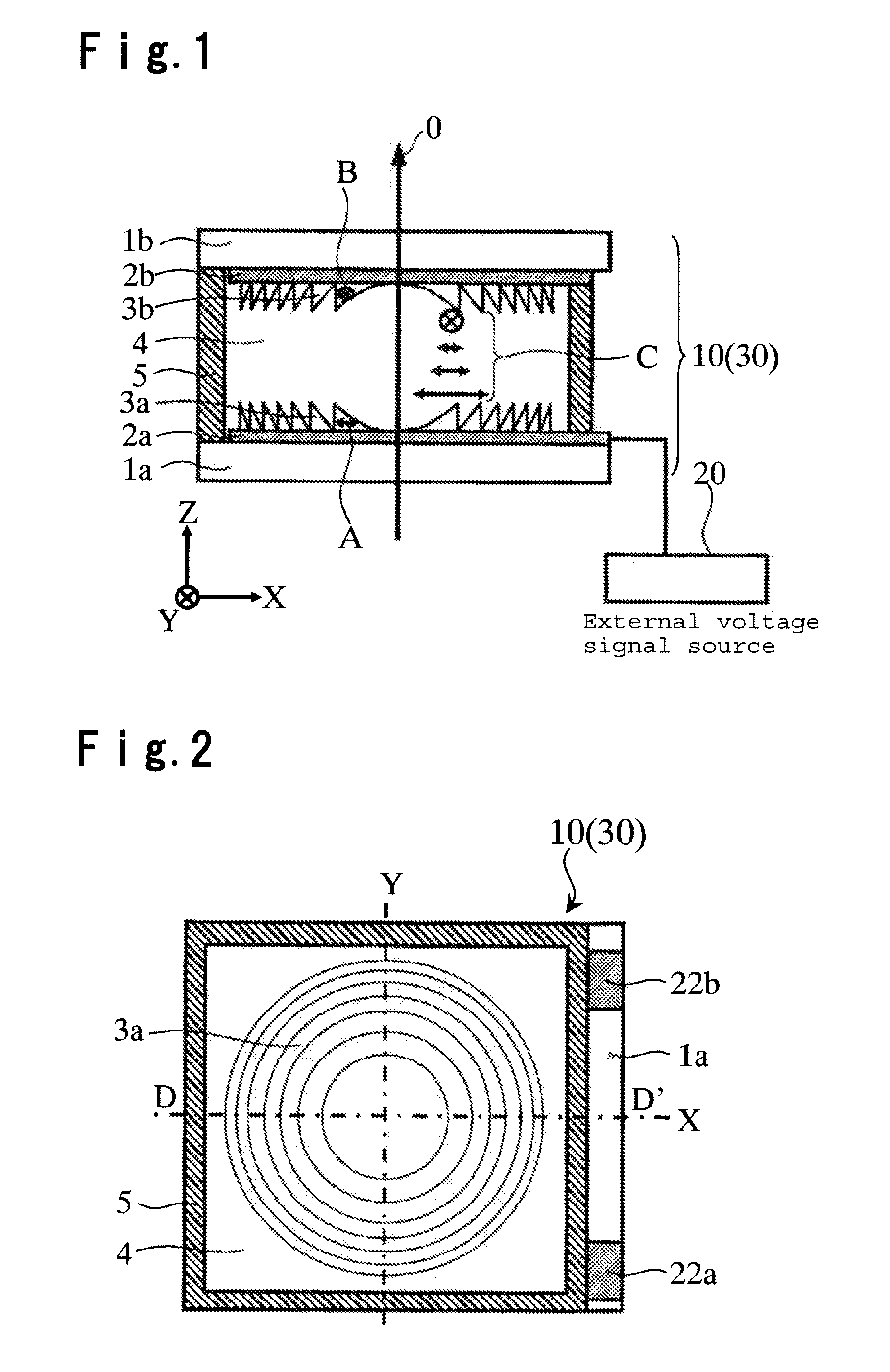
A liquid crystal diffraction lens element and an optical head device, which can switch focal lengths of both of outgoing light and returning light by a single element, are provided. The liquid crystal lens element comprises transparent substrates 1a, 1b, a liquid crystal 4 sandwiched between the transparent substrates 1a, 1b, transparent electrodes 2a, 2b, birefringent Fresnel lens members 3a, 3b each having a Fresnel lens shape and made of a birefringent material, and a seal 5, wherein the extraordinary refractive index direction A of the birefringent Fresnel lens member 3a and the extraordinary refractive index direction B of the birefringent Fresnel lens member 3b are perpendicular to each other, and the alignment direction of the liquid crystal 4 at the interface between the liquid crystal 4 and the transparent substrate 1a is perpendicular to the alignment direction of the liquid crystal 4 at the interface between the liquid crystal 4 and the transparent substrate 1b.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Linear illumination unit having plurality of LEDs
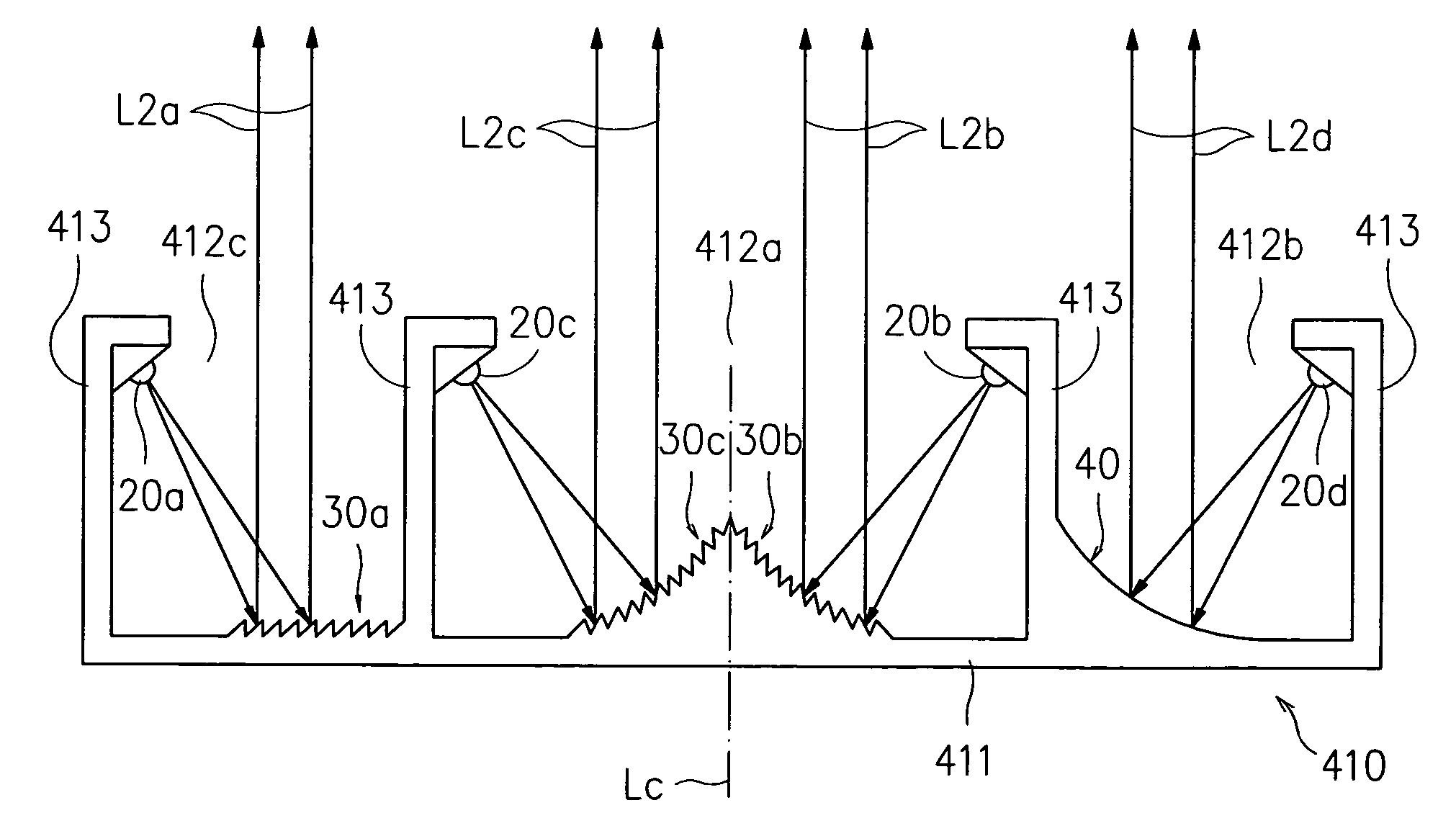
A linear illumination unit (30) has a line of unlensed LEDs (31) which emit light spreading out. The light is focused into a line by a Fresnel lens (33) which allows spread and mixing of light in the linear direction and limits spread in the ortliogonal direction. A Fresnel lens is particularly effective for this purpose. The housings 34 have slots 36 to help control light spread, and the housings are open-ended to allow spread of light in the linear direction beyond the confines of the, geometry of the units. Thus, units (30) may be interconnected to provide seamless linear light in a modular manner.
