Patents
Literature
463results about "Pressure/vacuum vessels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
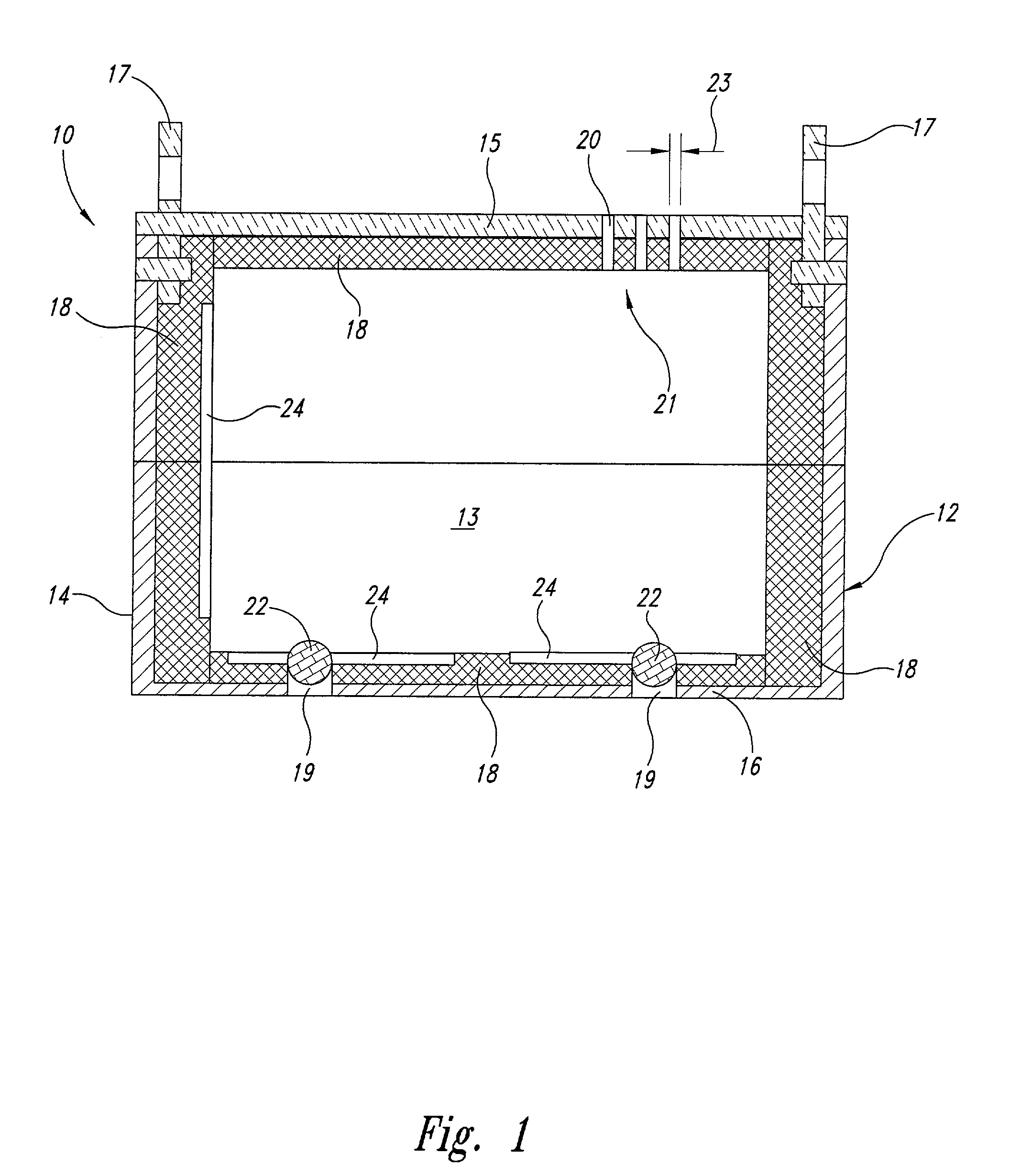
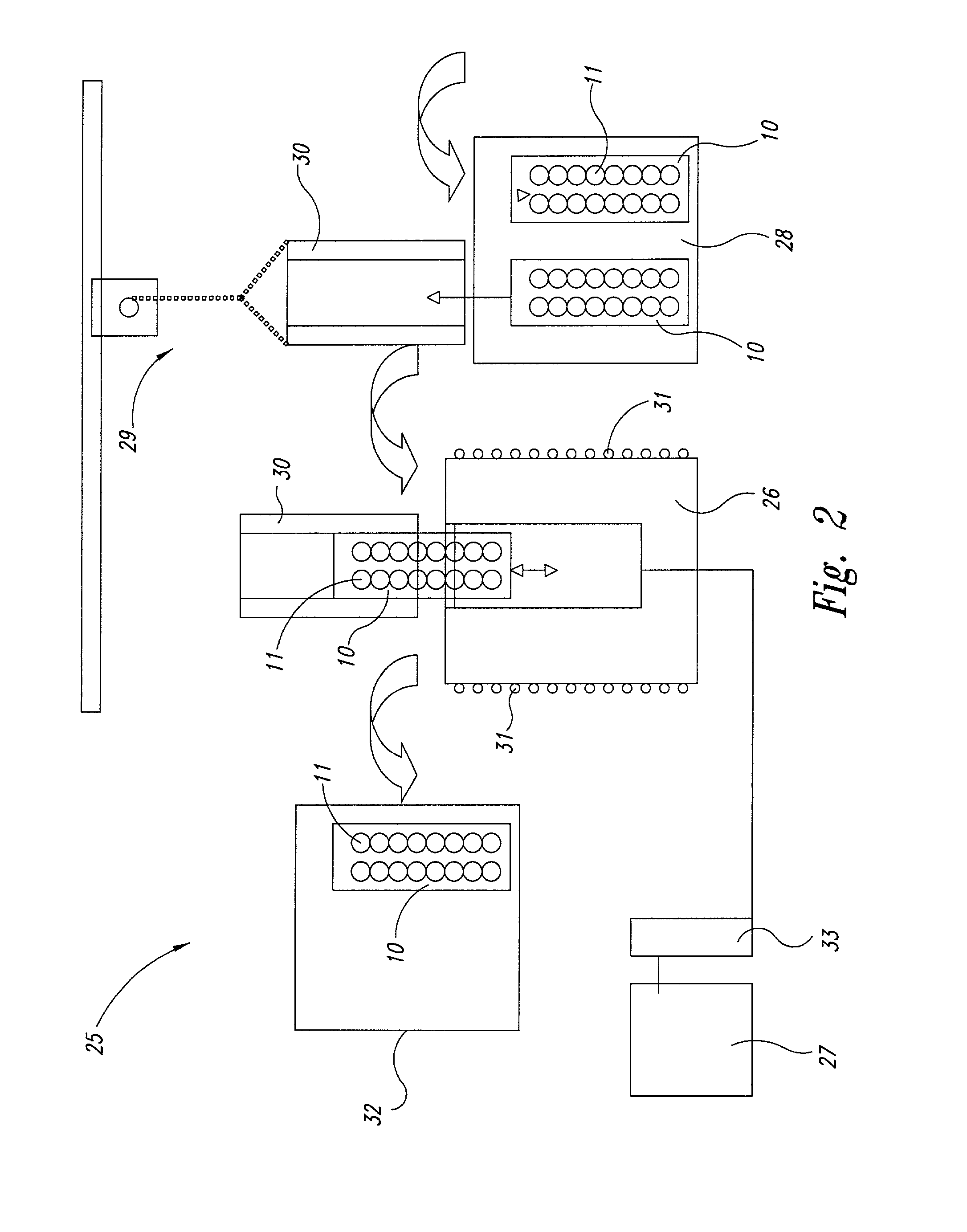
Apparatus and method for combinatorial chemistry synthesis
InactiveUS6045755AOvercome problemsImprove throughputEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisProcess engineering
In a first embodiment, this invention includes an integrated robot apparatus for performing combinatorial chemistry synthesis protocols and having interchangeable work-stations, robot arm tools, and reaction vessels and reaction vessel arrays. The work-stations and tools are specialized to perform tasks necessary for the synthesis in a plurality of the reaction vessels grouped in a plurality of the reaction vessel arrays. Preferably, these elements function interchangeably because they have standardized sizes and conformation. The work-stations and tools include those for fluid dispensing or aspirating from individual reaction vessels or from all the reaction vessels in an array simultaneously. The reaction vessels can include, alternatively, stackable, ball-sealed reaction vessels, microtitre-like reaction vessel arrays, arrays of independent reaction vessels, valve-sealed reaction vessels, septum-sealed reaction vessels, and syringe reaction vessels. In alternative embodiments, this invention includes these work-stations, tools, reaction vessels and reaction vessel arrays in various combinations or sub-combinations either for use in partially integrated robots or for manual or standalone use.
Owner:LION BIOSCIENCE AG
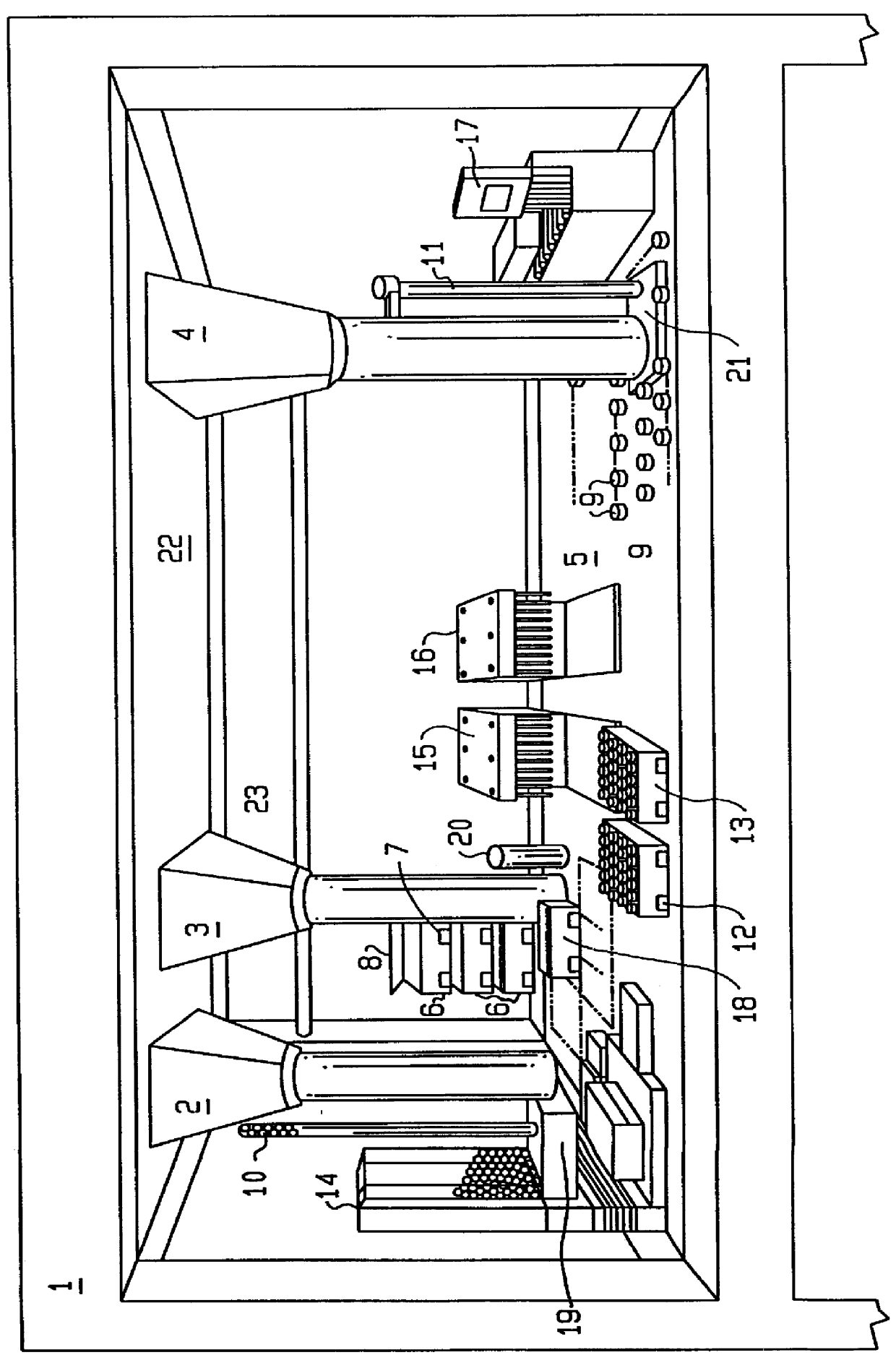
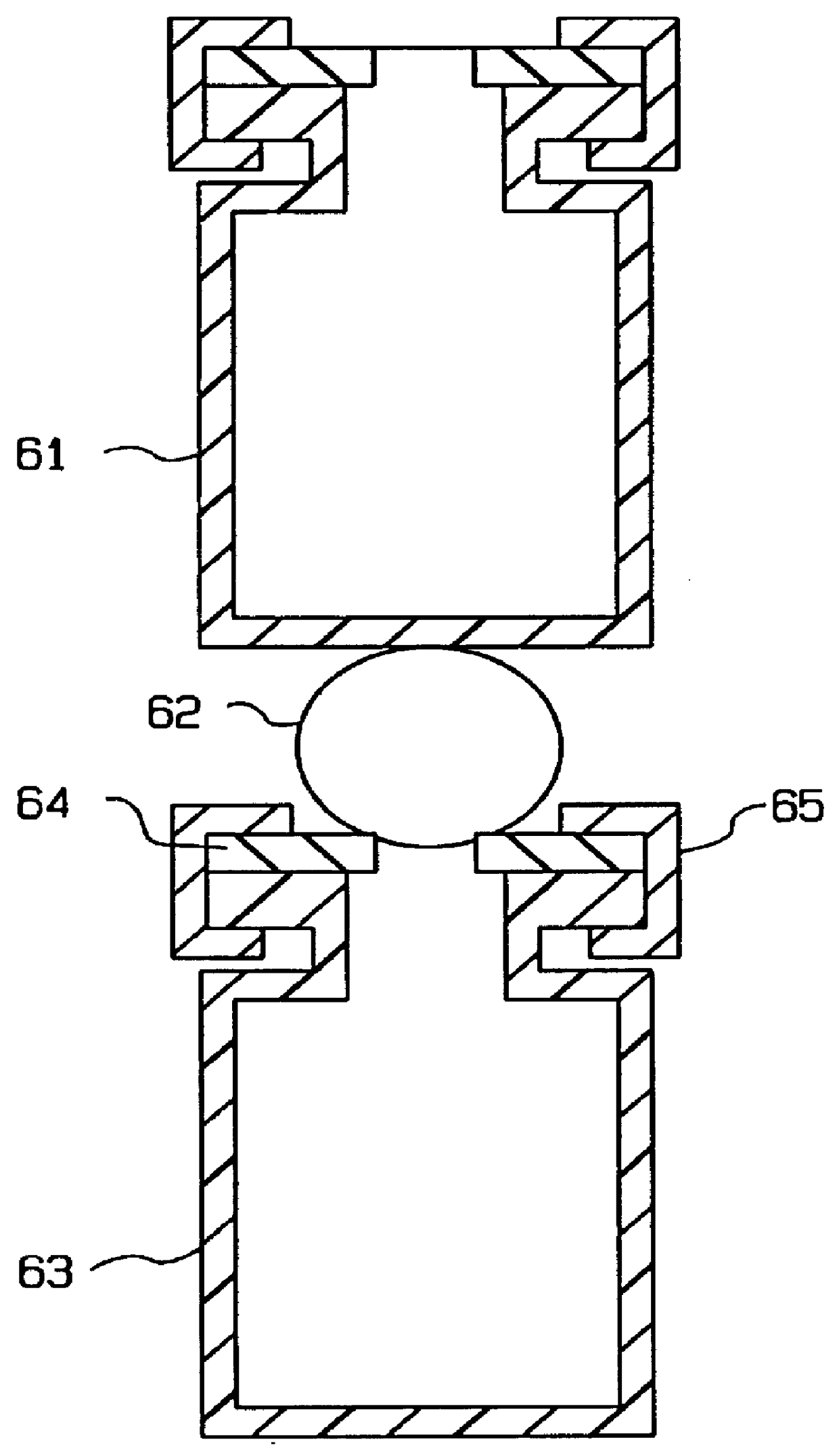
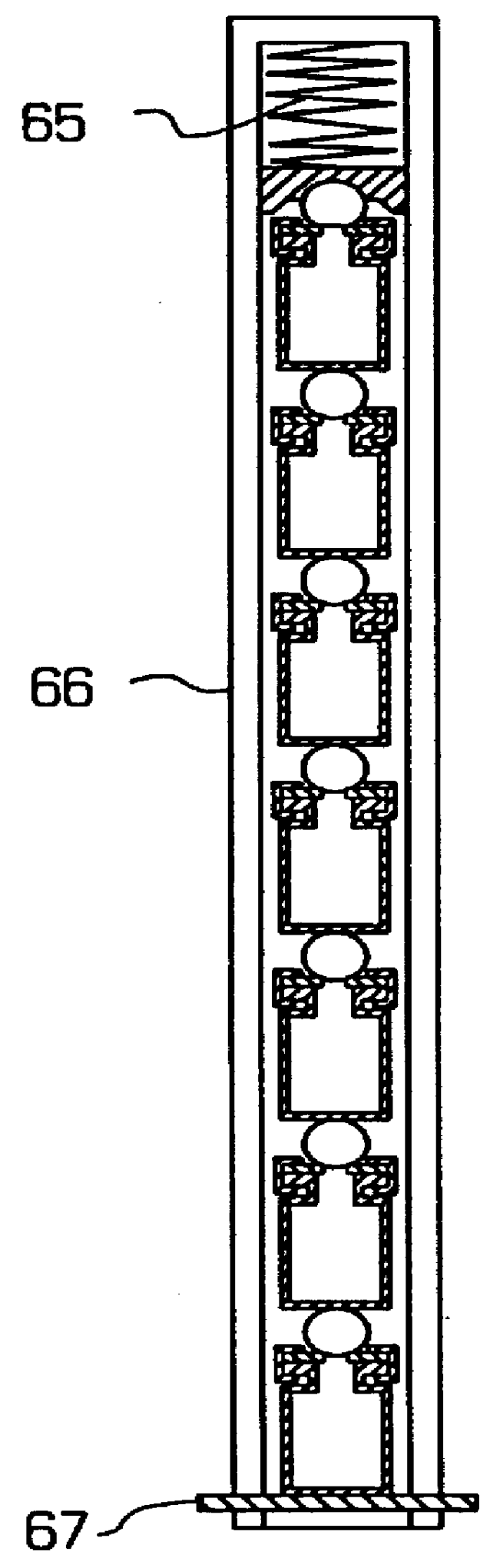
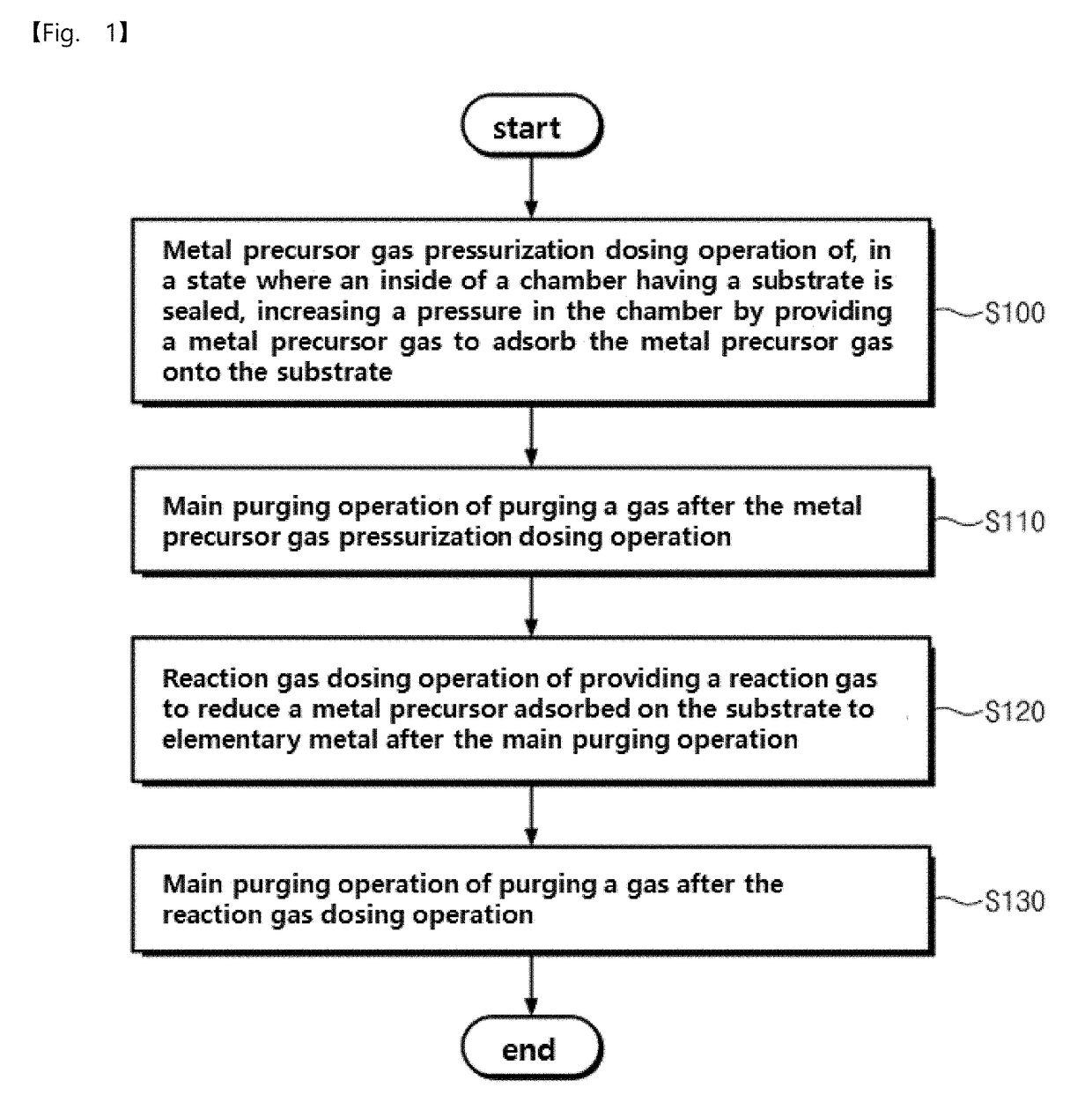
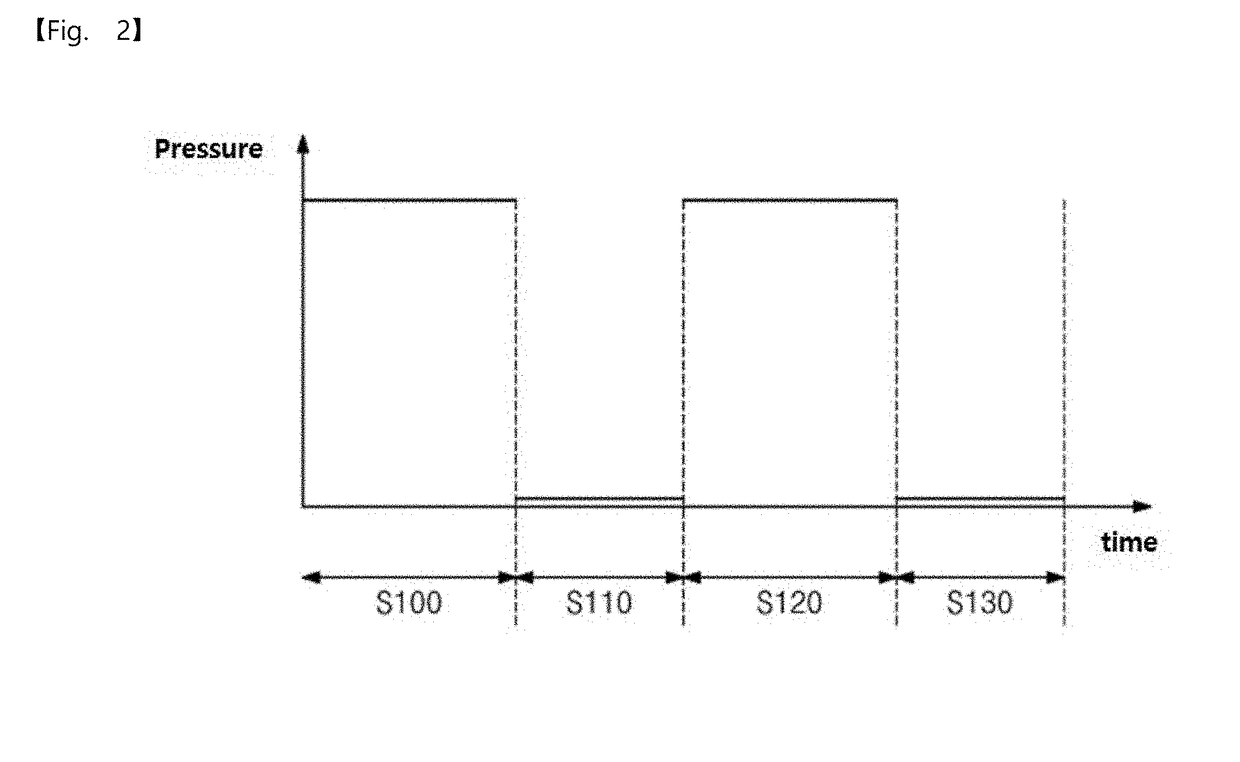
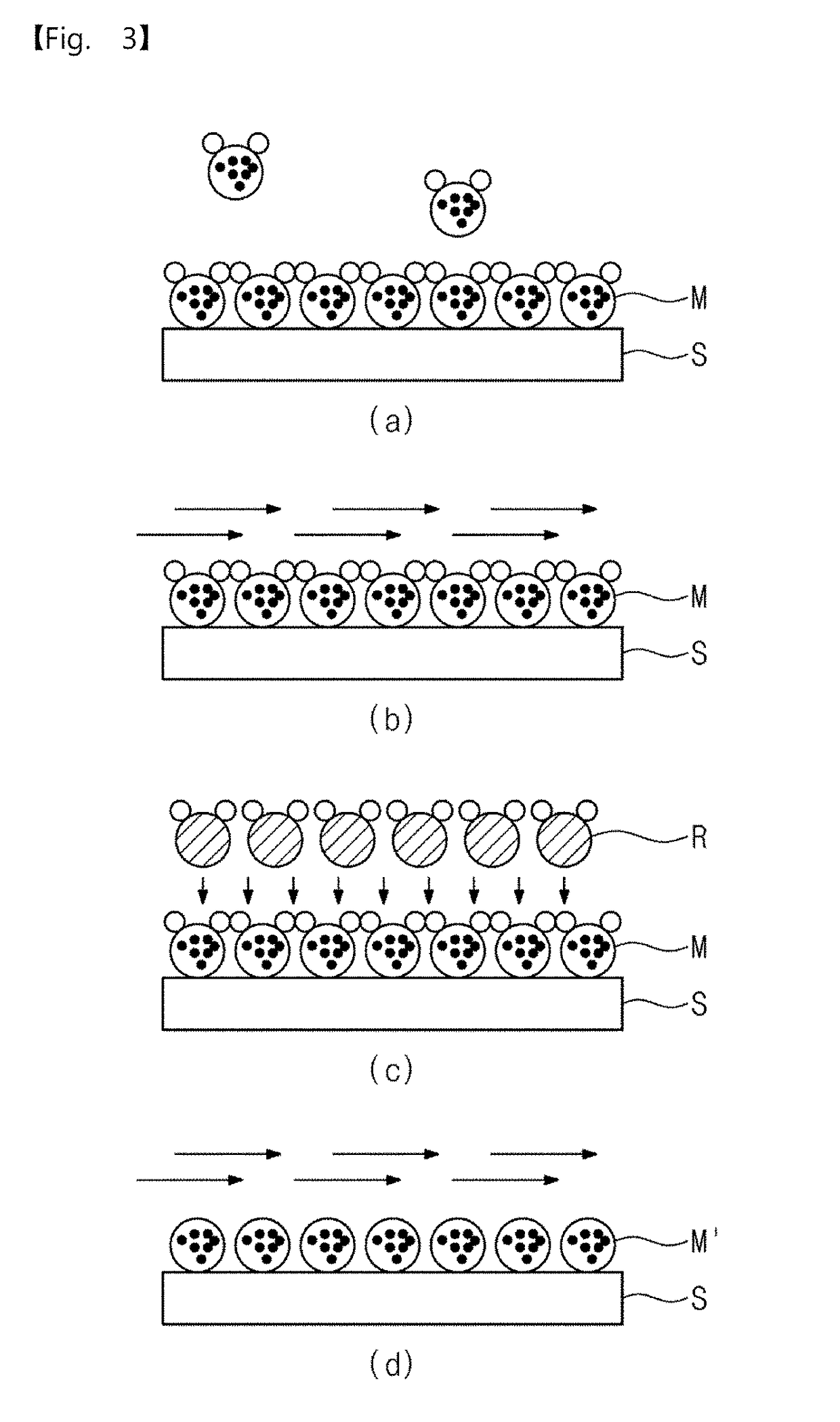
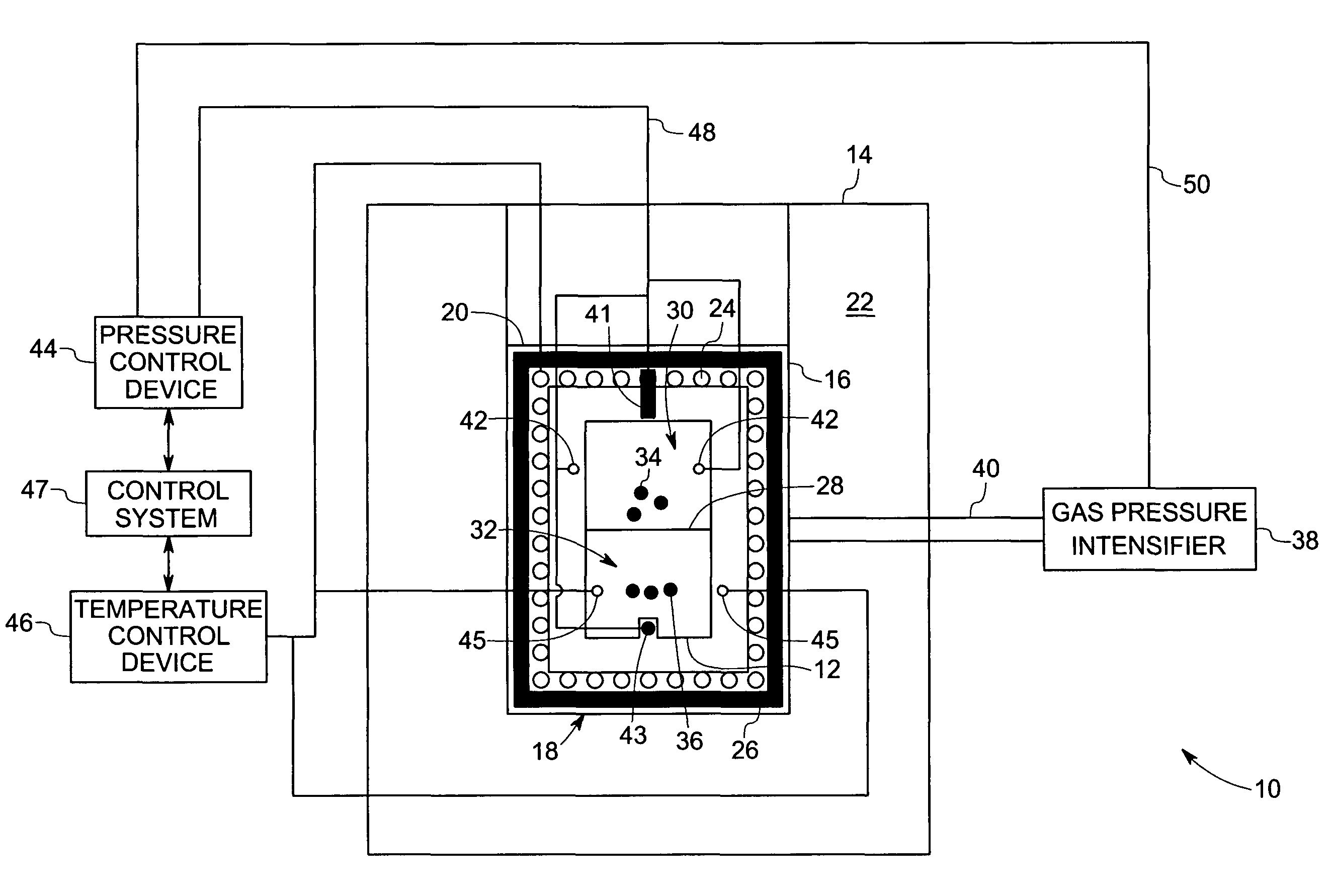
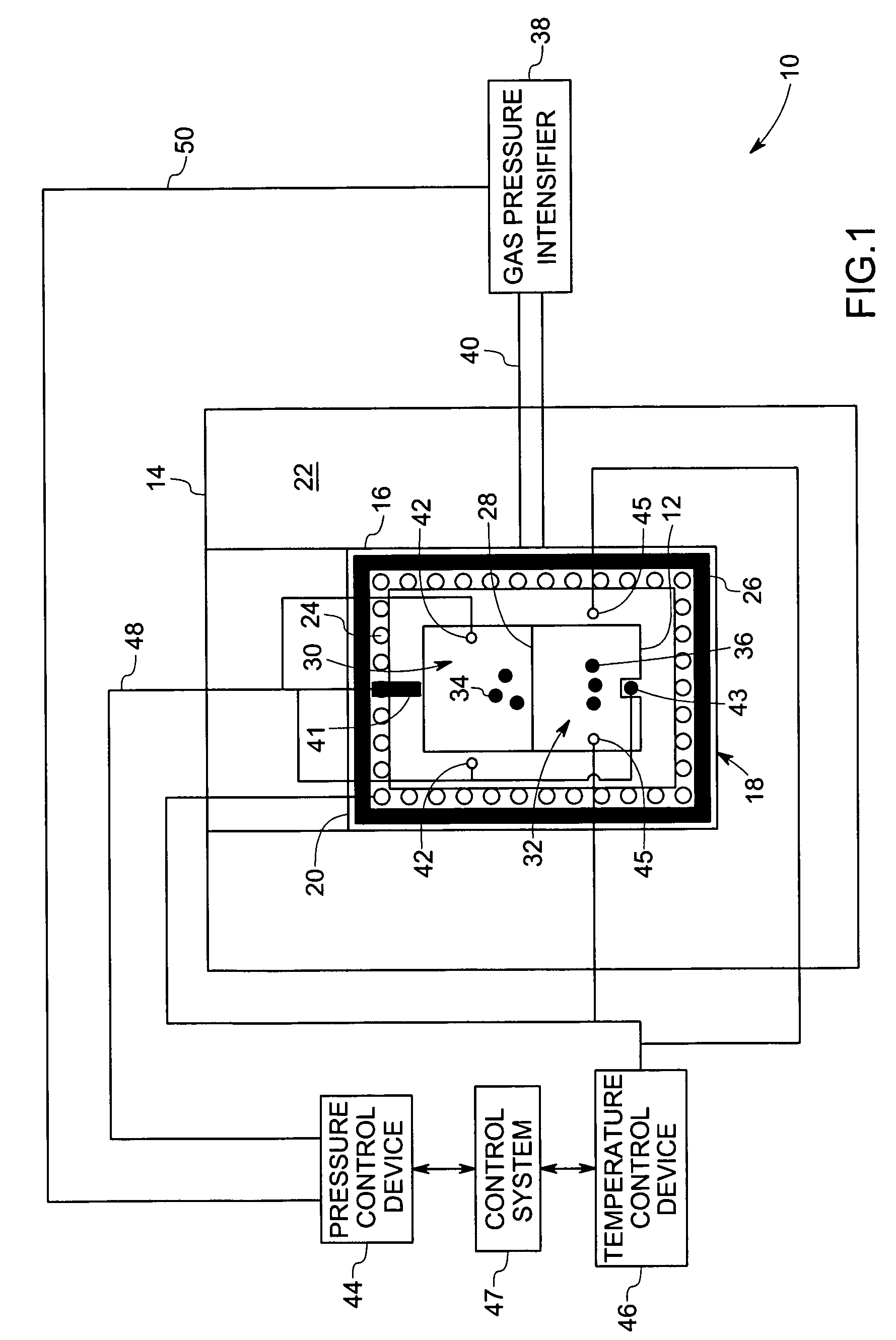
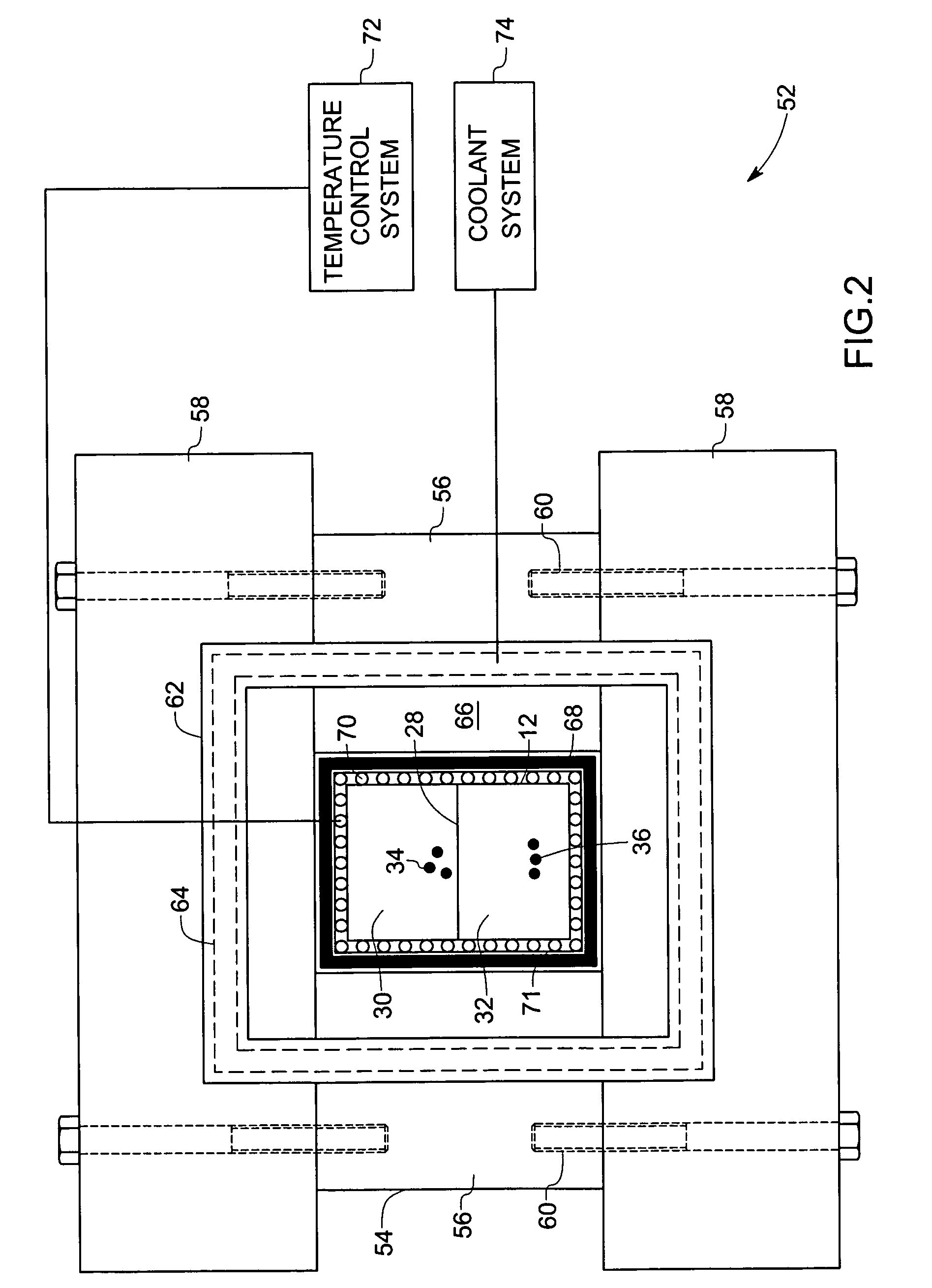
Pressurization type method for manufacturing metal monoatomic layer, metal monoatomic layer structure, and pressurization type apparatus for manufacturing metal monoatomic layer
ActiveUS20190062917A1High surface coverageReduce surface roughnessChemical vapor deposition coatingPressure/vacuum vesselsProduct gasMaterials science
