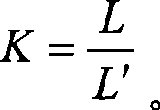Patents
Literature
873 results about "Focal surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
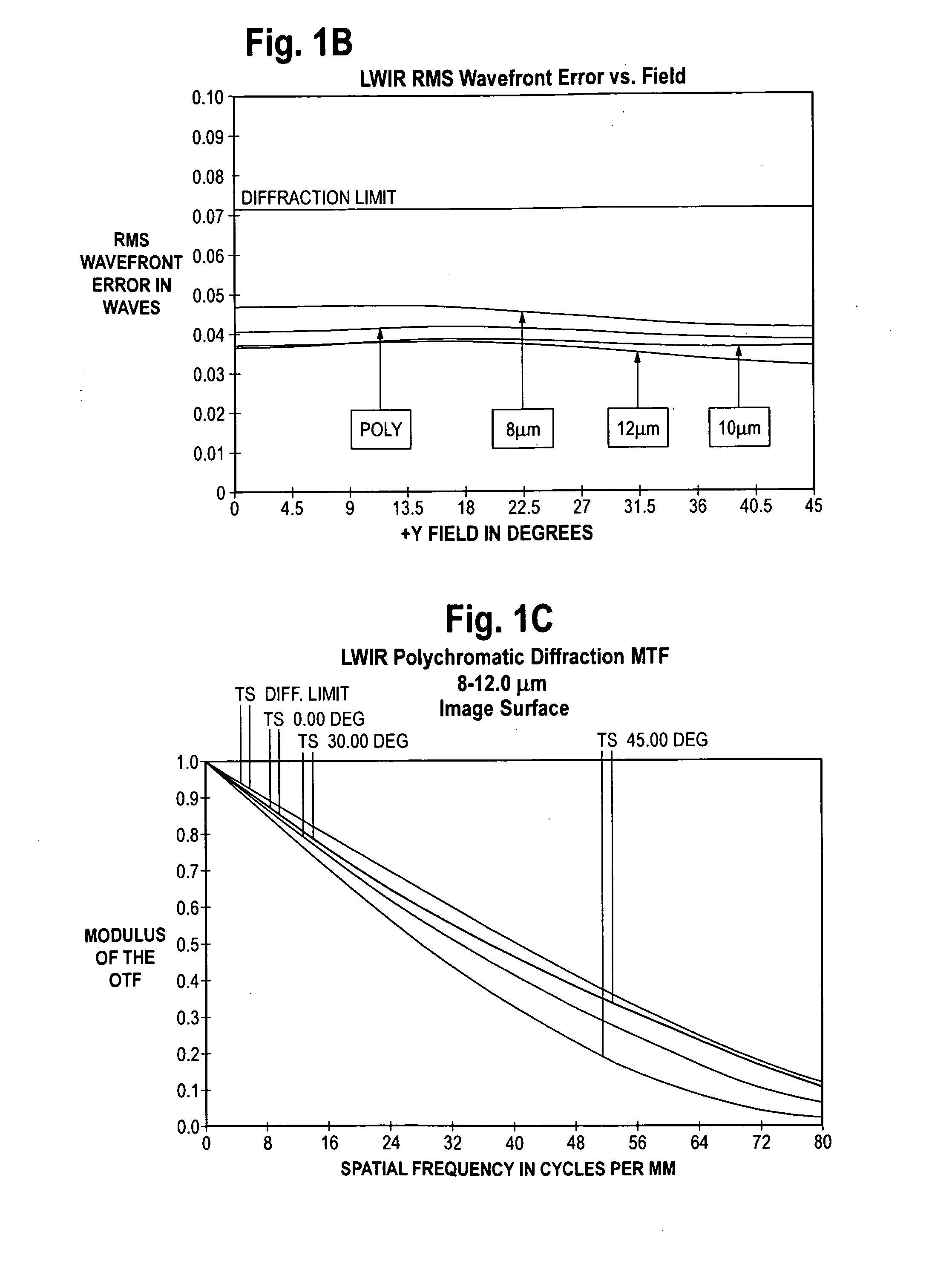
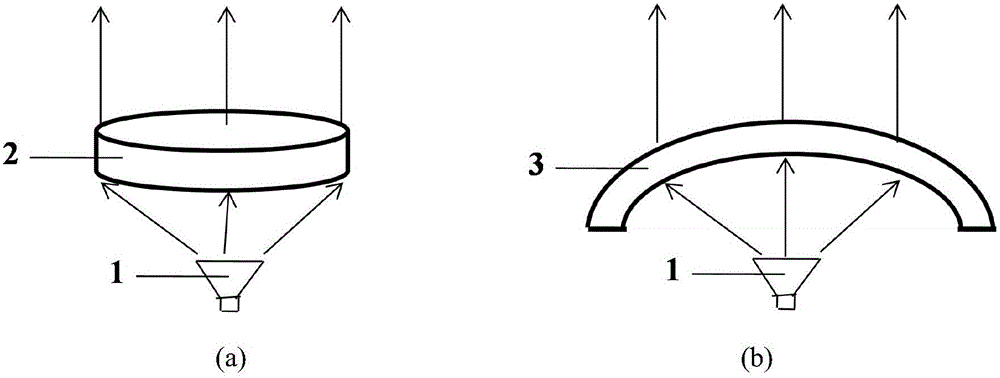
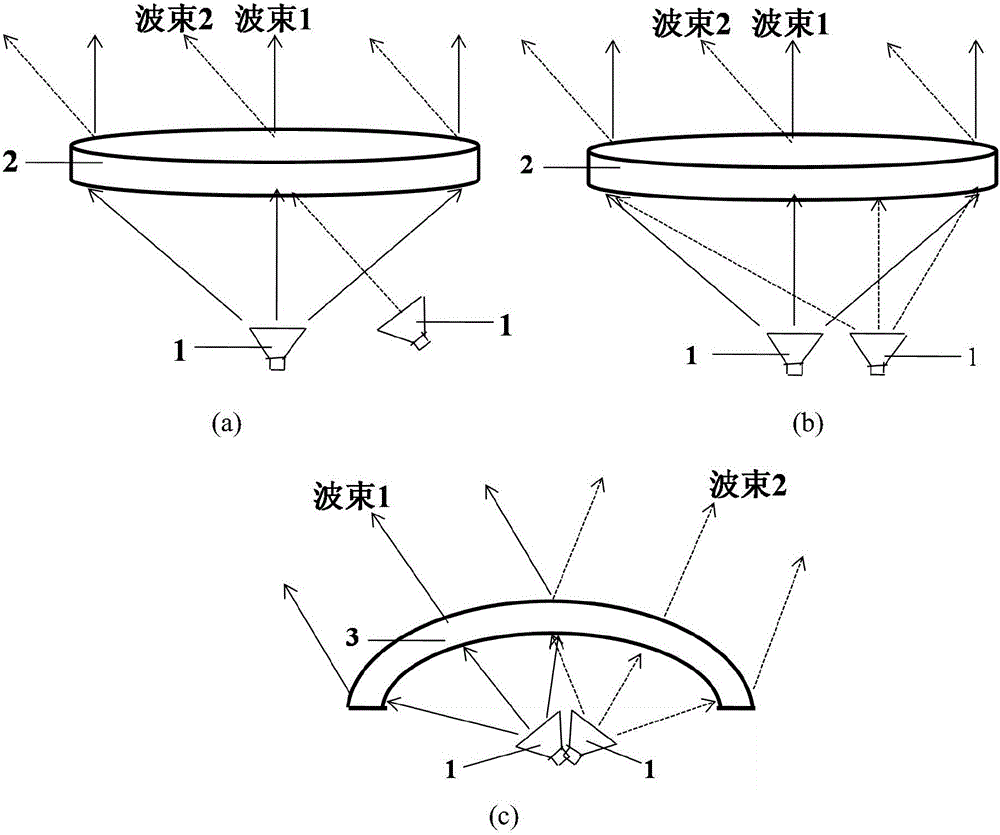
For a surface in three dimension the focal surface, surface of centers or evolute is formed by taking the centers of the curvature spheres, which are the tangential spheres whose radii are the reciprocals of one of the principal curvatures at the point of tangency. Equivalently it is the surface formed by the centers of the circles which osculate the curvature lines.
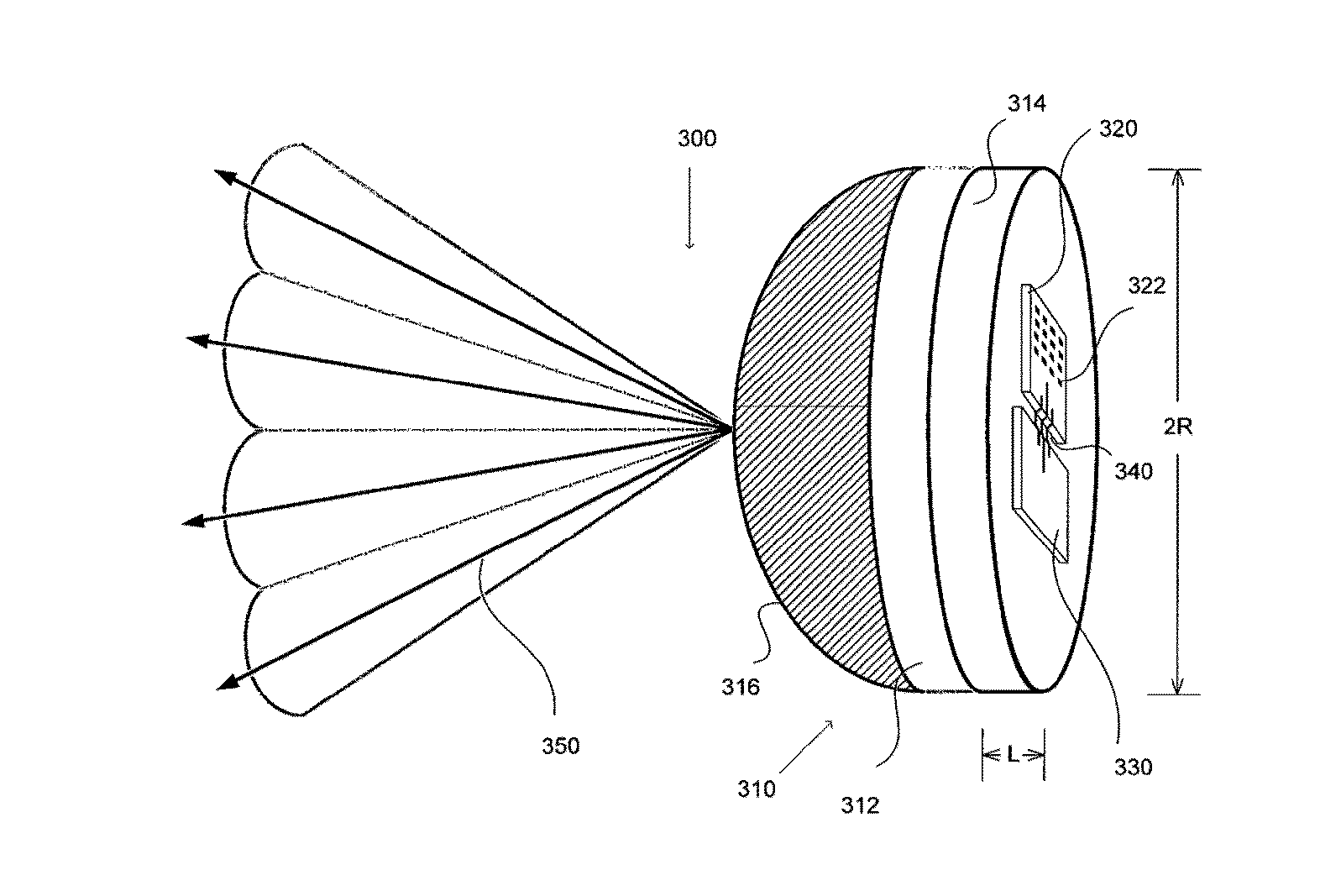
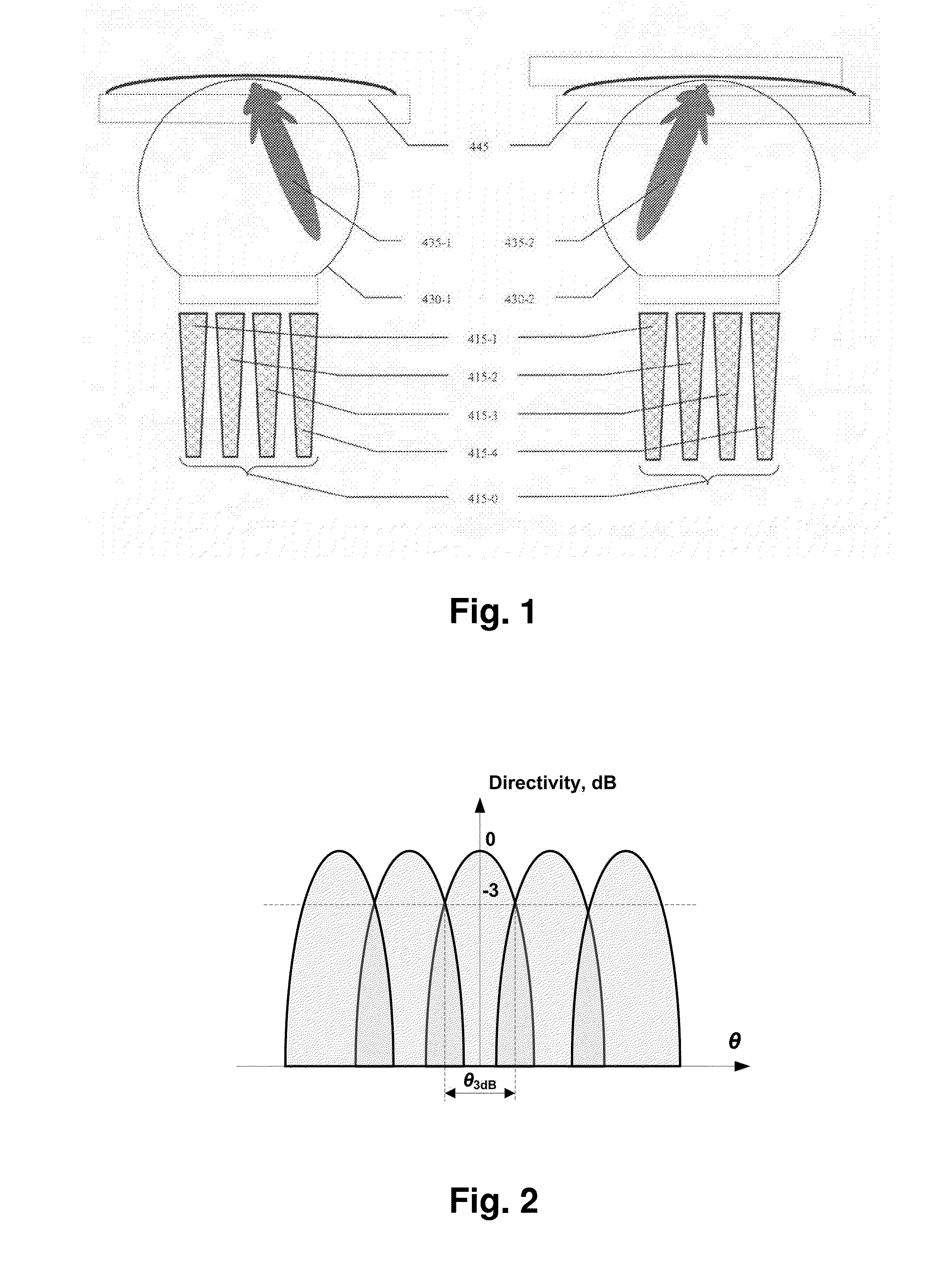
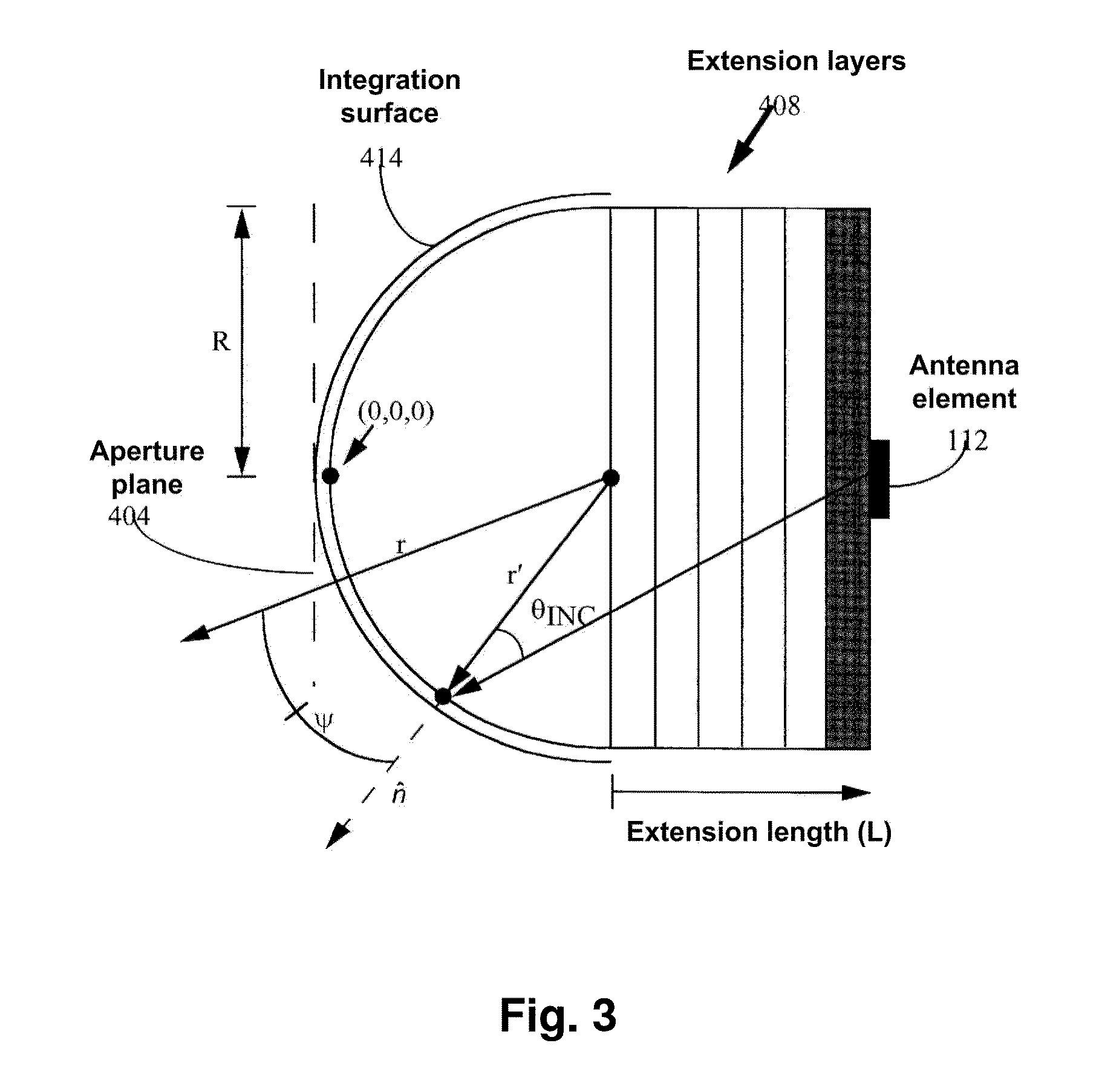
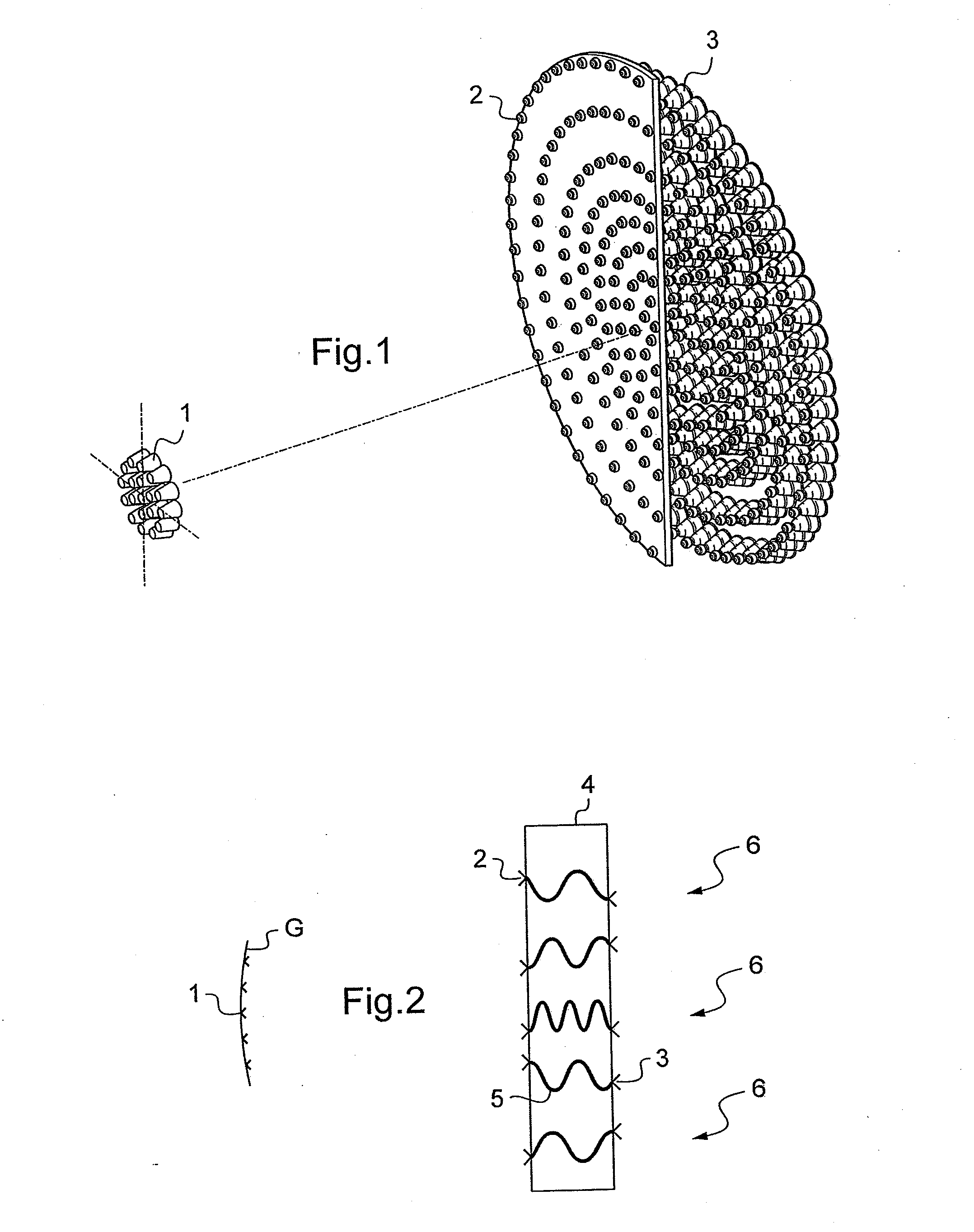
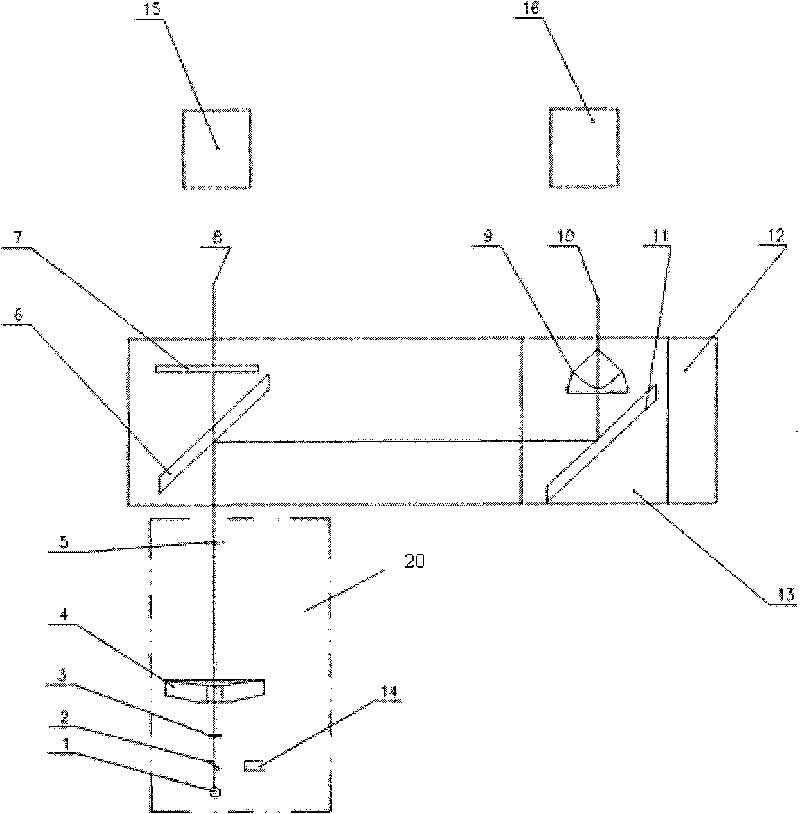
Lens antenna with electronic beam steering capabilities
InactiveUS20150116154A1Improve directivityImprove radiation efficiencyWaveguide hornsAntenna gainRadio relay
The invention discloses a lens antenna with high directivity intended for use in radio-relay communication systems, said antenna providing the capability of electronic steering of the main radiation pattern beam by switching between horn antenna elements placed on a plane focal surface of the lens. Electronic beam steering allows antenna to automatically adjust the beam direction during initial alignment of transmitting and receiving antennas and in case of small antenna orientation changes observed due to the influence of different reasons (wind, vibrations, compression and / or extension of portions of the supporting structures with the temperature changes, etc.). The technical