Patents
Literature
186 results about "Series expansion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, a series expansion is a method for calculating a function that cannot be expressed by just elementary operators (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division). The resulting so-called series often can be limited to a finite number of terms, thus yielding an approximation of the function. The fewer terms of the sequence are used, the simpler this approximation will be. Often, the resulting inaccuracy (i.e., the partial sum of the omitted terms) can be described by an equation involving Big O notation (see also asymptotic expansion). The series expansion on an open interval will also be an approximation for non-analytic functions.
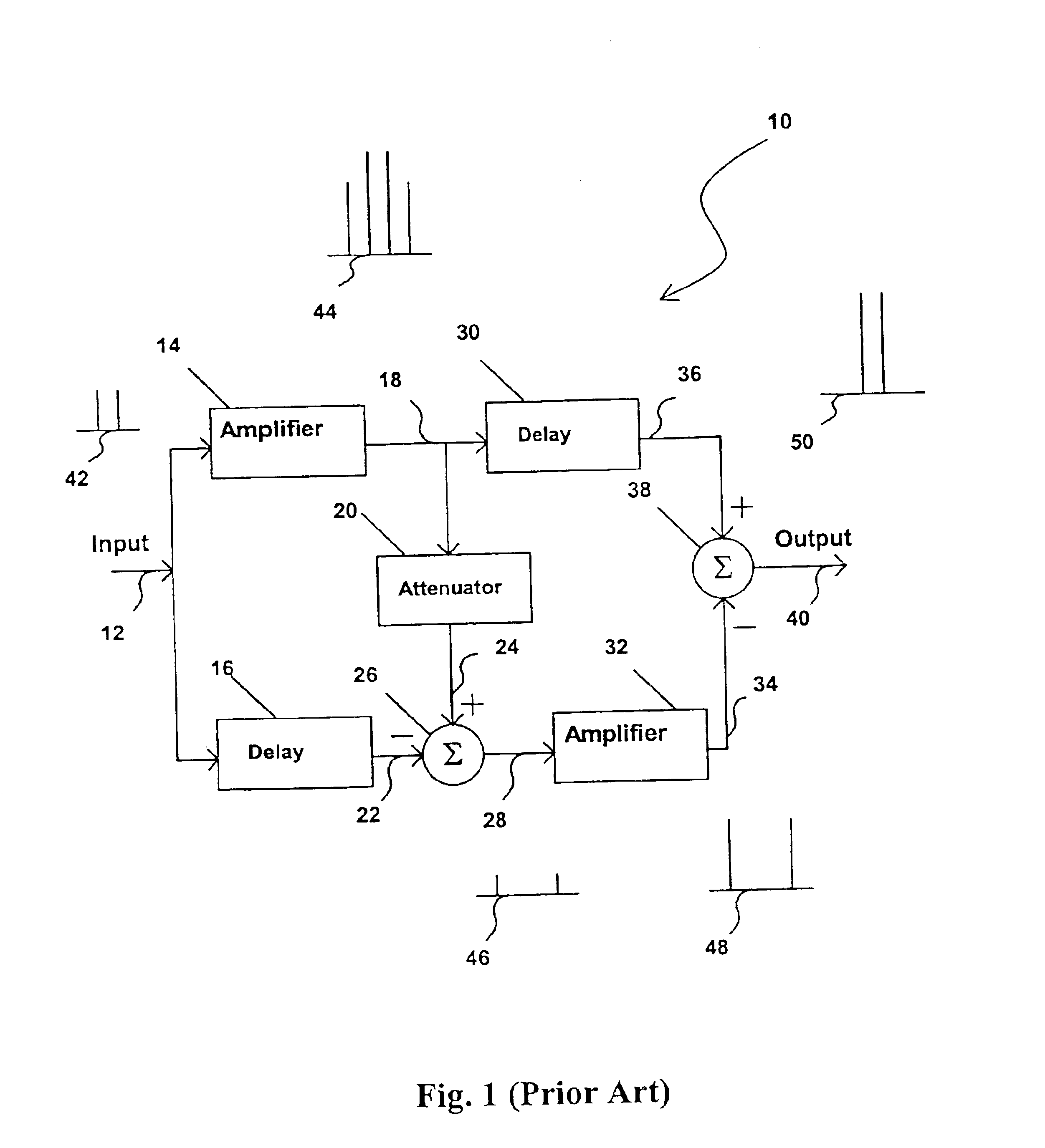
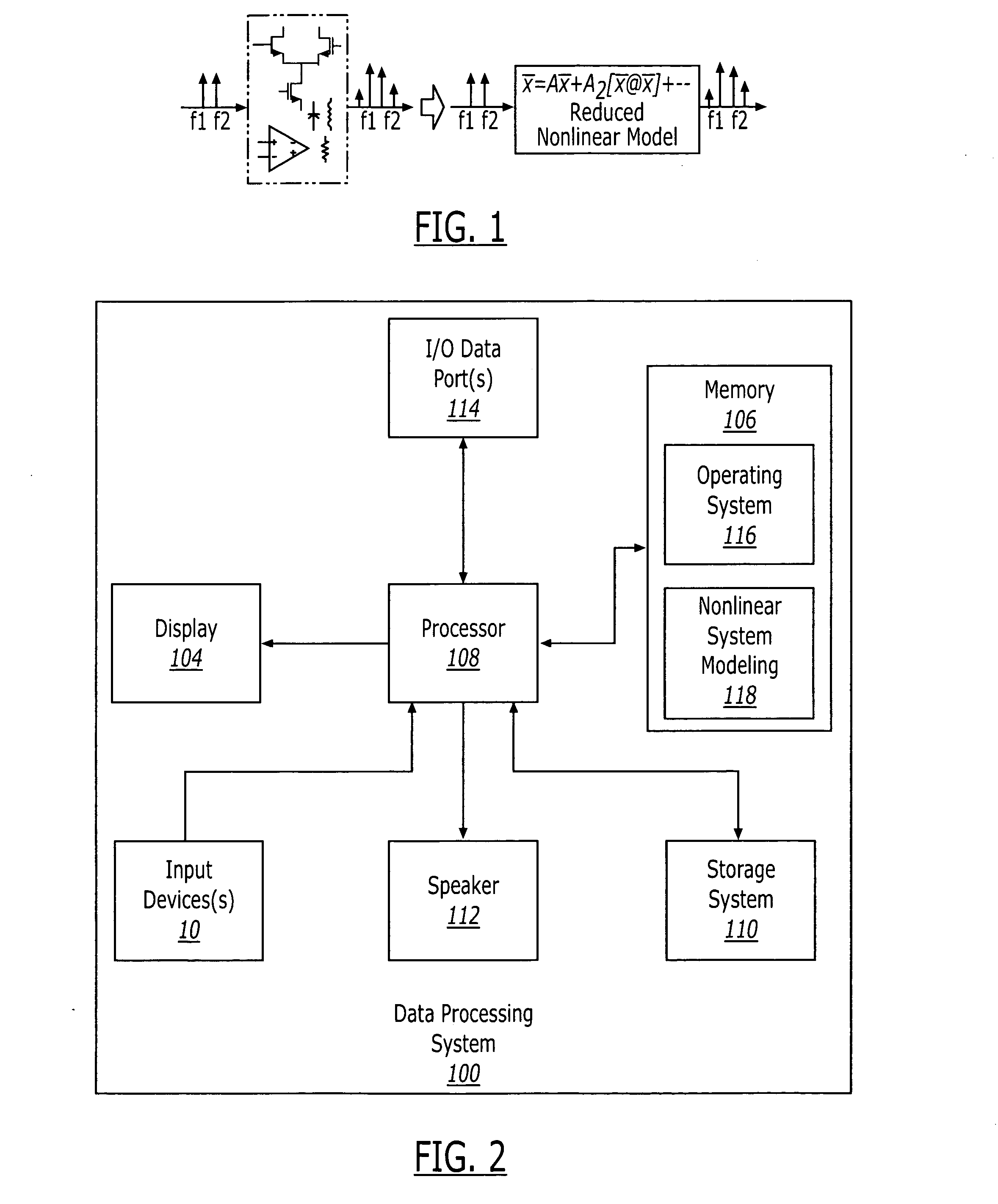
Trigonometric wave generation circuit using series expansion
InactiveUS20050262175A1Reduce circuit areaReduce functionMulti-frequency code systemsDigital function generatorsSinewave synthesisSeries expansion
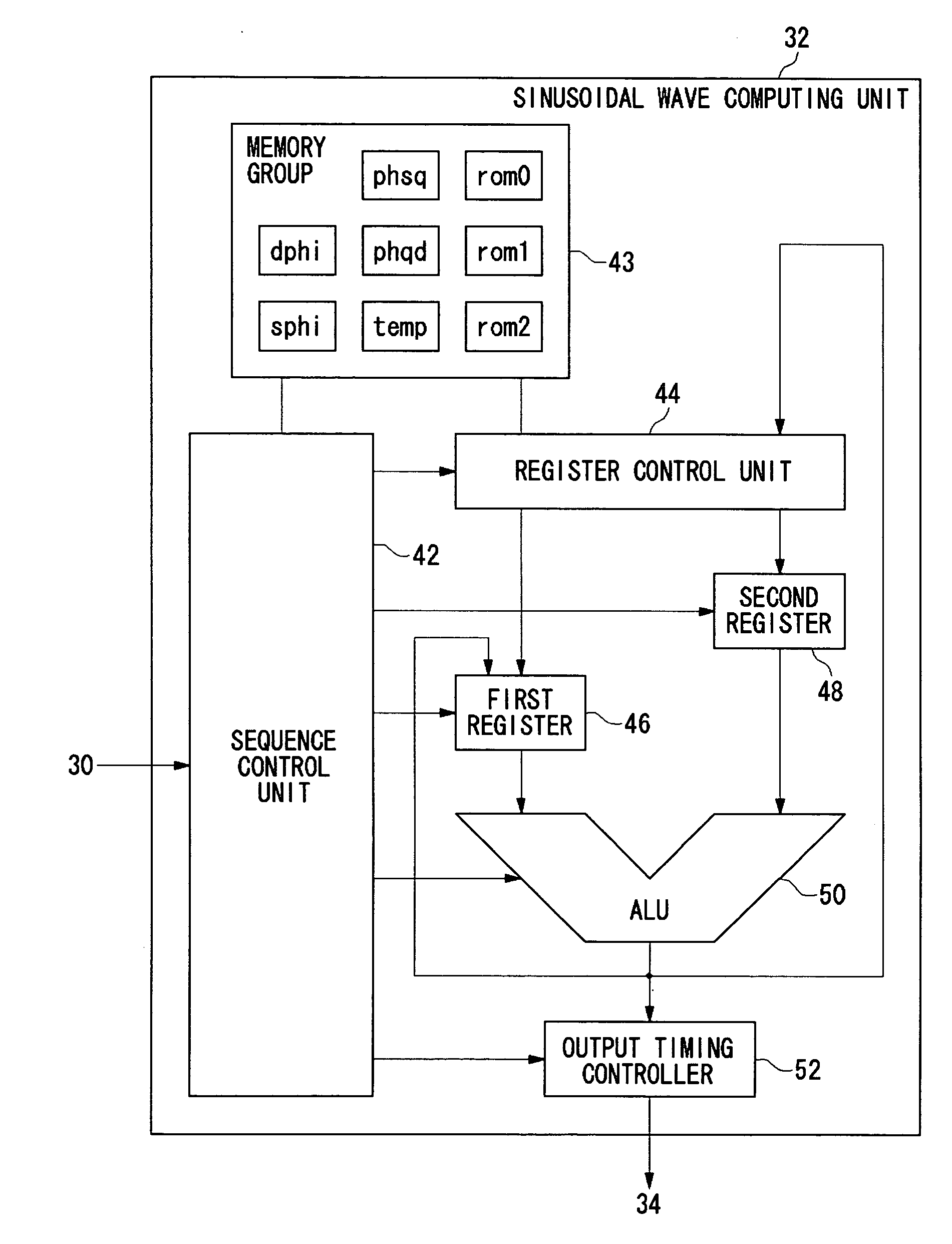
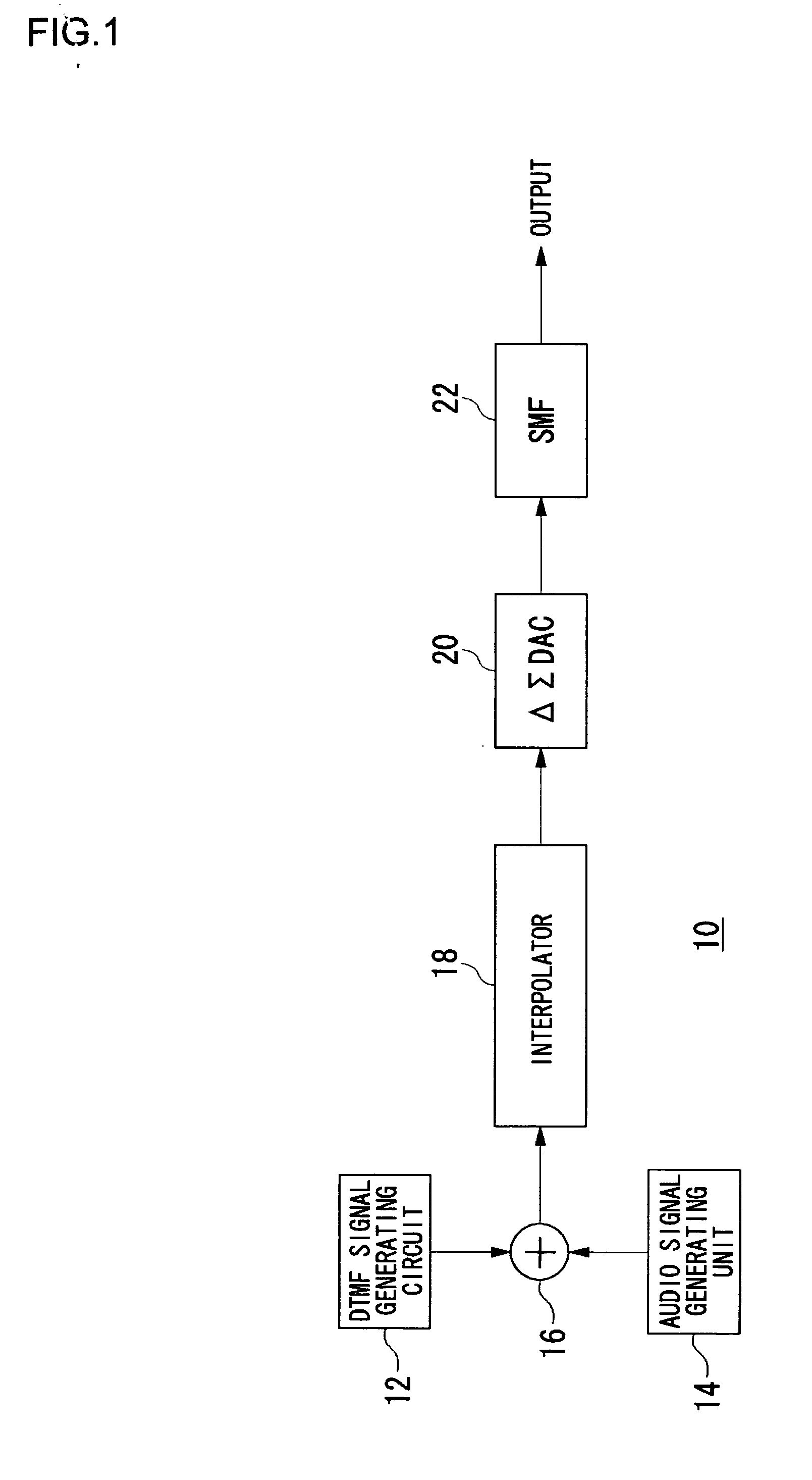
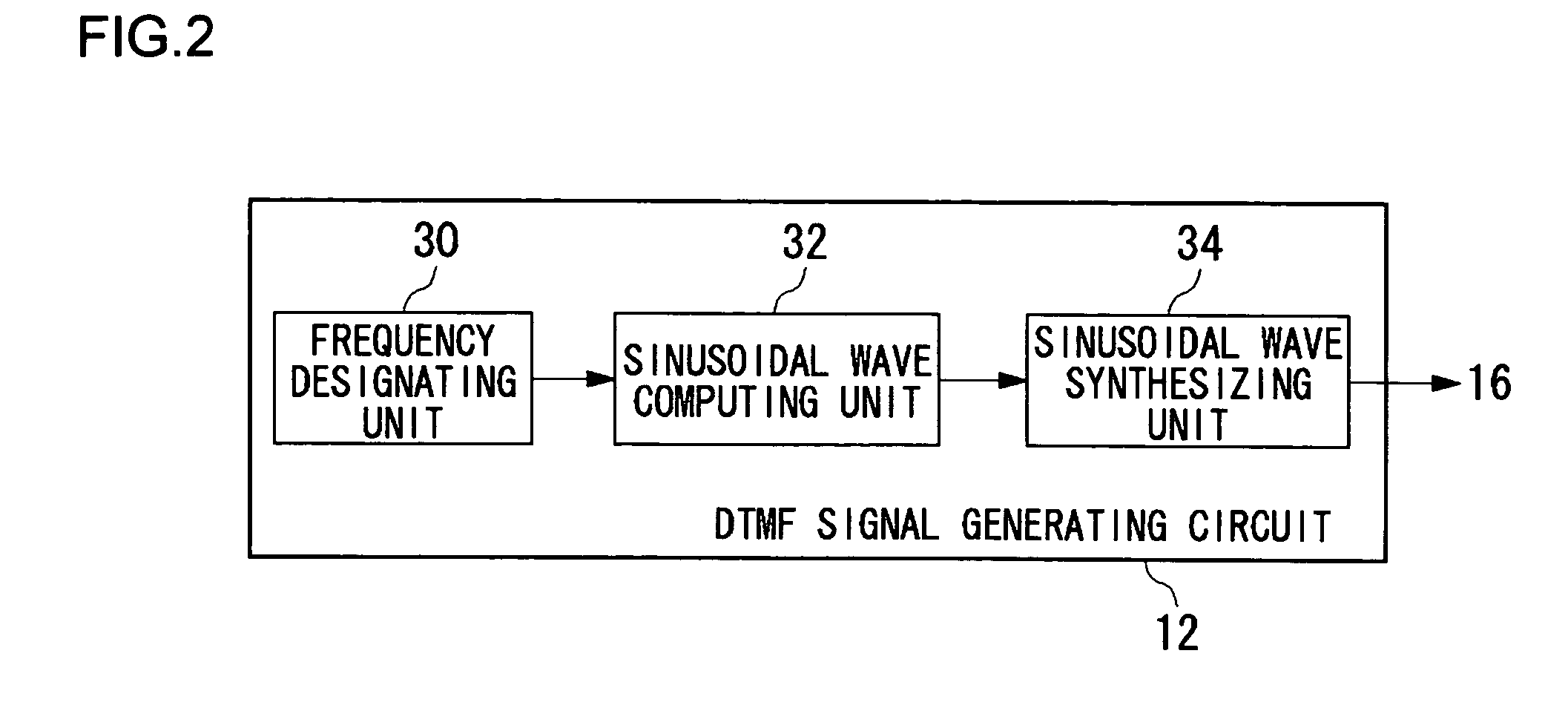
A DTMF signal generating circuit is provided with a frequency designating unit which designates frequencies to form a DTMF signal, a sinusoidal wave computing unit which computes sinusoidal waves by referring to frequencies designated by the frequency designating unit, and a sinusoidal wave synthesizing unit which synthesizes two sinusoidal waves computed by the sinusoidal wave computing unit. The sinusoidal wave computing unit is provided with operators such as an adder-subtracter and a multiplier and generates a sinusoidal wave by determining terms of a Taylor expansion of a sinusoidal function by arithmetic operation.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
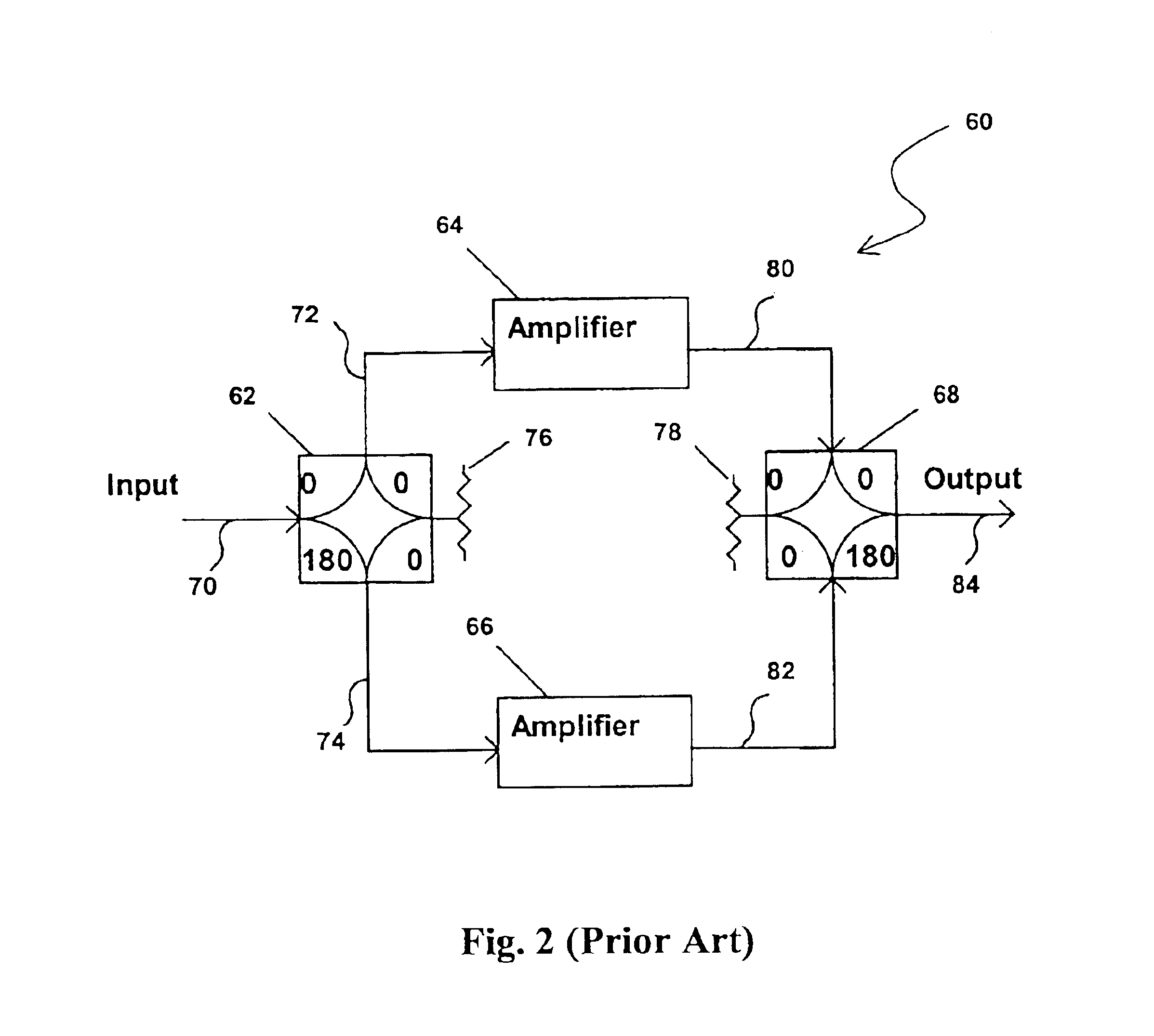
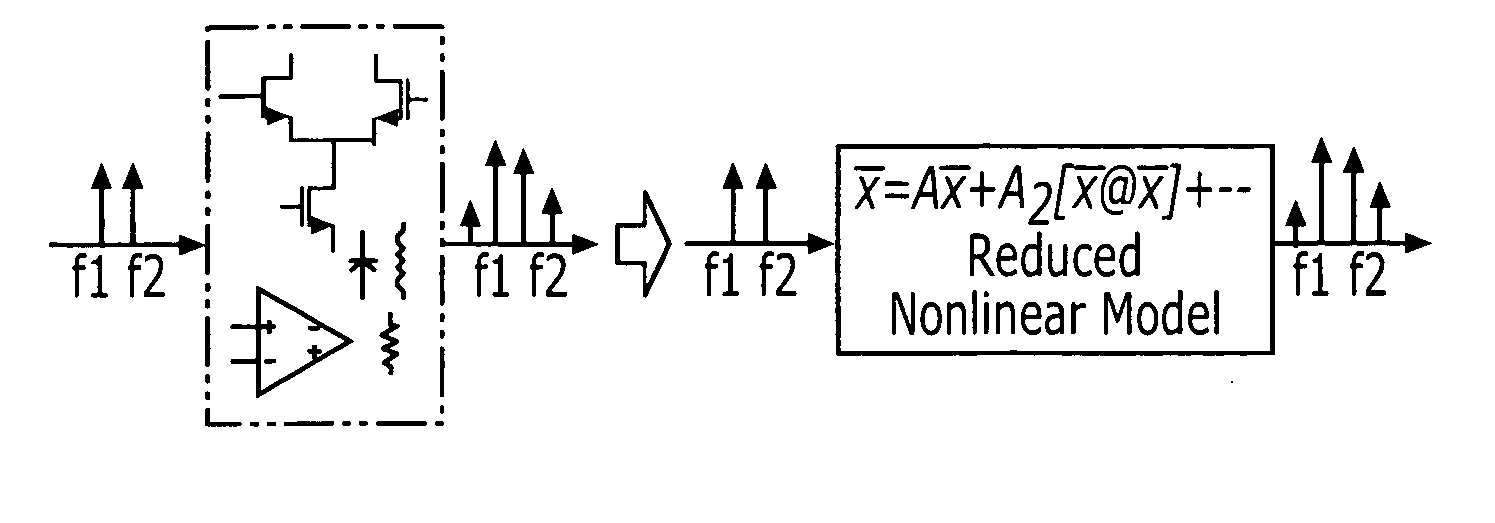
Methods and apparatus for using Taylor series expansion concepts to substantially reduce nonlinear distortion
InactiveUS6853247B2Reducing canceling nonlinearitiesReduce and cancel nonlinearitiesAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
Methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling nonlinearities of any order in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. In particular, methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling third order nonlinearities in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. A first coupler is used to split an input signal into two equal-amplitude in-phase components, each component is processed by two nonlinear devices with different nonlinearities, and a final combiner, such as a 180-degree hybrid, recombines the processed signals 180 degrees out of phase and substantially reduces and / or cancels the undesired nonlinear distortion components arising due to nonlinearities in the nonlinear devices.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
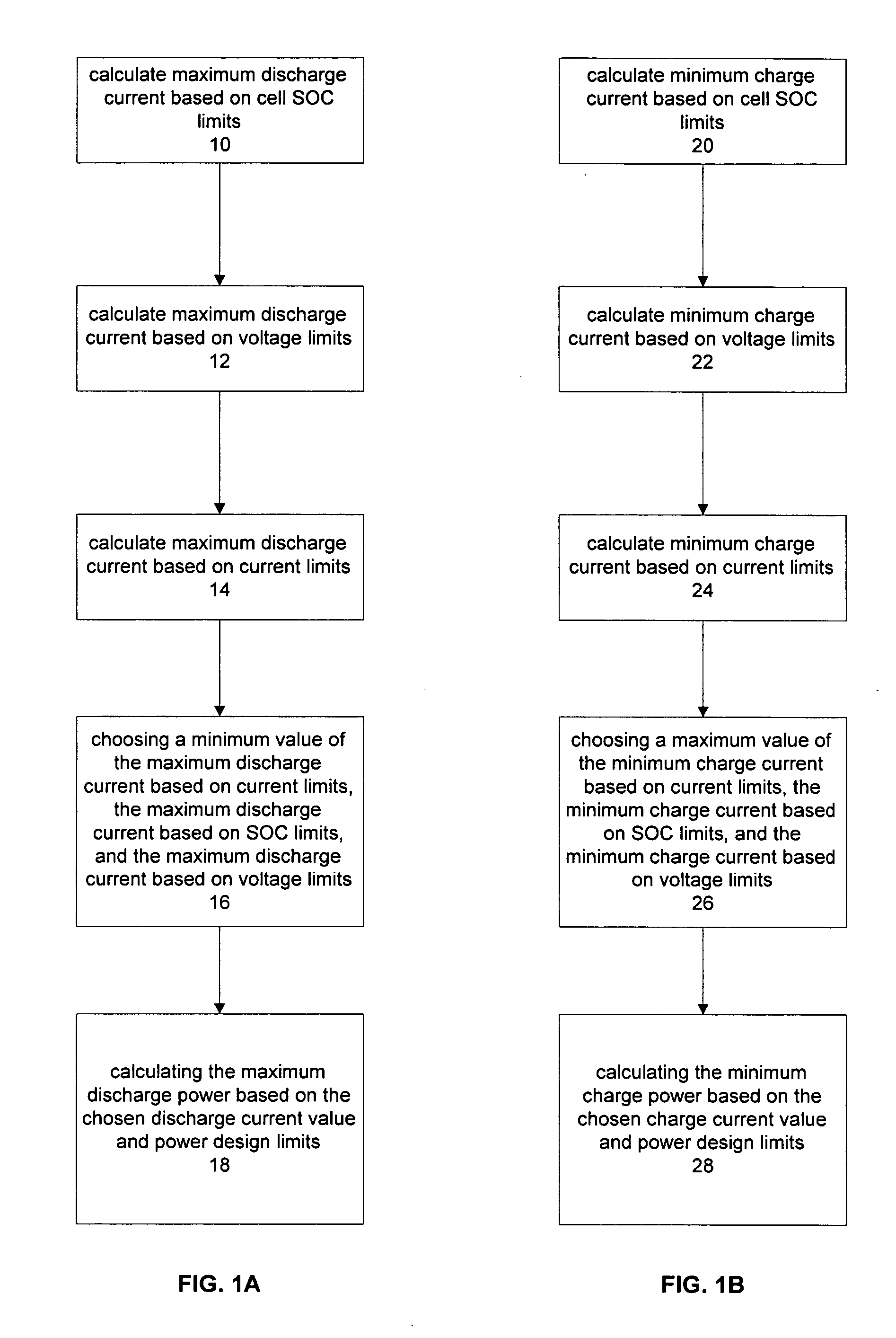
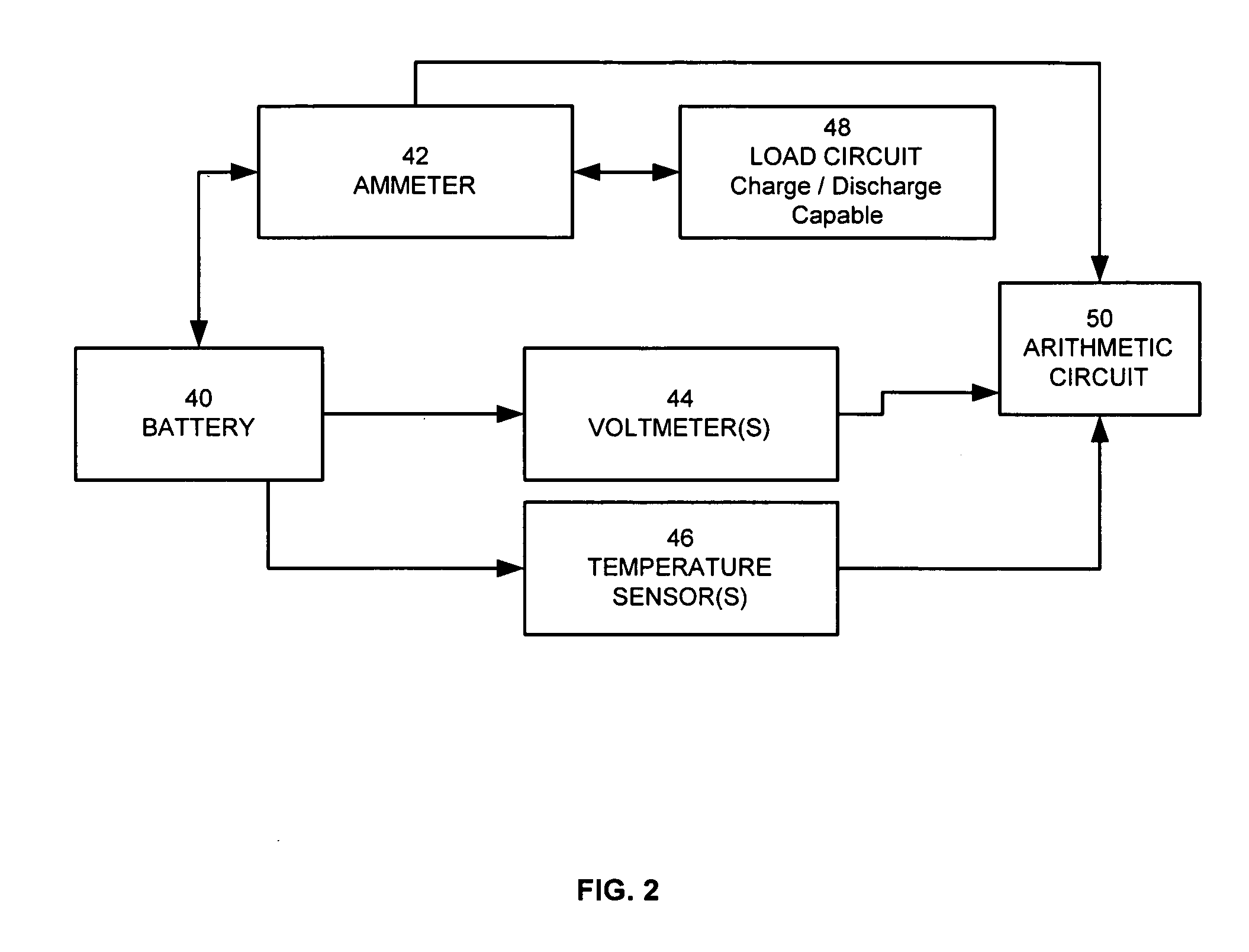
Method for calculating power capability of battery packs using advanced cell model predictive techniques
ActiveUS20050110498A1Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPower capabilityElectrical battery
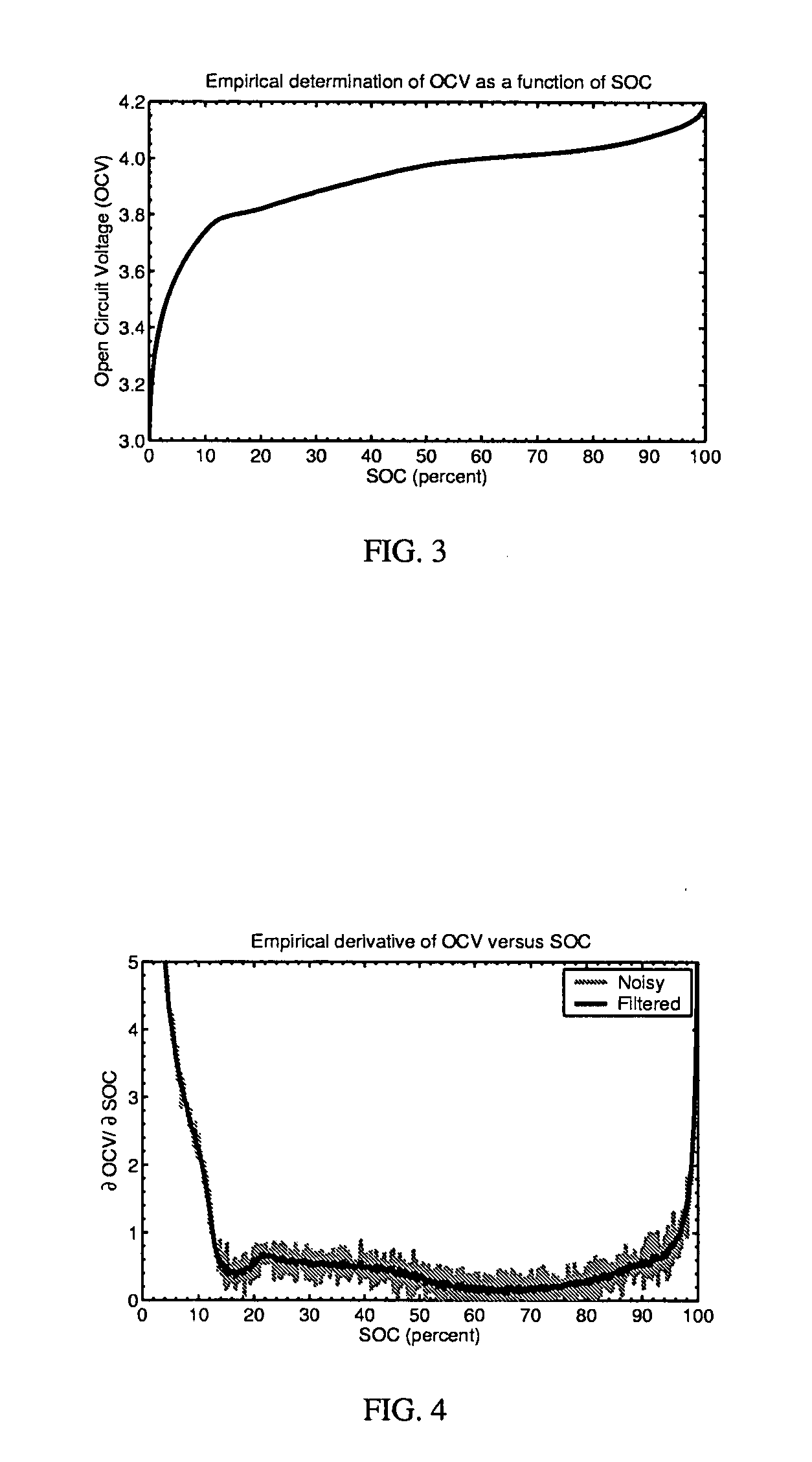
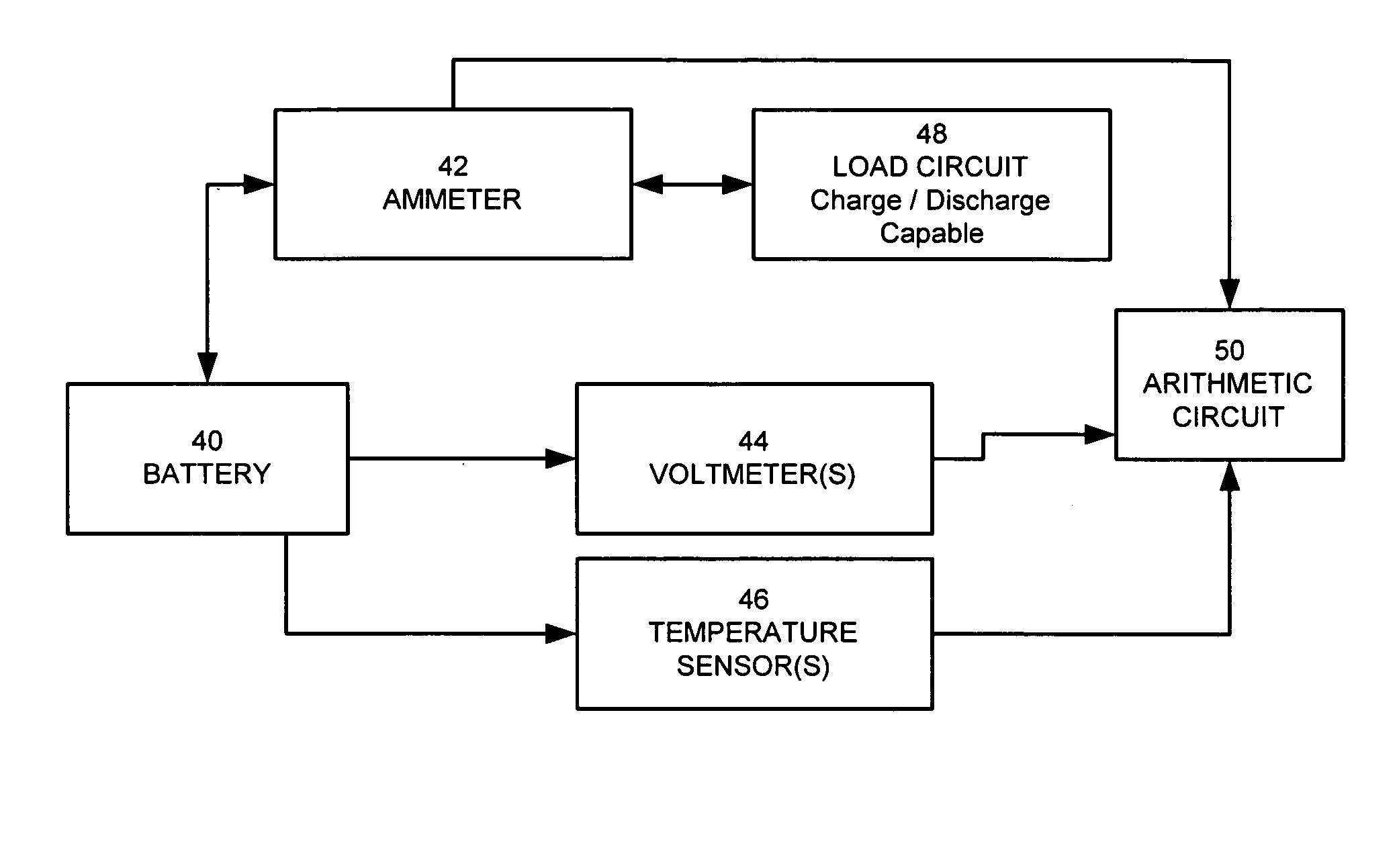
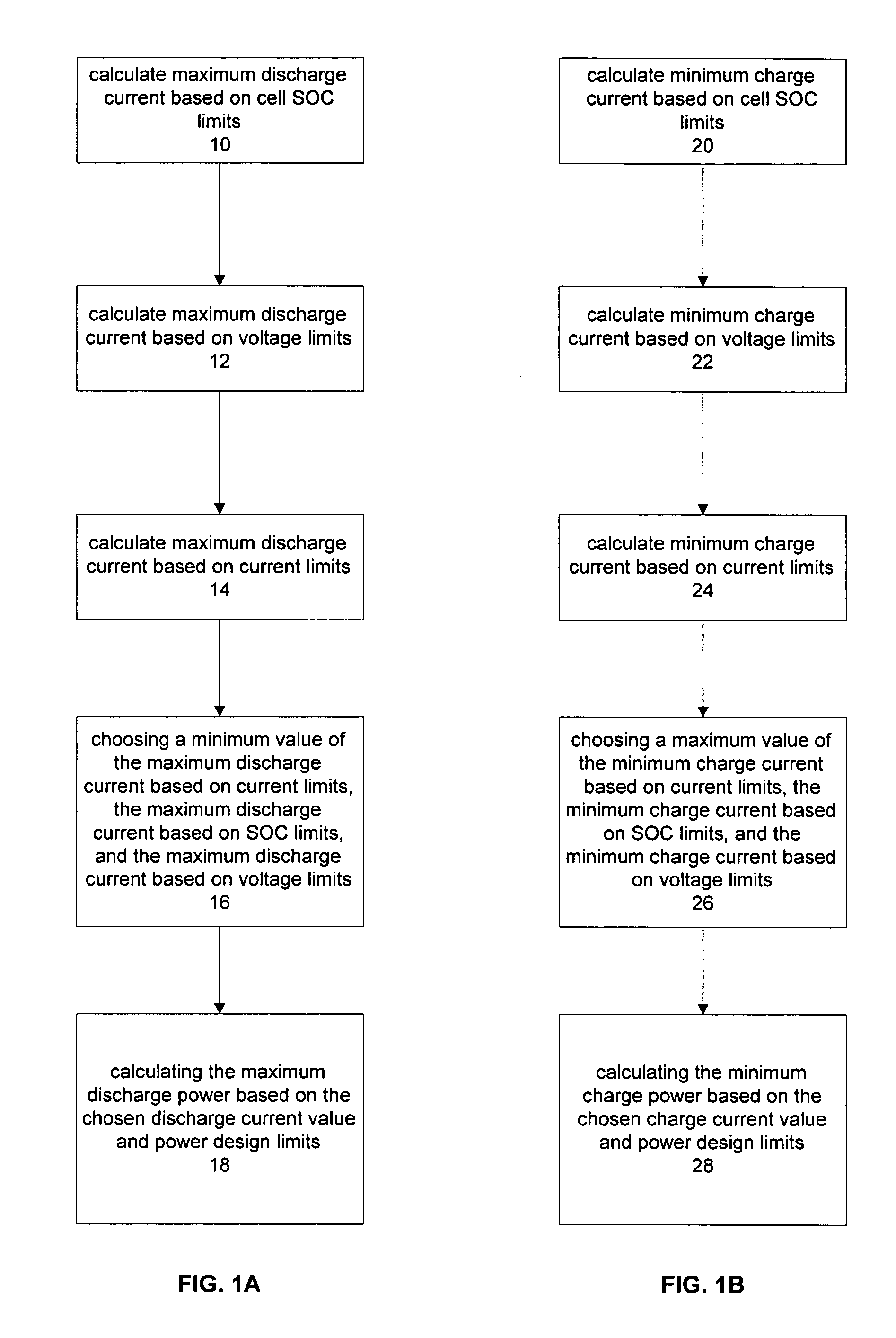
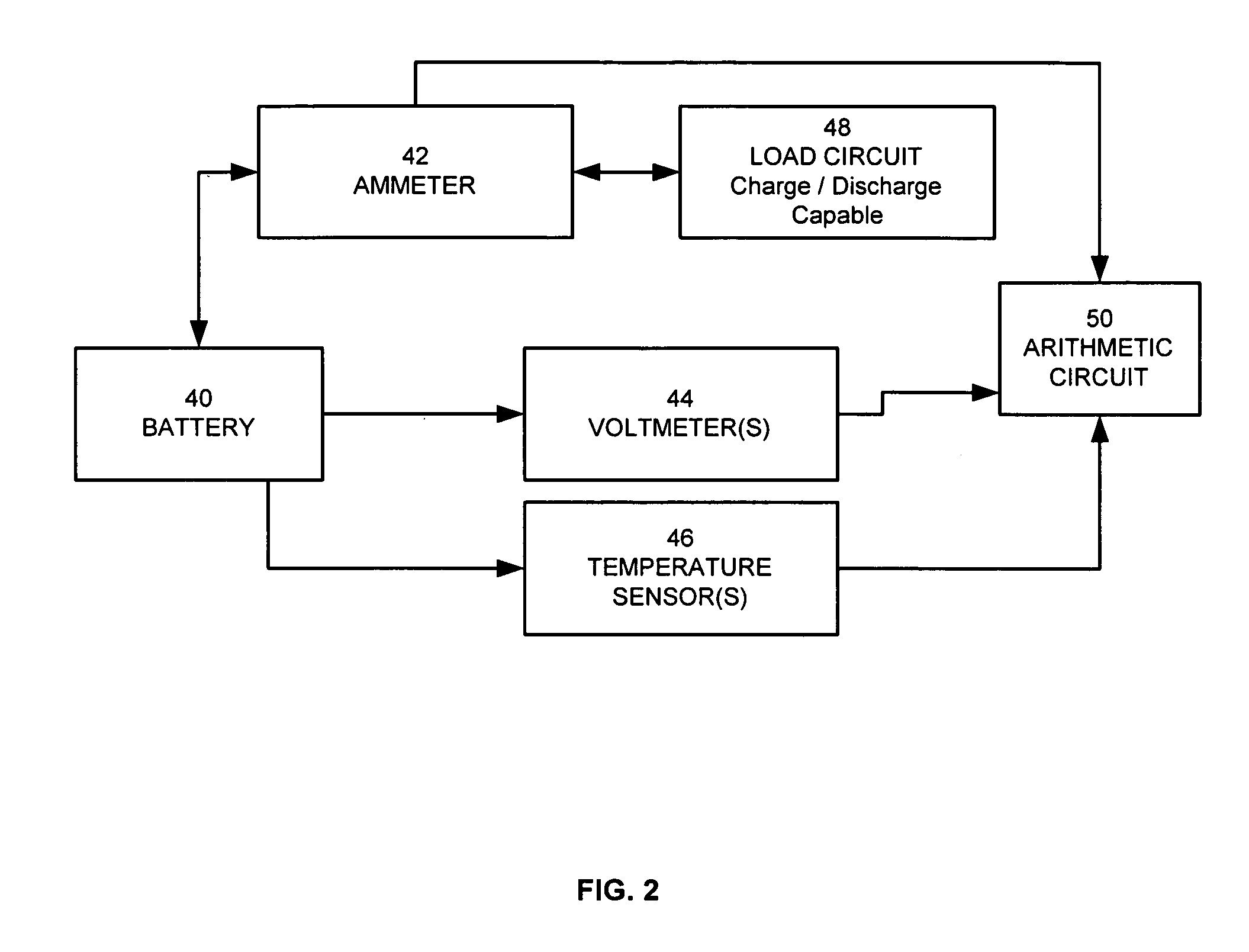
