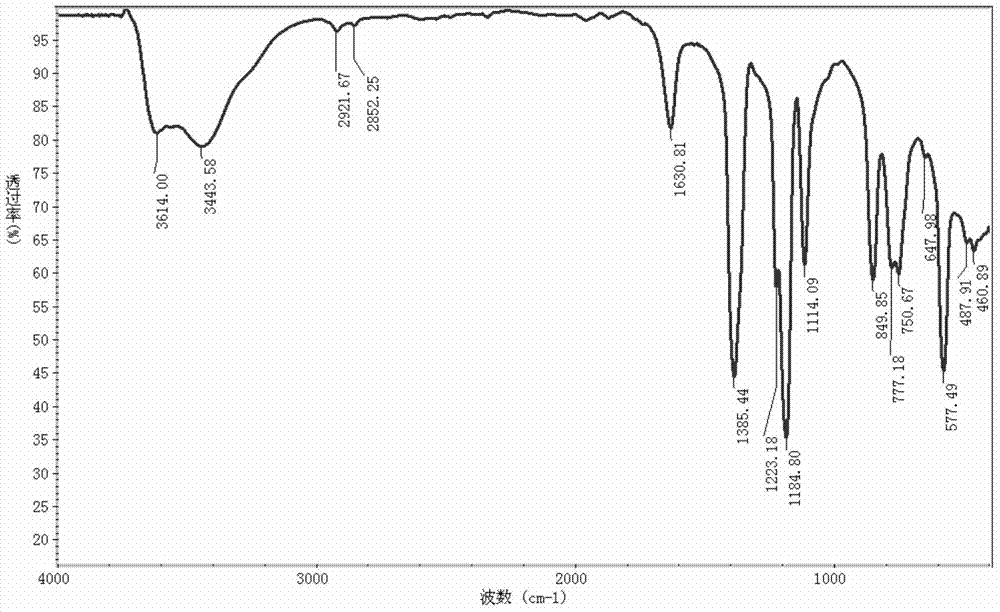
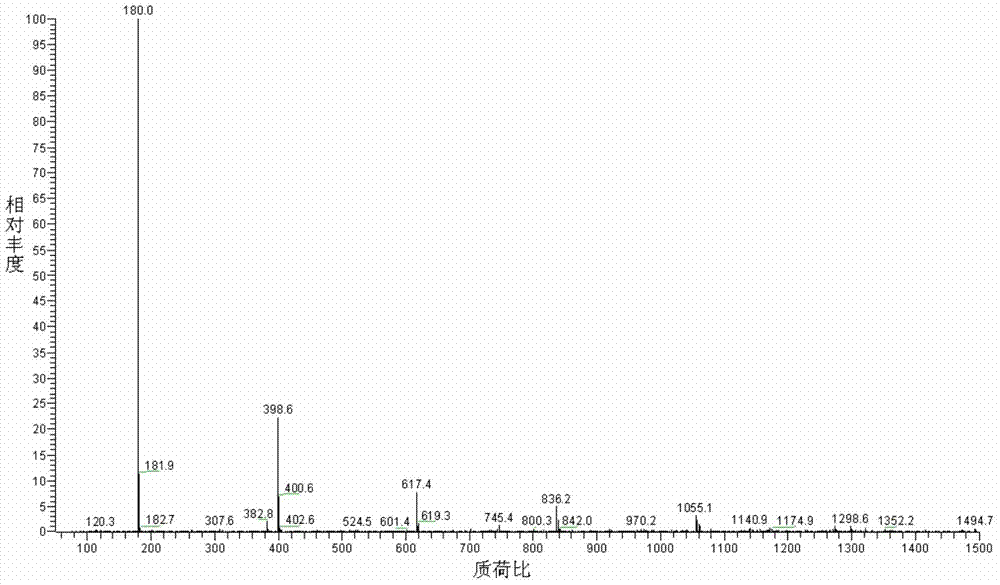
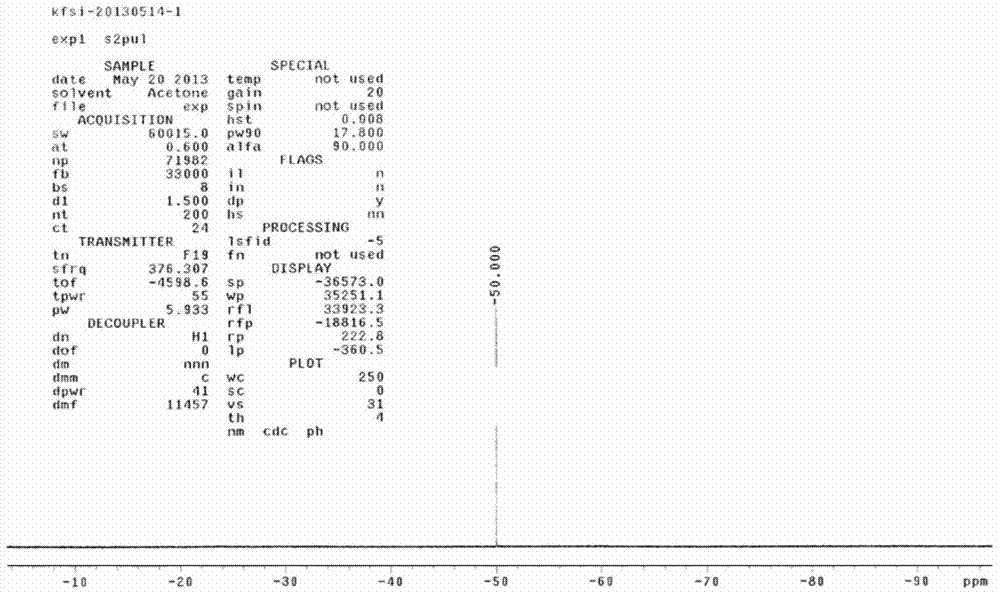
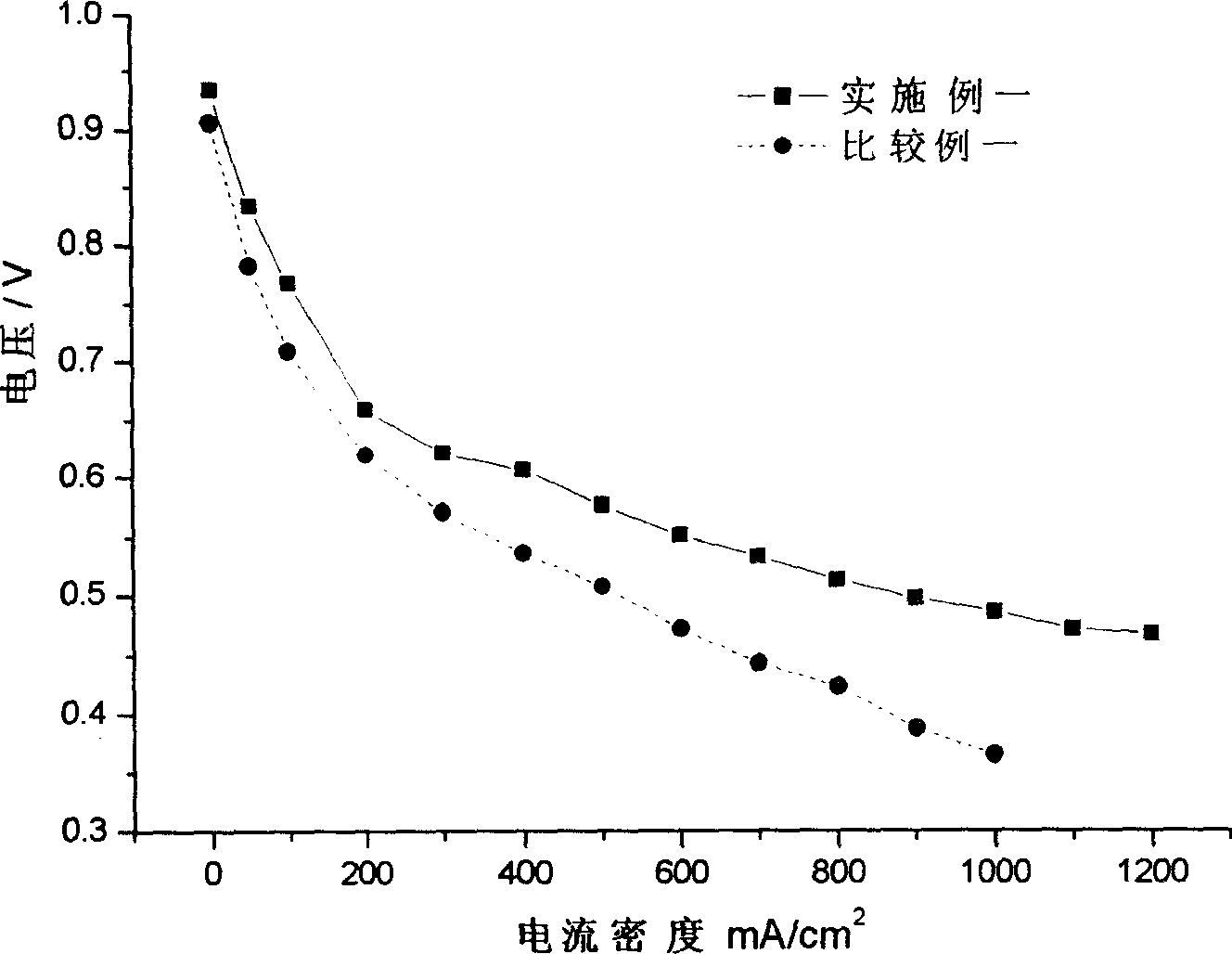
Patents
Literature
420 results about "Single displacement reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A single-displacement reaction, also known as a single-replacement reaction, is a chemical reaction in which one (or more) element(s) replaces an/other element(s) in a compound. This will most often occur if A is more reactive than B, thus giving a more stable product.
Preparation method of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide
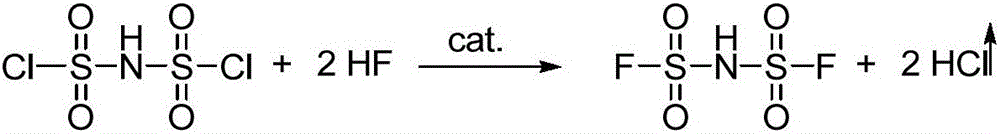
The present invention provides a preparation method of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide. The method comprises the following steps: A) reacting chlorosulfuric acid with ammonia in the presence of an organic base to obtain organic alkali salt of bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide; B) mixing the bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide obtained in the step A) with HF for a fluorinated reaction to obtain an organic alkali salt of bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide; C) mixing the organic alkali salt of bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide obtained in the step B) with an alkaline substance for a neutralization reaction to obtain a bis(fluorosulfonyl)amid metal salt crude product; D) purifying the bis(fluorosulfonyl)amid metal salt crude product obtained in the step C) to obtain bis(fluorosulfonyl)amid metal salt; and E) mixing the bis(fluorosulfonyl)amid metal salt obtained in the step D) with a lithium reagent for a replacement reaction, so as to obtain lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide. The preparation method provided by the invention has the characteristics of low raw material cost, low impurity content in the product and high yield of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide.
Owner:湖南福邦新材料有限公司
Nucleocapsid catalyst in use for fuel cell and preparation method
InactiveCN1872417ALarge specific surface areaCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationElectrode potentialStandard electrode potential
A core-shell catalyst with controllable granularity and thickness of catalyzing layer and high active specific surface area and catalytic efficiency for fuel battery is prepared through preparing the nanoparticles of the metal with low standard electrode potential, and using it to displace out the metal with high standard electrode potential to cover on the surface of said nanoparticle.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
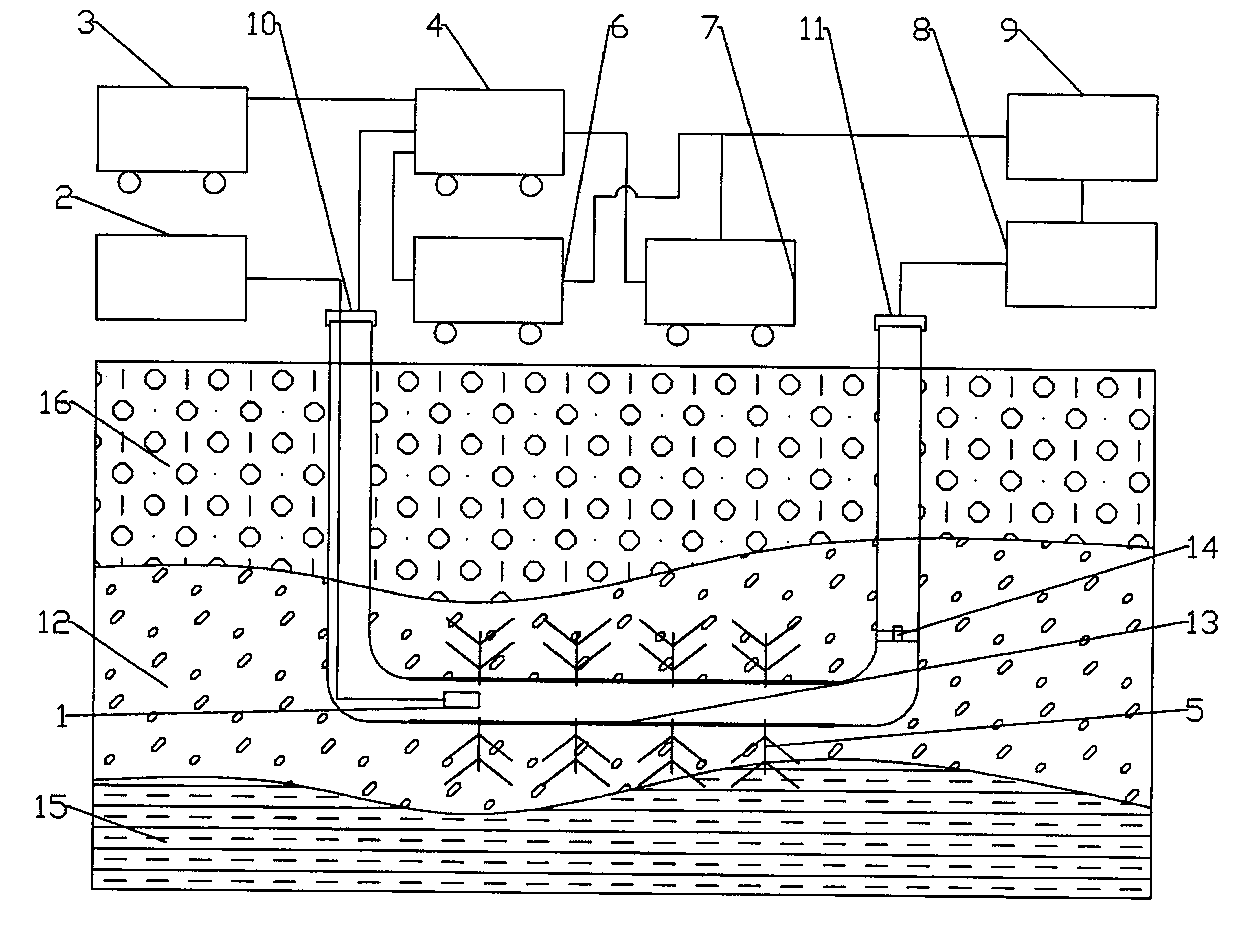
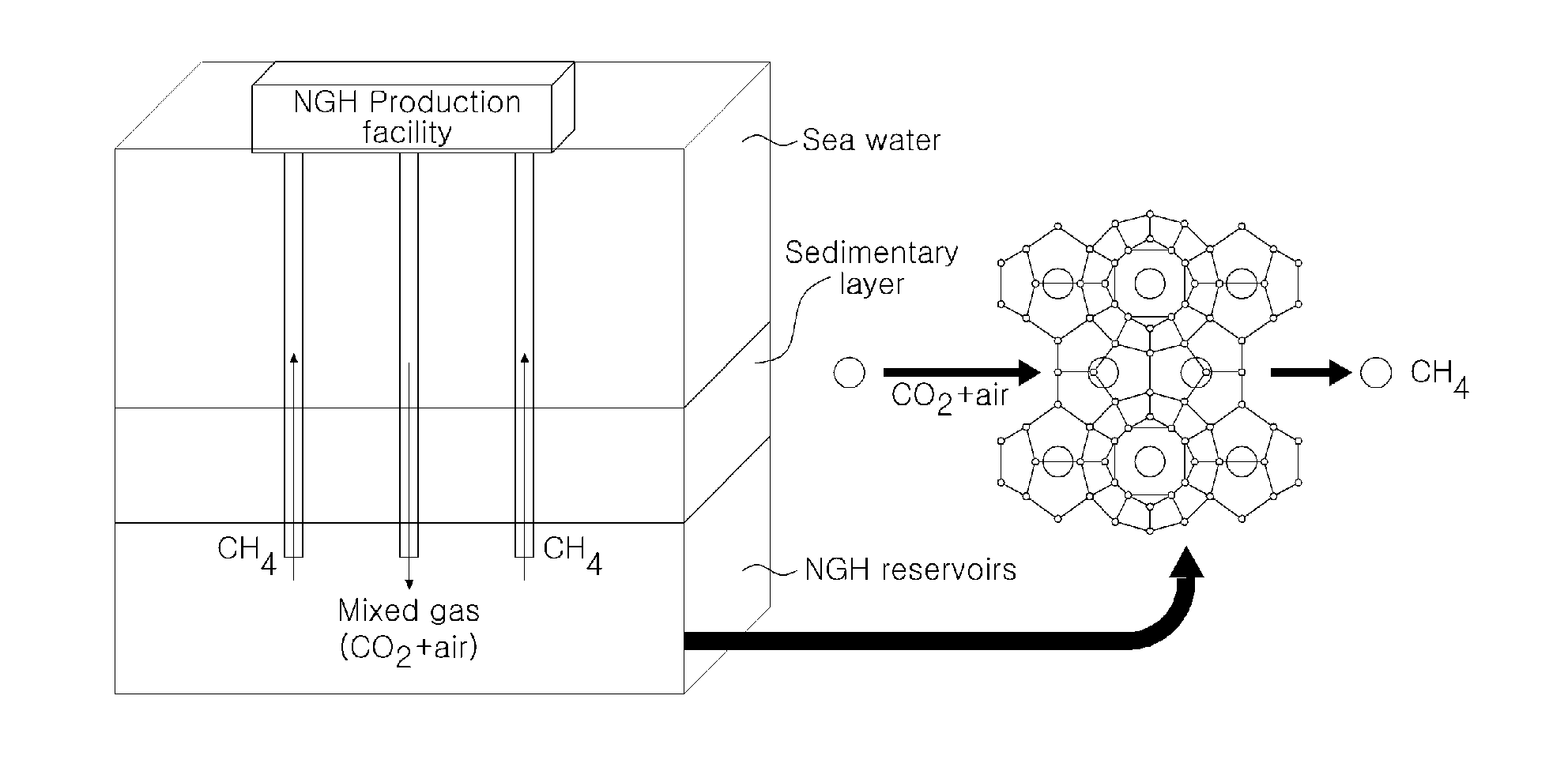
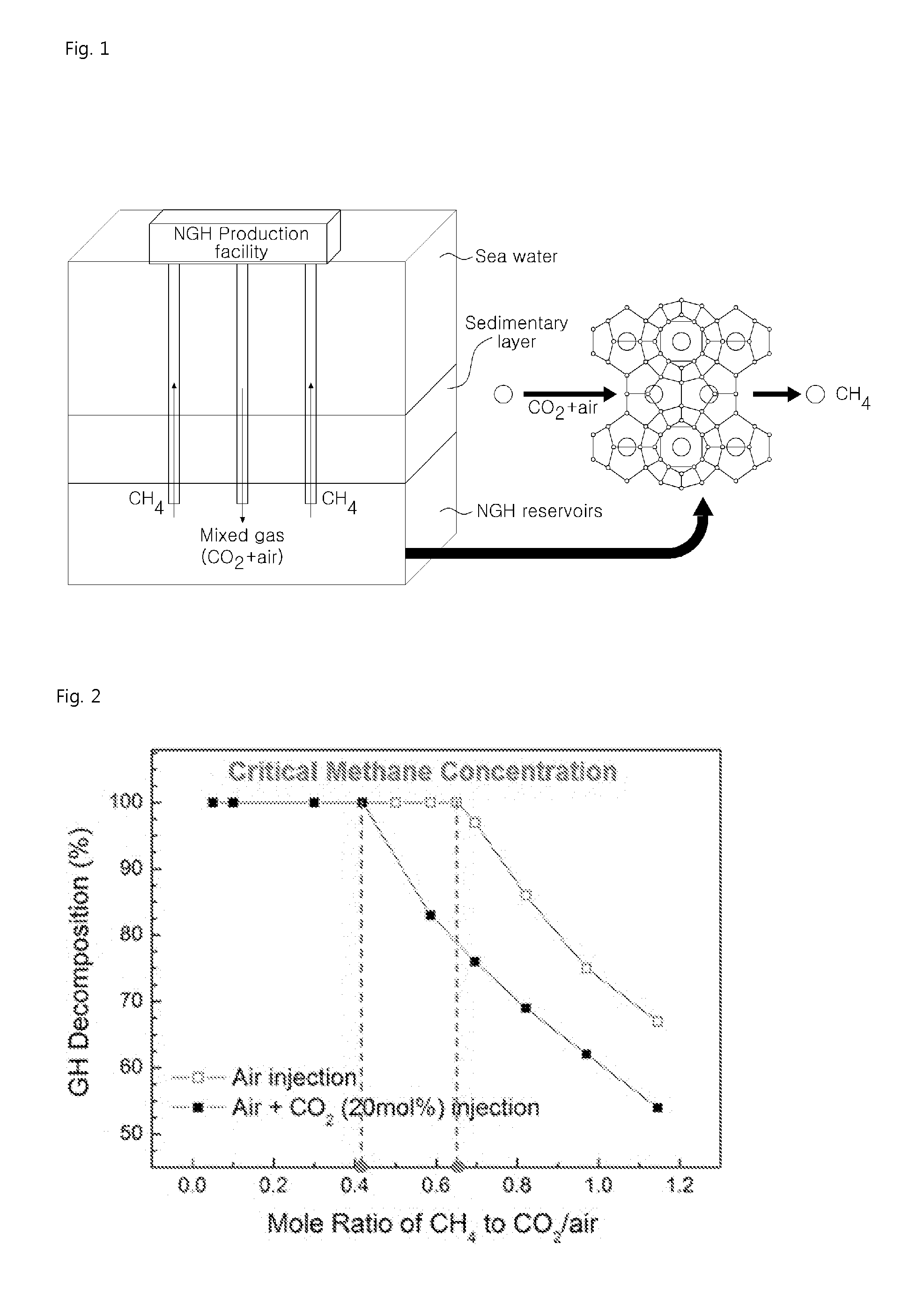
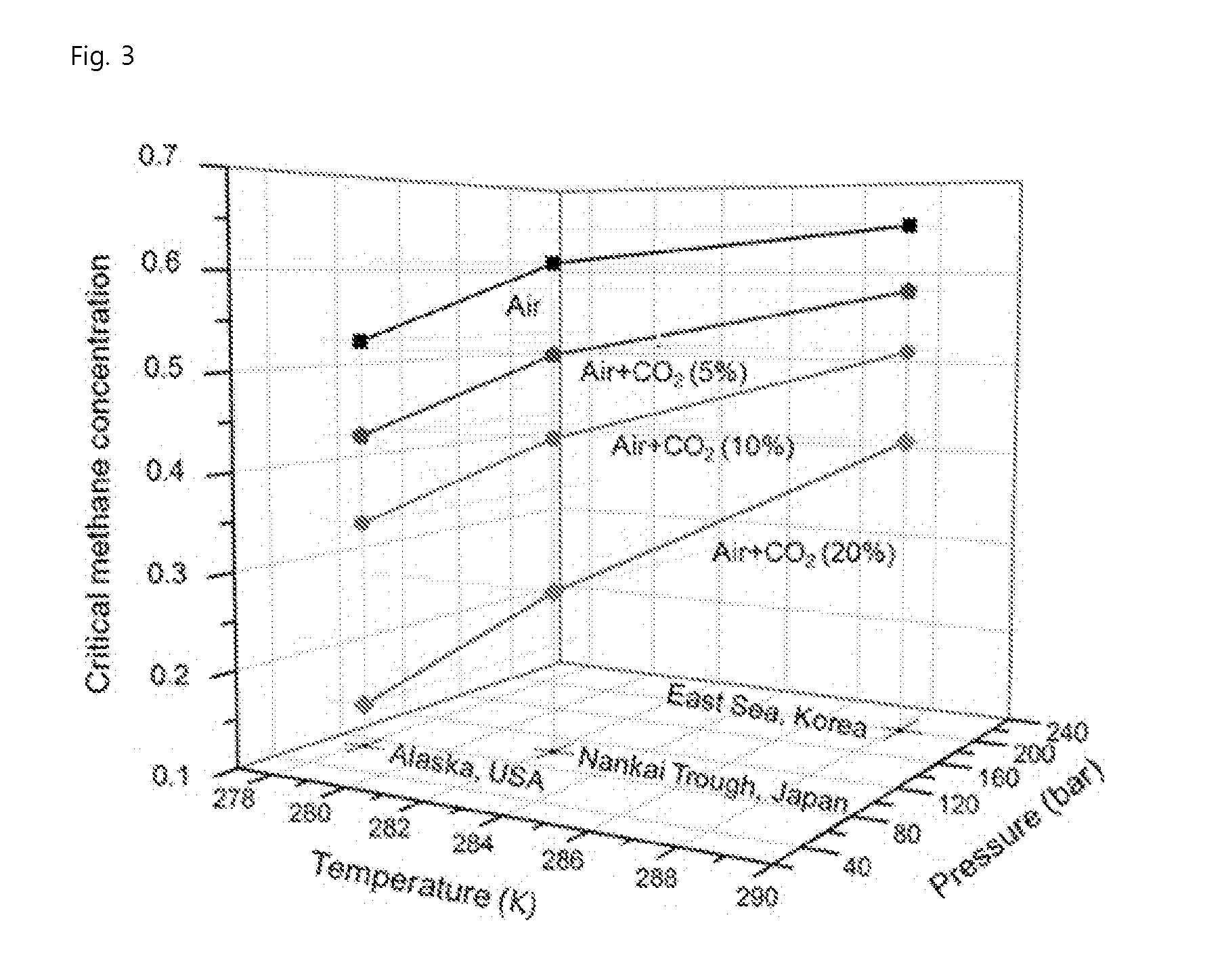
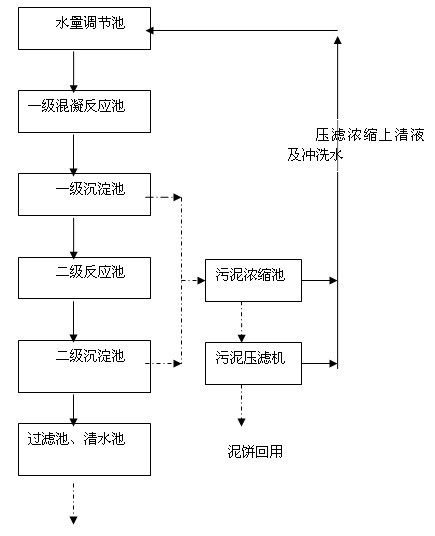
Method for extracting natural gas hydrate through CO2/N2 underground replacement
