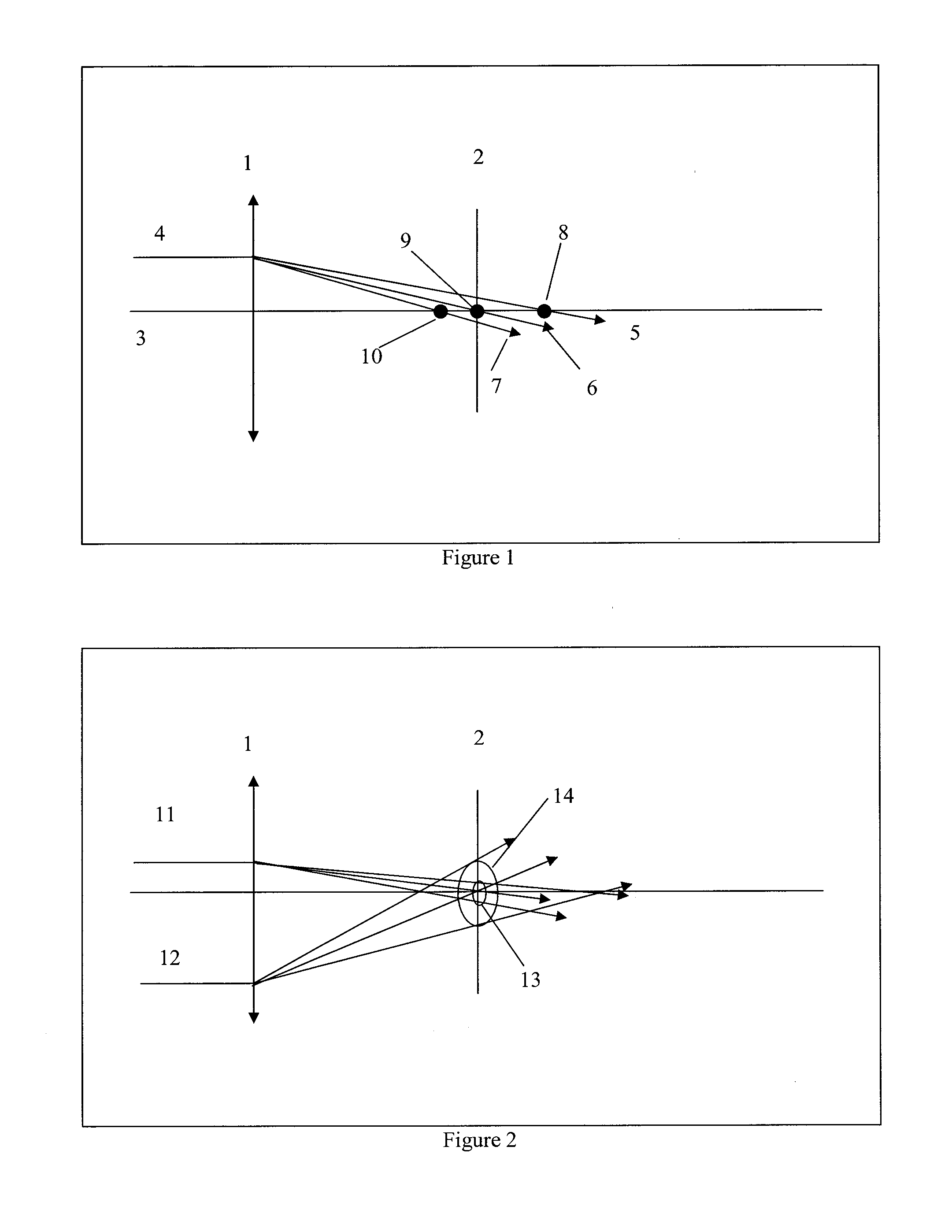Patents
Literature
70results about How to "Minimize aberration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
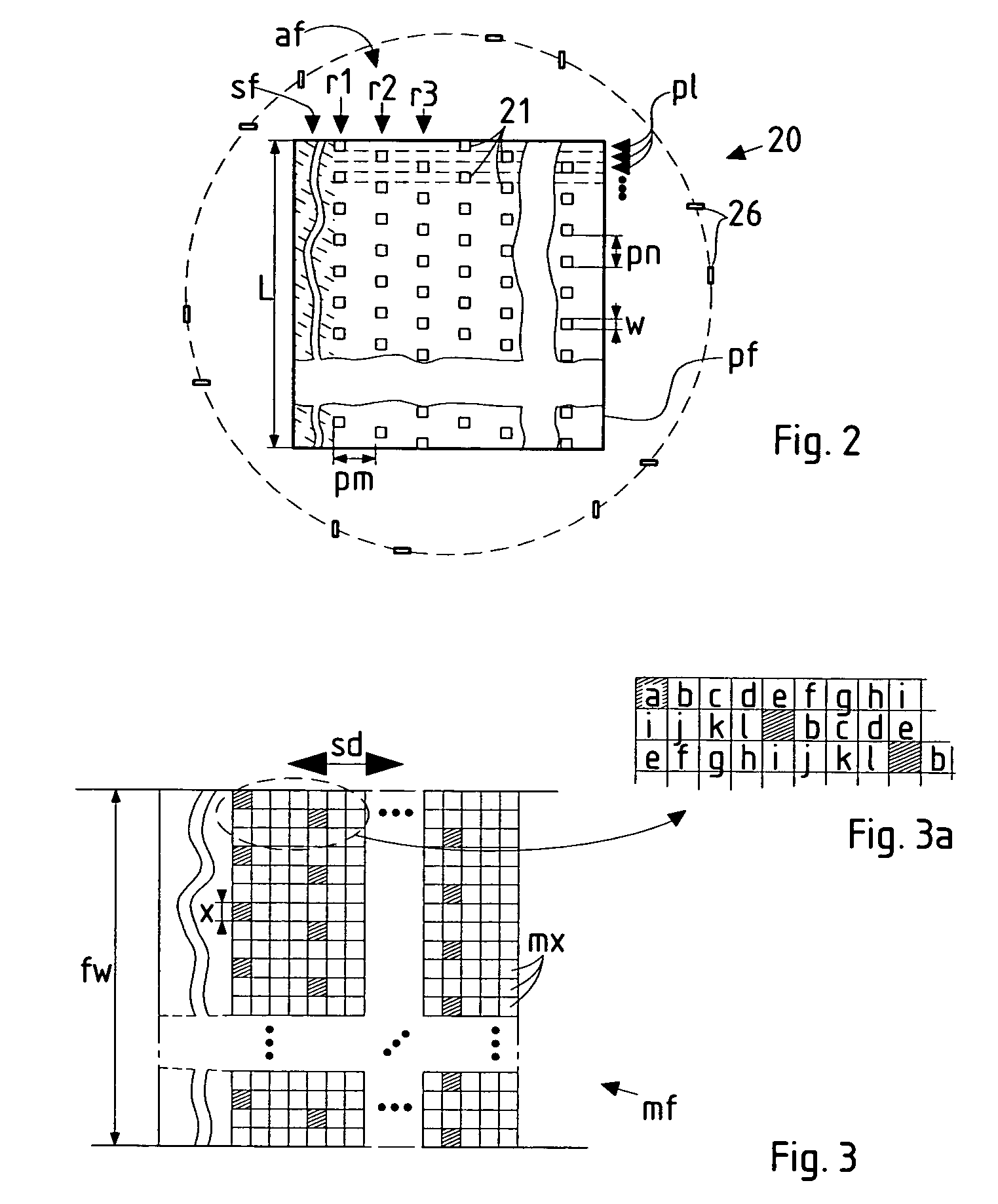
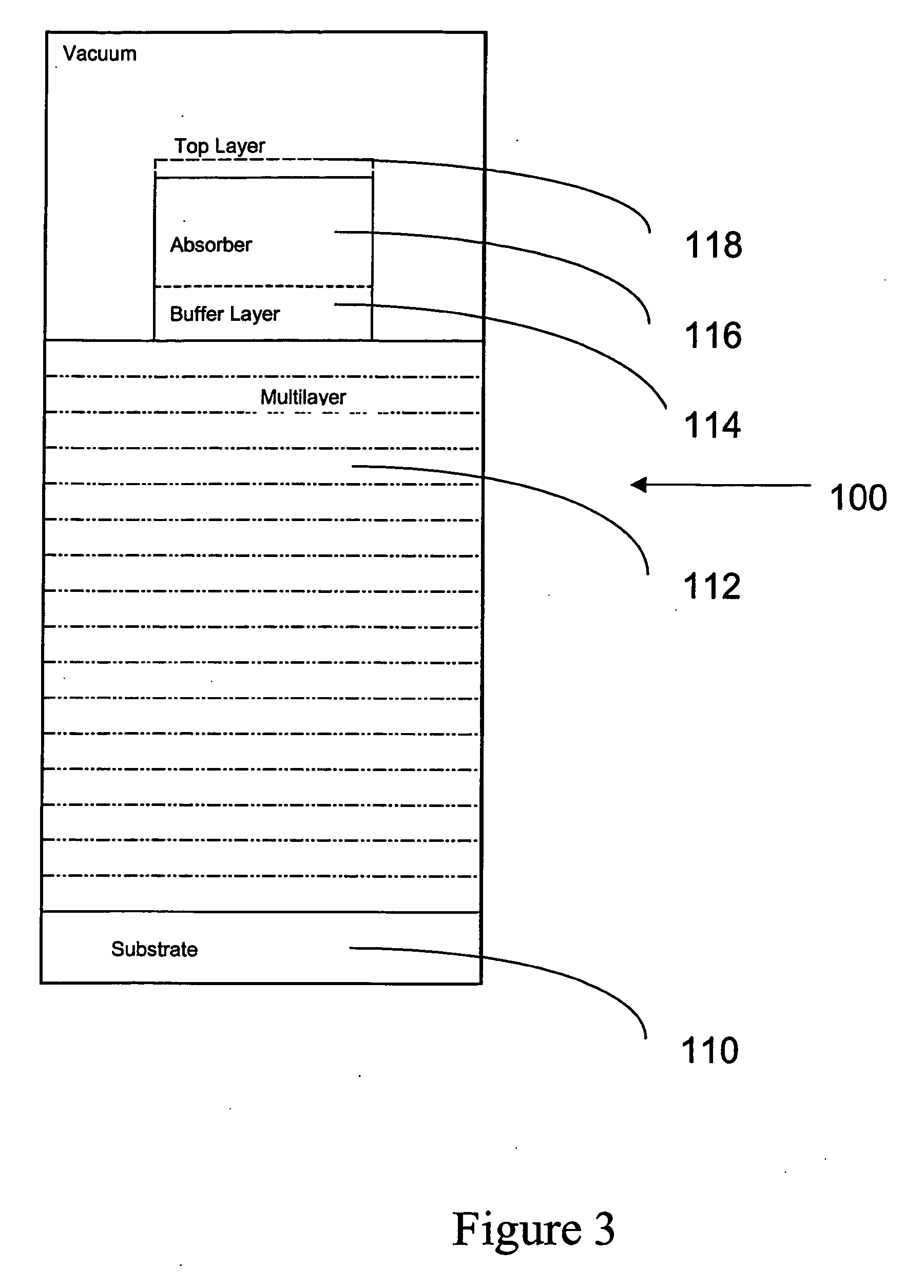
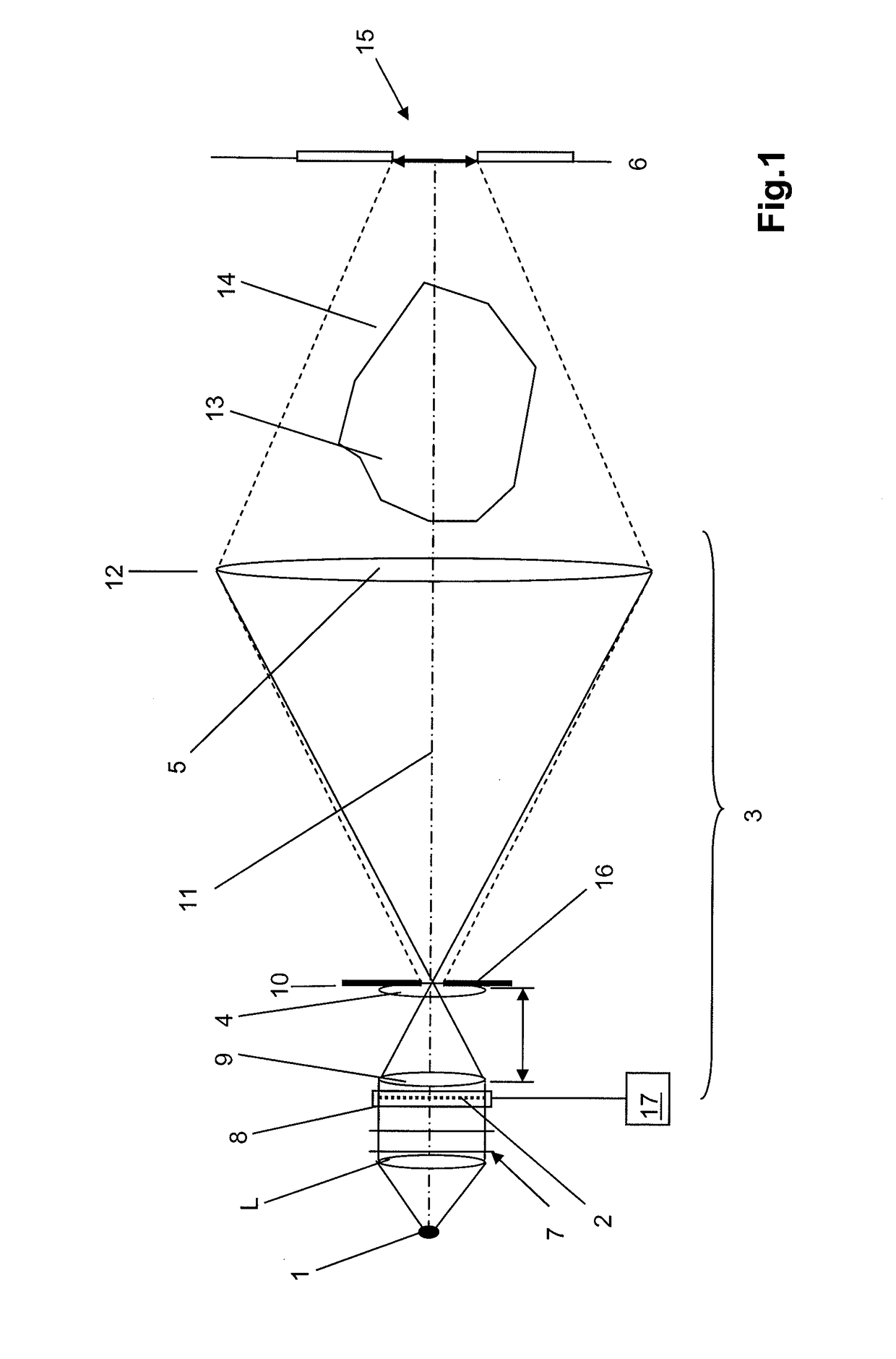
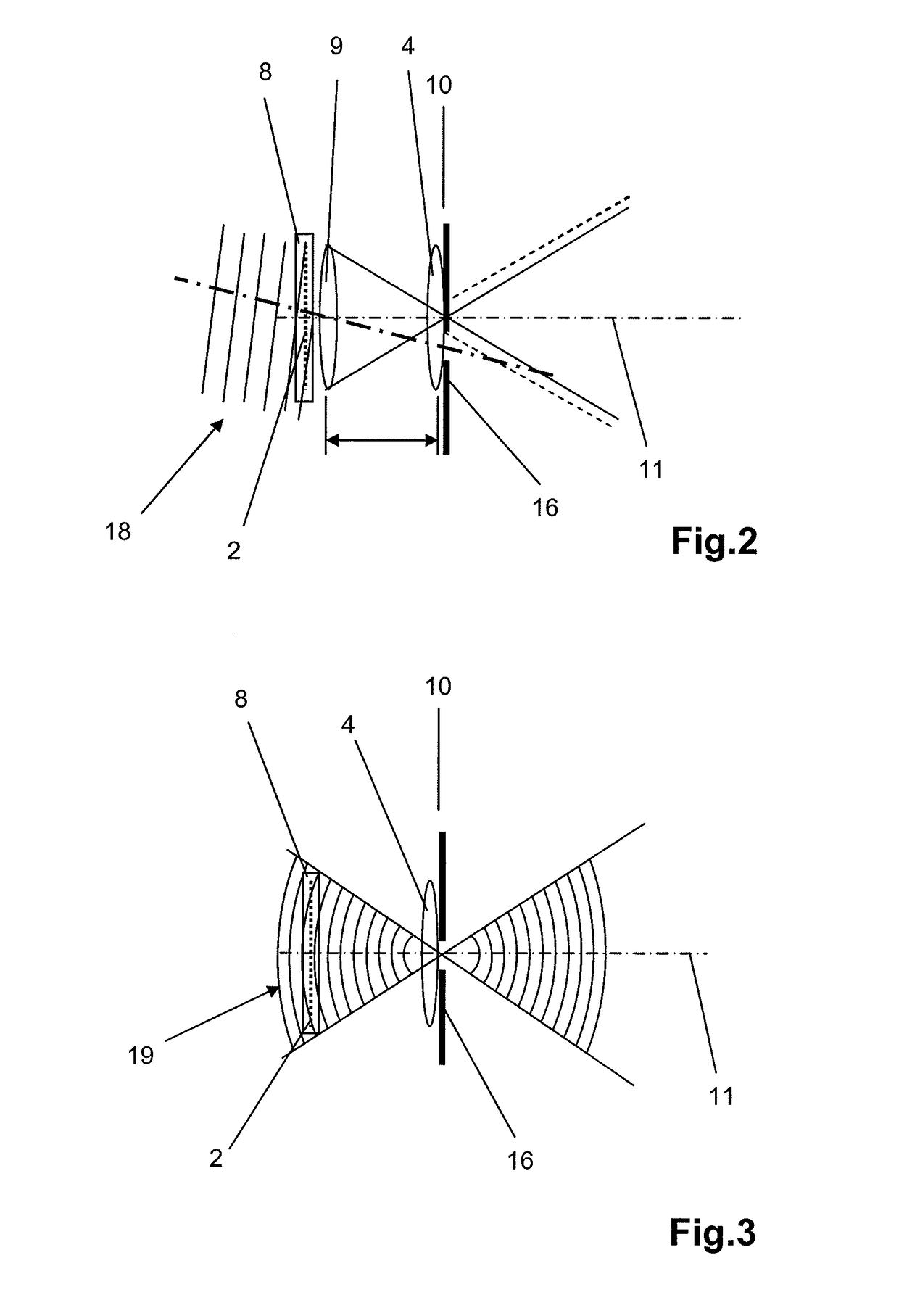
Particle-optical projection system
ActiveUS7388217B2Minimize distortionCompensation deviationElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsOptical axisProjection system
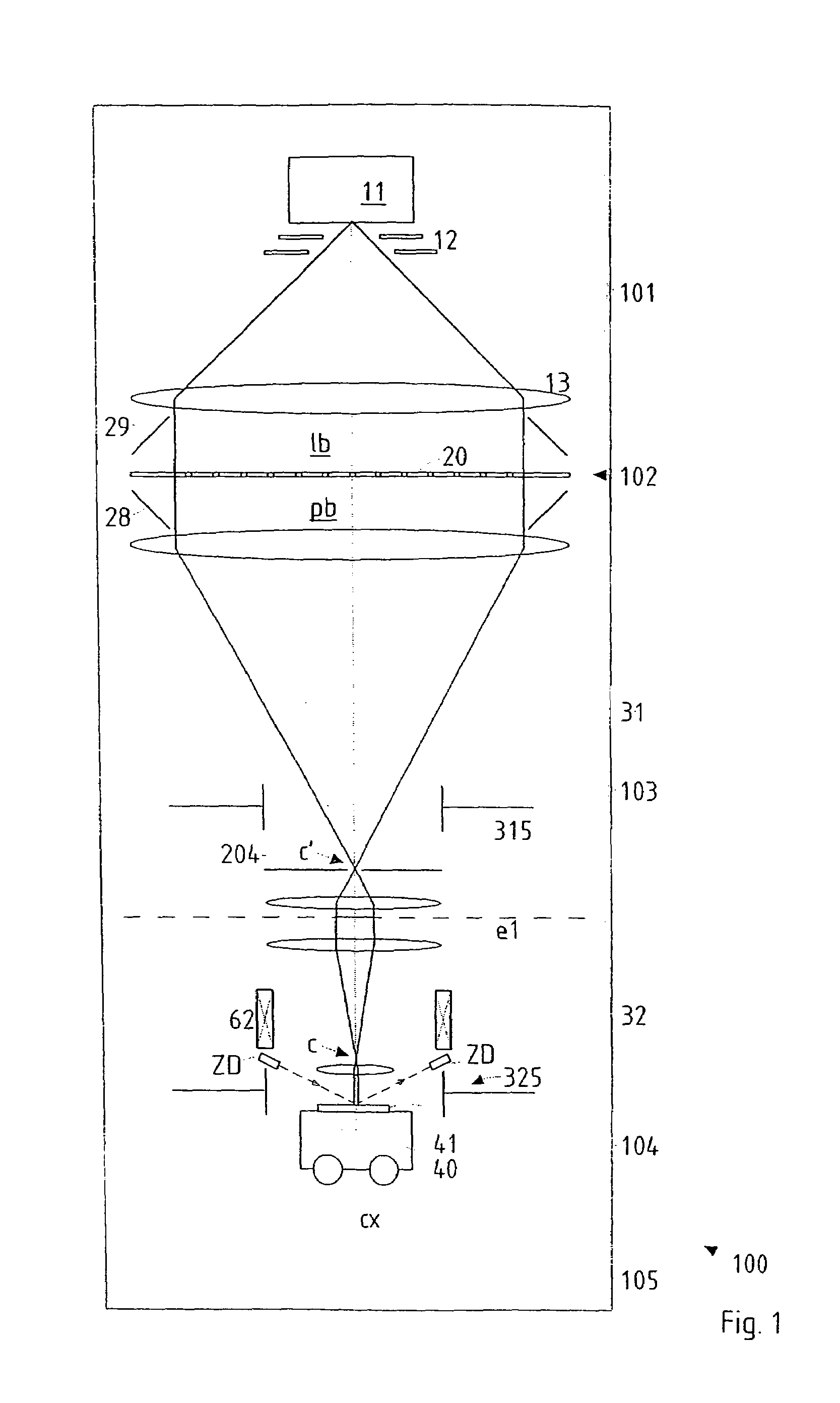
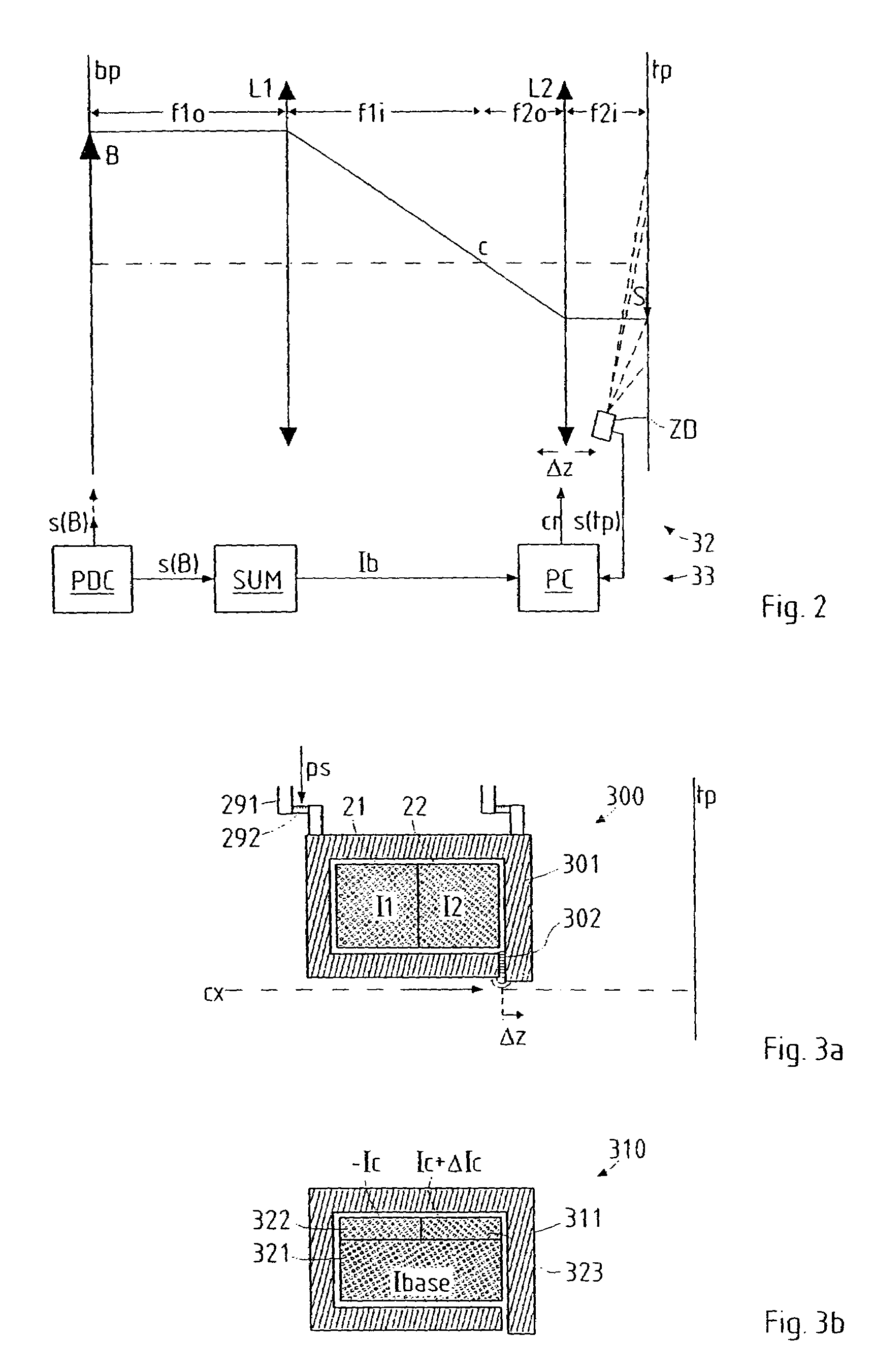
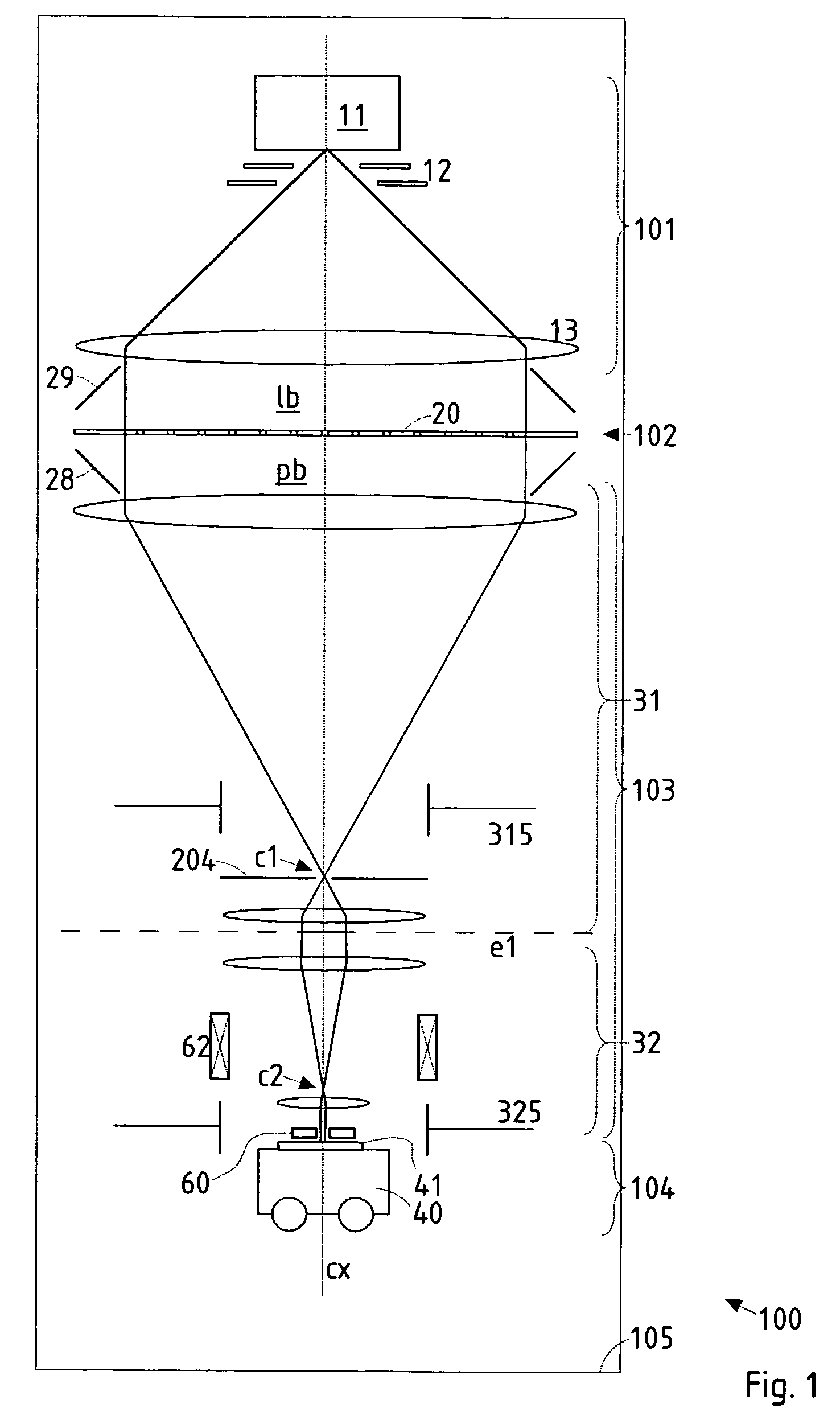
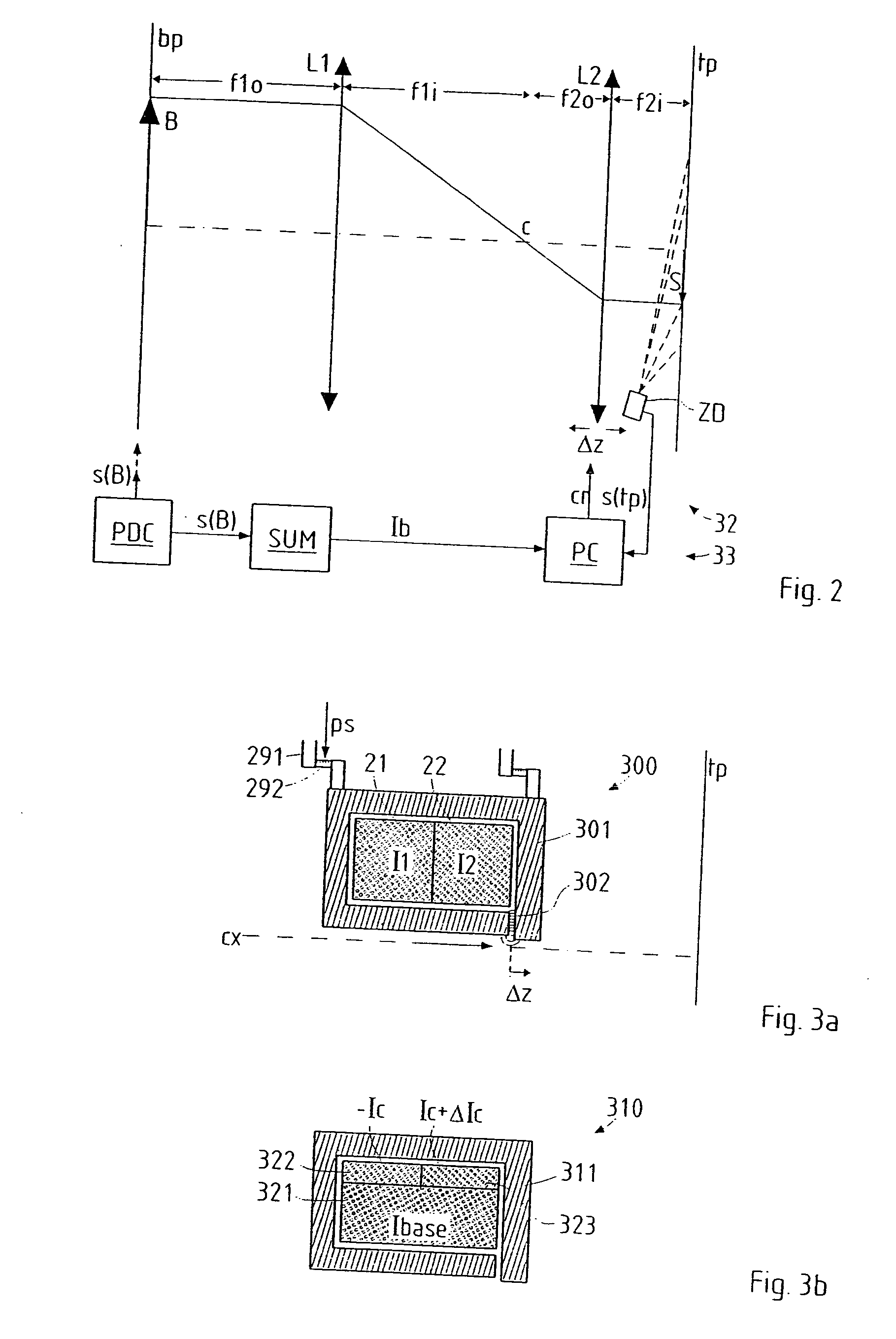
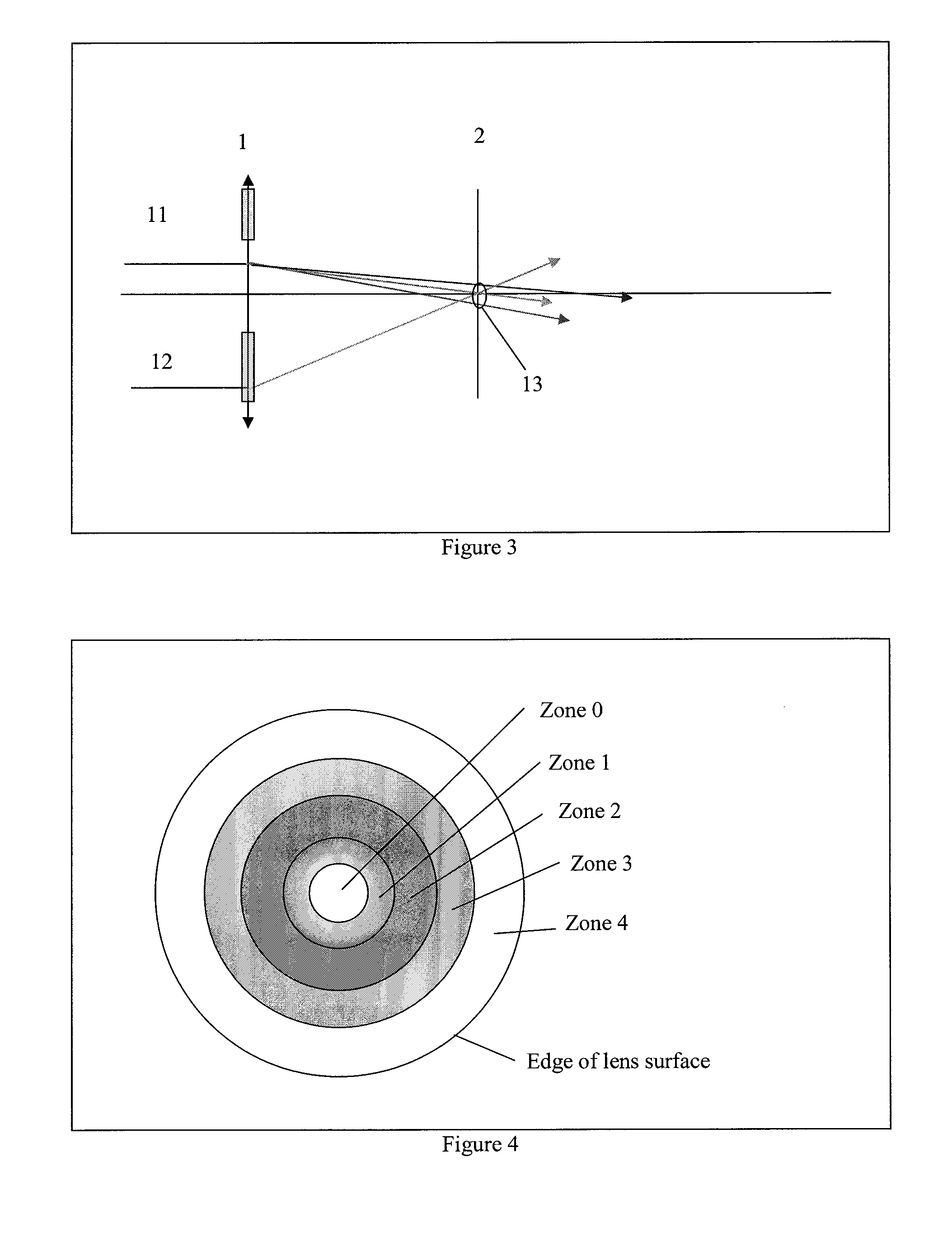
In a particle-optical projection system a pattern is imaged onto a target by means of energetic electrically charged particles. The pattern is represented in a patterned beam of said charged particles emerging from the object plane through at least one cross-over; it is imaged into an image with a given size and distortion. To compensate for the Z-deviation of the image position from the actual positioning of the target (Z denotes an axial coordinate substantially parallel to the optical axis), without changing the size of the image, the system includes a position detector for measuring the Z-position of several locations of the target, and a controller for calculating modifications of selected lens parameters of the final particle-optical lens and controlling said lens parameters according to said modifications.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
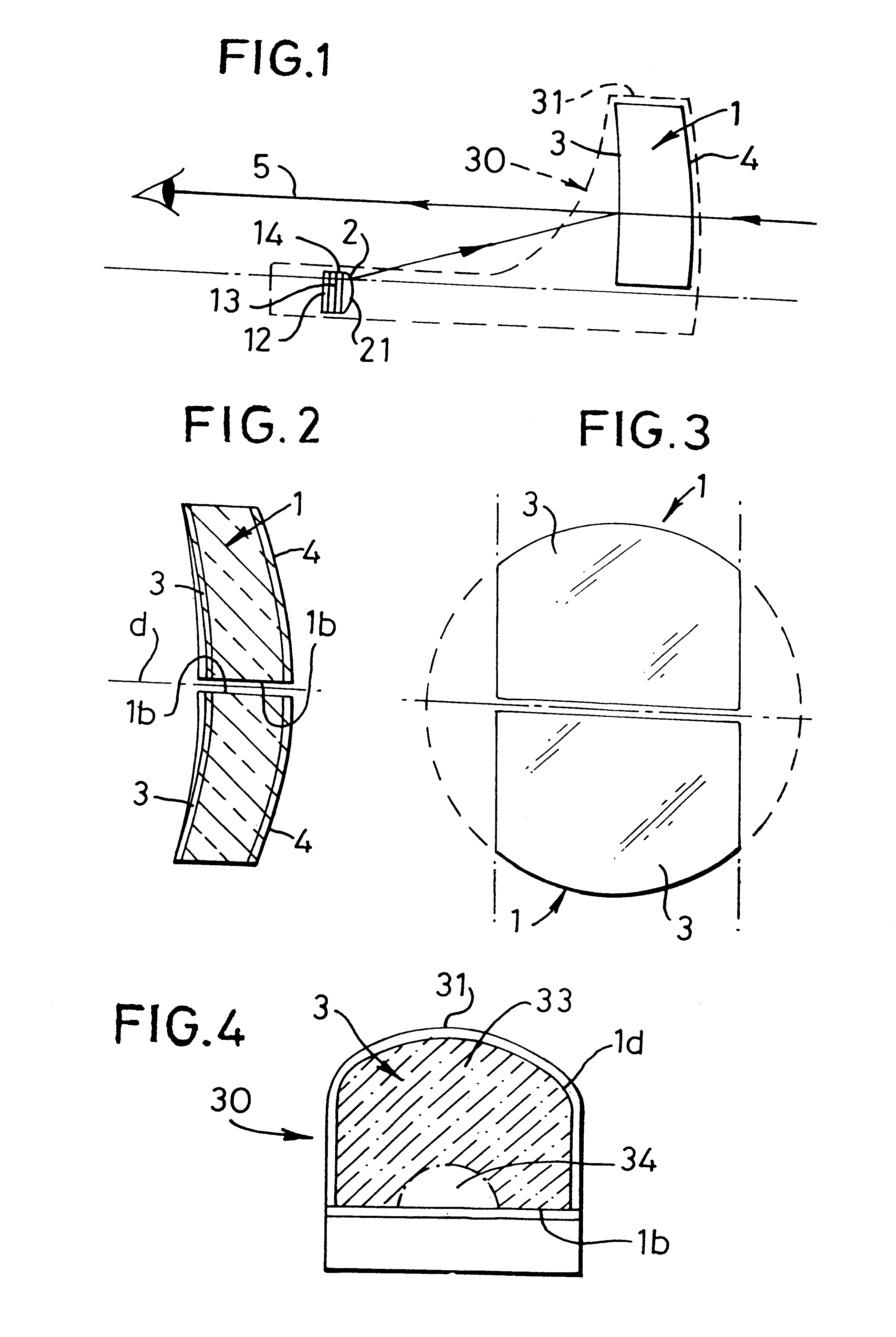
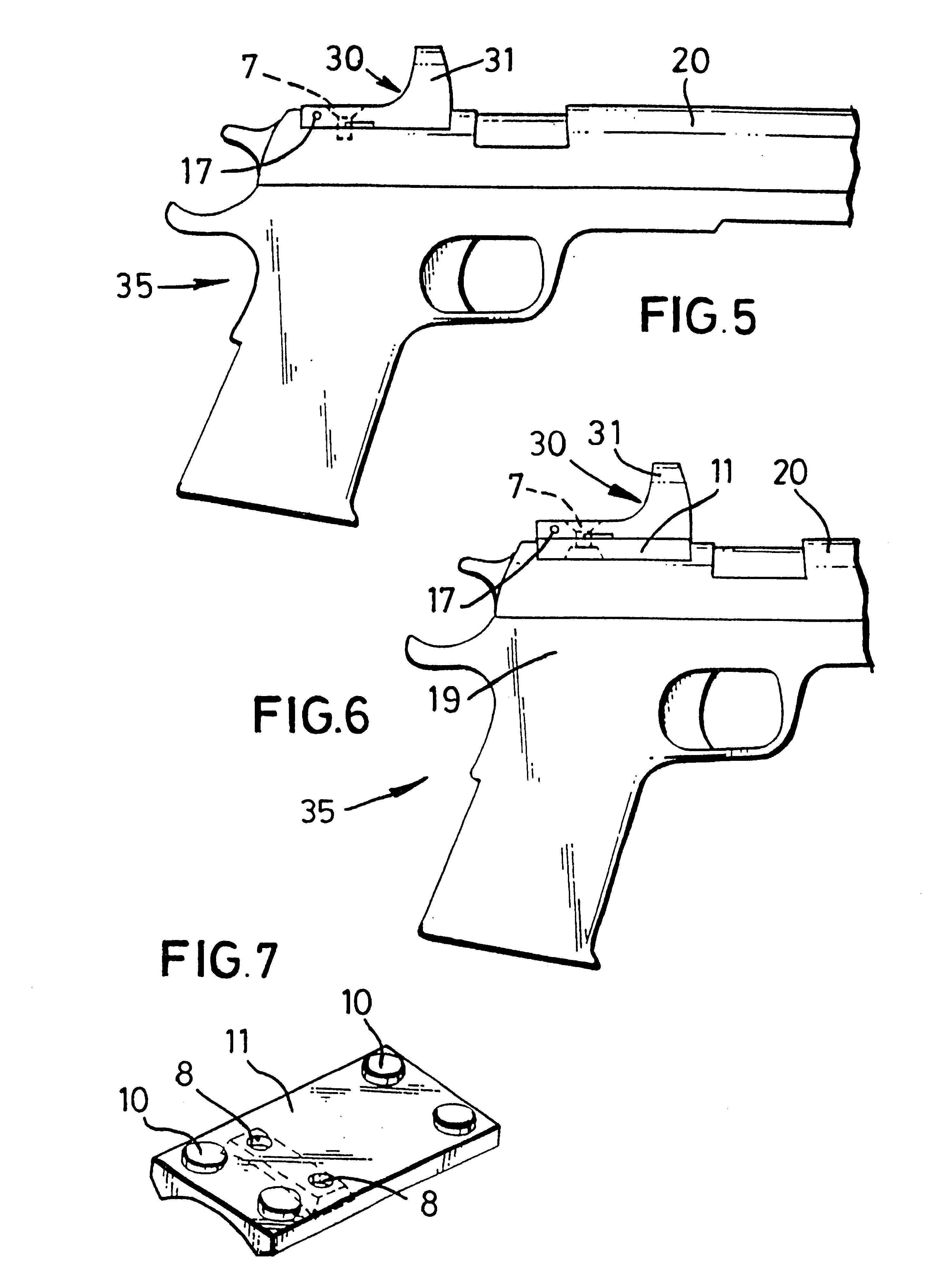
Optical sighting devices
Owner:LEUPOLD & STEVENS
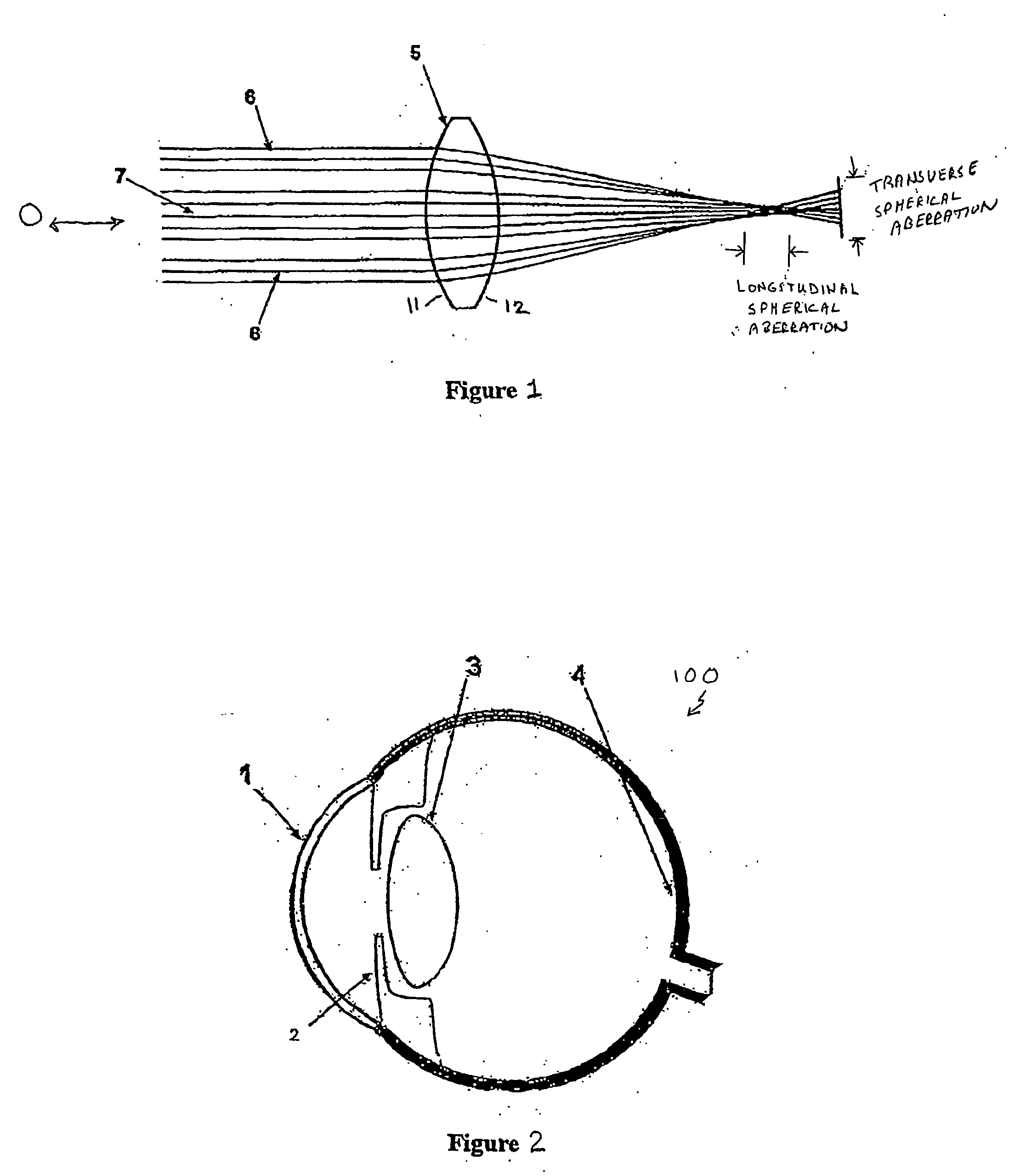
Aspheric lenses and lens family
InactiveUS20050203619A1Efficient processingPositive spherical aberrationIntraocular lensOptical partsWavefrontSpherical aberration
An aspheric IOL for use in an ocular system has no inherent spherical aberration. An aspheric IOL for use in an ocular system has a controlled amount of inherent negative spherical aberration such that the IOL induces no spherical aberration in a converging wavefront. The amount of negative spherical aberration is less than an amount necessary to counter balance the positive spherical aberration of the cornea. A family of aspheric IOLs made up of any two or more individual aspheric IOLs having different spherical aberration values and different lens shape factors. A lens constant, such as the A-constant, is kept constant throughout the family of lenses. In an aspect, the A-constant of a child-family of aspheric IOLs matches the A-constant of a parent-family of spherical IOLs. A method for designing a family of aspheric IOLs.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Aspheric lenses and lens family
ActiveUS20060030938A1Effectively process a finite amount of positive spherical aberrationPositive spherical aberrationIntraocular lensOptical partsWavefrontIntraocular lens
In an embodiment, an aspheric IOL for use in a pseudophakic ocular system has no inherent spherical aberration. In an embodiment, an aspheric IOL for use in a pseudophakic ocular system has a controlled amount of inherent negative spherical aberration such that the IOL induces no spherical aberration in a converging wavefront from a cornea passing through the lens. The amount of negative spherical aberration is less than an amount necessary to counter balance the positive spherical aberration of the cornea. In an aspect, the amount of inherent negative spherical aberration mimics that of a healthy natural crystalline lens in a relaxed state. An embodiment of the invention is directed to a family of aspheric IOLs made up of any two or more member aspheric IOLs each having different spherical aberration values and different lens shape