Patents
Literature
658 results about "Analysis sample" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sampling plan should be a clearly written document that contains precise details that an analyst uses to decide the sample size, the locations from which the sample should be selected, the method used to collect the sample, and the method used to preserve them prior to analysis.?
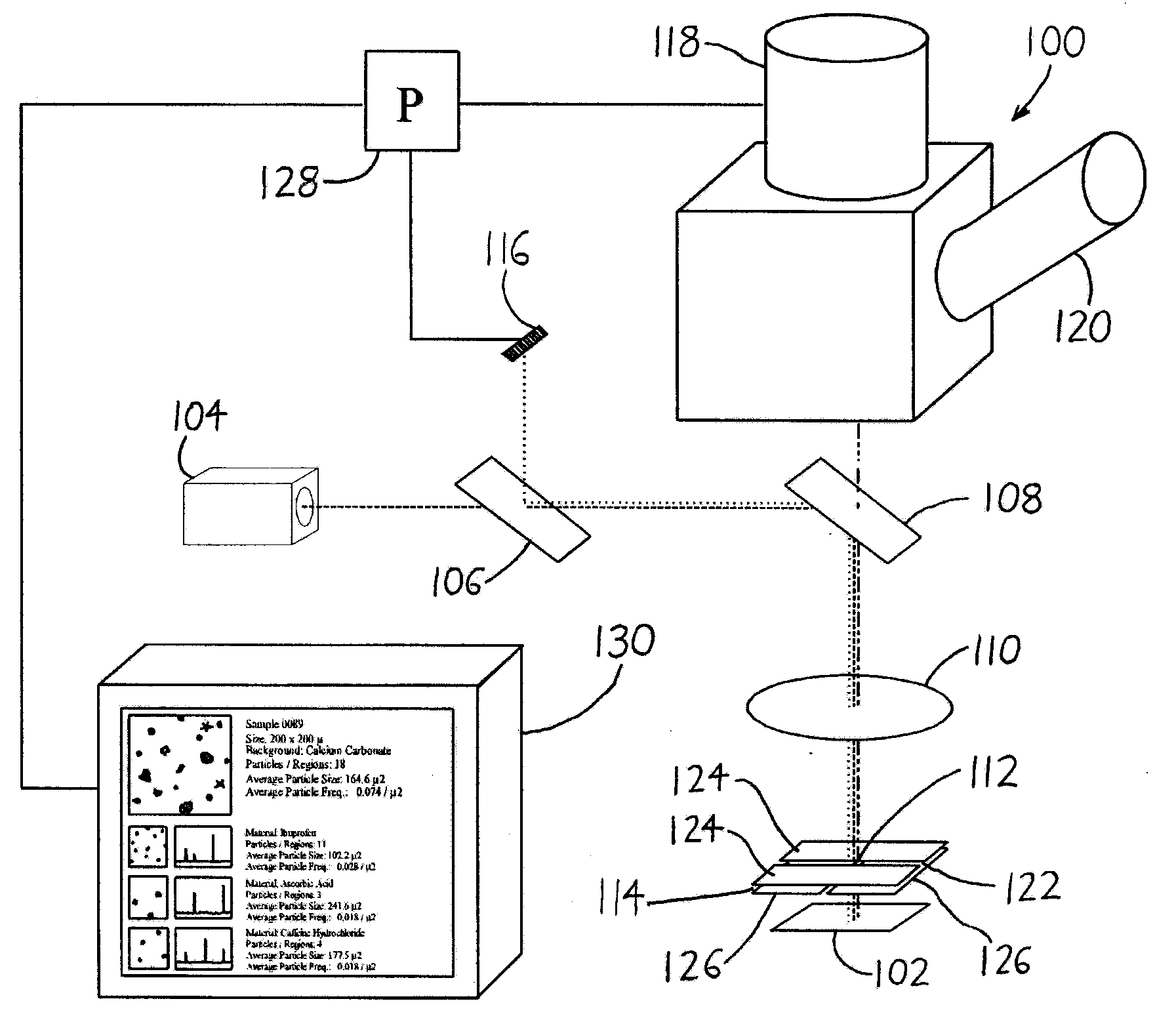
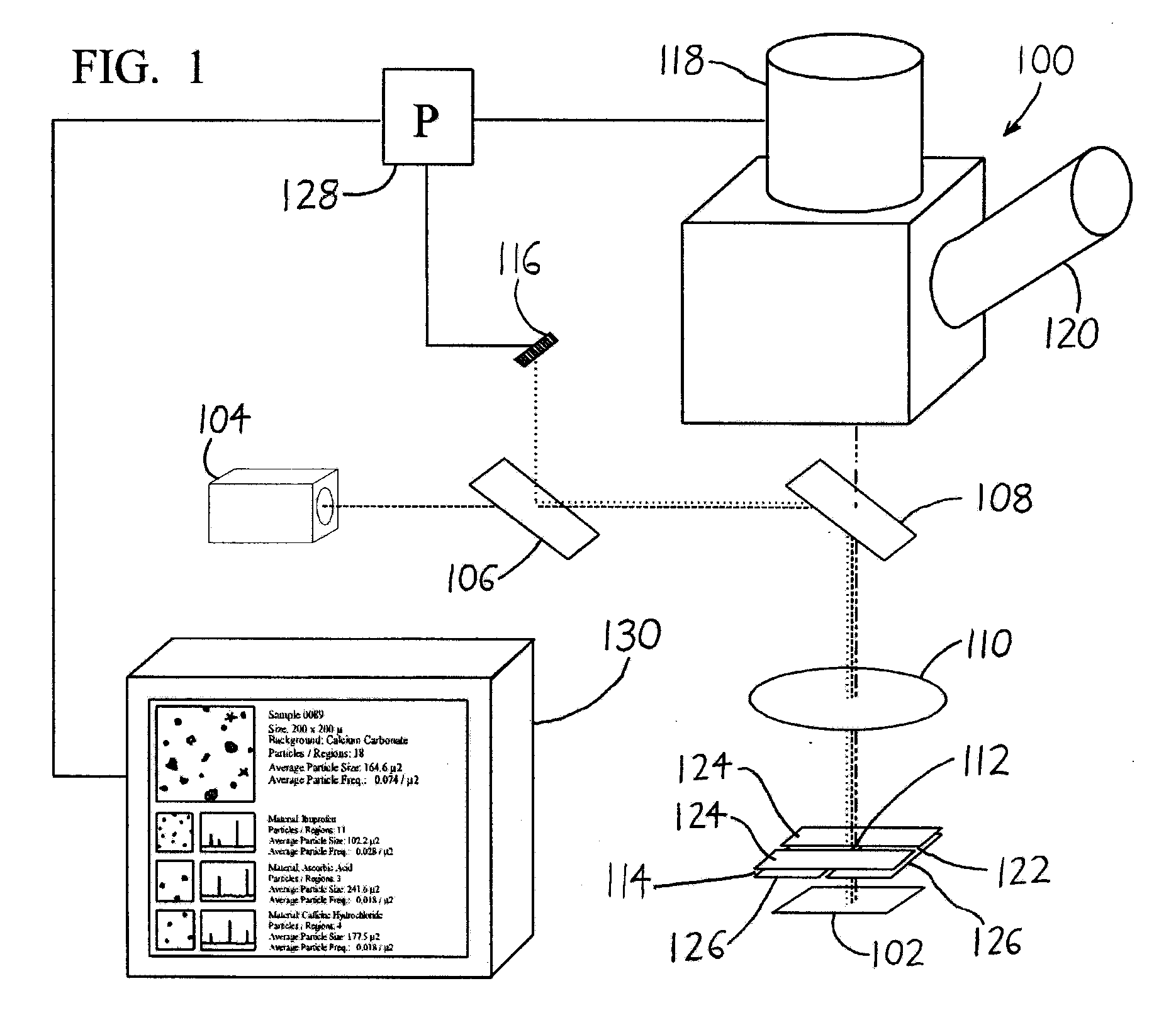
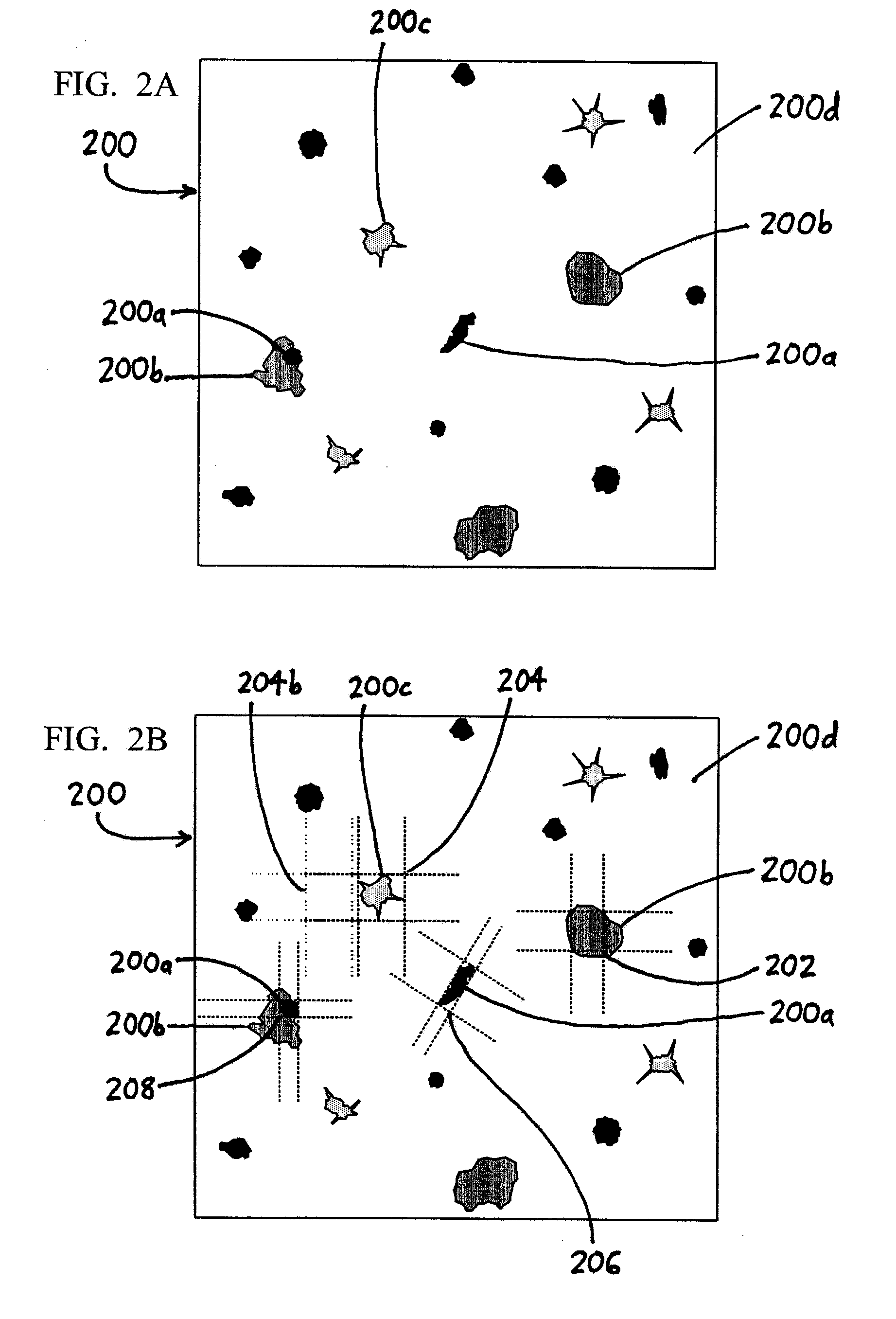
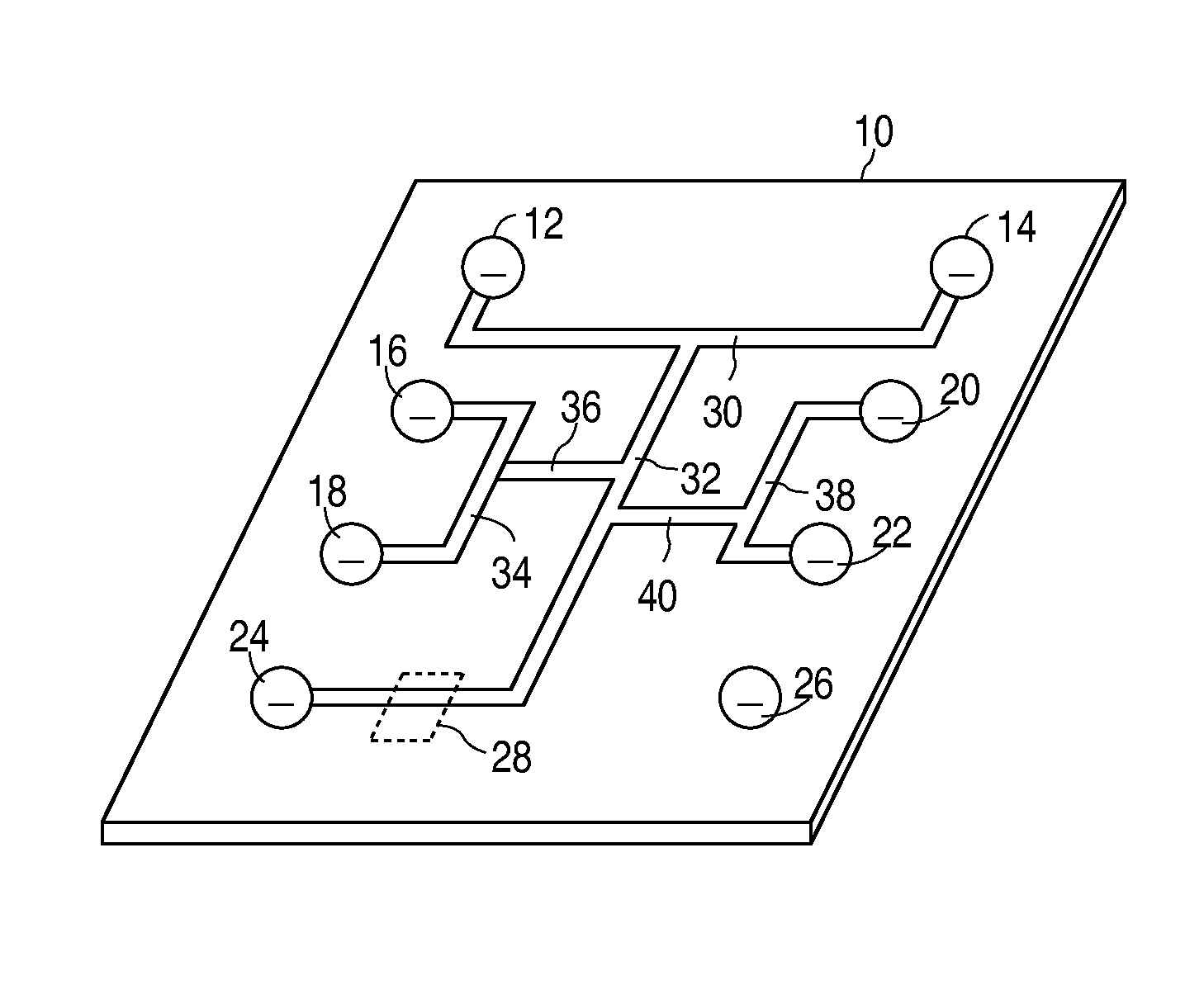
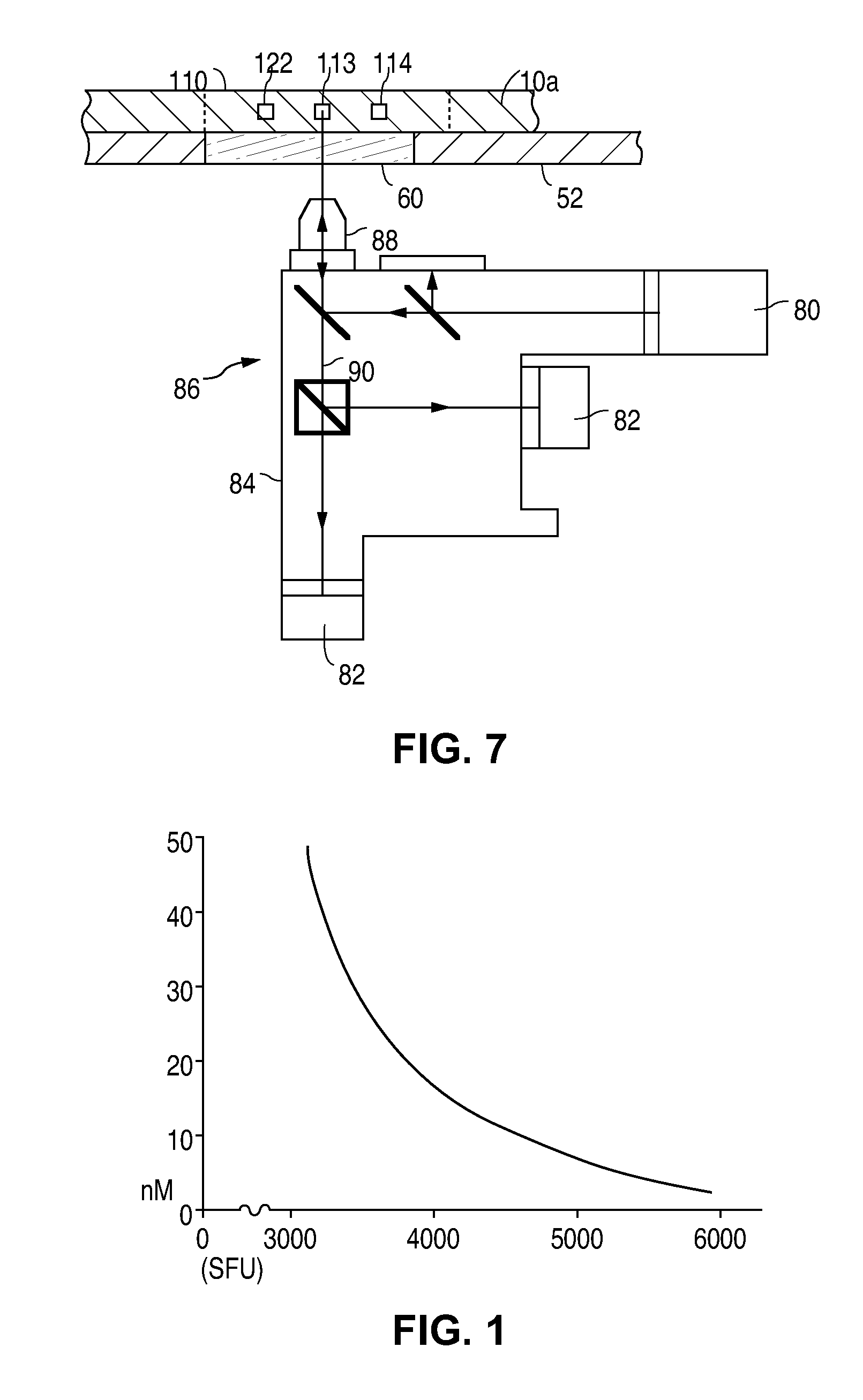
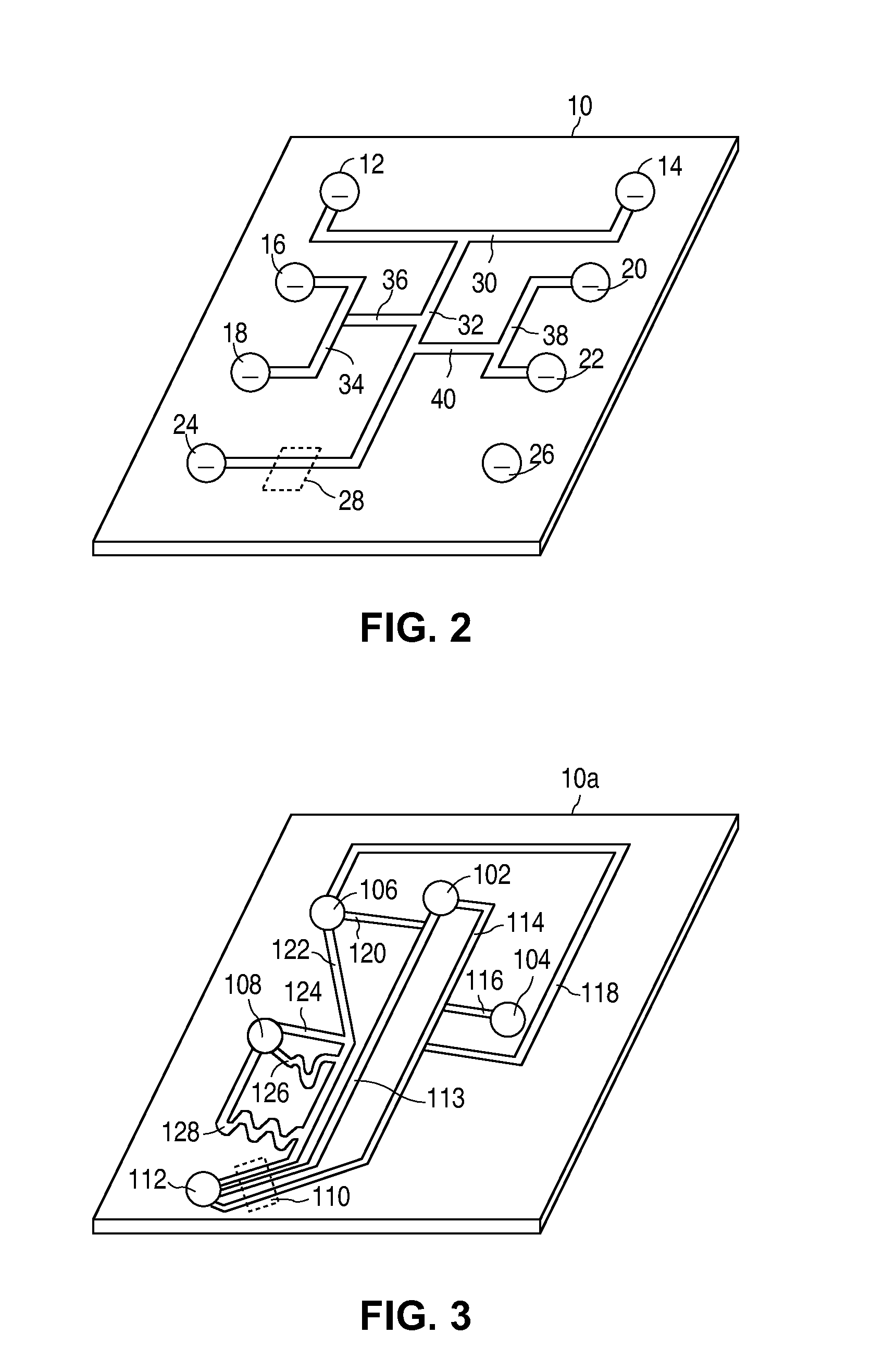
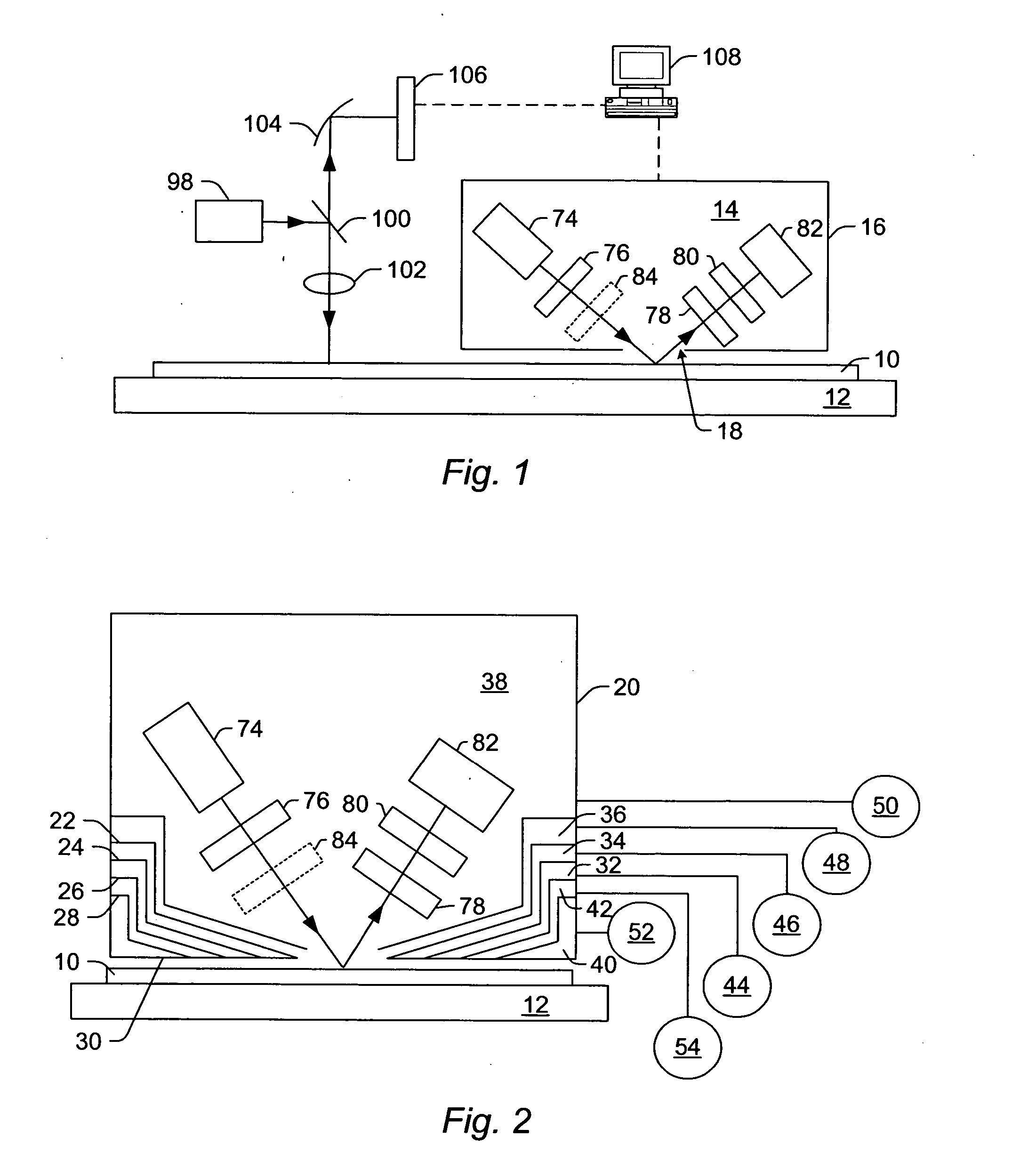
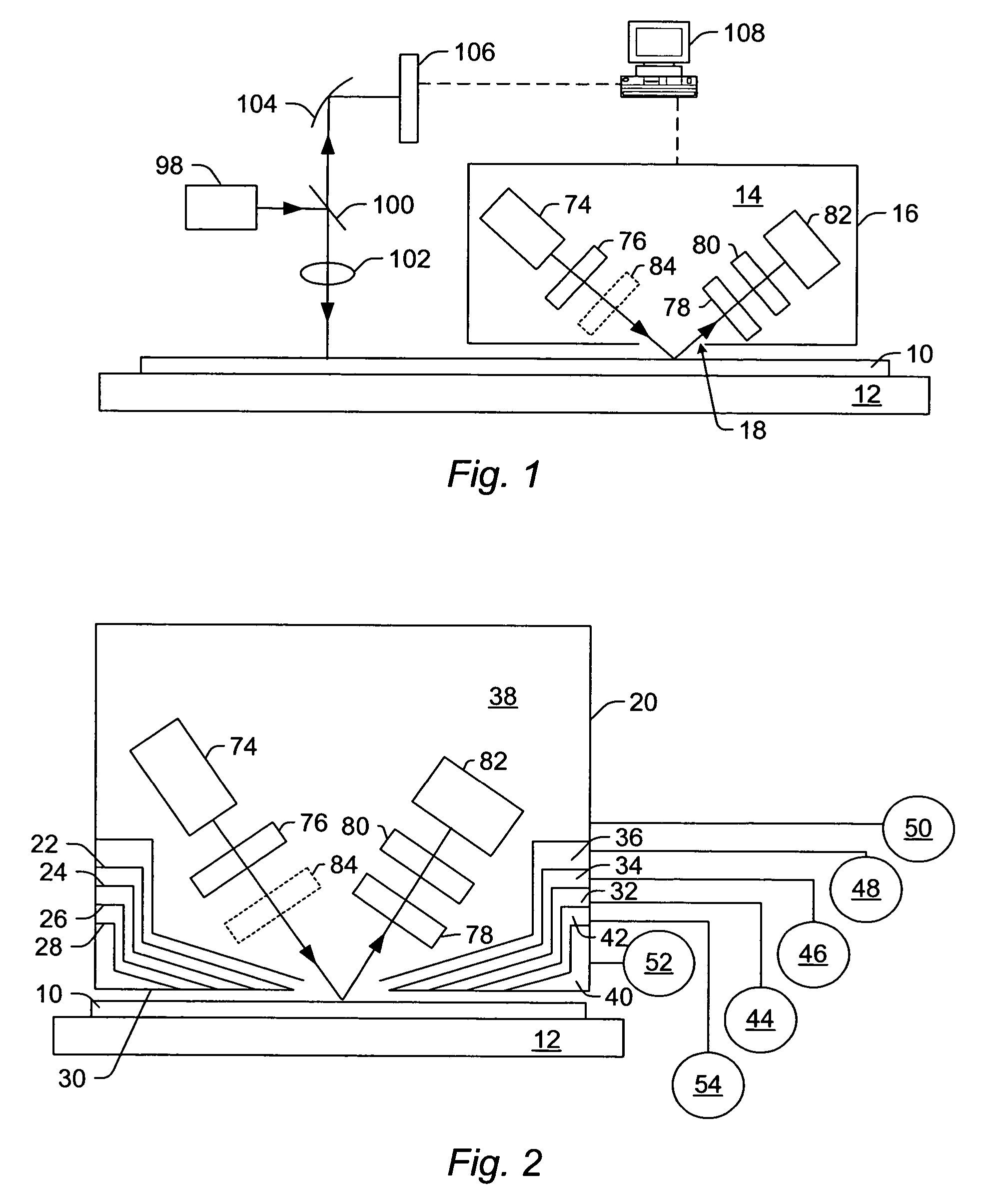
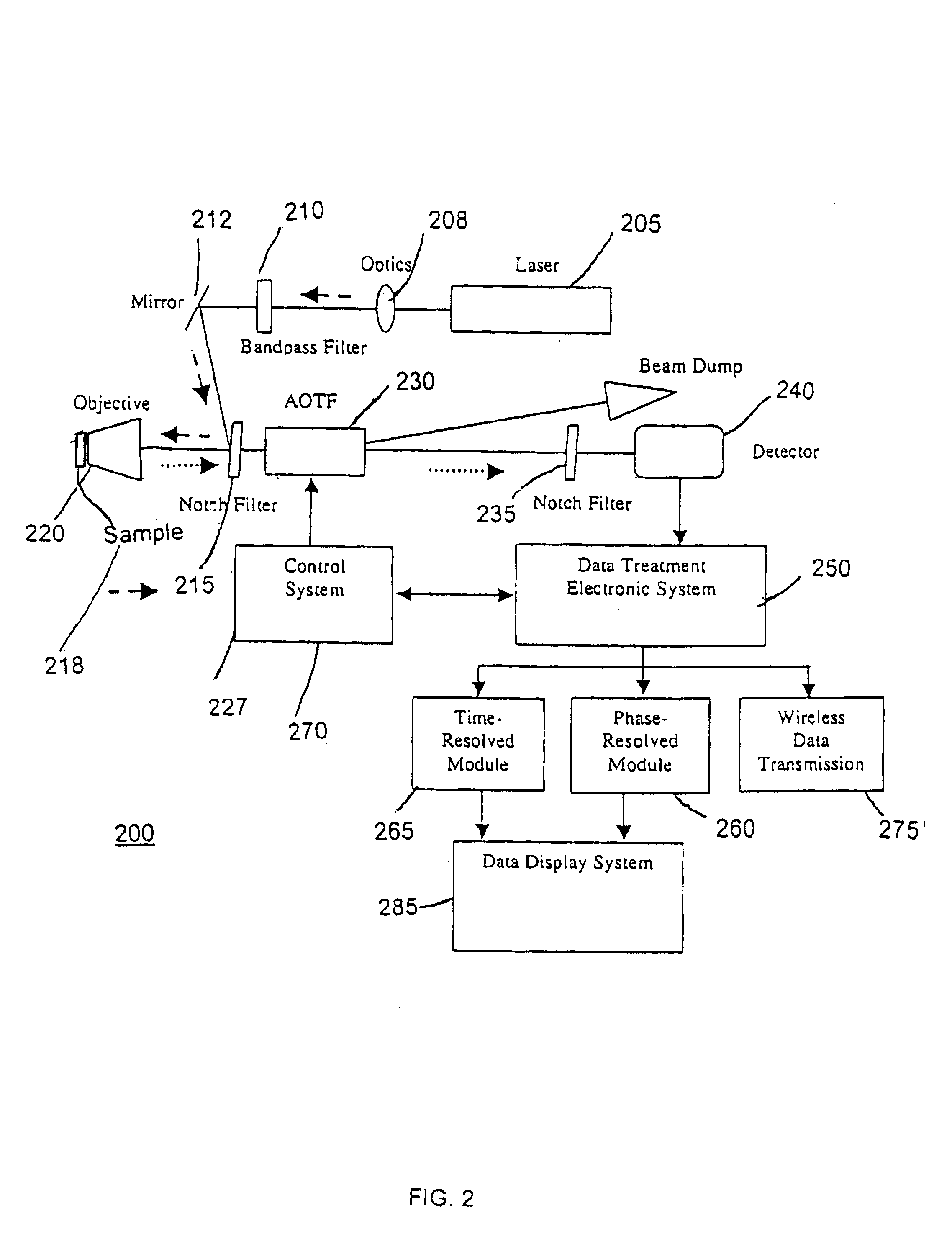
Spectroscopic microscopy with image-driven analysis
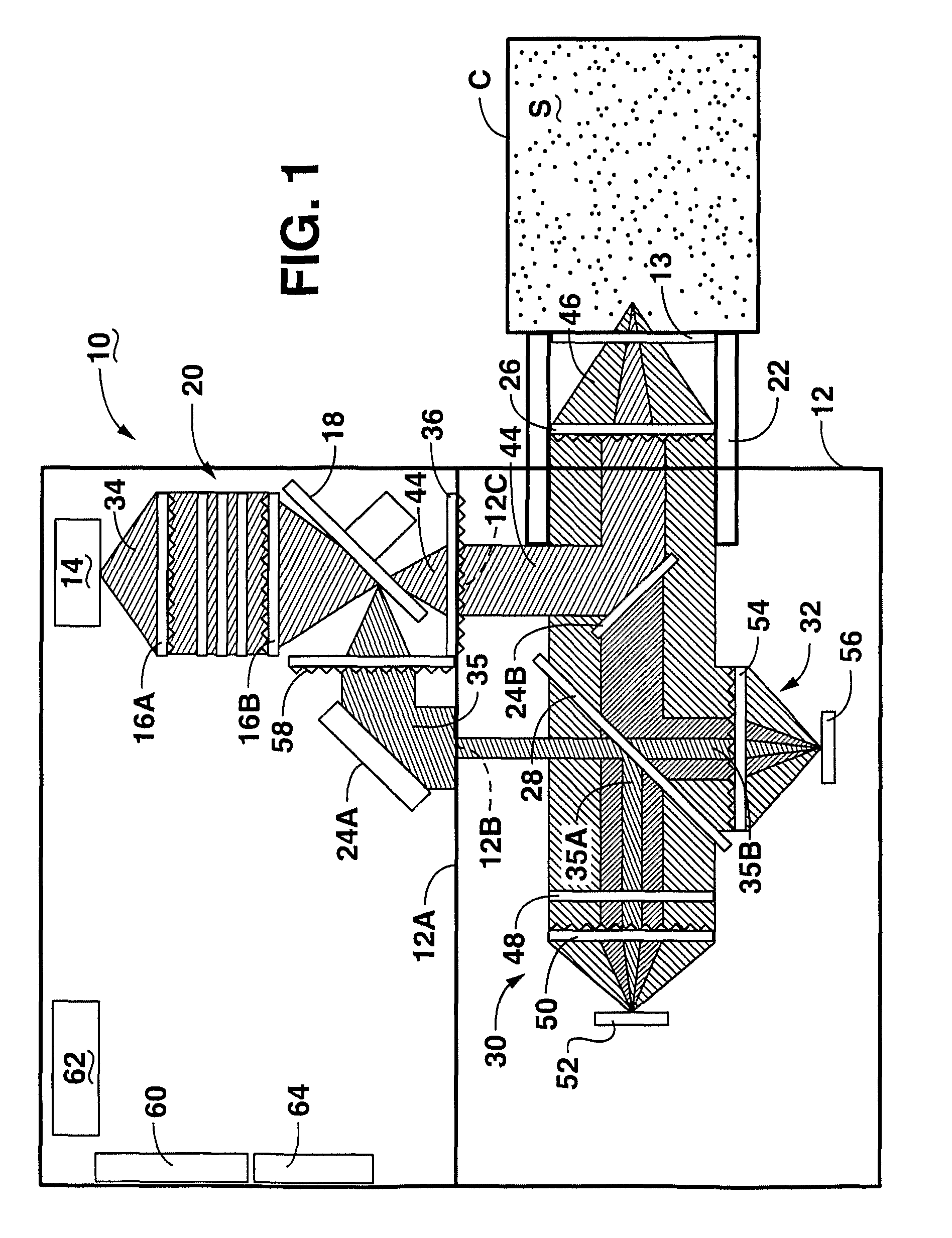
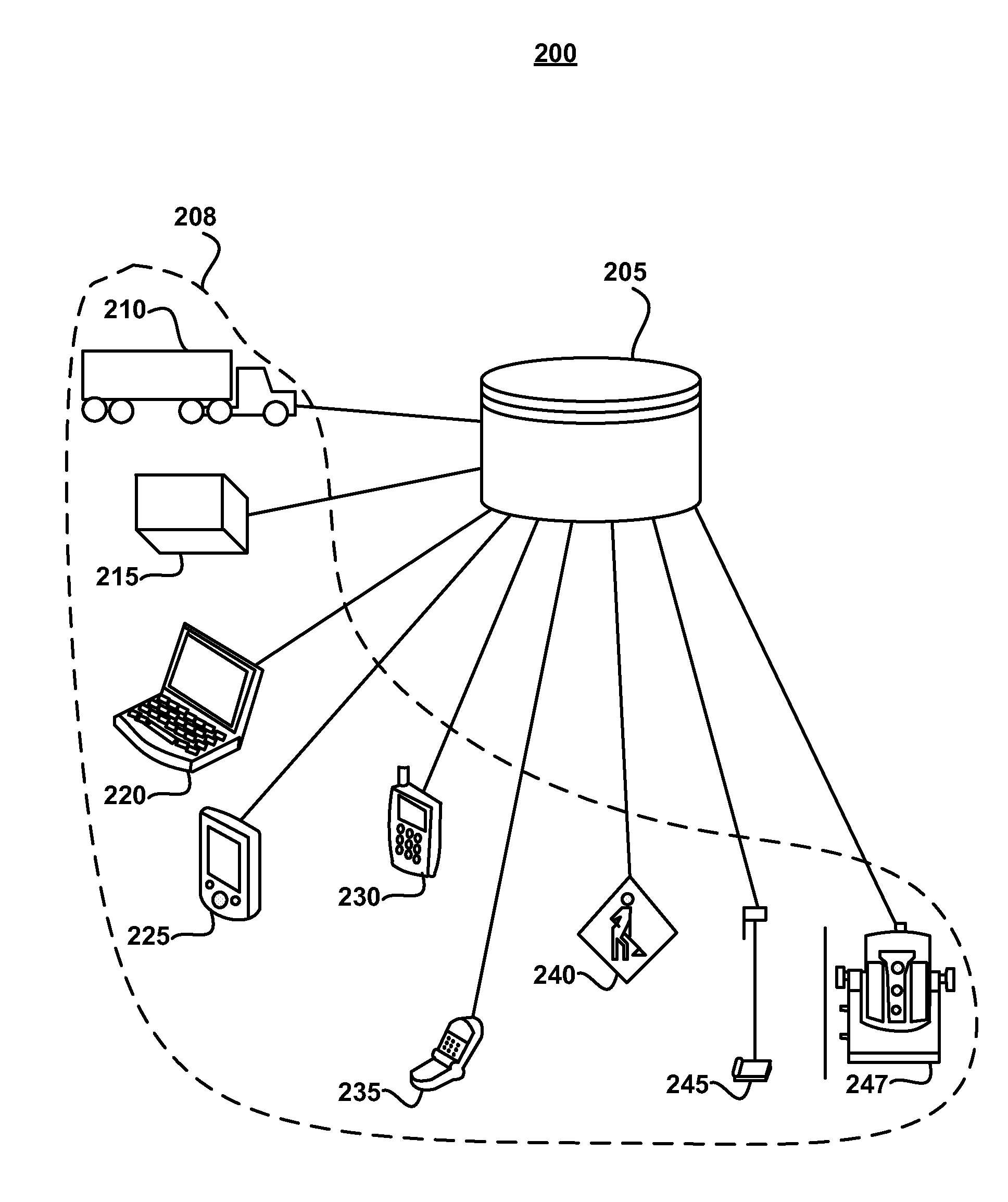
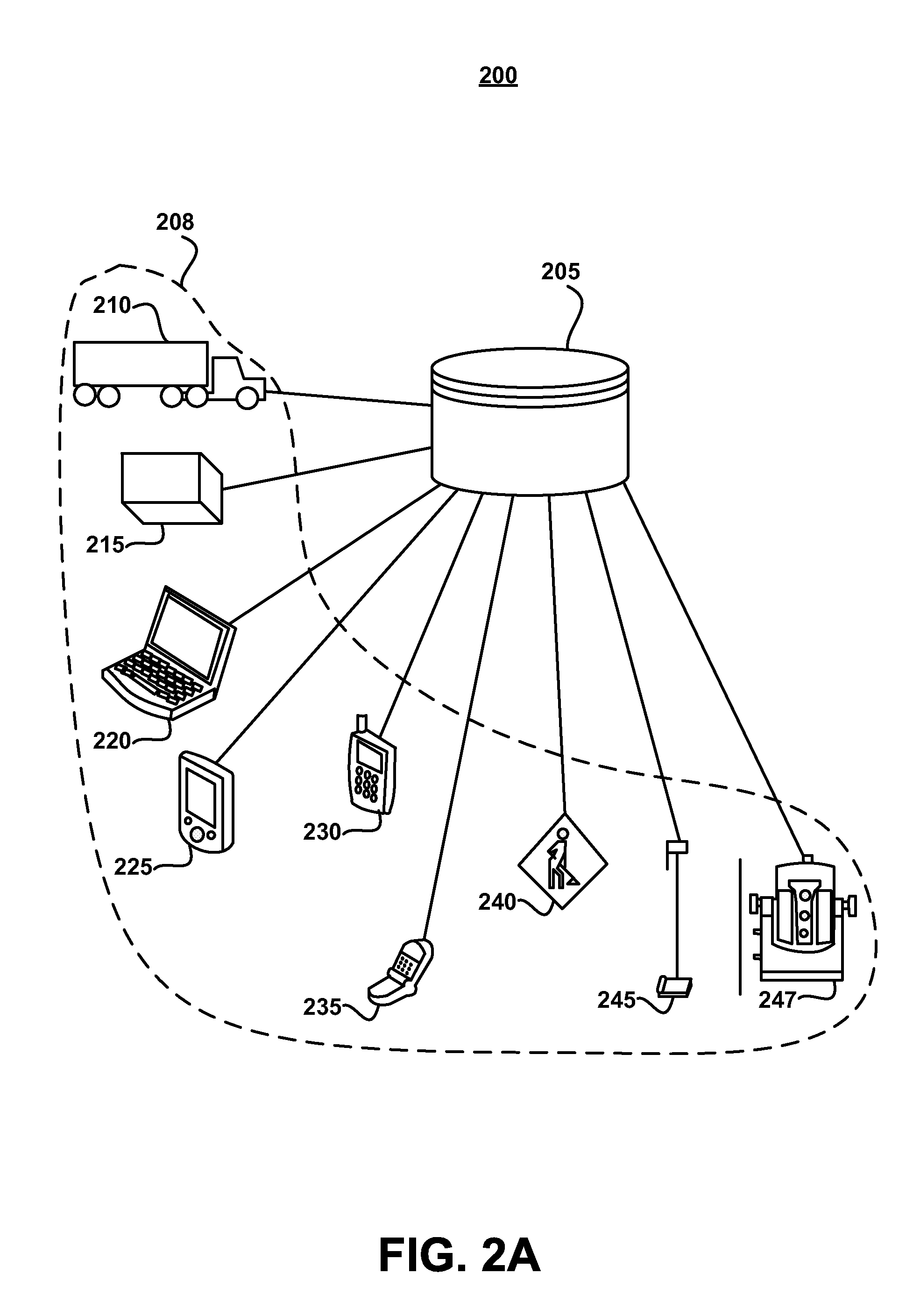
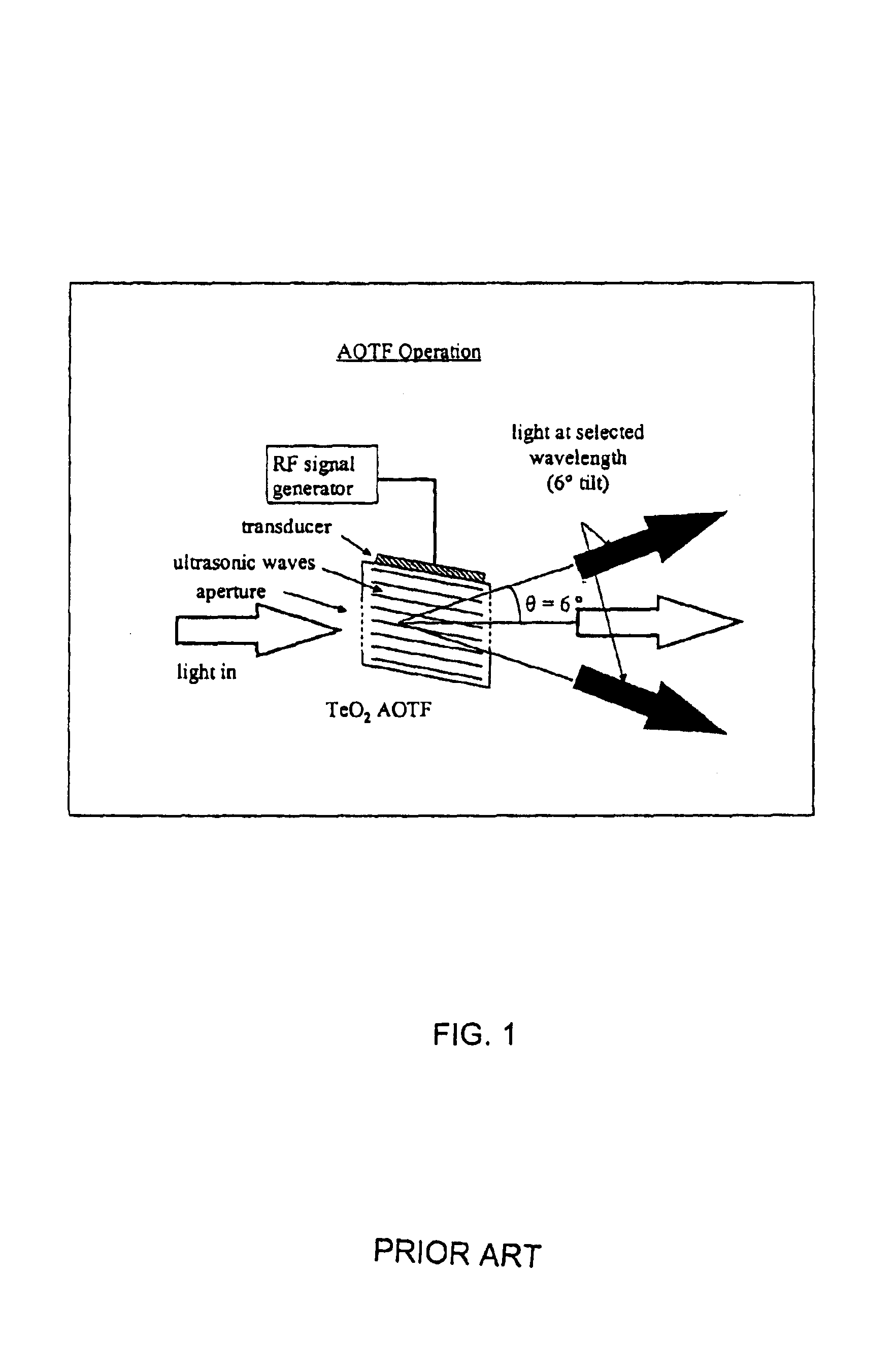
ActiveUS20080049220A1Easy to identifyArea maximizationRadiation pyrometryCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo imageAnalysis sample
In a spectroscopic microscope, a video image of a specimen is analyzed to identify regions having different appearances, and thus presumptively different properties. The sizes and locations of the identified regions are then used to position the specimen to align each region with an aperture, and to set the aperture to a size appropriate for collecting a spectrum from the region in question. The spectra can then be analyzed to identify the substances present within each region of the specimen. Information on the identified substances can then be presented to the user along with the image of the specimen.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRONICS SCI INSTR LLC
Optical analysis system and elements to isolate spectral region
