Patents
Literature
66 results about "Genome variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
GENOME VARIATIONS. Genome variations are differences in the sequence of DNA from one person to the next. Just as you can look at two people and tell that they are different, you could, with the proper chemicals and laboratory equipment, look at the genomes of two people and tell that they are different, too.
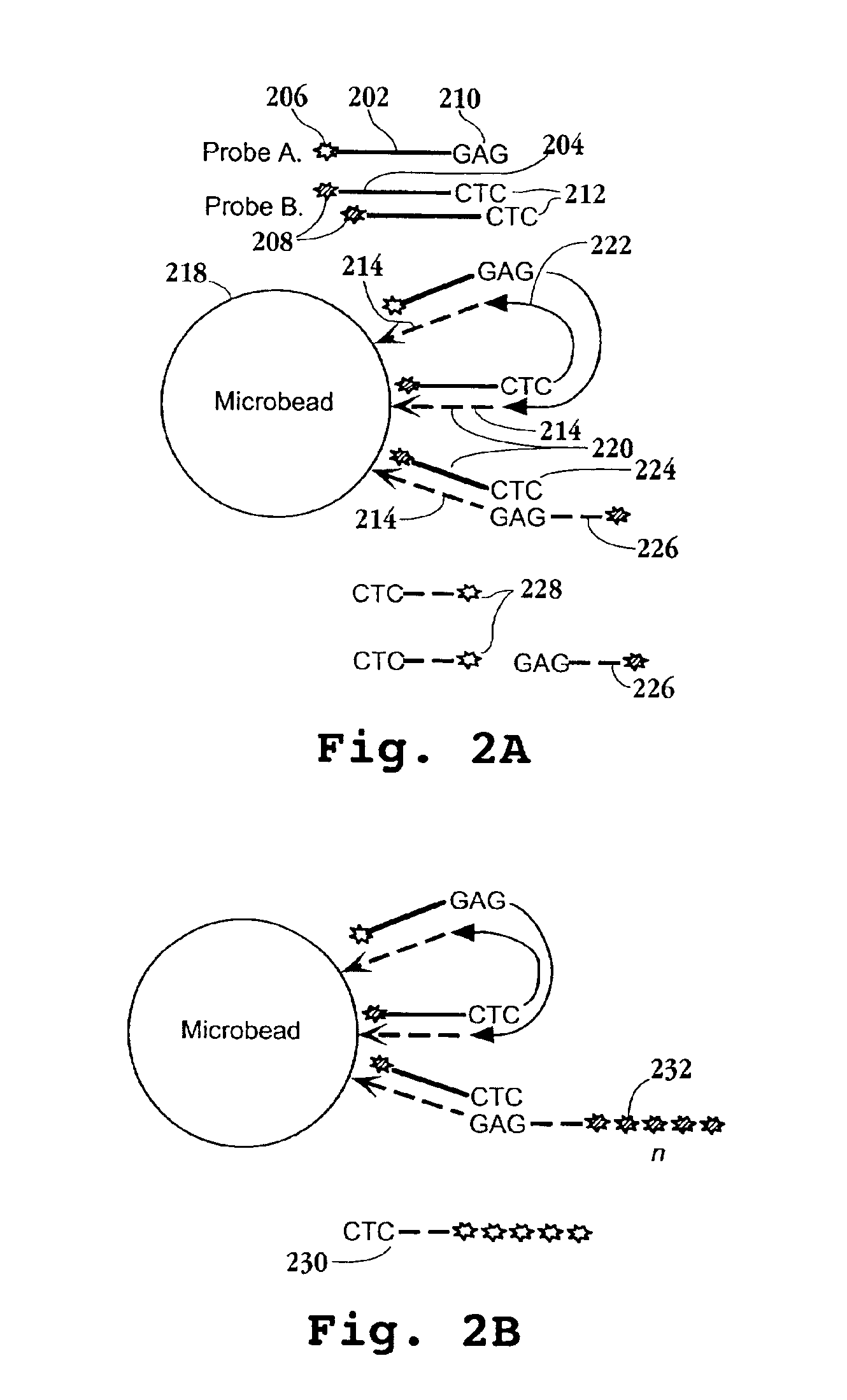
Arrayed biomolecules and their use in sequencing
InactiveUS7232656B2Reduce interferencePermit resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsGenome variationComputational biology
The invention is directed to a method for analysing genome wide variation in an individual. The method comprises randomly fragmenting the individual's genome and generating sequence reads of multiple bases on all fragments of the individual's genome, aligning the sequence reads generated with a known genomic reference sequence, and analysing variations between the sequence reads derived from the individual's genome and the known genomic reference sequence.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Method for determining relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6897023B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeFluorescence
Disclosed are methods for identifying nucleic acid sequences which are of different abundances in different nucleic acid source populations, e.g. differentially expressed genes or genomic variations among individuals or populations of individuals. In one embodiment, probes derived from the source nucleic acid populations are derivatized with a terminal sample ID (SID) sequence characteristic of that population. Upon competitive hybridization of the probes to a reference or index nucleic acid library containing all the sequences in the populations being compared, the SID tags remain single stranded, and those from the different sources are then annealed to one another. Unhybridized (remainder) SID sequences are then quantified. By labeling such remainder SID sequences with a fluorescent dye, FACS sorting of beads containing the hybridized probes can be carried out. The signal ratio upon which such sorting is based is enhanced compared to competitive hybridization using labeled probes without SID sequences.
Owner:THE MOLECULAR SCI INST +1
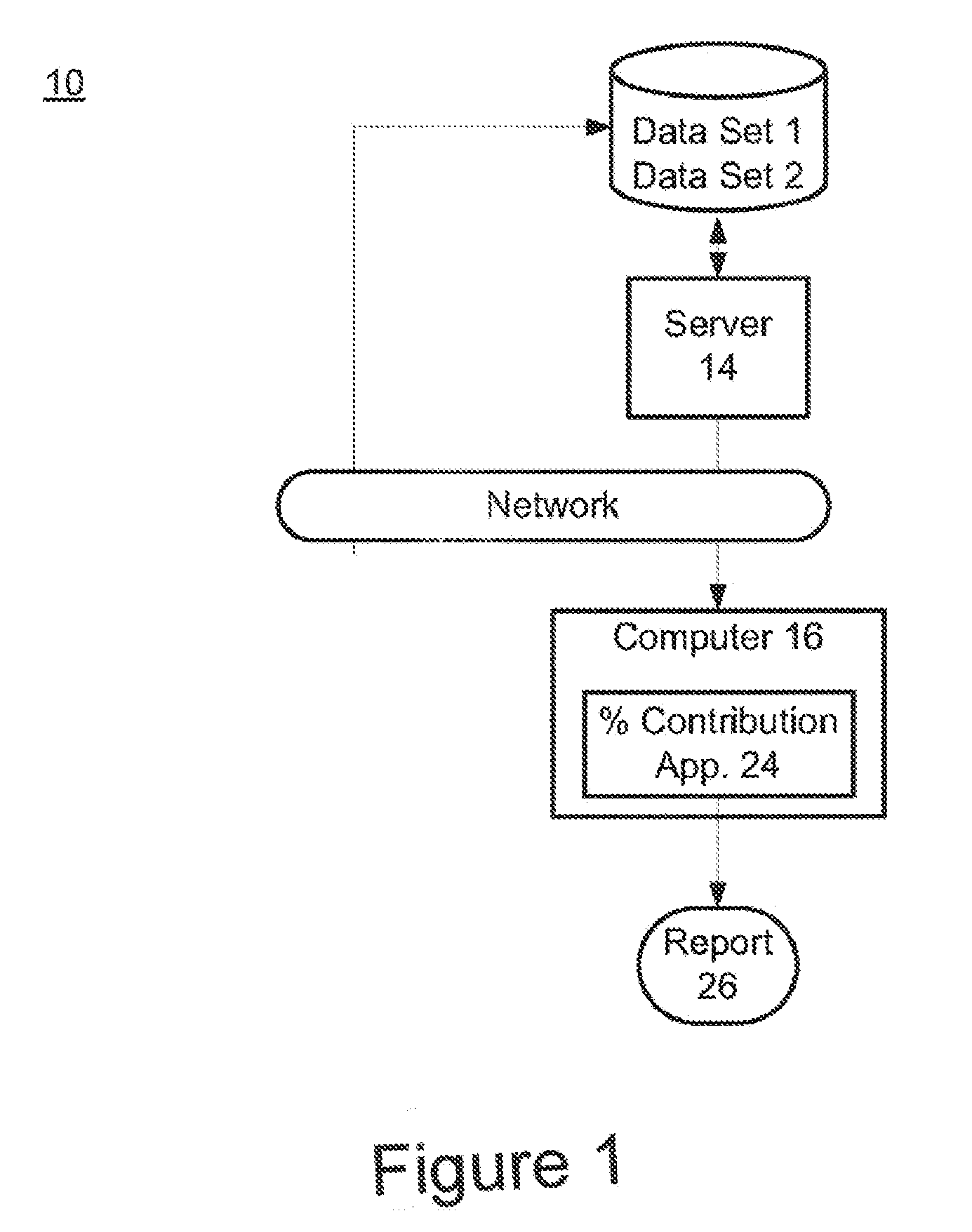
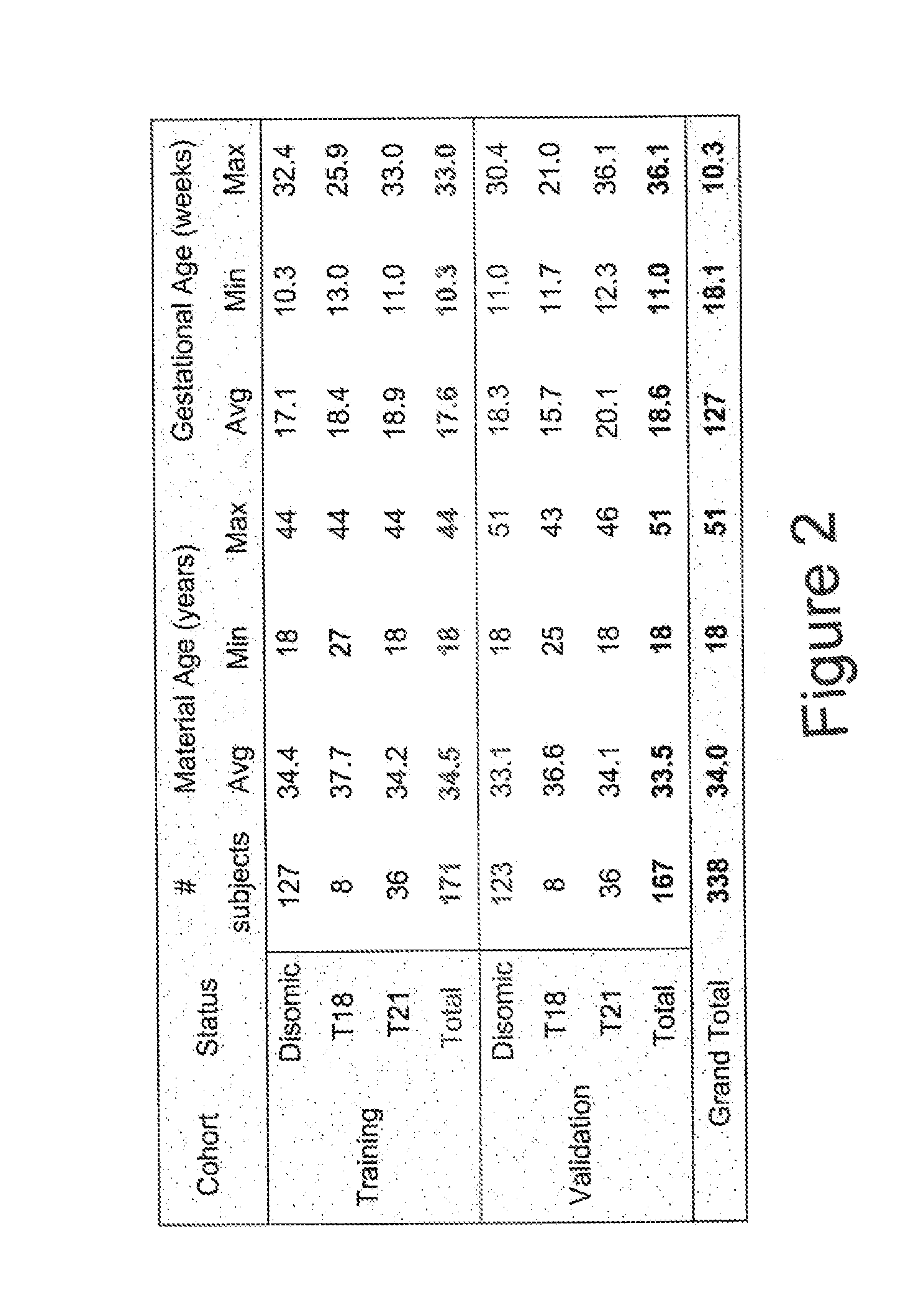
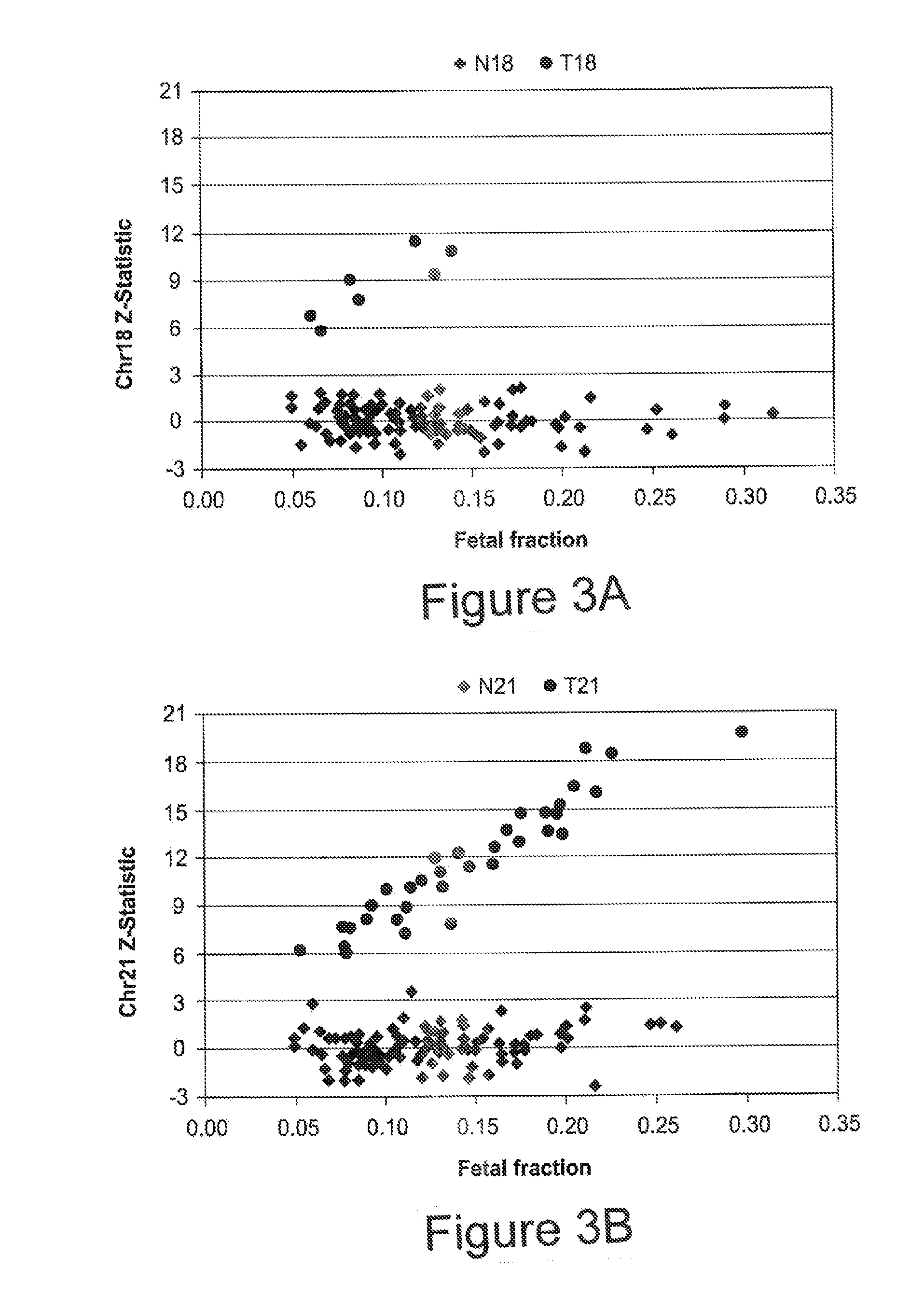
Risk calculation for evaluation of fetal aneuploidy
The present invention provides processes for determining accurate risk probabilities for fetal aneuploidies. Specifically, the invention provides non-invasive evaluation of genomic variations through chromosome-selective sequencing and non-host fraction data analysis of maternal samples.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Assay systems for determination of fetal copy number variation
The present invention provides processes for determining accurate risk probabilities for chromosome dosage abnormalities. Specifically, the invention provides non-invasive evaluation of genomic variations through chromosome-selective sequencing and non-host fraction data analysis of maternal samples.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
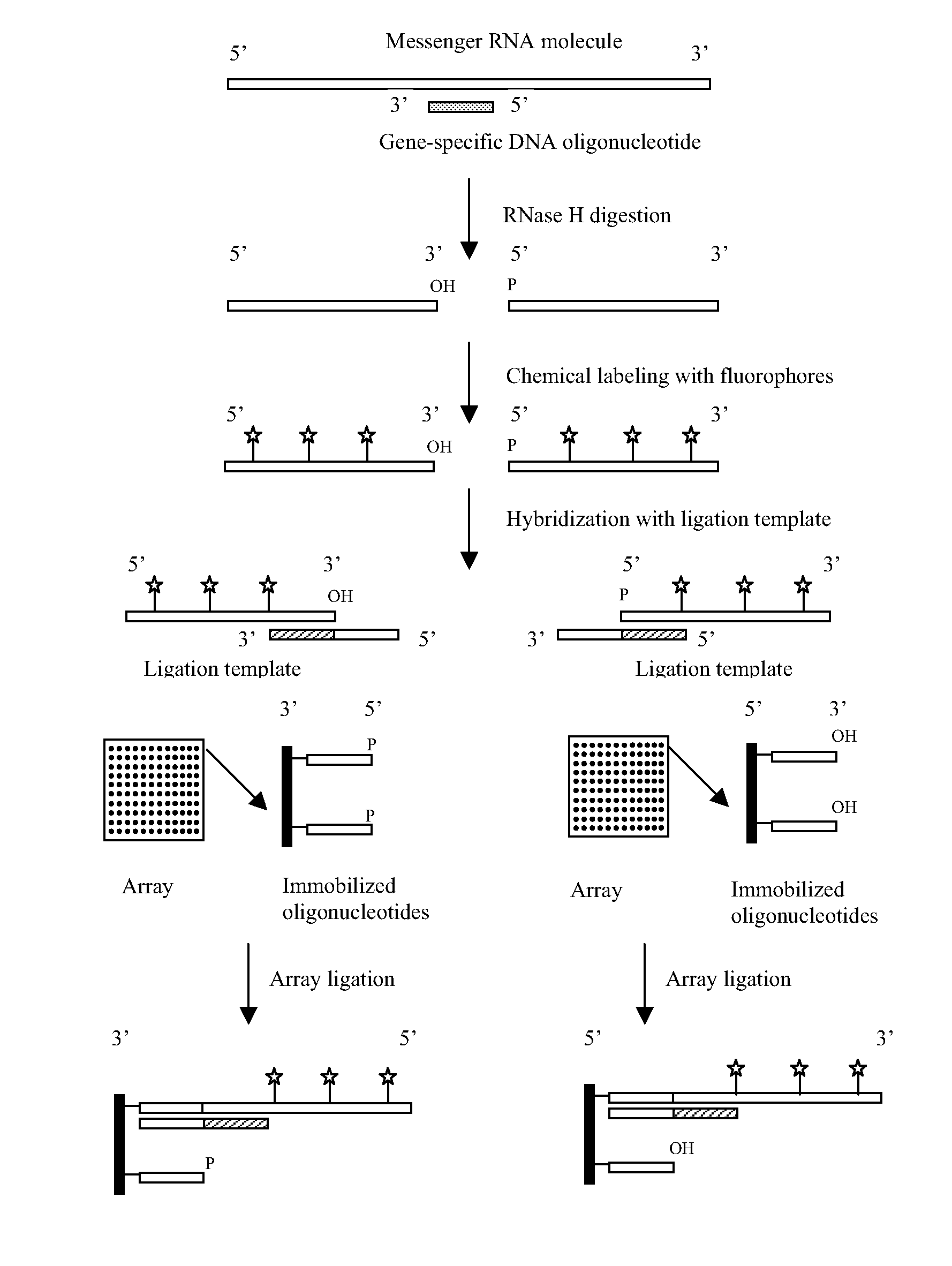
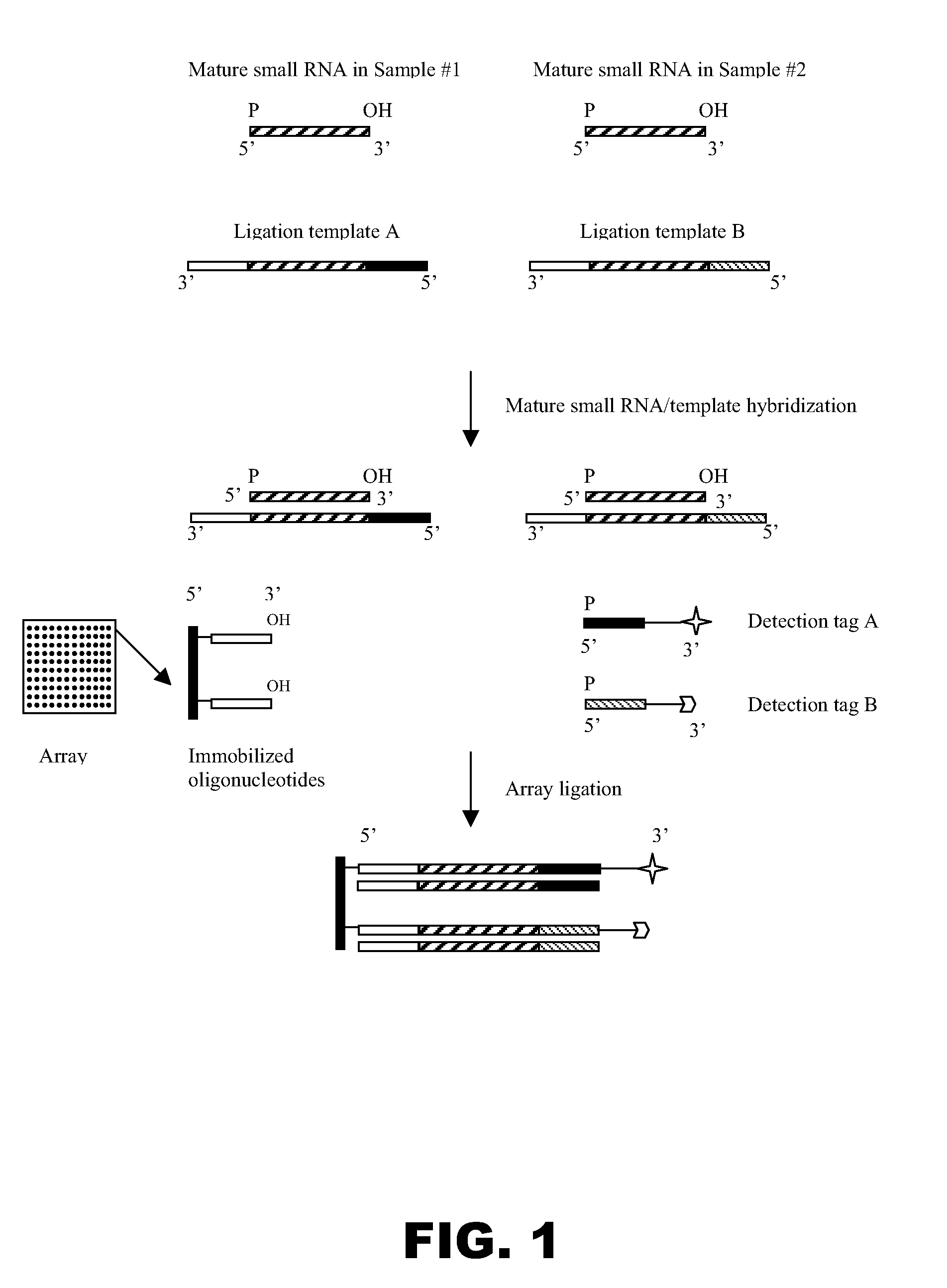
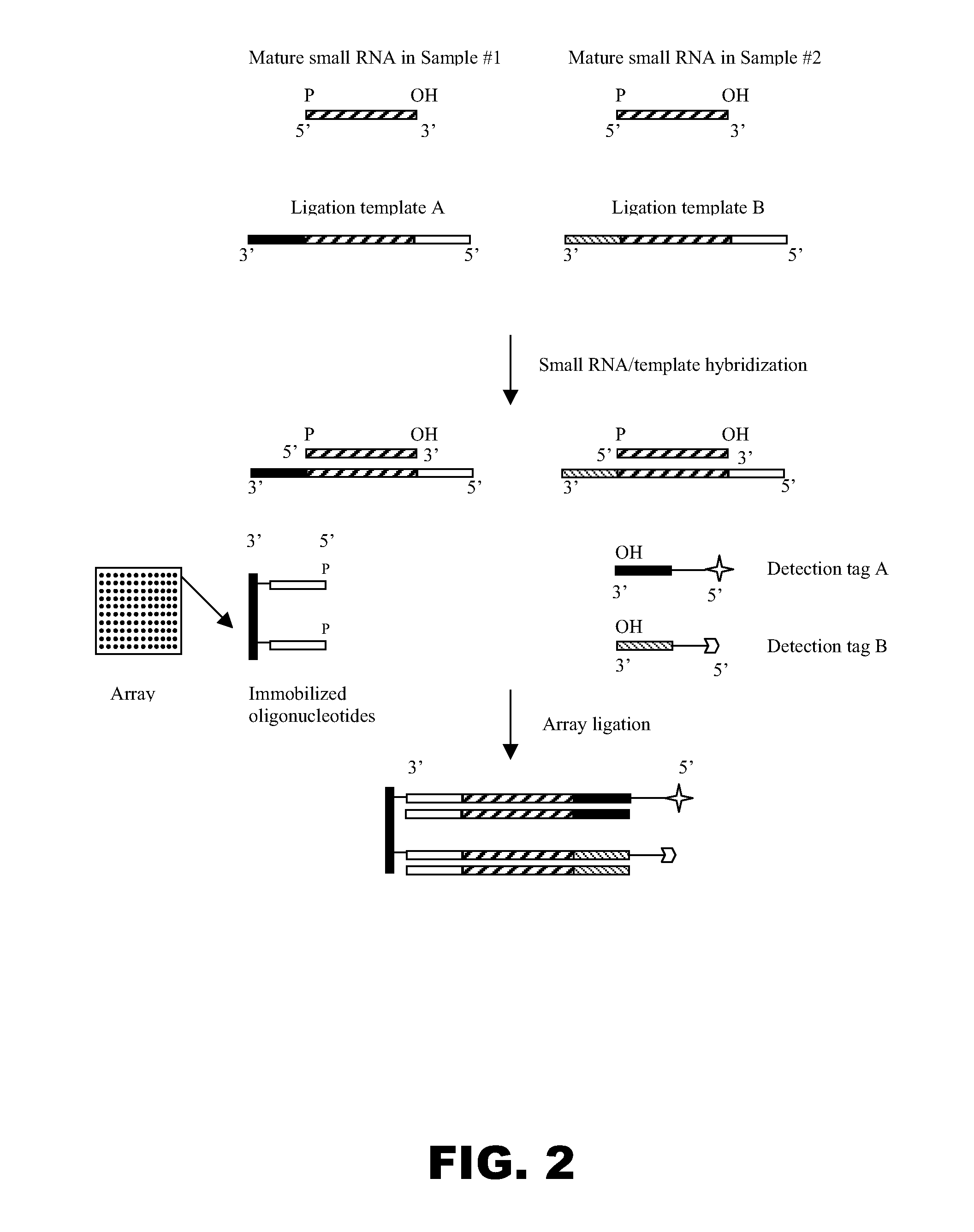
Universal ligation array for analyzing gene expression or genomic variations
InactiveUS20090061424A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene expressionGenome variation
The present invention provides an array system comprising a plurality of immobilized oligonucleotides comprising artificial sequences and a plurality of complementary ligation templates, as well as methods and kits for using the array system to analyze populations of nucleic acids. In particular, target nucleic acids are ligated to the immobilized oligonucleotides on the array in the presence of the complementary ligation templates.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Storage, retrieval, analysis, pricing, and marketing of personal health care data using social networks, expert networks, and markets
InactiveUS20150154646A1Facilitate communicationMedical communicationMedical data miningFinancial transactionBiological data