result of the invention is the increase of the antenna directivity with simultaneously provided capability of scanning the beam in a continuous angle range and also the increase of the antenna radiation efficiency and, consequently, the increase of the lens antenna gain. This result is achieved by the implementation of horn antenna elements with optimized geometry.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
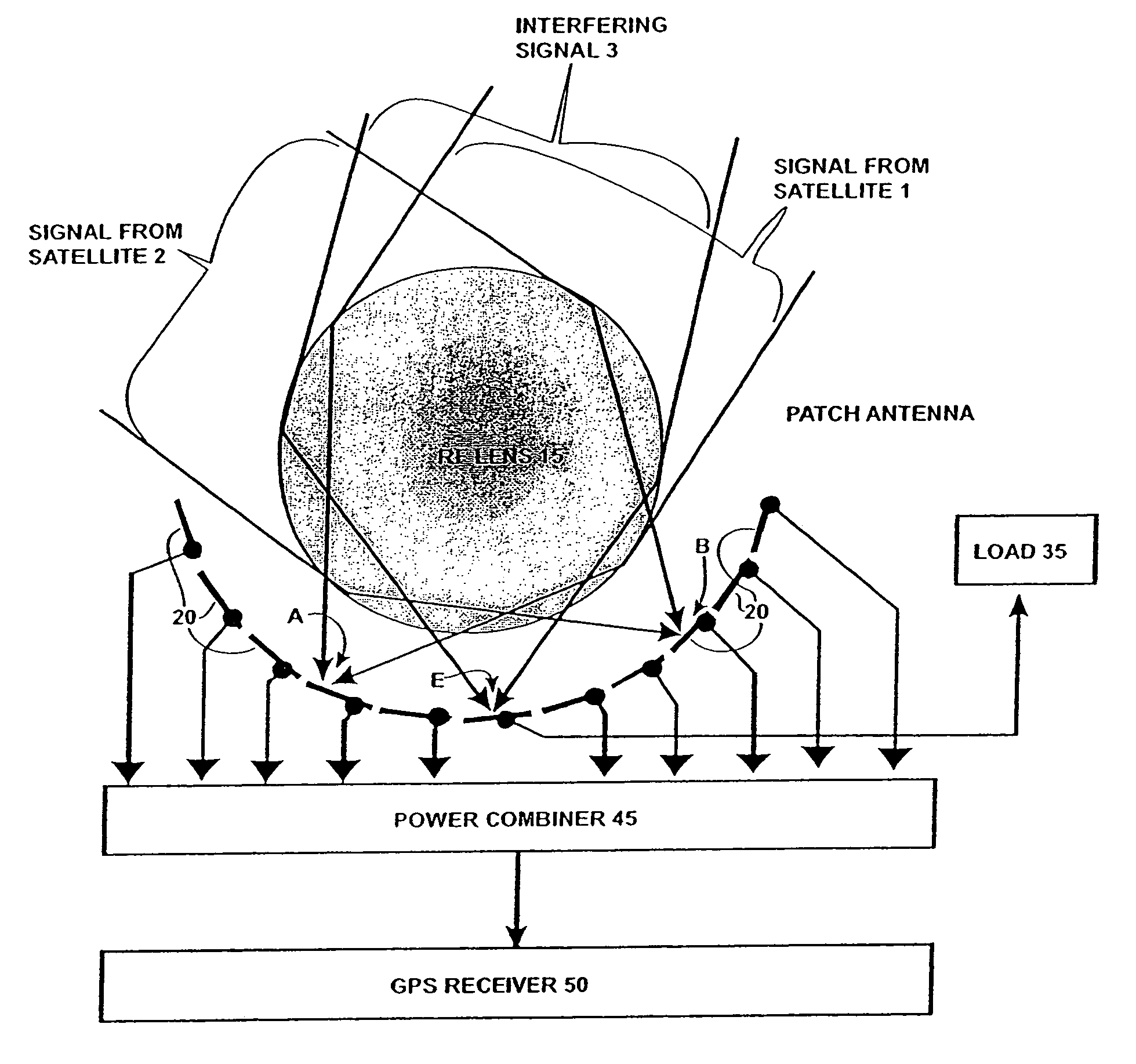
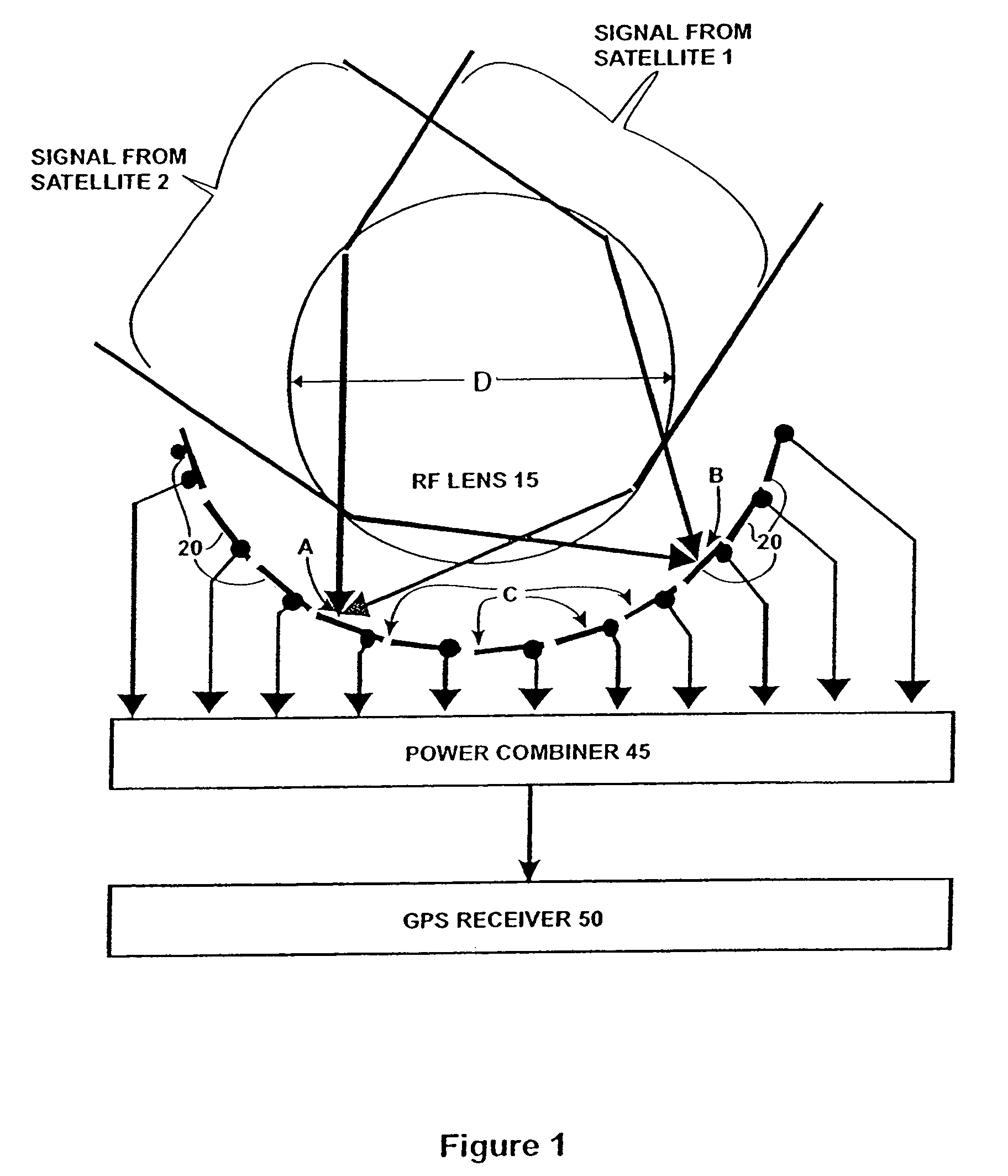
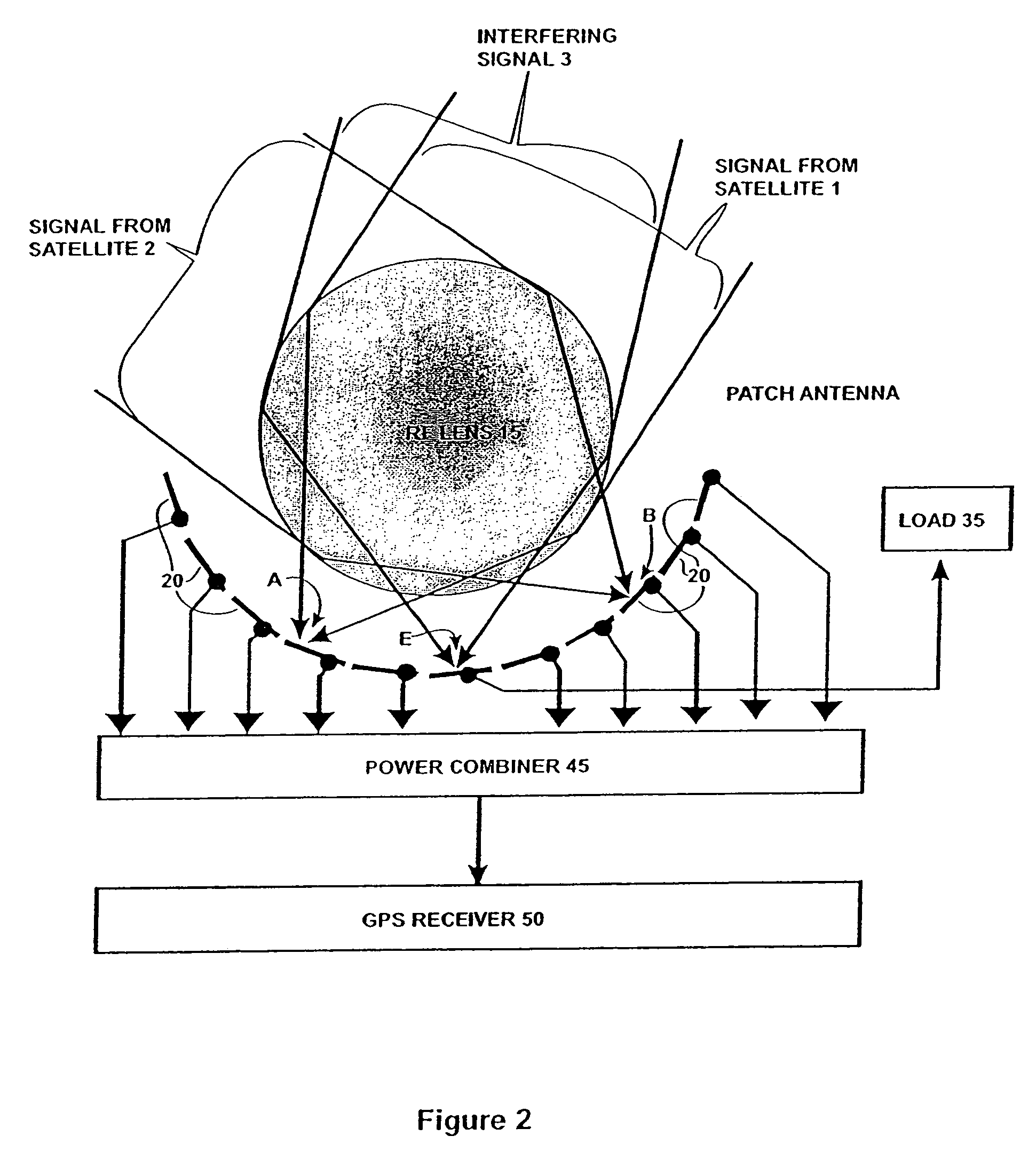
Antenna system and RF signal interference abatement method
InactiveUS7151508B2Reduce distractionsSimultaneous aerial operationsPosition fixationPower combinerGps receiver
Disclosed is an antenna system including a Luneberg Lens having a spherically shaped outer surface and a spherically shaped focal surface spaced from its outer surface with a plurality of patch antenna elements disposed along the focal surface of the Luneberg Lens; and a power combiner for combining signals received by said plurality of patch antenna elements. The disclosed antenna system may be used a part of a robust GPS system having a plurality of GPS satellites each transmitting a GPS signal; a plurality of airborne GPS platforms, each GPS platform including a GPS transmitter for transmitting its own GPS signal, the GPS signals being transmitted from the plurality of airborne GPS platforms being differentiated from the GPS signals transmitted by visible GPS satellites; and at least one terrestrially located GPS receiver for receiving the GPS signals transmitted by visible ones of the GPS satellites and by visible ones of said airborne GPS platforms.