The invention discloses a method for extracting natural gas hydrate through CO2 / N2 underground replacement. The method includes that CO2 / N2 is injected into a hydrate layer, temperature and pressure in a well are controlled, replacement reaction is carried out to obtain methane and CO2 / N2 hydrate, extracting of the natural gas hydrate is achieved, through the horizontal abutting joint well technology and the fracturing technology, the contact area of the reaction is enlarged, and extracting efficiency is improved; first, well drilling, well cementation and well completion of a horizontal abutting joint well are carried out, according to the layer thickness and the range of the hydrate, the length and the layer number of a horizontal well section are confirmed; then the fracturing technology is carried out on a layer to be extracted in the mode of staged fracturing; and fracturing fluid is removed, depressurizing extracting is carried out, after a period of time, extracting speed is reduced obviously, CO2 / N2 is injected in, the pressure in the well is controlled, and replacement extracting is carried out. Efficient replacement extracting of the natural gas hydrate is achieved, environment benefits and economical benefits are remarkable, and the method can be used for large-scale extracting of the natural gas hydrate in a freeze soil area and the natural gas hydrate.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
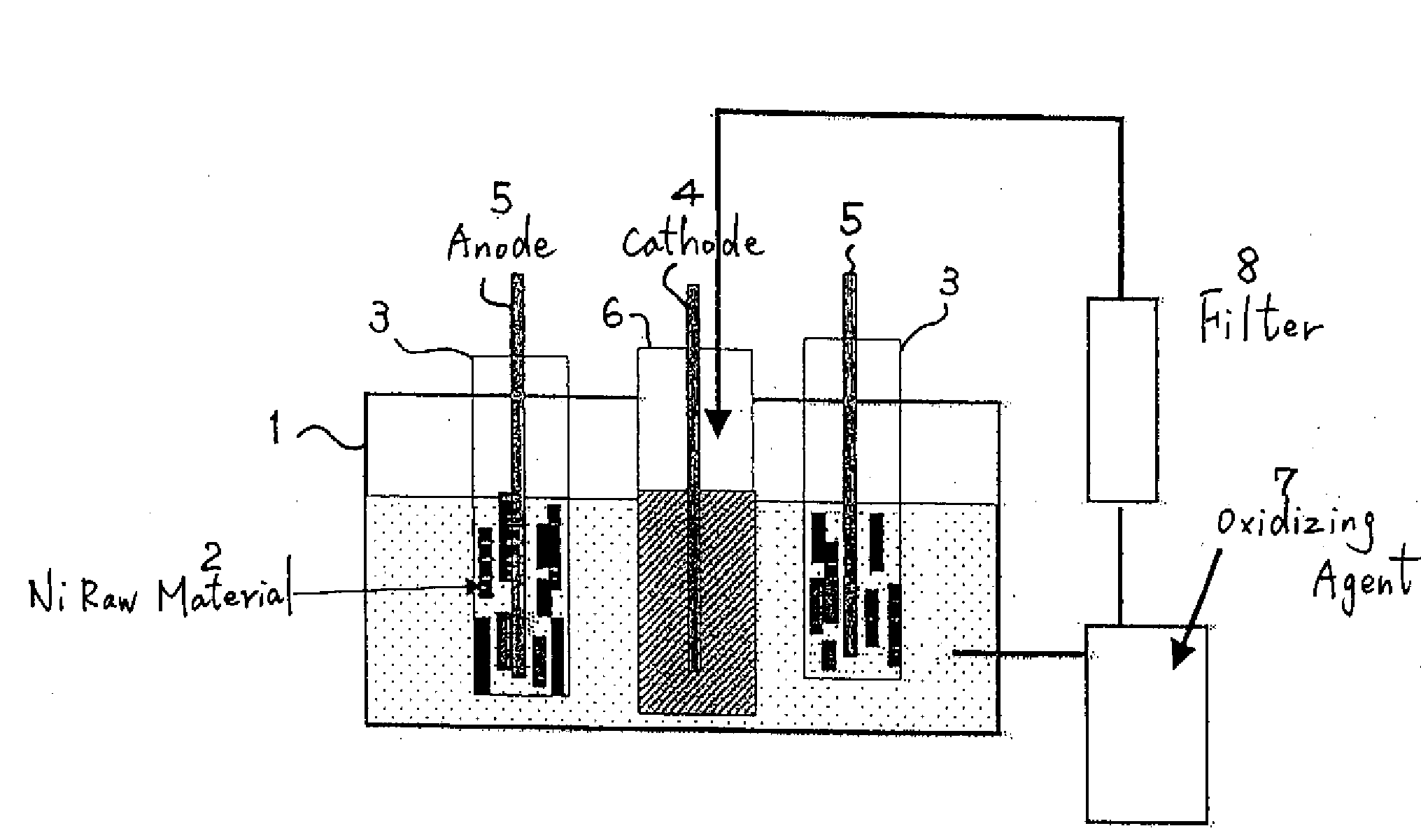
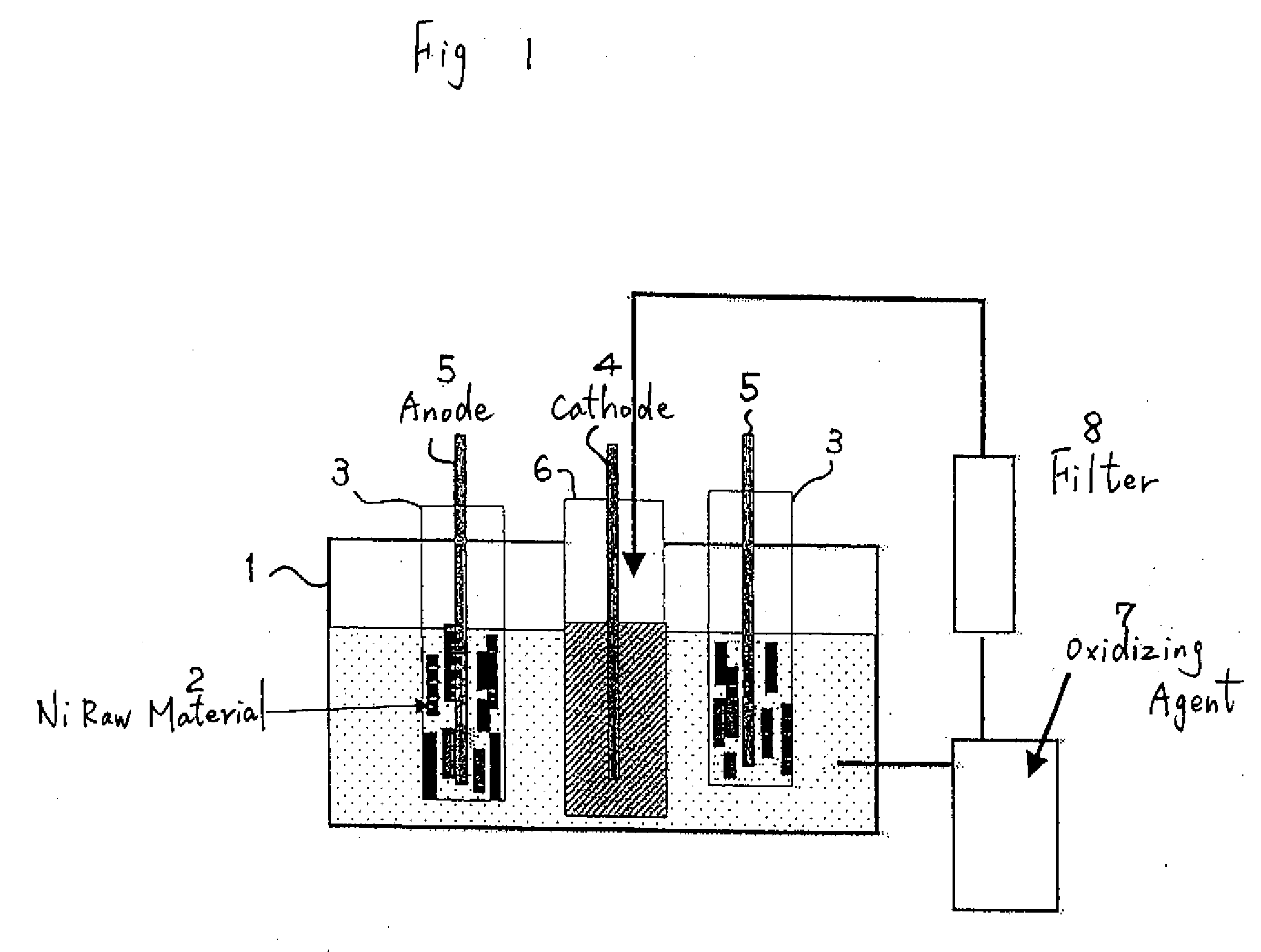
Manufacturing Method of High Purity Nickel, High Purity Nickel, Sputtering Target formed from said High Purity Nickel, and Thin Film formed with said Sputtering Target
InactiveUS20090004498A1Simple methodEfficient preparationPhotography auxillary processesPig casting plantsElectrolysisDisplacement reactions
Upon performing electrolysis with a solution containing nickel as the electrolytic solution, anolyte is adjusted to pH 2 to 5; impurities such as iron, cobalt and copper contained in the anolyte are eliminated by combining any one or two or more of the methods among adding an oxidizing agent and precipitating and eliminating the impurities as hydroxide, eliminating the impurities through preliminary electrolysis, or adding Ni foil and eliminating the impurities through displacement reaction; impurities are thereafter further eliminated with a filter; and the impurity-free solution is employed as catholyte to perform the electrolysis. The present invention relates to a simple method of performing electrolytic refining employing a solution containing nickel from nickel raw material containing a substantial amount of impurities, and provides technology on efficiently manufacturing high purity nickel having a purity of 5N (99.999 wt %) or more.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
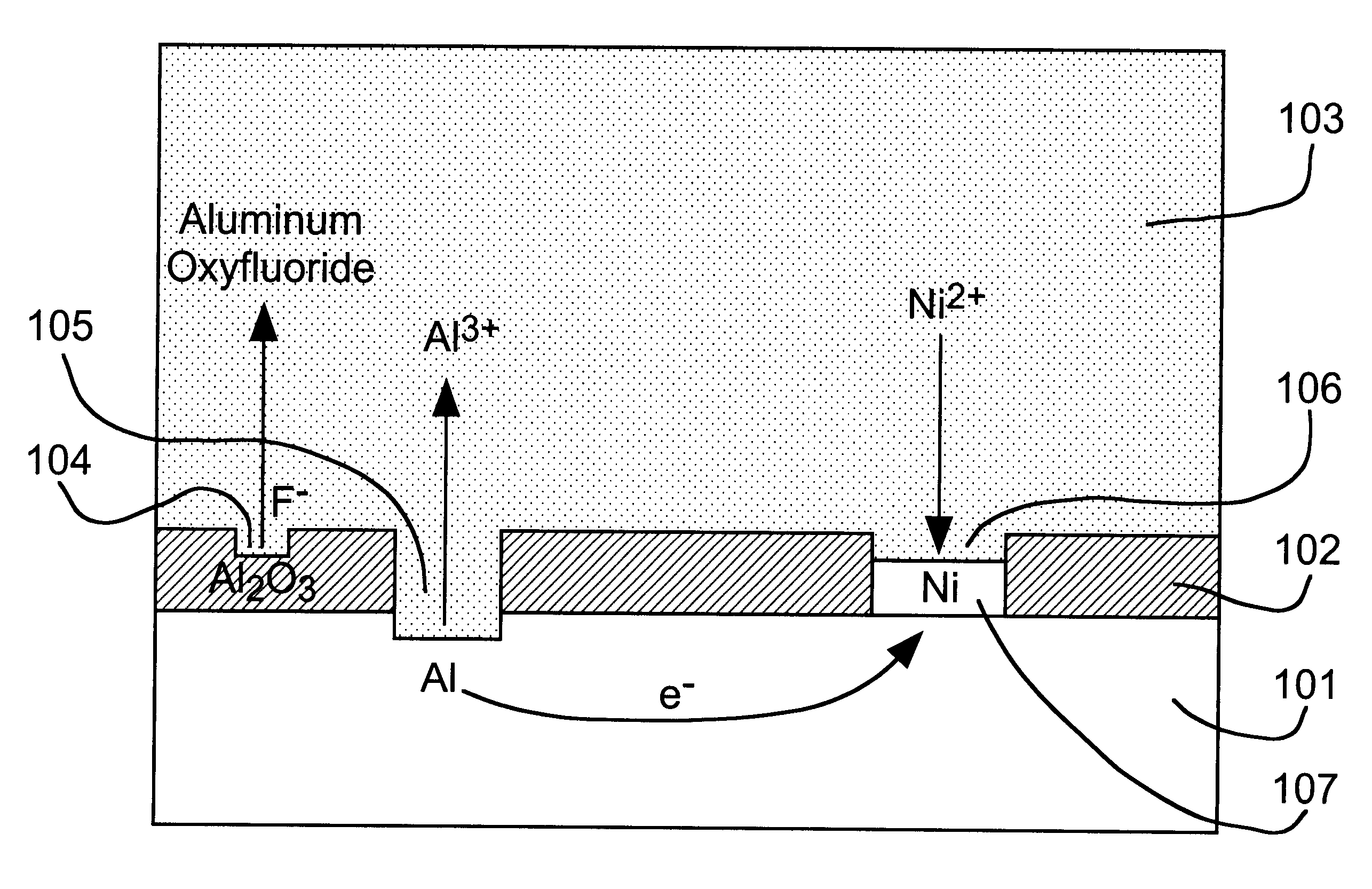
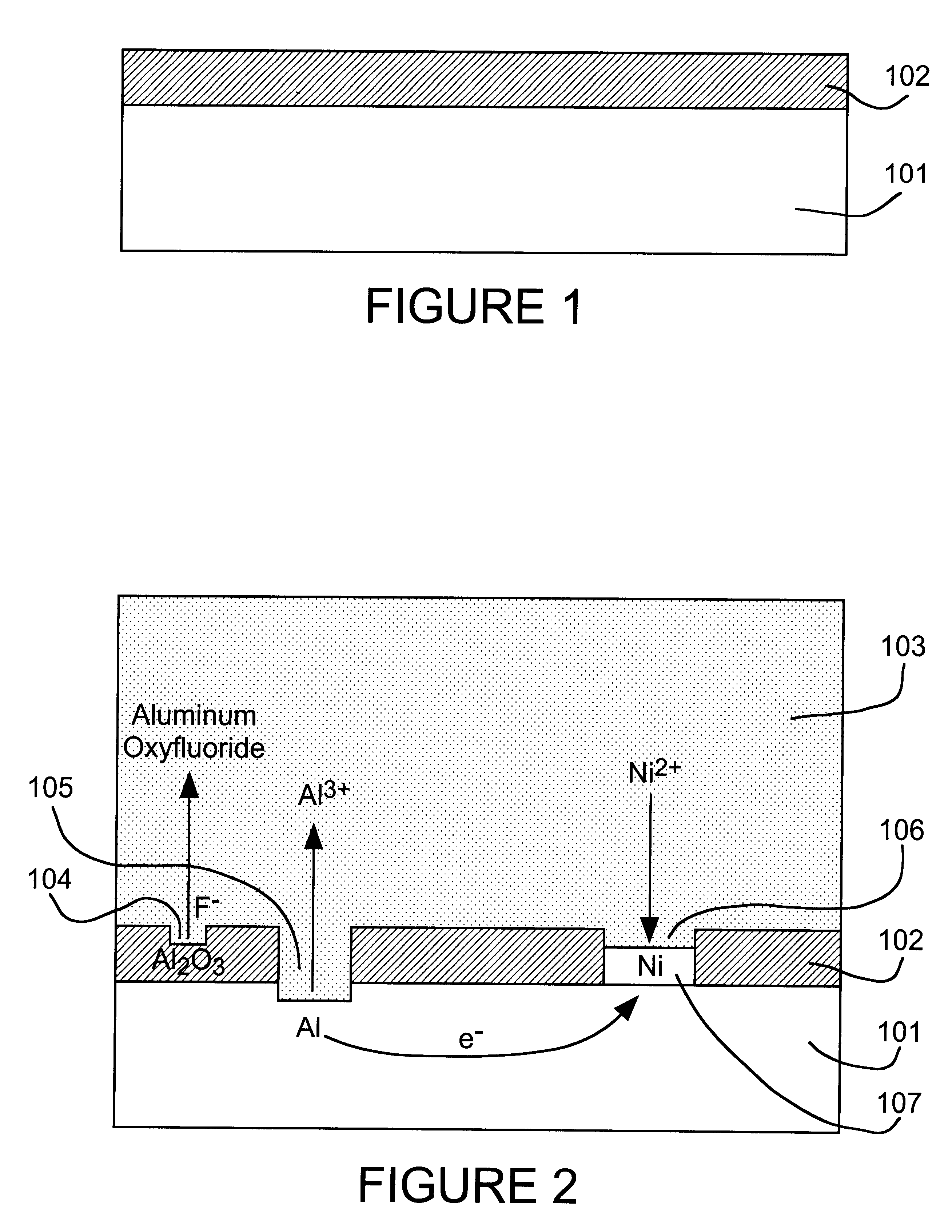
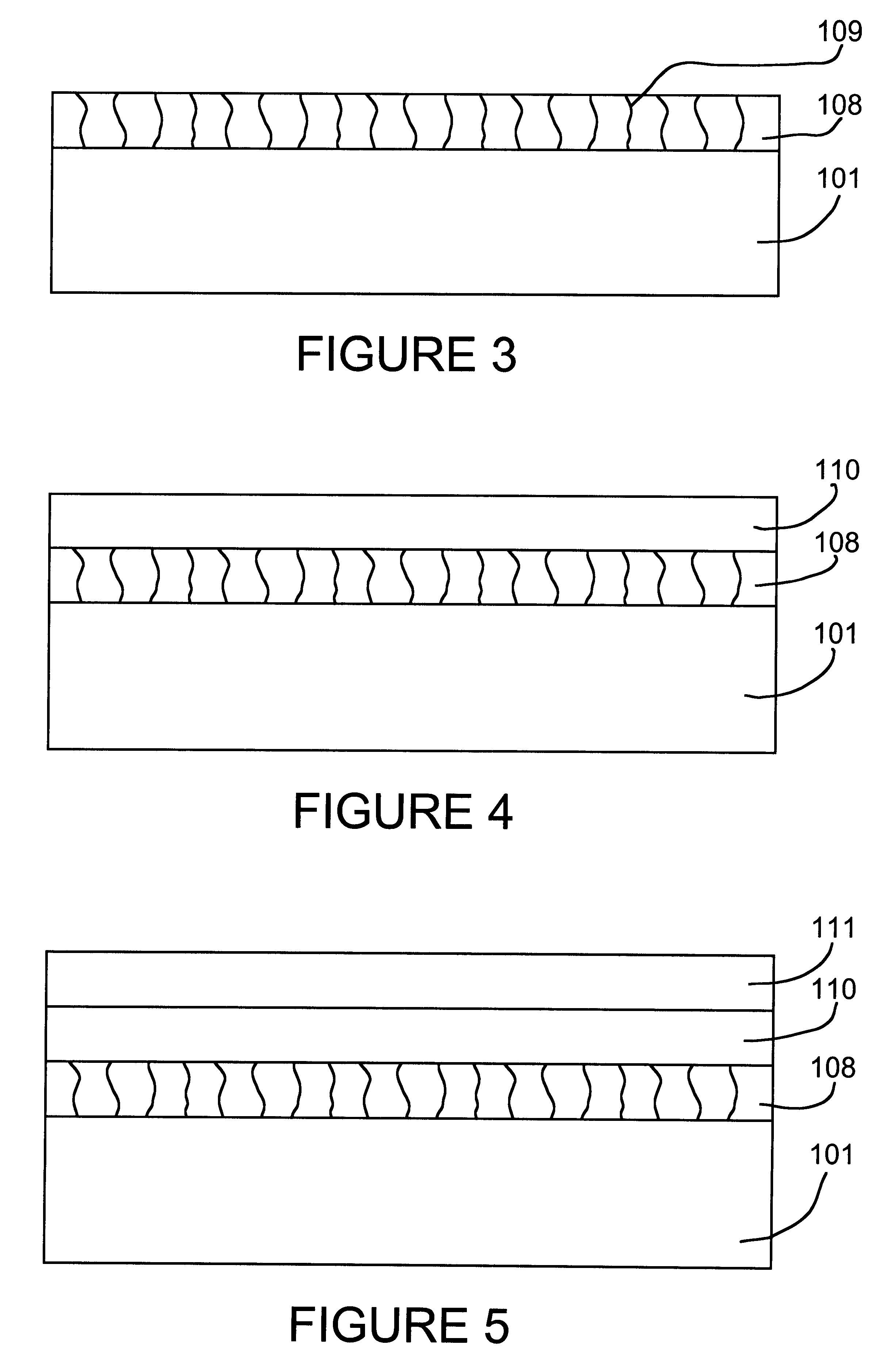
