Patents
Literature
198results about How to "Increase depth of focus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
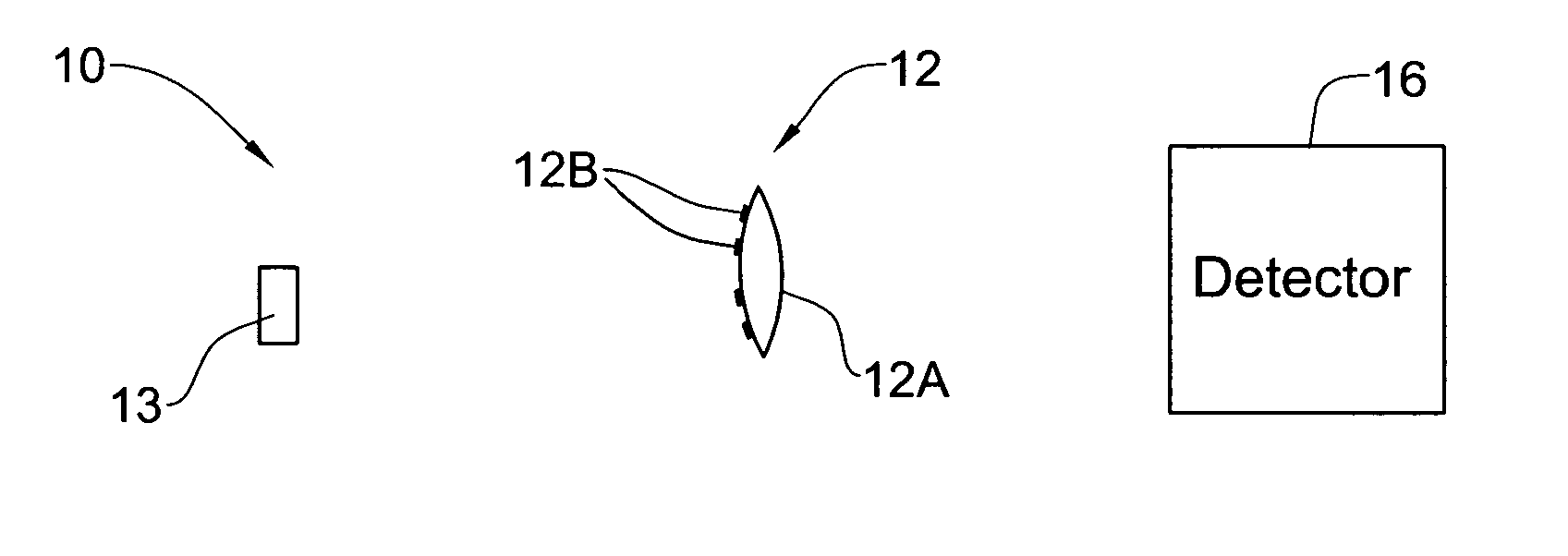
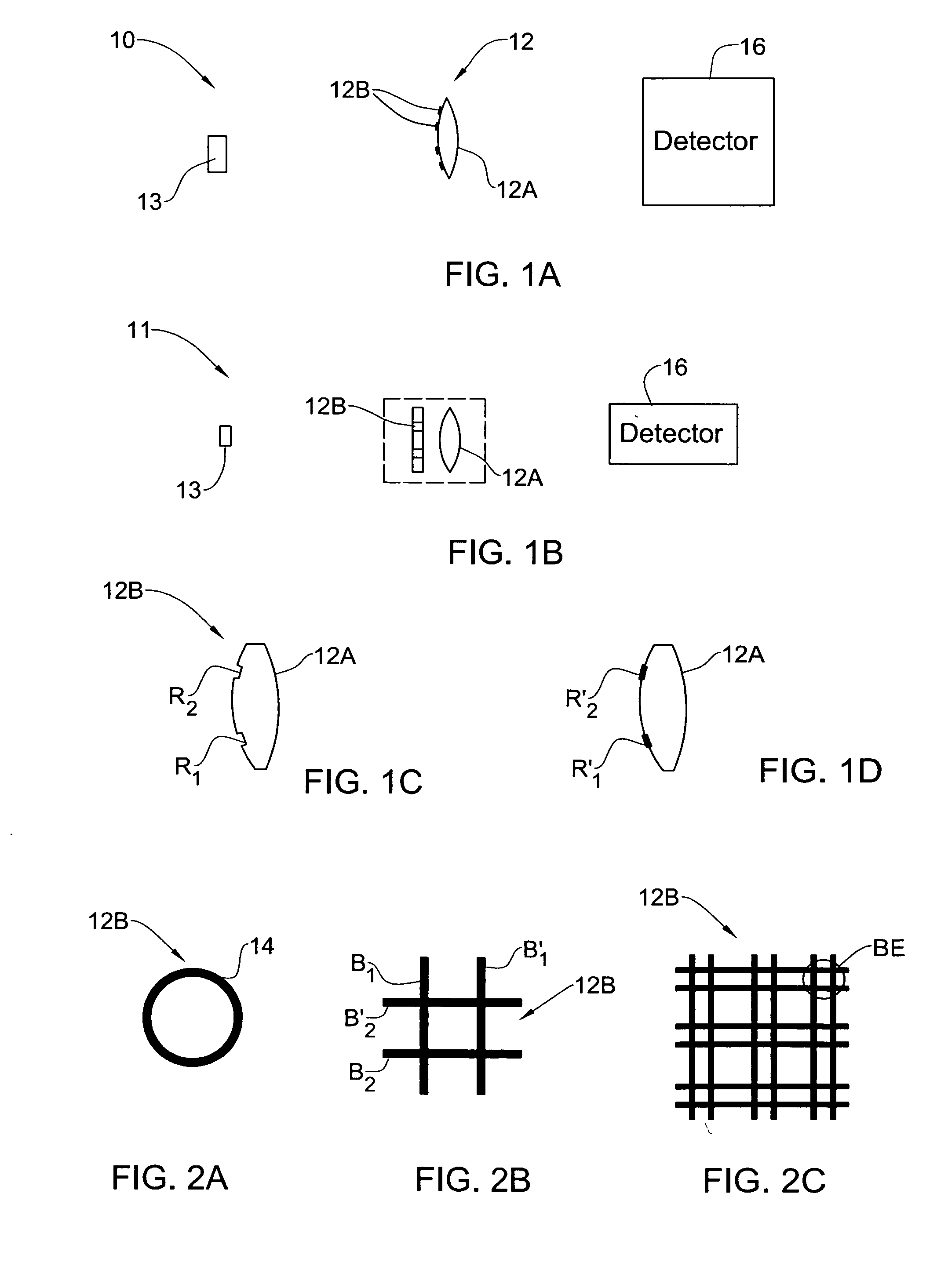
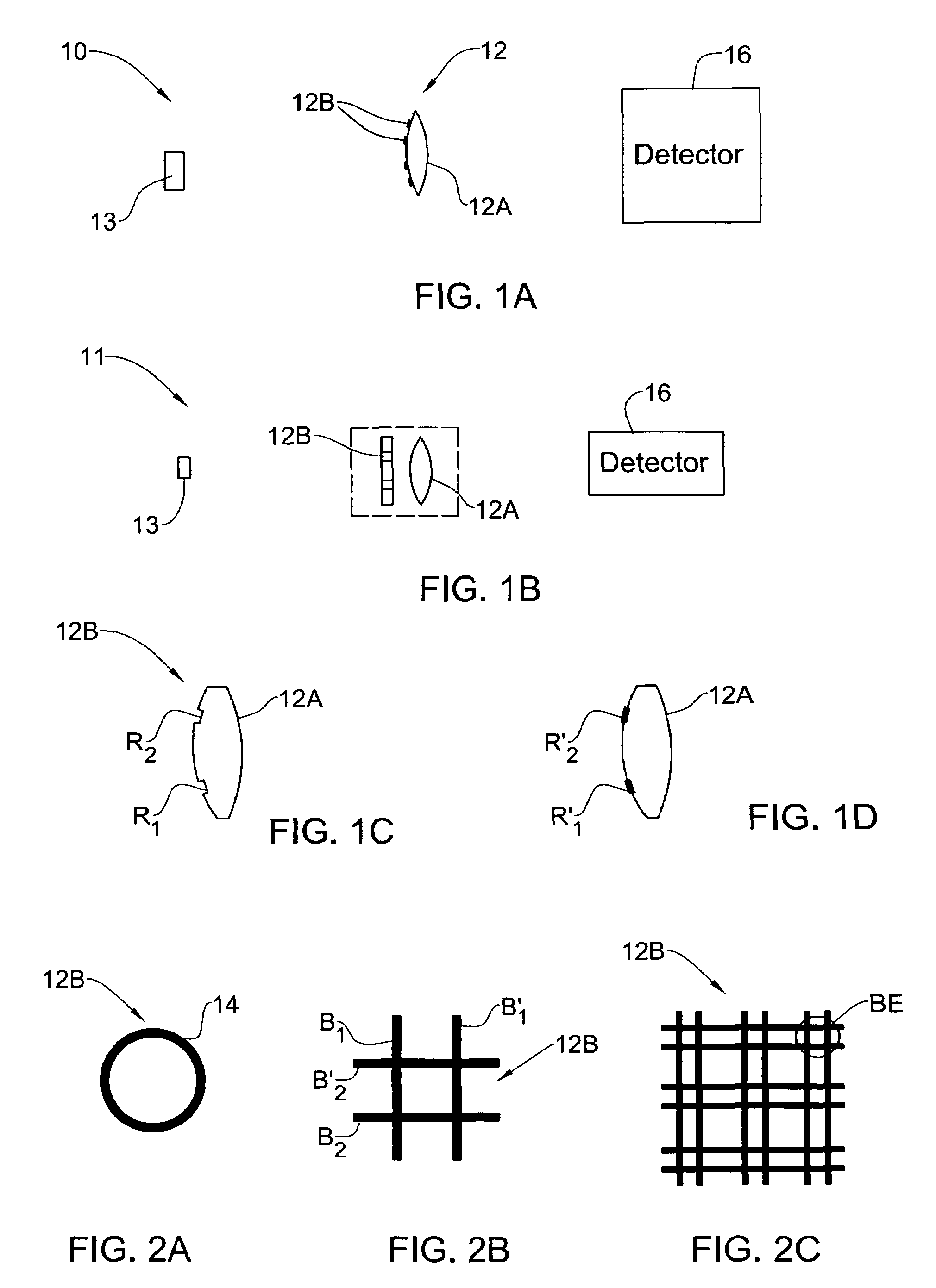
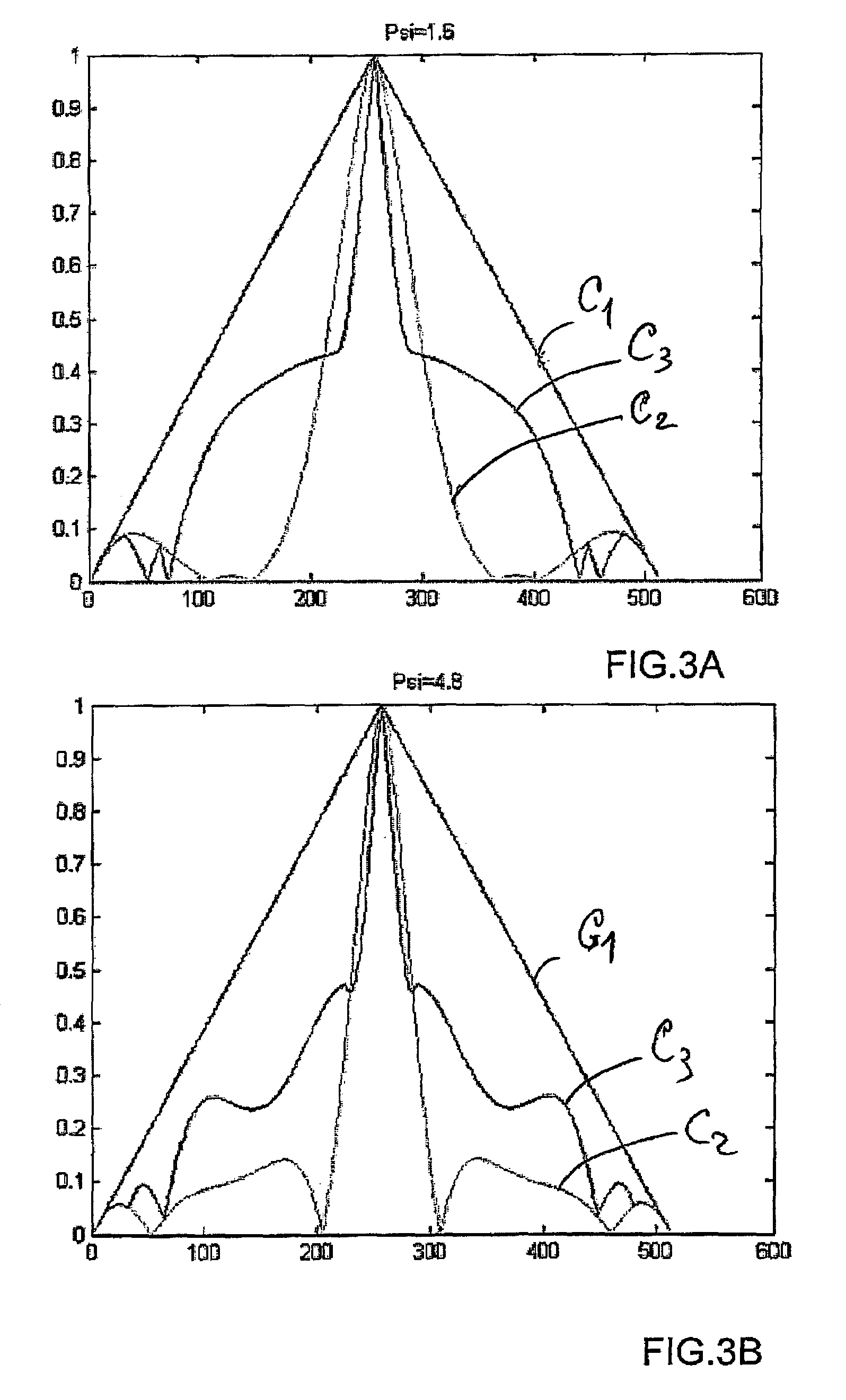
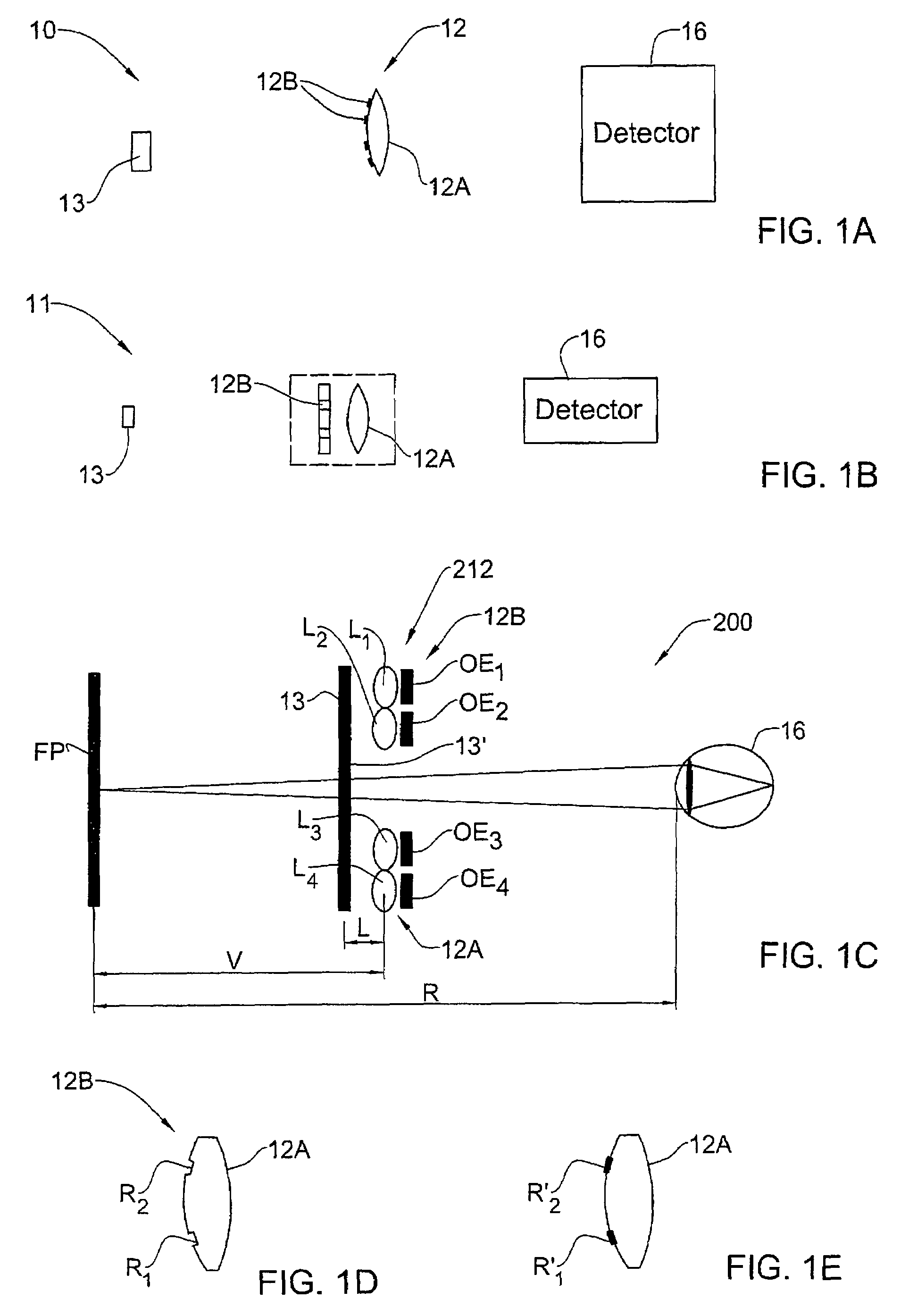
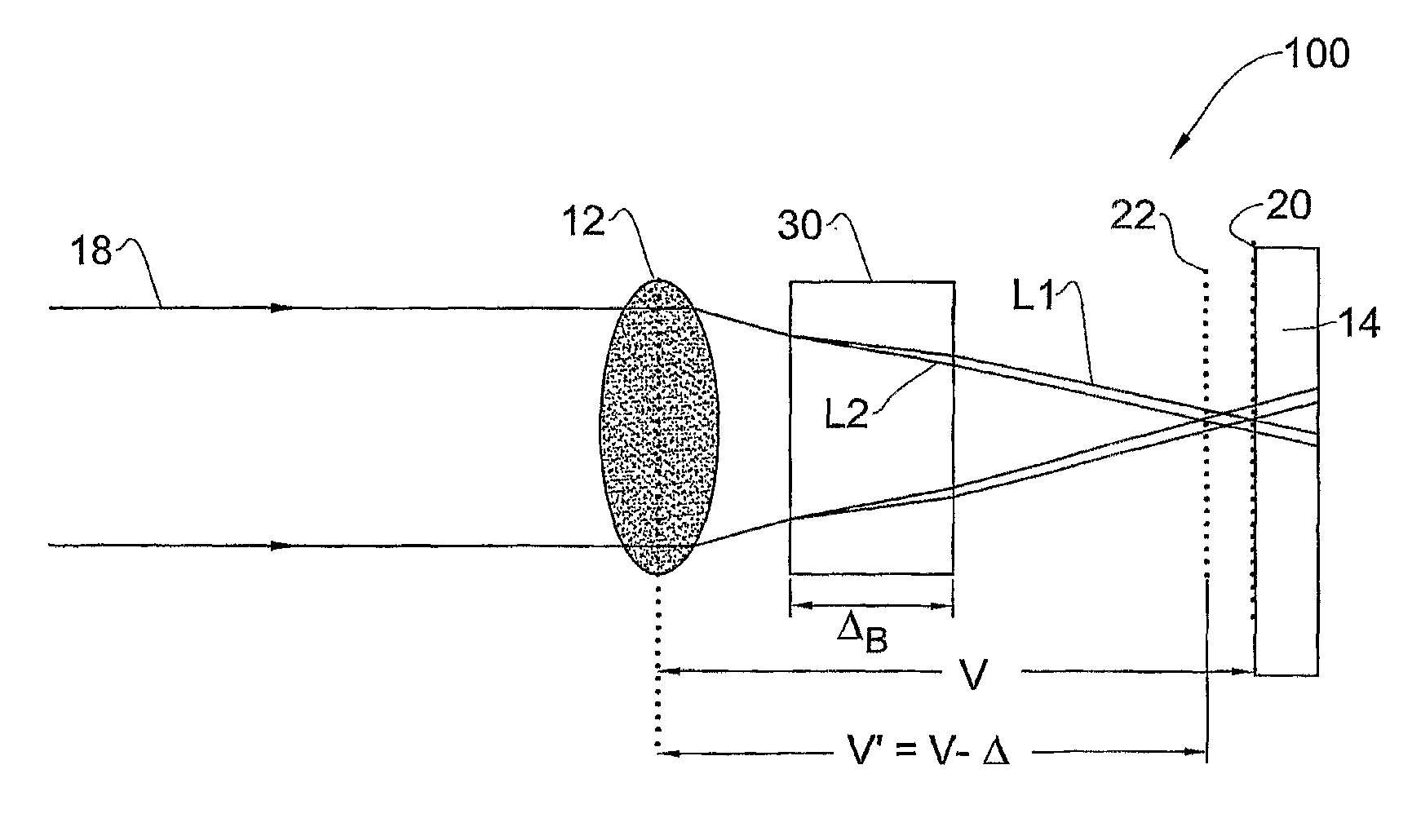
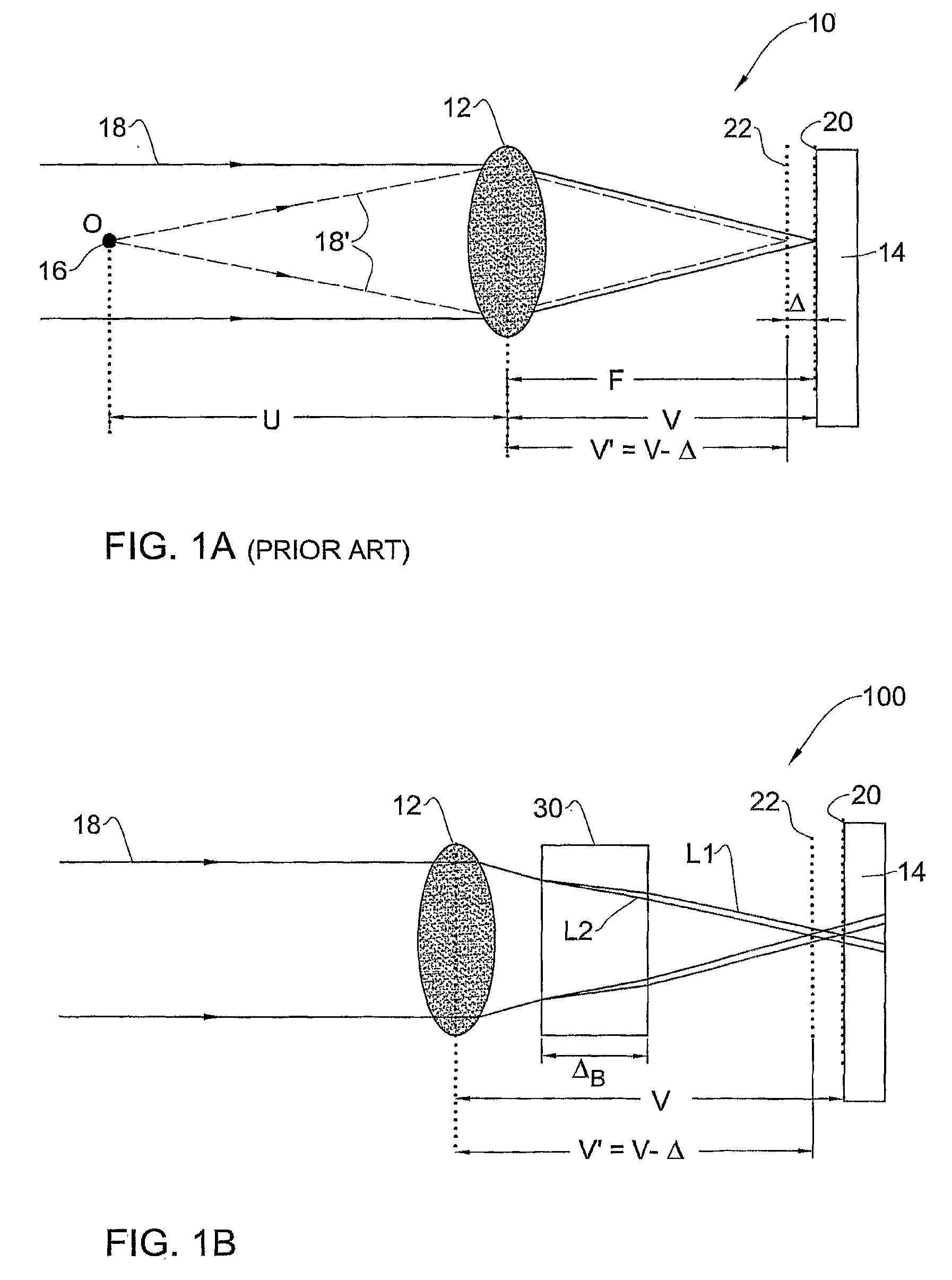
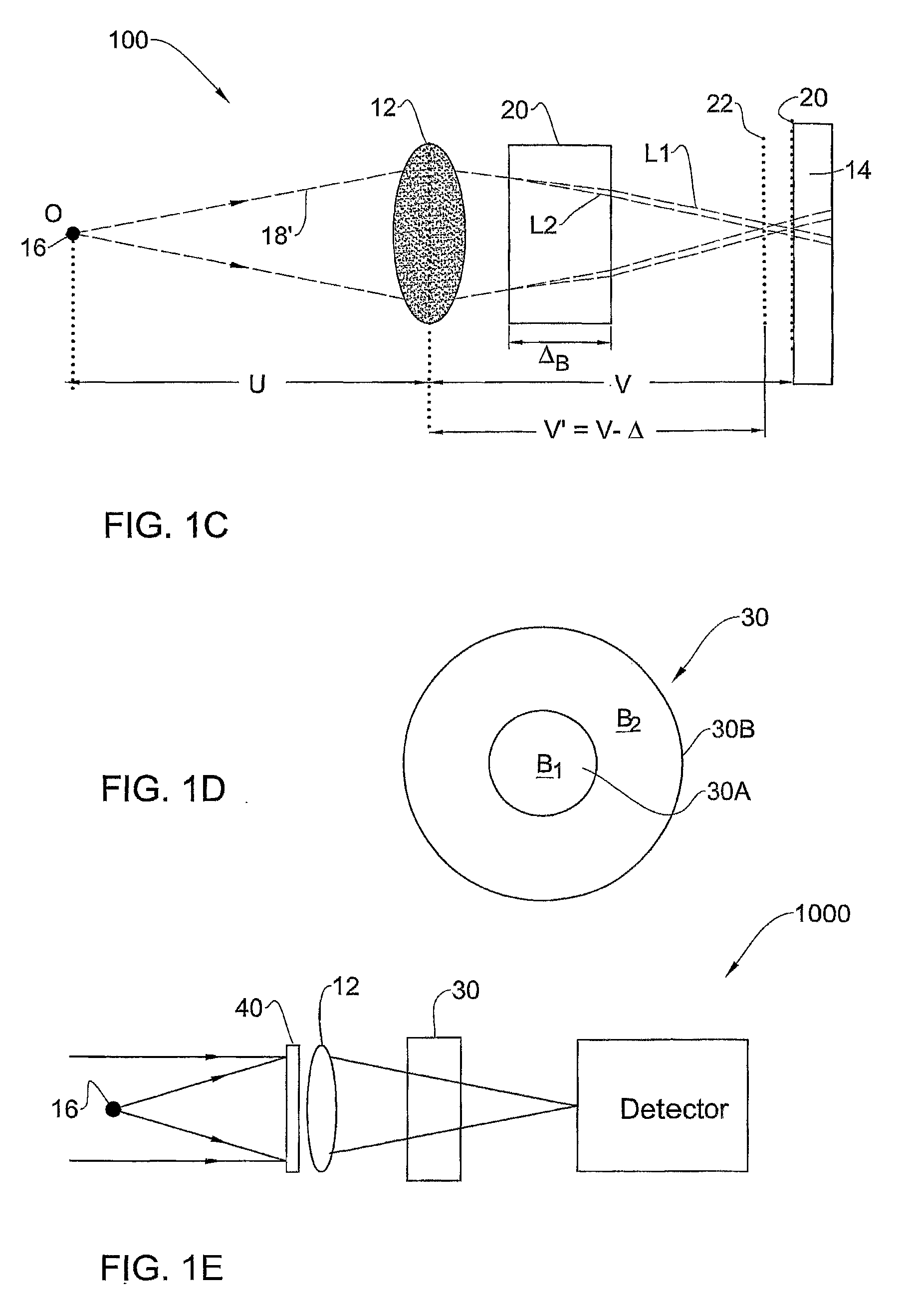
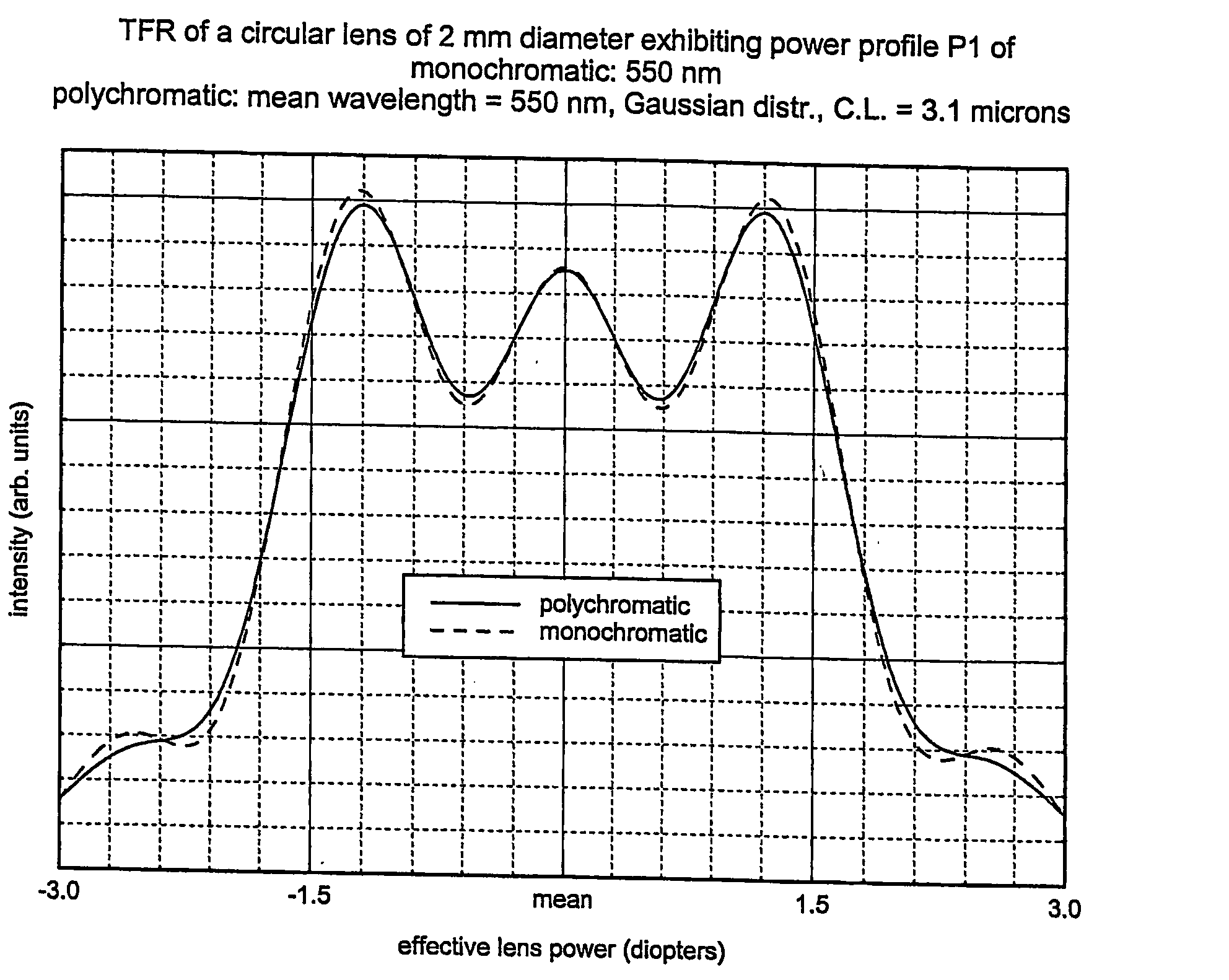
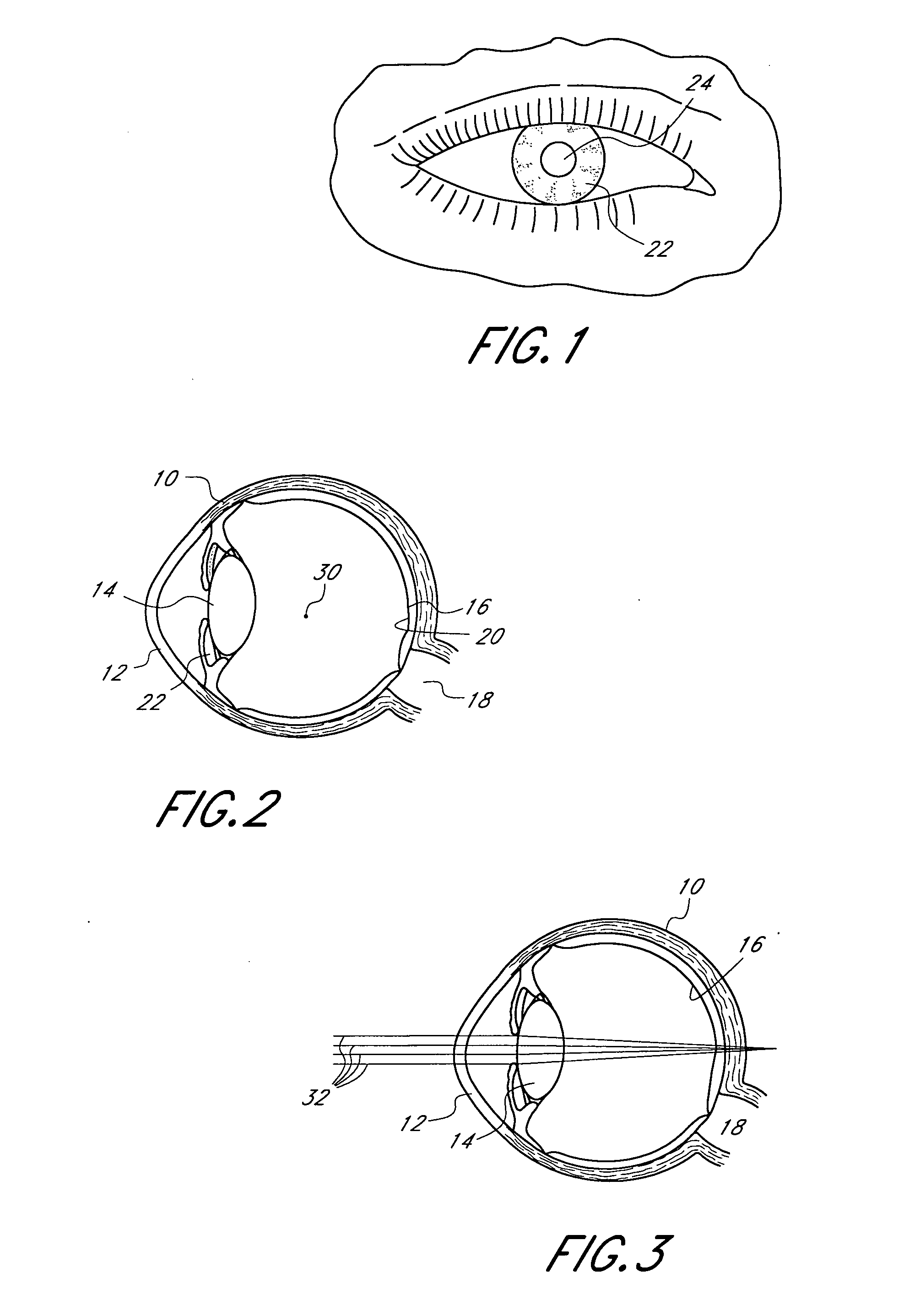
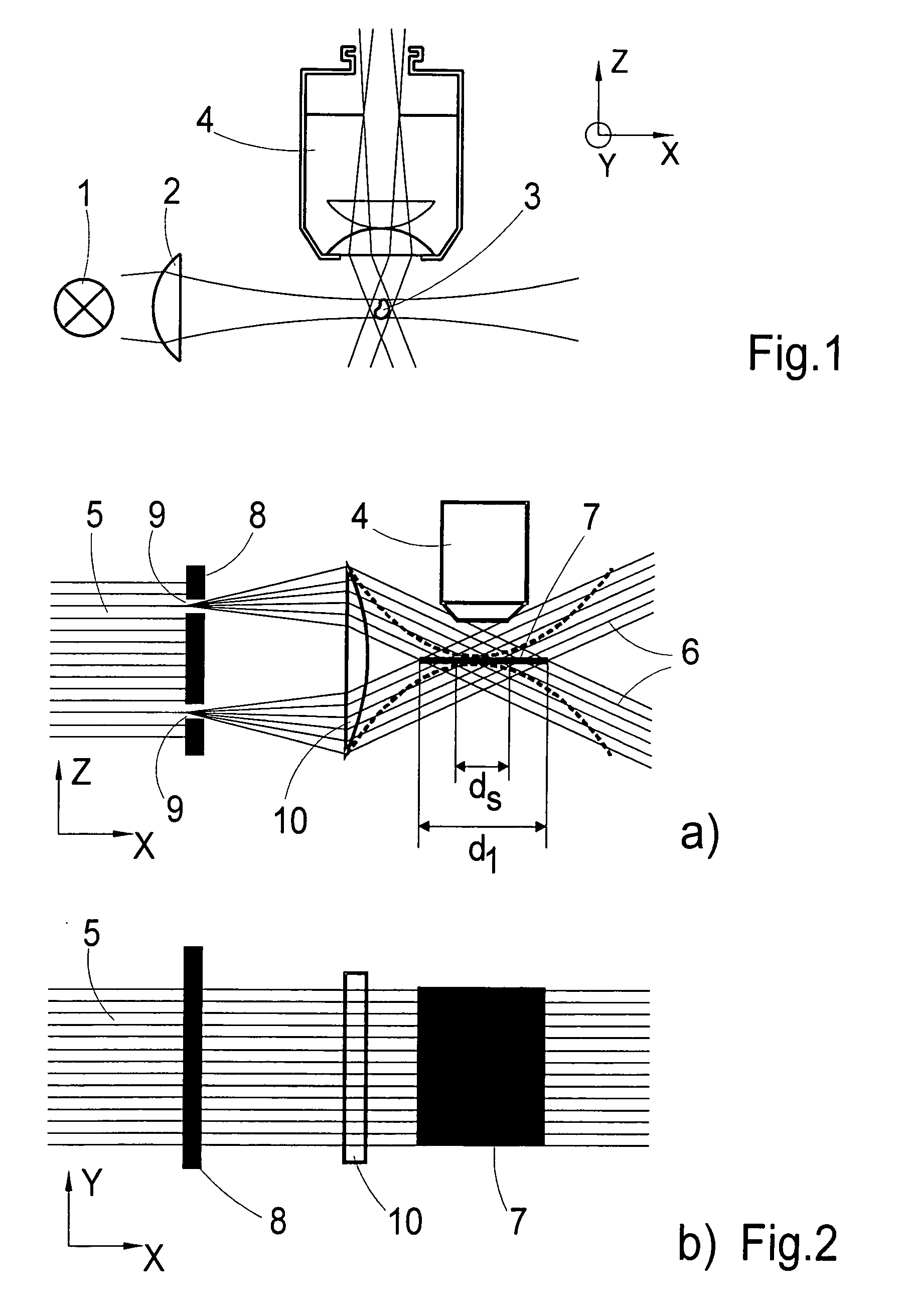
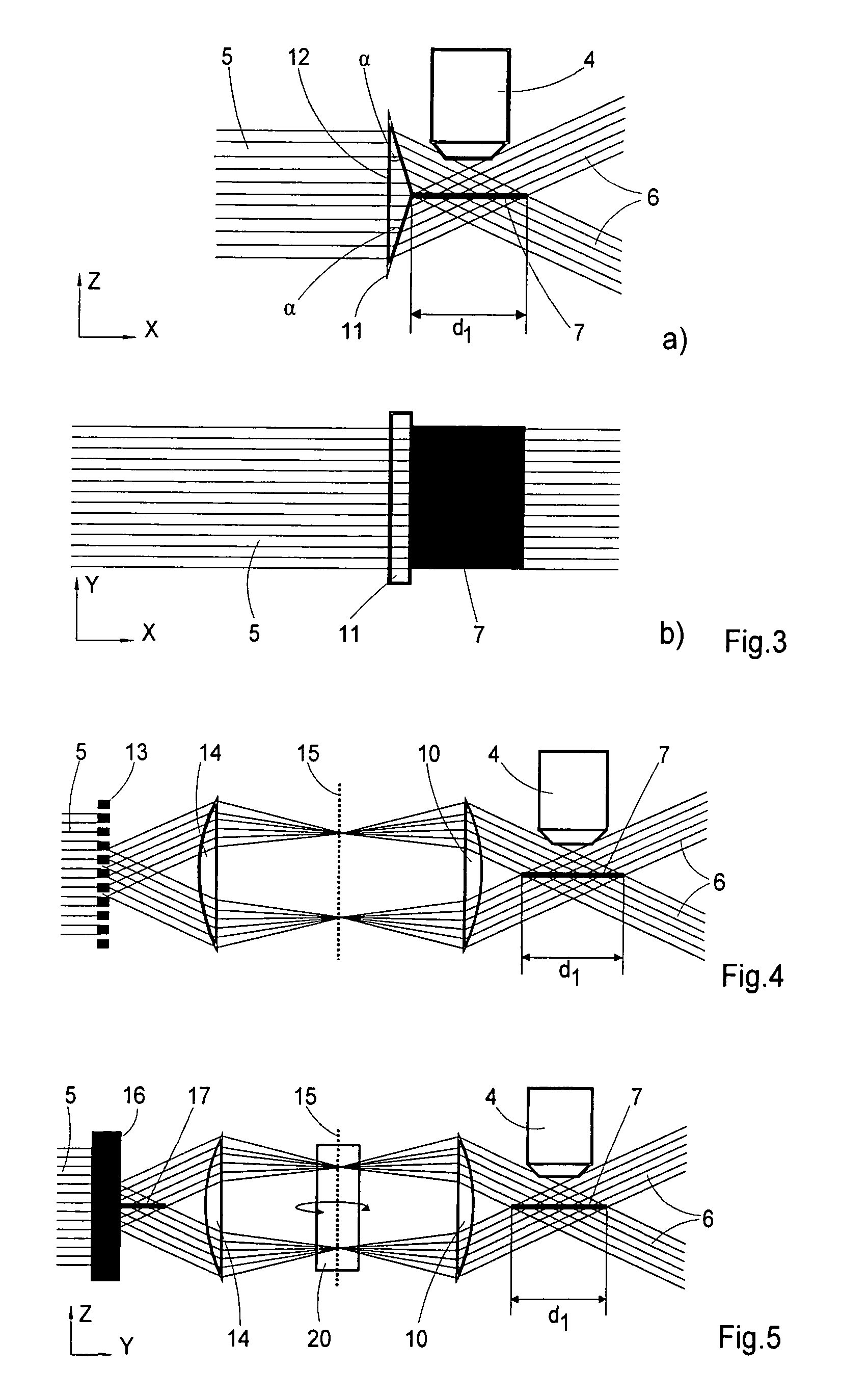
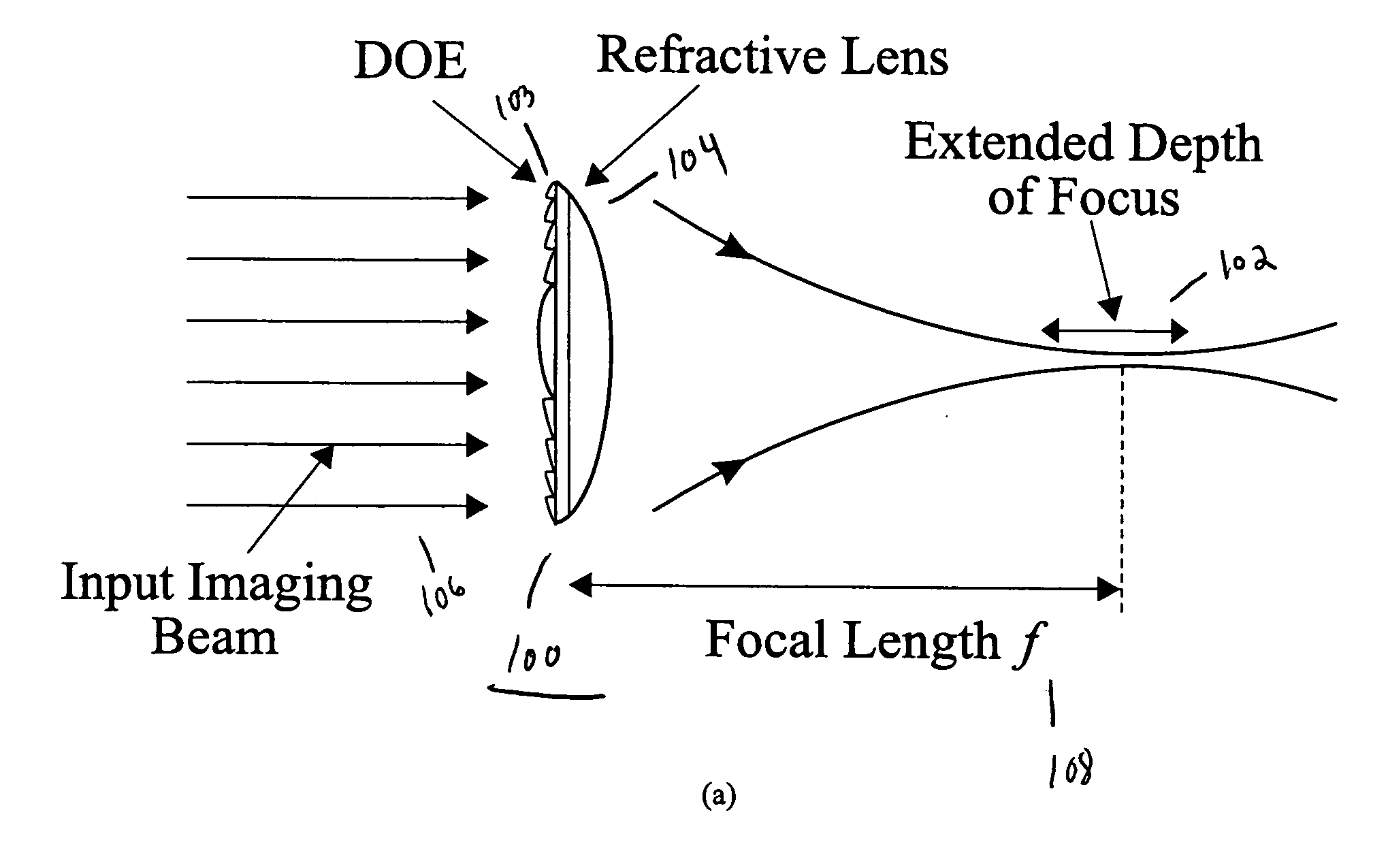
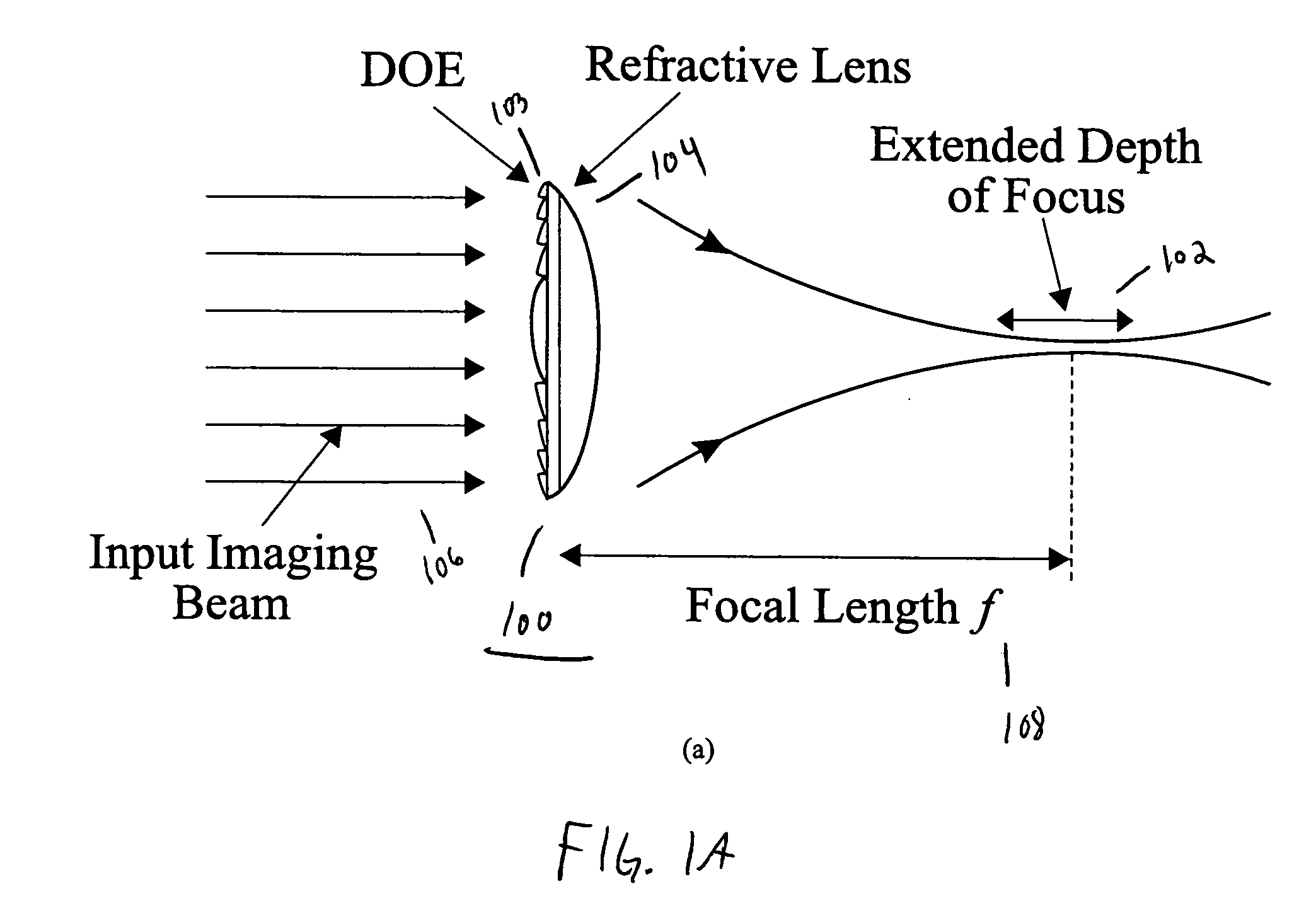
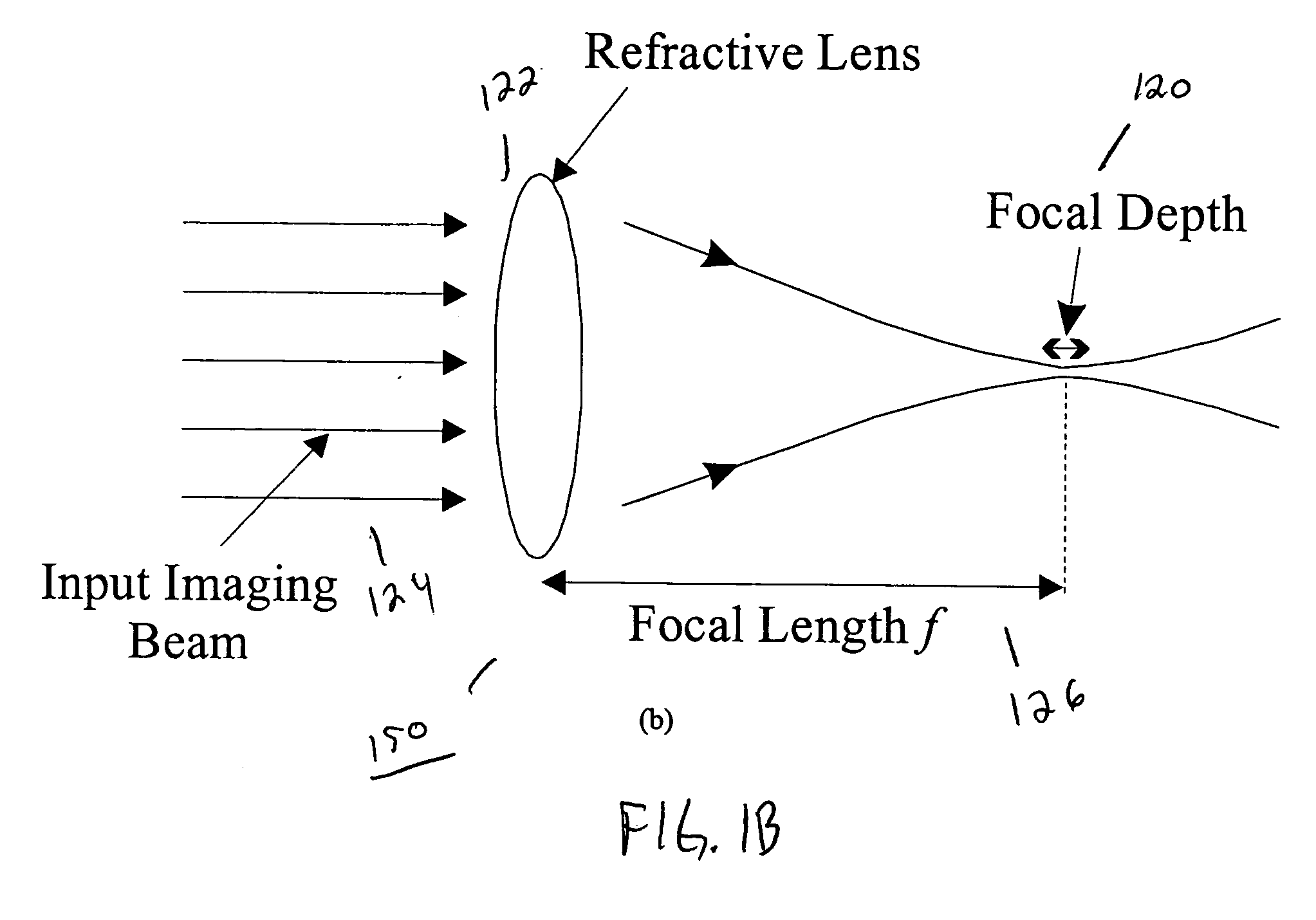
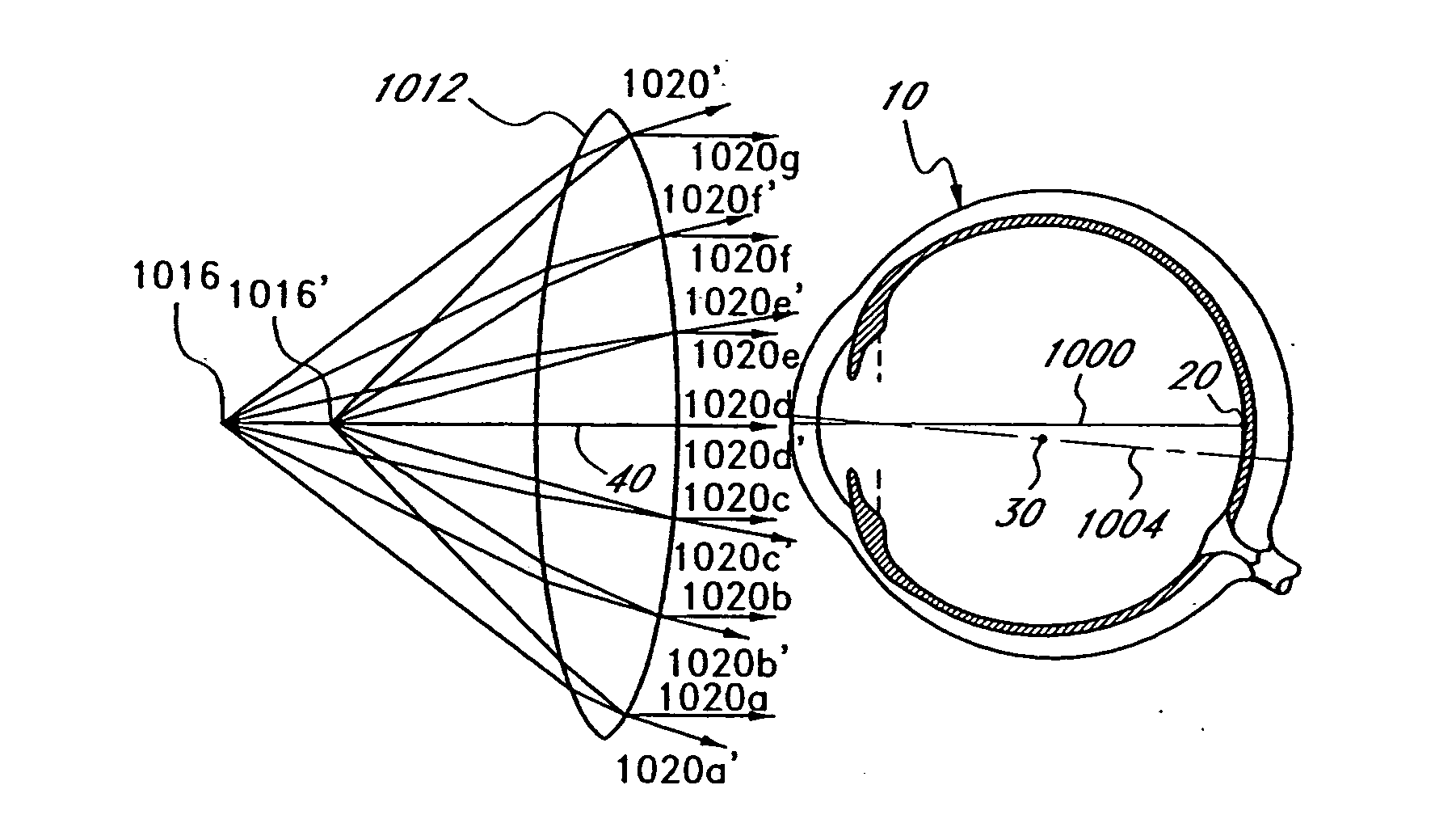
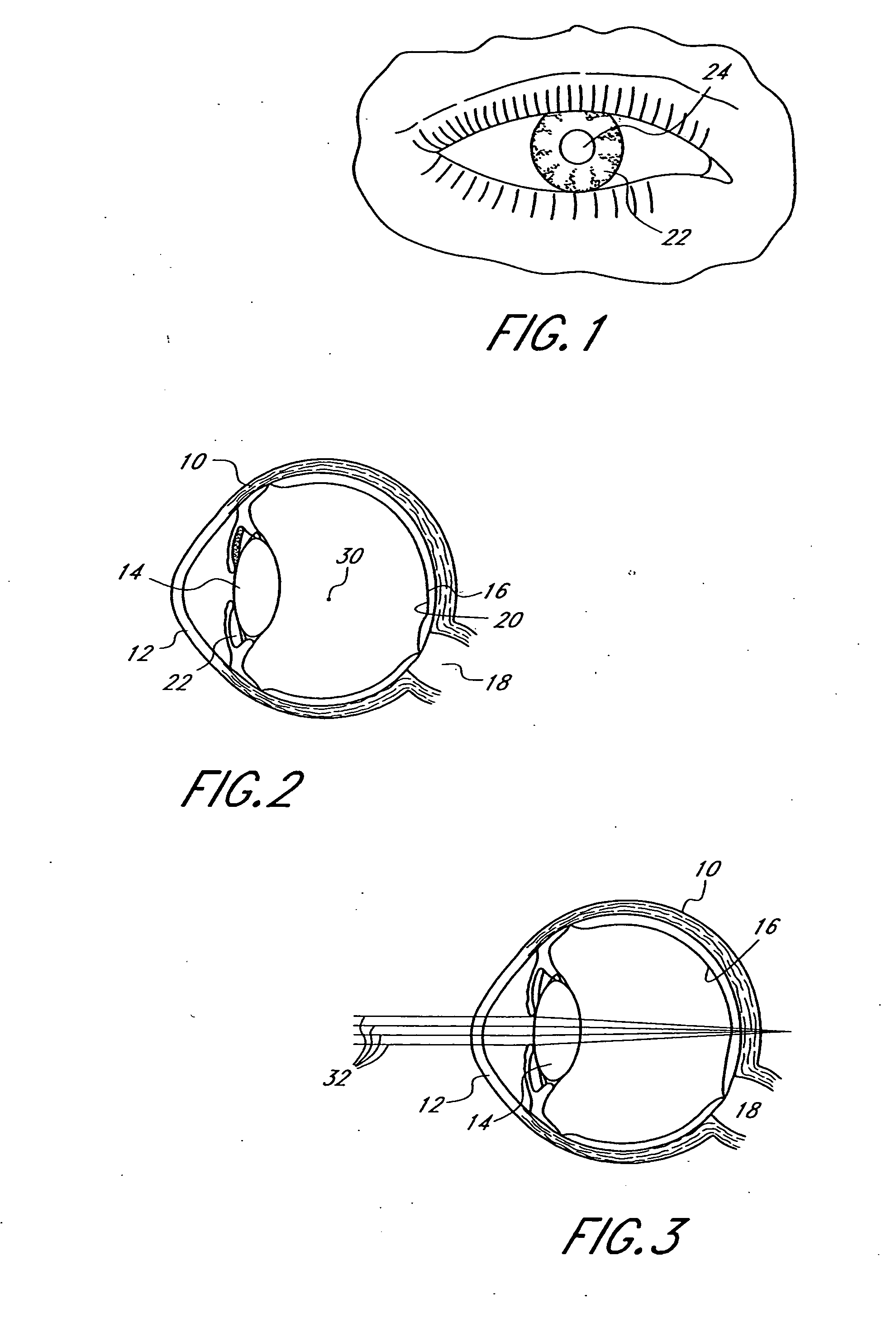
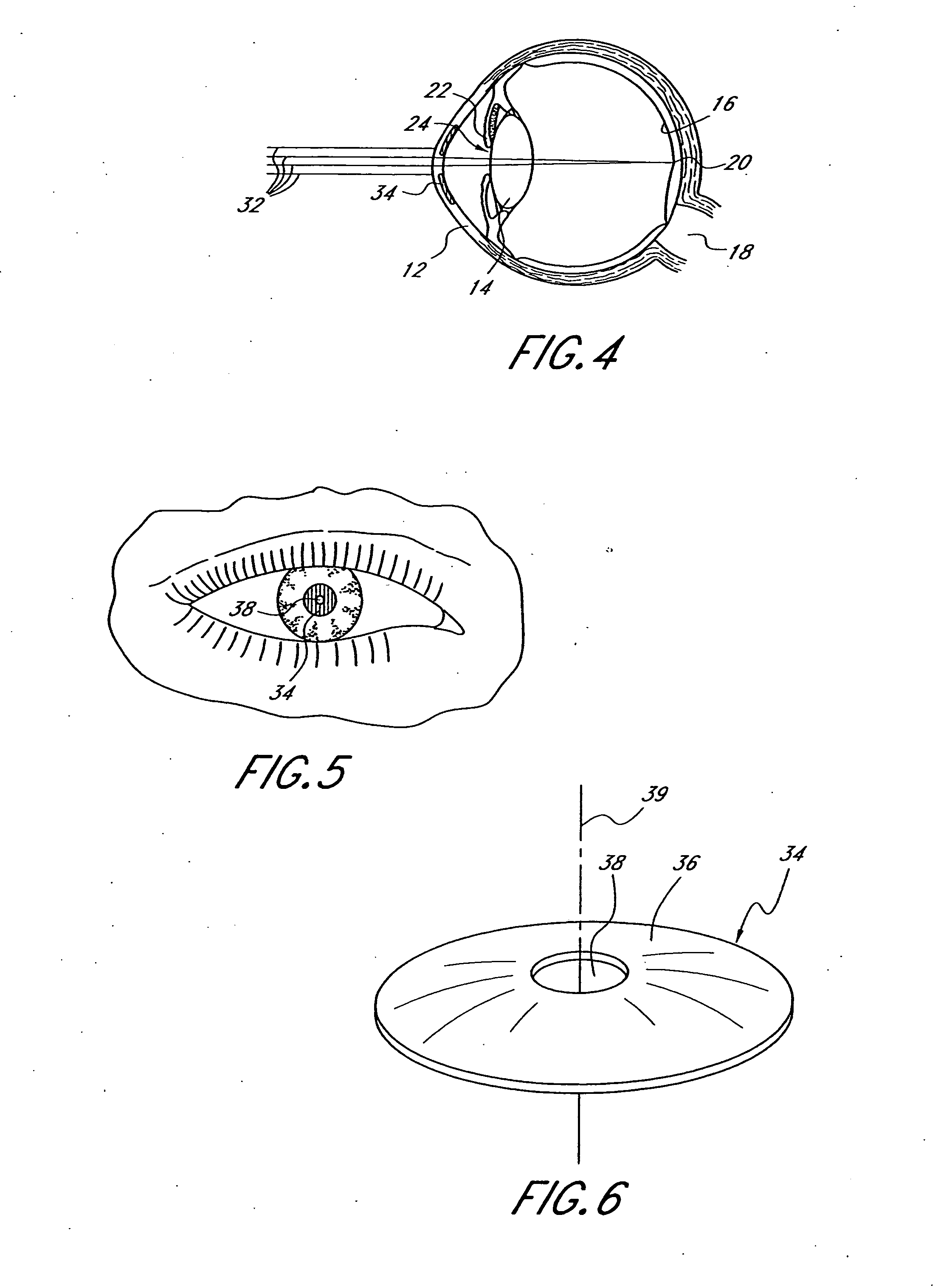
Optical method and system for extended depth of focus
ActiveUS20060034003A1Increase depth of focusEliminate needIntraocular lensOptical partsOptical propertyImaging lens
An imaging arrangement and method for extended the depth of focus are provided. The imaging arrangement comprises an imaging lens having a certain affective aperture, and an optical element associated with said imaging lens. The optical element is configured as a phase-affecting, non-diffractive optical element defining a spatially low frequency phase transition. The optical element and the imaging lens define a predetermined pattern formed by spaced-apart substantially optically transparent features of different optical properties. Position of at least one phase transition region of the optical element within the imaging lens plane is determined by at least a dimension of said affective aperture.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Optical method and system for extended depth of focus
ActiveUS7061693B2Increase depth of focusEliminate needIntraocular lensOptical partsOptical propertyImaging lens