ActiveUS7920258B2Useful and reliable capabilityImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical frequenciesAnalysis sample
A method of selecting components for a multivariate optical computing and analysis system to isolate a spectral region includes selecting a spectral region of interest; selecting a spectral element with a predetermined transmission characteristic to control a spectral range of an illumination source; illuminating a sample with the illumination source; and analyzing an optical frequency returned by the sample relative to the spectral region of interest.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
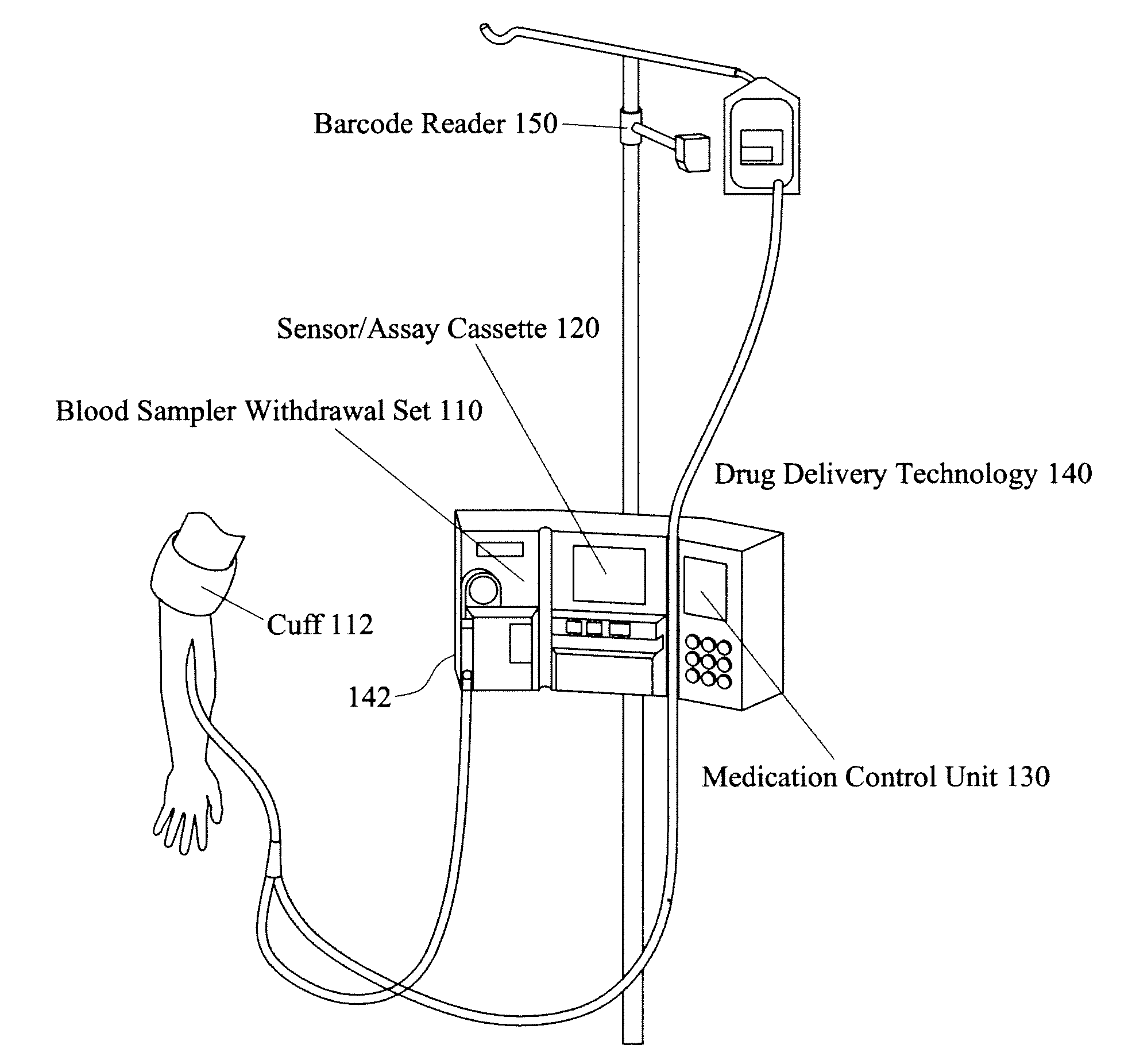
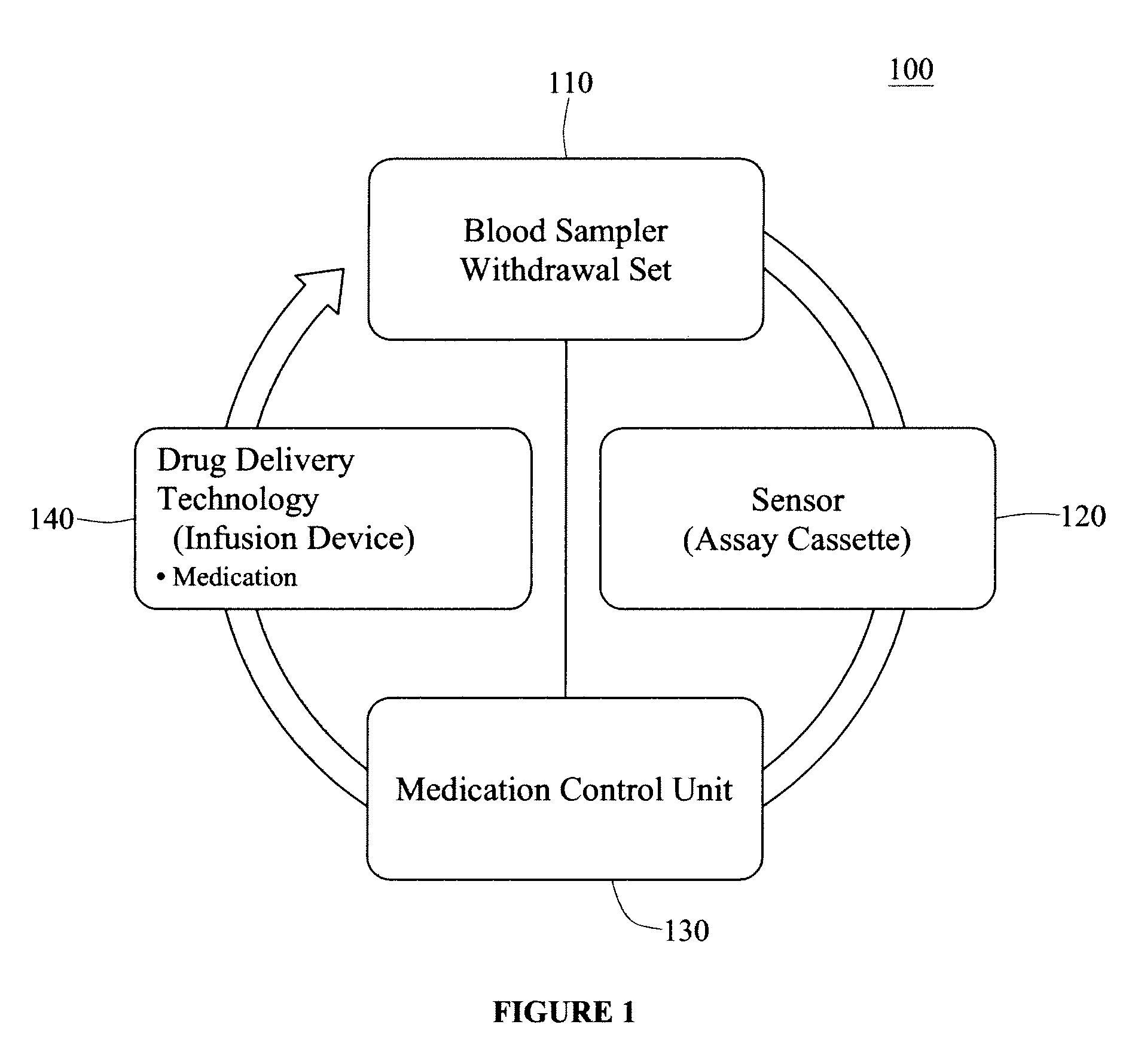
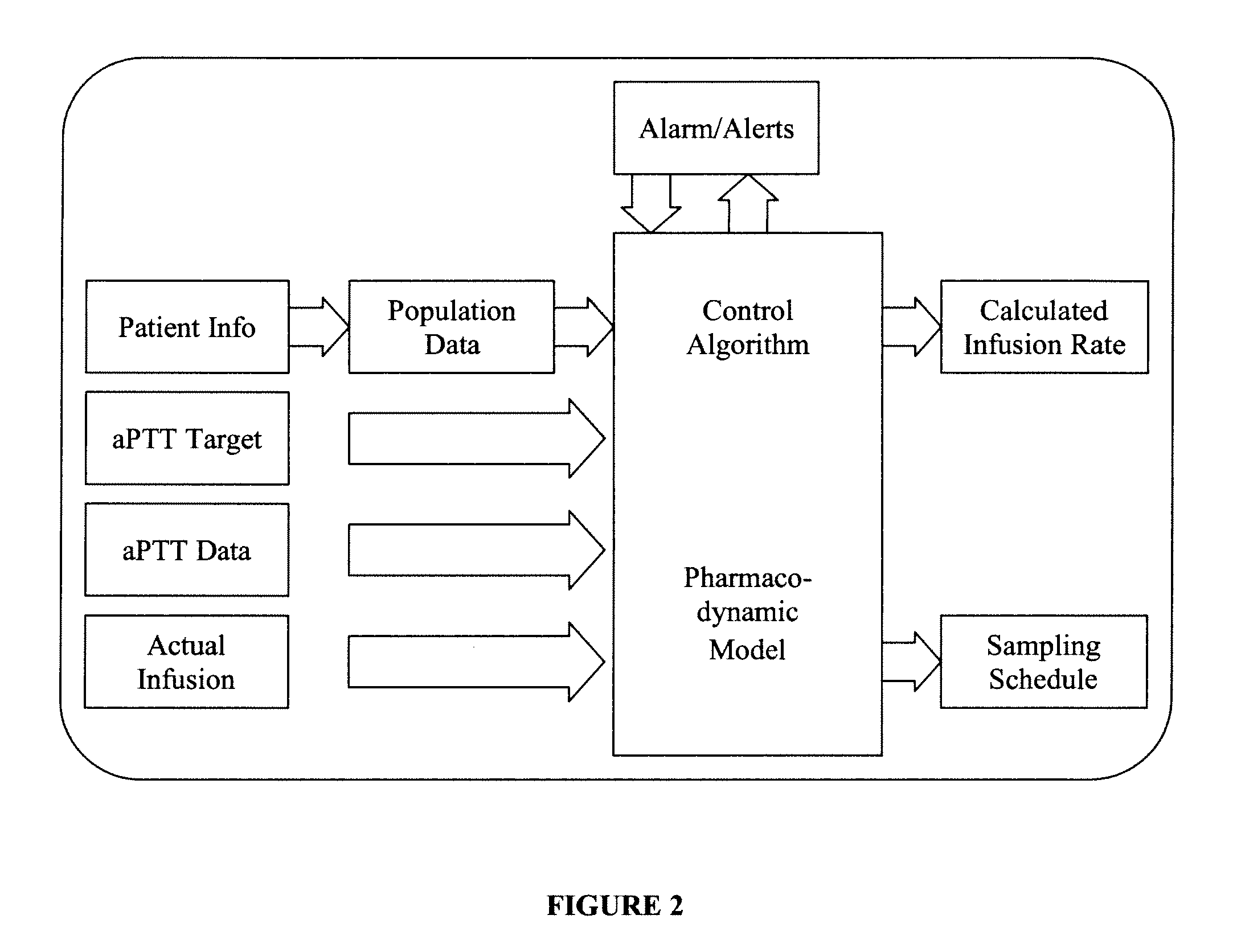
Integrated patient management and control system for medication delivery
InactiveUS20100036310A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsElectrotherapyPatient managementEmergency medicine
An integrated patient monitoring and control system is provided which includes a sample set, the sample set being adapted for coupling to the patient to obtain a specimen from the patient, a sensor, the sensor being adapted to receive the specimen from the sample set and to analyze the sample, a medication control unit, the medication control unit receiving information from the sensor, and utilizing that information to determine medication dosing information for the patient, and a medication administration system, the medication administration system receiving the dosing information from the medication control unit, and adapted to cause administration of the medication to the patient. If the sample set is adapted for blood draw, the system advantageously is performed in conjunction with a pneumatic pressure cuff, inflated so as to aid in blood draw.