Controlled plating on reactive metals
InactiveUS6503343B1Avoid consumptionInhibited porositySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectroless nickelSolubility
A direct displacement plating process provides a uniform, adherent coating of a relatively stable metal (e.g., nickel) on a highly reactive metal (e.g., aluminum) that is normally covered with a recalcitrant oxide layer. The displacement reaction proceeds, preferably in a nonaqueous solvent, as the oxide layer is dissolved by a fluoride activator. Halide anions are used to provide high solubility, to serve as an anhydrous source of stable metal ions, and to control the rate of the displacement reaction. A low concentration of activator species and little or no solution agitation are used to cause depletion of the activator species within pores in the surface oxide so that attack of the reactive metal substrate is minimized. Used in conjunction with electroless nickel deposition to thicken the displacement coating, this process can be used to render aluminum pads on IC chips solderable without the need for expensive masks and vacuum deposition operations. Such coatings can also be used to preserve or restore wire bondability, or for corrosion protection of aluminum and other reactive structural metals and alloys. A thin layer of immersion gold can be used to protect the thickened coating from oxidation. The solderable aluminum IC chip pads provide the basis for a maskless bumping process for flip chip attachment.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
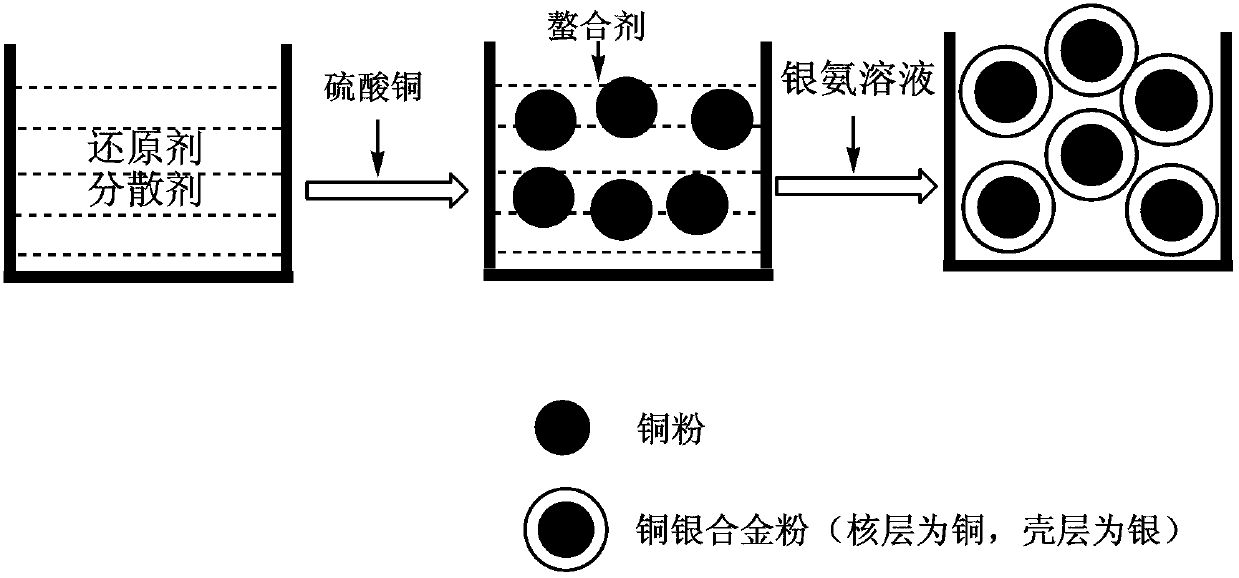
Method for preparing compact silver-coated copper powder by using one pot method
The invention relates to a method for preparing compact silver-coated copper powder by using the one-pot method. The silver-coated copper powder is in a coated core-shell structure, a core layer is made of copper, and a shell layer is made of silver. The preparation method includes: adding ammoniacal copper solution prepared by copper sulfate into aqueous solution containing reducing agent and dispersing agent to obtain copper powder suspension; adding water-soluble organic chelating agent into the suspension containing copper powder; adding ammoniacal silver solution prepared by silver nitrate into the suspension containing the copper powder to enable silver ions and the copper powder to be in a displacement reaction; after the displacement reaction finishes, additionally adding a certain amount of weak reducing agent to restore residual silver ions into silver; and filtering, washing and drying to obtain silver-coated copper powder with different grain diameters of 0.8-5 micrometers. The obtained silver-coated copper powder is uniform in silver coating of the shell layer, compact, good in conductivity, high in high-temperature oxidation resistance, and capable of being used for preparation of various electrode slurry sintered in the air.
