Patents
Literature
138 results about "Oblique projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
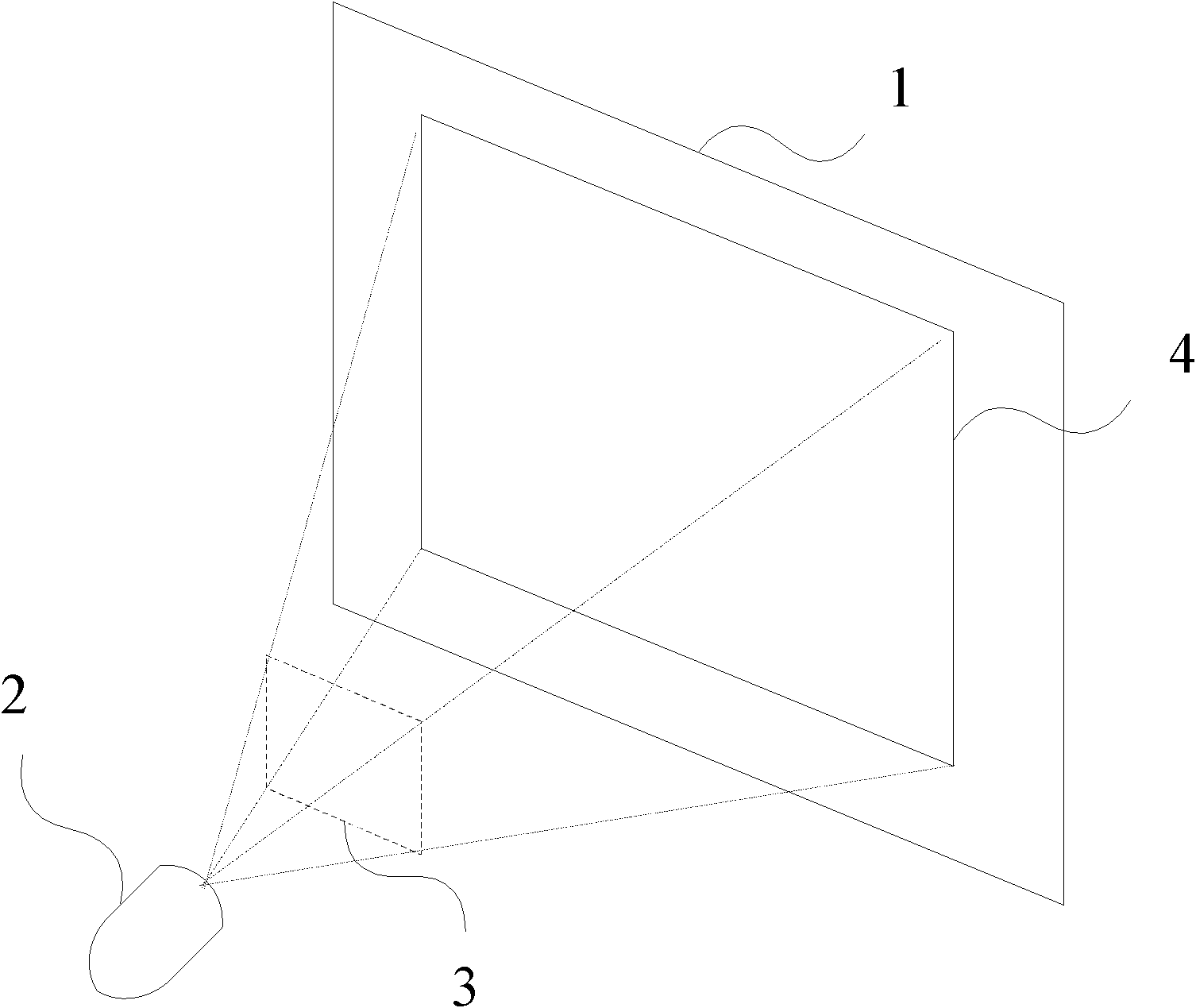
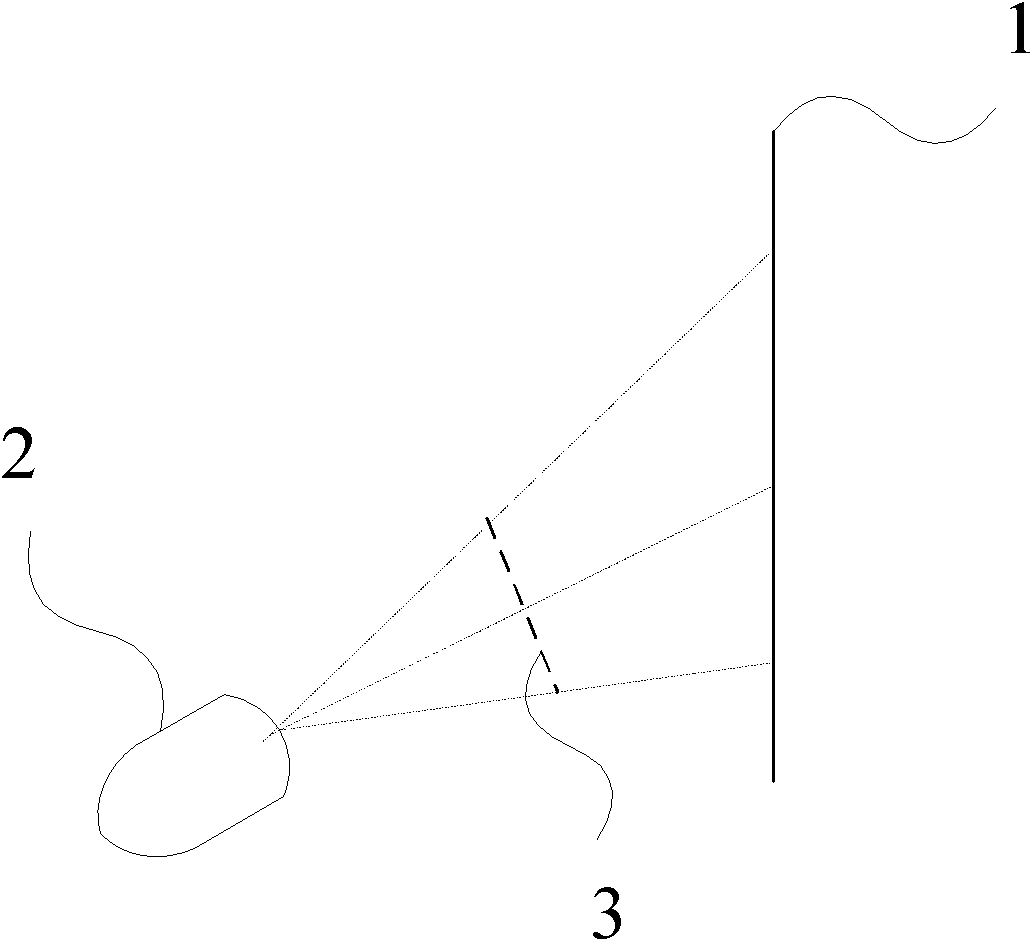
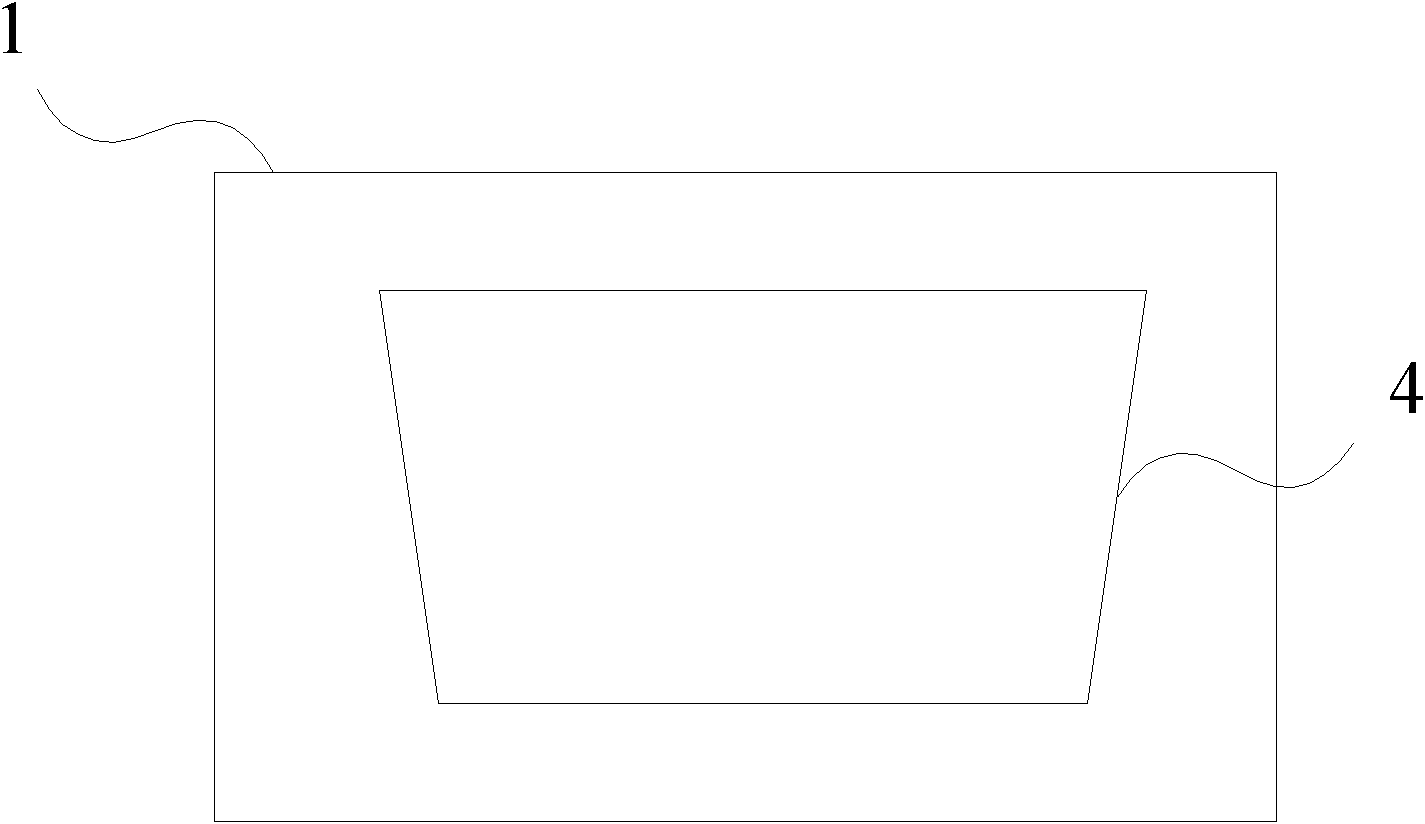
Oblique projection is a simple type of technical drawing of graphical projection used for producing two-dimensional images of three-dimensional objects. The objects are not in perspective, so they do not correspond to any view of an object that can be obtained in practice, but the technique does yield somewhat convincing and useful images.
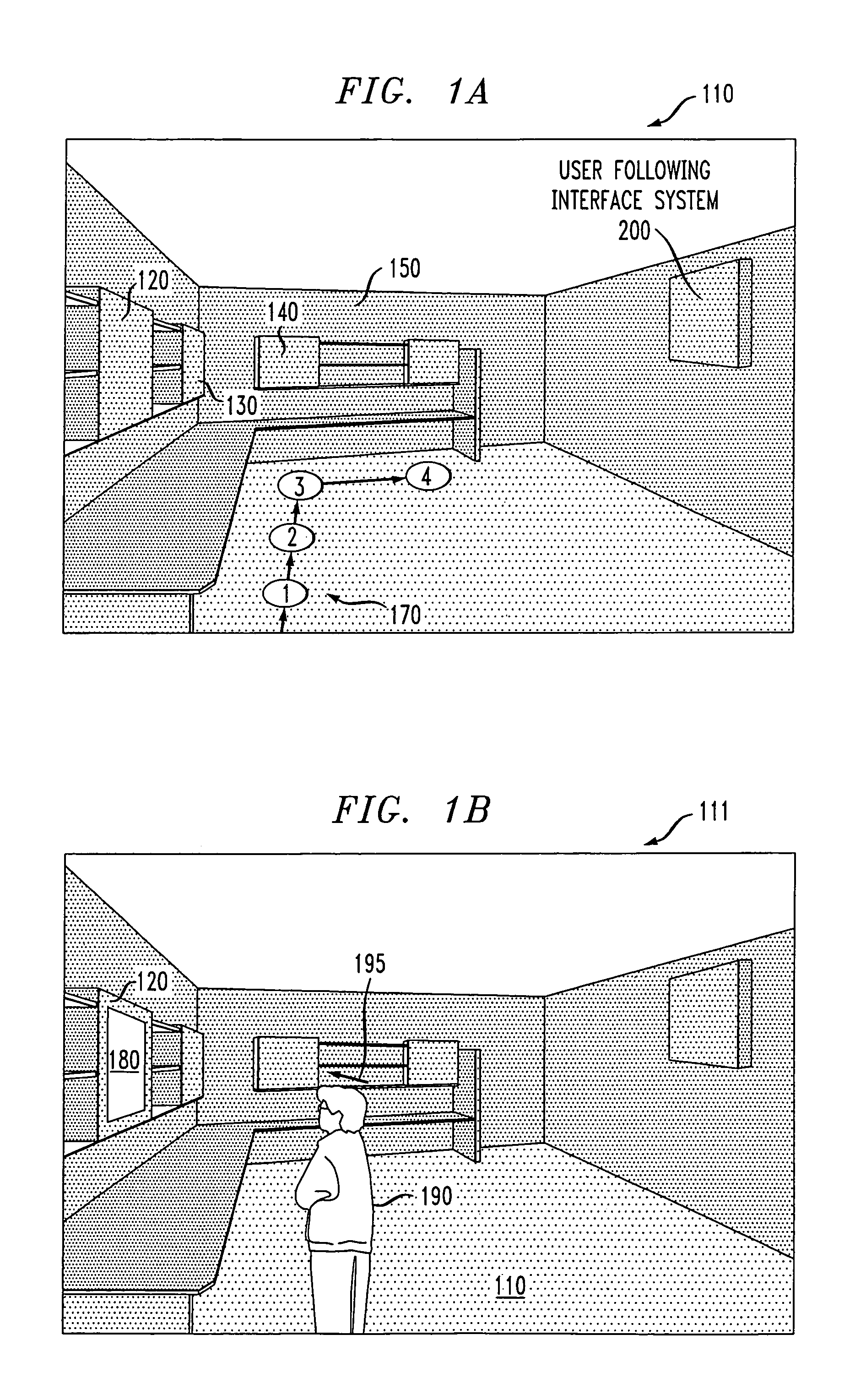
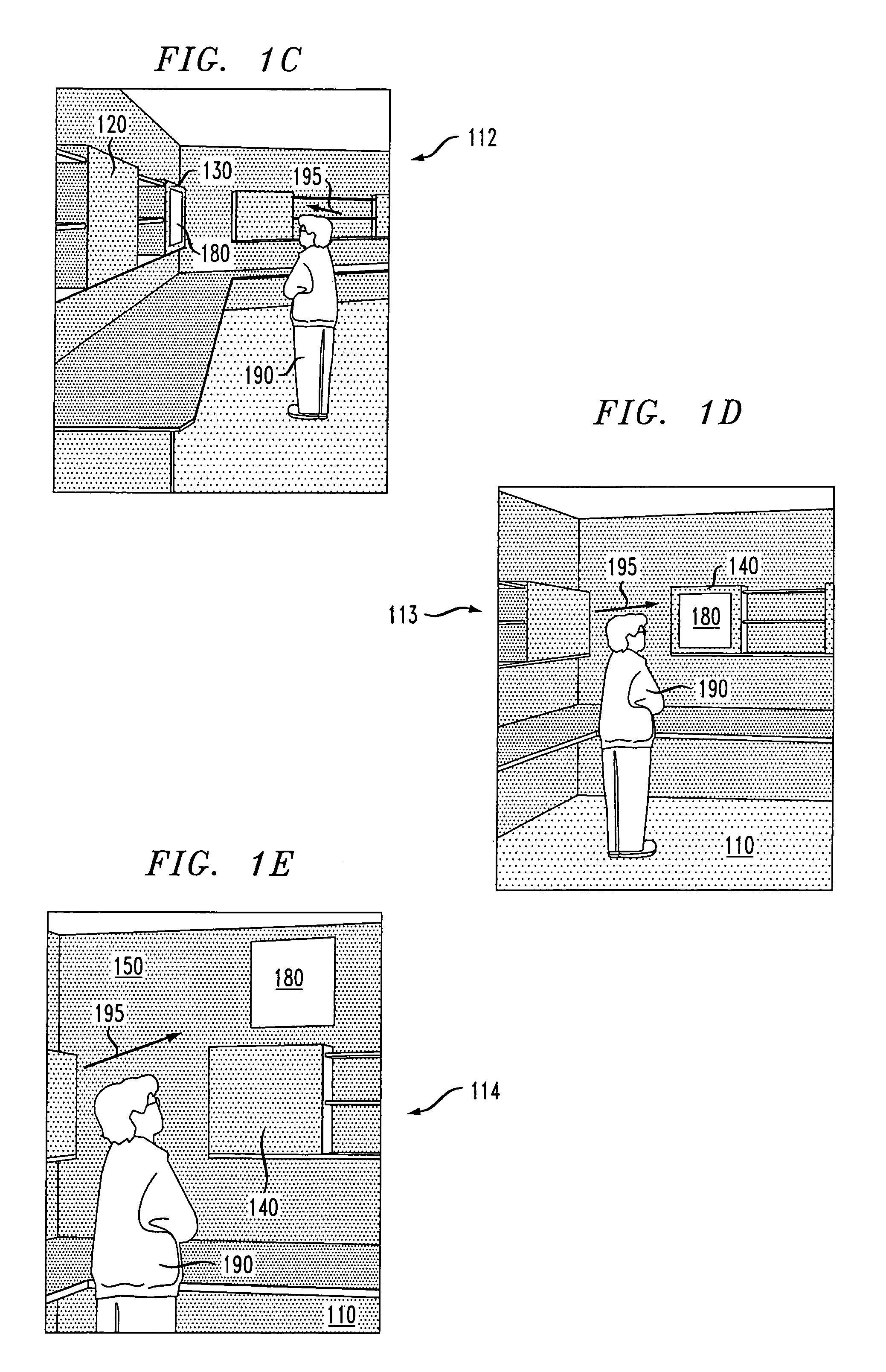
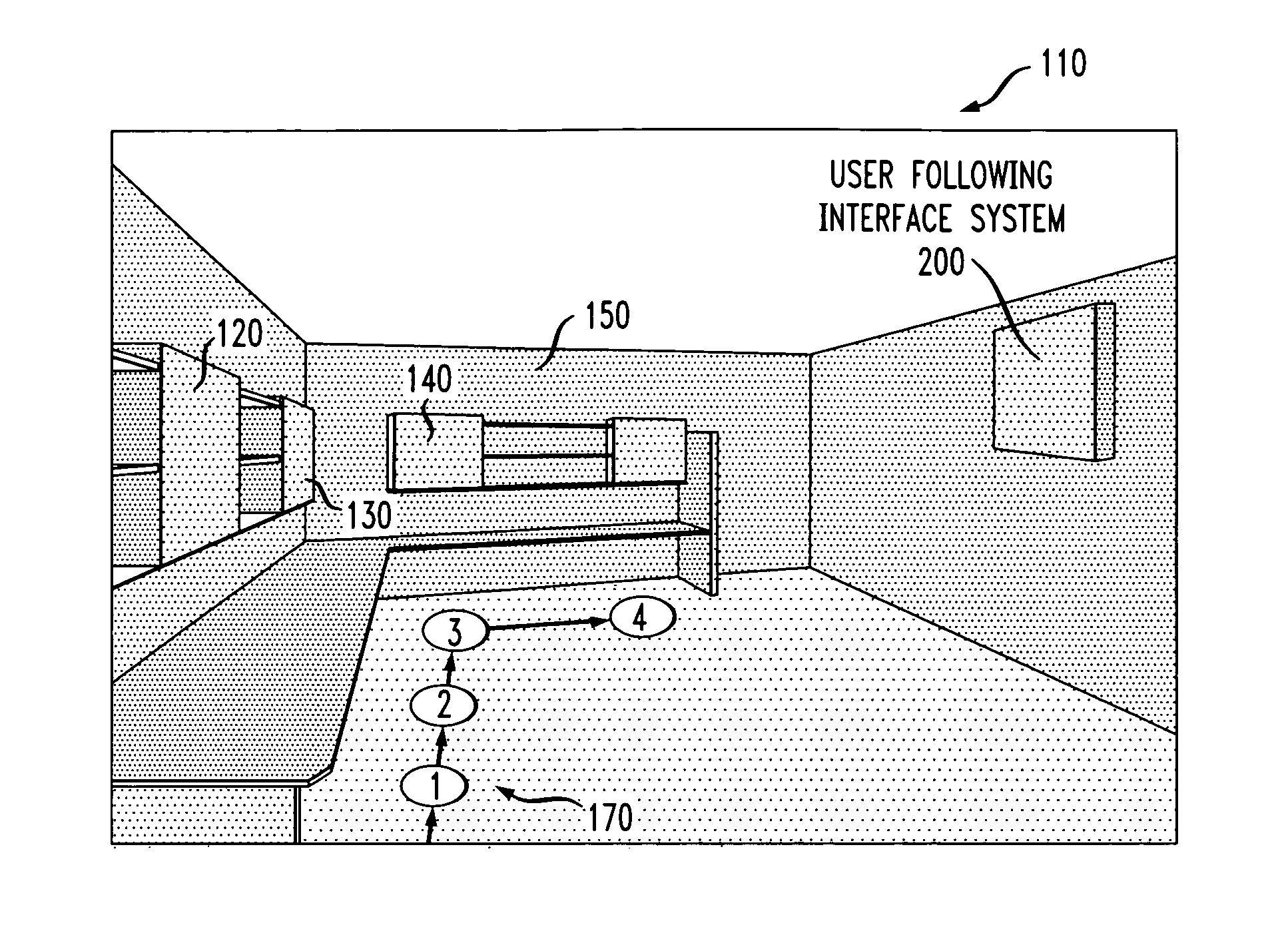
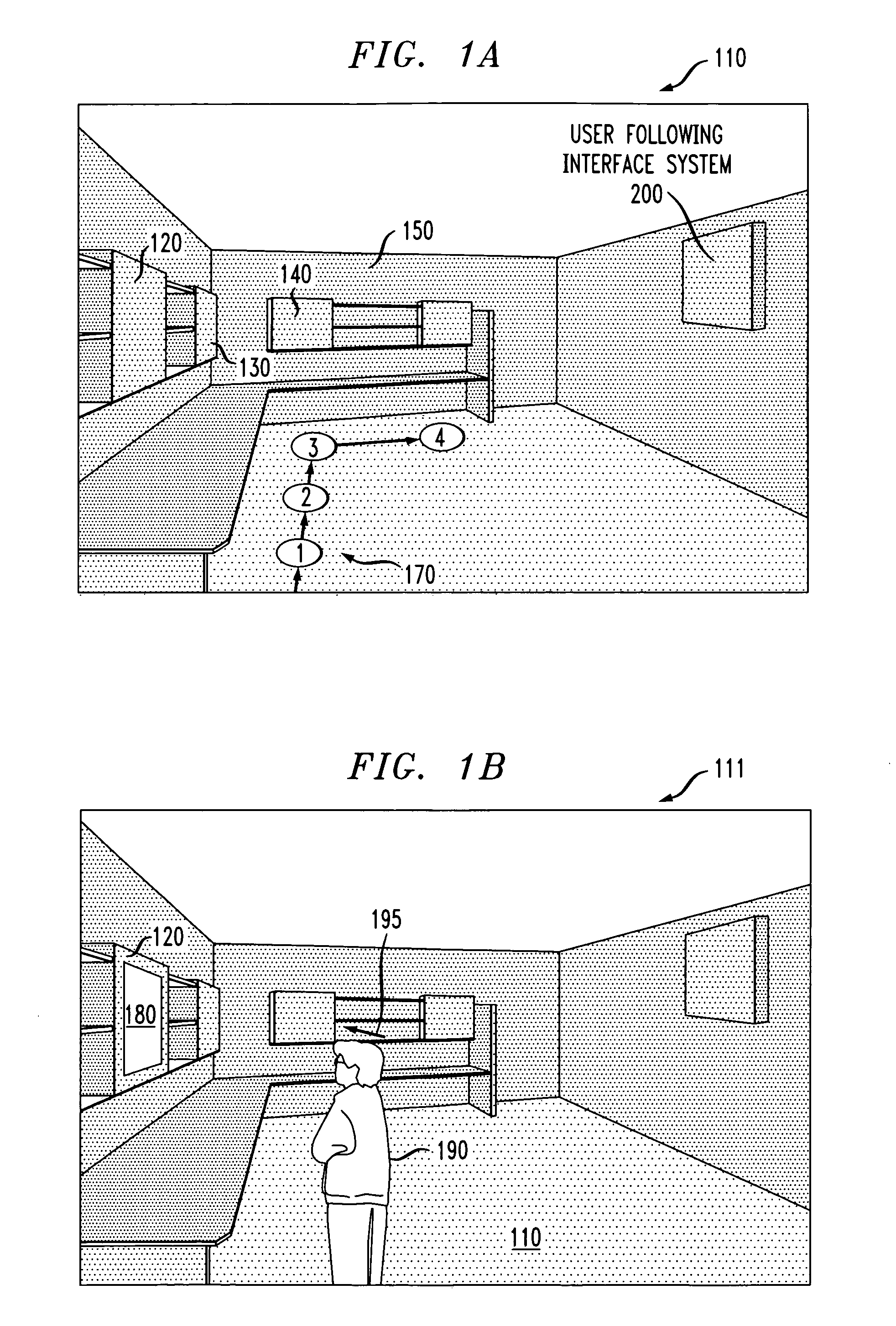
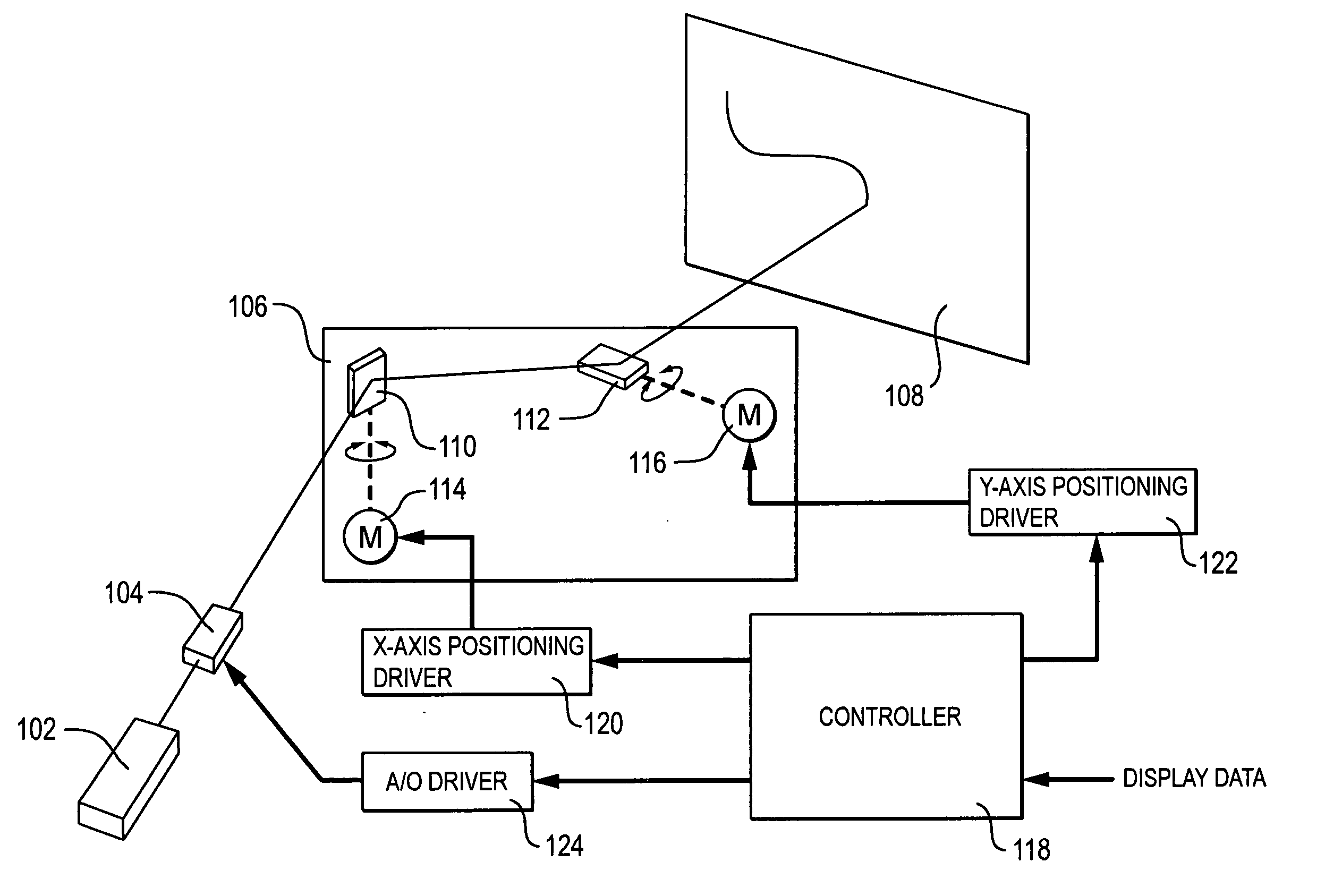
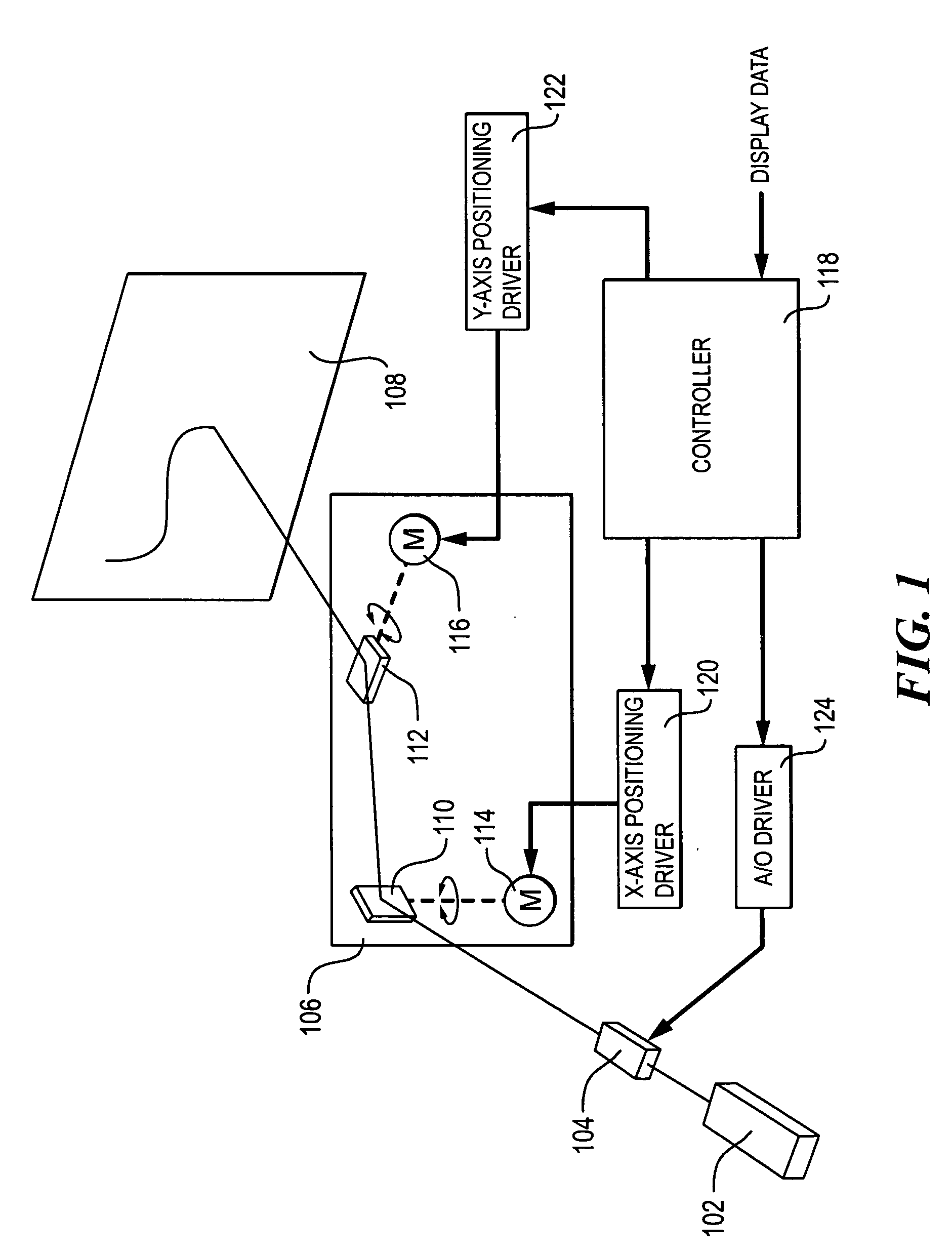
Method and system for a user-following interface
InactiveUS7134080B2Enhanced interactionTelevision system detailsProjectorsMedicineComputer graphics (images)
Techniques are disclosed for projecting an image onto a surface suitable for interaction with a user while avoiding user occlusion, and while correcting for distortion due to oblique projection. The displayed image moves to a suitable surface at a suitable size and orientation as a user moves around an environment, resulting in a user-following interface. Surfaces are selected in which the projected interface is not occluded by the user or other objects in the environment. Displayed images may be interactive, and moved into an interaction area on a suitable surface that is convenient for the user. The interaction area may or may not coincide with the display area. Adaptation of the projected interface is allowed so that the content of the display and the style of interaction widgets are modified based on distance from the user and orientation of the user with respect to a projected interface.
