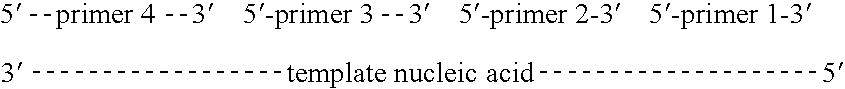Patents
Literature
2541results about "Libraries apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
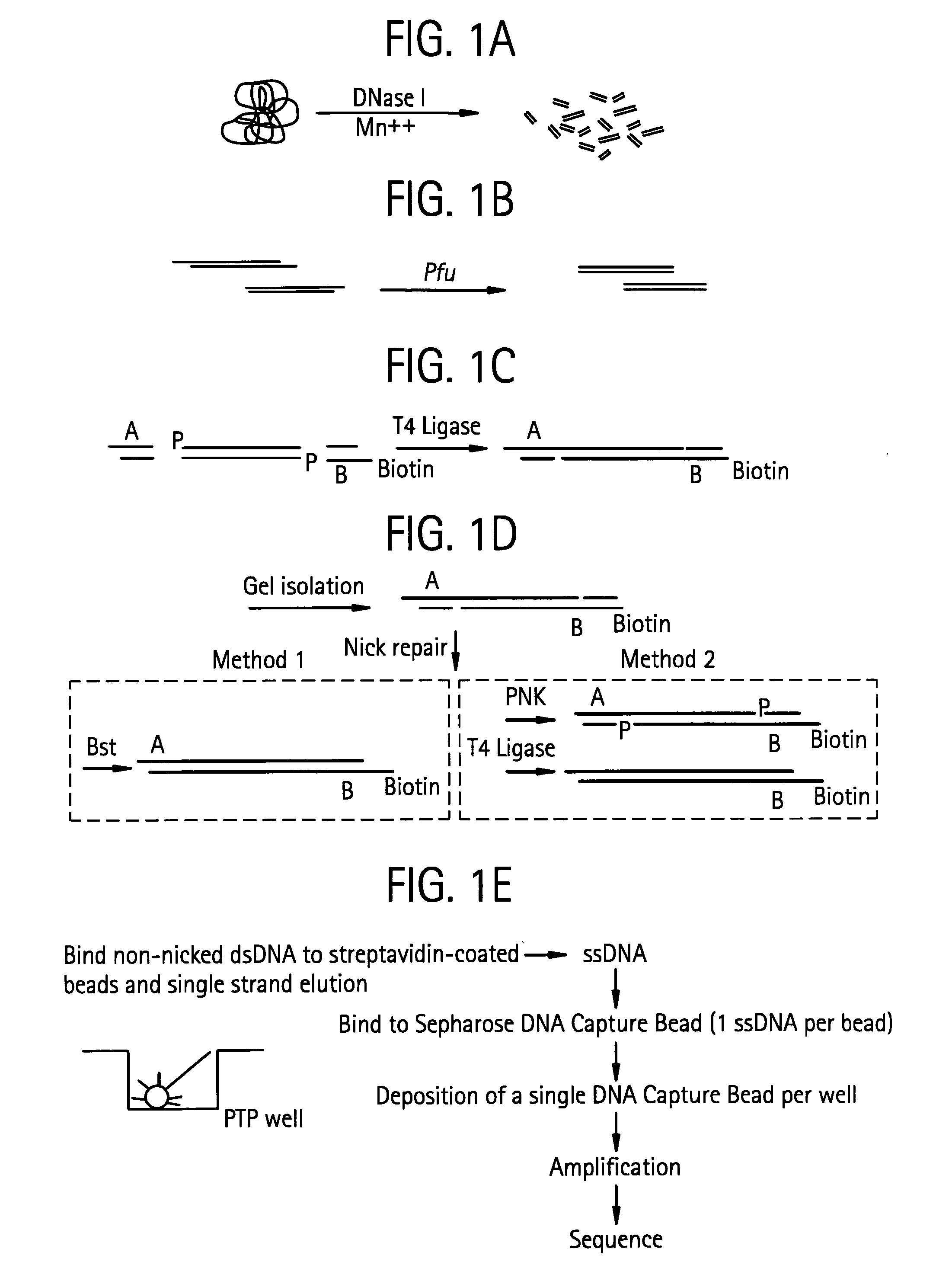
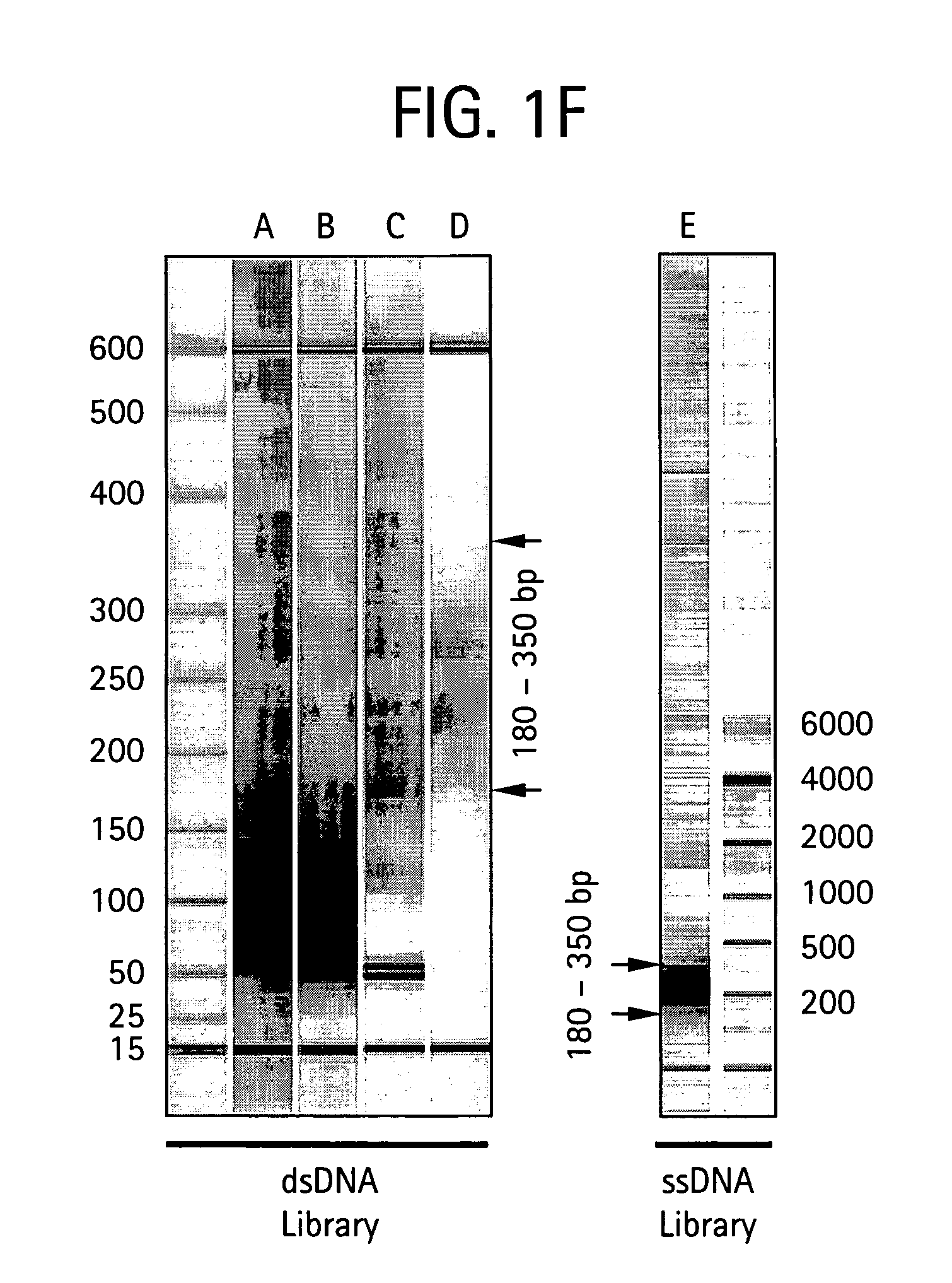
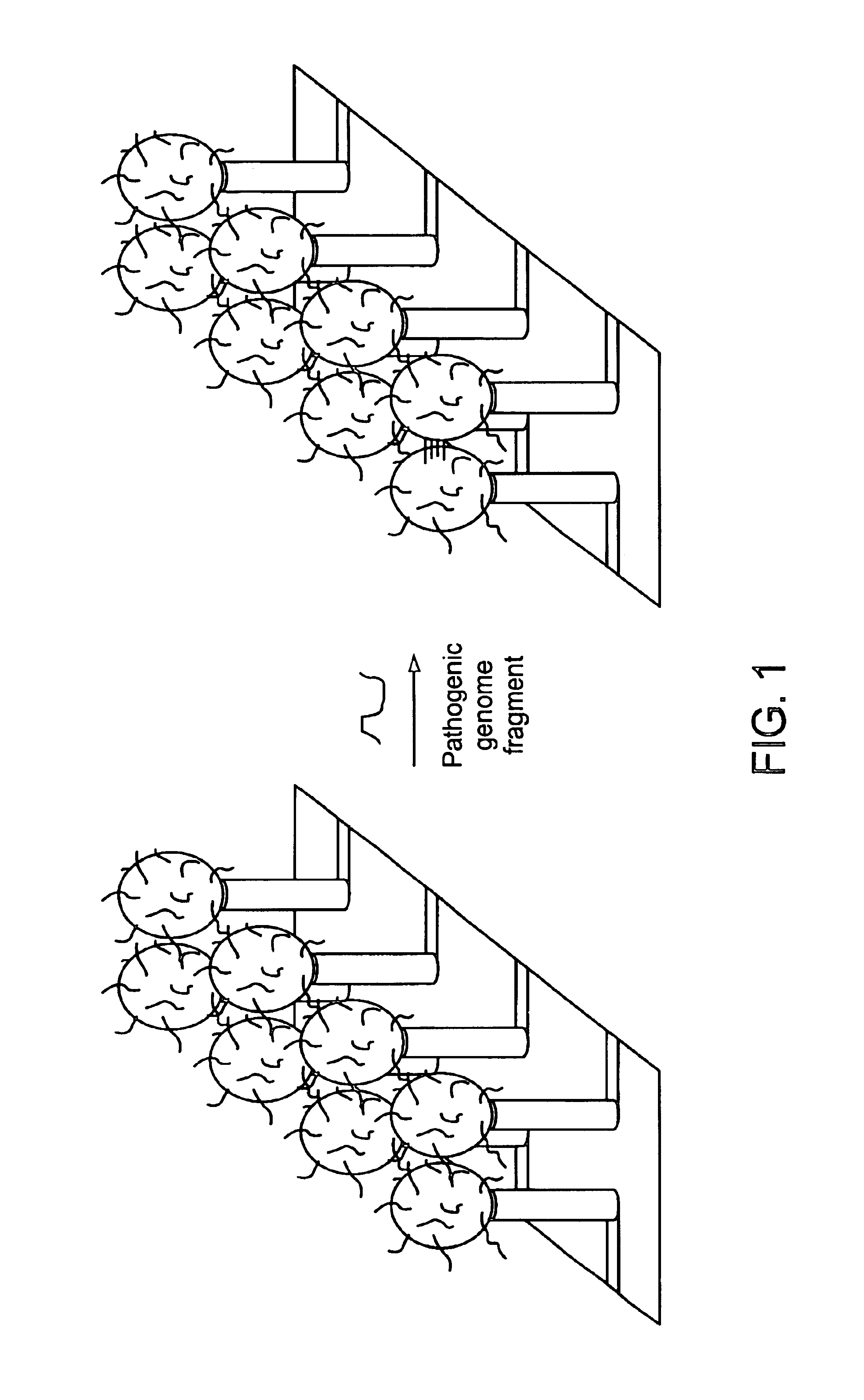
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
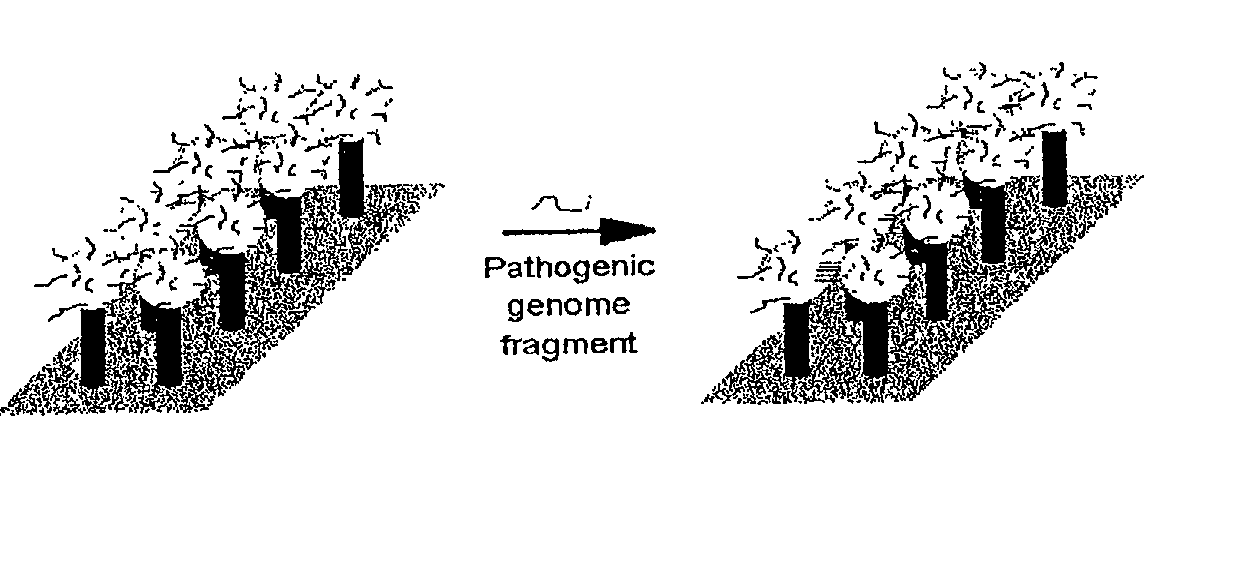
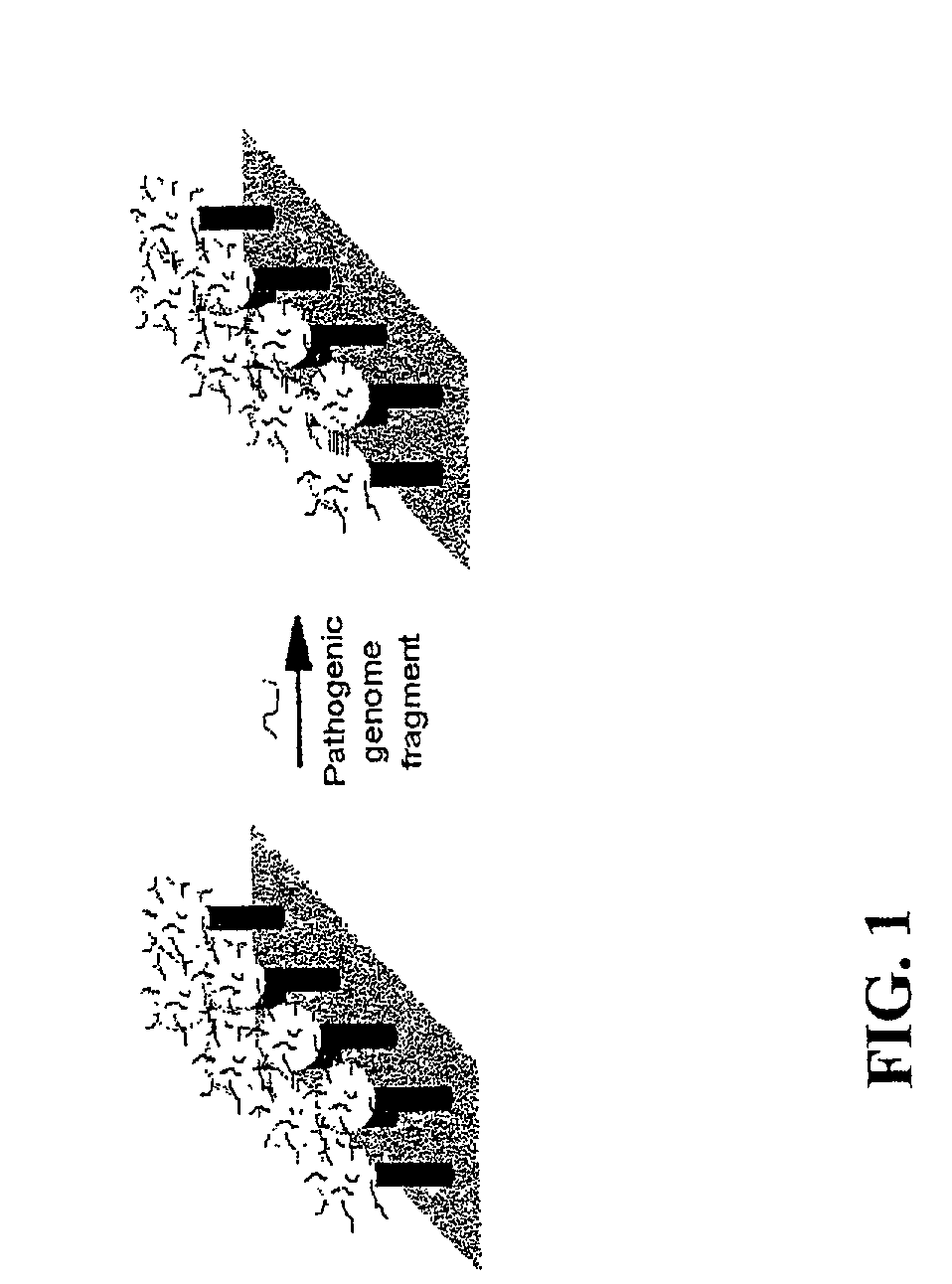
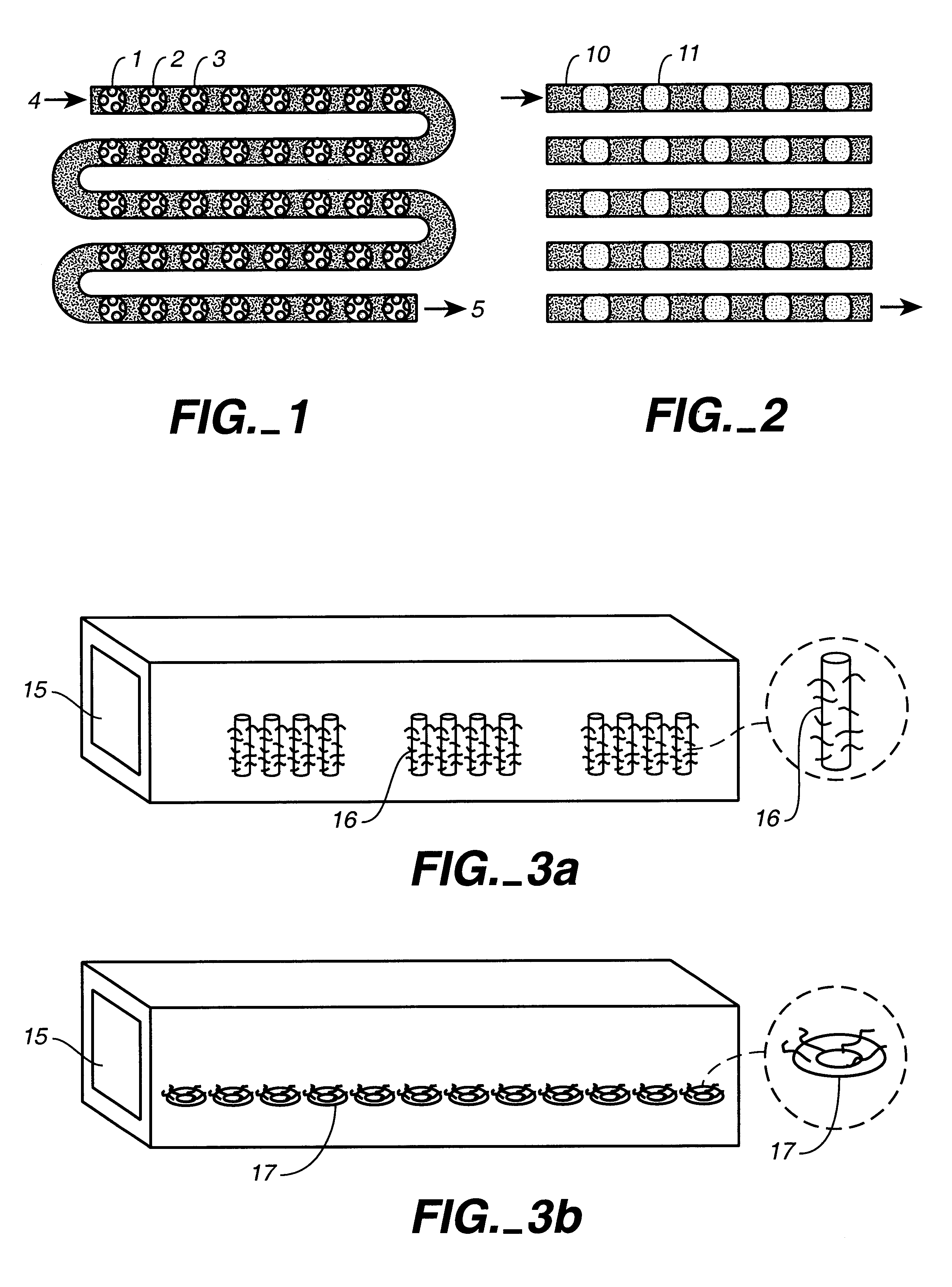
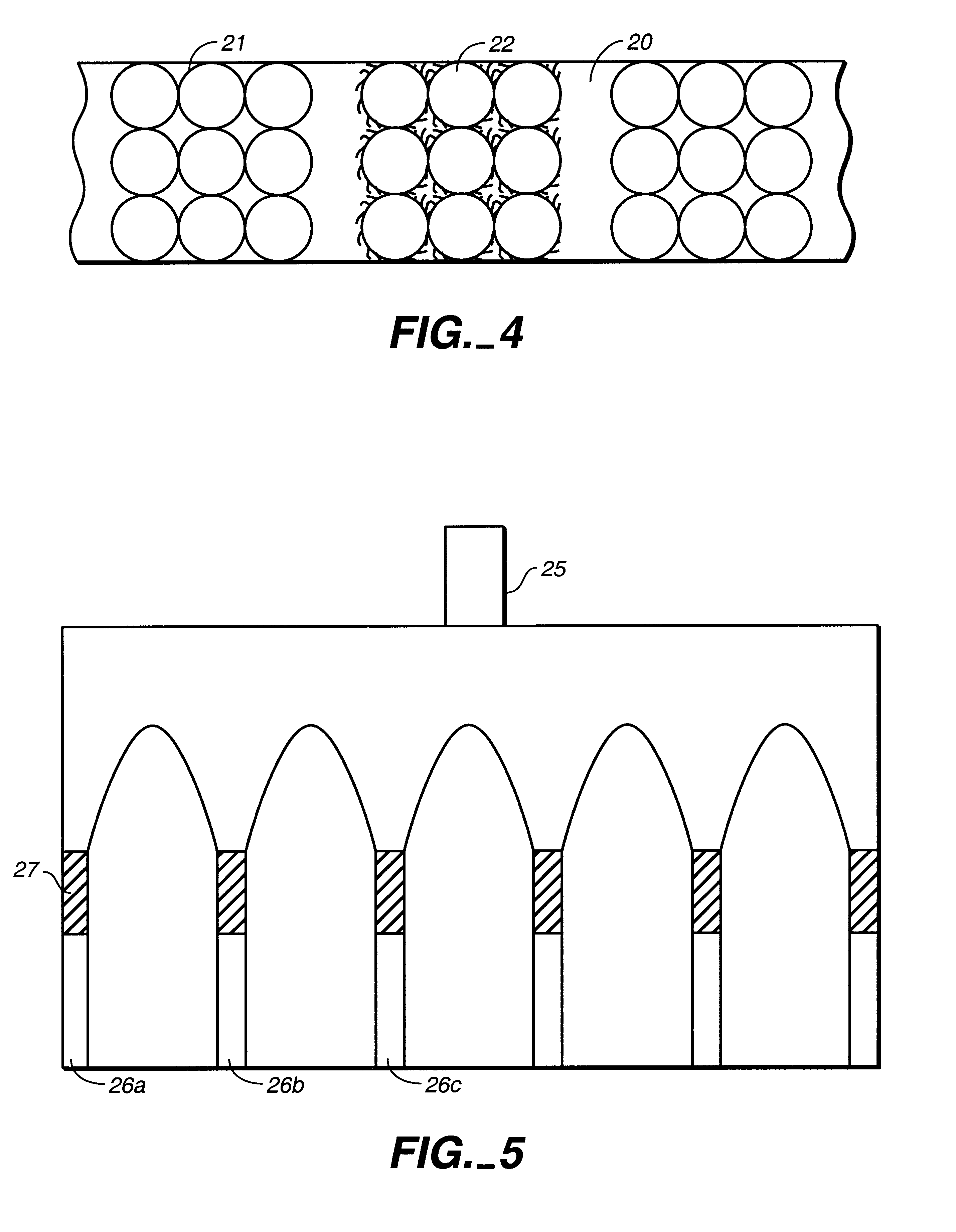
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
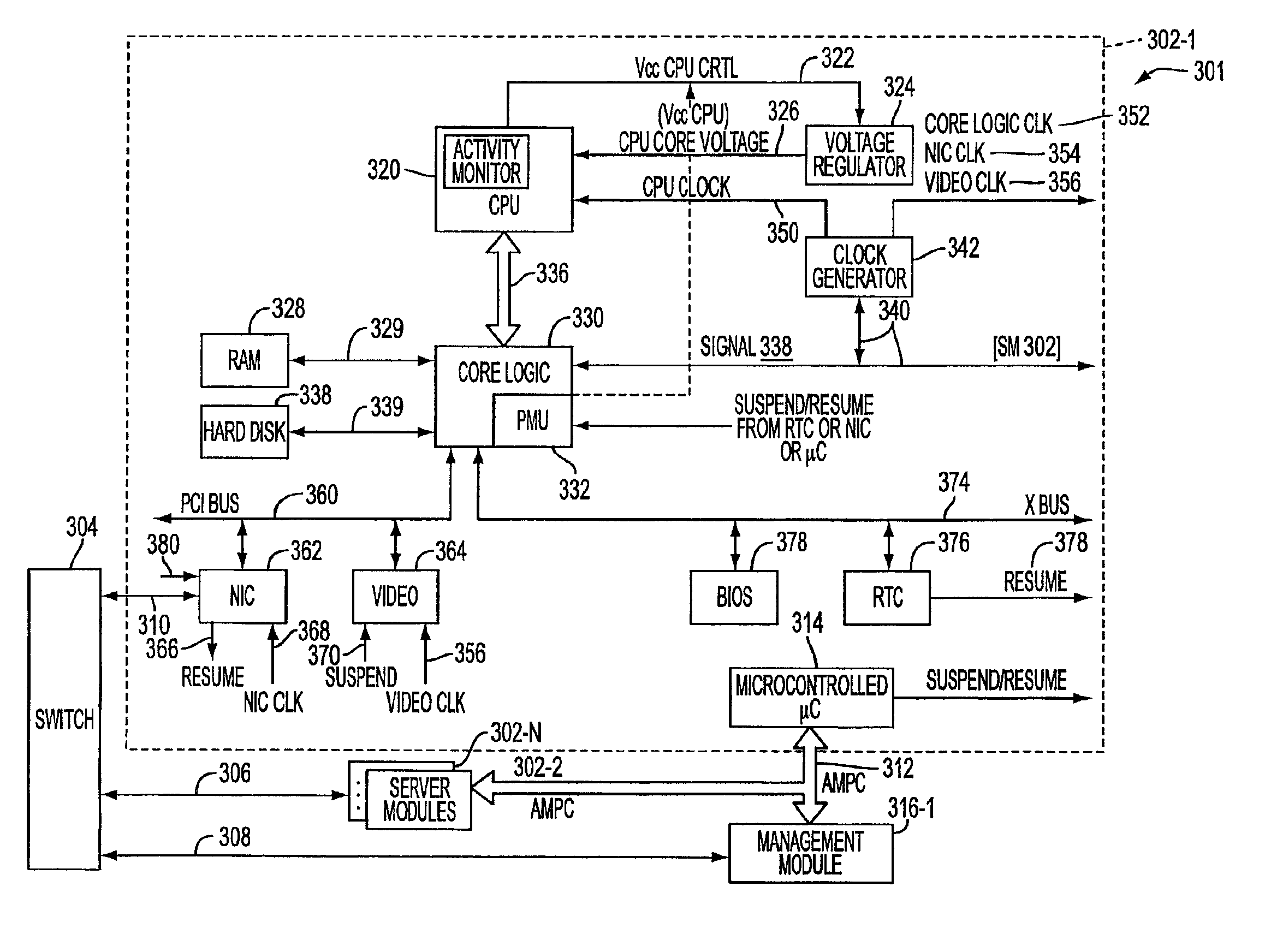
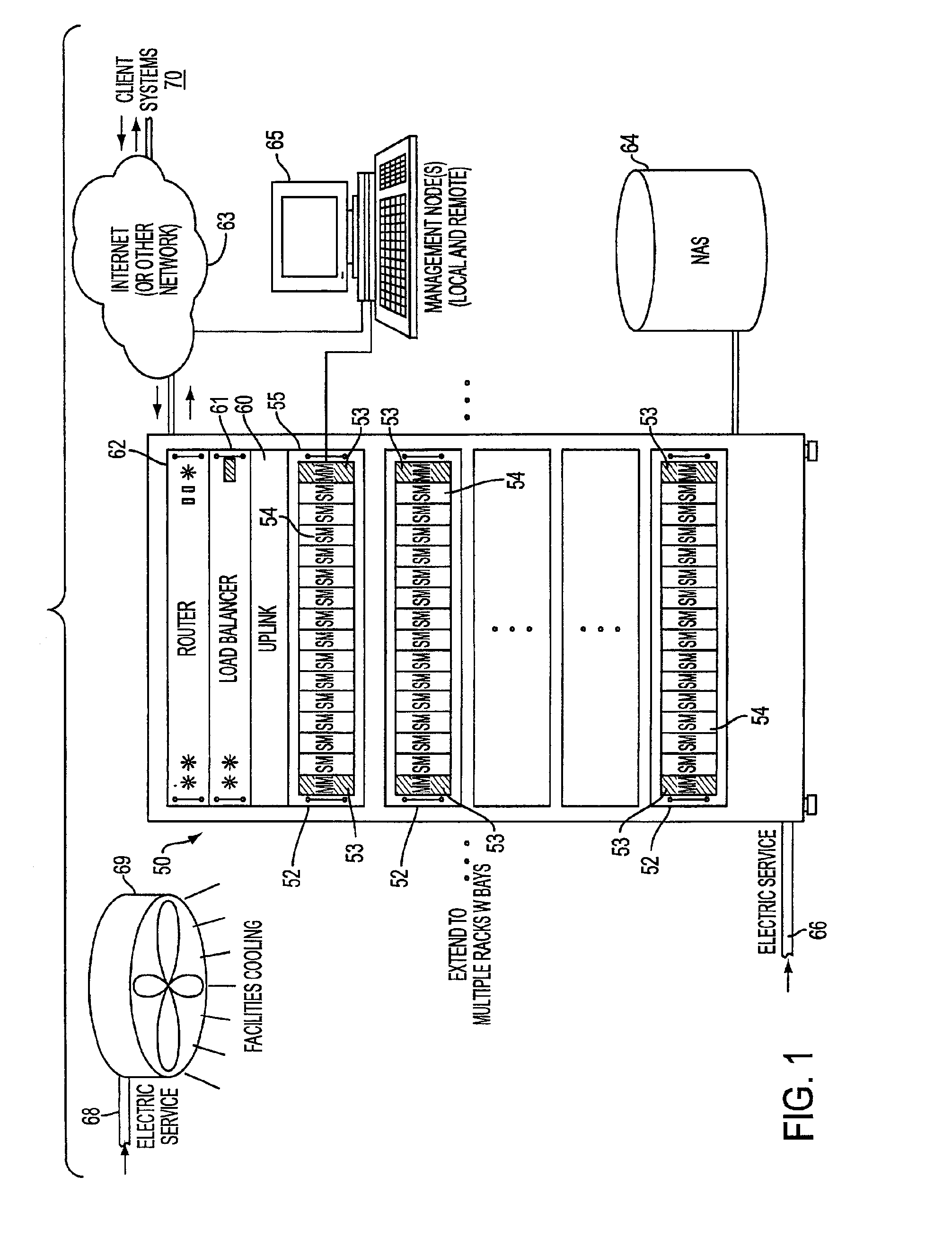
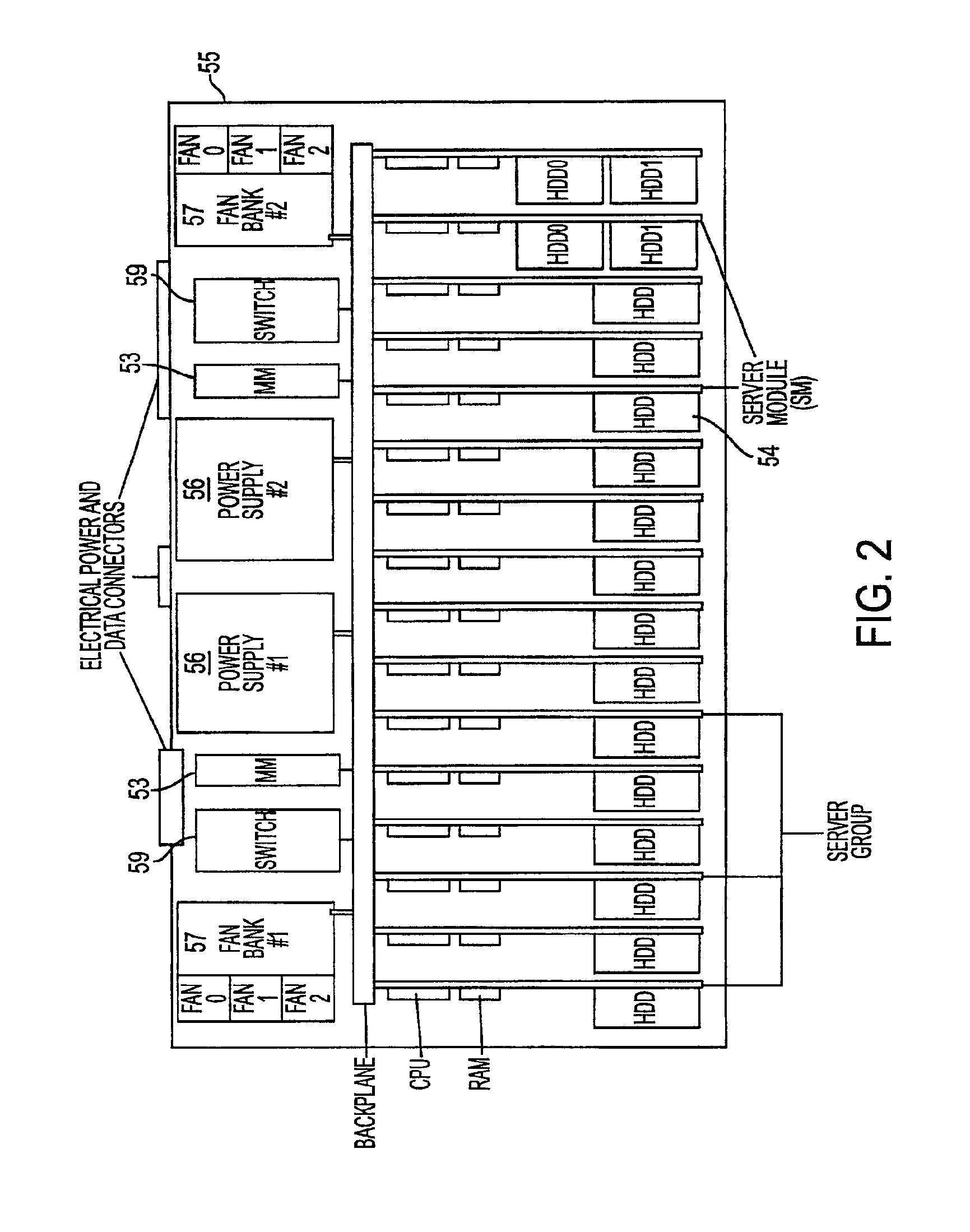
System, method, and architecture for dynamic server power management and dynamic workload management for multi-server environment
InactiveUS6859882B2Save energyConserving methodEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementNetwork architectureWorkload management
Network architecture, computer system and / or server, circuit, device, apparatus, method, and computer program and control mechanism for managing power consumption and workload in computer system and data and information servers. Further provides power and energy consumption and workload management and control systems and architectures for high-density and modular multi-server computer systems that maintain performance while conserving energy and method for power management and workload management. Dynamic server power management and optional dynamic workload management for multi-server environments is provided by aspects of the invention. Modular network devices and integrated server system, including modular servers, management units, switches and switching fabrics, modular power supplies and modular fans and a special backplane architecture are provided as well as dynamically reconfigurable multi-purpose modules and servers. Backplane architecture, structure, and method that has no active components and separate power supply lines and protection to provide high reliability in server environment.
Owner:HURON IP
Analying polynucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6054270AStable duplexReduce impactSequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesHybridization reactionSequence determination
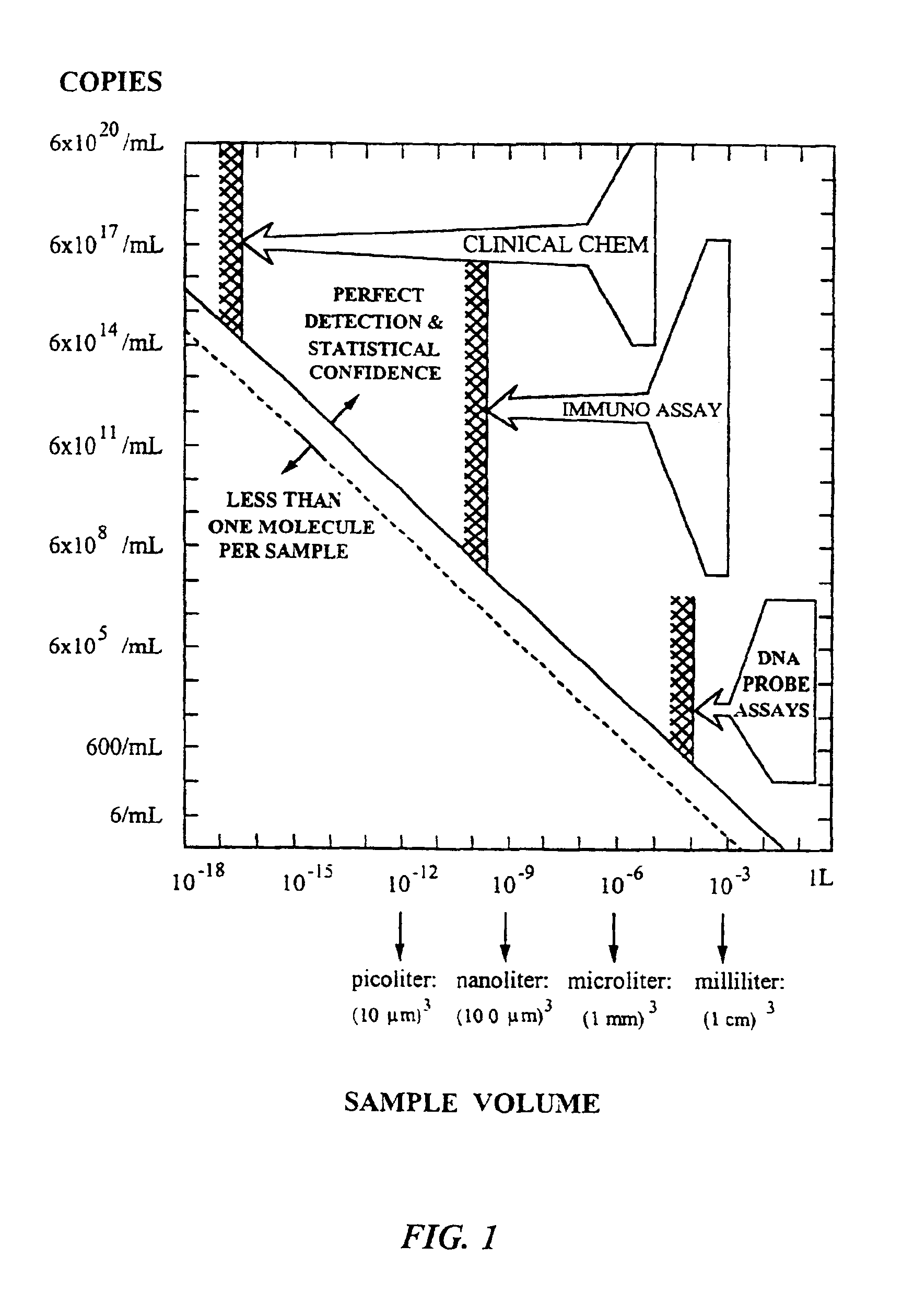
