Patents
Literature
271 results about "Object field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
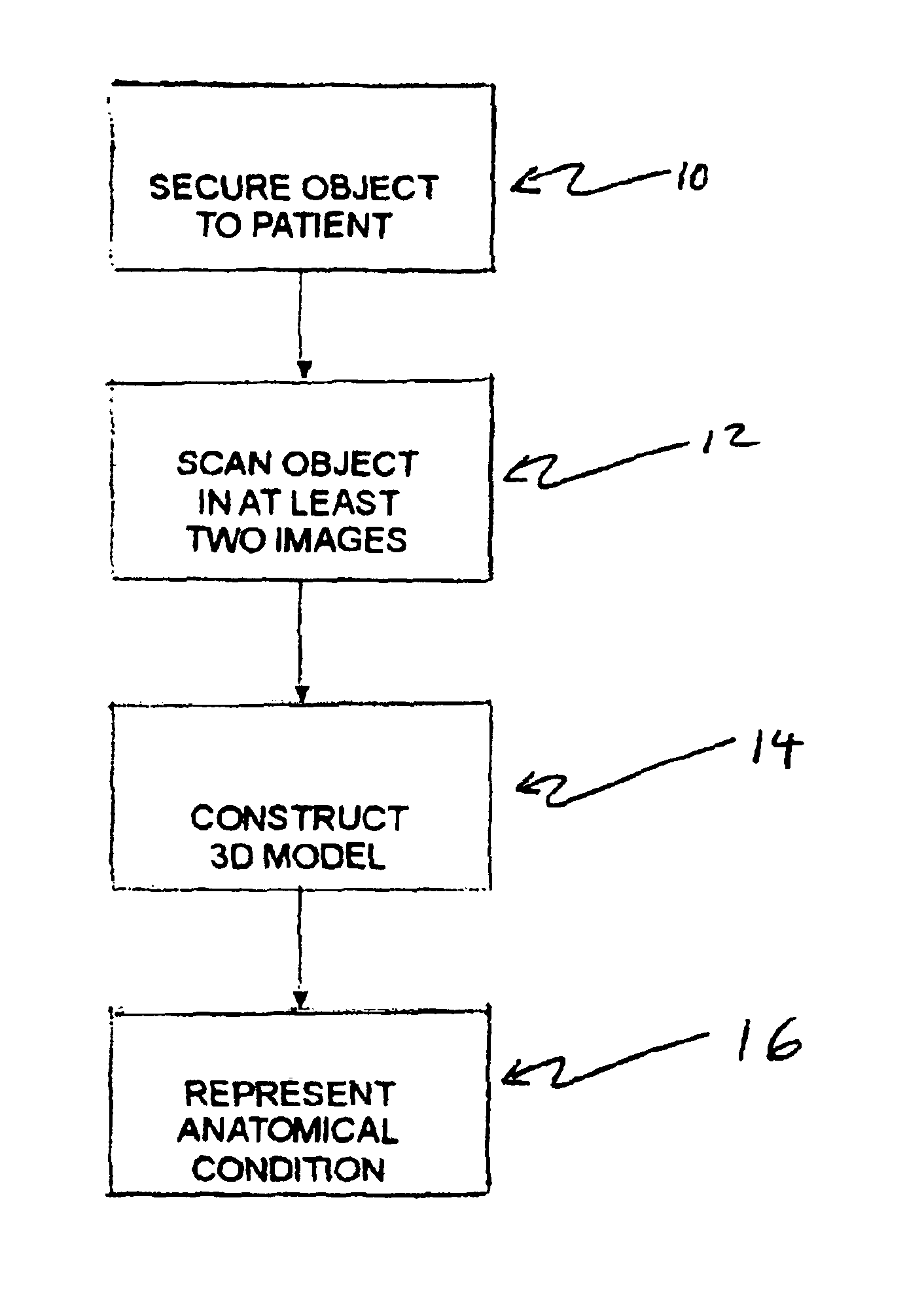
The Objects field contains the number of objects attached to a task or associated with a resource. There are several categories of Objects fields. Data Type Number. Objects (task field) Entry Type Calculated. How Calculated Project counts the number of objects linked to or embedded in a task.
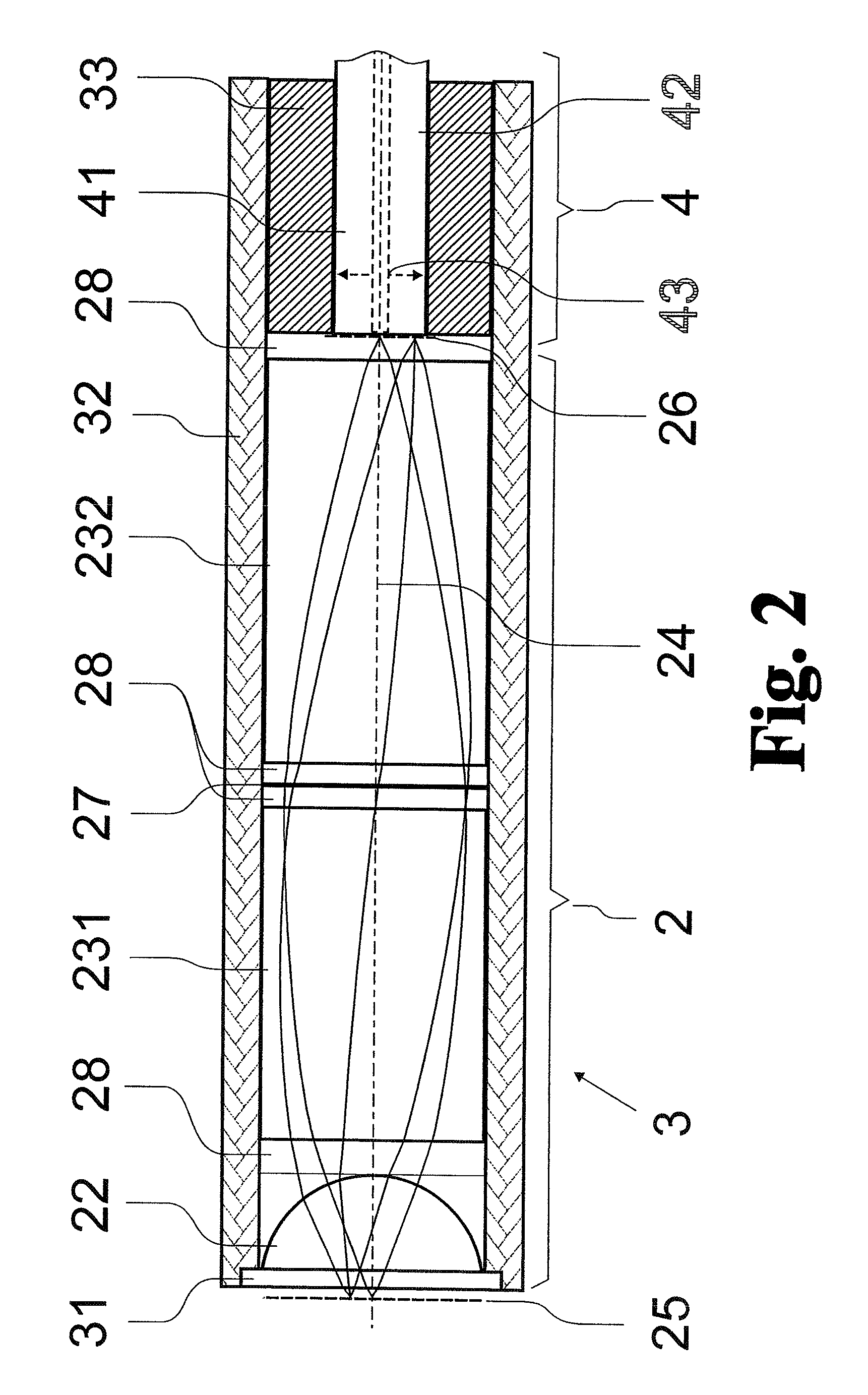
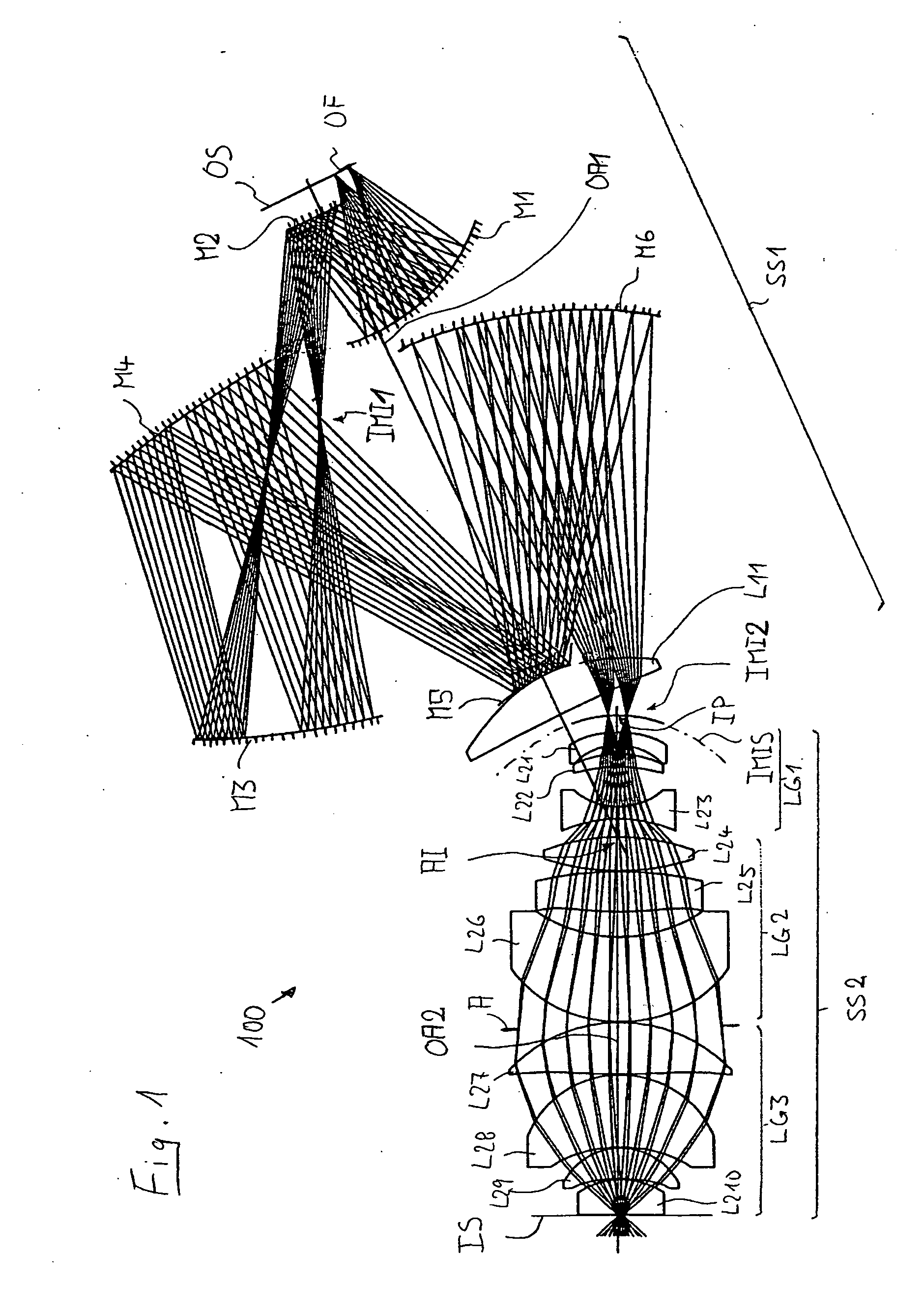
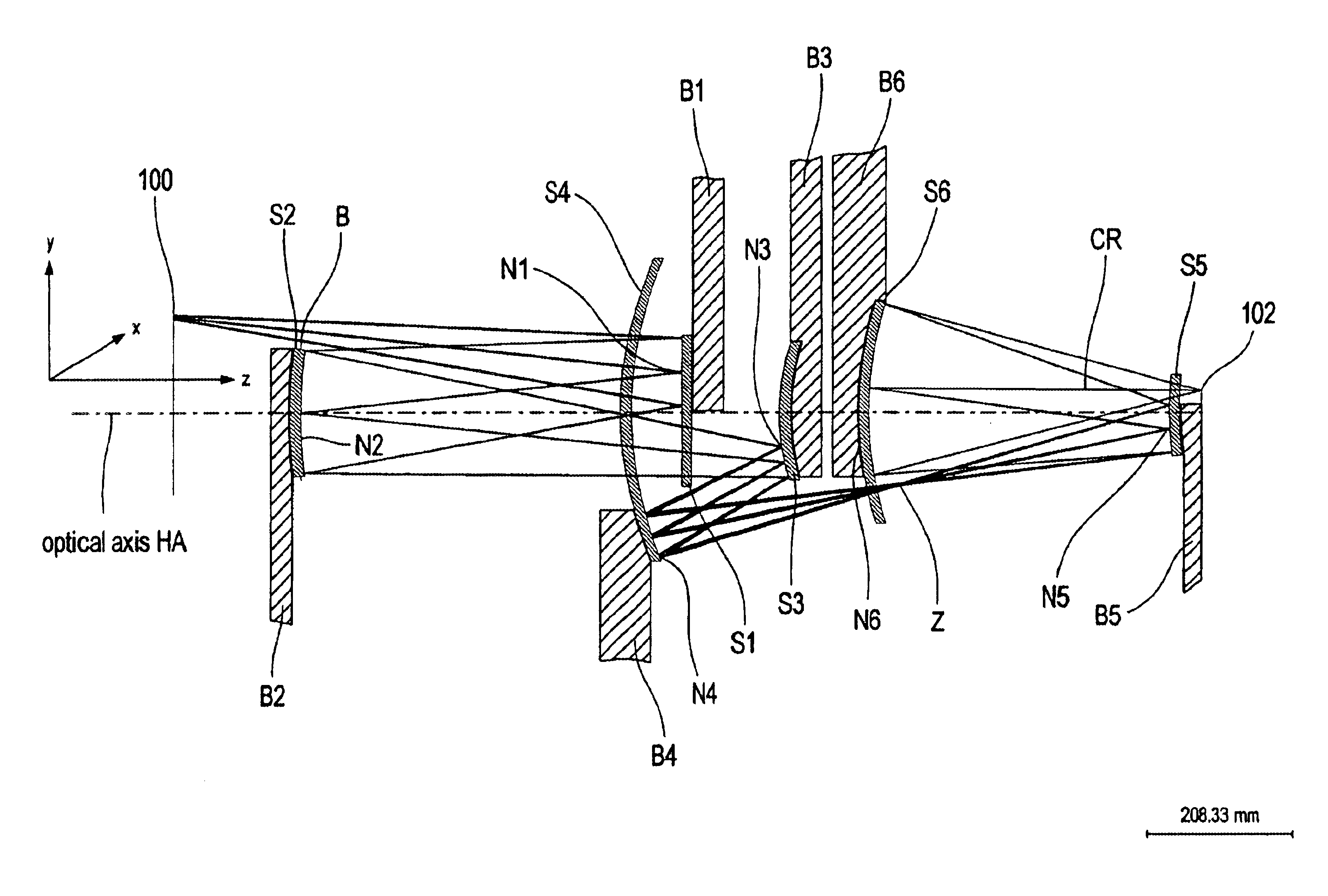
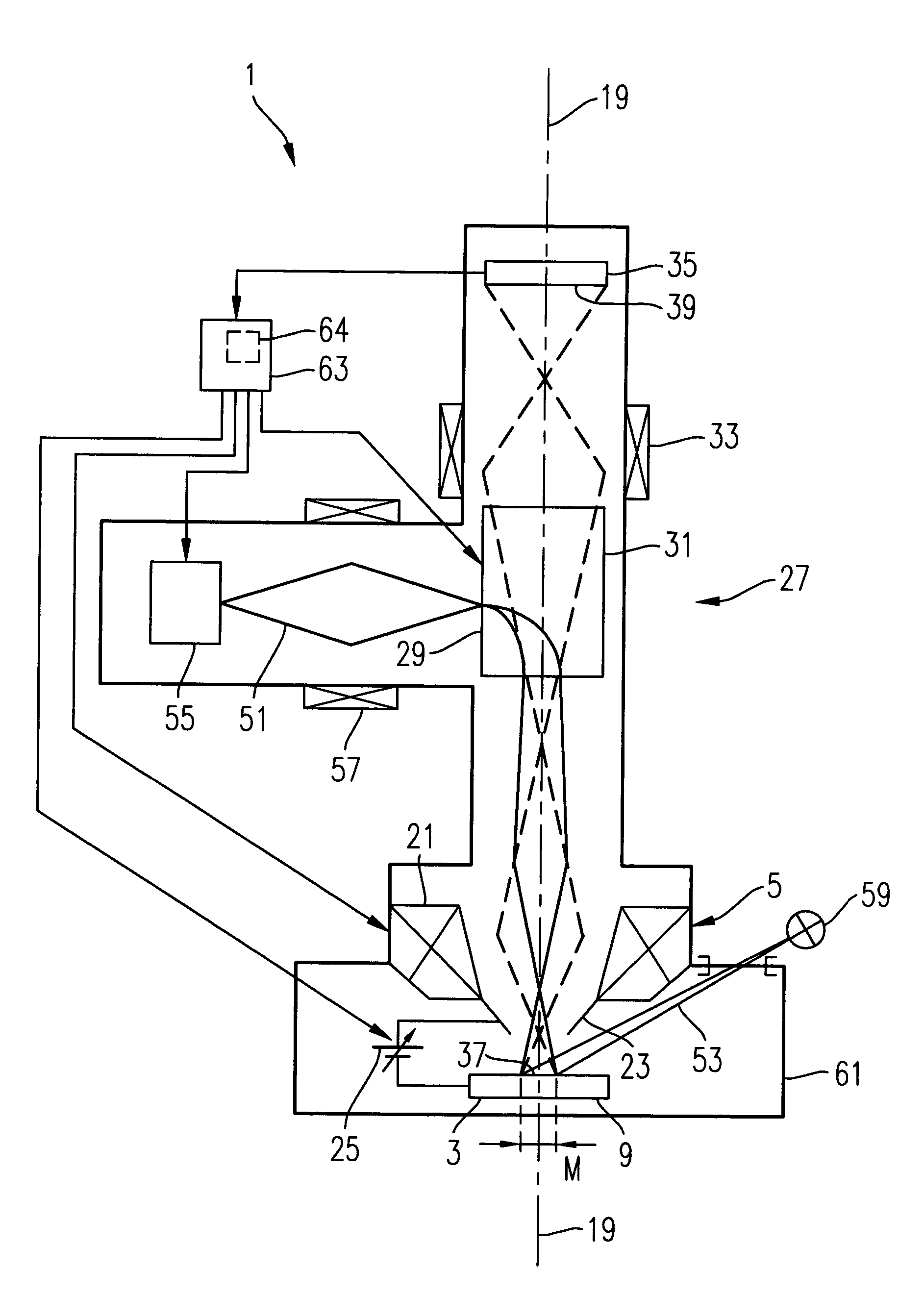
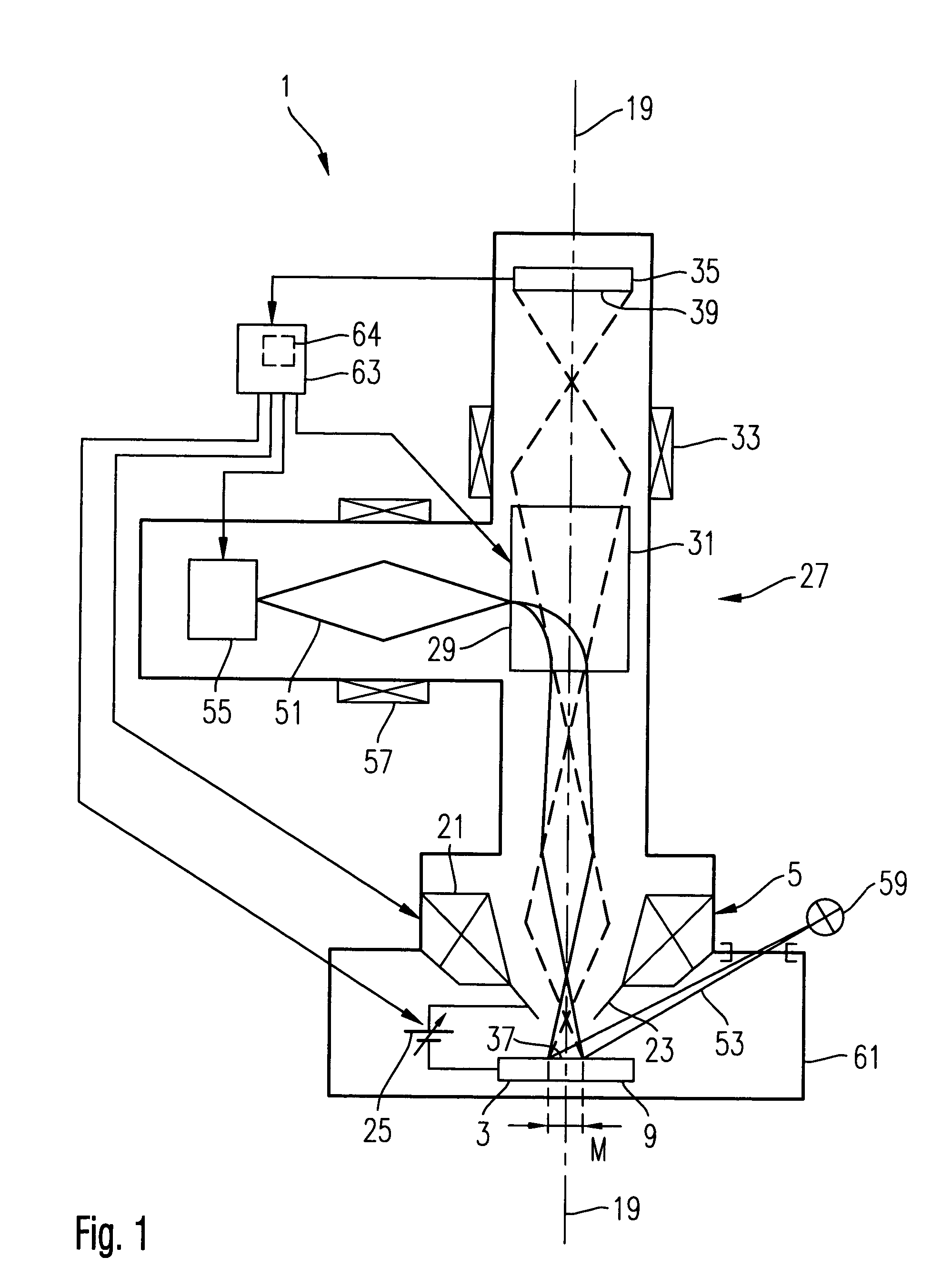
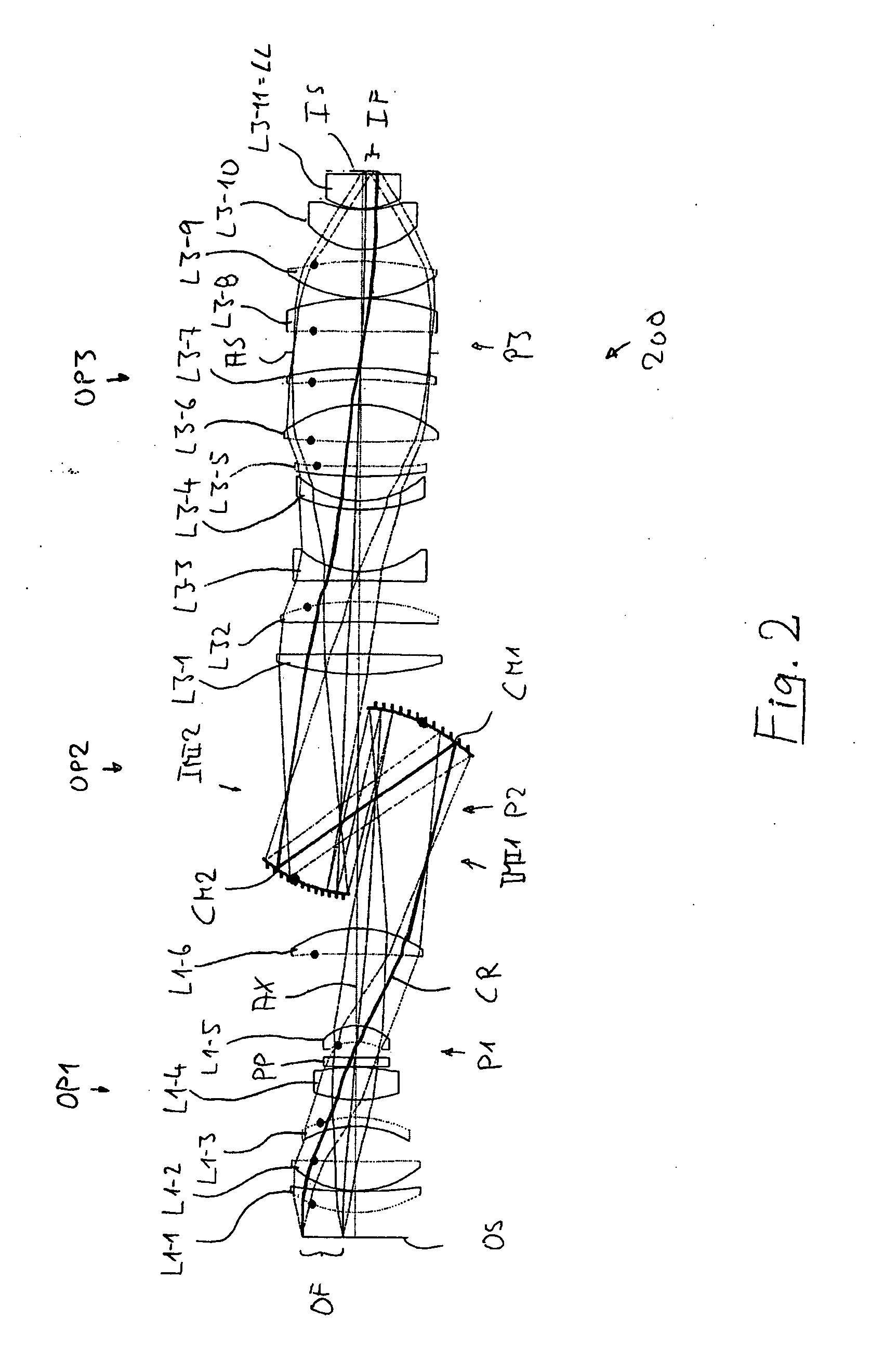
Catadioptric projection objective with geometric beam splitting
InactiveUS20050185269A1Easy to correctCorrect chromatic aberrationMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageBeam splitting
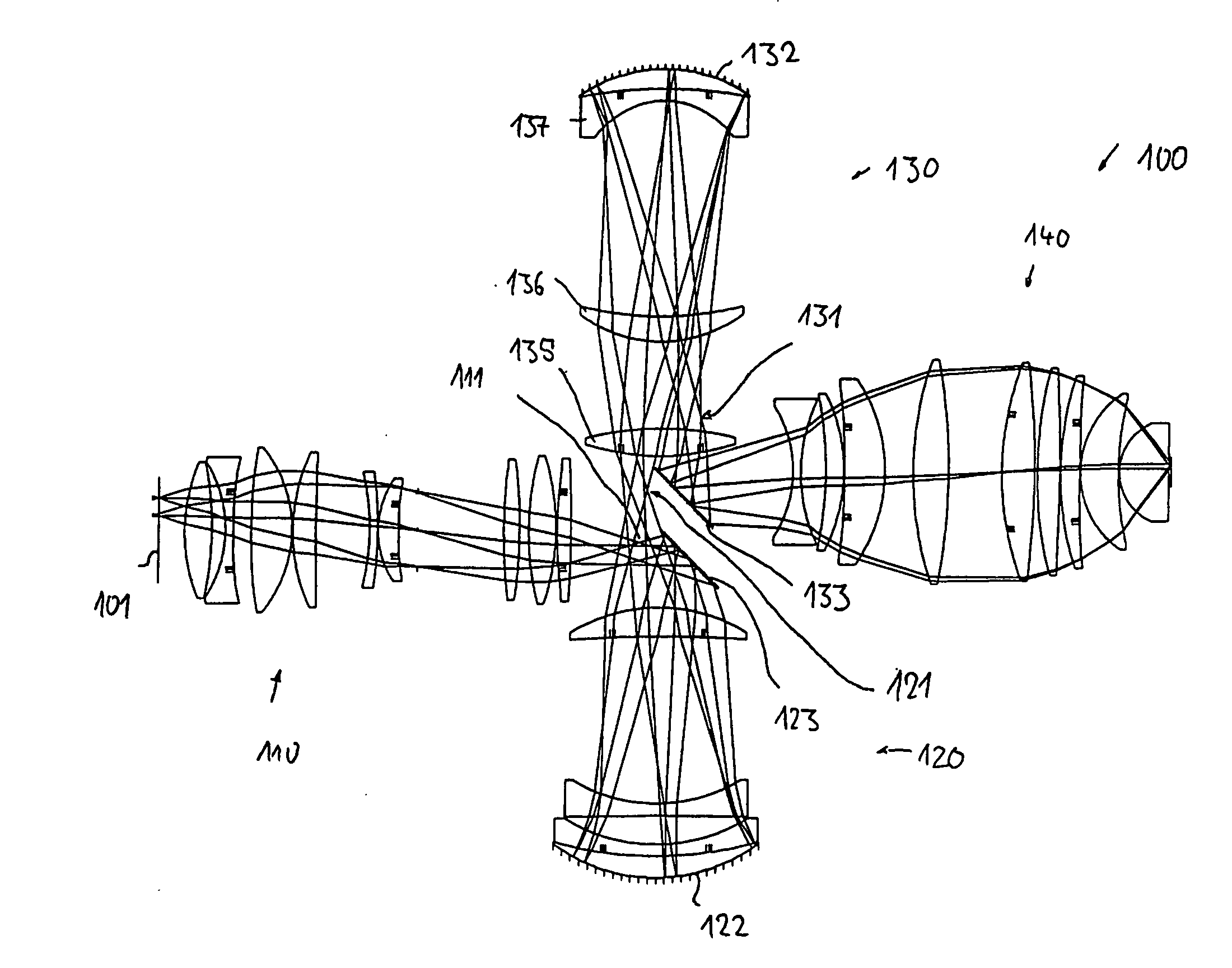
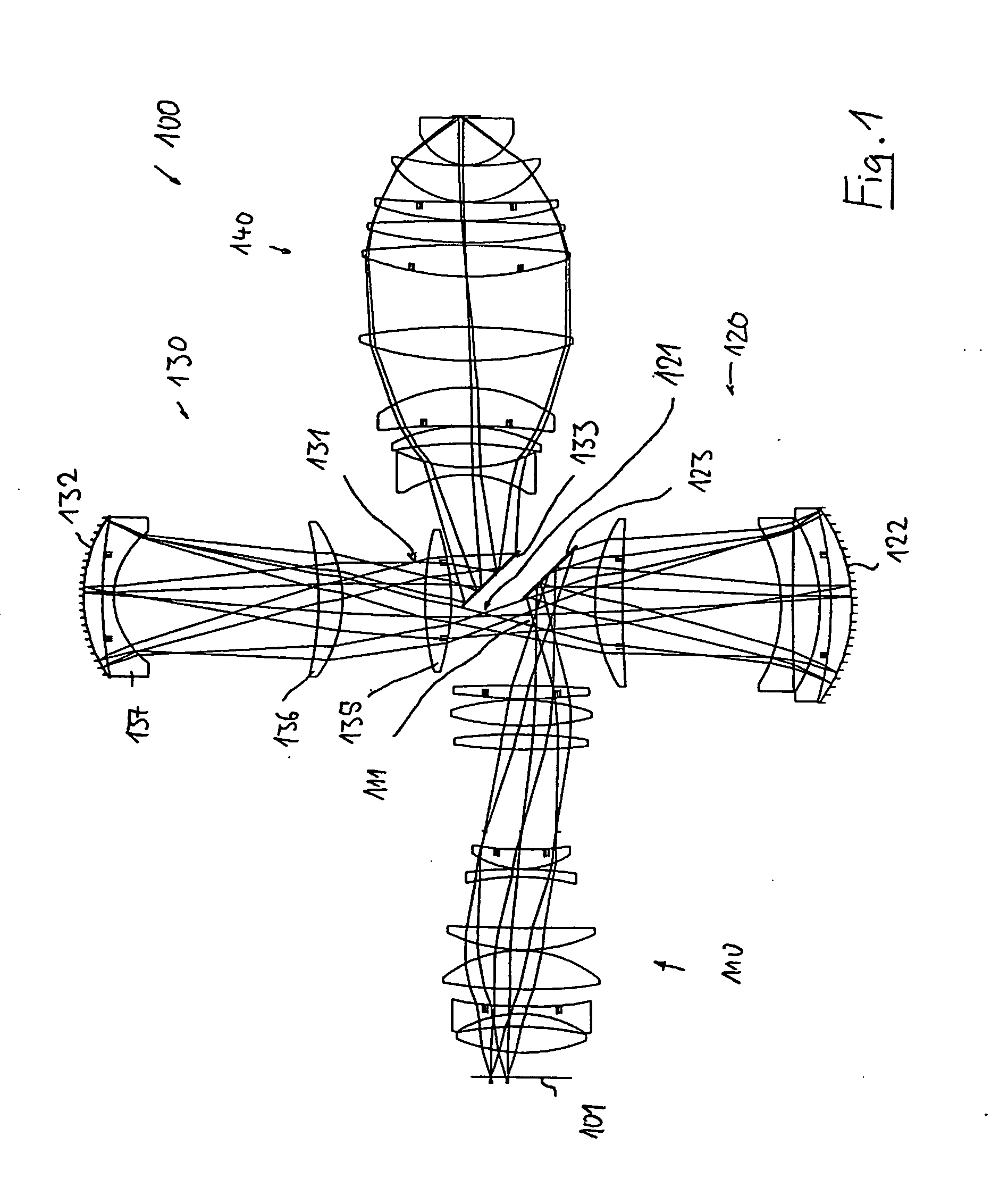
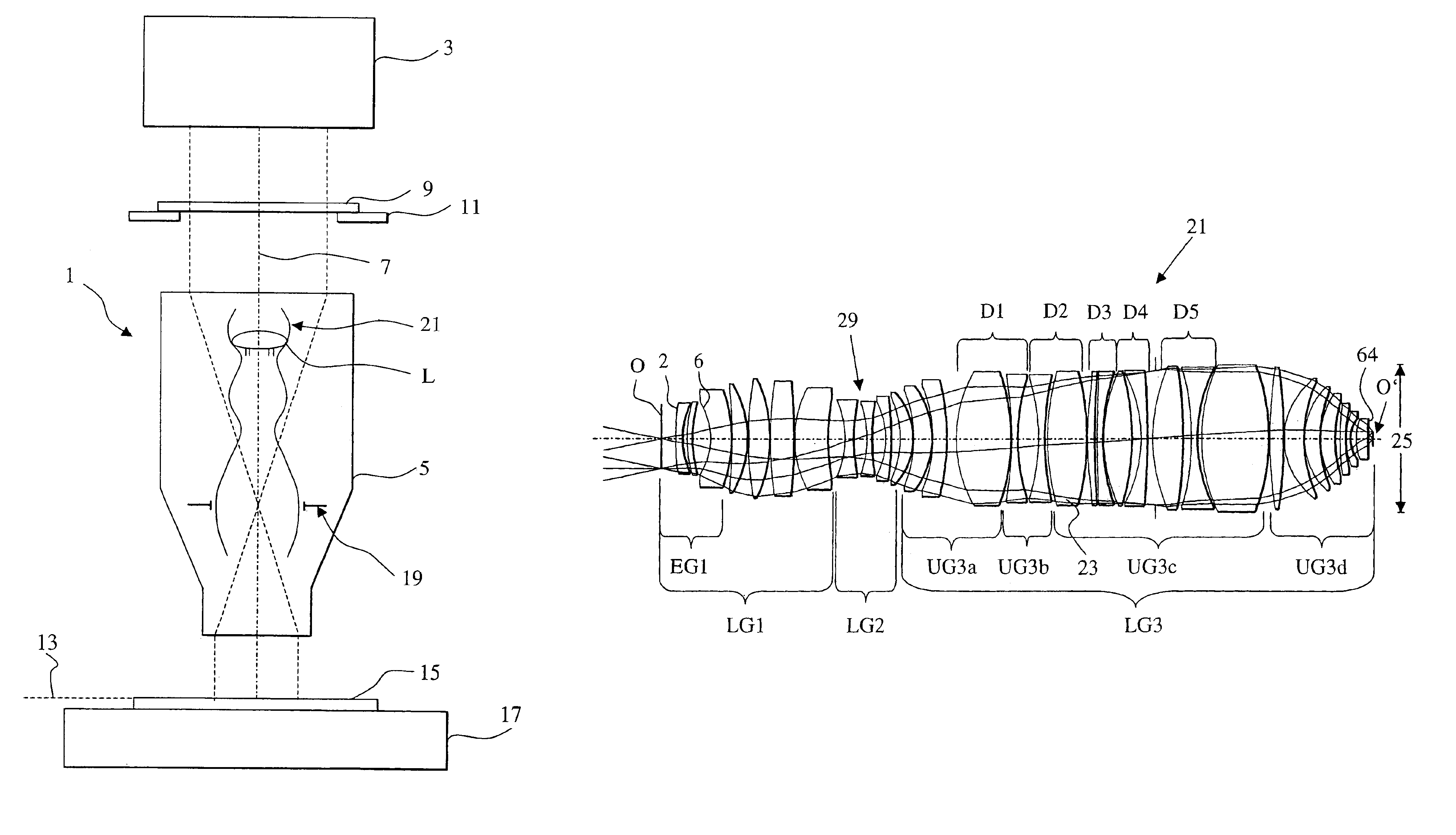
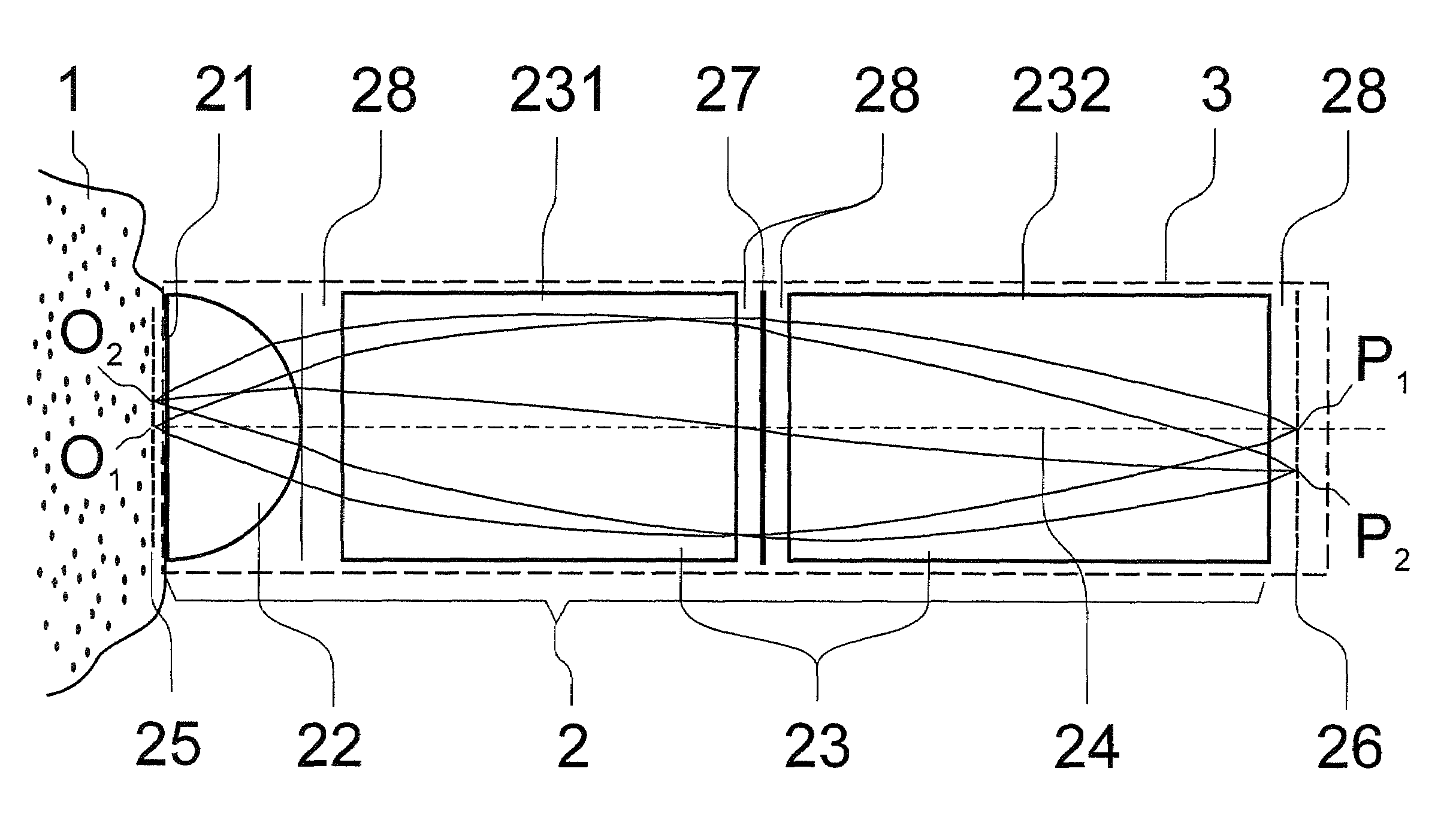
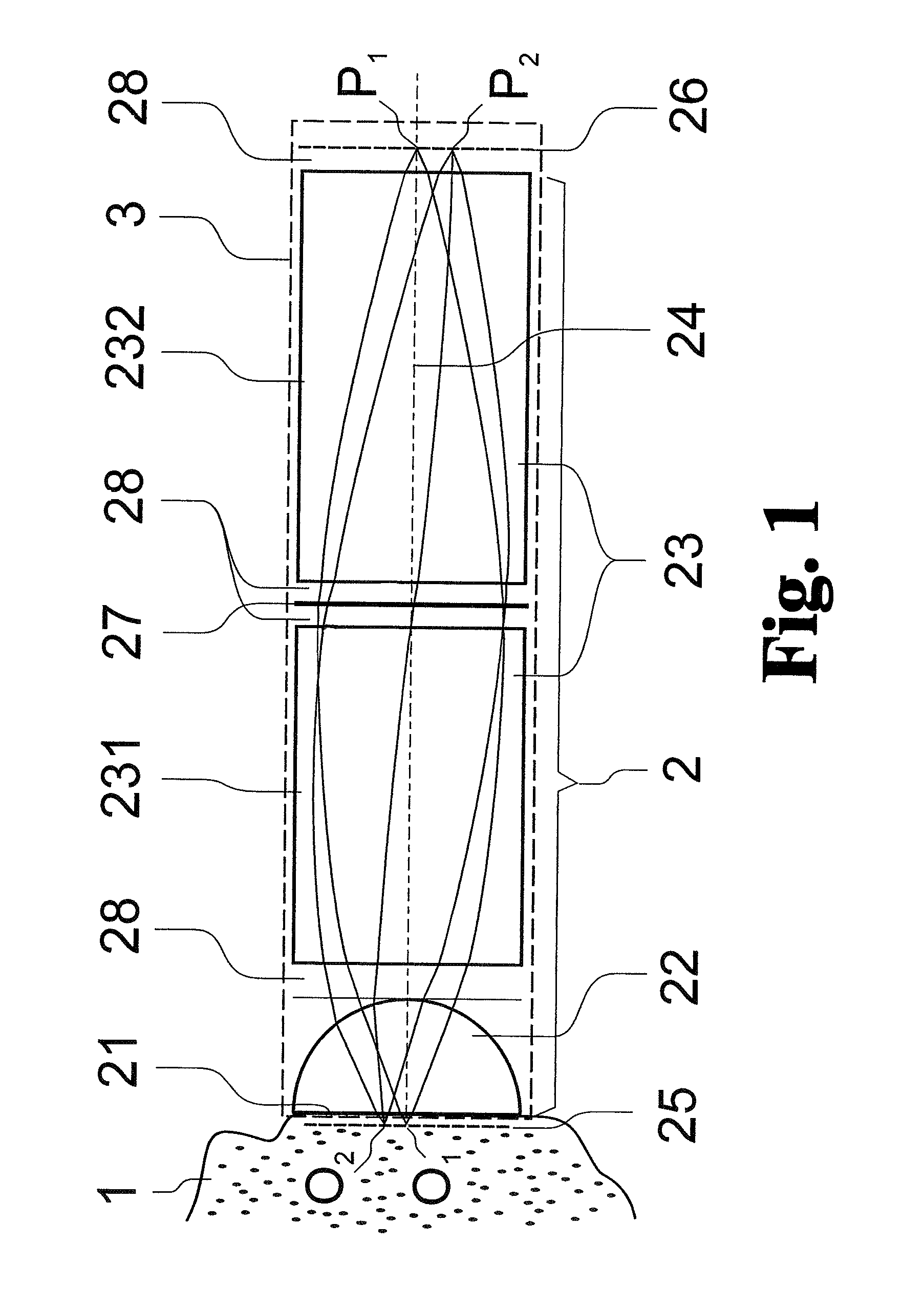
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern arranged on the object plane of the projection objective, on the image plane of the projection objective, comprising: a first objective part for imaging an object field in a first real intermediate image; a second objective part for producing a second real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the first objective part; and a third objective part for imaging the second real intermediate image on the image plane; wherein at least one of the objective parts is a catadioptric objective part with a concave mirror, and at least one of the objective parts is a refractive objective part and a folding mirror is arranged within this refractive objective part in such a way that a field lens is arranged between the folding mirror and an intermediate image which is closest to the folding mirror.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Plenoptic camera
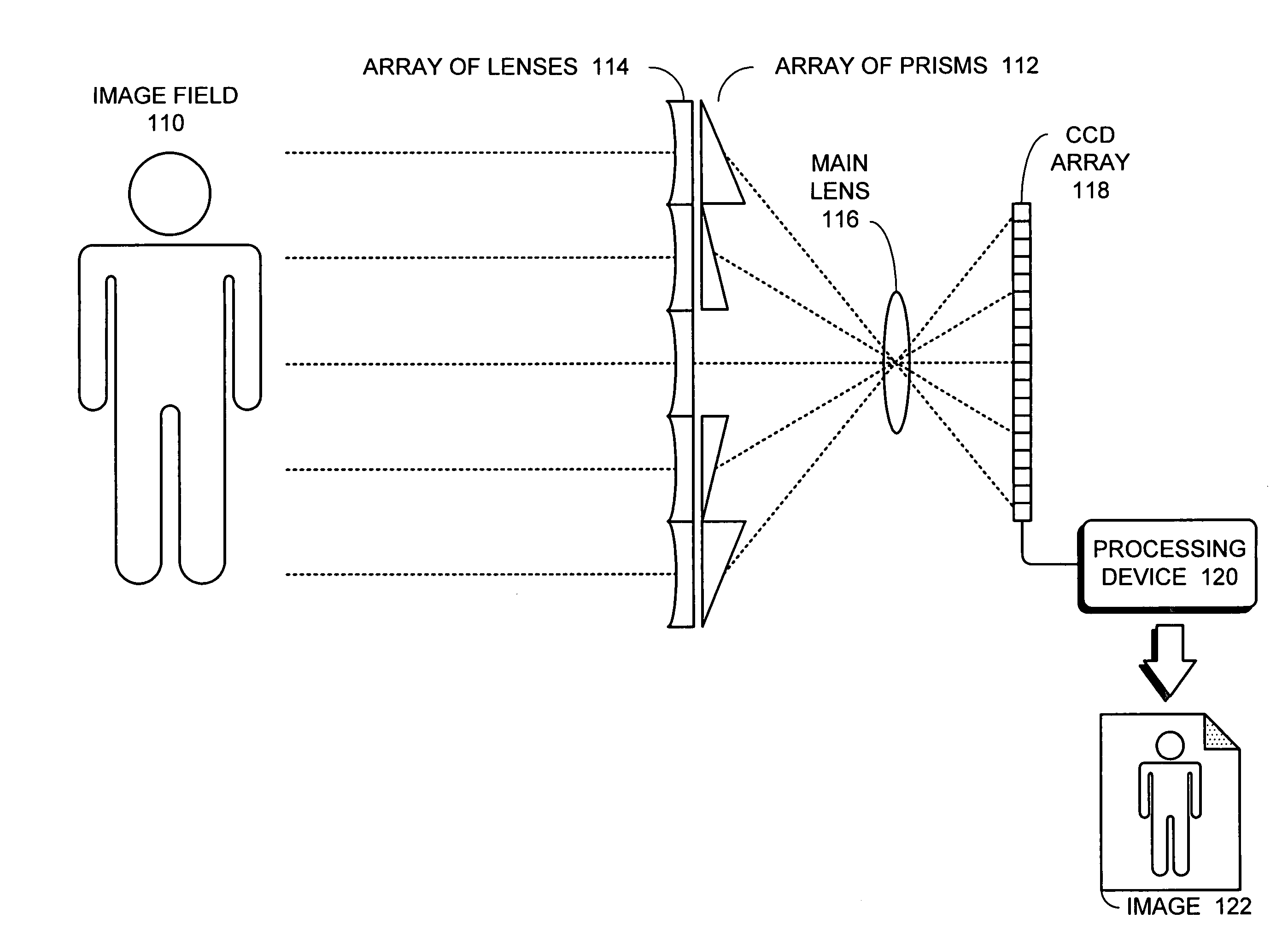
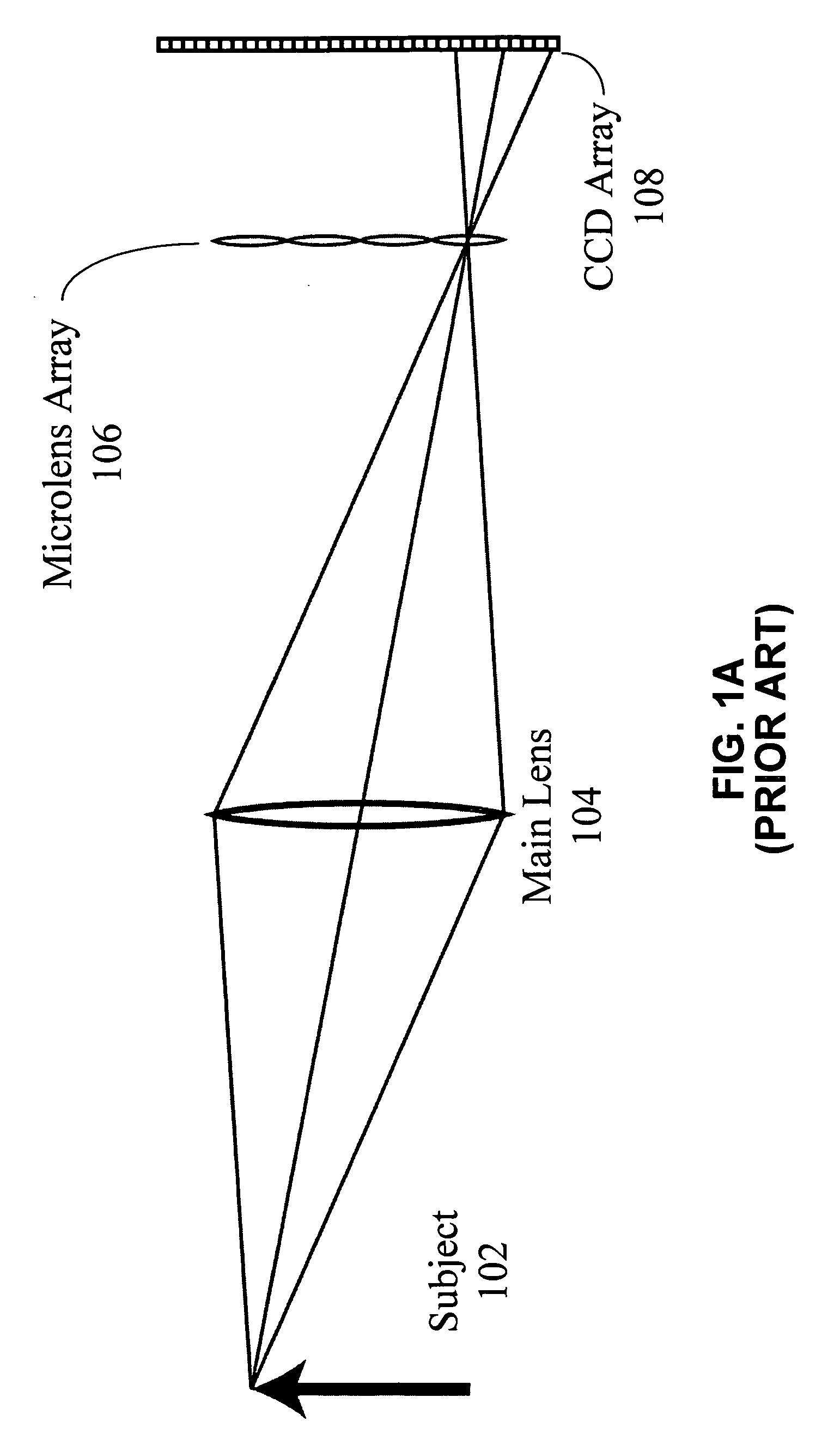
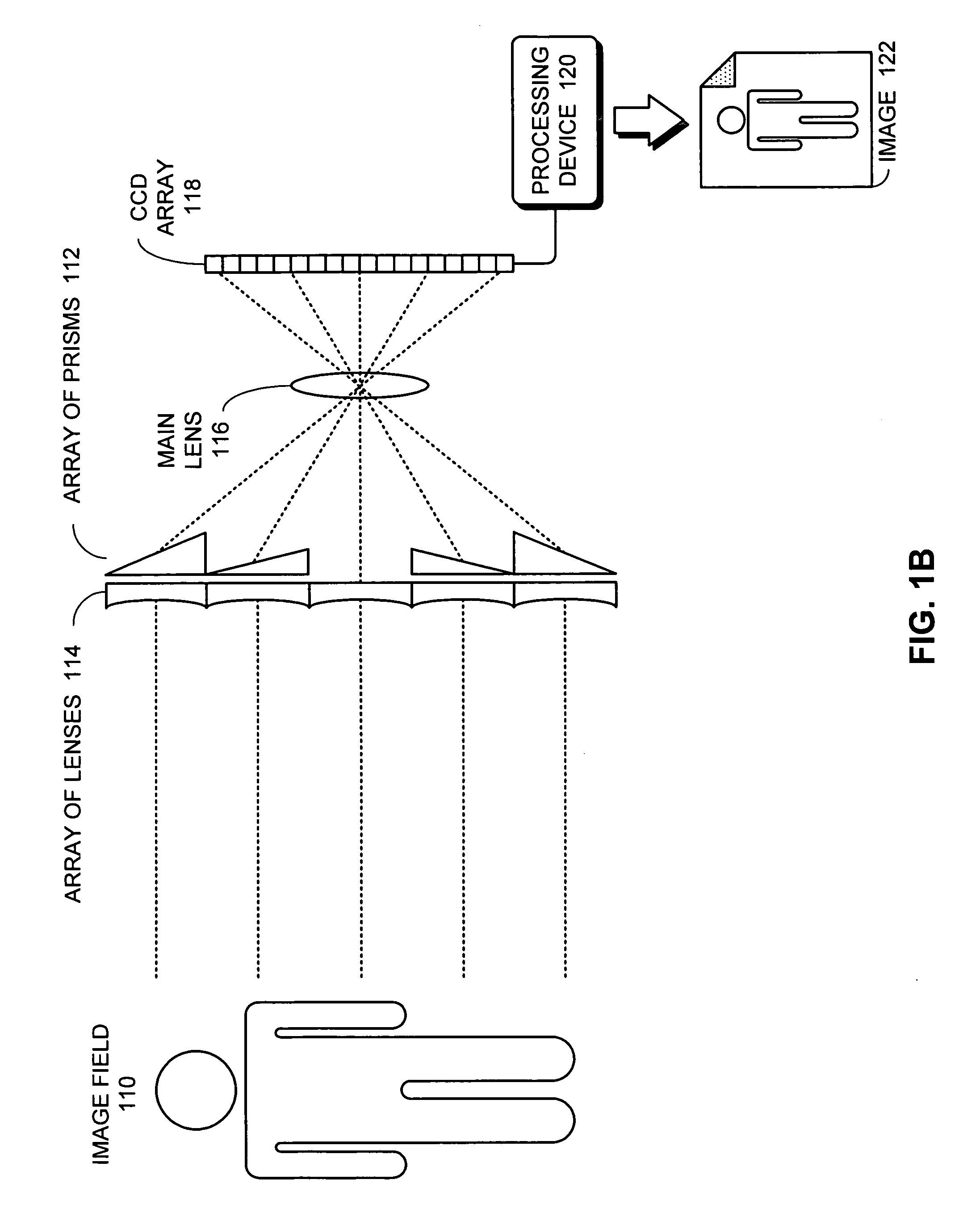
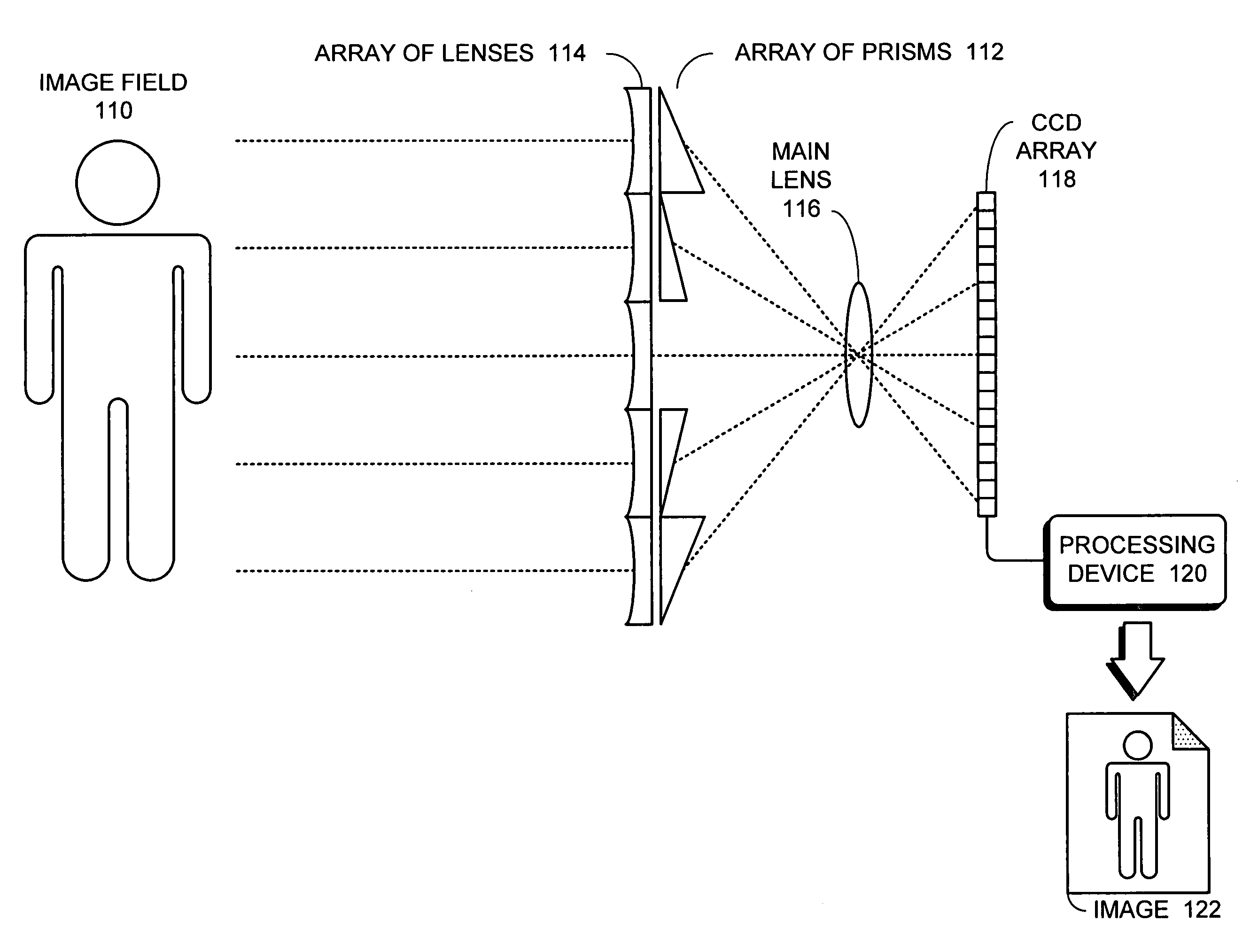