Owner:AUTOMEDICS MEDICAL SYST
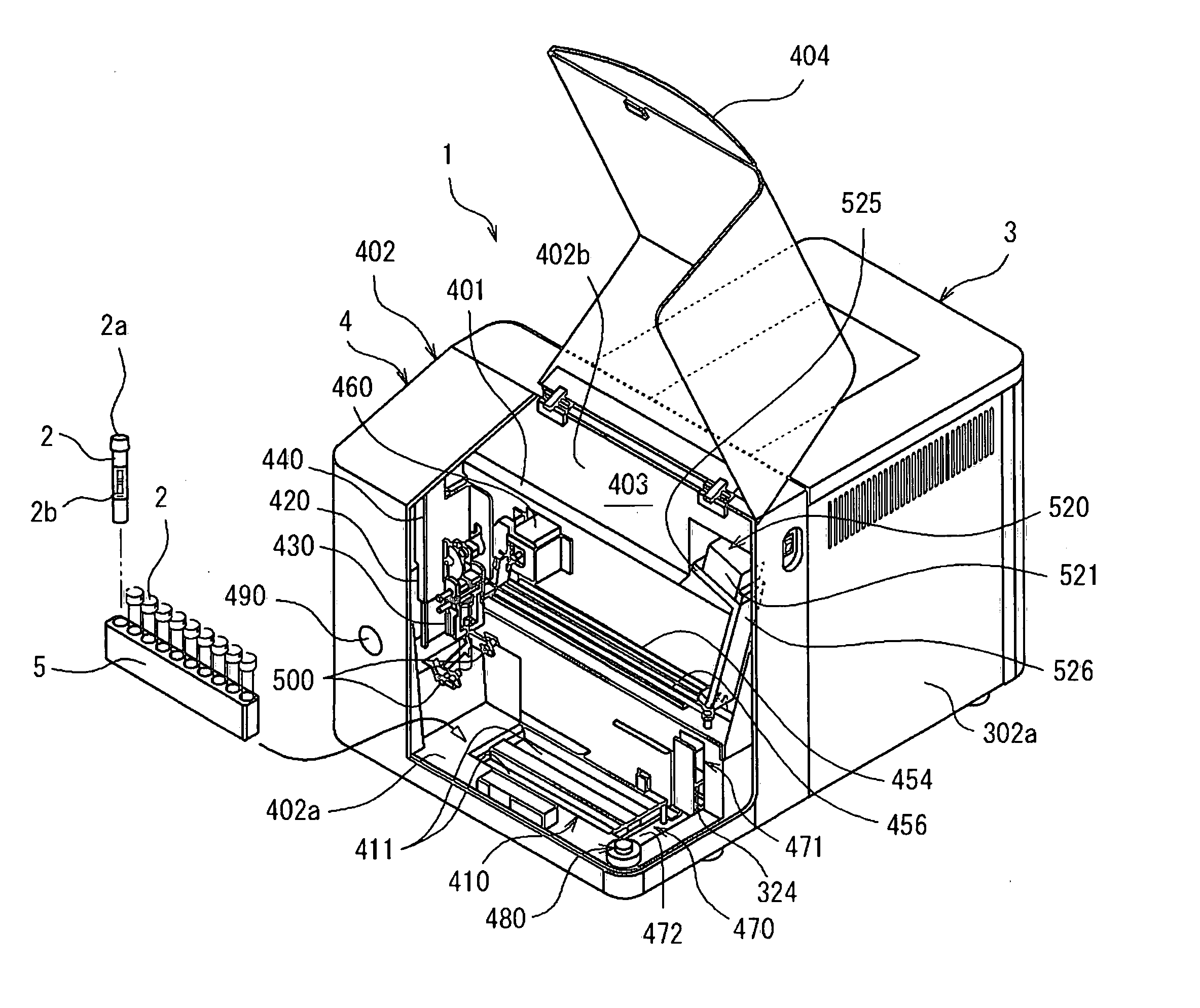
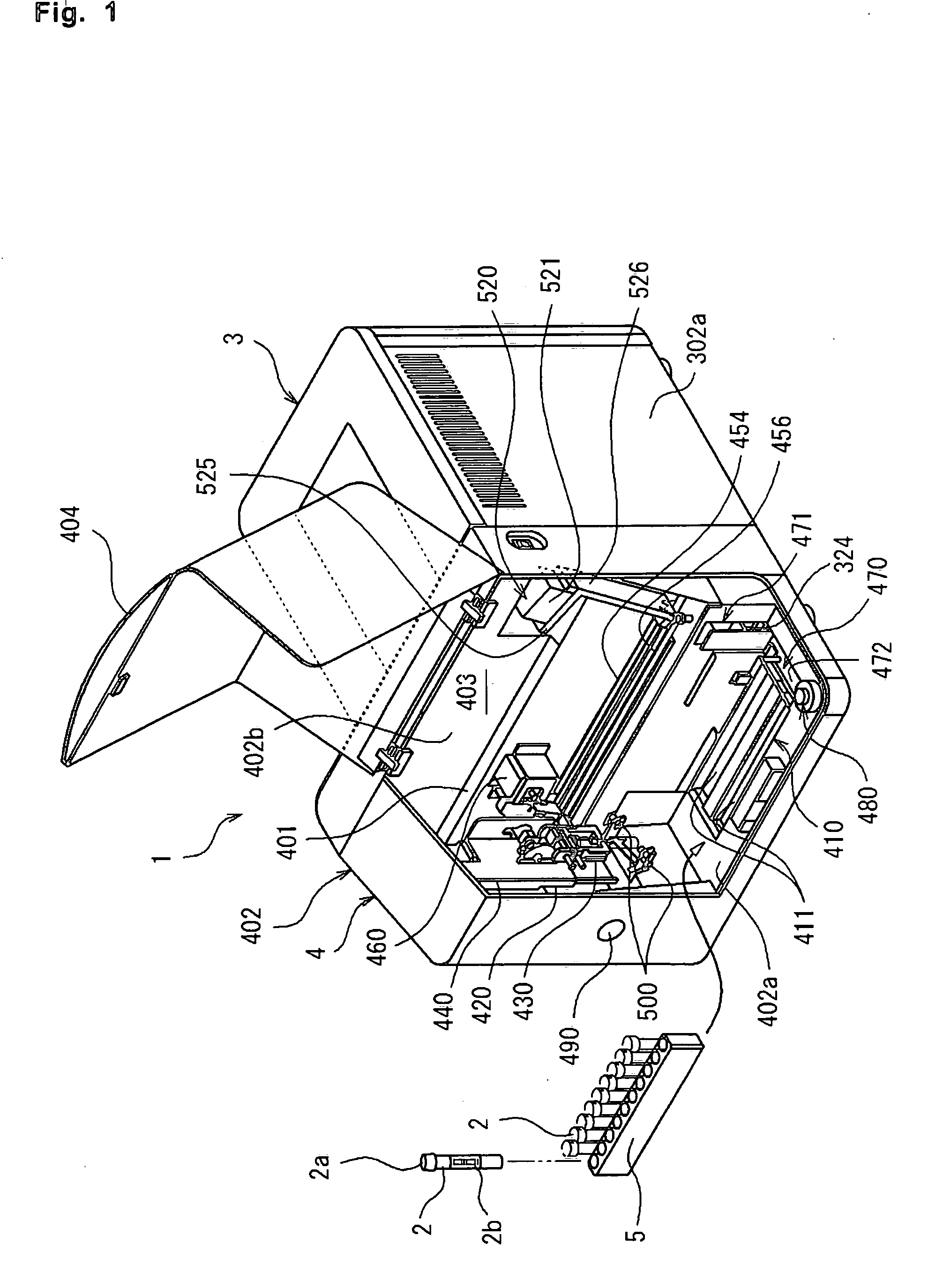
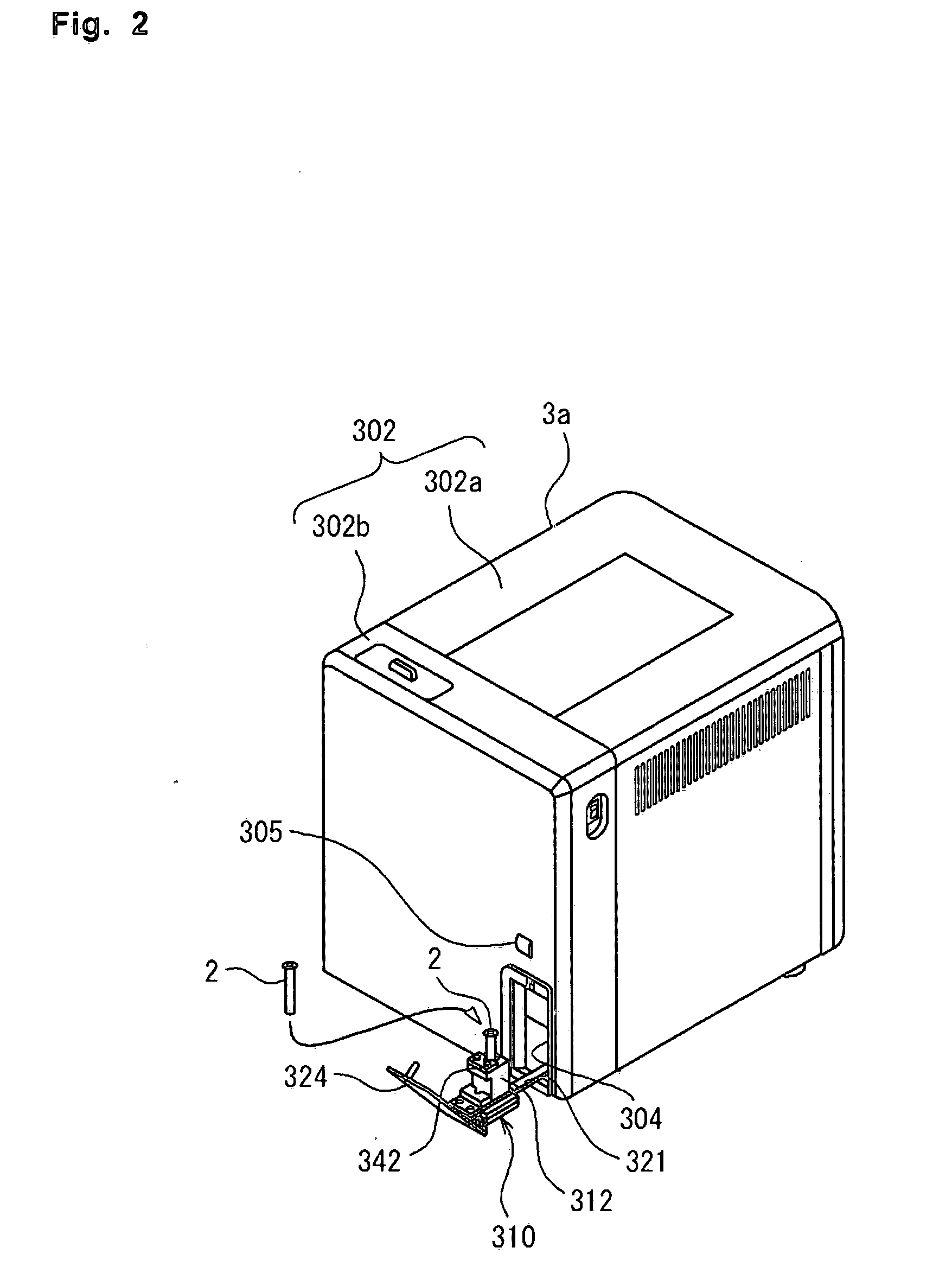
Sample analyzer and sample container supplying apparatus
ActiveUS20070110617A1Material analysis by optical meansLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringAnalysis sample
A sample analyzer for analyzing a sample comprising: a sample container receiver capable of receiving either one of a manually supplied sample container and an automatically supplied; a container holder receiver for receiving a container holder holding at least one sample container; a sample container supplier automatically for supplying, to the sample container receiver, a sample container held by the container holder received by the container holder receiver; an aspirator for aspirating a sample within a sample container received by the sample container receiver; and an analyzing part for analyzing the sample aspirated by the aspirator.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Automated sample analysis
ActiveUS7595197B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotomultiplierAnalysis sample
Samples of materials used in industrial processes are analyzed to determine the concentration of certain materials of interest. The quantitative analysis of samples for these materials is provided without the need for manual methods such as titration. Indicators such as fluorescent dyes for which the intensity of fluorescence is indicative of the concentration of a material of interest are used. The dyes are made to fluoresce by means of a light source, and a photomultiplier or other detector capable of measuring light intensity detects the resulting fluorescence. The intensity of fluorescence in the sample is compared to the intensities of fluorescence produced by samples with known concentrations of the material of interest to determine the concentration of the material of interest of the sample.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
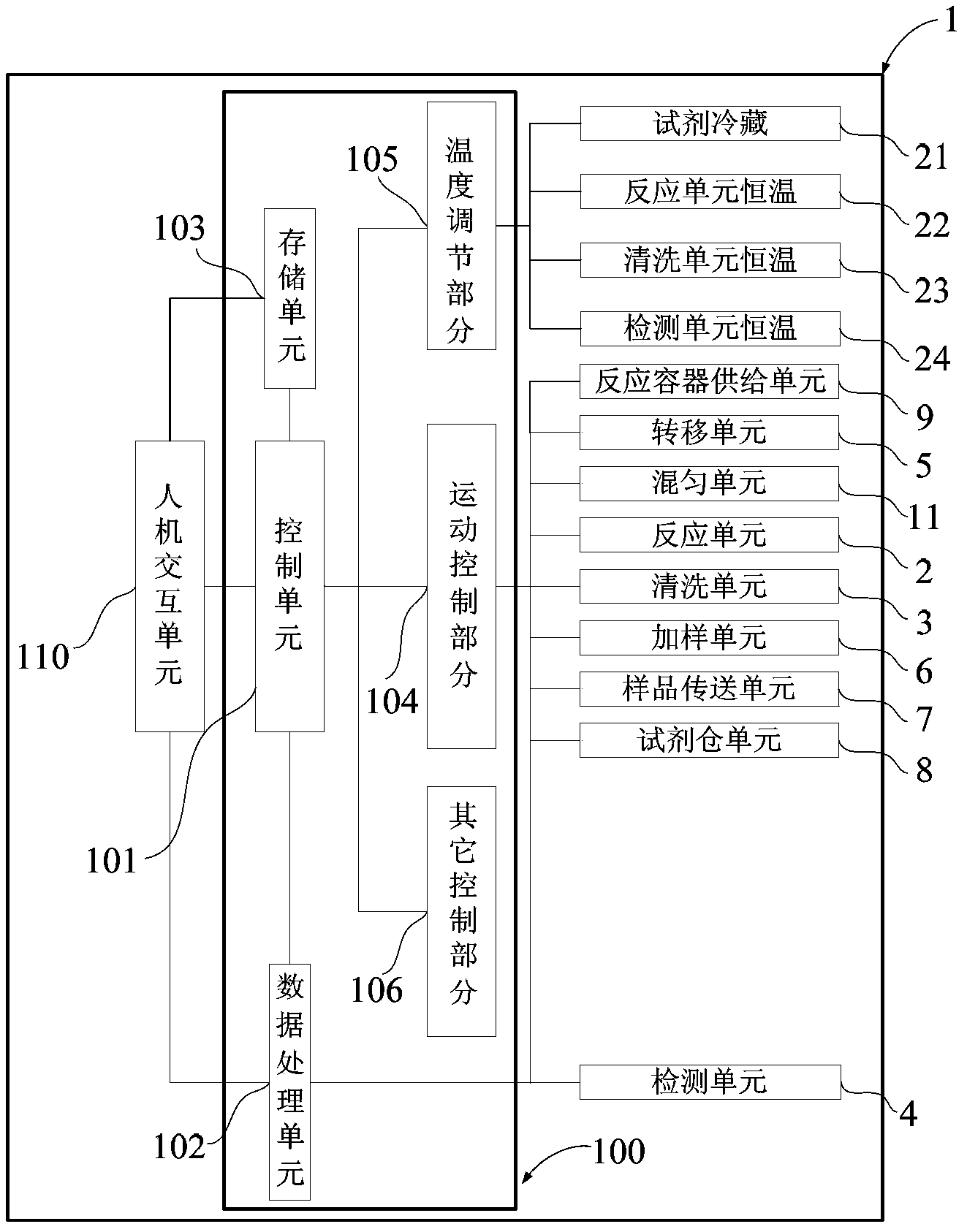
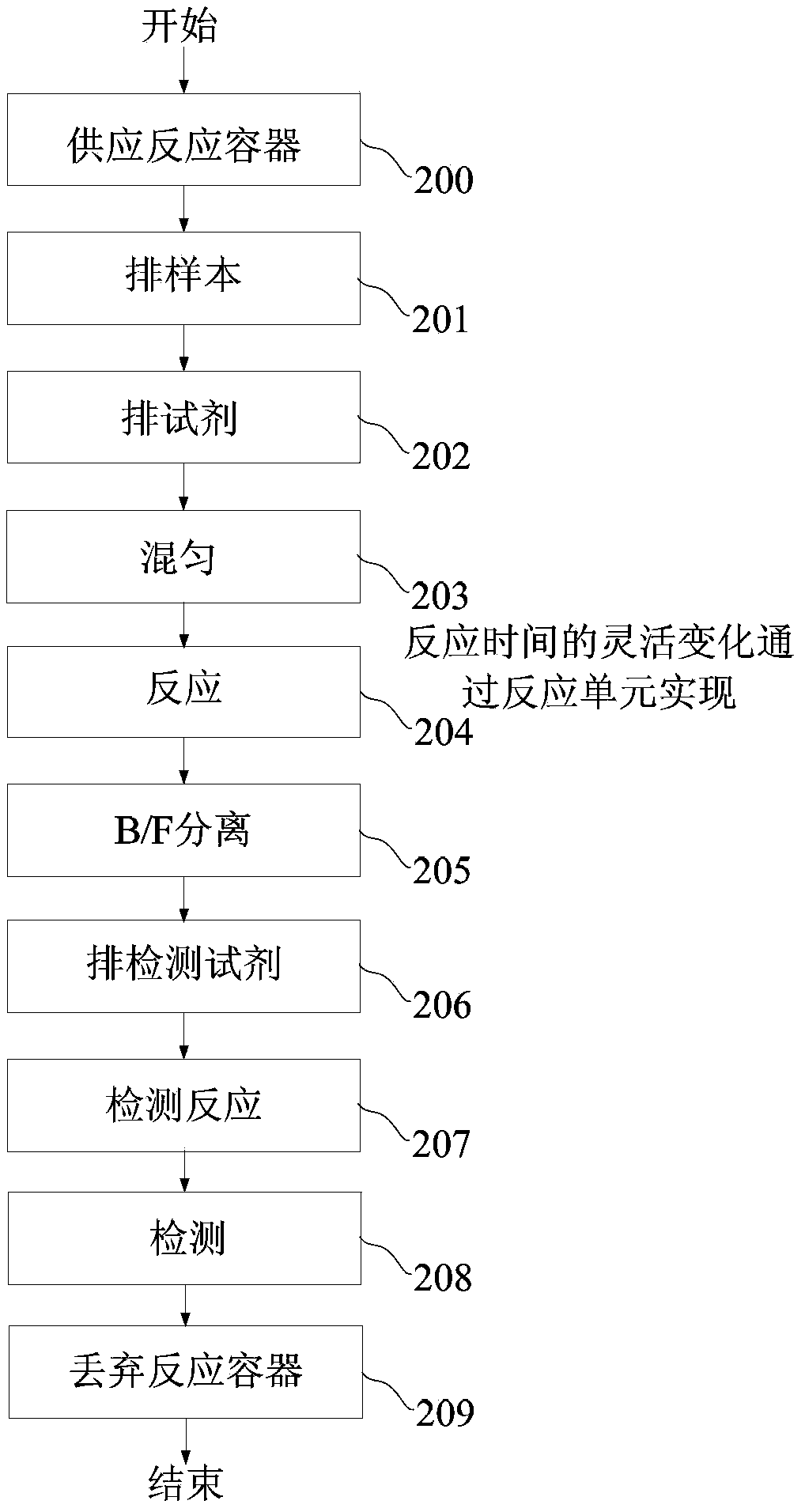
Automatic analysis apparatus and automatic analysis method
The invention relates to an automatic analysis apparatus. The apparatus includes a reaction container supply unit, a reagent warehouse receipt, a sample transfer unit, a reaction incubation unit, a cleaning and separating unit, a detection unit, a sample adding unit, a transfer unit and a control system. An automatic analysis method using the automatic analysis apparatus includes the following steps: (1) supplying a reaction container; (2) adding an analysis sample and an analysis reagent; (3) reacting; (4) cleaning, and separating; (5) adding a detection reagent; (6) reacting; and (7) detecting. The automatic analysis apparatus and the automatic analysis method can flexibly realize a variety of test modes and reaction times, reduce the size of a whole machine, reduce the cost, and make the whole machine have a compact structure; and the automatic analysis apparatus has scalability, can easily realize high speed test, and is suitable for analysis under different test modes and reaction times.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
System and method for detecting user attention
ActiveUS20070061851A1Reduce the burden onSolve the excessive calculationInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsExecution controlAnalysis sample
A system and method for conditioning execution of a control function on a determination of whether or not a person's attention is directed toward a predetermined device. The method involves acquiring data concerning the activity of a person who is in the proximity of the device, the data being in the form of one or more temporal samples. One or more of the temporal samples is then analyzed to determine if the person's activity during the time of the analyzed samples indicates that the person's attention is not directed toward the device. The results of the determination are used to ascertain whether or not the control function should be performed.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Optical analysis system and elements to isolate spectral region
ActiveUS20090219512A1Minimize band-edge effectUseful and reliable capabilityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical frequenciesAnalysis sample
A method of selecting components for a multivariate optical computing and analysis system to isolate a spectral region includes selecting a spectral region of interest; selecting a spectral element with a predetermined transmission characteristic to control a spectral range of an illumination source; illuminating a sample with the illumination source; and analyzing an optical frequency returned by the sample relative to the spectral region of interest.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
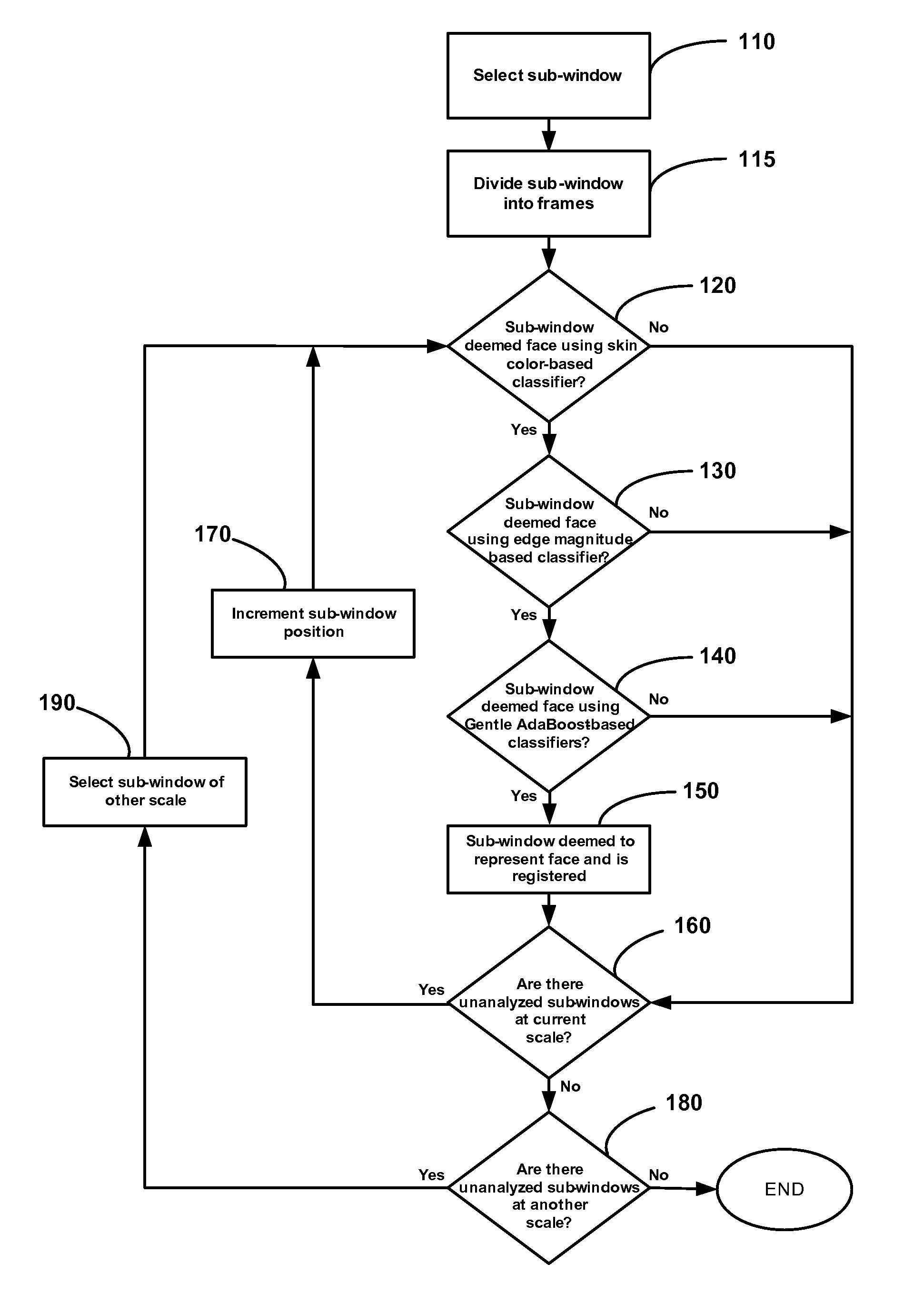
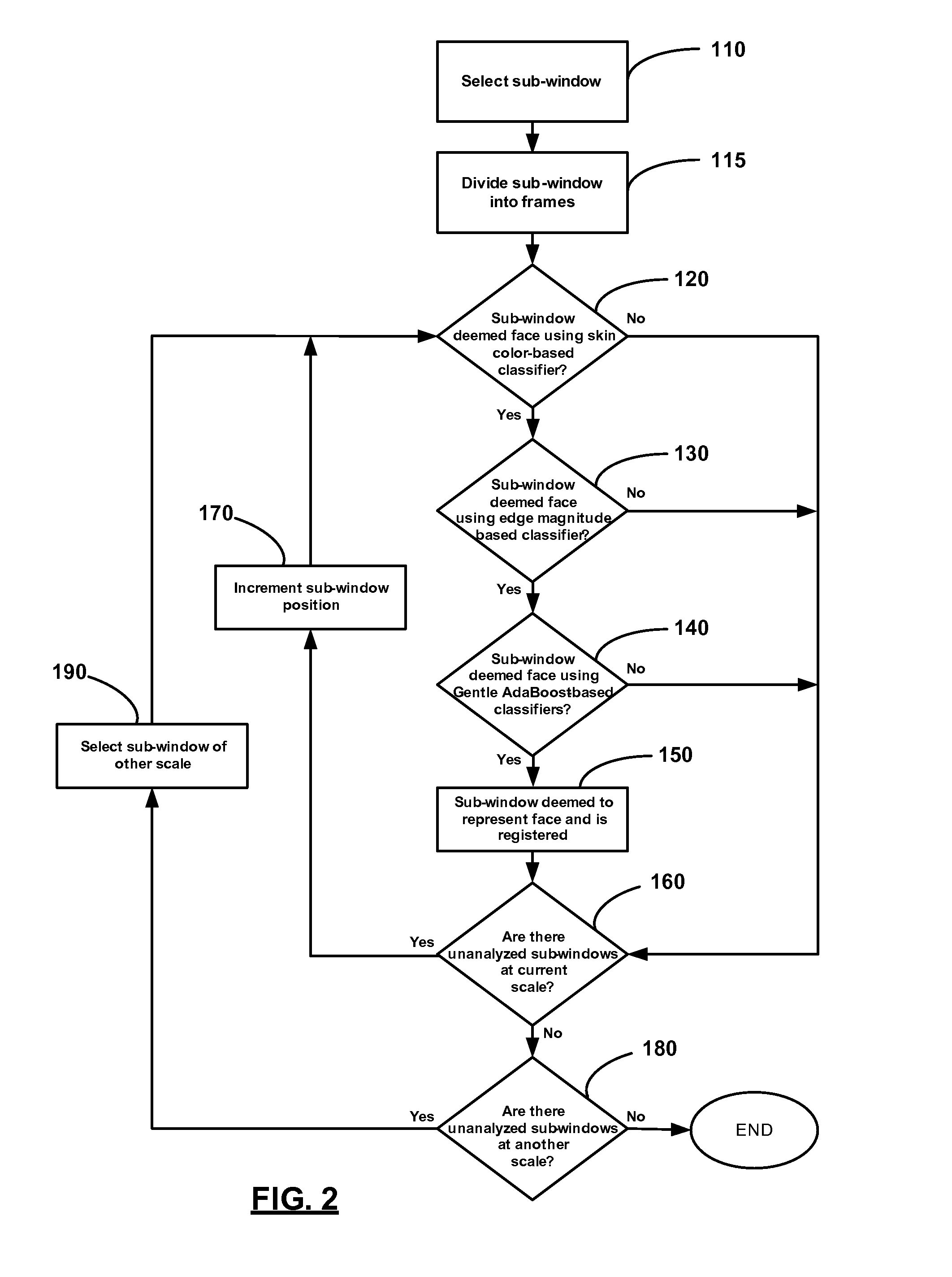
Method And Apparatus For Detecting Faces In Digital Images
InactiveUS20080107341A1Fast approachReduce computing costCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionDigital image
A method of detecting faces in a digital image comprises selecting a sub-window of the digital image. Sample regions of the sub-window are then selected. The sample regions are analyzed to determine if the sub-window likely represents a face.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
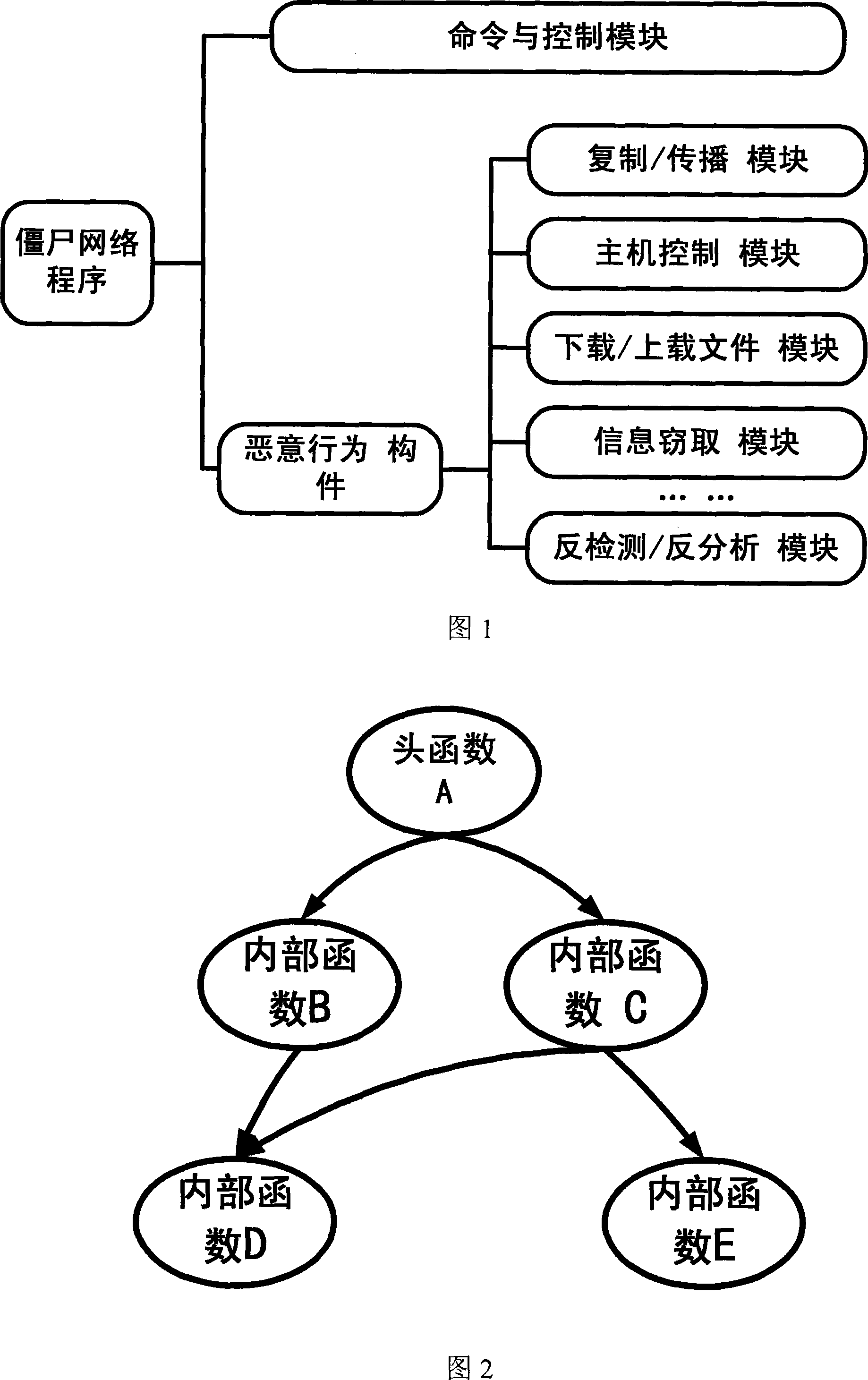
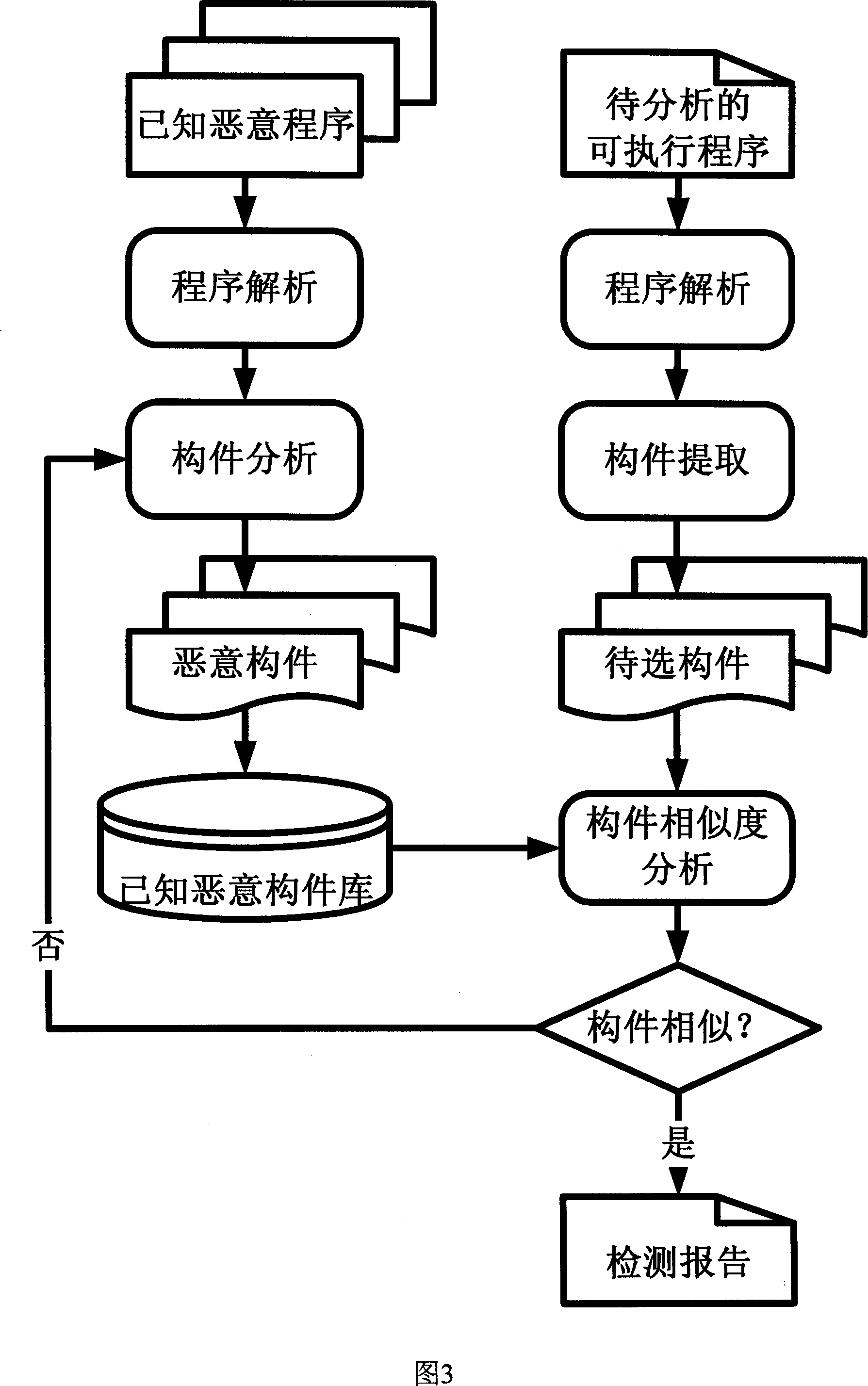
Malevolence code automatic recognition method
InactiveCN101140611ABroad analysis coverageImprove analysisPlatform integrity maintainanceSecuring communicationProgramming languageAnalysis sample
The invention belongs to the field of malicious code automatic analysis, and a malicious code automatic identification method. The invention first dismantles an executable program sample under analysis into components under analysis; then, compare a component under analysis with a component affected by known malicious behaviors, in order to automatically determine whether the sample under analysis is a malicious code. The invention has advantages of broad analysis coverage scope, high analysis speed on malicious samples, and updating malicious code behavior component library.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
System and method including analytical units
InactiveCN103119451ASimple structureHeating or cooling apparatusReagent containersAssayPhysical chemistry
Systems and methods for processing and analyzing samples are disclosed. The system may process samples, such as biological fluids, using assay cartridges which can be processed at different processing locations. In some cases, the system can be used for PCR processing. The different processing locations may include a preparation location where samples can be prepared and an analysis location where samples can be analyzed. To assist with the preparation of samples, the system may also include a number of processing stations which may include processing lanes. During the analysis of samples, in some cases, thermal cycler modules and an appropriate optical detection system can be used to detect the presence or absence of certain nucleic acid sequences in the samples. The system can be used to accurately and rapidly process samples.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Telematic asset microfluidic analysis
ActiveUS20110282631A1Saving time and effortImprove feature development and marketingValve arrangementsError detection/correctionAnalysis sampleTelematics
A fluid analyzing system wherein an electronic control module is coupled with an asset and a telematics device. The electronic control module initiates the acquisition of a sample of an asset's fluid and analyzes the sample in response to an analysis trigger. An asset management system located remotely from the asset and telematics device receives the results of the fluid analysis wirelessly via the telematics device.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Image type automatic analysis method for mesh adhesion rice corn
