Radar signal motion disturbance spatial-polarizational domain combined stable filtering method
A motion interference and radar signal technology, applied to radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not using array polarization information, low calculation amount, and high computational complexity, and achieve the effect of real-time and effective suppression of motion interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
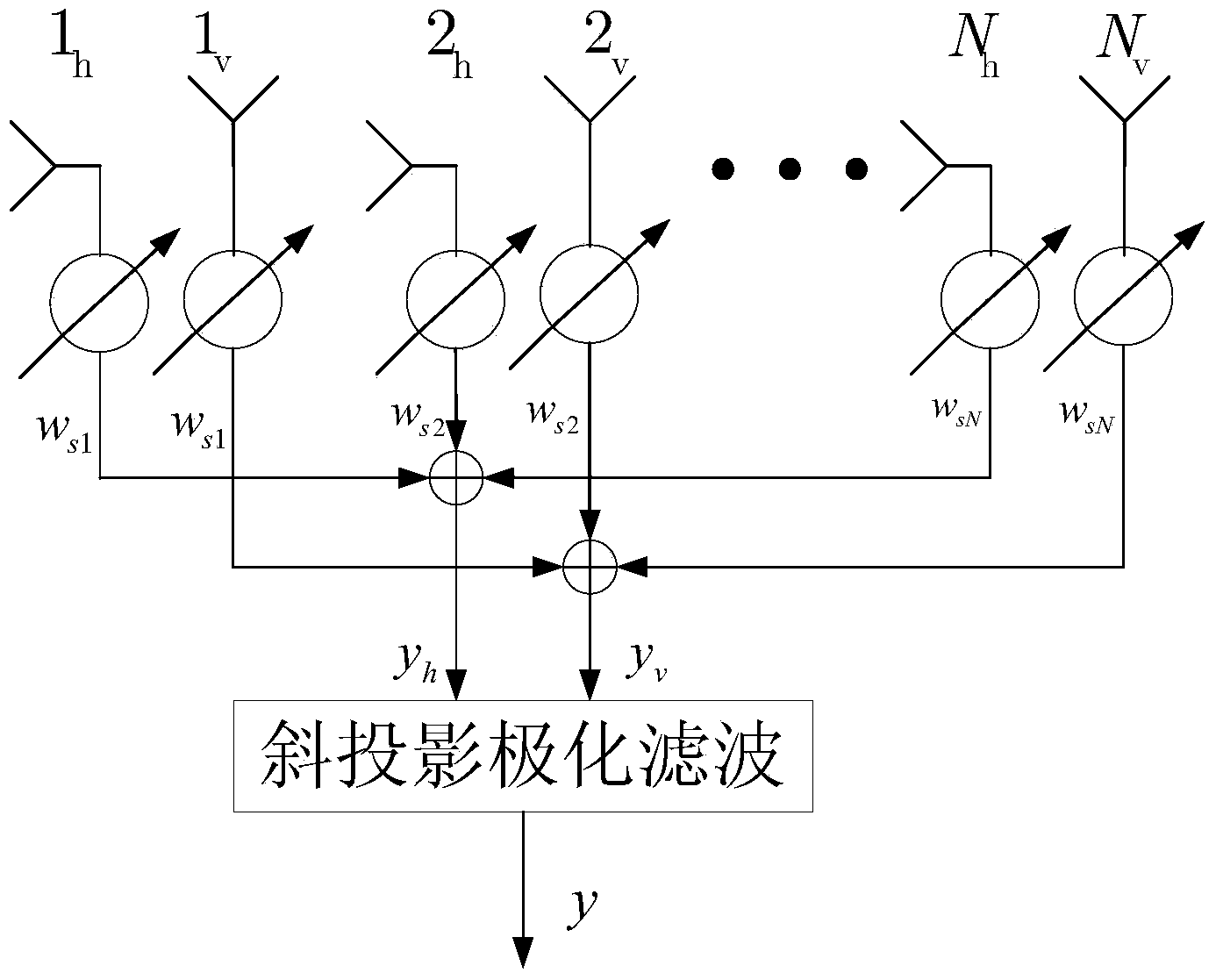
[0049] The present invention is a space-polarization domain joint robust filtering method for radar signal motion interference, referring to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention include as follows:
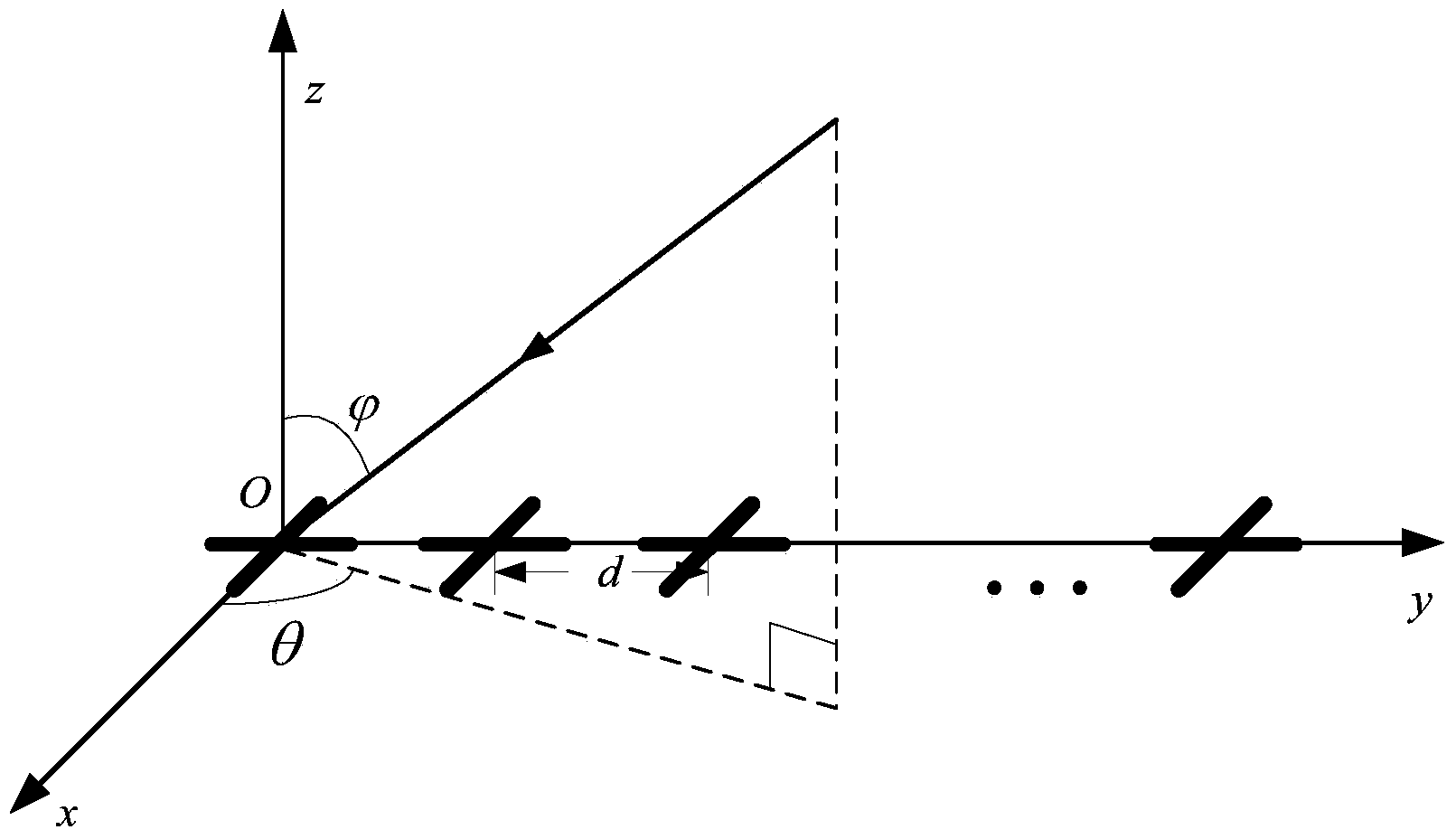
[0050] Step 1: The radar antenna array receives data X(t). For a half-wavelength equidistant antenna array composed of N orthogonal dipoles, see figure 2 , in this example the antennas are arranged equidistantly in the form of orthogonal dipoles, the total number of dipoles is N, and the distance between adjacent dipoles is d, represent the azimuth and elevation angles respectively, assuming that there is a target from direction, while there are a total of P disturbances from The direction is incident on the array, and the array receives the signal at time t, and the received data under a snapshot is expressed as:
[0051] X ( t ) = N ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] The radar signal motion interference airspace-polarization domain joint robust filtering method is the same as that in Embodiment 1