Systems and processes are provided for securely storing, retrieving, sharing, and selling private data, such as genome wide sequences, sequence related metadata, electronic healthcare data, biological data, demographic data, medical data, and other biomedical data, which, in turn, may allow the usage of genomic variations at multiple scales and across multiple population strata. In some examples, users may be matched with healthcare experts based on a medical need or interest. In other examples, an information-based market for utilizing the available data in a privacy-preserving manner may be provided. In these examples, individual or group data may be tracked, compared, rated, analyzed, and priced to allow individuals to establish connections and / or carry out financial transactions using their data with other participants, healthcare practitioners, and businesses.
Owner:SEQSTER PDM INC +1
Annotation method and annotation system of whole-genome variant data
InactiveCN106156538AAccurate NotesSolve the screening puzzleProteomicsGenomicsReference genesAllele frequency
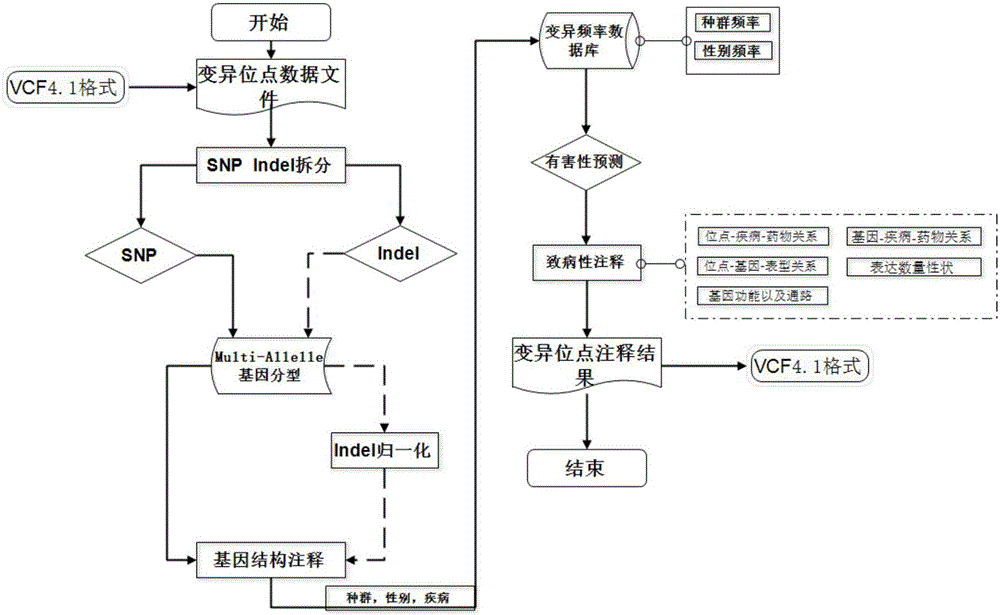
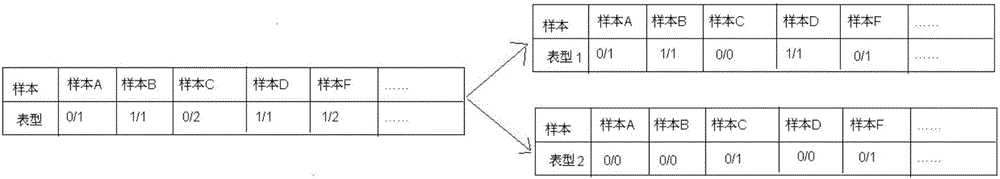
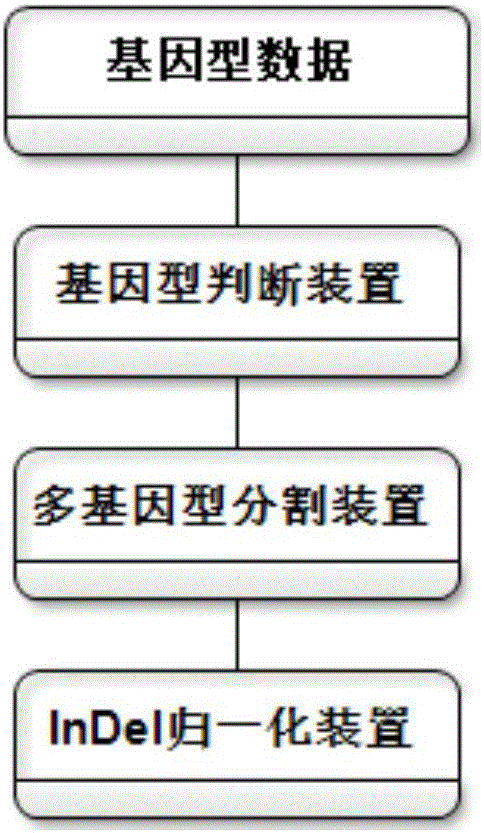
The invention discloses an annotation method and an annotation system of whole-genome variant data. The method comprises the following steps of S1, creating a variant data file, wherein the variant data are stored according to a national standard VCF format as an input file; S2, performing multi-allele genotyping, firstly performing genotype judgment, representing a basic group which is consistent with a reference genome by zero, and representing the basic groups which are inconsistent with the reference gene group by 1, 2, 3,..., then performing SNP and InDel multi-allele type resolution so that the allele type is represented by zero and one; S3, causing InDel generation position normalization, namely performing InDel generation position normalization according to a left justification and simplification normalization method; and S4, performing annotation, namely performing gene structure annotation, allele frequency annotation, variable site harm prediction and pathogenicity annotation. The annotation method and the annotation system improve integrity and accuracy of annotation information.
Owner:天津诺禾医学检验所有限公司
Gene analysis annotation method and device
ActiveCN107194208AAccurate annotation of genetic analysisEfficient annotation of gene analysisBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGene AnnotationChromosome number
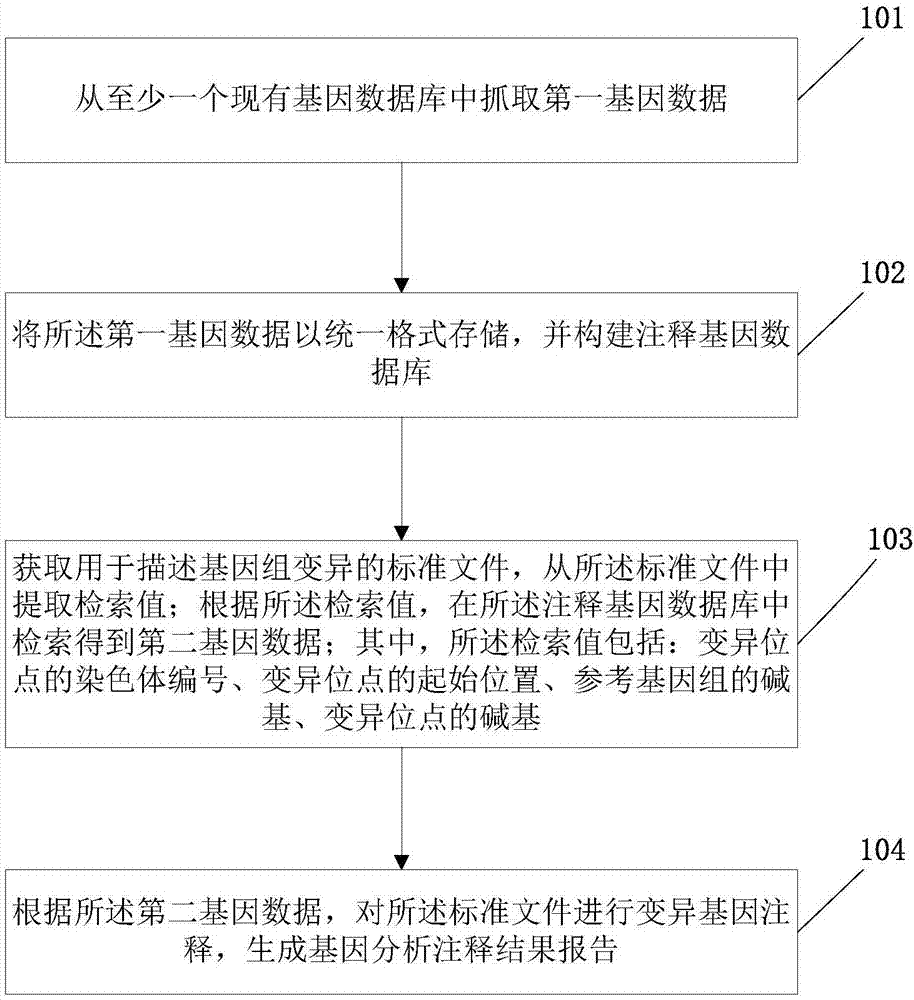
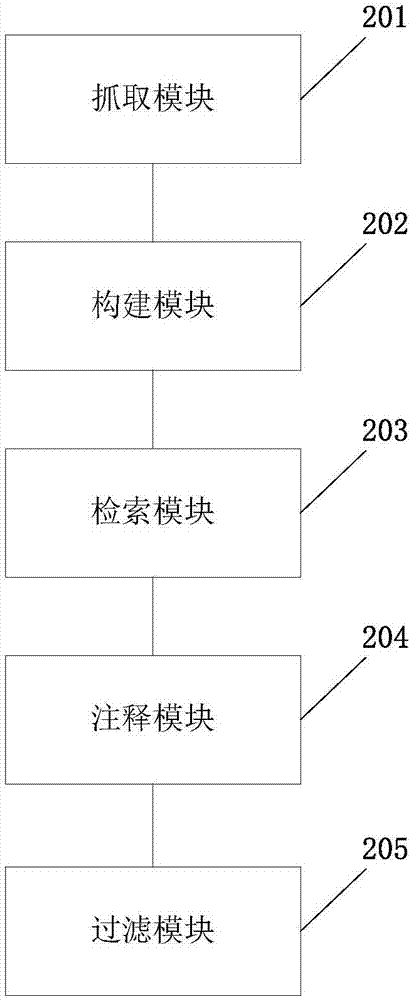
The invention discloses a gene analysis annotation method and device. The method comprises the following steps that: capturing first gene data from at least one existing gene database; storing the first gene data in a uniform format, and constructing an annotation gene database; obtaining a standard file used for describing genome variation, and extracting a retrieval value from the standard file; according to the retrieval value, carrying out retrieval in the annotation gene database to obtain second gene data, wherein the retrieval value comprises the chromosome number of a variation site, the starting position of the variation site, the basic group of a refereed genome and the basic group of the variation site; and according to the second gene data, carrying out gene annotation on the standard file, and generating a gene analysis annotation result report. By use of the method, the gene analysis annotation can be accurately and efficiently carried out.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS
Genome variation detection method and device
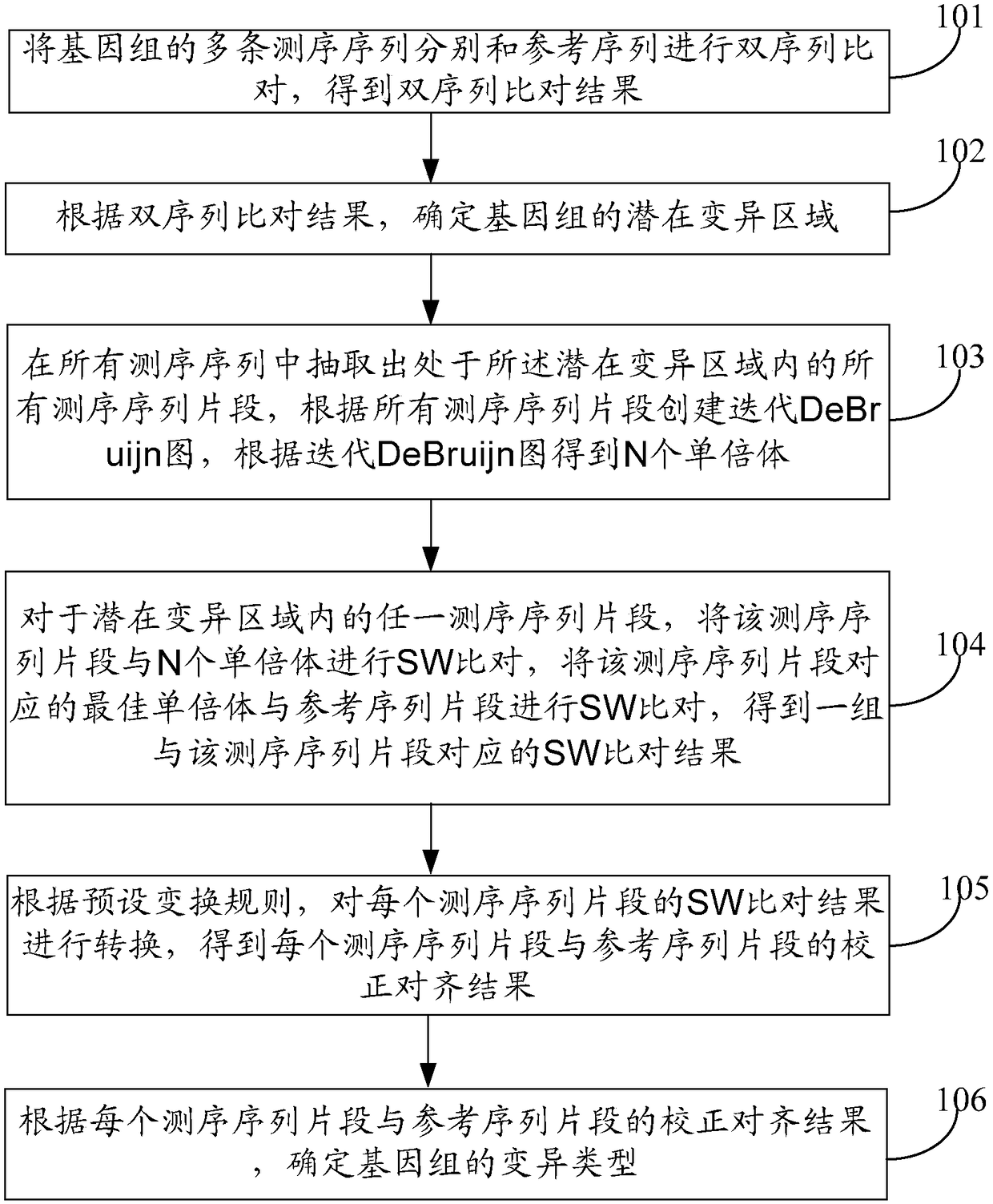
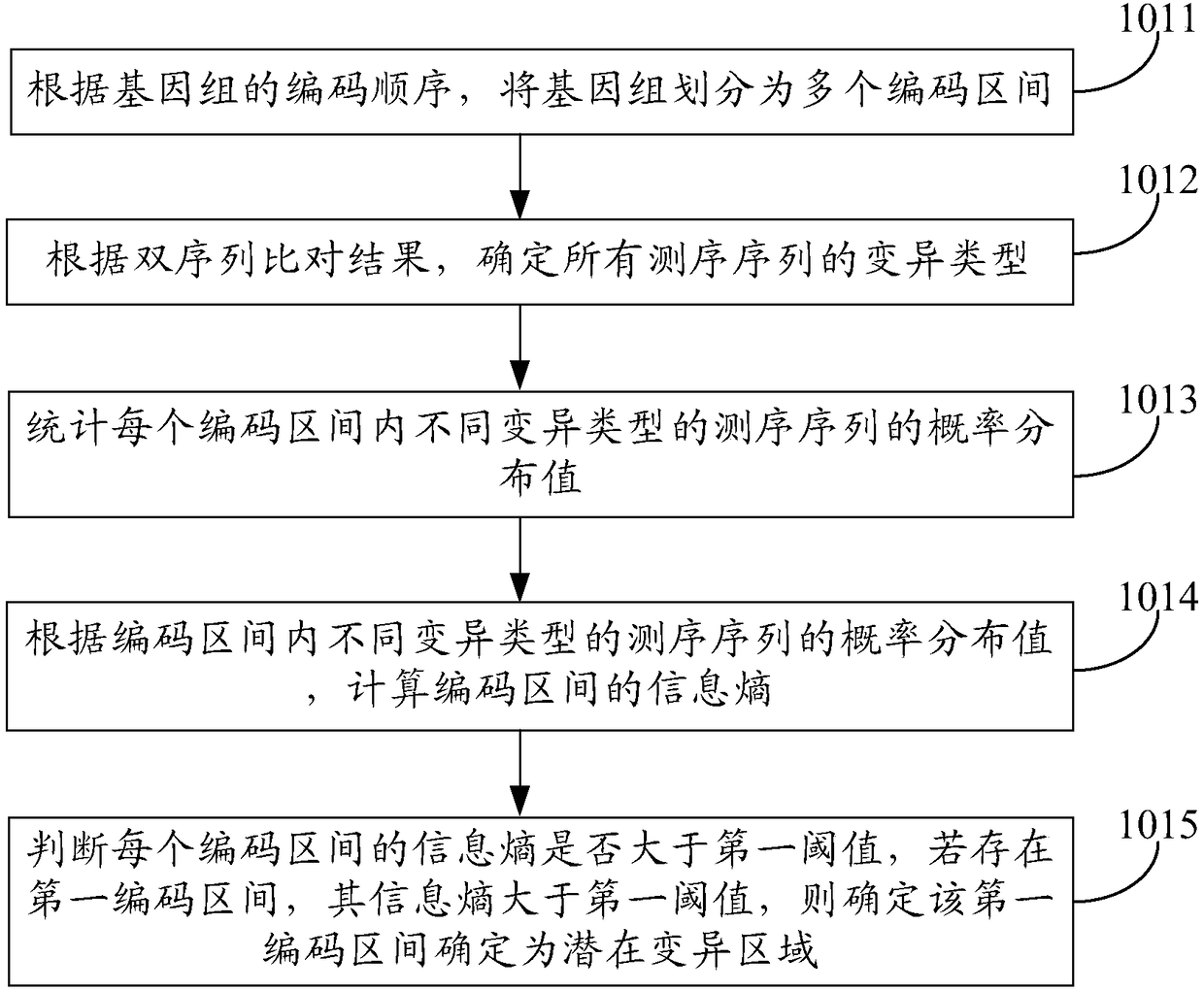
The invention discloses a genome variation detection method and device, relates to the field of bioinformatics researches, and aims at solving the problem that existing genome variation detection is low in efficiency and low in precision. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a potential variation area of a genome, carrying out local assembling on a sequencing sequence falling in the potential variation area to create an iterative DeBruijn graph, and obtaining haploids according to the iterative DeBruijn graph; and comparing the sequencing sequence with all the haploids, comparing the optimum haploids corresponding to the sequencing sequence with a reference sequence corresponding to the potential variation area to obtain a group of comparison results, transforming two comparison results in the group of comparison results by adoption of a preset transformation rule, obtaining a correction alignment result between the sequencing sequence and the reference sequence corresponding to the potential variation area, and determining a variation type of the genome according to the correction alignment result between the sequencing sequence and the reference sequence corresponding to the potential variation area.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Label-free sensing of pna-dna complexes using nanopores
