Patents
Literature
539 results about "Flat mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
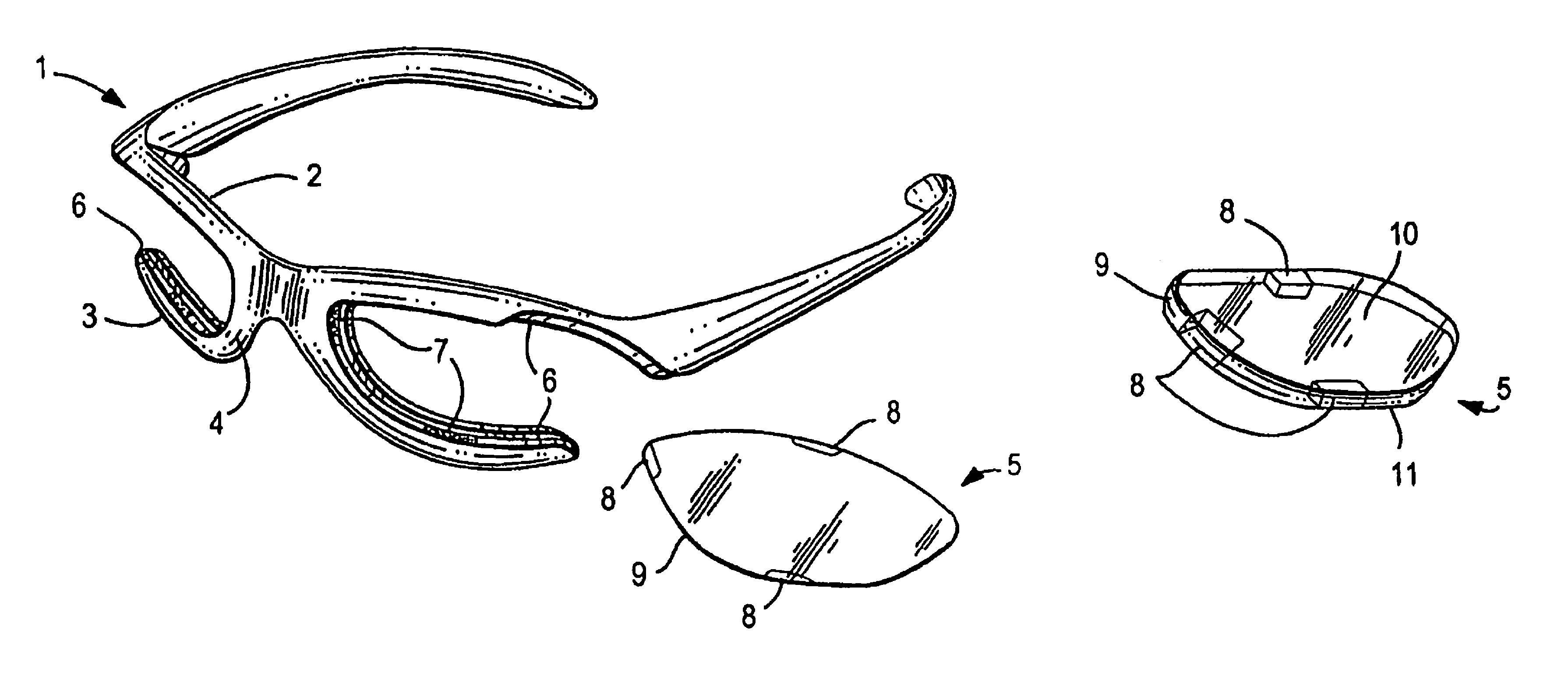
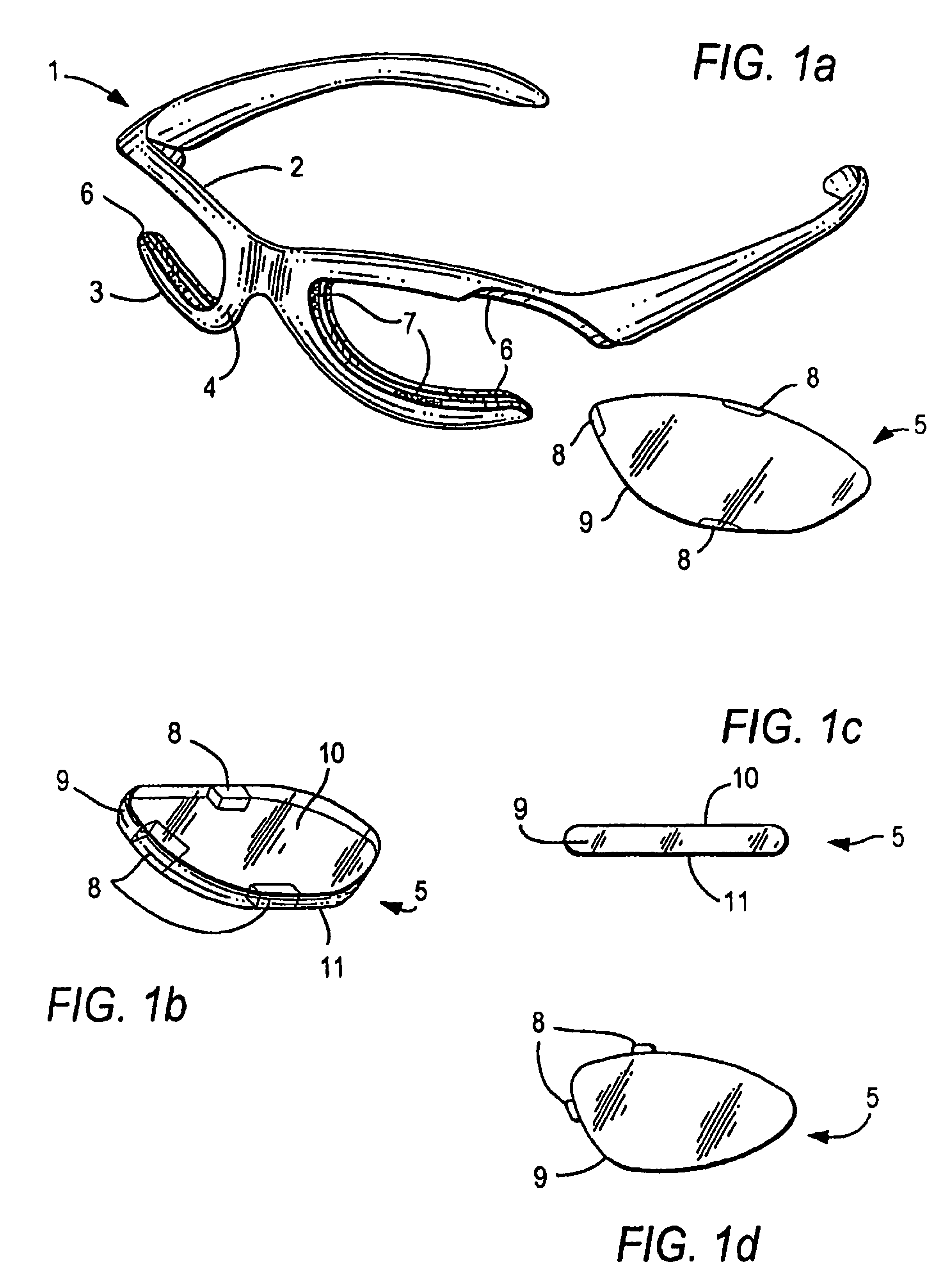
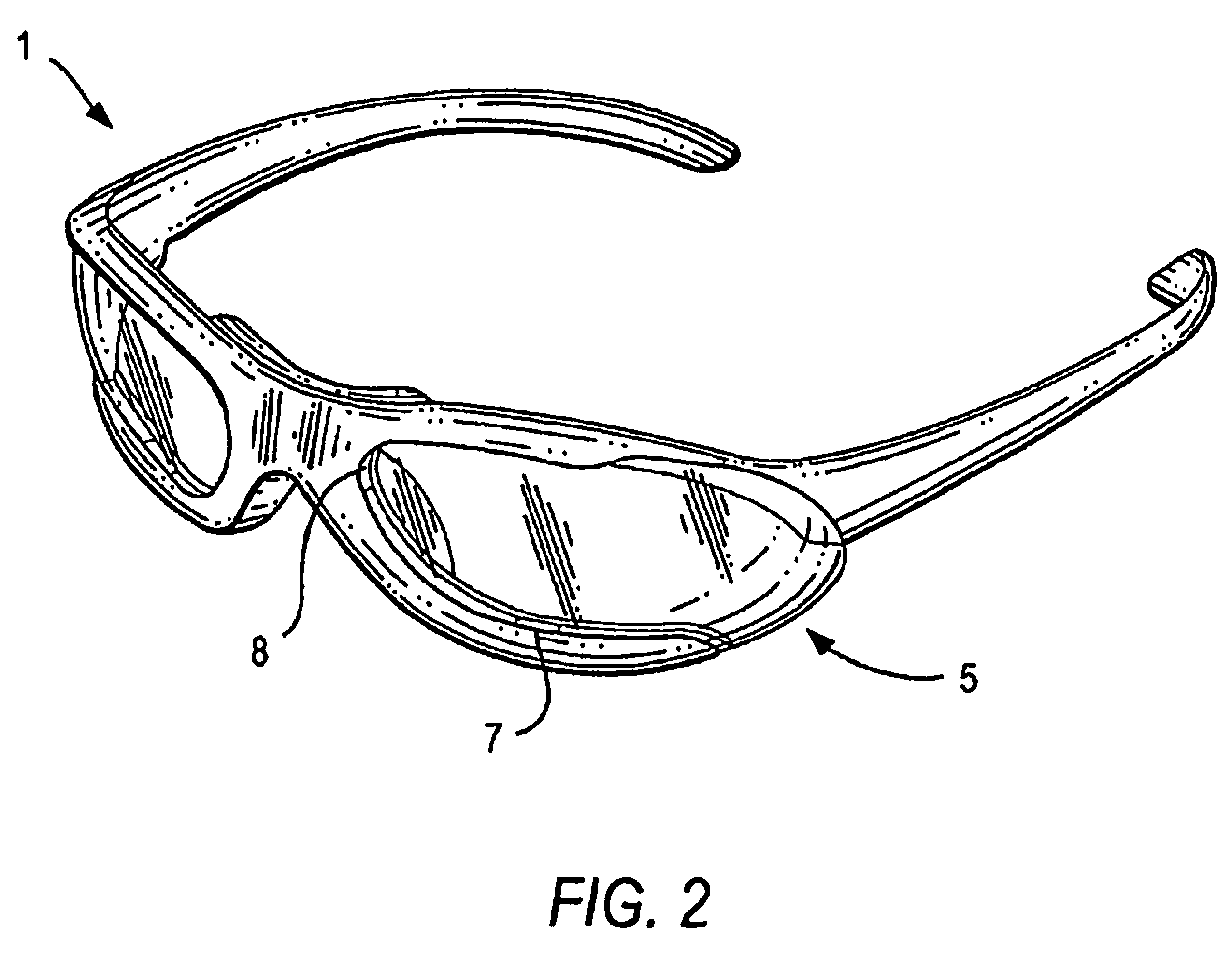
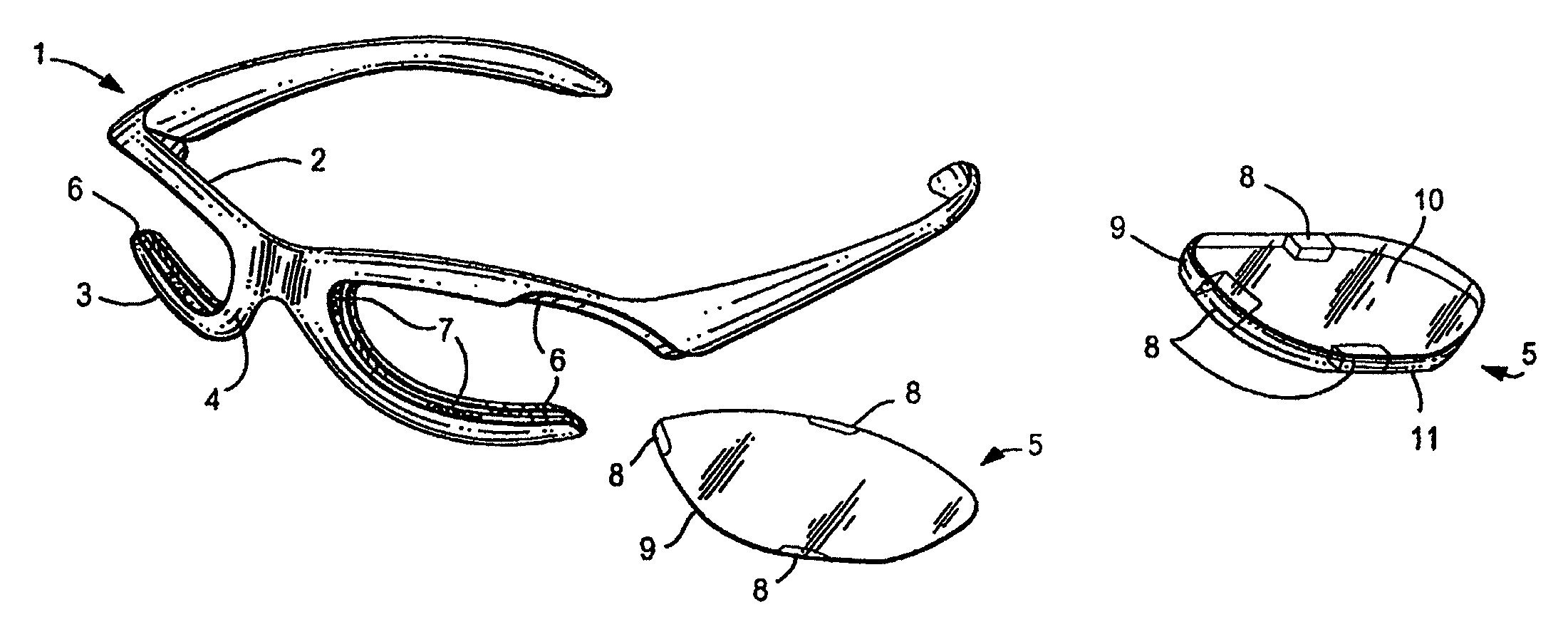
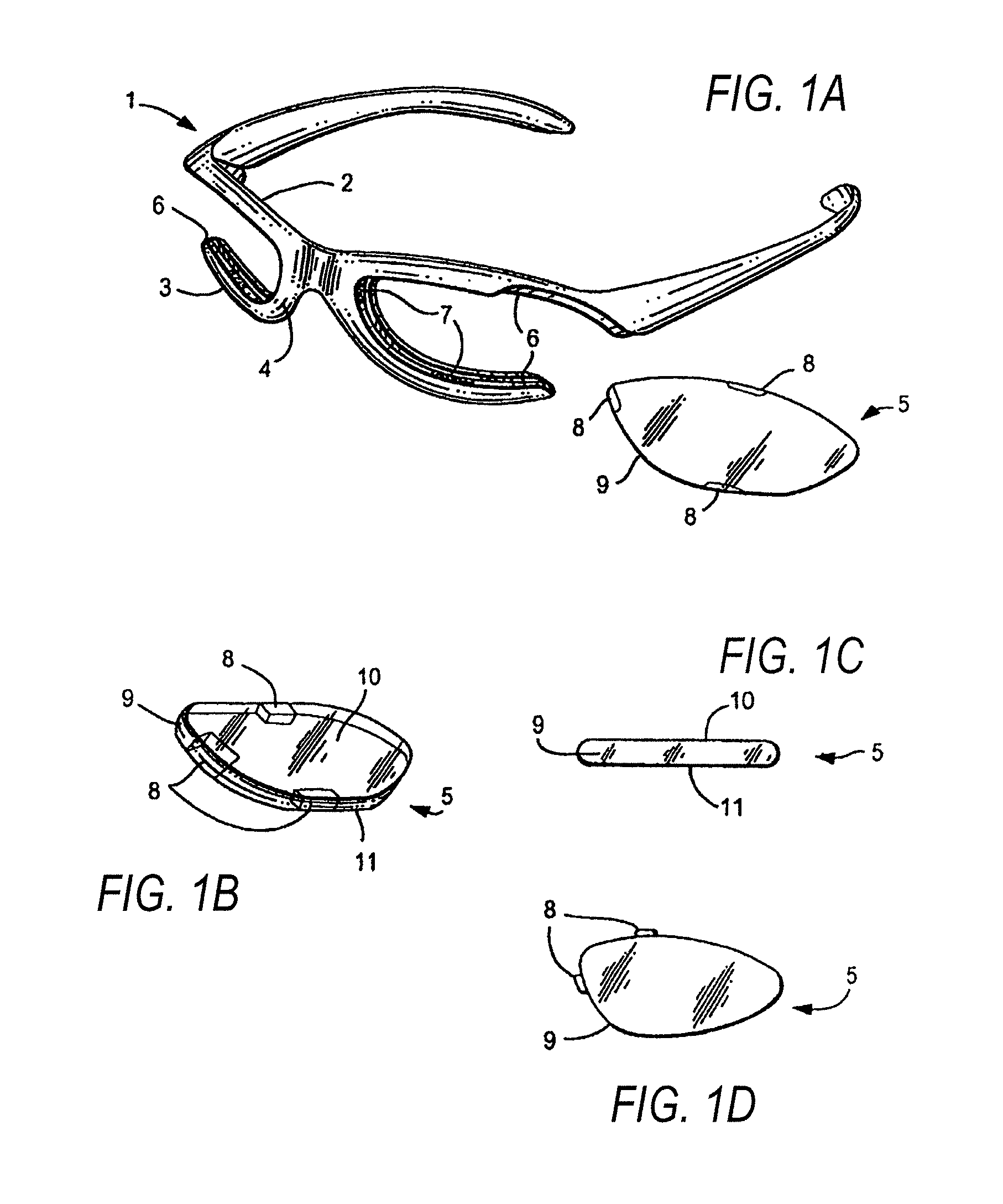
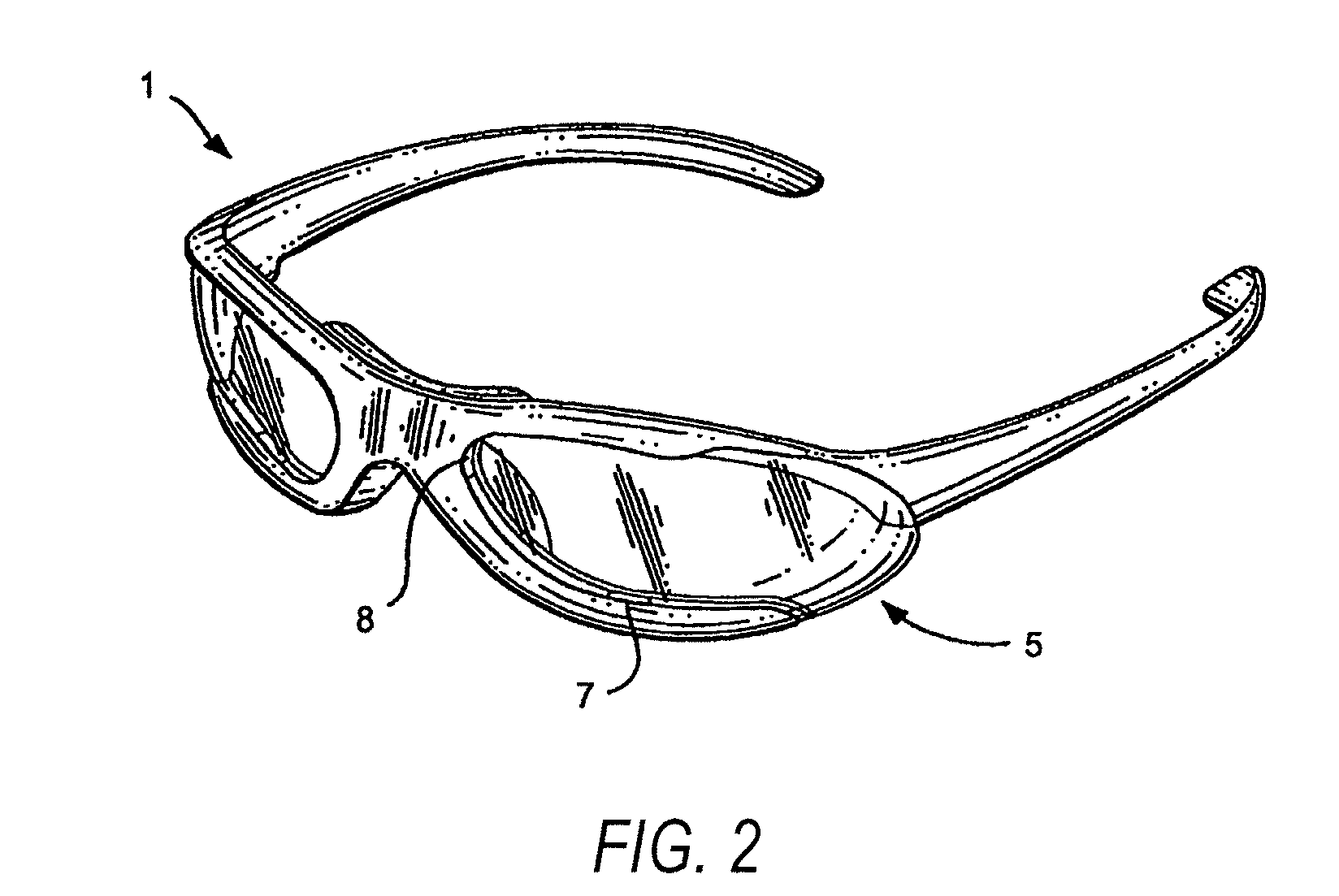
Eyewear frames with magnetic lens attachements
ActiveUS7850301B2Easy to changeRapid and simple interchangeSpectales/gogglesNon-optical partsCamera lensUses eyeglasses
The present invention illustrates various methods of attaching a pair of eyeglass lenses or a lens shield to an eyeglass frame using magnets or magnetically attractive material. The magnetic attachment methods are beneficial because they allow the user to have interchangeable lenses or shields for indoor and outdoor use, enhancing their visual acuity during work or play. The lenses may be tinted, prescription, protective eyewear, or plano. The magnetic lenses are convenient and user friendly, allowing intuitive, tool-less interchangeability with no need to twist or stress the frame. These methods of attachment require no specific instructions or tools when the user replaces lenses.
Owner:SWITCH VISION
Eyewear frames with magnetic lens attachments
ActiveUS8092007B2Easy to changeRapid and simple interchangeSpectales/gogglesNon-optical partsCamera lensUses eyeglasses
The present invention illustrates various methods of attaching a pair of eyeglass lenses or a lens shield to an eyeglass frame using magnets or magnetically attractive material. The magnetic attachment methods are beneficial because they allow the user to have interchangeable lenses or shields for indoor and outdoor use, enhancing their visual acuity during work or play. The lenses may be tinted, prescription, protective eyewear, or plano. The magnetic lenses are convenient and user friendly, allowing intuitive, tool-less interchangeability with no need to twist or stress the frame. These methods of attachment require no specific instructions or tools when the user replaces lenses.
Owner:SWITCH VISION
Flip-up convex mirror attachment
A flip-up convex mirror attachment for installation onto the original equipment mirror in vehicles with either a left-side or right-side driver. The flip-up convex mirror attachment attaches to the mirror surface of the original equipment interior mirror found in most motor vehicles. The flip-up convex mirror attachment contains an angled hinge block for creating a predefined offset angle between the flip-up convex mirror and the OEM mirror such that the reflected image on the side of the mirror nearest the driver is maintained at generally the same point behind the vehicle as the original equipment mirror. The wedge-based hinge assembly may be attached to the flat mirror surface on either a left-side or right-side driver vehicle and still maintain the desired angular offset between the OEM and flip-up convex mirrors.
