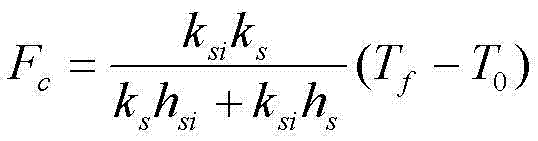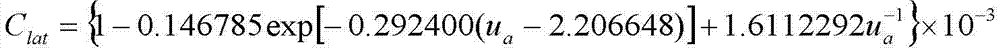Patents
Literature
35 results about "Thermodynamic equations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermodynamics is expressed by a mathematical framework of thermodynamic equations which relate various thermodynamic quantities and physical properties measured in a laboratory or production process. Thermodynamics is based on a fundamental set of postulates, that became the laws of thermodynamics.
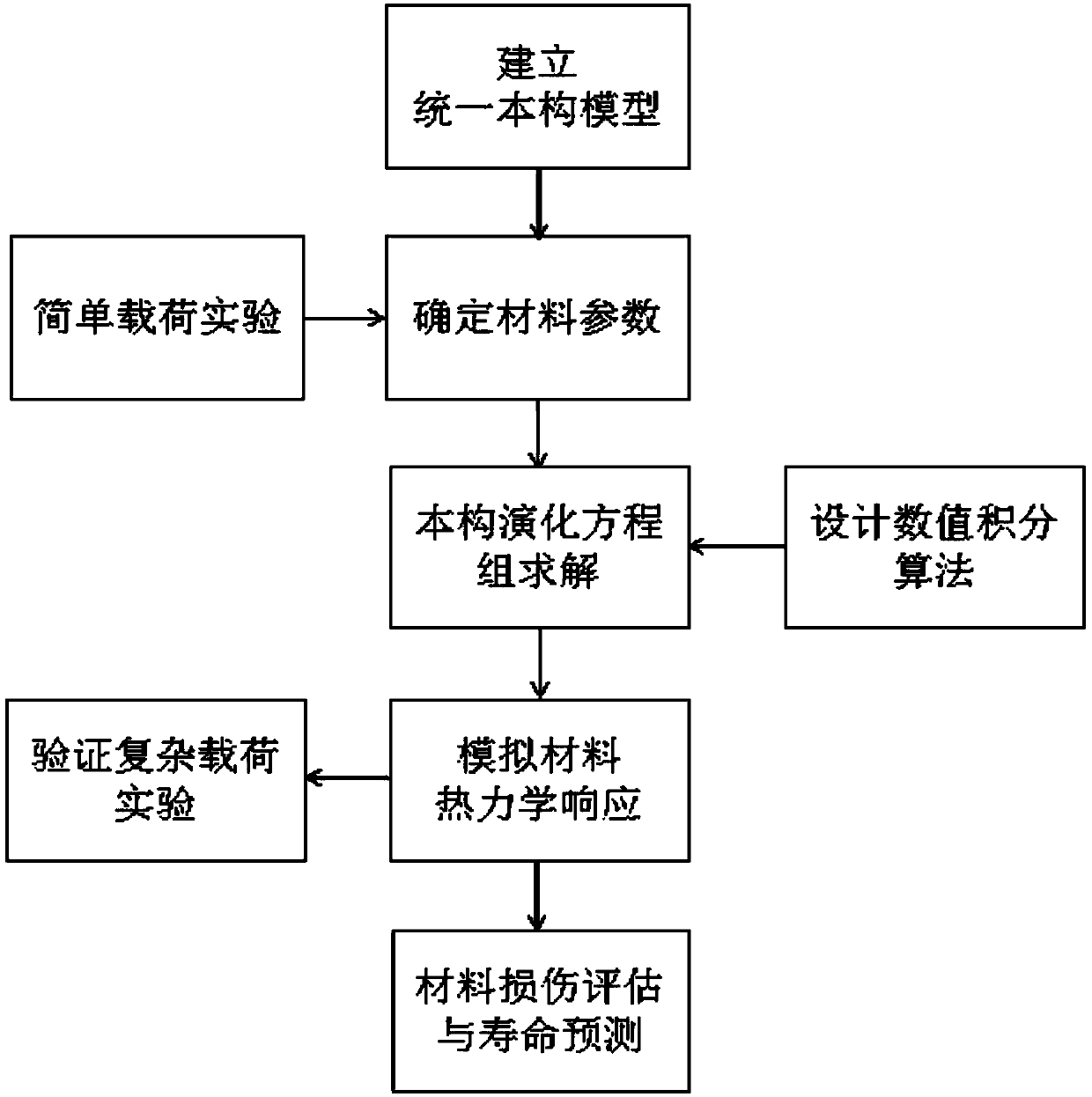
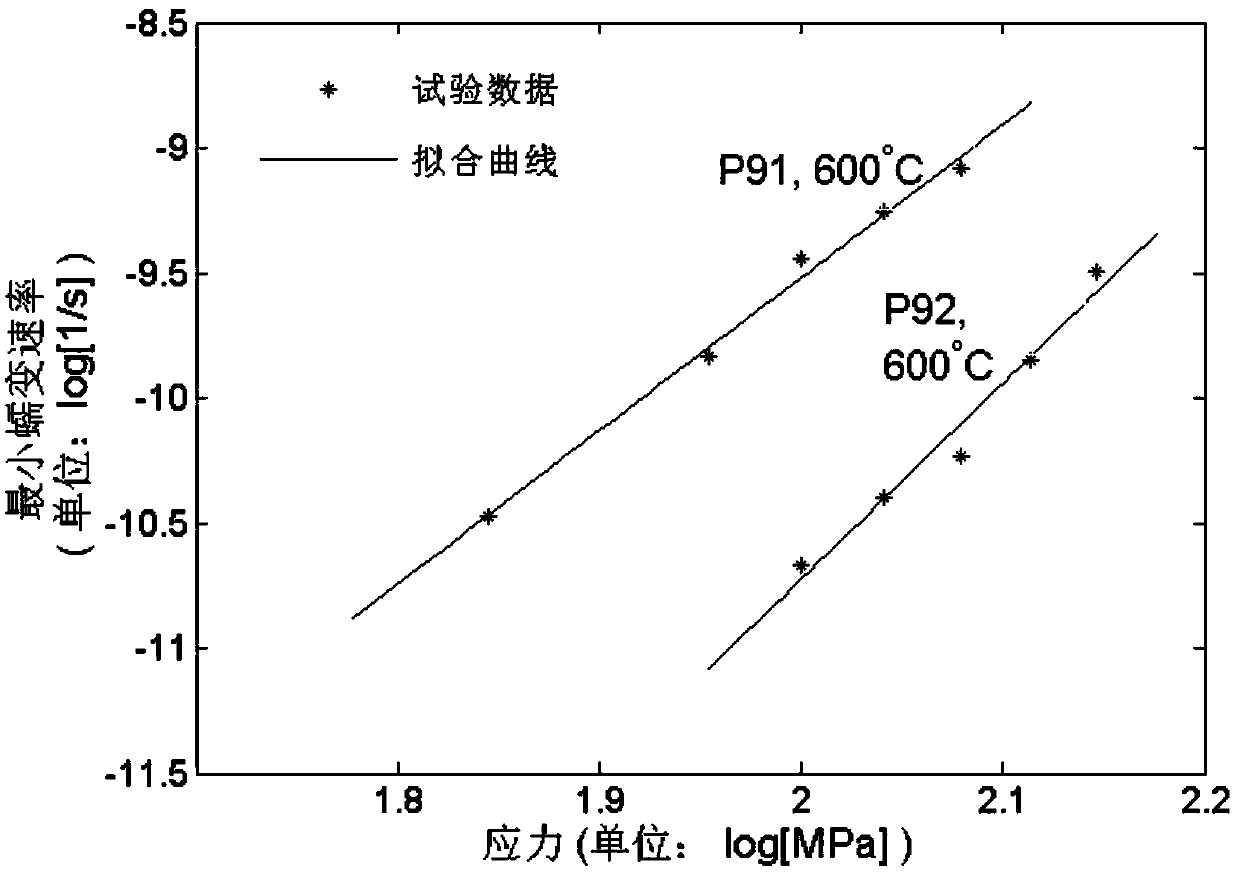
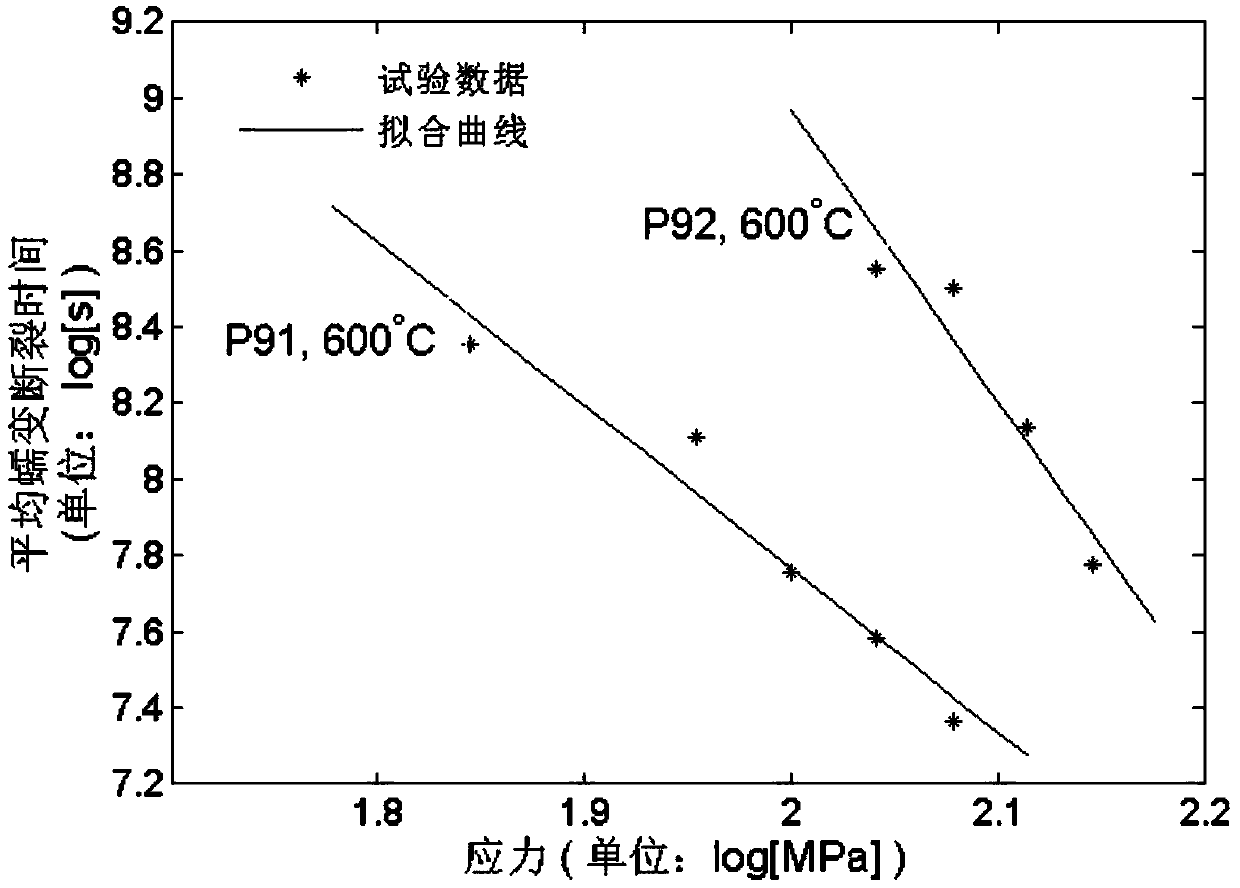
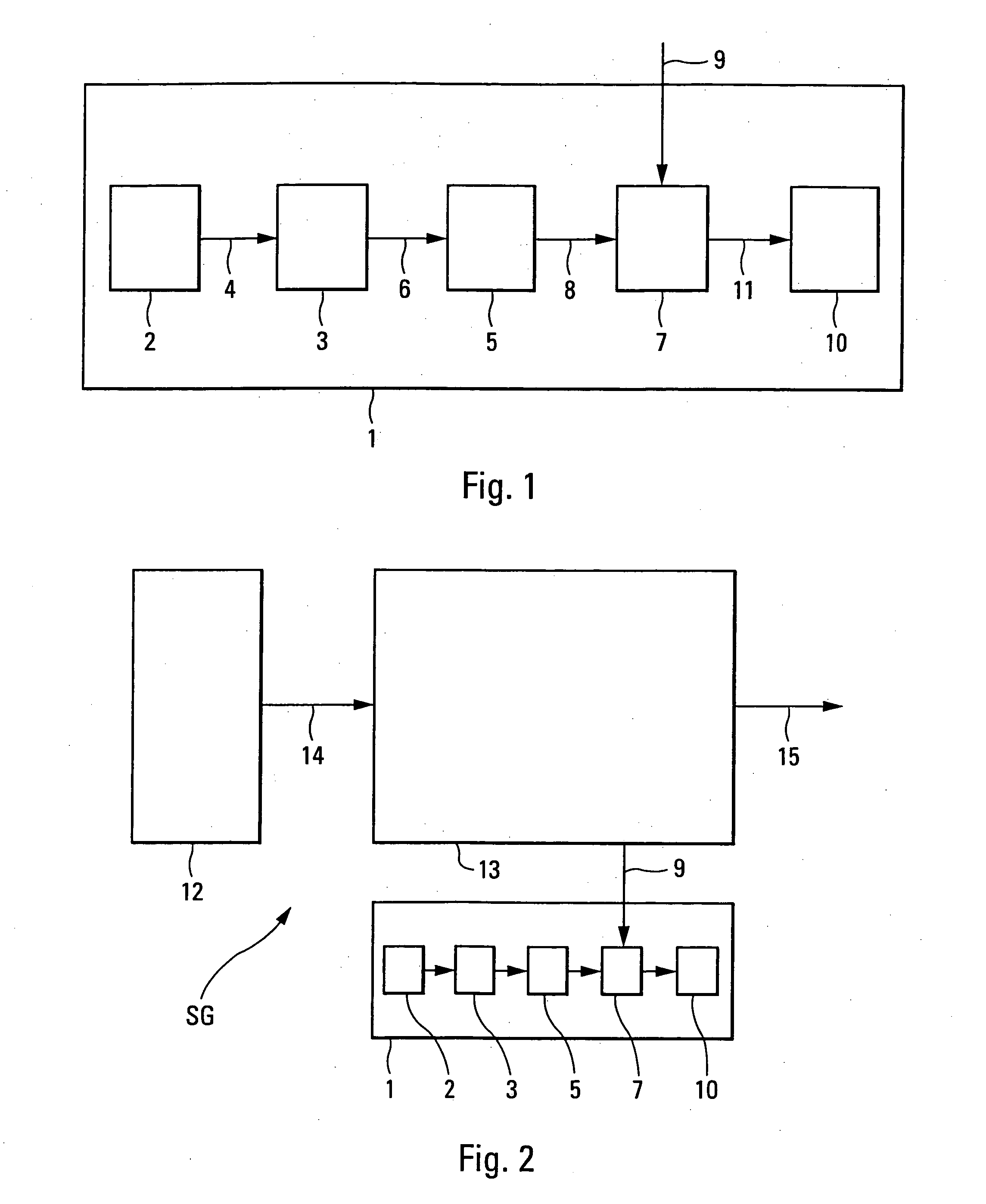
A prediction method for thermodynamic responses and fatigue-creep damage of a high-chrome steel material
ActiveCN108931448AAccurate predictionEffective simulationMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesSafety designThermodynamic process
A prediction method for thermodynamic responses and fatigue-creep damage of a high-chrome steel material is disclosed. The method includes constitutive model building, material parameter determination, numerical integration algorithm designing, damage analyzing, and the like. Compared with the prior art, the method can accurately simulate thermodynamic responses of the high-chrome steel material under different loading conditions, and can analyze fatigue, creep and fatigue-creep mutual damage of the material, thus providing a more reasonable and reliable theoretical model for service lifetimeprediction and safety design standards of supercritical generator unit components operated under complex changeable environments.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
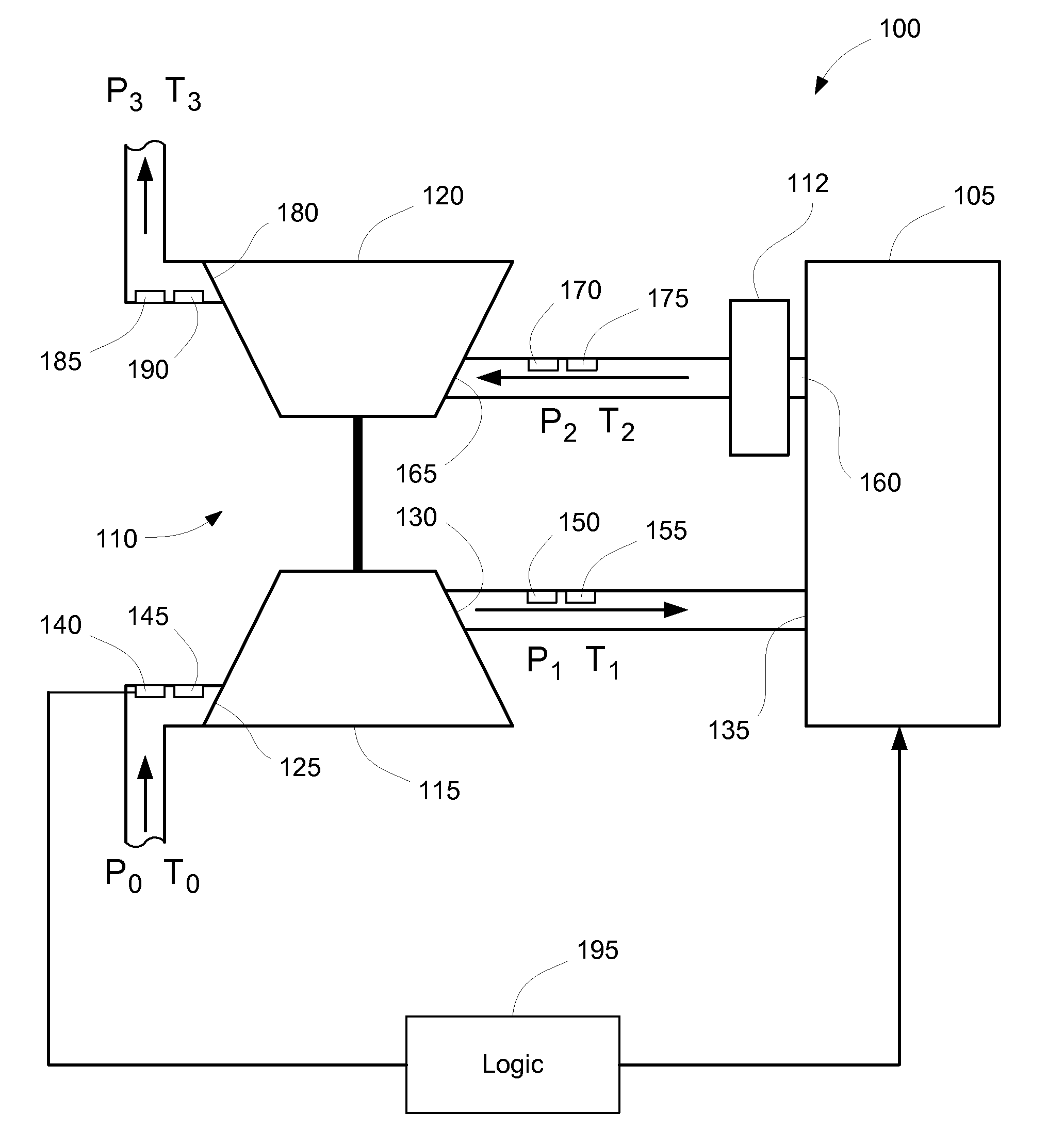
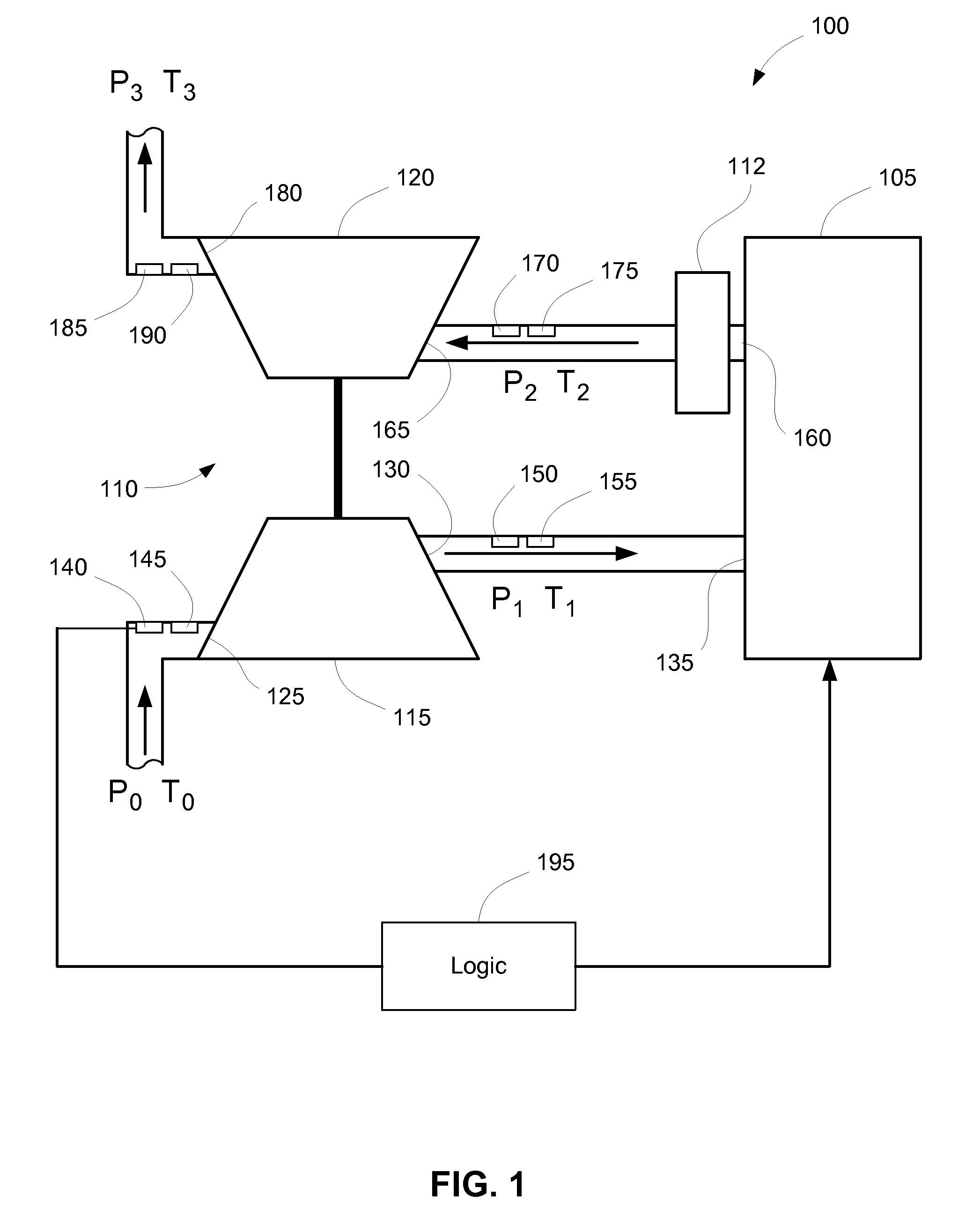
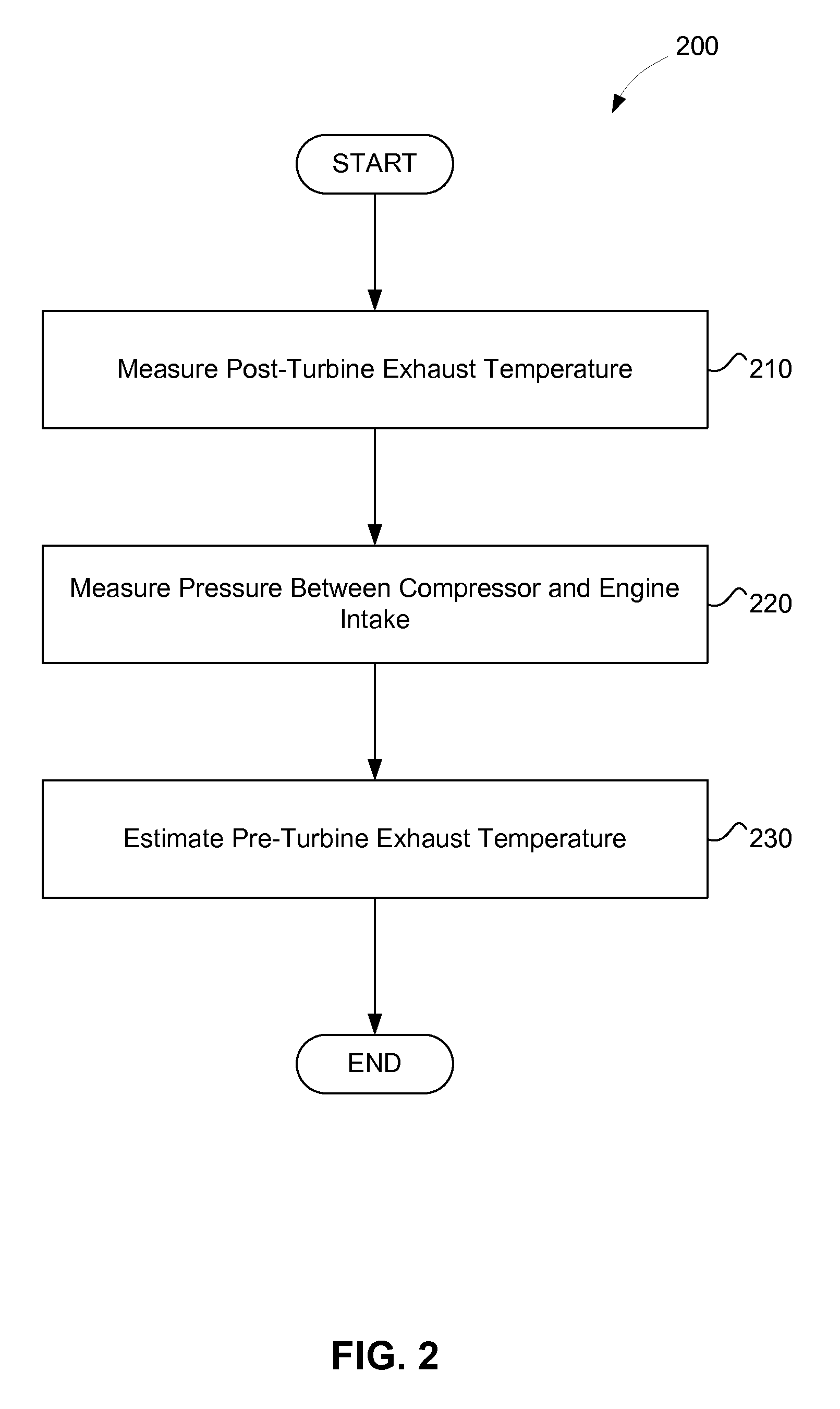
Estimating Pre-Turbine Exhaust Temperatures
InactiveUS20110154821A1Easy to operateInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlTurbochargerControl system
Methods are provided for estimating an exhaust temperature of an engine exhaust of a turbocharged engine prior to an inlet of the turbine of the turbocharger. These methods estimate the pre-turbine exhaust temperature based on thermodynamic equations and measured temperature and pressure values from elsewhere in the system. The estimated pre-turbine exhaust temperature can be used for controlling the engine, for verification of the emissions control system, and can also be compared against actual measurements of the pre-turbine exhaust temperature to evaluate engine performance. The present invention also provides turbocharged engine systems including sensors to make the required measurements and logic configured to estimate the pre-turbine exhaust temperature.