InactiveCN101281112AOvercoming problems that are difficult to analyze automaticallyRemove the restriction of non-stick placementImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansAutomatic segmentationSplit lines
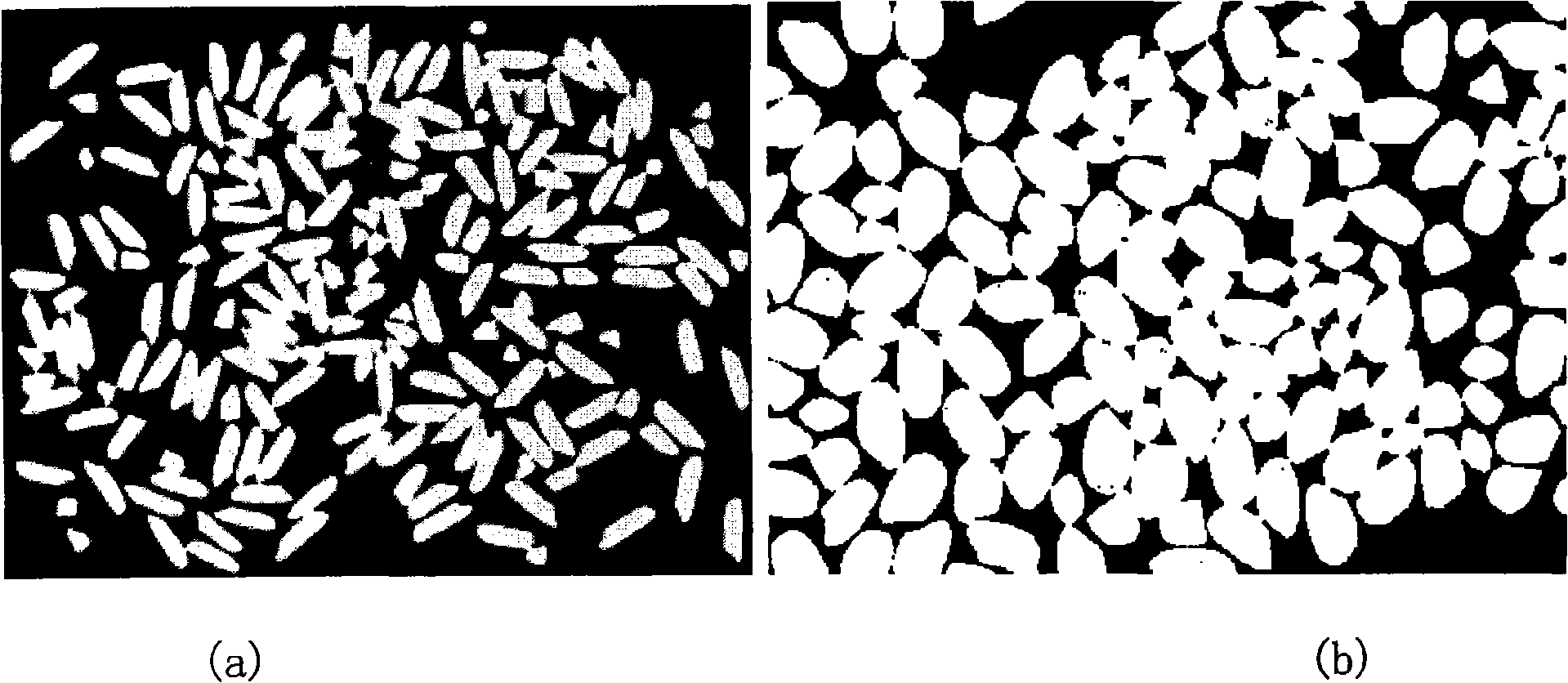
The invention discloses an image automatic analysis method for reticulate adhesion rice. The method firstly images rice under the grade of a reference backlight, and enables the reticulate adhesion rice to belong to the different local regions separately through an automatic segmentation. Secondly, the automatic segmentation includes that fat circular rice is carried on a distance transformation and a watershed transformation to be divided, as well as to use a circular template to get the concave angle point of long rice after the long rice is carried out watershed transformation, and the separation line can be determined and the wrong separation line can be removed according to the concave angle point. Different colors is using to color complete polished rice, broken rice and the rice whose length is in the critical region and to color background and chalkiness so as to figure out the grain number, the length, the width and the length to width ratio of each grain, finally, and the entire polished rice rate, the broken rice rate, the chalkiness degree and the chalkiness grain rate, and to form an analysis report. The invention overcomes the problem that the reticulate adhesion rice is difficult to be carried on automated analysis, and removes the limit of the request analysis sample is not in adhesion placing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
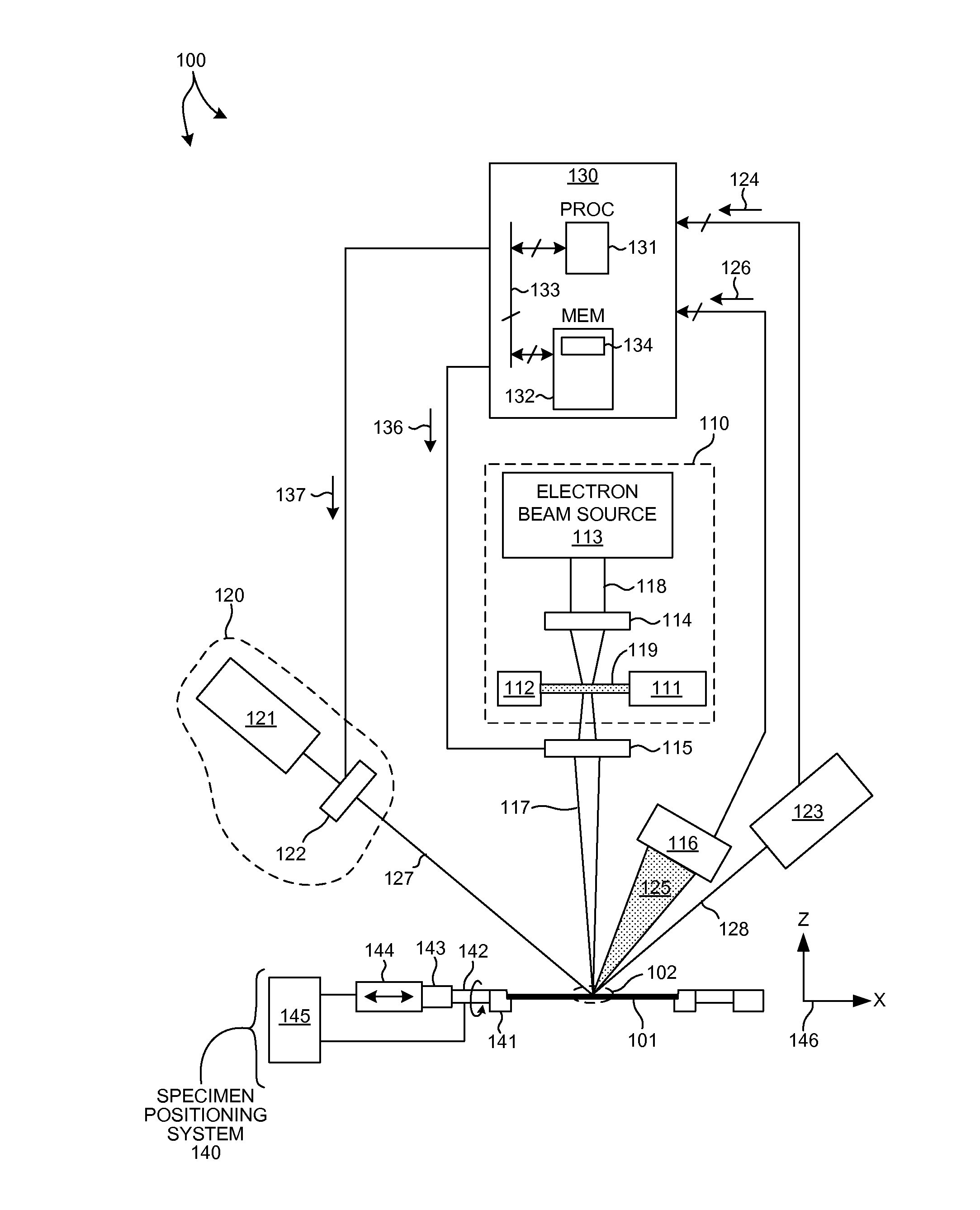
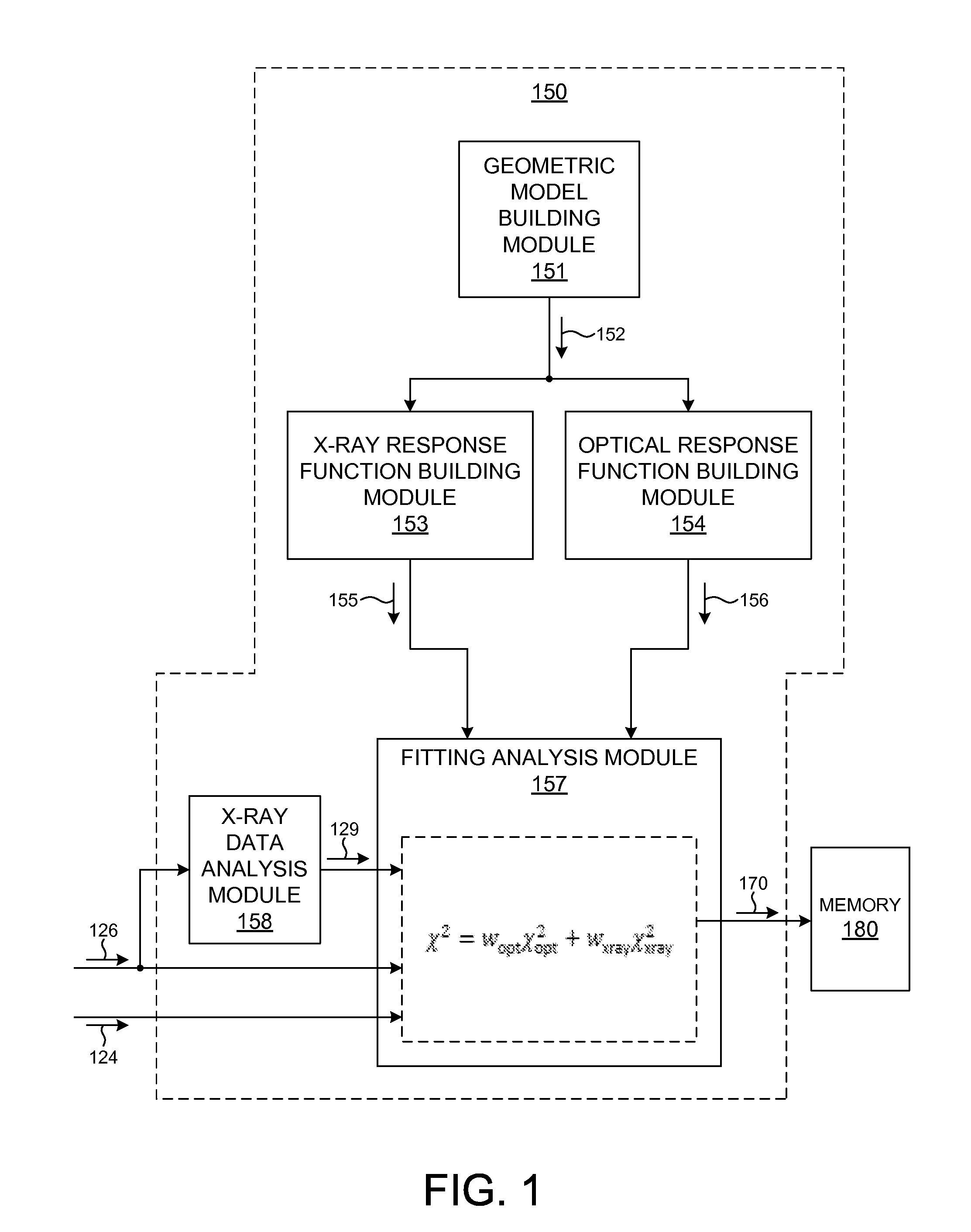
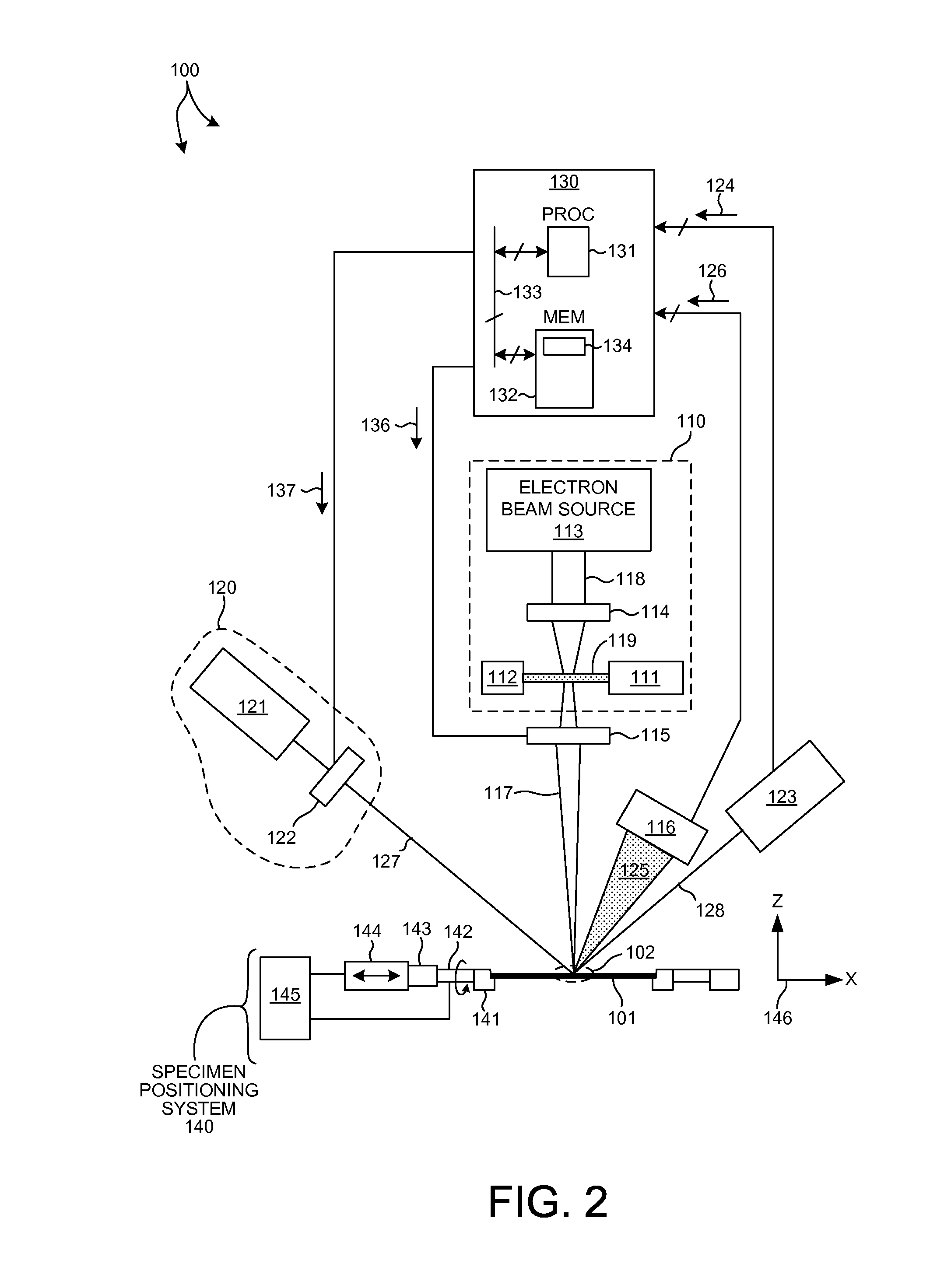
Combined X-Ray and Optical Metrology
ActiveUS20150032398A1Reduce in quantityReduce correlationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElemental compositionSoft x ray
Structural parameters of a specimen are determined by fitting models of the response of the specimen to measurements collected by different measurement techniques in a combined analysis. X-ray measurement data of a specimen is analyzed to determine at least one specimen parameter value that is treated as a constant in a combined analysis of both optical measurements and x-ray measurements of the specimen. For example, a particular structural property or a particular material property, such as an elemental composition of the specimen, is determined based on x-ray measurement data. The parameter(s) determined from the x-ray measurement data are treated as constants in a subsequent, combined analysis of both optical measurements and x-ray measurements of the specimen. In a further aspect, the structure of the response models is altered based on the quality of the fit between the models and the corresponding measurement data.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
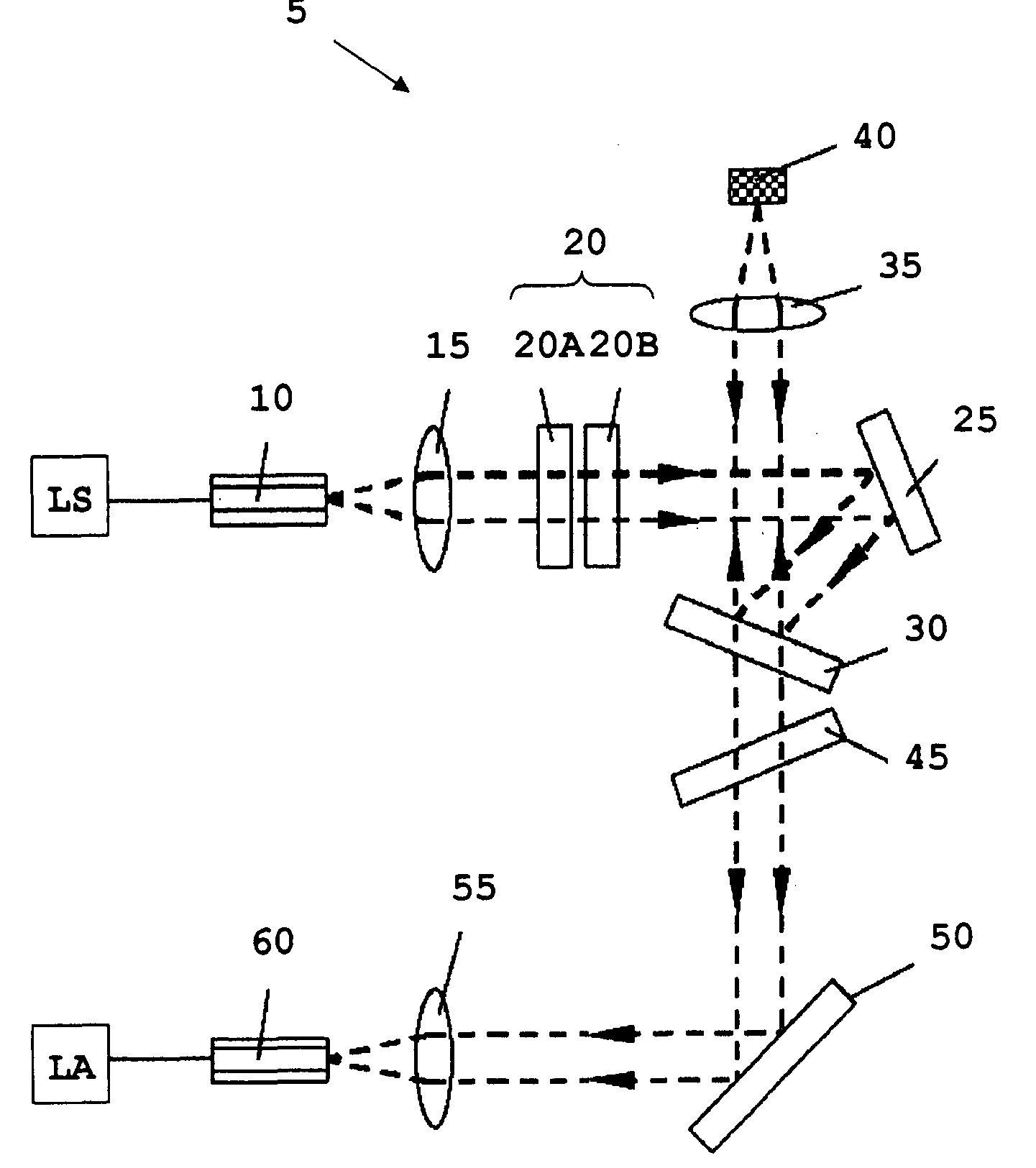
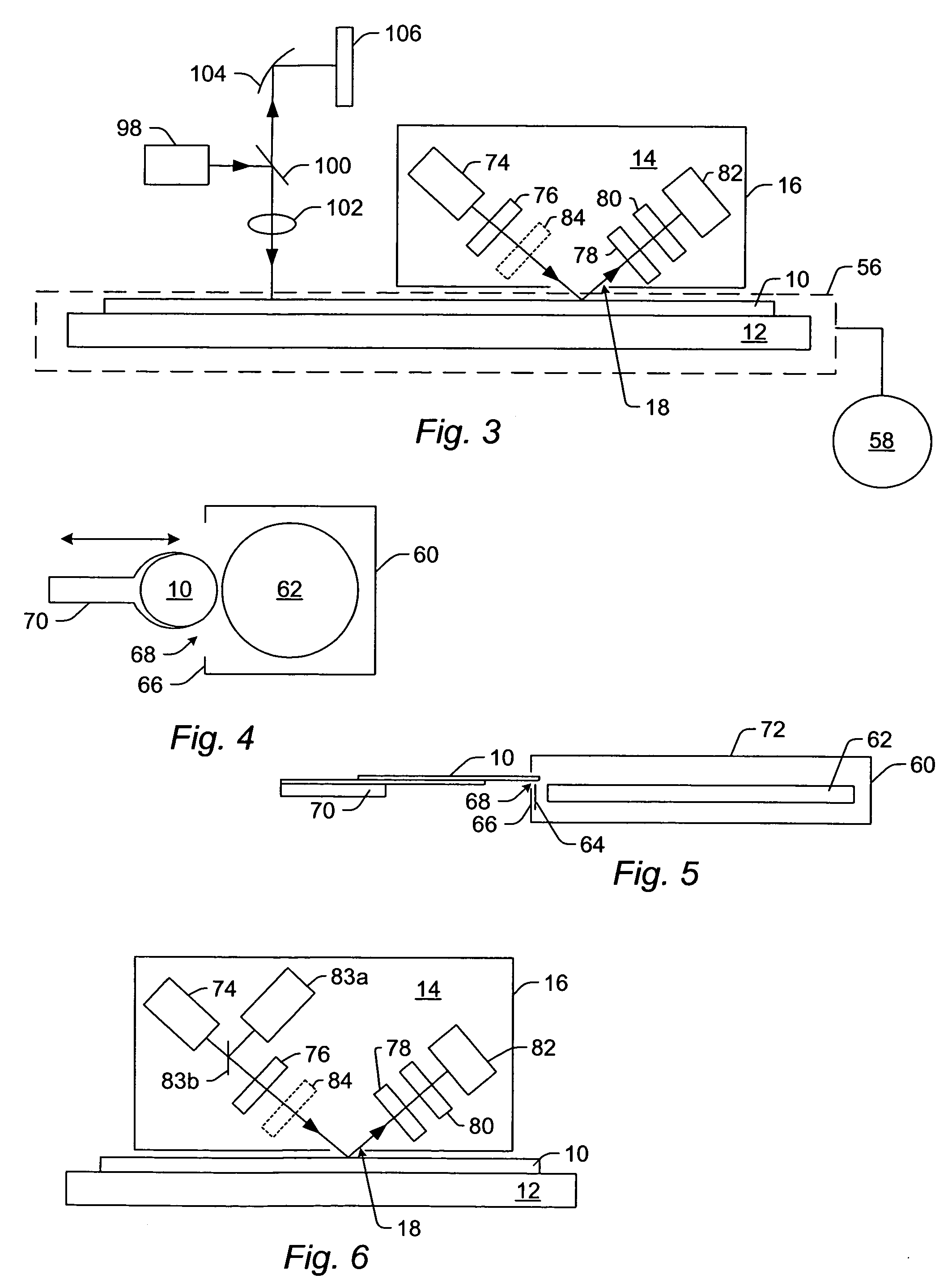
Method and apparatus for conducting Raman spectroscopy
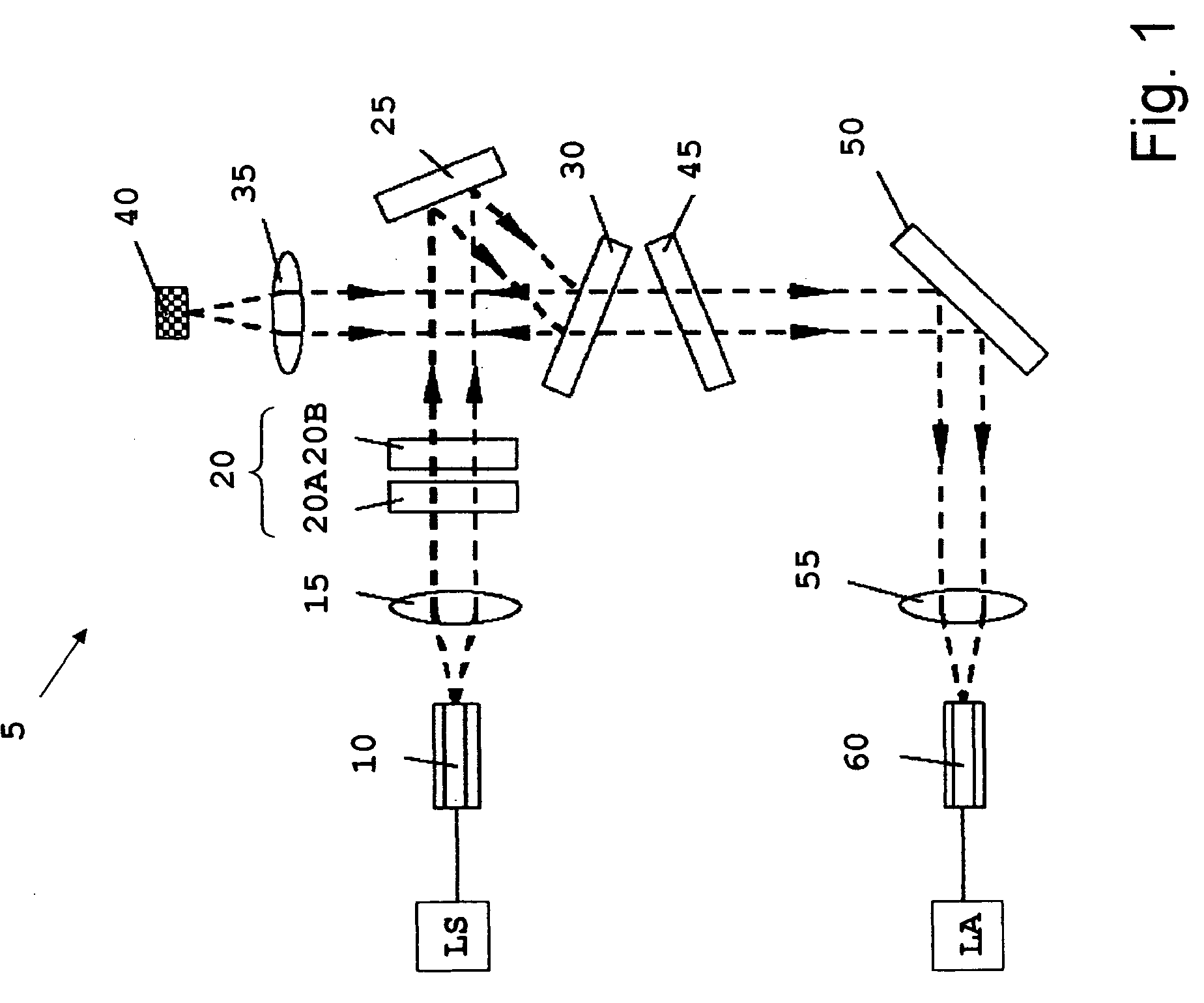
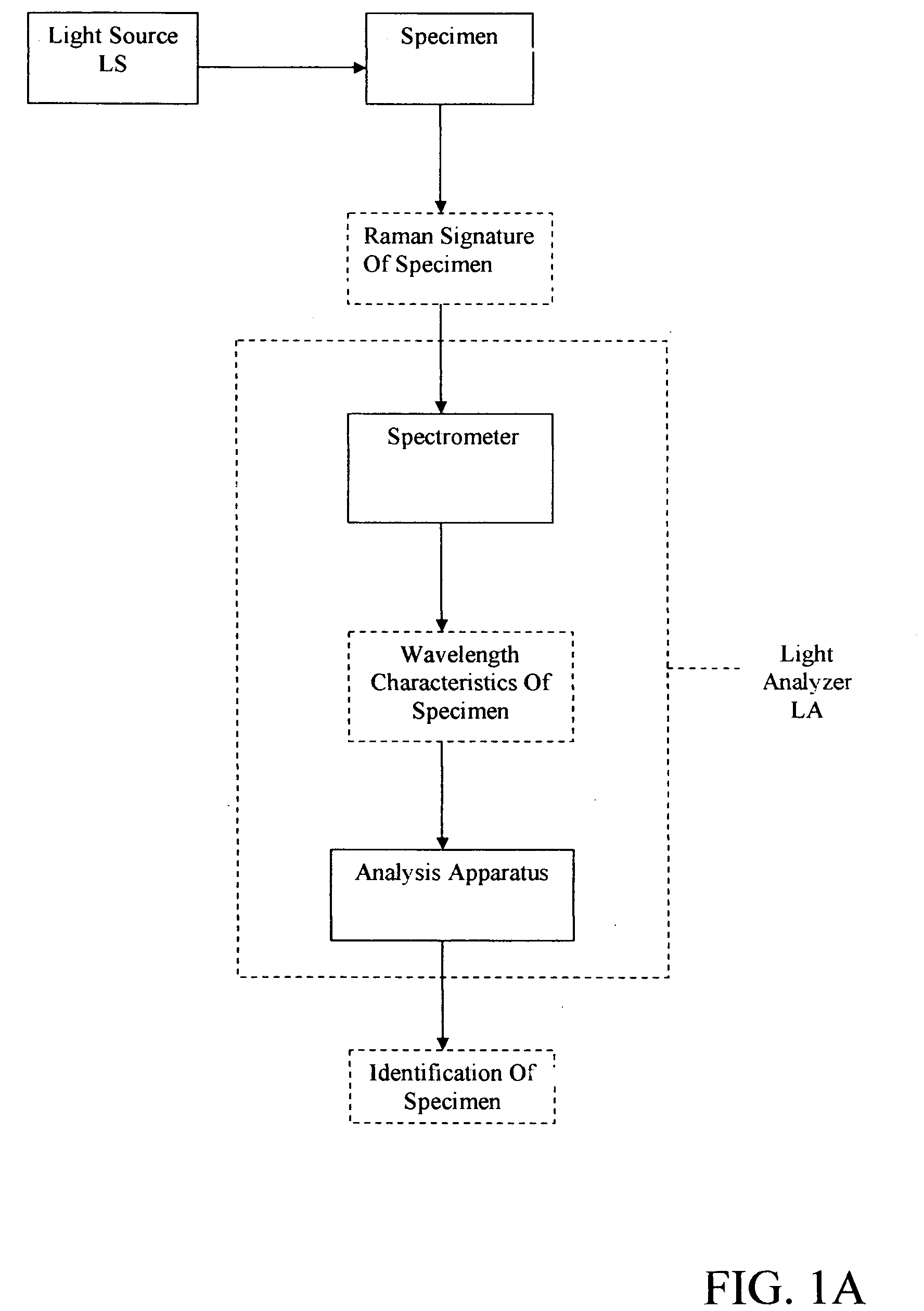
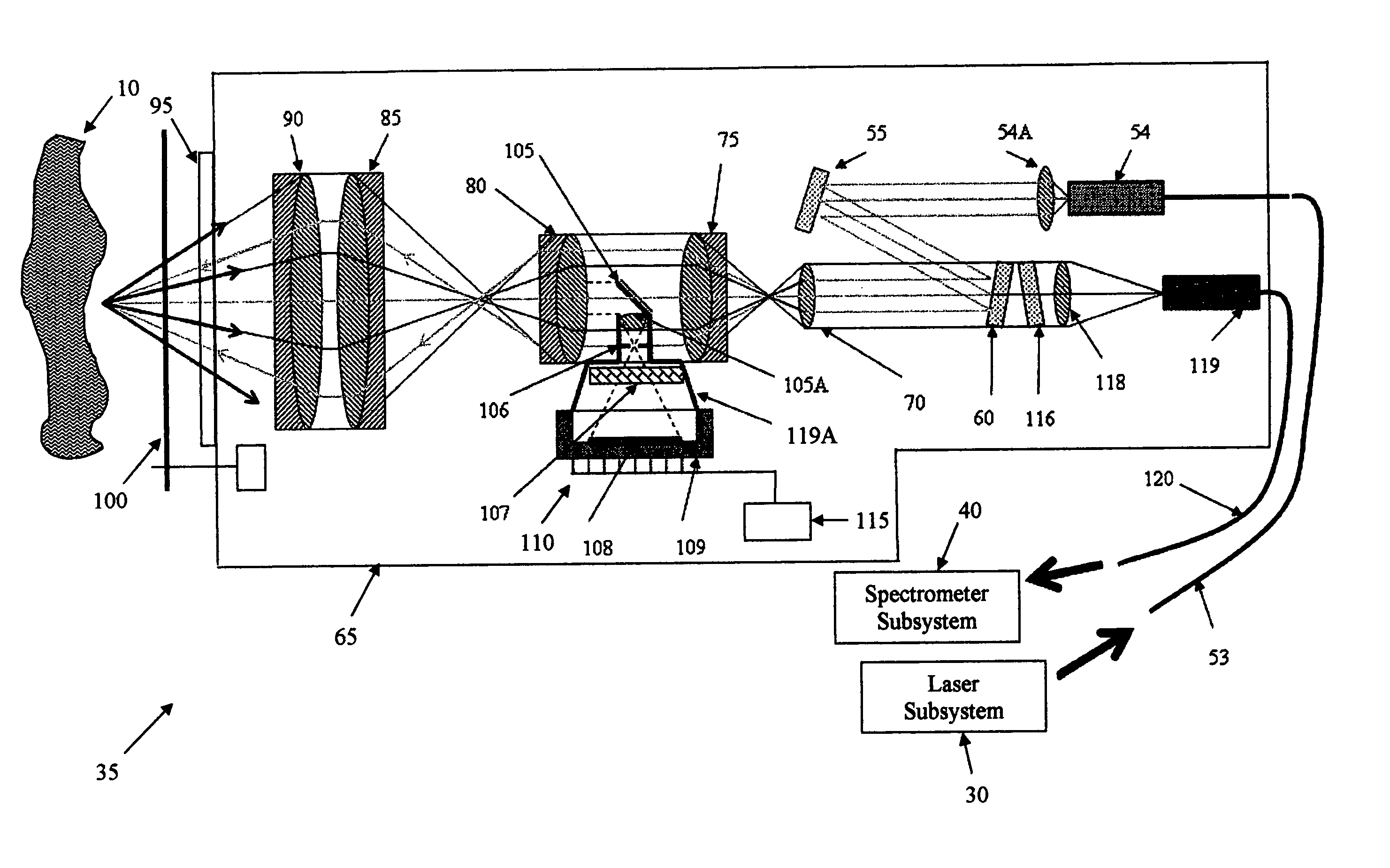
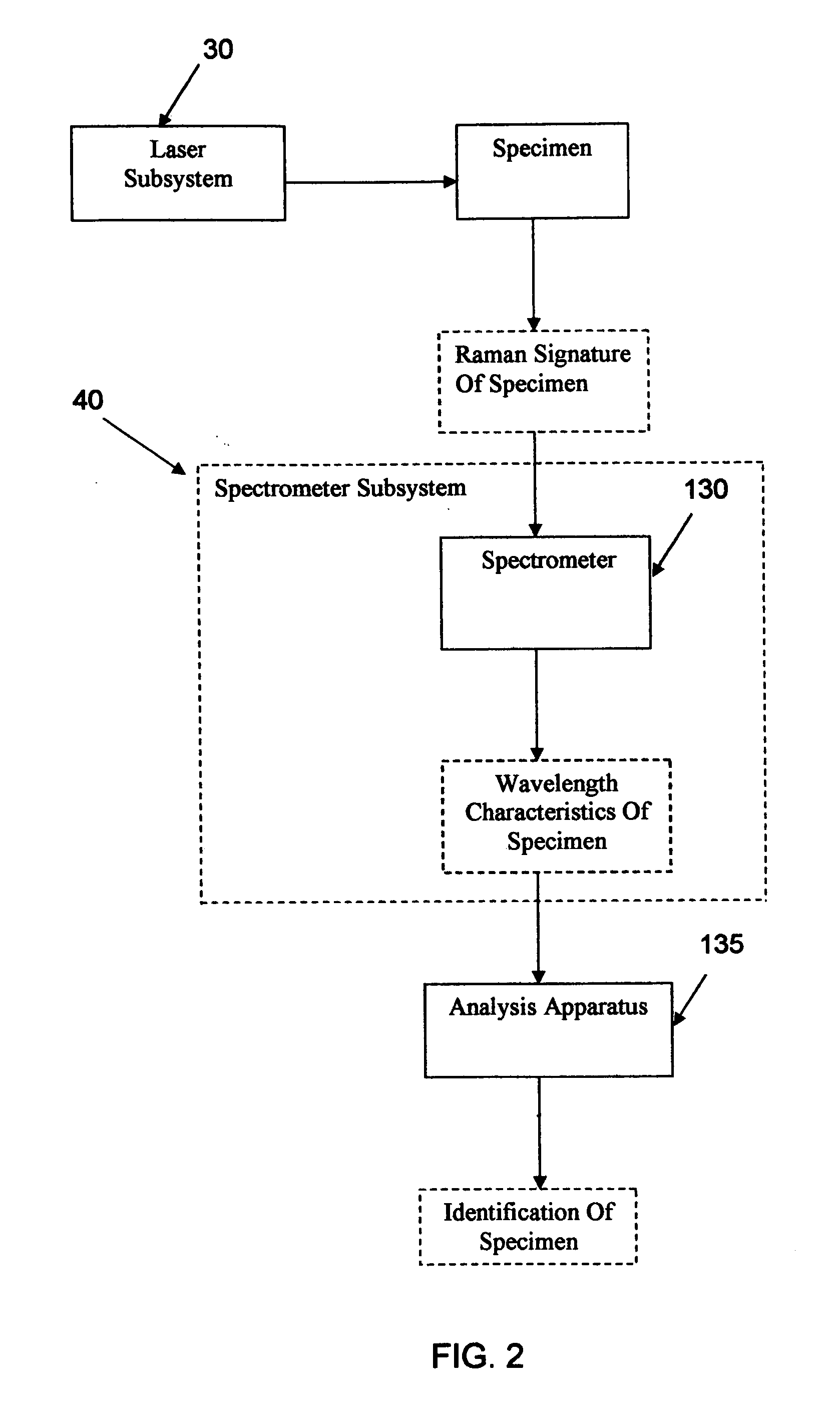
ActiveUS20050248759A1Keep distanceMaintain controlRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringDisplay deviceAnalysis sample
In another form of the present invention, there is provided a Raman probe comprising: a first optical fiber for receiving laser excitation light from a light source and transmitting the same; a first filter for receiving light from the first optical fiber and adapted to pass the laser excitation light and to block spurious signals associated with the light; a second filter for receiving light from the first filter and adapted to direct the light toward the specimen; focusing apparatus for receiving the light from the second filter, focusing the light on a specimen so as to generate the Raman signal, and returning the Raman signal to the second filter; wherein the second filter is further configured so that when the second filter receives the Raman signal from the focusing apparatus, the second filter filters out unwanted laser excitation light before directing the Raman signal to a second optical fiber; and a second optical fiber for receiving the Raman signal from the second filter and transmitting the same to a light analyzer. In another form of the present invention, there is provided a Raman probe comprising: a light source for generating laser excitation light; focusing apparatus for receiving the laser excitation light from the light source, focusing the laser excitation light on a specimen so as to generate the Raman signal, and returning the Raman signal to a light analyzer; and a light analyzer for analyzing the Raman signature of the specimen, whereby to identify the specimen; wherein the focusing apparatus is configured to permit the specimen to reside in a vial receptacle or at a target location remote from the vial receptacle. In another form of the present invention, there is provided a method for conducting Raman spectroscopy of a specimen, comprising: generating laser excitation light using a light source; passing the laser excitation light through a first filter so as to block spurious signals associated with the light; passing the laser excitation light through a second filter so as to direct the light toward the specimen; receiving the light from the second filter, focusing the light on a specimen so as to generate the Raman signal, and returning the Raman signal to the second filter; wherein the second filter is further configured so that when the second filter receives the Raman signal from the specimen, the second filter filters out unwanted laser excitation light; passing the filtered light received from the second filter to a light analyzer; and analyzing the Raman signature of the specimen so as to identify the specimen. In another form of the present invention, there is provided a Raman probe comprising: a housing; a light source disposed within the housing for generating laser excitation light; focusing apparatus disposed within the housing for receiving the laser excitation light from the light source, focusing the laser excitation light on a specimen so as to generate the Raman signal, and returning the Raman signal to a light analyzer; and a light analyzer disposed within the housing for analyzing the Raman signature of the specimen, whereby to identify the specimen; wherein the focusing apparatus is configured to permit the specimen to reside at a target location remote from the housing; and further comprising an optical shield mounted to the housing so as to be disposed between the specimen and the user, whereby to optically shield the user from the light source. In another form of the present invention, there is provided a Raman probe comprising: a housing; a light source disposed within the housing for generating laser excitation light; focusing apparatus disposed within the housing for receiving the laser excitation light from the light source, focusing the laser excitation light on a specimen so as to generate the Raman signal, and returning the Raman signal to a light analyzer; and a light analyzer disposed within the housing for analyzing the Raman signature of the specimen, whereby to identify the specimen; wherein the focusing apparatus is configured to permit the specimen to reside at a target location remote from the housing; and further comprising a camera mounted to the housing so that its field of view encompasses the target location, and a display mounted to the housing for displaying the image captured by the camera, whereby to permit the user to position the probe relative to the specimen while watching the display.
