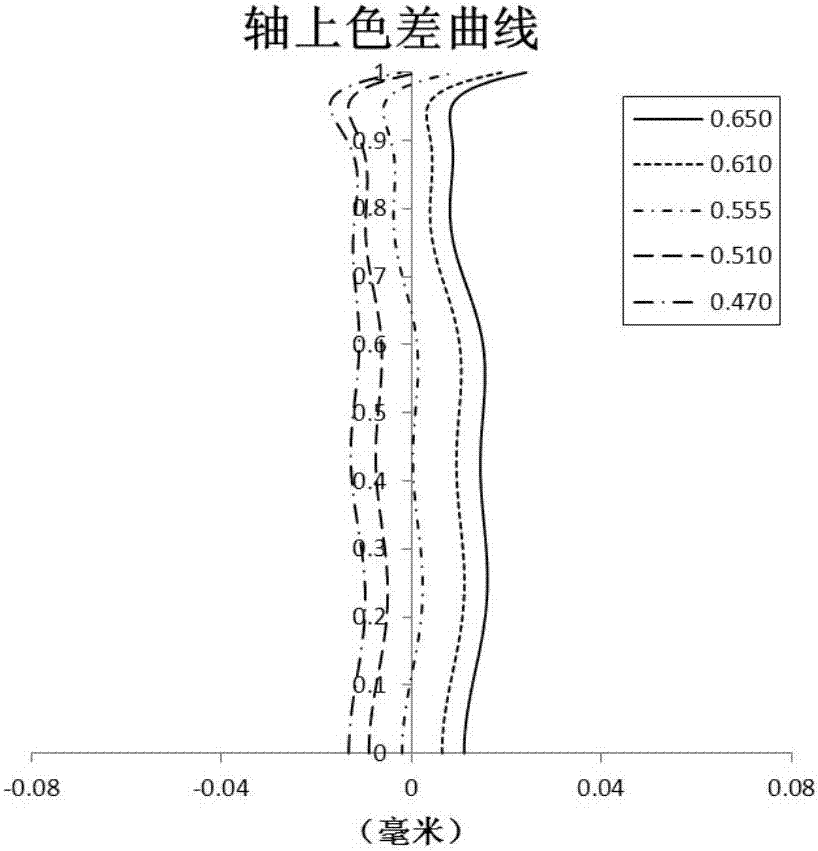
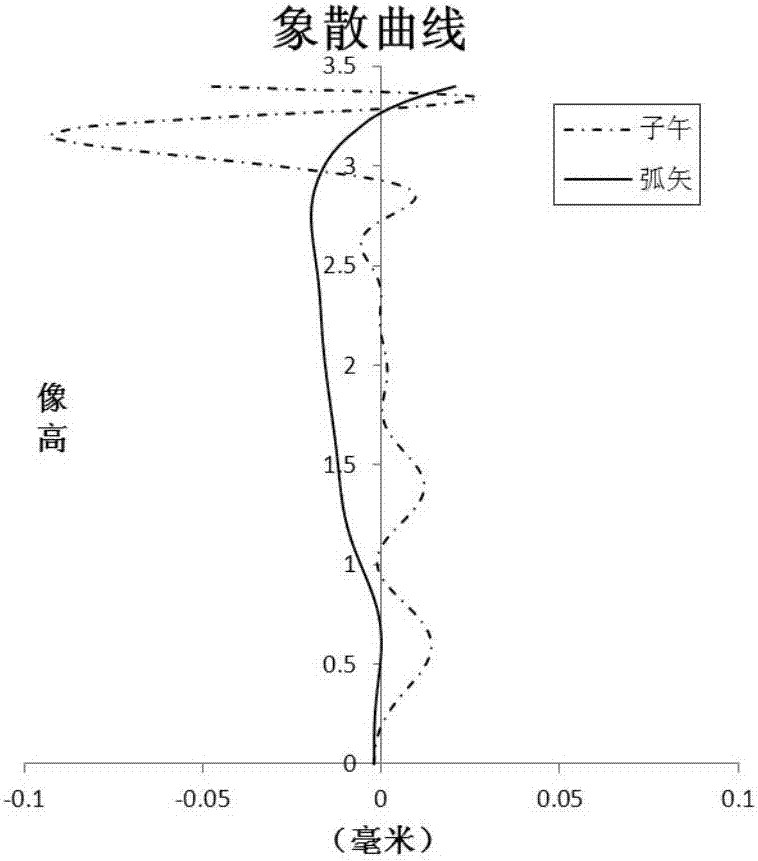
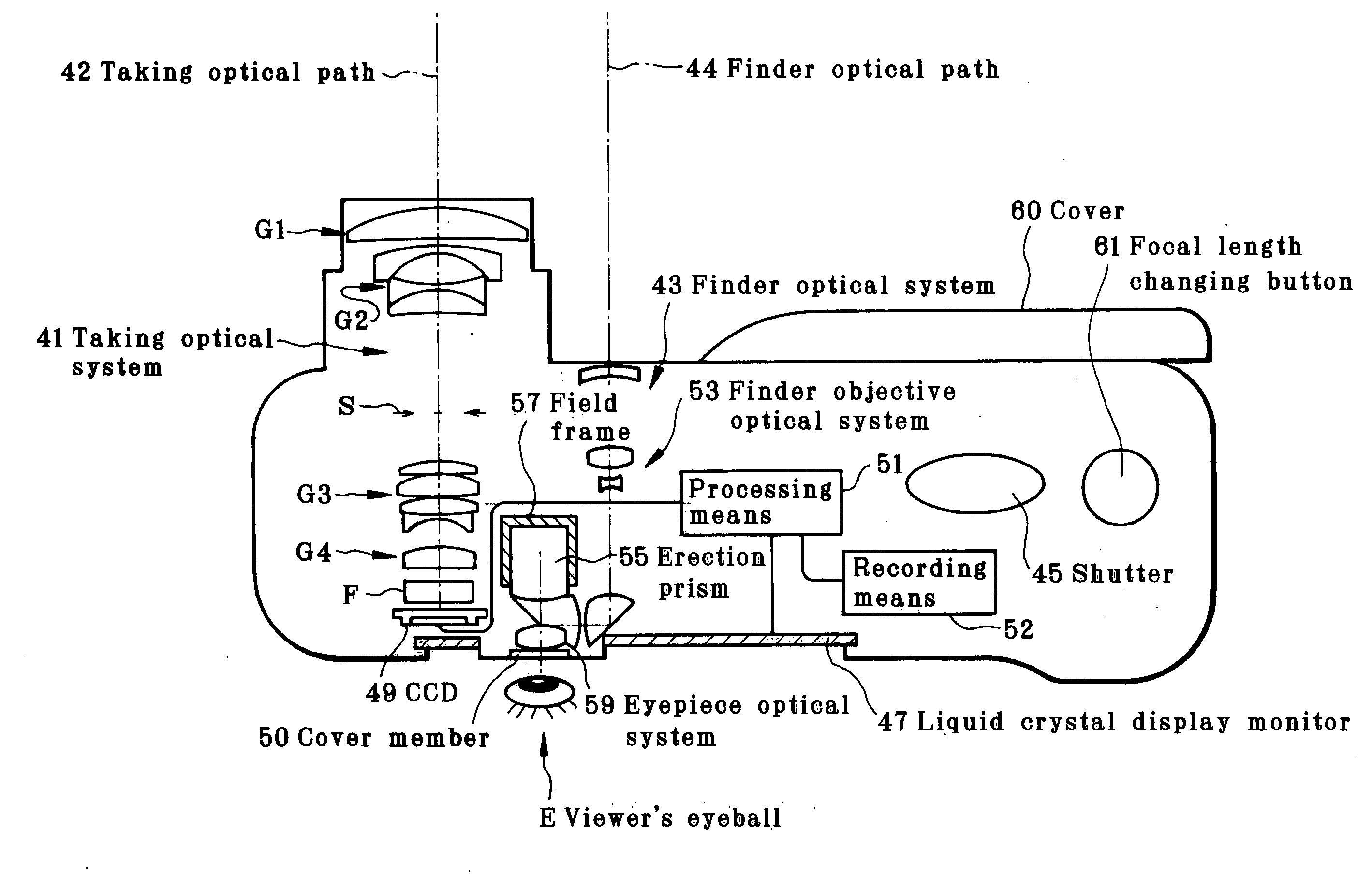
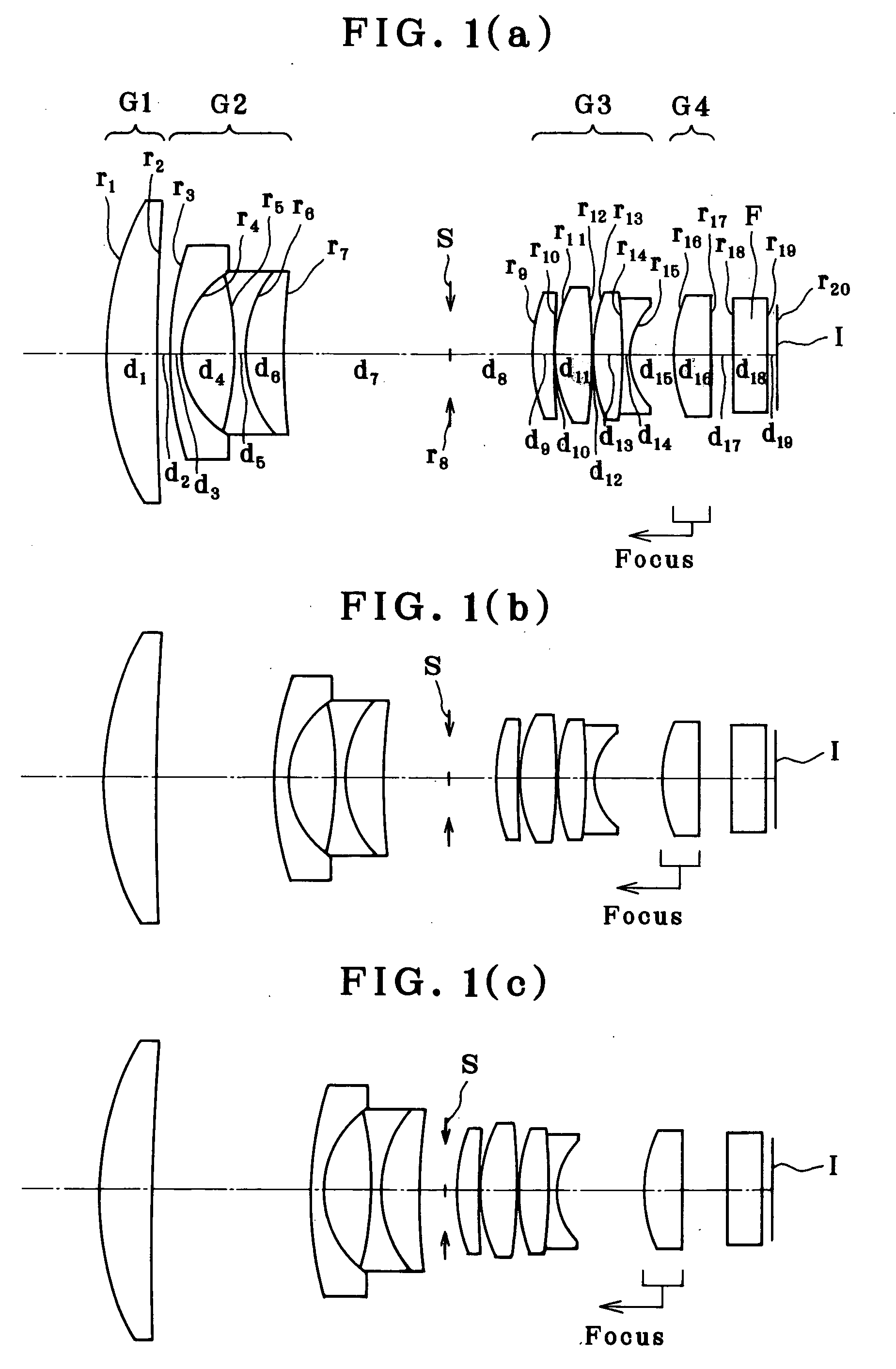
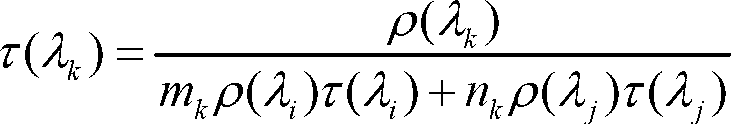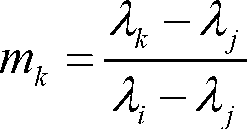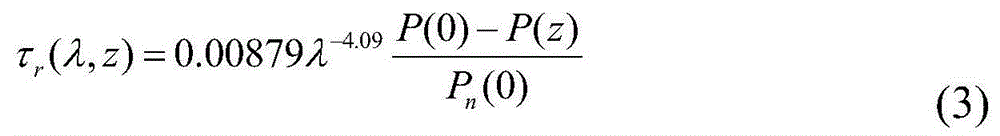Patents
Literature
901 results about "Entrance pupil" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
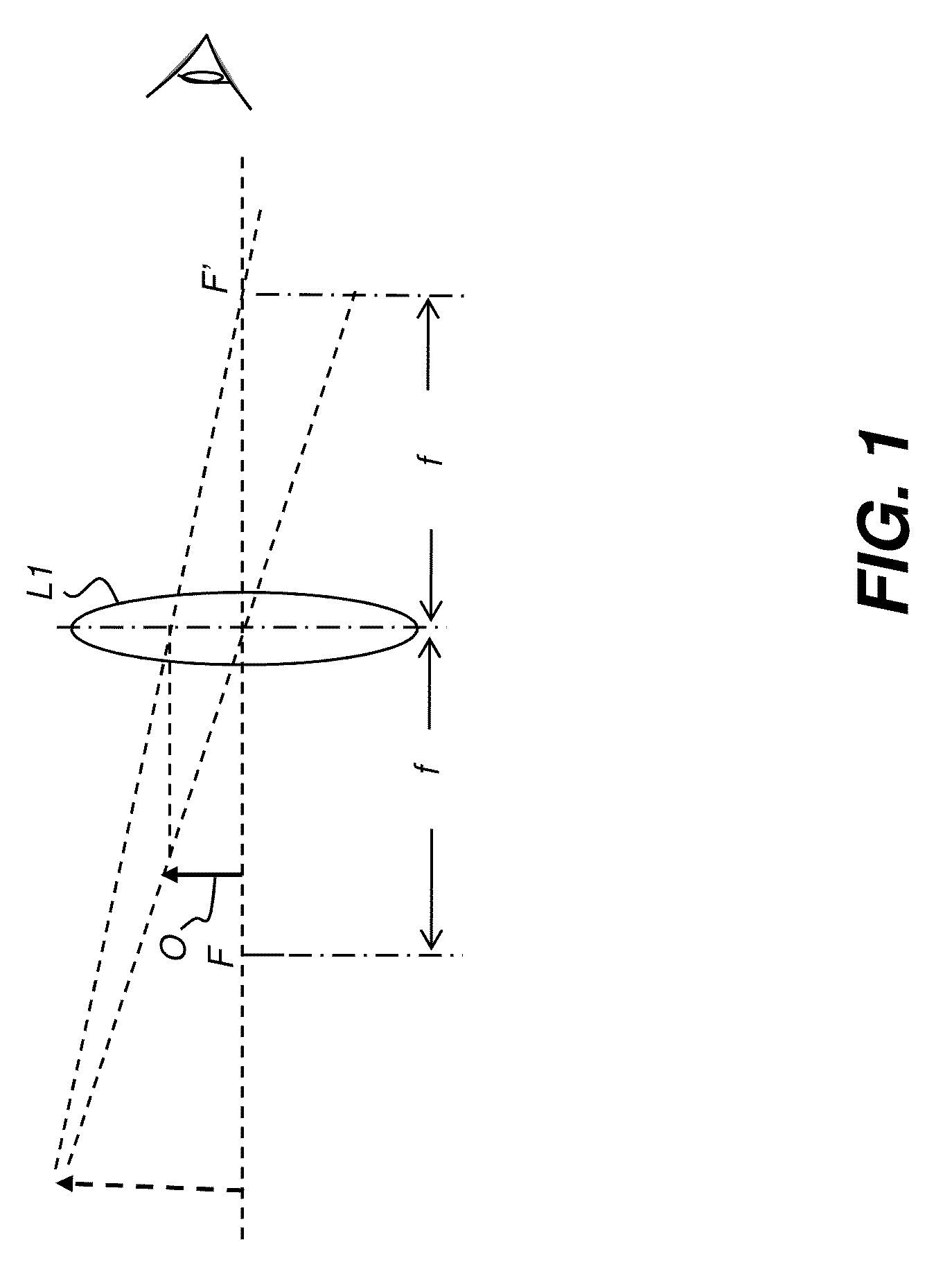
In an optical system, the entrance pupil is the optical image of the physical aperture stop, as 'seen' through the front of the lens system. The corresponding image of the aperture as seen through the back of the lens system is called the exit pupil. If there is no lens in front of the aperture (as in a pinhole camera), the entrance pupil's location and size are identical to those of the aperture. Optical elements in front of the aperture will produce a magnified or diminished image that is displaced from the location of the physical aperture. The entrance pupil is usually a virtual image: it lies behind the first optical surface of the system.
