Patents
Literature
172 results about "Standard electrode potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
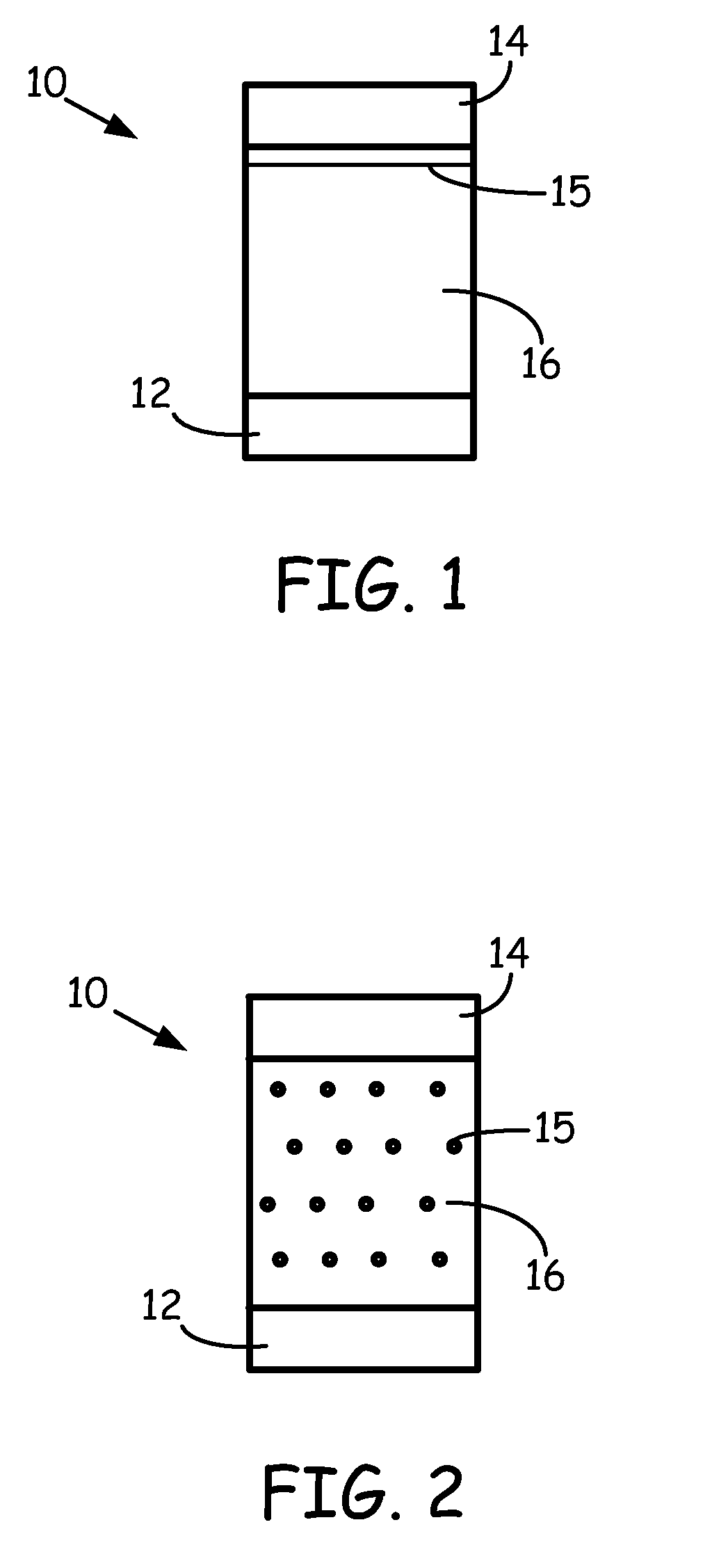
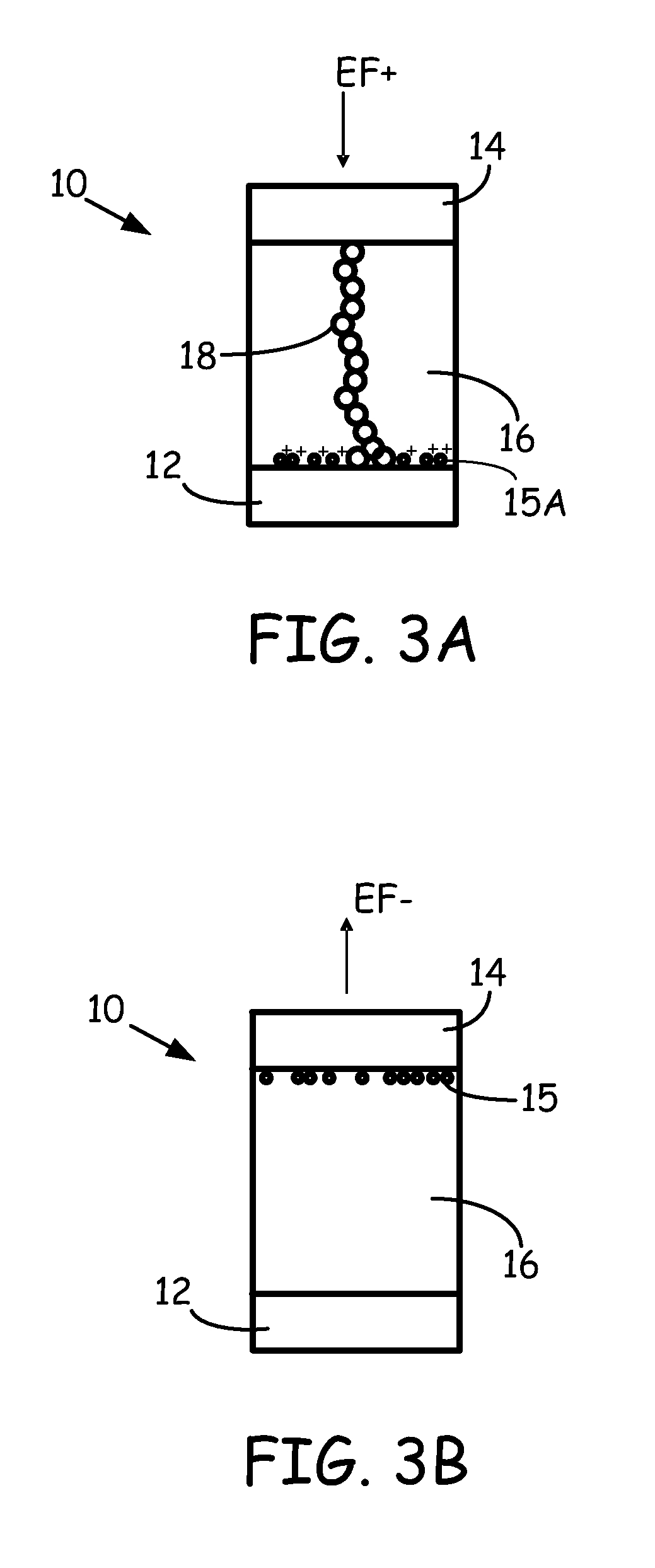
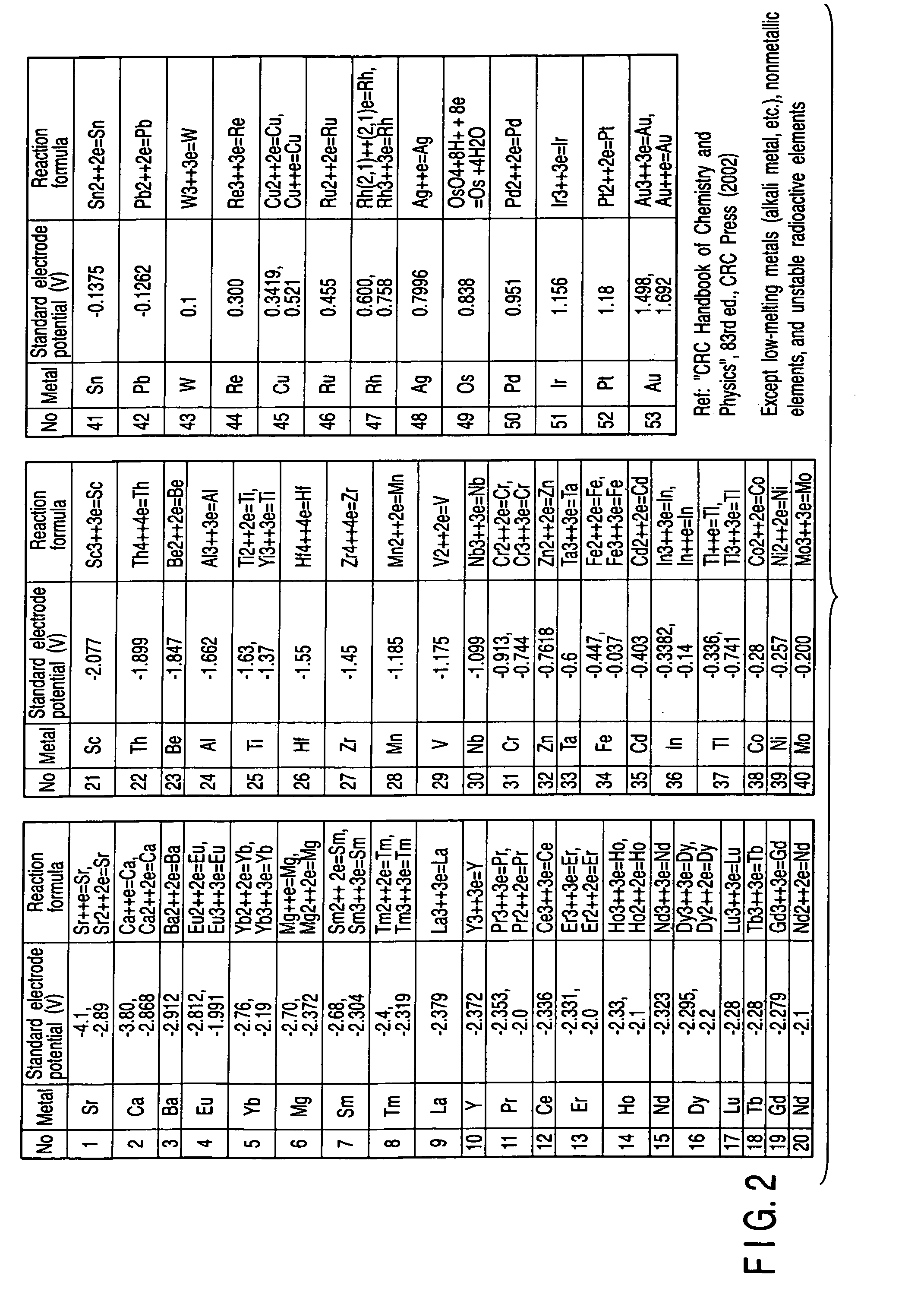
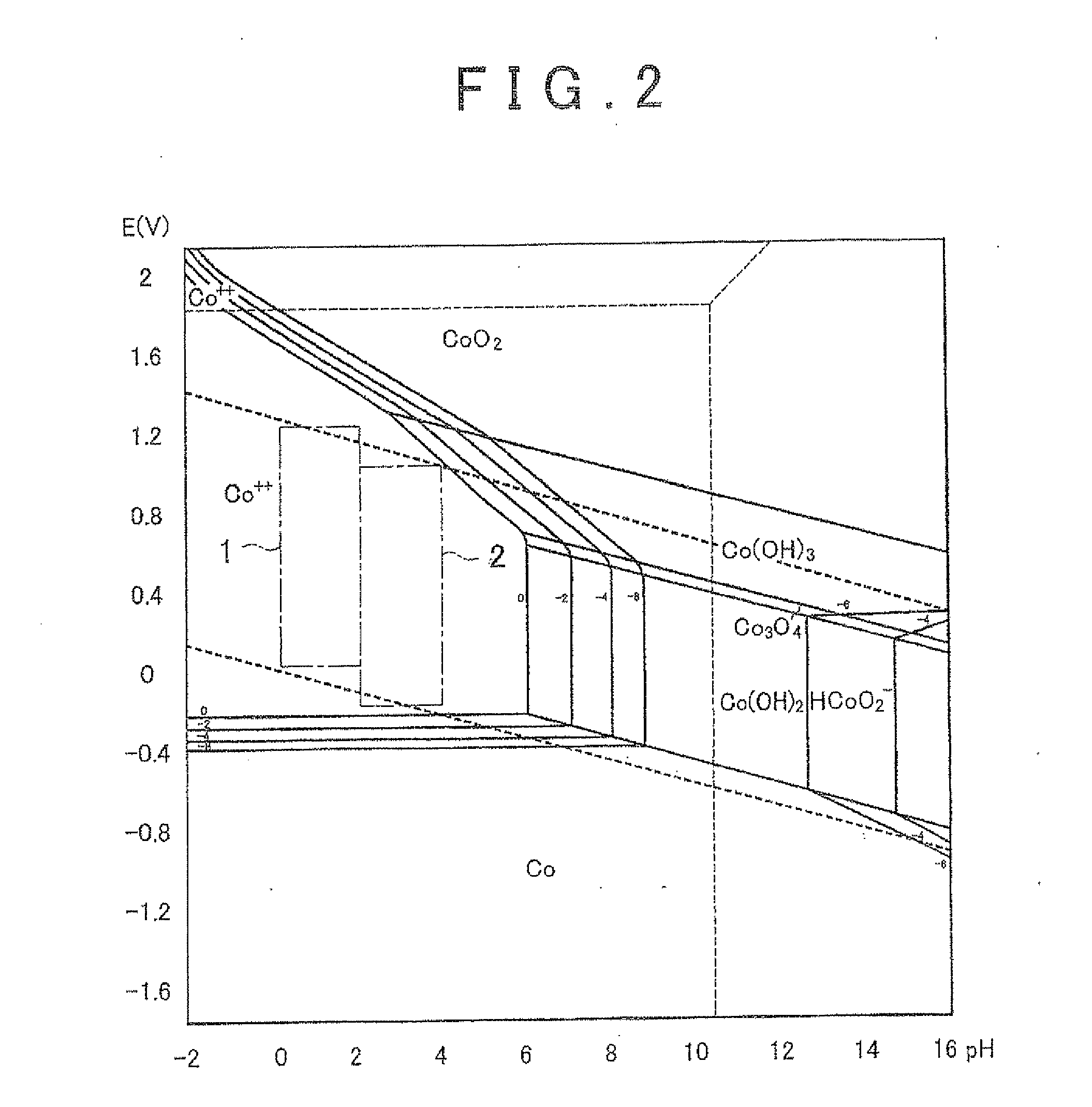
In electrochemistry, standard electrode potential is defined as the measure of the individual potential of reversible electrode at standard state with ions at an effective concentration of 1mol dm-3 at the pressure of 1 atm.
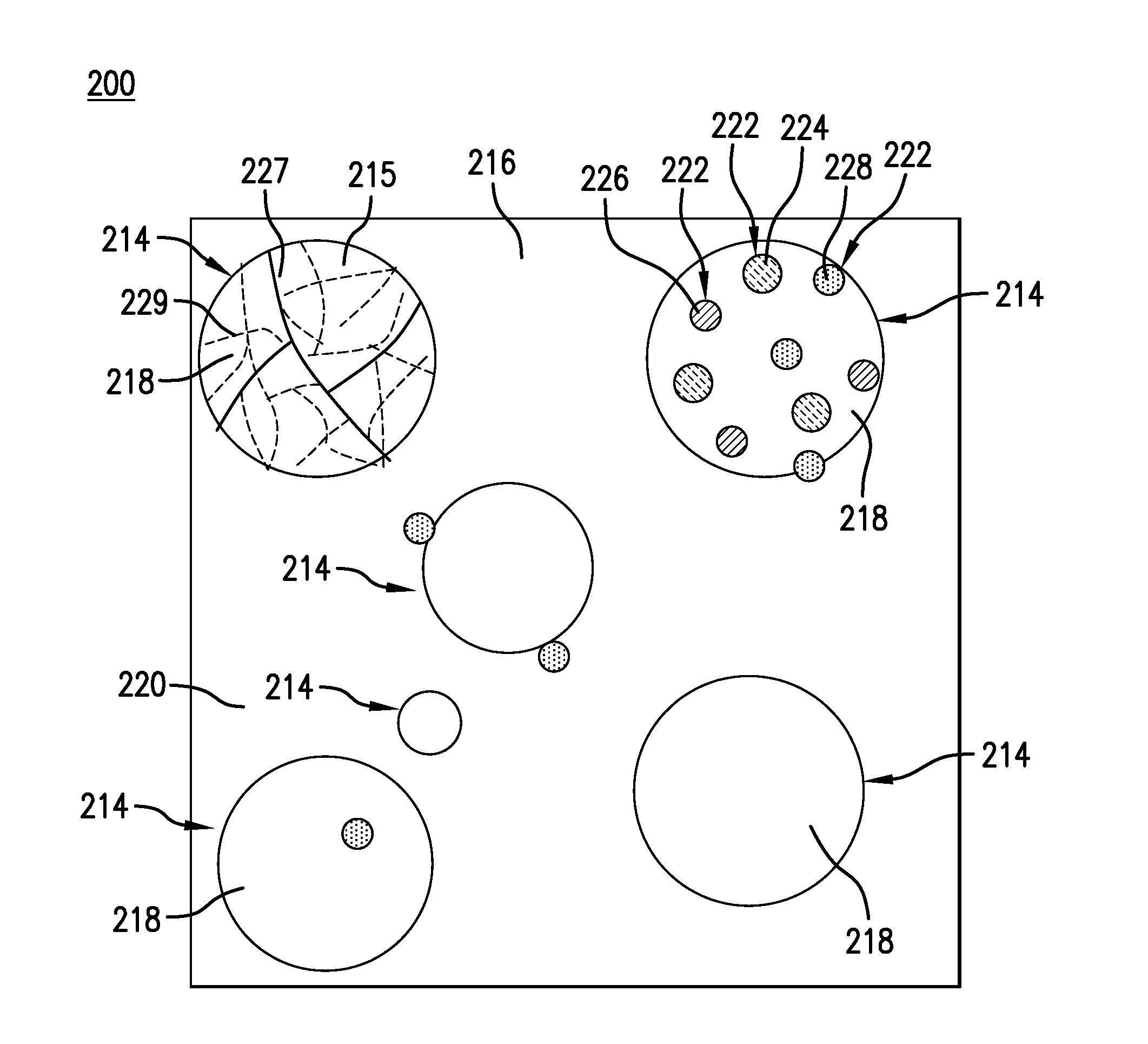
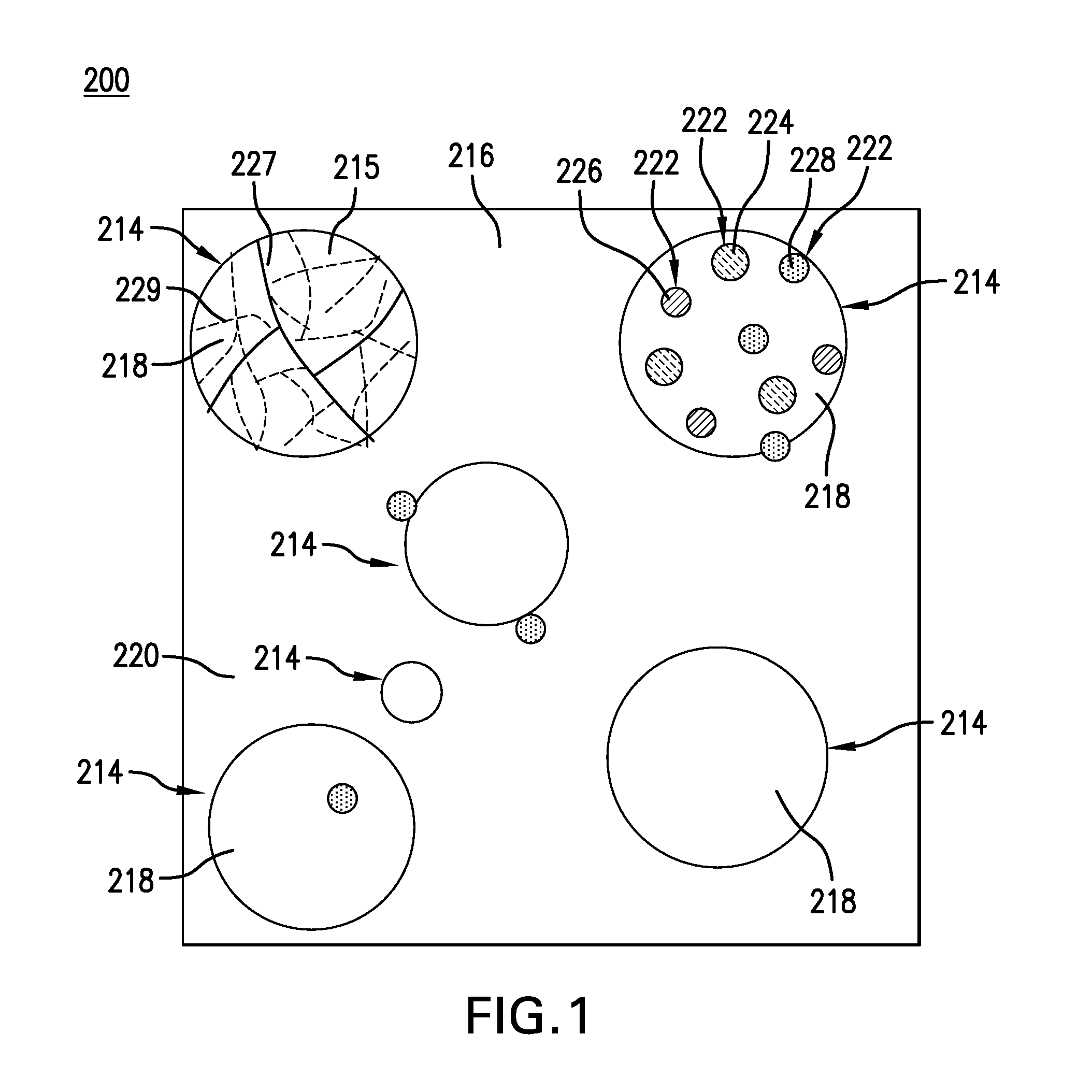
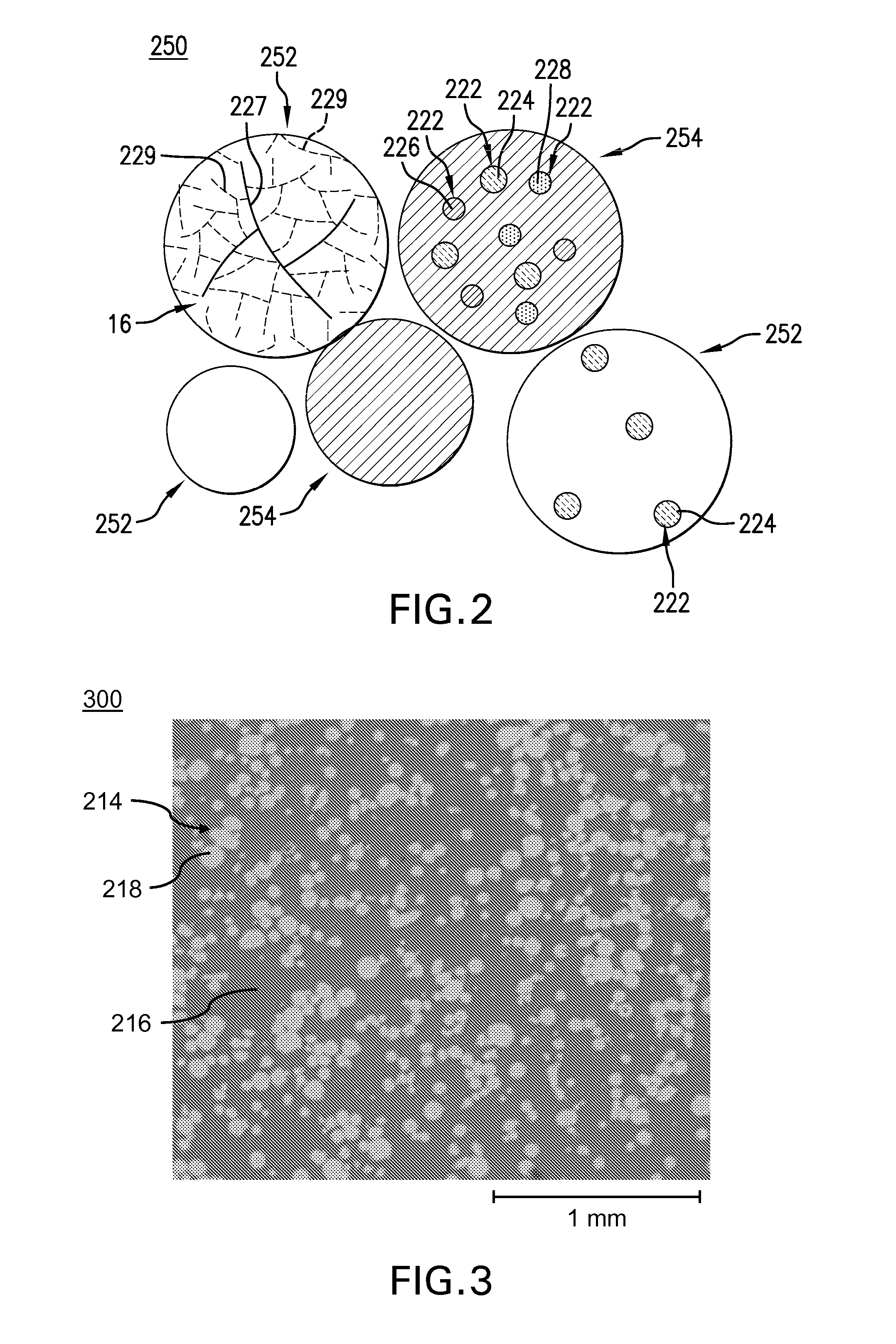
Ferrous disintegrable powder compact, method of making and article of same
ActiveUS20140262327A1Transportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusStandard electrode potentialAlloy
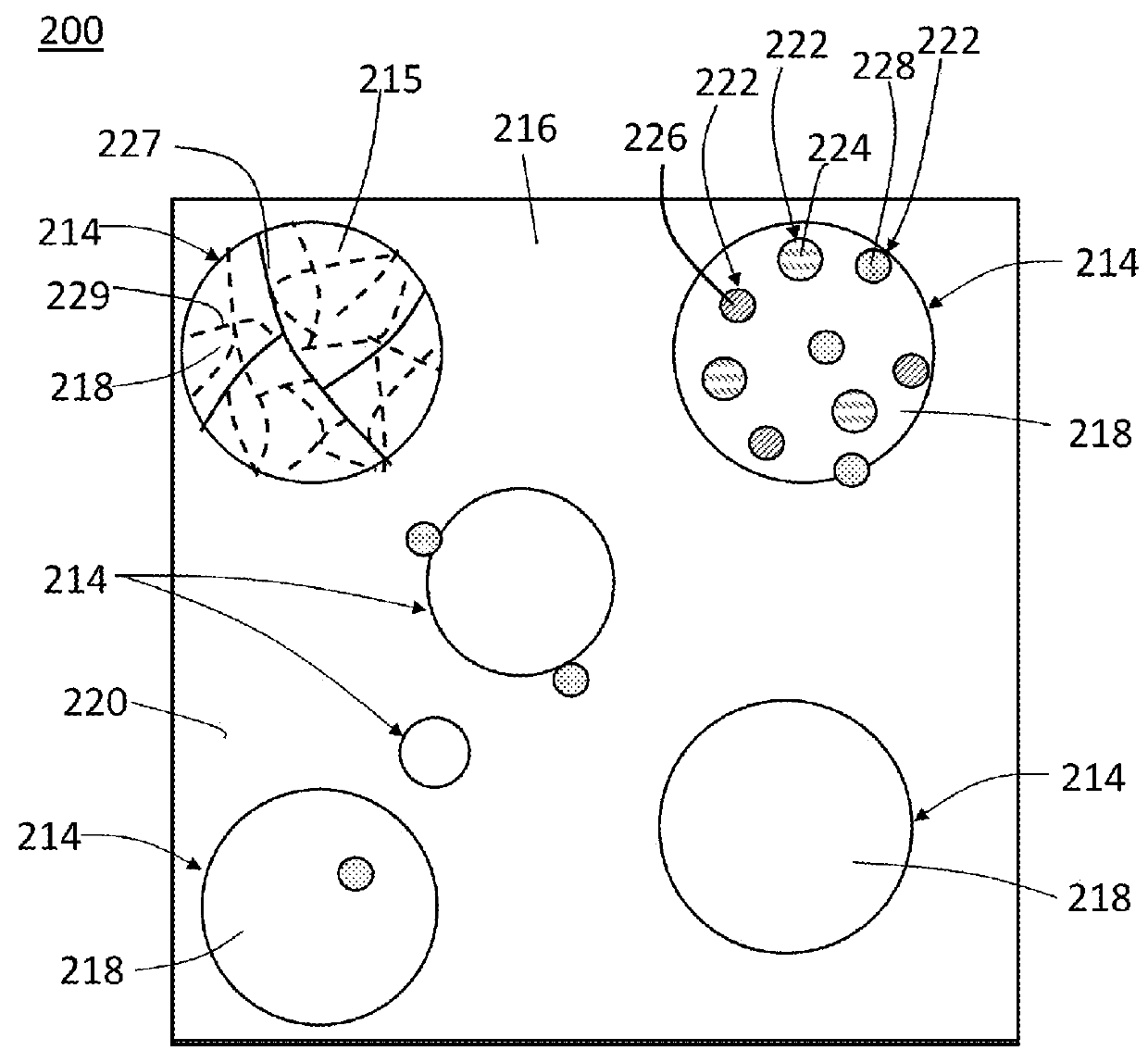
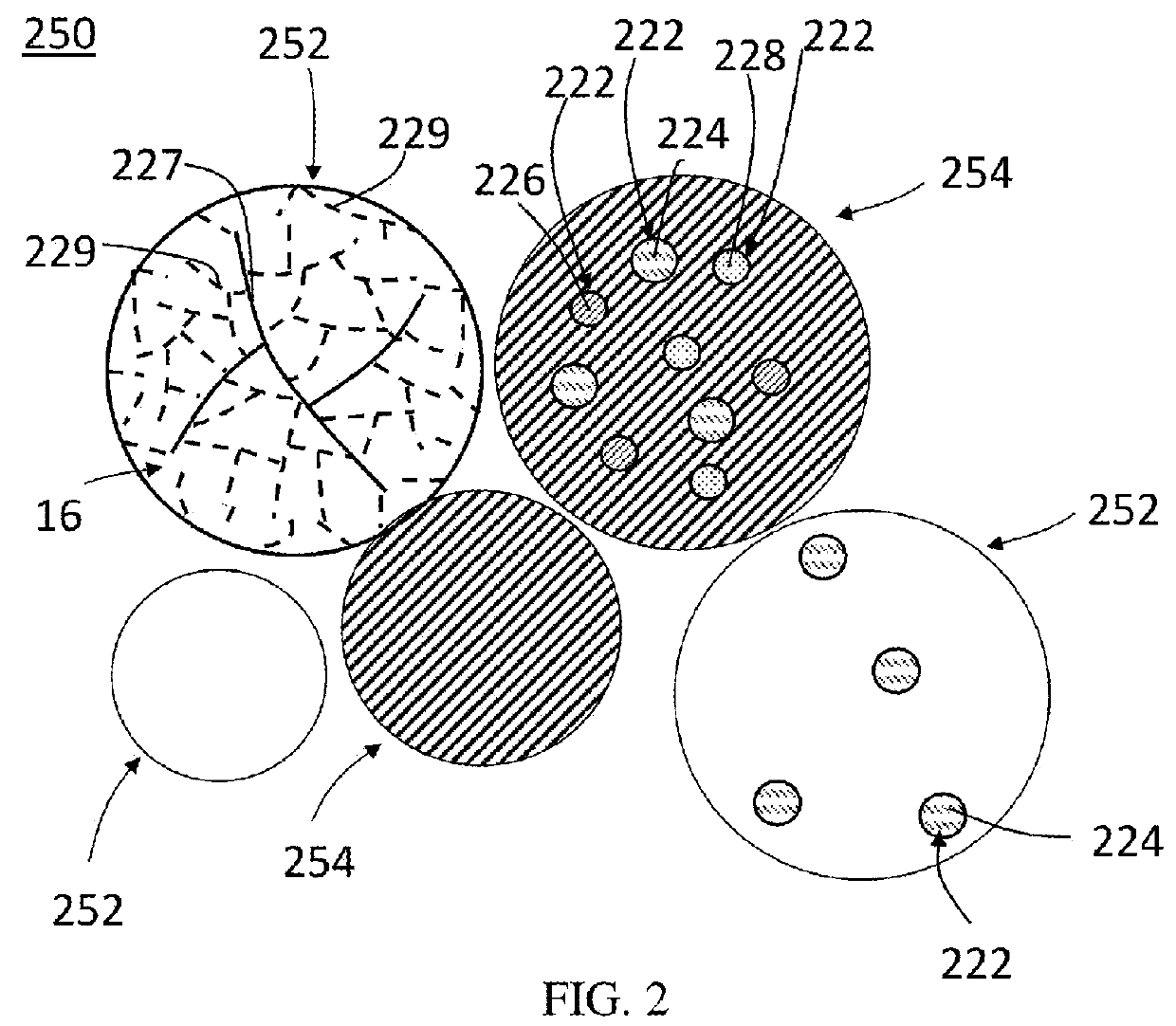
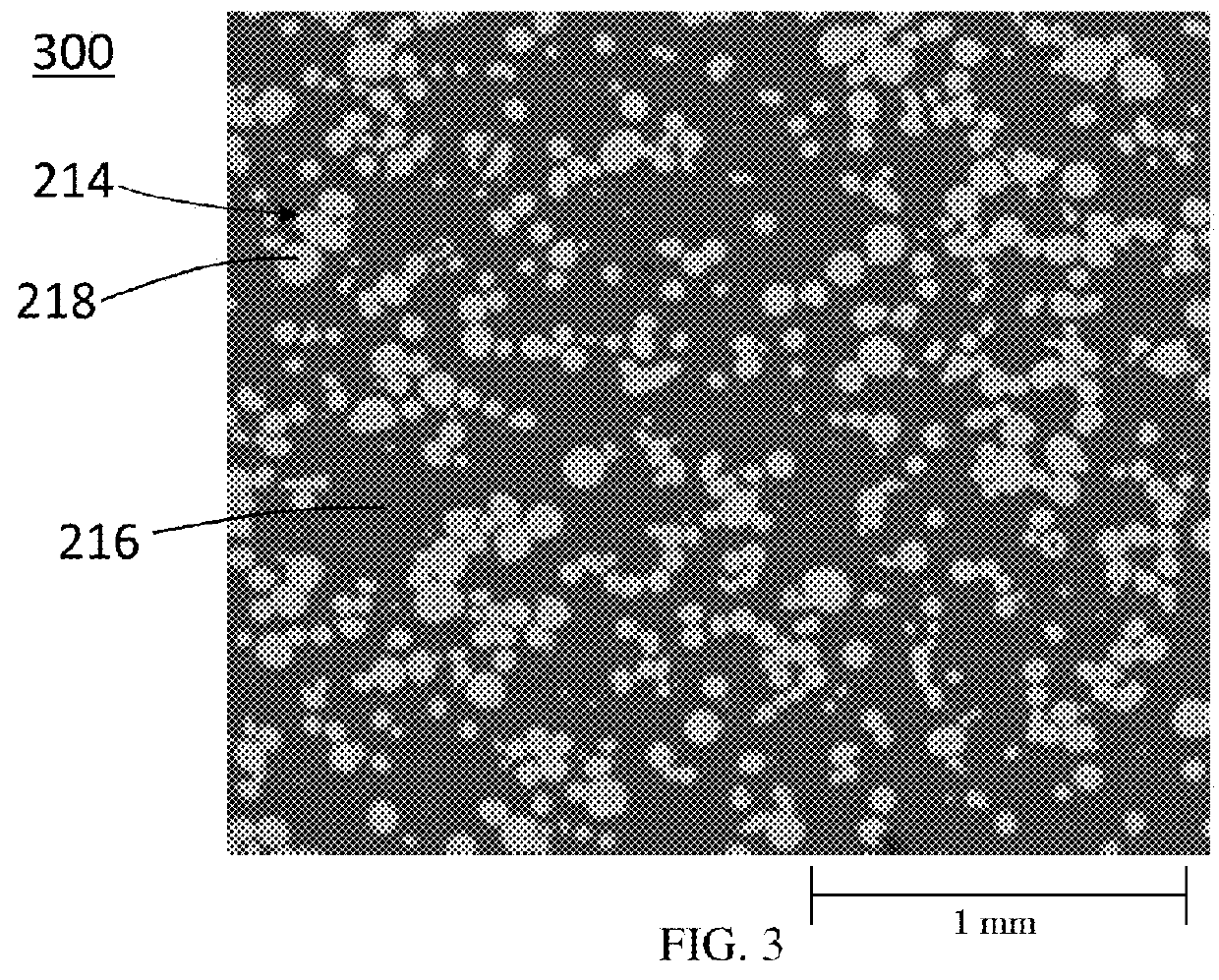
A disintegrable powder compact includes a matrix; a plurality of dispersed particles including a particle core material dispersed in the matrix; a ferrous alloy including carbon disposed in one of the matrix or particle core material; and a secondary element disposed in the other of the matrix or particle core material, the matrix and the plurality of dispersed particles having different standard electrode potentials. A process for preparing a disintegrable powder compact includes combining a primary particle including a ferrous alloy that includes carbon and a secondary particle to form a composition; compacting the composition to form a preform; and sintering the preform by forming a matrix, wherein the dispersed particles are dispersed in the matrix, the disintegrable powder compact is configured to disintegrate in response to contact with a disintegration fluid, and the primary particle and secondary particle have different standard electrode potentials.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Programmable resistive memory cell with sacrificial metal
