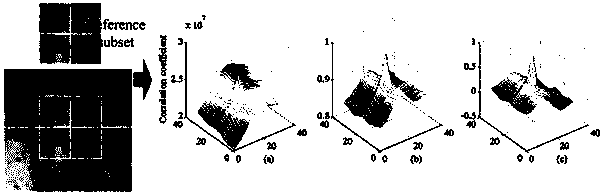
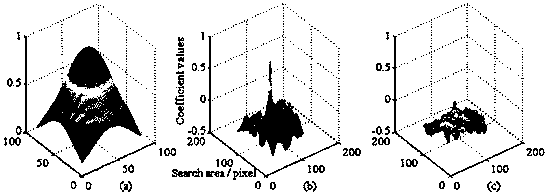
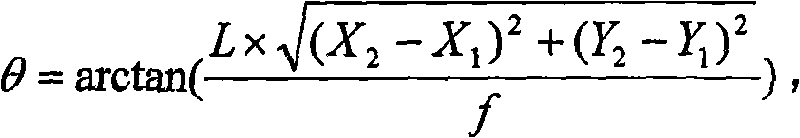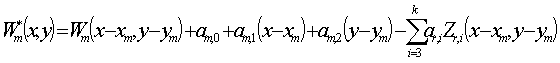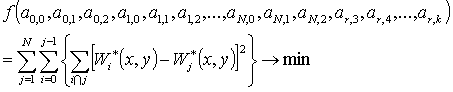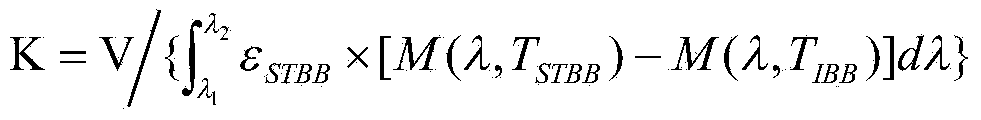Patents
Literature
216 results about "Standard plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Standard plane. [′stan·dərd ′plān] (crystallography) The crystal plane whose Miller indices are (111), that is, whose intercepts on the crystal axes are proportional to the corresponding sides of a unit cell.
Micro-engineered electron multipliers
ActiveUS7294954B2Accelerate emissionsEasy to manufactureMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesIn planeStandard plane
This invention provides for a simple method of fabricating miniature electron multipliers, in an in-plane configuration suitable for use with miniature analytic instruments such as mass filters. The materials involved are predominantly silicon and compatible oxides, allowing the possibility of integration with a mass filter formed in a similar materials system. The materials are selected simultaneously to withstand high voltages and to enhance secondary electron emission. Fabrication is based on standard planar processing methods. These methods also allow the construction of an integrated set of bias resistors in a multi-electrode device, so that the device may be operated from a single high-voltage source.
Owner:MICROSAIC SYST
Optical scanning apparatus and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20070030538A1Low costReduce in quantityInking apparatusOther printing apparatusStandard planeLight source
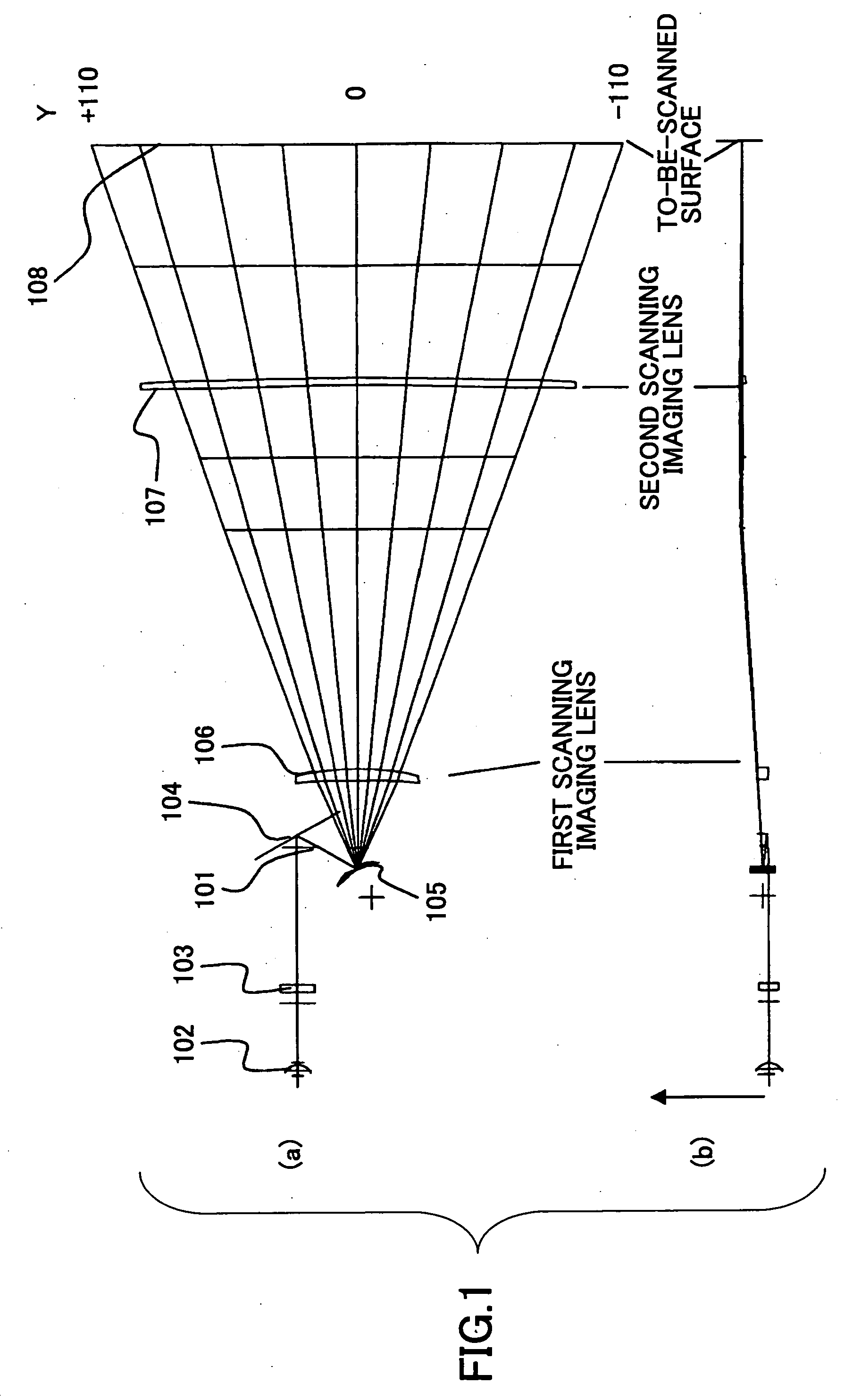
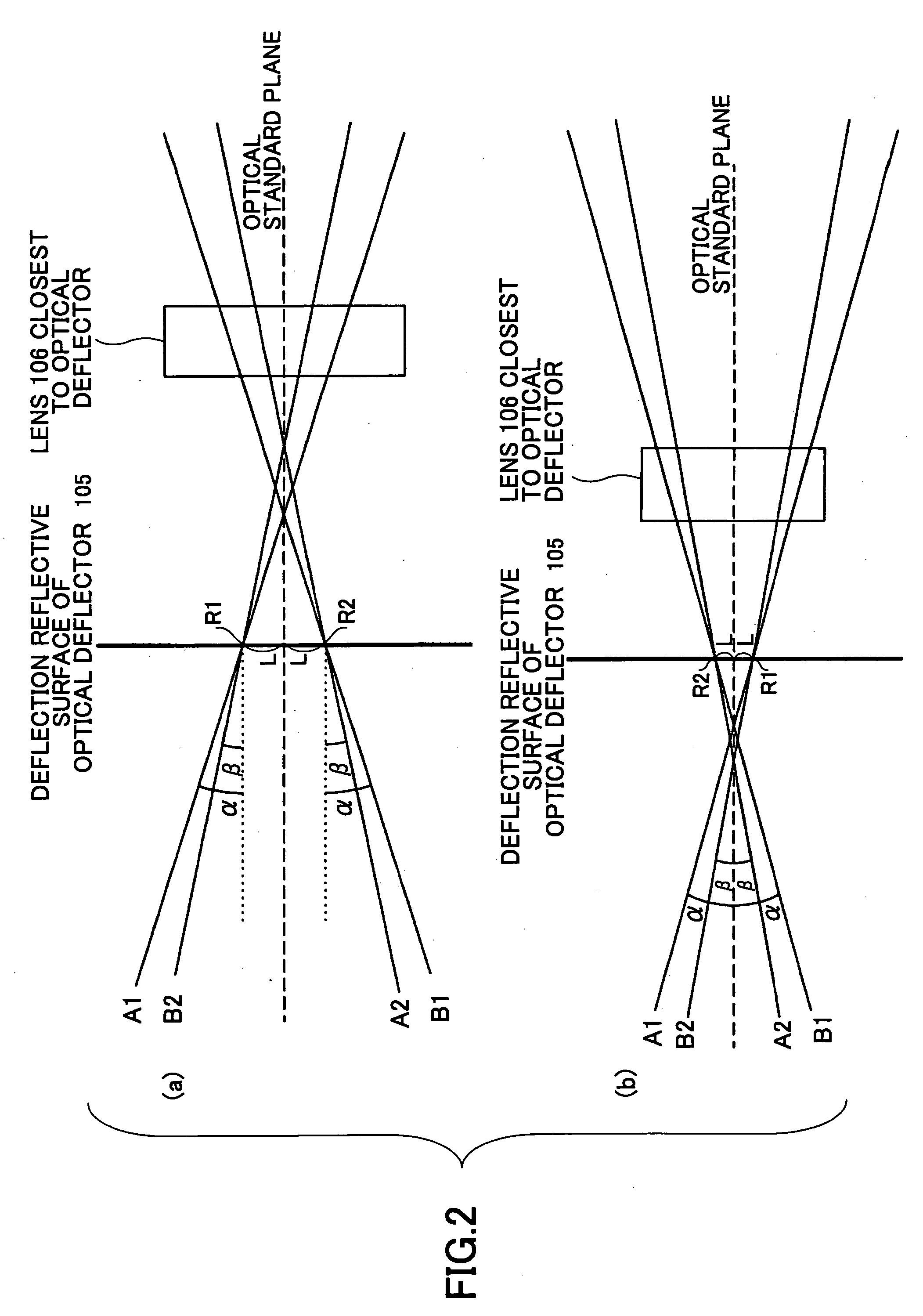
A light source part has a light source unit in which the plurality of light sources respectively emitting the light beams at angles different in a sub-scanning direction with respect to an optical standard plane, parallel to a main scanning direction and passing through a standard axis of a surface shape of a lens of the imaging part, which lens is closest to the deflecting part, and applied to the deflecting part at angles different in the sub-scanning direction, are integrally provided; and the plurality of light sources are inclined so that the plurality of light sources thus respectively emit the light beams at the angles different in the sub-scanning direction with respect to the optical standard plane.
Owner:RICOH KK
Device for detecting wave front of large-aperture optical system
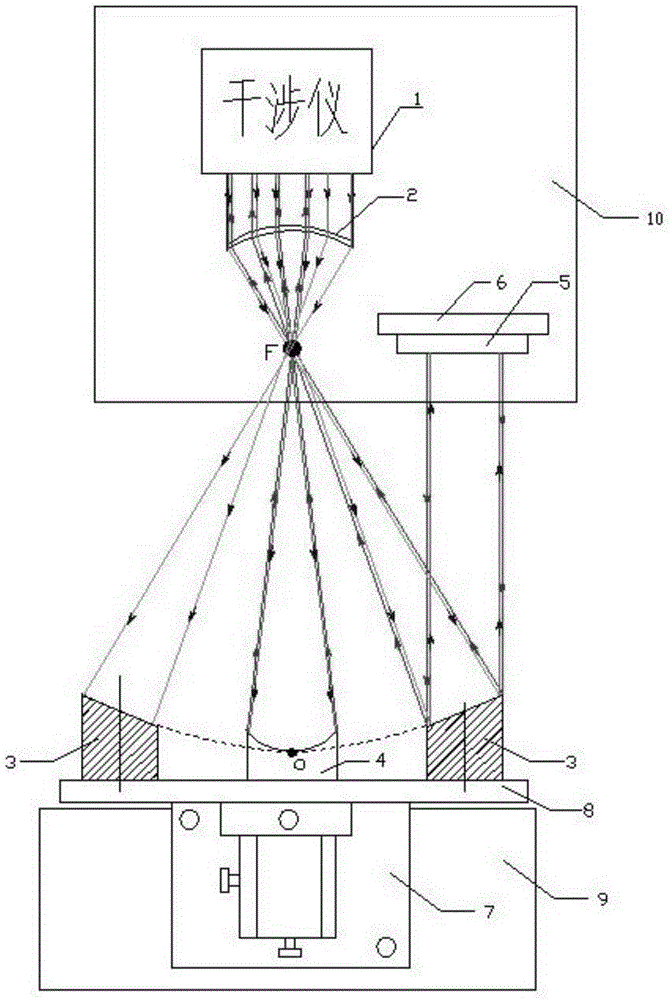
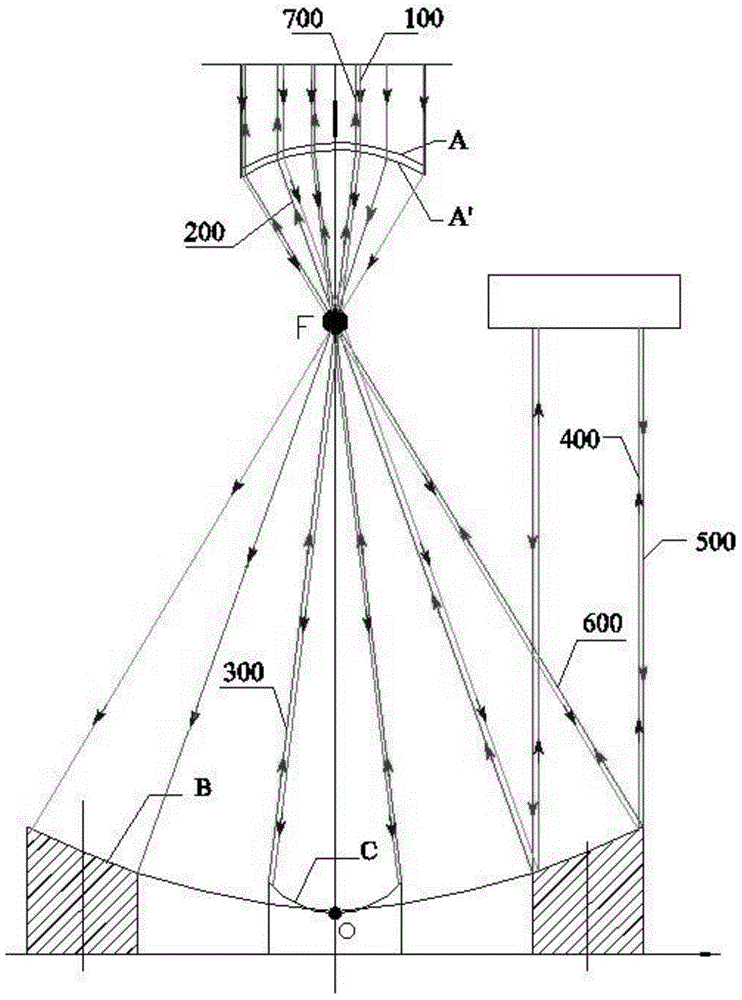
The invention relates to a device for detecting the wave front of a large-aperture optical system. The device comprises an interferometer, a five-dimensional adjustment platform, a numerical-control turntable, a numerical-control electric displacement platform, a self-collimation standard plane mirror, a two-dimensional adjustment rack and a computer control and data processing system. The device is characterized in that: the wave front of the large-aperture optical system is divided into a plurality of sub-aperture wave fronts, the interferometer and the self-collimation standard plane mirror detect the sub-aperture wave fronts of the large-aperture optical system, the numerical-control turntable and the numerical-control electric displacement platform control the standard plane mirror to move so as to scan the sub-aperture wave fronts, the interferometer detects and records the sub-aperture wave fronts, so that the detected sub-aperture wave fronts cover the whole large-aperture optical system; and the computer control and data processing system stitches the sub-aperture wave fronts through algorithms, so that the full-aperture wave front of the large-aperture optical system is obtained, and the detection on the wave front of the large-aperture optical system is finished. The device has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and capability of detecting the image quality of the wave front of a large-aperture optical system with the aperture of not less than 1000 mm.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large-caliber off-axis non-spherical measuring and calibration system
InactiveCN101858735AMake up for detection problemsAccurate measurementUsing optical meansGrinding machinesCamera lensOptical axis