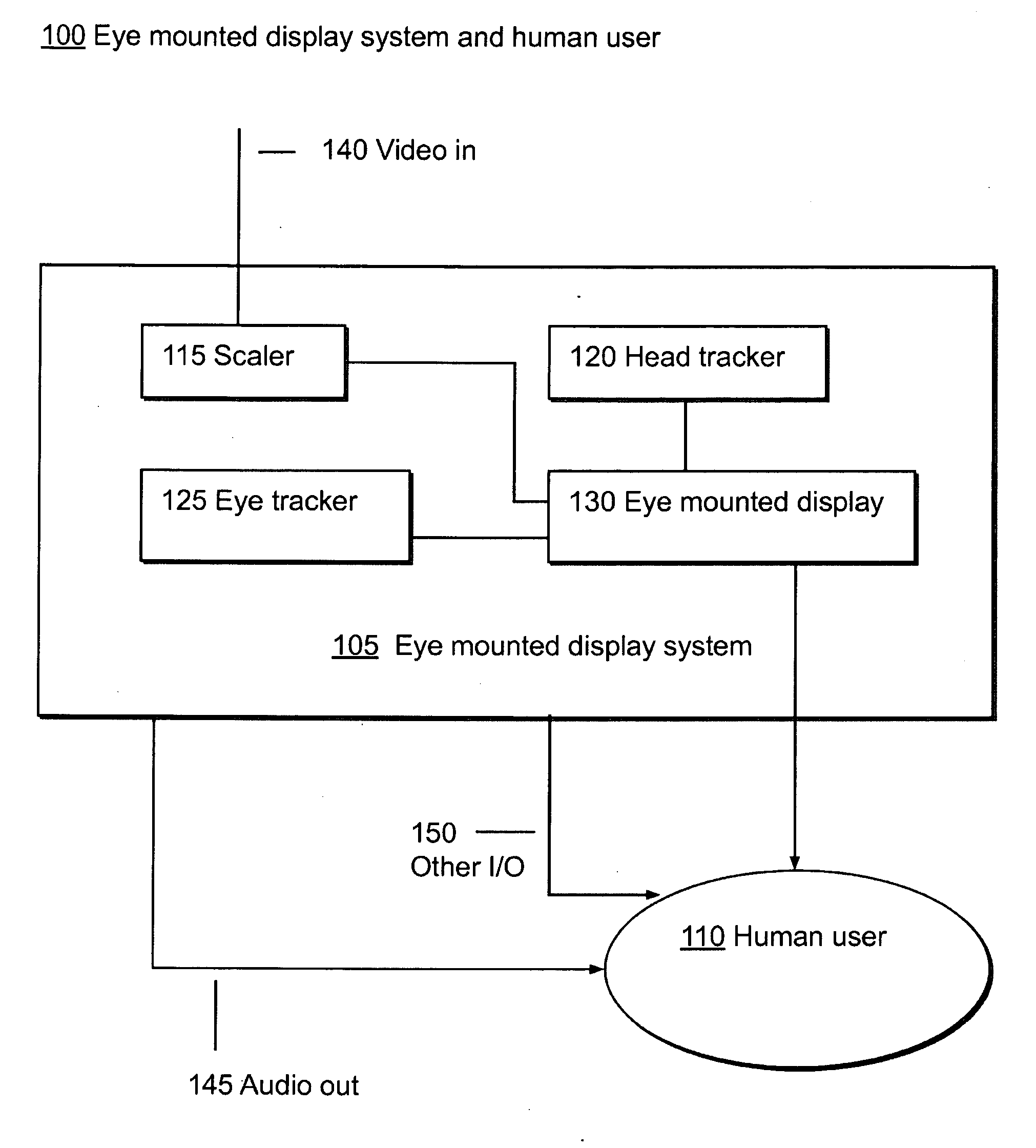
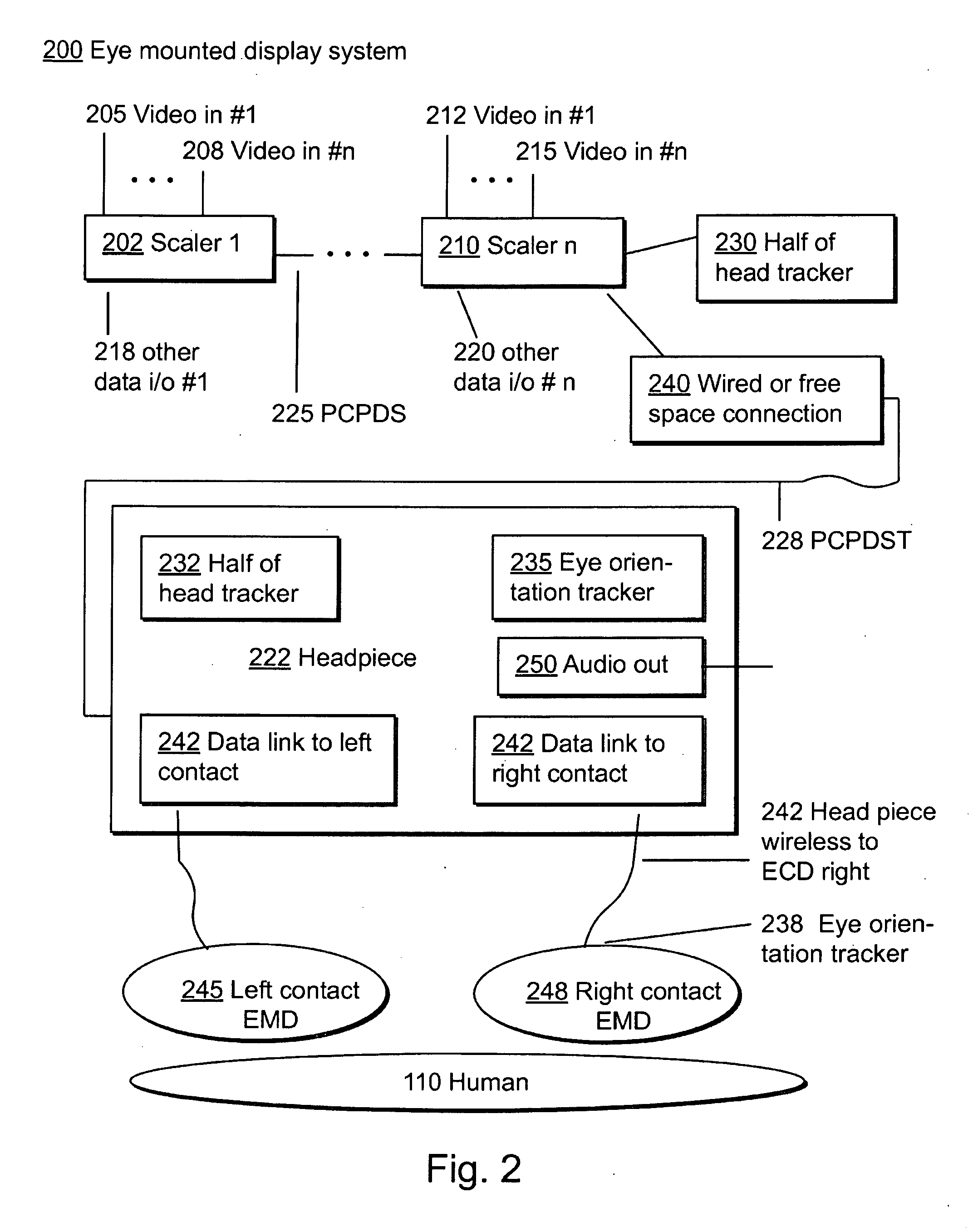
Eye Mounted Displays
InactiveUS20090189830A1Avoid and reduce interferenceVarious limitationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
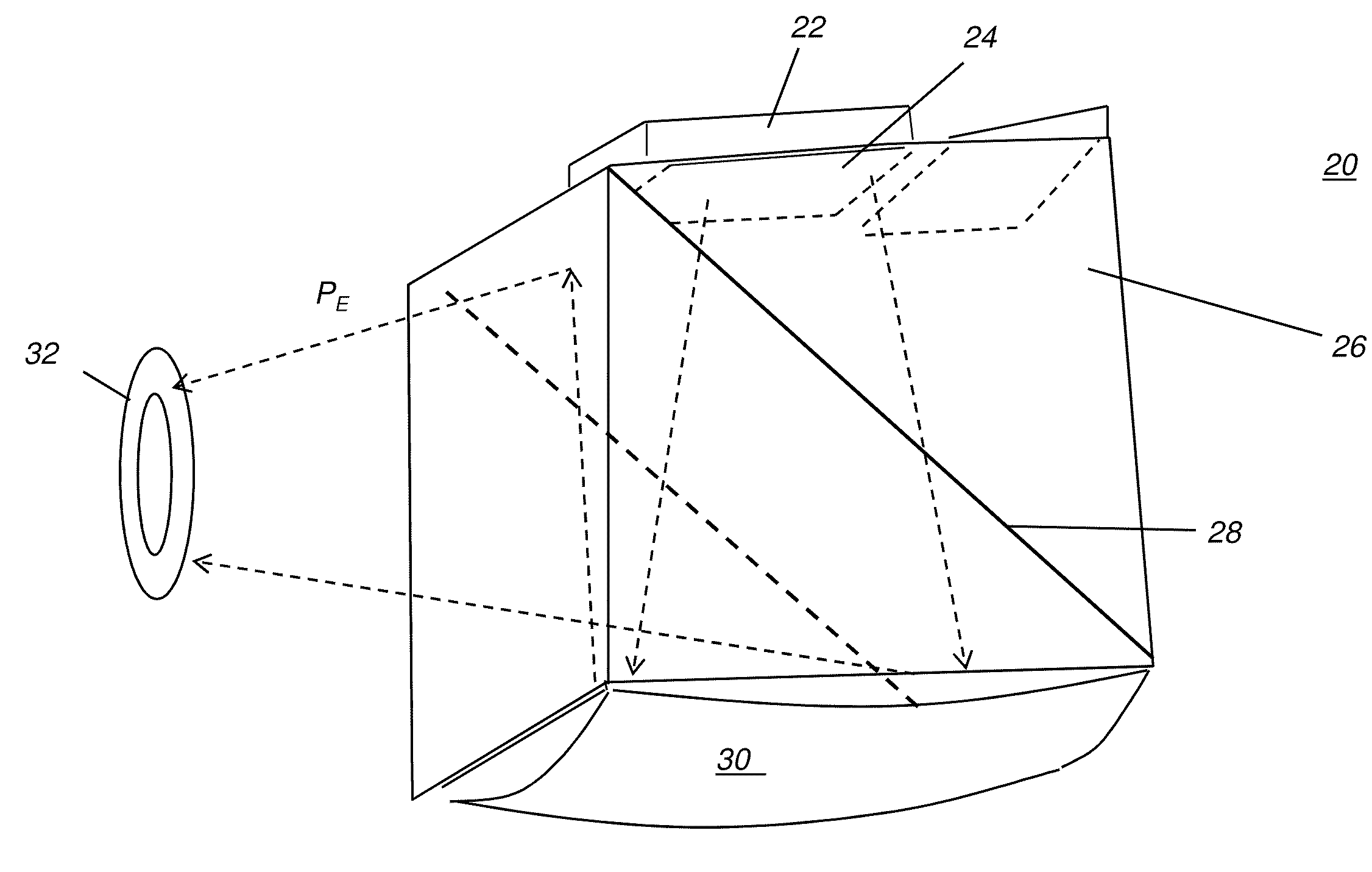
Head-mounted optical apparatus using an OLED display
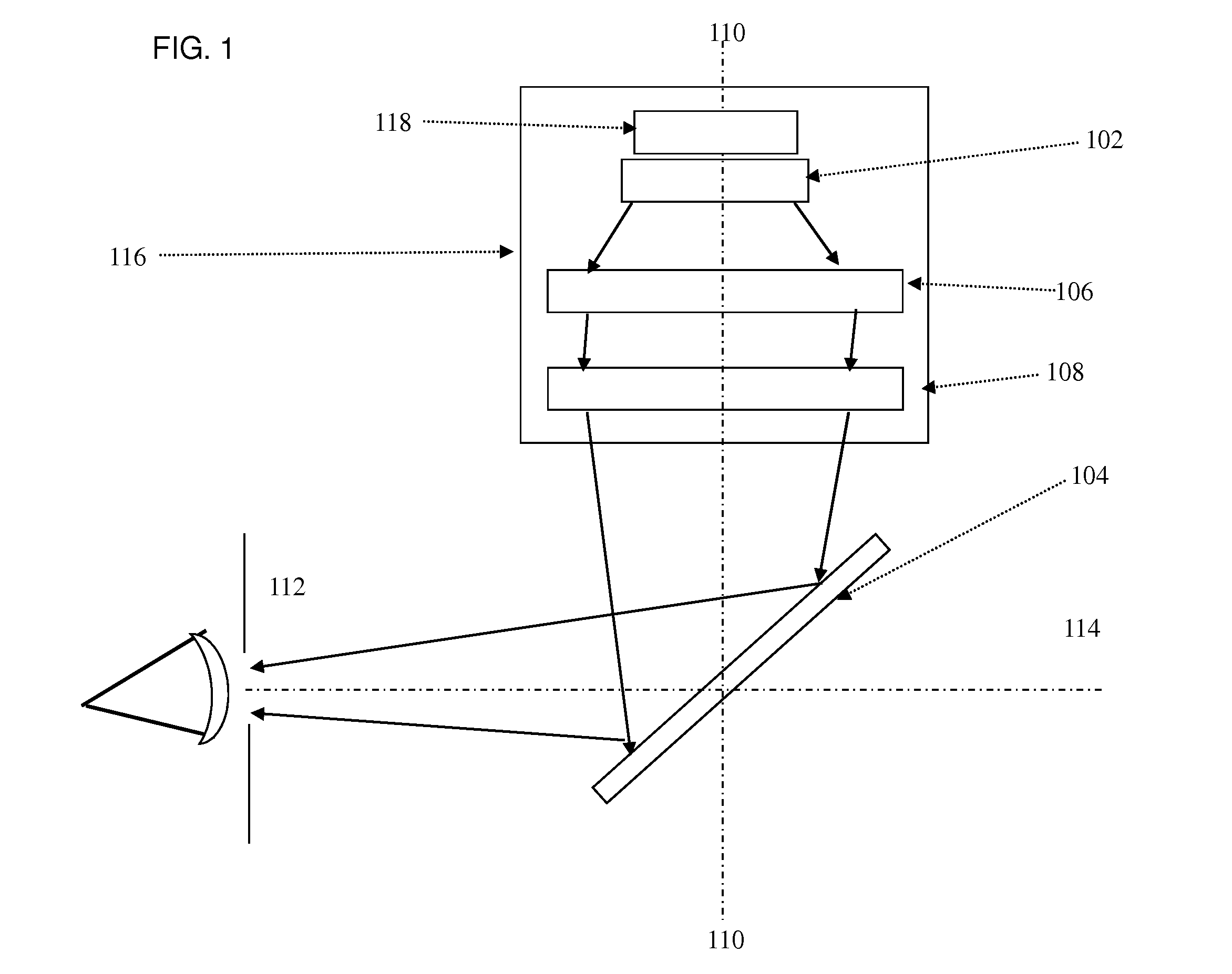
A see-through head-mounted optical apparatus for a viewer has at least one display module, each display module having a display energizable to form an image and a positive field lens optically coupled to the surface of the display and disposed to direct imaged light from the display toward a first surface of a prism. A curved reflector element is in the path of the imaged light through the prism and disposed at a second surface of the prism, opposite the first surface. The curved reflector element has a refractive surface and a curved reflective surface disposed to collimate imaged light received from the display and direct this light toward a beam splitter that is disposed within the prism and that is at an oblique angle to the collimated reflected light. The beam splitter redirects the incident collimated reflected light through the prism to form an entrance pupil for the viewer.
Owner:NVIS
Apparatus for head mounted image display
ActiveUS20100254017A1Additional imaging capabilityImprove toleranceAdditive manufacturing apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsBeam splitterOptical axis
Image display device having an image source generating an image, a beam splitter positioned at forty five degrees to the main optical path, to project and focus the image generated by the image source into the entrance pupil of the human eye, two achromatic standard doublet lenses positioned perpendicularly to the main optical path and placed between the image source and the beam splitter, and configured to amplify, collimate, and correct optical aberrations of said image, wherein the image source, beam splitter and the doublet lenses are in an on-axis configuration and the image display device comprises two mounting brackets parallel to the main optical axis, each having an extremity part holding an edge of the beam splitter and the other extremity pivotally attached to a housing, allowing the brackets and beam splitter to rotate in an axis perpendicular to the main optical path.
Owner:MIGUEL MARQUES MARTINS
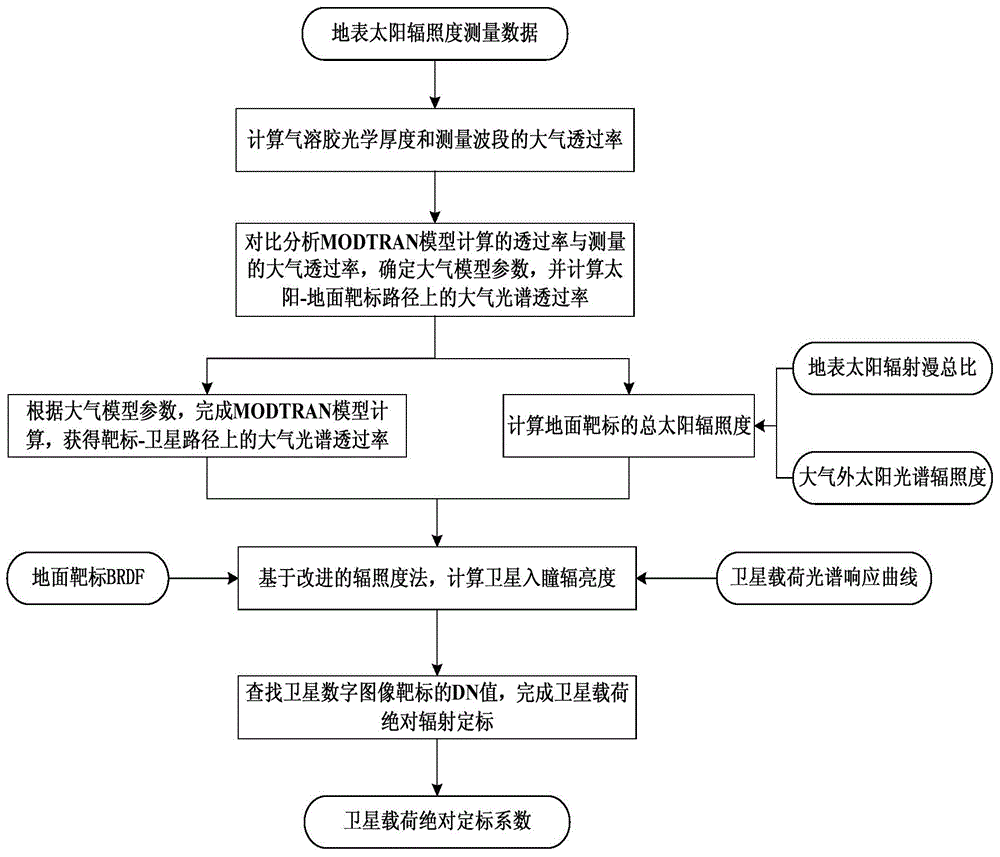
Satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval
InactiveCN103018736ASimulation is accurateAccurate entrance pupil radianceWave based measurement systemsMeteorological satelliteEntrance pupil
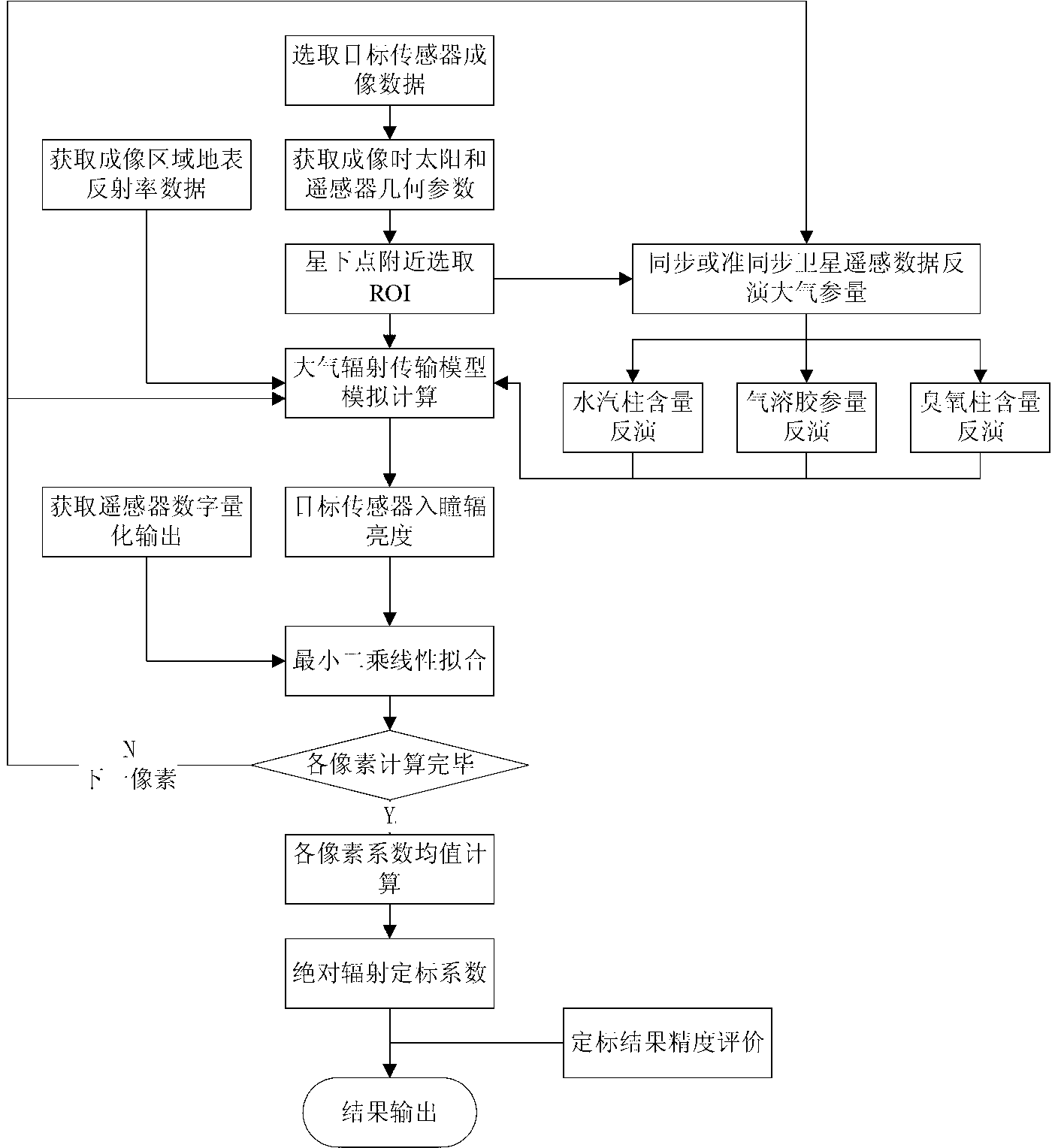
The invention discloses a satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval. The method includes nine steps. A surface reflectance is obtained through ground synchronous actual measurement during satellite crossing or historical data, imaging time and observation geometry parameters are obtained through remote sensing data head files, atmospheric parameters during imaging of synchronous crossing meteorological satellite sensors or related load retrieval remote sensors are utilized, the entrance pupil radiance of the remote sensors is calculated by an atmospheric radiation transmission model according to retrieval results of the atmospheric parameters, a calibration coefficient is calculated through a radiation calibration model, and thereby the on-orbit radiation calibration for a satellite-borne remote sensor is achieved. The satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on the atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval is a pixel-level calibration method and has the advantages that the accuracy is high, the costs are low, simultaneously, the high frequency calibration can be achieved, historical remote sensing data can be calibrated, and the method has a wide application prospect to remote sensing data processing methods and application technical fields.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Imaging optical system and exposure apparatus