A pressurization type method for manufacturing elementary metal may include a metal precursor gas pressurization dosing operation of, in a state where an outlet of a chamber having a substrate is closed, increasing a pressure in the chamber by providing a metal precursor gas consisting of metal precursors, thereby adsorbing the metal precursors onto the substrate, a main purging operation of purging a gas after the metal precursor gas pressurization dosing operation, a reaction gas dosing operation of providing a reaction gas to reduce the metal precursors adsorbed on the substrate to elementary metal, after the main purging operation, and a main purging operation of purging a gas after the reaction gas dosing operation.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Apparatus for processing materials in supercritical fluids and methods thereof
ActiveUS20060177362A1After-treatment apparatusUltra-high pressure processesHigh intensityPressure difference
An apparatus and method for processing materials in supercritical fluids is disclosed. The apparatus includes a capsule configured to contain a supercritical fluid, a high strength enclosure disposed about the capsule and a sensor configured to sense pressure difference between an interior and an exterior of the capsule. The apparatus also includes a pressure control device configured to adjust pressure difference of the capsule in response to the pressure difference sensed by the sensor. The apparatus further includes at least one dividing structure disposed within the capsule that divides the capsule into a seed growing chamber and a nutrient chamber.
Owner:SLT TECH
Apparatus for processing materials in supercritical fluids and methods thereof
ActiveUS7704324B2After-treatment apparatusUltra-high pressure processesHigh intensityPressure difference
An apparatus and method for processing materials in supercritical fluids is disclosed. The apparatus includes a capsule configured to contain a supercritical fluid, a high strength enclosure disposed about the capsule and a sensor configured to sense pressure difference between an interior and an exterior of the capsule. The apparatus also includes a pressure control device configured to adjust pressure difference of the capsule in response to the pressure difference sensed by the sensor. The apparatus further includes at least one dividing structure disposed within the capsule that divides the capsule into a seed growing chamber and a nutrient chamber.
