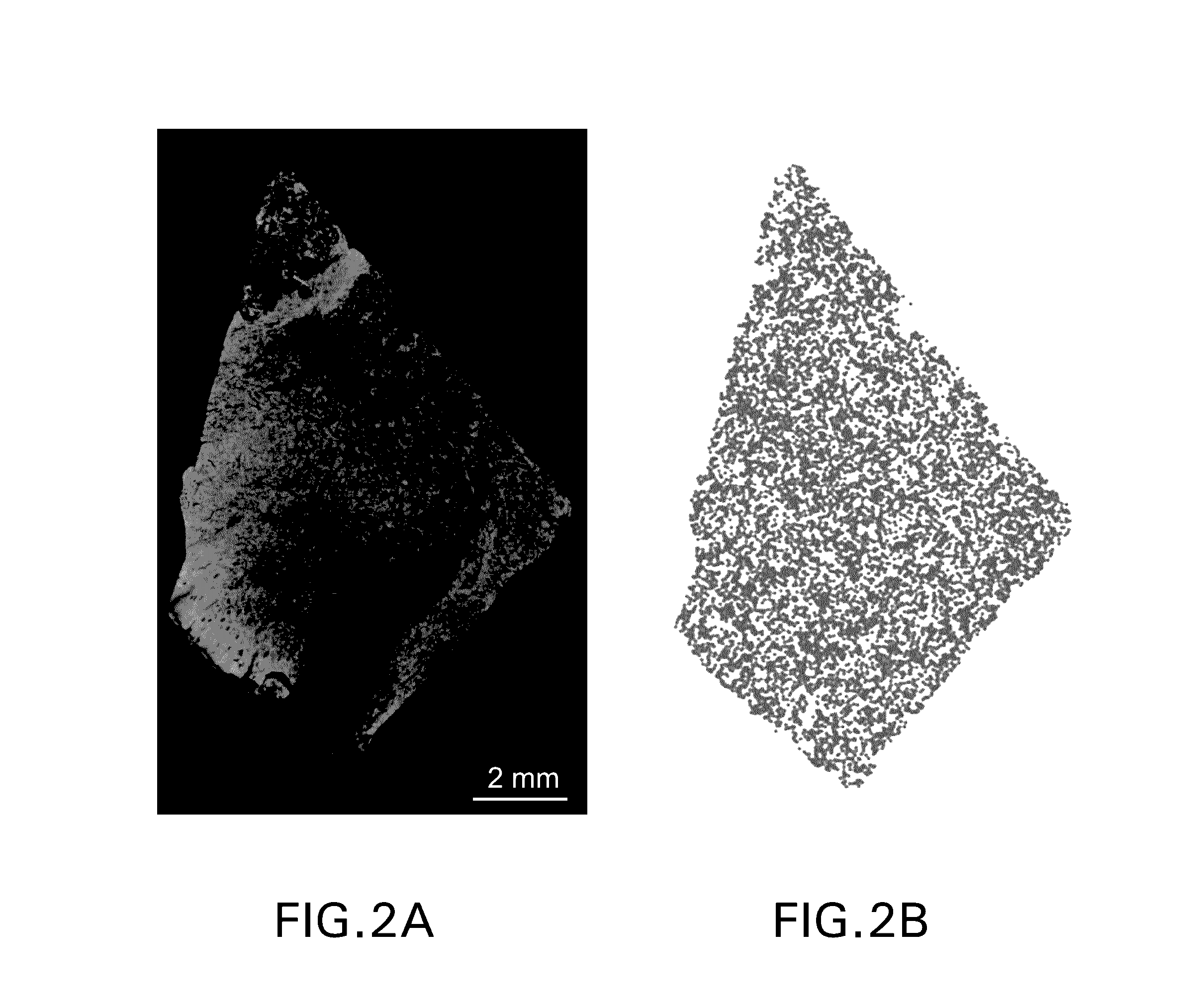
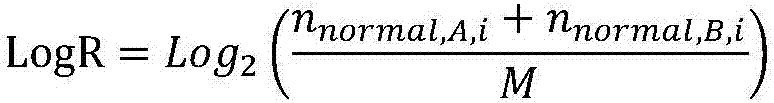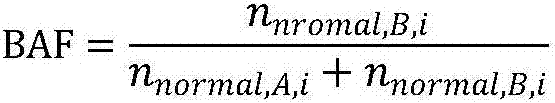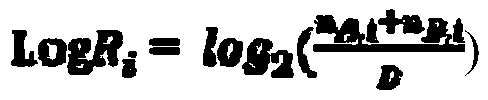Patents
Literature
408 results about "Tumor Sample" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
EGFR mutations
The present invention relates to mutations in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and methods of detecting such mutations as well as prognostic methods method for identifying a tumors that are susceptible to anticancer therapy such as chemotherapy and / or kinase inhibitor treatment. The methods involve determining the presence of a mutated EGFR gene or mutated EGFR protein in a tumor sample whereby the presence of a mutated EGFR gene or protein indicates the tumor is susceptible to treatment.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Methods of producing enriched populations of tumor-reactive t cells from tumor
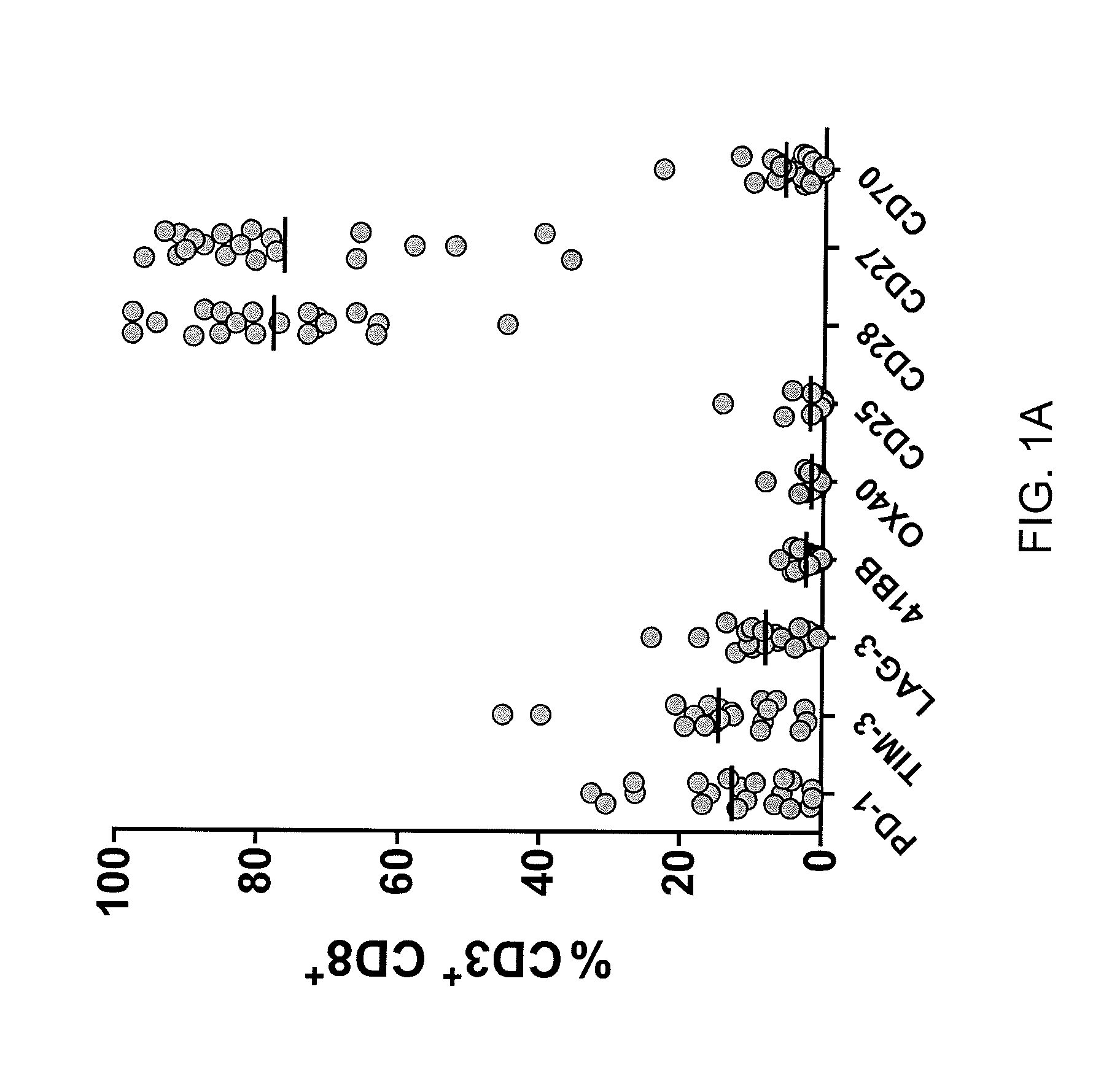
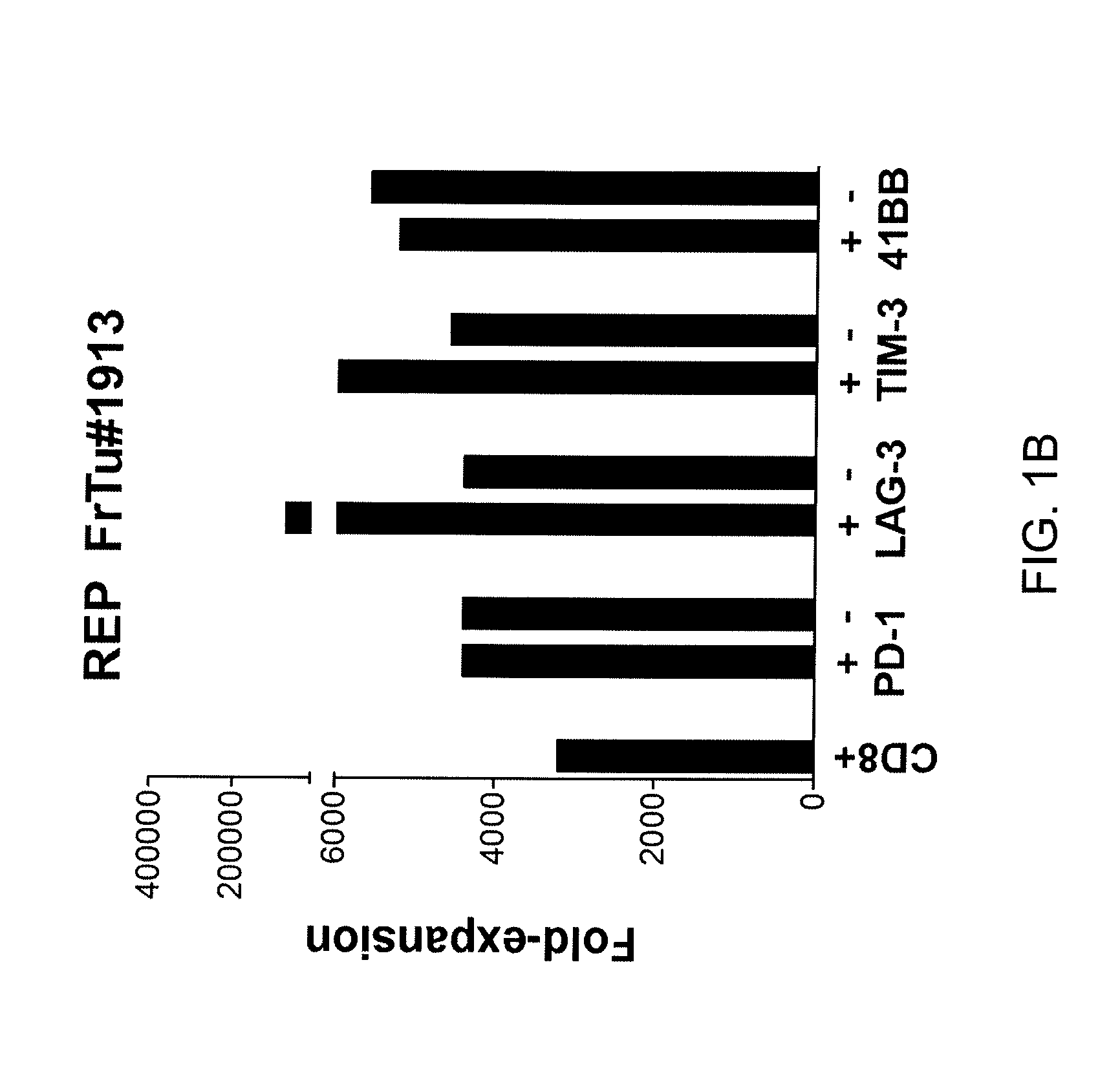
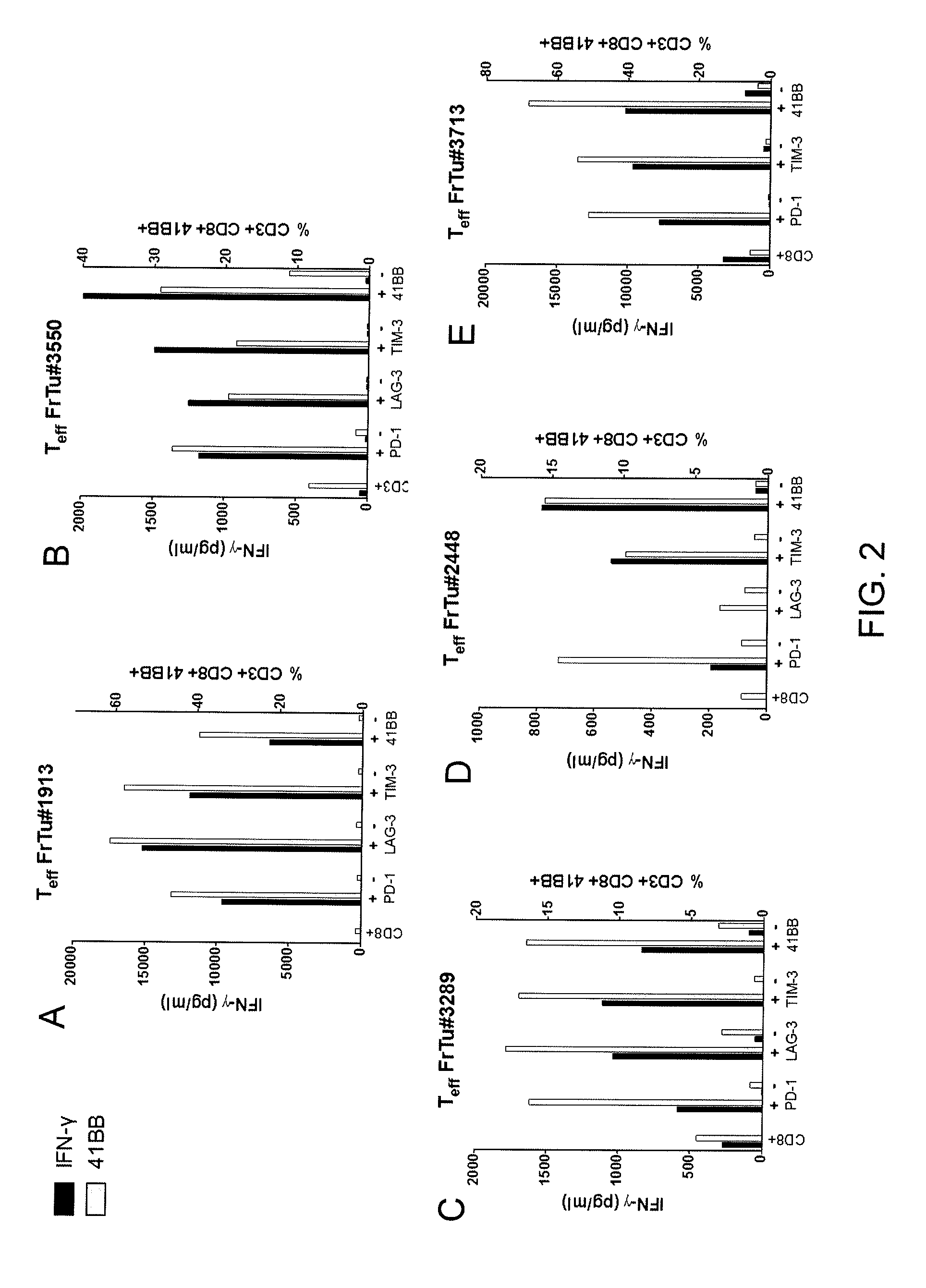
Methods of obtaining a cell population enriched for tumor-reactive T cells, the method comprising: (a) obtaining a bulk population of T cells from a tumor sample; (b) specifically selecting CD8+ T cells that express any one or more of TIM-3, LAG-3, 4-1BB, and PD-1 from the bulk population; and (c) separating the cells selected in (b) from unselected cells to obtain a cell population enriched for tumor-reactive T cells are disclosed. Related methods of administering a cell population enriched for tumor-reactive T cells to a mammal, methods of obtaining a pharmaceutical composition comprising a cell population enriched for tumor-reactive T cells, and isolated or purified cell populations are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
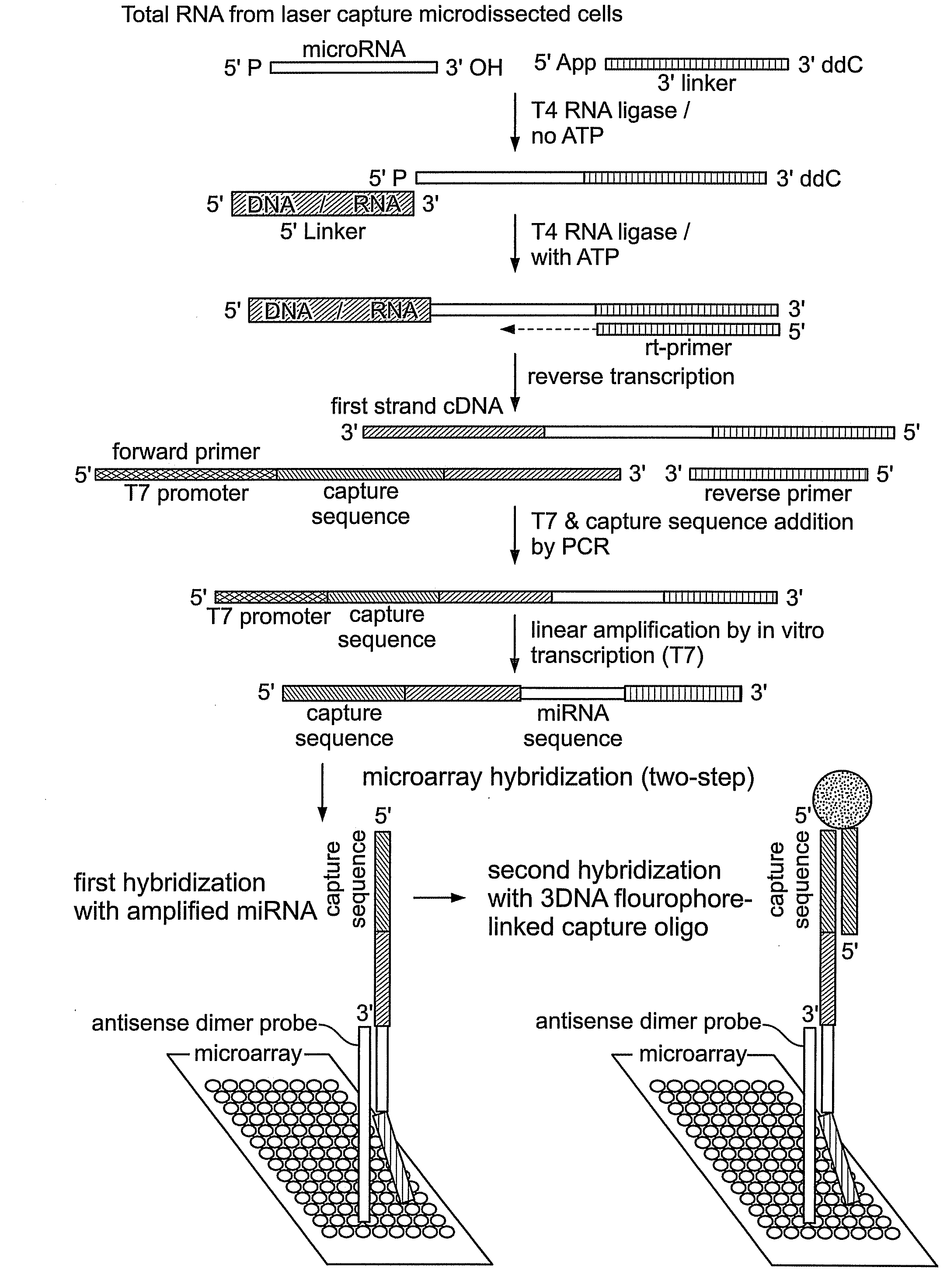
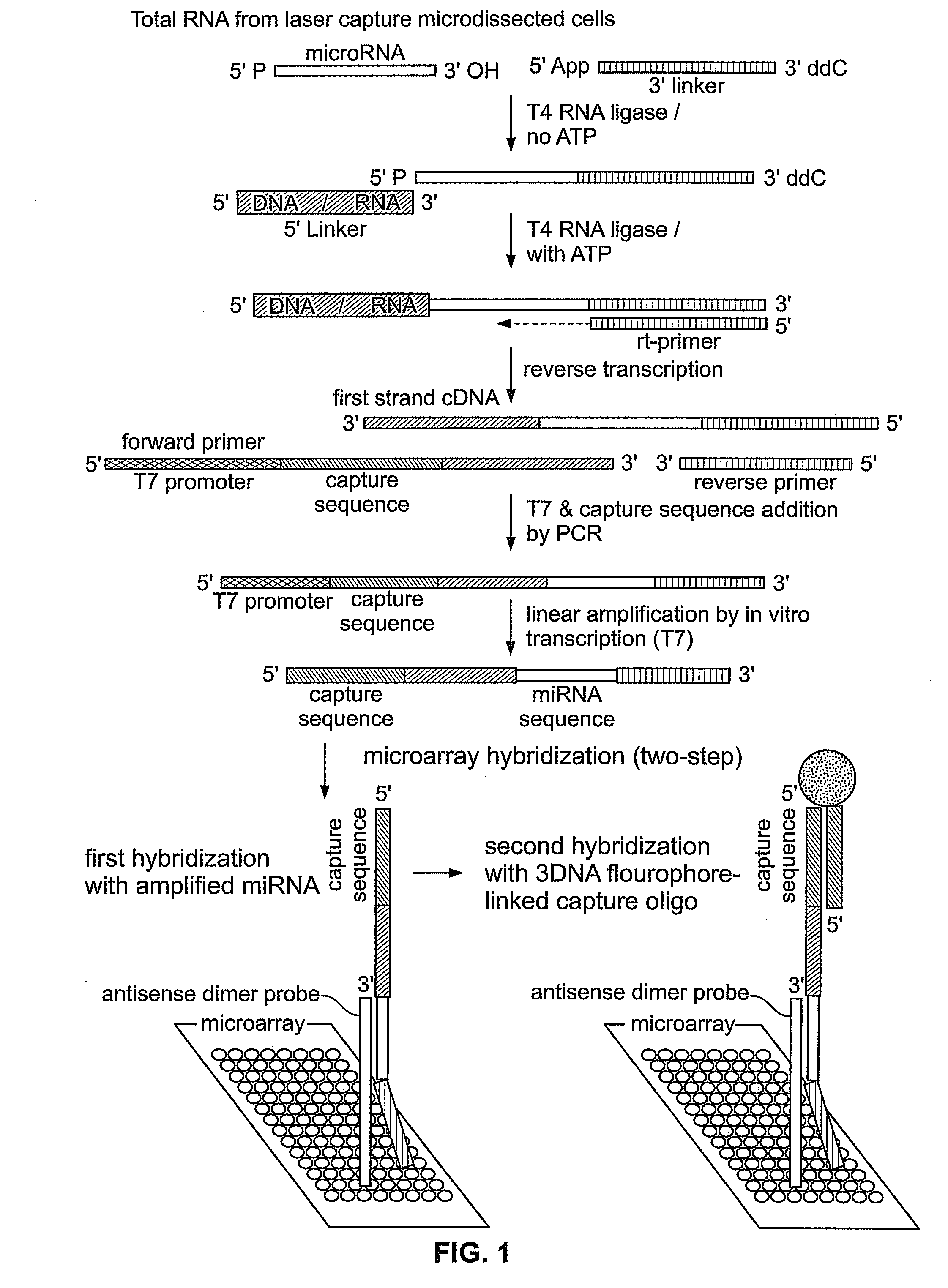
Reagents and Methods for miRNA Expression Analysis and Identification of Cancer Biomarkers
InactiveUS20090099034A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTumor BiomarkersTumor Sample
This invention provides methods for amplifying, detecting, measuring, and identifying miRNAs from biological samples, particularly limited amounts of a biological sample. miRNAs that are differentially expressed in tumor samples and normal tissues are useful as cancer biomarkers for cancer diagnostics.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
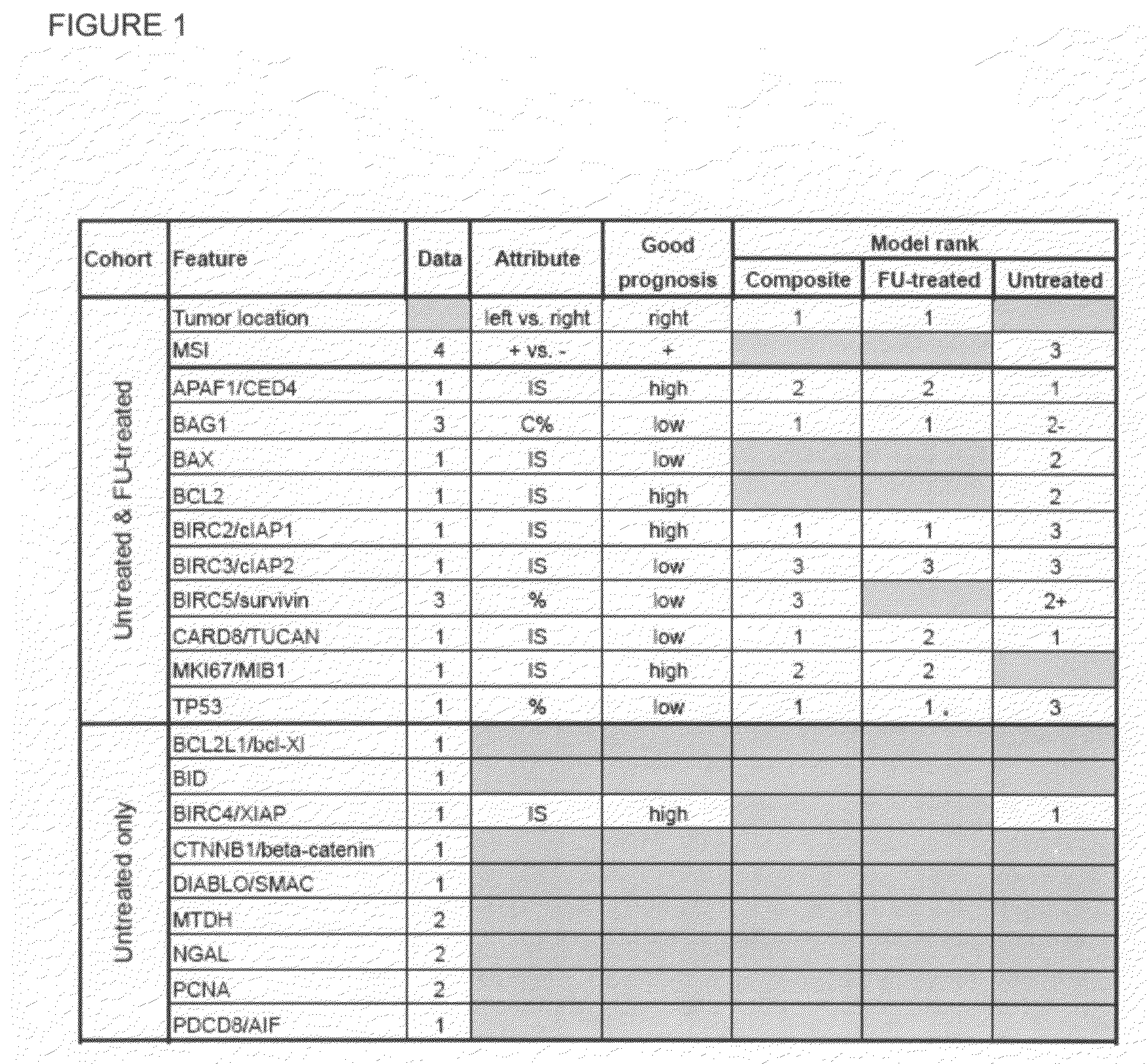
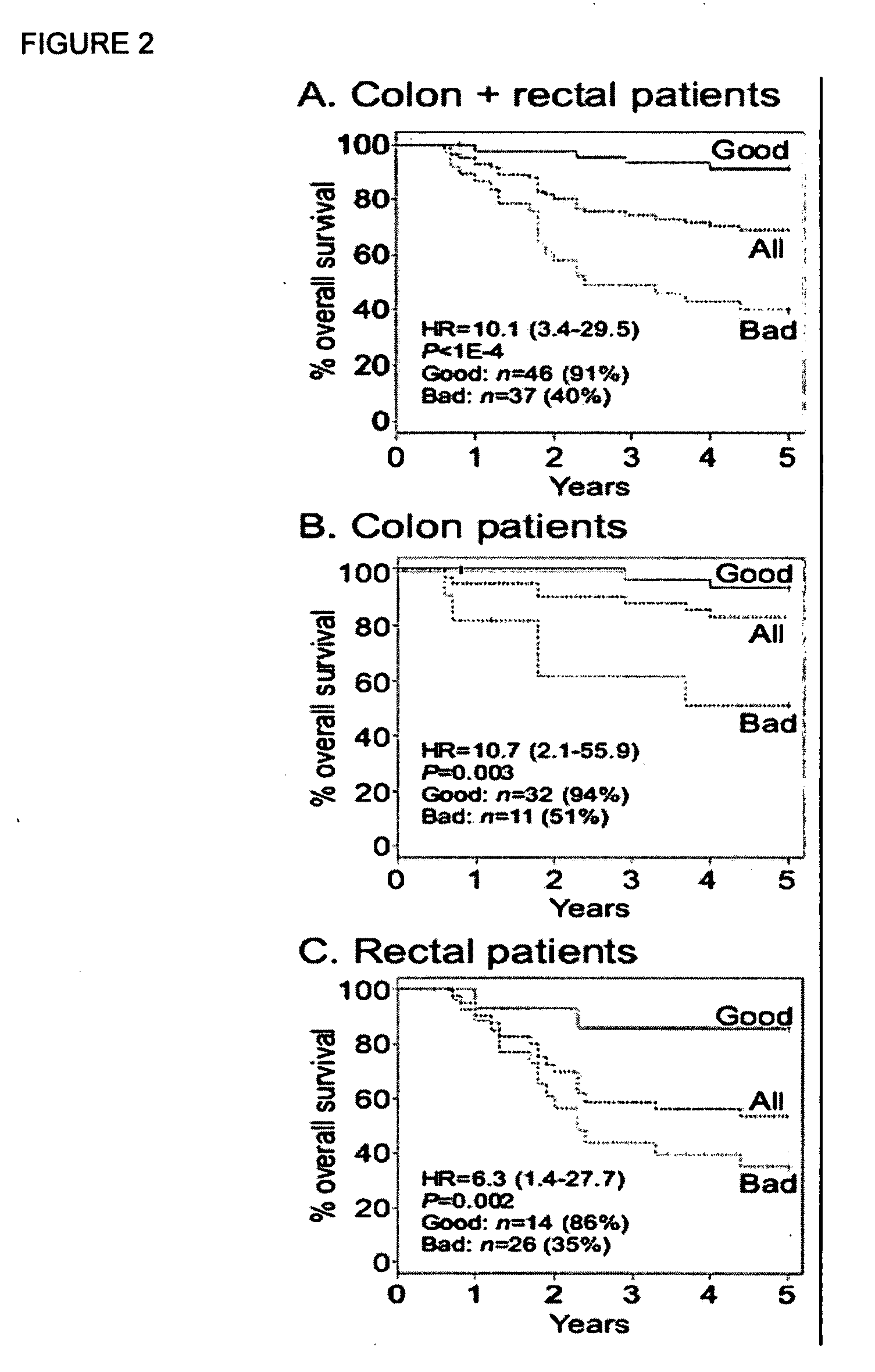
Diagnostic markers predictive of outcomes in colorectal cancer treatment and progression and methods of use thereof
Colorectal cancer patients with operable tumors must decide whether to receive adjuvant therapy after surgical resection in order to reduce their chances of recurrence. Current clinical guidelines are crudely based on the stage of the disease, as well as a few other clinicopathologic features. The instant invention integrates data from these clinicopathologic features with data on multiple biomarkers using advanced informatic methods to provide a far more accurate prediction of recurrence than the current guidelines. The instant invention consists of a panel of biomarker assays plus an algorithm into which the scored biomarker data, as well as standard clinicopathologic data, is entered. A tumor sample from an individual patient is submitted for test, and an individualized report is produced with a prognostic score that accurately reflects the patient's risk of recurrence. This helps guide the patient and his / her oncologist in their choice of whether to receive adjuvant treatment. Low-risk patients are spared the unnecessary toxicities associated with cytotoxic treatments, and high-risk patients are given the best chance for a cure, maximizing both life expectancy and quality of life.
Owner:LINKE STEVEN P +2
Method and quantification assay for determining c-kit/SCF/pAKT status
This invention provides methods for determining or predicting response to cancer therapy in an individual using differential image analysis of immunohistochemically stained tumor samples.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method for predicating homologous recombination deficiency mechanism and method for predicating response of patients to cancer therapy
InactiveCN107287285AInnovativeOvercoming the pitfalls of inaccurate forecastsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisAbnormal tissue growthPolymerase L