Owner:HRL LAB
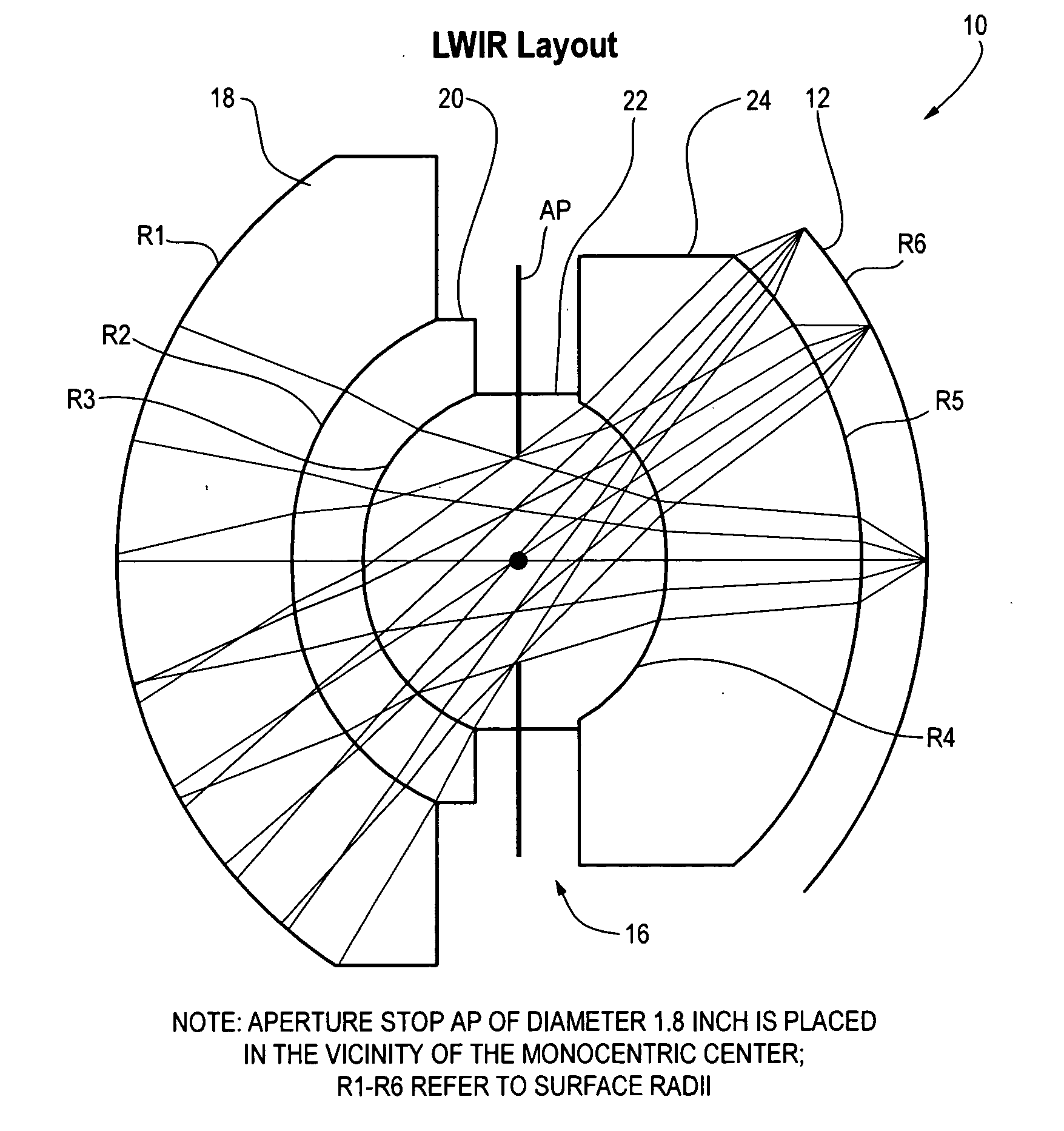
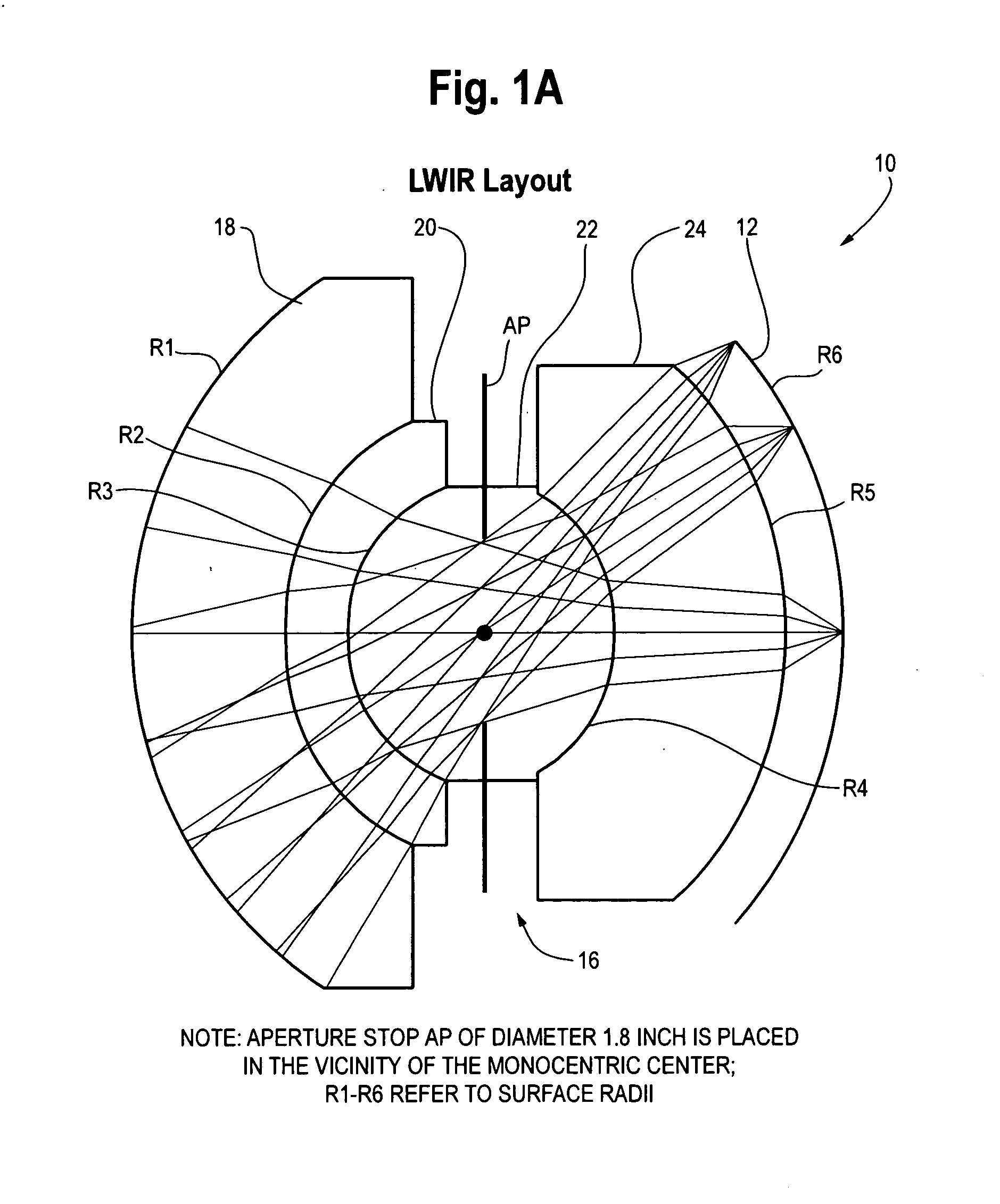
Wide field of view monocentric lens system for infrared aerial reconnaissance camera systems
ActiveUS20130076900A1Minimize chromatic aberrationMinimize spherical aberrationTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesAviationWide field
A wide field of view monocentric lens system for an infrared aerial reconnaissance camera includes front and rear lens shell elements and a core lens element, with the number of front and rear shell lens elements depending on the IR band of interest (LWIR, MWIR or SWIR). Infrared radiation entering the monocentric lens passes sequentially through the front shell lens element(s), the core lens element, and the rear shell lens element(s) and is focused onto a curved focal surface. The front shell lens element(s) and the rear shell lens element(s) are made of material having a relatively higher refractive index or a relatively higher optical dispersion, or both, in the band of interest, as compared to the core lens element.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
High gain, multi-beam antenna for 5g wireless communications
ActiveUS20170324171A1Improve directivityImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsFifth generationWeight gain
A high gain, multi-beam lens antenna system for future fifth generation (5G) wireless networks. The lens antenna includes a spherical dielectric lens fed with a plurality of radiating antenna elements. The elements are arranged around the exterior surface of the lens at a fixed offset with a predetermined angular displacement between each element. The number of beams and crossover levels between adjacent beams are determined by the dielectric properties and electrical size of the lens. The spherical nature of the dielectric lens provides a focal surface allowing the elements to be rotated around the lens with no degradation in performance. The antenna system supports wideband and multiband operation with multiple polarizations making it ideal for future 5G wireless networks.
Owner:AMPHENOL ANTENNA SOLUTIONS
Stereoendoscope wherein images having passed through plural incident pupils are transmitted by common relay optical systems
InactiveUS6976956B2Reduce the number of partsVariationEndoscopesEye treatmentLight guideImage formation
The illuminating light transmitted by the light guide inserted through the elongate inserted section is projected out of the distal end surface of the inserted section. The illuminated objects pass through the respective pupils of the two objective lens systems arranged in parallel within the distal end section of the inserted section and their images are formed on the focal surface. The respective images are transmitted to the rear side by one common relay lens system. The transmitted final images are formed respectively on the image taking surfaces of the image taking devices. The respective images photoelectrically converted by the respective image taking devices are processed to be signals, are displayed in the monitor and are stereo-inspected through shutter spectacles.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Spectral selection and image conveyance using micro filters and optical fibers
ActiveUS20060017928A1Eliminate needFacilitate transmissionColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical elementsFiberSpectral response
The present invention features a fiber optic imaging system for generating a customized spectral response comprising (a) an optional optical source for generating optical energy, (b) an optical system for focusing multi spectral optical energy to form a focal surface; (b) a fiber optic element for conveying the optical energy, wherein the fiber optic element has an input end optically coupled to the focal surface to receive the optical energy and an output end to transmit the conveyed optical energy; and (c) a spectral filter optically coupled to at least one of the input and output ends of the fiber optic element, wherein the spectral filter has a filter passband configured to provide the fiber optic element with a pre-determined wavelength transmittance capacity, such that only pre-determined wavelengths of the optical energy are transmitted through the output end, thus achieving a customized spectral response. The fiber optic imaging system may further comprise an imaging array optically coupled to the output end of the fiber optic element and configured to gather the transmitted optical energy and to convert it into a data signal corresponding to an image based on the customized spectral response. An example of this type of configuration is a spectrometer.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Overlay error measurement apparatus and method
ActiveCN103777467AReduce control difficultyHigh precisionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusBeam splittingLight beam
The invention provides an overlay error measurement apparatus and a method. According to the present invention, a wide waveband light source is adopted, the emitted wide waveband measurement light beam turns through a beam splitting prism, then is subjected to normal incidence on an overlay measurement label through an object lens, and produces diffraction, the diffraction light is received by a first detector after passing through the object lens and the beam splitting prism so as to measure the diffraction light intensity, and the asymmetry of the high-order diffraction light spectral intensity is further calculated so as to obtain the overlay error; and the adopted wide waveband has the wide measurement range, the good process adaptability is provided, and the normally-incident light beam is adopted so as to provide large depth of focus and reduce the control difficulty of the focal plane position measurement, such that the feasibility during actual measurement is increased, and the high precision measurement result can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Living body iris patterns collecting method and collector