Owner:AHURA CORP
Methods for measurement or analysis of a nitrogen concentration of a specimen
ActiveUS20050254049A1Improve accuracyMaintain calibrationPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsGate dielectricRefractive index
A method for measurement of a specimen is provided. The method includes measuring spectroscopic ellipsometric data of the specimen. The method also includes determining a nitrogen concentration of a nitrided oxide gate dielectric formed on the specimen from the spectroscopic ellipsometric data. A computer-implemented method for analysis of a specimen is also provided. This method includes determining a nitrogen concentration of a nitrided oxide gate dielectric formed on the specimen from spectroscopic ellipsometric data generated by measurement of the specimen. In some embodiments, the methods described above may include determining an index of refraction of the nitrided oxide gate dielectric from the spectroscopic ellipsometric data and determining the nitrogen concentration from the index of refraction. In another embodiment, the methods described above may include measuring reflectometric data of the specimen. The nitrogen concentration may be determined from the spectroscopic ellipsometric data in combination with the reflectometric data.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method and system for DNA analysis
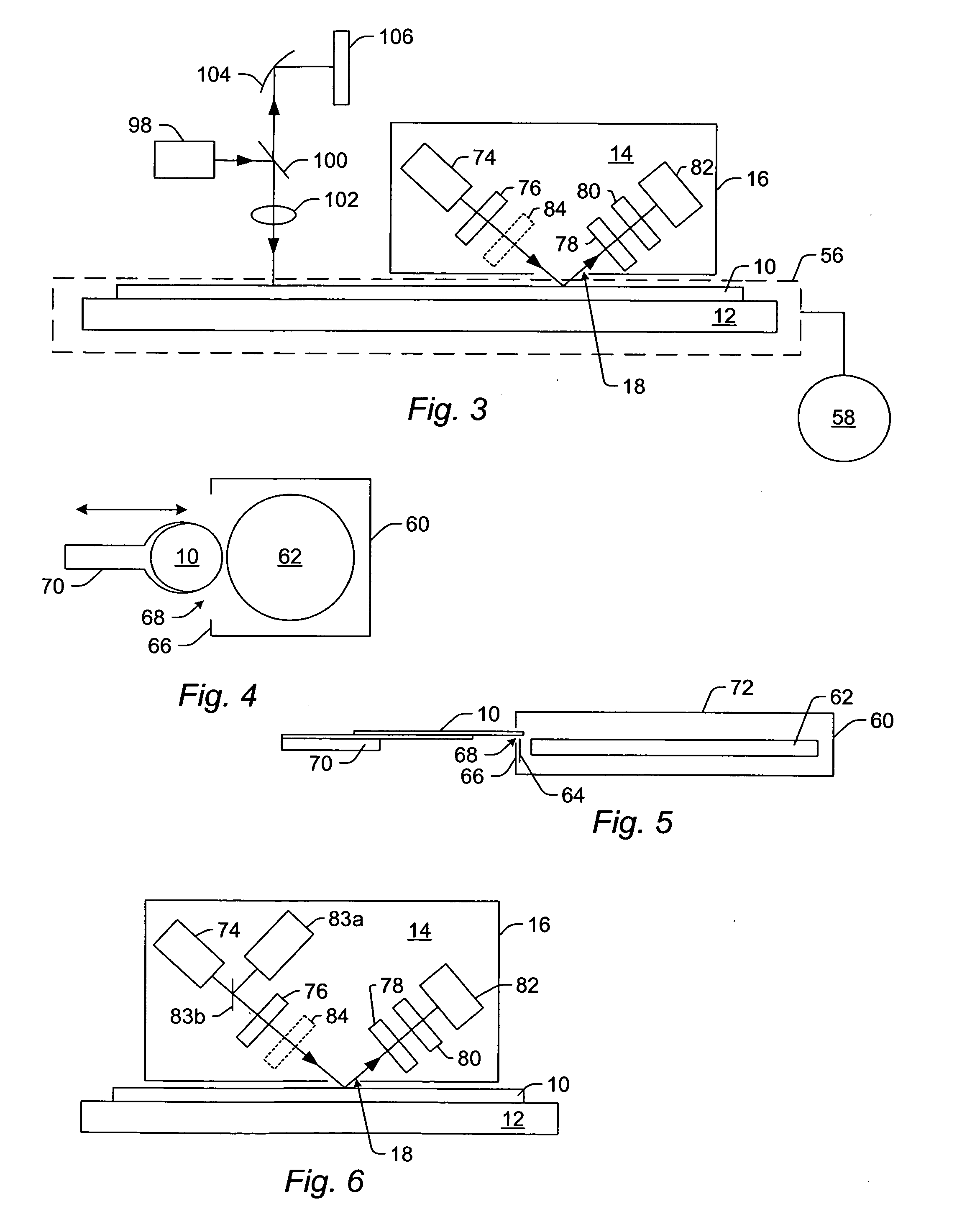
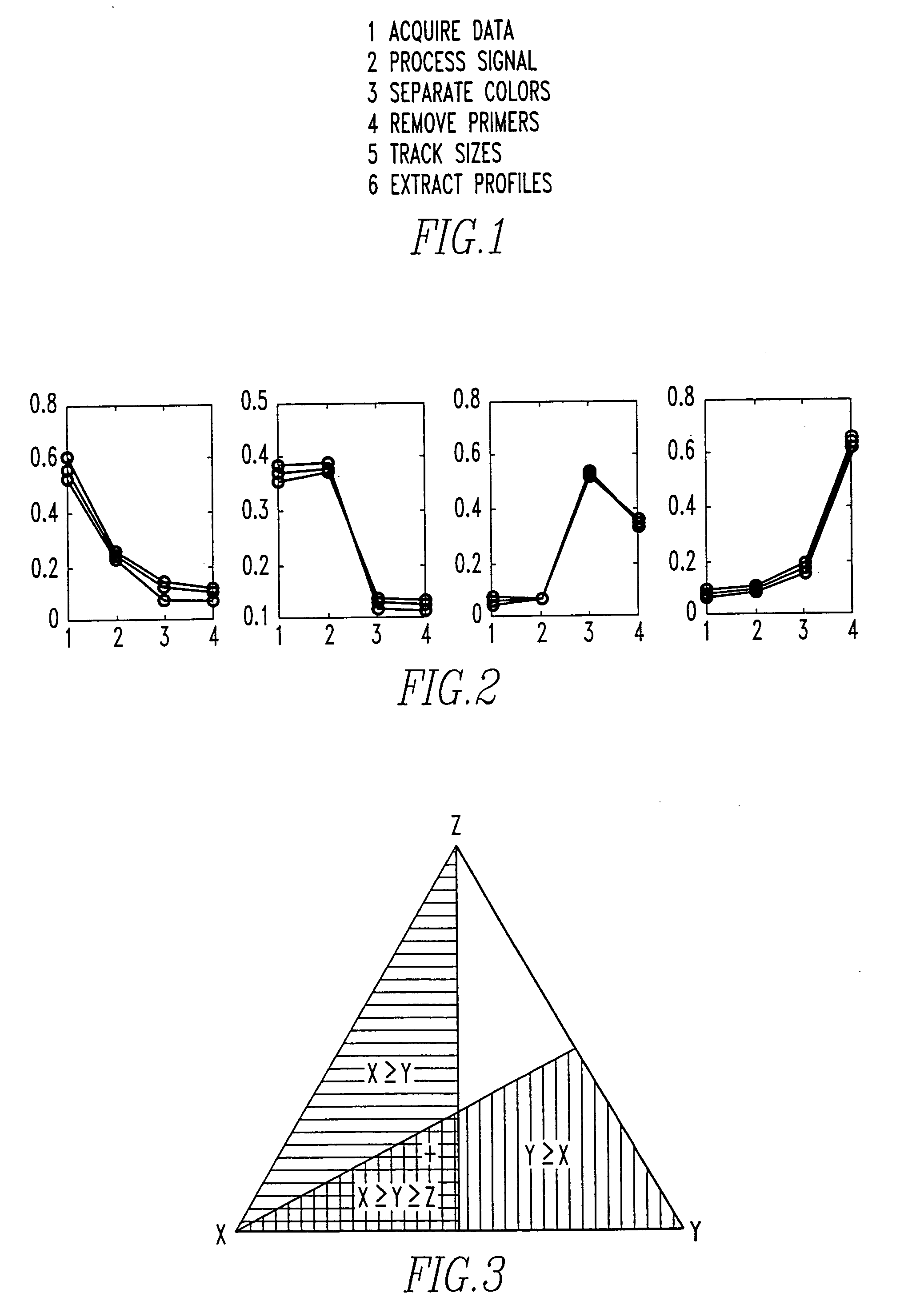
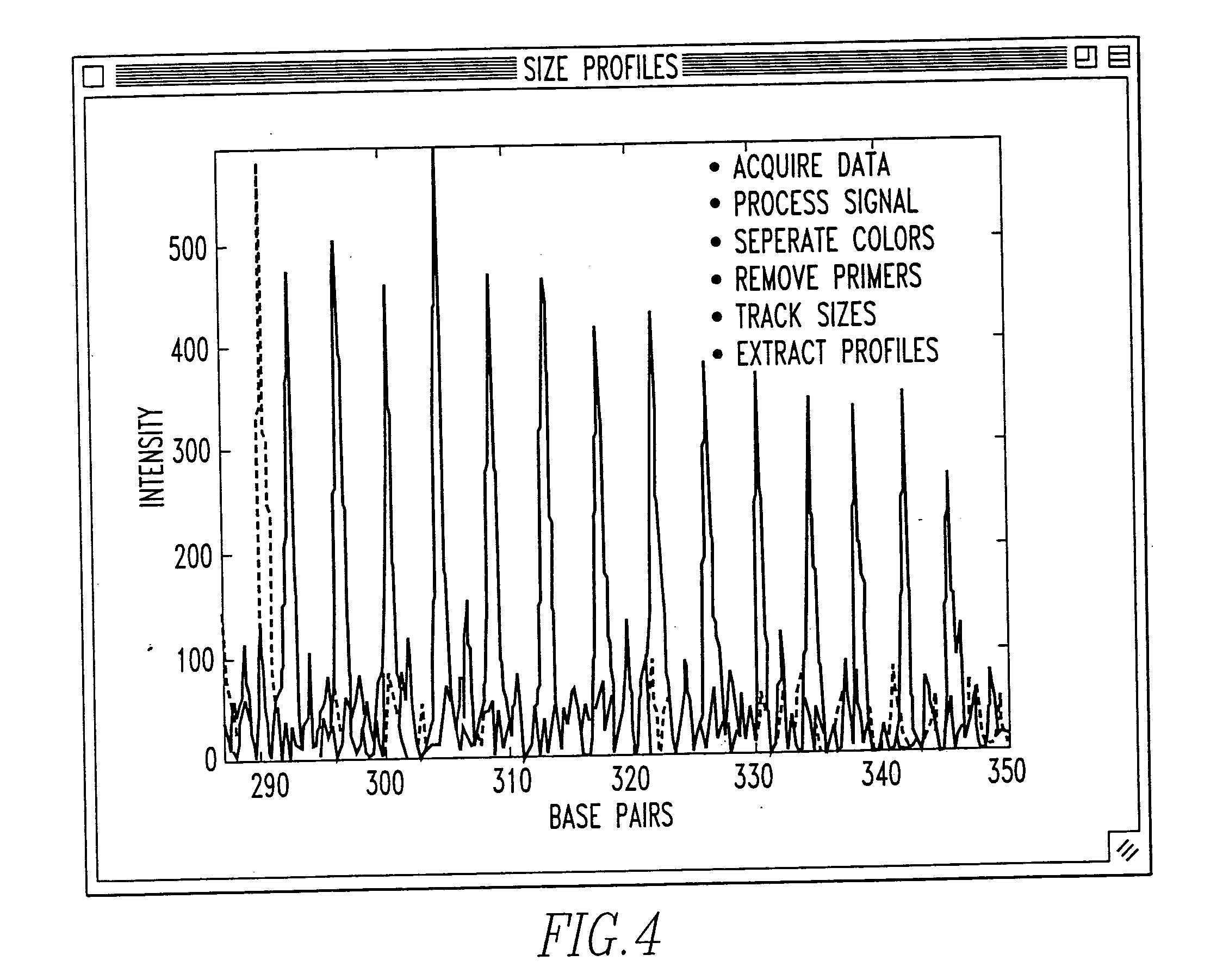
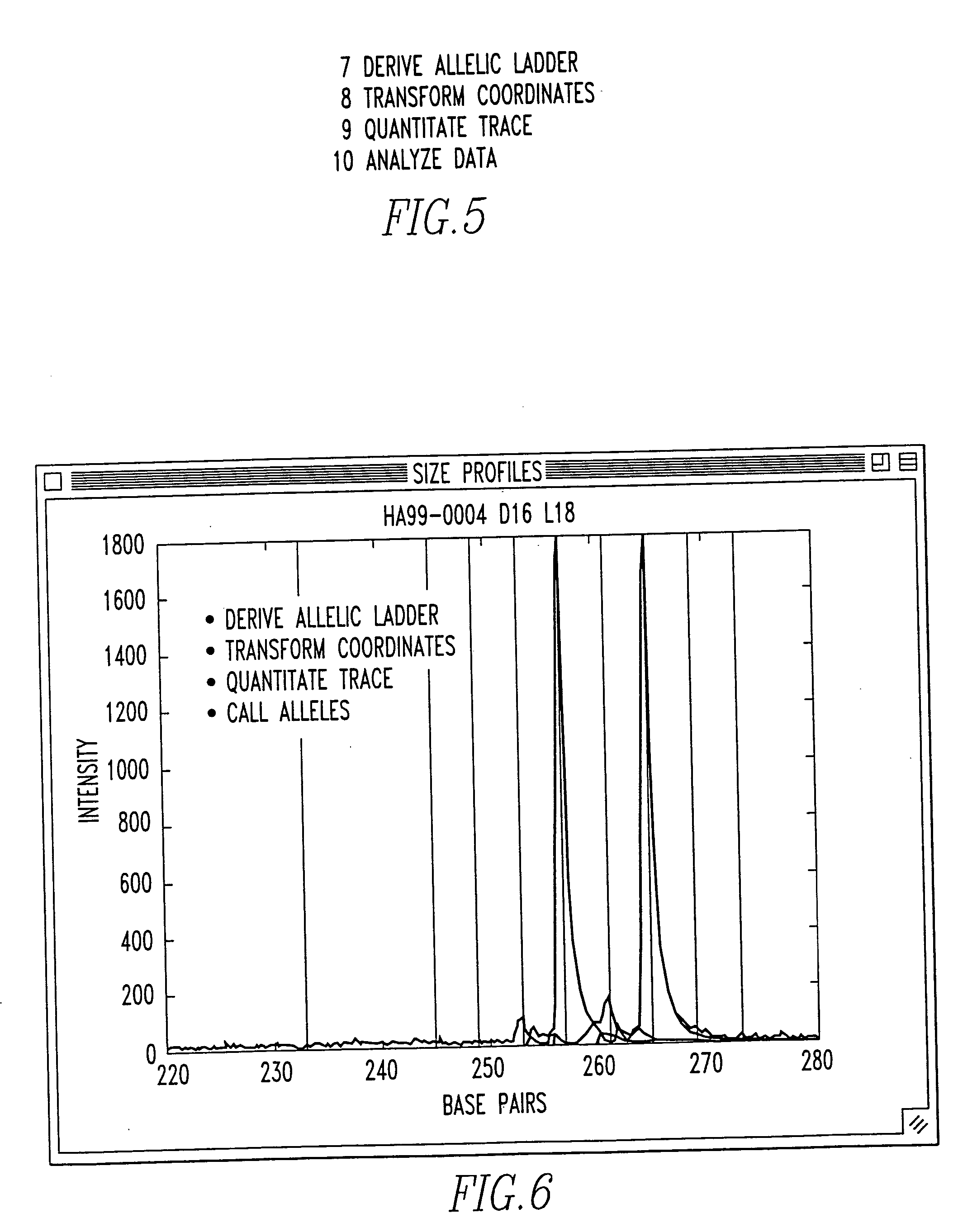
The present invention pertains to a process for automatically analyzing nucleic acid samples. Specifically, the process comprises the steps of forming electrophoretic data of DNA samples with DNA ladders; comparing these data; transforming the coordinates of the DNA sample's data into DNA length coordinates; and analyzing the DNA sample in length coordinates. This analysis is useful for automating fragment analysis and quality assessment. The automation enables a business model based on usage, since it replaces (rather than assists) labor. This analysis also provides a mechanism whereby data generated on different instruments can be confidently compared. Genetic applications of this invention include gene discovery, genetic diagnosis, and drug discovery. Forensic applications include identifying people and their relatives, catching perpetrators, analyzing DNA mixtures, and exonerating innocent suspects.
Owner:PERLIN MARK W
Method and apparatus for conducting Raman spectroscopy
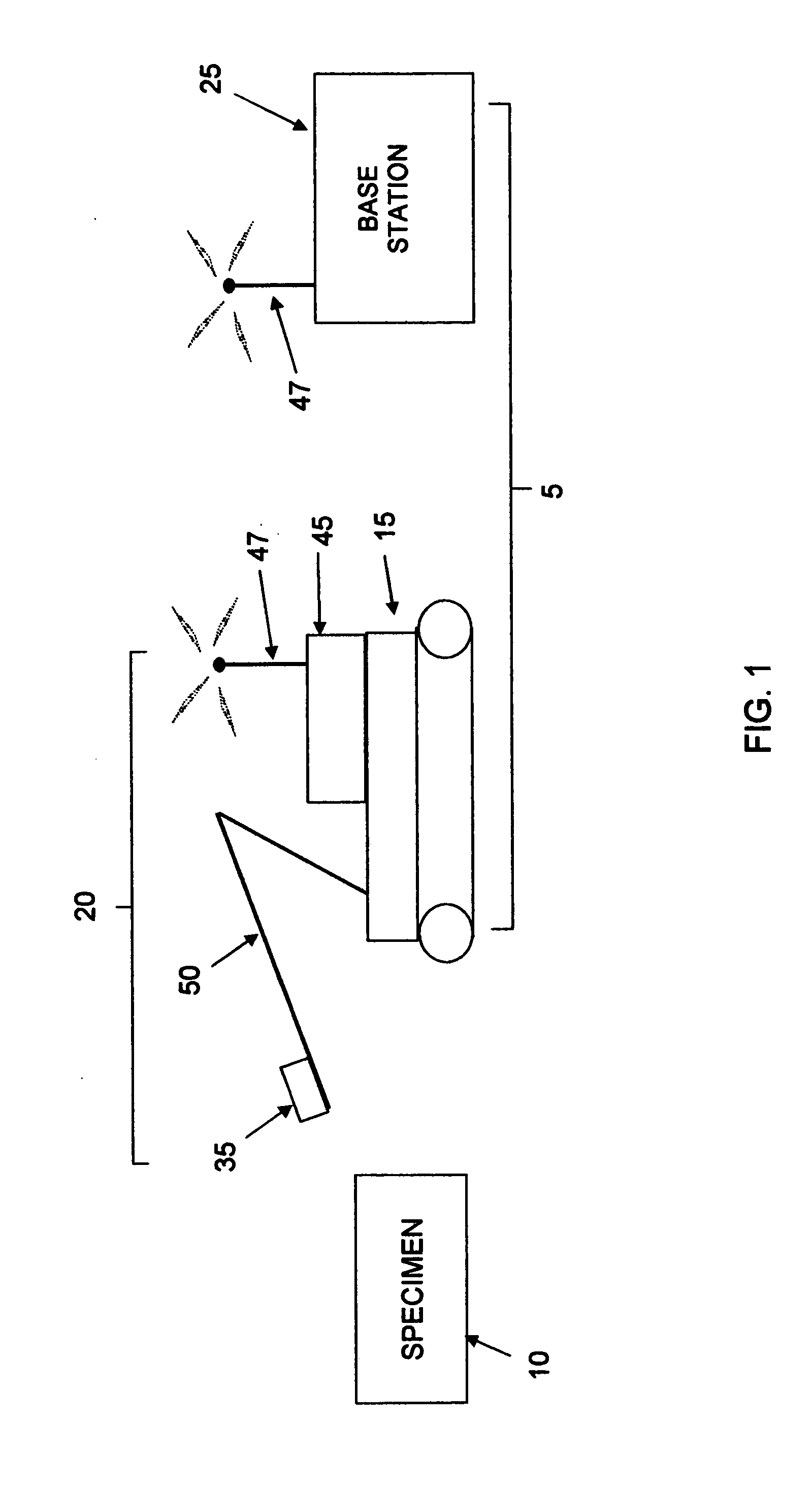
ActiveUS20070002319A1Simplify communication transmissionRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringRemote controlTeleoperated robot
A Raman probe assembly for analyzing a specimen, comprising: a light source for generating laser excitation light; a camera for capturing an image; a light analyzer for analyzing a Raman signature; and a light path for (i) delivering the laser excitation light from the light source to the specimen so as to produce the Raman signature for the specimen, (ii) capturing an image of the specimen and directing that image to the camera, and (iii) directing the Raman signature of the specimen to the light analyzer. A Raman probe assembly for analyzing a specimen, comprising: a light source for generating laser excitation light; a camera for capturing an image; a light analyzer for analyzing a Raman signature; a first light path for delivering the laser excitation light from the light source to the specimen so as to produce the Raman signature for the specimen; a second light path for capturing an image of the specimen and directing that image to the camera; a third light path for directing the Raman signature of the specimen to the light analyzer; wherein the a least a portion of the first light path, the second light path and the third light path are coaxial with one another. A Raman probe assembly for analyzing a specimen, comprising: a light source for generating laser excitation light; a light analyzer for analyzing a Raman signature; a light path for (i) delivering the laser excitation light from the light source to the specimen so as to produce the Raman signature for the specimen, and (ii) directing the Raman signature of the specimen to the light analyzer; wherein the assembly further comprises a probe body for housing the at least a portion of the light path, and a window, with the light path extending through the window; and further wherein the probe body further comprises a shutter / wiper disposed adjacent to the window. A Raman probe assembly for analyzing a specimen, comprising: a light source for generating laser excitation light; a light analyzer for analyzing a Raman signature; a light path for (i) delivering the laser excitation light from the light source to the specimen so as to produce the Raman signature for the specimen, and (ii) directing the Raman signature of the specimen to the light analyzer; and wherein the light analyzer comprises a transmitter for transmitting information using an Internet Web protocol. A method for identifying the nature of a specimen, the method comprising: providing a Raman probe assembly comprising: a light source for generating laser excitation light; a camera for capturing an image; a light analyzer for analyzing a Raman signature; a light path for (i) delivering the laser excitation light from the light source to the specimen so as to produce the Raman signature for the specimen, (ii) capturing an image of the specimen and directing that image to the camera, and (iii) directing the Raman signature of the specimen to the light analyzer wherein the assembly further comprises a probe body for housing the at least a portion of the light path, and a window, with the light path extending through the window; wherein the probe body further comprises a shutter / wiper disposed adjacent to the window; wherein the assembly is carried by a remote controlled robot; providing a base station for receiving the image, and for remotely controlling the robot, and for receiving information from the light analyzer; navigating the remote control robot from the base station to a position adjacent to the specimen; opening the shutter / wiper; using the camera to aim the probe body at the specimen; energizing the light source so that the laser excitation light is directed at the specimen; and analyzing the return light passed to the light analyzer so as to determine of the nature of the specimen.