factors. A lens constant, such as the well known A-constant, is kept constant throughout the family of lenses. An embodiment of the invention is directed to a multi-component accommodating intraocular lens (A-IOL). In a particular embodiment, the A-IOL introduces substantially no residual spherical aberration to a wavefront incident upon and passing through the A-IOL. According to an aspect, the A-IOL will have substantially no inherent spherical aberration. In an aspect, the posterior lens component of the A-IOL may have a diffractive or Fresnel optical surface to control a physical characteristic of the A-IOL. An embodiment of the invention is directed to a family of member A-IOLs where each member A-IOL has a first (1) surface and a fourth (4) surface characterized by a radius and a conic constant that remain substantially constant over the power range of the A-IOL family. An embodiment of the invention is directed to a family of member A-IOLs in which the accommodative amplitude per millimeter of anterior lens translational movement varies with A-IOL power over the power range of the family.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Advanced compact head up display
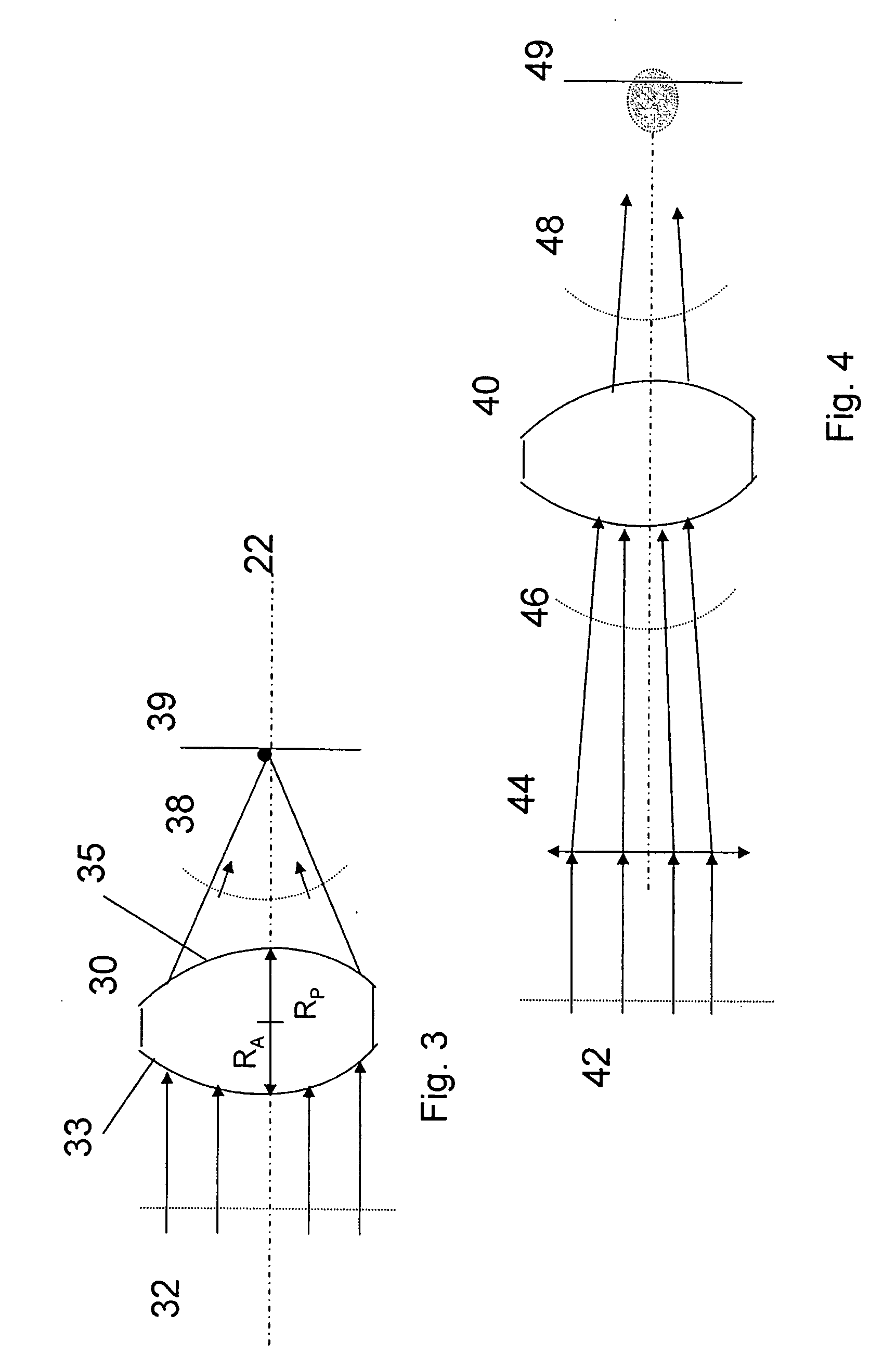
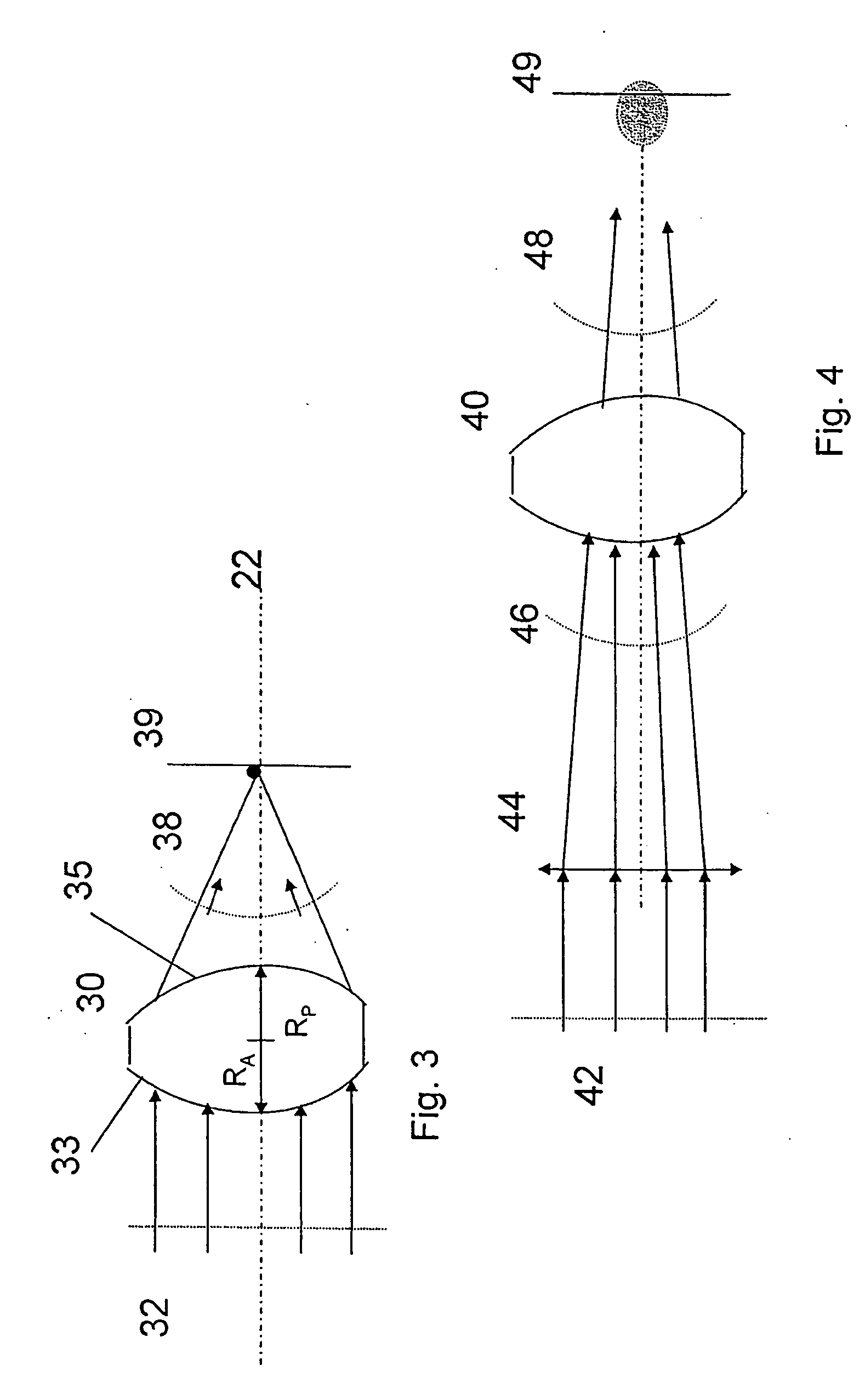
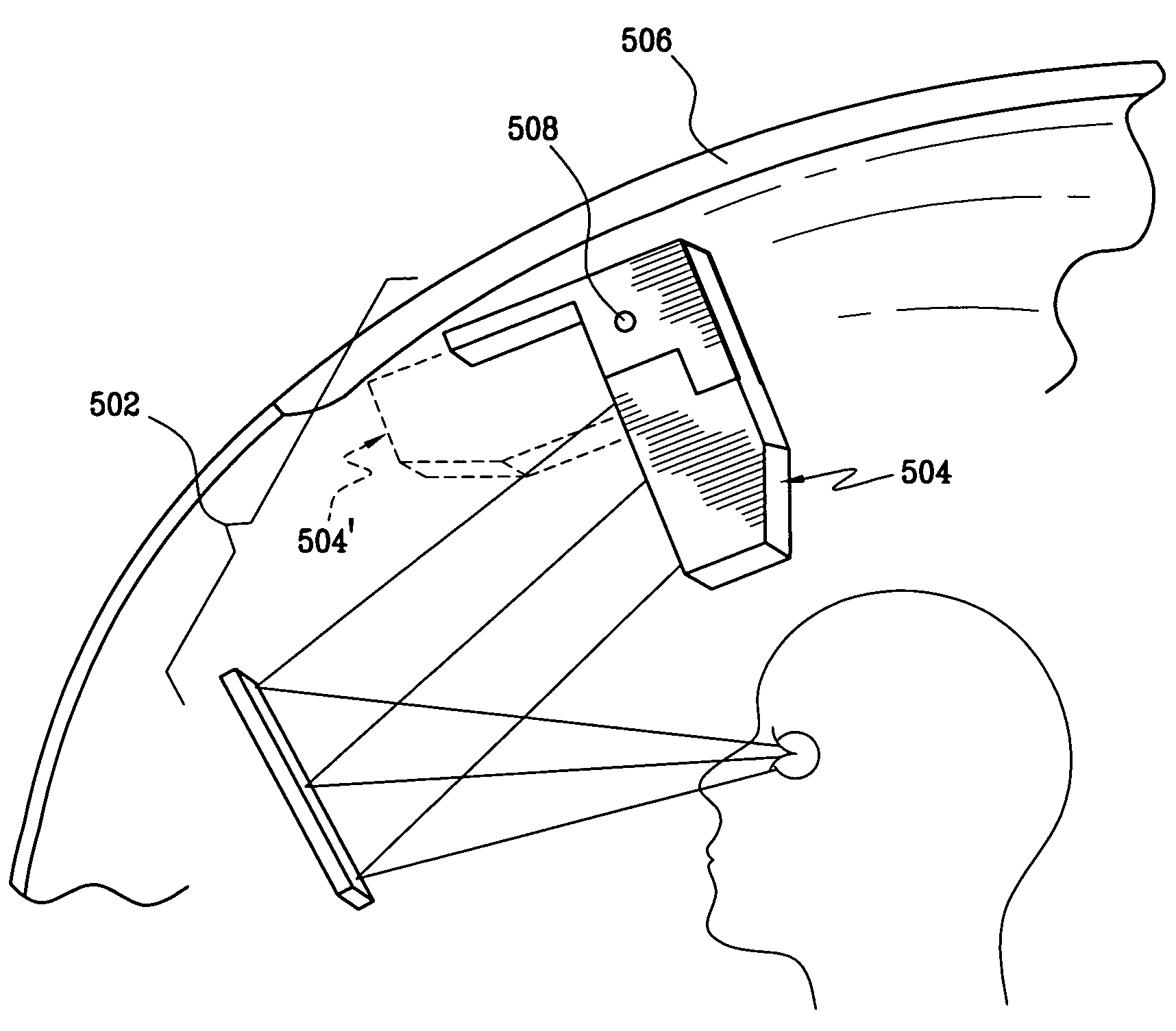
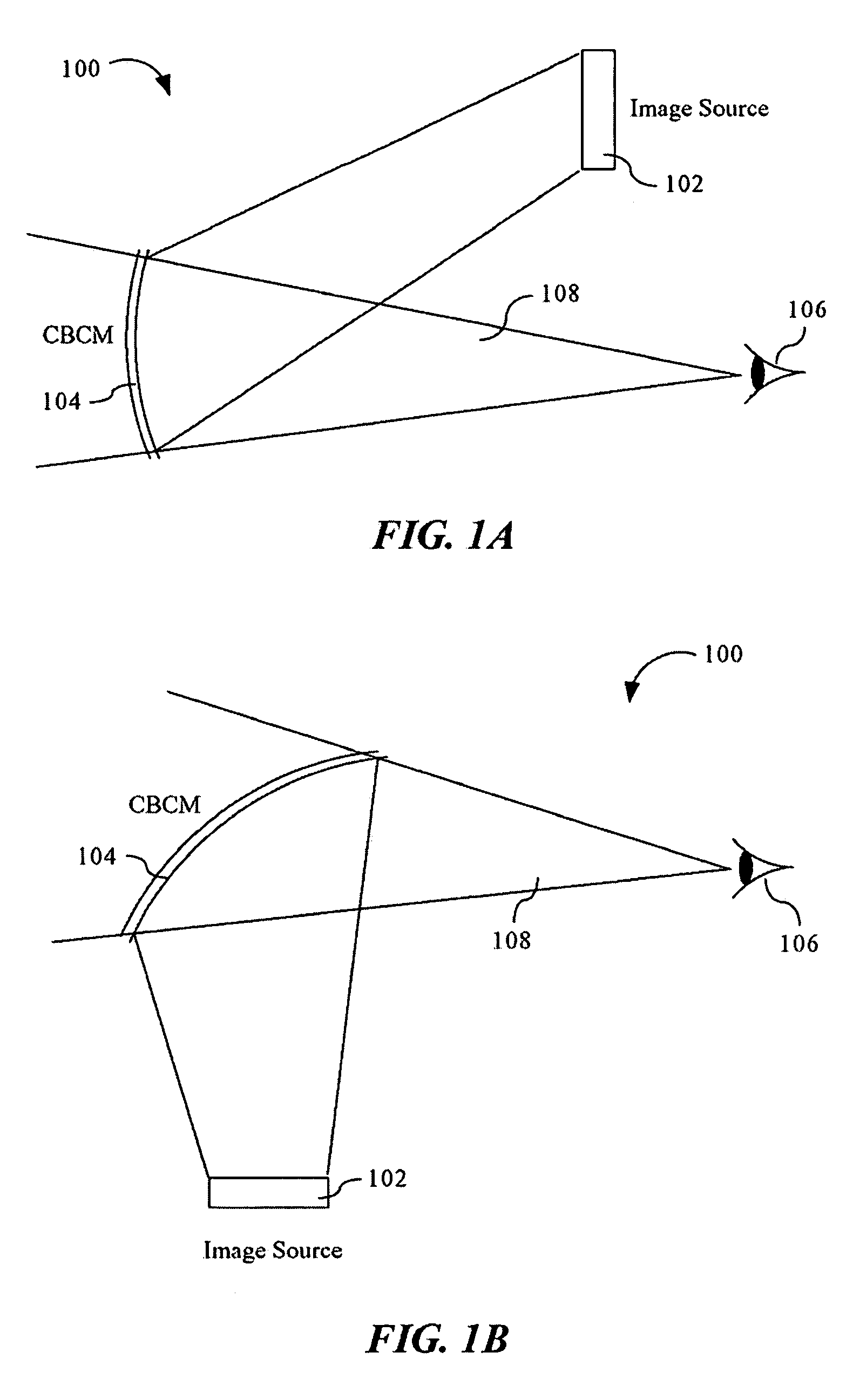
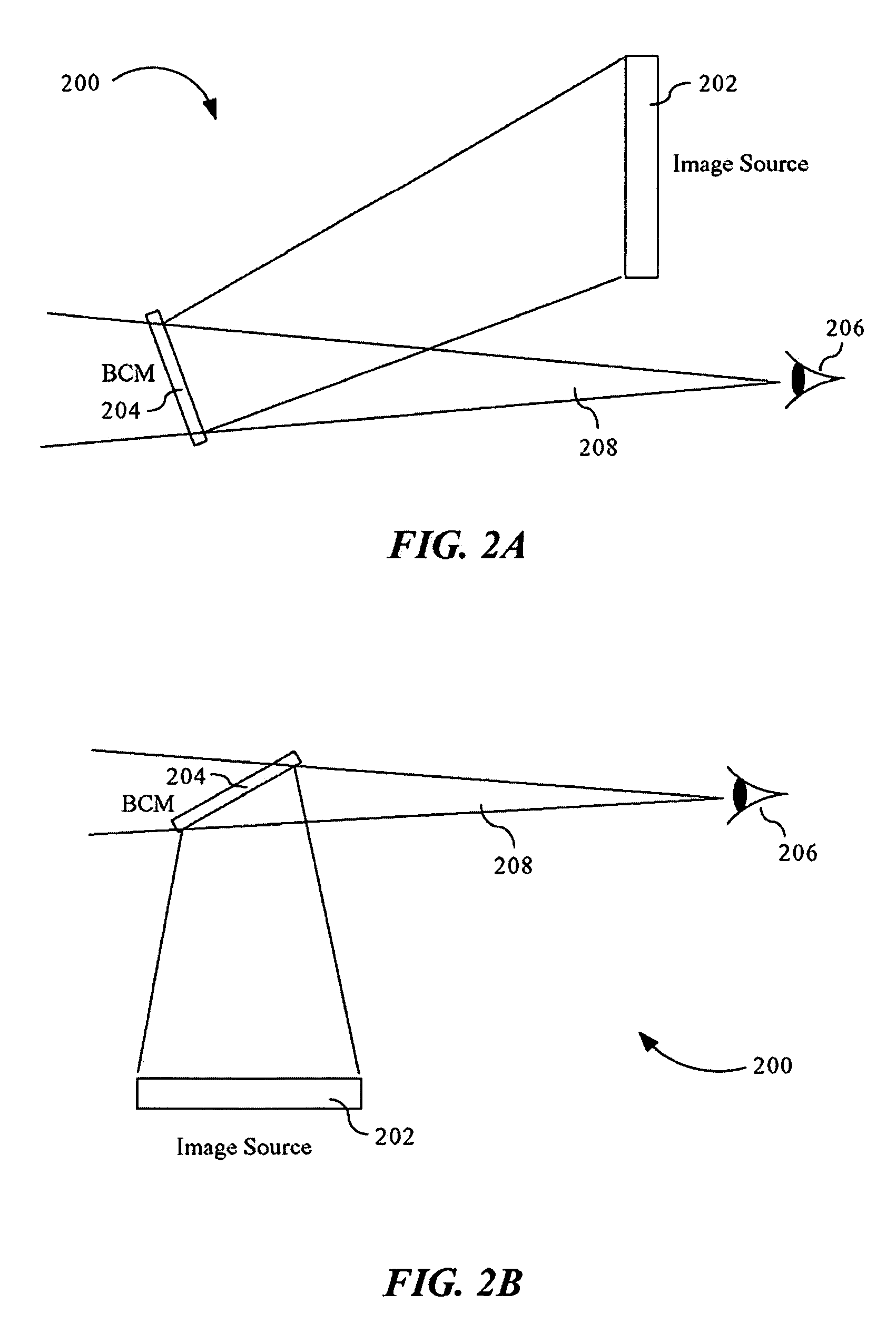
ActiveUS7095562B1Simplifies optical systemMinimize aberrationLighting support devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsHead-up displayDashboard
A head up display system for a vehicle that includes a compact image source for projecting an image. The compact image source may be foldable up toward or into a cockpit ceiling of the vehicle, be positioned within a dashboard of the vehicle, or located at another suitable position. A combiner reflects the projected image with optical power toward an observer for observation. The combiner is positioned so that the observer, in a line of sight, may see a visual exterior view of an outside scene through the combiner and the projected image in the combiner. In a preferred embodiment, the image source includes an illumination system that includes a high power light emitting diode (LED) array assembly. A Fresnel lens array is operatively associated with the LED array assembly for receiving light produced by the LED and providing a nearly collimated light output. A spatial light modulator receives the nearly collimated light output. The preferred combiner is a meniscus combiner that includes a meniscus lens; a multi-layer dichroic coating formed on a first surface of the meniscus lens; and, an anti-reflection coating formed on a second, opposite surface of the meniscus lens. The meniscus combiner preferably utilizes a non-symmetric aspheric meniscus lens.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
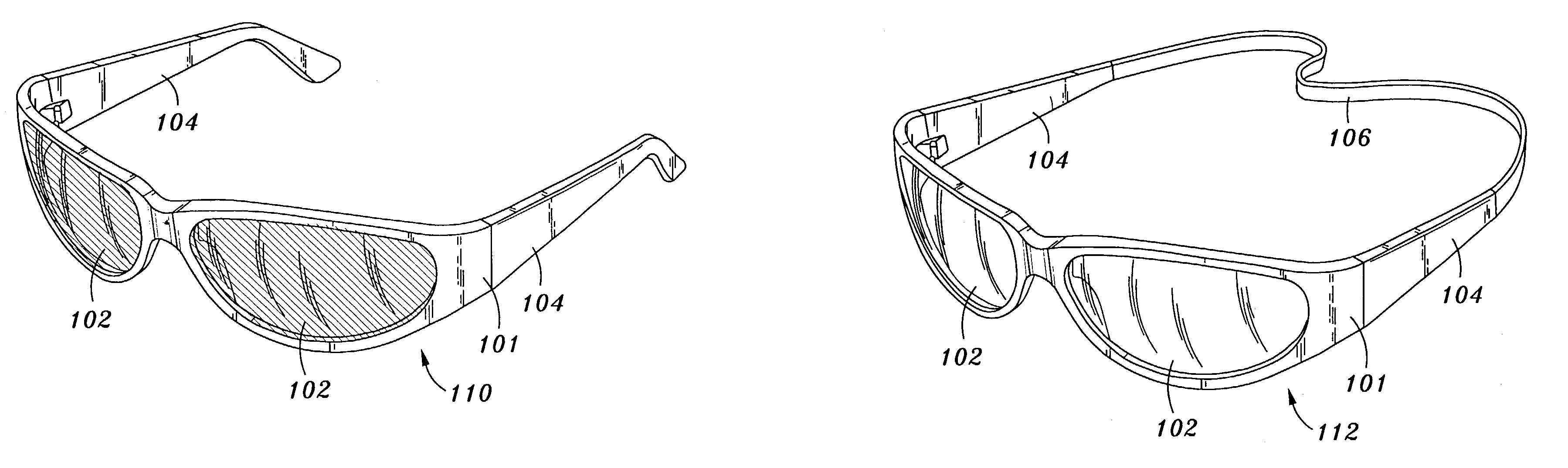
Blue blocking lens
InactiveUS6955430B2Maximizing visual acuity and blockageMinimize aberrationGogglesNon-optical partsCamera lensUses eyeglasses
An article of externally-worn eye wear, including, but not limited to, eyeglasses, sunglasses, goggles, and contact lenses. The eye wear includes a wavelength transmission blocker for blocking substantially all of light wavelengths throughout the blue light spectrum. The wavelength transmission blocker protects the eyes against the harmful effect of the blocked light. Also, since the eye wear is worn externally from the eye, and the user can remove the eye wear, the user can selectively block the light. As such, the eye wear can be worn to block potentially harmful light, or the eye wear can be removed if blocking the light would cause other hazards.
Owner:PRATT STEVEN G
Pattern-definition device for maskless particle-beam exposure apparatus
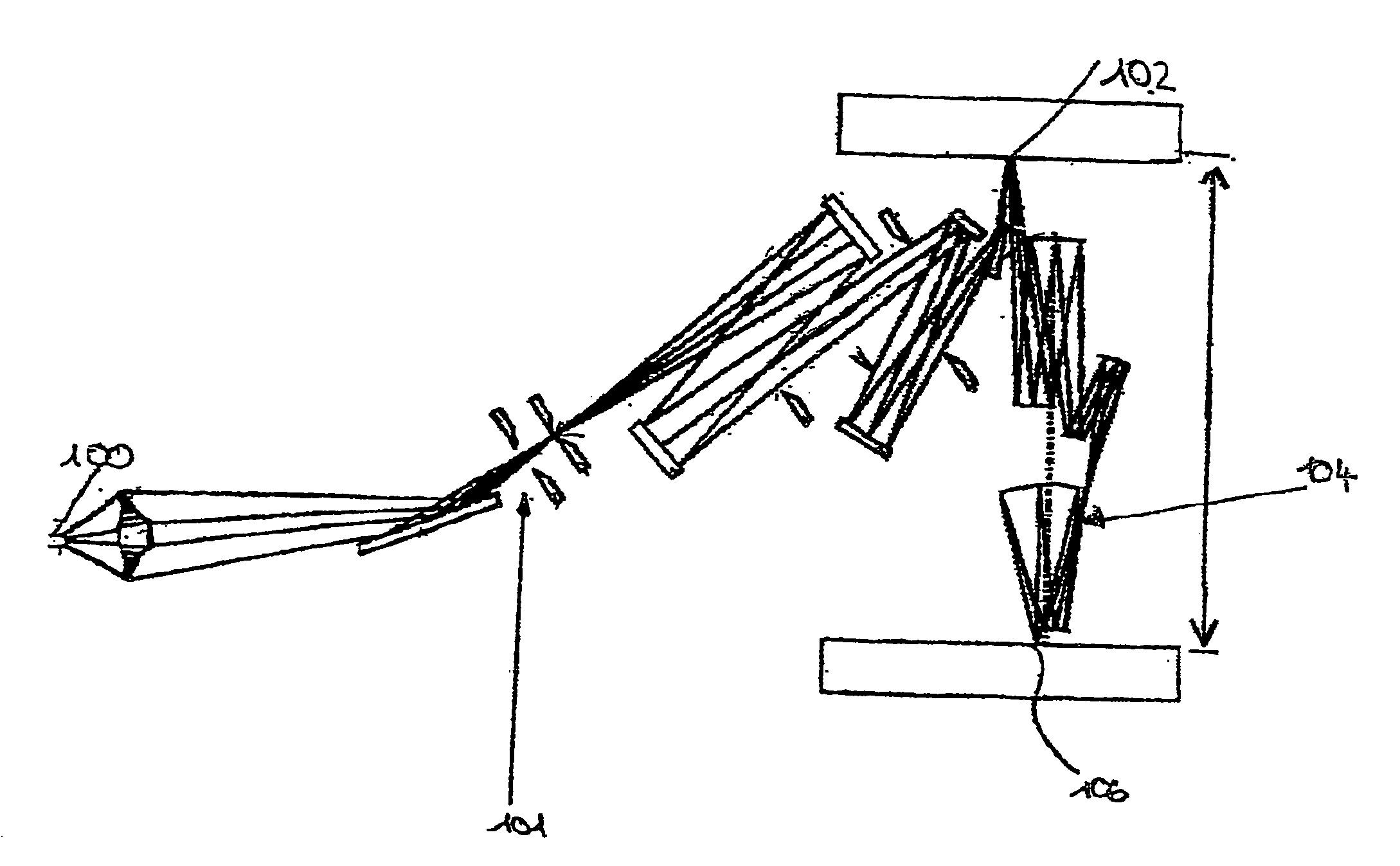