ActiveUS8097874B2Improve data retentionLow resistance stateBulk negative resistance effect devicesElectrical conductorStandard electrode potential
Programmable metallization memory cells include an electrochemically active electrode and an inert electrode and an ion conductor solid electrolyte material between the electrochemically active electrode and the inert electrode. A sacrificial metal is disposed between the electrochemically active electrode and the inert electrode. The sacrificial metal has a more negative standard electrode potential than the filament forming metal.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetoresistive element
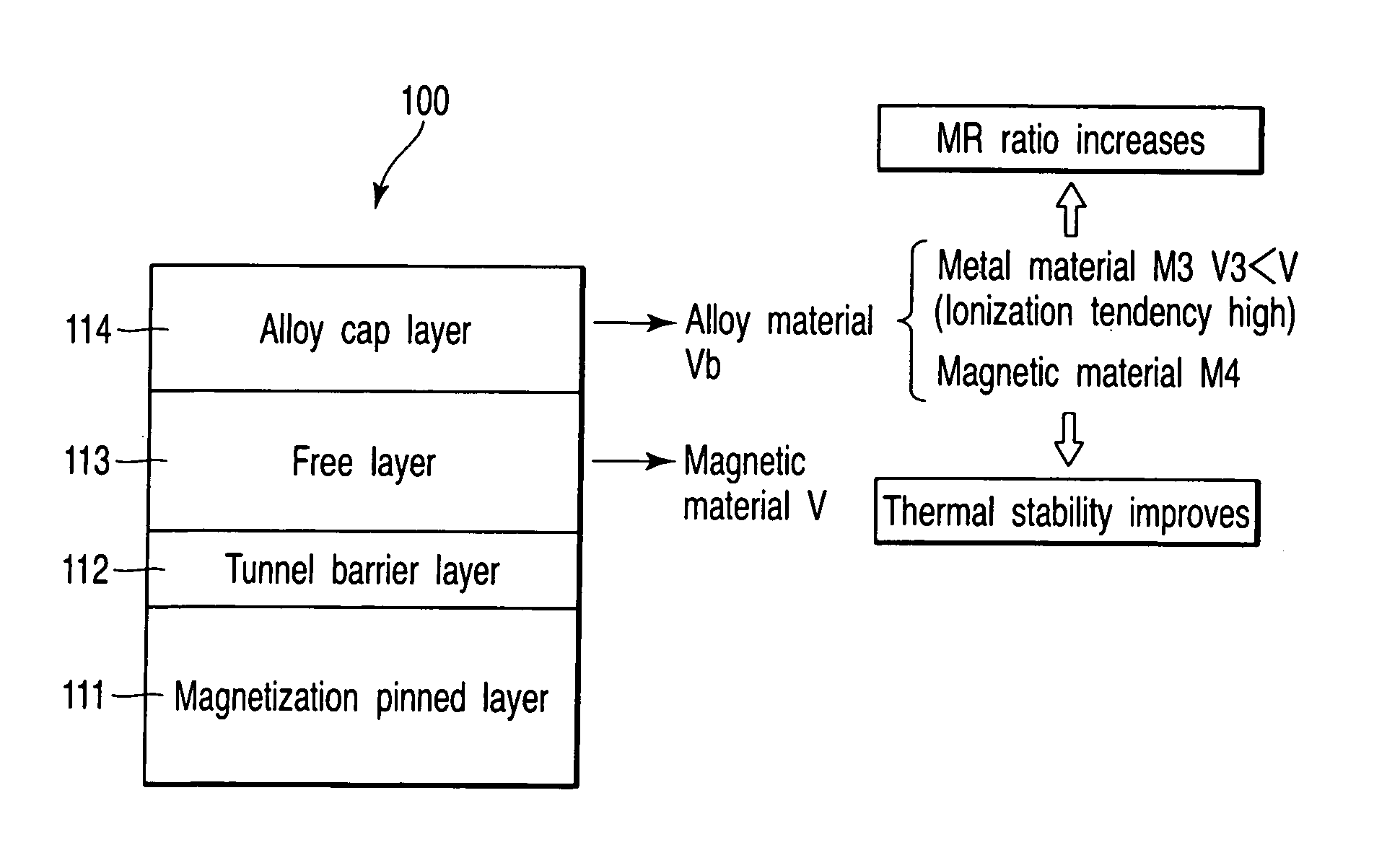
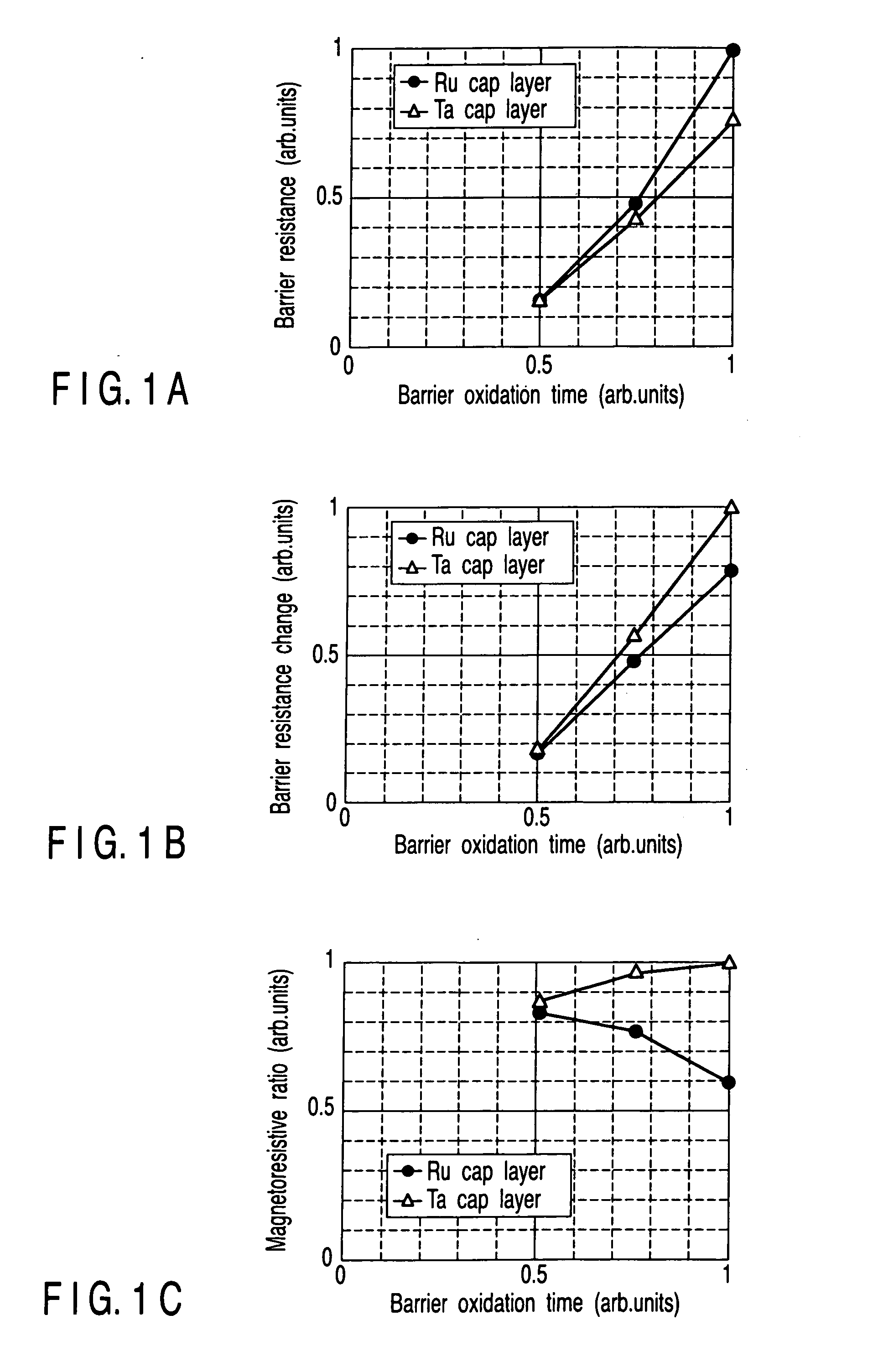
InactiveUS20070014149A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic reluctanceStandard electrode potential
A magnetoresistive element includes a first magnetic layer which includes a first surface and a second surface and has a first standard electrode potential, a second magnetic layer, a barrier layer which is provided between the second magnetic layer and the first surface of the first magnetic layer, and a nonmagnetic cap layer which contacts the second surface of the first magnetic layer and is formed from an alloy of a first metal material and a second metal material, the first metal material having a second standard electrode potential lower than the first standard electrode potential, the second metal material having a third standard electrode potential higher than the first standard electrode potential.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nucleocapsid catalyst in use for fuel cell and preparation method
InactiveCN1872417ALarge specific surface areaCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationElectrode potentialStandard electrode potential
A core-shell catalyst with controllable granularity and thickness of catalyzing layer and high active specific surface area and catalytic efficiency for fuel battery is prepared through preparing the nanoparticles of the metal with low standard electrode potential, and using it to displace out the metal with high standard electrode potential to cover on the surface of said nanoparticle.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus of generating electric power