The invention discloses a method for predicating a homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) mechanism and a method for predicating response of patients to cancer therapy and relates to the field of biological information predication. The method comprises the step of judging whether a tumor sample has homologous recombination deficiency or not according to one or more comprehensive values in a large-segment INDEL (Insertion / Deletion) fraction, a copy number variation fraction and a tumor mutation load fraction, wherein the comprehensive values can also comprise a loss of heterozygosity variation fraction. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, predication of a chromosome large-segment structure, a chromosome gene type number, a chromosome gene copy number, a chromosome variation interval and abnormal loss of heterozygosity and chromosome telomeric imbalance is realized, so that an evaluation range is more complete and HRD can be accurately predicated; the comprehensive values also can be used for determining whether the patients have response to a therapeutic regimen containing one or more of a PARP (Poly Adenosine Diphosphate Ribose Polymerase) inhibitor, an DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) injury inhibitor, a topoisomerase II / II+inhibitor, a topoisomerase I inhibitor and radiotherapy; the method is simple and has wide general applicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD
Immunohistochemical proximity assay for pd-1 positive cells and pd-ligand positive cells in tumor tissue
ActiveUS20160305947A1Easy to detectEasy to quantifyImage enhancementMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTumor SampleWilms' tumor
The present disclosure describes an IHC assay for detecting and quantifying spatially proximal pairs of PD-1-expressing cells (PD-1+ cells) and PD-Ligand-expressing cells (PD-L+ cells) in tumor tissue, and the use of the assay to generate proximity biomarkers that are predictive of which cancer patients are most likely to benefit from treatment with a PD-1 antagonist. The disclosure also provides methods for testing tumor samples for the proximity biomarkers, as well as methods for treating subjects with a PD-1 antagonist based on the test results.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Methods of classifying, diagnosing, stratifying and treating cancer patients and their tumors
InactiveUS7118853B2Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthKeratin
Owner:APPL GENOMICS INC +1
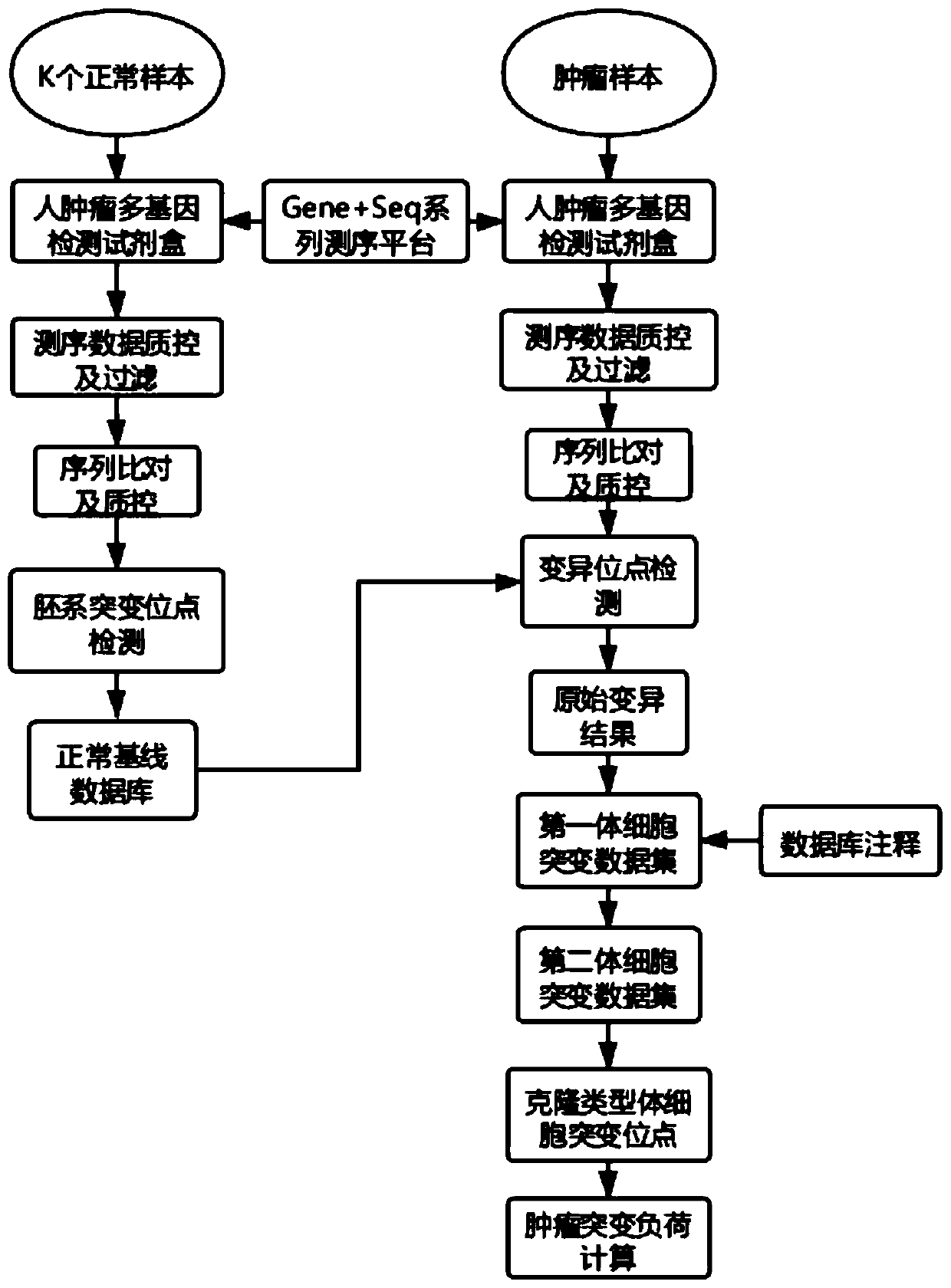
Tumor cloning mutation detection method and device based on next-generation sequencing and memory medium
ActiveCN108733975AAvoid influenceAccurate tumor clonal mutation type detection resultsSpecial data processing applicationsMutation frequencyMutation detection
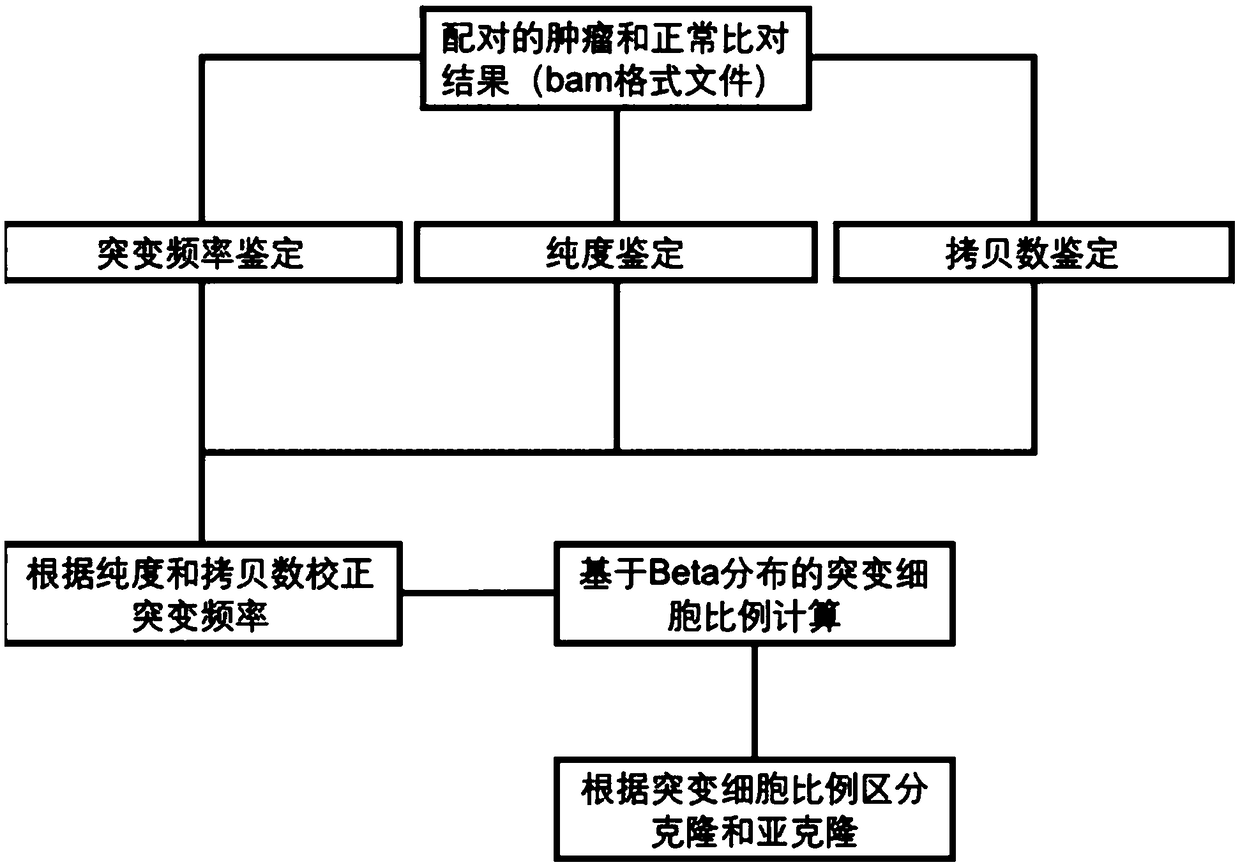
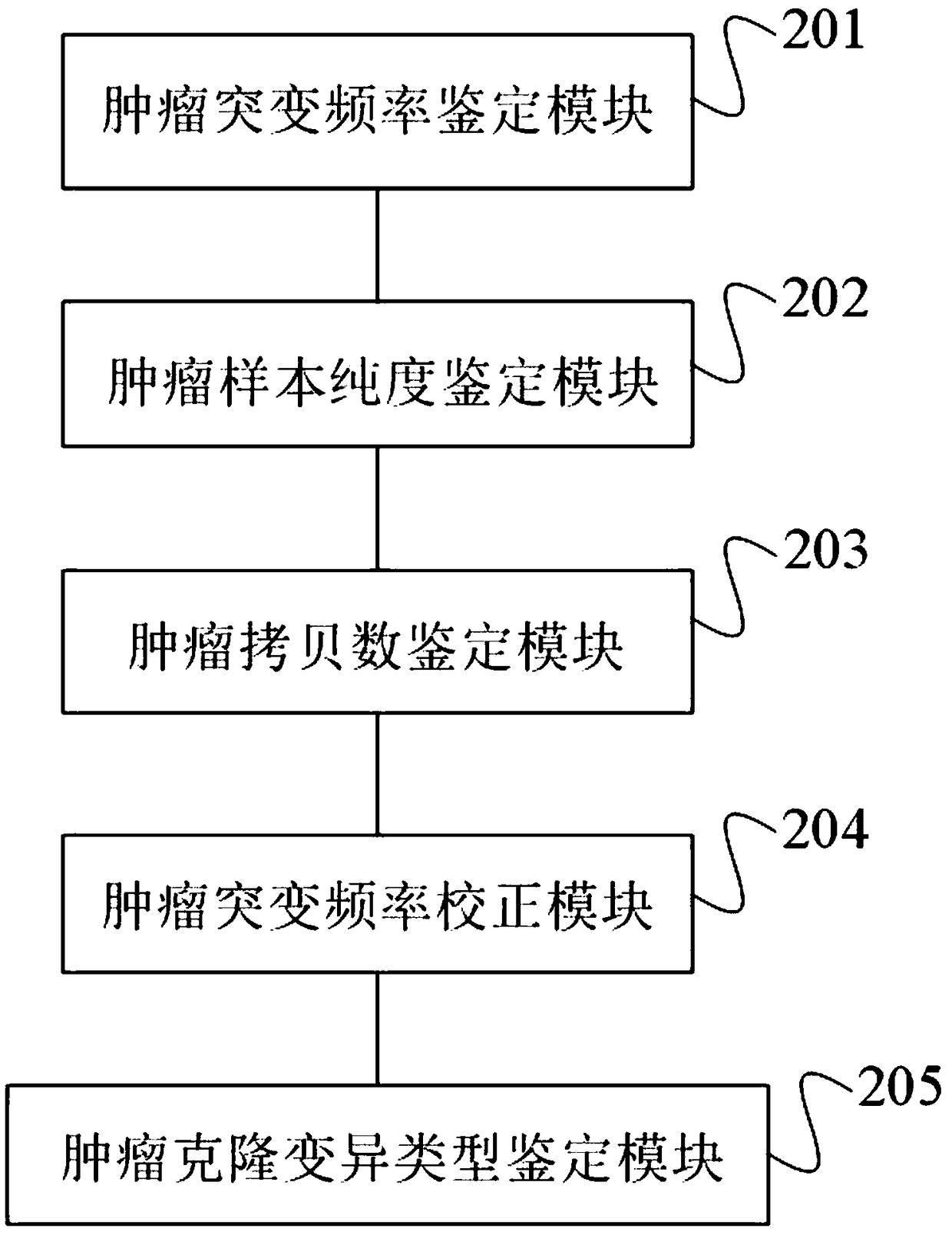
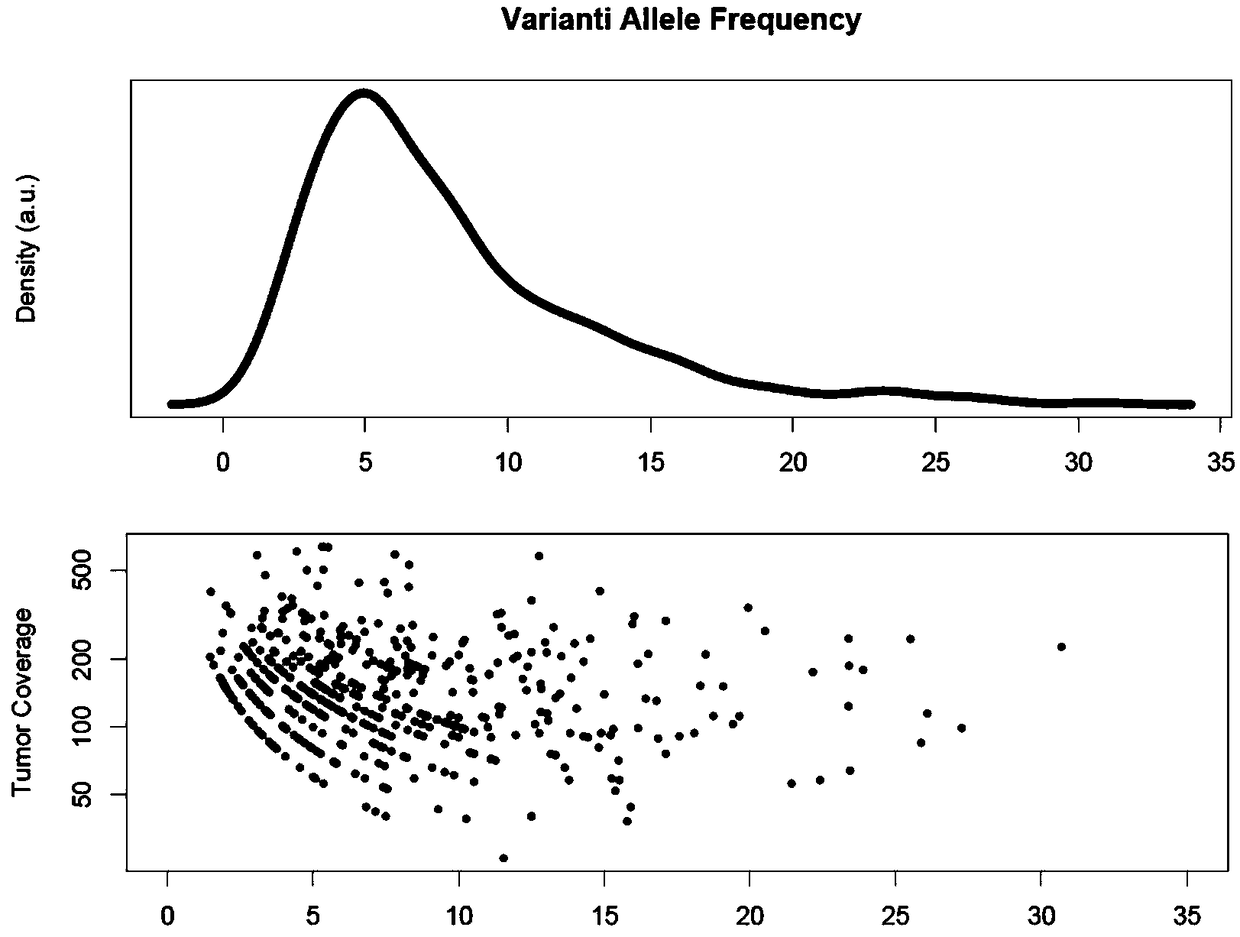
The invention discloses a tumor cloning mutation detection method and device based on next-generation sequencing and a memory medium. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps of carrying out mutation detection on a comparison file of paired tumor and normal samples through utilization of mutation detection software, computing a mutation frequency, and selecting segments with high sequencing quality as a statistics result; carrying out copy number and purity detection on the paired tumor and normal samples through utilization of purity detection software; combining small segments into big segments, and annotating the copy number in a mutation area; and computing a proportion of the mutation in a tested tumor tissue through utilization of a beta distribution model according to tumor sample purity and copy number detection results, thereby judging a tumor cloning mutation type. According to the method provide by the invention, influences of the sample purity and multiploidon the detection are avoided, the mutation type detection is relatively accurate, the subcloning mutation with clinical significance can be effectively identified, and the foundation for accurately and deeply researching a tumor cloning evolution process and searching a tumor therapy molecular mechanism is laid.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
Methods of classifying, diagnosing, stratifying and treating cancer patients and their tumors
InactiveUS20060040302A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCytokeratin
The invention provides a variety of reagents for use in the diagnosis and management of cancer, particularly breast cancer. cDNA microarray technology was used to identify genes whose expression profile across a large group of tumor samples correlates with that of cytokeratin 5 and cytokeratin 17, markers for basal cells of the normal mammary lactation gland. The invention demonstrates that tumors that express cytokeratin 5 / 6 and / or 17 have a poor prognosis relative to tumors overall. The invention provides basal marker genes and their expression products and uses of these genes for diagnosis of cancer and for identification of therapies for cancer. In particular, the invention provides basal marker genes including cadherin3, matrix metalloproteinase 14, and cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2. The invention provides antibodies to the polypeptides expressed by these genes and methods of use thereof.
