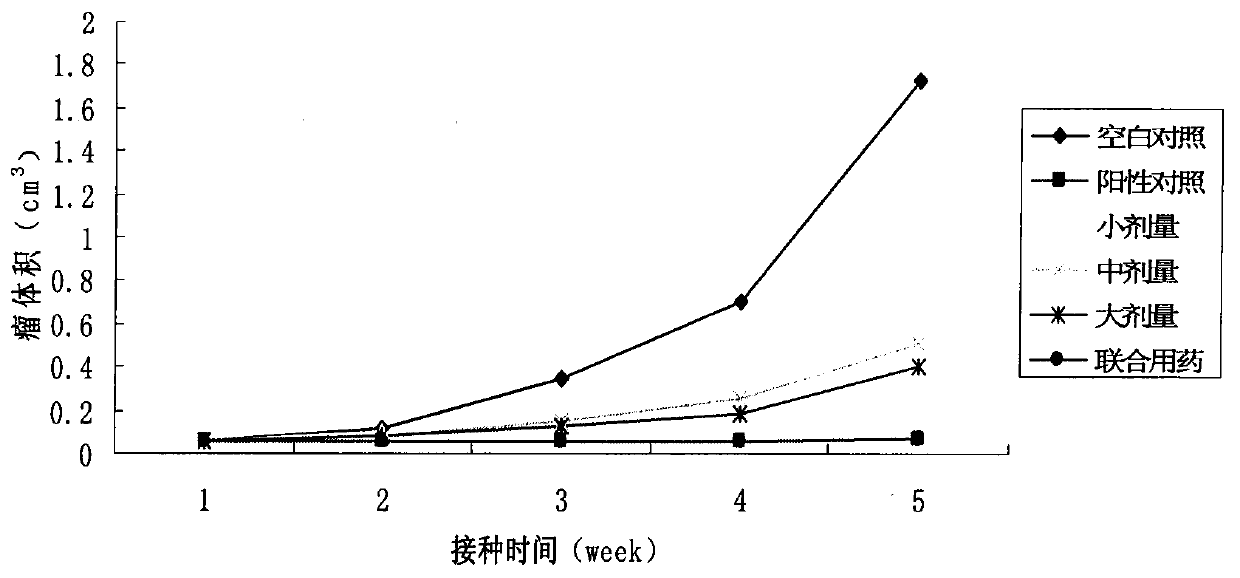
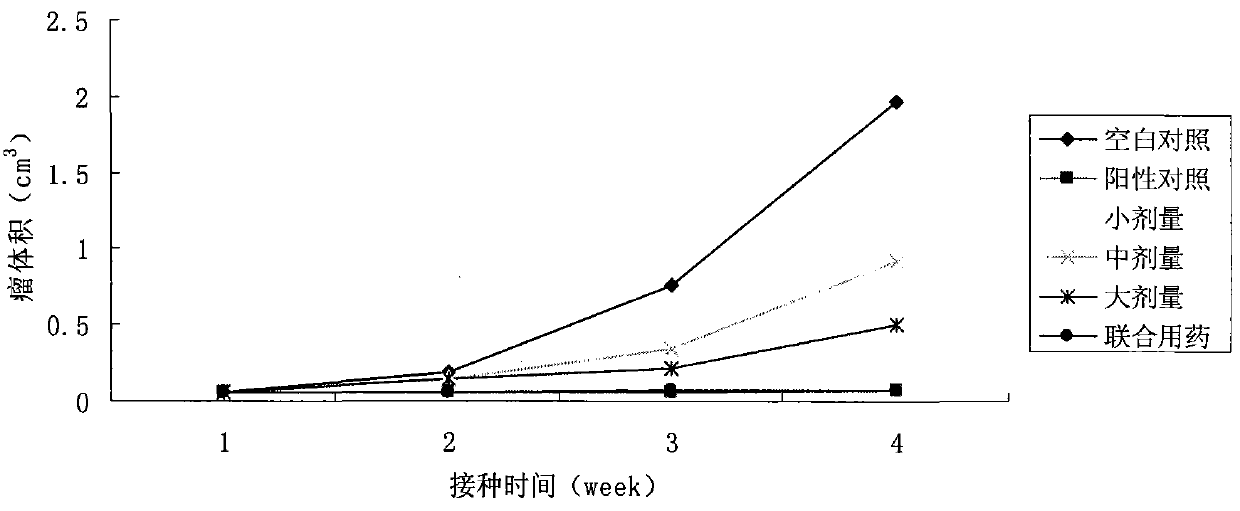
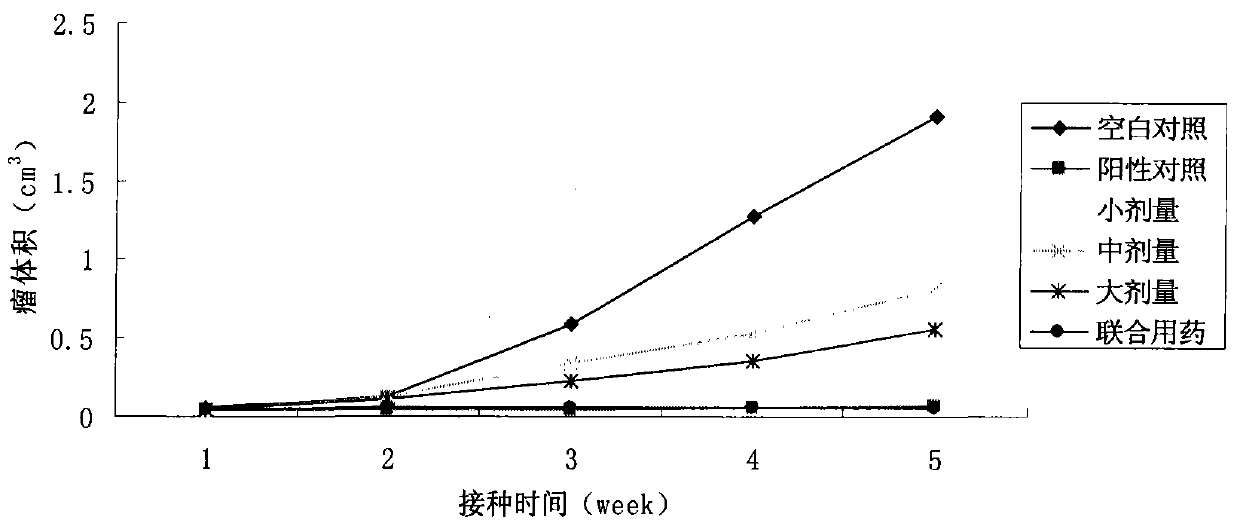
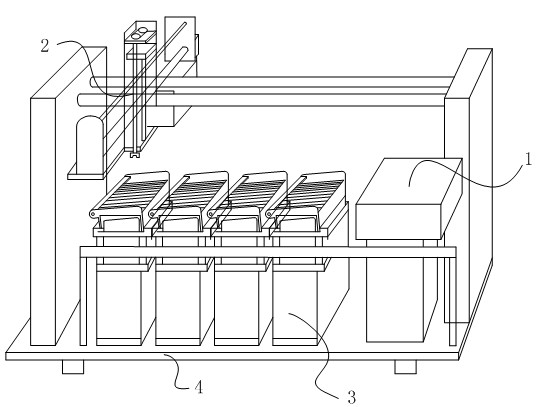
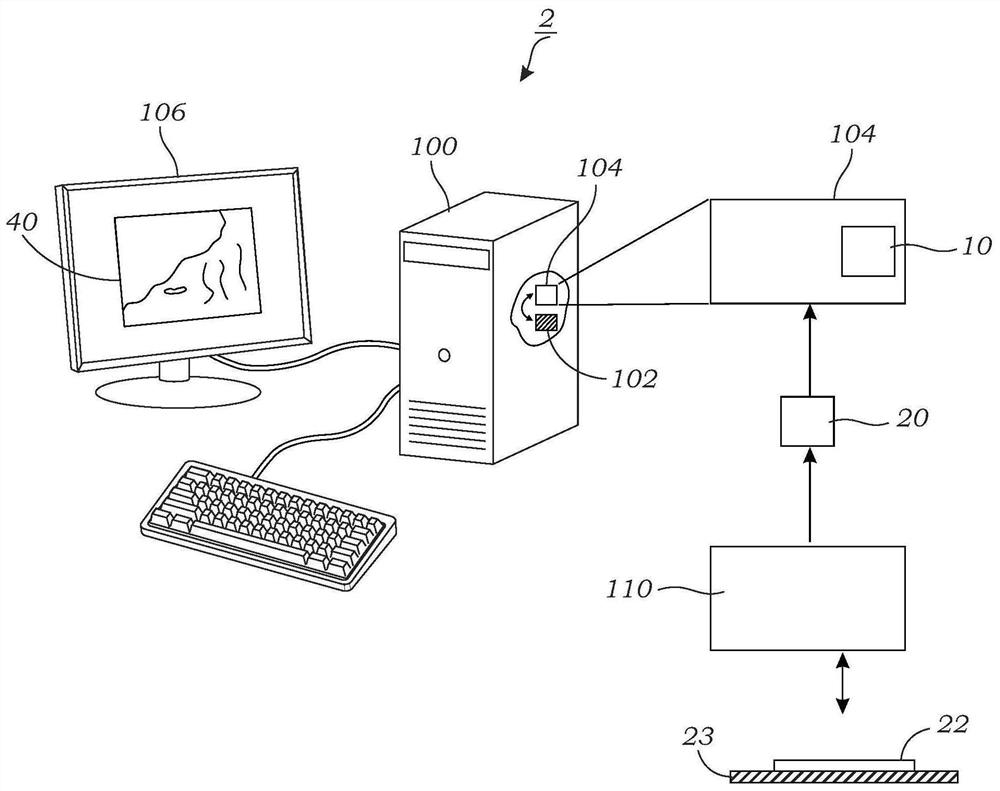
Patents
Literature
90 results about "Histochemical staining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
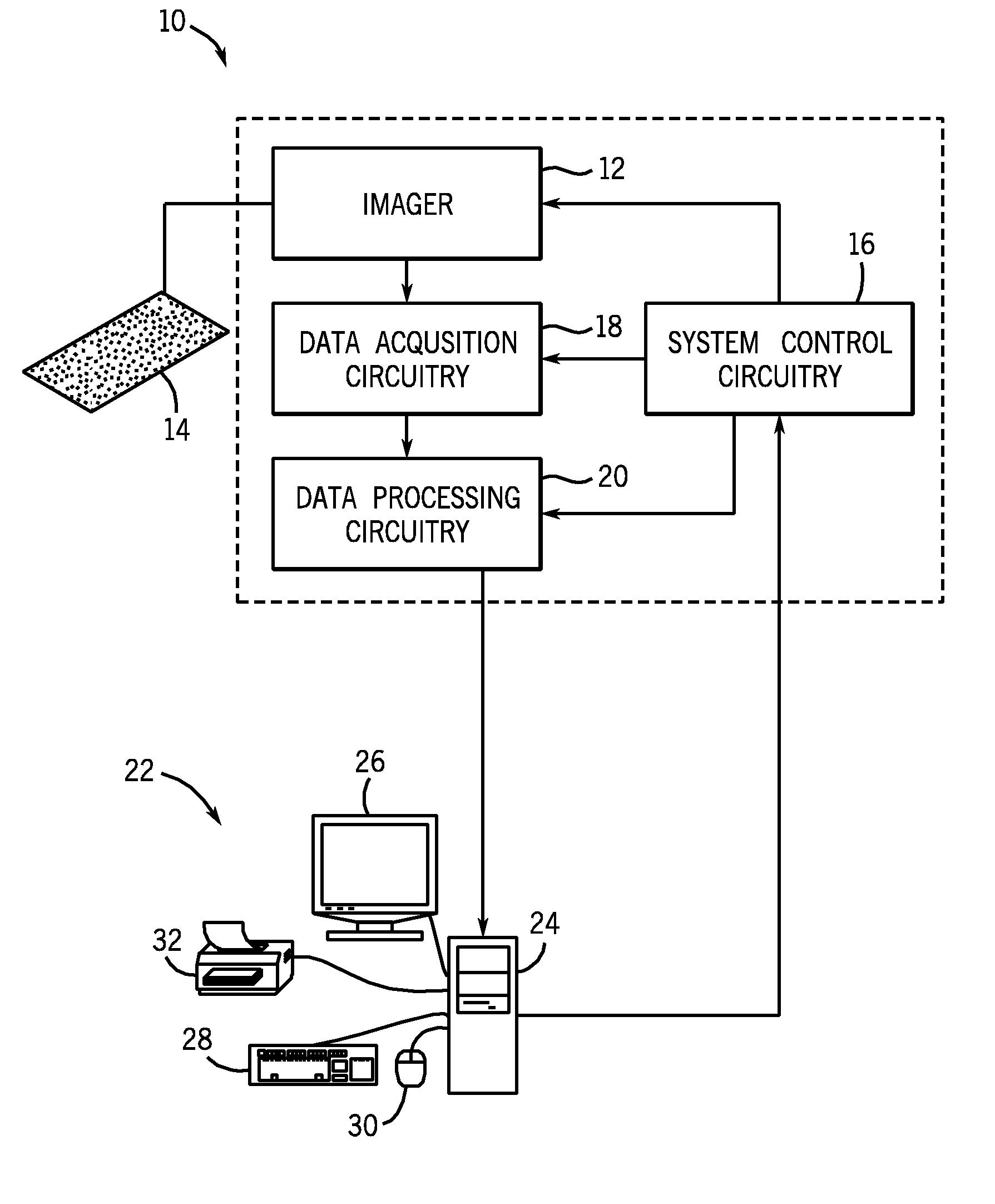
Methods for Assessing Molecular Expression of Subcellular Molecules
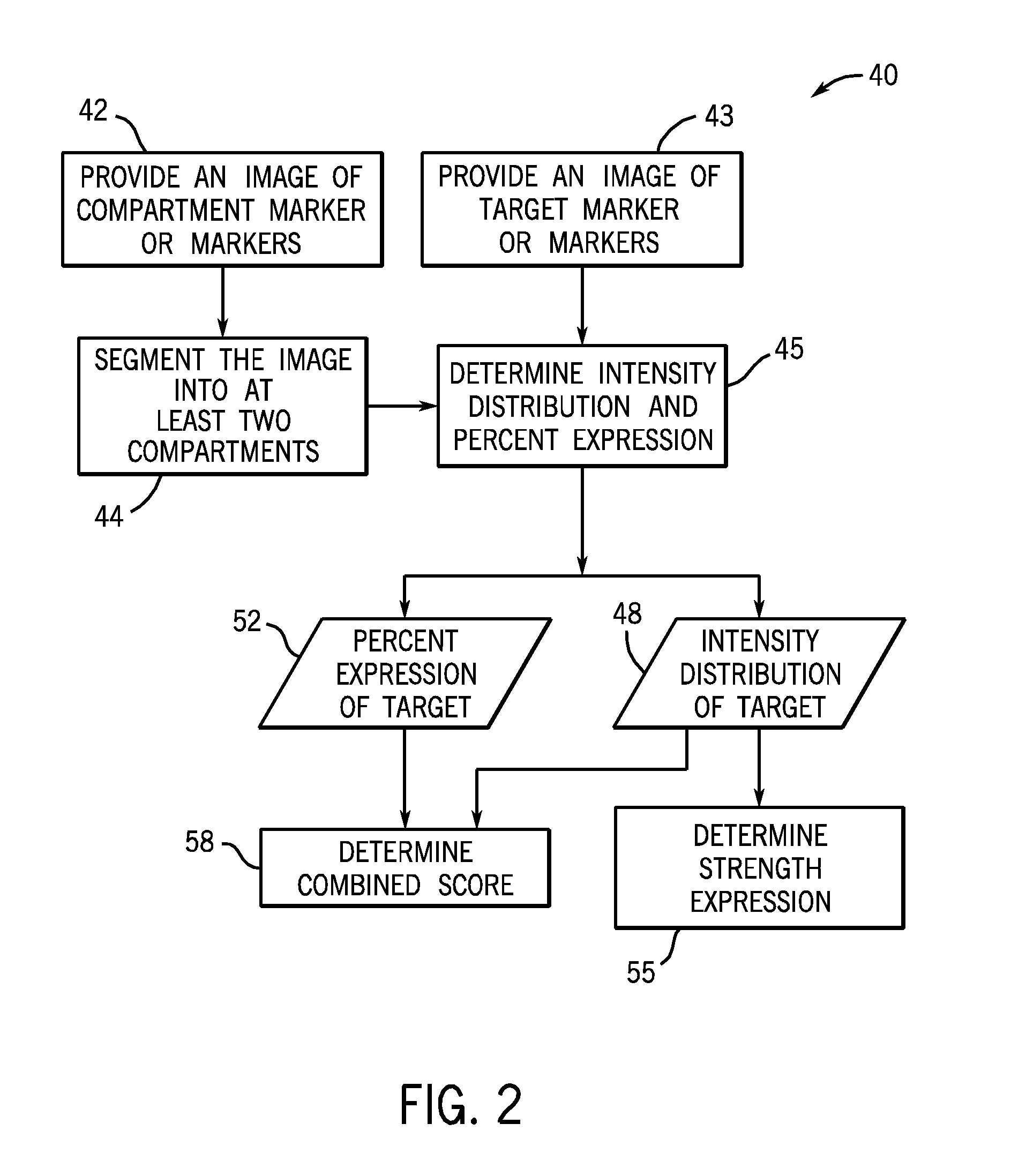
The present techniques provide fully automated methods for quantifying the location, strength and percent of expressed target molecules or other biological markers in immunohistochemically stained biological samples. The samples may be automatically segmented, for example into subcellular compartments, from images of compartmental markers. Then, the distribution of a target molecule on each of these compartments is calculated that includes the percentage and strength of expression. This is different than existing intensity or ratio based methods where abundant low expression levels are indistinguishable from scarce high expression levels.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