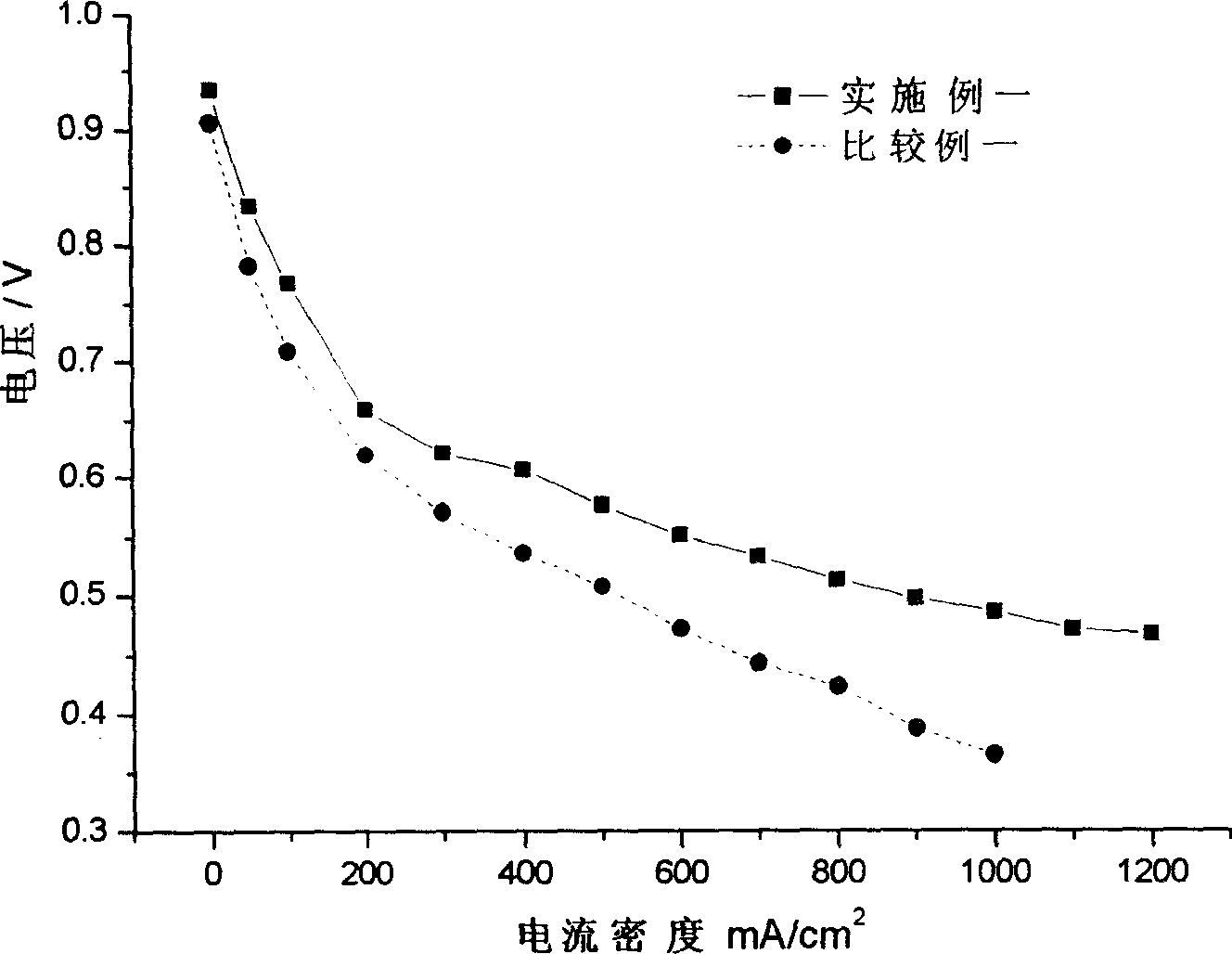
InactiveUS20070134520A1Enhance electrochemical reactionEffectively take out electrical energyFuel cell auxillariesBiochemical fuel cellsElectric power systemElectron donor
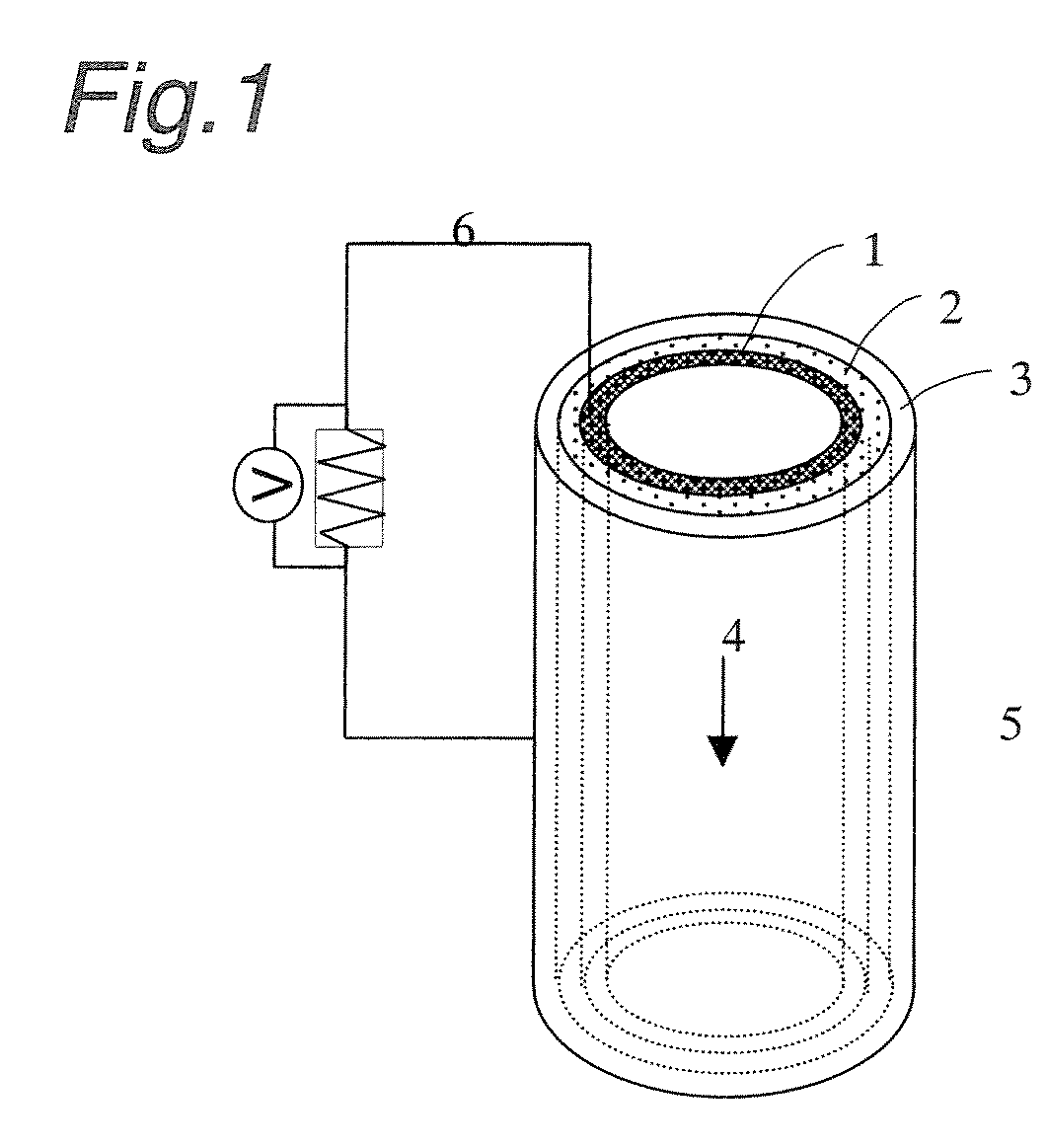
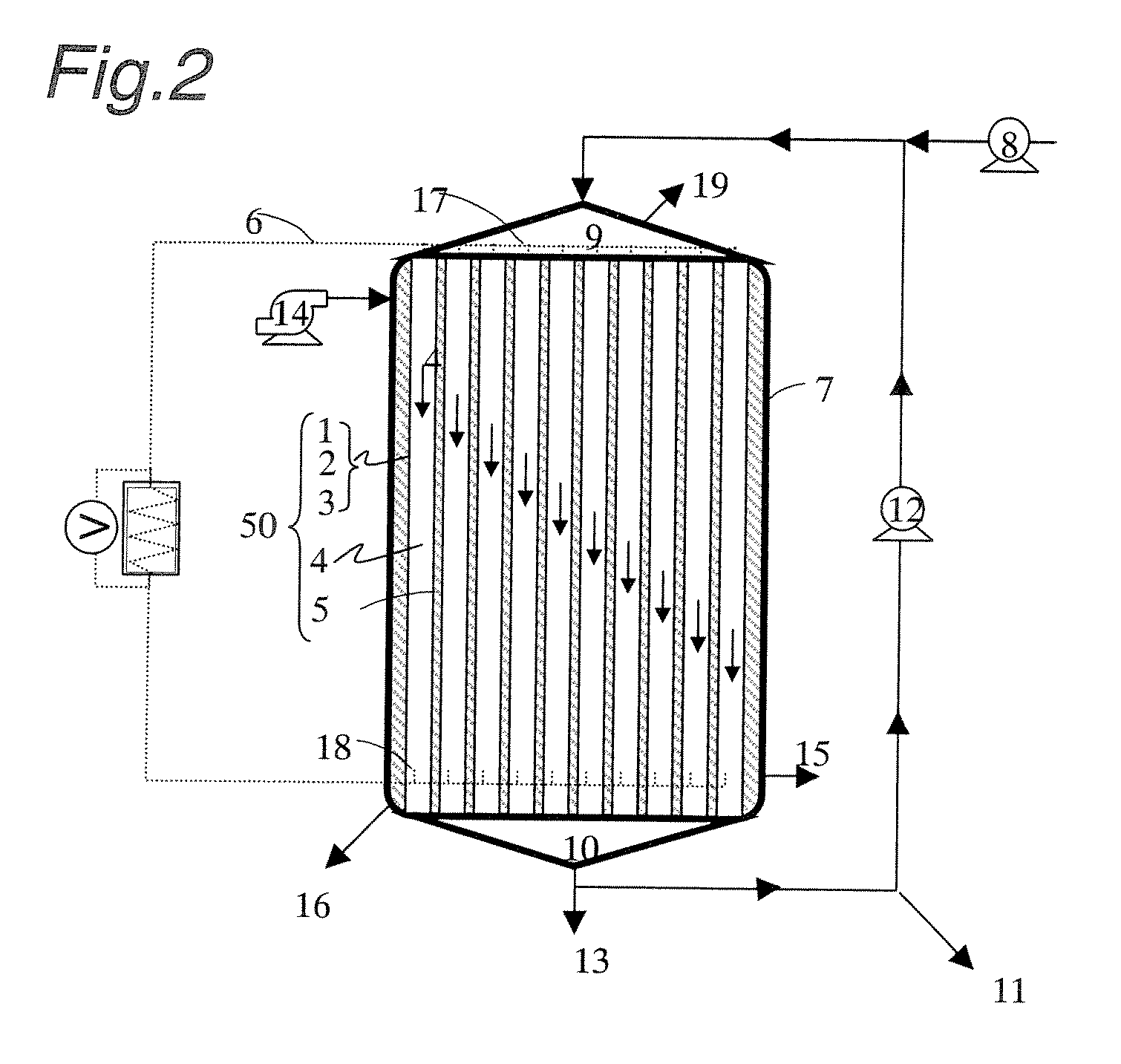
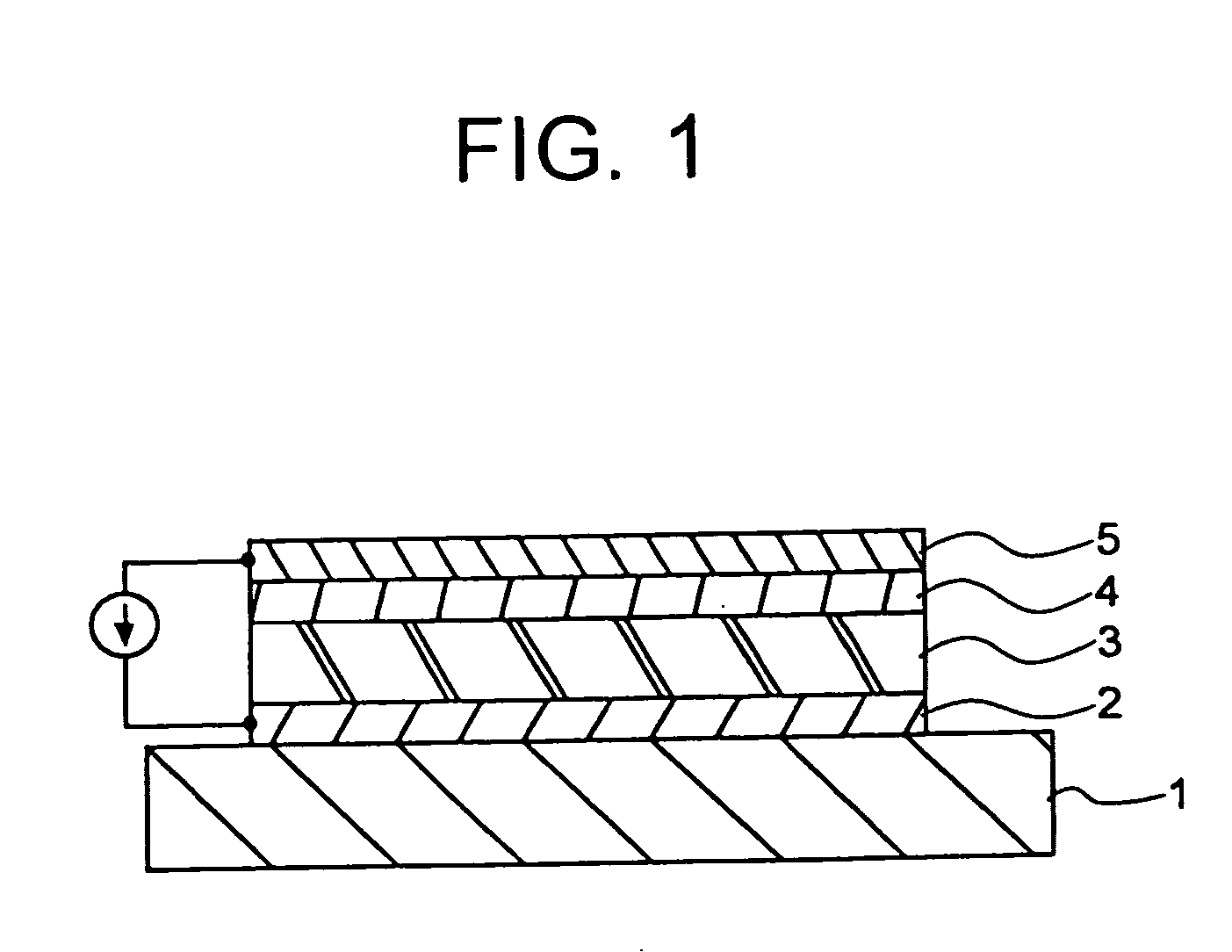
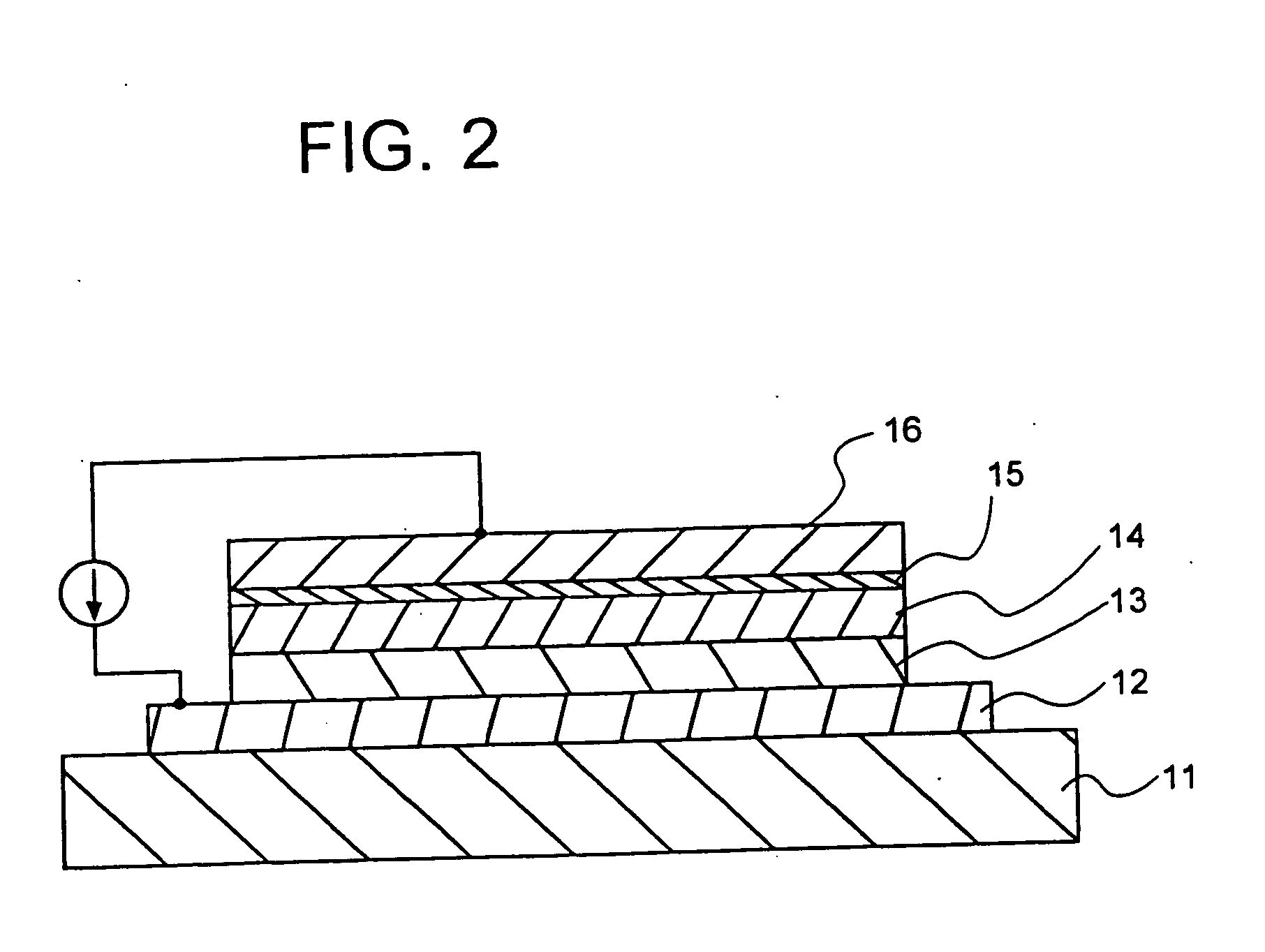
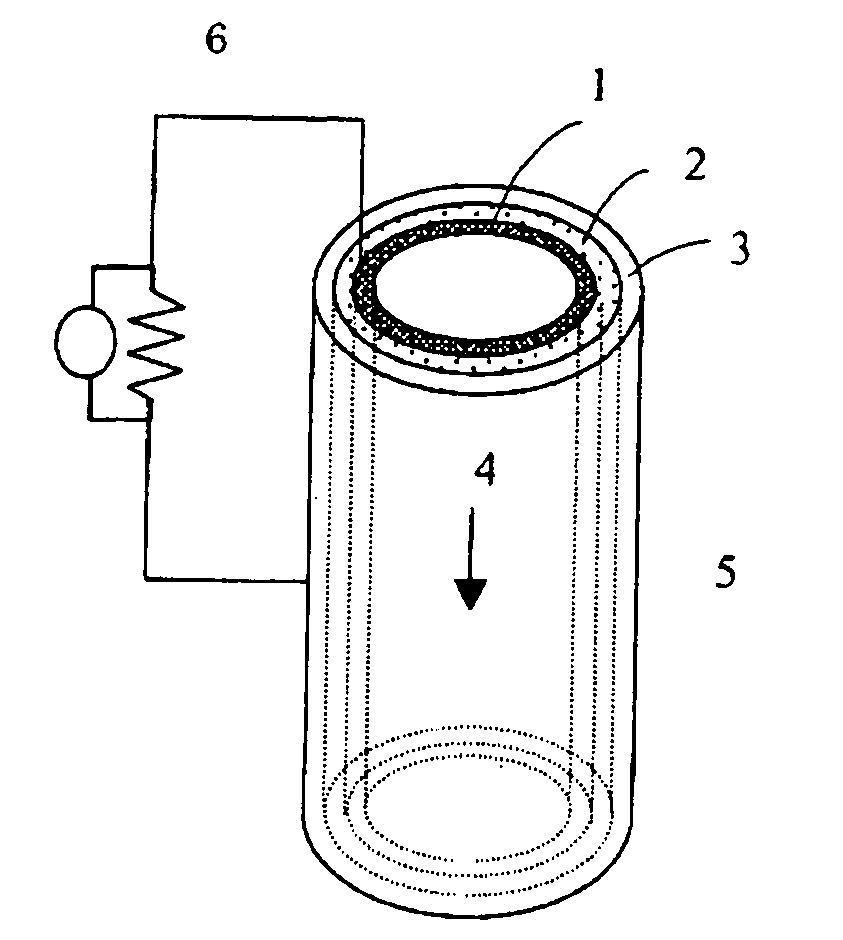
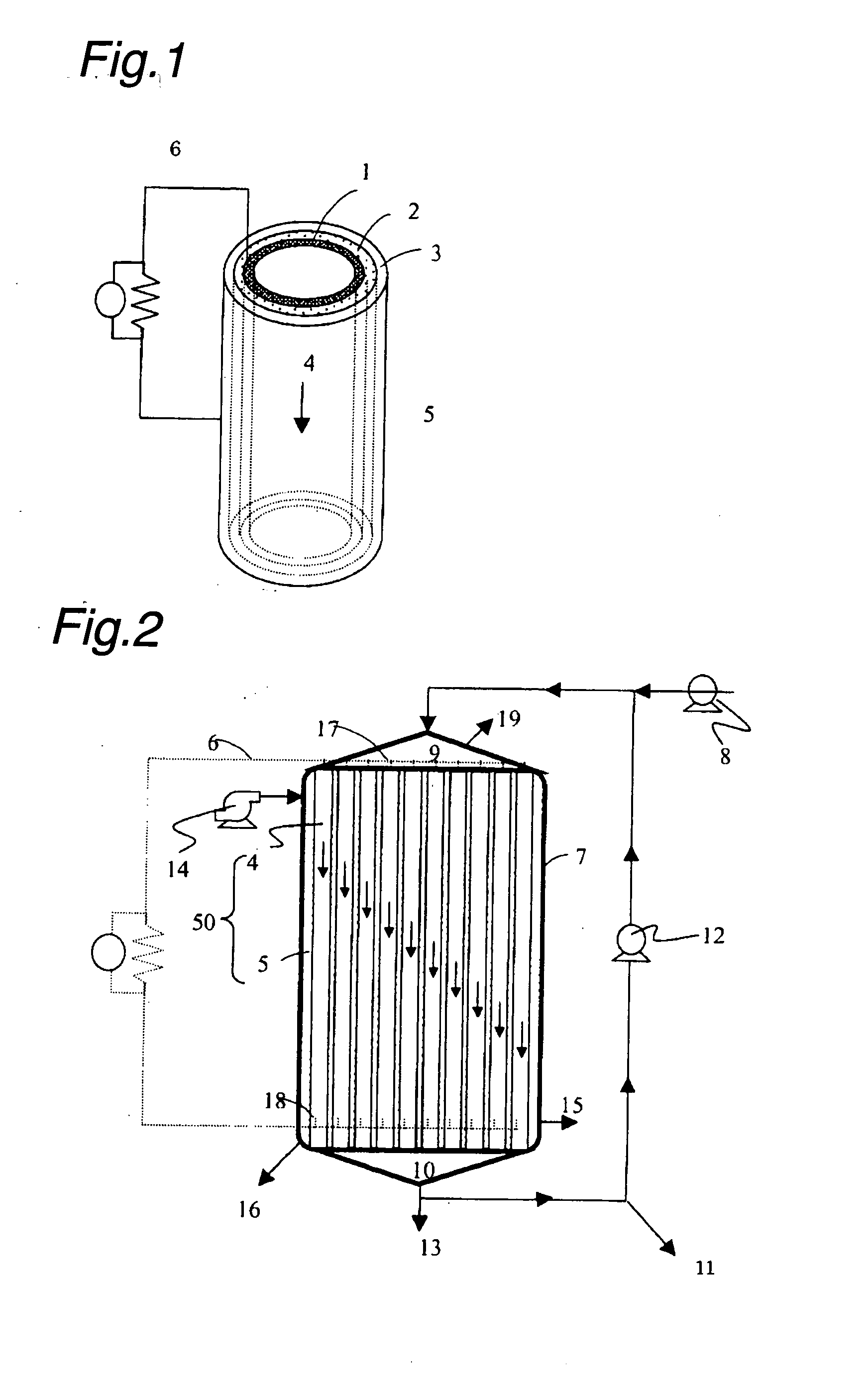
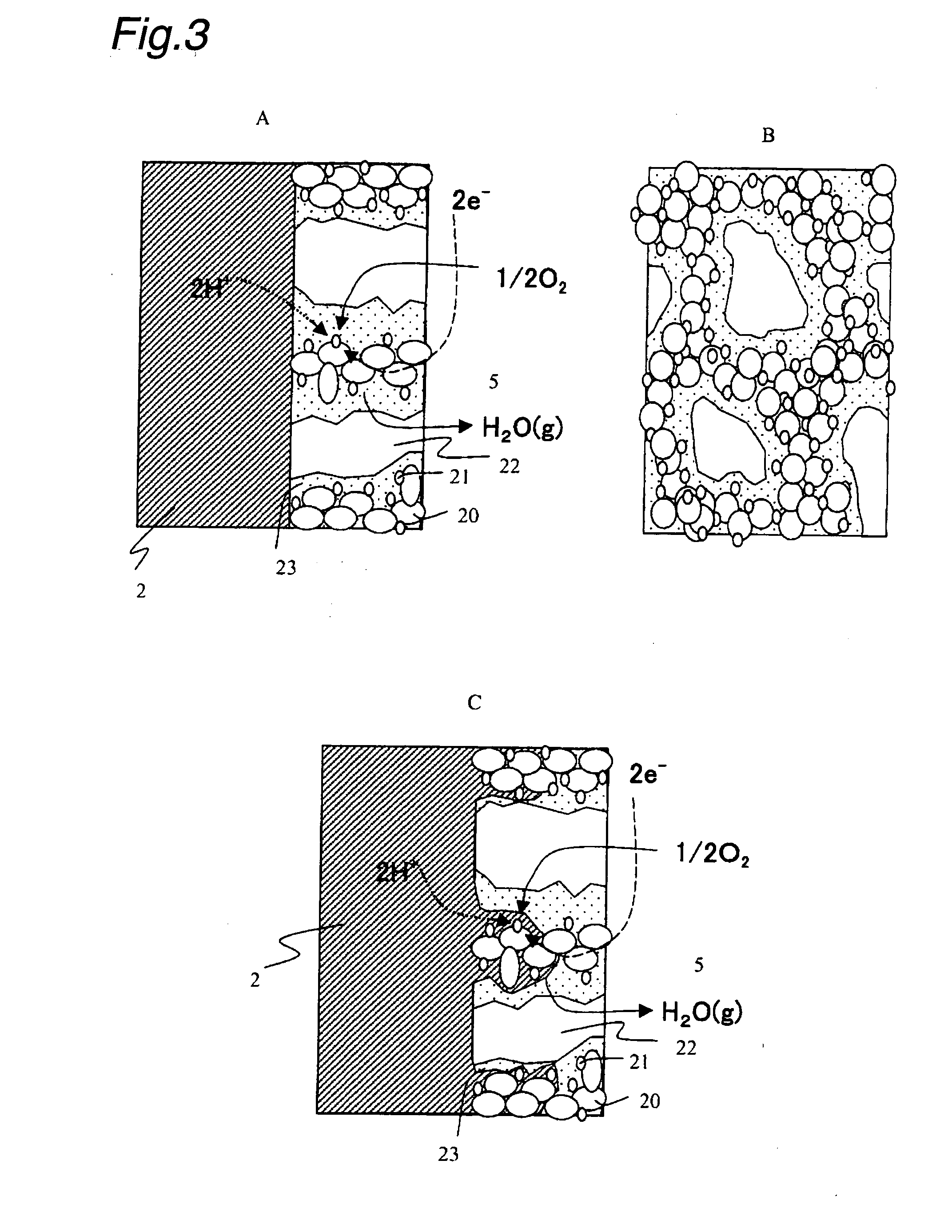
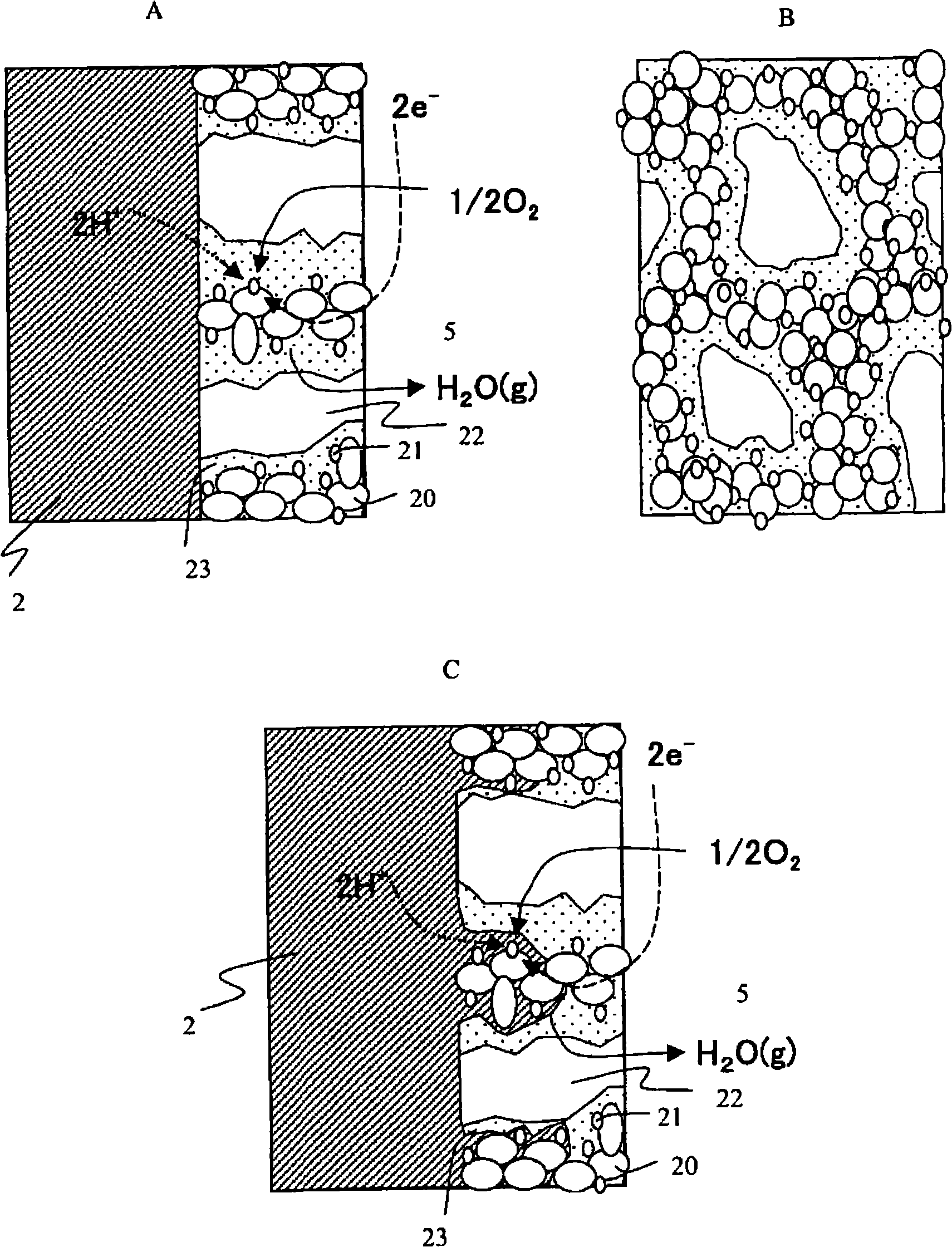
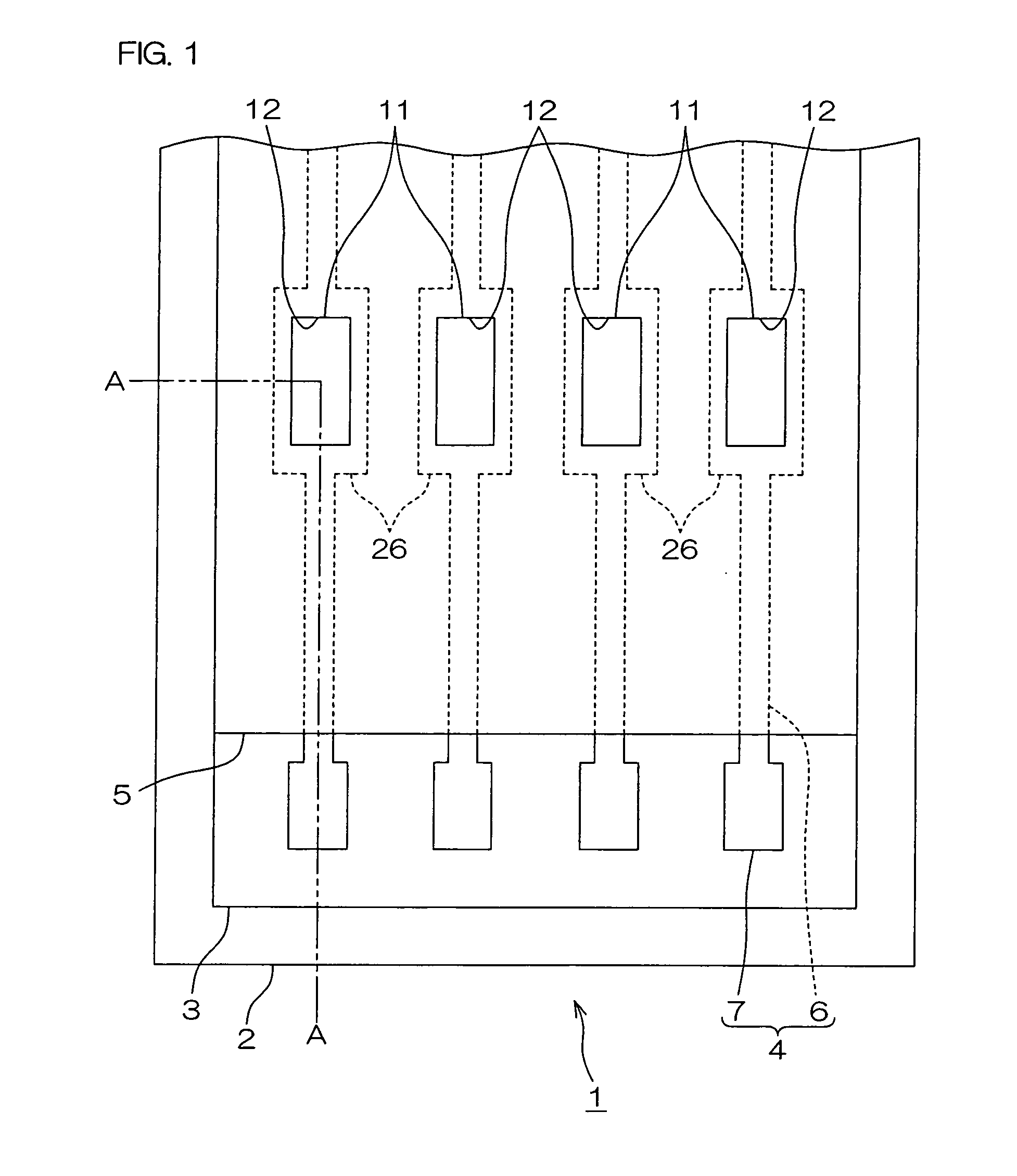
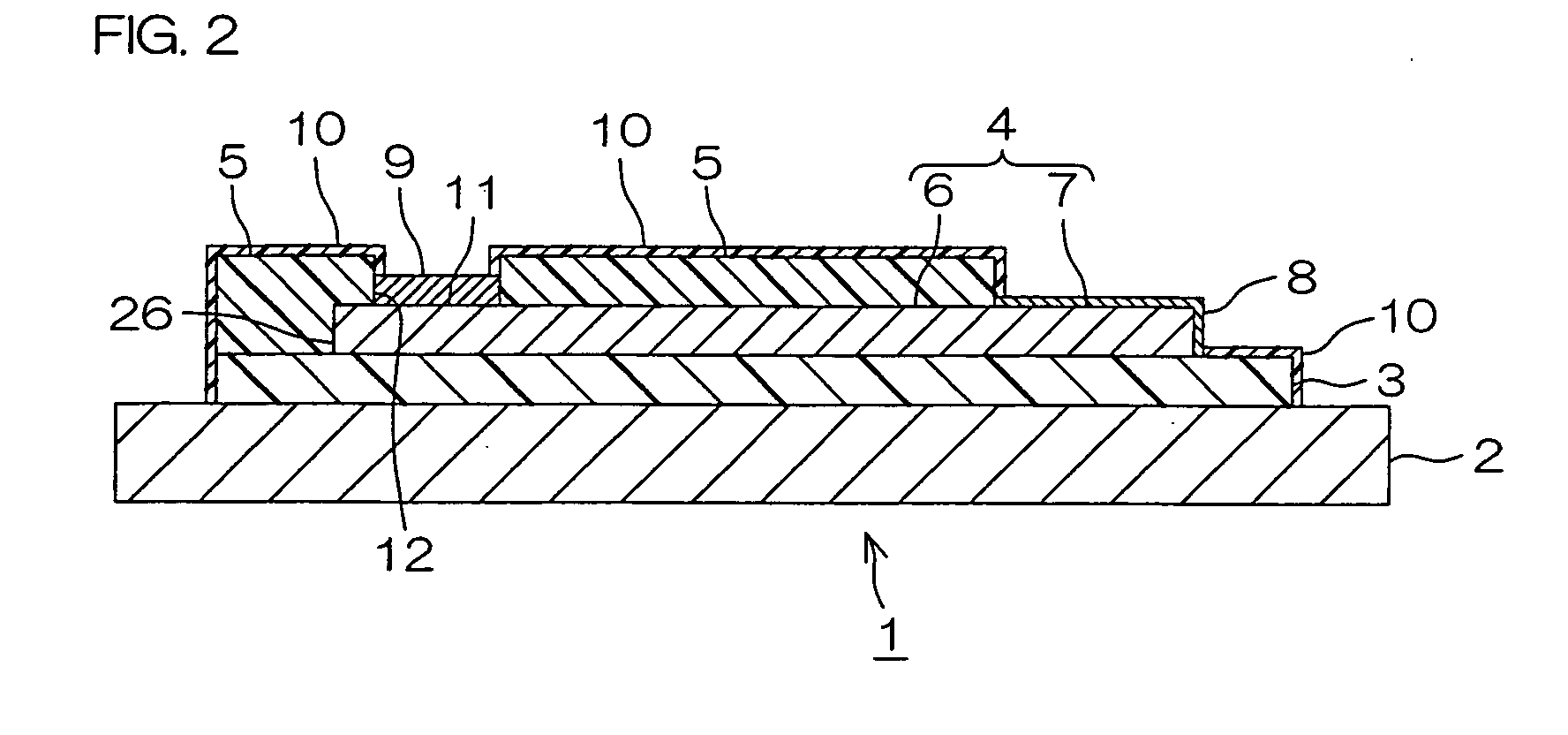
Power generation is performed by immobilizing an electron mediator having a standard electrode potential (E0′) at pH 7 in the range of −0.13 V to −0.28 V to one of a pair of electrodes to form an anode 1 and electrically connecting the other electrode as a cathode 3 to the anode 1 to form a closed circuit, bringing the anode 1 into contact with microorganisms capable of growing under anaerobic conditions and a solution or suspension 4 containing an organic substance to advance the oxidation reaction by microorganisms using the organic substance as an electron donor, separating the cathode 3 and the solution or suspension through an electrolyte membrane 2 to advance the reduction reaction using oxygen as an electron acceptor at the cathode, and accelerating the oxidation reaction in the biological system.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Piezoelectric device, liquid droplet discharging head using the device, and liquid droplet discharging apparatus using the head
InactiveUS20050052506A1Highly reliable piezoelectricInhibit deteriorationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyInking apparatusElectrode potentialMetallic materials