An imaging arrangement and method for extended the depth of focus are provided. The imaging arrangement comprises an imaging lens having a certain affective aperture, and an optical element associated with said imaging lens. The optical element is configured as a phase-affecting, non-diffractive optical element defining a spatially low frequency phase transition. The optical element and the imaging lens define a predetermined pattern formed by spaced-apart substantially optically transparent features of different optical properties. Position of at least one phase transition region of the optical element within the imaging lens plane is determined by at least a dimension of said affective aperture.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Imaging system and method for providing extended depth of focus, range extraction and super resolved imaging
InactiveUS7646549B2Improving geometrical resolutionIncrease depth of focusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsImaging lensField of view
An imaging system is presented for imaging objects within a field of view of the system. The imaging system comprises an imaging lens arrangement, a light detector unit at a certain distance from the imaging lens arrangement, and a control unit connectable to the output of the detection unit. The imaging lens arrangement comprises an imaging lens and an optical element located in the vicinity of the lens aperture, said optical element introducing aperture coding by an array of regions differently affecting a phase of light incident thereon which are randomly distributed within the lens aperture, thereby generating an axially-dependent randomized phase distribution in the Optical Transfer Function (OTF) of the imaging system resulting in an extended depth of focus of the imaging system. The control unit is configured to decode the sampled output of the detection unit by using the random aperture coding to thereby extract 3D information of the objects in the field of view of the light detector unit.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Fourier Ptychographic Imaging Systems, Devices, and Methods