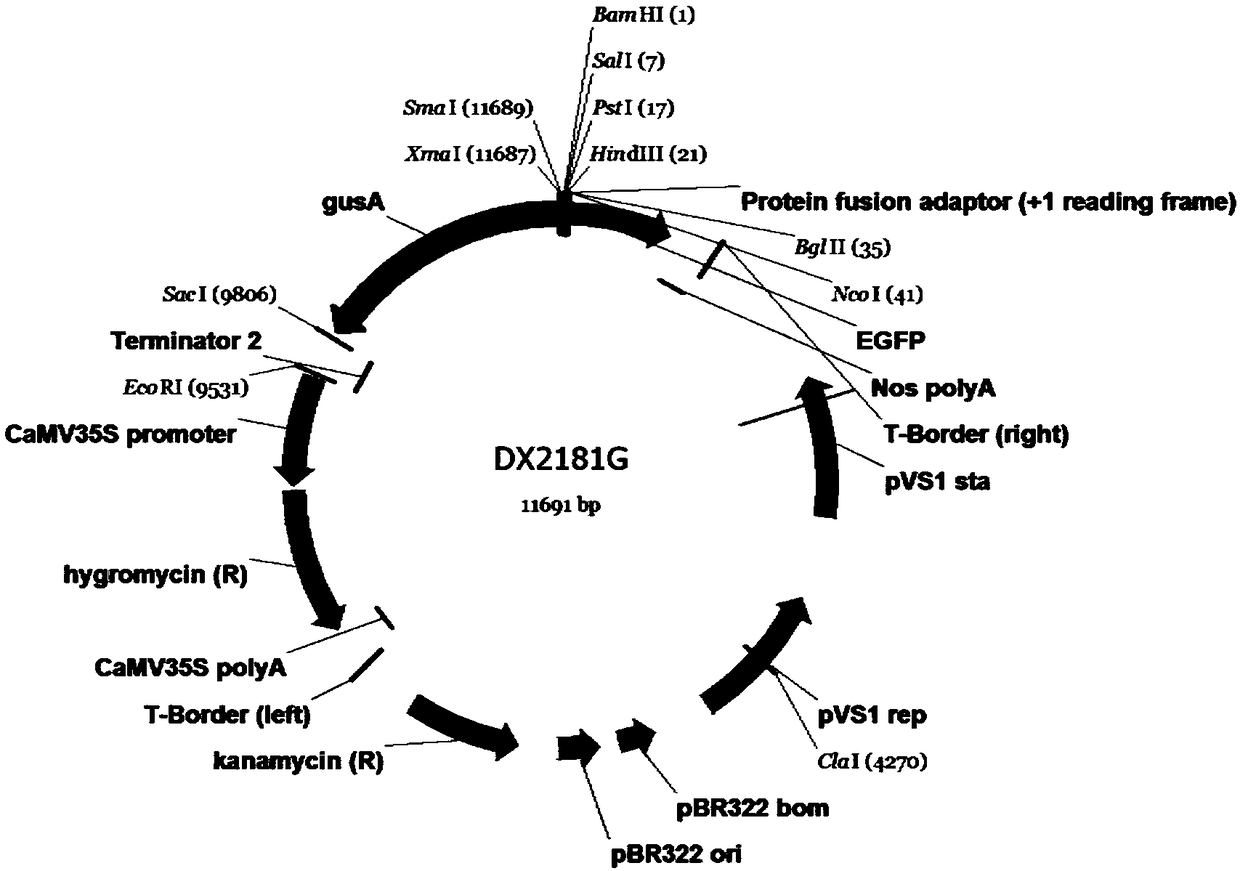
Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated and vacuum infiltration-assisted soybean genetic transformation method
InactiveCN102766650AImproves chances of intrusionHigh infection efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsHypocotylBacillus thuringiensis
The invention relates to an agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated and vacuum infiltration-assisted soybean genetic transformation method, and belongs to the technical fields of molecular biology and genetic engineering. The agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated and vacuum infiltration-assisted soybean genetic transformation method comprises the following steps of: selecting genotypes of soybean seeds, disinfecting the soybean seeds, and germinating; preparing bacterial liquid, which contains anti-nematode bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) genes, of agrobacterium