Owner:ROOSE ALISON L
Ultraviolet sterilizer for surgery
InactiveUS20110054574A1Prevent moistureAvoid burnsLight therapyRadioactive sourcesUv disinfectionArthroscopy
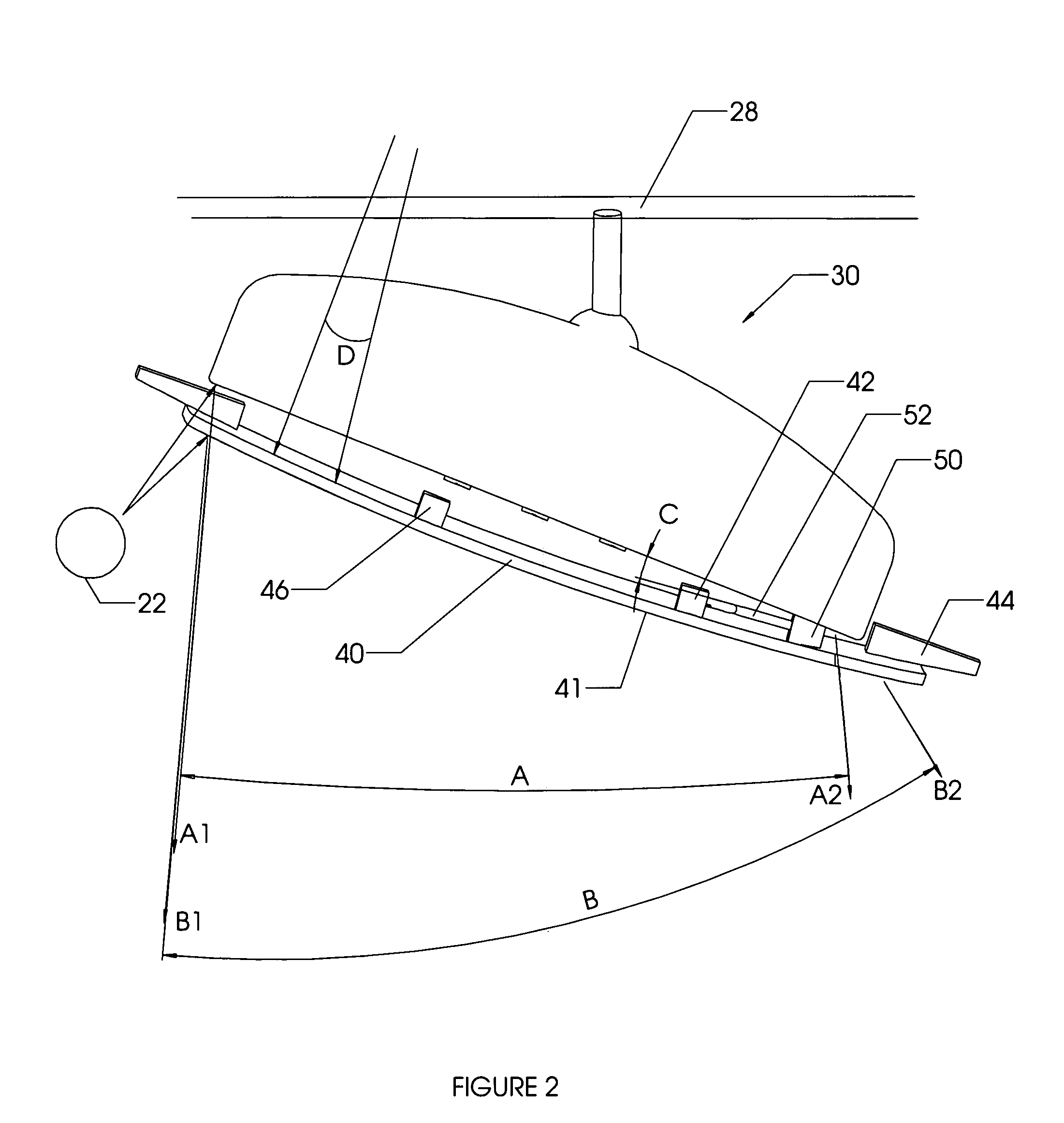
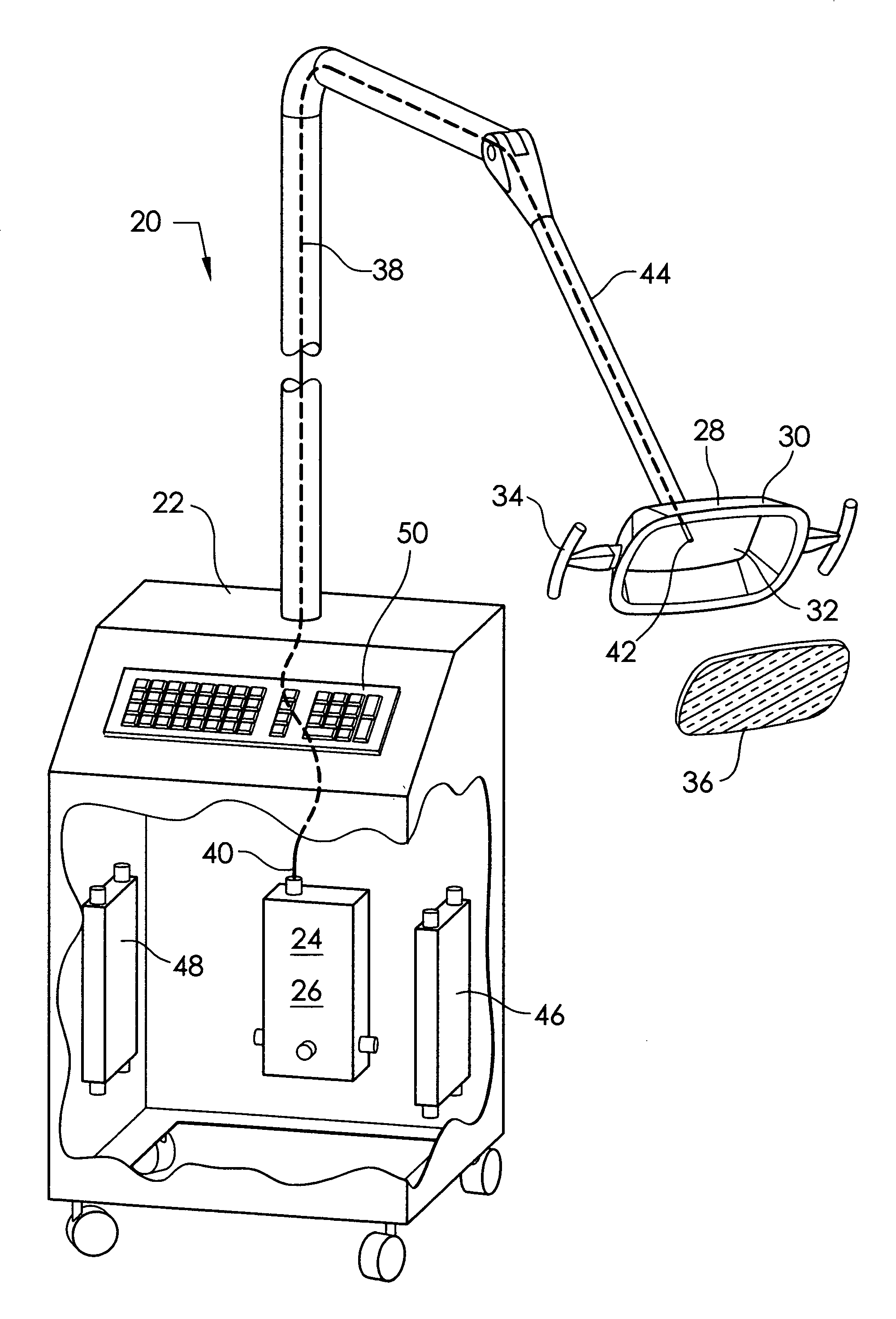
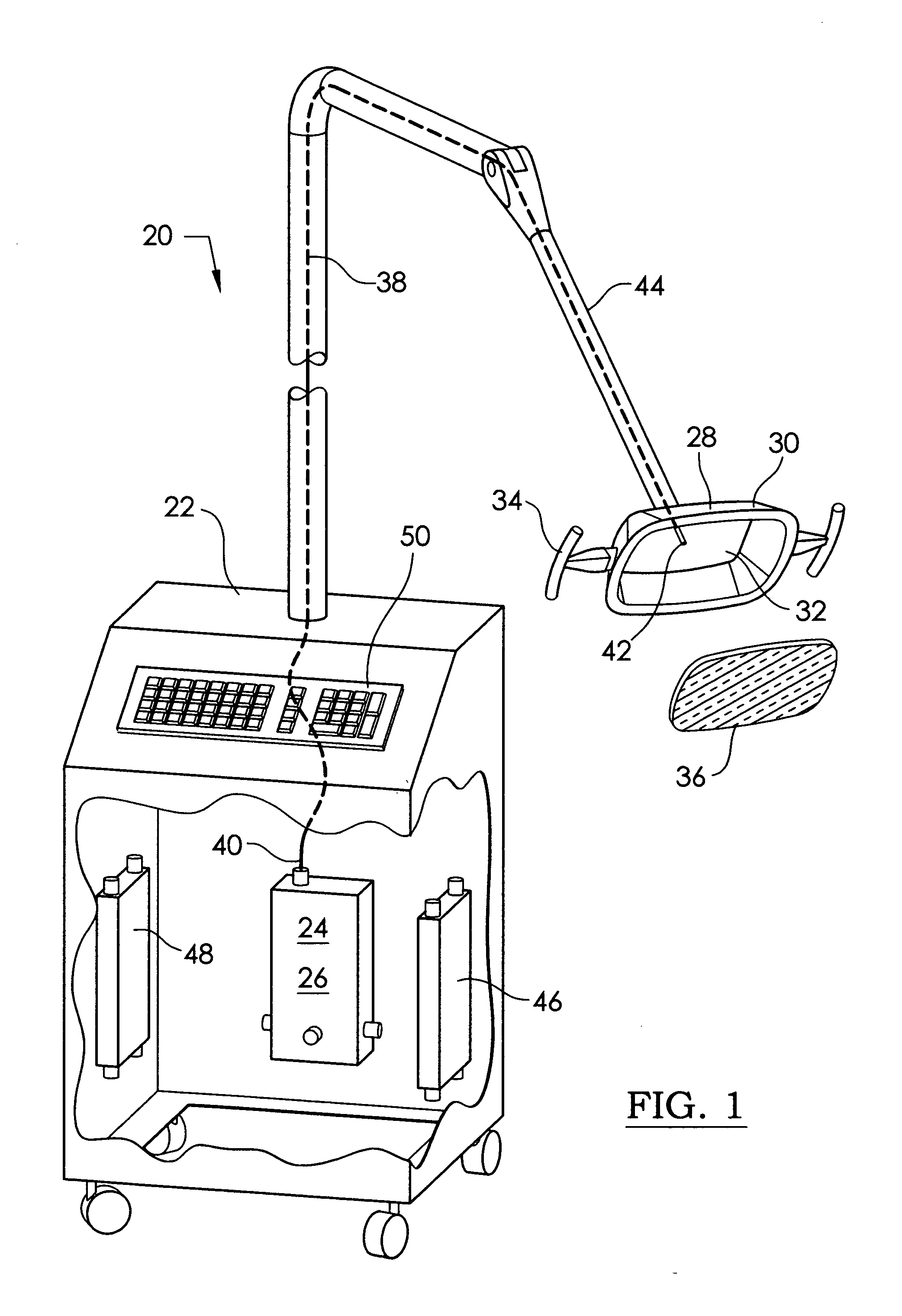
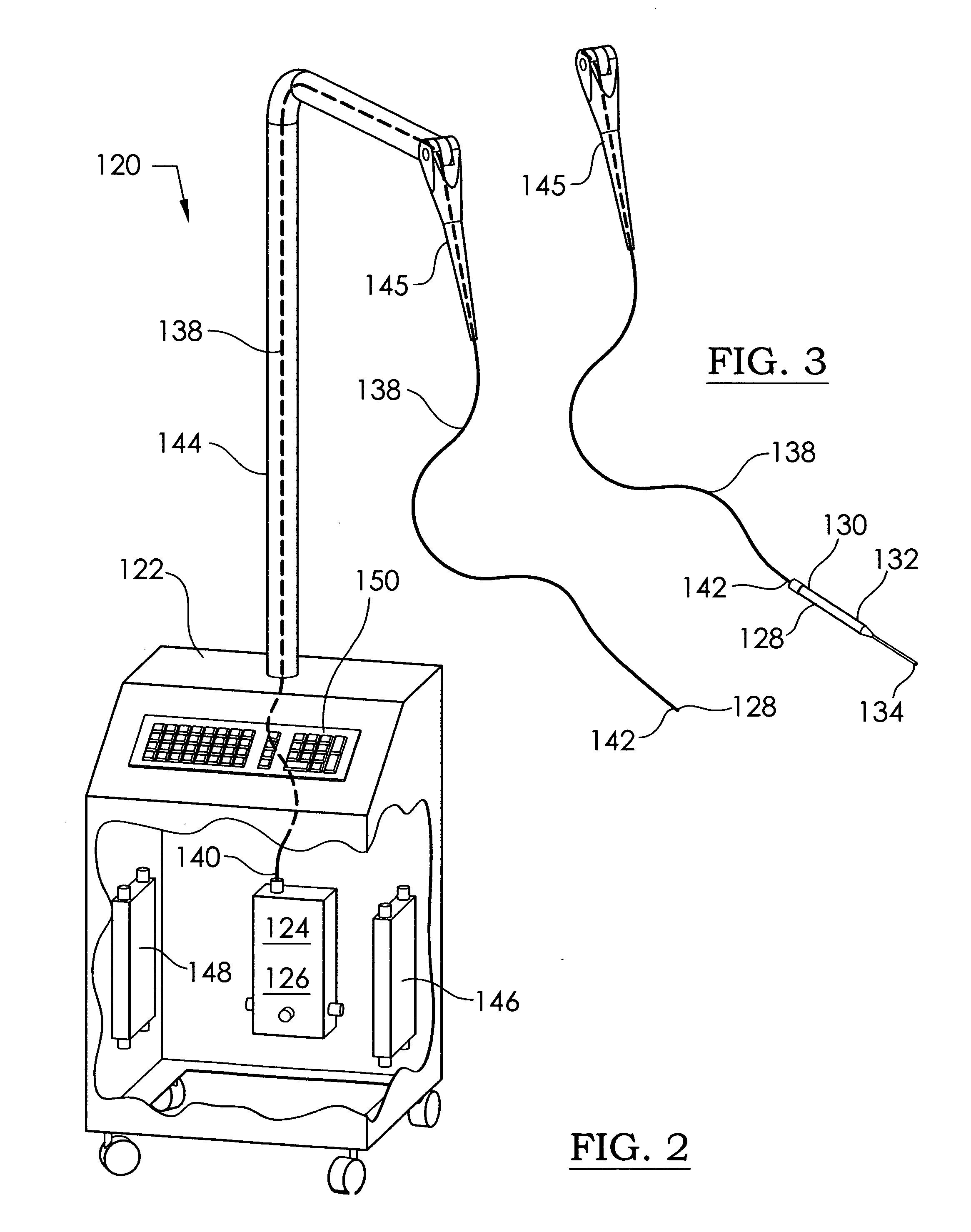
An ultraviolet sterilizer for use during surgery is mounted in a base cabinet. The UV light source can be a laser, or an LED. An optical frequency multiplier can be used that outputs UV of less than 280 nm, or greater than 320 nm, to avoid burning the patient. A visible LED aiming light directs the UV light toward the surgery. A crosshair image can be projected to position the light.One lamp has a housing, a cavity, a handle, and an ocular plate to pass the UV and the aiming light. An articulated arm allows selective positioning of the lamp. Another lamp has a stylus, a handle, and a tip small enough for easy insertion into a small incision for arthroscopy. A fiber optic cable connects the UV and the aiming light to the lamp. Lenses or filters can be used with the fiber optic cable.An electronic power supply and a CPU connect to the UV and the aiming light sources. A keyboard inputs commands to the CPU. A sensor provides feedback.Another UV sterilizer is mounted on a ceiling of the operating room. A lamp has a housing with a cavity. Either a curved or a flat substrate is mounted in the cavity. Solid state UV elements are arrayed on the substrate, along with visible LEDs for aiming. Either a curved or a flat mirror is disposed behind the substrate. An ocular plate passes the UV and the aiming light, and protects the elements from damage. The ocular plate is a diffuser, a filter, or a fresnel lens.
Owner:FELIX PERRY
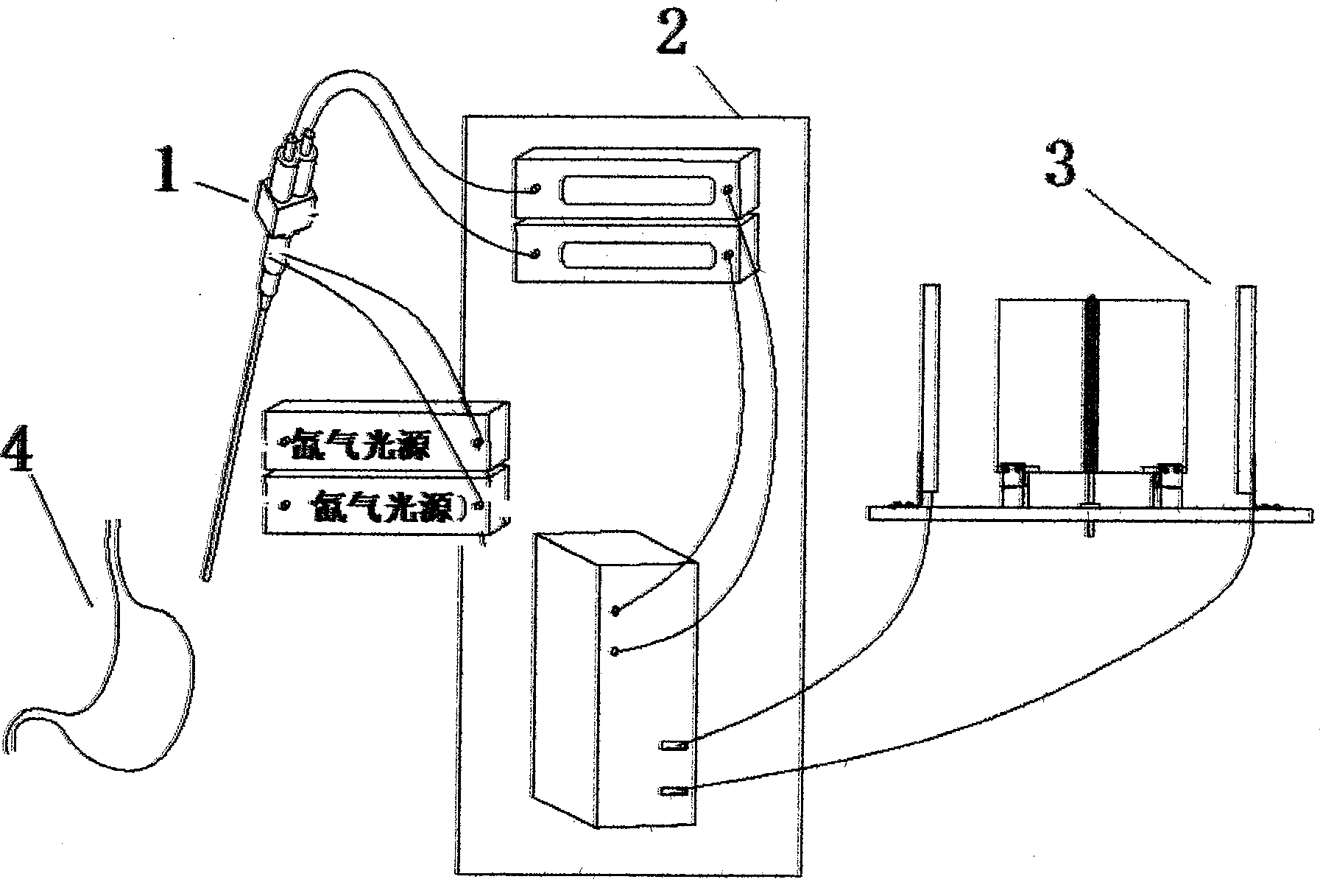
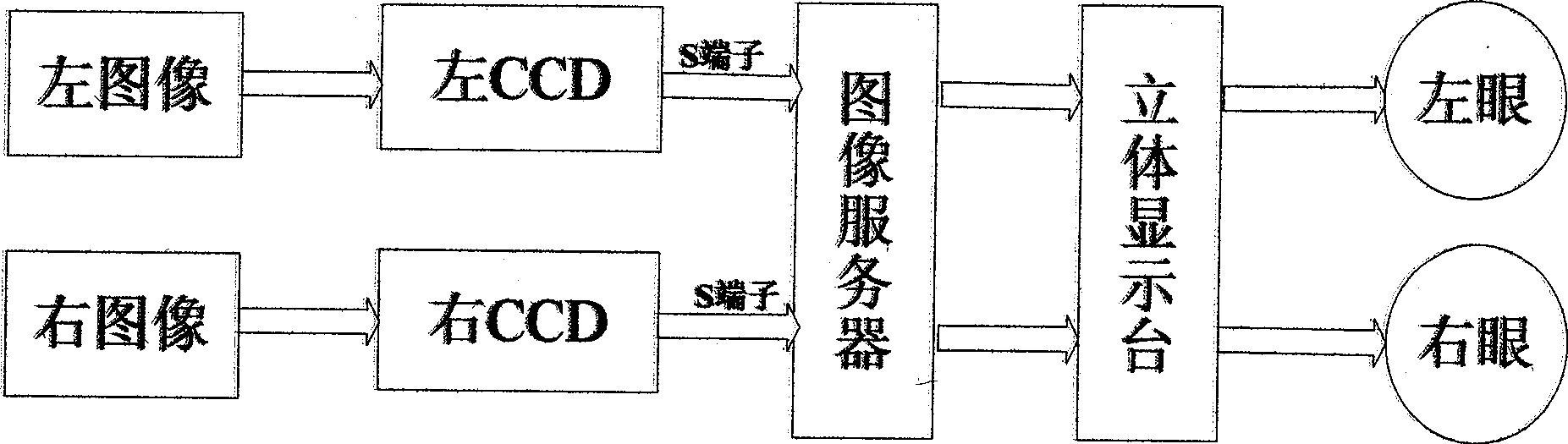
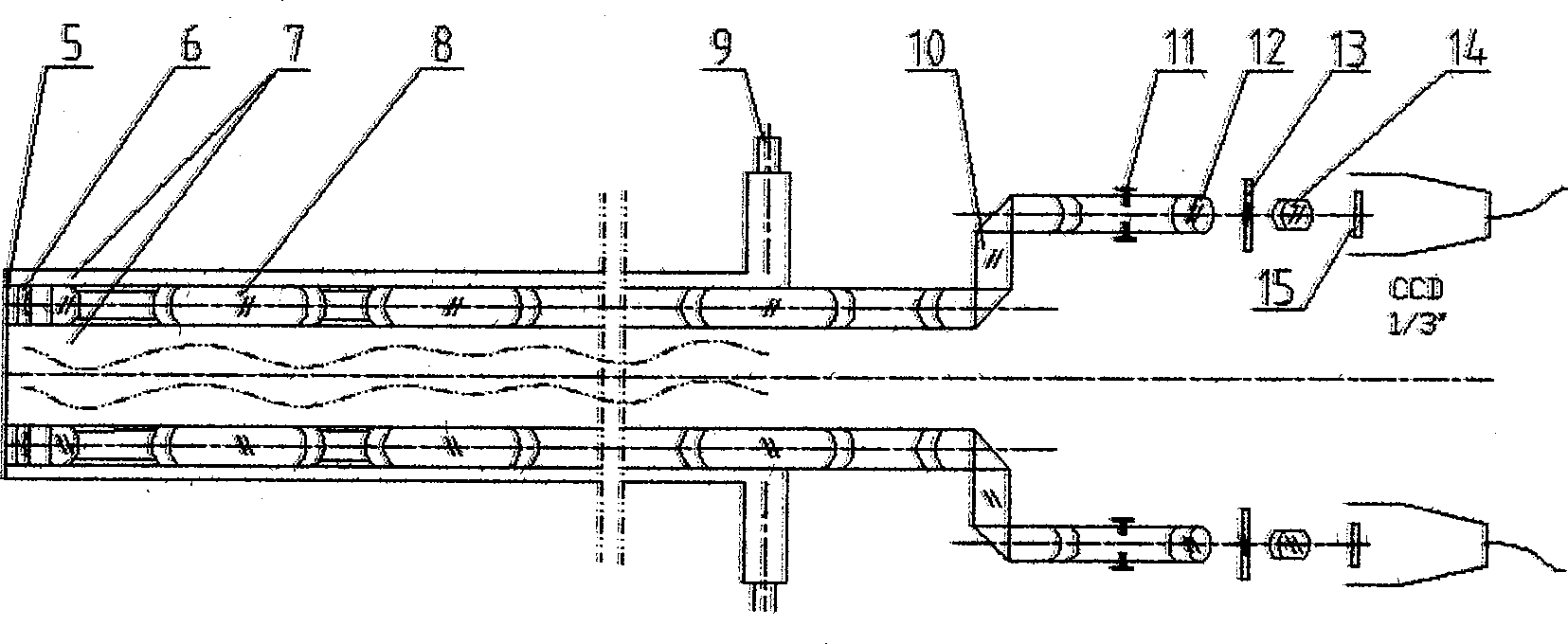
Binocular endoscope operation visual system
InactiveCN101518438AMeet the needs of 3D stereo visionStereoscopic effect is goodLaproscopesEndoscopesVideo memoryLaparoscopy
A binocular endoscope operation visual system mainly comprises a binocular endoscope, an image server and an endoscope stereo display unit. Two ways of clear abdominal cavity image video signals are obtained by the binocular endoscope, two ways of video streams enter a memory of an image processing server or a video memory by a two-way image capture card, and a left-way image and a right-way image which are processed are respectively displayed in a left displayer and a right displayer. By a flat mirror, the contents of the left displayer and the right displayer respectively enter the left eye and the right eye of an observer, thereby the stereo effect is realized. The binocular endoscope operation visual system is suitable for the circumstance of a medical surgical endoscope operation, can completely satisfy the stereoscopic vision requirement of a laparoscope operation of a minimally invasive operation robot, realizes the binocular stereoscopic vision real-time display in the laparoscope operation, has reliable performance, simple structure and high commercialization level, and adapts the germfree circumstances of the operation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
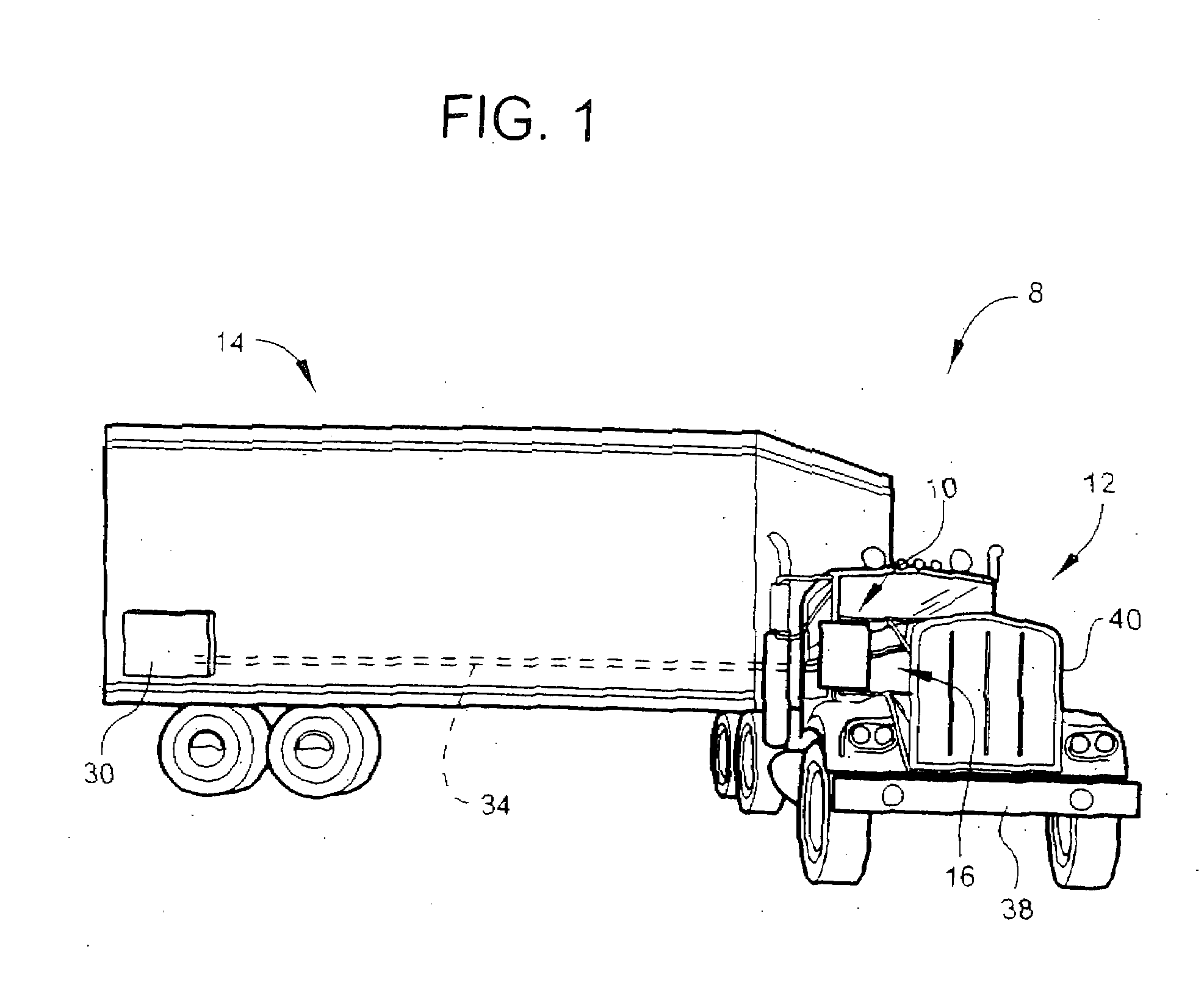
Mirror system for a trucking rig having a tractor and an articulated trailer
A mirror system for a tractor with an articulated trailer includes a mirror housing. The mirror housing is attached to the front end of the tractor on the passenger side. The mirror housing has a planar mirror. The planar mirror is adapted to move. The planar mirror moves allowing continuous observation of the passenger side rear corner of the trailer by a driver.