Owner:PURIFY SOLUTIONS INC
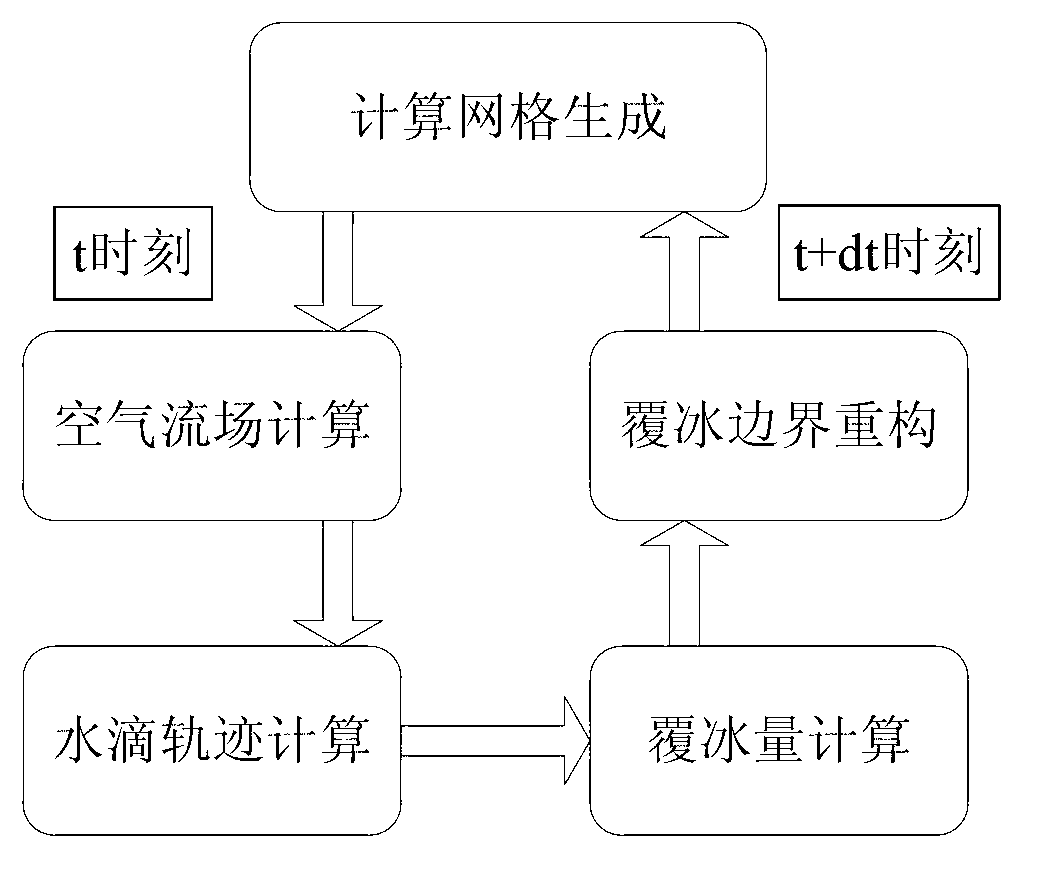
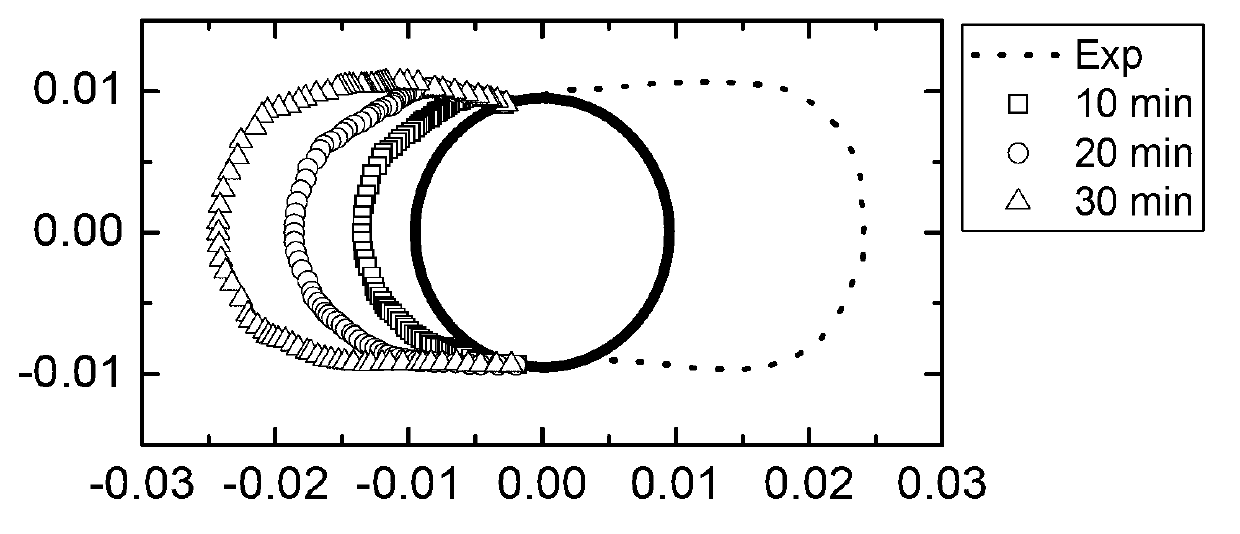
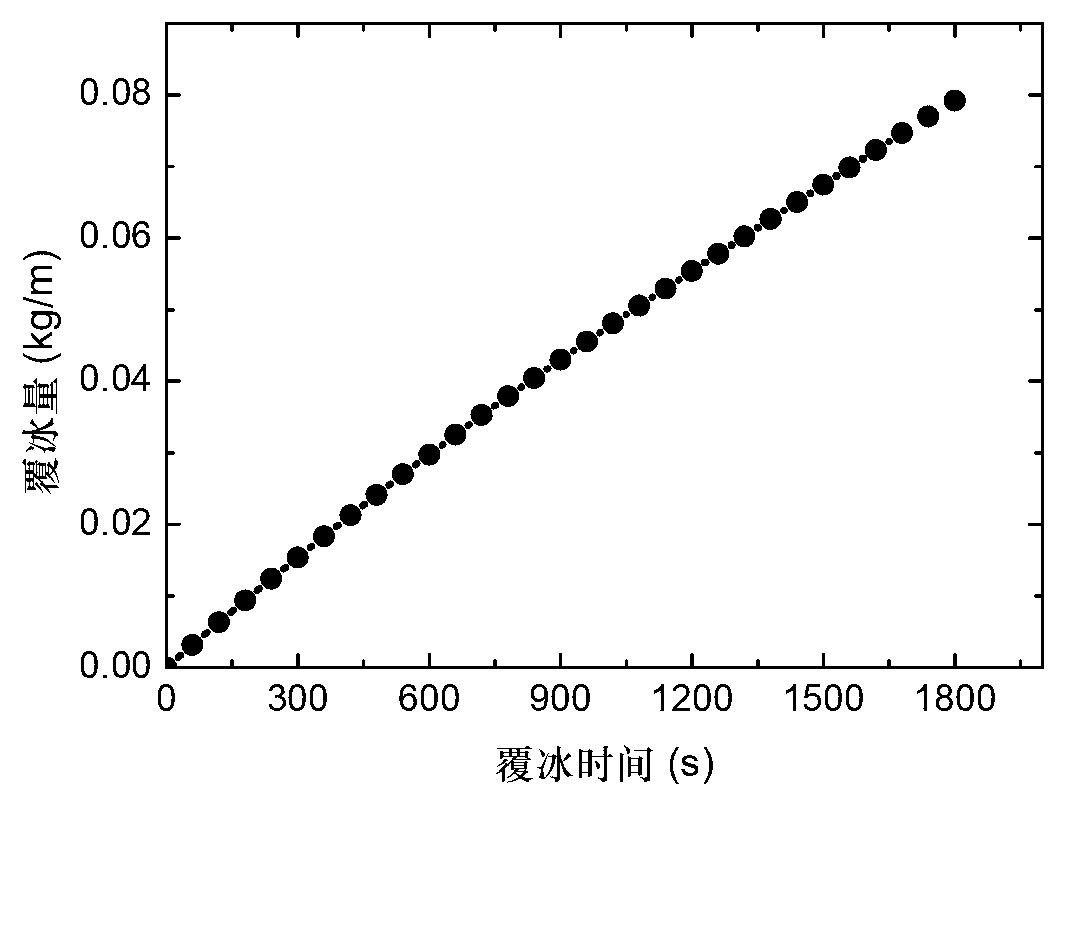
Two-dimensional numerical simulation method for icing process of power transmission line
The invention belongs to the field of electric power systems and relates to a two-dimensional numerical simulation method for an icing process of a power transmission line. Based on the lagrangian method, the invention provides the two-dimensional numerical simulation method for a surface rime icing process of the power transmission line. A Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equation and shear-stress-transport-k-omega (SST-k-omega) turbulence model of non-steady incompressible flow is solved by adopting a semi-implicit method for pressure linked equations (SIMPLE) algorithm on a staggered grid so as to obtain an air flow field; movement tracks of super-cooled water droplets in the flow field are tracked by adopting the lagrangian method to obtain the transient local collision rate of all control volumes on the surface of the power transmission line; solving is performed based on an icing thermodynamic equation established by a Messinger control volume method so as to obtain the rime icing temperature of all the control volumes, and the icing process is simulated by combining an icing time marching method. Indicated by results, predicted ice shapes are better fitted with test measurement data in literature, and therefore, the two-dimensional numerical simulation method for the icing process of the power transmission line is feasible and effective.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
System and method for efficient computation of simulated thermodynamic property and phase equilibrium characteristics using comprehensive local property models
A method of estimating a thermophysical property of a fluid using a local model is disclosed herein. The method includes generating, for use within the local model, a series expansion of thermodynamic equations relating to the thermophysical property and one or more derivatives involving the thermophysical property. The method further includes evaluating, based upon a set of specified values of parameters of the fluid, a first order term of the series expansion and a second order term of the series expansion. The values of the first order term and the second order term are then compared. A value of the thermophysical property is then automatically updated when the values of the first order term and the second order term are found to differ by more than a predefined amount.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOFTWARE LLC
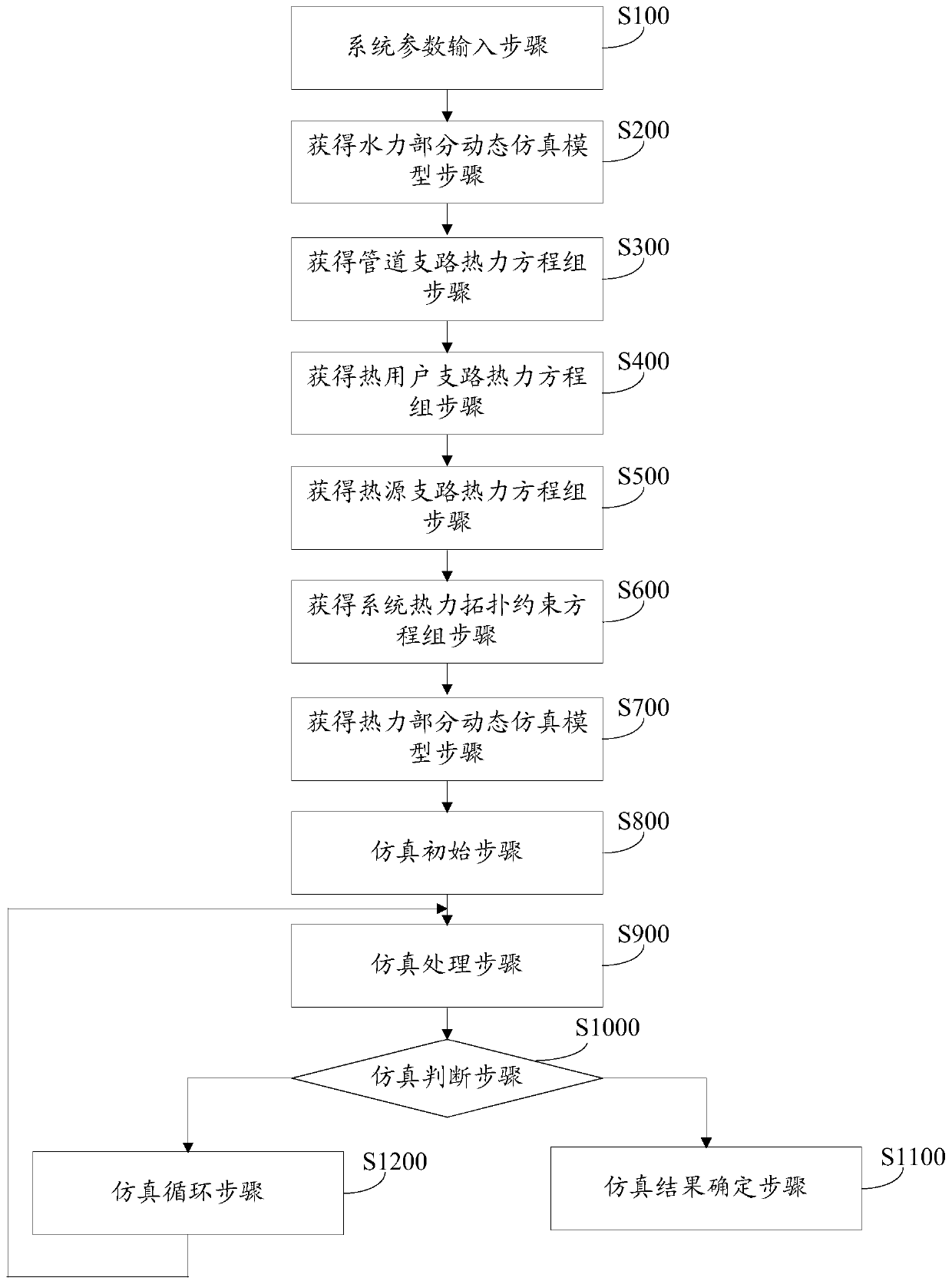
Comprehensive energy heat supply system dynamic simulation method and device based on expansion node method
ActiveCN110555264AMeet Simulation NeedsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringHeating system
The invention discloses a comprehensive energy heat supply system dynamic simulation method and device based on an expansion node method applied to a comprehensive energy heating system. The method comprises the following steps of: a system parameter input step, a step of obtaining a hydraulic part dynamic simulation model; a step of obtaining a pipeline branch thermodynamic equation set; a step of obtaining a heat consumer branch thermodynamic equation set, a step of obtaining a heat source branch thermodynamic equation set, a step of obtaining a system thermodynamic topology constraint equation set, a step of obtaining a thermodynamic part dynamic simulation model, a step of carrying out simulation initial, a step of carrying out simulation processing, a step of carrying out simulation judgment, a step of determining a simulation result and carrying out simulation circulation. The hydraulic dynamic state and the thermal dynamic state of the comprehensive energy heat supply system canbe simulated at the same time, and the simulation requirements of the comprehensive energy heat supply system in various application environments are met.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
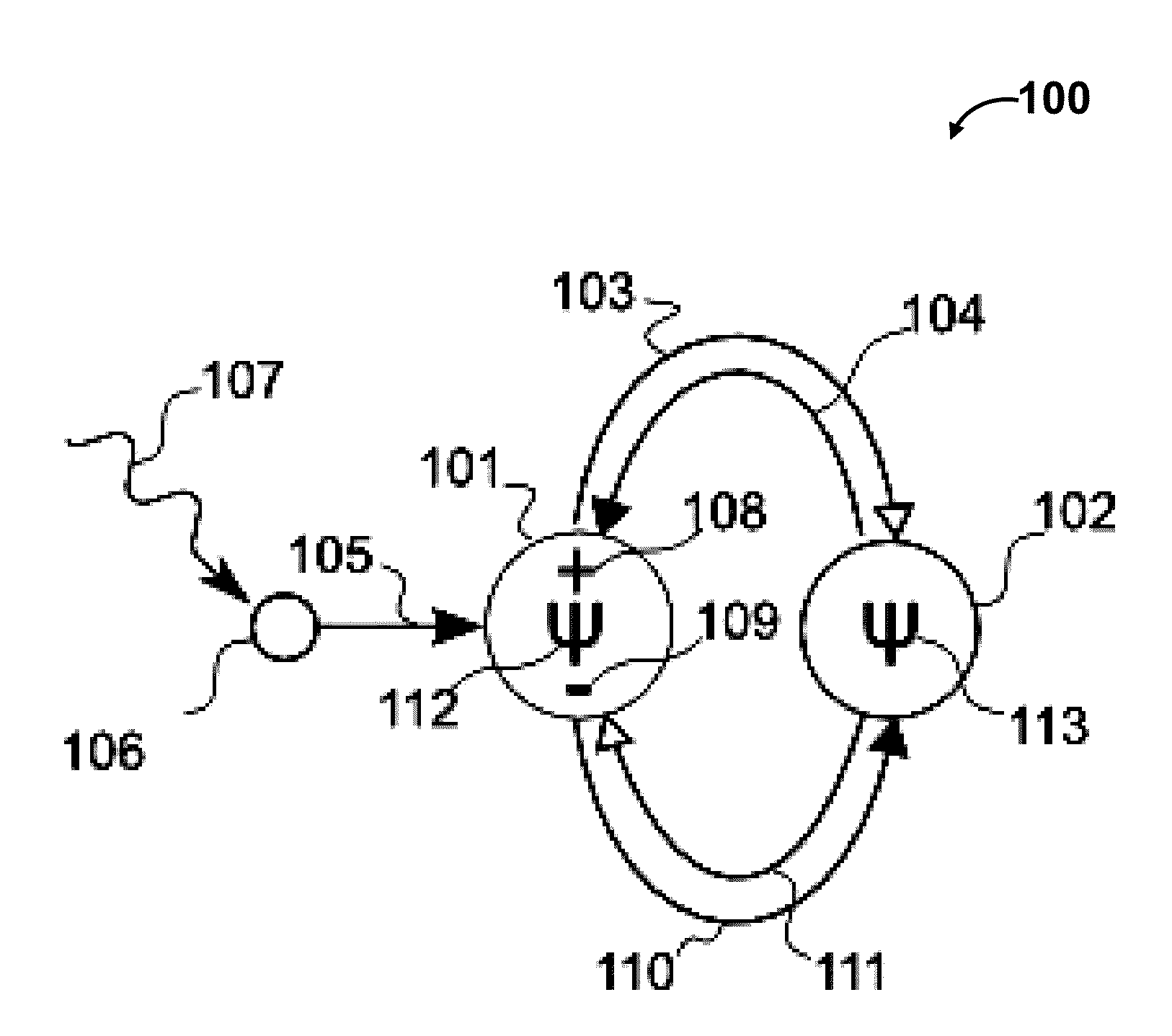
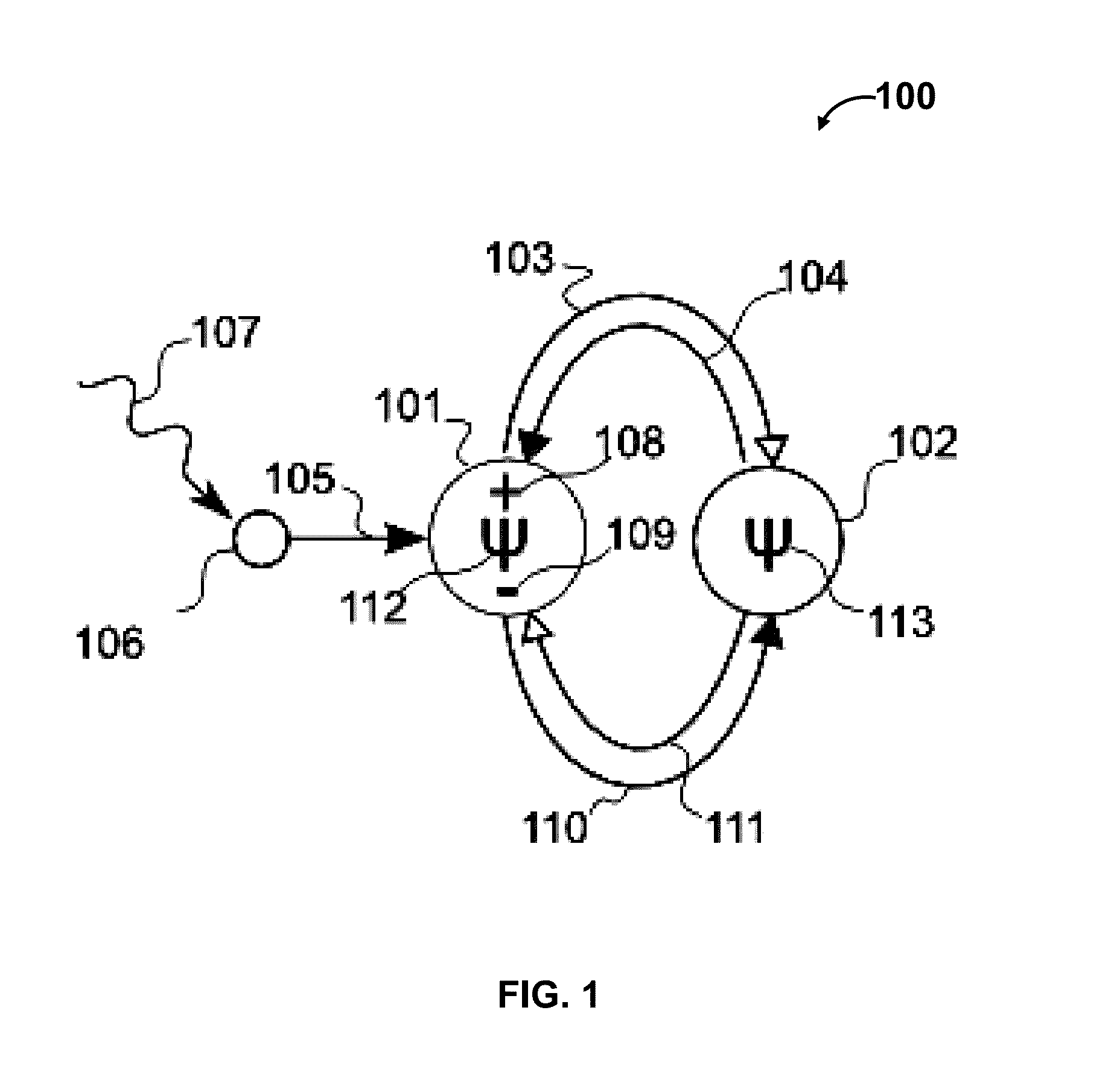
Methods and systems for thermodynamic evolution
ActiveUS8909580B2Maximize dissipation of energyLow mutation rateCAD circuit designKnowledge representationControl systemSelf adaptive
Methods and systems for thermodynamic evolution. Adaptive control systems are constructed based on the property of volatile matter to self-organize to maximize the dissipation of energy. The logical state of sensory nodes in a node circuit are set and projected into a network. Then, the system evaluates logical state of processing nodes by summing input currents of processing nodes and project processing node's state into network. The strength of processing node is increased such that logical state of sensory node matches with logical states of processing node by utilizing plasticity rule. The system is configured to maximize energy dissipation by creating weight structures to stabilize nodes with logical state. The internal positive feedback of node circuit forces competition between nodes such that one node is driven to high logical state and other nodes to low logical state.