The invention relates to a large-caliber off-axis non-spherical measuring and calibration system, which comprises an interference instrument, a standard lens, two plane concave lenses, a right-angle reflection prism, a standard plane reflection mirror and an off-axis non-sphere to be measured or calibrated. Standard parallel light which is transmitted from the interference instrument is focused on a focus point of the off-axis non-sphere to be measured or calibrated through the standard lenses, then the standard parallel light becomes parallel light after being reflected by the off-axis non-sphere and is reflected back along the original light path through the standard plane reflection mirror, finally the surface shape of the large-caliber off-axis non-sphere is analyzed and processed by image processing software of the interference instrument so as to complete the measurement of the large-caliber off-axis non-sphere. Narrow beam which is also transmitted from the center of the interference instrument enters the first plane concave lens along the direction of the main light axis, the narrow beam enters the right-angle reflection prism after being transmitted, the narrow beam deflects 90 degrees after being reflected by the right-angle reflection prism to enter the second plane concave lens, the narrow beam is finally emitted through the lowest point and the highest point of the off-axis non-sphere surface vector, and the standard plane reflection mirror is moved, so the beam is returned along the original path, the center of each element can be ensured to stay on the same height, and the geometric parameter measurement and calibration of the large-diameter off-axis non-sphere can be completed according to the known conditions.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
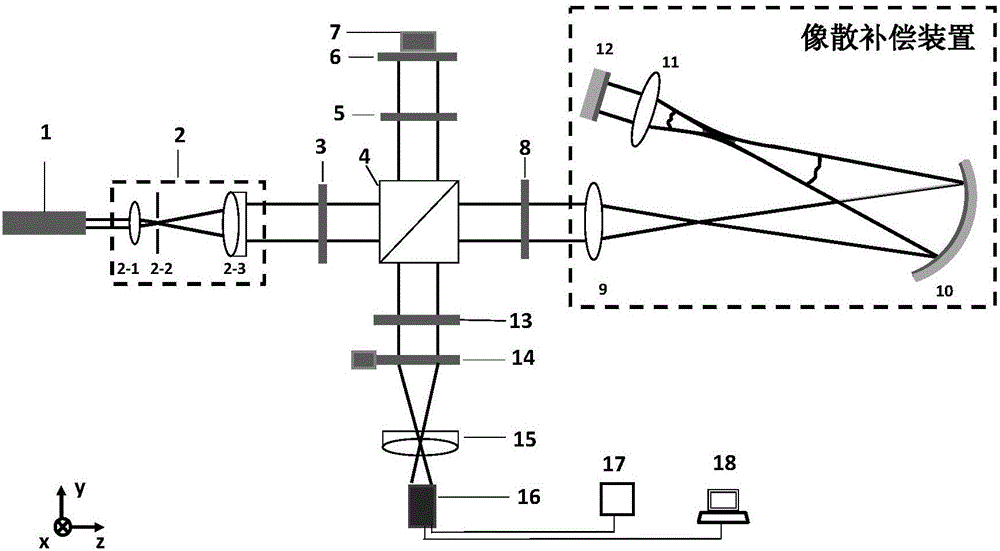
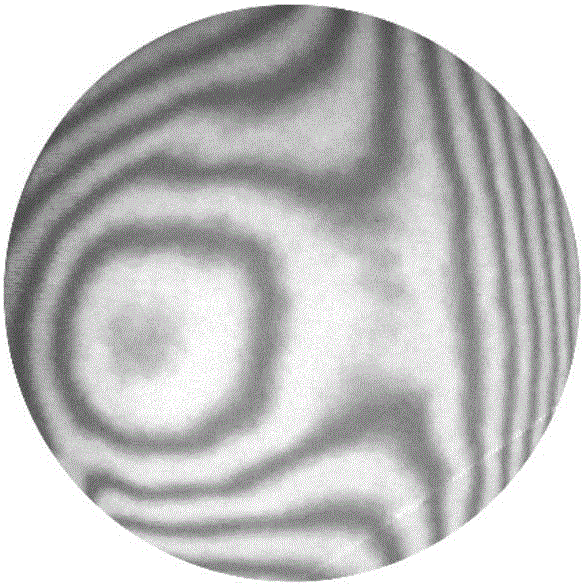
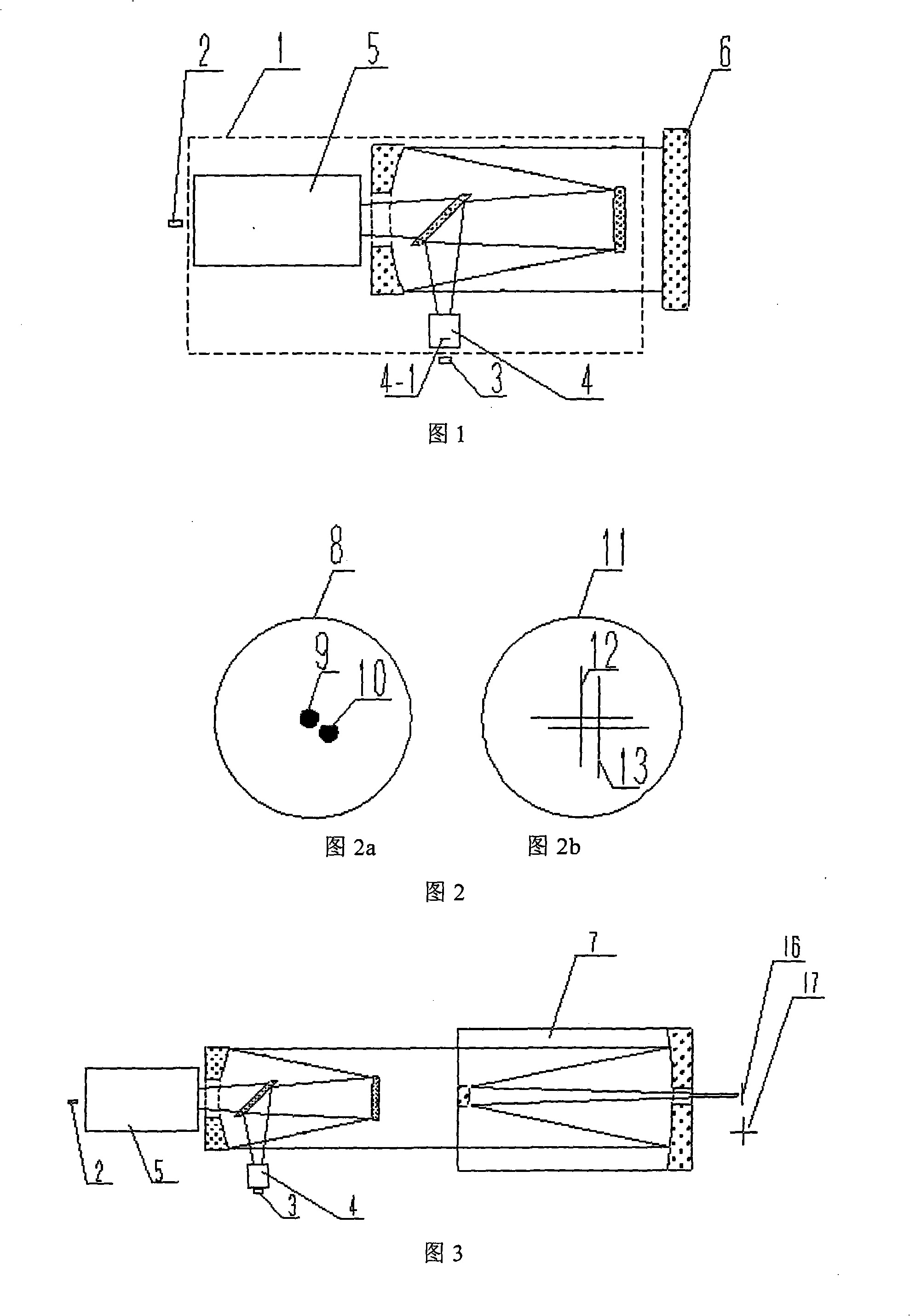
Astigmatic compensation type interference detecting device and method for optic free curved surfaces
The invention discloses an astigmatic compensation type interference detecting device and method for optic free curved surfaces. The device comprises He-He lasers, a beam expander, a 1 / 2 wave plate, a polarized beam splitter, a first 1 / 4 wave plate, a second 1 / 4 wave plate, a standard plane reflector, a phase shifter, a first convergent lens, a to-be-tested free curved surface, a second convergent lens, a plane reflector, a polarizer, a rotating frosted glass screen, an imaging objective lens, a detector, a displayer and a computer. The method comprises the steps of placing the to-be-tested free curved surface in an inclined state to make test beams come in a specific angle in an inclined mode to compensate for main surface shape astigmatic error components of the to-be-tested free curved surface, therefore reducing the degree of divergence of the subsequent test beams, and making the stripes discernable on the detector. The detector collects a series of phase-shifting interferograms which are treated with a wave front reconstruction algorithm to obtain a surface shape of the to-be-tested free curved surface. According to the astigmatic compensation type interference detecting device and method for optic free curved surfaces, the astigmatic compensation method is used for testing optic free curved surfaces for which the main surface shape error components are astigmatism, the stability is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Resetting and calibration of detector for visible and infrared composite light path light axis parallelism
InactiveCN101339013AImprove detection accuracyEasy to installUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesOptical axisStandard plane
The invention relates to a metnod for the assembling adjusting and standardization of a visible-infrared light compound optical path optical axis parallelism detector, which is characterized in that: placing a standard plane mirror on the back of the visible-infrared light compound optical path optical axis parallelism detector to roughly adjust the detector; placing a reflecting collimator and a high-temperature cross wire respectively on the back and the focal plane of the visible-infrared light compound optical path optical axis parallelism detector; electrifying the high-temperature cross wire to emit visible light wave and infrared light wave; adjusting the reflecting collimator to ensure the complete coincidence of the emitting visible cross wire image and the visible light image of the high-temperature cross wire on visible light CCD; adjusting the infrared part of the visible-infrared light compound optical path optical axis parallelism detector to ensure the completer coincidence of the infrared laser spot on infrared CCD and the infrared image of the high-temperature cross wire; standardizing the detector and calculating the optical axis parallelism difference between the visible light wave and the infrared light wave after the visible light and the infrared light gather in the same optical system with the help of software processing algorithm. The method has the advantages of convenient assembling adjustment and high precision.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
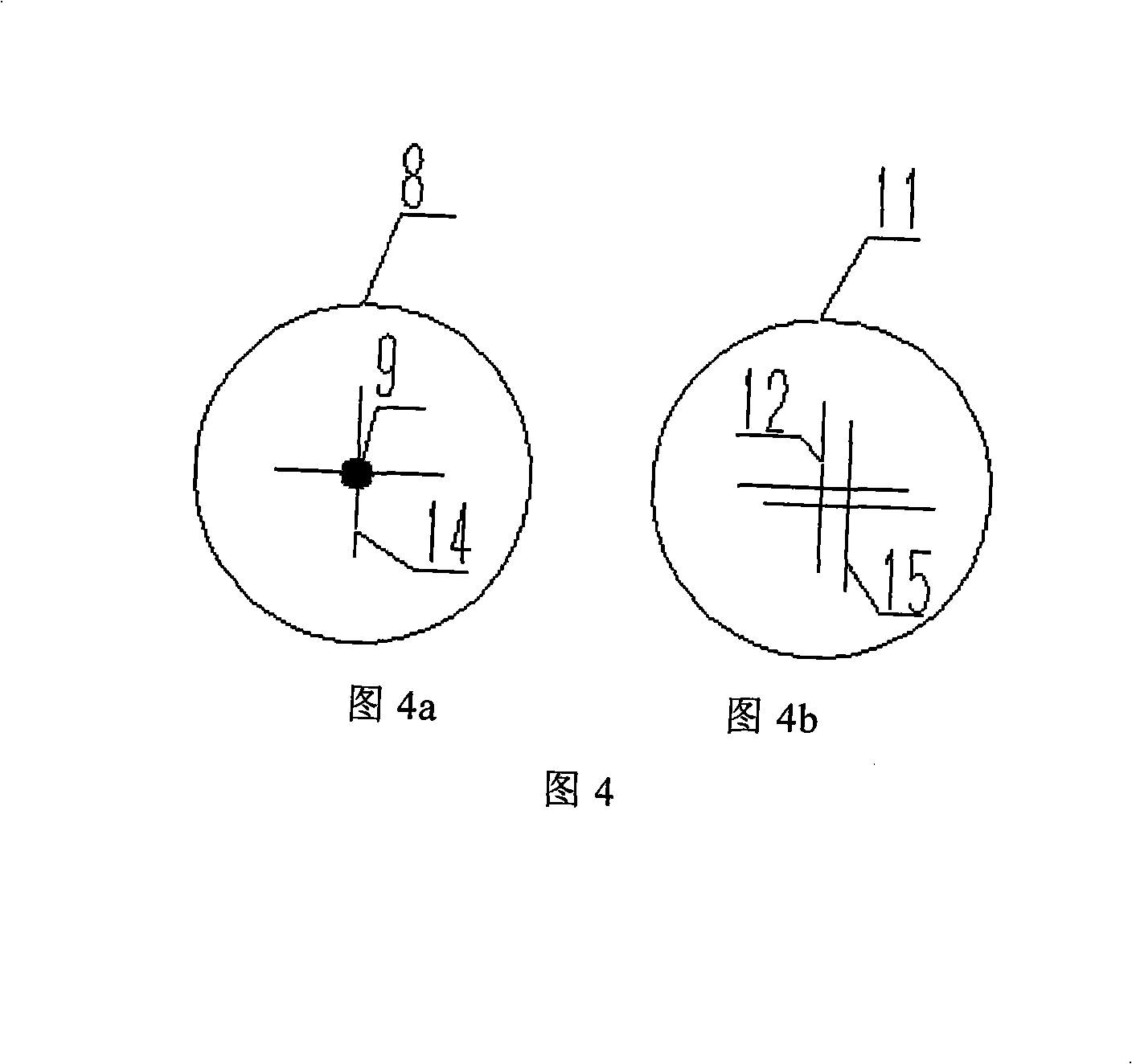
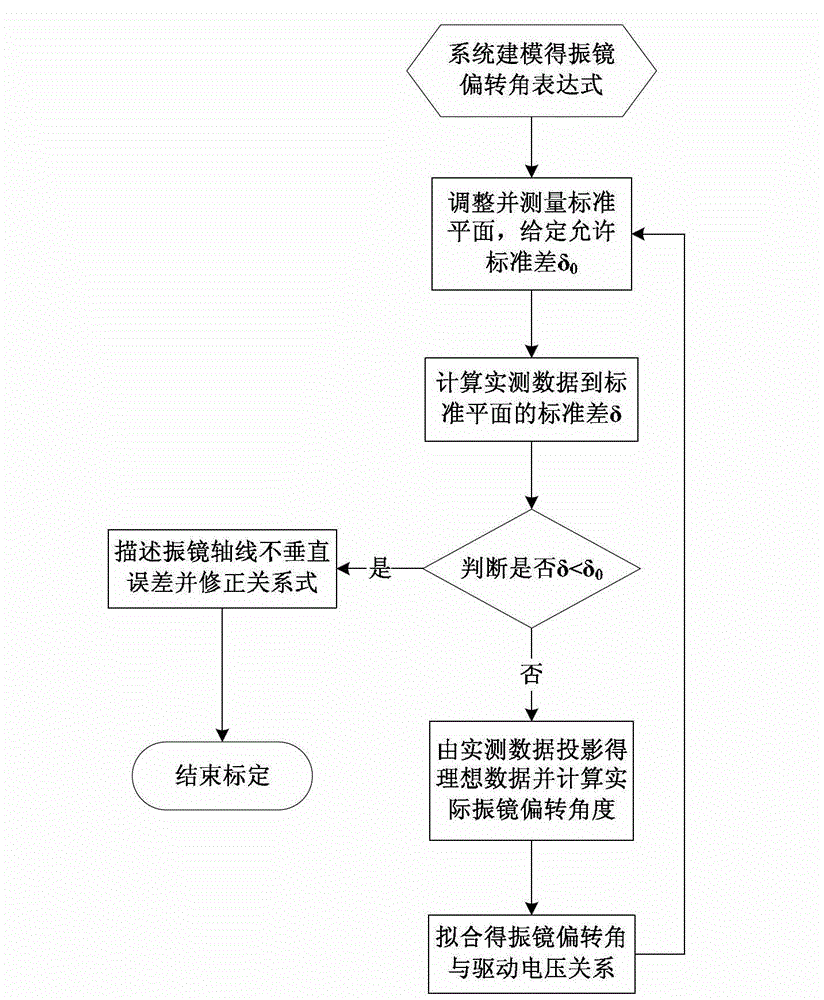
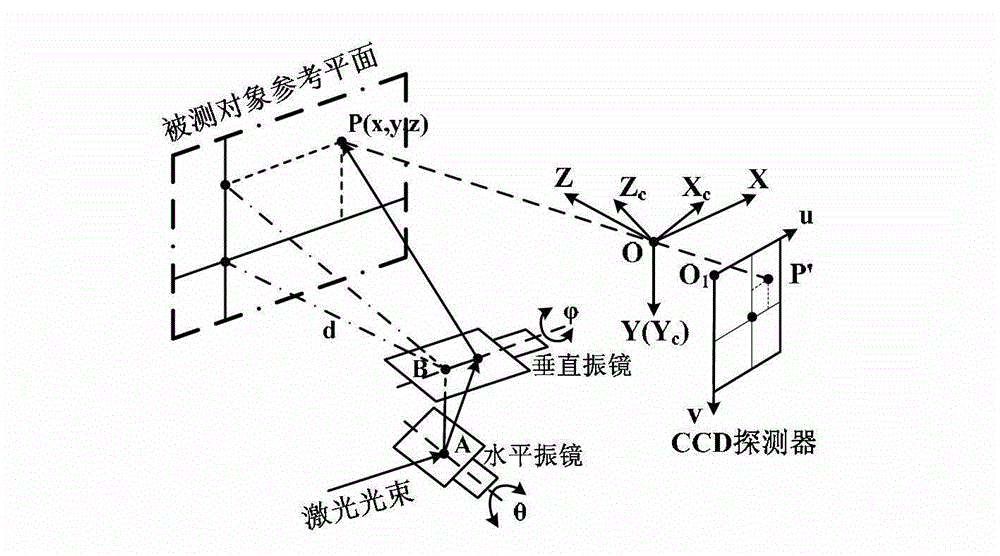
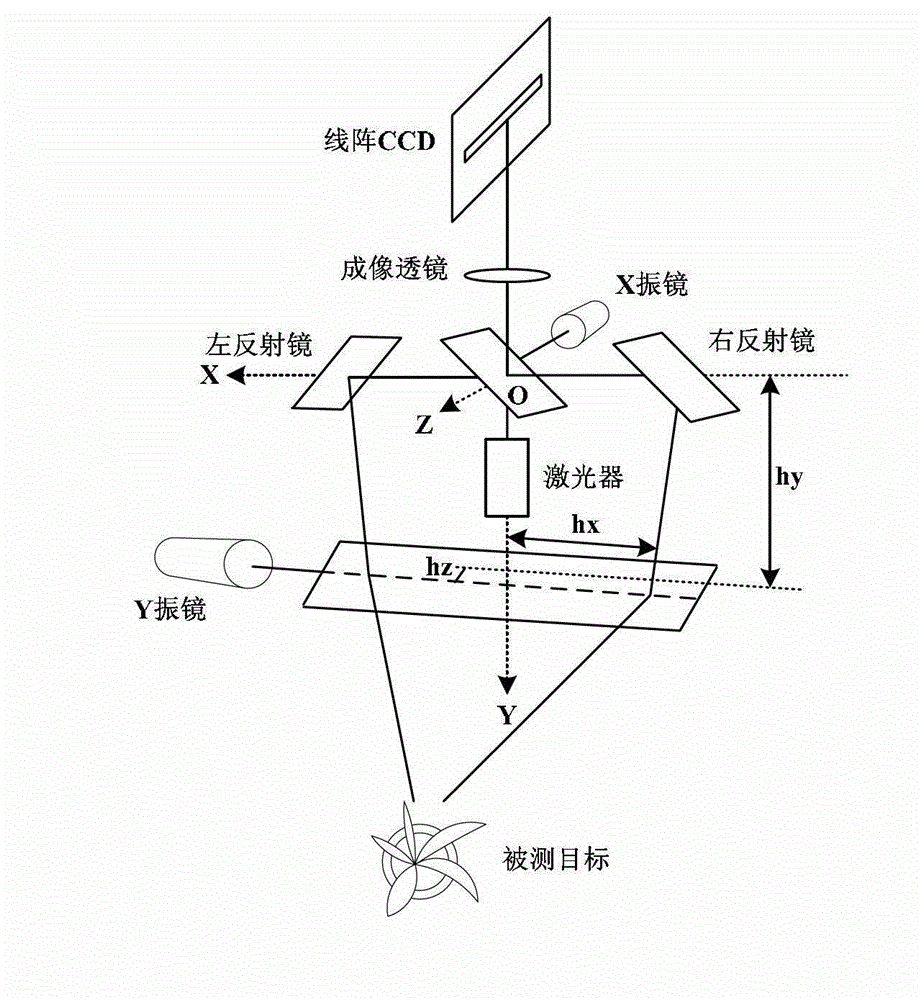
Calibration method of spot scanning galvanometer of three-dimensional measuring system
ActiveCN102941410AReduce the possibilityQuick calibrationUsing optical meansLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingStandard plane