Owner:BEALE HARRY A
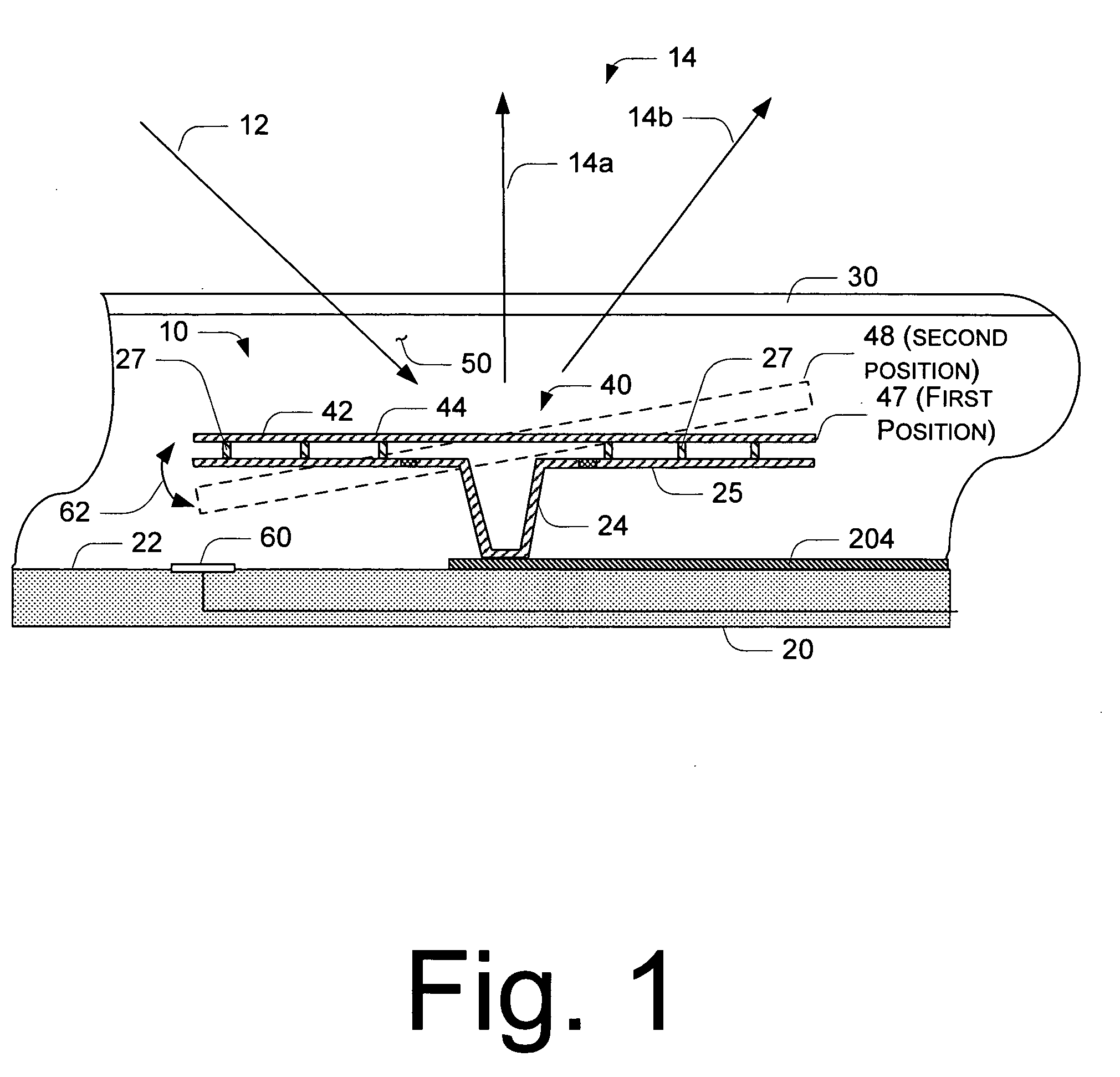
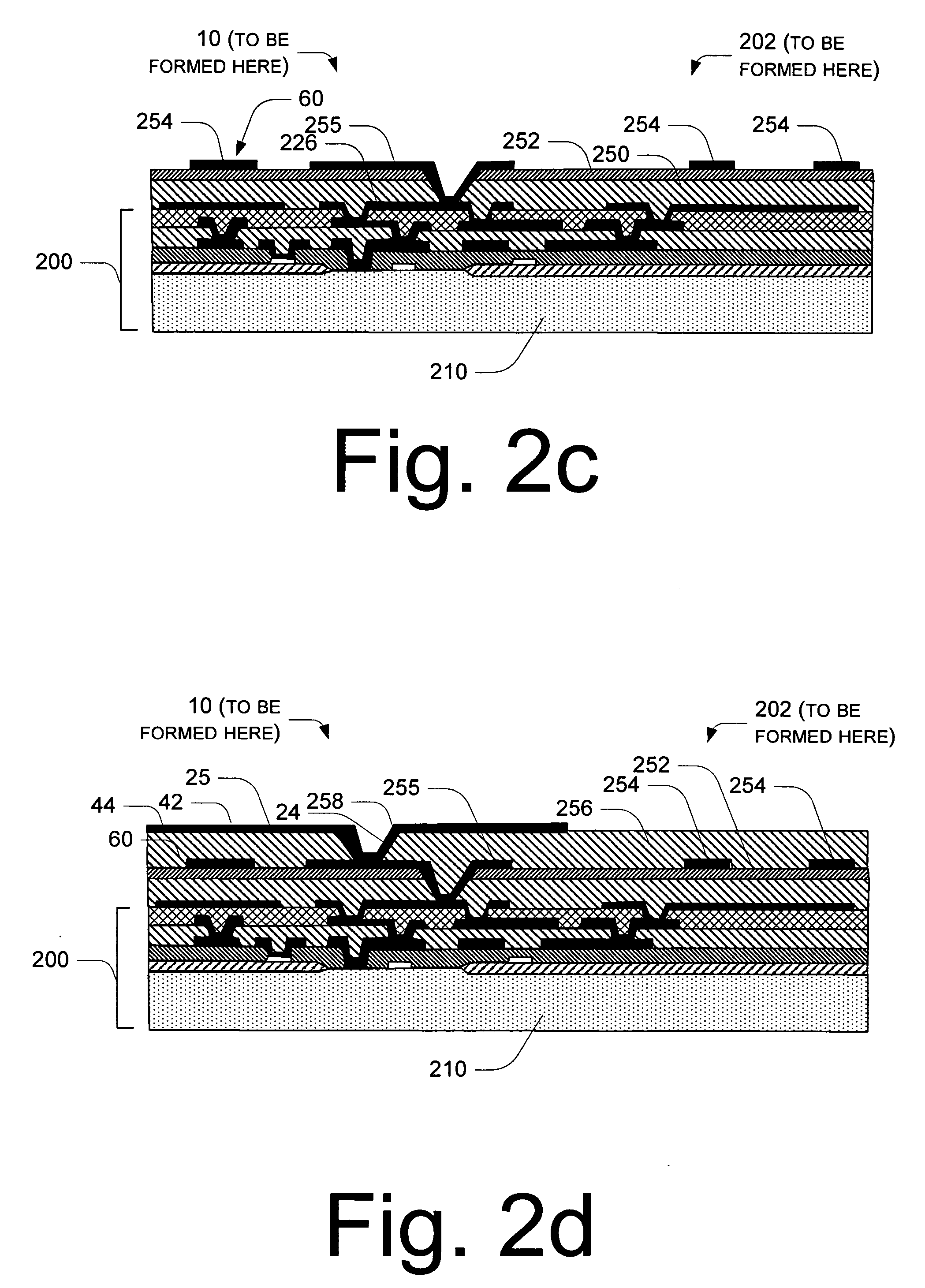
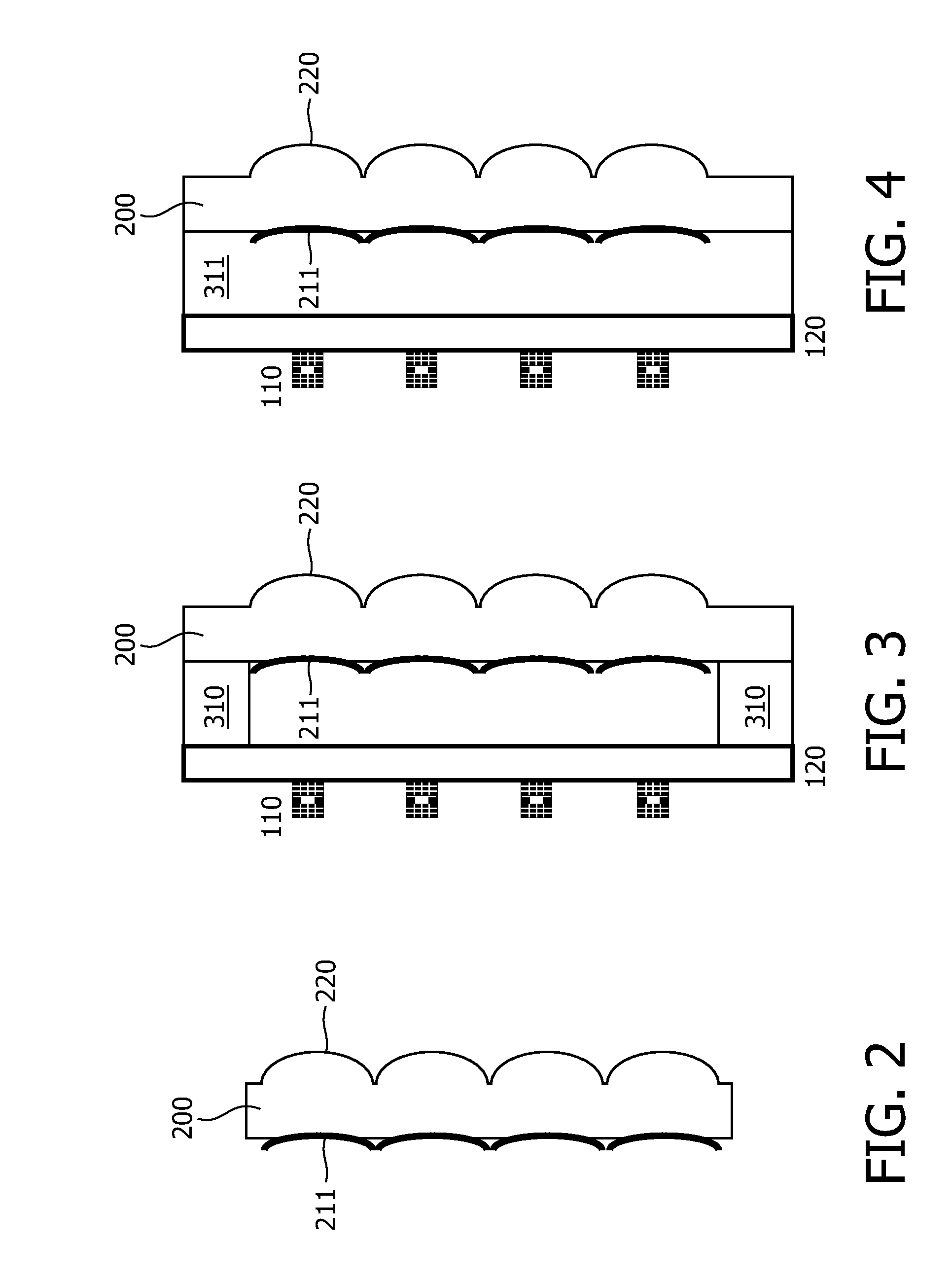
Method for forming a planar mirror using a sacrificial oxide
A micro electromechanical system (MEMS) mirror, comprising a displaceable hinged member, a mirror plate, and a plurality of mirror support elements. The mirror plate has a planar mirror face affixed thereto. The plurality of mirror support elements extend between the displaceable hinged member and the mirror plate.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Illumination optical system and exposure apparatus including the same
InactiveUS7538856B2Suppression of distortionConvenient lightingPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingIntegratorLight beam
Owner:CANON KK
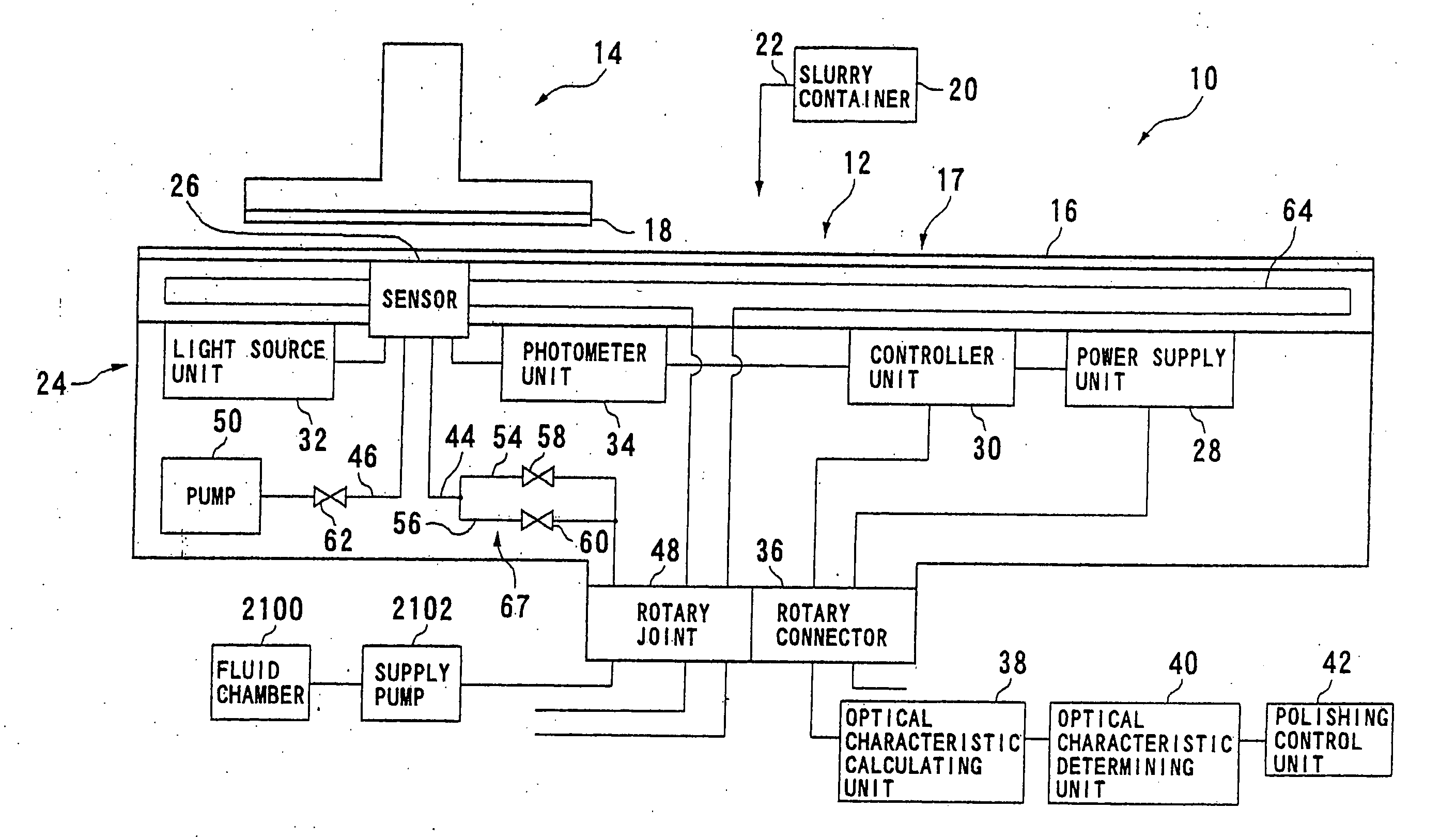
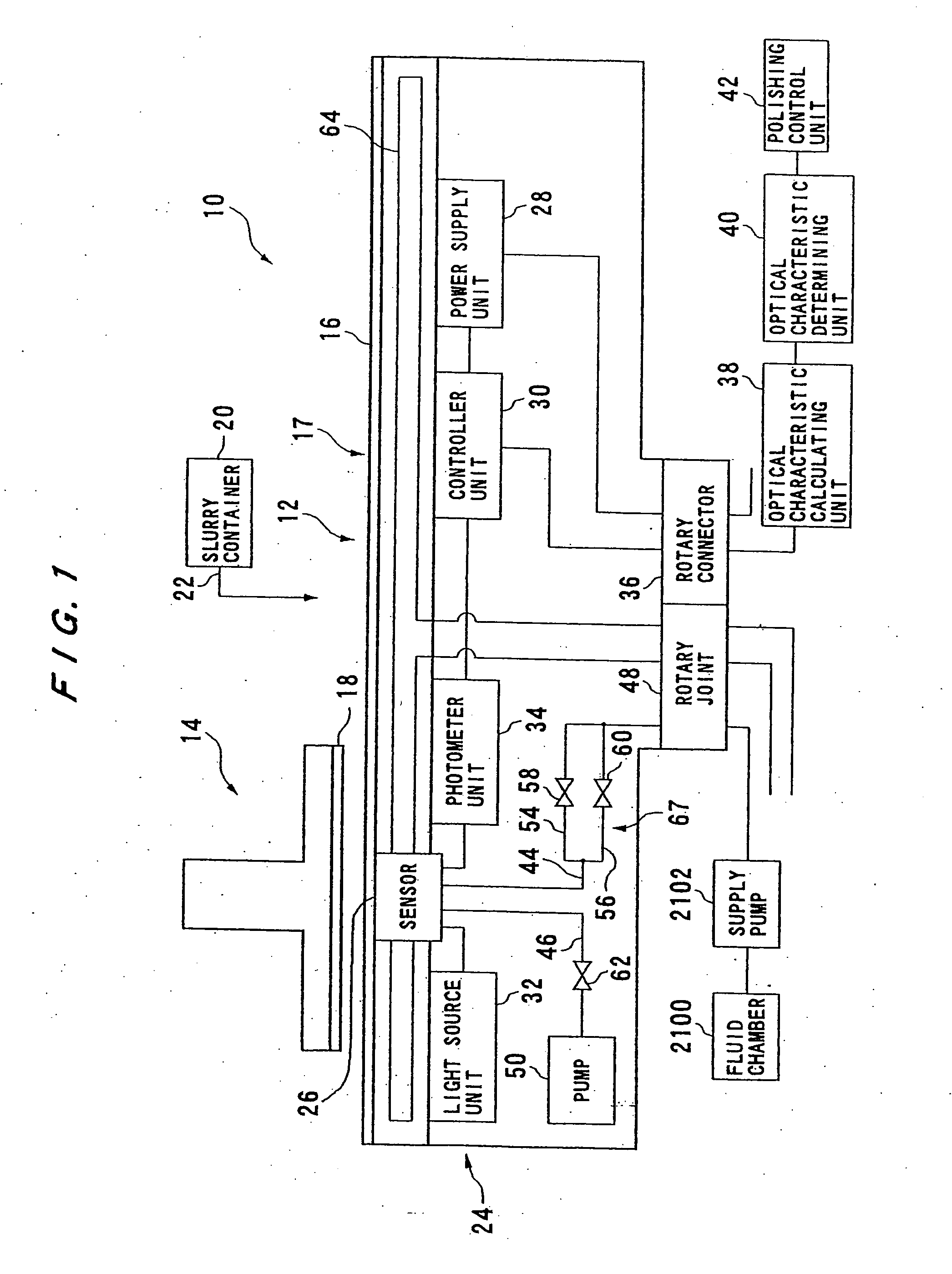
Polishing apparatus and method
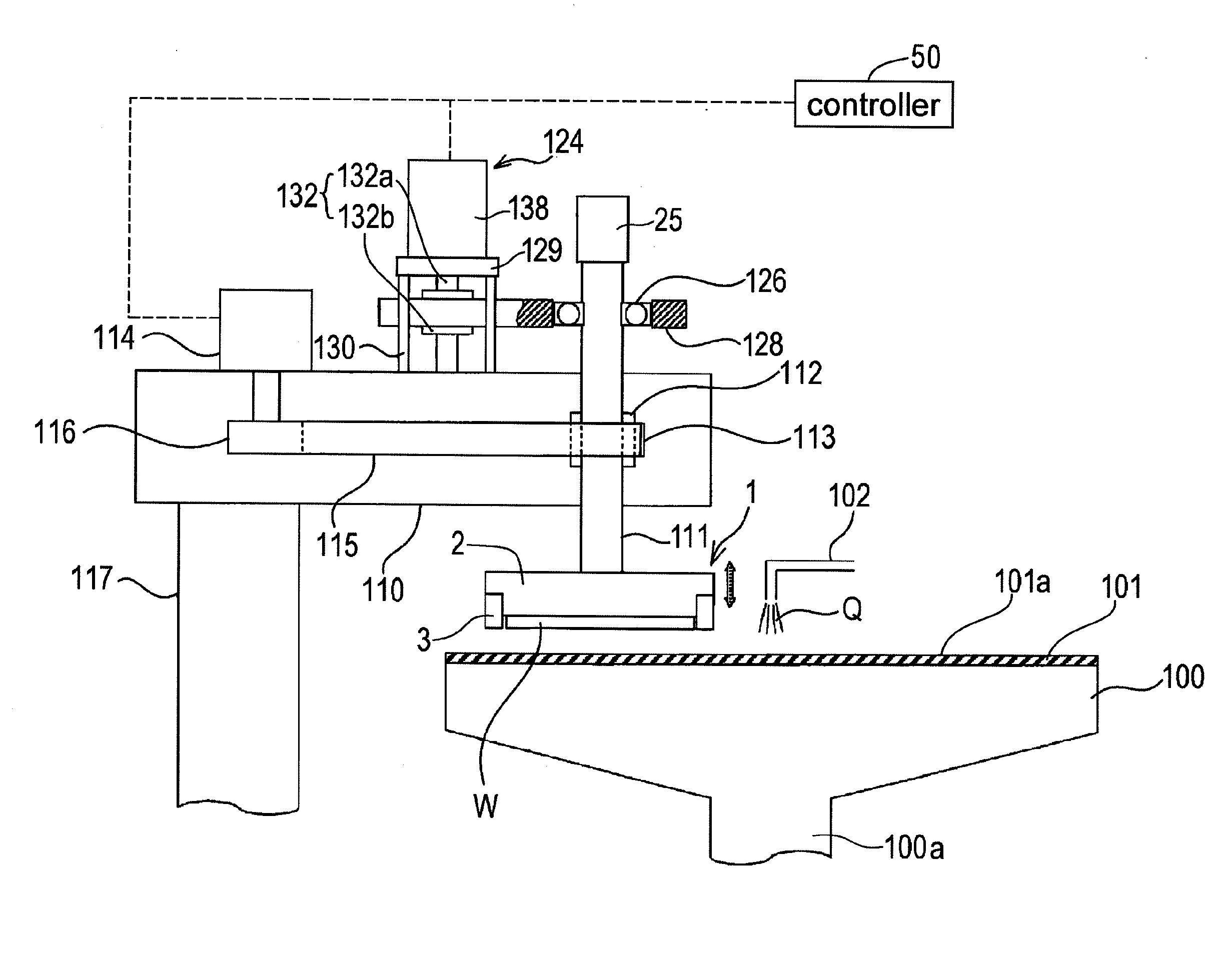
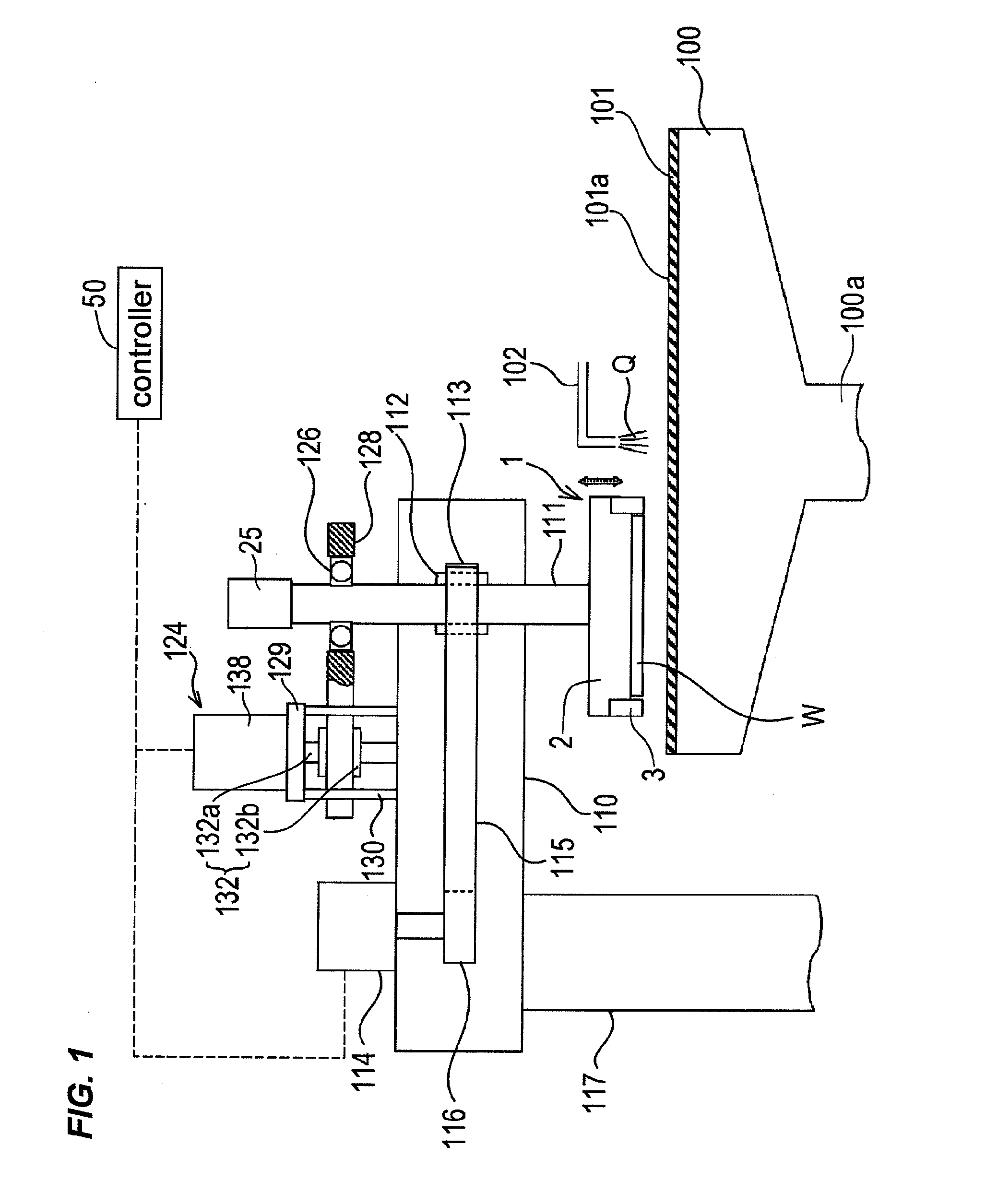
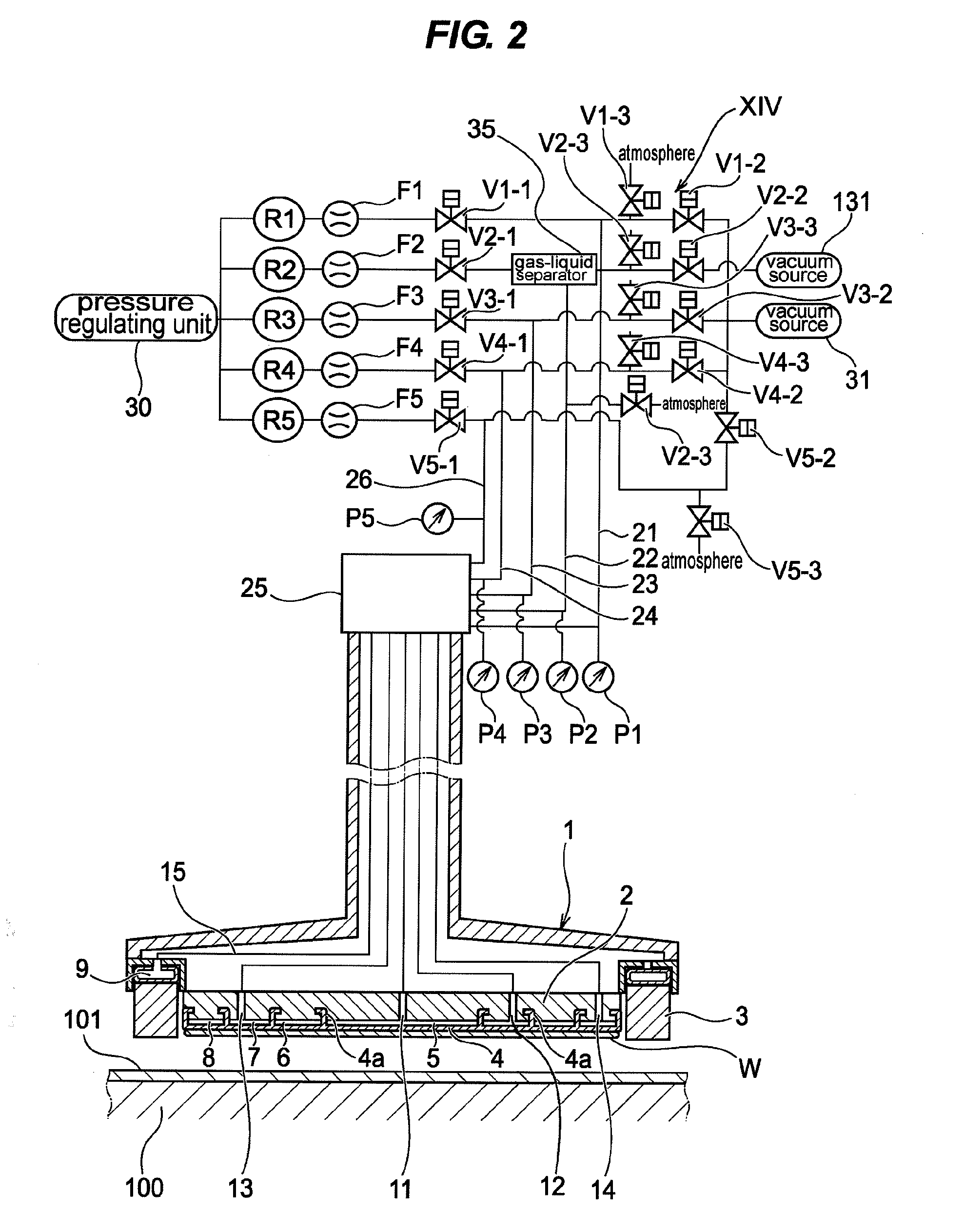
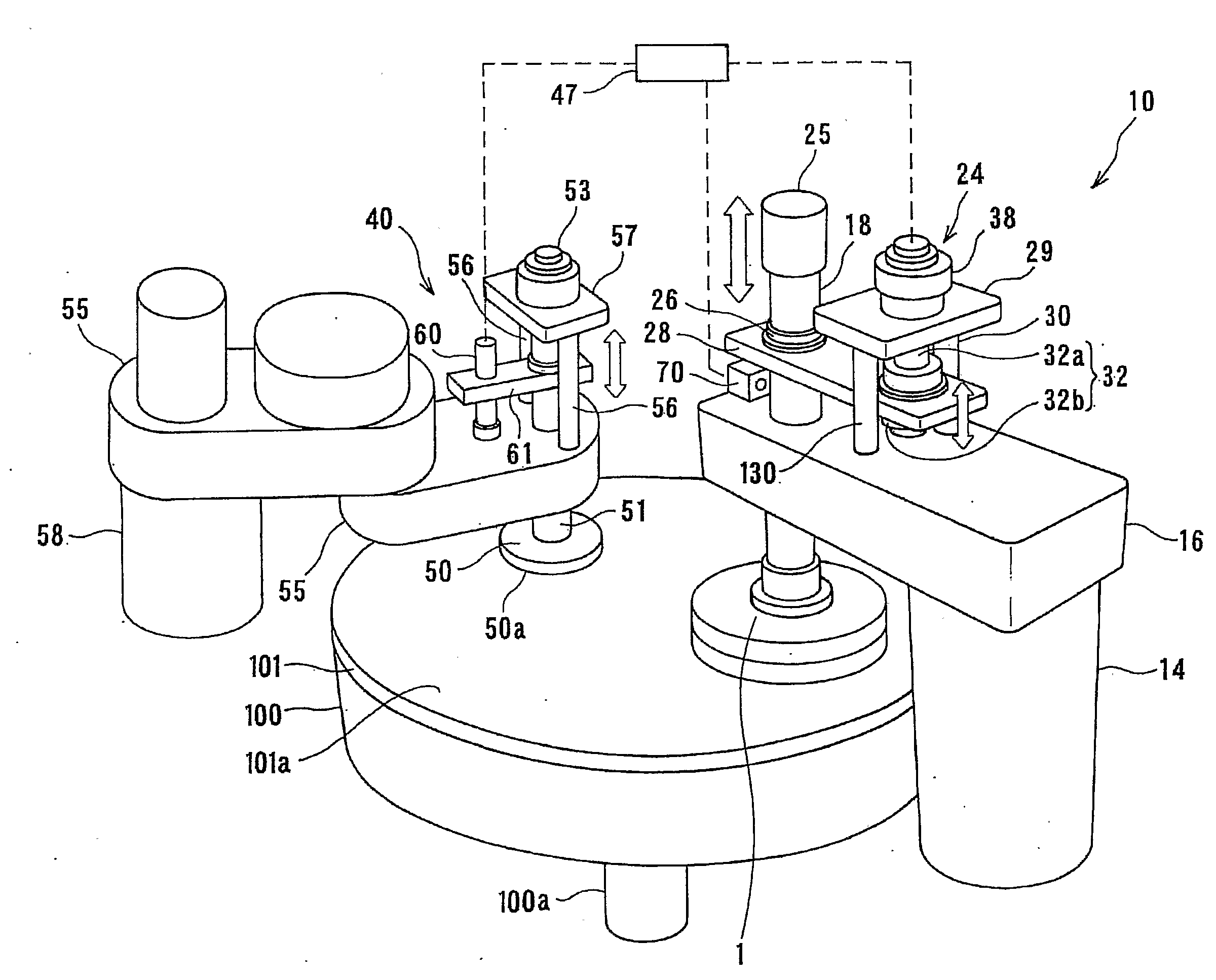
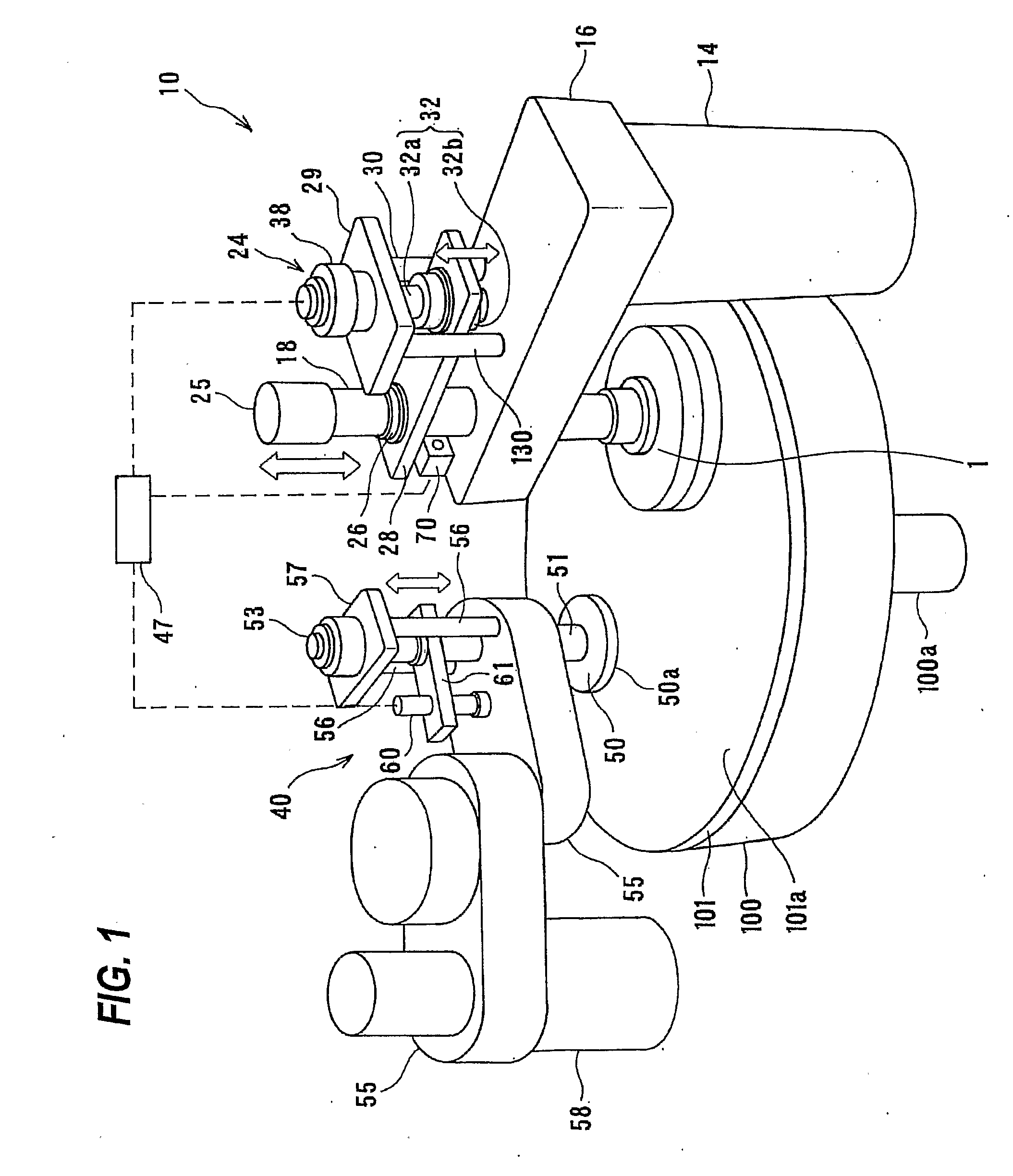
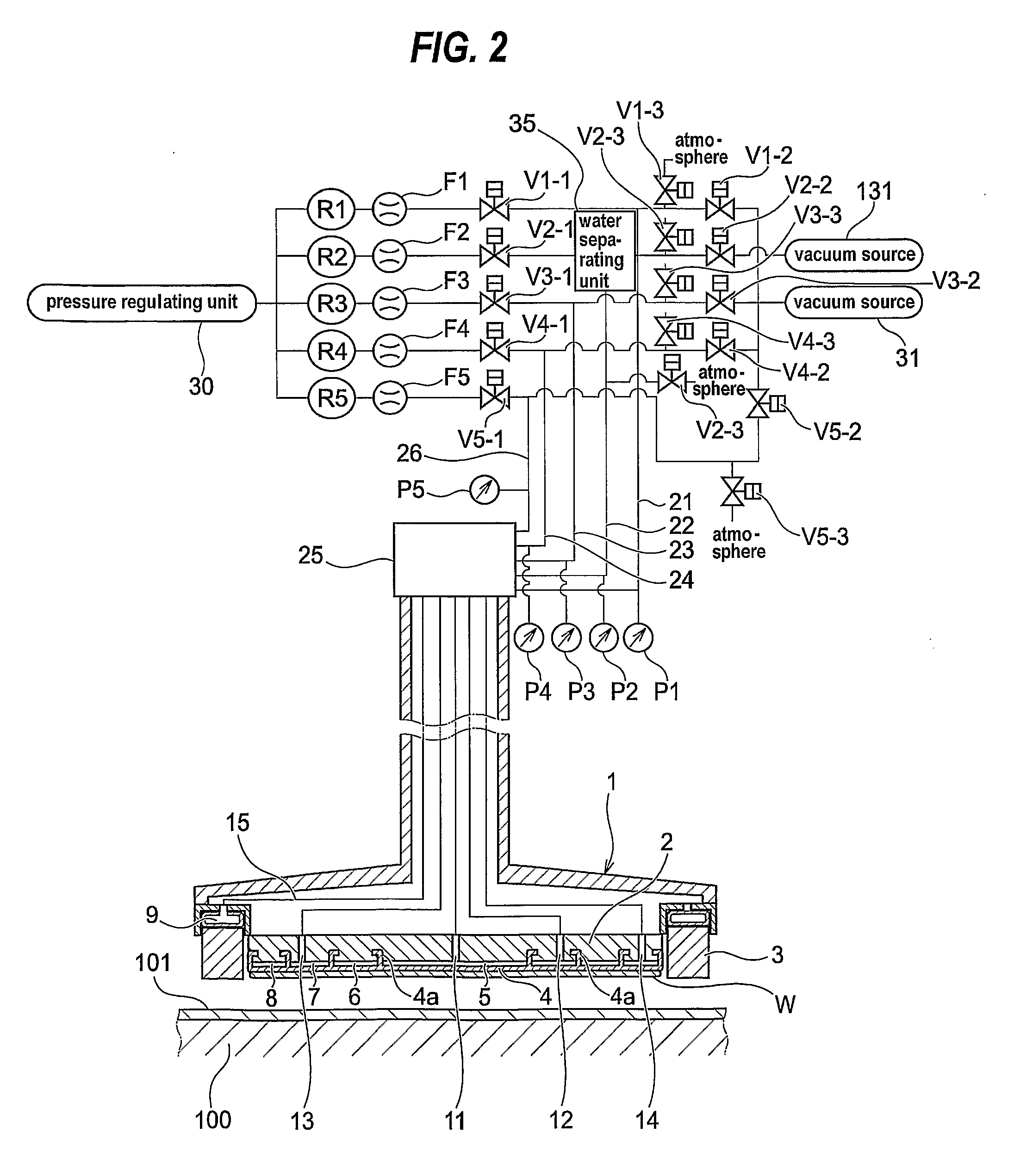
ActiveUS20120058709A1Preventing pressurizationReduce lossesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesThermal energyEngineering
A polishing is used for polishing a substrate such as a semiconductor wafer to a flat mirror finish. The polishing apparatus includes a polishing table having a polishing surface, a substrate holding apparatus configured to hold the substrate and to press the substrate against the polishing surface, and a controller. The substrate holding apparatus includes an elastic membrane configured to form a substrate holding surface which is brought into contact with the substrate, a carrier provided above the elastic membrane, at least one pressure chamber formed between the elastic membrane and the carrier, and an infrared light detector configured to measure thermal energy from the elastic membrane. The controller calculates an estimate value of a temperature of the elastic membrane using a measured value of the infrared light detector.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Method and apparatus for polishing a substrate
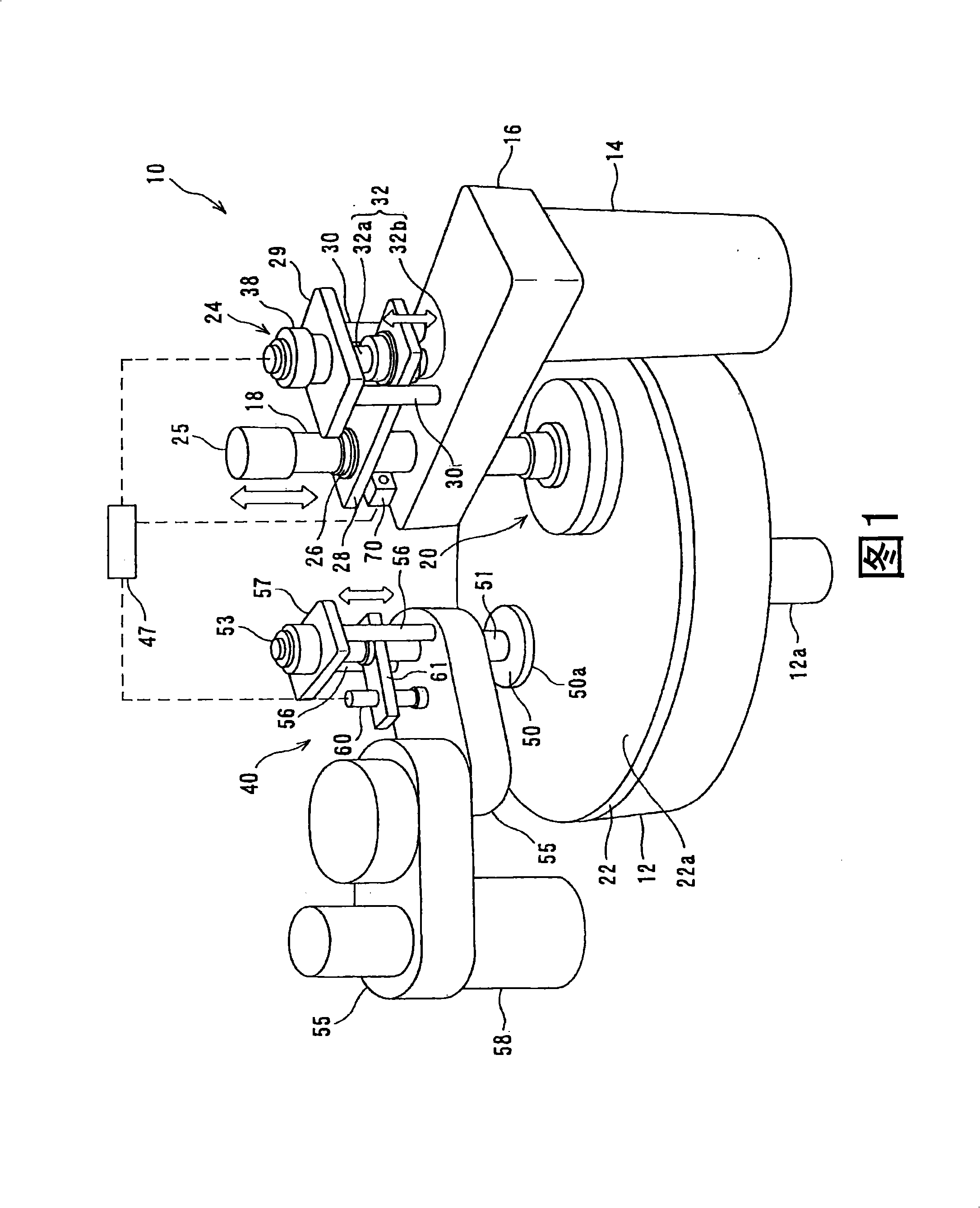
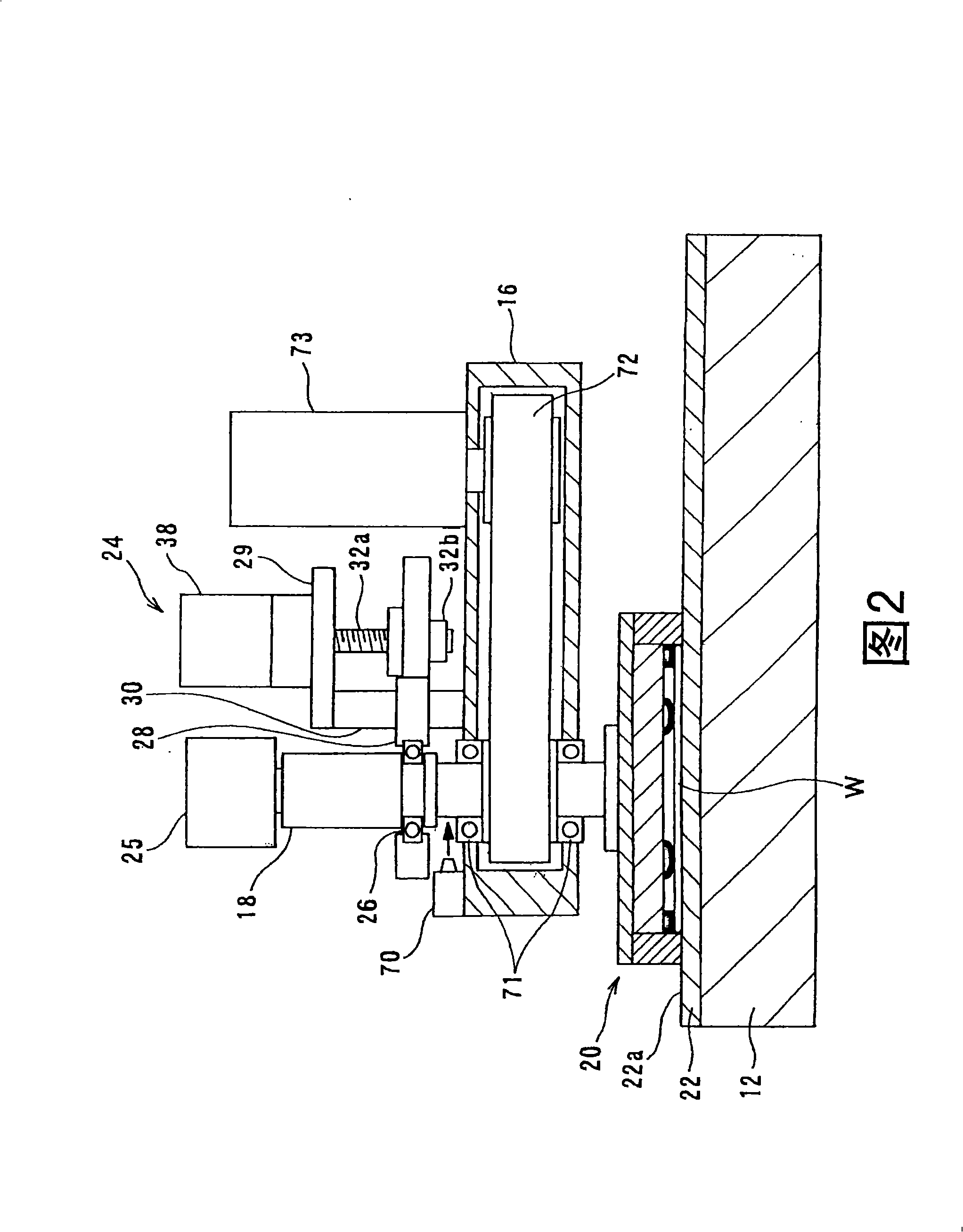
ActiveUS20110159783A1Suppression of deformationReducing stress appliedGrinding drivesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlat mirrorEngineering
A polishing method is used for polishing a substrate such as a semiconductor wafer to a flat mirror finish. A method of polishing a substrate by a polishing apparatus includes a polishing table (100) having a polishing surface, a top ring (1) for holding a substrate and pressing the substrate against the polishing surface, and a vertically movable mechanism (24) for moving the top ring (1) in a vertical direction. The top ring (1) is moved to a first height before the substrate is pressed against the polishing surface, and then the top ring (1) is moved to a second height after the substrate is pressed against the polishing surface.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Polishing apparatus