Owner:KNOWM TECH
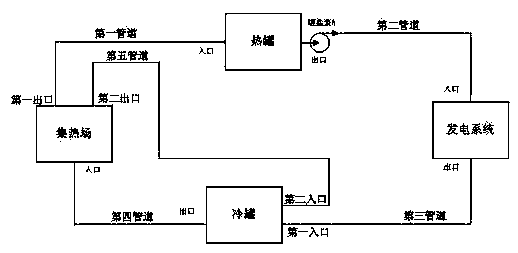
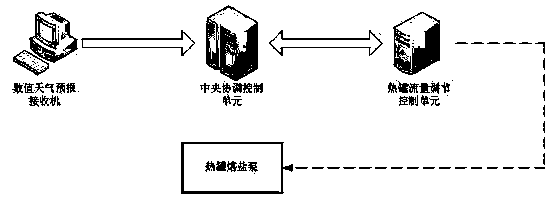
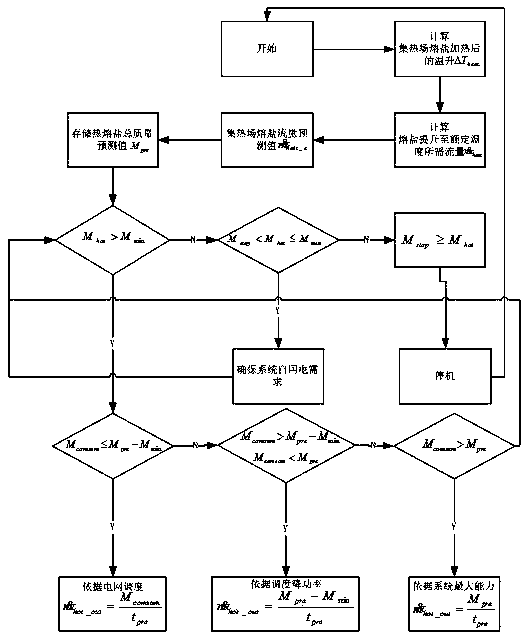
Heat tank control device, combined with weather prediction data, of groove type solar thermal electric power generation system
ActiveCN105371509AReduce the impactImprove grid-connected power generation reliabilityFrom solar energySolar heat devicesNumerical weather predictionPower grid
The invention relates to the technical field of solar groove type solar thermal electric power generation, in particular to a heat tank control device, combined with weather prediction data, of a groove type solar thermal electric power generation system. The heat tank control device comprises a numerical weather prediction receiver, a heat tank flow adjustment control unit and a central coordination control unit. The numerical weather prediction receiver receives numerical prediction data through the network. Numerical calculation is carried out through the numerical prediction data to solve a hydromechanical and thermodynamic equation set for describing the weather evolution process, and short-term solar resource prediction data are obtained. By means of the heat tank control device, combined with the weather prediction data, of the groove type solar thermal electric power generation system, the mass of hot melting salt stored in the system within a period in the future is estimated through numerical weather prediction, and flow control is carried out on a heat tank melting salt outlet pump according to the mass of the hot melting salt stored in a heat tank and the power grid dispatching power output requirement.
Owner:中国东方电气集团有限公司
Method of exploiting a fractured oil reservoir having a heterogeneous pore size
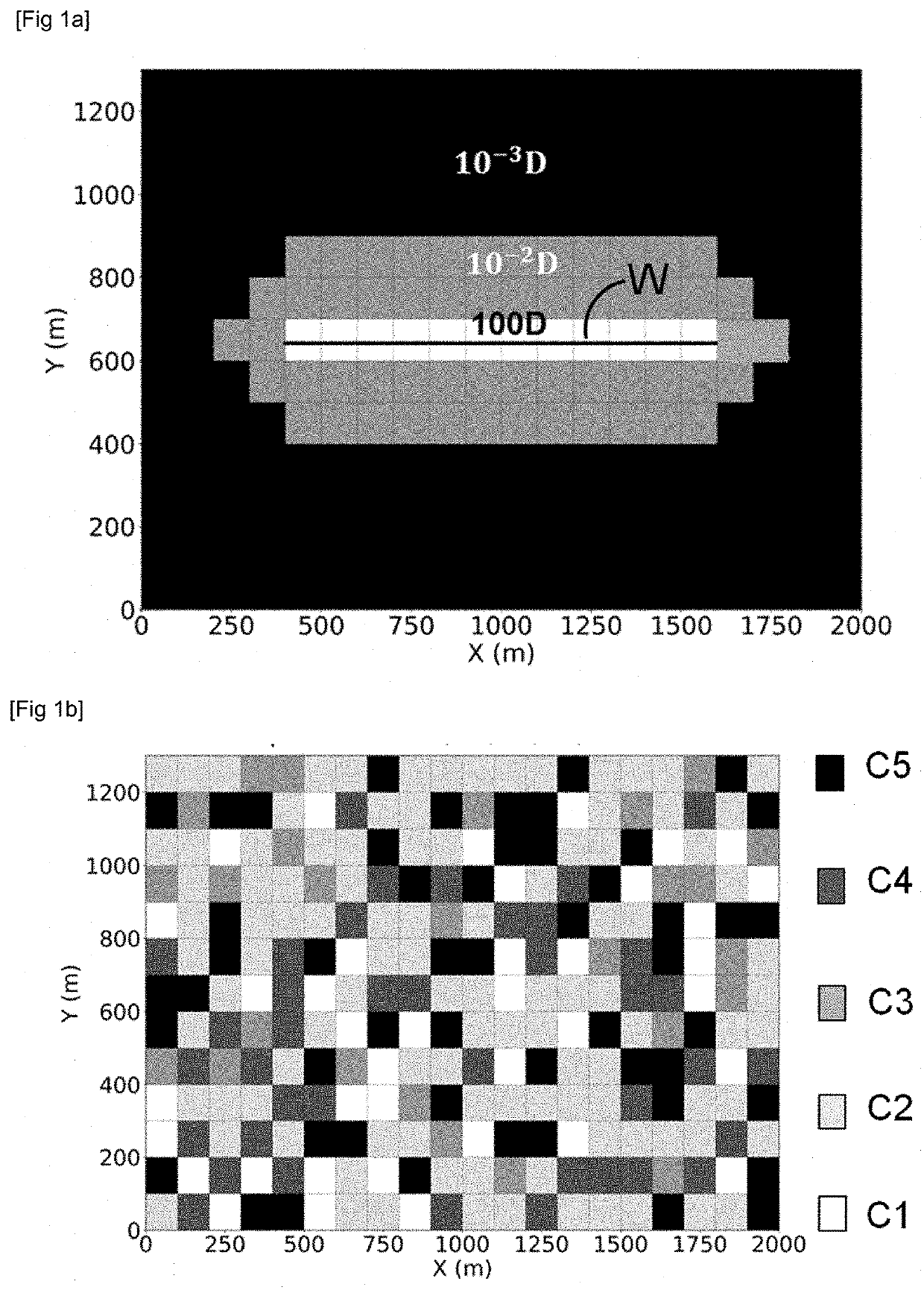
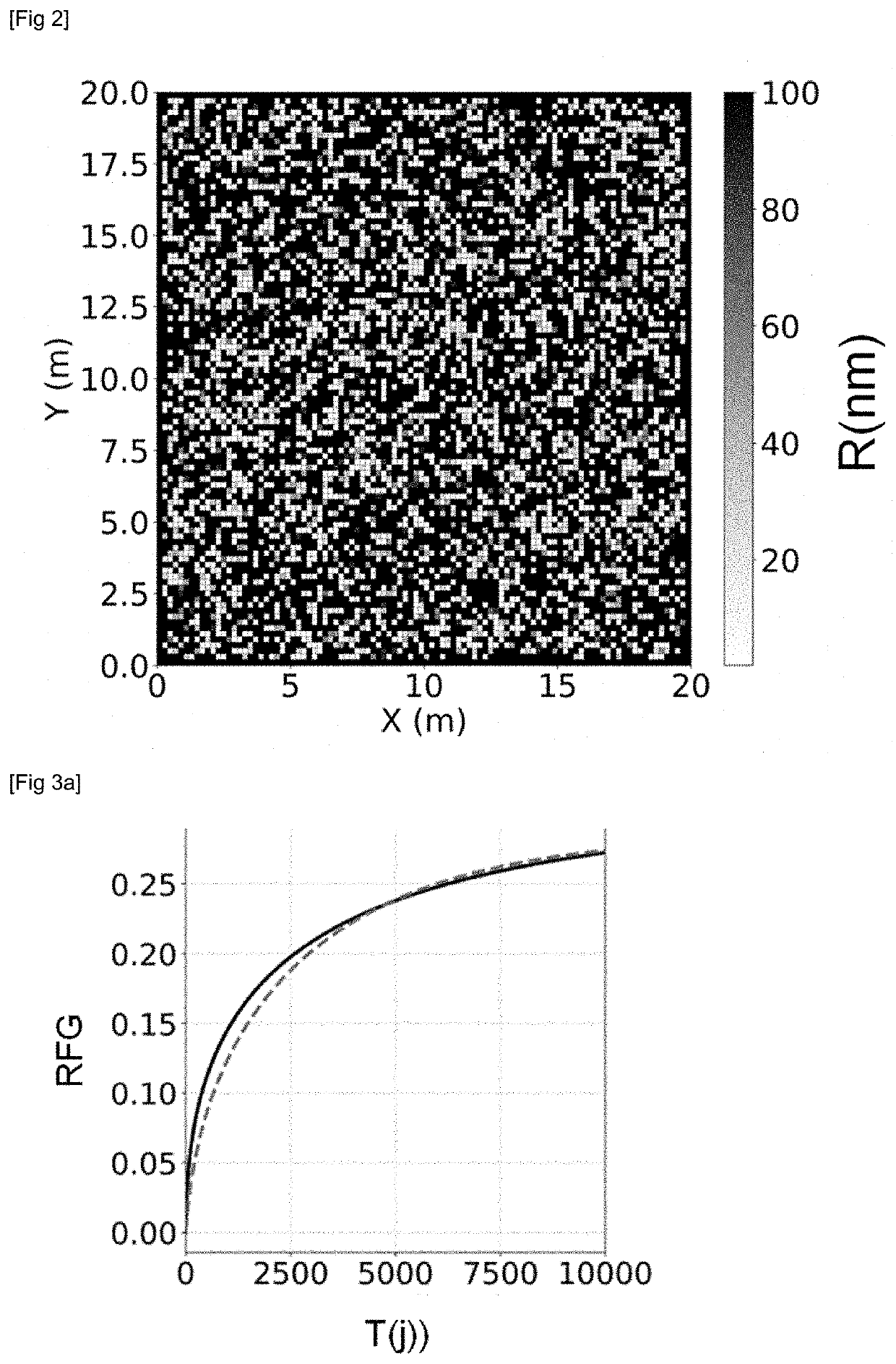
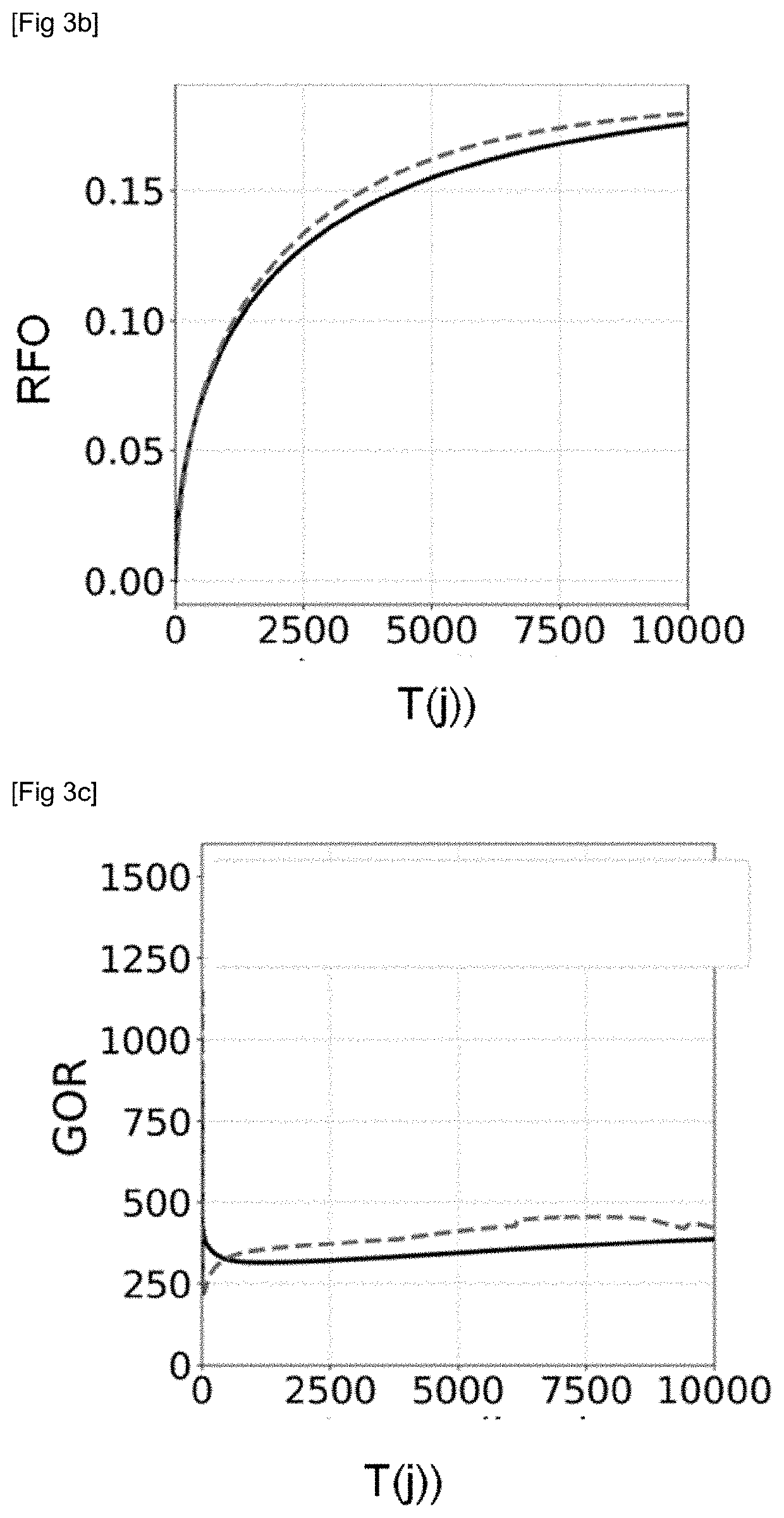
InactiveUS20200320239A1Improves flow simulationGood prediction of productionEarth material testingFluid removalPorosityCapillary pressure
The invention simulates flows in a geological reservoir having a heterogeneous pore size. From laboratory measurements on samples taken in the geological reservoir, pore size distribution classes are determined and a triple-porosity model representative of each class is determined. The flow simulator according to the invention implements the triple-porosity model, a thermodynamic equation of state accounting for an equivalent dimension of the pores of the small-size medium, fluid exchanges exclusively between the large-pore and small-pore media and between the small-pore and fracture media, and the capillary pressure as a function of the saturation in a small-pore medium.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
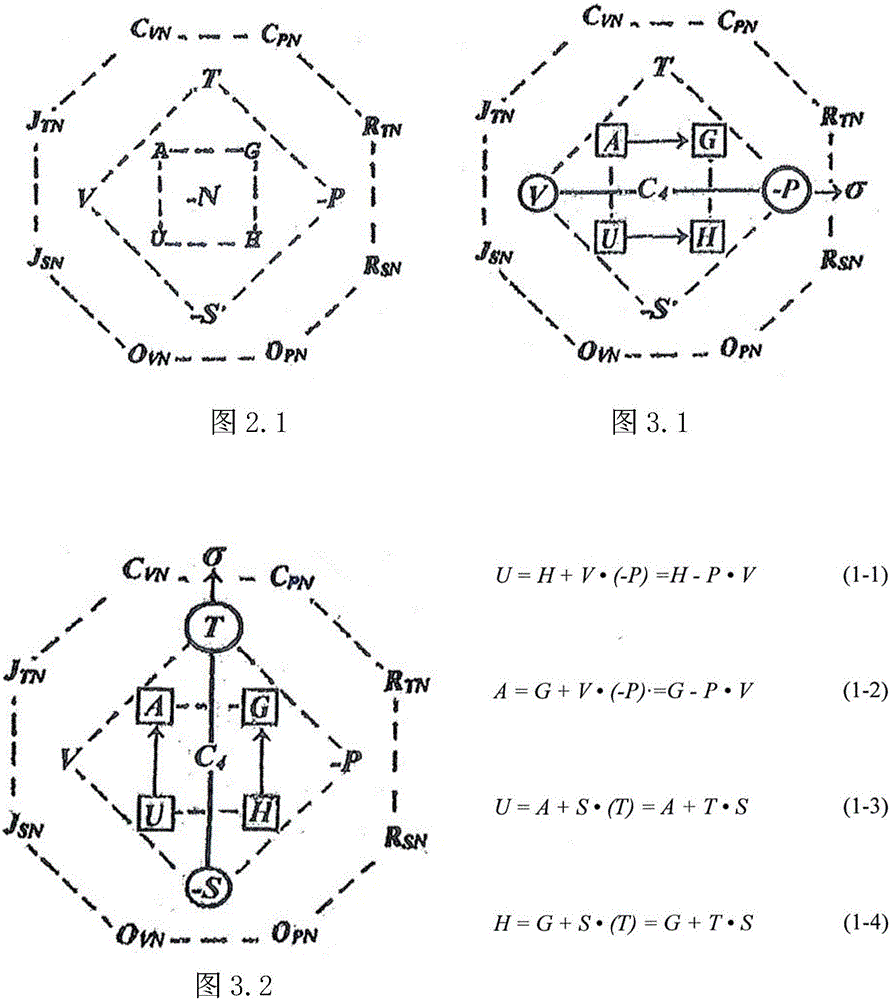
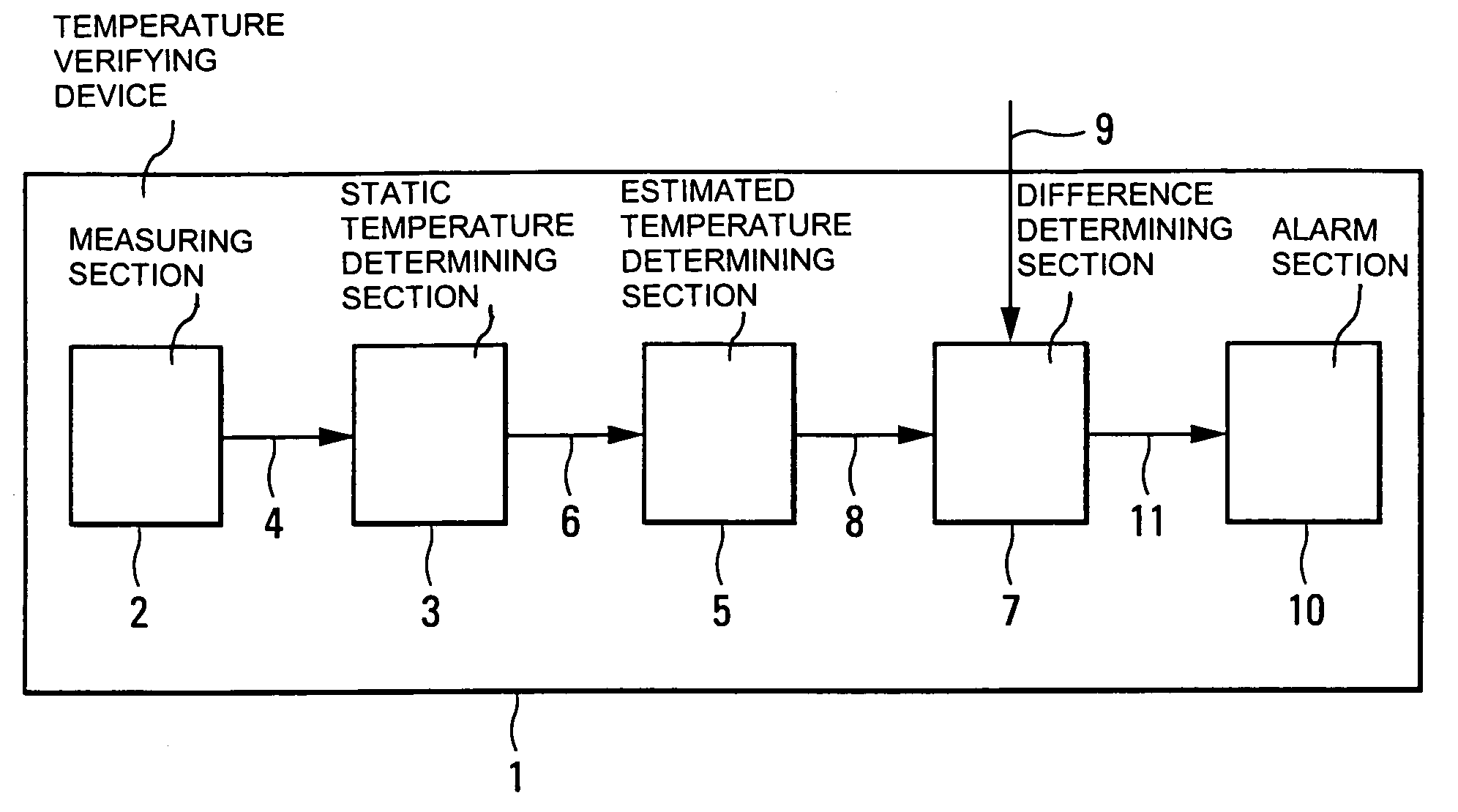
Method and device for verifying a temperature value at a destination altitude of an aircraft
The device comprises a means for measuring a dynamic temperature on the outside of the aircraft, a means for determining a static temperature around the aircraft, using said dynamic temperature, a means for determining, using said static temperature and a thermodynamic equation, a second temperature value corresponding to an estimated temperature at said destination altitude, a means for determining the difference between said first and second temperature values, and a means for emitting a warning signal when said difference is greater than a predetermined value.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Method for calculating alloy droplet deposition cooling rate
InactiveCN105689719ASimple processOptimization parametersAdditive manufacturing apparatusMathematical modelRegression analysis
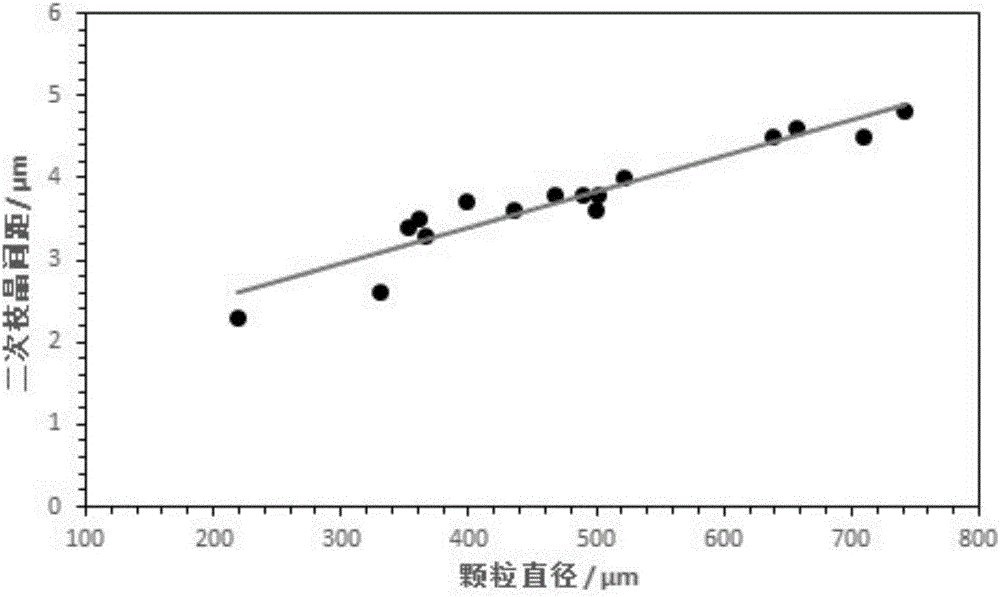
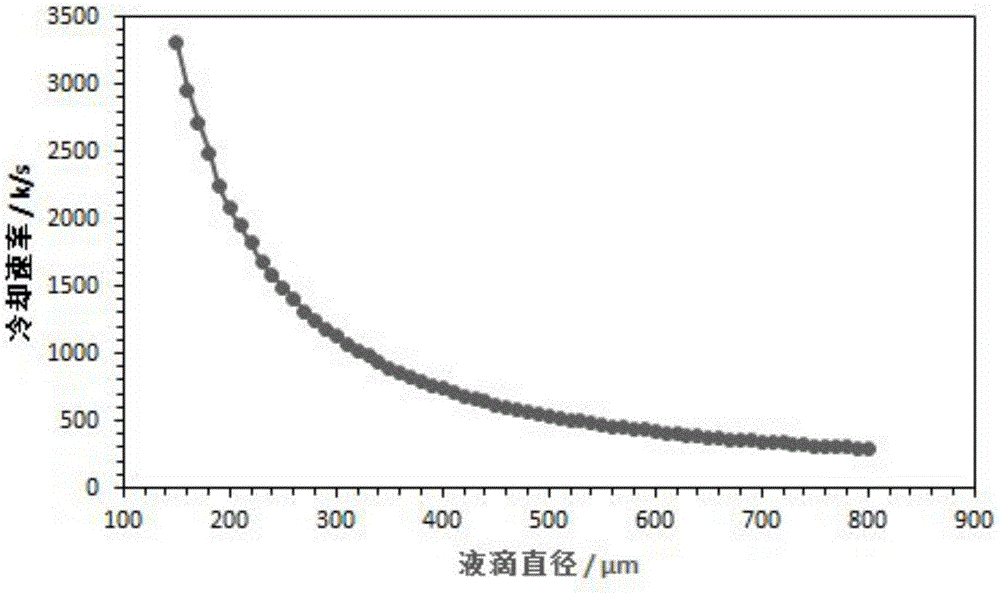
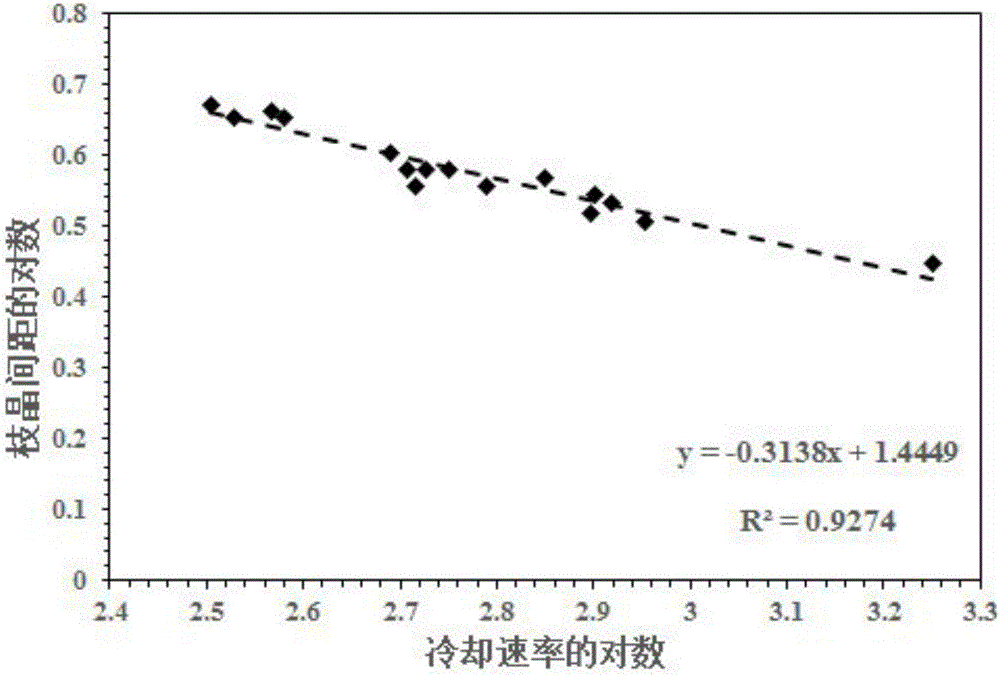