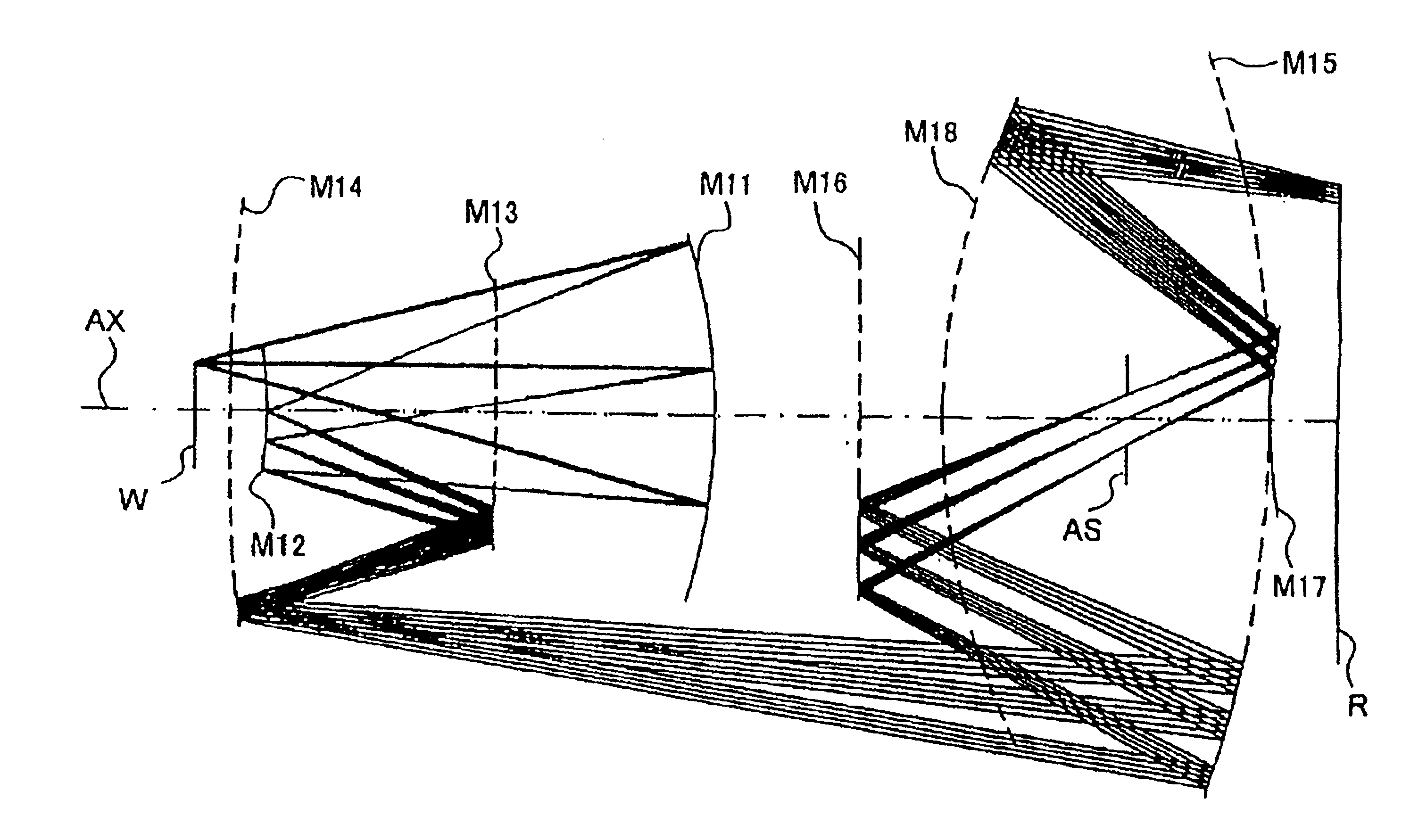
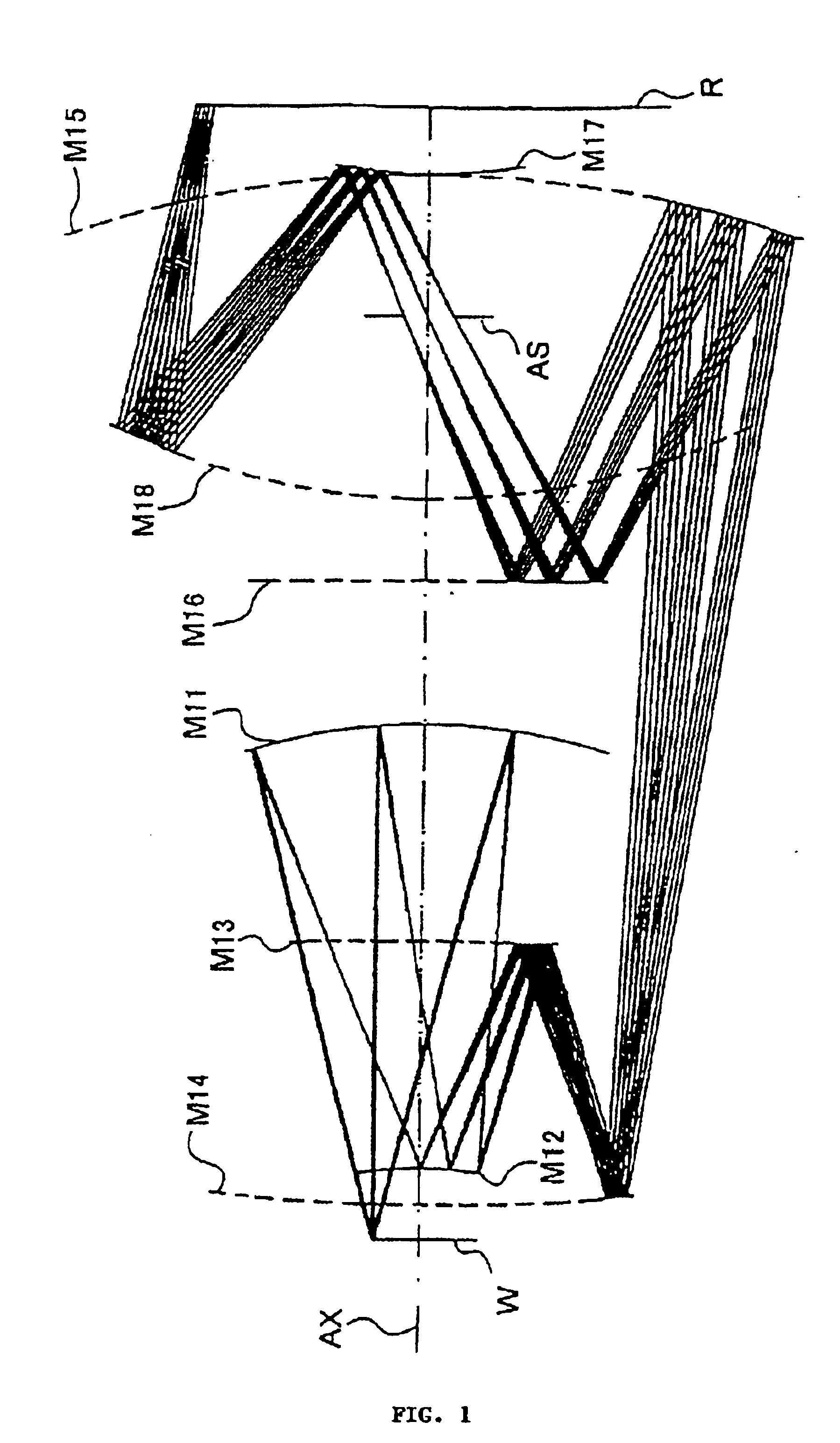
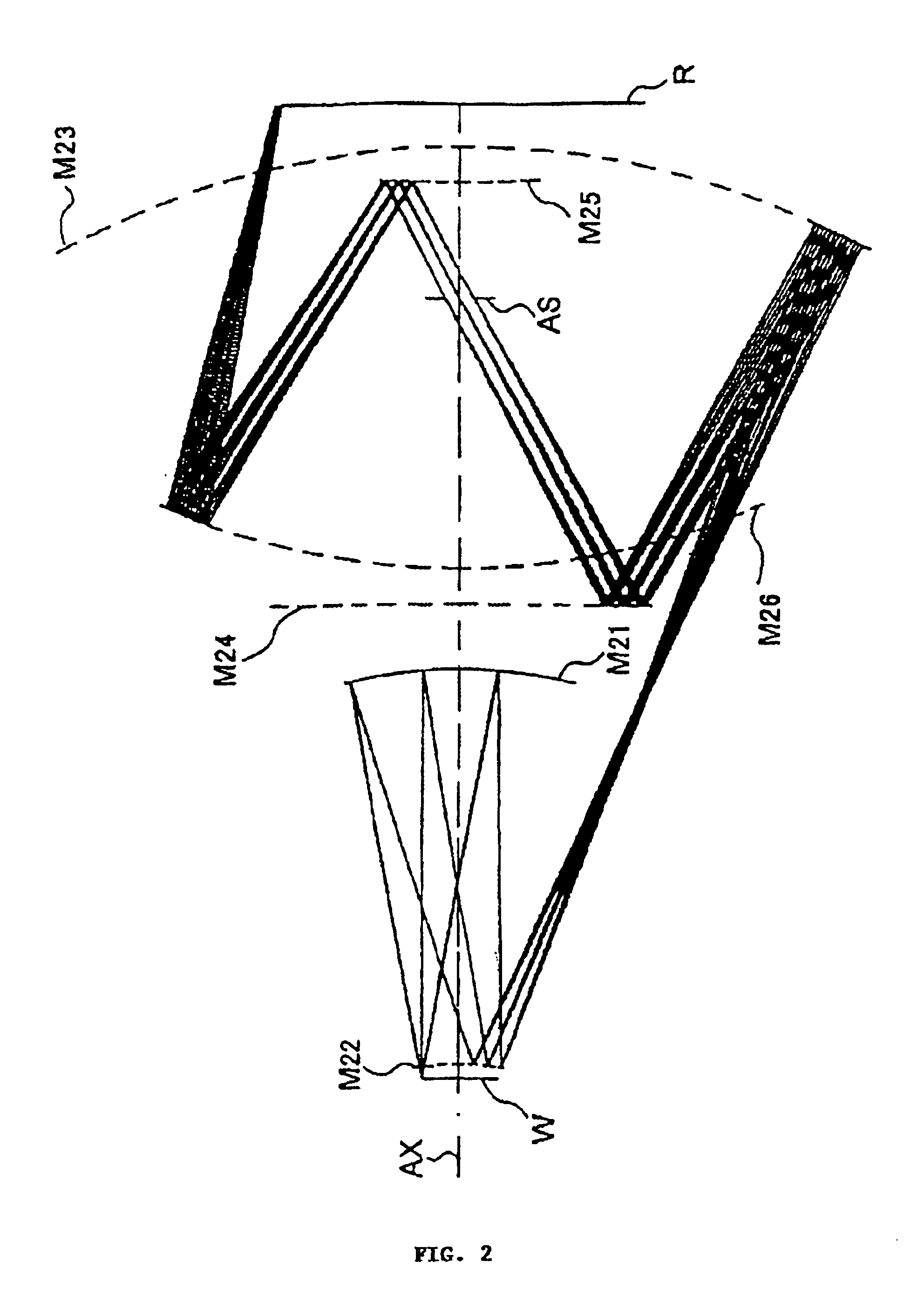
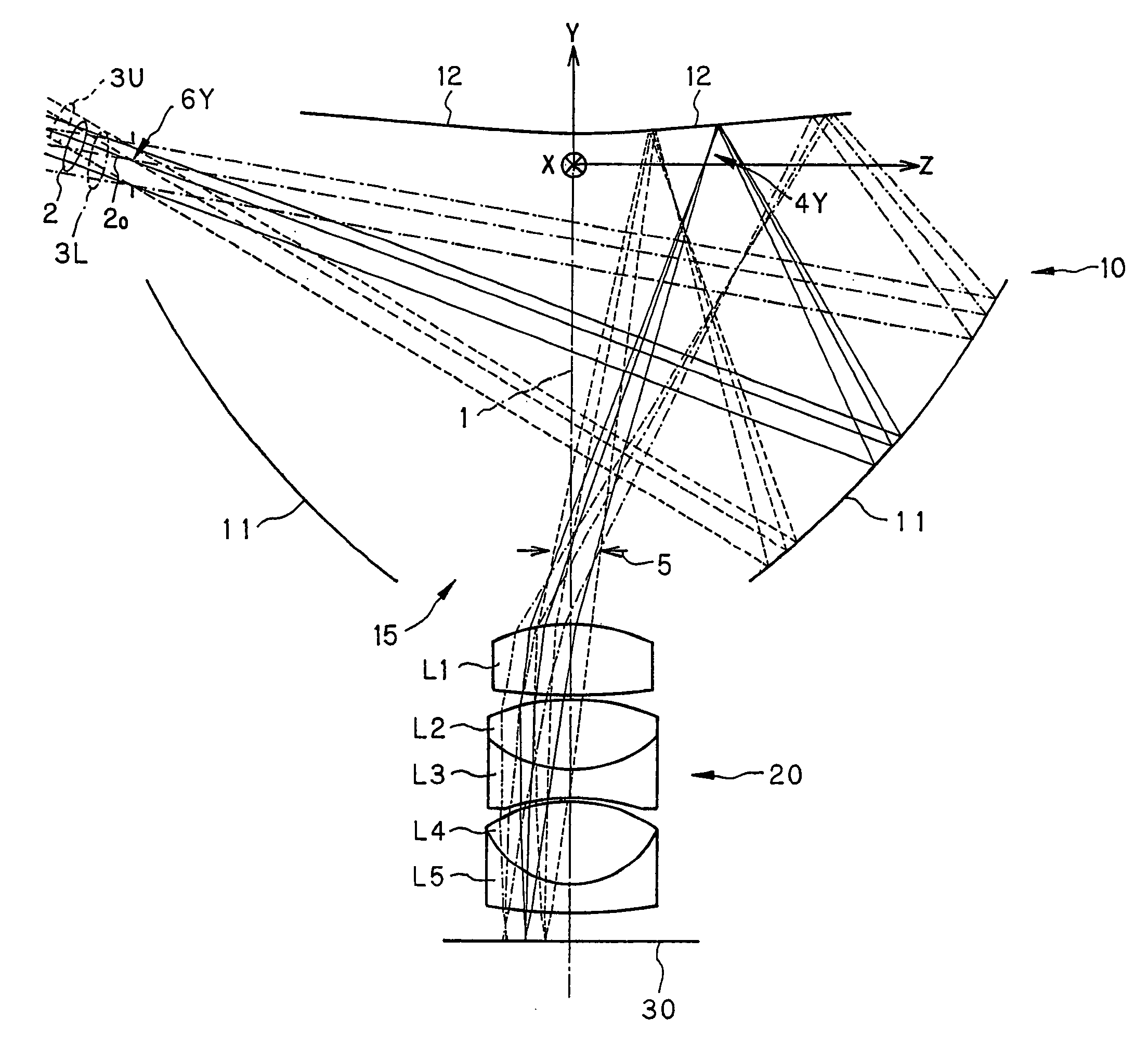
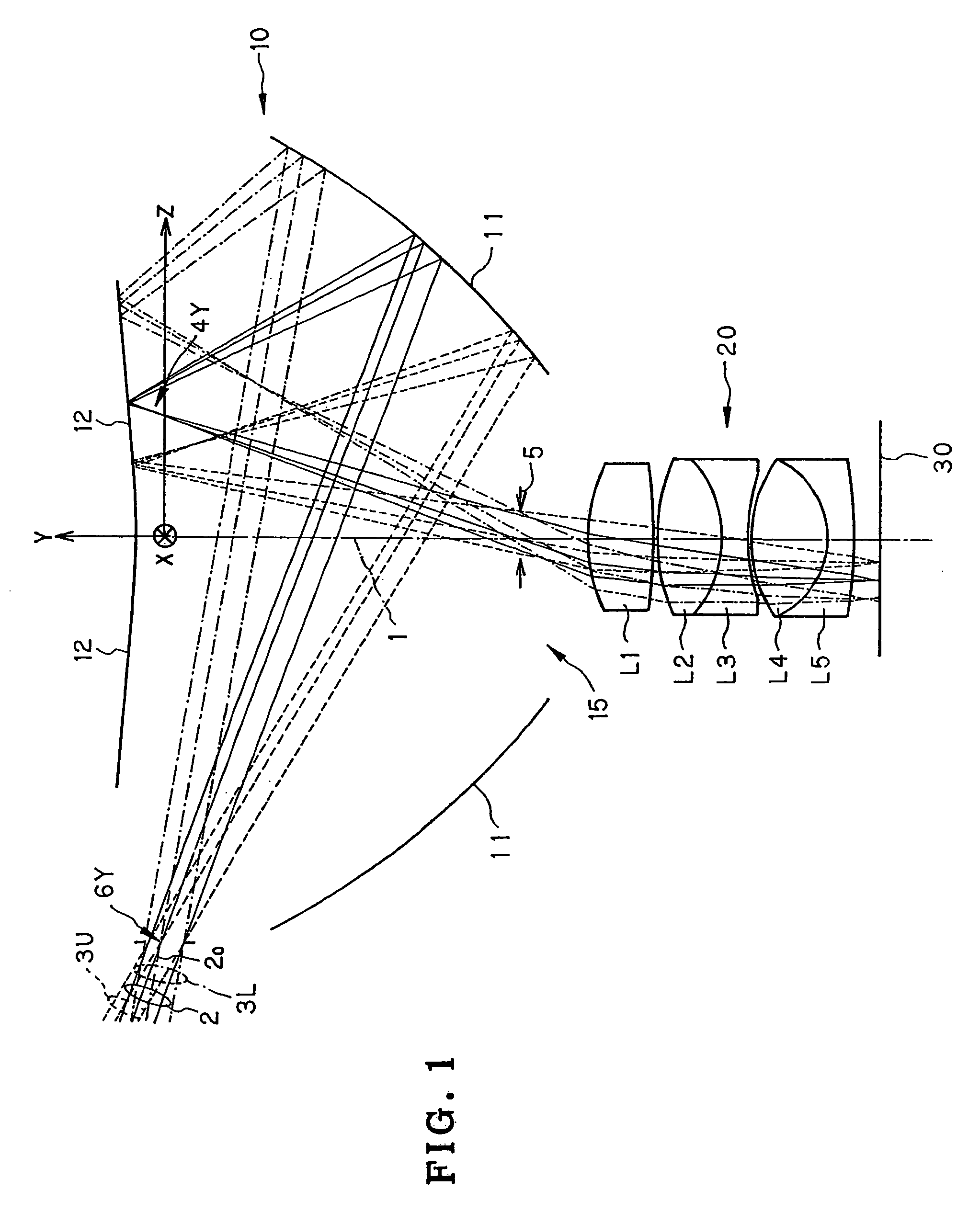
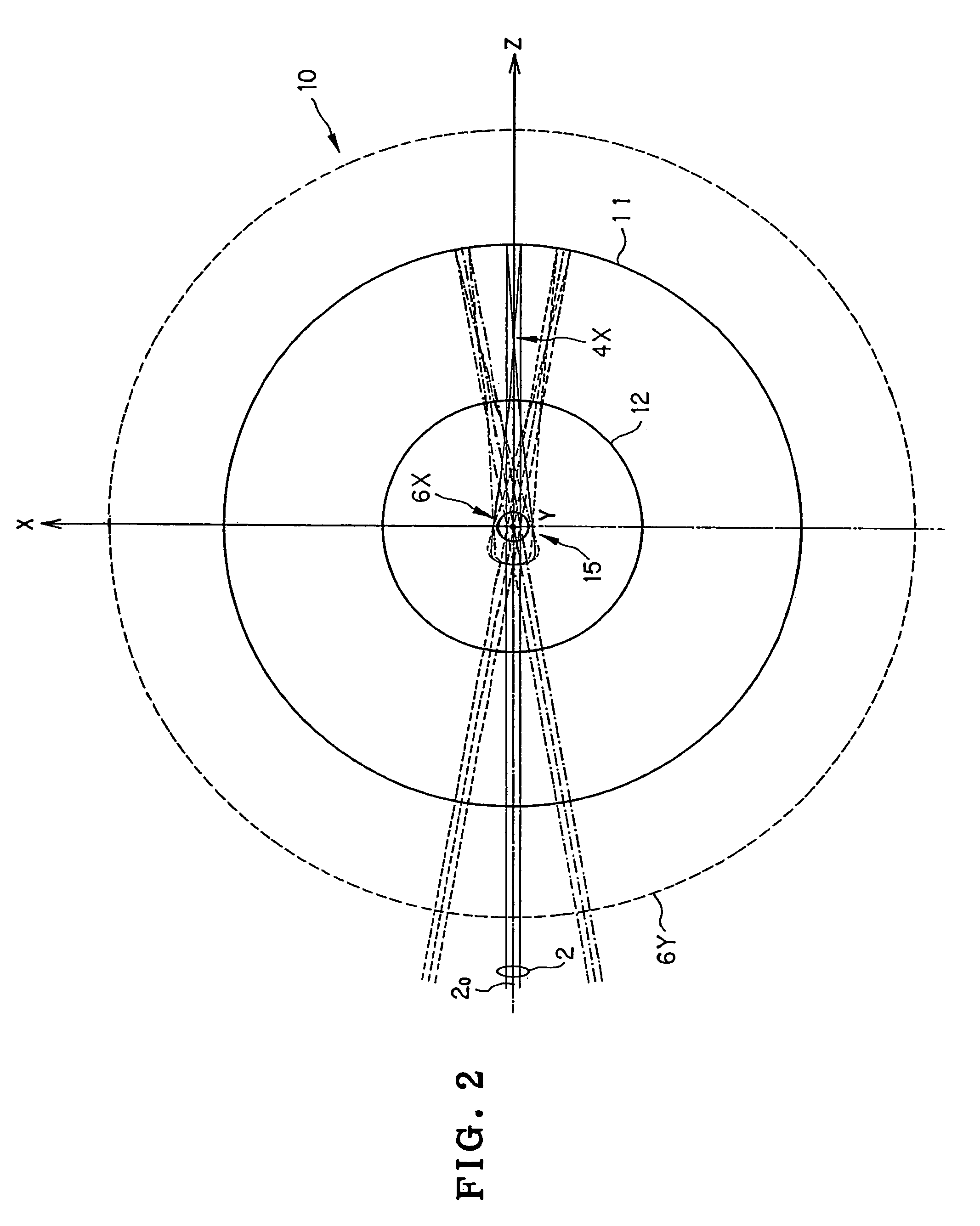
InactiveUS6781671B2MirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEntrance pupilImage-forming optical system
An imaging optical system may be capable of forming substantially in one or more second planes one or more complete and / or partial images of one or more objects arranged substantially in one or more first planes and may comprise one or more entrance pupils, at least one of which is located substantially on an opposite side of at least one of the first plane or planes from the imaging optical system exclusive of the at least one entrance pupil so located. Such imaging optical system may be constructed so as to be substantially telecentric on at least a same side thereof as at least one of the second plane or planes. Such imaging optical system may be such that all of the reflective surface or surfaces of the imaging optical system are located in one or more spaces substantially between at least one of the first plane or planes and at least one of the second plane or planes, inclusive, and / or such imaging optical system may further comprise one or more locations disposed in one or more optical paths from at least one of the first plane or planes to at least one of the second plane or planes, inclusive, and substantially optically conjugate to at least one of the first plane or planes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Endoscope objective lens with large entrance pupil diameter and high numerical aperture
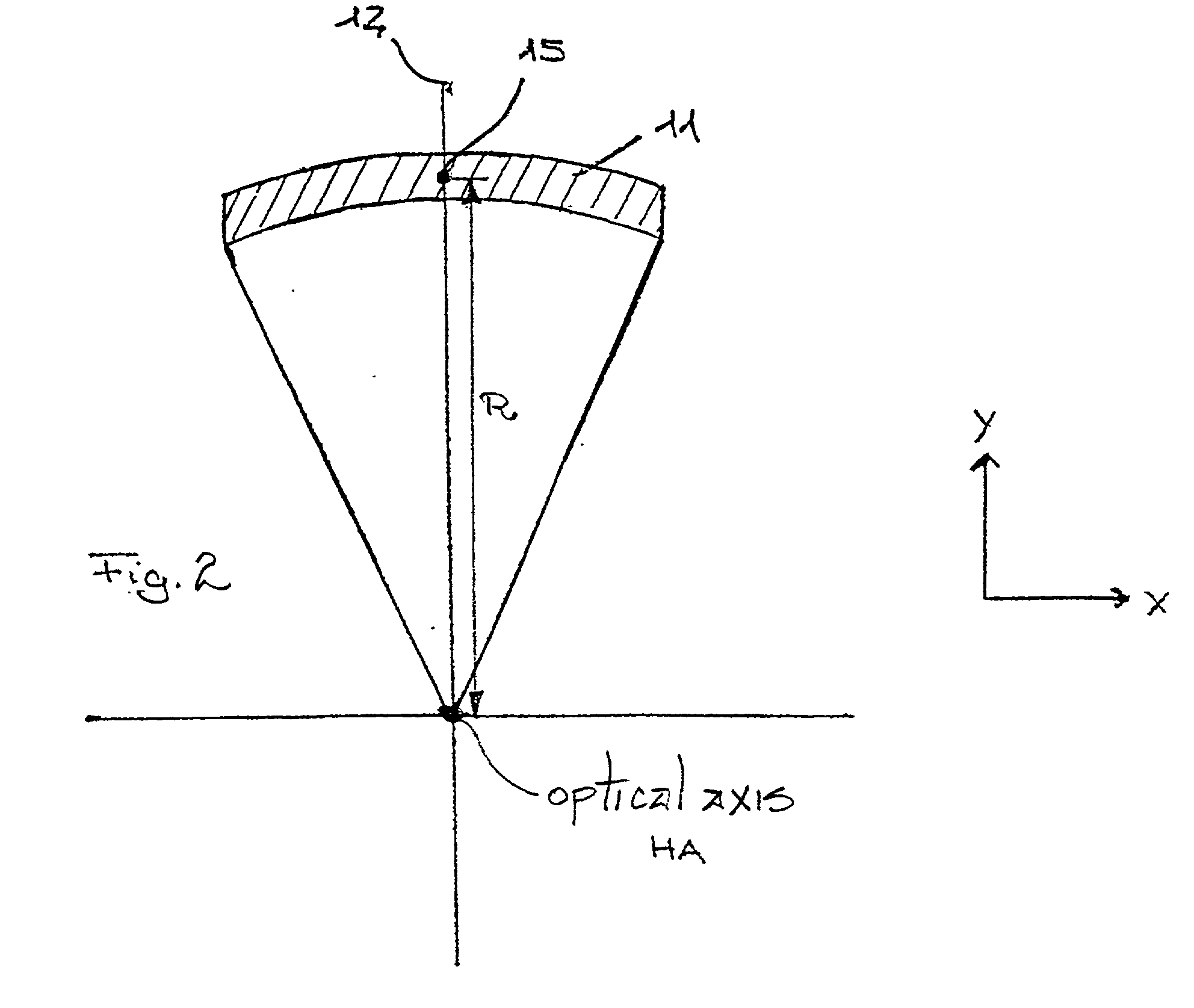
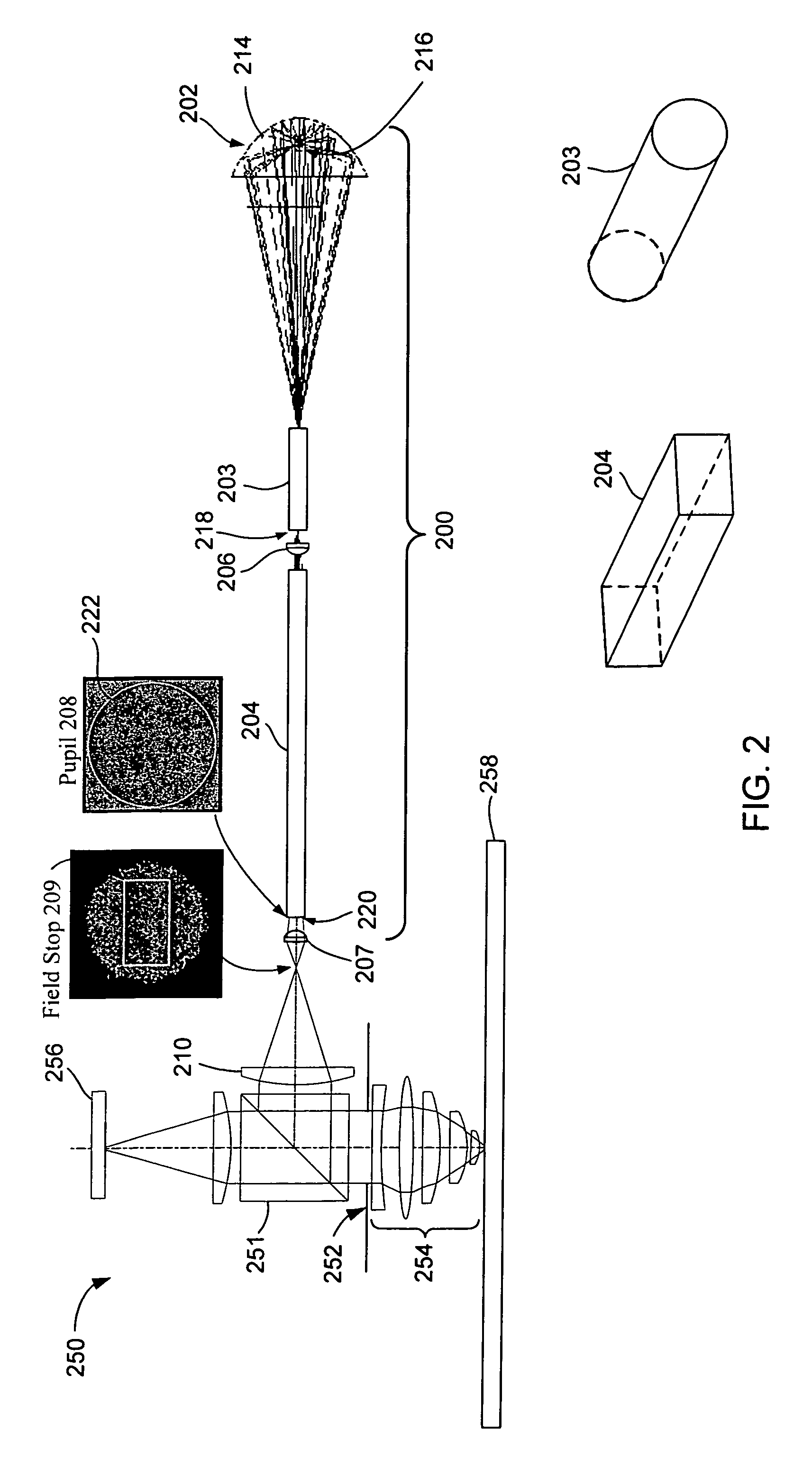
An endoscope objective lens for collecting combined bright field (white light) and fluorescence images includes a negative lens group, a stop, and a positive lens group. The lens has a combination of large entrance pupil diameter (≧0.4 mm) for efficiently collecting weak fluorescence light, large ratio between the entrance pupil diameter and the maximum outside diameter (Dentrance / Dmax larger than 0.2), large field of view (FFOV≧120°) and favorably corrected spherical, lateral chromatic and Petzval field curvature for both visible and near infrared wavelengths.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Camera lens
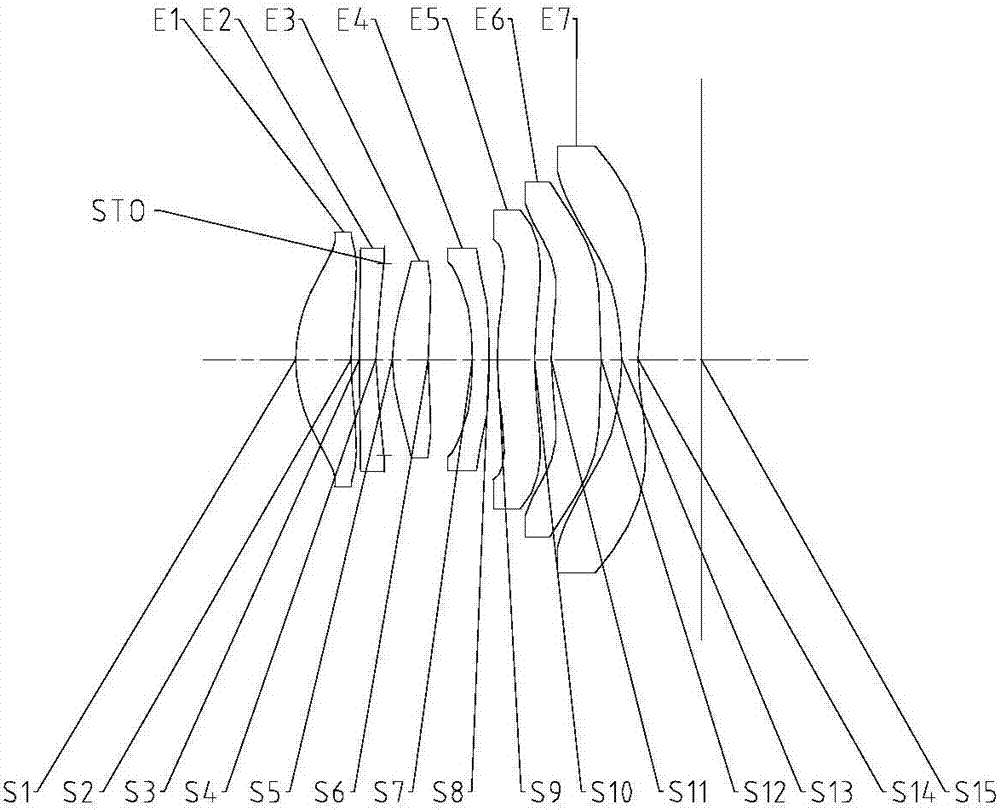
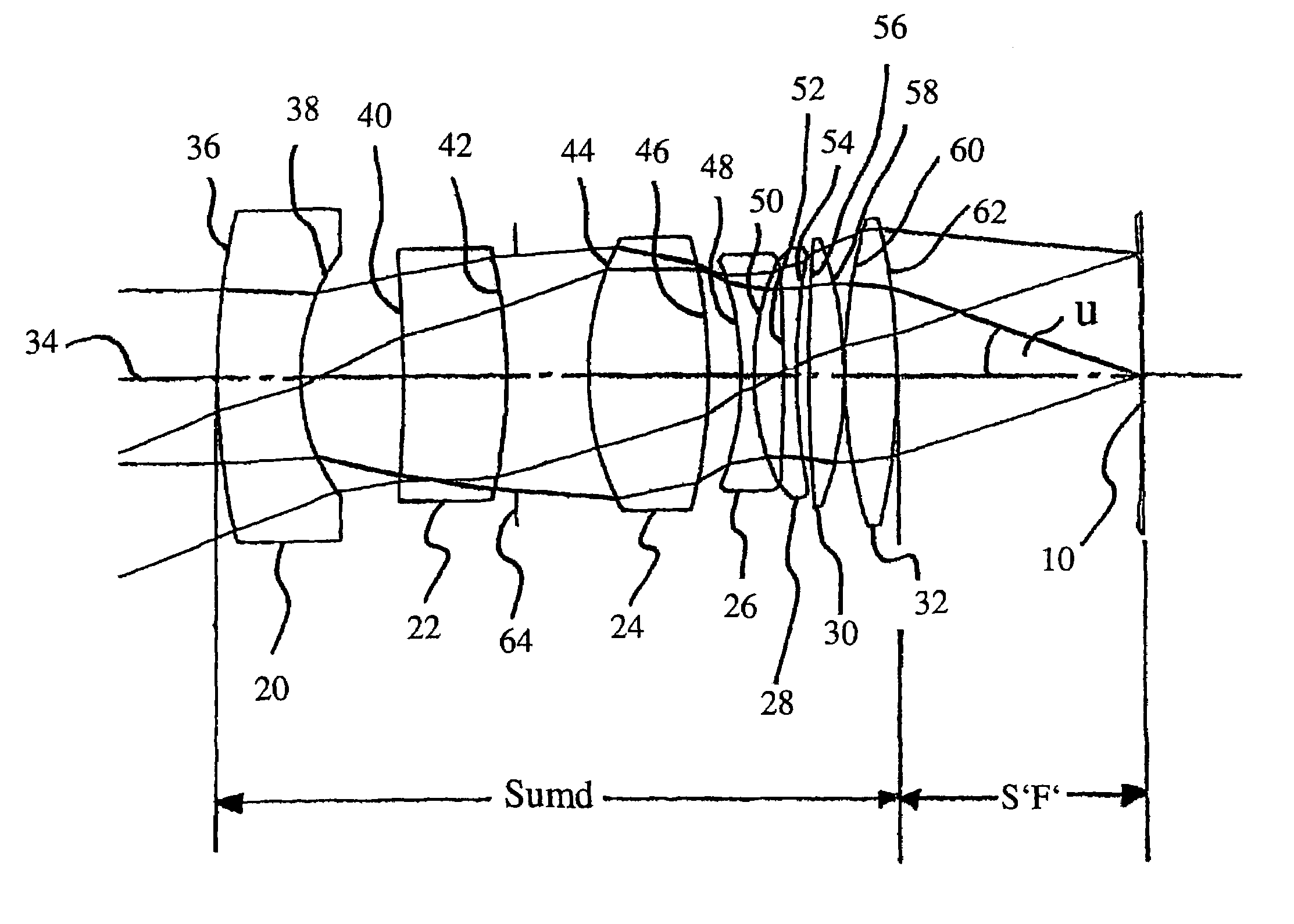
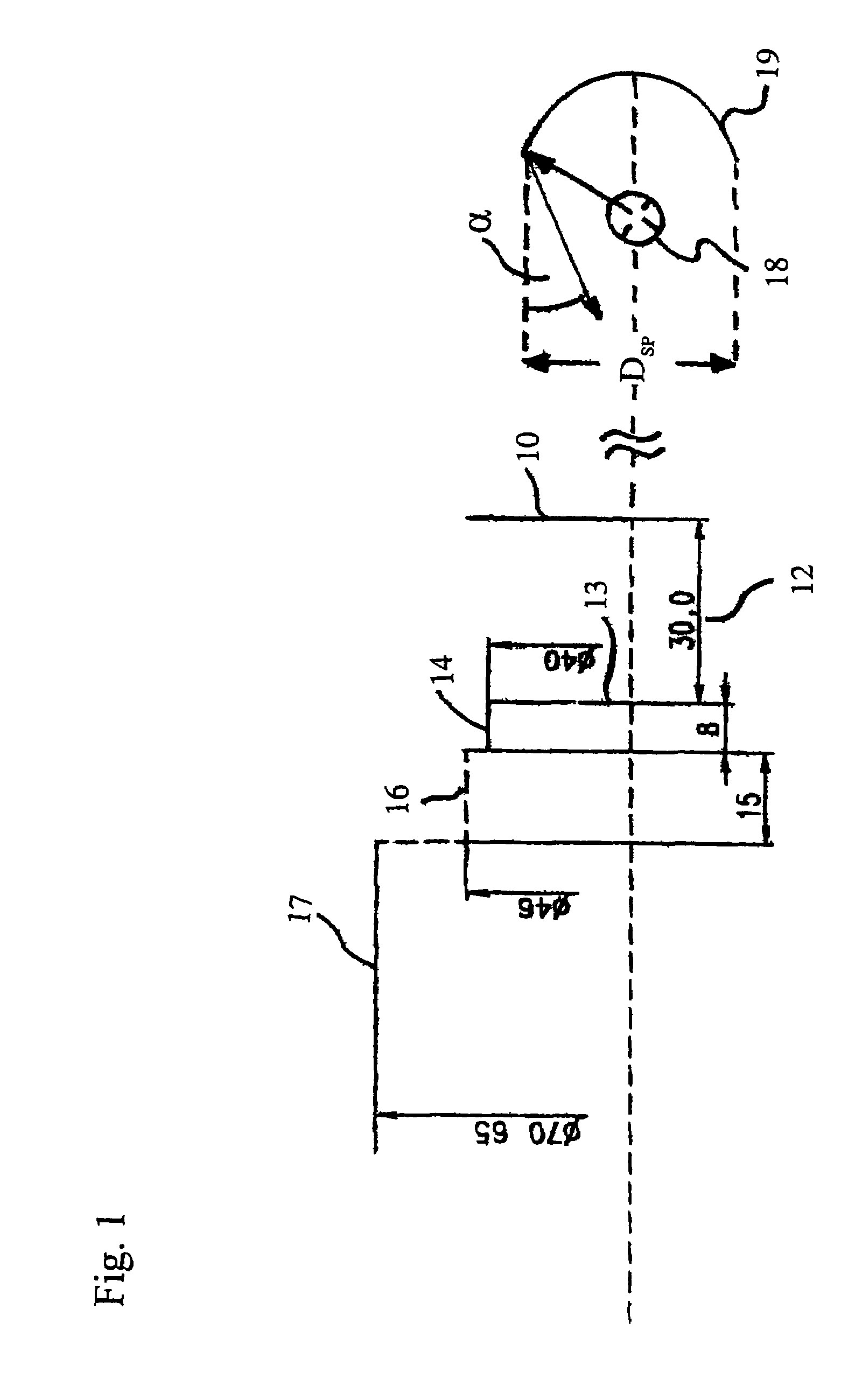
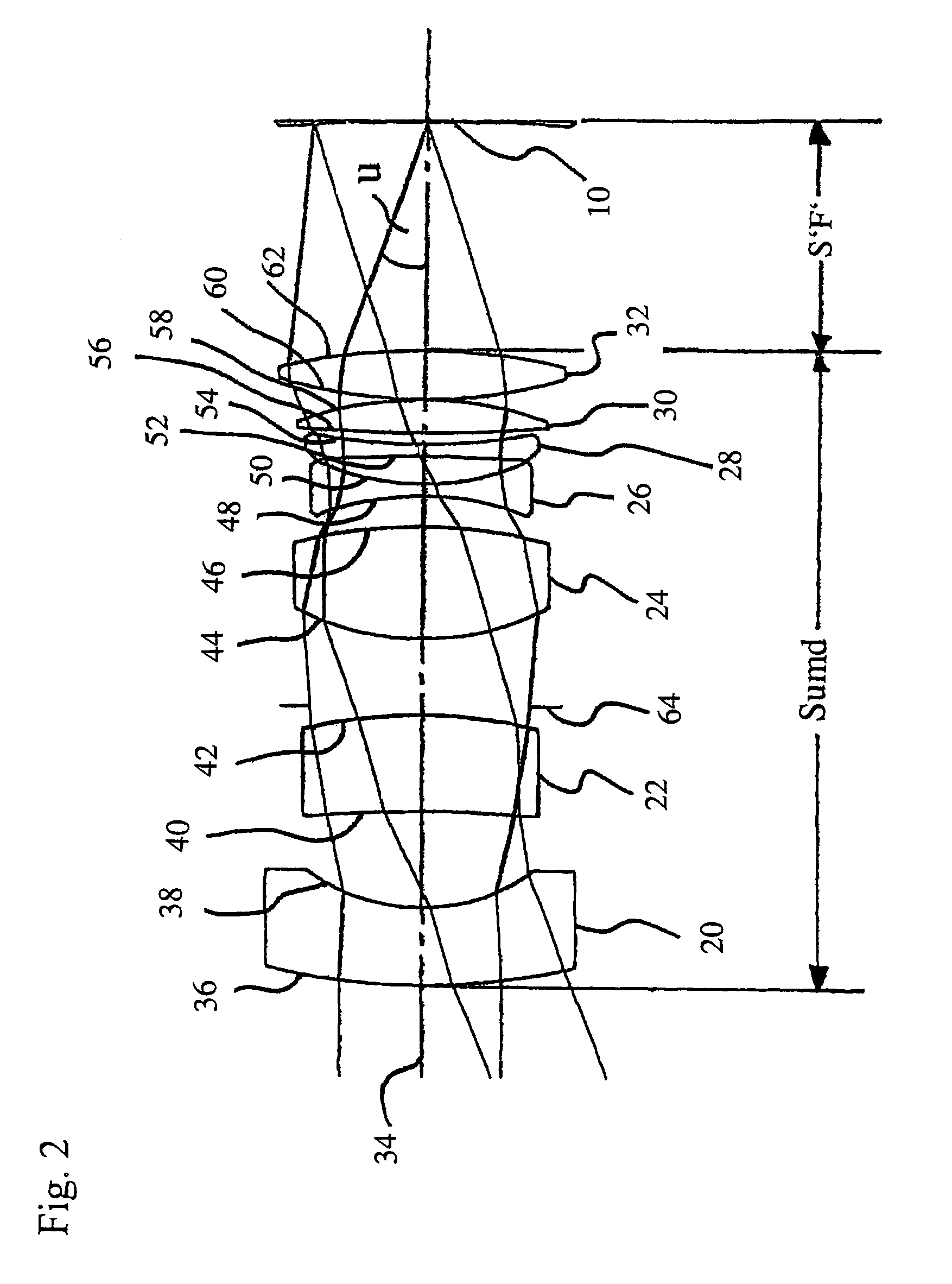
The invention relates to a camera lens. The camera lens has the total effective focal length f and entrance pupil diameter EPD, and the camera lens sequentially comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a sixth lens and a seventh lens from the object side to the image side along the optical axis. The first lens has positive power, and the object side face of the first lens is a convex face; the second lens has positive power, and the object side face and the image side face of the second lens are convex faces; the third lens has negative power, the fourth lens and the fifth lens each have positive power or negative power, the sixth lens has positive power or negative power, and the image side face of the sixth lens is a concave face at the paraxial position; the seventh lens has negative power, and the image side face of the seventh lens is a concave face at the paraxial position, wherein the total effective focal length f and entrance pupil diameter EPD meet the formula f / EPD<=1.9.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Stereoendoscope wherein images having passed through plural incident pupils are transmitted by common relay optical systems
InactiveUS6976956B2Reduce the number of partsVariationEndoscopesEye treatmentLight guideImage formation