A piezoelectric device includes a piezoelectric body layer, a first electrode layer at one face side of the piezoelectric body layer, and a second electrode layer at a side of a face of the same that is opposite to the side at which the first electrode layer is disposed. Higher potentials are applied to the first electrode layer and lower potentials are applied to the second electrode layer. The piezoelectric device features a metallic layer disposed in contact with a piezoelectric body layer surface at the side at which the first electrode layer is provided, and a metal oxide layer disposed in contact with a piezoelectric body layer surface at the side at which the second electrode layer is provided. The metallic layer is formed of a metallic material with a standard electrode potential greater than 0 V, and the metal oxide layer is formed of a metal oxide.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Lithium-ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20050186481A1Sufficient securityLarge capacityOrganic electrolyte cellsElectrolytesStandard electrode potentialRedox
A lithium-ion secondary battery 1 comprises an anode including a conductive anode active material containing layer containing an anode active material; a cathode including a conductive cathode active material containing layer containing a cathode active material; a nonaqueous electrolytic solution containing a lithium salt, propylene carbonate, and a linear carbonate; and a case accommodating the anode, cathode, and nonaqueous electrolytic solution in a closed state. The nonaqueous electrolytic solution further contains an additive satisfying the condition represented by expression (1): +0.9V≦(E2−E1)≦+2.5V, whereas the moisture content in the anode active material containing layer is regulated so as to satisfy the condition represented by expression (2): 40 ppm≦C1≦100 ppm. E1 is the standard electrode potential (V vs. SHE) of a redox pair Li / Li+, and E2 is the standard electrode potential (V vs. SHE) of a redox pair in the additive in expression (1); and Cl is the moisture content in 1 g of the material constituting the anode active material containing layer in expression (2).