InactiveUS20120276530A1Improve bindingImprove thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementNanomedicineDiseaseVirus
Embodiments disclosed herein relate to a method of detecting specific DNA sequences and the application of this method in the detection of pathogens, viruses, drug-resistant pathogens, genomic variations associated with disease / disorder susceptibility etc. based on specific signature sequences unique to the pathogens, viruses, drug-resistant pathogens or genomic variations. The method can also be used to distinguish a pool of same-sized dsDNA on the basis of sequence differences. The method uses non-optically labeled bis-PNA and / or gamma-PNA probes to tag specific target sequences for identification by solid-state nanopores.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Methods and Apparatus for Assigning a Meaningful Numeric Value to Genomic Variants, and Searching and Assessing Same
InactiveUS20120191366A1Easily parseReadily parsableBiological testingSequence analysisNumeric ValueReference genome
The present invention relates to methods, apparatus and computer systems for assigning a numerical value to a genotype at a single- or multi-base segment in an individual's genome to denote the presence of a match or a mismatch of a nucleic acid base sequence of one or more chromosomal copies of the segment, as compared to the nucleic acid base sequence at a reference genome segment that corresponds to the segment of the individual's genome. The methods involve assigning a single digit numerical value to the match or the mismatch of each chromosomal copy of the segment in the genome, so that the numerical value assigned to a mismatch is greater than the numerical value of the match. A null symbol is assigned to a no call determination. The assigned numerical values are summed and a total numerical value which is a single digit or a fixed number of digits is obtained. The steps are repeated to create a vector of total numerical values for the segment among the set of genomes, to thereby obtain a segment-specific pattern of genotype match / mismatch between a set of genomes and the nucleic acid base sequence at the reference genome segment. The segment-specific pattern, also referred to as a “diff pattern” can be used to filter or uncover specific trends or sub-patterns across a set of genomes, and more quickly identify genotypic / phenotypic relationships by identifying sites where the distribution of genotypes in the set of genomes relates in a distinctive, causal way to the distribution of a given phenotype among the individuals whose genomes are under study.
Owner:KNOME
Whole-exome sequencing data analysis method
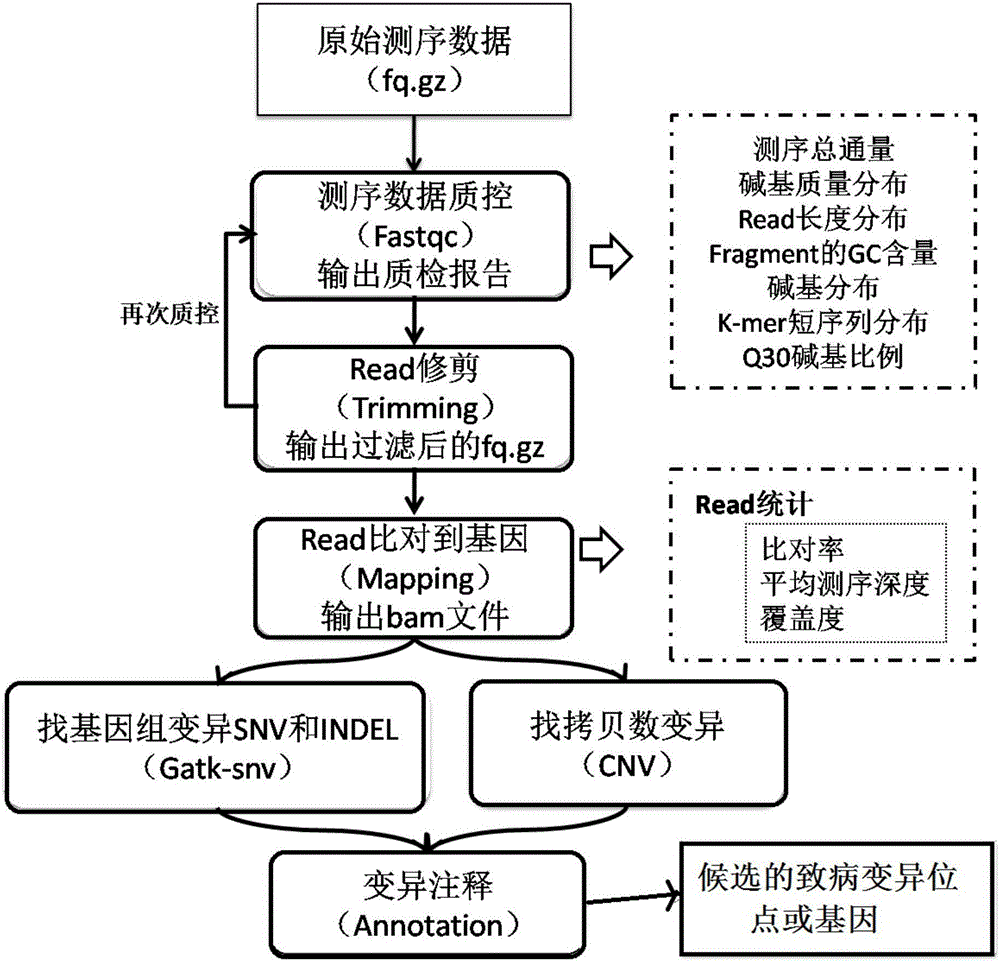
The invention provides a whole-exome sequencing data analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) quality control of sequencing data; 2) genome mapping of the sequencing data; 3) seeking of high-confidence genome mutation by the sequencing data; and 4) annotation of mutation sites. According to the method, the analysis of large-scale data is finished through simple parameter submitting, wherein the analysis of the large-scale data comprises quality detection of original data, data denoising and genome mapping of sequencing read; an upstream part takes over original sequencing data of a lower machine; the analysis of the sequencing data is finished through a parameter automated submitting and analysis module; and candidate pathogenic mutation sites and related genes are output, thereby providing a basis for later experimental verification.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
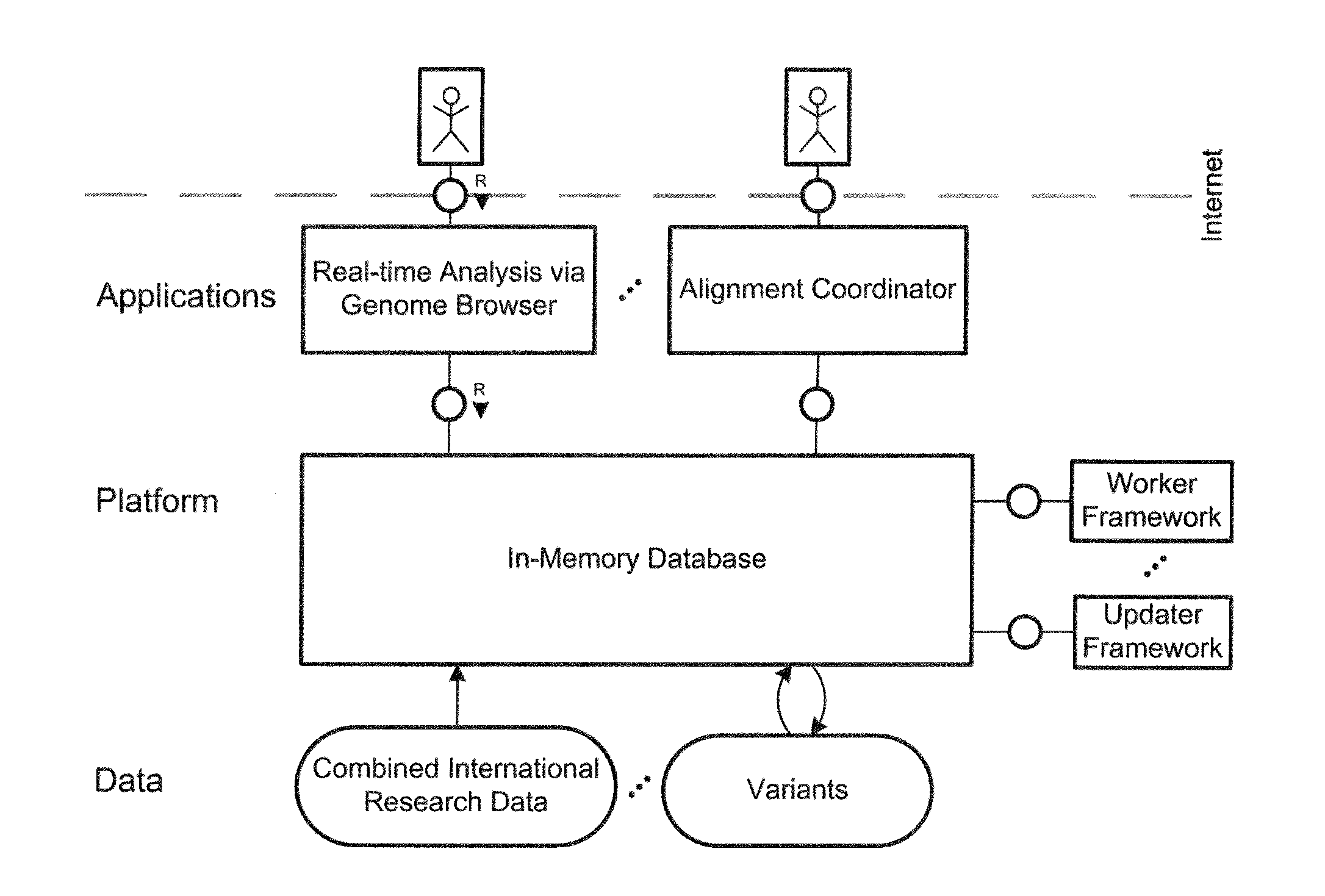
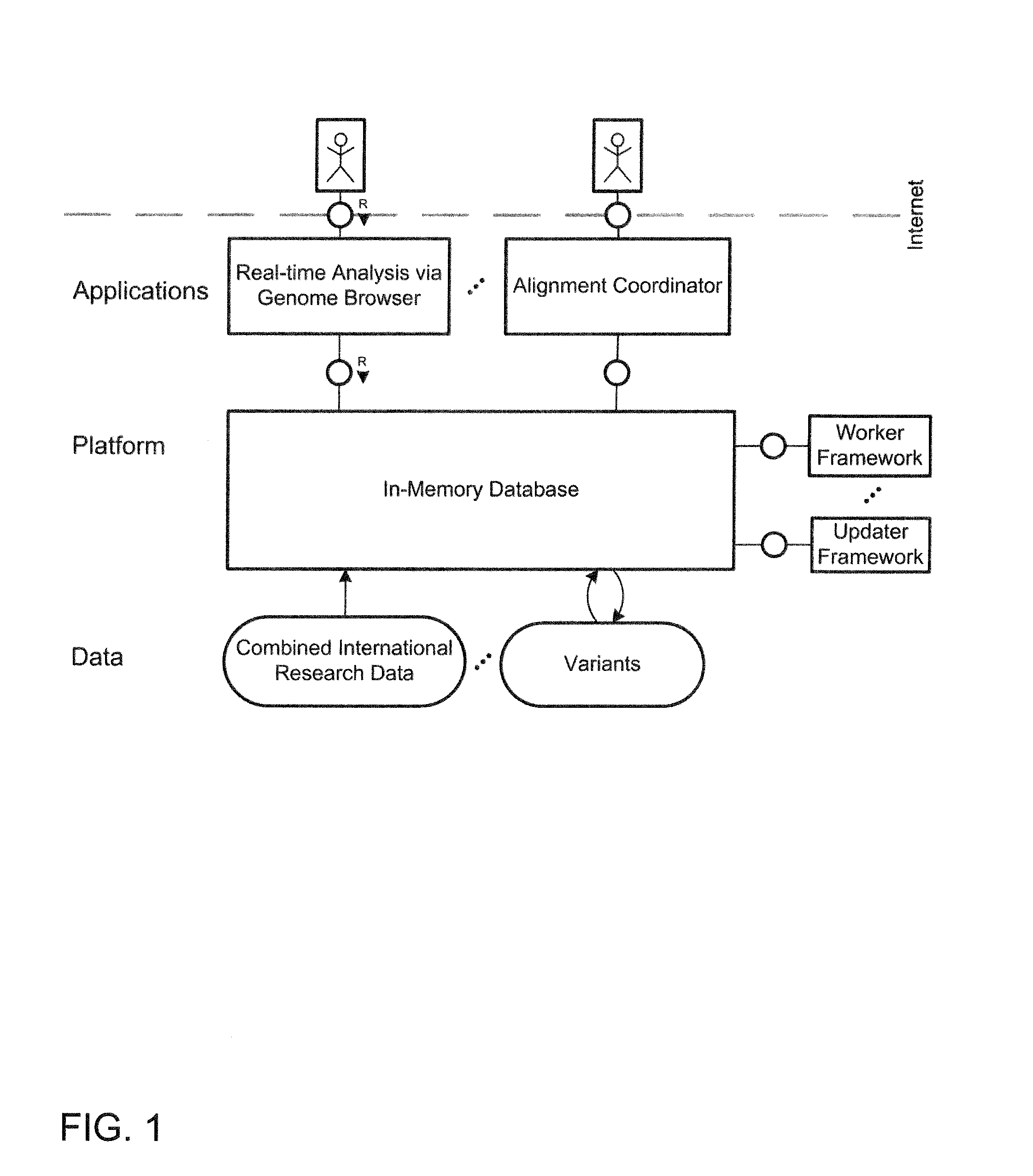
System and method for genomic data processing with an in-memory database system and real-time analysis
ActiveUS20140214333A1Quality improvementHigh-quality resultData visualisationBiological testingDiseasePersonalization
A system and a method for analyzing and evaluating genome data in the course of personalized medicine. In-memory technology is provided for processing of genome data and its real-time analysis as a holistic process in the course of personalized medicine. The cloud application helps physicians and researchers to identify the genetic roots for certain tumor types in the treatment of diseases correlating to genomic variants or mutations, such as cancer diseases. The system combines the latest international research results with patient-specific genomic data while eliminating the need for long-lasting manual searches of all dispositions in distributed international research and literature data sources.