Owner:江苏凯尚碳科技有限公司
Method for preparing diaminonaphthalene by catalytic hydrogenation of dinitronaphthalene
InactiveCN101575295AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationPalladium catalystReaction temperature
A method for preparing diaminonaphthalene by catalytic hydrogenation of dinitronaphthalene relates to a preparation technology of the diaminonaphthalene, which comprises the following steps: adding a palladium catalyst comprising active components and a carrier and adding the dinitronaphthalene and solvent to a stainless steel high-pressure reactor with an agitator, closing the reactor, replacing air in the reactor with nitrogen for at least three times and then replacing the nitrogen in the reactor with hydrogen for at least three times, and then filling the hydrogen in the reactor so that the reaction pressure in the reactor reaches 0.4-4.0MPa, heating the reactor so that the reaction temperature reaches 30-150 DEG C so as to carry out catalytic hydrogenation to prepare the diaminonaphthalene. The method adopts the hydrogenation reaction technology in the stainless steel high-pressure reactor with the agitator; a catalyst carrier is pretreated to improve the activity of the catalyst and reduce the consumption of the catalyst. By optimizing the technological conditions, the rate of conversion from the dinitronaphthalene to the diaminonaphthalene is effectively improved and high selectivity of the product diaminonaphthalene is maintained.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY +1
Preparation method of metal-based super-hydrophobic surface
InactiveCN104846376ASimple manufacturing processPreparation process safetyLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSpecial surfacesDisplacement reactionsAqueous solution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a metal-based super-hydrophobic surface. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) immersing a metal-based surface into an acid-salt mixed solution which comprises an acid, a metal salt and water, wherein metal in a metal base is subjected to a displacement reaction with the metal salt and is subjected to etching with the acid; (2) immersing the metal-based surface treated through the step (1) into a surface modification solution which is a perfluorosilane aqueous solution; and (3) drying and cooling the metal-based surface treated through the step (2), thus obtaining the metal-based super-hydrophobic surface. The metal-based super-hydrophobic surface prepared by using the method disclosed by the invention has excellent super-hydrophobic performance; the preparation process is simple and easy to carry out; the preparation course is safe and reliable; the preparation cycle is short; no expensive equipment or material is needed; the preparation cost is low; and a relatively good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
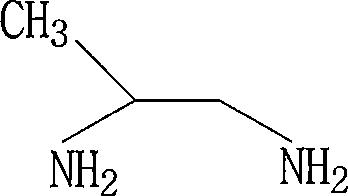
Method for synthesizing 1,2-propane diamine
InactiveCN101157617ARealize applicationSynthesis Process CleaningOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationHydrogenAmmonia
The invention relates to a synthetic method for 1, 2-propylene diamine which is produced by taking isopropyl alcohol as raw material and filling catalyst for pressurizing and heating reaction under hydrogen condition. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, isopropyl alcohol and catalyst are filled inside a reaction device; secondly, hydrogen is used for replacing the air inside the reaction device; thirdly, hydrogen and ammonia are continuously filled in for reaction under the temperature of 150 to 240 DEG C and the pressure of 10MPa to 13MPa, water is distilled through normal pressure after finishing the reaction, and then 1, 2-propylene diamine is obtained through vacuum distillation. The invention has the advantages that: (1) the technique process is clean with high product purity; (2) the cheap isopropyl alcohol is adopted as the raw material, thereby decreasing the cost; (3) the whole compound process can be operated continuously, thereby increasing the use rate of the device, satisfying the industrial demand and further decreasing the production cost; (4) the invention can apply the catalyst mechanically.
Owner:NANJING BAOCHUN CHEMICAL INDUSTRY CO LTD
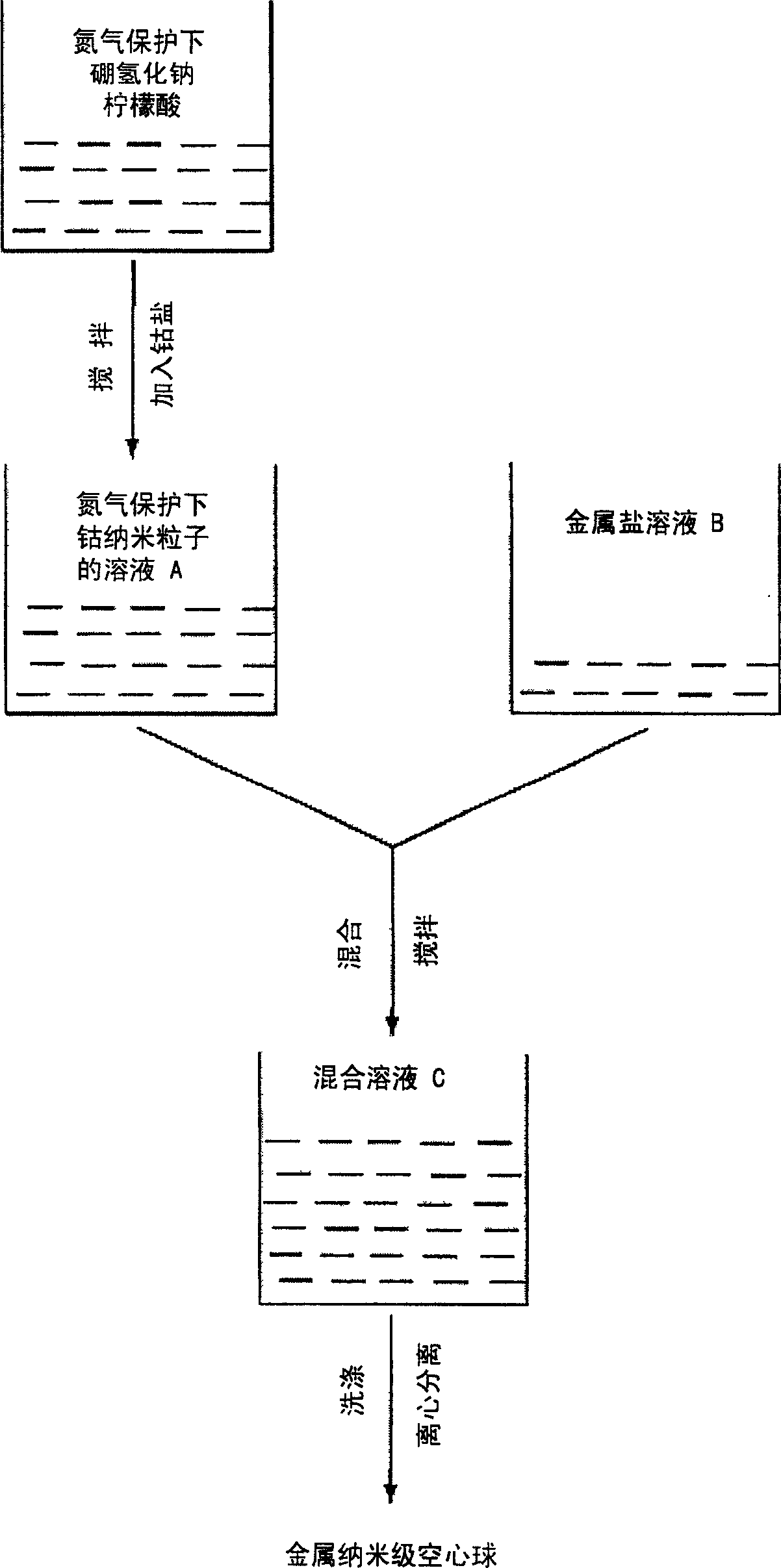
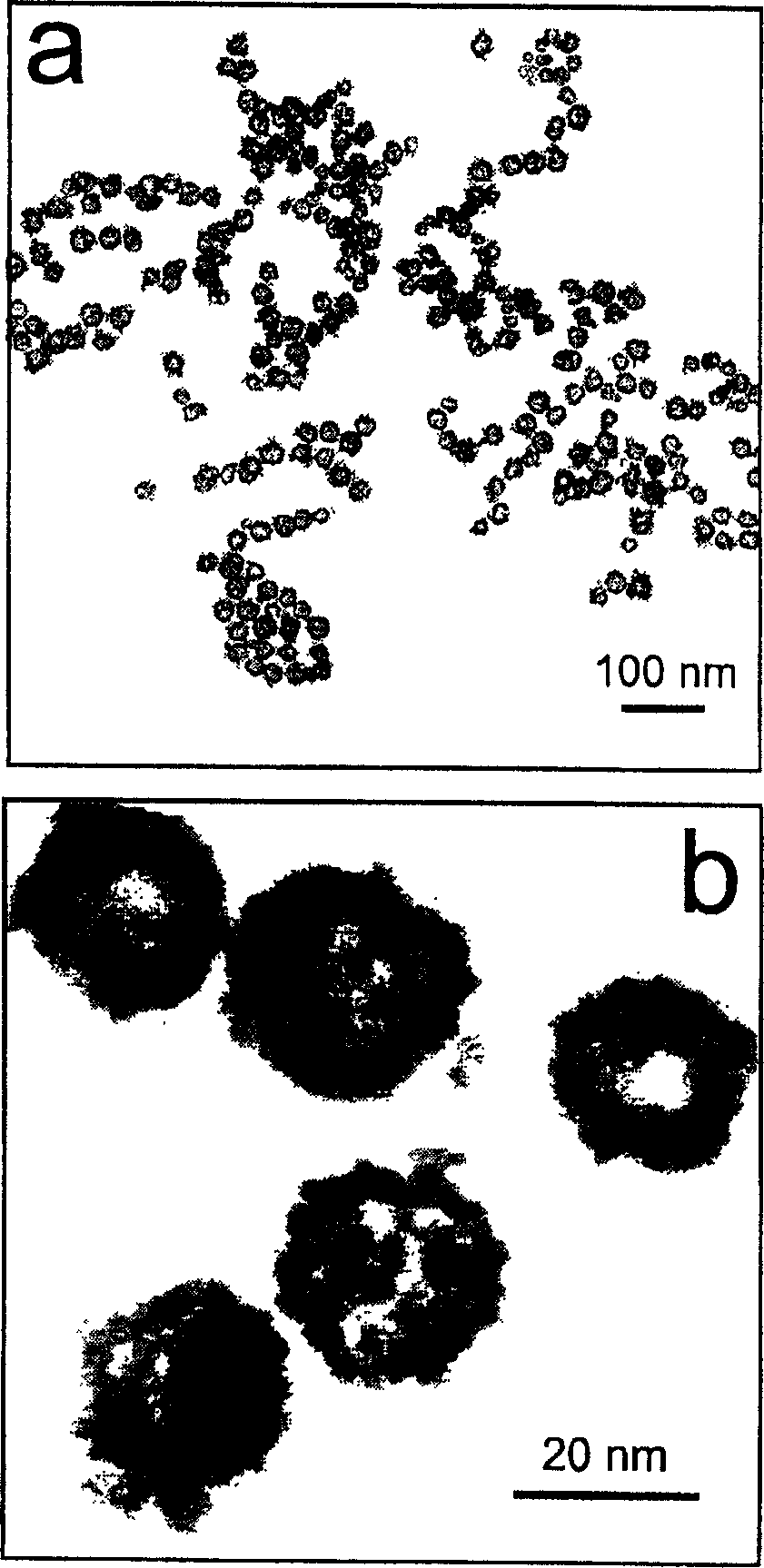
Method for preparing nano metal and bimetal hollow ball
InactiveCN1616165AAchieve preparationReduce energy consumptionCatalyst activation/preparationRoom temperatureLow density
The present invention relates to nano technology, and is the preparation process of nano hollow metal and bimetal ball. Nano cobalt particle used as the sacrificial template and metal salt solution produce replacement reaction to synthesize nano level hollow metal balls in large scale. The simple preparation process may be completed in room temperature simply and economically and may have huge industrial application foreground. Altering the reaction conditions can prepare nano level hollow metal balls of different sizes. The prepared nano level hollow metal ball has great specific surface area, low density, saving in material and low cost, and may find its wide application in catalyst and other fields.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