The invention discloses a calibration method of spot scanning a galvanometer of a three-dimensional measuring system. The calibration method comprises seven major steps as follows: firstly performing system modeling, so as to obtain a galvanometer deflection angle expression, then adjusting a standard plane to be positioned in a known position and perpendicular to a system main direction, measuring the plane, projecting measured data to the standard plane, so as to obtain ideal data, utilizing the data to calculate a galvanometer deflection angle, matching a relational expression between the galvanometer deflection angle and driving voltage, and measuring the standard plane again through the relational expression, and repeating the process till the standard deviation from the measured data to the standard plane is smaller than a set value, so as to obtain an accurate relational expression between the galvanometer deflection angle and the corresponding driving voltage, establishing the interactional relation between two galvanometers, describing the non-perpendicularity error of axes of the two galvanometers, and correcting the relational expression, so as to improve the calibration accuracy. The calibration method has higher practical value in the technical field of optical three-dimensional measurement and laser processing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
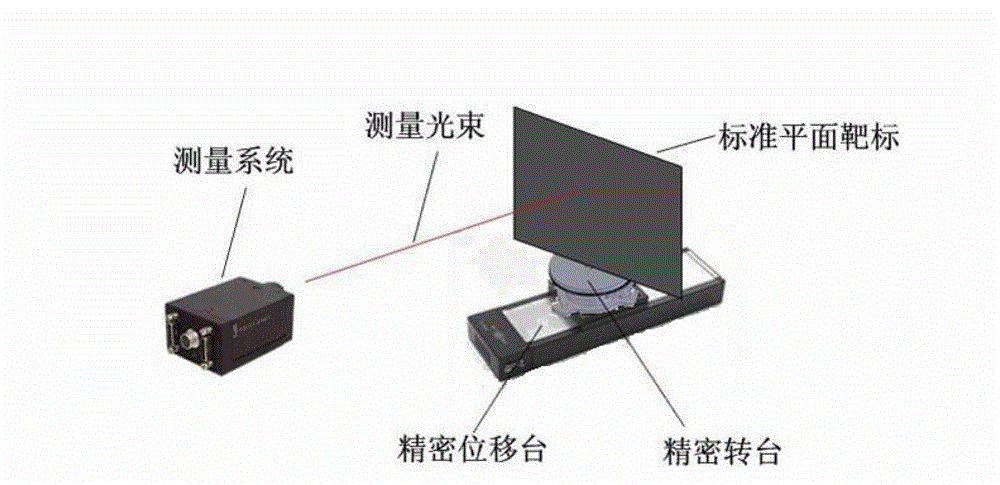
Calibration method of spot scanning three-dimensional topography measuring system
The invention discloses a calibration method of spot scanning a three-dimensional topography measuring system. The calibration method comprises three major steps as follows: firstly establishing a measuring system model and determining parameters to be calibrated, then taking a precise displacement platform, a precise rotating platform and a standard plane target as calibration devices, adjusting positions and postures of the calibration devices, so as to meet calibration requirements, driving the standard plane target to move and rotate through the precise displacement platform and the precise rotating platform, so as to obtain calibration data in all directions, and finally, solving the parameters to be calibrated through a method of maximum likelihood estimation, determining a system model, and realizing accurate calibration of the system. The calibration method has higher practical value and wide application prospect in the field of photoelectric measurement.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
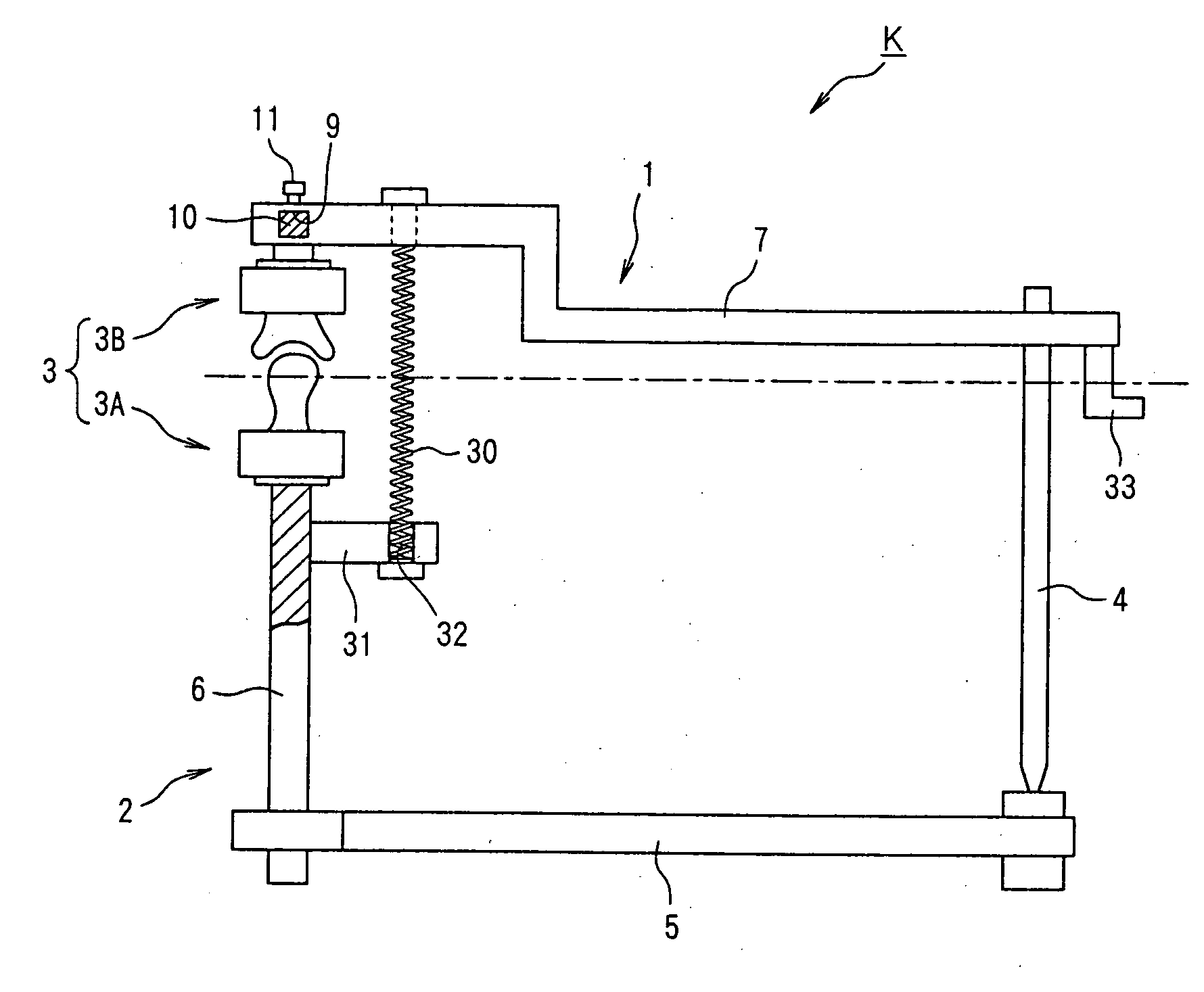
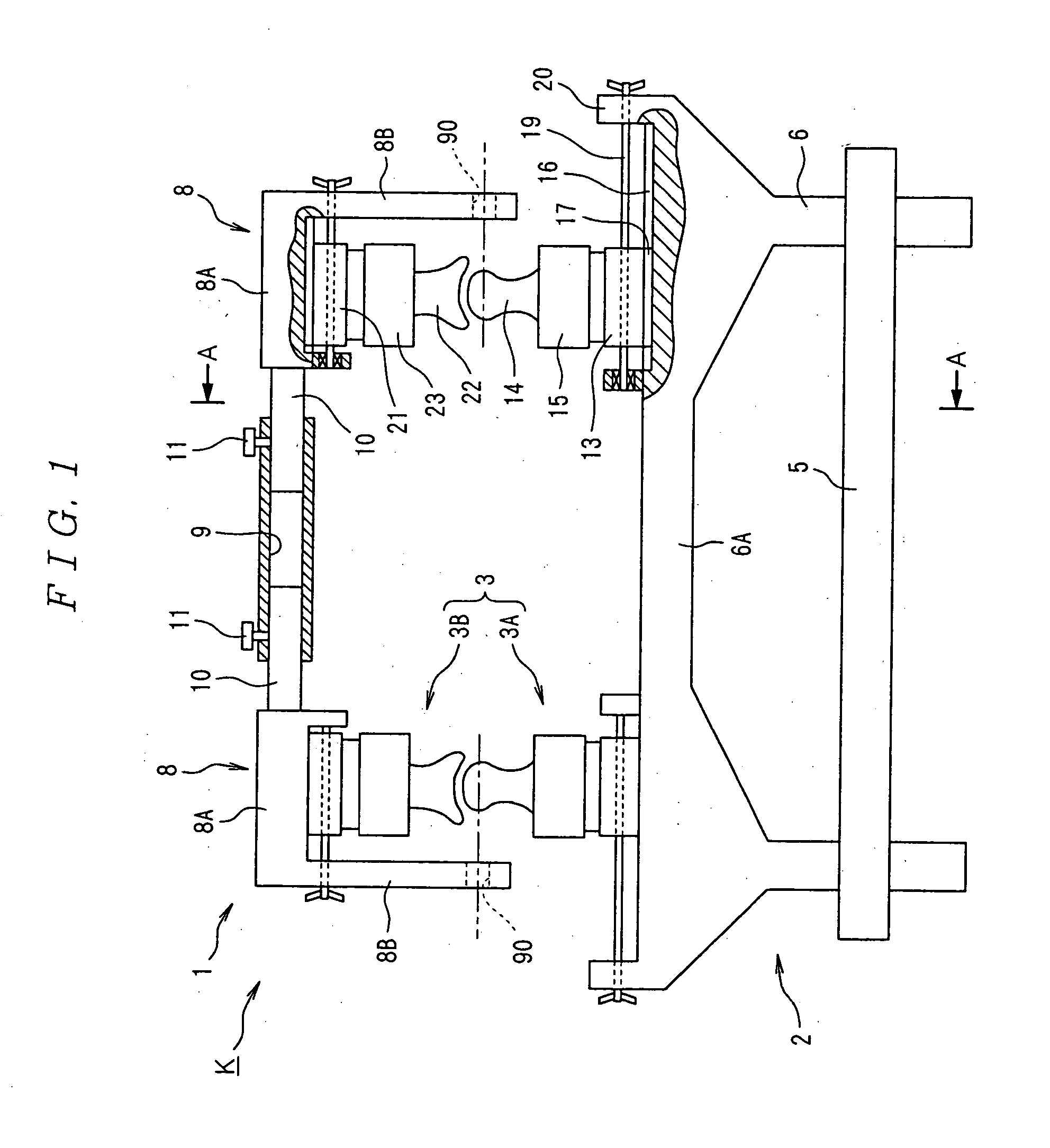
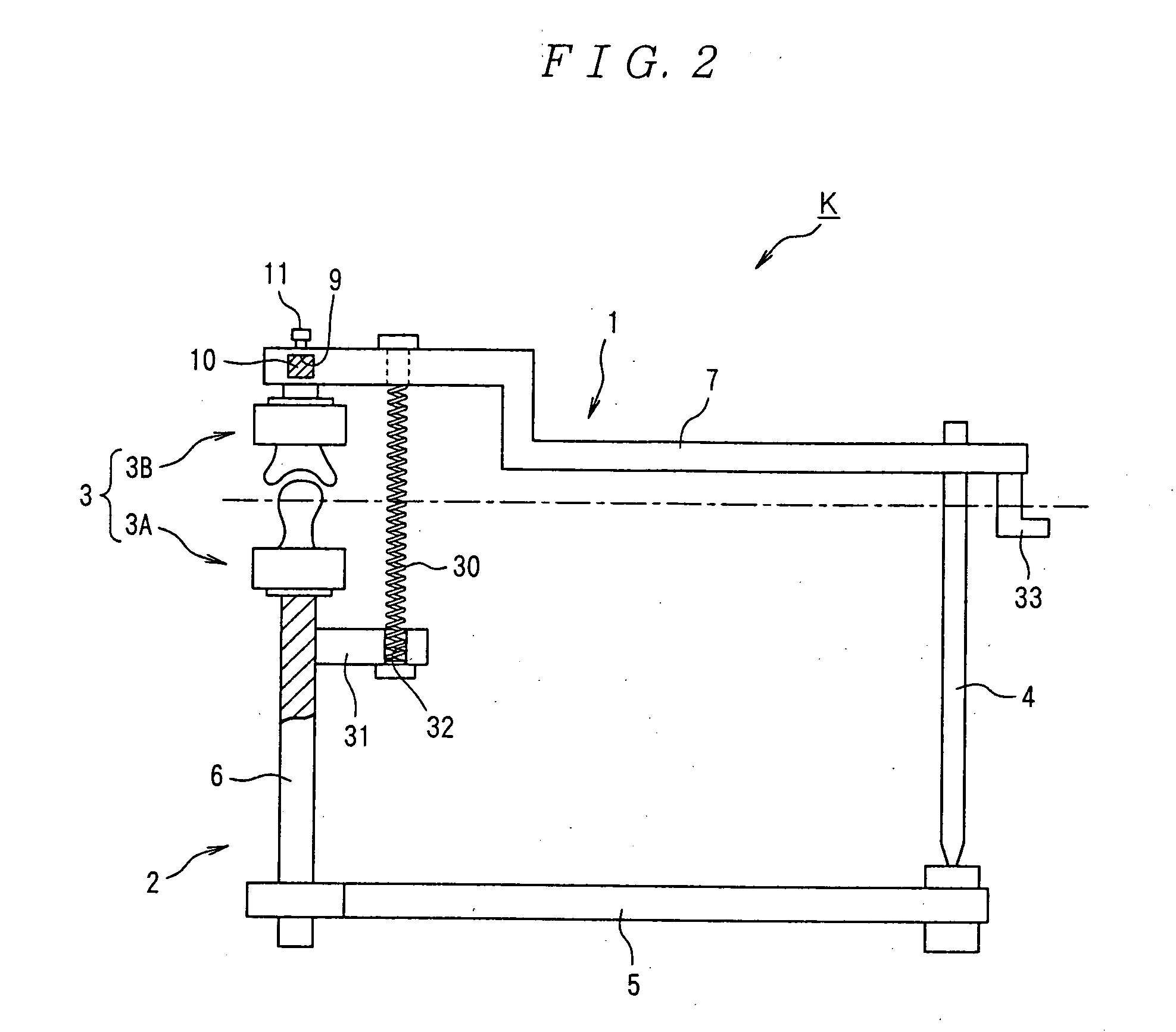
Occludator, face bow, occlusion-confirming system and temporomandibular joint-reproducing system
InactiveUS20050277086A1Easy to moveAdditive manufacturing apparatusDental articulators3d imageStandard plane
It is intended to provide an occludator whereby joint movements at occlusion being similar to the actual tempromandibular joint movements of an individual patient or ideal movements can be reproduced, and a face bow to be used for the occludator. To achieve this object, an occlusion plane against a standard plane is accurately drawn by using the above face bow F whereby the occlusion plane can be drawn at a high accuracy. A solid model of the tempromandibular joint similar to the tempromandibular joint form of an actual patient is used as the joint unit of the occludator K, while the positional relationship in the body at occlusion is three-dimensionally reproduced in the occludator I with the use of the above-described face bow F. It is also intended to provide an occlusion-confirming system and a tempromandibular joint-reproducing system with the use of an occludator whereby joint movements at occlusion being similar to the actual tempromandibular joint movements of an individual patient or ideal movements can be reproduced. To achieve this object, the tempromandibular joint of the body is photographed with a local X-ray CT device to give three-dimensional image data and then a solid model of the tempromandibular joint is constructed based on the three-dimensional image data. This solid model is employed as the joint unit of the occludator K and the positional relationship in the body at occlusion is three-dimensionally reproduced.
Owner:NIHON UNIVERSITY
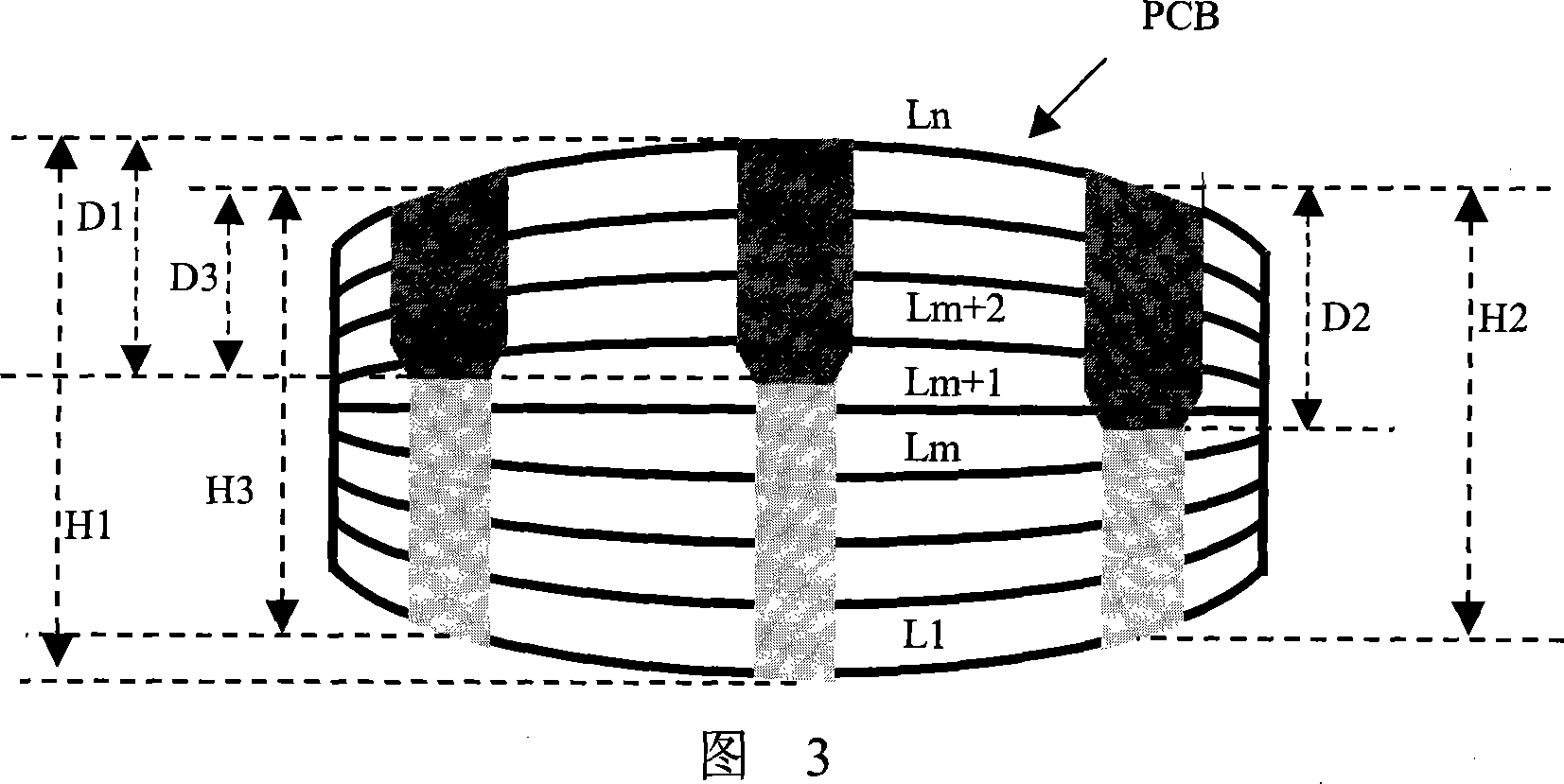
Method for deep drilling print circuit board
ActiveCN101094562AHigh control precisionEffects of reduced precisionConductive material mechanical removalStandard planeEngineering
The method comprises: setting the plane contacting with the PCB as a standard plane; recording the actual location height Hn of each point on PCB, and saving it into the storage software of the machine; selecting a target layer, setting a standard drilling depth D1 and standard plate thickness H1; the drilling depths of other points are Dn=D1*Hn / H1+ compensation value; according to the drilling depth Dn of each points, re-setting the parameters in the drilling program, and renewing each parameter in the storage software in machine; finally, according to Dn value, modifying the program-controlled instruction.