Owner:IBM CORP
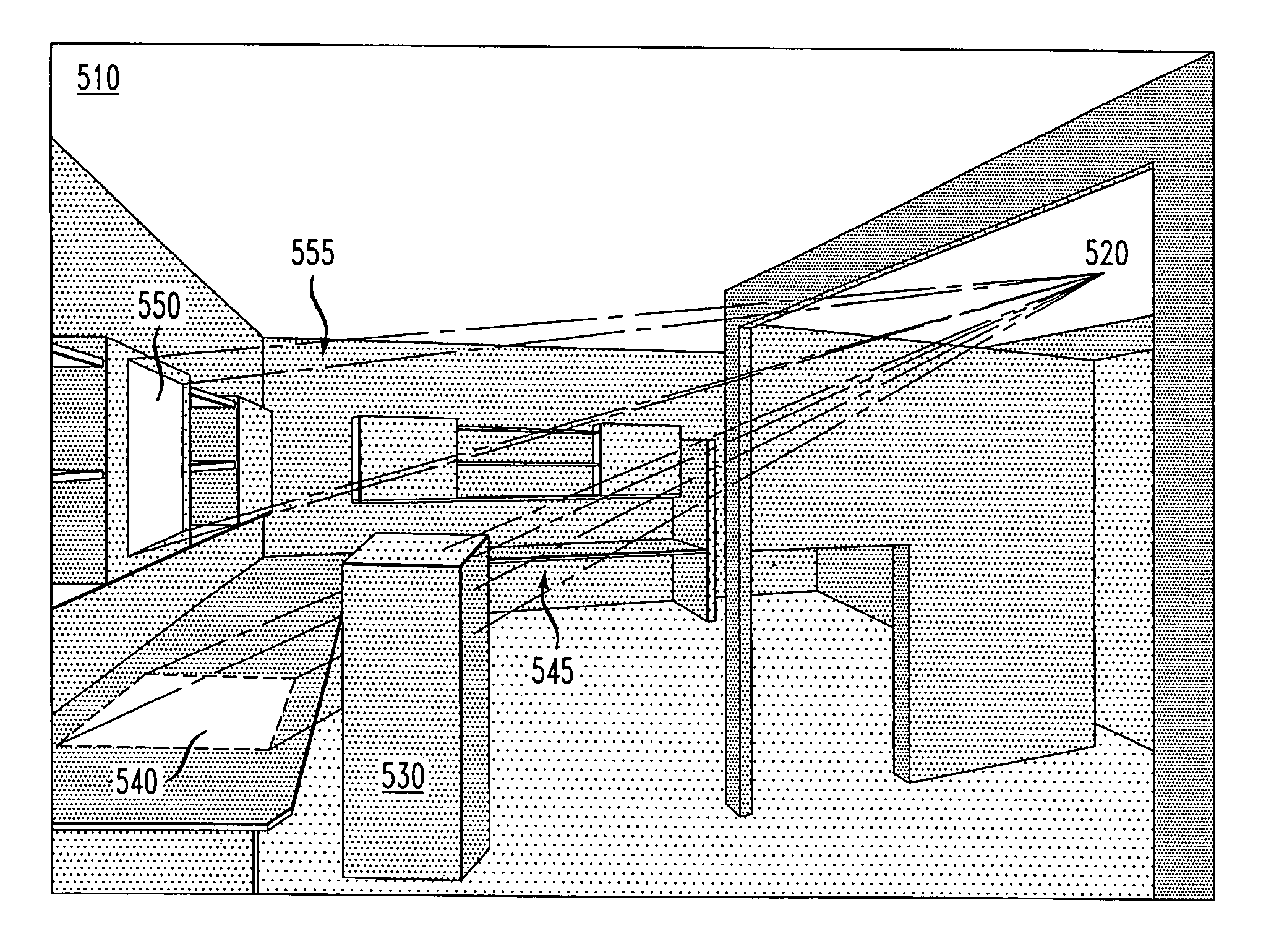
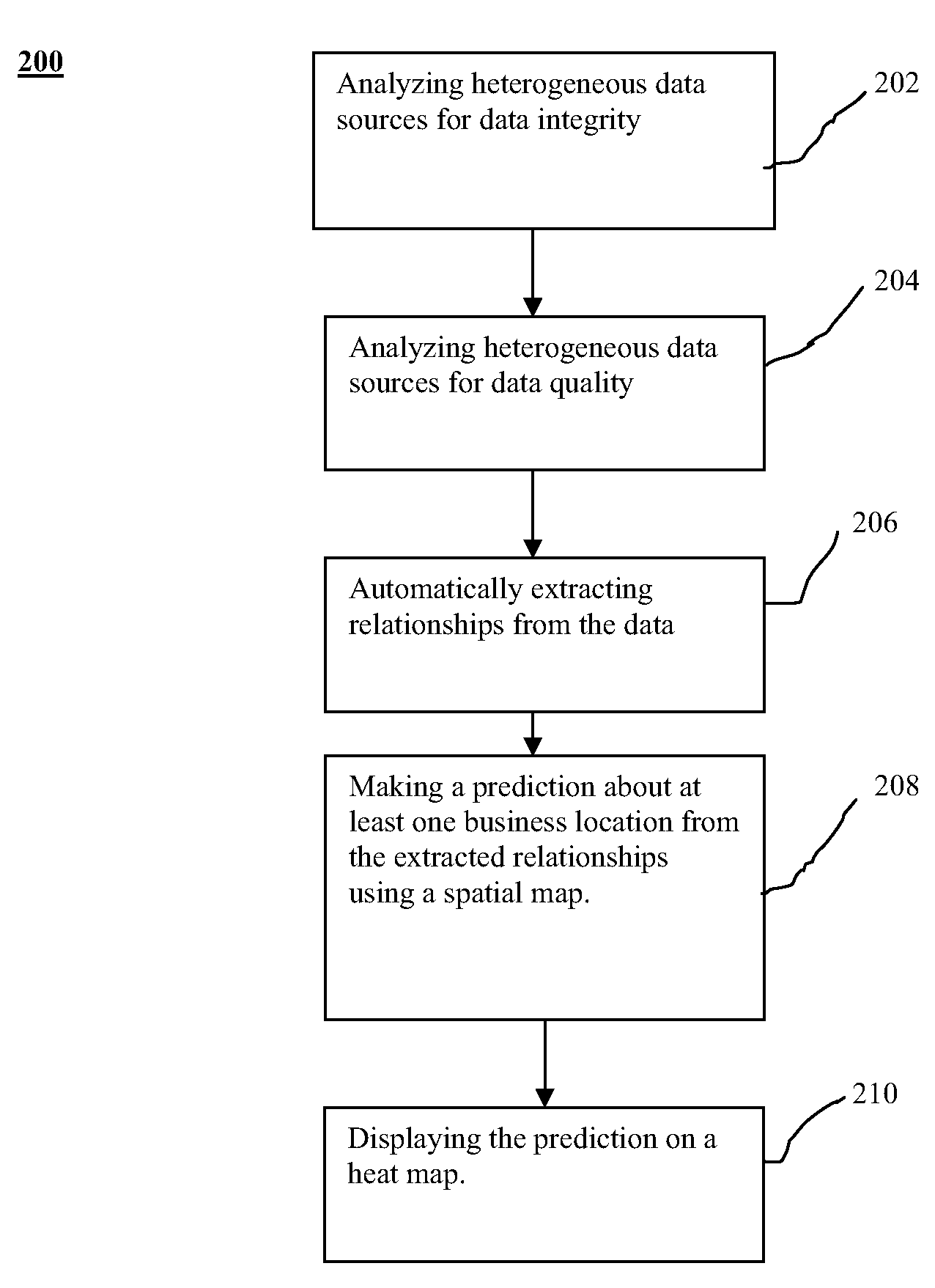
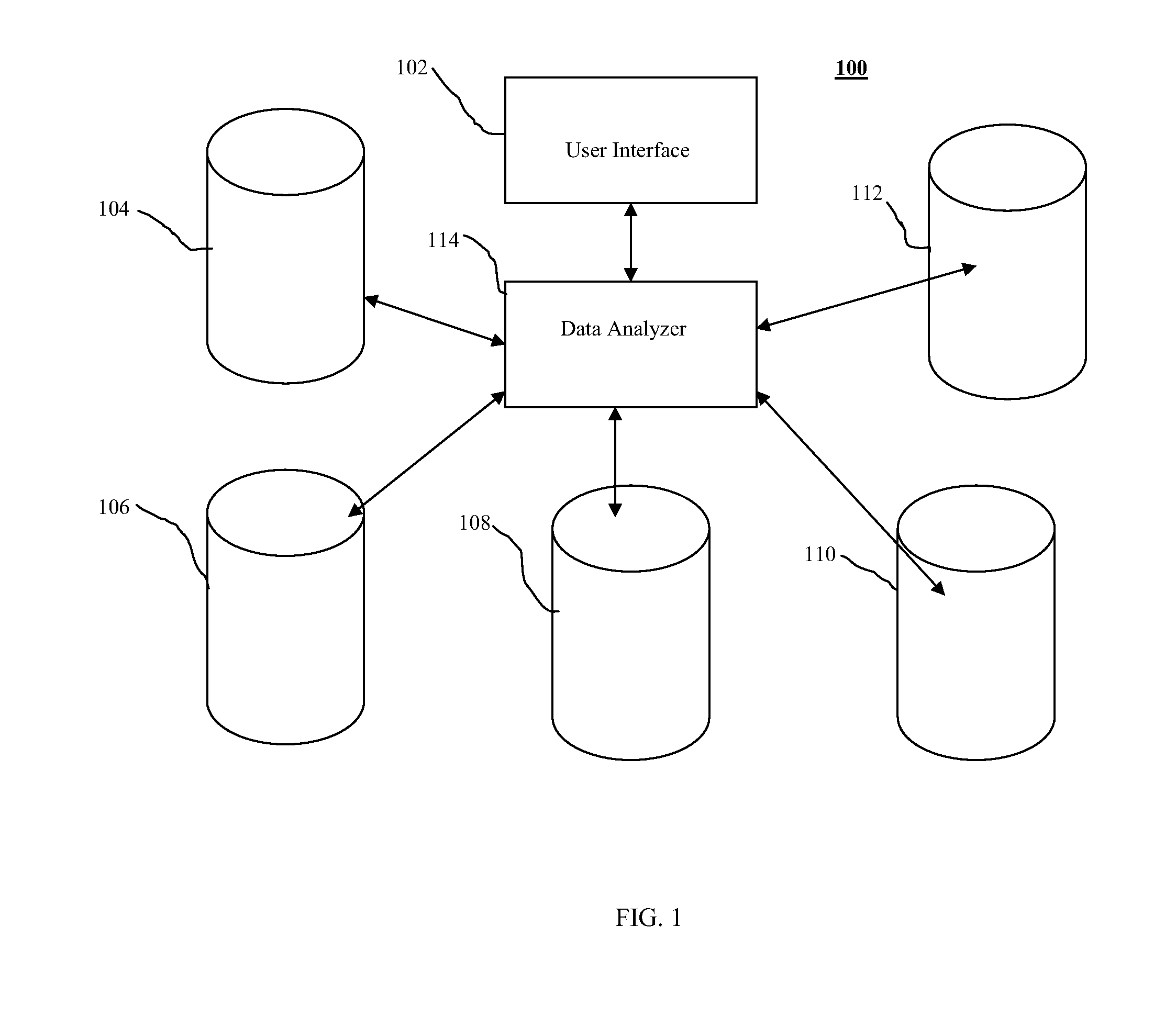
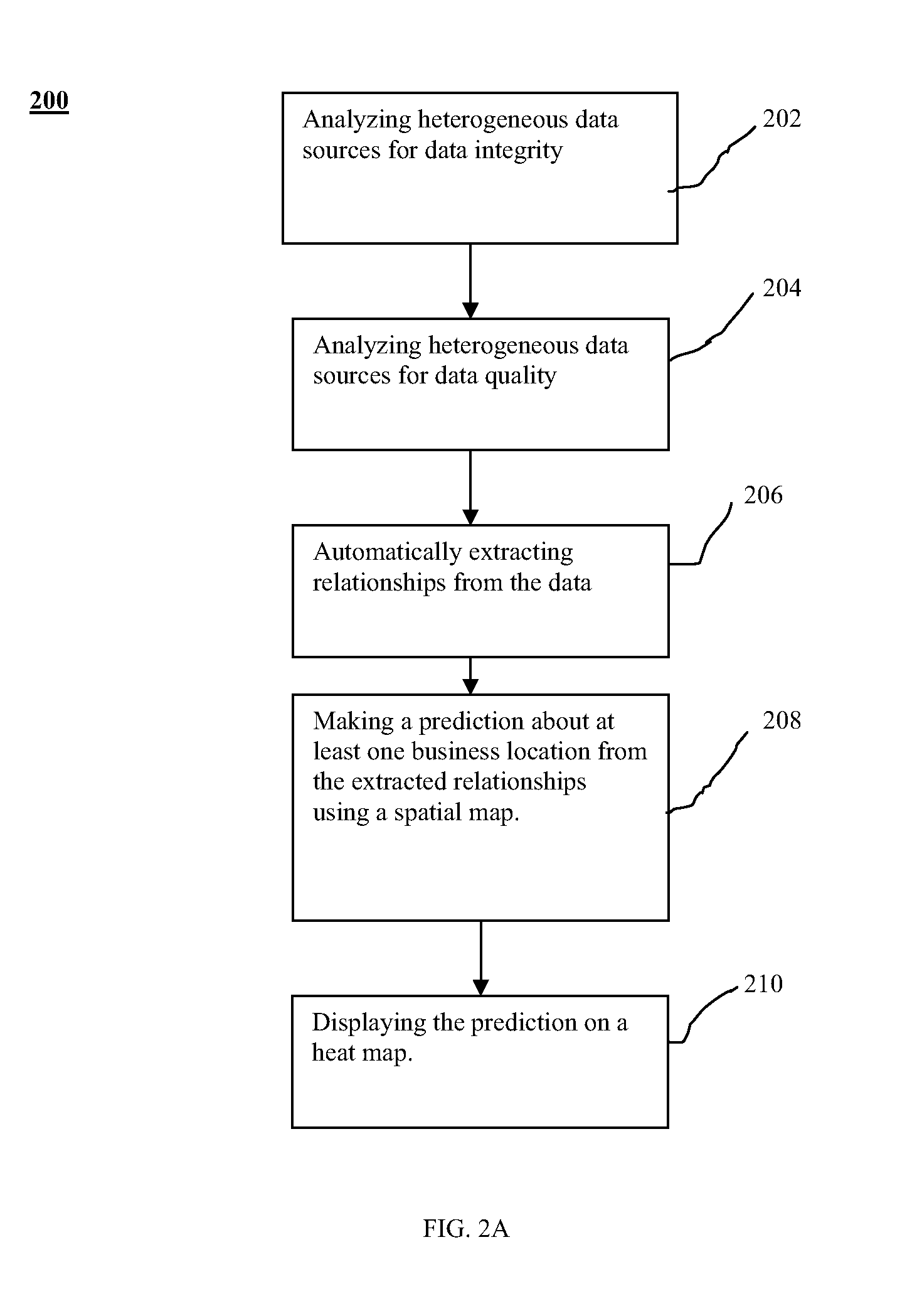
Method and system for displaying predictions on a spatial map
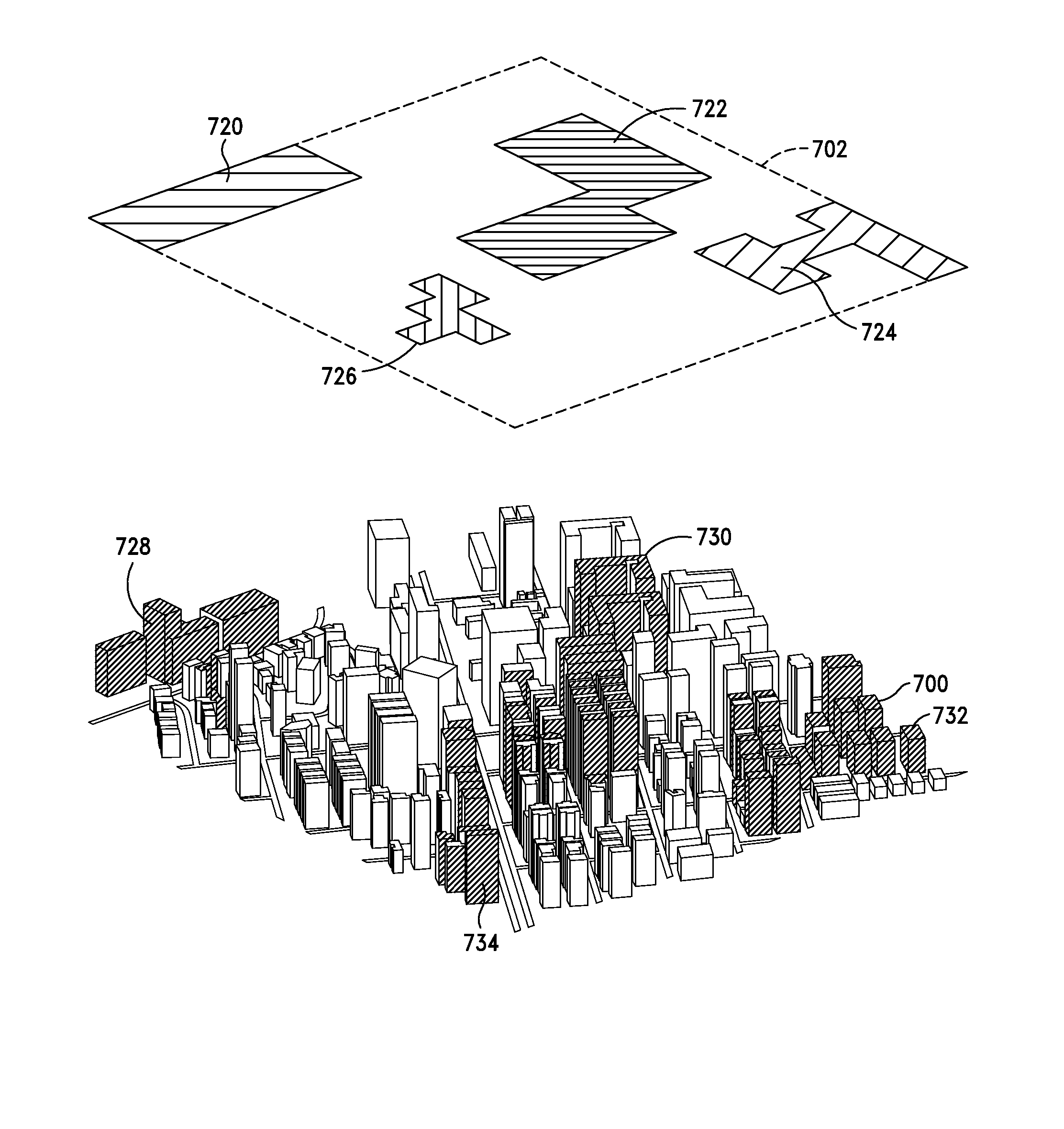
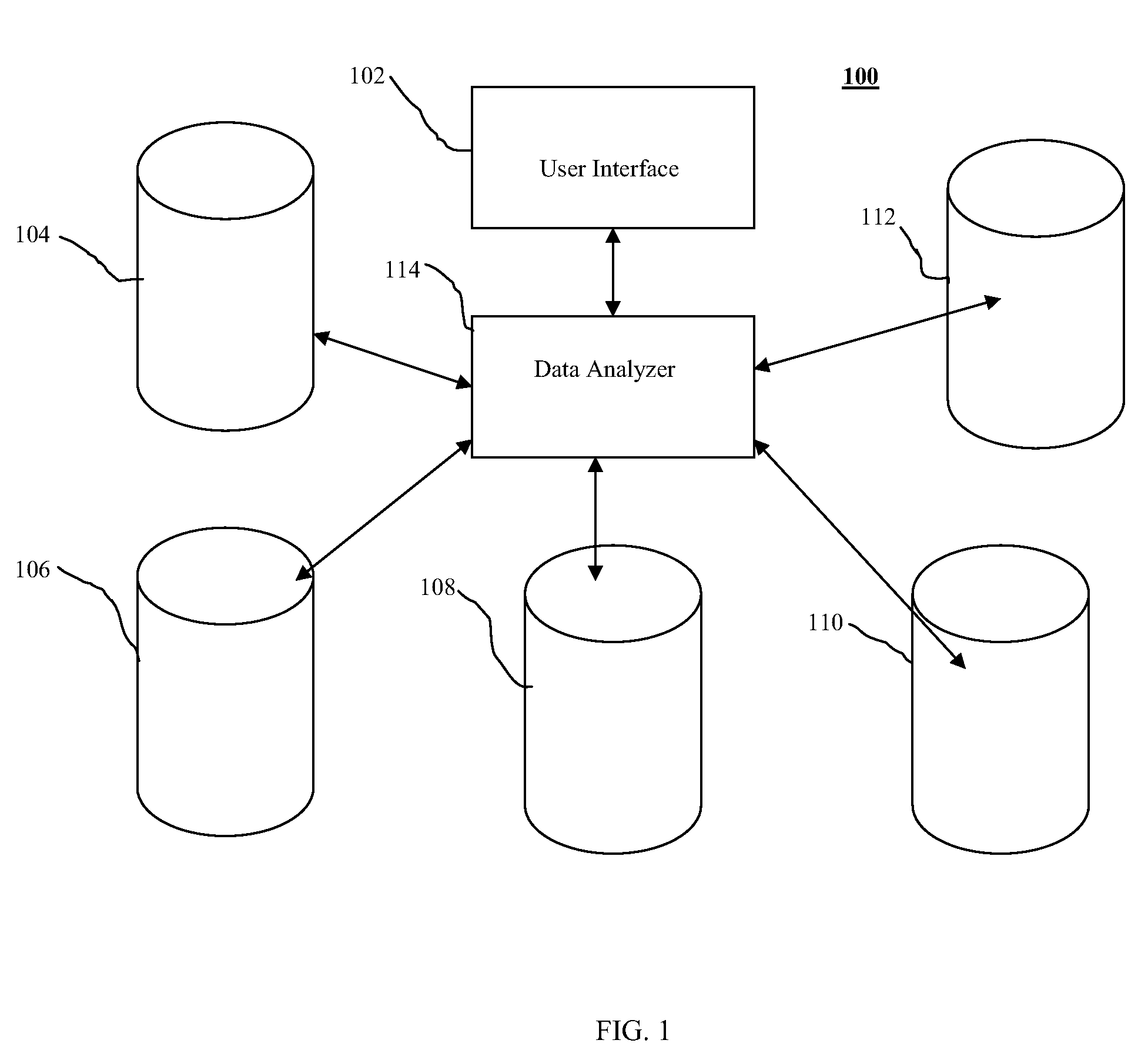
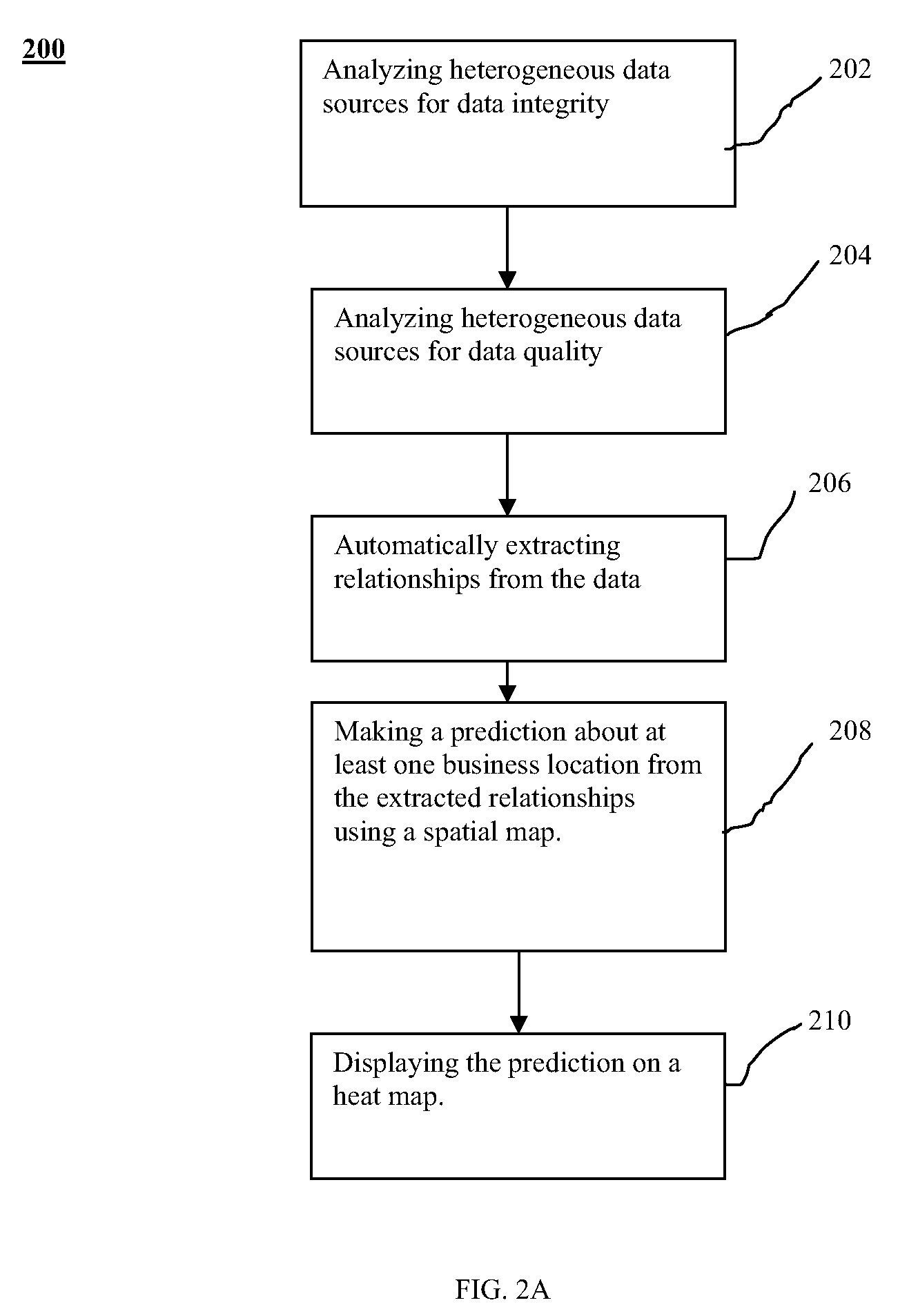
A method and system for displaying predictions on a spatial map includes using a data analyzer for analyzing heterogeneous data having a spatial component to find utilizable data and using machine learning to automatically extract relationships from the utilizable data. The extracted relationships are used to make a prediction about at least one location on the spatial map and present that prediction in an oblique or perspective view. An interface presents the prediction on the spatial map in the form of a heat map overlying a 3-D topographical map. Although the 3-D map can be shown as any form of graphical projection including an oblique projection or orthographic projection, preferably a perspective view is used. It is also preferred that the graphical projection be interactive. The heat map may be 2-D or 3-D and be selectively displayed depending on the preference of a user.