InactiveUS6939208B2Maintain performanceHigh yieldEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
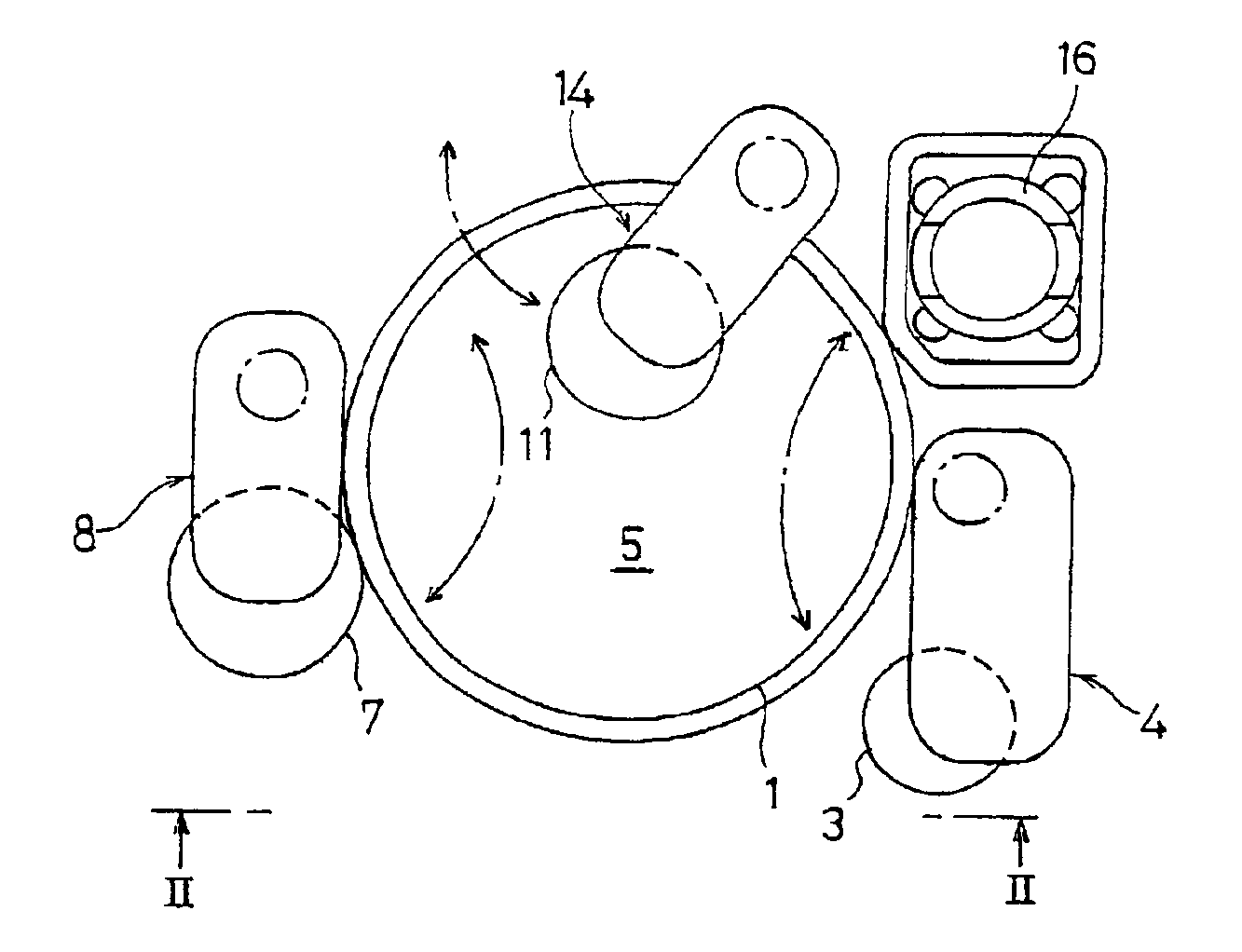
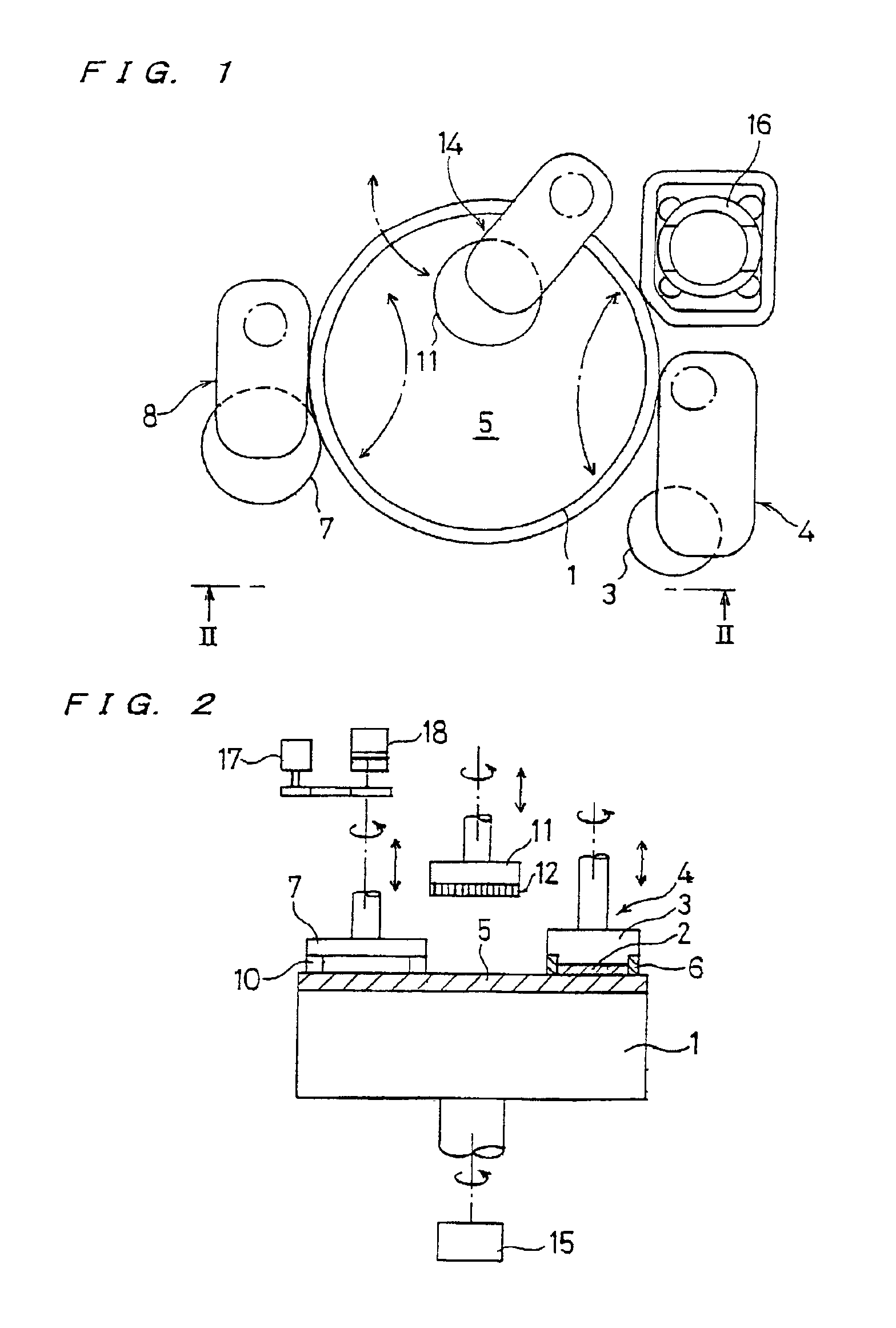
The present invention relates to a polishing apparatus for polishing a workpiece, such as a semiconductor wafer, to a flat mirror finish. The polishing apparatus comprises a polishing table having a polishing surface, and a top ring, and the workpiece is interposed between the polishing table and the top ring, and pressed at a predetermined pressure to polish the workpiece. The polishing apparatus comprises at least two dressing units for dressing the polishing surface by being brought into contact with the ppolishing surface, which is a surface of a polishing cloth.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Head-up display device
ActiveUS20150098029A1Reduce the amount of lightAvoid breakingStatic indicating devicesPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsHead-up displayInfrared
Provided is a head-up display (HUD) device capable of effectively preventing damage to a liquid-crystal display device due to entry of exterior light. A HUD device has a liquid-crystal panel, and is provided with a liquid-crystal display device for realizing a transparent display using light from a backlight, a control means for controlling the liquid-crystal display device, and an optical system for reflecting the display light outputted by the liquid-crystal display device onto a windshield. A flat mirror constituting the optical system allows infrared rays of incident light to pass behind the mirror and reflects the visible light. The HUD device is provided with an infrared-ray sensor positioned behind the flat mirror, and the control means reduces the brightness of the light of the backlight or extinguishes the backlight when the strength detected by the infrared-ray sensor exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:NIPPON SEIKI CO LTD
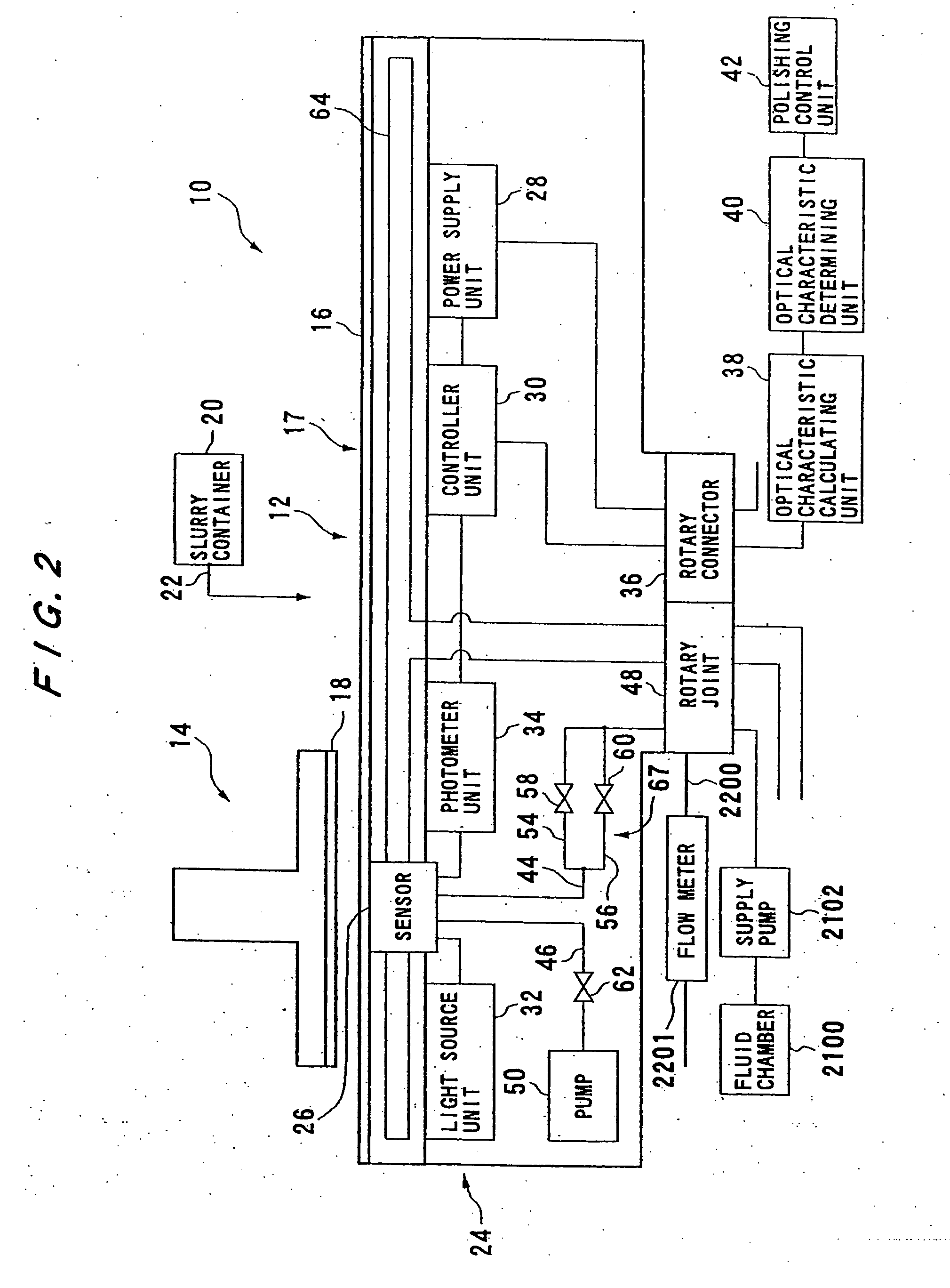
Polishing apparatus
ActiveCN101254586ASolve the real problemIncrease Cumulative Polishing TimePolishing machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl theorySemiconductor
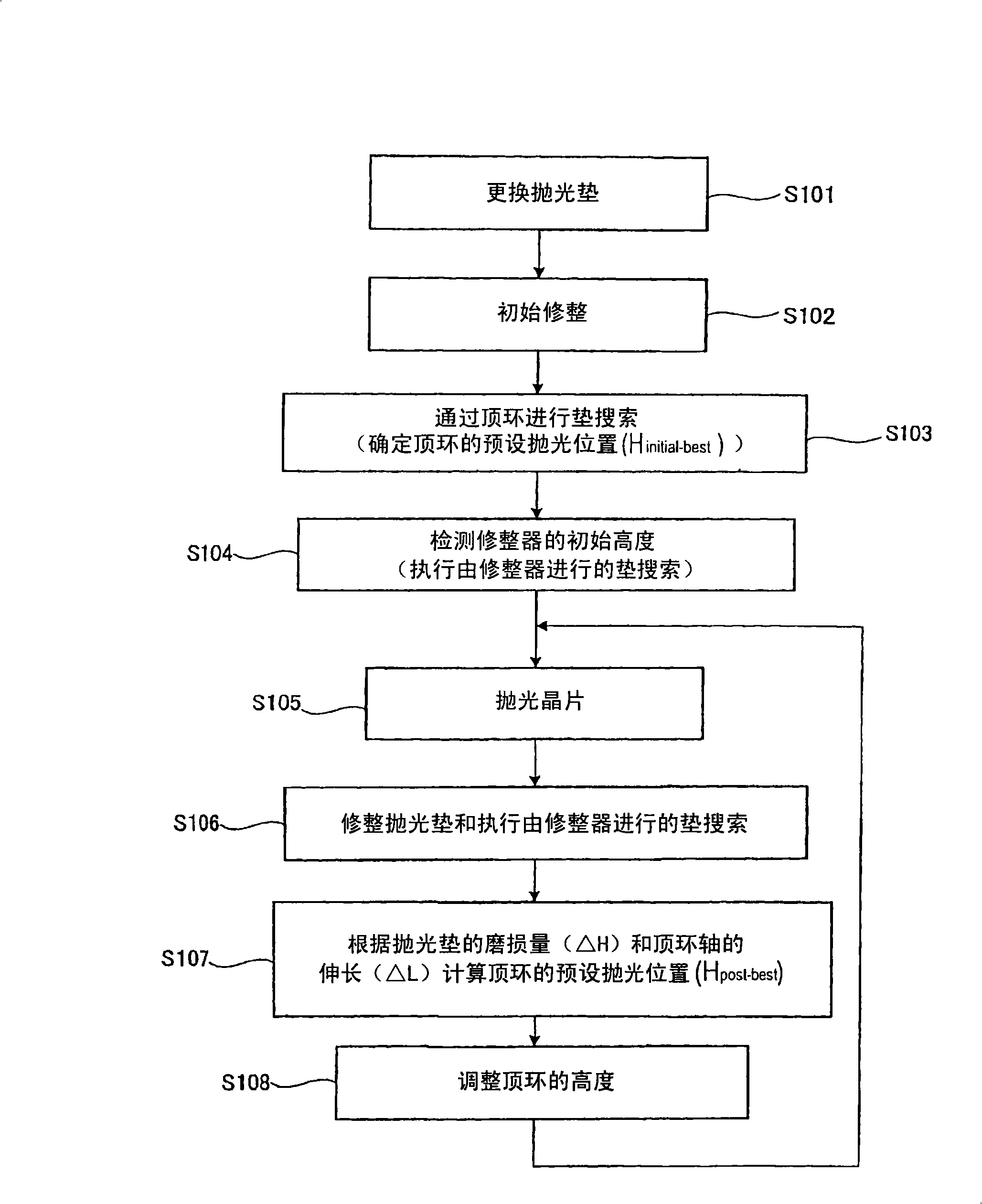
A polishing apparatus is used for polishing a substrate such as a semiconductor wafer to a flat mirror finish. The polishing apparatus includes a polishing table having a polishing surface, a top ring configured to hold and press the substrate against the polishing surface, a top ring shaft configured to lift and lower the top ring, and an elongation detecting device configured to detect an elongation of the top ring shaft. The polishing apparatus further includes a controller configured to set a vertical position of the top ring at the time of polishing, and control a lifting and lowering mechanism to lower the top ring to a preset polishing position as the set vertical position. The controller corrects the preset polishing position based on the elongation of the top ring shaft which has been detected by the elongation detecting device.