The invention discloses a method for calculating the alloy droplet deposition cooling rate and belongs to the technical field of 3D printing technologies. According to the method for calculating the alloy droplet deposition cooling rate, on the basis of a thermodynamic equation, a mathematic model of the cooling rate and the dendritic structure character is built, and accordingly the cooling rate is calculated according to droplet structure evolution. In the solidification process, the influence of crystalline latent heat is taken into account, the droplet ejecting speed is combined, the heat exchanging condition of the droplet movement process and the external environment is considered, and the variable relationship of the cooling rate of droplets with different diameters is calculated. According to the dendrite spacing dimension, a semi-empirical formula of the cooling rate and the secondary dendrite spacing is built and derived through regression analysis; by observing and measuring the dendritic structure of the deposition droplets, the cooling rate of the deposition droplets in the 3D printing process is obtained. According to the calculation method, the relationship between the 3D printing material structure and the cooling rate can be built, and deposition droplet solidification structure evolution of 3D printing can be effectively predicted, adjusted and controlled. The method for calculating the alloy droplet deposition cooling rate is mainly used for 3D printing technology control.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
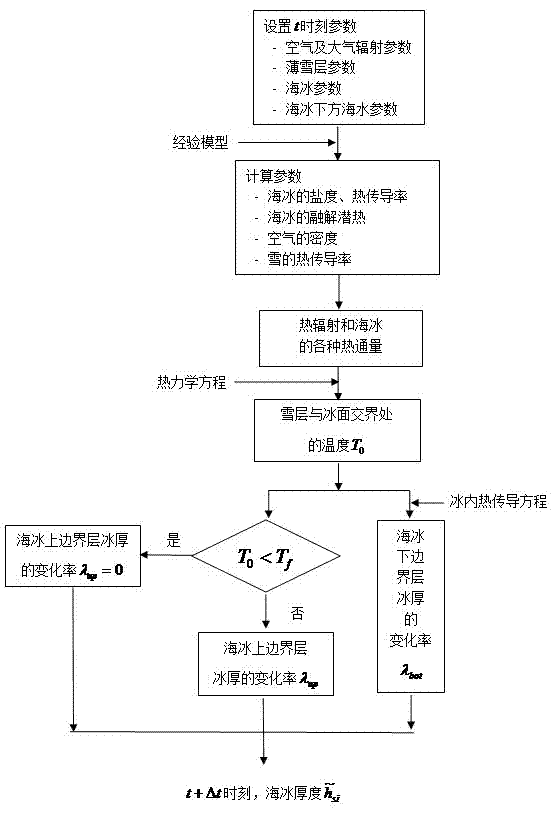
Method for simulating generating and thawing process of sea ice covered by thin snow
InactiveCN102902843AAvoid layered computingImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsHeat fluxLong wave radiation
The invention discloses a method for simulating the generating and thawing process of sea ice covered by thin snow. The method comprises the steps of: setting the sea ice covered by the thin snow and environmental parameters of the sea ice; calculating parameters such as salinity, heat conductivity, and melting latent heat of the sea ice; calculating the solar shortwave radiation, the atmosphere long wave radiation and various heat fluxes of the sea ice according to the environmental parameters; calculating the temperature at the boundary of a snow layer and an ice surface according to a thermodynamic equation; and judging whether the upper boundary layer of the sea ice is thawed or not, if so, calculating the change rate of the ice thickness of the upper boundary ice layer; calculating the change rate of the thickness of the lower boundary layer of the sea ice according to an internal heat conduction equation; and finally calculating the thickness of the sea ice according to the change rates of the thicknesses of the upper and lower boundary layers of the sea ice. The method has the characteristic of high calculation efficiency and can be used for the simulation on the generating and thawing process of the sea ice covered by thin snow.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
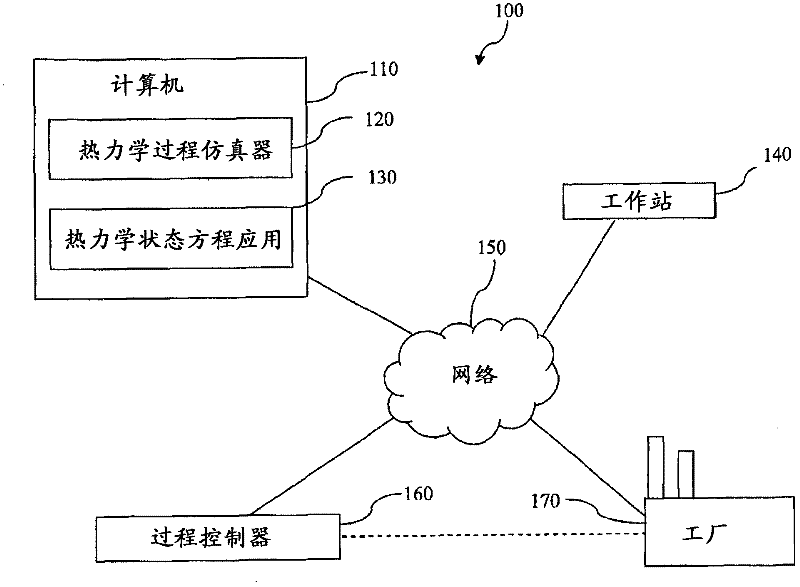
Thermodynamic process control based on pseudo-density root for equation of state
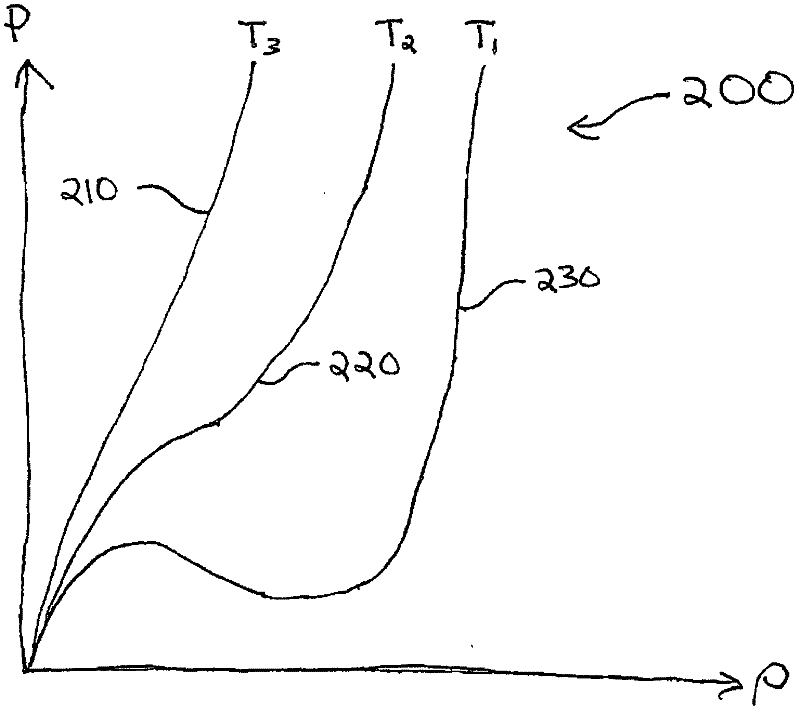
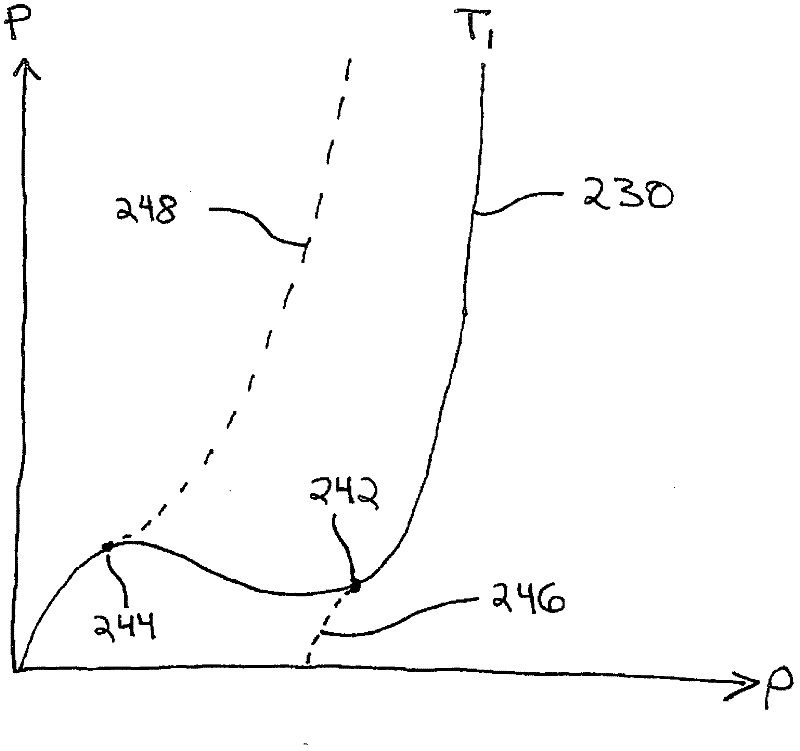
InactiveCN102597988ASimulator controlMultiple digital computer combinationsThermodynamic stateEquation of state
A thermodynamic modeling system comprising a computer, a thermodynamic process simulation application, and a thermodynamic equation of state application is provided. The thermodynamic equation of state application determines a density root based on a first and second point of departure from an equation of state and based on a first and a second extrapolation equation. The first departure point satisfies the equation the partial derivative of pressure with respect to density equals a first constant times the pressure divided by the density plus a second constant. The density root is determined as a pseudo-density in a phase two when the specified pressure is greater than the second departure point pressure and in a phase one when the specified pressure is less than the first departure point pressure.; The thermodynamic process simulation application invokes the thermodynamic equation of state application to determine a result based on the density root.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
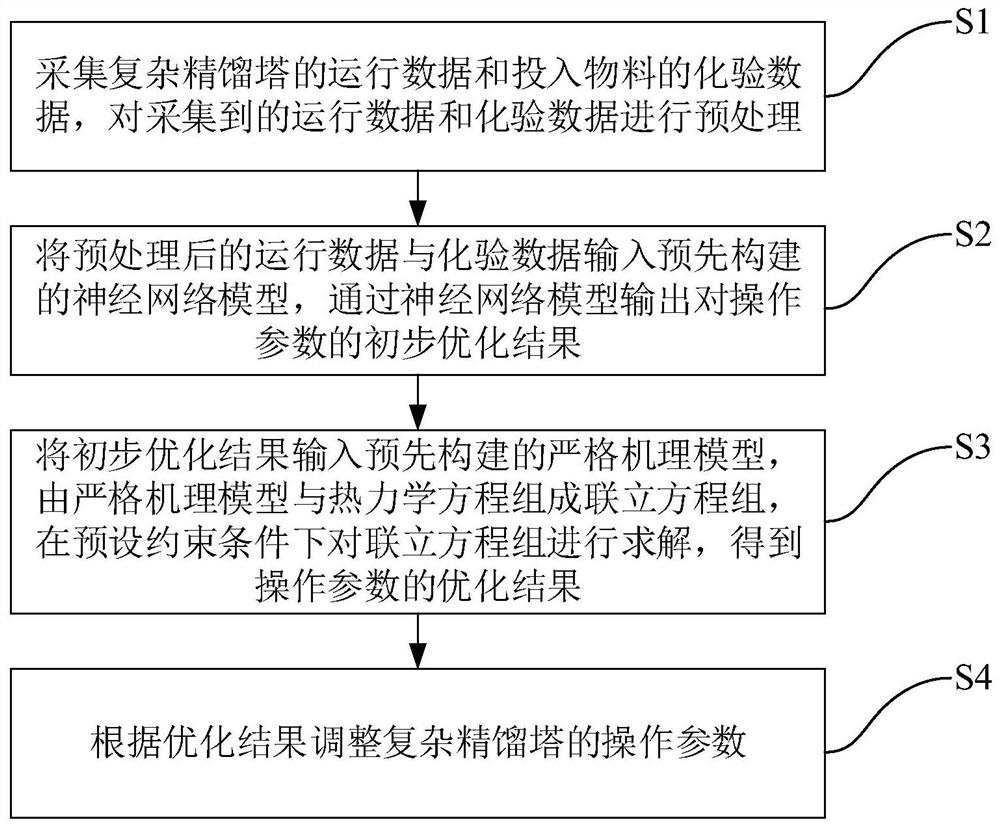
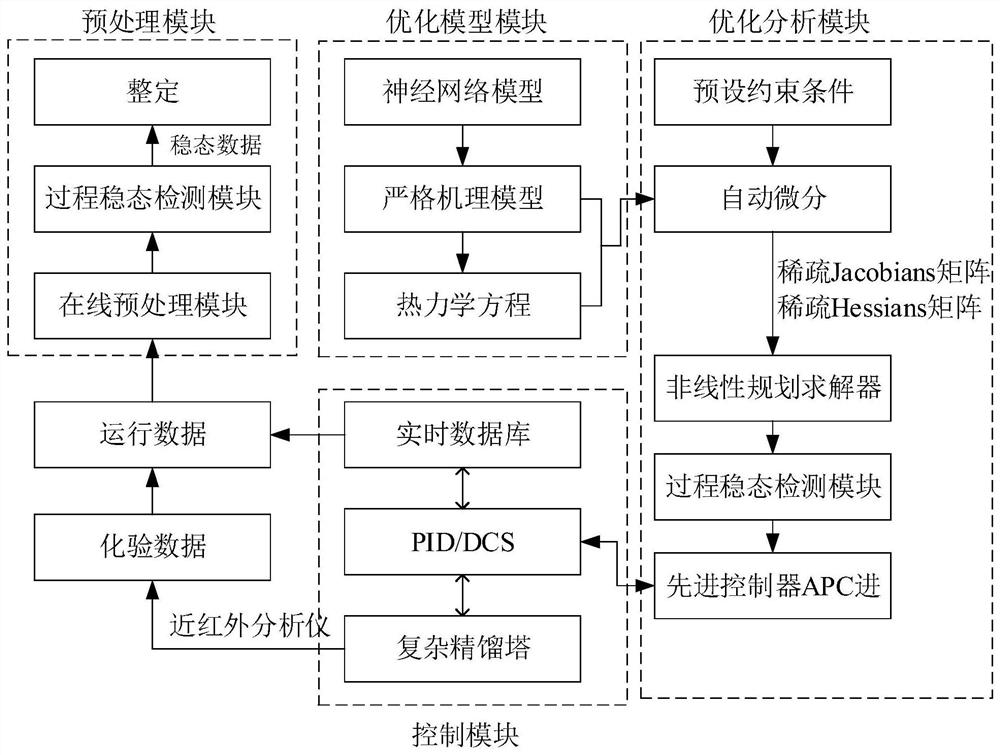
Operating parameter optimization method for complex rectifying tower
PendingCN112597430AReduce complexityMeet actual response needsForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationAssayAlgorithm
The invention provides an operating parameter optimization method for a complex rectifying tower, which comprises the following steps: acquiring operating data of the complex rectifying tower and assay data of input materials, and preprocessing the acquired data; inputting the preprocessed operation data into a neural network model, and outputting a preliminary optimization result of the operationparameters through the neural network model; inputting the preliminary optimization result into a strict mechanism model, forming a simultaneous equation set by the strict mechanism model and a thermodynamic equation, and solving the simultaneous equation set under a preset constraint condition to obtain an optimization result of the operation parameter; adjusting operation parameters of the complex rectifying tower according to an optimization result. Operation parameters of the complex rectifying tower are optimized twice by combining the neural network model and the strict mechanism model,the neural network model obtains a preliminary optimization result of the operation parameters firstly, and the convergence rate and robustness during subsequent solving of the strict mechanism modelare increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUPCON TECH +1
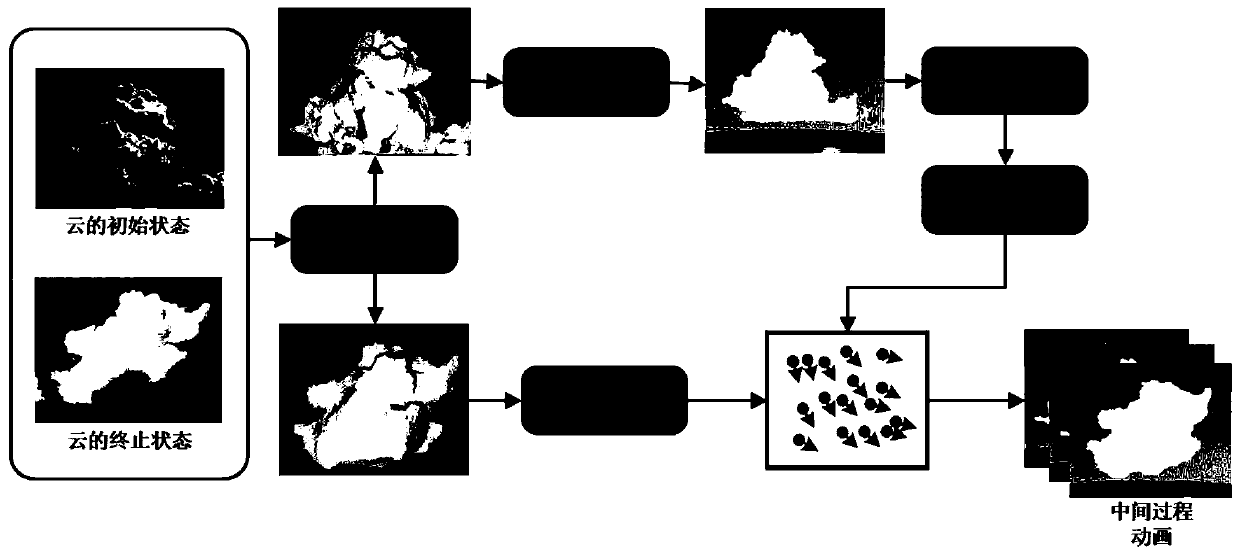
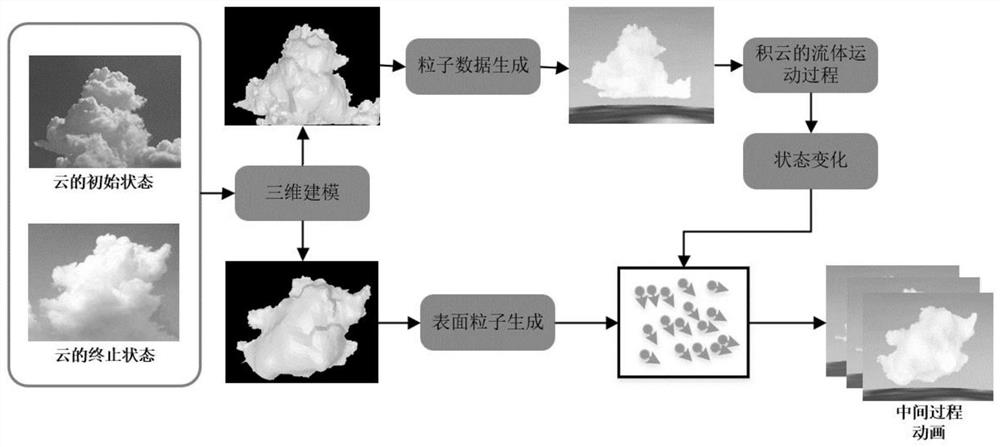
Three-dimensional cloud motion evolution method based on physics
ActiveCN110096766AEasy to implementImprove Simulation EfficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsCouplingComputer graphics
The invention discloses a three-dimensional cloud motion evolution method based on physics, belongs to the field of computer graphics, and can realize automatic evolution from an initial three-dimensional cloud shape motion to a target shape by taking two natural cloud images as input. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, respectively reconstructing a three-dimensional cumulative cloud model from two given cumulative cloud natural images, and carrying out particle sampling on a first three-dimensional cumulative cloud model to obtain cloud particle data; secondly, solving a thermodynamic equation, a state change equation and a motion equation of the cumulative cloud in an atmospheric motion process to realize a physical motion process of the cumulative cloud; thirdly, adopting the PBF method to keep the density of cloud particles unchanged in the movement process, and to guarantee incompressibility of the accumulated cloud in the movement process; then, performing surfaceparticle sampling on the target shape, and achieving coupling of cloud particles and the target shape in combination with a fluid-solid interaction strategy; and finally, adjusting an external forceapplied to the cloud in the movement process according to the movement states of the time frames before and after the cloud, and driving the physical movement process of the cloud until the final shape is consistent with the target shape.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
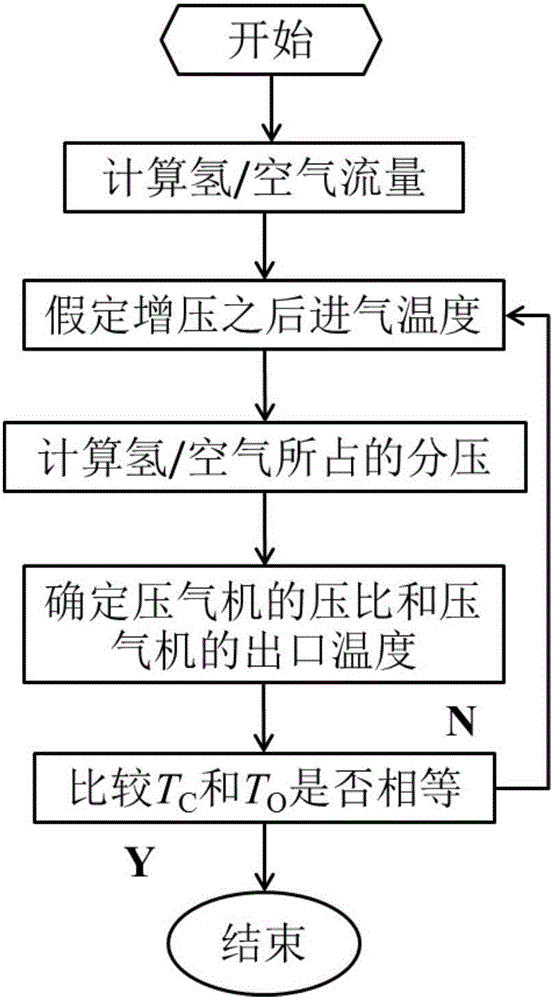
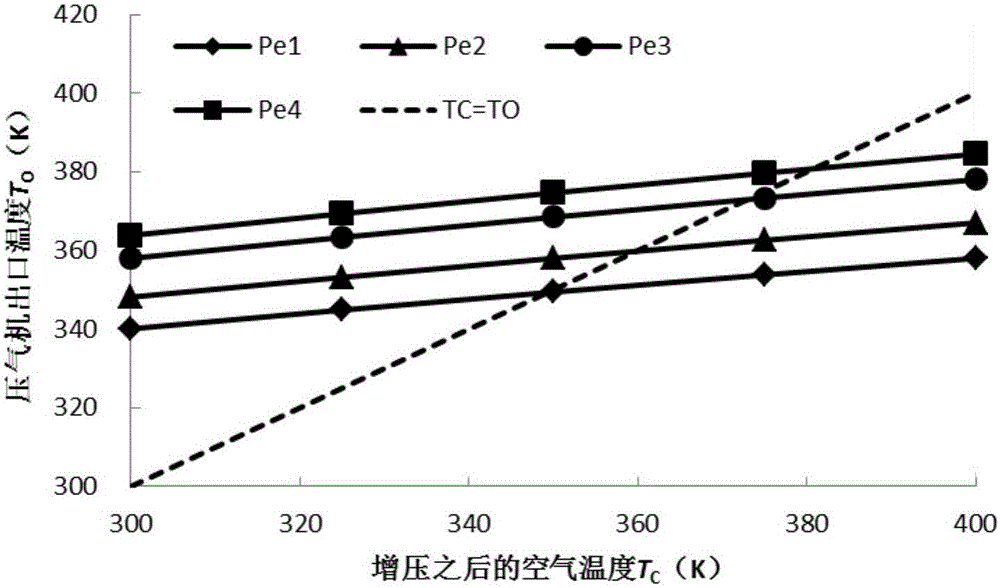
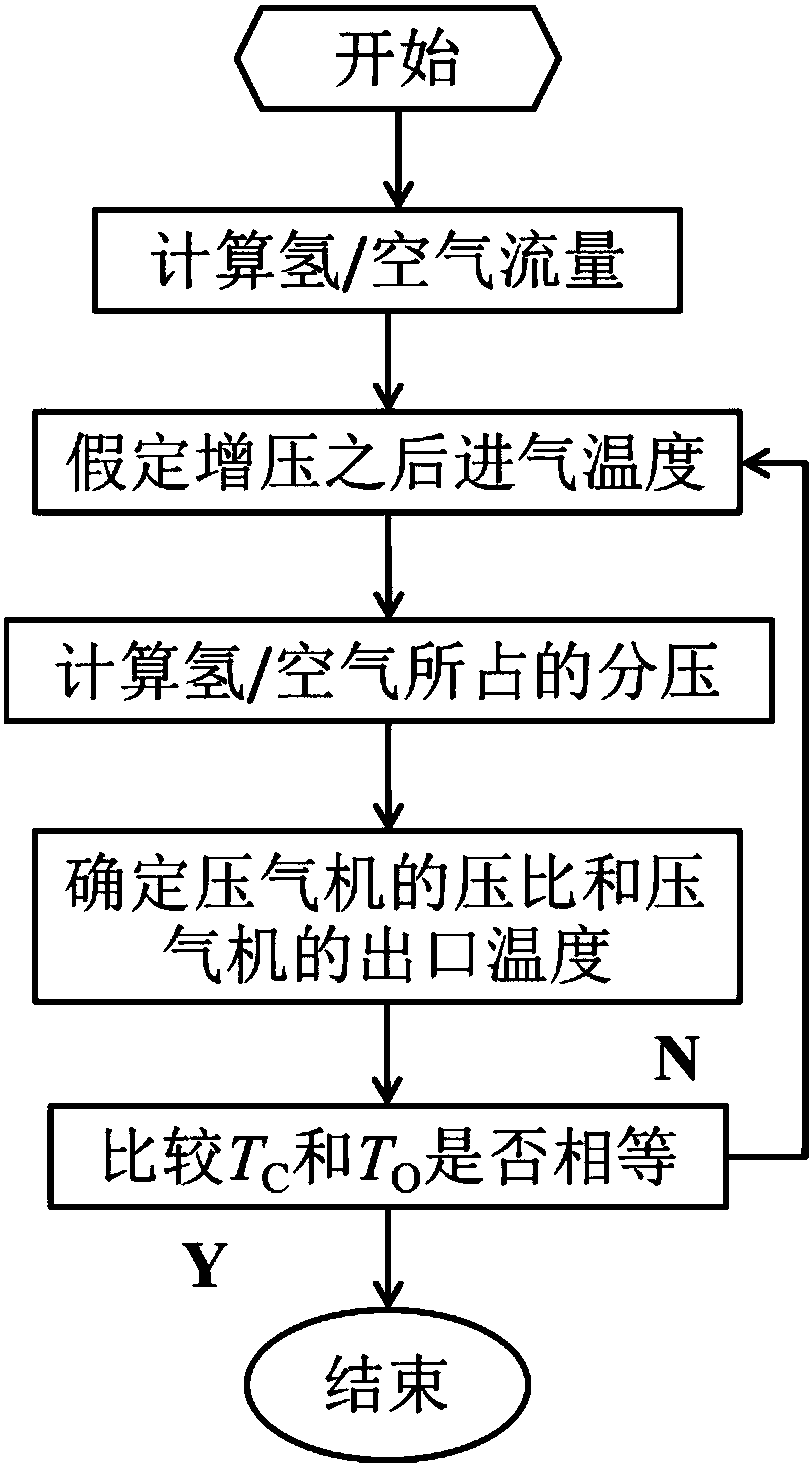
Compressor type selection method suitable for supercharged hydrogen internal combustion engines
ActiveCN105955926ATemperature correctionThe result is accurateComplex mathematical operationsHydrogenCombustion
The invention discloses a compressor type selection method suitable for supercharged hydrogen internal combustion engines. Through a given target value and the basic parameters of an engine, the fuel, entering an air cylinder, of the conventional engines is liquid and does not generate partial pressure; the hydrogen internal combustion engines take hydrogen as fuel, and after entering the air cylinder, the gas fuel generates partial pressure and the influences, caused by the partial pressure generated by the gas fuel, on the pressure ratio calculation of the compressor is considered; therefore, according to the method disclosed in the invention, the partial pressure, in the air cylinder, of the hydrogen and the air is calculated to serve as total pressure in the air cylinder, and then the pressure ratio of the compressor is calculated; moreover, a plurality of compressor outlet temperatures are selected in a reasonable range according to experience values at the outlet of the compressor, after obtaining the pressure ratio, a theoretical value of the compressor outlet temperature is obtained through a thermodynamic equation, and the pressure ratio obtained when the selected experience value of the compressor outlet temperature is approximately equal to the thermodynamic equation is taken as the final result, so that the modification of the temperature after the supercharging is realized and more accurate result can be obtained.