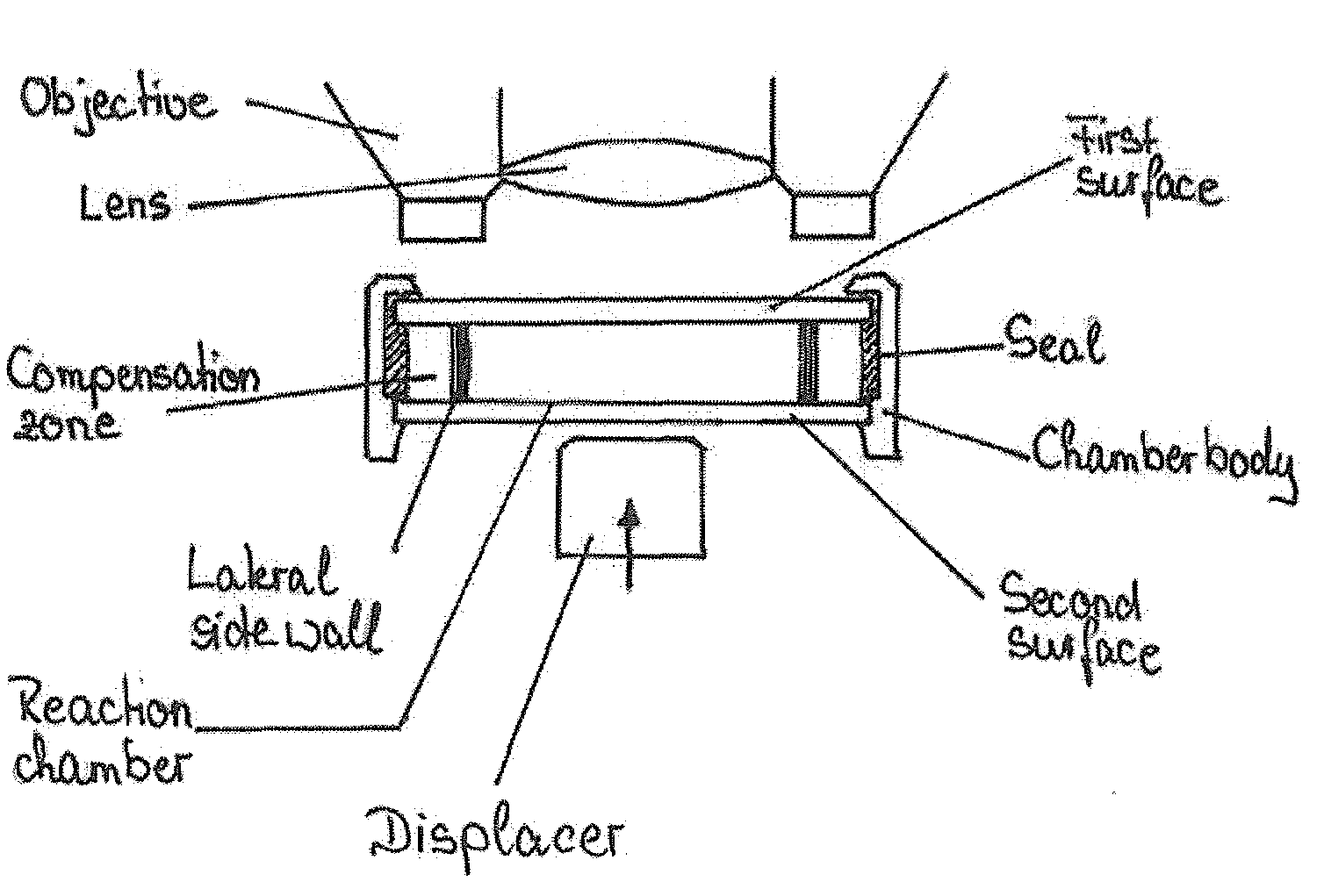
Device and method for the detection of particles
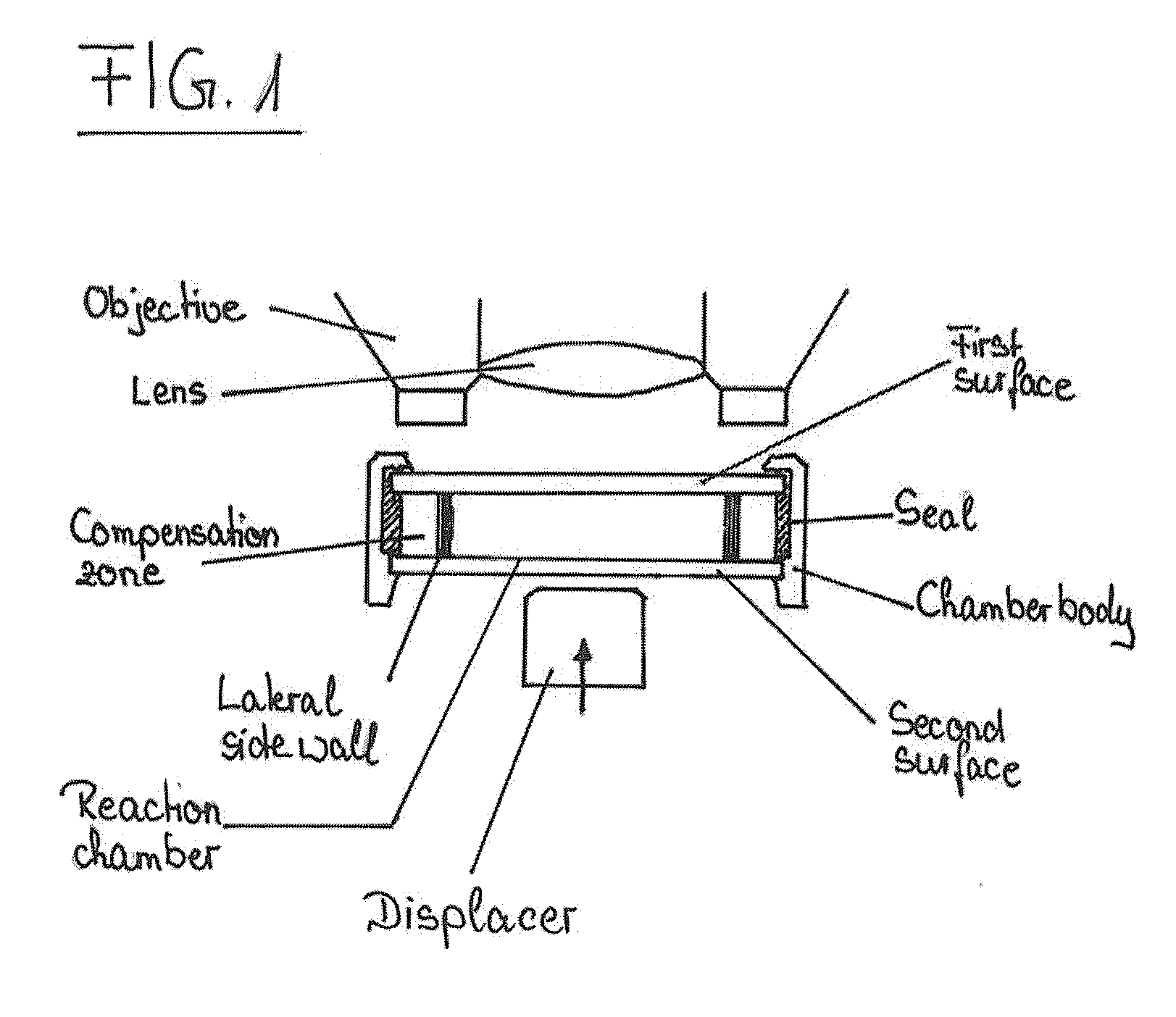
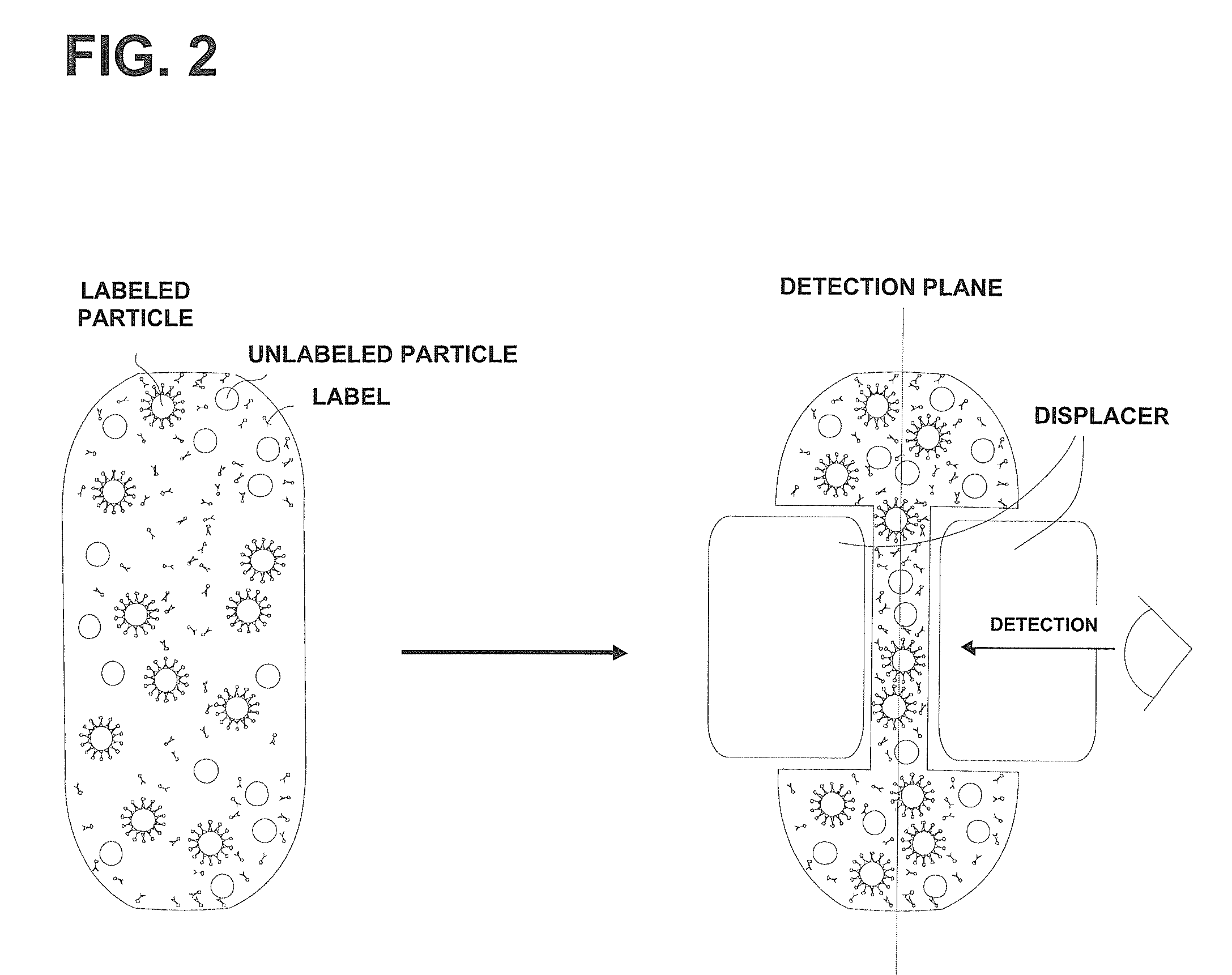
ActiveUS20090079963A1Lower the volumeReduce distanceShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingReaction chamberPhysics
The present invention relates to devices and methods for the qualitative and / or quantitative detection of particles. In particular, the invention relates to devices for the detection of particles, comprising a reaction chamber formed within a chamber body between a first surface and a second surface, wherein the second surface is located opposite to the first surface, and one or more displacers, wherein the distance between the first surface and the second surface is variable via the one or more displacers at least in one or more parts of the surface area of the first surface and / or the second surface. The invention also relates to corresponding methods for the detection of particles, comprising positioning a sample supposed to comprise one or more species of particles to be detected in a reaction chamber, displacing at least a part of the sample within the reaction chamber via the one or more displacers; and detecting / determining a value indicative for the presence and / or number of one or more species of particles.
Owner:CLONDIAG GMBH
Low temperature high pressure gas hydrate replacement reaction kettle and system
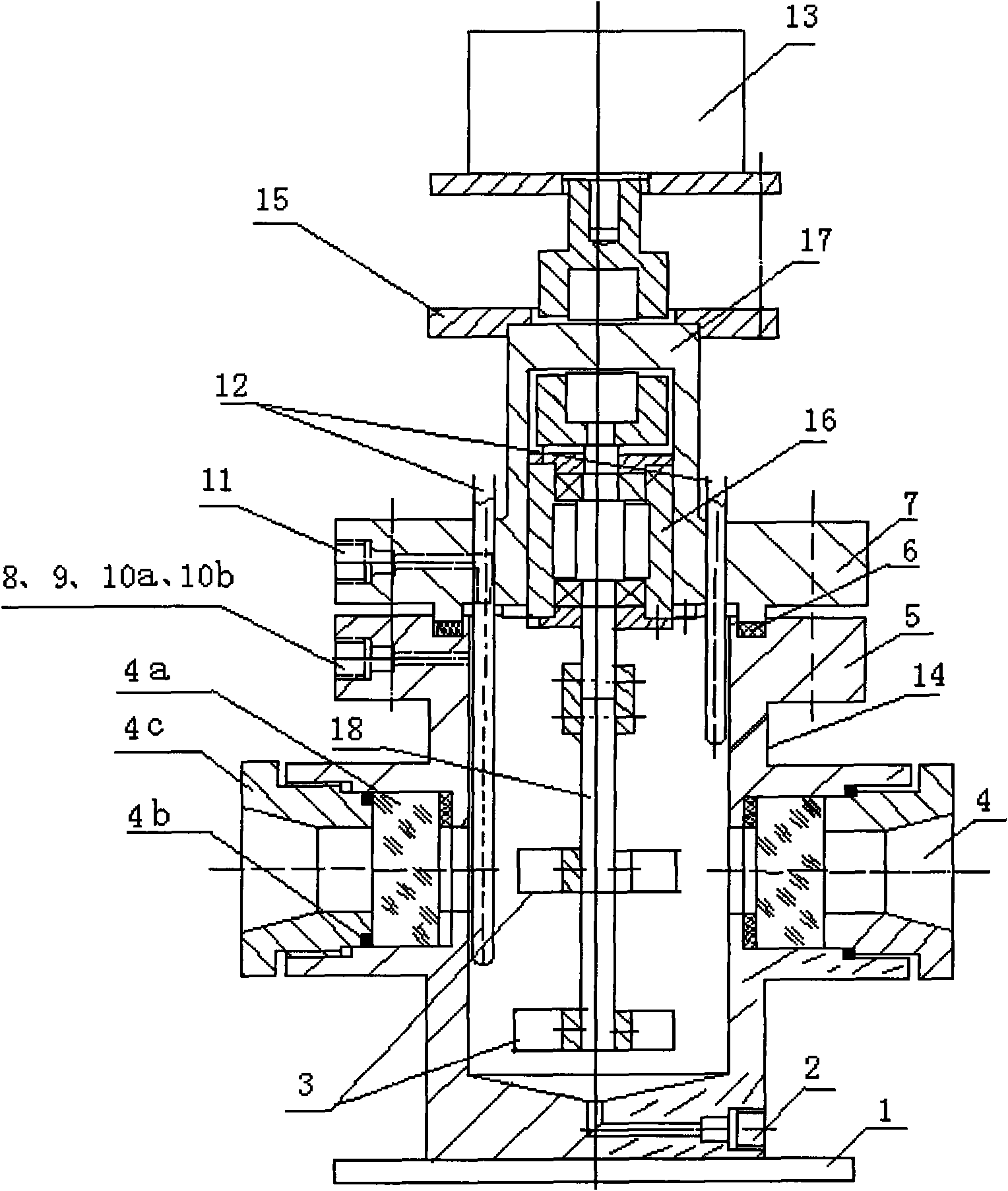
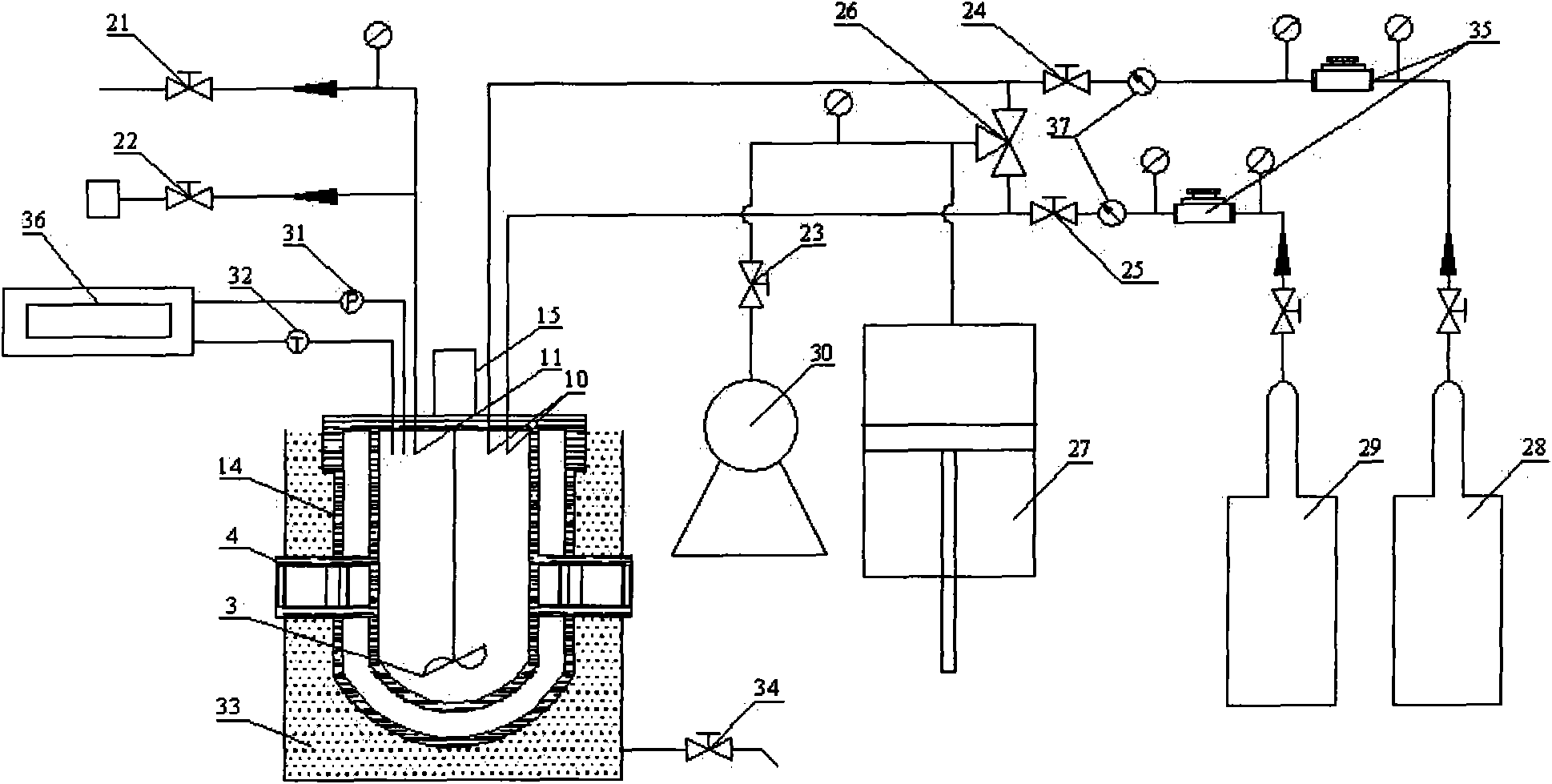
InactiveCN101612539ASolve the problem of poor performance of high-pressure rotary sealsGuaranteed uptimeChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPressure/vacuum vesselsWater bathsGas phase
The invention relates to a low temperature high pressure gas hydrate replacement reaction kettle and a system used for replacement reaction of gas hydrate. The whole reaction kettle is soaked in a constant low temperature water bath to keep the low temperature, and a vacuum system performs vacuum pump in the low temperature high pressure reaction kettle through a gas inlet, a gas phase component detection system performs gas collection and analysis through a gas collection opening, a pressure control system is connected with the gas inlet of the low temperature high pressure reaction kettle to ensure the pressure required by the low temperature high pressure reaction kettle, a data acquisition system is connected with a temperature detection opening and a pressure detection opening of the low temperature high pressure reaction kettle to acquire system data. In the invention, static sealing replaces dynamic sealing, thus solving the problem of poor performance of high pressure rotary sealing, and having the advantages of reliable running and no noise. The phenomenon occurring in the reaction kettle can also be observed by a visible window in real time, and the gas component alteration in the gas hydrate solid phase can be measured by a Raman spectrometer in real time.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Nano core-shell type copper-nickel bimetal powder body and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN101209493AOvercome the disadvantage of easy oxidationMeet the requirement of transparent appearanceCoatingsThioureaConductive materials
The invention relates to a bimetal powder of copper and nickel and a preparation method thereof. The invention solves the defect of easy oxidation of the simple substance nanometer copper powder and improves the use effect of the ordinary copper nickel composite powder. Referring to the prior art, the invention firstly prepares a nanometer copper powder, the copper powder is stirred and dispersed homogeneously in the water, and suspension liquid of the copper powder is prepared; the suspension liquid of the copper powder is blended with the nickel sulfate solution comprising macromolecule protective agent and special copper coordination agent thiourea so as to cause a replacement reaction between nickel ion and the copper; surfaces of the ultrafine copper particles are partly or all coated with the nickel, thus forming the core-shell copper-nickel bimetal nanometer powder. The bimetal powder can be taken as lubricant, lubricating grease extreme pressure-antiwear additives, additives in powder metallurgy, or as porous materials, antibacterial materials, antifouling coatings, conductive materials, magnetic materials, self-lubricating materials, antifriction materials, diamond tools, and raw materials or additives of electrical carbon products.