InactiveCN1584917AImprove clarityThe characteristic texture is obviousCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityIris image
A method for collecting living body iris image includes confirming dynamic image being eye image, counting up eye image grey scale value to find out initial pupil centre, collecting a series of eye image in different focal surface to make image quality evaluation in order to confirm the best quality iris image.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Simulator of star sensor
ActiveCN102116642AVerify measurement accuracyOvercoming the problem of poor simulation accuracy of angular distance between satellitesMeasurement devicesAngular distancePoint target
The invention provides a simulator of a star sensor. The simulator comprises a collimating objective lens, wherein a focal plane of the collimating objective lens is provided with a star point target; the star point target is imaged at infinity through the collimating objective lens; a light splitting component is arranged between the collimating objective lens and the star point target; the focal plane of a light splitting optical path on the side face of the light splitting component is also provided with a detection target; the star point target is fixed on a focal plane adjusting mechanism; and a target lighting device is used for lighting the star point target. In the simulator, a technology which is different from the scheme of the conventional star simulator is adopted, so that the problem of poor accuracy of simulation of angular distance between stars of the conventional star simulator is solved; and the simulator can be used for extremely-high-accuracy simulation of a star and asteroid array of an asteroid autonomous navigation extremely-high-accuracy star sensor, verification of measurement accuracy and autonomous navigation and positioning accuracy of the star sensor, and has broad application prospect in research of a deep space autonomous navigation sensor.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
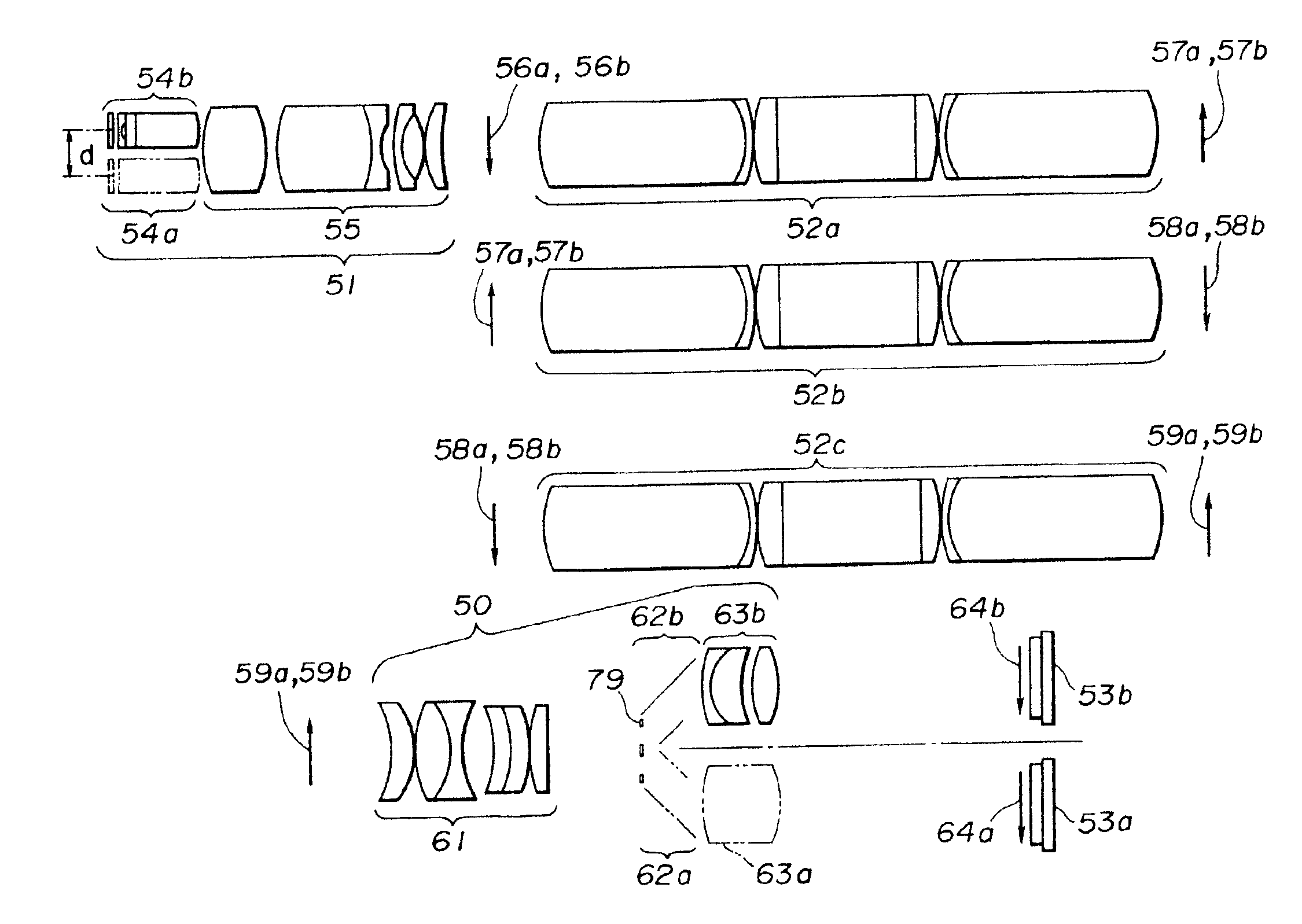
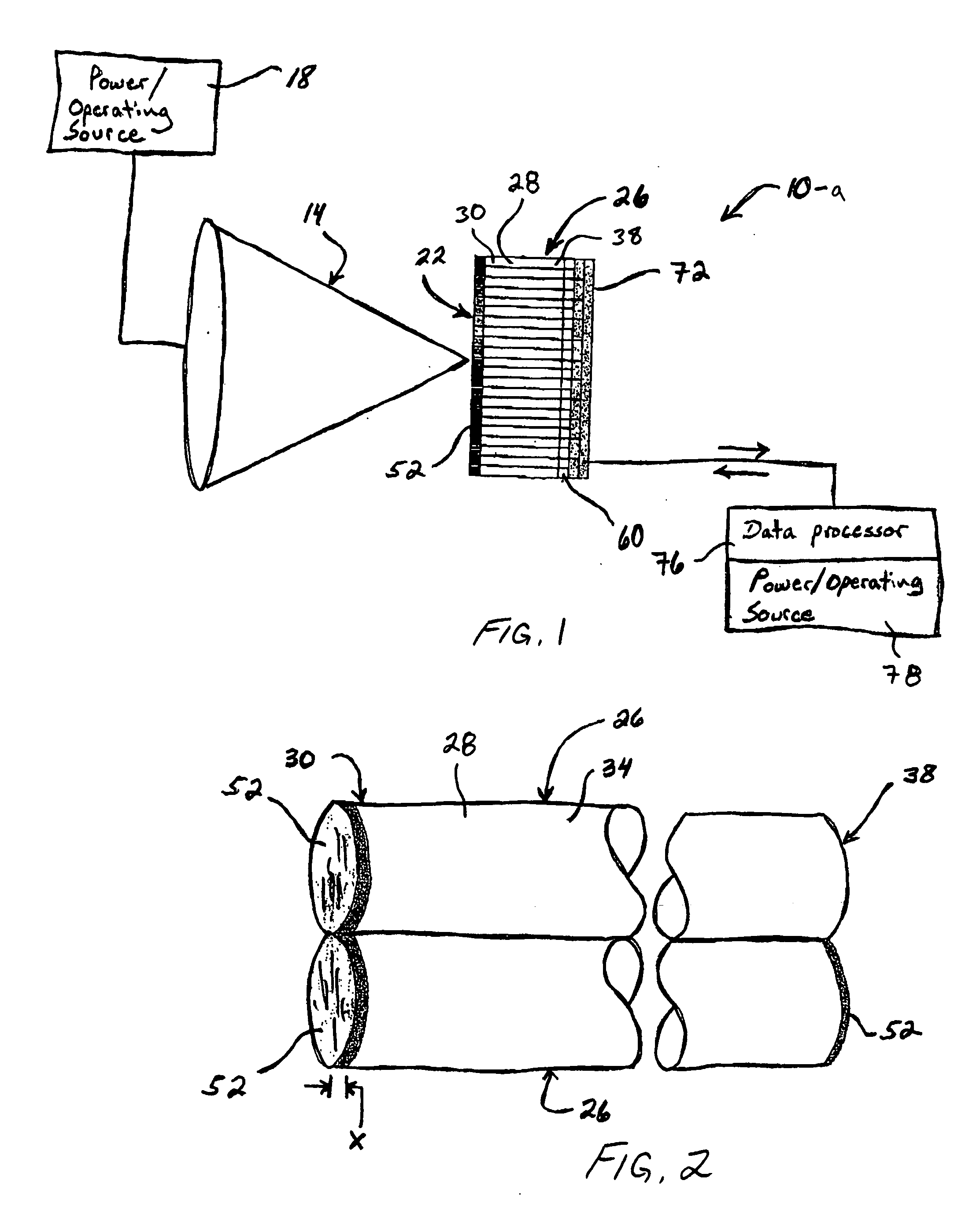
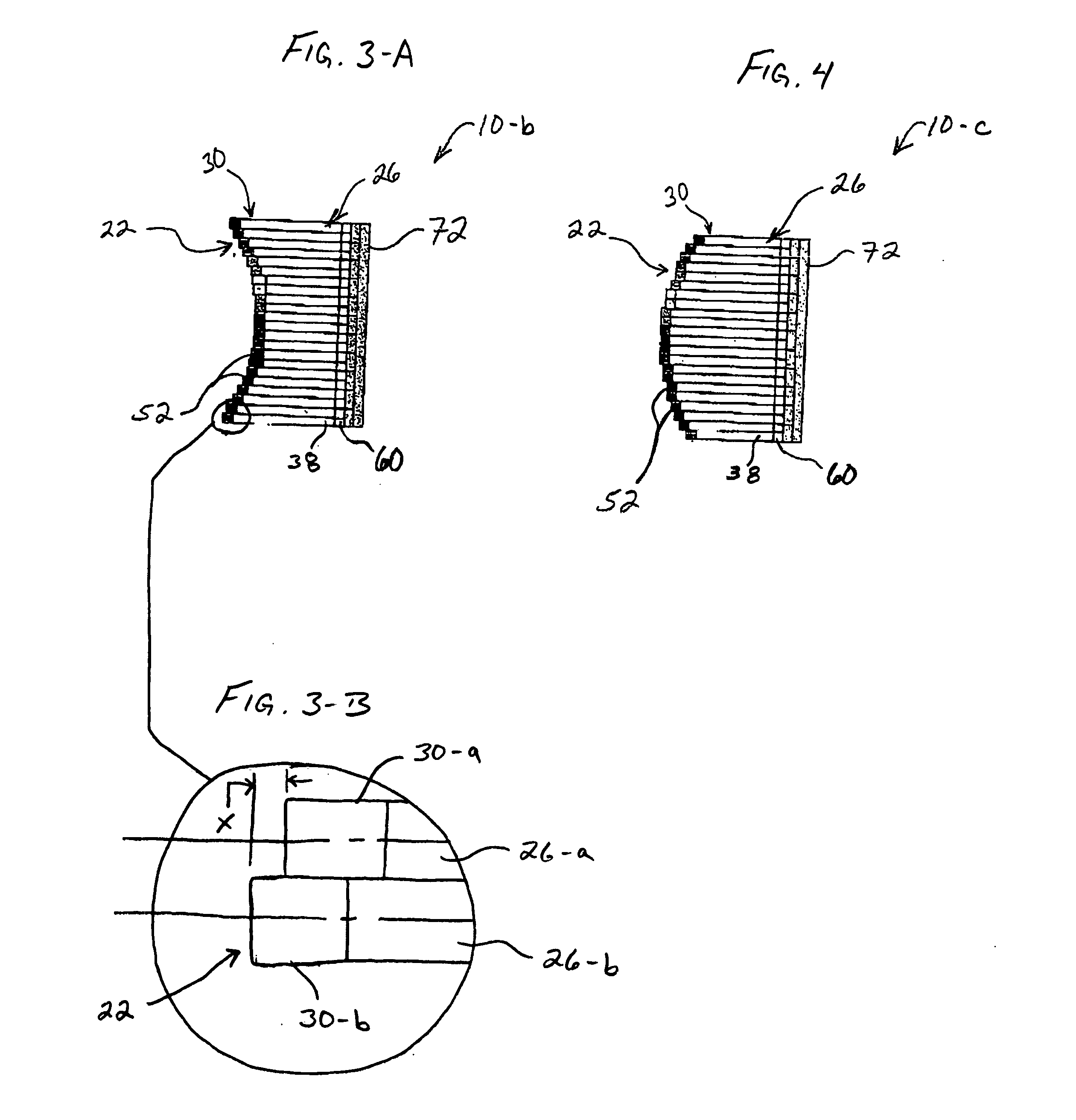
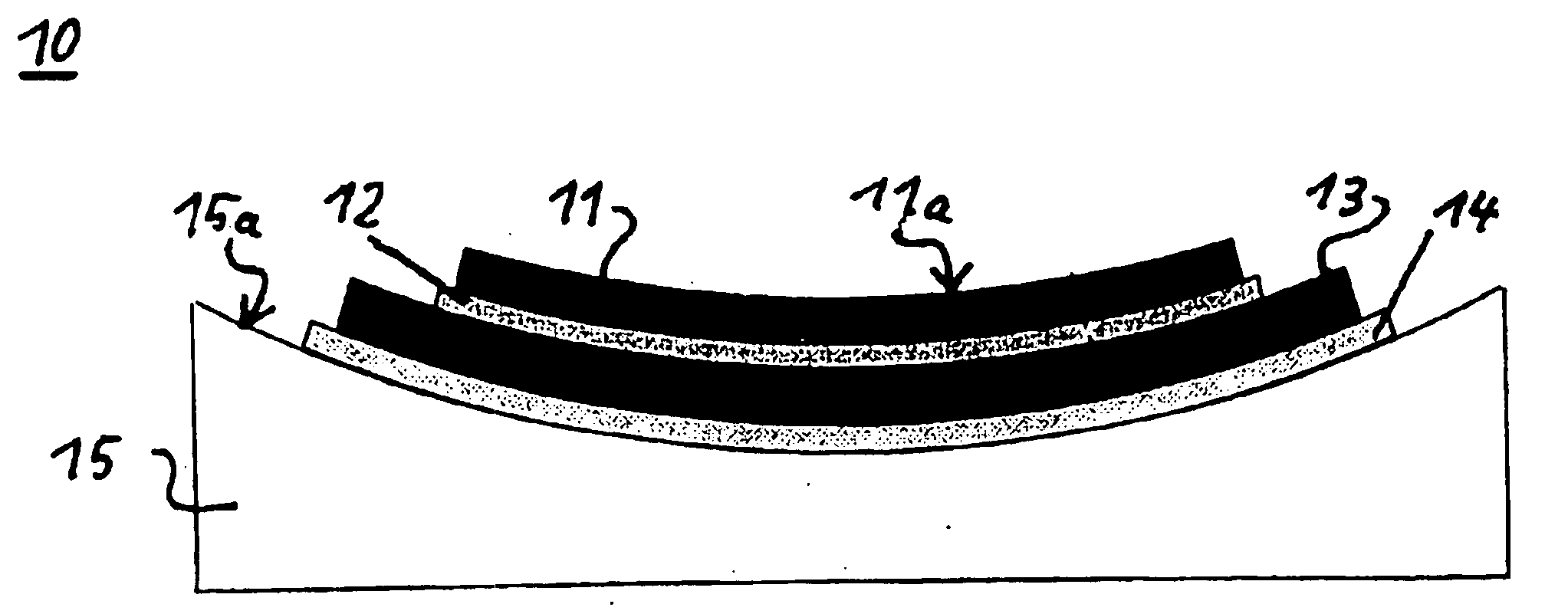
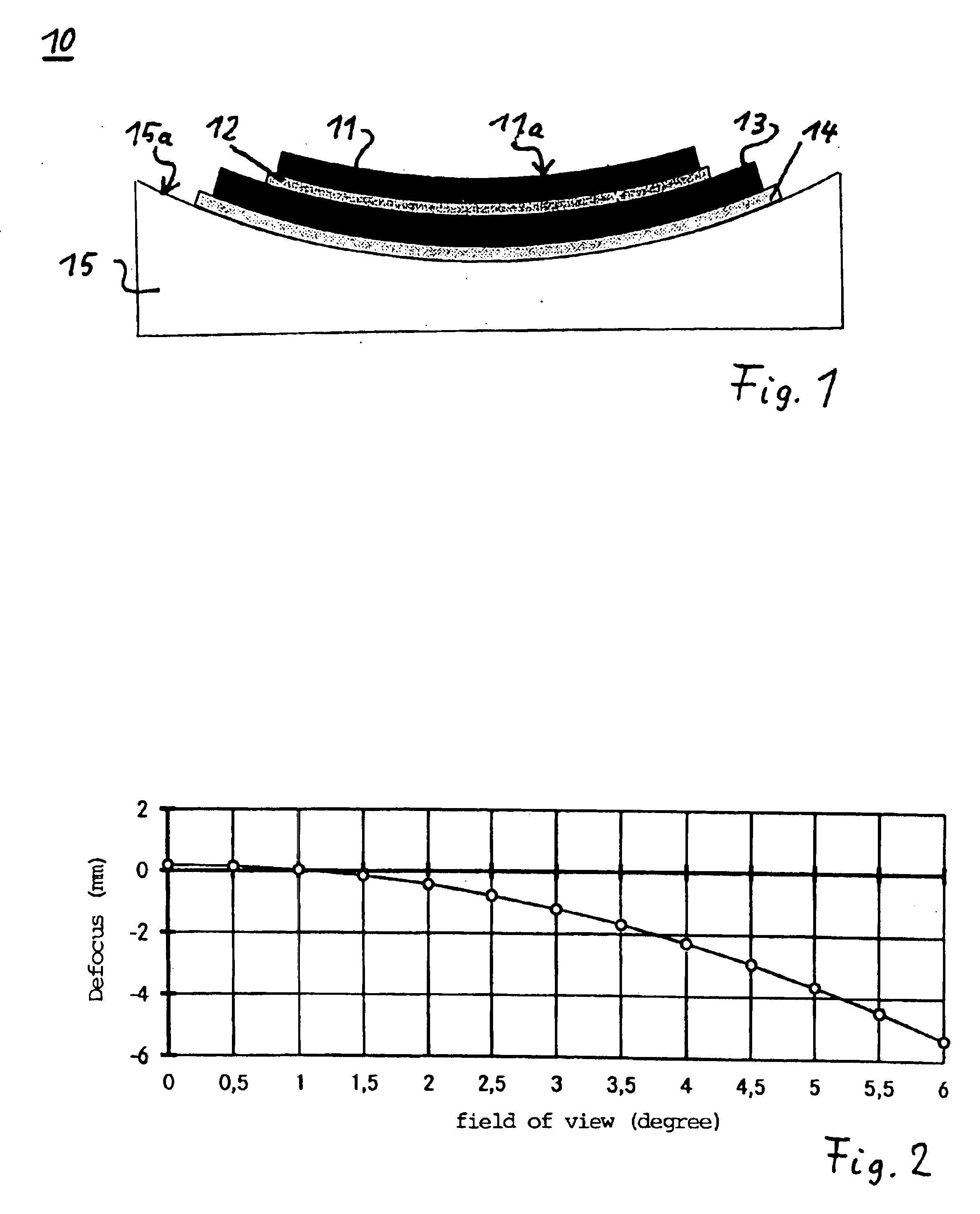
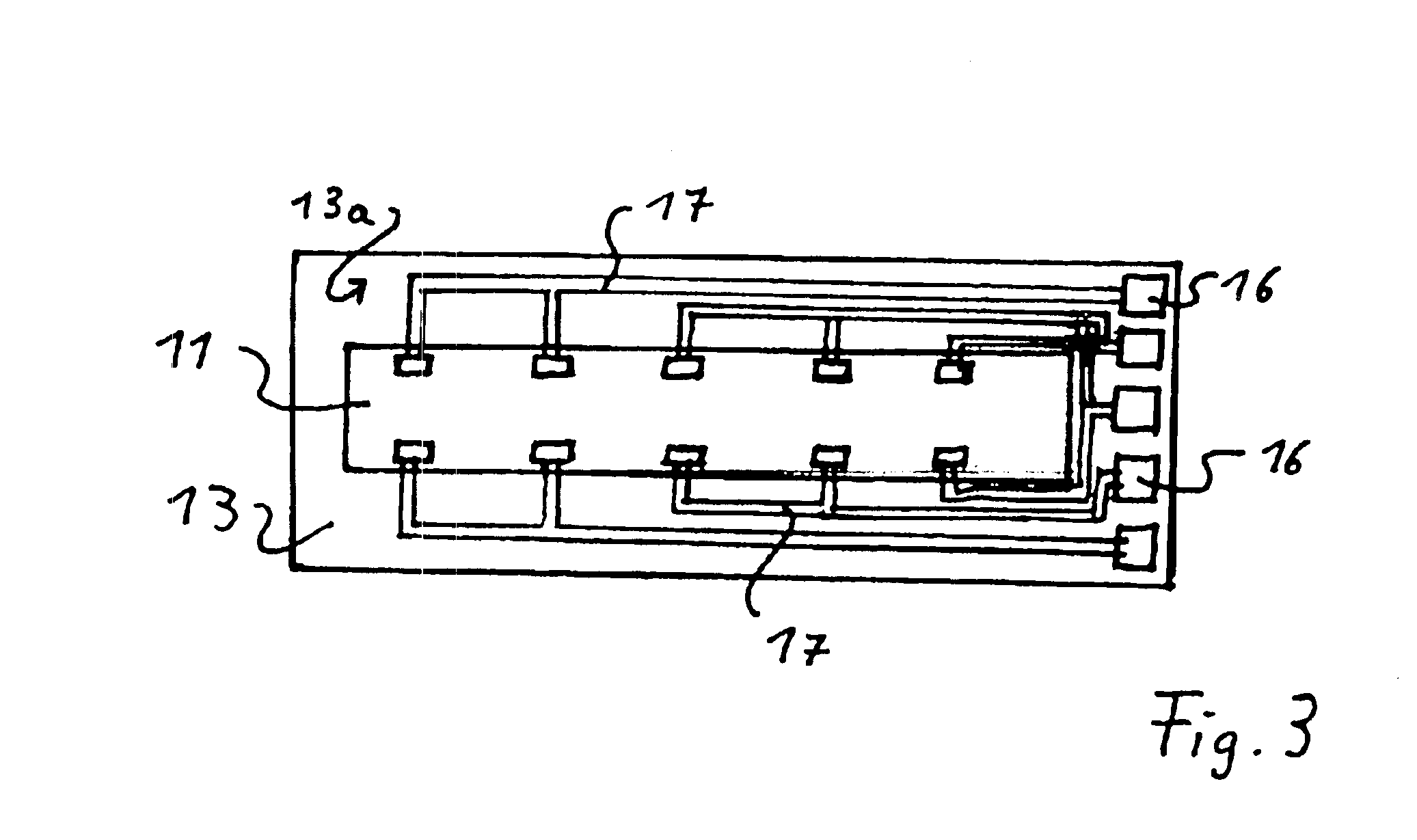
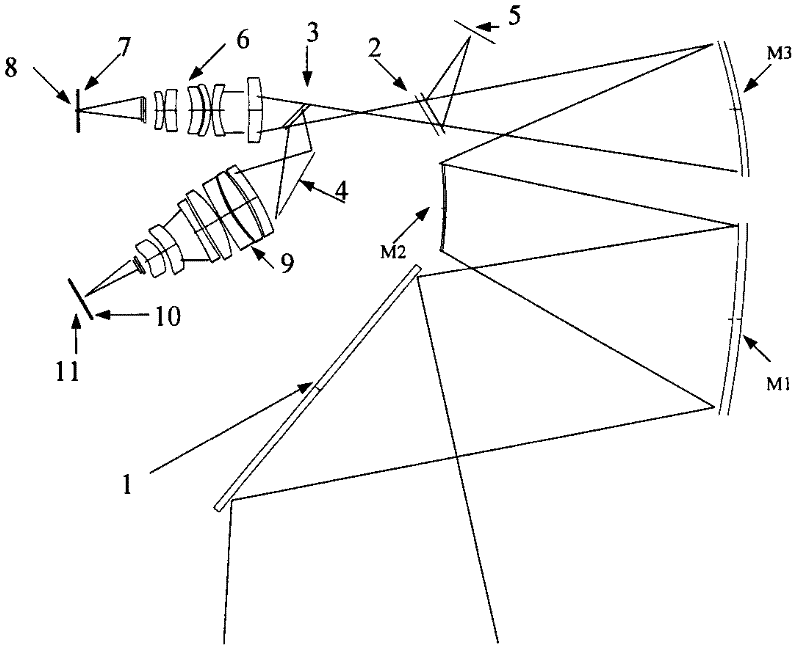
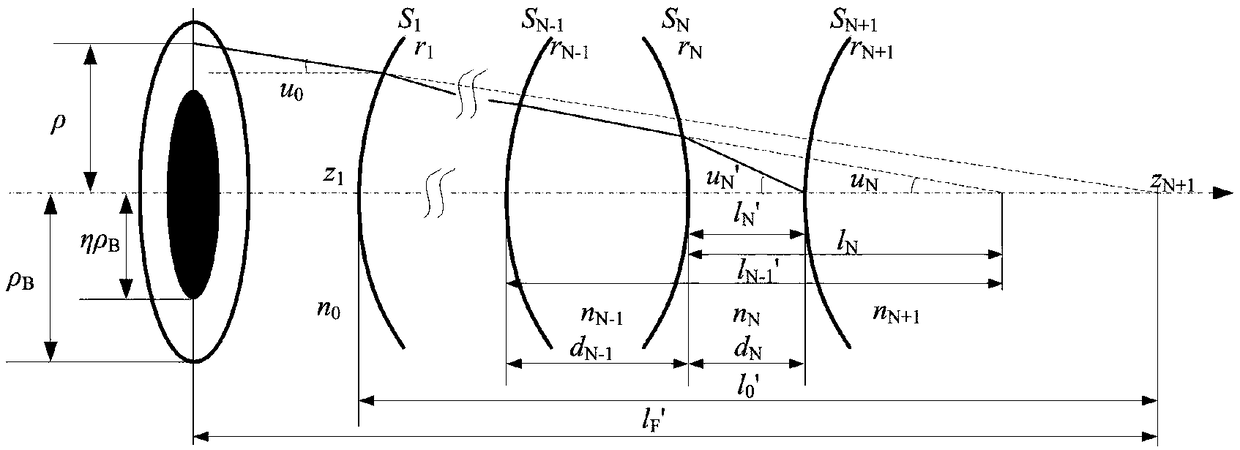
Focal surface and detector for opto-electronic imaging systems, manufacturing method and opto-electronic imaging system
InactiveUS6849843B2Reduce the numberReduce thicknessTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage recordingOpto electronic
The focal surface for an opto-electronic imaging system includes an arrangement of detectors for image recording and a detector carrier or a FPA carrier for holding the detectors. The detectors are each made of at least one solid state element that is bonded to a flexible carrier substrate. The focal surface, or the detectors, respectively, exhibits a curvature, such that a curved field of view can be recorded. In a method for manufacturing a focal surface for opto-electronic imaging systems, at least one solid state element is bonded to a flexible carrier substrate to form flexible detectors, whereby a detector carrier provides a curvature and the flexible detectors are adapted to the curvature of the detector carrier. To manufacture a detector according to the present invention, a solid state element is thinned and bonded to a flexible carrier substrate, such that it is formed in a flexible manner and can be adapted to a curvature of a field of view. An opto-electronic imaging system according to the present invention with front optics for capturing an image and a detector arrangement that is arranged in a focal surface of the front optics, in which the detector arrangement is arranged in the focal surface in a curved manner.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
Spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system
InactiveCN102508361AReduce in quantityNo color differenceRadiation pyrometryCoatingsSpectral bandsLarge range
The invention discloses a spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system, which comprises a switching reflector, a main optical off-axis three-reflector system, a medium- and short-wave focus-free relaying optical system and a long-wave focus-free relaying optical system, wherein a radiation light beam of an imaging target enters from the switching reflector, and is divided into light rays in three channels, namely a visible multispectral channel, a short-wave / medium-wave channel and a long-wave infrared channel, by color division sheets after passing through the main optical off-axis three-reflector system; the light ray in the visible multispectral channel is reflected by the first color division sheet, and then full-color multispectral imaging is realized through a five-color device; the light rays in the short-wave / medium-wave channel and the long-wave infrared channel are transmitted / reflected by the second color division sheet, respectively pass through the own focus-free relaying optical systems, and then are focused on a focal surface for imaging after being subdivided by filters. The spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system has the advantages of large view field, large relative aperture, wide spectral range, high subdivision degree, compact structure, small volume, light weight and the like; and large-range, all-day and high-resolution dynamic and stable detection can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