This invention provides an apparatus and method for analyzing a polynucleotide sequence; either an unknown sequence or a known sequence. A support, e.g. a glass plate, carries an array of the whole or a chosen part of a complete set of oligonucleotides which are capable of taking part in hybridization reactions. The array may comprise one or more pair of oligonucleotides of chosen lengths. The polynucleotide sequence, or fragments thereof, are labelled and applied to the array under hybridizing conditions. Applications include analyses of known point mutations, genomic fingerprinting, linkage analysis, characterization of mRNAs, mRNA populations, and sequence determination.
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH
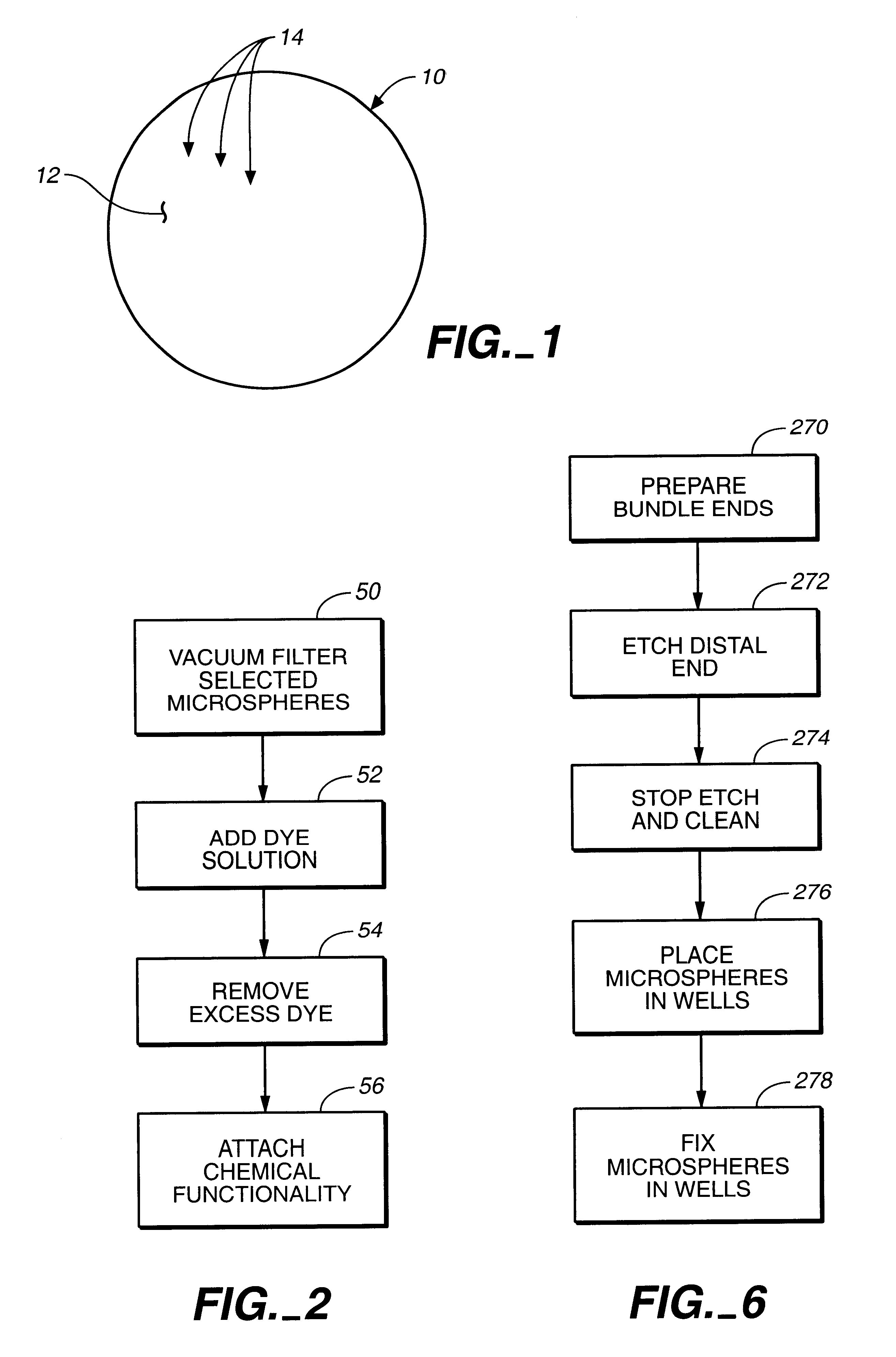
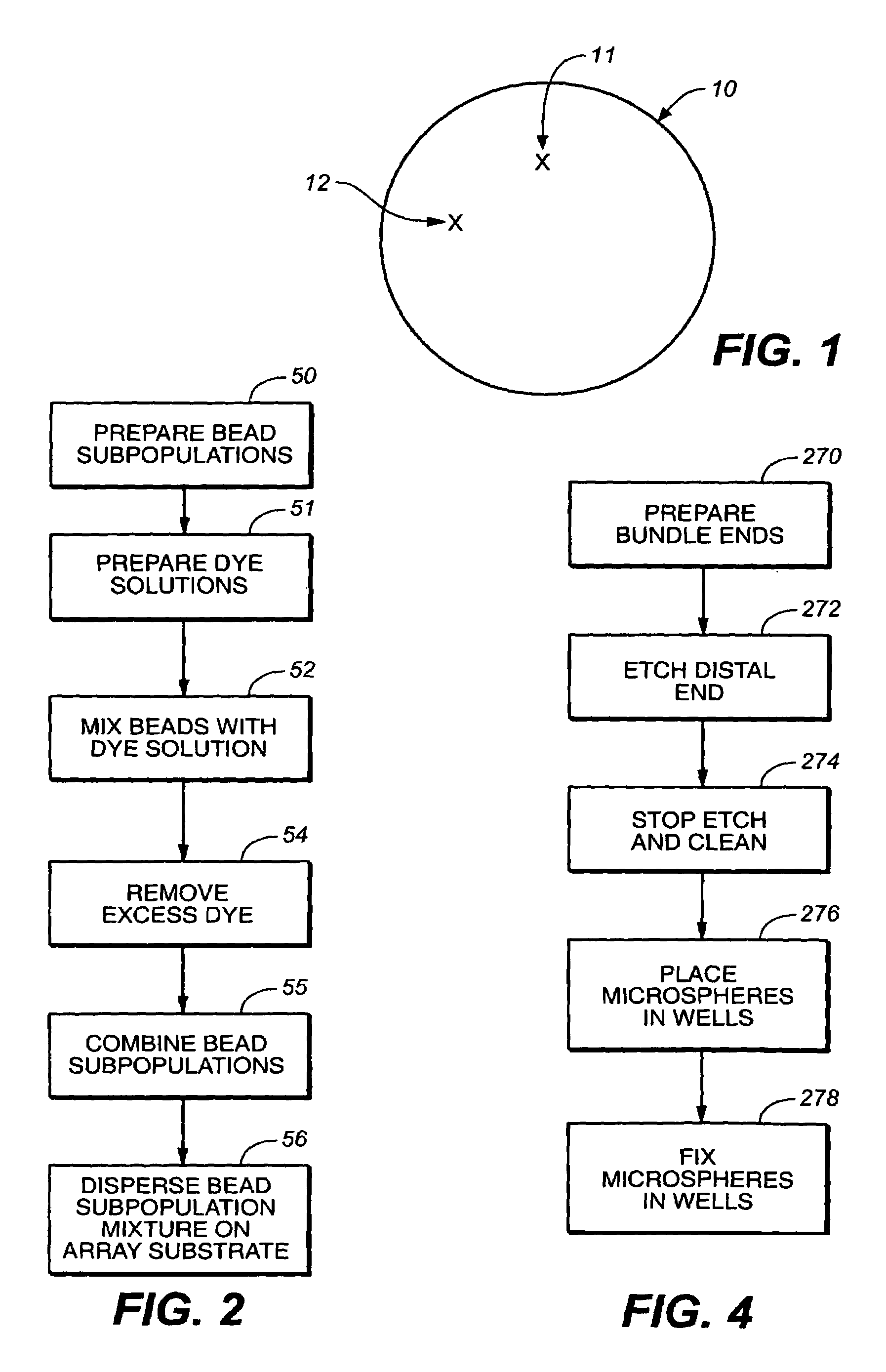
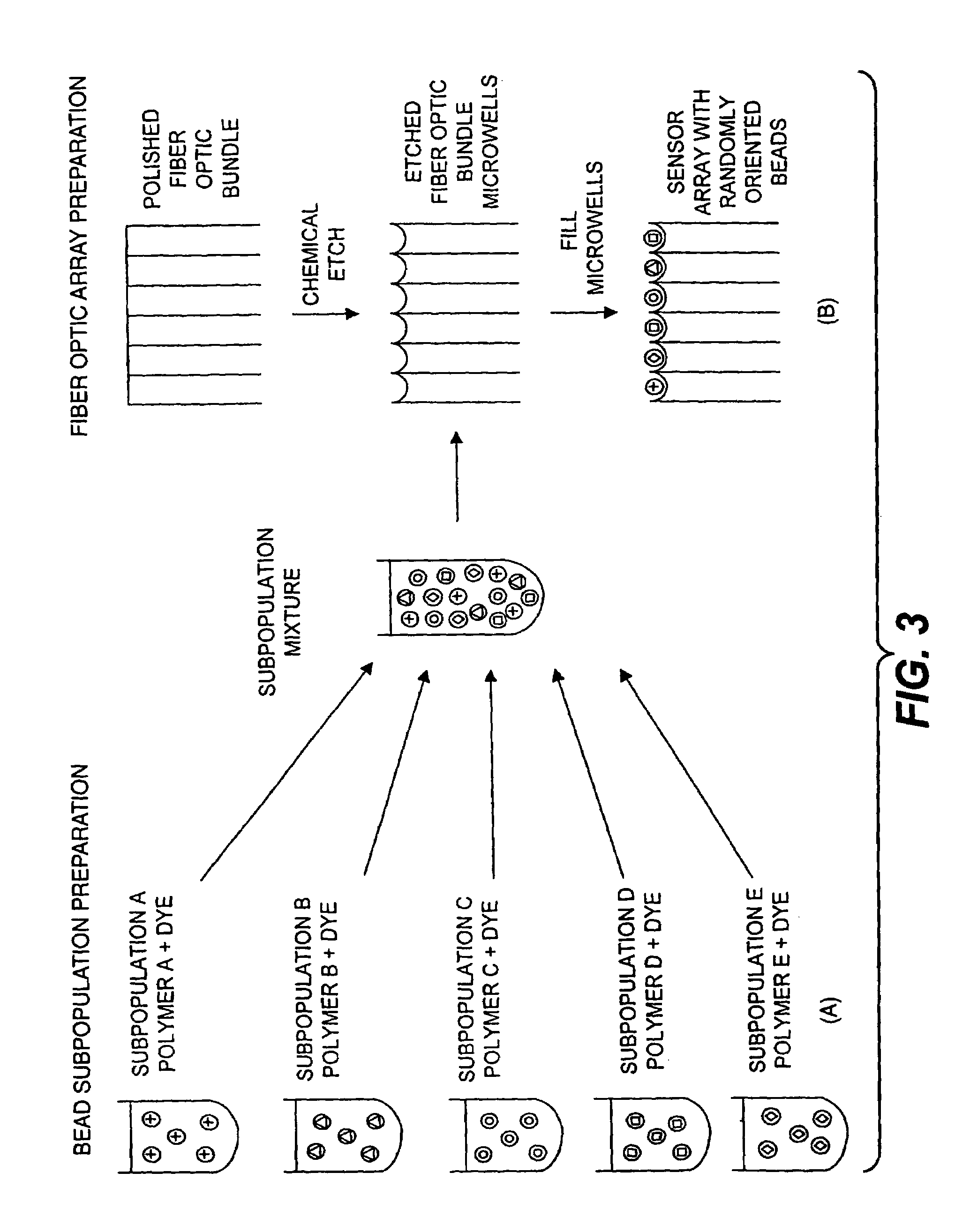
Target analyte sensors utilizing microspheres
A microsphere-based analytic chemistry system and method for making the same is disclosed in which microspheres or particles carrying bioactive agents may be combined randomly or in ordered fashion and dispersed on a substrate to form an array while maintaining the ability to identify the location of bioactive agents and particles within the array using an optically interrogatable, optical signature encoding scheme. A wide variety of modified substrates may be employed which provide either discrete or non-discrete sites for accommodating the microspheres in either random or patterned distributions. The substrates may be constructed from a variety of materials to form either two-dimensional or three-dimensional configurations. In a preferred embodiment, a modified fiber optic bundle or array is employed as a substrate to produce a high density array. The disclosed system and method have utility for detecting target analytes and screening large libraries of bioactive agents.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGETHE
Miniaturized cell array methods and apparatus for cell-based screening
InactiveUS6103479AImprove throughputIncrease contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyTemporal informationHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention discloses devices and methods of performing high throughput screening of the physiological response of cells to biologically active compounds and methods of combining high-throughput with high-content spatial information at the cellular and subcellular level as well as temporal information about changes in physiological, biochemical and molecular activities. The present invention allows multiple types of cell interactions to be studied simultaneously by combining multicolor luminescence reading, microfluidic delivery, and environmental control of living cells in non-uniform micro-patterned arrays.