Owner:APPL GENOMICS INC +1
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods for cancer
InactiveUS20180037655A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementBladder cancerPd l1 expression
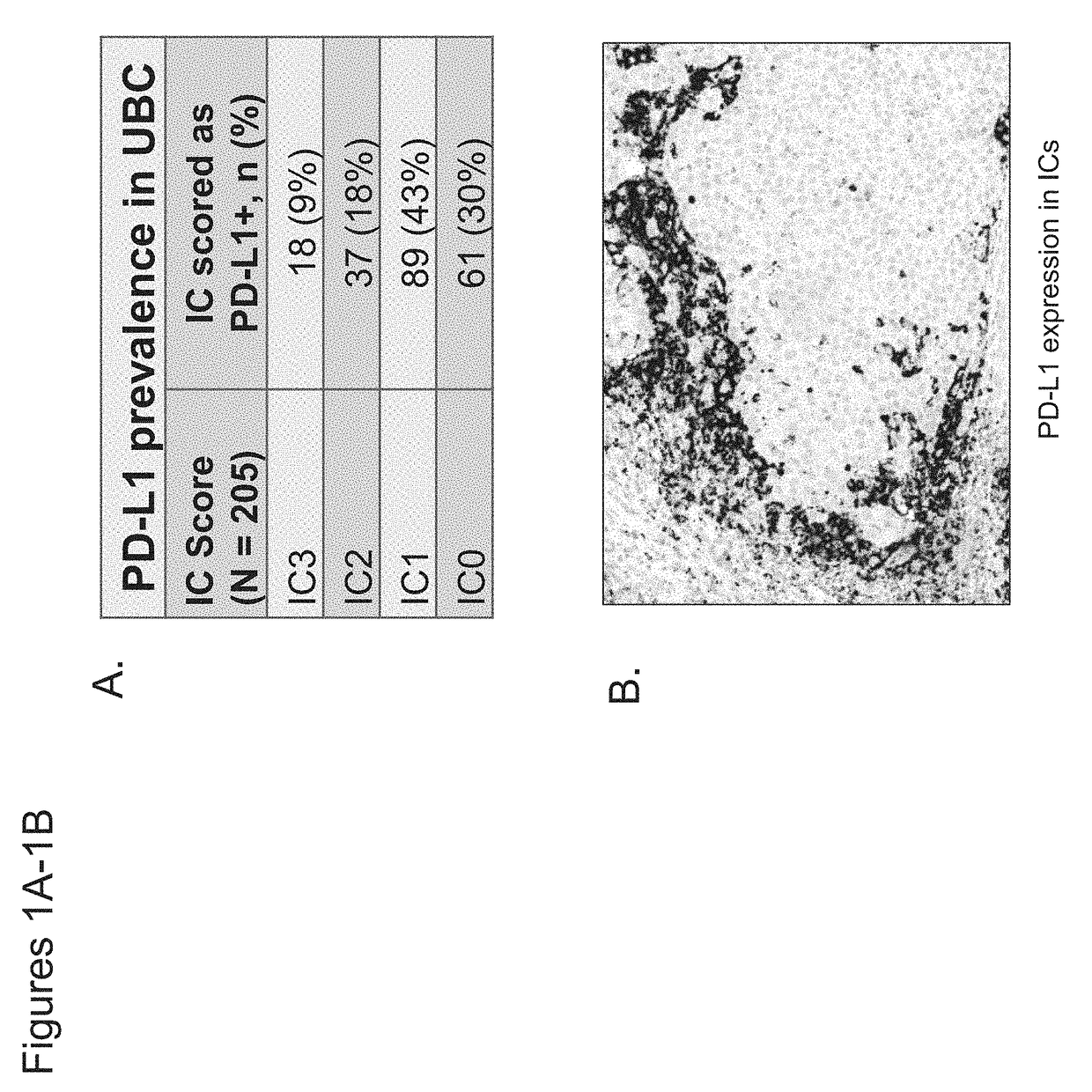
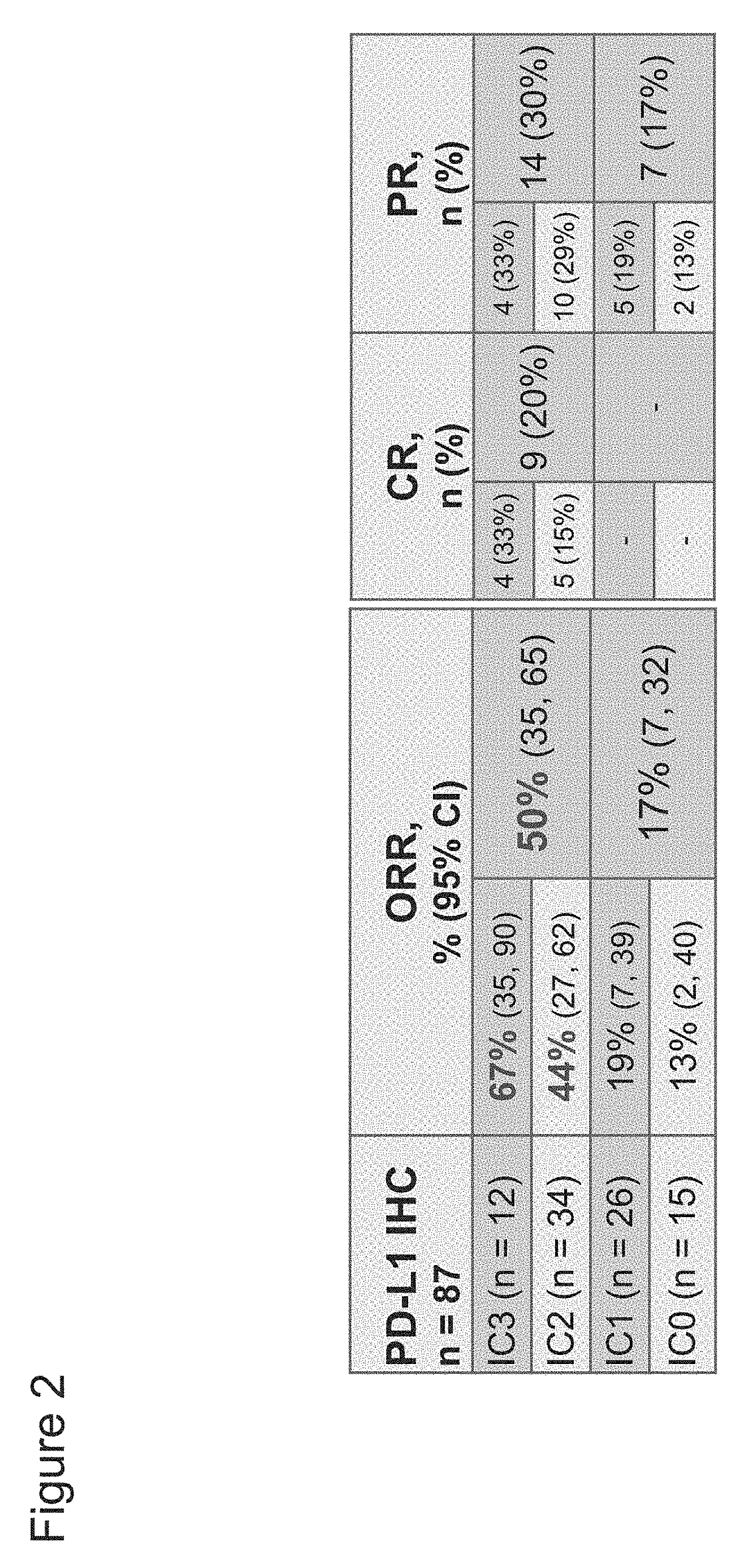
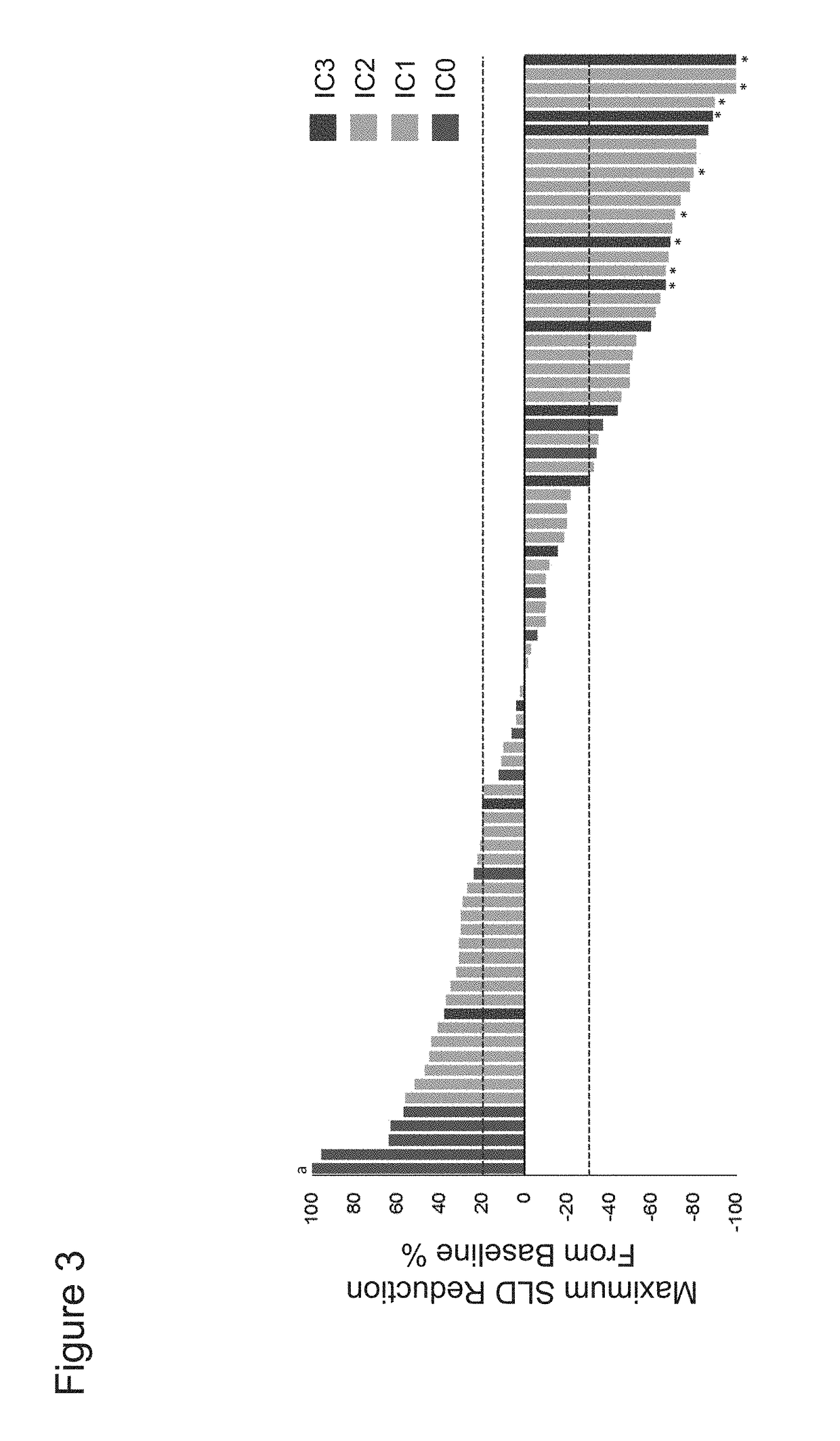
The present invention provides therapeutic and diagnostic methods and compositions for cancer, for example, bladder cancer. The invention provides methods of treating bladder cancer, methods of determining whether a patient suffering from bladder cancer is likely to respond to treatment comprising a PD-L1 axis binding antagonist, methods of predicting responsiveness of a patient suffering from bladder cancer to treatment comprising a PD-L1 axis binding antagonist, and methods of selecting a therapy for a patient suffering from bladder cancer, based on expression levels of a biomarker of the invention (e.g., PD-L1 expression levels in tumor-infiltrating immune cells in a tumor sample obtained from the patient) and / or based on the determination of a tumor sample subtype.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for primary culture of tumor cells
InactiveCN103865876AIncrease success rateGood removal effectTumor/cancer cellsSingle cell suspensionBovine serum albumin
The invention discloses a method for primary culture of tumor cells and relates to the field of cell biology. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a tumor sample is prepared into a single-cell suspension liquid by use of an enzyme method or a mechanical method, and then tumor cell bladders are prepared by use of a serum-free suspension culture method, wherein alkaline fibroblast growth factors, epidermal growth factors, insulin and bovine serum albumin need to be added during a culturing process, then the growth factors are removed, and the culture is implemented in a general culture medium to obtain adherent cells capable of realizing continuous passage. The method disclosed by the invention is short in culture period and has the effect of increasing the success rate of the primary culture of tumors.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
EGFR and kras mutations
InactiveUS20110081651A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementKras mutationBRCA2 Mutation
The present invention relates to mutations in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and KRAS and methods of detecting such mutations as well as prognostic methods for identifying tumors that are susceptible to anticancer therapy such as chemotherapy and / or kinase inhibitor treatment. The methods involve determining the presence of a mutated EGFR gene or mutated EGFR protein and / or a mutated KRAS gene or mutated KRAS protein in a tumor sample.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method and display for multivariate classification
InactiveUS6868342B2Quick classificationSimple processData visualisationDigital computer detailsObject basedMultivariate classification
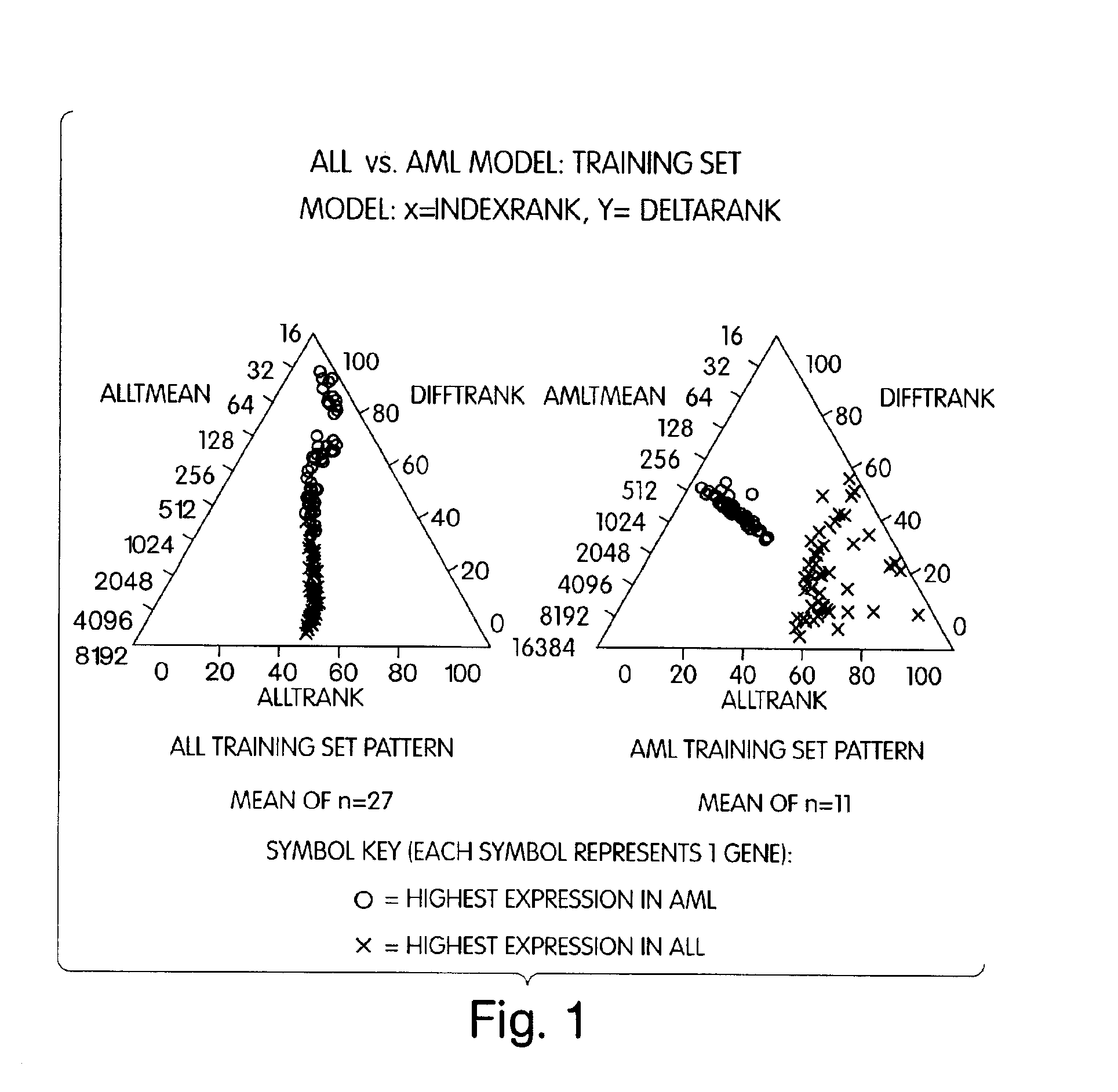