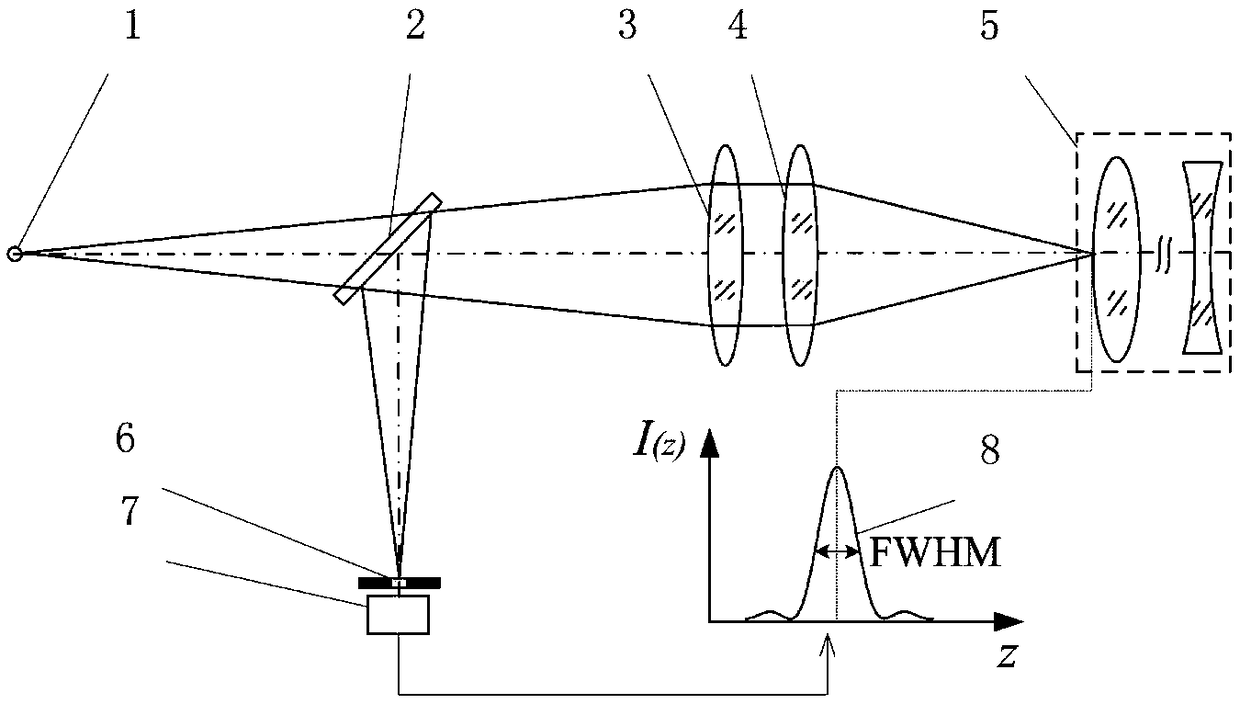
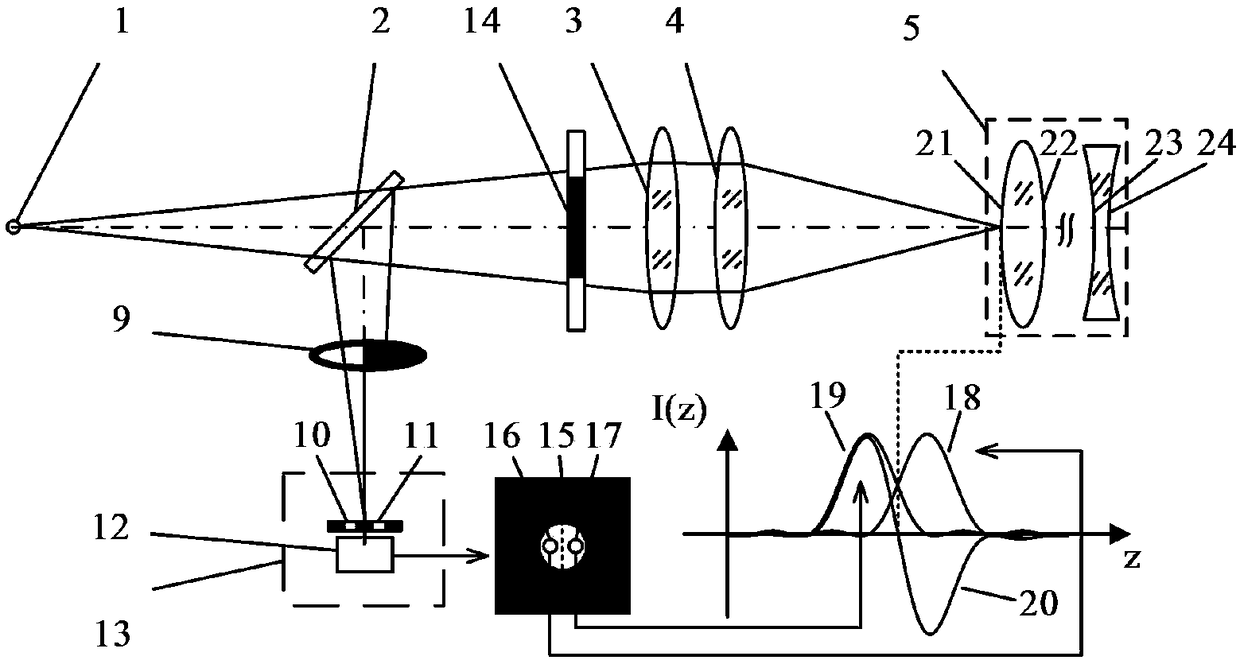
Laser differential confocal tomography focusing method and device
ActiveCN109253989AImprove focus accuracyReduce the impactAnalysis by material excitationLight beamTomography
The present invention relates to a laser differential confocal tomography focusing method and device, and relates to the technical field of optical imaging and detection. The method uses a rear pupilto block half of a measurement beam, uses a spectroscopic differential confocal detection system to detect the unblocked measurement beam, and uses an absolute zero point of a differential confocal response curve to achieve high precision tomographic focusing. The method organically combines a laser differential confocal technique and a ray tracing technique to establish a ray tracing and compensation model to eliminate influence among each fixed focal surface parameters, and achieves fast trigger of focus through data near a linearly fitting absolute zero point. The method can obtain the differential confocal response curve by using only one detector, and realizes the tomographic focusing through the absolute zero point of the differential confocal response curve, greatly simplifies system structure, in the same time, avoids error introduced by adjustment inaccuracy, and greatly improves precision of focusing. The method will provide a new technical approach to the field of confocal imaging / detection.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
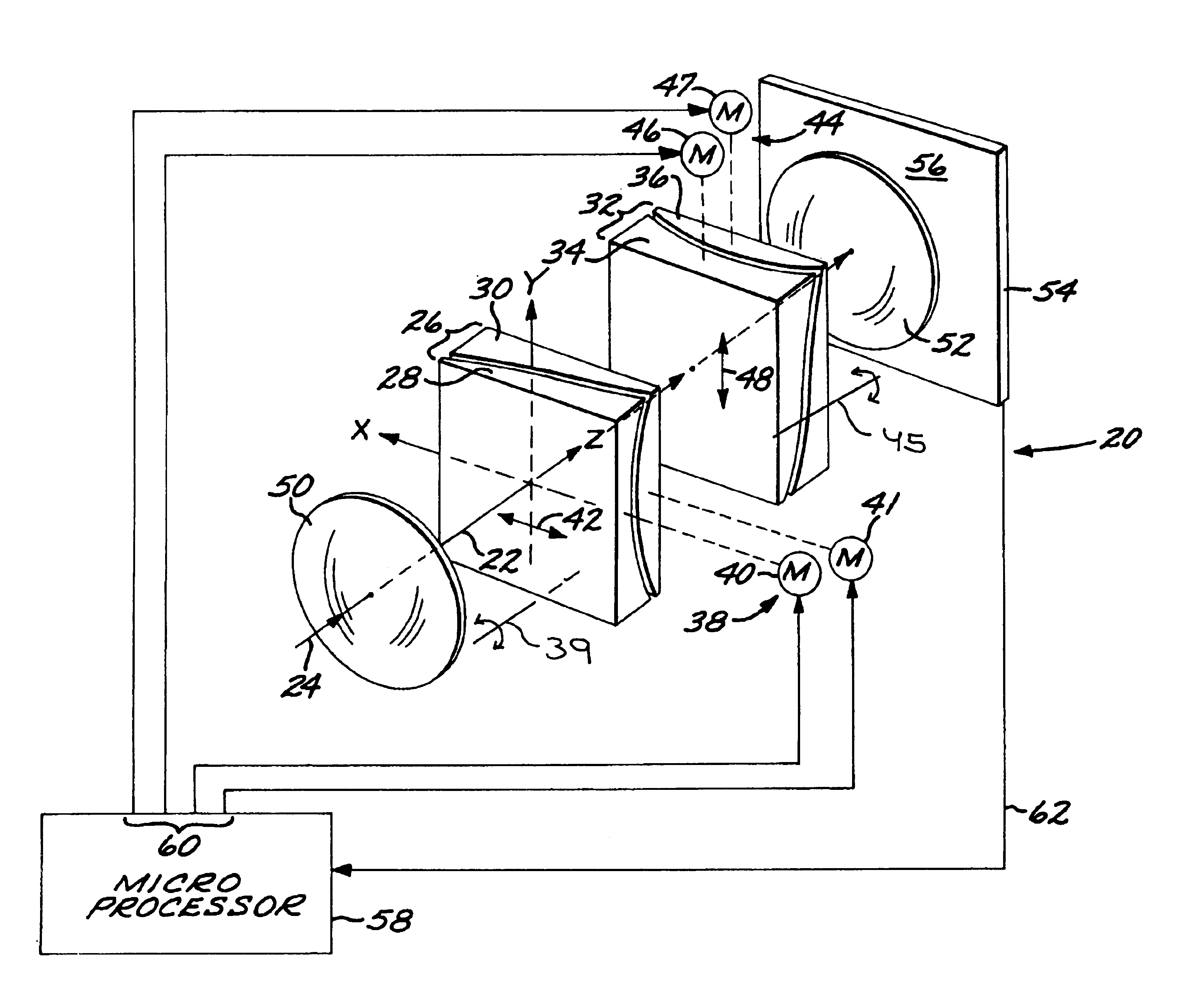
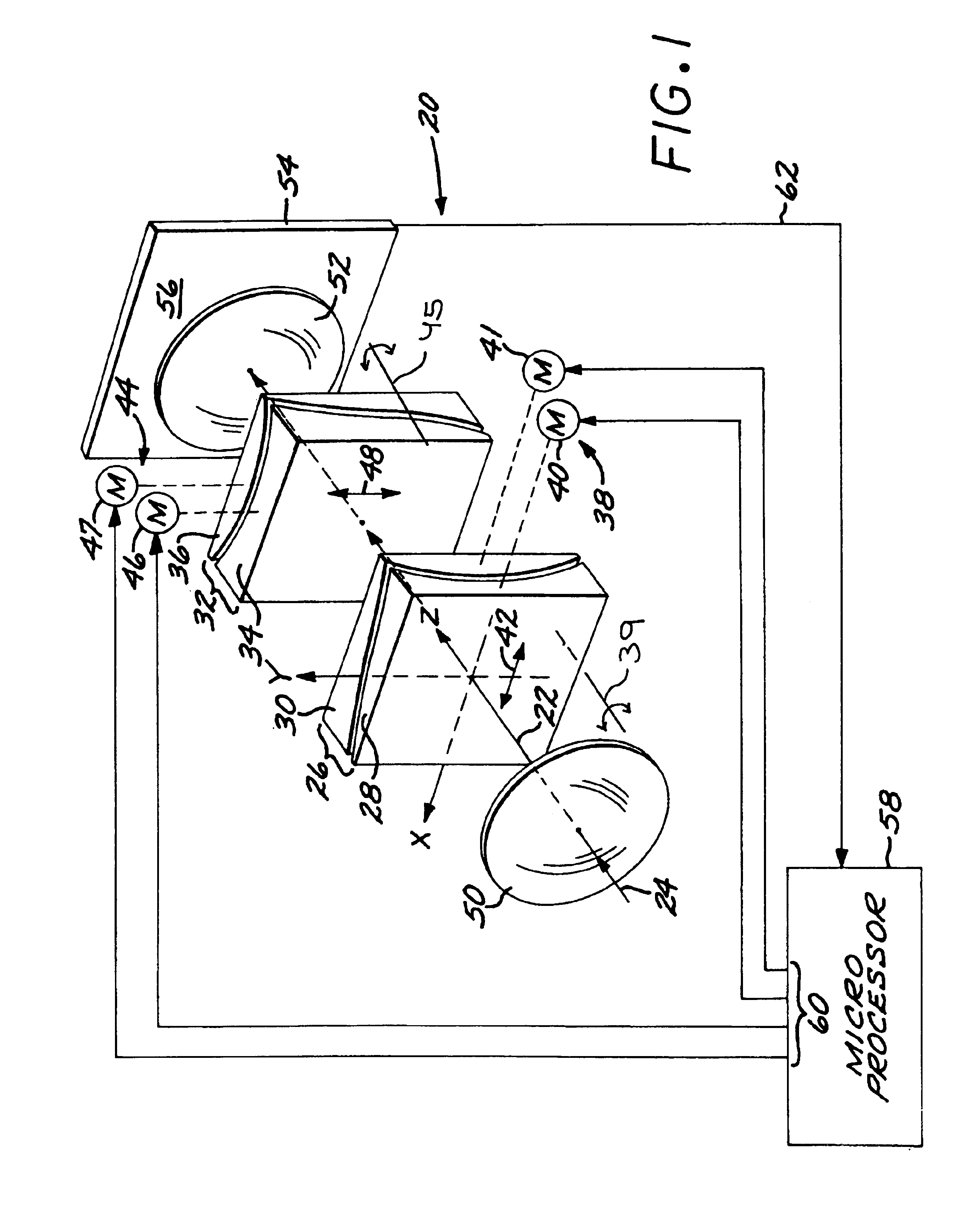
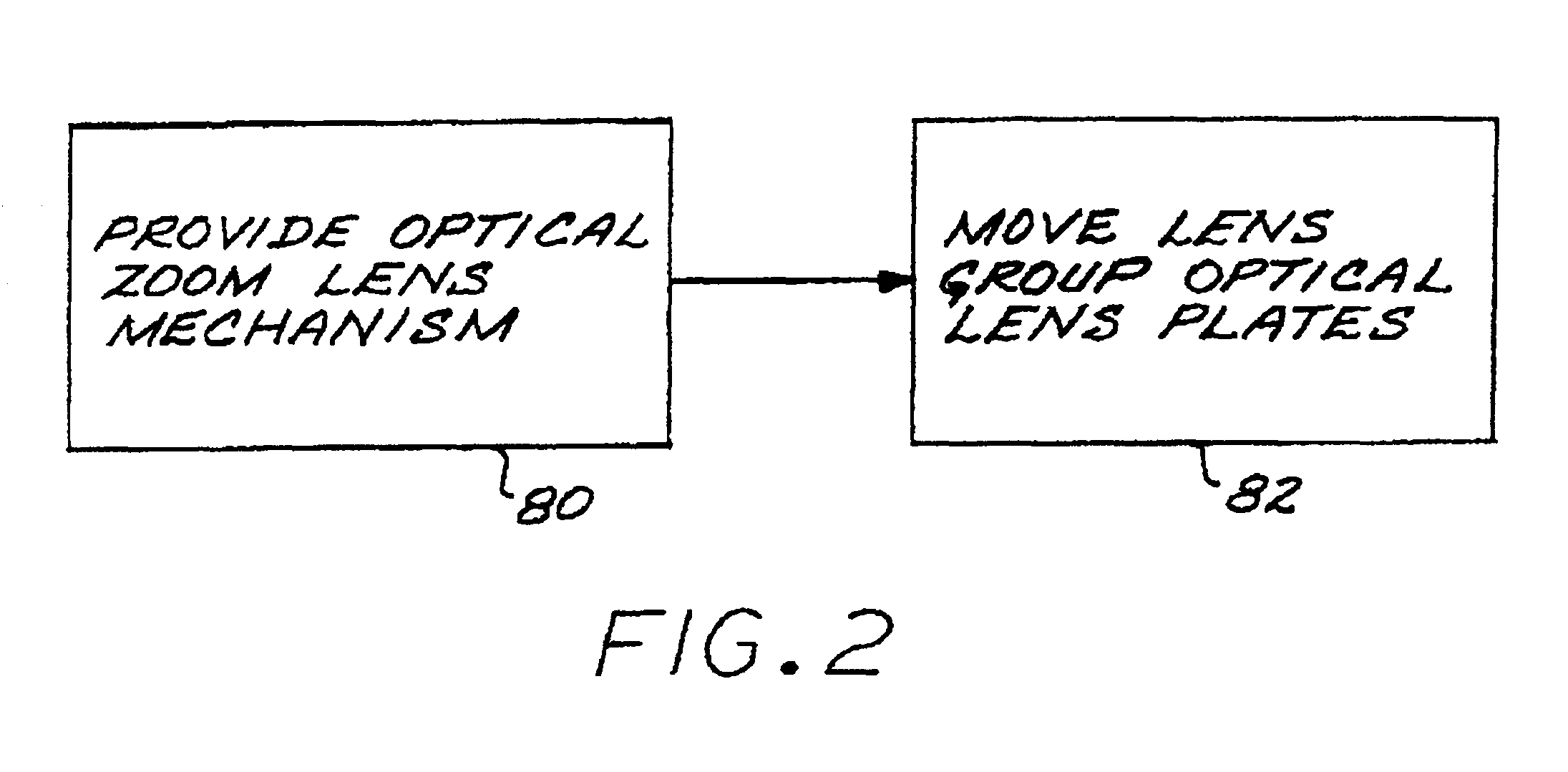
Orthogonal movement lateral shift zoom lens
An optical zoom lens mechanism is arranged along an optical axis and produces a zooming effect by a transverse movement of transparent elements perpendicular to the optical axis. A first lens group has two adjacent, rotationally nonsymmetric transparent first optical lens plates that are each rotationally nonsymmetric relative to the optical axis, and a first-group drive is operable to move the first optical lens plates together and relative to each other in a first-movement radial direction relative to the optical axis. A second lens group has two adjacent, rotationally nonsymmetric transparent second optical lens plates that are each rotationally nonsymmetric relative to the optical axis, and a second-group drive is operable to move the second optical lens plates together and relative to each other in a second-movement radial direction relative to the optical axis. The second-movement radial direction is angularly rotated from the first-movement radial direction by a nonzero, preferably about 90 degrees, rotational angle about the optical axis. The first optical lens plates and the second optical lens plates are shaped so that the relative movement of the first optical lens plates and second optical lens plates produces an optical zoom relative to a focal surface. The drives may be driven by a controller, such as a feedback controller having an imaging sensor located at the focal surface, and a microprocessor controller receiving an output of the imaging sensor and having a control output signal set operably connected to the drives.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
Regulating and calibrating method for linear array CCD scanning detection system
InactiveCN101365144AEasy to implementImprove calibration accuracyImage analysisTelevision systemsProduction lineImaging processing
The invention discloses an adjustment and calibration method for a linear-array CCD scanning and detecting system, which comprises the following steps of (1) arranging a plurality of equally-spaced vertical lines and two paralleled horizontal lines which are processed with high precision on a target; (2) arranging target pieces on production lines, adjusting a target plane and a detected plane on the same plane and enabling the target vertical lines to be in parallel with the forward direction of a conveyor belt; (3) gathering a target image, adjusting the array direction of a linear-array CCD camera to be perpendicular to the movement direction of the conveyor belt according to the image processing result, and also adjusting the target to be positioned on the front focal surface of an image-forming system; (4) gathering the target image after the adjustment, handling the image to obtain the position of each line of the target, and then evaluating a calibration parameter. The invention can be used for the on-site calibration of the linear-array CCD scanning and detecting system, and has the characteristics of fast adjustment and simple calibration.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Physical parameter common-channel phase-shift digital holographic microscopic device based on diffraction grating
ActiveCN102147233AVibration insensitiveImprove stabilityUsing optical meansDigital holographic microscopyBeam splitting