Owner:SLT TECH
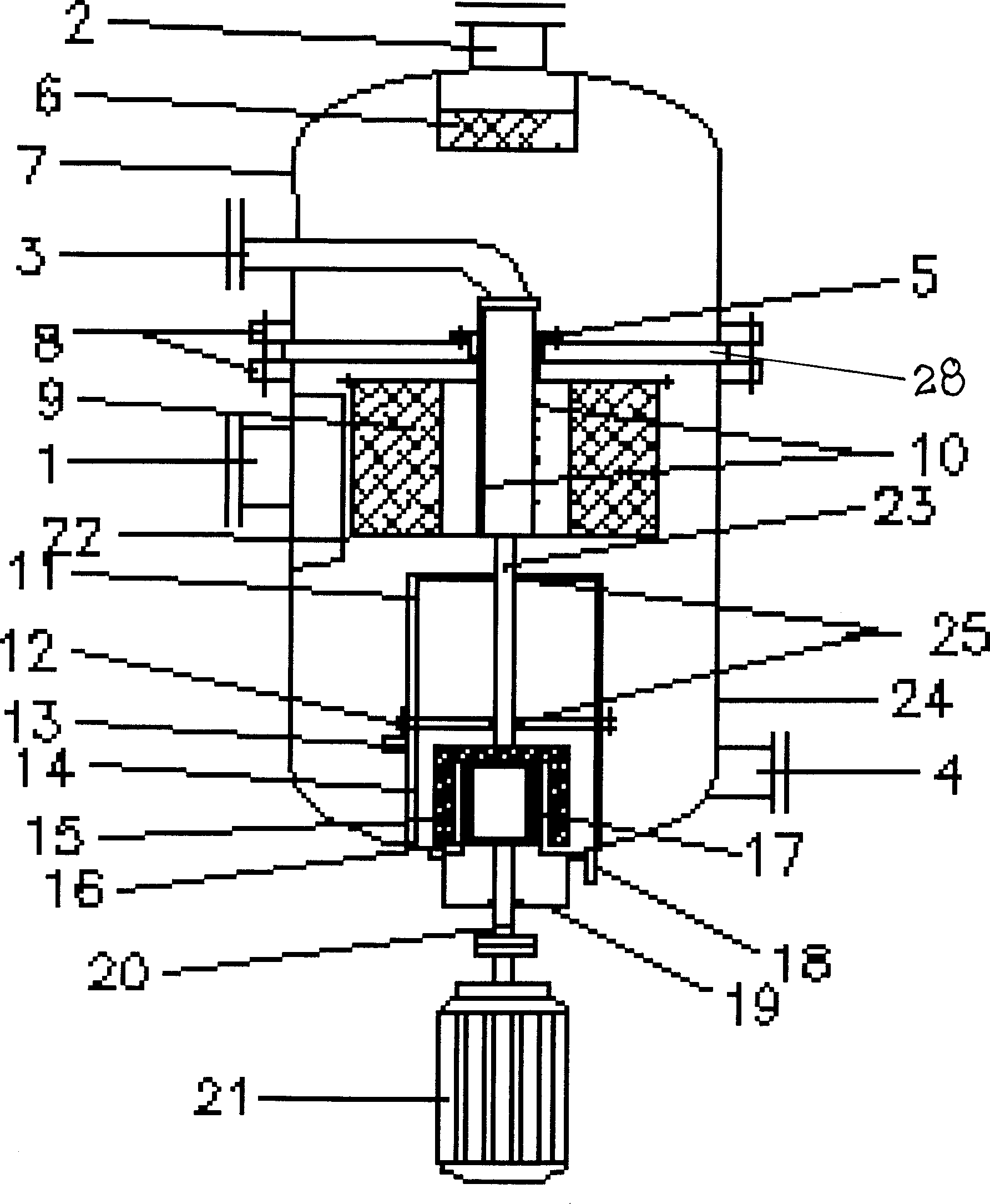
High-pressure rotary bed gas-liquid mass-transferring and reaction equipment in superheavy force field
InactiveCN1428189AOvercome deficienciesOvercome defectsLiquid-gas reaction processesPressure/vacuum vesselsDrive shaftEngineering
The present invention relates to a gas-liquid mass transfer and reaction equiopment of high-pressure rotating bed in ultragravity force field. Said invention drive equipment is a magnetic drive equipment, including driving portion, driving magnetic stell protecting cover positioned on the exterior of the machine shell and driving magnetic steel and driving shaft which are placed in the protecting cover and driven portion, driven magnetic steel protecting cover positioned in the interior of the machine shell and driven magnetic steel and driven shaft which are placed in the driven magnetic steel protecting cover. The driving portion and driven portion are separatedy by means of magnetic isolation cover between both them. Said invention adopts band pressure design and measures of internal and internal magnetic steel protecting cover, magnetic steel cooling system, high-effective coating layer and others so as to raise mass transfer effect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Chemical reaction apparatus and power supply system
InactiveUS20040148858A1Improve energy efficiencySuppress heat lossChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsFuel cell auxillariesChemical reactionEngineering
A chemical reaction apparatus includes a solid body which has an outer surface, and in which at least one flow path which allows a chemical medium to flow is formed. This body has a heating element which heats the chemical medium in the flow path to accelerate a chemical reaction of the chemical medium, and a heat radiation preventing film which covers at least a portion of the outer surface of the body, and prevents radiation of heat generated by the heating element from a portion of the outer surface.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Foam extrusion apparatus
InactiveUS6113374AEasy to disassembleIncrease the sectionConfectionerySweetmeatsNarrow rangeFree rotation
An extrusion system utilizes single or tandem extruders and a mixer-cooler to extrude a foamable extrudate through a die in a sealable chamber. The foamable extrudate is shaped and calibrated within the chamber. The die is mounted on the end of a gel tube projecting through a gland seal in a fixed bulkhead forming the upstream end of the chamber. The gel tube and mixer-cooler are mounted on a movable carriage, movement of which may be used to adjust the die with respect to shaping and calibrating equipment inside the chamber. The mixer-cooler achieves a selected narrow range of uniform viscosity of the melt at the die depending on the size of the product and density. The chamber is preferably a vacuum chamber producing low density foams. The product exits the chamber to atmosphere on a