Owner:EBARA CORP
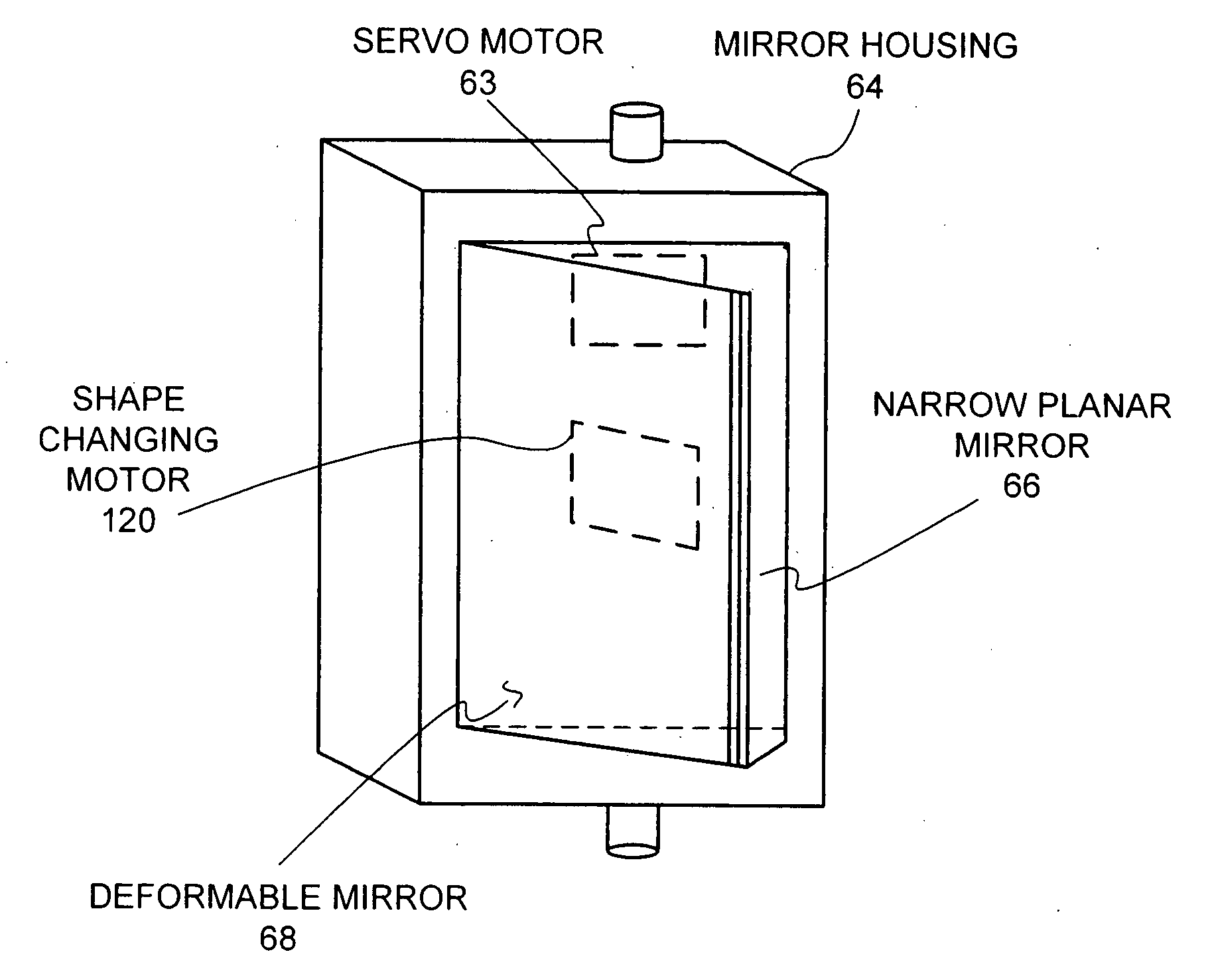
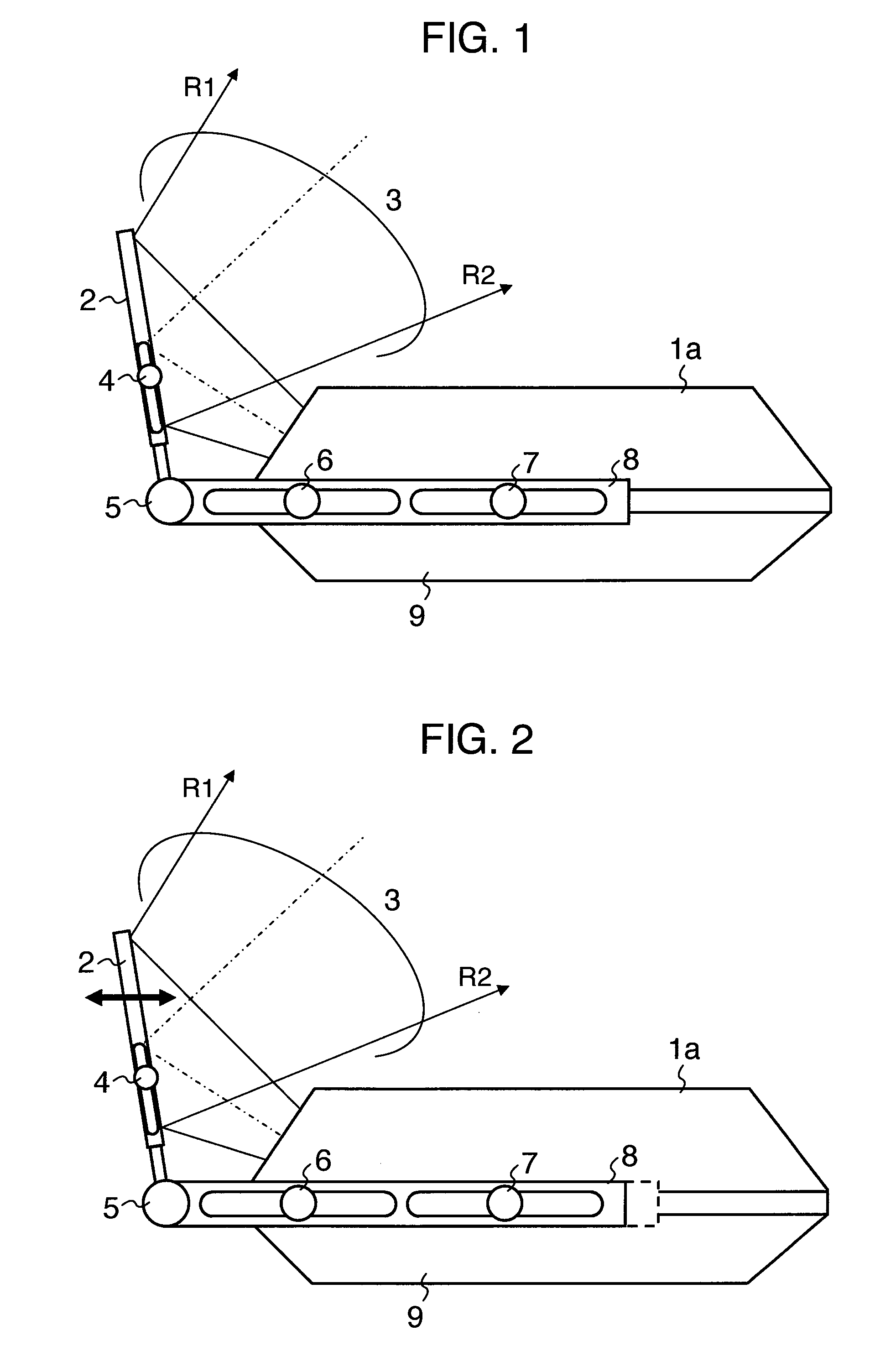
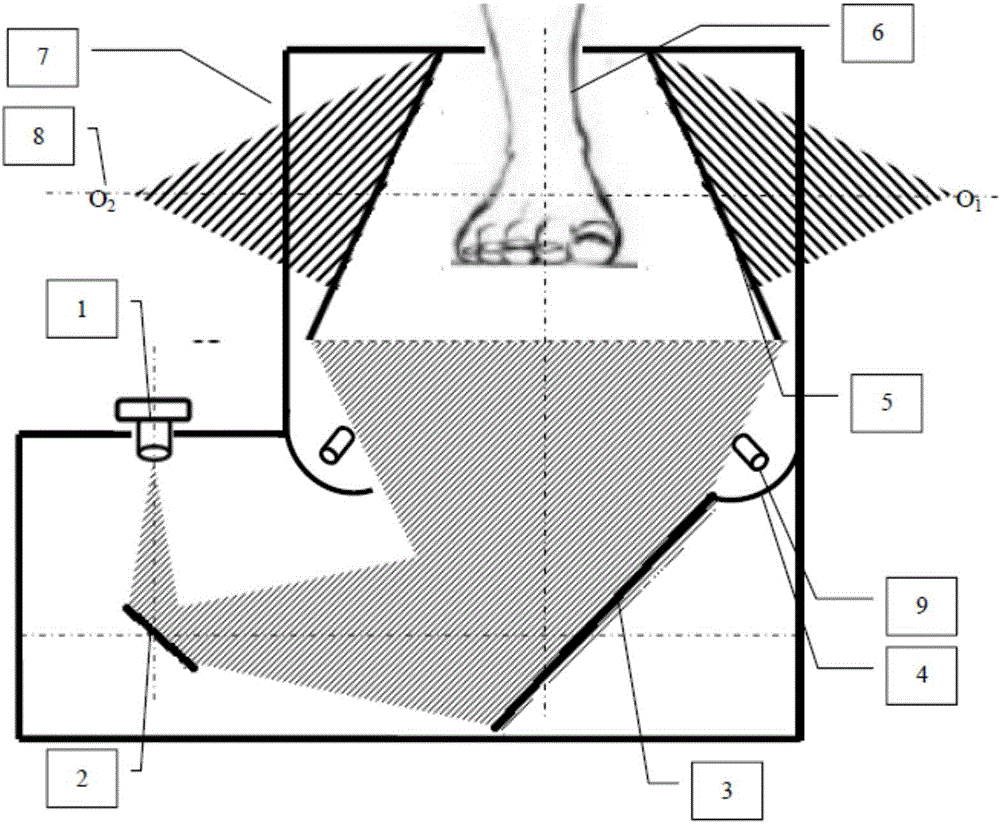
Secondary reflection light gathering and heat collecting device with compound curved surface
InactiveCN101660845ALower relative altitudeLow costMirrorsSolar heat devicesLight energyCollector device
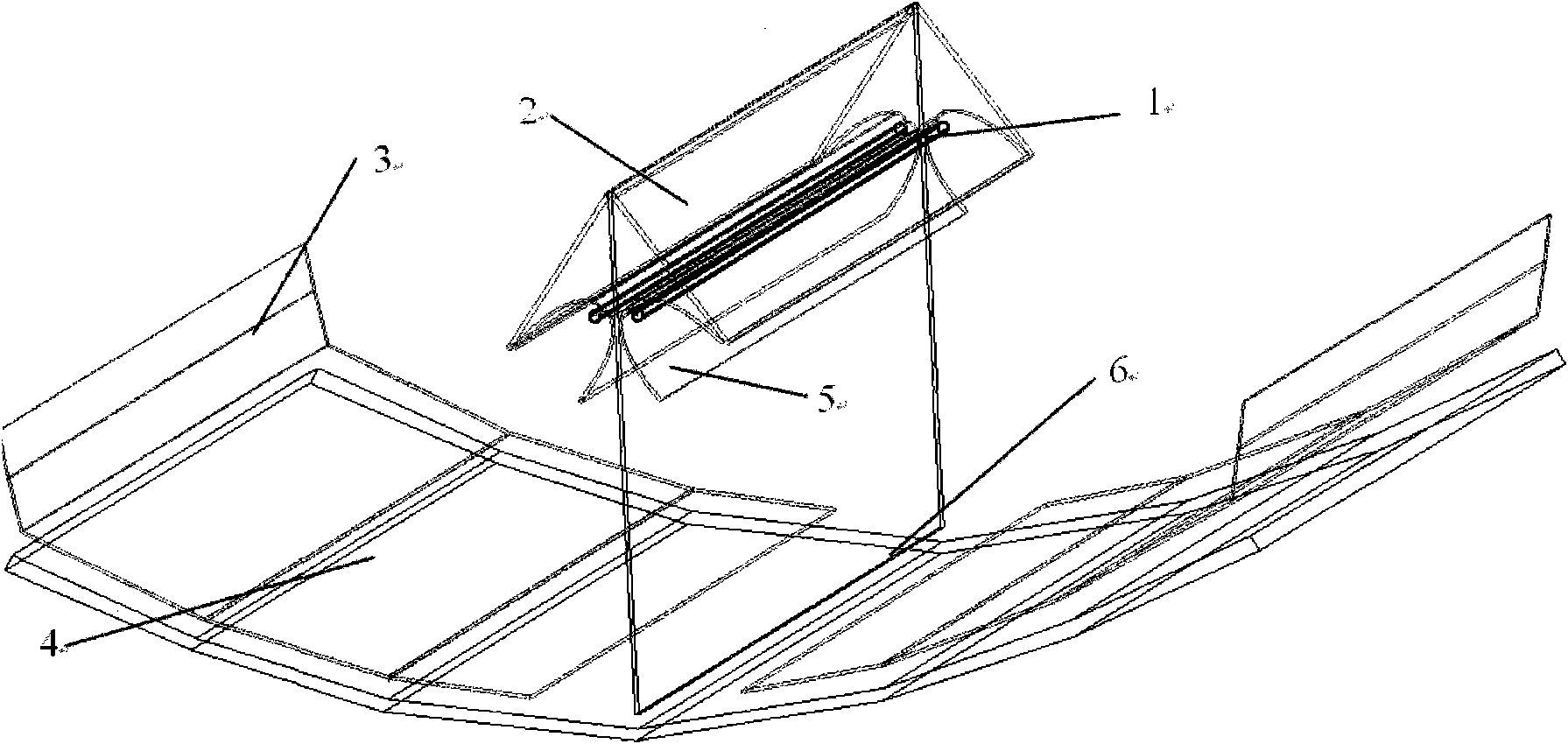
The invention provides a secondary reflection light gathering and heat collecting device with a compound curved surface, which relates to a solar slot type light gathering and heat collecting device and comprises a heat collecting tube (1), a plane primary reflector (2), a refracting plane secondary reflector (3), a compound circular arc primary reflector (4), a compound paraboloid secondary reflector (5) and a supporting frame (6), wherein the heat collecting tube (1) comprises two parallel heat collecting tubes and is positioned in the compound paraboloid secondary reflector (5), and the supporting frame (6) is positioned below the compound circular arc primary reflector (4) and used for fixing the compound circular arc primary reflector (4). By adopting the design of combination of onesupporting frame and two heat collecting tubes, the cost and the height of the heat collecting device can be remarkably reduced; by adopting the compound paraboloid secondary reflector, the requirement on the tracking accuracy is reduced; by adopting the compound circular arc primary reflector, the degree of freedom of the design is increased; and by adopting the design of combination of the planereflector and the refracting plane, the utilization ratio of the light energy is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Headlamp with a continuous long-distance illumination without glaring effects
InactiveUS7452115B2Efficient use ofImprove viewing effectVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceForward lookingStandard illuminant
Owner:ALCELIK TURHAN
Ophthalmic photographic apparatus
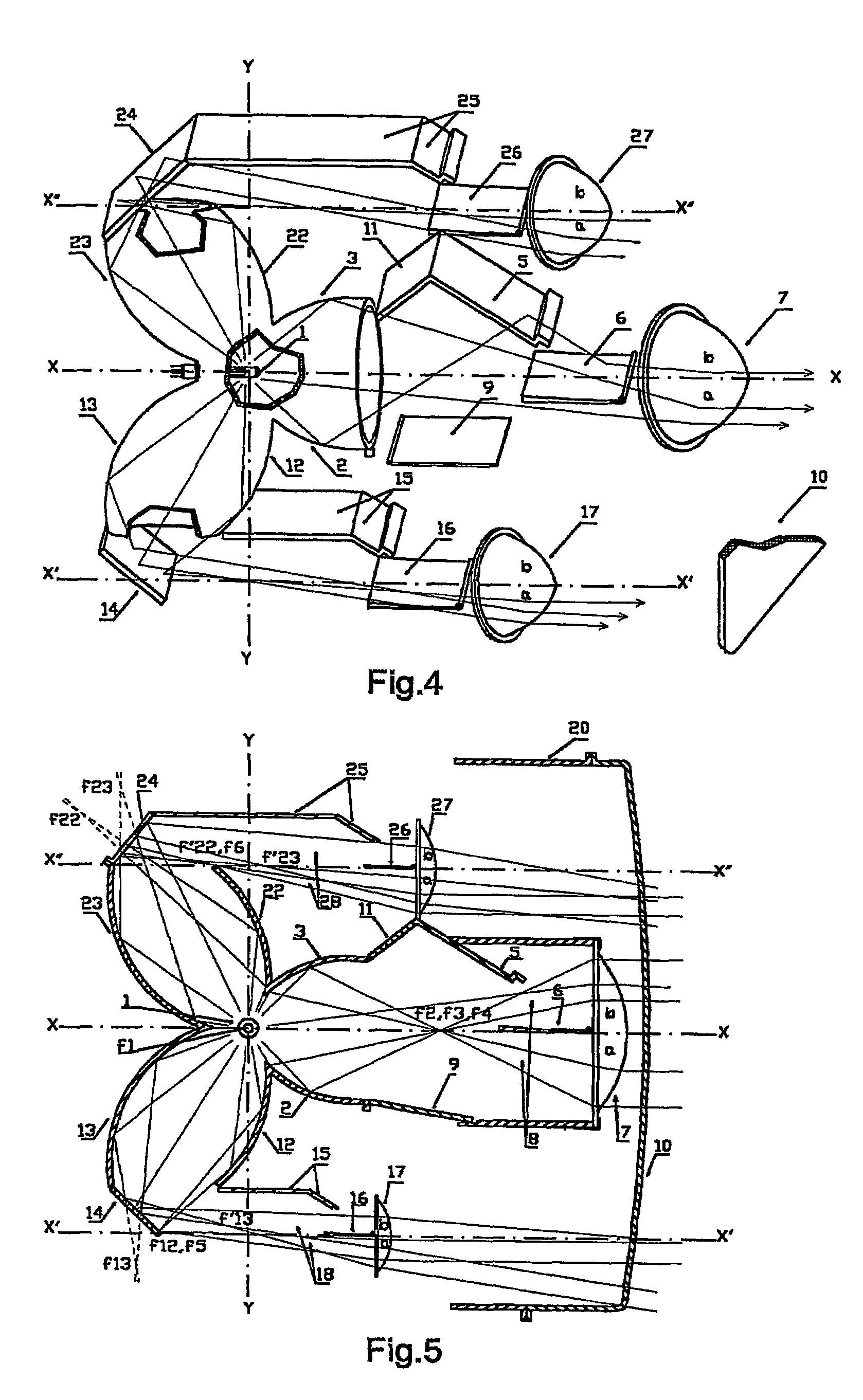
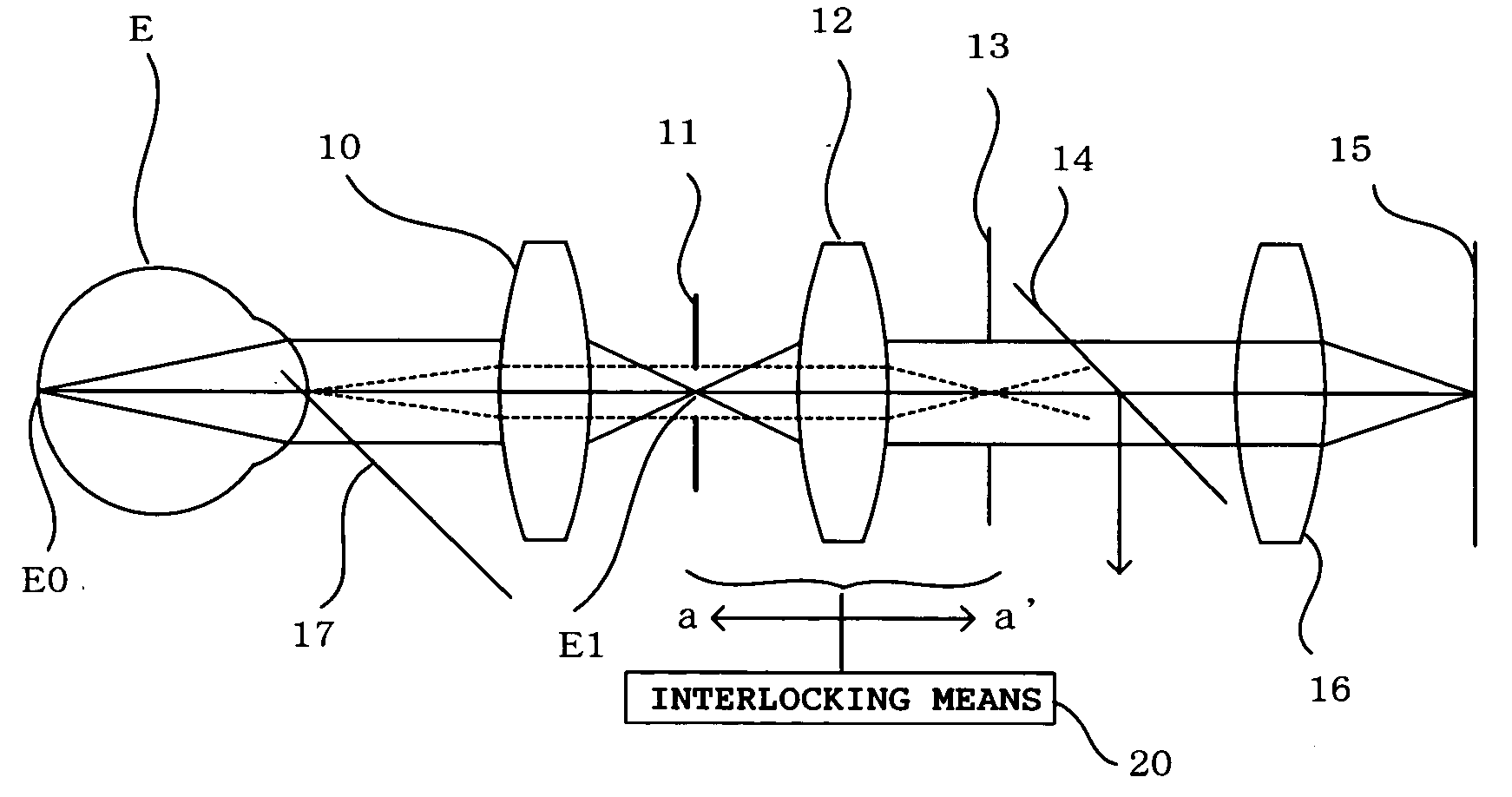
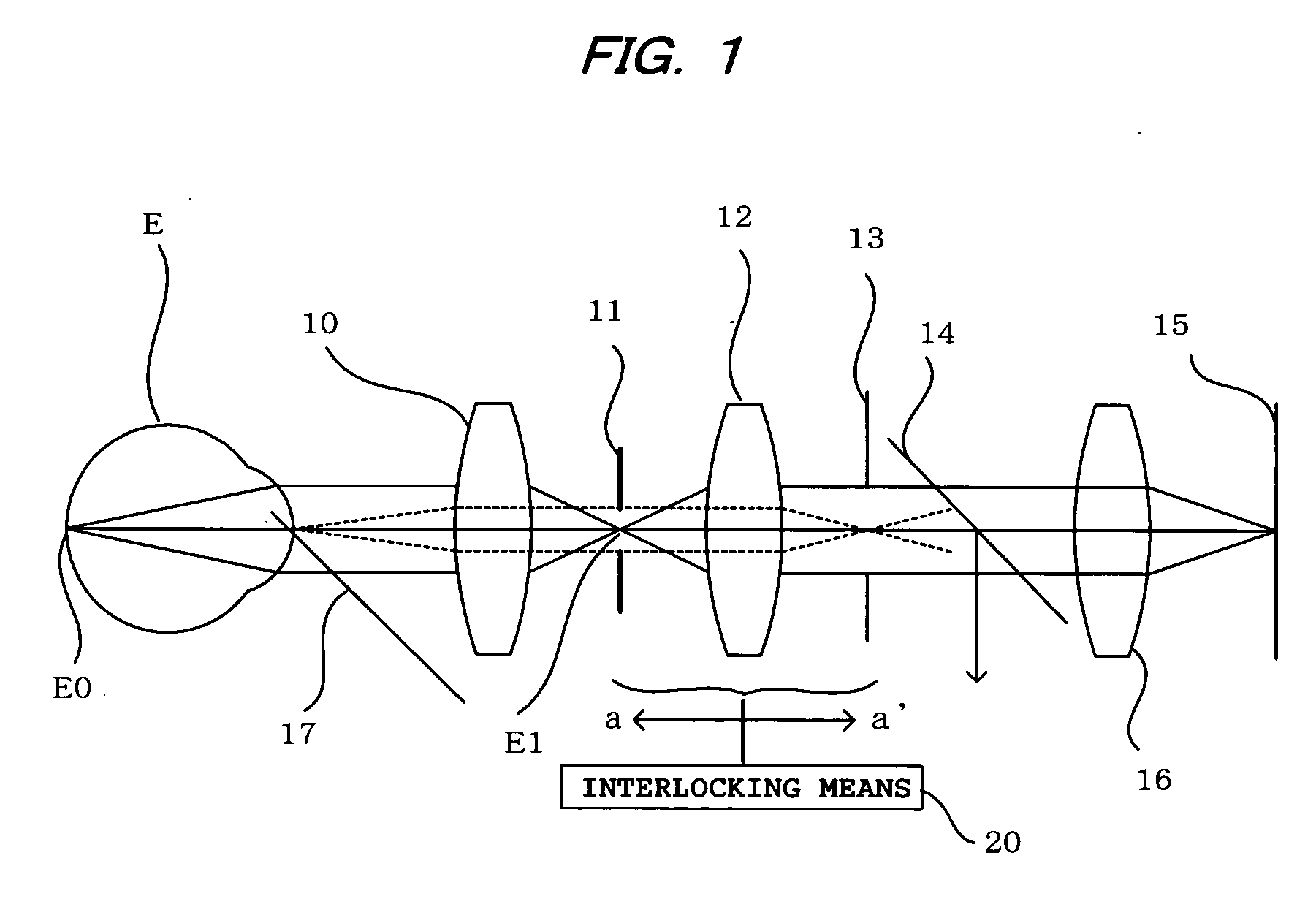
An ophthalmic photographic apparatus comprises a photographic mask for defining a fundus photography range, a photographic stop for eliminating light reflected from an anterior portion of the eye, and a focusing lens for bringing the fundus into focus. Interlocking means are provided to move the photographic mask and the photographic stop in an interlocked manner relative to the movement of the focusing lens in such a way that with respect to a photographic optical system the photographic mask may be kept at a position substantially conjugate with an imaging plane of a CCD and the photographic stop may be kept at a position substantially conjugate with an anterior portion of the eye. The CCD is located at the image-side focal plane of the image-formation lens, the mask is located on the object-side focal plane of the focusing lens, and the photographic stop is located on the image-side focal plane of the focusing lens. These three components are moved as one unit when the system is adjusted to focus on the fundus.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD +1
Oblique projection optical system and projection type display apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20100171937A1Shorten the timeReduce development costsProjectorsColor television detailsOptical axisProjection screen
A projection type display apparatus including an oblique projection optical system having a plurality of lenses is disclosed. A lens nearest to a projection screen has a vertical effective image area through which a light flux passes. The lens is arranged at a position not including an optical axis shared by the largest number of lenses among the plurality of lenses. A flat mirror for returning the optical path is arranged between the particular lens and the projection screen at a predetermined angle to the optical axis. An enlarged image obtained by the light flux returned by the flat mirror is formed toward a display screen.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
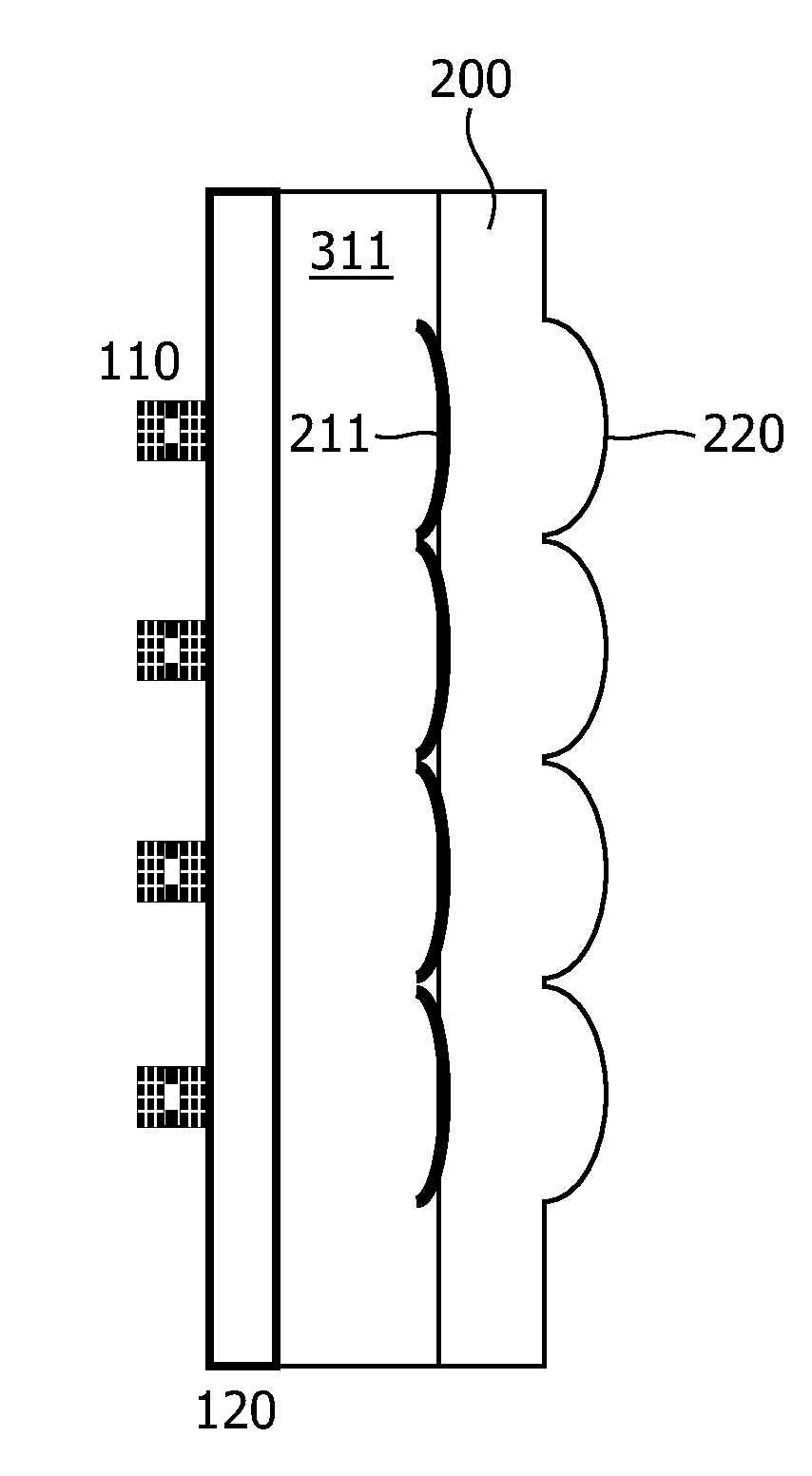
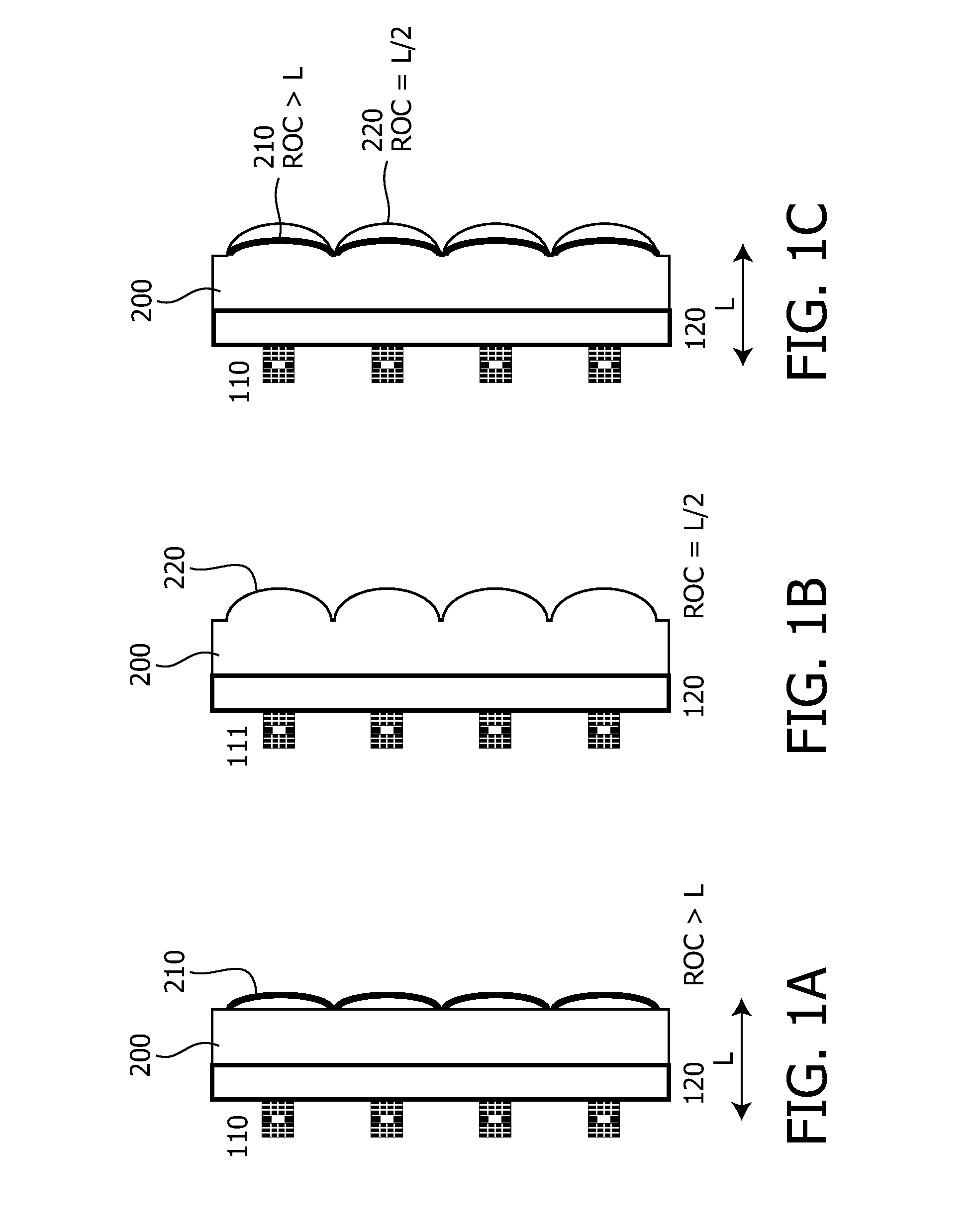
Optical element for vertical external-cavity surface-emitting laser