Owner:WUS PRINTED CIRCUIT (KUNSHAN) CO LTD
Surveymeter for parallelism of optical axis of visible and infrared light wave
InactiveCN101446485AReduce experimental riskHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesOptical axisStandard plane
The invention relates to a surveymeter for parallelism of optical axis of visible and infrared light wave, comprising an infrared light part and a visible light part. Firstly, aiming is operated by employing visible light, the visible light emitted by a visible light source lightens up a cross wire by a cross-linegraticule, an emergent visible cross wire image is formed on a visible light CCD, after being reflexed by an infrared beam splitter, a secondary mirror, a primary mirror and a standard flat mirror, the emergent visible light returns to the visible light CCD by the optical devices and forms a return cross wire image, and a system is adjusted to superpose the emergent visible cross wire image and the return cross wire image, thereby completing instrument aiming. Then infrared light is employed for detecting, iraser emitted by an infrared laser passes through a series of optical elements of the infrared light part, and an emergent infrared spot and a return infrared spot on an infrared CCD are extracted by measurement software. Error value of the parallelism can be obtained by formula computing. The surveymeter of the invention adopts the visible light to aim and the infrared light to detect the parallelism error, thereby reducing experiment risk while improving measurement precision.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting large-caliber large-relative-aperture parabolic reflector surface shape error
ActiveCN103575233AIncrease horizontal resolutionLower requirementUsing optical meansOptical axisStandard plane
The invention relates to a method for detecting a large-caliber large-relative-aperture parabolic reflector surface shape error. An existing method is high in cost and low in accuracy and efficiency. The method includes the steps of selecting a transmission standard lens, adjusting the position of a laser wave surface interferometer, adjusting a focus of a tested parabolic reflector to be coincided with a focus of the laser wave surface interferometer, adjusting the optical axis of the tested parabolic reflector to enable the optical axis of the tested parabolic reflector and the optical axis of the laser wave surface interferometer to be coaxial, adjusting a standard plane reflector, rotating the laser wave surface interferometer to enable the laser wave surface interferometer to be aligned with a first annular sub-aperture A, and repeating the sixth step and the seventh step according to a sub-aperture division scheme. The method for detecting the large-caliber large-relative-aperture parabolic reflector surface shape error is low in cost and high in accuracy and efficiency.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Flatness and inclination optical measurement method
InactiveCN106248005AReduce the difficulty of measurementLow costUsing optical meansClassical mechanicsStandard plane
The invention discloses a method for measuring approximate plane flatness and inclination by using optical technology. First artificially define a standard plane that is close to the actual measured plane, and place a planar laser generator at a certain distance from the standard plane, so that there is a non-90° angle between the laser plane and the standard mathematical plane, then There will be a linear area illuminated by the laser on the measured surface. According to the difference between the projection of the area and the intersection line between the laser plane and the standard mathematical plane on the measured surface, the corresponding position relative to the The bump gap value for the standard plane. Take pictures of the measured surface irradiated by the laser through a digital camera, collect the data of these deviations, use a computer to analyze and calculate, and obtain the overall flatness data of the measured plane and the inclination relative to the standard plane. The invention provides a convenient, accurate, fast and low equipment cost method for measuring the flatness and inclination of various approximate planes.
Owner:欧阳一平
Sub-aperture stitching-based high-accuracy planar optical element face type detection method
The invention relates to a sub-aperture stitching-based high-accuracy planar optical element face type detection method. A detection device comprises a two-dimensional translation table, an interferometer and a standard planar lens. The method specifically comprises the following steps: fixing a planar optical element on the two-dimensional translation table and arranging the interferometer aiming at the position of the planar optical element; adjusting the two-dimensional translation table to reach a specified target distribution region to align an exit pupil of the interferometer with a geometric central part of the planar optical element; sampling, measuring and calculating the geometric central part by the interferometer to obtain sub-aperture face type information; and repeating the steps until the measurement of all sub-apertures is finished, thereby realizing sub-aperture measurement of the planar optical element. According to the method, the complete face type of the measured planar element is restored through a certain stitching algorithm aiming at the characteristic of higher planarity of the face type of the high-accuracy planar optical element, and an economic and effective detection method is provided for checking the face type of the high-accuracy planar optical element.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
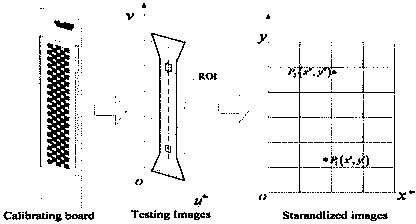
Tensile sample deformation measurement method based on digital image correlation
InactiveCN103913375AAvoid markingFast measurement speedUsing optical meansStrength propertiesPhase correlationTest sample
The invention provides a tensile sample deformation measurement method based on digital image correlation. The tensile sample deformation measurement method mainly applies an image correlation method and combines a measurement method based on a standard surface to realize high-speed and high-precision measurement of a test sample. The tensile sample deformation measurement method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out integer pixel positioning based on the image correlation; 2, carrying out sub pixel positioning based on two-dimension curved surface fitting; and 3, carrying out image mapping positioning based on the standard surface. The three steps are organically combined to form a main body of the whole method. The tensile sample deformation measurement method has the beneficial effects that a standard plane mapping method is combined by adopting a simplified digital image correlation method so that the test sample is prevented from being marked; an operation flow is simplified, the measurement speed and the precision of the deformation of the test sample are improved, and the practicability of the system is improved.
Owner:JINAN SHIDAI SHIJIN TESTING MACHINE GRP
Detection device and detection method of off-axis parabolic mirror surface shape precision
ActiveCN105115444AAccurate measurementLarge measuring rangeUsing optical meansPlane mirrorStandard plane
The invention relates to a detection device of off-axis parabolic mirror surface shape precision. The detection device is composed of a Fizeau interferometer, a standard spherical mirror, an auxiliary concave spherical column, a base disc, a five-dimensional adjusting frame, a standard plane mirror, a two-dimensional adjusting frame, a supporting fixing bottom plate, a first base and a second base; the Fizeau interferometer is provided with the standard spherical mirror; the standard spherical mirror is a light beam output window of the Fizeau interferometer; the base disc is located below the Fizeau interferometer; the base disc is provided with an off-axis parabolic mirror to be detected and the auxiliary concave spherical column; the base disc is located at the top surface of the five-dimensional adjusting frame; the standard plane mirror is arranged at the bottom surface of the two-dimensional adjusting frame; and the two-dimensional adjusting frame is located above the off-axis parabolic mirror to be detected. With the detection device of the off-axis parabolic mirror surface shape precision of the invention adopted, the surface shape precision of the off-axis parabolic mirror can be accurately and quickly detected.