Owner:STOCKERYALE IRL
Ultraviolet sterilizer for surgery
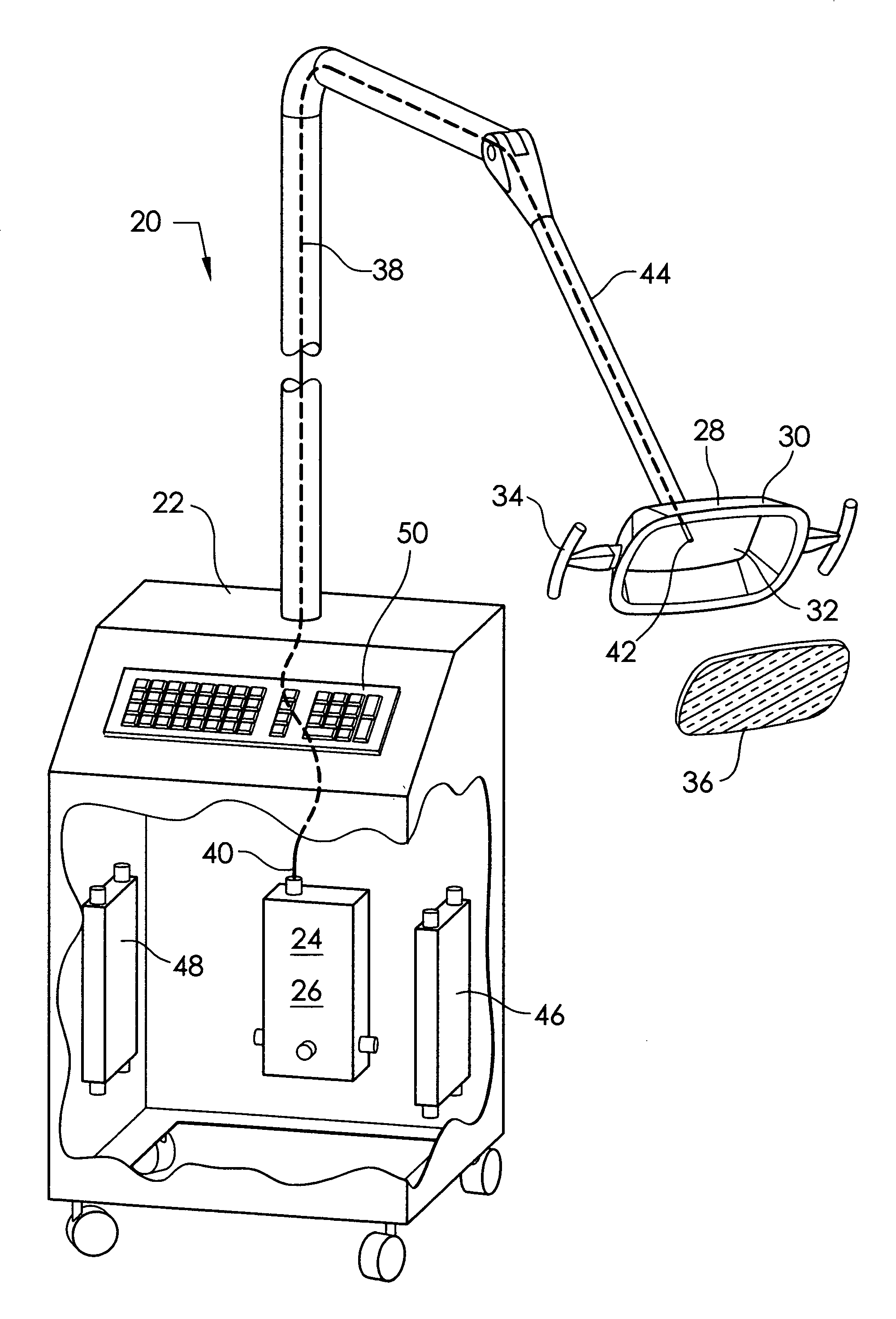
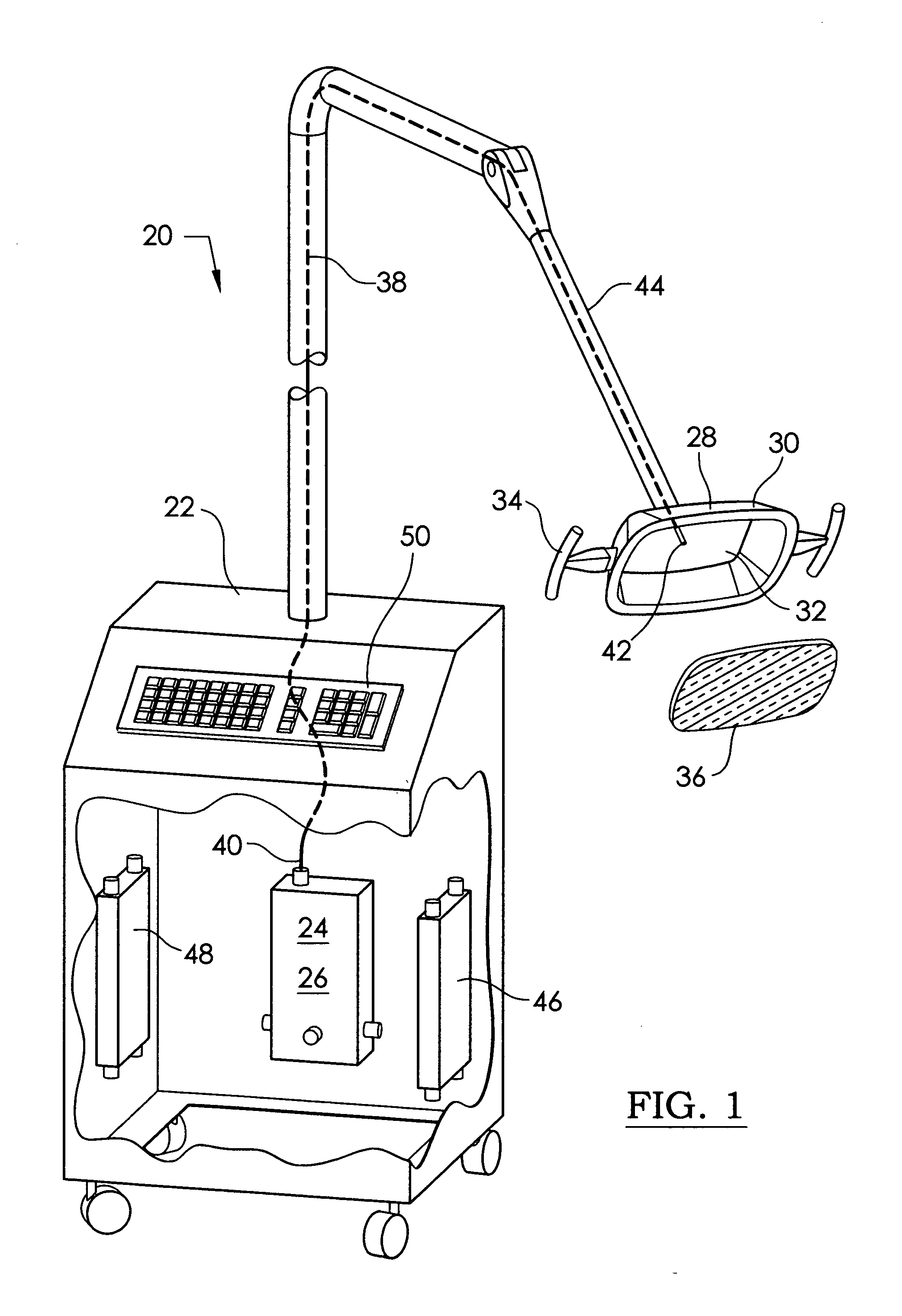
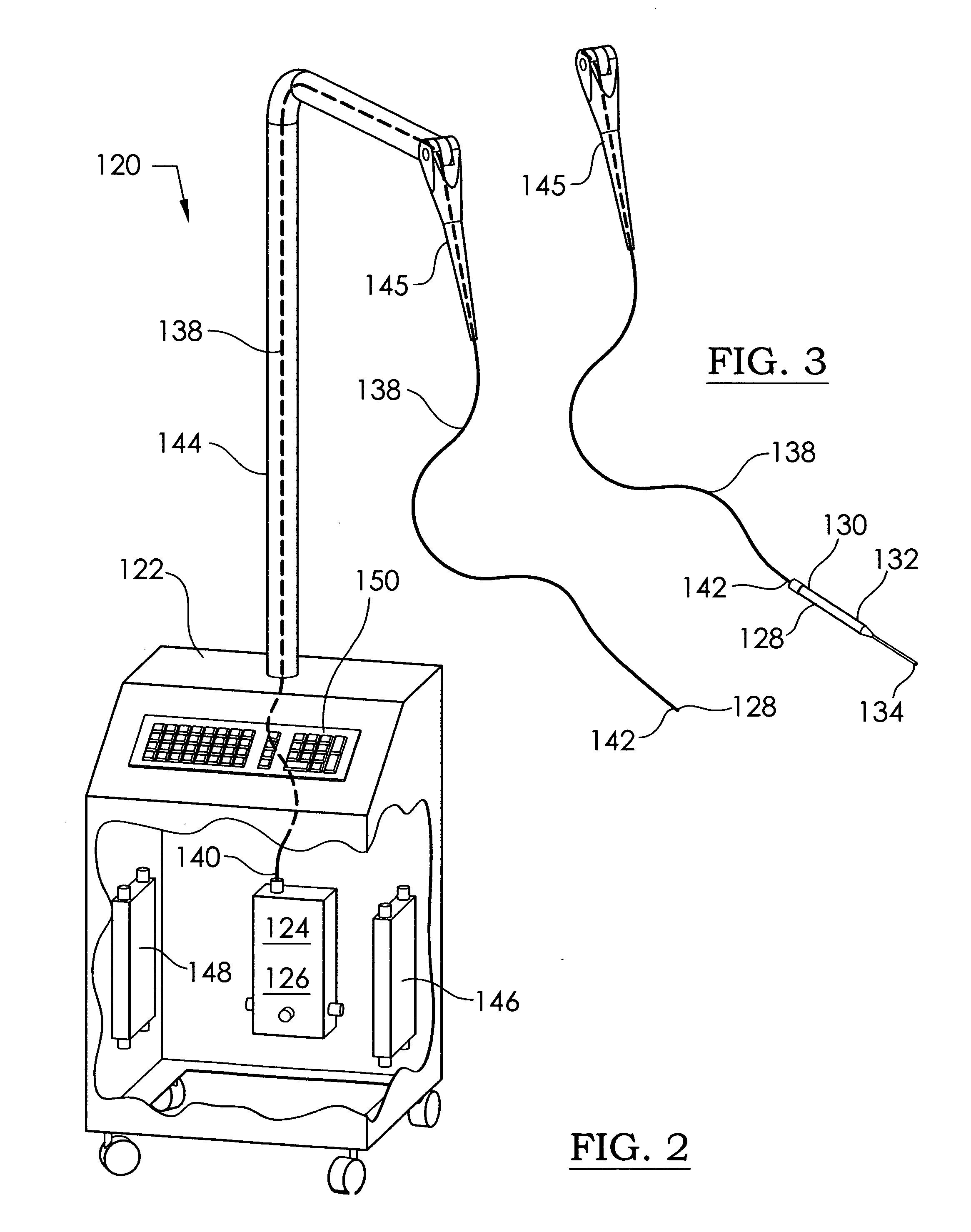
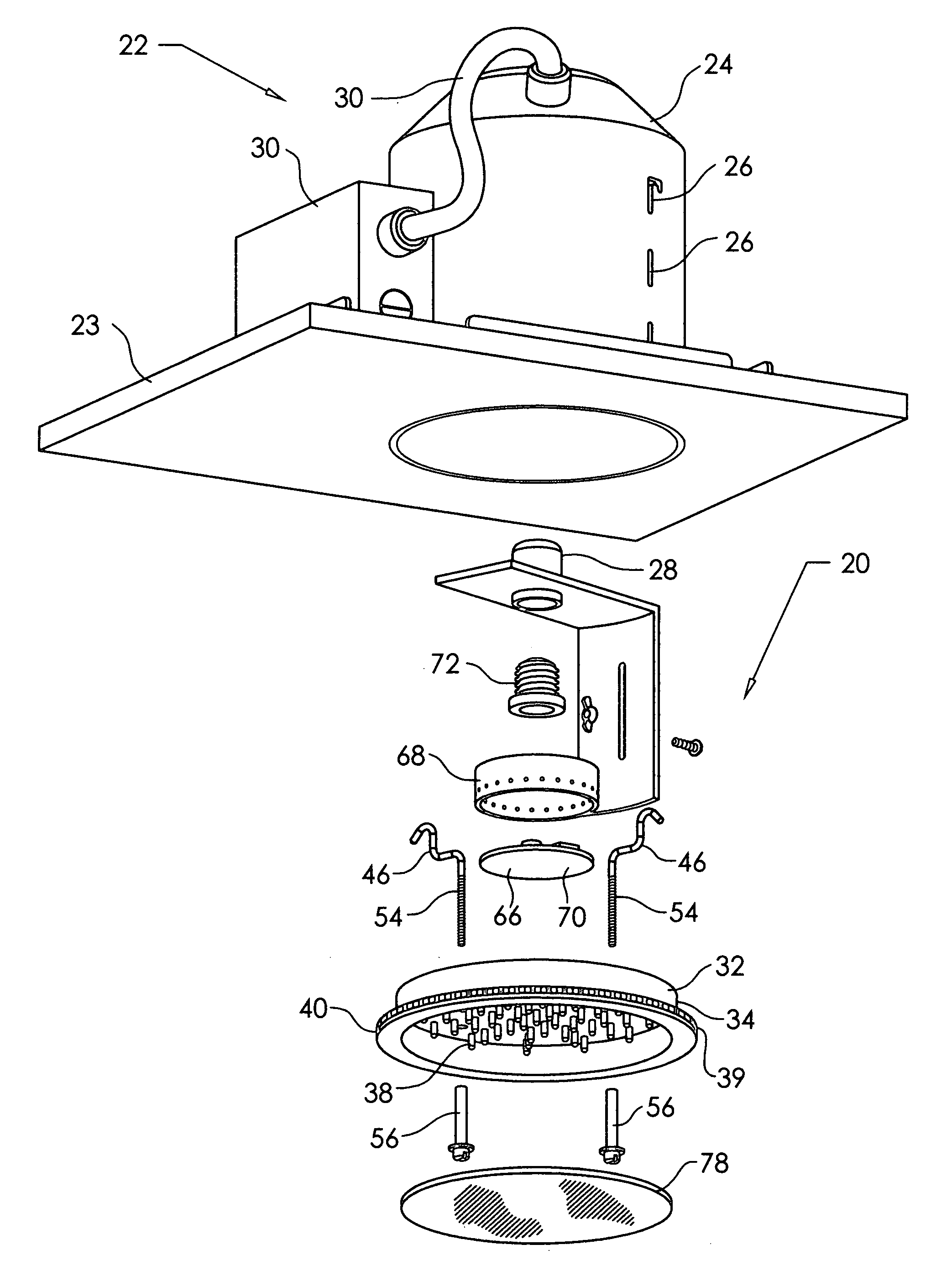
InactiveUS20110054574A1Prevent moistureAvoid burnsLight therapyRadioactive sourcesUv disinfectionArthroscopy
An ultraviolet sterilizer for use during surgery is mounted in a base cabinet. The UV light source can be a laser, or an LED. An optical frequency multiplier can be used that outputs UV of less than 280 nm, or greater than 320 nm, to avoid burning the patient. A visible LED aiming light directs the UV light toward the surgery. A crosshair image can be projected to position the light.One lamp has a housing, a cavity, a handle, and an ocular plate to pass the UV and the aiming light. An articulated arm allows selective positioning of the lamp. Another lamp has a stylus, a handle, and a tip small enough for easy insertion into a small incision for arthroscopy. A fiber optic cable connects the UV and the aiming light to the lamp. Lenses or filters can be used with the fiber optic cable.An electronic power supply and a CPU connect to the UV and the aiming light sources. A keyboard inputs commands to the CPU. A sensor provides feedback.Another UV sterilizer is mounted on a ceiling of the operating room. A lamp has a housing with a cavity. Either a curved or a flat substrate is mounted in the cavity. Solid state UV elements are arrayed on the substrate, along with visible LEDs for aiming. Either a curved or a flat mirror is disposed behind the substrate. An ocular plate passes the UV and the aiming light, and protects the elements from damage. The ocular plate is a diffuser, a filter, or a fresnel lens.