InactiveUS20130223466A1Increase brightnessLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionOptical radiationLength wave
The present invention relates to an optical element for VEC-SELs or VECSEL arrays. The optical element is formed of a substrate (200) which is transparent at least in a wavelength region of optical radiation. A first interface of the- substrate (200) comprises one or several curved regions forming part of an optical lens or of an array of optical lenses (220) integrated in the substrate (200). The substrate (200) further comprises one or several optical mirrors (210) formed on a second interface of the substrate (200) opposing the first interface or embedded in the substrate (200). The optical mirrors (210) are arranged and designed to back reflect a fraction of optical radiation incident on the first or second interface. The optical mirrors (210) are flat mirrors or curved mirrors having a radius of curvature different from the radius of curvature of the curved region (220). The optical element allows the fabrication of a VECSEL or VECSEL array having a high brightness without the requirement of additional adjustments during fabrication. The VECSEL are arranged at a distance (L) to the optical mirrors (210) and this equals the length of the external cavity. The ROC of the optical lens may be chosen to ROC=L / 2 and for the optical mirror ROC>L. The cavity length may be adjusted by a monolithic spacer (120)
Owner:TRUMPF PHOTONIC COMPONENTS GMBH
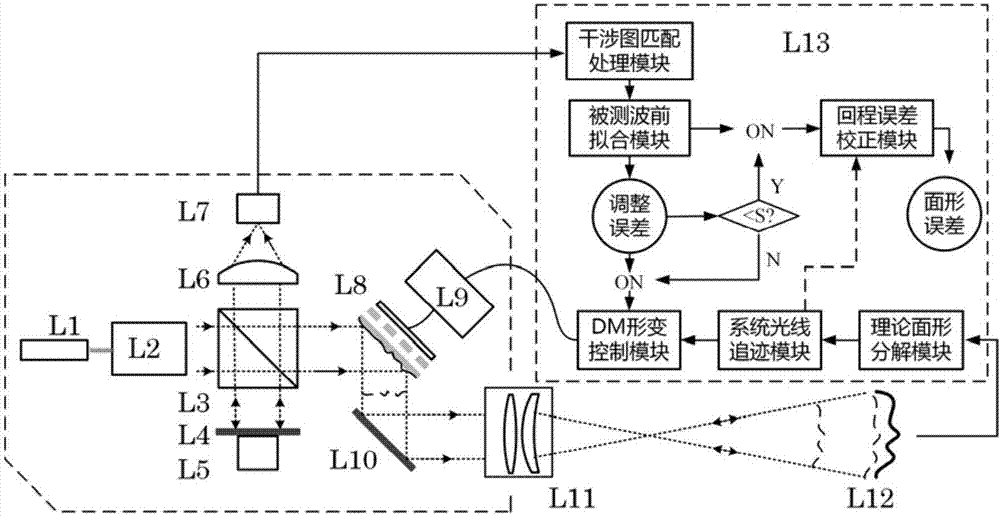
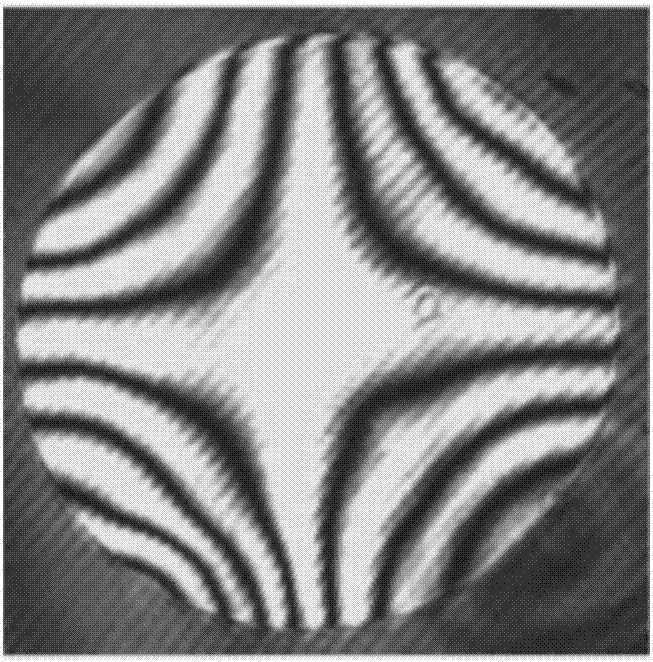
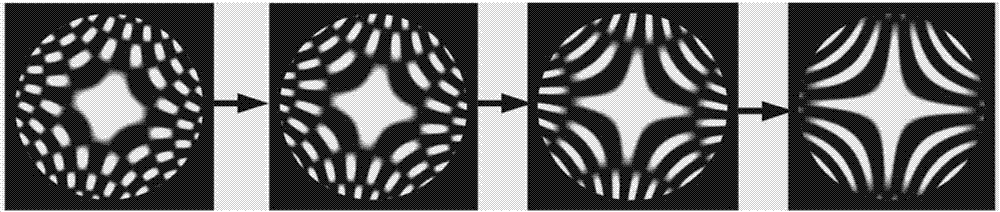
Adaptive non-zero digit interference detecting system for optical free curved surface
ActiveCN106918303AImplement non-zero bit detectionAchieving Adaptive CompensationUsing optical meansHysteresisBeam splitter
The invention discloses an adaptive non-zero digit interference detecting system for an optical free curved surface. The system comprises a free curved surface non-zero digit interference detecting system and an adaptive data processing and controlling system, wherein the free curved surface non-zero digit interference detecting system comprises a frequency stabilized laser, a collimating system, a beam splitter, a reference flat mirror, an imaging lens, a detector, a deformable reflector DM, a reflector and an aplanat. The adaptive data processing and controlling system comprises a system laser tracing module, a theoretical surface decomposition module, a DM deformation control module, an interferogram coupling processing module, a detected wavefront fitting module and a hysteresis error correction module. The adaptive non-zero digit interference detecting system can realize compensation for different Zernike low-order aberration by means of the continuous deformable reflector DM. Deformation of the deformable reflector is guided through the system laser tracing module, so that high-precision universal detection for a large-curvature changing free curved surface is realized.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Switchable Viewing Angle Display
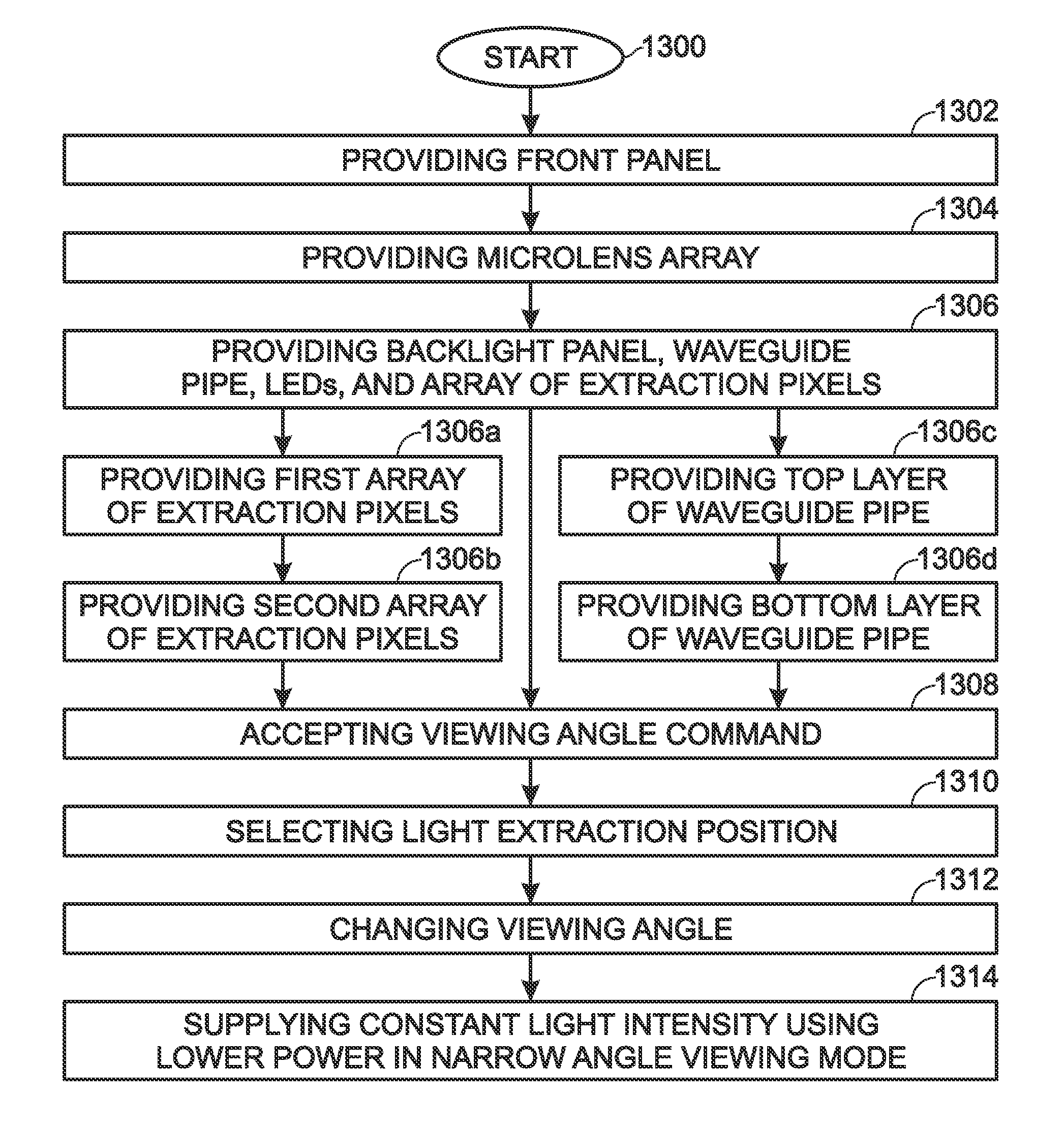
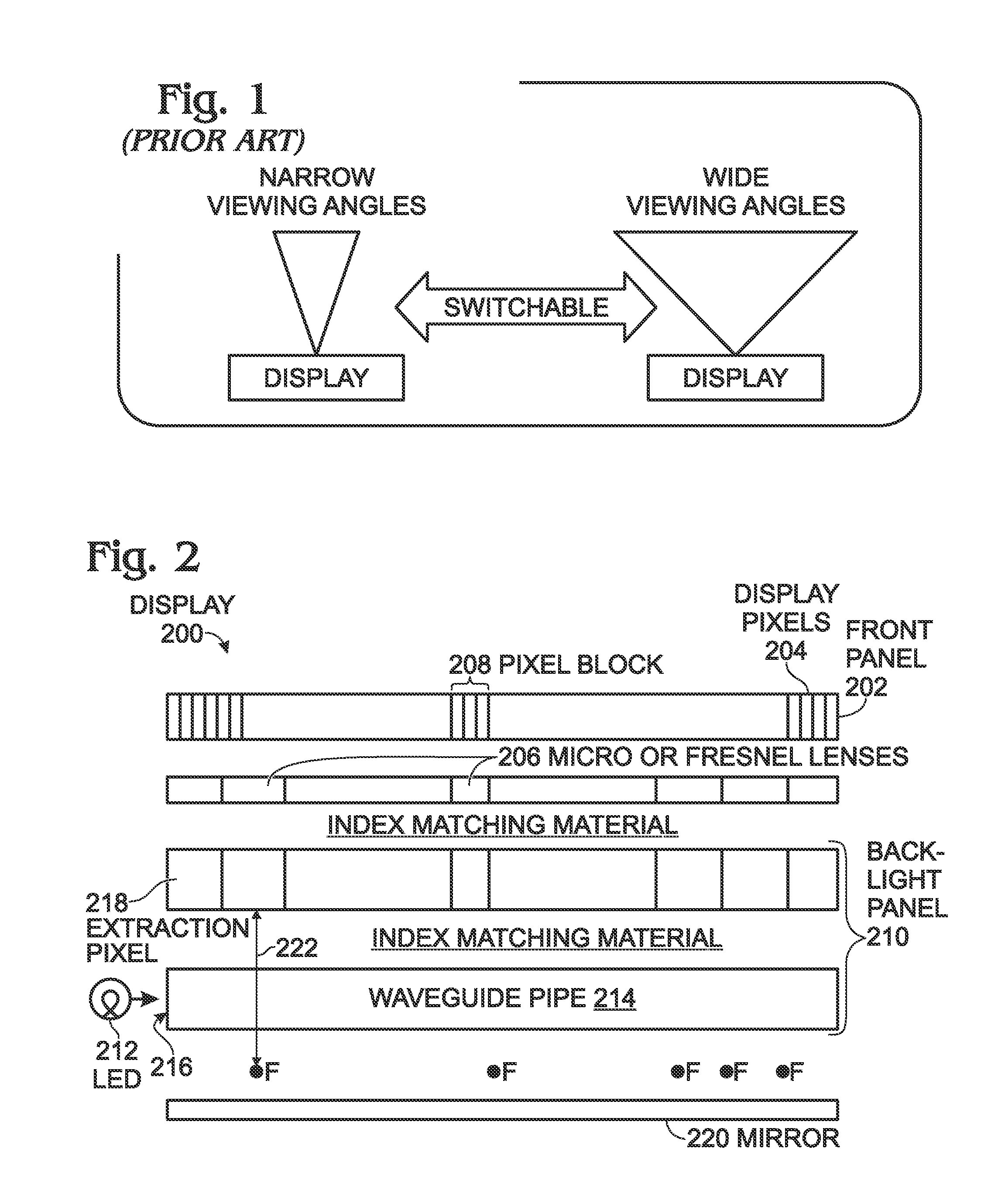
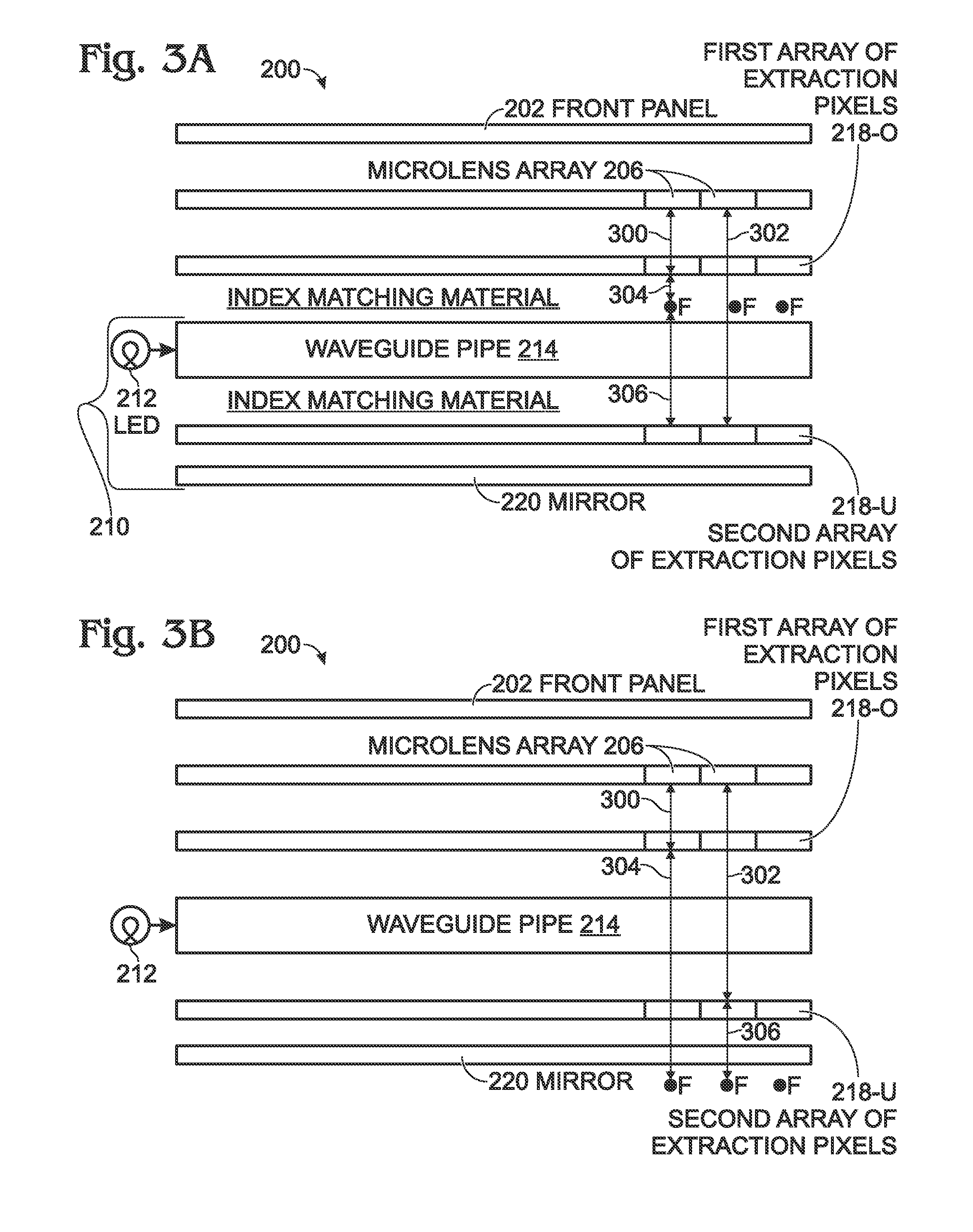
InactiveUS20120050342A1Reduce intensitySame brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceMicro lens array
A switchable viewing angle display method is provided, using arrayed microlenses and a waveguide pipe with selectable light extraction positions. The method provides a front panel array of display pixels. Also provided is an array of microlenses underlying the array of display pixels. Each microlens has a focal point and each microlens is associated with a corresponding block of display pixels. A backlight panel has an edge-coupled waveguide pipe with an optical input connected to a column of light emitting diodes (LEDs). The backlight panel includes an array extraction pixels, each extraction pixel underlying a corresponding microlens, and the backlight panel also includes a planar mirror underlying the waveguide pipe. In response to a display viewing angle change command, a waveguide pipe's light extraction position selected, which is the distance between the extraction pixels and their corresponding microlenses, and the display viewing angle is changed.