Owner:CELLOMICS
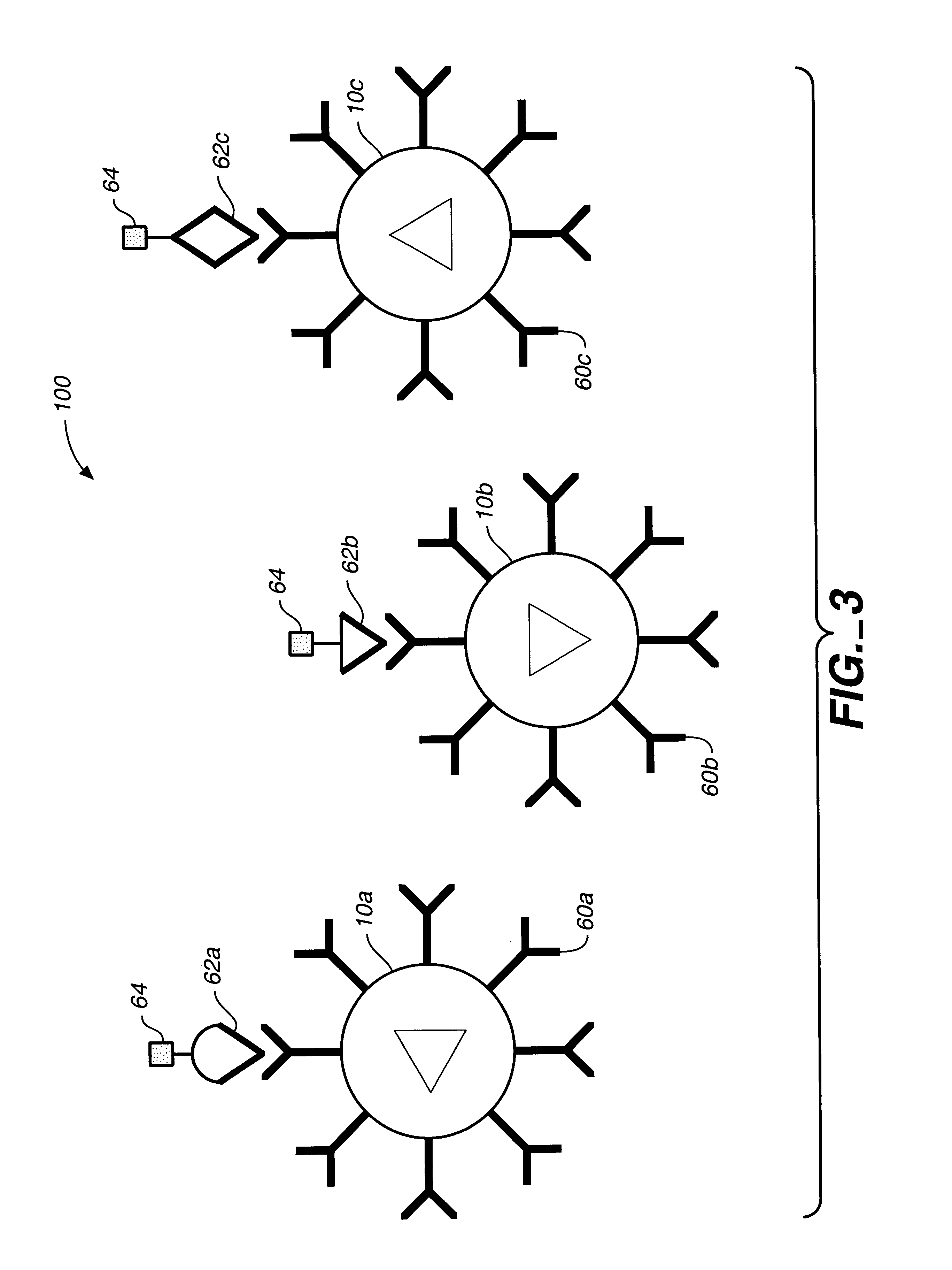
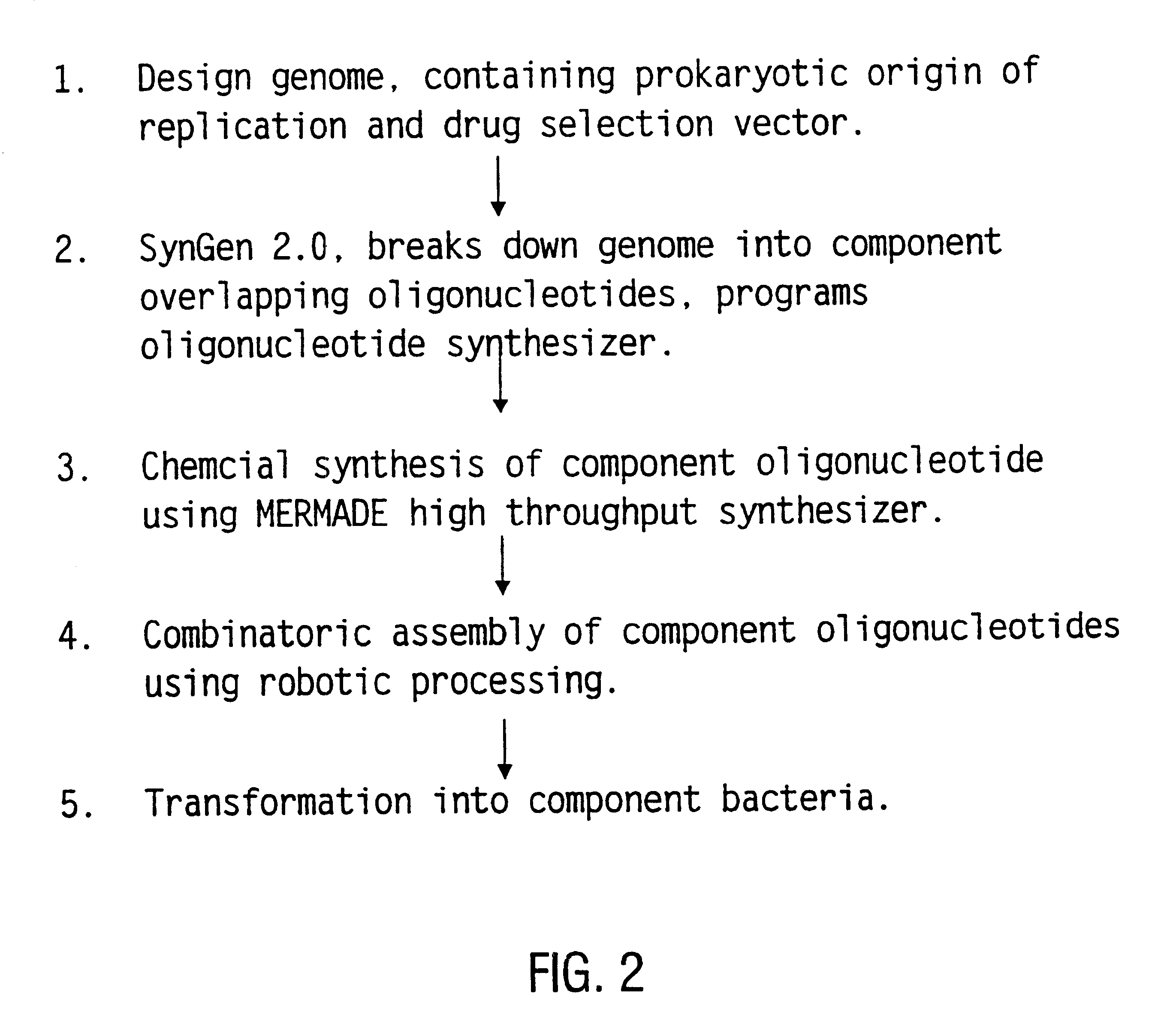
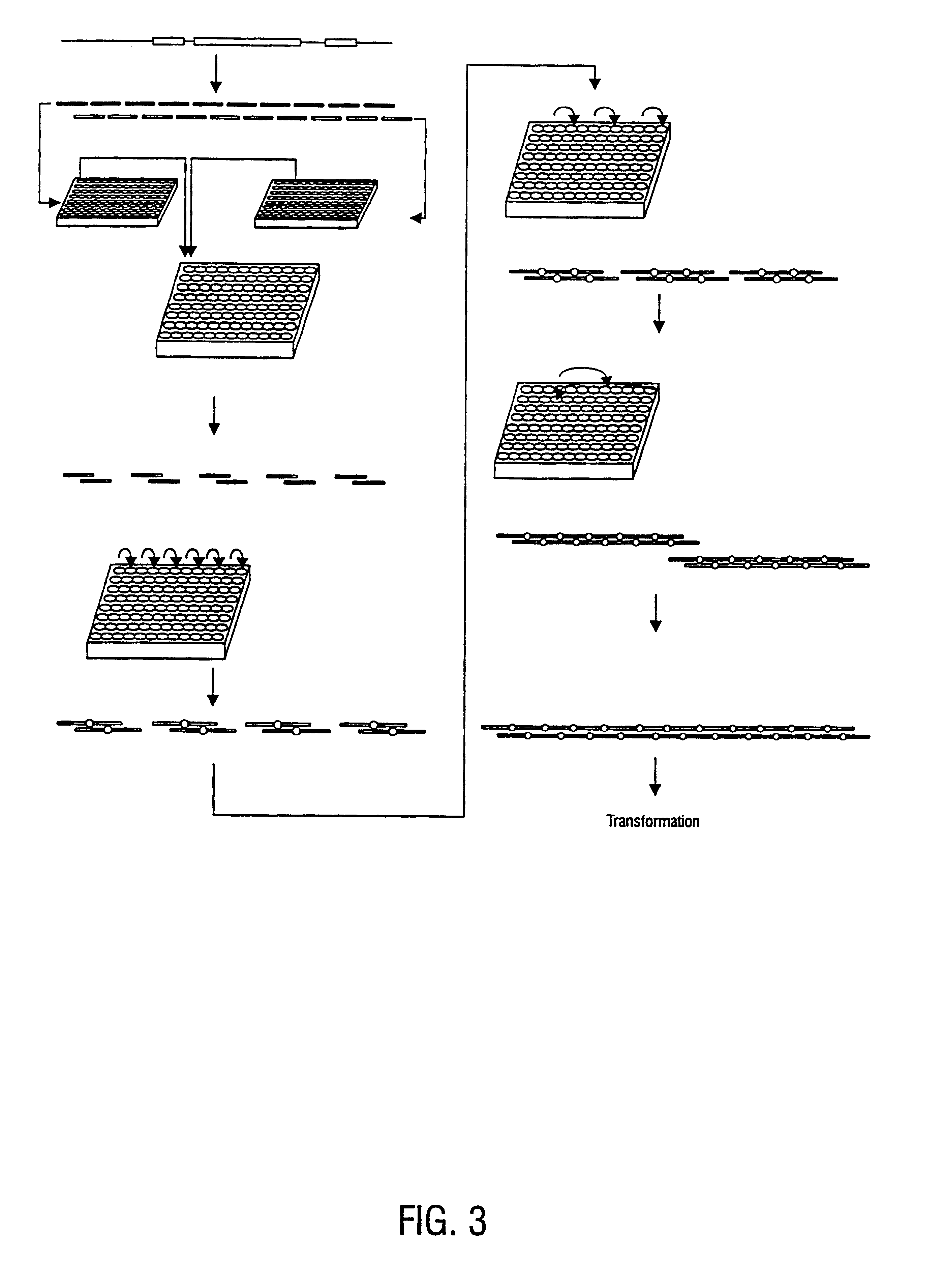
Method for the complete chemical synthesis and assembly of genes and genomes
InactiveUS6521427B1BiocideSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisHuman genome database
The present invention relates generally to the fields of oligonucleotide synthesis. More particularly, it concerns the assembly of genes and genomes of completely synthetic artificial organisms. Thus, the present invention outlines a novel approach to utilizing the results of genomic sequence information by computer directed gene synthesis based on computing on the human genome database. Specifically, the present invention contemplates and describes the chemical synthesis and resynthesis of genes defined by the genome sequence in a host vector and transfer and expression of these sequences into suitable hosts.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US) +3
Capillary electroflow apparatus and method
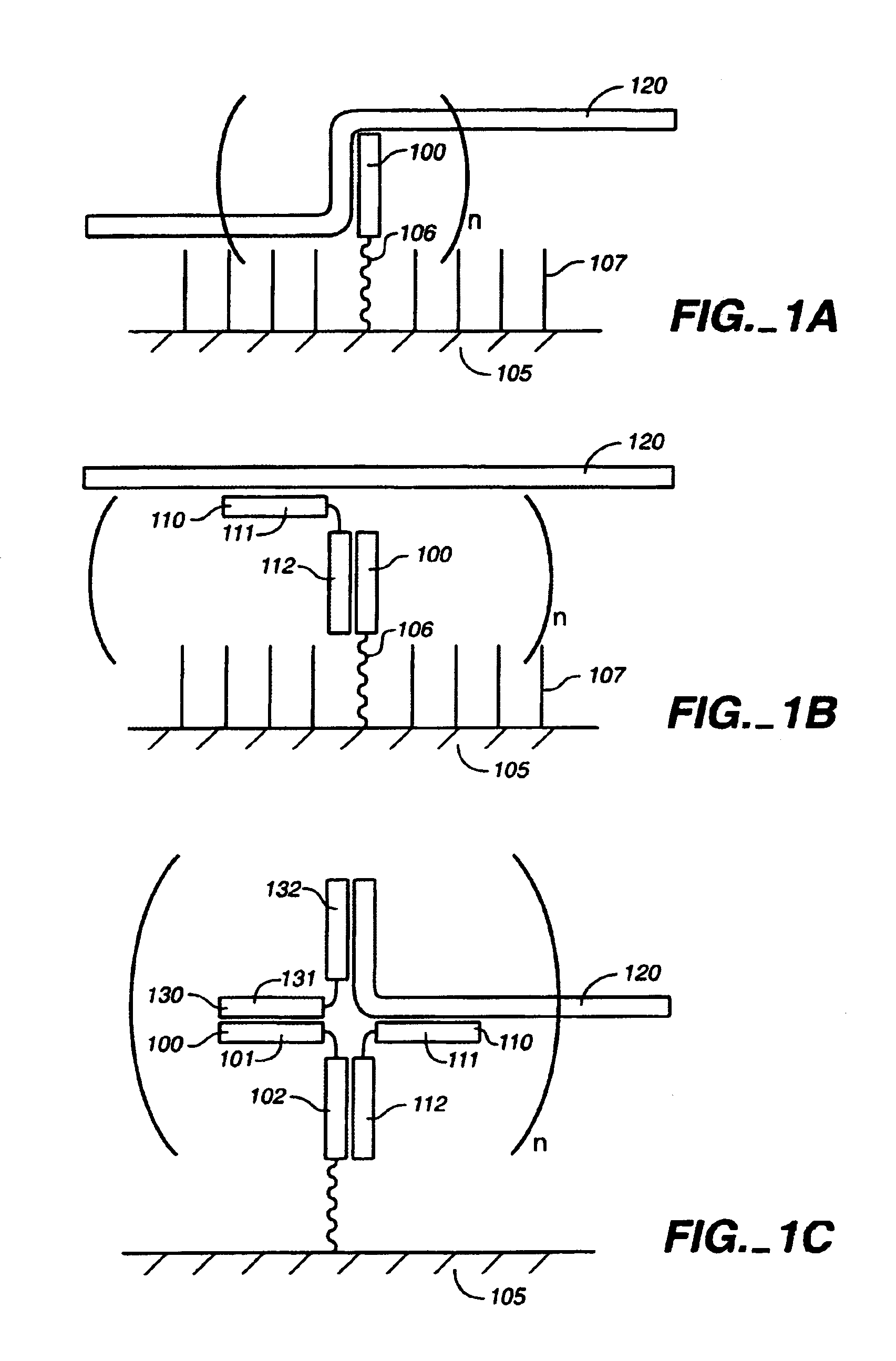
The present invention concerns an apparatus for conducting a microfluidic process. The apparatus comprises integral first and second plates. The first plate comprises an array of sample receiving elements for receiving a plurality of samples from an array of sample containers and dispensing the samples. The second plate comprises a planar array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels for conducting a microfluidic process. Also disclosed is a method for processing an array of samples. At least a portion of each sample in an array of sample wells is simultaneously transferred to a corresponding array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels by means of a corresponding array of sample receiving elements that is in integral fluid communication with the array of microfluidic networks. The samples are then processed. Also disclosed is a device for conducting a microfluidic process wherein the device comprising a planar substrate having a planar array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels for conducting a microfluidic process. A plurality of such devices may be present on a continuous sheet. The invention further includes kits for carrying out microfluidic processes comprising an apparatus as described above.