Owner:SHANGHAI MODERN ADVANCED ULTRA PRECISION MFG CENT
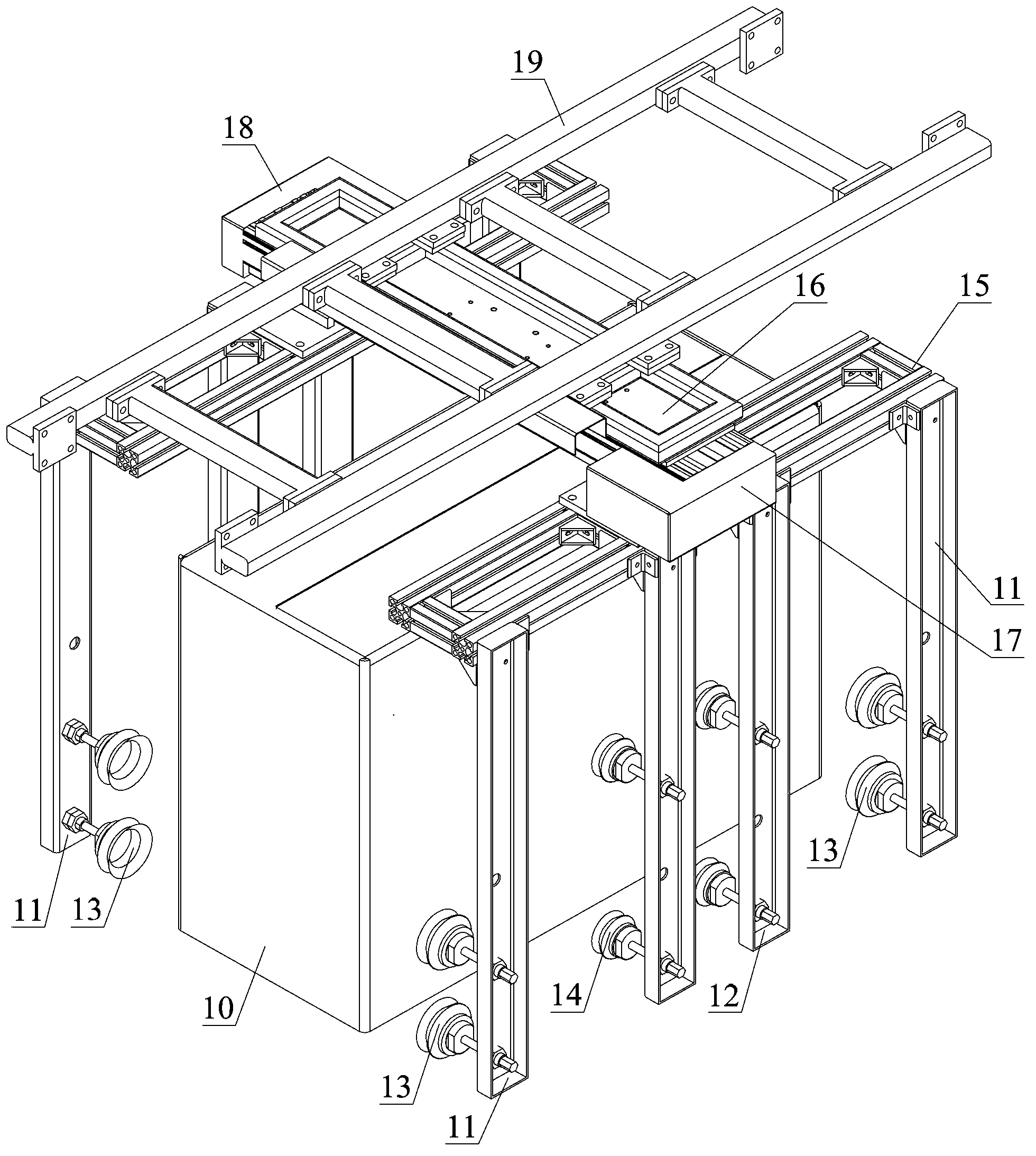
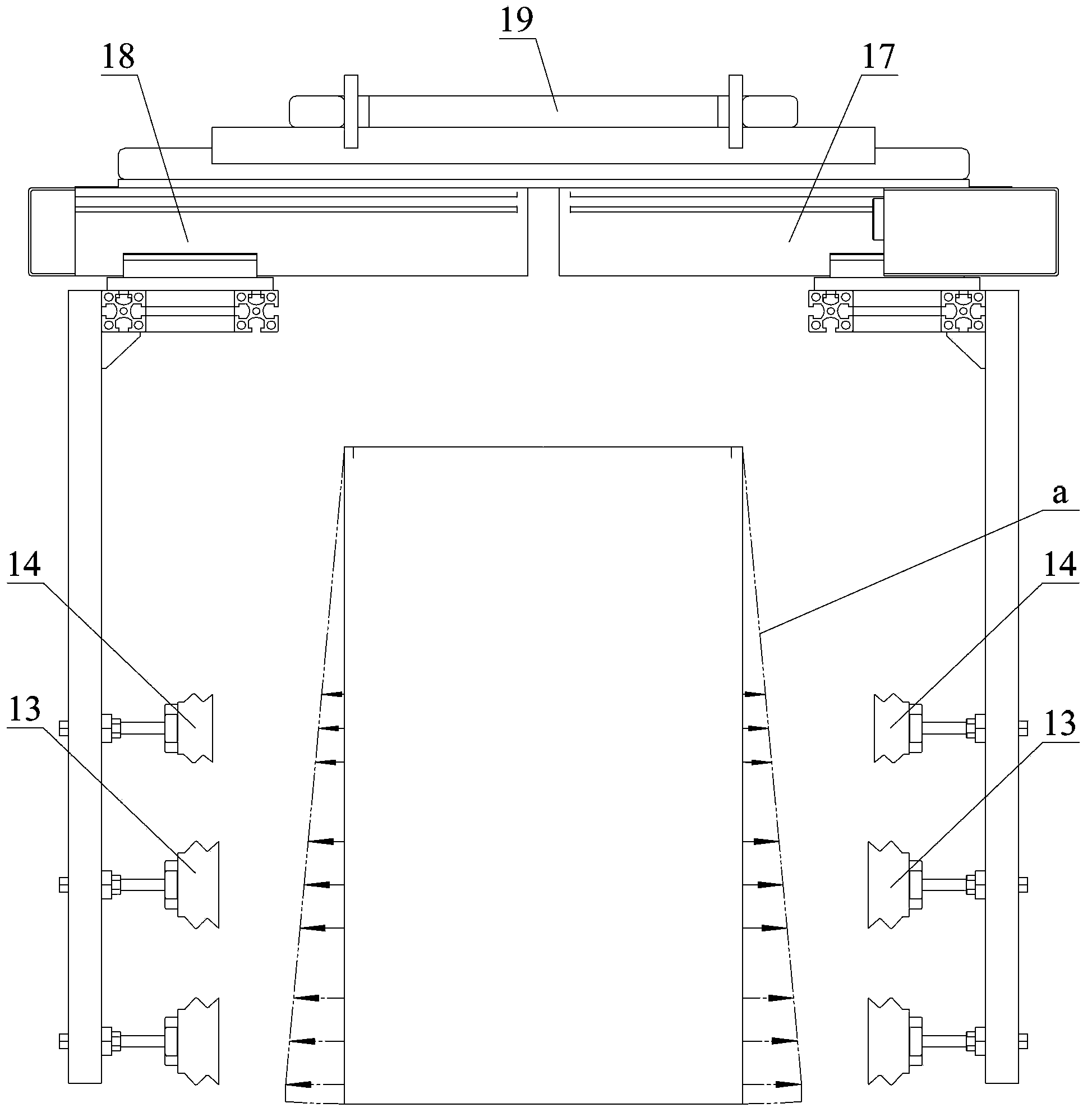
Packaging box automatic box sleeving device and electric appliance packaging production line
ActiveCN104210705AImprove nesting efficiencyAlleviates the need to adjust boxes to keep nesting operations running smoothlyPackagingProduction lineStandard plane
The invention discloses a packaging box automatic box sleeving device which comprises an imbibition box mechanism. The imbibition box mechanism comprises a sucking jaw group formed by at least two sucking jaws placed on the same side. The sucking jaw group comprises a packaging box end sucking jaw (11) provided with an end sucking disc (13) and a packaging box middle sucking jaw (12) provided with a middle sucking disc (14). The distance between the working face of the end sucking disc (13) and the standard plane of a surface to be adsorbed of a packaging box is smaller than the distance between the working face of the middle sucking disc (14) and the standard plane. The sucking jaw group has a box expanding stroke far away from the standard plane. When the packaging box has an effect on an electric appliance under the effect of the packaging box automatic box sleeving box, the packaging box cannot interfere with the electric appliance easily, then the situation that an operator needs to adjust the packaging box to guarantee the fact that box sleeving operation is carried out smoothly is relieved, and accordingly the box sleeving efficiency of the electric appliance is improved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
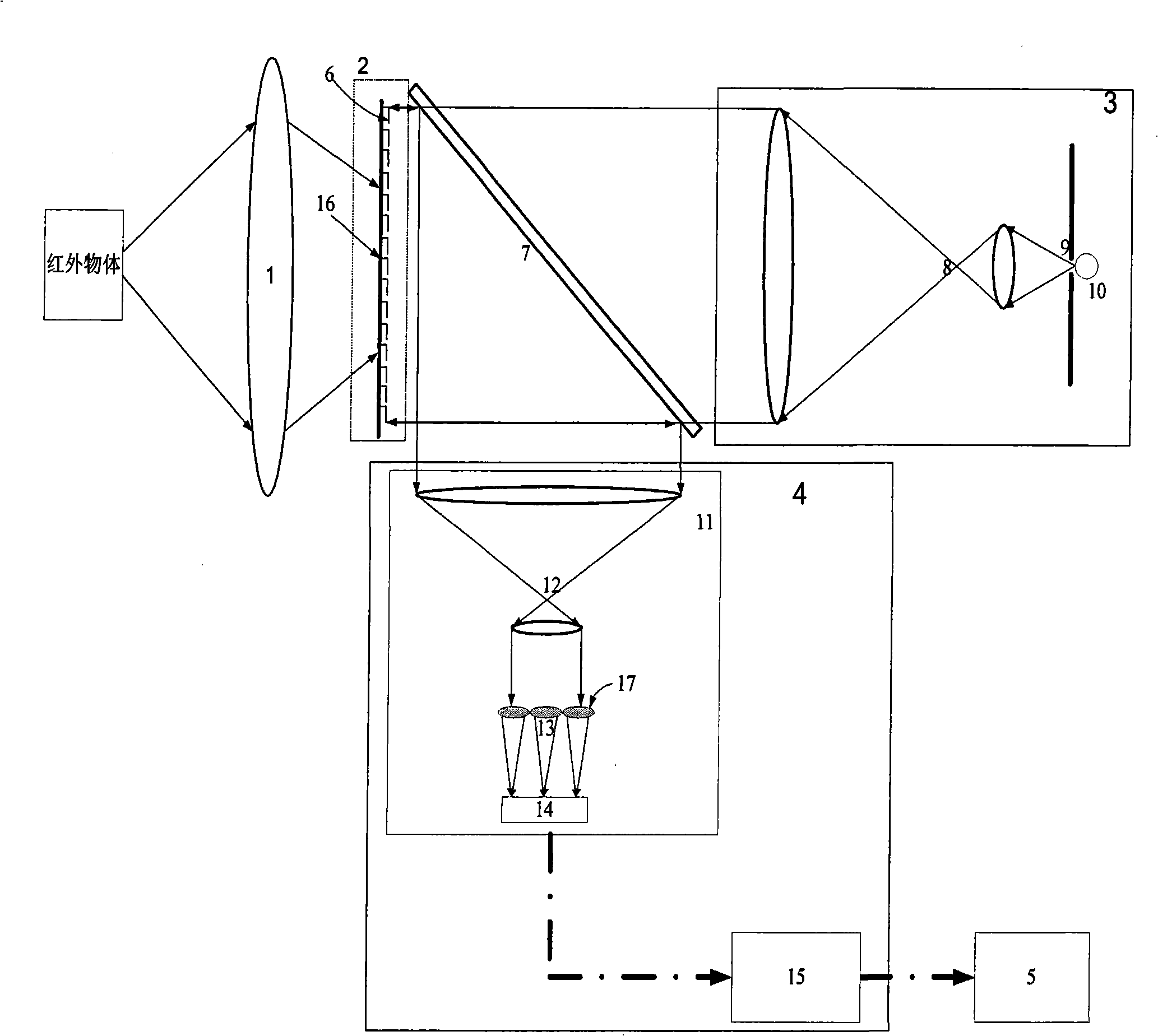
Opto-mechanics infrared imager based on hartmann wavefront sensor
InactiveCN101285709AHigh sensitivityIncrease frame rateOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryHigh frame rateWavefront sensor
The invention relates to a photodynamic infrared imaging instrument based on a Hartmann wavefront sensor. The invention comprises an infrared imaging system, a focal plane array, a cold light source system, an optical readout system and an IR image restorator; an infrared object images on the focal plane array by the infrared imaging system; infrared thermal radiation gets an FPA unit in the focal plane array to produce slight deformation, then standard plane waves emitted by the cold light source system irradiate on the FPA unit by a spectroscope and are reflected in order that the wavefront information with a slight surface-shape change can enter the optical readout system by the spectroscope; wavefront detection is carried out on the wavefront information by the Hartmann wavefront sensor of the optical readout system, then the thermotropic corner information of each FPA unit is extracted from the wavefront information detected by the optical readout system and reconstructed to an infrared image of a detected object by the IR image restorator according to relative algorithm. The photodynamic infrared imaging instrument utilizes the Hartmann wavefront sensor, has the advantages of detecting wavefront signals in high precision and high frame rate and improves the sensitivity of the photodynamic infrared imaging instrument, thereby acquiring the infrared image with better quality.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Micro-impulse measuring method based on multi-beam laser heterodyne second harmonic method and torsion pendulum method
InactiveCN102322997AImprove collection effectFast operationApparatus for force/torque/work measurementLinearityMeasurement precision
The invention relates to a micro-impulse measuring method, in particular to a micro-impulse measuring method based on a multi-beam laser heterodyne second harmonic method and a torsion pendulum method. The micro-impulse measuring method solves the problem of low measurement accuracy caused by poor laser difference frequency signal acquisition effect and low signal processing speed when the existing method of using multi-beam laser heterodyne to measure micro-impulses is adopted. By using the multi-beam laser heterodyne second harmonic method in the micro-impulse measuring method, the measurement of the micro-impulses is converted into the measurement of the swinging angle of a torsion pendulum, the information of the swinging angle to be measured can be obtained indirectly through the measurement of the thickness of a standard plane mirror, the measurement accuracy is effectively improved, the measured impulses are in a linear relation with the incident angles when a rotating angle issmaller than 5 degrees, the measurement error is smaller than 0.5 percent, the requirement on the measurement of the impulse of a laser micro-thruster can be satisfied, and a very good measurement means for evaluating the performance of the laser micro-thruster is provided.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for quickly measuring object surface steps through spectrum confocal line scanning
ActiveCN109781015AQuick measurementAchieving height measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansFast measurementDiffusion function
The invention discloses a method for rapidly measuring object surface steps through spectrum confocal line scanning. The method comprises: a spectrum confocal line scanning device is built; a standardplane mirror is detected, the position of the standard plane mirror is moved in the axial direction, meanwhile, the coordinate position of the standard plane mirror is monitored, and the dispersion focusing range of a chromatic dispersion focusing element and the wavelength-position relation curve of the spectrum confocal line scanning device are calibrated; the standard plane mirror is replacedwith a sample for detection, and the surface of the sample is placed in a dispersion focusing range of the chromatic dispersion focusing element; an intensity point spread function of a return signalof a spectrograph is analyzed, a peak coordinate position is calculated by using a centroid method to obtain a return signal wavelength, and according to the wavelength-position relation curve, the maximum height difference of the surface of the sample is decoded, and the steps of the surface of the sample are rapidly calculated. The method has the beneficial effects that the structure is simple,the measurement speed is high, precision is high, the application range is wide, and the method is suitable for precise measurement of transparent or opaque steps, grooves, inclined surfaces and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Fabrication method of cylindrical gratings
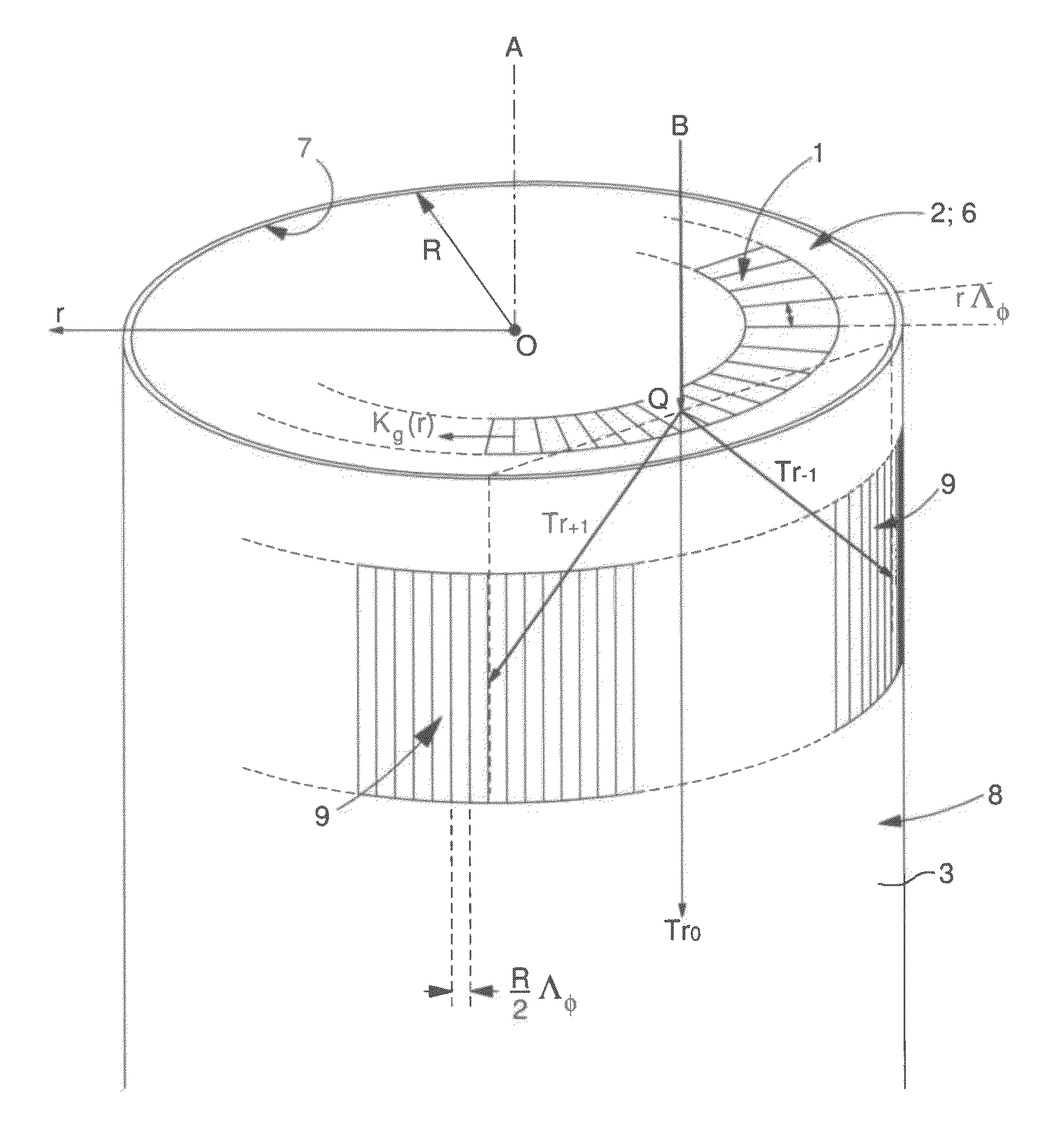
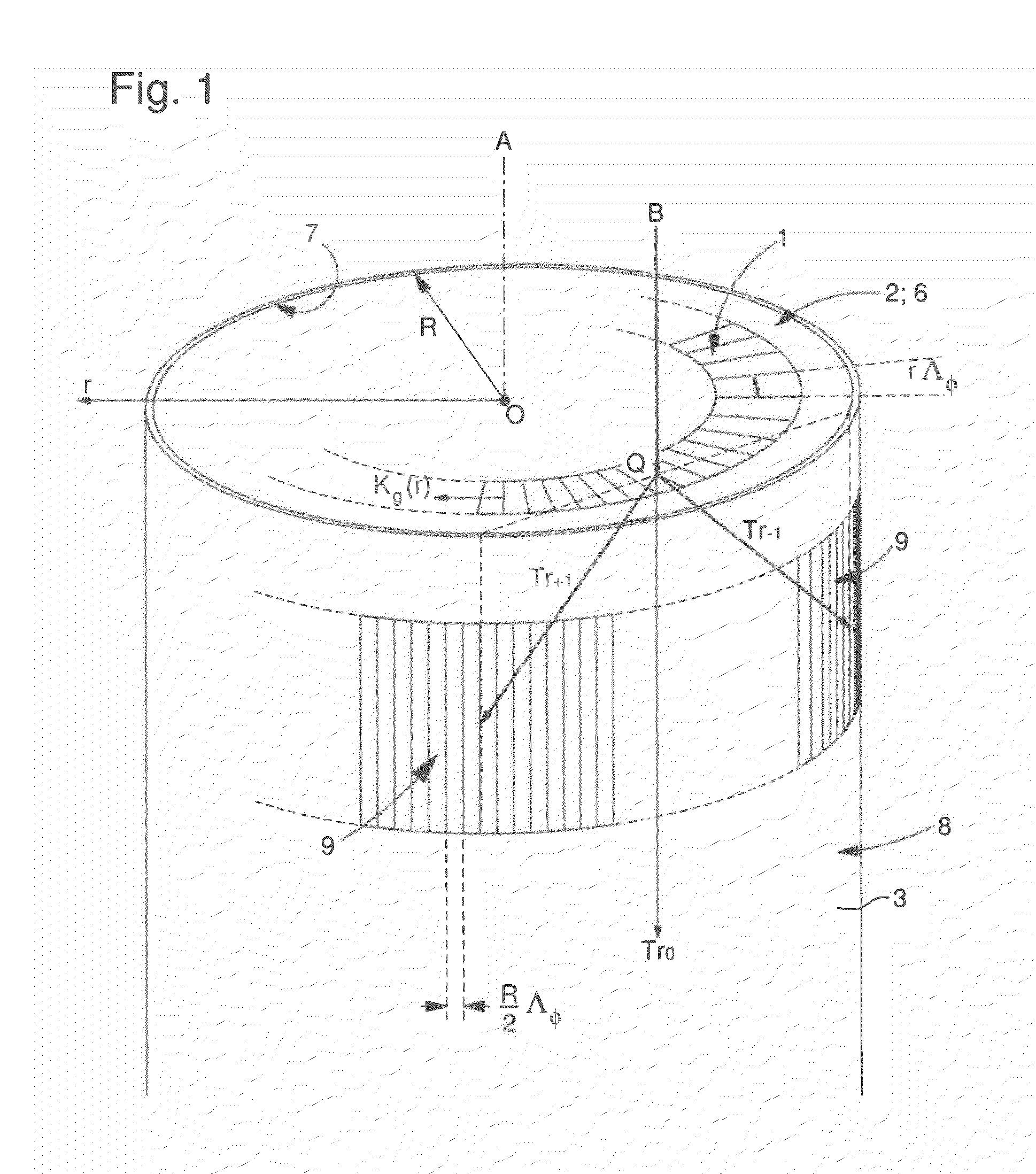
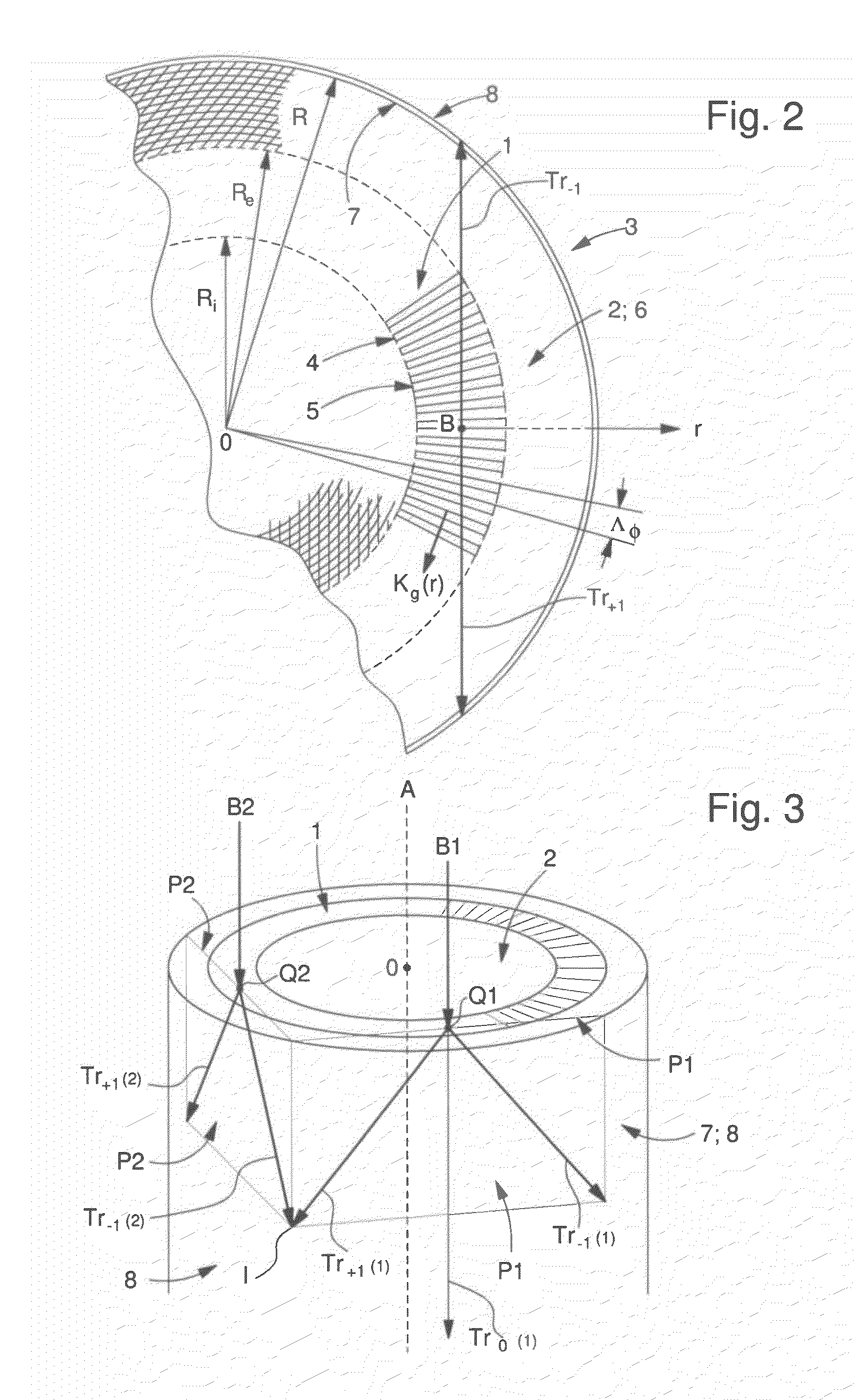
ActiveUS20130052592A1Easy to writeSimplifies mask fabricationOptical articlesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDiffraction orderLight beam
A phase mask method to geometrically transform and to optically transfer a standard planar radial grating pattern into a cylindrical photoresist pattern at the circularly cylindrical wall of a given element. The planar radial grating pattern can be written with an integer number of lines having strictly constant period without any stitching problem. The photolithographic transfer is made by an illumination device providing a normal incident beam on the phase mask. The annular radial grating diffracts this normal incident beam, formed by plane waves, into two cylindrical waves of the first diffraction order (Tr+1 and Tr−1)) which impinge on the circularly cylindrical wall and interfere in a photoresist layer deposited on the circularly cylindrical wall to give rise to an interferogram.