[0075] In step 2, for the first M snapshot data of the received data X(t), use the PASTd algorithm to obtain the interference signal subspace at time t=i (i=1,2,...,M)
[0076] (1) Initialize d p (0) and u p (0)(p=1,2,...,P), i=0;
[0077] (2) i=i+1,x 1 (i)=X h (i);
[0078] (3) Calculate u in turn when p takes (1,2,...P) p (i):
[0079] y p ( i ) = u p H ( i - 1 ) x 1 ( i )
[0080] d p (i)=βd p (i-1)+|y p (i)| 2 , β is the forgetting factor
[0081] e p (i)=x p (i)-u p (i-1)y p (i), e p (i) is the estimation error
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0089] The joint robust filtering method of radar signal motion interference airspace-polarization domain is the same as that of Embodiment 1-2
[0090] In step 3, the orientation estimate (θ 1 (t), θ 2 (t),...,θ P (t)), where the polarization vector of a fast-moving interference is expressed as The power series expansion of the perturbation with the spatial domain polarization state model and the first-order approximation are obtained to obtain the spatial domain polarization state model a n (n=0,1) is the first-order coefficient of the real part power series expansion of the polarization space state disturbance, b n (n=0,1) is the first-order coefficient of the power series expansion of the imaginary part of the state disturbance in the polarization space domain. In order to facilitate the solution, a mathematical transformation will be performed to solve the polarization ratio vector P J Transformed into the easy-to-calculate polarization parameter vector Ρ=[1 (b 0 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Snr | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com