Owner:SAAMA TECH LLC
Method and system for a user-following interface
InactiveUS20070013716A1Enhanced interactionTelevision system detailsProjectorsDisplay deviceOblique projection
Techniques are disclosed for projecting an image onto a surface suitable for interaction with a user while avoiding user occlusion, and while correcting for distortion due to oblique projection. The displayed image moves to a suitable surface at a suitable size and orientation as a user moves around an environment, resulting in a user-following interface. Surfaces are selected in which the projected interface is not occluded by the user or other objects in the environment. Displayed images may be interactive, and moved into an interaction area on a suitable surface that is convenient for the user. The interaction area may or may not coincide with the display area. Adaptation of the projected interface is allowed so that the content of the display and the style of interaction widgets are modified based on distance from the user and orientation of the user with respect to a projected interface.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
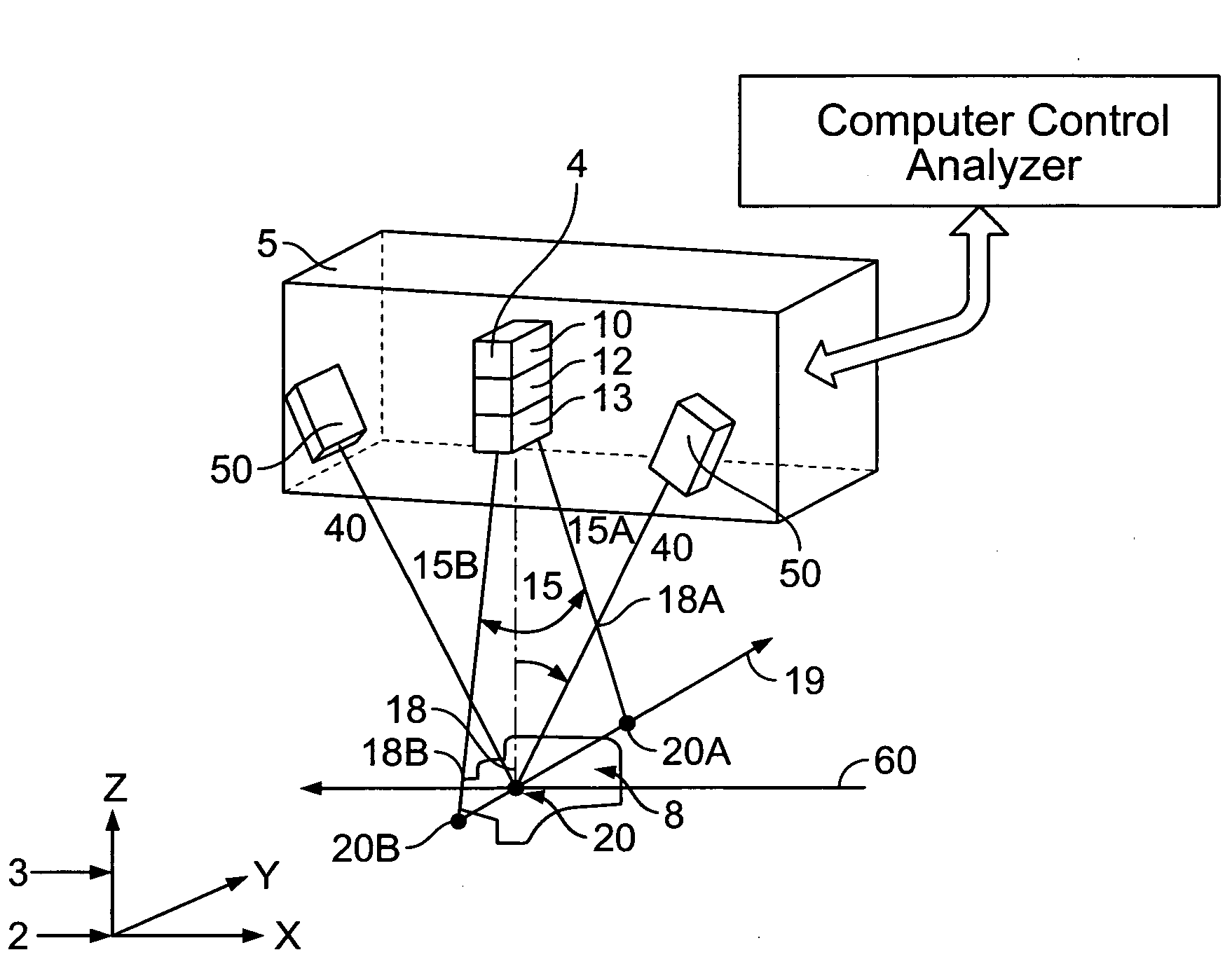
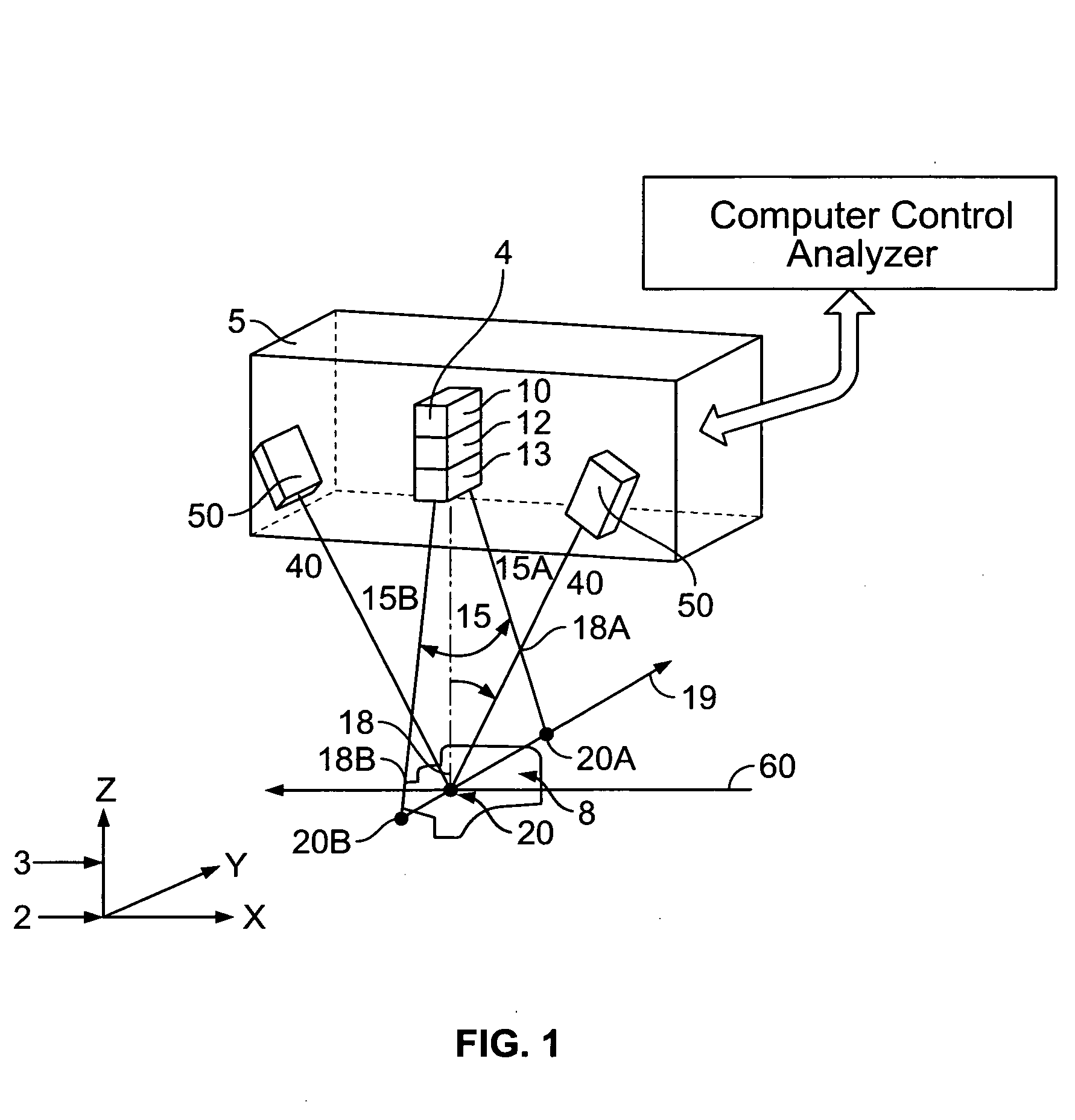
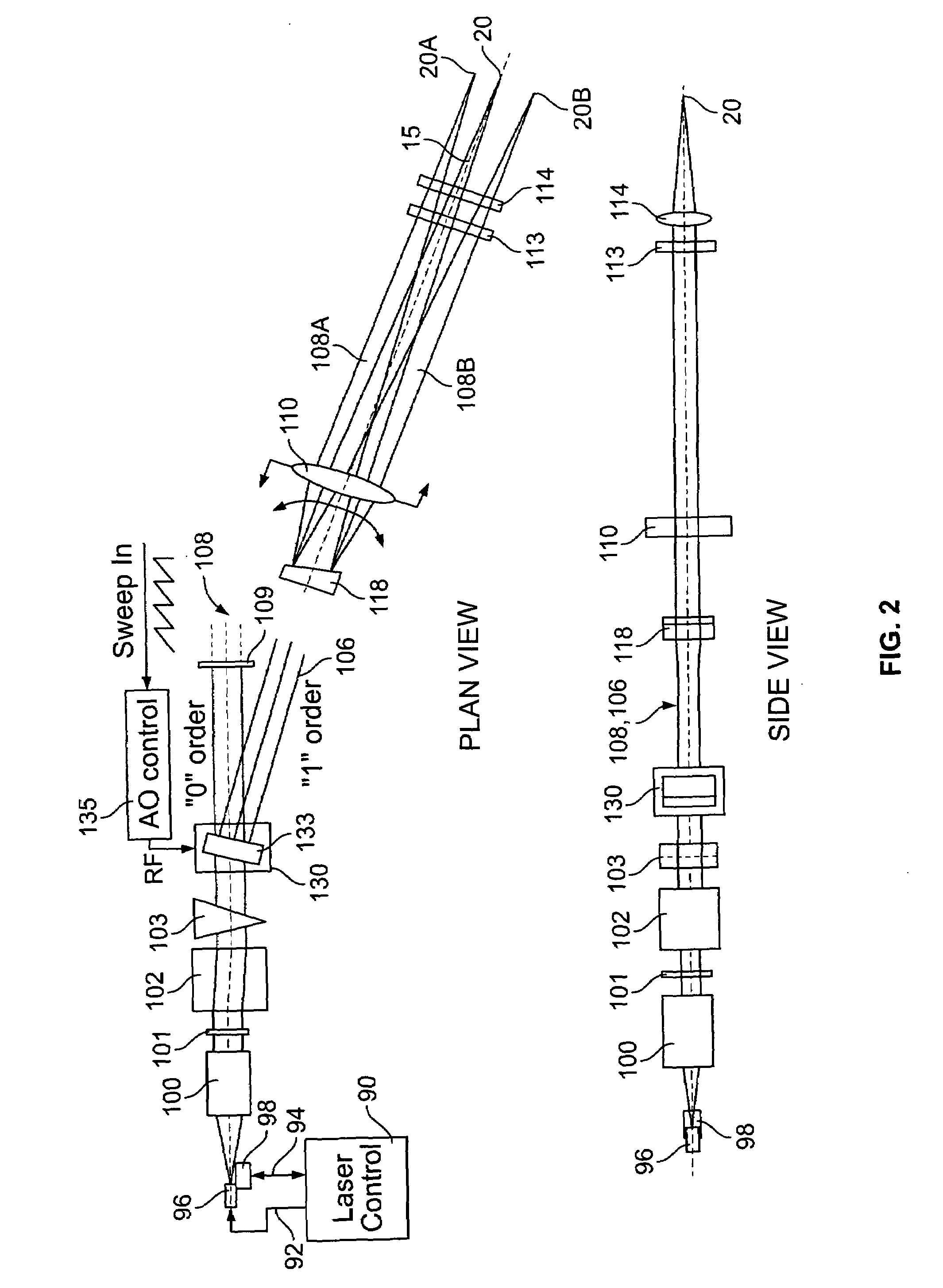
Method and system for providing a high definition triangulation system
ActiveUS20080165357A1Precise positioningSmall spot sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansOphthalmologyTriangulation
A triangulation system including a laser beam, optics focusing the laser beam on an object, a light detection unit detecting light reflected from the object due to impingement of the beam on the object, and an arrangement for determining, based on the detected light, object feature dimensions. The wavelength of the laser beam may be shorter than of infrared radiation, which allows for a reduced spot size without significant loss of depth of field. So as to reduce aberrations or a sensitivity to aberrations due to the shortened wavelength, the system may include (i) a polarization dependent coating matching the index of refraction of an element of the light detection unit to that of air for a range of angles, (ii) tilted projection optics, (iii) a prism wavefront corrector, and / or (iv) a positioning assembly, which provides for increased precision in positioning the laser diode with respect to a collimator lens.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Method and system for displaying predictions on a spatial map
A method and system for displaying predictions on a spatial map includes using a data analyzer for analyzing heterogeneous data having a spatial component to find utilizable data and using machine learning to automatically extract relationships from the utilizable data. The extracted relationships are used to make a prediction about at least one location on the spatial map and present that prediction in an oblique or perspective view. An interface presents the prediction on the spatial map in the form of a heat map overlying a 3-D topographical map. Although the 3-D map can be shown as any form of graphical projection including an oblique projection or orthographic projection, preferably a perspective view is used. It is also preferred that the graphical projection be interactive. The heat map may be 2-D or 3-D and be selectively displayed depending on the preference of a user.
Owner:SAAMA TECH LLC
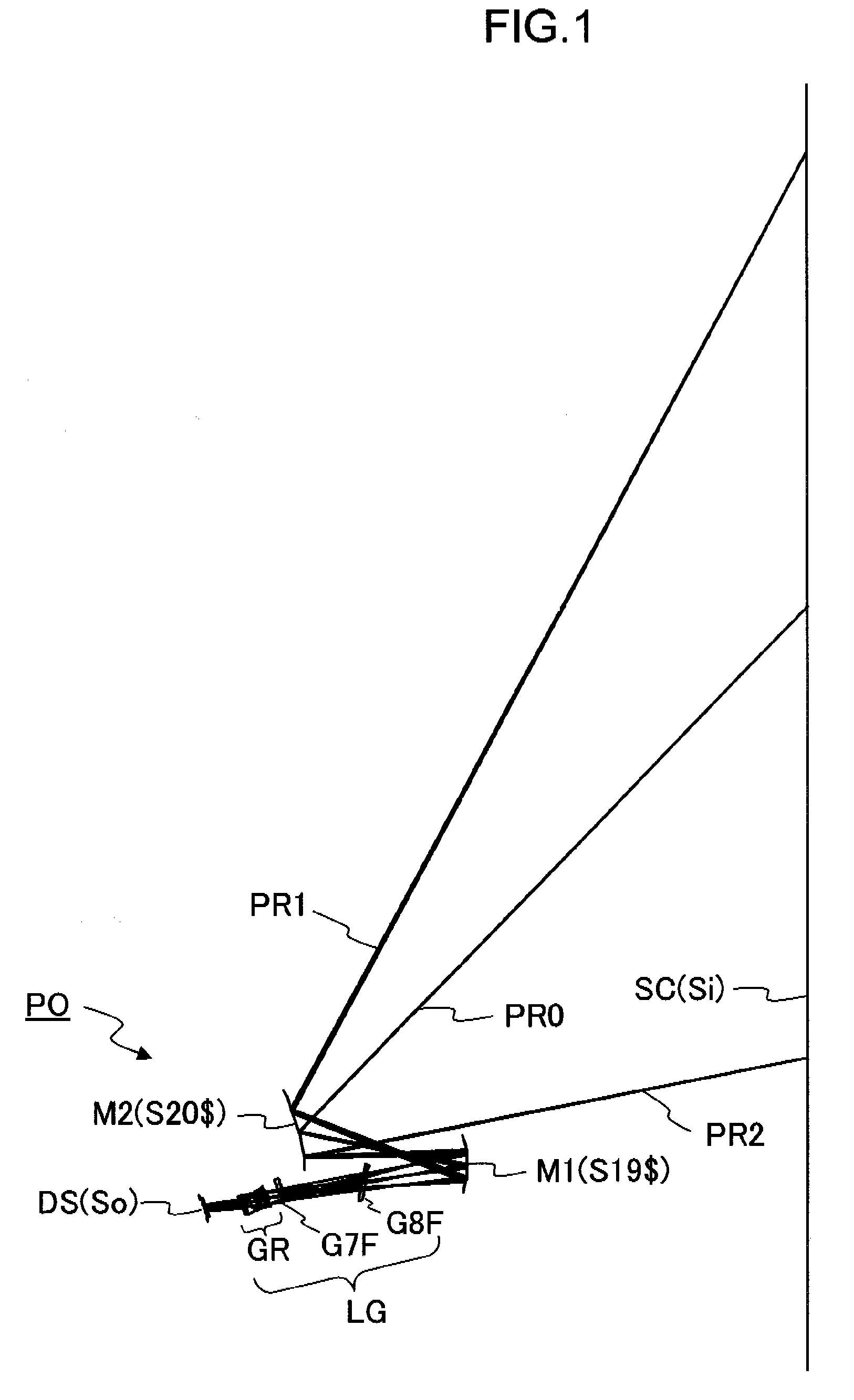
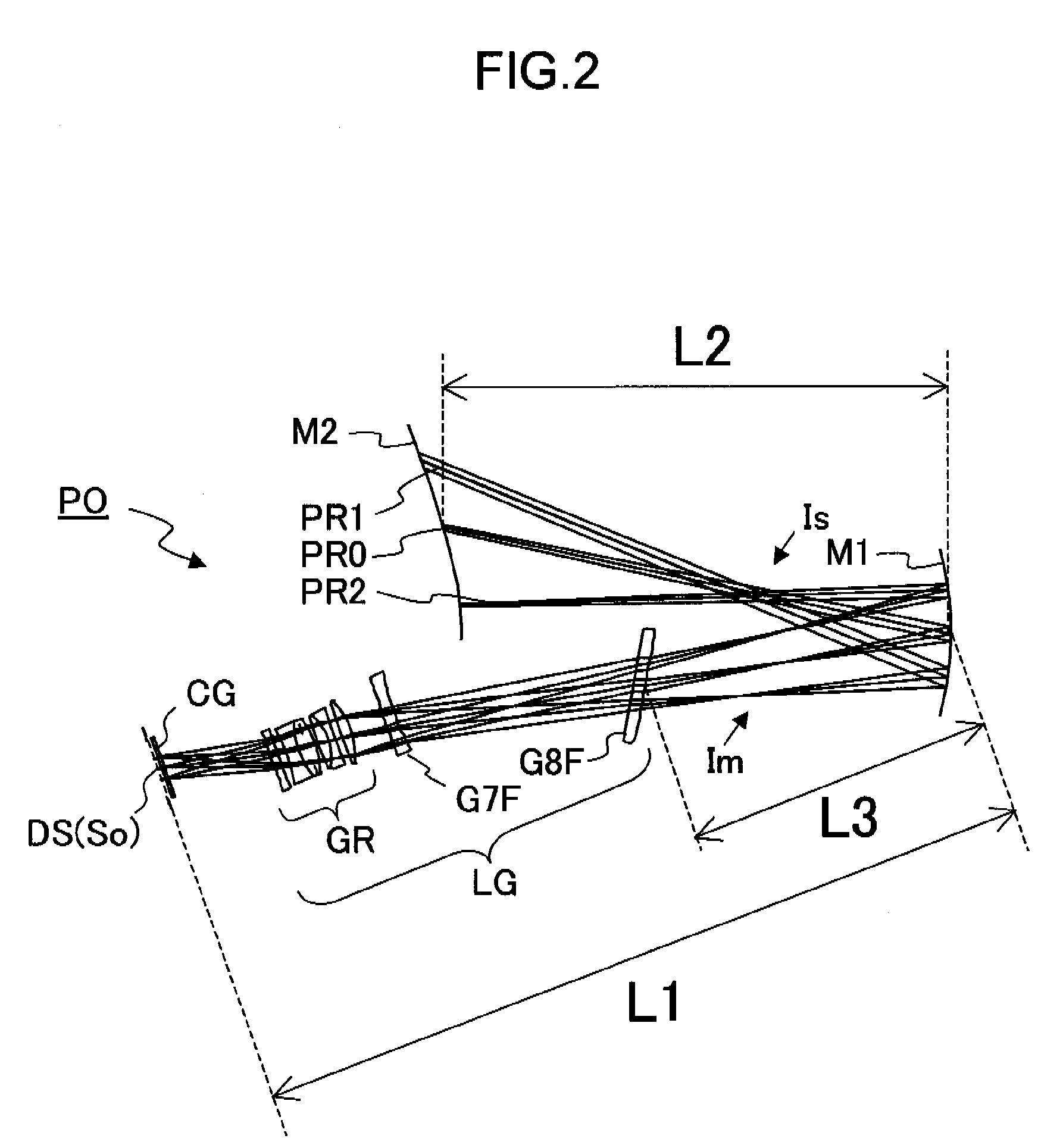
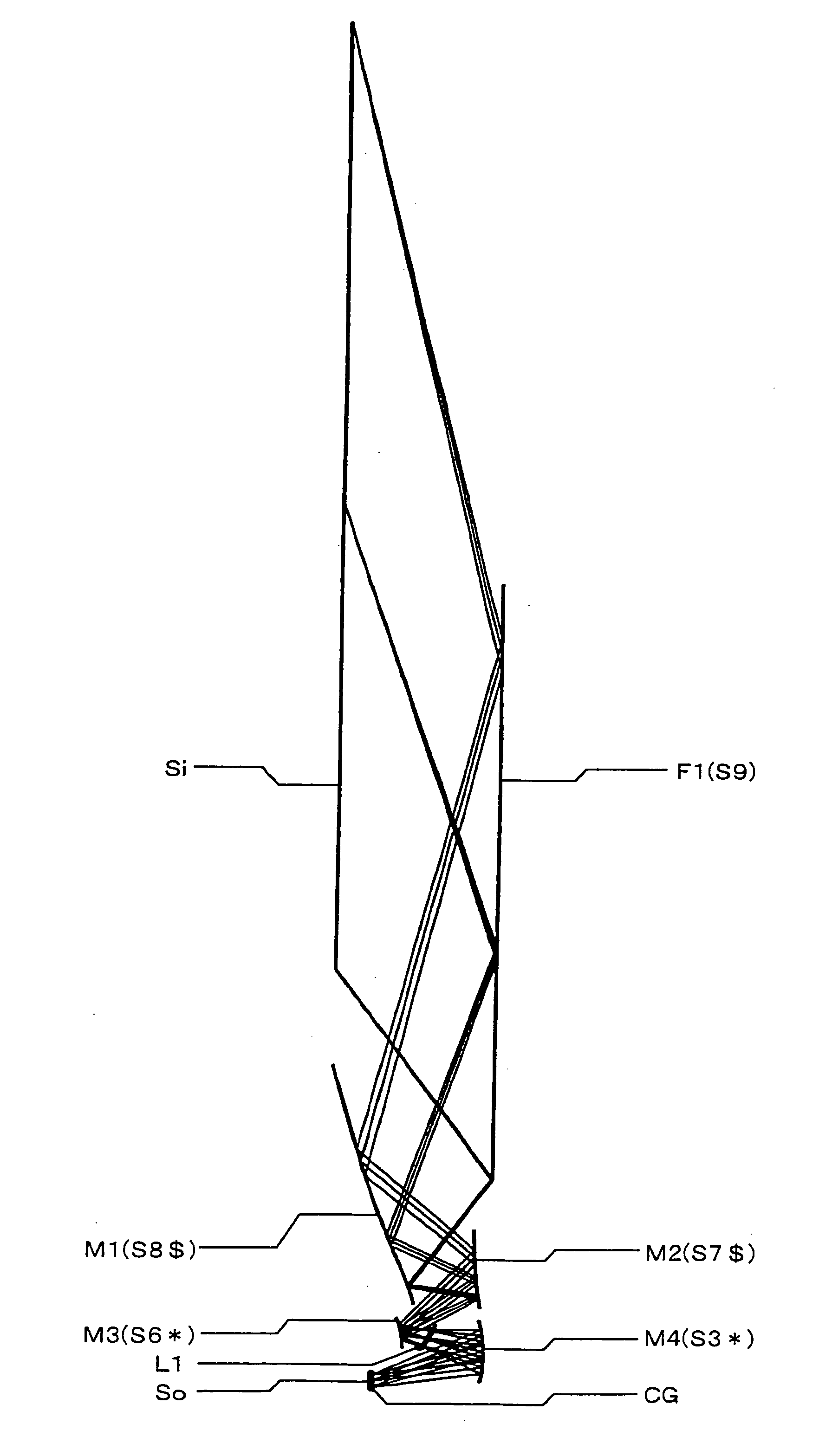
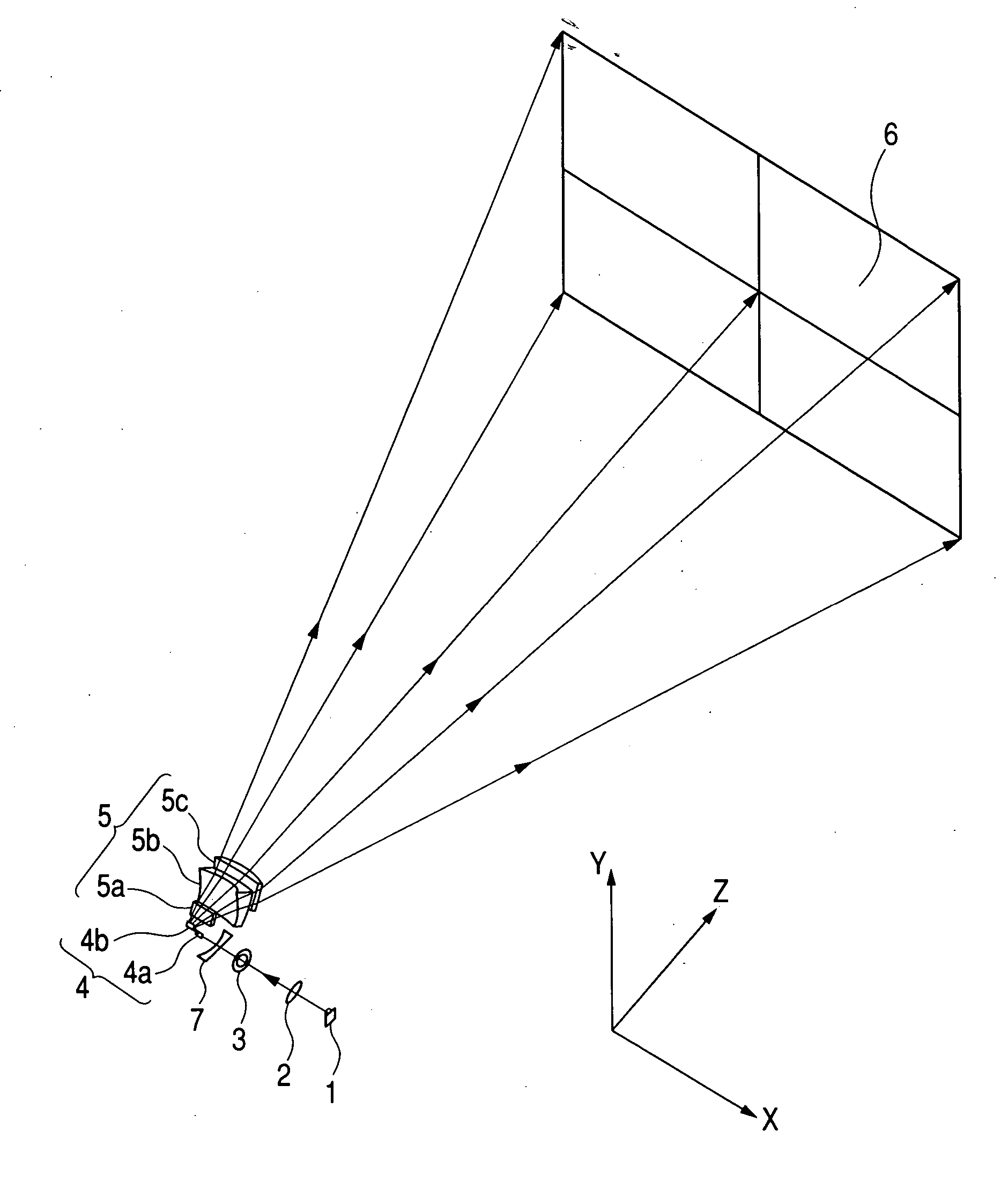
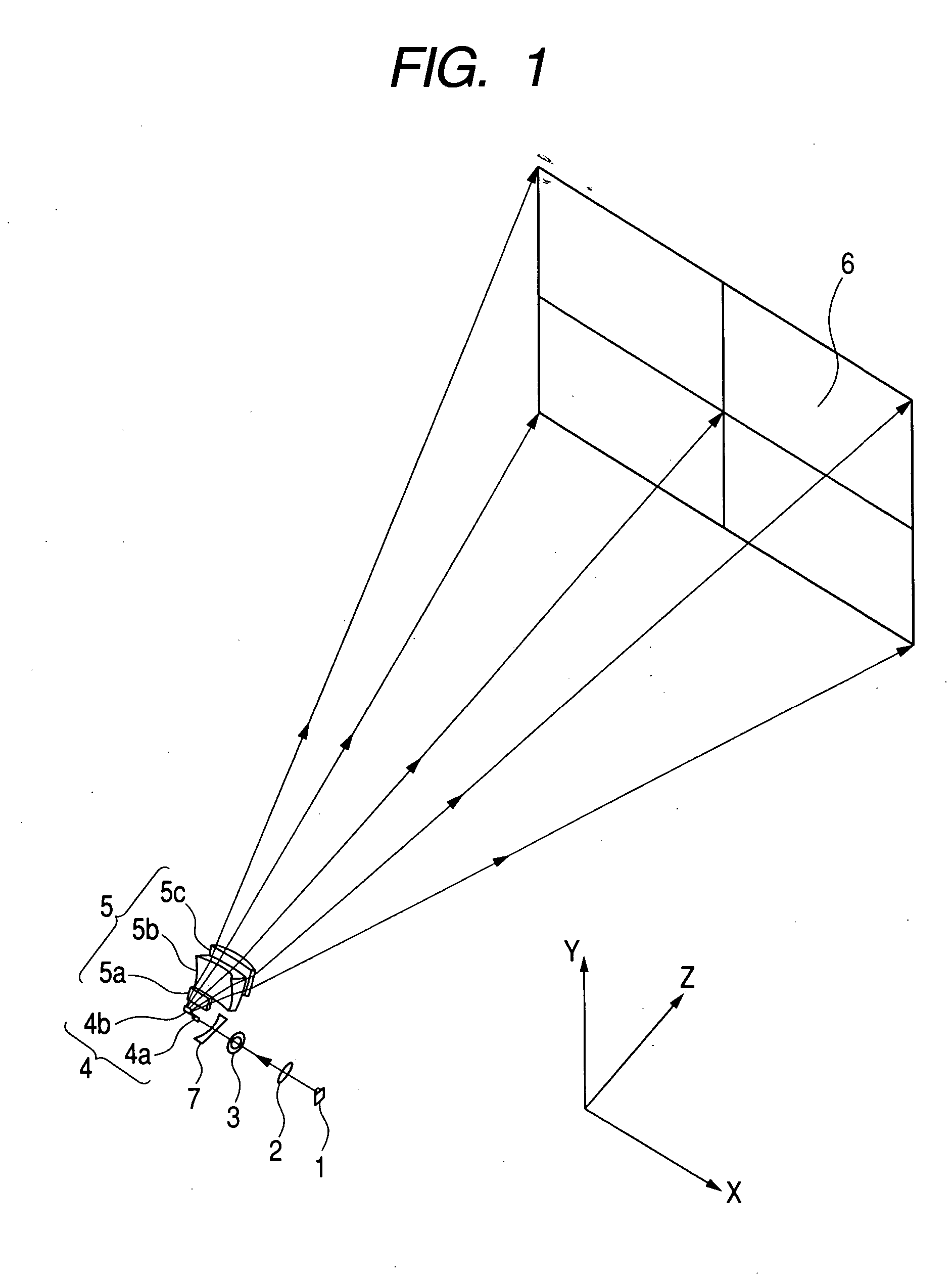
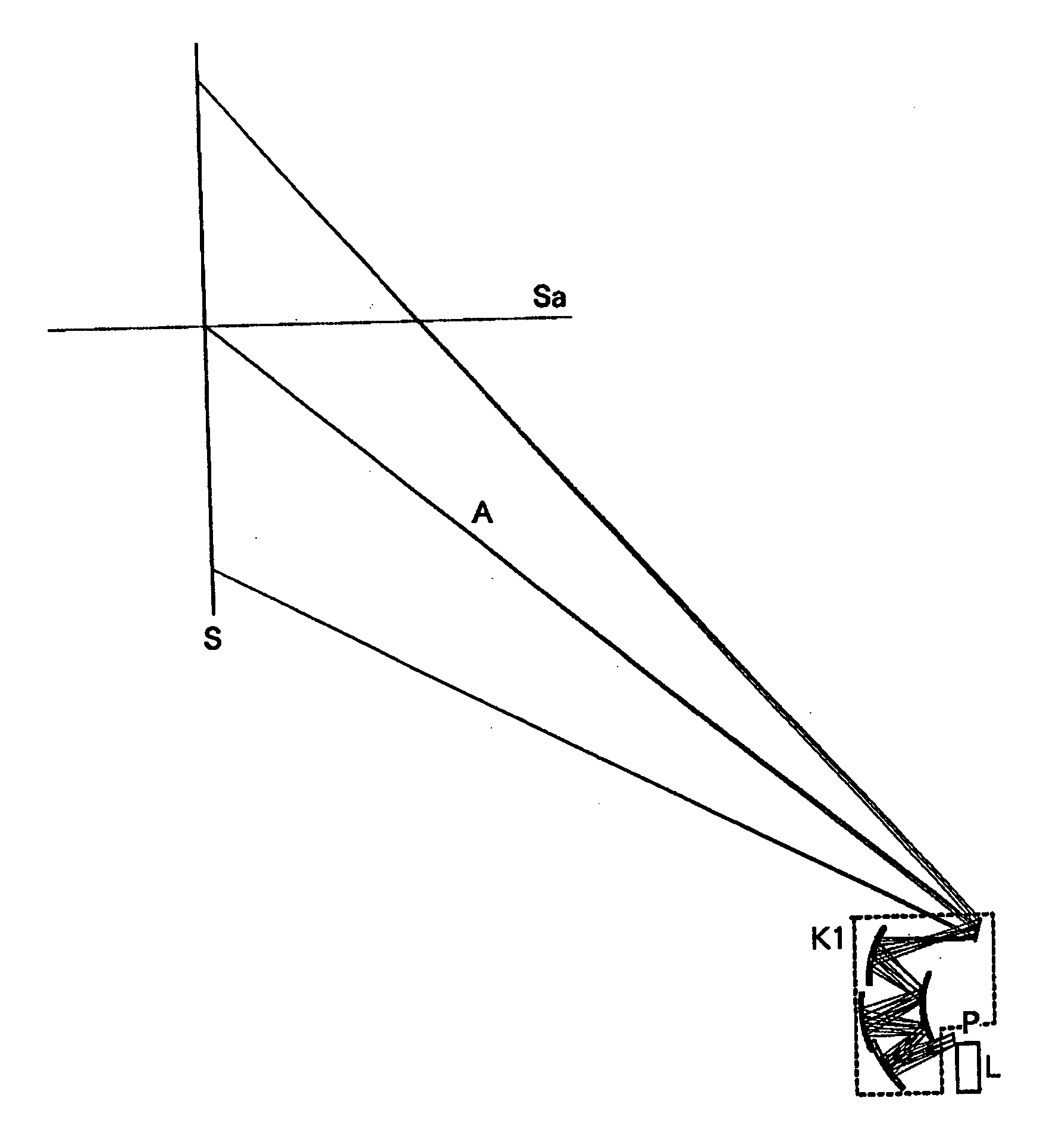
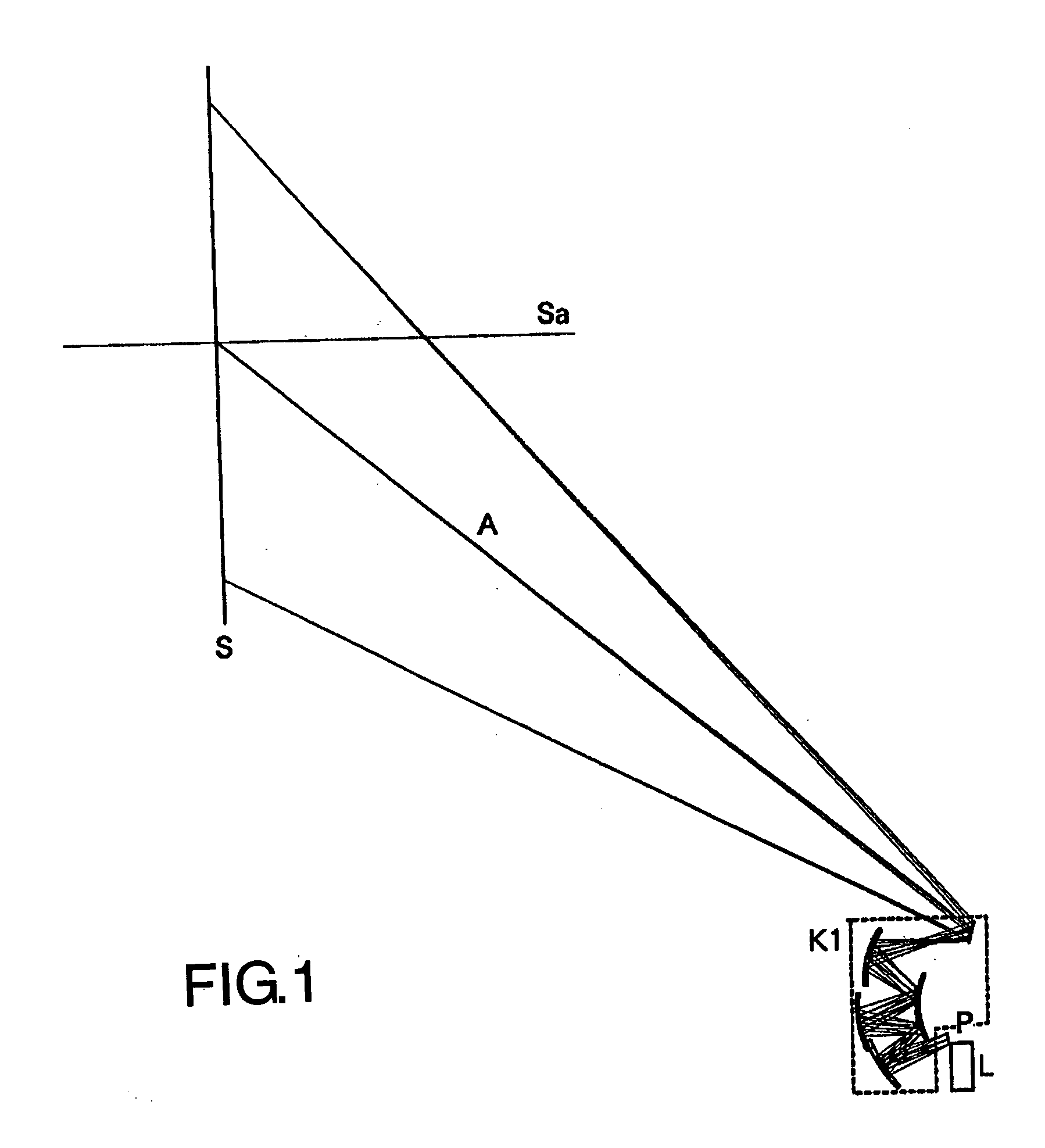
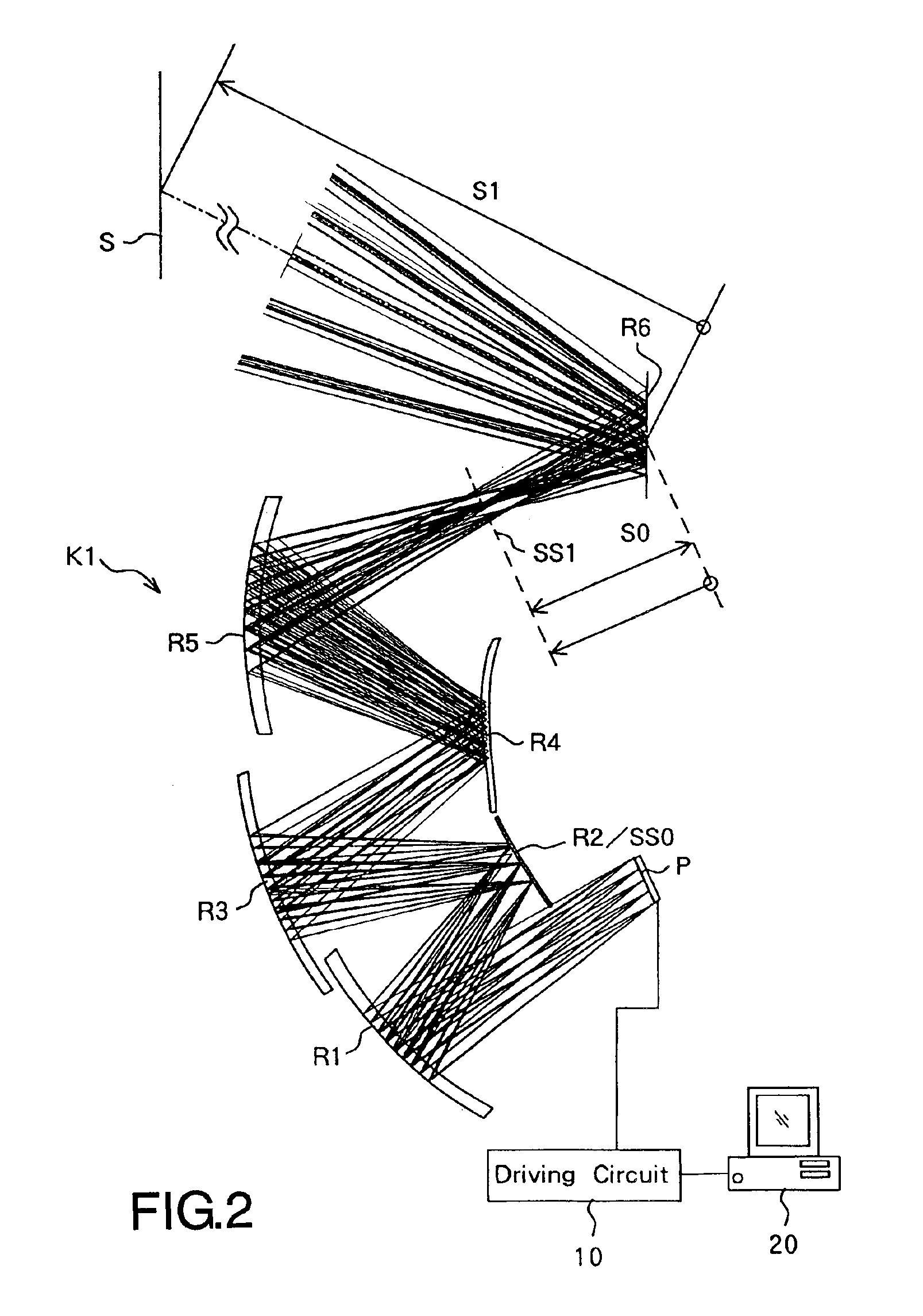
Oblique projection optical system
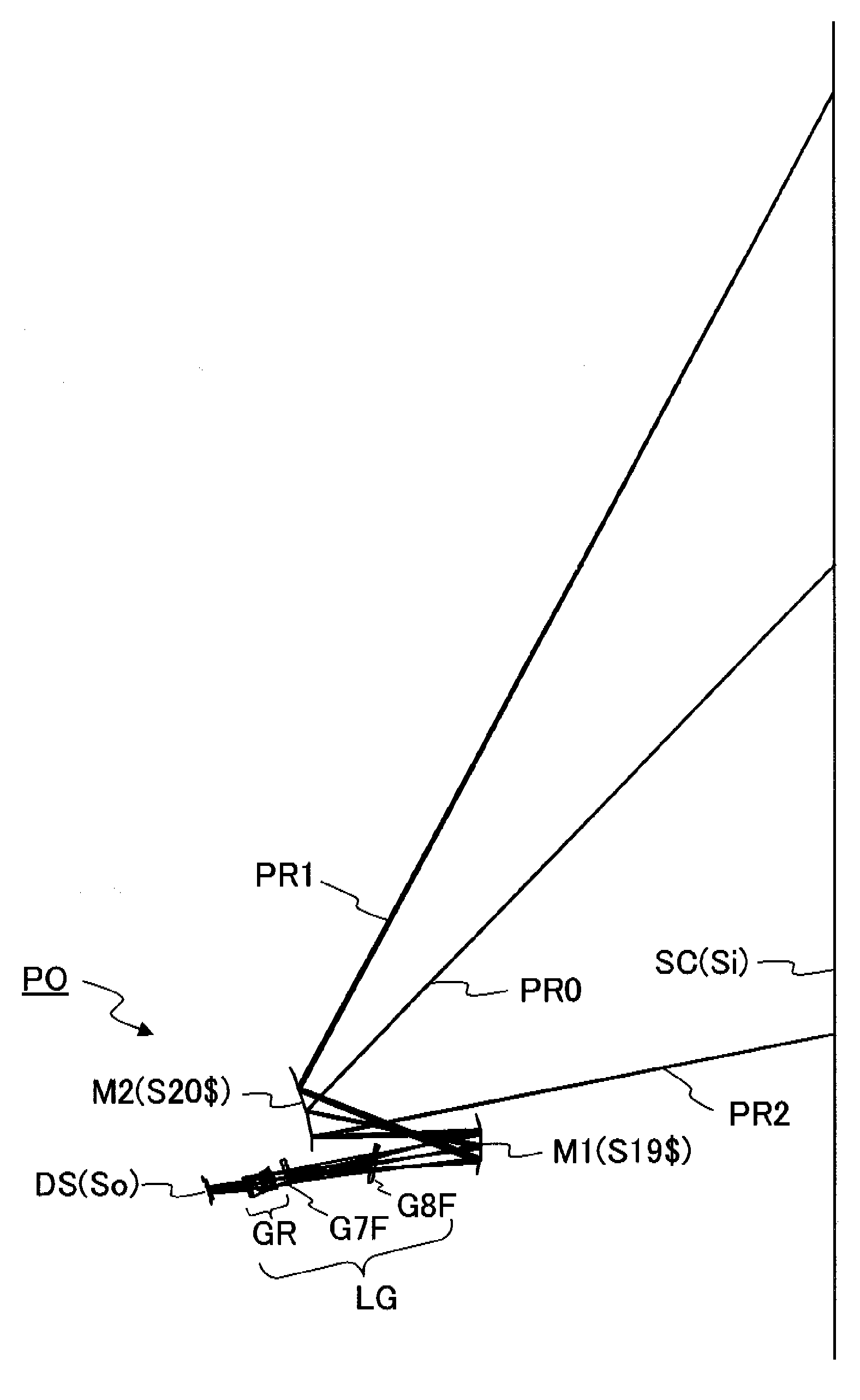
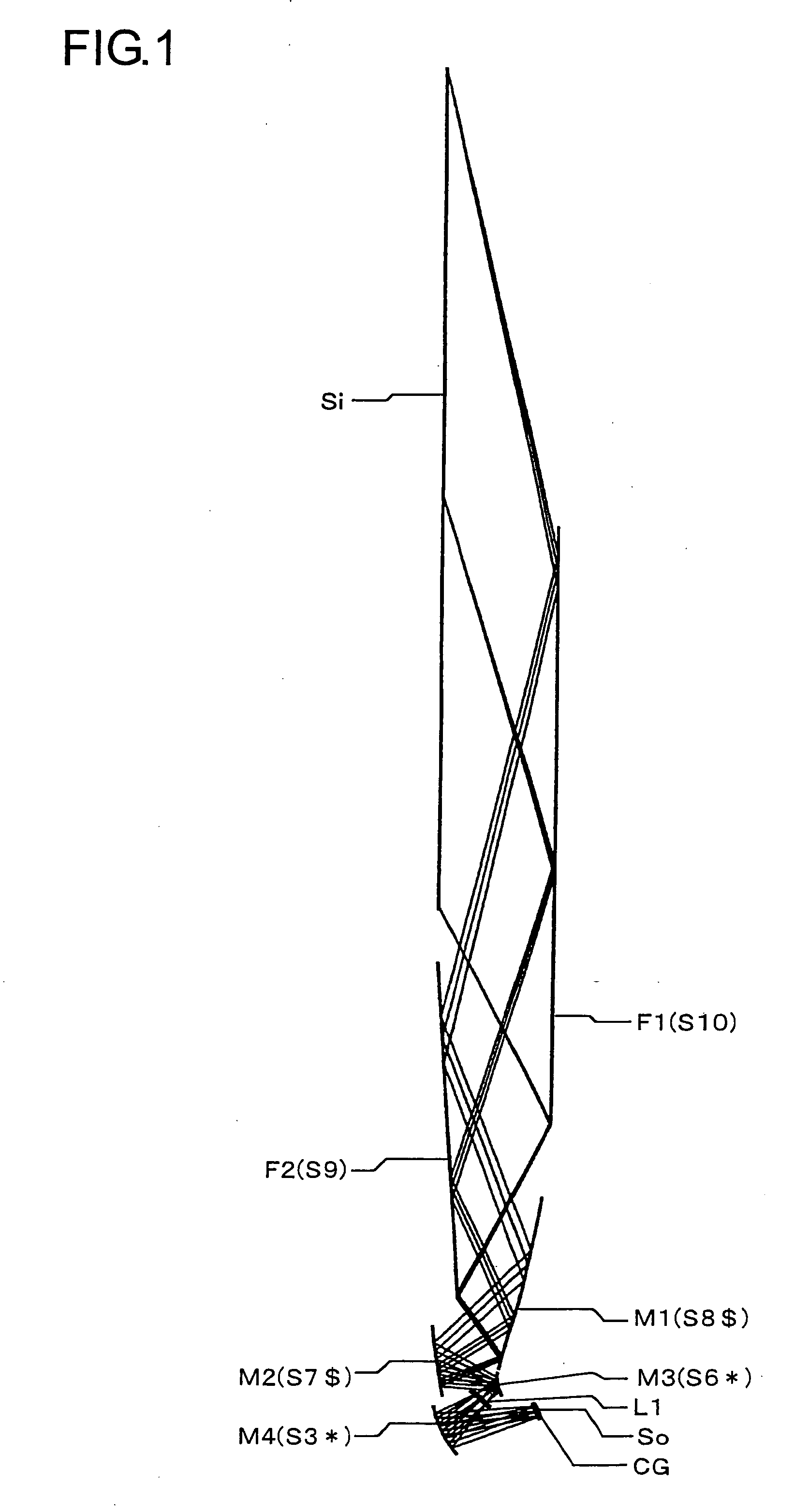
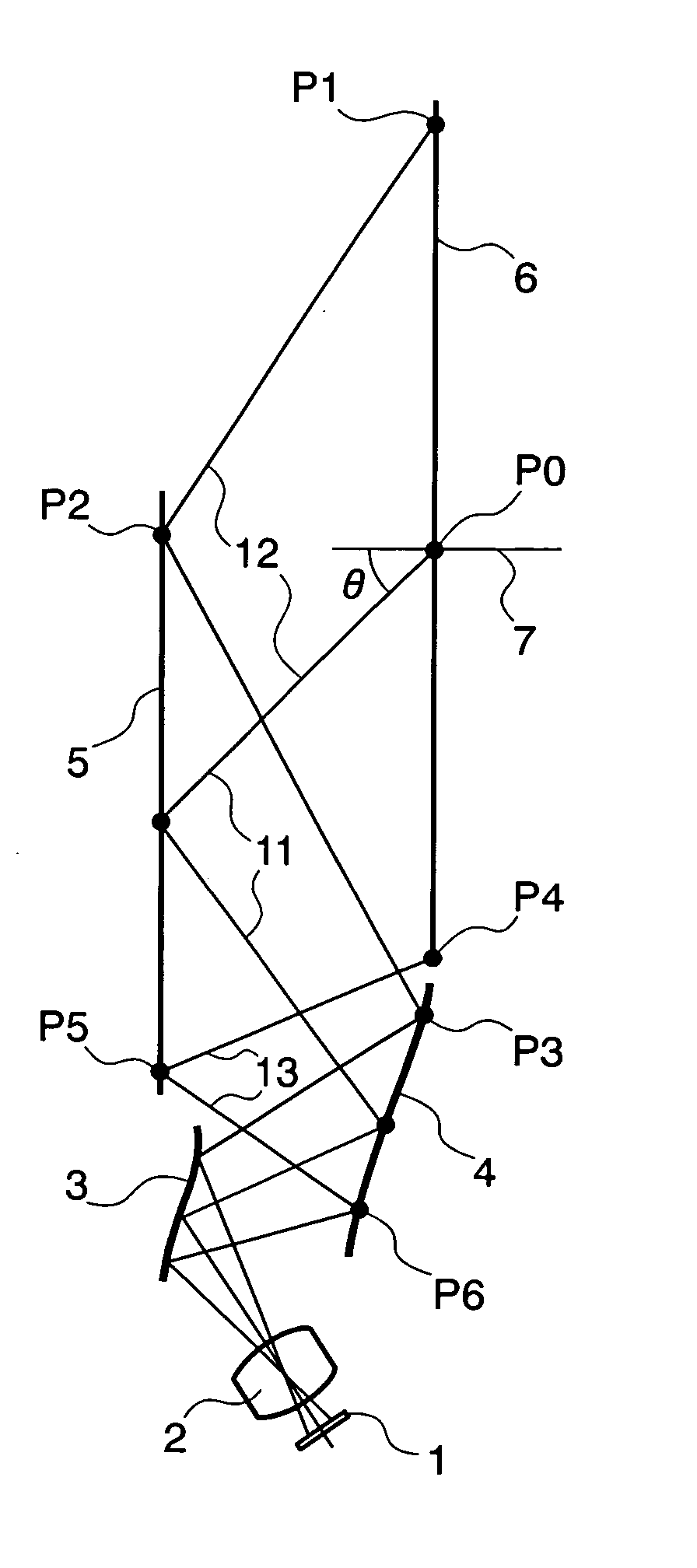
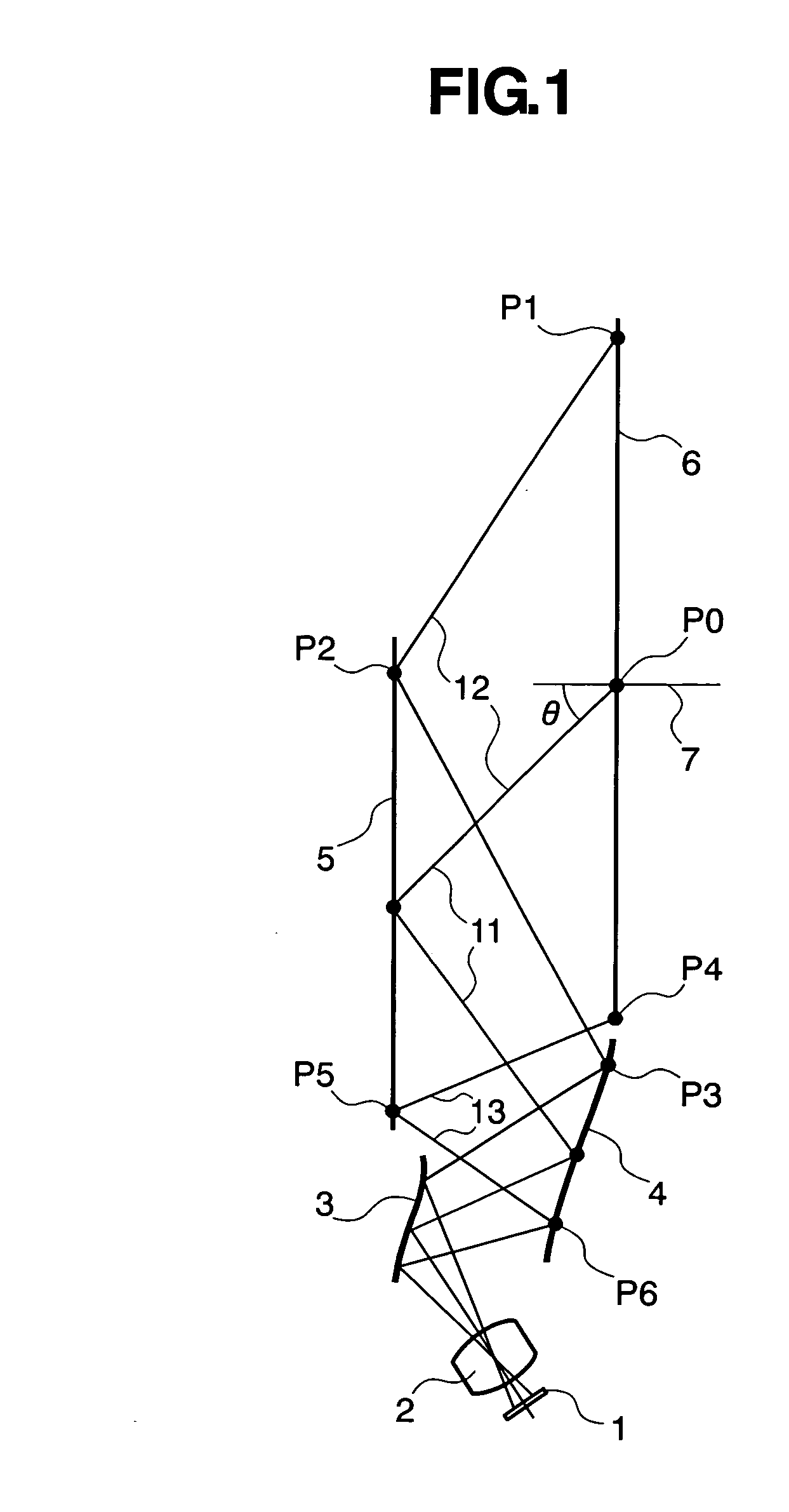
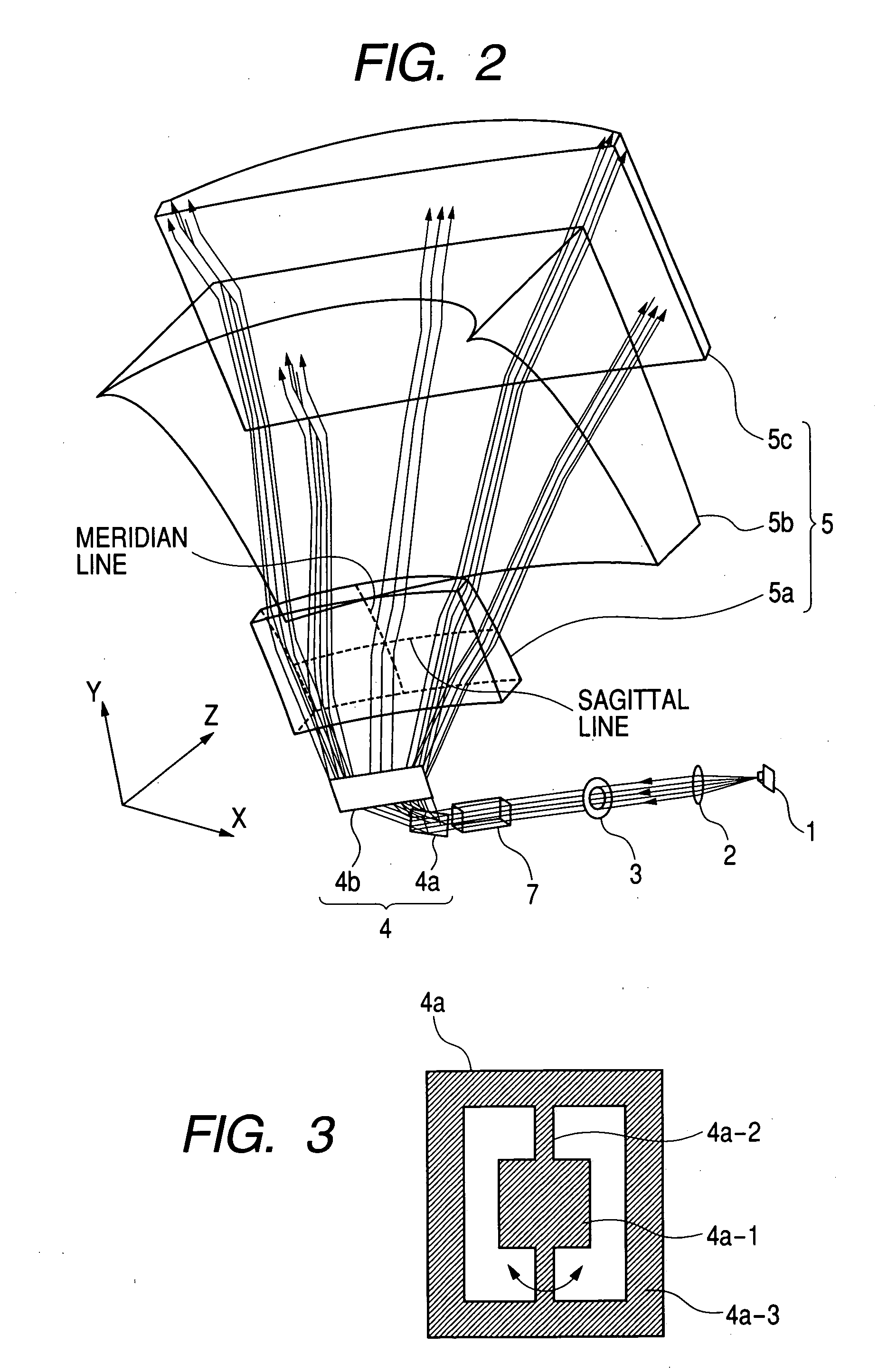
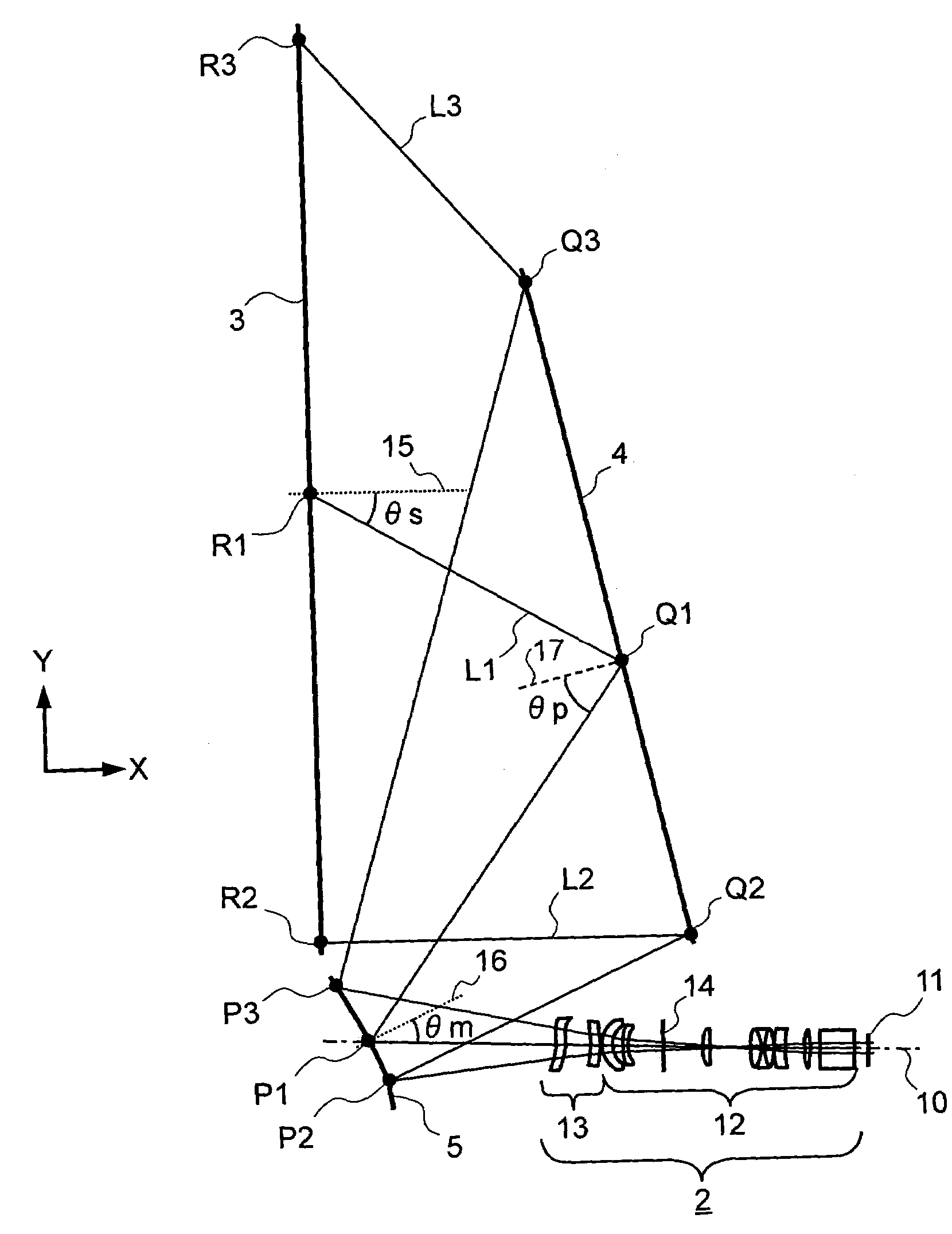
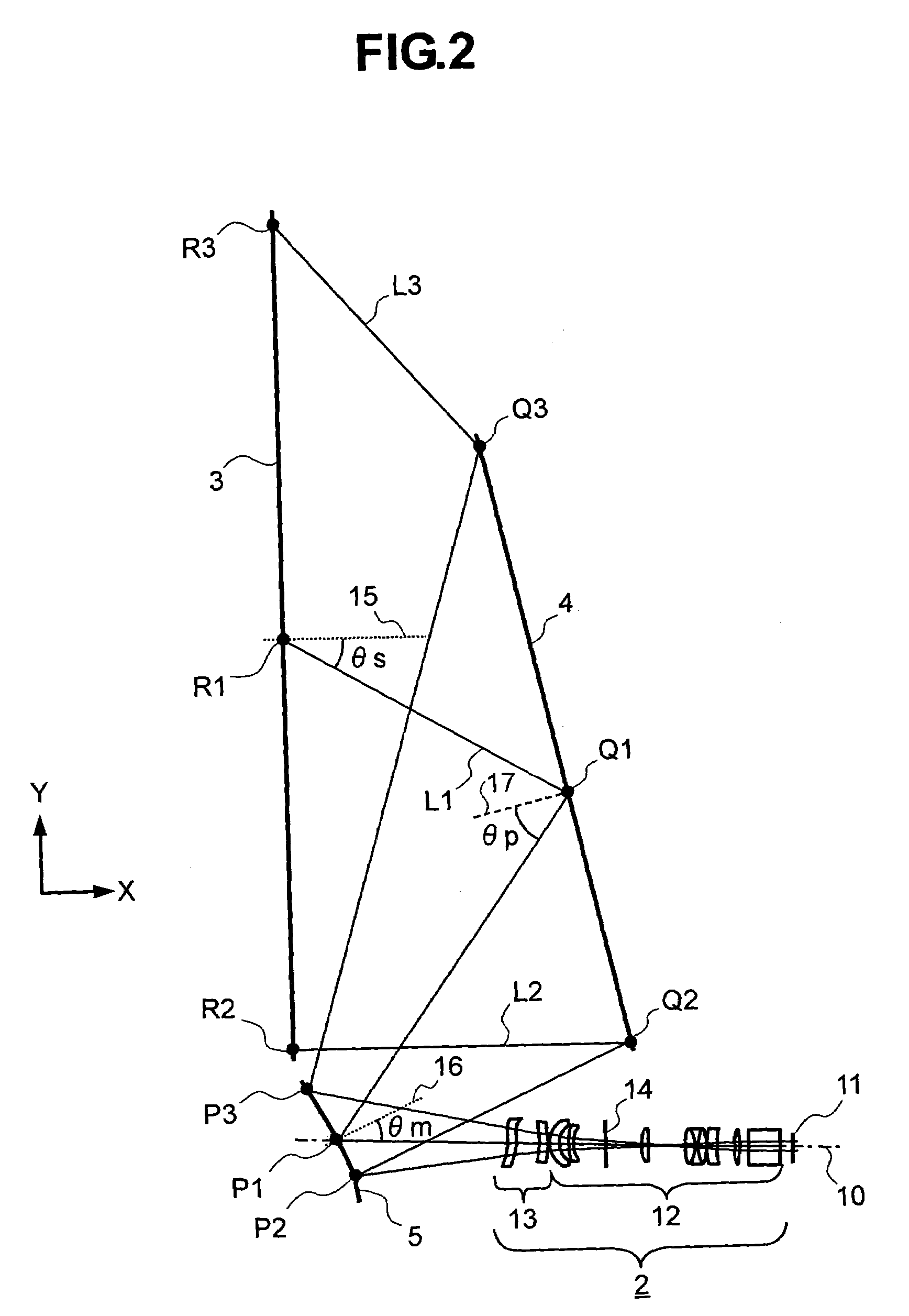
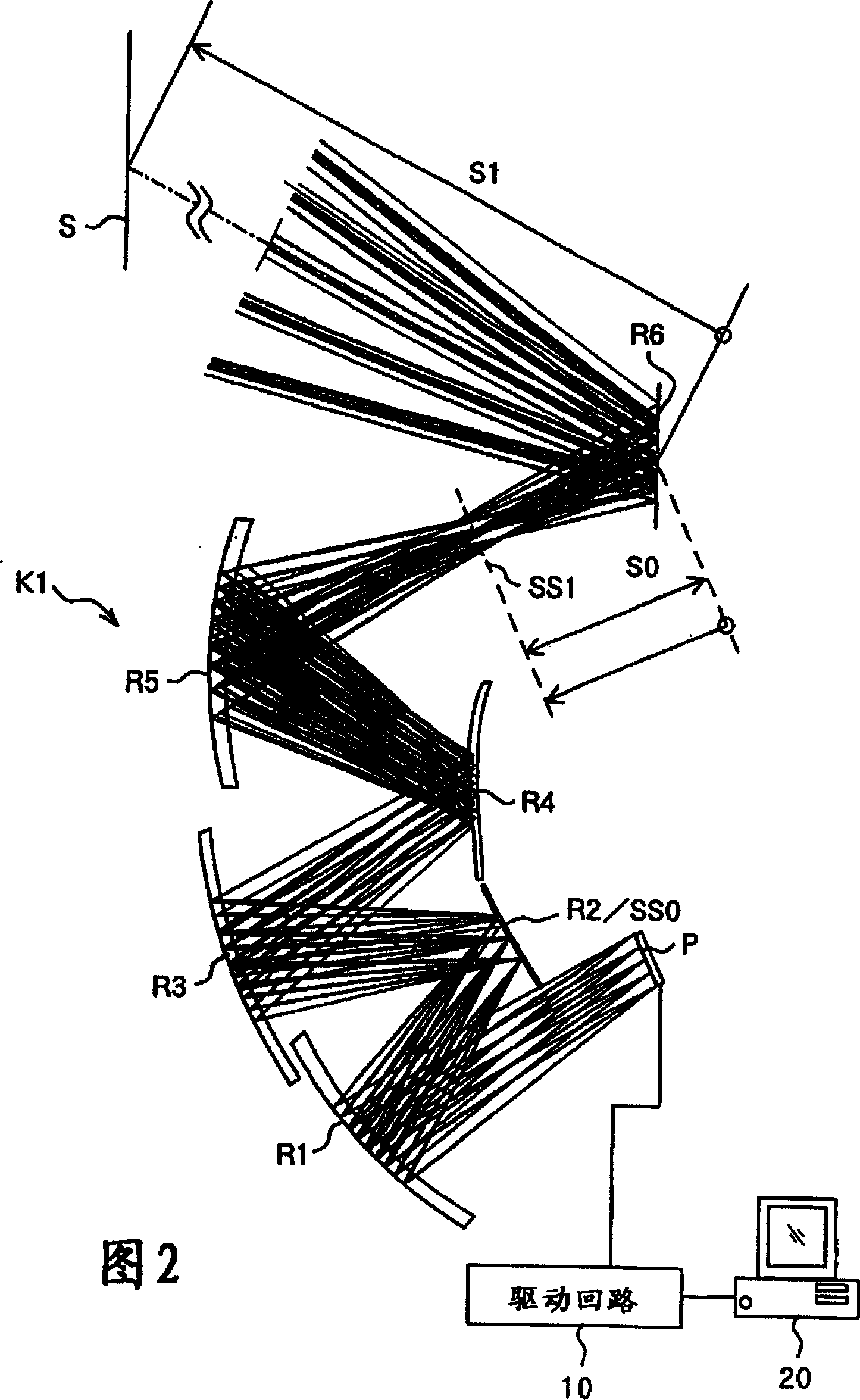
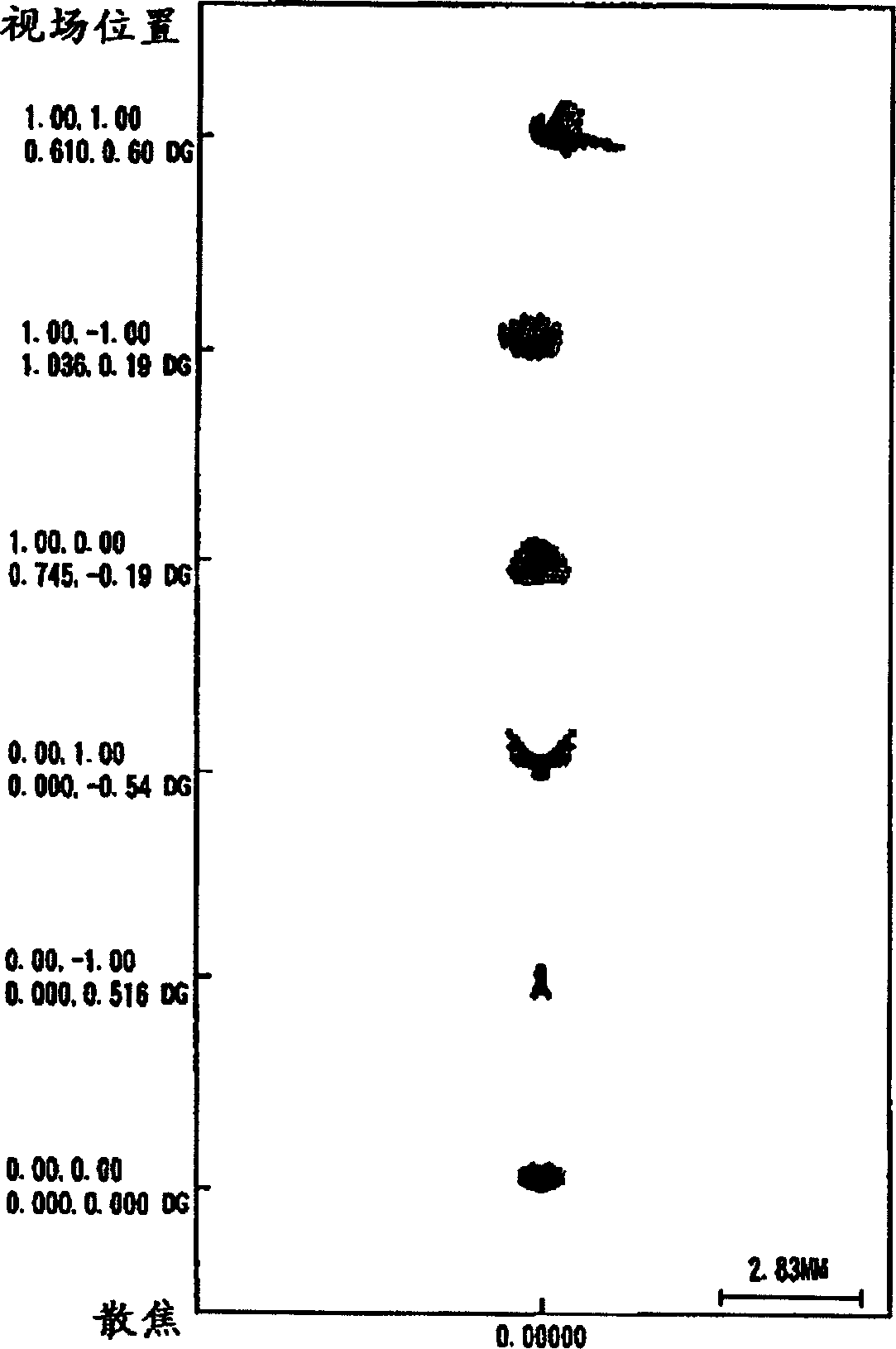
An oblique projection optical system enlarges an image formed on a display device surface, and obliquely projects the enlarged image on a screen surface. The oblique projection optical system has, in the order from a reduction side: a refraction optical portion having a positive optical power, a concave reflection surface having a positive optical power, and a convex reflection surface having a negative optical power. The refraction optical portion includes a rotationally symmetric coaxial refraction group. An intermediate image of the image formed on the display device surface is formed between the refraction optical portion and the concave reflection surface. An aperture stop image is formed between the concave reflection surface and the convex reflection surface. The concave reflection surface and the convex reflection surface fulfill prescribed conditional formulae.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Oblique projection optical system and projection type display apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20100171937A1Shorten the timeReduce development costsProjectorsColor television detailsOptical axisProjection screen