Owner:SICK AG
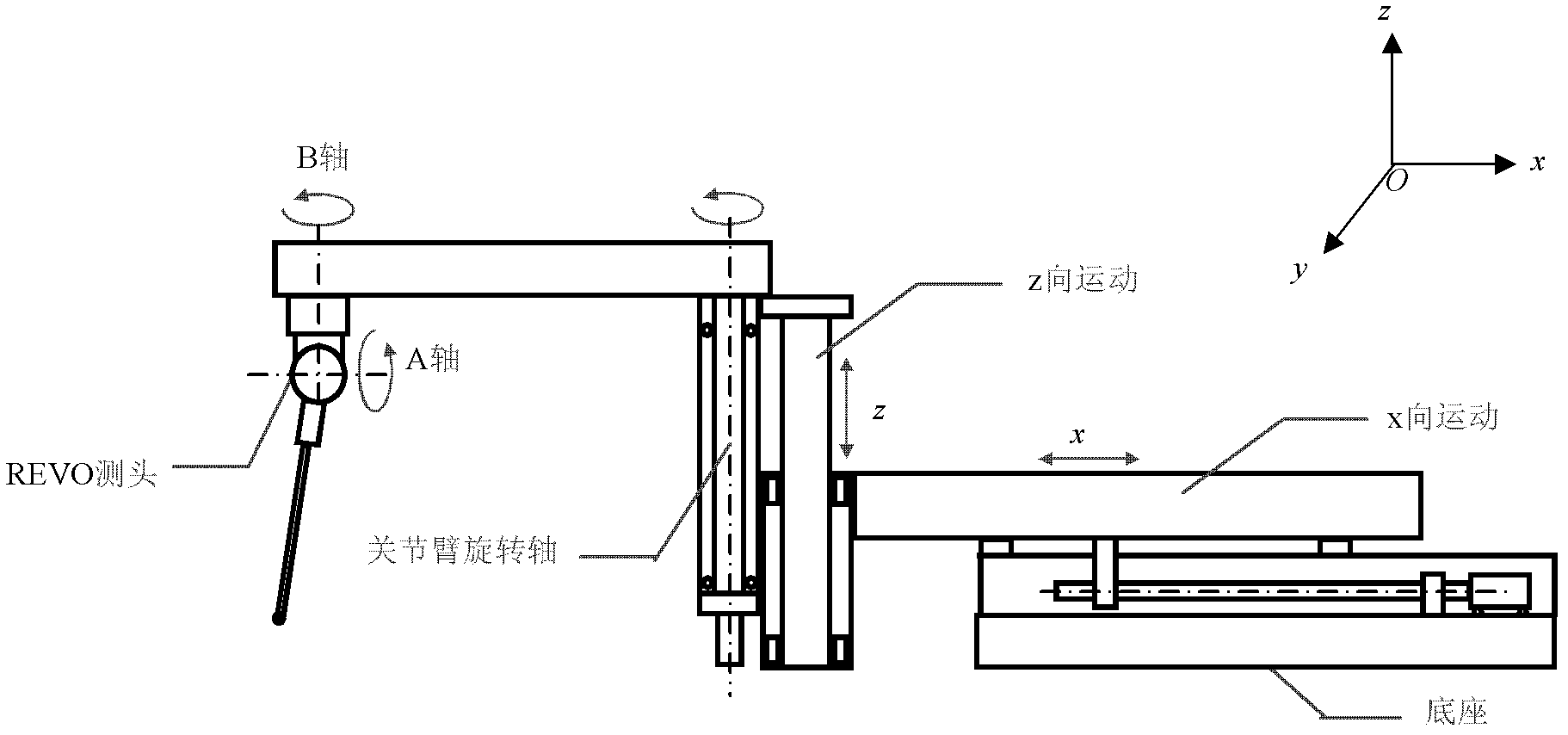
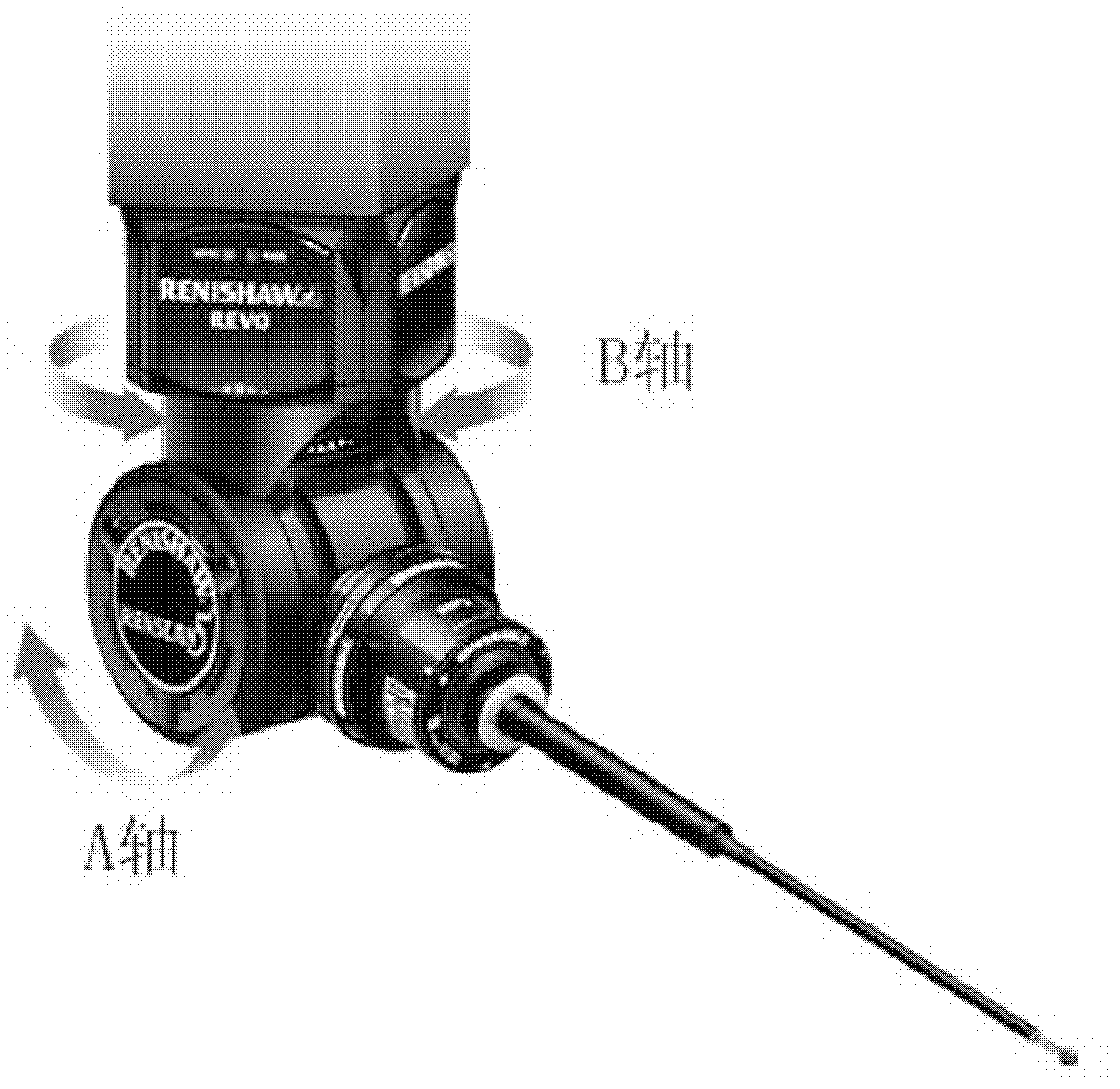
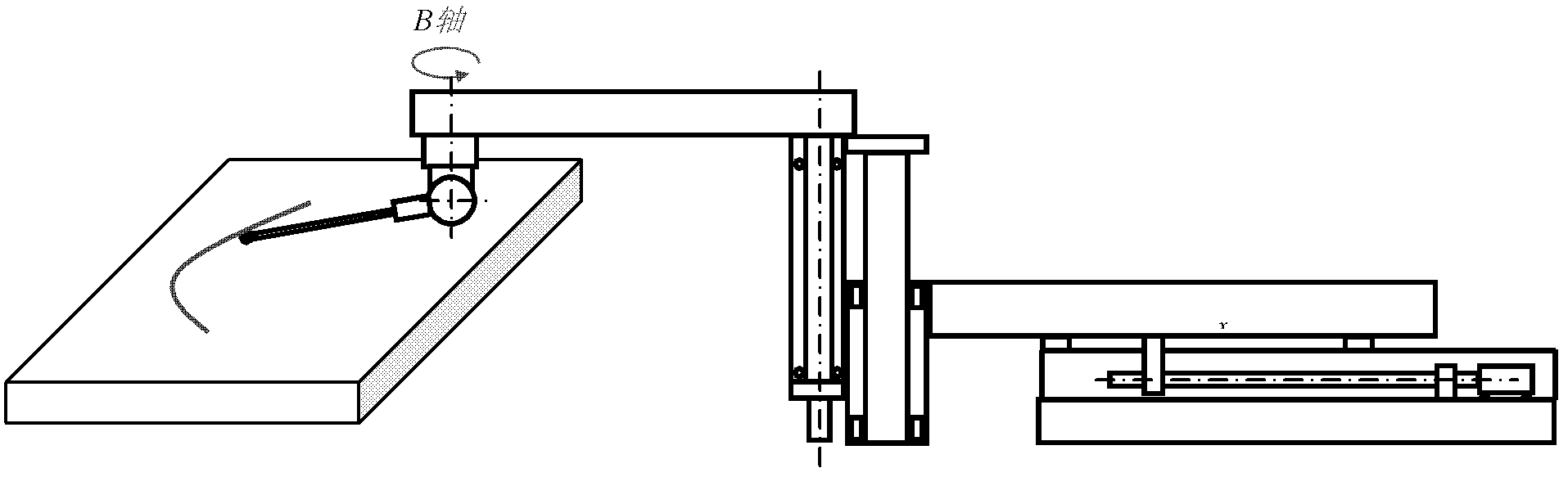
REVO (Resident Encrypted Variable Output) measuring head position posture calibrating method in joint arm type coordinate measuring machine
InactiveCN102636137AHigh measurement accuracyMeasurement devicesStandard planeCoordinate-measuring machine
The invention belongs to the field of testing technology and instrument and provides a calibrating method of a joint arm type coordinate measuring machine which can improve the measuring precision. According to the technical scheme adopted by the invention, an REVO (Resident Encrypted Variable Output) measuring head position posture calibrating method in the joint arm type coordinate measuring machine is carried out on a measuring machine device and the method comprises the following steps of: establishing a coordinate system, wherein an X axis is parallel to an x-directional movement axis of the REVO measuring head and a Z axis is parallel to a z-directional movement axis of the REVO measuring head; calibrating the parallelism depth of a B axis of the REVO measuring head and the z-directional movement axis: in order to determine a parallelism depth error on an xoy coordinate plane of the A axis of the Revo measuring head corresponding to the x-directional movement axis, vertically placing the other plane on a standard plane which is vertically placed and carrying out measurement. The REVO measuring head position posture calibrating method in the joint arm type coordinate measuring machine is mainly used for measuring.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for adjusting optical axis parallelism of multi-optical-axis imager
InactiveCN103116209AGuaranteed image qualityParallelism Tuning RealizationMountingsOptical axisPlane mirror
The invention relates to a method for adjusting optical axis parallelism of a multi-optical-axis imager. The method includes the steps: assembling a standard plane mirror on an interferometer and adjusting a single-mode dual-plane reflector to be self-aligned; inversely placing an optical-mechanical structure of the multi-optical-axis imager between the interferometer and the single-mode dual-plane reflector; adjusting a mounting base surface of the multi-optical-axis imager to be perpendicular to the optical axis of the interferometer; assembling a standard spherical mirror on the interferometer and adjusting the position and the inclination angle of a first channel optical-mechanical system on the mounting base surface to enable the first channel optical-mechanical system and a standard spherical mirror system to be confocal; and adjusting the position and the inclination angle of a second channel optical-mechanical system on the mounting base surface to enable the second channel optical-mechanical system and the standard spherical mirror system to be confocal. In the method, no special devices are needed, multi-optical-axis parallelism and system wave aberration can be simultaneously adjusted, and adjusting precision and efficiency are effectively improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
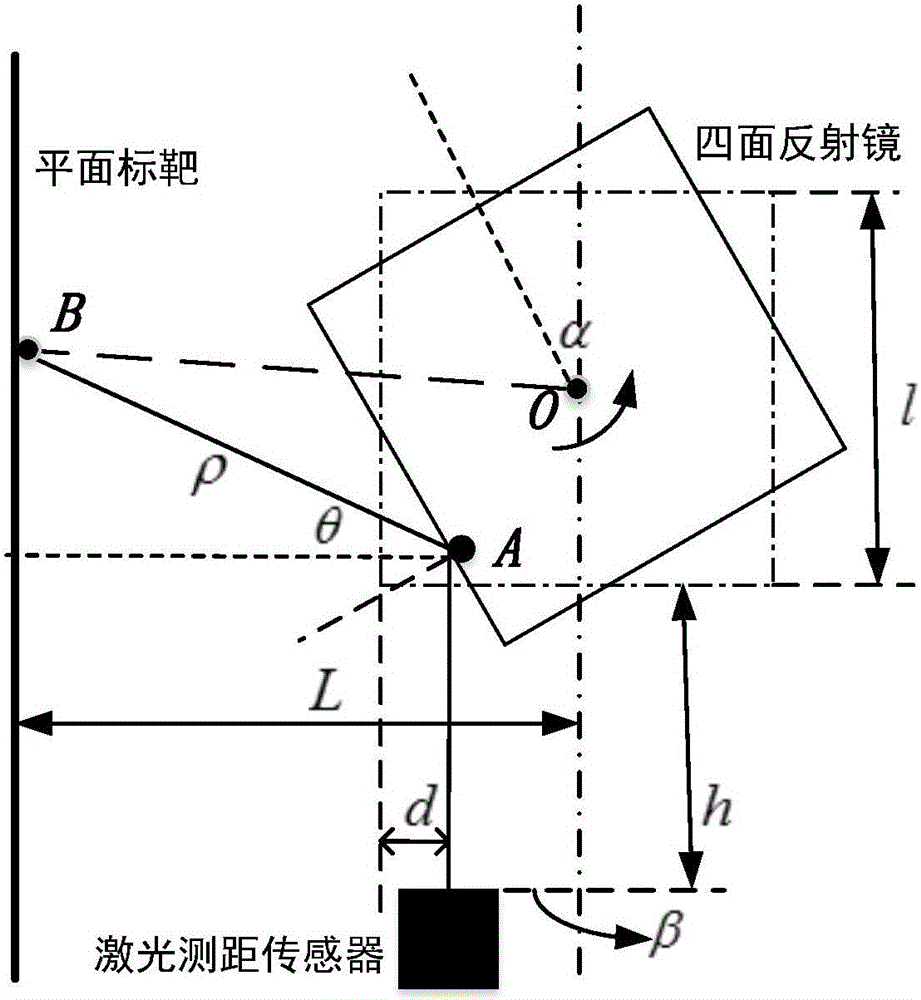
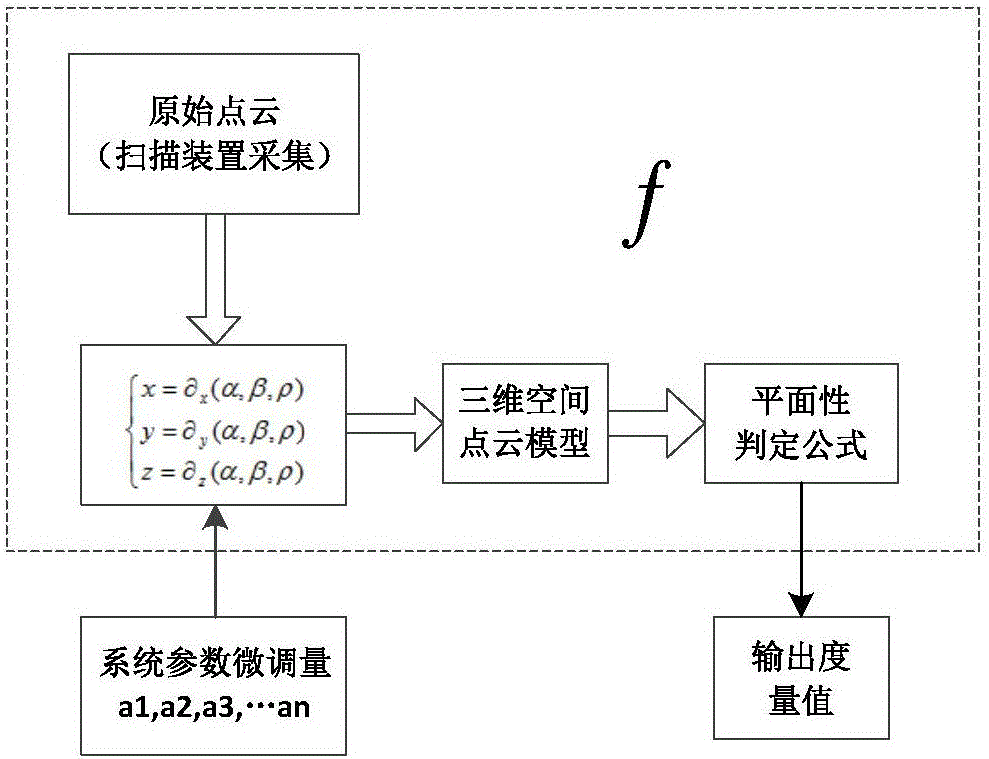
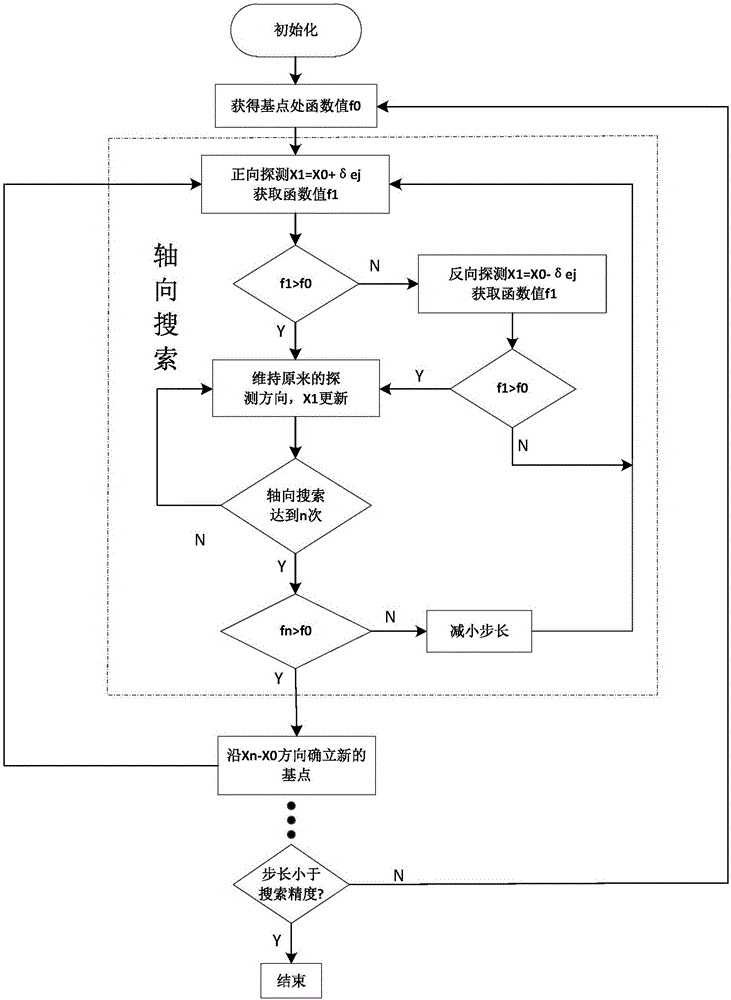
Three-dimensional laser scanning device system parameter calibration method
The invention discloses a three-dimensional laser scanning device system parameter calibration method. Since laser scanning device system parameters have inherent mechanical installation and measurement errors during measuring, each parameter needs to be tuned slightly on the basis of the measured value. The invention discloses a reliable method for obtaining system parameter fine-tuning amount. The method is characterized by, to begin with, obtaining a point cloud model of a standard plane target through a three-dimensional laser scanning device; then, determining an evaluation index serving as a metric of precision of the point cloud model to enable the fine-tuning amount of the system parameters and the metric of precision of the point cloud model to be in a function relationship; and finally, searching a group of system parameter fine-tuning amount capable of enabling the point cloud model precision to be the highest, that is, precision metric value to get the optimum value, through a pattern search method, and thus the group of fine-tuning amount is the optimum system parameter fine-tuning amount. Result shows that after the system parameters are calibrated through the method above, the precision of point cloud data obtained by the scanning device in scanning a three-dimensional space scene is effectively improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
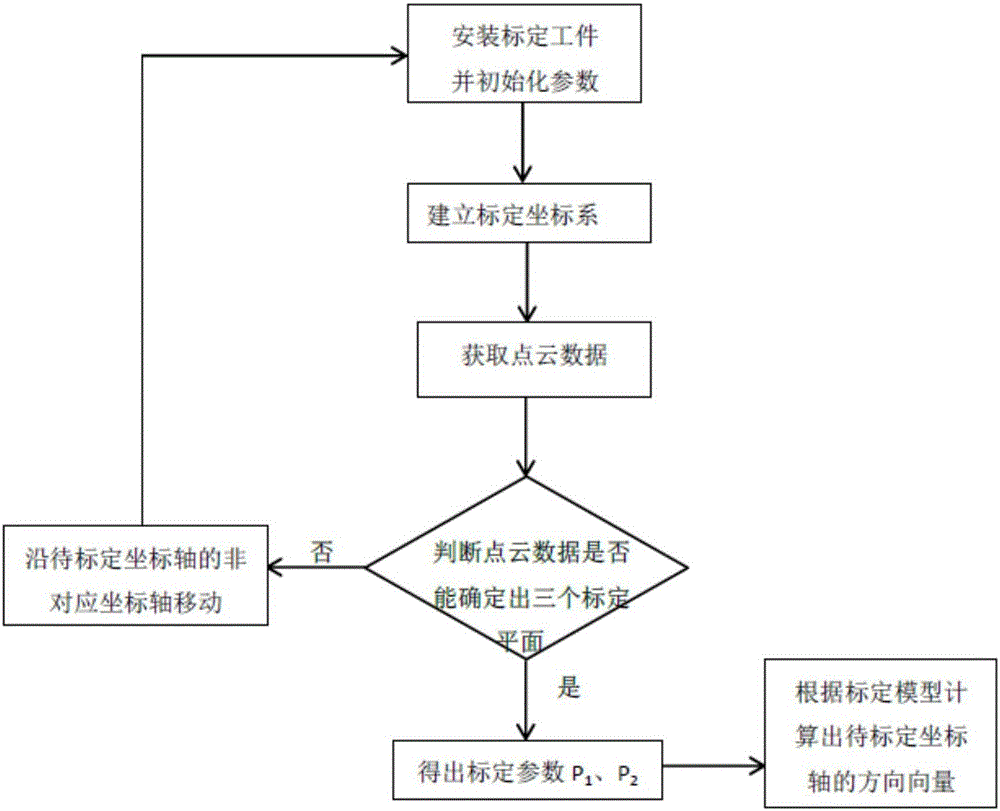
Calibration method for linear radar measurement system based on standard plane
The invention discloses a calibration method for a linear radar measurement system based on a standard plane, which comprises the following steps: step one, a linear laser sensor is enabled to be connected to a numerically-controlled moving platform, and a selected tetrahedron calibration workpiece is installed in the measurement system; step two, a calibration coordinate system is built according to a coordinate axis to be calibrated in a linear laser sensor coordinate system and a non-correspondence coordinate axis of the coordinate axis to be calibrated in a world coordinate system; step three, point cloud data of the calibration workpiece in the linear sensor coordinate system is acquired through the linear laser sensor; step four, calibration parameters in the calibration coordinate system are calculated according to the point cloud data acquired in the step three; step five, a direction vector of the coordinate axis to be calibrated is calculated according to the calibration parameters in the step four and a calibration model; and step six, the linear laser sensor moves along the direction of the other coordinate axis to be calibrated in the linear laser sensor coordinate system, executing the above steps in a repeated manner so as to acquire a direction vector of the other coordinate axis to be calibrated. The calibration method is high in reliability and small in system error.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Infrared radiometer calibration method on basis of standard plane source black body