Owner:北京氢燃科技有限公司
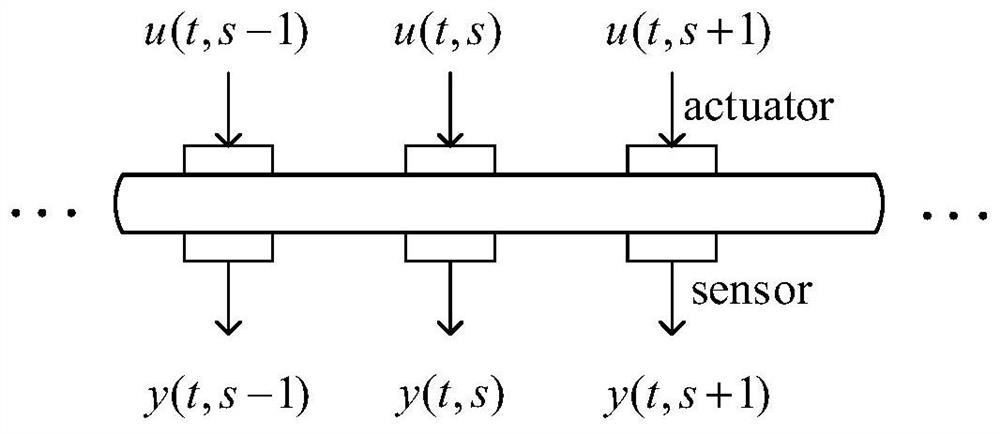
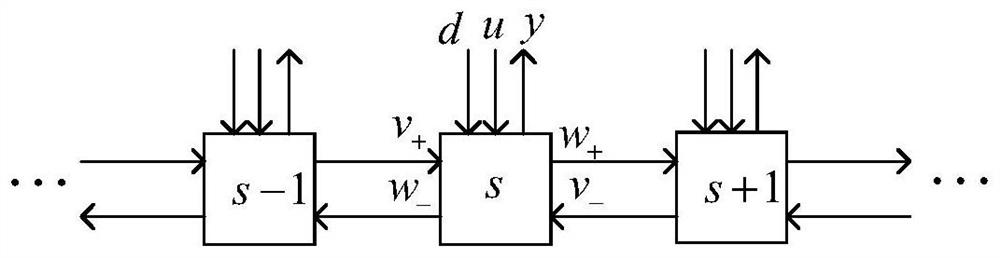
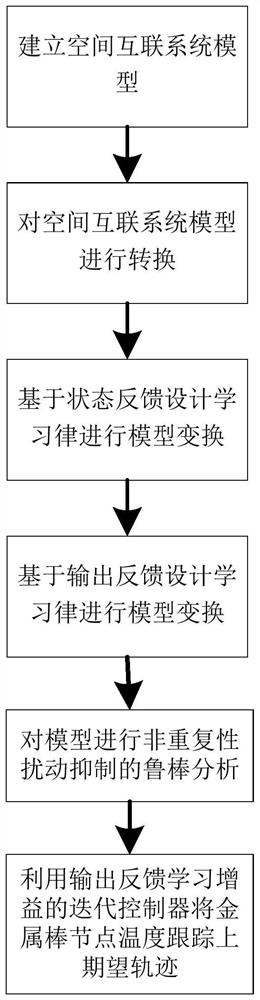
Robust heuristic iterative learning control method for metal bar temperature distribution system
ActiveCN112327971ASimple methodEasy to implementAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesAlgorithmLinear matrix
The invention discloses a robust heuristic iterative learning control method for a metal bar temperature distribution system, and relates to the field of iterative learning control. The robust heuristic iterative learning control method comprises the steps of: carrying out discretization of a metal bar thermodynamic equation through employing a finite difference method for a metal bar system to obtain a partial recursion equation, and converting the partial recursion equation into a spatial interconnection system model; converting the spatial interconnection system model into an equivalent one-dimensional dynamic model by using a lifting vector technology; designing a controller based on state feedback; constructing a controller based on output information by using the controller; converting a controlled object into an equivalent discrete repetitive process according to a designed iterative learning law; and converting a controller comprehensive problem into a linear matrix inequalitybased on stability analysis of a repetitive process. The robust heuristic iterative learning control method is simple and easy to implement, solves the problem of non-convex stability generally causedby static output feedback, considers the problems of model uncertainty and disturbance suppression of the system, and has good control performance and robustness.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
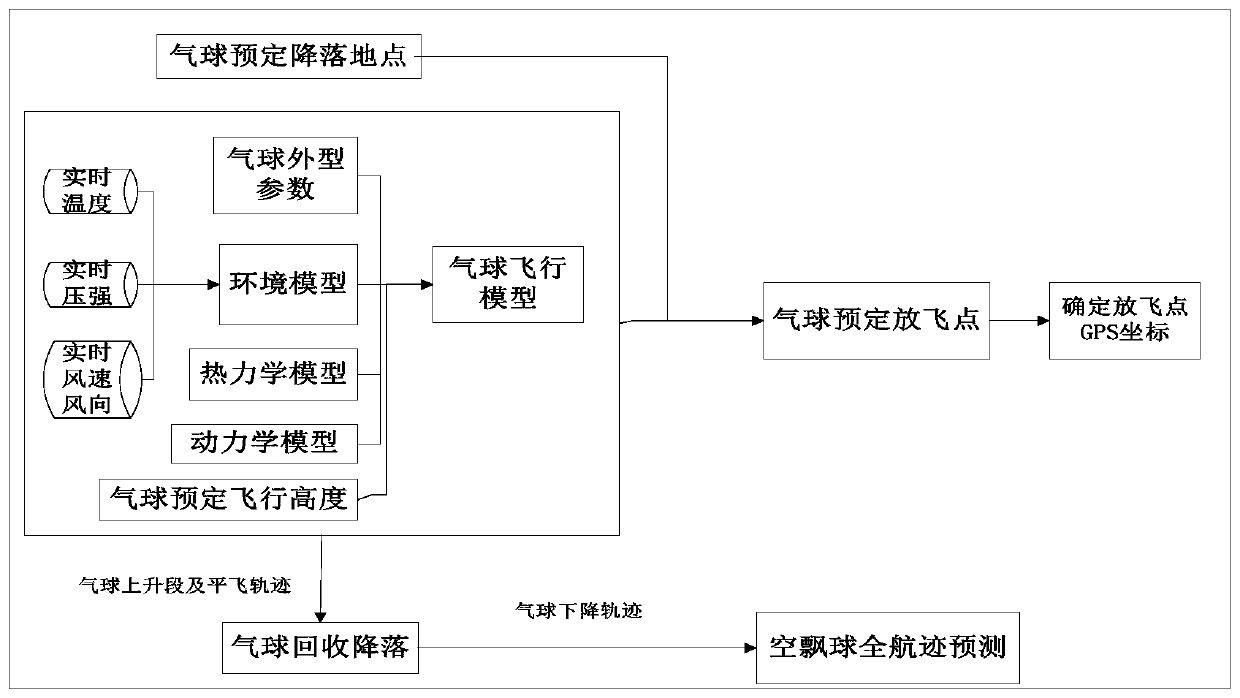
Medium-low altitude balloon flight path prediction method
PendingCN110889256AControllable flightImprove forecast accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationKinematics equationsClassical mechanics
The invention belongs to the technical field of balloon flight path planning, and discloses a medium-low altitude balloon flight path prediction method, which comprises the steps of obtaining balloonsystem parameters, and a predetermined task flight height and a landing point of a balloon; carrying out interpolation to obtain environmental parameters of the balloon at any height from the ground to the flight height of the predetermined task; calculating the balance weight of the balloon when the balloon flies on the ground; establishing a thermodynamic equation in the balloon rising process,a kinetic equation, and a kinematic equation; predicting to obtain a flying point of the balloon, a rising track of the balloon from the ground to the starting point of the level flying stage and a motion track of the balloon in the level flying stage. The problem of balloon flight path prediction and planning is solved, the balloon can complete a flight task according to the planning path and height, and high-precision prediction of the flight path of the medium-low altitude balloon is realized.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL TYPE FLIER RES INST
Thermodynamics circulation system achieving heat circulation through environment working media and application
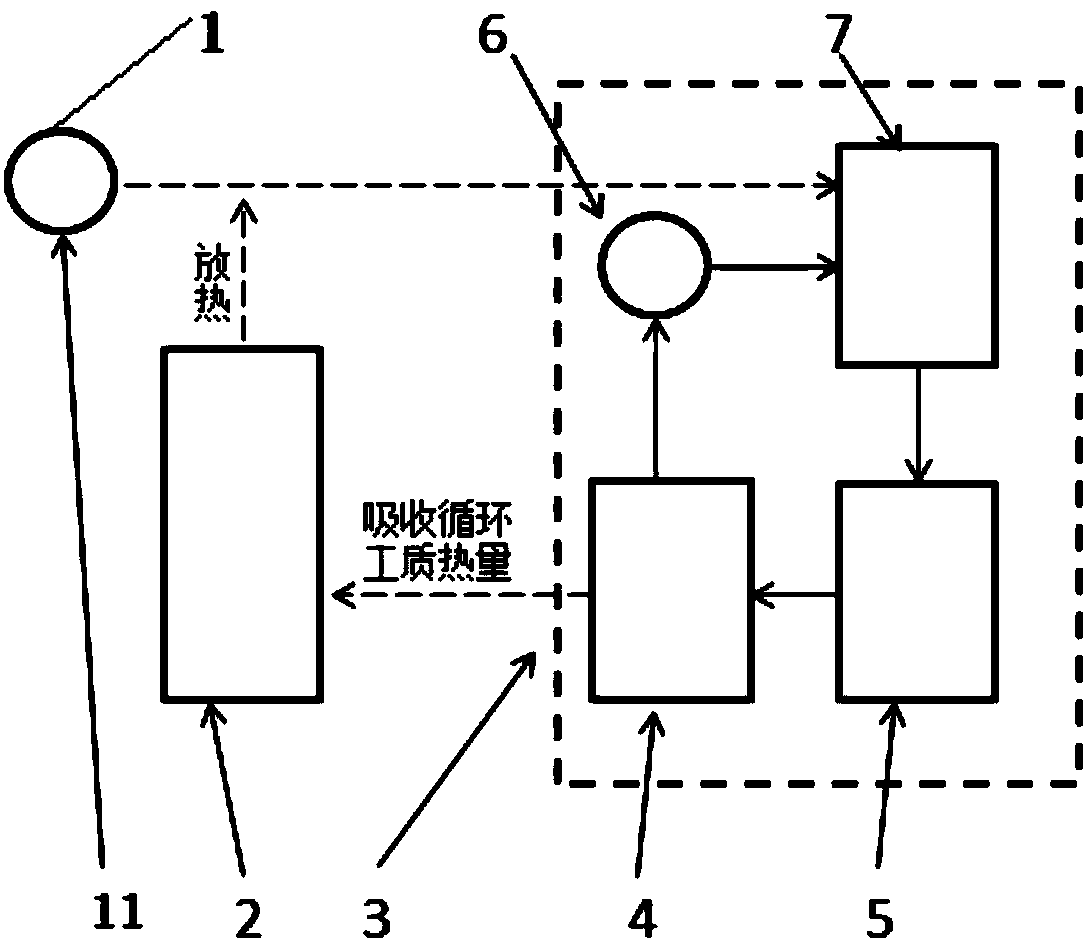
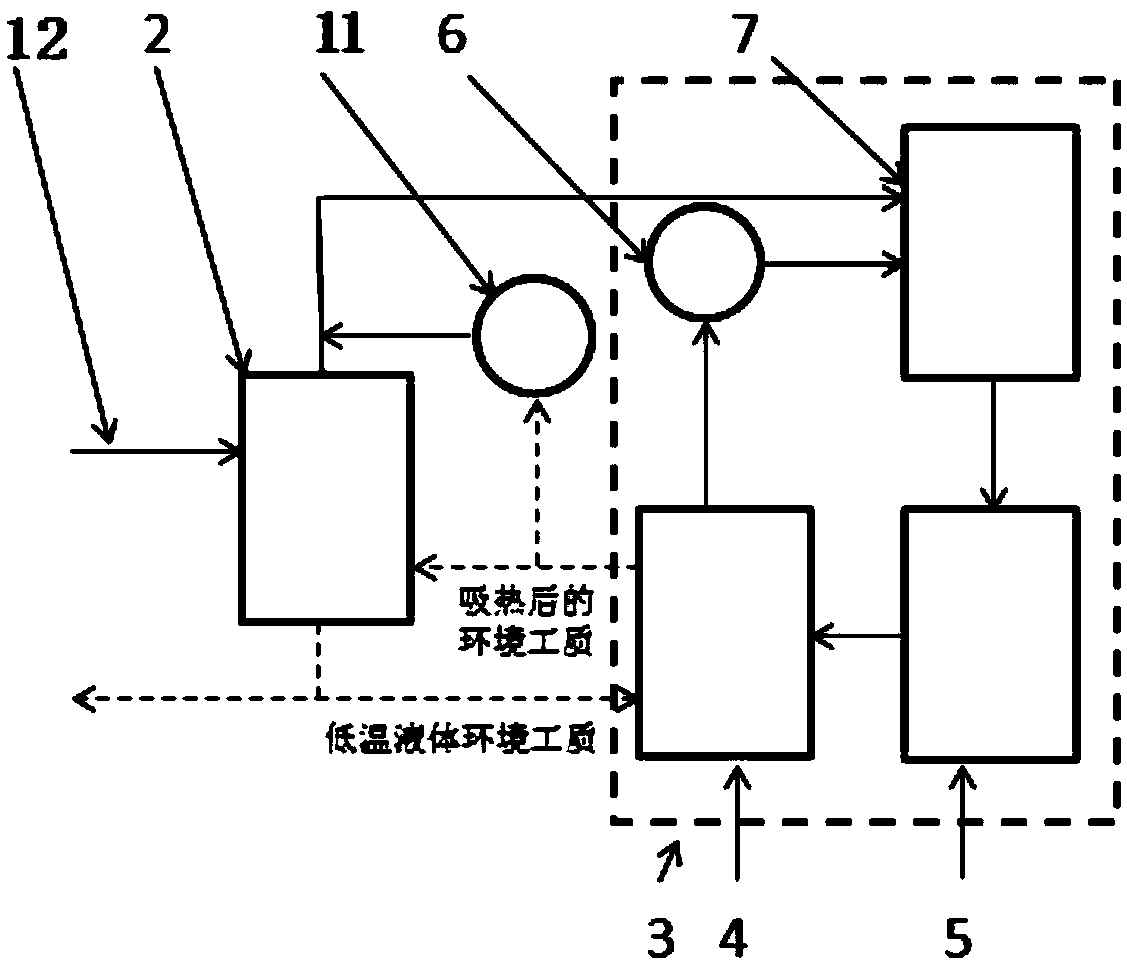
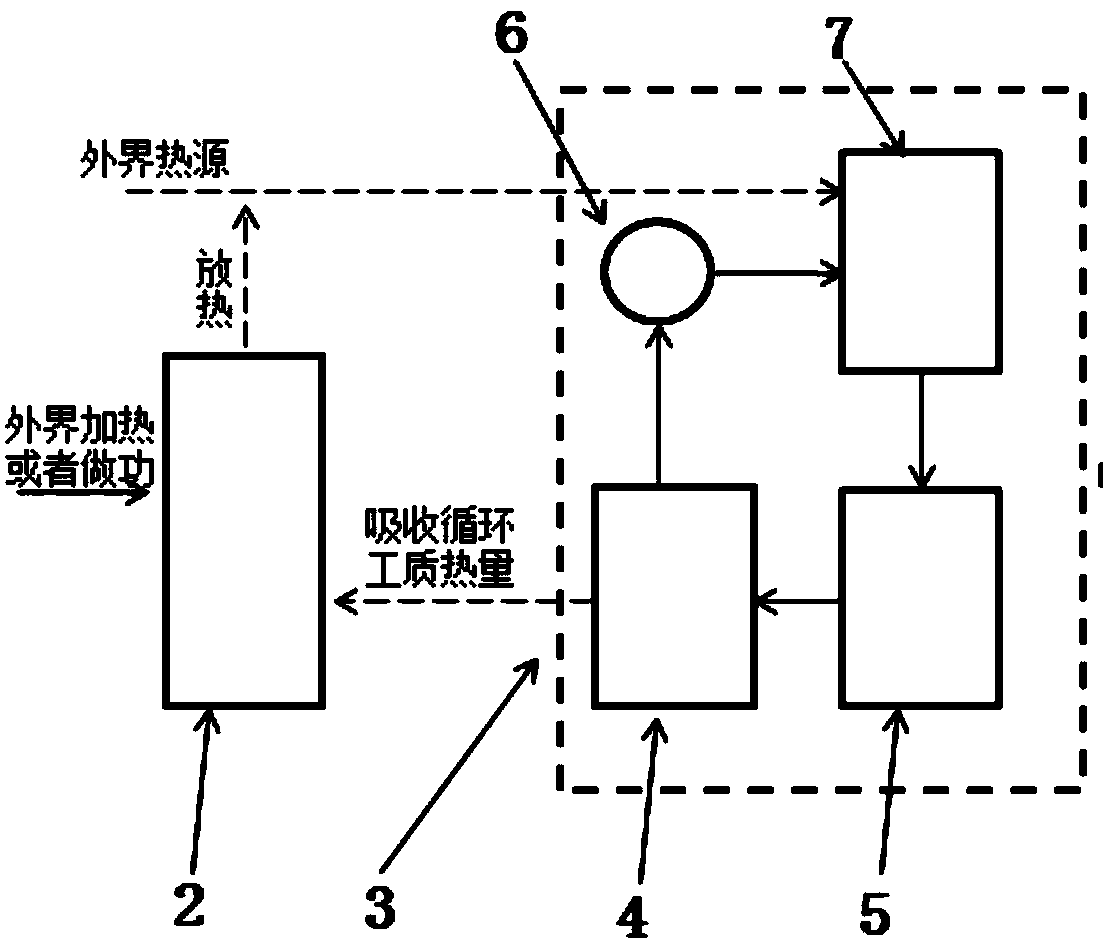
ActiveCN105783300AIncrease profitEmission reductionCompression machines with non-reversible cycleRefrigeration componentsArtificial environmentEngineering
The invention discloses a thermodynamics circulation system achieving heat circulation through environment working media and application. The system comprises an environment working medium system and a thermodynamics circulation system body. The thermodynamics circulation system body comprises a circulating working medium evaporator, a circulating working medium expansion device, a circulating working medium condenser and a circulating working medium pump which are circularly connected in sequence. In addition, in order to convert low-level energy into high-level energy, an external heat source is further introduced. According to the thermodynamics circulation system achieving heat circulation through the environment working media, an artificial environment serves as a part of a low-temperature heat source and a high-temperature heat source of the thermodynamics circulation system body, phase change heat of the thermodynamics circulation system body can be transferred to the environment working media, the heat is transmitted to the thermodynamics circulation system body again by means of energy conversion of the environment working media, and the utilizing rate of energy is increased.
Owner:西安新港分布式能源有限公司
Small room refrigerating and fresh air generating method
InactiveCN107477755ASimple processEasy to controlSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusFresh airAir change
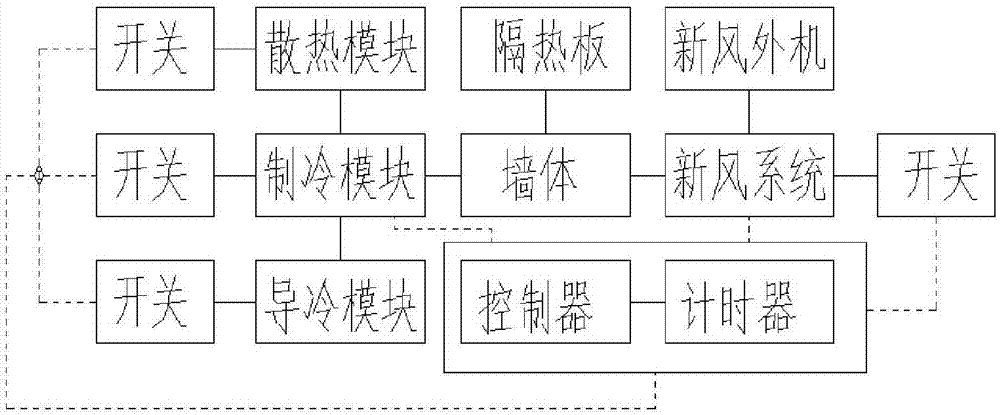
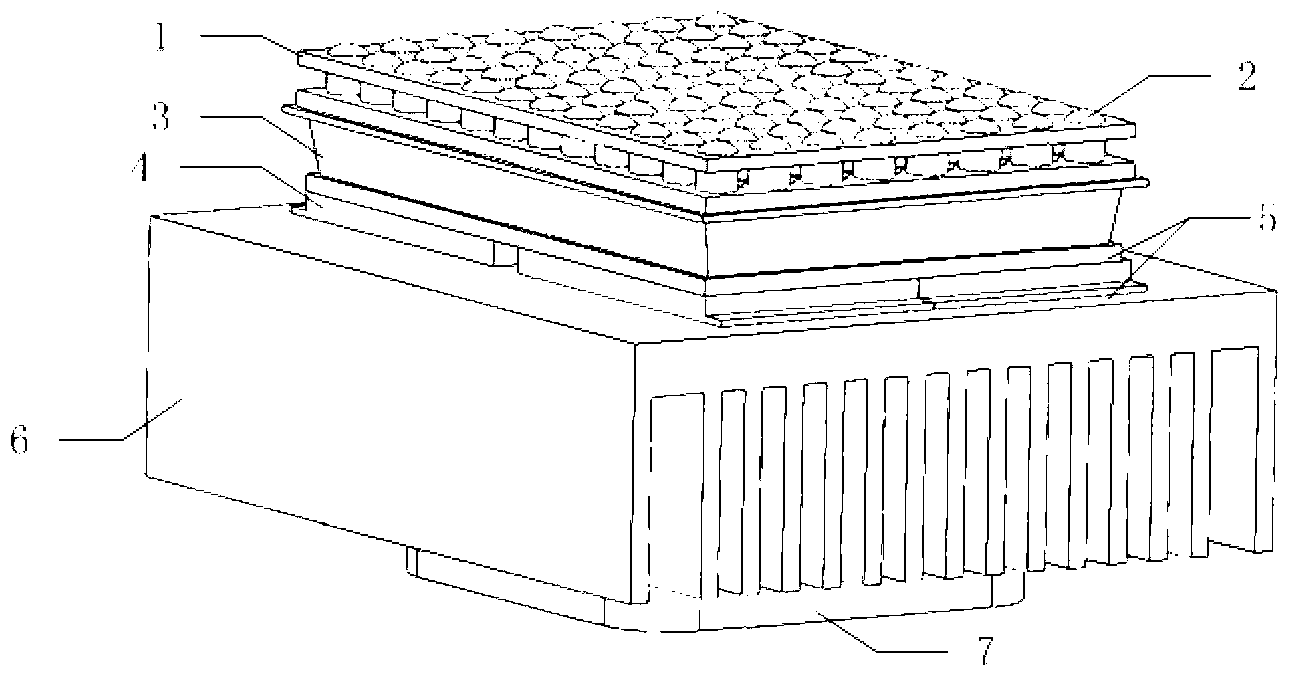
The invention discloses a small room refrigerating and fresh air generating method. The method comprises the following steps that a refrigerating module and a fresh air system are arranged on the inner side of a wall body in a spaced mode, and a radiating module and a cold guiding module are provided; the indoor size of a small room is calculated, the indoor temperature of the small room is measured, and parameters are calculated according to a thermodynamic equation; and a controller controls the switch sequence and opening and closing time of the refrigerating module, the radiating module, the cold guiding module and the fresh air system, and refrigerating and fresh air feeding are achieved, and finally thermal is balanced or the system is closed. The method is delicate in conception, automatic and flexible in process and suitable for small room rapid and balanced refrigerating and fresh air feeding and is a good choice for cooling and air change in summer.