rhizogene K599; transforming the agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated soybeans; performing histochemical staining analysis on transgenic roots; and performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection on the transgenic roots. According to the method, an agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated and vacuum infiltration-assisted transformation method is applied to the soybeans for the first time, and hairy roots of soybean roots are transformed successfully; the disinfected soybean seeds are planted in sterile vermiculite and are germinated, the injury of epidermic meristematic cells is caused at the upper end of hypocotyl, the agrobacterium rhizogene is infected under the vacuum condition, and genetic transformation is performed to obtain the soybean transgenic hairy roots containing the anti-nematode BT genes. By implementing the agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated and vacuum infiltration-assisted soybean genetic transformation method, the opportunity of the invasion of the agrobacterium rhizogenes can be improved fully, the infection efficiency of the agrobacterium rhizogenes can be improved obviously, and the transformation rate of the soybeans is improved effectively.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
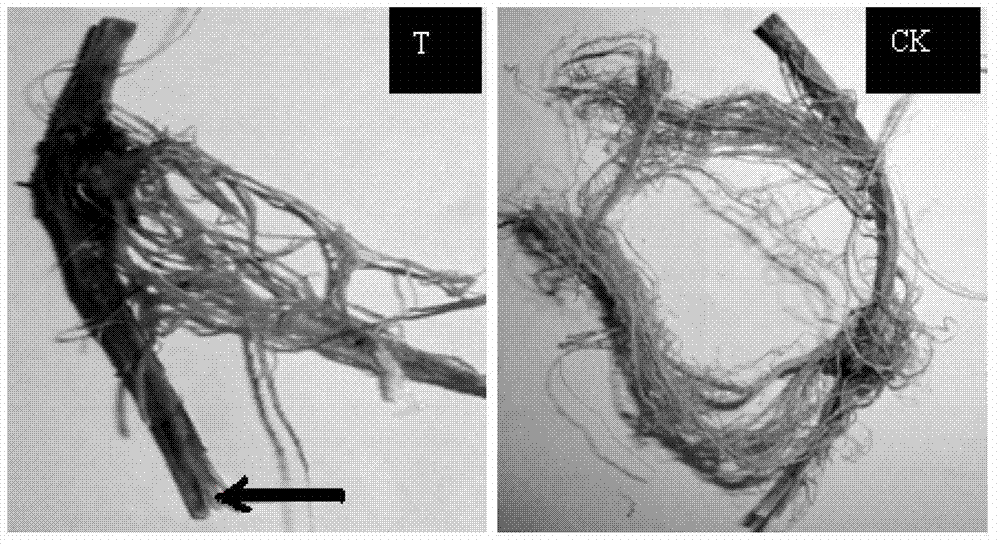
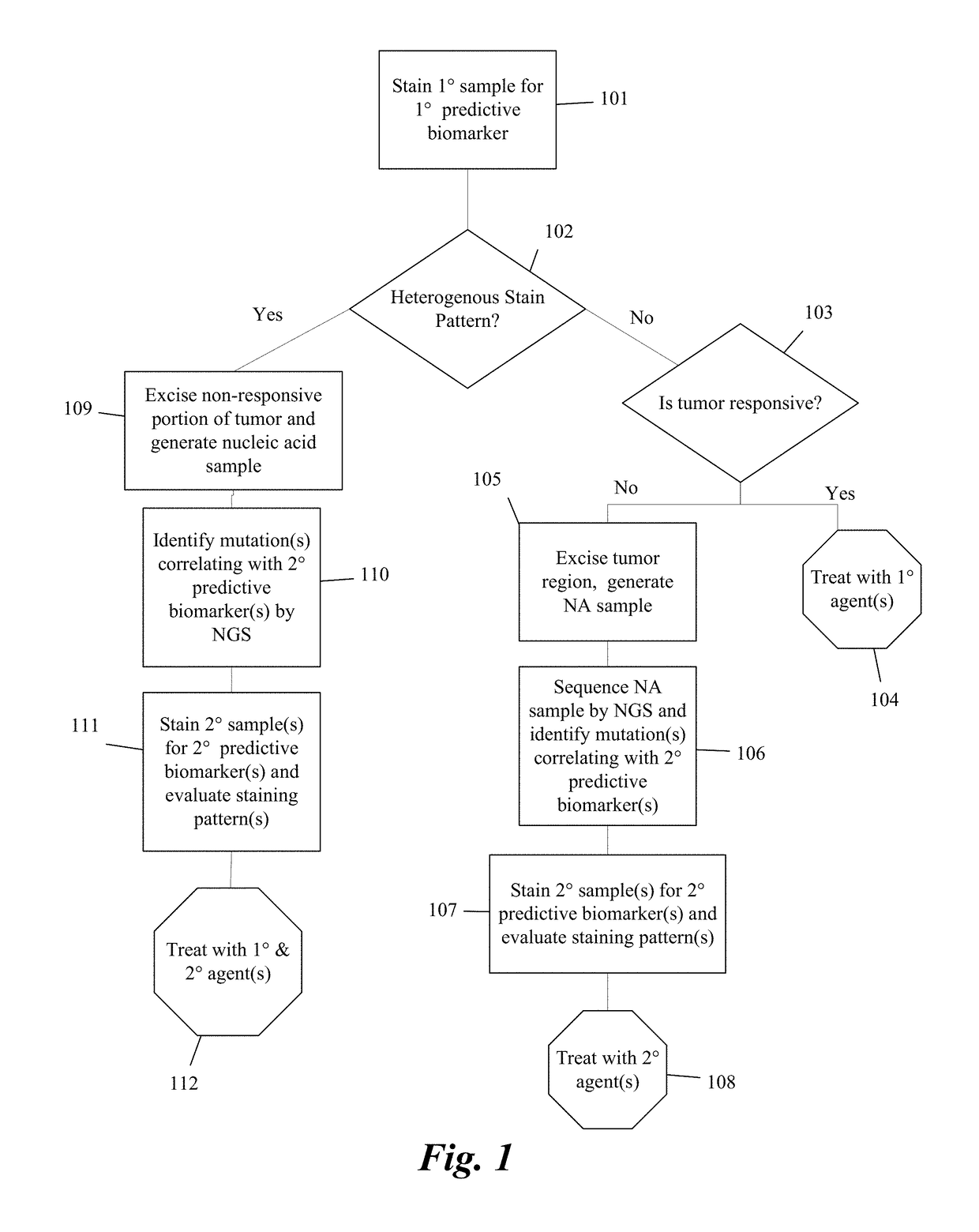
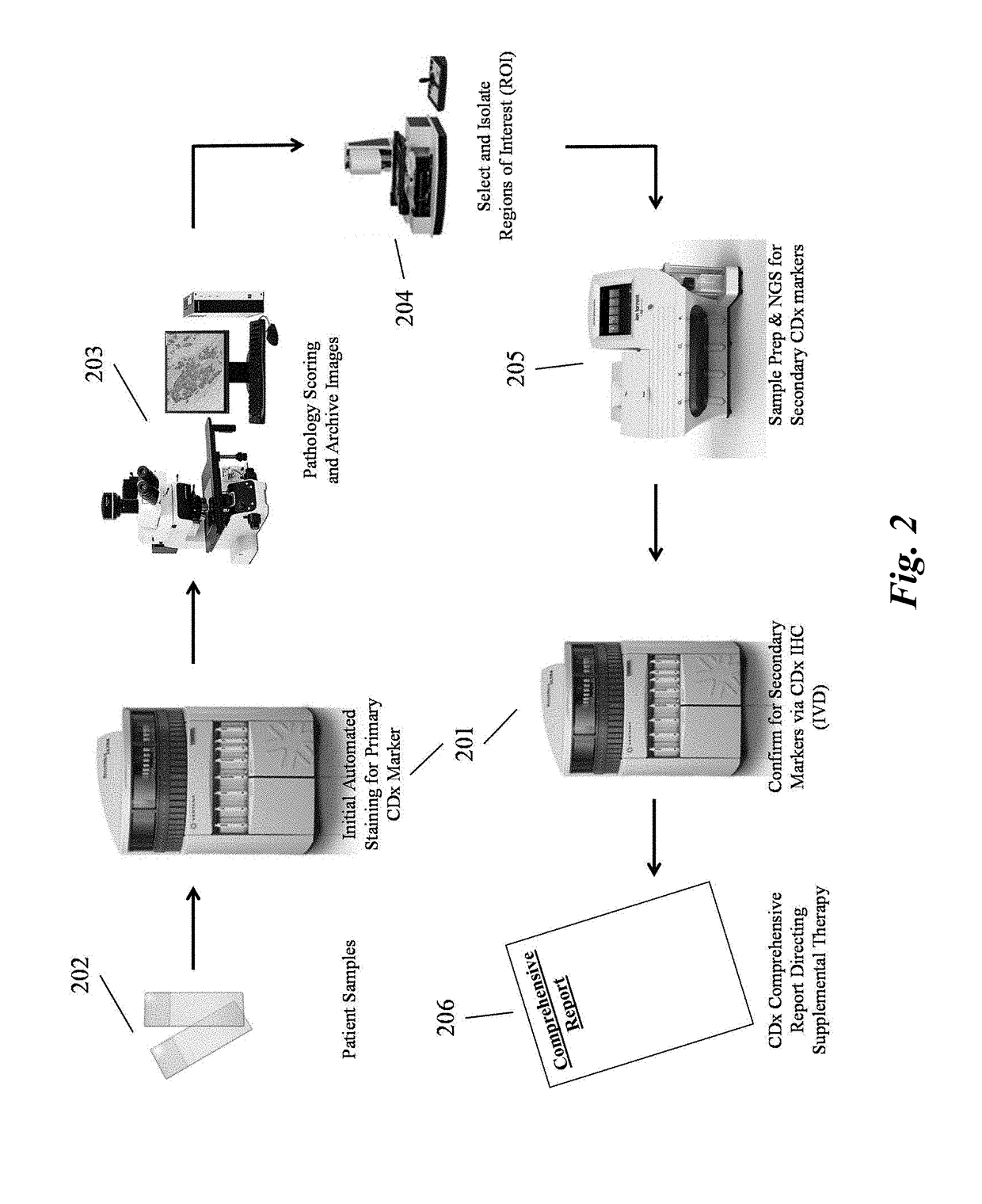
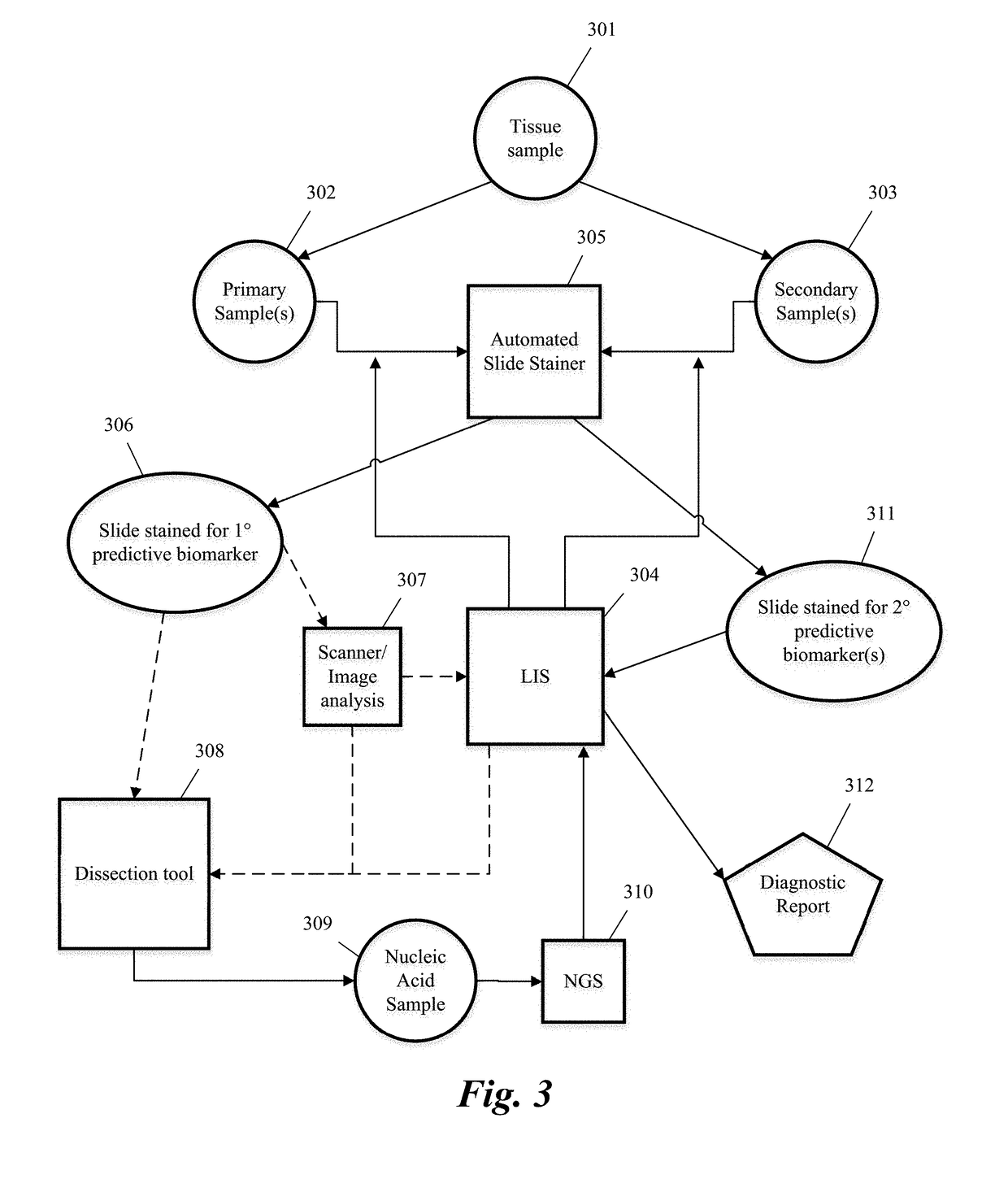
Predictive diagnostic workflow for tumors using automated dissection, next generation sequencing, and automated slide stainers
PendingUS20180340870A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationRegimenMedicine
Systems and methods for selecting therapeutic agents for cancers using next generation sequencing, automated dissection, and / or automated slide stainers are disclosed. Non-responsive regions of a tumor sample having a heterogenous staining pattern for a predictive biomarker are excised using an automated dissection tool. Mutations linked to additional predictive biomarkers are identified in the excised