Owner:ACLARA BIOSCIENCES INC
Apparatus and method for transferring liquids
InactiveUS6284113B1Sequential/parallel process reactionsSludge treatmentElectricityMechanical engineering
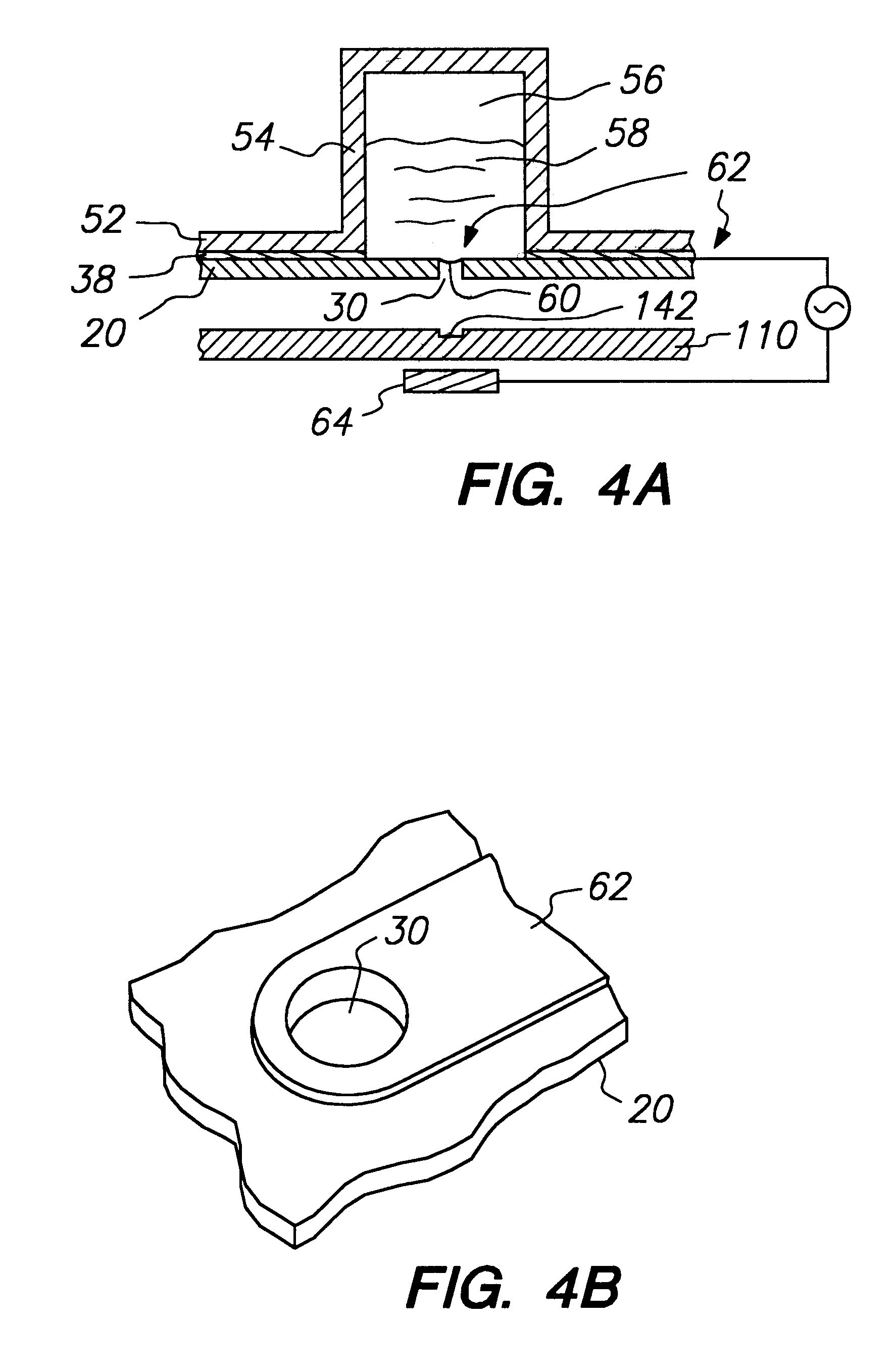
The present invention concerns devices, apparatus and methods for transferring liquids. One aspect of the present invention is a device comprising a plate having a plurality of transfer elements. Each of the transfer elements comprises an aperture in the plate where the aperture is capable of being electrically activated. The plate has one of more attaching elements for attaching the plate to a multiwell plate to form a sealed system except for the apertures of the transfer elements. Usually, the device is adapted for sealing attachment to a multiwell plate. In a method in accordance with the present invention a quantity of liquid is disposed to a second side of a plate having a plurality of apertures in the plate. The apertures are capable of being electrically activated. The liquid is present in a closed well except for the apertures in the plate. To simultaneously expel liquid from the apertures, the apertures are electrically activated. Also disclosed are kits comprising a device in accordance with the present invention.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Microfluidic Devices and Methods of Use in The Formation and Control of Nanoreactors
InactiveUS20100137163A1Material nanotechnologyCompound screeningHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysEmulsion
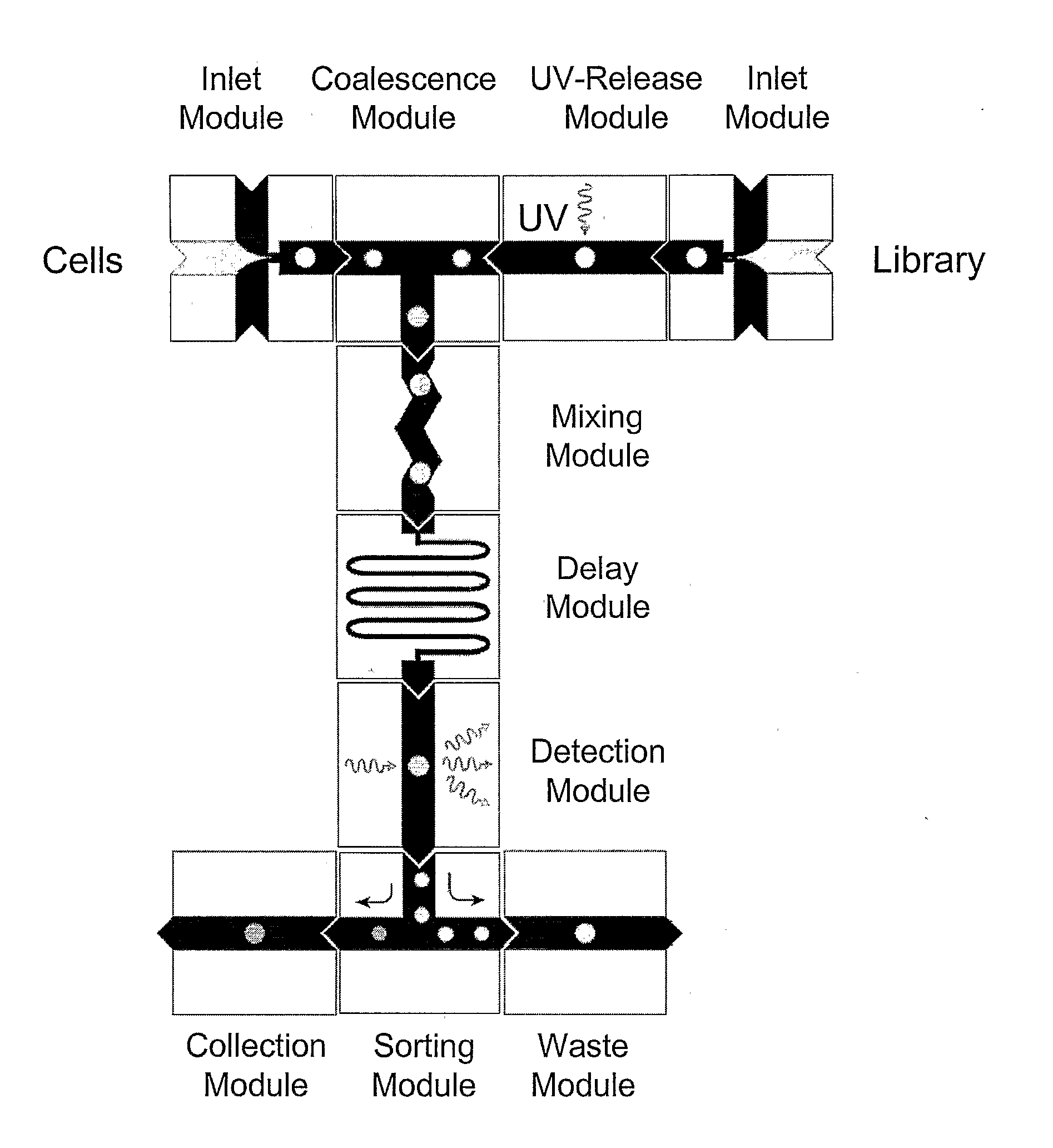
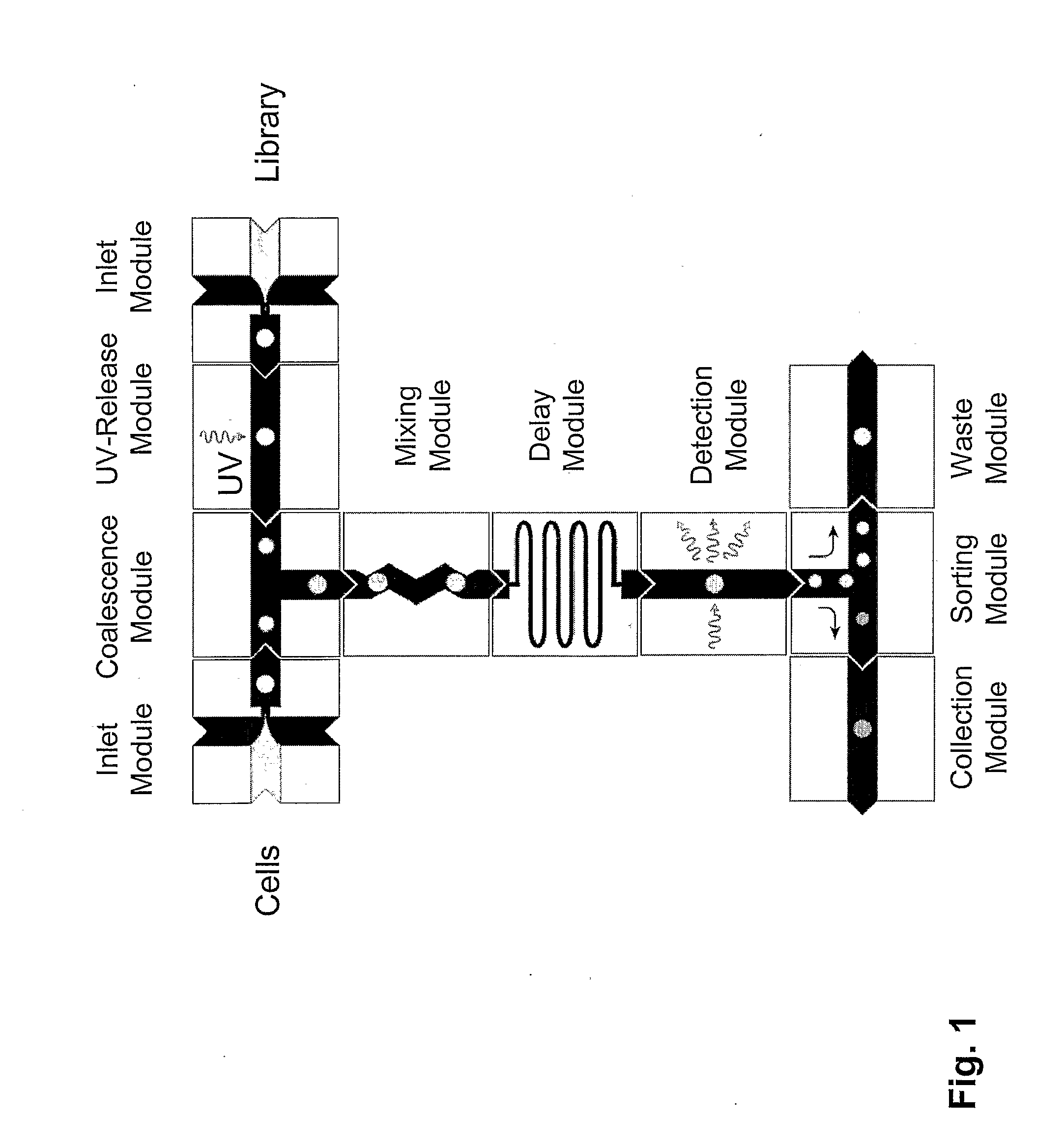
The present invention provides novel microfluidic devices and methods that are useful for performing high-throughput screening assays and combinatorial chemistry. Such methods can include labeling a library of compounds by emulsifying aqueous solutions of the compounds and aqueous solutions of unique liquid labels on a microfluidic device, which includes a plurality of electrically addressable, channel bearing fluidic modules integrally arranged on a microfabricated substrate such that a continuous channel is provided for flow of immiscible fluids, whereby each compound is labeled with a unique liquid label, pooling the labeled emulsions, coalescing the labeled emulsions with emulsions containing a specific cell or enzyme, thereby forming a nanoreactor, screening the nanoreactors for a desirable reaction between the contents of the nanoreactor, and decoding the liquid label, thereby identifying a single compound from a library of compounds.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
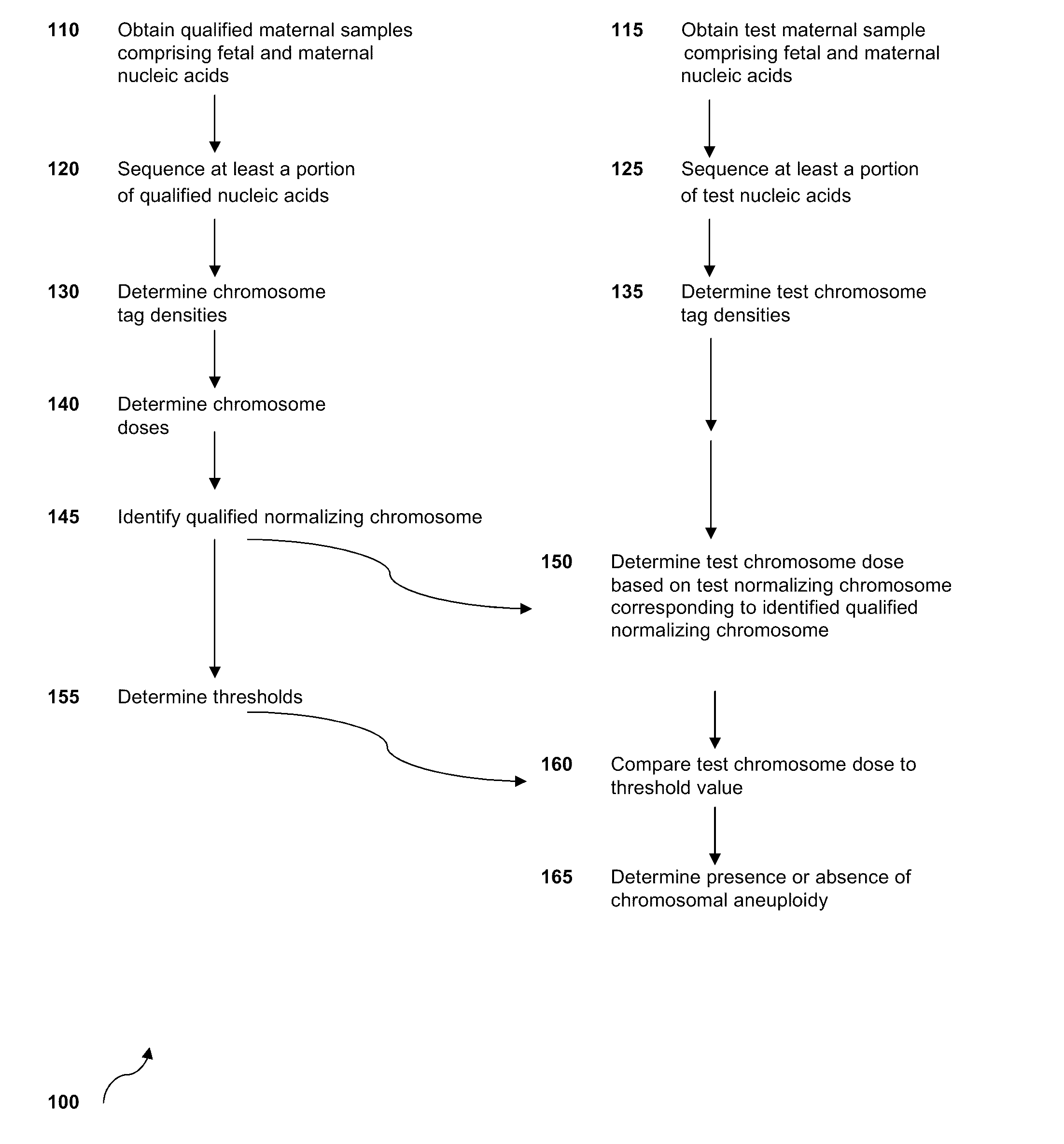
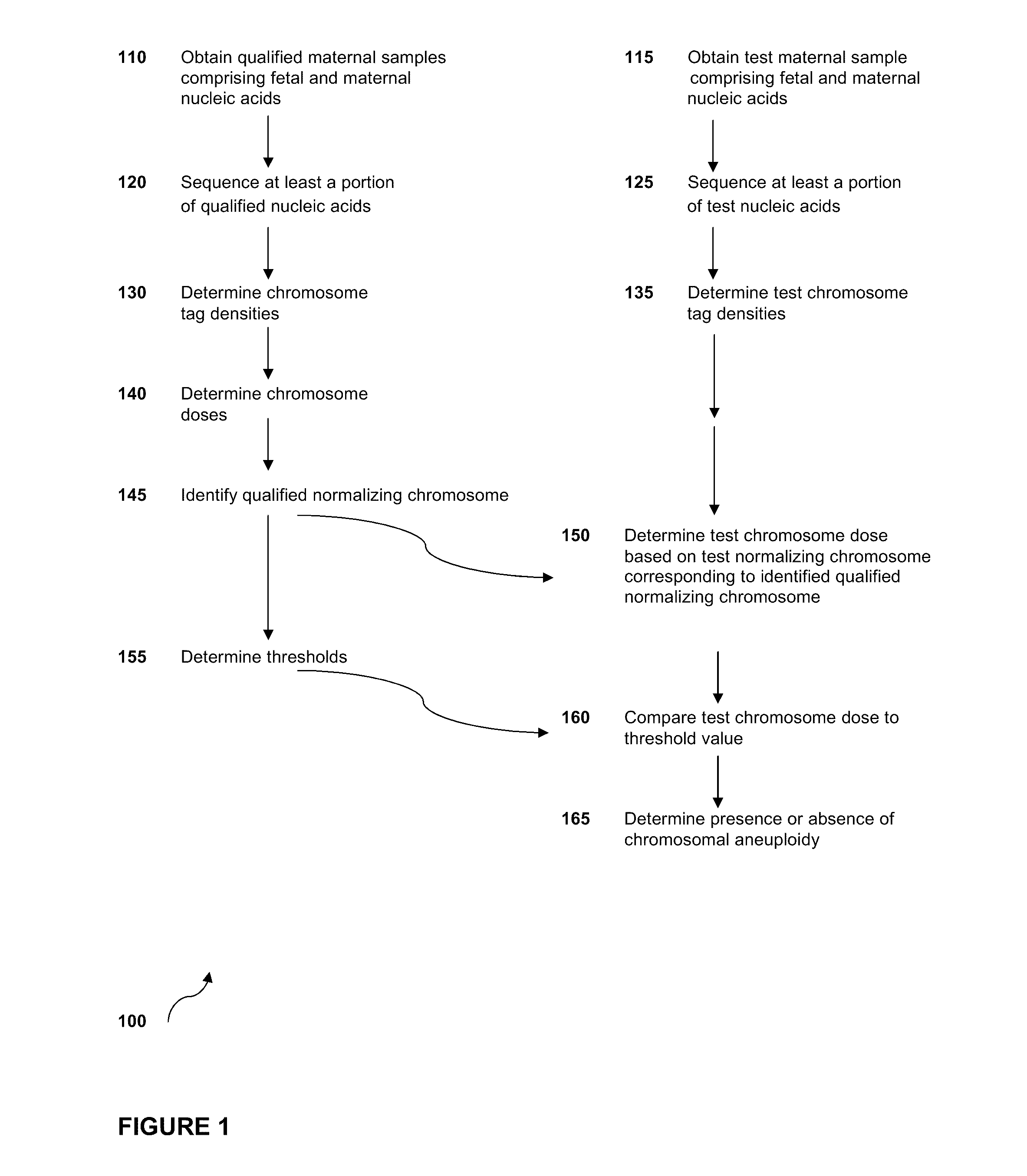
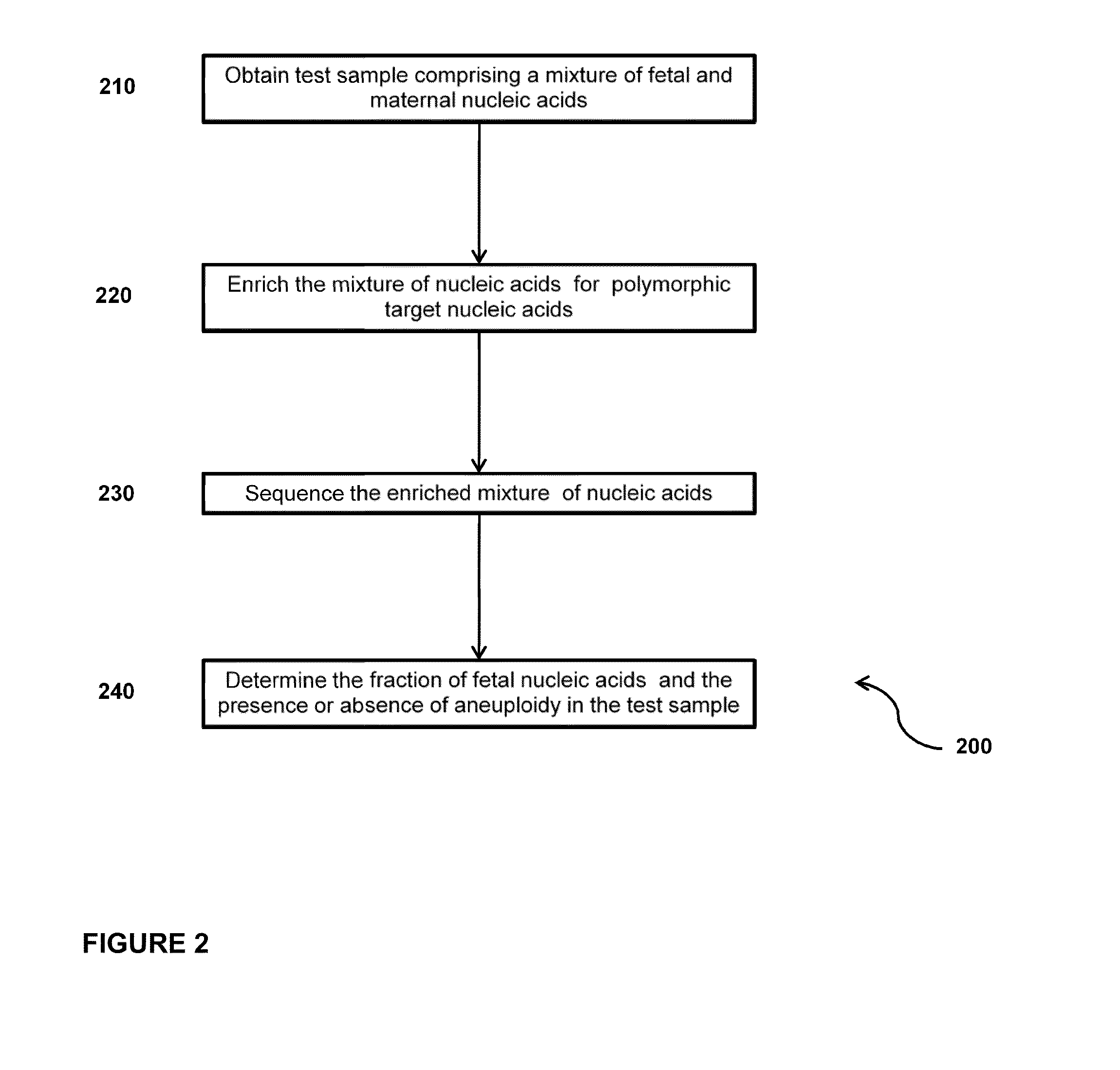
Sequencing methods and compositions for prenatal diagnoses
ActiveUS20110201507A1Quality improvementEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPrenatal diagnosisGenetics
The invention provides methods for determining aneuploidy and / or fetal fraction in maternal samples comprising fetal and maternal cfDNA by massively parallel sequencing. The method comprises a novel protocol for preparing sequencing libraries that unexpectedly improves the quality of library DNA while expediting the process of analysis of samples for prenatal diagnoses.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Arrayed biomolecules and their use in sequencing
InactiveUS7232656B2Reduce interferencePermit resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsGenome variationComputational biology
The invention is directed to a method for analysing genome wide variation in an individual. The method comprises randomly fragmenting the individual's genome and generating sequence reads of multiple bases on all fragments of the individual's genome, aligning the sequence reads generated with a known genomic reference sequence, and analysing variations between the sequence reads derived from the individual's genome and the known genomic reference sequence.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
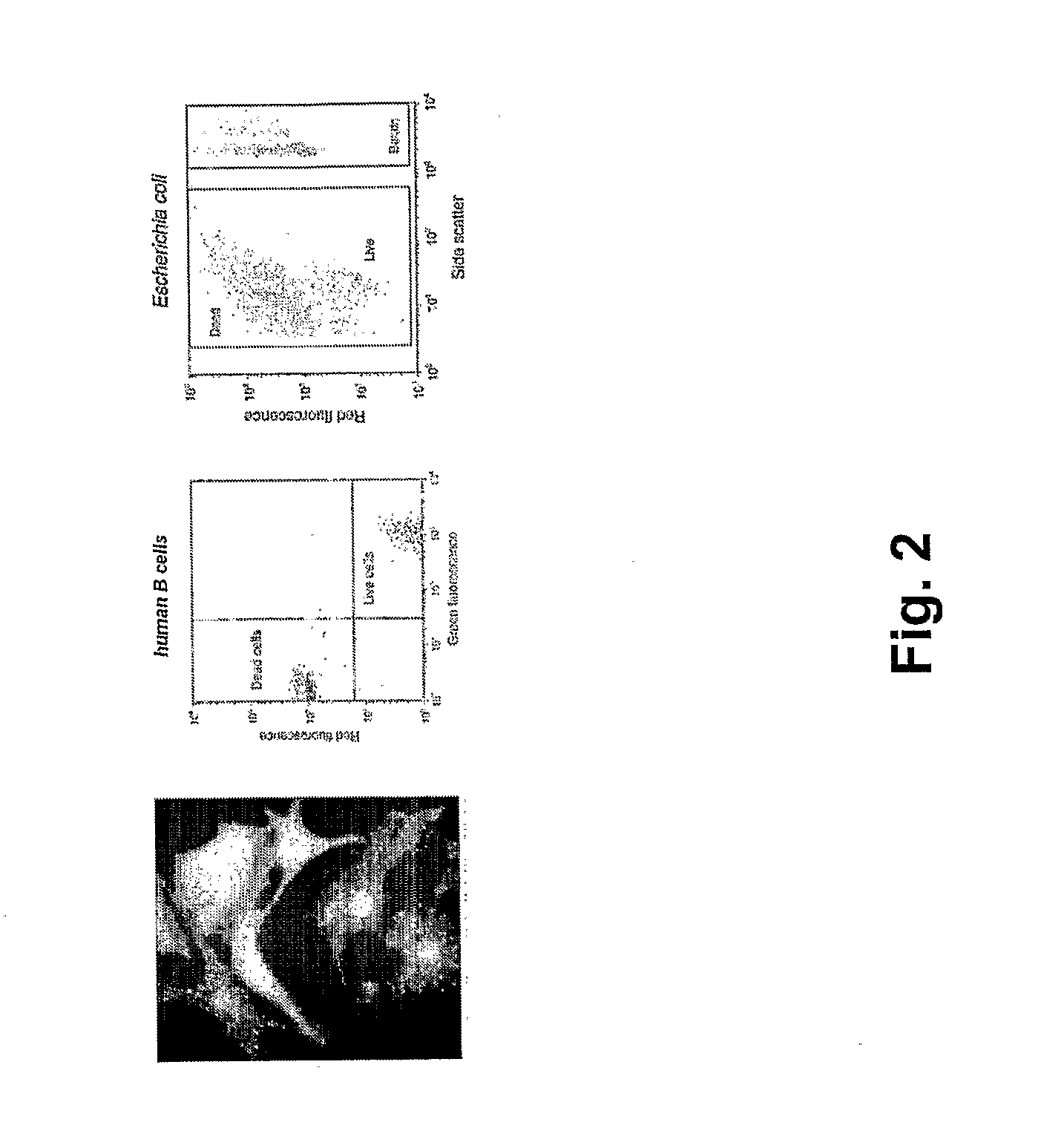
Nucleic acid amplification with continuous flow emulsion
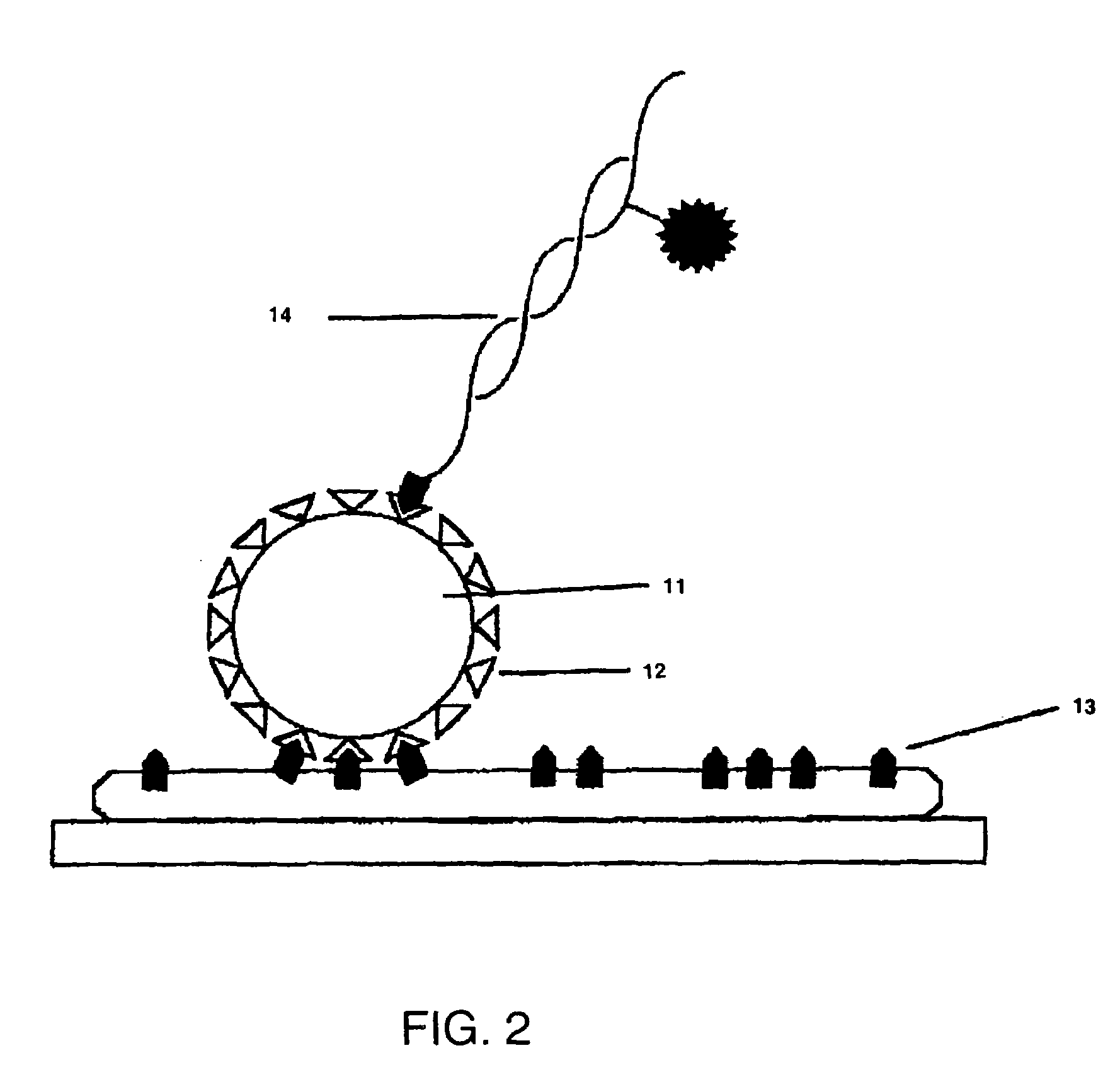
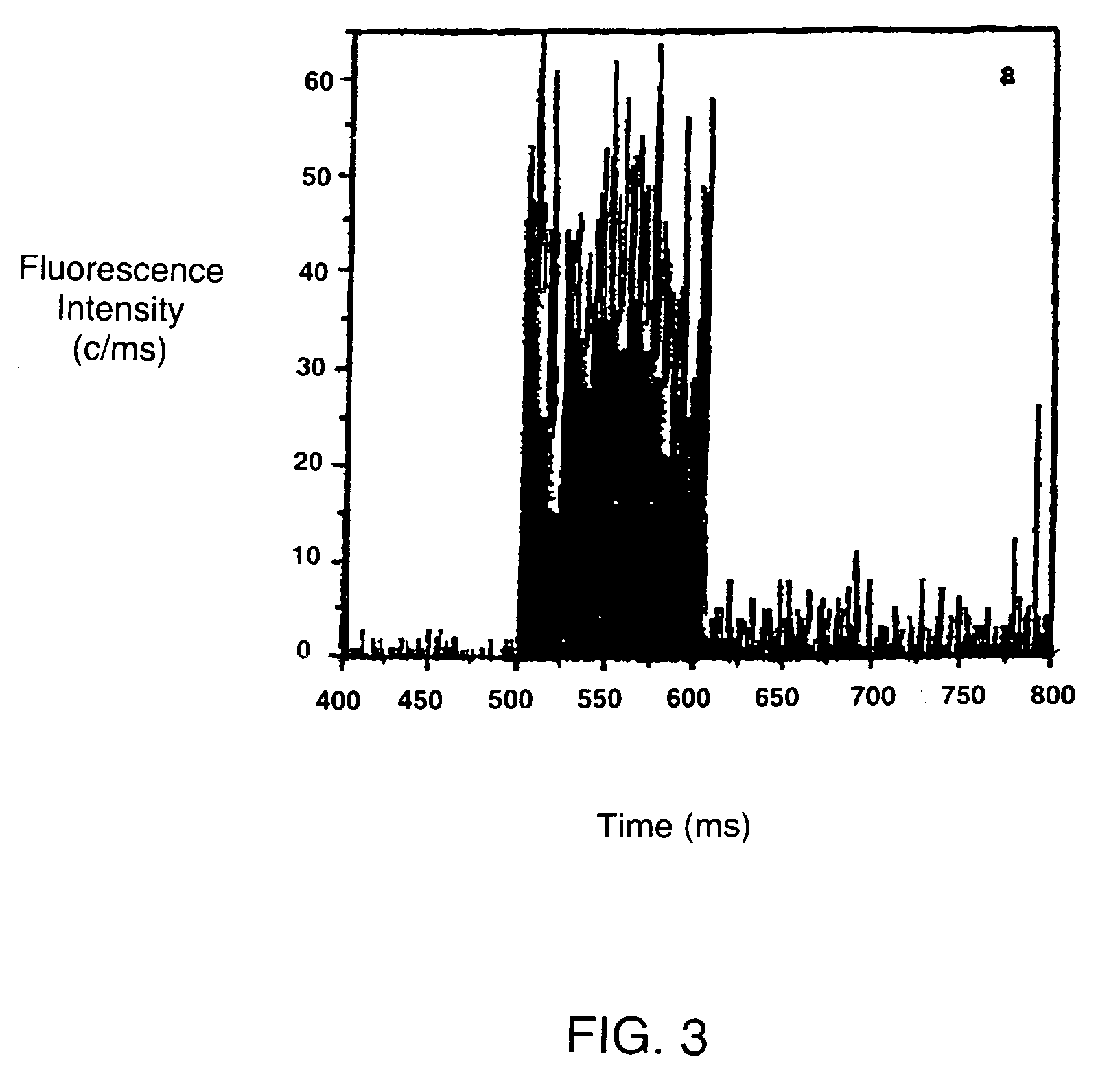
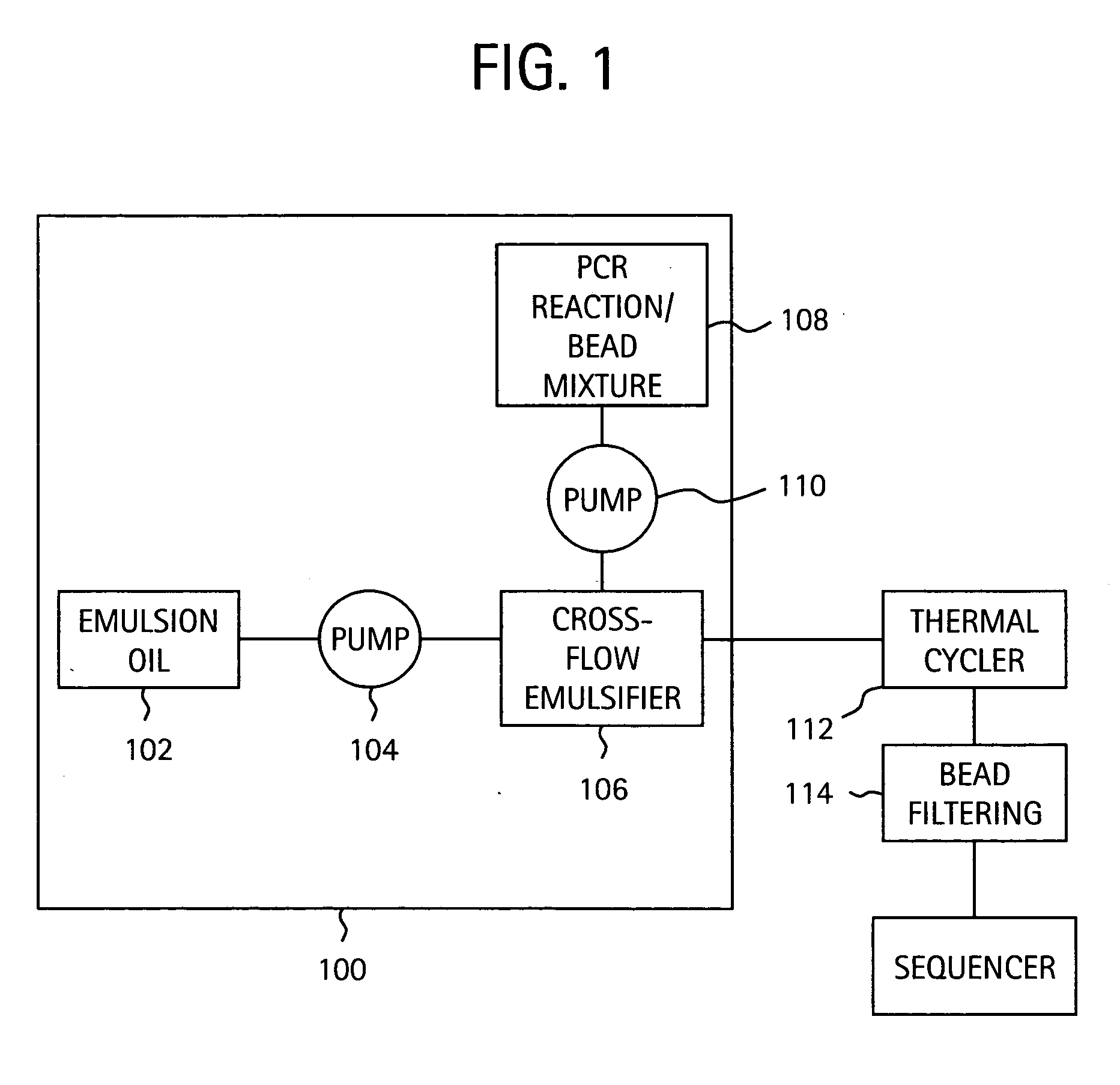
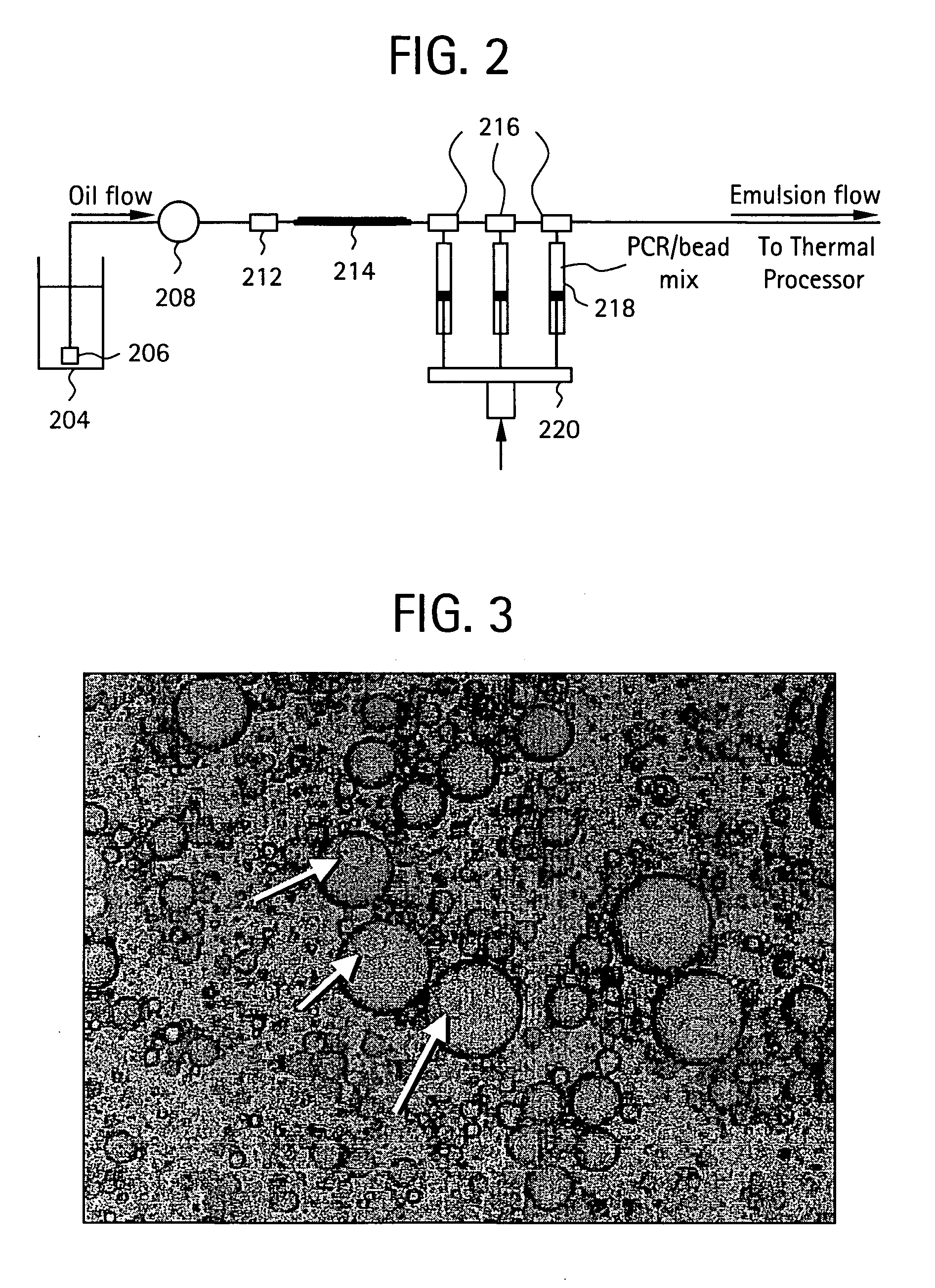
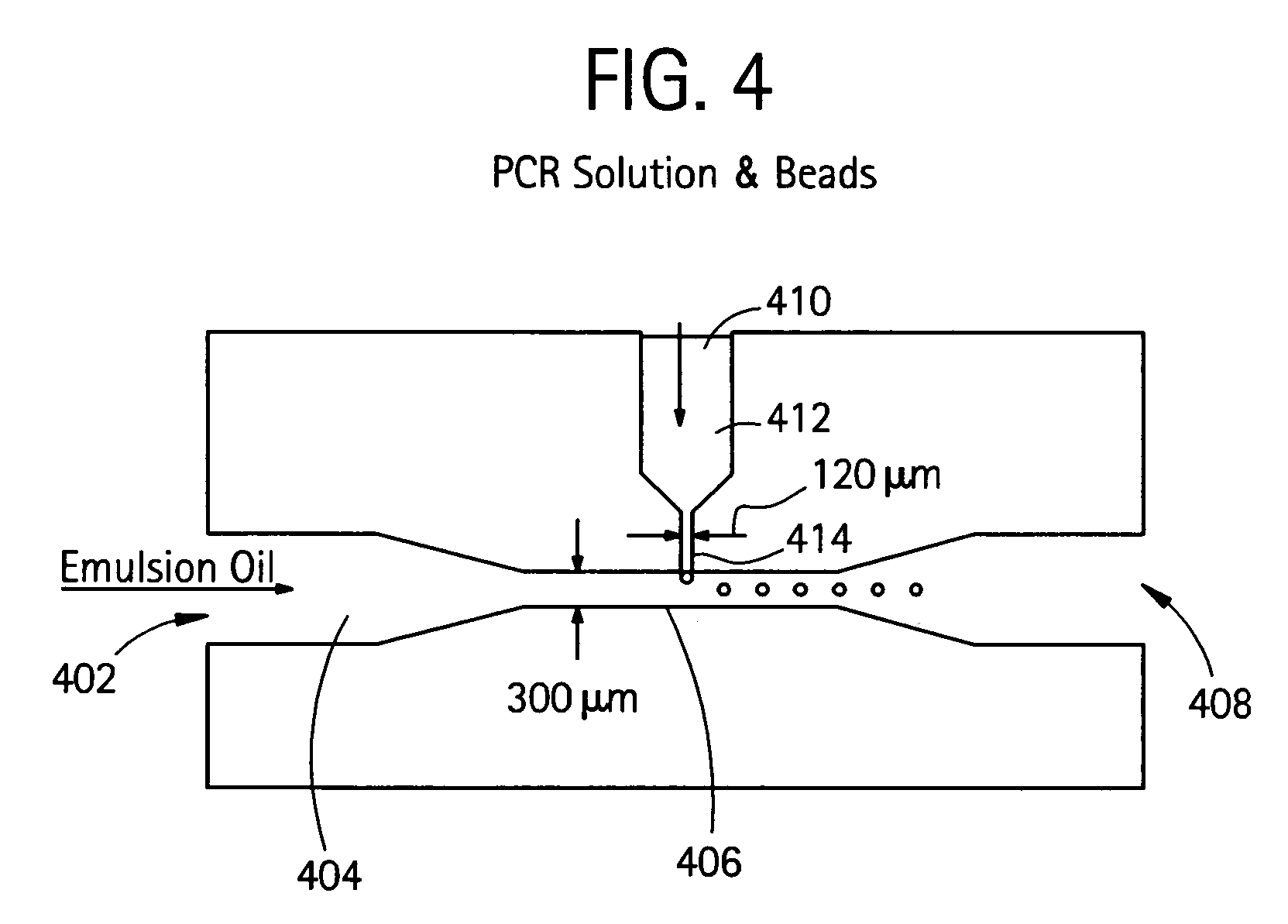
InactiveUS20050227264A1Rapid and economical mannerReduce nozzle cloggingHeating or cooling apparatusFlow mixersMicroreactorGenetic Materials