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Organic EL device and preparation method
InactiveUS20050064241A1Improve efficiencyHigh ease of handlingDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic layerStandard electrode potential
In an organic EL device comprising a cathode, an anode, and two or more stacked organic layers therebetween including a light emitting layer, an electron injecting organic layer containing an organic salt or complex of a metal having a standard electrode potential of more negative than −1.8 V at 25° C. is formed close to the cathode by coating, and an organic layer containing a high molecular weight EL material is disposed close to the electron injecting organic layer. A multilayer structure of organic layers can be formed by coating, and the organic EL device has a high luminance, high efficiency, high reliability, long life and ease of handling.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION +1
Metal nanowires, method for producing the same, and aqueous dispersion thereof
ActiveUS20090226753A1Good dispersionGood storage stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsElectrode potentialLong axis
The present invention provides metal nanowires including at least silver, and a metal other than silver, wherein the metal other than silver has a standard electrode potential more positive than the standard electrode potential of silver, and the metal nanowires have a long-axis length of 1 μm or more and a short-axis length of 300 nm or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of producing core-shell catalyst particle and core-shell catalyst particle produced by this production method
InactiveUS20120010069A1Maintain durabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesElutionStandard electrode potential
A method of producing a core-shell catalyst particle, the method including: preparing a core particle that contains an alloy including a first core metal having a standard electrode potential of at least 0.6 V and a second core metal having a standard electrode potential lower than that of the first core metal; eluting the second core metal at least at a surface of the core particle, the elution being carried out under conditions at which an equilibrium is maintained for the first core metal between a metal state and a hydroxide and at which an equilibrium is maintained for the second core metal between a metal state and a metal ion; and, with the core particle being designed as a core portion, coating this core portion with a shell portion after the elution of the second core metal.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
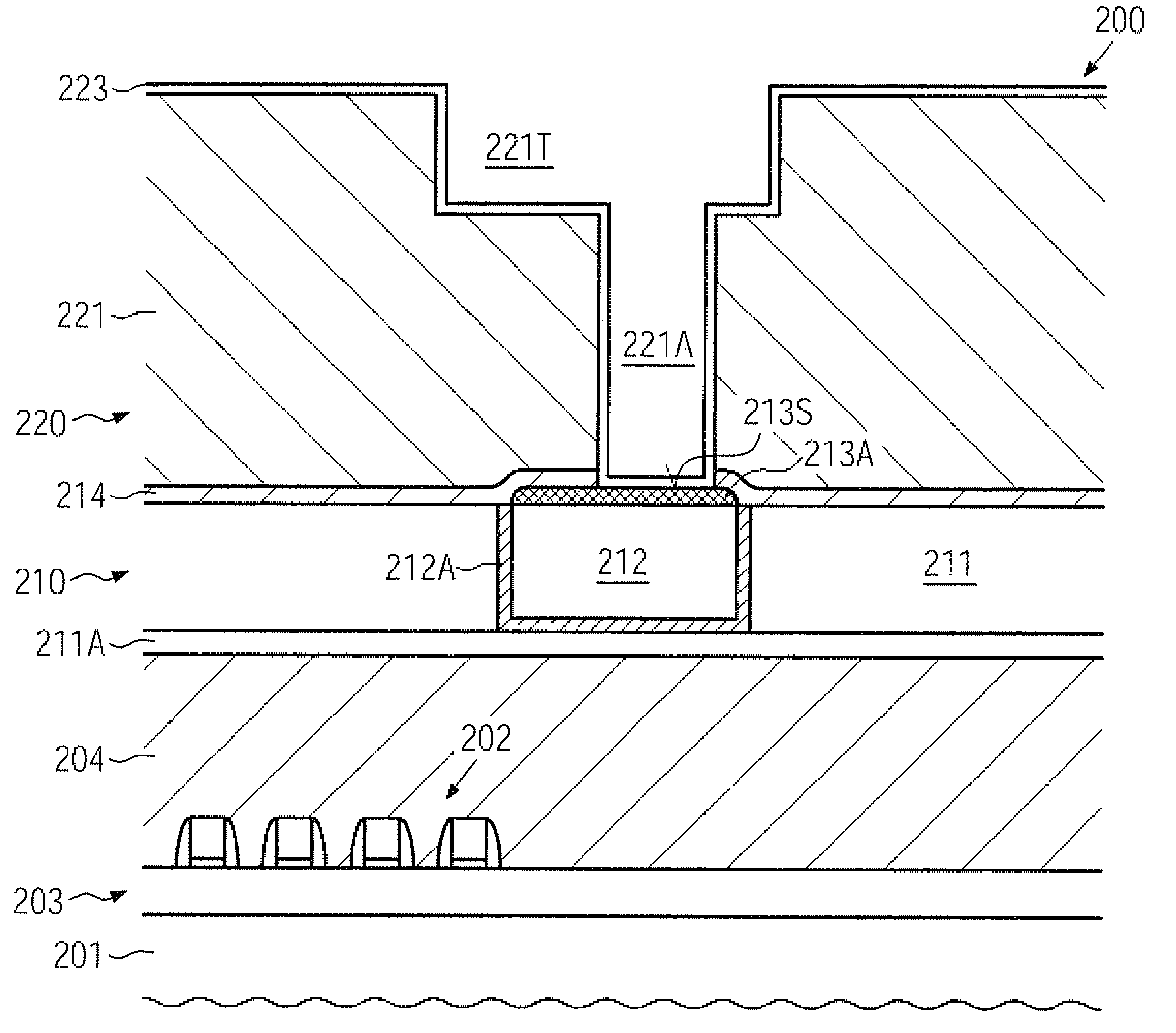
Metal cap layer of increased electrode potential for copper-based metal regions in semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20090243109A1Increased etch resistivityResist attackSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrode potentialStandard electrode potential
A conductive cap material for a copper region may be provided with enhanced etch resistivity by taking into consideration the standard electrode potential of one or more of the species contained therein. For example, instead of a conventionally used CoWP alloy, a modified alloy may be used, by substituting the cobalt species by a metallic species having a less negative standard electrode potential, such as nickel. Consequently, device performance may be enhanced, while at the same time the overall process complexity may be reduced.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
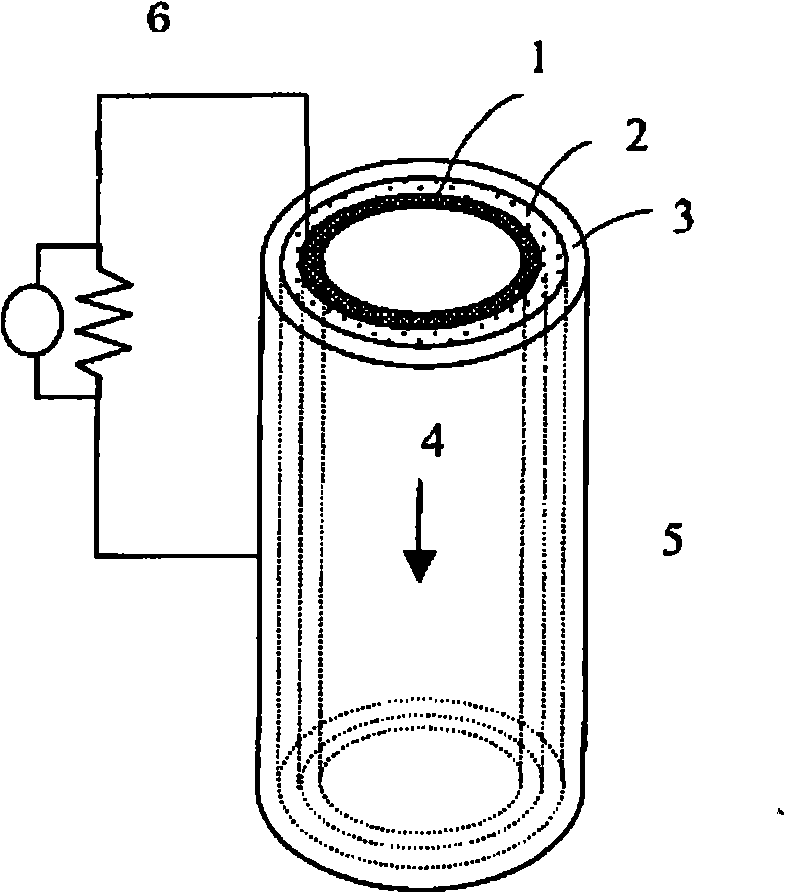
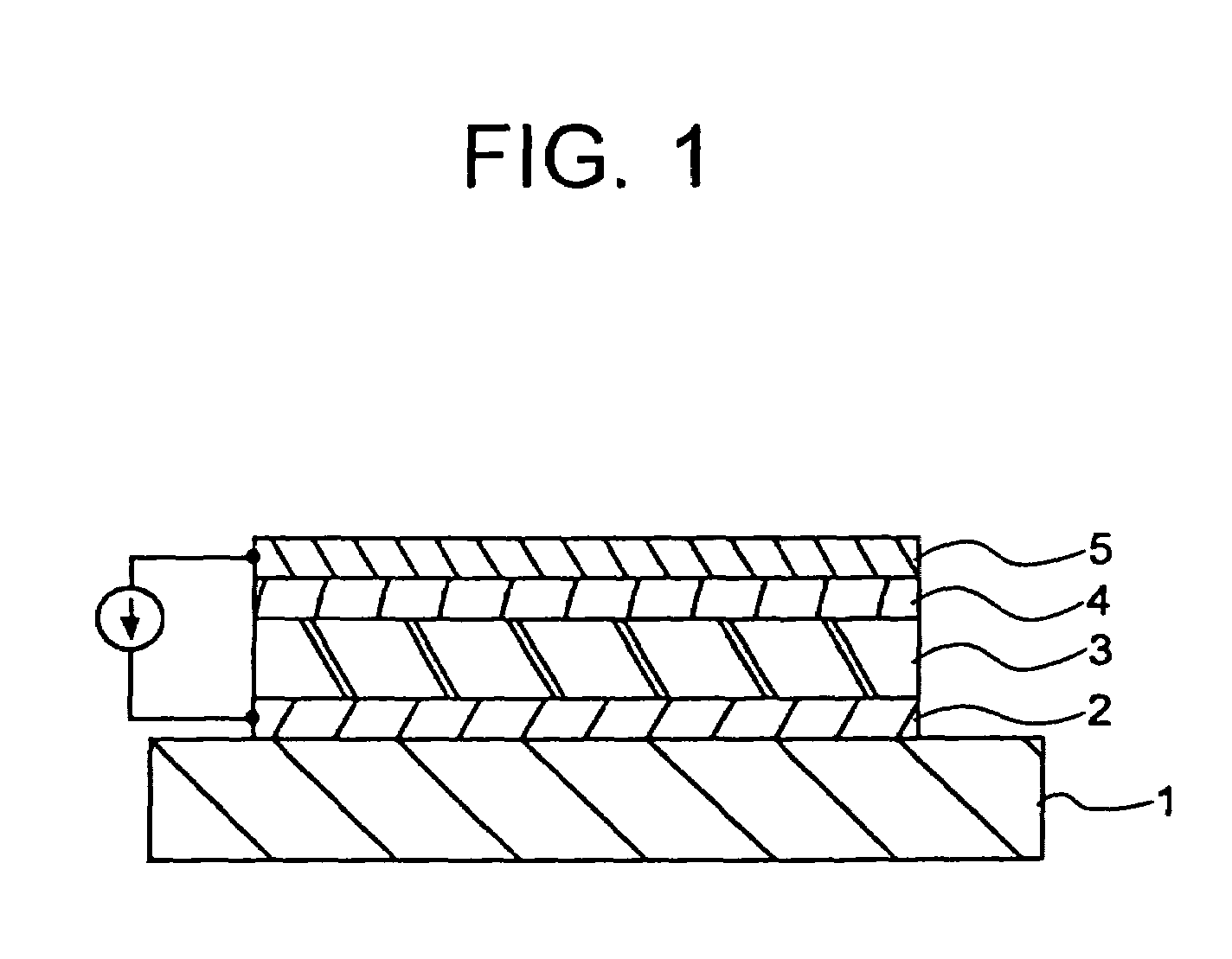
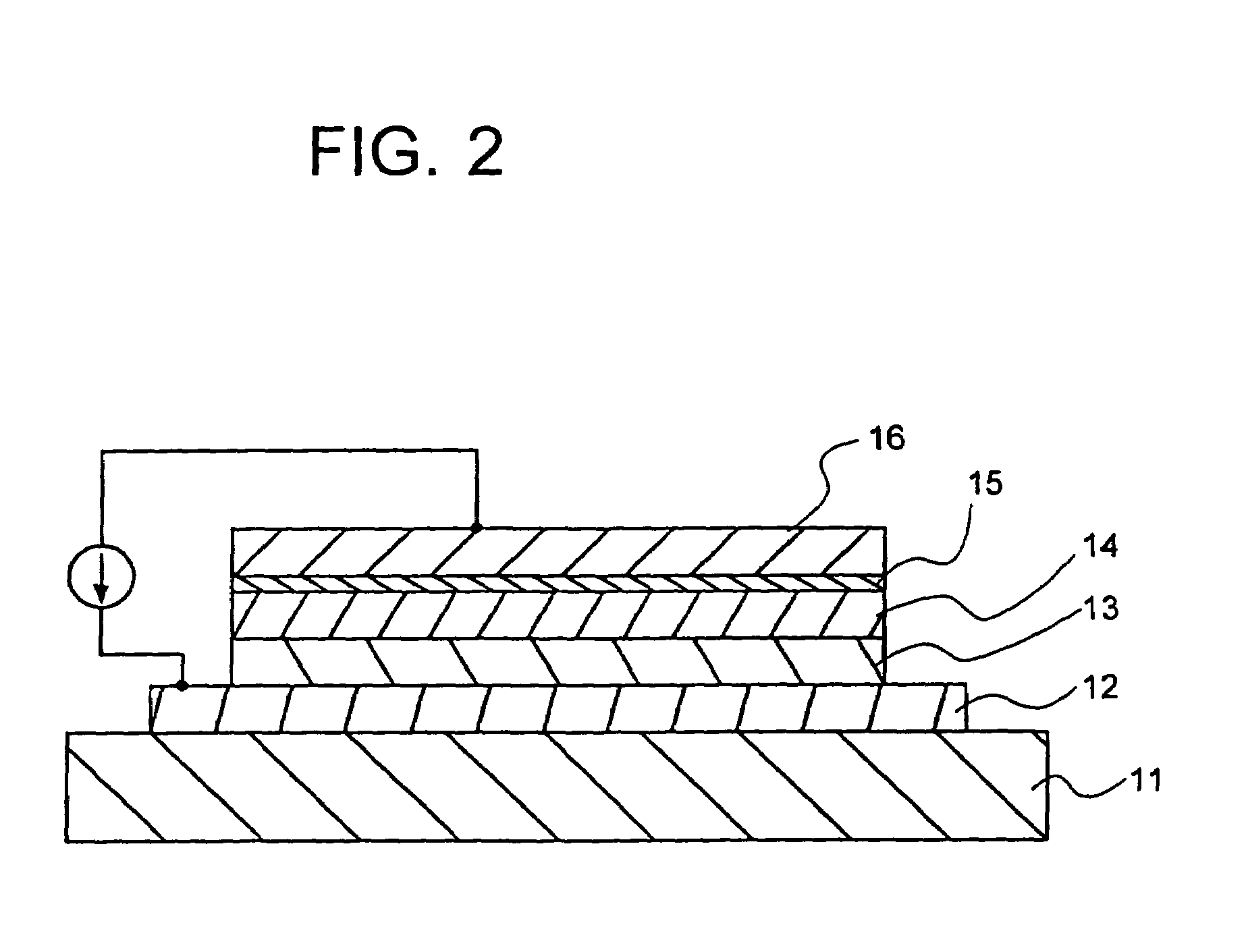
Anode for Bioelectric Power Generation And Power Generation Method And Apparatus Utilizing Same
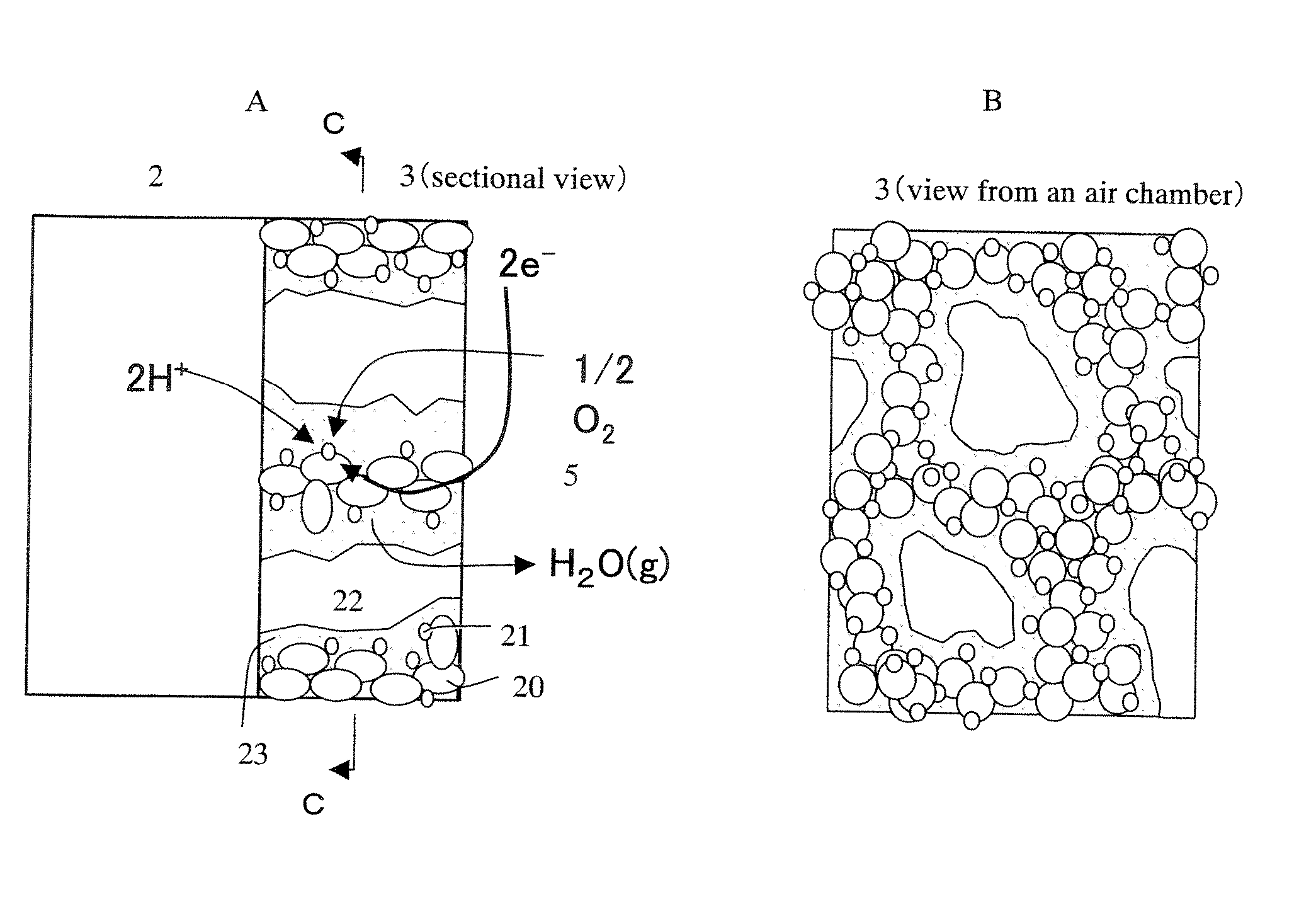
InactiveUS20090297890A1Efficient biological power generationSimple equipmentCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsOvervoltageHydrophilic polymers
A method and a device for obtaining electric energy efficiently from a hydrous organic substance by suppressing the activation overvoltage of an anode low and thereby obtaining a sufficiently low anode potential. The power generating device comprises an anaerobic region (4) including microorganisms which can grow under anaerobic conditions, solution or suspension containing an organic substance, an electron mediator and an anode (1), an aerobic region (5) including molecular oxygen and a cathode (3), and a diaphragm (2) defining the anaerobic region (4) and the aerobic region (5), wherein a closed circuit (6) is formed by connecting the anode (1) and the cathode (3) electrically with a power utilization apparatus, and oxidation reaction of microorganisms using the organic substance in the anaerobic region (4) as electron donor and a reduction reaction using oxygen in the aerobic region (5) as electron acceptor are utilized. The anode (1) includes a conductive substrate having a surface coated at least partly with a hydrophilic polymer layer, an electron mediator is introduced into the hydrophilic polymer layer with chemical bond, and the anode (1) has a standard electrode potential (E0′) at pH 7 in a range of −0.13 V to −0.28 V.