Owner:TAICANG SANYI HEATING & CHILLING PROJECT CO LTD
Equivalent analysis circuit of gene amplification instrument thermal cycling system based on thermoelectric cooler (TEC)
InactiveCN103268376AAvoid the modeling processAvoid parsingSpecial data processing applicationsCapacitanceEngineering
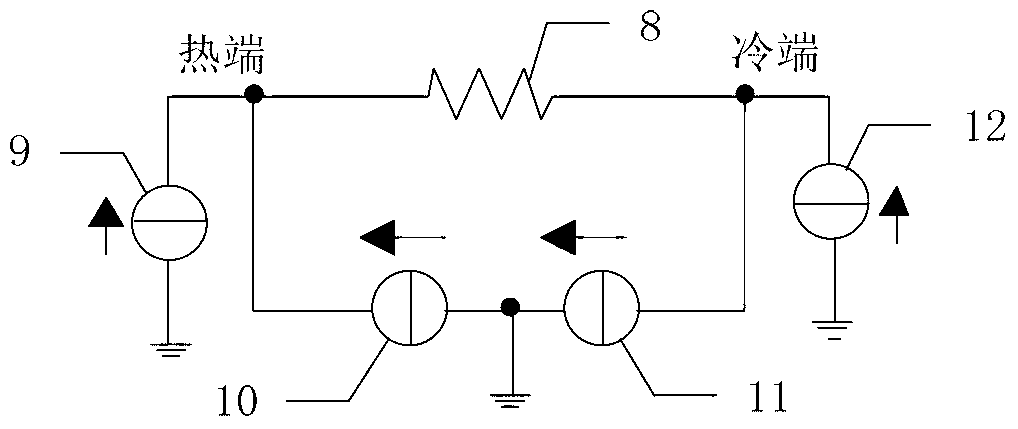
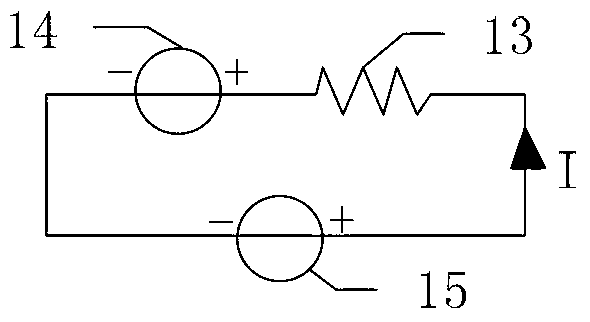
The invention discloses an equivalent analysis circuit of a gene amplification instrument thermal cycling system based on a thermoelectric cooler (TEC). Thermal physical parameters of heat q, temperature T, thermal resistance and thermal capacity C in a heat transfer process of the thermal cycling system are replaced by electrical physical parameters of current I, voltage U, resistance R and capacitance c respectively in an equivalent mode. A thermal cycling system pure circuit model based on the TEC is built. Parameter calculation is performed on electrical apparatus elements of the circuit model according to physical parameters supplied by manufacturers, simulation analysis of the equivalent analysis circuit of the thermal cycling system is achieved by combining software of Multisim and the like, and steady state and dynamic performances of the thermal cycling system are studied and evaluated through simulation results. The equivalent analysis circuit of the gene amplification instrument thermal cycling system based on the TEC successfully avoids that modeling and analysis are performed on the heat transfer process of the thermal cycling system through a method by building of a complicated thermodynamic equation, greatly simplifies a thermal performance analysis process of the thermal cycling system, and can provide visual reference for design and optimization of the thermal cycling system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
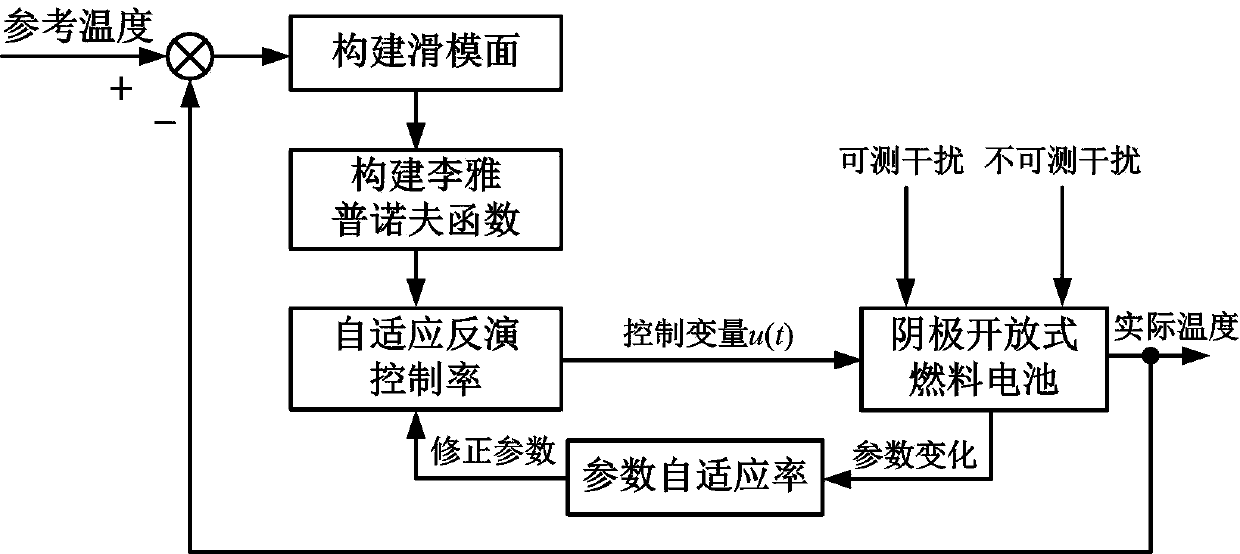
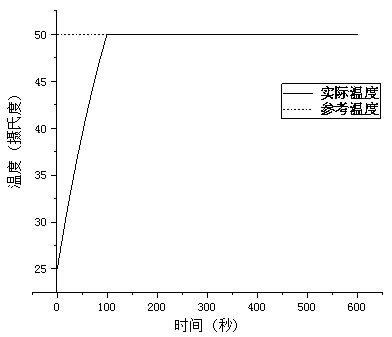
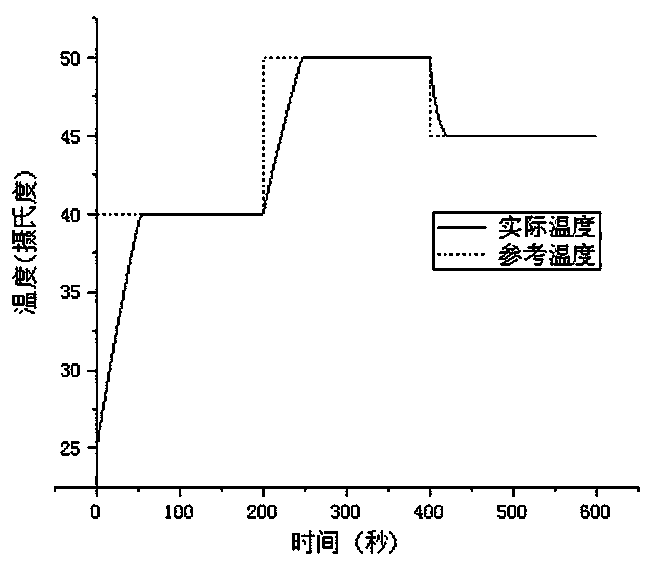
Temperature adaptive control method for cathode open type fuel cell
ActiveCN110112444AIncrease working temperatureMake up for uncertaintyFuel cellsTemperature controlFuel cells
The invention relates to a temperature adaptive control method for a cathode open type fuel cell. The method comprises steps that a cathode open type fuel cell temperature model is established, various thermodynamic equations are expanded, physical quantities other than the fuel cell stack temperature and a forced heat convection transfer coefficient are further constantized, a state equation consisting of the fuel cell stack temperature and the forced heat convection transfer coefficient is established, a sliding mode surface of temperature tracking control is defined, a Lyapunov function isconstructed, a controller based on adaptive inversion sliding mode control strategy is designed in combination with the state equation, temperature control of the cathode open type fuel cell stack isrealized, and an adaptive system parameter changes.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for obtaining specified thermodynamic function of nanometer material
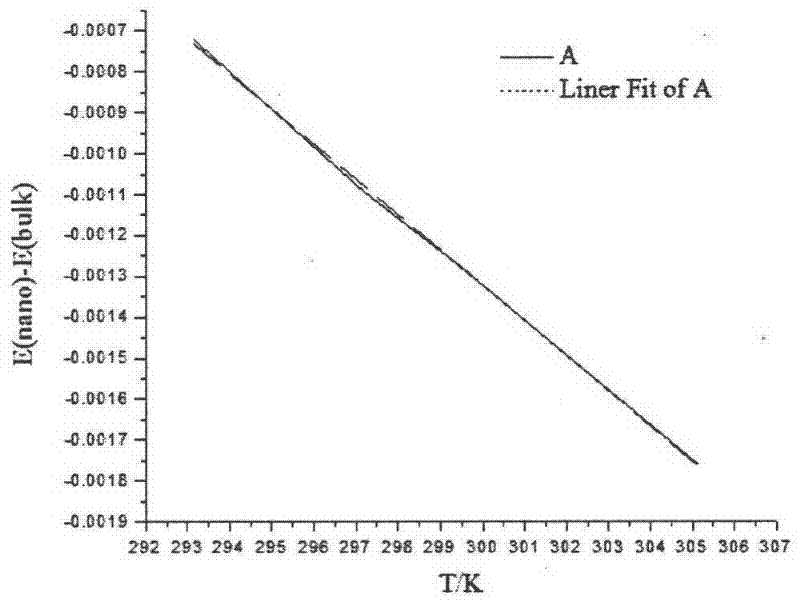
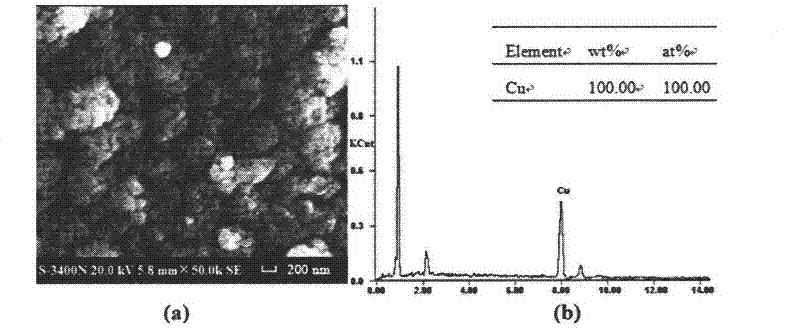
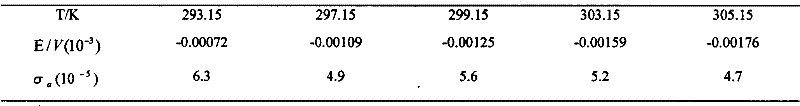
InactiveCN102507672AEasy to operateEasy to implementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrode potentialPotential change
The method provided by the invention comprises the steps as follows: measuring electrodynamic potential of a battery made of nanometer material and corresponding bulk material at different temperatures, determining a fitting equation of which the electrodynamic potential changes along with the temperature, calculating difference between thermodynamic functions when the nanometer material and the block material are 298.15 K through a thermodynamic relational expression, and finding out the specified thermodynamic function of the bulk material, so that standard molar entropy of the nanometer material, standard molar Gibbs free energy, standard molar enthalpy and thermal effects of the batteries are obtained. The method can be widely applied to researches of standard electrode potential of nanometer materials with different shapes, sizes and structures and specified thermodynamic functions of the nanometer materials.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
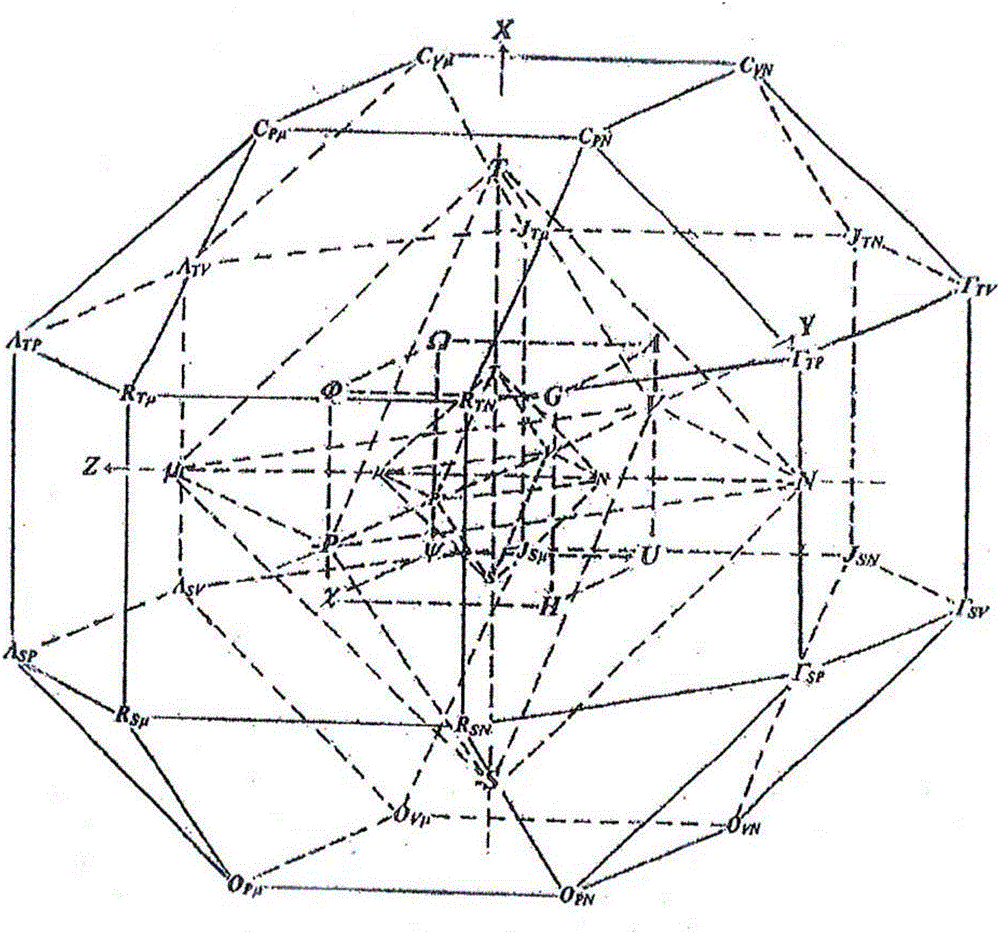
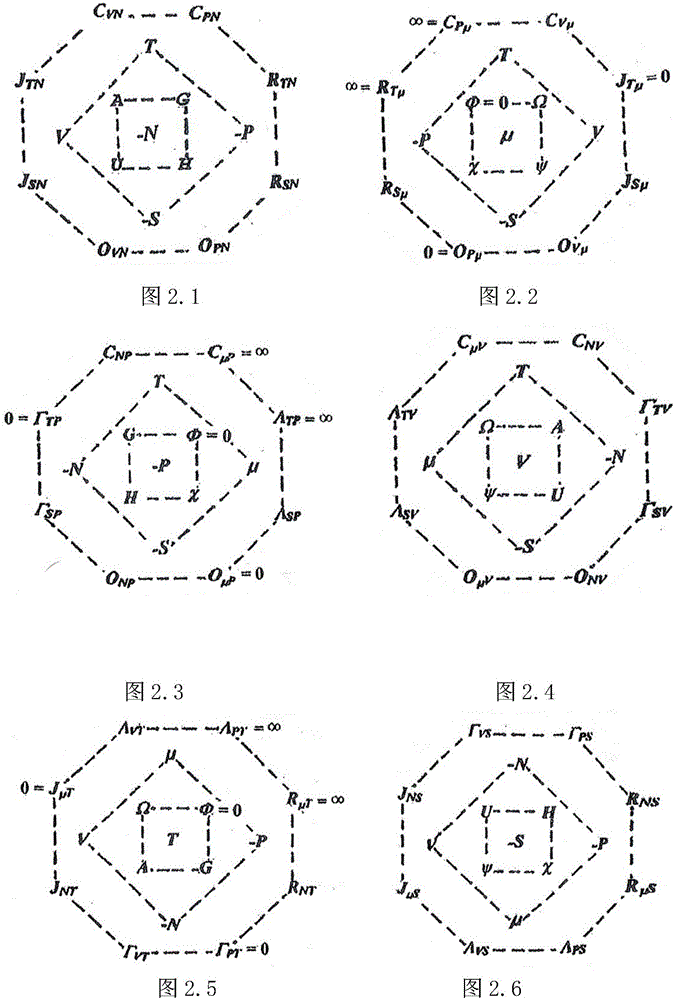
Thermodynamic concentric multi-layer multi-face shell model and simple symmetrical graphic interpretation
PendingCN106021823ASimple and reliable descriptionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputer scienceSHELL model
The invention provides a thermodynamic concentric multi-layer multi-face shell model and a simple symmetrical graphic interpretation. According to the invention, symmetry existing in thermodynamics is disclosed through geometry, and a large amount of thermodynamic relationships are concluded and demonstrated through direct symmetry, so that thermodynamics becomes simple. According to physical meanings, 44 thermodynamic variables of four types of a unit single phase system are uniformly reasonably arranged on the peak of a concentric multi-layer multi-face shell to form a self-consistent complete thermodynamic model; according to a symmetrical equivalence principle, 12 specially-created active patterns are overlapped on a fixed two-dimensional {1, 0, 0} projection drawing for symmetry transformation for describing more than 300 thermodynamic relationships of 12 kinds one by one; and the created patterns and obtained CP variable results are utilized to simply reliably derive a parameter expression for any required partial derivative.
Owner:李震川
Method and device for verifying a temperature value at a destination altitude of an aircraft
InactiveUS7334939B2Rapidly and accurately verifyingThermometer detailsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringAirplane
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
A physics-based method for 3D cloud motion evolution
ActiveCN110096766BEasy to implementImprove Simulation EfficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsComputational physicsComputer graphics
The invention discloses a physics-based three-dimensional cloud motion evolution method, which belongs to the field of computer graphics. The method takes two natural cumulus images as input, and can realize automatic motion evolution from an initial three-dimensional cumulus shape to a target shape. Firstly, the three-dimensional cumulus model is reconstructed from two given natural images of cumulus, and the particle sampling is performed on the first three-dimensional cumulus model to obtain cloud particle data; secondly, the thermodynamic equation and state of cumulus in the process of atmospheric movement are solved Change equations and motion equations to realize the physical movement process of cumulus clouds; again, use the PBF method to maintain the density of cloud particles during the movement process to ensure the incompressibility of cumulus clouds during the movement process; then, through the target shape Surface particle sampling, combined with the fluid-solid interaction strategy, realizes the coupling between cloud particles and the target shape; finally, according to the motion state of the cumulus before and after the time frame, the external force received by the cumulus during the movement is adjusted, and the physical movement process of the cumulus is driven until The final shape matches the target shape.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
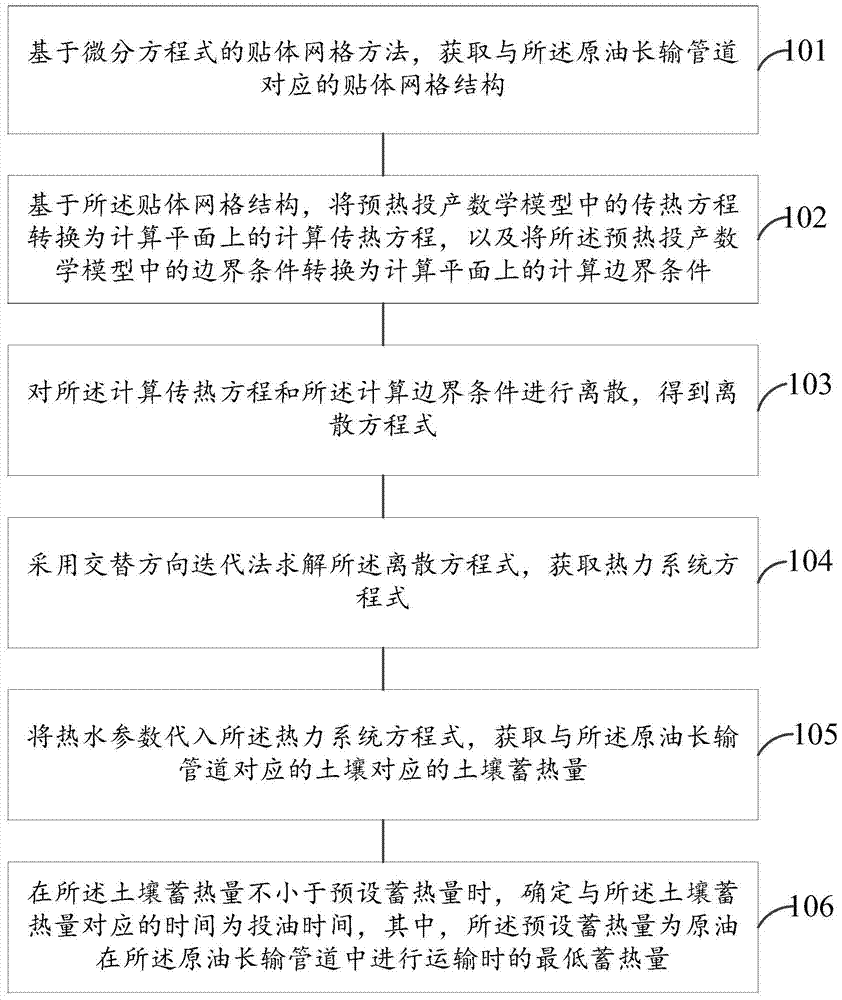
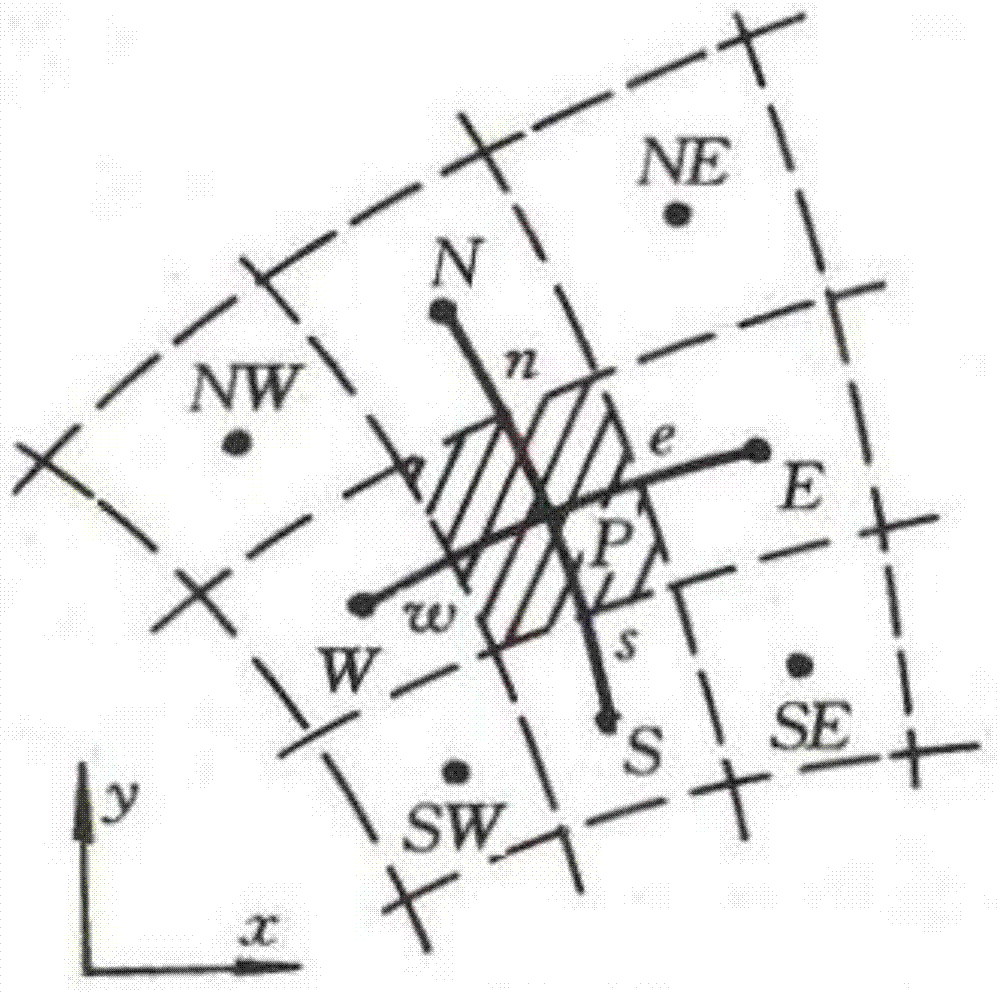
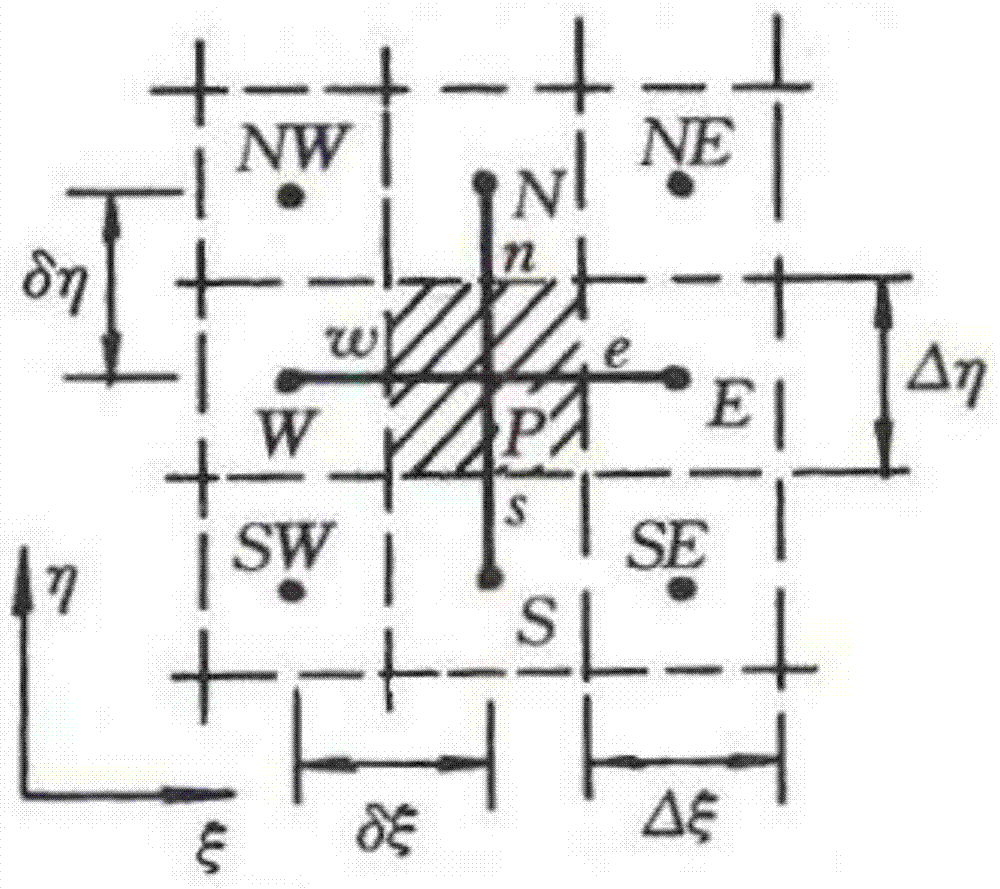
A Preheating and Production Unsteady Prediction Method for Waxy Crude Oil Long-distance Pipeline
ActiveCN104318080BFit closelySmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a non-steady-state prediction method for preheating and putting into production of a long-distance crude oil pipeline containing waxy crude oil. Based on a body-fitted grid method based on differential equations, a body-fitted grid structure corresponding to the long-distance crude oil pipeline is obtained; based on the Body-fitted grid structure, transforming the heat transfer equation and boundary conditions in the preheating and commissioning mathematical model into calculation heat transfer equations and calculation boundary conditions on the calculation plane; discretizing the calculation heat transfer equation and the calculation boundary conditions , to obtain the discrete equation; use the alternating direction iteration method to solve the discrete equation to obtain the thermal system equation; substitute the hot water parameters into the thermal system equation to obtain the soil heat storage corresponding to the soil corresponding to the long-distance crude oil pipeline; When the heat storage amount in the soil is not less than the preset heat storage amount, the time corresponding to the heat storage amount in the soil is determined as the oiling time.