Owner:SHARP KK
High fill-factor bulk silicon mirrors
InactiveUS7209274B2Improve performanceLarge optical surfaceMirrorsMountingsEngineeringAngular rotation
A method and apparatus for fabricating a MEMS apparatus having a device layer with an optical surface that is supported by a pedestal on a planar support layer that is suspended for movement with respect to a base support by hinge elements disposed in a different plane from the planar support layer. The surface area of the optical surface is maximized with respect to the base support to optimized the fill factor of the optical surface and afford a high passband. The height of the pedestal is selected to position the device layer sufficiently above the base support to afford an unobstructed predetermined angular rotation about each axis. The hinges may be made of thin-film material, fabricated by way of surface micromachining techniques. The hinges are disposed underneath the device layer enabling the optical surface to be maximized so that the entire surface becomes usable (e.g., for optical beam manipulation). MEMS devices afford an array of MEMS mirrors with a high optical fill factor and high passband. Further, use of both bulk and surface micromachining techniques gives a MEMS device with a large and flat mirror and flexible hinges capable of a substantial rotational range at modest electrostatic drive voltages.
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
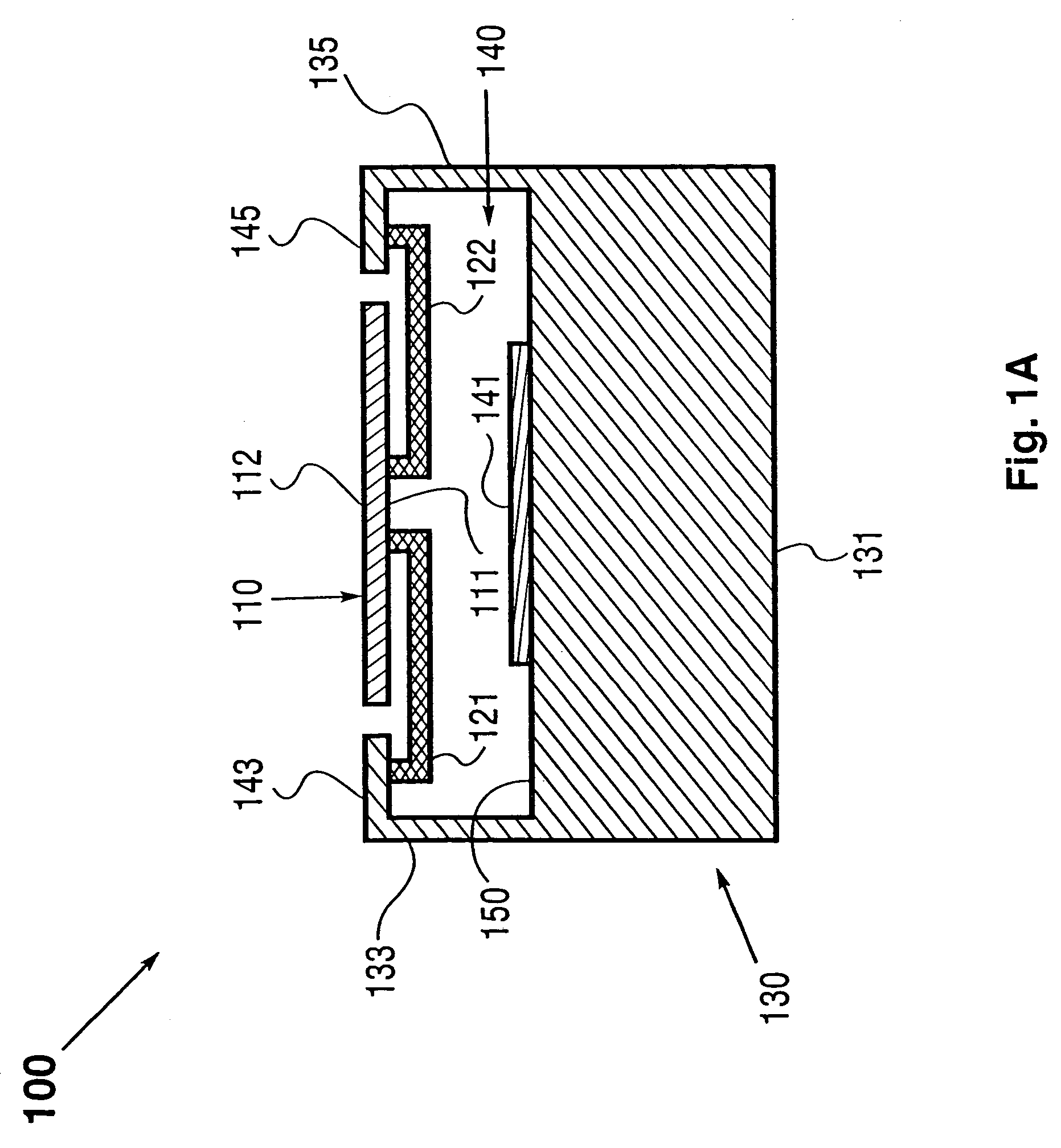
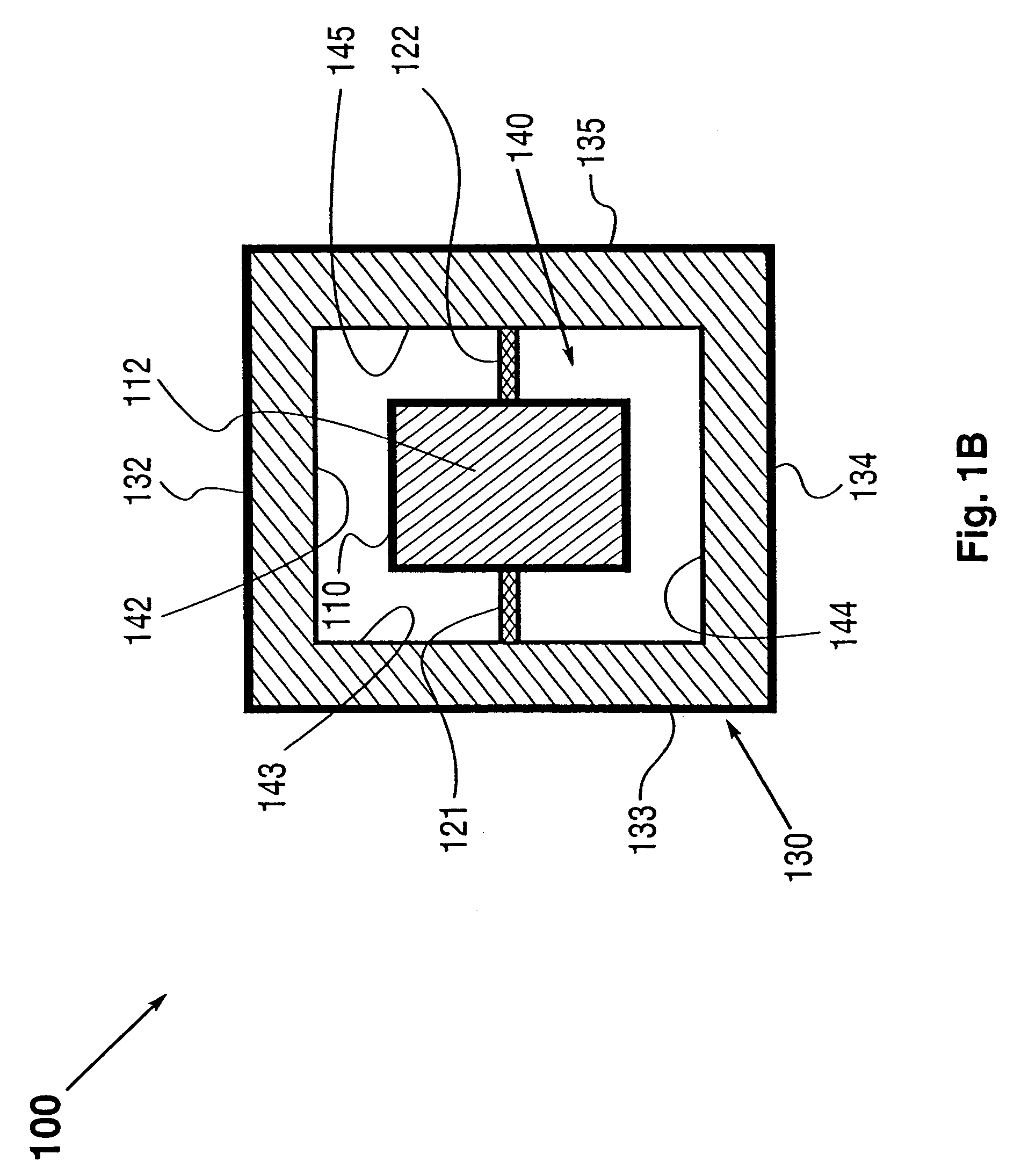
Method and apparatus for beam deflection
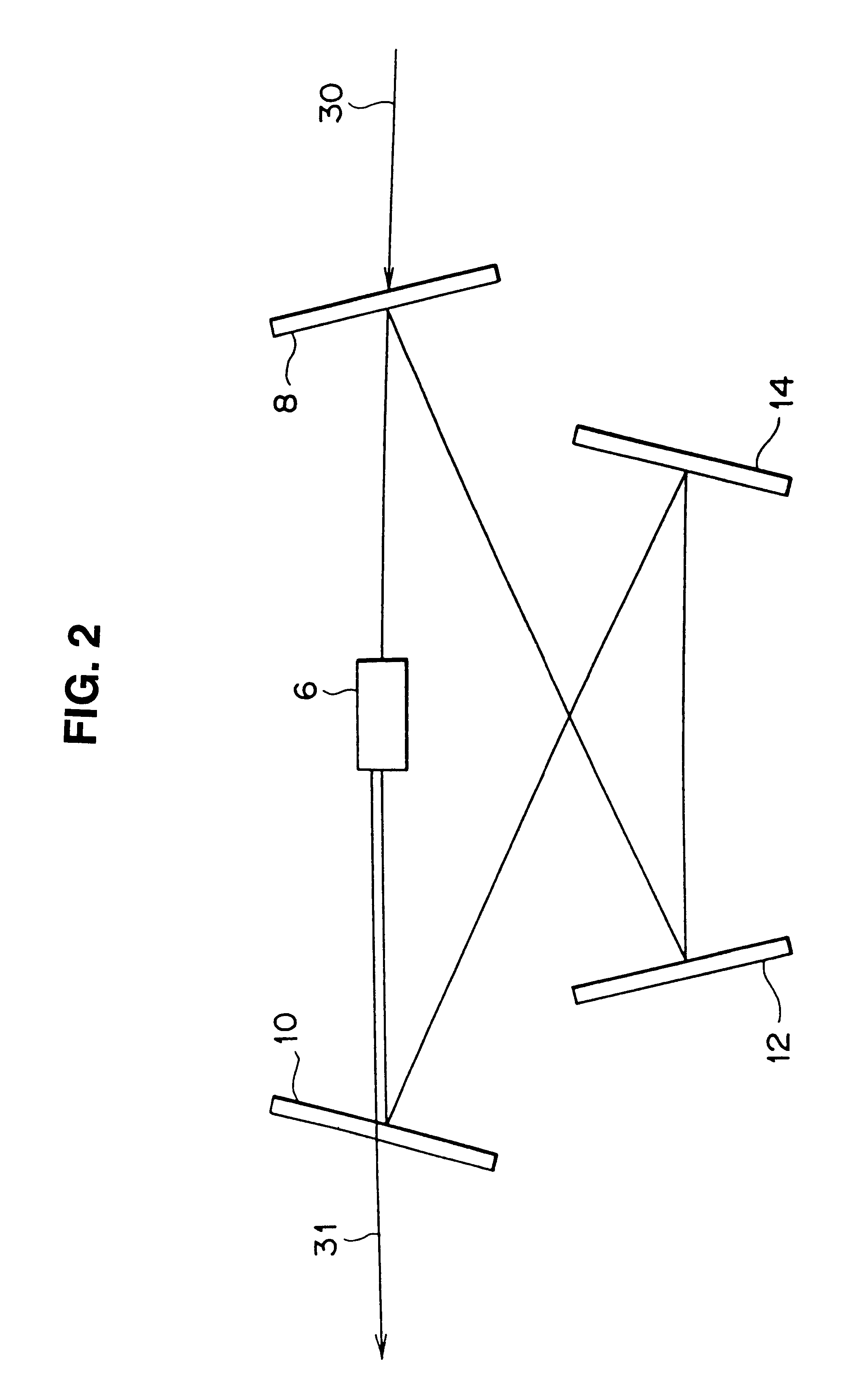
The invention provides a method and apparatus for directing a radiation beam (504, 606) in a desired direction. There is provided a movable member (10) supported for movement by a fixed member (40) and the movable member has an optical element, e.g a flat mirror (30) fixedly attached thereto. In one embodiment the mirror scans a radiation beam incident thereon in one plane. In a second embodiment, the radiation beam is scanned in two mutually perpendicular planes. A magnetic element (50) having a north and a south magnetic pole is fixedly attached to the movable member (10). A magnetically permeable stator element (70) that is stationary with respect to the movable member (10) and the magnetic element (50) is placed in the field of the magnetic element such that the stator element and said magnetic element mutually generate a magnetic traction force between them. A current coil (60) is wound around a portion of the stator element (70) and a current driver (400) is provided for driving a current in the current coil (60). The current induces an electromagnetic force in the stator element (70) and the electromagnetic force acts on the magnetic element (50) for controlling movement of the optical element (30) with respect to the fixed element (40). A radiation beam source (502) may be directed onto the movable mirror surface (30) and scanned by the movement of the mirror to direct the radiation beam in a desired propagation direction. Alternately, a radiation source (604) may be attached to the movable member (10) and pointed in a desired direction.
Owner:THE GSI GRP LLC +1
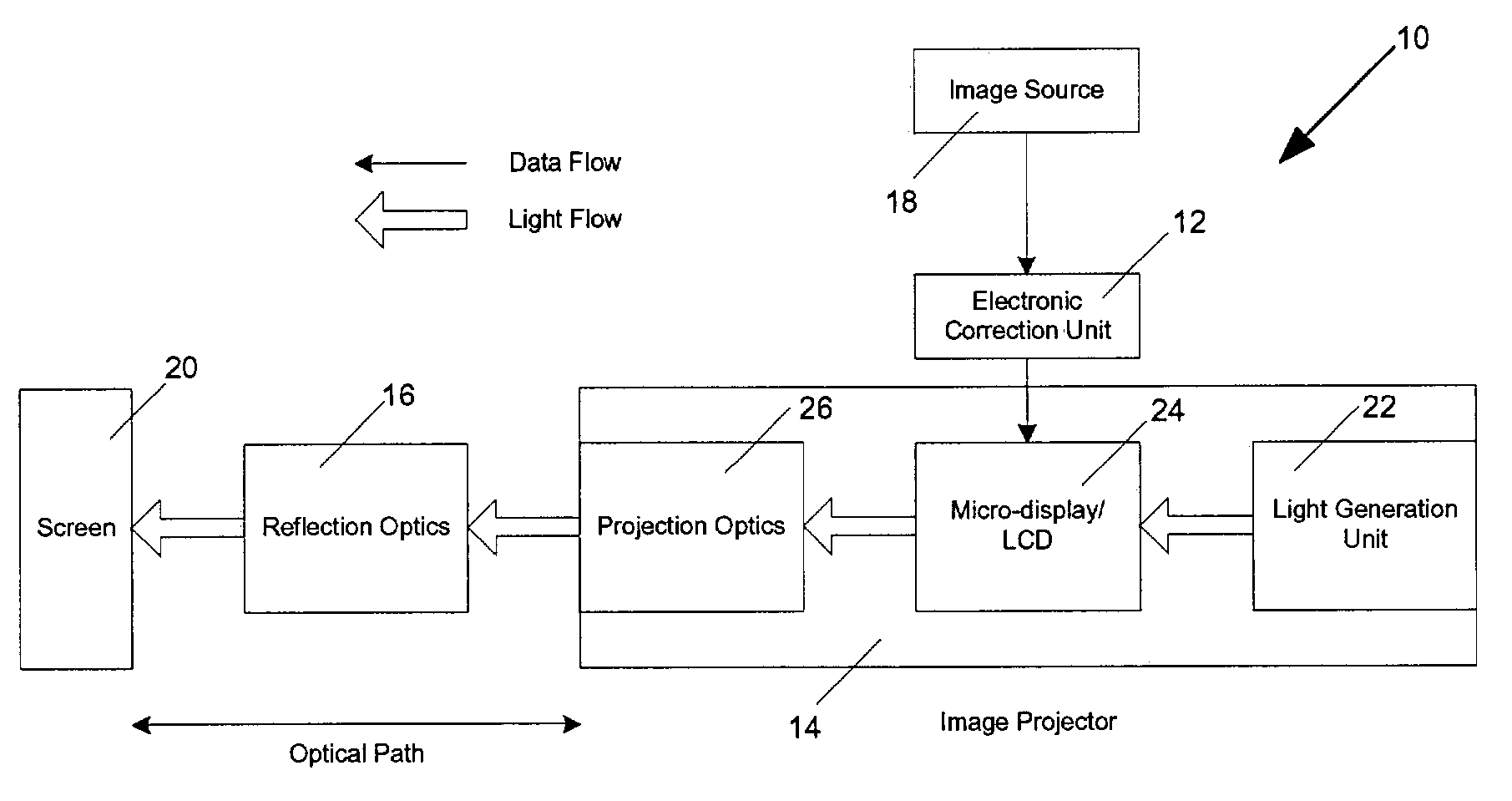
Short throw projection system and method
ActiveUS7239360B2Remove distortionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsOptical reflectionProjection optics
A short throw projection system and method for displaying a corrected optical image on a projection screen based on input image data that includes an electronic correction unit, an image projector and a reflection assembly. The electronic correction unit receives the input image data and generates pre-distorted image data. The image projector receives the pre-distorted image data from the electronic correction unit and projects a pre-distorted optical image that corresponds to the pre-distorted image data or a pre-distorted image compensated by the projection optic distortion. The optical reflection assembly is positioned in the optical path of the pre-distorted optical image to project an optical image on the projection screen. The reflection assembly can consist of various combinations of curved and planar mirrors as desired. The electronic correction unit is encoded to pre-distort the geometry of the image represented by the image data such that when the pre-distorted optical image is projected through the image projector and reflected within the reflection assembly, the optical and geometric distortions associated with the image projector and the mirrors within the reflection assembly are eliminated in the displayed optical image.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Polishing apparatus
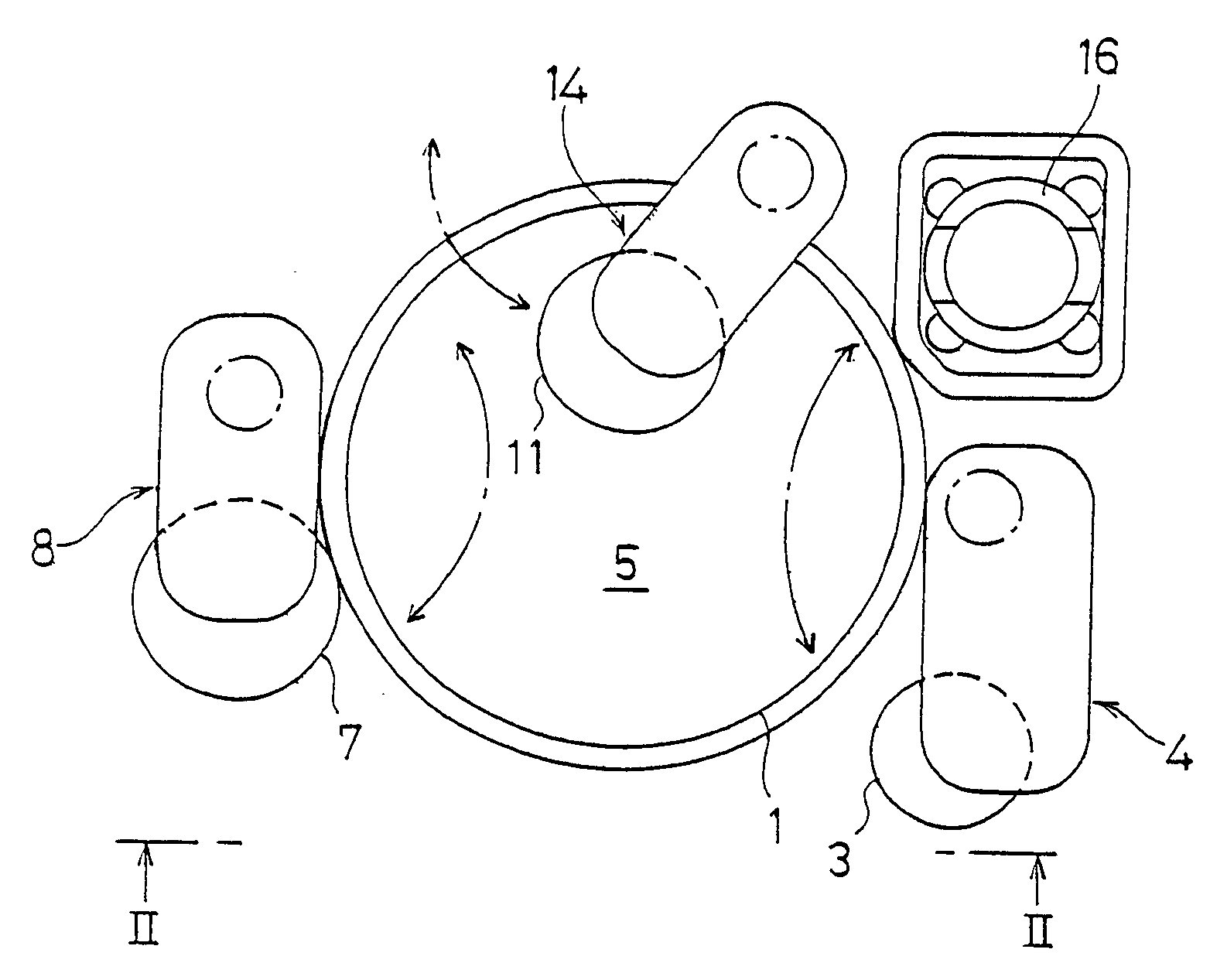
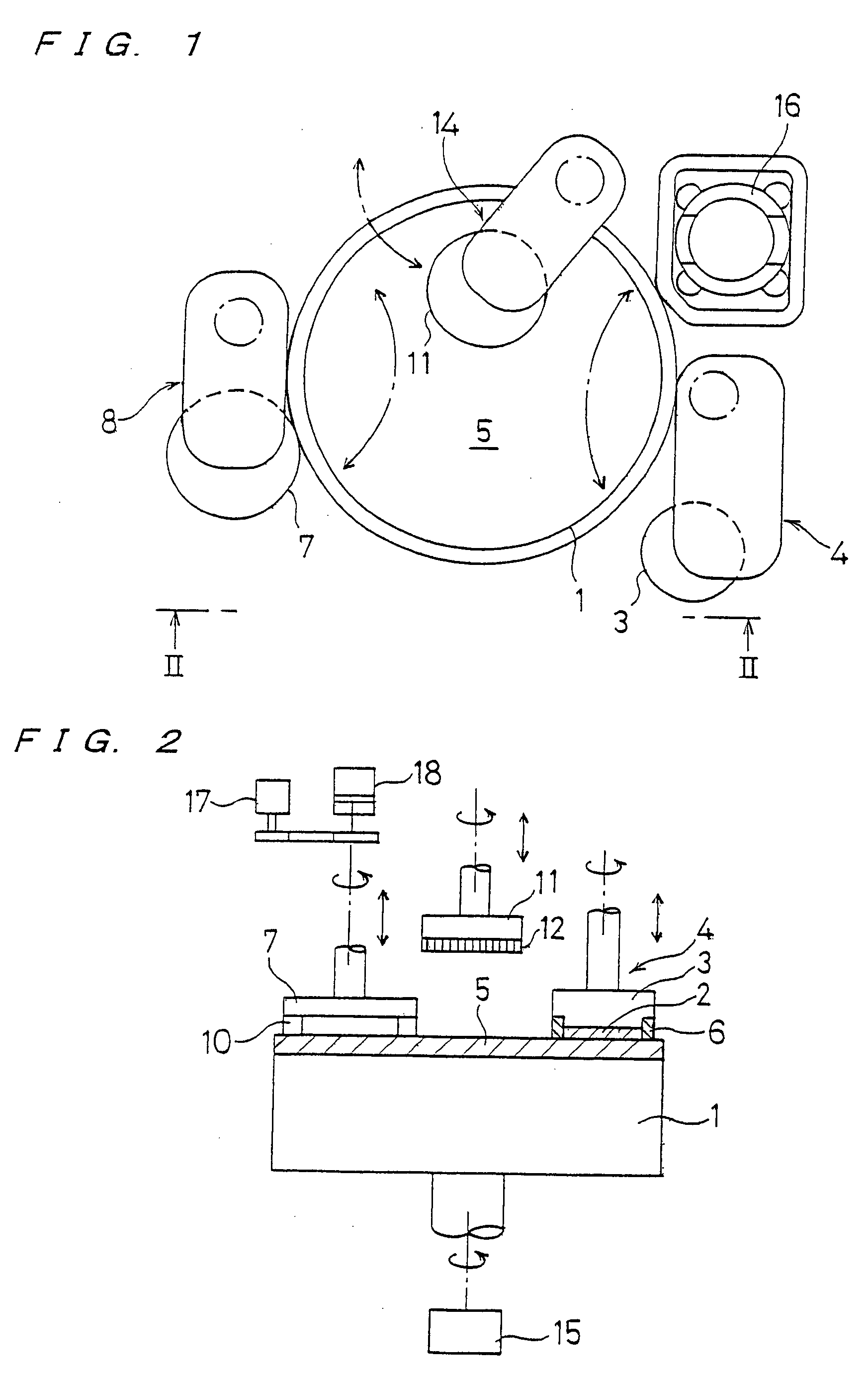
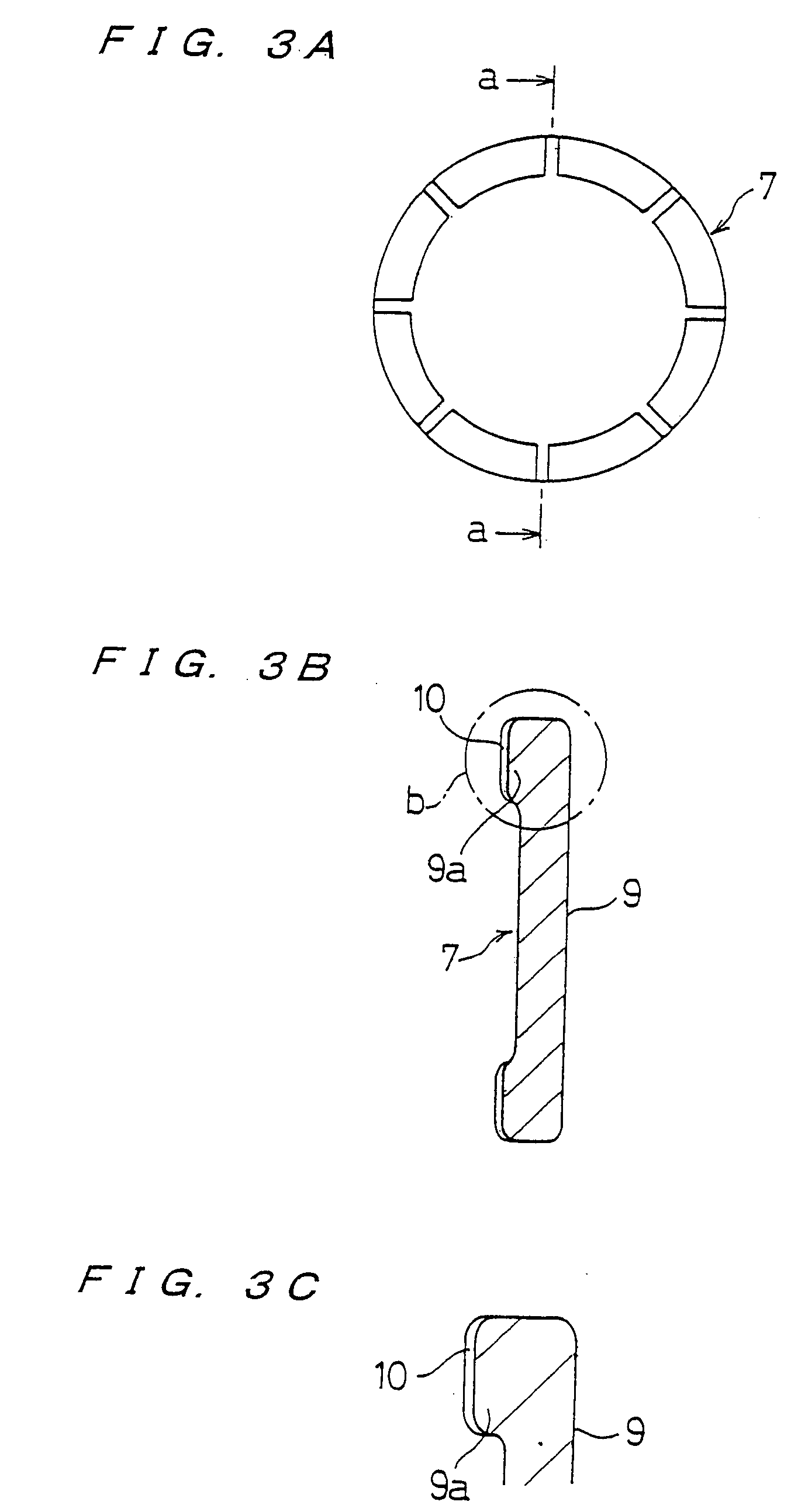
InactiveUS20050191949A1Maintain performanceHigh yieldPolishing machinesGrinding drivesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to a polishing apparatus for polishing a workpiece, such as a semiconductor wafer, to a flat mirror finish. The polishing apparatus comprises a polishing table having a polishing surface, and a top ring, and the workpiece is interposed between the polishing table and the top ring and pressed at a predetermined pressure to polish the workpiece. The polishing apparatus comprises at least two dressing units for dressing the polishing surface by being brought into contact with the ppolishing surface, which is a surface of a polishing cloth.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Real-person shoe type copying device and shoe tree manufacturing method based on single-eye multi-angle-of-view robot vision
InactiveCN104573180AIncrease silhouetteConstraints for adding silhouettesSpecial data processing applications3D modellingPlane mirrorImage segmentation
The invention discloses a real-person shoe type copying device based on single-eye multi-angle-of-view robot vision. The device comprises a single-eye multi-angle-of-view 3D (Three-dimensional) vision box and a computer, wherein the single-eye multi-angle-of-view 3D vision box is used for shooting images of a foot of a real person at five different angles of view; the computer is used for achieving the 3D reconstruction of the foot of the real person and automatically generating a 3D printing file; a plane mirror rectangular bucket-type cavity is formed inside the single-eye multi-angle-of-view 3D vision box and consists of four trapezoidal mirror planes; the upper part of a mirror body is large, and the lower part of the mirror body is small; the mirror planes face the inner side of a cavity body; a light source used for providing uniform soft lighting for the foot of the real person is arranged at the lower part of the plane mirror rectangular bucket-type cavity; cameras used for obtaining the images of the foot of the real person at multiple angles of view according to the refraction and reflection principle of the mirror planes are further arranged in the single-eye multi-angle-of-view 3D vision box; the computer comprises a single-eye multi-angle-of-view 3D vision calibrating unit, an image division, conversion and correction unit, a real person foot surface shape measurement unit and an automatic STL (Standard Template Library) file generation unit. The invention further discloses a shoe tree manufacturing method based on the single-eye multi-angle-of-view robot vision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Laser beam generating apparatus
A laser beam in the ultraviolet region is generated at high power for along period. A green laser beam generated by a laser oscillator comes incident into a resonator from behind a first curved mirror, and circulates there, reflected by each mirror. By passing a barium borate crystal, it causes a secondary harmonic (a laser beam in the ultraviolet region) to be generated, which is taken out of the resonator via a second curved mirror. The beam waist of the laser beam passing the barium borate crystal is set to 46 mum, about double the conventional thickness, by adjusting the distance between the first curved mirror and a second flat mirror. As a result, the power density of the laser beam in the barium borate crystal is reduced to ¼ of the value according to the related art, and it is made possible to avoid rapid degradation of the barium borate crystal by excessive squeezing of the laser beam.