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for estimating discharge and charge power of battery applications, including battery packs used in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Electric Vehicles (EV). One charge / discharge power estimating method incorporates voltage, state-of-charge (SOC), power, and current design constraints and works for a user-specified prediction time horizon Δt. At least two cell models are used in calculating maximum charge / discharge power based on voltage limits. The first is a simple cell model that uses a Taylor-series expansion to linearize the equation involved. The second is a more complex and accurate model that models cell dynamics in discrete-time state-space form. The cell model can incorporate a inputs such as temperature, resistance, capacity, etc. One advantage of using model-based approach is that the same model may be used in both Kalman-filtering to produce the SOC and the estimation of maximum charge / discharge current based on voltage limits.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Method for calculating power capability of battery packs using advanced cell model predictive techniques
ActiveUS7321220B2Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPower capabilityEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for estimating discharge and charge power of battery applications, including battery packs used in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Electric Vehicles (EV). One charge / discharge power estimating method incorporates voltage, state-of-charge (SOC), power, and current design constraints and works for a user-specified prediction time horizon Δt. At least two cell models are used in calculating maximum charge / discharge power based on voltage limits. The first is a simple cell model that uses a Taylor-series expansion to linearize the equation involved. The second is a more complex and accurate model that models cell dynamics in discrete-time state-space form. The cell model can incorporate a inputs such as temperature, resistance, capacity, etc. One advantage of using model-based approach is that the same model may be used in both Kalman-filtering to produce the SOC and the estimation of maximum charge / discharge current based on voltage limits.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
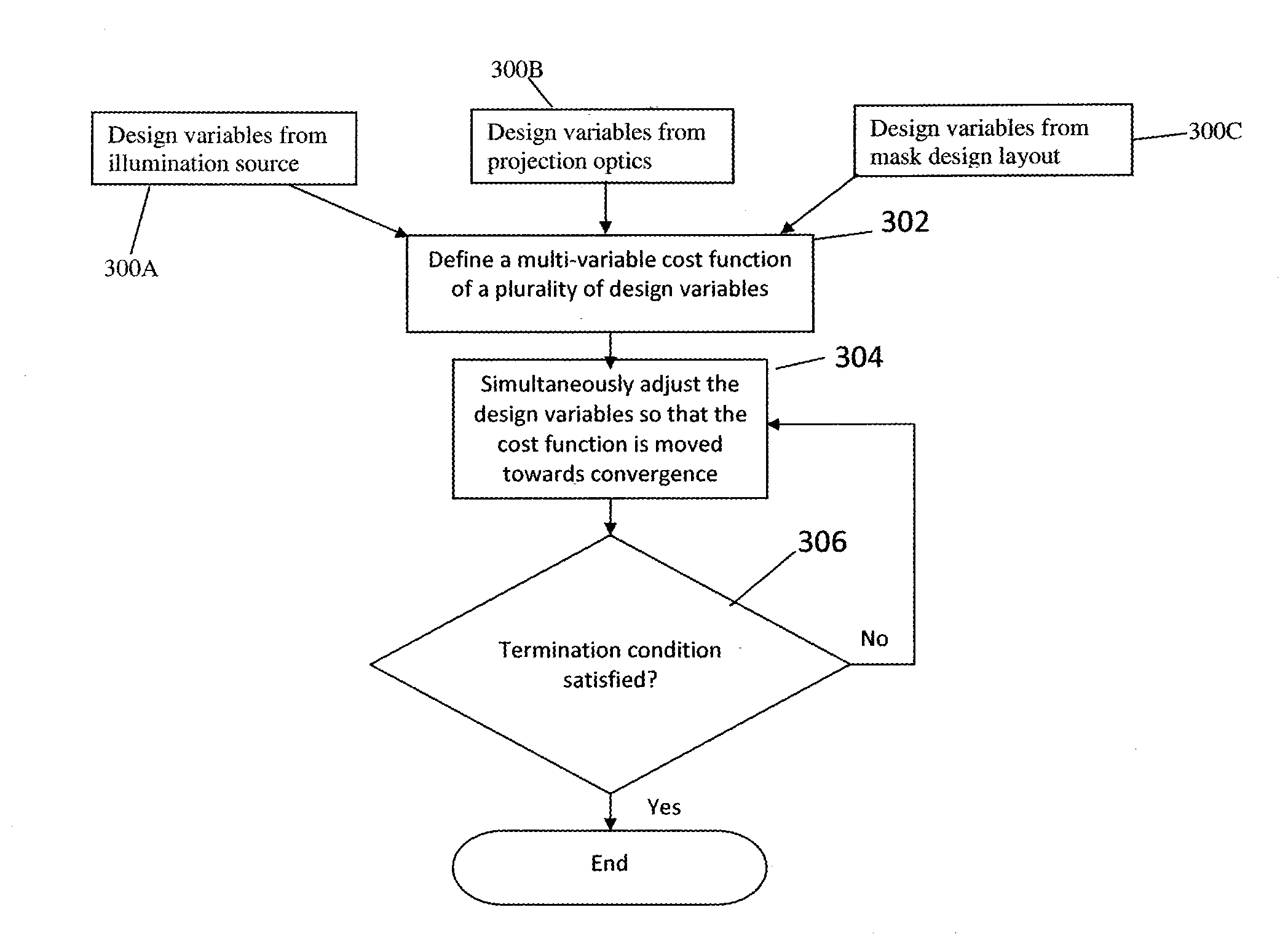
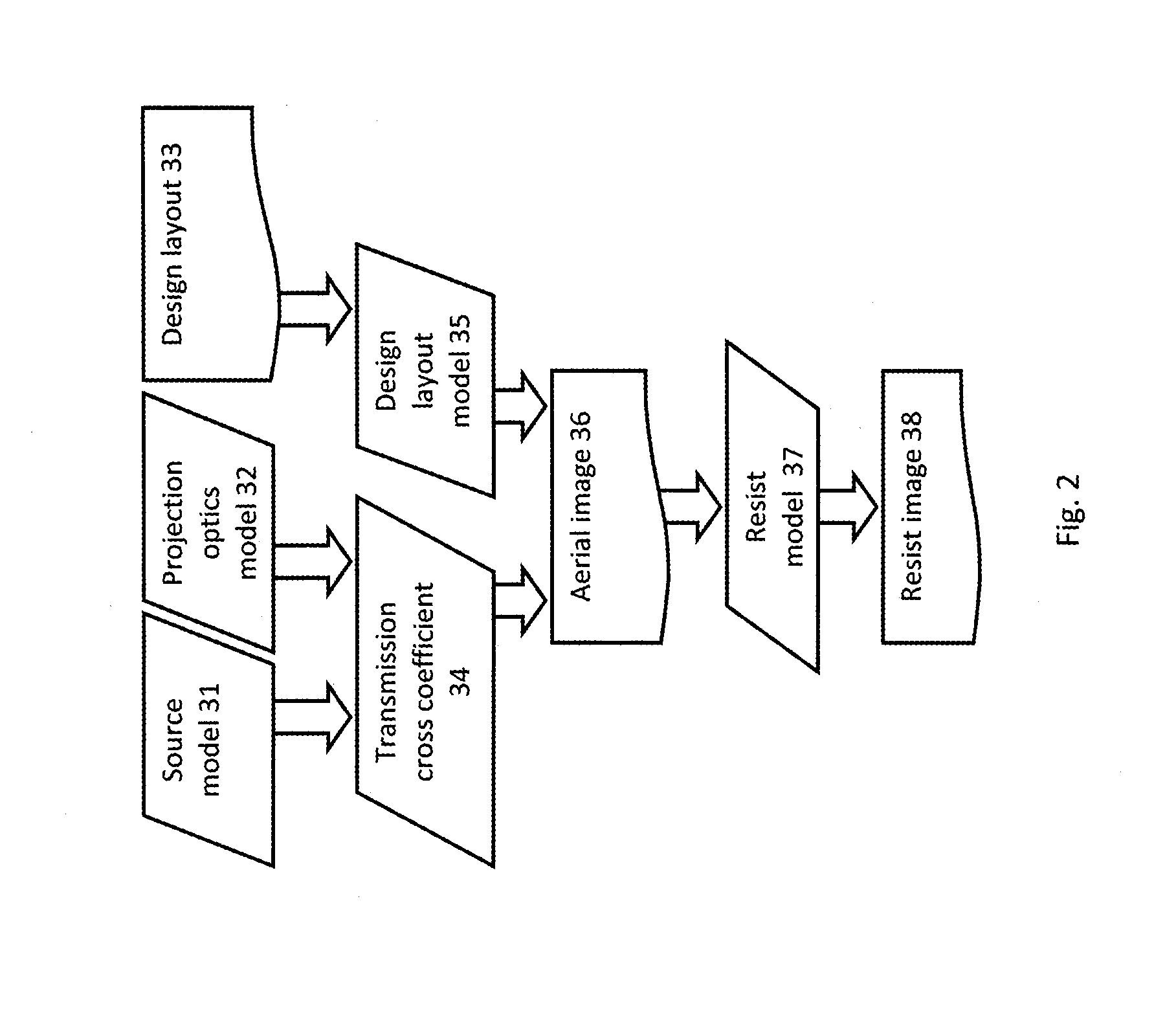
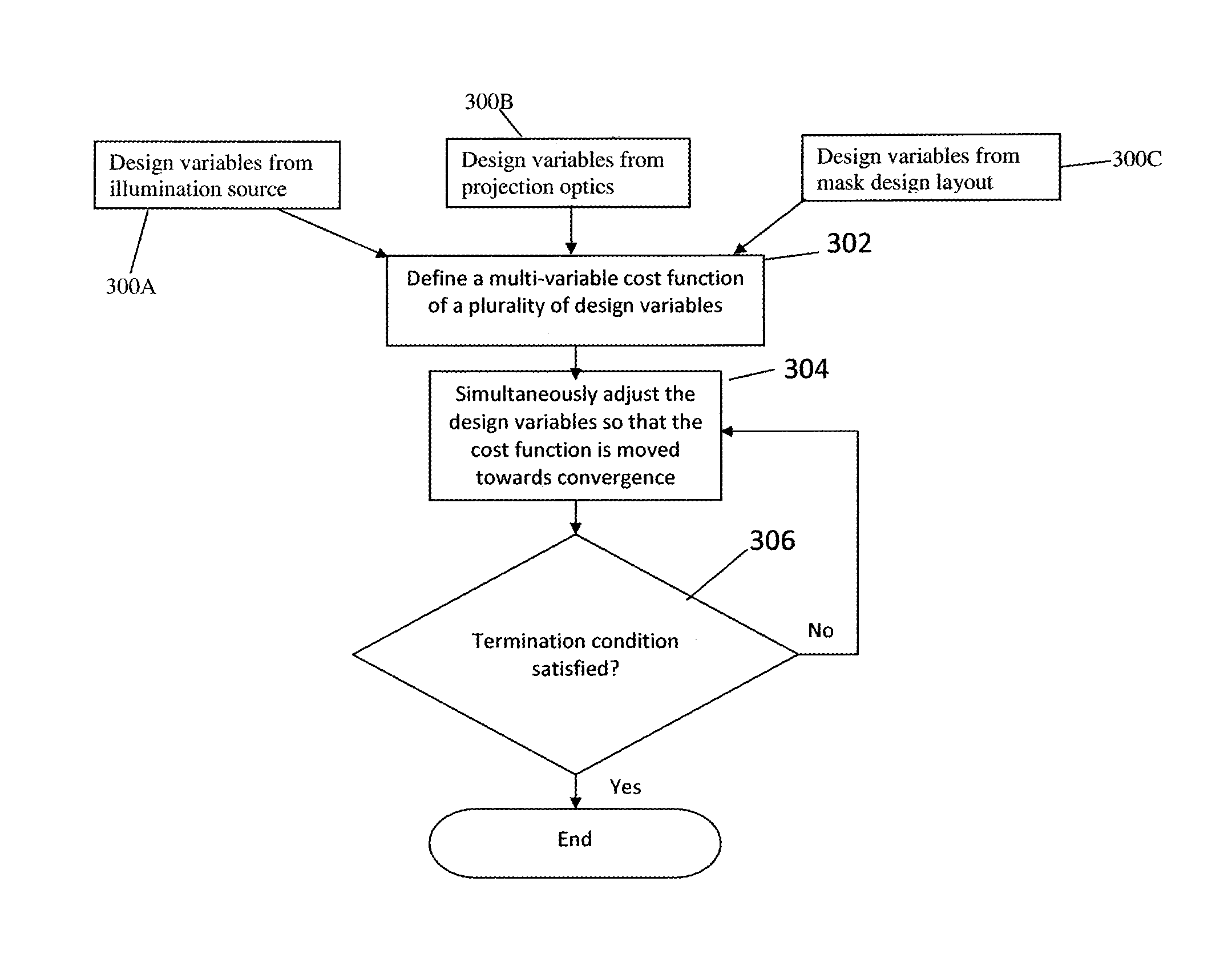
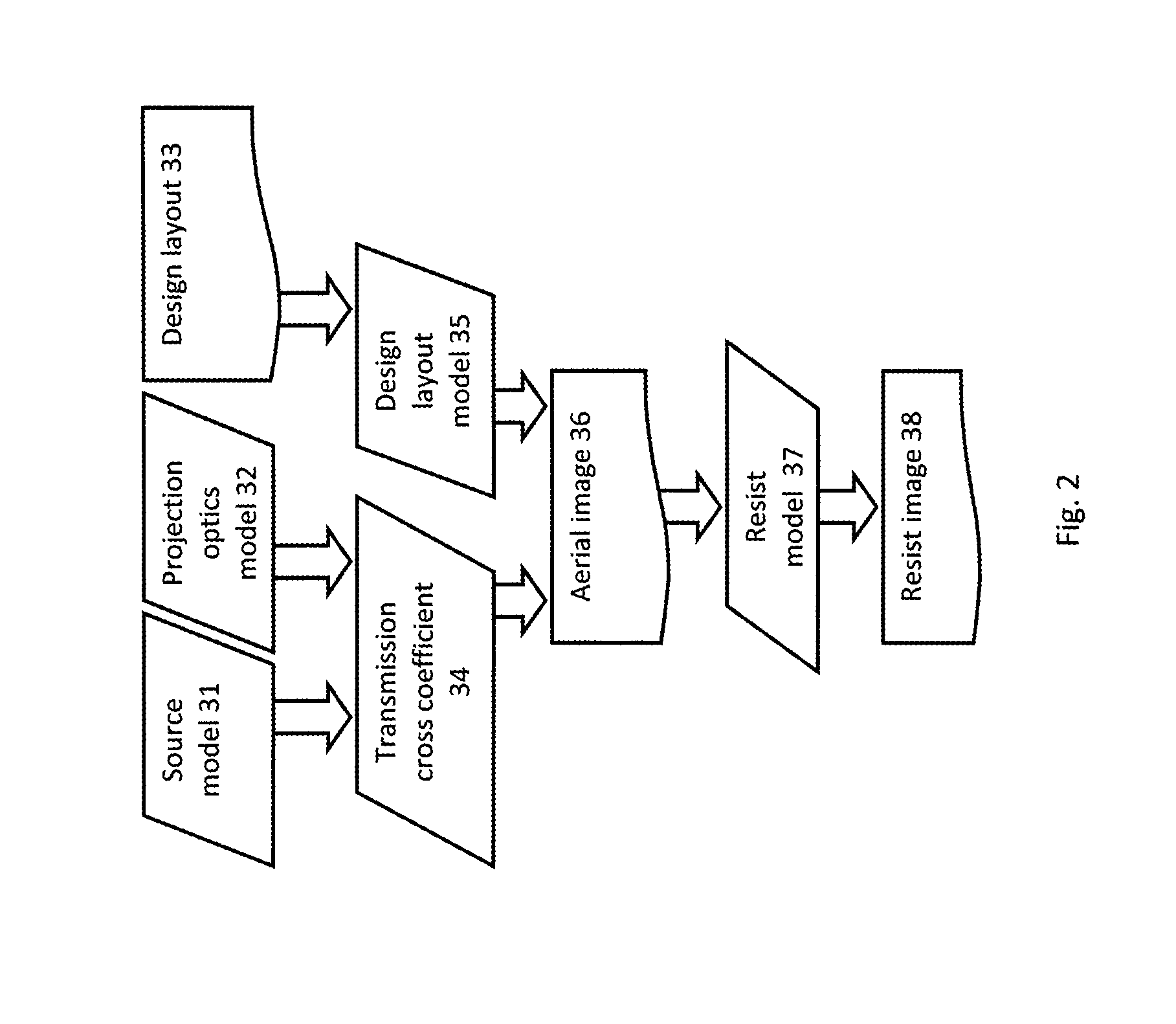
Optimization of Source, Mask and Projection Optics
ActiveUS20120117522A1Optimize and improveEasy to optimizePhotomechanical apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationProjection opticsWavefront
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for optimizing a lithographic projection apparatus including optimizing projection optics therein, and preferably including optimizing a source, a mask, and the projection optics. The projection optics is sometimes broadly referred to as “lens”, and therefore the joint optimization process may be termed source mask lens optimization (SMLO). SMLO is desirable over existing source mask optimization process (SMO), partially because including the projection optics in the optimization can lead to a larger process window by introducing a plurality of adjustable characteristics of the projection optics. The projection optics can be used to shape wavefront in the lithographic projection apparatus, enabling aberration control of the overall imaging process. According to the embodiments herein, the optimization can be accelerated by iteratively using linear fitting algorithm or using Taylor series expansion using partial derivatives of transmission cross coefficients (TCCs).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
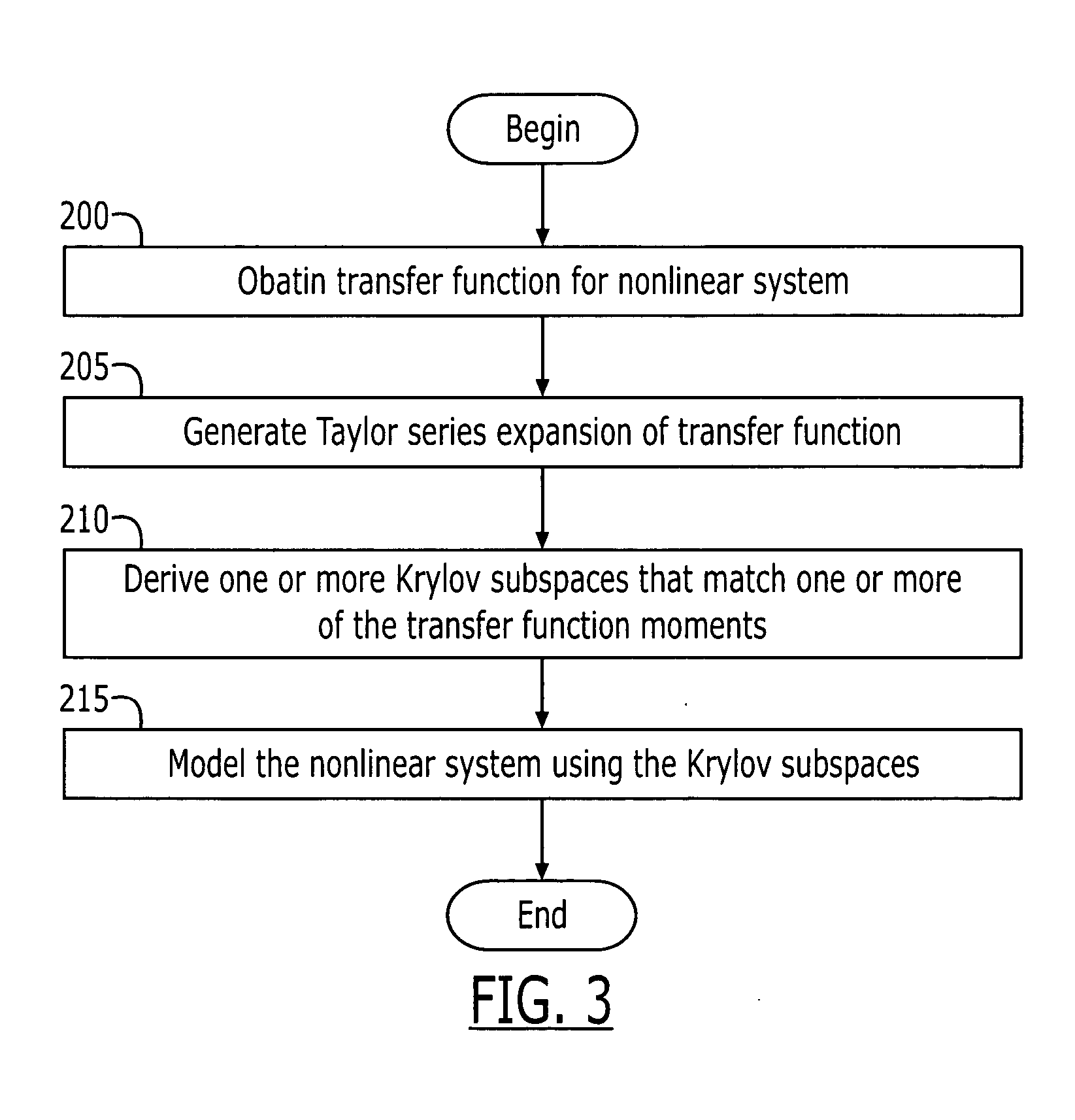
Methods, systems, and computer program products for modeling nonlinear systems
InactiveUS20050021319A1Computation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designEngineeringSeries expansion