continuous basis through a submerged orifice in a water baffle immersion seal. The mixer-cooler enables a large size low density product to be produced with uniform cellular structure without cell collapse or density gradients, as the product is subjected to the pressure and temperature transformations passing from the chamber to atmosphere through the water. The seal includes the submerged orifice with a free wheeling guiding system upstream of the orifice. Immediately ahead of the guiding system, the parameters of the foam extrudate are sensed to control the configuration of the orifice on a continuous basis. Before the extrudate passes into the water baffle seal it moves over a floating dancer roll, the position of which controls a haul-off such as a vacuum belt at the tail end of the system. This avoids pushing on the extrudate.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Carbon material and method for producing same
ActiveUS20120315482A1High crystallinityShorten the time periodFrom gel stateMaterial nanotechnologyPrillLithium-ion battery
There are provided a cluster of thin sheet graphite crystals or the like which is useful as an electrode material for lithium ion batteries, hybrid capacitors and the like, and a method for efficiently producing the same at high productivity. The method is one for producing a cluster of thin sheet graphite crystals composed of aggregates in such a state that thin sheet graphite crystals extend from the inside toward the outside, comprising charging a powdery and / or particulate material of an organic compound pre-baked to an extent of containing remaining hydrogen in a graphite vessel, and subjecting the powdery and / or particulate material together with the vessel to hot isostatic pressing treatment (HIP treatment) using a compressed gas atmosphere under the predetermined conditions.
Owner:INCUBATION ALLIANCE
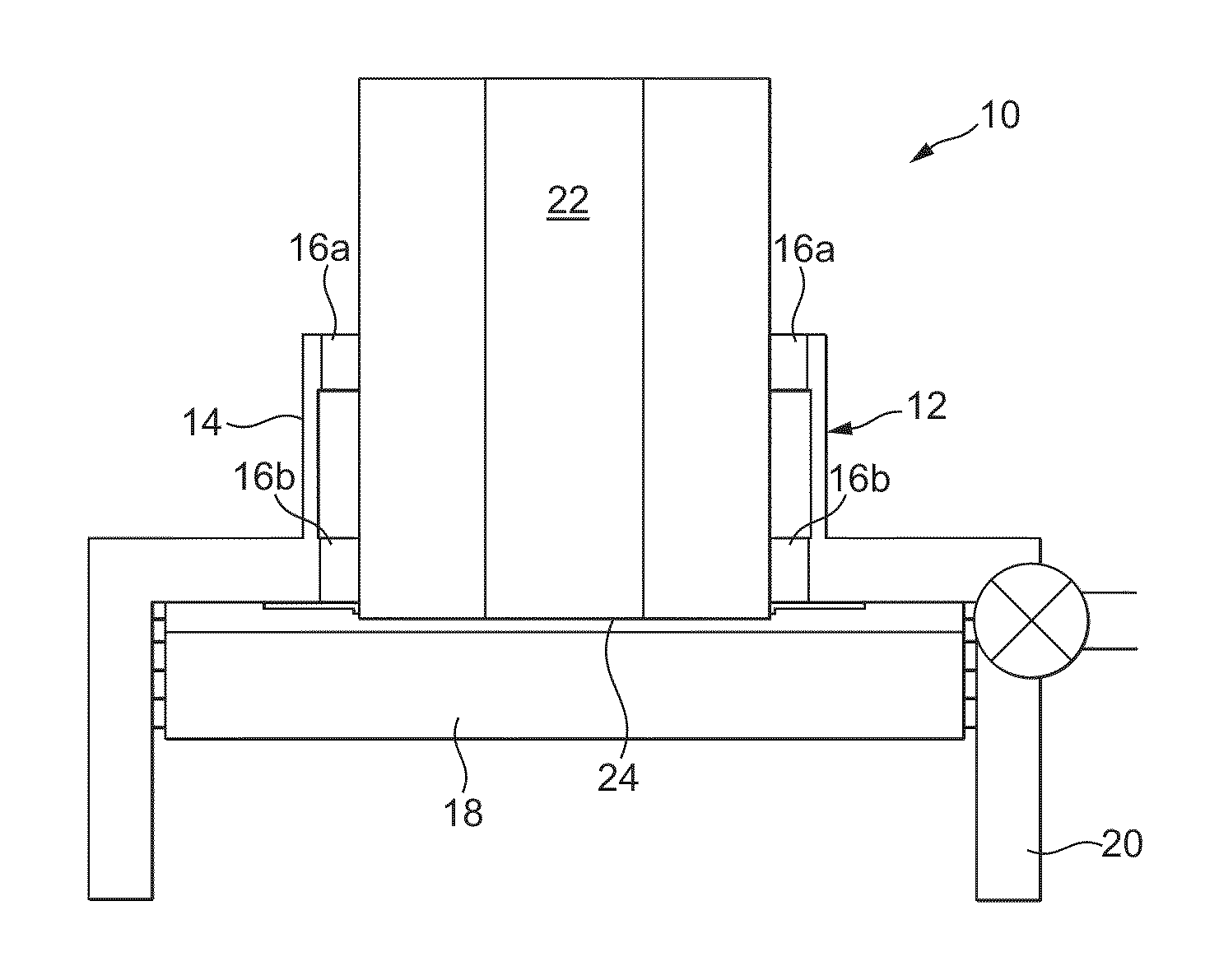
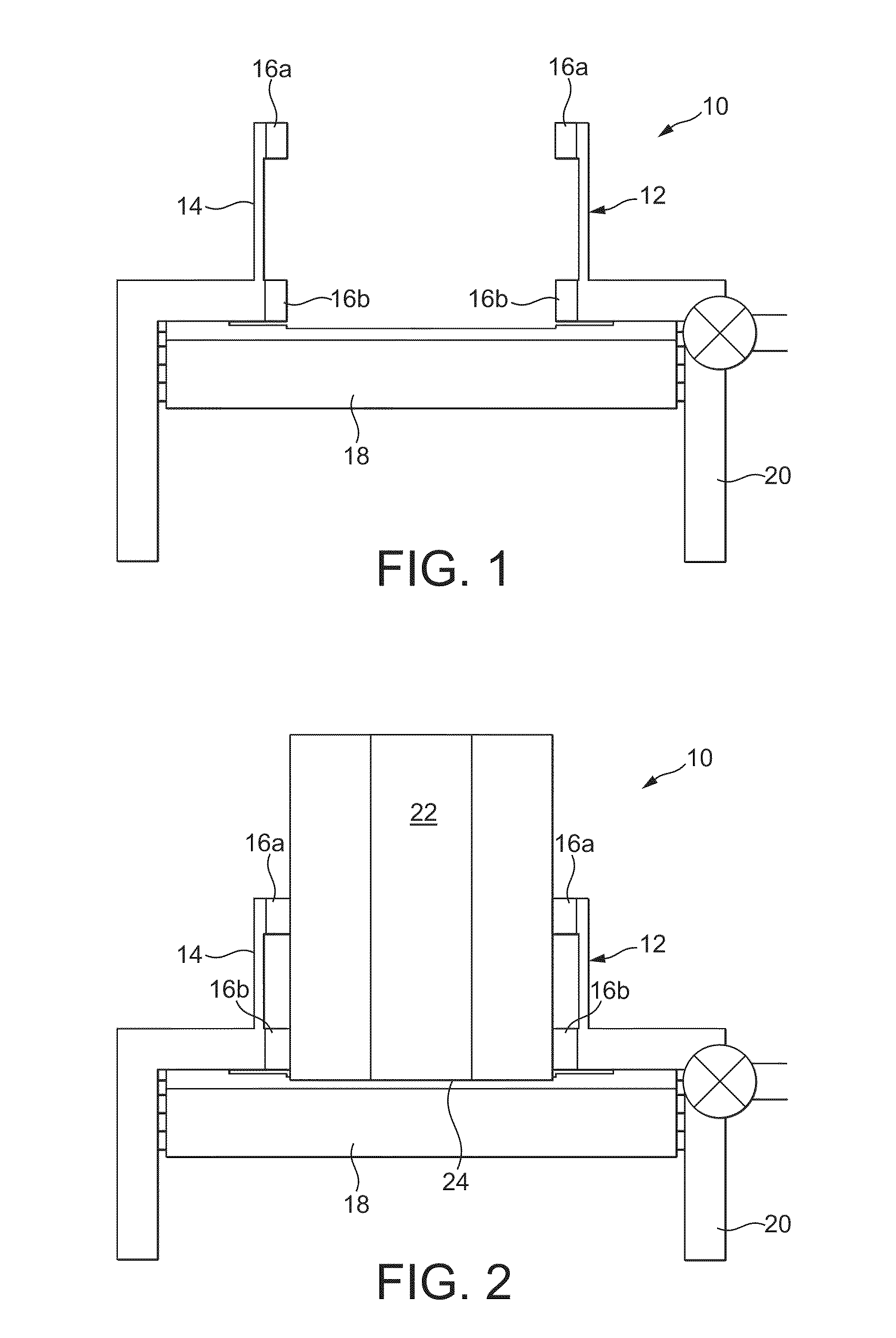
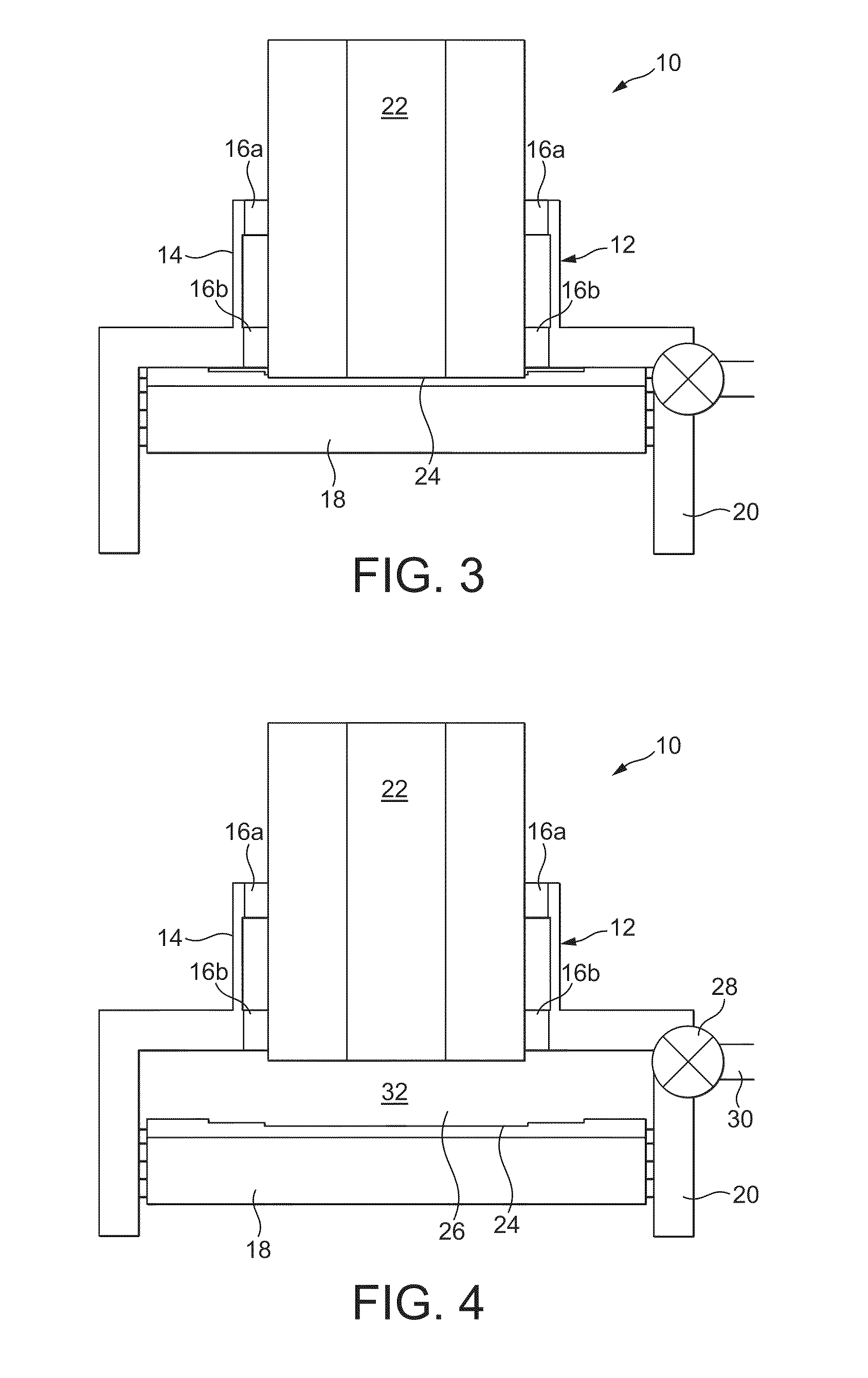
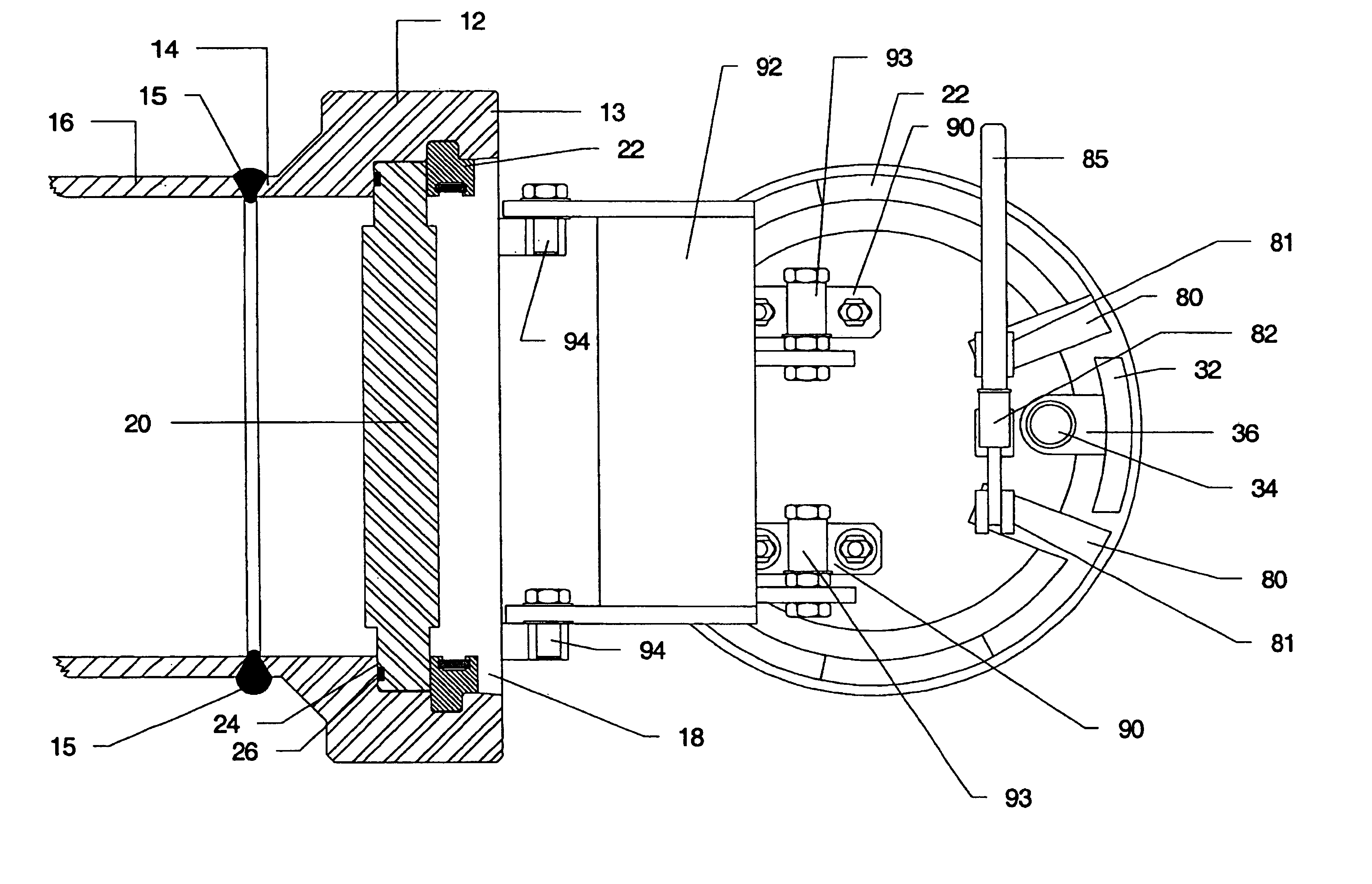
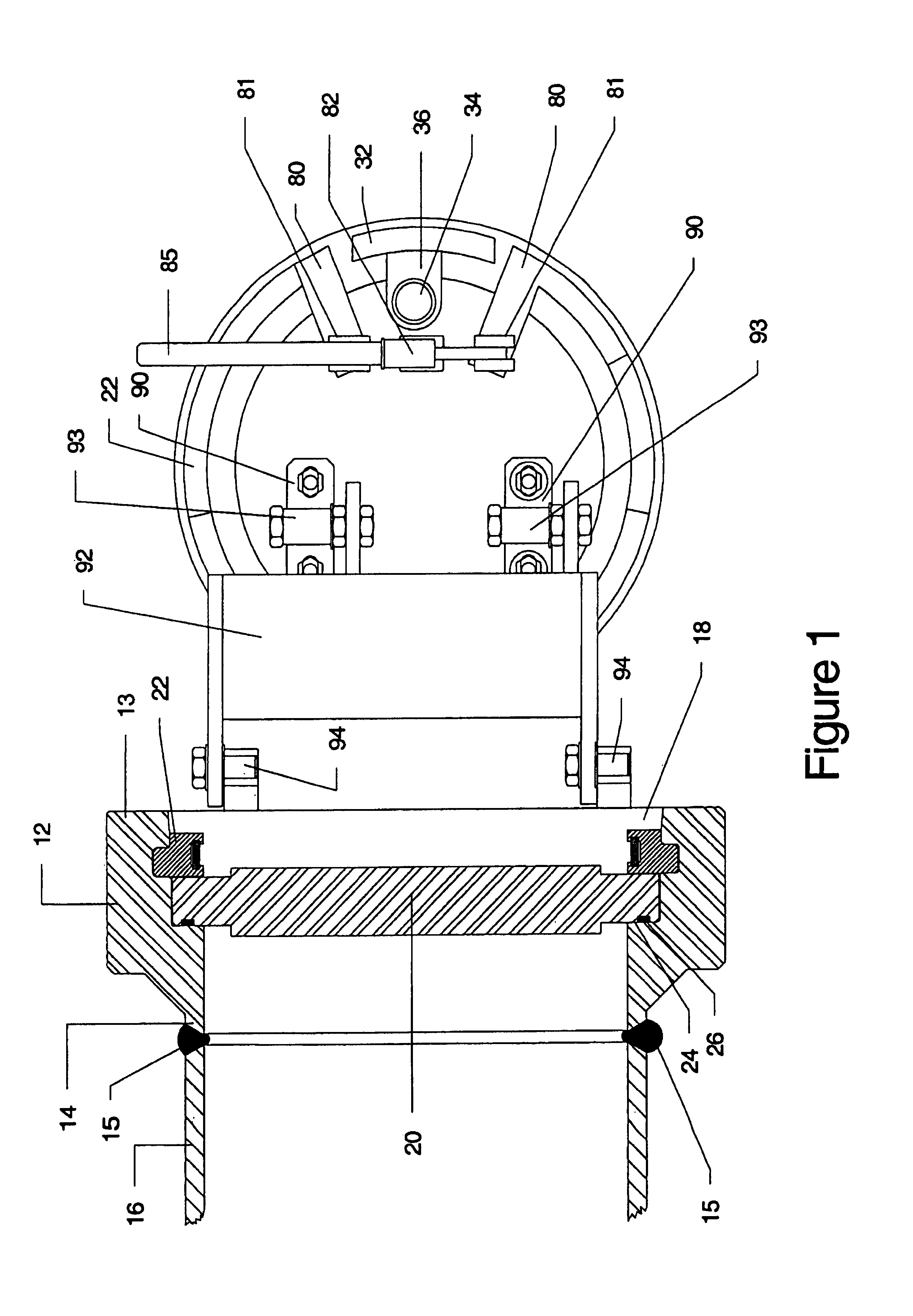
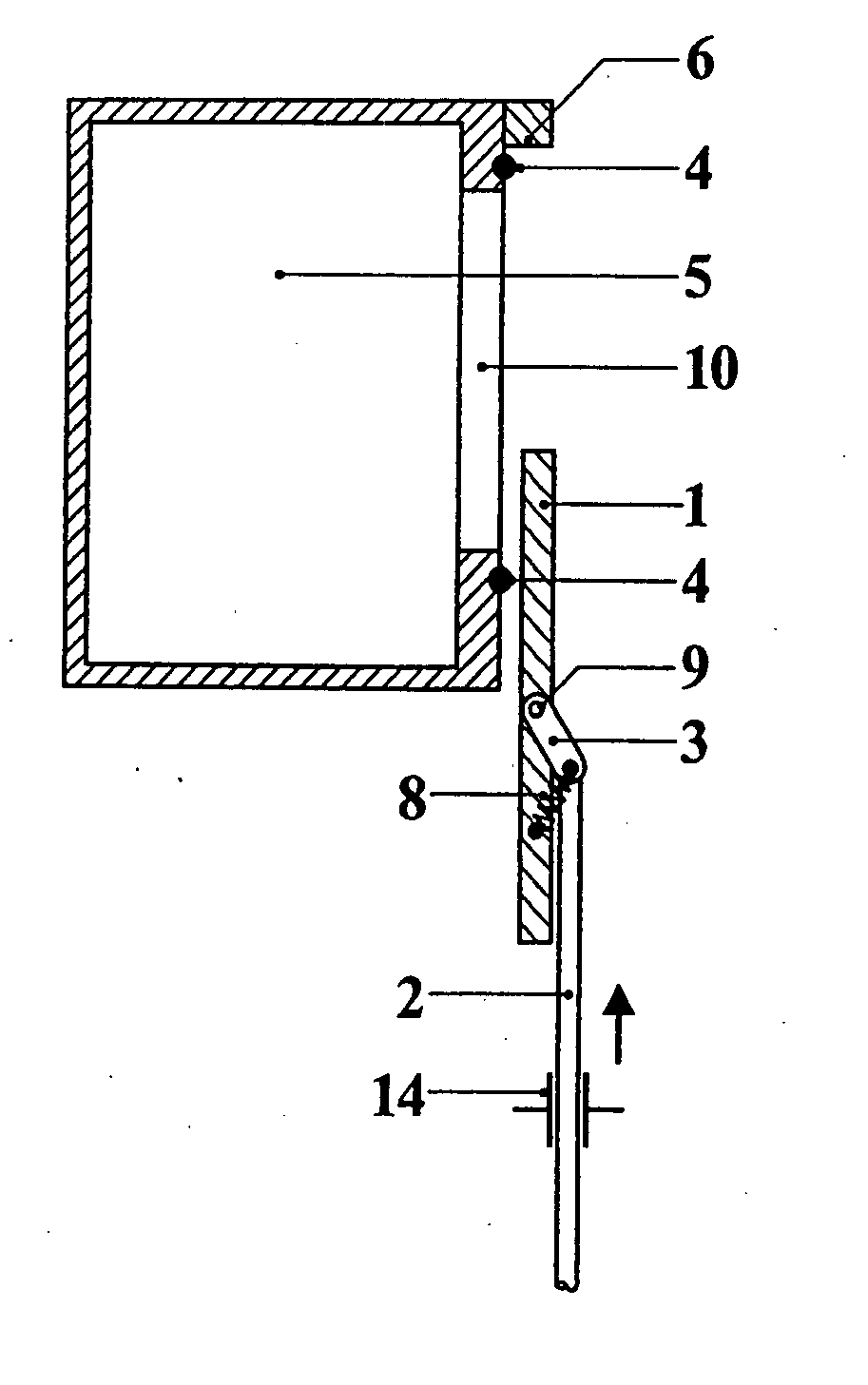
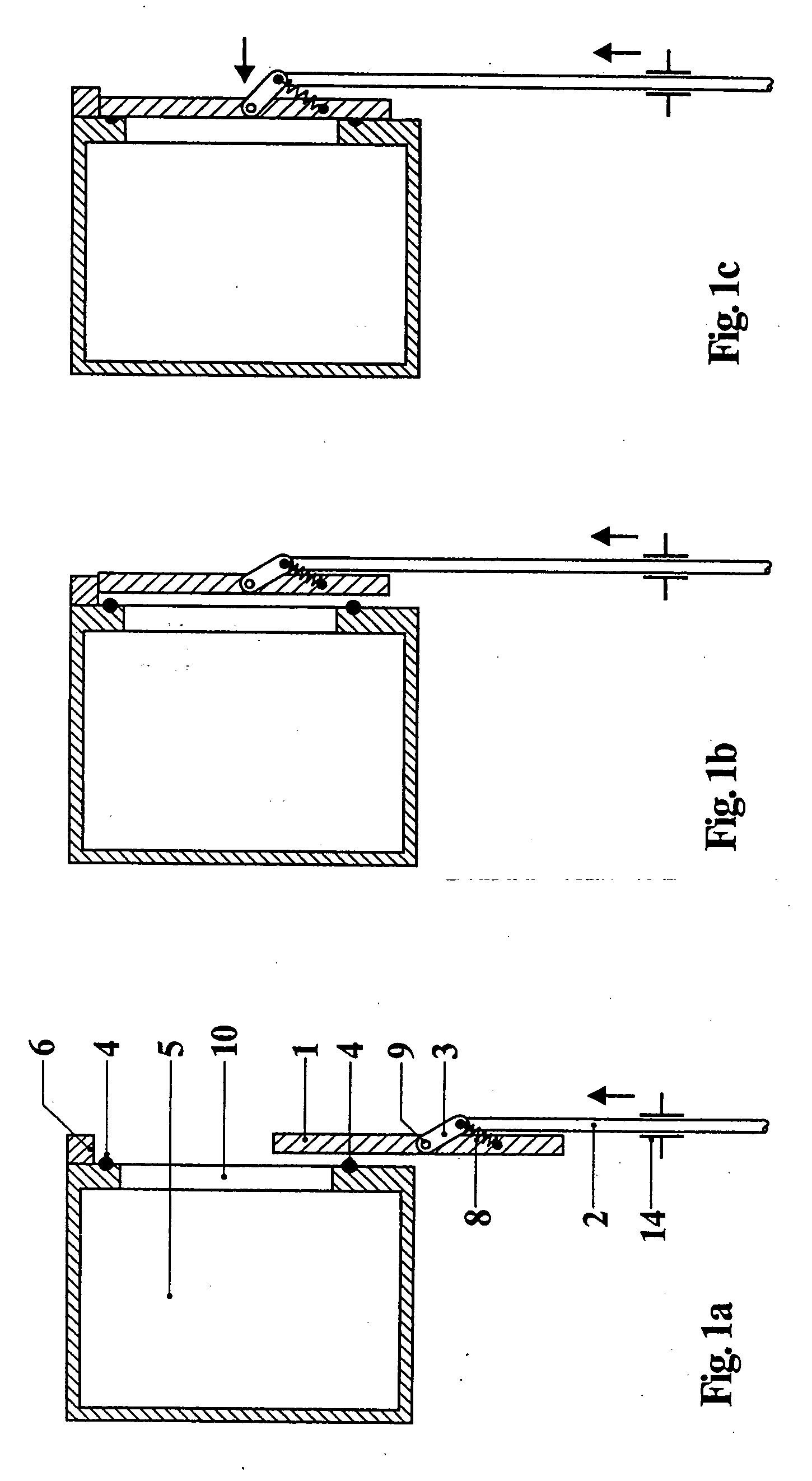
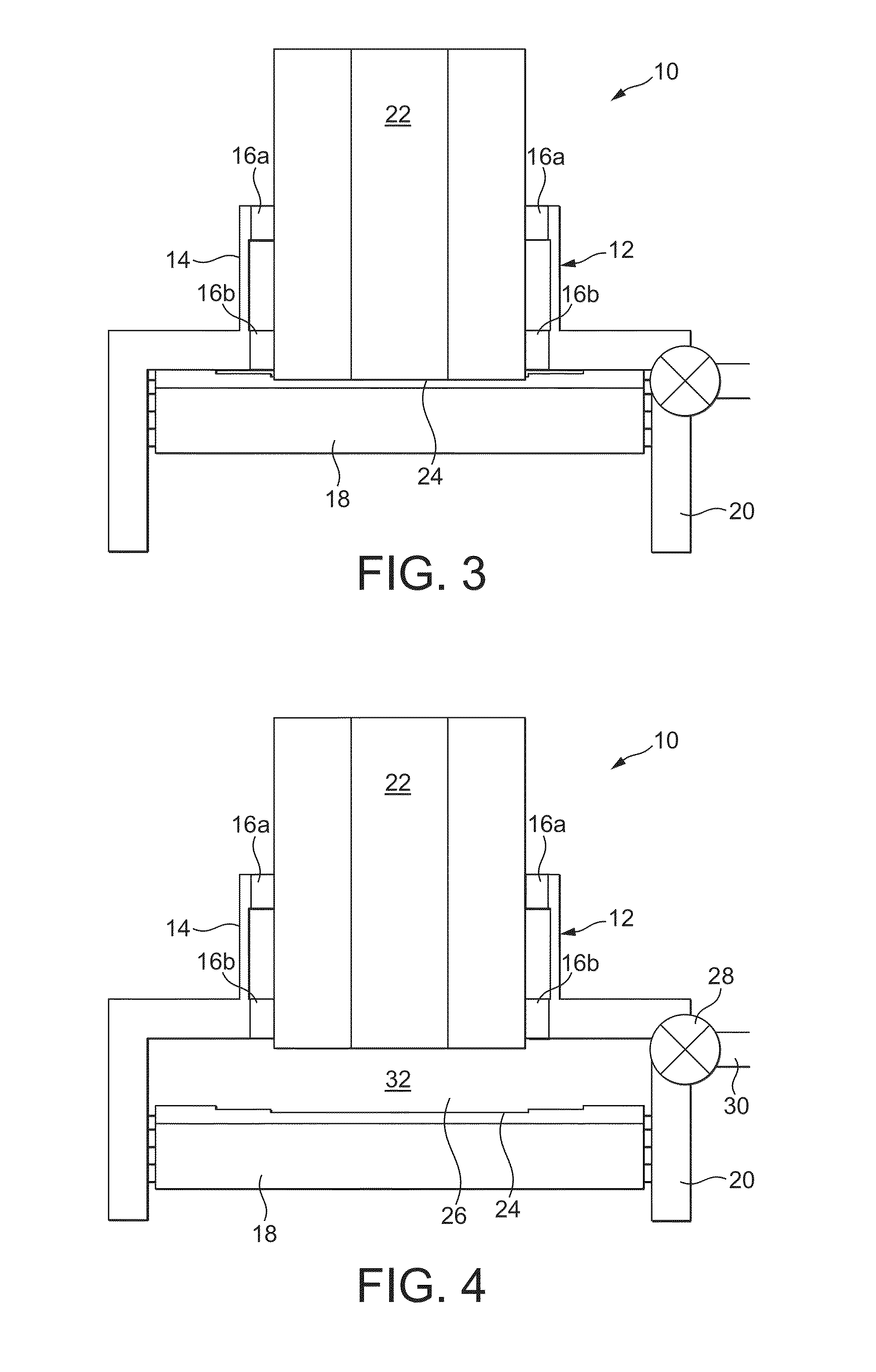
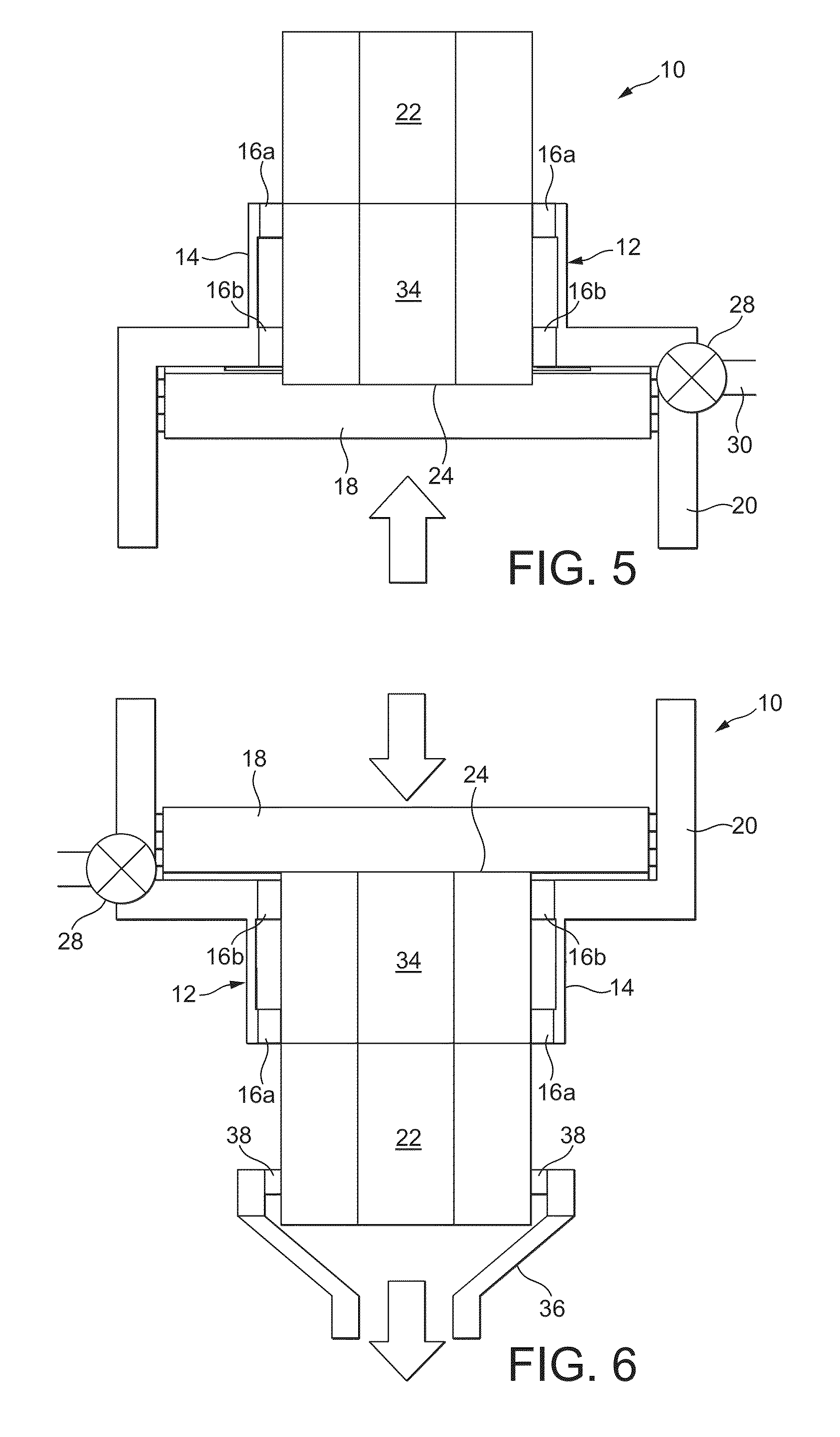
Closure for a pressure vessel and method
InactiveUS7036674B2Easy to closeEasy to openContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsVacuum pressureEngineering
A closure assembly 10 contains positive and / or vacuum pressure within a pressure vessel 16 having a neck 12. A circumferential locking member 22 supported on a door 20 locks the door to the neck, and is radially moveable between an open position and a closed position. A seal 26 between the neck and the door maintains fluid-tight integrity. A lever or other hand powered operator may be used for moving the locking member between the open position and the closed position. The locking member may include locking segments interconnected to form the circumferential locking member.