Owner:EBARA CORP
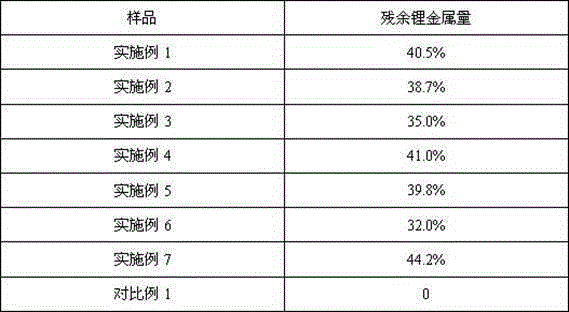
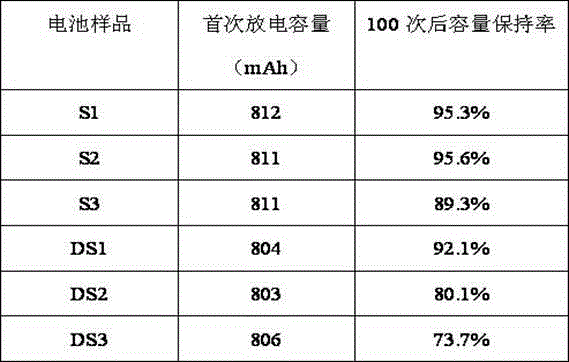
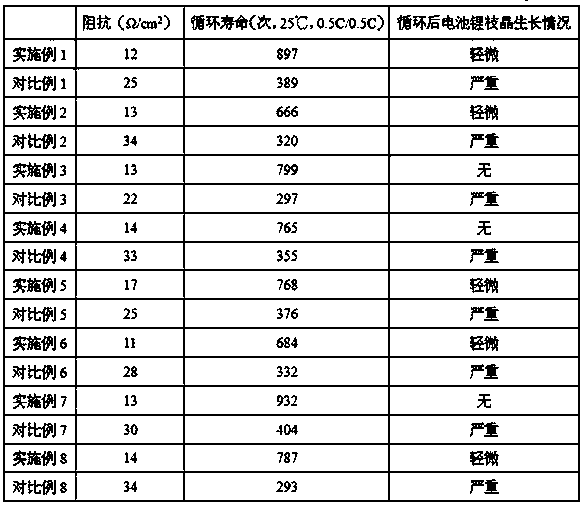
Passivation lithium powder and preparing method thereof, positive electrode material with addition of passivation lithium powder and battery
ActiveCN105762328AEasy to prepareIncrease energy densityCell electrodesElectrode potentialHigh energy
The invention provides a passivation lithium powder and a preparing method thereof, a positive electrode material with addition of the passivation lithium powder and a battery; the passivation lithium powder includes lithium powder particles and a metal layer coating the surface of the lithium powder particles; a metal in the metal layer comprises one or more of copper, nickel, iron, zinc, lead, silver, cadmium and cobalt, and the standard electrode potential of the metal in the metal layer is in a range of -0.7 to 1.3 V. The passivation lithium powder provided by the invention can make the lithium powder particles stably exist in air for a long time. The passivation lithium powder is added to the positive electrode material of the battery, so the purpose of lithium supplement can be controllable to achieve, and the prepared battery has relatively high energy density.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Anode for biological power generation and power generation method and device utilizing it
A method and a device for obtaining electric energy efficiently from an organic substance containing water by suppressing the activation overvoltage of an anode low and thereby obtaining a sufficiently low anode potential. The power generating device comprises an anaerobic region (4) including microorganisms which can grow under anaerobic conditions, solution or suspension containing an organic substance, an electron mediator and an anode (1), an aerobic region (5) including oxygen in molecular state and a cathode (3), and a diaphragm (2) defining the anaerobic region (4) and the aerobic region (5), wherein a closed circuit (6) is formed by connecting the anode (1) and the cathode (3) electrically with a power utilization apparatus, and oxidation reaction of microorganisms using the organic substance in the anaerobic region (4) as electron donor and a reduction reaction using oxygen in the aerobic region (5) as electron receptor are utilized. The anode (1) includes a conductive substrate having a surface coated at least partially with a hydrophilic polymer layer, an electron mediator is introduced into the hydrophilic polymer layer while boded chemically, and standard electrode potential (E0') at pH7 is in the range of -0.13V to -0.28V.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Preparation method of Raman scattering substrate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Raman scattering substrate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: providing a carbon nanotube film structure which comprises a plurality of carbon nanotubes connected by a van der waals force; and infiltrating at least part of the carbon nanotube film structure in a first solution until a plurality of metal particles are deposited on the surface of the carbon nanotube film structure, wherein the first solution comprises a plurality of metal ions, and a standard electrode potential of the metal ion is larger than Fermi energy of the carbon nanotube.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Silicon wafer cleaning agent and use method thereof
InactiveCN101880609AEasy to operateWill not bring inSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic non-surface-active detergent compositionsOrganic baseStandard electrode potential
The invention discloses a silicon wafer cleaning agent and a use method thereof. The silicon wafer cleaning agent consists of oxidant, organic base, penetrant and water, and the volume ratio of the components is as follows: oxidant : organic base : penetrant : water equal to 0.02-0.1:1-4:0.5-1:30-50; the standard electrode potential of the oxidant is not less than 1.7V, and the oxidant is ozone or hydrogen peroxide; the organic base is selected from one or more of the following components: triethanolamine, sodium alkoxide, sodium alkyl, lithium alkyl, lithium amide and quaternary ammonium base; and the penetrant is fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether or sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate. The cleaning agent can be simply operated, silicon wafer cleaning does not become complex, the cost is low, no pollution is generated, and the cleaning agent cannot bring impurities to stain silicon wafers, and is environment-friendly.
Owner:GD SOLAR
Method for inhibiting yellow smog during pickling of silicon materials
InactiveCN102020280ADoes not affect cleaning qualityImprove protectionSilicon compoundsElectrode potentialStandard electrode potential
The invention relates to the fields of photovoltaic or semiconductors, in particular to a method for inhibiting yellow smog during pickling of silicon materials. The main chemical components of the yellow smog are nitrogen oxides, such as nitric oxide, nitrogen monoxide, nitrogen dioxide and nitrogen tetroxide gas. The invention adopts the technical scheme that silicon material to be pickled is put in a mixed solution of mixed acid and strong oxidizer, wherein the mixed acid comprises hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, or other inorganic acids or organic acids, and the strong oxidizer is a standard oxidant of which the electrode potential is higher than that of the nitric acid and can be hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, manganese dioxide or ozone. By adopting the technical scheme, the quality for cleaning the silicon material cannot be influenced while the yellow smog is inhibited.
Owner:JIANGXI SAI WEI LDK SOLAR HI TECH CO LTD
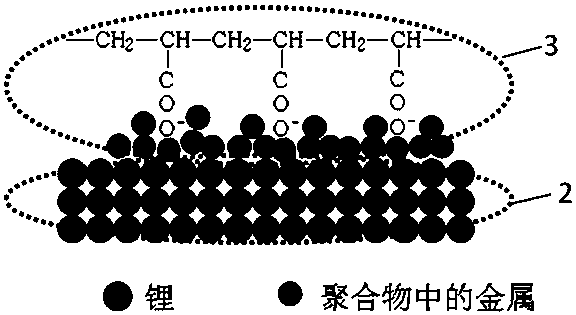
A polymer-protected lithium anode and a preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109216652AIncrease elasticityImprove lithium ion conductivityNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesInterfacial impedanceInterfacial adhesion