Owner:HAILIAN INST OF LUBRICATING MATERIALS SHANGHAI
Preparation method of gluconic acid and its salt
InactiveCN1594265AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid salt preparationCatalytic oxidationGluconic acid
The invention relates to the preparation method of gluconic acid and its salt, wherein Au / C catalyst liquid phase catalytic oxidation glucose is employed to synthesize calcium gluconae through calcium hydrate neutralization, based on this, the replacing reaction of magnesium, zinc and ferrous sulfate is utilized to obtain the corresponding glucoheptonates, and glucose acid is obtained through sulfuric acid replacement reaction.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
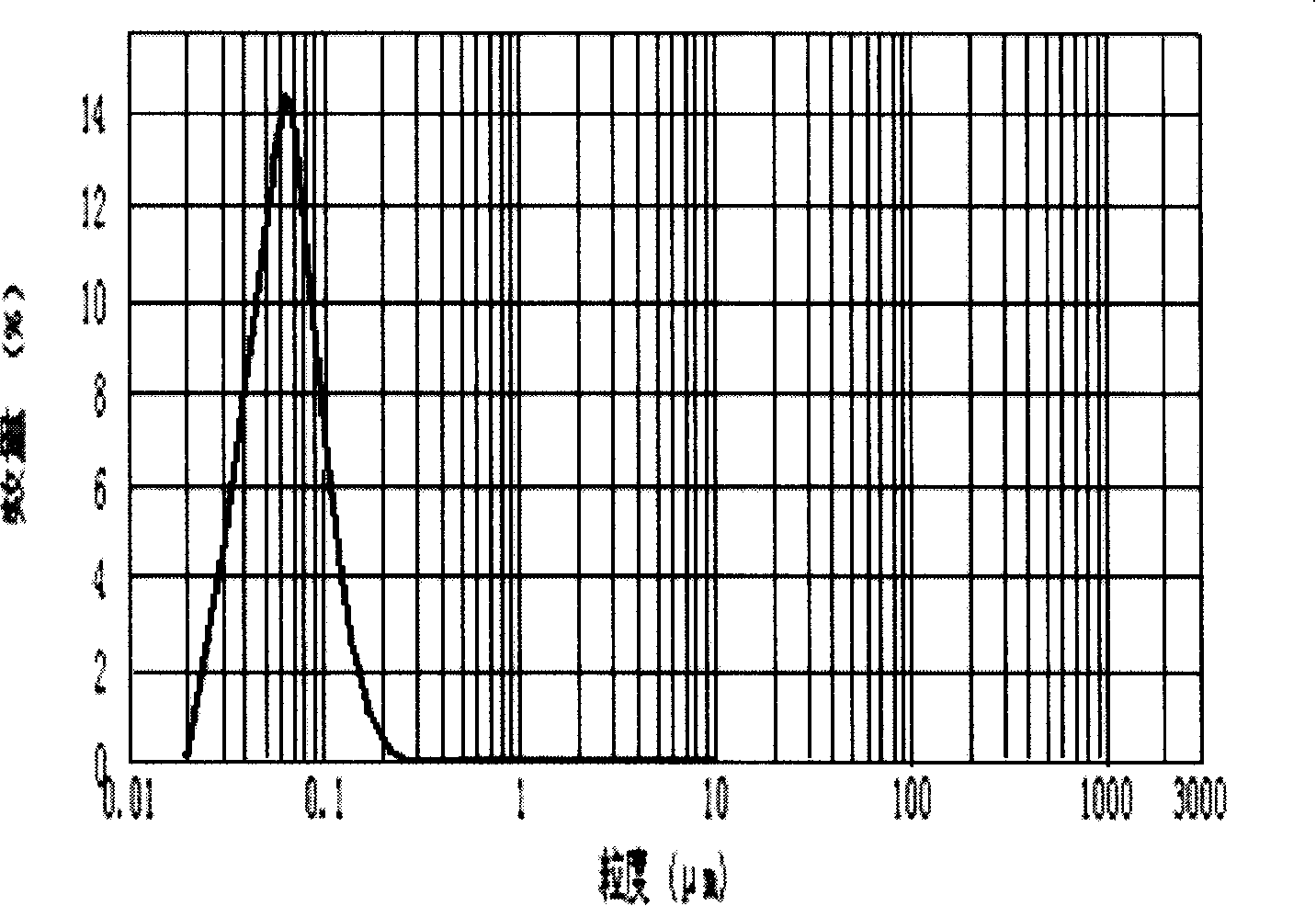
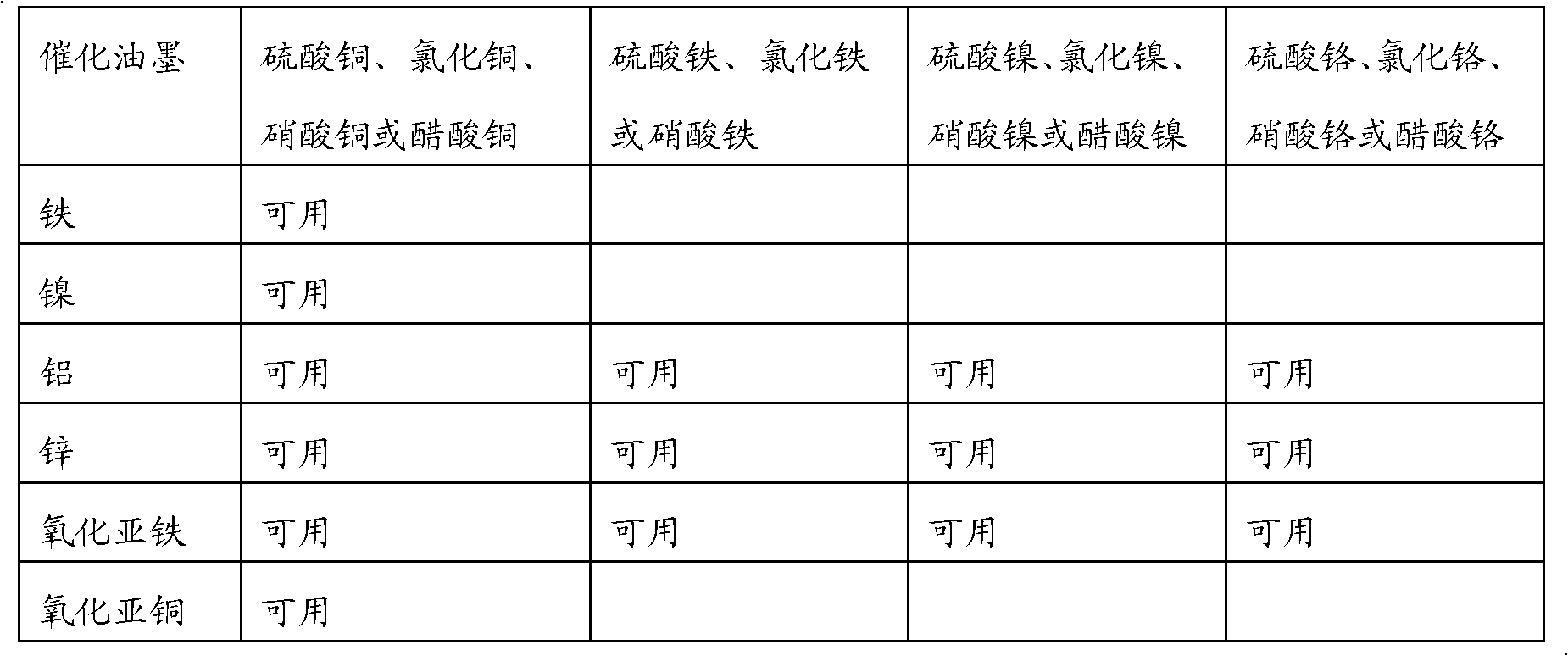
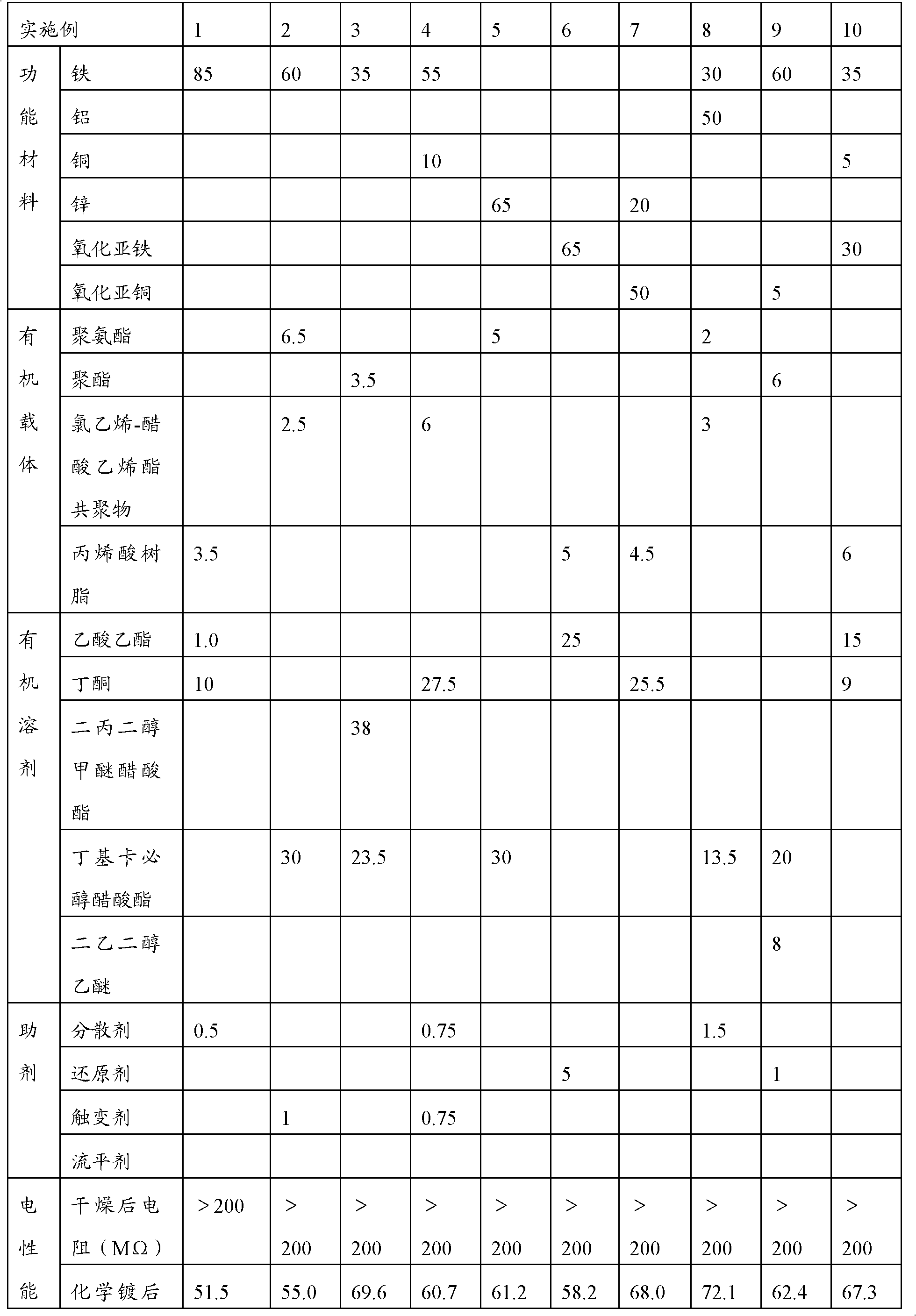
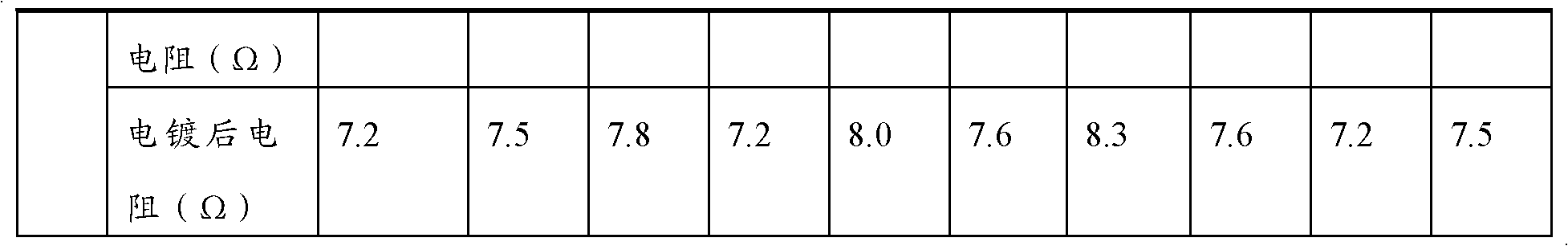
Method for utilizing base metal catalytic ink to manufacture printed circuit
InactiveCN102573313ALow priceReduce manufacturing costInksConductive pattern formationElectrical conductorDisplacement reactions
The invention provides a method for utilizing base metal catalytic ink to manufacture a printed circuit. The method is characterized in that: the ink mainly is composed of 10% to 90% of functional materials, 2% to 18% of organic carriers and 8% to 72% of organic solvents, wherein the functional materials are formed by metal or / and metal oxide powder, the metal is one selected from the group of iron, nickel, aluminum, and zinc, or a mixture of at least two metals in random mixing proportion selected from the group of iron, nickel, aluminum, zinc, and copper, and a metal oxide is selected from ferrous oxide or / and cuprous oxide. According to the invention, traditional printing modes of screen printing, gravure printing and the like can be employed to manufacture lines on insulation base material, and then the insulation base material is put into a replacement reaction solution for a displacement reaction to form a conductor printed circuit. The method has the following advantages: (1) the ink does not contain precious metals of silver, gold and the like, and manufacture cost of related products is greatly reduced; (2) the method is simple; (3) the manufactured printed circuit is reliable, electric conductivity is good, and application is wide.