Owner:HASSO PLATTNER INSTITUT FUR SOFTWARESYSTTECHN
Risk calculation for evaluation of fetal aneuploidy
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
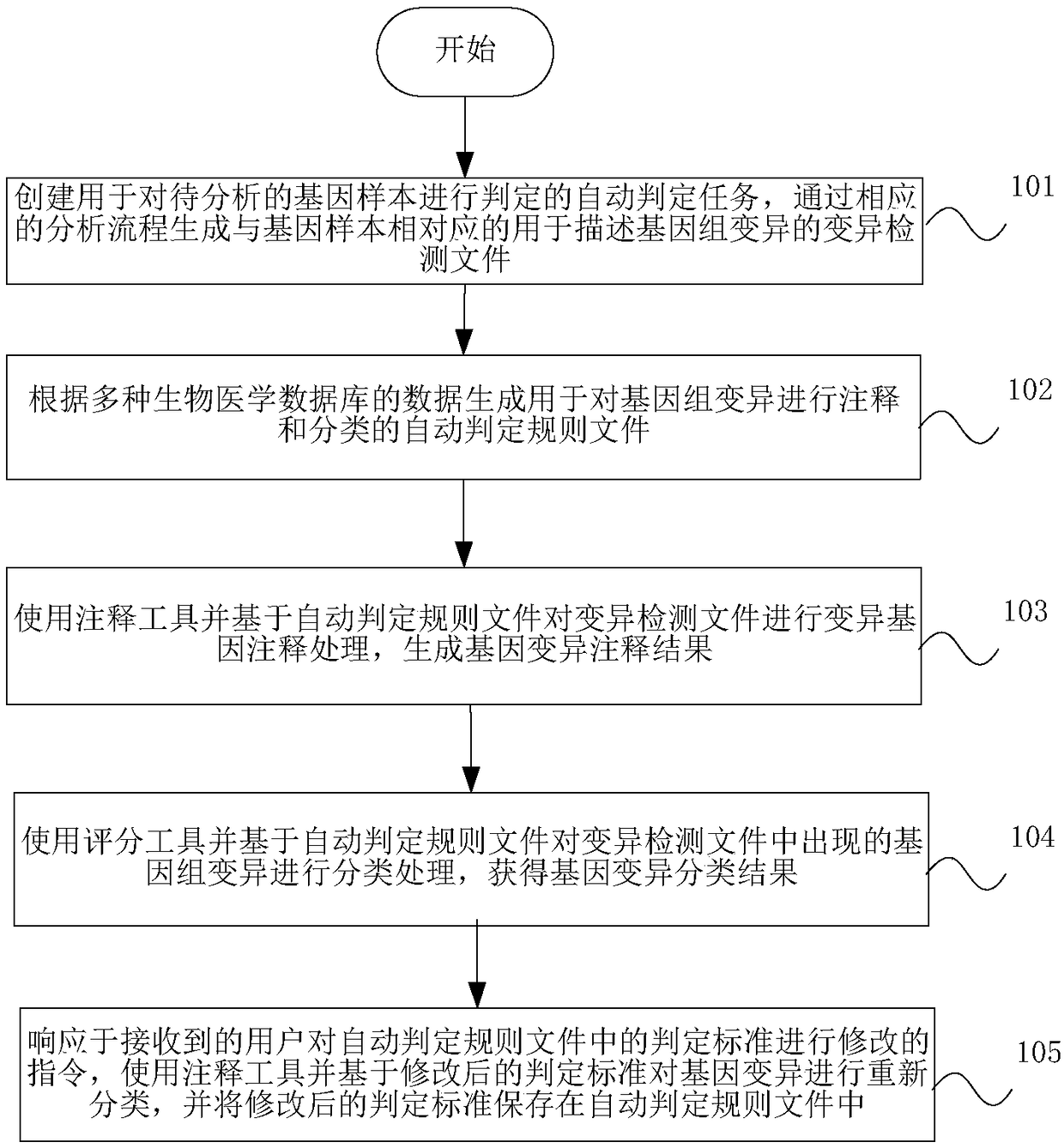
Genetic variation determination method and system and storage medium
The invention discloses a genetic variation determination method and system and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: an automatic determination rule file is generated for annotating and classifying the genomic variation according to the data of multiple biomedical databases; and mutant gene annotation processing is performed on the variation detection file by using an annotation toolbased on the automatic determination rule file, the genomic variation in the variation detection file is classified by using a scoring tool based on the automatic determination rule file, the geneticvariation is reclassified by using the scoring tool based on the modified determination criterion, and the modified determination criterion is saved in the automatic determination rule file. Accordingto the genetic variation determination method and system and the storage medium, gene analysis and annotation can be more accurately and efficiently performed, the interpreter can be assisted to moreefficiently apply the evaluation criterion, automatic analysis on the massive variation site information can be realized and the accuracy and the determination speed of genetic variation determination can be improved.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS
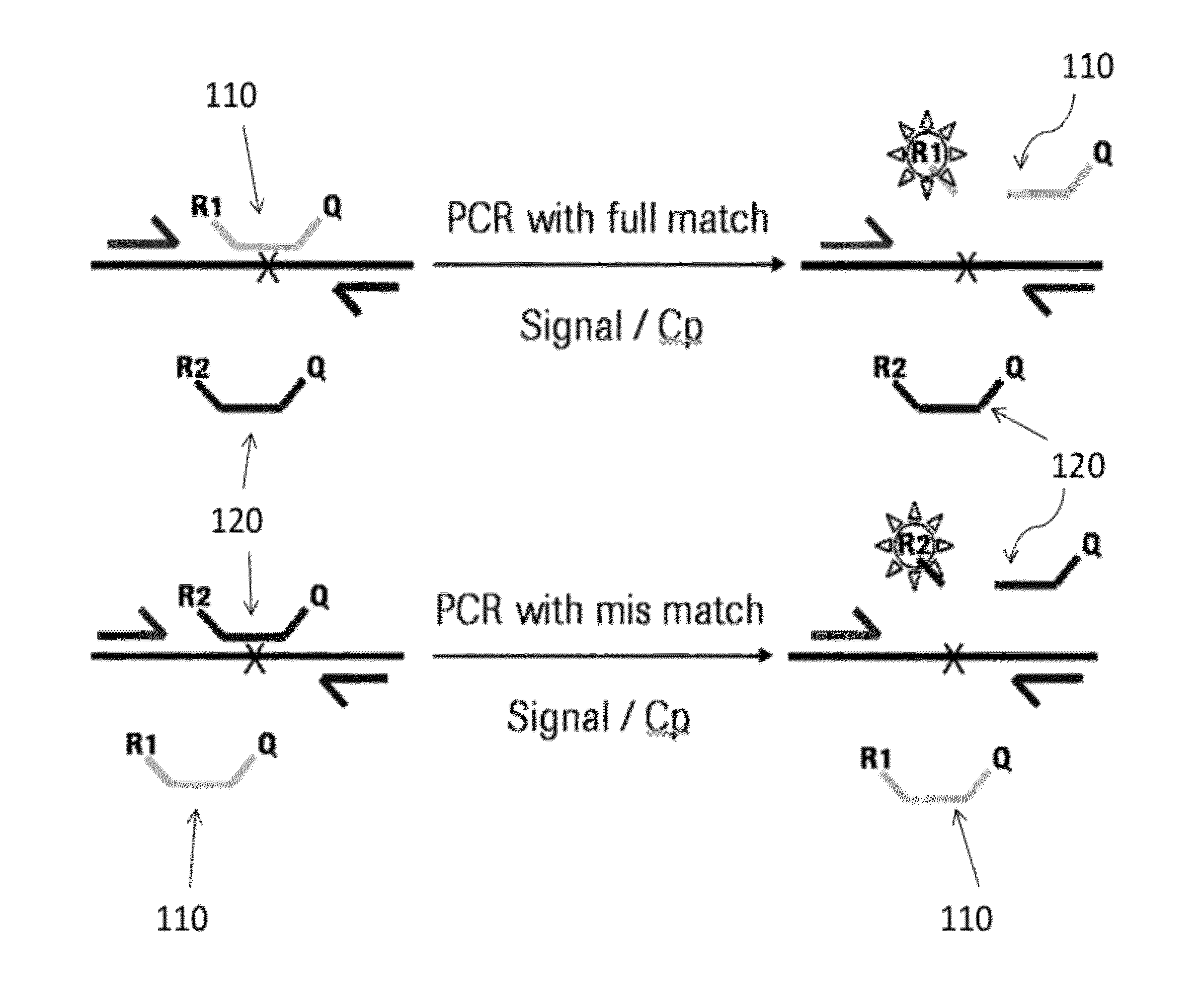
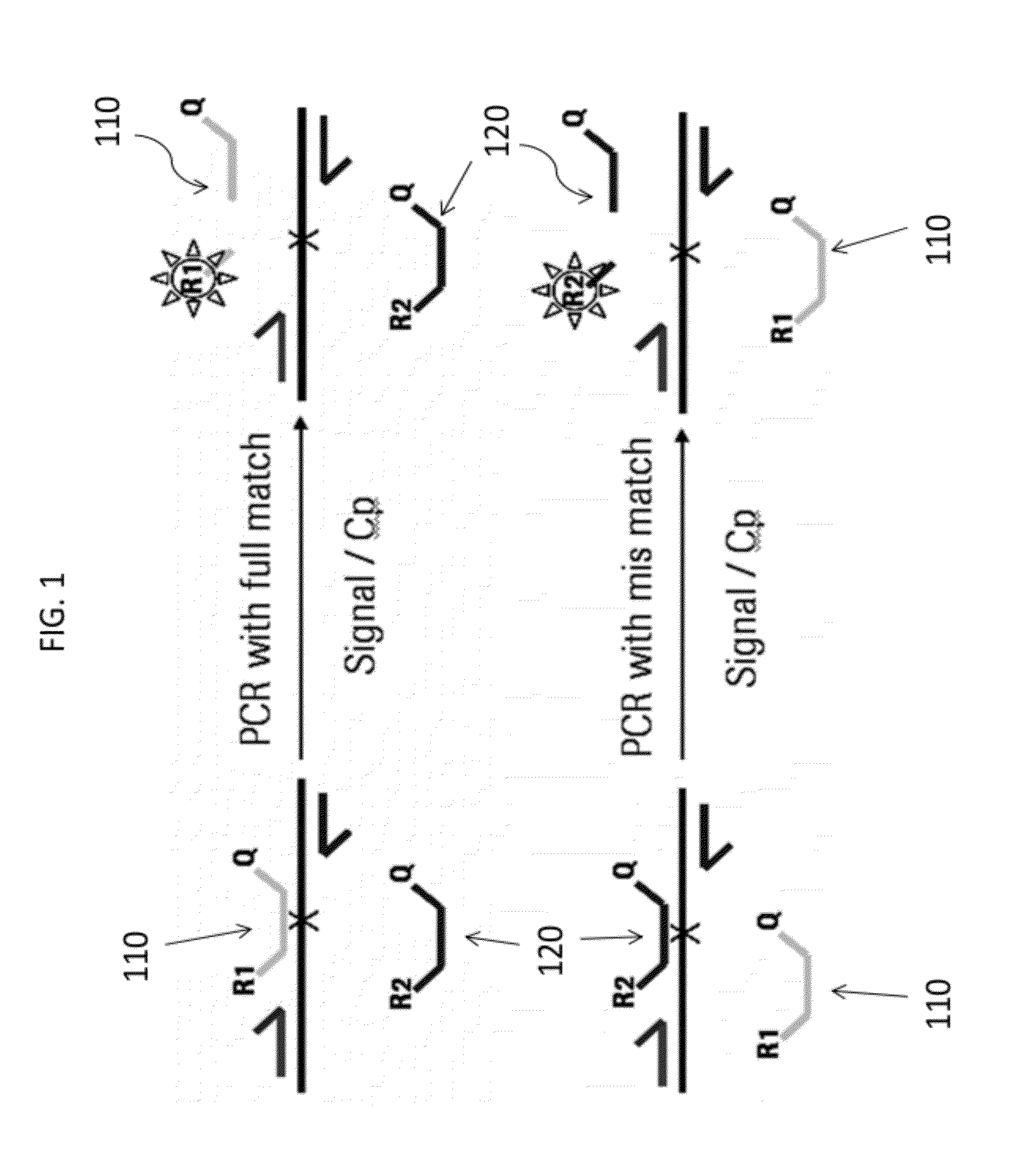
Type of universal probe for the detection of genomic variants
InactiveUS20120225428A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceLocked nucleic acidNucleotide composition
The present disclosure relates to a composition comprising a first set of probes and a second set of probes, composed of one or more DNA nucleotide(s) and five or more LNA (locked nucleic acid) nucleotides, wherein the base at a discriminating position differs for a first probe of the first set and a first probe of the second set. The present disclosure relates to the composition comprising a plurality of probes in each of the first and second set of probes, wherein the probes in each set differ in one, two, or three LNA random position(s). Further, the present disclosure relates to a method of detecting genomic variants by means of the aforementioned probes.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Pulsed field gel electrophoresis method for S.paratyphi A
InactiveCN102305823AImprove the ability to distinguishMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEnzyme digestionDigestion
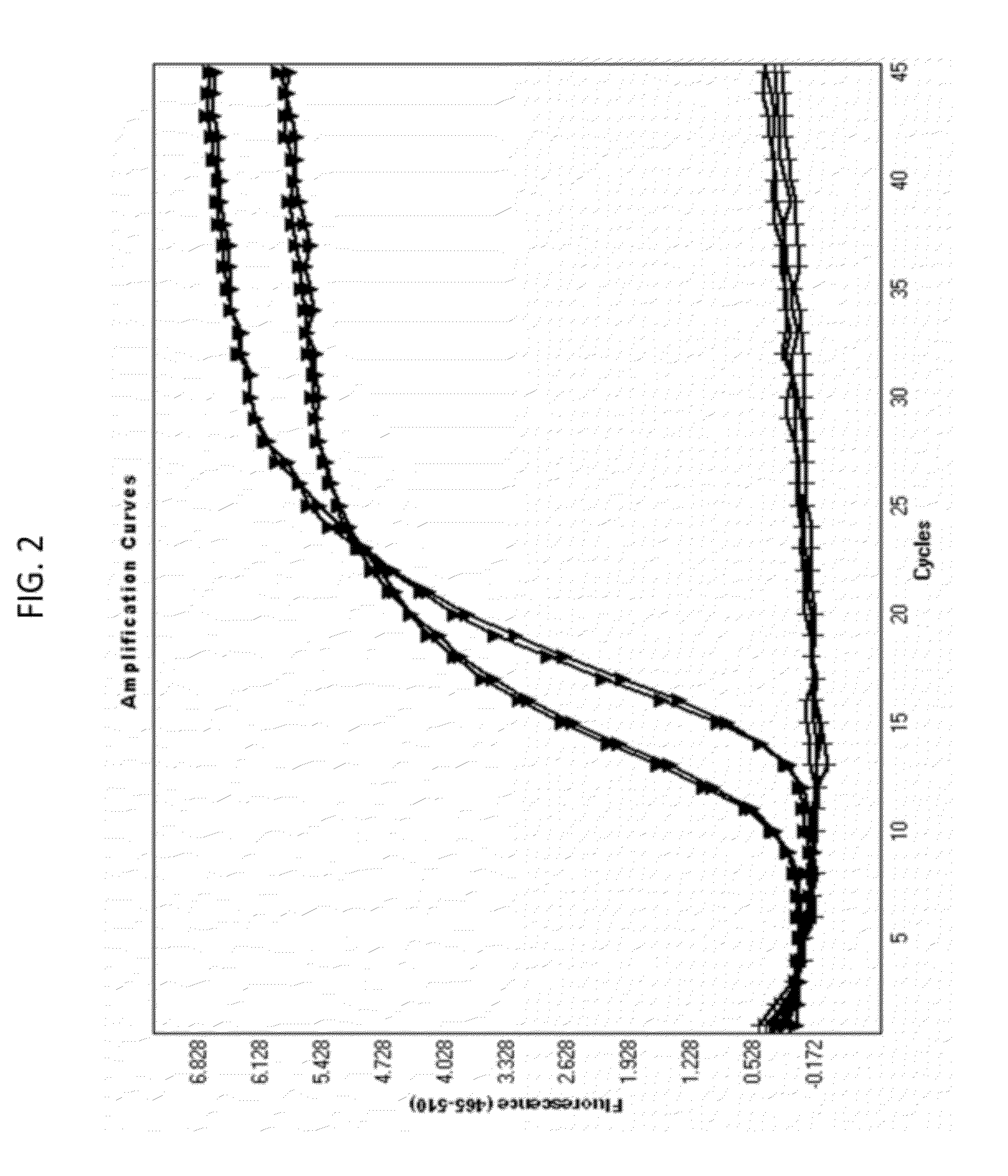
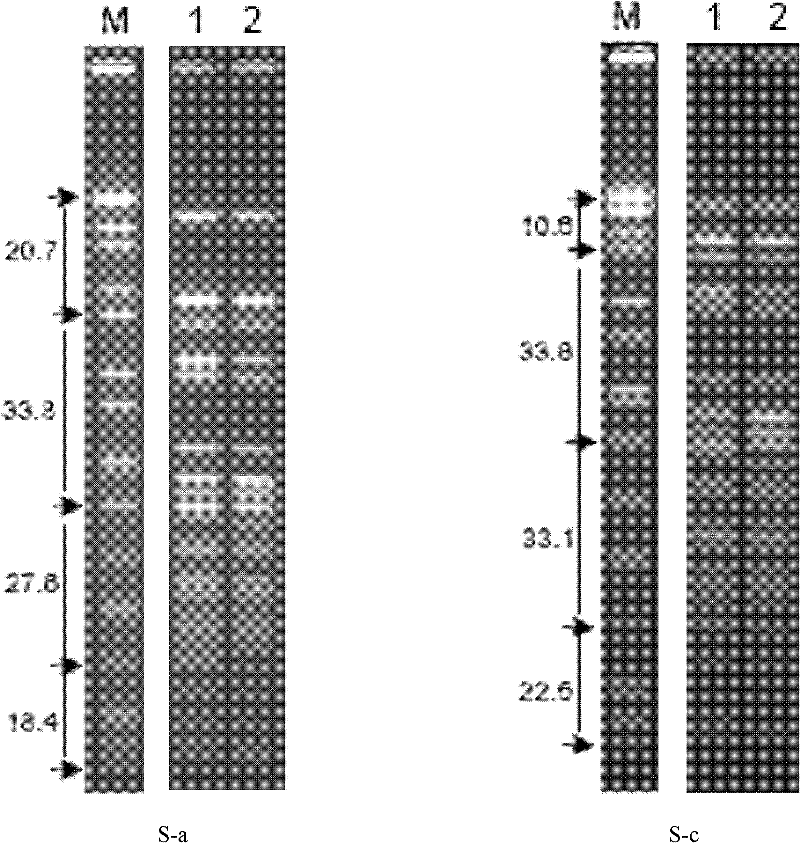
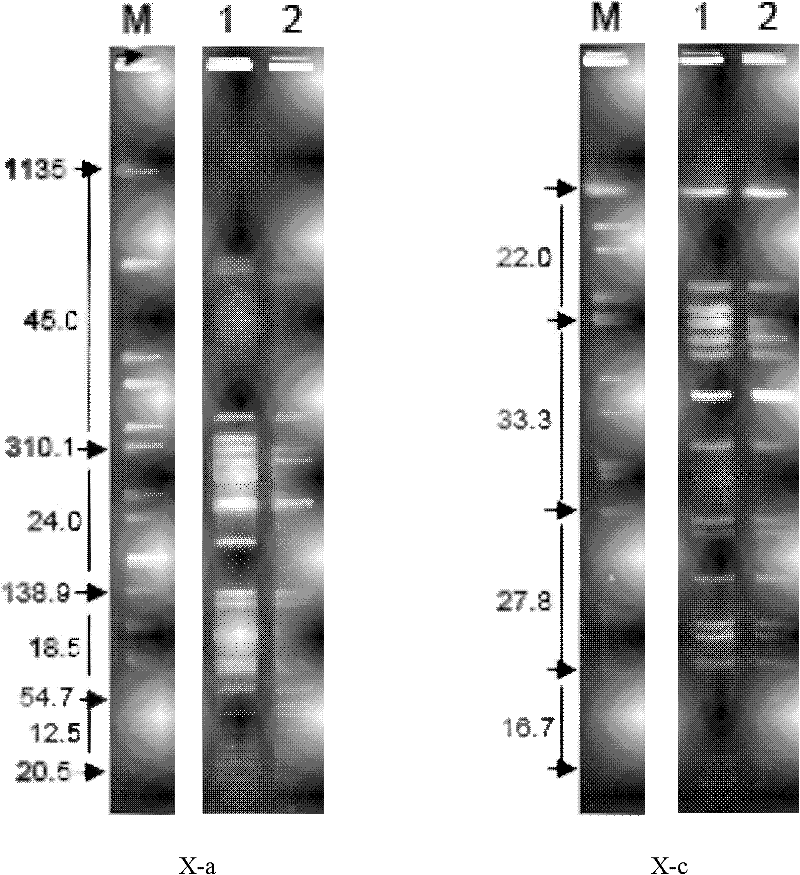
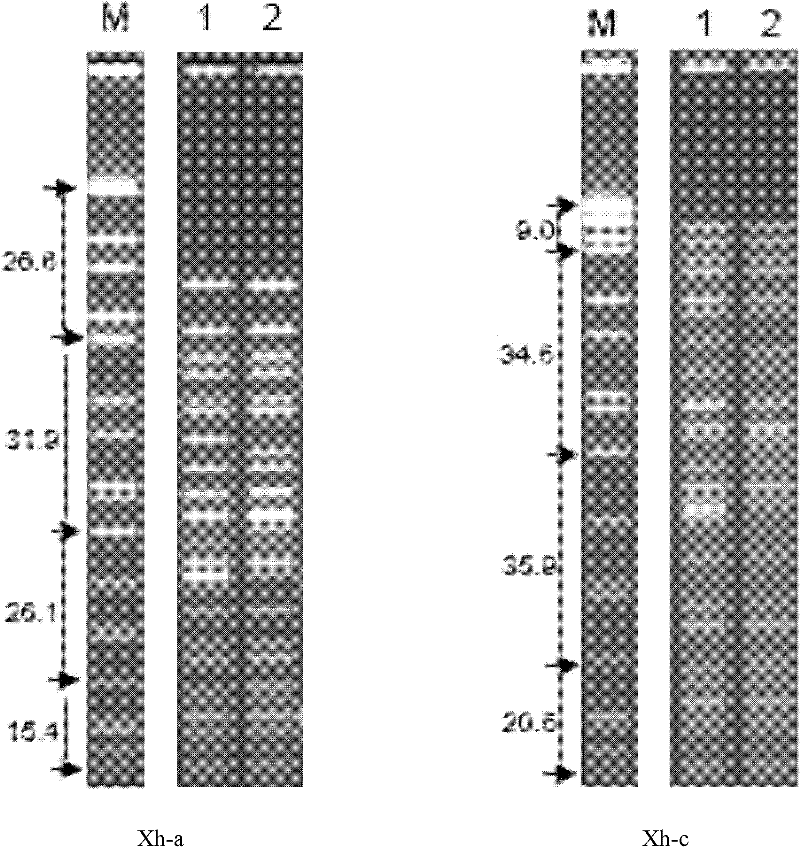
The invention provides a pulsed field gel electrophoresis method for S.paratyphi A. S.paratyphi A which is obtained through separation is used as an analysis sample, and the method sequentially comprises the following steps of: preparing a gel block, performing lysis, washing the gel block, performing enzyme digestion on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in the gel block, and injecting the sample and performing electrophoresis. The steps of preparing the gel block, performing lysis, washing the gel block, and injecting the sample are performed according to the conventional pulsed field gel electrophoresis method; in the step of performing enemy digestion on the DNA in the gel block, Spe I is used as a preferred enzyme, Xba I is used as a secondarily selected enzyme, and Xho I is used as the third kind of enzyme; in the electrophoresis parameters, the pulse time corresponding to Spe I enzyme is 1 to 20s, 19 to 20h; the pulse time corresponding to Xba I enzyme is 1.5 to 29s, 19 to 20h; and the pulse time corresponding to the Xho I enzyme is 2.2 to 29s, 19 to 20h. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantage that the resolution ratio of S.paratyphi A is improved obviously, and can be effectively applied to the detection of molecular classification or genome variation of S.paratyphi A.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Method for recognizing contribution proportion of kiwi fruit hybrid patients on filial generation genome
ActiveCN106755300AImprove accuracyFacilitate early screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationConfidence intervalKiwi fruit
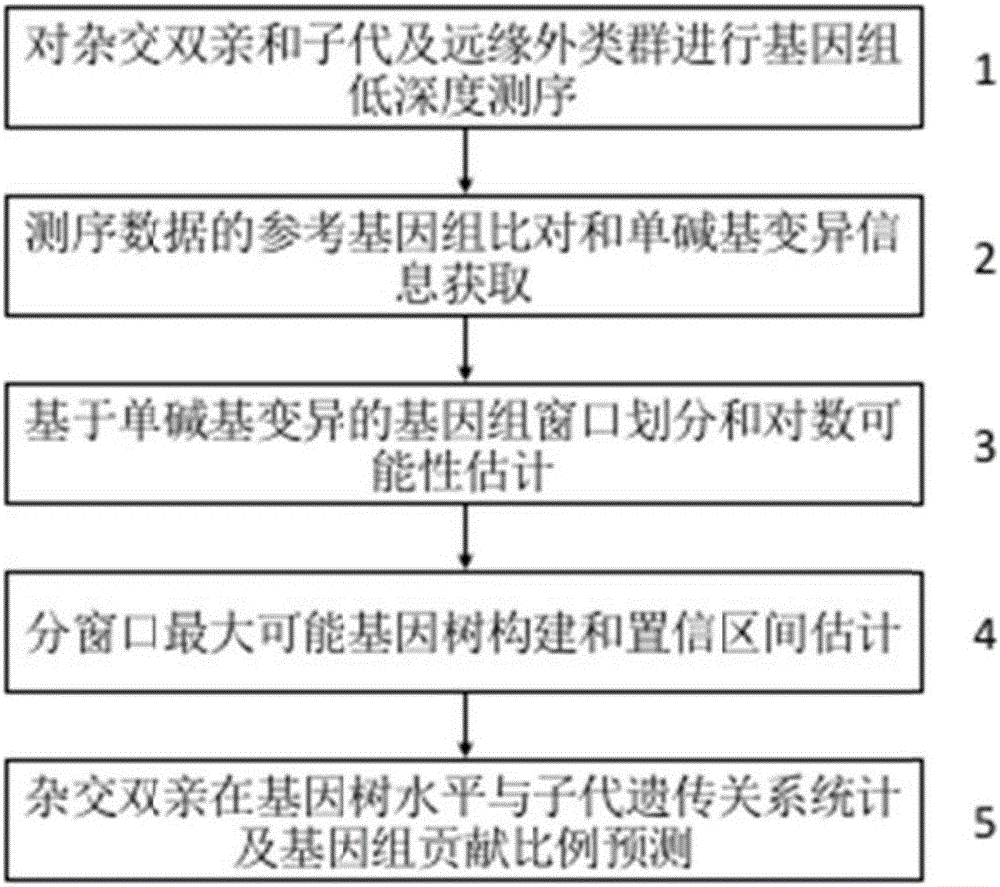
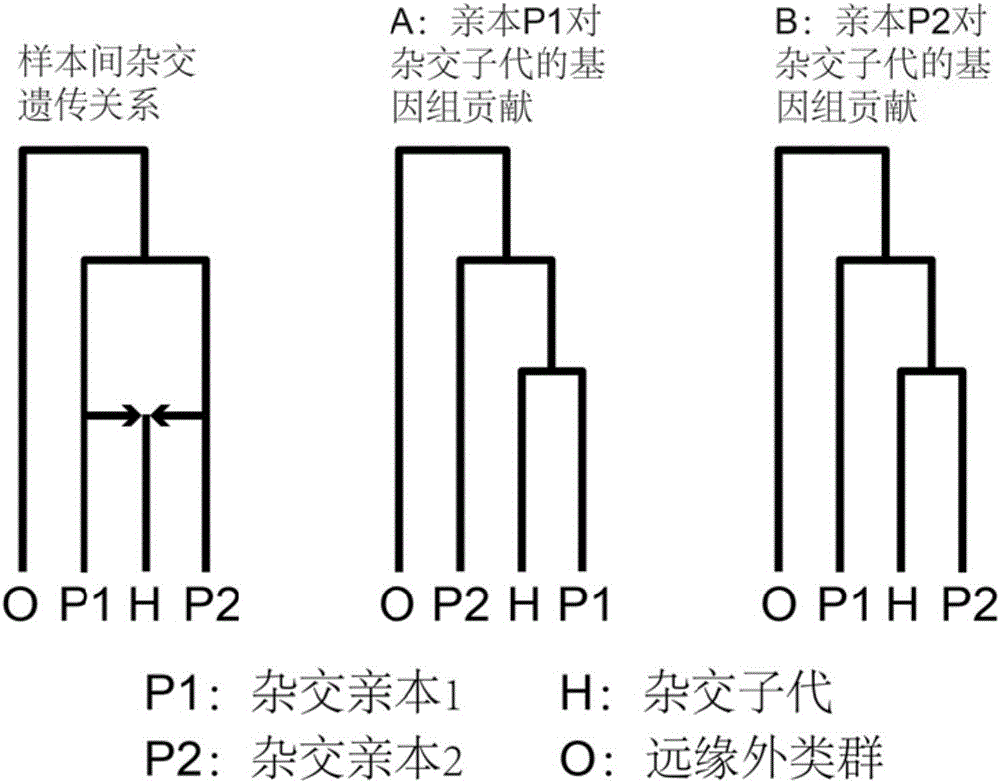
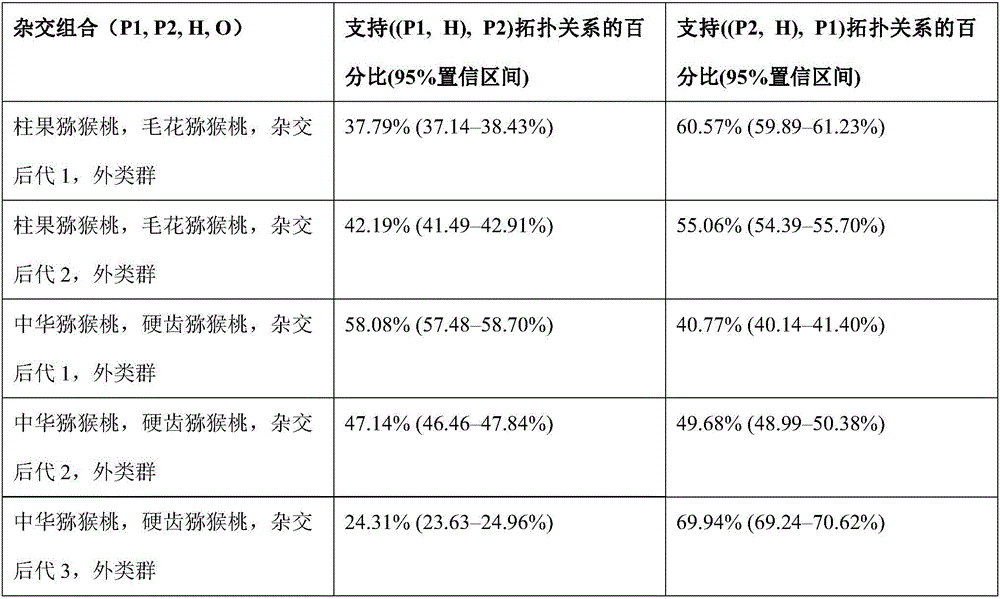