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods and devices / systems for amplifying genetic material and may include providing a water-in-oil emulsion in a continuous flow. The emulsion may include a plurality of water droplets comprising microreactors. Each of the plurality of microreactors may include a single bead capable of capturing a nucleic acid template, a single species nucleic acid template and sufficient reagents to amplify the copy number of the nucleic acid template. The method also includes flowing the emulsion across a first temperature zone and a second lower temperature zone to thermally process the microreactors to amplify the nucleic acid template by polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Method for separating analyte from a sample
InactiveUS6893879B2Improve elution efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSporeChemical reaction
An analyte is separated from a fluid sample by introducing the sample into a cartridge having an extraction chamber containing capture material for capturing the analyte. The sample is forced to flow through the extraction chamber to capture the analyte with the capture material in the extraction chamber. The captured analyte is then eluted from the extraction chamber by forcing an elution fluid to flow through the extraction chamber. The cartridge may optionally include a lysing region for lysing sample components (e.g., cells spores, or microorganisms), a waste chamber for storing waste fluid, and reaction or detection chambers for chemically reacting or detecting the eluted analyte.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Nanopore sequencing devices and methods
ActiveUS20100331194A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes arrays of nanopores having incorporated electronic circuits, for example, in CMOS. In some cases, the arrays of nanopores comprise resistive openings for isolating the electronic signals for improved sequencing. Methods for controlling translocation of through the nanopore are disclosed.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Apparatus and method for combinatorial chemistry synthesis
InactiveUS6045755AOvercome problemsImprove throughputEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisProcess engineering
In a first embodiment, this invention includes an integrated robot apparatus for performing combinatorial chemistry synthesis protocols and having interchangeable work-stations, robot arm tools, and reaction vessels and reaction vessel arrays. The work-stations and tools are specialized to perform tasks necessary for the synthesis in a plurality of the reaction vessels grouped in a plurality of the reaction vessel arrays. Preferably, these elements function interchangeably because they have standardized sizes and conformation. The work-stations and tools include those for fluid dispensing or aspirating from individual reaction vessels or from all the reaction vessels in an array simultaneously. The reaction vessels can include, alternatively, stackable, ball-sealed reaction vessels, microtitre-like reaction vessel arrays, arrays of independent reaction vessels, valve-sealed reaction vessels, septum-sealed reaction vessels, and syringe reaction vessels. In alternative embodiments, this invention includes these work-stations, tools, reaction vessels and reaction vessel arrays in various combinations or sub-combinations either for use in partially integrated robots or for manual or standalone use.
Owner:LION BIOSCIENCE AG
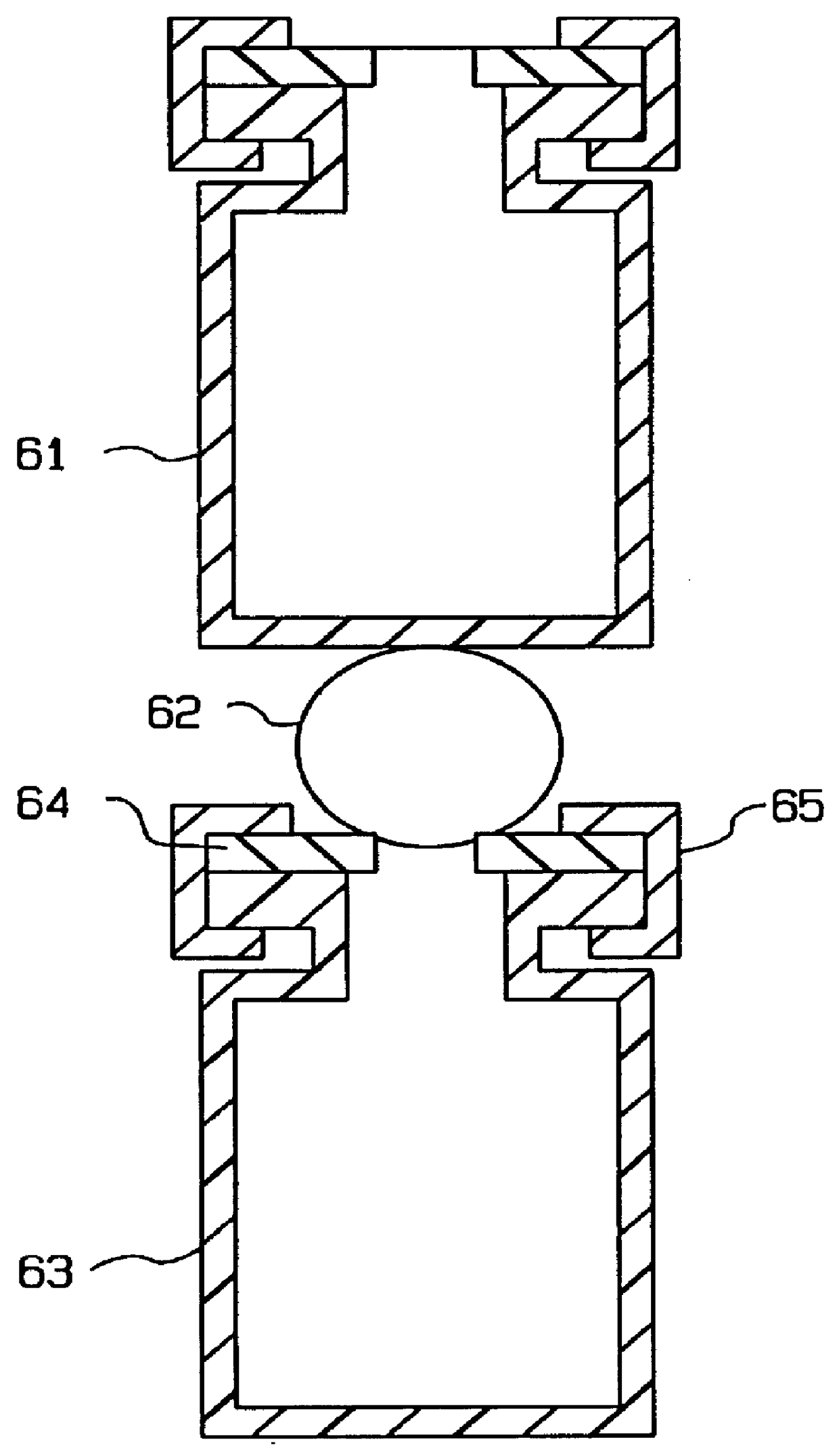
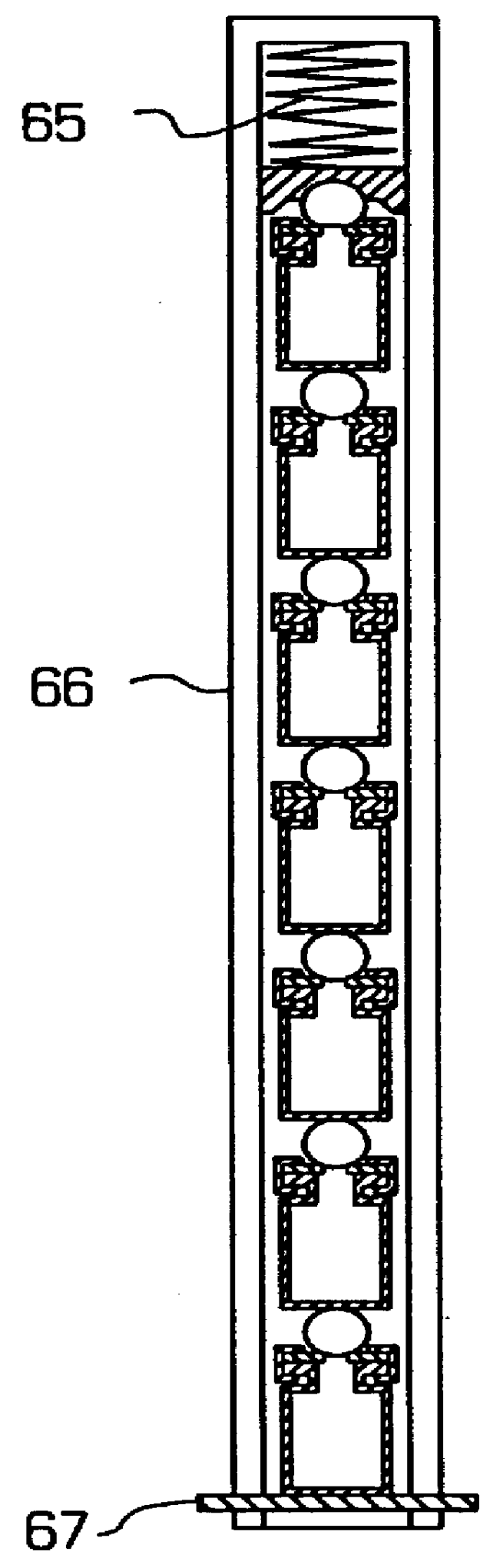
Method and apparatus for acoustically controlling liquid solutions in microfluidic devices
InactiveUS6948843B2Improve reaction speedAccelerating molecular interactionSequential/parallel process reactionsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSound sourcesAcoustic energy
Acoustic energy is used to control motion in a fluid. According to one embodiment, the invention directs acoustic energy at selected naturally occurring nucleation features to control motion in the fluid. In another embodiment, the invention provides focussed or unfocussed acoustic energy to selectively placed nucleation features to control fluid motion. According to one embodiment, the invention includes an acoustic source, a controller for controlling operation of the acoustic source, and one or more nucleation features located proximate to or in the fluid to be controlled.