ActiveUS20140118529A1Increase depth of focusAberration correctionColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsImage resolutionHigh resolution image
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Intra-ocular lens or contact lens exhibiting large depth of focus
ActiveUS7287852B2Increase depth of focusLarge depth of fieldIntraocular lensOptical partsIntra ocular lensContact lens
Owner:FIALA WERNER J
Optical method and system for extended depth of focus
ActiveUS7365917B2Increase depth of focusEliminate needSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensOptical propertyImaging lens
An imaging arrangement and method for extended the depth of focus are provided. The imaging arrangement comprises an imaging lens having a certain affective aperture, and an optical element associated with said imaging lens. The optical element is configured as a phase-affecting, non-diffractive optical element defining a spatially low frequency phase transition. The optical element and the imaging lens define a predetermined pattern formed by spaced-apart substantially optically transparent features of different optical properties. Position of at least one phase transition region of the optical element within the imaging lens plane is determined by at least a dimension of said affective aperture.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
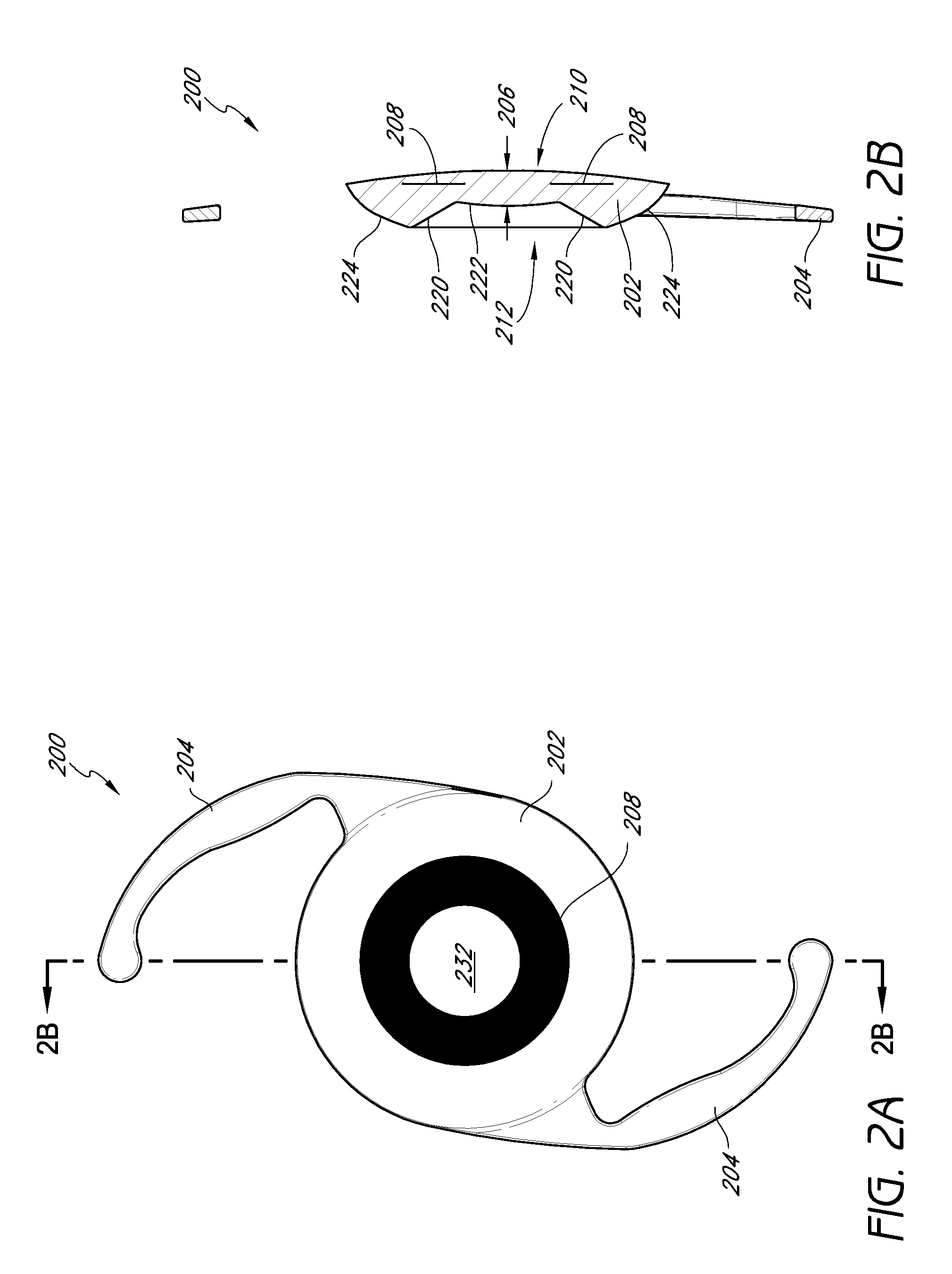
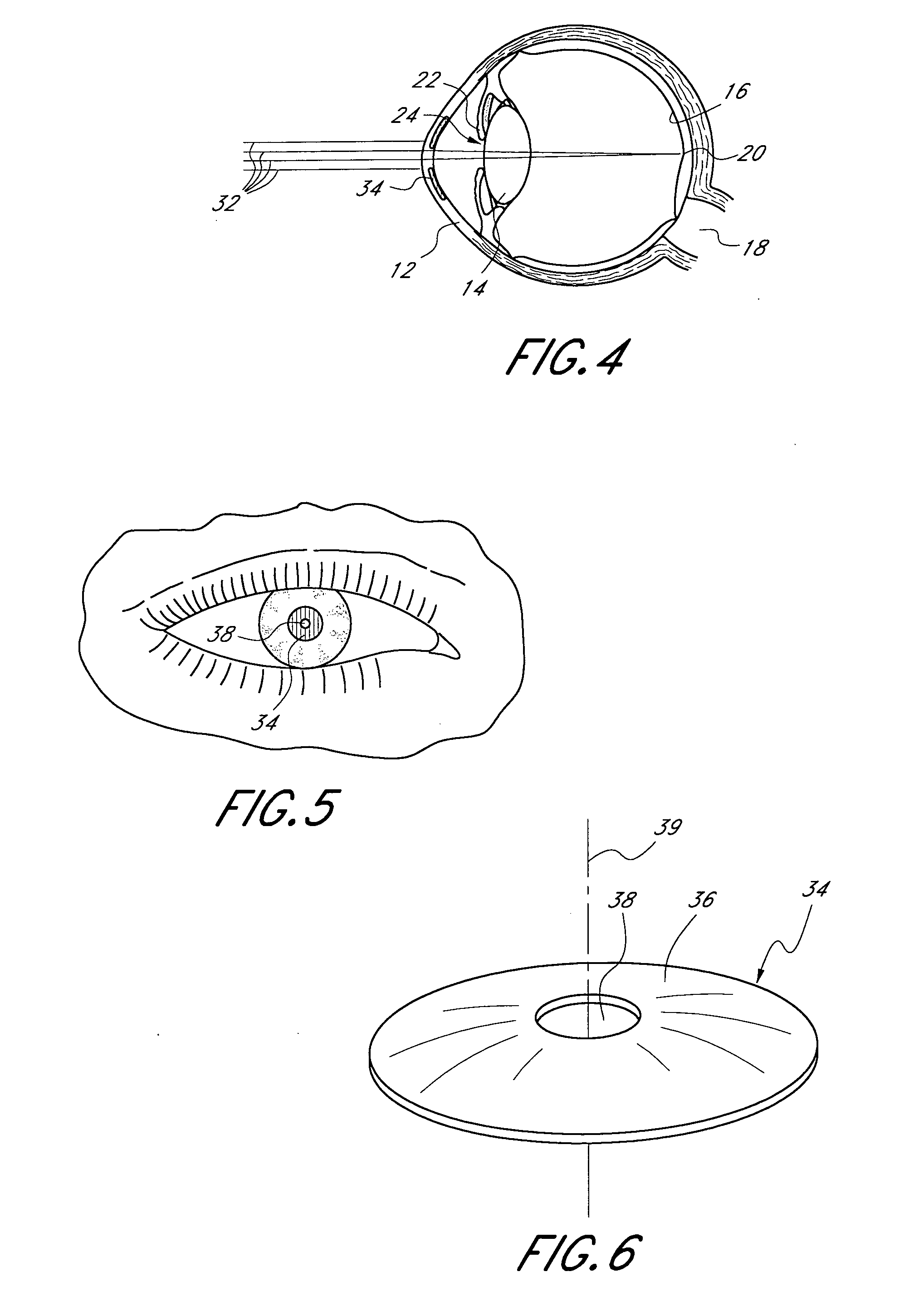
Masked intraocular implants and lenses
ActiveUS20110040376A1Improve eyesightIncrease depth of focusOptical articlesIntraocular lensMedicineOptical power
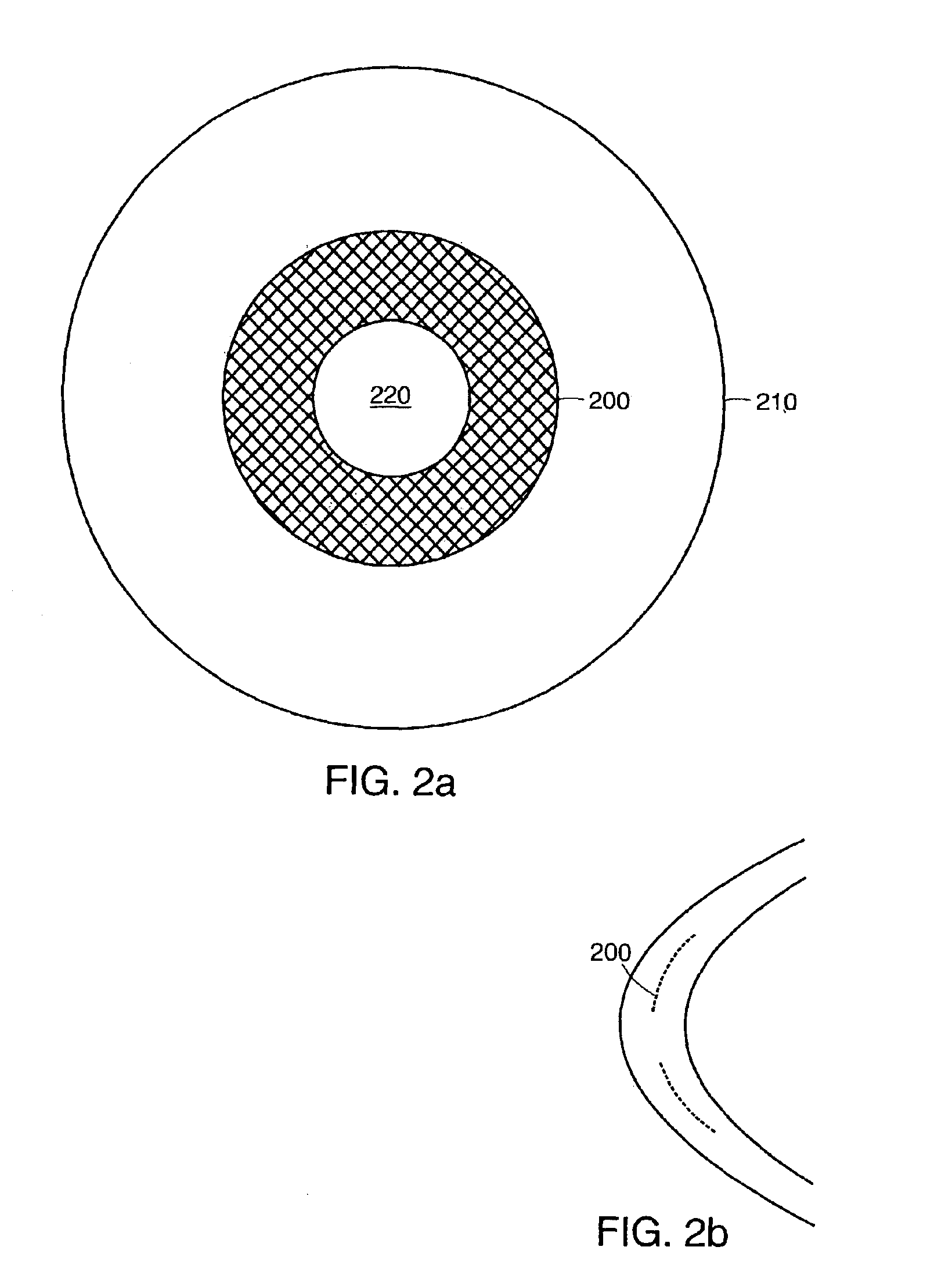
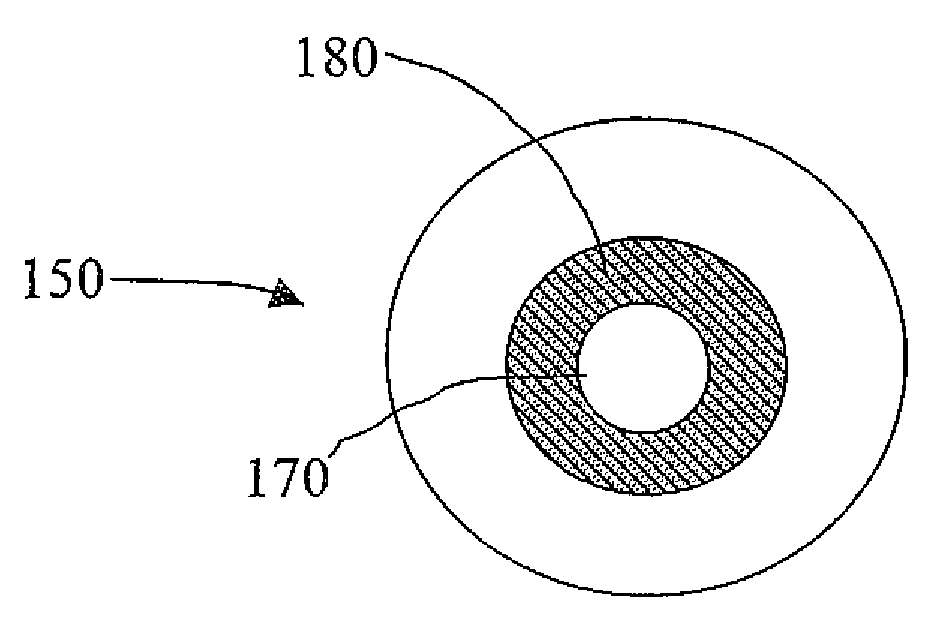