According to some embodiments of the present invention, a nonlinear system may be modeled by obtaining a transfer function for the nonlinear system and generating a Taylor series expansion of the transfer function. The Taylor series expansion includes a plurality of moments respectively corresponding to a plurality of coefficients of the Taylor series terms. At least one Krylov subspace is derived that matches at least one of the plurality of moments. The nonlinear system is modeled using the at least one Krylov subspace.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
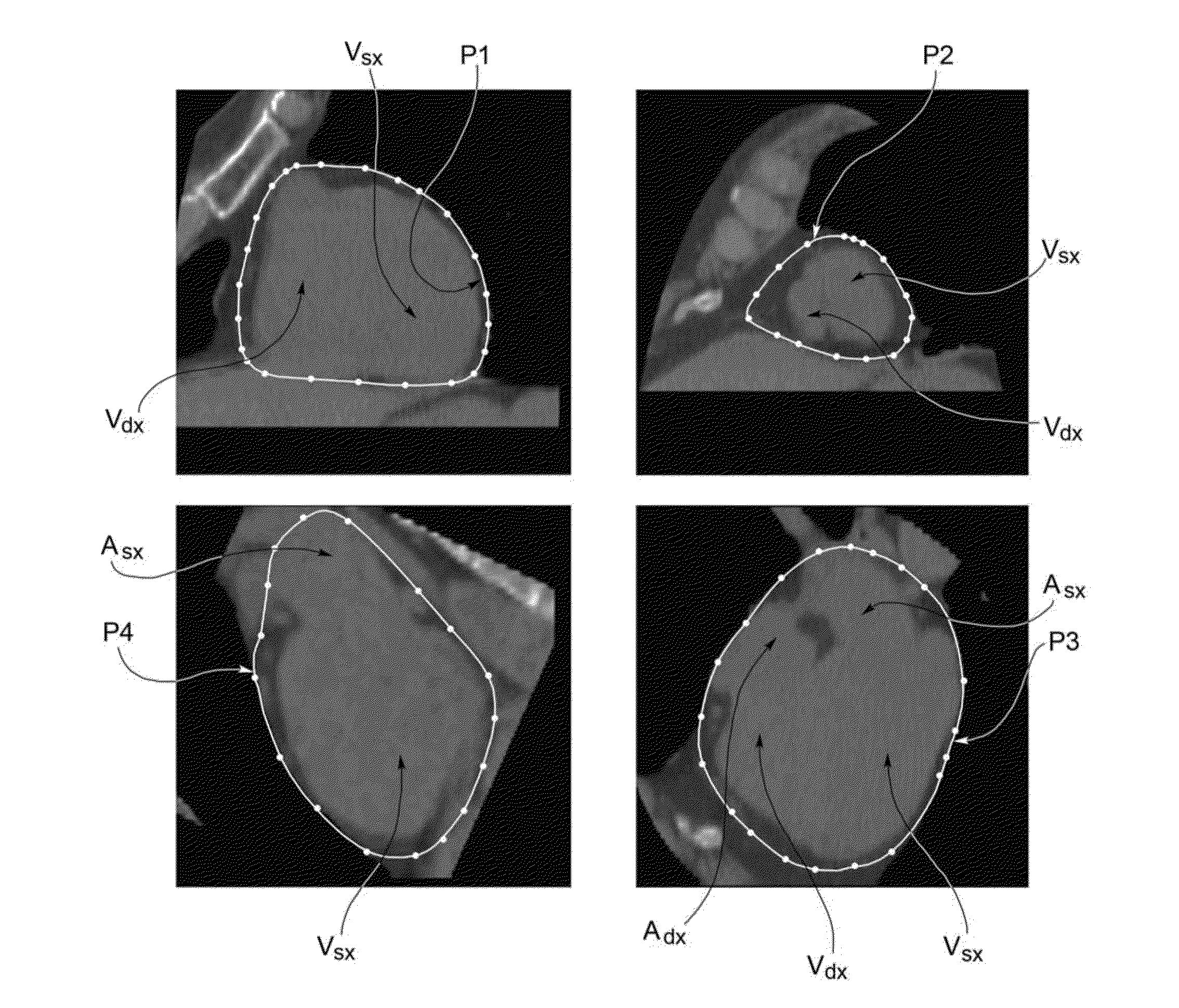
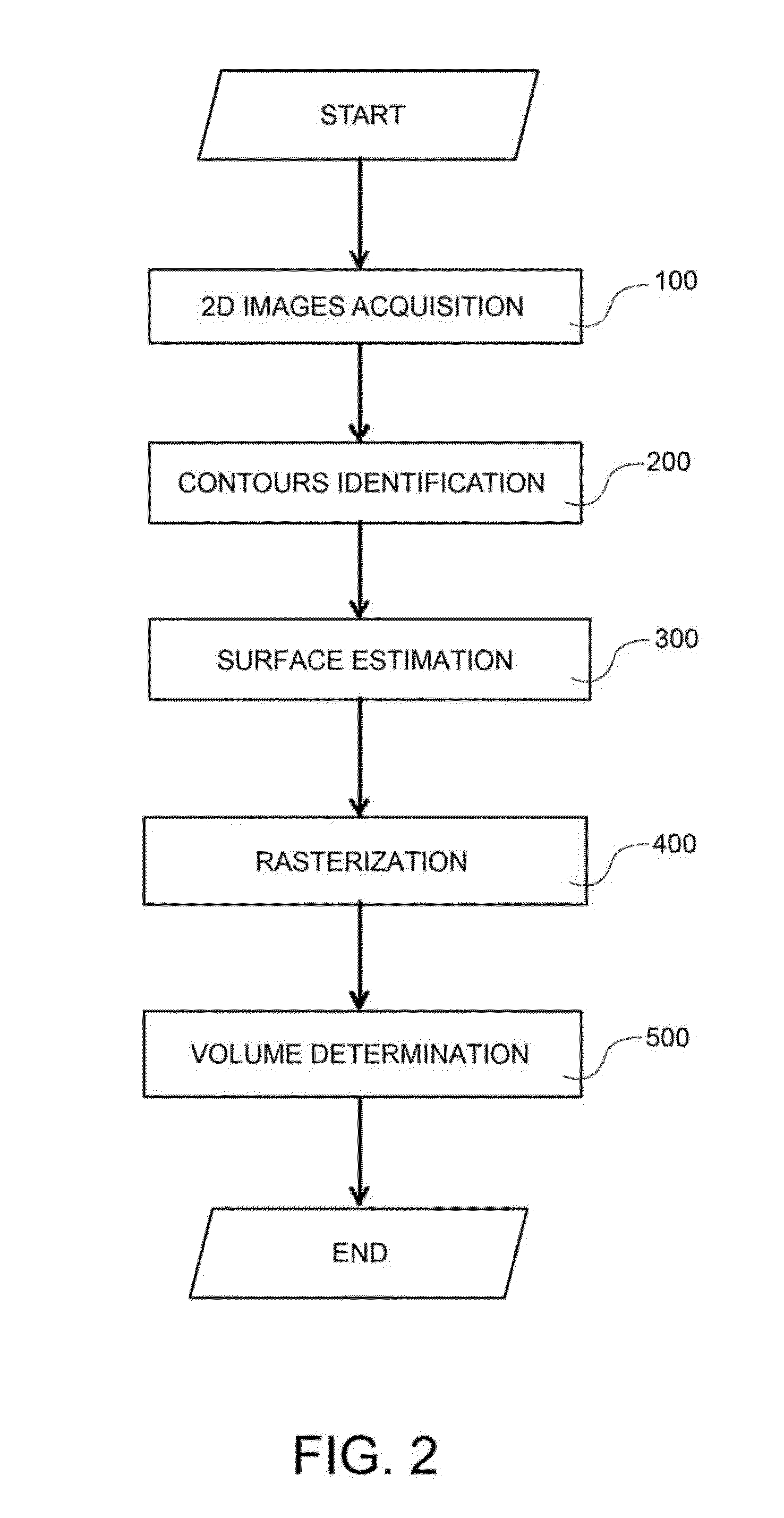
Methods and systems for determining the volume of epicardial fat from volumetric images
InactiveUS20130190592A1Easy to useDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementVoxelSeries expansion
Methods and systems are provided for determining the volume of epicardial fat of a heart, which include acquiring a plurality of volumetric image data representing the heart; morphologically characterizing a volume of interest represented by the volumetric image data, including identifying a predetermined number of reference contours of the heart; estimating the epicardial surface, Σ, according to a three-dimensional series expansion of vector spherical harmonic functions based on the reference contours; and determining the volume of epicardial fat based on the voxels which are located inside the estimated epicardial surface, Σ, and which have a grey level within a predetermined range, characteristic of fatty tissue.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Random reactive optimization method for power distribution network including wind power plant
ActiveCN103401248AStochastic Power Flow AccurateReduce installed capacitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationSeries expansionElectric field
The invention provides a random reactive optimization method for a power distribution network including a wind power plant, which is used for eliminating adverse effects caused by various undetermined factors of the power distribution network and keeping the power distribution network run in a qualified voltage state. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly, establishing a probability calculation model considering various random factors; secondly, establishing determining trend including a fan equivalent circuit, establishing a random trend model for the power distribution network including the wind power plant in combination with a semi invariant and Gram-Charlier series expansion method, and solving the voltage of each node and the probability distribution of reactive output of a generator; and lastly, establishing a reactive optimization model including the wind power plant by taking the voltage of each node and the probability distribution of the reactive output of the generator as the chance constraints of reactive optimization, taking the reactive output limit of the wind power plant as a constraint condition and taking a minimum active consumption expected value as a target function, and solving by using a genetic algorithm.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for calculating probability power flow of power system containing wind farm
InactiveCN103208798AEliminate errorsImprove calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsNormal densityPower flow