The present invention represents a new approach to data analysis for multivariate classification, particularly as used in medical diagnostics. The invention is in part an intuitive decision making tool for rapid classification of “objects” (e.g., cell, tissue or tumor samples) from evaluation of many simultaneous “variables” (e.g., quantitative gene expression profiles). The data analysis methods of the invention provide the end user with a simplified and robust output for diagnostic classification of objects based on identifying and evaluating multiple variables of predetermined diagnostic relevance. The raw data generated by analysis of the variables is transformed by application or appropriate algorithms to scaleless rank differentials between the variables. The rank orders of variables are used to classify tissues based on readily observable user interfaces, such as a graphical (e.g., visual) user interface or an auditory user interface.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Compositions and methods for diagnosing, evaluating and treating cancer
ActiveUS20160326593A1Decreases potential evolutionary capacityImprove treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisGenetic ChangeTumor Sample
The present invention relates to methods of determining a cancer treatment prognosis for a subject in need thereof by evaluating epigenetic and genetic changes within a tumor sample from the subject. The present invention further provides methods of treating cancer in a subject by evaluating epigenetic and genetic changes within a tumor sample from the subject. In addition, the present invention provides methods of screening test agents to identify agents that decrease tumor cell plasticity.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +3
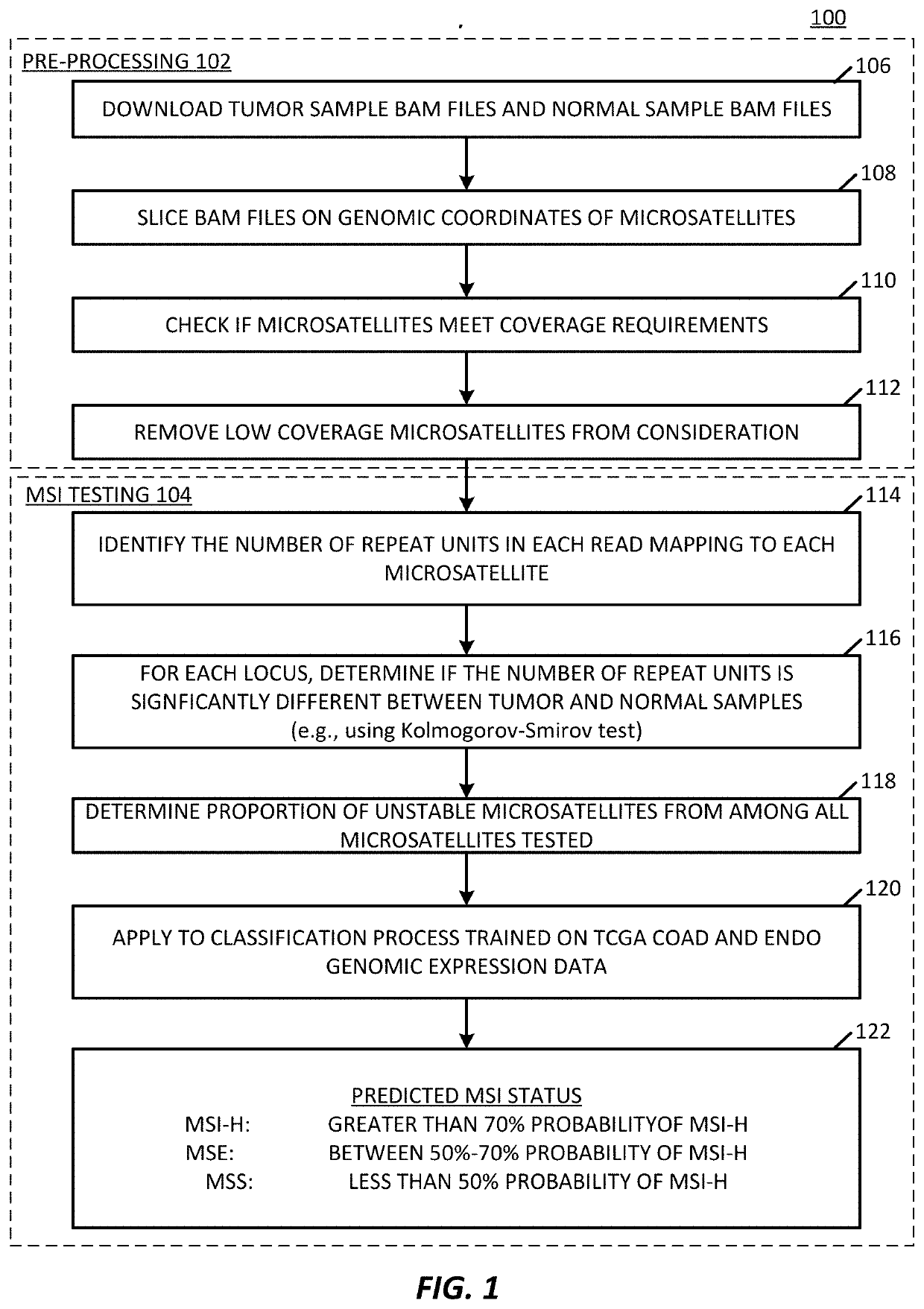
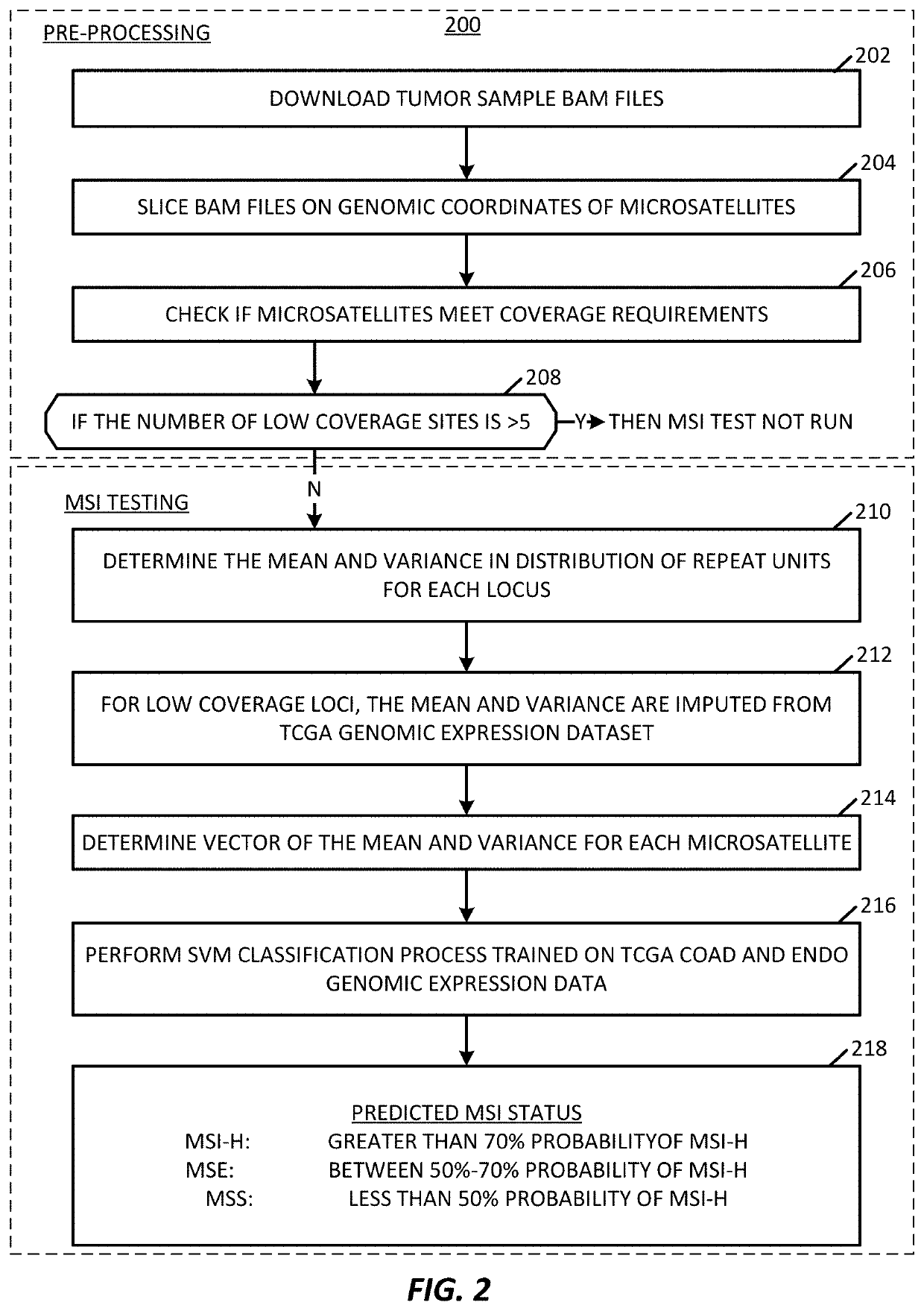
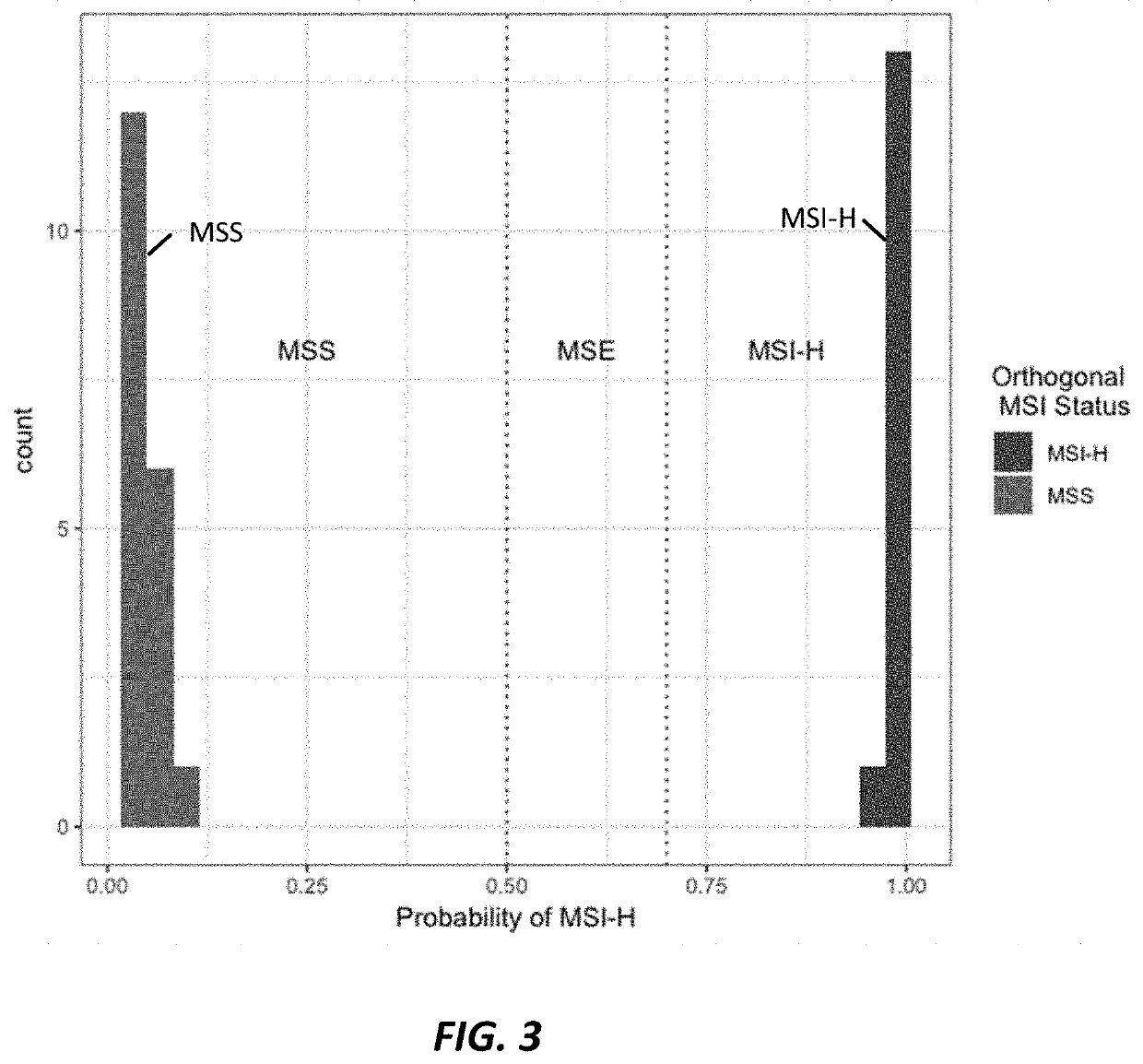
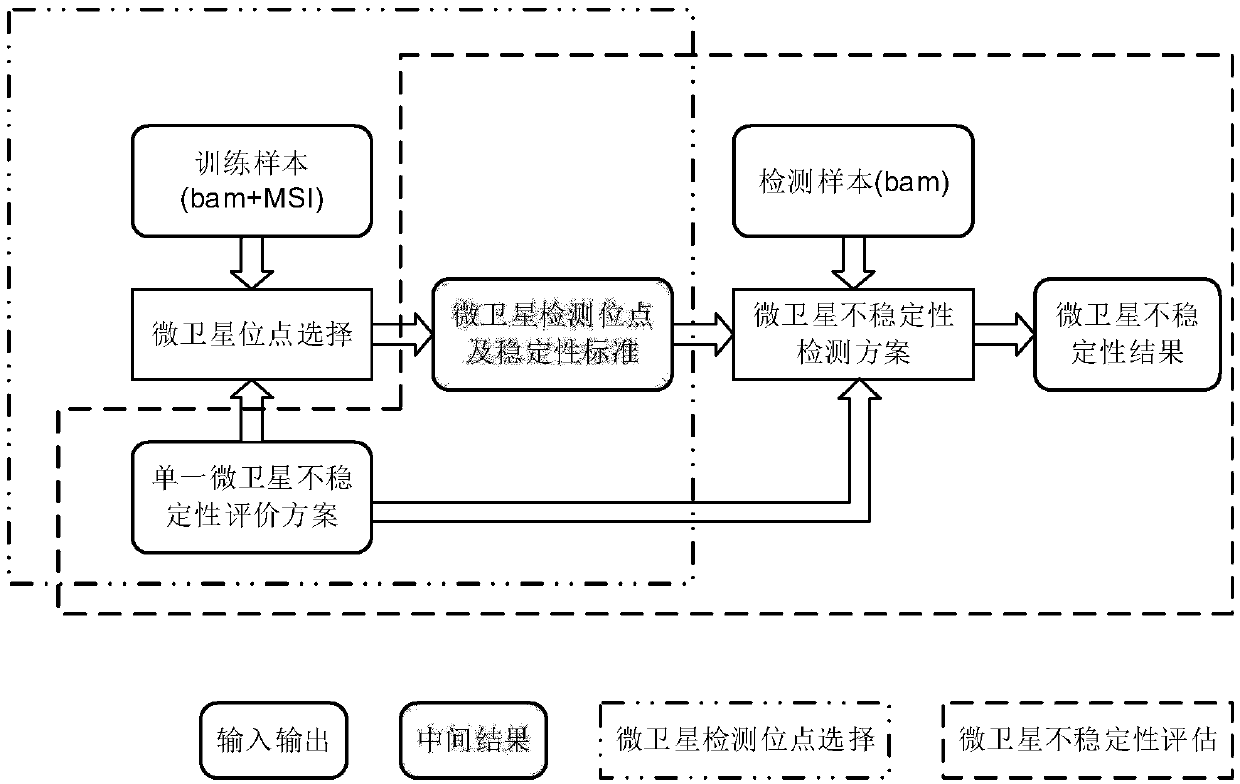
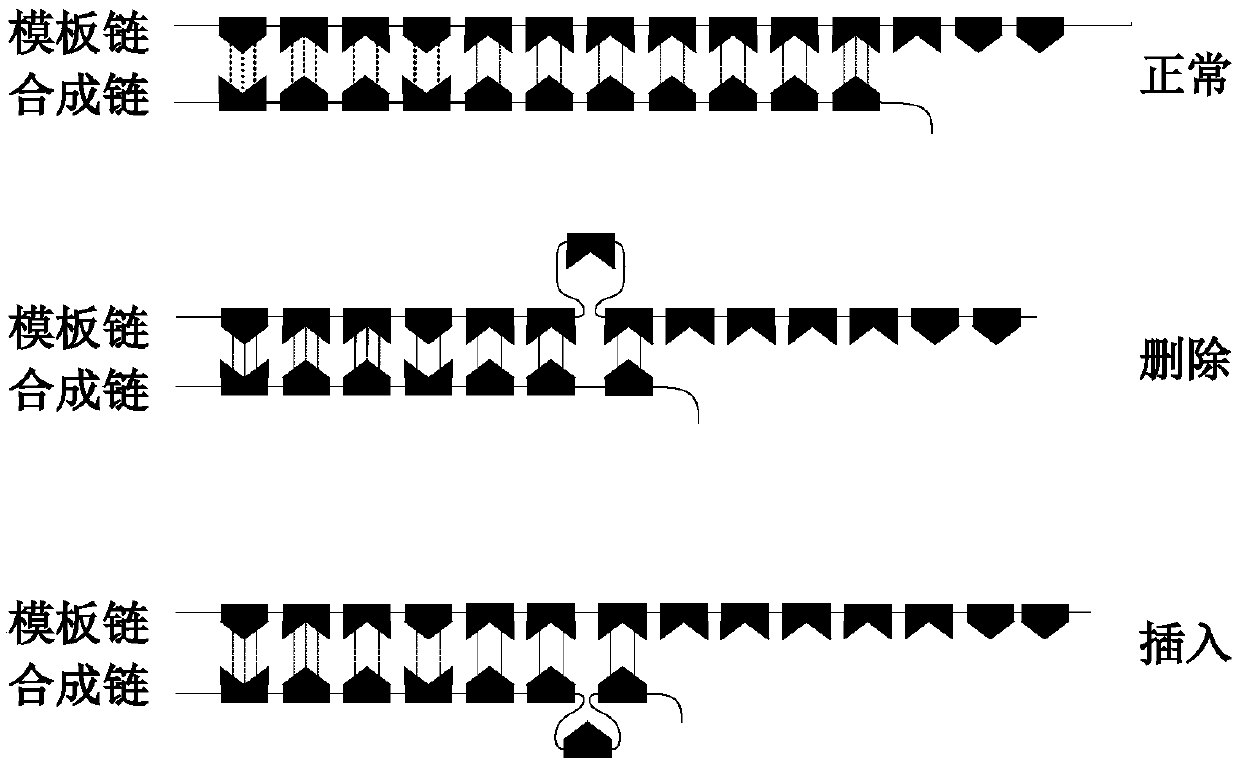
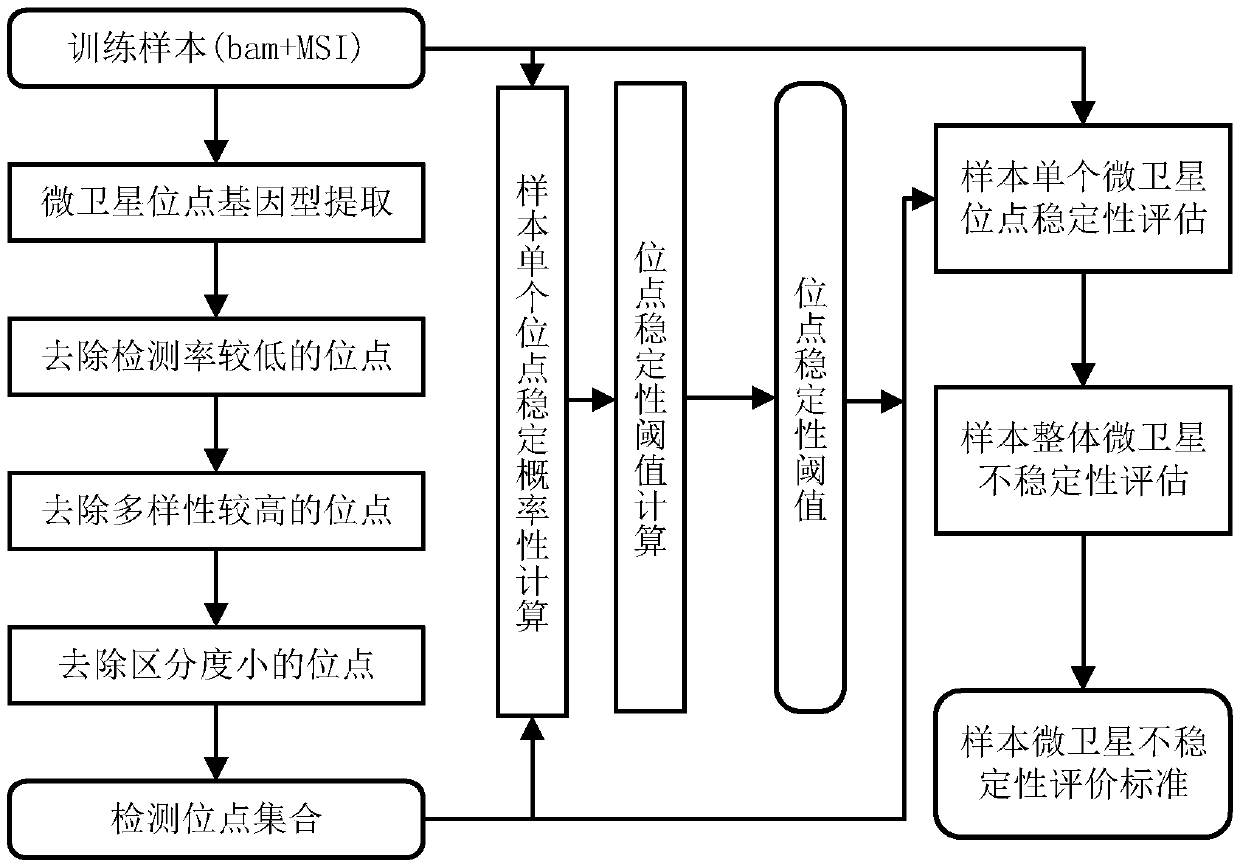
Microsatellite instability determination system and related methods
Methods and systems for determining microsatellite instability (MSI) directly from microsatellite region mappings for specific loci in the genome are provided. Techniques include an MSI assay that may be deployed in a paired form, that is, as tumor sample and matched normal sample MSI assay, or an unpaired form, that is, as a tumor-only MSI assay. The techniques provide an automated process for MSI determination by mapping read counts in tumor samples and normal samples and comparing the two, for an identified set of 43 microsatellite loci.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS INC
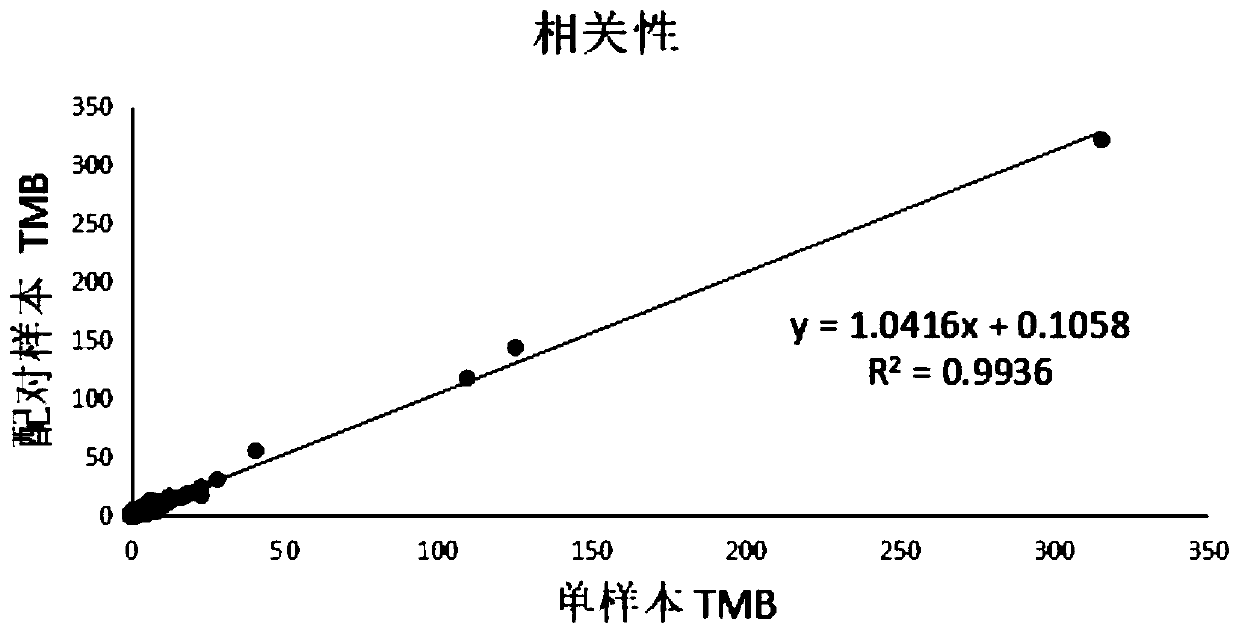
Method and device for detecting tumor mutation load based on single sample
ActiveCN111321140AAccurate detectionReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsHuman tumorData set
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a method and a device for detecting tumor mutation load based on a single sample. According to the device, a probe combination comprises probes that capture the exon region of a gene shown in Table 1, an intron promoter fusion breakpoint region of a gene shown in Table 2, and a coding region region of a gene shown in Table 3. A human tumor polygene detection kit comprises the probe combination. The TMB detection method based on the single sample comprises the following steps: access to target area of the tumor samples under test sequencing data, with the reference genome comparison, based on comparing the results obtained, detecting mutation loci, filtering original variable results with normal sample normal baseline database coincidence loci, filtering the high frequency reproductive mutation locus of a first cell mutation data set, screening the clonal somatic cell mutation locus of a second somatic cell mutation data set and calculating TMB. This method can accurately detect TMB of tumor samples without pairing samples.