Owner:PIPECHINA SOUTH CHINA CO
A compressor type selection method suitable for pressurized hydrogen internal combustion engine
ActiveCN105955926BTemperature correctionThe result is accurateComplex mathematical operationsHydrogenCombustion
The invention discloses a compressor type selection method suitable for supercharged hydrogen internal combustion engines. Through a given target value and the basic parameters of an engine, the fuel, entering an air cylinder, of the conventional engines is liquid and does not generate partial pressure; the hydrogen internal combustion engines take hydrogen as fuel, and after entering the air cylinder, the gas fuel generates partial pressure and the influences, caused by the partial pressure generated by the gas fuel, on the pressure ratio calculation of the compressor is considered; therefore, according to the method disclosed in the invention, the partial pressure, in the air cylinder, of the hydrogen and the air is calculated to serve as total pressure in the air cylinder, and then the pressure ratio of the compressor is calculated; moreover, a plurality of compressor outlet temperatures are selected in a reasonable range according to experience values at the outlet of the compressor, after obtaining the pressure ratio, a theoretical value of the compressor outlet temperature is obtained through a thermodynamic equation, and the pressure ratio obtained when the selected experience value of the compressor outlet temperature is approximately equal to the thermodynamic equation is taken as the final result, so that the modification of the temperature after the supercharging is realized and more accurate result can be obtained.
Owner:北京氢燃科技有限公司
A test method for dew point temperature of fuel cell humidification reaction gas
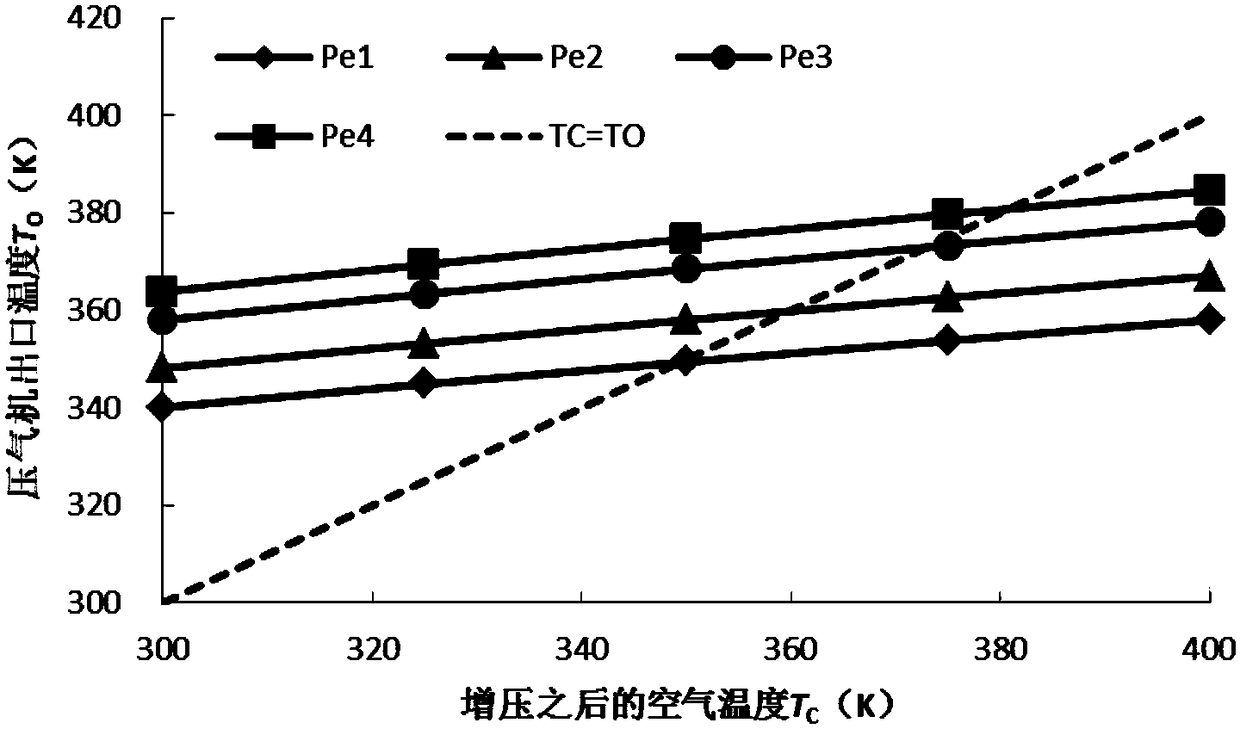
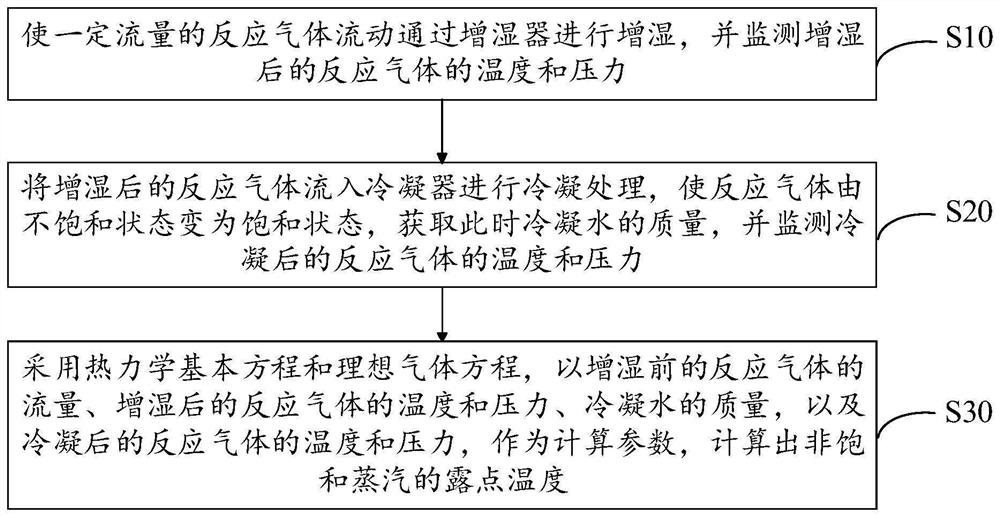
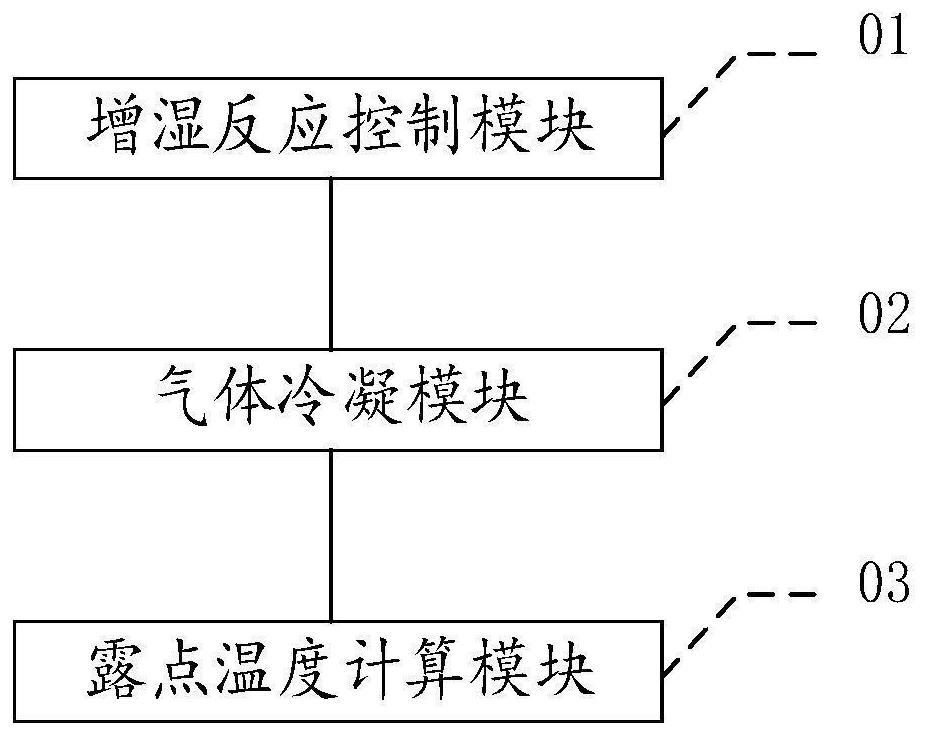
ActiveCN111933974BMeasuring equipment is simpleThe calculation result is accurateFuel cellsFuel cellsEngineering
The invention discloses a method for testing the dew point temperature of humidification reaction gas of a fuel cell, which comprises: making a certain flow rate of reaction gas flow through a humidifier for humidification, and monitoring the temperature and pressure of the humidified reaction gas; The wet reaction gas flows into the condenser for condensation treatment, so that the reaction gas changes from an unsaturated state to a saturated state, obtain the quality of condensed water at this time, and monitor the temperature and pressure of the condensed reaction gas; use the basic thermodynamic equation and ideal The gas equation calculates the dew point temperature of unsaturated steam based on the flow rate of the reaction gas before humidification, the temperature and pressure of the reaction gas after humidification, the quality of condensed water, and the temperature and pressure of the reaction gas after condensation. The method for testing the dew point temperature of the fuel cell humidification reaction gas provided by the invention has simple measuring equipment, and the dew point temperature after gas humidification can be directly calculated through the basic laws of thermodynamics and the ideal gas state equation, so that the test result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:北京国鸿氢能科技有限公司 +1
Thermodynamic cycle system and application of heat cycle through environmental working fluid
ActiveCN105783300BIncrease profitEmission reductionCompression machines with non-reversible cycleRefrigeration componentsWorking fluidArtificial environment
The invention discloses a thermodynamics circulation system achieving heat circulation through environment working media and application. The system comprises an environment working medium system and a thermodynamics circulation system body. The thermodynamics circulation system body comprises a circulating working medium evaporator, a circulating working medium expansion device, a circulating working medium condenser and a circulating working medium pump which are circularly connected in sequence. In addition, in order to convert low-level energy into high-level energy, an external heat source is further introduced. According to the thermodynamics circulation system achieving heat circulation through the environment working media, an artificial environment serves as a part of a low-temperature heat source and a high-temperature heat source of the thermodynamics circulation system body, phase change heat of the thermodynamics circulation system body can be transferred to the environment working media, the heat is transmitted to the thermodynamics circulation system body again by means of energy conversion of the environment working media, and the utilizing rate of energy is increased.
Owner:西安新港分布式能源有限公司
Modeling method for three-dimensional hydrodynamic numerical model of large shallow lake
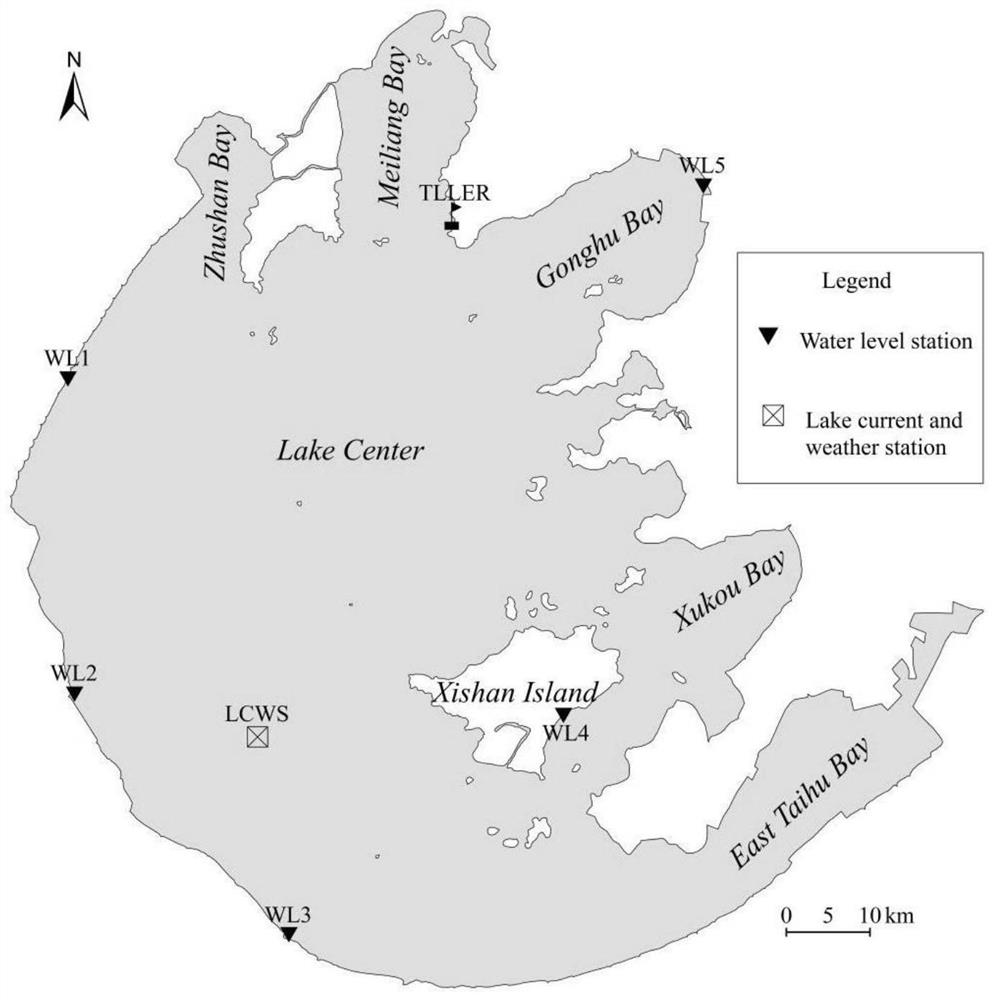
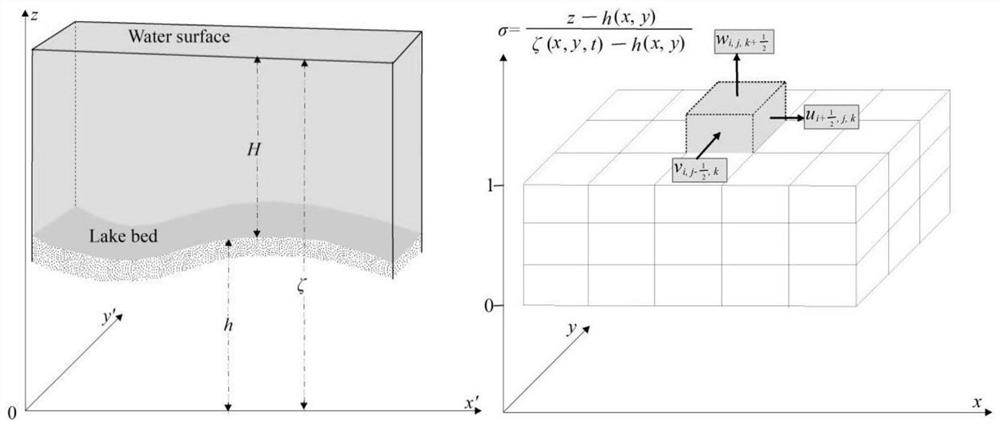
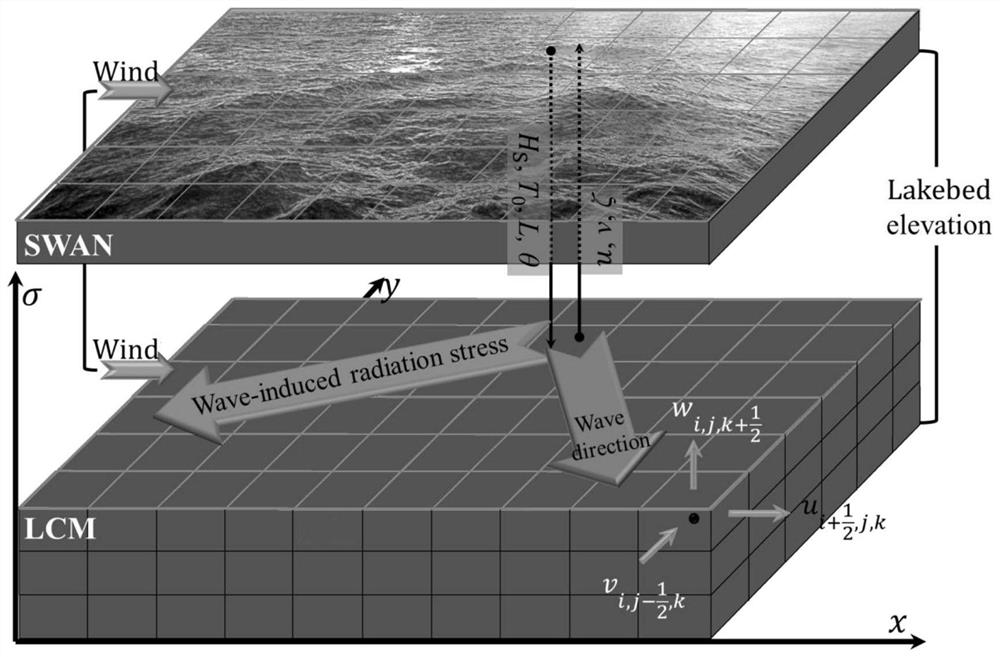
PendingCN112749520AAchieve couplingImprove simulation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingHeat fluxGlobal wind patterns
The invention relates to a modeling method for a three-dimensional hydrodynamic numerical model of a large shallow lake. The method comprises the steps of establishing a three-dimensional lake flow numerical model LCM and a shallow water storm numerical model SWAN for a modeling area, wherein the LCM model is established in a sigma coordinate system, the control equations are a continuous equation, a momentum conservation equation and a thermodynamic equation, and the momentum conservation equation comprises a wave-induced radiation stress item; applying boundary conditions to the LCM, wherein the boundary conditions comprise a water-gas boundary condition, a water-soil boundary condition and heat flux, wind stress is applied to the water-gas boundary, and lake bed friction resistance is considered on the water-soil boundary; and finally, establishing a wind wave and lake flow coupled numerical model WHM-3D based on the LCM and the SWAN. The WHM-3D model established by the modeling method disclosed by the invention has the capability of simulating spatial and temporal changes of wave characteristic elements; the simulation precision of the flow velocity is obviously improved, and the movement process of the wind-generated water body in the Taihu Lake under the prevailing wind field condition can be more accurately simulated.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com