The invention discloses a method for calculating the probability power flow of a power system containing a wind farm. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, calculating the power of the wind farm and probability distribution of load power; 2, calculating deterministic power flow of the power system containing the wind farm by a Newton method, and solving a sensitivity matrix S0; 3, calculating the each-order cumulant of each node injection vector; 4, solving the each-order cumulant of a state variable according to the each-order cumulant of the injection vector; and 5, solving a probability density function and a cumulative distribution function according to Gram-Charlier series expansion. By the method, errors caused by solving through a cumulant method when the wind farm is processed as a simplified PQ model with a constant power factor can be effectively reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Dynamical probability load flow calculation method with consideration of wind power integration
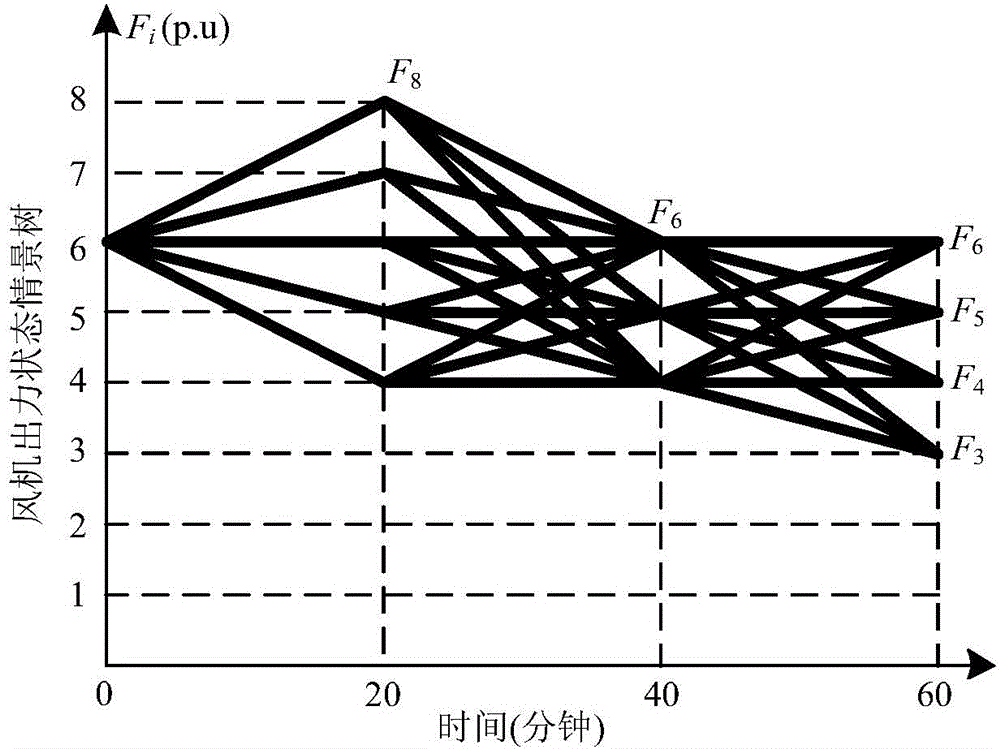
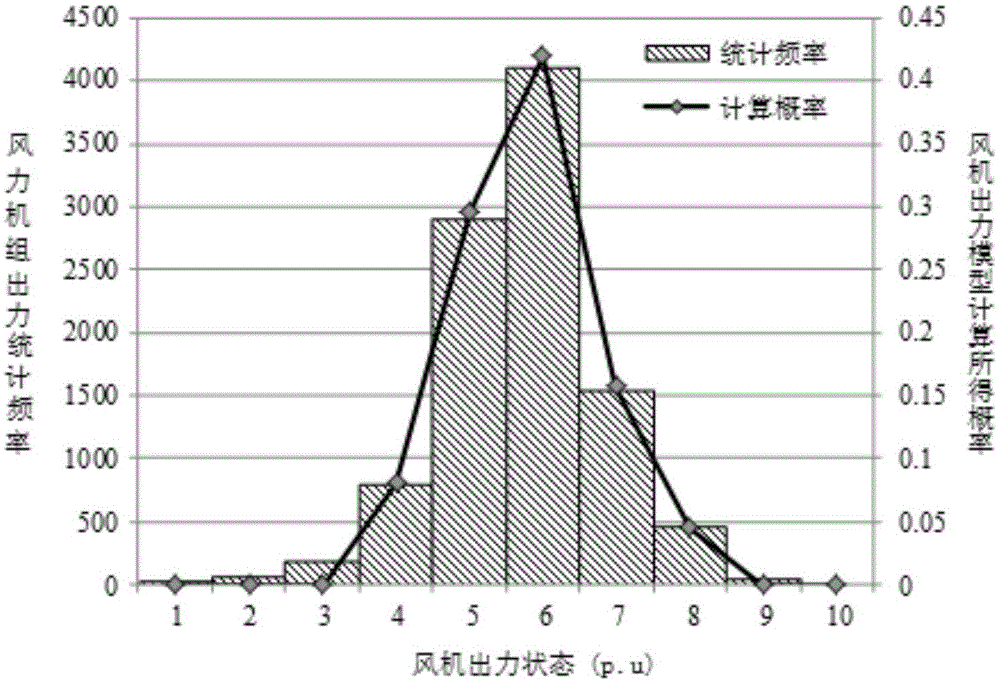
InactiveCN103986156AAccurately describe the law of changeEffectively reflect time series volatilitySpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsElectricityMarkov chain
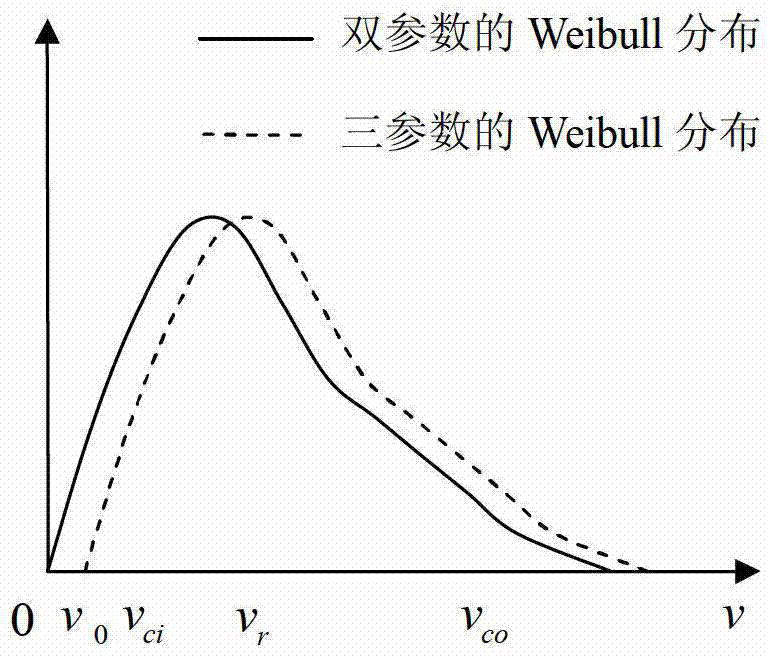
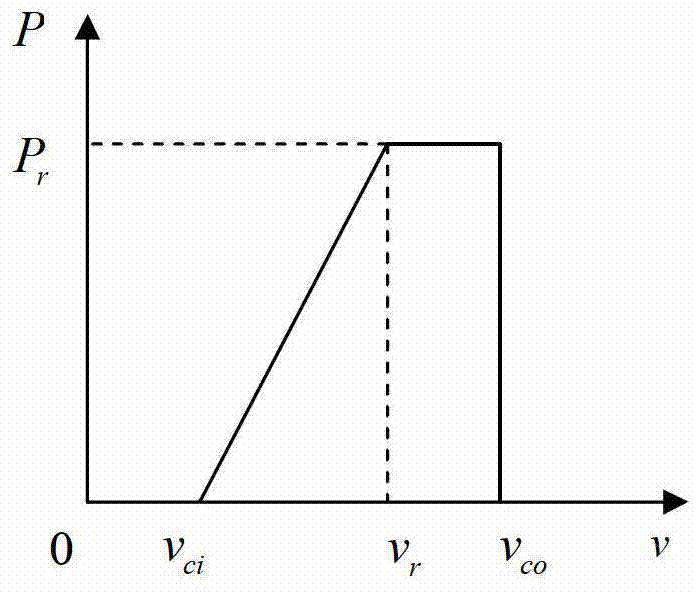
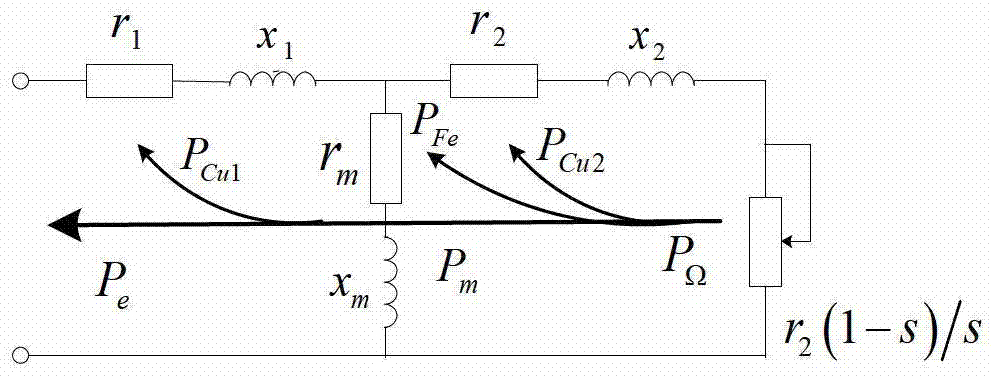
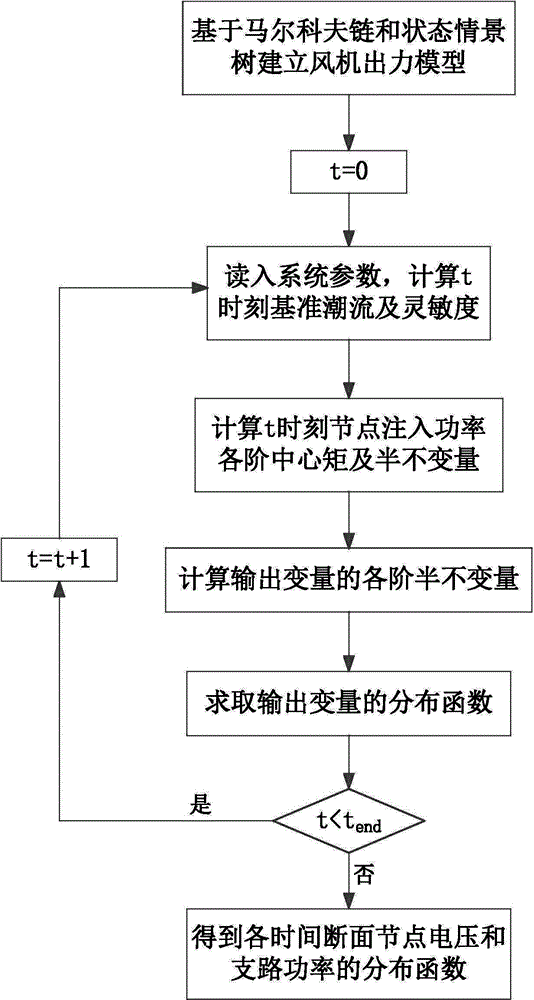
The invention discloses a dynamical probability load flow calculation method with consideration of wind power integration. A draught-fan output model is established on the basis of the Markov chain and a state scenario tree, draught-fan output historical data are normalized, states are partitioned, and a state transfer matrix is obtained according to the change relations between the states; according to the draught-fan output state at the current moment and the state transfer matrix, the most possible states of the draught-fan output at the next moment and the probabilities of the most possible states are predicted, repeated analysis is conducted, and the state scenario tree in a future period is generated; multi-period and multi-state distribution of the draught-fan output is obtained through the state scenario tree; probability load flow calculation based on the semi-invariant method and improved Von-Mises series expansion is conducted on each time section. Calculation results can reflect the relations between probability load flows of a power grid in different time periods, probability distribution of the draught-fan output states can be reasonably predicted, the change rule of the draught-fan output states is accurately described, and the method is used for comprehensively assessing safety and stability of a power system achieving wind power integration.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
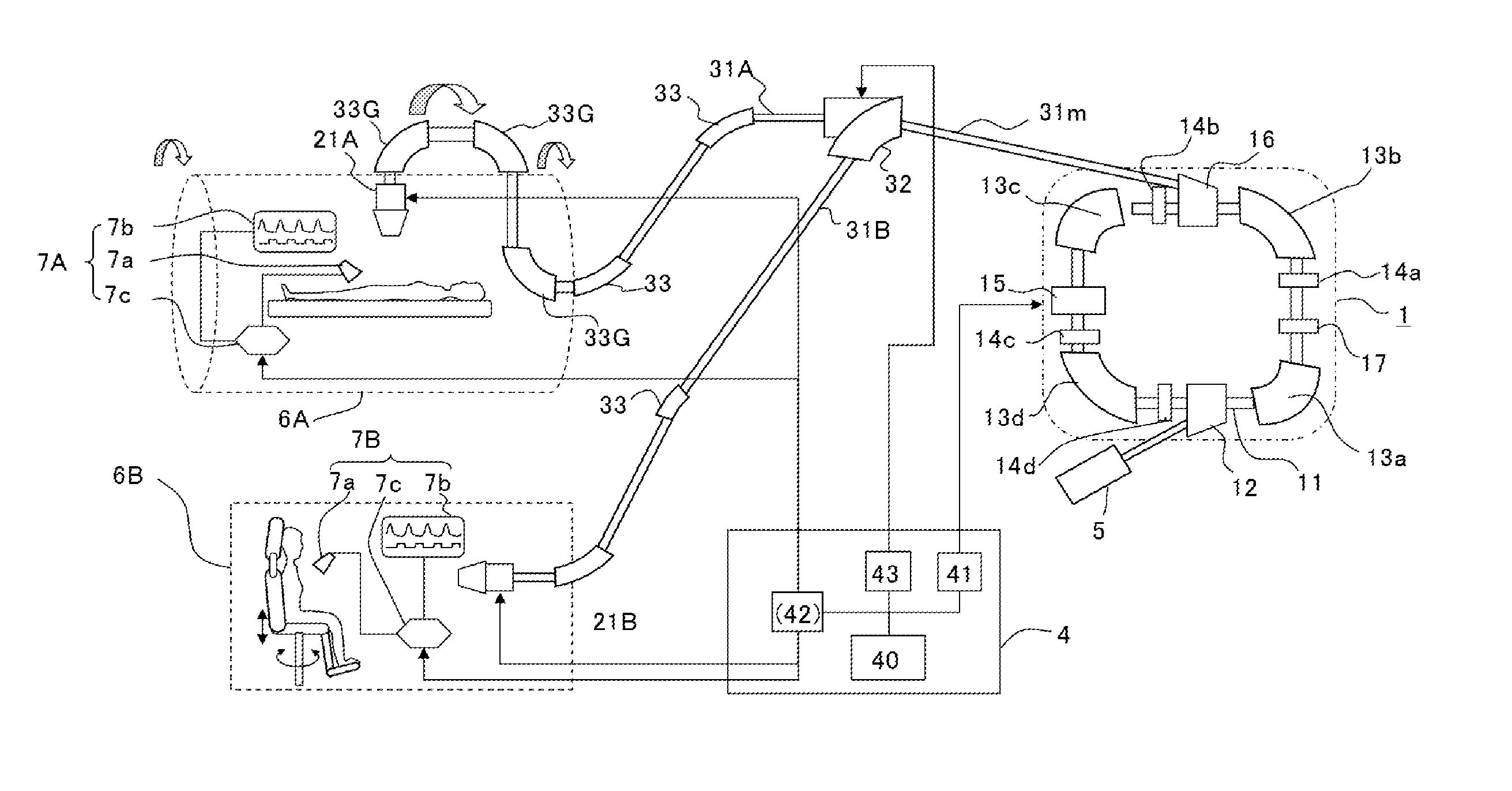
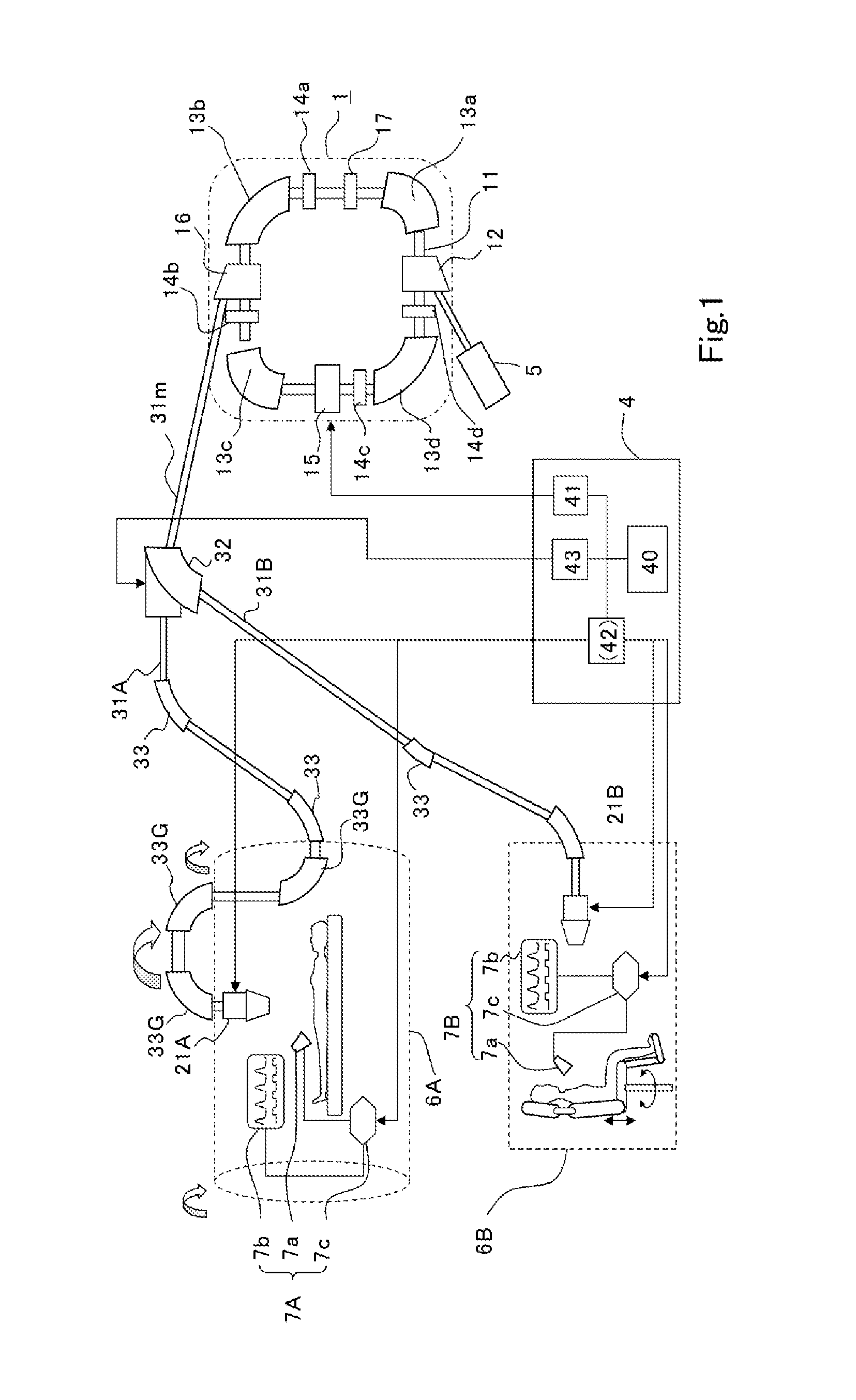
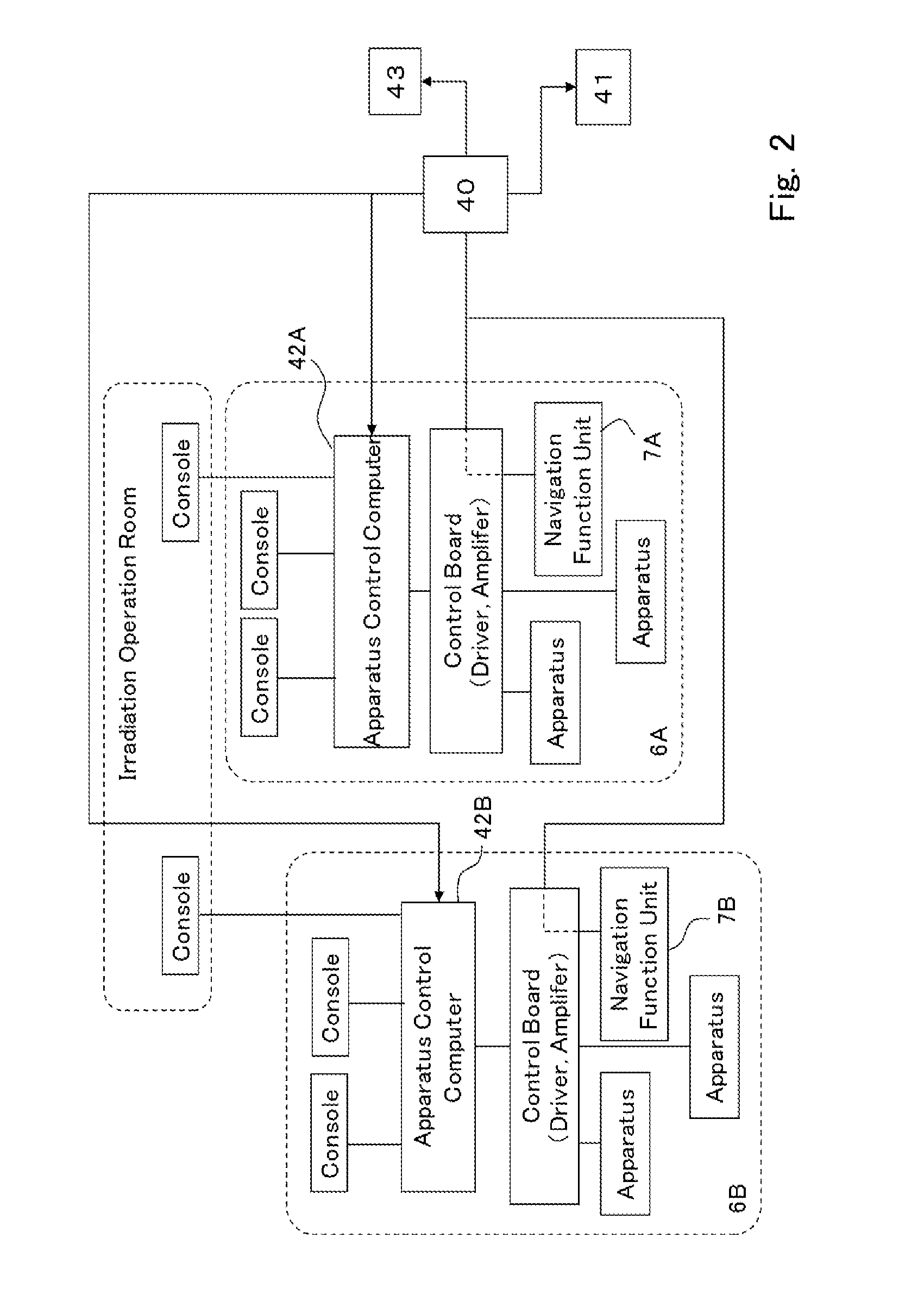
Respiratory induction apparatus, respiratory induction program, and particle beam therapy system
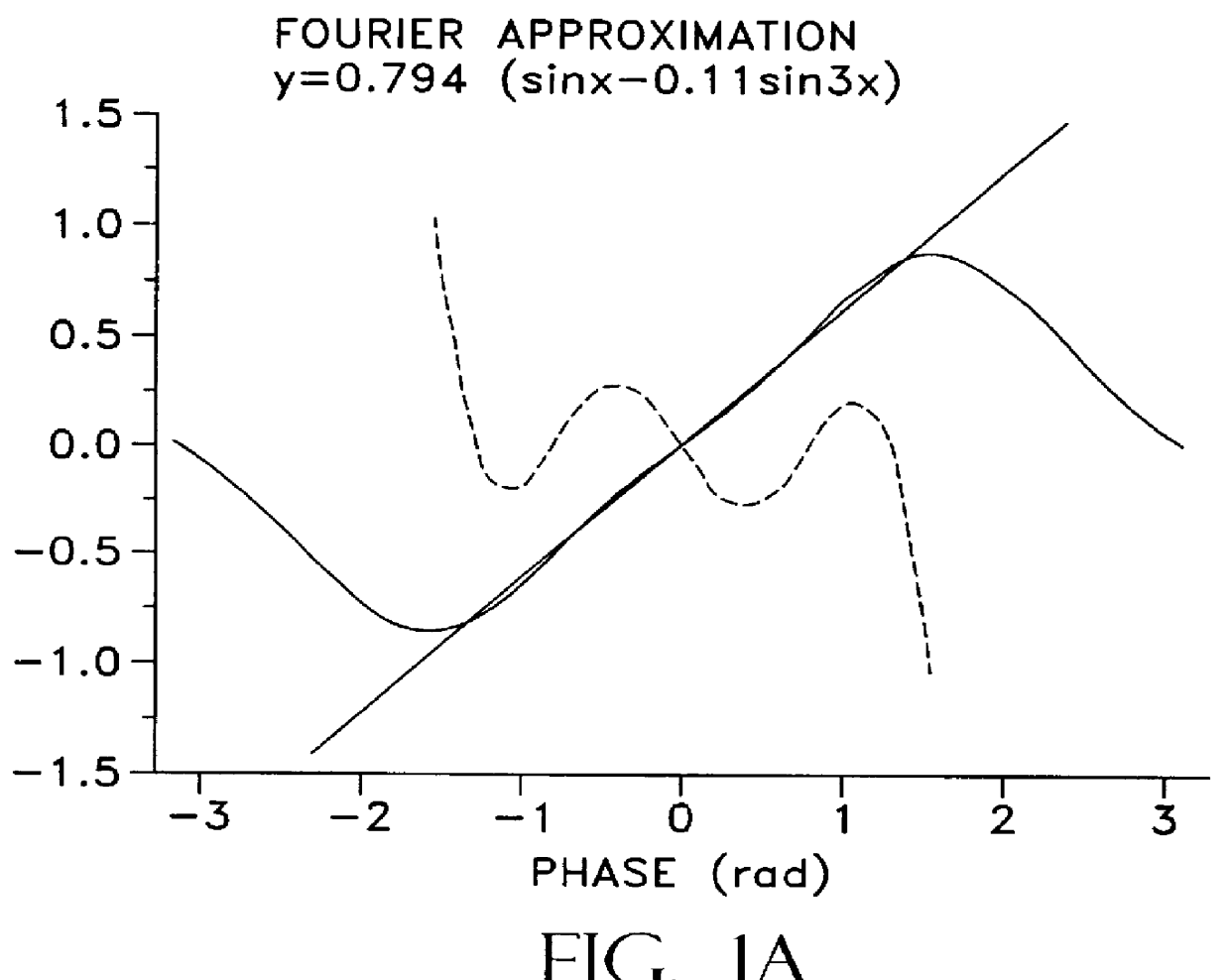
The objective is to obtain a respiratory induction apparatus and a particle beam therapy system in which respiration can appropriately be induced by accurately evaluating the respiration. There are provided a respiratory induction control unit (7cC) that generates a desired respiratory signal (Rtj(t)) for respiratory induction; a real respiration measurement unit (7a) that outputs a real respiratory signal (Rrl(t)) obtained by measuring real respiration of a patient; and a respiration evaluation unit (7cE) in which by, as a unit, utilizing data of a single period (Tres) of the desired respiratory signal (Rtj(t)), there is calculated a pair of coefficients (a1 and b1), of trigonometric functions, which correspond to the 1st-order terms by means of Fourier series expansion of data of the desired respiratory signal (Rtj(t)) and data of the real respiratory signal (Rrl(t)), which is acquired in synchronization with the data of the desired respiratory signal (Rtj(t)), and there are performed comparisons between the respective gains (Gtj and Grl) and between the respective phases (φtj and φrl), which are obtained from the coefficients (a1 and b1), so that there is evaluated a misalignment of the real respiration from the desired respiratory signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