Owner:苏州吉因加生物医学工程有限公司 +1
Gene-based algorithmic cancer prognosis
InactiveUS20080275652A1Guaranteed monitoring effectMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAbnormal tissue growthTumor Sample
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
EGFR mutations
The present invention relates to mutations in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and methods of detecting such mutations as well as prognostic methods method for identifying a tumors that are susceptible to anticancer therapy such as chemotherapy and / or kinase inhibitor treatment. The methods involve determining the presence of a mutated EGFR gene or mutated EGFR protein in a tumor sample whereby the presence of a mutated EGFR gene or protein indicates the tumor is susceptible to treatment.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
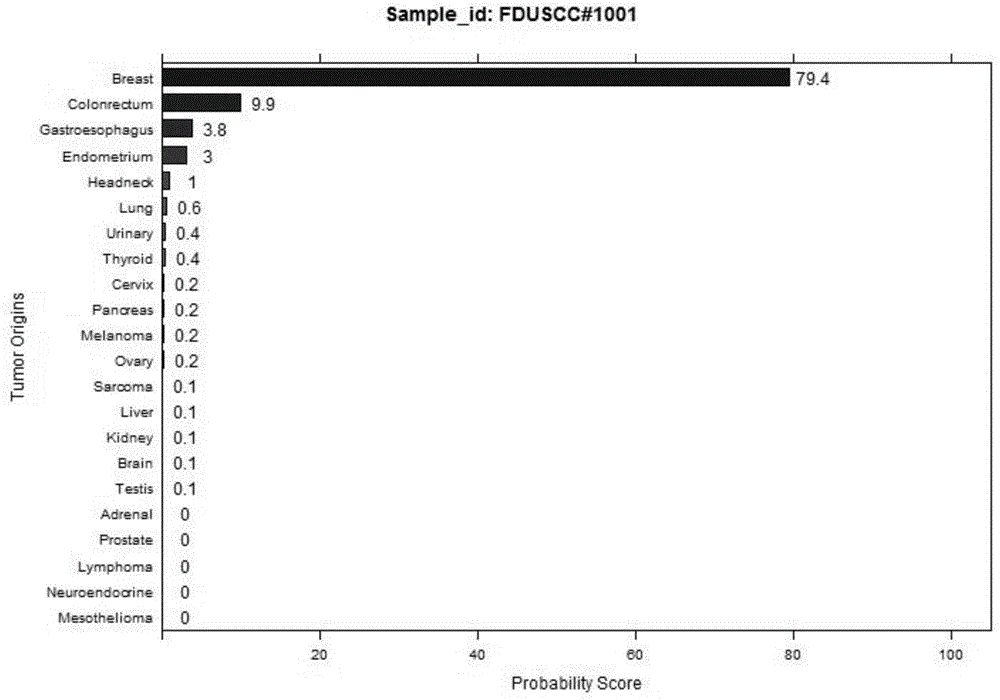
Group of genes for tumor molecular subtyping and application thereof
ActiveCN105087568AImprove living conditionsRealize personalized medicineNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAGR2Cancer type
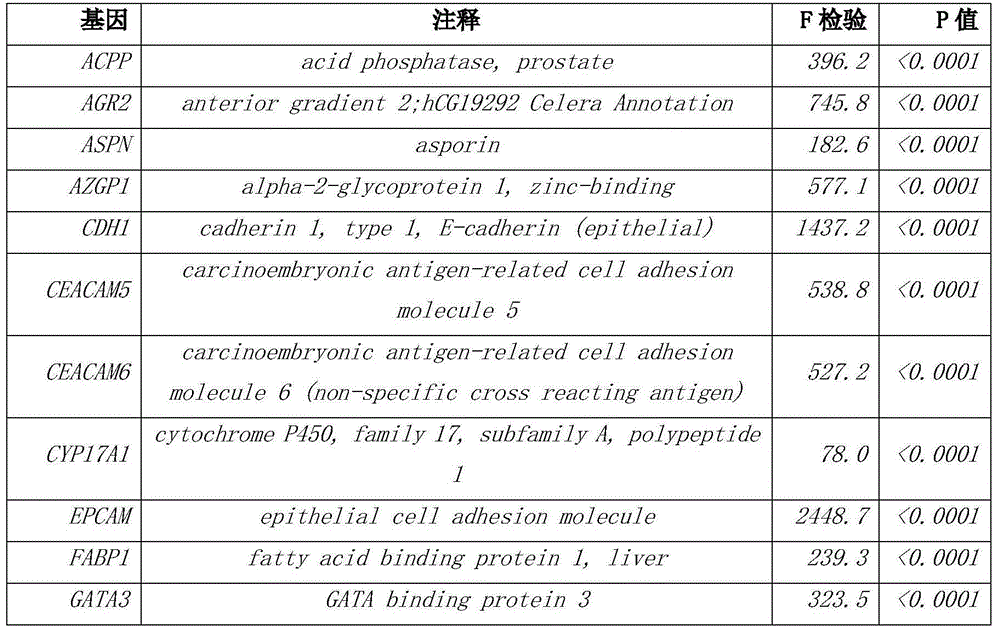
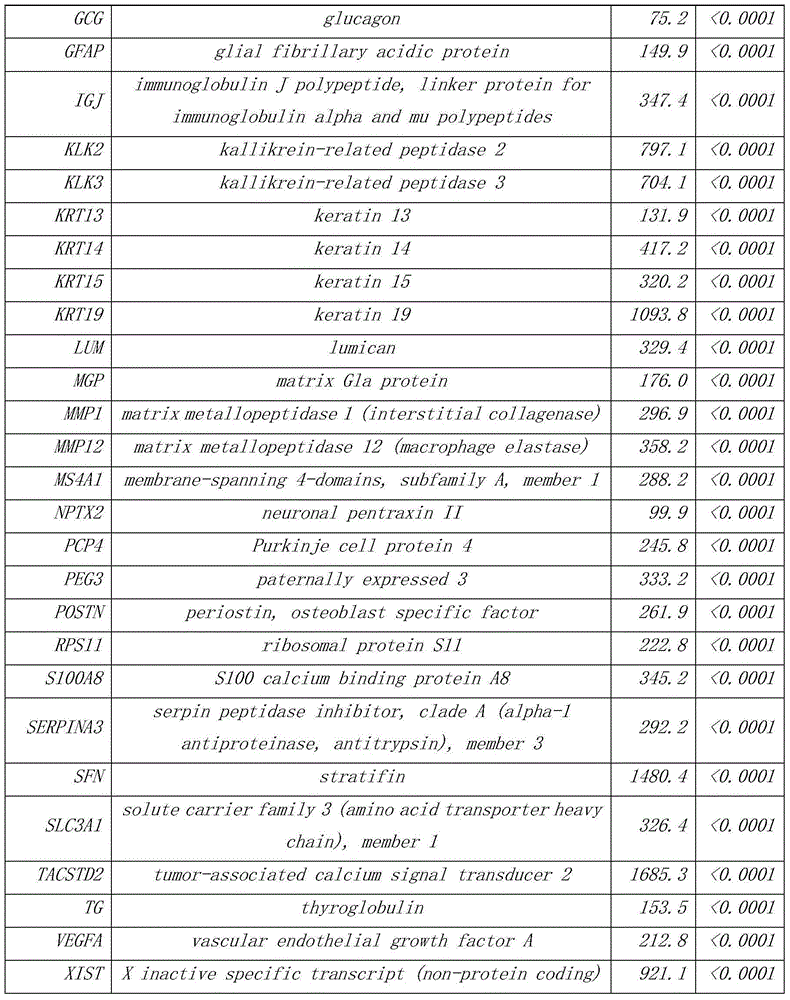
The invention discloses a group of genes for tumor molecular subtyping. The group of genes includes 38 genes such as an ACPP gene and an AGR2 gene. Moreover, the invention further discloses a kit for tumor molecular subtyping and application of the kit. The group of genes is beneficial to the recognition of the tissue sources of tumors. After a tumor sample is obtained, the tissue source and cancer type of the tumor sample can be judged objectively and accurately through detection and conjoint analysis of the gene group, so that a patient can be treated specifically.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANQING BIOTECH CO LTD
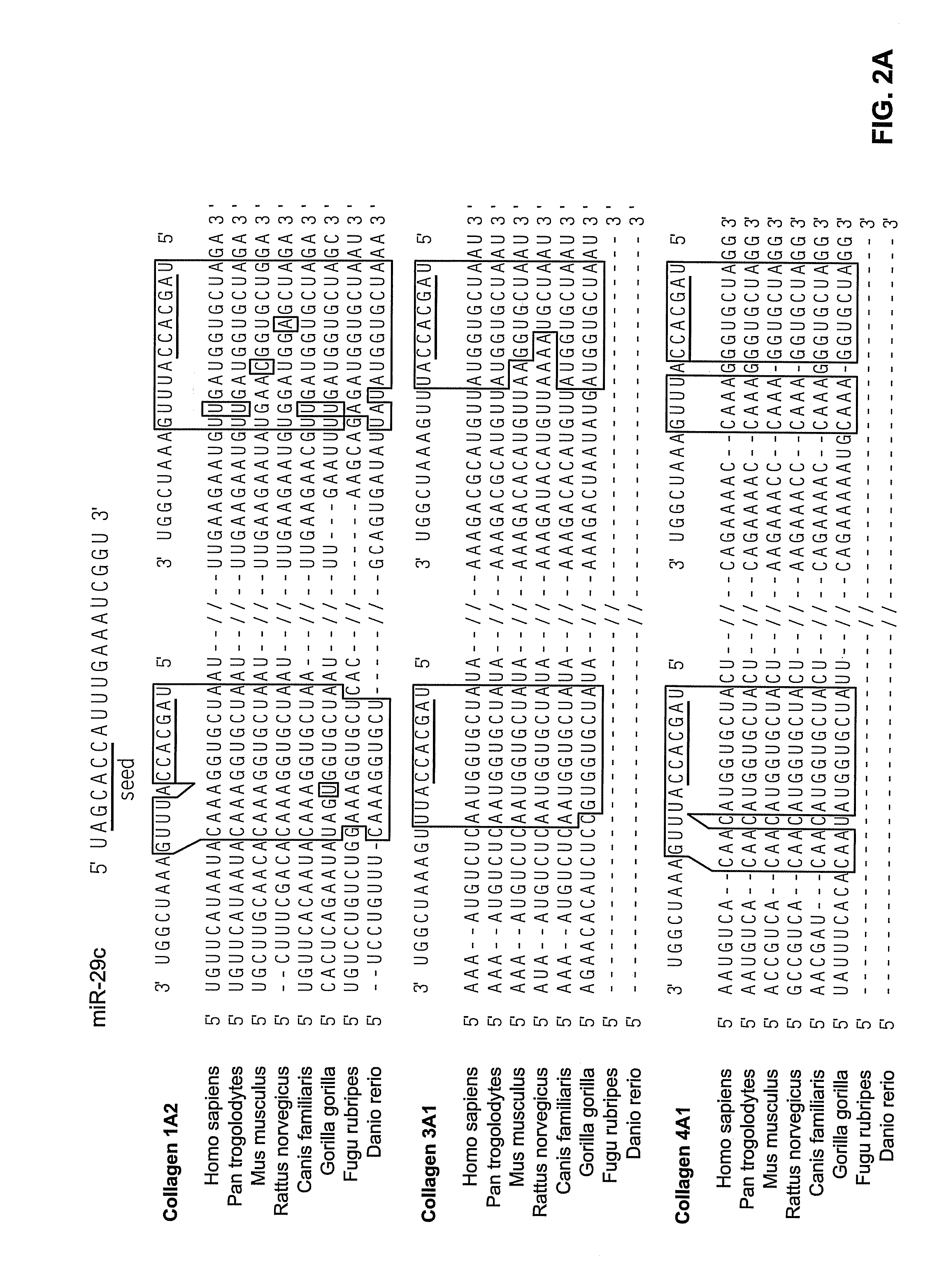
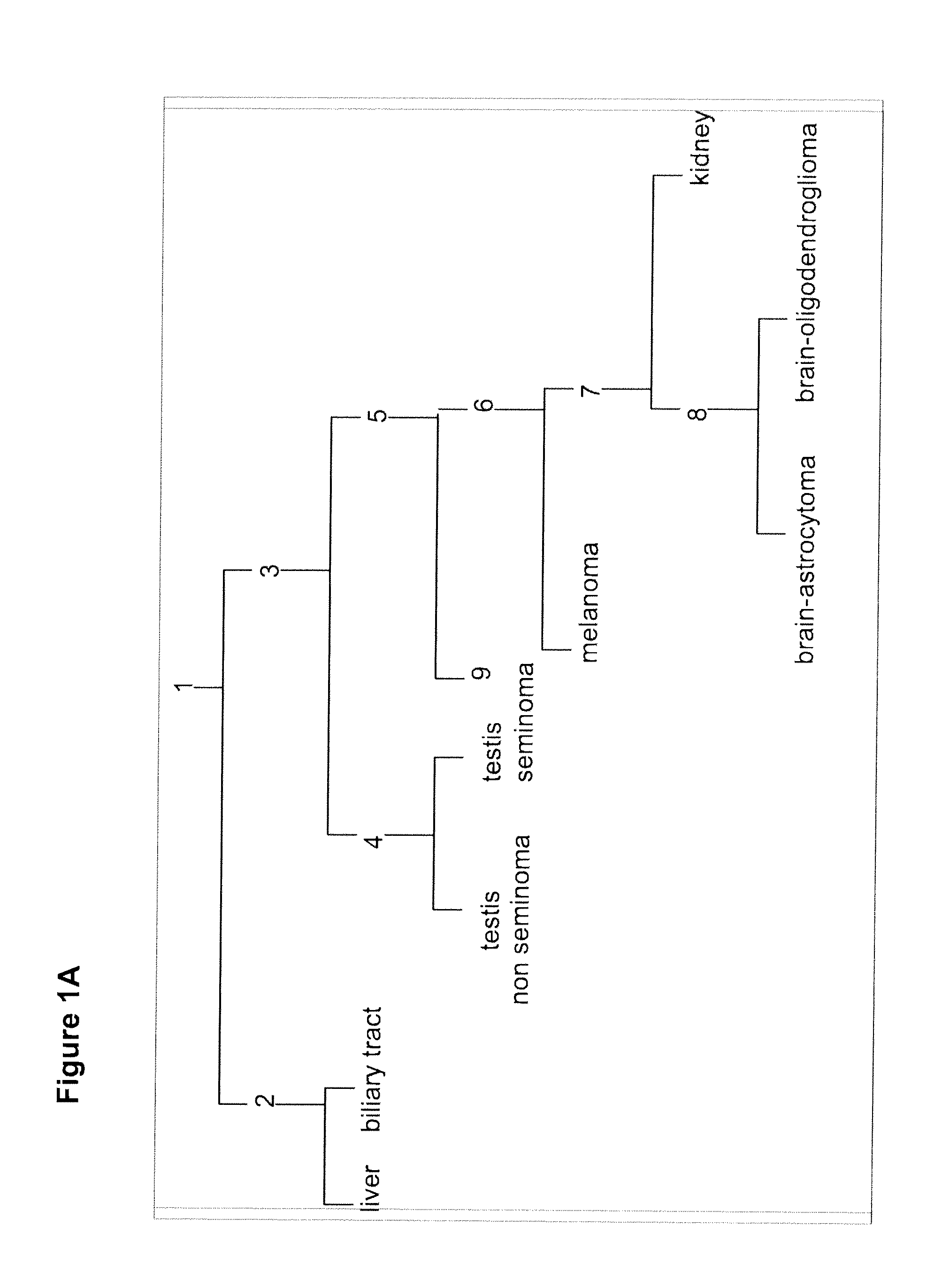
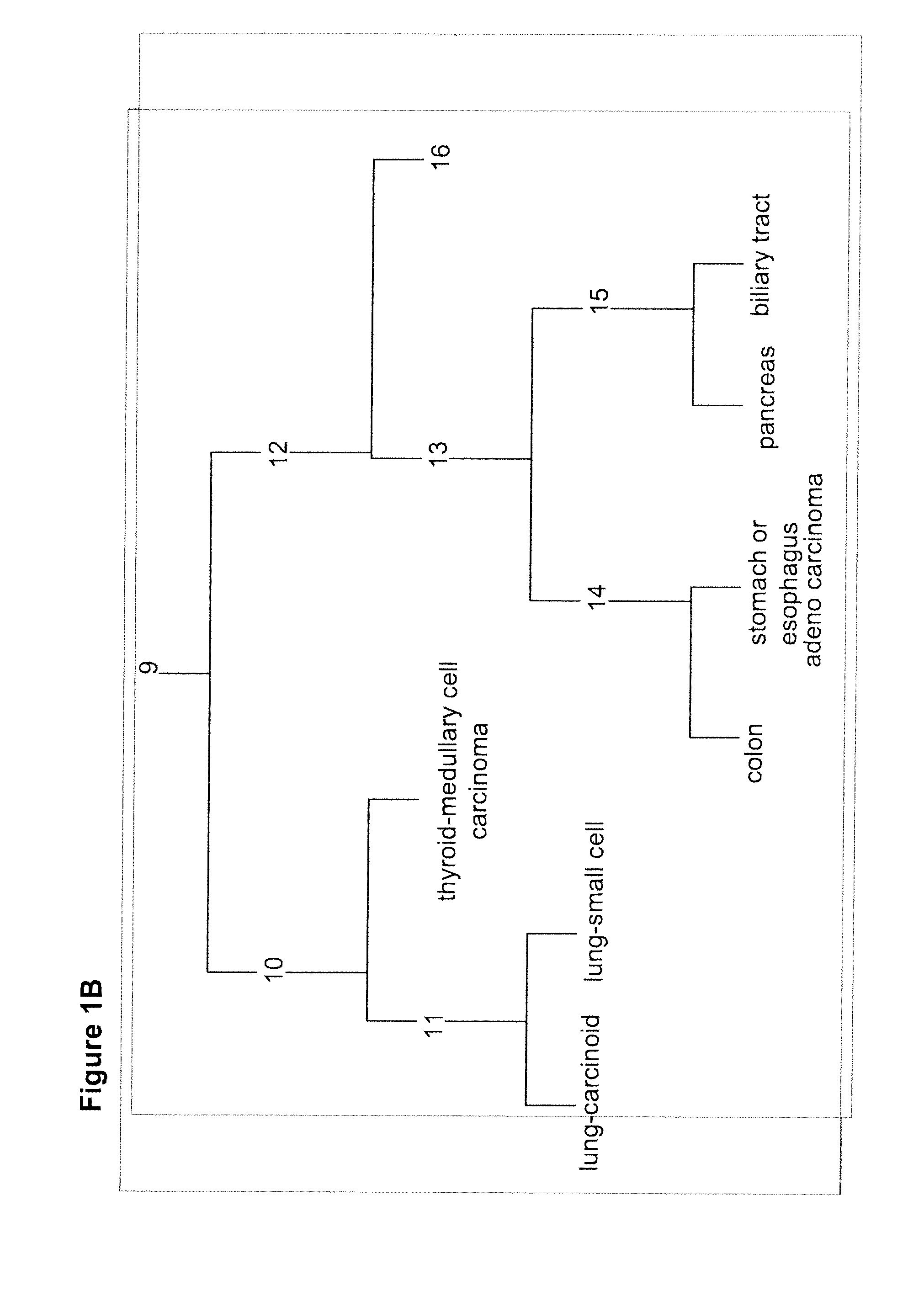
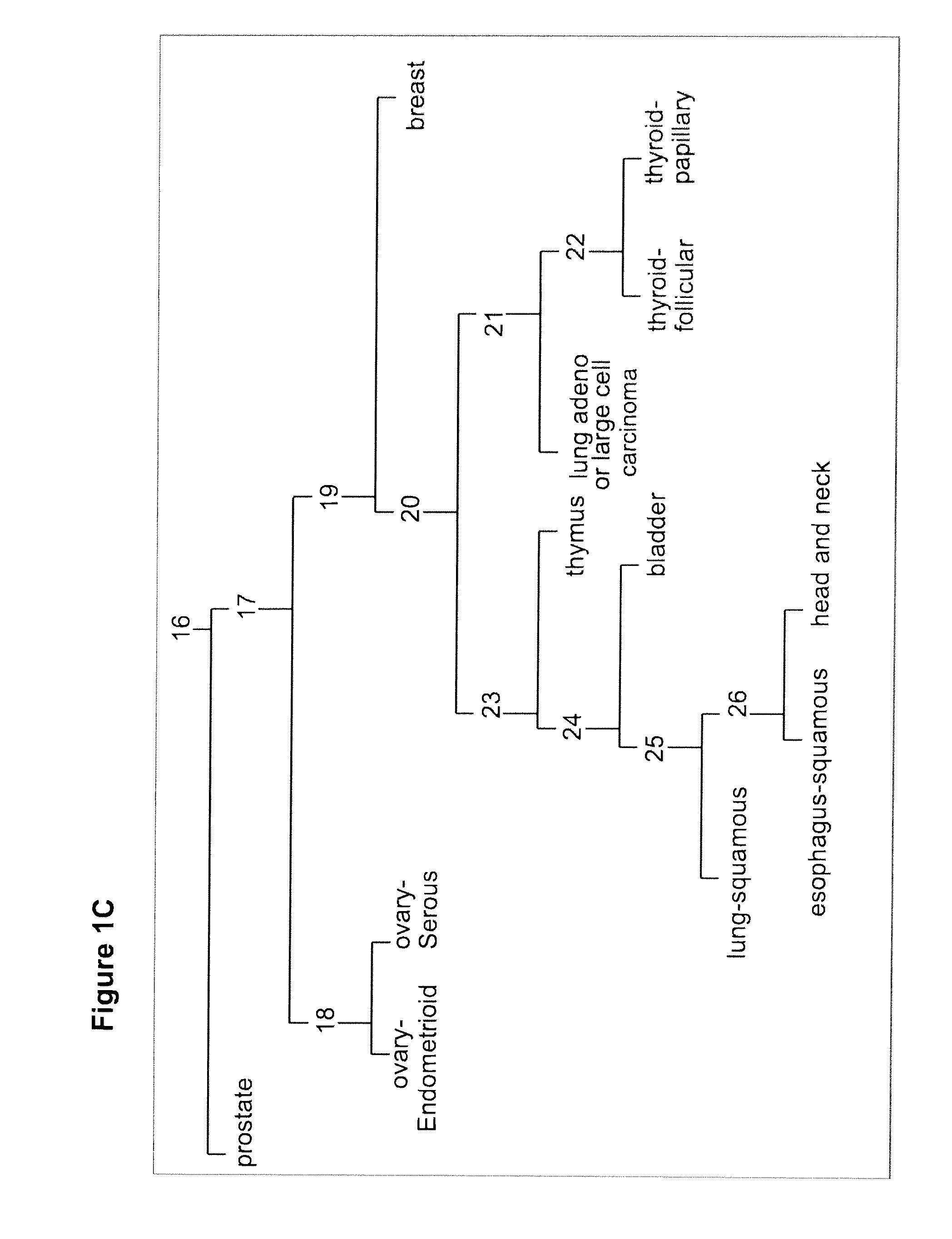
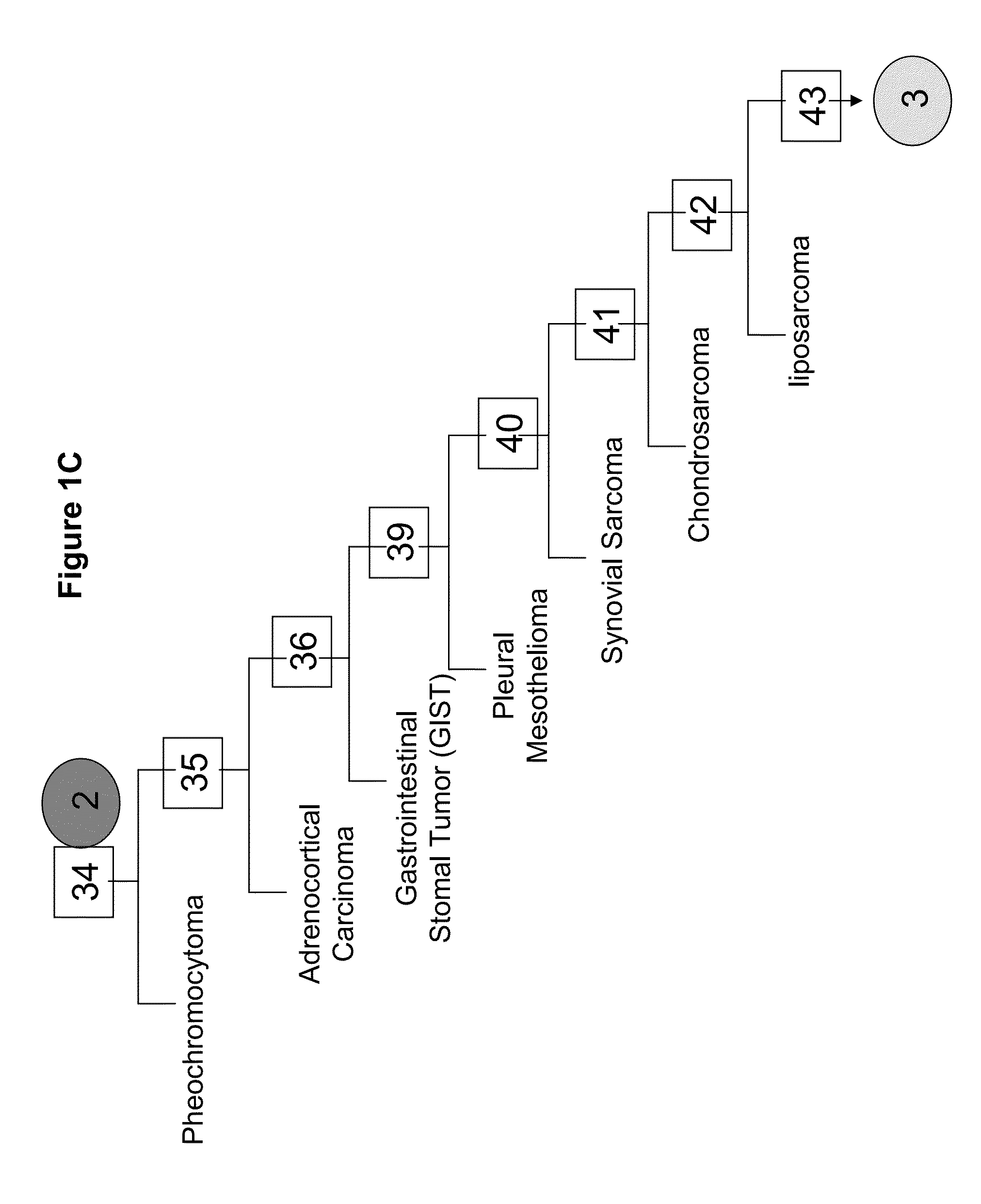
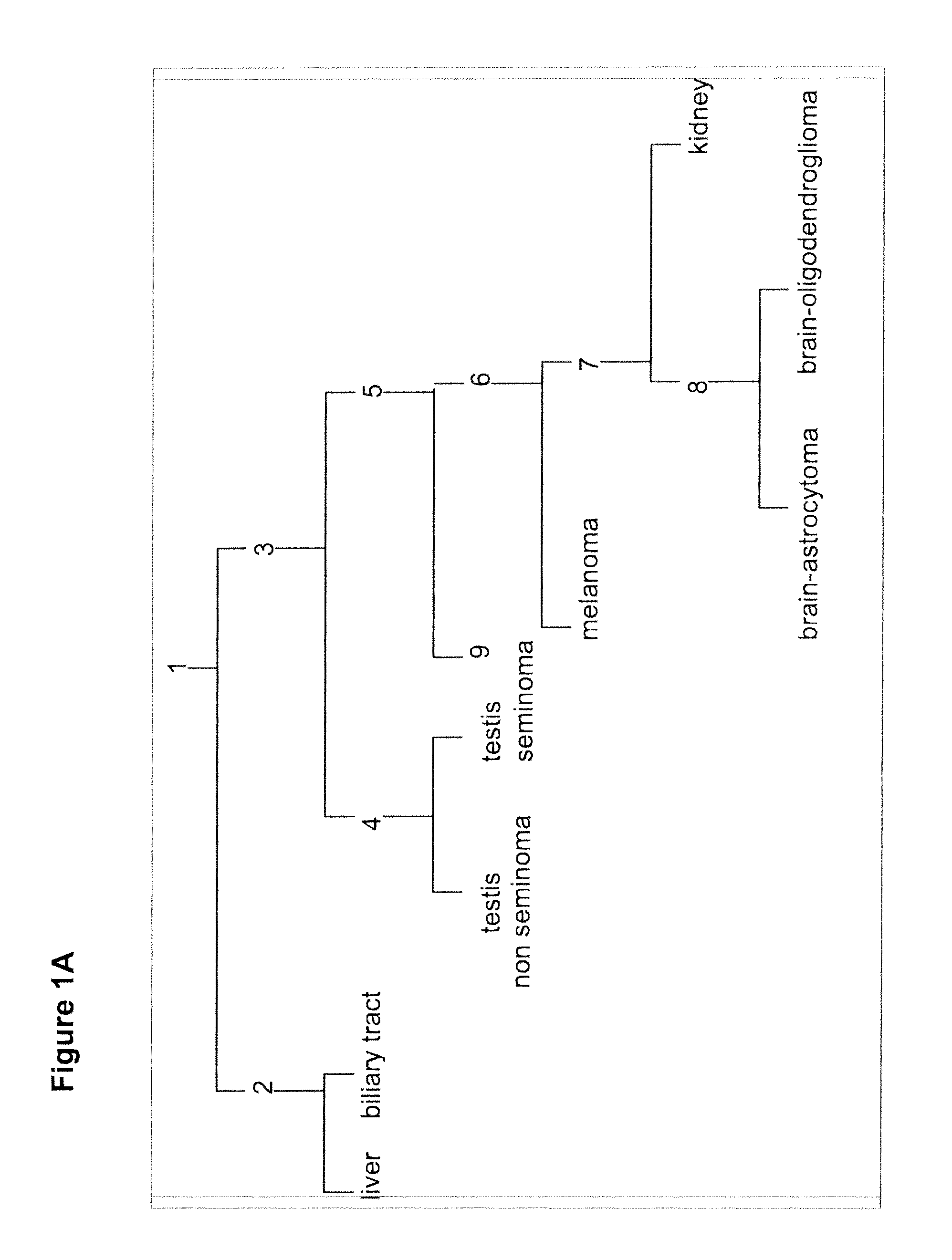
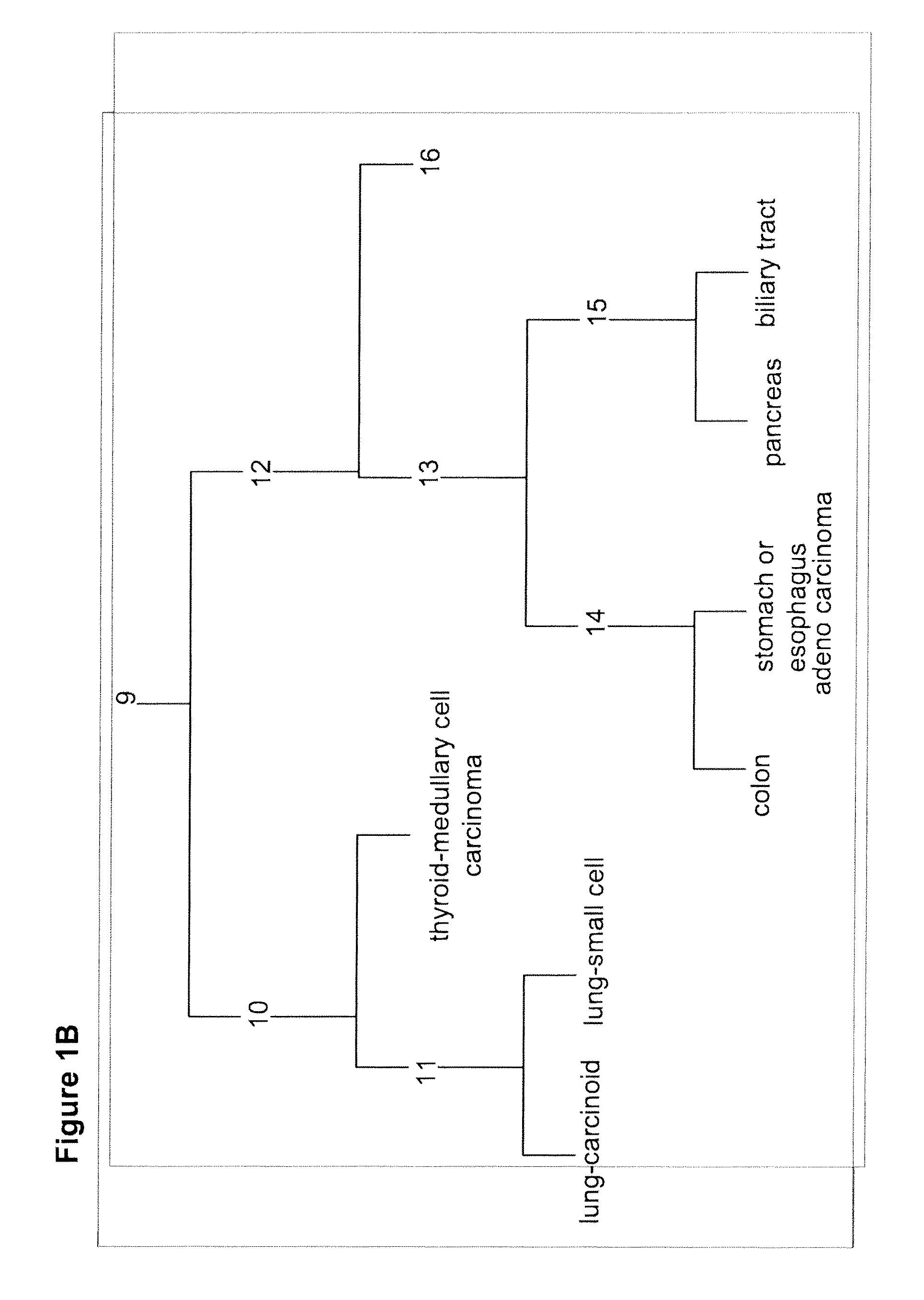
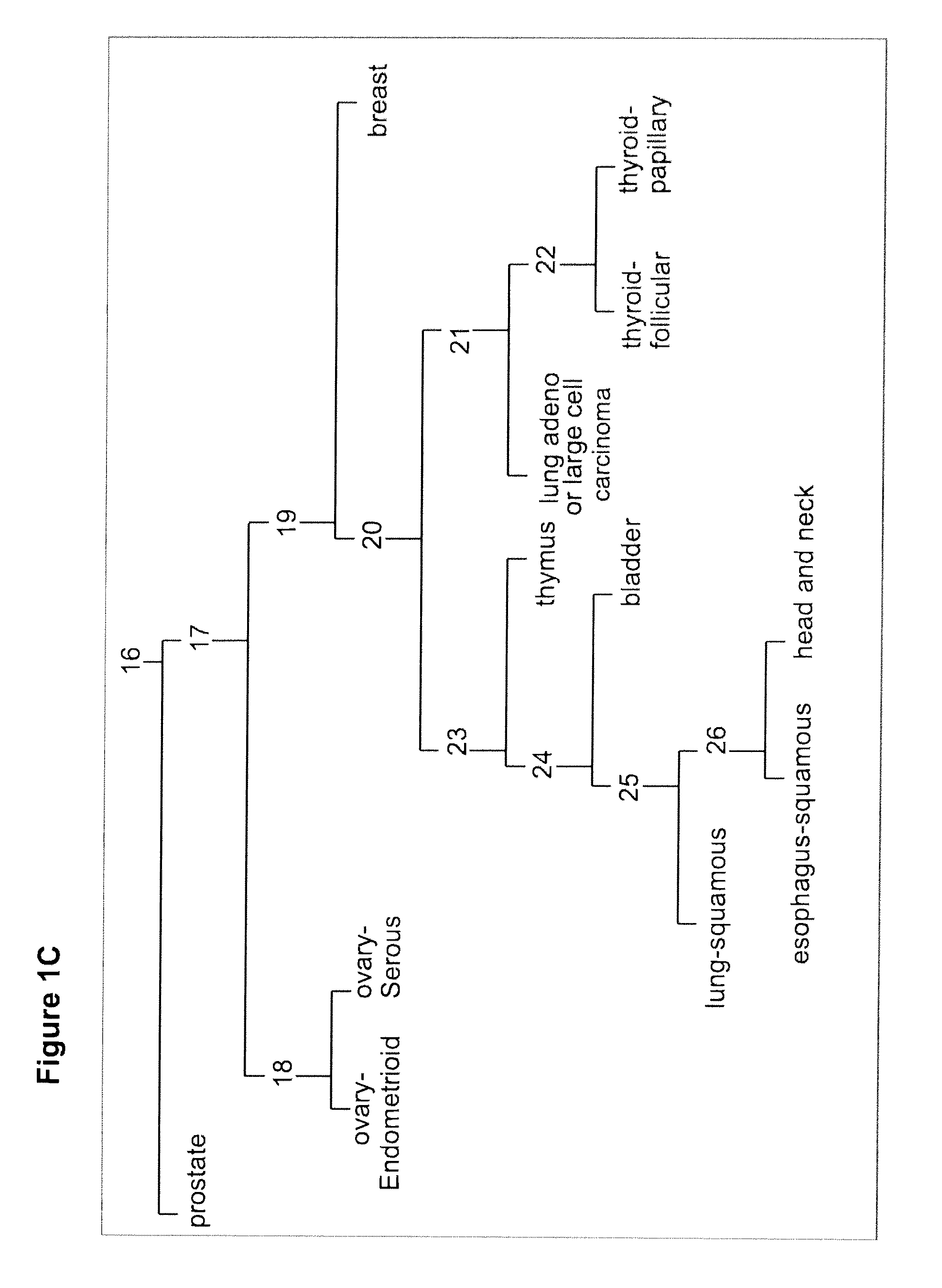
Gene expression signature for classification of tissue of origin of tumor samples