The illuminating light transmitted by the light guide inserted through the elongate inserted section is projected out of the distal end surface of the inserted section. The illuminated objects pass through the respective pupils of the two objective lens systems arranged in parallel within the distal end section of the inserted section and their images are formed on the focal surface. The respective images are transmitted to the rear side by one common relay lens system. The transmitted final images are formed respectively on the image taking surfaces of the image taking devices. The respective images photoelectrically converted by the respective image taking devices are processed to be signals, are displayed in the monitor and are stereo-inspected through shutter spectacles.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Optical system
ActiveUS8072693B2Reduce lightHigh resolutionPanoramic photographyOptical elementsLight beamOptic system
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Imaging optical system and exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20030076483A1MirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEntrance pupilImage-forming optical system
An imaging optical system may be capable of forming substantially in one or more second planes one or more complete and / or partial images of one or more objects arranged substantially in one or more first planes and may comprise one or more entrance pupils, at least one of which is located substantially on an opposite side of at least one of the first plane or planes from the imaging optical system exclusive of the at least one entrance pupil so located. Such imaging optical system may be constructed so as to be substantially telecentric on at least a same side thereof as at least one of the second plane or planes. Such imaging optical system may be such that all of the reflective surface or surfaces of the imaging optical system are located in one or more spaces substantially between at least one of the first plane or planes and at least one of the second plane or planes, inclusive, and / or such imaging optical system may further comprise one or more locations disposed in one or more optical paths from at least one of the first plane or planes to at least one of the second plane or planes, inclusive, and substantially optically conjugate to at least one of the first plane or planes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
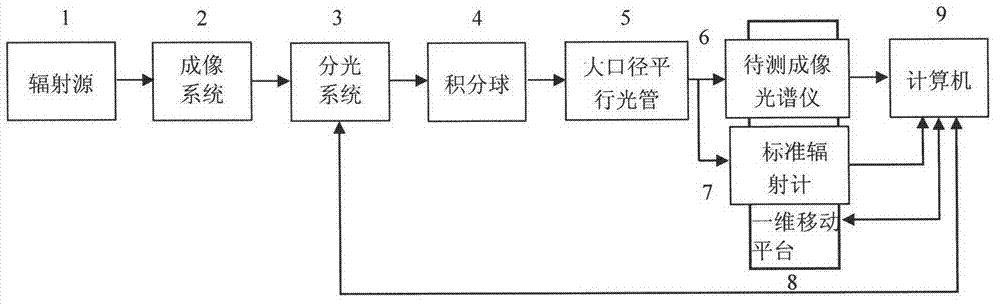
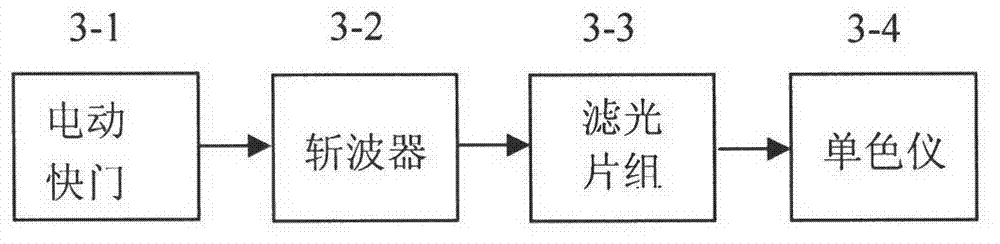
Imaging spectrometer absolute radiation calibration method
ActiveCN102829868ARealize full-band absolute radiometric calibrationSolving the challenge of absolute radiometric calibrationSpectrum investigationIlluminanceRadiometer
The invention discloses an imaging spectrometer absolute radiation calibration method and belongs to the field of optical metrological testing. The method utilizes a high-stability radiation source combination imaging system, a beam-splitting system and an integrating sphere to generate uniform monocolor radiation through a heavy-caliber parallel collimator to form collimated radiation to be received by a standard radiometer with a precise diaphragm and a measured imaging spectrometer, spectral radiant luminance on an entrance pupil face of the measured imaging spectrometer is calibrated by the standard radiometer, and full wavelength absolute radiation calibration of the imaging spectrometer can be realized. The imaging spectrometer absolute radiation calibration method solves the problem of absolute radiation calibration of current imaging spectrometers, measuring of responsivity uniformity of the imaging spectrometer can also be realized, and the imaging spectrometer absolute radiation calibration method has the advantages of high calibration accuracy and wide application prospect.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二0五研究所
Otoscope