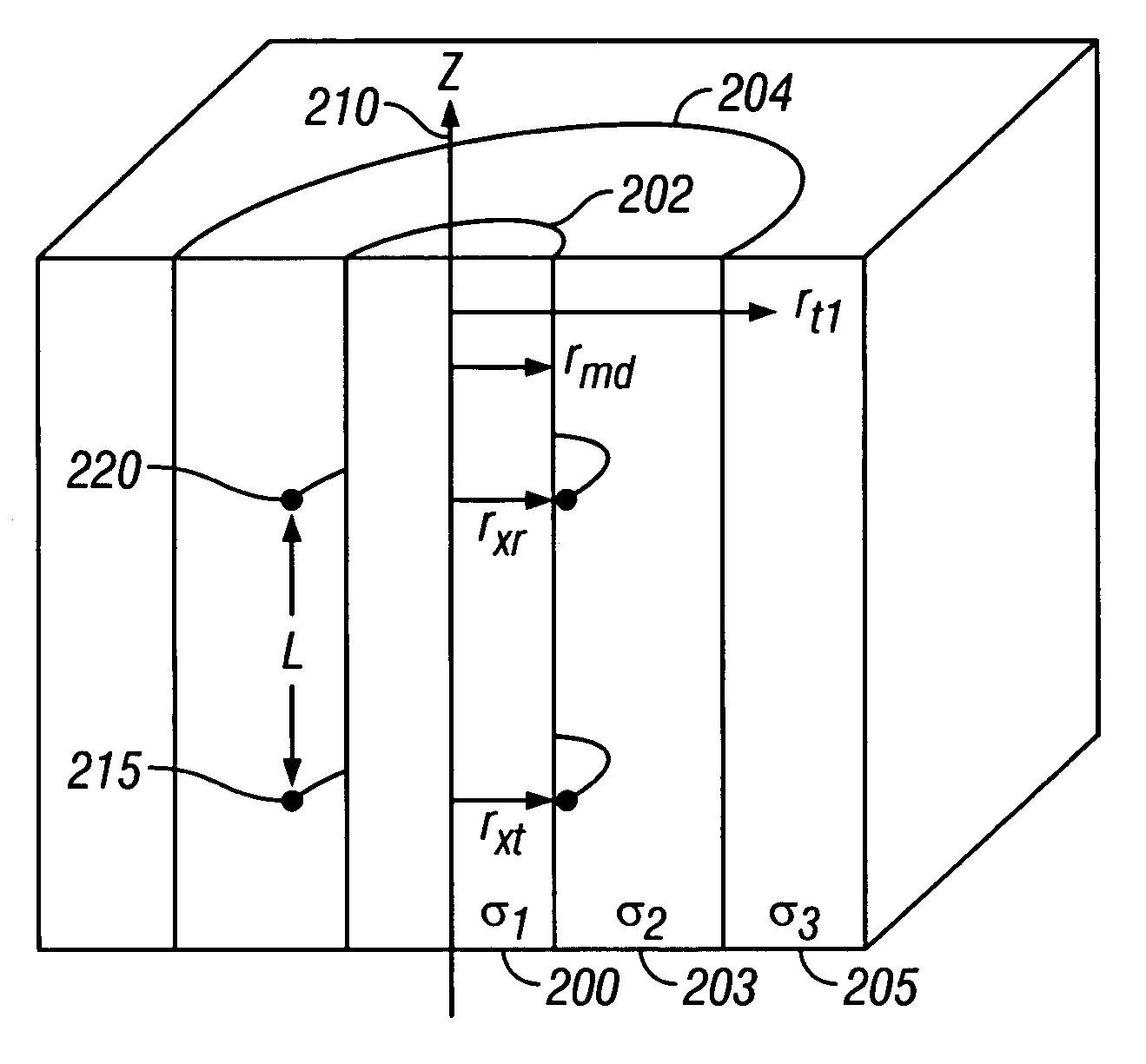
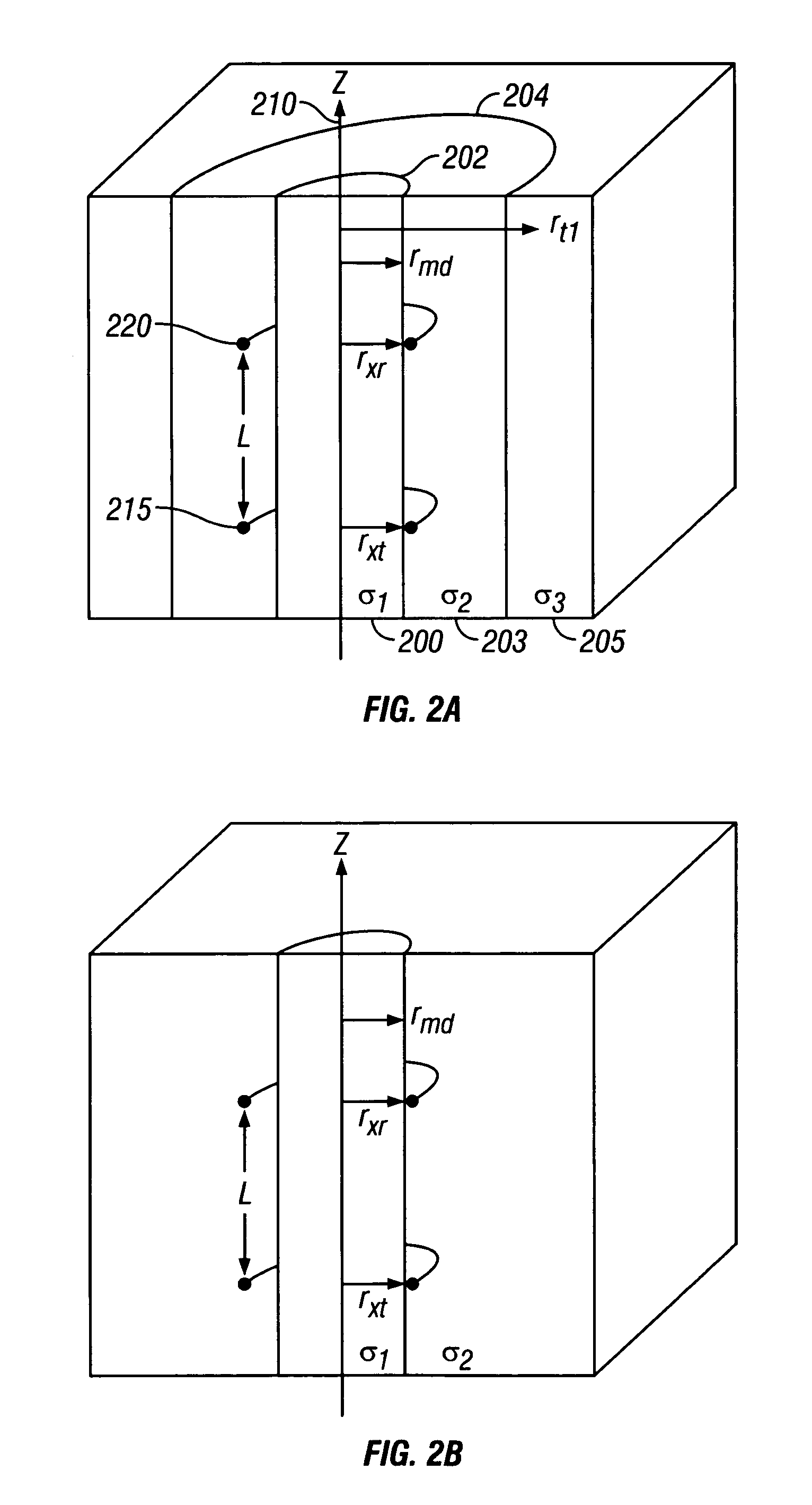
Deep resistivity transient method for MWD applications using asymptotic filtering
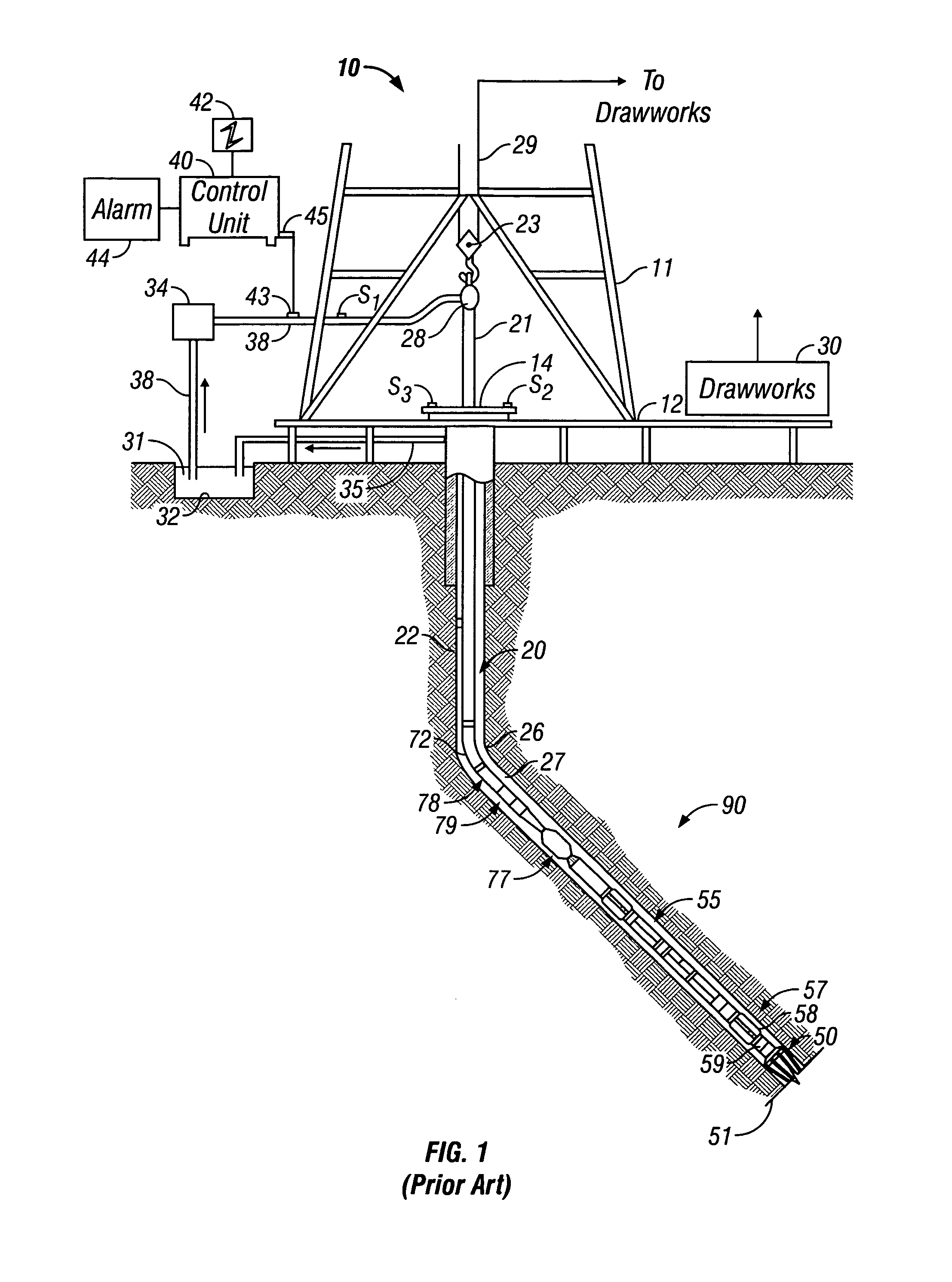
ActiveUS7027922B2Reduce impactExclude influenceElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveySeries expansionEnvironmental geology
A method is discussed of obtaining a parameter of interest of an earth formation, typically a formation resistivity or a distance to a bed boundary, in conditions where an induction tool is using having a body with finite, non-zero conductivity. The method substantially removes the effects of the conductivity of the tool from the signal received from the earth formation. A Taylor series expansion in one half of odd integer powers of time is used to represent the received signal. At least one leading term of the Taylor series expansion can be subtracted from the second signal. A filtering operation is applied to the second signal to remove the terms most dominated by pipe effects. Typical filtering operations can be a differential filtering operation or an integral filtering operation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
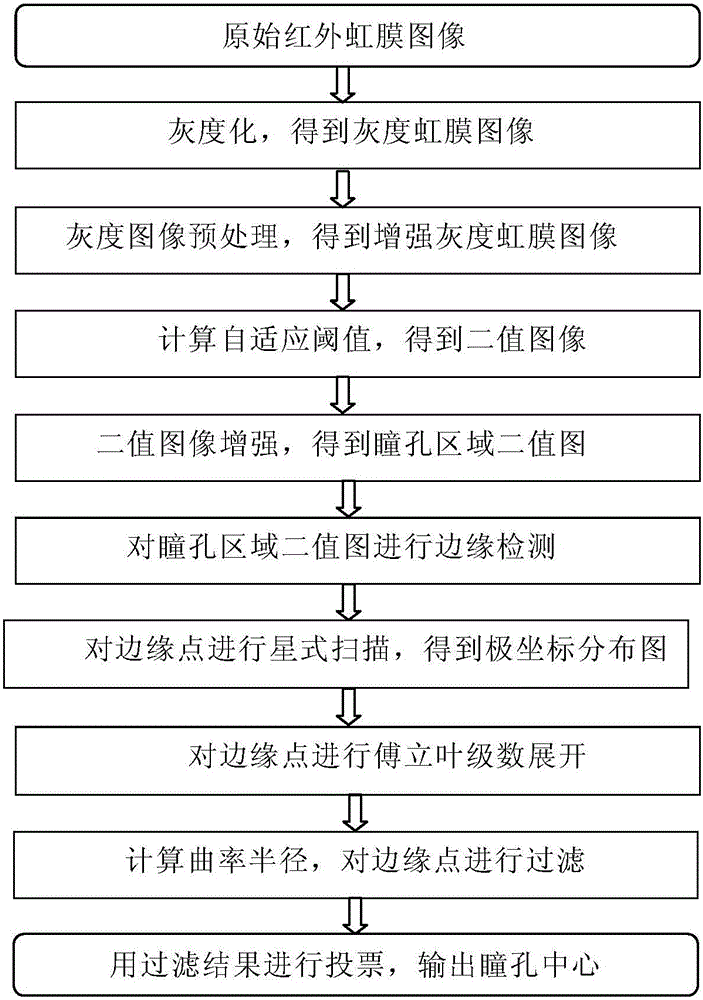
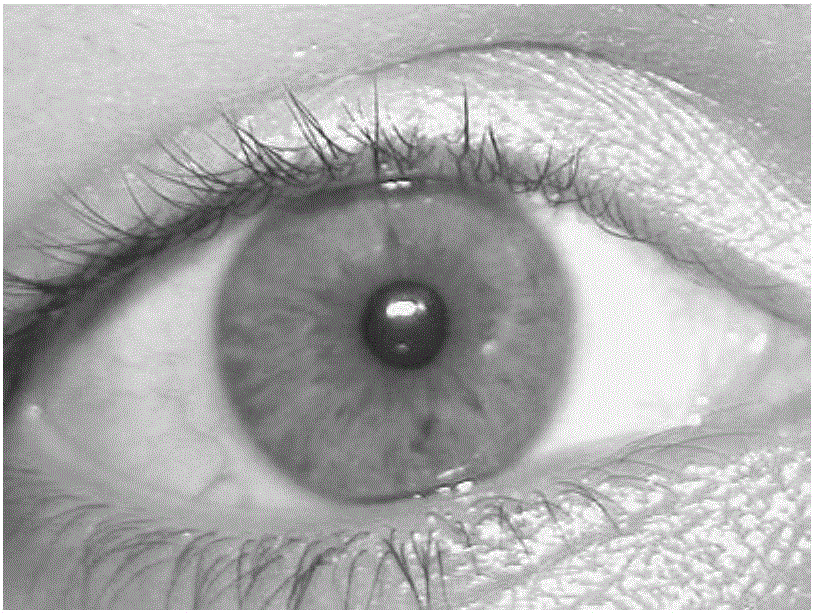
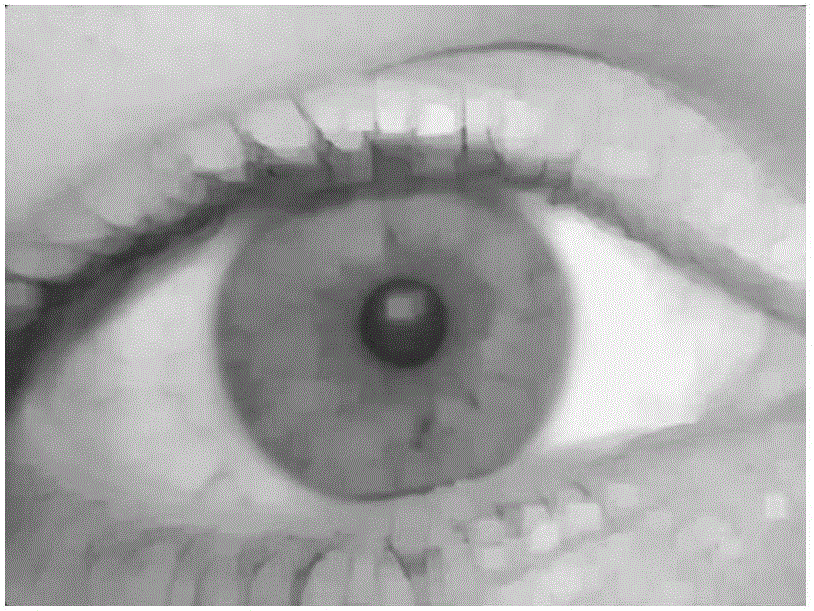
Pupil center positioning method for iris recognition
The invention relates to a pupil center positioning method for iris recognition. The method includes the following steps that: (1) graying processing is carried out on an original iris image; (2) a gray image is preprocessed; (3) binarization processing is carried out on the gray iris image; (4) a binary image is preprocessed; (5) edge detection is carried out on the binary image; (6) star type scanning is carried out on edge points, so that a polar coordinate distribution diagram is obtained; (7) Fourier series expansion is carried out; (8) the radius of curvature of the edge of the image is calculated, and the edge points are filtered; and (9) filtering results are voted, and a pupil center or location failure is outputted. According to the pupil center positioning method for iris recognition of the invention adopted, according to the gray and shape characteristics of a pupil in the infrared iris image, binarization and edge shape analysis are carried out, and problems in pupil center determination can be solved.
Owner:北京极创未来科技有限公司
Method and device for controlling fast periodic motion
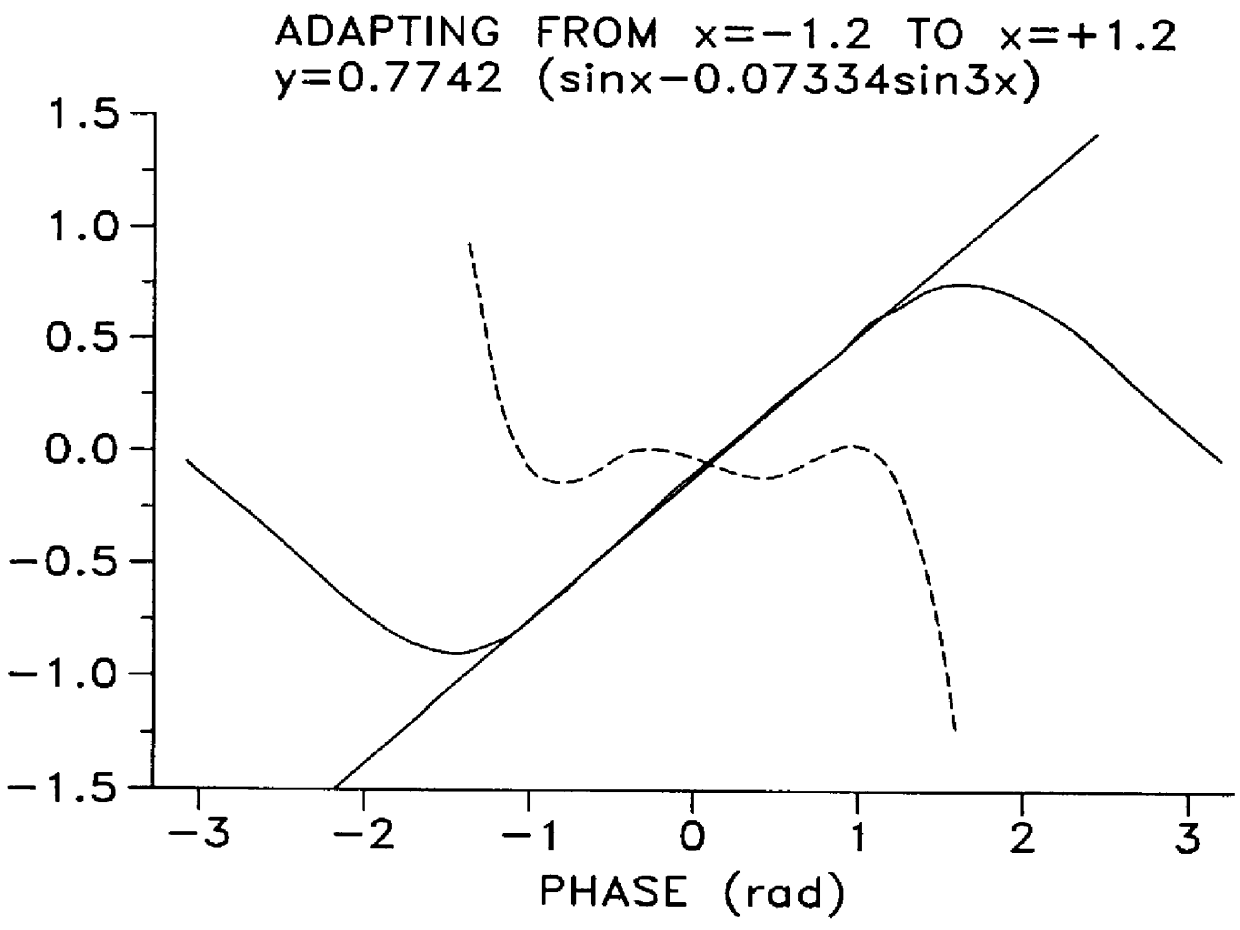
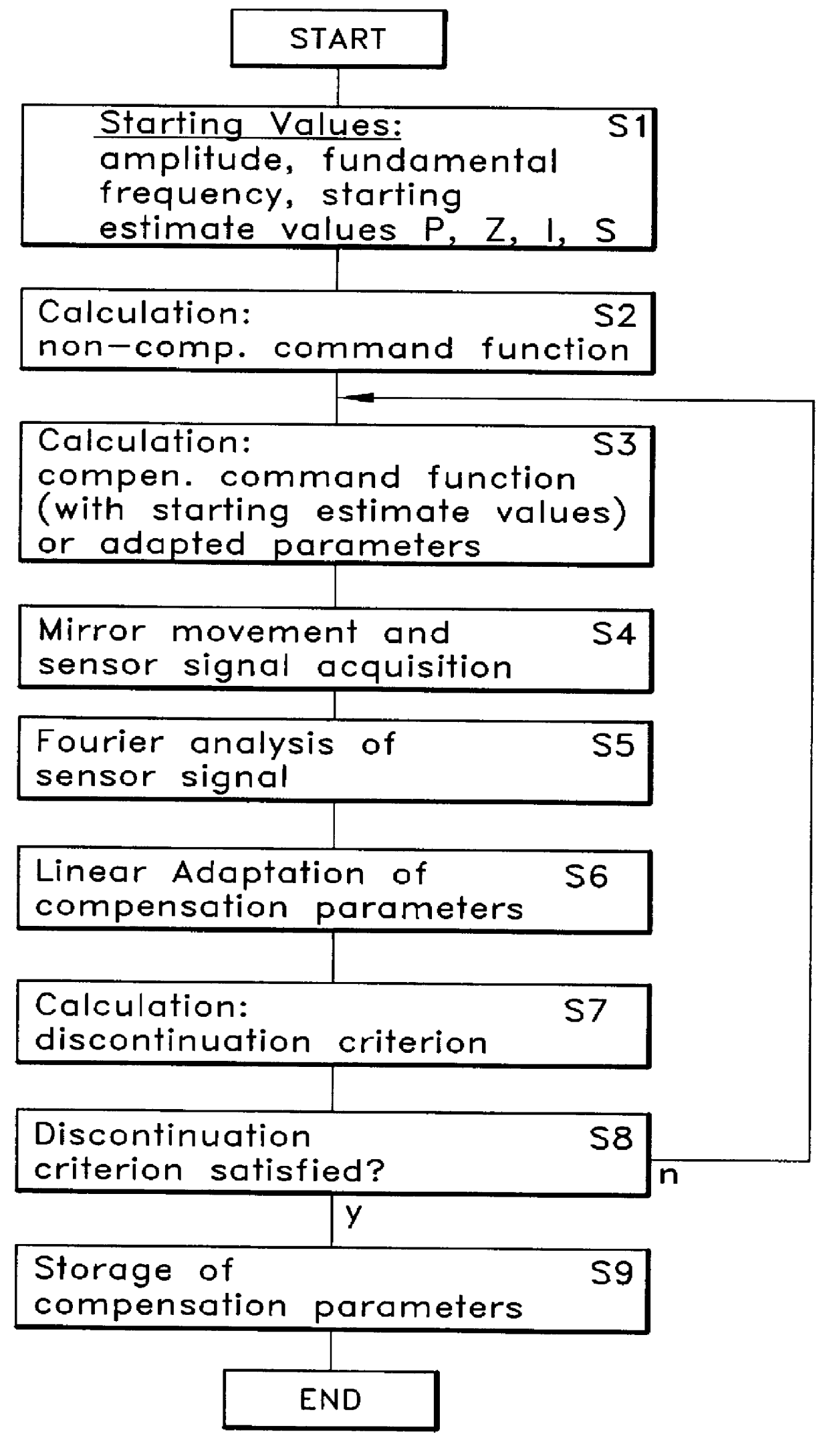
InactiveUS6040567AImprove accuracyIncrease frequencyMaterial analysis by optical meansCounting objects on conveyorsClosed loopSeries expansion
A method for moving an object such that a location coordinate of the object is adapted at least in one periodic sub-interval to a aim function y<<(t) comprises parameterizing the aim function as a series expansion in accordance with determining n command parameters a1, a2, . . . an, for which an optimization criterion is satisfied in the periodic sub-interval for a command function and signalling the object such that the location coordinate thereof corresponds to the command function. In a closed loop method for setting a controlled variable for a driver function of an engine with amplitude attenuating and phase delay the driver function is formed with amplitude / phase compensation parameters.