Owner:AHURA CORP
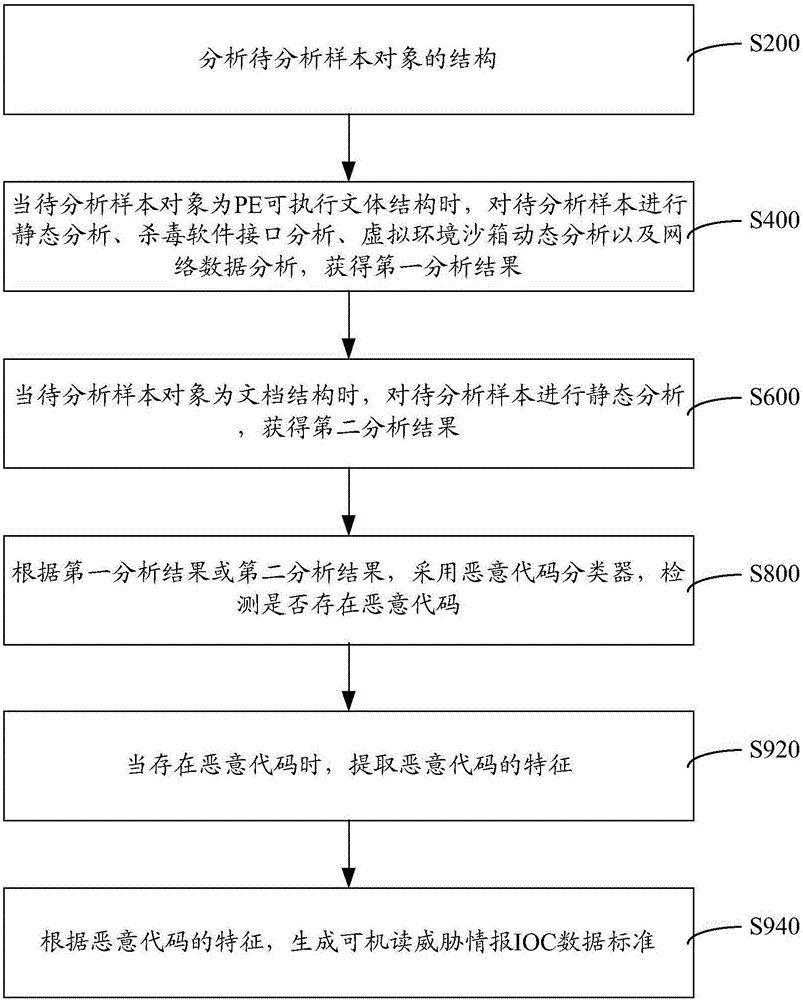
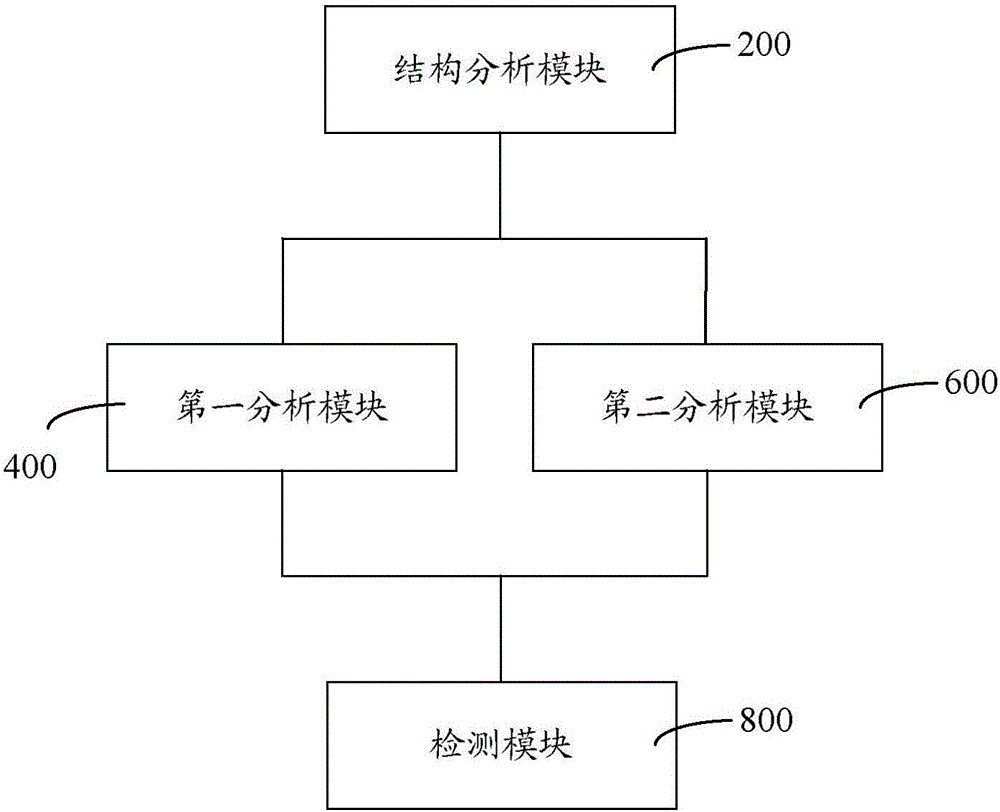
Malicious code detection method and system
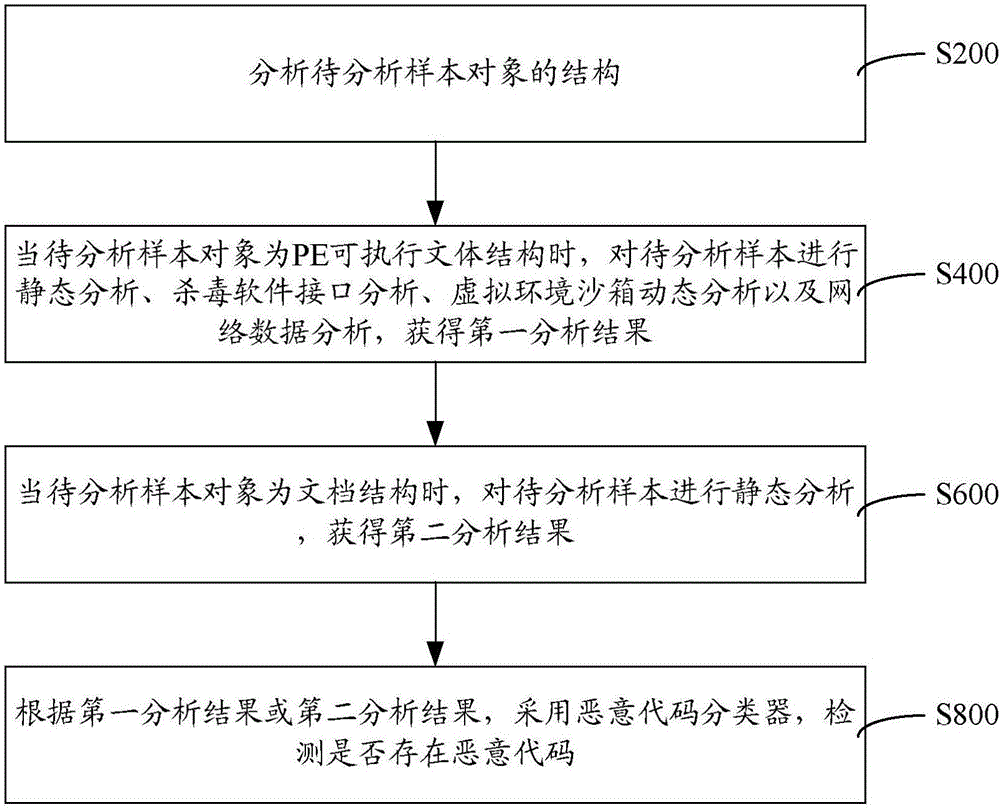
InactiveCN106778268AReliable analysis and identification abilityPlatform integrity maintainanceStatic timing analysisData profiling
The invention provides a malicious code detection method and system. The malicious code detection method comprises the following steps: analyzing a structure of a to-be-analyzed sample object; when the to-be-analyzed sample object is of a PE executable stylistic structure, performing static analysis, antivirus software interface analysis, dynamic virtual environment sandbox analysis and network data analysis on the to-be-analyzed sample object and obtaining a first analysis result; when the to-be-analyzed sample object is of a text structure, performing static analysis on the to-be-analyzed sample object and obtaining a second analysis result; detecting whether a malicious code exists or not by adopting a malicious code classifier according to the first analysis result or the second analysis result. In the whole process, data structures of different sample object types are analyzed; static analysis, antivirus software interface analysis, dynamic virtual environment sandbox analysis and network data analysis are adopted; the analysis and identification abilities are reliable, and a source of a network attack incident can be traced.
Owner:广东省信息安全测评中心 +1
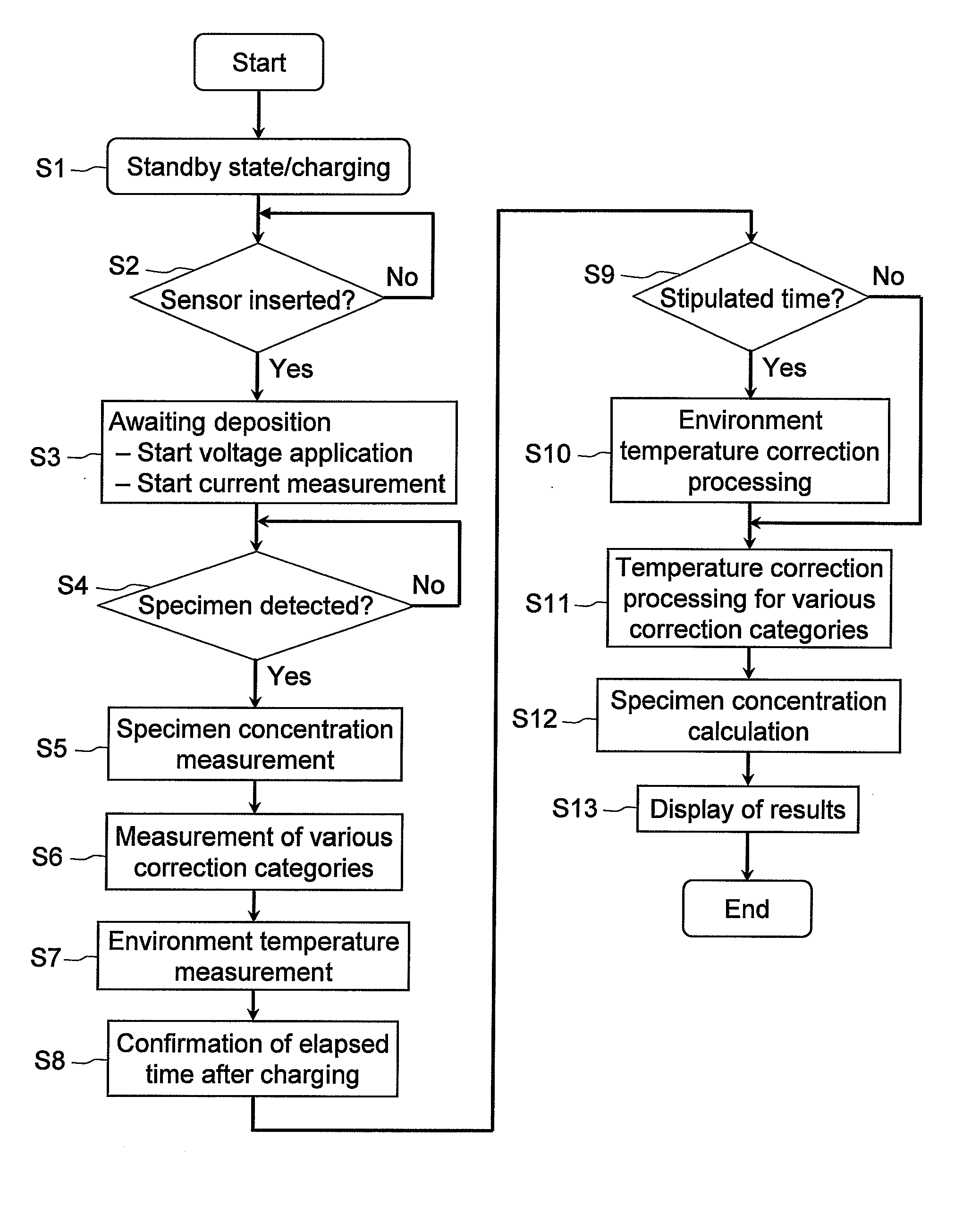
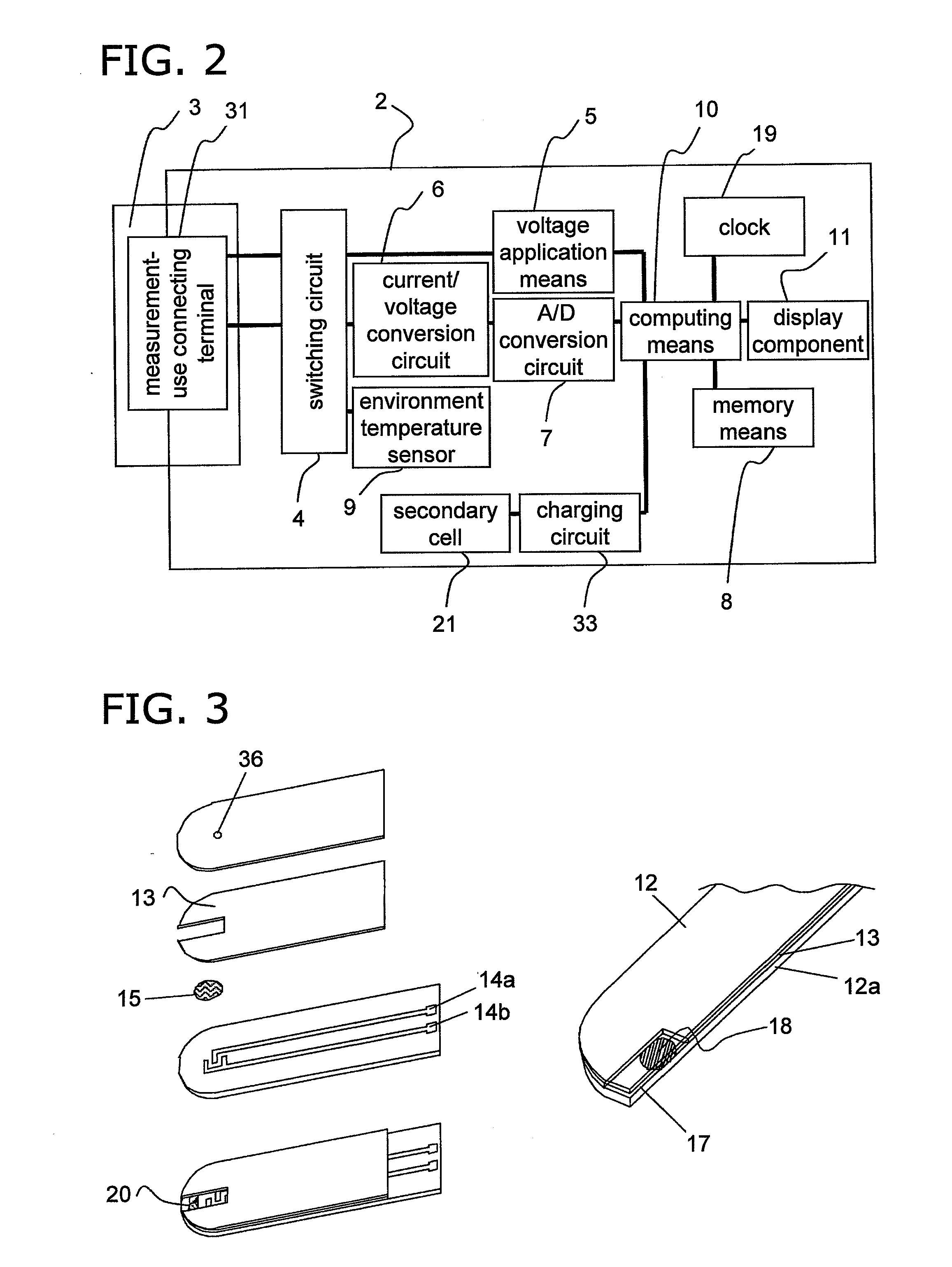
Environment temperature measuring method, liquid sample measuring method, and measuring device
InactiveUS20100268475A1Accurate temperatureAccurate correctionThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionMeasurement deviceAnalysis sample
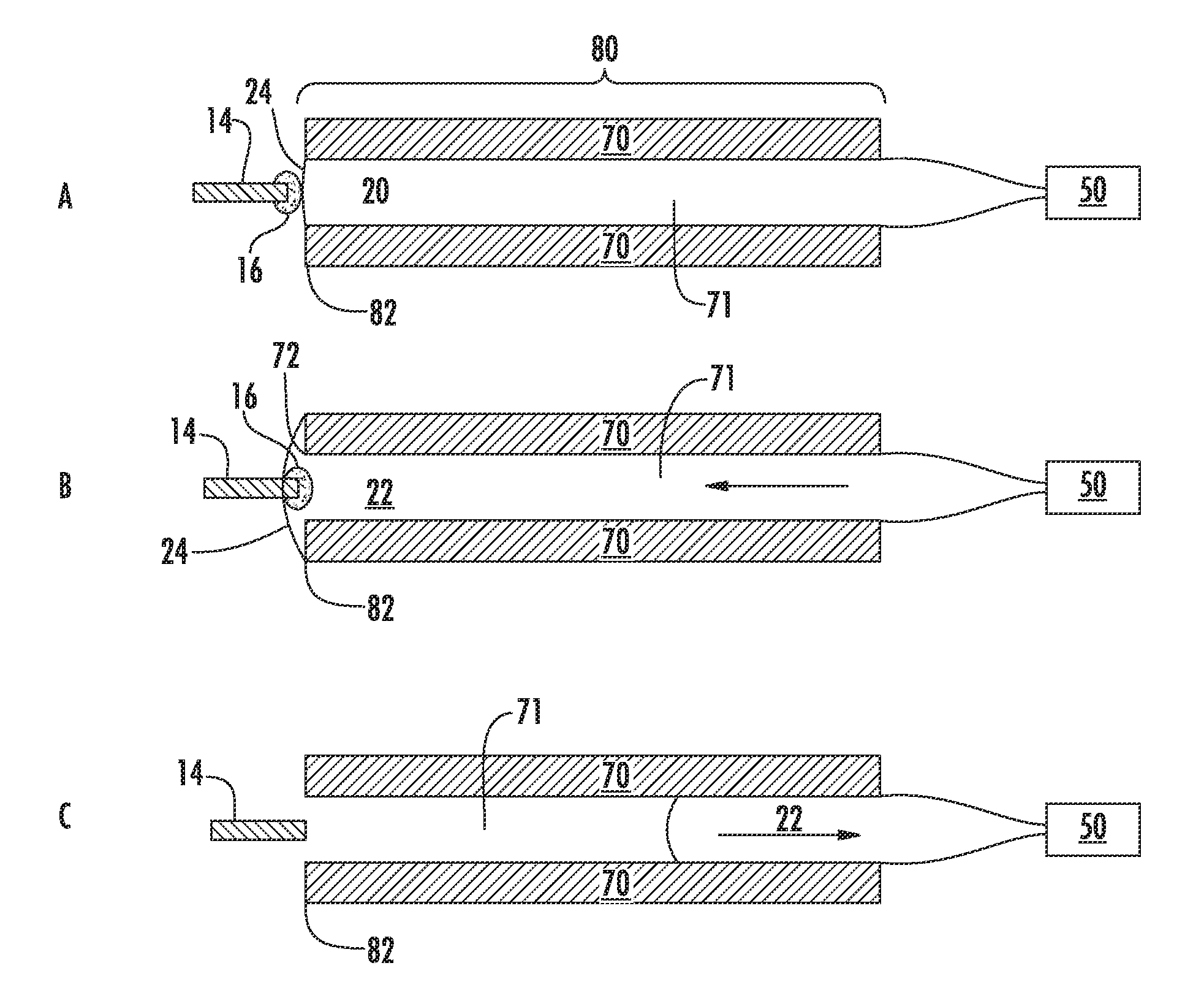
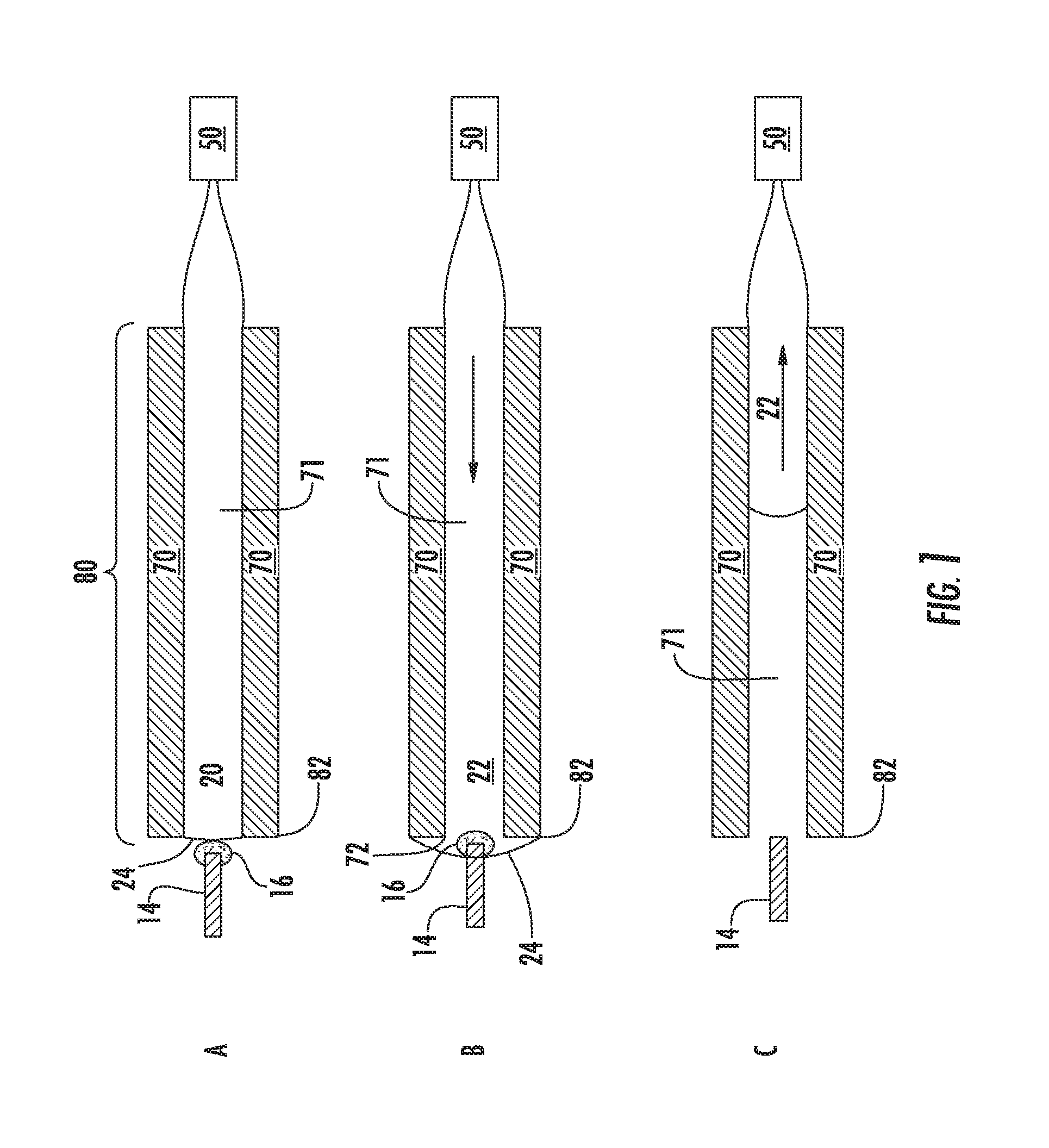
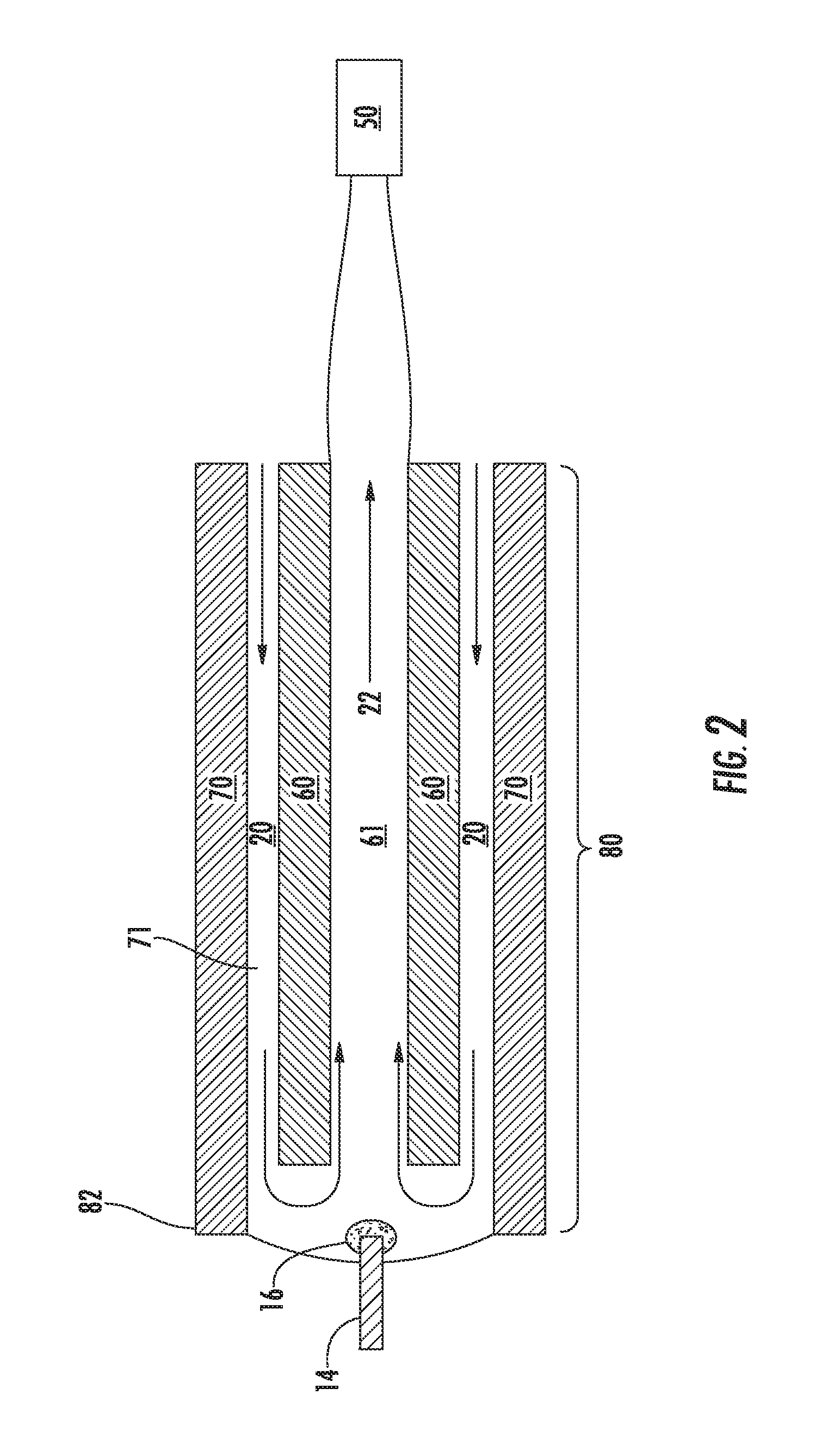
A cavity (17) in which an analysis sample is held and measurement is performed, and an electrode system (14) for measuring the concentration of the sample in the cavity (17) are provided on a biosensor (1). A secondary cell (21) and an environment temperature sensor (9) are provided inside the measuring device (2). The environment temperature during charging is measured in real time by specifying the environment temperature during charging from the time required to charge the secondary cell (21) and the environment temperature during charging. The measured analysis sample concentration is corrected for temperature with high accuracy from the environment temperature information obtained during charging, in a temperature correction step 09, and thus an analysis result with extremely high accuracy is obtained.