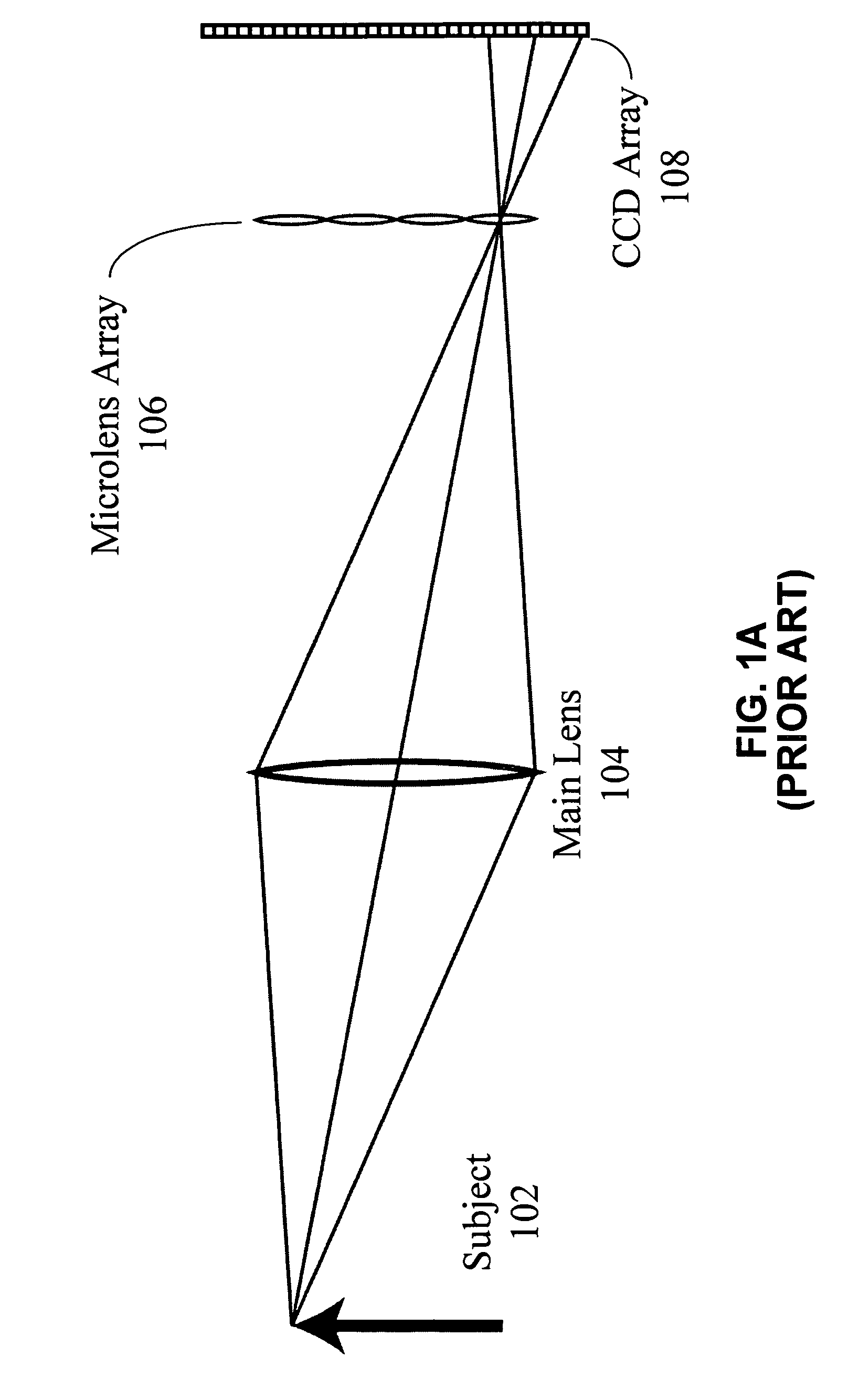
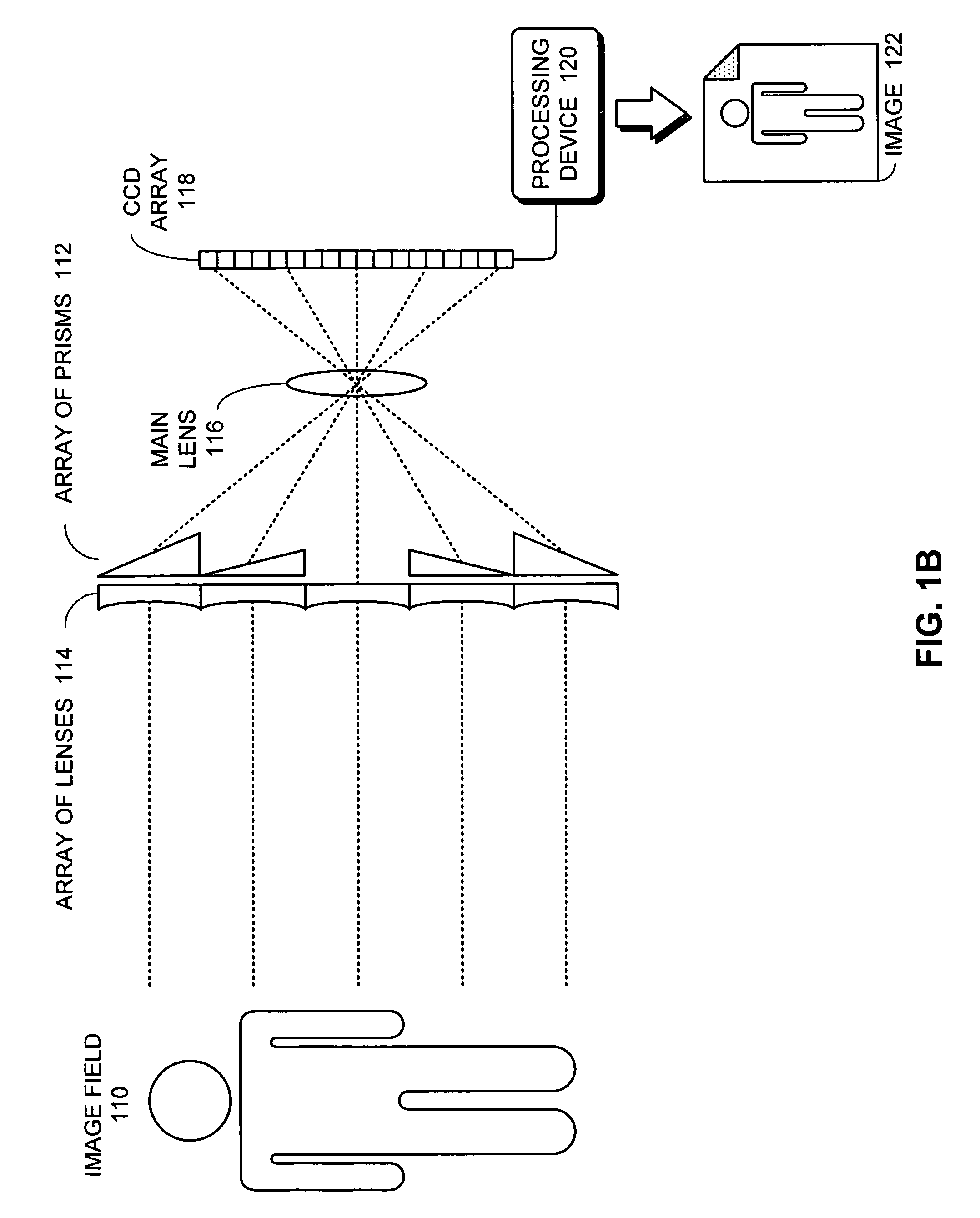
One embodiment of the present invention provides a plenoptic camera which captures information about the direction distribution of light rays entering the camera. Like a conventional camera, this plenoptic camera includes a main lens which receives light from objects in an object field and directs the received light onto an image plane of the camera. It also includes a photodetector array located at the image plane of the camera, which captures the received light to produce an image. However, unlike a conventional camera, the plenoptic camera additionally includes an array of optical elements located between the object field and the main lens. Each optical element in this array receives light from the object field from a different angle than the other optical elements in the array, and consequently directs a different view of the object field into the main lens. In this way, the photodetector array receives a different view of the object field from each optical element in the array. COLOR DRAWINGS The patent or application file contains at least one drawing executed in color. Copies of this patent or patent application publication with color drawing(s) will be provided by the Office upon request and payment of the necessary fee.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Plenoptic camera
InactiveUS7620309B2Television system detailsColor television detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
One embodiment of the present invention provides a plenoptic camera which captures information about the direction distribution of light rays entering the camera. Like a conventional camera, this plenoptic camera includes a main lens which receives light from objects in an object field and directs the received light onto an image plane of the camera. It also includes a photodetector array located at the image plane of the camera, which captures the received light to produce an image. However, unlike a conventional camera, the plenoptic camera additionally includes an array of optical elements located between the object field and the main lens. Each optical element in this array receives light from the object field from a different angle than the other optical elements in the array, and consequently directs a different view of the object field into the main lens. In this way, the photodetector array receives a different view of the object field from each optical element in the array.