An otoscope permitting examination of a patient's ear is defined by an instrument head including a proximal end and a distal insertion portion that is insertable into the ear. The otoscope includes an imaging lens train disposed within the instrument head, wherein each of the imaging lens train, an eyepiece and a distal opening of said insertion portion are aligned along an optical axis. The otoscope further includes a focusing mechanism for selectively moving at least one of the imaging lens train and the optics contained within the eyepiece relative to one another along the optical axis. The imaging lens train and the optics in the eyepiece define an optical system such that an entrance pupil is substantially located in the distal insertion portion of the instrument head, thereby enabling the entire tympanic membrane to be viewed at once by the user.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Optical Informational Recording/Reproduction Device and Method
InactiveUS20080192311A1Accurate recordExact reproductionOptical beam sourcesRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsRecording layerEntrance pupil
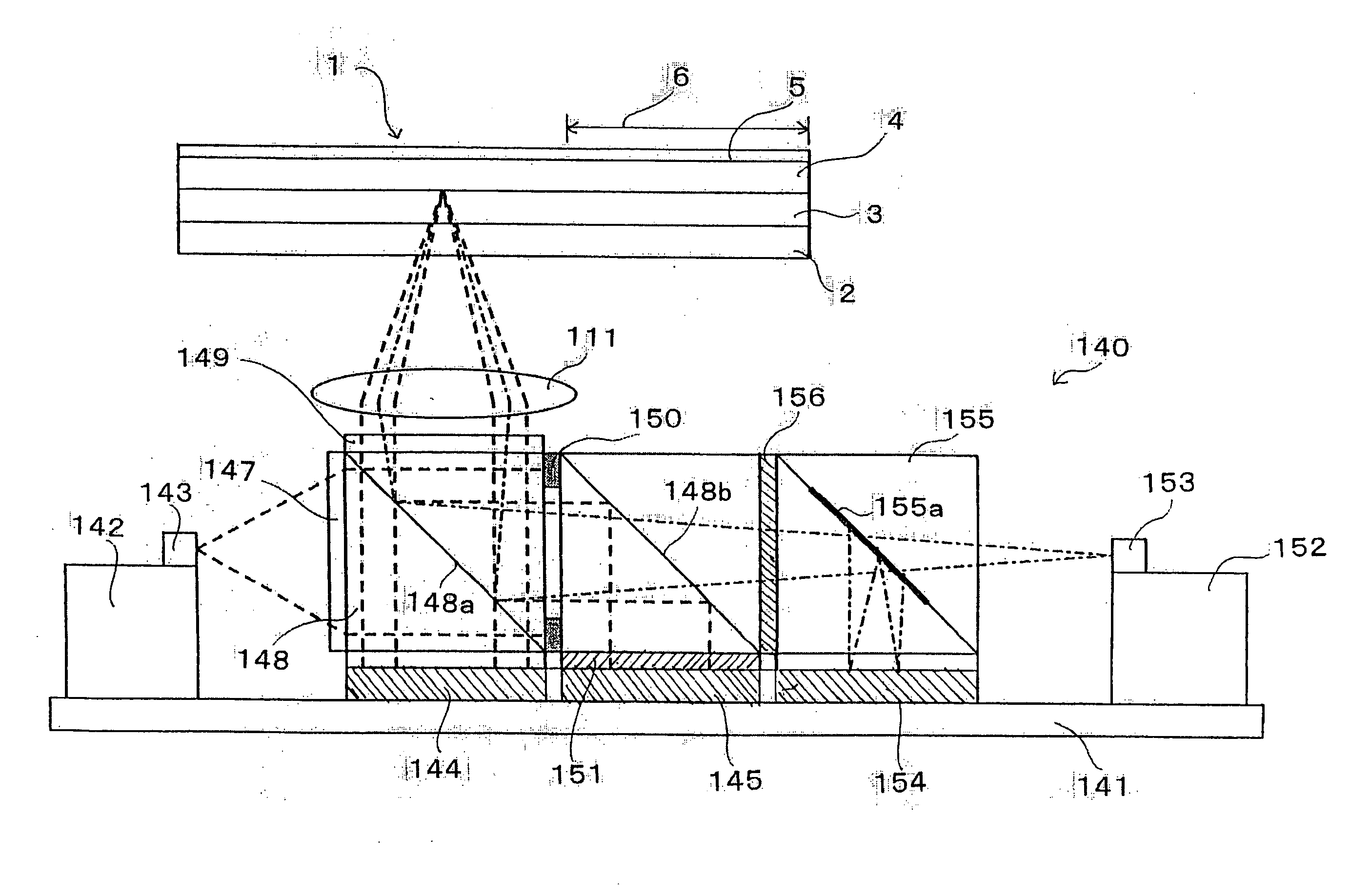
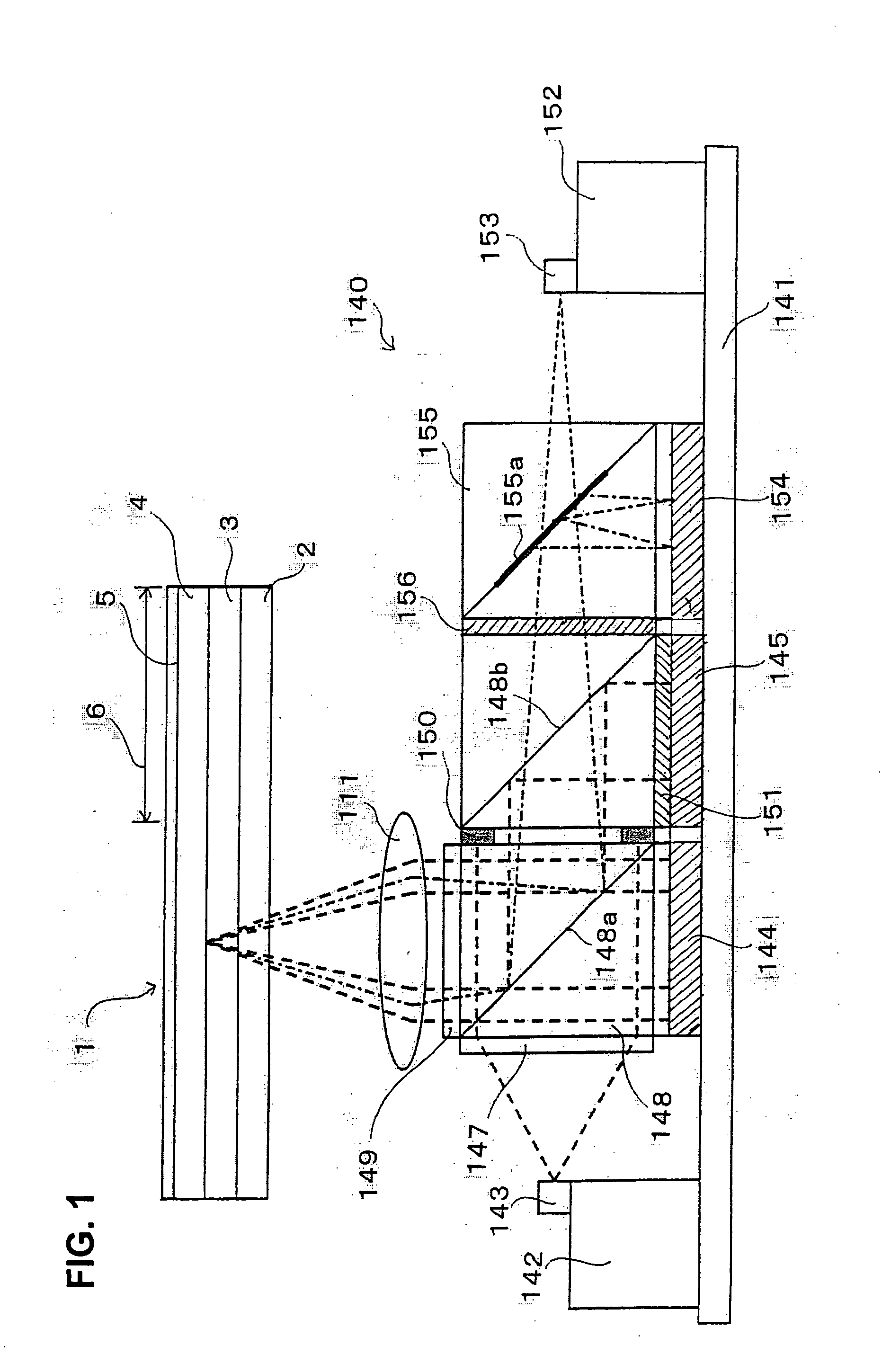
An optical information recording device, a reproduction device, and a method enabling include a first spatial light modulator I for generating information light by spatially modulating light from a light source 143 by a plurality of pixels and a second spatial light modulator R for generating reference light by spatially modulating light from a light source by a plurality of pixels. The area I of the information light and the area R of the reference light on the entrance pupil surface of an objective lens 111 are formed such that one area surrounds the other area. The reference light is spatially modulated by the second spatial light modulator R such that interference is not easily generated between the reference lights in the information recording layer 3.
Owner:OPTWARE
Optical imaging lens
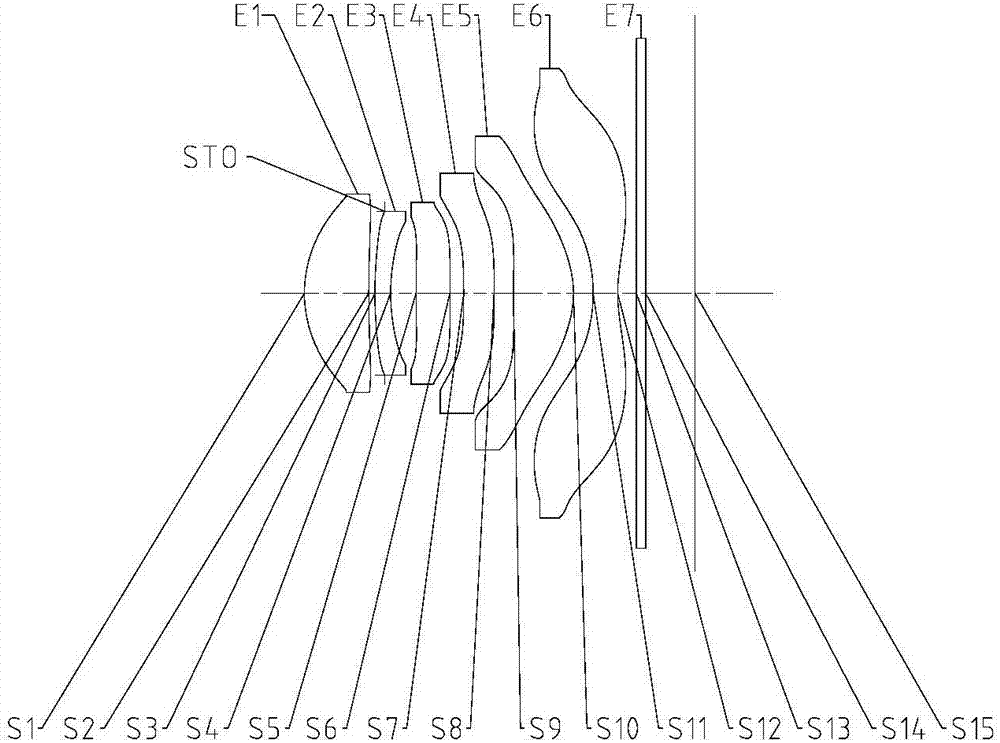
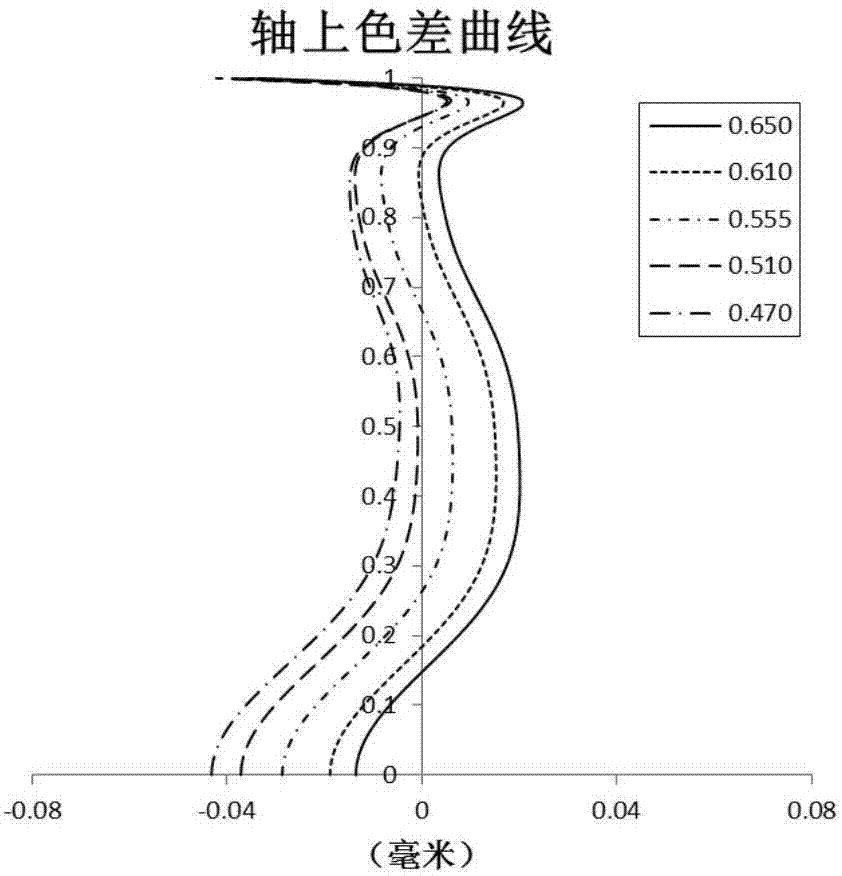
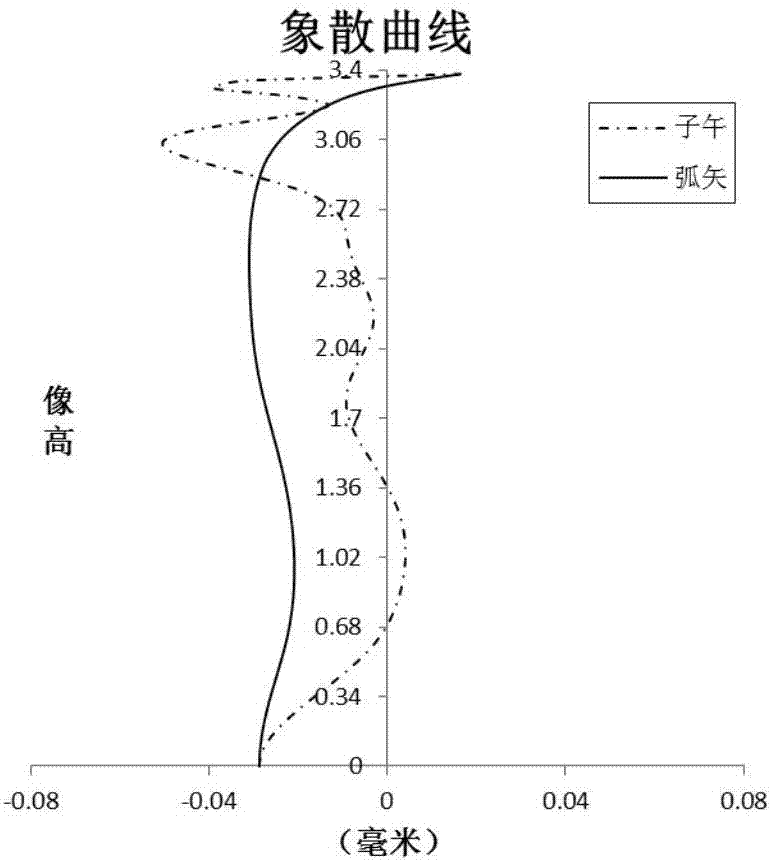
The application discloses an optical imaging lens, comprising a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a sixth lens and a seventh lens sequentially from the object side to the image side along an optical axis. The first lens has positive focal power, the object side of the first lens is a convex face, and the image side thereof is a concave face. The second lens has negative focal power, the object side of the second lens is a convex face, and the image side thereof is a concave face. The third lens has positive or negative focal power. The fourth lens has positive or negative focal power, and the object side of the fourth lens is a concave face. The fifth lens has positive or negative focal power. The sixth lens has positive or negative focal power. The seventh lens has negative focal power, the object side of the seventh lens is a concave face, and the image side thereof is a concave face. Total effective focal length f of the optical imaging lens and EPD (entrance pupil diameter) thereof meets f / EPD< / =1.70.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Taking apparatus
InactiveUS20070177047A1Implementation processSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight sensingMedicine
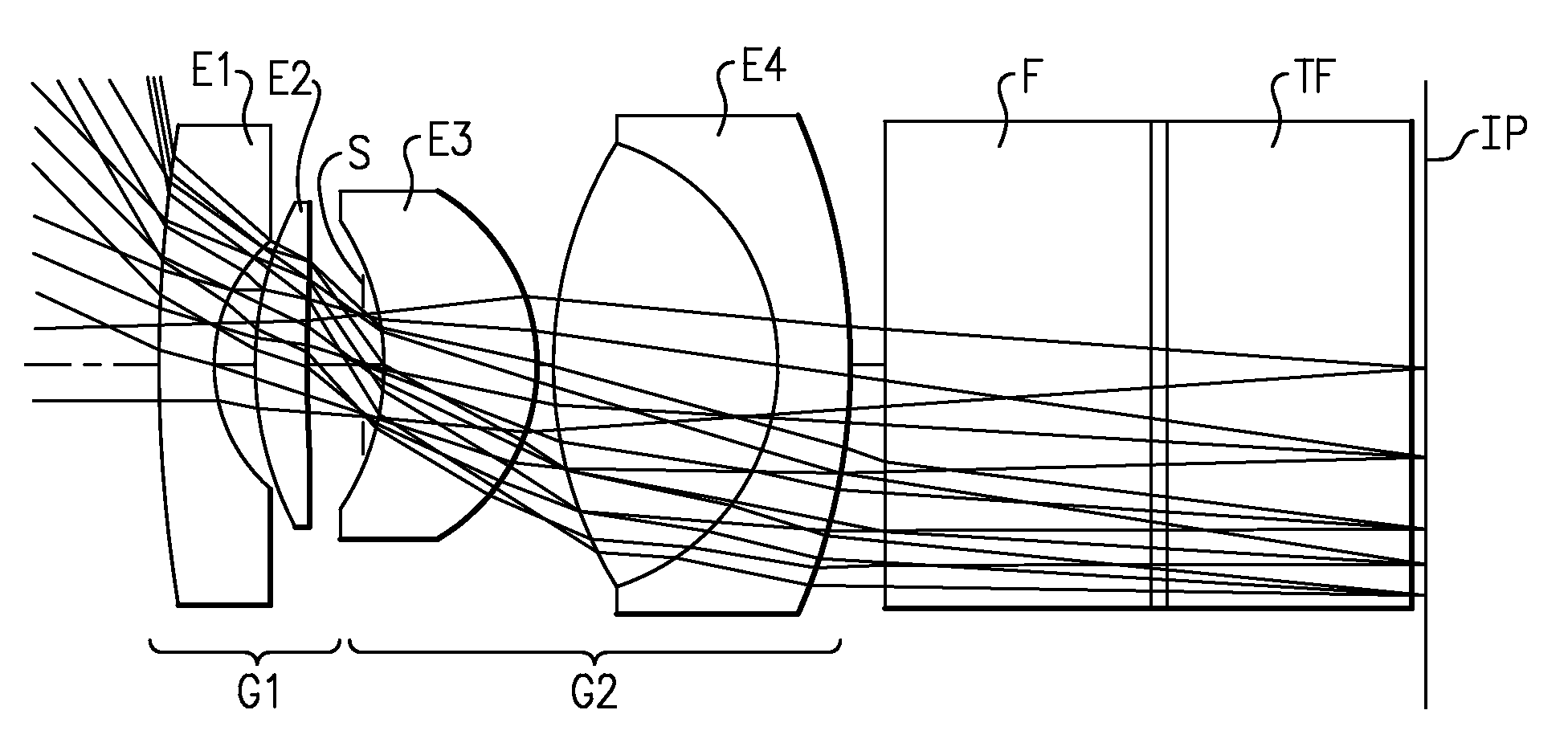
The present invention concerns an imaging apparatus which works for size reductions, power savings, the efficient attainment of the quantity of light sensed, and prevention of contrast decreases due to a diffraction phenomenon, is well fit for the taking and appreciation of common still pictures, and comprises a taking lens and electronic imaging device combination that takes full advantage of the characteristics of an imaging device. The imaging apparatus comprises a taking optical system, and an electronic imaging device which is located on an image side of said taking optical system, includes an imaging plane I with a plurality of two-dimensionally arranged light sensors, and is adapted to convert an image formed through said imaging optical system into electrical signals. In at least one taking state, the apparatus satisfies at the same time condition (1) about relations of the area of the entrance pupil to the focal length of the taking optical system, condition (2) about the number of effective pixels of the imaging plane, condition (3) about the effective area of the imaging plane, and condition (4) about the division of the effective area of the imaging plane by the number of effective pixels.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