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
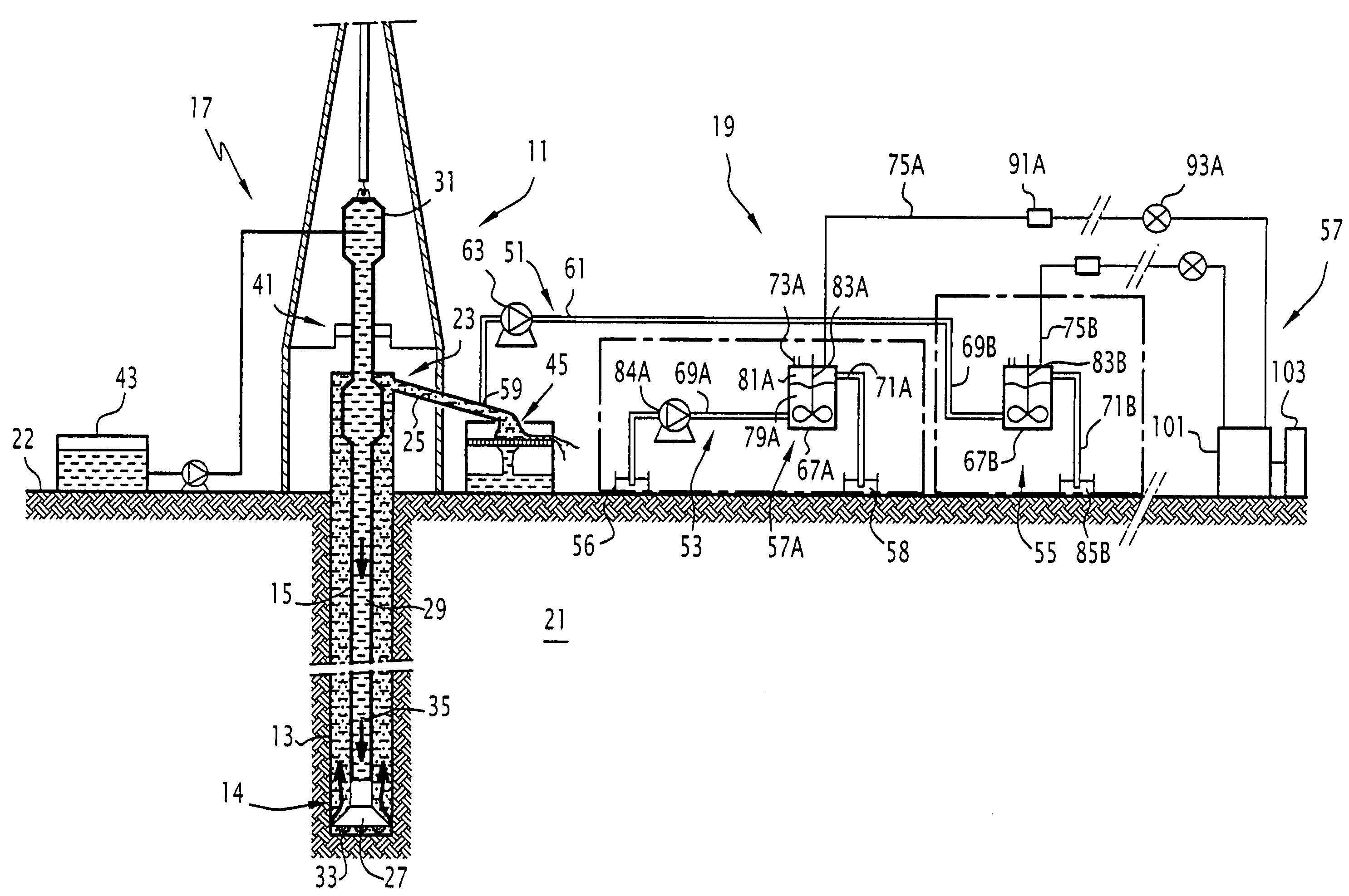
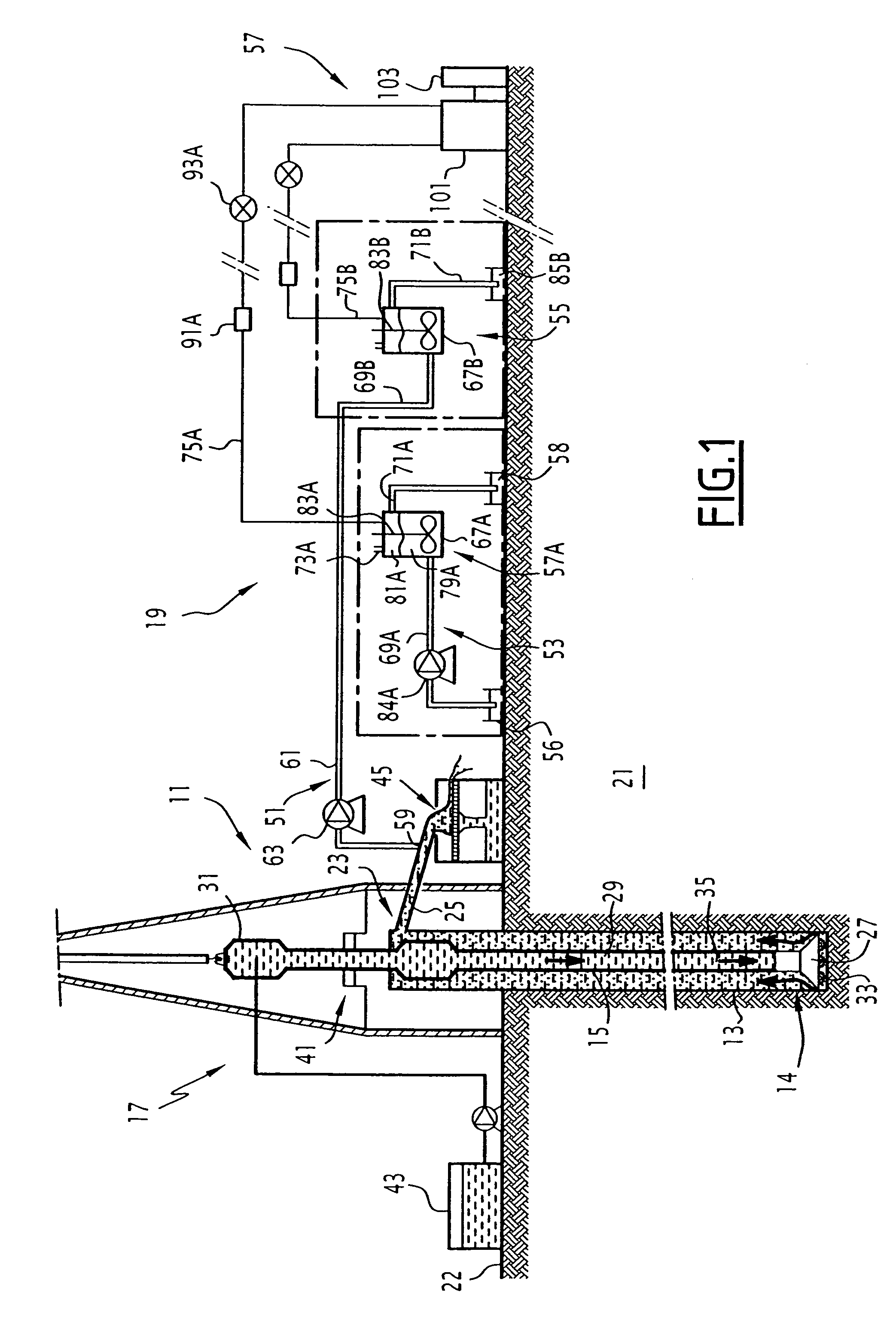
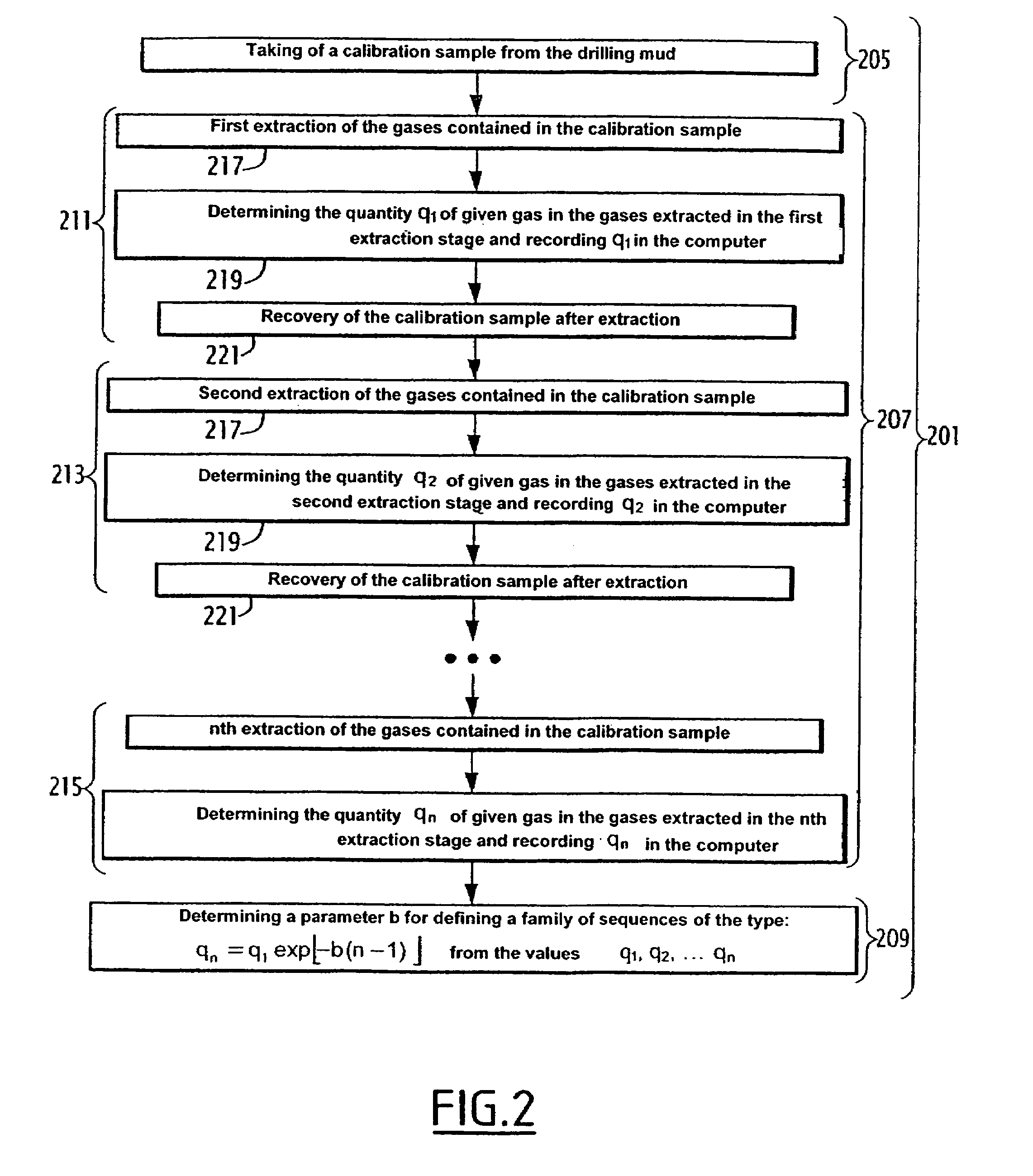
Method for determining the content of at least one given gas in a drilling mud, associated device and rig
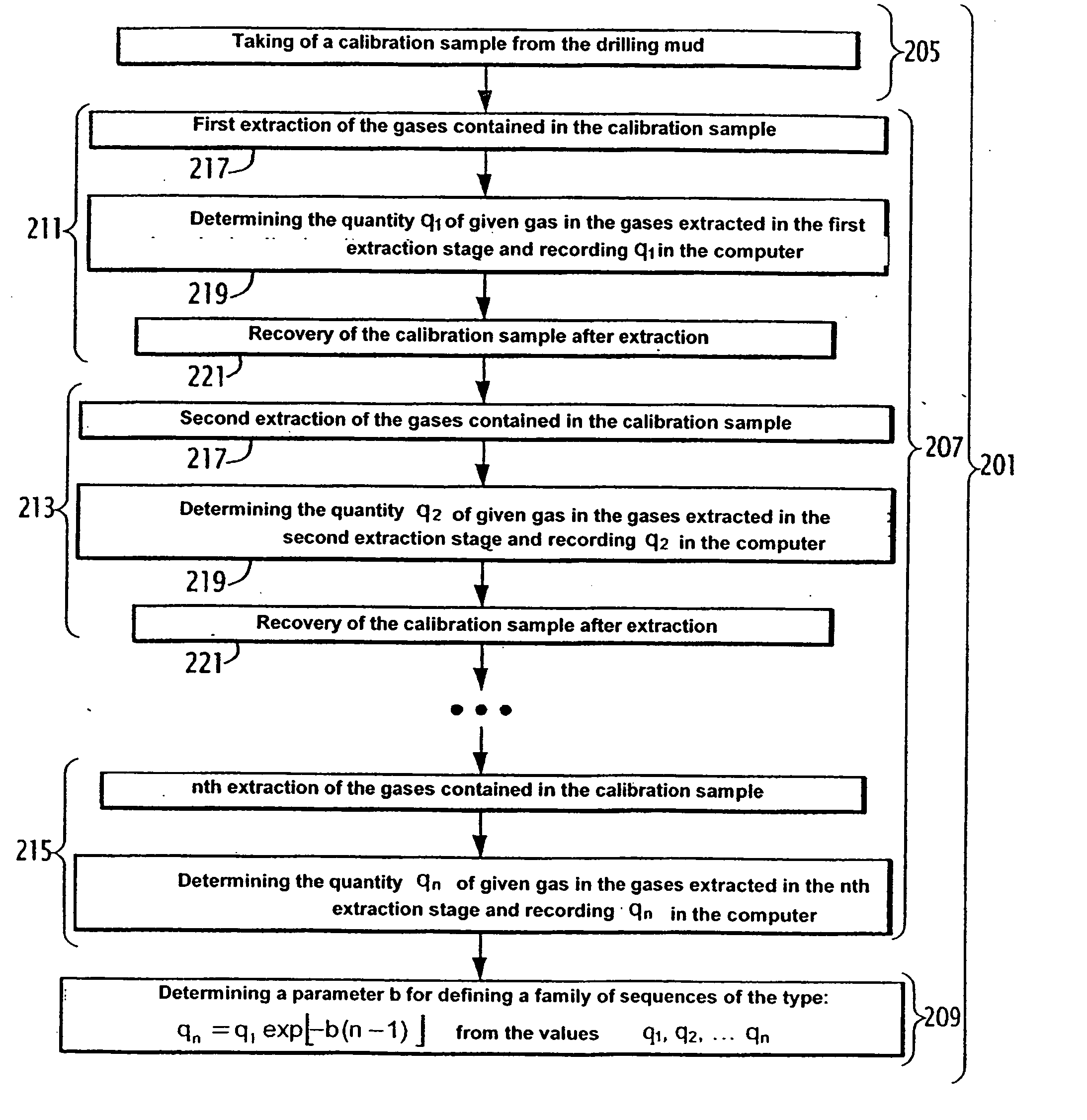
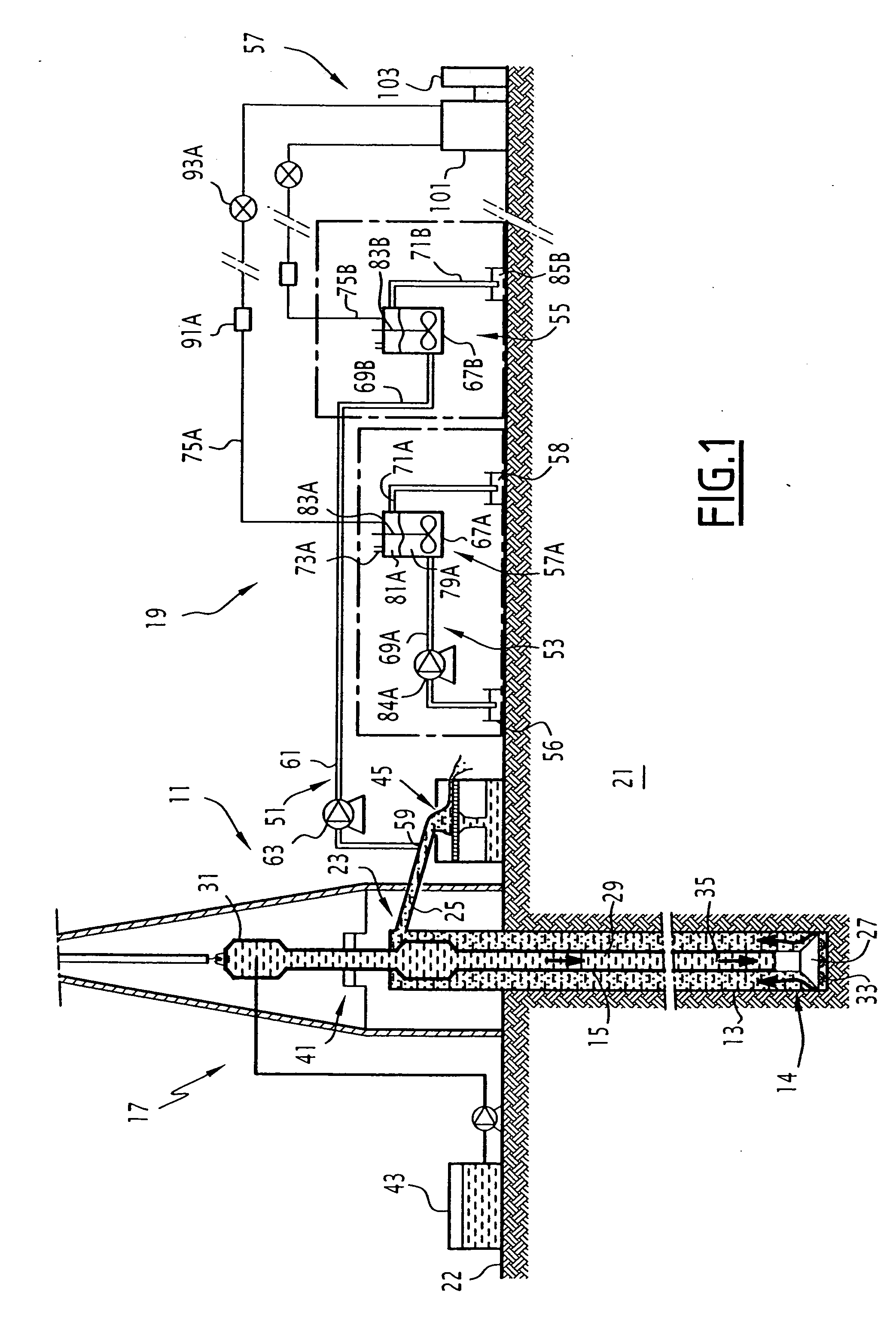
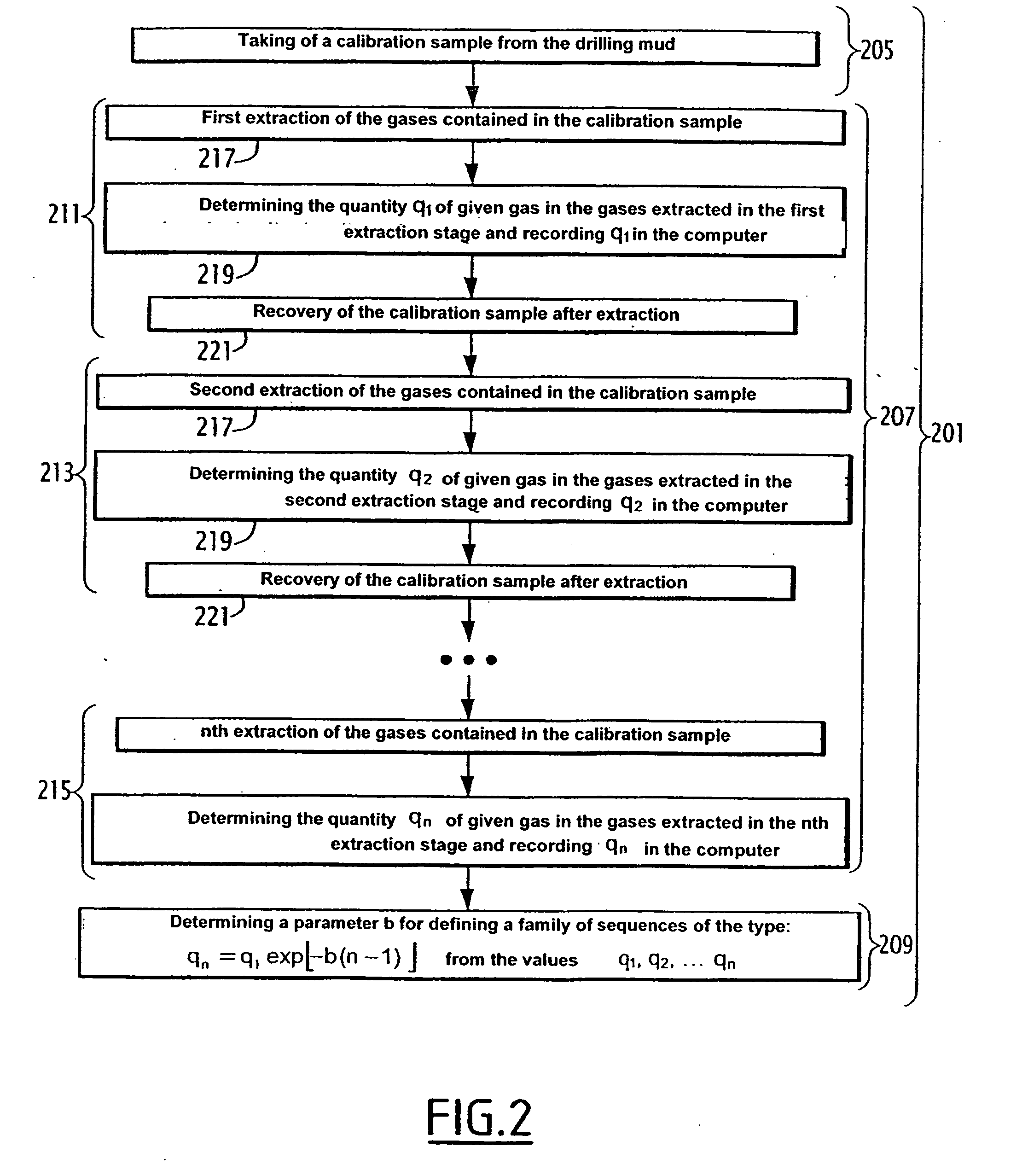
ActiveUS7392138B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWithdrawing sample devicesWell drillingProduct gas
A method includes the phases of measuring the quantity of a given gas in the gases extracted from a calibration sample of a calibration mud, in at least two stages for extraction under predetermined conditions. A family of curves representing the extraction, under the predetermined conditions, of the given gas from the drilling mud, is established on the basis of the measurements carried out. The method also includes the phases of measuring the quantity of given gas in the gases extracted from an analysis sample of the drilling mud in an extraction stage, under the predetermined conditions; and computing the given gas content of the drilling mud on the basis of the measured quantity of given gas and of a curve of the family.
Owner:GEOSERVICES EQUIP SAS
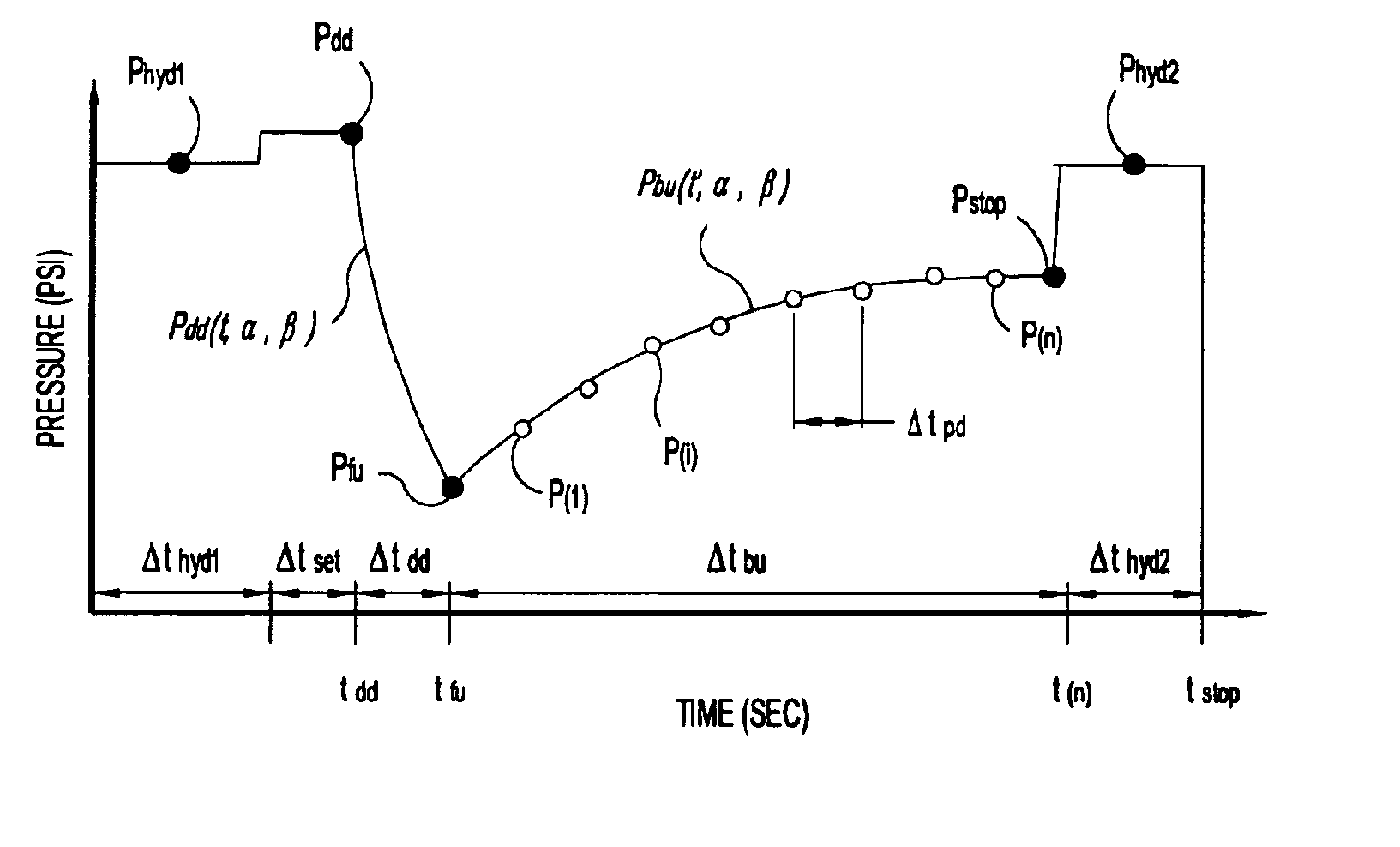
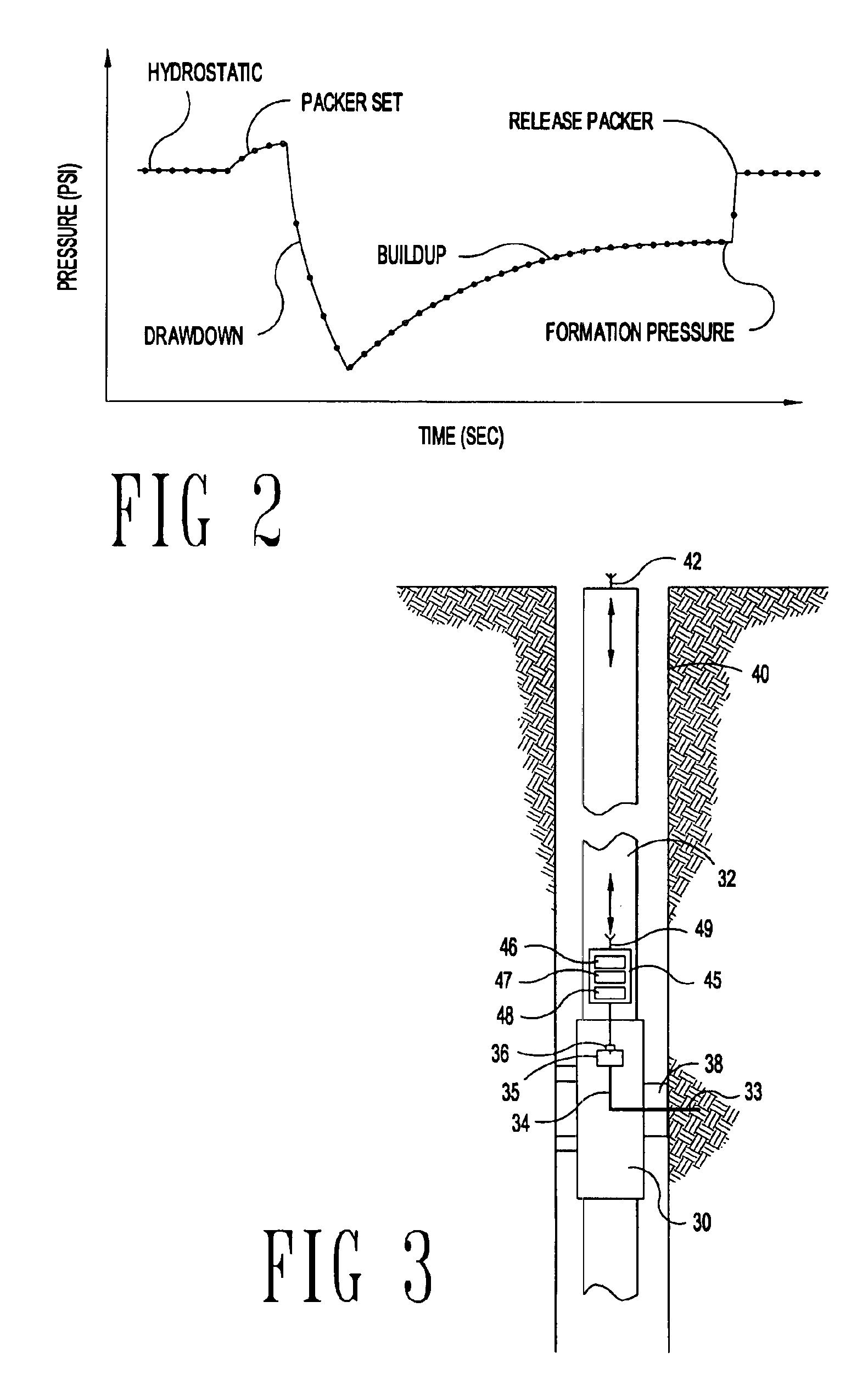
Formation testing while drilling data compression
A compression scheme for reducing the amount of data that must be transmitted uplink from a formation test while drilling apparatus. Periodic samples are taken within the formation test apparatus and prior to transmitting data uplink, the samples are analyzed to generate curve fit parameters that define a curve that most closely fits the sampled data. A minimal set a data points, time variables, and curve fit parameters are transmitted to the surface where the transmitted data is used to reconstruct the formation pressure test curve. A quality of fit value is also transmitted with the minimal data set as an indication of the quality of the fit between the reconstructed data and the actually sampled data points.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods for measurement or analysis of a nitrogen concentration of a specimen
ActiveUS7349079B2Improve accuracyPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsGate dielectricRefractive index
A method for measurement of a specimen is provided. The method includes measuring spectroscopic ellipsometric data of the specimen. The method also includes determining a nitrogen concentration of a nitrided oxide gate dielectric formed on the specimen from the spectroscopic ellipsometric data. A computer-implemented method for analysis of a specimen is also provided. This method includes determining a nitrogen concentration of a nitrided oxide gate dielectric formed on the specimen from spectroscopic ellipsometric data generated by measurement of the specimen. In some embodiments, the methods described above may include determining an index of refraction of the nitrided oxide gate dielectric from the spectroscopic ellipsometric data and determining the nitrogen concentration from the index of refraction. In another embodiment, the methods described above may include measuring reflectometric data of the specimen. The nitrogen concentration may be determined from the spectroscopic ellipsometric data in combination with the reflectometric data.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
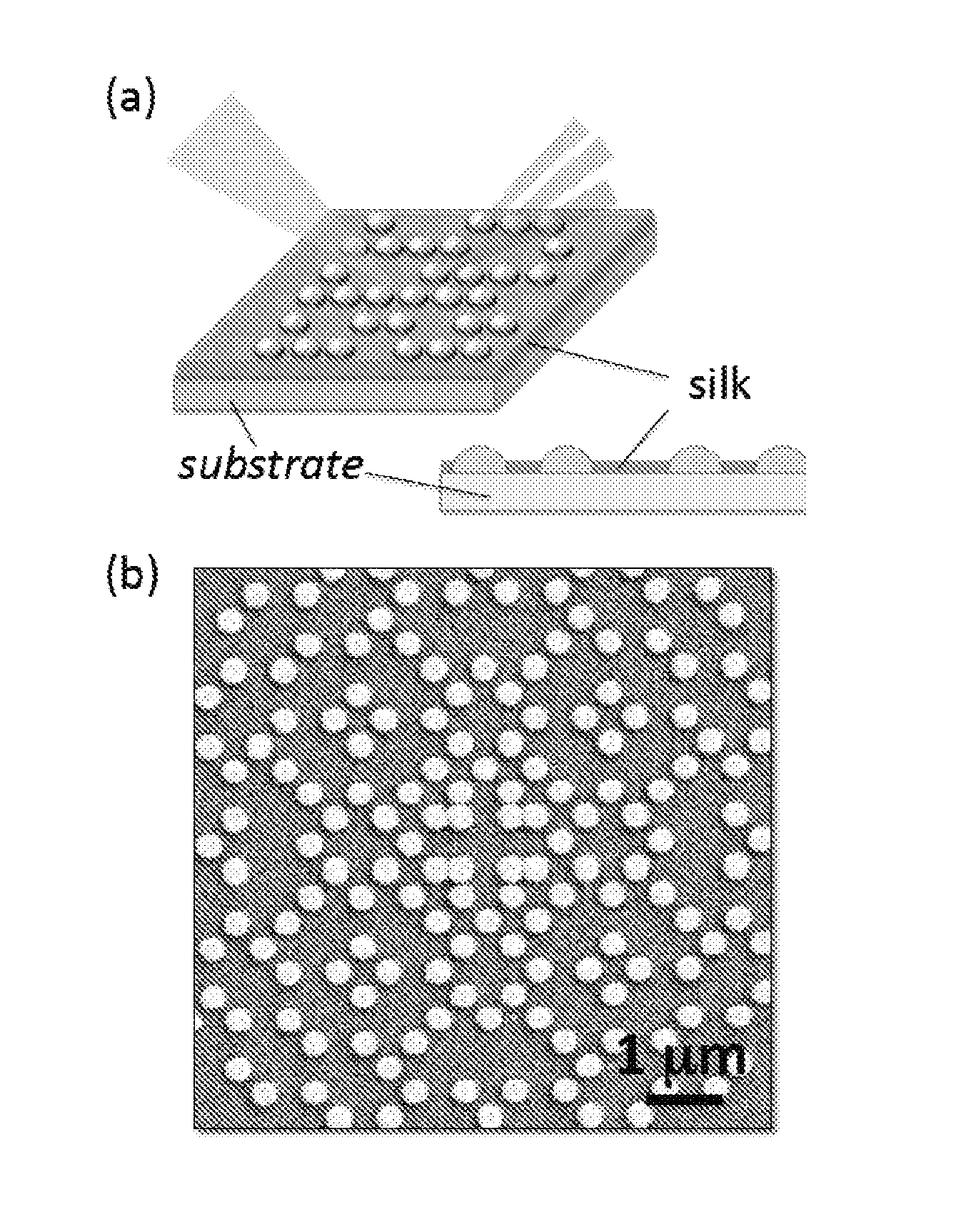
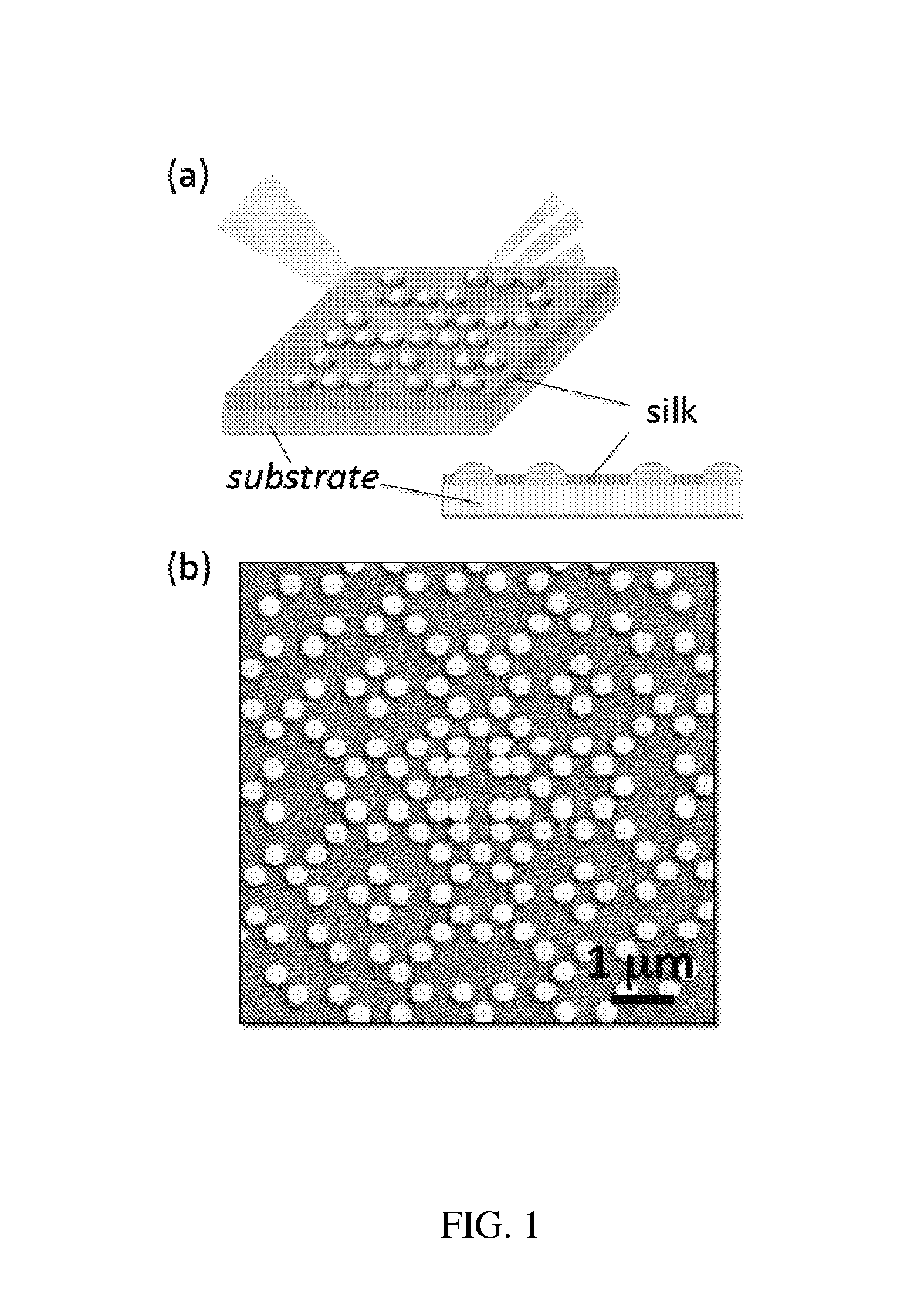
Silk based biophotonic sensors
InactiveUS20130330710A1High sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyPhotonic sensorPeriodic nanostructures
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV +1
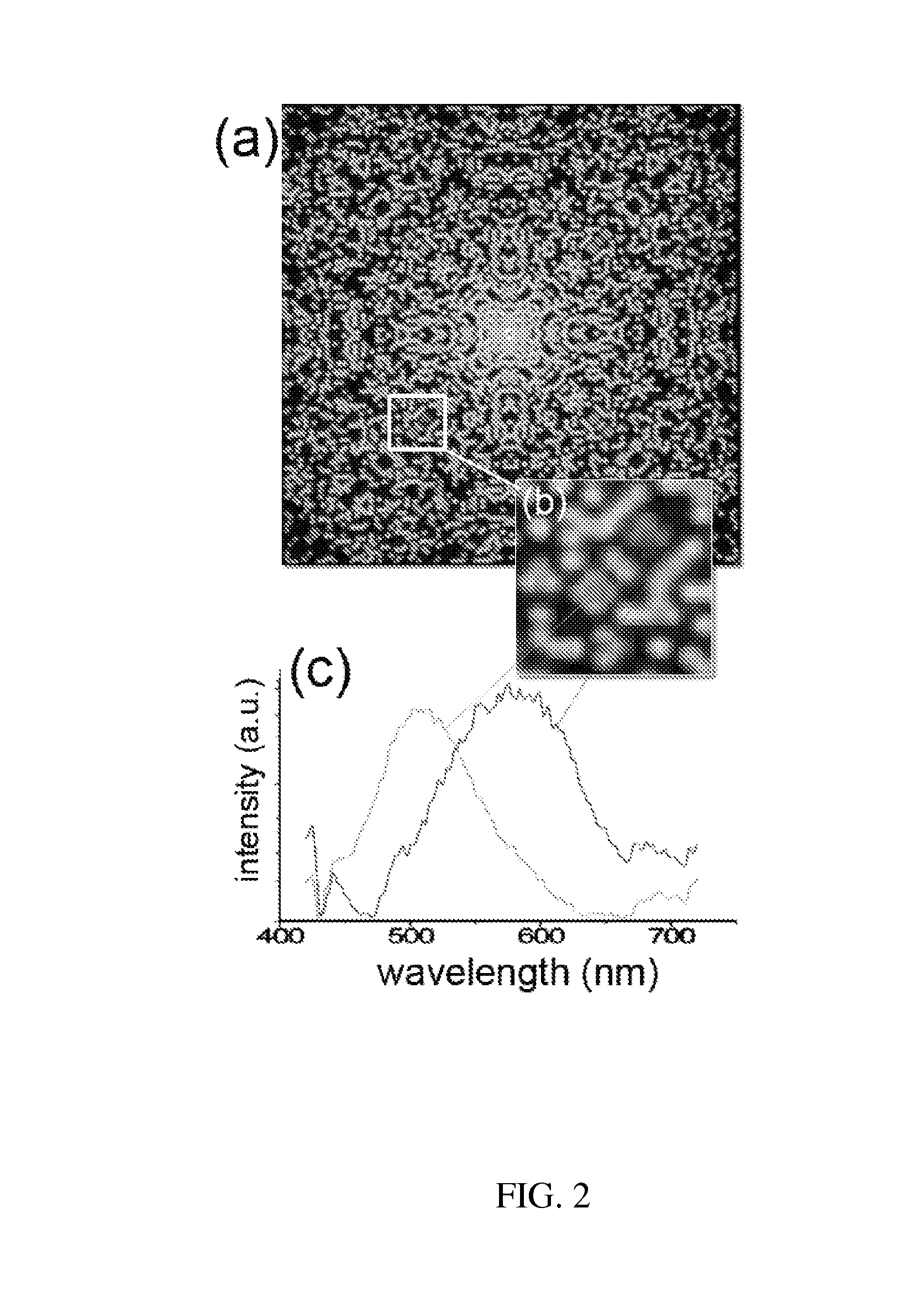
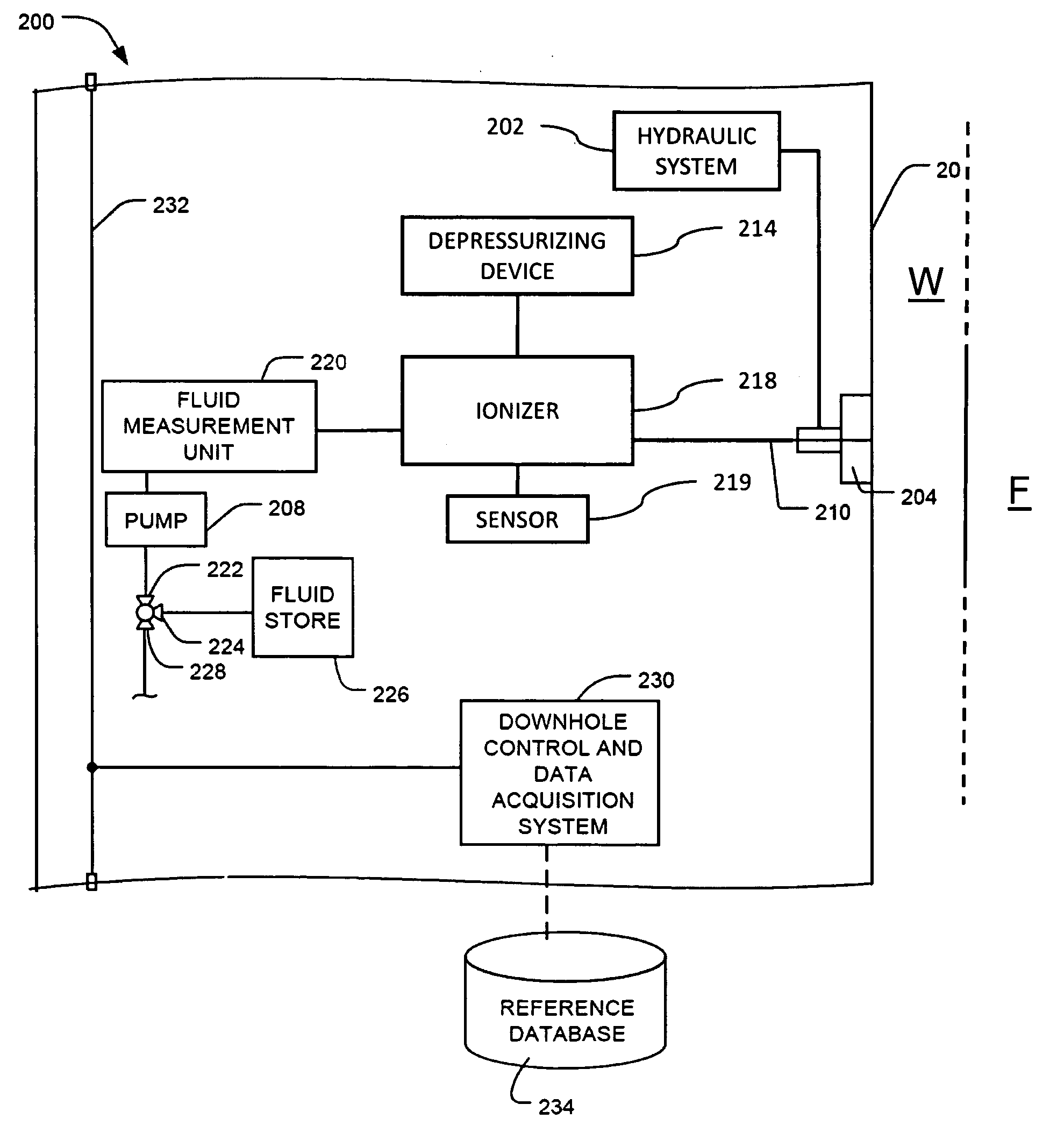
Apparatus and methods to analyze downhole fluids using ionized fluid samples
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
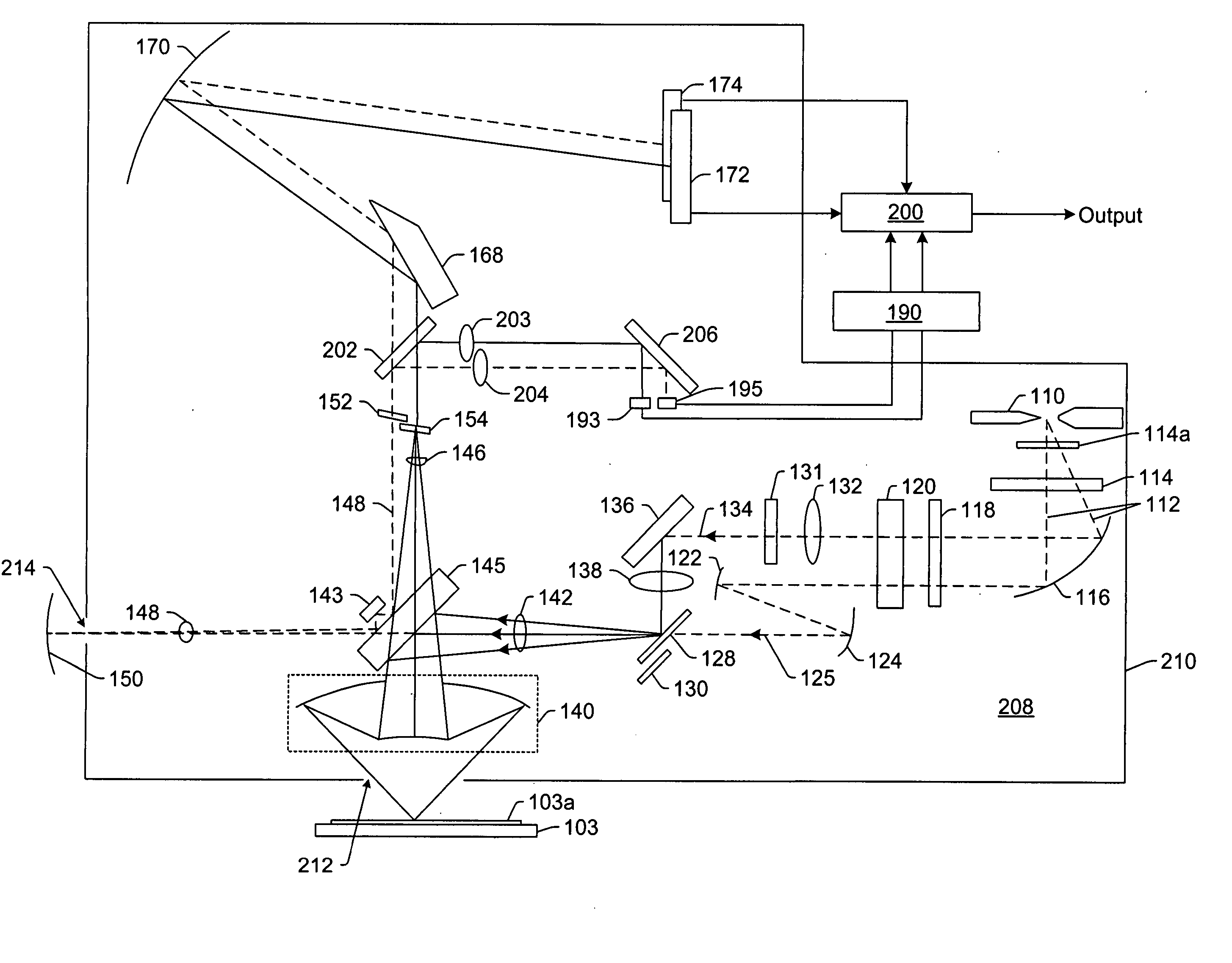
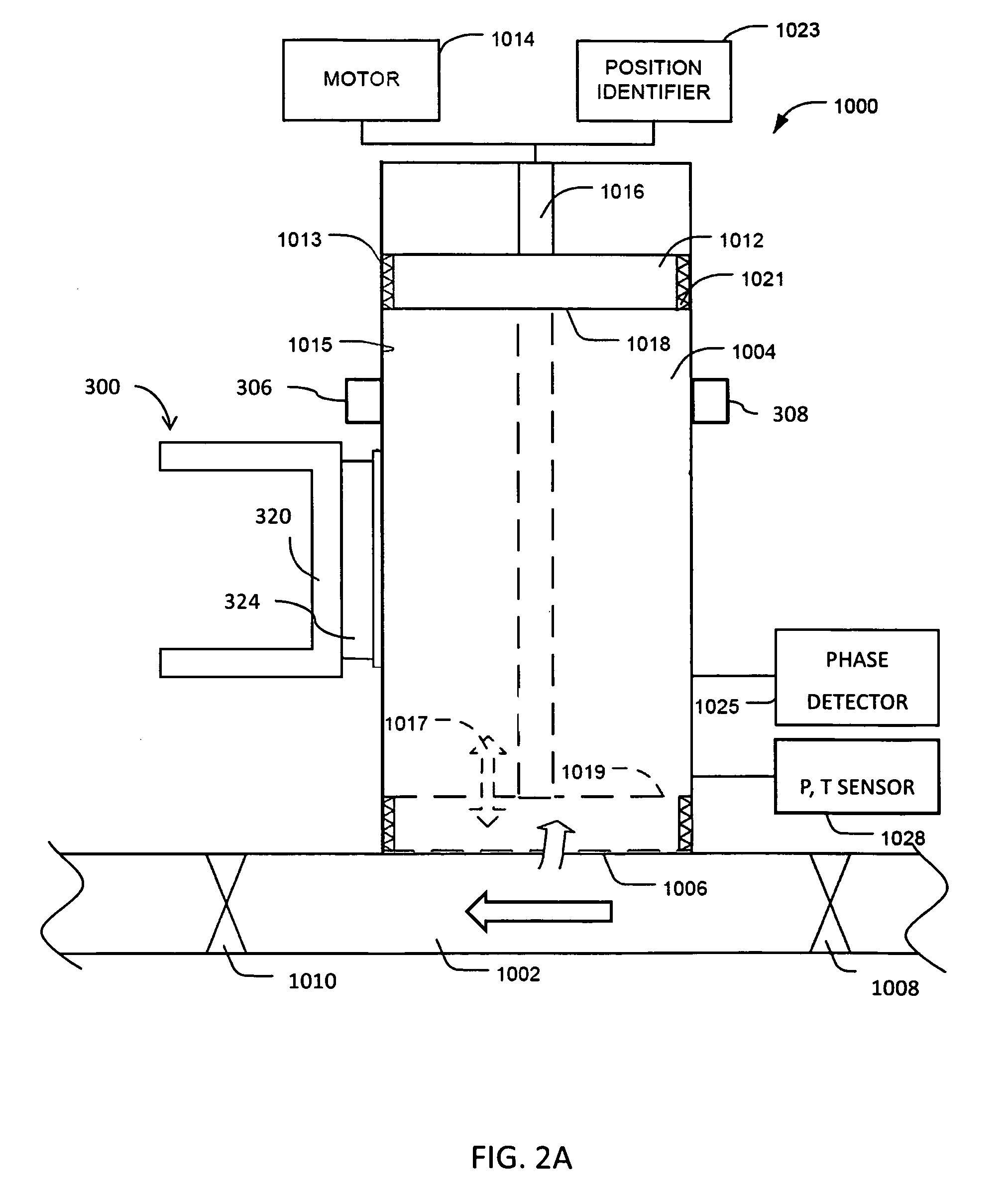
Device for high spatial resolution chemical analysis of a sample and method of high spatial resolution chemical analysis
ActiveUS20120053065A1Increase lateral distanceParticle separator tubesLibrary screeningChemical compositionImage resolution