Owner:ESS TECH INT INC
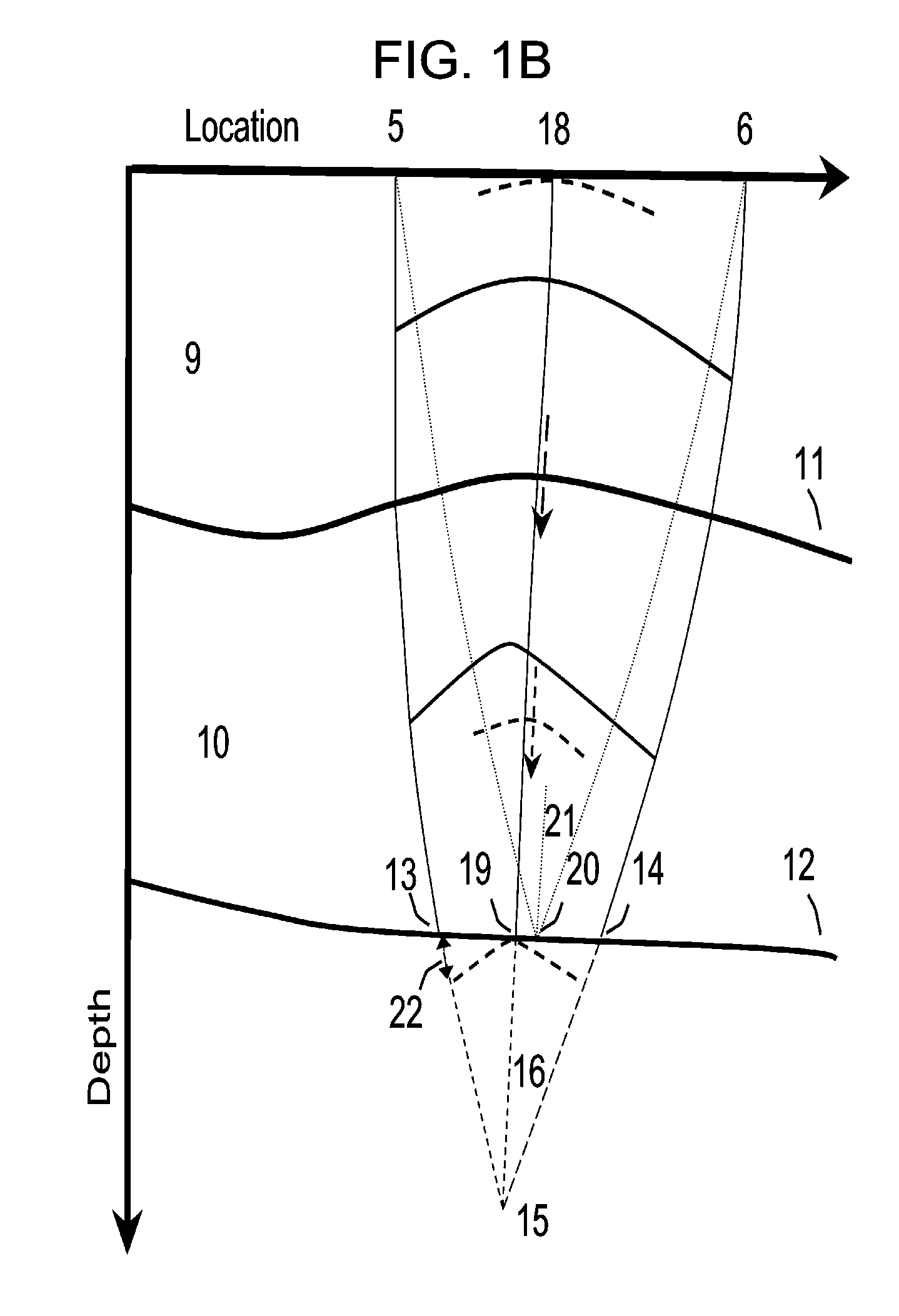
Determination of depth moveout and of residual radii of curvature in the common angle domain
InactiveUS20100118652A1Reduce workloadSeismic signal processingSeries expansionSignal-to-noise ratio
A method is disclosed for processing seismic data. The method includes prestack depth migrating seismic measurements to compute common angle domain image gathers with an initial depth model. Residual moveout analysis is performed in the common angle domain, moveout corrections are derived in terms of the residual radii of curvature at zero reflection angle. Corrections for larger reflection angles are obtained from separate analyses for the coefficients of suitable series expansions. The residual radii of curvature at zero reflection angle can be used to improve the signal to noise ratio of the migrated data and to assess or improve the velocity model used for the prestack depth migration.
Owner:SCHNEIDER JORG FRIEDRICH
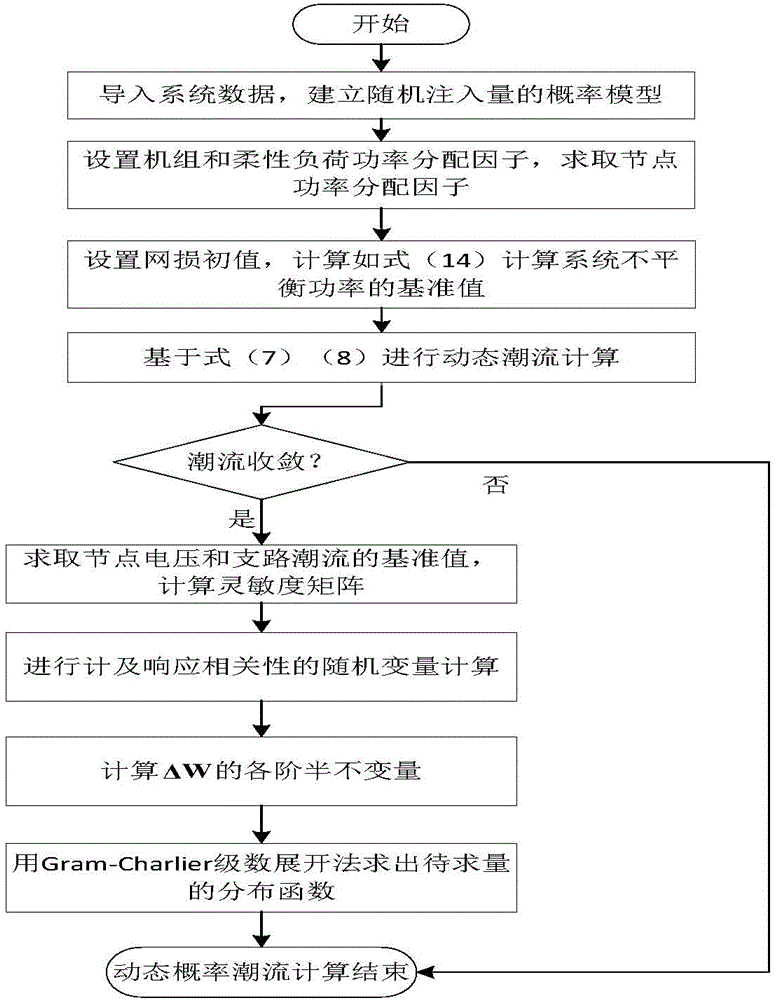
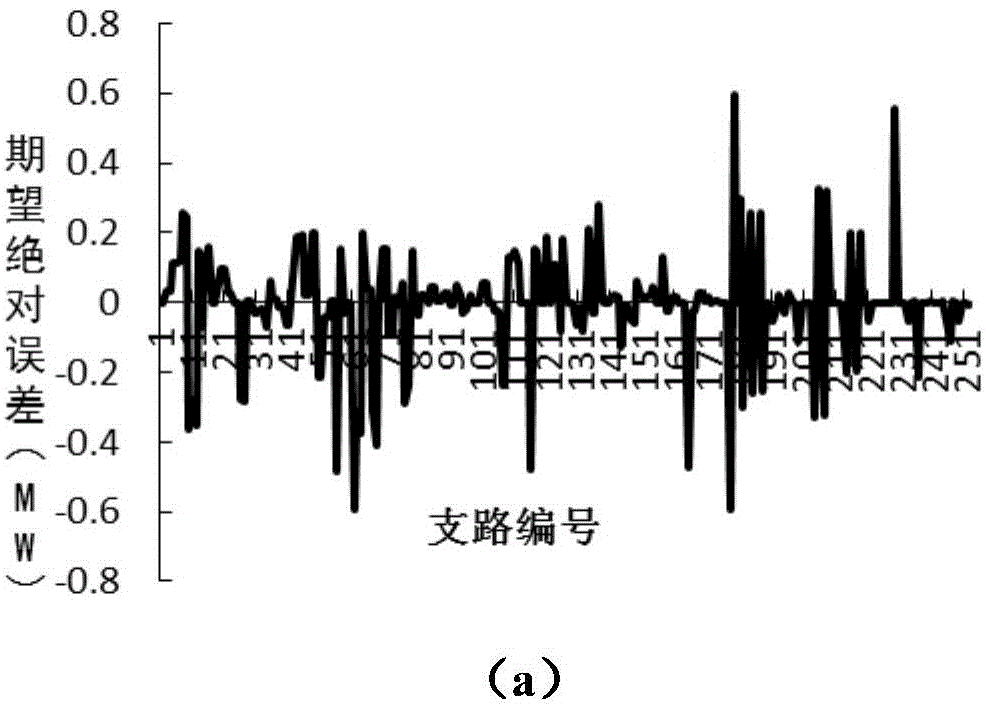
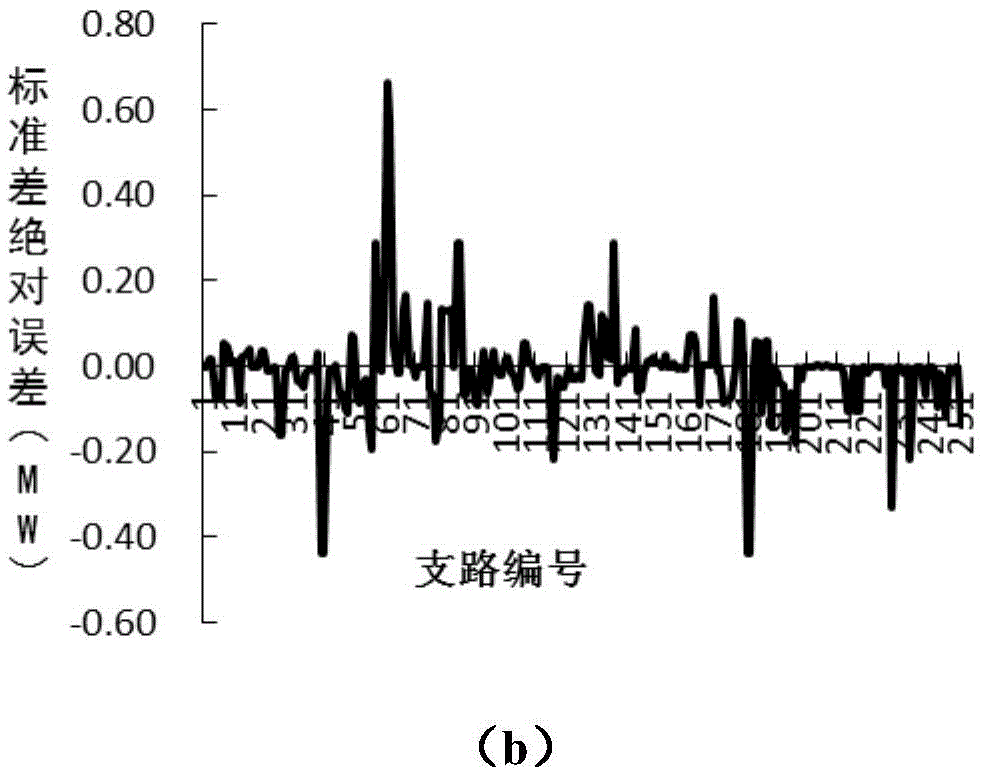
Dynamic probability load flow calculation method taking response correlation into account
ActiveCN104410069AFast convergenceComplex mathematical operationsAc network circuit arrangementsInjection volumeProbit model
The invention relates to a dynamic probability load flow calculation method taking response correlation into account. The method comprises the following steps: (1) creating a probability model of dynamic random injection volume; (2) performing optimized analysis and calculation on imbalance power of a system, creating a dynamic load flow model for reference value distribution of the imbalance power of the system, and working out node voltage and a branch load flow reference value as well as a related sensitivity matrix; (3) performing random variable calculation taking interaction correlation into account, calculating each-order semi-invariant of a random variable, and working out each-order semi-invariants of the node voltage and the branch load flow random quantity by a linearization method based on sensitivity; (4) working out a distribution function to be calculated by a Gram-Charlier series expansion method. The dynamic probability load flow calculation method has the benefits that on one hand, a distribution method for imbalance power of dynamic load flow is used for improving the convergence of random load flow based on semi-invariant when the imbalance power of the system is relatively high, and on the other hand, the response correlation of the random variable can be taken into account.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Preparation technology of phosphorus nitrogen series expansion type fire retardant
The present invention discloses a preparation process of phosphonitrogen series expanded fire-retarding agent and fire-retarding agent prepared according to said preparation process. Said preparation process includes the following steps: making polybasic alcohol be reacted with phosphorus oxychloride, making the obtained product undergo the processes of hydrolysis and solution pH value regulation, then making said product be reacted with cyanurotriamide, the described polybasic alcohol includes pentaerythritol and dipentaerythritol, then using surfactant to make surface modification treatment so as to obtain the invented fire-retarding agent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
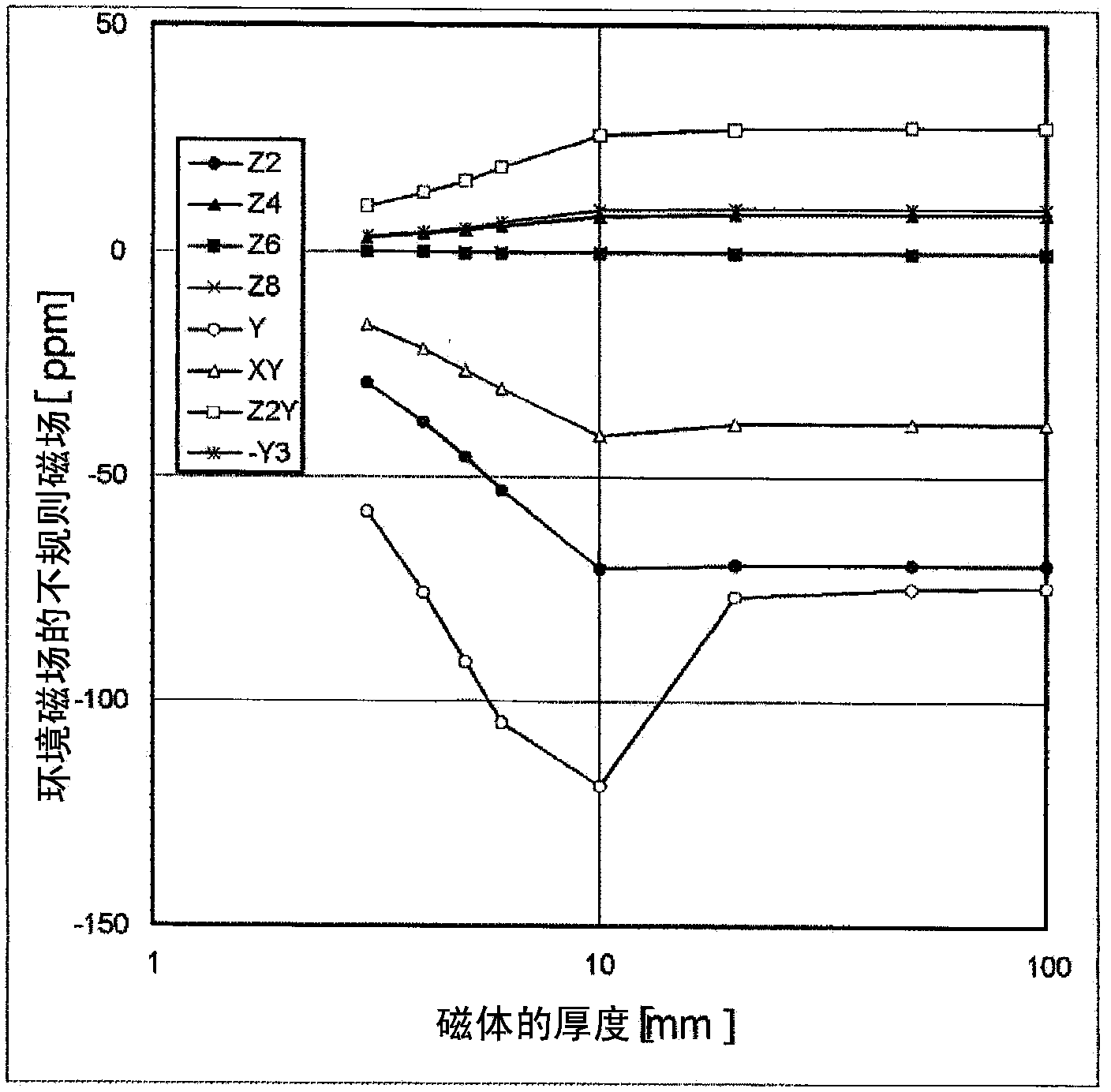
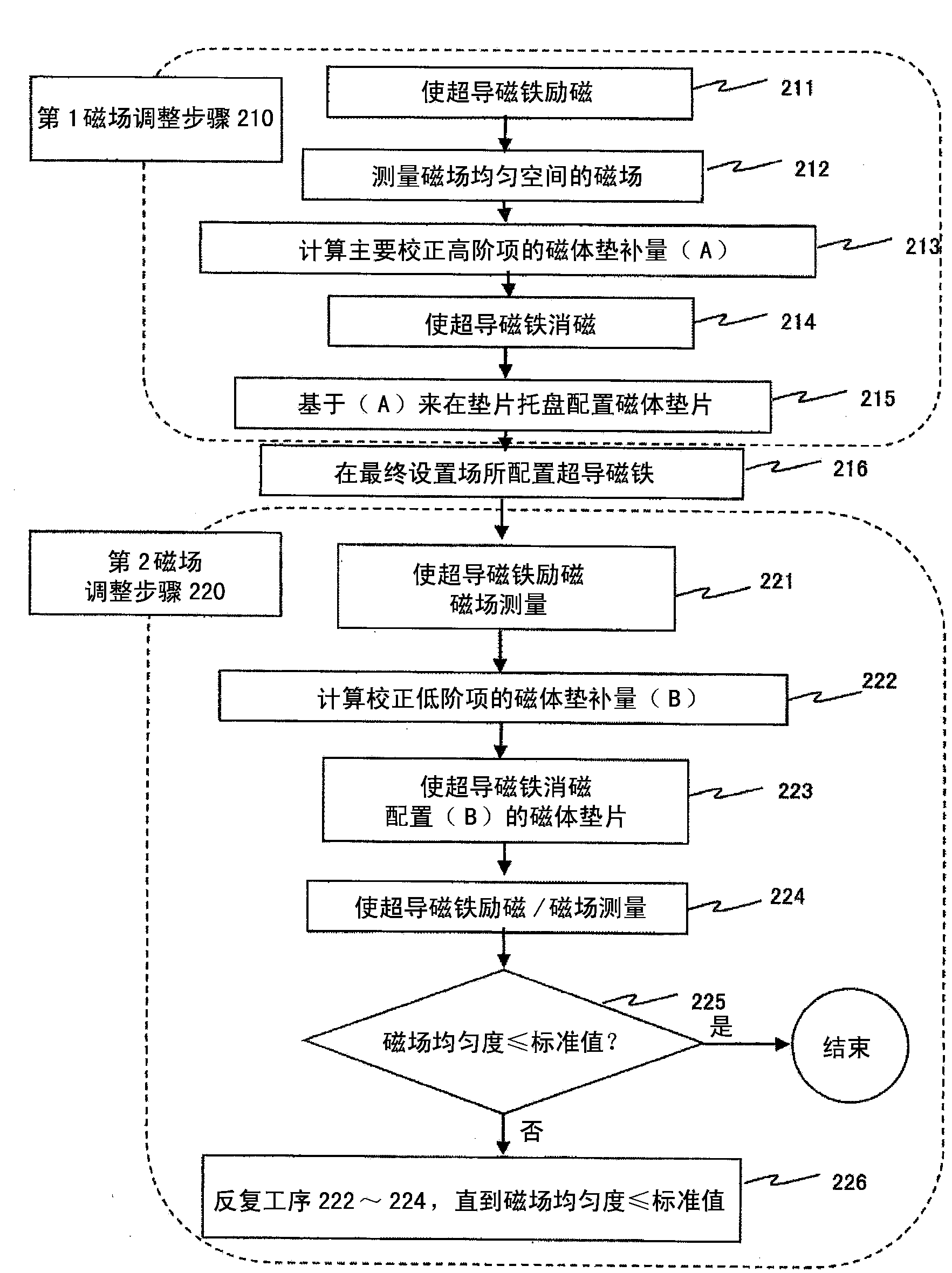
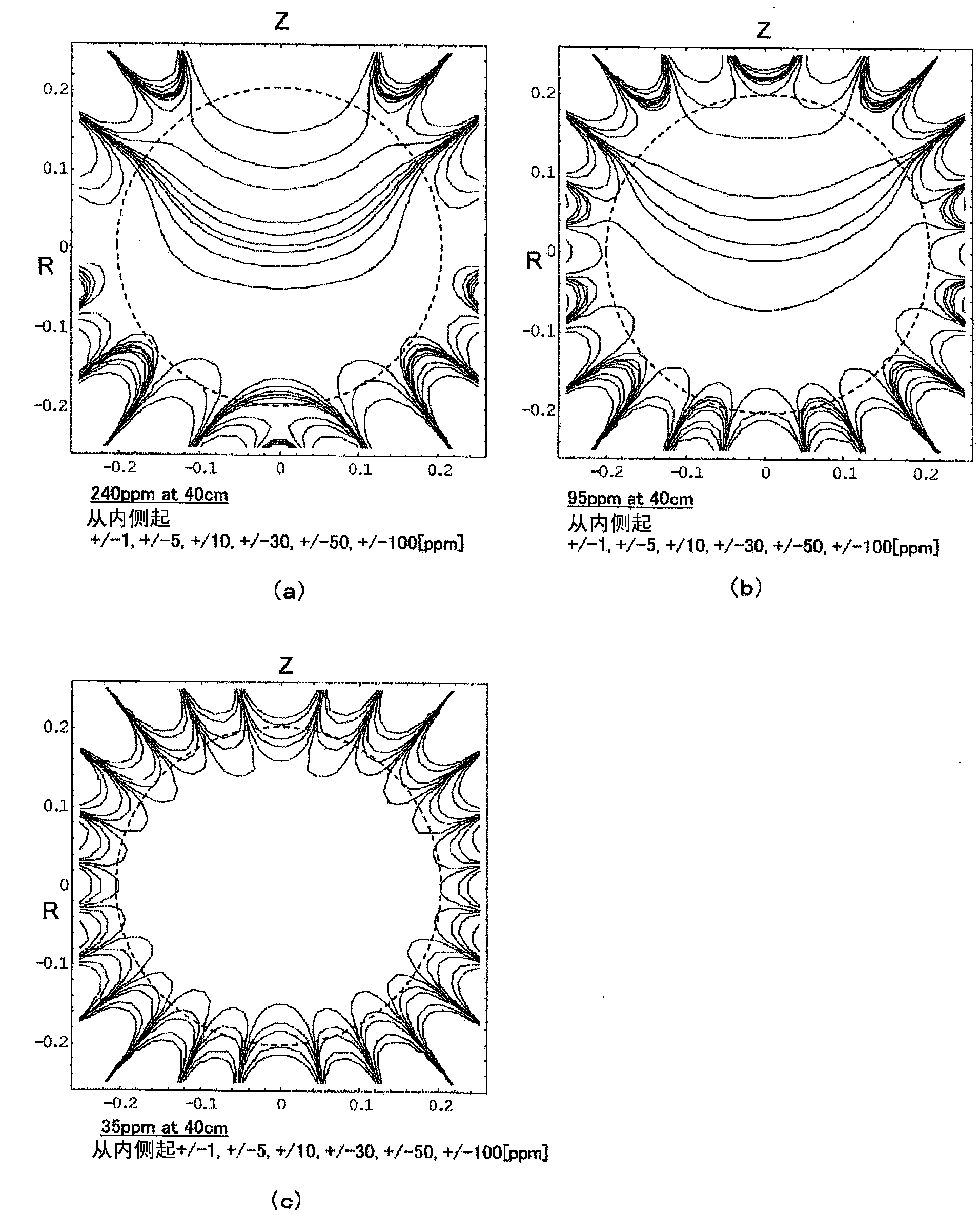
Method for adjusting static magnetic field homogeneity, static magnetic field generation device for magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic field adjustment system, and program
ActiveCN103442635AReduce processLabor savingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSeries expansionMagnet
In order to avoid the duplication of the period and cost required for magnetic field adjustment, minimize the magnetic field adjustment period in a final installation site, and achieve highly efficient magnetic field adjustment of a magnet, a method for adjusting the homogeneity of a static magnetic field generated in a measurement space by a static magnetic field generation means by disposing a magnetic field correction means for generating a corrected magnetic field with respect to the static magnetic field comprises: a step for measuring the static magnetic field generated by the static magnetic field generation means; a step for expanding the spatial distribution of the measured static magnetic field in a series; a first magnetic field adjustment step for correcting a high-order term irregular magnetic field component among irregular magnetic field components expanded in a series; and a second step for adjusting a low-order irregular magnetic field component, the second step being performed after the first adjustment step.