Owner:FELIX PERRY
LED conversion system for recessed lighting
Owner:SELL TIMOTHY L
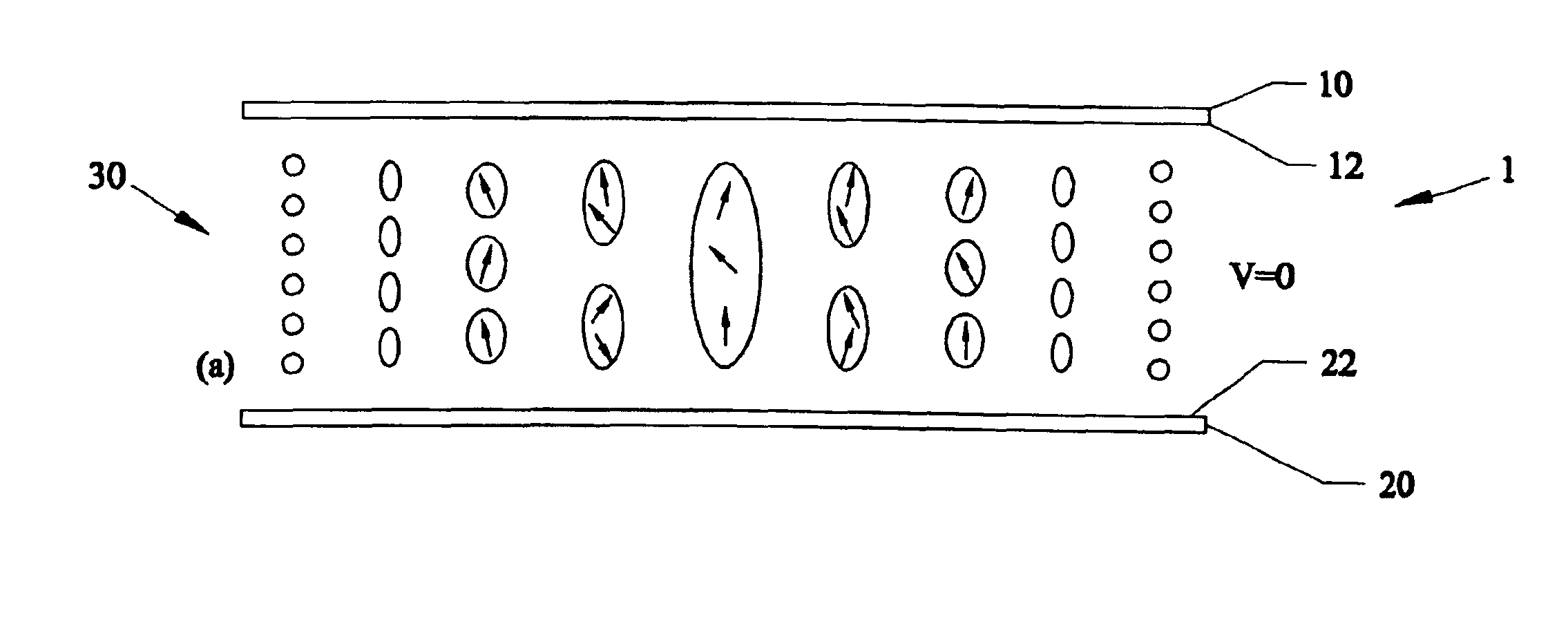
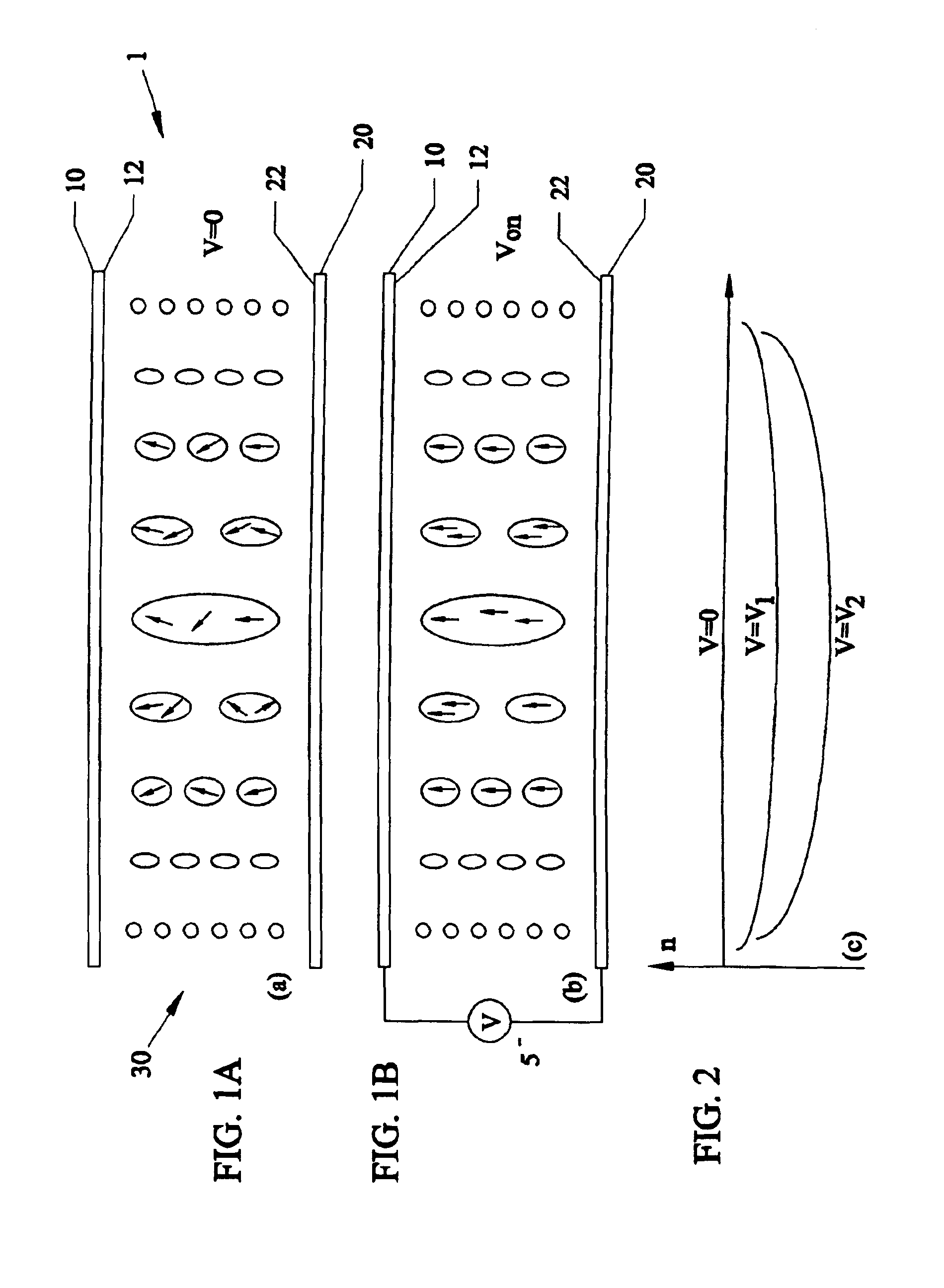
Tunable electronic lens and prisms using inhomogeneous nano scale liquid crystal droplets
InactiveUS6864951B1Simple manufacturing processLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsCamera lensFresnel lens
Using inhomogeneous sized liquid crystal (LC) droplets for lens and prisms. For forming a positive lens, the LC droplet size can gradually increase from the center to the side edges. For forming a negative lens, the LC droplet size can gradually decrease from the center to the side edges. The lens can be created by Ultra Violet light exposure to patterns. The lens can be tuned by applying voltage to the droplets. The inhomogeneous droplets can also be used in Fresnel lens and prisms. Applications of the invention can be used for eyeglasses, arrays, camera type zoom lenses and beam steering applications.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Reflective illumination device
InactiveUS7530712B2Improve efficiencyIncrease illuminationPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesFresnel lensReflection illumination
Owner:IND TECH RES INST +1
Display device
ActiveUS20100259566A1Simple and light-weightedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay boardFresnel lens
A direct-viewing type display device according to the present invention includes: at least one display panel having a display region and a frame region formed outside of the display region; and at least one Fresnel lens plate disposed on a viewer side of the at least one display panel with a predetermined interval therefrom. The Fresnel lens plate includes a Fresnel lens region at a position overlapping a region that contains a portion of the frame region of the display panel and a portion of a peripheral display region within the display region that adjoins the portion of the frame region along a first axis. A portion of display light exiting the portion of the peripheral display region is emitted from a region of the Fresnel lens region that overlaps a portion of the frame region, or a region outside the region, toward the viewer side. According to the present invention, there is provided a direct-viewing type display device in which a frame region of a display panel, or a joint in the case of tiling, is made unlikely to be seen, with a structure which is more simple and light-weighted than conventionally.