ActiveUS7084411B2Minimize aberrationThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsParticle beamEngineering
In a pattern-definition device (102) for use in a particle-beam exposure apparatus, a beam of electrically charged particles is patterned through a plurality of apertures. The device comprises at least one deflector array means having a plurality of openings surrounding the beamlets, wherein for each opening are provided at least two deflecting electrodes to which different electrostatic potentials are appliable, thus correcting the path of the beamlet(s) passing through the respective opening according to a desired path through the device (102). According to a partition of the plurality of apertures into a set of subfields (Aij), the deflecting electrodes belonging to the same subfield (Aij) have common electric supplies. Thus, the electrostatic potentials of the deflecting electrodes belonging to the same subfield (Aij) are constant or linearly interpolated between basic potentials fed at basic points (Pij) of the respective subfield.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
Meniscus head up display combiner
A meniscus combiner for a head up display (HUD) system. The meniscus combiner includes a meniscus lens; a multi-layer dichroic coating formed on a first surface of the meniscus lens; and, an anti-reflection coating formed on a second, opposite surface of the meniscus lens. The meniscus combiner preferably utilizes a non-symmetric aspheric meniscus lens which simplifies the optical system of the image source (overhead or in-dash unit) minimizing aberrations and minimizing costs. The meniscus combiner may be fabricated utilizing a number of lens sections which may be bonded together and blended. Use of multiple lens sections provides the ability to easily optimize the lens design. Alternatively, the meniscus combiner can be fabricated from a single lens.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Data storage system and methods using diffractive near-field optics
InactiveUS6396789B1Minimize aberrationLow costOptical flying-type headsNanoinformaticsOptical pathOptical radiation
An optical assembly suitable for use with an optical medium for the storage and retrieval of data, the optical assembly comprising: a source of illumination for providing a beam of optical radiation, an objective lens disposed in the optical path of the beam for redirecting the beam to the optical medium, and a diffractive optical element disposed between the redirected beam of radiation and the optical medium such that at least a portion of the redirected beam of radiation passes through a surface of the diffractive optical element and is reflected to the objective lens.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Blue blocking tens
InactiveUS7255435B2Maximizing visual acuity and blockageMinimize aberrationGogglesIntraocular lensLength waveVisual acuity
An article of an eye wear worn externally upon an eye, having an article which article comprises a wavelength transmission blocker. The wavelength transmission blocker has a lutein assimilated therein for preventing radical damage in the eye. The wavelength transmission blocker is sized and configured to maximize visual acuity and block at least 80% of light wavelengths throughout a blue light spectrum set in a range from about 400 nm to about 510 nm. Preferably, the wavelength transmission blocker is operative to block substantially 100% of light wavelengths lower than 420 nm, and to block about 99% light wavelength at 420 nm and about 20% of light wavelength at 510 nm. Preferably, the wavelength transmission blocker blocks a gradually reduced percentage of light wavelengths between 420 nm to 510 nm. The wavelength transmission blocker is also operative to block a portion of light wavelengths between 510 nm to 650 nm.