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Refractive projection objective with a waist
InactiveUS6891683B2Beneficial longitudinal chromatic aberrationIncrease the number ofMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical axisLight beam
A refractive projection objective for use in microlithography with lenses made exclusively of one and the same material has an image-side numerical aperture larger than 0.7. A light bundle defined by the image-side numerical aperture and by the image field has within the objective a variable light-bundle diameter smaller than or equal to a maximum light-bundle diameter. In a length interval measured on the optical axis from the system diaphragm towards the object field and at least equaling the maximum light-bundle diameter, the variable light-bundle diameter exceeds 85% of the maximum light-bundle diameter.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Default schema mapping
InactiveUS6076090AData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSchema mappingObject Class
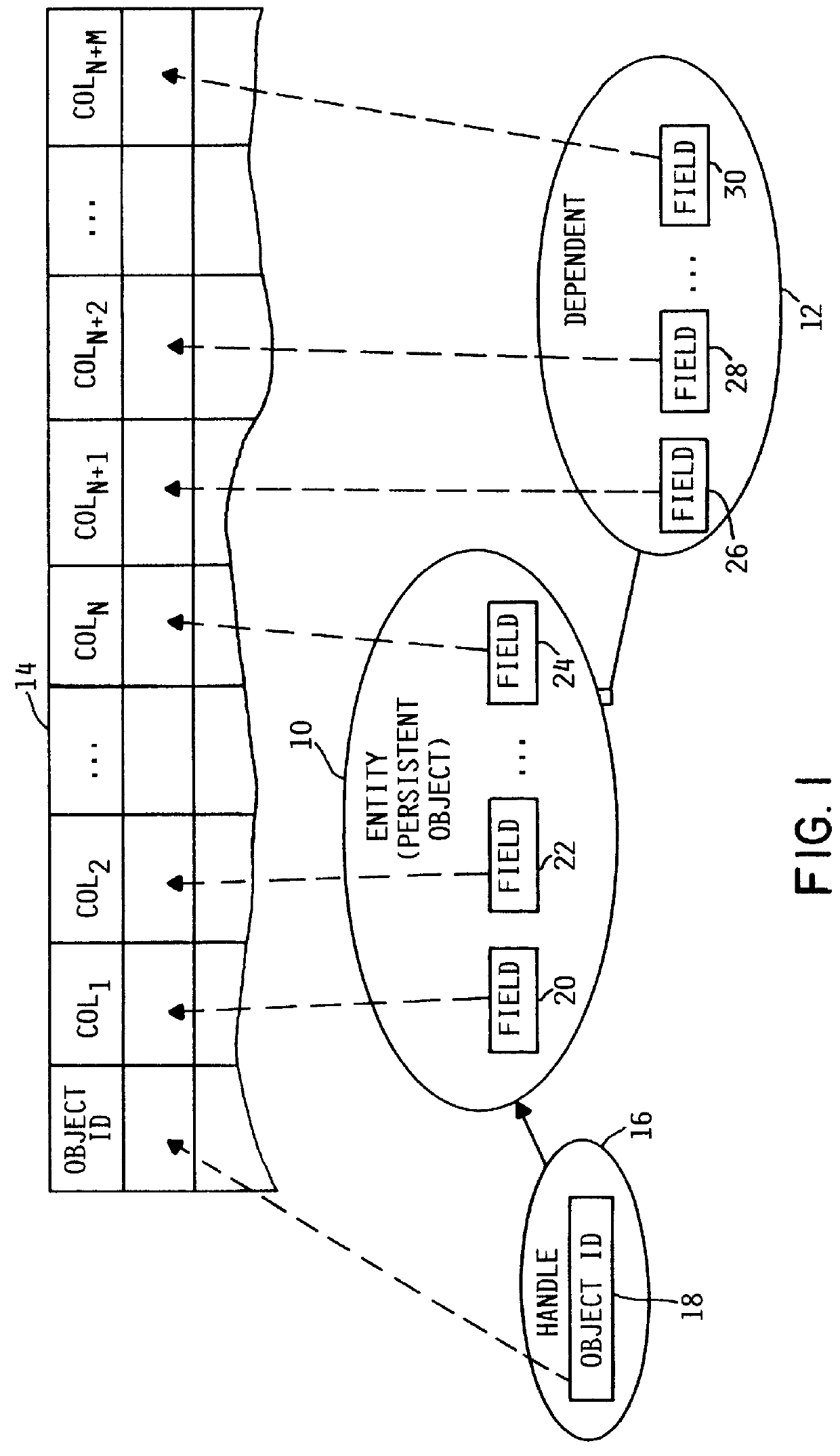
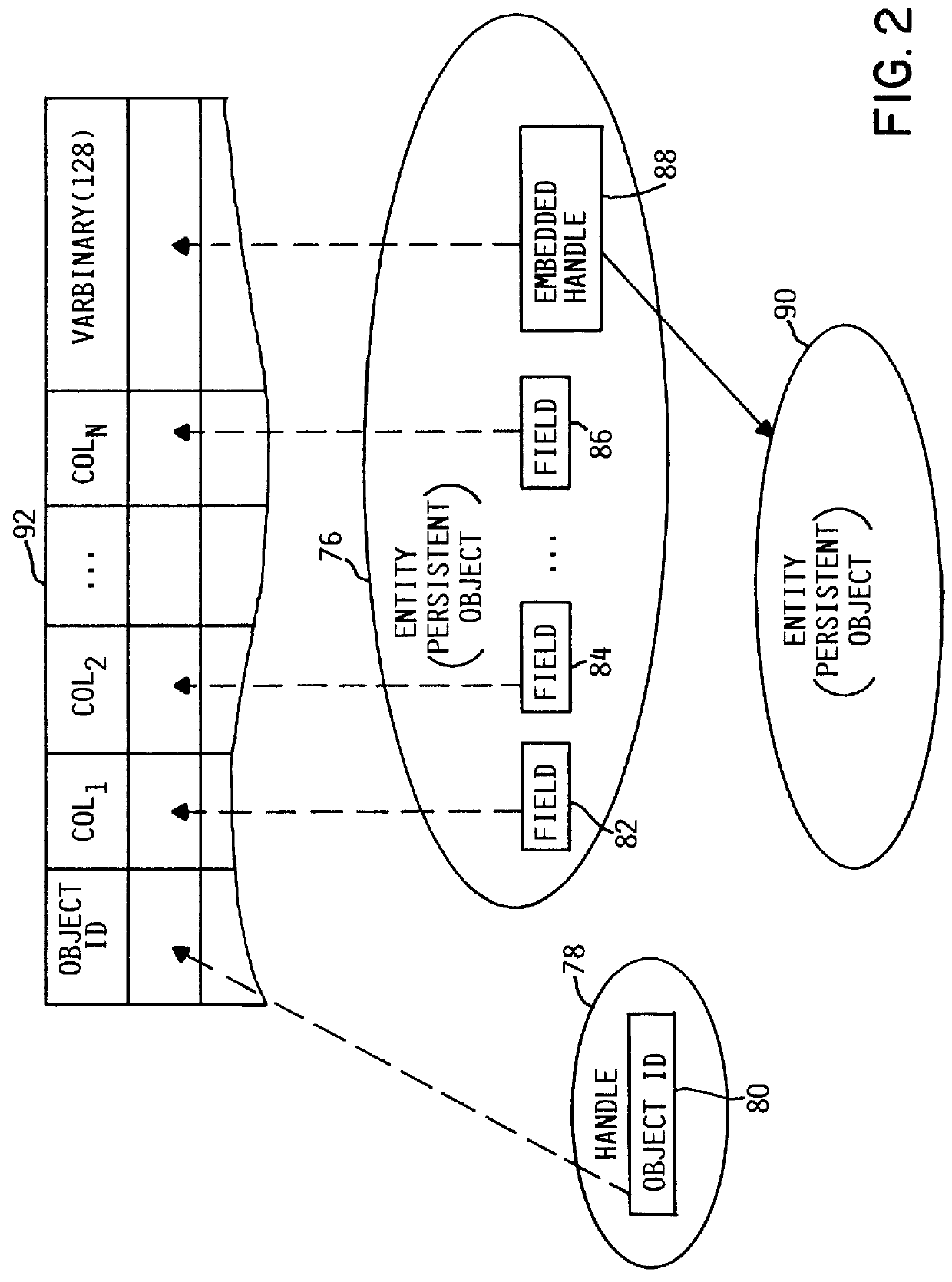
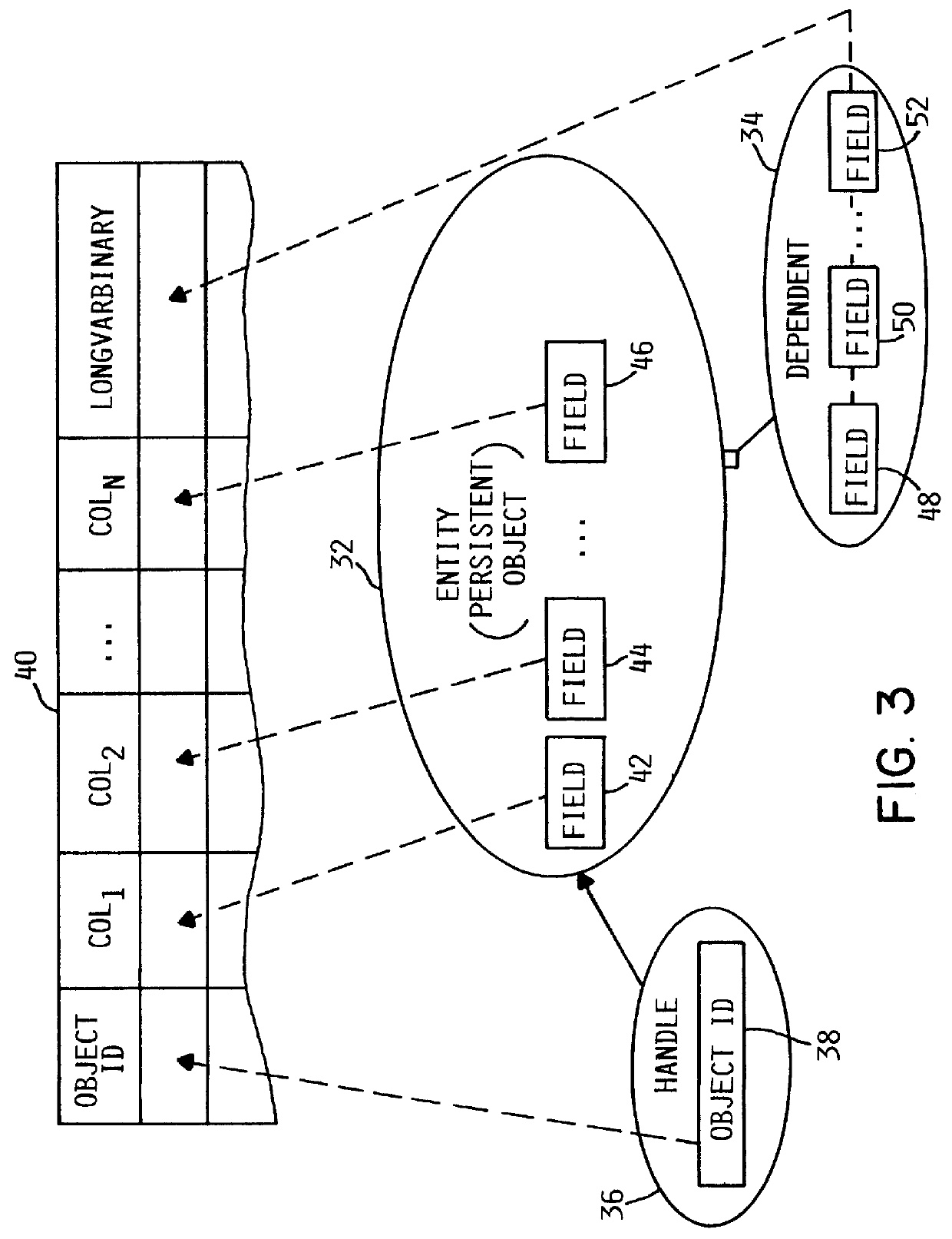
A method and system for persisting an object in a relational database schema by creating a new relational table at application program run-time for each class of objects to be persisted. The method may generate a schema map object for each class of objects to be persisted. The schema map object may be generated in response to the first transaction in which an object of a certain class is to be persisted and remains in memory for persisting, querying, restoring or deleting objects of that class. The schema map object determines the fields of each class of objects to be persisted, defines one or more columns in the table in accordance with the data types of the fields, and controls the passing of data between the table and the object fields.