ActiveCN103743489AEliminate the effects of additional radiationRadiation pyrometryTemperature controlEmissivity
The invention discloses an infrared radiometer proportional constant calibration method on the basis of a standard plane source black body and belongs to the field of infrared optimal radiation. The calibration method aims at the characteristics that a chopper of a current infrared radiometer is sprayed with high-emissivity black paint and the current infrared radiometer is provided with four temperature probes; when the temperature of the chopper is equal to that of a built-in temperature control reference black body, a signal is acquired, so that additional radiation of the chopper is avoided entering a detector; and moreover, in the signal acquiring process, the environment temperature, the temperature in a shell and the temperature of the chopper are requested to be equal to enable radiation among the environment, the shell and the chopper is dynamically balanced, and thus, influence of additional radiation of the chopper, the inside of the shell, the environment and the like can be eliminated. In addition, in the calibration method, calibration of a plurality of temperature points is also carried out in a common environment temperature range, so that the defect of replacing a plane with points in a conventional method, i.e. one temperature point replaces a plurality of temperature points to carry out calibration, is overcome. Compared with the prior art, the infrared radiometer proportional constant calibration method has higher accuracy.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
Method for measuring three-dimensional surface shape of membrane mirror
InactiveCN102410819AImprove real-time performanceImprove accuracyUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceFourier transform on finite groups
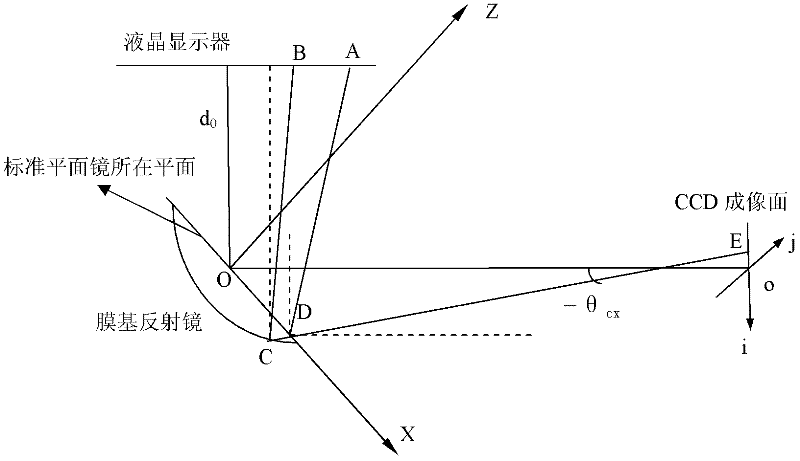
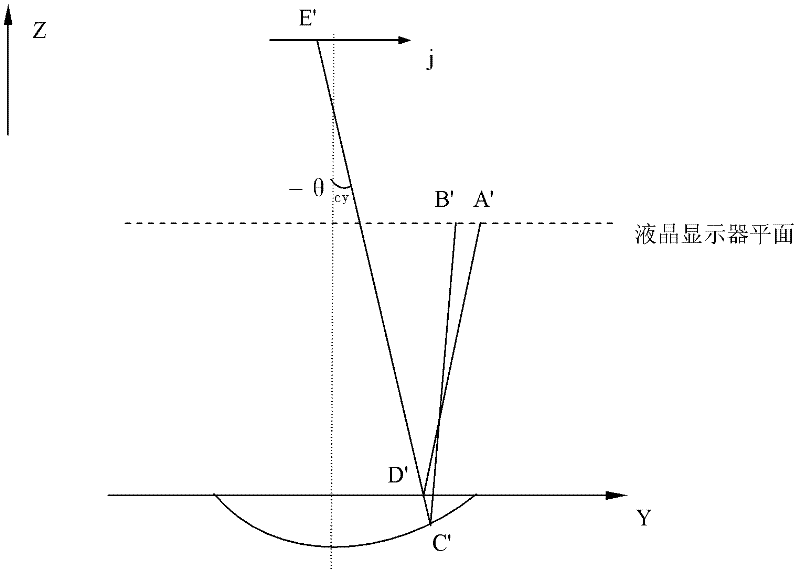
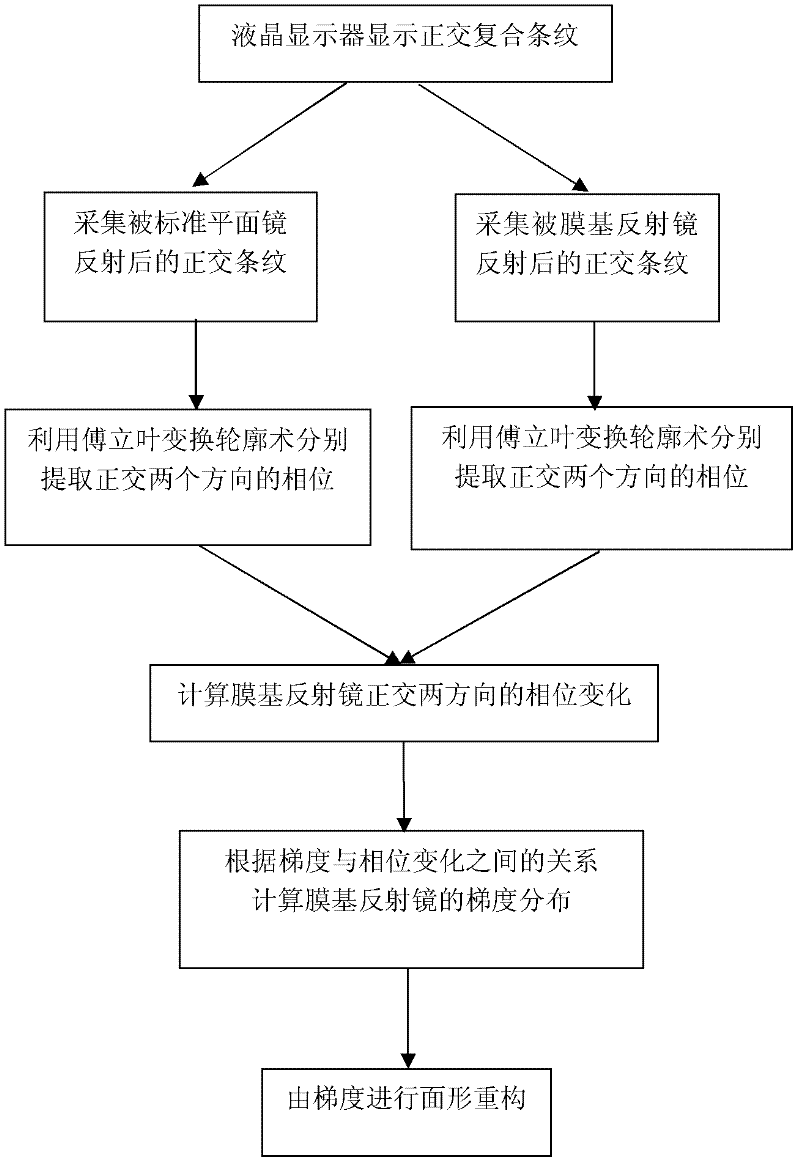
The invention discloses a method for measuring a three-dimensional surface shape of a membrane mirror. A measuring system comprises a liquid crystal display, a standard planar mirror, a charge coupled device (CCD), an image acquisition card, a computer and the like, wherein the liquid crystal display displays orthogonal sine stripes input through the computer; the CCD acquires compound stripes which are reflected by the standard planar mirror and the membrane mirror; and the system extracts phases in two orthogonal directions by using Fourier transformation profilometry, calculates phase changes in the two orthogonal directions caused by the membrane mirror, calculates gradient distribution of the membrane mirror according to a relation between gradient and the phase changes, and reconfigures the surface shape according to the gradient. By adopting an orthogonal sine stripe reflection technology, measurement of the surface shape of the membrane mirror can be realized only by acquiringa frame of bar graph reflected by the standard planar mirror and the membrane mirror respectively. A measuring device is simple, low in cost and high in instantaneity; and the problem that the three-dimensional surface shape of the membrane mirror is difficult to measure can be solved effectively.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
A processing method for the seam of a cylinder block
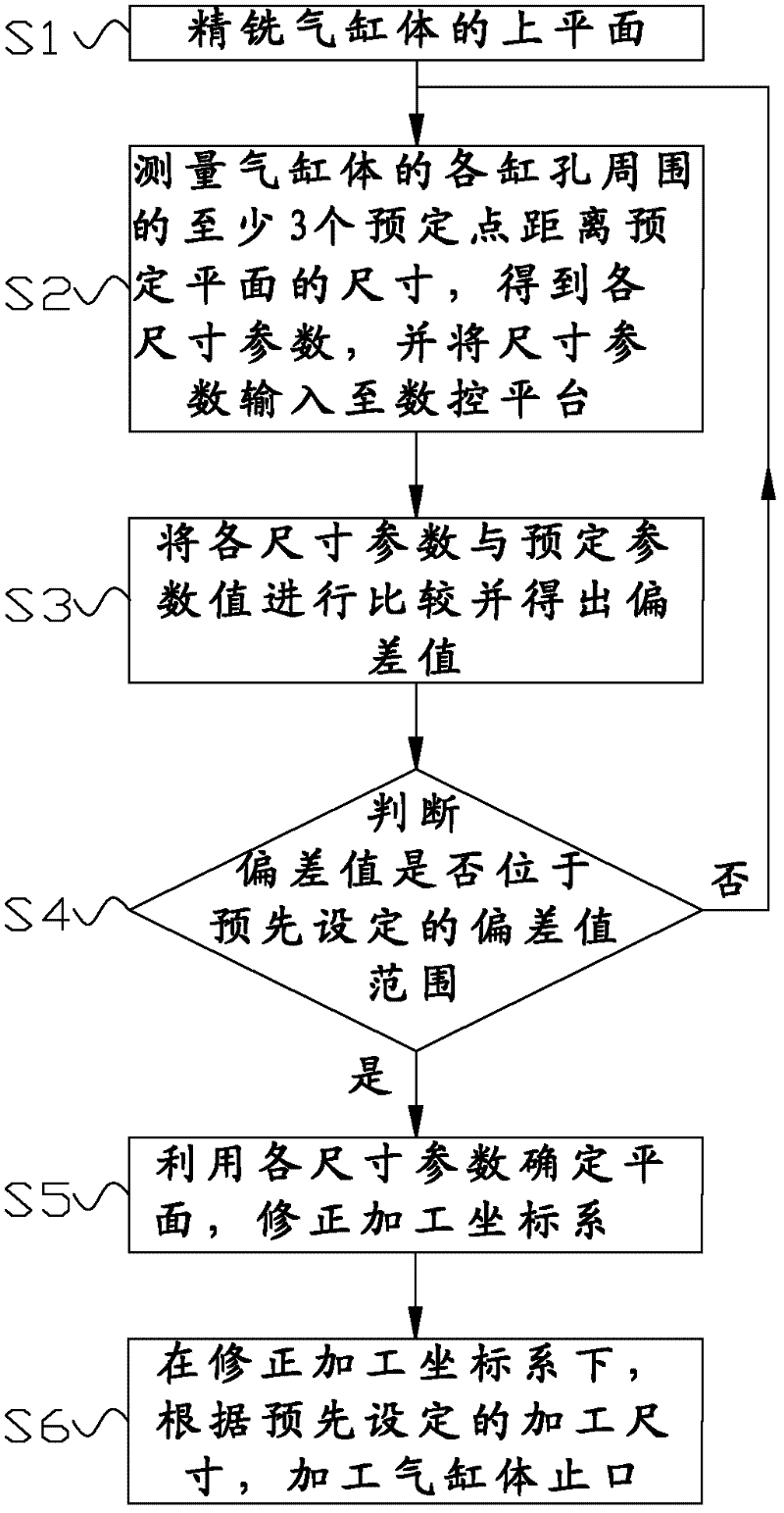
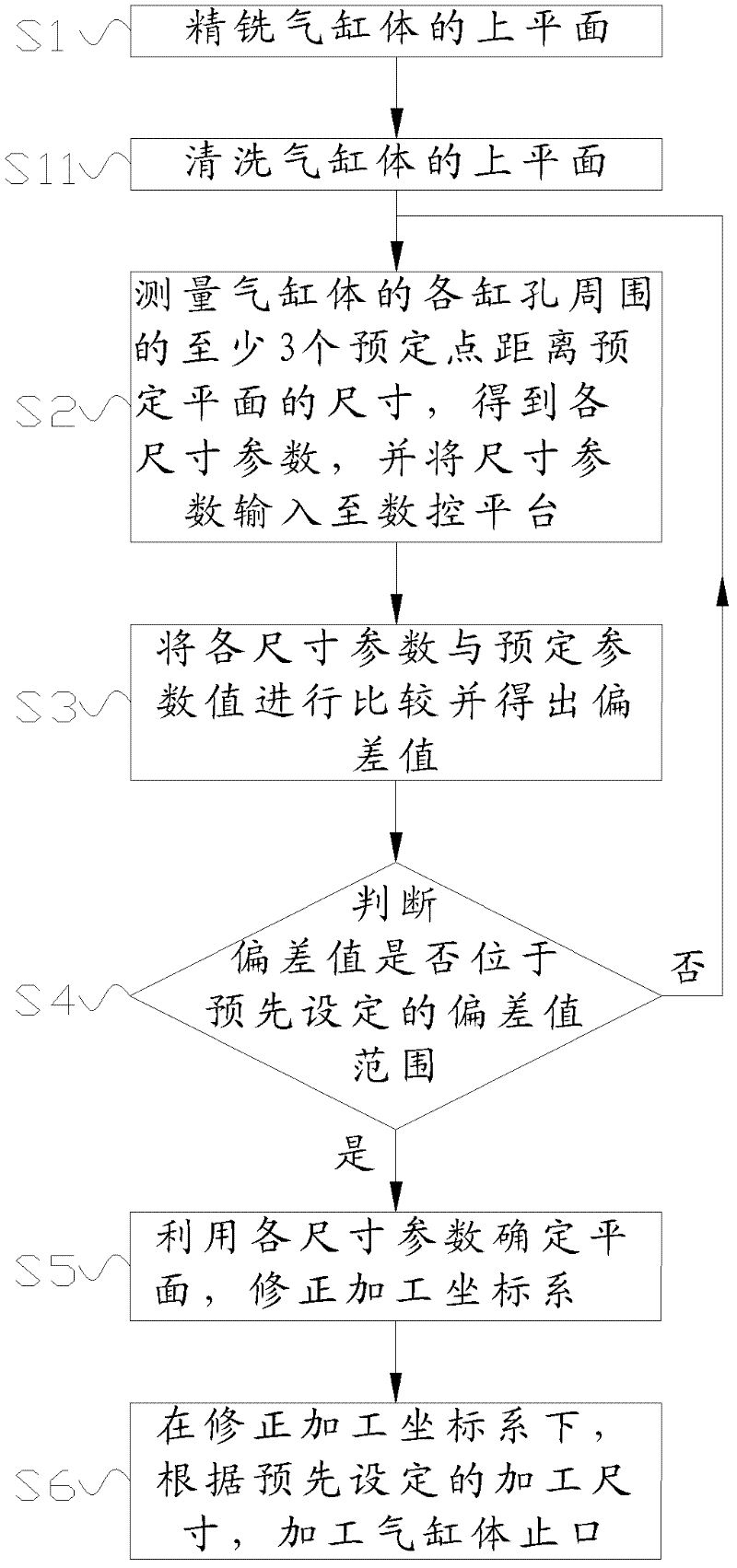
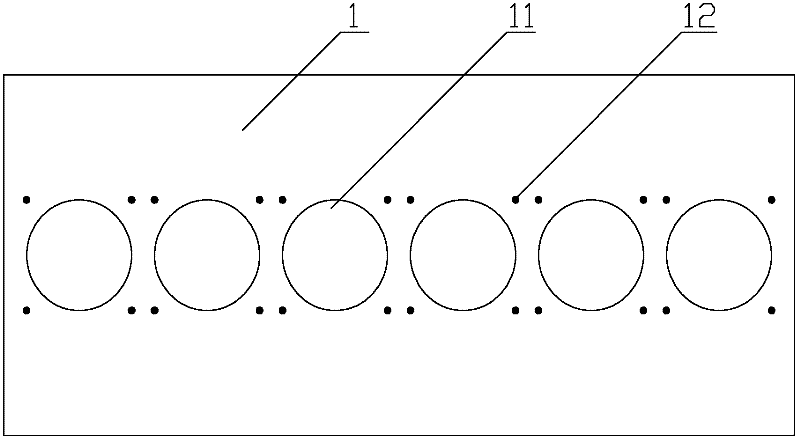
InactiveCN102284729AImprove processing qualityHigh precisionMilling equipment detailsNumerical controlManufacturing cost reduction
The invention discloses a method for processing a stop mouth of an air cylinder body. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) finely milling the upper plane of the air cylinder; 2) measuring the sizes of at least three preset points at the periphery of each cylinder hole of the air cylinder body away from the preset plane to obtain each size parameter and inputting the size parameters into a numerical control platform, wherein the preset plane is parallel with the standard plane of the upper plane of the air cylinder body; 3) comparing each size parameter with the preset parameter value to obtain an offset value; 4) judging whether the offset value is in the preset offset value range, if so, turning to the step 5), and otherwise, turning to the step 2); 5) determining the plane byutilizing each size parameter and amending a processing coordinate system; and 6) under the amended processing coordinate system, processing the stop mouth of the air cylinder body according to the preset processing size. By the processing method provided by the invention, the processing precision of the stop mouth of the air cylinder body can be improved, consistency of products can be improved,processing rework rate and rejection rate are reduced, and manufacturing cost is reduced.