ActiveUS20110312530A1Accurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTumor SampleBiology
The present invention provides a process for classification of cancers and tissues of origin through the analysis of the expression patterns of specific microRNAs and nucleic acid molecules relating thereto. Classification according to a microRNA tree-based expression framework allows optimization of treatment, and determination of specific therapy.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
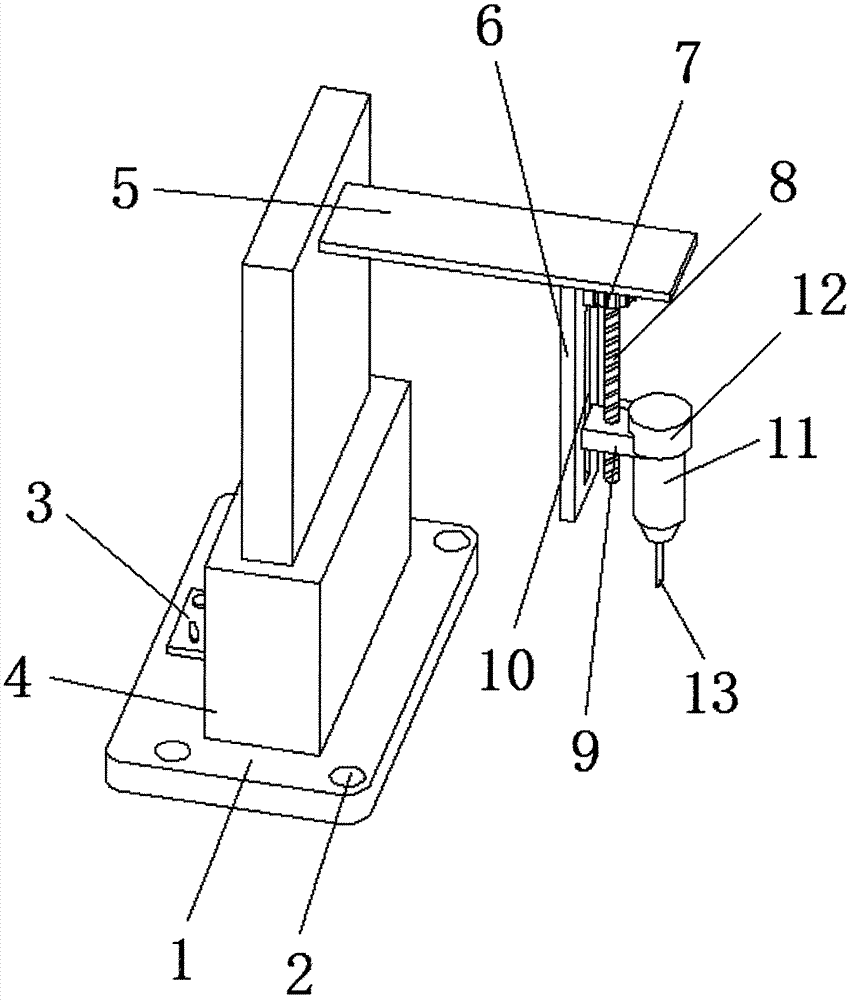
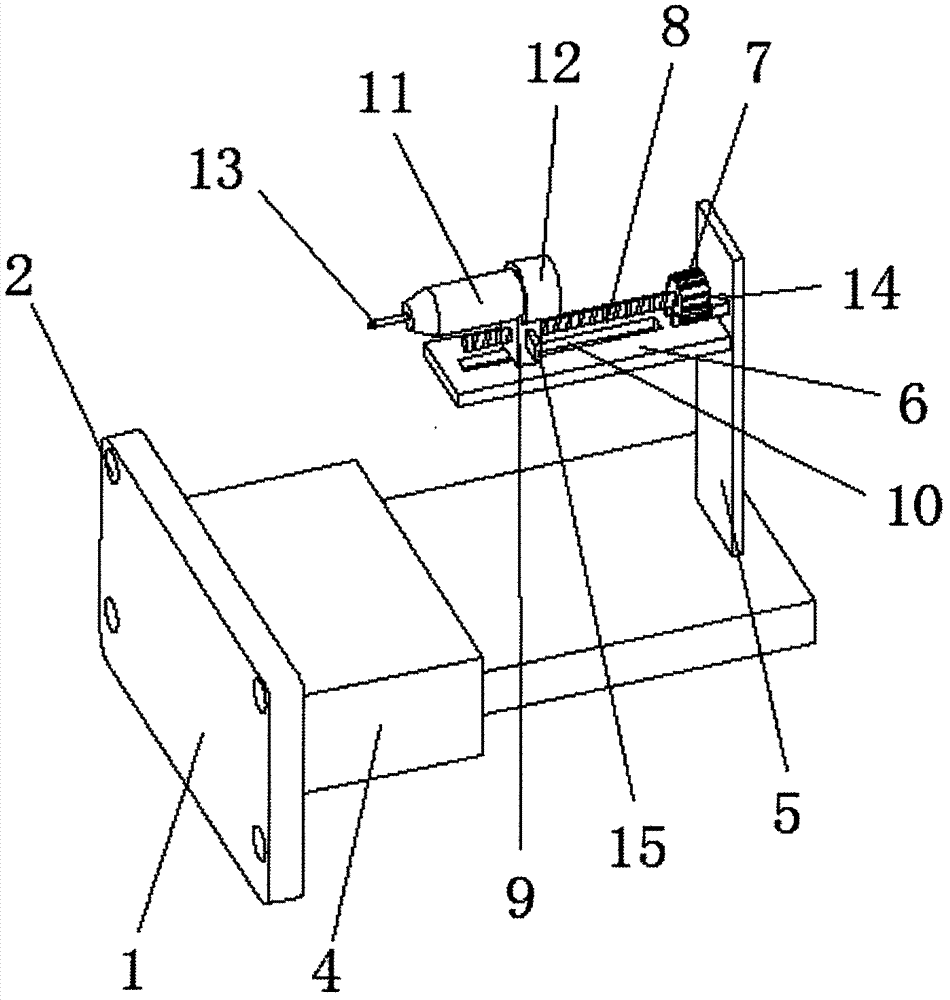
Medical clinical tumor sampling device
InactiveCN107115128ANot easy to hurtLess likely to be injured againSurgical needlesTumor SampleEngineering
The invention discloses a medical clinical tumor sampling device. The medical clinical tumor sampling device comprises an installing plate; a PLC controller and an electric stretchable rod are arranged on the upper surface of the installing plate respectively, the input end of the PLC controller is electrically connected with the output end of an externally-arranged power source, the input end of the electric stretchable rod is electrically connected with the output end of the PLC controller, a fixing plate is arranged on the side surface of the stretchable end of the electric stretchable rod, a connecting plate is arranged on the lower surface of the fixing plate, and a stepper motor is installed on the side surface of the connecting plate. According to the medical clinical tumor sampling device, a manual-sucking sample collecting mode is replaced with the electric mode, the sucking force is easy to grasp, and harm to patients is not prone to occurrence; as controlling is carried out through the PLC controller, controlling is concentrated and capable of saving force, and operation is easy; movement of a sampling pipe and movement of a sampling needle head are controlled by the stepper motor, the internal inserting depth of the patients can be determined, the accuracy is high, and secondary damage to the patients is avoided; meanwhile, a distance measuring sensor is arranged and used for measuring the inserting depth of the sampling needle head, and the accuracy is increased.