Owner:SHARP KK
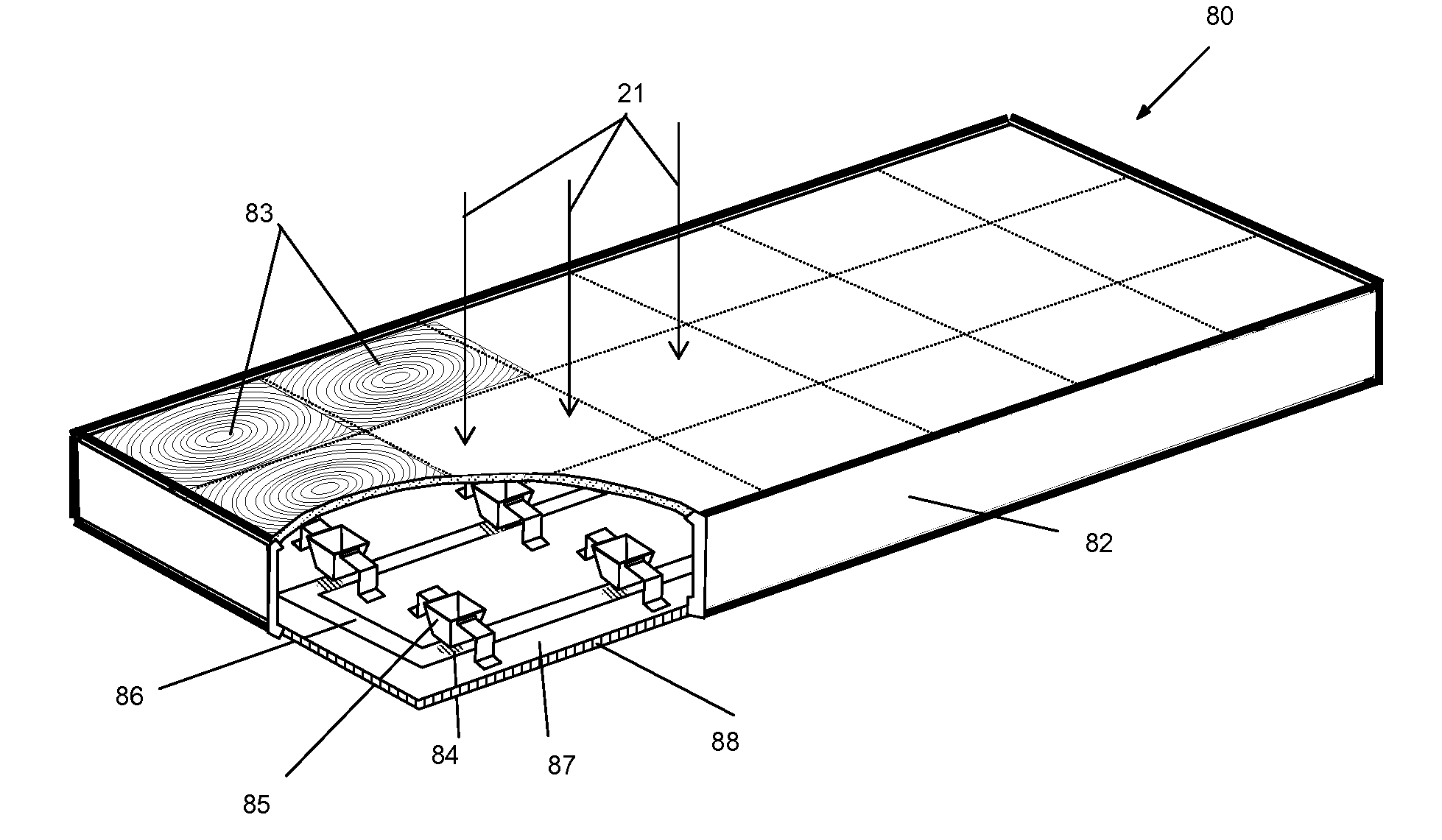
Methods and systems to form high efficiency and uniform fresnel lens arrays for ultrasonic liquid manipulation
ActiveUS8319398B2Vibration measurement in solidsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFresnel lensRadio frequency
Apparatus and methods to form high efficiency and uniform Fresnel lens arrays for ultrasonic liquid manipulation are provided. An ultrasonic transducer array may be fabricated by forming top and bottom electrodes on top and bottom surfaces of a sensor plate. The ultrasonic transducer array may generate ultrasonic energy to manipulate one or more samples. Each of the top and bottom electrodes may be coupled to a radio frequency source and arranged to form one of a solid shape or a pattern. Additional apparatus and methods are disclosed.
Owner:MICROSONIC SYST
Reflective illumination device
InactiveUS20070217193A1Improve efficiencyIncrease illuminationPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesFresnel lensOptoelectronics
A reflective illumination device is disclosed, which is comprised of a light-guiding screen with light reflecting ability and at least a directional light source; wherein the light-guiding screen includes a reflecting surface having a semi-Fresnel lens structure arranged thereon. The semi-Fresnel lens structure, being designed basing on the principle of Fresnel lens, is the equivalent of a parabolic mirror that has spiral cut ridges for focusing light to a focal point, whereas the profile of the ridges can be a planar surface, a curved surface or the combination thereof. By arranging the reflecting surface with semi-Fresnel lens structure at the bottom of the light-guiding screen and each light source at a circumferential side wall of the light-guiding screen, the light beams emitting from each light source can be reflected out of the light-guiding screen by a specific angle as the direction of the light beams is adjusted to pour on the semi-Fresnel lens structure by a specific angle matching the configuration of the same.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST +1