Owner:ROBBINS & MYERS ENERGY SYST
Coating a monolith substrate with catalyst component
ActiveUS20110268624A1Careful and accurate loadingAvoid lostExhaust apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingHoneycombChemistry
A method of coating a honeycomb monolith substrate comprising a plurality of channels with a liquid comprising a catalyst component comprises the steps of: (i) holding a honeycomb monolith substrate substantially vertically; (ii) introducing a pre-determined volume of the liquid into the substrate via open ends of the channels at a lower end of the substrate; (iii) sealingly retaining the introduced liquid within the substrate; (iv) inverting the substrate containing the retained liquid; and (v) applying a vacuum to open ends of the channels of the substrate at the inverted, lower end of the substrate to draw the liquid along the channels of the substrate.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
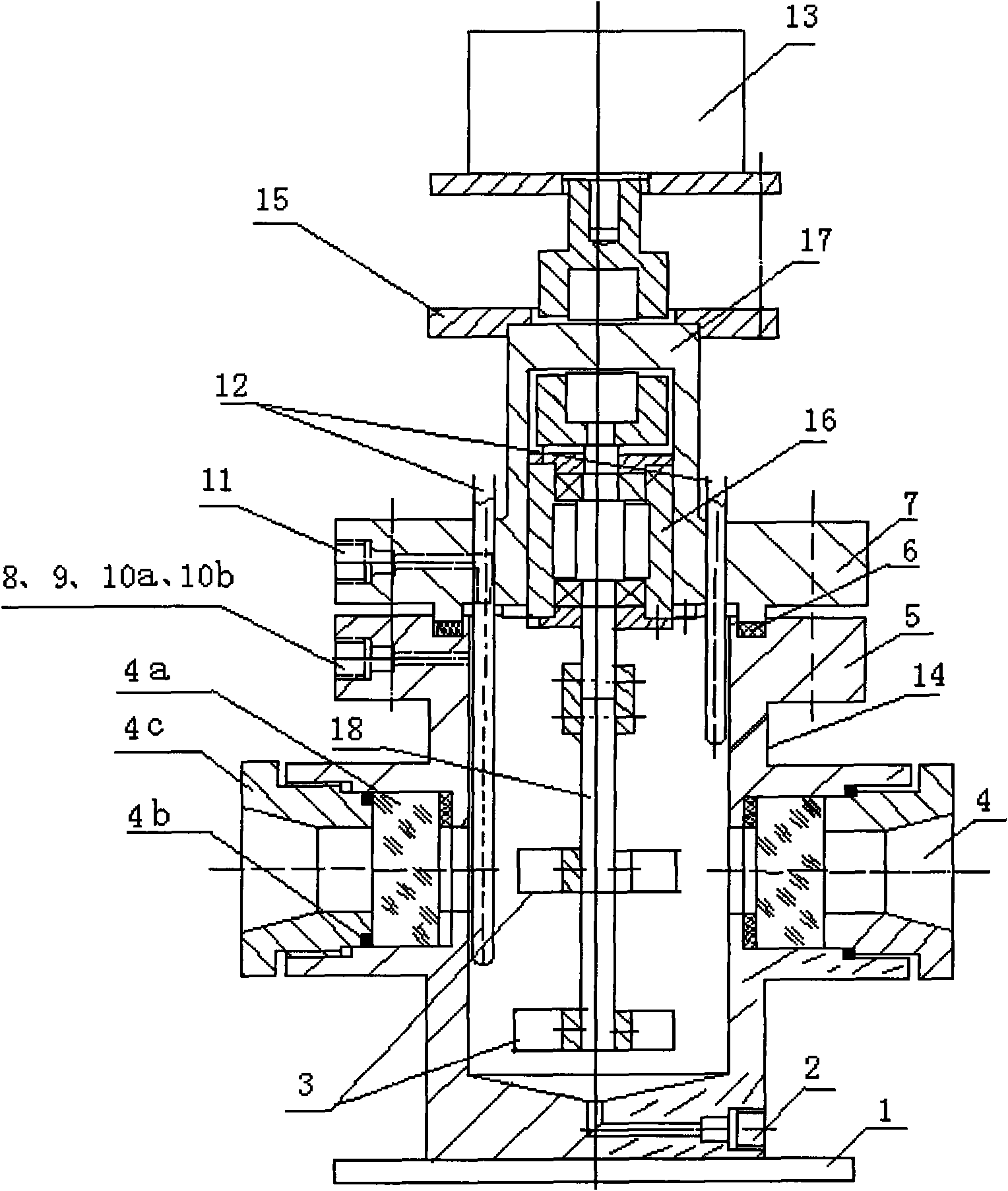
Low temperature high pressure gas hydrate replacement reaction kettle and system
InactiveCN101612539ASolve the problem of poor performance of high-pressure rotary sealsGuaranteed uptimeChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPressure/vacuum vesselsWater bathsGas phase
The invention relates to a low temperature high pressure gas hydrate replacement reaction kettle and a system used for replacement reaction of gas hydrate. The whole reaction kettle is soaked in a constant low temperature water bath to keep the low temperature, and a vacuum system performs vacuum pump in the low temperature high pressure reaction kettle through a gas inlet, a gas phase component detection system performs gas collection and analysis through a gas collection opening, a pressure control system is connected with the gas inlet of the low temperature high pressure reaction kettle to ensure the pressure required by the low temperature high pressure reaction kettle, a data acquisition system is connected with a temperature detection opening and a pressure detection opening of the low temperature high pressure reaction kettle to acquire system data. In the invention, static sealing replaces dynamic sealing, thus solving the problem of poor performance of high pressure rotary sealing, and having the advantages of reliable running and no noise. The phenomenon occurring in the reaction kettle can also be observed by a visible window in real time, and the gas component alteration in the gas hydrate solid phase can be measured by a Raman spectrometer in real time.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Closure for a pressure vessel and method
InactiveUS7051897B2Easy to closeEasy to openValve arrangementsContainer filling methodsVacuum pressurePressure vessel
A closure assembly 10 contains positive and / or vacuum pressure within a pressure vessel 16 having a neck 12. A circumferential locking member 22 supported on a door 20 locks the door to the neck, and is radially moveable between an open position and a closed position. A seal 26 between the neck and the door maintains fluid-tight integrity. A lever or other hand powered operator may be used for moving the locking member between the open position and the closed position. The locking member may include locking segments interconnected to form the circumferential locking member.
Owner:ROBBINS & MYERS ENERGY SYST +1
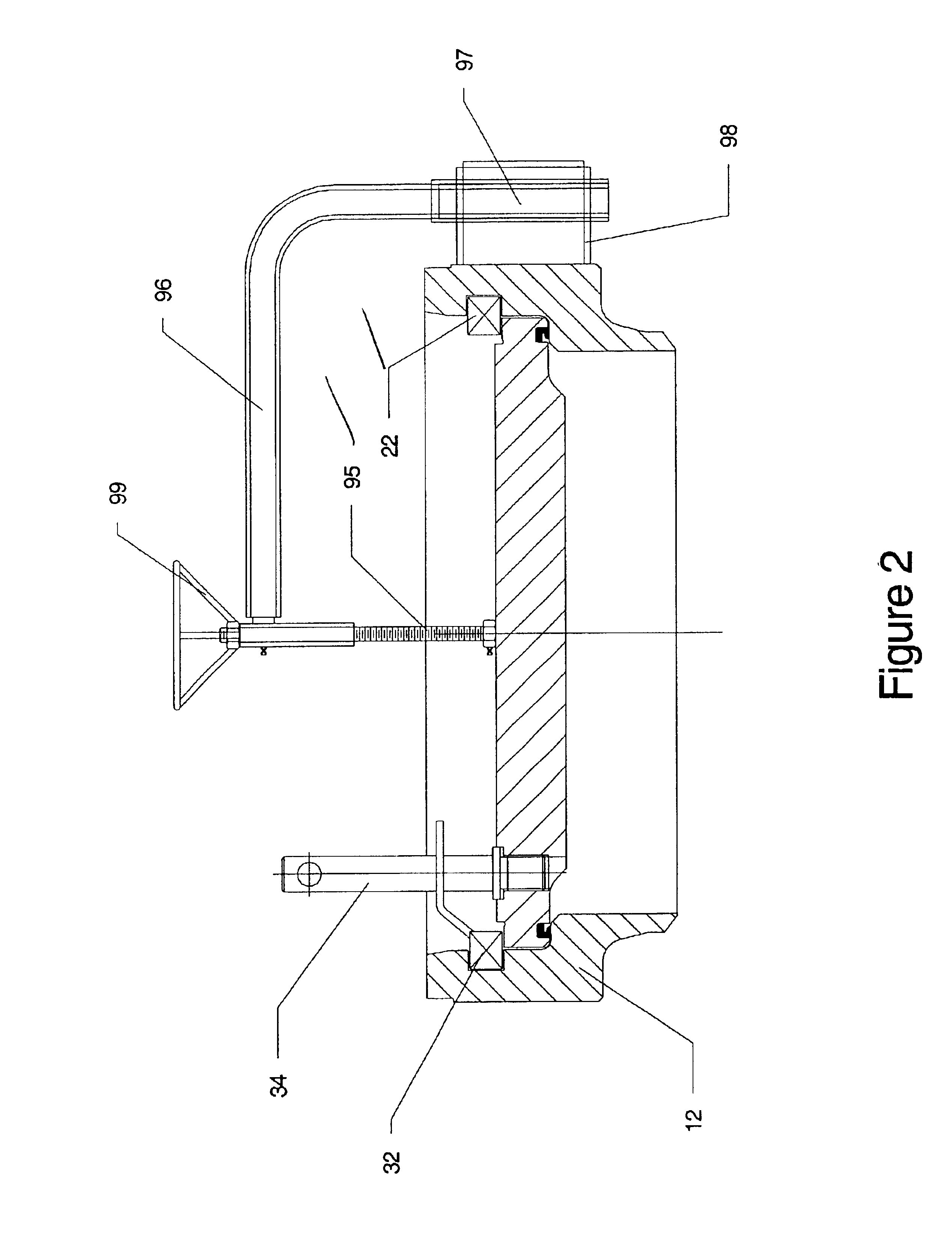
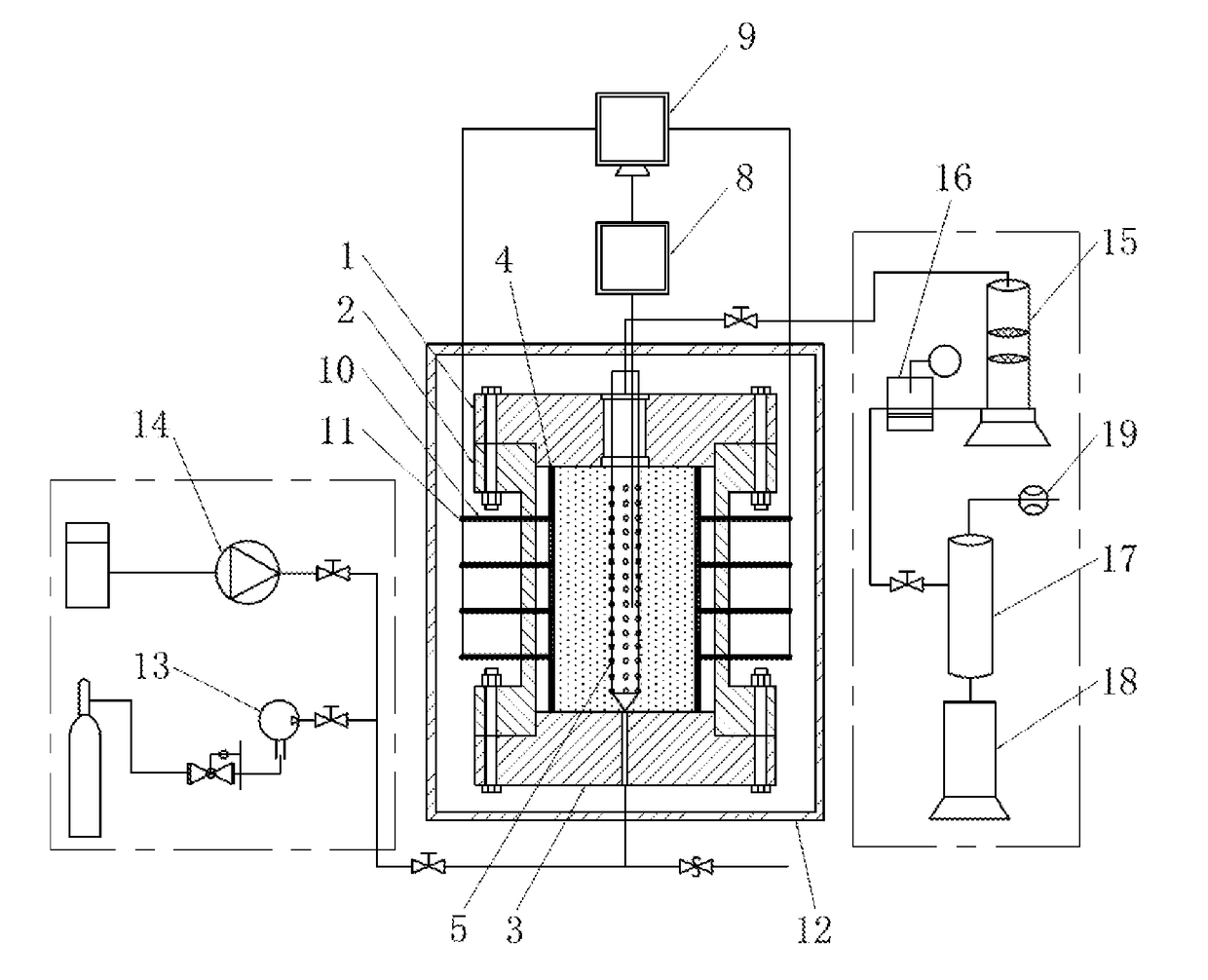
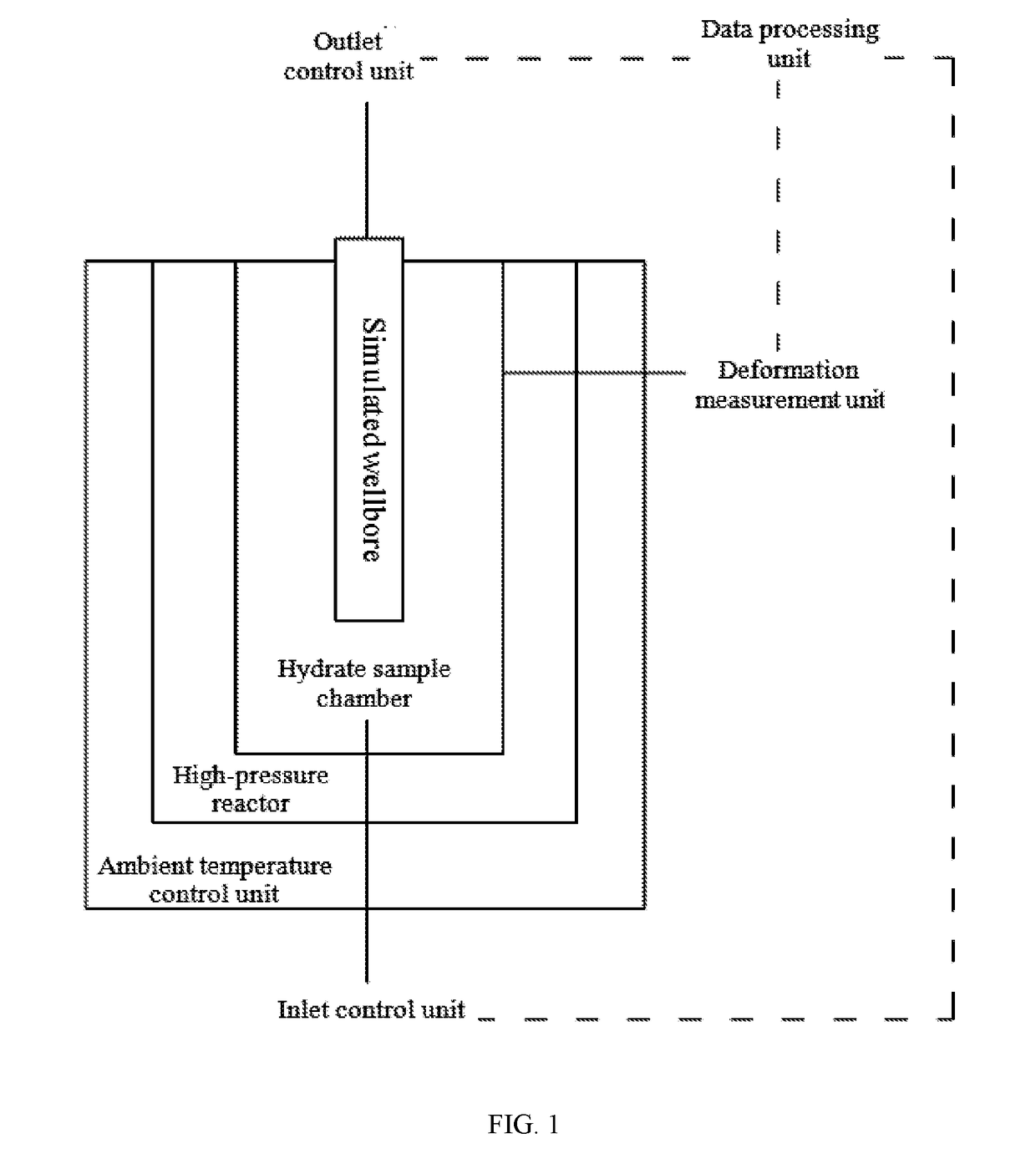
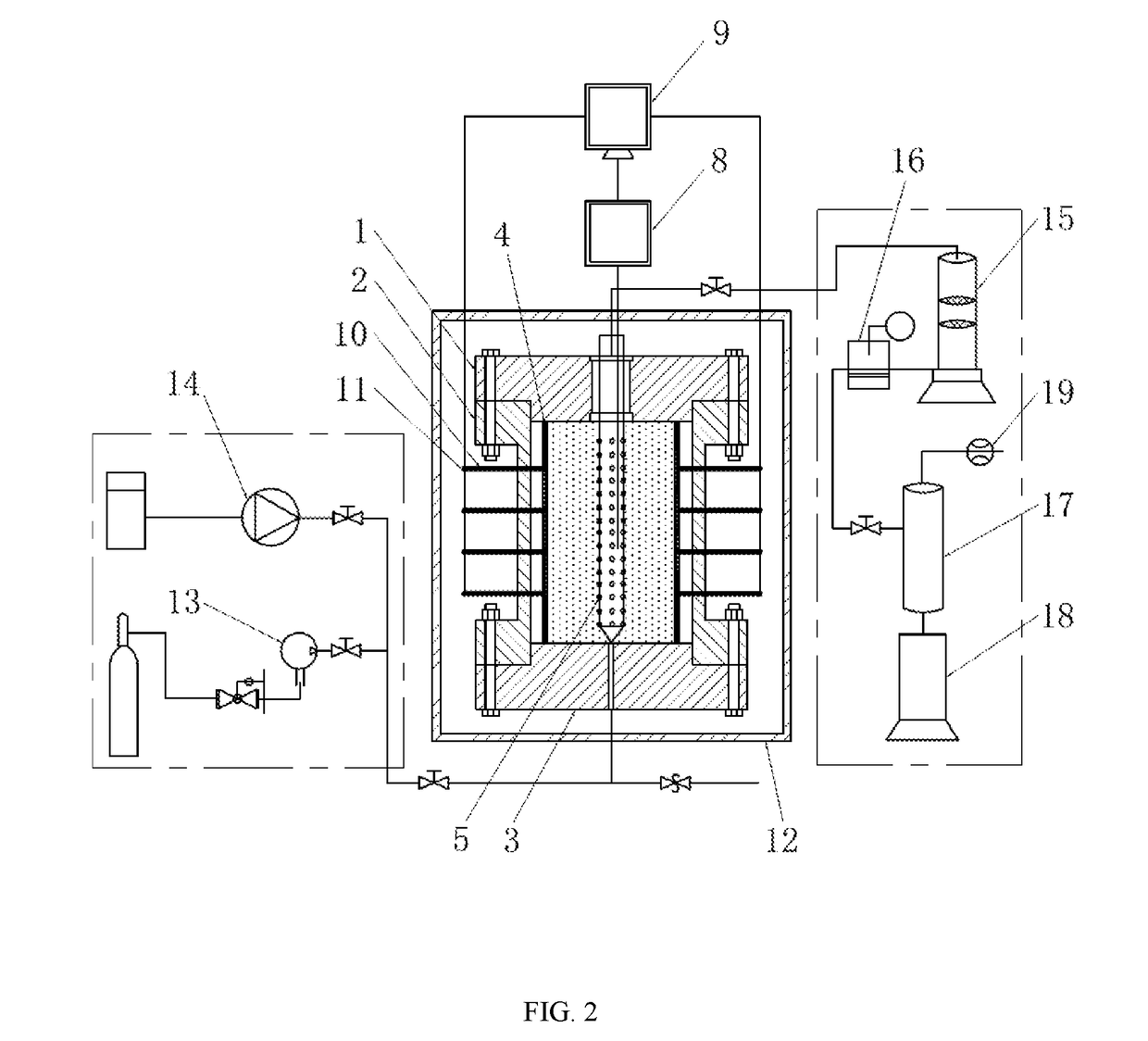
Experimental device and method for studying relationship between sediment yield behavior and radial deformation of porous media during exploitation of natural gas hydrates
ActiveUS20180172574A1Accurate measurementGood effectEarth material testingPressure/vacuum vesselsDecompositionPorous medium
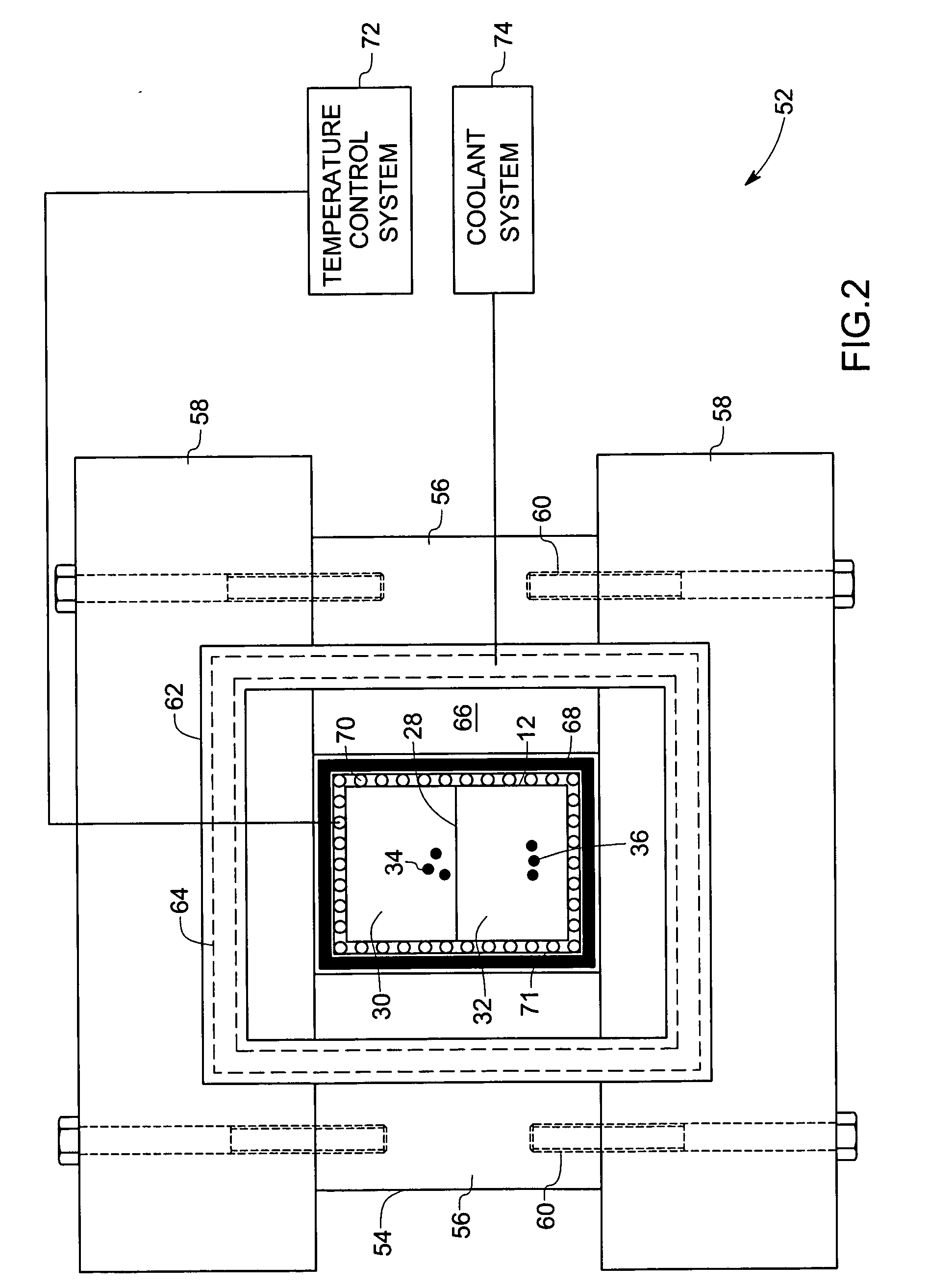
Disclosed is an experimental device for studying the sediment yield behavior and the radial deformation of porous media during the exploitation of natural gas hydrates, comprising a high-pressure reactor, a hydrate sample chamber, a simulated wellbore, a deformation measurement unit, an ambient temperature control unit, an outlet control unit, an inlet control unit and a data processing unit. Further disclosed is a method using the above-mentioned experimental device to carry out experiments. The experimental device and method according to the present invention can conveniently measure the deformation of the porous media during the decomposition of the hydrates and simulate the sediment producing situation in the wellbore, can simulate the sediment yield problem during the exploitation of natural gas hydrates as well as the gas-liquid-solid flowing problem in the wellbore during the exploitation of natural gas hydrates, and can accurately obtain the gas-solid-liquid three-phase yields in real time during the decomposition of natural gas hydrates. Being simple to operate and easy to control, and suitable for various sizes and shapes of reactors, it can provide basic experimental data and a theoretical basis for the technologies of hydrate exploitation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