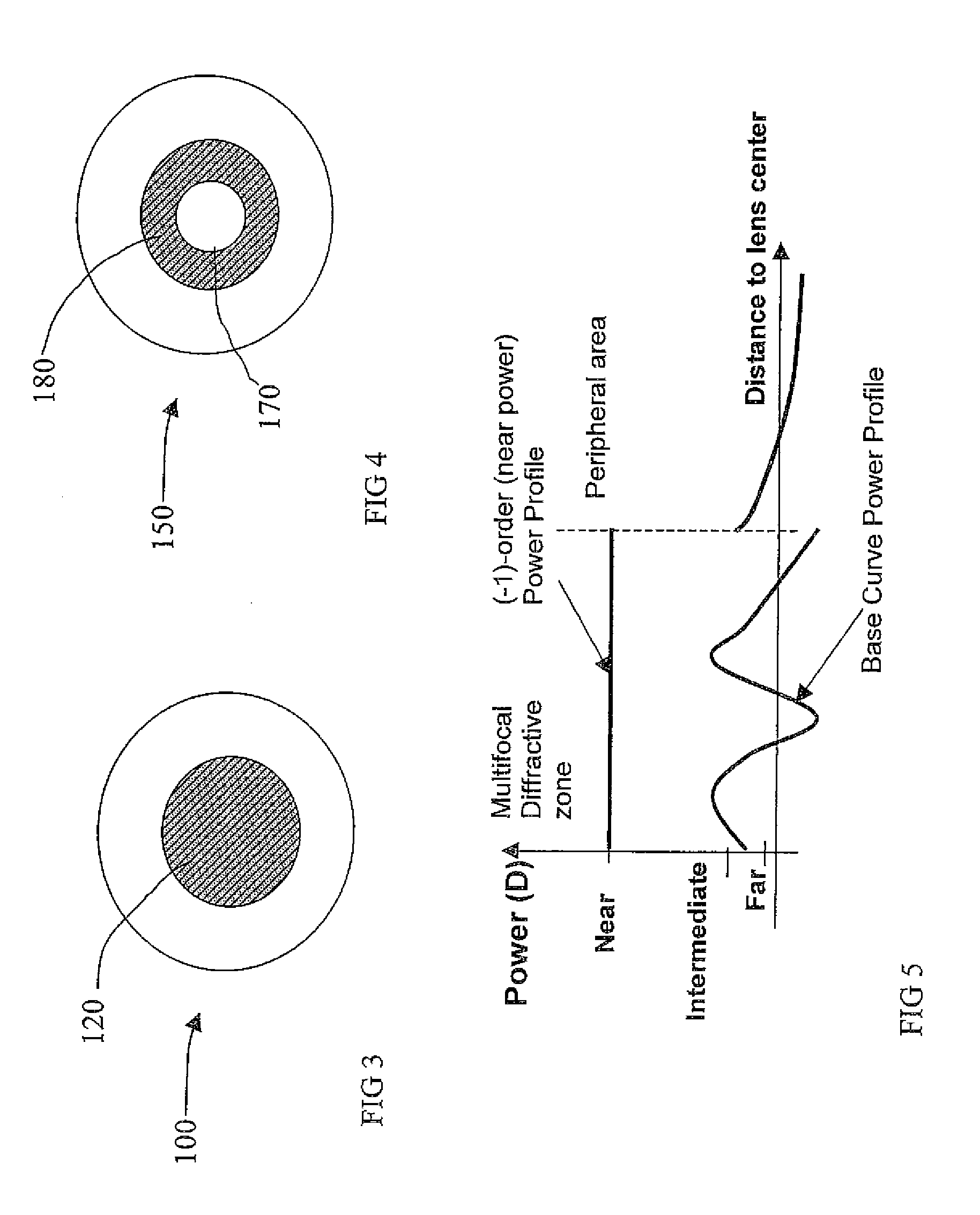
Intraocular implants and methods of making intraocular implants are provided. The intraocular implants can improve the vision of a patient, such as by increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. In particular, the intraocular implants can include a mask having an annular portion with a relatively low visible light transmission surrounding a relatively high transmission central portion such as a clear lens or aperture. This construct is adapted to provide an annular mask with a small aperture for light to pass through to the retina to increase depth of focus. The intraocular implant may have an optical power for refractive correction. The intraocular implant may be implanted in any location along the optical pathway in the eye, e.g., as an implant in the anterior or posterior chamber.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Method of making an ocular implant
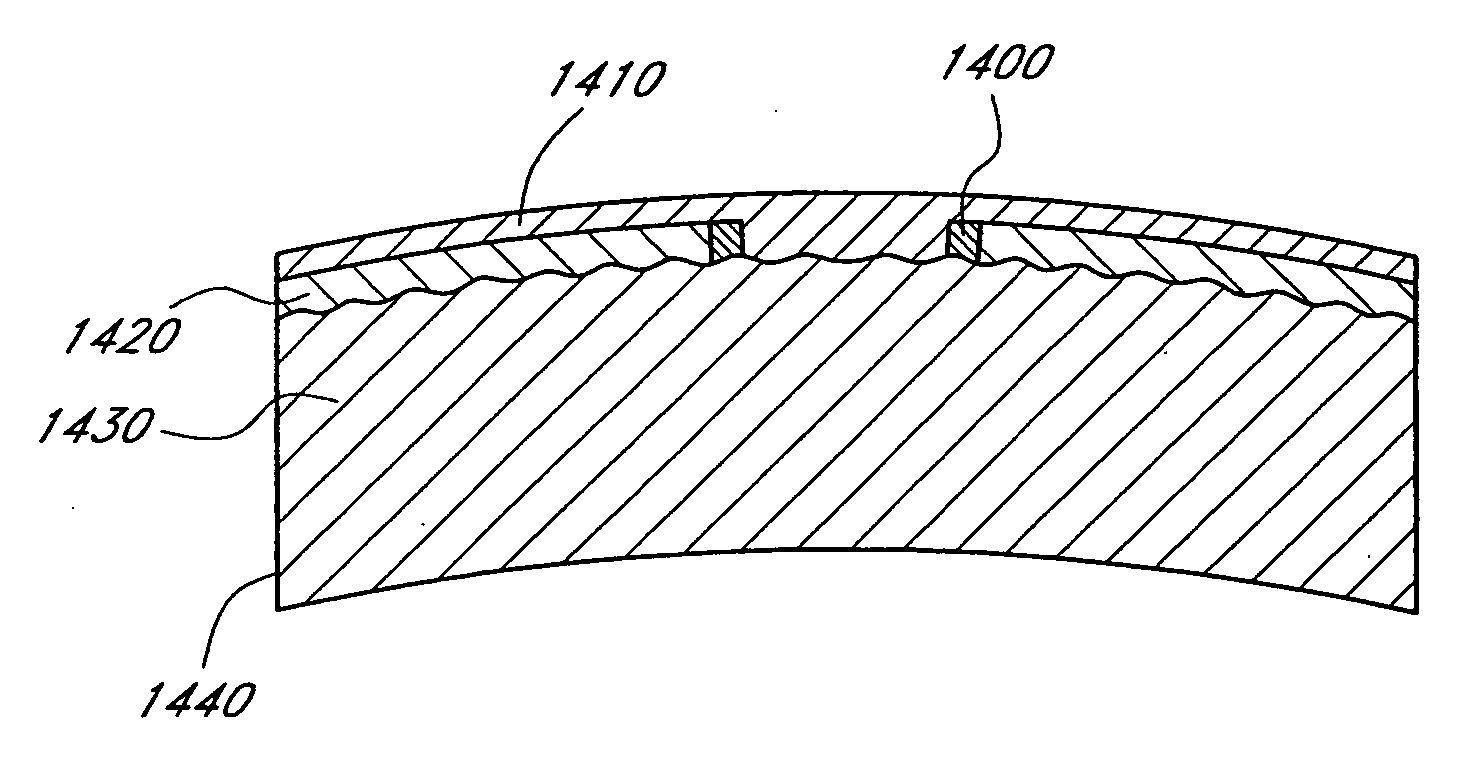
InactiveUS20060113054A1Increased depth of focusIncrease depth of focusEye implantsCosmetic implantsBiomedical engineeringMask layer
A method of making a mask configured to improve the depth of focus of an eye of a patient is provided. A substrate with a mask forming feature is provided. The mask forming feature comprises a forming surface that extends from an outer periphery. The forming surface is centered on a central axis of the mask forming feature. A release layer is formed on the forming surface. A mask layer is formed such that the release layer is between the mask layer and the substrate. The mask layer is formed of a biocompatible metal. A surface of the mask layer opposite the release layer is configured to not corrode. The mask layer is separated from the substrate.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
All Optical System and Method for Providing Extended Depth of Focus of Imaging