The invention relates to a polymer-protected lithium anode and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of lithium ion batteries. The lithium negative electrode comprises a current collector, two opposite sides of the current collector are respectively provided with lithium-containing material layers, and the outer sides of each lithium-containing material layer are coated with a polymer. The invention has the advantages that: Polyacrylate metal salt (non-Li salt) or polymethacrylate metal salt (non-Li salt) was selected as the polymer to protect lithium anode, in which the standard electrode potential of the metal was higher than Li, which would be deposited at the interface between the lithium anode and the polymer protective layer during the charging process, so asto improve the interfacial adhesion and reduce the interfacial impedance. Moreover, the deposited metal can be used as the skeleton structure on the surface of lithium anode to improve the cycling stability of lithium anode. These polymers have excellent elasticity and lithium ion conductivity, which can further reduce the interfacial impedance.
Owner:ZHUHAI COSMX BATTERY CO LTD
Organic EL device and preparation method
InactiveUS7018724B2Improve efficiencyEasy to handleDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesStandard electrode potentialOrganic layer
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION +1
Optical element molding die and method for molding optical element
InactiveUS20100119782A1Increased durabilityImprove accuracyAnodisationLayered productsConvex structureStandard electrode potential
An optical element molding die is designed for molding an optical element having a concave-convex structure. The optical element can be manufactured by a wet system that enables element formation over a large area and a curved surface, without using a lithographic process, and is advantageous in terms of mass production and equipment cost. The optical element molding die includes a substrate having a surface with a negative standard electrode potential in the oxidation reaction and an anodic oxidation layer provided on the substrate. A protective layer with the positive standard electrode potential is provided between the substrate and the anodic oxidation layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical film
InactiveUS20060127604A1Increased durabilityDesired optical properties to be obtained easilyLiquid crystal compositionsSolid-state devicesOptical propertyStandard electrode potential
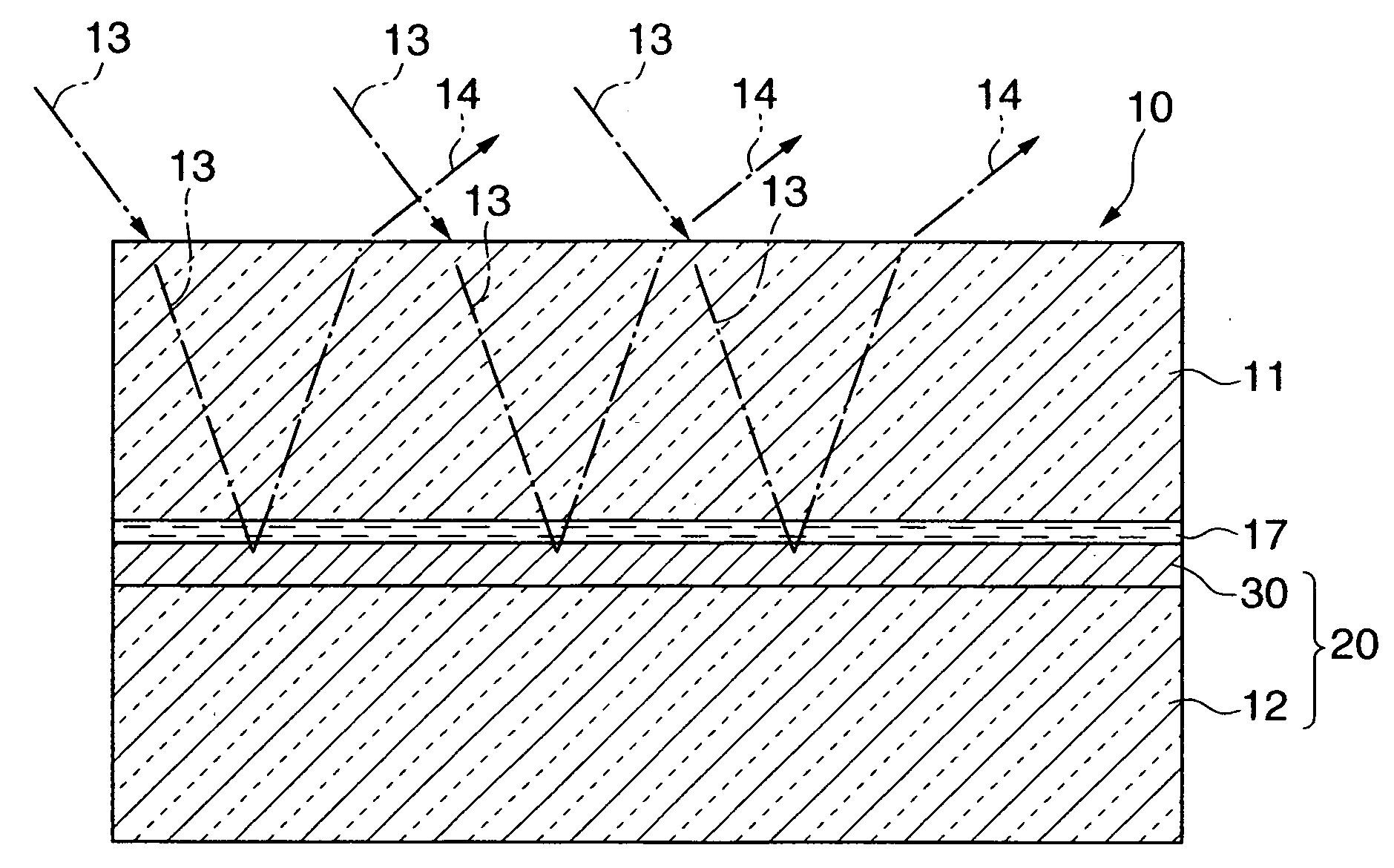
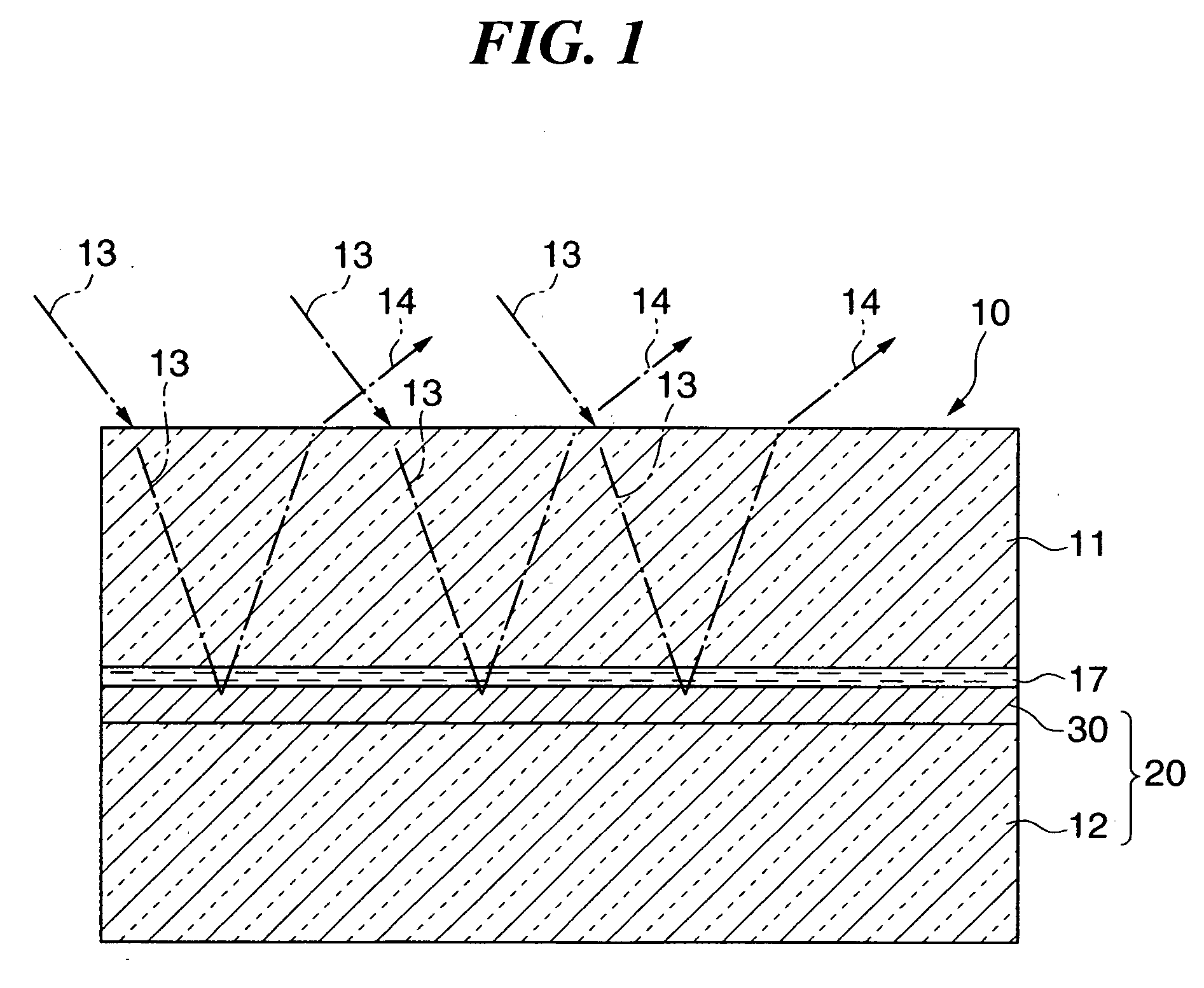
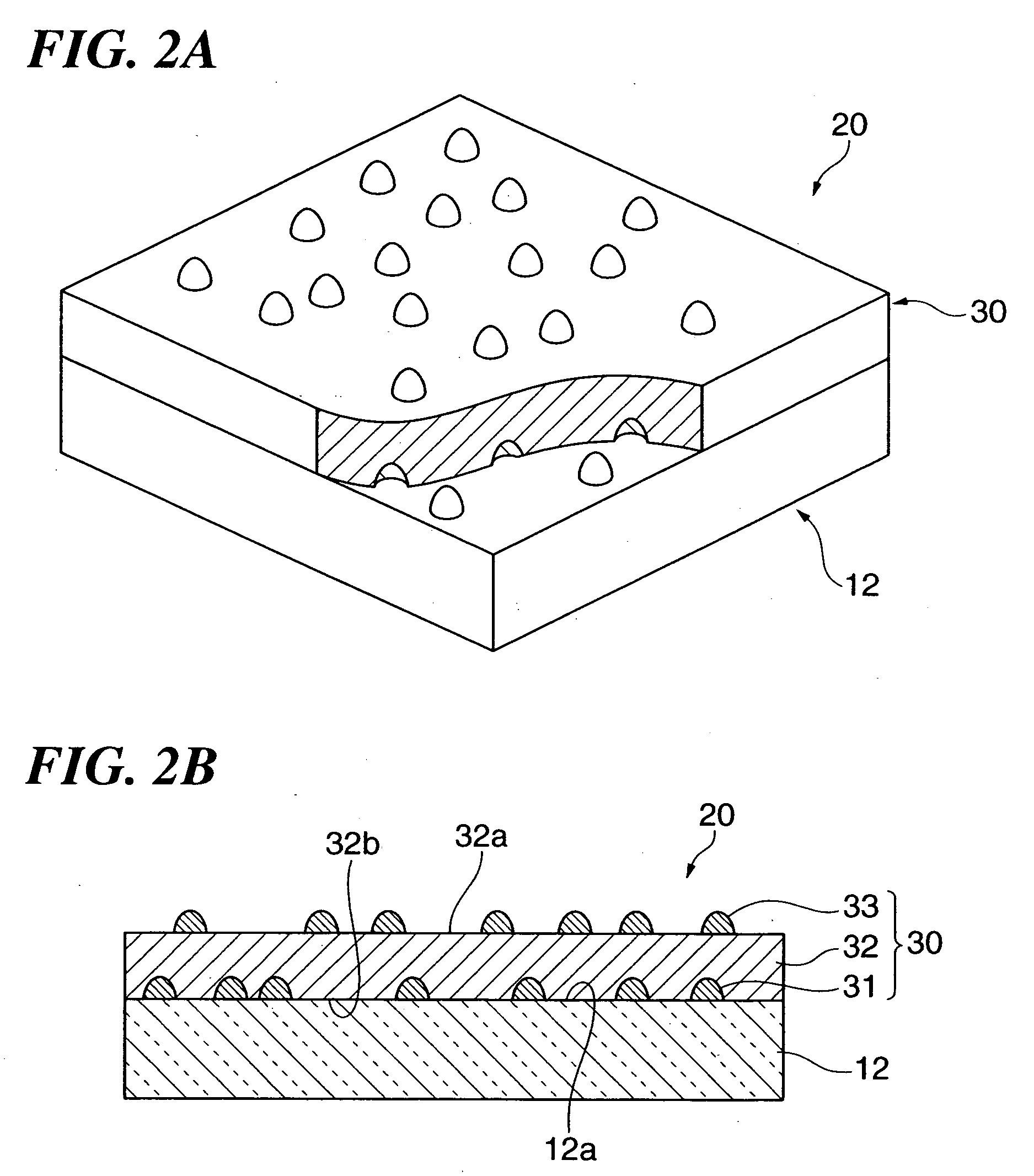
An optical film which enables desired optical properties to be obtained easily, and enables the durability to be improved. A metal film 32 is formed on an inner major surface 12a of a glass substrate 12. A plurality of first island structures 33 is formed scattered as islands on an inner major surface 32a of the metal film 32. A plurality of second island structures 31 is formed scattered as islands on the inner major surface 12a of the substrate 12. At least one set of the plurality of first island structures 33 and the plurality of second island structures 31 are made of at least one selected from the group consisting of metals and metal oxides having a different standard electrode potential to a metal of the metal film 32.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Chemical-mechanical polishing liquid and its application method
ActiveCN102464944AChemical Mechanical Polishing AccelerationFast polishingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolishing compositions with abrasivesStandard electrode potentialNanotechnology
Owner:ANJI MICROELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
High-purity antimony producing method by two-section fused salt electrolysis method
InactiveCN104313643AOptimizing Electrolysis ParametersSimple processStandard electrode potentialElectron
The invention relates to a high-purity antimony producing method by a two-section fused salt electrolysis method. The high-purity antimony producing method includes: a step of adding smashed antimony blocks and a fused salt electrolyte into an electrolytic cell comprising a first graphite electrode and a second graphite electrode; a step of electrolyzing firstly by an anode method, wherein the first electrode is set as an anode, the second electrode is set as a cathode, in an anode region, the antimony and impurity metals lose electrons, become positive ions, enter the fused salts, migrate to the surface of the cathode under actions of an electric field and diffusion and receive the electrons, and the impurity metals, which have standard electrode potentials lower than the standard electrode potential of the antimony, comprising Na, K, Zn, Cd, Fe, Pb, Sn, Cu and Ni are removed; and a step electrolyzing firstly by a cathode method, wherein the first electrode is set as a cathode, the second electrode is set as an anode, the reduced antimony elementary substance is adopted as a cathode, and nonmetal impurity elements comprising As, S and Bi are removed. The high-purity antimony producing method adopts the two-section fused salt electrolysis method, and optimizes electrolysis parameters to obtain antimony having purity of 99.99%. The high-purity antimony producing method is simple in process and suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:贵州重力科技环保股份有限公司
Producing method of wired circuit board
InactiveUS20080134500A1Efficient removalPrevent discolorationPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsConductive polymerStandard electrode potential
A producing method of a wired circuit board includes the steps of preparing a wired circuit board having an insulating layer and a conductive pattern including a wire covered with the insulating layer and a terminal portion exposed from the insulating layer, disposing a contact member formed of a material having a standard electrode potential lower than that of a conductive material forming the conductive pattern such that the contact member is in contact with the conductive pattern and exposed from the insulating layer, and dipping the wired circuit board including the disposed contact member in a polymerization solution of a conductive polymer to form a semiconductive layer on the surface of the insulating layer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method for preparing molten-salt electrolyte containing low-valent titanium chloride and method for extracting titanium