Owner:IBM CORP
Display system having a three-dimensional convex display surface
ActiveUS20050017924A1Television system detailsBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsComputer graphics (images)Projection system
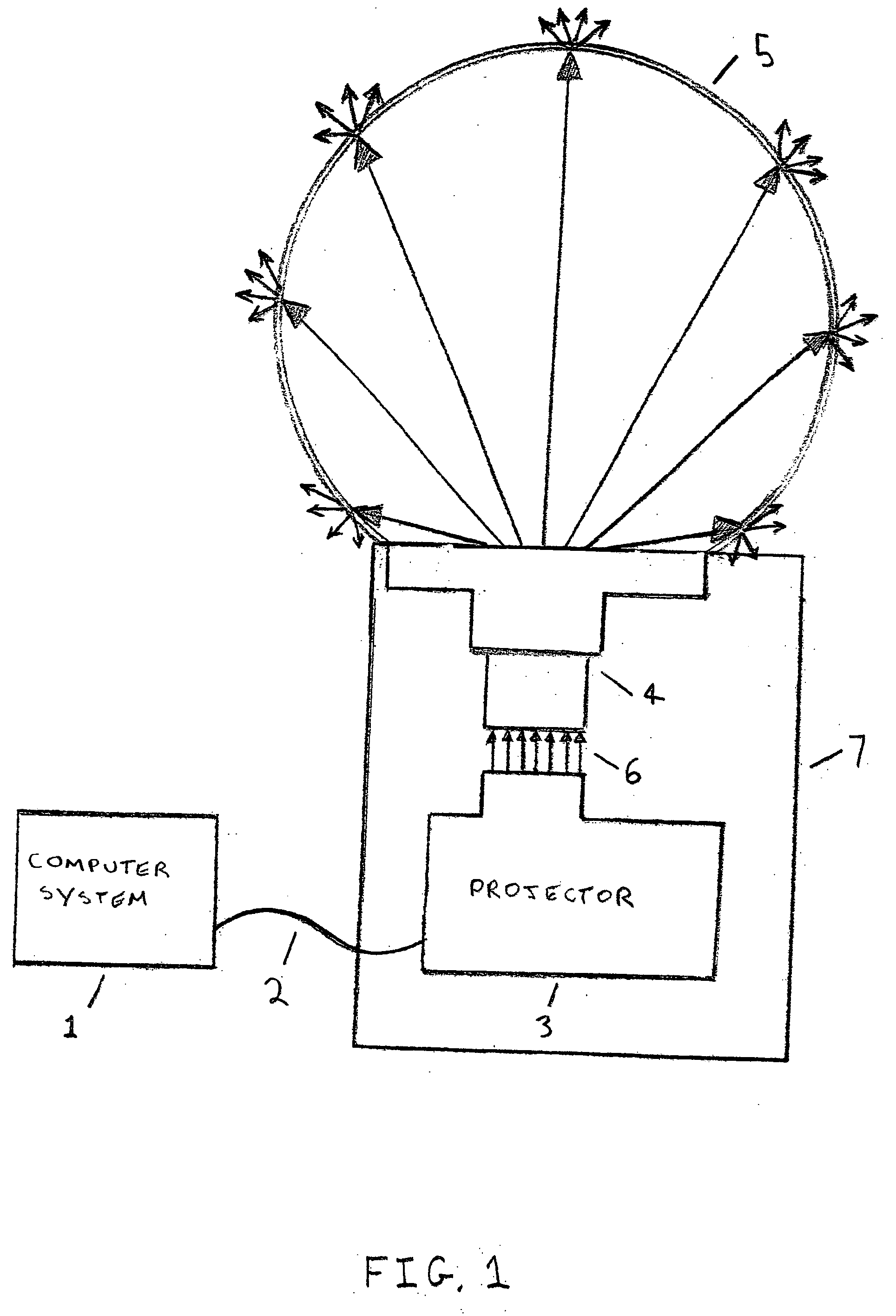
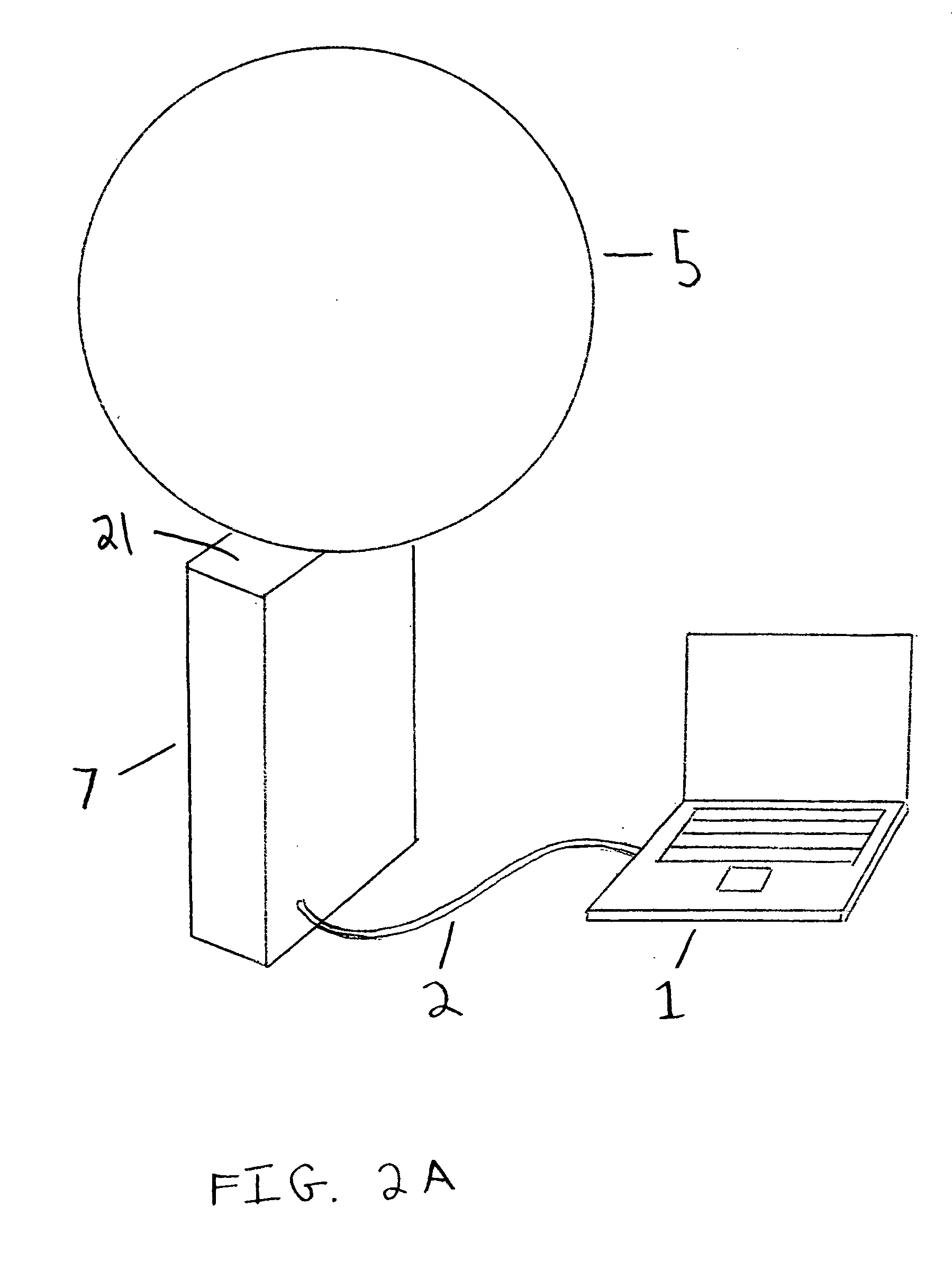
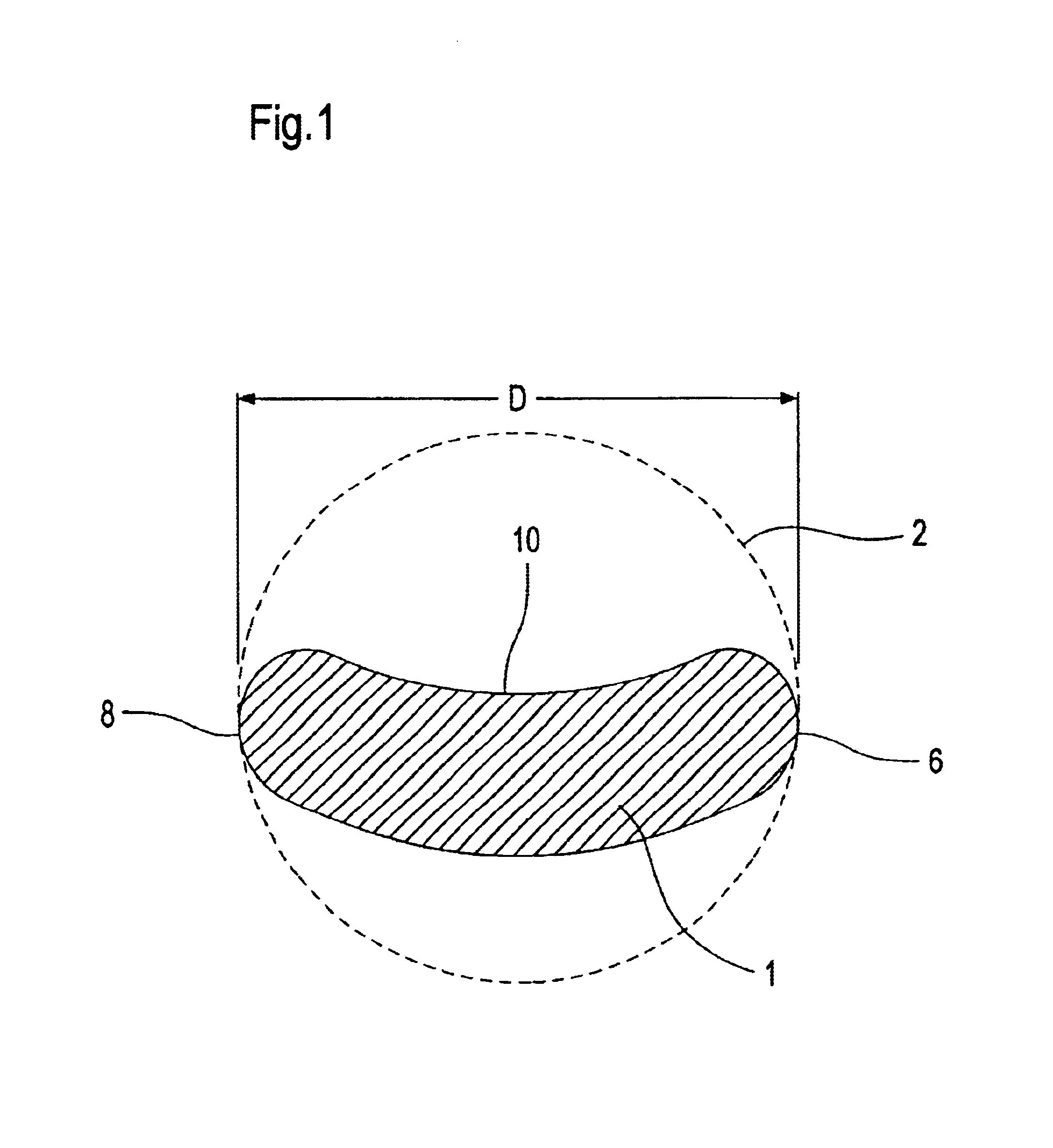
A display system has a display surface having a three-dimensional convex shape. A projection system projects an object field onto a continuous image field located on the interior of the display surface the display surface is extensive in its coverage, for example subtending an angle of at least 240 degrees to provide greater hemispherical coverage.
Owner:GLOBAL IMAGINATION
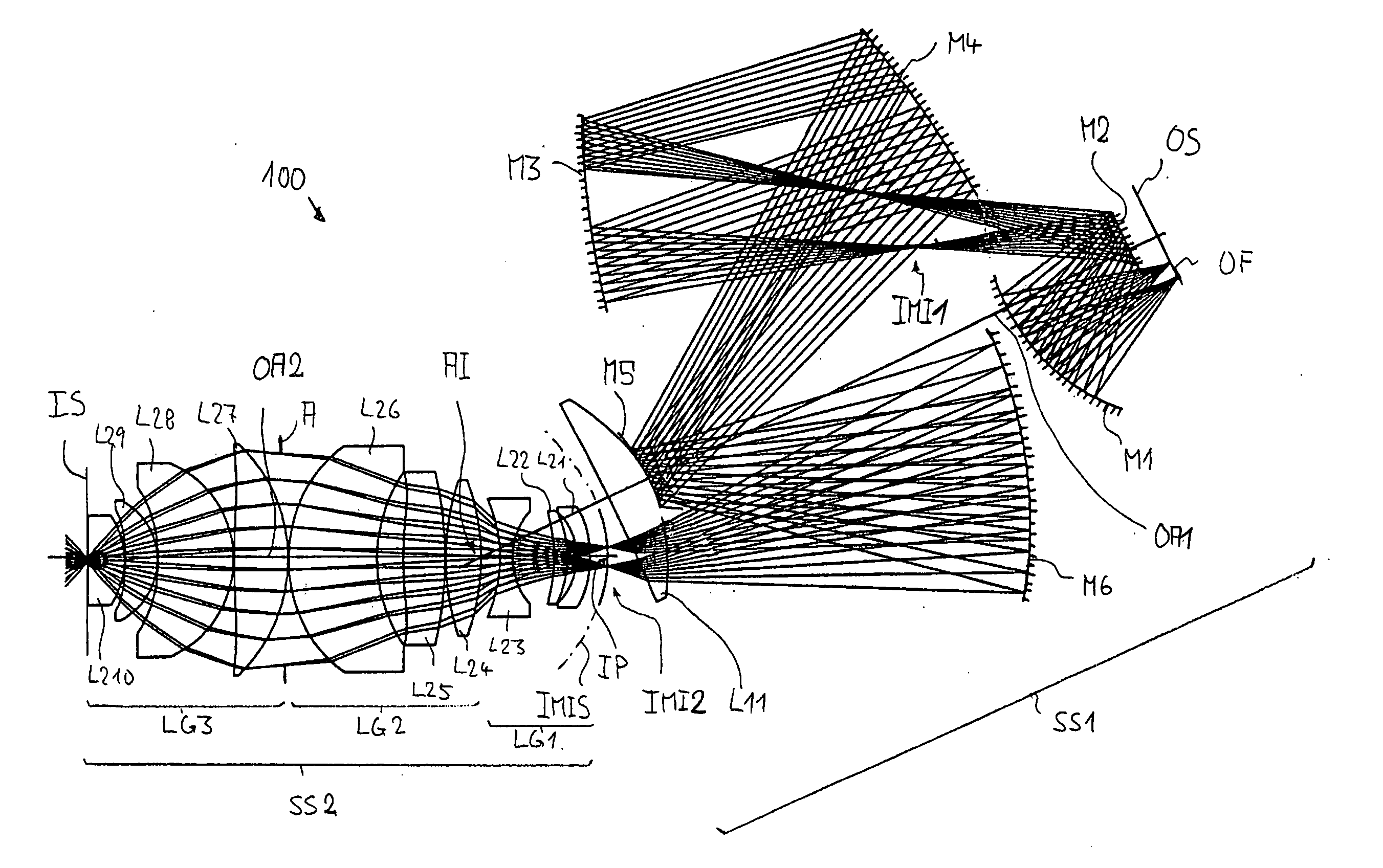
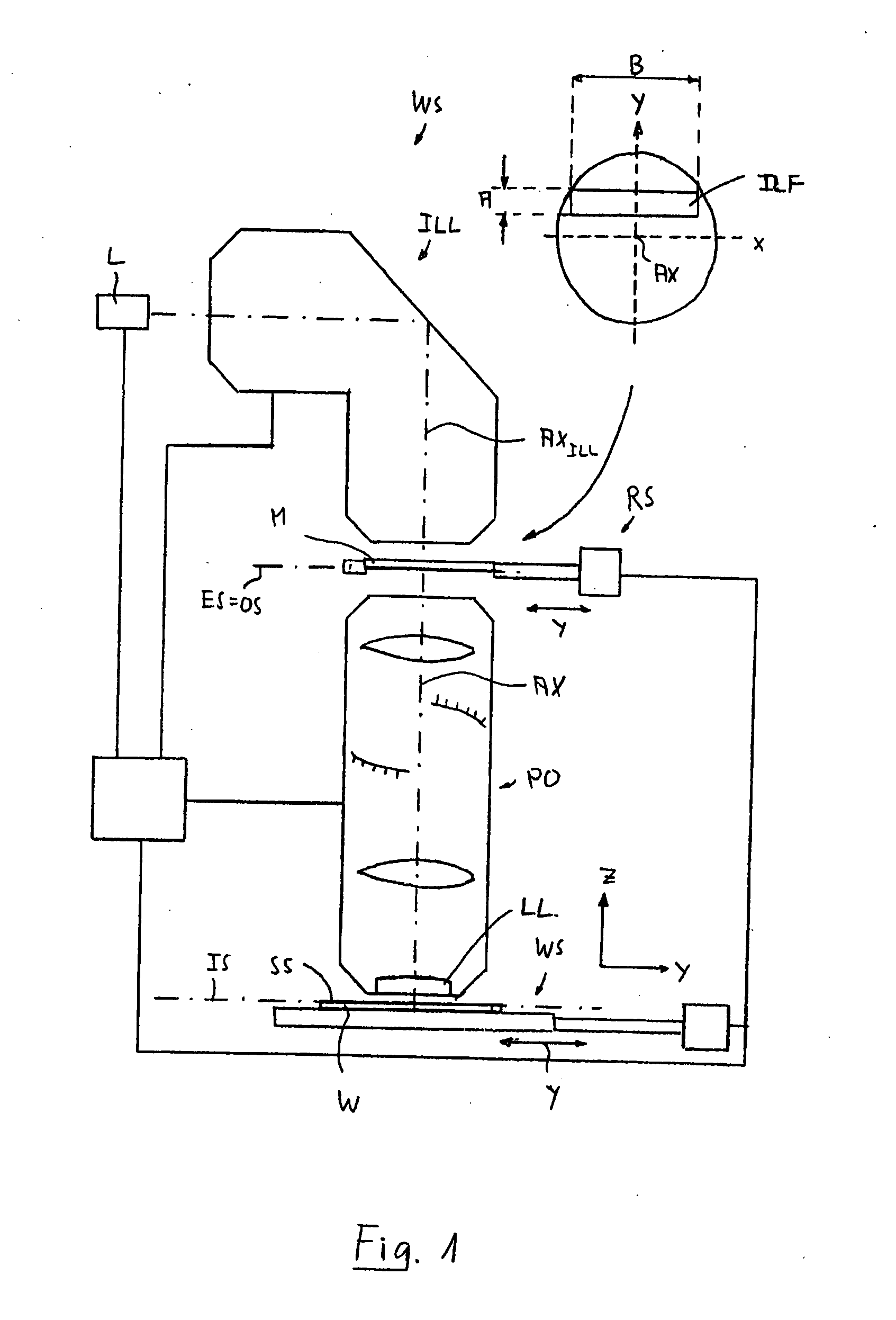
Miniaturized optically imaging system with high lateral and axial resolution
ActiveUS7511891B2Improve efficiencyHigh resolutionPhotometryMicroscopesTransmission systemObject field
The invention is directed to a miniaturized optically imaging system with high lateral and axial resolution for endomicroscopic applications. To provide a miniaturized optical head which permits an appreciable increase in photon efficiency with high lateral and axial spatial resolution compared to conventional GRIN optics the plane side of a refractive, plano-convex, homogeneous lens defines a plane entrance surface of the optical system, and first and second GRIN lenses are arranged along the optical axis orthogonal to the entrance surface, wherein the first GRIN lens being arranged downstream of the refractive lens for reducing the divergence of the highly divergent light bundle transmitted from the object through the refractive lens, and the second GRIN lens being provided for adapting the light bundle transmitted by the first GRIN lens to the aperture and object field size of the downstream transmission system.
Owner:GRINTECH
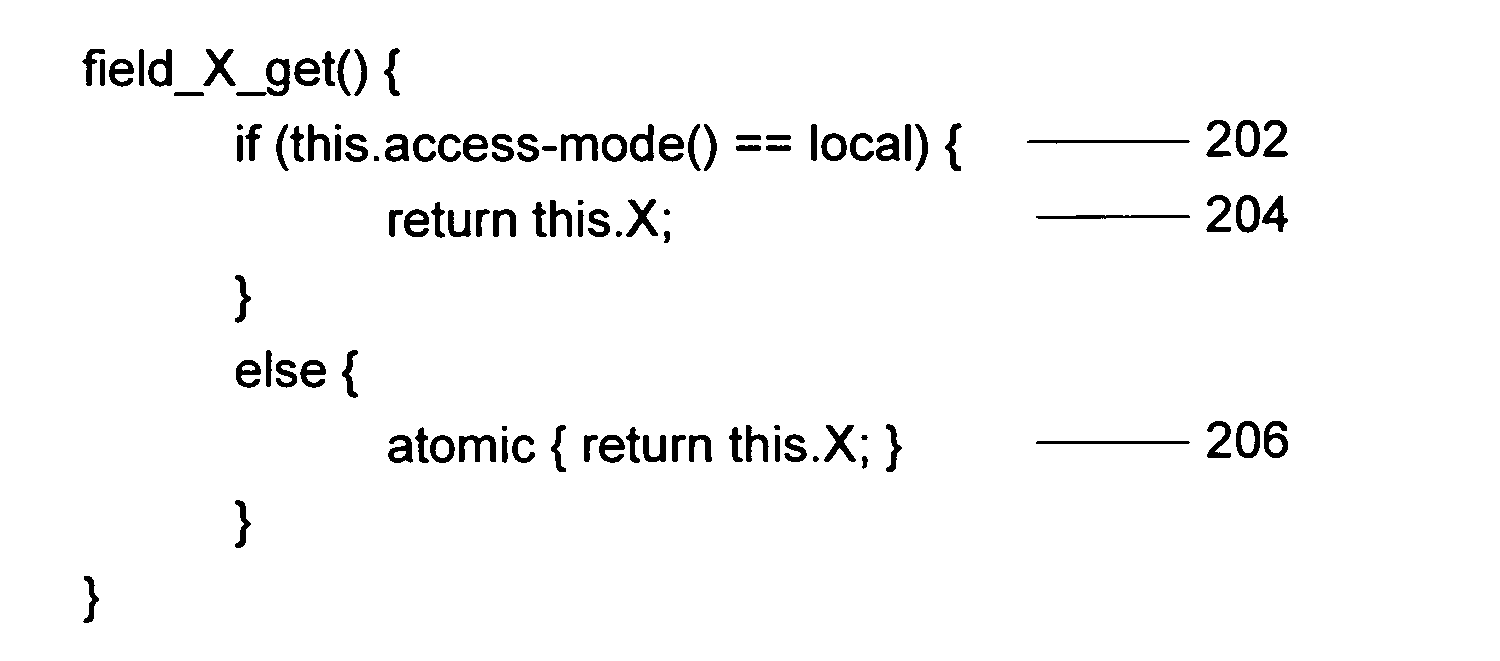
Method and apparatus for improving transactional memory interactions by tracking object visibility
ActiveUS20070150509A1Avoid overheadAvoid accessSpecific program execution arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageVisibility
In a multi-threaded computer system that uses transactional memory, object fields accessed by only one thread are accessed by regular non-transactional read and write operations. When an object may be visible to more than one thread, access by non-transactional code is prevented and all accesses to the fields of that object are performed using transactional code. In one embodiment, the current visibility of an object is stored in the object itself. This stored visibility can be checked at runtime by code that accesses the object fields or code can be generated to check the visibility prior to access during compilation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Imaging system
InactiveUS20060198018A1High image side numerical apertureSmall amountPhotomechanical apparatusMicroscopesIntermediate imageOptical axis
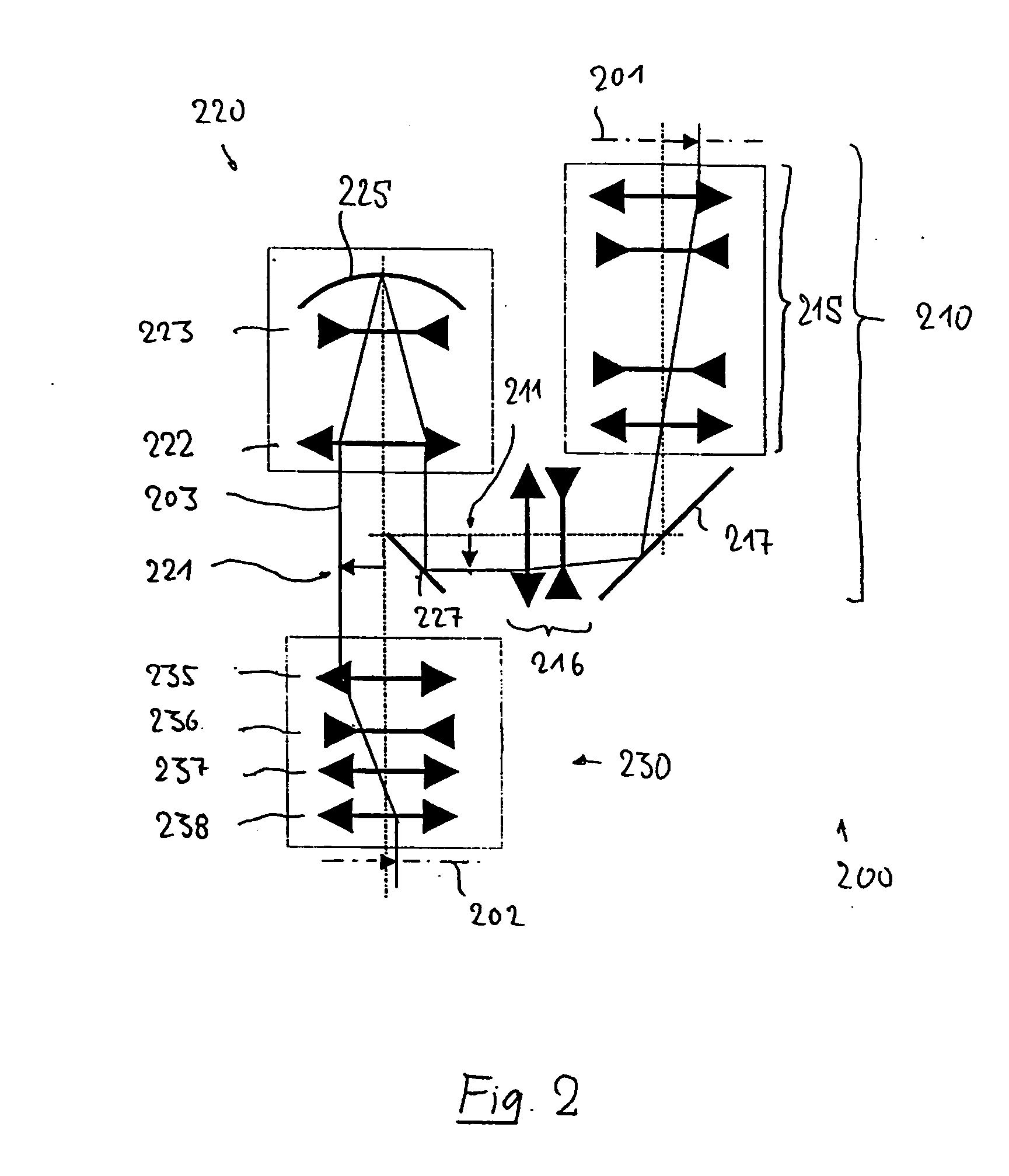
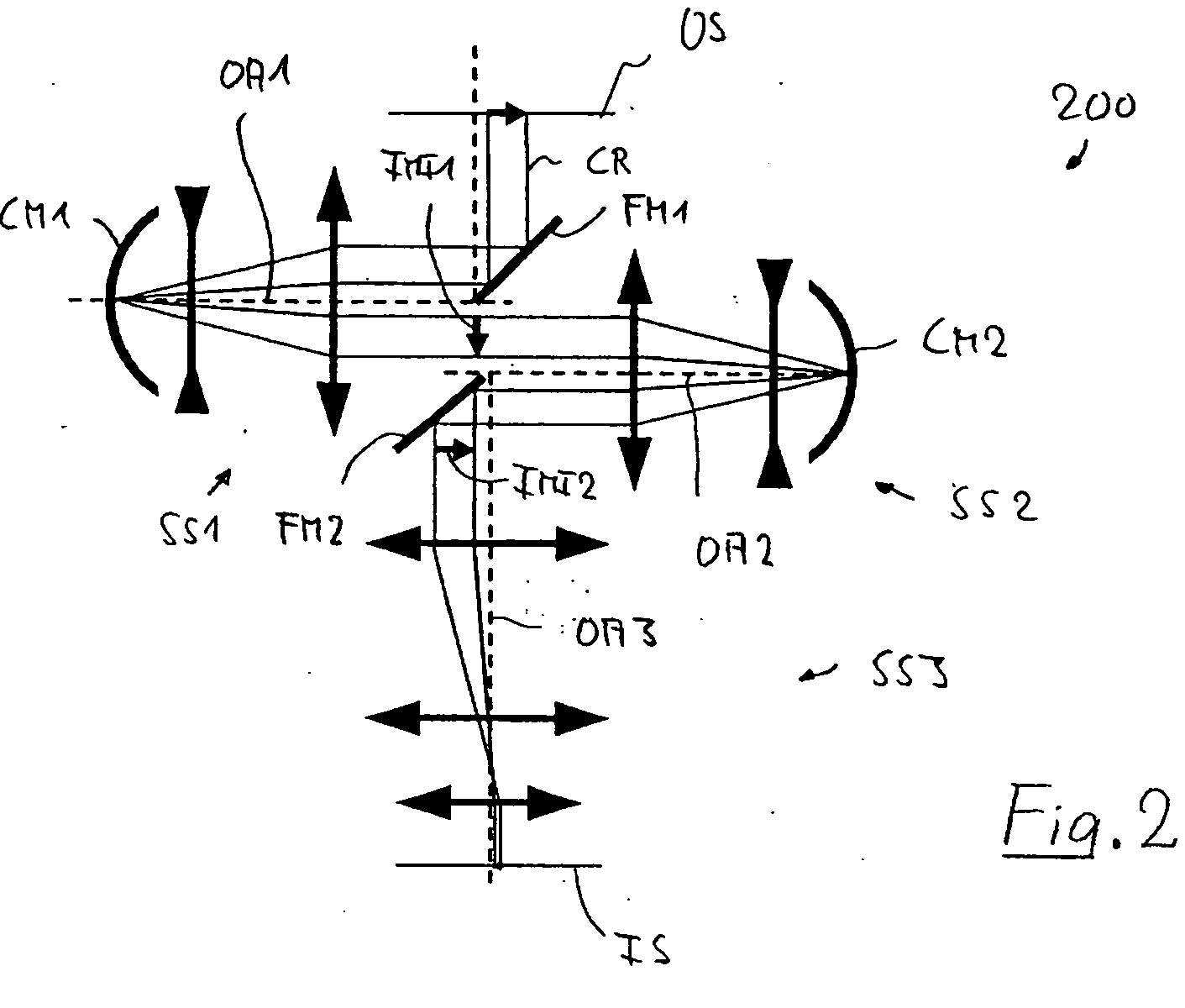
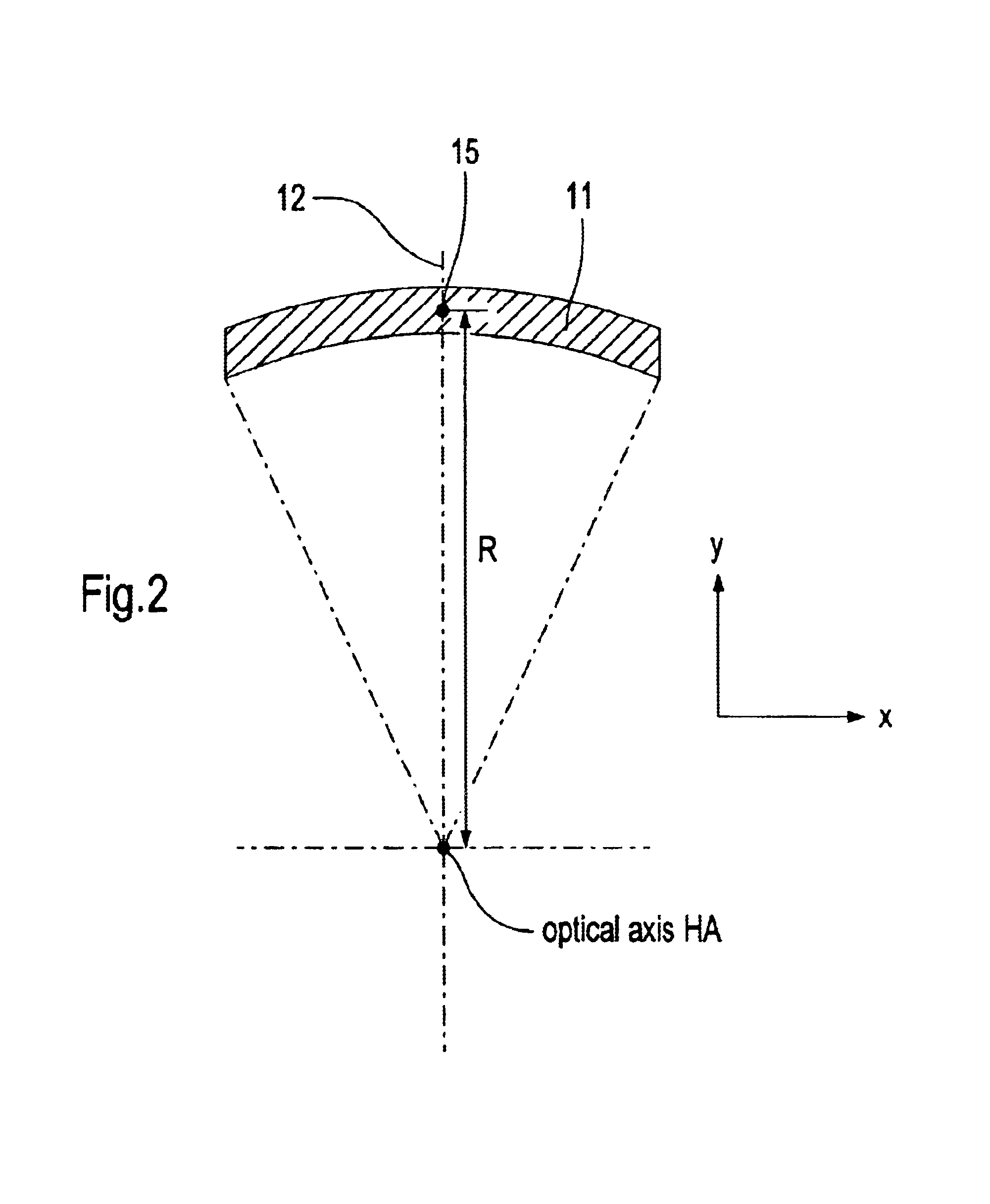