Owner:PRATT STEVEN G
Optical disk apparatus using tilt and aberration correction control system
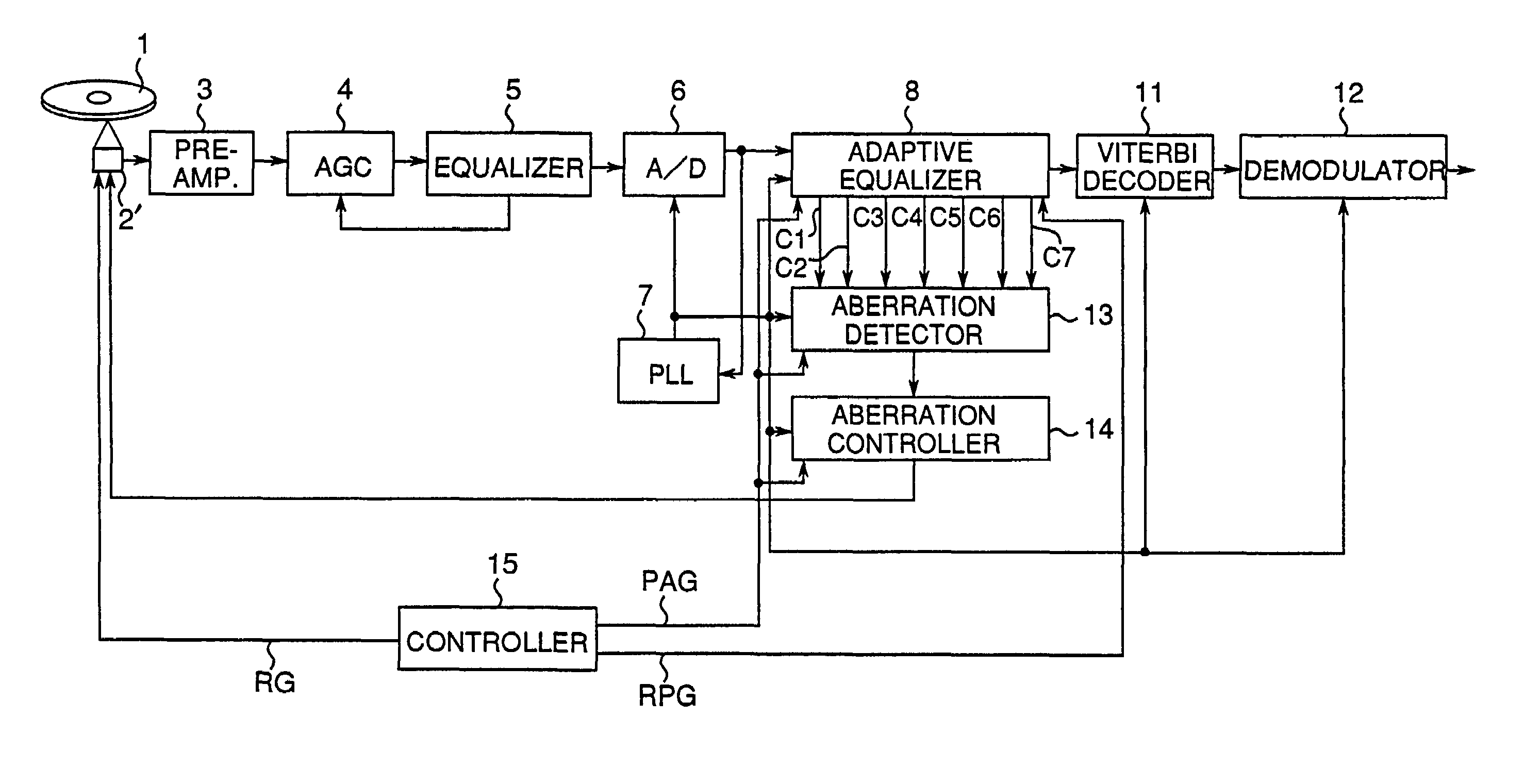
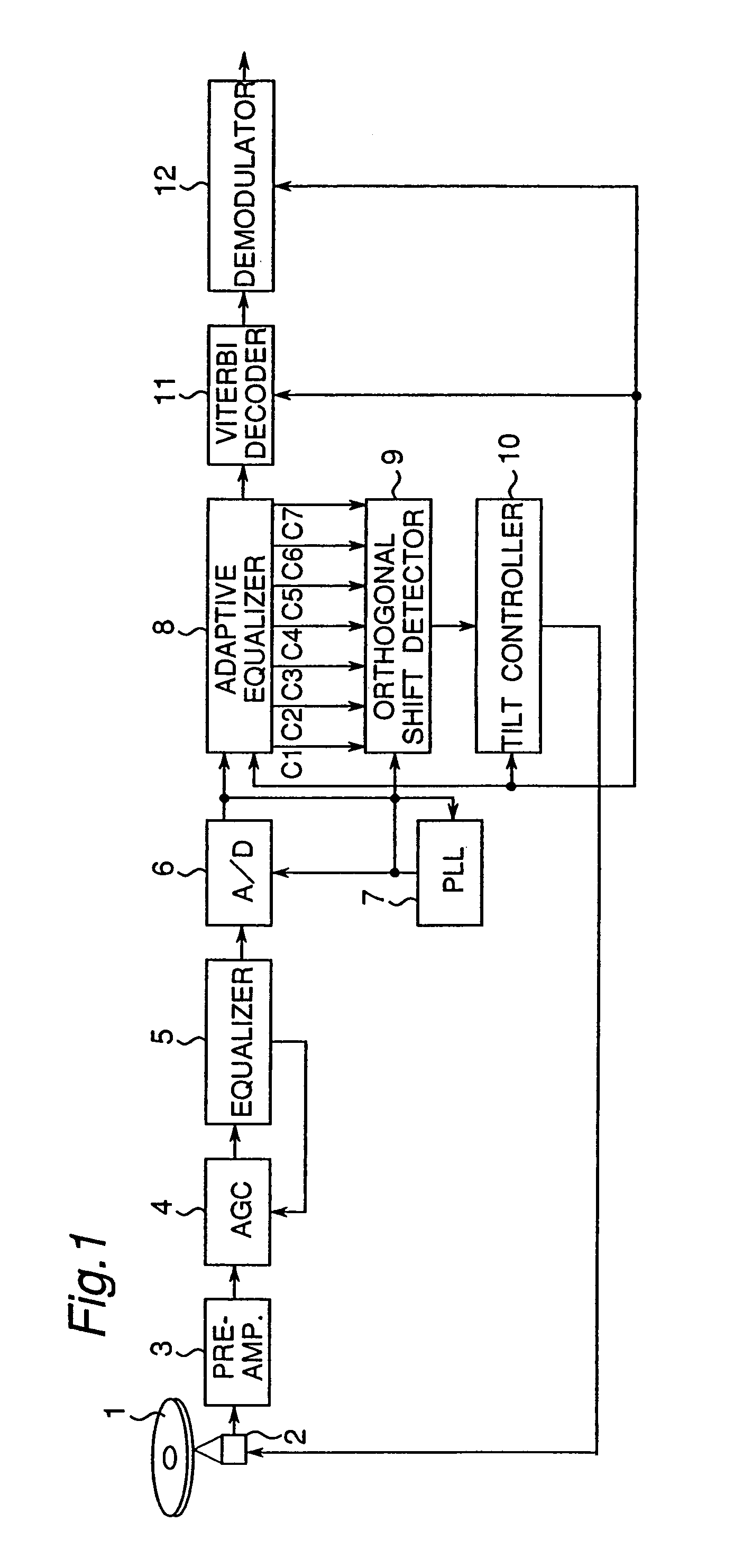
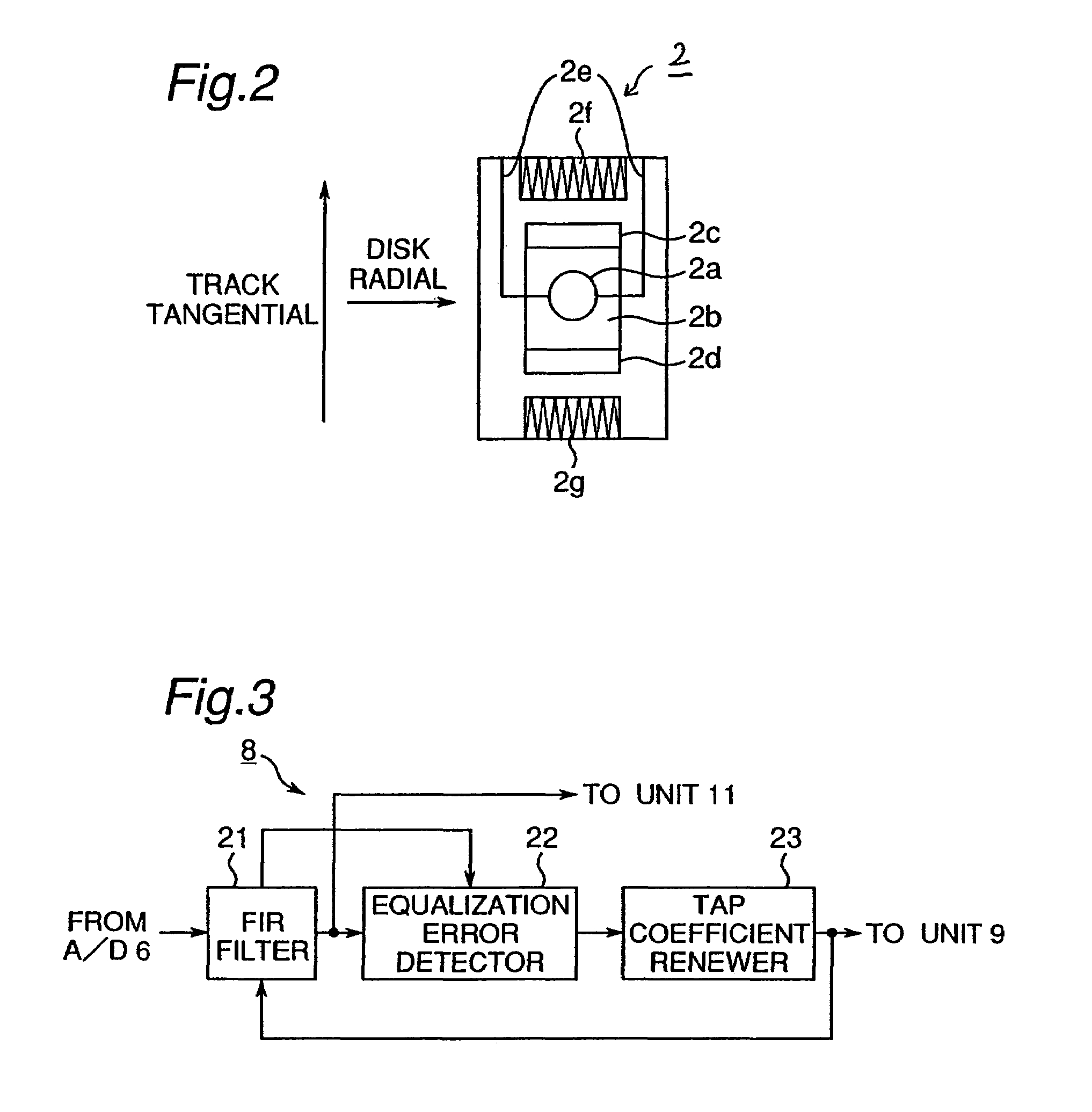
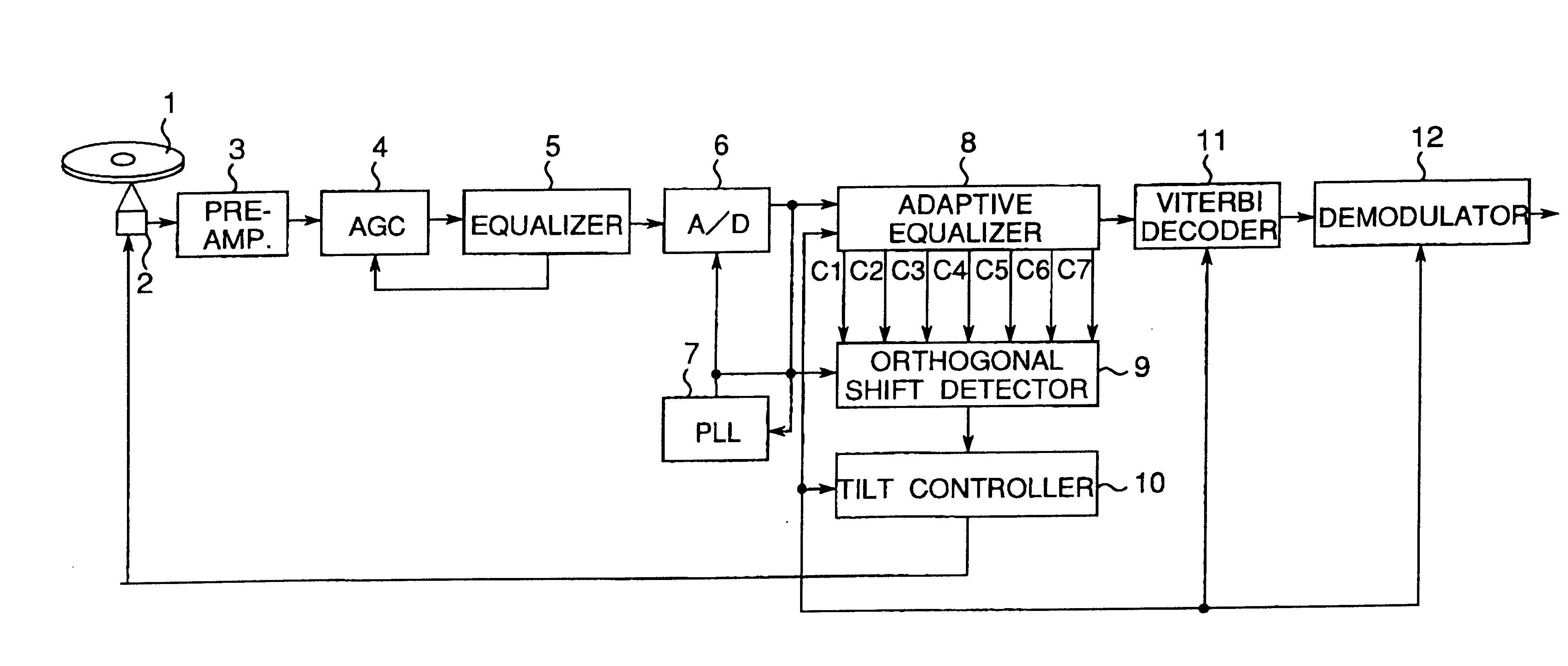
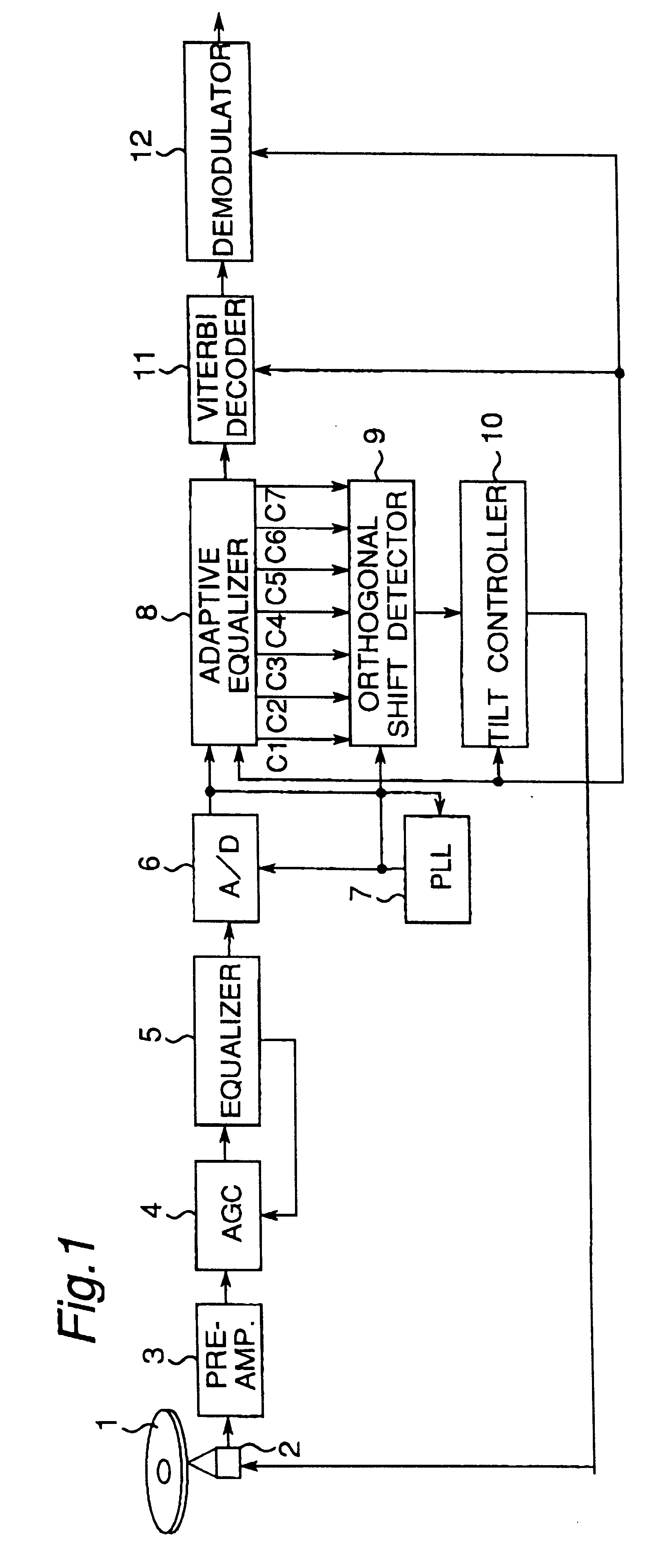
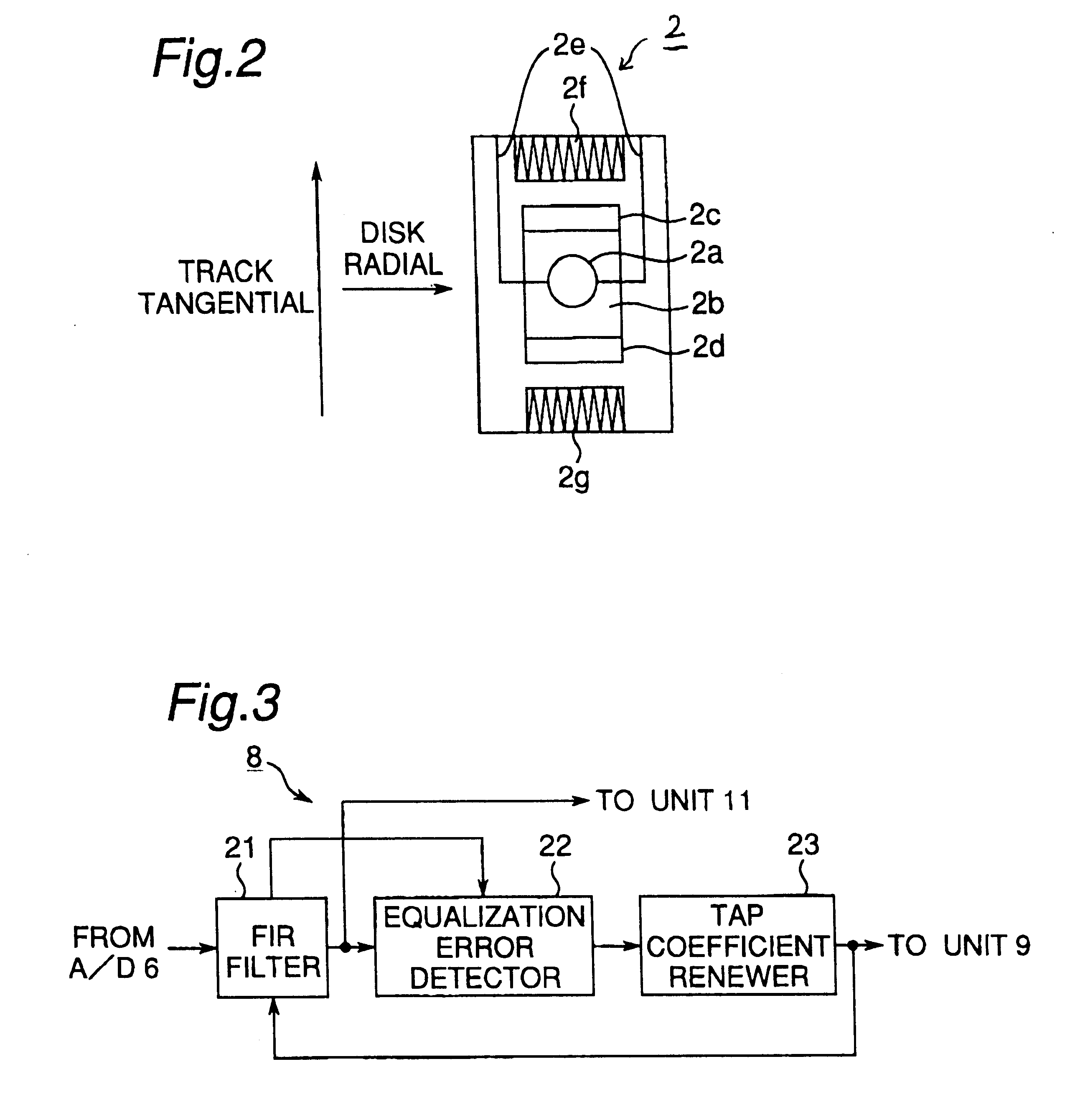
InactiveUS7145848B2Error minimizationMinimize orthogonal shift of light beamCombination recordingTelevision system detailsOptical axisControl system
A tilt control apparatus includes an orthogonal shift detector (9) which detects an orthogonal shift by comparing a pair of a plurality of tap coefficients (C1, . . . , C7) of a FIR filter and generates an orthogonal shift signal, and an actuator varies the inclination of the optical axis of the light beam to correct the orthogonal shift, and a tilt controller (10) controls the drive of the actuator in accordance with the orhogonal shift signal to minimize the orthogonal shift. In the information recording operation, the orthogonal shift obtained based on a recording track is previously stored in a temporary storage portion and the stored orthogonal shift is used to conduct the tilt control.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Blue blocking lens
InactiveUS20050043793A1Maximizing visual acuity and blockageMinimize aberrationMirrorsGogglesLength waveVisual acuity
An article of an eye wear worn externally upon an eye, having an article which article comprises a wavelength transmission blocker. The wavelength transmission blocker has a lutein assimilated therein for preventing radical damage in the eye. The wavelength transmission blocker is sized and configured to maximize visual acuity and block at least 80% of light wavelengths throughout a blue light spectrum set in a range from about 400 nm to about 510 nm. Preferably, the wavelength transmission blocker is operative to block substantially 100% of light wavelengths lower than 420 nm, and to block about 99% light wavelength at 420 nm and about 20% of light wavelength at 510 nm. Preferably, the wavelength transmission blocker blocks a gradually reduced percentage of light wavelengths between 420 nm to 510 nm. The wavelength transmission blocker is also operative to block a portion of light wavelengths between 510 nm to 650 nm.
Owner:PRATT STEVEN G
EUV Exposure Apparatus
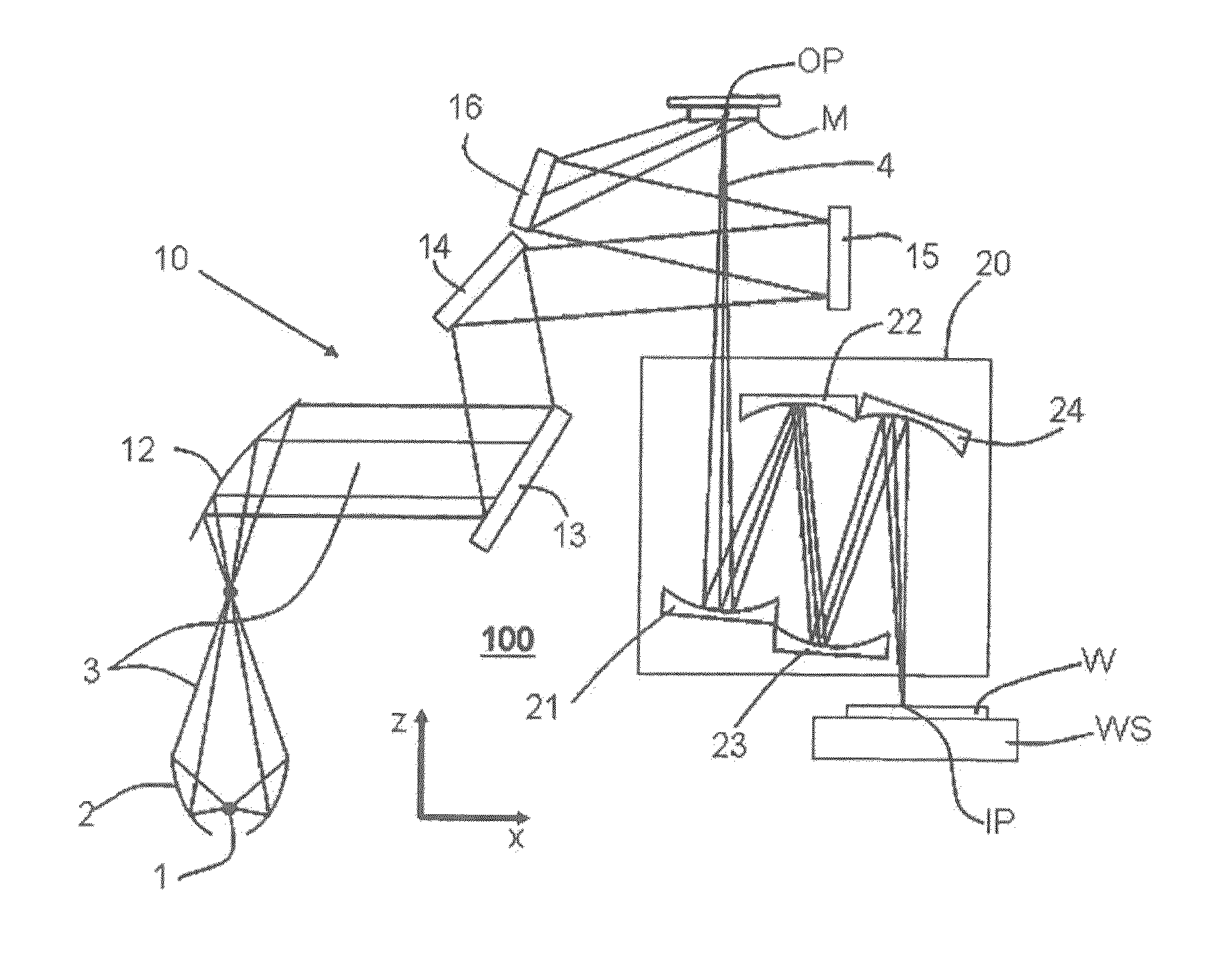
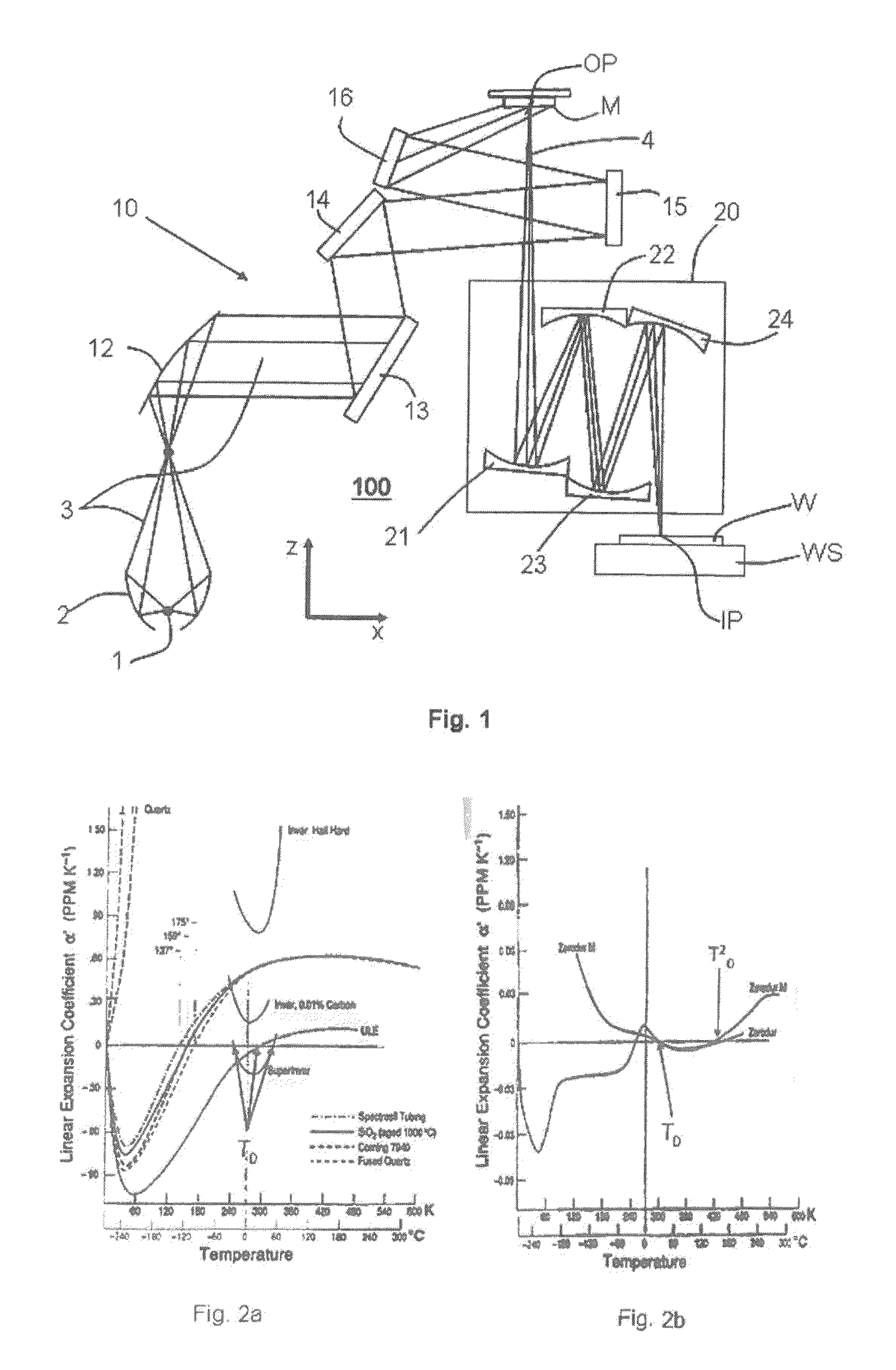
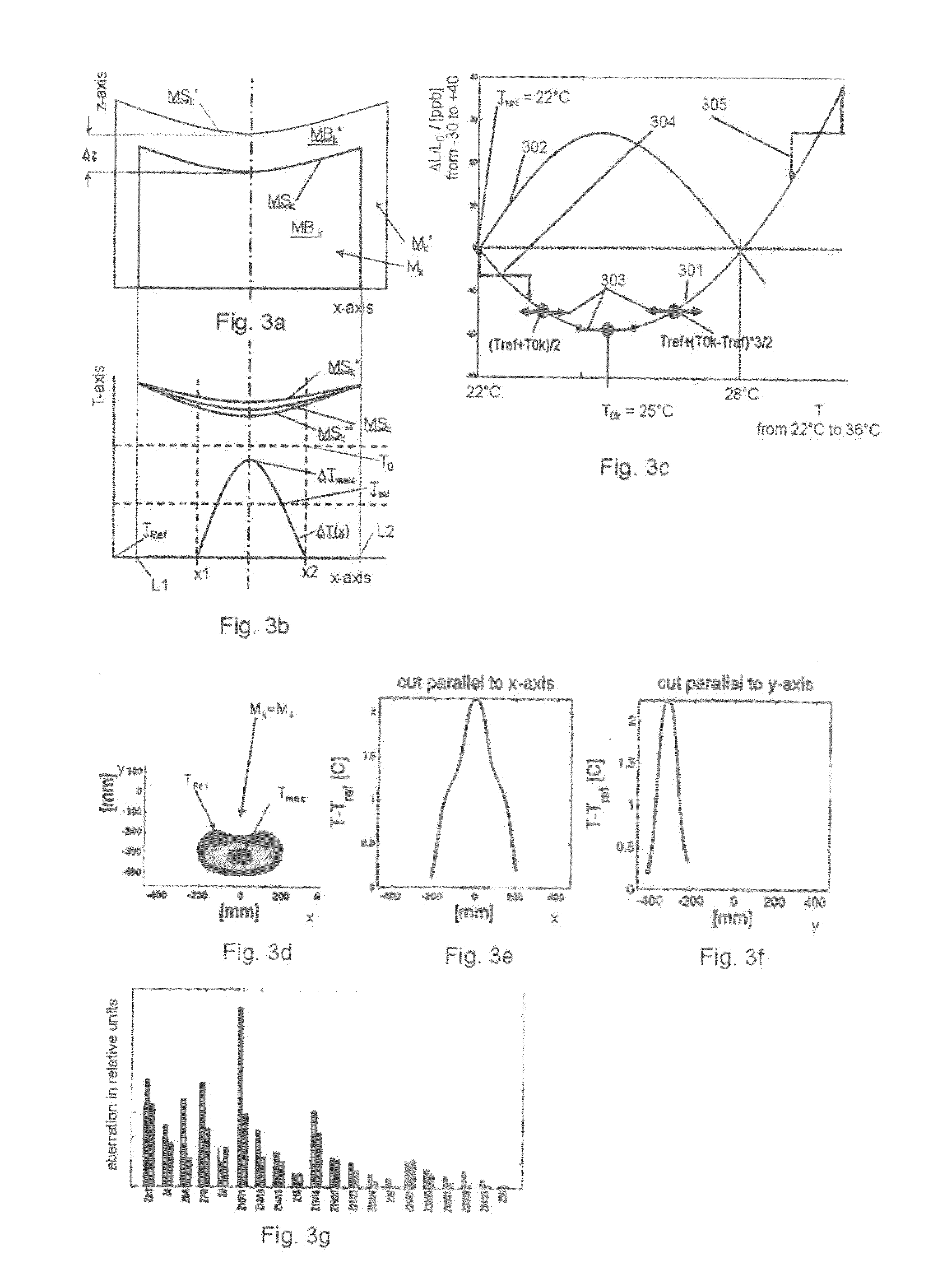
ActiveUS20130141707A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingThermal expansionProjection lens
A projection lens of an EUV-lithographic projection exposure system with at least two reflective optical elements each comprising a body and a reflective surface for projecting an object field on a reticle onto an image field on a substrate if the projection lens is exposed with an exposure power of EUV light, wherein the bodies of at least two reflective optical elements comprise a material with a temperature dependent coefficient of thermal expansion which is zero at respective zero cross temperatures, and wherein the absolute value of the difference between the zero cross temperatures is more than 6K.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Optical component that includes a material having a thermal longitudinal expansion with a zero crossing
ActiveUS20050207001A1Minimize aberrationLow thermal expansionMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusThermal expansionLighting system
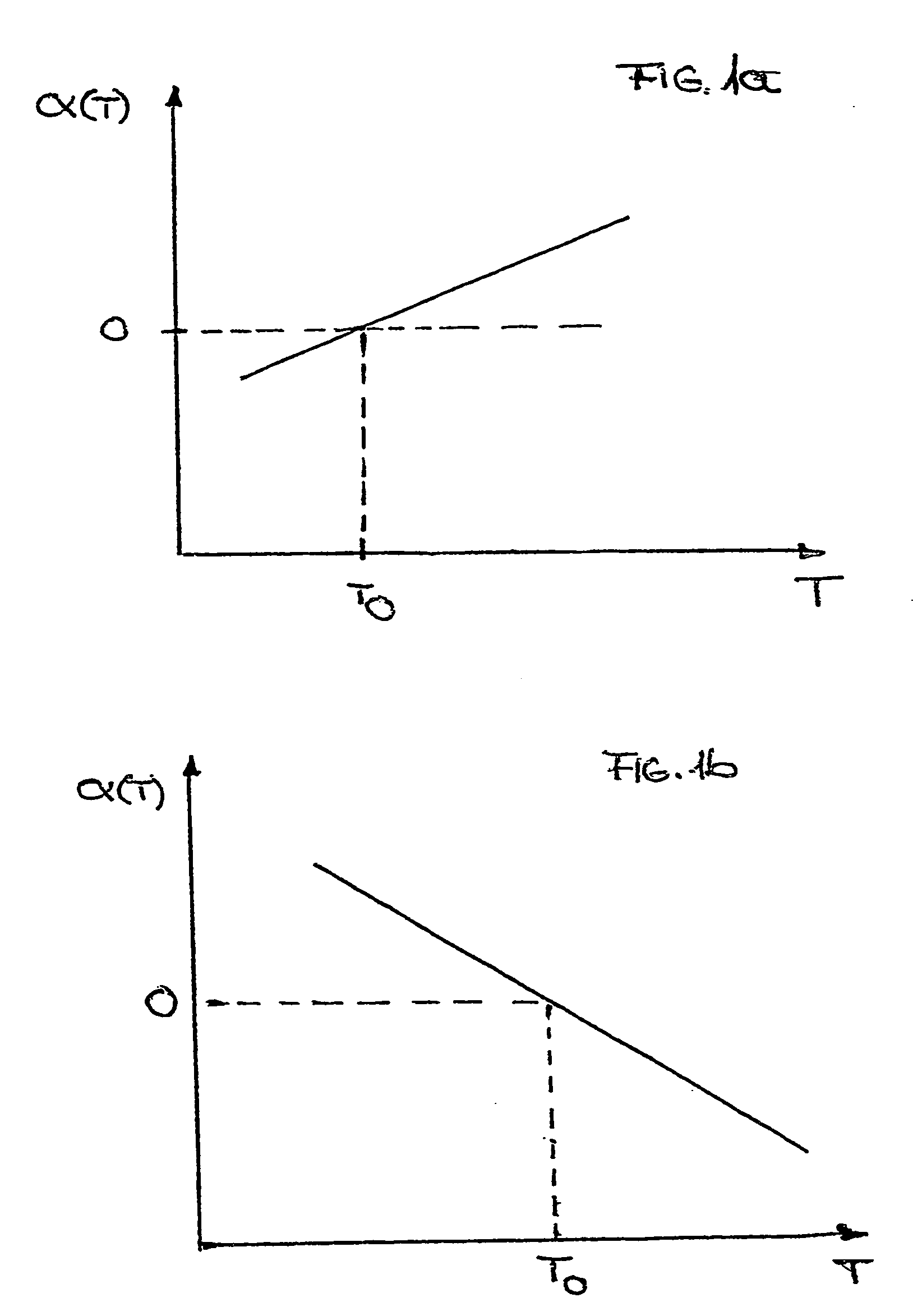
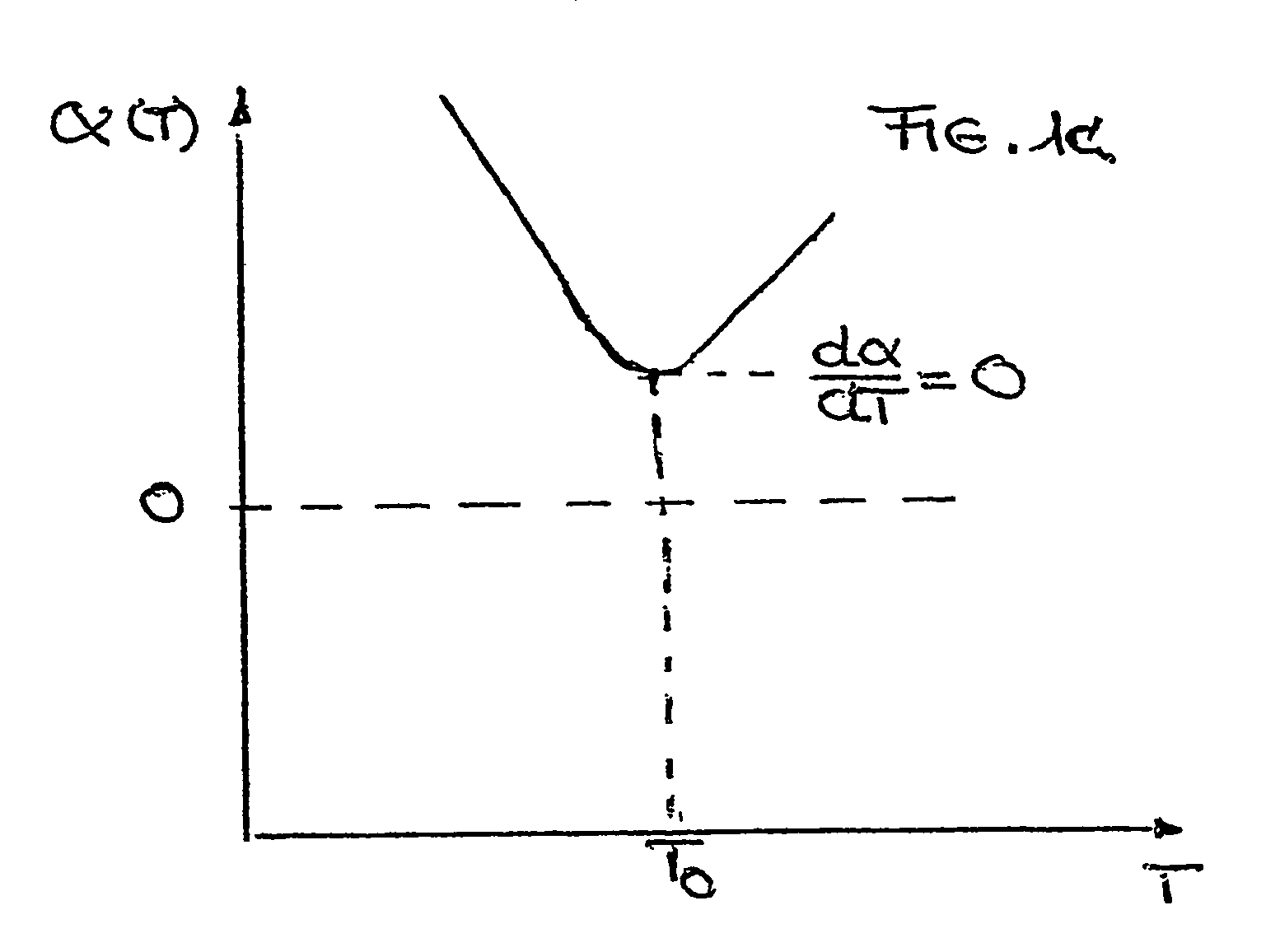
There is provided an optical component. The optical component includes a material having a surface that heats to a maximum temperature (Tmax) when subjected to radiation. The material has a temperature-dependent coefficient of thermal expansion (α(T)) of about zero at a temperature T0 that is approximately equal to Tmax. The optical component is suitable for use in any of an illumination system, a projection objective or a projection exposure system, as employed, for example, for EUV microlithography.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Beam altering fiber lens device and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20030165292A1Reduce in quantityEfficient couplingOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingCoupling light guidesFiberOptical axis