Dynamic image modulation transfer function measuring device
The invention relates to a dynamic image modulation transfer function measuring device belonging to the field of optical property tests and sequentially comprising a point light source, a collimator objective, a pupil coupling system and a photoelectronic imaging system along the light propagating direction, and also comprising a driver, a motor, a lead screw, a computer and an image collector card, wherein the pupil coupling system adopts parallel light incidence and parallel light emergence; the entrance pupil of the pupil coupling system and the exit pupil of the collimator objective have same size and same position; the exit pupil of the pupil coupling system and the entrance pupil of the photoelectronic imaging system have same size and same position; the pupil coupling system is dismantled, and the exit pupil of the collimator objector and the entrance pupil of the photoelectronic imaging system have same size and same position; and the time difference of image acquisition of the photoelectronic imaging system and the travel of a sliding block I is set by a hardware delay circuit or software delay program. The device can not only eliminate image vignetting caused by target travel, but also can realize time comparison of the measurement result and the theoretical model.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Device and method for focusing and leveling based on microlens array
InactiveCN101201549ALow stability requirementsReduce difficultyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLight spotMicro-Opto-Electro-Mechanical Systems
The invention discloses a method and a device based on focusing and leveling of a lenticule array and belongs to the technical field of opto-electrical detection. The invention comprises an emitting part and a receiving part, wherein, the emitting part comprises a light source, a focusing lens, a pinhole filter, a beam expanding lens, an optimal entrance pupil device, a lenticule array and a steering mirror; the receiving part comprises a steering mirror, a lenticule array, a focusing lens, a scan mirror of a micro-opto-electro-mechanical-system (OMEMS), a pinhole filter and a detector. The invention adopts the optimal entrance pupil device to control light entrance quantity and then improve measuring light spot, or the quantity of the imaging point can be controlled by the state of a switch to adapt to different exposure viewing field; the invention adopts the lenticule array to replace a slit array; the scan mirror of the micro-opto-electro-mechanical-system (OMEMS) is adopted to replace the single lens scan; the difference receiving method is adopted and then the requirement for stability of the light source is decreased and higher measuring accuracy can be acquired.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
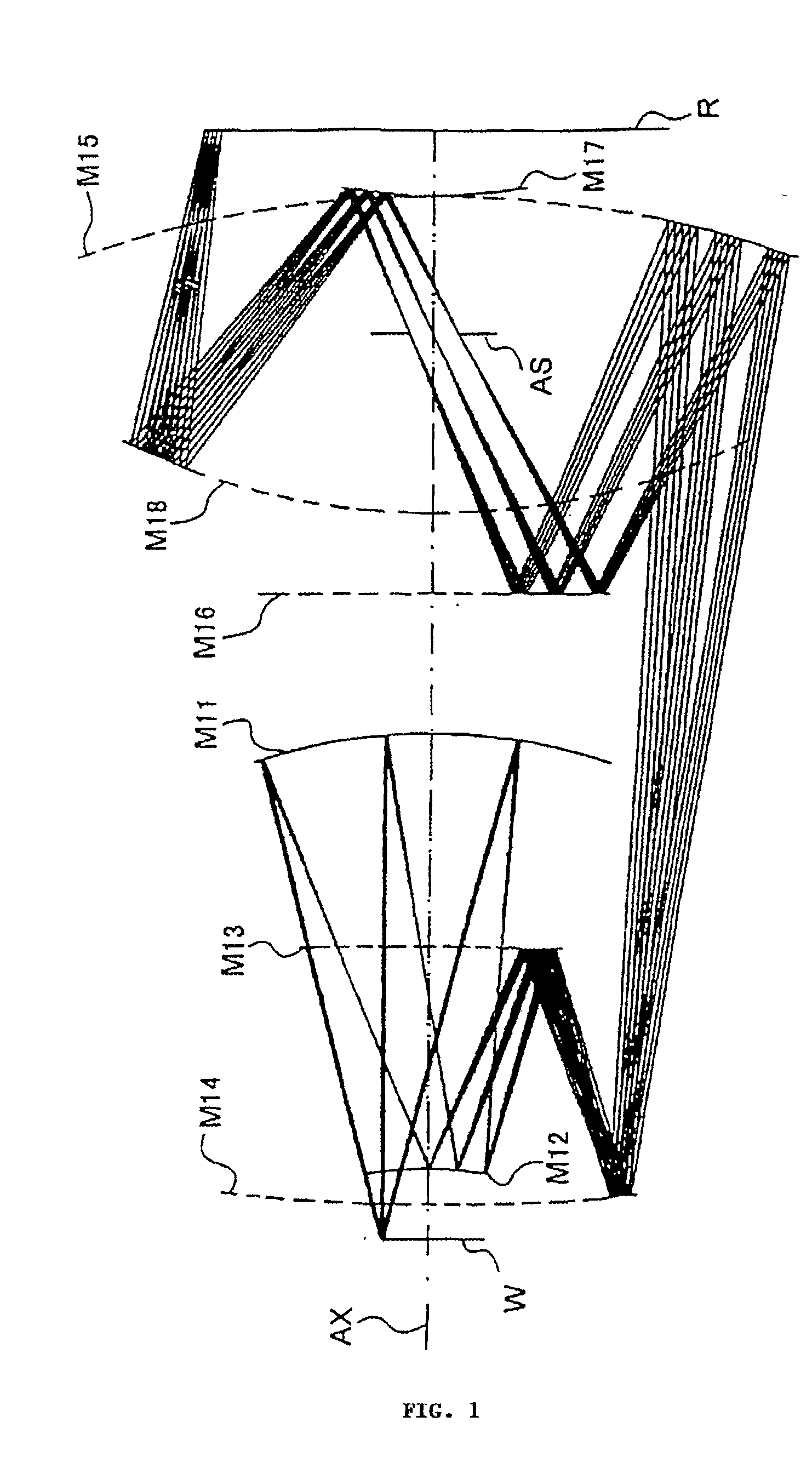
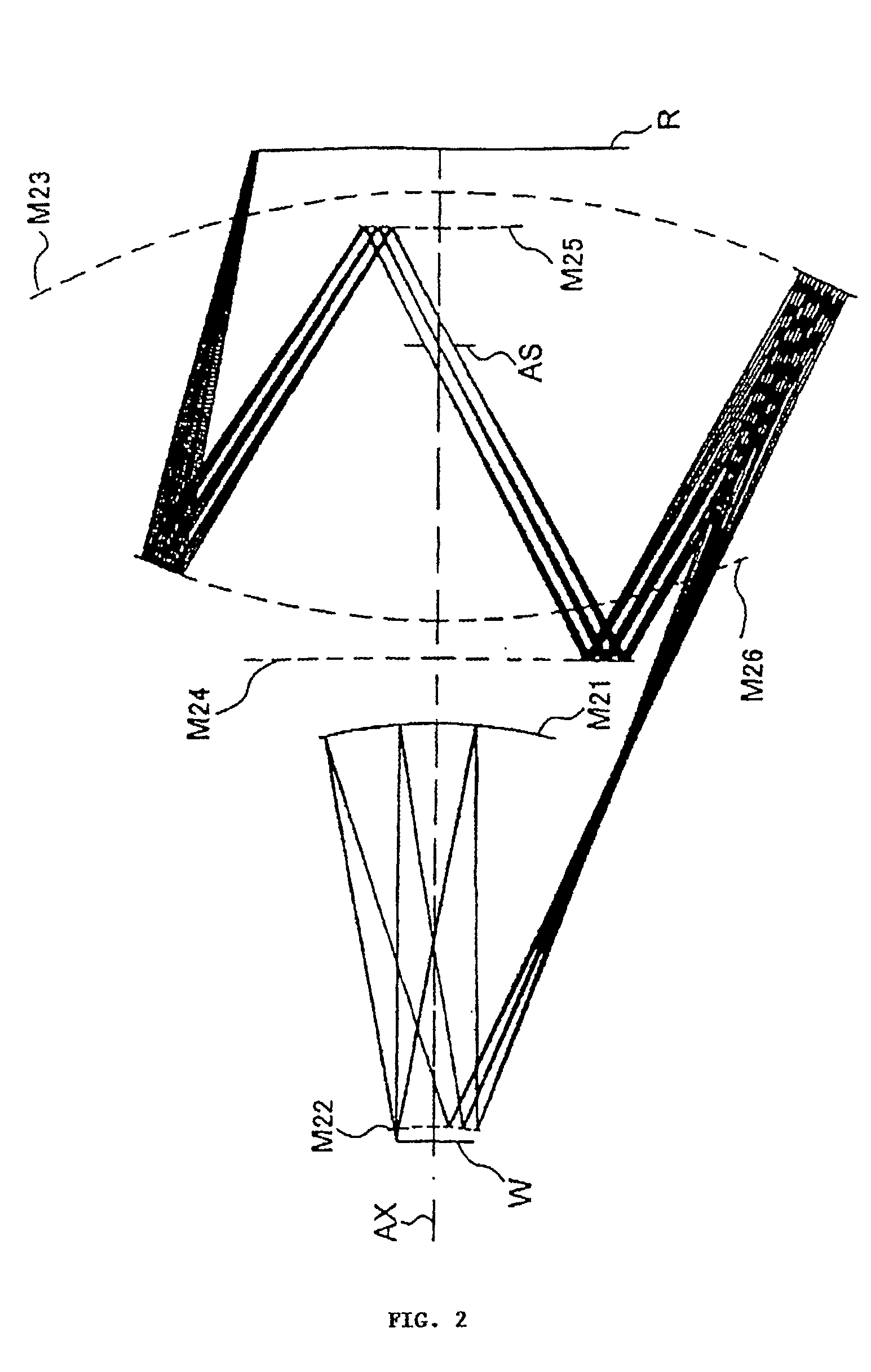
6-mirror microlithography projection objective
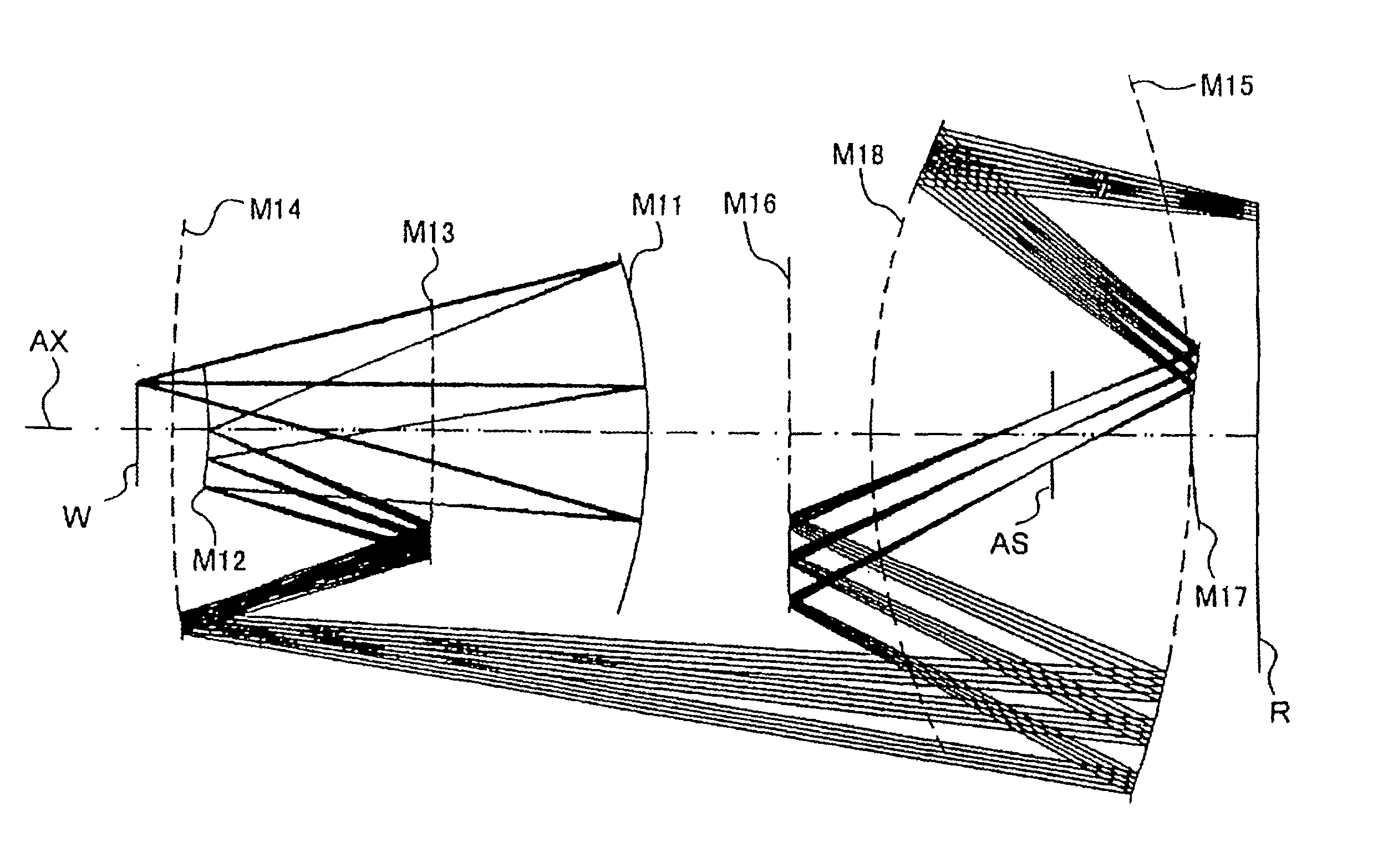
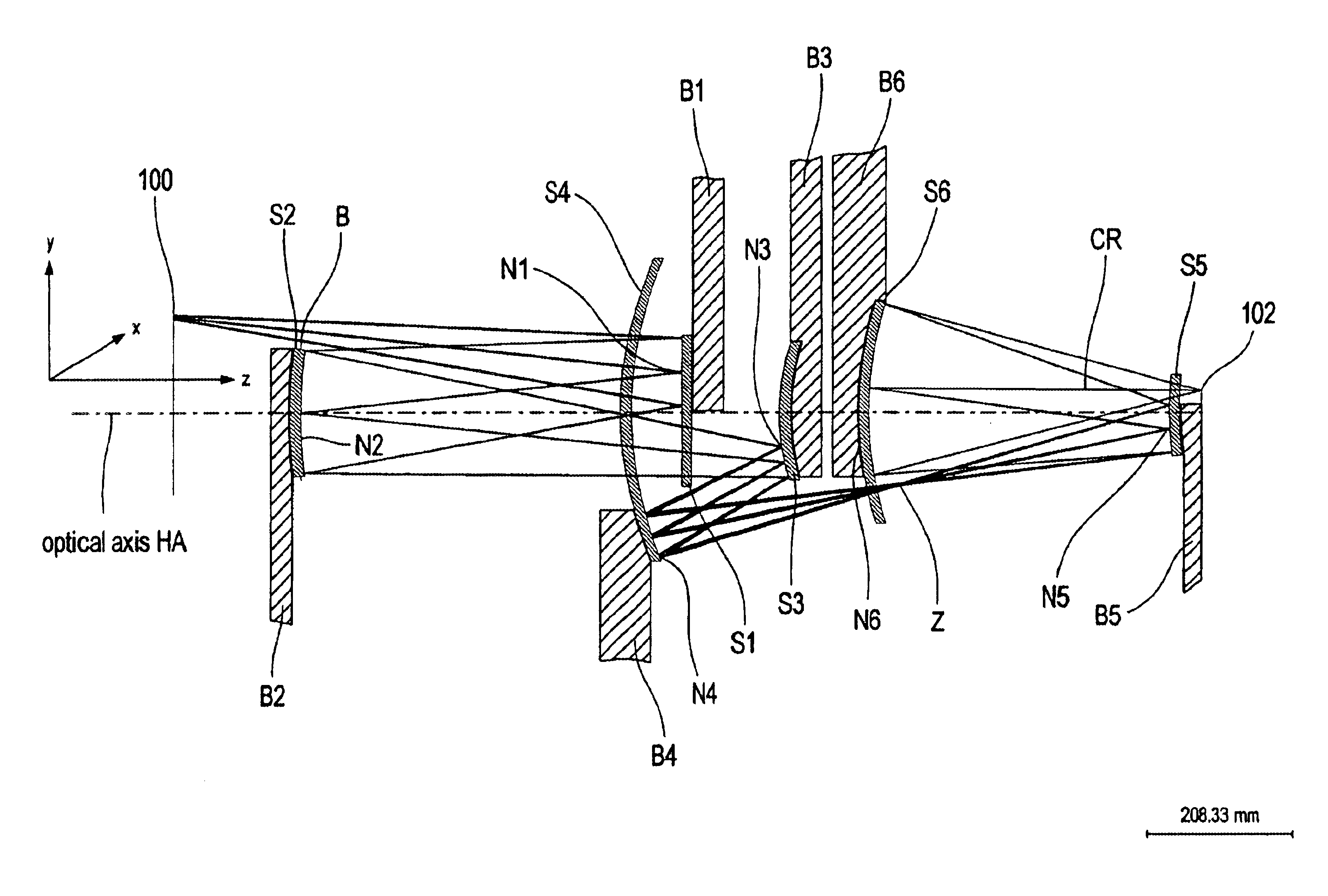
InactiveUS20020056815A1Increase the number ofMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusExit pupilAxis of symmetry
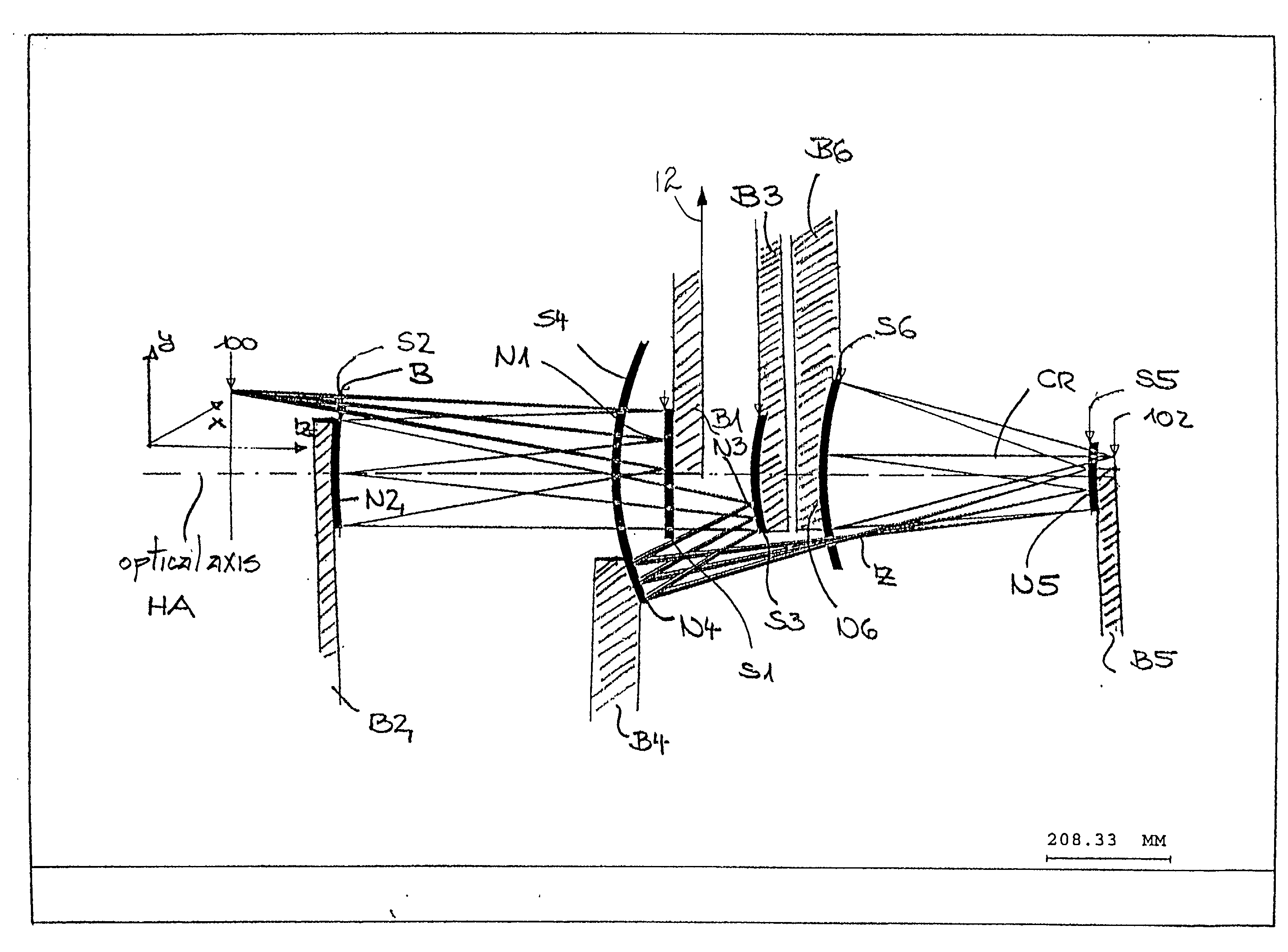