Owner:SEMITEL ELECTRONICS
A method for preparing silver plated copper powder
InactiveCN1704502AWith room temperature oxidation resistanceFlat surfaceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSilver plateAmmonium hydroxide
The invention relates to a process for preparing silver-plated copper powder, which comprises using chelation extracting agent during the silver-plated copper powder production from silver ammonia solution, obtaining cheliform compounds with the obtained Cu2++ and loading into organic phase. The silver-plated copper powder have high oxidization resistance under normal temperature.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Precipitation reduction method of preparing nano-cobalt powder
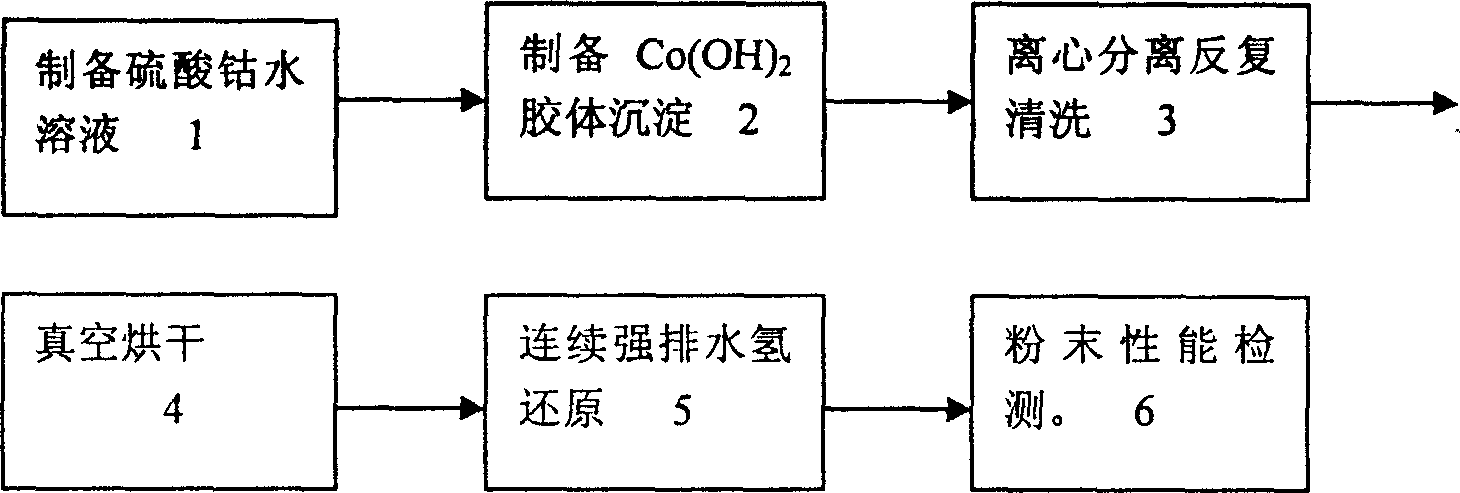
A process for preparing cobalt nanoparticles by deposition-reduction method includes such steps as displacing reaction between the aqueous solution of soluble Co salts and NaOH or KOH to obtain the nano-colloid deposit of Co(OH)2, centrifugal separation of mother liquid, washing repeatedly, centrifugal separation of waste liquid, vacuum drying, and reducing by H2.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
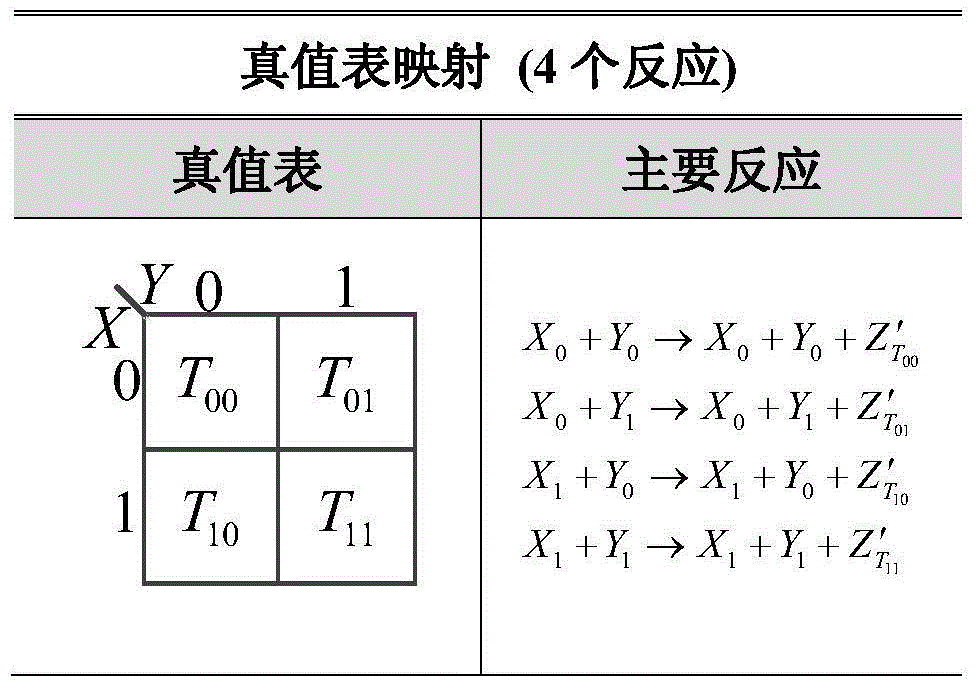
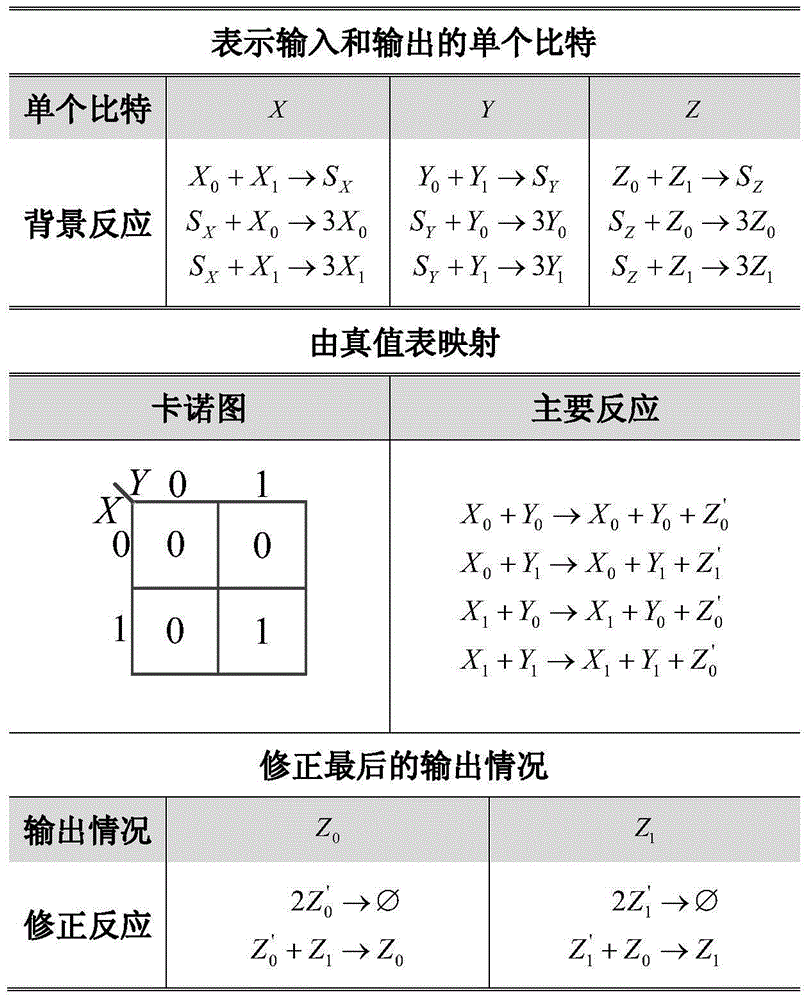
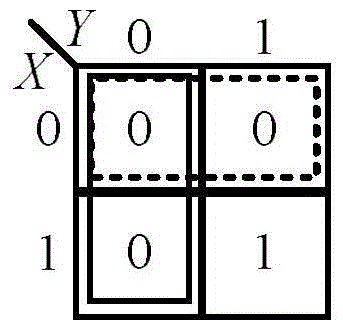
DNA molecular chain displacement reaction based method for extracting CRNs for realizing combinational logic
ActiveCN105046102AReduce energy consumptionGeneralSpecial data processing applicationsTruth valueChemical reaction
The present invention discloses a DNA molecular chain displacement reaction based method for extracting CRNs for realizing combinational logic. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, according to a set logic function, obtaining a truth table that reflects input and output logic relationships, and obtaining, through mapping, a proforma chemical reaction network from the truth table; and step 2, simplifying the proforma chemical reaction network obtained in the step 1 by using a Karnaugh map simplification approach, to obtain a proforma chemical reaction network for realizing a combinational logic function. The method provided in the present invention is mainly used for obtaining the chemical reaction network that represents logical relationships in a DNA molecular chain displacement reaction; the CRNs is obtained by mainly using the truth table in electronics and the Karnaugh map simplification approach; CRNs that indicate logical relationships can be obtained without considering the specific circuit architecture; the CRNs are simplified; and energy consumption is effectively reduced. Meanwhile, the method provided in the present invention is more general, straightforward and more convenient in operation.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
Preparation method of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide
ActiveCN106241757AHigh purityLow impurity contentNitrosyl chlorideChemical synthesisSulfate radicals
The invention relates to the field of chemical synthesis, and concretely relates to a preparation method of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide. The preparation method of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out a displacement reaction on bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide and LiX, wherein X is selected from Cl, Br and I; 2, mixing a proper amount of hydrogen chloride with a reaction solution obtained through the displacement reaction; and 3, carrying out solid-liquid separation on a reaction solution obtained in step 2, concentrating the obtained liquid phase, adding a poor solvent to crystallize, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain the bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide. The preparation method of bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide allows highly pure LiFSI to be obtained, and has the advantages of realization of stable quality and high yield of the above product, effective reduction of the content of potassium ions, sodium ions, chloride ions, sulfate radicals, water and other impurities, simple operating steps, reasonable production cost, high safety, and suitableness for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEMSPEC CORP
Method for preparing titanium-containing zeolite molecular sieve by natural zeolite modification
InactiveCN101182005AStrong redoxGood solid acidityMolecular sieve catalystsCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesIon exchangeHeteroatom
The invention relates to a method used for preparing zeolite molecular sieve containing titanium by modification of natural zeolite, and uses the natural zeolite as a raw material and the zeolite molecular sieve containing titanium is obtained through ion exchange, chemical dealumnization treatment and gas-solid isomorphous substitution reaction. The mole ratio of Si and Ti of molecular sieve skeleton is 20 to 100. The invention brings metallic titanium which has special catalytic performance to the skeleton of the natural zeolite, which greatly promotes grade of natural zeolite products, widens the application range of the natural zeolite and provides a way with low cost, convenient operation and environment protection to prepare heteroatom zeolite molecular sieve.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for constructing super-hydrophobic membrane on surface of copper matrix
InactiveCN102230169ALow toxicityExcellent superhydrophobic propertiesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCarboxylic acidSurface modification
The invention relates to a method for constructing a super-hydrophobic membrane on the surface of a copper matrix, and relates to a method for constructing a super-hydrophobic membrane, which solves the problems of complex steps of constructing the super-hydrophobic surface and large toxicity of raw materials in the conventional method. In the method, a sliver layer with a micro-nanometer structure is generated by replacement reaction of copper and silver nitrate, a rough surface is constructed on the copper matrix, and a self-assembly membrane is formed on a silver surface by utilizing long-chain carboxylic acid to reduce surface energy. When the method is used, the construction of the rough surface and surface modification are completed in one step, equipment and a process is simple, and the method is easy to operate; and the toxicity of the raw materials is low, and environmental pollution is small. The method is suitable for the large-scale industrial production of the super-hydrophobic membrane.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for Recovering Methane Gas from Natural Gas Hydrate by Injecting CO2 and Air Mixed Gas
The present invention relates to a method for recovering methane gas from natural gas hydrates. In particular, it includes the step of adding a gas mixture containing air and carbon dioxide to an NGH of deep sea and the step of replacing the methane gas with gas mixture and the step of decomposition-replacement of methane hydrate.In accordance with the present invention, the invention is possible use as a technique for recovery of methane gas in the all-weather to induce replacement reaction using a gas mixture when the temperature of the technology applied is low and to induce degradation of solid methane hydrate by mixing gas when the temperature of the region technique is applied is high.Further, the method makes it possible to reduce costs than using conventional methods because the air is collected directly from the NGH reservoirs and compressed and is injected as a mixture with carbon dioxide and, there is no need to transport the infusion another gas. The invention may be widely used in the production of natural gas more effectively.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for treating manganese-containing wastewater generated during electrolytic manganese processing
InactiveCN102115284ALow costGuarantee sustainable developmentSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater contaminantsManganeseEmission standard
The invention discloses a method for treating manganese-containing wastewater generated during electrolytic manganese processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, pretreating manganese-containing wastewater; adding sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to be 9.3+0.10; adding carbonate capable of undergoing a displacement reaction with Mn<2+> to generate a MnCO3 sediment; then, adding a flocculant and fully stirring, wherein the addition amount of the flocculant is 0.12-0.35 percent of the wastewater amount; leading the wastewater to enter a primary sedimentation tank, standing still, sedimenting MnCO3 and separating the MnCO3 from liquid; then, adding sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to 9.7+0.10; adding perhydrol and the flocculant; and leading the wastewater enter a secondary sedimentation tank and standing still to generate a Mn(OH)2 sediment; and adding an acid or alkali substance to adjust the pH value of the Mn(OH)2 sediment so that related indexes can reach an emission standard. The method disclosed by the invention is a production type treatment method for resource recycling, can be used for recycling manganese resources, has lower treatment cost and is beneficial to decrease of the costs of enterprises for treating the manganese-containing wastewater.