A multi-lens apparatus for altering the mode field of an optical signal is disclosed. The apparatus includes an optical fiber having a core region defining an optical axis and a GRIN-fiber lens positioned in relation to one end of the optical fiber. A biconic lens including an external surface defined by two different curves disposed substantially orthogonal to one another, a major curve C1 and a minor curve C2, with C1 and C2 intersecting at or near the optical axis is positioned in relation to an end of the GRIN-fiber lens remote from the fiber. A method of manufacturing a multi-lens apparatus for altering the mode field of an optical signal, and an optical assembly are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Aspheric lenses and lens family
ActiveUS7905917B2Effectively process a finite amount of positive spherical aberrationPositive spherical aberrationIntraocular lensOptical partsCamera lensIntraocular lens
In an embodiment, an aspheric IOL for use in a pseudophakic ocular system has no inherent spherical aberration. An embodiment of the invention is directed to a family of aspheric IOLs in which a lens constant, such as the well known A-constant, is kept constant throughout the family of lenses. An embodiment of the invention is directed to a multi-component accommodating intraocular lens (A-IOL) having substantially no inherent spherical aberration. An embodiment of the invention is directed to a family of member A-IOLs where each member A-IOL has a first (1) surface and a fourth (4) surface characterized by a radius and a conic constant that remain substantially constant over the power rage of the A-IOL family.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
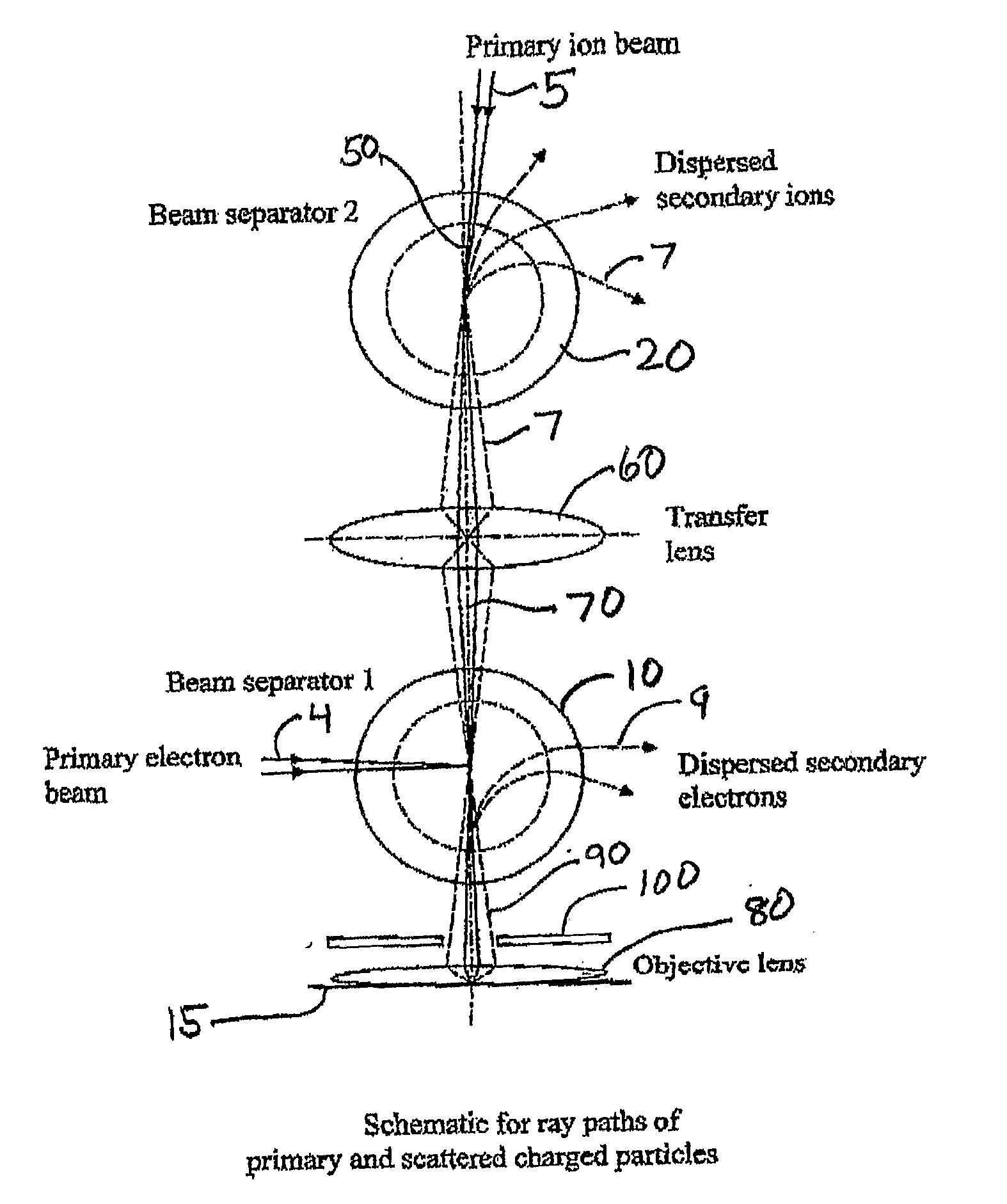
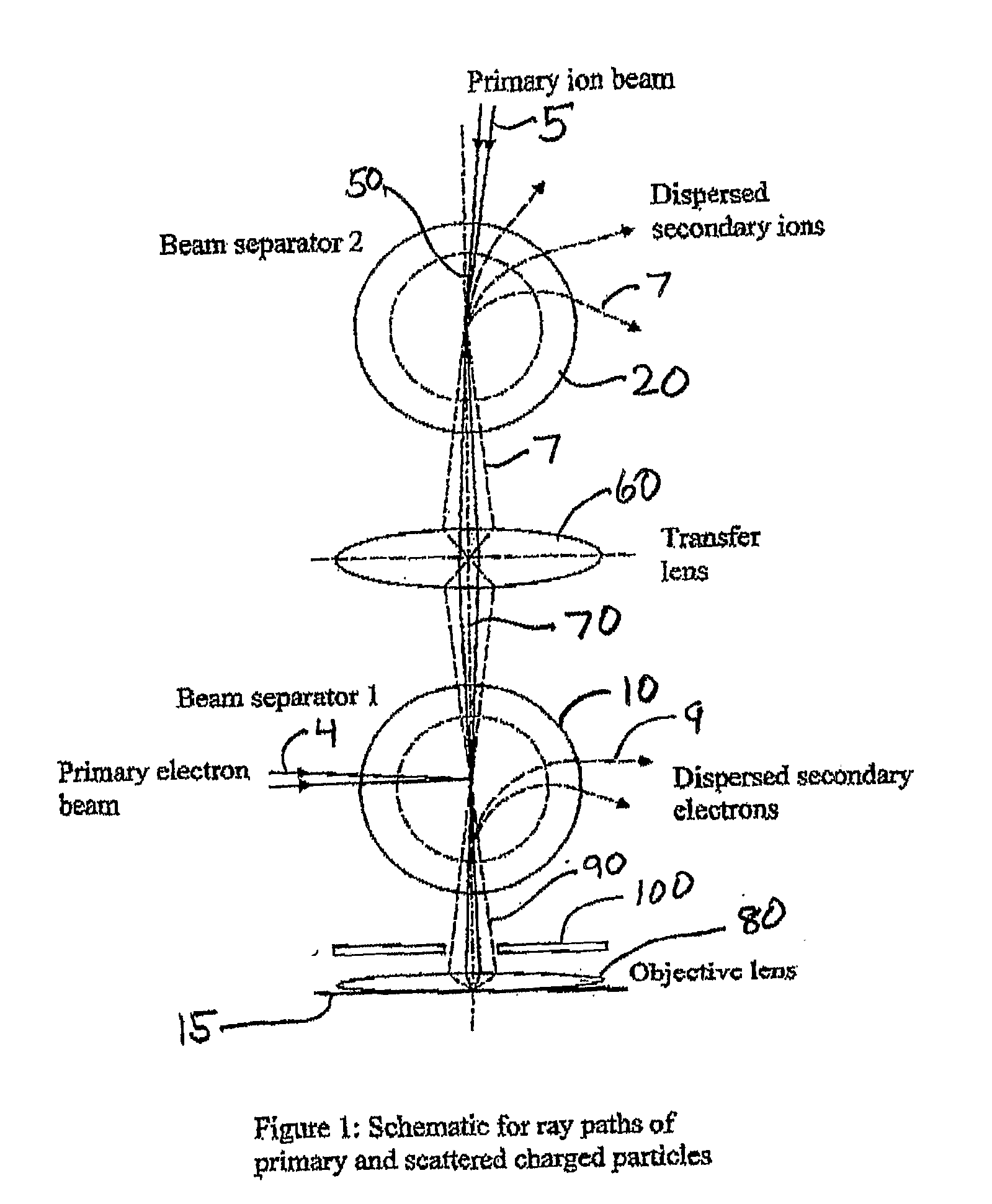
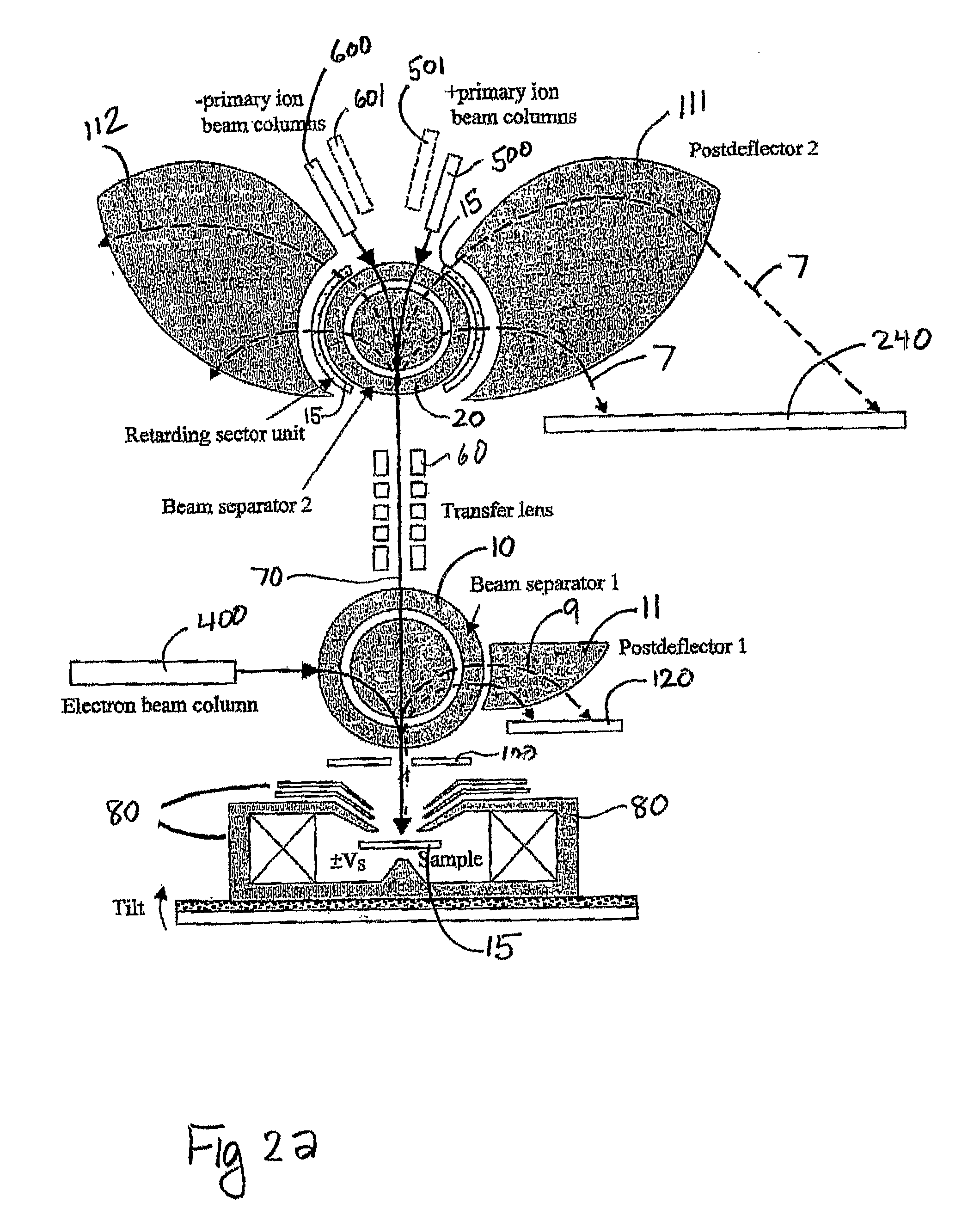
Multi-beam ion/electron spectra-microscope
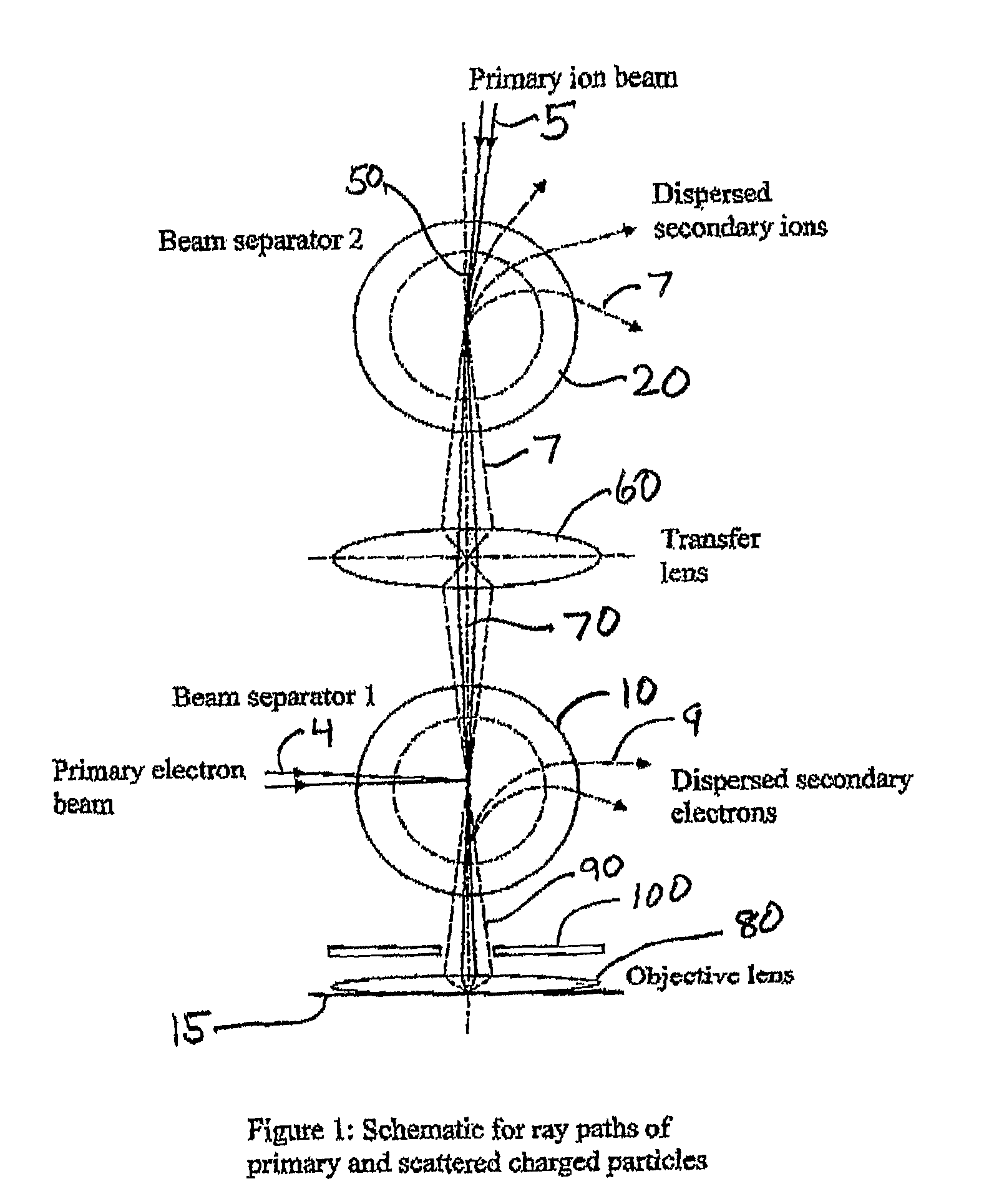
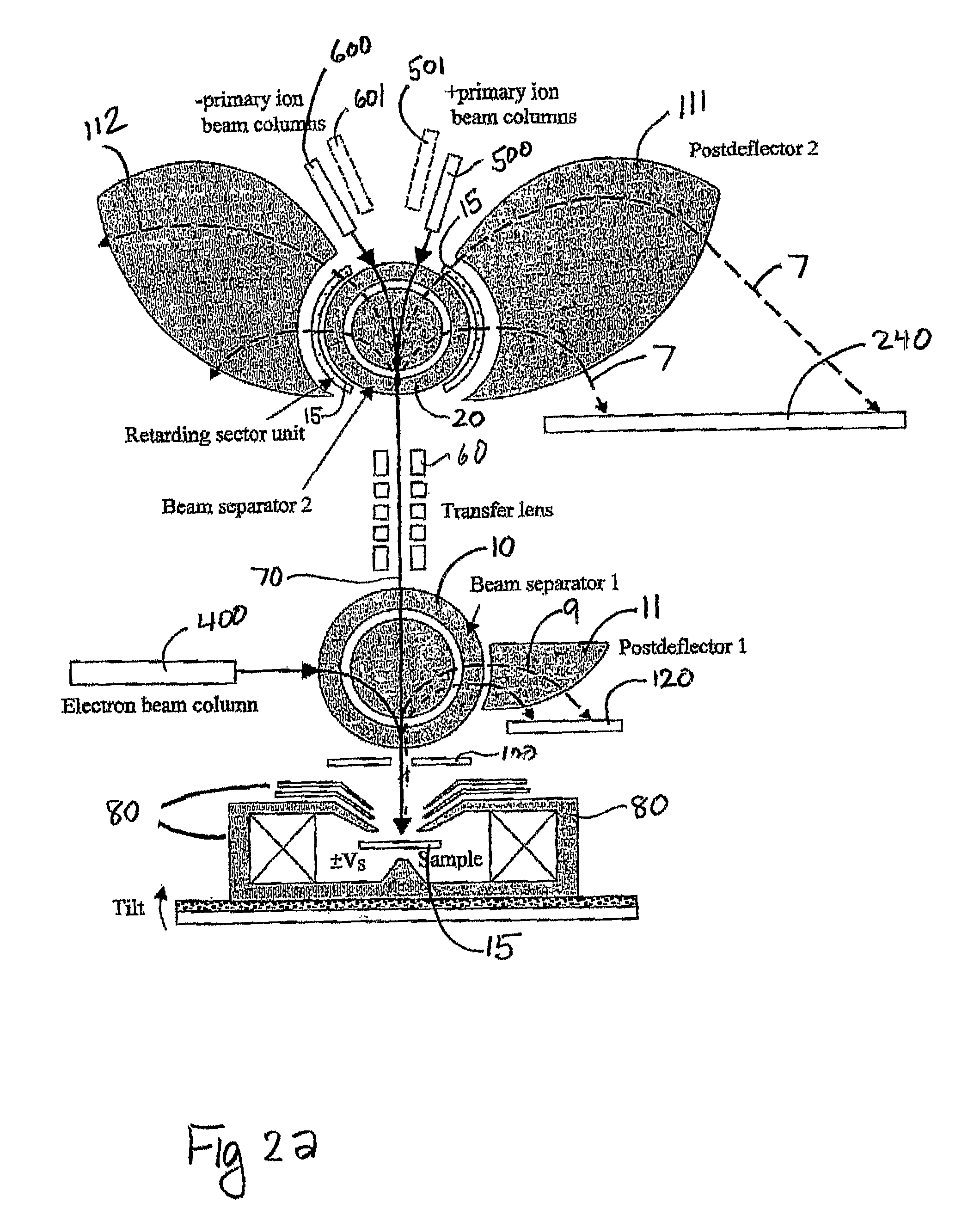
ActiveUS20090321634A1Minimize aberrationSmall tendencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesSecondary electronsInstrumentation
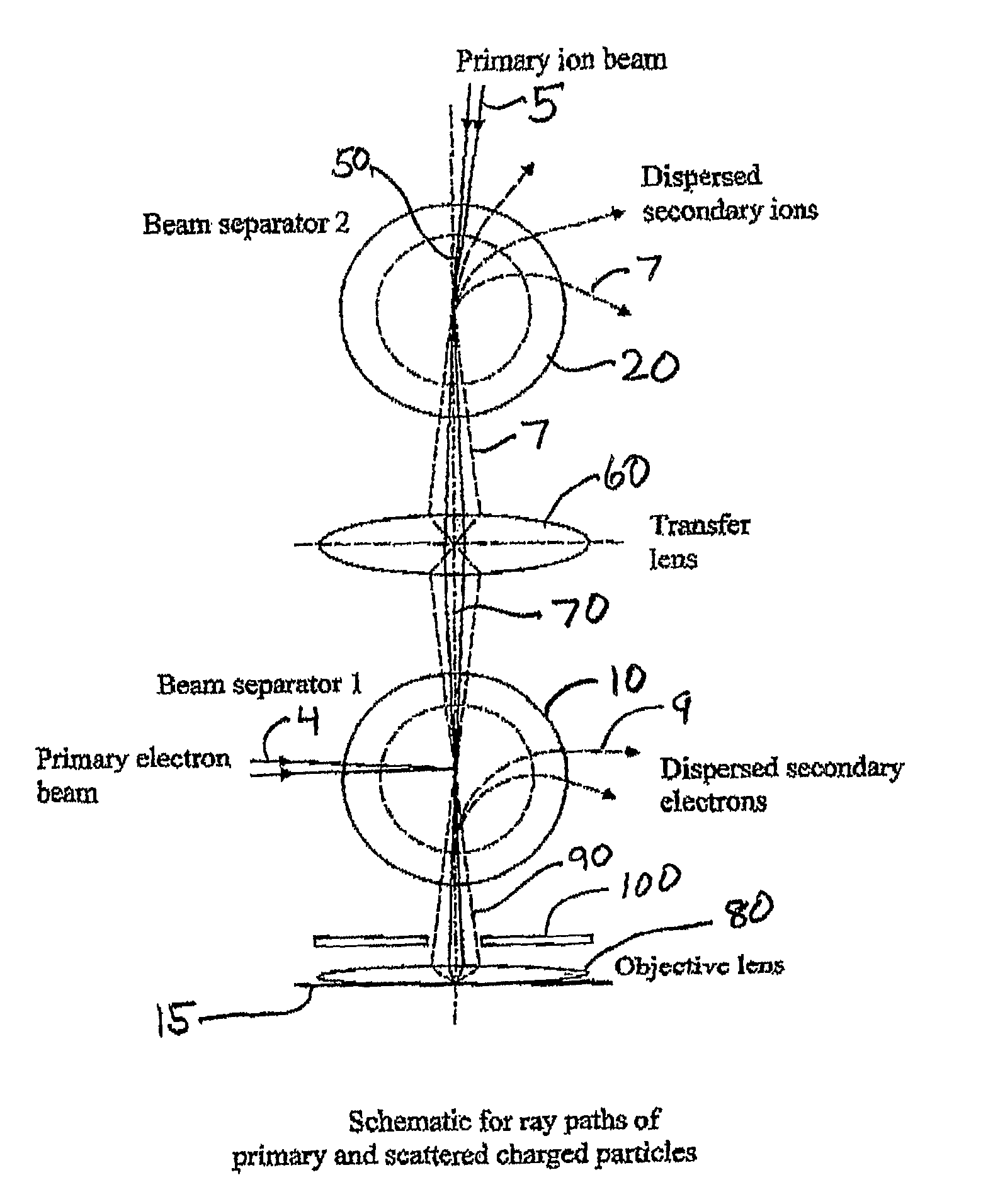
This invention is a multi-beam charged particle instrument that can simultaneously focus electrons and a variety of positive and negative ions, such as Gallium, Oxygen and Cesium ions, onto the same material target. In addition, the instrument has provision to simultaneously capture the spectrum of both secondary electrons and ions. The highly dispersive, high resolution mass spectrometer portion of the instrument is expected to detect and identify secondary ion species across the entire range of the periodic table, and also record a portion of their emitted energy spectrum. The electron energy spectrometer part of the instrument is designed to acquire the entire range of scattered electrons, from the low energy secondary electrons through to the elastic backscattered electrons.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
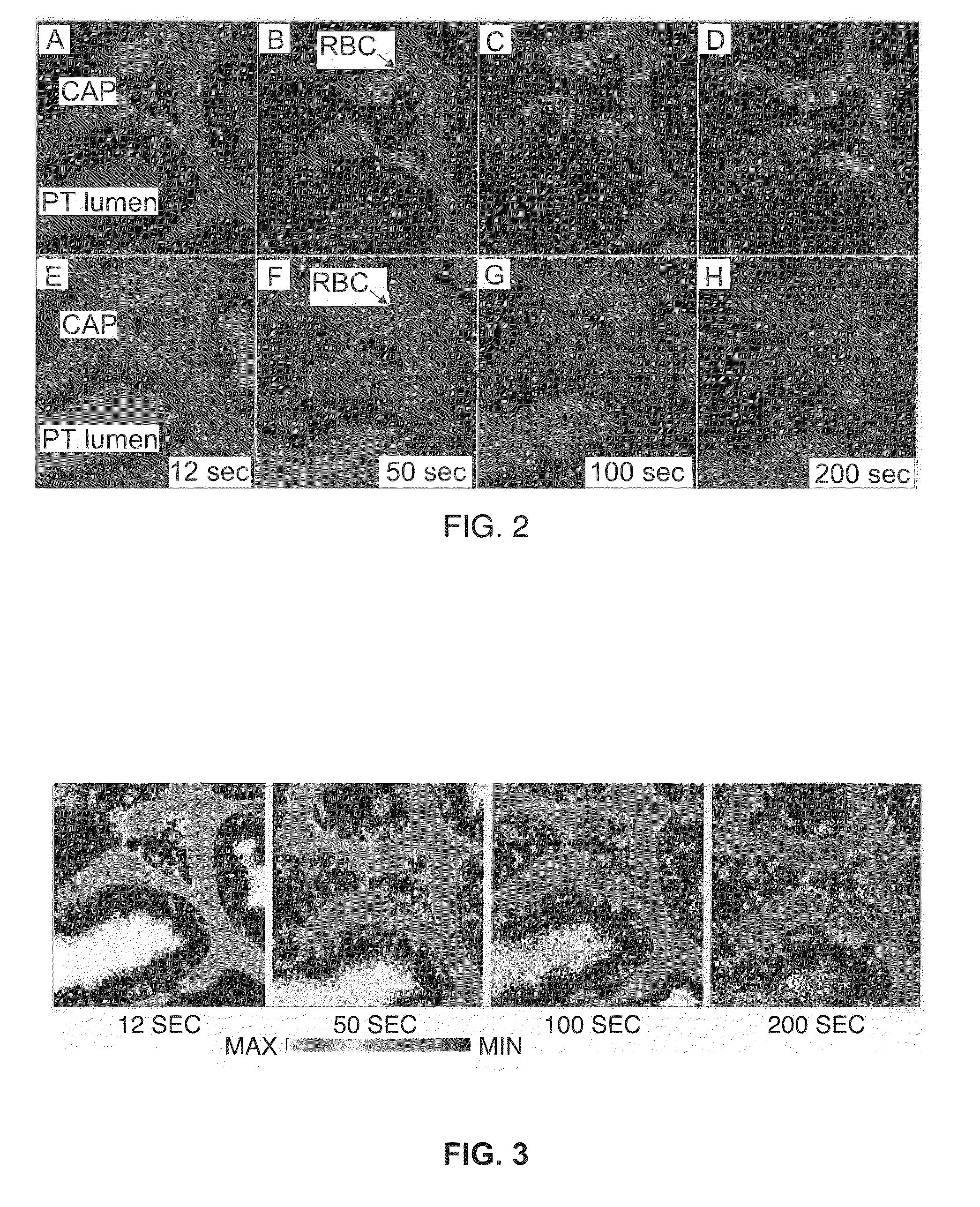
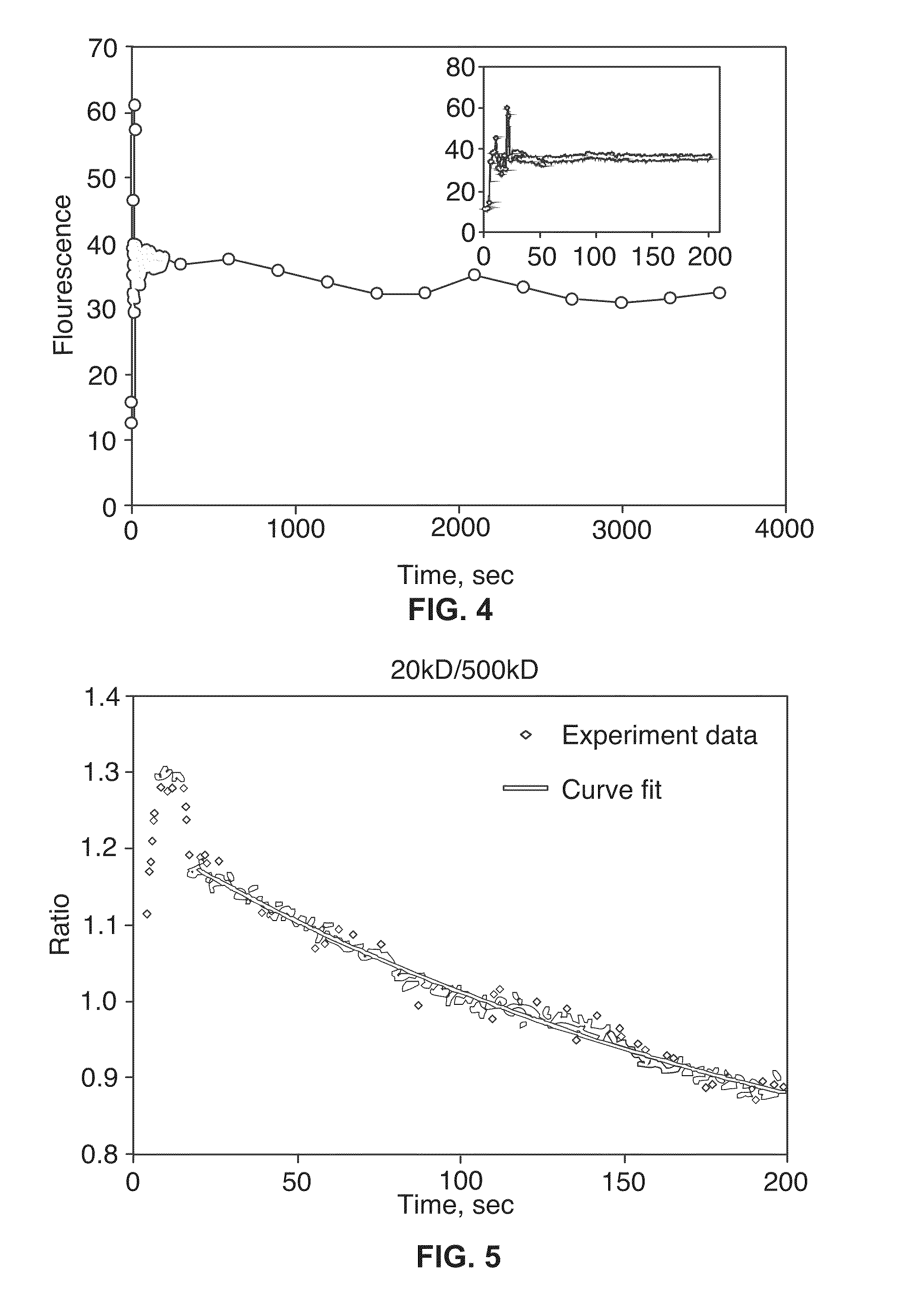
Renal Function Analysis Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20090285761A1Minimize aberrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryFluorescenceFiltration
A method for measuring a glomerular filtration rate in a mammalian kidney comprises a source of reporter and marker fluorescent molecules. The fluorescent molecules are introduced into the blood stream of a mammalian subject. Over a period of time, a measurement of the intensities of the reporter and marker fluorescent molecules is taken. A ratio is calculated to determine the health of the subject's kidney. This method measures volume of plasma distribution based on a fluorescence of a marker molecule relative to a fluorescence of a reporter molecule.