Owner:刘晓
Methods and systems for evaluating tumor mutational burden
ActiveCN109196359AQuality improvementImprove efficiencyNucleotide librariesLibrary tagsTumor SampleOncology
Methods of evaluating tumor mutational burden in a sample, e.g., a tumor sample or a sample derived from a tumor, from a subject, are disclosed.
Owner:FOUND MEDICINE INC +1
Gene expression signature for classification of tissue of origin of tumor samples
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Gene expression signature for classification of tissue of origin of tumor samples
ActiveUS8802599B2Accurate identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor SampleBiology
The present invention provides a process for classification of cancers and tissues of origin through the analysis of the expression patterns of specific microRNAs and nucleic acid molecules relating thereto. Classification according to a microRNA tree-based expression framework allows optimization of treatment, and determination of specific therapy.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Microsatellite instability detecting system and method based on genome sequencing
ActiveCN109637590AReduce limitationsRelieve painSequence analysisInstrumentsGenomic sequencingWhole genome sequencing
The invention discloses a microsatellite instability detecting system and method based on genome sequencing. The method comprises the steps that microsatellite detecting site selection is conducted, wherein an effective detecting site is selected according to sequencing data of a certain tumor sample, the threshold value of the instability of a single microsatellite corresponding to the effectivedetecting site and the evaluation standard of the instability of the microsatellite of a certain tumor sample are computed; microsatellite instability detection is conducted on a detected sample according to the threshold value of the instability of the single microsatellite corresponding to the effective detecting site and the evaluation standard of the instability of the microsatellite of the certain tumor sample. The system and the method have the advantages that the system and the method do not rely on a control sample, the pain on a detected person caused by sampling can be reduced, all genetic information of the detected person is included in the control sample, the probability of privacy leakage of the detected person can be reduced by not using the control sample, and the detectioncost can be reduced by not detecting the control sample; the operation is convenient, the cost is low, and the confidence level is high.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
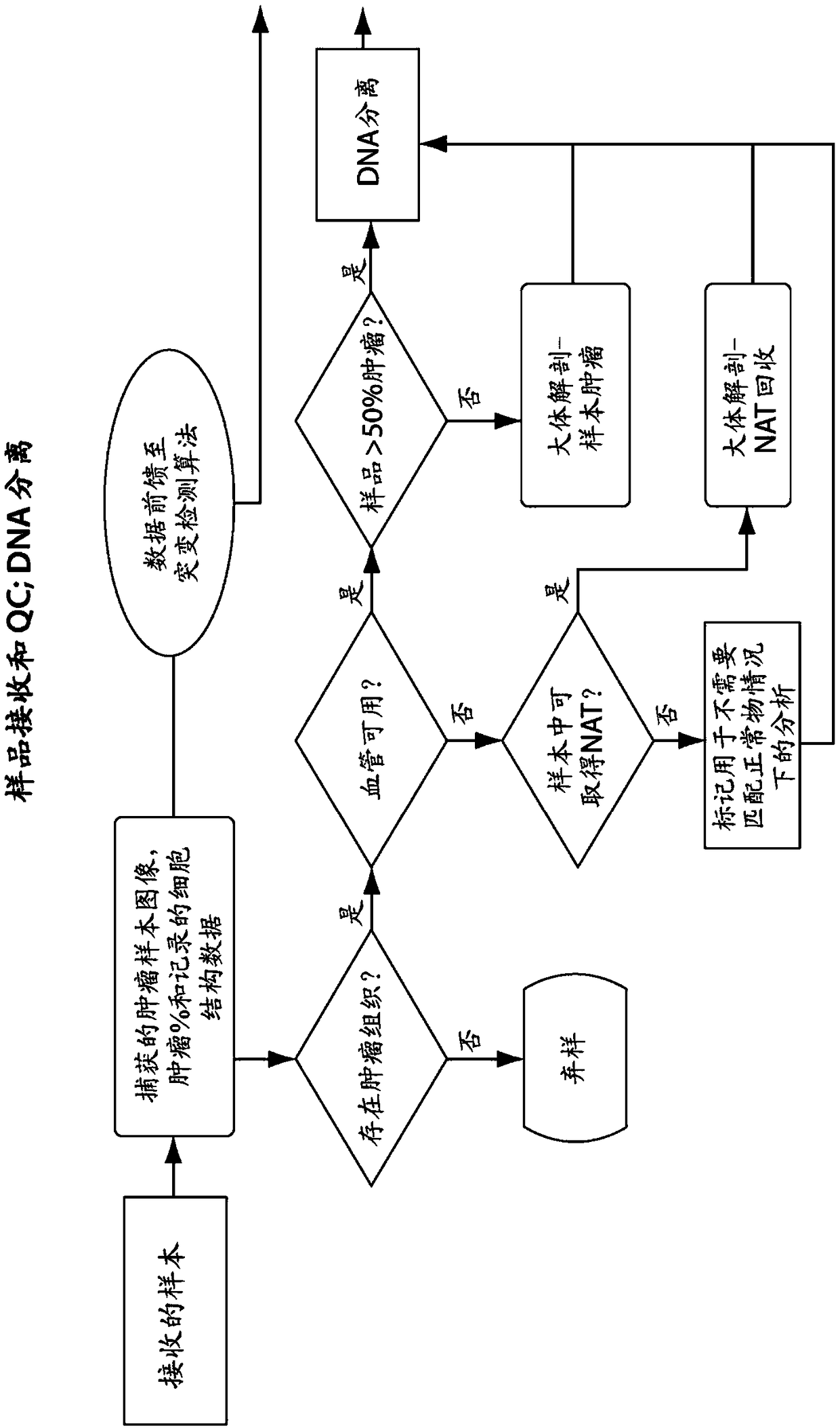
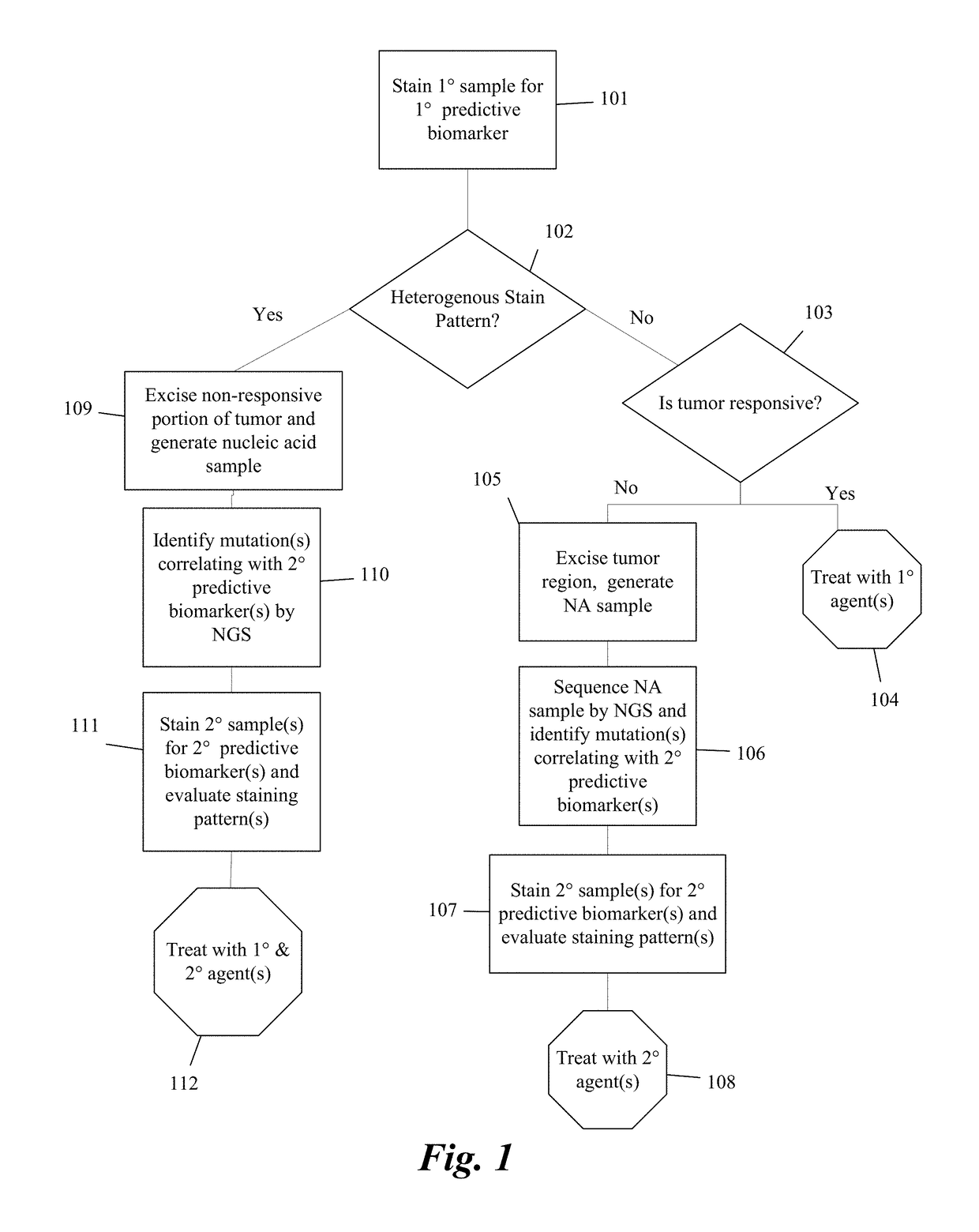
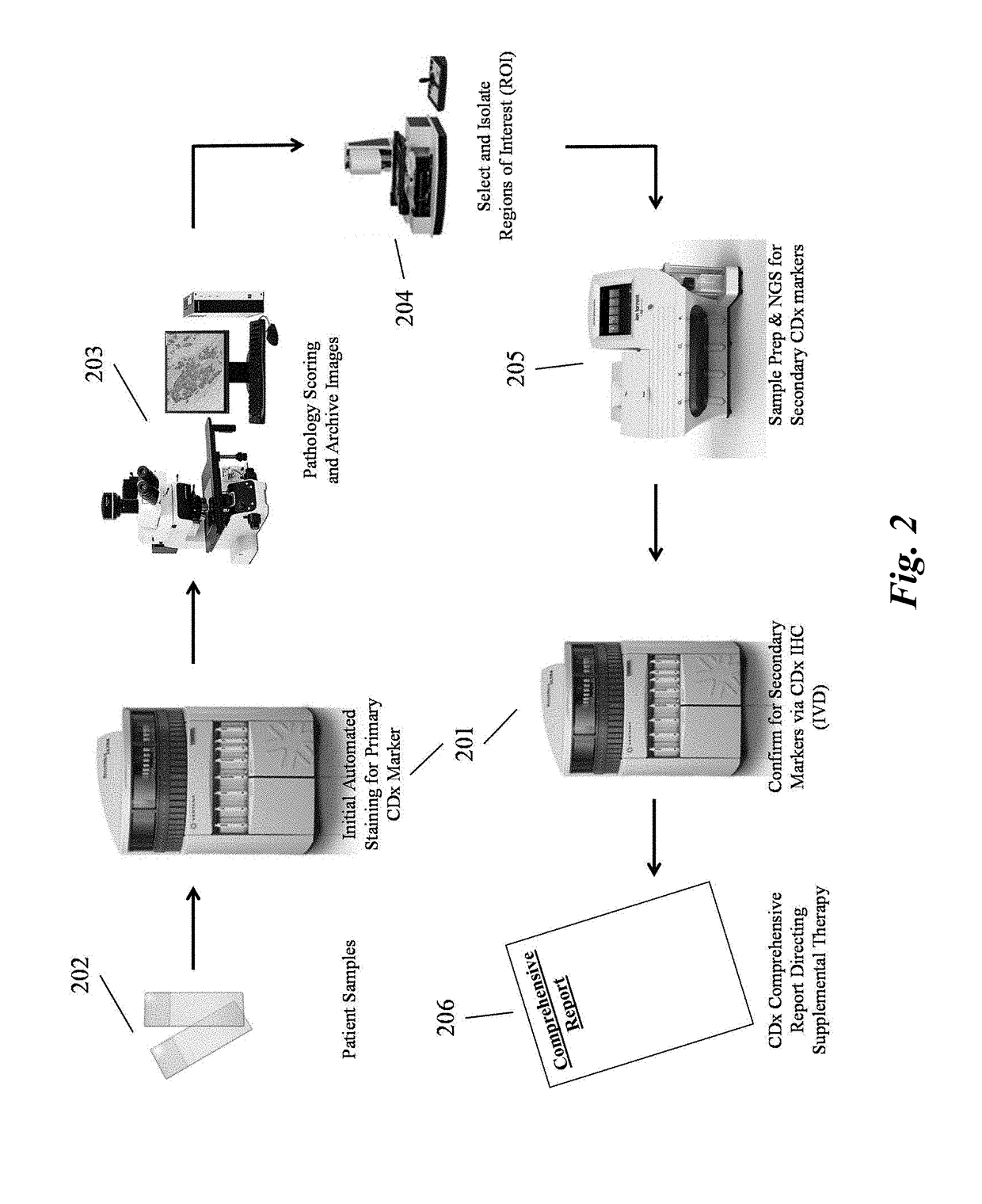
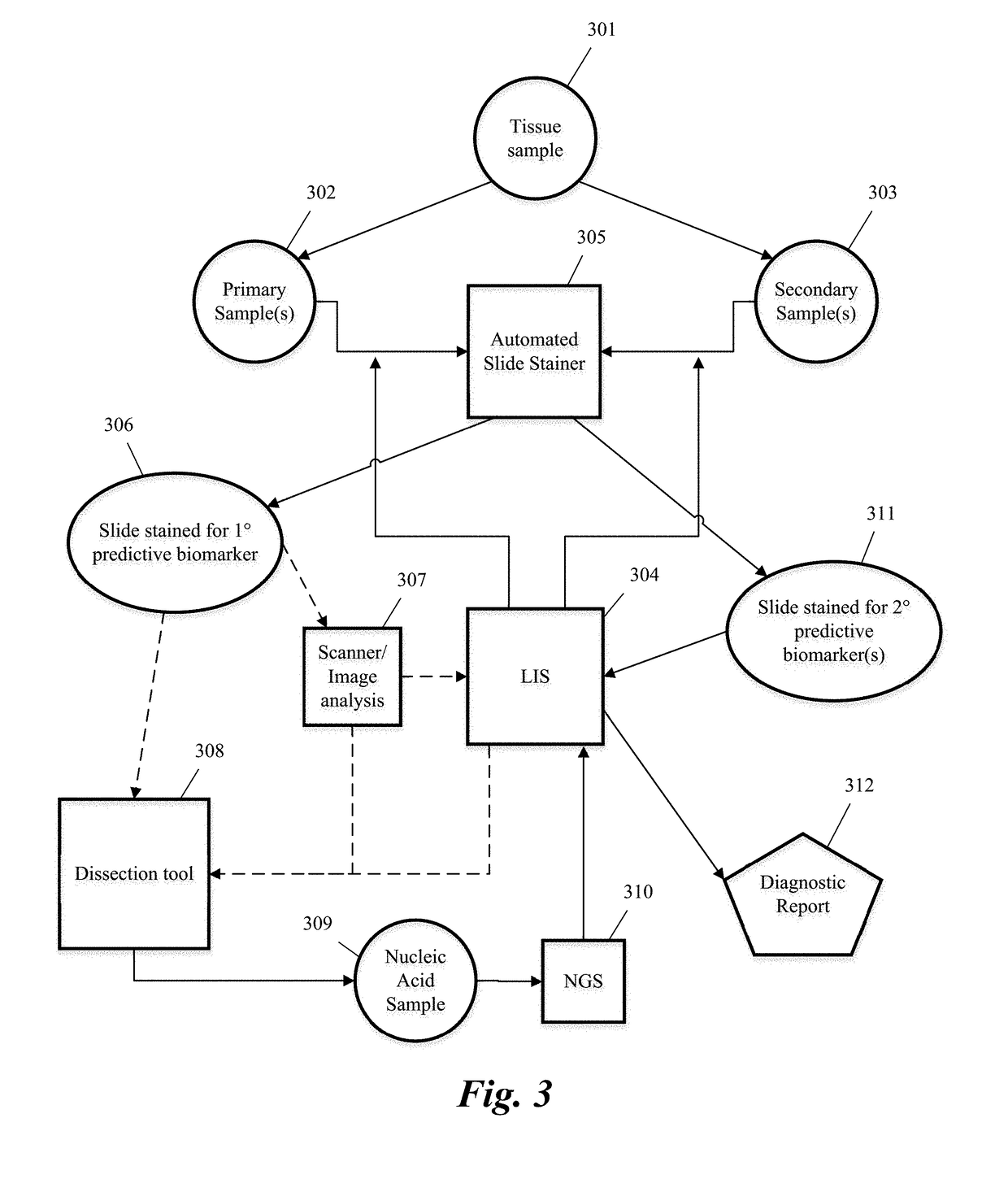
Predictive diagnostic workflow for tumors using automated dissection, next generation sequencing, and automated slide stainers
PendingUS20180340870A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationRegimenMedicine
Systems and methods for selecting therapeutic agents for cancers using next generation sequencing, automated dissection, and / or automated slide stainers are disclosed. Non-responsive regions of a tumor sample having a heterogenous staining pattern for a predictive biomarker are excised using an automated dissection tool. Mutations linked to additional predictive biomarkers are identified in the excised portion of the sample by next generation sequencing. The relevance of the additional predictive biomarker(s) is confirmed by histochemical staining. Therapeutic courses may then be selected on the basis of the staining patterns of the predictive biomarkers.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Molecular markers predicting response to adjuvant therapy, or disease progression, in breast cancer
Predicting response to adjuvant therapy or predicting disease progression in breast cancer is realized by (1) first obtaining a breast cancer test sample from a subject; (2) second obtaining clinicopathological data from said breast cancer test sample; (3) analyzing the obtained breast cancer test sample for presence or amount of (a) one or more molecular markers of hormone receptor status, one or more growth factor receptor markers, (b) one or more tumor suppression / apoptosis molecular markers; and (c) one or more additional molecular markers both proteomic and non-proteomic that are indicative of breast cancer disease processes; and then (4) correlating (a) the presence or amount of said molecular markers and, with (b) clinicopathological data from said tissue sample other than the molecular markers of breast cancer disease processes. A kit of (1) a panel of antibodies; (2) one or more gene amplification assays; (3) first reagents to assist said antibodies with binding to tumor samples; (4) second reagents to assist in determining gene amplification; permits, when applied to a breast cancer patient's tumor tissue sample, (A) permits observation, and determination, of a numerical level of expression of each individual antibody, and gene amplification; whereupon (B) a computer algorithm, residing on a computer can calculate a prediction of treatment outcome for a specific treatment for breast cancer, or future risk of breast cancer progression.