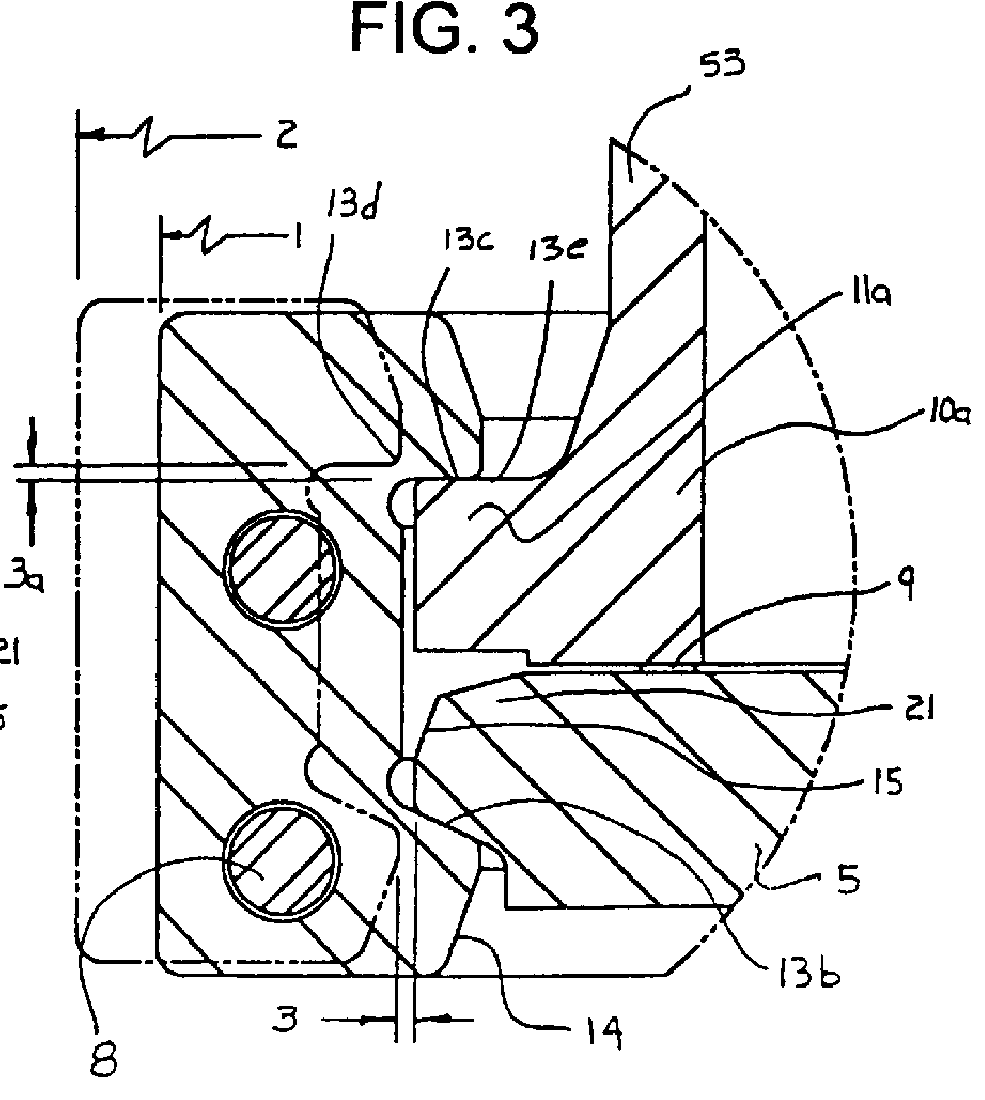
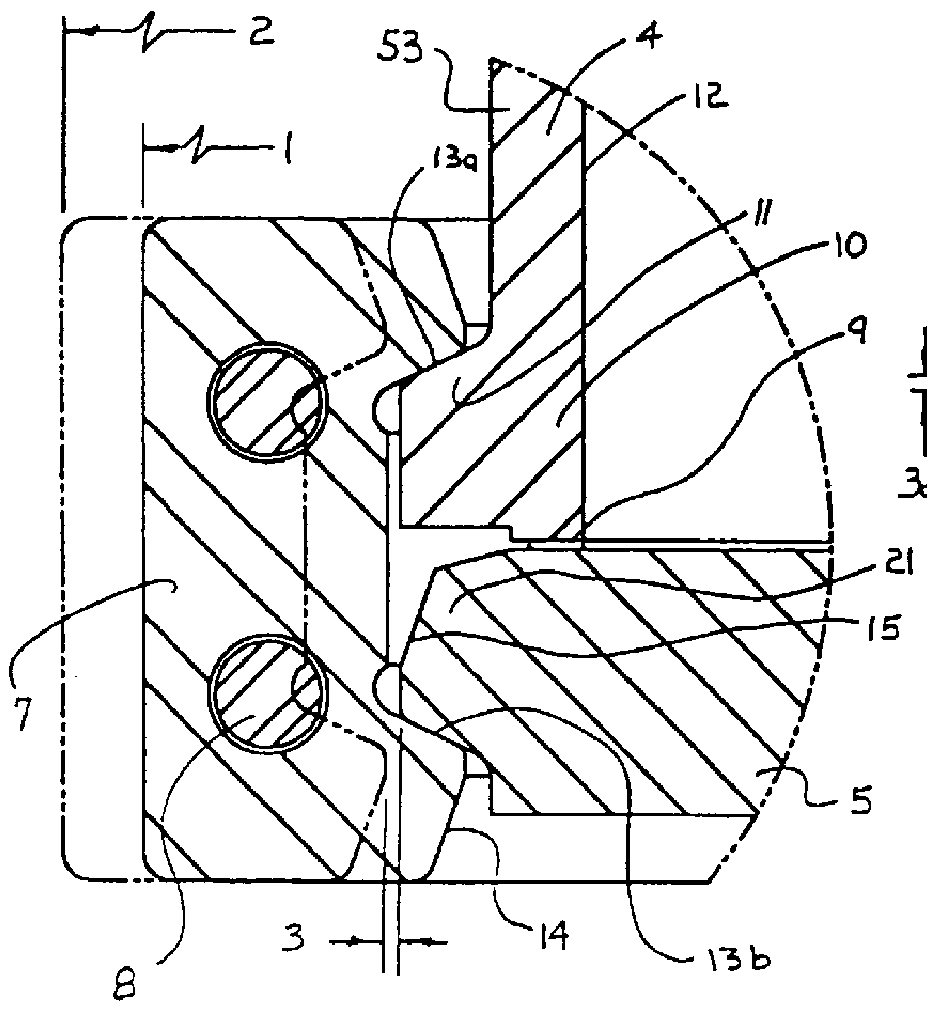
Shaft sealing apparatus
InactiveUS7055825B2Improve featuresSmall sizeEngine sealsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDrive shaftSurface roughness
Herein disclosed is a shaft sealing apparatus which comprises a vacuum casing formed with a vacuum chamber, a driving shaft having an outer cylindrical surface and movably extending in the vacuum chamber of the vacuum casing, and a sealing ring in the form of an annular ring shape and including a sealing lip held in contact with the outer cylindrical surface of the driving shaft, an annular spring member operative to impart a force to the sealing lip to ensure that the sealing lip is held in tight contact with the outer cylindrical surface of the driving shaft, and a peripheral portion radially outwardly extending from the sealing lip, in which the outer cylindrical surface of the driving shaft is smaller in surface roughness Ra than 0.1 (μm).
Owner:TEIJIN SEIKI CO LTD
Shaft sealing assembly for vacuum processing apparatus
InactiveUS7090222B2Improve featuresSmall sizeEngine sealsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDrive shaftSurface roughness
Herein disclosed is a shaft sealing apparatus which comprises a vacuum casing formed with a vacuum chamber, a driving shaft having an outer cylindrical surface and movably extending in the vacuum chamber of the vacuum casing, and a sealing ring in the form of an annular ring shape and including a sealing lip held in contact with the outer cylindrical surface of the driving shaft, an annular spring member operative to impart a force to the sealing lip to ensure that the sealing lip is held in tight contact with the outer cylindrical surface of the driving shaft, and a peripheral portion radially outwardly extending from the sealing lip, in which the outer cylindrical surface of the driving shaft is smaller in surface roughness Ra than 0.1 (μm).
Owner:TEIJIN SEIKI CO LTD
Closure for a pressure vessel and method
InactiveUS20050161957A1Easy to closeEasy to openValve arrangementsContainer filling methodsVacuum pressureEngineering
A closure assembly 10 contains positive and / or vacuum pressure within a pressure vessel 16 having a neck 12. A circumferential locking member 22 supported on a door 20 locks the door to the neck, and is radially moveable between an open position and a closed position. A seal 26 between the neck and the door maintains fluid-tight integrity. A lever or other hand powered operator may be used for moving the locking member between the open position and the closed position. The locking member may include locking segments interconnected to form the circumferential locking member.
Owner:R & M ENERGY SYST
Methods for introduction of a reactive material into a vacuum chamber
InactiveUS20100111750A1Contamination of materialApparatus using atomic clocksSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReactive materialVacuum chamber
Methods for the introduction of a reactive material into a vacuum chamber while minimizing or eliminating the simultaneous introduction of contaminating materials or substances. As a result, contaminating materials and substances that can interfere with any measurements or other processes that occur in the vacuum chamber are minimized or eliminated.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Pressure vessel door seal mechanism
Owner:BURCELL TECH INC
Method for high pressure treatment of substances under controlled temperature conditions
ActiveUS7220381B2Prevent heat lossReduce heatFood preservationLavatory sanitoryEngineeringHigh pressure
A product carrier for use in pressure processing substances is substantially fluidically closed, and is insulated, to prevent heat transfer from the product being treated to the cooler wall of the pressure vessel. The insulating material has compression heating properties, such that as the product is pressurized, the temperature of the insulation increases as does the temperature of the product and pressure media, thereby helping to prevent heat transfer from the product to the surrounding media and pressure vessel wall.
Owner:AVURE TECH
Vacuum lock
InactiveUS20060033061A1High degreeImprove securityAir-pressure/air-lock chambersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSlide plateVacuum chamber