Inflatable fresnel lens solar concentrator for space power
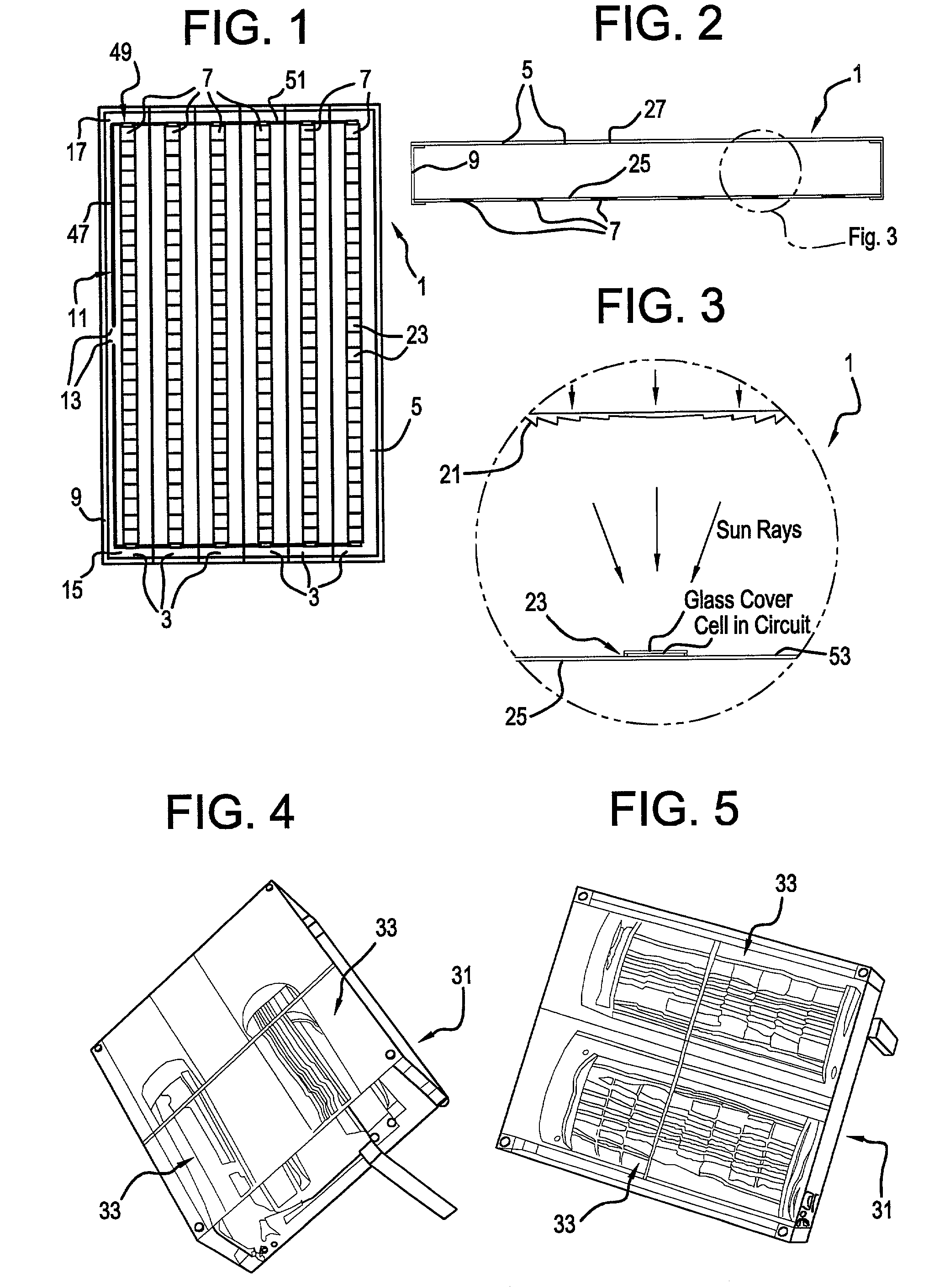
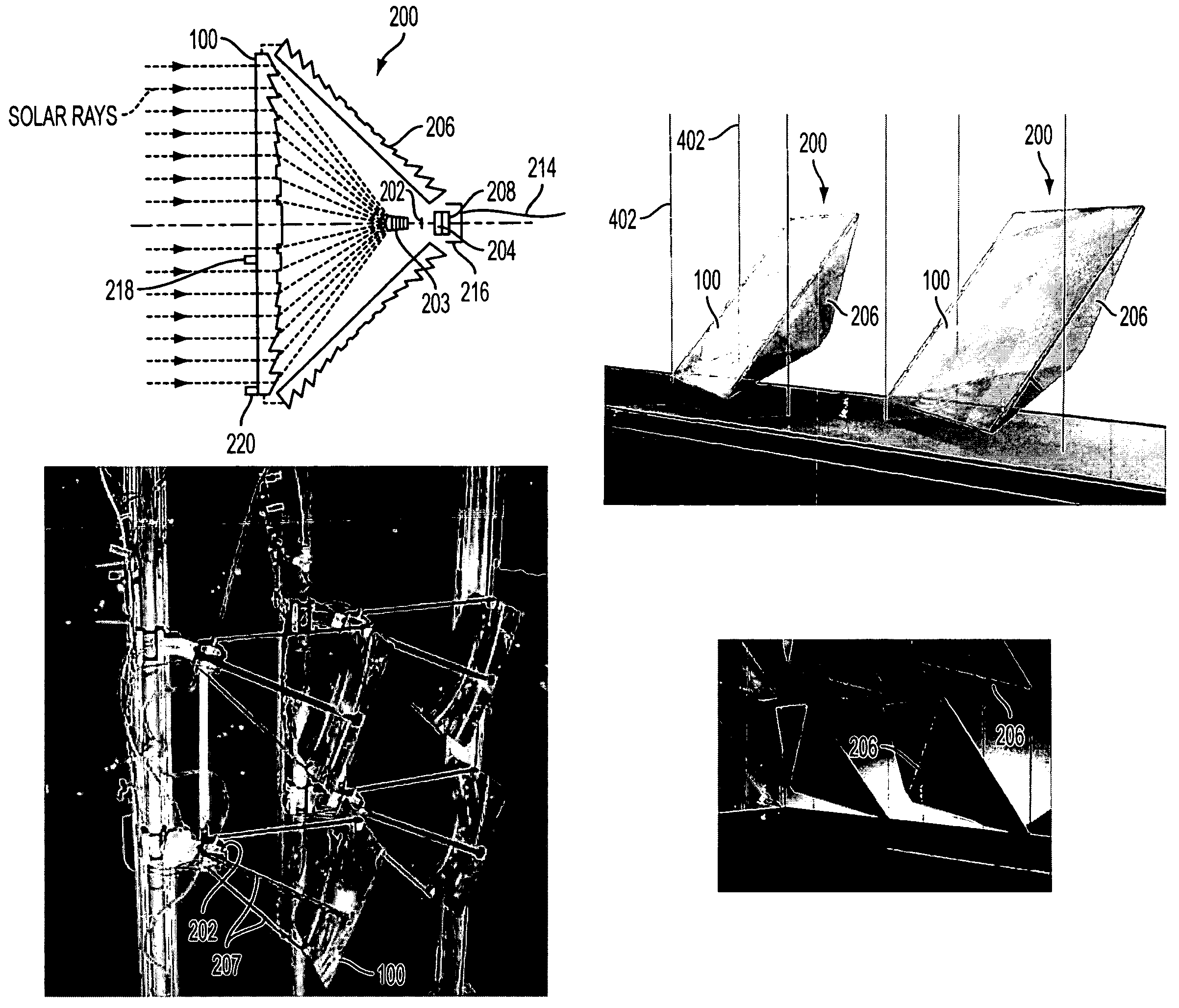
InactiveUS6111190AImprove toleranceReduce quality problemsSolar heating energyCosmonautic vehiclesSpace powerEngineering
A novel, high-efficiency, extremely light-weight, inflatable refractive solar concentrator for space power is described. It consists of a flexible Fresnel lens, flexible sides, and a back surface, together enclosing a volume of space which can be filled with low pressure gas to deploy the concentrator on orbit. The back surface supports the energy receiver / converter located in the focal region of the Fresnel lens. The back surface can also serve as the waste heat radiator. Prior to deployment, the deflated flexible lens and sides are folded against the back surface to form a flat, low-volume package for efficient launch into space. The inflatable concentrator can be configured to provide either a line focus or a point focus of sunlight. The new inflatable concentrator approach will provide significant advantages over the prior art in two different space power areas: photovoltaic concentrator arrays and high-temperature solar thermal conversion systems. Photovoltaic concentrator arrays using the new inflatable lens will be much lighter than prior space concentrator arrays. In addition, for photovoltaic concentrator arrays, the new inflatable lens will eliminate the need for a fragile glass superstrate to support the lens, substantially improving robustness of the lens. Solar thermal concentrator arrays using the new inflatable lens will be much lighter than prior art space concentrators which used parabolic mirrors. In addition, for solar thermal applications in space, the new inflatable lens will eliminate the need for high surface accuracy, which has been a significant problem for prior art concentrators.
Owner:ENTECH INC +1
Liquid crystal lens and imaging lens device