Owner:PHARMACOPHOTONICS INC
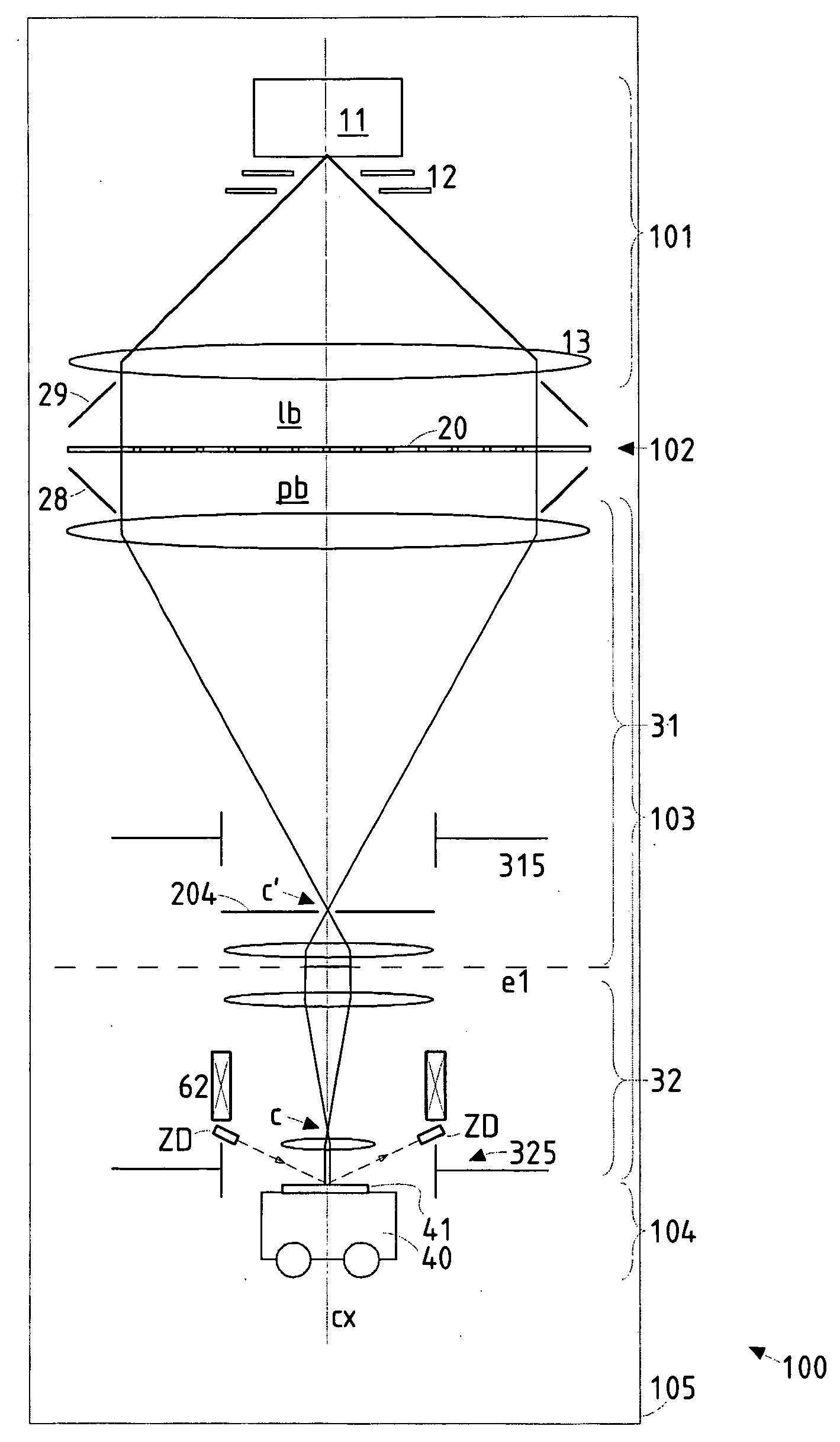
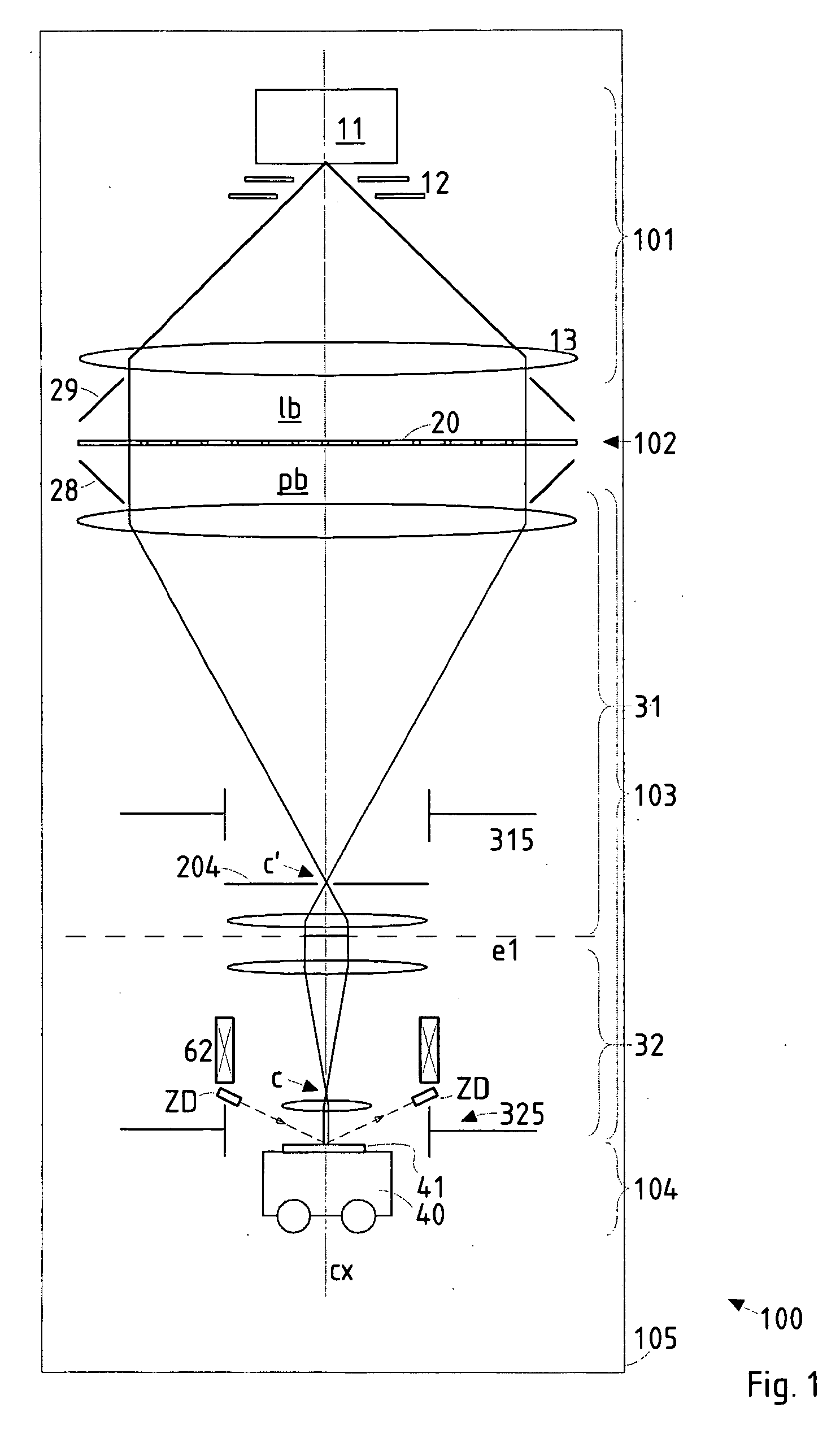
Particle-optical projection system
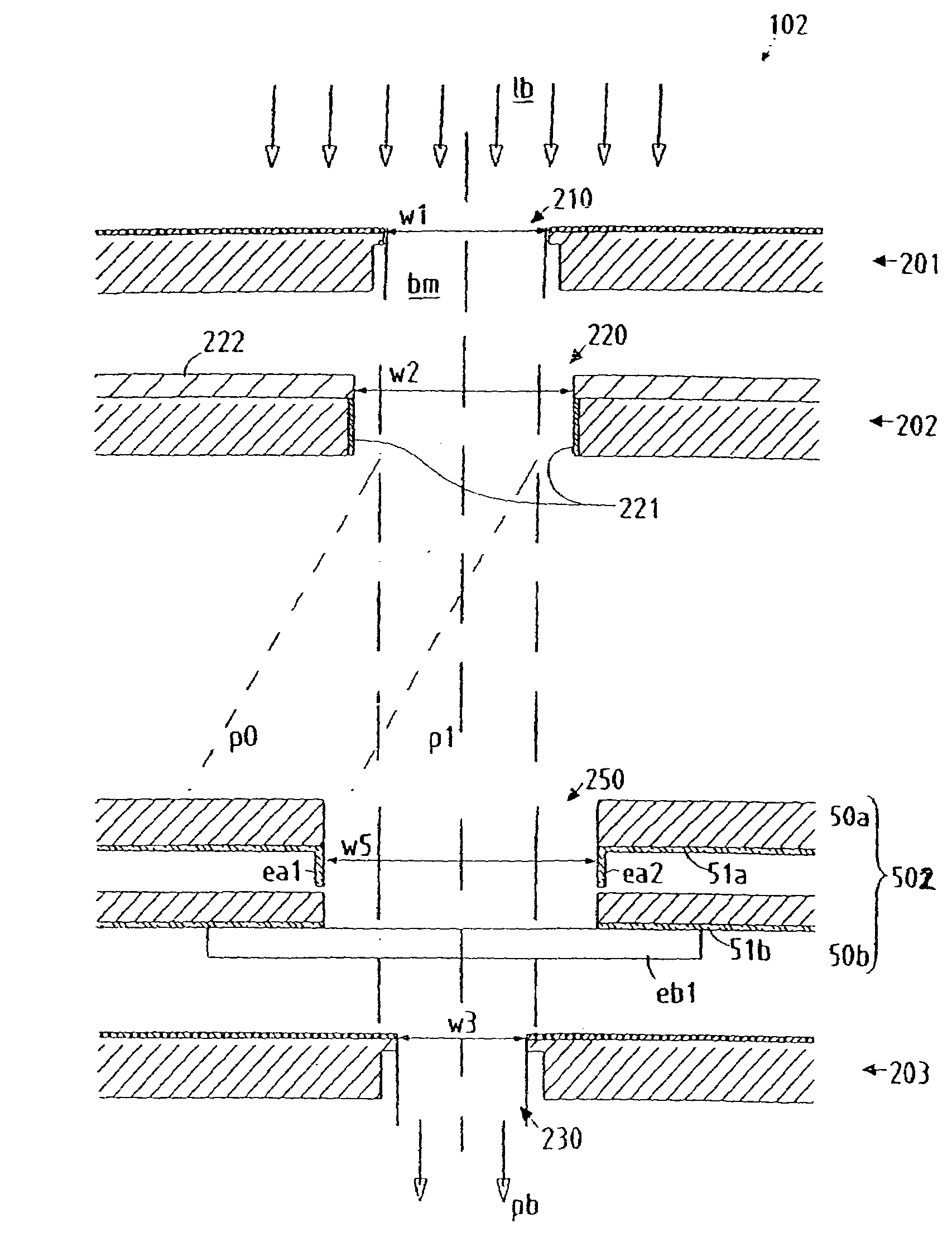
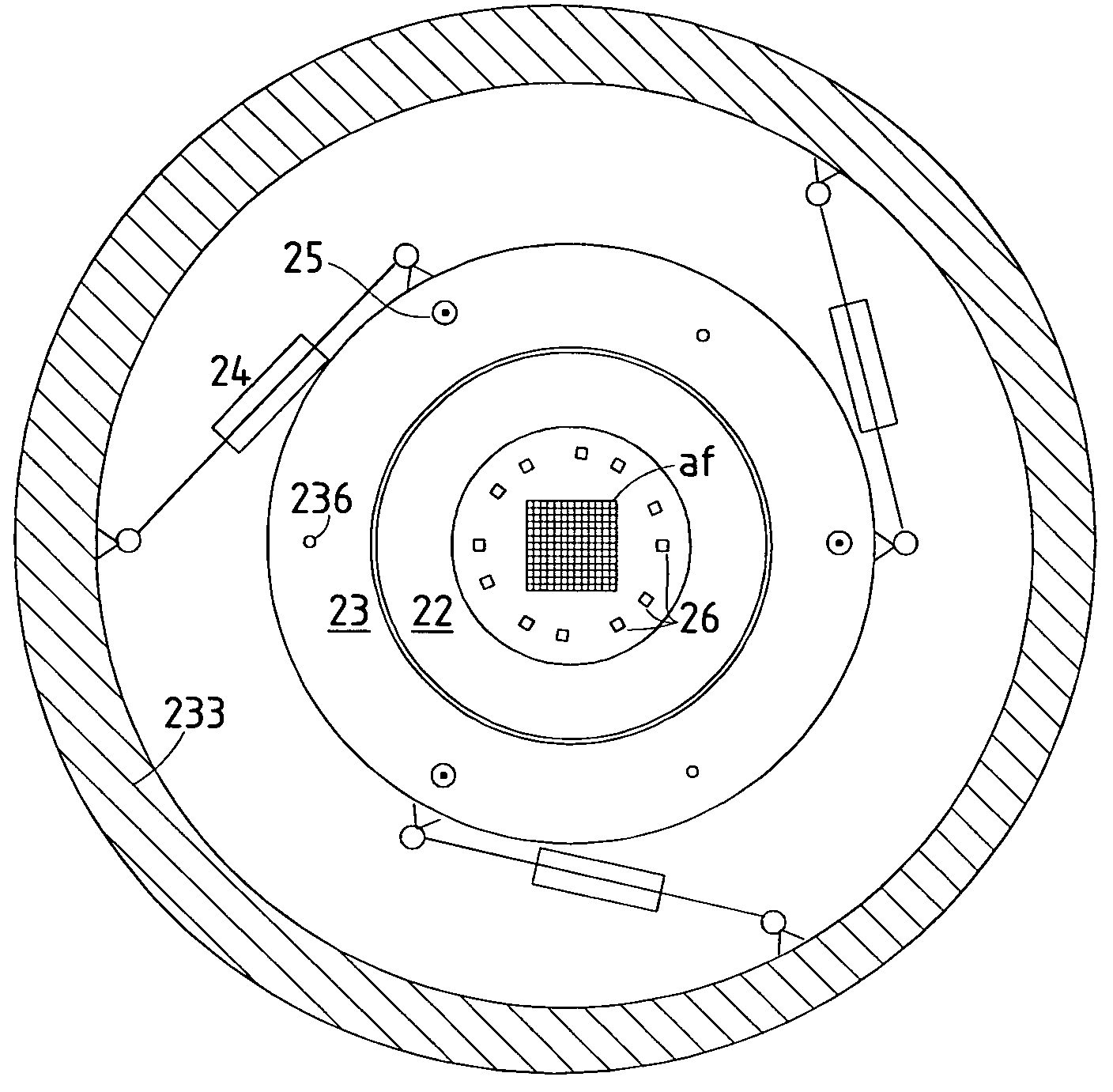
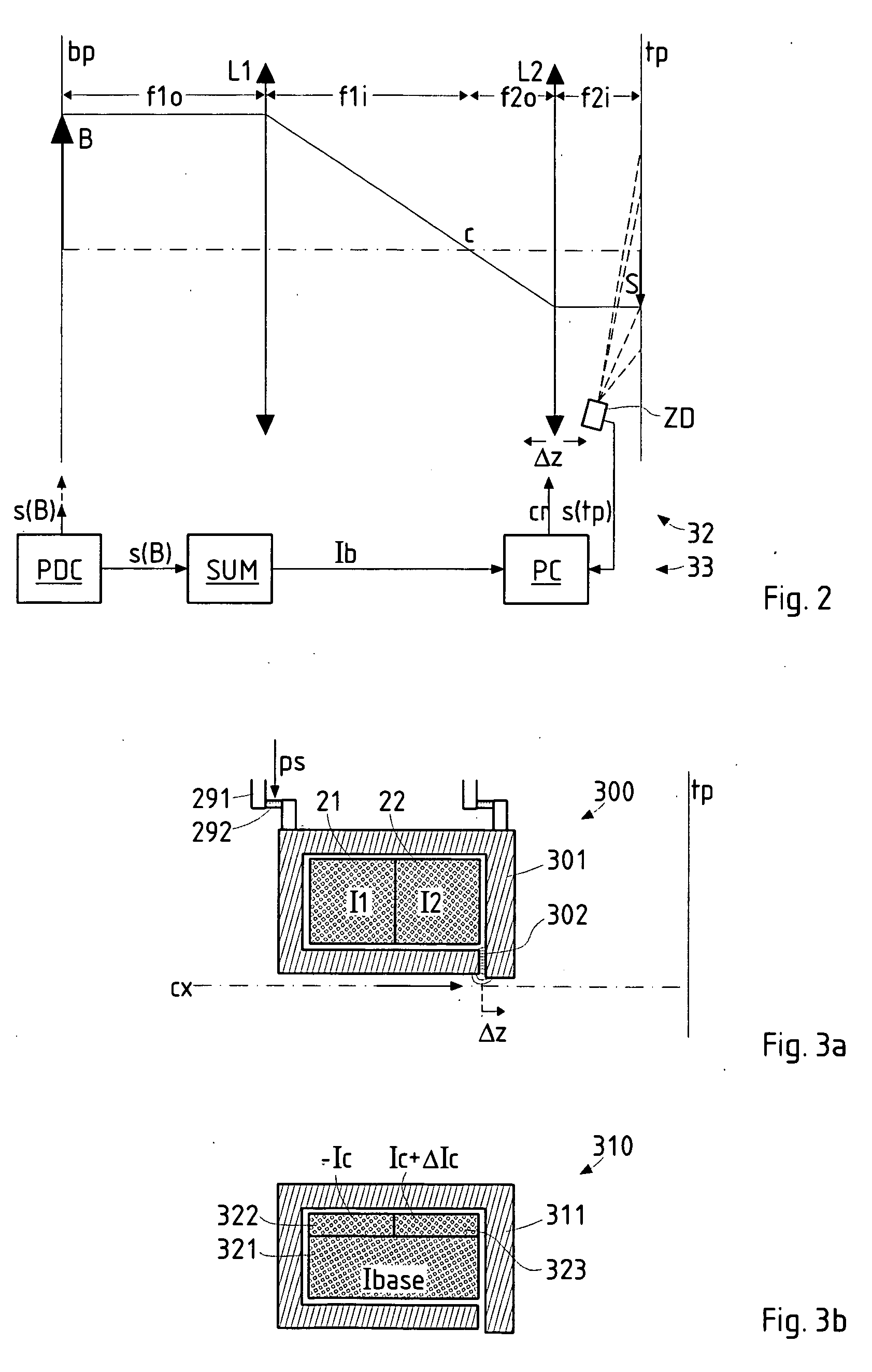
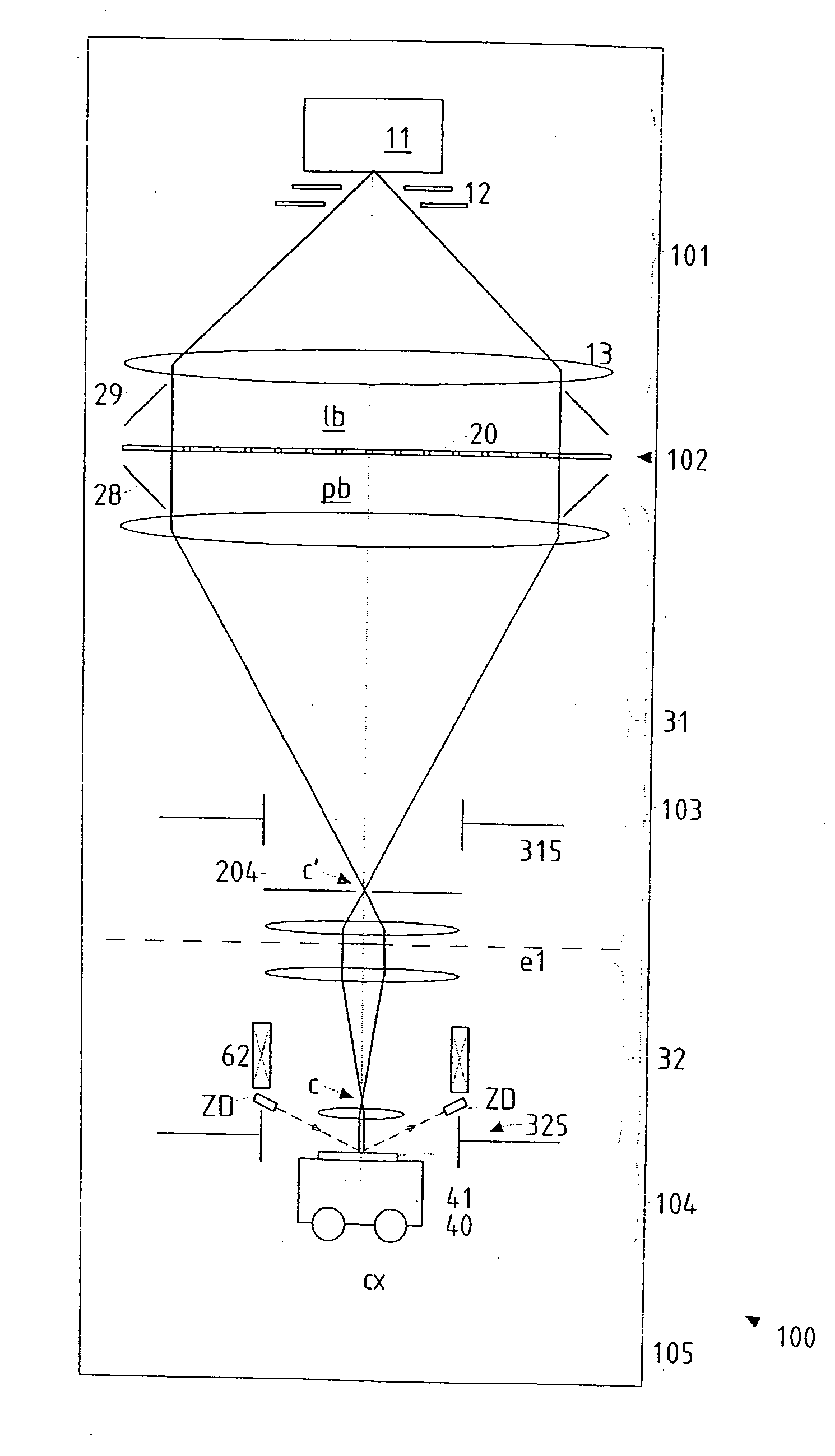
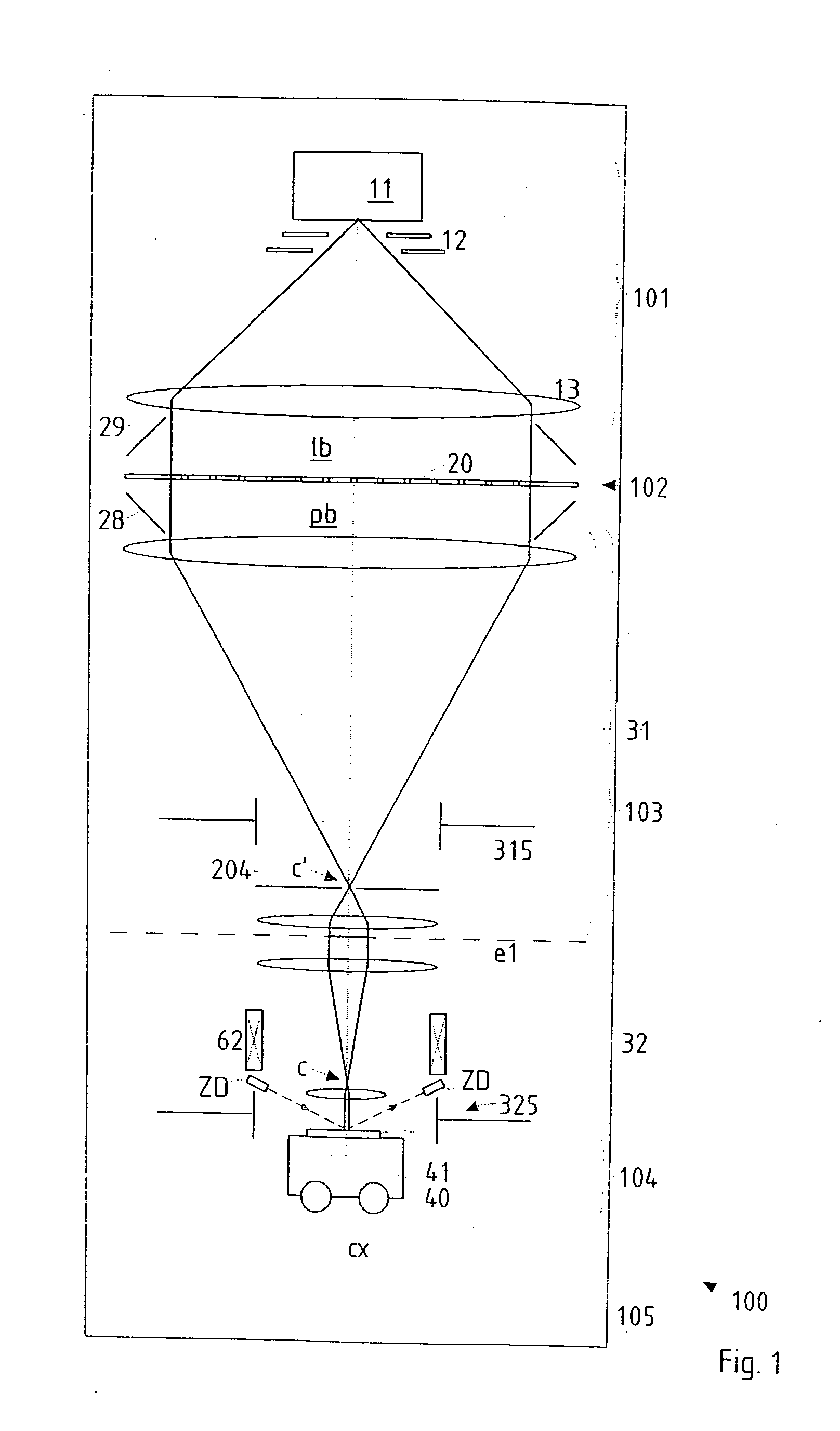
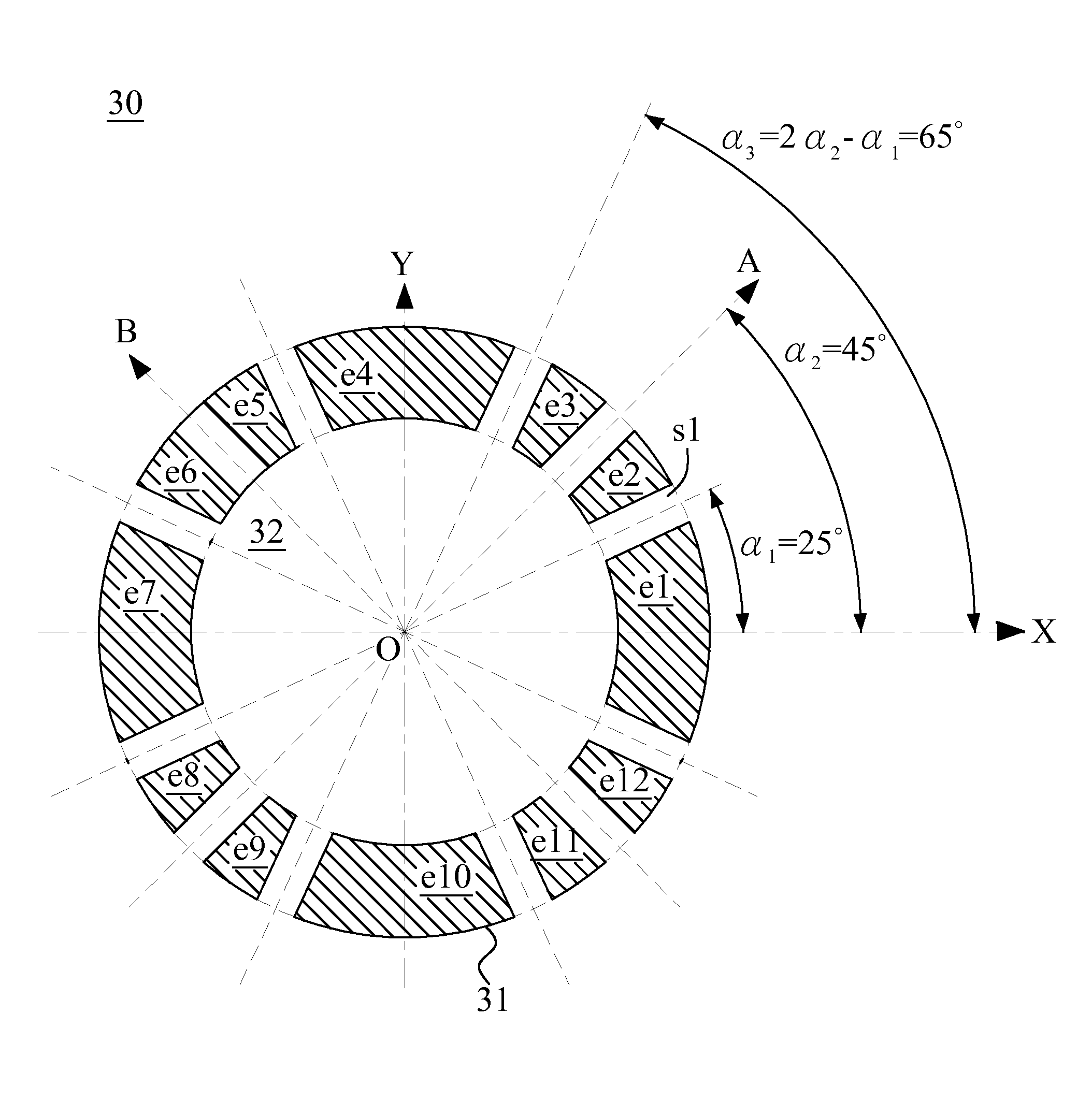
InactiveUS20050201246A1Minimize image distortionMinimize distortionTrack finding/aligningNanoinformaticsDistortionPhysics
In a particle-optical projection system (32) a pattern (B) is imaged onto a target (tp) by means of energetic electrically charged particles. The pattern is represented in a patterned beam (pb) of said charged particles emerging from the object plane through at least one cross-over (c); it is imaged into an image (S) with a given size and distortion. To compensate for the Z-deviation of the image (S) position from the actual positioning of the target (tp) (Z denotes an axial coordinate substantially parallel to the optical axis cx), without changing the size of the image (S), the system comprises a position detection means (ZD) for measuring the Z-position of several locations of the target (tp), a control means (33) for calculating modifications (cr) of selected lens parameters of the final particle-optical lens (L2) and controlling said lens parameters according to said modifications.