A vacuum lock on a vacuum chamber has a lockable gate opening with a substantially vertical gate and the following characteristics: the gate is a sliding plate displaceable parallel to the opening; the gate is connected via a driving rod on a side oppose the opening and is supported at a distance in the sliding direction; this connection is via a guidance mechanism such that in the presence of a blockage of the closing process, the gate is laterally pressed on a seal encompassing the opening; and a spring element is provided to narrowly compensates the weight of the gate. This ensures that in the event of a operator error or unintentional reaching into the opening during a closing process, injuries cannot occur and a high degree of safety is ensured.
Owner:OC OERLIKON BALZERS AG
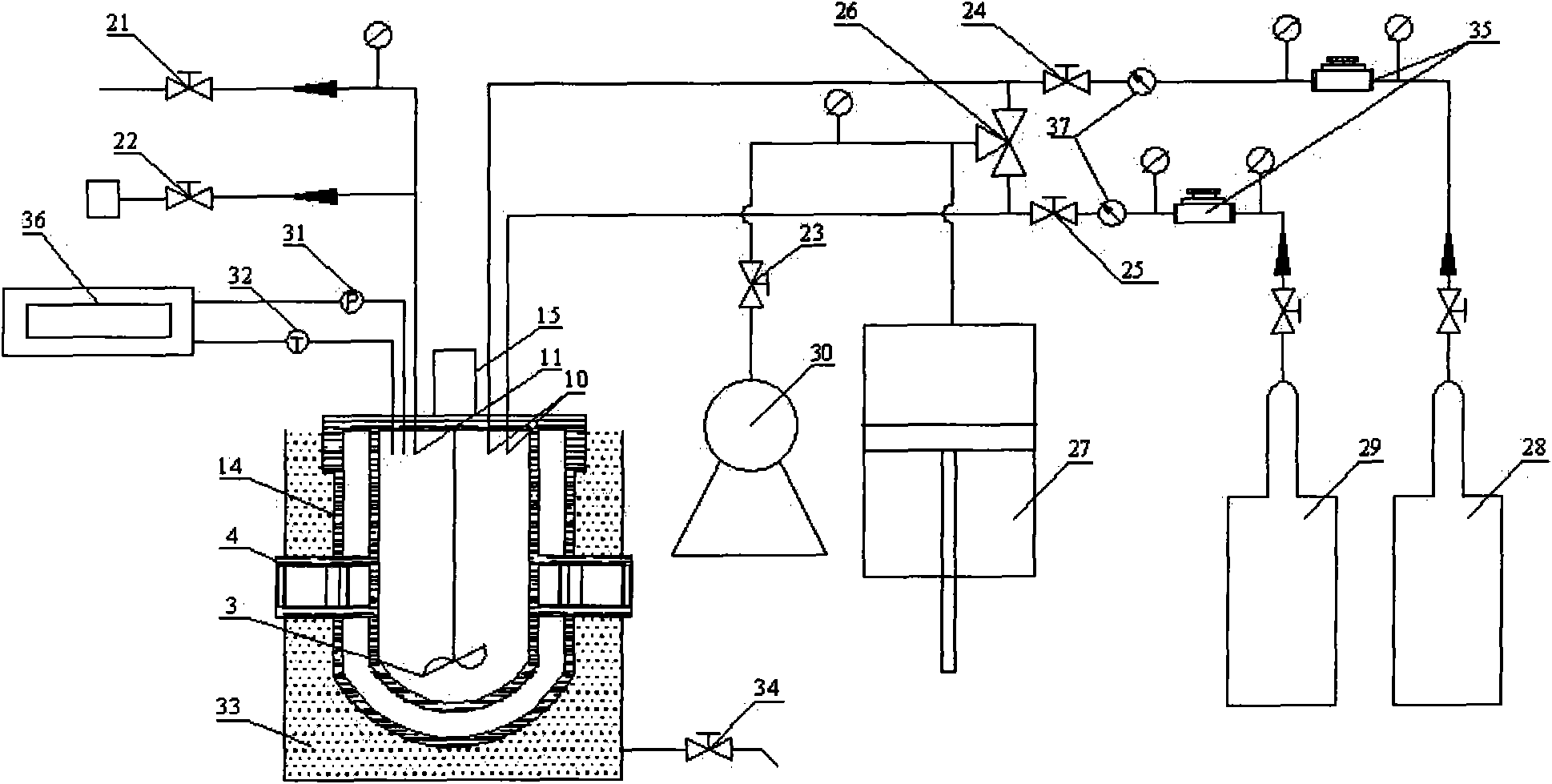
Visual reaction kettle and visualized experimental system and method for replacing natural gas hydrate
InactiveCN106000229AEasy to control temperatureSimple structureGaseous fuelsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsGas cylinderData acquisition
The invention relates to a visual reaction kettle and a visualized experimental system and method for replacing natural gas hydrate. The reaction kettle used by the system comprises a barrel, a front flange, a rear flange and glass; the front flange, the rear flange and the barrel are each of a hollow structure, the glass is embedded on the hollow structure of the front flange and the hollow structure of the rear flange respectively, and the front flange, the rear flange and the glass are used for sealing the barrel; the barrel is provided with multiple connectors; the system comprises a sampling tank, a vacuum pump, a first natural gas bottle, a carbon dioxide gas bottle, a second natural gas bottle, an environmental climate case, a beaker, a sensor, an image acquisition device and a data acquiring and processing device. By means of the experimental system, the process of replacing the natural gas hydrate with carbon dioxide at different phase states can be carried out, macroscopic thermodynamic and dynamic data in the replacing process is obtained, and meanwhile the dynamic characteristics, the heat-fluid-solid coupling phenomenon and the hydrate form change in the replacing process are recorded; the visual reaction kettle and the visualized experimental system and method for replacing the natural gas hydrate can be used for observing the natural gas hydrate generation phenomenon.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
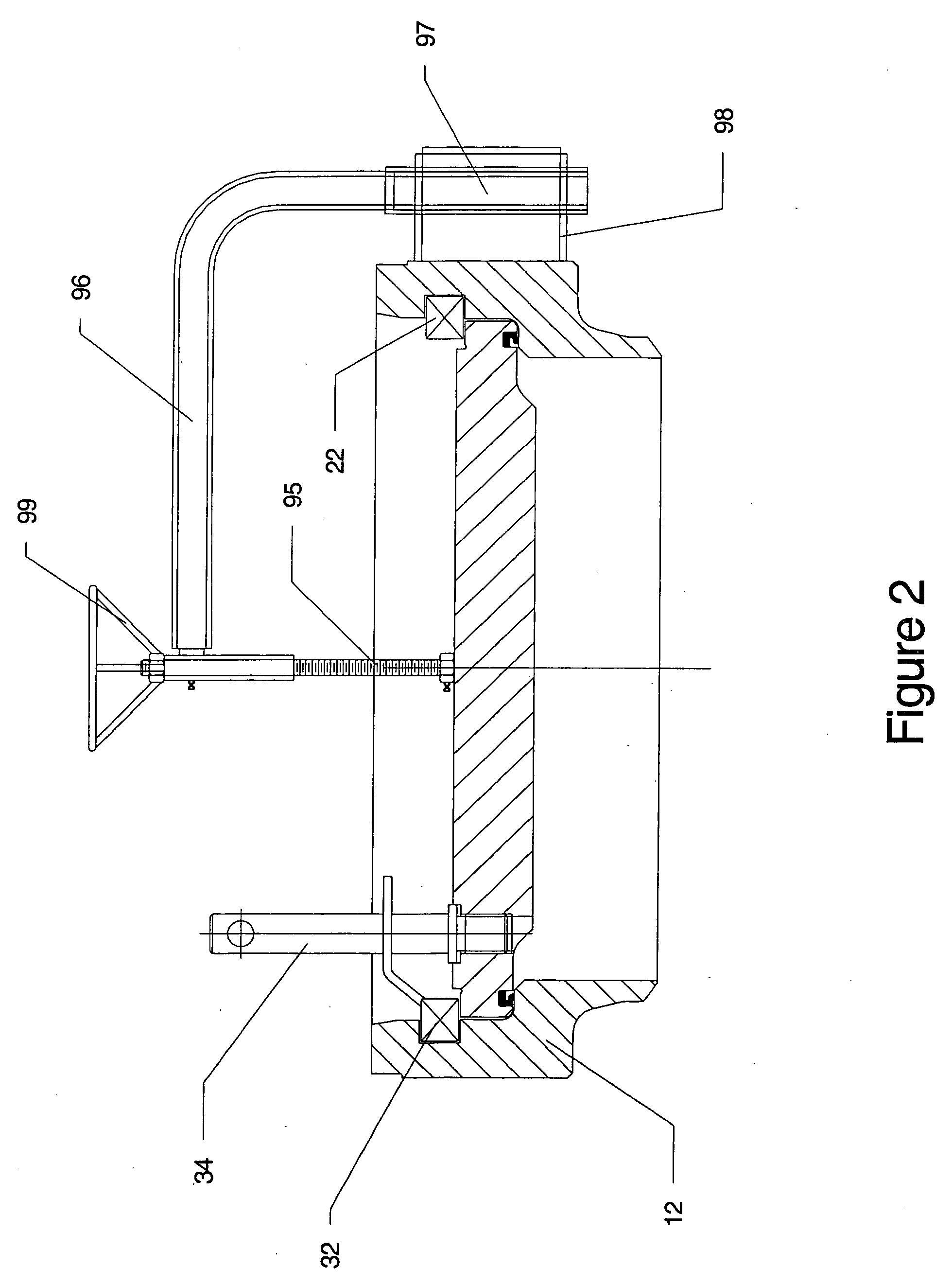
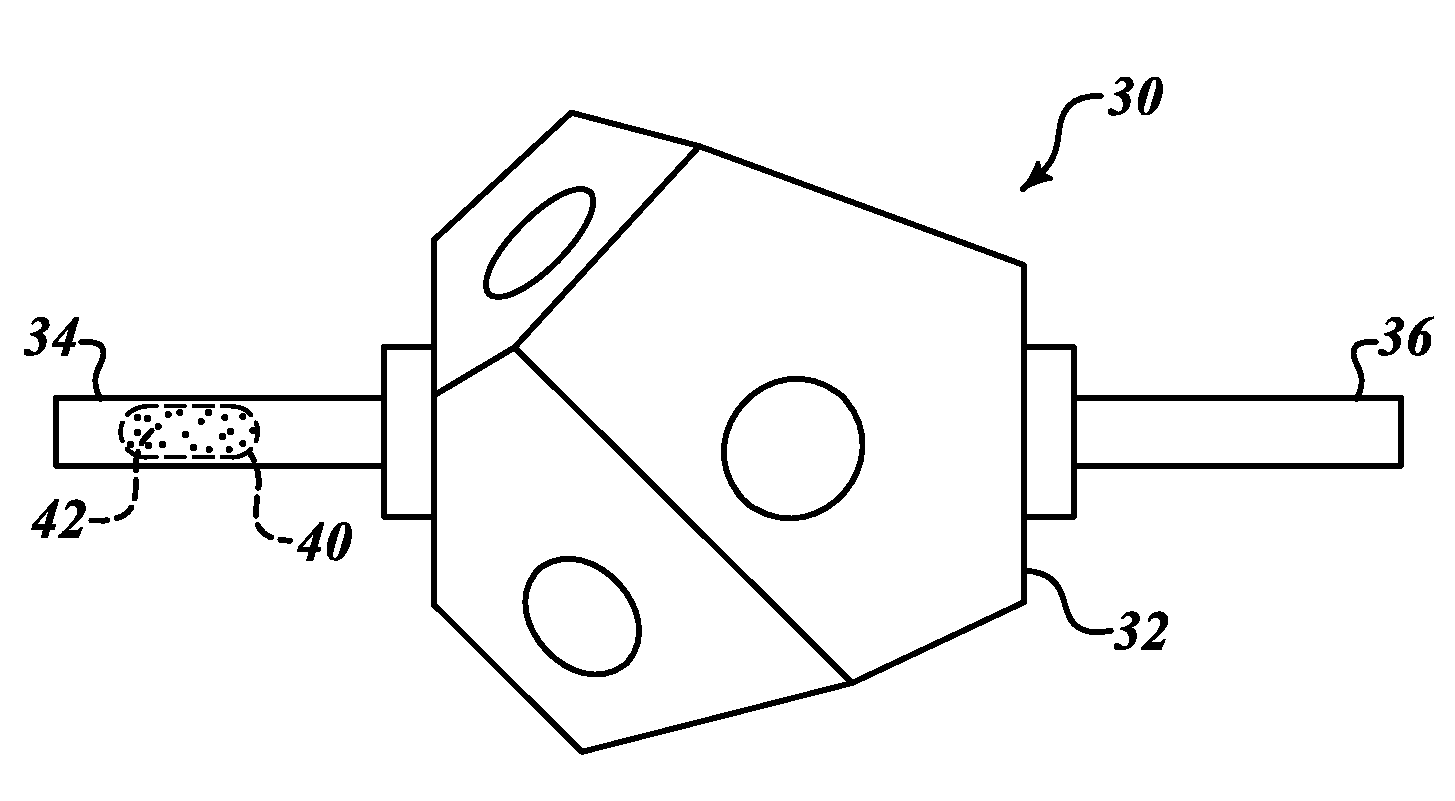
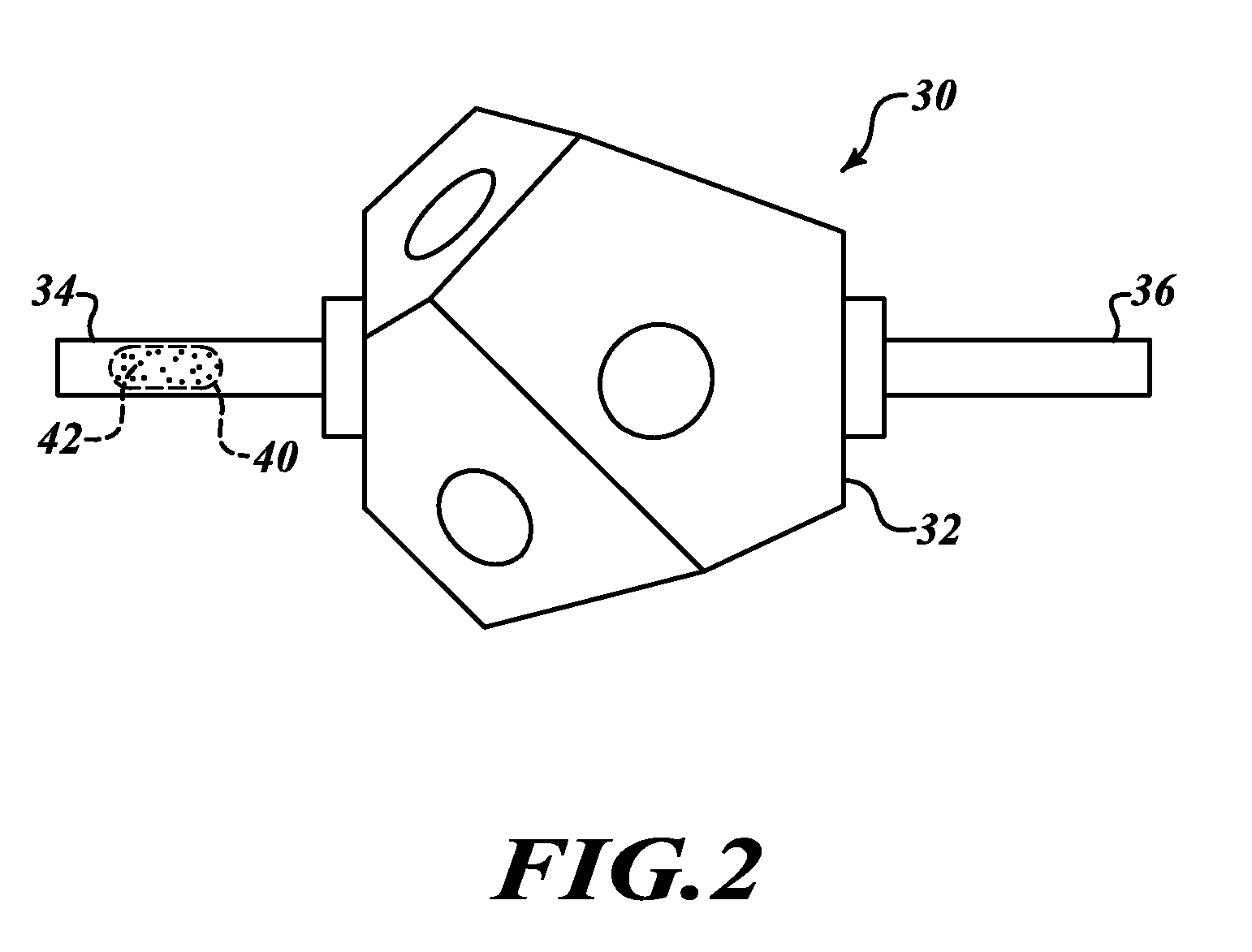
Compositions, methods and apparatuses for preserving platelets
InactiveUS7202020B2Dead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsBlood plasmaPlasma concentration
Owner:HUMAN BIOSYST
Coating a monolith substrate with catalyst component
ActiveUS8703236B2Low viscosityShorten drying timeGaseous chemical processesMolecular sieve catalystsPtru catalystHoneycomb like
A method of coating a honeycomb monolith substrate comprising a plurality of channels with a liquid comprising a catalyst component comprises the steps of: (i) holding a honeycomb monolith substrate substantially vertically; (ii) introducing a pre-determined volume of the liquid into the substrate via open ends of the channels at a lower end of the substrate; (iii) sealingly retaining the introduced liquid within the substrate; (iv) inverting the substrate containing the retained liquid; and (v) applying a vacuum to open ends of the channels of the substrate at the inverted, lower end of the substrate to draw the liquid along the channels of the substrate.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
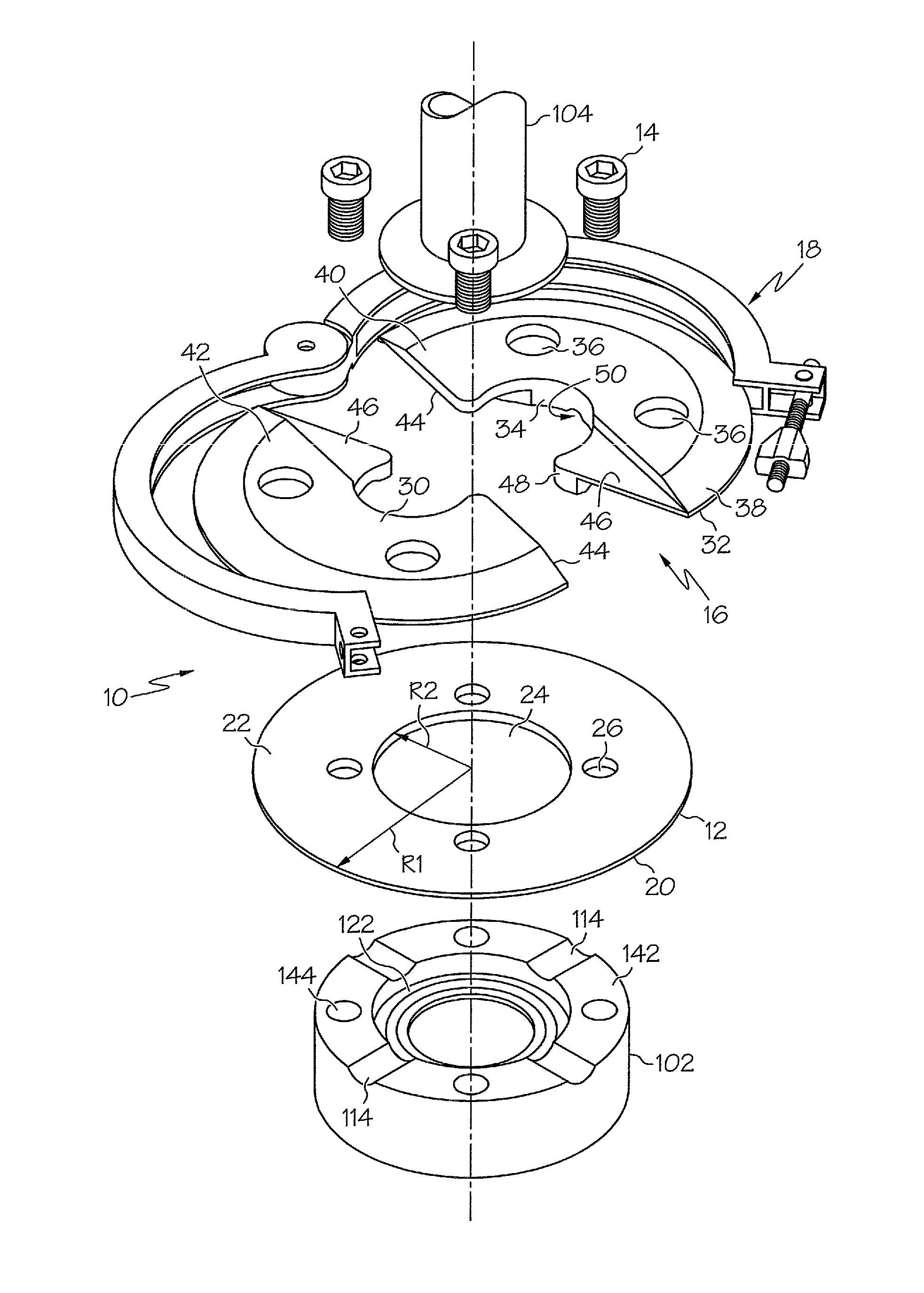
Clamp adapter assembly
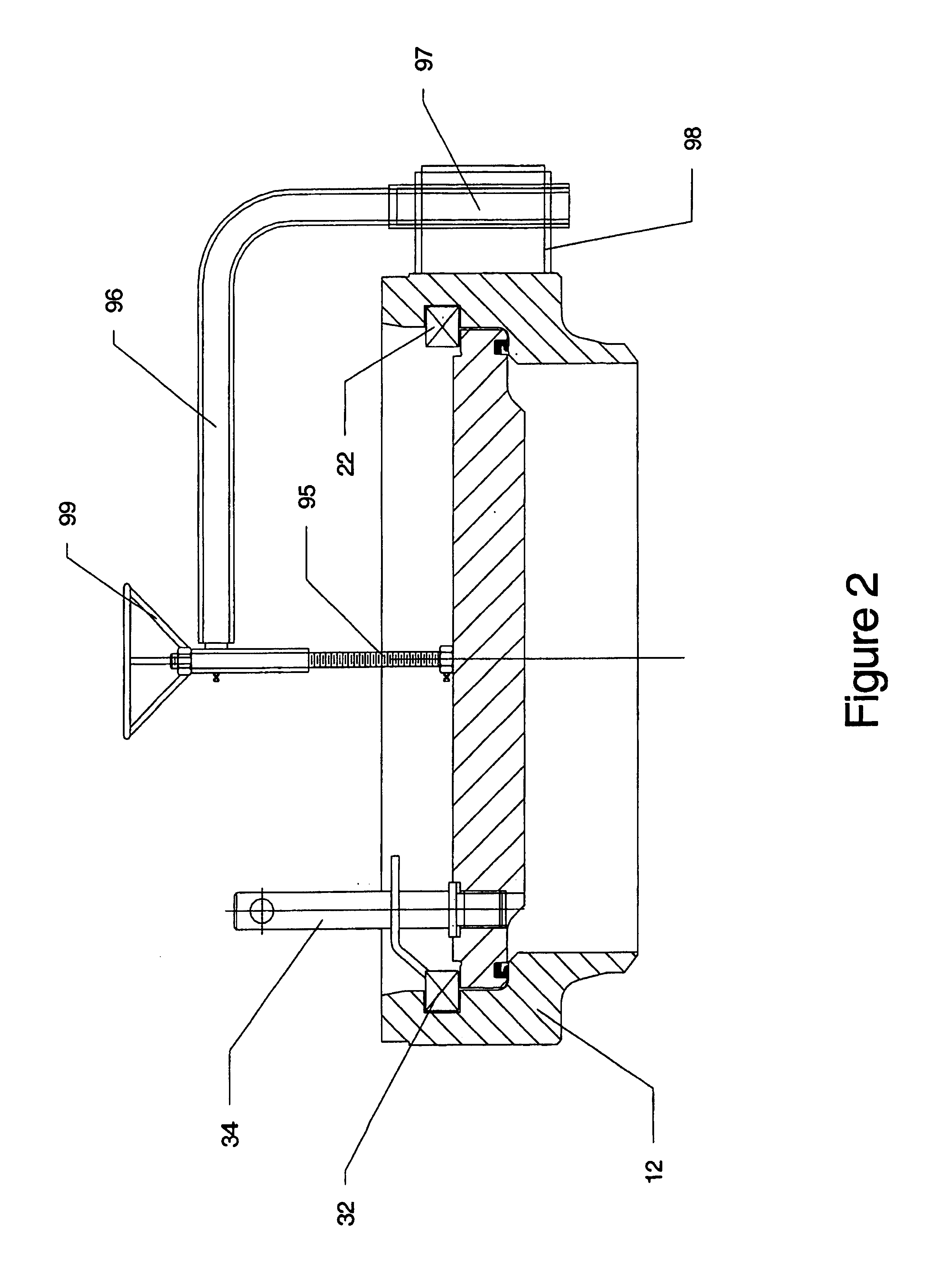
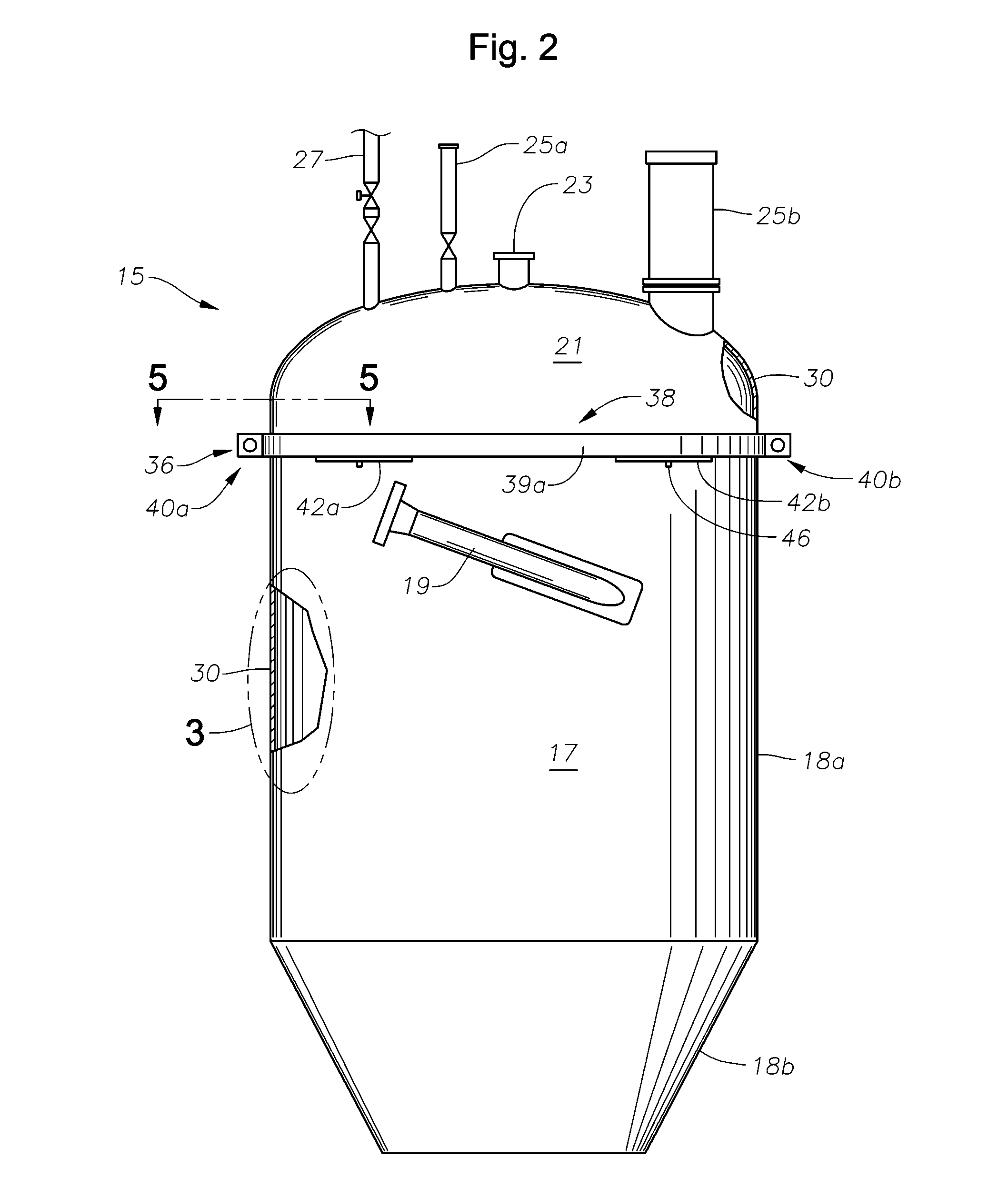
A clamp adapter assembly for connecting an instrument to a pressure vessel. The clamp adapter assembly allows an operator to convert a bolt connection base known in the art into a base suitable for utilizing a clamped connection similarly known in the art. The connection assembly includes a bottom plate, at least one fastener to fasten the bottom plate to a base, a top retaining plate, and a clamp. The peripheral portions of the bottom plate and top retaining plate may be beveled in order to be received within a tri-clamp. The top retaining plate may include two sections that overlappingly engage one another.
Owner:SRM
Automatic suction structure of a vacuum container
InactiveUS7721771B2Easy to operateSimple structureLiquid fillingClosuresEngineeringAutomatic testing
The present invention provides an improved automatic suction structure of a vacuum container. The structure includes a pumping unit, a power supply, a vacuum releaser and a vacuum detector. The structure allows for automatic air suction, automatic detection, safety power disconnection and continuous vacuuming as well as easy operation. The present invention guarantees improved quality and convenient operation.