Owner:重庆武陵锰业有限公司
Method for preparing nano noble metal hydrogenation catalyst by substitution method and its use
InactiveCN1775361ASimple preparation techniquePromote regenerationCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNitro compoundDisplacement reactions
The present invention relates to a method for preparing nano noble metal hydrogenation catalyst by using chemical displacement process and its application. It is characterized by that it utilizes metal elementary substance M and salt of noble metal N and makes them undergo the process of displacement reaction to produce elementary substance N, in which the N represents Ru, Rh, Pd, Pt and Ir or their mixture, M represents Zn, Al, Fe, Co and Ni. When the M is terrifically excess, N / M type metal loaded nano noble metal can be produced; and When the N and M are approximate to stoichiometry, the highly-dispersed nano N colloid can be formed, after the stabilizing agent is added, the load type N / S can be prepared, in which S represents C, Al2O3, SiO2, MgO, ZrO2 and CeO2. Said catalyst can be used for hydrogenation reaction of various compounds.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Graphene oxide composite aerogel and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105536774AImprove adsorption catalytic activityHigh mechanical strengthWaste water treatment from plant processingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFreeze-dryingOxide composite
The present invention belongs to the field of porous catalyst materials, and specifically discloses a graphene oxide composite aerogel and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method is as follows: mixing graphene oxide powder and water in solid-liquid ratio of 1: 2 to 1: 6 for ultrasonic dispersion; under stirring conditions, adding nanoscale MnO2 powder, performing hydrothermal reaction, after the reaction is stopped, cooling to room temperature, filtering, washing a filter cake with water, and drying; placing an obtained solid material in an alcohol solution for substitution reaction to obtain a graphene oxide composite hydrogel; finally freeze-drying the graphene oxide hydrogel, and then cooling to obtain the graphene oxide composite aerogel. The catalyst preparation method is simple and easy to operate, the graphene oxide composite aerogel is high in stability, and the catalytic ozonation treatment effect of the graphene oxide composite aerogel is good, and an effective method is provided for advanced treatment of papermaking wastewater.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for carbon supported ultra-low platinum catalytic electrode preparation by indirect galvanic deposit
InactiveCN101359744AGood dispersionGood size controlCell electrodesFuel cell detailsPlatinum saltsPorous carbon
The invention provides a method for preparing a carbon-supported ultra-low platinum catalytic electrode by means of indirect electrodeposition, which belongs to the fuel cell technique field. The method comprises the steps: transition metal M (such as: Cu, Co, Ni and the like) nano-particles in an aqueous solution are highly dispersed and deposited on a porous carbon electrode (PCE) bonded with perfluoro-sulfonated resin through a four-step electrodeposition method, then the obtained M / PCE electrode is immerged into a platinum salt solution for preparing the carbon-supported ultra-low platinum catalytic electrode through displacement reaction. The invention has the advantages of simple process and low costs. The prepared carbon-supported ultra-low platinum catalytic electrode has the advantages of low platinum loading, high electro-catalytic performance, good dispersion of platinum nano-particles and controllable sizes, and can replace the existing commercial platinum carbon (Pt / C) catalyst.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Sulfurated modified Fe-Cu bimetallic material, preparation method and method for removing chromium-containing wastewater
ActiveCN107200392AIncrease the active siteFacilitated releaseTransportation and packagingWater contaminantsCopper saltChromium
The invention relates to a sulfurated modified Fe-Cu bimetallic material, a preparation method and a method for removing chromium-containing wastewater. In the sulfurated modified Fe-Cu bimetallic material, the molar ratio of sulfur to iron is (0.05-0.06): 1, and the mass ratio of iron to copper is 10: (0.1-4). The preparation method comprises the following steps: in a buffer solution with an acidic environment, performing a reaction on zero-valent iron and soluble sulfate to obtain sulfurated modified zero-valent iron; performing a replacement reaction on the sulfurated modified zero-valent iron and bivalent copper salt to obtain the sulfurated modified Fe-Cu bimetallic material. The heavy metal chromium removing efficiency of the sulfurated modified Fe-Cu bimetallic material is much higher than that of the zero-valent iron, and the reactivity of the sulfurated modified Fe-Cu bimetallic material is also higher than those of a sulfurated modified zero-valent iron material and a Fe-Cu bimetallic material, so that removal of pollutants is effectively accelerated; in addition, the sulfurated modified Fe-Cu bimetallic material has the advantages of small chemical dosage, high reaction speed rate, relatively wide pH adaptability, and the like, and has a wide application prospect in heavy metal-containing wastewater treatment.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
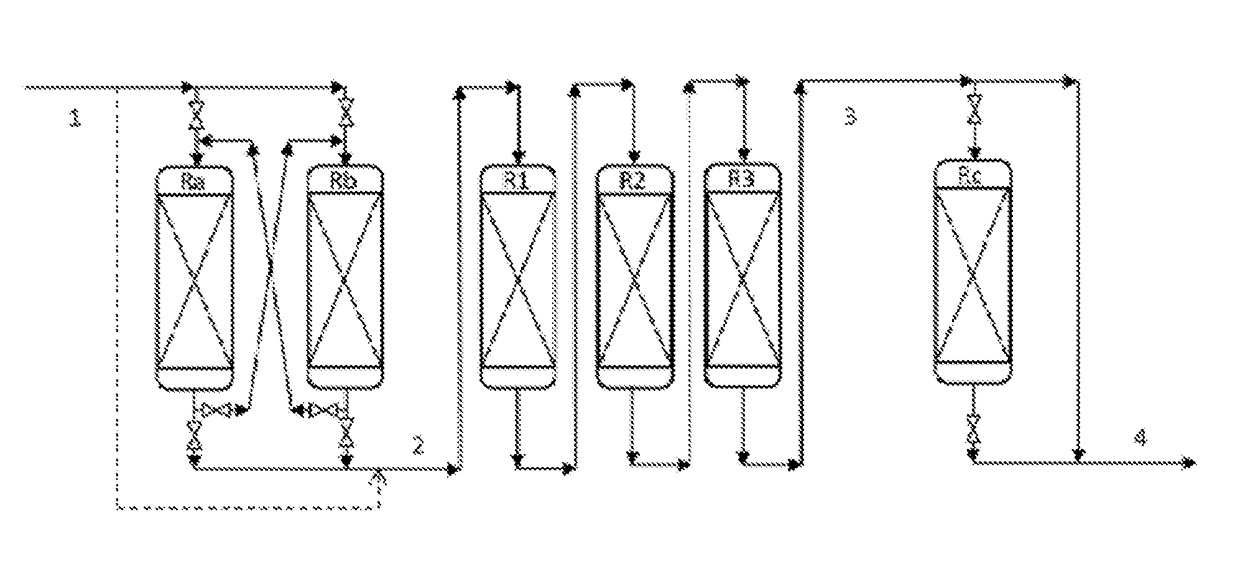
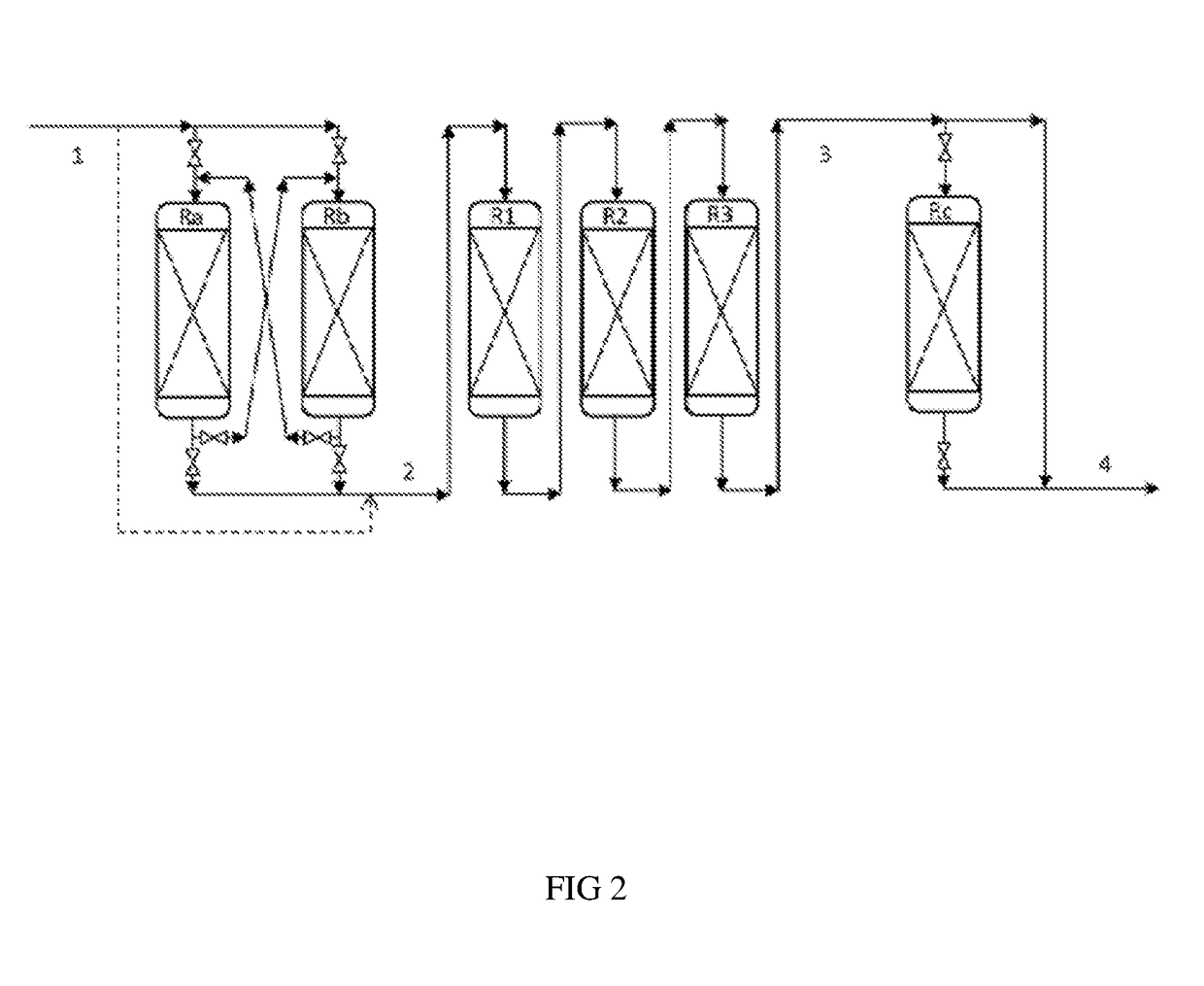
Conversion process comprising at least one step for fixed bed hydrotreatment and a step for hydrocracking in by-passable reactors
ActiveUS20170355914A1Lower overall pressure dropModerate temperatureHydrocarbon oil crackingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesFixed bedMetal
The invention concerns a process for the treatment of a hydrocarbon feed in order to obtain a heavy hydrocarbon fraction with a low sulphur content, said process comprising the following steps: a) an optional step for hydrodemetallization carried out in permutable reactors, b) a step for fixed bed hydrotreatment of the effluent obtained from step a), c) a step for hydrocracking of the effluent obtained in step b) in by-passable reactors, d) a step for separation of the effluent obtained from step c).
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Vulcanization method of hydrofining catalyst
ActiveCN103059910AImprove deep hydrodesulfurization activityAvoid vulcanization aloneCatalyst activation/preparationRefining to eliminate hetero atomsVulcanizationHydrogen
The invention discloses a vulcanization method of a hydrofining catalyst. The method comprises: first, under a nitrogen atmosphere, raising the catalyst bed temperature to 120-180DEG C, and starting injection of vulcanization startup oil; after complete moistening, raising the catalyst bed temperature to 230-260DEG C, using hydrogen sulfide-containing hydrogen to replace nitrogen in the reaction system, and beginning to injecting a vulcanizing agent into the reaction system; and when the purity of hydrogen in a circulation gas is greater than 75%, carrying out vulcanization according to a normal vulcanization process. According to the invention, the introduction of hydrogen sulfide and injection of the vulcanizing agent are carried out under a higher temperature, low temperature individual vulcanization of Co and / or Ni can be avoided, so that under a high temperature and in the presence of hydrogen sulfide, Mo and / or W, and Co and / or Ni can be vulcanized at the same time to form a high activity Mo(W)-Co(N)-S active phase. The method provided in the invention is in favor of improving the deep hydrodesulfurization activity of the catalyst.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Copper-based nano catalyst for preparing high-carbon alcohol from synthetic gas as well as preparation method and application thereof
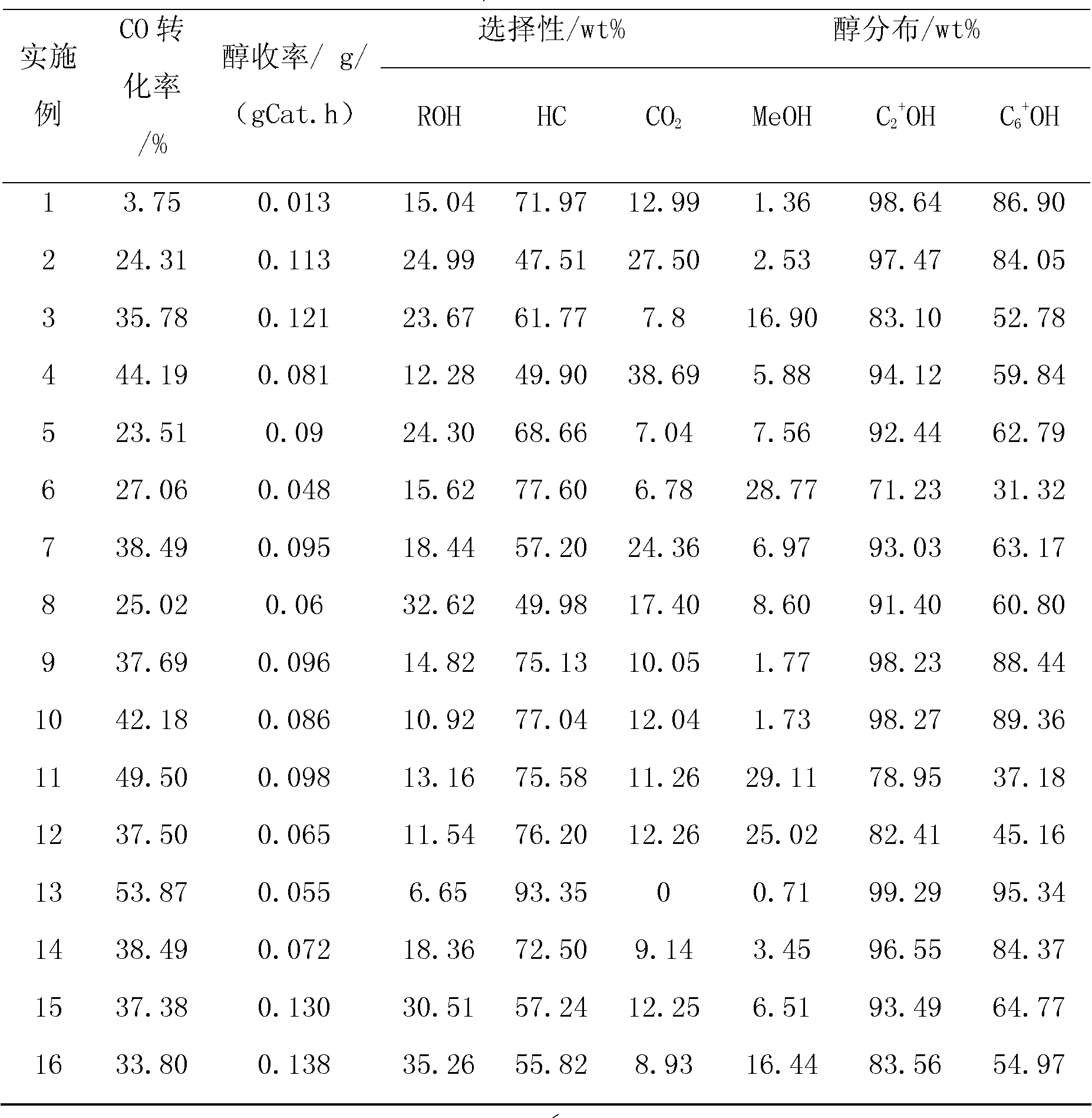
ActiveCN102500374ASmall particle sizeLarger than surfaceOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationNano catalystSyngas
The invention discloses a copper-based nano catalyst for preparing high-carbon alcohol from synthetic gas as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst is a copper-based polymetallic nano catalyst, which is composed of copper and at least one Fischer-Tropsch component. The preparation method is selected from one of replacement reaction method, step-by-step reduction method and simultaneous reduction method. The catalyst disclosed by the invention is small in particle size, large in specific surface and high in utilization rate; the preparing process is simple and convenient for operation; and when the catalyst is used for the synthesis of high-carbon alcohol from synthetic gas, by controlling the component and ratio of the catalyst, the selectivity of the alcohols higher than ethanol in the obtained alcohols is up to 95wt% and the selectivity of high-carbon alcohols higher than hexanol reaches more than 80wt%.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com