portion of the sample by next generation sequencing. The relevance of the additional predictive biomarker(s) is confirmed by histochemical staining. Therapeutic courses may then be selected on the basis of the staining patterns of the predictive biomarkers.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Embedding medium suitable for plant tissue frozen section and frozen section method
InactiveCN102816401AOvercome the problem that it is easily soluble in fixative and cannot be fixed first and then slicedSlice flatDead plant preservationPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyCellulose
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method and application of tissue slice for observing temporal-spatial distribution of early embryo development in vivo
InactiveCN102944456AObservation continuityEasy to observe continuityPreparing sample for investigationCooking & bakingFluorescence
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a tissue slice for observing temporal-spatial distribution of early embryo development in vivo. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 4% paraformaldehyde fixing, upward gradient ethanol dehydration, wax dipping, embedding, serial section, baking, dewaxing and downward gradient ethanol rehydration are performed in sequence on oviducts or uterine tissues which contain mice embryos in every period, and finally, after haematoxylin-eosin staining is performed on the tissues in the slice, neutral gum is used for sealing the slice, or after immunofluorescence histochemical staining is performed on the slice, a fluorescence resistant quenching sealing agent is used for sealing the slice. The tissue slice disclosed by the invention can be used for manufacturing a map of early mice embryo development and detecting the expression of Crb3 in the mice embryos in every period of development in vivo. The preparation method has the advantages that positions of all organs in the embryos can be relatively fixed, so that the position change of embryo cells in a genital tract and the continuity of embryo development can be conveniently observed, the structure is clear, and the tissue slice is convenient to store.