InactiveCN103147096AIncrease response rateThe process can be continuousMetal chlorideAlkaline earth metal
The invention provides a method for preparing molten-salt electrolyte containing low-valent titanium chloride and a method for extracting titanium. The method for preparing molten-salt electrolyte comprises the following steps: mixing alkali chloride and / or alkaline-earth metal chloride with a pre-set amount of metal chloride to form mixture, wherein the standard electrode potential of metal ions in the metal chloride is more positive than the standard electrode potential of divalent or trivalent titanium ion; with the electrode containing the metal titanium as an anode and the mixture as molten-salt electrolyte, configuring a cathode and electrolyzing so that all the metal chloride in the mixture is deposited on the cathode, wherein the obtained molten salt is the molten-salt electrolyte containing the low-valent titanium chloride. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the molten-salt electrolyte containing low-valent titanium chloride can be prepared under the conditions that the molten-salt electrolyte is not polluted and test devices are not corroded, the reaction rate is high, and the technical processes are continuous.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
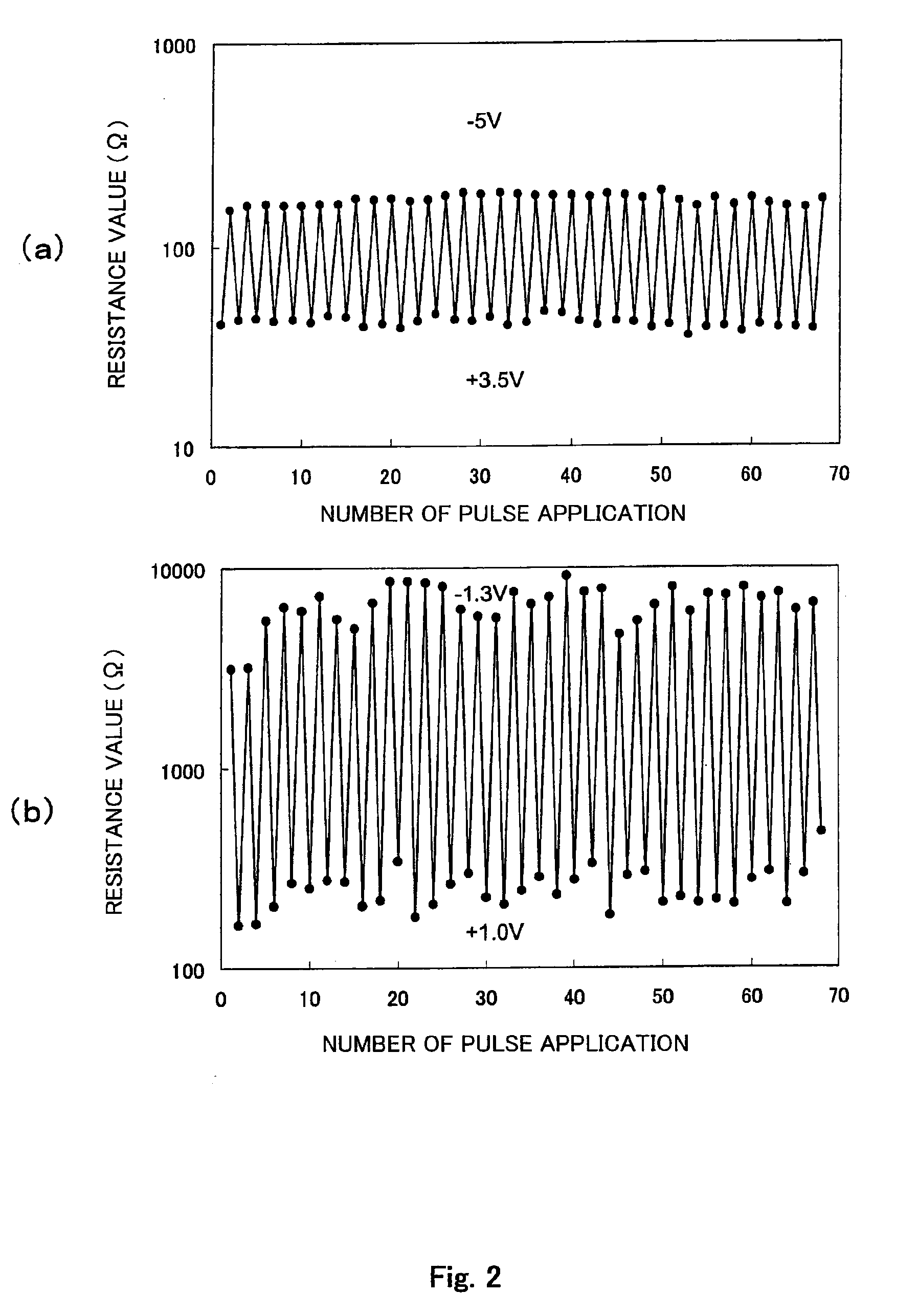
Nonvolatile memory element, nonvolatile memory apparatus, and method of writing data to nonvolatile memory element
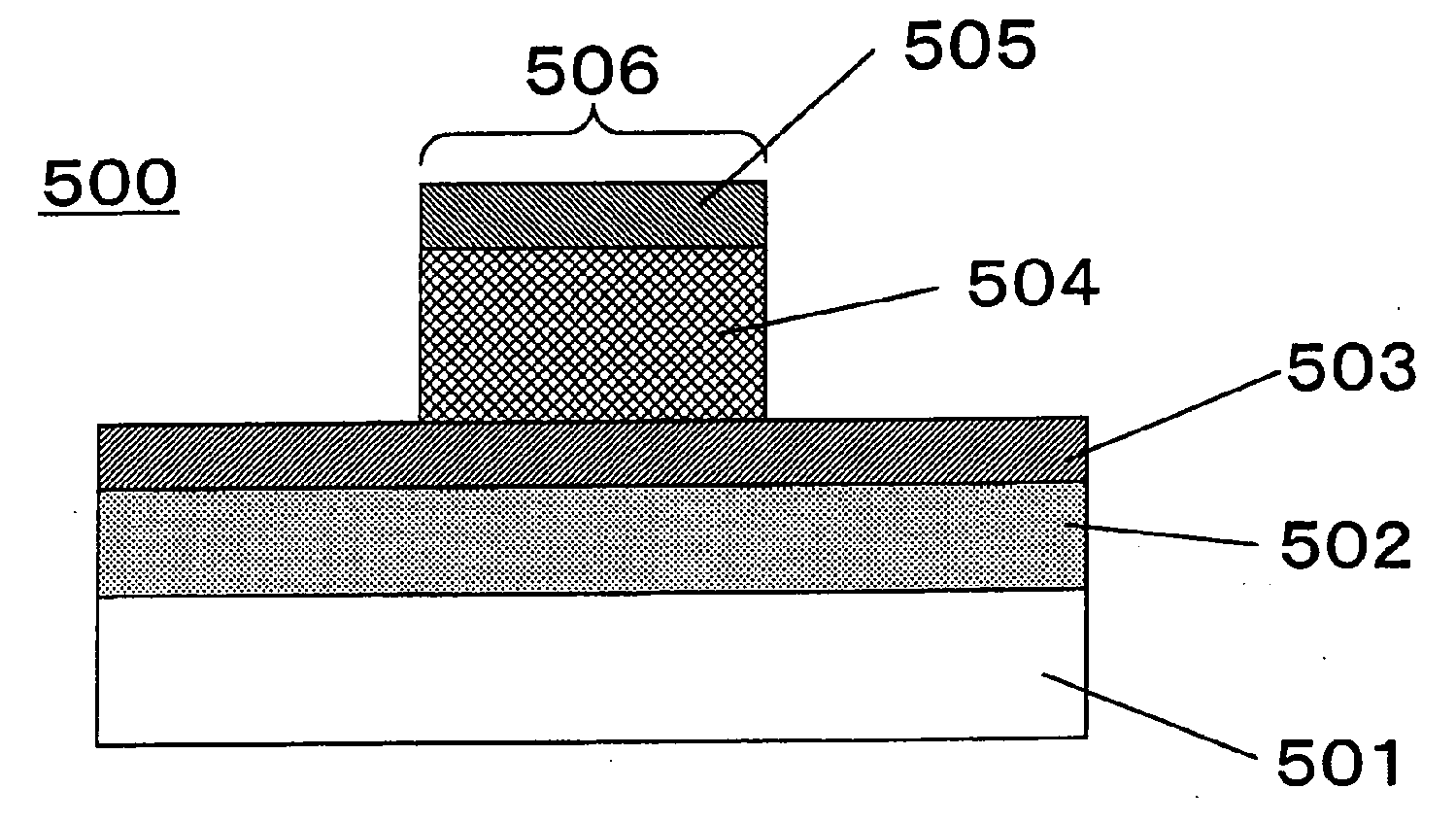
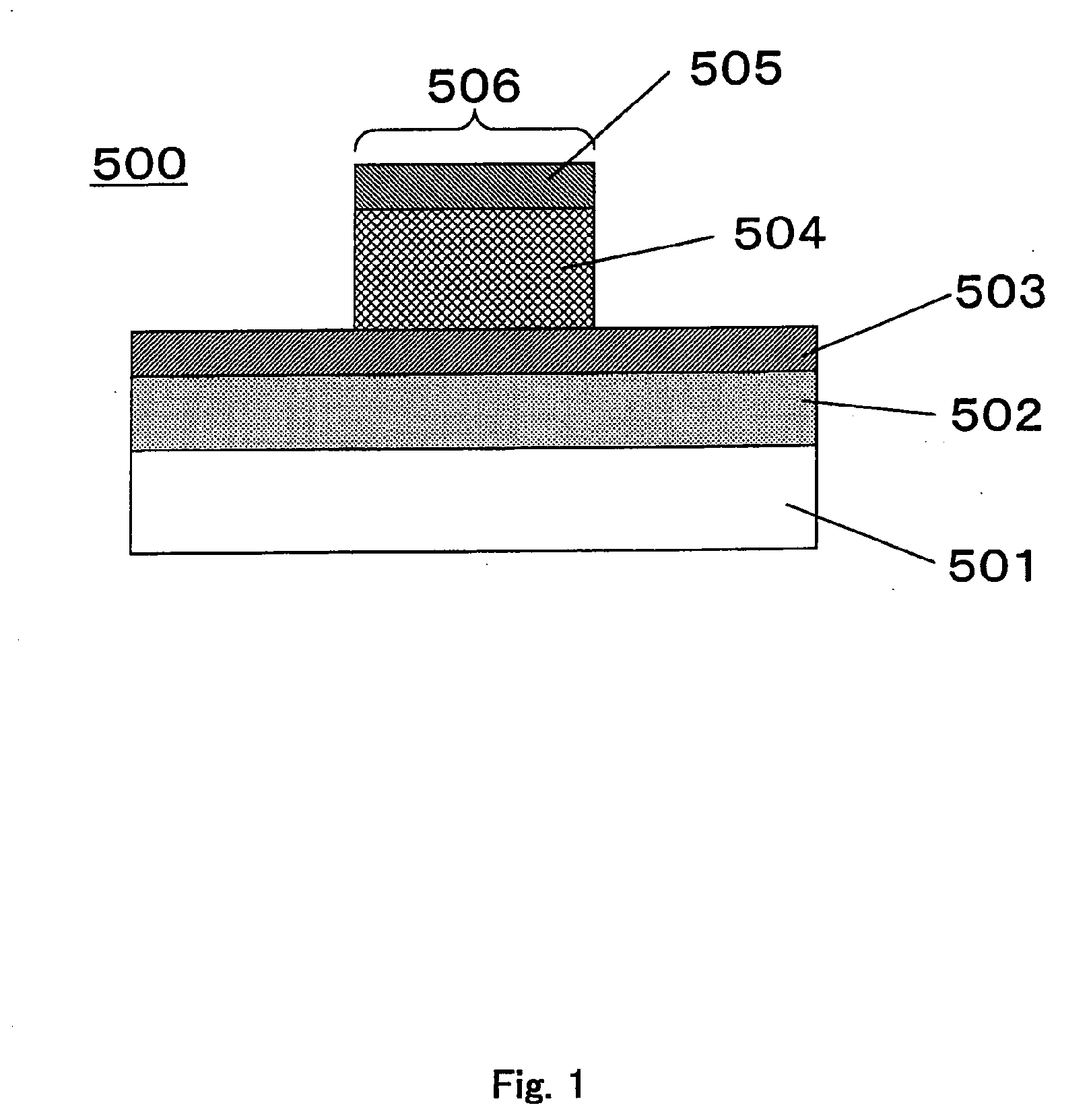
InactiveUS20100188884A1Stable characteristicsDigital storageBulk negative resistance effect devicesStandard electrode potentialHafnium
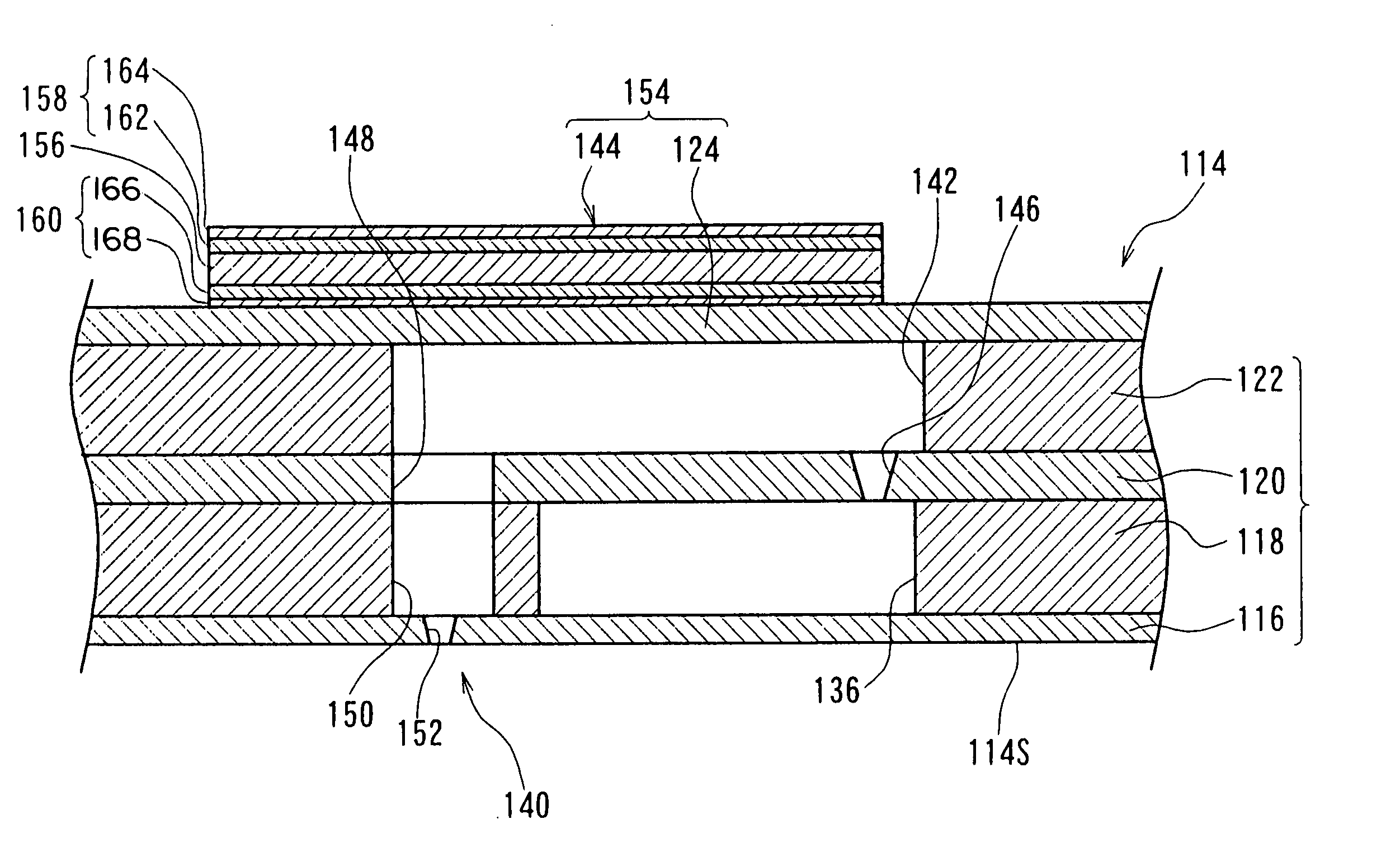
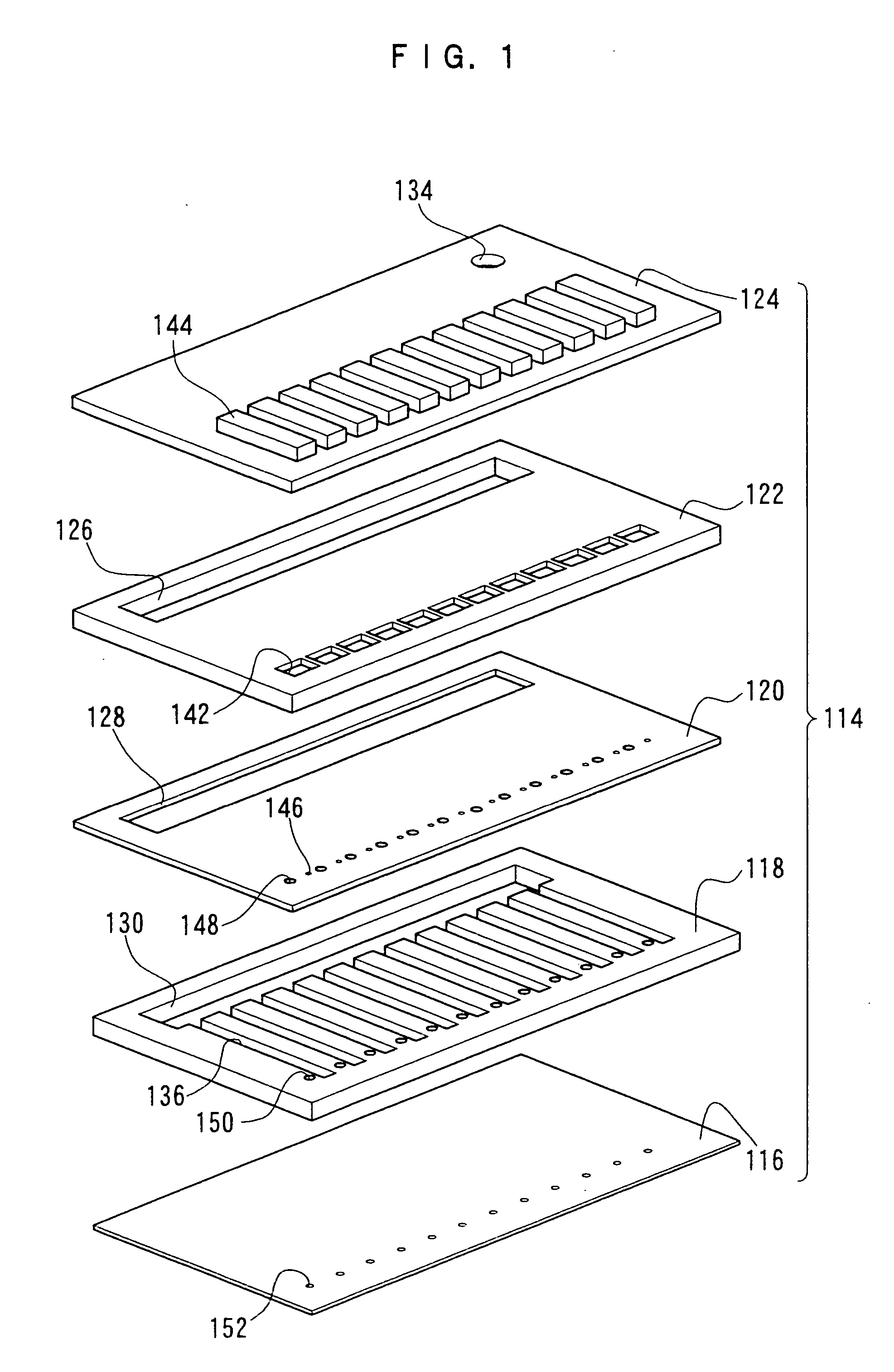
A nonvolatile memory element comprises a first electrode (503), a second electrode (505), and a resistance variable layer (504) disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode, a resistance value between the first electrode and the second electrode being switchable reversibly in response to positive and negative electric signals applied between the first electrode and the second electrode; wherein the resistance variable layer includes an oxygen-deficient hafnium oxide; wherein the first electrode and the second electrode comprise elements which are different from each other; and wherein a standard electrode potential V1 of an element forming the first electrode, a standard electrode potential V2 of an element forming the second electrode and a standard electrode potential V0 of hafnium satisfy a relationship of V1<V2 and V0<V2.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
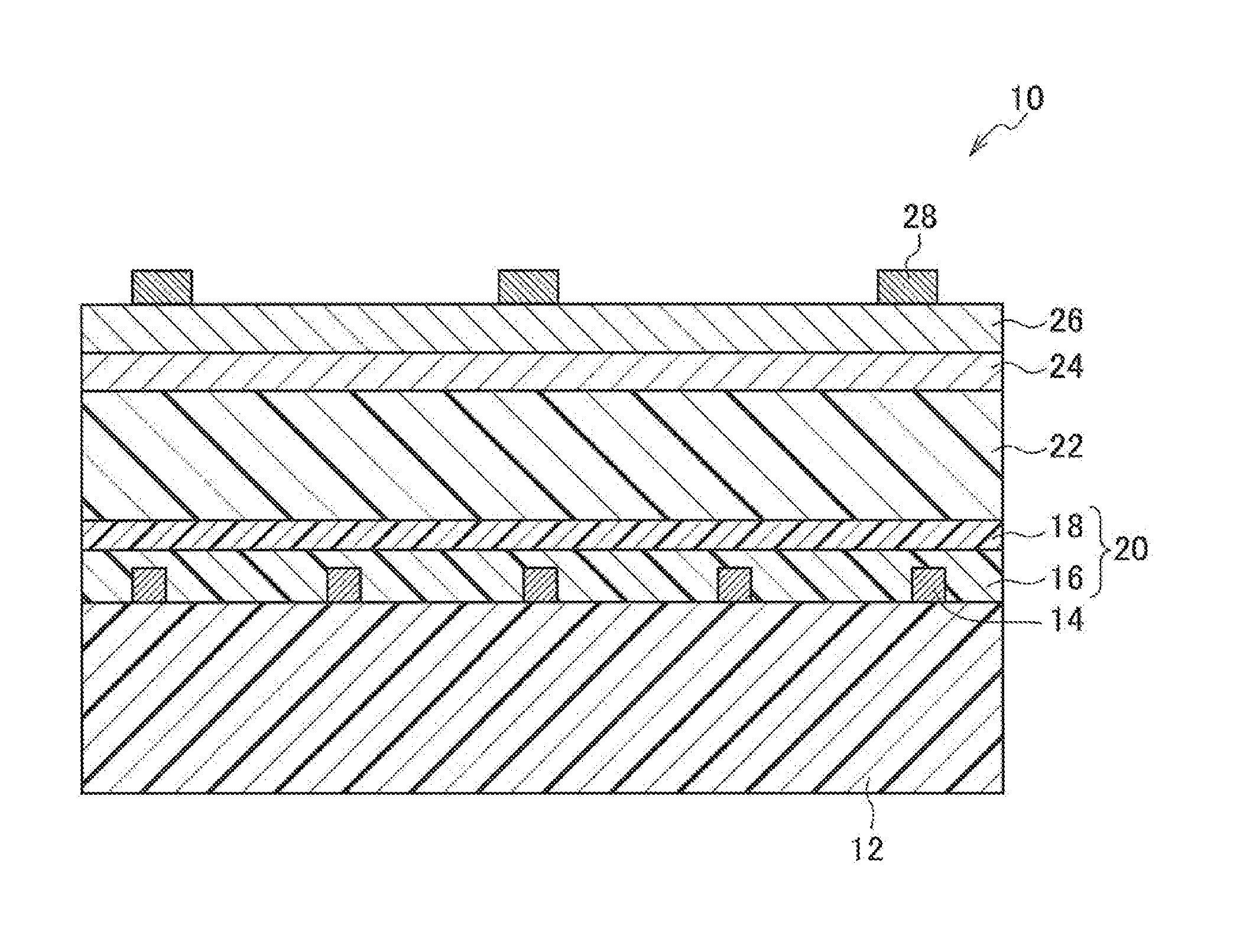
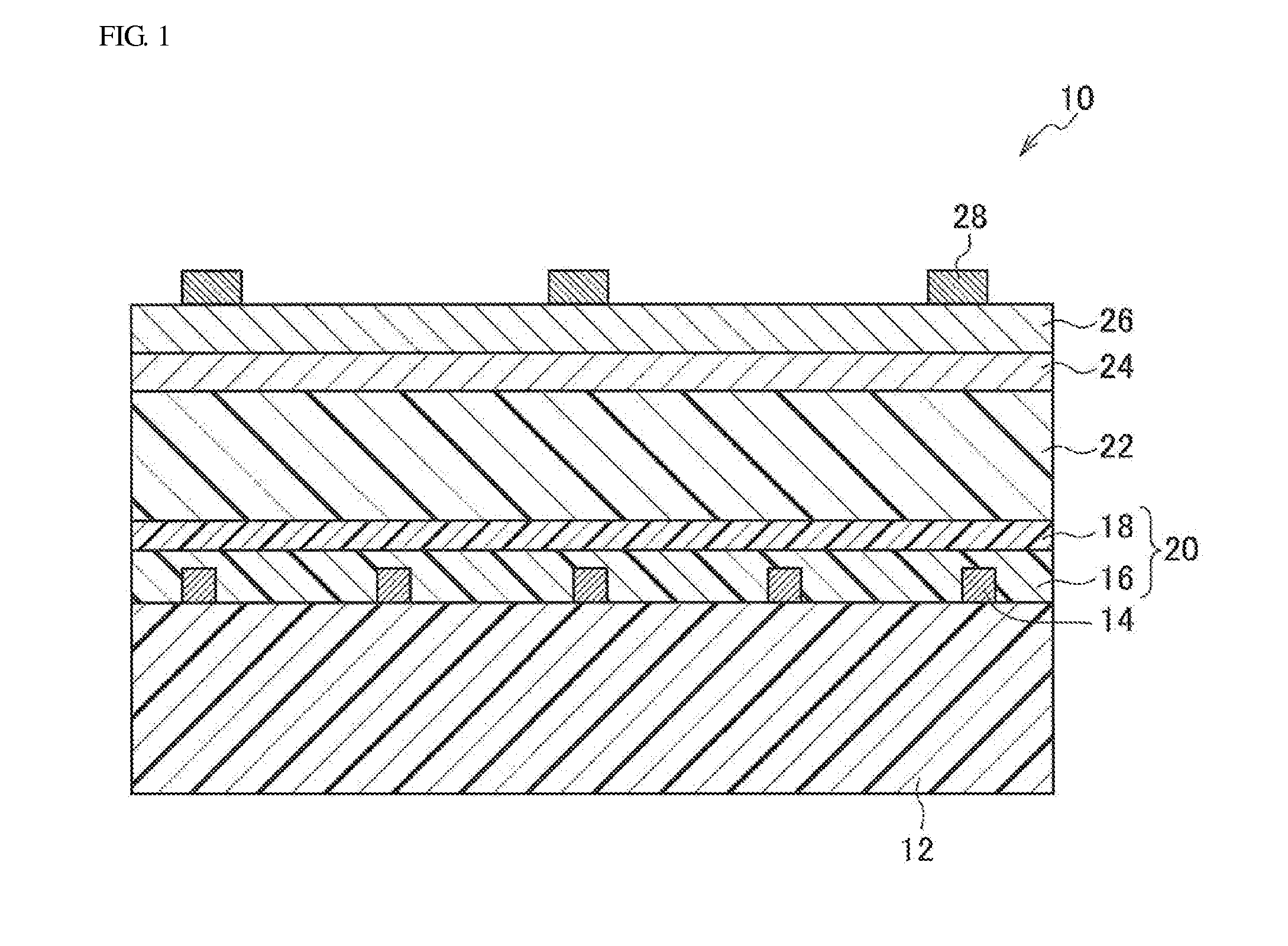
Solar cell
InactiveUS20130180586A1Deterioration in photovoltaic characteristics due to degradation of the negative electrode is suppressedFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsStandard electrode potentialPhotoelectric conversion
A solar cell 10 has a support 12, a positive electrode 20 disposed on the support, a photoelectric conversion layer 22 disposed on the positive electrode, a translucent metal negative electrode 26 which is disposed on the photoelectric conversion layer and is provided with a positive standard electrode potential, and an additional metal electrode 28 for the negative electrode, the additional metal electrode being disposed so as to be in contact with the metal negative electrode and being provided with a standard electrode potential that is less than the standard electrode potential of the metal negative electrode.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
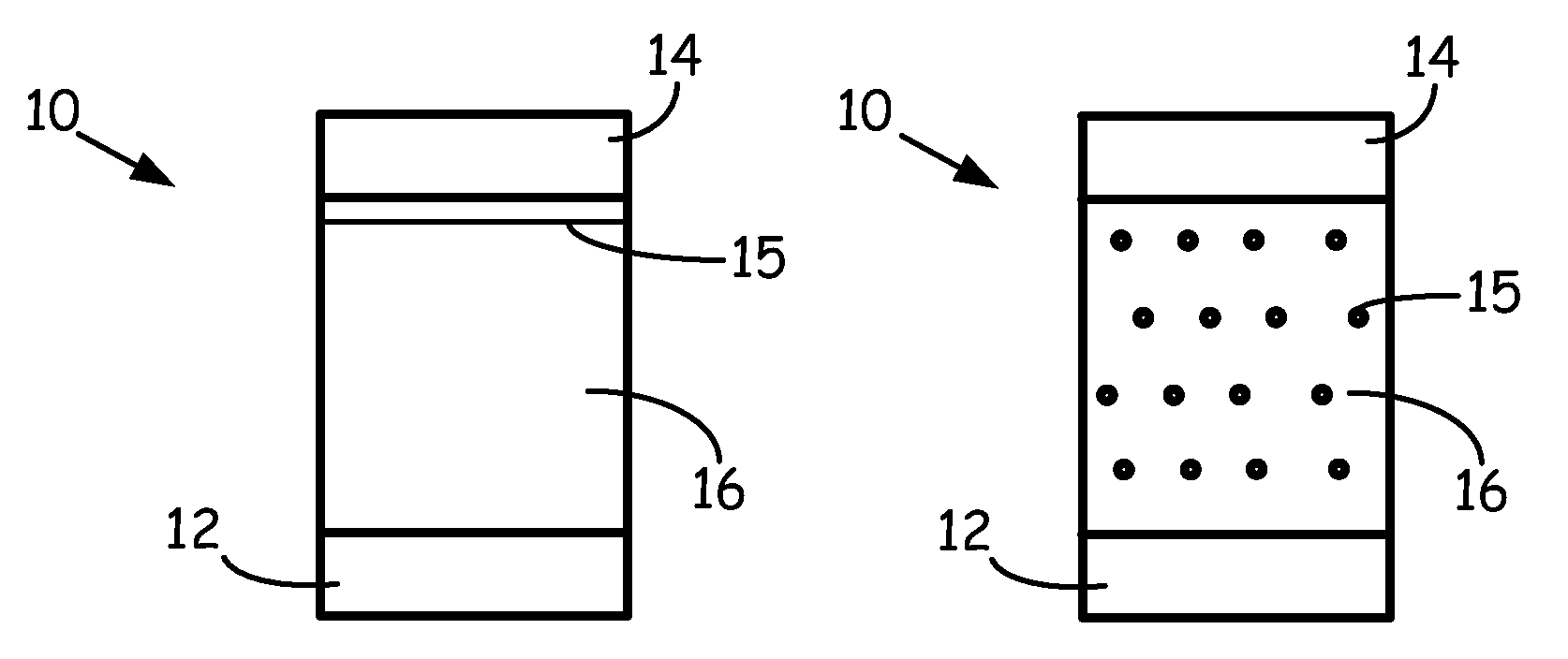
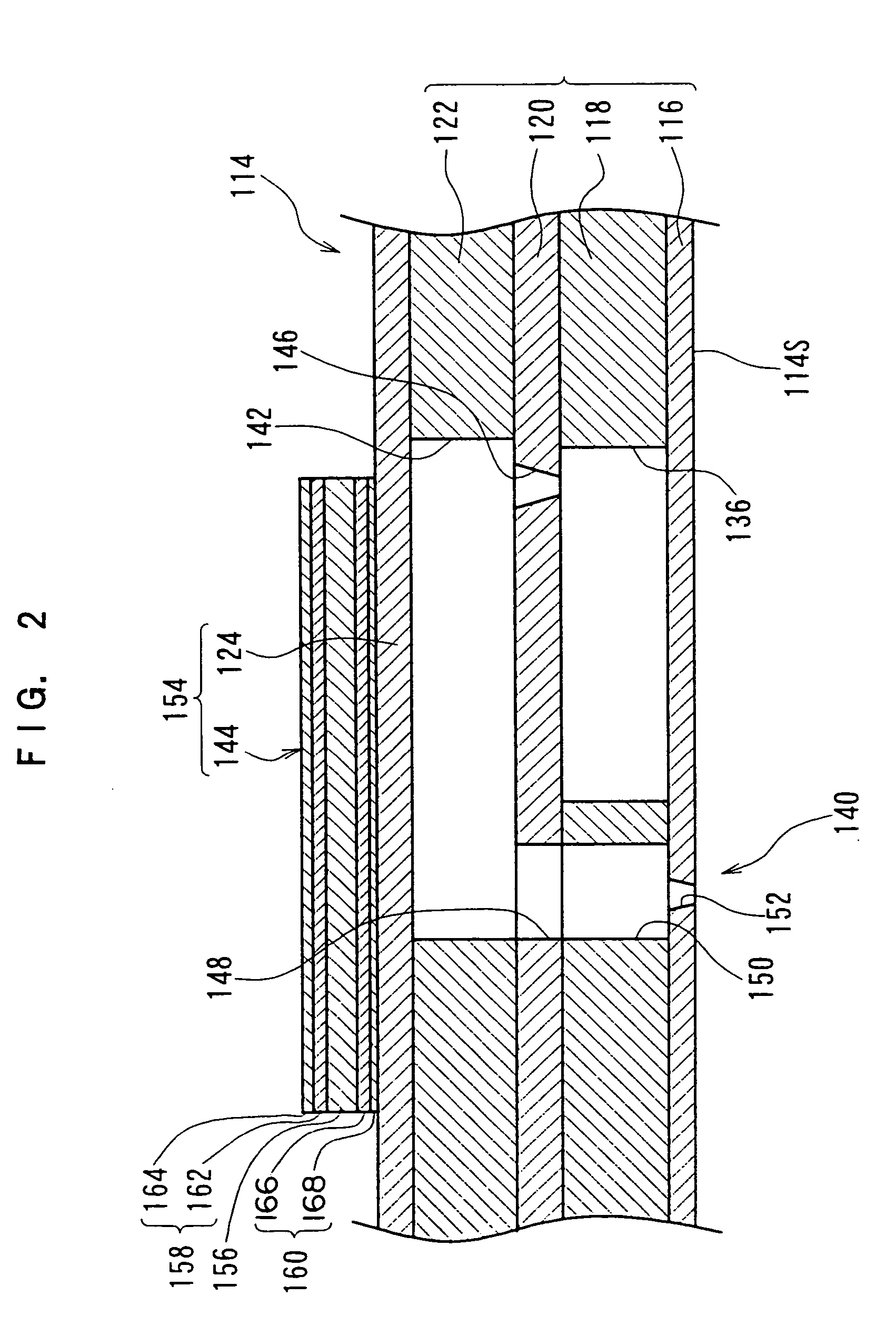
Ferrous disintegrable powder compact, method of making and article of same
ActiveUS20160032671A1Transportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusStandard electrode potentialAlloy
A process for preparing a disintegrable powder compact, the process comprises: combining: a primary particle comprising a ferrous alloy which comprises carbon; and a secondary particle to form a composition; compacting the composition to form a preform; and sintering the preform to form the disintegrable powder compact by forming a matrix from one of the primary particle or the secondary particle; and forming a plurality of dispersed particles from the other of the primary particle or the secondary particle, wherein the dispersed particles are dispersed in the matrix, the disintegrable powder compact is configured to disintegrate in response to contact with a disintegration fluid, and the primary particle and secondary particle have different standard electrode potentials.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Preparation process of radioactive isotope cadmium-109
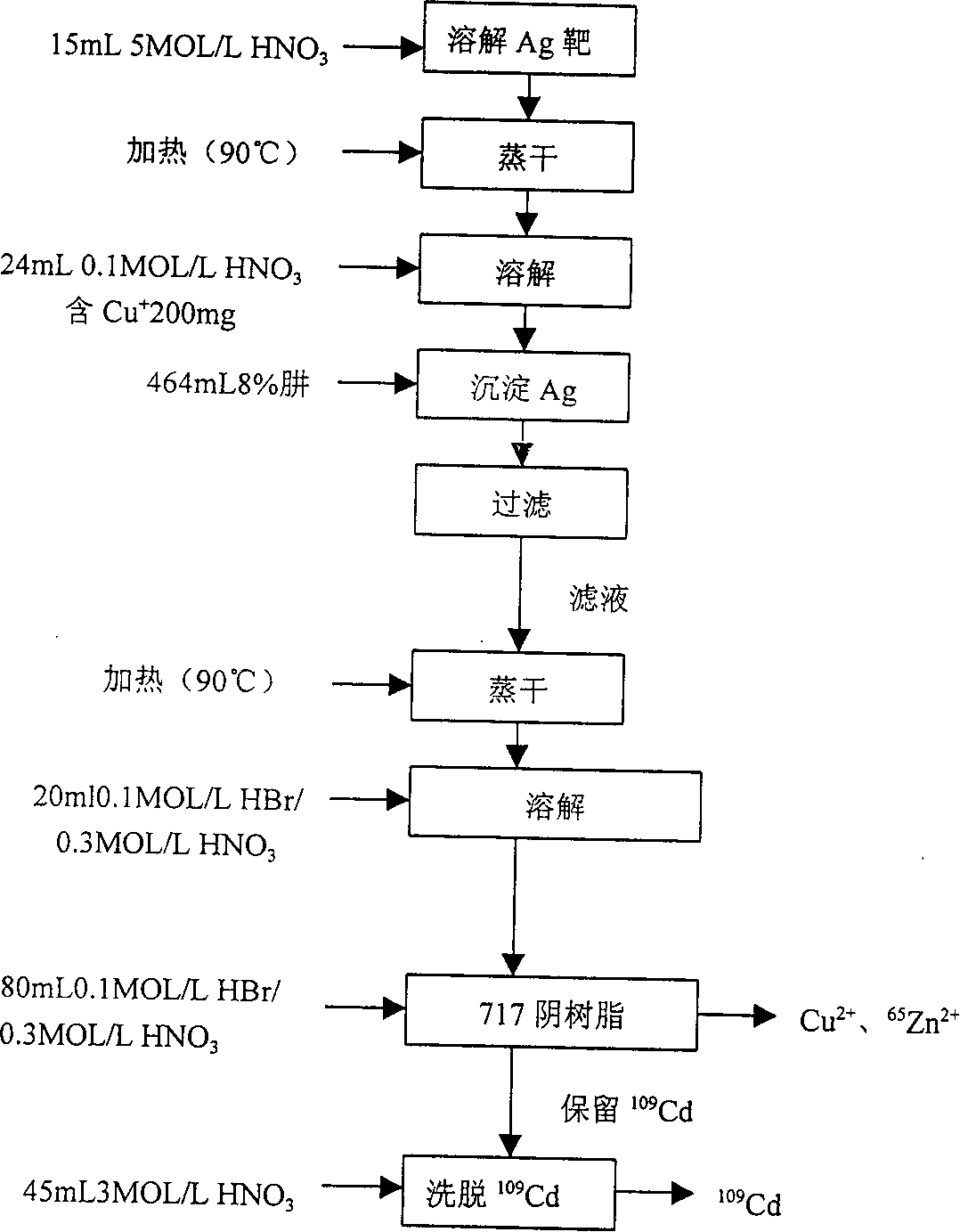
InactiveCN1341761AConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsHydrazine compoundStandard electrode potential
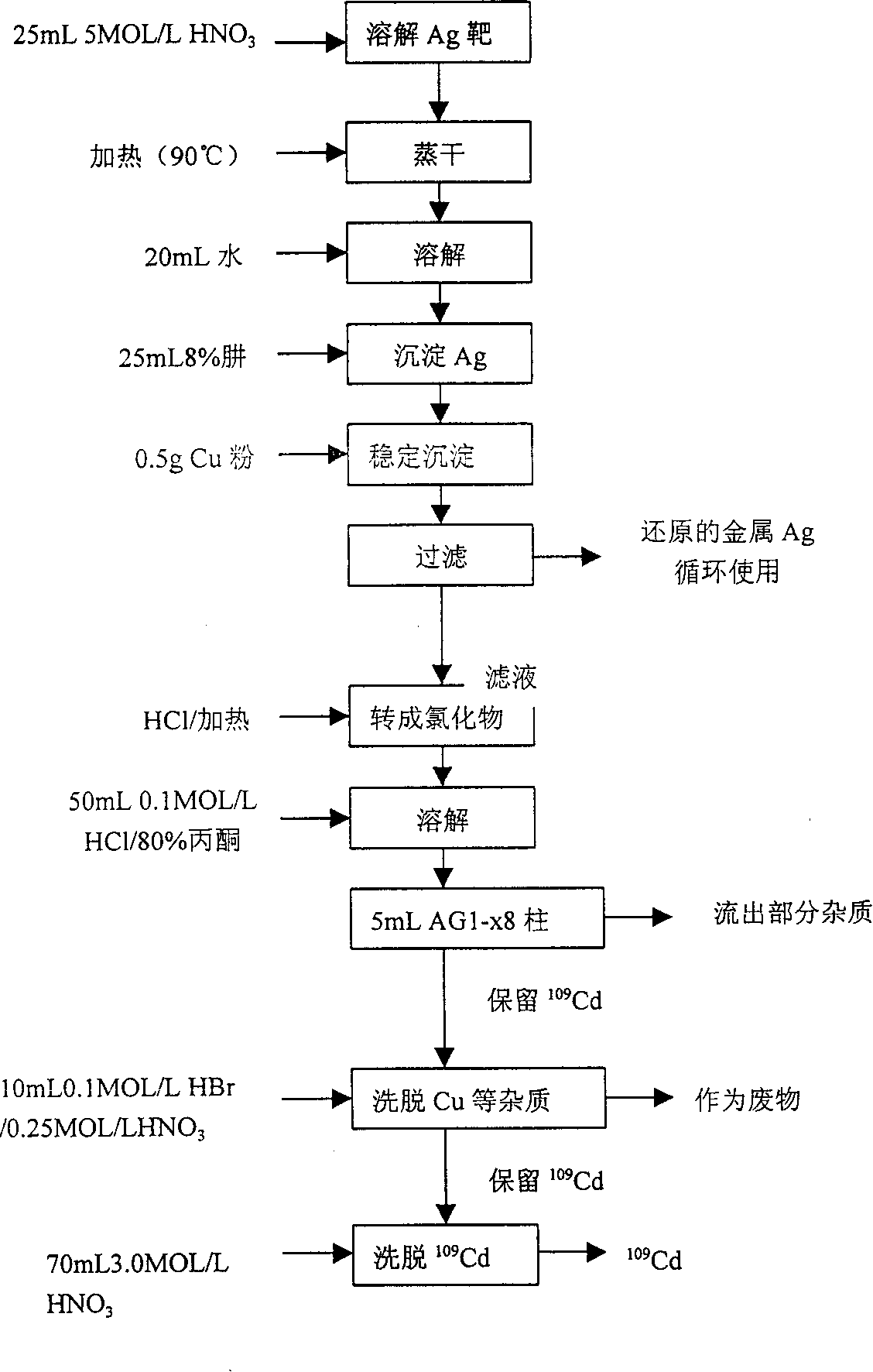
The preparation process of radioisotope cadmium-109 (109Cd) relates to the separation and purification process of radioisotope cadmium-109 produced by utilizing proton beam accelerated by cyclotron to bombard silver target. It is characterized by that according to the principle of oxidation-reduction potential firstly adding metal ion whose standard electrode potential value of greater than cadmium ion and less than silver ion as protecting agent of cadmium ion in the silver target dissolved liquor, then adding excess hydrazine hydrate to quantitatively reduce silver ion, and also partially reduce added protecting agent so as to make cadmium ion do not be reduced.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Metal nanowires, method for producing the same, and aqueous dispersion thereof
ActiveUS8349467B2Good dispersionImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyMetal-working apparatusStandard electrode potentialLong axis
The present invention provides metal nanowires including at least silver, and a metal other than silver, wherein the metal other than silver has a standard electrode potential more positive than the standard electrode potential of silver, and the metal nanowires have a long-axis length of 1 μm or more and a short-axis length of 300 nm or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com