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Focusing system and method for a charged particle imaging system
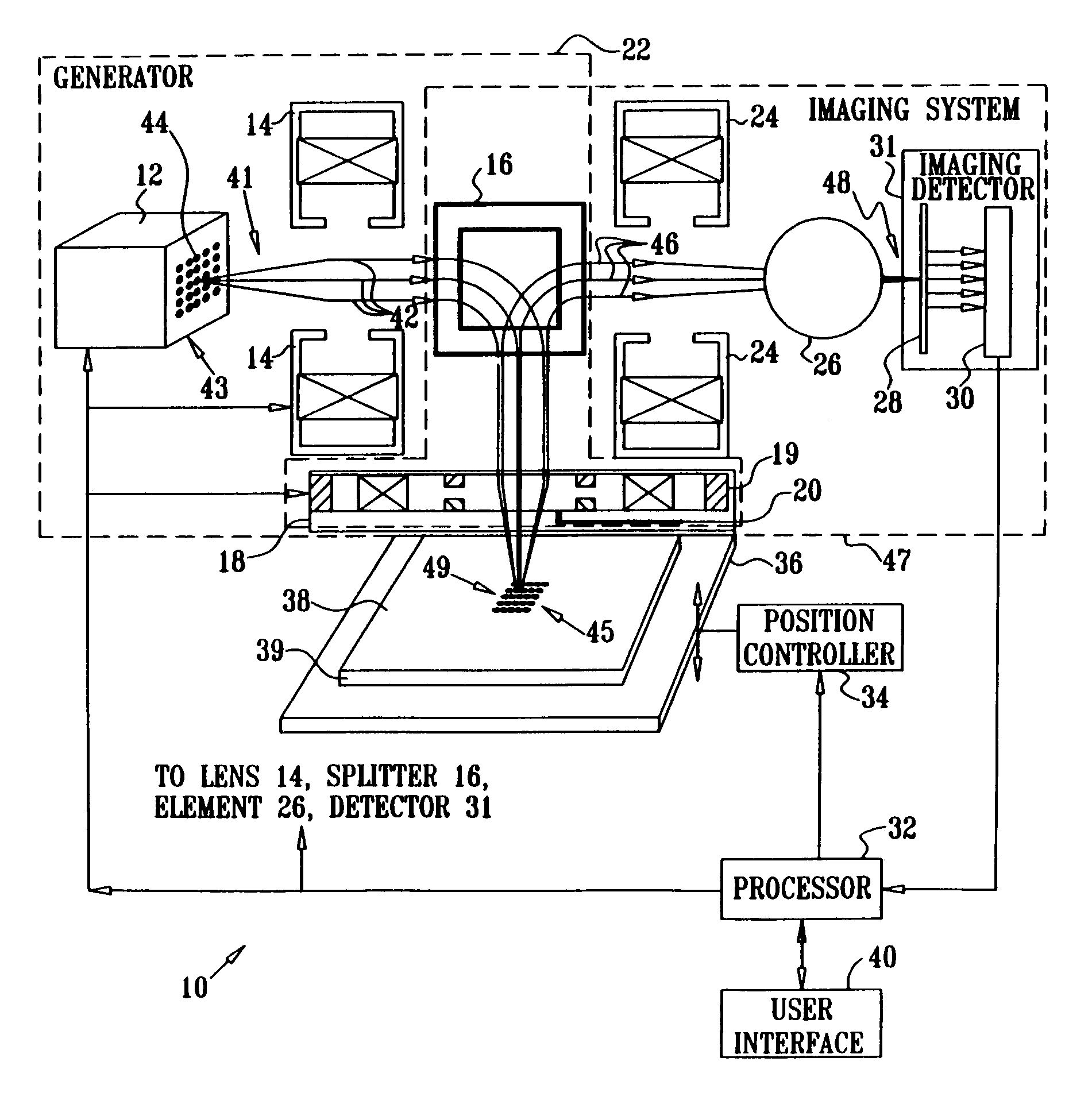
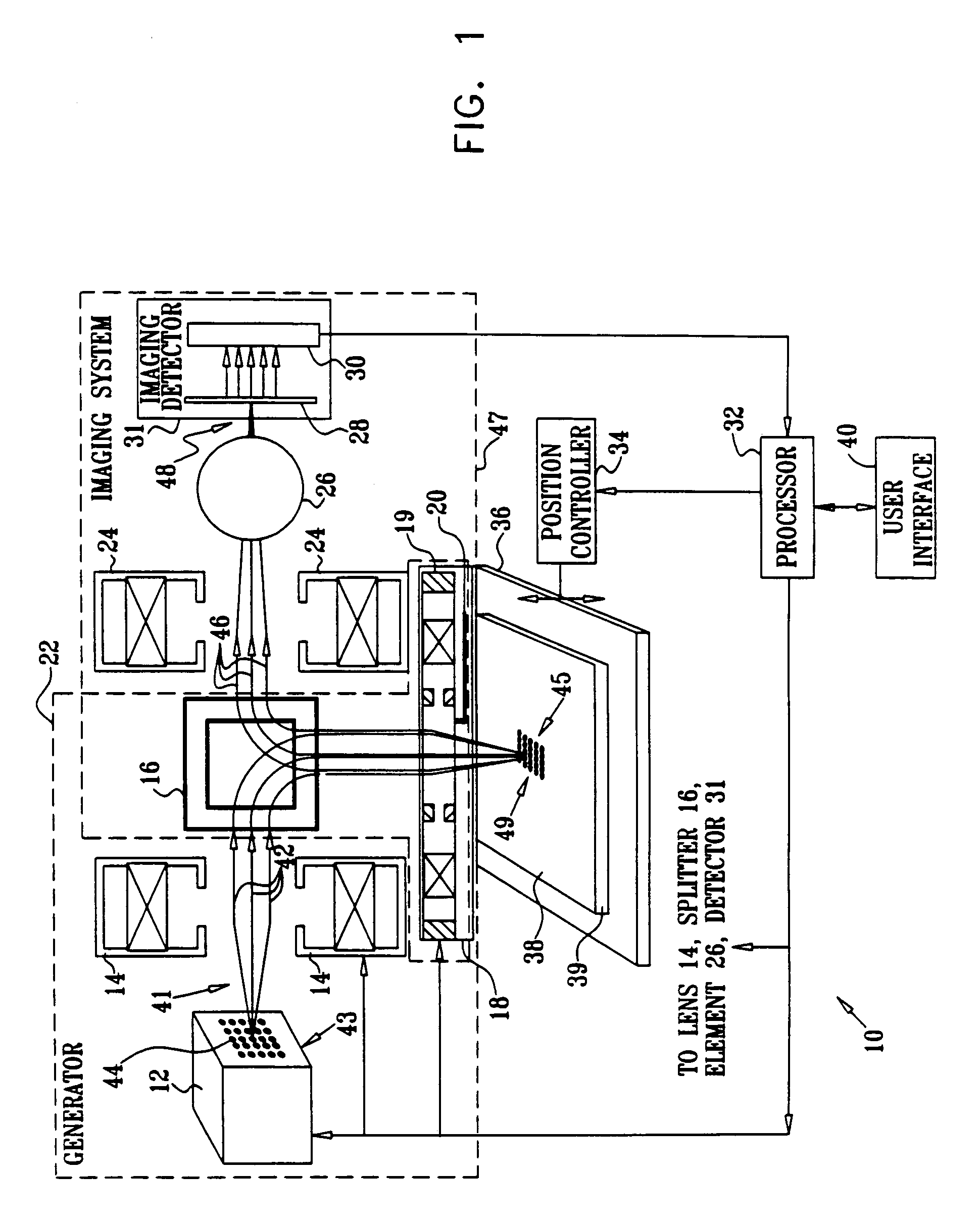
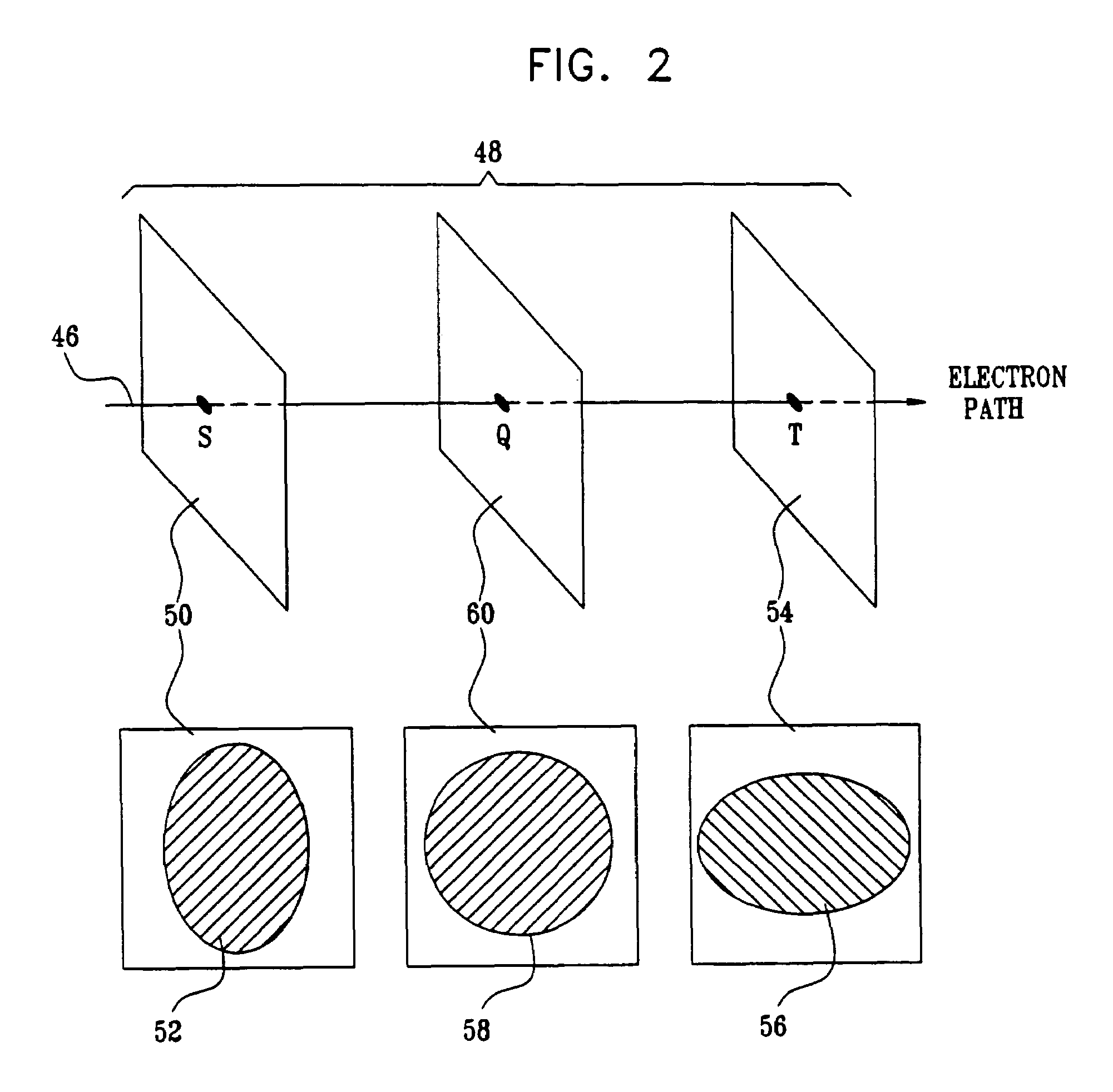
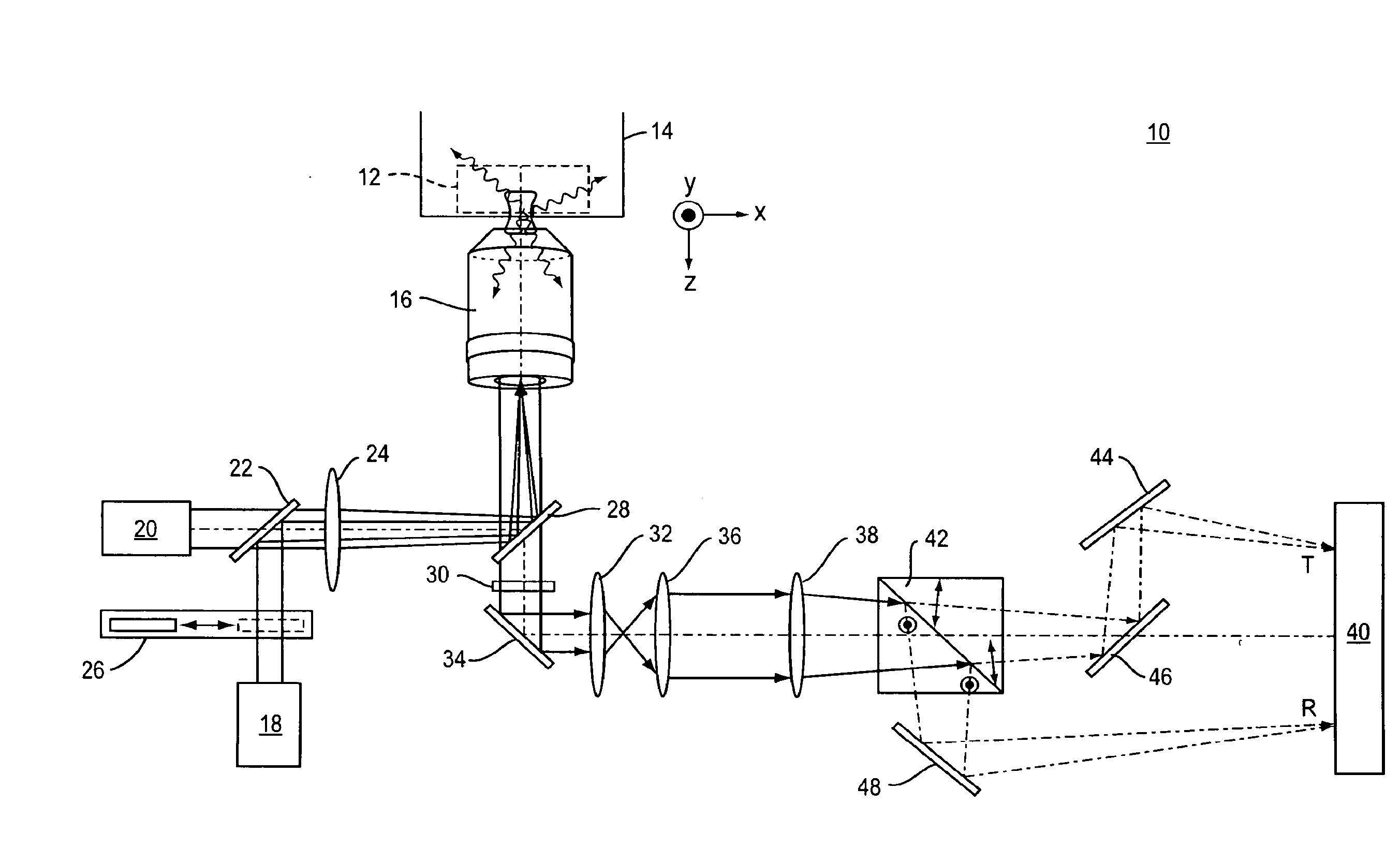
ActiveUS7696497B2Minimize aberrationEfficient and effectiveStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansMolecular physicsCharged particle beam
Apparatus for focusing a charged particle beam onto a surface, including a charged particle beam generator which is adapted to project the charged particle beam onto a location on the surface, thereby causing charges to be emitted from the location. The apparatus further includes an imaging detector which is adapted to receive the charges so as to form an image of the location, and an aberrating element which is positioned before the imaging detector and which is adapted to produce an aberration in the image. A processor is adapted to receive the image and to adjust at least one of the charged particle beam generator and a position of the surface in response to the aberration.