A projection type display apparatus including an oblique projection optical system having a plurality of lenses is disclosed. A lens nearest to a projection screen has a vertical effective image area through which a light flux passes. The lens is arranged at a position not including an optical axis shared by the largest number of lenses among the plurality of lenses. A flat mirror for returning the optical path is arranged between the particular lens and the projection screen at a predetermined angle to the optical axis. An enlarged image obtained by the light flux returned by the flat mirror is formed toward a display screen.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Projection display and method for displaying an overall image for projection free-form surfaces or tilted projection surfaces
A projection display with an imaging system is described, which is implemented to generate individual images in a distribution, such as a two-dimensional distribution, of sub-areas of an imaging plane of the imaging system, and a multi-channel optics that is configured to map one allocated individual image or one allocated sub-area of the imaging system each per channel, such that the mapping of the individual images is at least partly superimposed to an overall image in a projection surface, wherein the projection surface is a non-planar free-form surface, such as a curved surface, and / or tilted with respect to the imaging plane, and the imaging system is implemented such that constellations of points in the sub-images, each superimposed in a respective common point in the overall image by the multi-channel optics, differ depending on what distance the respective common point in the overall image has to the multi-channel optics.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Projective texture mapping-based oblique projection distortion correction method
InactiveCN102014259AAvoid disadvantagesAvoid limitationsTelevision system detailsProjectorsTransformation parameterProjection screen
The invention discloses a projective texture mapping-based oblique projection distortion correction method. The projective texture mapping-based oblique projection distortion correction method comprises the following steps of: 1, establishing models of a projector, a projection screen and an observer; 2, mapping a texture image to the projection screen through projective texture mapping, wherein the observer is regarded as a virtual projector; 3, applying colors to the projection screen after the projective texture mapping and acquiring a deformed image that a virtual observer observes, wherein the projector is regarded as the virtual observer and the deformed image is a pre-deformed image that a projection system needs during image correction; and 4, applying the pre-deformed image in the step 3 serving as a projected image to the actual projection system to realize geometric distortion correction of the projected image. By the projective texture mapping-based oblique projection distortion correction method, defects and limitation of estimating projection transformation parameters are overcome and cost is reduced.
Owner:杭州华泰医疗科技有限公司
Oblique projection optical system
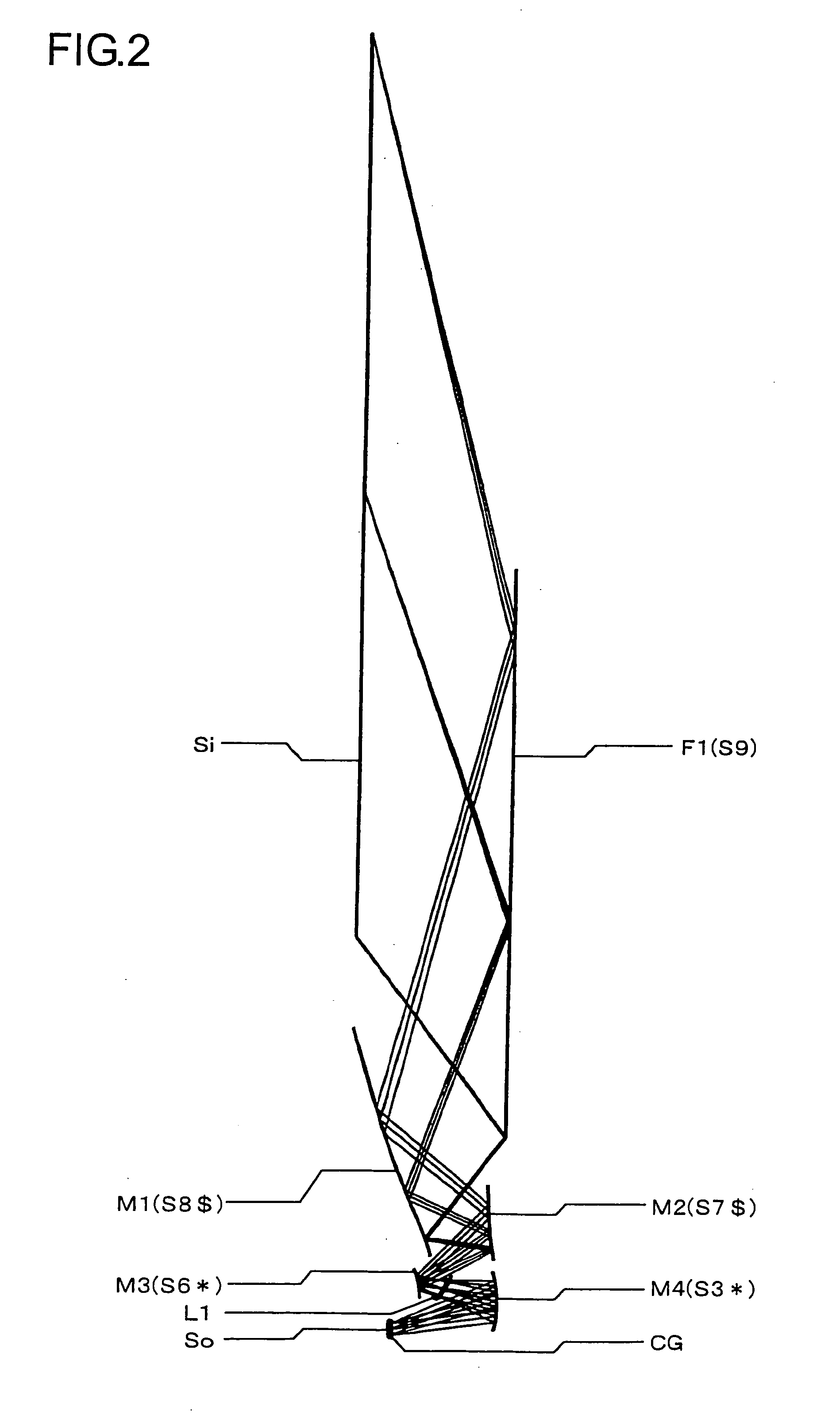
InactiveUS20060164605A1Good optical performanceCost advantageBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsOptical elementsOptical powerOblique projection
In an oblique projection optical system for performing enlargement projection from a primary image surface on the reduction side to a secondary image surface on the enlargement side, at least one reflective surface having an optical power is provided, and, assuming that of the aforementioned surfaces, the reflective surface located on the most secondary image surface side in the optical path is a first curved reflective surface, the first curved reflective surface has a portion having a positive optical power and a portion having a negative optical power.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
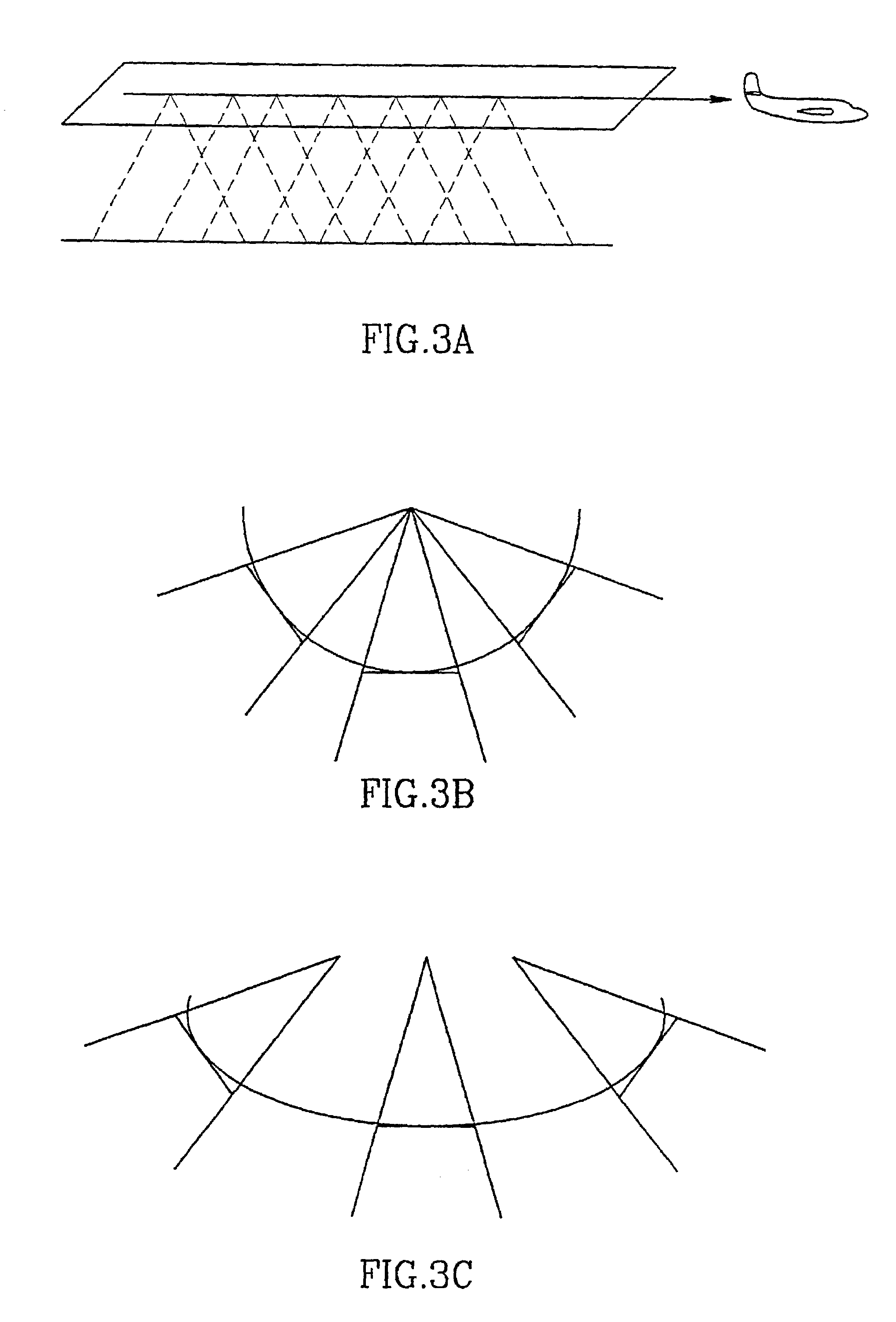
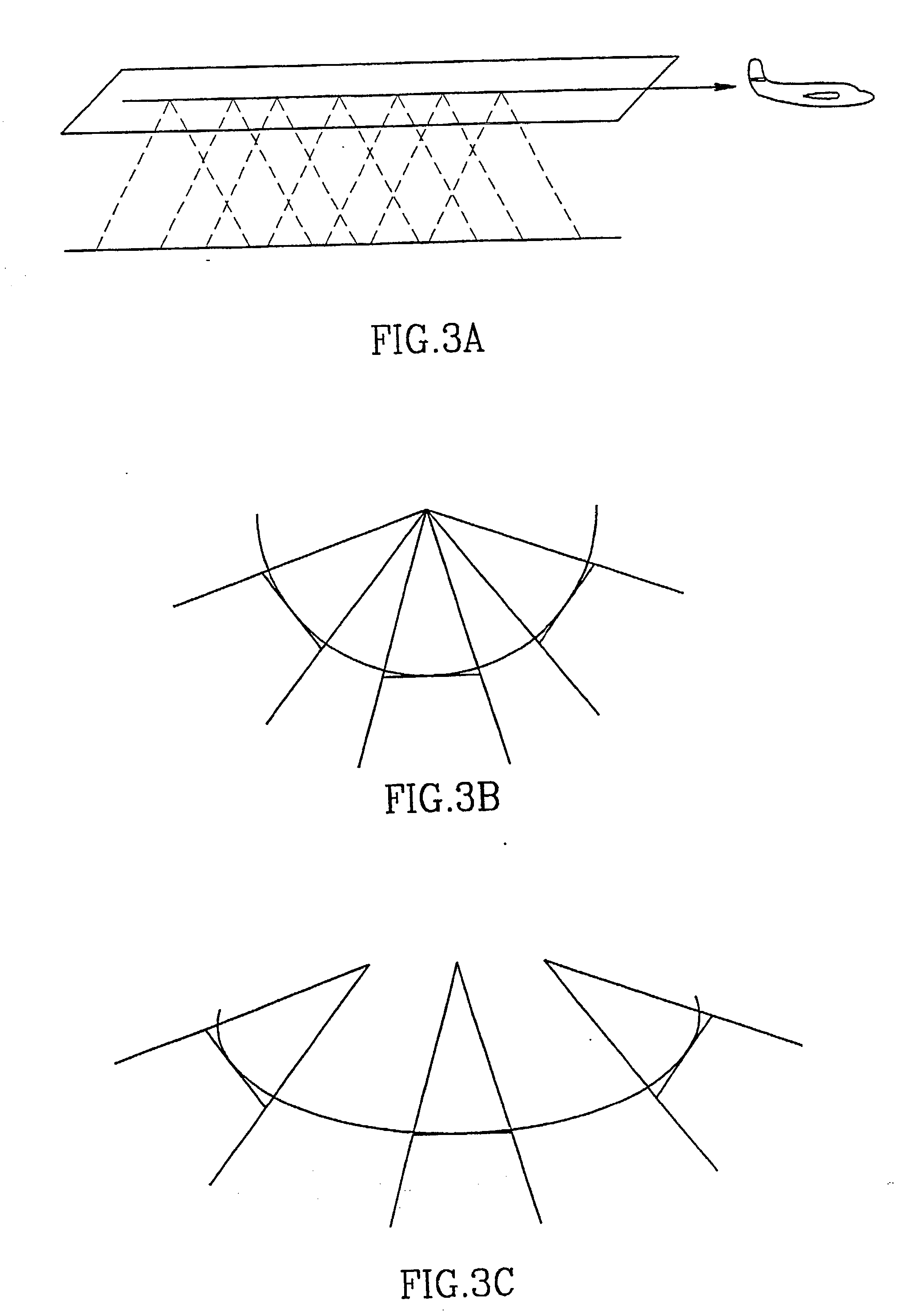
Generalized panoramic mosaic
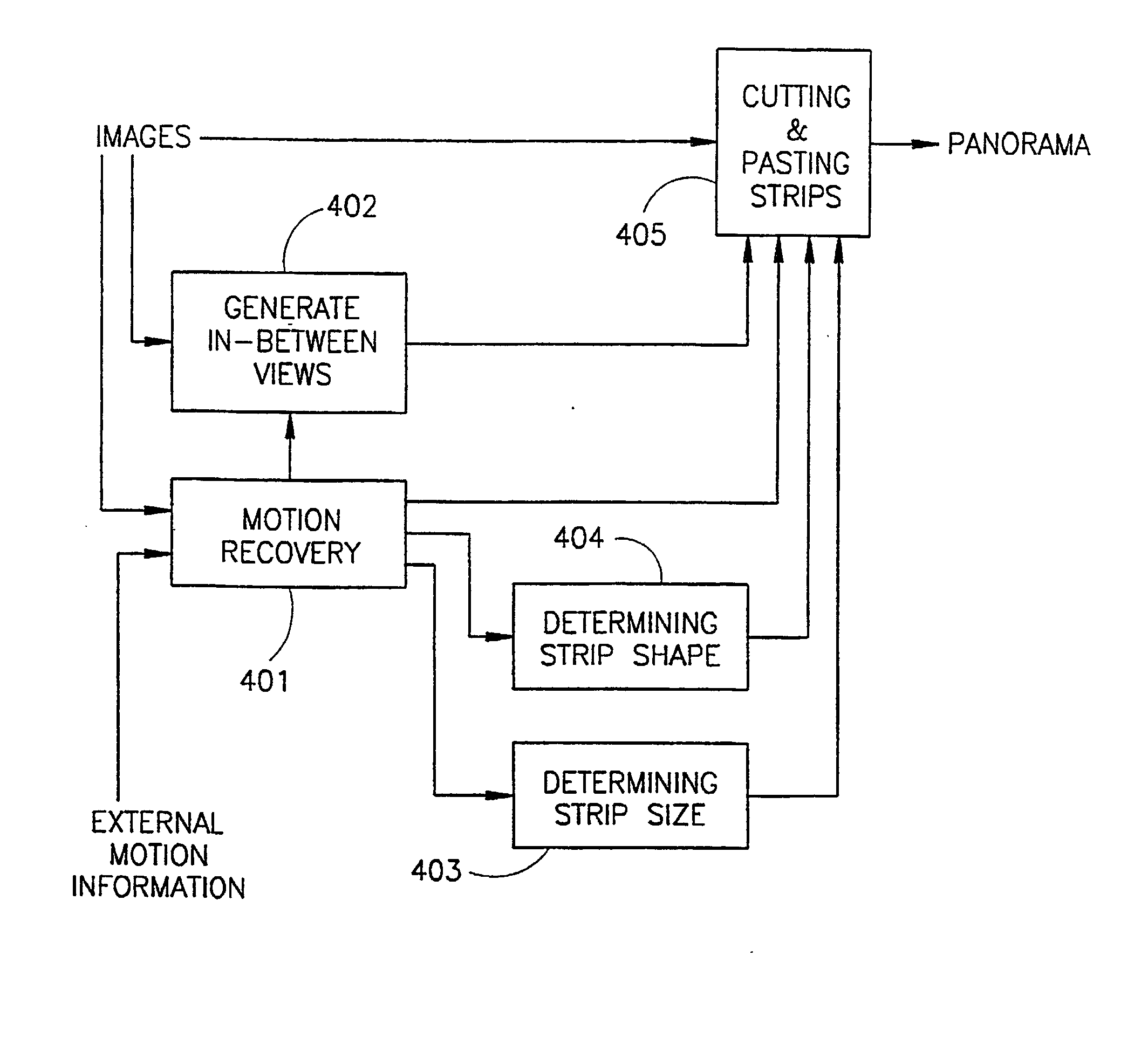
Video mosaicing is commonly used to increase the visual field of view by pasting together many video frames. The invention provides for image mosaicing for general camera motion, including forward camera motion and zoom. After computing the motion between the images in a sequence, strips are selected from individual frames such that the strips are approximately perpendicular to the optical flow. The strips are warped such that the optical flow becomes parallel, and are pasted to a panoramic mosaic. The warping transformation on the strips, which results in making the optical flow to be parallel, can be modeled by an oblique projection of the image onto a cylindrical surface whose central axis is the trajectory of the camera. In addition, this invention uses view interpolation to generate dense intermediate views between original video frames, such that these intermediate views are used to overcome effects of motion parallax when creating panoramic mosaics.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREW UNIV OF JERUSALEM LTD
Generalized panoramic mosaic
InactiveUS20030076406A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsParallaxVisual field loss