InactiveUS20090116096A1High quality imagingPrecise designPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsCamera lensImaging lens
An imaging system and method are presented. The system comprises an imaging lens unit, an imaging detector, and a birefringent element located between the imaging lens unit and the imaging detector. The system is thus configure and operable to provide in-focus imaging of objects located at both near-field and far-field ranges. Also provided is an optical device configured to be mounted on an imaging lens, being one of the following: a lens of an individual's glasses, on a contact lens, and an eye internal lens. The optical device is configured to be located between the imaging lens and the retina and comprises a birefringent element, to thereby provide in-focus imaging onto the retina of the objects located at both near-field and far-field ranges therefrom.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Intra-ocular lens or contact lens exhibiting lardge depth of focus
ActiveUS20060176572A1Easy to manufactureIncrease depth of focusIntraocular lensOptical partsIntra ocular lensDepth of focus
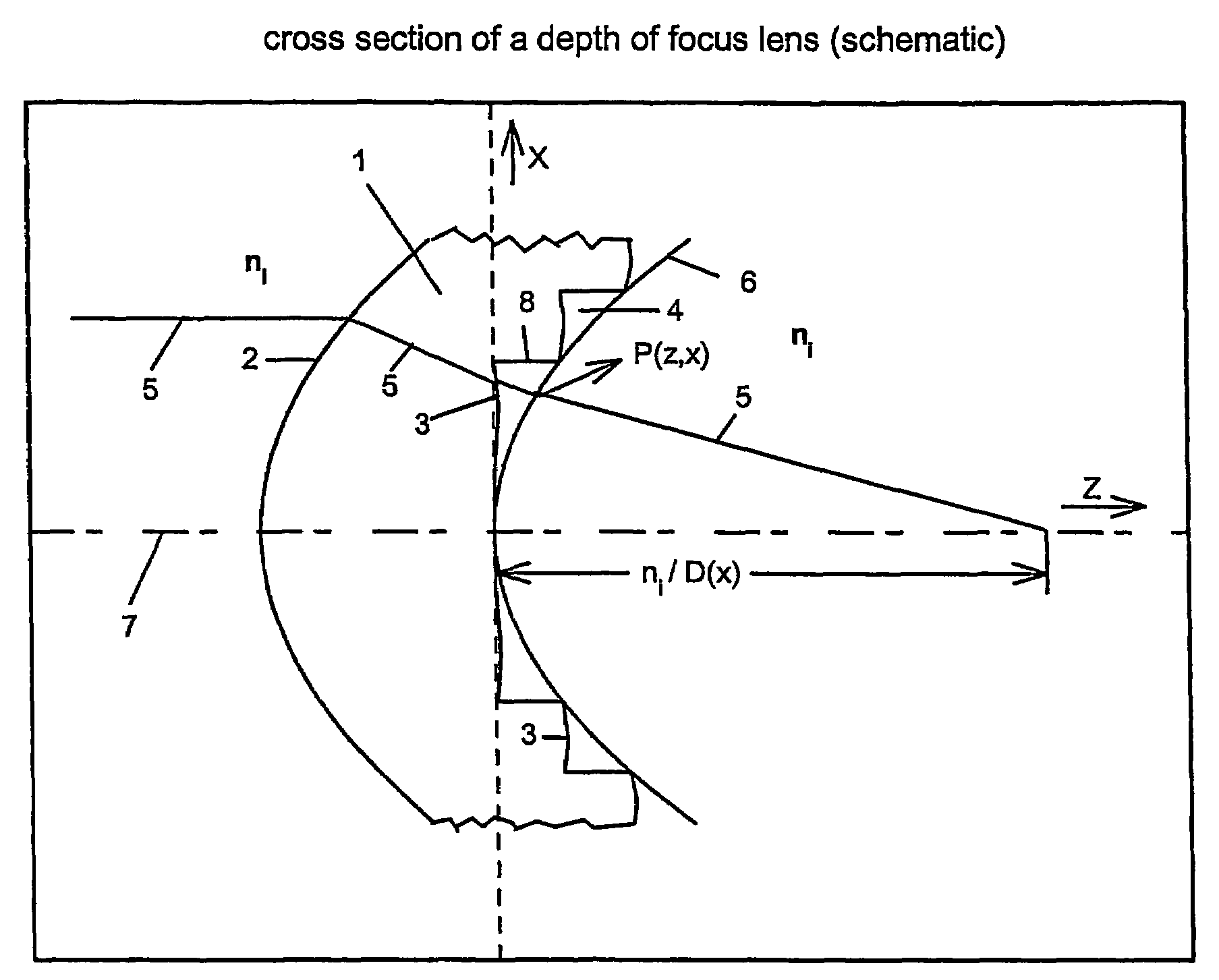
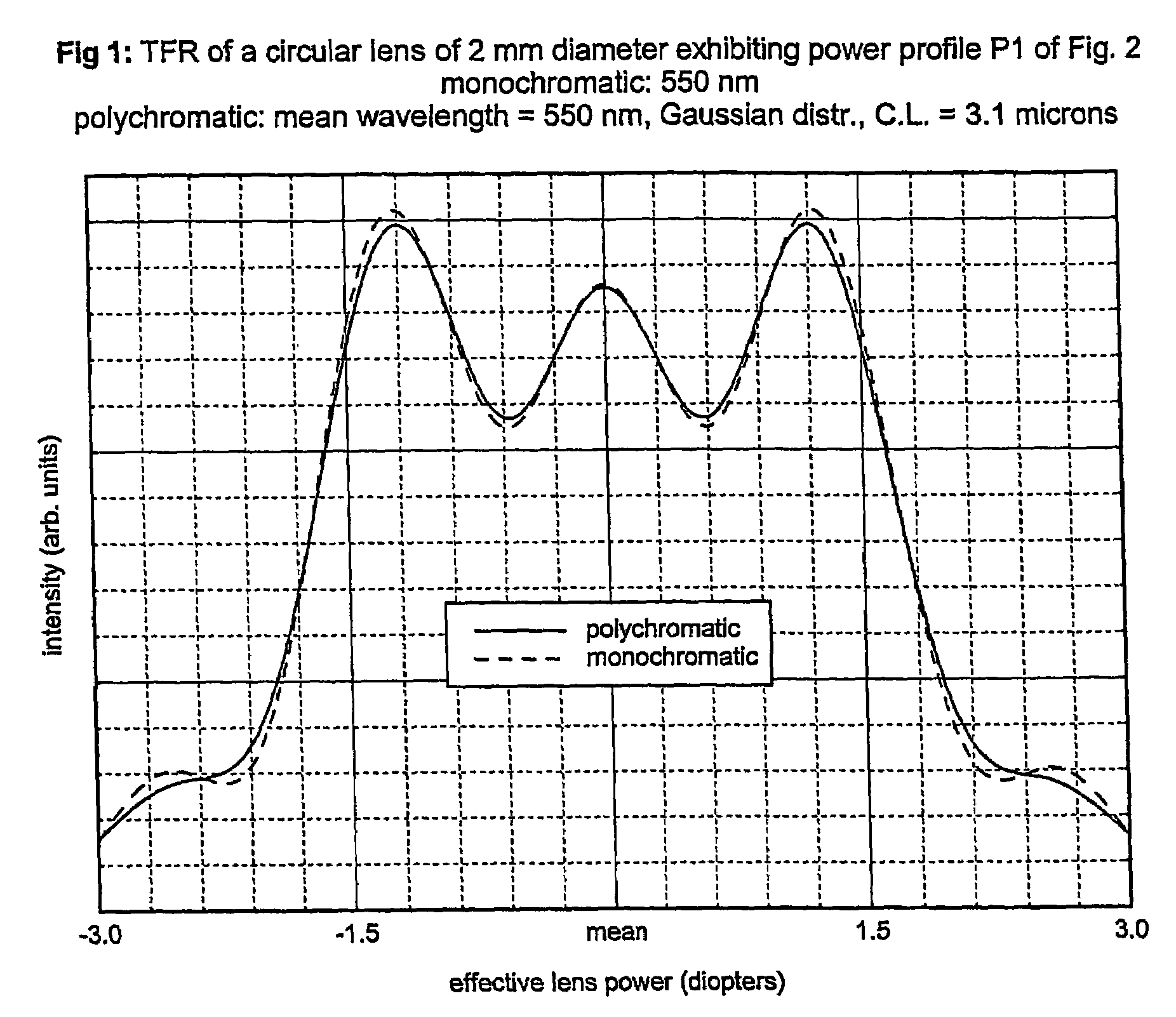
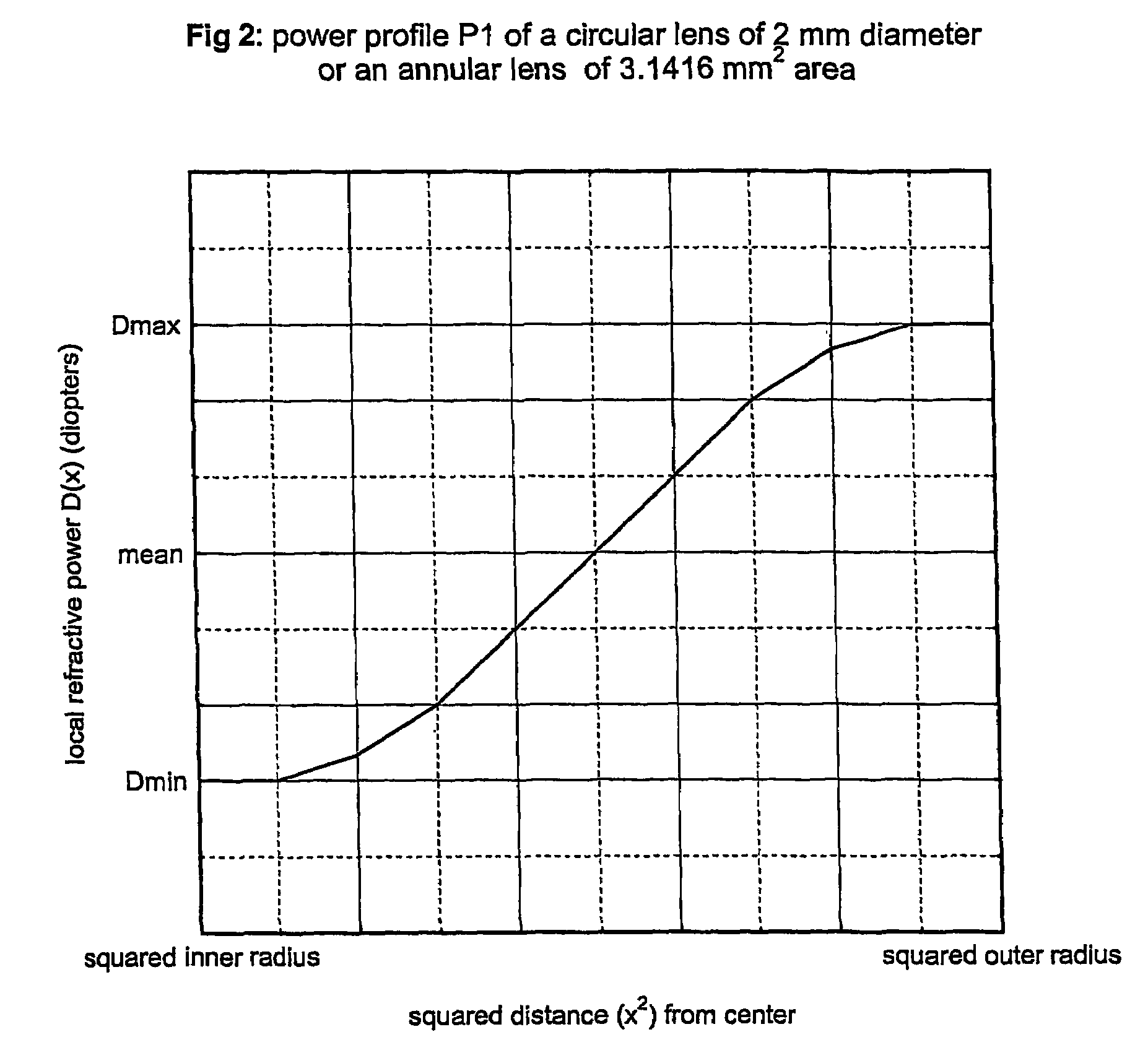
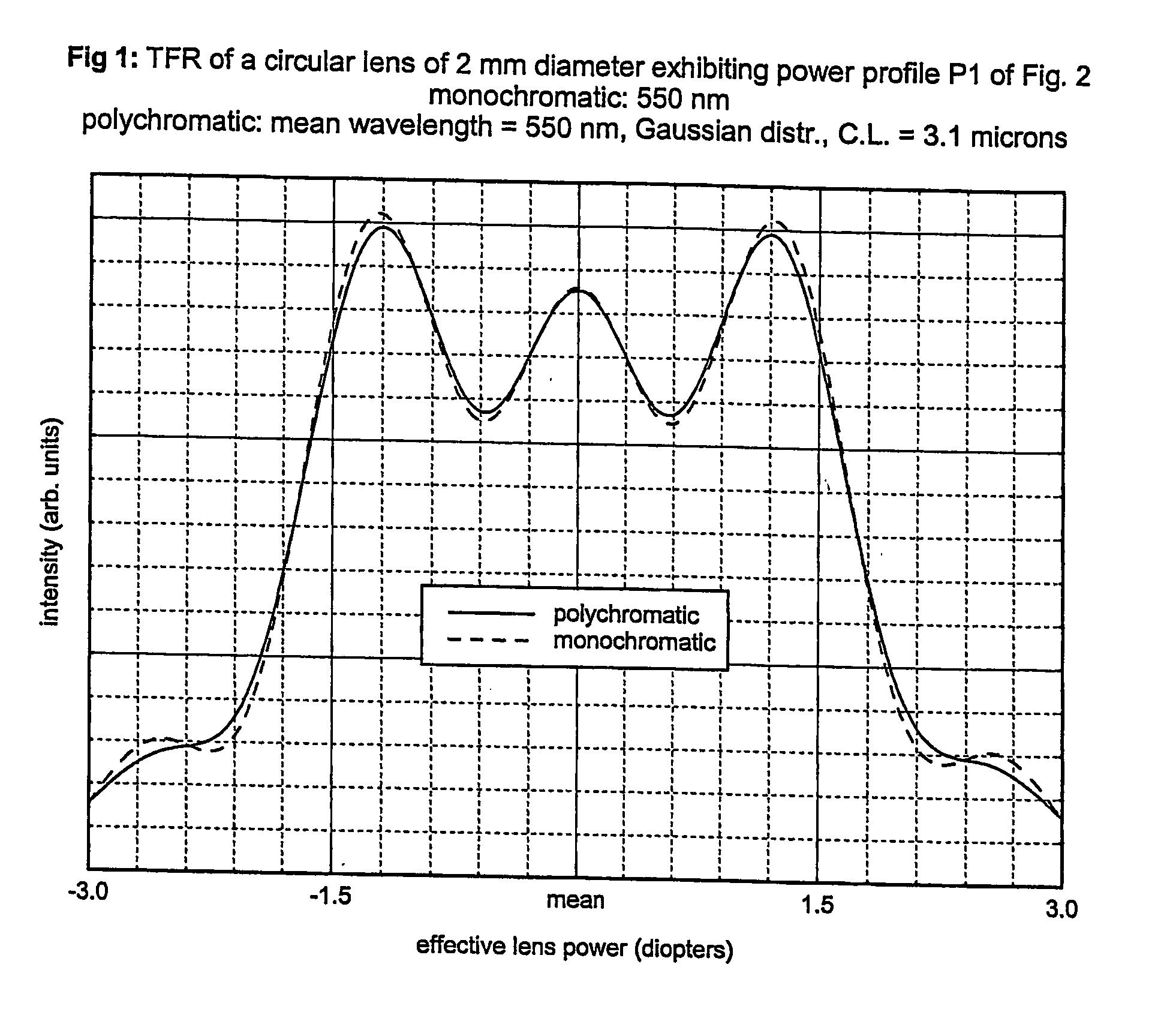
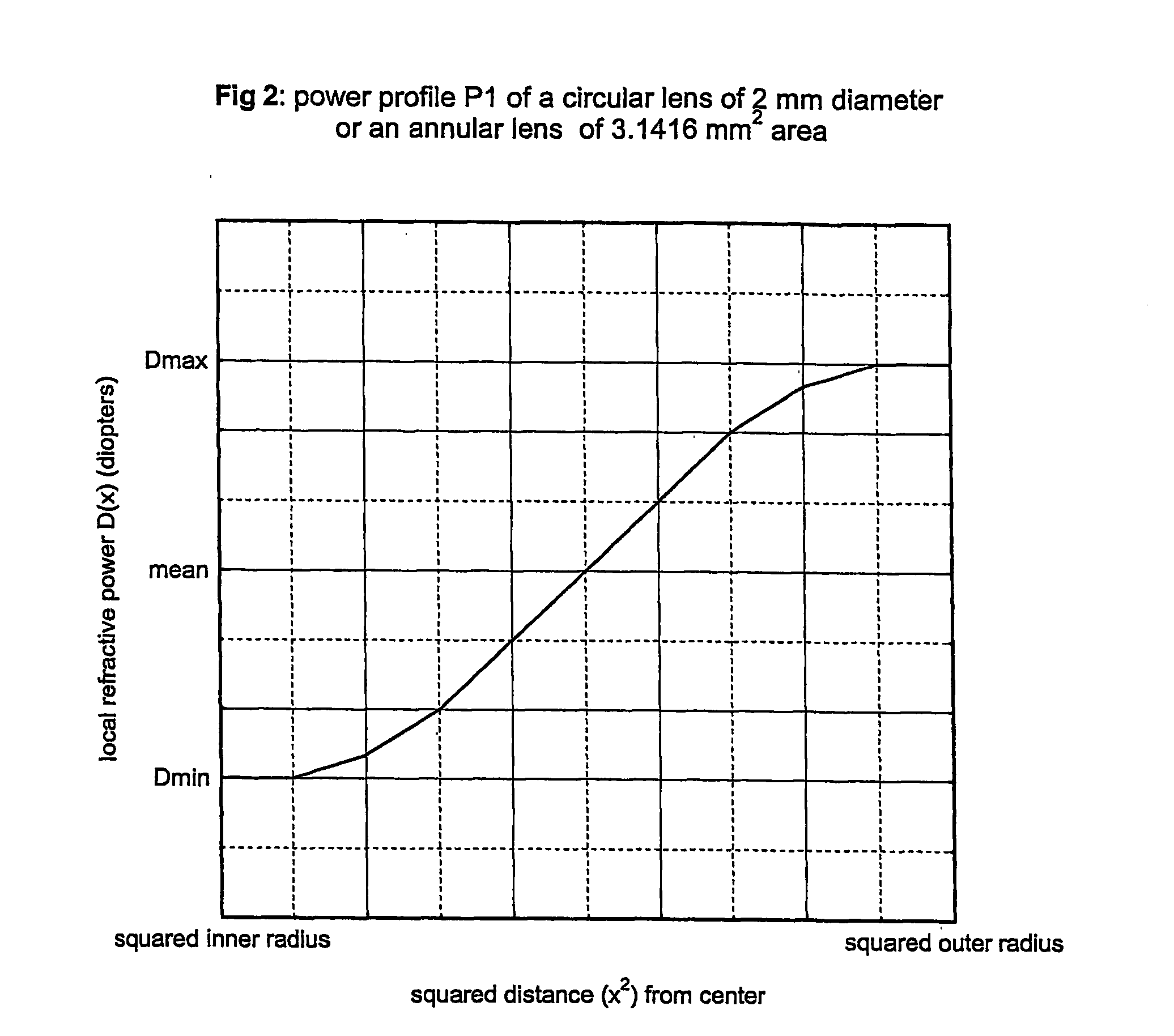
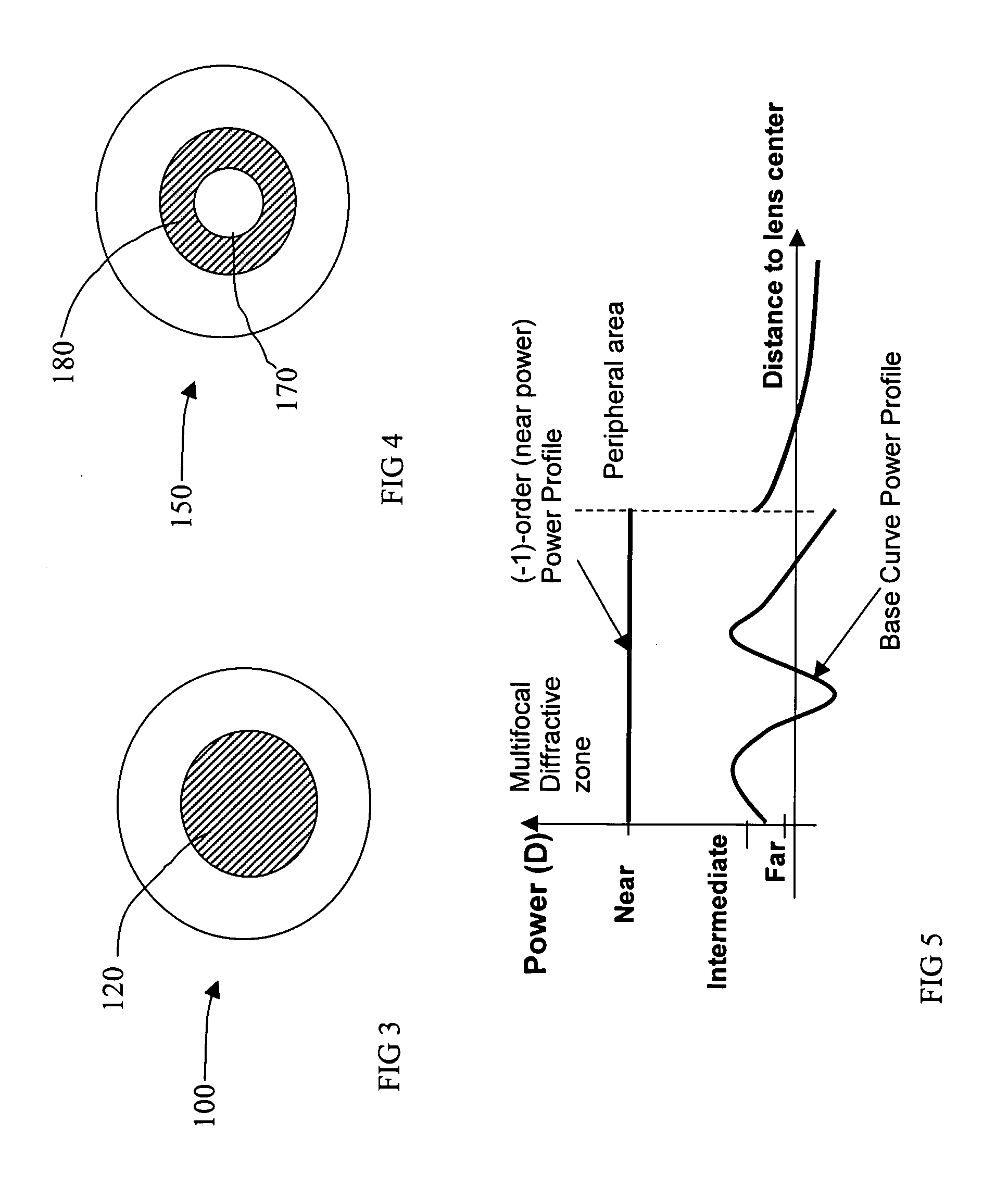
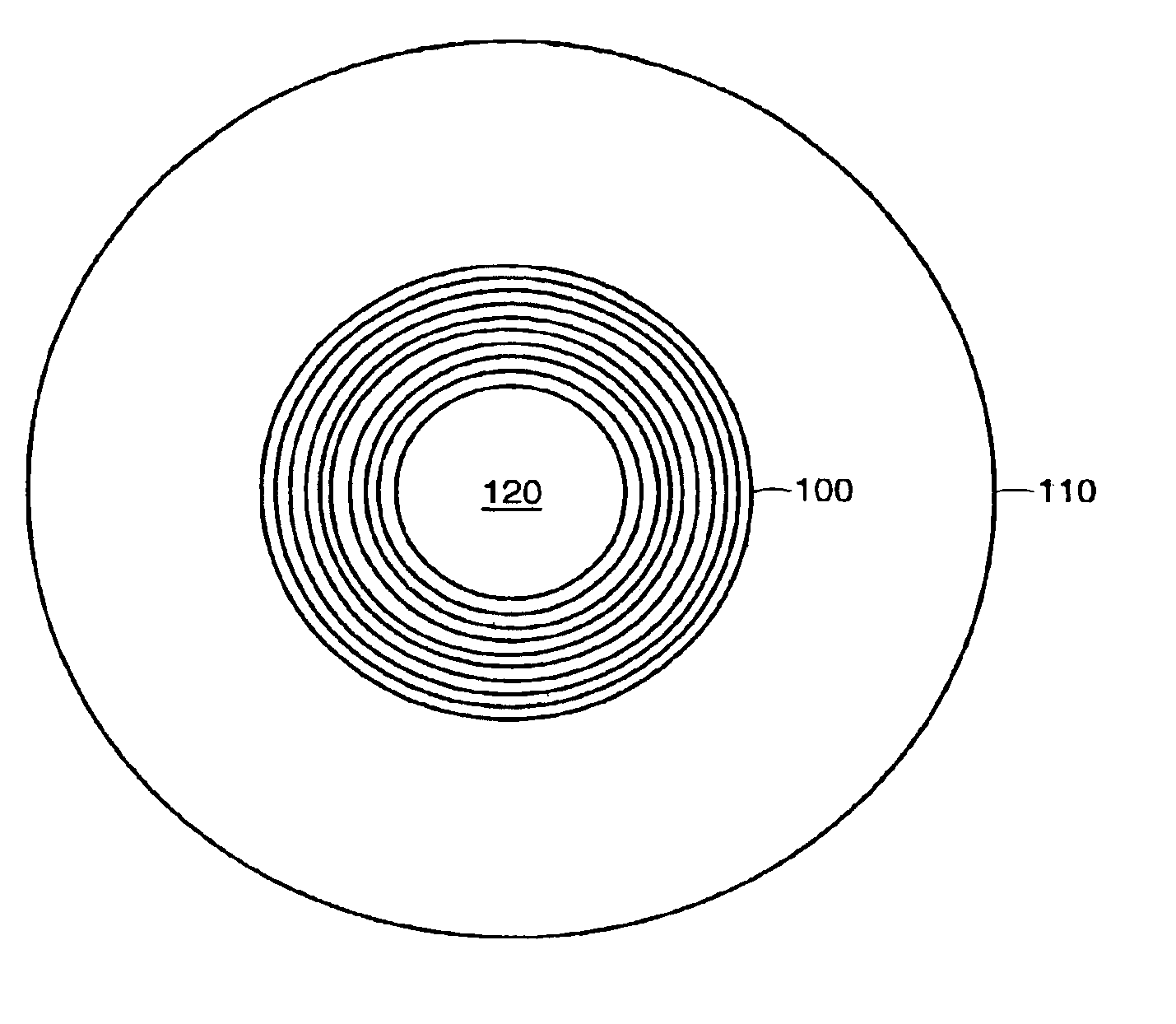
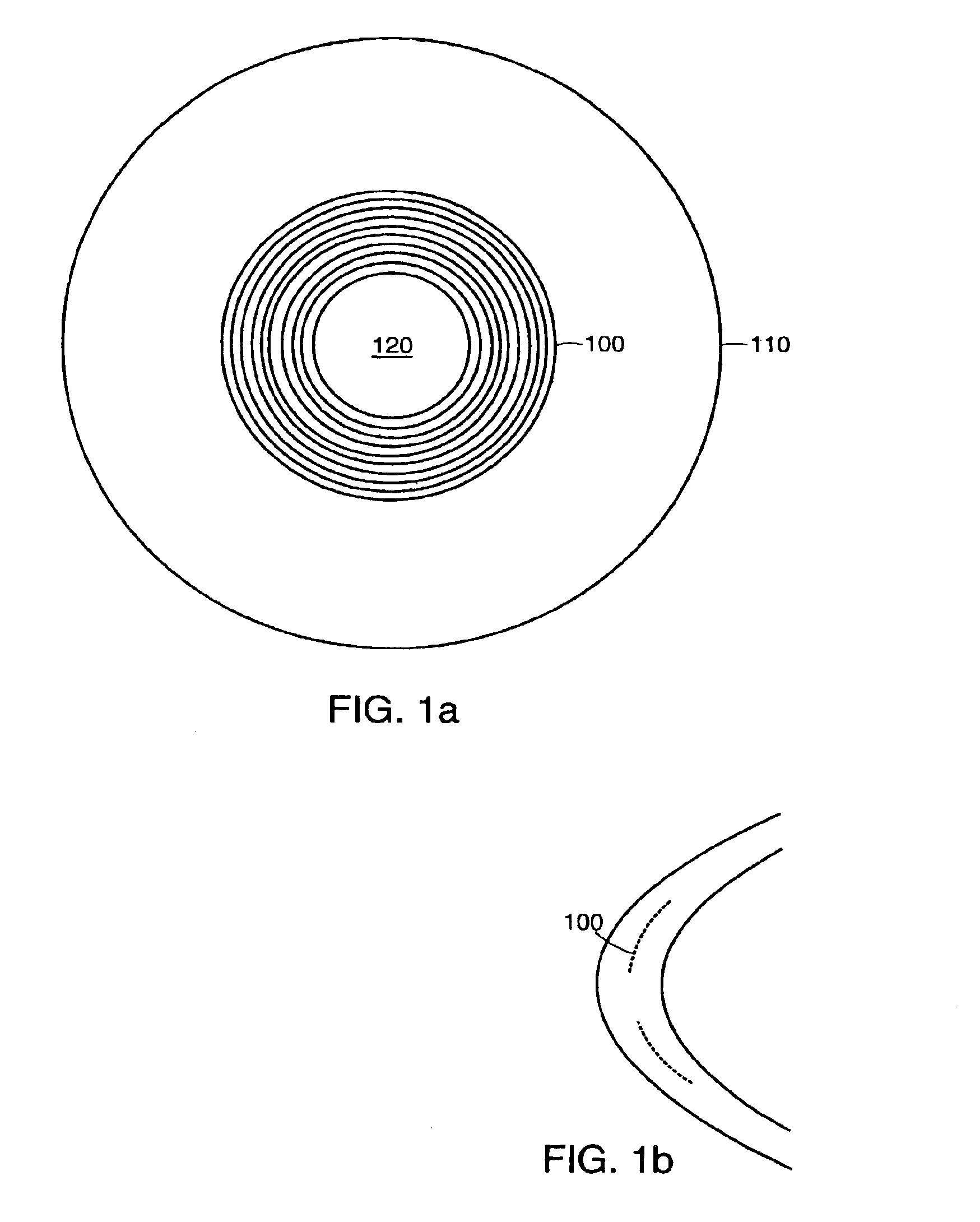
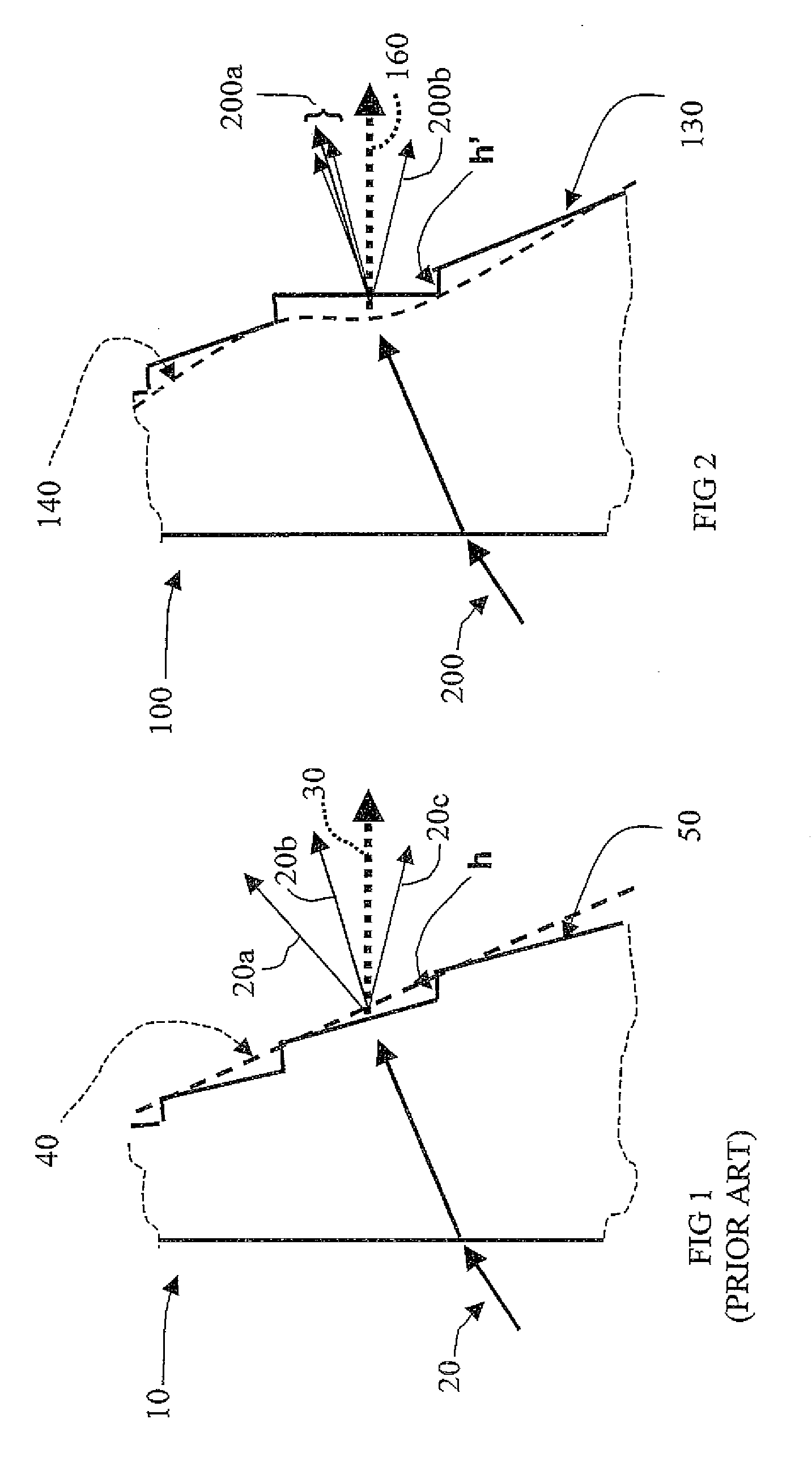
Circular and annular lens zones are disclosed which, at a given lens area, exhibit a depth of focus of a lens of considerably smaller area. The large depth of focus is achieved by imparting the lens zones a refractive power profile. An assembly of such large depth of focus lens zones represents a lens of large diameter which lens, in polychromatic light, exhibits essentially the same depth of focus as the lens zones from which it is composed.