Owner:CARL ZEISS AG +1
Deformable mirror actuation system
InactiveUS6989922B2Stable controlImprove performanceMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSet screwMetrology
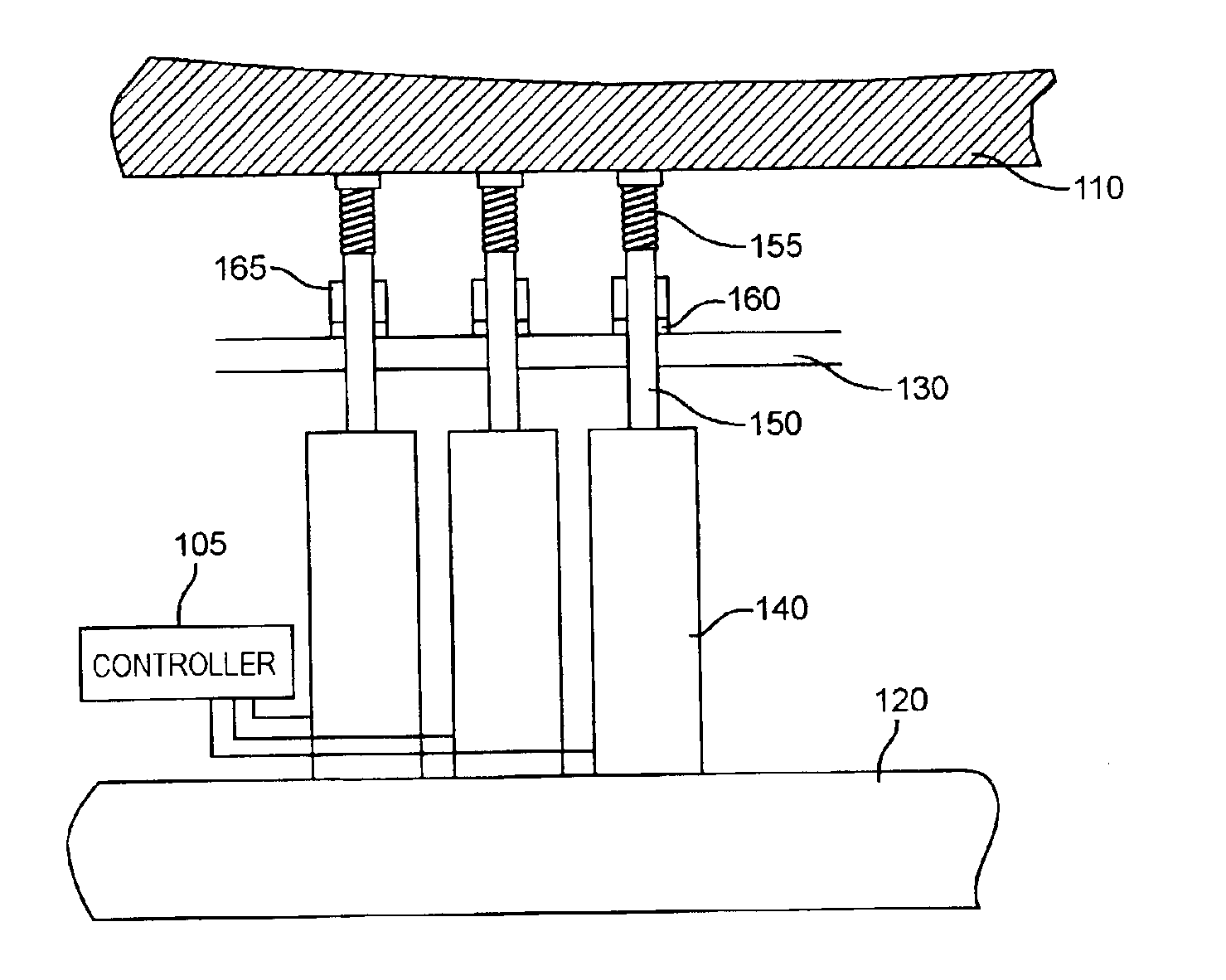
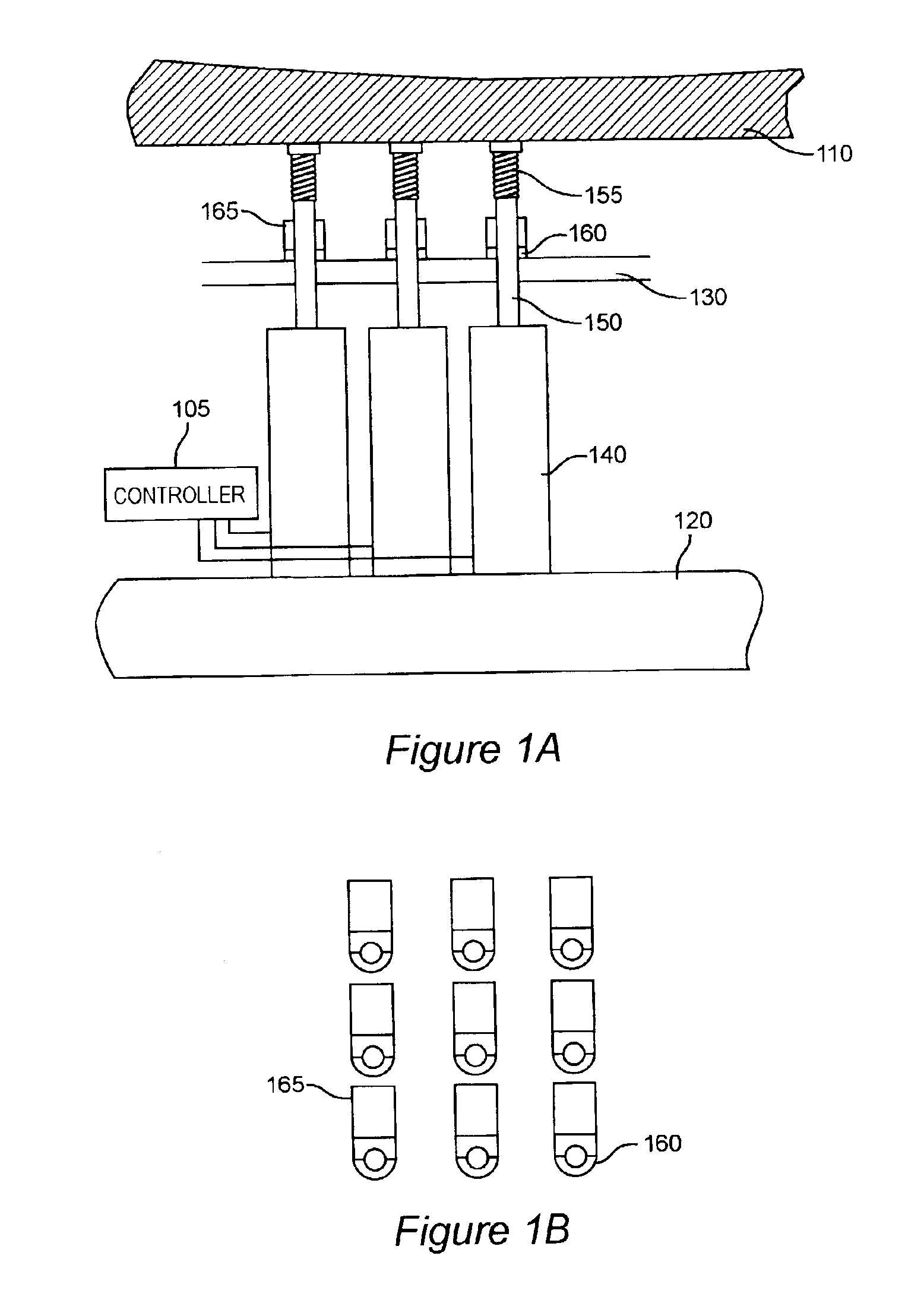
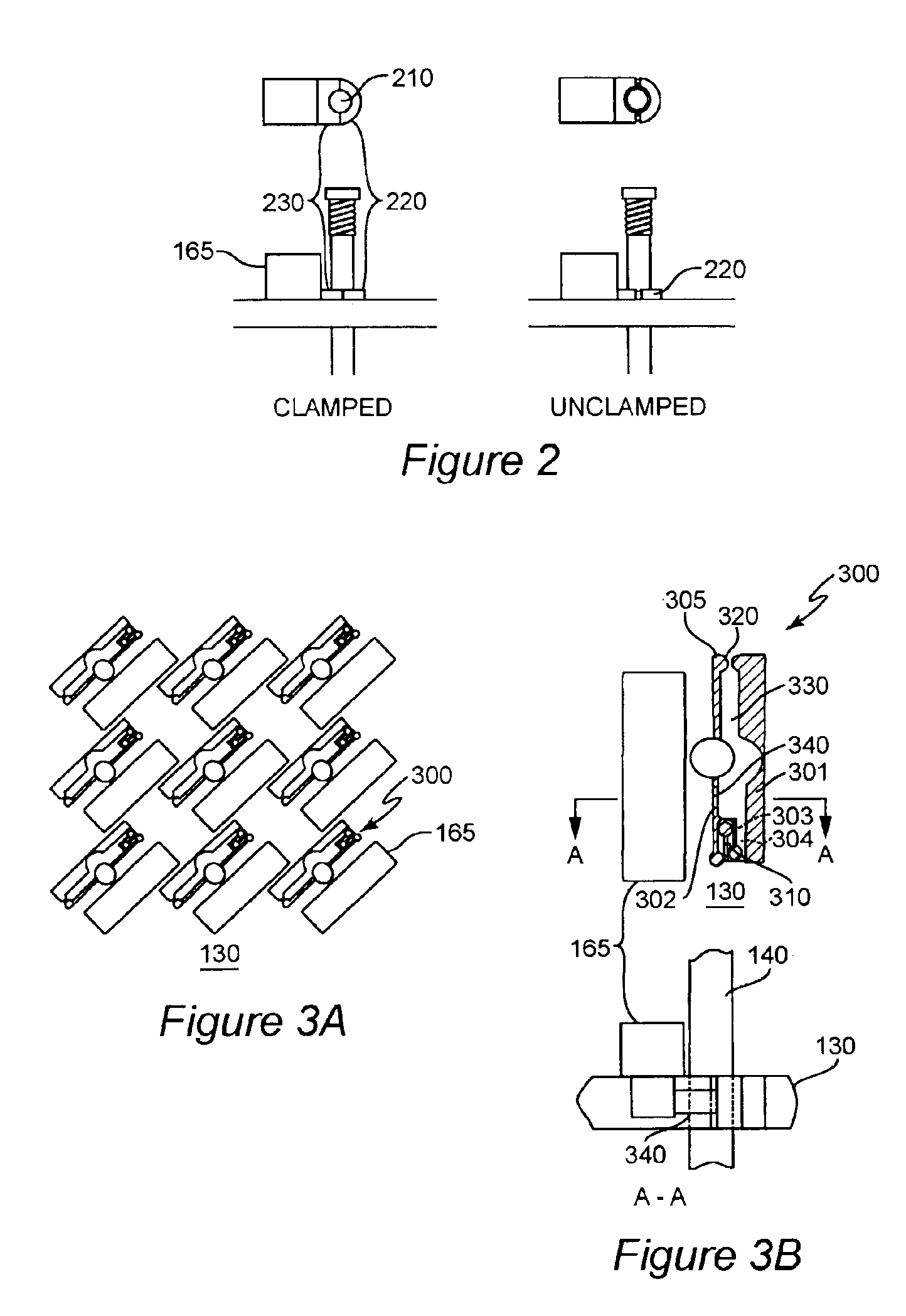
Mechanical control and actuation of an adaptive optical element provides highly stable and repeatable correction of the shape of an optical element to an accuracy of a small fraction of a very short wavelength of light, responsive to a metrology source and sensor arrangement. Actuators in the form of individual set-screws or other actuators capable of axially positioning a shaft are driven by a robotic screw driver with four degrees of freedom or one or more linear actuators to exert force on the mirror. Positive or negative force may be used for outward and / or inward deflection of the mirror. When a desired force is developed on the mirror through a mechanical linkage, the linkage may be clamped by a passive clamp which may be released by an actuator such that the adjustment is maintained while the linear actuator and the clamp actuator are turned off; yielding a highly stable adjustment while effectively removing sources of actuator drift, noise, vibration and heating which may adversely affect stability.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Multi-beam ion/electron spectra-microscope
InactiveUS7947951B2Good dispersionMinimize aberrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesSecondary electronsOxygen
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Particle-optical projection system
ActiveUS20070125956A1Minimize distortionCompensation deviationStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsOptical axisProjection system
In a particle-optical projection system a pattern is imaged onto a target by means of energetic electrically charged particles. The pattern is represented in a patterned beam of said charged particles emerging from the object plane through at least one cross-over; it is imaged into an image with a given size and distortion. To compensate for the Z-deviation of the image position from the actual positioning of the target (Z denotes an axial coordinate substantially parallel to the optical axis), without changing the size of the image, the system includes a position detector for measuring the Z-position of several locations of the target, and a controller for calculating modifications of selected lens parameters of the final particle-optical lens and controlling said lens parameters according to said modifications.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Optical disk apparatus using tilt and aberration correction control system
InactiveUS6577568B1Error minimizationMinimize aberrationRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical axisLight beam
A tilt control apparatus includes an orthogonal shift detector (9) which detects an orthogonal shift by comparing a pair of a plurality of tap coefficients (C1, . . . , C7) of a FIR filter and generates an orthogonal shift signal, and an actuator varies the inclination of the optical axis of the light beam to correct the orthogonal shift, and a tilt controller (10) controls the drive of the actuator in accordance with the orhogonal shift signal to minimize the orthogonal shift. In the information recording operation, the orthogonal shift obtained based on a recording track is previously stored in a temporary storage portion and the stored orthogonal shift is used to conduct the tilt control.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
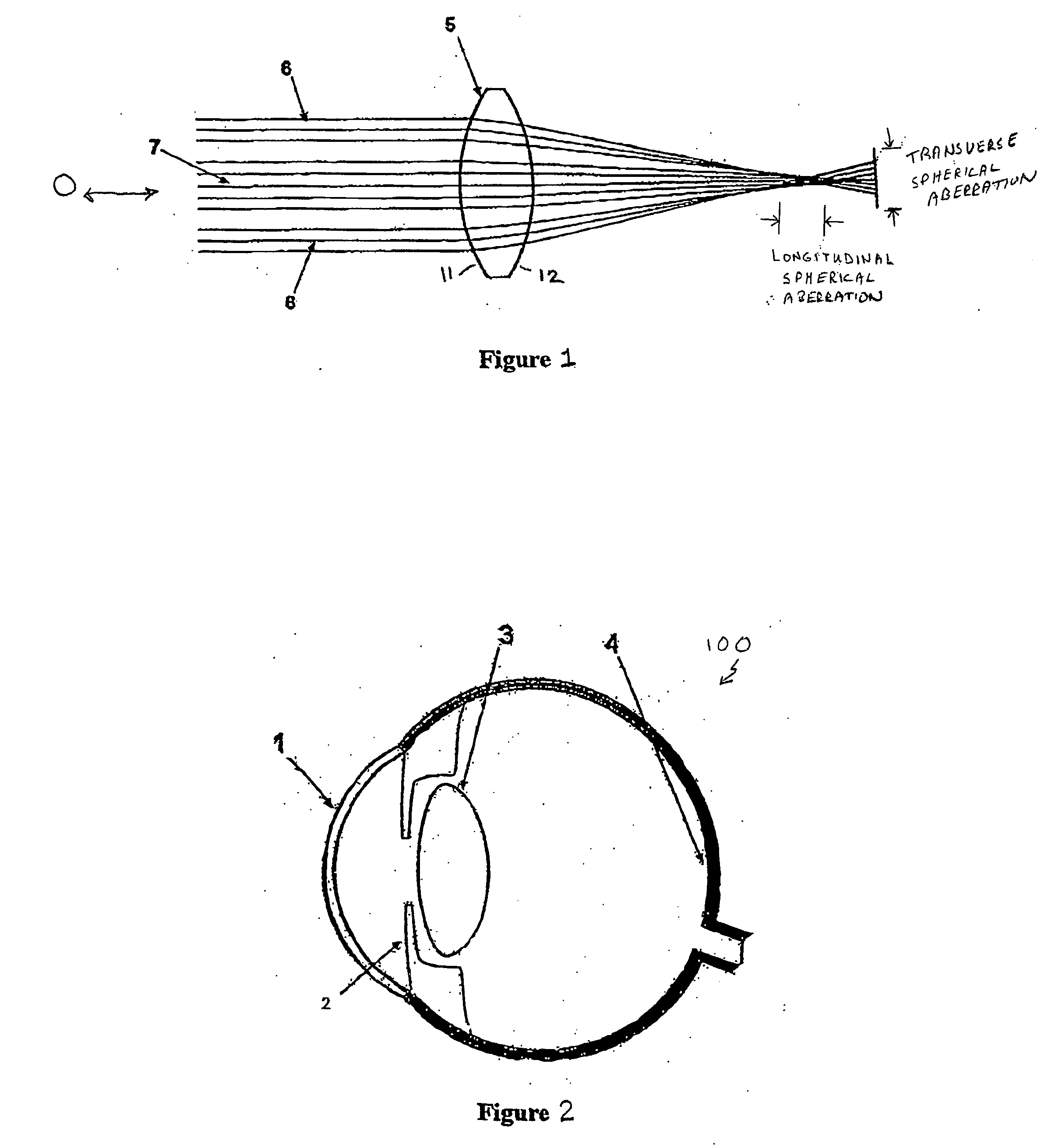
Progressive chromatic aberration corrected ocular lens
InactiveUS20100103371A1Reduce chromatic aberrationMinimize aberrationSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensPhysicsCamera lens
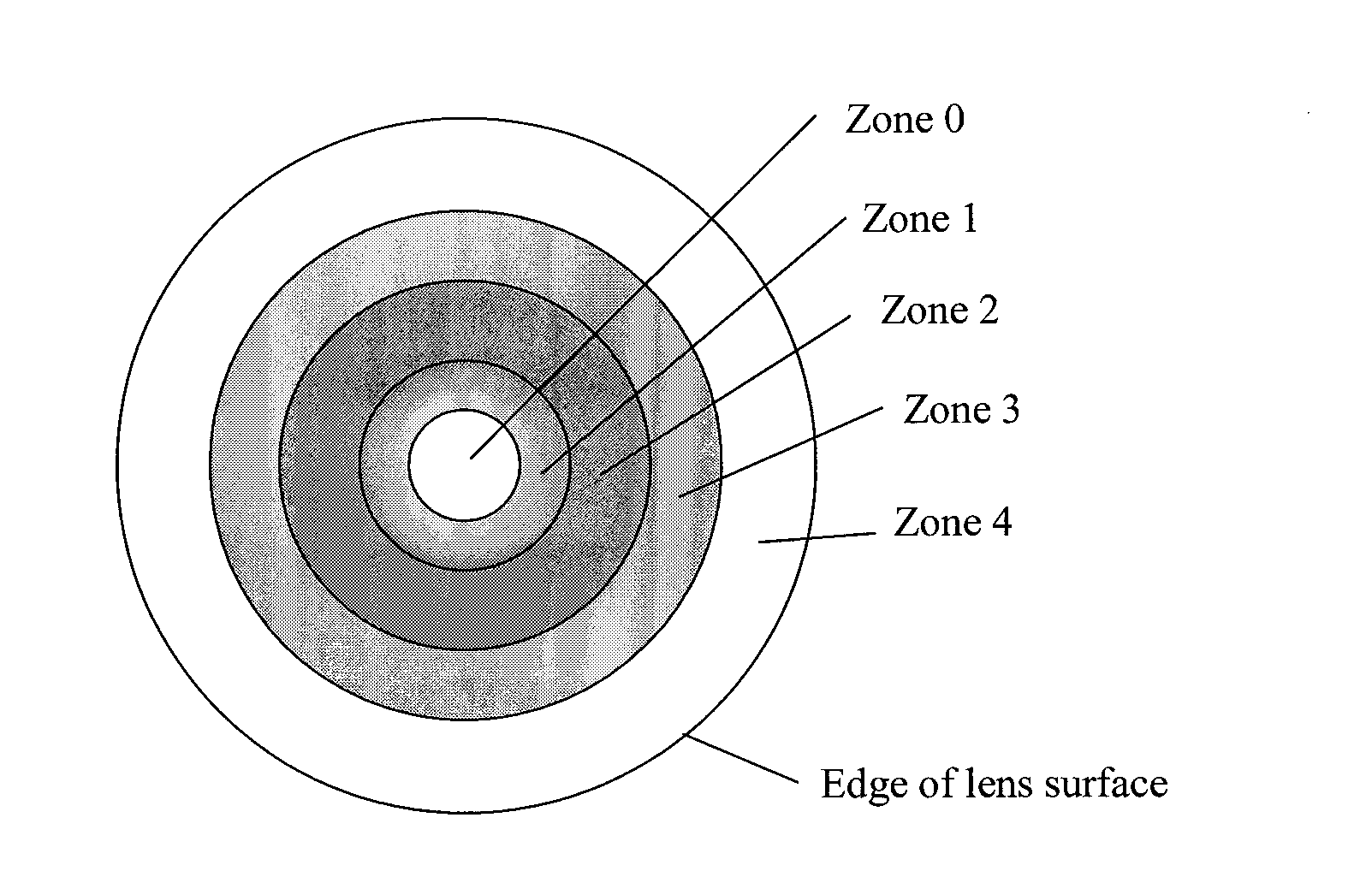
A method to reduce ocular chromatic aberrations using a lens or other spatial structure to selectively band-pass filter transmitted light of certain wavelengths. The ocular lens overcomes the negative effects of the wavelength band pass filter lenses while maintaining its ability to reduce the negative effects of chromatic aberration. The band-pass filter is applied in one or more concentric zones and or angular regions. The lens power is adjusted in concert with the band-pass filter wavelength to minimize aberrations. Variations include the application of the band-pass filter being applied to an angular region and no filter is applied to another. Alternatively the band-pass filter is not applied to one or more concentric ring regions and is applied to one or more angular regions. The band-pass filter can be applied to the surface of the lens or spatial structure, or applied to the lens material.
Owner:SARVER EDWIN J +1
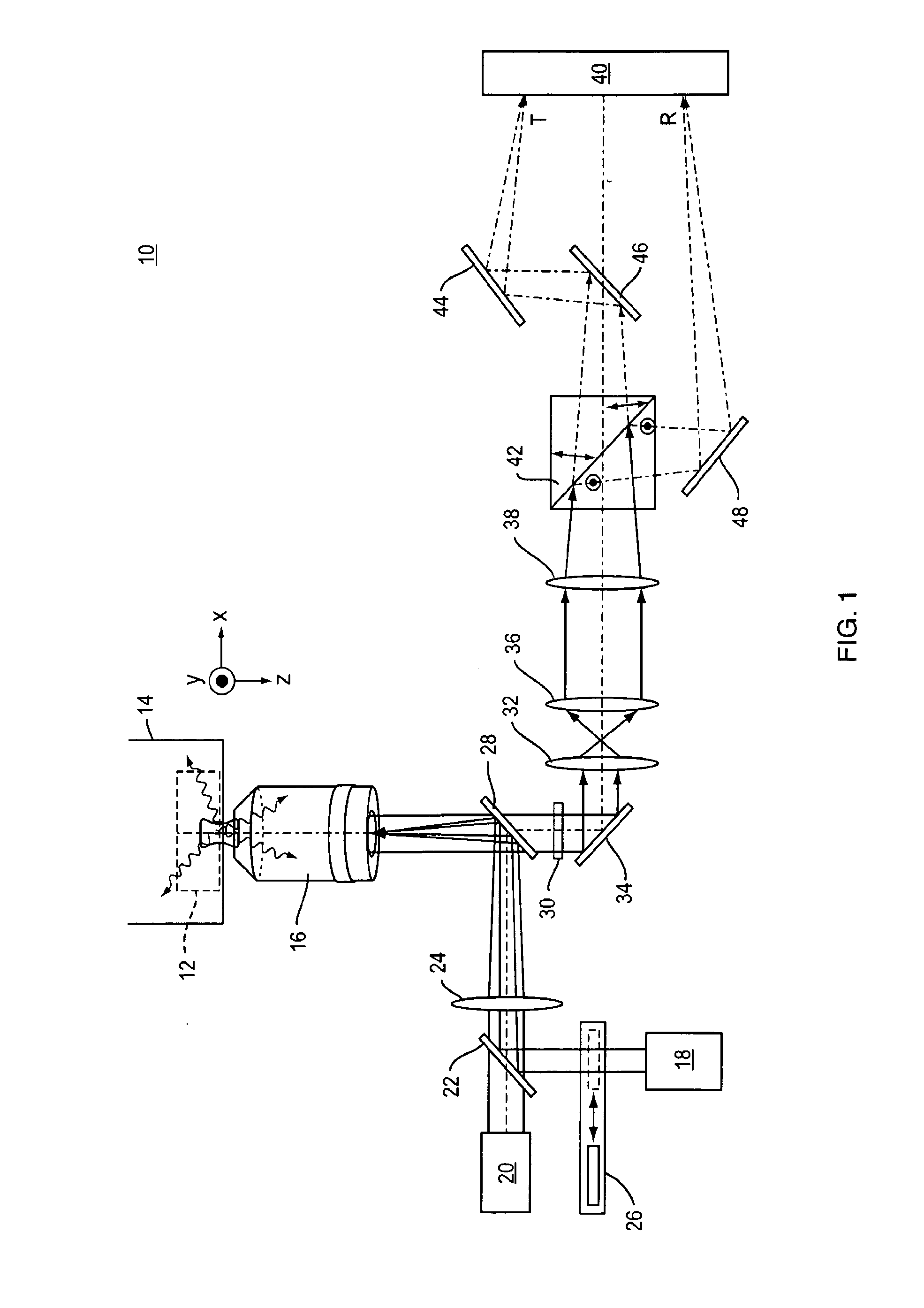
Nanoscale imaging of molecular positions and anisotropies
InactiveUS20120018651A1High resolutionImprove spatial resolutionRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotometryBeam splitterLight beam
A Polarization Fluorescence Photoactivation Localization Microscopy (P-FPALM) system and method are provided to simultaneously image the localizations and fluorescence anisotropics of large numbers of single molecules within a sample. The system modifies known FPALM systems by adding a polarizing beam splitter. The beam splitter polarizes emissions perpendicular and parallel to an axis in the sample to allow spatially separate imaging of fluorescence emitted from a sample. The system includes lenses and mirrors so that the separate, polarized beams are detected simultaneously. The present invention includes methods of using the system to image localizations and fluorescence anisotropics of single molecules, and methods of using data obtained with the system to predict 3-D orientation of the molecules. The system and method achieve substantially improved lateral resolution within even dense samples over known microscopic imaging techniques, and does not compromise speed or sensitivity.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MAINE
Use of a reticle absorber material in reducing aberrations
InactiveUS20050221238A1Enhance the imageMinimize formationPhoto-taking processesNanoinformaticsLight beamReticle
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Projection device and method for holographic reconstruction of scenes
ActiveUS20150355597A1Reconstructed simply and inexpensivelyQuality improvementTelevision system detailsHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesFrequency spectrumDiffraction order
A holographic reconstruction of scenes includes a light modulator, an imaging system with at least two imaging means and an illumination device with sufficient coherent light for illumination of hologram coded in the light modulator. The at least two imaging means are arranged such that a first imaging means is provided for the magnified imaging of the light modulator on a second imaging means. The second imaging means is provided for imaging of a plane of a spatial frequency spectrum of the light modulator in a viewing plane at least one viewing window. The viewing window corresponds to a diffraction order of the spatial frequency spectrum.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Wien filter
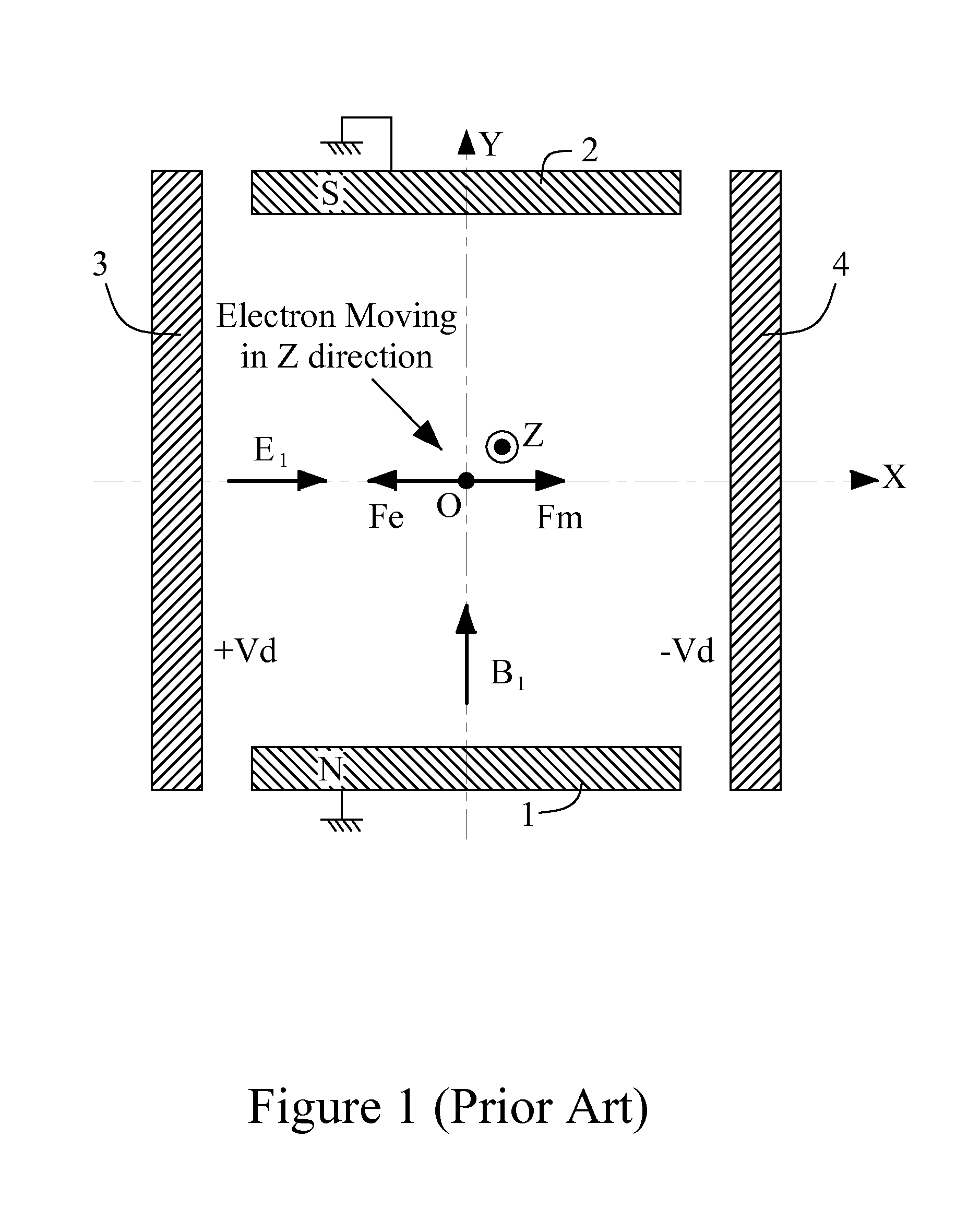
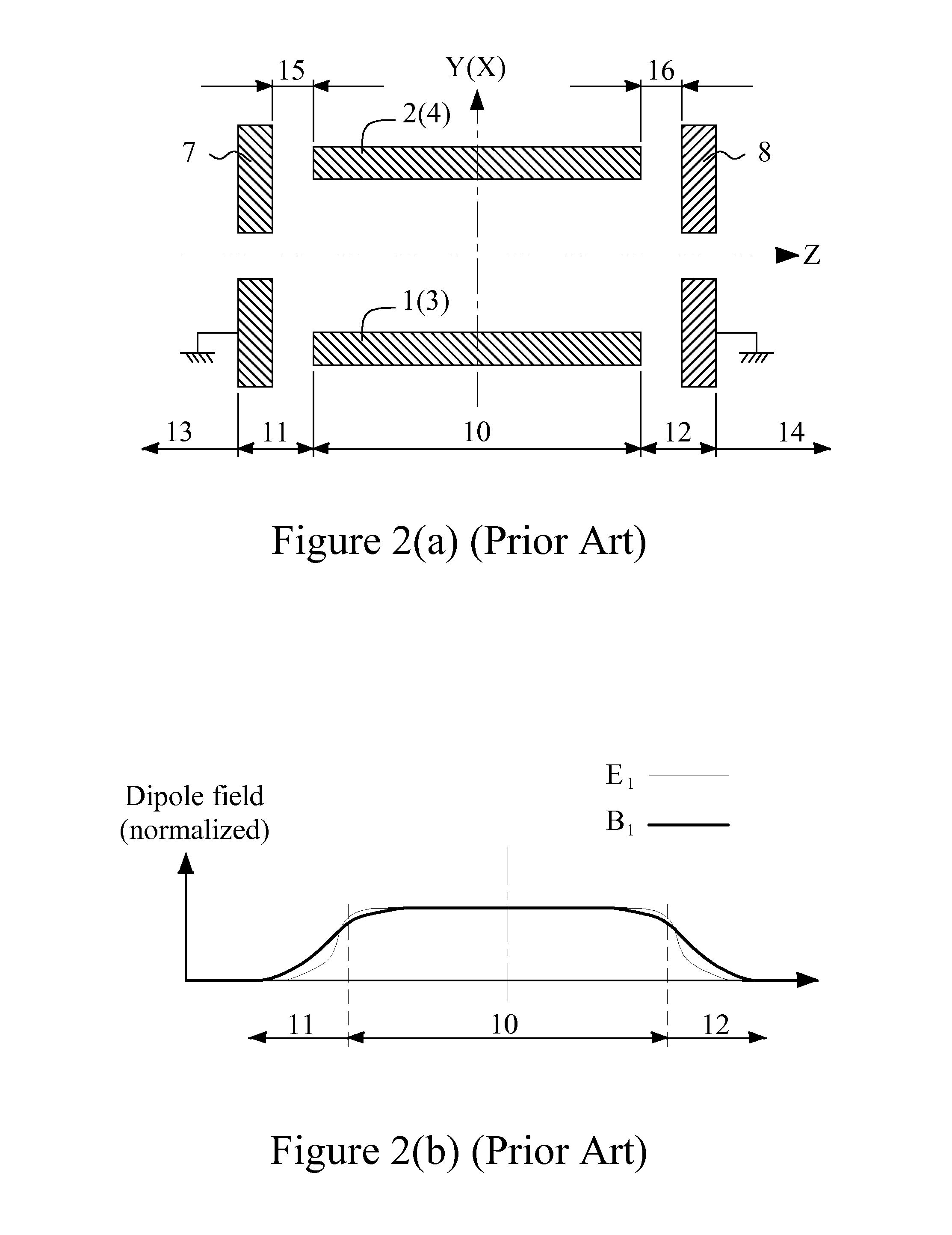
ActiveUS8436317B1Minimize aberrationReduced structureStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsHarmonicWien filter
This invention provides a multi-pole type Wien filter, which acts more purely approaching its fundamentally expected performance. A 12-electrode electric device acts as an electric deflector, or acts as an electric deflector and an electric stigmator together. A cylindrical 4-coil magnetic device with a magnetic core acts as a magnetic deflector. Both can produce a dipole field while only incurring a negligibly-small 3rd order field harmonic. The magnetic core enhances the strength and more preciously regulates the distribution of the magnetic field originally generated by the coils. Then two ways to construct a Wien filter are proposed. One way is based on both of the foregoing electric and magnetic devices, and the other way is based on the foregoing electric device and a conventional magnetic deflector. The astigmatism in each of such Wien filters can be compensated by the electric stigmator of the electric device.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Projection device and method for the holographic reconstruction of scenes
ActiveUS20170082976A1Reconstructed simply and inexpensivelyQuality improvementHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsDiffraction orderFrequency spectrum
A holographic reconstruction of scenes includes a light modulator, an imaging system with at least two imaging means and an illumination device with sufficient coherent light for illumination of hologram coded in the light modulator. The at least two imaging means are arranged such that a first imaging means is provided for the magnified imaging of the light modulator on a second imaging means. The second imaging means is provided for imaging of a plane of a spatial frequency spectrum of the light modulator in a viewing plane at least one viewing window. The viewing window corresponds to a diffraction order of the spatial frequency spectrum.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com