Owner:HITACHI HEALTHCARE MFG LTD
On-board SAR image automatic target positioning method
InactiveCN101339244AAchieve absolute positioningIncrease computing speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOn boardSeries expansion
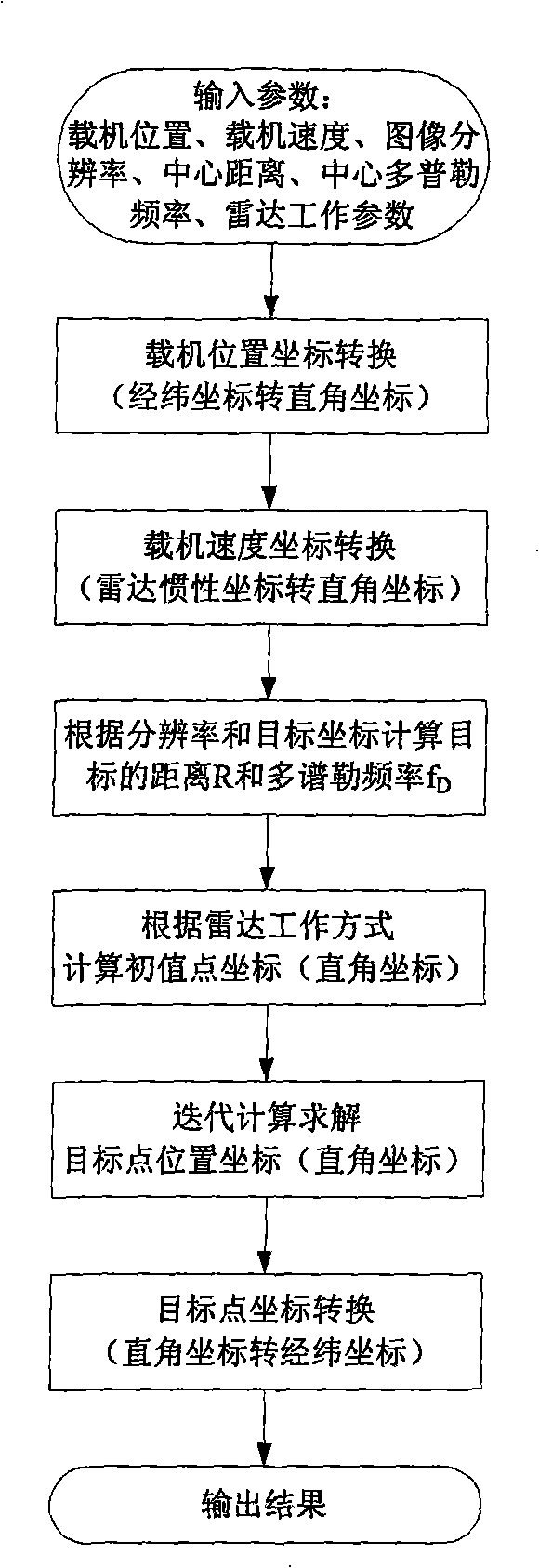
The invention relates to an airborne SAR image automatic target positioning method, which convert the coordinates of a target in the SAR image into an actual geographic coordinates of the target on the earth by utilizing the flight information (location, speed, etc.) of an aerial carrier and the SAR image information (resolution, center distance, central Doppler frequency, etc.). Based on a range-Doppler equation, the invention combines an earth model equation to carry out an target location, which not only can realize an absolute localization without a control point, but also considers the influence of the earth model on positioning accuracy; on the other hand, Taylor series expansion is used for carrying out the linearization of nonlinear equations; an iterative method is adopted to solve the equation, thus improving the positioning speed; meanwhile, the initial value point of an iterative computation is appropriately selected according to the operation mode of radar, thereby controlling a converging direction in the iteration and avoiding a target confusion. As a positioning method without the control point, the automatic target positioning method of the invention has the advantages of high accuracy and high speed, thereby being capable of carrying out a real-time processing and suitable to various airborne SAR systems.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
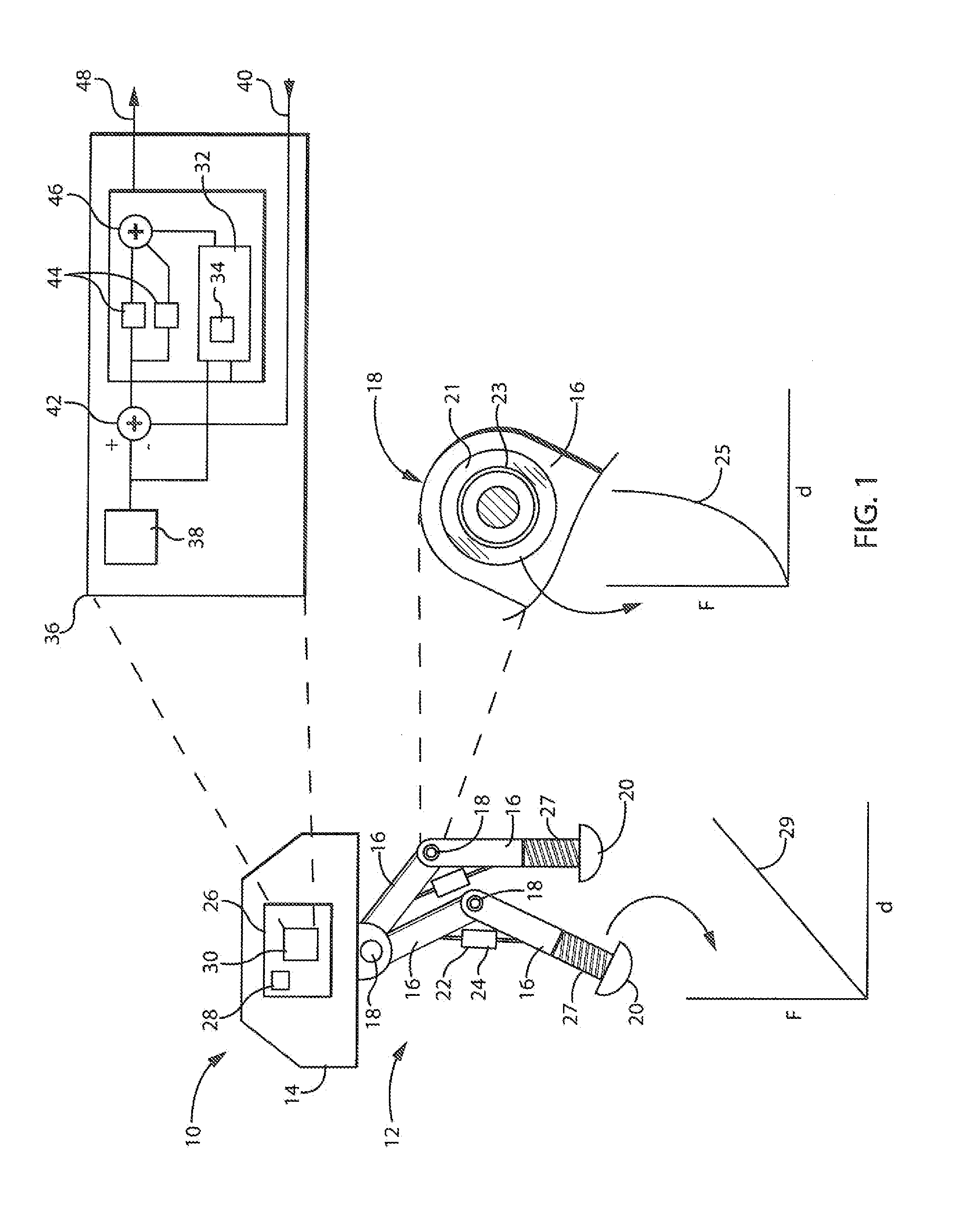
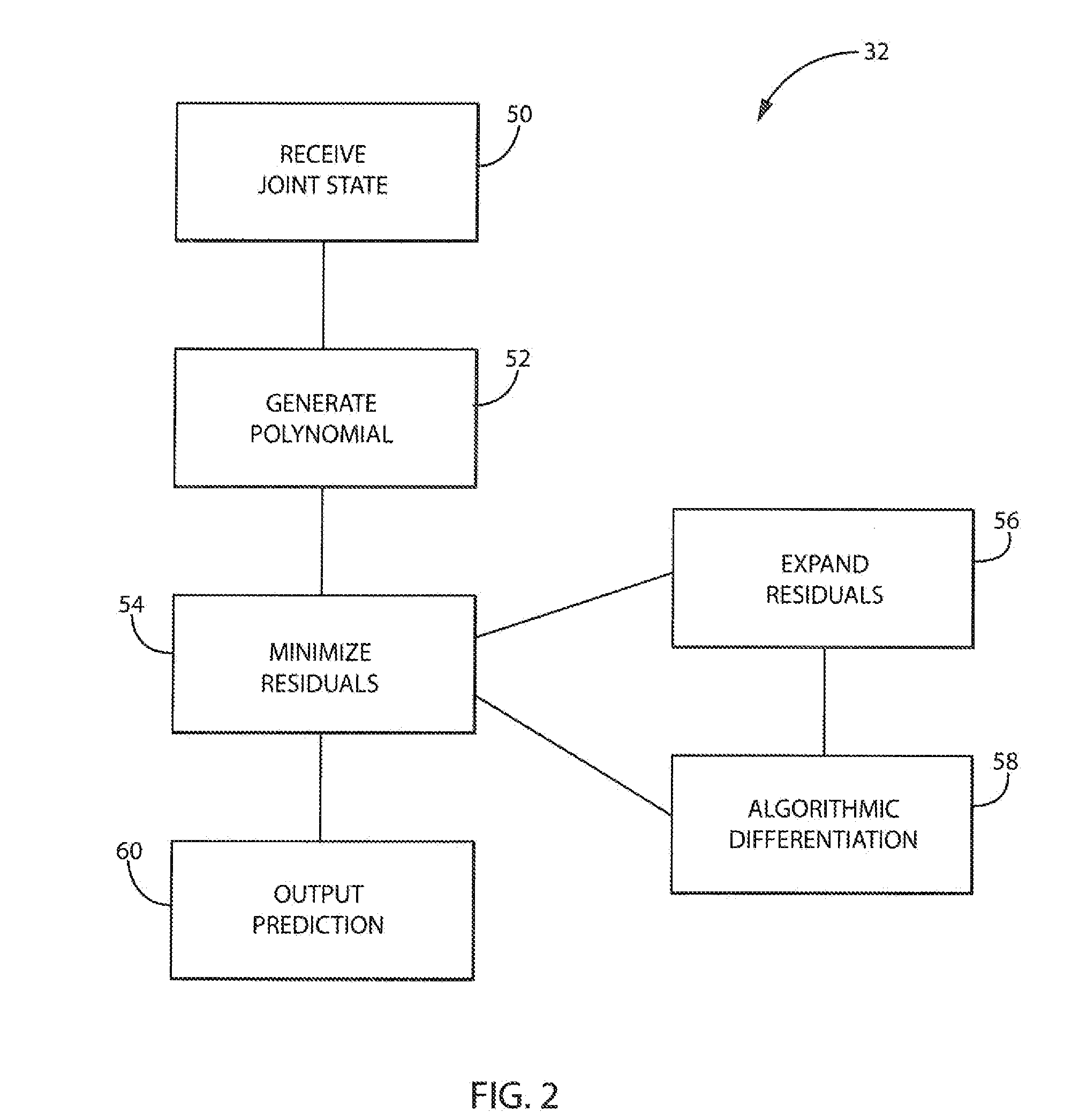
Dynamic Predictor for Articulated Mechanisms
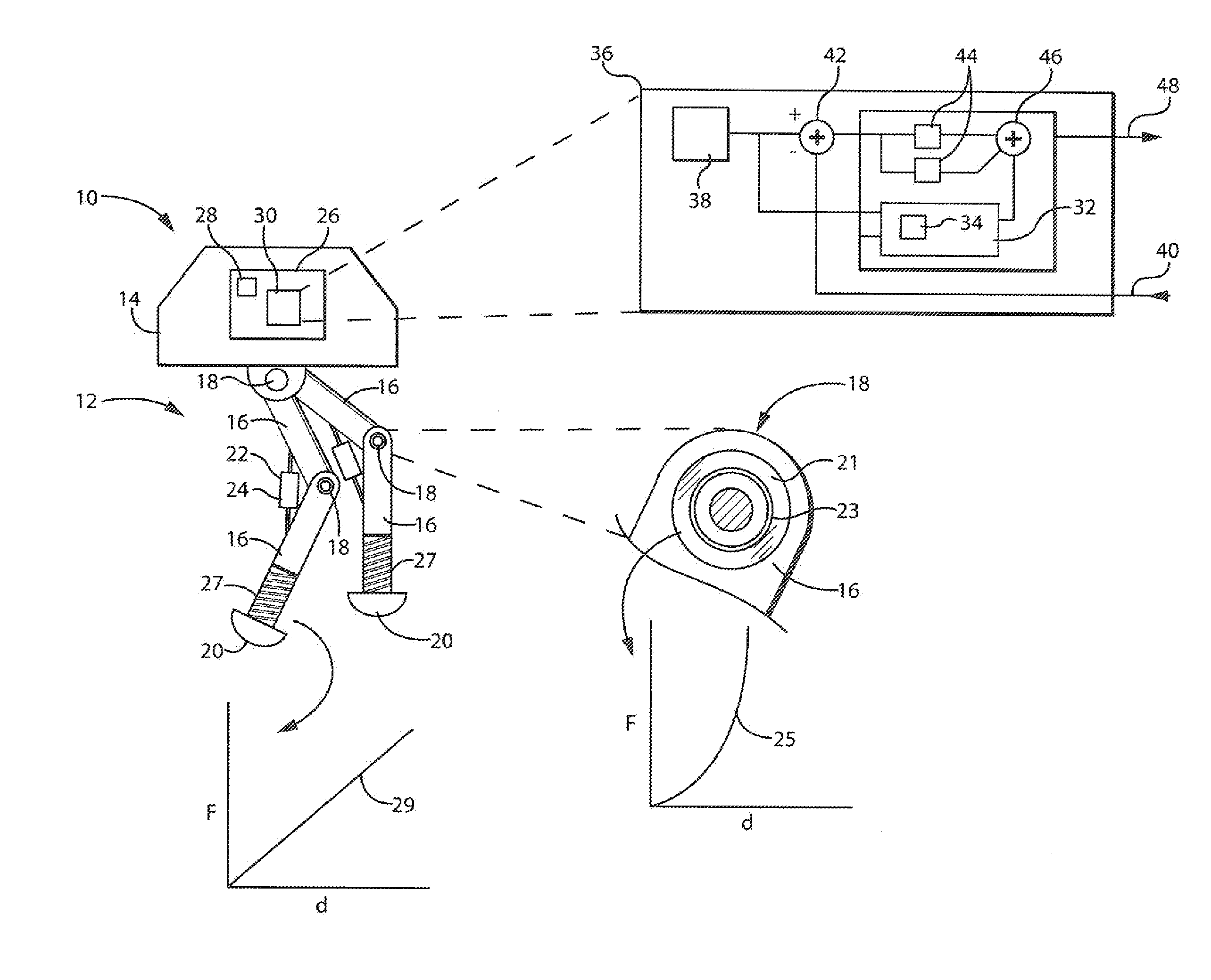
ActiveUS20150005941A1Stable and accurate solutionImproved polynomial approximationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEquation of the centerEngineering
A dynamic predictor usable for rapid and accurate calculation of joint commands of an articulated dynamical mechanism describes the relationship between the joints in the form of a differential equation. The predictor solves this differential equation for predicted joint states by fitting a polynomial equation having free parameters describing the predicted joint states to the differential equations by minimizing the differential equation residuals. This minimization employs a series expansion allowing algorithmic differentiation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Rapid probabilistic load flow calculation method considering static power frequency characteristics of electric power system
InactiveCN103825269AComplete Comprehensive AssessmentReduce computationSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsNormal densityGram
The invention discloses a rapid probabilistic load flow calculation method considering the static power frequency characteristics of an electric power system. The rapid probabilistic load flow calculation method comprises the steps that electric power system parameters needed by conventional load flow calculation are extracted from the electric power system and are initialized; a frequency variable to be solved is added to a conventional load flow calculation model, an improved rapid decoupling load flow module is established, and the normal state of the node voltage, the system frequency and the branch power of the variable to be solved are worked out; cumulants of each order of the node voltage, the system frequency and the branch power are worked out; through Gram-Charlier series expansion, the cumulative probability distribution function and the probability density function of the node voltage, the system frequency and the branch power of the variable to be solved are worked out. According to the rapid probabilistic load flow calculation method, the influence of uncertain factors on the system frequency in the electric power system and the distribution characteristics of the system frequency are considered in the process of probabilistic load flow analysis, the calculation speed is high, and a complete comprehensive assessment can be provided for the safe and economical operation analysis and the stability analysis of the electric power system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +3
Method and apparatus for high-order differential mobility separations
InactiveUS20070069120A1Reduce contributionTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNon symmetricMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention relates generally to separation of ions based on their transport properties. More particularly, the invention relates to separation of ionic mixtures and characterization of ions in gases using higher-order differential ion mobility spectrometry (HODIMS) enabled by asymmetric waveforms of fundamentally new types. The invention discloses a method and apparatus for separation of ionic mixtures and characterization, identification, or quantification of ions in a gas based substantially on the terms of third or higher order in a series expansion of ion mobility as a function of electric field intensity. This is achieved using a periodic, time-dependent electric field with novel waveform profiles that cancel or substantially reduce the contributions to time-averaged ion motion of the leading n (where n≧2) terms of that expansion, thereby achieving ion separations based substantially on the (n+1)th term. Separations using HODIMS with different n are expected to be highly orthogonal, enabling multidimensional separations employing HODIMS analyzers of different orders. The expected high orthogonality between HODIMS and mass spectrometry or ion mobility spectrometry would make HODIMS / MS and HODIMS / IMS combinations powerful analytical tools of broad utility.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Optimization of source, mask and projection optics
ActiveUS8893060B2Optimize and improveEasy to optimizeDesign optimisation/simulationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusProjection opticsWavefront
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
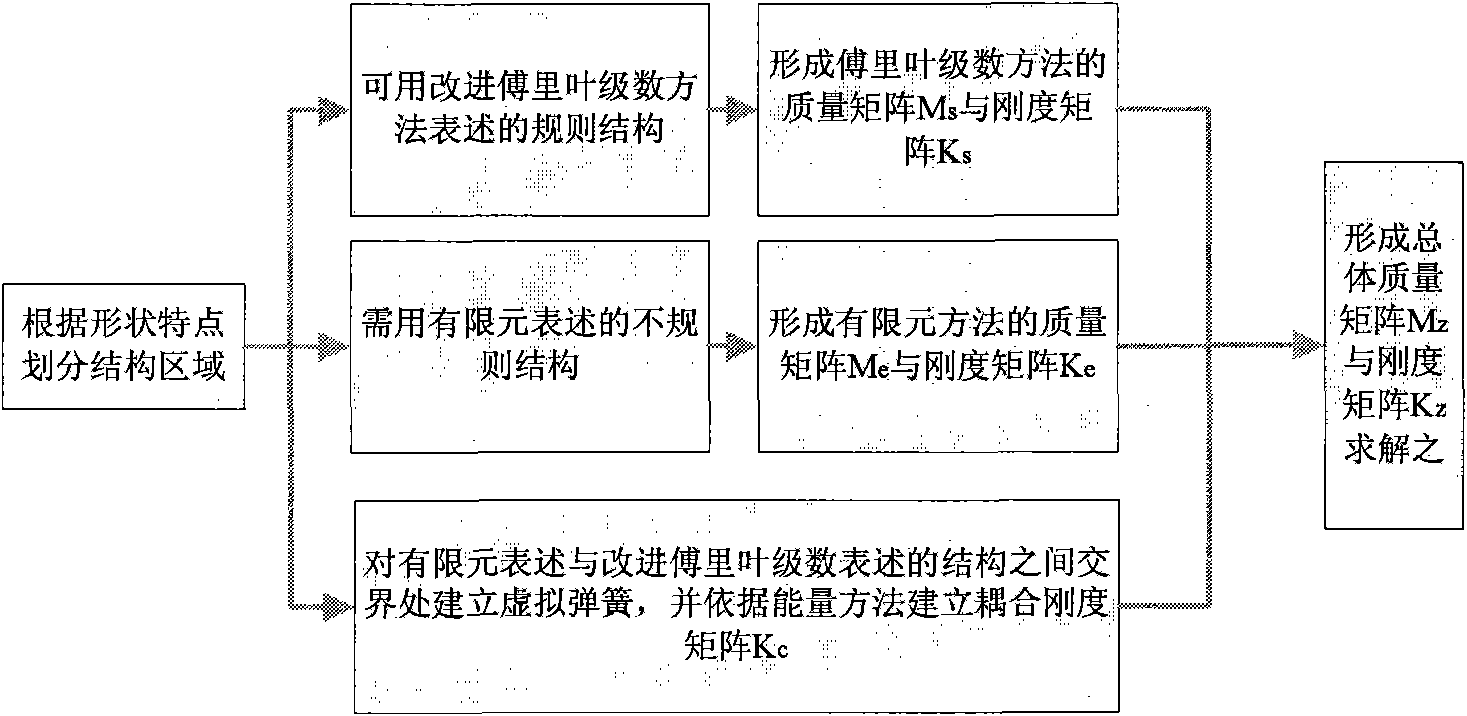
Structural vibration analysis method based on finite element method and generalized Fourier series method
InactiveCN101887474AFast convergenceSave resourcesSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy variationExtended finite element method
The invention aims at providing a structural vibration analysis method based on a finite element method and a generalized Fourier series method, which comprises the following steps of: dividing a structure region to be subjected to vibration analysis to respectively and correspondingly form a finite element expression region and a generalized Fourier series expression region; dividing the finite element grids of the finite element expression region to form a corresponding quality stiffness matrix, and selecting a corresponding assumption displacement form according to the characteristics of the generalized Fourier series expression region to form a quality stiffness matrix; subsequently, establishing a virtual spring between the two regions, and converting the potential energy of the virtual spring into an overall coupling stiffness matrix by using an energy variation method; then, arranging the formed quality stiffness matrices according to displacement to form an overall structure quality stiffness matrix; and solving linear equations to obtain an unknown coefficient in corresponding node displacement and series expansion. When applied to a large complex structure, the method not only can obtain precision higher than the finite element method, but also can save a large amount of calculation cost.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