The present invention provides an imaging lens device, which has a widely extended focusing range and exhibits good resolution over the entire focusing range. The imaging lens device comprises a liquid crystal lens for focusing an object at a prescribed distance, comprising a liquid crystal layer, a first transparent substrate disposed adjacent to one surface of the liquid crystal layer and having a first electrode and having Fresnel lens surface formed on the boundary with the liquid crystal layer, a second transparent substrate disposed adjacent to the other surface of the liquid crystal layer and having a second electrode; a controller for changing the refractive index of the liquid crystal layer for extraordinary ray by changing electric voltage applied between the first electrode and the second electrode; and an imaging element for taking an image of the object. The liquid crystal lens functions as a diffractive optical element for an extraordinary ray when the liquid crystal layer has a prescribed refractive index for an extraordinary ray incident upon the liquid crystal layer.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Planar solar concentrator power module
InactiveUS7872192B1Low costEasy customer acceptanceSolar heating energySolar heat devicesFresnel lensSolar power
A planar concentrator solar power module has a planar base, an aligned array of linear photovoltaic cell circuits on the base and an array of linear Fresnel lenses or linear mirrors for directing focused solar radiation on the aligned array of linear photovoltaic cell circuits. The cell circuits are mounted on a back panel which may be a metal back plate. The cell circuit area is less than a total area of the module. Each linear lens or linear mirror has a length greater than a length of the adjacent cell circuit. The cell circuit may have cells mounted in shingle fashion to form a shingled-cell circuit. In an alternative module, linear extrusions on the circuit element have faces for mounting the linear mirrors for deflecting sun rays impinging on each mirror onto the shingled-cells. The linear extrusions are side-wall and inner extrusions with triangular cross-sections. The circuit backplate is encapsulated by lamination for weather protection. The planar module is generally rectangular with alternating rows of linear cell circuits and linear lenses or linear mirrors.