The invention regards to a microlithography projection objective for short wavelengths, preferably <=193 nm, with an entrance pupil and an exit pupil for the imaging of an object field in an image field, which represents a segment of a ring field, wherein the segment has an axis of symmetry and an extension perpendicular to the axis of symmetry, and the extension is at least 20, and preferably 25 mm. The microlithography projection objective comprises a first (S1), a second (S2), a third (S3), a fourth (S4), a fifth (S5), and a sixth mirror (S6) in centered arrangement relative to an optical axis, whereby each of these mirrors has a off-axis segment, in which light beams impinge, which have been guided through the projection objective. whereby as a function of the numerical aperture NA of the exit pupil, the diameter of the off-axis segment of the first, second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth mirrors is <=1200 mm*NA.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
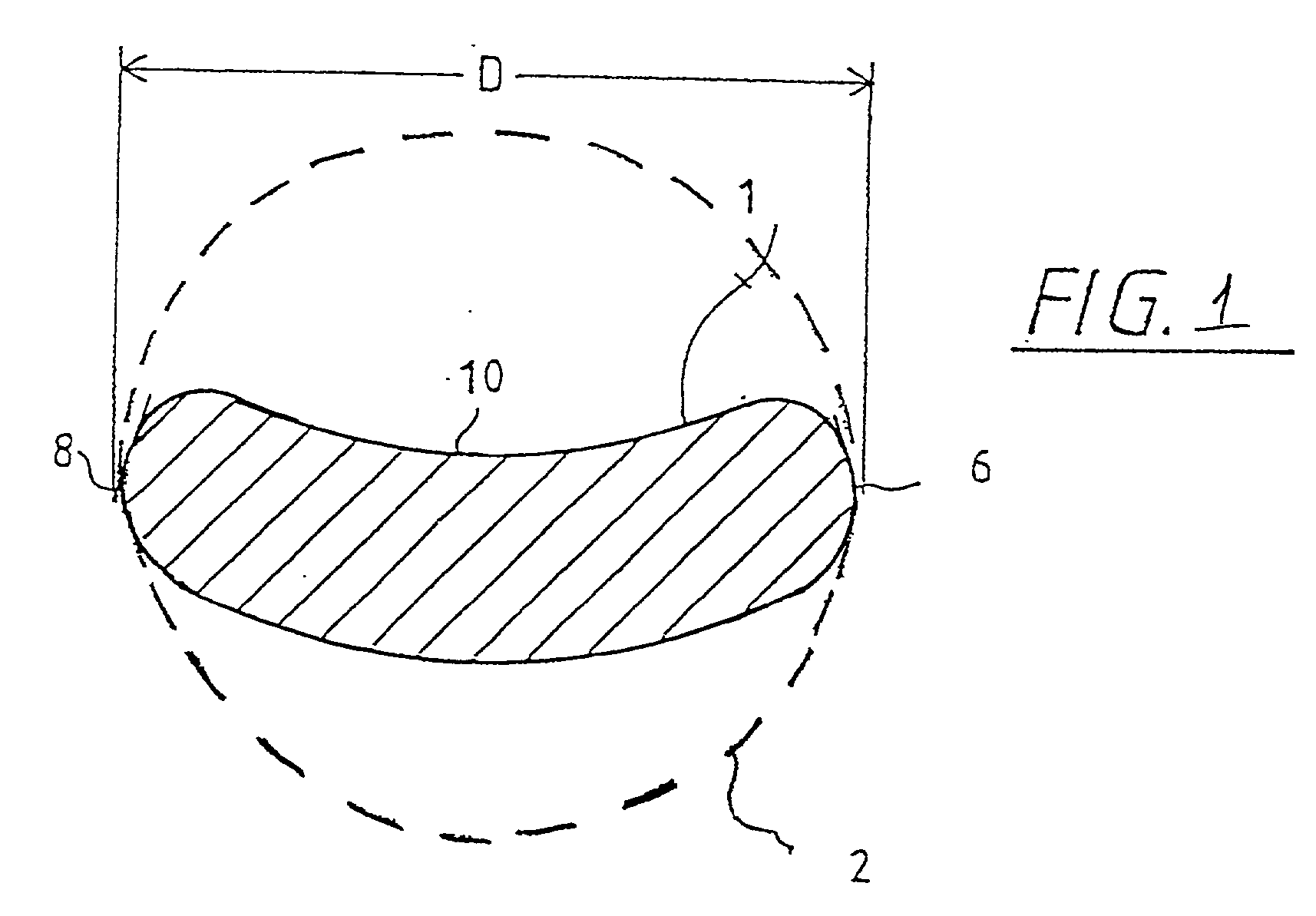
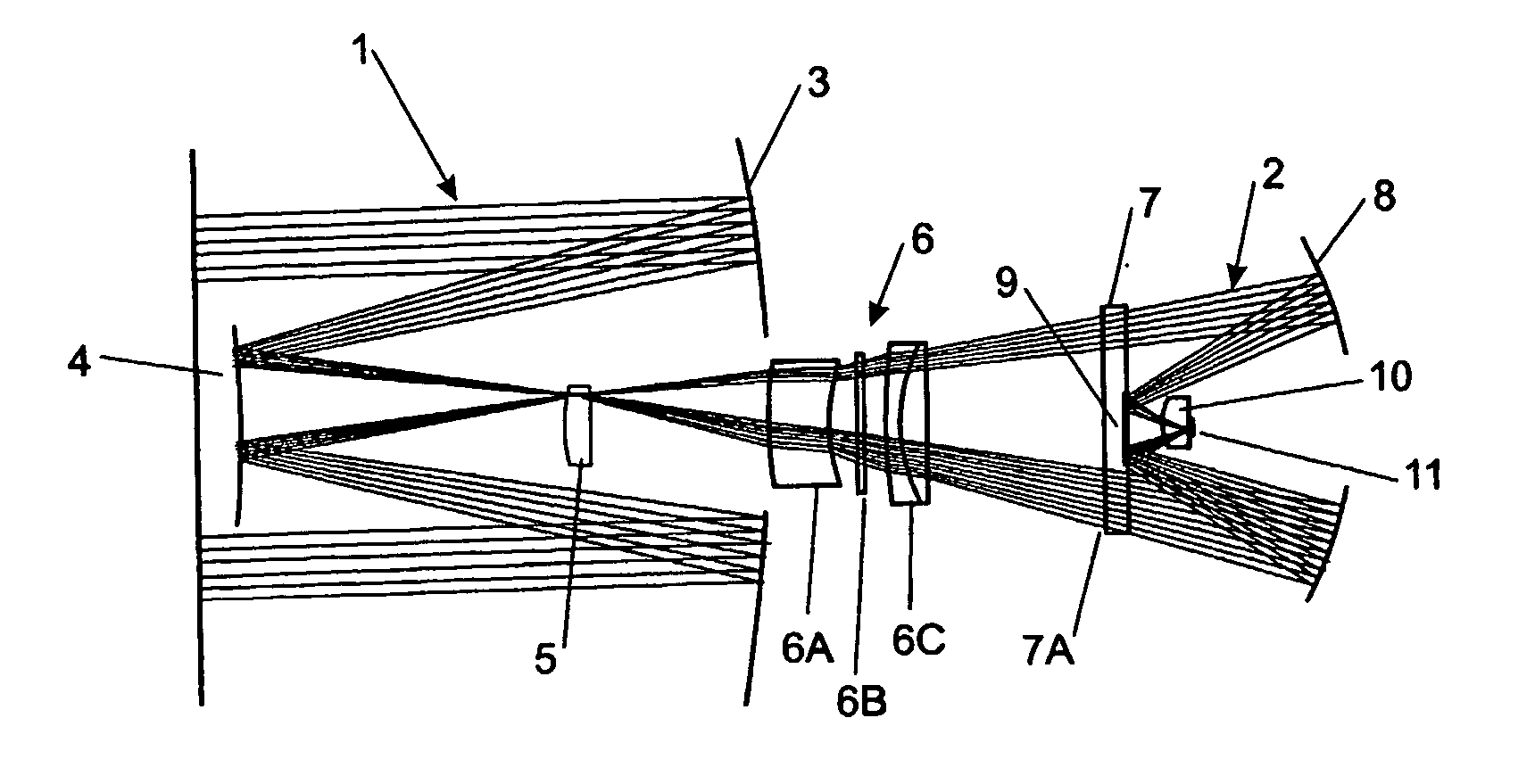
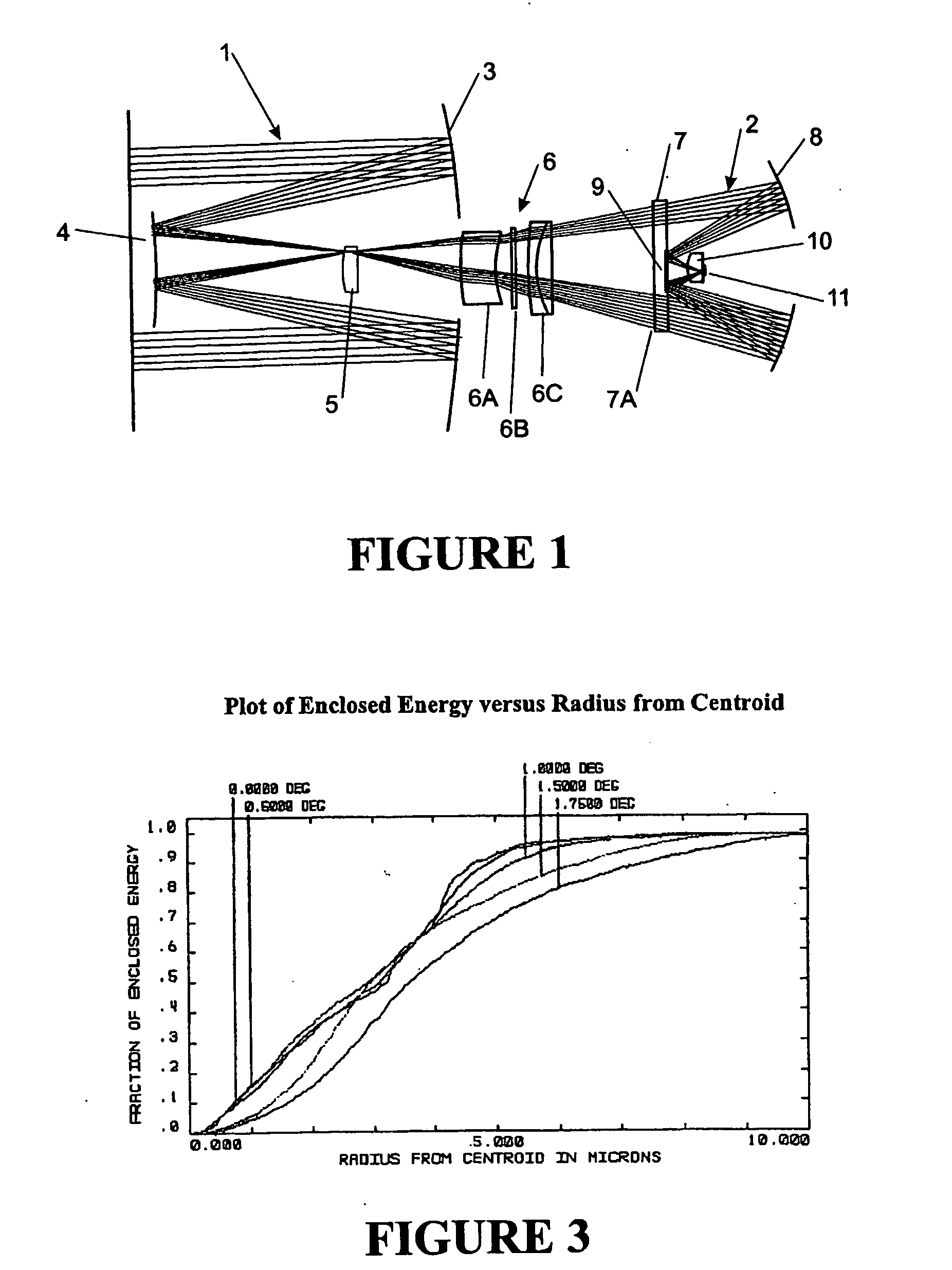
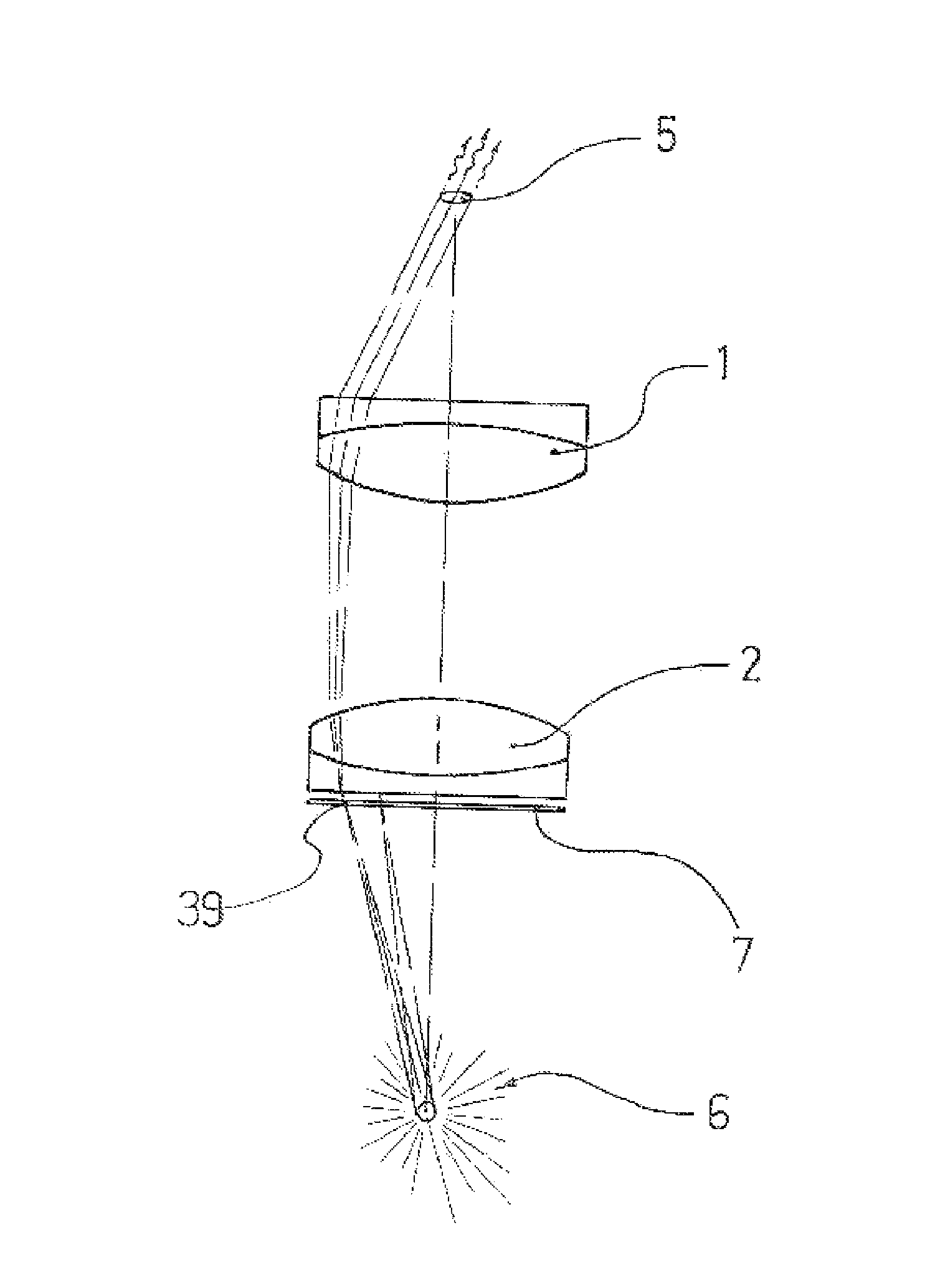
Optical imaging system with aberration correcting means
An optical system includes a front end (1), a rear end image relay (2), an image transfer means (5) adapted to image the aperture stop of the rear end image relay (2) to a position where it forms the entrance pupil of the optical imaging system, and aberration correcting means (6, 7), including a lens (7) having an aspheric surface (7A) at or adjacent the aperture stop of the rear end image relay (2) and a meniscus lens (6A) to correct for both primary and higher order spherical aberration, the aspheric surface (7A) being sufficiently aspherical that chromatic error introduced by lens (7) cancels at least a major part of chromatic error introduced by the meniscus lens (6). The aberration correcting means may further include a multiple component lens (6C) to also cancel chromatic error. The front and rear ends may include one or more mirrors in different configurations.
Owner:IND RES LTD
Laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared common-aperture three-band imaging system
ActiveCN103278916AReduce volumeExcellent aberration correctionOptical elementsBeam splitterImaging quality
The invention relates to a laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared common-aperture three-band imaging system, which comprises an entrance pupil shared by each band, a primary mirror, a secondary convex mirror, a middle / long-wavelength infrared optical path imaging lens group, a laser converging light spot receiving unit, a middle- and long-wavelength infrared band beam splitter, a middle- and long-wavelength infrared dual-band imaging lens group and a detection image surface, wherein the reflection surface of the primary mirror is a concave surface, and a hole is formed in the center of the primary mirror. The system can be used for realizing the common-aperture collection of scene infrared radiation energy of the same object and laser echo energy reflected by the object; and the entrance pupil is positioned in front of the primary mirror, the secondary mirror is used for the beam splitting of laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared bands, and a dichroic mirror is inclined to split middle-wavelength infrared light and long-wavelength infrared light, so that the system is compact in structure, the utilization rates of optical energy and space of the system are increased, the aberration correction and beam focusing of middle- and long-wavelength infrared bands are facilitated respectively, and the imaging quality is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
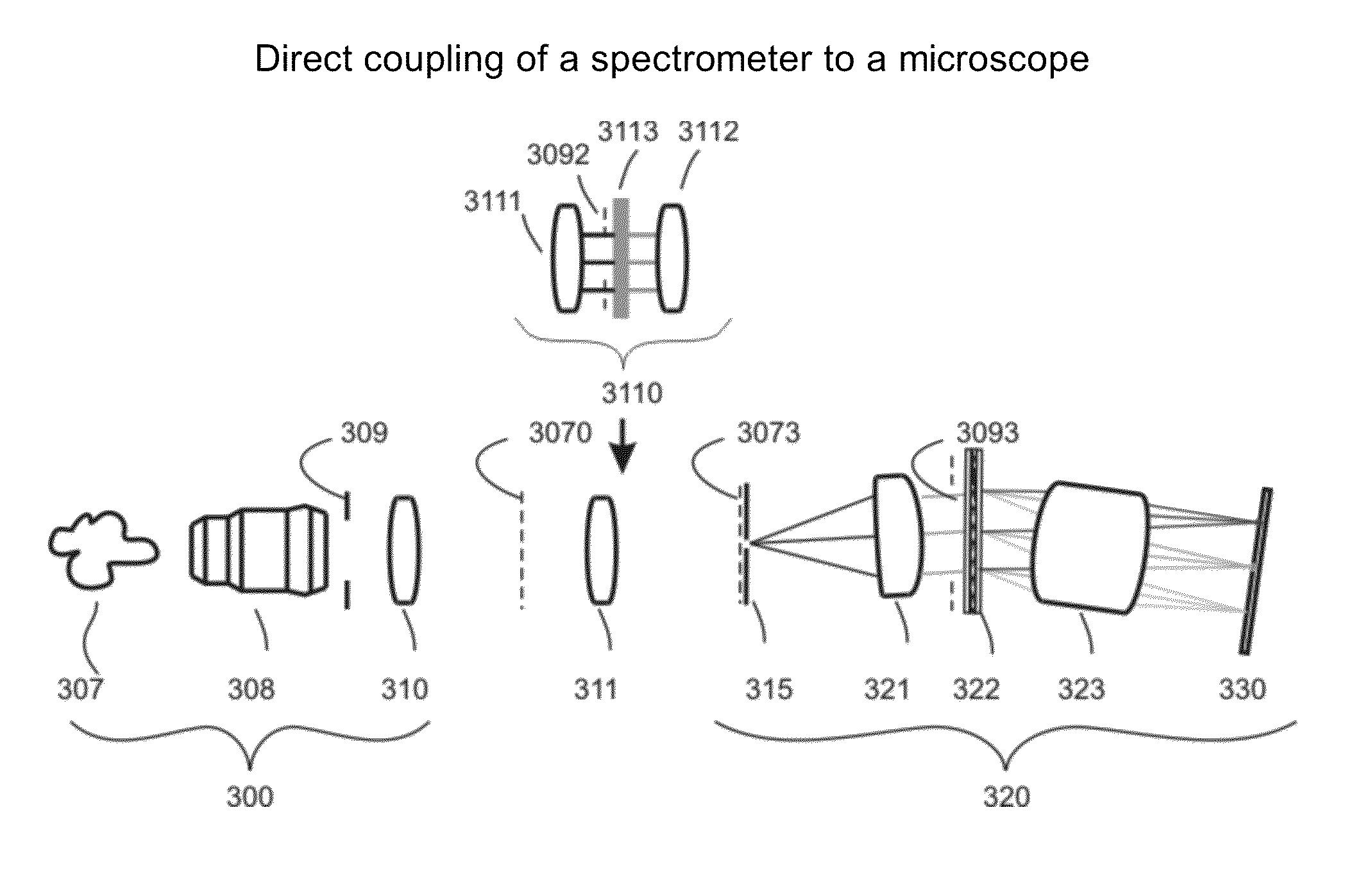
Optimal coupling of high performance line imaging spectrometer to imaging system
An optical coupling relay system has an imaging optical system having an object plane, an exit pupil and an image plane. An image analyzer has an image plane and an entrance pupil, and a detector is located in a detector plane and contains photosensitive material. An optical coupling relay couples the optical system to the image analyzer, for projecting the image produced by the imaging optical system into the image plane of the image analyzer and simultaneously for projecting the exit pupil of the imaging optical system into the entry pupil of the image analyzer.