The invention discloses a method for recognizing the contribution proportion of kiwi fruit hybrid patients on a filial generation genome. The method comprises the following steps of performing genome low-depth sequence testing on hybrid parents and filial generations and distant hybrid outgroup; performing sequence testing data reference genome comparison, and obtaining single basic group variation information; performing single basic group variation-based genome window division and log probability estimation; performing sub window maximum possible gene tree building and confidence interval estimation; performing gene tree level and filial generation genetic relationship statistics and genome contribution ratio prediction on the hybrid parents. The whole genome variation information is used for analyzing the evolution genetic relationship of the hybrid patients and the hybrid filial generation, so that the prediction of the hybrid filial generation characteristic properties realizes high accuracy; meanwhile, by using the method, the magnitude and the direction of the possibly existing phenotypic characteristic variation are predicted in the baby period of the hybrid filial generation formation; the early stage screening of the hybrid strains can be greatly promoted; the labor and material cost can be reduced; the resource mining and utilization efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Multiple primers, kit and method for high-throughput sequencing of enterovirus
InactiveCN110387438AComprehensive detection effectPerfect analysis techniquesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnterovirusGenotype
The invention discloses multiple primers and a kit for high-throughput detecting of a whole genome of enterovirus, and a high-throughput sequencing analysis method. Compared with the prior art, specific primers do not need to be used for detecting a certain generic type one by one in a targeted mode any more, but multiple PCR is utilized to conduct genomic amplification on various enterovirus subtypes through an experiment, the virus subtypes are accurately distinguished and identified, and the accuracy rate is higher, and repeatability is better; high-depth sequencing is adopted, the enough detection depth is ensured, and thus false positive is lower; and through the detection method, the gene types of the enterovirus are rapidly identified, genome variable site, diversity and recombination analysis of viruses can be further provided, and the important scientific basis of prevention and control over the enterovirus is provided.
Owner:广东省公共卫生研究院 +1
Gene for regulating and controlling corn flowering period, promoter, and application of gene and promoter
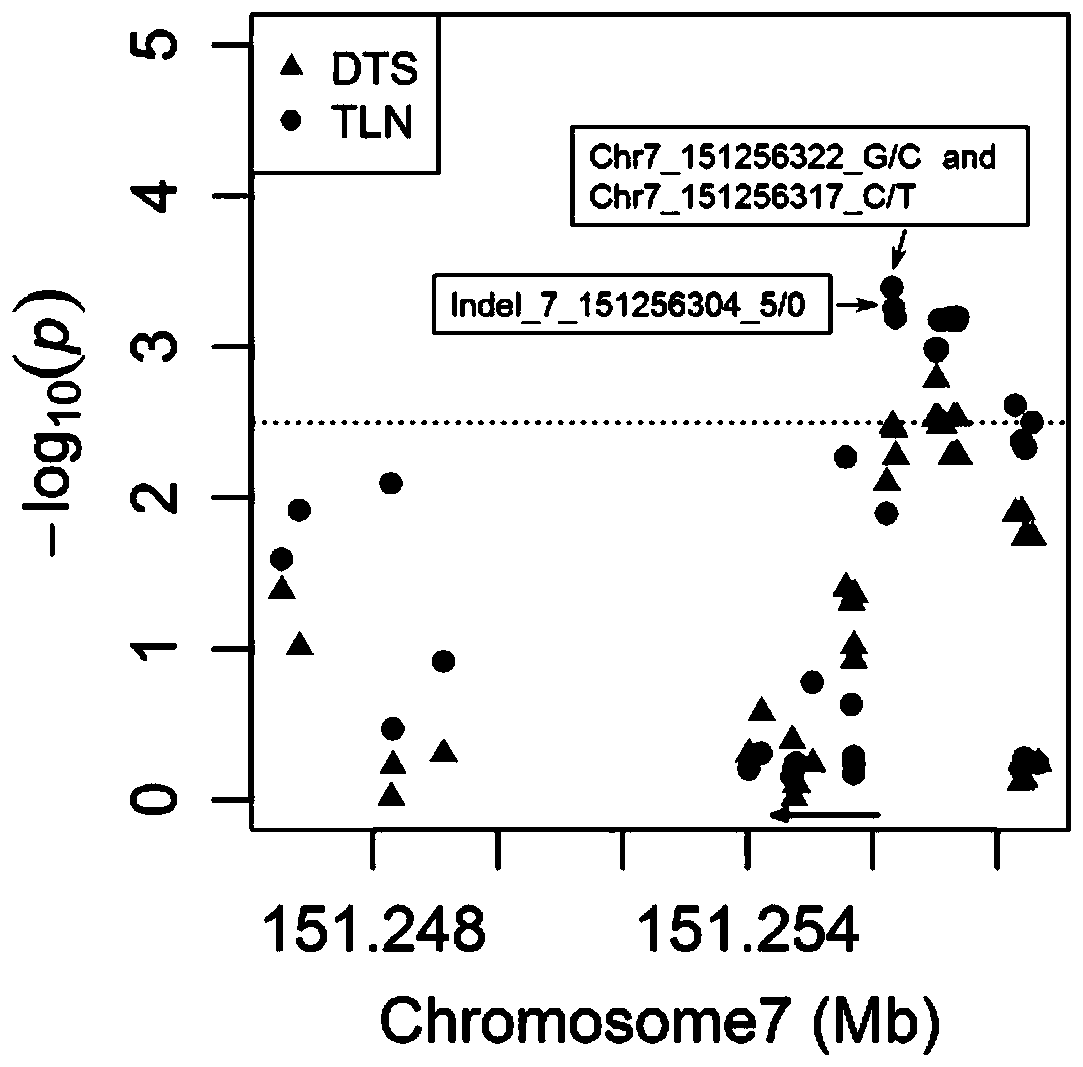
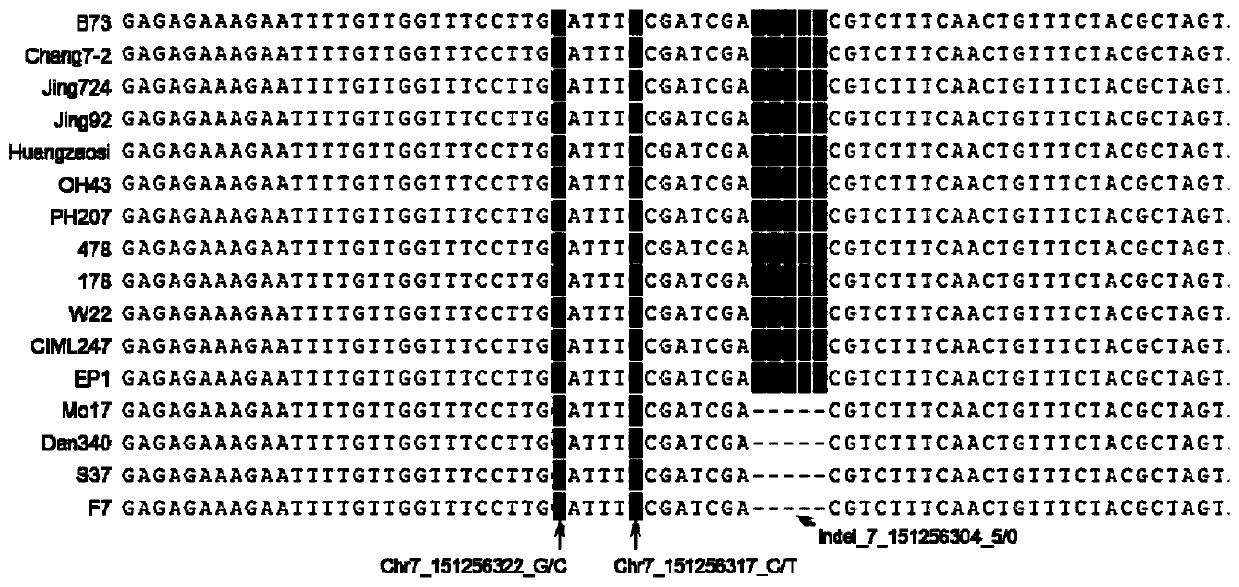
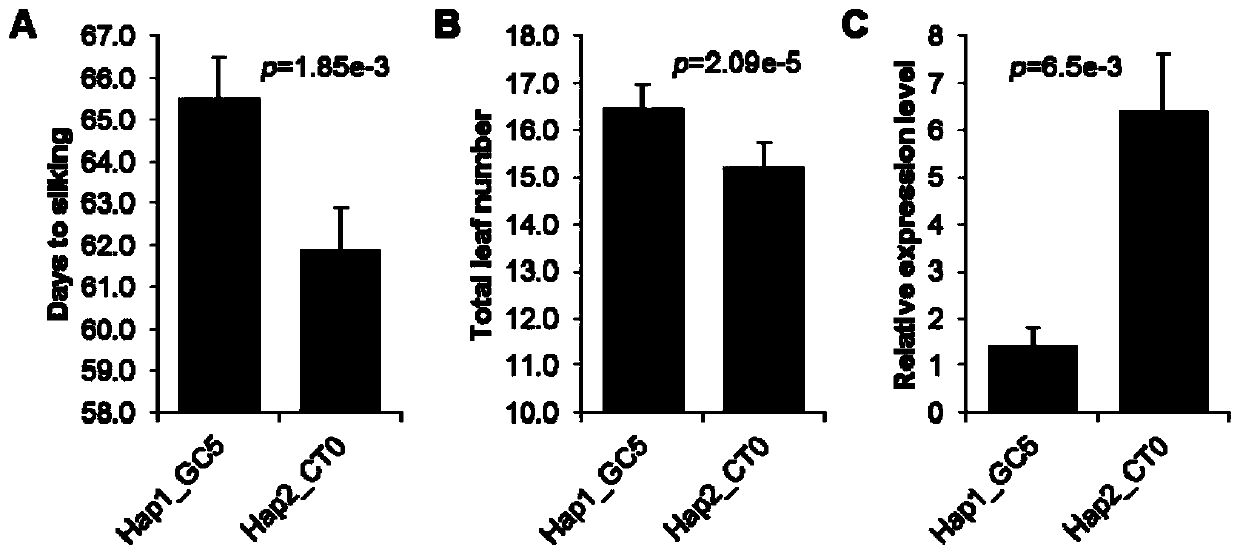
The invention discloses a gene for regulating and controlling the corn flowering period, a promoter, and application of the gene and the promoter. Firstly, a key genome region for regulating and controlling the corn flowering period or the leaf quantity is provided; the polyribonucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID No. 1; the condition that a ZmSBP29 gene has the function of regulating and controlling the corn flowering period and the leaf quantity is proved by a genetics and molecular biology method. The invention further provides a key genome variation for regulating and controlling the expression quantity of the ZmSBP29 gene, and creates a transgenic event for overexpression of the ZmSBP29 gene; the key genome variation and the transgenic event can be applied to the improvement of thecorn flowering period and plant type, and can also be applied to corn high yield and adaptive breeding.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Seed selection and cultivation method for novel-variety Jinliu early-red peach tree
The invention provides a seed selection and cultivation method for a novel-variety Jinliu early-red peach tree. The seed selection method for the novel-variety Jinliu early-red peach tree is characterized by comprising the steps that seed selection is carried out, a branch with fruits obviously different from other branches is selected from the whole peach tree, and the branch is marked and observed if the fruits on the branch are obviously larger than other fruits; a traditional tree fruit breeding method is combined with the modern molecular biological technique, precocious peach breeding work is carried out, and the effect is significant. On the basis of bud mutation, seed selection, top grafting identification, clone breeding and the like in the fruit tree breeding theory, an SSR and SRAP molecular marker technology is further utilized for bud mutation identification, the genome DNA variation range and site are found, it is verified that the genes of the novel variety are changed, true bud mutation occurs on the novel variety, and the good property can be stably inherited.