An imaging system for imaging an object field arranged in an object surface of the imaging system onto an image field arranged in an image surface of the optical system while creating at least one intermediate image including: a first imaging subsystem for creating the intermediate image from radiation coming from the object surface, the first imaging subsystem having a first optical axis; and a second imaging subsystem different in construction from the first imaging subsystem for imaging the intermediate image onto the image surface, the second imaging subsystem having a second optical axis; wherein the first optical axis is offset with respect to the second optical axis by an axis offset at the intermediate image and wherein the intermediate image has a correction status adapted to the axis-offset such that the correction status of the image field is essentially free from aberrations caused by the axis-offset.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Endoscope objective
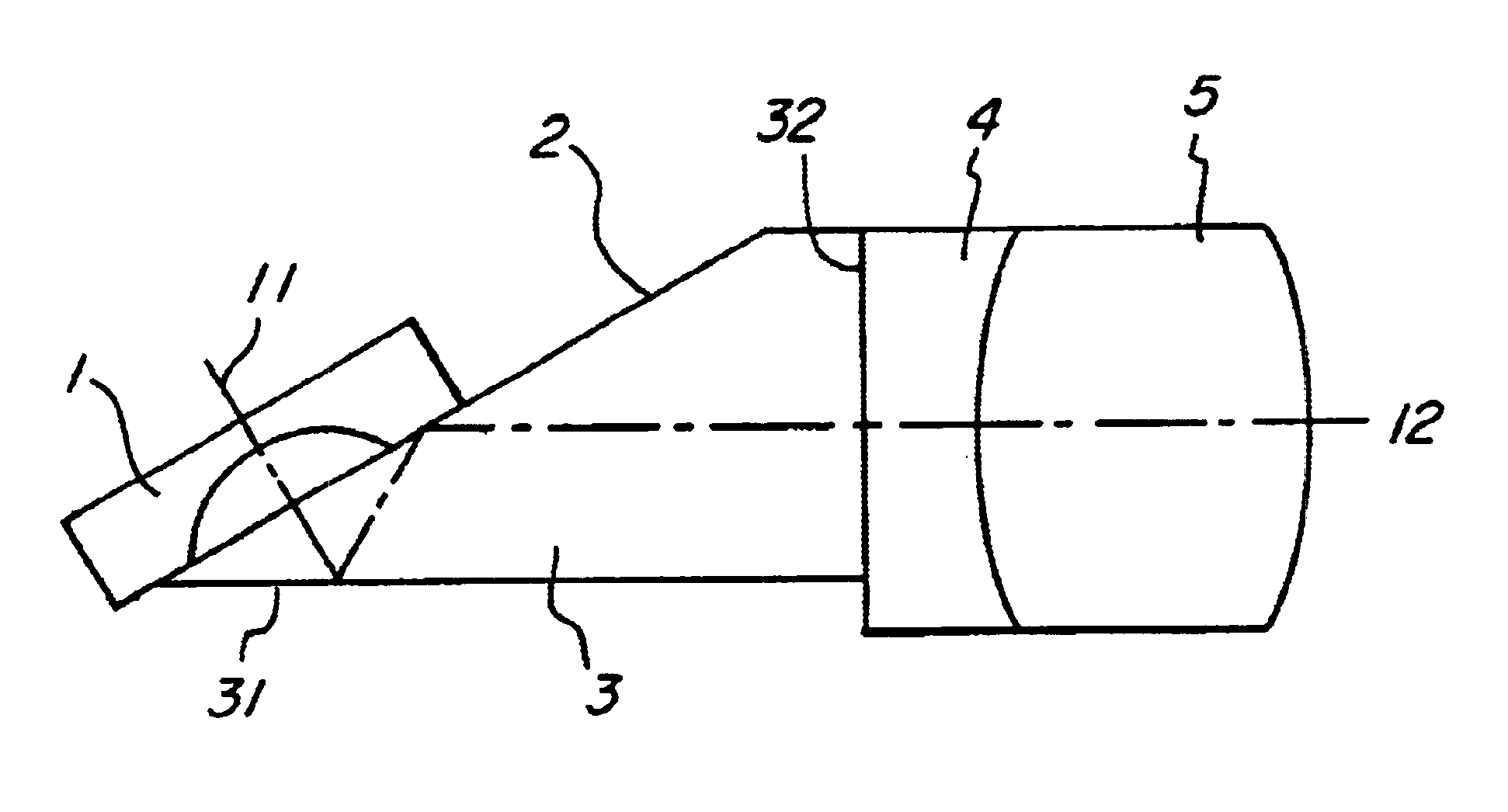
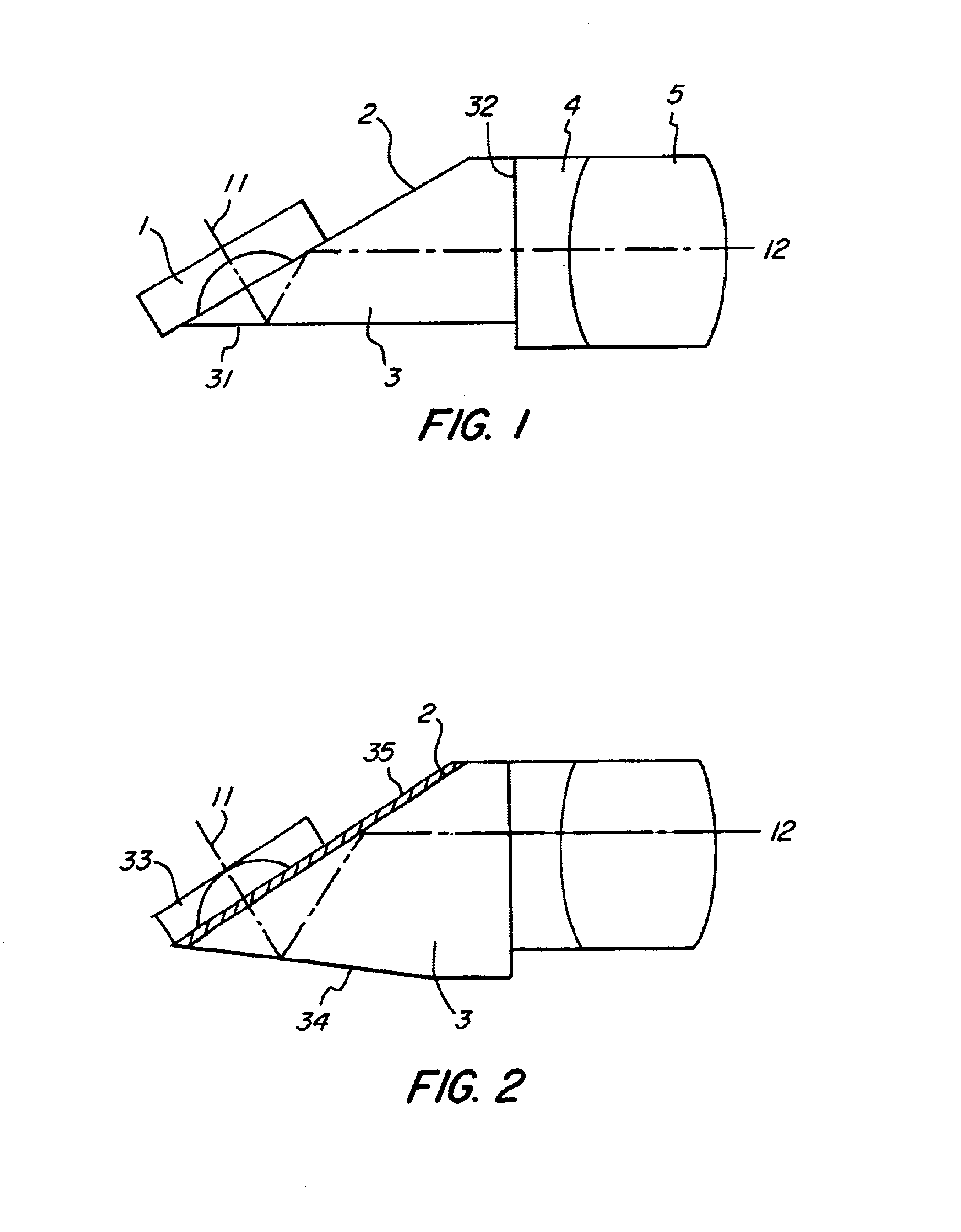
InactiveUS6635010B1Simple and low-cost techniqueSmall reflectionSurgeryEndoscopesGlass coverRefractive index
Endoscope objective having a viewing direction including an angle< >0° relative to the longitudinal axis of the endoscope, comprising a lens system imaging the object field into a single image plane disposed orthogonally on the longitudinal axis, and a prism unit disposed downstream of the distal window of the endoscope along the imaging path, in which the beam is reflected on two boundary surfaces such that the beam will be deflected in the prism unit from the desired viewing direction into the longitudinal axis of the endoscope, wherein a coating is applied on at least one surface on the prism unit, which comprises a thin layer having a refractive index smaller than the refractive index of the material which said prism unit is made of, so that total reflection against the layer occurs. The invention is characterized by the provision that the coating is applied to that surface of the prism unit which faces the glass cover of the endoscope.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
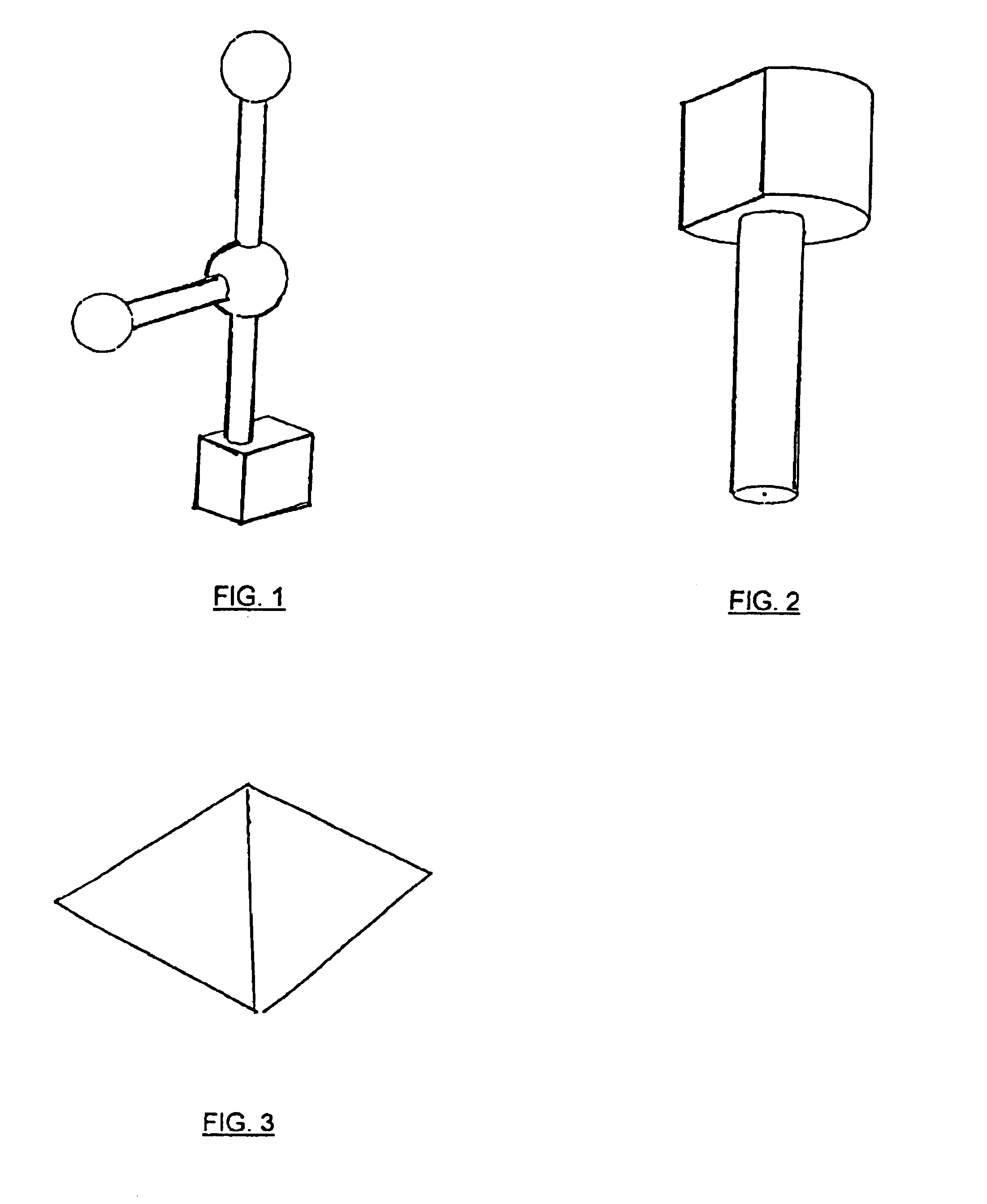
Method and system for three-dimensional modeling of object fields
InactiveUS6925198B2Definition of image is lowEnabling useImage enhancementImpression capsImage processing softwareDimensional modeling
A method and system for creating three-dimensional models of implant-bearing dental arches, and other anatomical fields of view, employs three-dimensional scanning means to capture images of an anatomical field of view wherein there have been positioned (and preferably affixed to an anatomical feature) one or more three-dimensional recognition objects having a known geometry, such as a pyramid or a linked grouping of spheres. Image processing software is employed to locate and orient said recognition objects as reference data for stitching multiple images and thereby reconstructing the scanned field of view. Recognition objects placed in areas of low feature definition enhance the accuracy of three-dimensional modeling of such areas.
Owner:ATLANTIS COMPONENTS
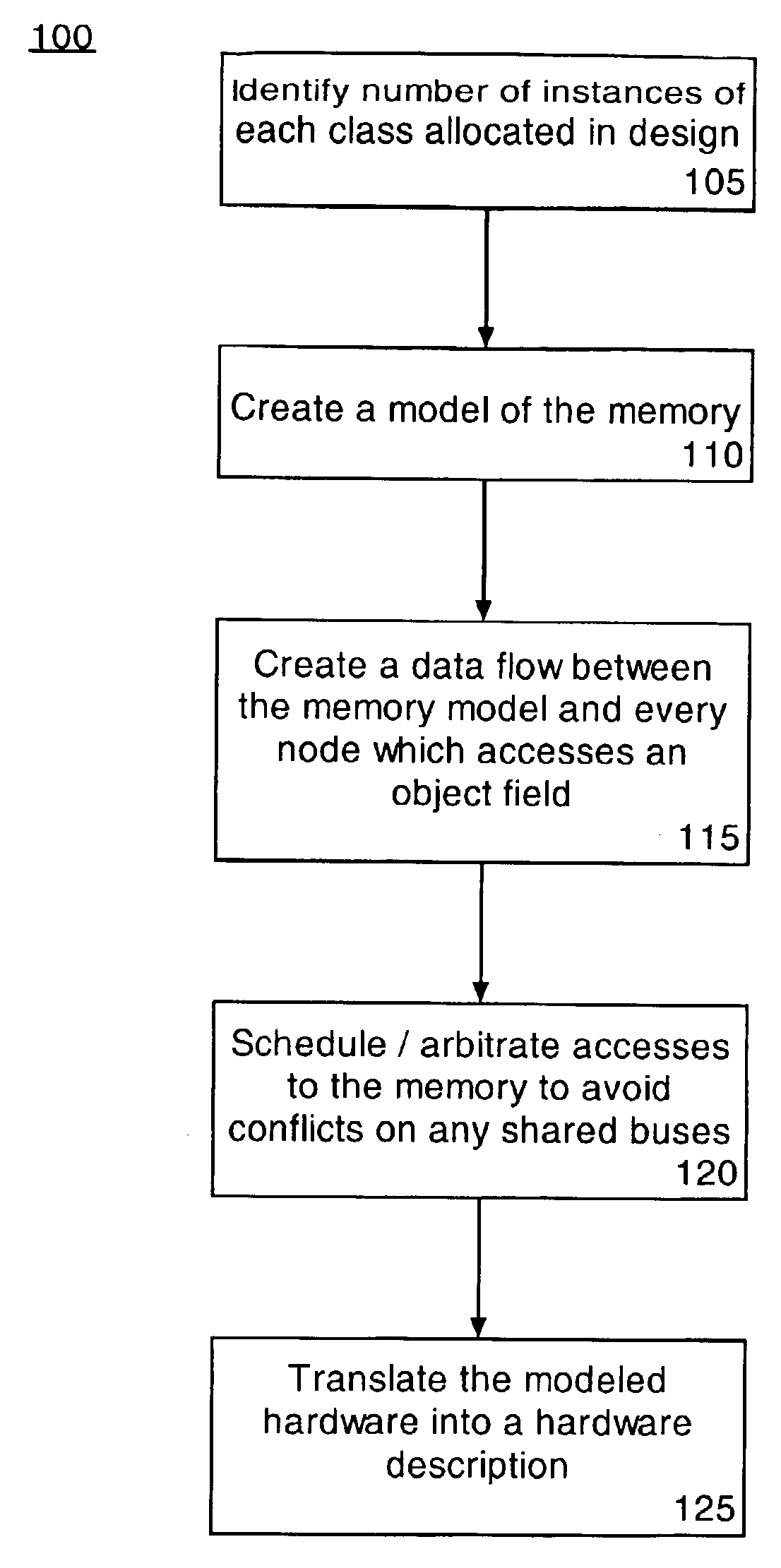
Method of transforming software language constructs to functional hardware equivalents
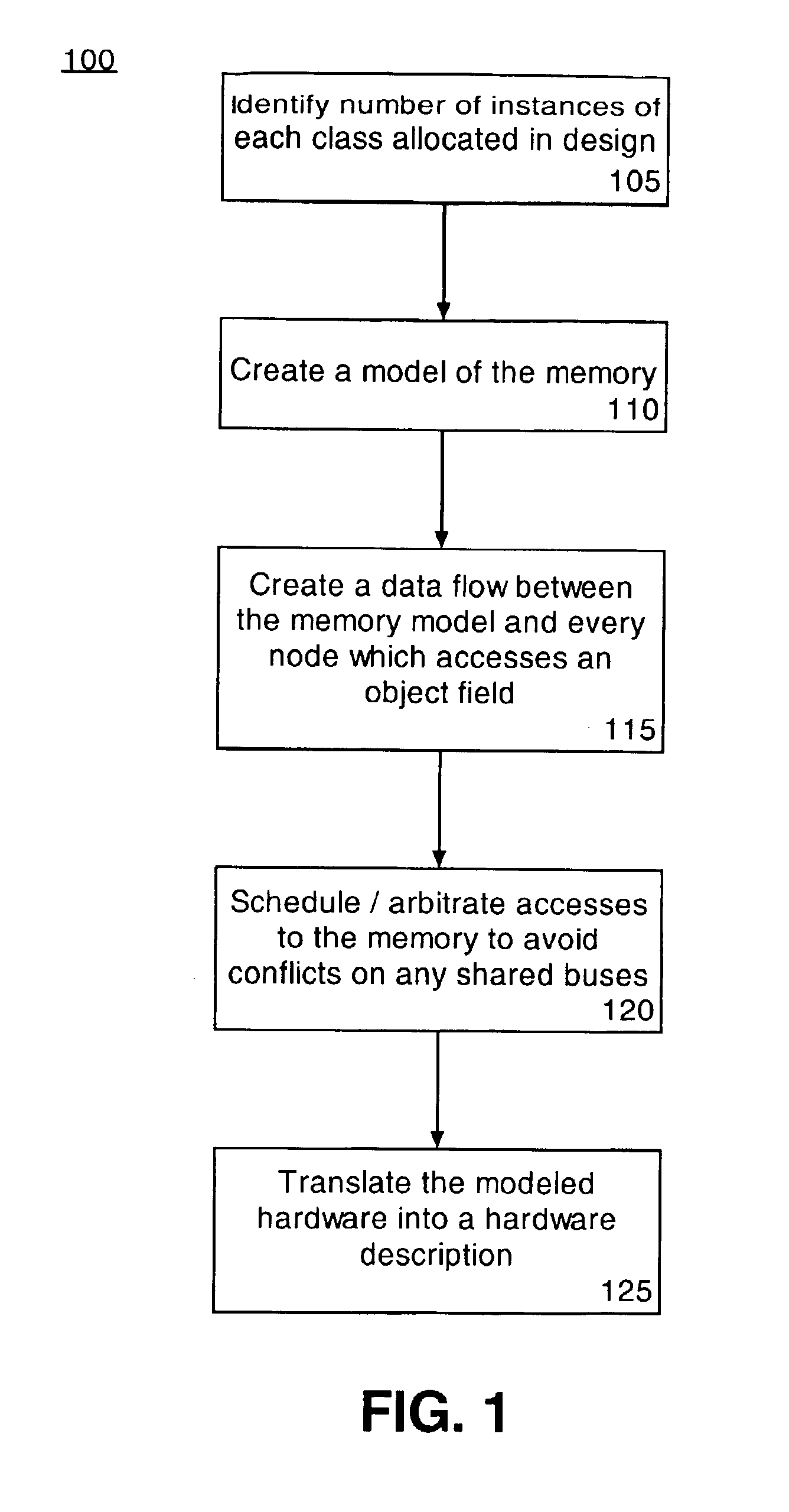
A method of designing an integrated circuit using a general purpose programming language can include identifying (105) a number of instances of each class allocated in a programmatic design implemented using the general purpose programming language and modeling (110) the global memory of the programmatic design. A data flow between the modeled global memory and instructions of the programmatic design which access object fields can be determined (115) and access to the modeled global memory can be scheduled (120). The programmatic design can be translated (125) into a hardware description of the integrated circuit using the modeled global memory, the data flow, and the scheduled memory access.