The invention relates to a physical parameter common-channel phase-shift digital holographic microscopic device based on a diffraction grating, which comprises a lighting unit, a microscopic unit, an interference generating unit and an imaging unit, wherein the lighting unit and the microscopic unit are respectively arranged at two sides of a sample; the lighting unit comprises a laser and a light intensity controller arranged in front of the laser; the microscopic unit comprises a second telescope unit which consists of a microobjective and a third lens; the sample is placed on the front focal plane of the second telescope unit; the interference generating unit comprises a beam splitting unit, a filtering unit, a beam combining unit and a contrast control unit sequentially arranged in the light path direction; and the imaging unit comprises a CCD (charge coupled device) camera which is arranged on the rear focal plane of a seventh lens. The digital holographic microscopic device has the advantages of good stability and no sensitivity to ambient vibration.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-profile lens antenna capable of realizing wide-angle scanning
InactiveCN105742824AOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to conformal designLow profileAntennasDistribution characteristicBeam scanning
The invention relates to a low-profile lens antenna capable of realizing wide-angle scanning. The lens antenna comprises a lens and a feed source positioned on the focal plane of the lens; beam scanning and tracking can be realized by mechanical control on the feed source; the lens has an electromagnetic wave focusing function, and the appearance of the lens can be flat-plate-shaped or curved-surface-shaped, and conformal design with a carrier platform can be realized; the effective dielectric constant distribution characteristic of the lens is that the effective dielectric constants are decreased from the center to the edges along the horizontal and longitudinal directions; the regulation and control on the effective dielectric constants can be realized by changing the structure or dimensions of the metamaterial units; and the assembling and preparation of the lens at a low cost is realized by multiple metamaterial panels in a stacked manner. The low-profile lens antenna has the characteristics of broadband, high gain, low profile, easy conformal property and the like, and is particularly suitable for high-gain conformal vehicle-mounted or missile-borne platforms in the fields of communication measurement and control, and the like.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Convex lens focal length measuring device and method
ActiveCN104111163AHigh precision measurementIntuitive interference patternTesting optical propertiesFiberPoint light source
Disclosed is a convex lens focal length measuring device and method. The device is composed of a 1053 nm fiber point light source, a laser range finder, a precise moving guide rail, a convex lens to be measured, a shearing interference plate, a frosted glass screen and a CCD (charge coupled device). A user observes the fringe pattern formed on the shearing interference plate by output beams through the CCD after the lens is collimated, then adjusts the moving direction and the position of the fiber point light source on the precise moving guide rail, enables the 1053 nm point light source to finally be positioned on a focal plane, and then obtain the focal length of the lens through measurement of the laser range finder. The convex lens focal length measuring device has the advantages of being simple in structure, convenient to adjust and high in measuring precision and can help evaluate the optical quality of the convex lens through transverse shearing interference fringes generated during the measuring process to provide valuable detecting data for installation, calibration and optical manufacture of convex lenses.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Continuous multi-satellite tracking
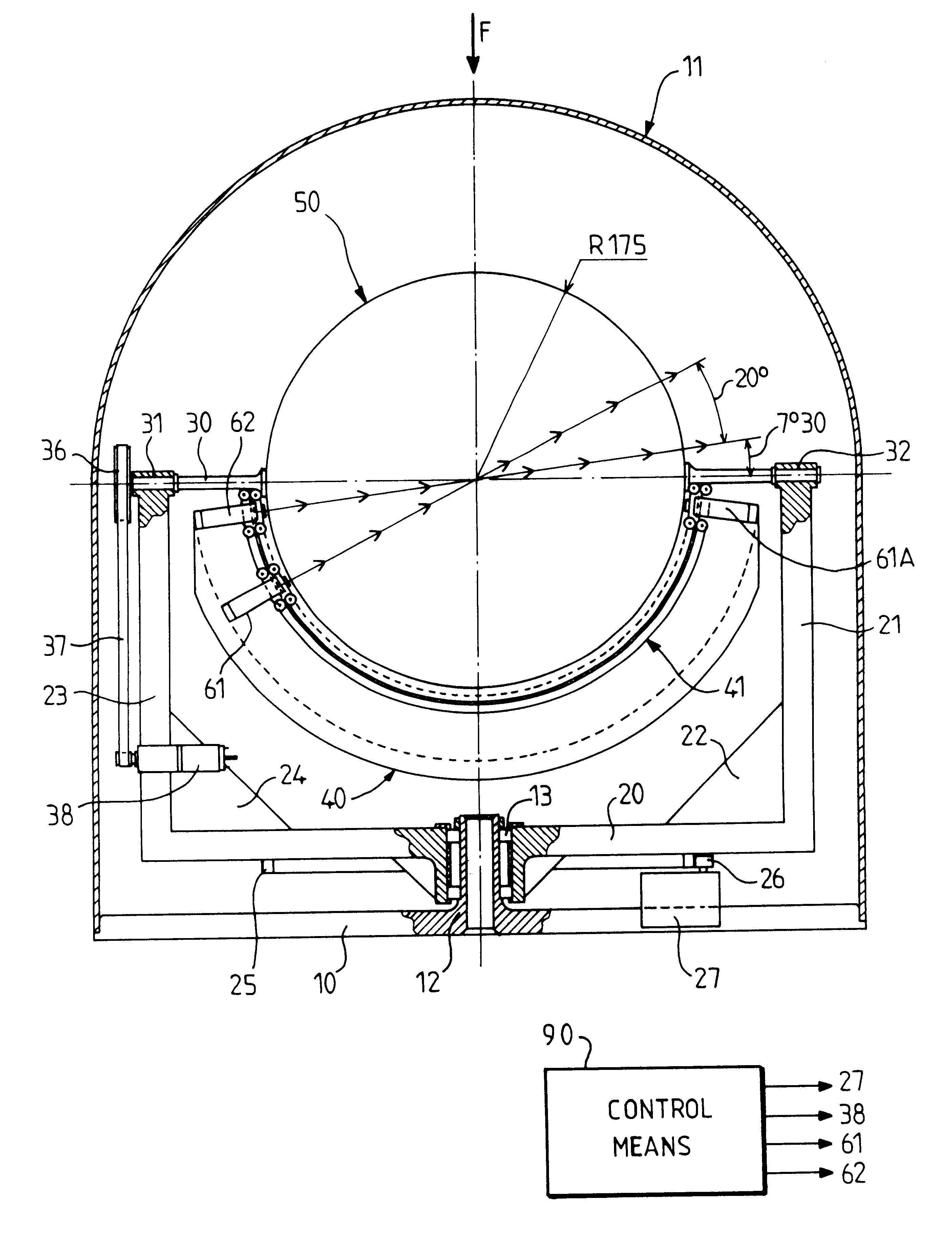
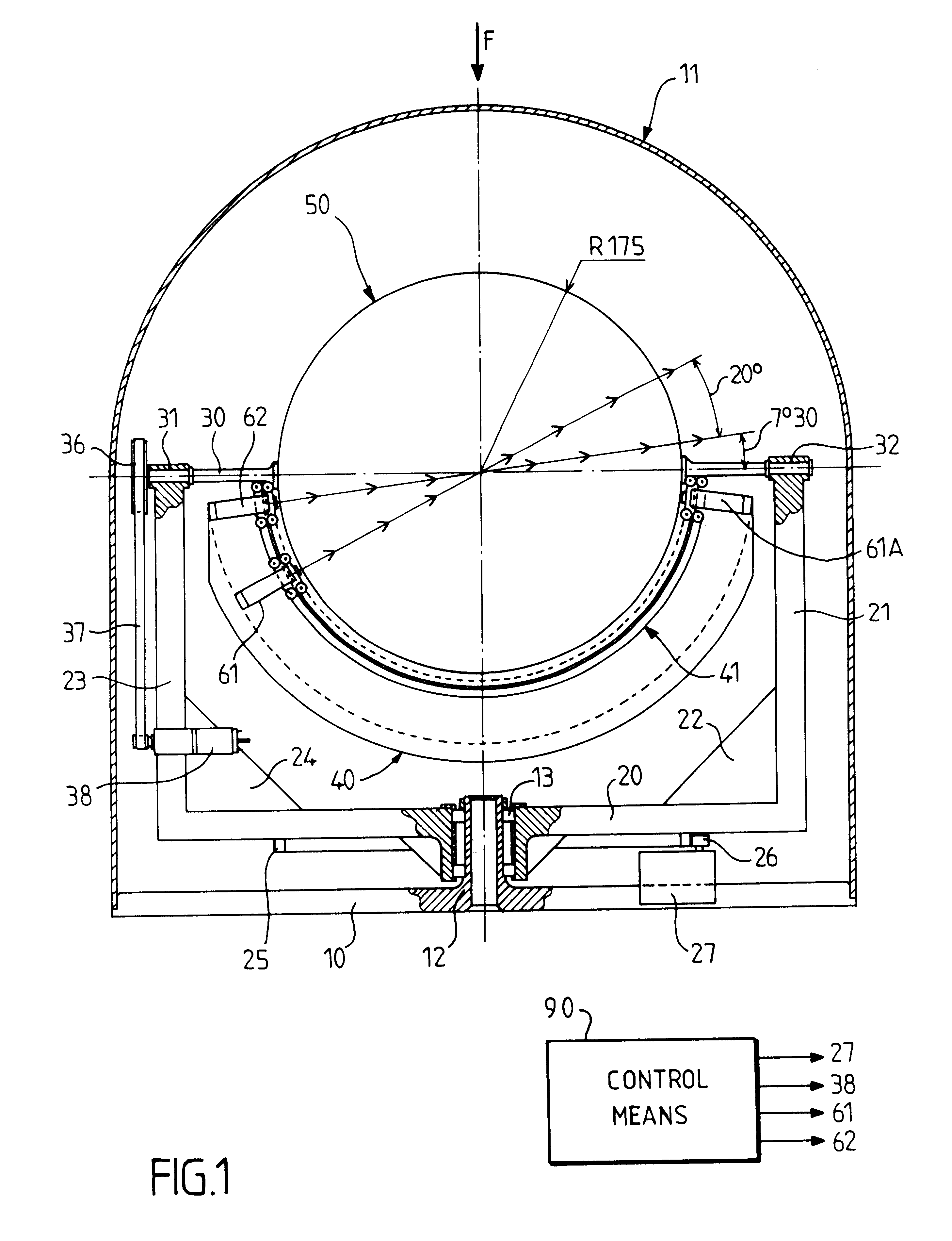
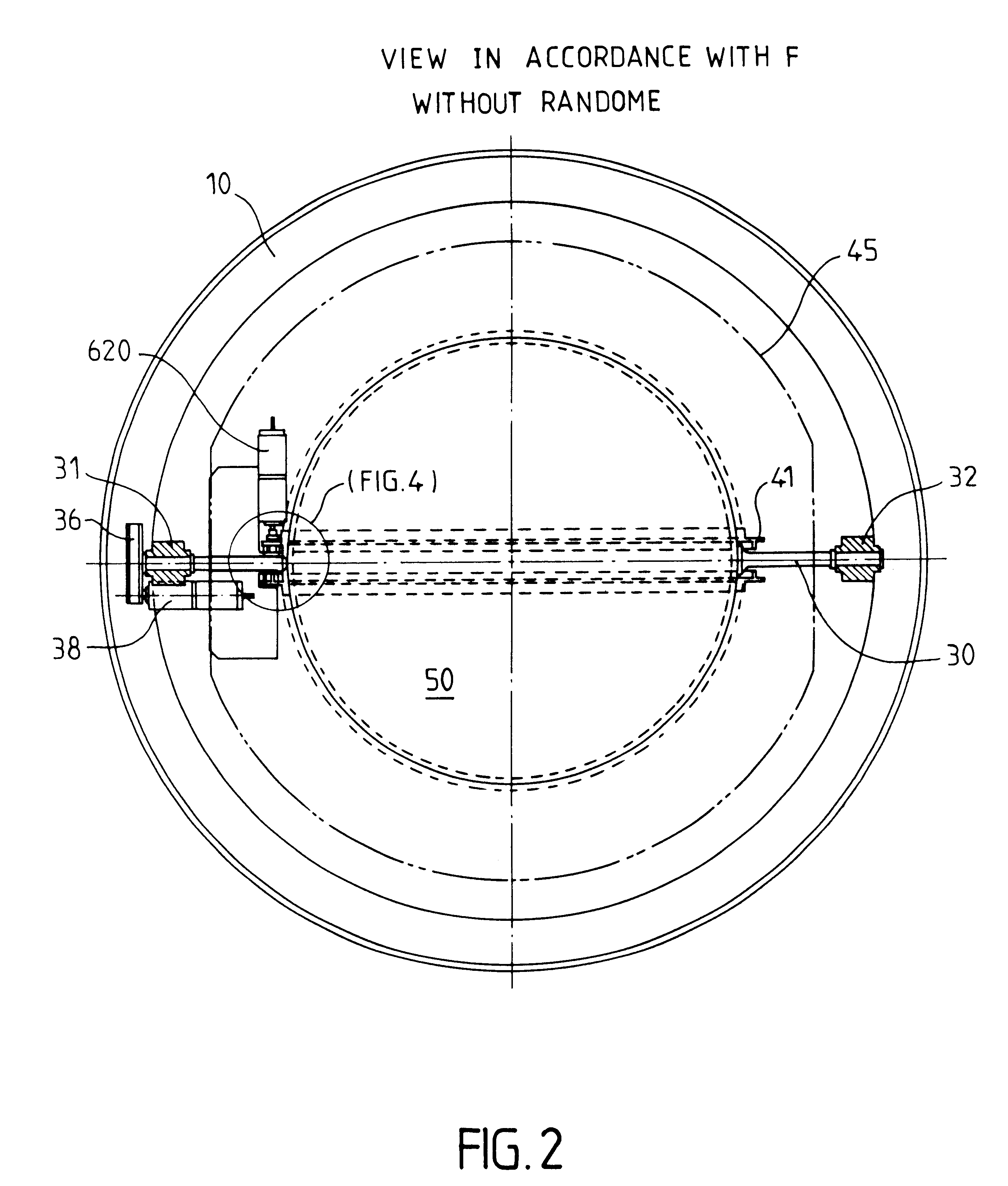
The pointing of at least two sensors (61, 62) is ensured through a Luneberg lens (50). A first frame (20) pivoting on a support (10), supports in pivoting manner a second frame (30), which can in turn support the lens (50). The second frame (30, 40) supports at least one rail (41) for guiding the sensors in the vicinity of the focal surface of the lens. Control means (90) act on the mount as a function of data concerning the position of satellites to be sighted. They are arranged so as to temporarily stop the sighting of one of the satellites, bring the mount into an opposite position on the focal surface, whilst continually sighting the other satellite, and resume the sighting of both satellites, the two sensors then being in an inverted position on the rail.
Owner:ELECTRONIQUE MARCEL DASSAULT SA
Novel ultra wide angle lens
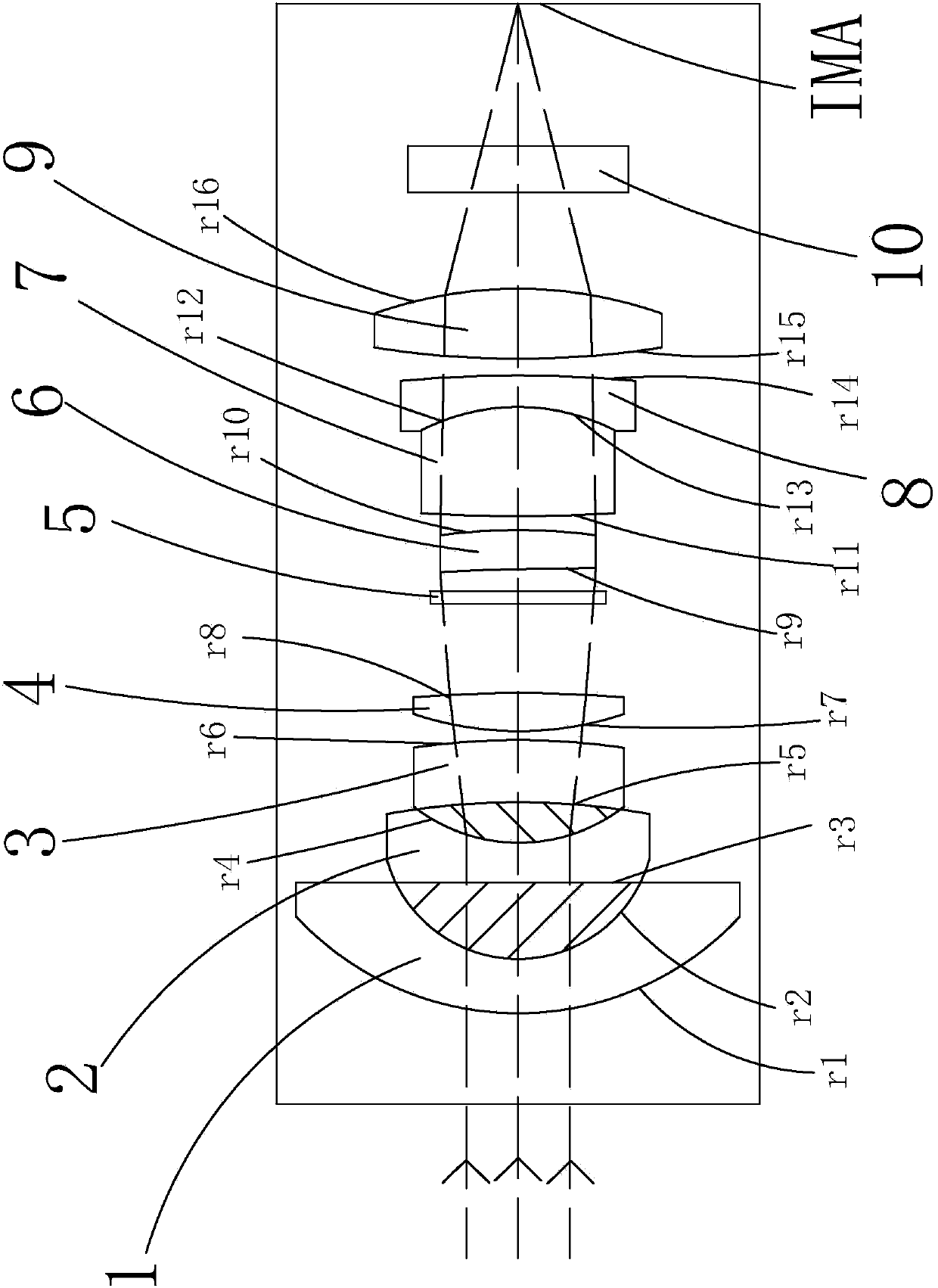
The invention discloses a novel ultra wide angle lens. The novel ultra wide angle lens comprises a lens shell. Pieces of optical glass sequentially arranged from the object space to the image space inside the lens shell include a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a diaphragm component, a fifth lens, a sixth lens, a seventh lens and an eighth lens, wherein the first lens is a strawhat-type lens with the negative focal power, the second lens is a biconcave lens or a plane concave lens with the negative focal power, the third lens is a falcate lens or a biconvex lens with the positive focal power, the fourth lens is a falcate lens or a biconvex lens with the positive focal power, the fifth lens is a falcate lens or a biconvex lens with the positive focal power, the sixth lens is a biconvex lens with the positive focal power, the seventh lens is a falcate lens with the negative focal power, the eighth lens is a biconvex lens with the positive focal power, and the eighth lens is connected with a color filter. The visible light wave band and the near-infrared wave band guided in by the lens are focused in the same focal plane, so that the novel ultra wide angle lens can conduct clear imaging in the day and night modes.