Owner:JX CRYSTALS
Concentrating type solar collection and daylighting system within glazed building envelopes
A Fresnel lens including a substantially polygonal focusing portion adapted to focus solar radiation to a area having the same geometry as the focusing portion of the lens. Also a solar module including the Fresnel collecting lens and a substantially polygonal photovoltaic cell. The photovoltaic cell is mounted at distance from the Fresnel collecting lens so that the size of the area substantially matches the size of the photovoltaic cell. Also a solar panel having multiple modules within a glazed building envelope system. The solar panel also includes an actuating mechanism within the glazed window envelope system. The actuating mechanism is operatively connected to the plurality of solar modules and is adapted to move the solar modules to track the sun.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
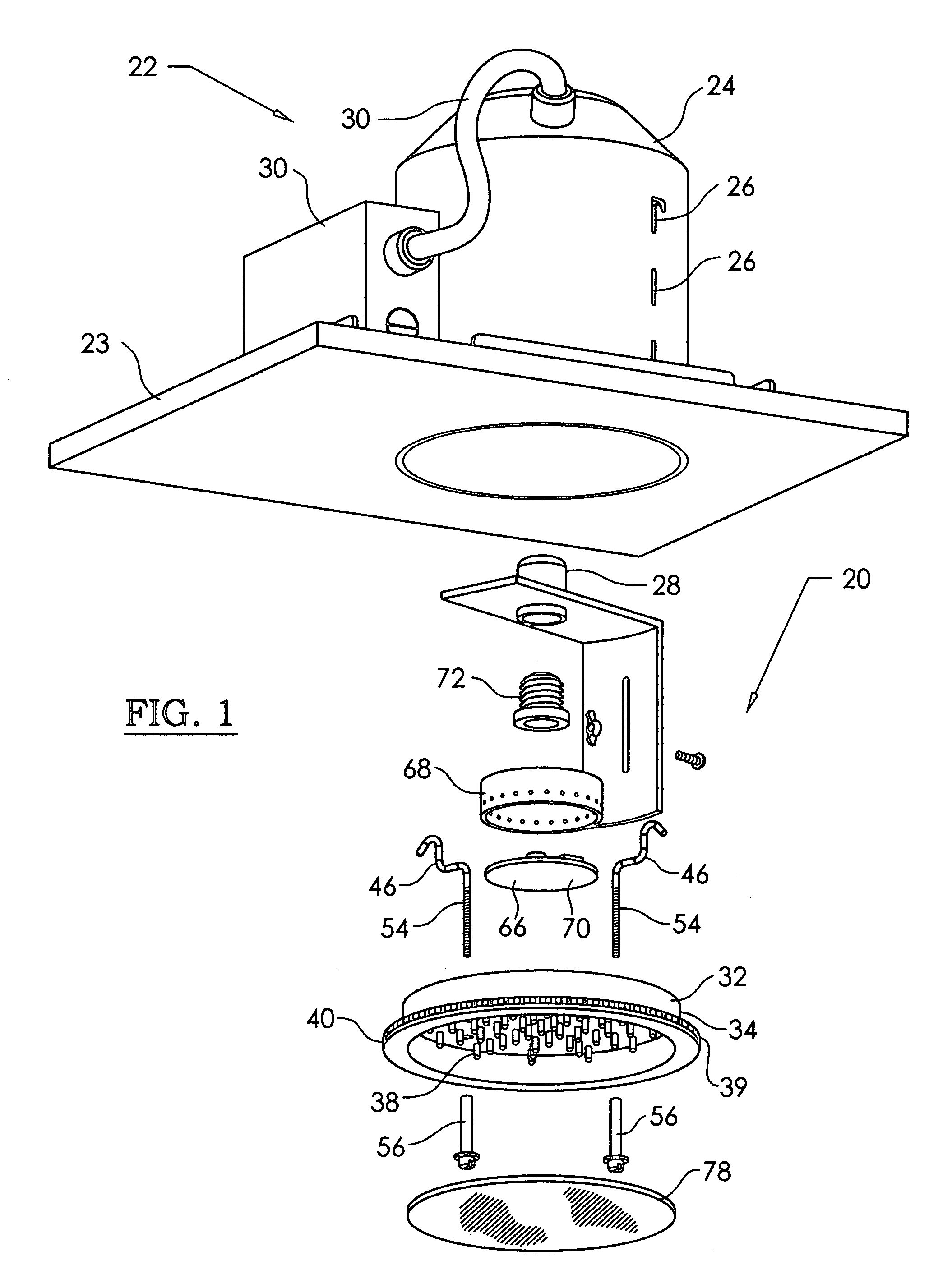
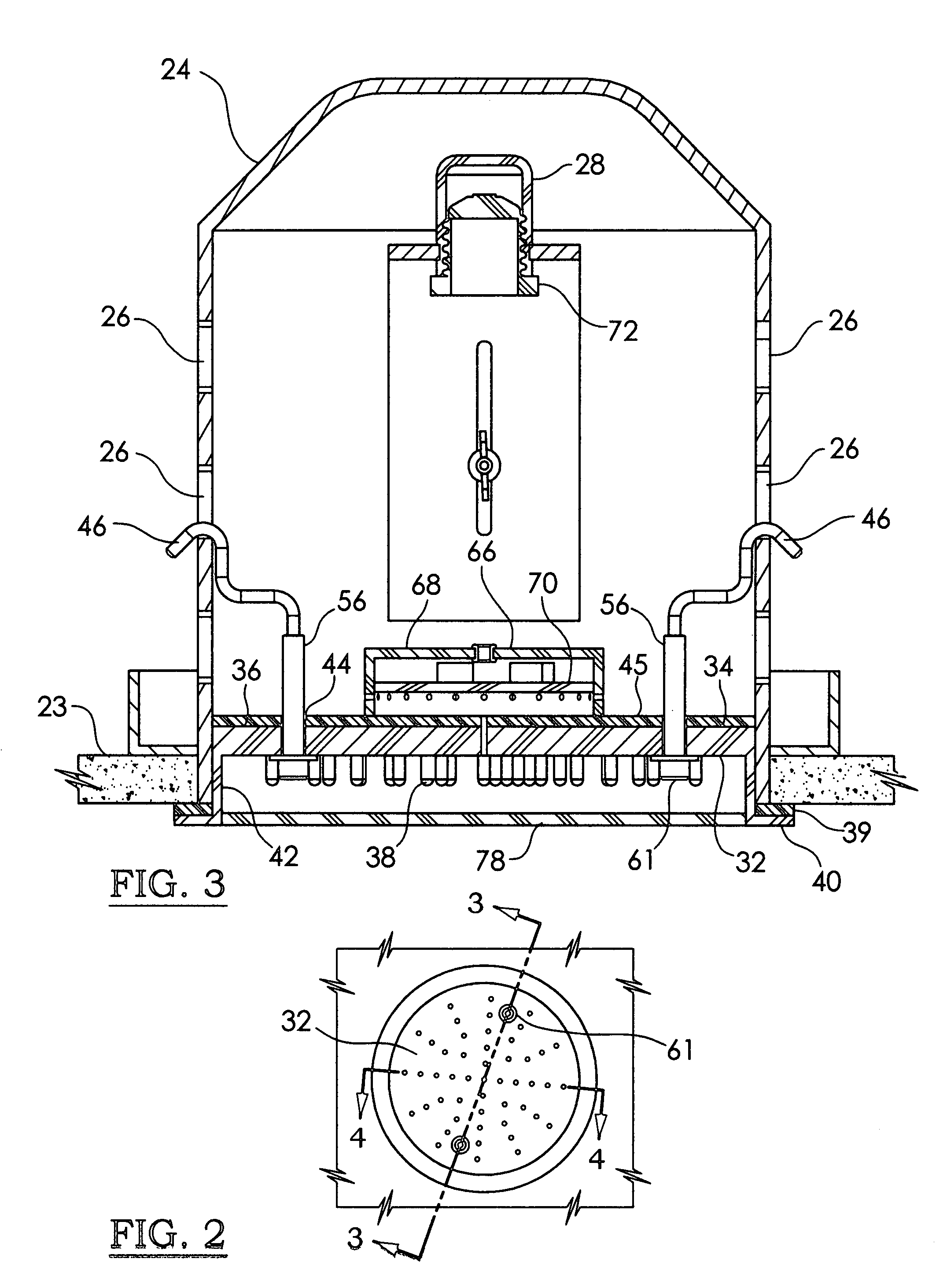
Compact light emitting diode retrofit lamp and method for traffic signal lights
A high power LED lamp and method for retrofitting conventional traffic signal lamps. The LED lamp includes a housing, a power supply disposed in the housing, a plurality of LEDs mounted to a substantially planar mounting surface in the housing and electrically connected to the power supply for producing diverging light, and a threaded electrical connector extending from the housing. The method includes replacing a conventional incandescent light bulb with the LED lamp, and installing a Fresnel lens inside the traffic signal lamp that collimates and just fills and illuminates the outer lens of the traffic signal lamp.
Owner:LEOTEK ELECTRONICS
Variation of power levels within an LED array
