Whole genome DNA sequence splicing sequencing method
A DNA sequence, whole genome technology, applied in the field of whole genome DNA sequence splicing and sequencing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] 1. Proteinase K / phenol method to extract genomic DNA from blood samples. To ensure the integrity of the DNA (more than 150kb), after phenol extraction, the aqueous phase DNA was transferred to a dialysis bag (dialysis molecular weight cut-off 1000kDa), and dialyzed at 4 degrees Celsius for 3 hours. Subsequent operations will be carried out directly in the dialysis bag until the DNA fragments are attached to the sequencing plate. Before each step of the enzyme reaction, the dialysis bag was dialyzed against 10 times more buffer solution (the same buffer solution as the reaction system) for 30 minutes at 4°C. When performing the enzymatic reaction, place the dialysis bag into a 50ml tube containing a small amount of buffer. After the enzyme reaction, put more than 10 times the amount of buffer in the dialysis bag (matching the next reaction), and perform two dialysis to remove the remaining enzyme and buffer from the previous reaction. For a small amount of DNA samples,...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In the aforementioned operations, the amount of actual DNA fragments used is relatively large, and the preliminary operation process is cumbersome. Therefore, we tried to adopt an improved strategy, adding asymmetric Adapters on both sides of the genomic DNA fragments at the beginning of the experiment. Specific steps are as follows:
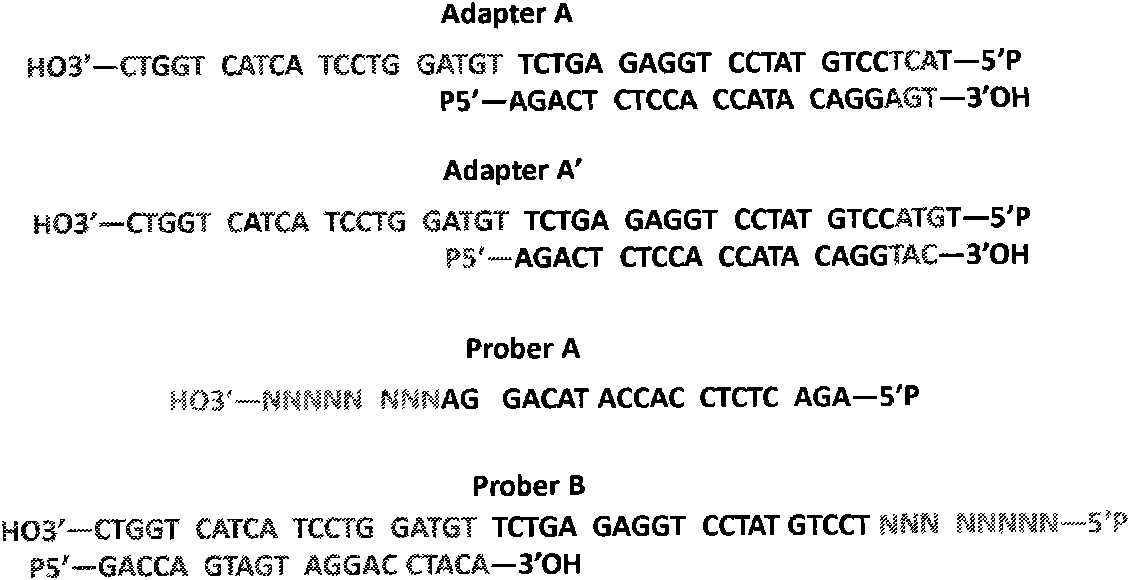
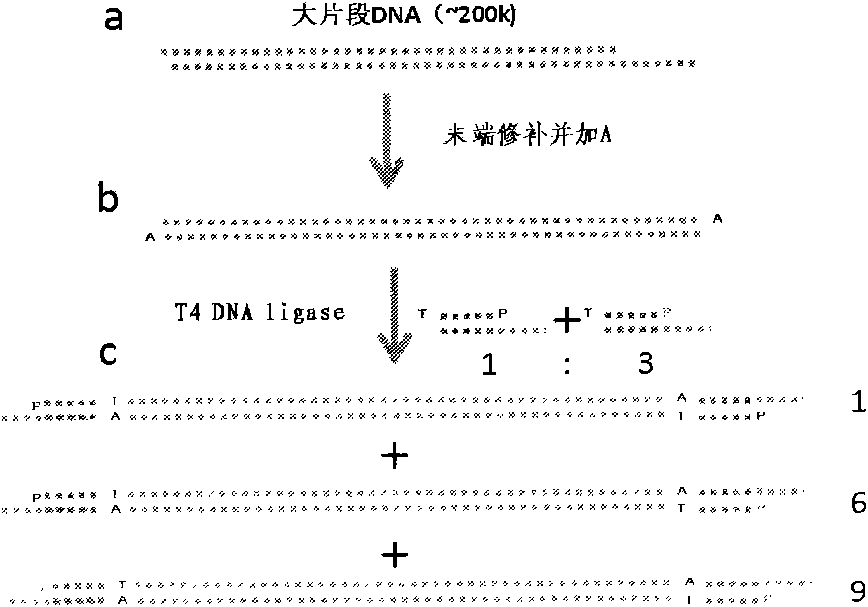
[0044] 1. After following step 2 in Example 1, we added Adapter A and A' in a ratio of 1:3, and then added T4 DNA ligase, and the reaction time was 3 hours at 15 degrees Celsius. At this time, the ratio of DNA fragments containing Adapter A at both ends, Adapter A and A' at both ends, and Adapter A' at both ends is 1:6:9 ( figure 2 ).
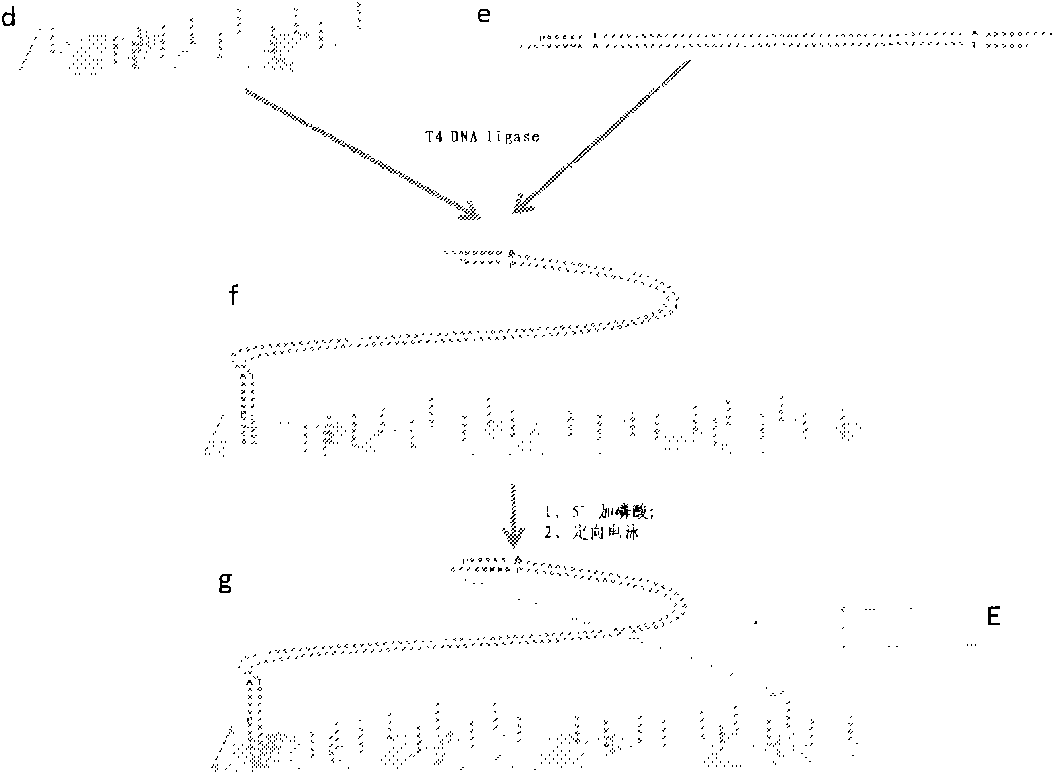
[0045]2. Import the genomic DNA fragments into the sequencing plate, add T4 DNA ligase, and react at 15 degrees Celsius for 3 hours. At this time, only the DNA fragment containing Adapter A at least at one end is anchored, and the rest of the DNA fragments are still in a free state. After flow wash, o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com