Owner:CHOU MING SHI
Microwave autoclave
InactiveUS20070108194A1Synthetic resin layered productsOhmic-resistance heatingEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
An autoclave for pressure and temperature treatment of objects comprises a pressure container having a pressure resistant wall which encloses a pressure chamber for receiving the objects to be treated, said pressure chamber having a free inner diameter of at least 1.5 m; and a heat source for heating the objects received in said pressure chamber, said heat source including a plurality of microwave sources irradiating microwave radiation, which are arranged outside said pressure container. Said microwave sources are distributed over said pressure resistant wall at an areal density of at least 4 microwave sources per square meter surface area of said pressure resistant wall; and the microwave radiation irradiated by said microwave sources is coupled through said pressure resistant wall into said pressure chamber.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV +1
Sealing structure for processing reaction chamber by semiconductor
ActiveCN101515538AIncrease the lengthExtended pathElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound (substance)Engineering
The invention relates to a sealing structure for processing a reaction chamber by semiconductor, which comprises cover plates which are mutually connected and jointly form the reaction chamber, a side wall of the chamber and an electrostatic clamping disc, wherein the joint of the side wall of the chamber and the cover plates and / or electrostatic clamping disc is provided with a clamping piece provided with a sealing piece; and the joint of the side wall of the chamber and the cover plates and / or electrostatic clamping disc is at least provided with a curved surface connecting part, and the inclination angle between the curved surface connecting part and the joint is between 0 and 90 degrees. The length of a gap is lengthened by changing the shape of the gap between the sealing surfaces of the vacuum ends, thereby prolonging the route by which chemical gases and plasmas reach a sealing ring and reducing the amount of the chemical gases and plasmas reaching the sealing ring; and simultaneously, the passing difficulty of the chemical gases and plasmas are greatly increased due to the curved shape, thereby prolonging the service life of the sealing ring.
Owner:BEIJING NAURA MICROELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
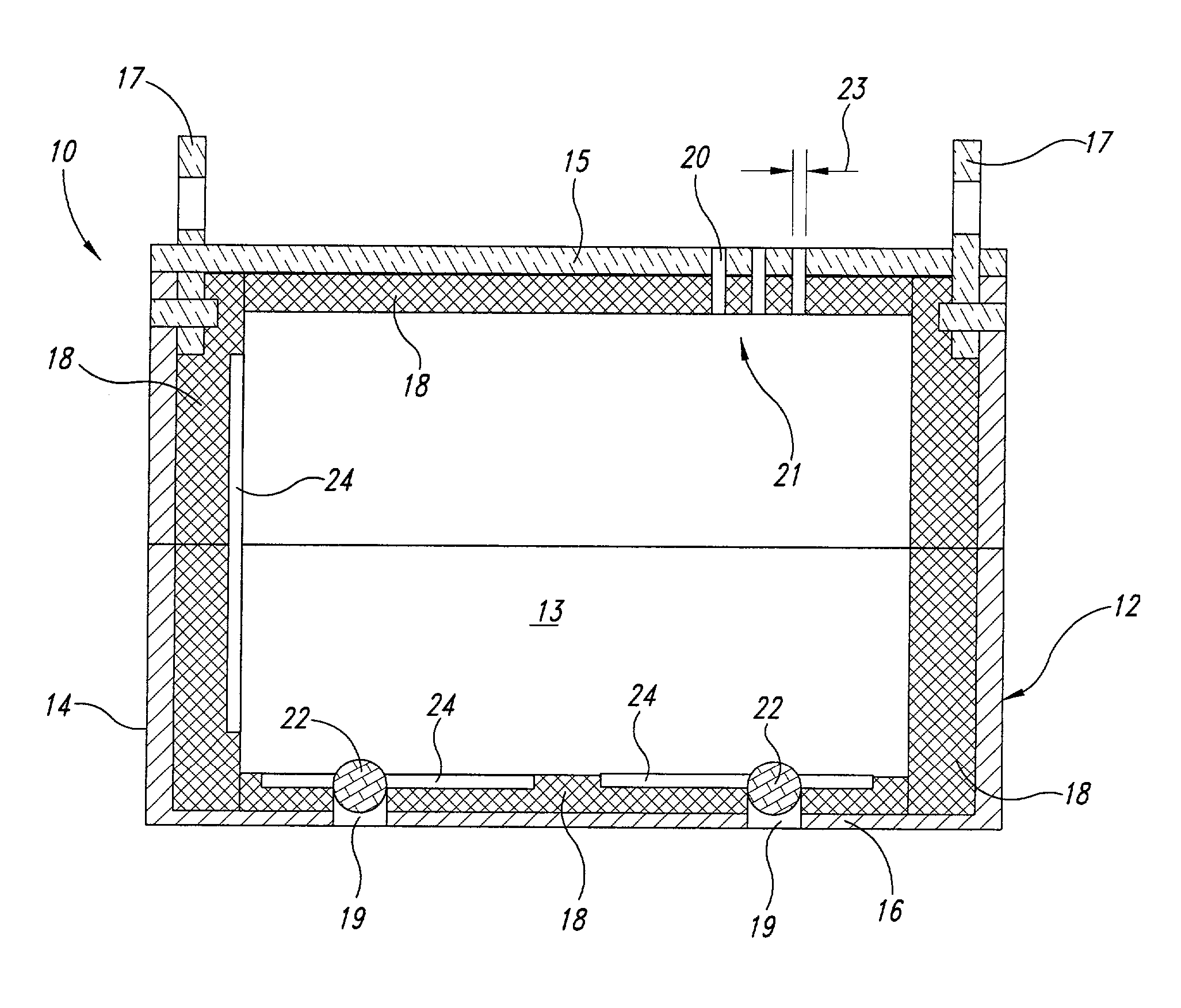
Separation Vessels For Use In Polymerization Processes And Methods For Cleaning Same
InactiveUS20120240960A1Reduce downtimeEasy and less-expensive to implementHollow article cleaningCleaning using toolsHigh pressureActuator
Both a system and method for cleaning a low pressure separation vessel of a high pressure polyethylene polymerization plant are provided. The system includes a polytetrafluoroethylene lining that covers the interior surfaces of the vessel, and a cover mounting assembly including an annular clamp for detachably mounting a cover over the vessel. The mounting assembly includes a clamp actuator for quickly securing and releasing the cover with respect to a top rim of the vessel. The vessel is drained of liquid polyethylene and allowed to cool to ambient temperature, thus creating a frozen “skin” of polyethylene around the interior surfaces of the vessel. The clamp actuator releases the cover. The polyethylene skin is peeled off the interior sides the vessel and gathered up at the top to form a neck, thus peeling the polyethylene skin away from the polytetrafluoroethylene lining along with any degraded polymers or other impurities that have accumulated on the interior surfaces of the vessel.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Remotely operable pressure vessel system
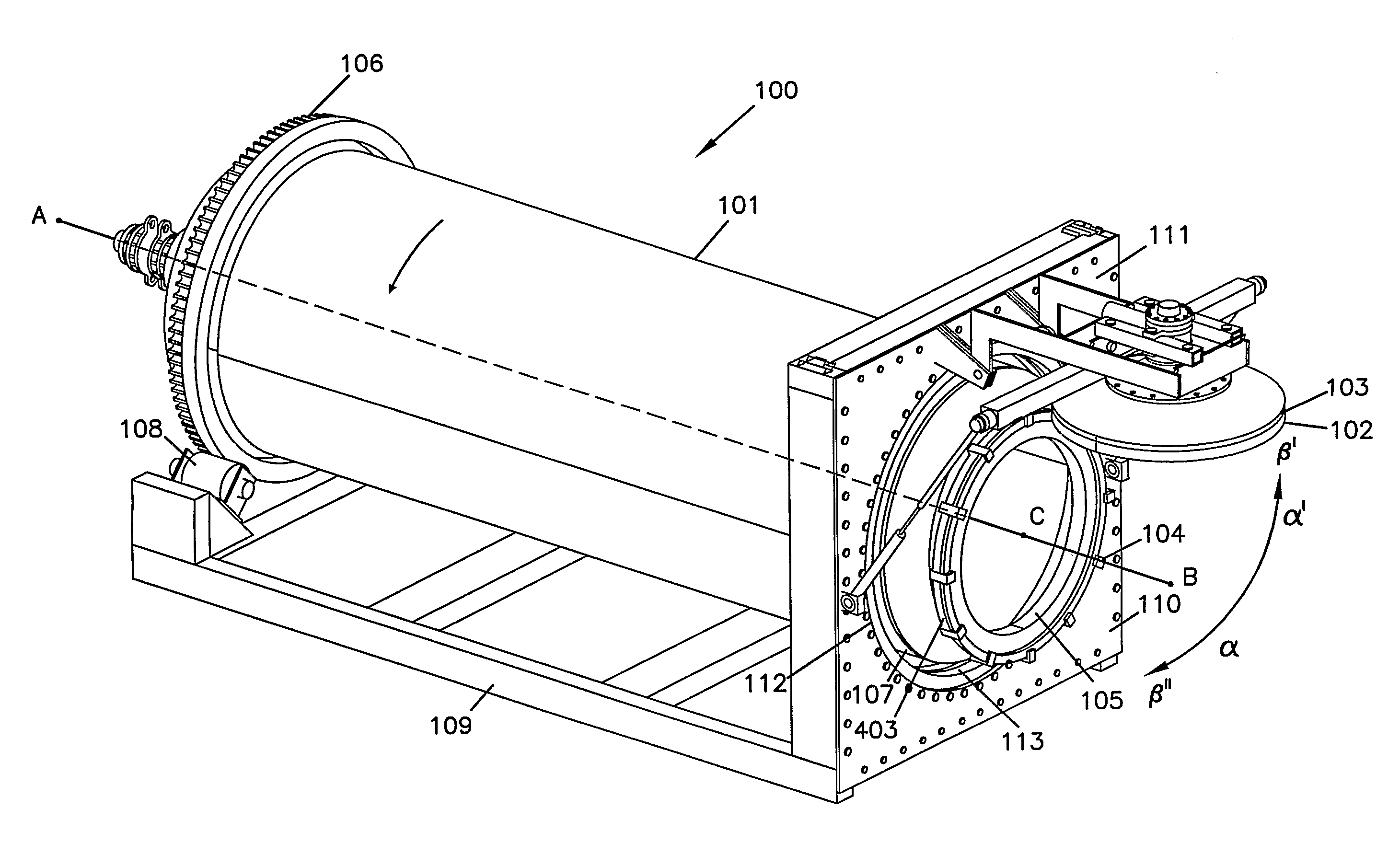
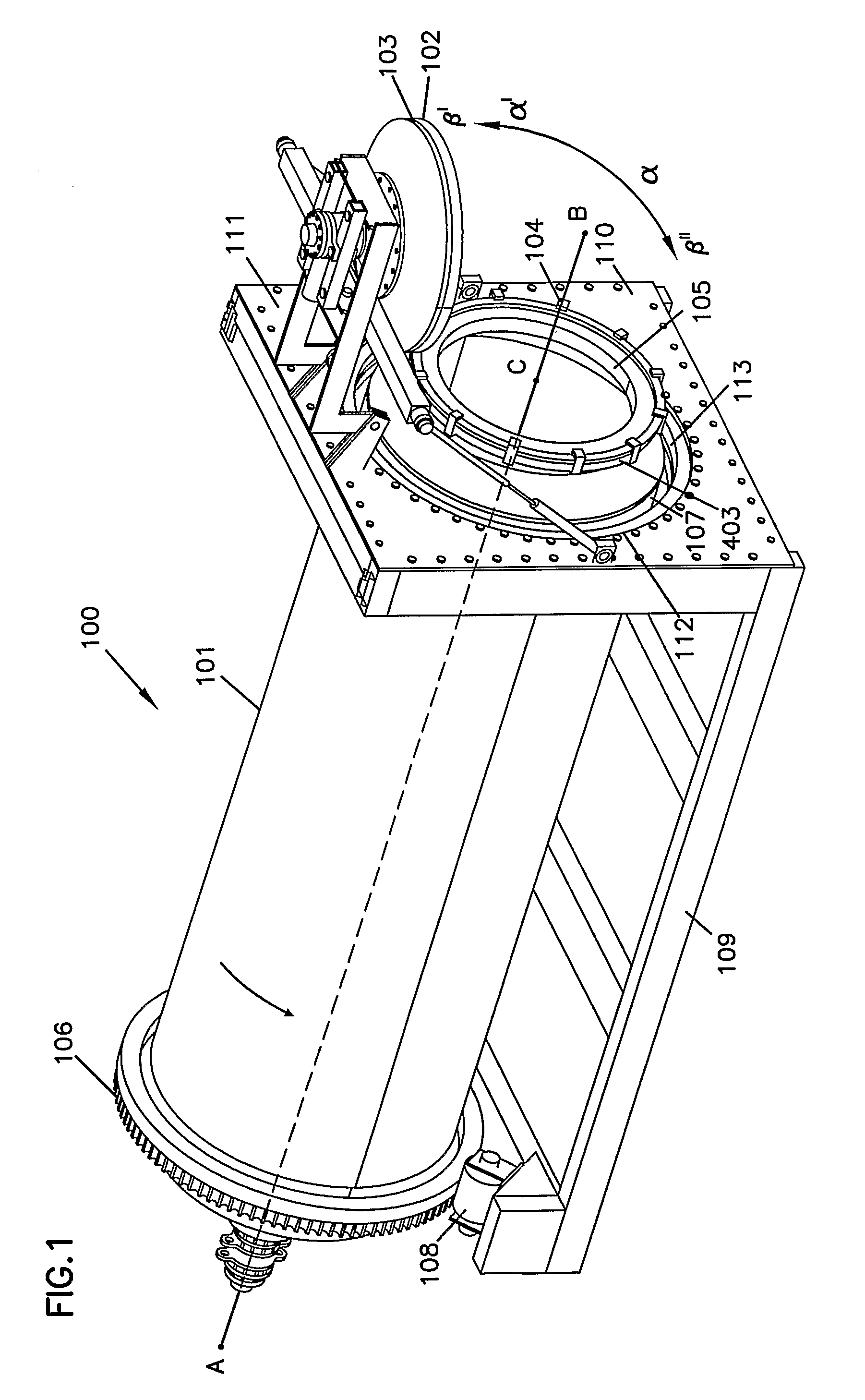
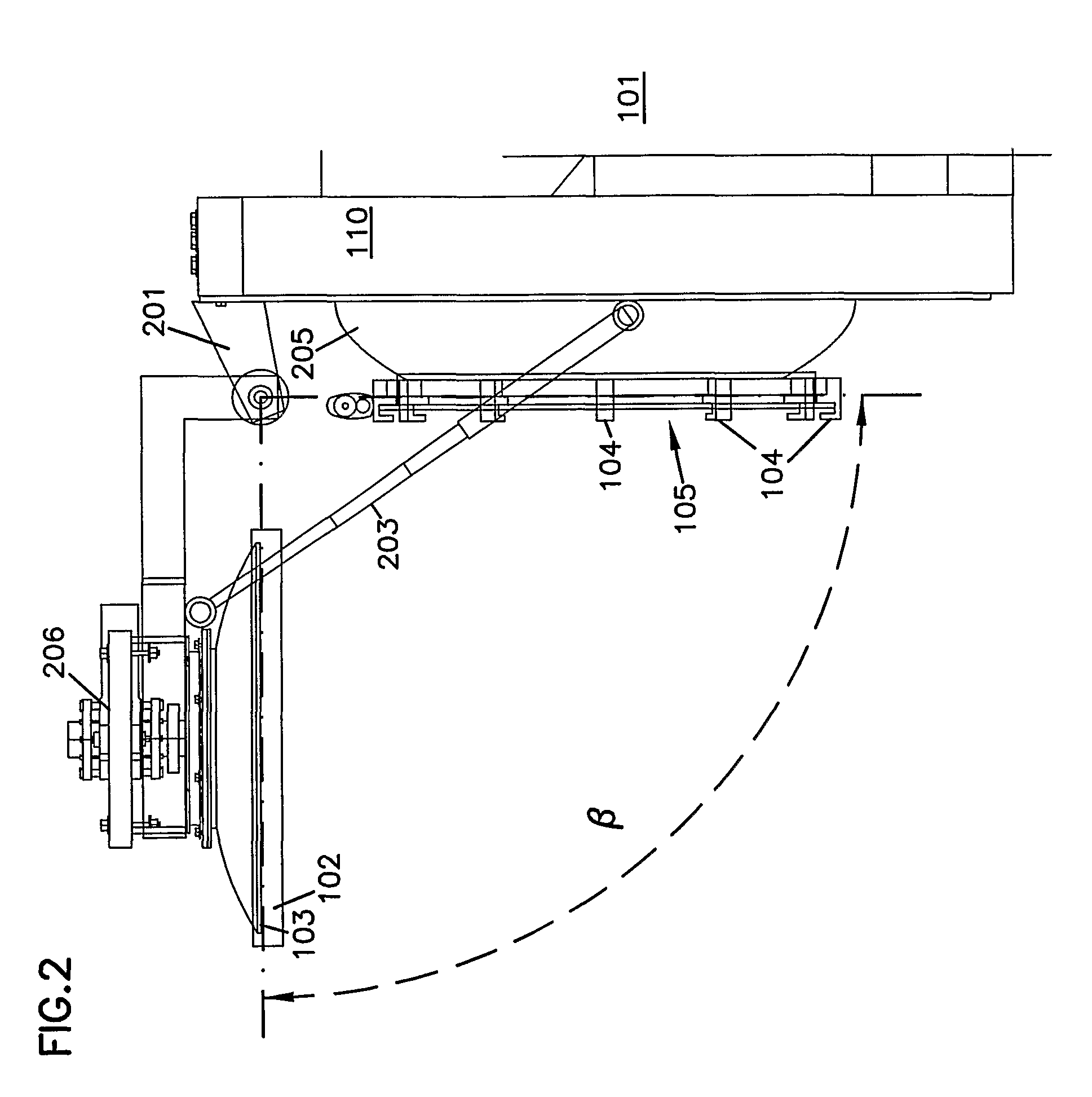
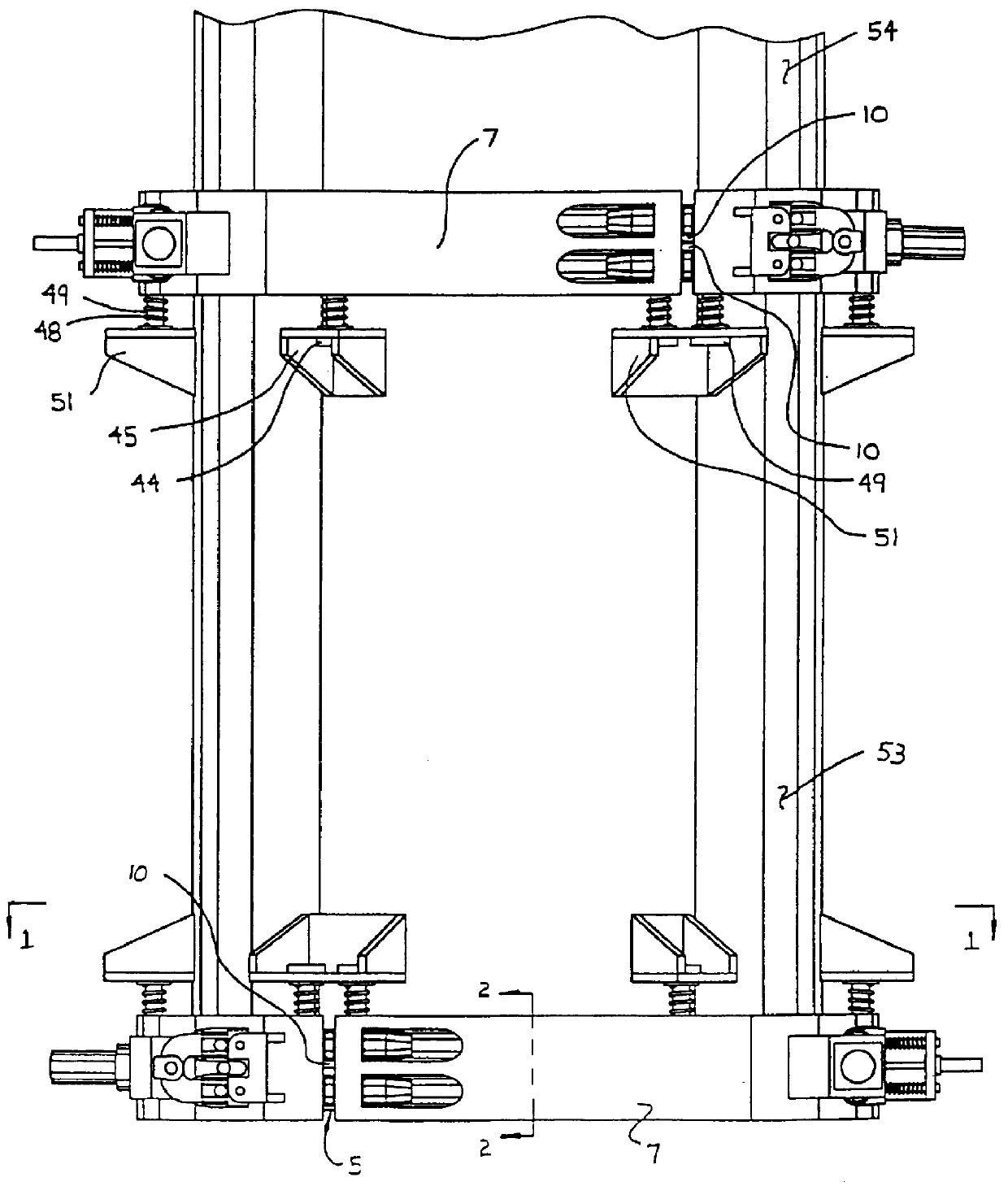
InactiveUS6022454AFor quick maintenanceCharging-discharging device combinationsRetortsMarine engineeringStructural unit
The present invention provides a substantially remote operable system for connecting and disconnecting a vessel. The system comprises substantially a remotely operable joint connector for connecting and disconnecting structural units. The system and the method using the system may also comprise a remote operable closure transport for removing a vessel closure from an opening in the vessel, and a substantially remote operable removal system for allowing material to be emptied from the vessel to increase operational efficiency.
Owner:AUTOMATED CONNECTORS HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com