Video mosaicing is commonly used to increase the visual field of view by pasting together many video frames. The invention provides for image mosaicing for general camera motion, including forward camera motion and zoom. After computing the motion between the images in a sequence, strips are selected from individual frames such that the strips are approximately perpendicular to the optical flow. The strips are warped such that the optical flow becomes parallel, and are pasted to a panoramic mosaic. The warping transformation on the strips, which results in making the optical flow to be parallel, can be modeled by an oblique projection of the image onto a cylindrical surface whose central axis is the trajectory of the camera. In addition, this invention uses view interpolation to generate dense intermediate views between original video frames, such that these intermediate views are used to overcome effects of motion parallax when creating panoramic mosaics.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
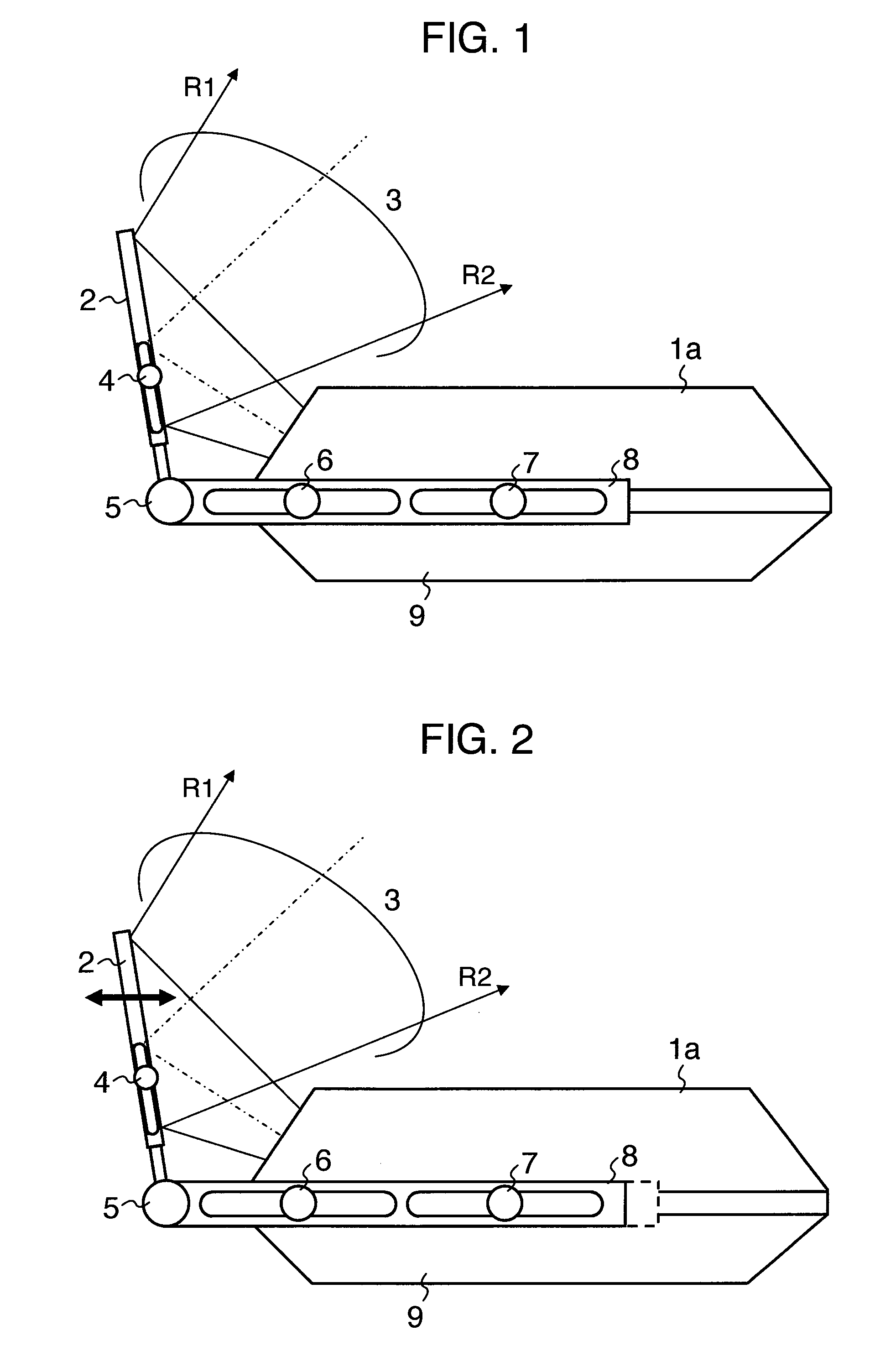
Projection image display apparatus and projection optical unit to be used therein
ActiveUS20060092385A1Reducing trapezoidal distortionOptical depth of smallTelevision system detailsMirrorsProjection imageLight beam
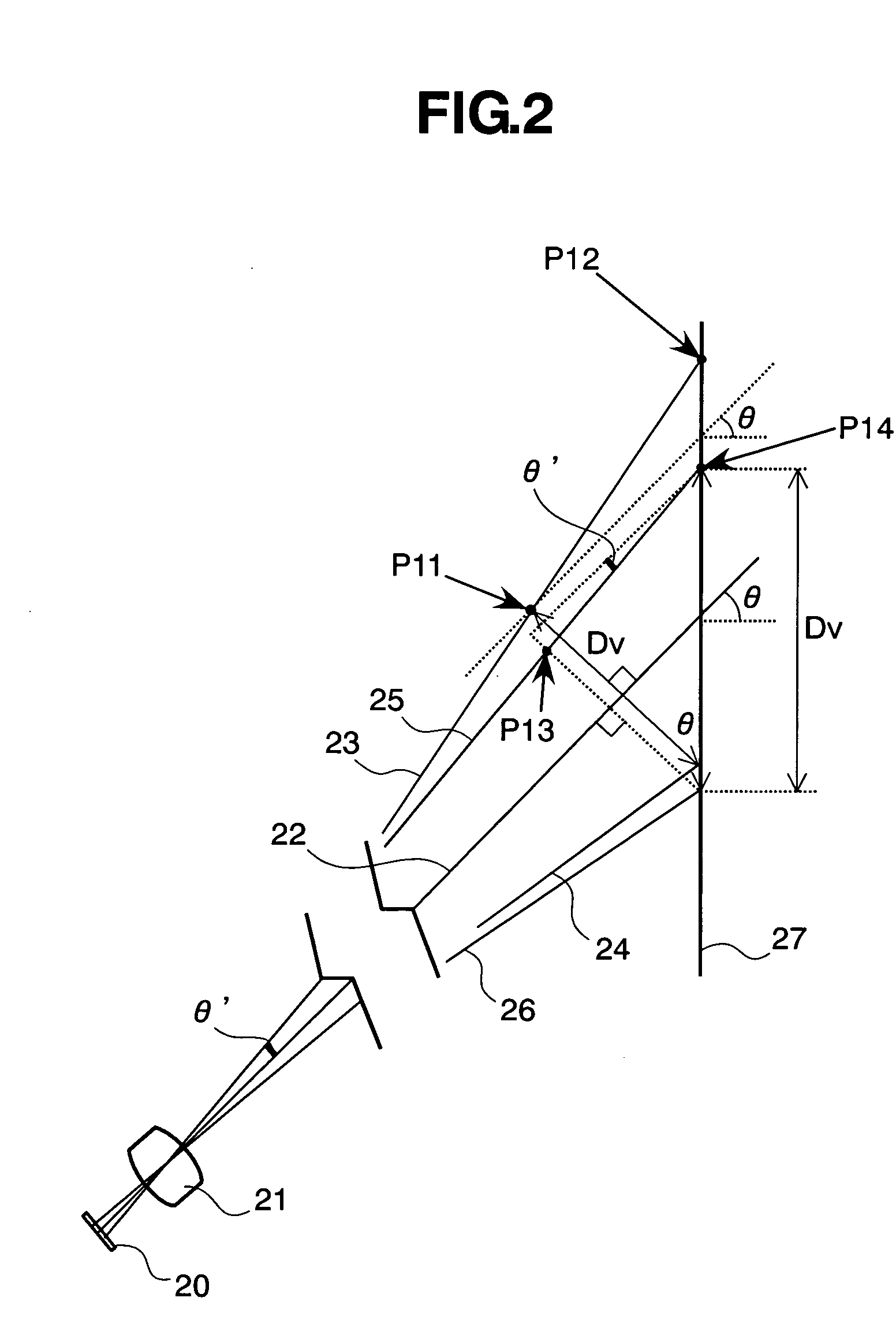
In a projection type image display apparatus, for enlarging an image on a image display apparatus 1 by means of a projection lens 2, thereby projecting the enlarged image onto a screen 6, obliquely, being inclined thereto, between the projection lens 2 and a rear-surface mirror 5, there are disposed free shaped surface mirrors 3 and 4, each having a free shaped surface for compensating a trapezoidal distortion due to oblique projection of the enlarged image. The surface configuration of the free shaped surface mirror is so shaped as to satisfy a following equation: |L1−L2|>1.4·Dv if assuming that a distance for a light beam of an upper end of the enlarged image to reach the screen after being reflected upon a free shaped surface is “L1”, a distance for a light beam of a lower end of the enlarged image to reach the screen after being reflected upon the free shaped surface is “L2”, and a distance from an upper end of an image on the screen to a lower end thereof is “Dv”.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
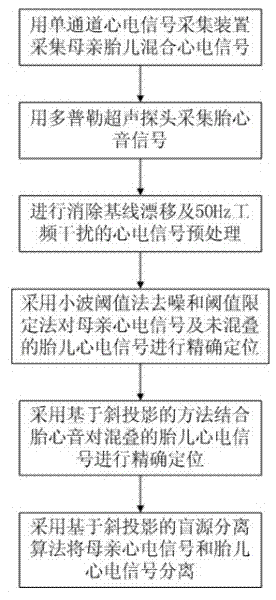
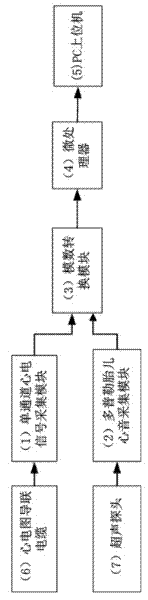
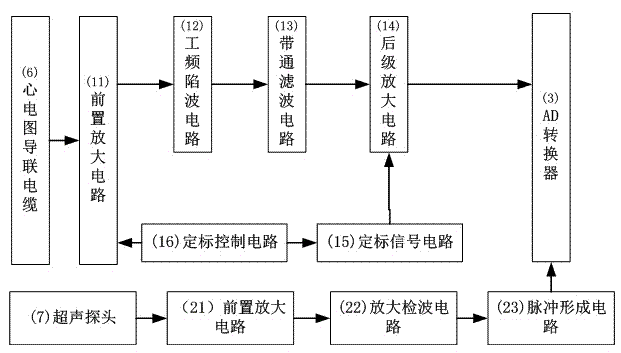
Single-channel fetal electrocardiogram blind separation device based on oblique projection and separation method
The invention relates to a single-channel fetal electrocardiogram blind separation device based on oblique projection and a separation method. The separation device comprises a single-channel electrocardiogram signal acquisition module, a Doppler fetal heart sound acquisition module, an analog to digital conversion module, a microprocessor and a PC (personal computer) upper computer for separating and displaying signals. A switch-in end of the single-channel electrocardiogram signal acquisition module for acquiring aliasing electrocardiogram signals is connected with an electrocardiogram lead cable, an input end of the Doppler fetal heart sound acquisition module for acquiring fetal heart sound signals is connected with an ultrasonic probe, a switch-out end of the single-channel electrocardiogram signal acquisition module and a switch-out end of the Doppler fetal heart sound acquisition module are respectively connected with an analog input end of the analog to digital conversion module, a data output port of the analog to digital conversion module is connected with the microprocessor, and the microprocessor is connected with the PC upper computer. The separation method includes a fetal electrocardiogram QRS (quantum resonance spectrometer) wave group positioning method based on oblique projection and single-channel fetal electrocardiogram signal blind separation based on oblique projection. The separation device is reasonable in design and is convenient and practical; and the separation method is convenient and practical.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Two-dimensional scanning apparatus and scanning type image displaying apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20050117188A1Quality improvementCorrect image distortionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight beamDistortion
A two-dimensional scanning apparatus has light source means, deflecting means for deflecting a beam emitted from the light source means in a two-dimensional direction, and scanning optical means for directing the beam deflected by the deflecting means onto a surface to be scanned. The scanning optical means has one or more scanning optical element, and one or more surfaces of one or more of the aforementioned one or more scanning optical elements are anamorphic surfaces, and the anamorphic surfaces on the aforementioned one or more surfaces are anamorphic surfaces monotonously changing in a radius of curvature of which the absolute value of the radius of curvature in a first one-dimensional direction continuously decreases from one side toward the other side along a second one-dimensional direction orthogonal to the first one-dimensional direction. Thus, there can be supplied a two-dimensional scanning apparatus which can well correct TV distortion caused by the two-dimensional deflection of the beam by the deflecting means and trapezoid distortion caused by an image being obliquely projected onto a surface to be scanned, and a scanning type image displaying apparatus using the same.