Owner:TIANJIN XUEXIANG FRUIT & VEGETABLE
Human respiratory virus targeted enrichment capture probe set and application thereof
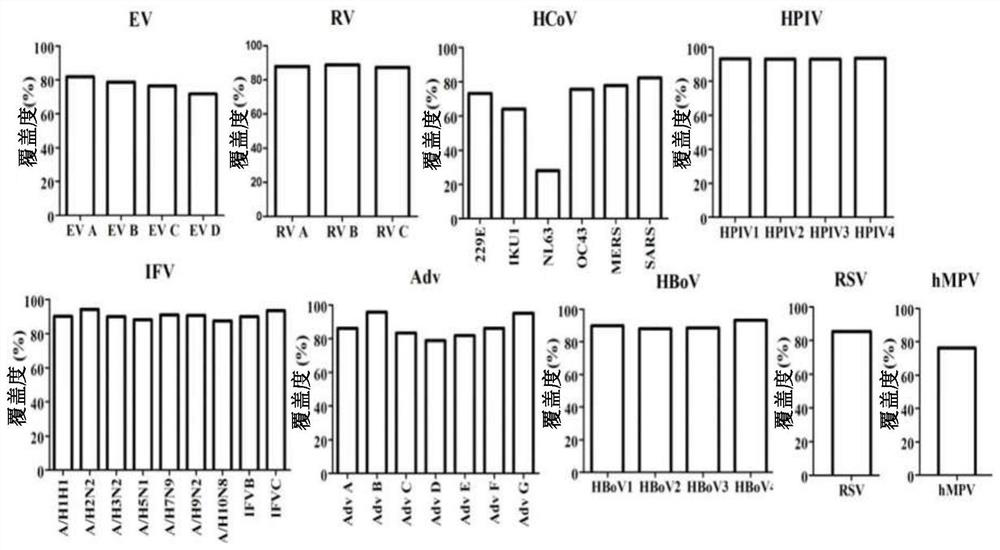
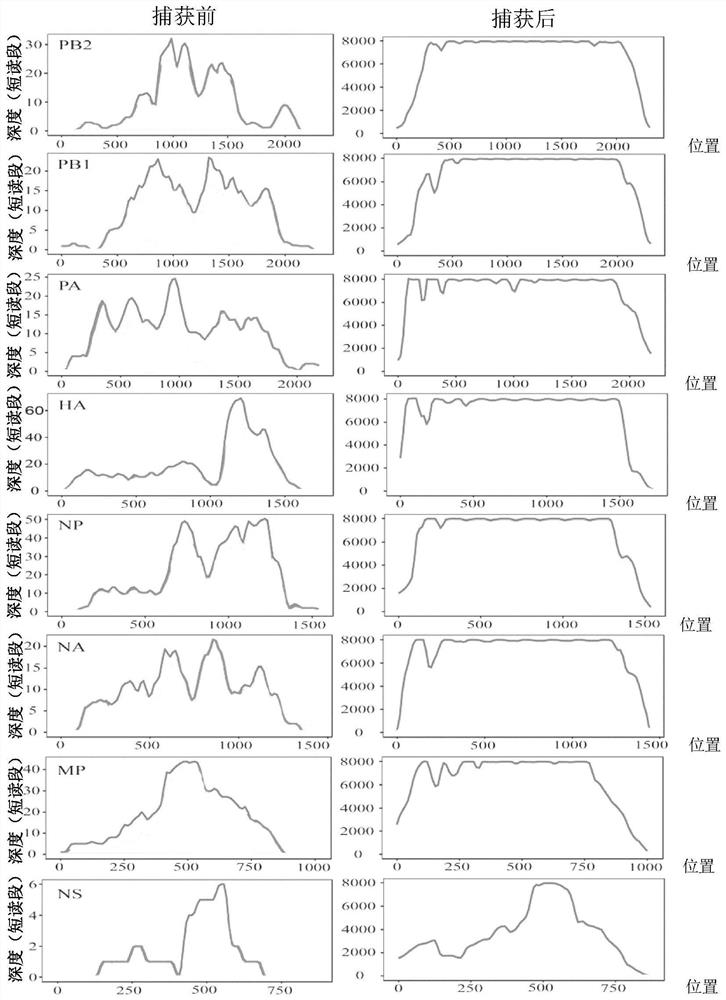
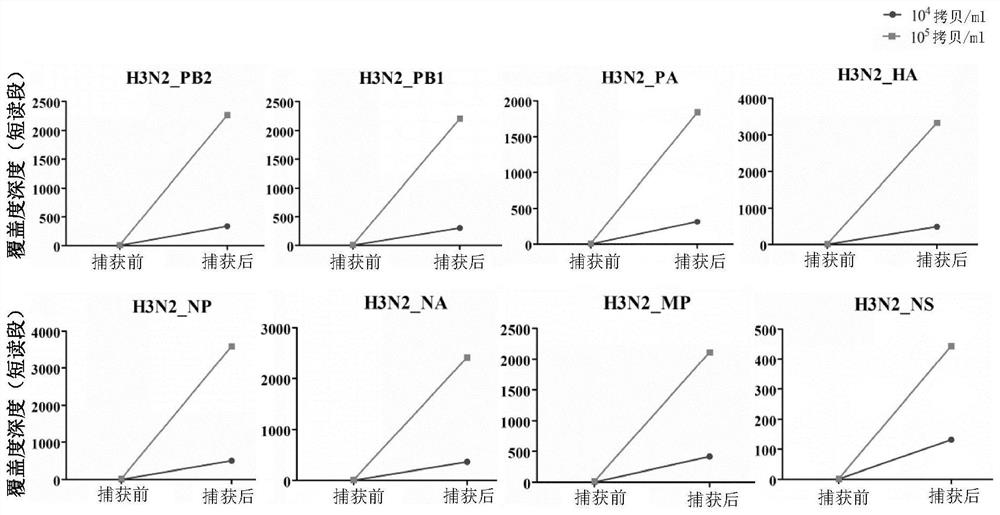
The invention relates to the field of human respiratory virus diagnosis, and provides a method for generating a targeted enrichment capture probe set for human respiratory viruses. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a gene sequence of a virus infecting a human respiratory tract; designing a probe through a sliding window method, and performing exhaustion of all possible nucleicacid sequences; filtering the obtained nucleic acid sequences; filtering out sequences highly homologous with the human genome in a nucleic acid sequence library; and clustering the probe sequences. The invention also relates to application of the probe set obtained through the method to preparation of a next-generation sequencing library of human respiratory viruses, so that whole genome sequenceinformation is obtained, the genome variation is identified, potential epidemic propagation characteristics of viruses are evaluated, and early warning and prevention and control of respiratory diseases are guided.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Comprehensive methods for detecting genomic variations
InactiveUS20180135120A1Enabling detectionFacilitates emergenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNucleotide
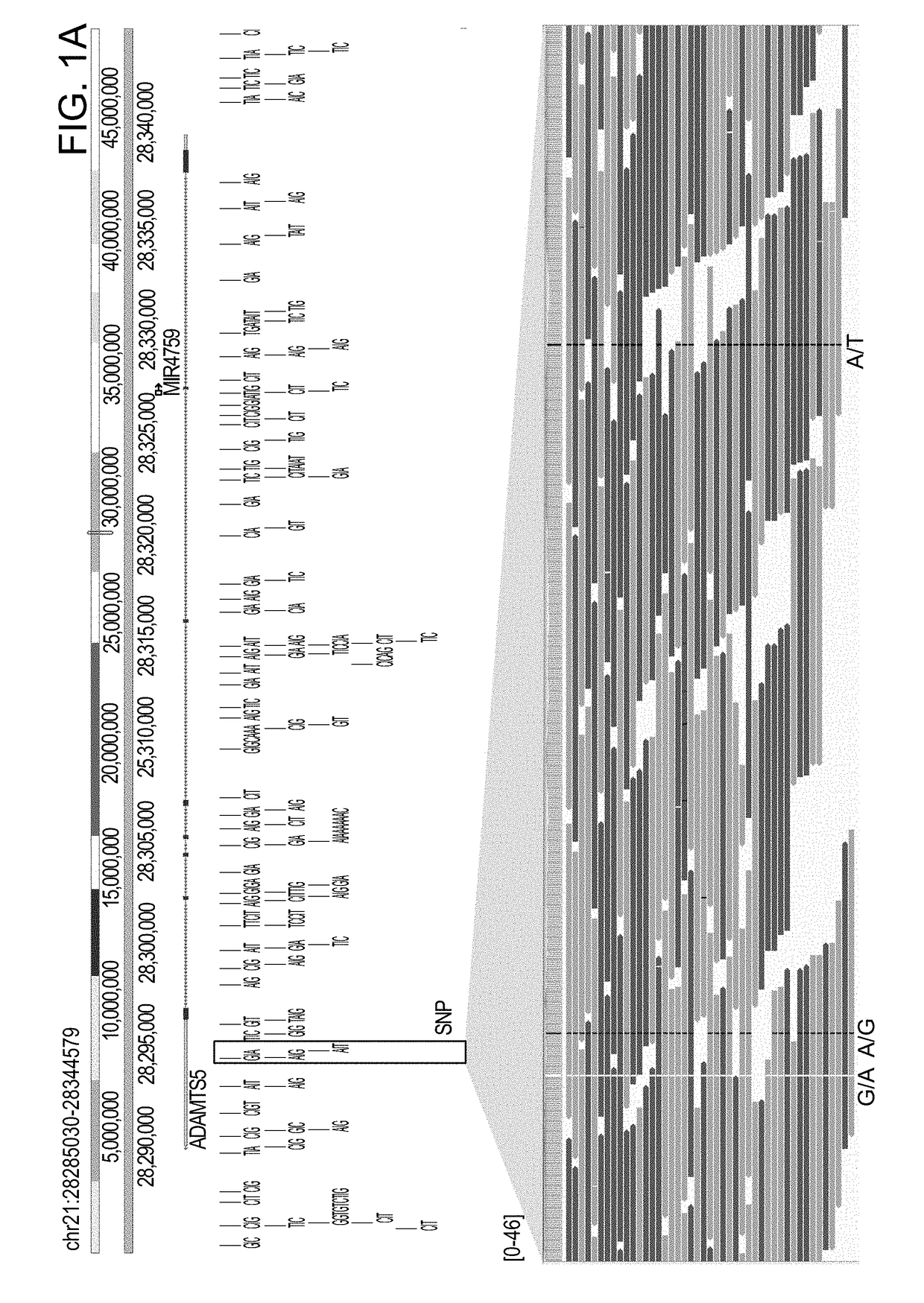
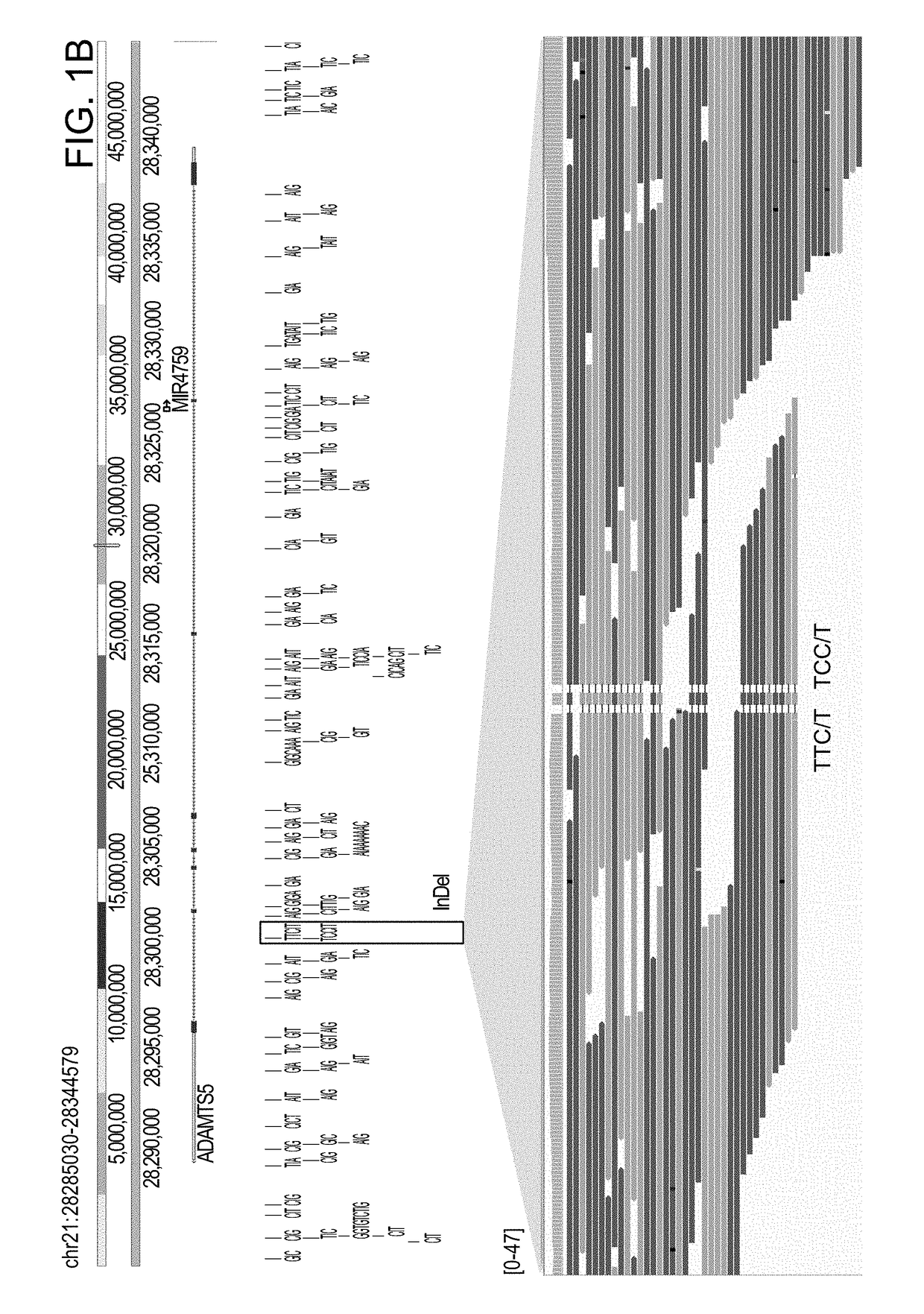
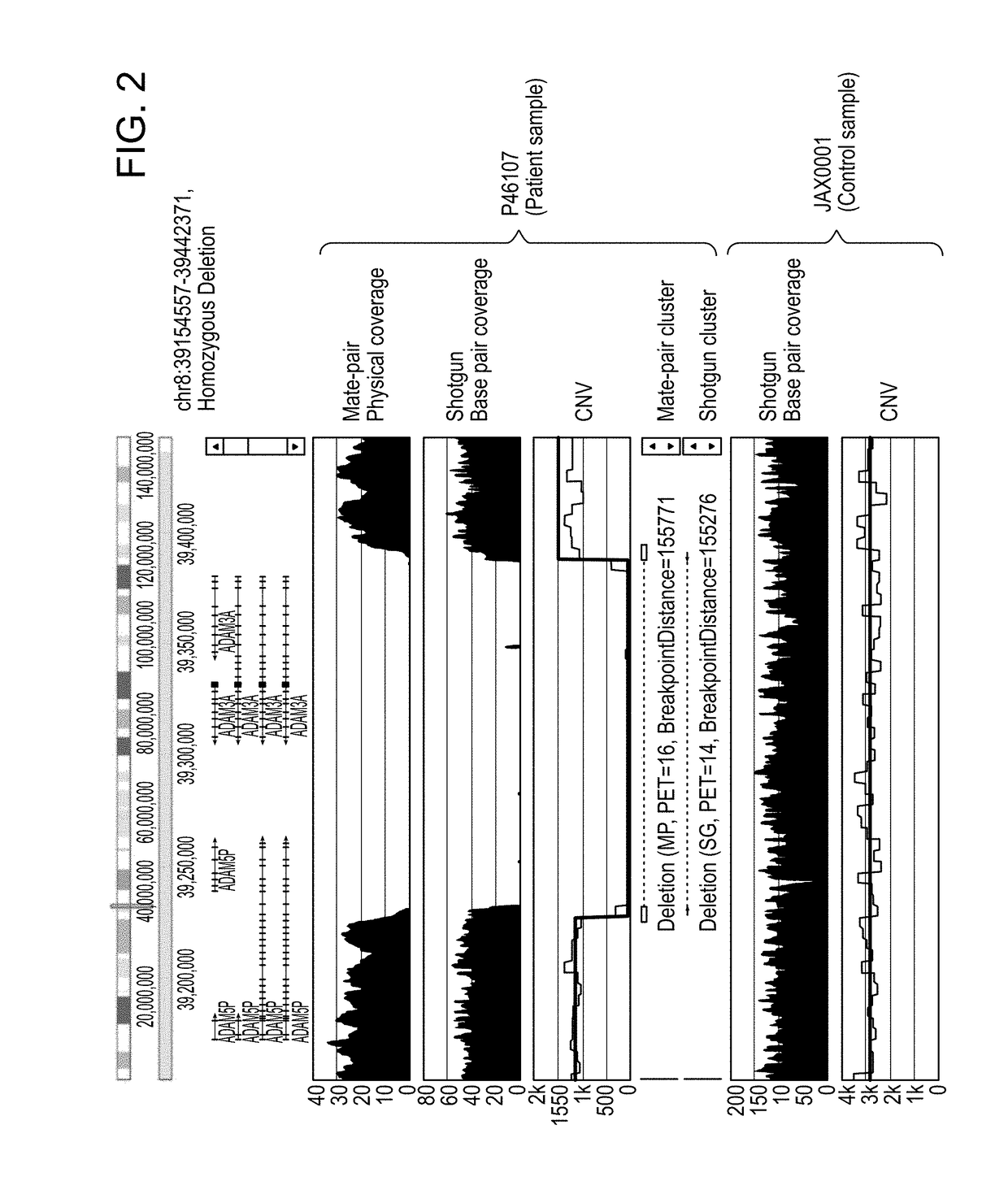
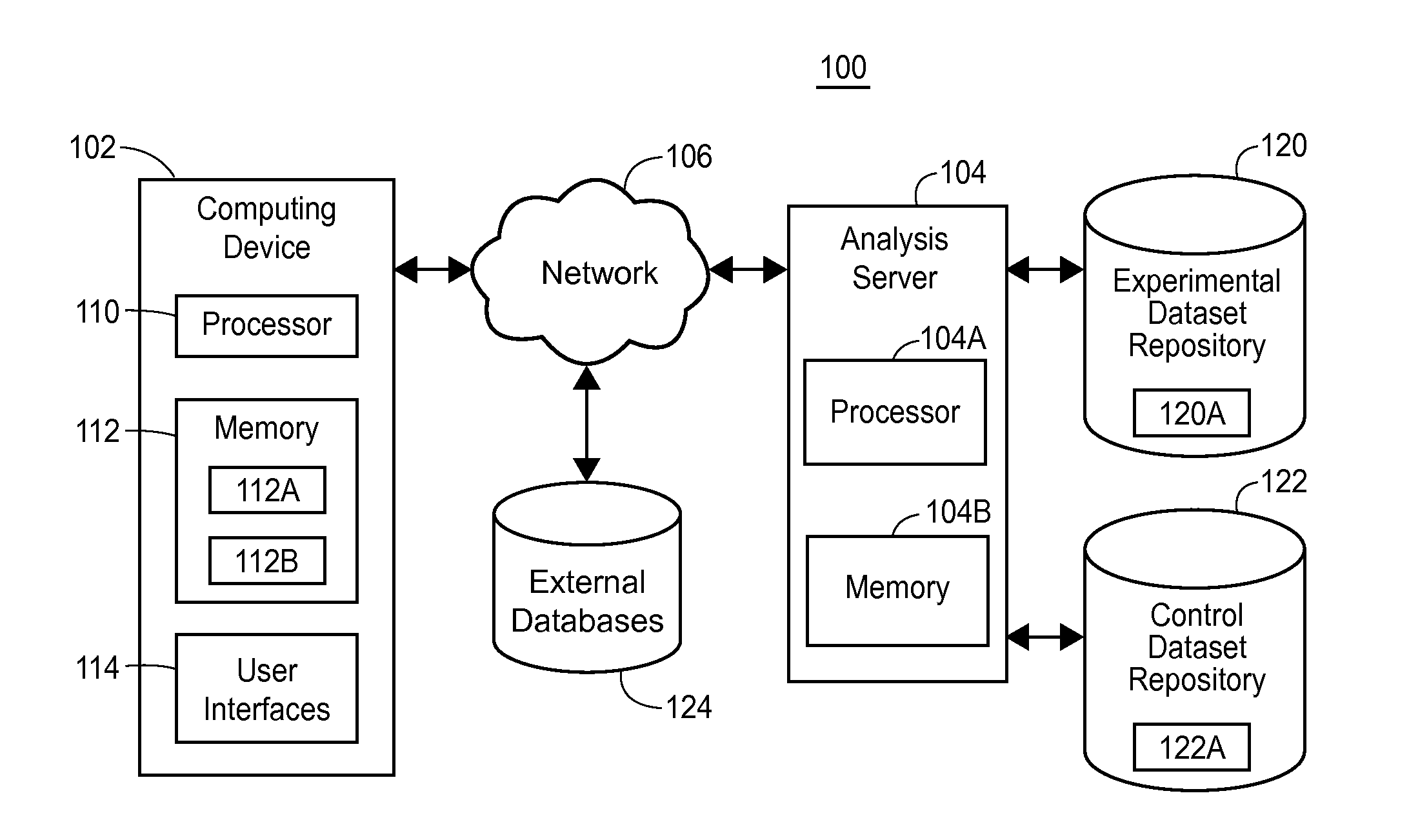
The invention described herein provides methods and systems for comprehensive genomic analysis that enables the detection of a broad range of genomic variations, including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), small insertions or deletions (indels), Tandem Base Mutations (TBM), copy number variations (CNVs), structural variations (SVs), and combination thereof, in a single assay.The invention can be used, for example, to analyze the complicated underlying genomic defects in diseases and conditions such as Autism spectrum disorders (ASD), cancers, Alzheimer's disease, and other neurological disorders.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE
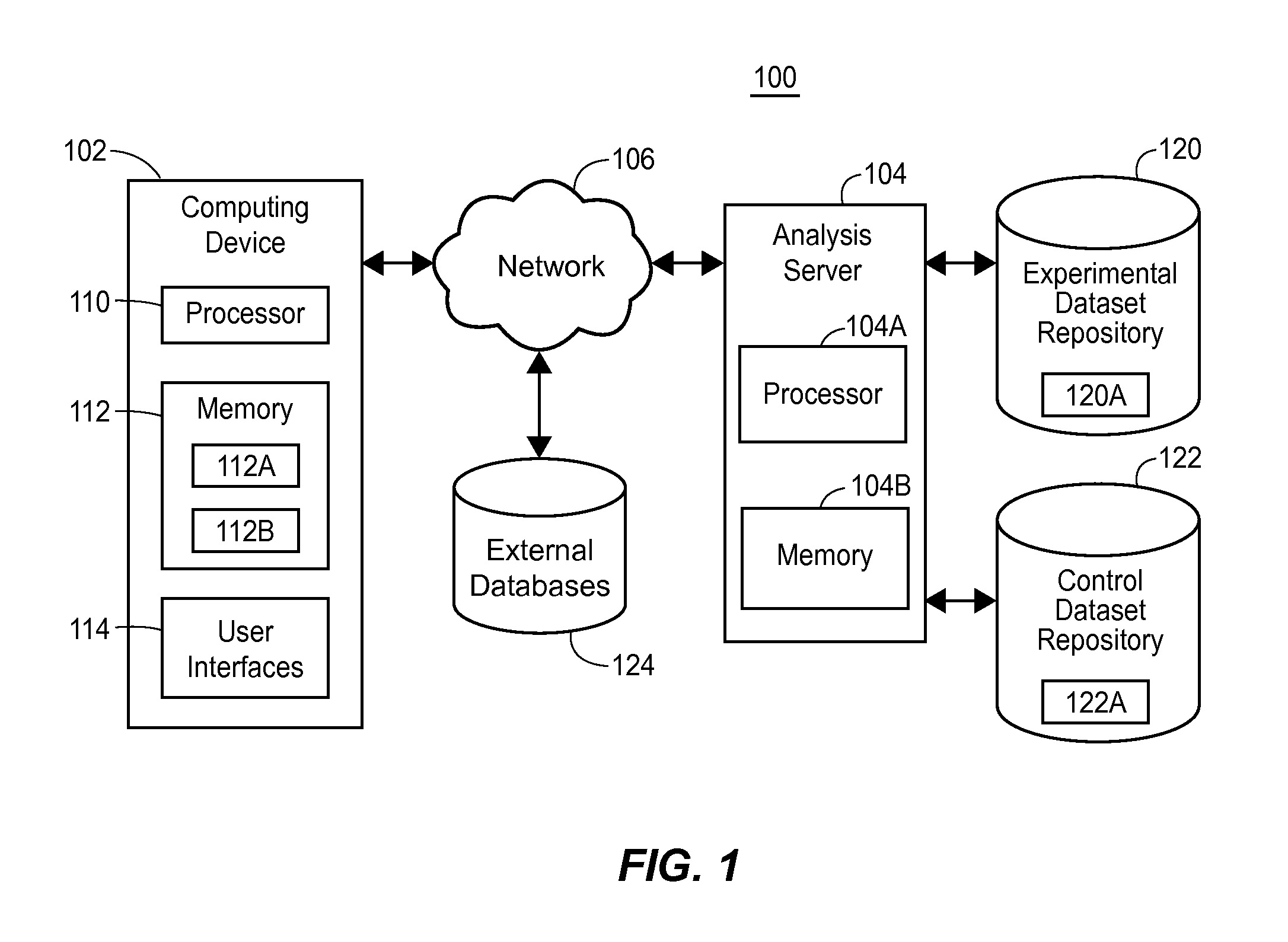
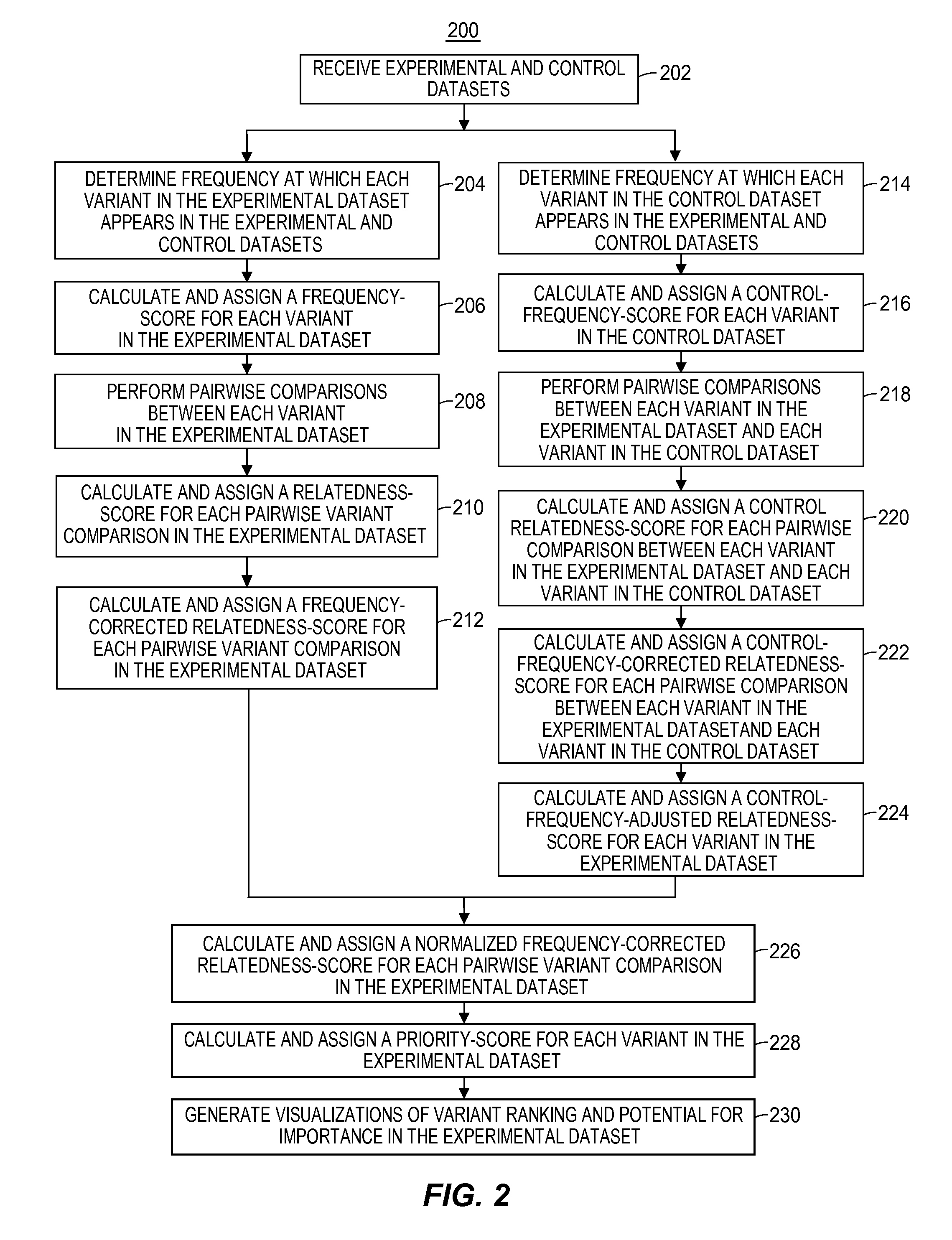
Systems and methods for genomic variant analysis
A genomic variant analysis method and computer system utilizing information related to variant frequency and biological consequence to determine the relative statistical significance of each variant in given genome sequence datasets. The method and system perform both variant frequency normalization and universal pairwise variant comparisons across the given genome sequence datasets to automatically identify the likelihood of any given variant as contributing to disease process or biological phenomenon under study and organize the results into a priority ranking. The priority ranking is then used to categorize the results into biologically-related data subsets for display to indicate potential for importance.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
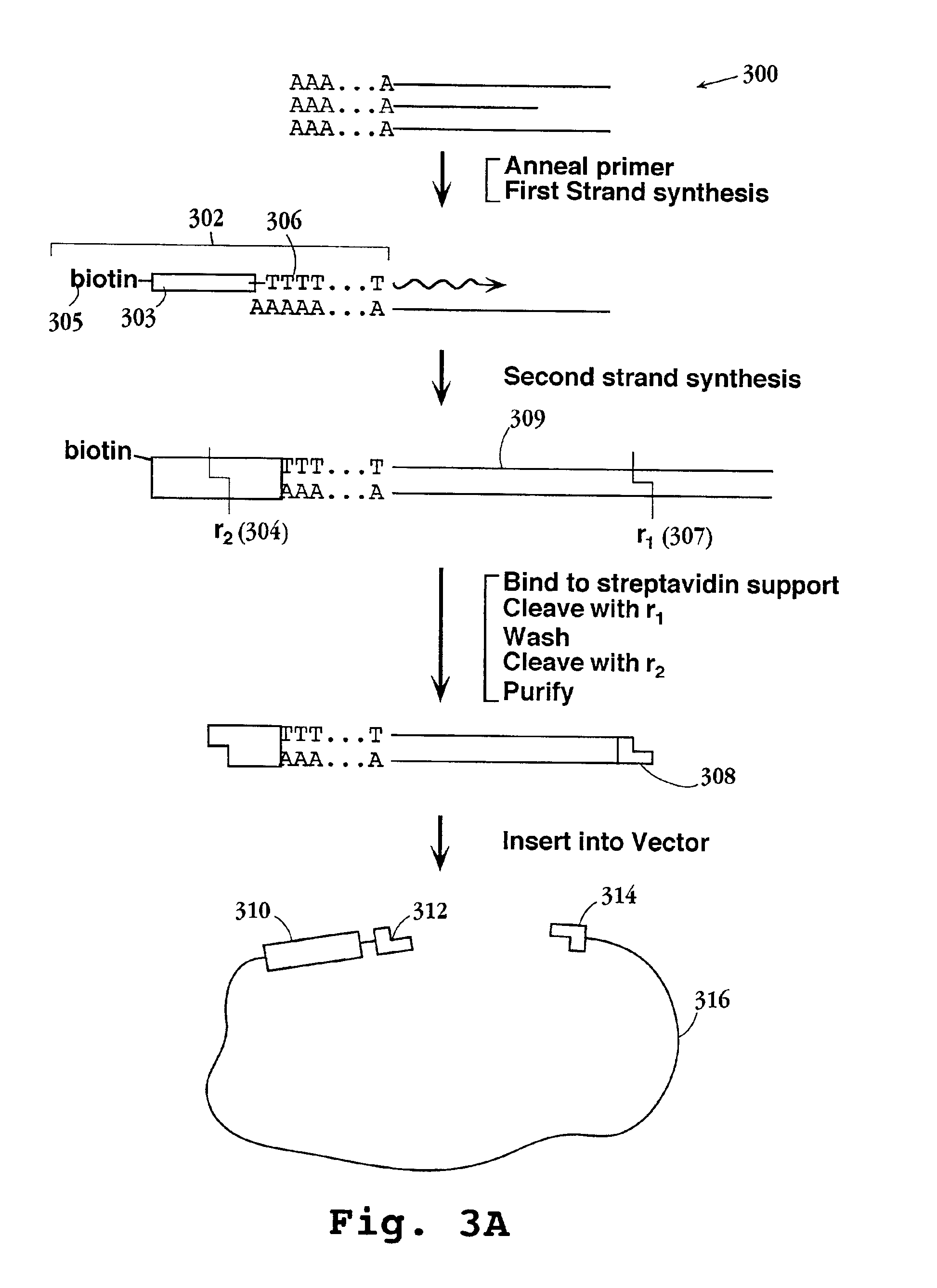
Whole genome DNA sequence splicing sequencing method