Owner:舜宇光学(中山)有限公司
Large view field off-axis three-reflector system and adjusting method
ActiveCN105242387ASimple structureReduce the difficulty of assembly and adjustmentOptical elementsHyperboloidSystems design
The invention relates to a large view field off-axis three-reflector system and an adjusting method. The large view field off-axis three-reflector system comprises a main mirror, a secondary mirror, an aperture diaphragm, a third mirror and a focal plane. The main mirror is an off-axis hyperboloid reflector; the secondary mirror is a protruding spherical surface reflection mirror; the third mirror is an off-axis secondary recessed flat spherical mirror; the master axes of the master mirror and the third mirror are superposed as a reference axis; the aperture diaphragm is successively arranged on the secondary mirror; the optical axis of the secondary mirror is superposed with the master axis of the third mirror; a target light ray from infinity enters the secondary mirror after reflection of the main mirror and enters the third mirror through the reflection of the secondary mirror; and then the light ray is imaged on the focal surface. The invention solves the contradiction between the large view field off-axis three-reflector system, the processing and adjusting. The large view field off-axis three-reflector system adopts a simple structure and can realize the wide width imaging, wherein the effective view field reaches 12 degree*3.5 degree.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Off-axis alignment system and alignment method
ActiveCN103777476AWill not affect detection resultsRequirement to eliminate coherencePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingPrism
The present invention relates to an off-axis alignment system and a method thereof. The off-axis alignment system comprises an illumination module, an interference module and a detection module, wherein the illumination module comprises a light source, multi-wavelength incidence optical fibers and a light splitting element, the interference module comprises a polarization beam splitter, the one polarization beam splitter side relative to the one side of the illumination module and the detection module is provided with a first 1 / 4 wave plate and a first reflecting mirror, the other two sides of the polarization beam splitter are respectively provided with a second 1 / 4 wave plate and a cube-corner prism, and a third 1 / 4 wave plate, a second reflecting mirror and a lens, the second reflecting mirror is positioned on the rear focal plane of the lens, the center of the bottom surface of the cube-corner prism is positioned on the optical axis of the lens, and the detection module comprises a detection lens set, a polarization device, detection optical fibers and a photoelectric detector. According to the present invention, the grating double-diffraction technology of the off-axis alignment system is adopted, the incidence light beam passes through the alignment label twice, and the secondary diffraction light beam direction is completely opposite to the original incidence direction, such that it is ensured that the detection result is not affected when the alignment label is subjected to inclination and / or defocusing.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Grating-based phase difference wavefront sensor
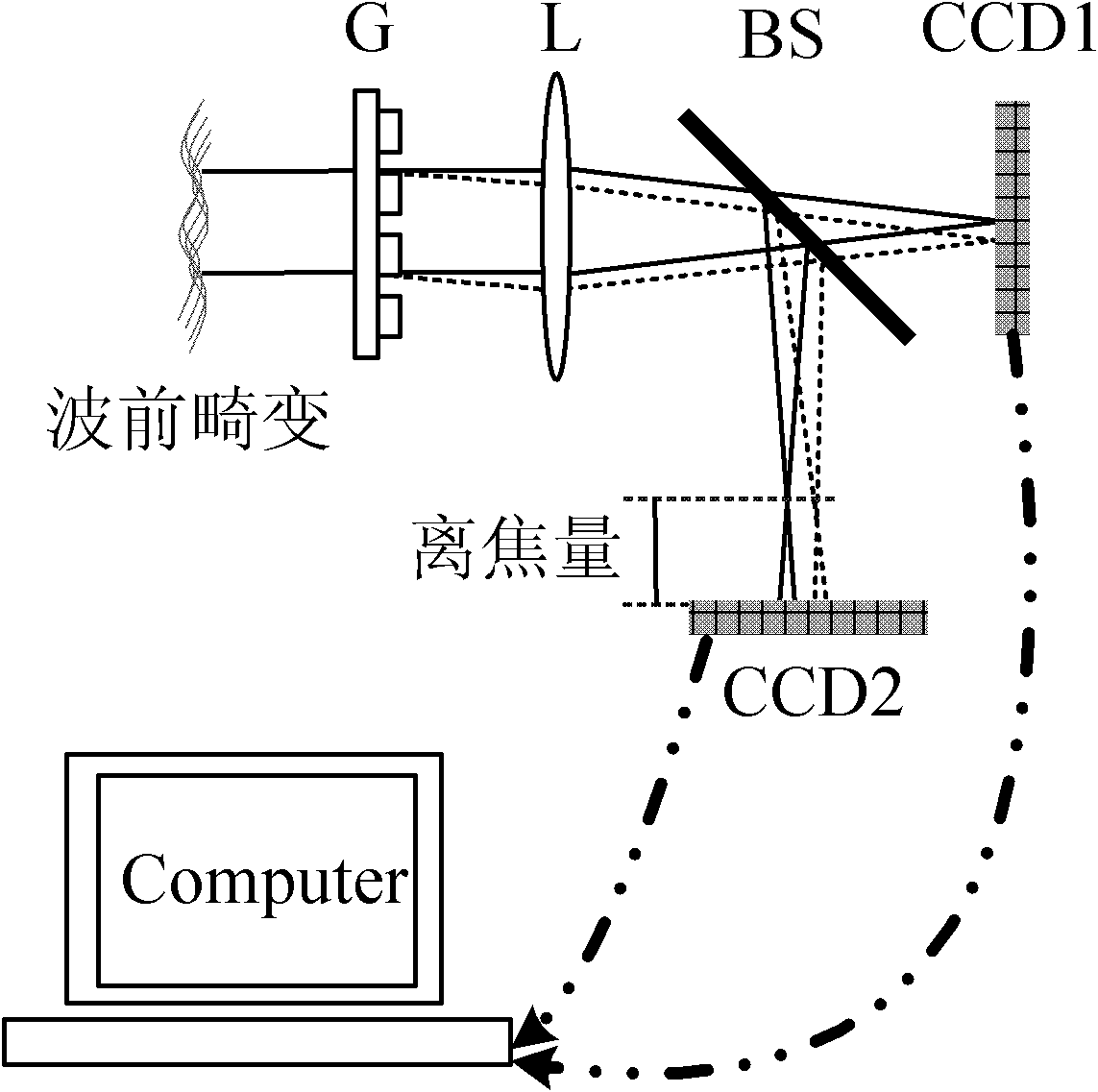
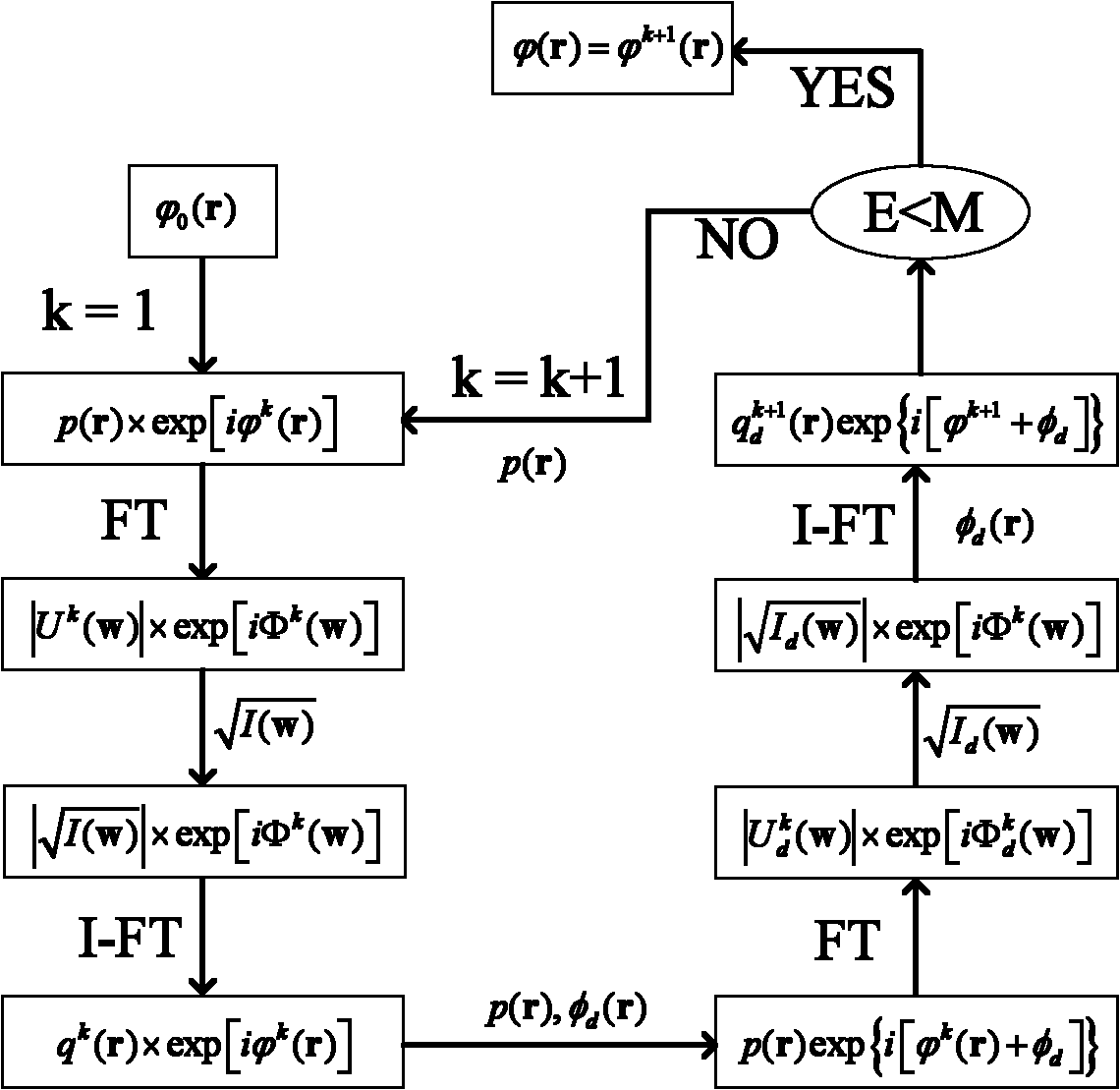
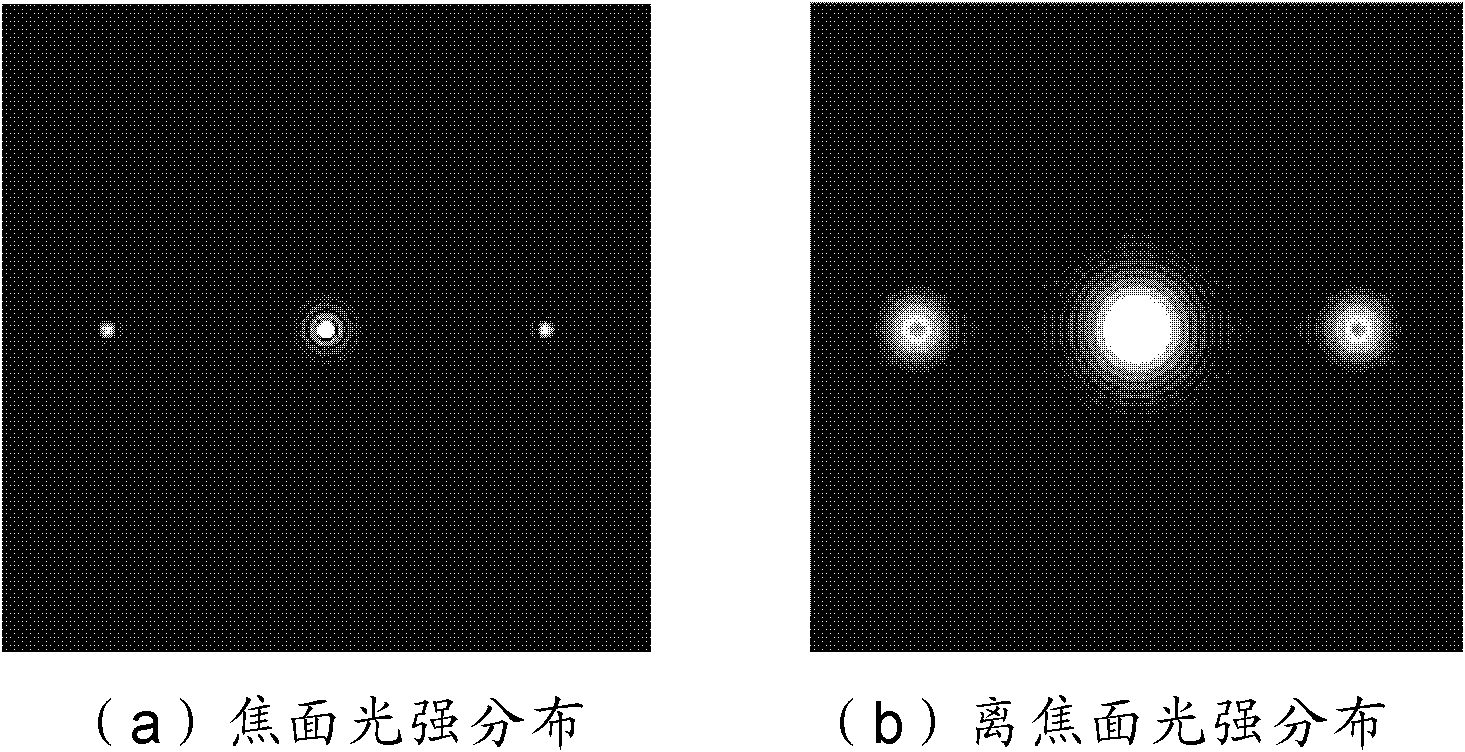
The invention discloses a grating-based phase difference wavefront sensor which comprises a grating, a lens, a spectroscope, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) imaging detector, a computer and the like, wherein a parallel light beam containing wavefront distortion is directly irradiated onto the surface of the grating; and the light beam is divided into multiple beams of light with different intensities and same phase after being transmitted by the grating and is imaged on a CCD photosensitive surface by the lens. According to two or multiple grating diffraction spots, the light intensity distribution of the spots can be more accurately calculated by a corresponding algorithm. According to focal plane and defocusing surface light intensity distribution, the computer can restore to obtain wavefront distortion information to be detected. In the grating-based phase difference wavefront sensor, the CCD imaging detector can be used for collecting the high-frequency ingredient of the light intensity distribution which can not be measured in the common condition, the detection precision of the phase difference wavefront sensor is effectively improved, and the phase difference wavefront sensor has obvious advantages in the fields of optical detection, adaptive optics, high-resolution imaging and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
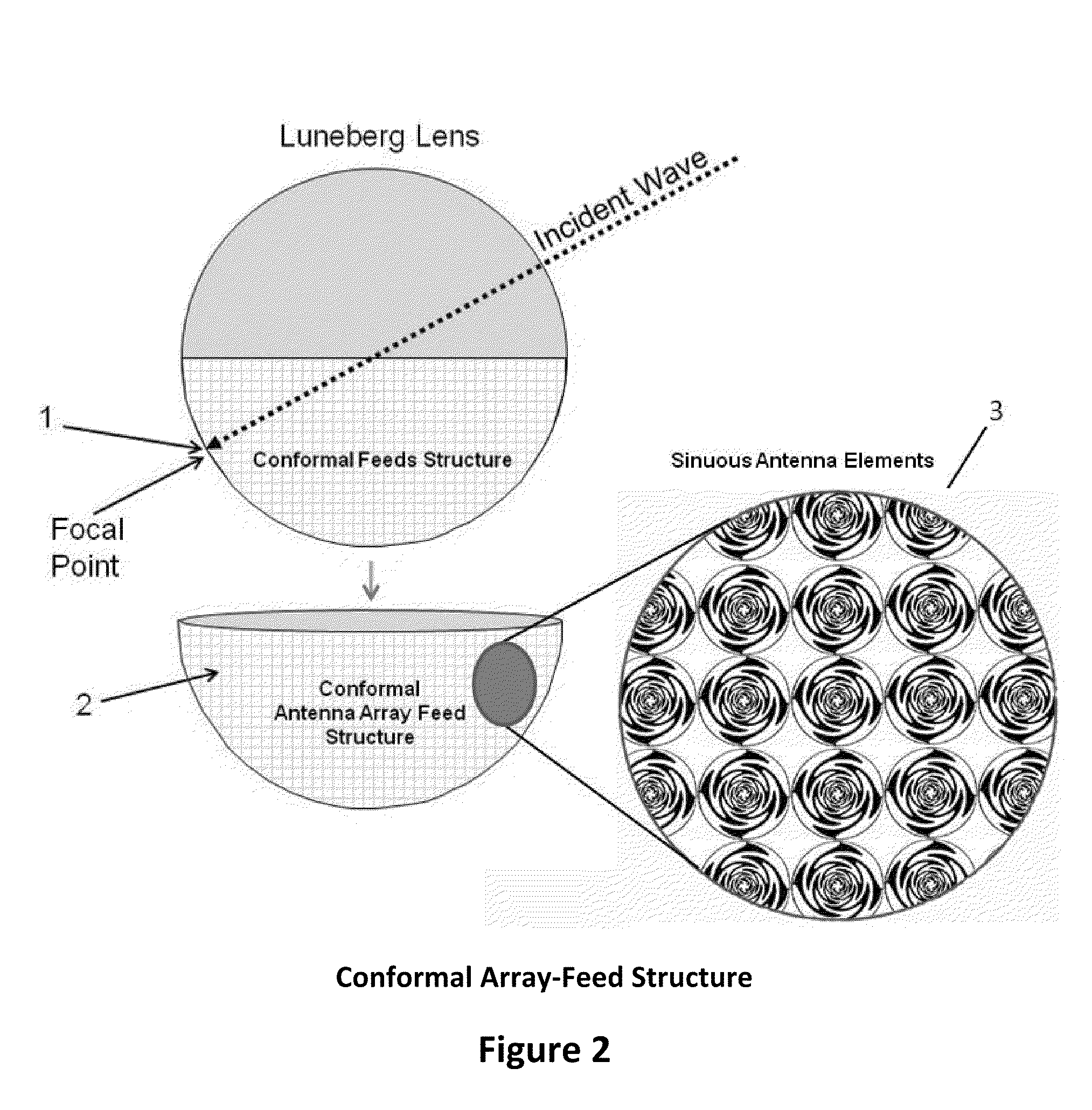
Multibeam Active Discrete Lens Antenna
ActiveUS20100207833A1Improve Radiation PerformanceReduce volumeWaveguide type devicesSpace fed arraysAudio power amplifierRadiating element
A multibeam antenna comprising: a plurality of primary radiating elements, each associated to a respective beam; and an active radiating structure comprising a first planar array of radiating elements, a second planar array composed by a same number of radiating elements, a set of connections between each radiating element of the first planar array and one corresponding element of the second planar array, and a set of power amplifiers for amplifying signals transmitted through said connections; wherein: the relative positions of the radiating elements of the first and second planar arrays and phase delays introduced by said connections are such that the radiating structure forms an active discrete converging lens; and said primary radiating elements are clustered on a focal surface of said lens, facing the first planar array; characterized in that said first and second planar arrays are both aperiodic. A method of manufacturing such an antenna.