Owner:FIALA WERNER J
Single microstructure lens, systems and methods
ActiveUS20110149236A1Increase depth of focusSuppresses the distinct bifocalitySpectales/gogglesComputer-aided planning/modellingImaging qualityCircular surface
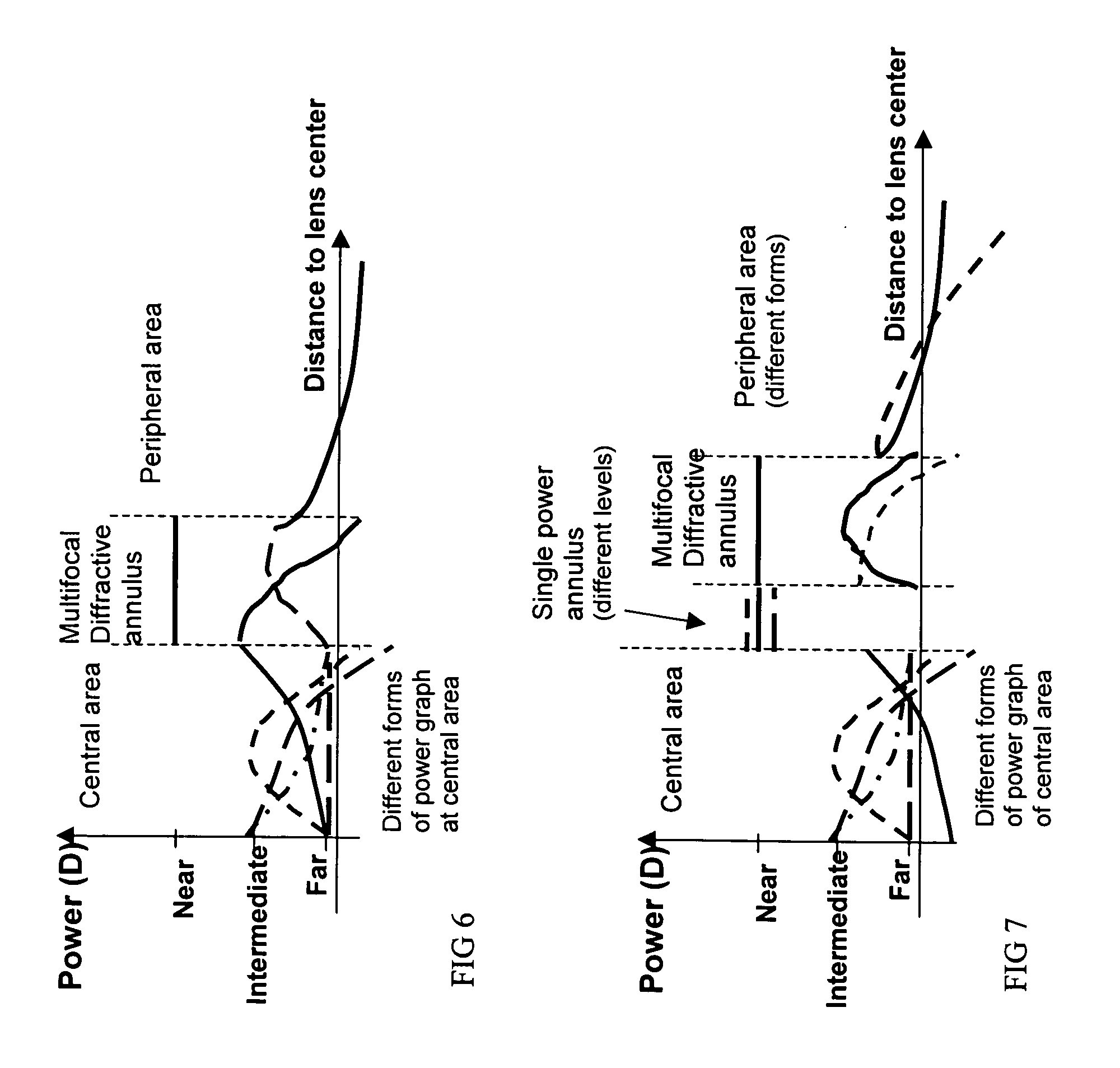
Systems and methods for providing enhanced image quality across a wide and extended range of foci encompass vision treatment techniques and ophthalmic lenses such as contact lenses and intraocular lenses (IOLs). Exemplary IOL optics can include a circular surface structure which acts as a diffractive or phase shifting profile. In some cases, a single ring IOL includes an anterior face and a posterior face, where a profile can be imposed on the anterior or posterior surface or face. The profile can have an inner portion such as a microstructure or central echelette, and an outer portion. Between the inner portion and the outer portion, there may be a transition zone that connects the inner and outer portions.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
System and method for aligning an optic with an axis of an eye
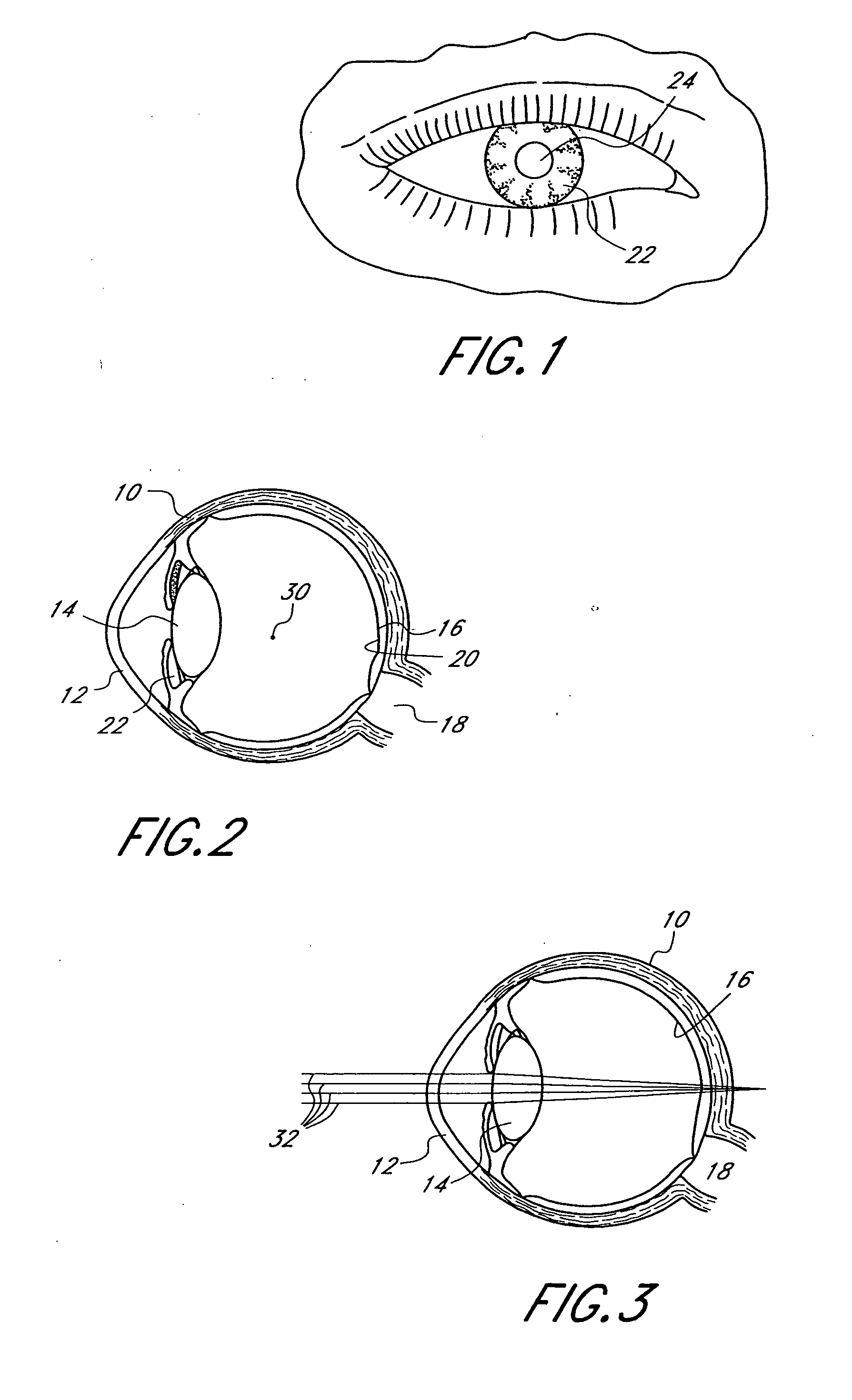
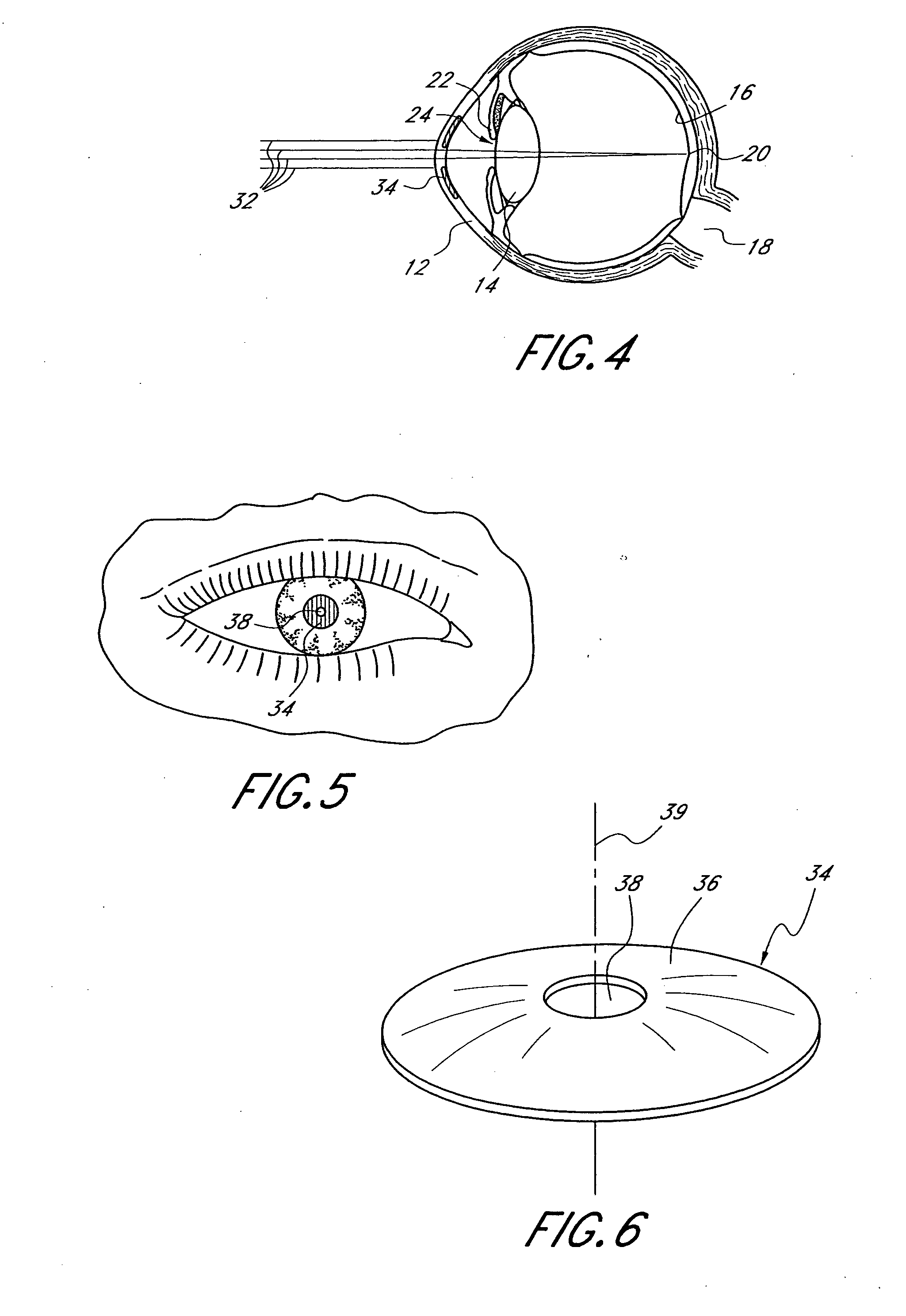
InactiveUS20060184243A1Increase depth of focusSmall sizeLaser surgeryEye implantsPupilComputer science
A method increases the depth of focus of an eye having a line of sight. A pharmacologic agent is applied to the eye to cause a reduction in the size of the pupil of the eye. The pupil is aligned with a visible feature of a mask comprising a pin-hole aperture. The pin-hole aperture is centered on a mask axis. The alignment causes the mask axis to be substantially aligned with the line of sight of the eye. The mask is applied to the eye of the patient while maintaining the alignment of the visible feature of the mask and the pupil.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal design for ocular implant
ActiveUS20100161048A1Reduce step heightIncrease depth of focusIntraocular lensMedicineOptical energy
A radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL for ocular implant is provided. The ocular implant can comprise a radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal intraocular lens optic and a number of haptics. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL may pass optical energy in both photopic and mesopic conditions. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL includes a number of radially segmented apodization zones, each radially segmented apodization zones having a unique focal length. The haptics mechanically couple to the apodized diffractive multifocal IOL optic in order to position and secure the apodized diffractive multifocal IOL within the eye. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL may include both a diffractive region and a refractive region.
Owner:ALCON INC
Aspheric multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS20070258143A1Increase depth of focusAdd depthSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensAnterior surfaceRefractive index
A multifocal ophthalmic lens includes a lens element having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, a refractive zone, or base surface having aspherically produced multifocal powers disposed on one of the anterior and posterior surfaces; and a near focus diffractive multifocal zone disposed on one of the anterior and posterior surfaces.
Owner:VISION ADVANCEMENT LLC
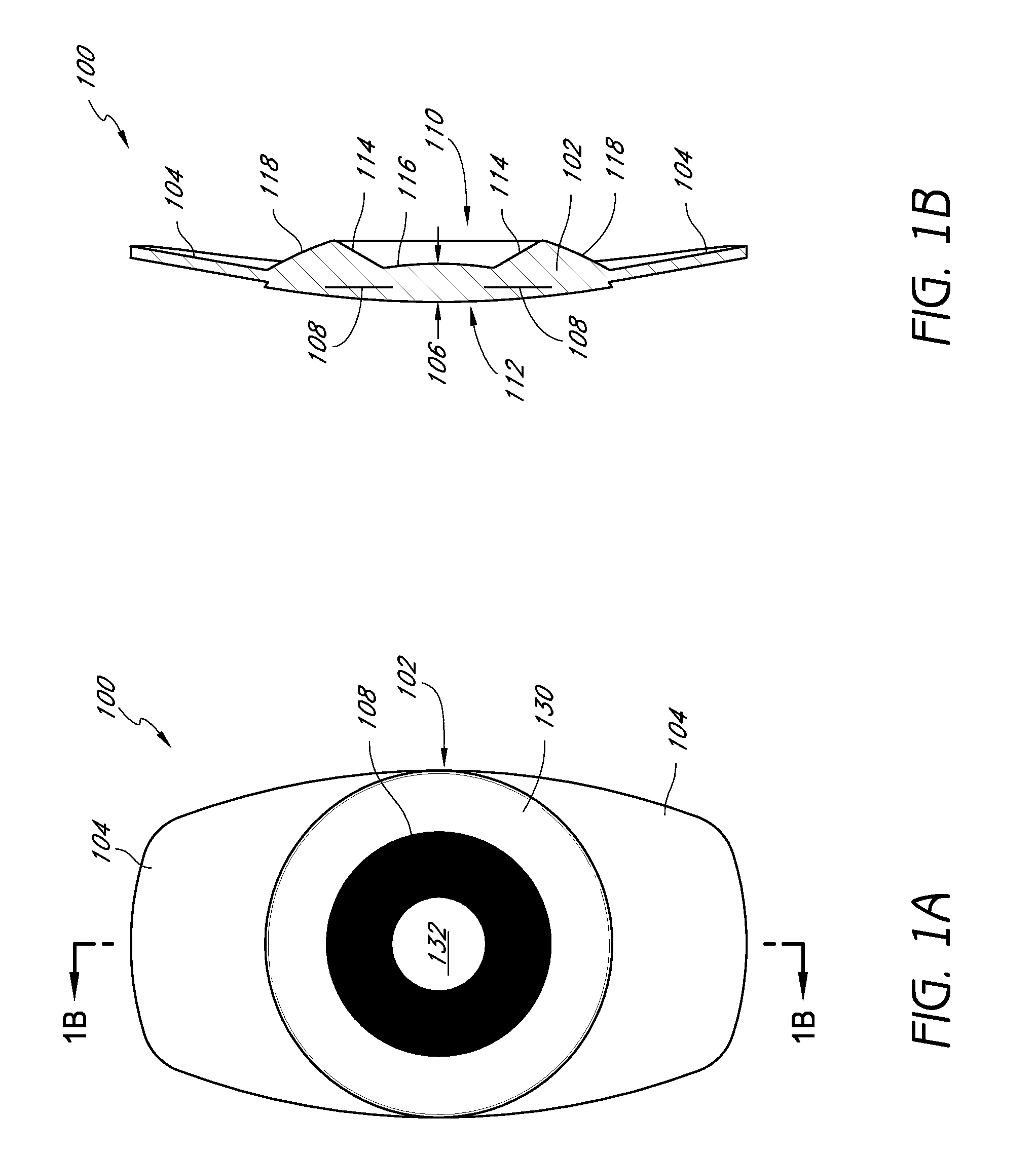
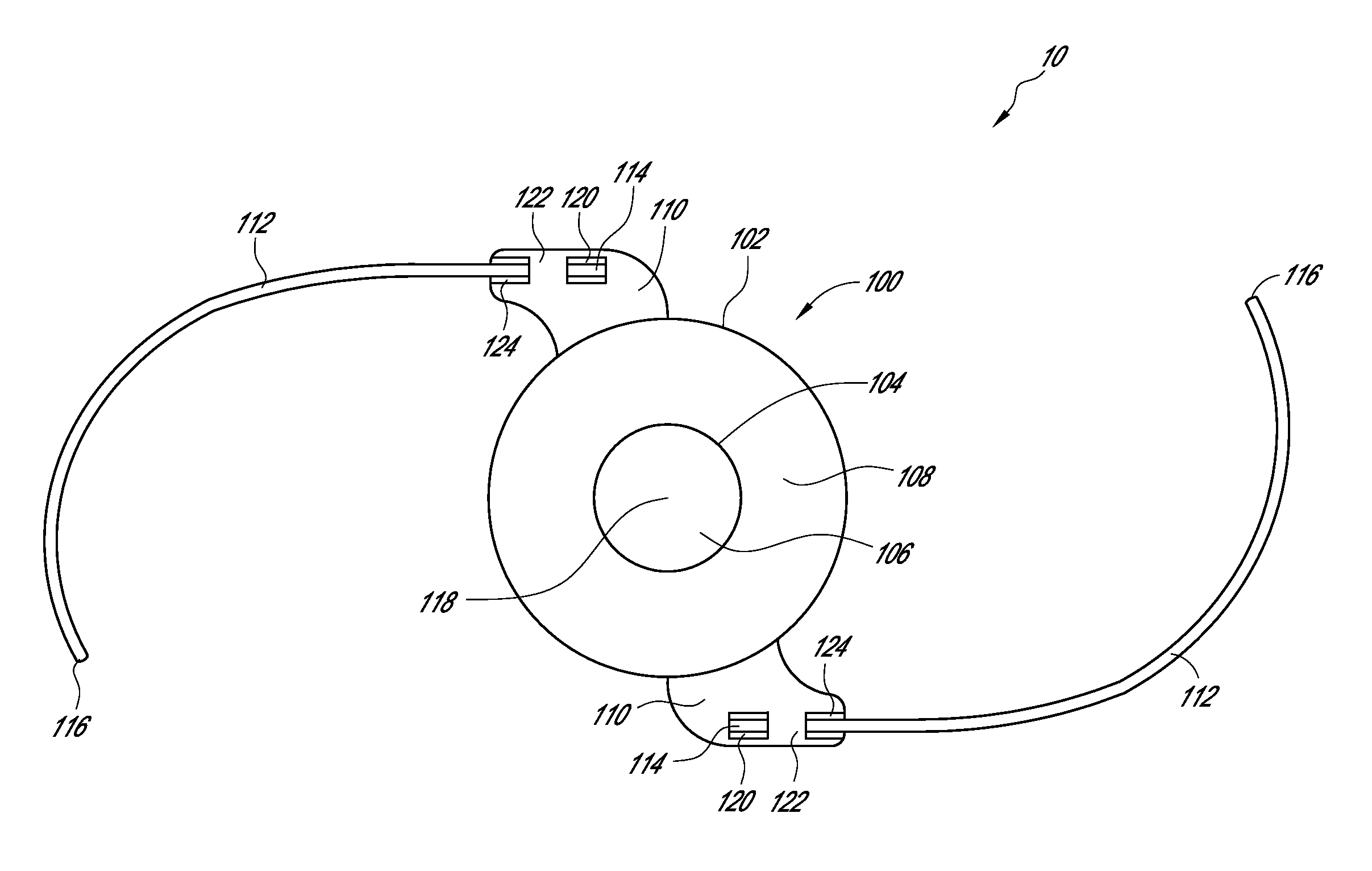
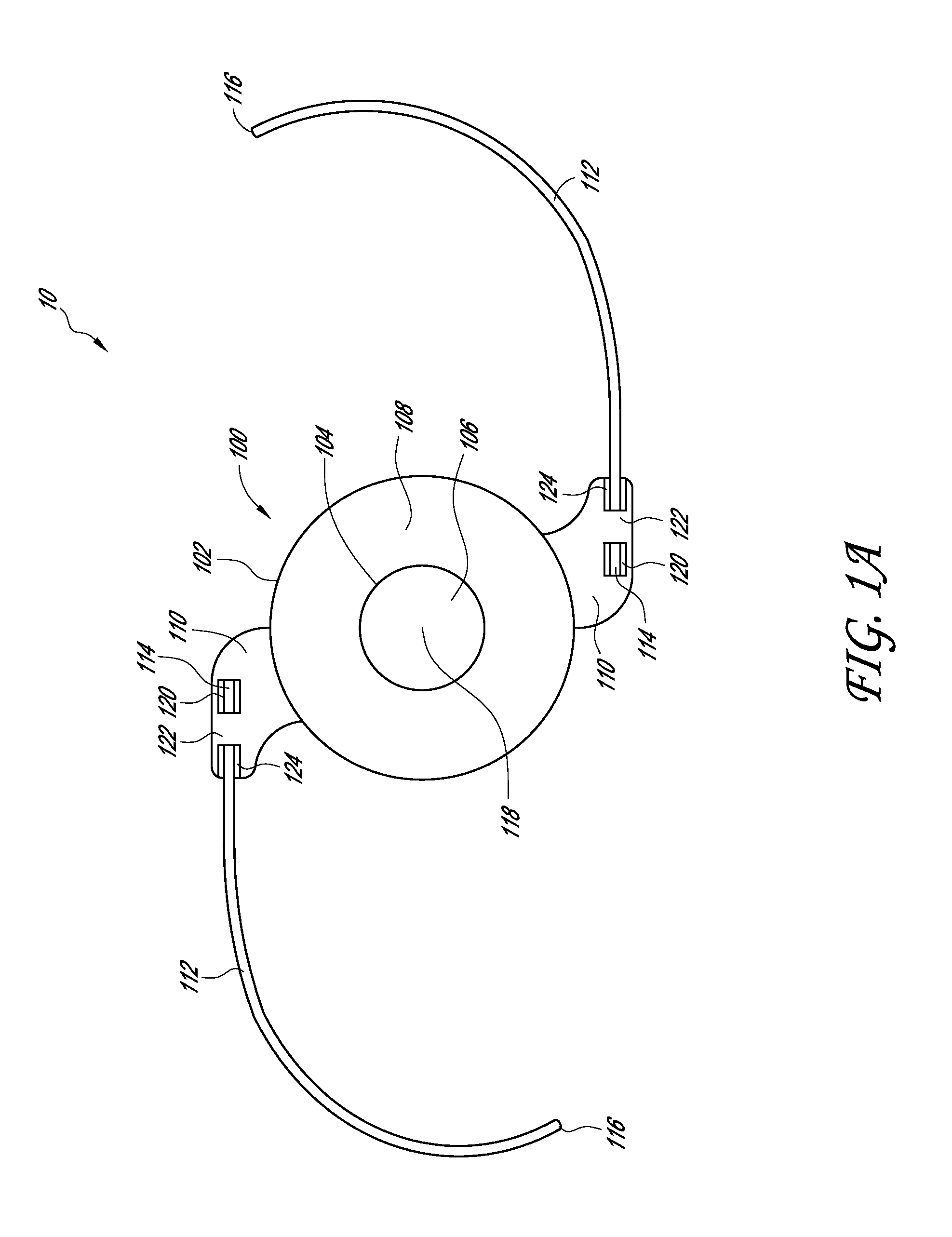
System and method for increasing the depth of focus of the human eye
InactiveUS6874886B2Increase depth of focusPrevent deviationSpectales/gogglesMembranesLight reflectionFace shield
A method and apparatus for increasing the depth of focus of the human eye is comprised of a lens body, an optic in the lens body configured to produce light interference, and a pinhole-like optical aperture substantially in the center of the optic. The optic may be configured to produce light scattering or composed of a light reflective material. Alternatively, the optic may increase the depth of focus via a combination of light interference, light scattering, light reflection and / or light absorption. The optic may also be configured as a series of concentric circles, a weave, a pattern of particles, or a pattern of curvatures. One method involves screening a patient for an ophthalmic lens using a pinhole screening device in the lens to increase the patient's depth of focus. Another method comprises surgically implanting a mask in the patient's eye to increase the depth of focus.