Owner:COVARIS INC
Self-encoding fiber optic sensor
InactiveUS7115884B1Overcome limitationsEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensor arrayLight energy
Self-encoding microspheres having distinct characteristic optical response signatures to specific target analytes may be mixed together while the ability is retained to identify the sensor type and location of each sensor in a random dispersion of large numbers of such sensors in a sensor array using an optically interrogatable encoding scheme, resulting in a microsphere-based analytic chemistry system. Individual microsphere sensors are disposed in microwells at a distal end of a fiber bundle and are optically coupled to discrete fibers or groups of fibers within the bundle to form an optical fiber bundle sensor. The identities of the individual sensors in the array are self-encoded by exposing the array to a reference analyte while illuminating the array with excitation light energy. A single sensor array may carry thousands of discrete sensing elements whose combined signal provides for substantial improvements in sensor detection limits, response times and signal-to-noise ratios.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS20020172963A1High precisionHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
Compositions for the electronic detection of analytes utilizing monolayers
Owner:OSMETECH TECH +2
Modular point-of-care devices, systems, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090088336A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalytePoint of care device
The present invention provides devices and systems for use at the point of care. The methods devices of the invention are directed toward automatic detection of analytes in a bodily fluid. The components of the device are modular to allow for flexibility and robustness of use with the disclosed methods for a variety of medical applications.
Owner:LABRADOR DIAGNOSTICS LLC
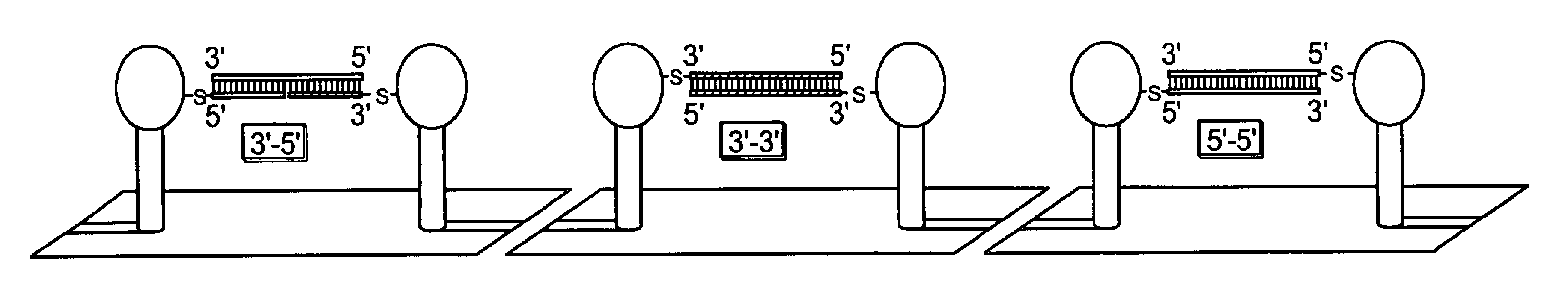
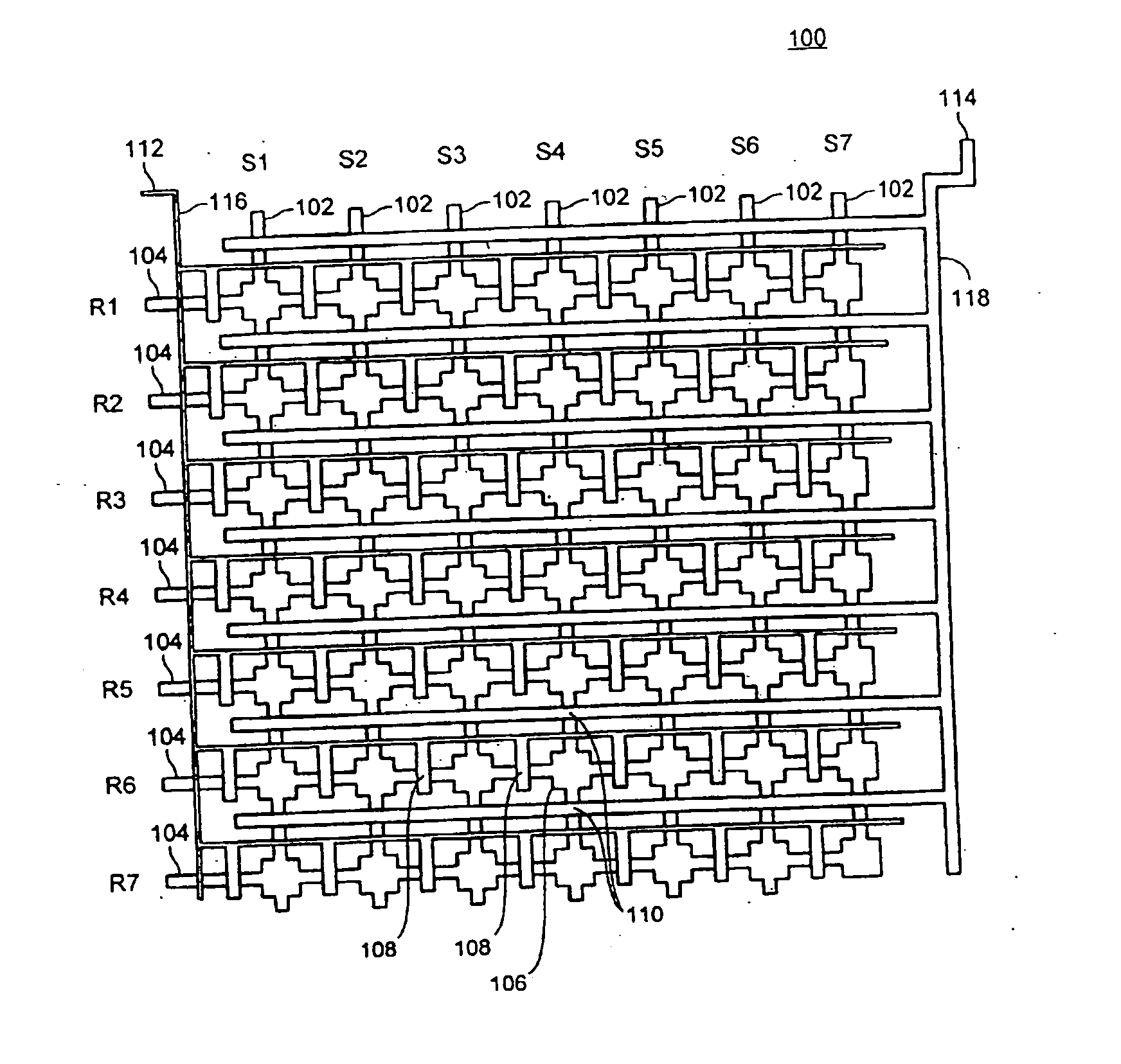
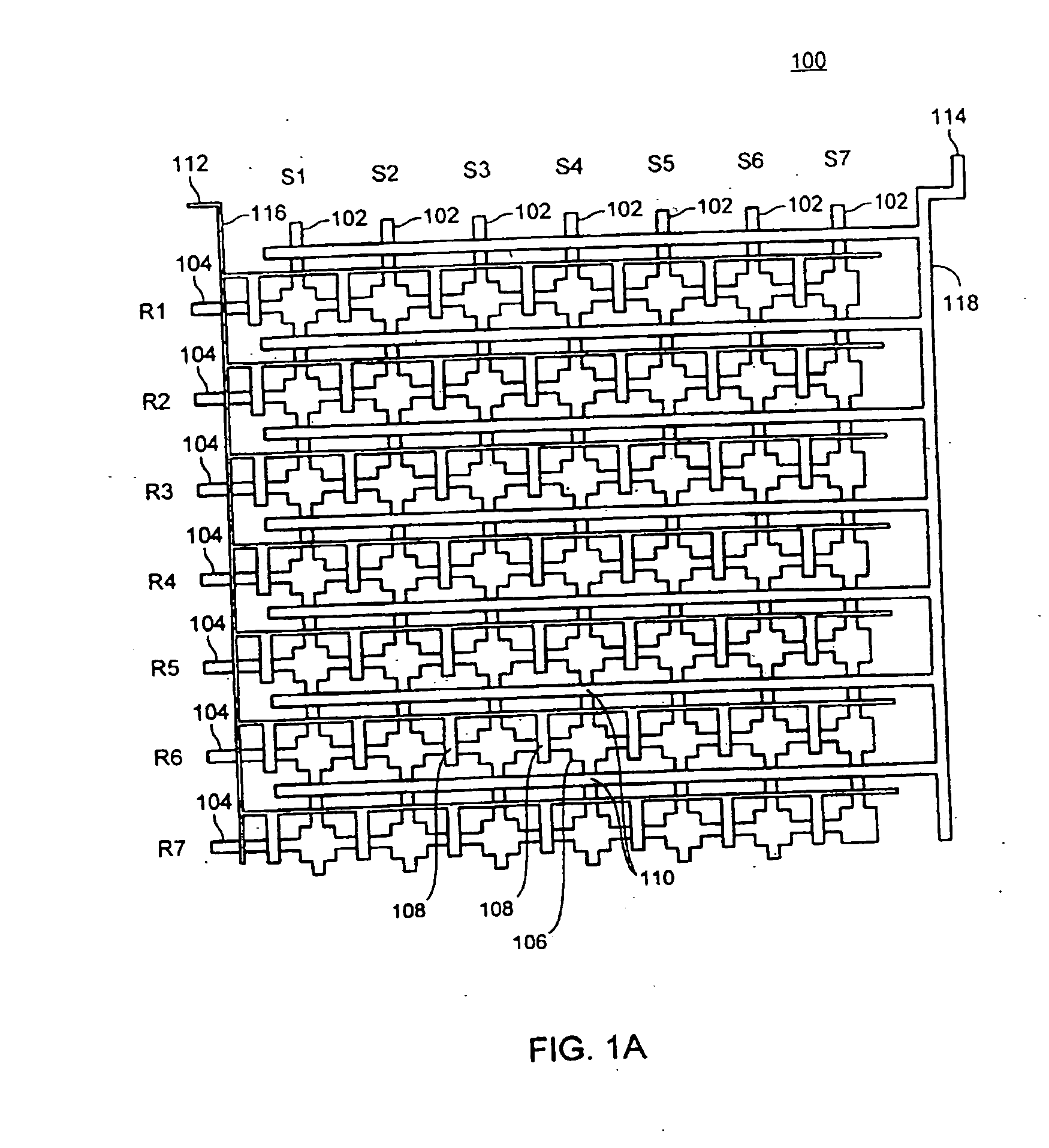
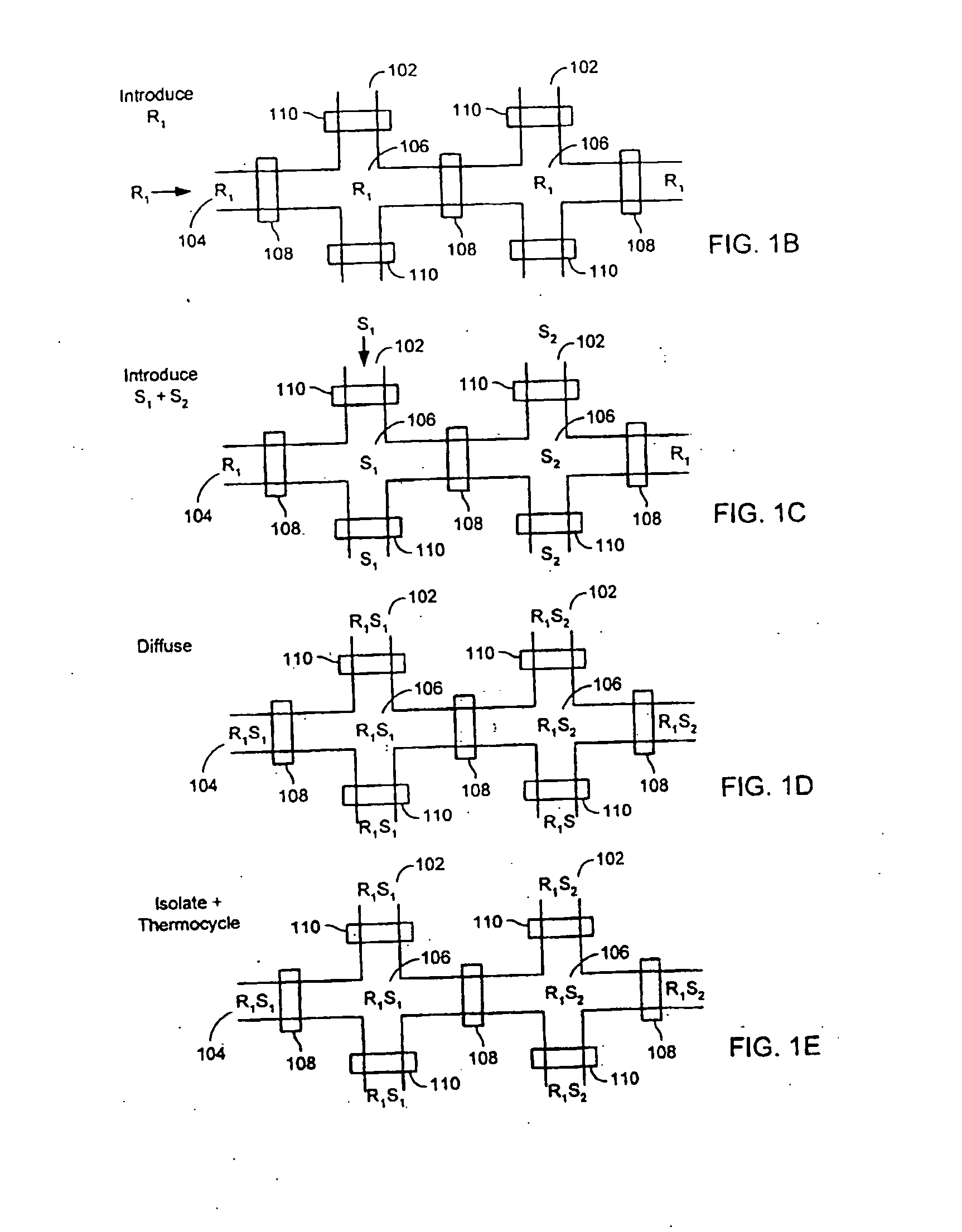
Oligonucleotide arrays and their use for sorting, isolating, sequencing, and manipulating nucleic acids
InactiveUS6322971B1Increase in hybridization specificityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyHybridization ArrayBioinformatics
Ligation methods for manipulating nucleic acid stands and oligonucleotides utilizing hybridization arrays of immobilized oligonucleotides. The oligonucleotide arrays may be plain or sectioned, comprehensive or non-comprehensive. The immobilized oligonucleotides may in some cases be binary oligonucleotides having constant as well as variable segments. Some embodiments include amplification of ligated products.
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY
Microfluidic devices comprising biochannels
InactiveUS6875619B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteBiological organism
The present invention is directed to a variety of microfluidic devices with configurations including the use of biochannels or microchannels comprising arrays of capture binding ligands to capture target analytes in samples. The invention provides microfluidic cassettes or devices that can be used to effect a number of manipulations on a sample to ultimately result in target analyte detection or quantification.
Owner:CLINICAL MICRO SENSORS +1
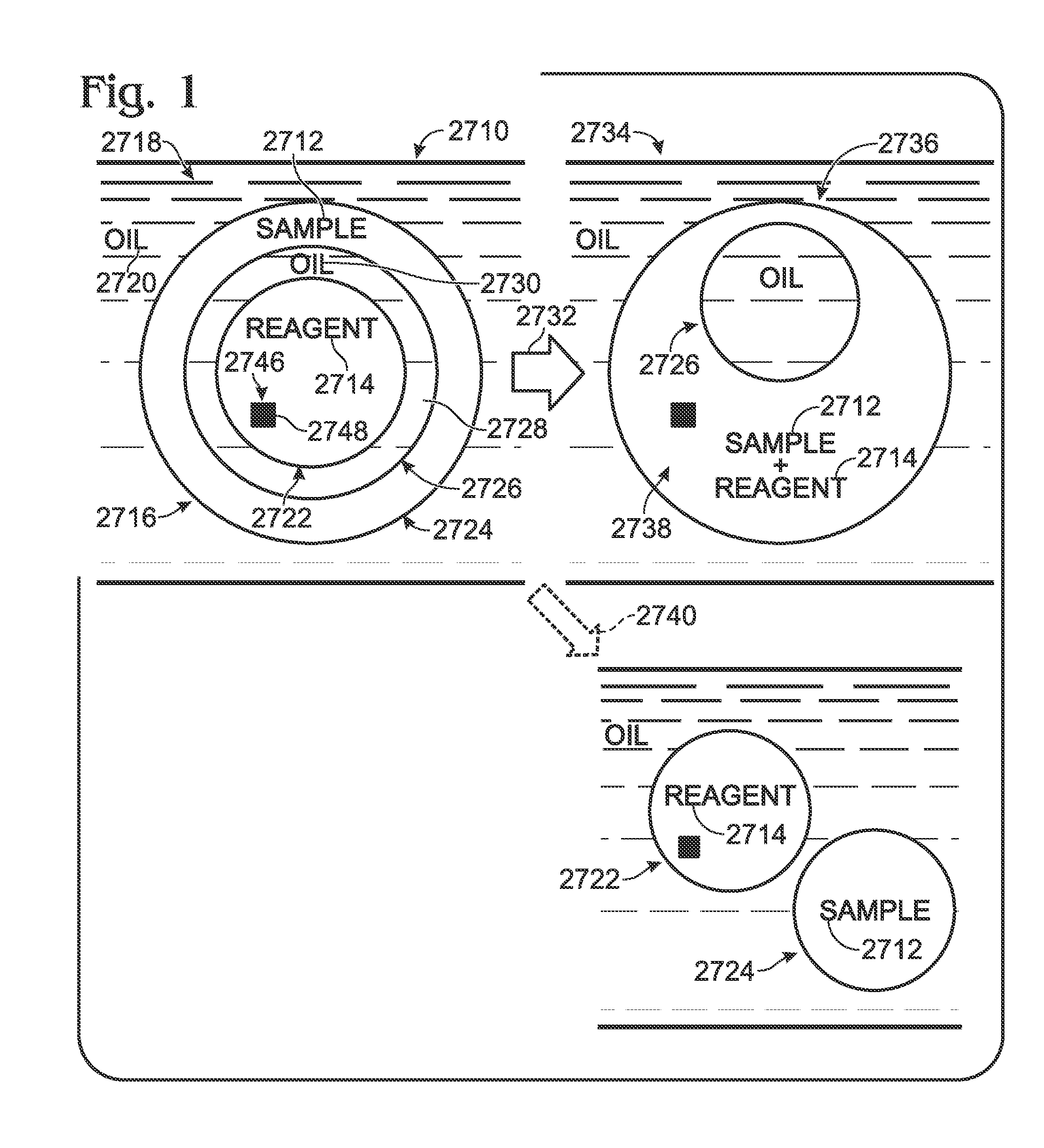
System for mixing fluids by coalescence of multiple emulsions