A system and method for analyzing a chemical composition of a specimen are described. The system can include at least one pin; a sampling device configured to contact a liquid with a specimen on the at least one pin to form a testing solution; and a stepper mechanism configured to move the at least one pin and the sampling device relative to one another. The system can also include an analytical instrument for determining a chemical composition of the specimen from the testing solution. In particular, the systems and methods described herein enable chemical analysis of specimens, such as tissue, to be evaluated in a manner that the spatial-resolution is limited by the size of the pins used to obtain tissue samples, not the size of the sampling device used to solubilize the samples coupled to the pins.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Integrated tunable optical sensor (ITOS) system
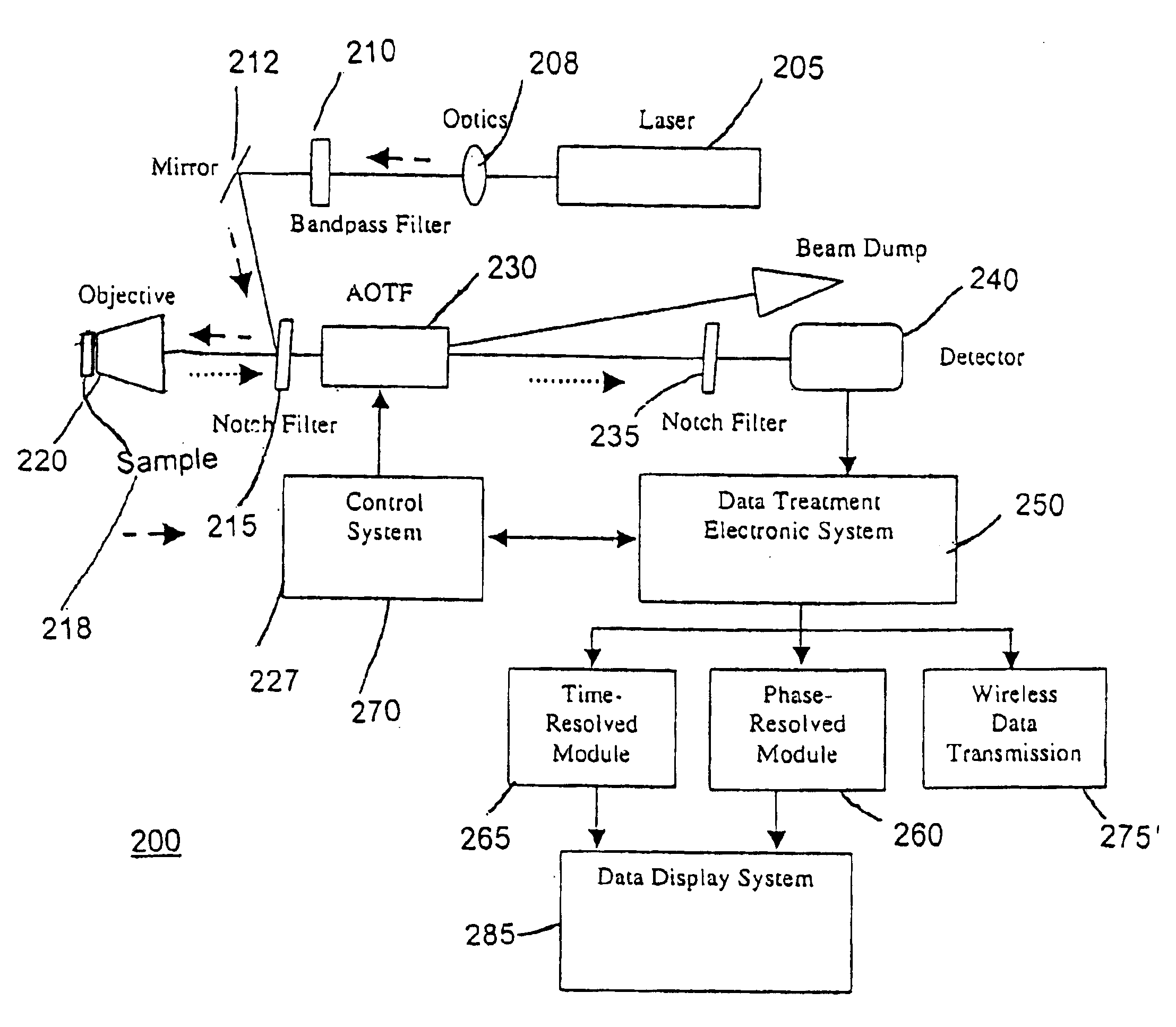
A scanning tunable detection system and related method for analyzing samples includes a source of time varying excitation signals and a tunable optical filter for selectively transmitting time-varying optical signals emanated from a sample following irradiation with the time varying excitation signals. A detector is provided for converting the time-varying optical signals to electrical detection signals. The system can identify components in a sample using phase sensitive or time sensitive detection. A slew scan mode can be used to permit slow scanning through spectral regions rich in information but quickly in regions without such information.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
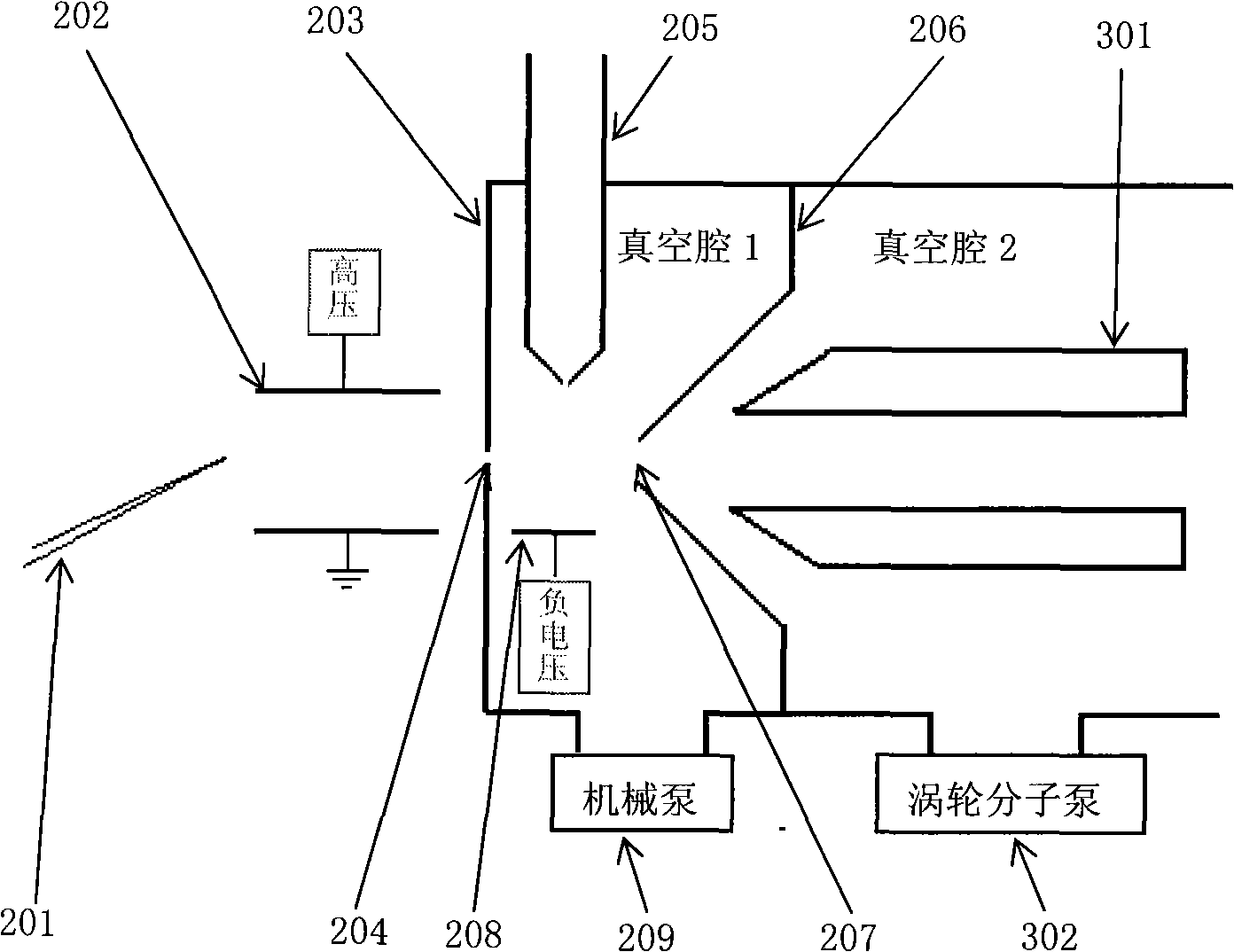
Method and apparatus for ionizing mass spectrographic analysis sample
InactiveCN101281165ASimple structureEasy to operateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometersESI mass spectrometryElectricity
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
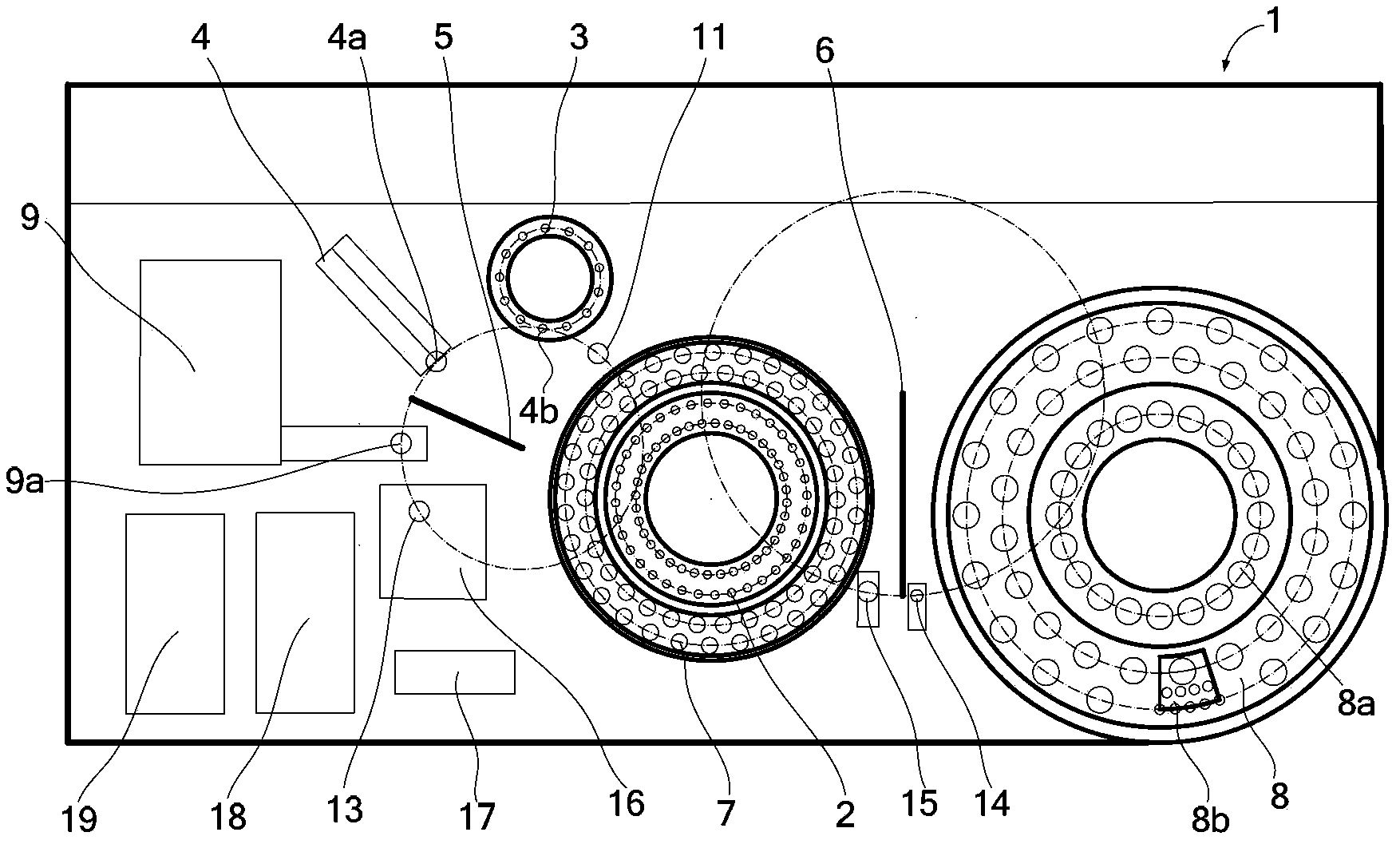
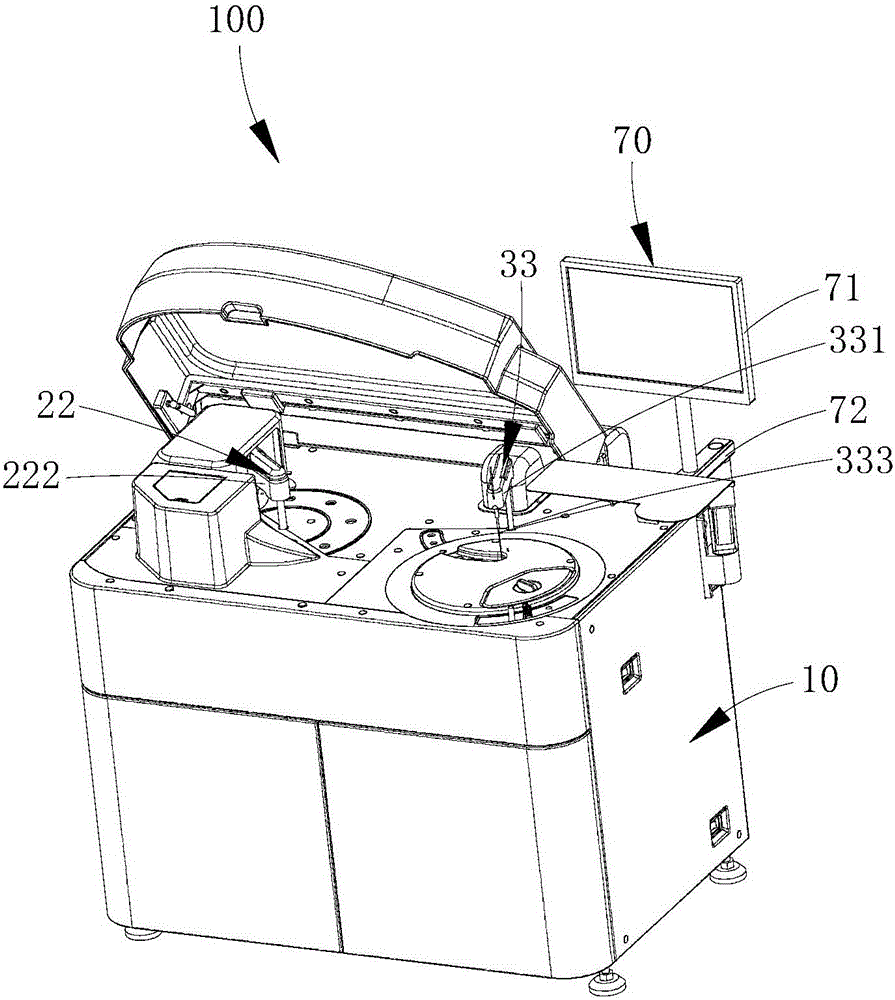
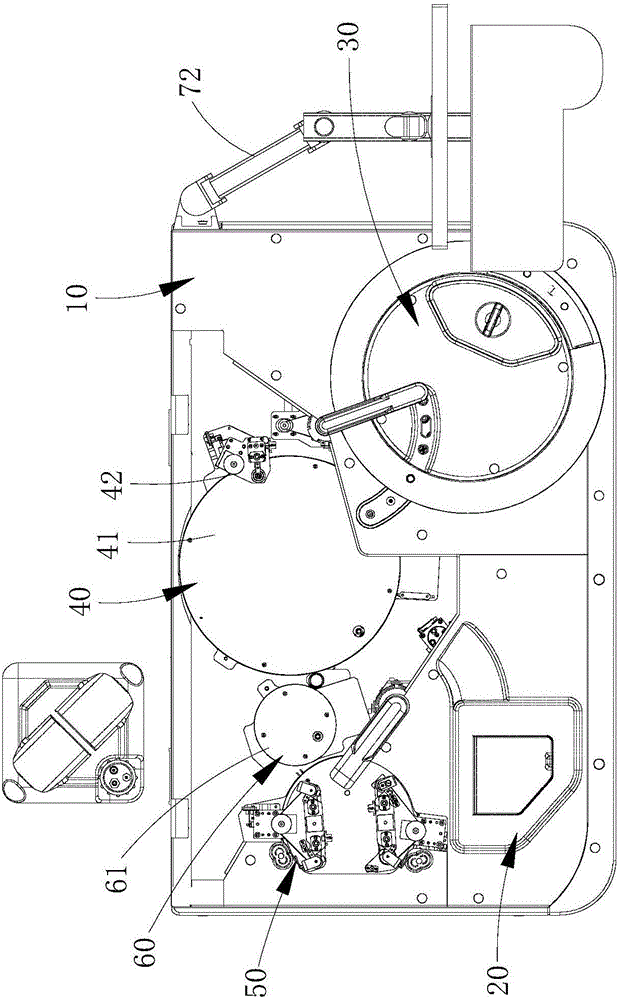
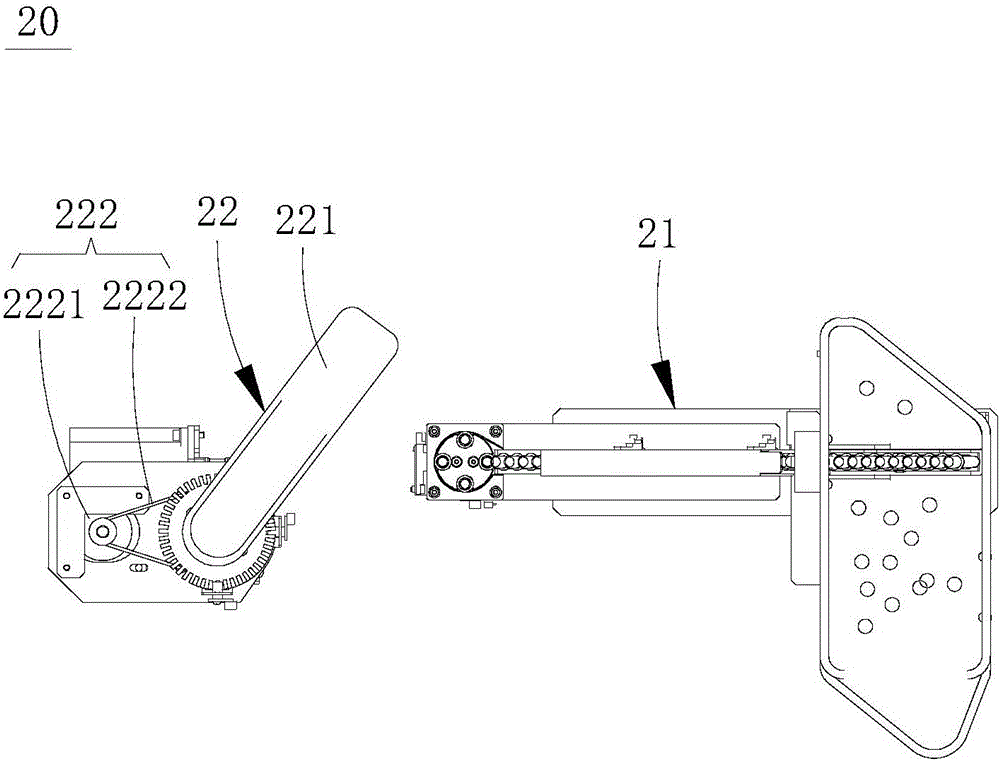
Full-automatic chemiluminescence immunity analyzer
ActiveCN106199025AAvoid individual differencesAvoid manual errorMaterial analysisControl systemTransfer system
A full-automatic chemiluminescence immunity analyzer comprises a frame, a transferring system, a sampling system, an incubation system, a cleaning system, an optical detection system and a control system. The transferring system comprises a cup feeding mechanism, a cup inlet and a grasping mechanism; the sampling system comprises a sample tray, a reagent tray, a sample adding mechanism and two first driving sources; the incubation system comprises an incubation tray, a second driving source and a mixing mechanism; the cleaning system comprises a cleaning plate and a third driving source; the optical detection system comprises photometric plate and an optical collection mechanism. When sample analysis is required, the full-automatic chemiluminescence immunity analyzer is started and controlled to operate by the control system, and then the transferring system, the sampling system, the incubation system, the cleaning system and the optical detection system operate correspondingly, so that all operations are automatic operations. The full-automatic chemiluminescence immunity analyzer has advantages that probabilistic problems including individual differences, manual errors, operational nonuniformity and the like of manual operations are avoided effectively, and accuracy in chemiluminescence immunity analysis is improved.
Owner:深圳雷杜生命科学股份有限公司
Method for determining the content of at least one given gas in a drilling mud, associated device and rig
ActiveUS20060224333A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWithdrawing sample devicesWell drillingAnalysis sample
The method includes the phases of measuring the quantity (q1, q2) of given gas in the gases extracted from a calibration sample of a calibration mud, in at least two stages for extraction under predetermined conditions; and establishing a family (310) of curves (303, 305, 309) representing the extraction, under the predetermined conditions, of the given gas from the drilling mud, on the basis of the measurements carried out. It also includes the phases of measuring the quantity (qd1) of given gas in the gases extracted from an analysis sample of the drilling mud in an extraction stage, under the predetermined conditions; and computing the given gas content of the drilling mud on the basis of the measured quantity (qd1) of given gas and of a curve (309) of said family (310).
Owner:GEOSERVICES EQUIP SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com