Owner:HEALTHCARE ROYALTY PARTNERS II
Method of making an ocular implant
InactiveUS20060271184A1Increase depth of focusEye implantsCosmetic implantsOcular implantBiomedical engineering
A method of making a mask configured to improve the depth of focus of an eye of a patient is provided. A substrate with a mask forming feature is provided. The mask forming feature comprises a forming surface that extends from an outer periphery. The forming surface is centered on a central axis of the mask forming feature. A release layer is formed on the forming surface. A mask layer is formed such that the release layer is between the mask layer and the substrate. The mask layer is formed of a biocompatible metal. A surface of the mask layer opposite the release layer is configured to not corrode. The mask layer is separated from the substrate.
Owner:HEALTHCARE ROYALTY PARTNERS II
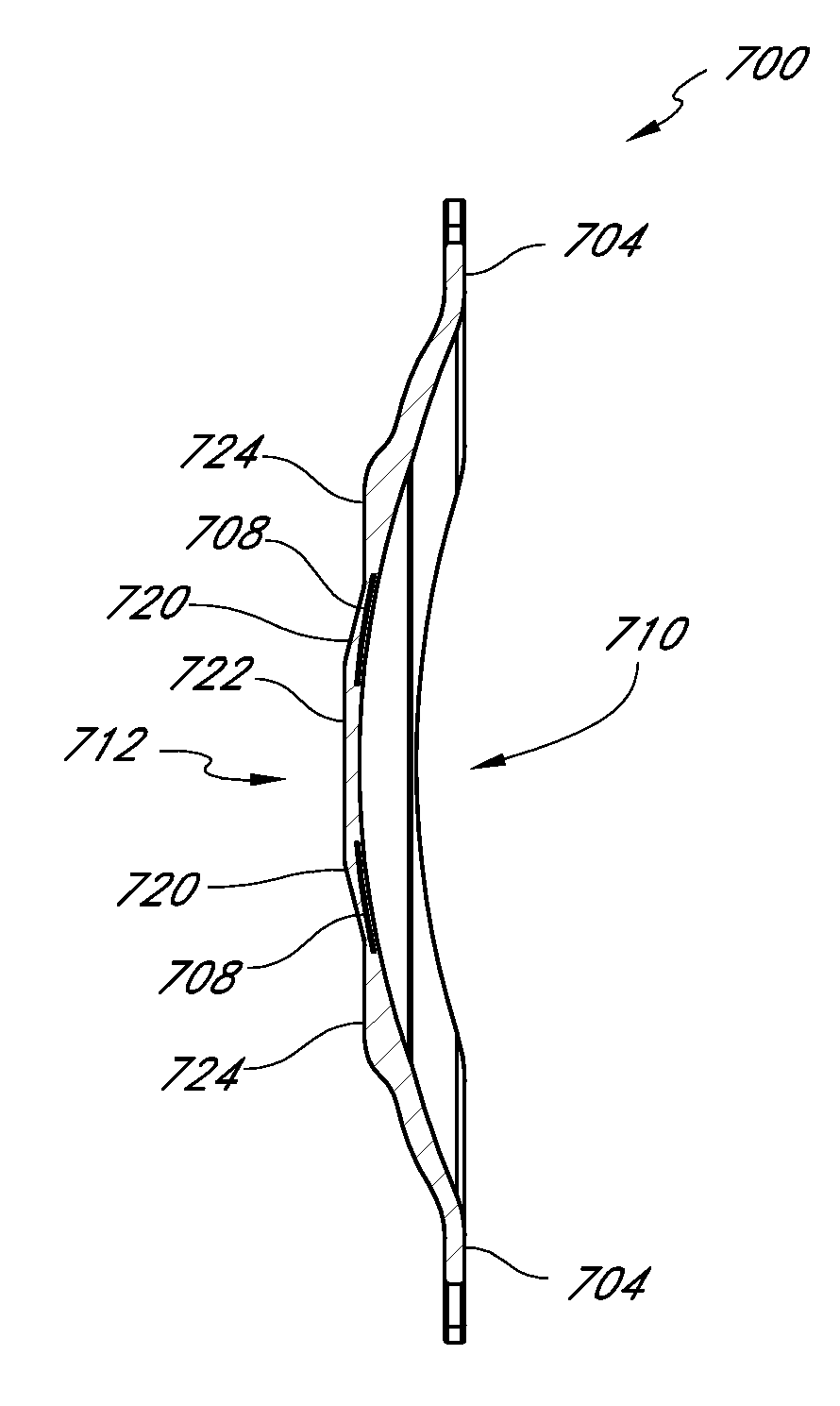
Intraocular lens with extended depth of focus
InactiveUS20100161051A1Add depthSolve lack of contrastSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensOptical axisAnterior surface
An ophthalmic lens is disclosed, one embodiment comprising an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface disposed about an optical axis, wherein at least one of the surfaces has a profile characterized by superposition of a base profile and an auxiliary profile, the auxiliary profile comprising a continuous pattern of surface deviations from the base profile. The auxiliary profile is a sinusoidal profile and can be amplitude modulated, frequency modulated or both amplitude and frequency modulated. The ophthalmic lens can be an IOL.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
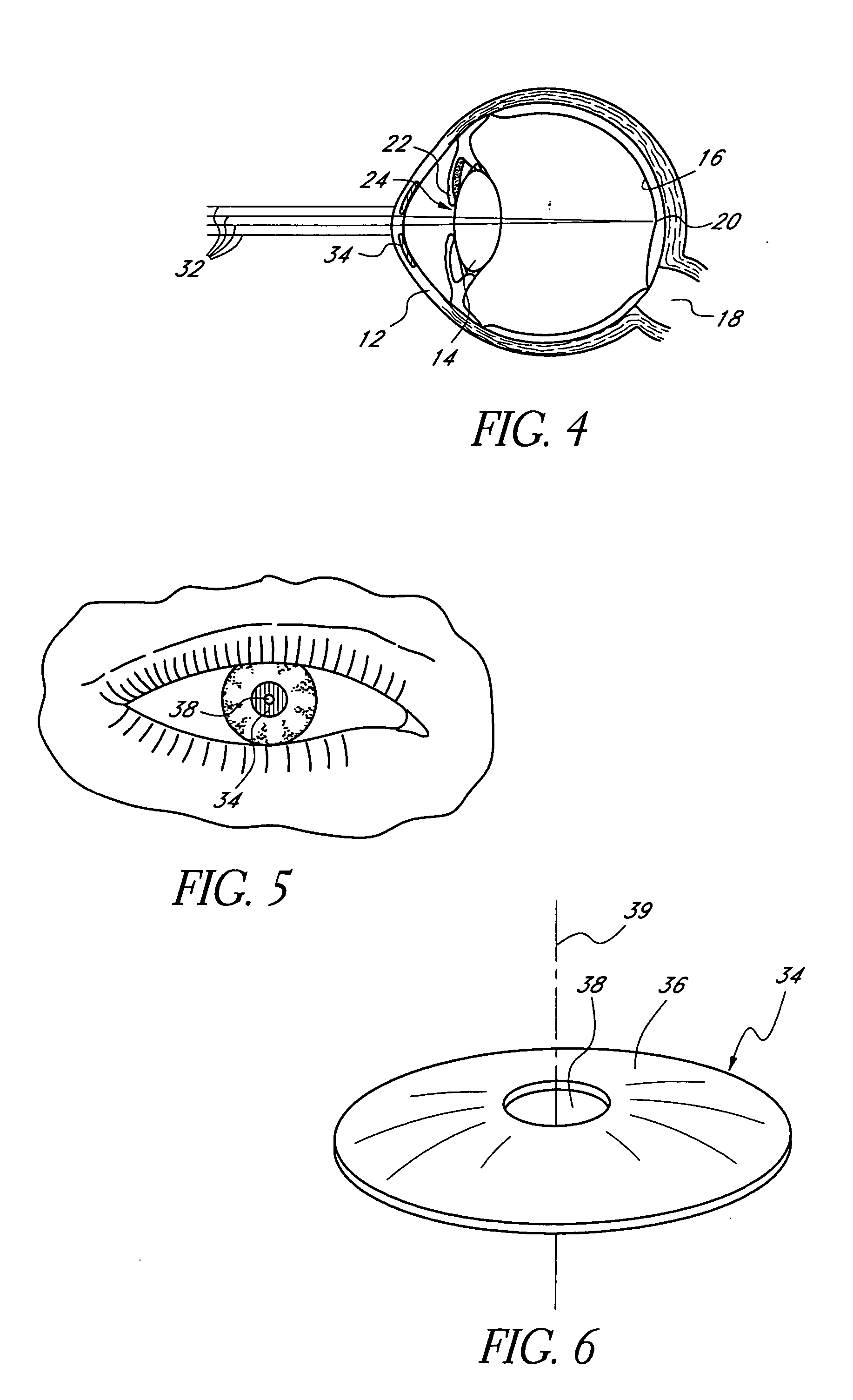
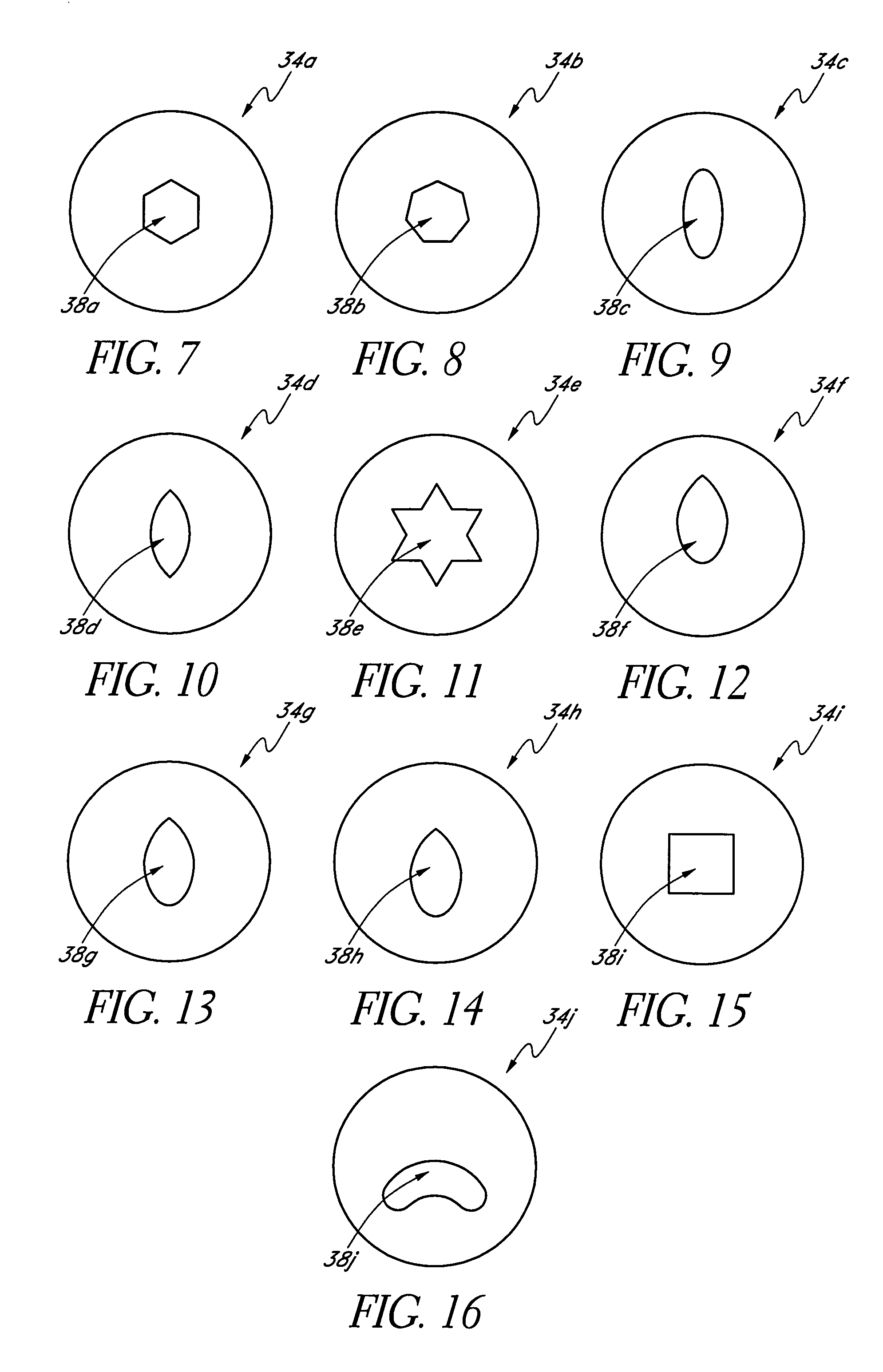
Mask configured to maintain nutrient transport without producing visible diffraction patterns
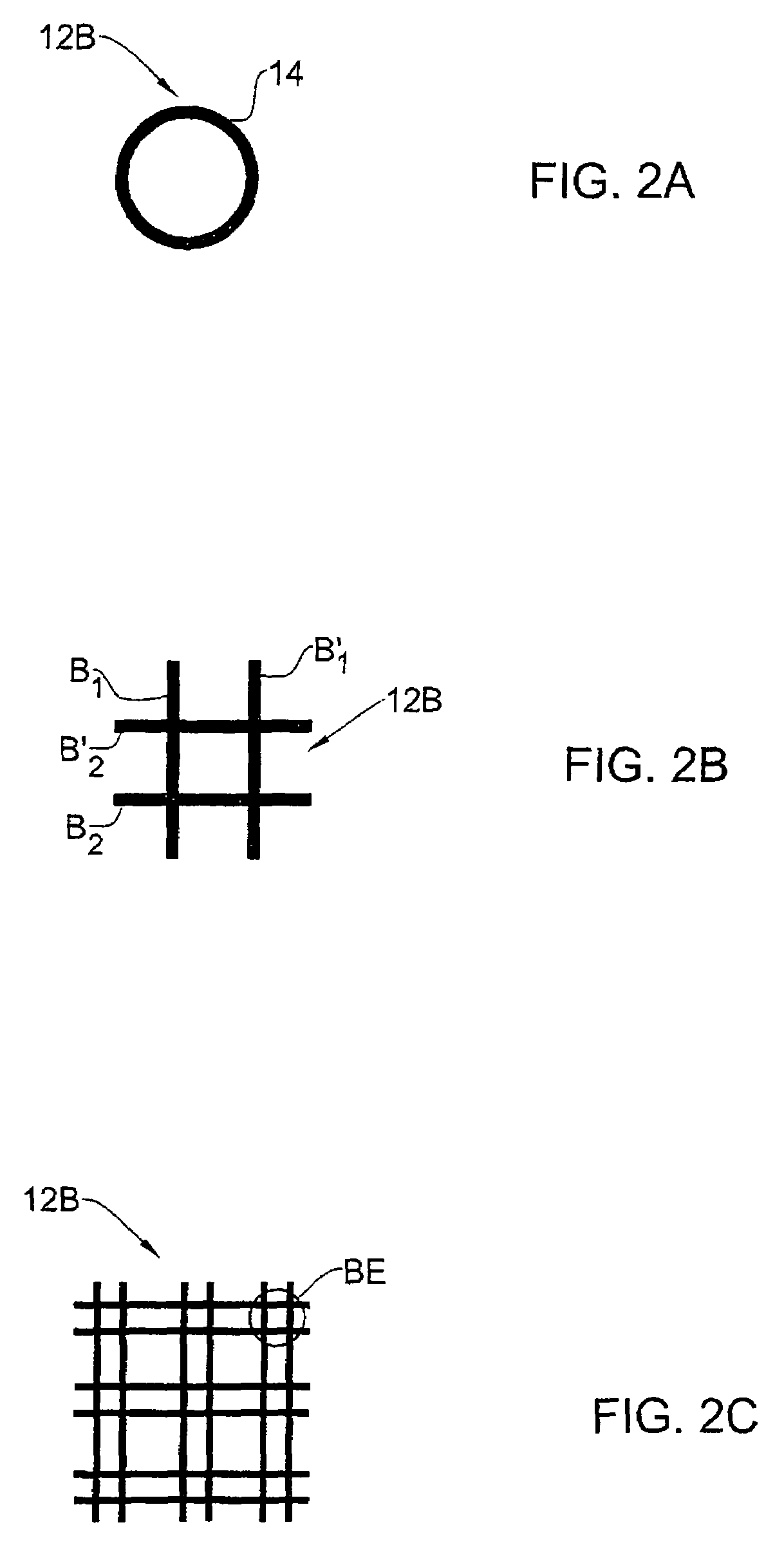
InactiveUS20060079959A1Increase depth of focusEliminate DiffractionSpectales/gogglesSenses disorderAnterior surfaceCorneal layer
A mask configured to be implanted in a cornea of a patient to increase the depth of focus of the patient includes an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a plurality of holes. The anterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a first corneal layer. The posterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a second corneal layer. The plurality of holes extends at least partially between the anterior surface and the posterior surface. The holes of the plurality of holes are configured to substantially eliminate visible diffraction patterns.
Owner:CHRISTIE BRUCE A +2
Masked ocular device for implantation adjacent to an intraocular lens
The present application describes a device and methods that use a small-aperture mask surgically implanted in the optical path to improve the depth of focus of, for example, a pseudophakic patient. The device can be inserted adjacent to an intraocular lens (IOL). The device may include one or more connectors for attaching the device to an intraocular lens.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Multi-ring lens, systems and methods for extended depth of focus
ActiveUS20140168602A1Increase depth of focusSuppress the distinct bifocalitySpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsImaging qualityEye lens
Systems and methods for providing enhanced image quality across a wide and extended range of foci encompass vision treatment techniques and ophthalmic lenses such as contact lenses and intraocular lenses (IOLs). Exemplary IOL optics can include an aspheric refractive profile imposed on a first or second lens surface, and a diffractive profile imposed on a first or second lens surface. The aspheric refractive profile can focus light toward a far focus. The diffractive profile can include a central zone that distributes a first percentage of light toward a far focus and a second percentage of light toward an intermediate focus. The diffractive profile can also include a peripheral zone, surrounding the central zone, which distributes a third percentage of light toward the far focus and a fourth percentage of light toward the intermediate focus.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Method and apparatus for aligning a mask with the visual axis of an eye
InactiveUS20060271026A1Increase depth of focusMaintain alignmentSurgical instrument detailsEye diagnosticsOptometryDepth of focus
A method is provided for increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. A visual axis of the eye is aligned with an instrument axis of an ophthalmic instrument. The ophthalmic instrument has an aperture through which the patient may look along the instrument axis. A first reference target is imaged on the instrument axis at a first distance with respect to the eye. A second reference target is imaged on the instrument axis with the ophthalmic instrument at a second distance with respect to the eye. The second distance is greater than the first distance. Movement is provided such that the patient's eye is in a position where the images of the first and second reference targets appear to the patient's eye to be aligned. A mask comprising a pin-hole aperture having a mask axis is aligned with the instrument axis such that the mask axis and the instrument axis are substantially collinear. The mask is applied to the eye of the patient while the alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis is maintained. Maintaining alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis may be facilitated by capturing an image of the eye.