The invention which relates to a whole genome DNA sequence splicing sequencing method belongs to the biotechnological field. The invention which improves the preparation of present DNA sequencing substrates, and brings forward a new sequence splicing method can be applied to DNA detection associated with the biology, the medical science, and sidelines of the agriculture, the forestry and the animal husbandry. The invention relates to a series of DNA-associated operations comprising the steps: adding asymmetric junctions to two ends of the genome DNA; anchoring one end to a plane sustenance fully distributed with amplification primers; anchoring the other end of an orientated DNA fragment through methods of electrophoresis and the like; manufacturing and enlarging incisions on a DNA duplex; connecting to 5' terminals of the incisions with sequencing primers containing random ends; connecting the amplification primers with the sequencing primers through a singe-stranded DNA ligase; and increasing the incision number to generate local DNA fragments which can be sequenced. Compared with present sequencing technologies, the method of the invention allows each of the local DNA fragments to reserve distance information, and a complete genome sequence to be obtained through marking splicing results of the local sequences with distances as weights. The method of the invention has protruding advantages in splicing of unknown biological genomes and detection of the genome variation.
Owner:陈先锋
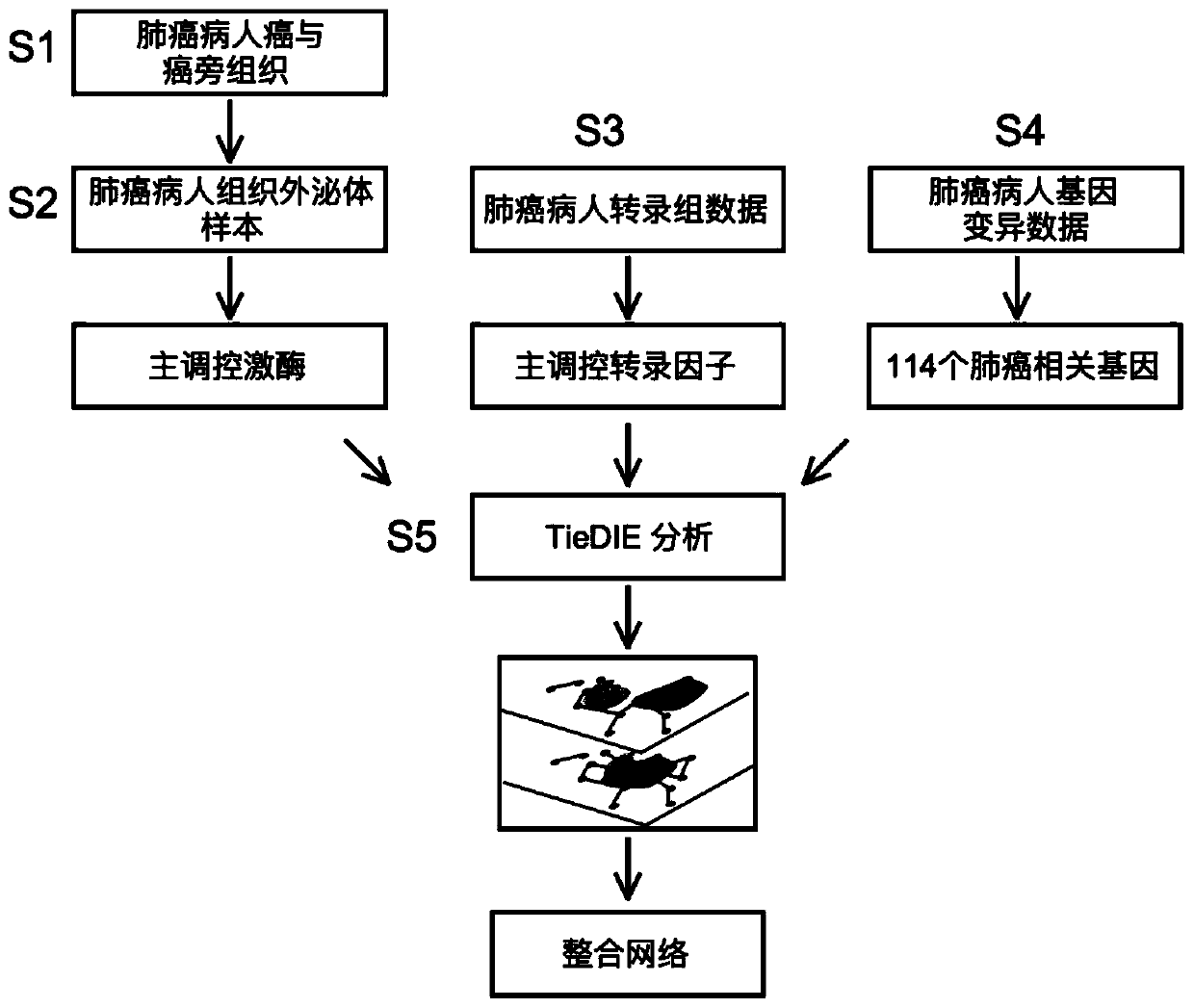
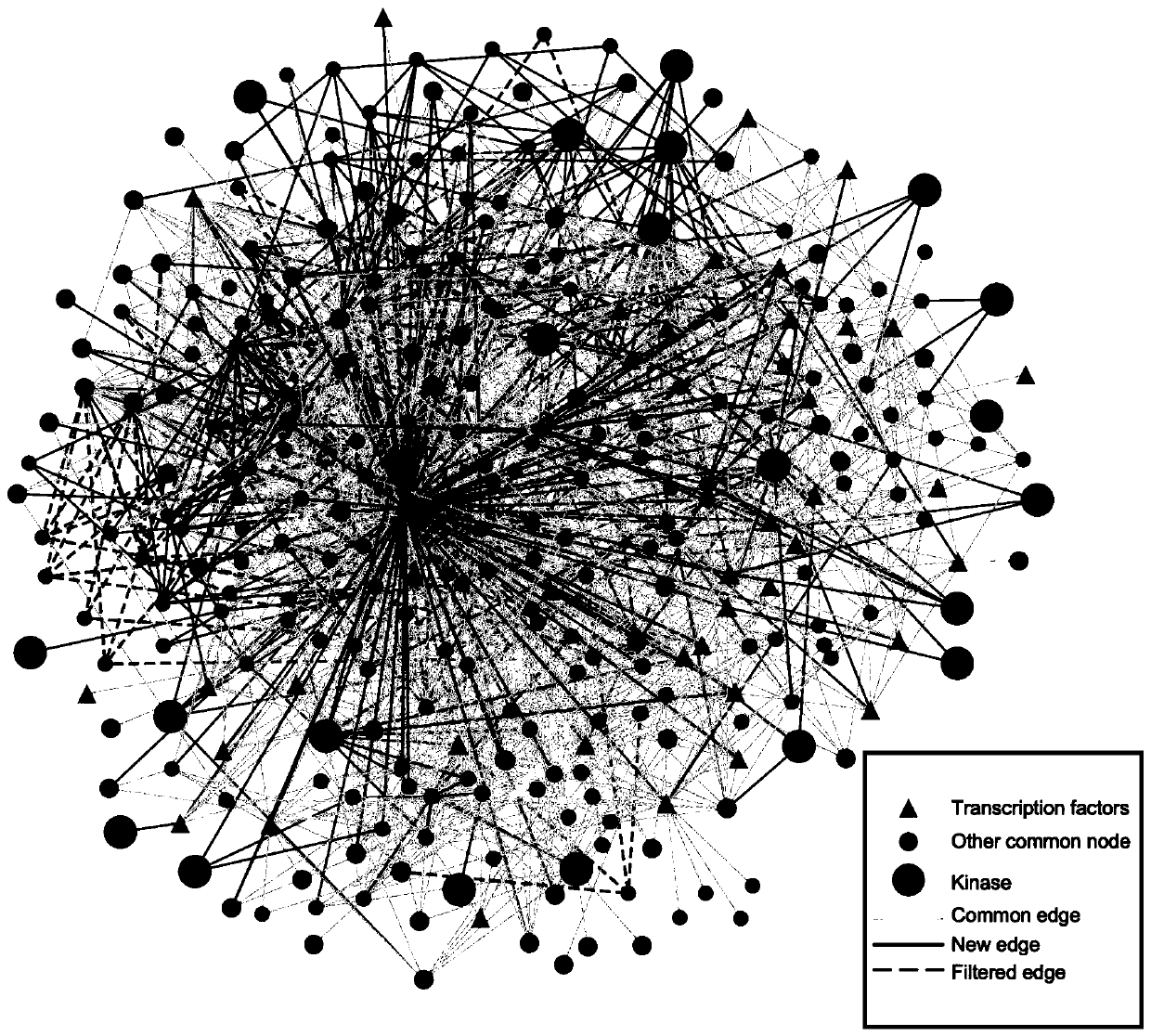
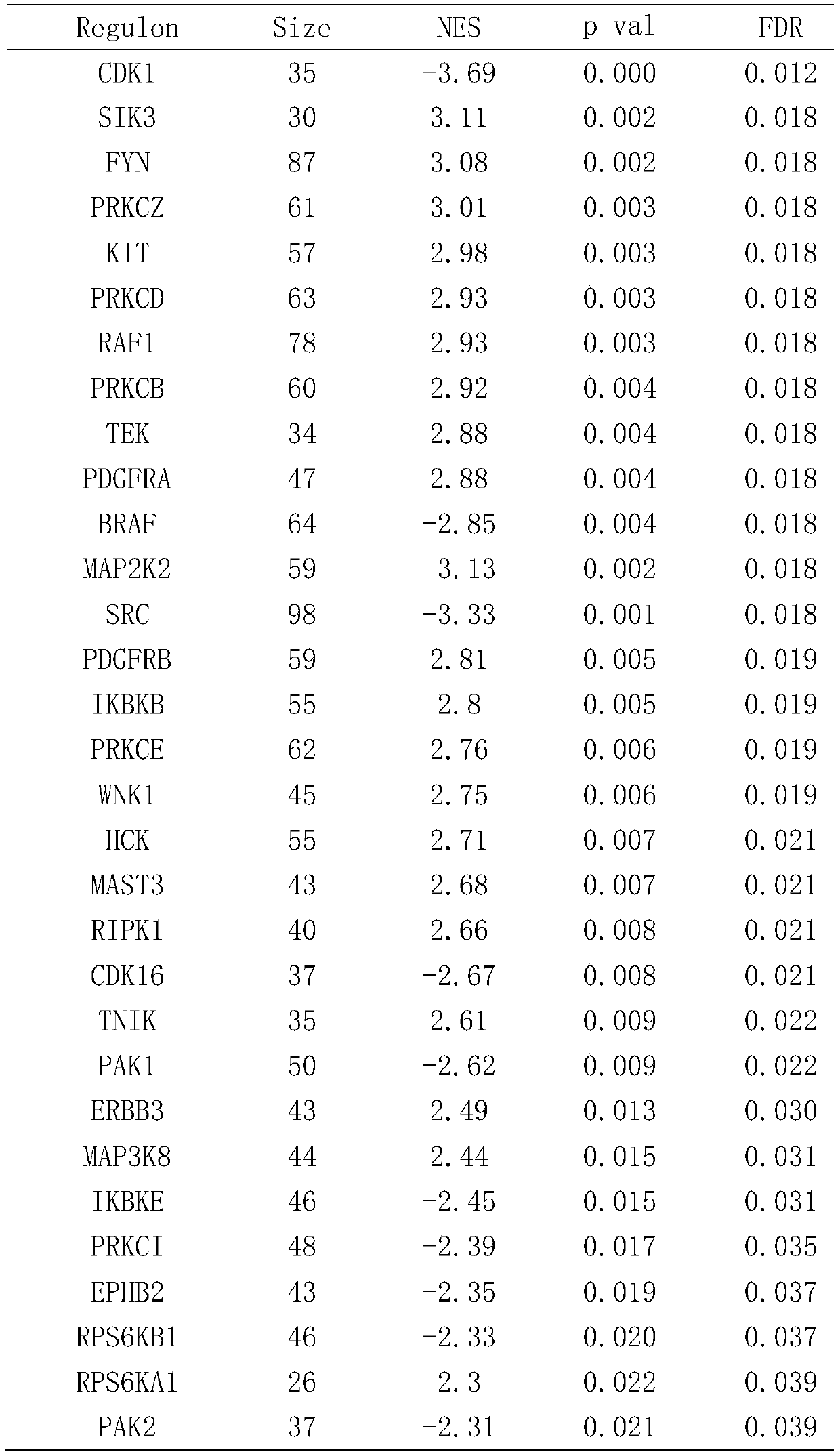
Tissue exosome phosphorylated proteome-based multi-omics analysis method
ActiveCN110957007ALarge amount of informationUniversalMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsSequence analysisDisease
The invention provides a tissue exosome phosphorylated proteome-based multi-omics analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, separating exosomes of a tissue sample and specifically enriching phosphorylated proteins; S2, carrying out sequencing analysis on the enriched phosphorylated protein to obtain main regulation kinase; S3, analyzing transcriptome data of the tissue sample to obtain a main regulation transcription factor; S4, analyzing the genome variation data of the tissue sample to obtain a tumor-related gene; and S5, performing strategy analysis on the analysis data obtained in the steps S2, S3 and S4 to obtain a cancer-related main regulation kinase network and a drug action target. The method is suitable for the joint analysis technology of phosphorylated proteome sequencing data, transcriptome data and gene mutation data of any disease exosome sample, and a foundation is laid for exploring markers related to diseases and selecting more effective and accurate disease treatment targets.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and device for simultaneously detecting DNA methylation and genome variation and storage medium
ActiveCN112634984AShort cycleHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsDNA methylationMutation detection
The invention discloses a method and device for simultaneously detecting DNA methylation and genome variation and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: a methylation site restoration step: restoring a methylation site into an original C basic group or G basic group according to the DNA methylation information of a to-be-detected sample, and obtaining the restored sequencing data of the to-be-detected sample; and mutation detection: taking the repaired sequencing data of the sample to be detected as an input sample for mutation detection, and carrying out mutation detection on the sample to be detected to obtain genome mutation information of the sample to be detected. According to the method, the DNA methylation information and the genome variation information of the sample to be detected can be simultaneously obtained by sequencing the DNA library of the sample to be detected once, so that not only is the genome variation detection period shortened, but also false positive mutation caused by DNA methylation is prevented from being detected; thereby improving the genome variation detection precision.