Owner:CANON KK
Projection apparatus and transparent screen for it
ActiveUS20100290010A1Aberration correctionLow costBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsTelevision systemsFresnel lensReflection loss
There is provided a projection apparatus using an oblique projection optical system, which generates little reflection loss by providing a linear Fresnel lens at an incident surface in the case where the apparatus is used as a linear system, wherein said linear Fresnel lens makes total reflection of image light, and is capable of obtaining total surface property with good brightness in a region with small incident angle onto a screen, by using a total reflection Fresnel lens and a refraction Fresnel lens in combination. In addition, total surface property with further good brightness can be obtained by using a plurality of projection image display apparatuses in the same projection apparatus.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Projection type image display
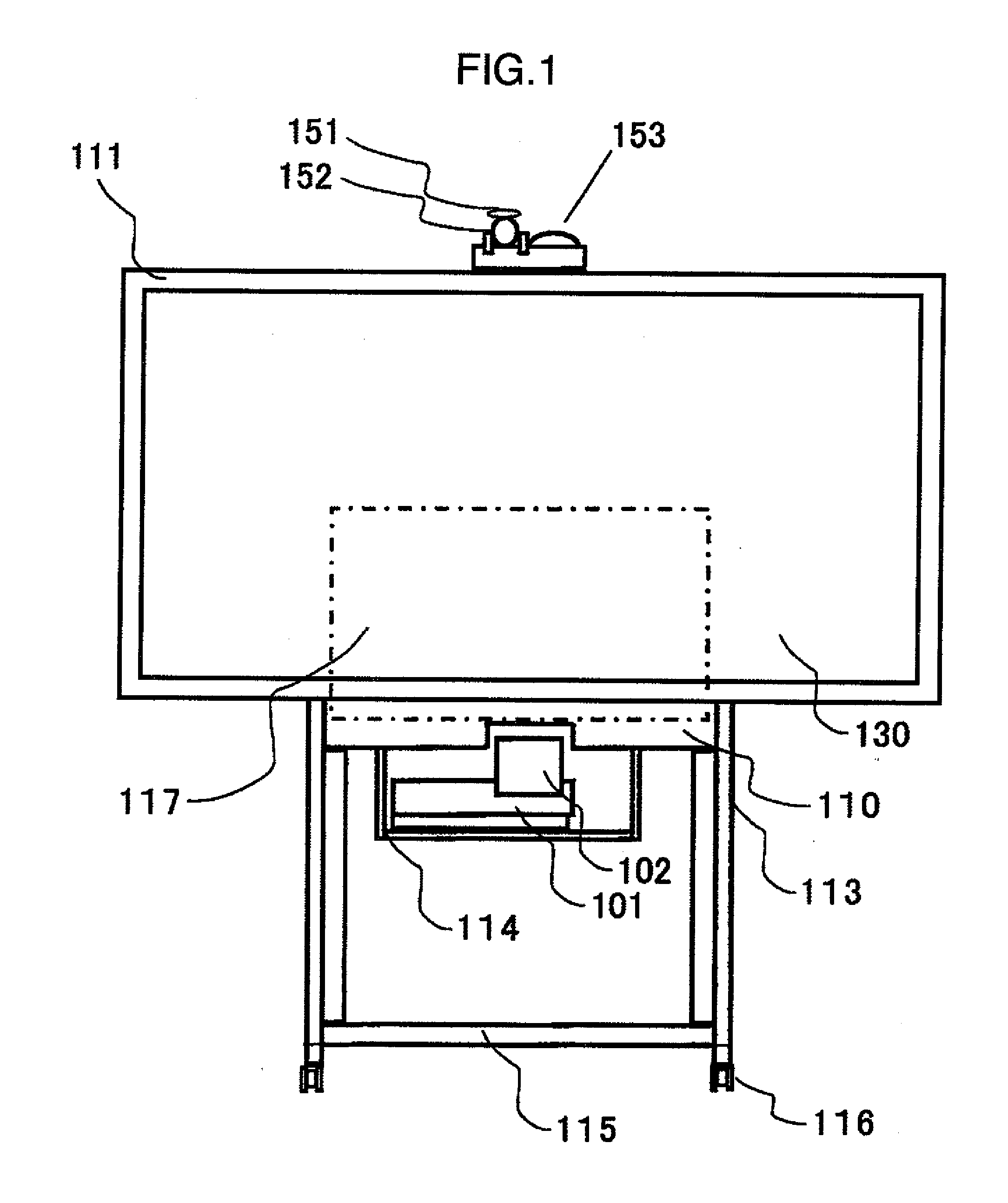
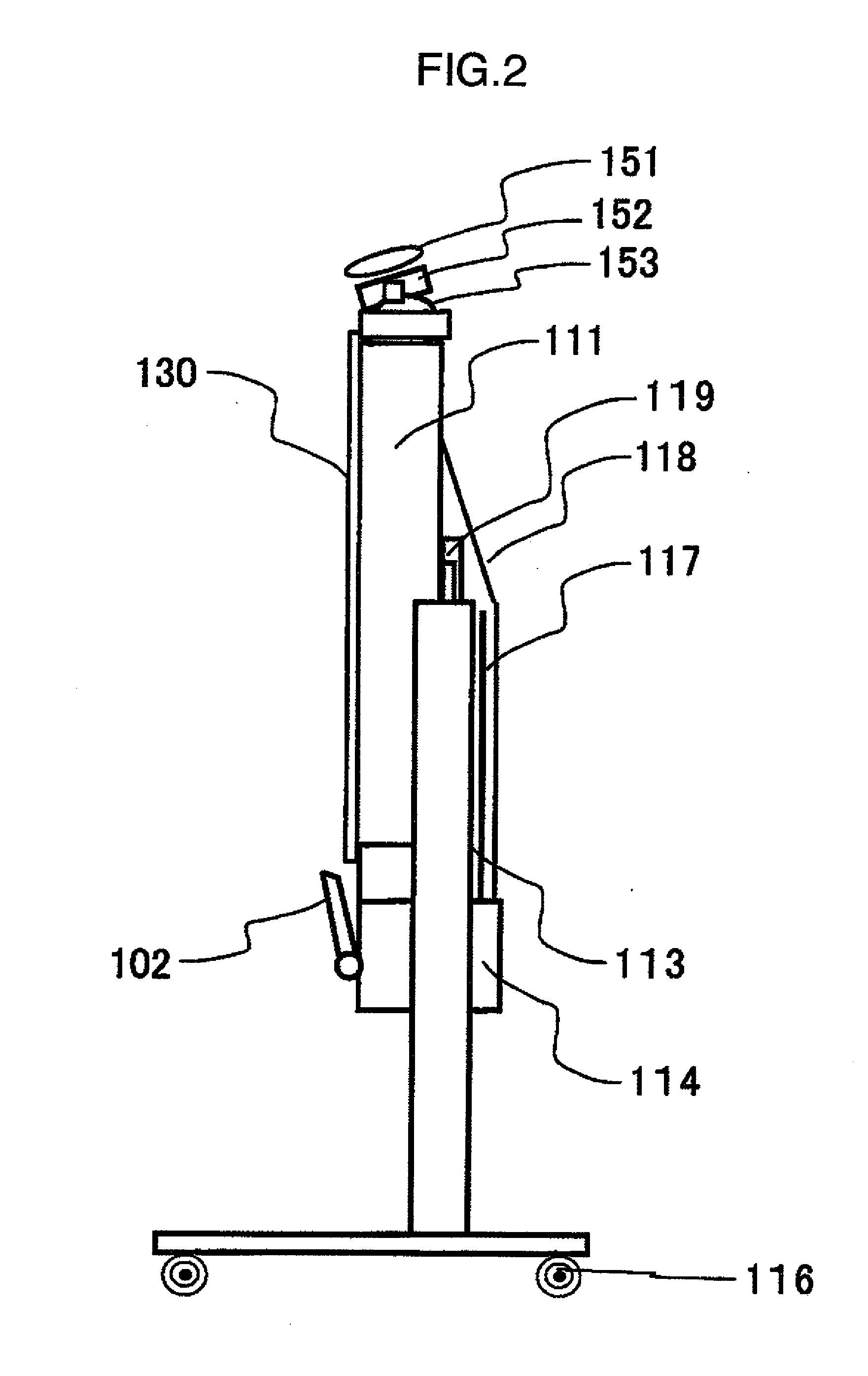
InactiveUS7535648B2Reduce changesTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementFree formProjection screen
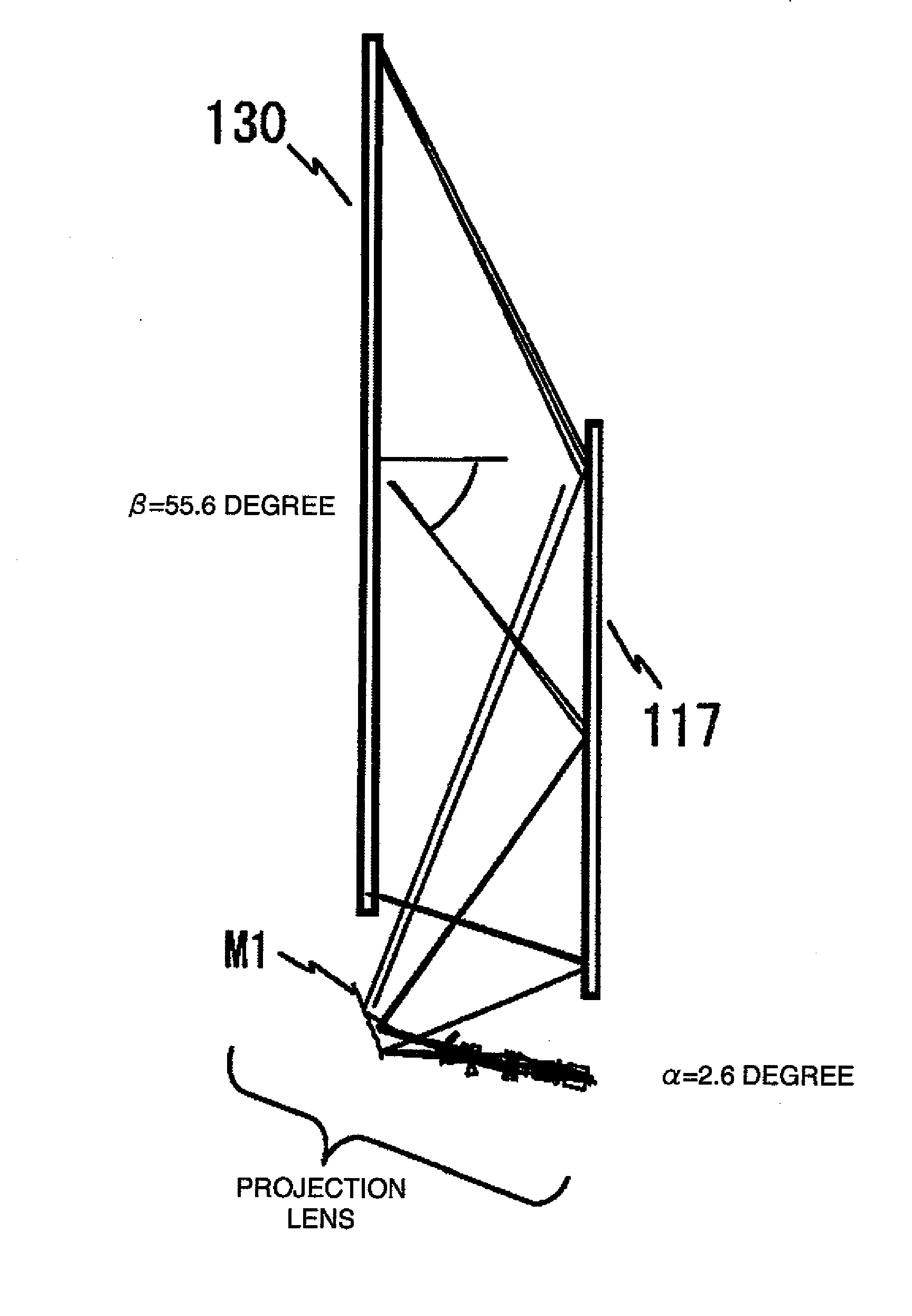
An image that has been displayed on the display screen of an image generator is first passed through a projection lens section consisting of a front group and a rear group. Next after being reflected on the reflecting surface of a free-form surface mirror, the image is further reflected by a planar reflecting mirror and then obliquely projected from the lower section of a projection screen onto the screen. The front group of the projection lens section is provided for enlarging the image. In order to correct aberration due to oblique projection onto the projection screen, the rear group uses a free-form surface lens that forms a concave shape with respect to the exit side of light from the lens. The free-form surface mirror corrects trapezoidal distortion due to oblique projection onto the projection screen. The free-form surface lens in the rear group of the projection lens section can accommodate changes in environmental conditions by using one edge as a reference edge and rendering the other edge expandable. The free-form surface mirror can likewise use one edge as a reference edge and render the other edge expandable. For adjustment, the free-form surface mirror can also be pivoted about the reference edge.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
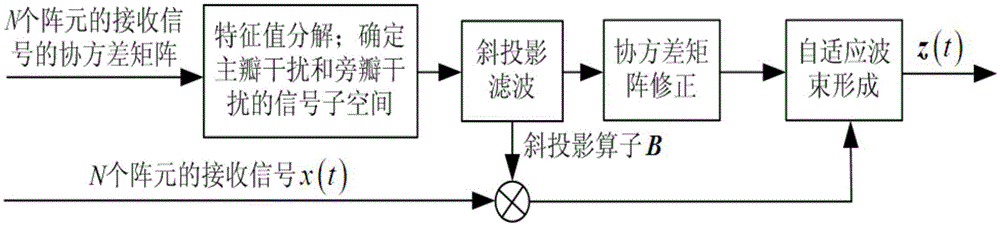
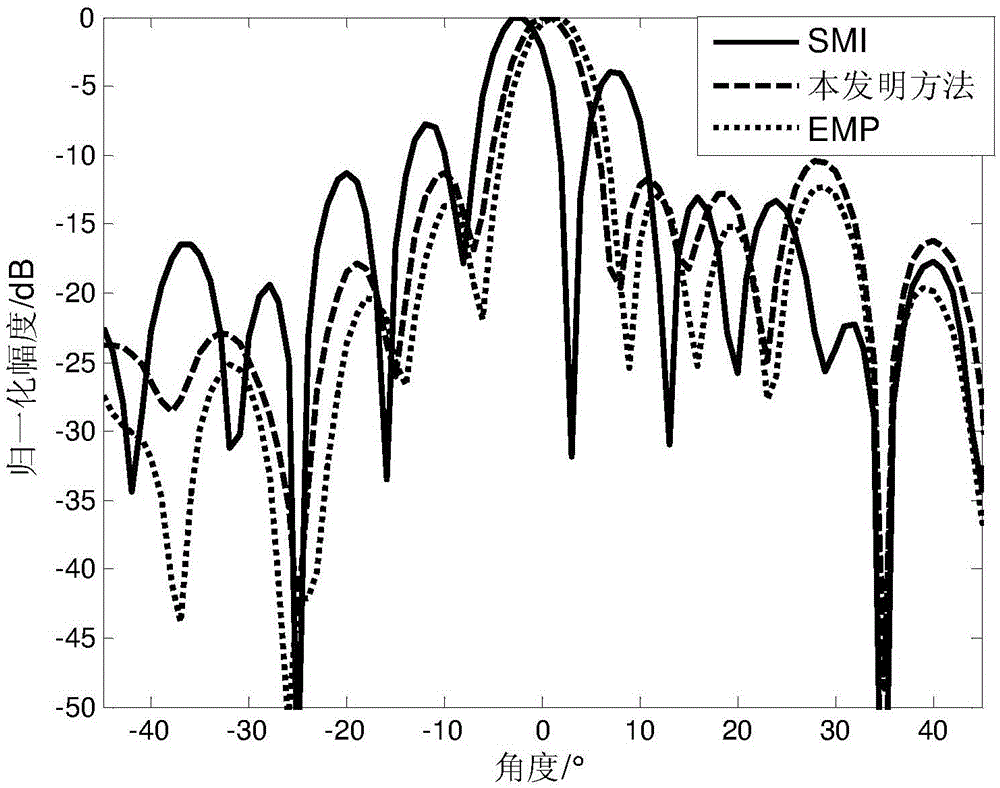
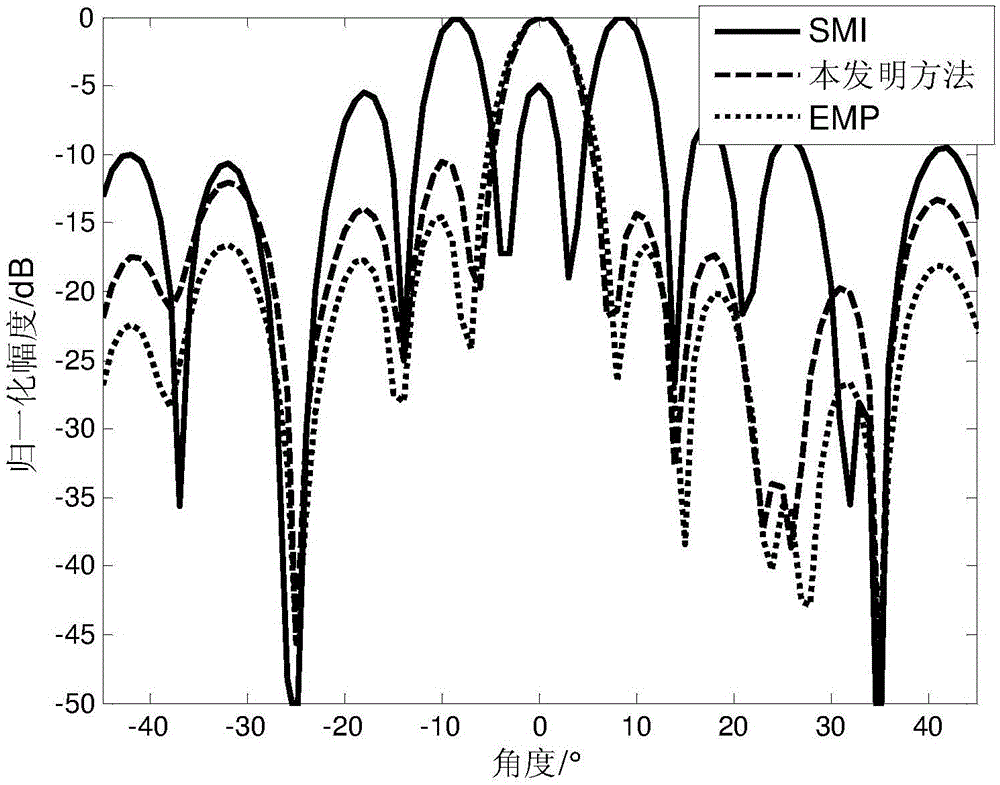
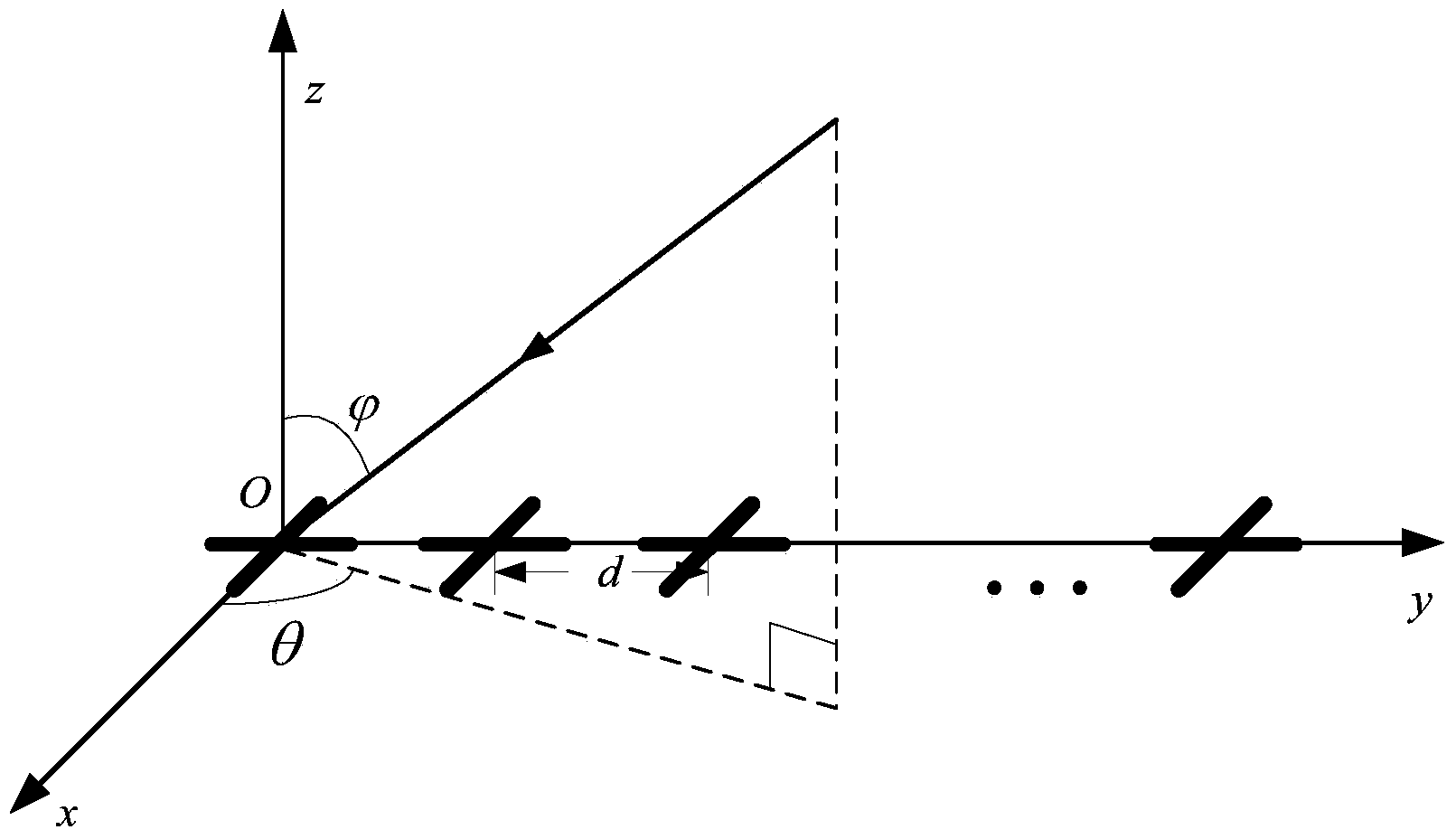
Radar adaptive beam forming method based on oblique projection filtration
The invention discloses a radar adaptive beam forming method based on oblique projection filtration. The method comprises the following steps: (1) signals received by N array elements in an array are set to be x(t), and interference and noise are included; a covariance matrix Rxx for the signals x(t) received by the N array elements is built, eigenvalue decomposition is carried out on the matrix, and interference signal subspace UJ and noise signal subspaceUn are obtained; (2) an interference judgment rule is built, and signal subspace Em for main lobe interference and signal subspace for side lobe interference are determined respectively in the interference signal subspace UJ; (3) an oblique projection operator B is built to carry out oblique projection filtration treatment on the signals x(t) received by the N array elements, signals y(t) after oblique projection filtration treatment are obtained, and a covariance matrix Ryy is built; (4) noise in the covariance matrix Ryy for the signals y(t) after oblique projection filtration treatment is corrected, and a covariance matrix R after correction is obtained; and (5) according to the covariance matrix R after correction, adaptive beam forming is carried out on the signals x(t) received by the N array elements, and signals z(t) after adaptive beam forming are obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Programmable laser illuminated sign apparatus
A self-contained sign, illuminated by laser or other source of substantially parallel beams, presenting intensely lighted and vividly colored displays, is programmable to display one or more user designed images through controlled deflection of projected beams. The sign comprises a backlit illuminated apparatus of low depth to display dimension ratio, astigmatically correcting distortion of the projected dot resulting from oblique projection angles, such correction occurring in the projected beam's light path prior to controlled beam deflection. Embodiments further normalize obliquely incident light by employing a transmissive refractive right angle structure. Distortion of a projected image is minimized by appropriate pre- or post-processing of display data. Embodiments enable animation of images and are adaptable to networked control.