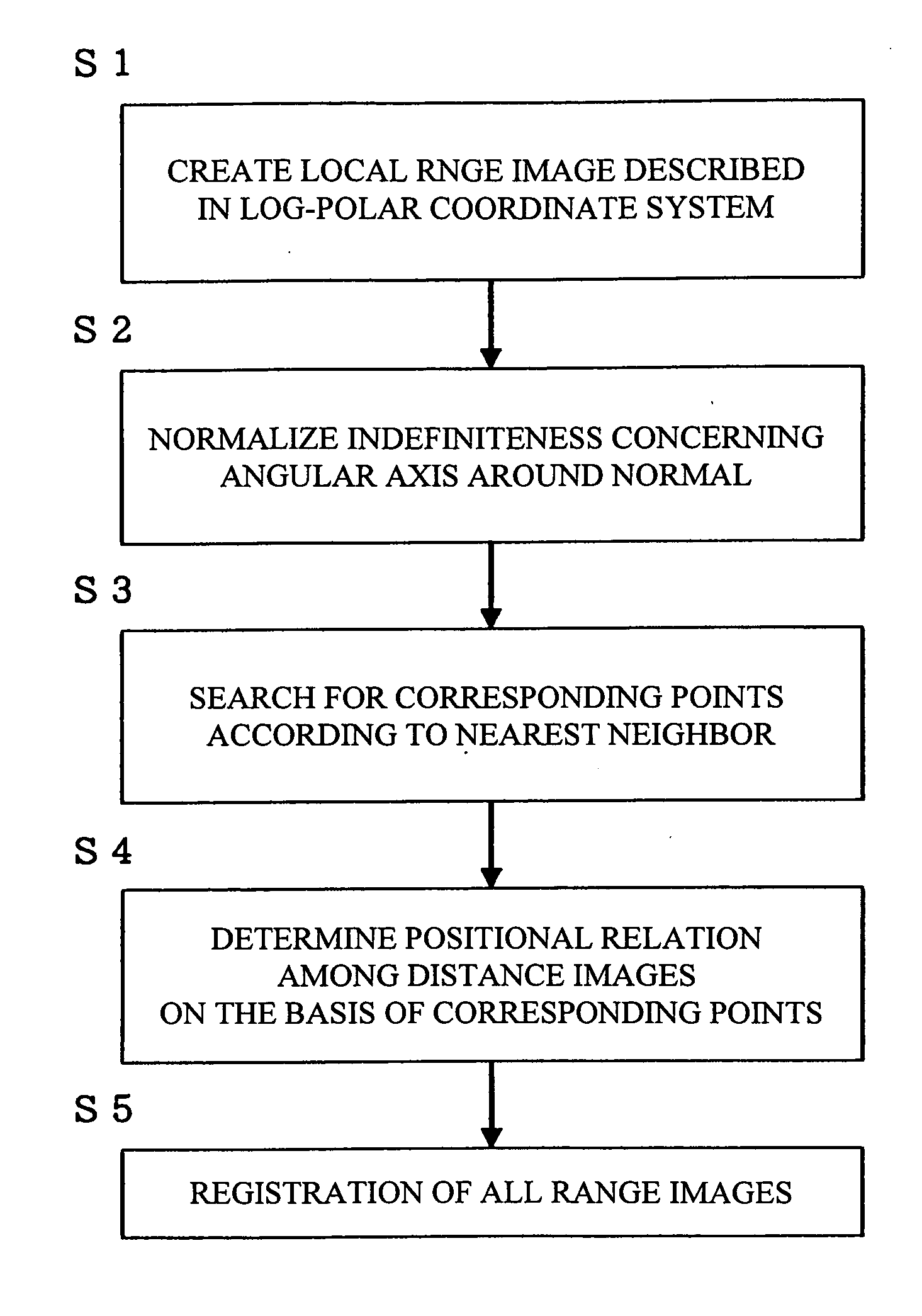
Method And Program For Registration Of Three-Dimensional Shape
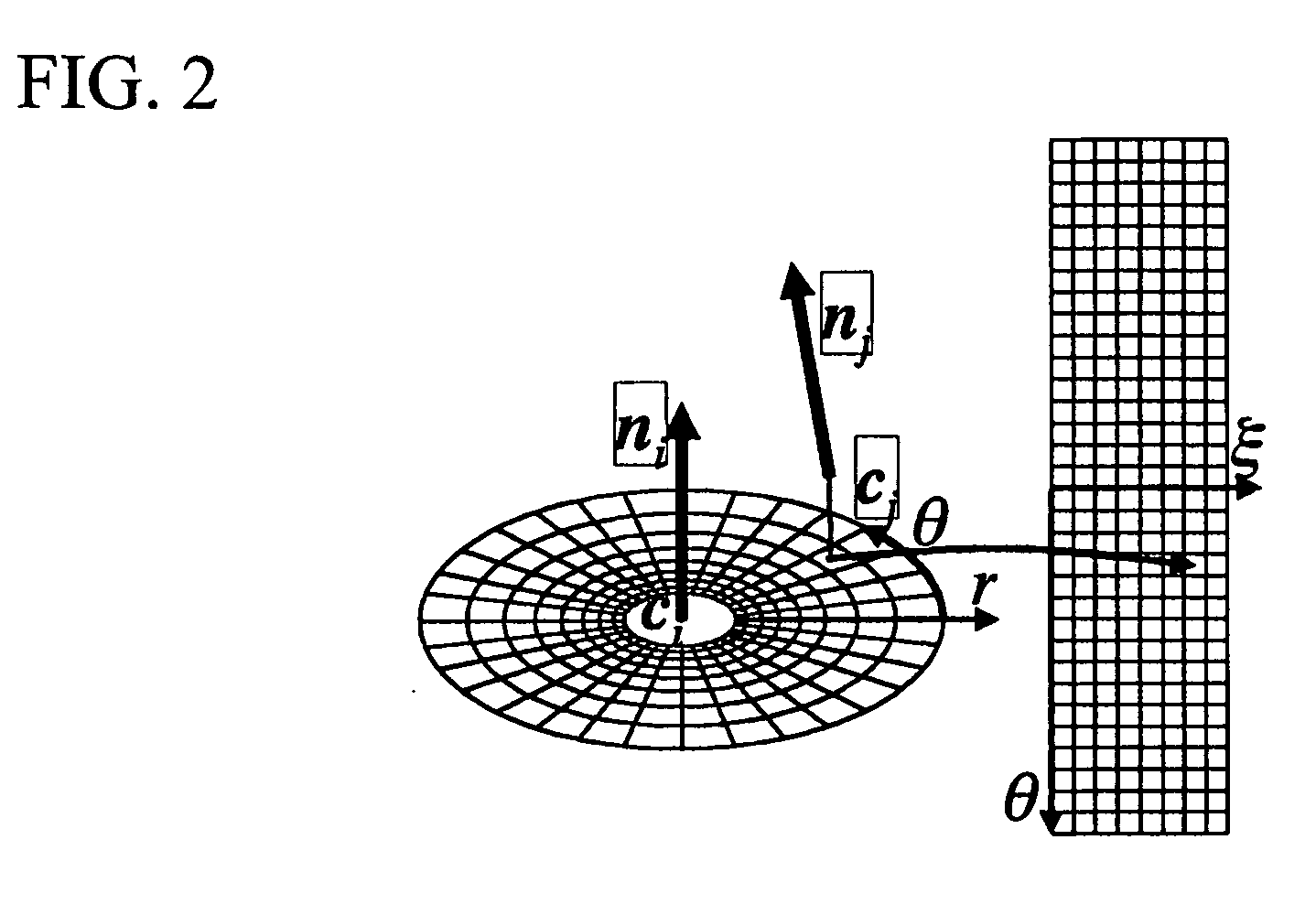
ActiveUS20090128546A1Rich relevant informationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
As a feature, a local range image described in a log-polar coordinate system with a tangential plane set as an image plane is used. In a created image, ambiguity concerning an angular axis around the normal is normalized as a power spectrum using Fourier series expansion and changed to an amount invariable with respect to rotation. The power spectrum is dimensionally compressed by expanding the power spectrum in a peculiar space using a peculiar vector. Corresponding points are searched by nearest neighbor in a dimensionally compressed space to calculate a correspondence relation among the points. Wrong correspondence is removed by verification to determine a positional relation among range images. A reliable correspondence relation is narrowed down by verification by cross-correlation and a RANSAC to create a tree structure representing a link relation among the range images. A shape mode is created by applying a simultaneous registration method to plural range images of the tree structure using a result of this registration as an initial value.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
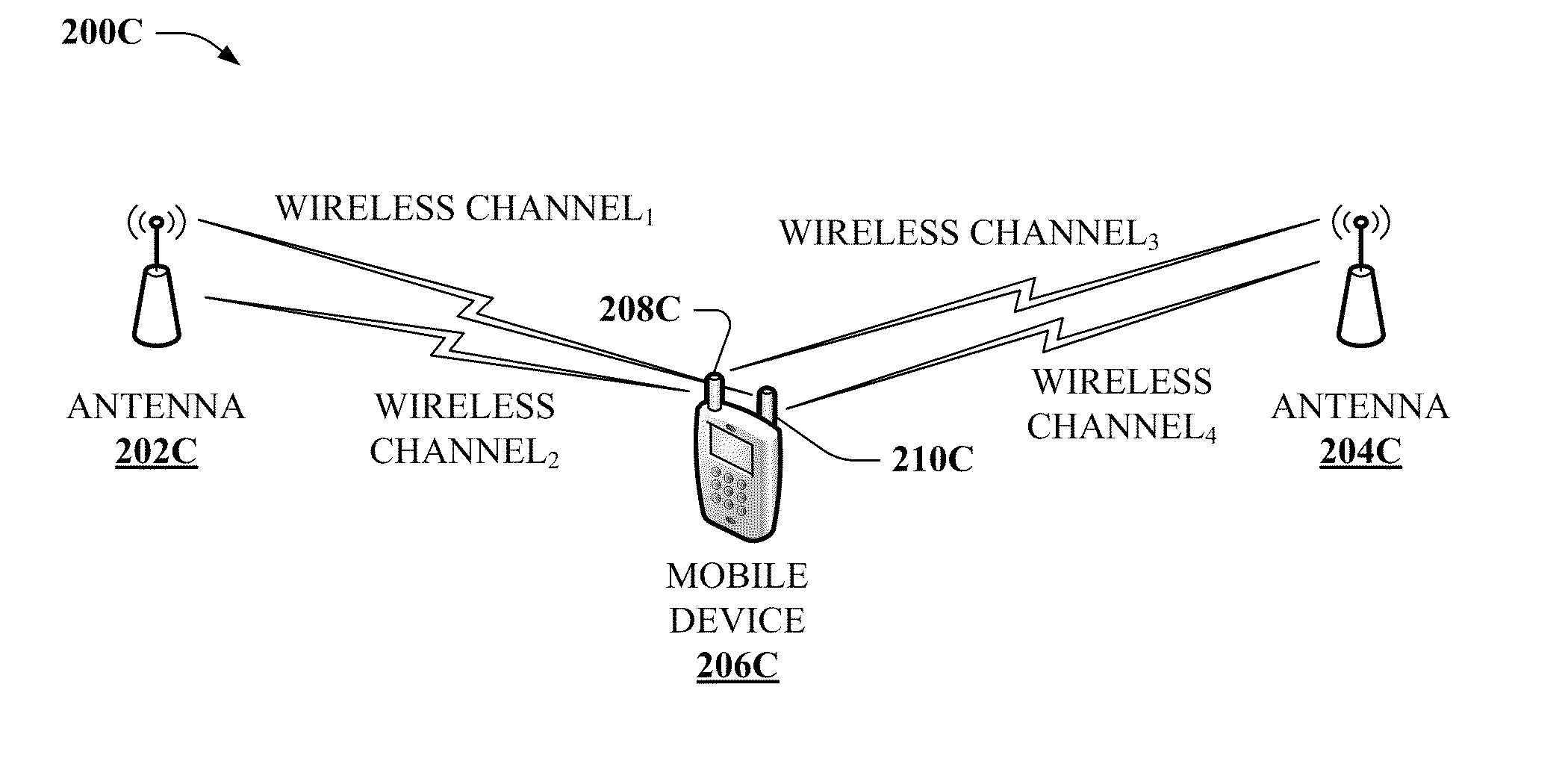
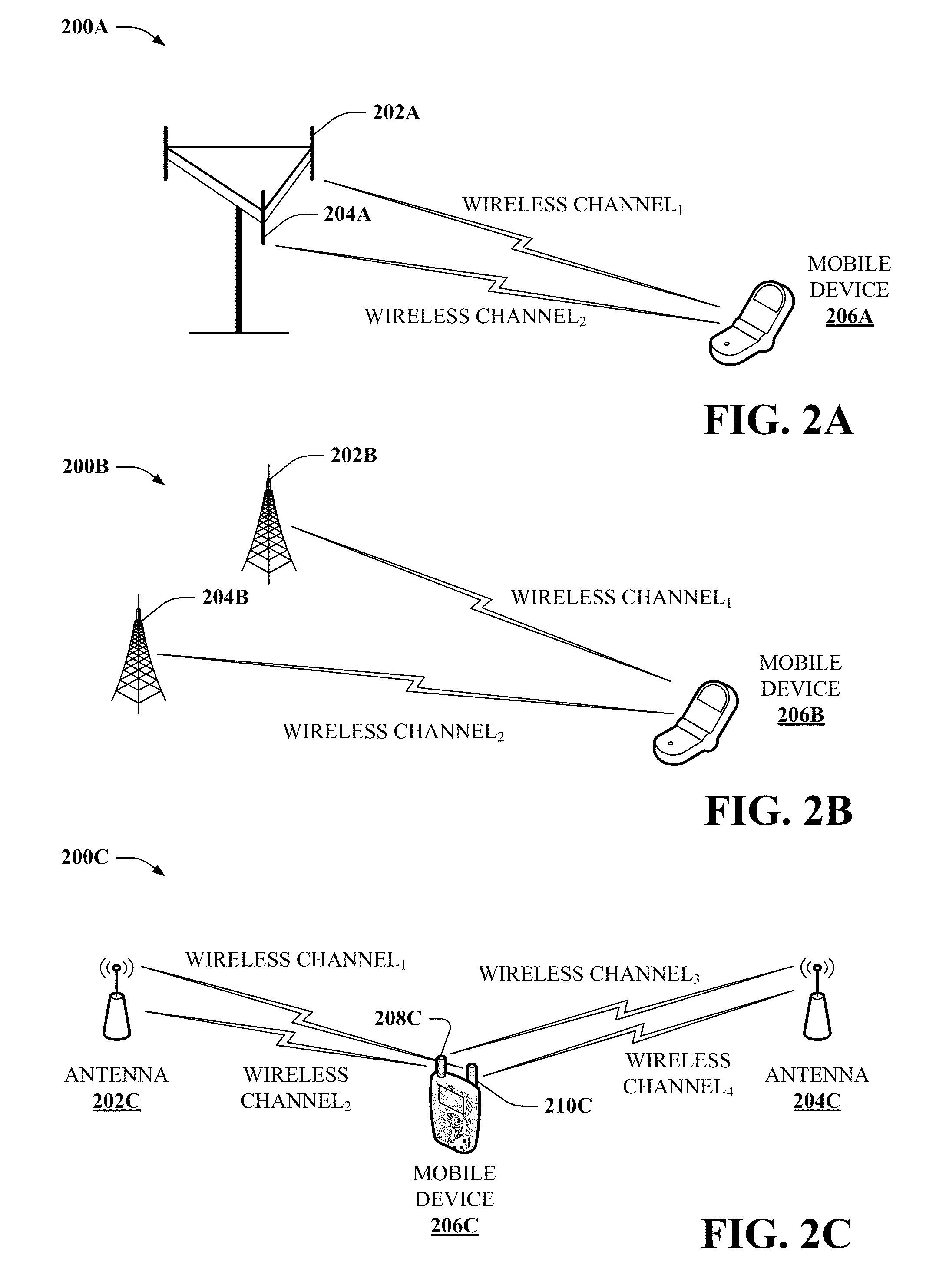
Multi-term demapping for multi-channel wireless communication
InactiveUS20110206151A1Reduce complexityAvoid processing overheadAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsData streamRound complexity
Providing for reduced complexity or improved accuracy in de-mapping received wireless data streams for multi-channel wireless communication is described herein. By way of example, a low-complexity likelihood algorithm can be employed to de-map data bits from the wireless data streams. In one particular example, the likelihood algorithm can approximate a received bit with a subset of received wireless symbols correlated the bit, reducing algorithm complexity. In other examples, a limited set of received wireless symbols can be employed for the subset, further reducing algorithm complexity. According to at least one other example, logarithmic terms of the algorithm can be approximated with non-logarithmic functions, such as a look-up table, series expansion, polynomial approximation, or the like. These approximations can enhance symbol de-mapping accuracy while maintaining or improving processing overhead for a wireless receiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Deep resistivity transient method for MWD applications using asymptotic filtering
ActiveUS20050049791A1Reduce impactExclude influenceElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyEngineeringSeries expansion
A method is discussed of obtaining a parameter of interest of an earth formation, typically a formation resistivity or a distance to a bed boundary, in conditions where an induction tool is using having a body with finite, non-zero conductivity. The method substantially removes the effects of the conductivity of the tool from the signal received from the earth formation. A Taylor series expansion in one half of odd integer powers of time is used to represent the received signal. At least one leading term of the Taylor series expansion can be subtracted from the second signal. A filtering operation is applied to the second signal to remove the terms most dominated by pipe effects. Typical filtering operations can be a differential filtering operation or an integral filtering operation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Performance evaluation of multicarrier channels
InactiveUS7131038B2Lower performance requirementsError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/correctionSeries expansionSymbol error rate
A method and apparatus determines an uncoded bit error rate pb based on a target symbol error rate εs. The uncoded bit error rate pb is determined based on a weighted series expansion of the target symbol error rate εs, comprising weights W that are a function of a maximum number of symbol errors that can be corrected t and a number of symbols in an information field K. The maximum number of symbol errors t and the number of symbols in the information field K is selected such that the uncoded bit error rate pb that produces a symbol error rate that is less than or equal to the target symbol error rate εs is largest.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
System and method for efficient computation of simulated thermodynamic property and phase equilibrium characteristics using comprehensive local property models
A method of estimating a thermophysical property of a fluid using a local model is disclosed herein. The method includes generating, for use within the local model, a series expansion of thermodynamic equations relating to the thermophysical property and one or more derivatives involving the thermophysical property. The method further includes evaluating, based upon a set of specified values of parameters of the fluid, a first order term of the series expansion and a second order term of the series expansion. The values of the first order term and the second order term are then compared. A value of the thermophysical property is then automatically updated when the values of the first order term and the second order term are found to differ by more than a predefined amount.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOFTWARE LLC
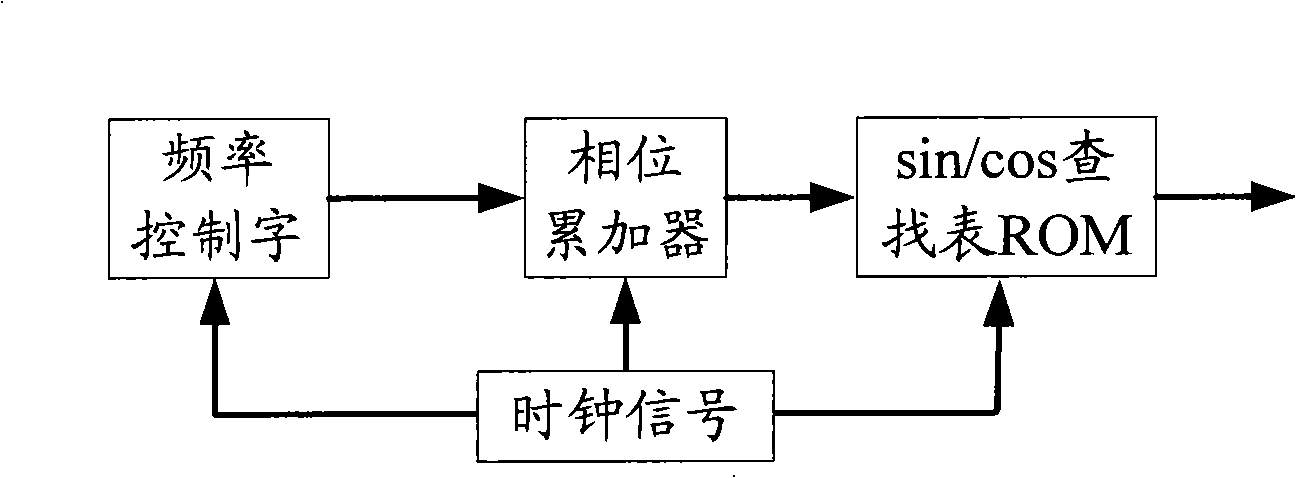
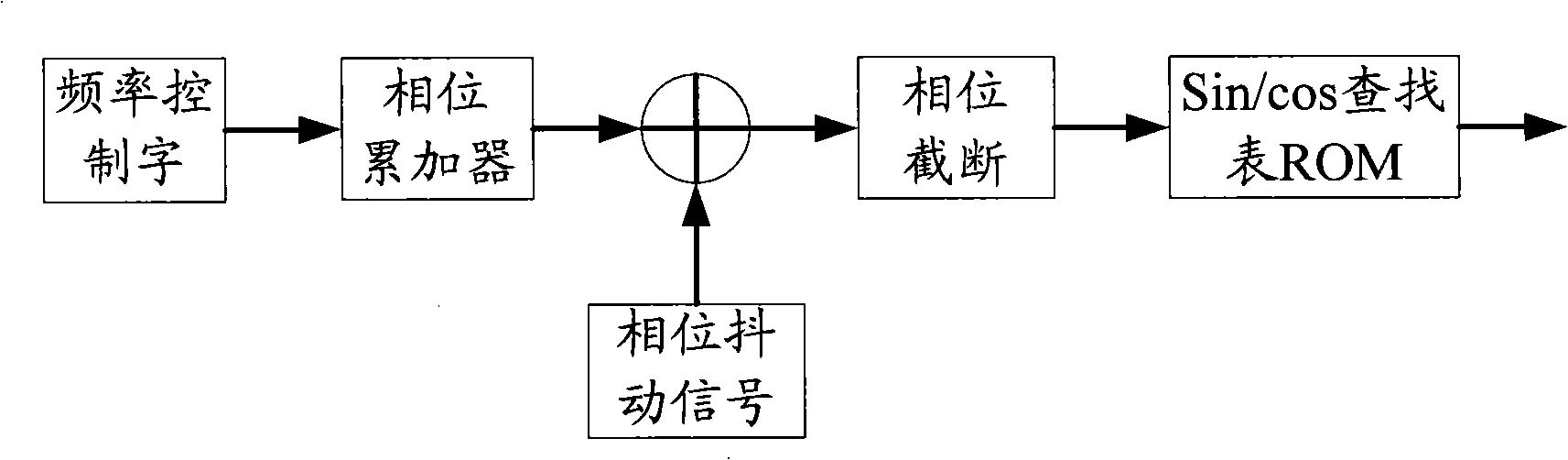
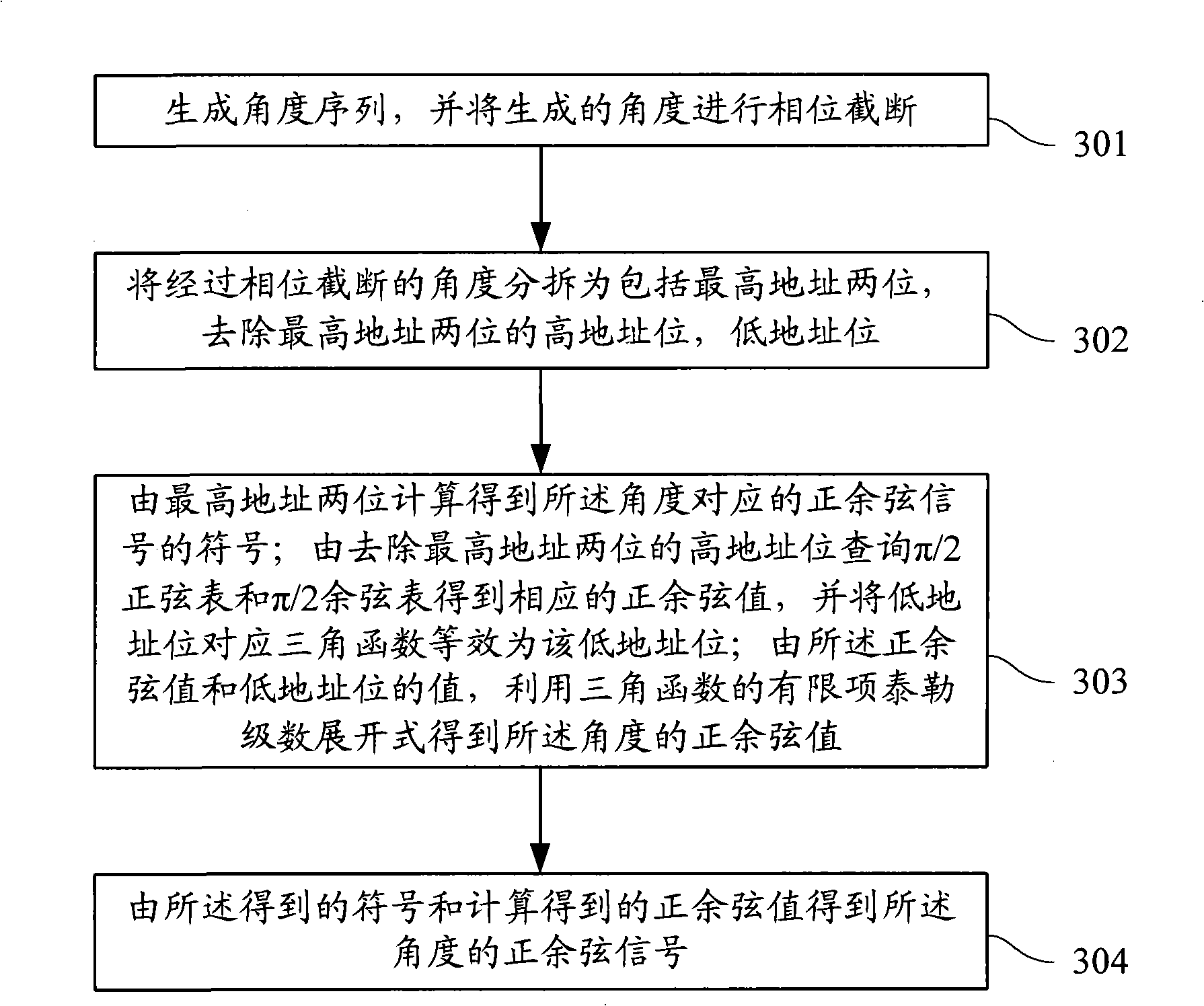
Method and digital control oscillator for sinusoidal and cosine signal generator
ActiveCN101335509ASmall footprintReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlSinusoidal oscillations train generatorNumerical controlPhase truncation
The invention discloses a method for producing sine and cosine signals, which comprises the steps that: an angle sequence is generated; the generated angle is treated with phase truncation; the angle after the phase truncation is parted into a high address bit including highest two address bits and a high address bit, the highest two address bits of which are wiped off, and a low address bit; the symbols of the sine and cosine signals corresponding to the angle are calculated by the highest two address bits; the corresponding sine and cosine values are obtained by inquiring a Pi / 2 sine table and a Pi / 2 cosine table with the high address bit, the highest two address bits of which are wiped off; the low address bit is corresponded to a trigonometric function for being equivalent to the value of the low address bit; a finite term Tylor series expansion of the trigonometric function is utilized for obtaining the sine and cosine values of the angle by the sine and cosine values and the value of the low address bit; the sine and cosine signals of the angle are obtained by the obtained symbols and the calculated sine and cosine values. The invention also discloses a numerical control oscillator. By utilizing the method, the space occupied by storage lists can be effectively compressed under the condition that phase-truncated word length is not increased.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com