Owner:北京吉因加医学检验实验室有限公司
Streptococcus agalactiae attenuated strain YM001 genome sequence feature and use thereof
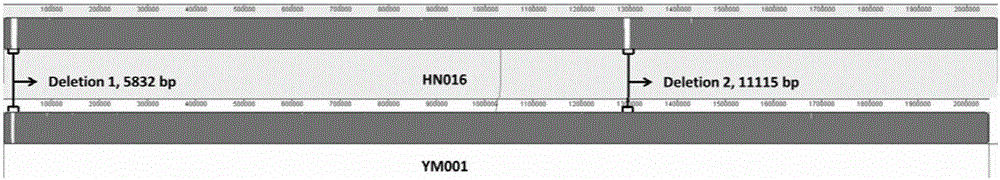
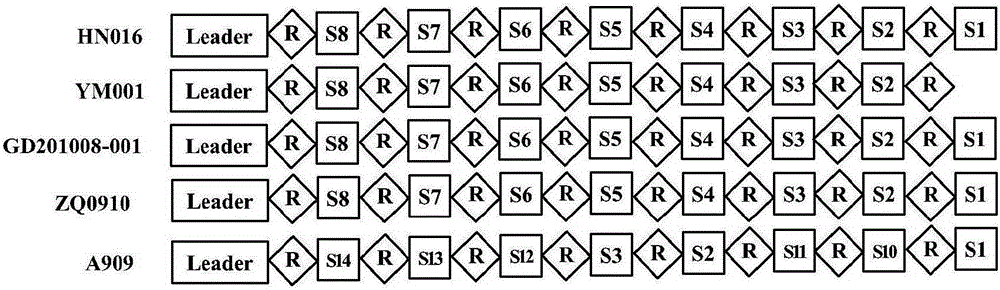
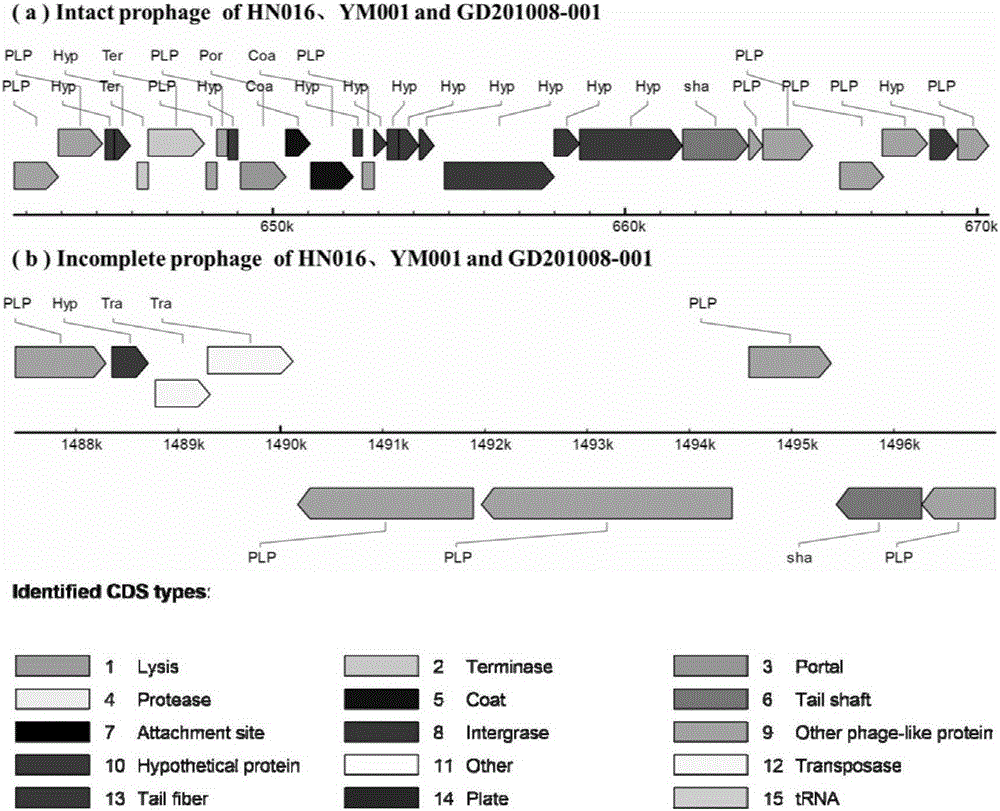
The invention relates to a streptococcus agalactiae attenuated strain YM001 genome sequence feature and a use thereof, especially relates to a streptococcus agalactiae attenuated strain genome sequence feature and concretely relates to streptococcus agalactiae attenuated strain whole genome sequencing, sequence analysis and genome comparison analysis. Compared with a maternal wild virulent strain HN016 genome, the YM001 genome has two large fragment losses, the loss sizes are 5832 bp and 11115 bp, and three rRNA and eleven tRNA gene losses and ten functional gene losses or function damage are caused. Compared with the HN016 genome, the YM001 genome has ten small fragment losses and 28 mononucleotide variants. The YM001 genome variation feature can be used for protection of attenuated strain YM001 intellectual property and construction and screening of a streptococcus agalactiae attenuated strain.
Owner:GUANGXI ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Method for predicting liver cancer feature type, electronic equipment and computer storage medium
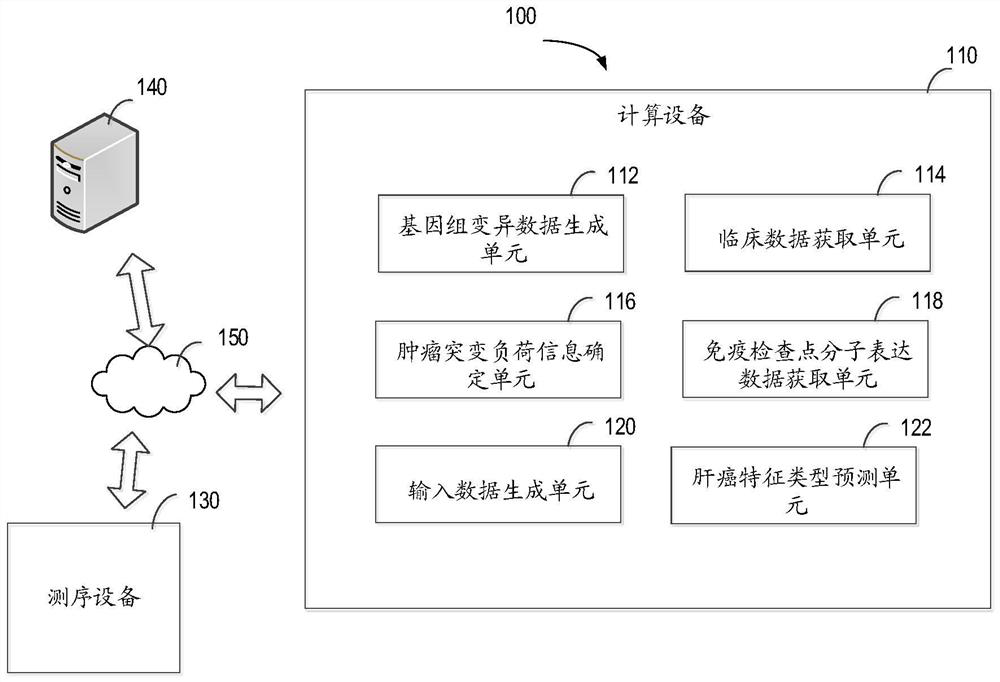
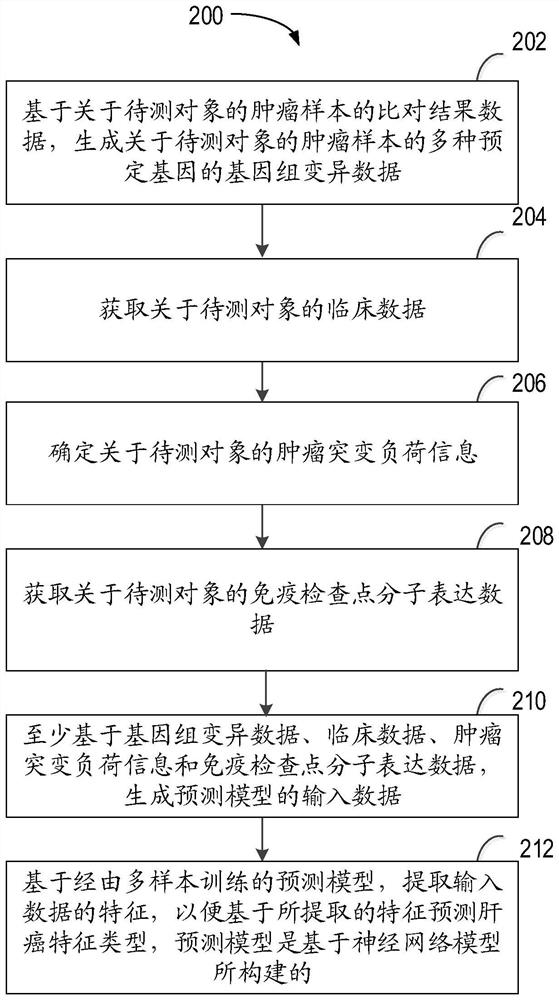
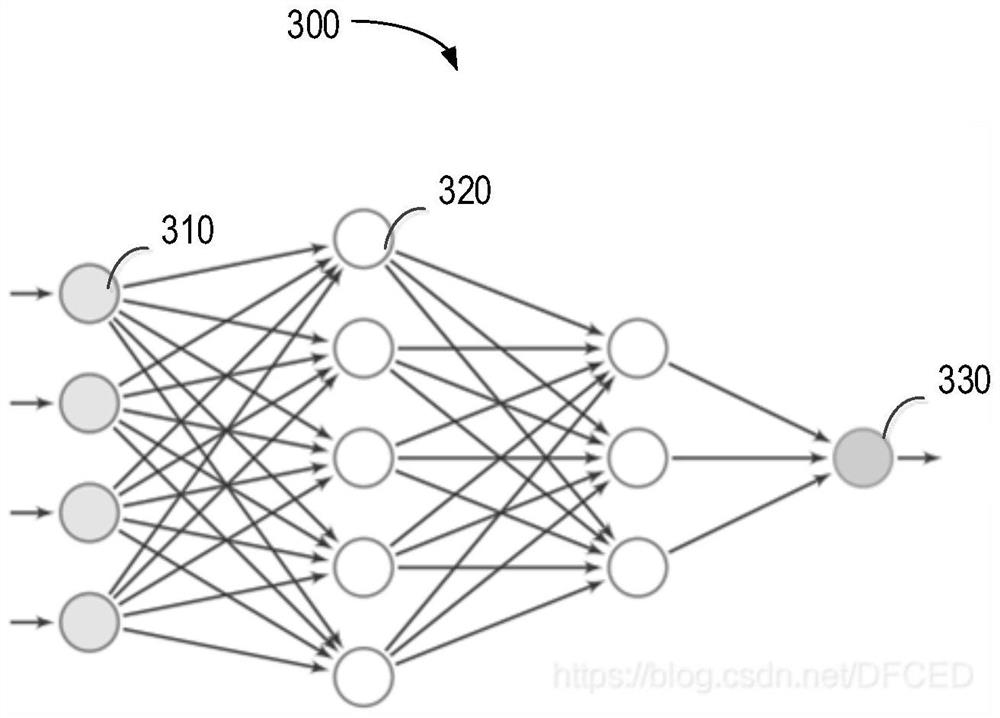
ActiveCN114446393AImprove reliabilityStrong generalizationBiostatisticsProteomicsTumor SampleEngineering
The invention relates to a method for predicting liver cancer feature types, computing equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: based on comparison result data about a tumor sample of a to-be-detected object, generating genome variation data about multiple predetermined genes of the tumor sample of the to-be-detected object; acquiring clinical data about the to-be-detected object; determining tumor mutation load information about the to-be-detected object; obtaining immune checkpoint molecular expression data of the to-be-detected object; generating input data of a prediction model at least based on the genome variation data, the clinical data, the tumor mutation load information and the immune checkpoint molecular expression data; and based on a prediction model trained by multiple samples, the prediction model is constructed based on a neural network model. According to the method, the reliability of predicting the liver cancer feature type can be improved, and good generalization of clinical application is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD +1
Methods for analyzing genomic variation within cells
ActiveUS10760121B2Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresDiseaseHeteroplasmy
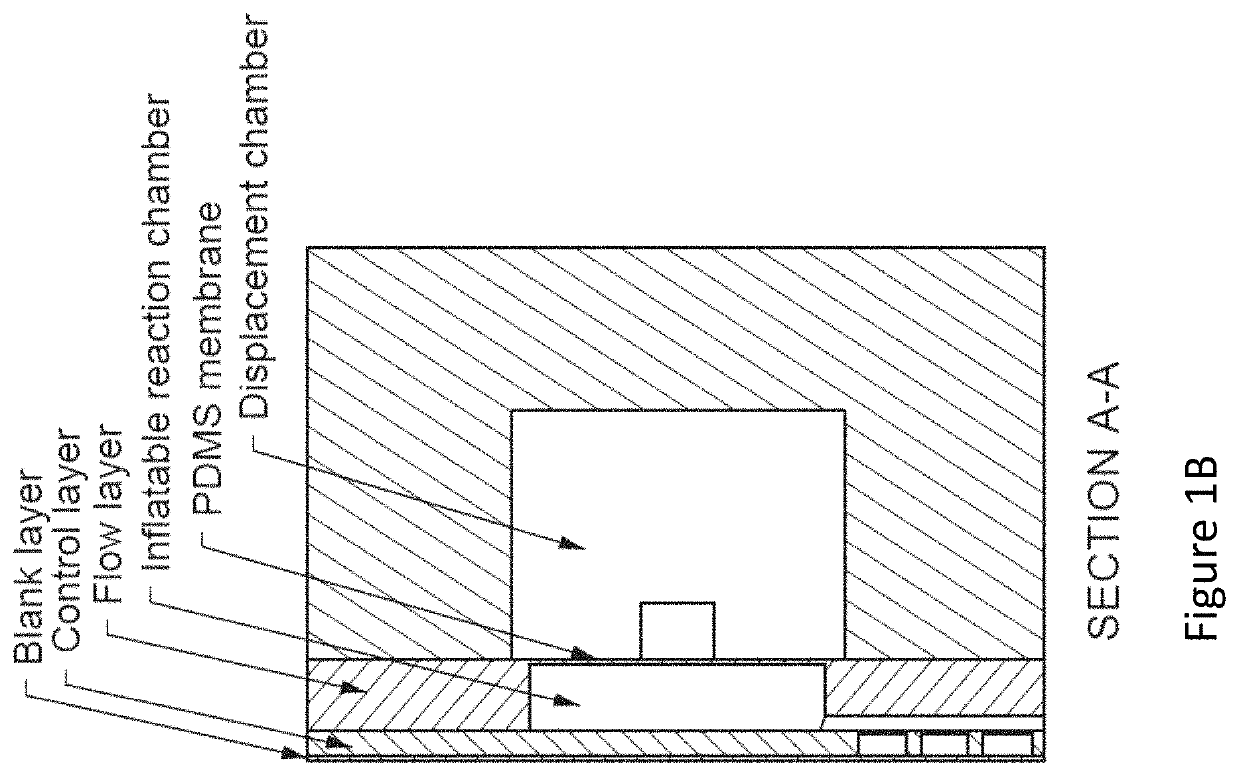
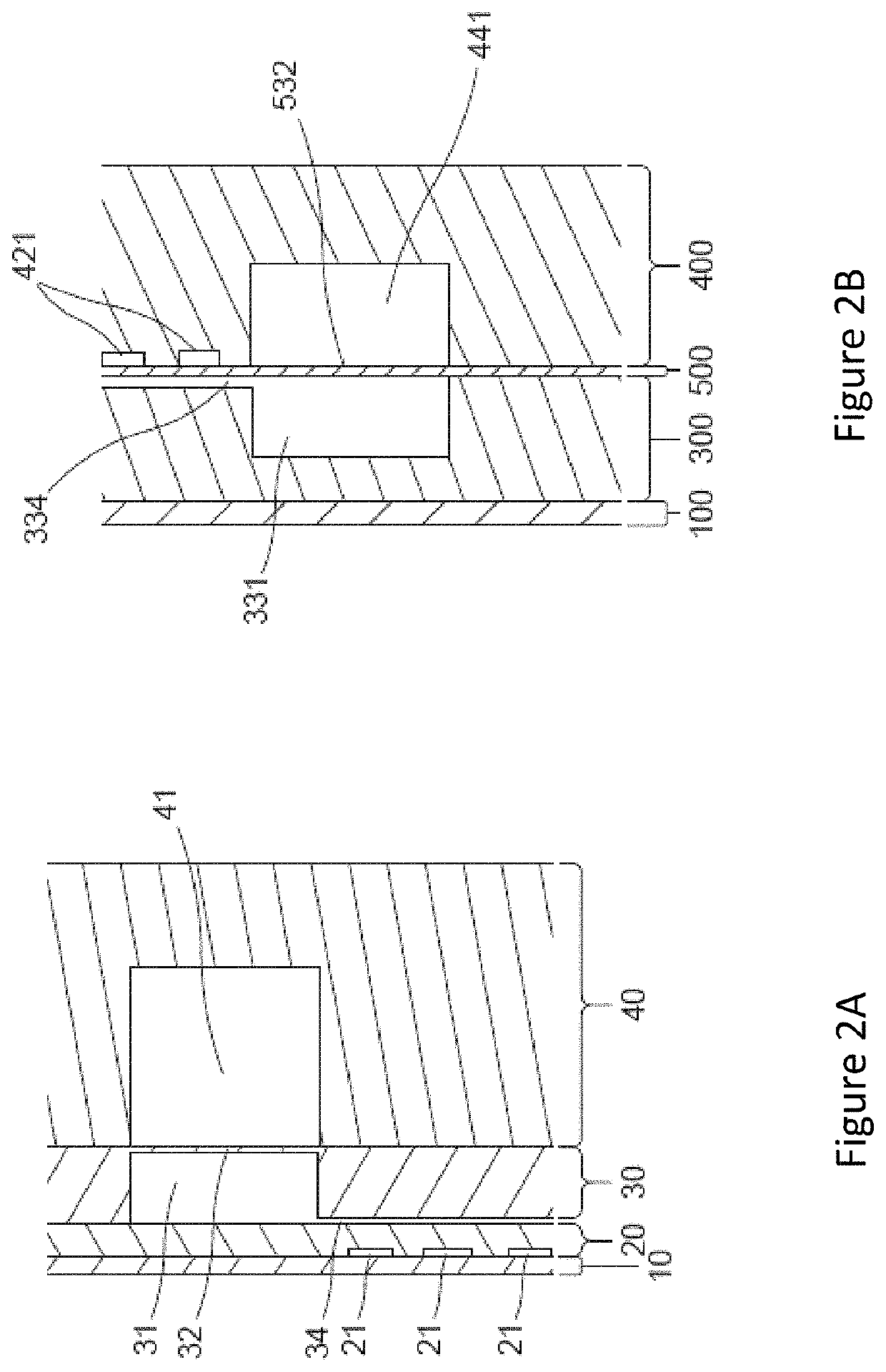
Methods, devices and systems for analyzing precious samples of cells, including single cells are provided. The methods, devices, and systems in various embodiments of the invention are used to assess genomic heterogeneity, which has been recognized as a central feature of many cancers and plays a critical role in disease initiation, progression, and response to treatment. The methods devices and systems are also used to analyze embryonic biopsies for preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). In one embodiment, the devices, systems and methods provided herein allow for the construction of genomic and RNA-seq libraries without a pre-amplification step.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com