Owner:GREENCO LLC DBA LFI INT
Projection optical system, projection image display device and image display system
InactiveCN1479131AShort throw distanceCompact structureTelevision system detailsProjectorsProjection imageDisplay device
Owner:CANON KK
Back projection-type screen and back projection-type projection device
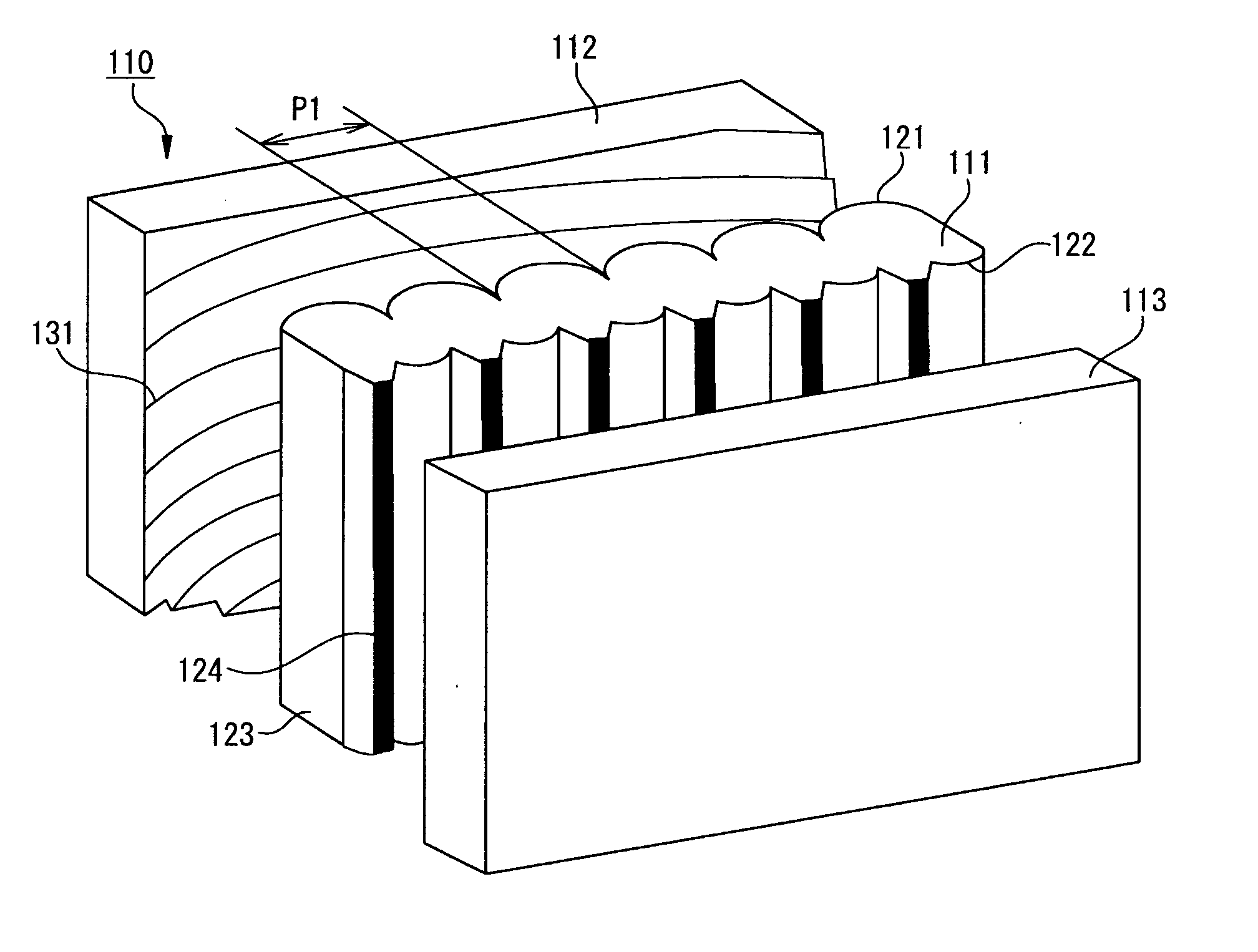
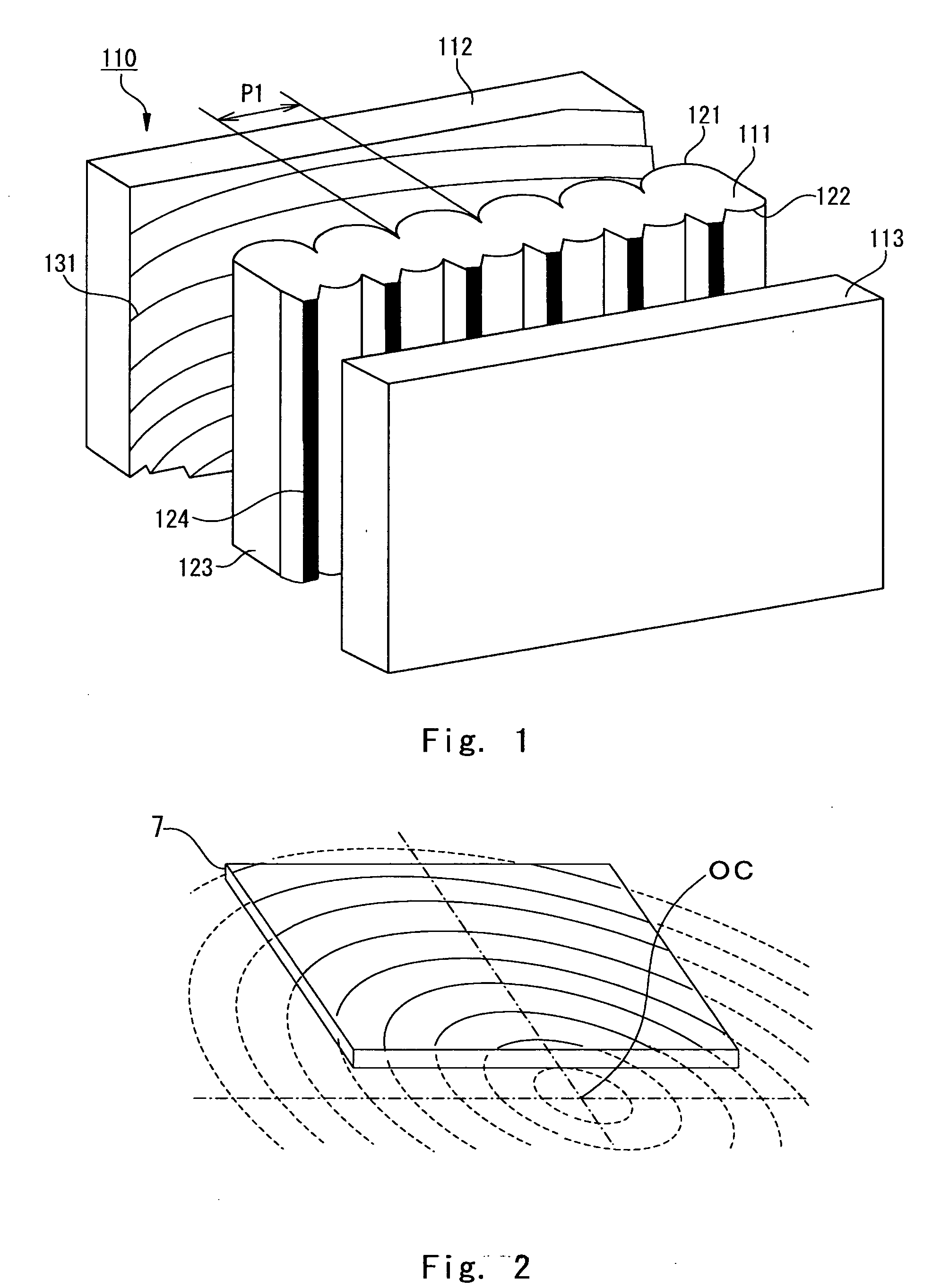
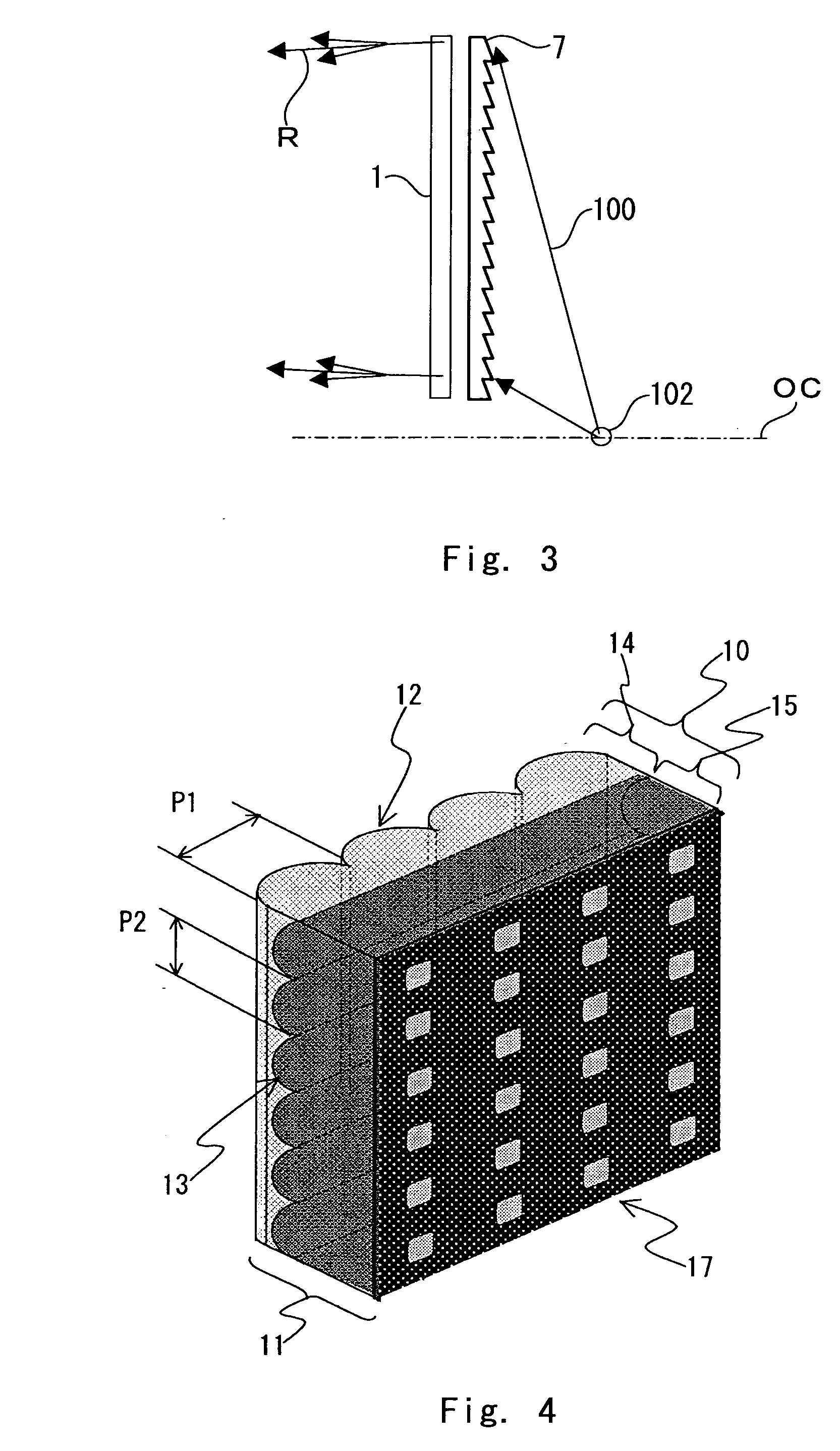
A rear projection-type screen and a rear projection-type projection device, in which contrast is enhanced, unevenness of an external light absorption layer is reduced, moiré trouble is suppressed, damage due to contact between sheets is suppressed, and the entire projection device can be reduced in size and weight. The rear projection-type screen is the so-called oblique projection system where the optical center of a Fresnel lens sheet 7 is located at a position outside a display screen area, above or below the screen. The lens array 12 of a lenticular lens sheet 1 is arranged substantially in the vertical direction. Moiré can be reduced by setting the pitch of Fresnel lens and the lens pitch of the lenticular lens sheet within a predetermined range.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
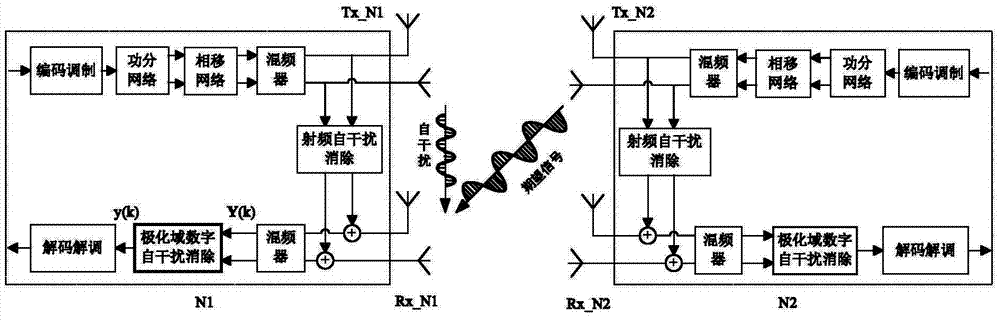
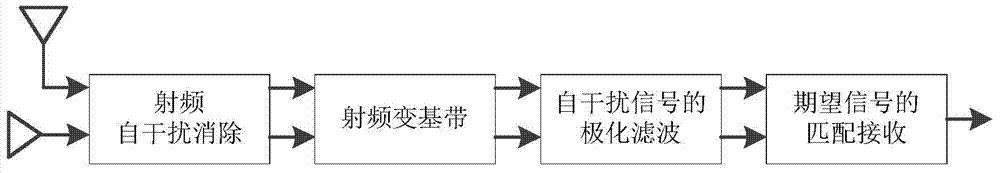
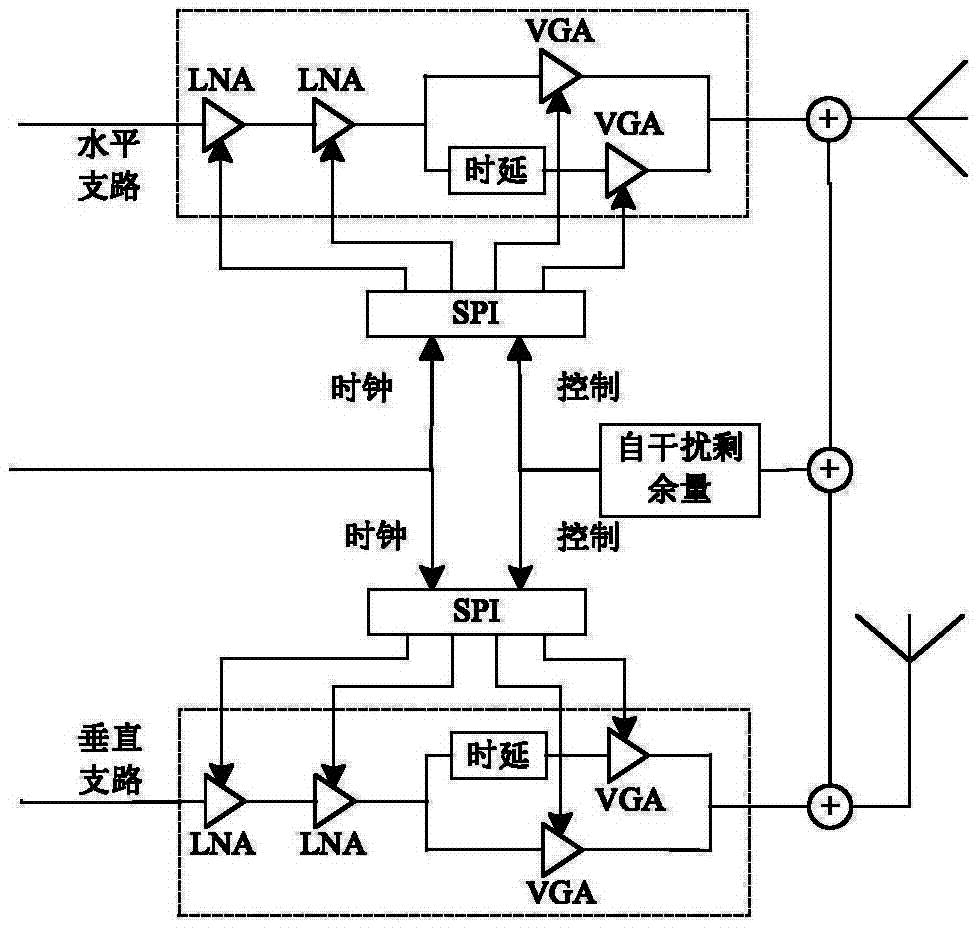
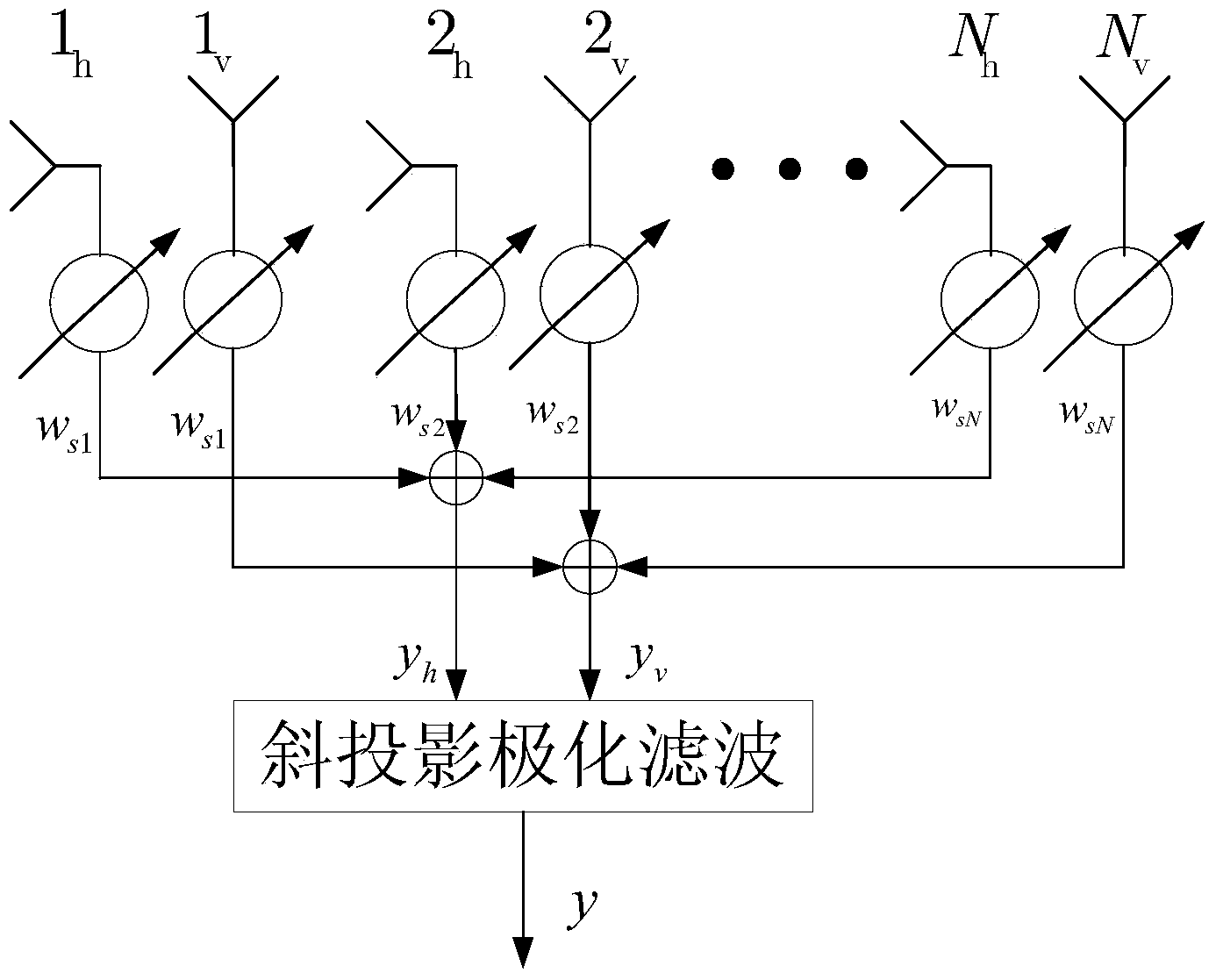
Method for eliminating self-interferences of cascade time-frequency domain and polarization domain processing during full-duplex communication
ActiveCN104125180AOvercoming overlapping and indistinguishable problemsAvoid reuseTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDuplex signal operationSelf interferenceDigital signal processing
The invention provides a method for eliminating self-interferences of cascade time-frequency domain processing and polarization domain processing during full-duplex communication and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. A quadrature dual polarized antenna used for transmitting and receiving polarization signals is equipped at every communication node, and a local node is subjected to polarized digital signal processing. The method includes that self-interferences of radio frequency of a time-frequency domain are eliminated by a receiving end; polarized signals subjected to radio frequency self-interference elimination are transmitted to a base band via down conversion, an oblique projection polarization filtering operator is constructed according to a transcendental self-interference polarization state and an expected signal polarization state, and polarization filtering is performed; matching and receiving of expected signals are performed according to the principle that the output signal to interference plus noise power ratio is maximum. The method for eliminating self-interferences of cascade time-frequency domain processing and polarization domain processing during full-duplex communication has the advantages that the problem that self-interferences and expected signals in a traditional scheme are overlapped and difficult to distinguish, self-interference elimination is performed by utilizing polarized dimensionality information of the signals in the base band, repeated utilization of time frequency information is avoided, self-interference elimination gain is increased and the purpose of eliminating self-interferences is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Projection optical system, projection type image display apparatus, and image display system
ActiveUS20040027544A1Short throw distanceCompact structureTelevision system detailsProjectorsImage formationLuminous flux
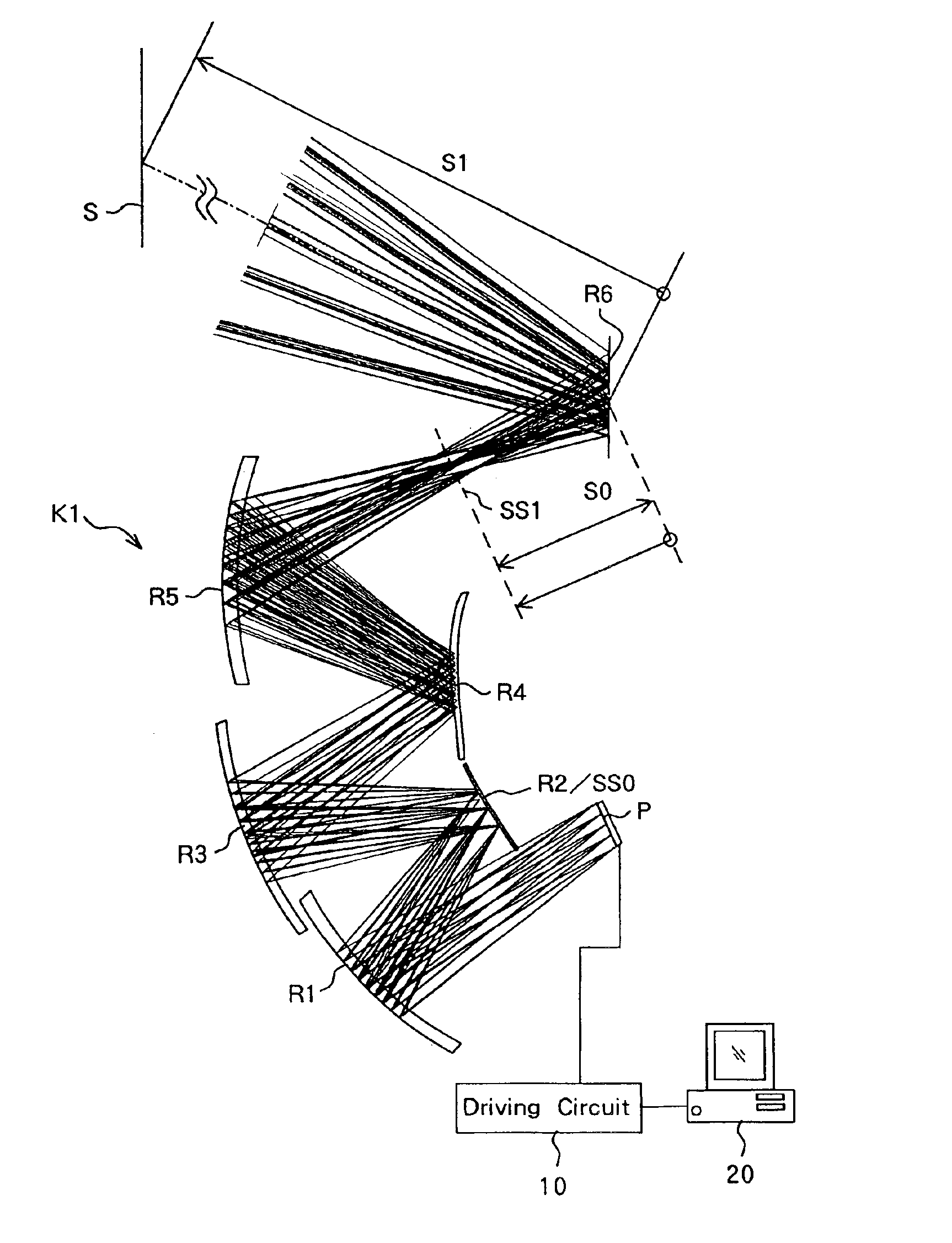
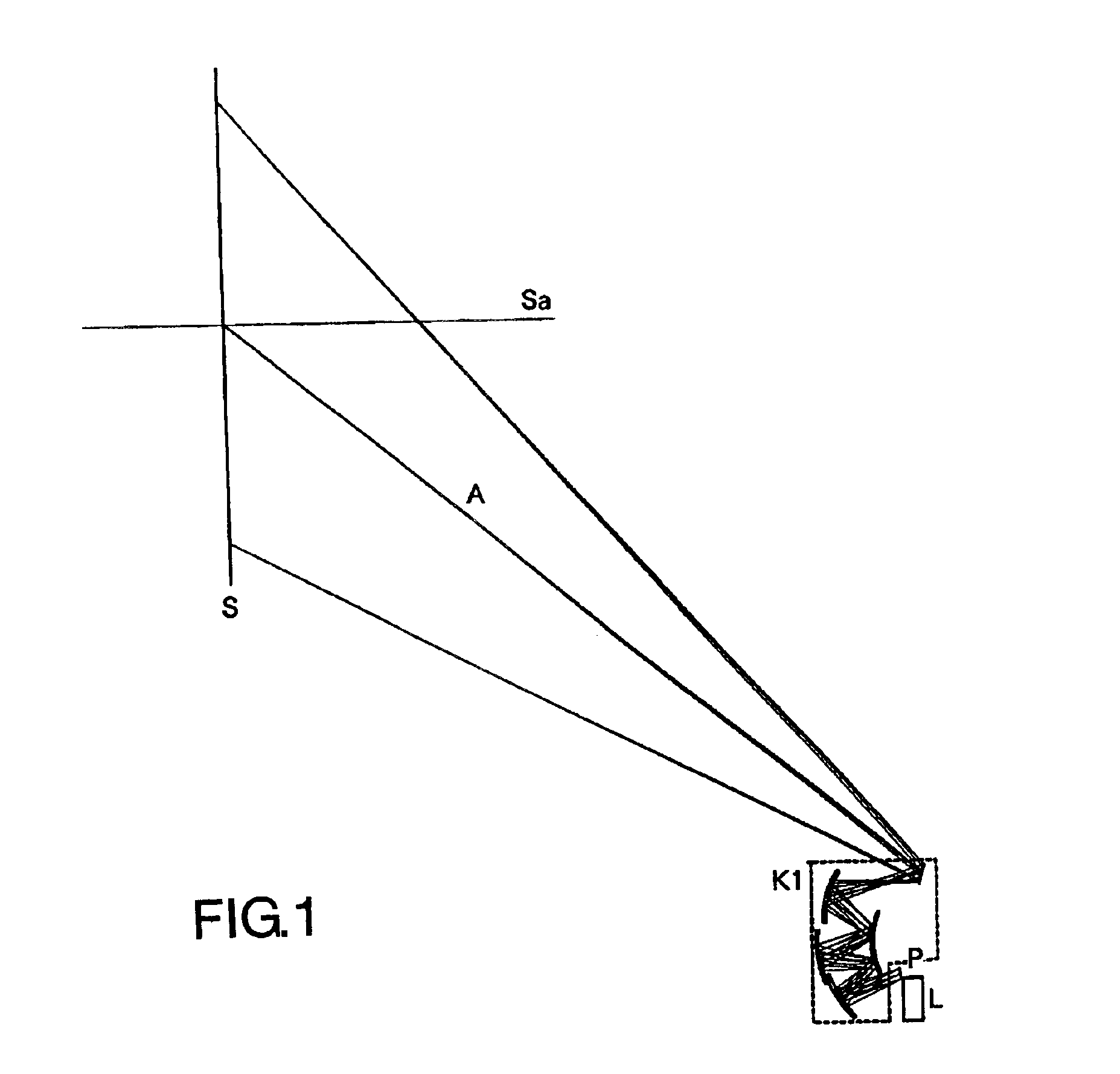
A projection optical system which has a short projection distance and a compact structure, and allows oblique projection. The projection optical system projects luminous flux from an image forming element for forming an original image onto a projection surface which is oblique to a central principal ray which is a principal ray of luminous flux traveling from the center of the original image to the center of a finally formed image. The system includes a plurality of reflecting surfaces each having a curvature. In addition, the projection optical system satisfies a predetermined expression (1).