Owner:PAWLUCZYK ROMUALD +1
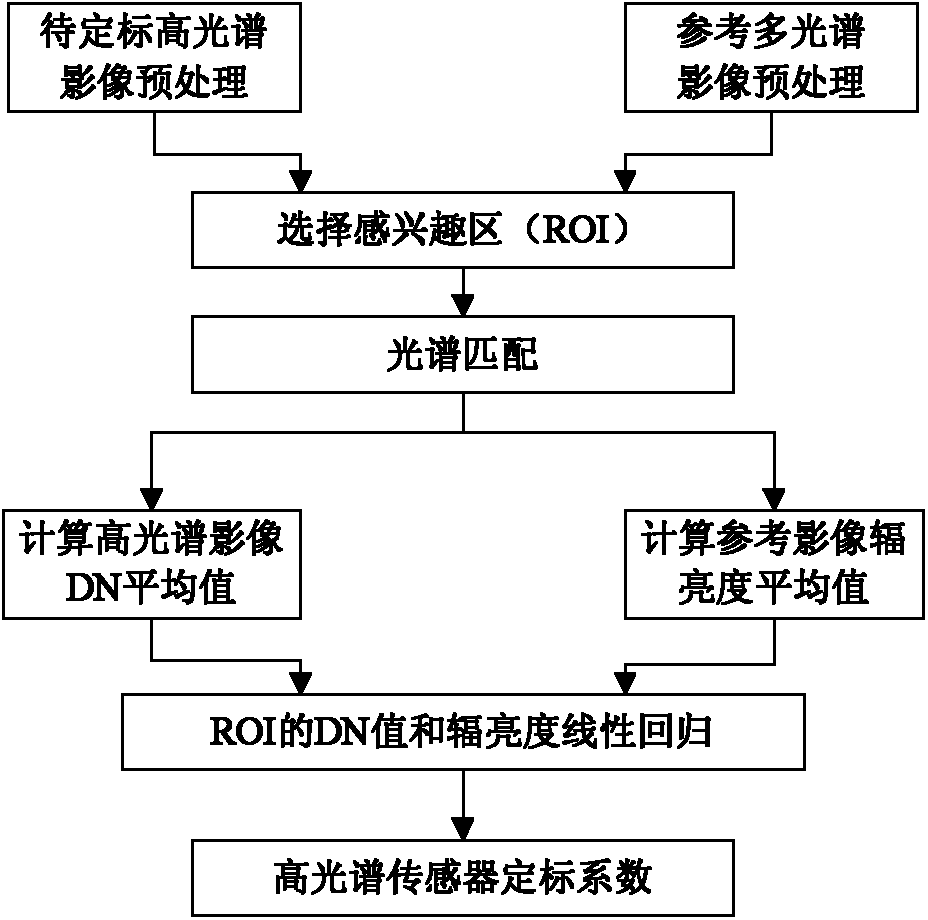
A cross-radiation calibration method for hyperspectral sensors based on multispectral sensors
InactiveCN102279393AAchieving Cross Radiation CalibrationReduce mistakesWave based measurement systemsLightnessEntrance pupil
The invention discloses a cross radiometric calibration method of a hyper-spectral sensor based on a multi-spectral sensor. The method is used for solving the cross radiometric calibration problem of the hyper-spectral sensor without a matched reference hyper-spectral image. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting cloudless hyper-spectral image data; selecting a multi-spectral reference image according to the hyper-spectral data; selecting a uniform ground object on the image as an interesting region; performing geometric precise correction of the two images; calculating entrance pupil radiances of various types of wave bands of the two sensors by using an atmospheric radiation transmission model; solving spectrum matching factors of various types of corresponding wave bands according to a certain rule; solving the entrance pupil radiances of the various types of wave bands of the hyper-spectral sensor by using the spectrum matching factors and the multi-spectral data; and linearly fitting pixel DN (Digital Number) values in the interesting region of the hyper-spectral image to be calibrated and the radiances of corresponding pixels of the multi-spectral reference image after being corrected through the spectrum matching factors to obtain calibration coefficients of the various types of wave bands of the hyper-spectral sensor. The method has the advantages of good stability, high reliability, high precision and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Uniform pupil illumination for optical inspection systems
ActiveUS7001055B1Improve resolutionHigh sensitivityLighting elementsMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionPupil
An illuminator for uniformly illuminating an entrance pupil of an inspection system in order to increase inspection resolution and sensitivity and improve system-to-system matching is described. The illuminator incorporates at least two lightpipes for spatially and angularly distributing light rays from the illuminator uniformly across the entrance pupil. The illuminator also results in spatial and angular uniformity at the field stop plane. In one embodiment, one lightpipe has a circular shape and a second lightpipe has a rectangular shape.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
High-aperture wide angle cinema projection lens
Owner:JOS SCHNEIDER OPTISCHE WERKE AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT
6-mirror microlithography projection objective
InactiveUS6867913B2Improve accessibilitySmall dimensionMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusExit pupilAxis of symmetry
There is provided a microlithography projection objective for short wavelengths, with an entrance pupil and an exit pupil for imaging an object field in an image field, which represents a segment of a ring field, in which the segment has an axis of symmetry and an extension perpendicular to the axis of symmetry and the extension is at least 20 mm. The objective comprises a first (S1), a second (S2), a third (S3), a fourth (S4), a fifth (S5) and a sixth mirror (S6) in centered arrangement relative to an optical axis. Each of these mirrors have an off-axis segment, in which the light beams traveling through the projection objective impinge. The diameter of the off-axis segment of the first, second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth mirrors as a function of the numerical aperture NA of the objective at the exit pupil is ≦1200 mm * NA.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Infinity display with autostereoscopic capability
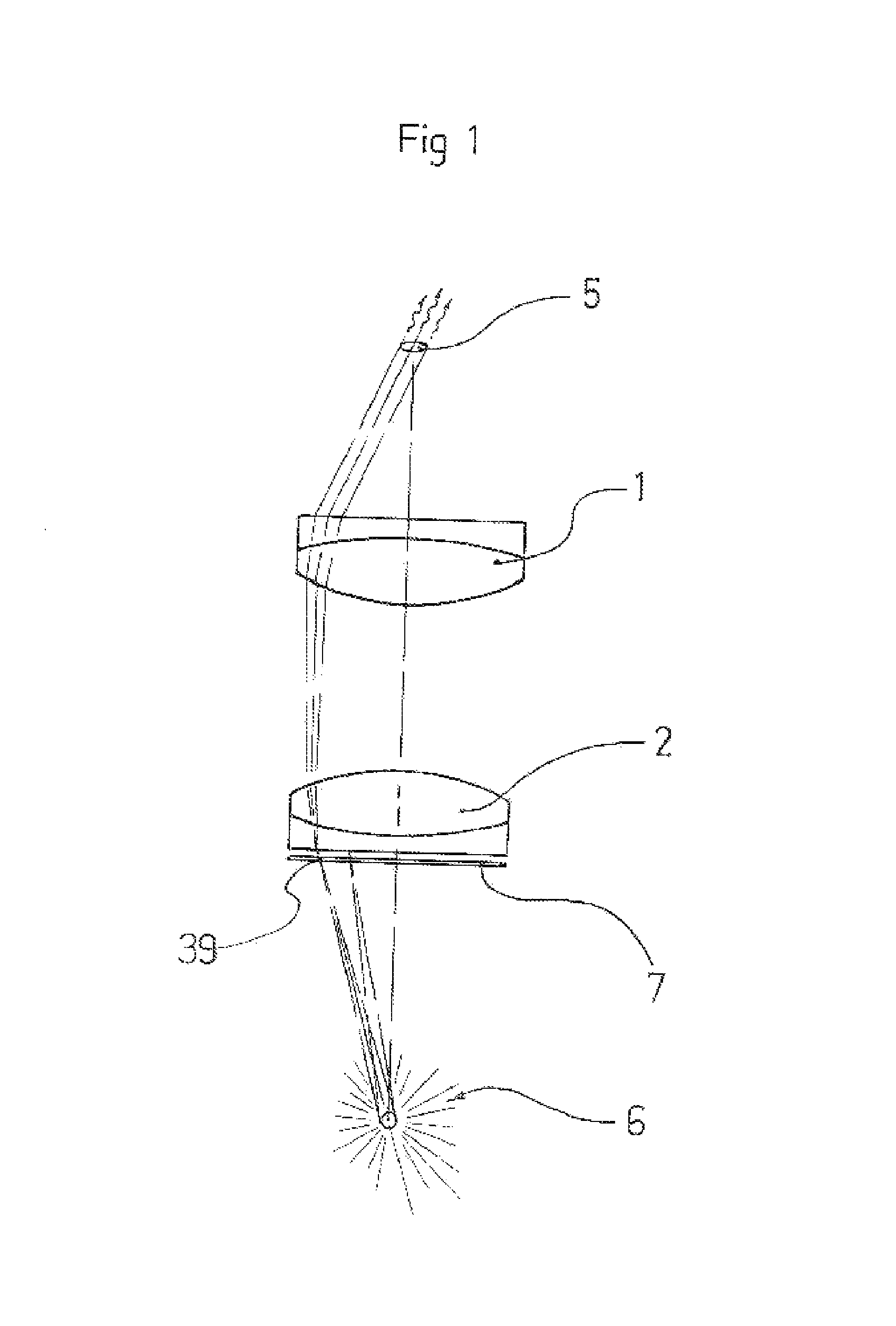
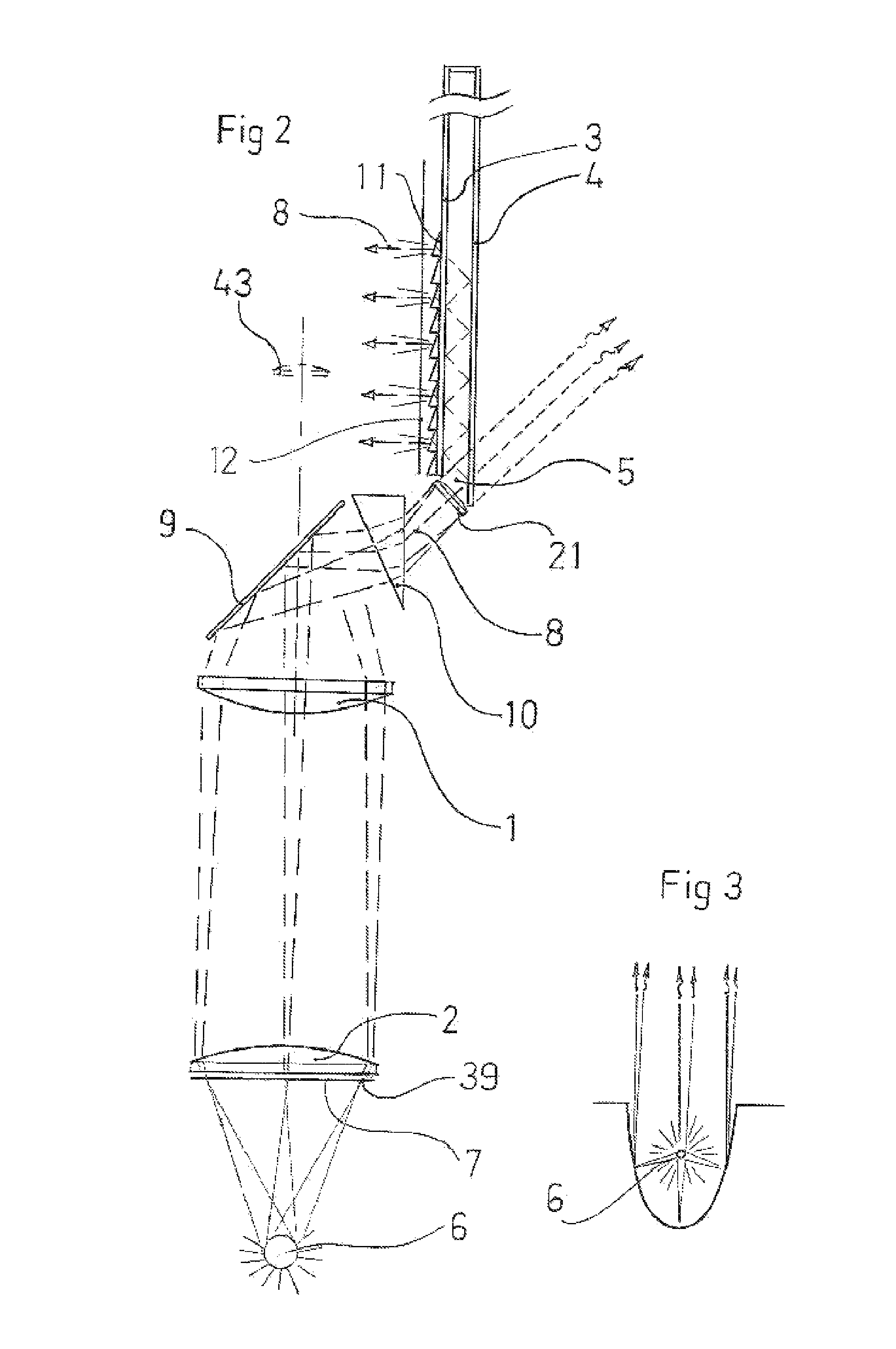
ActiveUS8068285B1Easy to displayMore compactPolarising elementsEducational modelsSpatial light modulatorLight guide
An infinity display device with autostereoscopic capability having one or more high lumen light sources 6, a transmissive spatial light modulator (SLM) 7, light collimating optics and a rectilinear light guide. Once the light has passed through the SLM 7 an objective 2 converges the image encoded rays toward a point 43 representing the entrance pupil 5 of said light guide. A second lens 1 then collimates the rays in one plane (Tangential) while a lenticular array 13 is used for collimating rays in the second plane (Sagittal). Next, a first surface mirror 9 reflects all said rays toward a triangular prism 10, where they undergo colour separation before entering the light guide. The light guide may itself consist of two, parallel, first surface mirrors 3&4 one of which is partially transmissive. Finally a Fresnel screen 11 tilts the light toward the observer.
Owner:INNERSCENE LTD
Method for determining the configuration of an ophthalmic lens, ophthalmic lens produced according to said method, and method for producing said lens
ActiveUS8240850B2Add depthIncrease depth of focusSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsOptical correctionVisual acuity
The invention relates to a method for making an ophthalmic lens intended to correct the visual acuity of a user, comprising the steps of determining the shape of a base optical corrective element, determining the profile of a phase element structure, said determination comprising the steps of defining a desired depth of focus of said ophthalmic lens; calculating the phase distribution to be created at the entrance pupil of the lens, selecting a phase distribution and performing an iterative calculation to obtain the depth of focus, finding the phase which minimizes the differences between the effective phase distribution and the desired phase distribution and of converting the phase data into geometrical data to define the profile of the phase distribution structure and juxtaposing the resulting phase element structure and the base optical corrective element.
Owner:SAV IOL
Optical imaging lens
The invention discloses an optical imaging lens. The optical imaging lens comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens and a sixth lens in order from an object side to an image side along an optical axis. The first lens and the fifth lens have positive power. The second lens, the third lens and the fourth lens have positive power or negative power. The object side of the first lens and the image side of the fifth lens are convex sides. The image side of the second lens, the object side of the sixth lens and the image side of the sixth lens are concave sides. According to the total effective focal length f of the optical imaging lens and the entrance pupil diameter EPD of the optical imaging lens, f / EPD is less than or equal to 1.8.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Method and device for on-orbit absolute radiation calibration
InactiveCN104880702AImproving the accuracy of on-orbit absolute radiometric calibrationEasy to handleWave based measurement systemsAbsolute calibrationIlluminance
The invention discloses a method for on-orbit absolute radiation calibration, which comprises the steps of: conducting root calculation on optical thickness of an aerosol; determining parameters of an MODTRAN model according to atmospheric spectral transmittance of a measured wave band; adopting the MODTRAN model with determined parameters, and calculating to obtain atmospheric spectral transmittance on a ground target-satellite path; calculating total solar irradiance on the surface of a target; and calculating entrance pupil radiance of a satellite; looking up DN values of gray scale targets on a satellite digital image, and determining absolute calibration parameters of load carried by the satellite by combining the DN values with the entrance pupil radiance corresponding to the ground target. The invention further discloses a device for on-orbit absolute radiation calibration. By adopting the method and the device for on-orbit absolute radiation calibration, the atmospheric parameter processing procedure for on-orbit absolute radiation calibration of a remote sensing satellite is simplified, and an atmospheric transmission model most accordant with the actually-measured atmospheric condition can be determined, thereby improving the on-orbit absolute radiation calibration precision of the remote sensing satellite.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
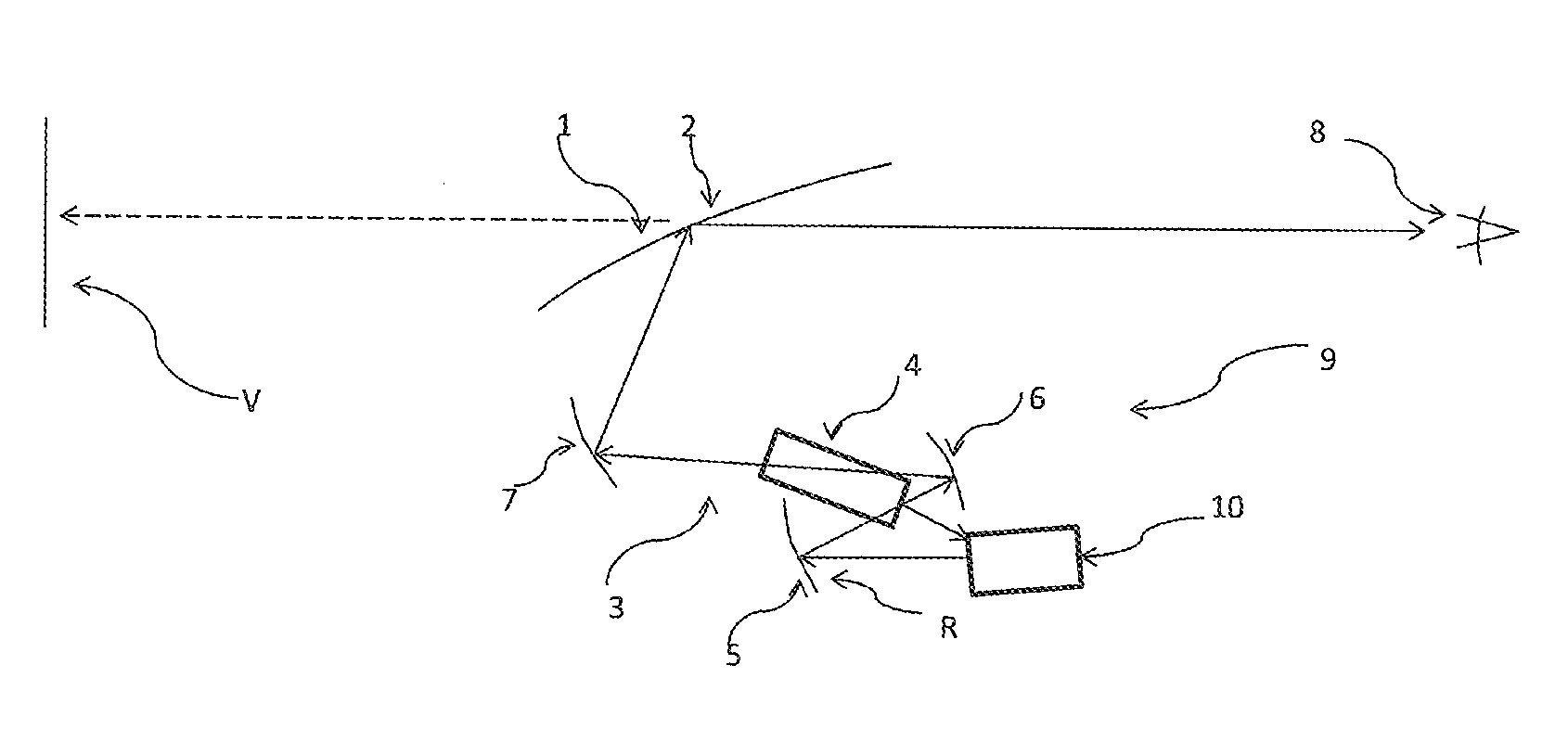
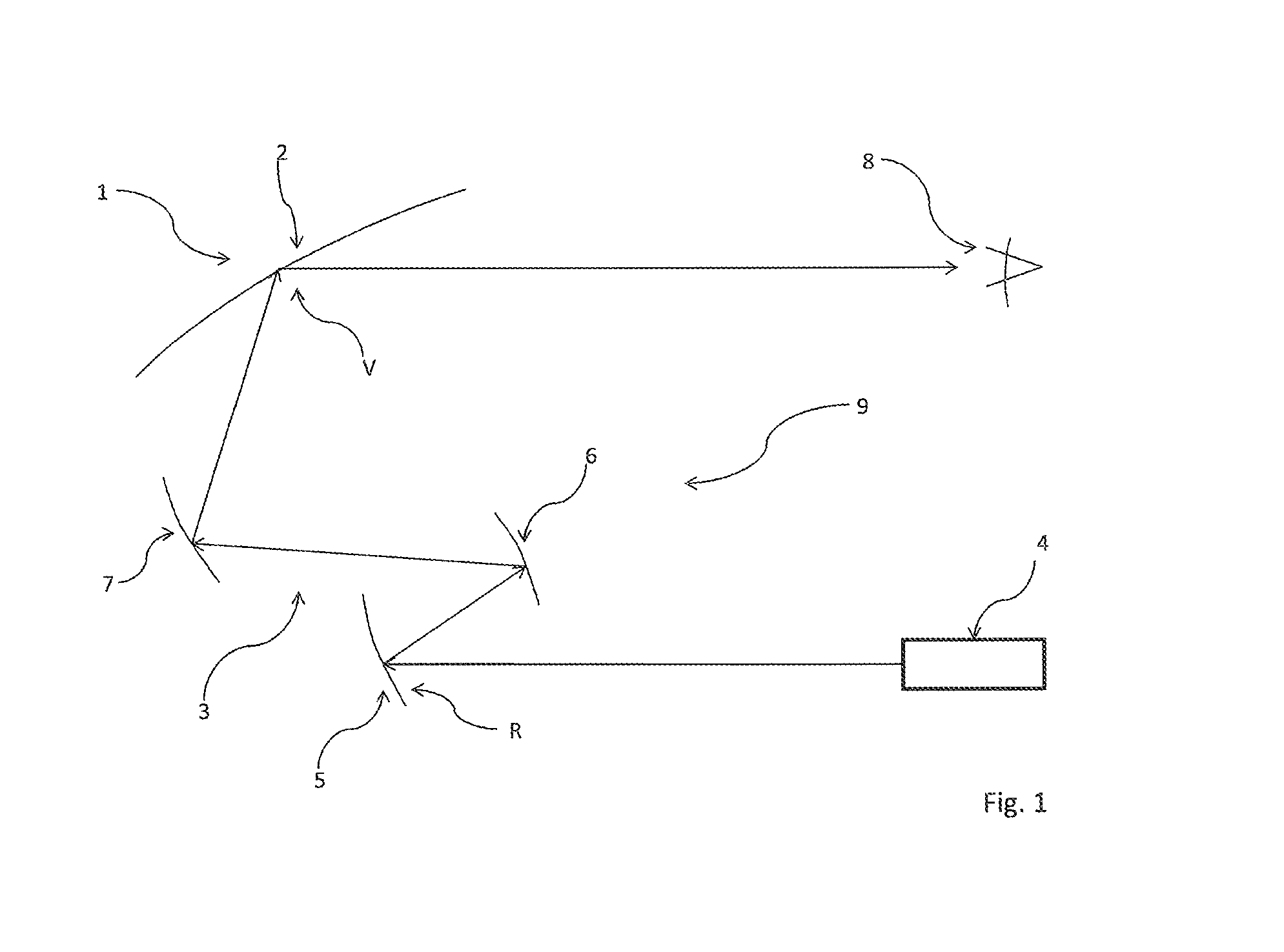
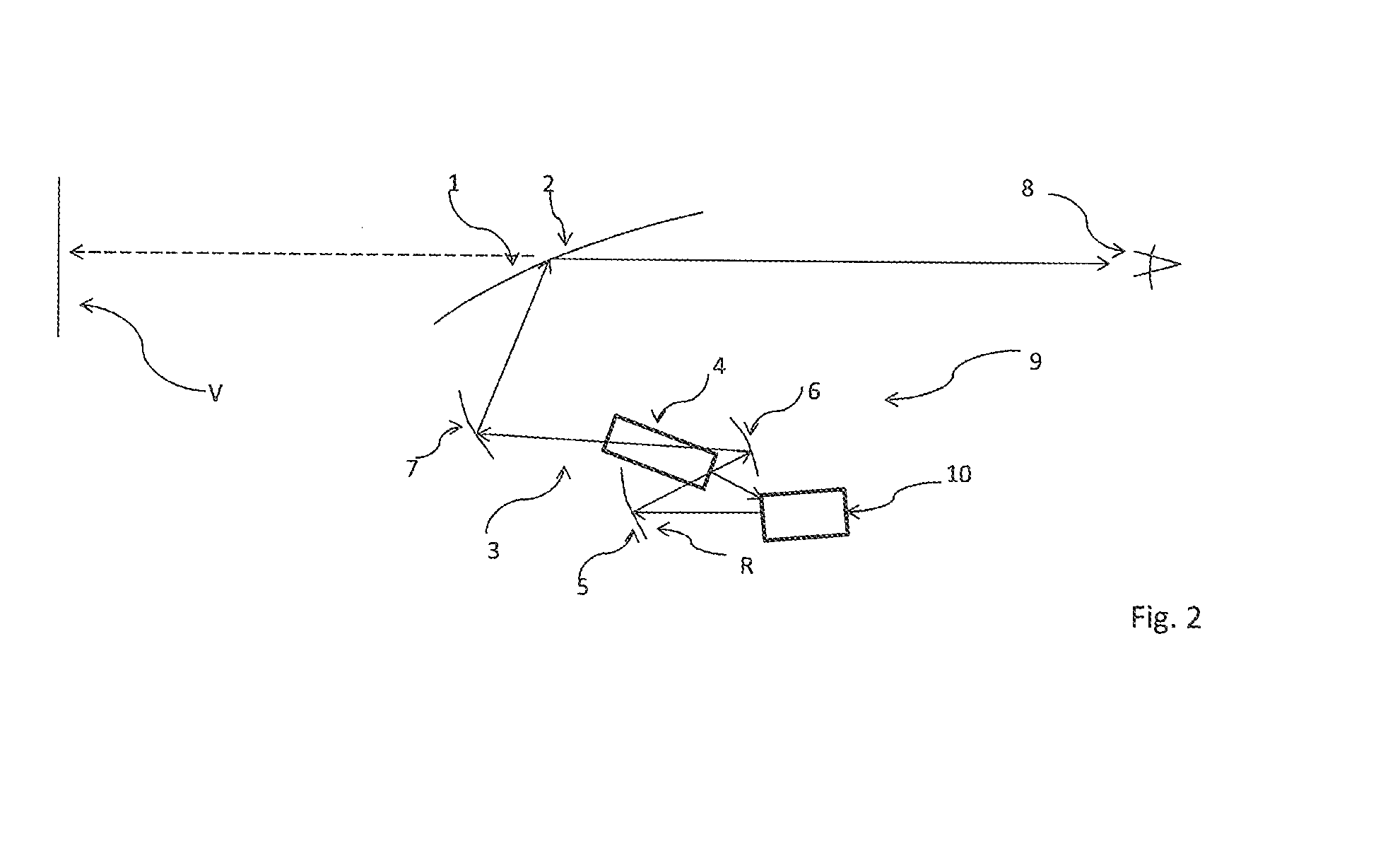
Device for projecting an image into a display area, having a screen for displaying an intermediate image
ActiveUS20140247433A1Effective displayDisplay brightProjectorsOptical elementsIntermediate imageComputer graphics (images)
Device (1) for projecting an image into a display area (2), with an imager (31) generating the picture, a first projection device (30) for generating a real intermediate image (R), a screen (5) onto which the first projection device (32) projects the intermediate image (R) and to a second projection device (9) projecting the intermediate image (R) into the display area (2). In order to project the image with the least possible loss of brightness, the invention provides that main beam directions (H, H′, H″) of the screen (5) point into an entrance pupil (20) of the second projection device (9).
Owner:JABIL OPTICS GERMANY GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com