Owner:XILINX INC
Exoscope
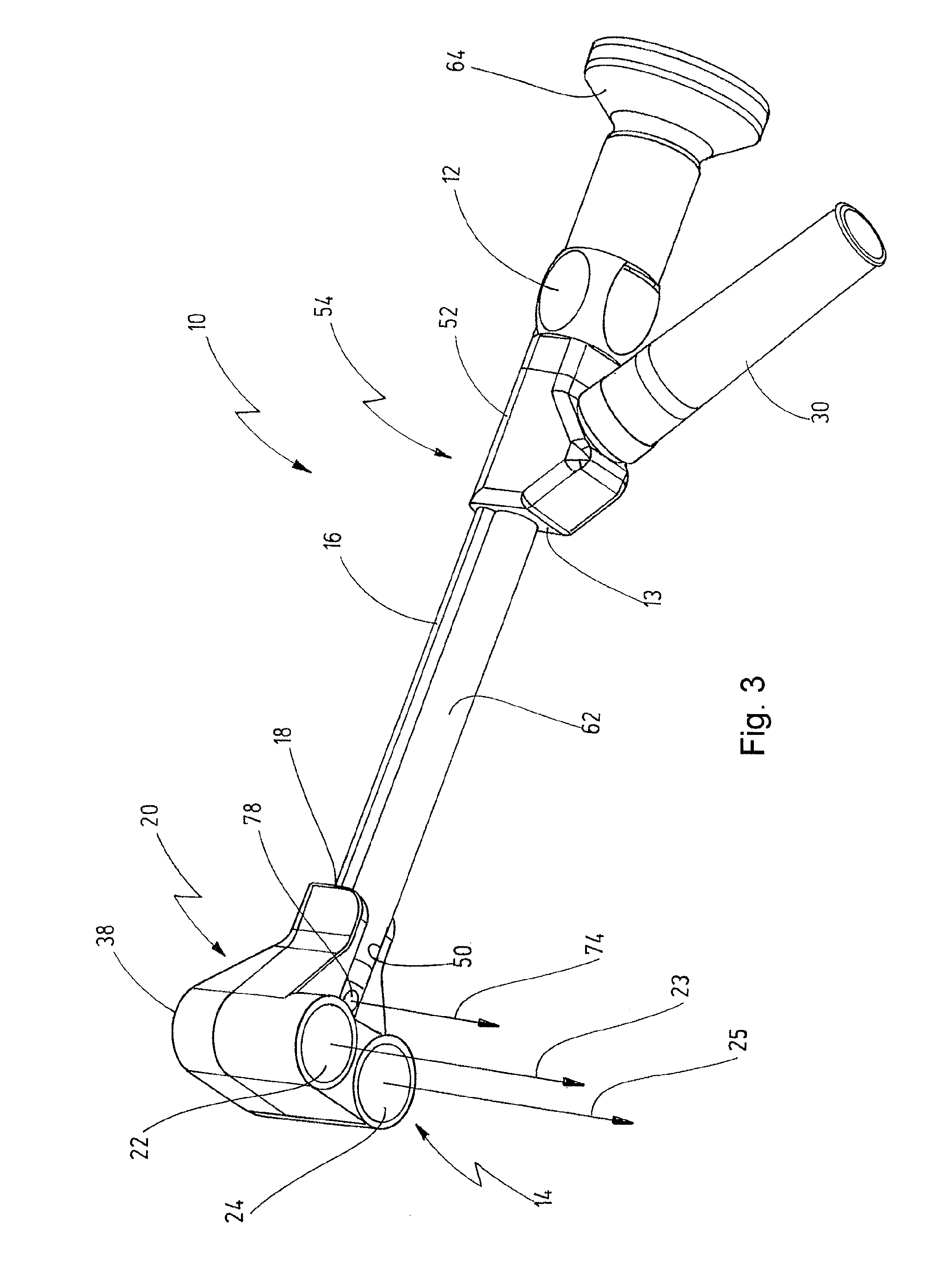
ActiveUS20120265023A1Strong and stable structureSufficient lightingEndoscopesSurgical field illuminationRadiation exposureObject field
An exoscope serves for observing and illuminating an object field on a patient from a position set apart from the patient's body. A lens system serves to observe the object field and an illumination serves to illuminate the object field. A distance between the lens system and the object field can be modified by a bracket. A shaft comprises on its distal end a head member that is widened in comparison to it, so that the illumination reaches into the distal-side head member. Positioned in the head member is at least one radiating illumination unit whose radiant characteristic can be adjusted in such a way that the object field can be illuminated homogeneously at all possible distances from the lens system. Supply lines for the at least one illuminating unit are positioned in the shaft.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
6-Mirror projection objective with few lenses
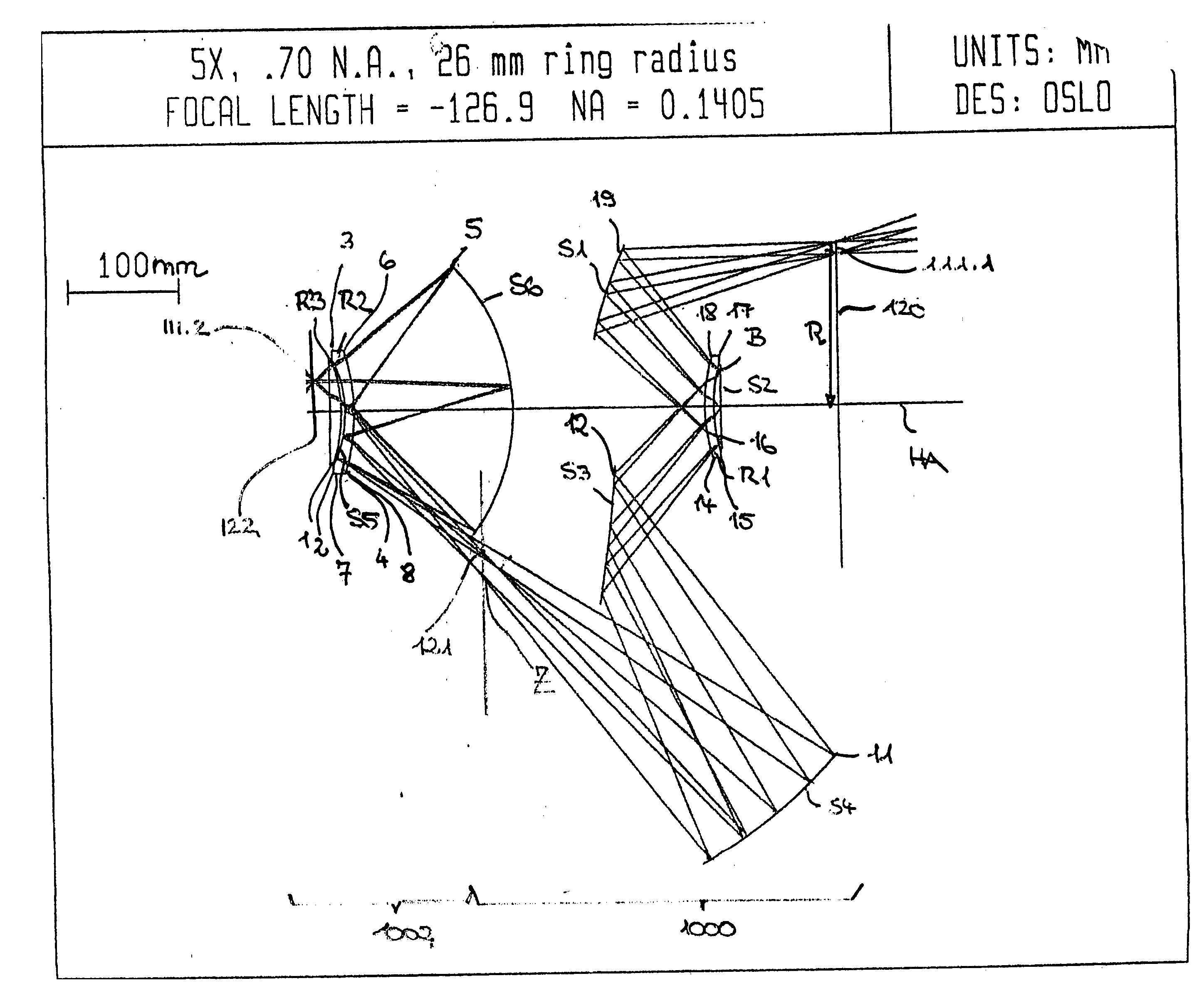
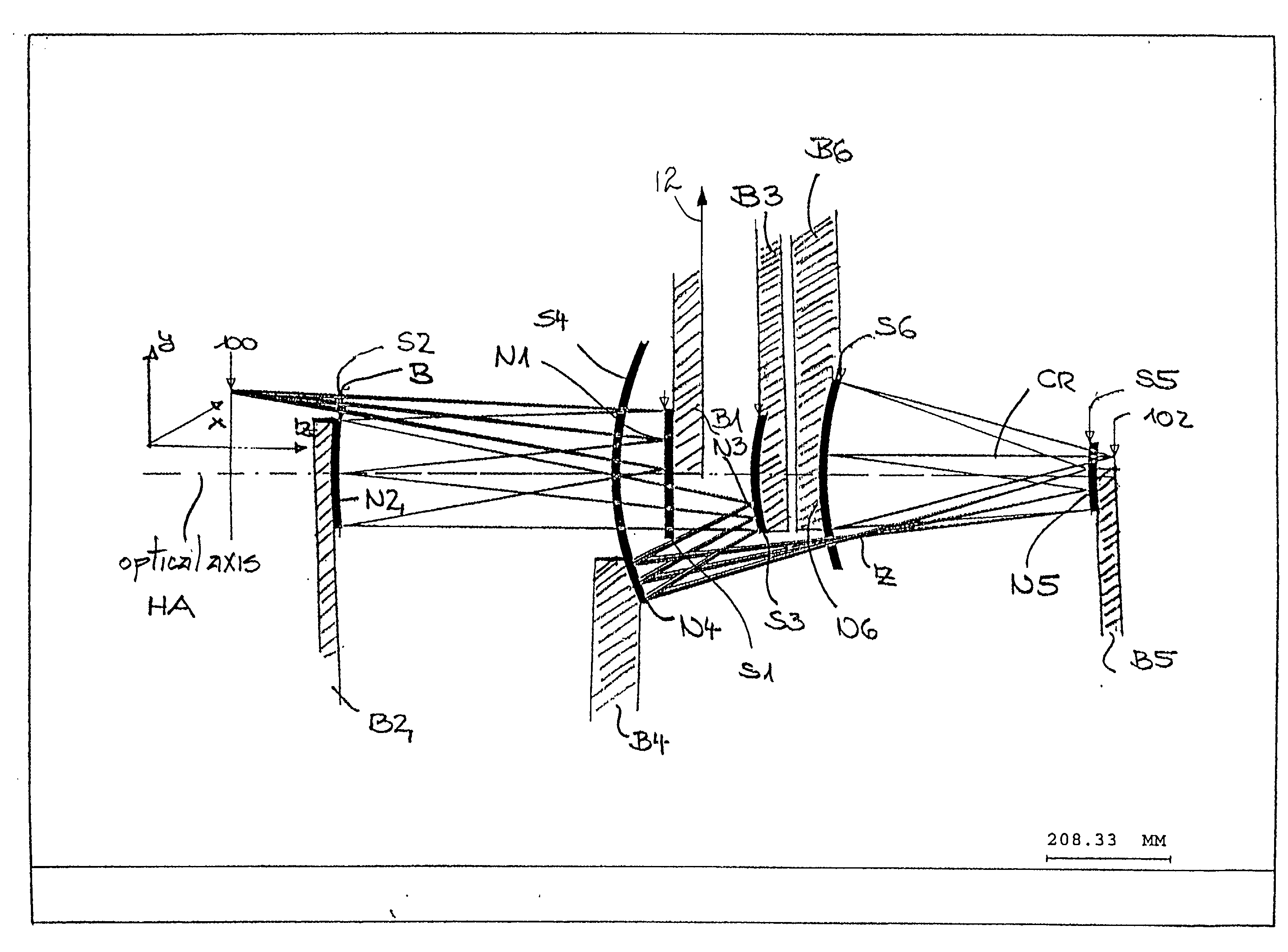
There is provided a projection objective for wavelengths of <=193 nm for imaging an object field in an object plane into an image field, in an image plane. The projection objective includes a first reflective optical element, a second reflective optical element, a third reflective optical element, a fourth reflective optical element, a fifth reflective optical element, and a sixth reflective optical element, and a refractive optical element. The reflective and refractive optical elements each have an off axis segment with a diameter. The projection objective has an image-side numerical aperture >=0.65, and the off axis segment of the refractive optical element has a diameter that is less than 1 / 3<rd >of the distance from the object plane to the image plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
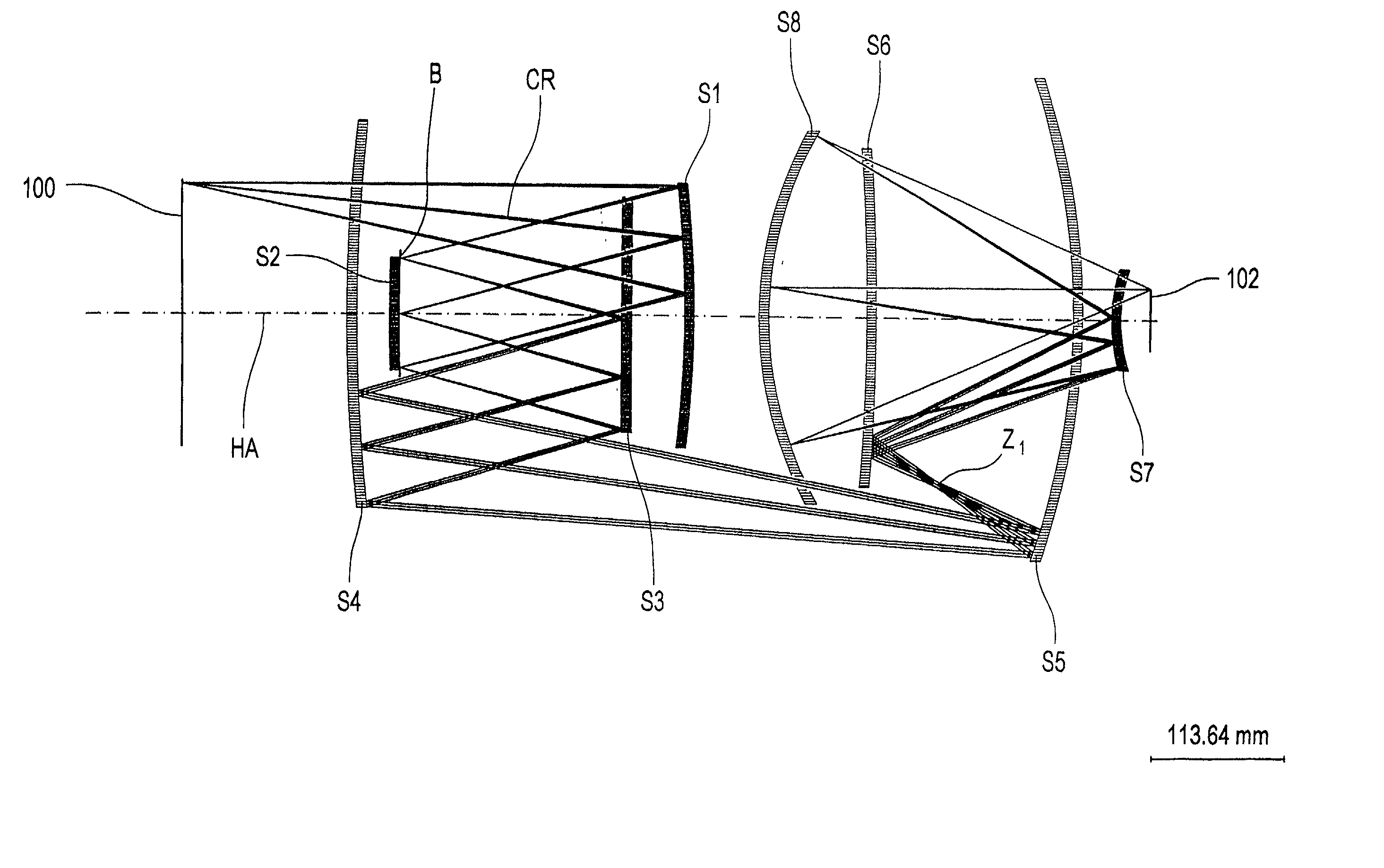
8-Mirror microlithography projection objective
A projection objective provides a light path for a light bundle from an object field in an object plane to an image field in an image plane. The projection objective comprises a first mirror (S1), a second mirror (S2), a third mirror (S3), a fourth mirror (S4), a fifth mirror (S5), a sixth mirror (S6), a seventh mirror (S7), and an eighth mirror (S8). The light path is provided via the eight mirrors, the light bundle includes light with a wavelength in the range of 10-30 nm, and the light path is free of shading.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060138349A1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisObject field
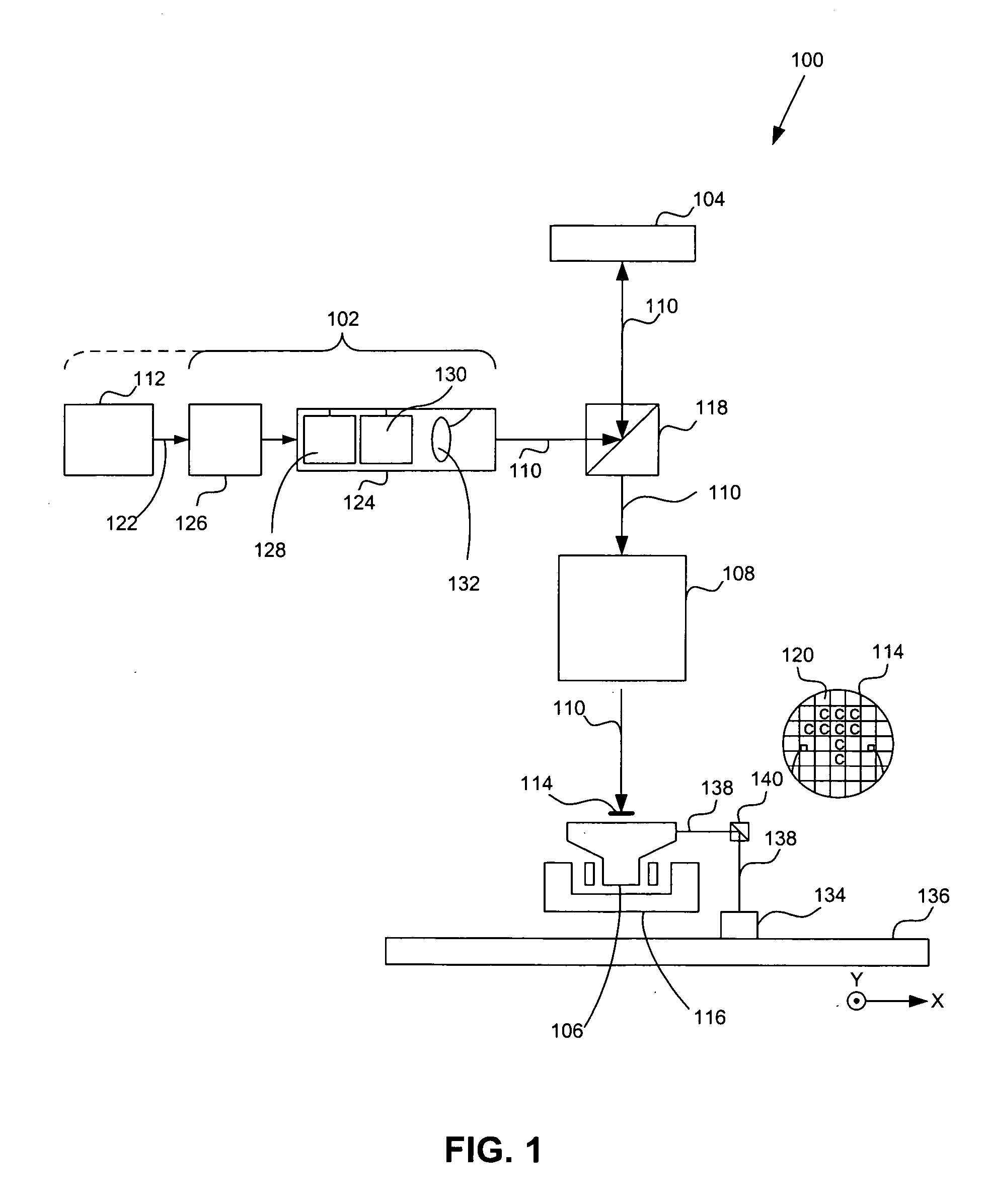
A system and method are used to direct a radiation beam to illuminate non-perpendicularly a patterning array of individually controllable elements used for patterning the radiation beam. The individually controllable elements can change a telecentricity of the radiation beam. Projection of the radiation beam onto the individually controllable elements can be by a concave mirror or use a folding mirror placed in an object field of the individually controllable elements. Alternatively, the individually controllable elements can change the optical axis of the radiation beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV +1
6-mirror microlithography projection objective
InactiveUS20020056815A1Increase the number ofMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusExit pupilAxis of symmetry
The invention regards to a microlithography projection objective for short wavelengths, preferably <=193 nm, with an entrance pupil and an exit pupil for the imaging of an object field in an image field, which represents a segment of a ring field, wherein the segment has an axis of symmetry and an extension perpendicular to the axis of symmetry, and the extension is at least 20, and preferably 25 mm. The microlithography projection objective comprises a first (S1), a second (S2), a third (S3), a fourth (S4), a fifth (S5), and a sixth mirror (S6) in centered arrangement relative to an optical axis, whereby each of these mirrors has a off-axis segment, in which light beams impinge, which have been guided through the projection objective. whereby as a function of the numerical aperture NA of the exit pupil, the diameter of the off-axis segment of the first, second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth mirrors is <=1200 mm*NA.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
EUV Exposure Apparatus
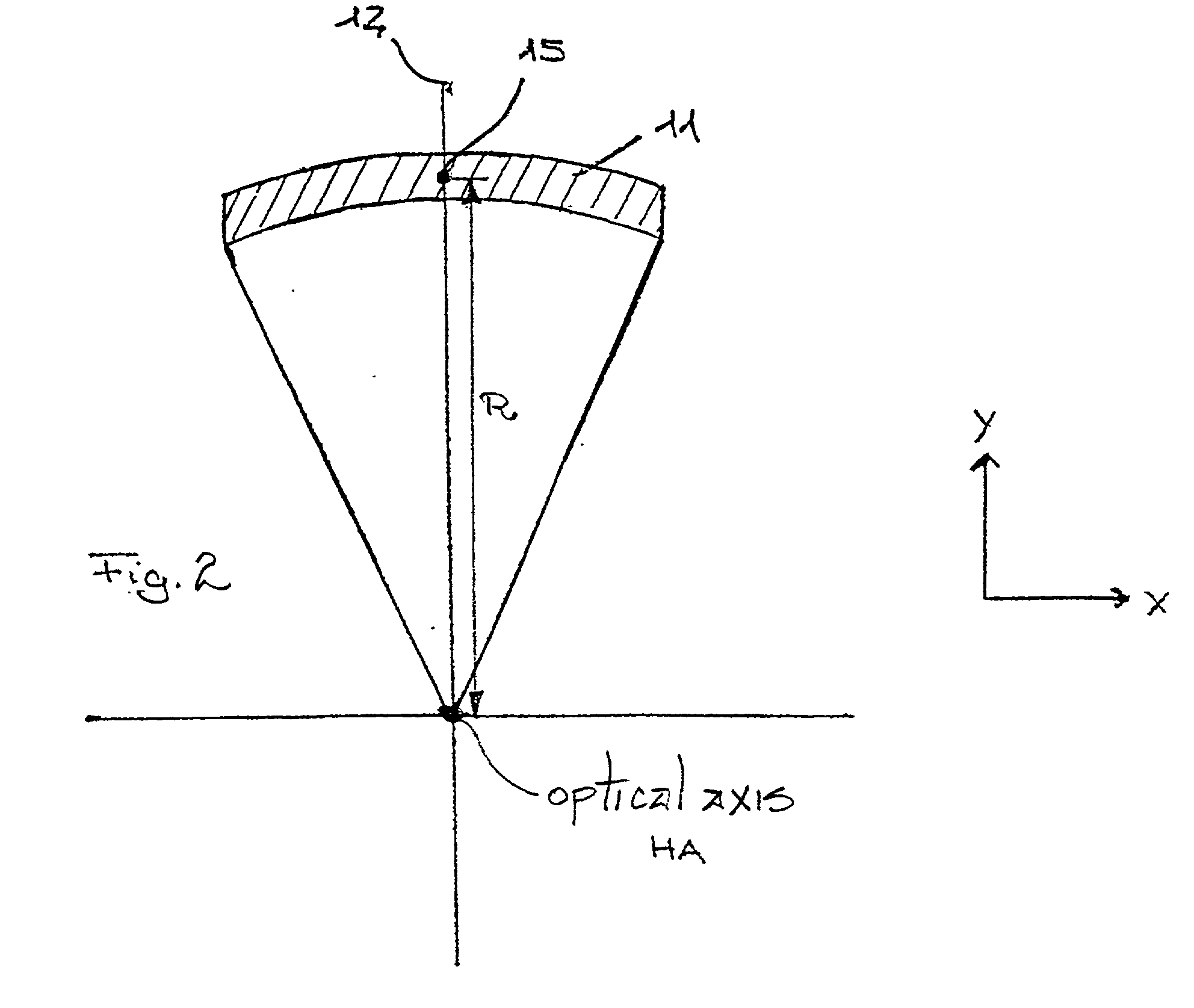
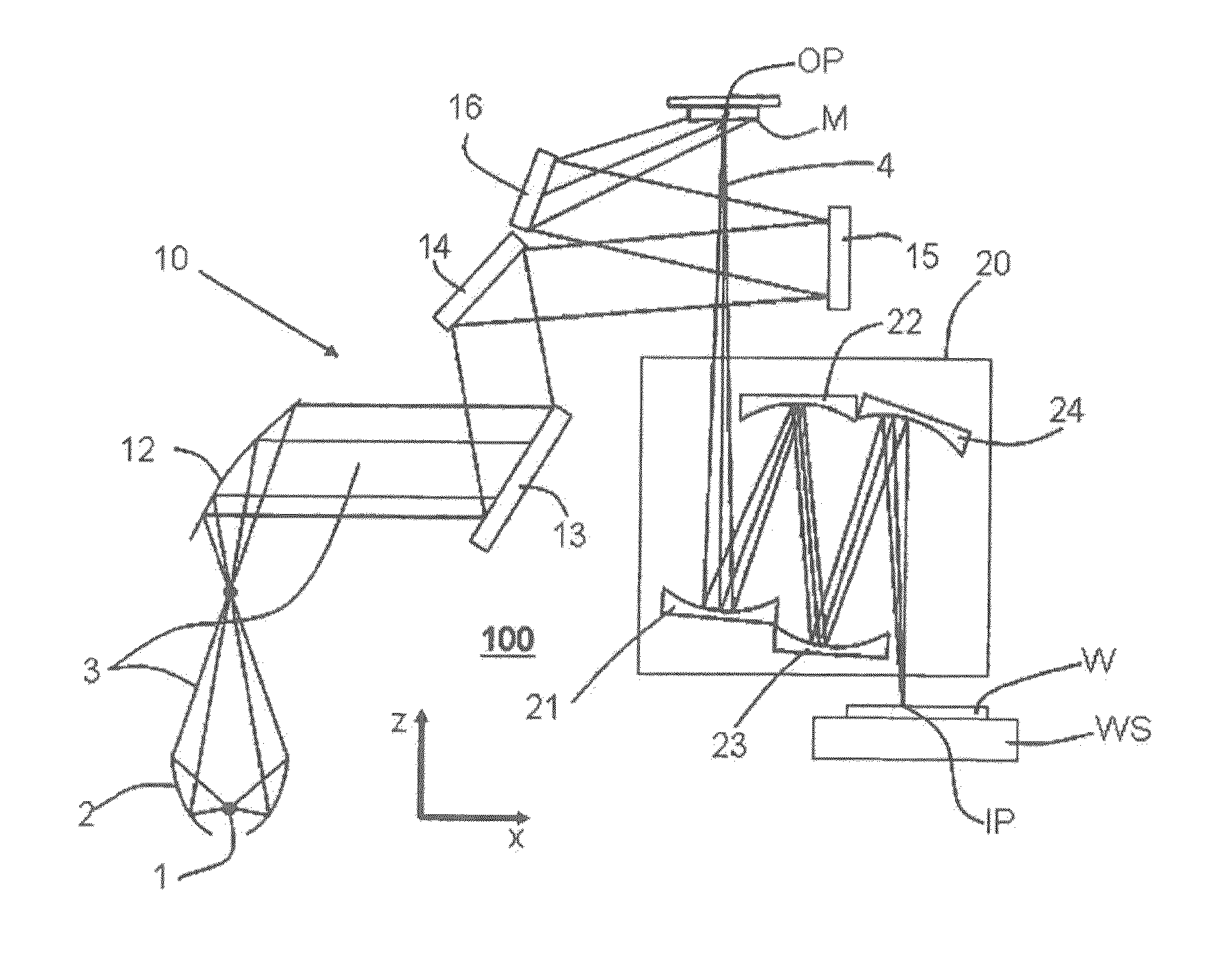
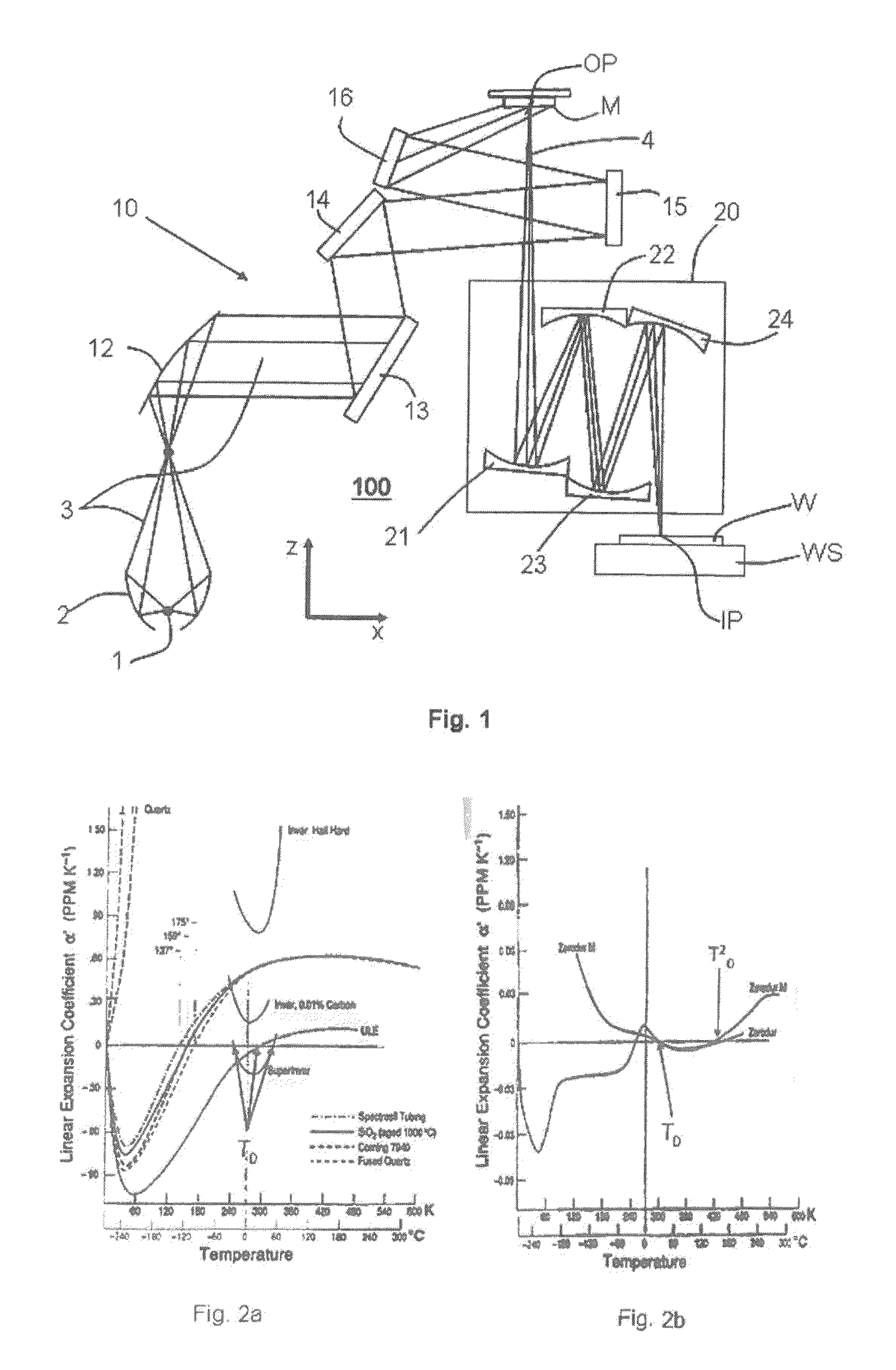
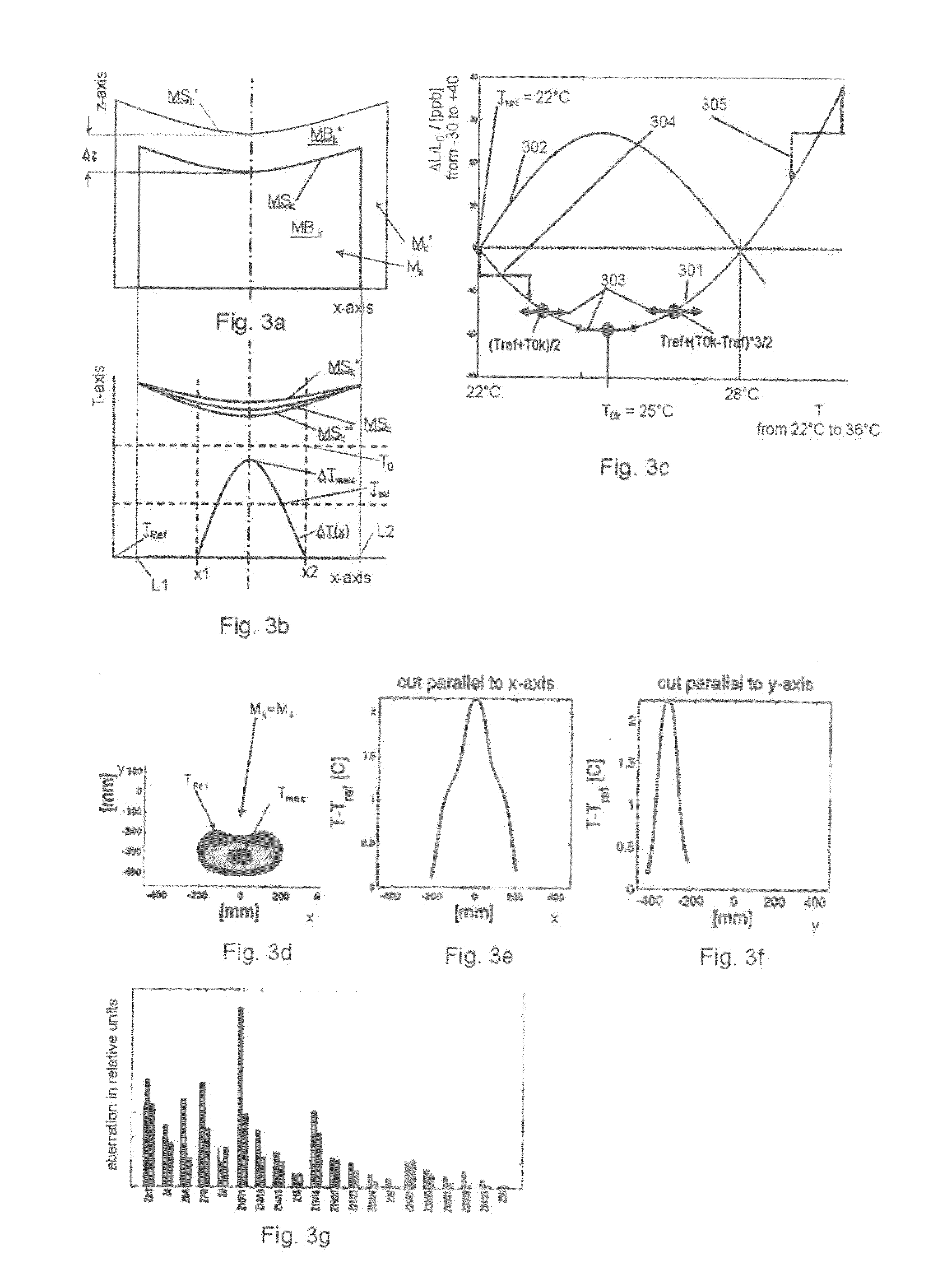
ActiveUS20130141707A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingThermal expansionProjection lens
A projection lens of an EUV-lithographic projection exposure system with at least two reflective optical elements each comprising a body and a reflective surface for projecting an object field on a reticle onto an image field on a substrate if the projection lens is exposed with an exposure power of EUV light, wherein the bodies of at least two reflective optical elements comprise a material with a temperature dependent coefficient of thermal expansion which is zero at respective zero cross temperatures, and wherein the absolute value of the difference between the zero cross temperatures is more than 6K.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
6-mirror projection objective with few lenses
InactiveUS6912042B2Easy to installEasy alignmentPhotomechanical apparatusMicroscopesLength waveNumerical aperture