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
Method for measuring cone angle of cone mirror
InactiveCN102818542AGuaranteed detection accuracyThe principle is simpleUsing optical meansOptical axisPlane mirror
The invention relates to a method for measuring the cone angle of a cone mirror, which utilizes a device comprising an interferometer, a standard plane mirror, the measured cone mirror, a rotating platform, a cube and an optical platform. Firstly, the rotating platform is vertical to an optical axis; then the measured cone mirror is placed at the center of the rotating platform; one generating line or one conical surface of the cone mirror is regulated to be vertical to the optical axis; by utilizing the auto-collimation reflection of the generating line and the surrounding region thereof or the conical surface, zero-interference strips are formed by reference light inside the interferometer; the rotating platform is rotated so that the other generating line or the other conical surface at the side corresponding to the rotating platform is vertical the optical axis, and the zero-interference strips are formed in the same way; and at the time, the rotating angle of the rotating platform and the cone angle are supplementary angles, so that the accurate value of the cone angle can be calculated. The detection method provides an effective method for measuring the cone angle under the high accuracy, has a simple structure and has high application value.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rapid phase-height mapping calibration method
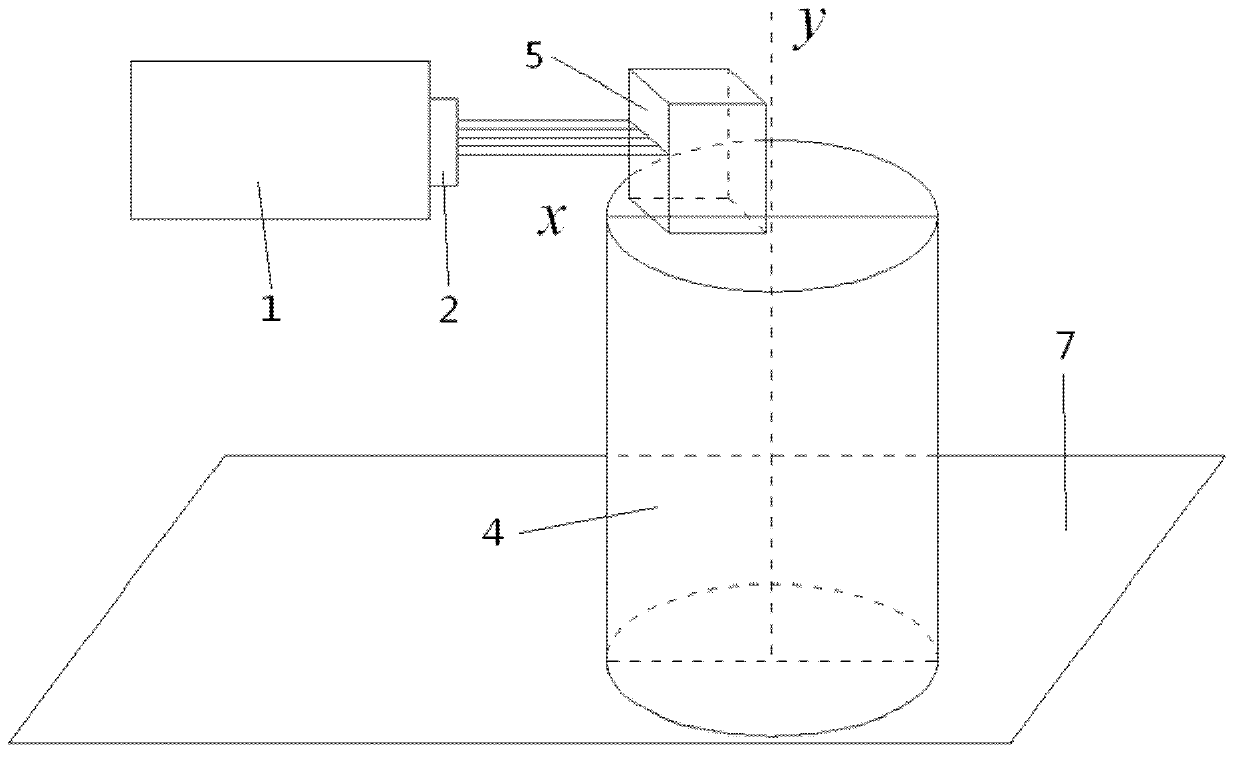
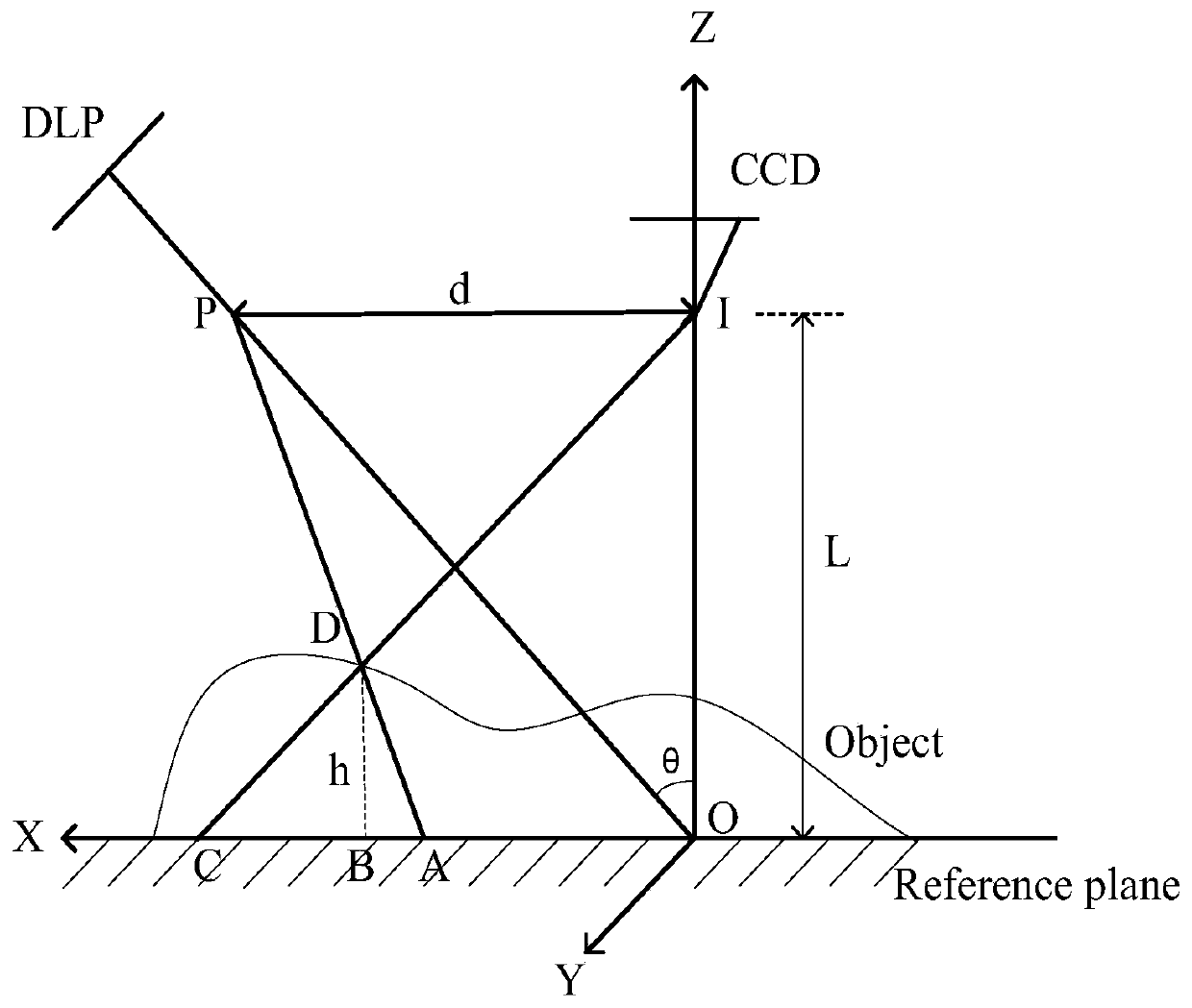
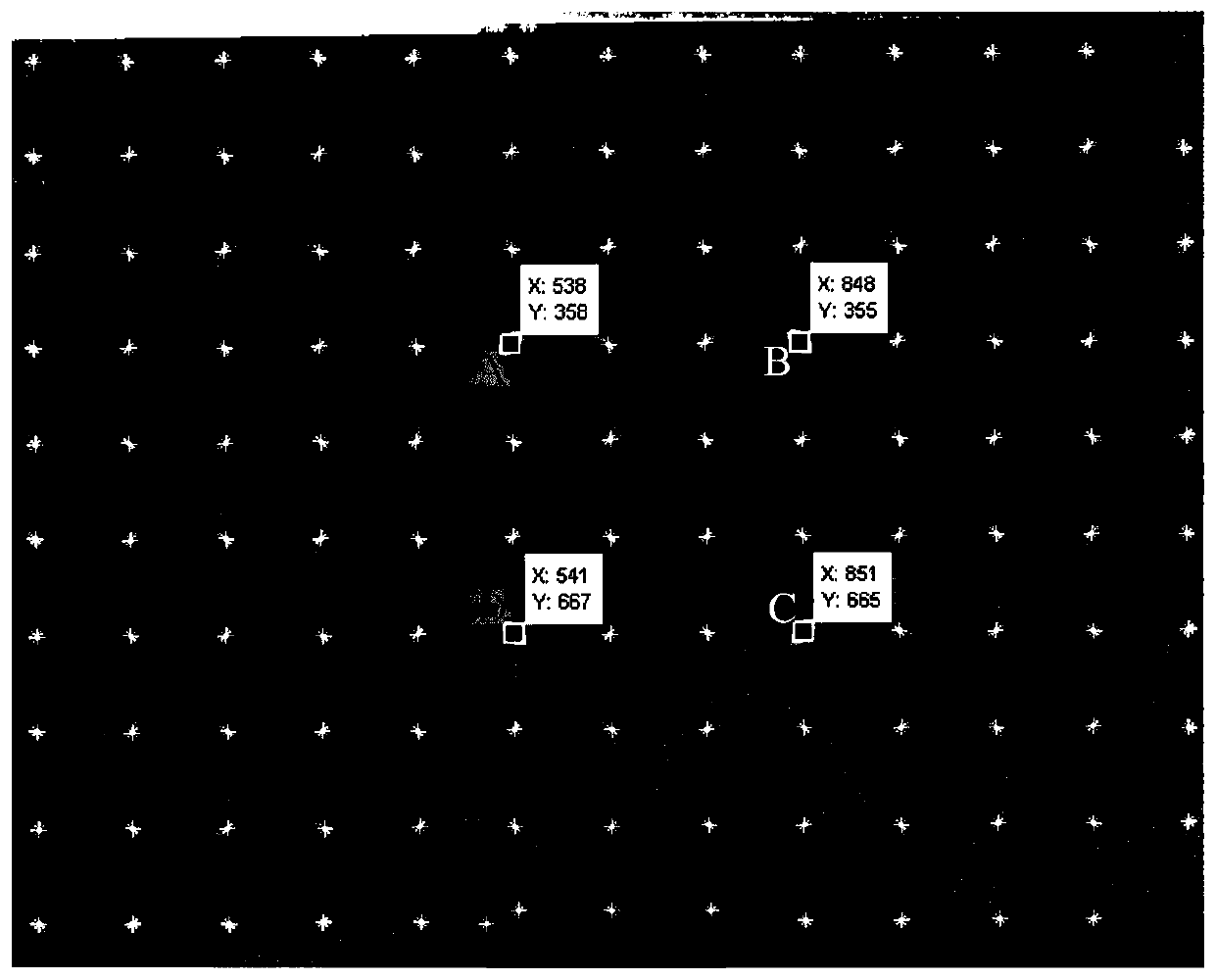
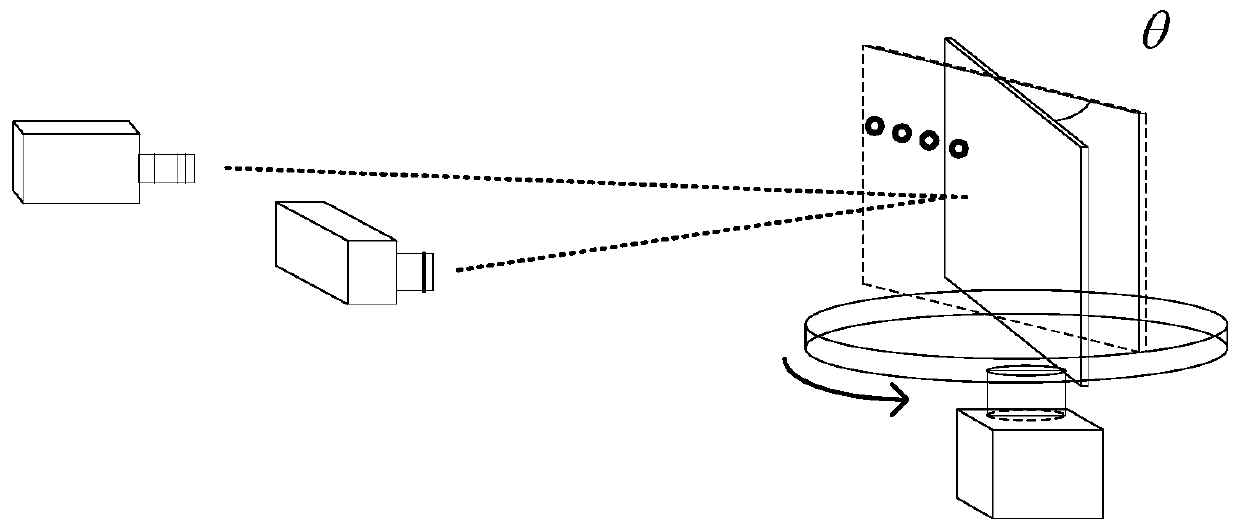
The invention discloses a rapid phase-height mapping calibration method. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a three-dimensional measurement system; using a Harris corner detectionalgorithm for detecting the difference value of pixel coordinate values of checkerboard specific points shot by a camera to adjust the optical axis of the CCD camera to be perpendicular to a referenceplane; respectively obtaining high-precision absolute phase values of the standard plane before and after rotation through a time phase unwrapping method based on period correction; carrying out two-dimensional identification on the mark points on the rotated standard plane by using a centroid method to obtain pixel coordinates, and searching the absolute phase value of the corresponding mark point in the absolute phase value data of the corresponding standard plane; and fitting a plurality of virtual planes by using the slope of the standard plane and the absolute phase value of the mark point before rotation, and optimizing and solving system parameters by using a least square method to complete phase-height calibration. According to the invention, the calibration speed of the three-dimensional measurement system is greatly improved, and the method has potential application prospect and practical value in the field of desktop three-dimensional scanners.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com