Owner:EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY
Parallelism detector for optical axis of multi-optical system
InactiveCN101718534AReduced precision requirementsImprove parallelismUsing optical meansOptical axisPrism
The invention relates to a parallelism detector for an optical axis of a multi-optical system. A first half-reflecting semi-permeable mirror of the detector is fixed on a guide rail, and a calibration reflection mirror is movably connected with the guide rail through a two-dimensional adjusting mechanism; a refluxing reflection mirror is movably connected with a guide rail sliding block through the two-dimensional adjusting mechanism, and the guide rail sliding block can move along the guide rail; a crosshair division plate is positioned on a focal surface of a collimating system, and a light source irradiates one side of the crosshair division plate; one path of collimated light beams emitted from the collimating system permeates the first half-reflecting semi-permeable mirror and is then incident upon the calibration reflecting mirror, and the other path of the collimated light beams is incident upon a cone prism after reflected through the first half-reflecting semi-permeable mirror and the refluxing reflection mirror. The invention can be flexibly applied to the parallelism detection of optical axes of various multi-optical systems and has simple processing and manufacturing, low cost, convenient installation and debugging and convenient detection and calibration.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large-field-of-view high-resolution microscopic imaging device and iterative reconstruction method based on a large illumination numerical aperture
ActiveCN107065159AEasy control programmingIncrease the apertureColor television detailsMicroscopesMicroscopic imageEffect light
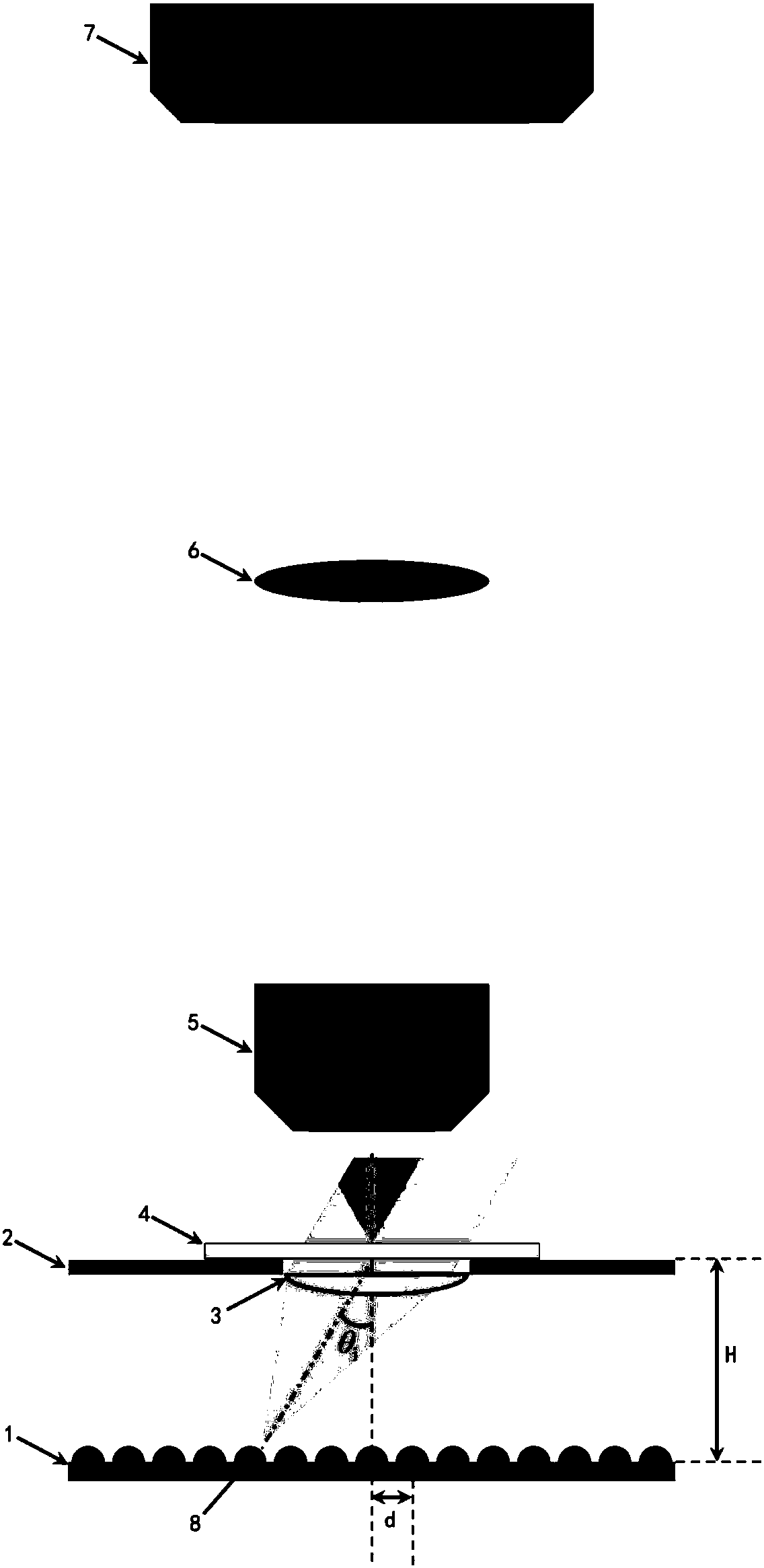
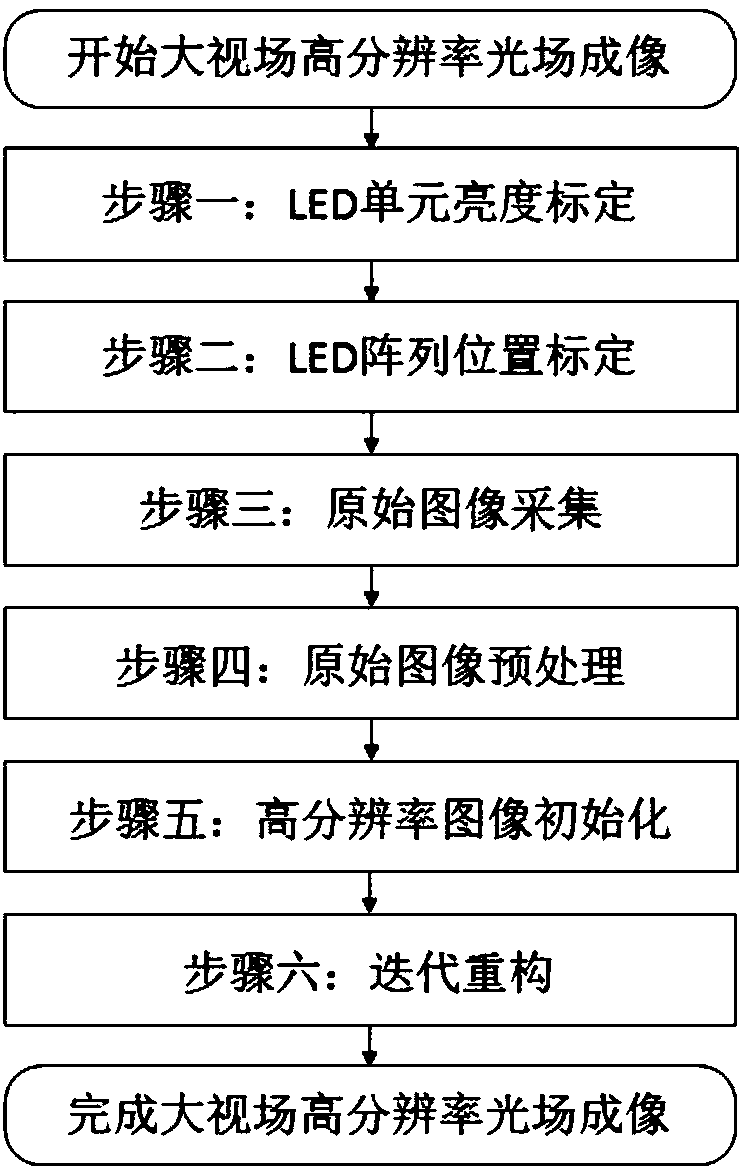
The invention discloses a large-field-of-view high-resolution microscopic imaging device and iterative reconstruction method based on a large illumination numerical aperture. The large-field-of-view high-resolution microscopic imaging device comprises an LED array, an objective table, a condenser lens, a microscopic objective lens, an imaging mirror, and a camera. The LED array is arranged on the front focal plane of the condenser lens. The light emitted by the i-th illuminated LED unit on the LED array is converted into parallel light by the convergence of the condenser lens to be emitted to a sample to be detected. The sample to be detected is placed on the objective table. A part of diffractive light transmitting the sample to be detected is collected by a microscopic objective lens and is emitted to the image plane of the camera by the convergence of the imaging mirror. A formed light intensity map is recorded by the camera. The large-field-of-view high-resolution microscopic imaging device ensures the programming controllability of the lighting direction, ensures that the illumination numerical aperture as high as 1.20 so as to obtain a reconstructed resolution up to 0.15[mu]m.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for multi-focal-plane object imaging under microscopic vision
InactiveCN102968792ARapid positioningCalculation speedImage enhancementImage analysisOptical axisThree-dimensional space
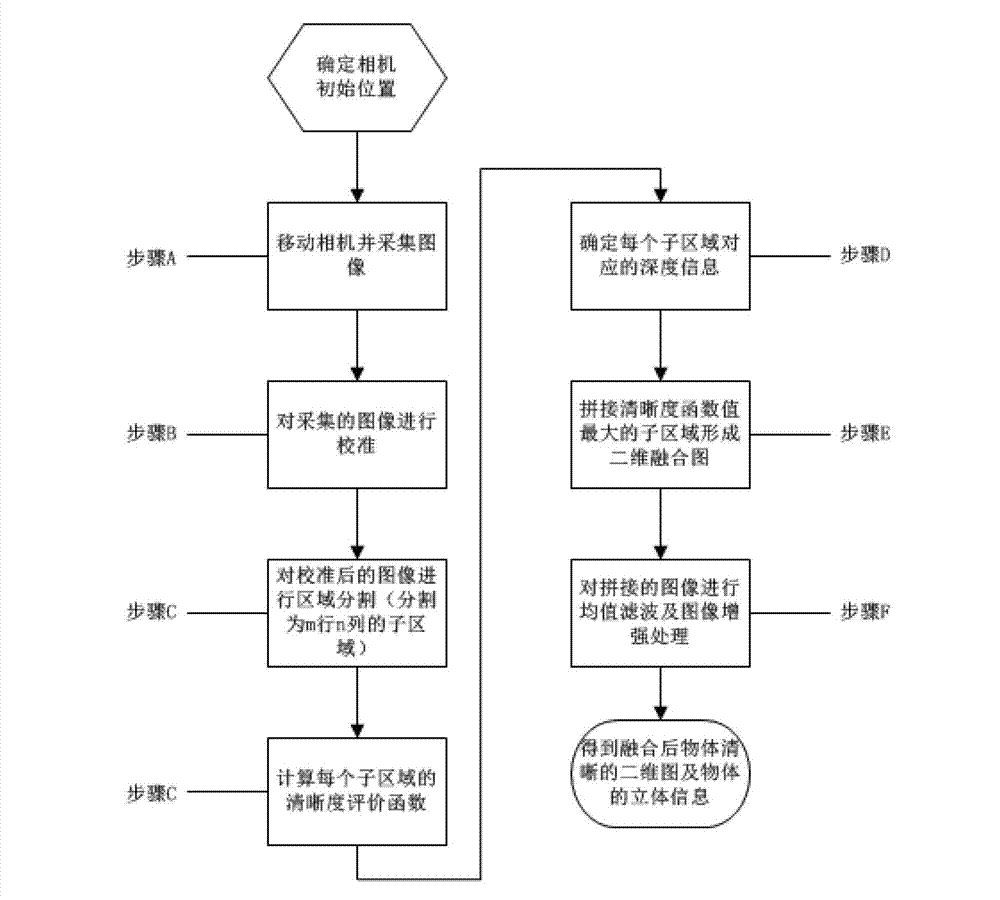
The invention provides a method for multi-focal-plane object imaging under microscopic vision. The method comprises moving a camera along the direction of a primary optical axis, collecting a plurality of images of a multi-focal-plane object, forming an image sequence, and enabling the plurality of images to record the process of vagueness to clearness and then to vagueness of imaging of the multi-focal-plane object; correcting images in the image sequence, and enabling regions of the surface in which the multi-focal-plane object is located according to the images to be the same; dividing each image in the image sequence into sub-regions with m lines and n columns, performing definition evaluation on each sub-region image, and obtaining definition evaluation function values of each sub-region image; finding out a corresponding image serial number when the definition evaluation function value is the maximum for each sub-region, obtaining the position of the camera relative to the object at the time, and obtaining depth information of the sub-region in a three-dimensional space through position information of the camera relative to the object. According to the method, the depth information of the object in the regions can be positioned rapidly.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Resetting and calibration of detector for visible and infrared composite light path light axis parallelism
InactiveCN101339013AImprove detection accuracyEasy to installUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesOptical axisStandard plane
The invention relates to a metnod for the assembling adjusting and standardization of a visible-infrared light compound optical path optical axis parallelism detector, which is characterized in that: placing a standard plane mirror on the back of the visible-infrared light compound optical path optical axis parallelism detector to roughly adjust the detector; placing a reflecting collimator and a high-temperature cross wire respectively on the back and the focal plane of the visible-infrared light compound optical path optical axis parallelism detector; electrifying the high-temperature cross wire to emit visible light wave and infrared light wave; adjusting the reflecting collimator to ensure the complete coincidence of the emitting visible cross wire image and the visible light image of the high-temperature cross wire on visible light CCD; adjusting the infrared part of the visible-infrared light compound optical path optical axis parallelism detector to ensure the completer coincidence of the infrared laser spot on infrared CCD and the infrared image of the high-temperature cross wire; standardizing the detector and calculating the optical axis parallelism difference between the visible light wave and the infrared light wave after the visible light and the infrared light gather in the same optical system with the help of software processing algorithm. The method has the advantages of convenient assembling adjustment and high precision.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three light wave transversal shearing interference apparatus and method for extracting differential phase
InactiveCN101451890ALow coherence requirementsReduce spatial coherenceOptical measurementsGratingSpatial light modulator
The invention provides a device of a tri-light wave for transverse clipping interference and a method for extracting the difference phase. The device comprises a light source, a to-be measured object, a first lens, a space light modulator, a second lens and a charge coupled device; the to-be measured object is located on the focus plane of the first lens; the base focus plane of the first lens; the space light modulator is located at the front focus plane of the second lens; the charge coupled device is located on the back focus plane of the second lens; the light source, the to-be measured object, the first lens, a space light modulator and the second lens and a charge coupled device form the coaxial device. The invention uses the calculating a spatial light modulator on the cosine of the computer-generated hologram grating to control the +- 1-ordered diffraction light of the relative phase shift of zero level and the shear volume, you can generate real-time dynamic shear interferogram phase-shifting, interference by Figure intensity calculated differential phase calculation. The present invention has a simple, compact structure, high precision control, dynamic control and so on.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
System for testing optical axis of broadband multi-sensor electro-optic apparatus
InactiveCN101008563AEasy to adjustUsing optical meansOptical apparatus testingOptical testOptical axis
This invention relates to one wide band multi-sensor device light axis test system in optical test technique, which comprises the following steps: fixing the devices with different wave lengths into guide rail and moving their focus parts onto parallel focus surface through adjusting system in cross or star holes; receiving laser spot CCD receive system parts; using parallel light tube to make cross or star point hole onto tested system each optical display to receive test system laser.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Volumetric direction-finding system using a Luneberg Lens
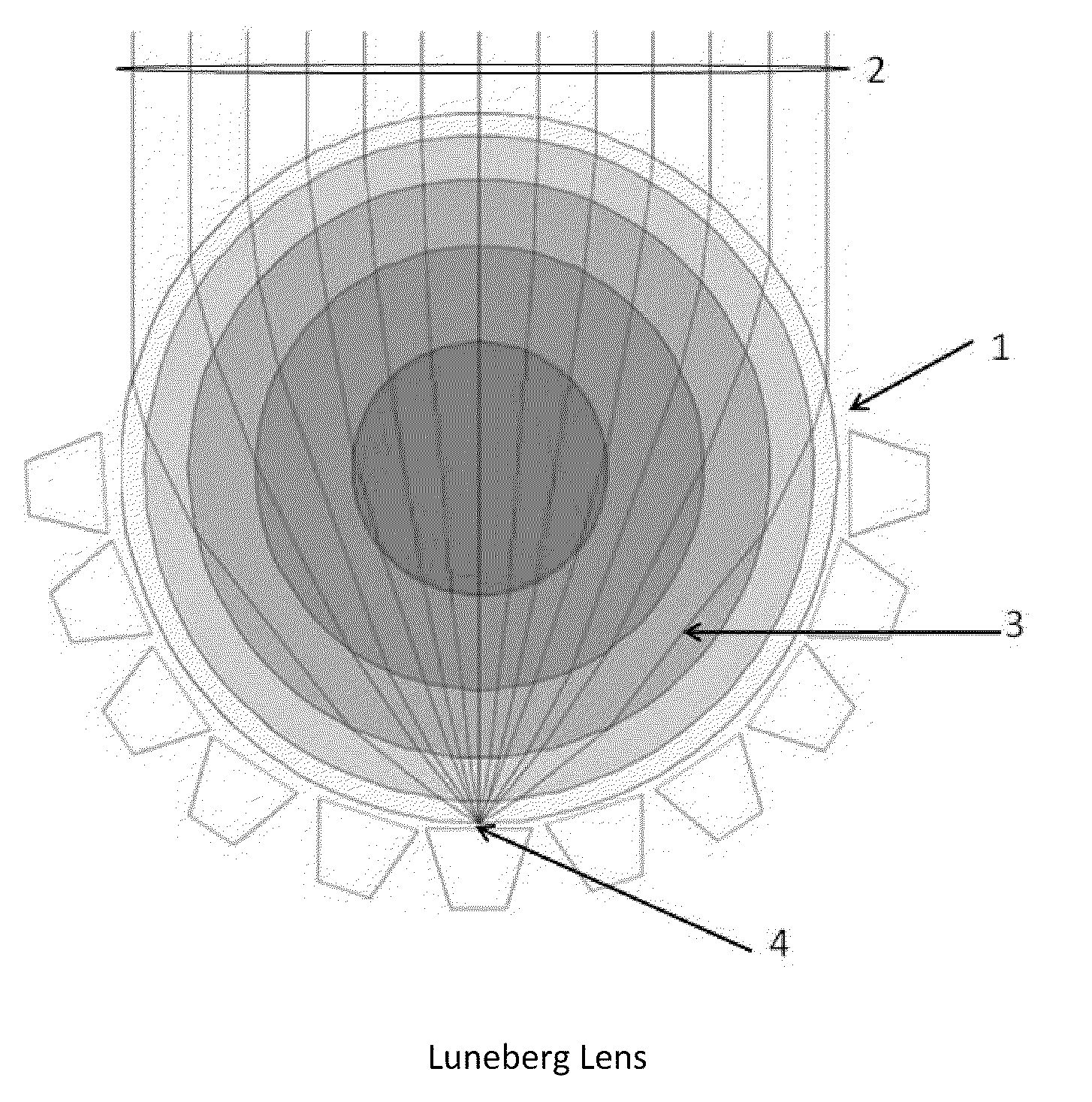
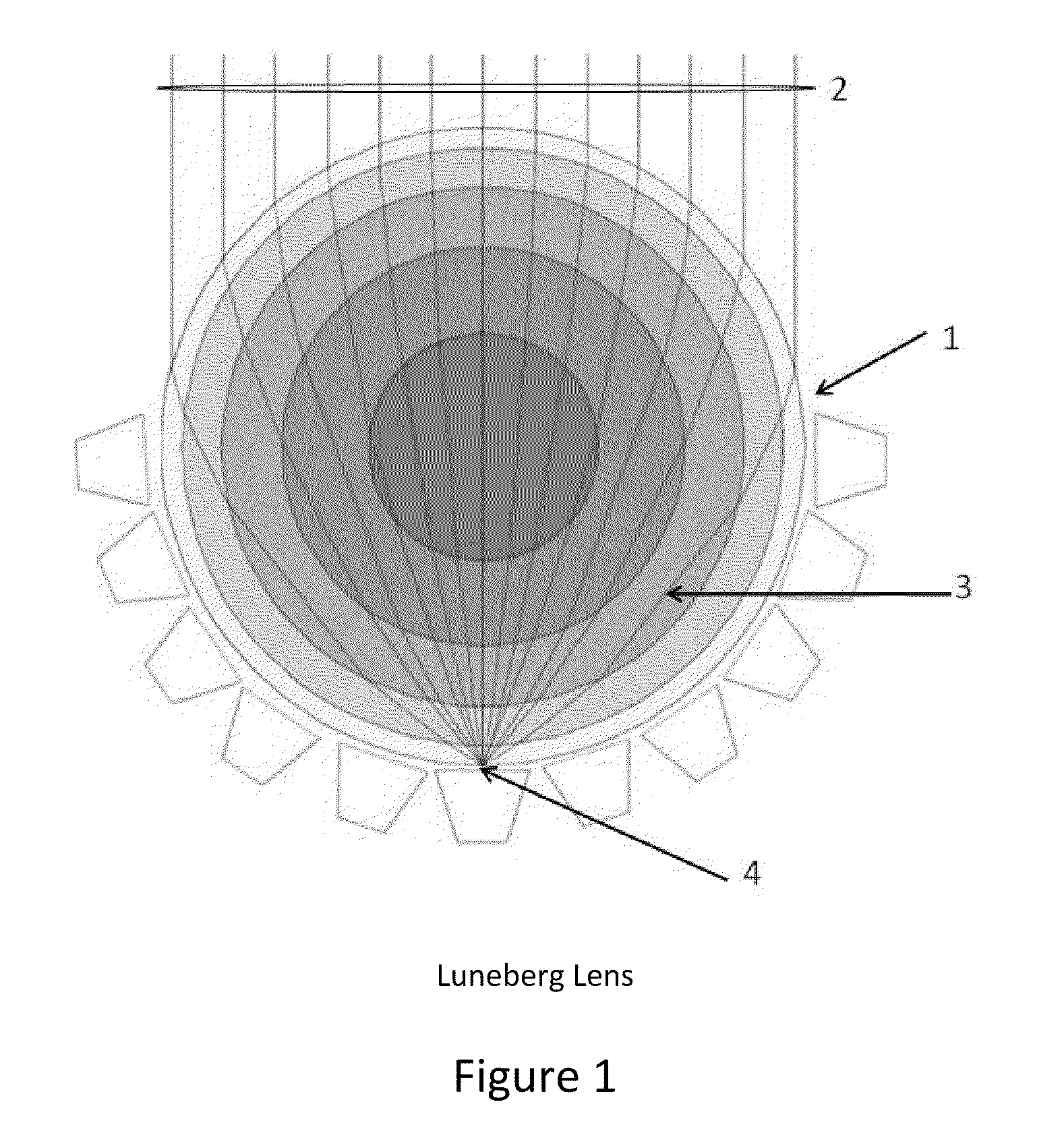
InactiveUS7688263B1High sensitivityImprove accuracyPosition fixationDirection findersSpherical shapedEngineering
Disclosed is an Radio Frequency (RF) receiving system methodology, utilizing an Luneberg Lens having a spherically shaped outer surface and a semi-spherical shaped focal surface composed of near-equally spaced frequency-independent antenna elements disposed uniformly to cover the semi-spherical focal surface of the Luneberg Lens; and radio frequency (RF) power splitters and combiners for combining the RF energy received by the antenna elements; forming rows and columns; thereby reducing the number of required RF receiver channels for subsequent processing, where the maximum row / column and differential amplitude comparison is used for deriving volumetric direction finding (DF) of intercepted signals; as part of a robust signal detection and direction-finding (DF) system; for detecting and processing a plurality of signals emanating from surface and airborne platforms within the hemisphere, where each surface and airborne platform include transmitters for transmitting navigation, communication and radar signals.
Owner:OXLEY ROGER DALE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com