Owner:SONY CORP
Eyewear frames with magnetic lens attachments
ActiveUS8641188B2Easy to changeRapid and simple interchangeSpectales/gogglesGogglesCamera lensUses eyeglasses
The present invention illustrates various methods of attaching a pair of eyeglass lenses or a lens shield to an eyeglass frame using magnets or magnetically attractive material. The magnetic attachment methods are beneficial because they allow the user to have interchangeable lenses or shields for indoor and outdoor use, enhancing their visual acuity during work or play. The lenses may be tinted, prescription, protective eyewear, or plano. The magnetic lenses are convenient and user friendly, allowing intuitive, tool-less interchangeability with no need to twist or stress the frame. These methods of attachment require no specific instructions or tools when the user replaces lenses.
Owner:SWITCH VISION
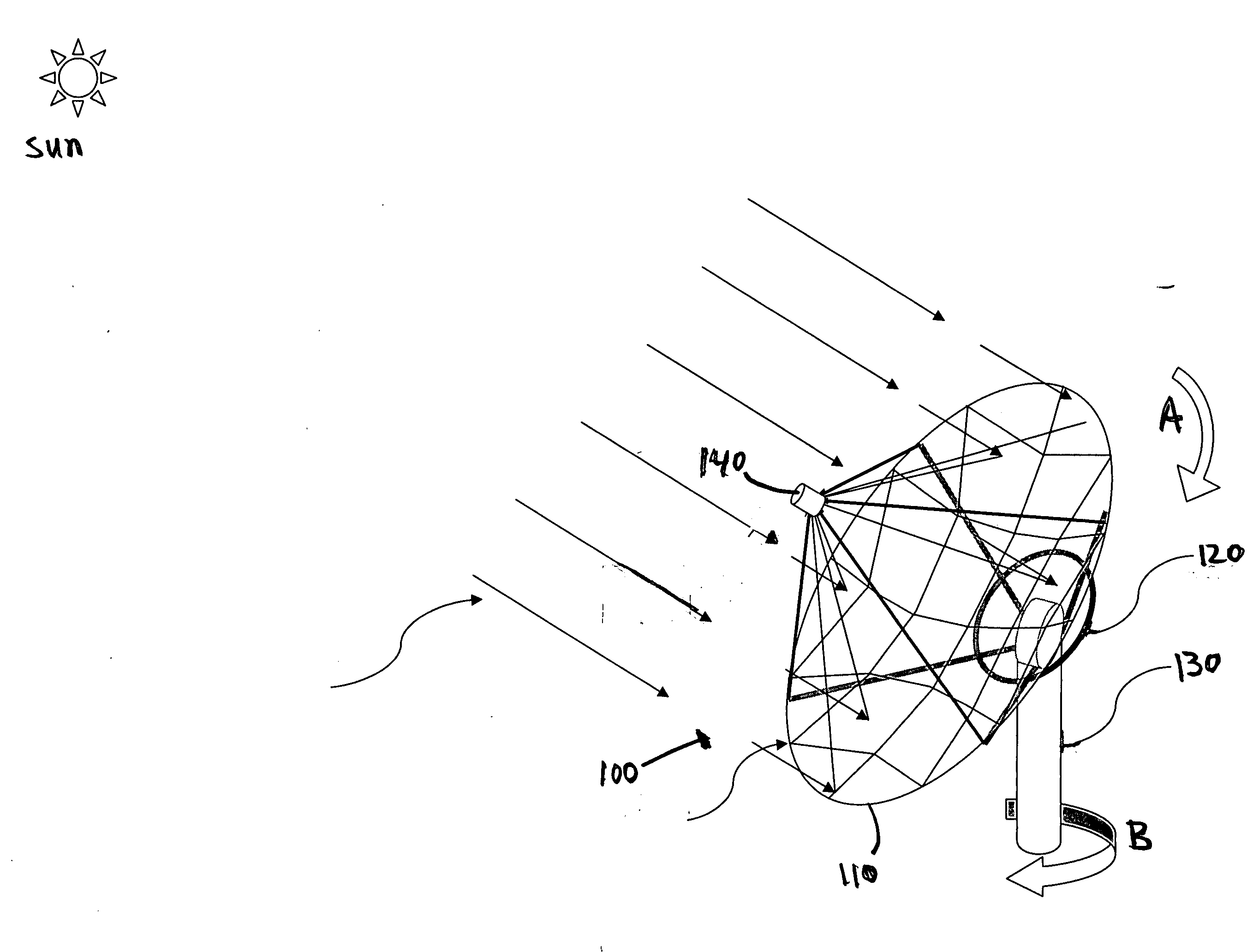
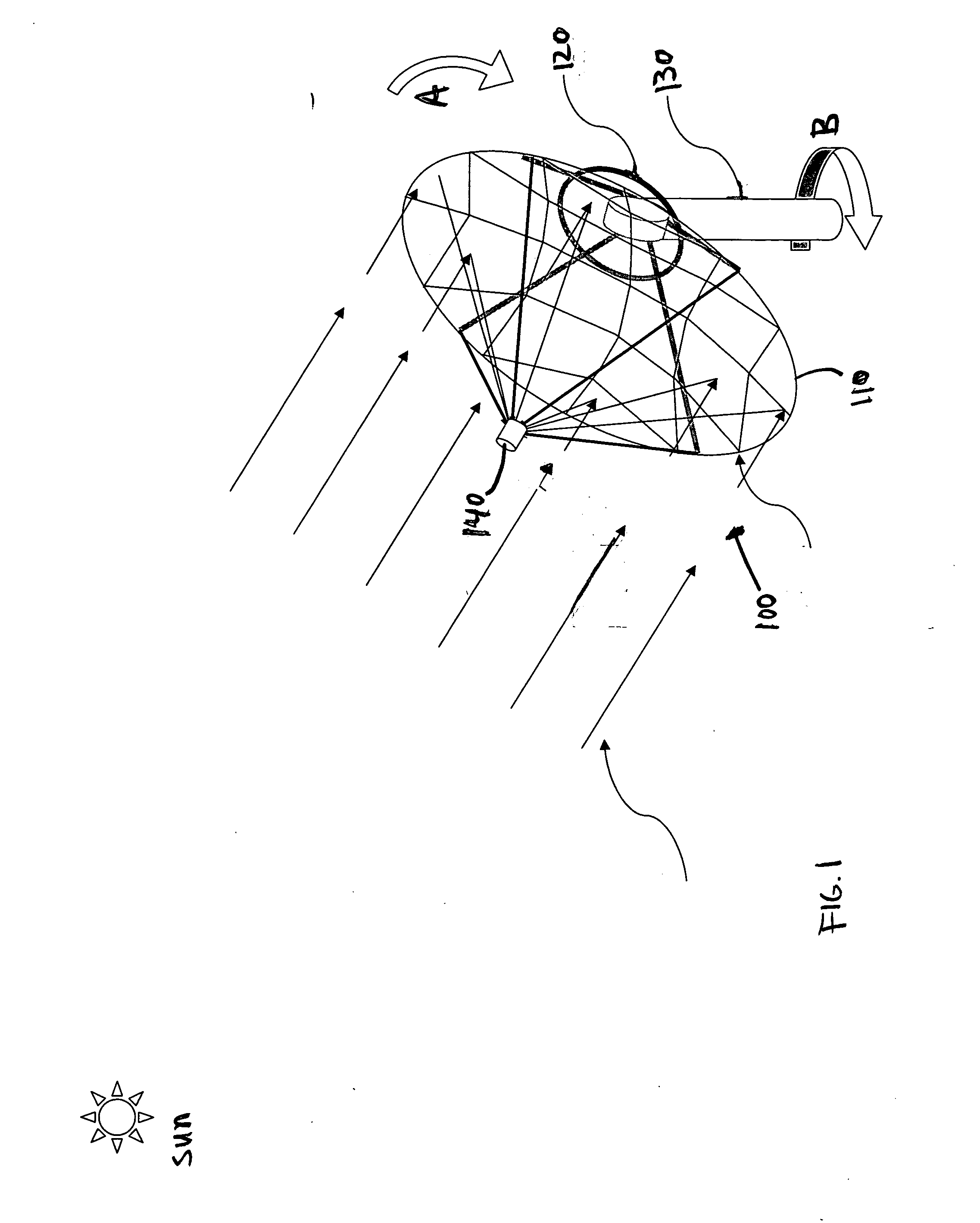
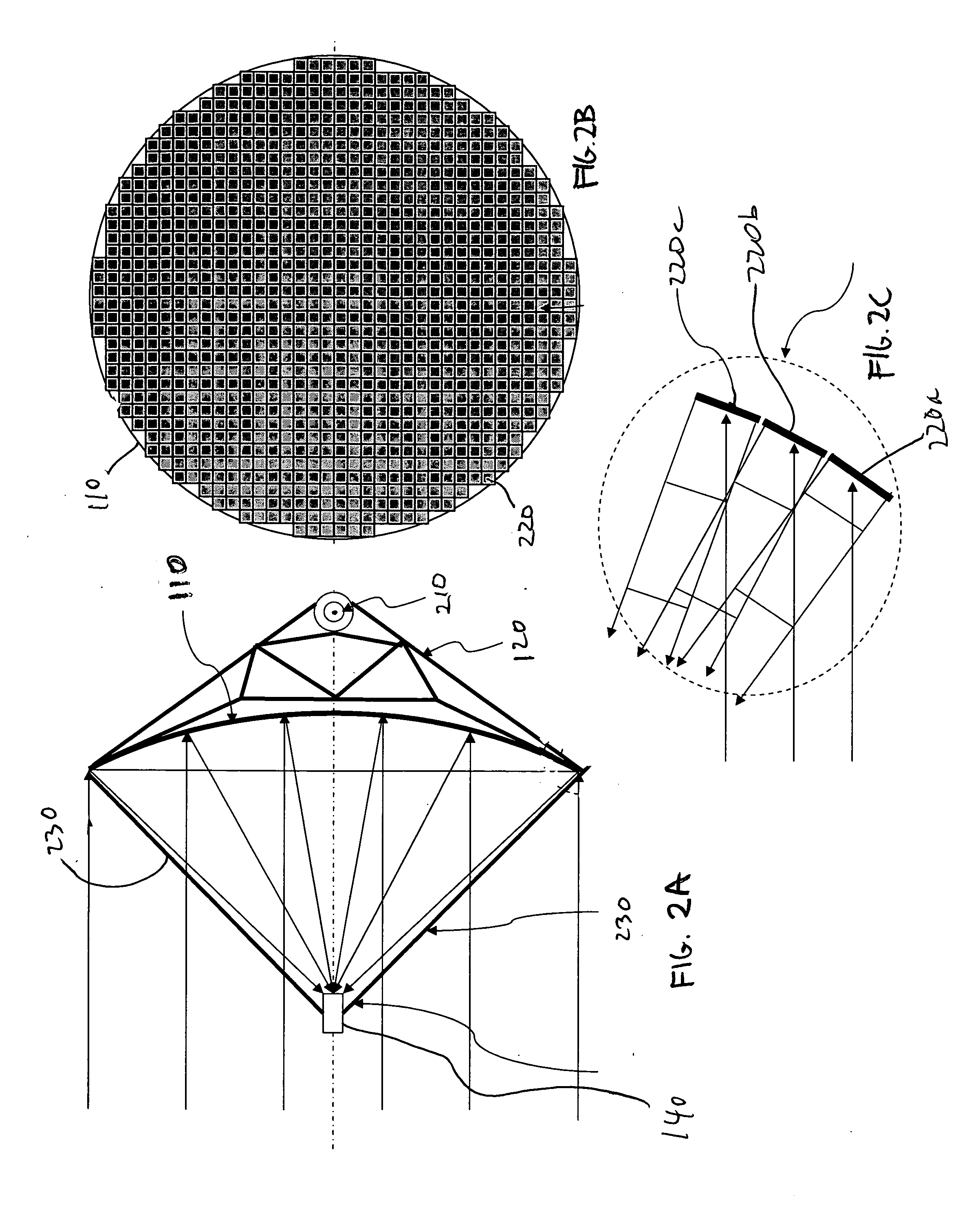
Aligned multiple flat mirror reflector array for concentrating sunlight onto a solar cell
InactiveUS20090084375A1Great contributionSolar heating energySolar heat devicesSolar cellFlat mirror
An aligned multiple flat mirror reflector array for concentrating sunlight onto a solar cell is disclosed. The reflector array includes a concentrating dish and a plurality of flat mirrors disposed on an inside surface of the concentrating dish, the plurality of flat mirrors being disposed and aligned on the inside surface of the concentrating dish such that sunlight impinging upon each of the plurality of flat mirrors is reflected upon the solar cell.
Owner:XIE JINCHUN
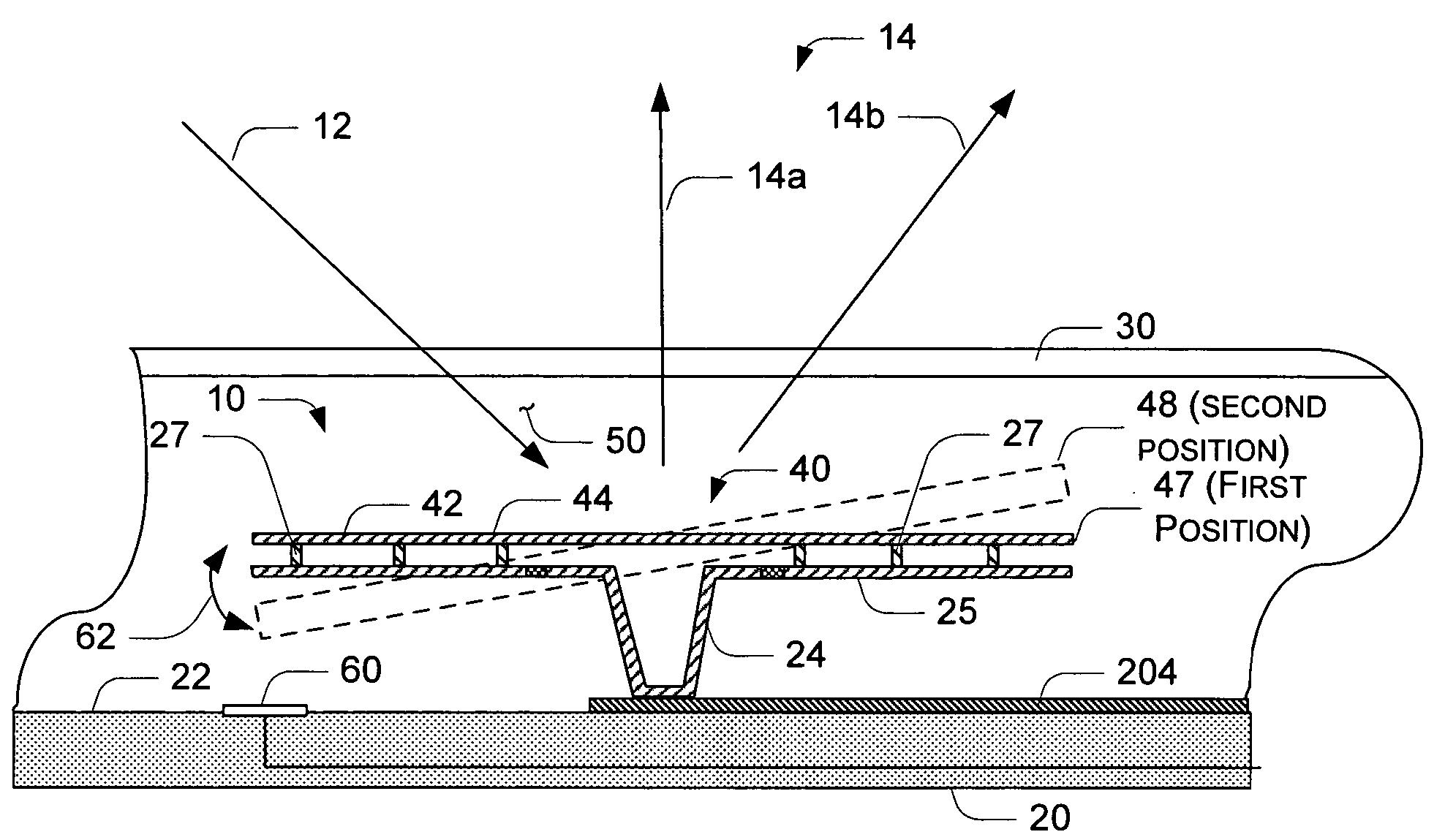
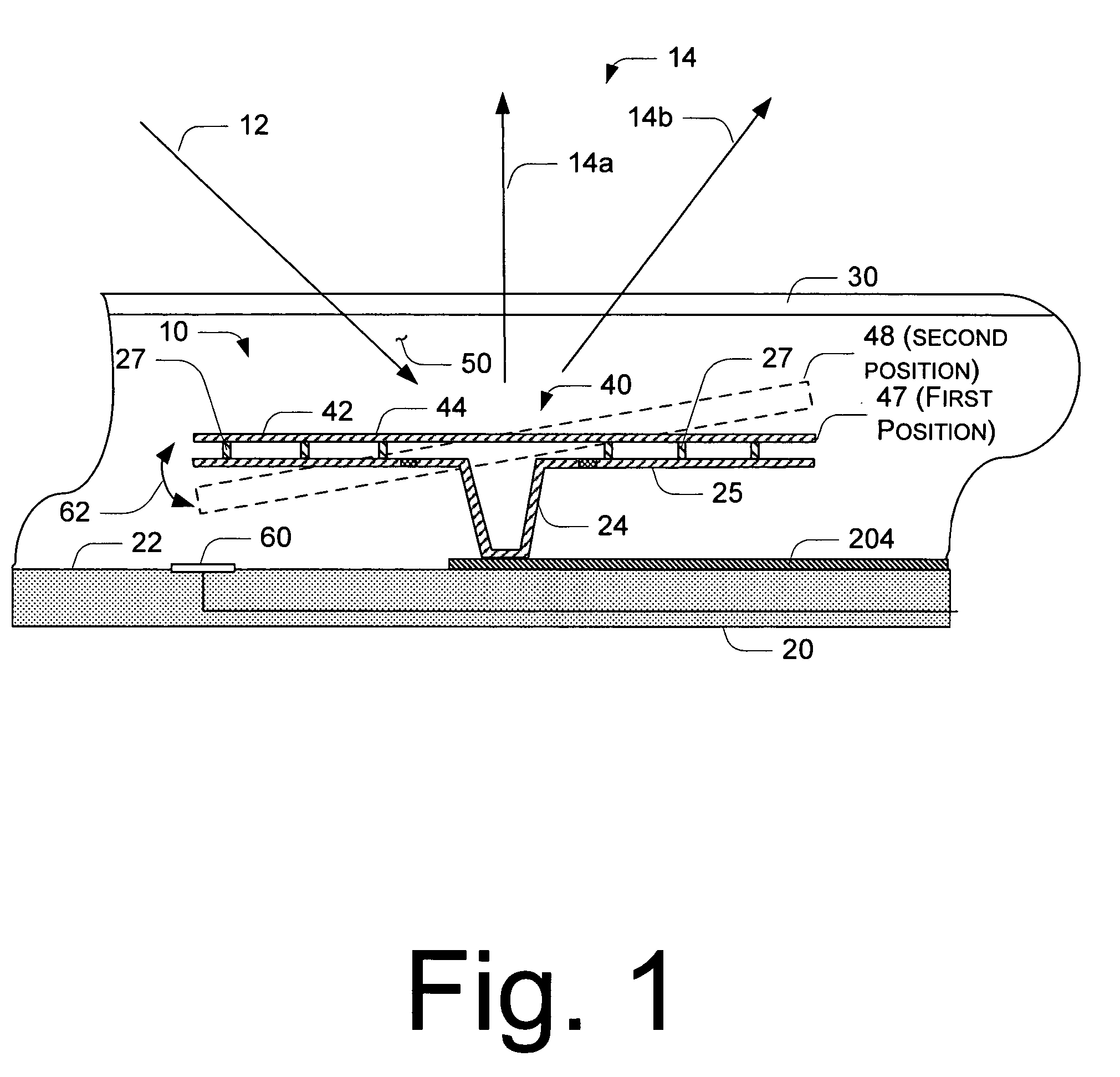
Substrate polishing apparatus
InactiveUS20070173177A1Reduce impactMaintaining measuring capability of measuringPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesEngineeringLight emission
A substrate polishing apparatus is used to polish a surface of a substrate such as a semiconductor wafer to a flat mirror finish. The substrate polishing apparatus has a polishing table and a polishing pad mounted on the polishing table for polishing a semiconductor substrate. The polishing pad has a through hole formed therein. The substrate polishing apparatus also has a light emission and reception device for emitting measurement light through the through hole formed in the polishing pad to the semiconductor substrate and receiving reflected light from the semiconductor substrate so as to measure a film on the semiconductor substrate. The light emission and reception device is disposed in the polishing table. The substrate polishing apparatus includes a supply passage for supplying a fluid to a path of the measurement light. The supply passage has an outlet portion detachably mounted on the polishing table. The substrate polishing apparatus also includes a protection cover mounted on the polishing table and fitted into the through hole when the polishing pad is attached to the polishing table.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Method for forming a planar mirror using a sacrificial oxide
InactiveUS7273693B2Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringFlat mirror
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com