ActiveUS20110053798A1High-confidence resultLower the volumeSequential/parallel process reactionsHeating or cooling apparatusEmulsionChemistry
System, including methods, apparatus, compositions, and kits, for the mixing of small volumes of fluid by coalescence of multiple emulsions.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
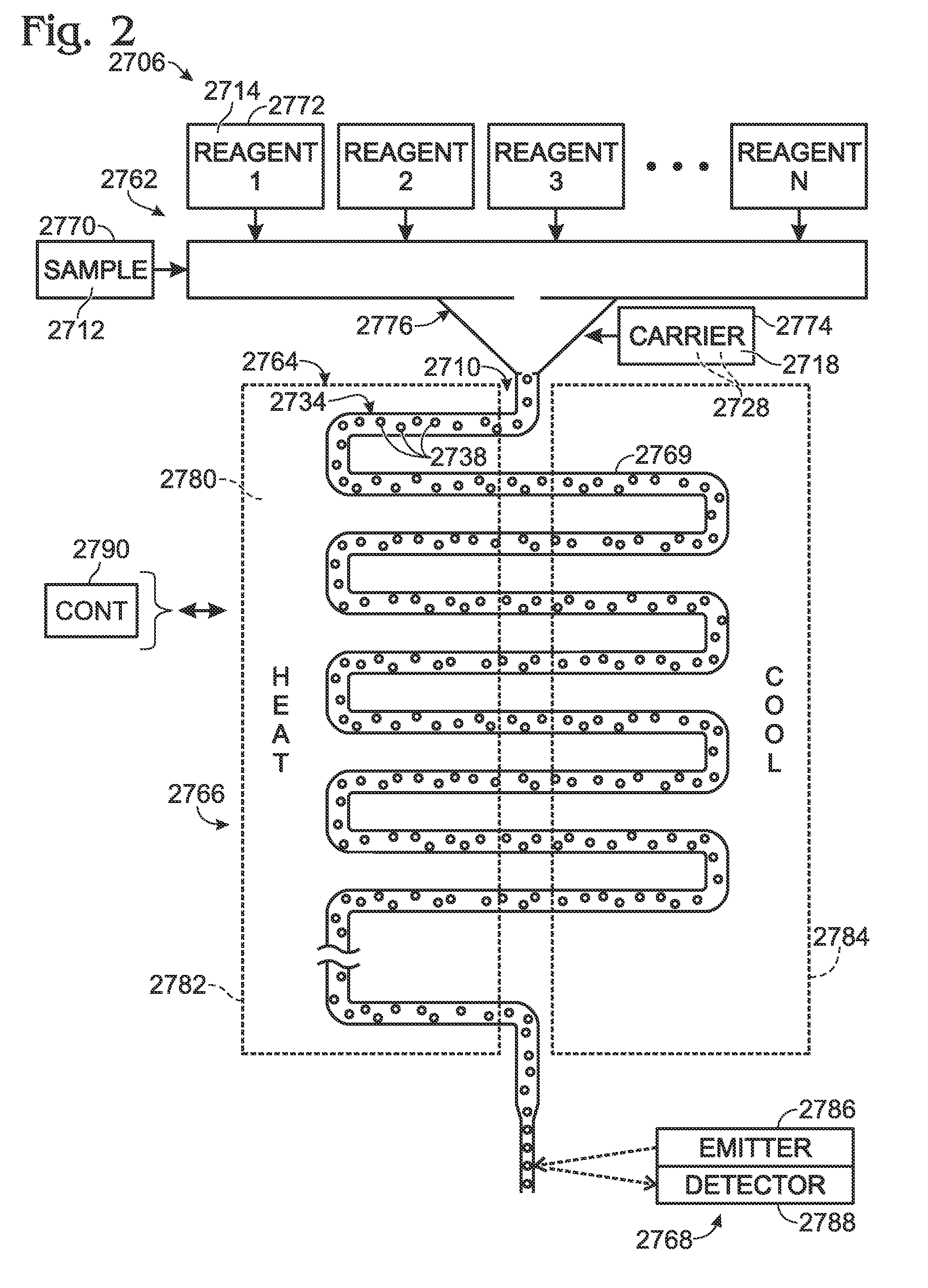
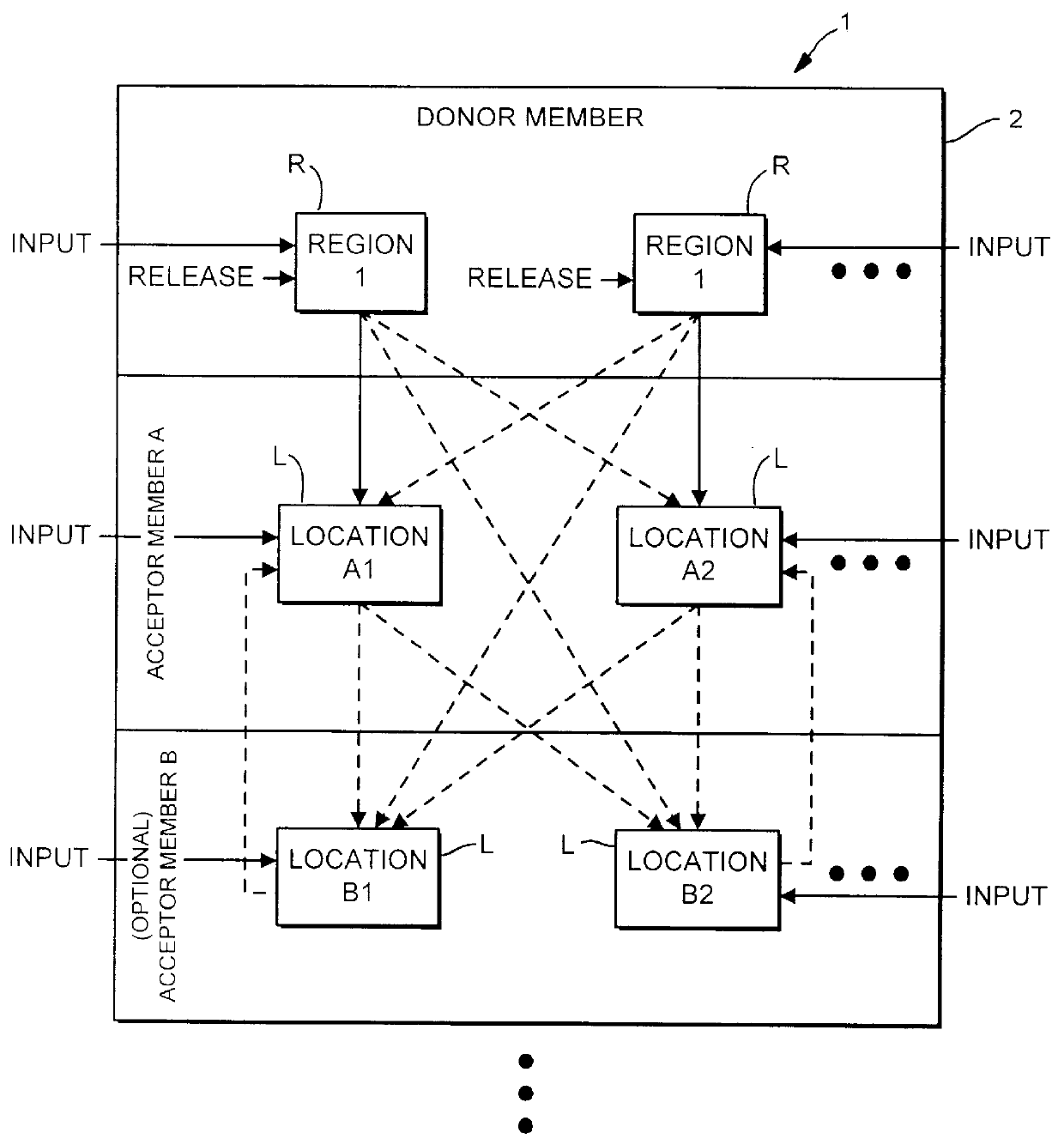
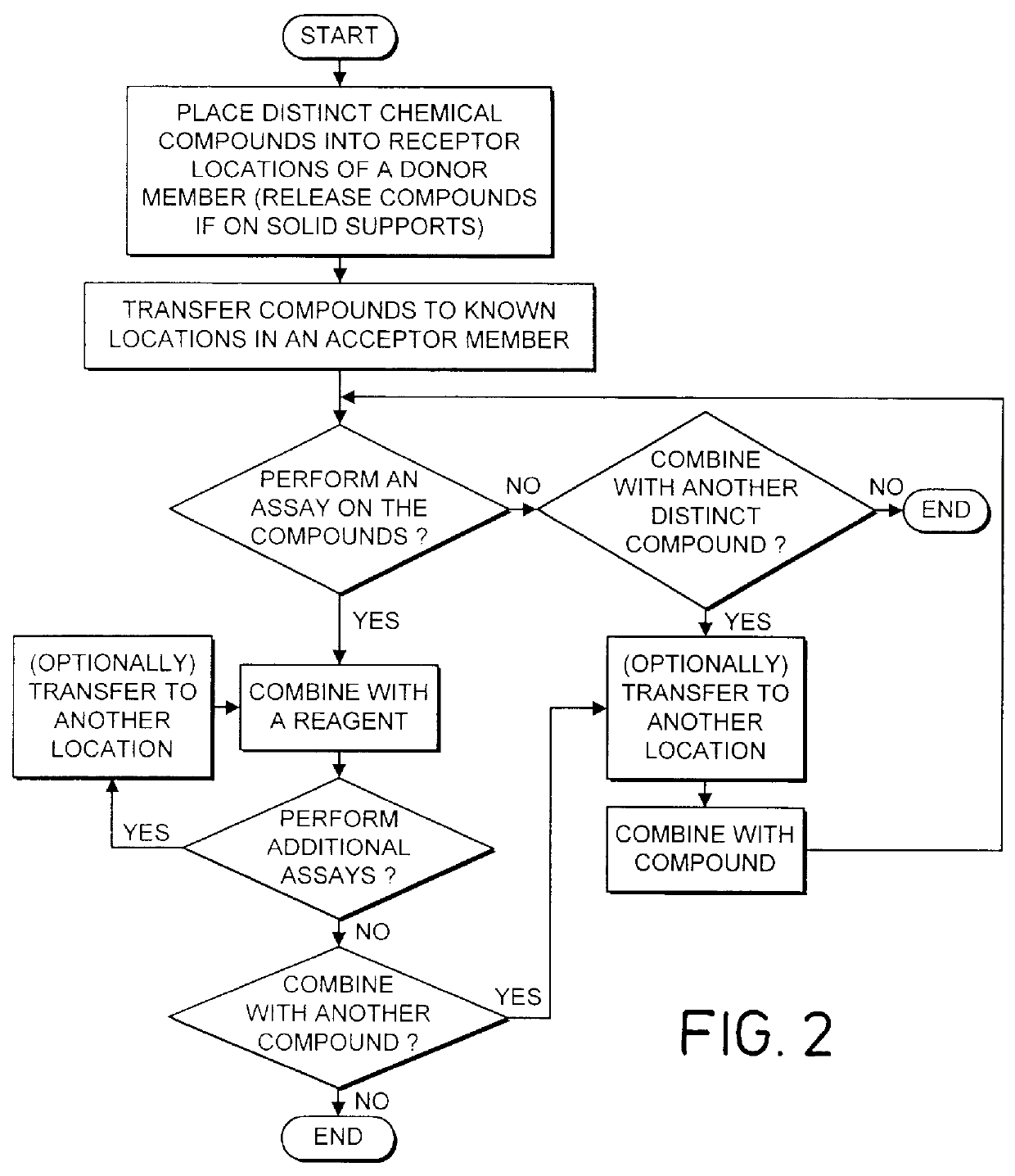
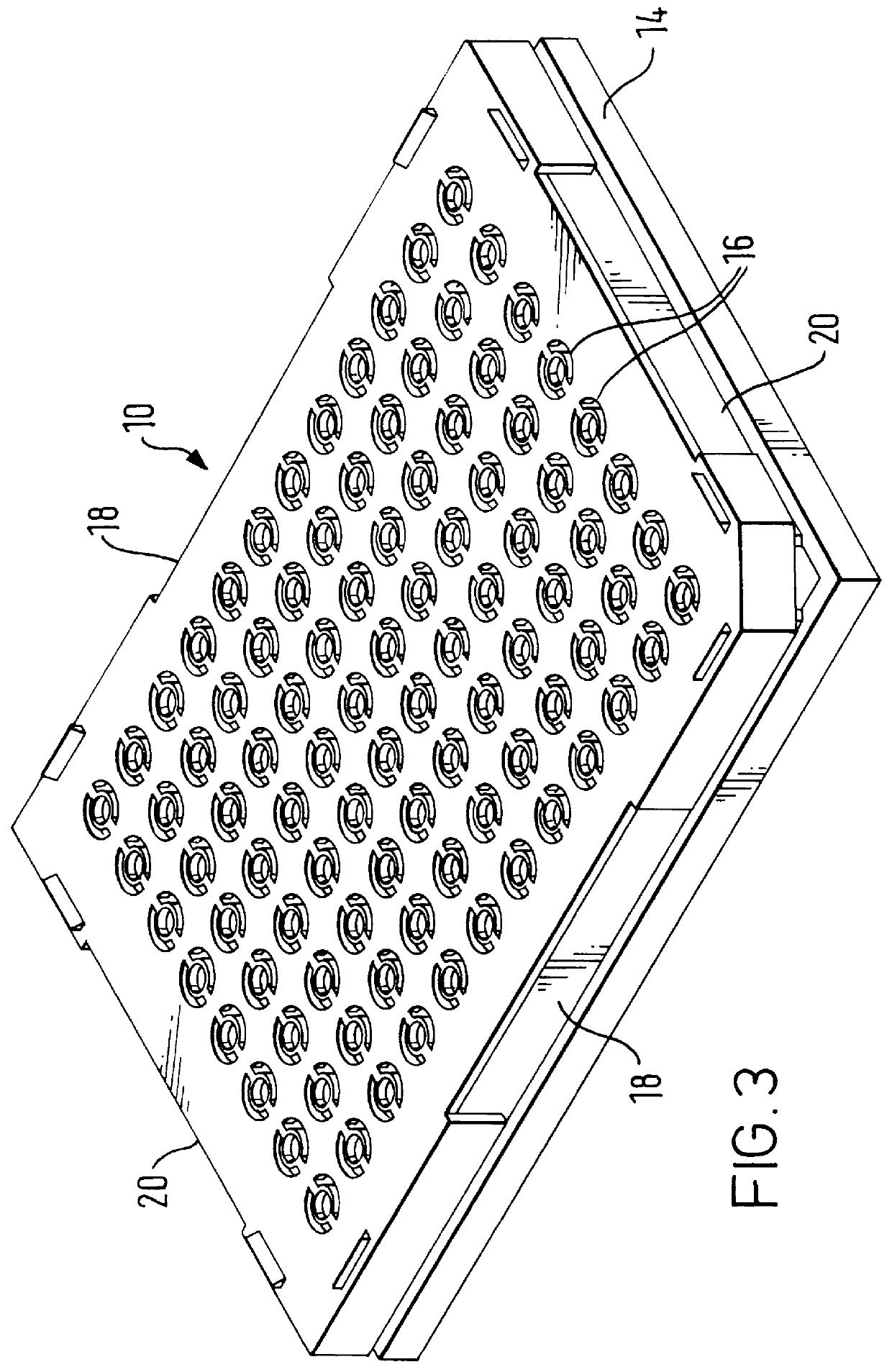
Method and apparatus for transferring and combining reagents
InactiveUS6083761AEasy to carryEfficient transferSequential/parallel process reactionsWithdrawing sample devicesChemical compositionCentrifugation
The invention provides exemplary systems, methods, and apparatus for distinctly allocating liquids containing chemical compositions or compounds to known locations in an organized manner so that assays may be performed on the compositions, or so that the chemical compositions may be combined with other distinct chemical compositions or reagents prior to evaluation. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention includes a multiwell plate for handling articles such as resin beads suspended in a liquid. The plate comprises a plurality of wells. The wells in turn have a capillary hole that is adapted to (i) retain articles in the well, and (ii) retain liquid in the well while the liquid is not subjected to extrinsic forces, such as centrifugation or vacuum.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP +1
Multifunctional and multispectral biosensor devices and methods of use
InactiveUS6743581B1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectromagnetic radiationBiology
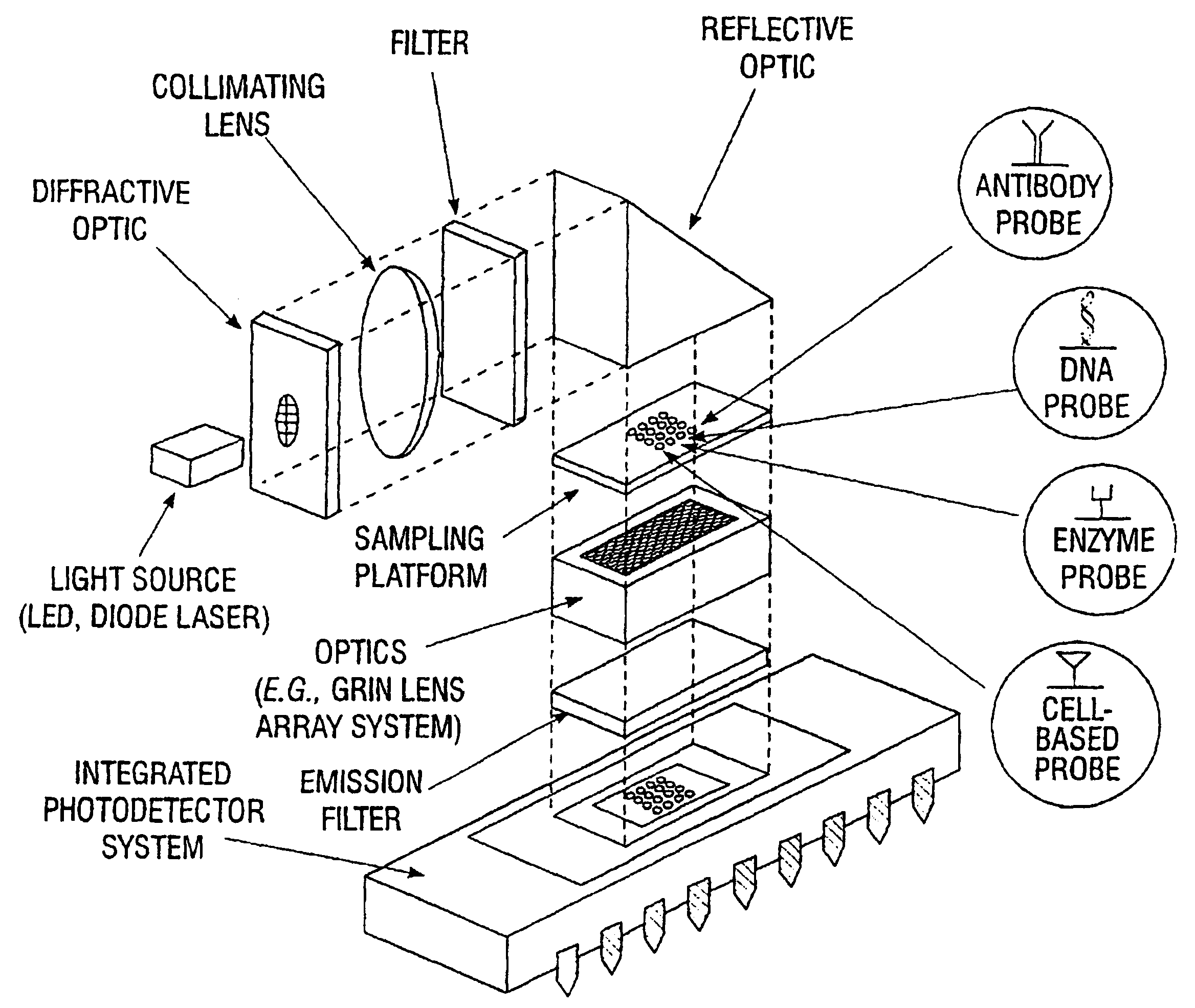
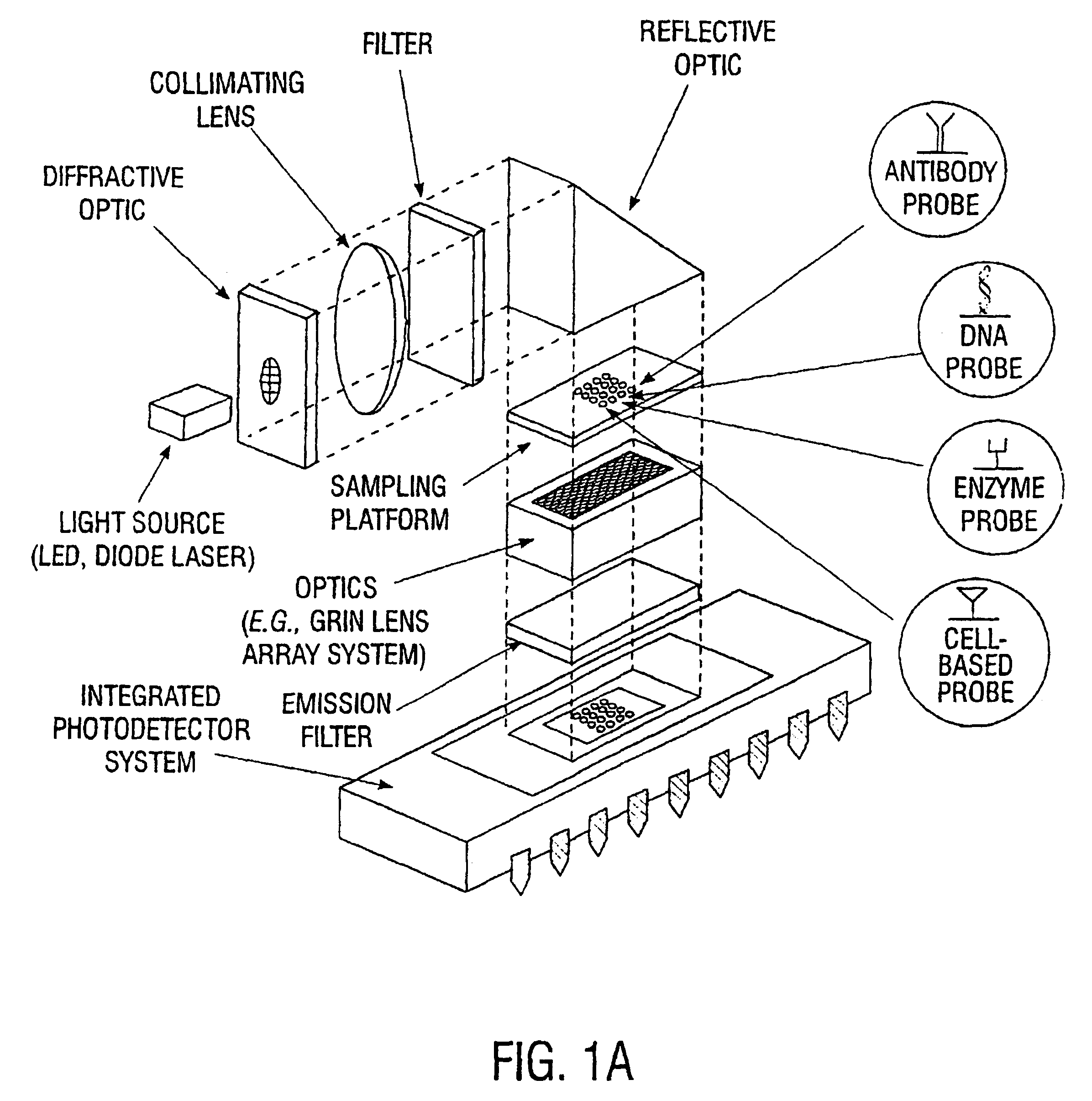
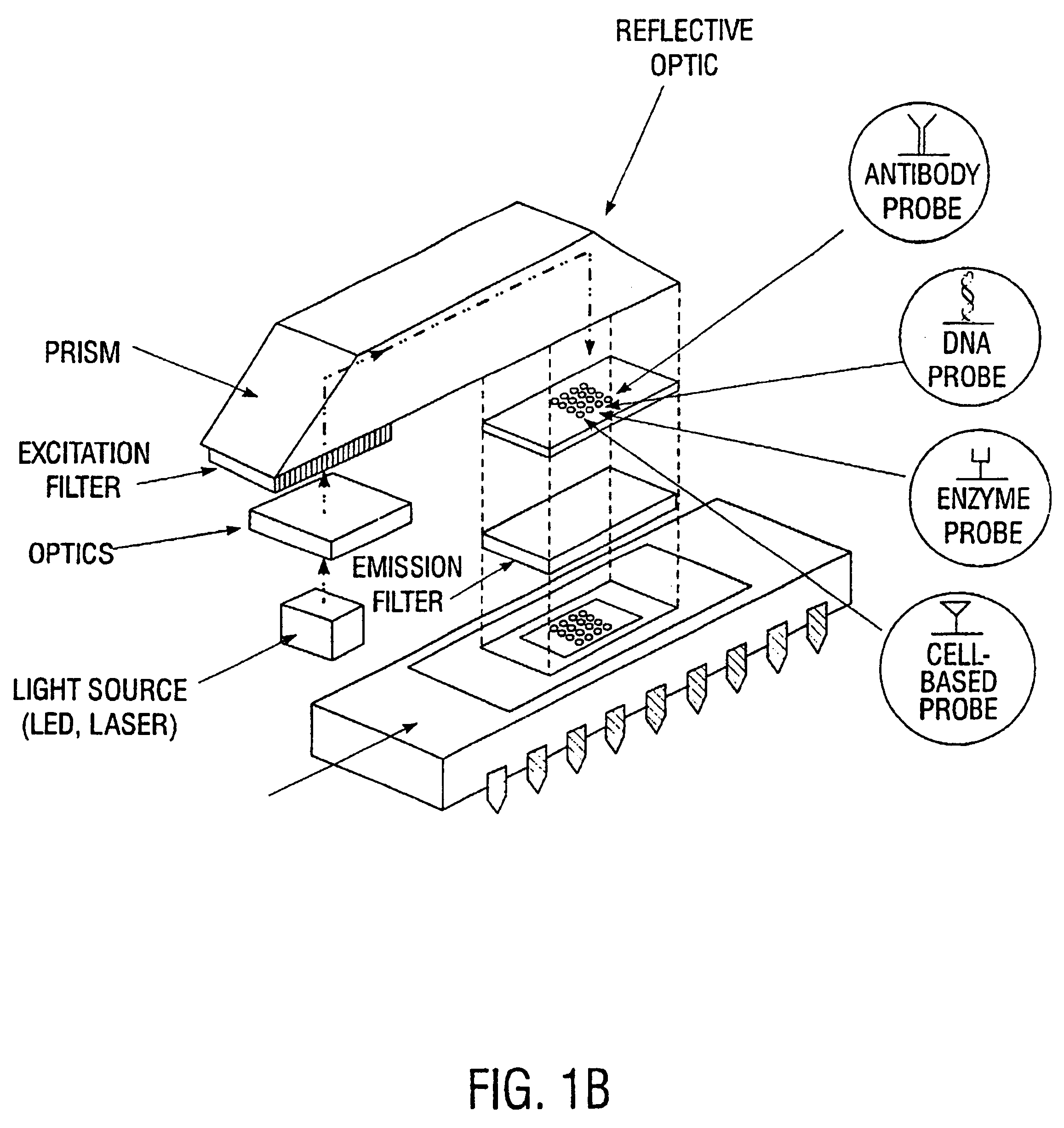
An integrated biosensor system for the simultaneously detection of a plurality of different types of targets includes at least one sampling platform, the sampling platform including a plurality of receptors for binding to the targets. The plurality of receptors include at least one protein receptor and at least one nucleic acid receptor. At least one excitation source of electromagnetic radiation at a first frequency is provided for irradiating the receptors, wherein electromagnetic radiation at a second frequency different from the first frequency is emitted in response to irradiating when at least one of the different types of targets are bound to the receptor probes. An integrated circuit detector system having a plurality of detection channels is also provided for detecting electromagnetic radiation at said second frequency, the detection channels each including at least one detector.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS6958216B2High sensitivityImprove portabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
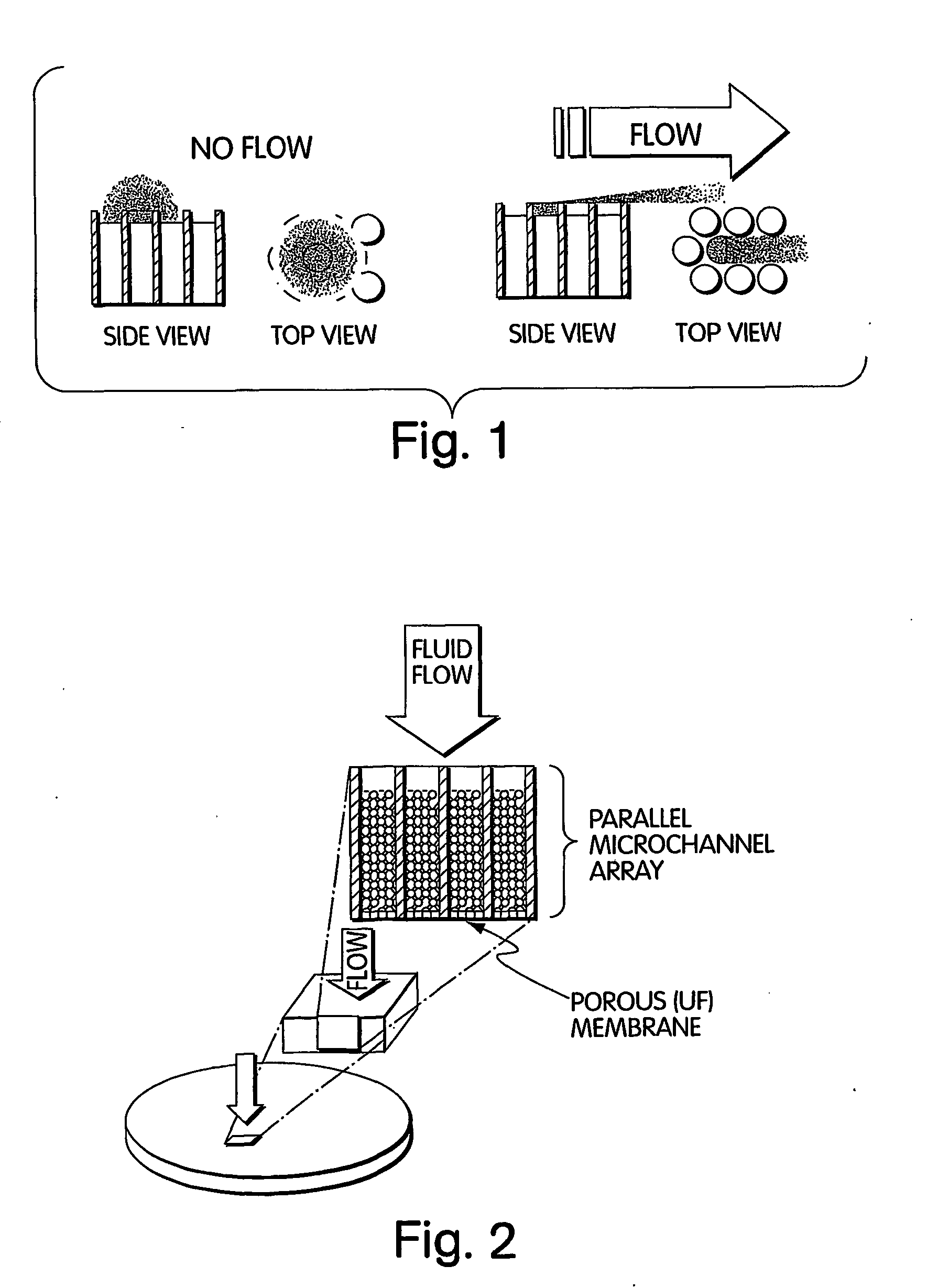
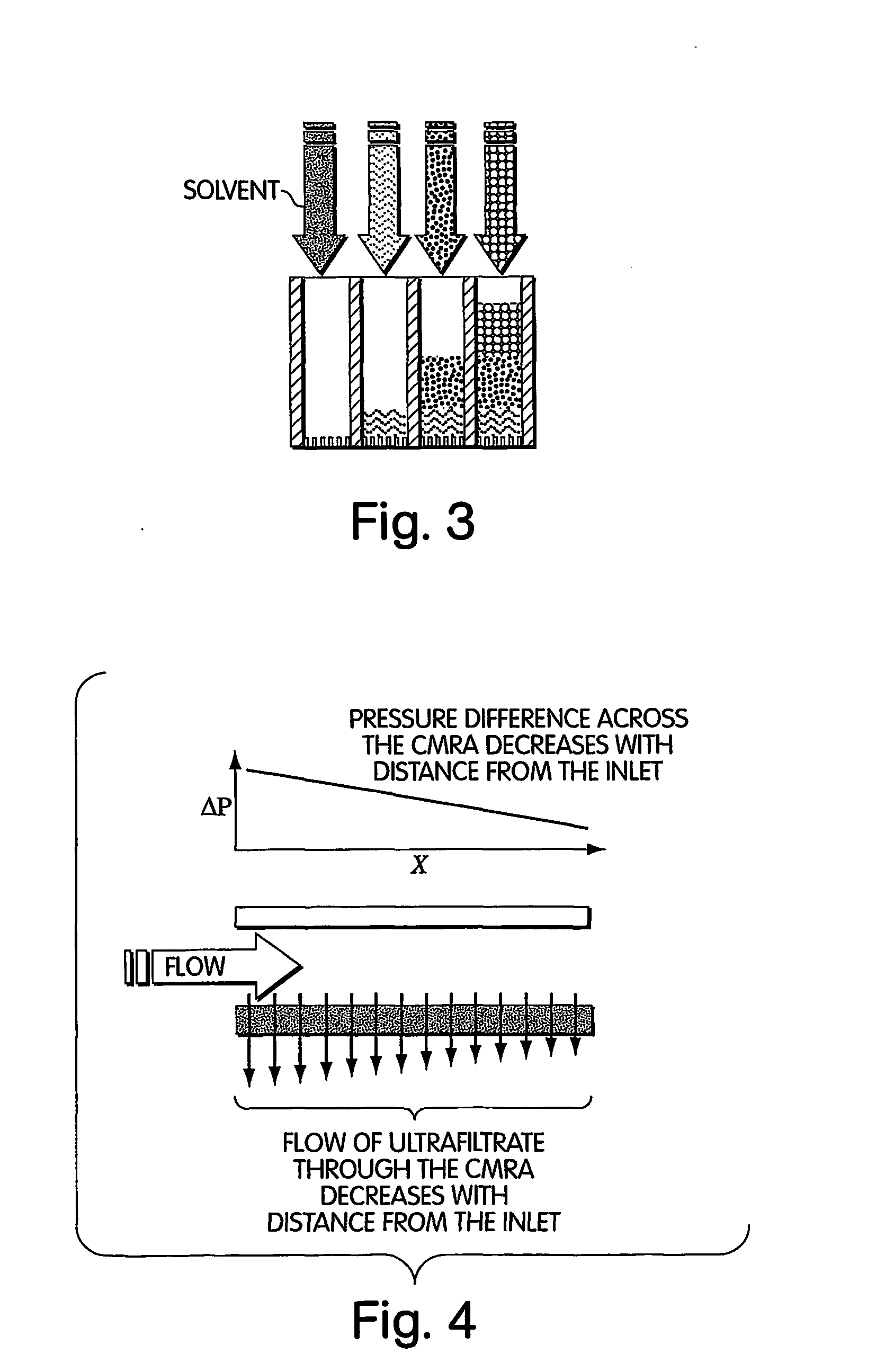
Method for isolation of independent, parallel chemical micro-reactions using a porous filter
InactiveUS20050009022A1Fast deliveryFaster more complete removalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesChemical reactionCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to the field of fluid dynamics. More specifically, this invention relates to methods and apparatus for conducting densely packed, independent chemical reactions in parallel in a substantially two-dimensional array. Accordingly, this invention also focuses on the use of this array for applications such as DNA sequencing, most preferably pyrosequencing, and DNA amplification.