There is provided a projection objective for wavelengths of ≦193 nm for imaging an object field in an object plane into an image field, in an image plane. The projection objective includes a first reflective optical element, a second reflective optical element, a third reflective optical element, a fourth reflective optical element, a fifth reflective optical element, and a sixth reflective optical element, and at least one refractive optical element. The refractive optical elements has a used area with a diameter. The projection objective has an image-side numerical aperture ≧0.65, and the used area of the refractive optical element has a diameter that is less than ⅓rd of the distance from the object plane to the image plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Exoscope
ActiveUS8702602B2Strong and stable structureSufficient lightingEndoscopesSurgical field illuminationFluenceObject field
An exoscope serves for observing and illuminating an object field on a patient from a position set apart from the patient's body. A lens system serves to observe the object field and an illumination serves to illuminate the object field. A distance between the lens system and the object field can be modified by a bracket. A shaft comprises on its distal end a head member that is widened in comparison to it, so that the illumination reaches into the distal-side head member. Positioned in the head member is at least one radiating illumination unit whose radiant characteristic can be adjusted in such a way that the object field can be illuminated homogeneously at all possible distances from the lens system. Supply lines for the at least one illuminating unit are positioned in the shaft.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
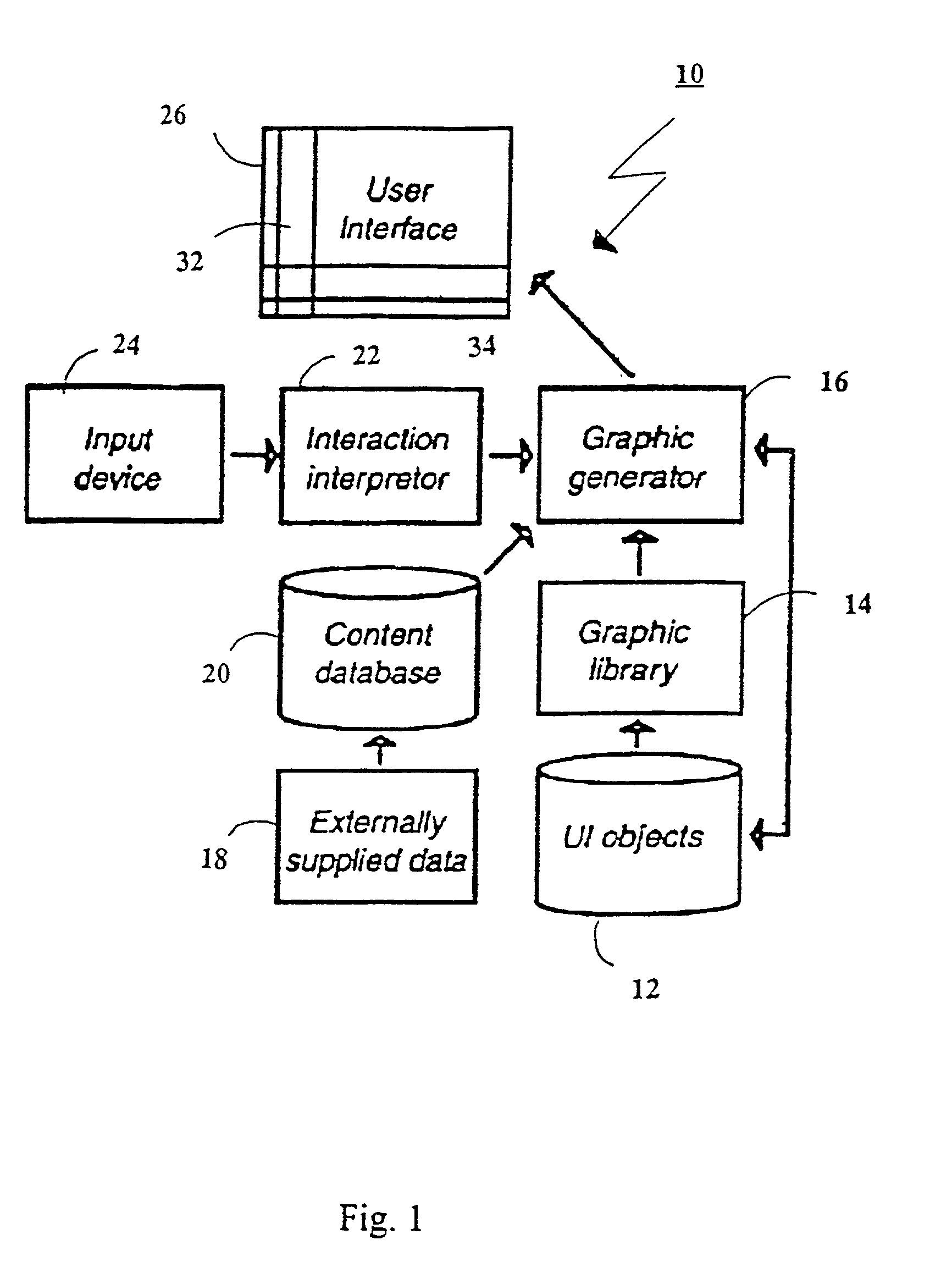
System and method for building wireless applications with intelligent mapping between user interface and data components
ActiveUS8108830B2Drive down the complexity involvedReduce resource utilizationDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsWireless Application ProtocolPresentation Manager
A system and method for generating a screen element, based on a data object, of a component application is disclosed. The component application includes a data component having a data field definition and a screen component having a screen element definition. A mapping manager identifies a mapping present in the screen component. The mapping specifies dynamic relationships between the screen component and the data component by an identifier, and for selecting the data component mapped by the mapping according to the mapping identifier. The mapping manager maintains dynamic integrity and automatically synchronizes changes between the screen component and the corresponding data component. A data manager obtains a data object field value corresponding to the data field definition of the mapped data component; and a presentation manager generates a screen element from the screen element definition to include the data object field value.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Display system having a three-dimensional convex display surface
ActiveUS7352340B2Television system detailsBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A display system has a display surface having a three-dimensional convex shape. A projection system projects an object field onto a continuous image field located on the interior of the display surface the display surface is extensive in its coverage, for example subtending an angle of at least 240 degrees to provide greater hemispherical coverage.
Owner:GLOBAL IMAGINATION
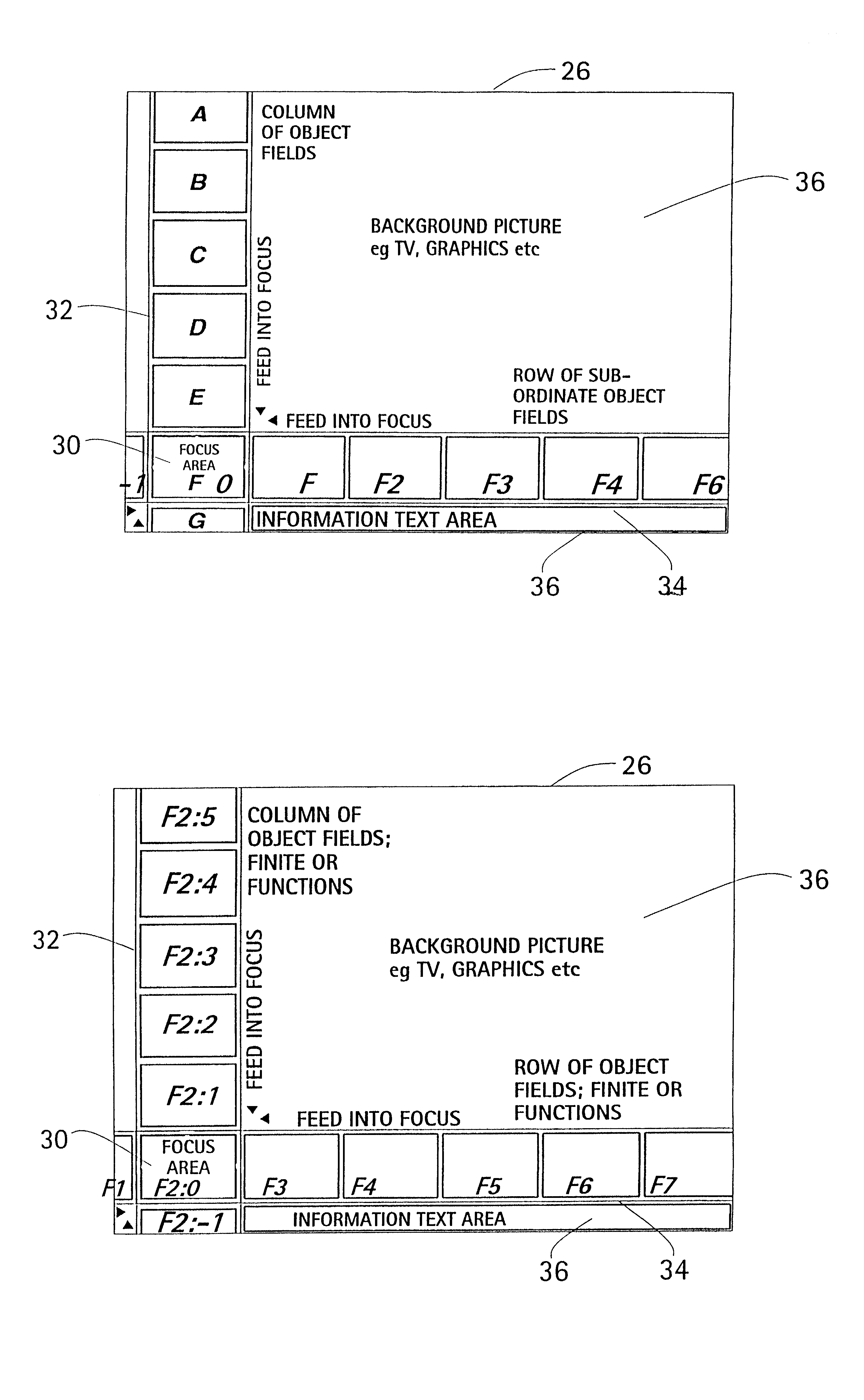
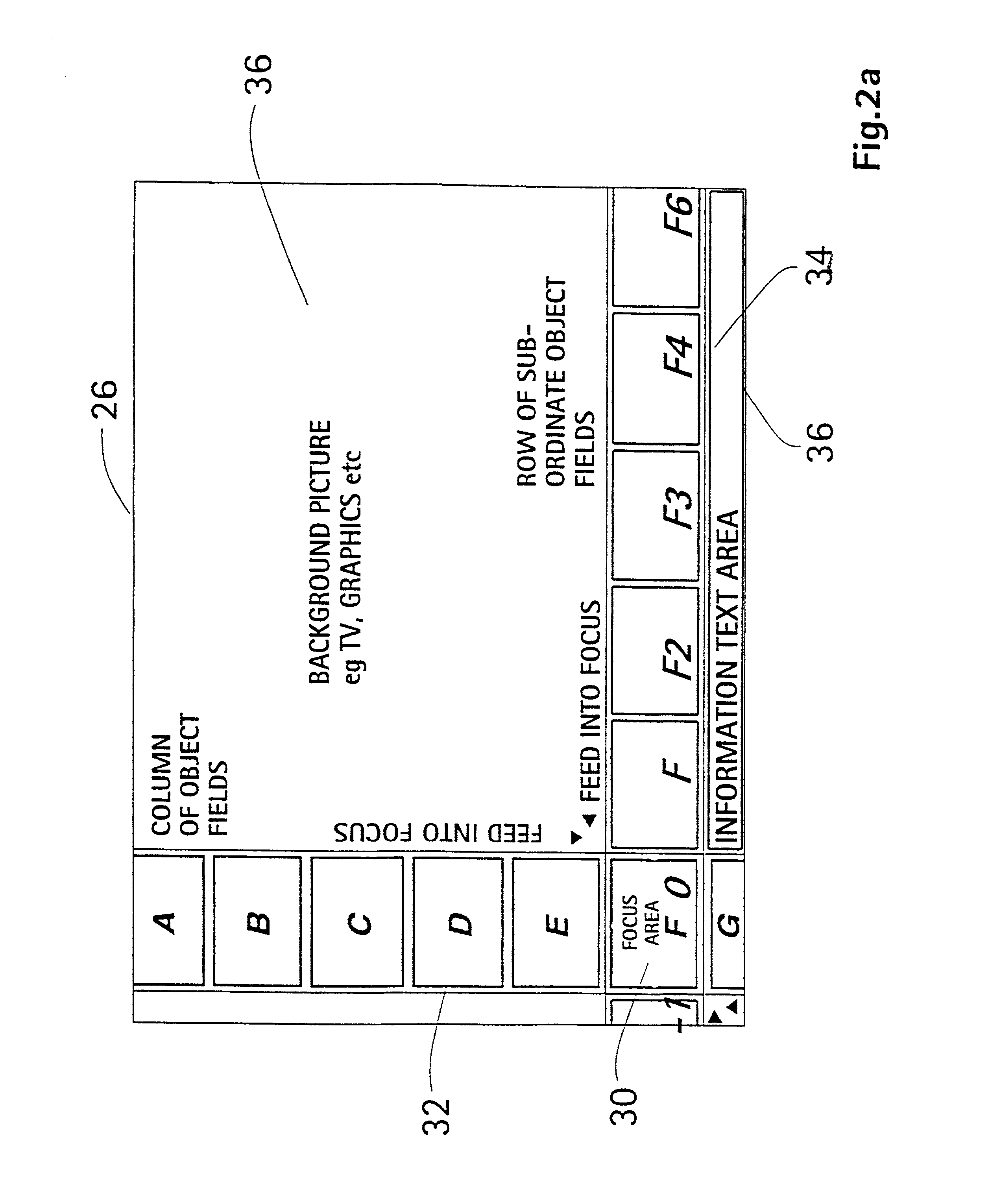
Method and an arrangement for scrollable cross point navigation in a user interface
InactiveUS7293241B1Data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingHuman–computer interactionUser interface
The invention relates to a method and an arrangement for scrollable cross point navigation on a user interface in order to select a feature by combining object fields. Bars, where at least one of them is scrollable, have object fields which overlap and combine each other when scrolled or put to a visible focus area in the user interface at the cross point of the bars. Object fields in the focus area select a feature connected to a combination of fields, which is chosen by a confirmation action.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
6-mirror microlithography projection objective
InactiveUS6867913B2Improve accessibilitySmall dimensionMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusExit pupilAxis of symmetry
There is provided a microlithography projection objective for short wavelengths, with an entrance pupil and an exit pupil for imaging an object field in an image field, which represents a segment of a ring field, in which the segment has an axis of symmetry and an extension perpendicular to the axis of symmetry and the extension is at least 20 mm. The objective comprises a first (S1), a second (S2), a third (S3), a fourth (S4), a fifth (S5) and a sixth mirror (S6) in centered arrangement relative to an optical axis. Each of these mirrors have an off-axis segment, in which the light beams traveling through the projection objective impinge. The diameter of the off-axis segment of the first, second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth mirrors as a function of the numerical aperture NA of the objective at the exit pupil is ≦1200 mm * NA.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Monitoring system for monitoring the progress of neurological diseases
ActiveUS7494464B2Optimize treatment planImprove monitoring qualitySurgeryEndoscopesNervous systemImaging processing
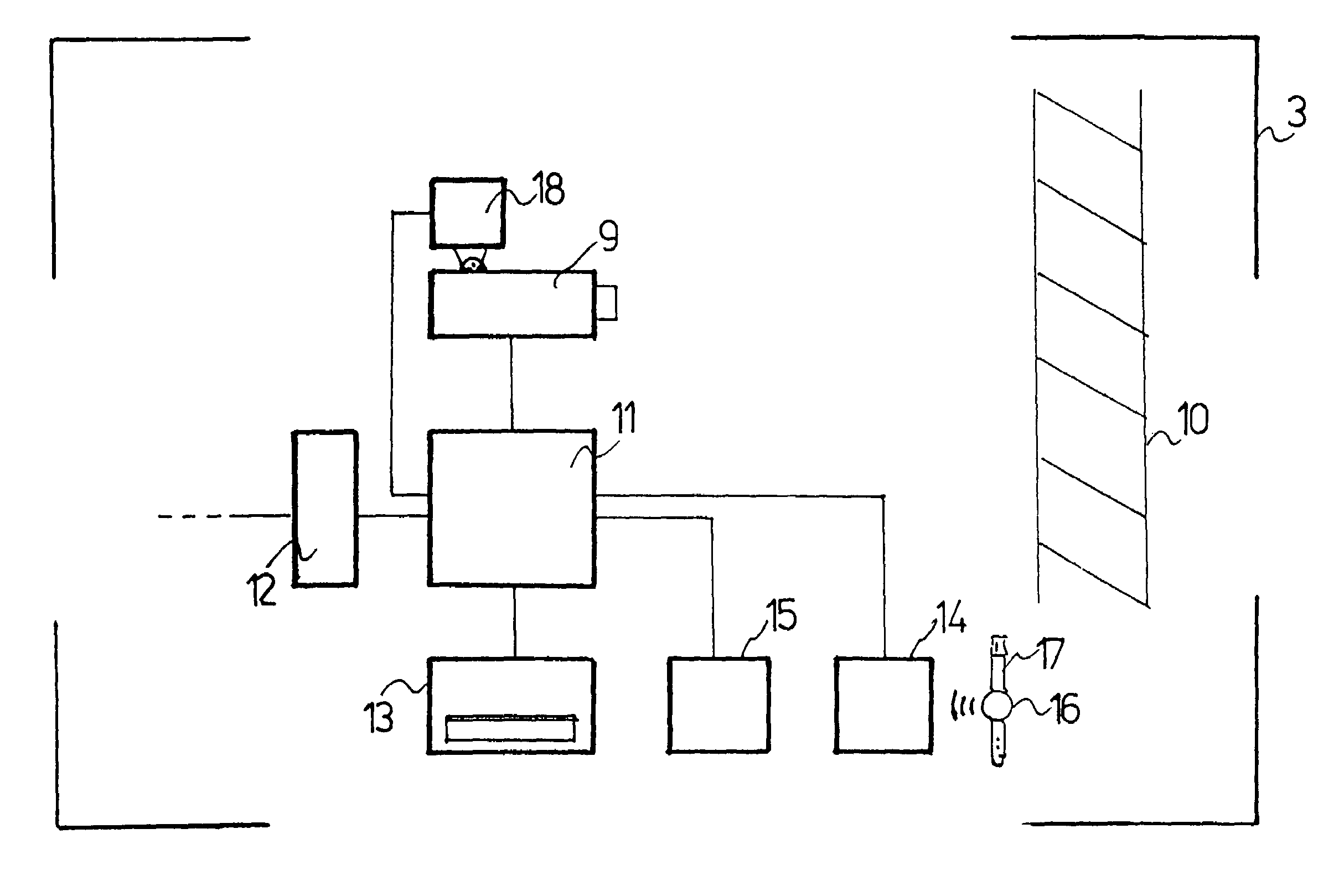
The invention concerns a monitoring system for monitoring patients with disturbed motor function. The monitoring system is characterized by at least one observation station (3) with an electronic camera for recording video motion pictures and devices (10) for marking an object field to be covered by the camera (9), a storage device for the digital storage of video pictures of a patient, which are to be recorded at preselected intervals by the camera in the movement station, an image processing system for processing the video pictures recorded in time intervals to obtain a shortened video picture sequence, and a video display device for displaying the video picture sequence.