Owner:SILVESTRINI THOMAS A +3
Microscope
InactiveUS20100265575A1Increase depth of focusShadowing is preferably also reduced or preventedMicroscopesAcute angleLight beam
A microscope including an imaging objective for imaging a sample on a detector and means for illuminating the sample with a light sheet in the focus plane of the imaging objective. The illumination means includes an illumination source which emits coherent light, and Bessel optics which generate at least two plane waves from the light beam and give propagation directions for the plane waves. The propagation direction of each of the plane waves encloses an acute angle with the focus plane in each instance, the magnitude of the acute angle being identical for each of the plane waves, so that the plane waves undergo constructive interference in the focus plane so that a light sheet is generated. Similarly, the illumination means can also include an optical element by which a rotationally symmetric Bessel beam is generated from the light beam for dynamic generation of a light sheet.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
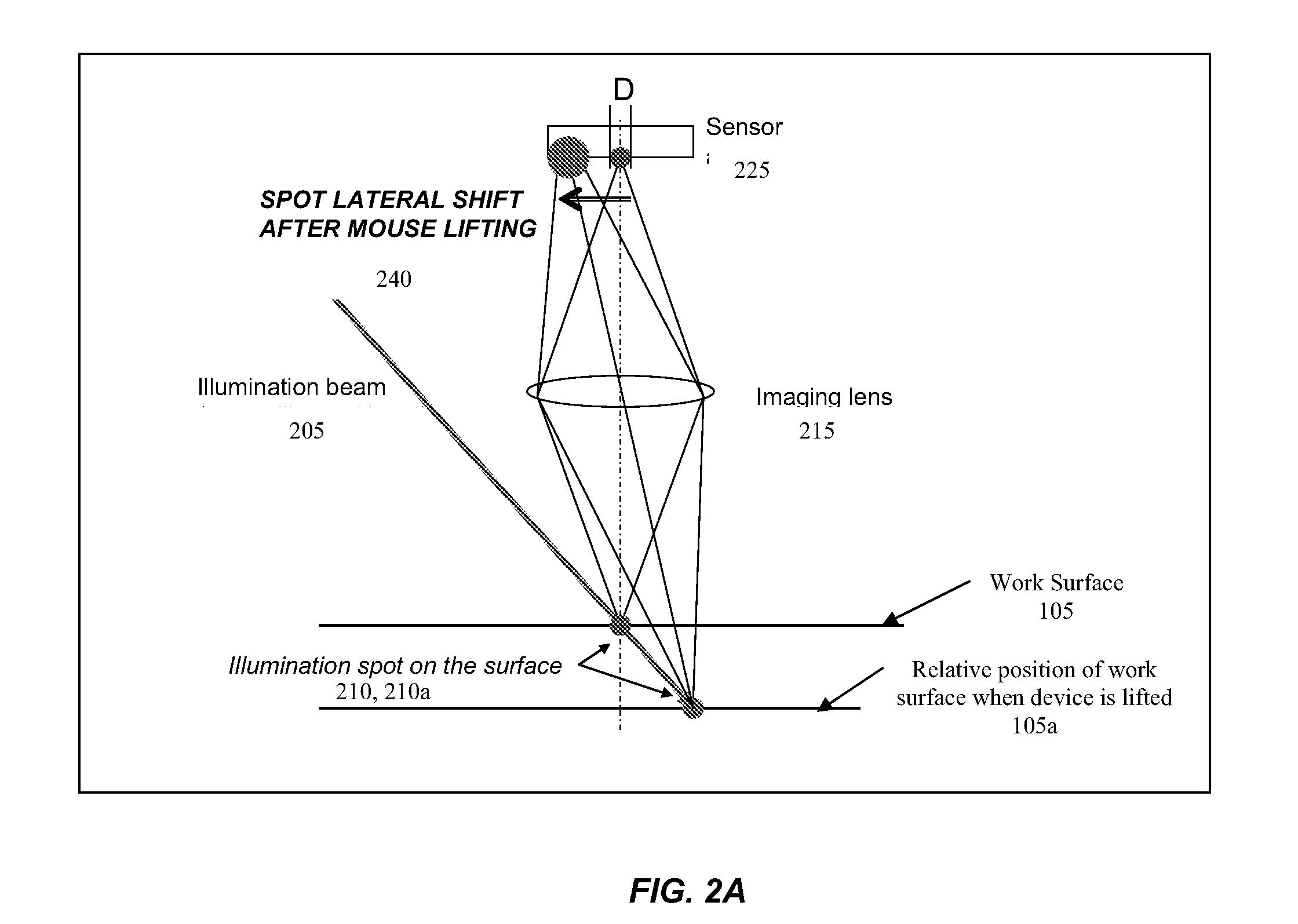
System and method for accurate lift-detection of an input device
InactiveUS20090135140A1Accurate detectionEasy to trackInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsCapacitanceDielectric
Various systems and methods are employed for lift-detection. Beam triangulation can be used, and in one embodiment, an optical lift detection module is separate from the optical tracking module. In one embodiment, a capacitive lift detection technique is used. A capacitor is built into the bottom case of the mouse. When the mouse is resting on a surface, the surface material serves as a dielectric for the capacitor, while air serves as the dielectric when the mouse is lifted. This dielectric change leads to a change in the capacitance value, leading to detection of lift. In one embodiment, a capacitor with an easily compressable material inserted between the two electrodes is used. In another embodiment, a mechanical plunger with an elastic membrane is used for lift detection. Lift detection can be tunable and / or customizable. The actual height of the life can be detected, rather than simple on-off notifications.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
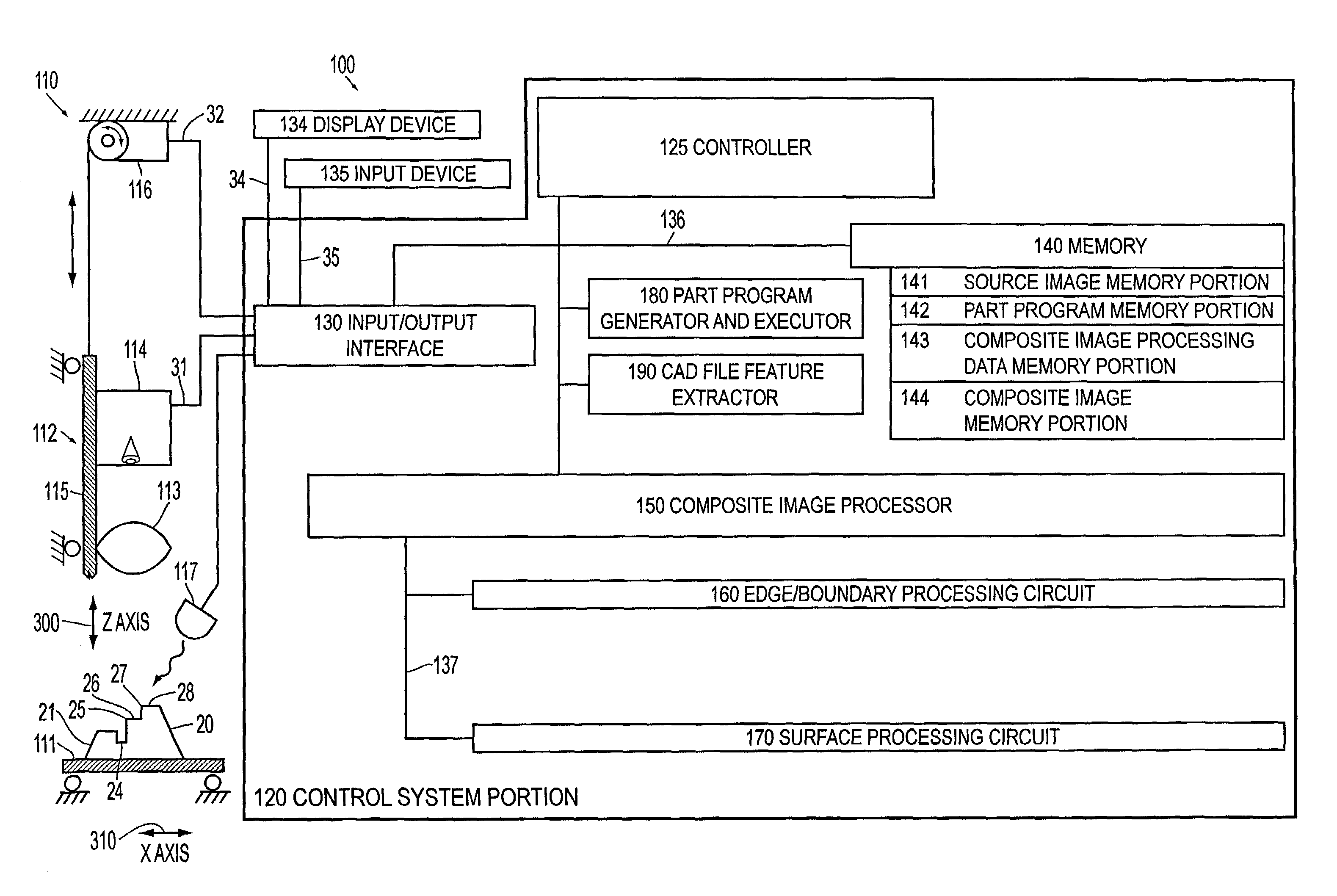
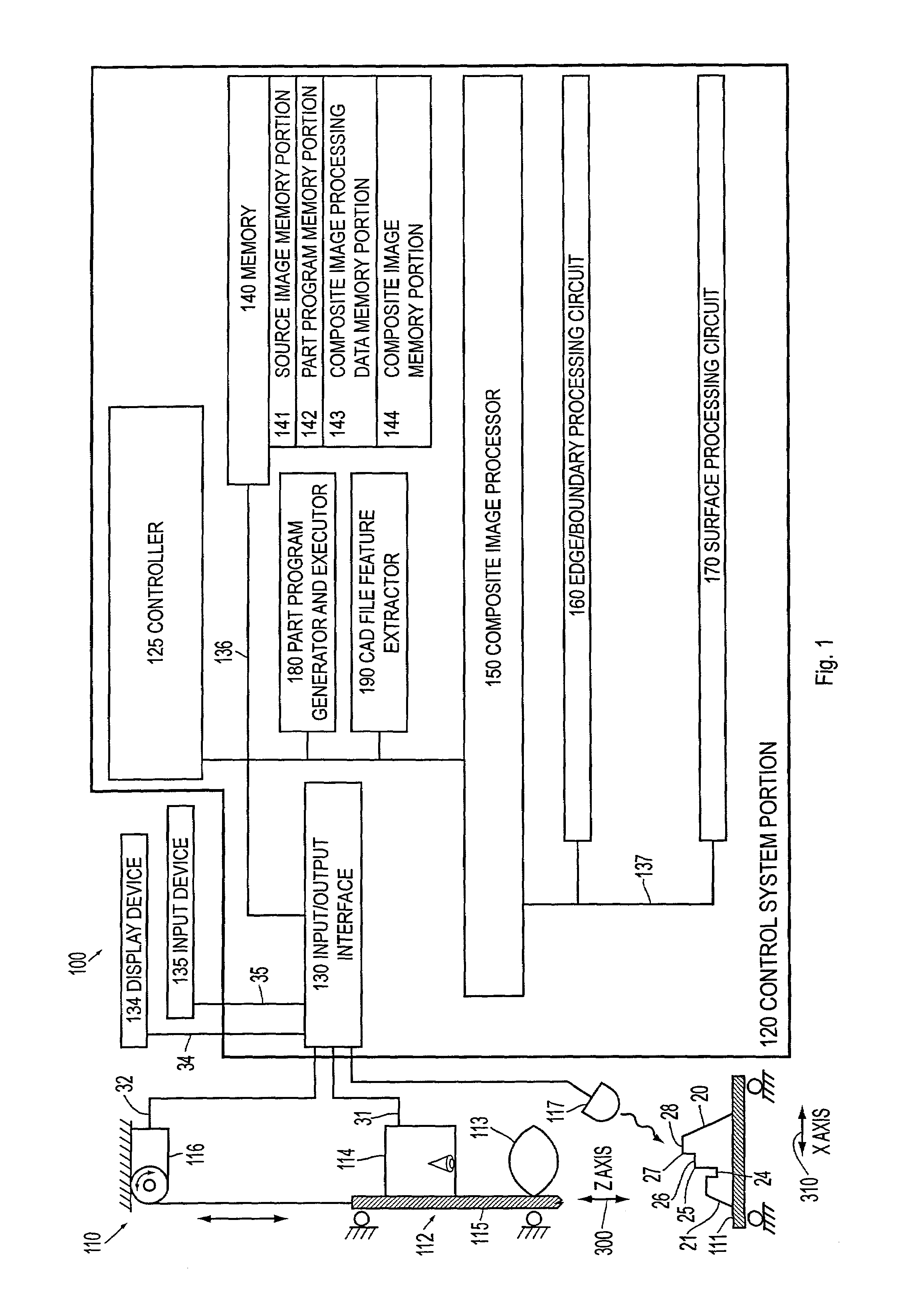
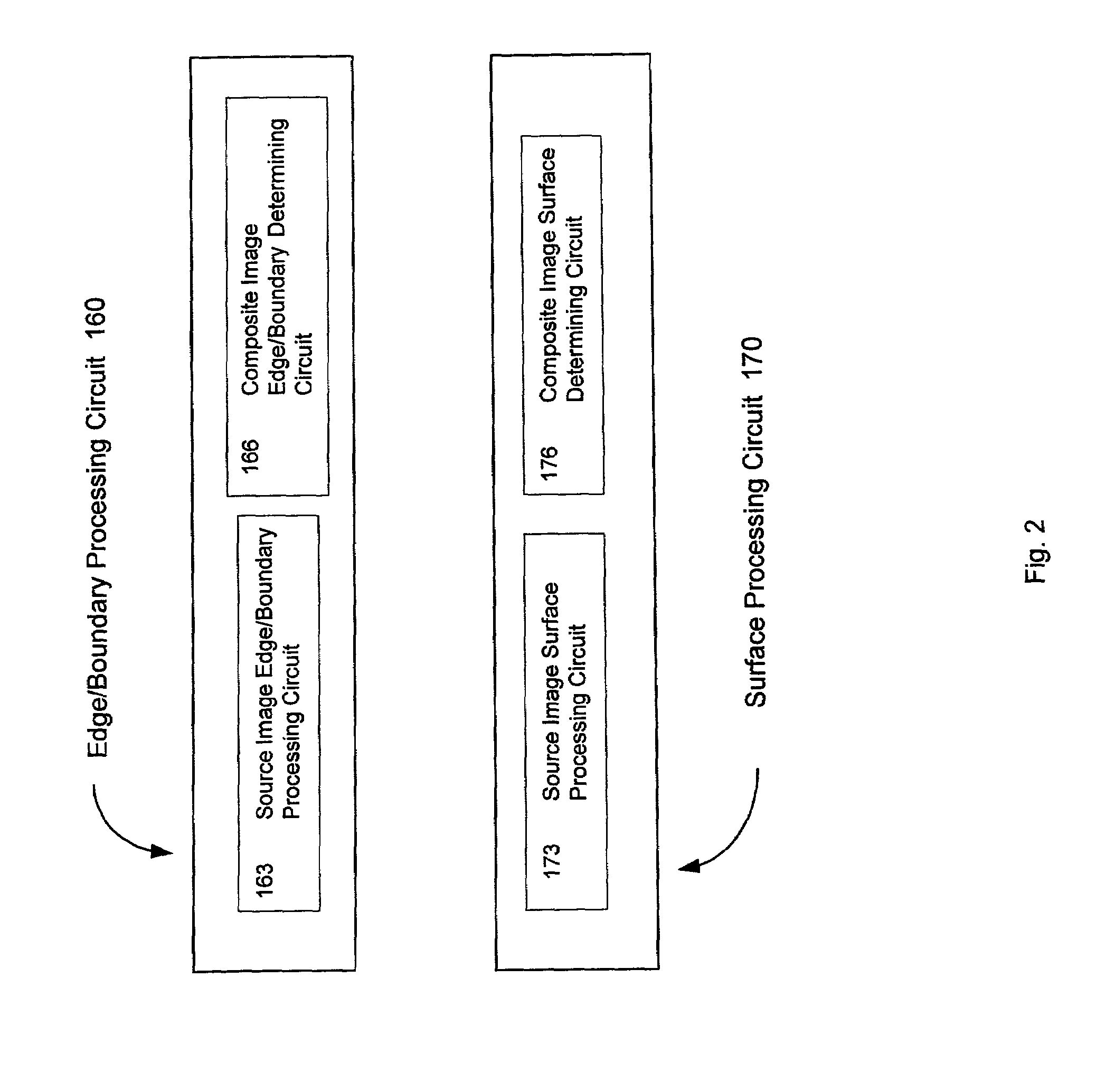
Systems and methods for constructing an image having an extended depth of field
InactiveUS7058233B2Keep detailsRobust and reliable resultImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionDepth of fieldSource image
Systems and methods are provided for constructing a composite image having an extended depth of focus from a plurality of spatially congruent source images of lesser depth of focus. The systems and methods are relatively fast, preserve detail, provide robust results on a variety of unpredictable workpiece features and configurations, and tend to suppress or reduce out-of-focus artifacts. The composite image is constructed by edge and / or boundary analysis to identify well-focused edges or boundaries in the source images. Each particular edge or boundary in the composite image is determined based on the source image containing the best-focused instance of each particular edge or boundary. The composite image is constructed outside of the previously constructed portions by surface analysis to identify well-focused surfaces in the source images, Each particular surface portion in the composite image is determined based on the source image with the best-focused instance of each particular surface portion.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lens with multifocal base surface
ActiveUS20100066973A1Increase costHigh quality multifocal opticSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsAnterior surfaceRefractive index
A multifocal ophthalmic lens includes a lens element having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, a refractive zone, or base surface having produced multifocal powers disposed on one of the anterior and posterior surfaces; and a near focus diffractive multifocal zone disposed on one of the anterior and posterior surfaces.
Owner:PORTNEY VALDEMAR
Using the light adjustable lens (LAL) to increase the depth of focus by inducing targeted amounts of asphericity
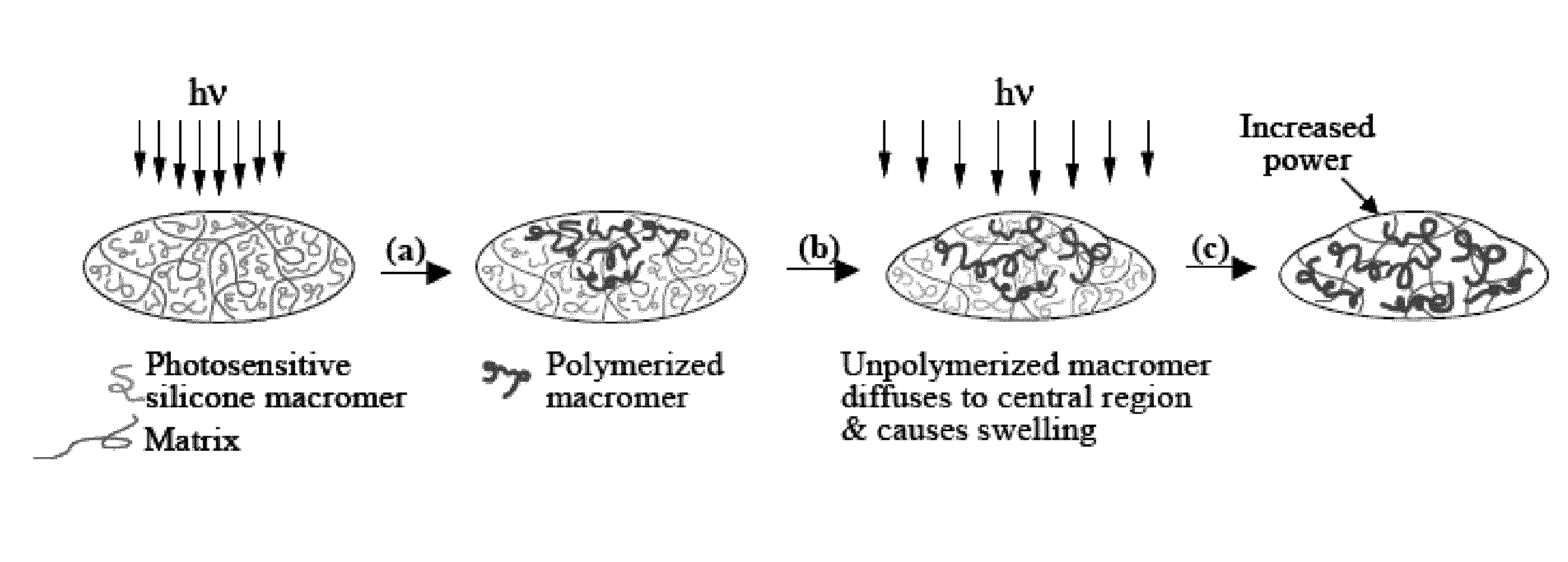
ActiveUS20130072591A1Increase depth of focusEasy to adjustOptical articlesIntraocular lensOptical propertyMedicine
In general, the present invention relates to optical elements, which can be modified post-manufacture such that different versions of the element will have different optical properties. In particular, the present invention relates to lenses, such as intraocular lenses, which can be converted into aspheric lenses post-fabrication. Also, the present invention relates to a method for forming aspheric lenses post-fabrication.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
Achromatic imaging lens with extended depth of focus
InactiveUS20060082882A1Reduce overall chromatic aberrationIncrease depth of focusDiffraction gratingsMountingsImage resolutionOptoelectronics
A lens includes a diffractive surface having an etched structure and a refractive surface having a curved structure. The lens reduces chromatic aberration of incident light and extends depth of focus. In one alternative, the etched structure is a calculated phase pattern or a pattern that is embossed or diamond tuned. In another alternative, the curved structure is convex shaped or concave shaped. In yet another alternative, the lens is an imaging lens wherein high lateral resolution of incident light is preserved.
Owner:NEW SPAN OPTO TECH
Method and apparatus for aligning a mask with the visual axis of an eye
InactiveUS20060270946A1Increase depth of focusMaintain alignmentEye diagnosticsOphthalmology departmentOptometry
A method is provided for increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. A visual axis of the eye is aligned with an instrument axis of an ophthalmic instrument. The ophthalmic instrument has an aperture through which the patient may look along the instrument axis. A first reference target is imaged on the instrument axis at a first distance with respect to the eye. A second reference target is imaged on the instrument axis with the ophthalmic instrument at a second distance with respect to the eye. The second distance is greater than the first distance. Movement is provided such that the patient's eye is in a position where the images of the first and second reference targets appear to the patient's eye to be aligned. A mask comprising a pin-hole aperture having a mask axis is aligned with the instrument axis such that the mask axis and the instrument axis are substantially collinear. The mask is applied to the eye of the patient while the alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis is maintained. Maintaining alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis may be facilitated by capturing an image of the eye.
Owner:SILVESTRINI THOMAS +3
Modified monovision by extending depth of focus
InactiveUS20120123534A1Enhance through-focus binocular visual performanceReduce gapSpectales/gogglesSurgical instrument detailsIntraocular lensVisual perception
Depth-of-focus (DoF) is extended in a presbyopic patient by inducing different higher order aberrations, e.g. spherical aberration, to each of the two eyes. That method will result in improving binocular through-focus visual performance and outperform traditional monovision. The aberration can be induced in any suitable way, such as by an intraocular lens or a contact lens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Multiocular Intraocular Lens System
InactiveUS20100004742A1Increase accommodation amplitudeIncrease depth of focusIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCapsular bag
An accommodating intraocular lens having anteriorly and posteriorly movable extended portions, such as T-shaped haptics, extending from a central optic to be implanted within a human eye, and a second optic spaced from the posterior optic. The first optic is intended to be implanted in the capsular bag, and the second optic may be located in the capsular bag, in the sulcus, or in the anterior chamber. The second optic can be spaced from and fixed to the first optic and this lens assembly implanted in the capsular bag.
Owner:C& C VISION INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com