Owner:WEINER MICHAEL P +4
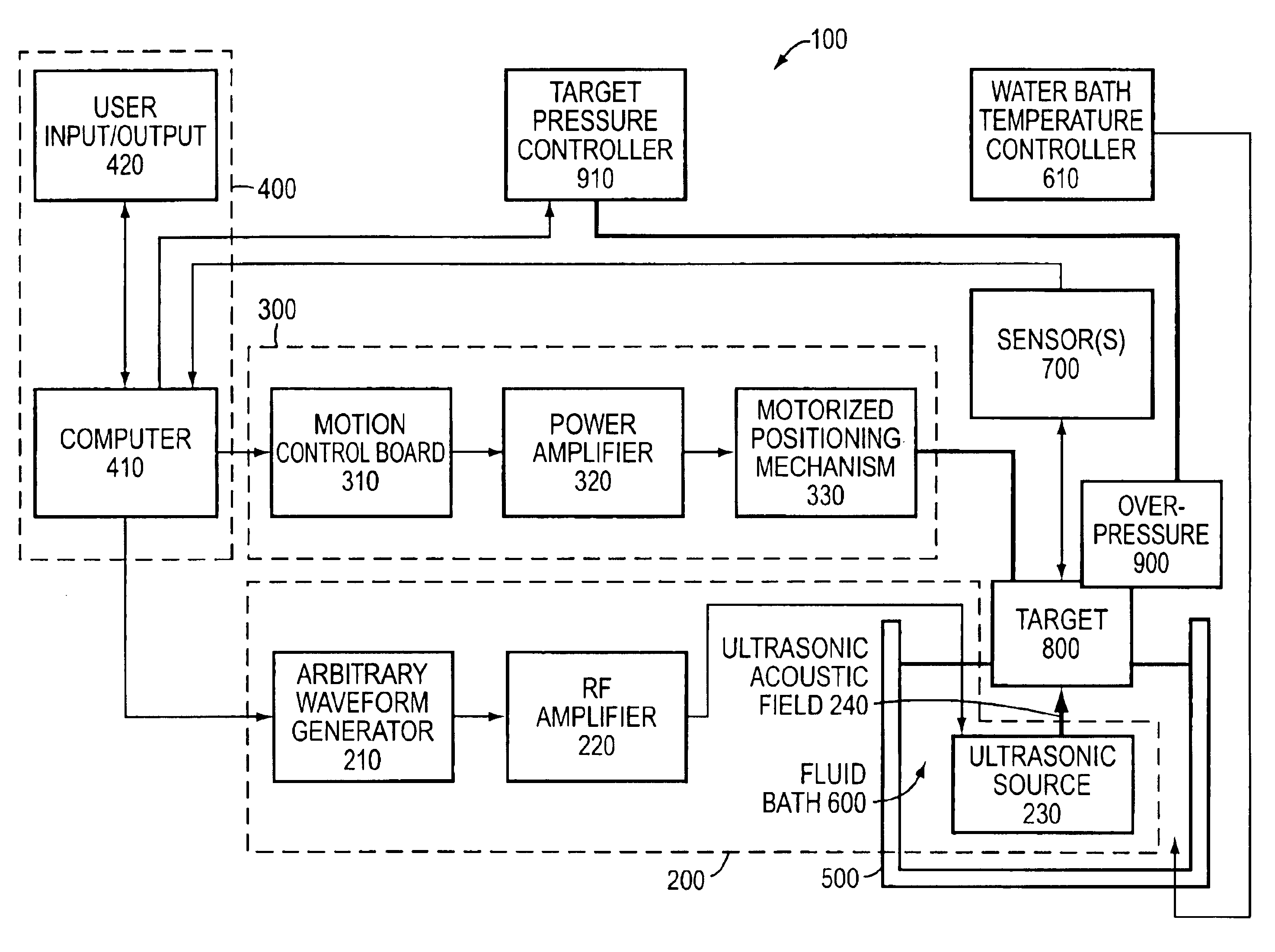
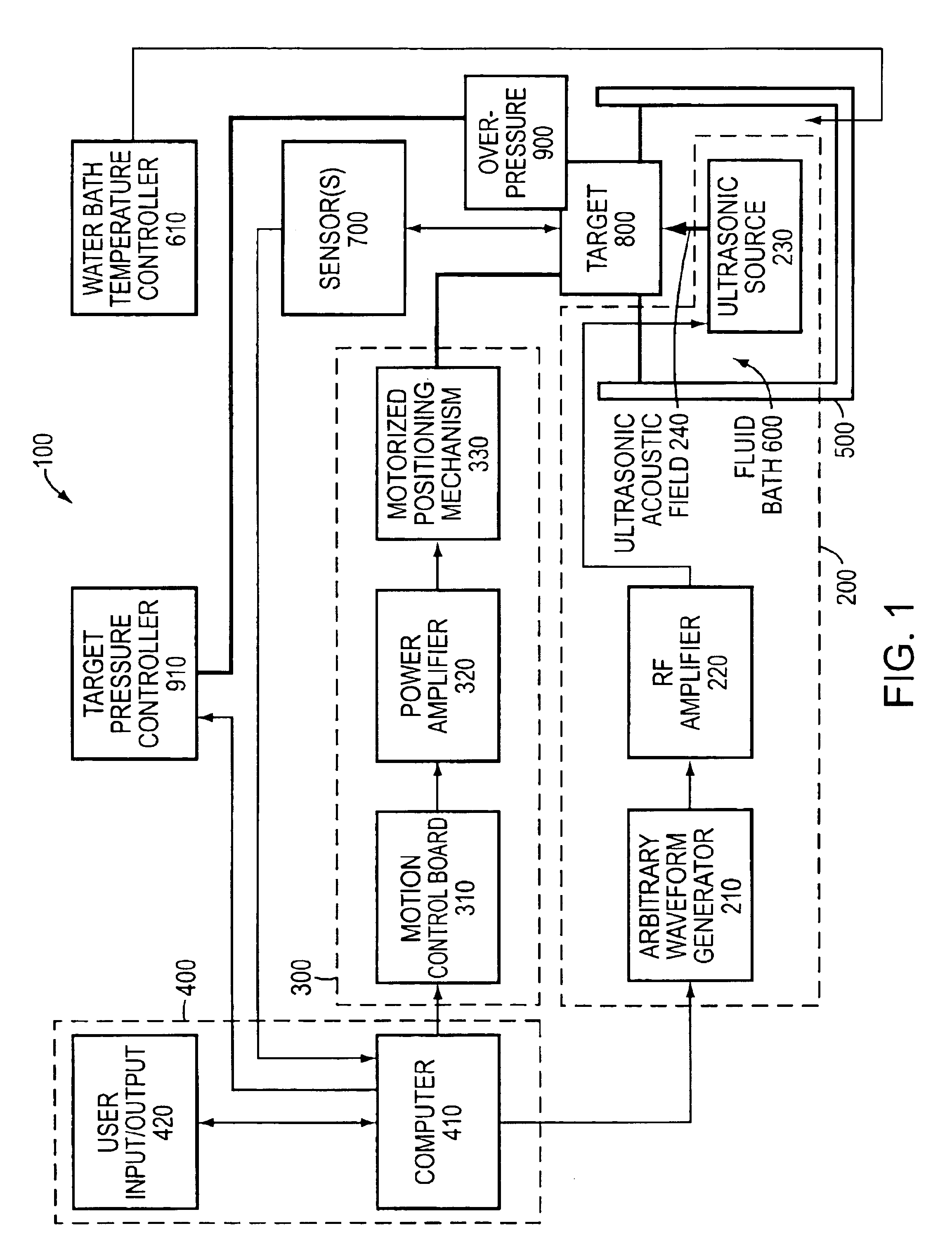
Systems and methods for characterization of materials and combinatorial libraries with mechanical oscillators
InactiveUS6182499B1Optical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologySonificationVisual perception
Methods and apparatus for screening diverse arrays of materials are provided. In one aspect, systems and methods are provided for imaging a library of materials using ultrasonic imaging techniques. The system includes one or more devices for exciting an element of the library such that acoustic waves are propagated through, and from, the element. The acoustic waves propagated from the element are detected and processed to yield a visual image of the library element. The acoustic wave data can also be processed to obtain information about the elastic properties of the library element. In another aspect, systems and methods are provided for generating acoustic waves in a tank filled with a coupling liquid. The library of materials is then placed in the tank and the surface of the coupling liquid is scanned with a laser beam. The structure of the liquid surface disturbed by the acoustic wave is recorded, the recorded disturbance being representative of the physical structure of the library. In another aspect of the invention, a mechanical resonator is used to evaluate various properties (e.g., molecular weight, viscosity, specific weight, elasticity, dielectric constant, conductivity, etc.) of the individual liquid elements of a library of materials. The resonator is designed to ineffectively excite acoustic waves. The frequency response of the resonator is measured for the liquid element under test, preferably as a function of time. By calibrating the resonator to a set of standard liquids with known properties, the properties of the unknown liquid can be determined. An array of library elements can be characterized by a single scanning transducer or by using an array of transducers corresponding to the array of library elements. Alternatively, multiple resonators of differing design may be used to evaluate each element of a library of elements, thus providing improved dynamic range and sensitivity.
Owner:FREESLATE
Microfluidic device and methods of using same
ActiveUS20050019792A1Prevent evaporationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlGenotyping
A variety of elastomeric-based microfluidic devices and methods for using and manufacturing such devices are provided. Certain of the devices have arrays of reaction sites to facilitate high throughput analyses. Some devices also include reaction sites located at the end of blind channels at which reagents have been previously deposited during manufacture. The reagents become suspended once sample is introduced into the reaction site. The devices can be utilized with a variety of heating devices and thus can be used in a variety of analyses requiring temperature control, including thermocycling applications such as nucleic acid amplification reactions, genotyping and gene expression analyses.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
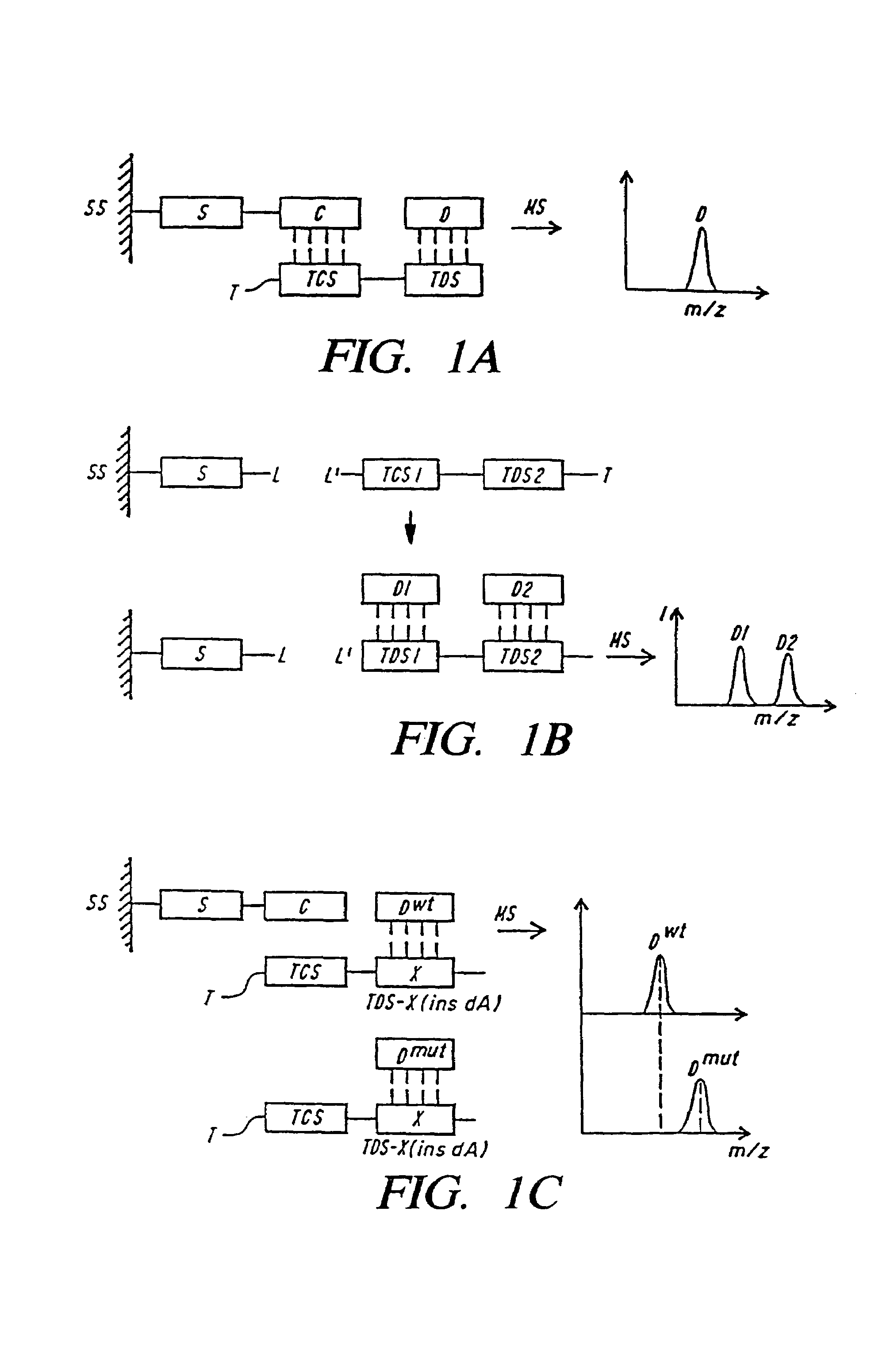
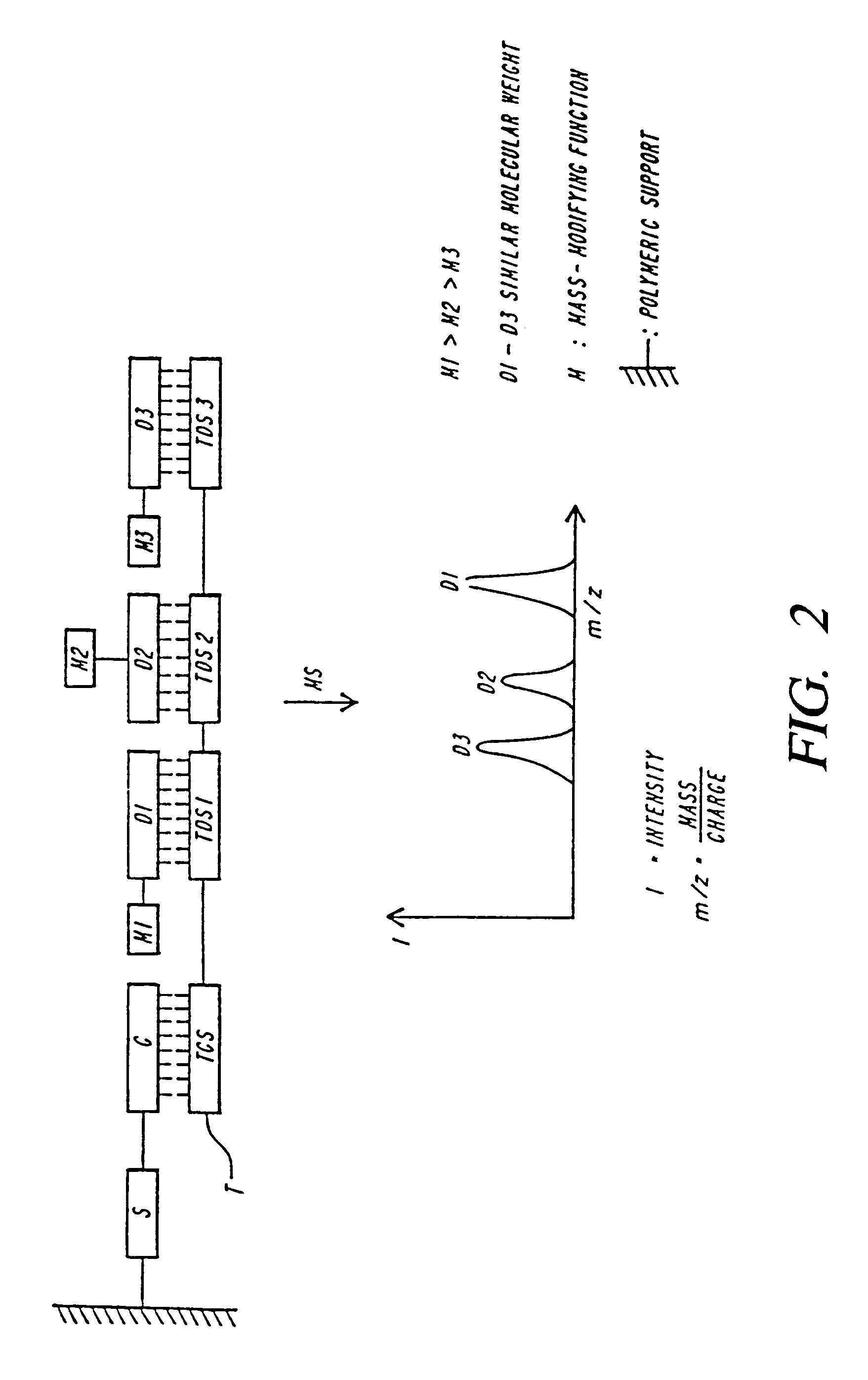
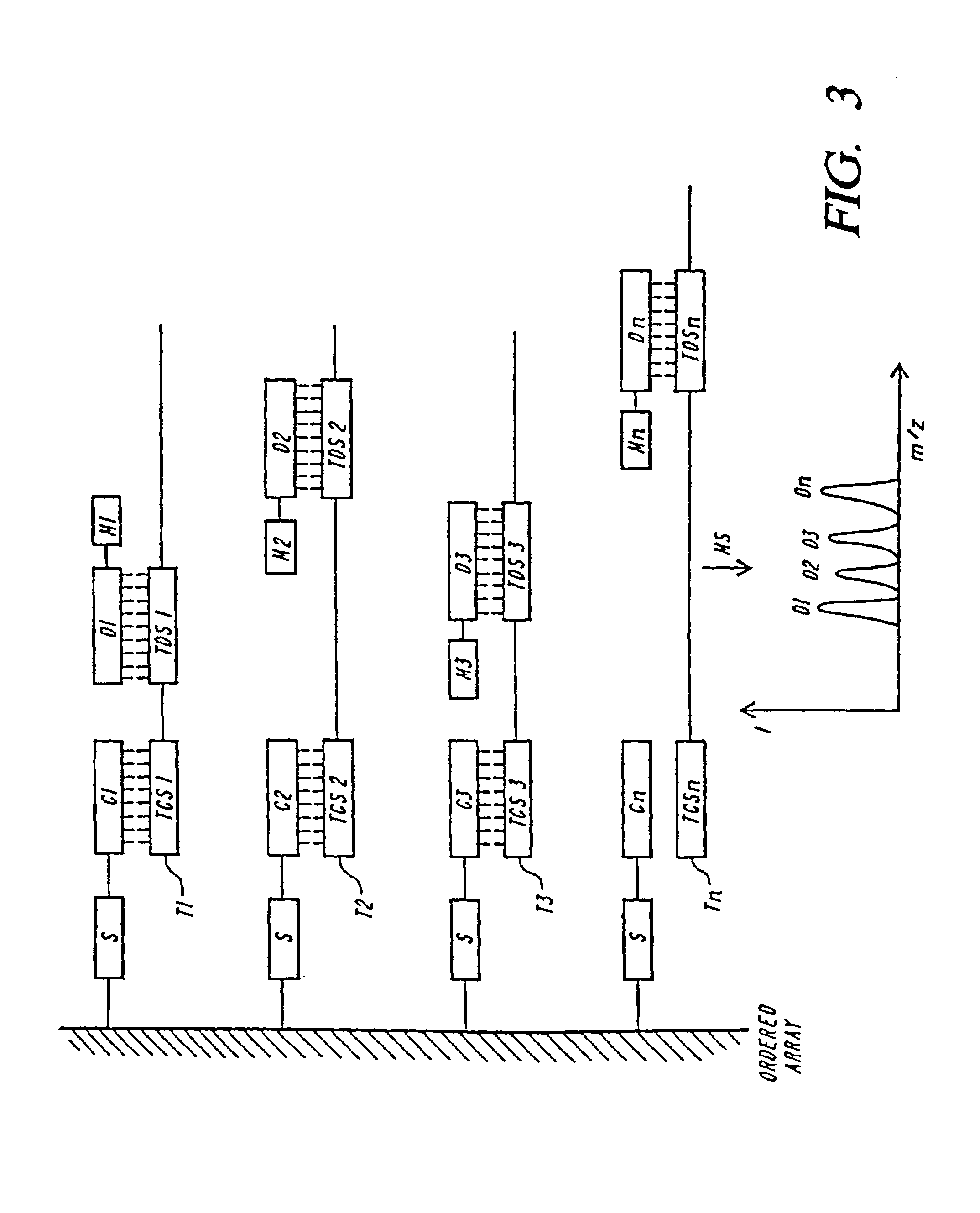
DNA diagnostics based on mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7198893B1Increase mass resolution massIncrease mass mass accuracyPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsMass spectrometry imagingOrganism
Fast and highly accurate mass spectrometry-based processes for detecting a particular nucleic acid sequence in a biological sample are provided. Depending on the sequence to be detected, the processes can be used, for example, to diagnose a genetic disease or chromosomal abnormality; a predisposition to a disease or condition, infection by a pathogenic organism, or for determining identity or heredity.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com