Owner:RZESNITZEK ALEXANDER +2
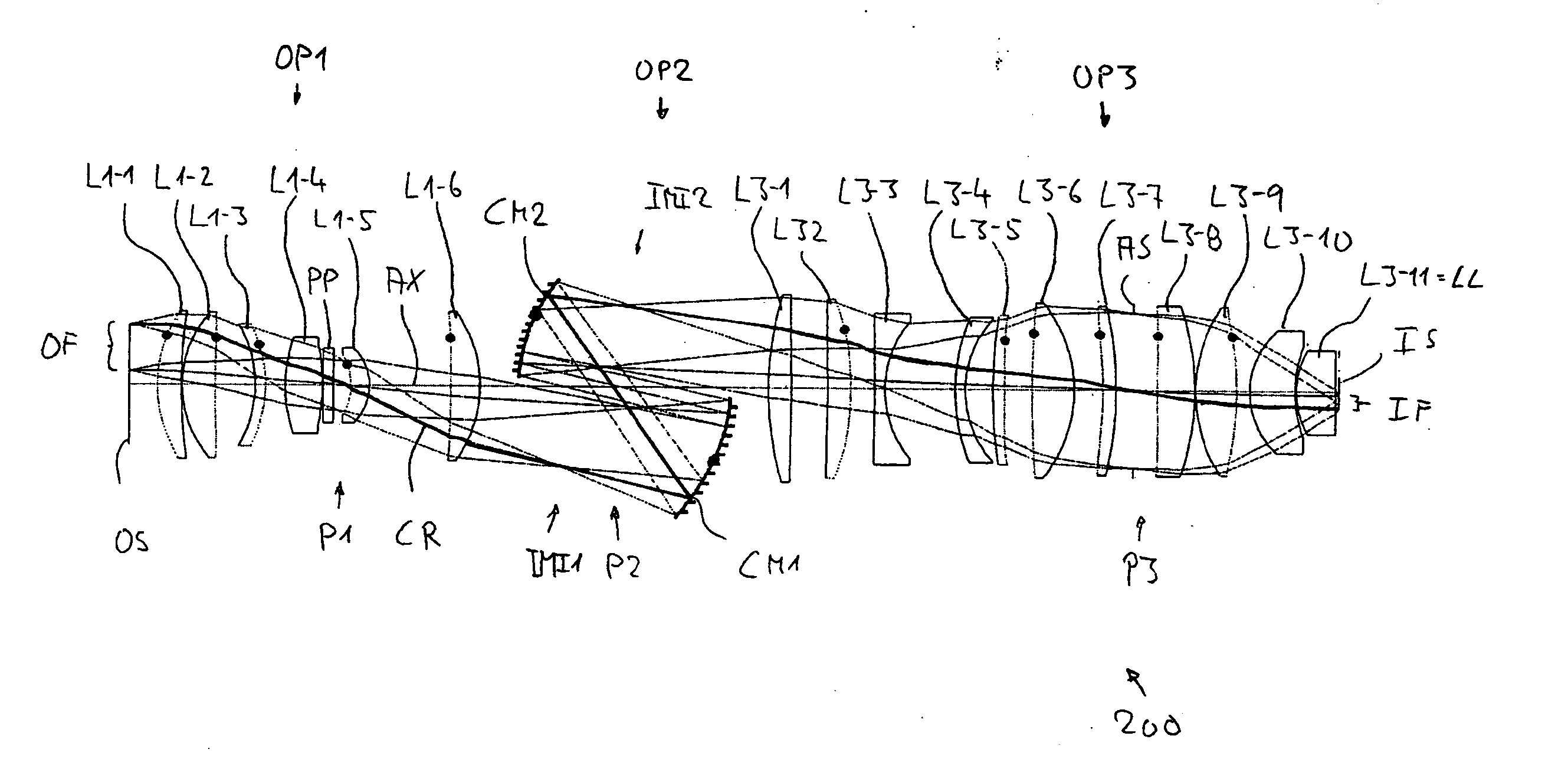
Catadioptric Projection Objective
InactiveUS20080037111A1Simple designEasy to correctMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageImage plane
A catadioptric projection objective for projecting a pattern arranged in the object plane of the projection objective into the image plane of the projection objective, having: a first objective part for projecting an object field lying in the object plane into a first real intermediate image; a second objective part for generating a second real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the first objective part; a third objective part for generating a third real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the second objective part; and a fourth objective part for projecting the third real intermediate image into the image plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
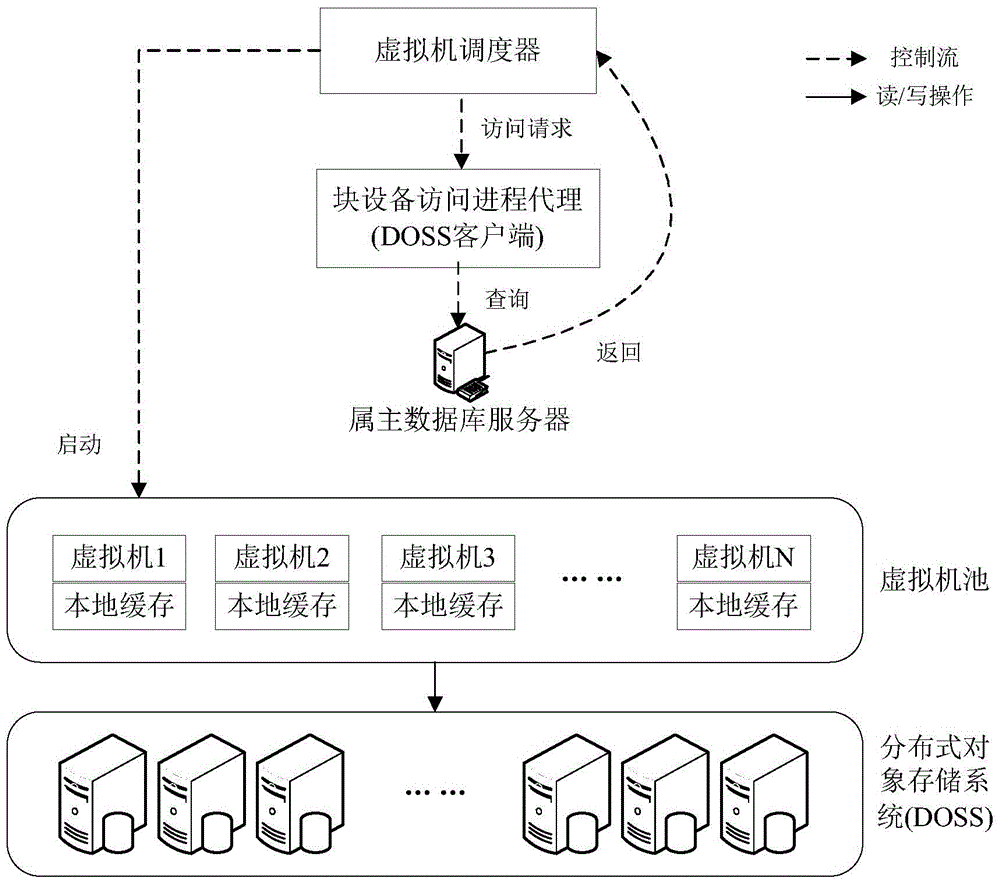
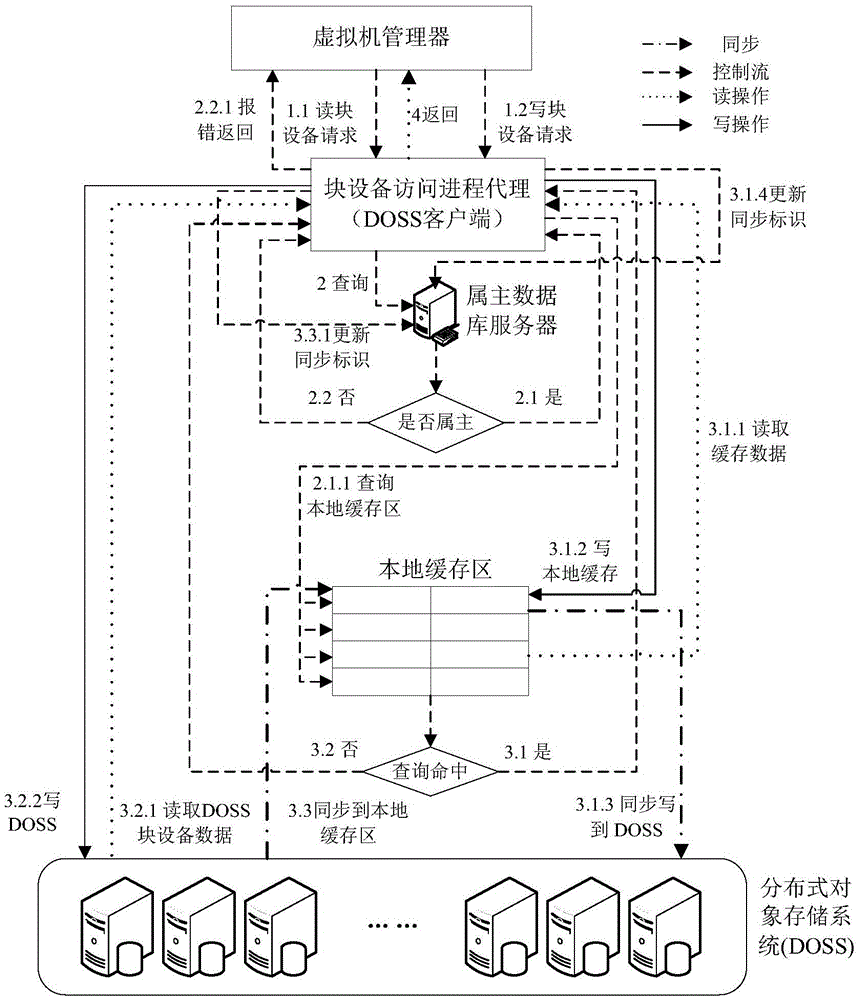
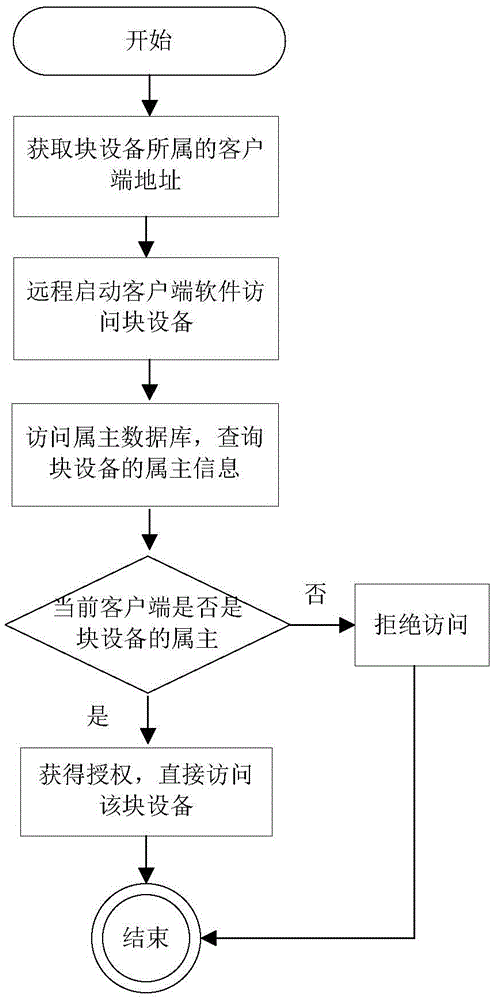
Method for multiple virtual machines to access distributed object storage system
ActiveCN105549905AIncrease I/O transfer bandwidthImprove response speedInput/output to record carriersSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAccess timeDistributed object
The invention relates to a method for accessing a distributed object storage system through a mode of designing a local cache in a client under the architecture of the distributed object storage system. The method comprises a reading operation: when reading the object file data of the distributed object storage system, firstly, searching an object file in the local cache of the client, if the object file is not searched in the local cache, reading the object file from the distributed object storage system, storing in the local cache system of the client, if the object file is searched in the cache, not reading the object file from the distributed object storage system; writing operation: when writing object field data in the distributed object storage system, firstly writing the object file data in a local cache, after finishing writing, marking that the object file is not synchronized, returning, and then writing the object file data written in the local cache in the distributed object storage system by a cache synchronous service module. Through the invention, the number of access times to the distributed object storage system can be reduced; the I / O throughput of accessing the file system by the virtual machine is improved; and the response time of an access request is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +1
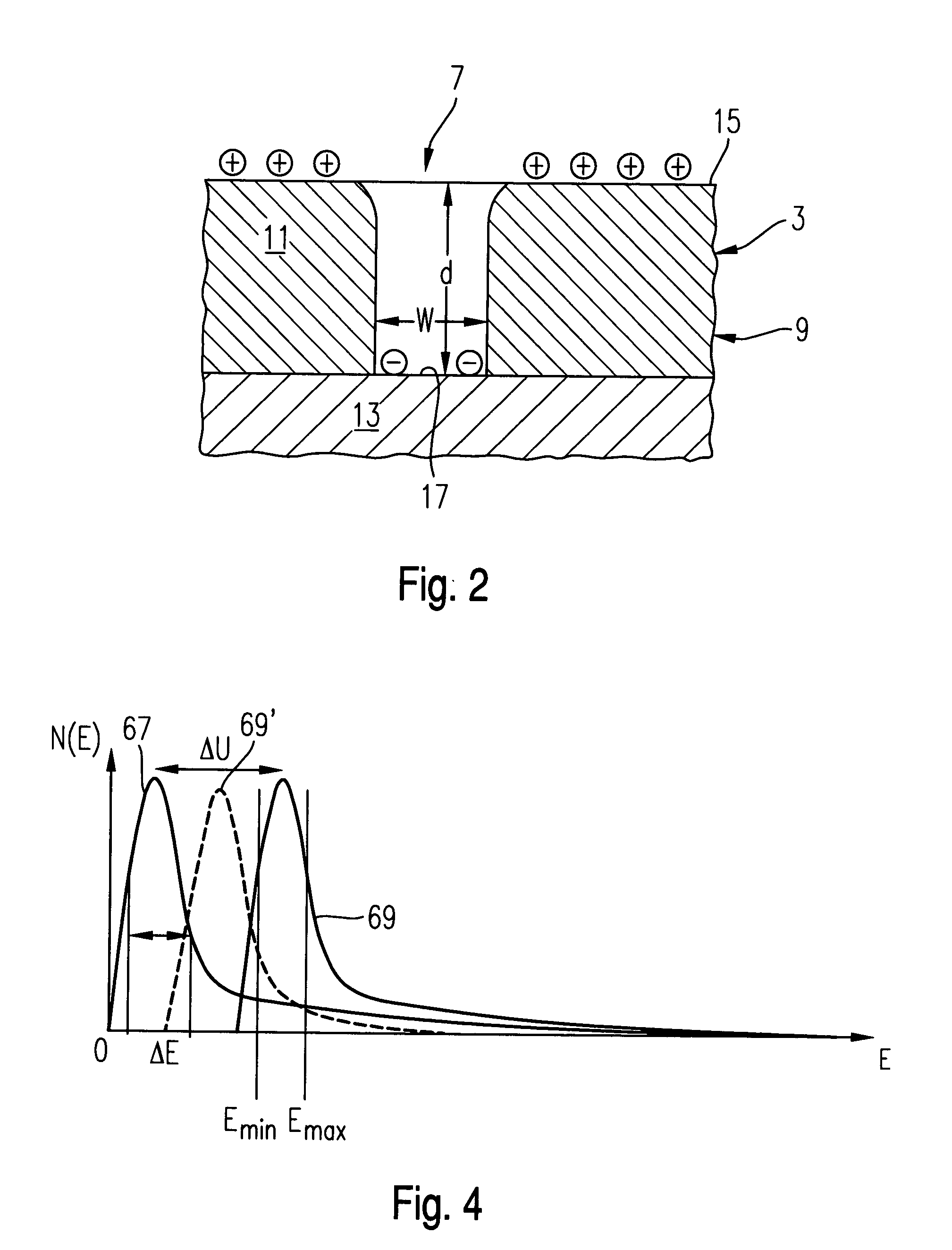
Method for the electron-microscopic observation of a semiconductor arrangement and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS20040065827A1Producing an excessive and uncompensatable image blurHigh resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectron microscopeSecondary electrons
A method for the electron-microscopic observation of a semiconductor arrangement is provided. It includes providing an electron microscopy optics for imaging secondary electrons emanating from the semiconductor arrangement within an extended object field on a position-sensitive detector, providing an illumination device for emitting a primary energy beam, directing the primary energy beam to at least the object field for extracting there secondary electrons from the semiconductor arrangement. The semiconductor arrangement comprises a region with an upper surface provided by a first material and a recess with a high aspect ratio which is surrounded by the upper surface and has a bottom provided by a second material.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Projection objective and projection exposure apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20080037112A1Reduce in quantityReduce the total massPhotomechanical apparatusMicroscopesLithographic artistMaterial consumption
A reduction projection objective for projection lithography has a plurality of optical elements configured to image an effective object field arranged in an object surface of the projection objective into an effective image field arranged in an image surface of the projection objective at a reducing magnification ratio |β|<1. The optical elements form a dry objective adapted with regard to aberrations to a gaseous medium with refractive index n′<1.01 filling an image space of finite thickness between an exit surface of the projection objective and the image surface. The optical elements include a largest lens having a maximum lens diameter Dmax and are configured to provide an image-side numerical aperture NA<1 in an effective image field having a maximum image field height Y′. With COMP=Dmax / (Y′·(NA / n′)2) the condition COMP<15.8 holds. Preferred embodiments have relatively small overall numbers of lenses which allows to fabricate the projection objectives relatively small in size with relatively low material consumption, yielding high performance, light weight, compact reduction projection objectives for dry lithography.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
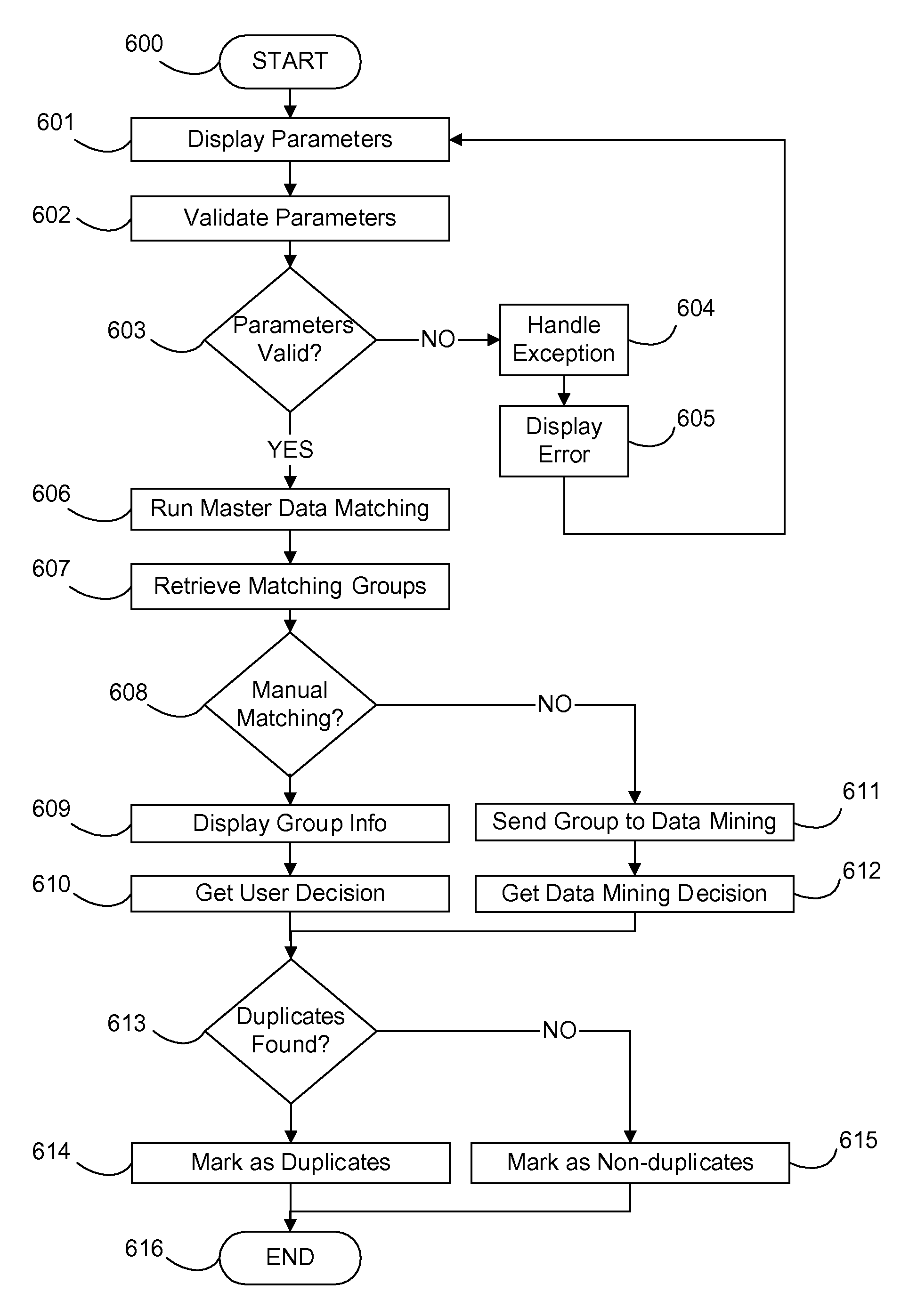
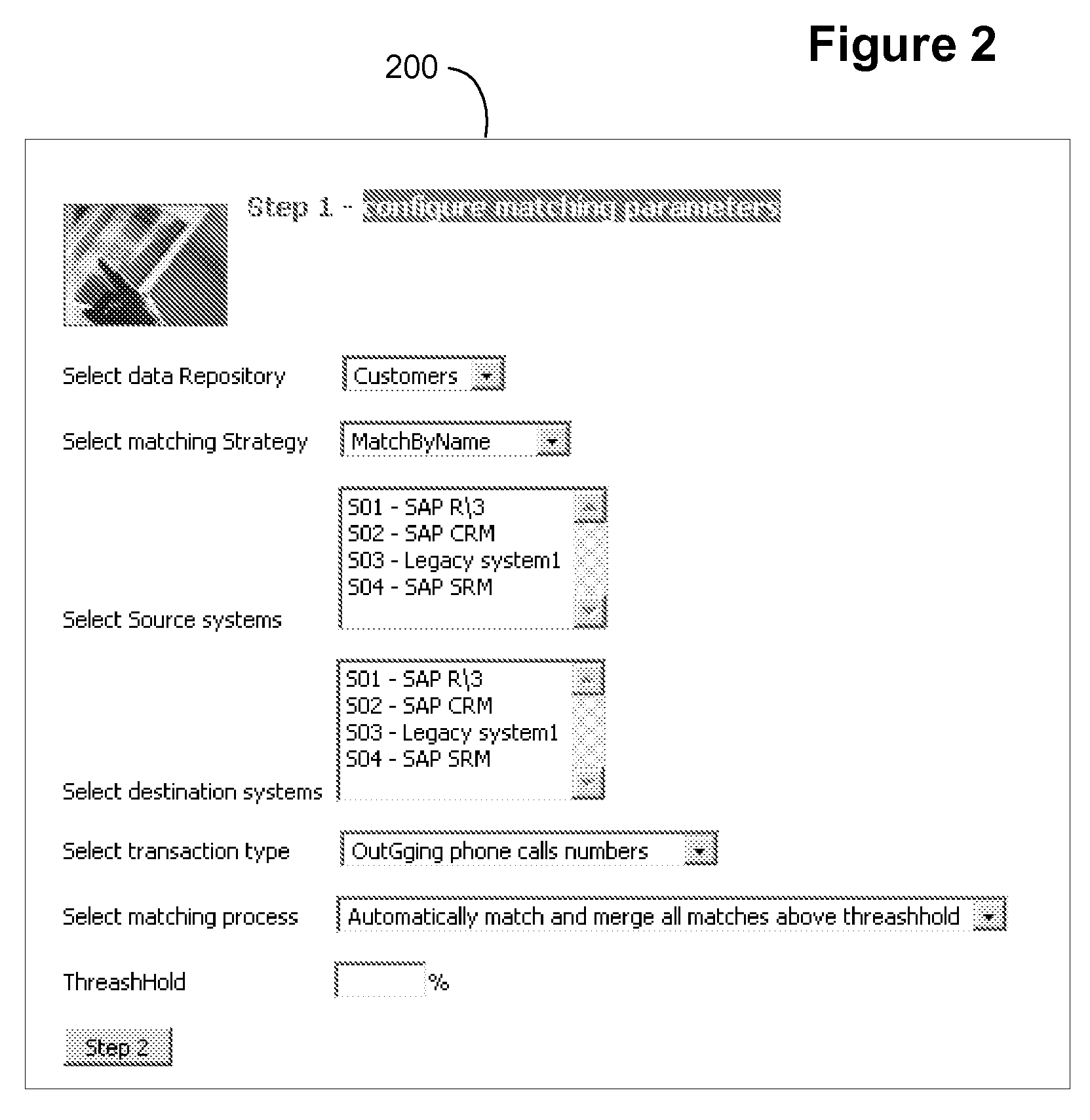
System and method for matching similar master data using associated behavioral data
ActiveUS20080162580A1Retain de-duplication accuracyAccelerating transactionDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData matchingTheoretical computer science
A system and method for matching similar master data using associated behavioral data, for example transactional data. Matching accuracy is significantly increased. Master data may be thought of as nouns. Behavioral data is associated with master data as verbs are related to nouns. Specifically, behavioral data is data associated with an action taken by a master data object. Behavioral data may include temporal and non-temporal data. Temporal data for example may include time and / or duration that a behavior occurred. Non-temporal data may include a physical location, a product, a phone number or any other quantity other than time. Using behavioral data in duplication testing adds another dimension to de-duplication that is not achieved through comparison of master data object fields alone. For example, a duplication test on two similar “person” records with similar “name” field values is improved by comparing associated “behavior” data, (phone numbers called by each “similar person”).
Owner:SAP AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com