Owner:LINKE STEVEN +2
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods for cancer
ActiveUS20190219586A1Conducive to survivalImprove survivalCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsTissues tumorMelanoma
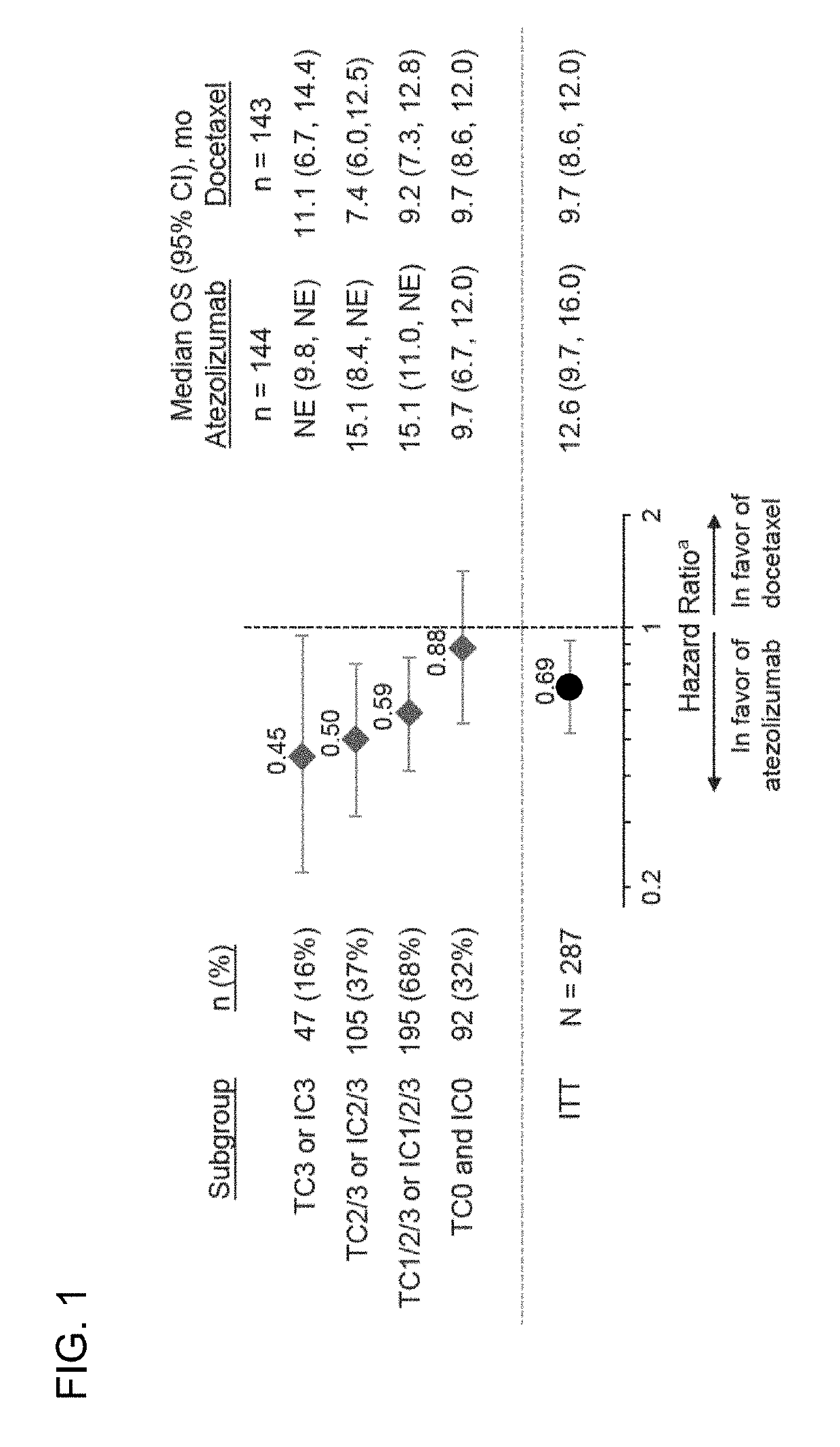
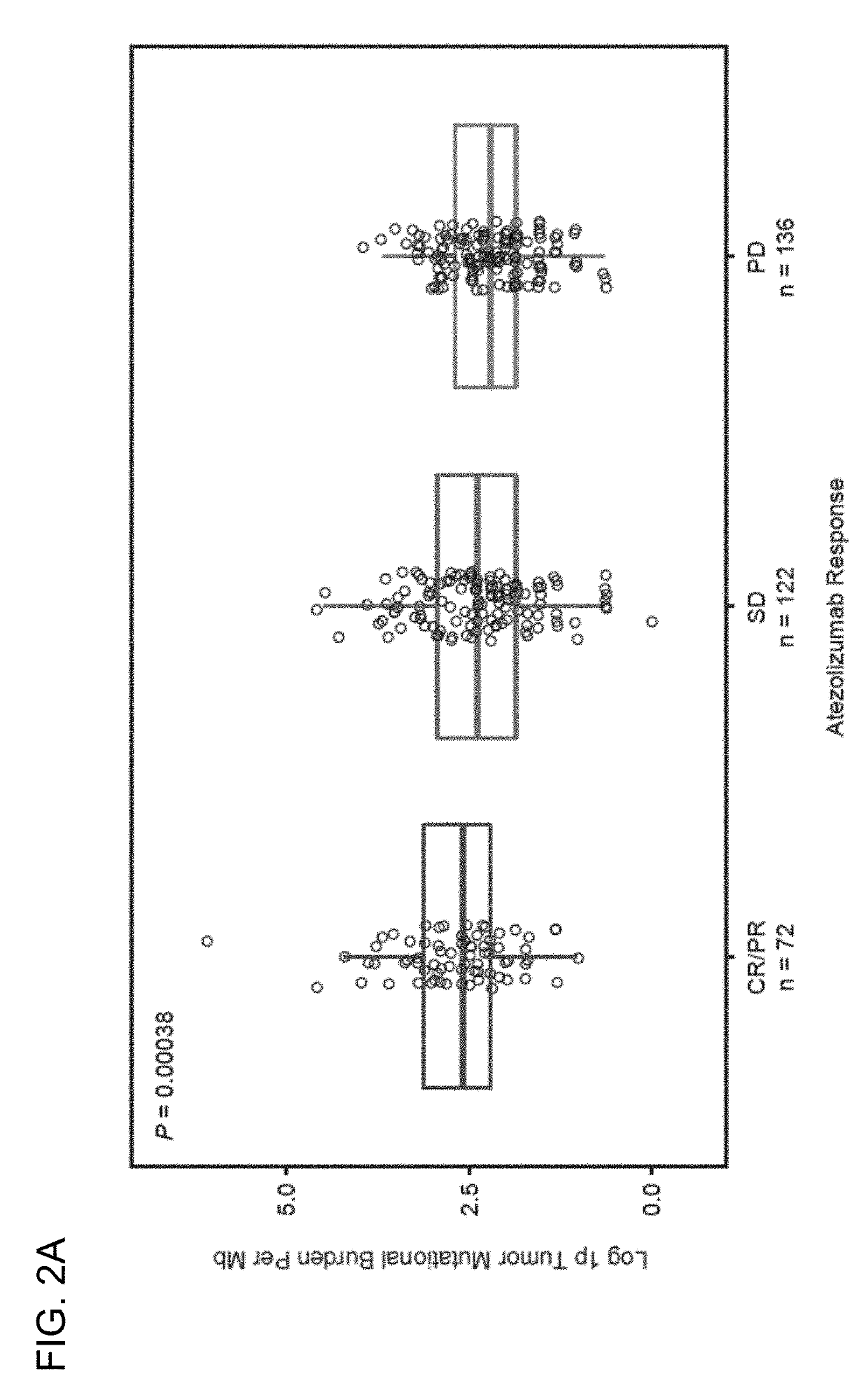
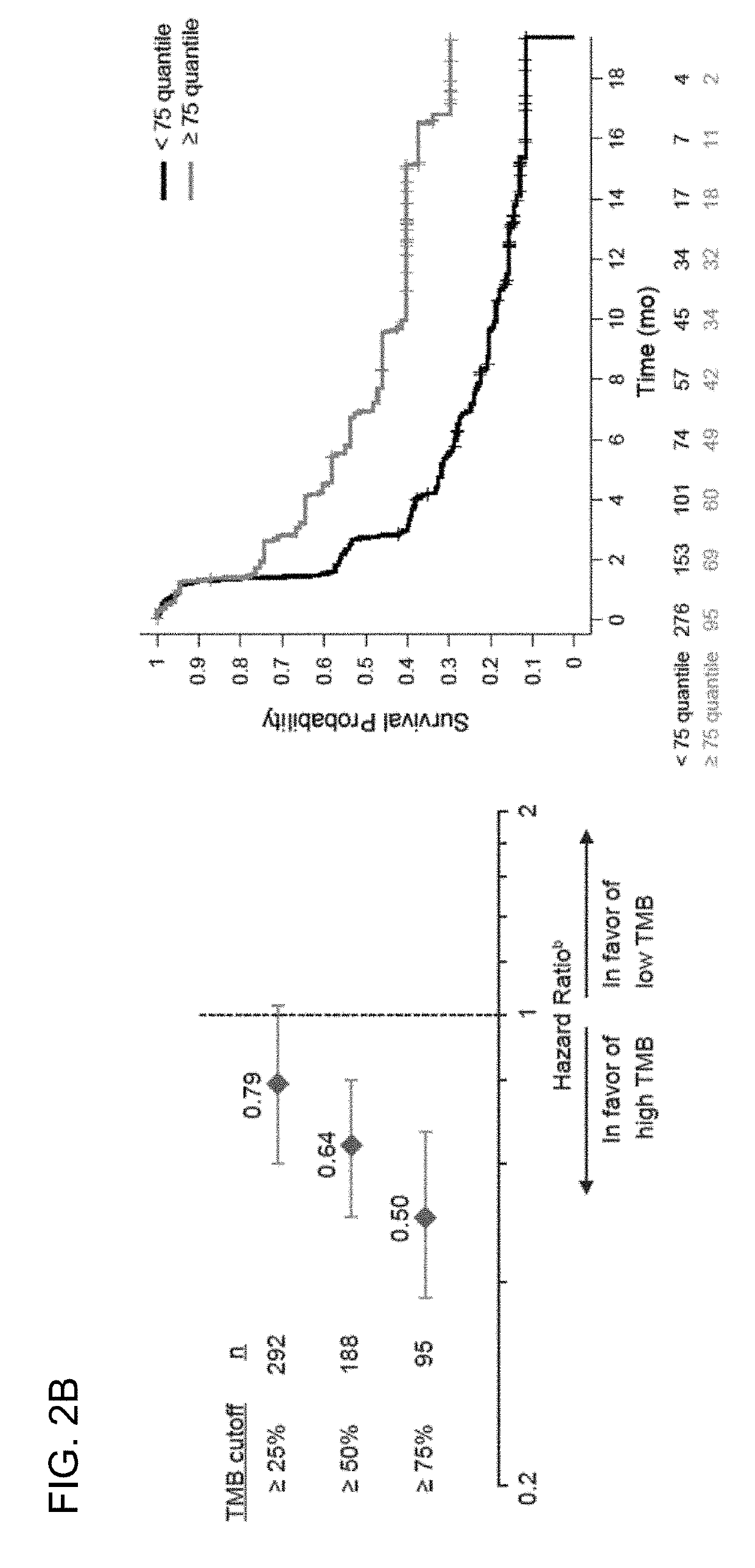
The present invention provides therapeutic and diagnostic methods and compositions for cancer, for example, lung cancer (e.g., NSCLC), bladder cancer (e.g., UC), kidney cancer (e.g., RCC), breast cancer (e.g., TNBC), or melanoma. The invention provides methods of treating cancer (e.g., lung cancer (e.g., NSCLC), bladder cancer (e.g., UC), kidney cancer (e.g., RCC), breast cancer (e.g., TNBC), or melanoma), methods of determining whether a patient suffering from cancer (e.g., lung cancer (e.g., NSCLC), bladder cancer (e.g., UC), kidney cancer (e.g., RCC), breast cancer (e.g., TNBC), or melanoma) is likely to respond to treatment comprising a PD-L1 axis binding antagonist, methods of predicting responsiveness of a patient suffering from cancer (e.g., lung cancer (e.g., NSCLC), bladder cancer (e.g., UC), kidney cancer (e.g., RCC), breast cancer (e.g., TNBC), or melanoma) to treatment comprising a PD-L1 axis binding antagonist, and methods of selecting a therapy for a patient suffering from cancer (e.g., lung cancer (e.g., NSCLC), bladder cancer (e.g., UC), kidney cancer (e.g., RCC), breast cancer (e.g., TNBC), or melanoma), based on a tissue tumor mutational burden (tTMB) score, which reflects somatic mutation levels of genes in a tumor tissue sample obtained from the patient, alone or in combination with PD-L1 expression levels (e.g., PD-L1 expression levels in tumor or tumor-infiltrating immune cells in a tumor sample (tumor area) obtained from the patient).
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Methods for predicting sensitivity of tumors to arginine deprivation
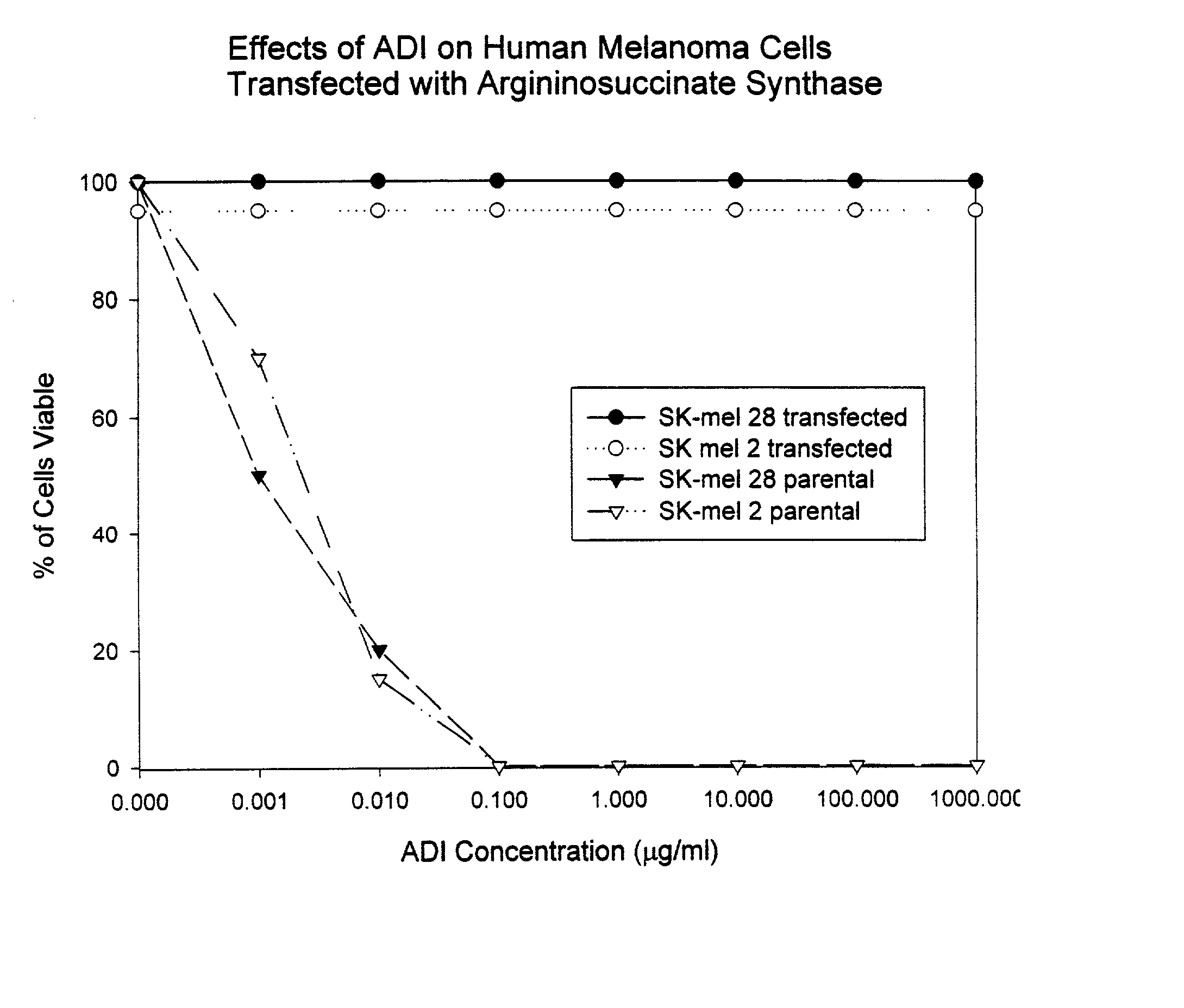
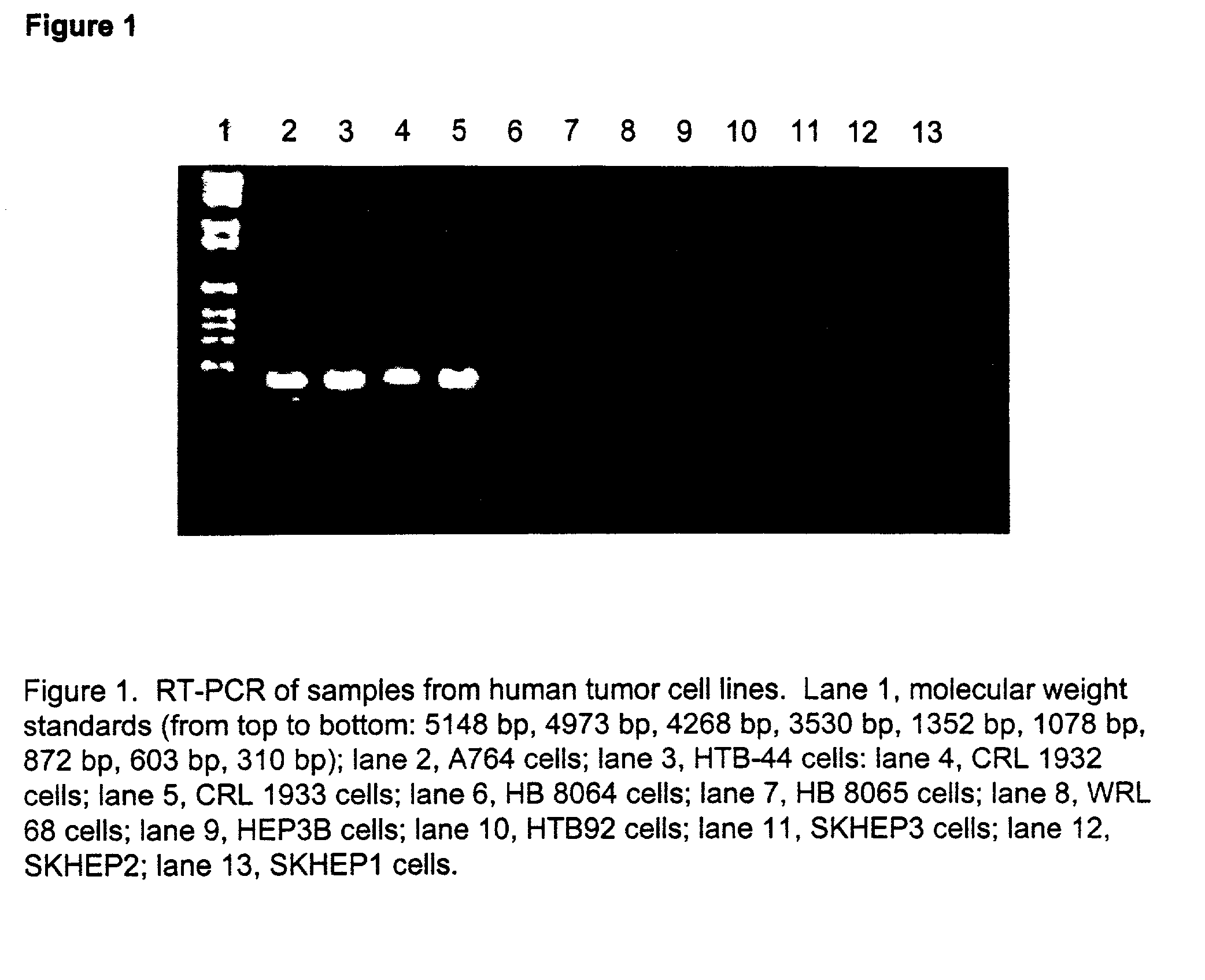
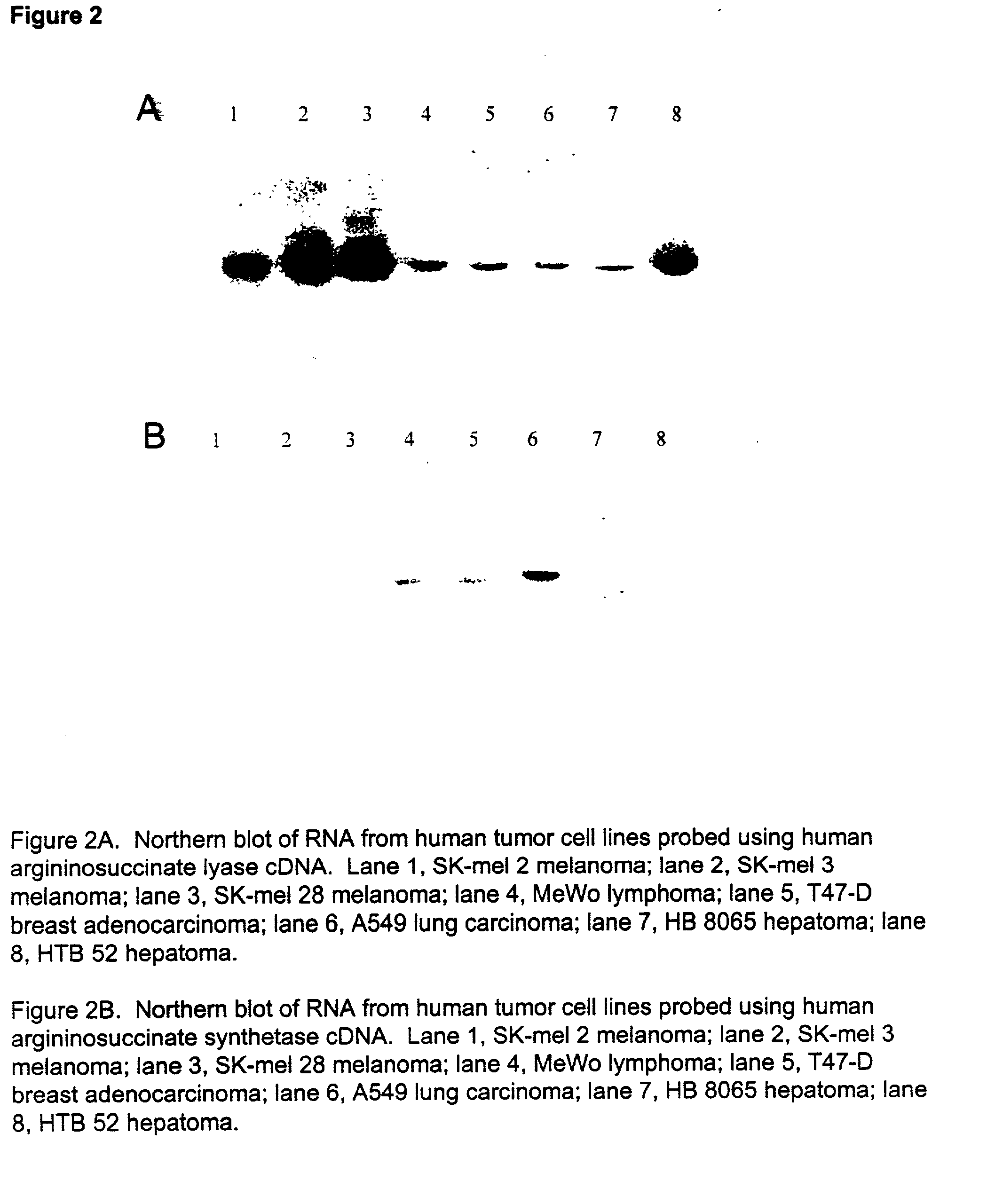
InactiveUS20050063942A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthUrea cycle enzymes
The present invention provides methods for determining which cancer patients are susceptible to arginine depletion therapy and methods for treating cancer. The present invention also provides methods for predicting the appropriateness of arginine deprivation therapy for a cancer patient. The methods generally comprise obtaining a tumor sample from the cancer patient and detecting the presence or absence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in the tumor sample. The absence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in the tumor sample is indicative of a cancer patient who is a candidate for arginine deprivation therapy, and the presence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in said tumor sample is indicative of a cancer patient who is not a candidate for arginine deprivation therapy. Prior to, simultaneous with, or after testing the tumor sample, the method further comprises the steps of obtaining a non-cancerous sample from the cancer patient and detecting the presence or absence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in the non-cancerous sample, wherein the absence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in the non-cancerous sample and absence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in the tumor sample is indicative of a cancer patient who is not a good candidate for arginine deprivation therapy, the presence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in the non-cancerous sample and the absence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in the tumor sample is indicative of a cancer patient who is a good candidate for arginine deprivation therapy, and the presence of evidence of urea cycle enzyme expression in the tumor sample is indicative of a cancer patient who is not a candidate for arginine deprivation therapy.
Owner:PHOENIX PHARMACOLOGICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com