InactiveUS20060109648A1Differ in their performanceNon-electric lightingLighthouseFresnel lensHigh flux
A lighting device having a plurality of high flux LEDs mounted on a heat sink and surrounded by a diffuser and a power supply that provides independent power to individual sets of the LEDs. The heat sink serves to transfer heat from the LEDs to the outside environment. In one embodiment the lighting device is positioned within a fresnel lens to produce a distribution of light.
Owner:PHAROS MARINE AUTOMATIC POWER
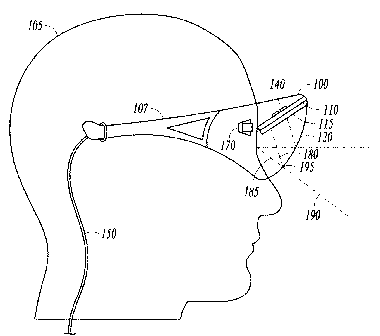
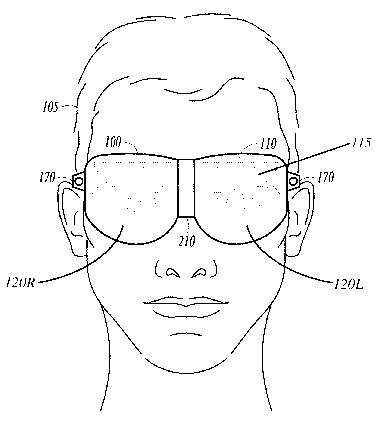
Head-mounted display apparatus employing one or more fresnel lenses
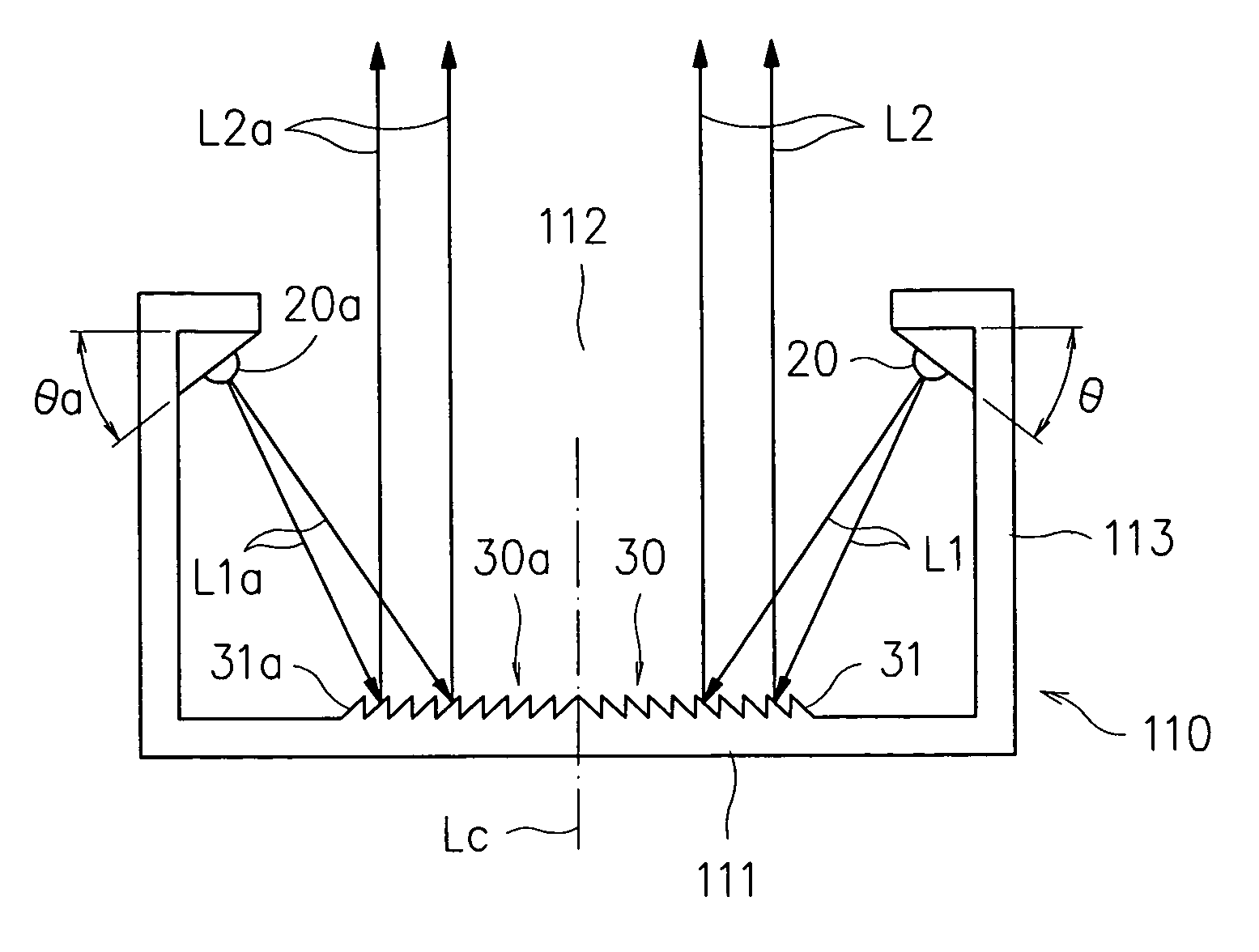
InactiveCN103261943AUse in any combinationNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingEye corneasFresnel lens
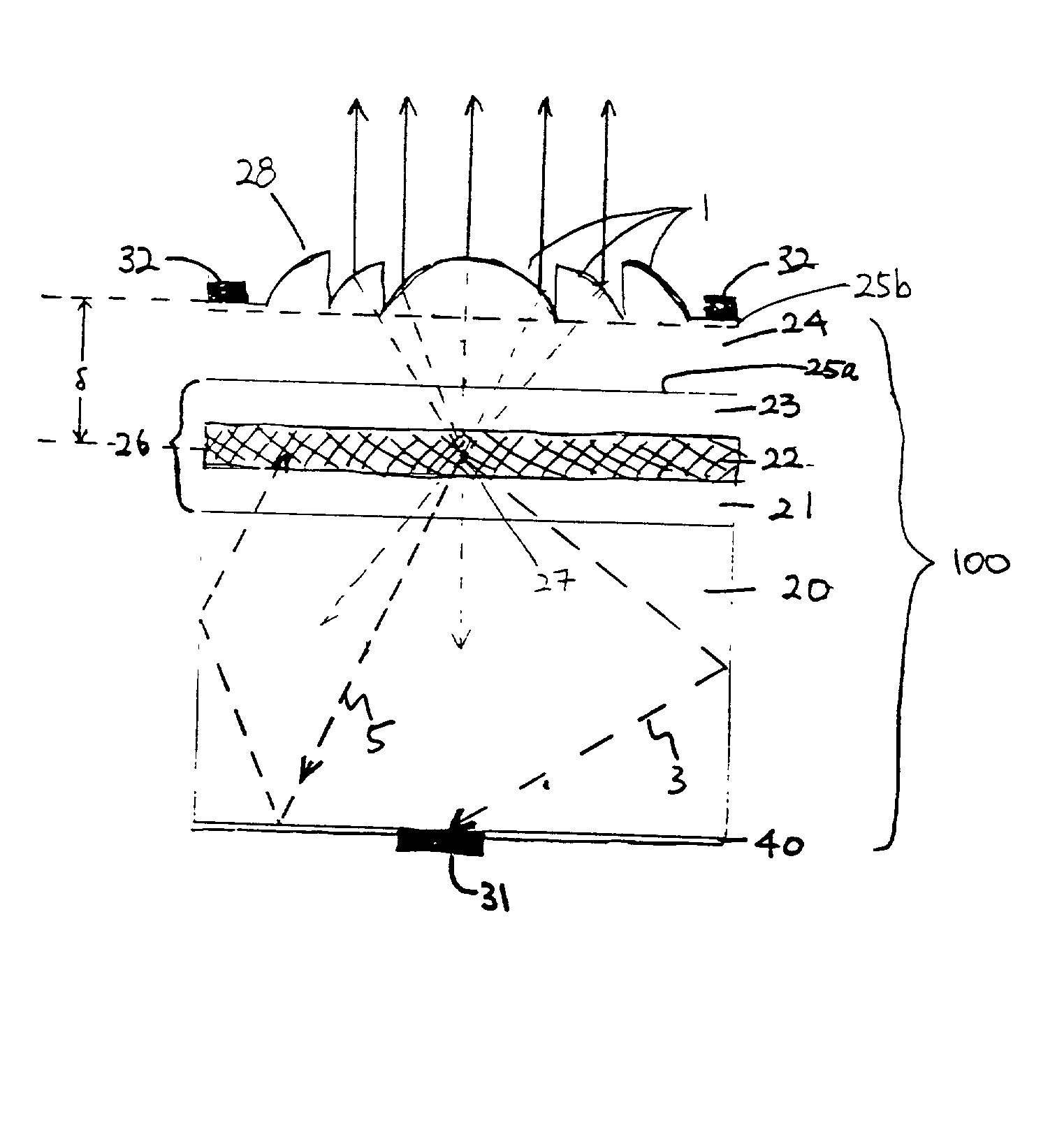
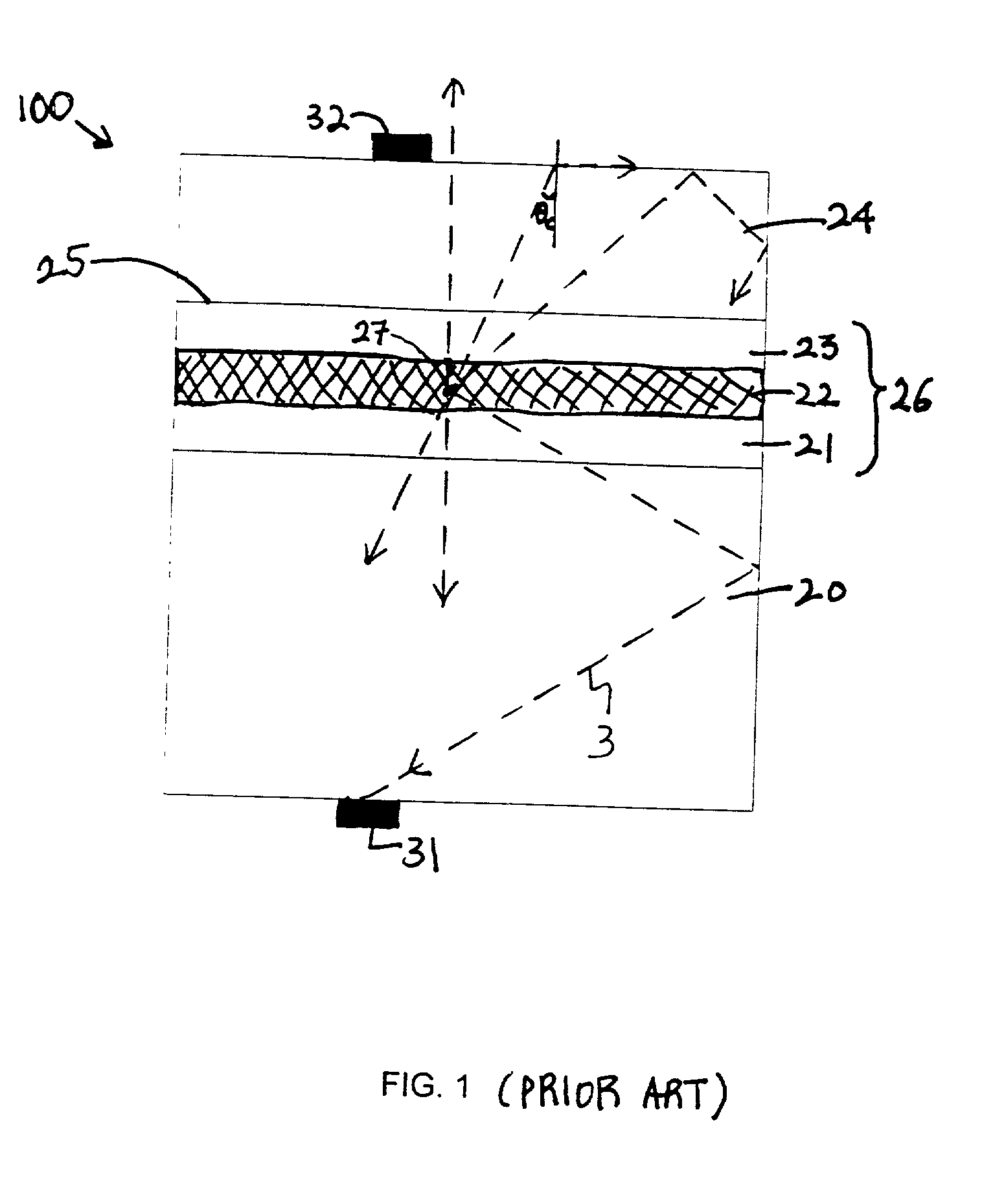
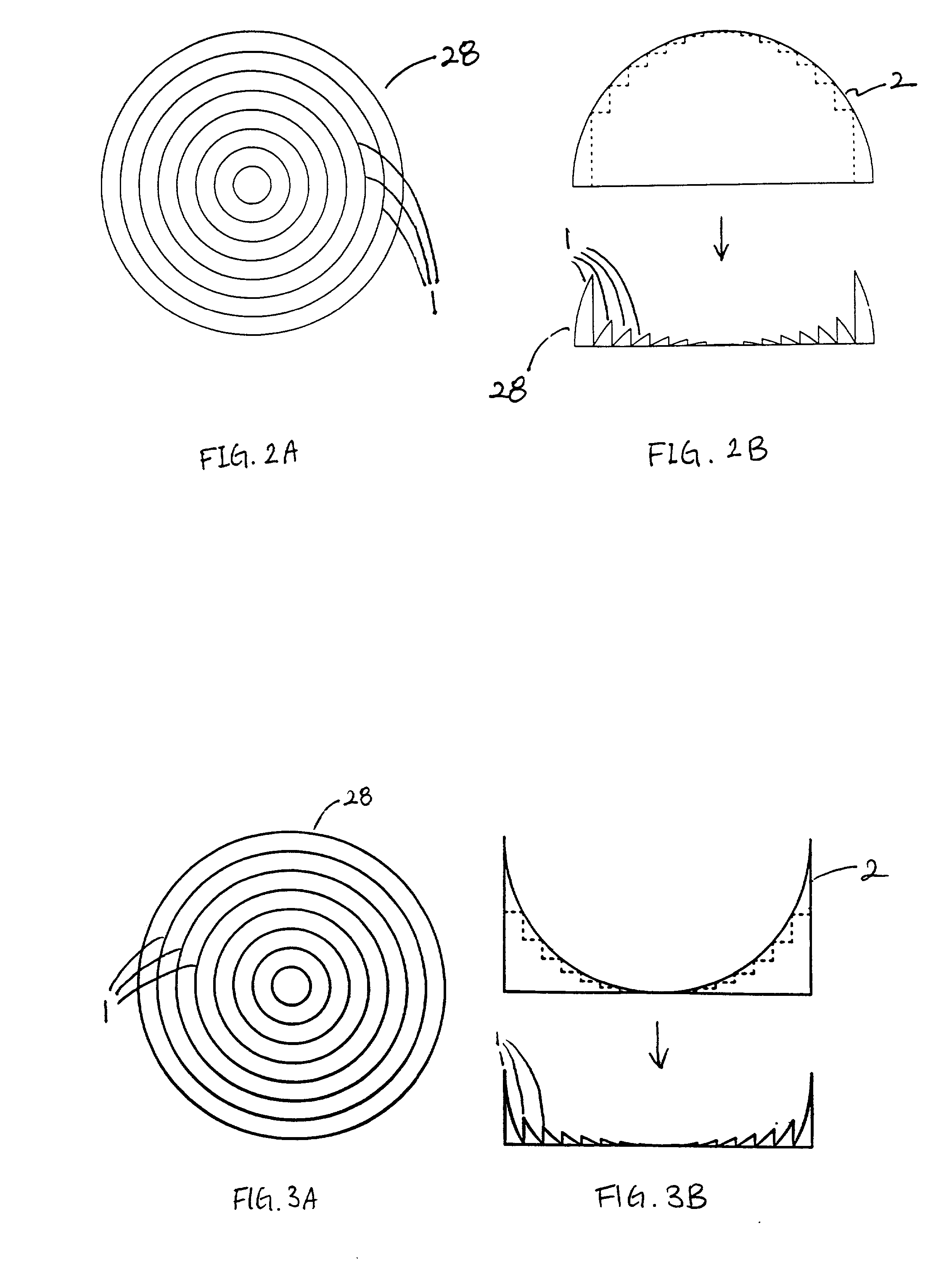
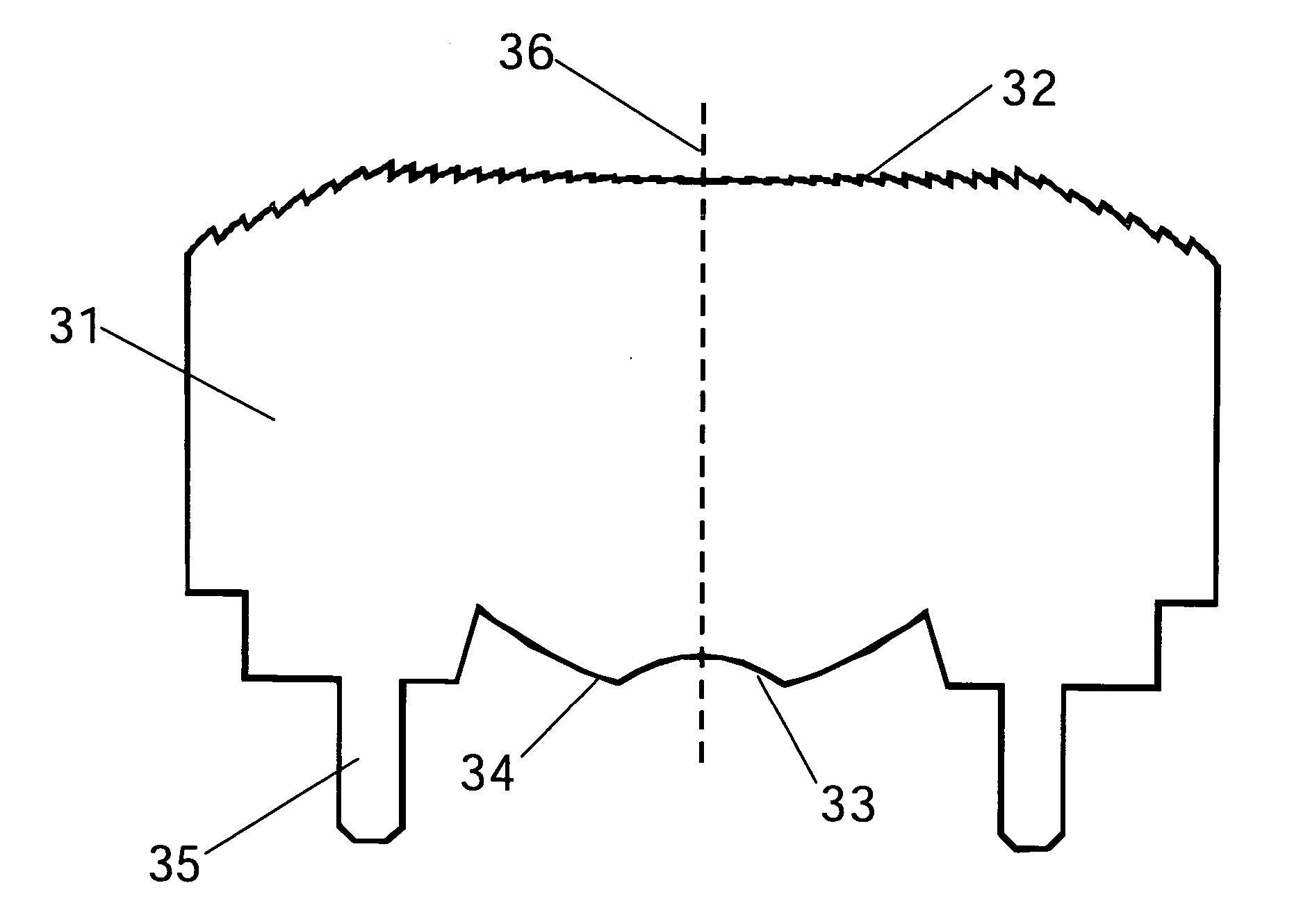
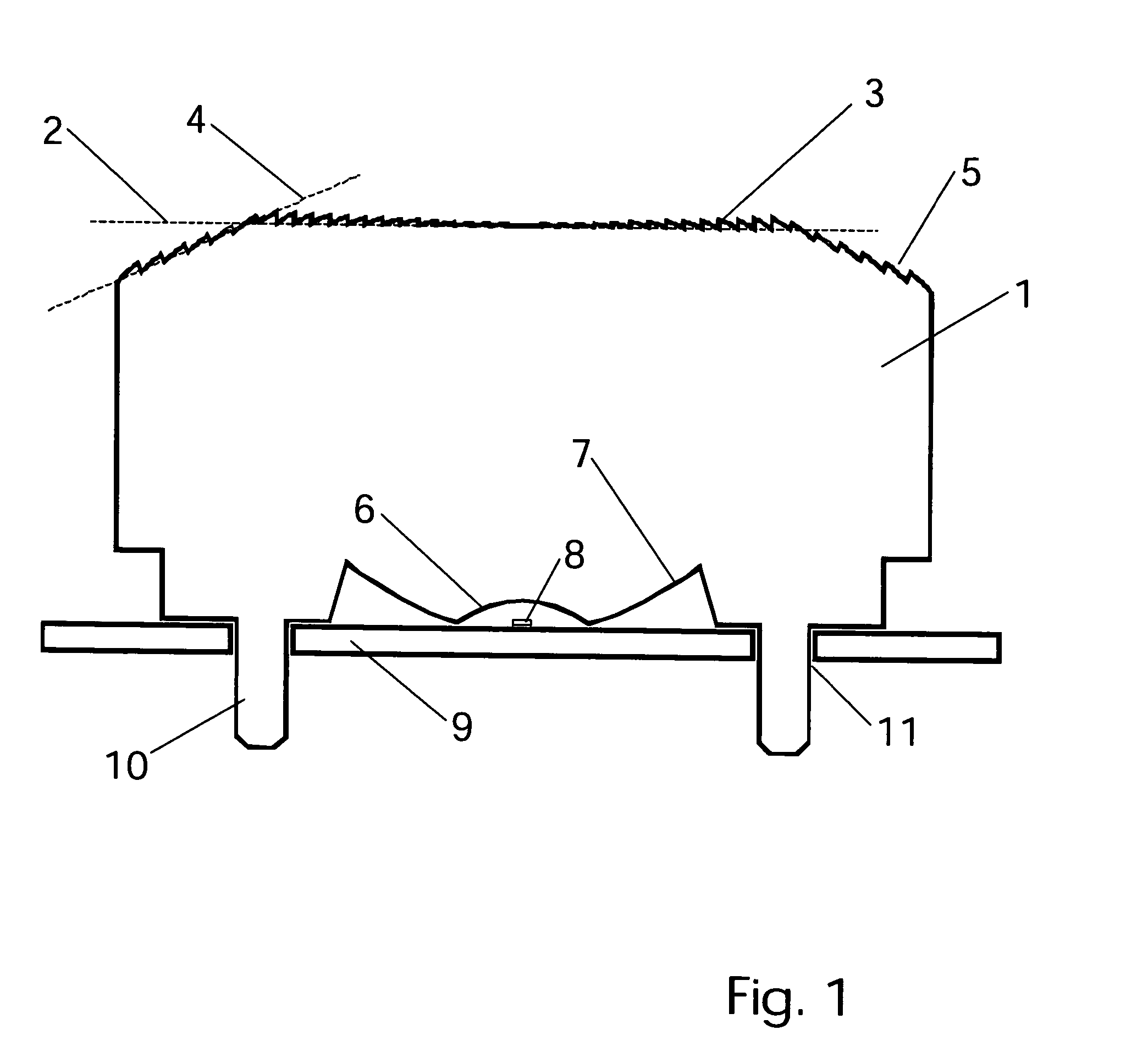
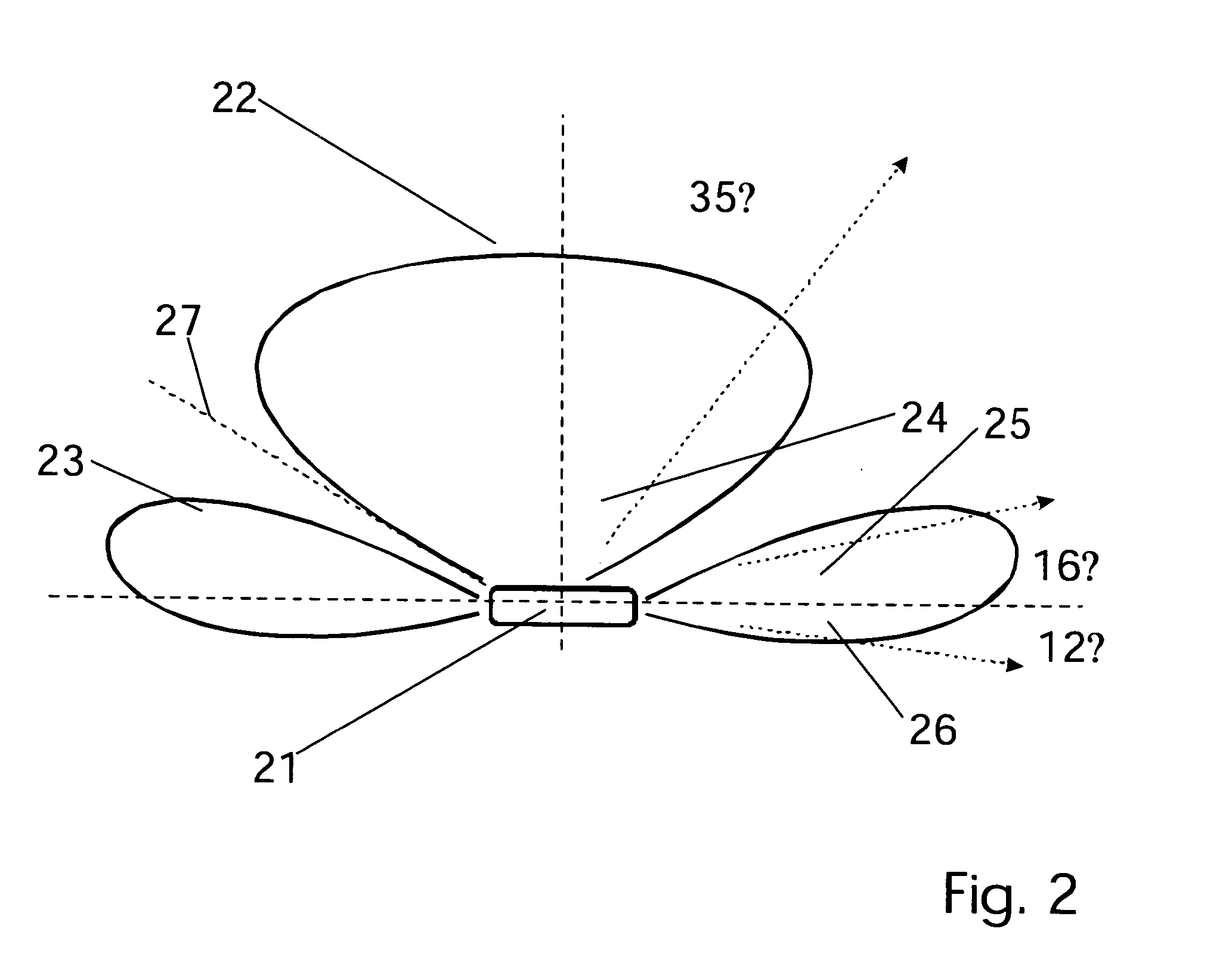
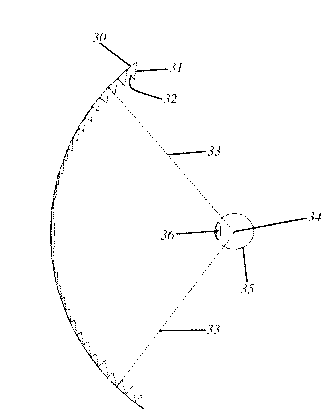
Head-mounted displays (100) are disclosed which include a frame (107), an image display system (110) supported by the frame (107), and a Fresnel lens system (115) supported by the frame (107). The HMD (100) can employ a reflective optical surface, e.g., a free-space, ultra-wide angle, reflective optical surface (a FS / UWA / RO surface) (120), supported by the frame (107), with the Fresnel lens system (115) being located between the image display system (110) and the reflective optical surface (120). The Fresnel lens system (115) can include at least one curved Fresnel lens element (820). Fresnel lens elements (30) for use in HMDs are also disclosed which have facets (31) separated by edges (32) which lie along radial lines (33) which during use of the HMD pass through a center of rotation (34) of a nominal user's eye (35) or through the center of the eye's lens (36) or are normal to the surface of the eye's cornea.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com