Owner:CANON KK
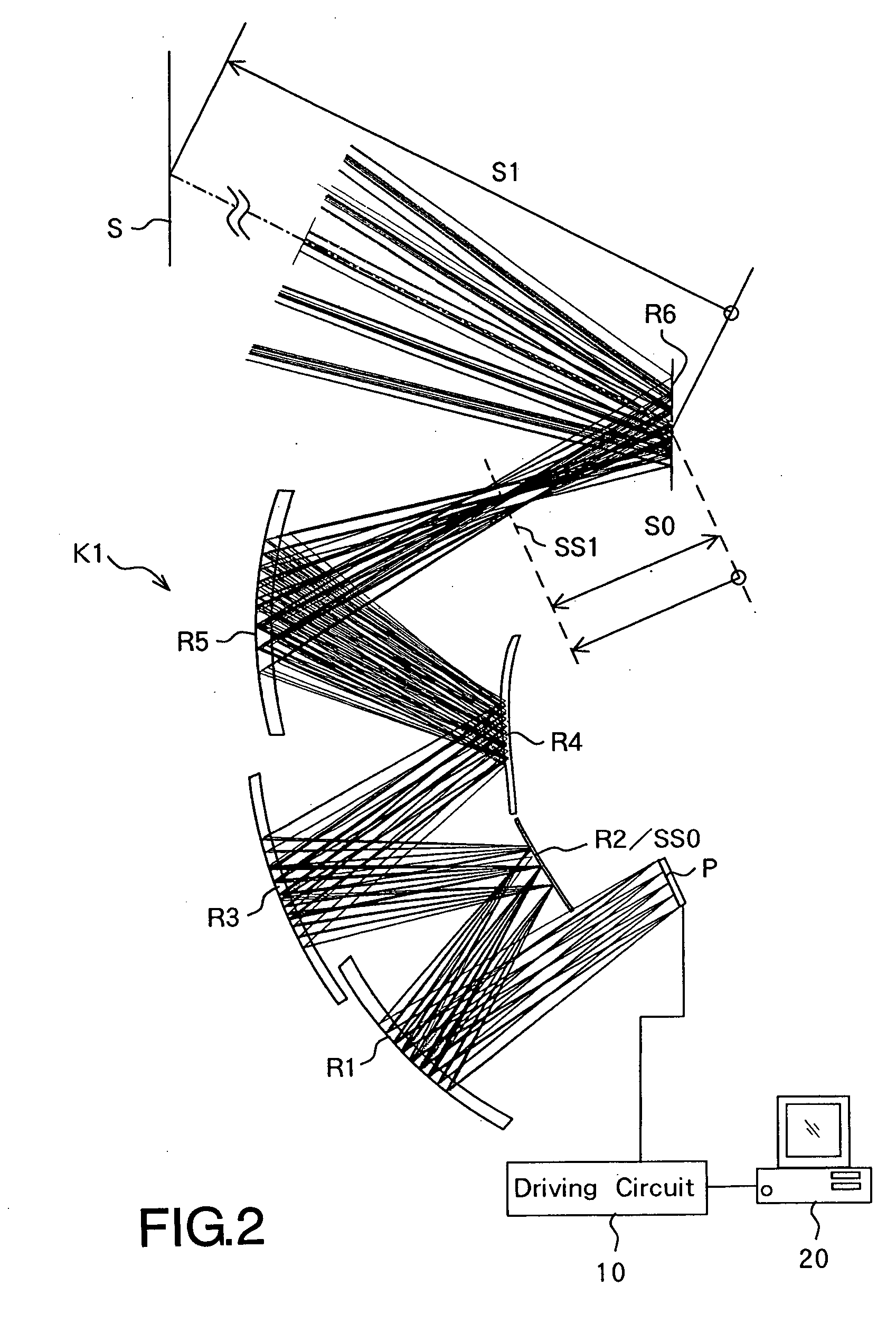
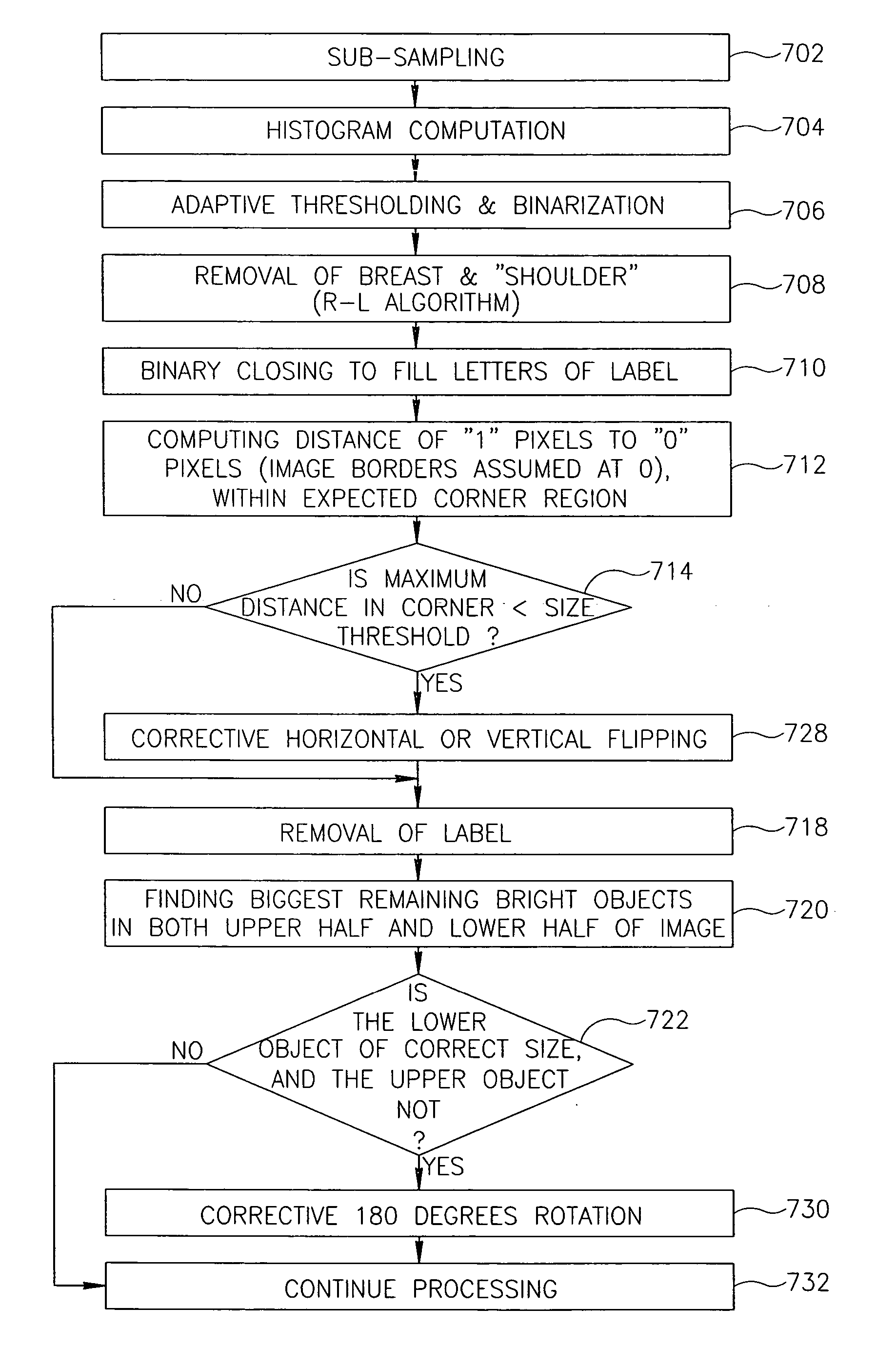
Workstation for computerized analysis in mammography and methods for use thereof
A method for determining if the digitized image of a scanned film mammogram represents a left or right breast. The method also determines if the projection therein represents a craniocaudal projection or mediolateral oblique projection. Additionally, the method allows for automatic ordering of a set of digitized images according to a pre-selected order. A method is also provided for determining if the digitized image of a scanned film mammogram represents an improperly flipped or rotated view, automatically correcting the problem. Additionally the present invention provides for easy restarting of a workstation when the processing and / or scanning systems crash or an examination fails.
Owner:CADVISION MEDICAL TECH
Radar signal motion disturbance spatial-polarizational domain combined stable filtering method
ActiveCN103728601AMotion Interference SuppressionImplement joint filteringWave based measurement systemsChannel dataSignal subspace
The invention discloses a radar signal motion disturbance spatial-polarizational domain combined stable filtering method. The method comprises, firstly, performing real-time estimation of disturbance signal subspace on the horizontal channel data of a polarized sensitive array through a PASTd (projection approximation subspace tracking with deflation) algorithm and meanwhile estimating the azimuth angles of disturbance signals through an MUSIC (multiple signal classification) algorithm; then estimating disturbance spatial-polarizational models through the estimated disturbance signal azimuth angles, and after obtaining the disturbance spatial-polarizational models, performing spatial domain orthogonal projection filtering through the disturbance subspace obtained during the disturbance angle real-time estimation process; lastly, performing oblique projection polarization filtering. The radar signal motion disturbance spatial-polarizational domain combined stable filtering method is simple and practical, can accurately estimate the disturbance signal directions and timely achieve spatial-polarizational domain combined disturbance suppression through spatial-polarizational characteristic models and accordingly can be applied to suppression of motion disturbance in the fields of radars, communication and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Laser projector
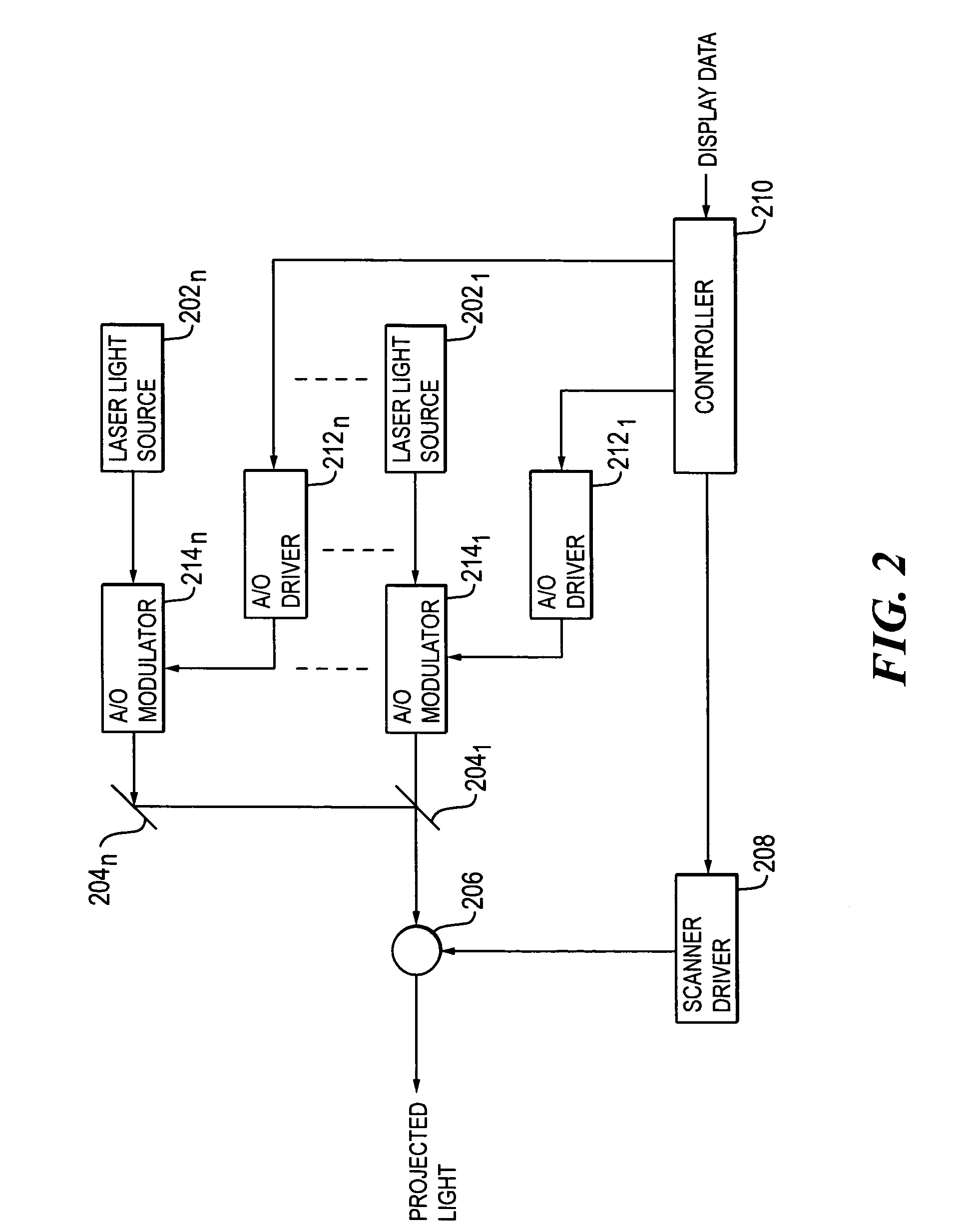
ActiveUS20110134499A1Fast scanningDegree of reductionProjectorsColor television detailsLight beamOblique projection
A two-dimensional image is displayed on a screen (SC) by scanning the screen (SC) two-dimensionally with light beams from a laser light source (1) that are deflected to orthogonally-intersecting first and second scanning directions by means of a mirror (10) in a deflection apparatus (3). The deflection apparatus (3) is arranged to incline obliquely in the second scanning direction (e.g. vertical direction) lower in a scanning speed than the first scanning direction (e.g. horizontal direction), and performs an oblique projection onto the screen (SC). Assuming a direction in which the incidence angle of a light beam deflected by the deflection apparatus (3) and entering the screen (SC) increases in the second scanning direction is positive side, the light beam from the laser light source (1) impinges on the deflection apparatus (3) from the negative side in the second scanning direction, and the normal to the mirror (10) in the deflection apparatus (3) in a state where the center of the screen is displayed inclines to the negative side in the second scanning direction with respect to the normal to the screen (SC).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Medical Multi-Wavelength Lasers
InactiveCN102280807ACompact structureImprove scalabilityLaser detailsSelective reflectionOblique projection
The invention discloses a medical multi-wavelength laser device. In one case, the multi-wavelength laser is generated by the fundamental frequency light through a modulator, and a resonant cavity is generated by a selective reflection mirror and a total reflection mirror, and the structure is compact. . It is also possible to expand the diversity of output wavelengths through simple frequency doubling combined with the cooperation of the above-mentioned selective reflector and total reflector, which is easy to expand. The selection and adjustment of multiple wavelengths depend on liquid-optic switches and shutters, which are easy to adjust and work safely and reliably. Another situation is to further include a second total reflection mirror for the laser with the first output wavelength inclined at 45 degrees on the projection optical path of the second selective reflection mirror. Through structural integration, it is convenient to adjust and obtain in multiple directions, and the structure tends to be more compact.
Owner:山东瑞华同辉光电科技有限公司
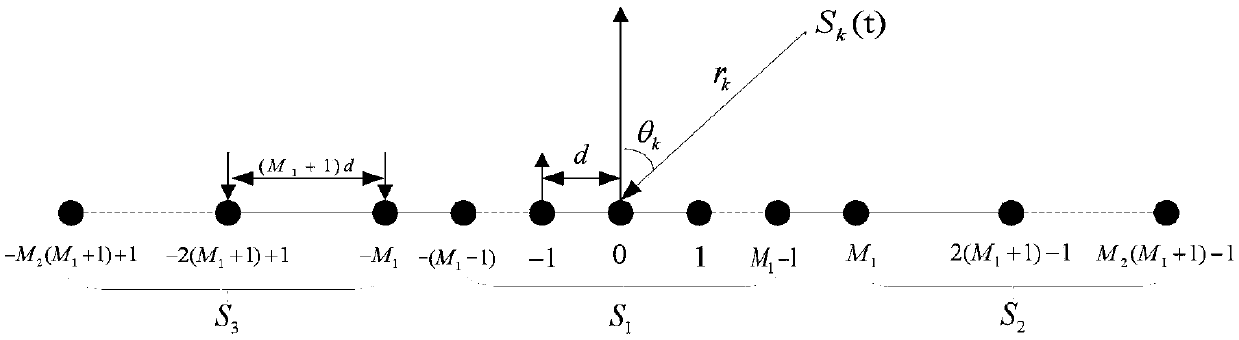
Hybrid field signal source positioning method based on symmetrical nested array
InactiveCN108919178AReduce computational complexityOvercoming noisePosition fixationComputation complexityNested arrays
The invention provides a hybrid field signal source positioning method based on a symmetrical nested array. The hybrid field signal source positioning method comprises the following steps that an antenna array is set, wherein the antenna array is the symmetrical nested array; a far-field signal DOA is estimated to obtain an estimation value of the far-field signal DOA; the near field component isseparated from the far field component; a fourth-order cumulant virtual difference array of a near-field signal is calculated; an estimation value of the near-field signal DOA is obtained by using spectral peak search; and according to the near-field signal DOA estimation value, the near-field signal distance is estimated to obtain a near-field signal distance estimation value. The hybrid field signal source positioning method uses mixed-order statistics, and compared with a second-order statistic algorithm, the hybrid field signal source positioning method solves the problems of Gaussian noise interference and reduction of degree of freedom by half; the symmetric nested array and the fourth-order cumulant virtual differential array are used for improving the estimation accuracy of far-field DOA, near-field DOA and a near-field distance; oblique projection technology is utilized to separate the far-field and near-field components, and thus, it is not necessary to distinguish the far-field signal from the near-field signal according to distance parameters; and therefore, the number of search is reduced, and the computational complexity of the algorithm is further reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
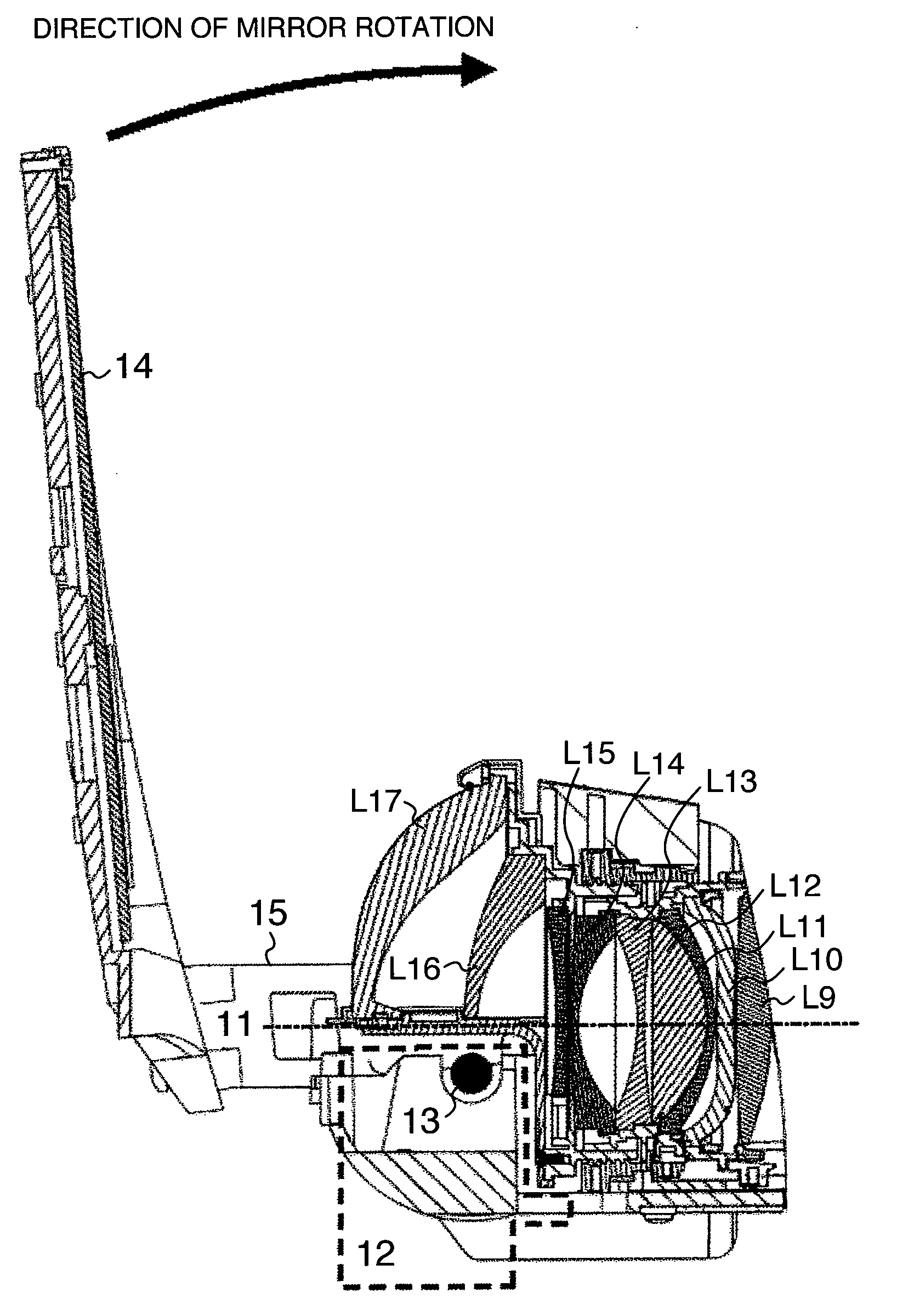
Rear projection optical system
InactiveUS7021770B2Improve imaging effectPermit miniaturizationBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsOptical elementsProjection opticsFree form
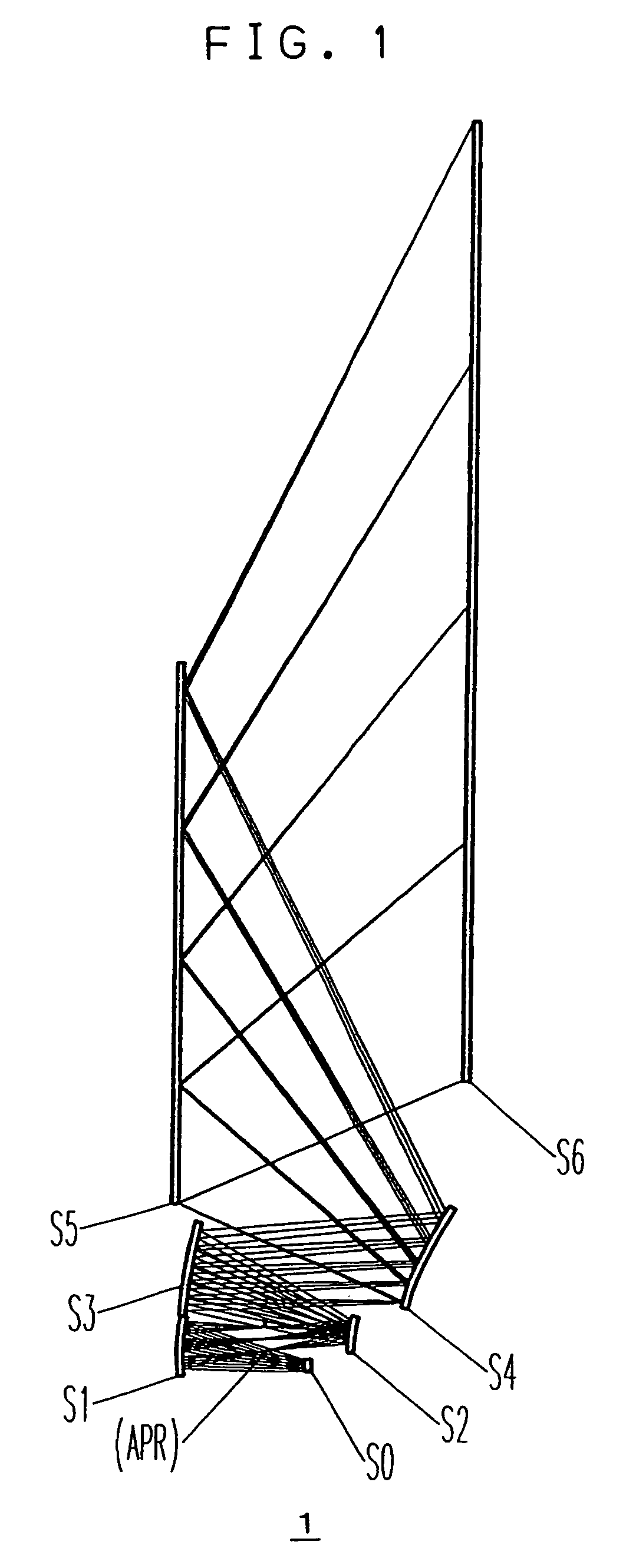
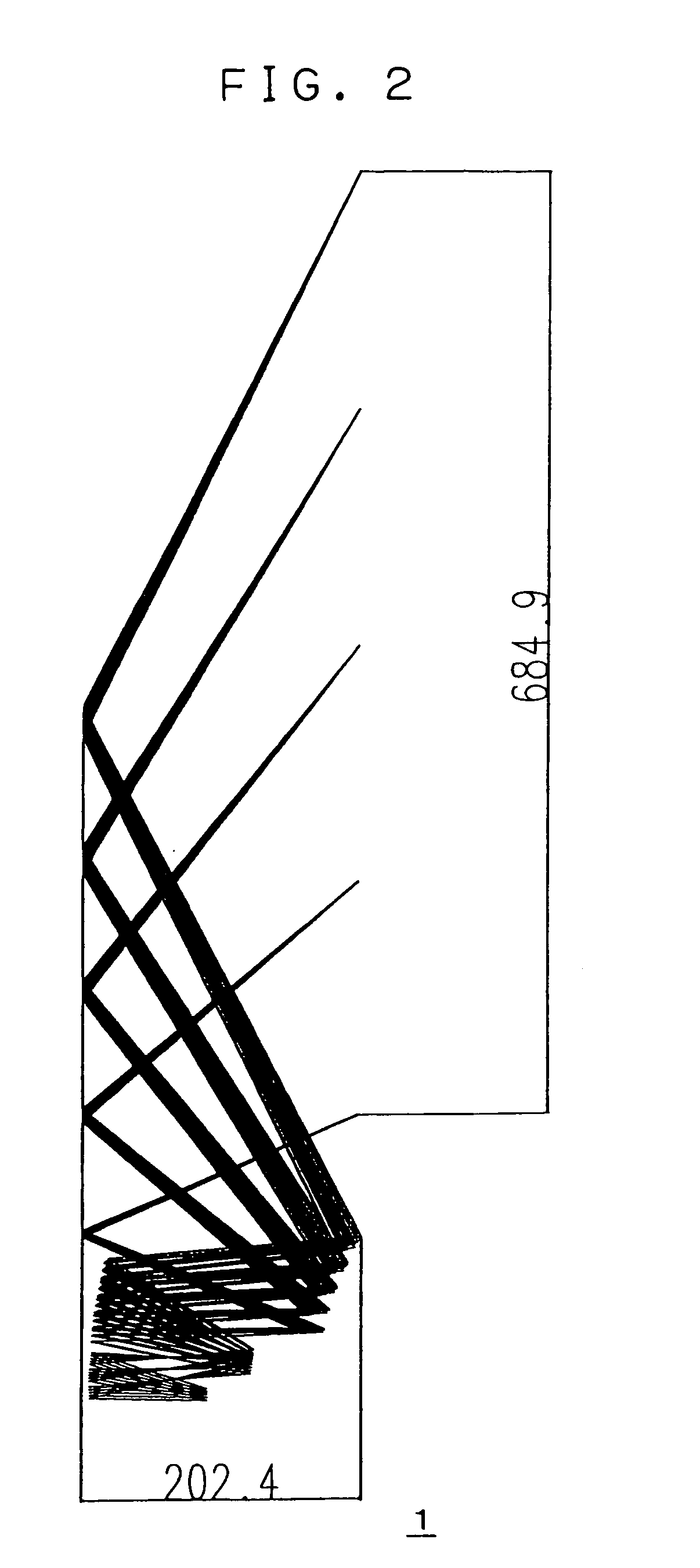
An oblique projection optical system for leading rays of light from a display surface on which an image is displayed to a projection surface in such a way that the ray of light from the center of the display surface is obliquely incident on the projection surface in order to project a magnified image of the image displayed on the display surface onto the projection surface includes a plurality of reflecting surfaces having a power. At least two of the reflecting surfaces have a free-form curved surface, and, of all the reflecting surfaces, the one closest to the projection surface has a negative power and at least one of the other has a positive power. Alternatively, in a rear projection optical system having a projection optical system for projecting an image displayed on a panel display surface onto a screen surface, the projection optical system includes at least four curved-surface reflecting mirrors.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Projection optical system, projection type image display apparatus, and image display system
InactiveUS6951395B2Short throw distanceCompact structureTelevision system detailsProjectorsImage formationOblique projection
A projection optical system which has a short projection distance and a compact structure, and allows oblique projection. The projection optical system projects luminous flux from an image forming element for forming an original image onto a projection surface which is oblique to a central principal ray which is a principal ray of luminous flux traveling from the center of the original image to the center of a finally formed image. The system includes a plurality of reflecting surfaces each having a curvature. In addition, the projection optical system satisfies a predetermined expression (1).
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com