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Human stomache cancer endothelial-cell specific combination short peptide series
This invention belongs to the biomedicine field, involves screening phage peptide library in vitro to get GEBPs. This invention utilizes Transwell co culturing technology to set up culture in vitro models of endothelial cell of stomach cancer blood vessel, through screening phage peptide library in vitro, get GEBPs. The peptides have certain theory meaning and great potential applying value to the research such as stomach cancer diagnosis, blood vessel targeted cure, etc.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
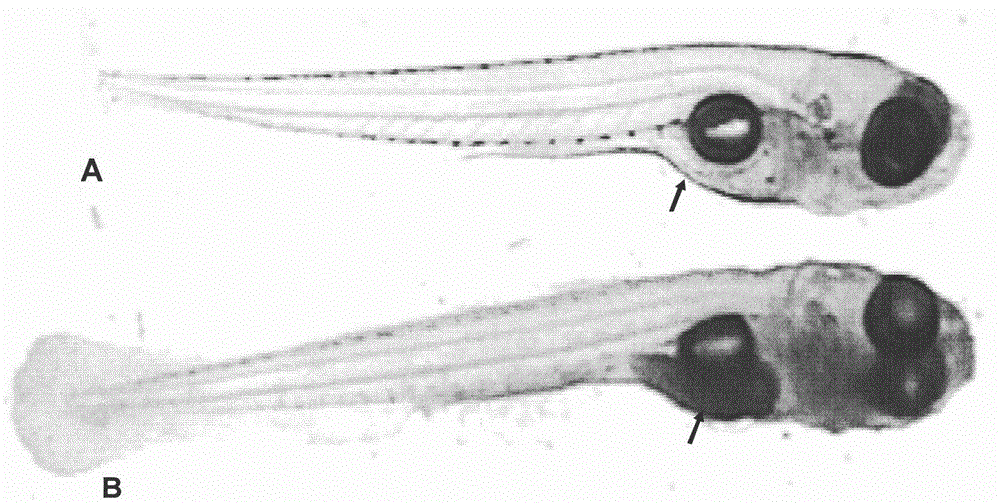
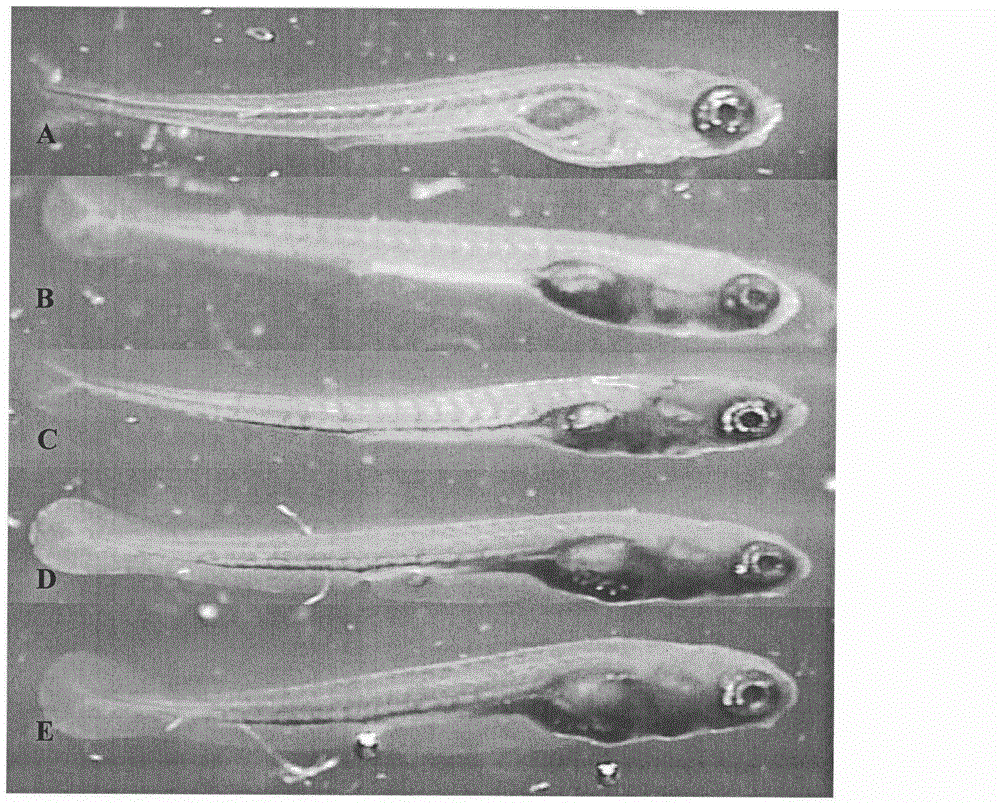
Building method and application of zebra fish hyperlipidemia model
InactiveCN102907357ATrue reflection absorptionTrue reflection distributionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseYolk
The invention relates to a building method of a zebra fish hyperlipidemia model and application of the animal model to hyperlipidemia disease research and lipid-lowering drug screening. The building method of the zebra fish hyperlipidemia model mainly includes the steps of zebra fish selection, feeding of zebra fish by yolk powder, histochemical staining or fluorescent staining, image analysis and / or microwell plate analysis and statistical analysis. The building method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, rapidity, economy, high efficiency, high throughput and the like, and the model can be used for hyperlipidemia disease research and lipid-lowering drug screening. The building method and application of the zebra fish bacterial infection model are of great significance to acceleration of research and development on lipid-lowering drugs and improvement on treatment of patients suffering from hyperlipidemia.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUANTE BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
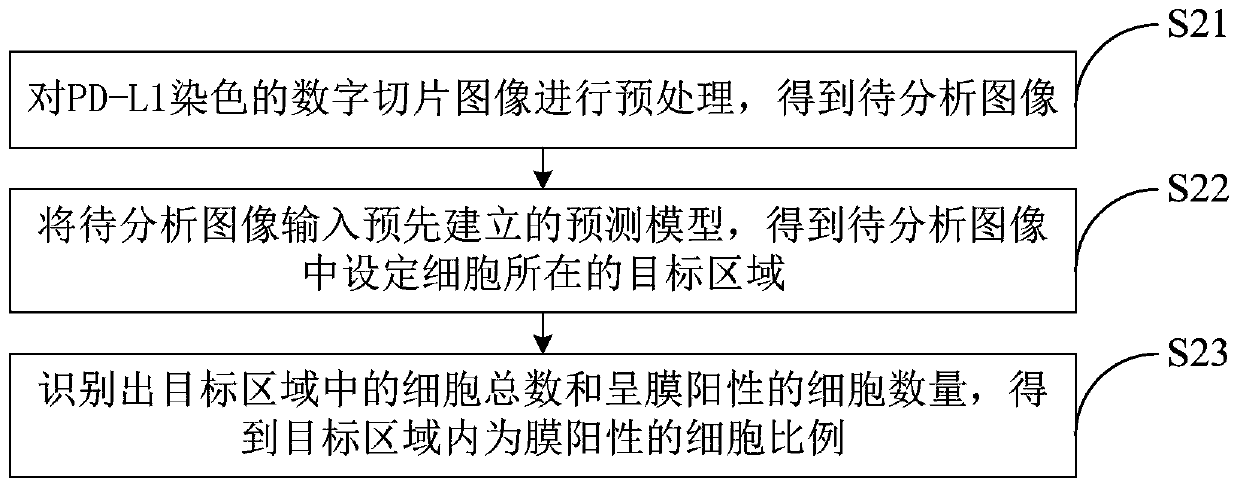
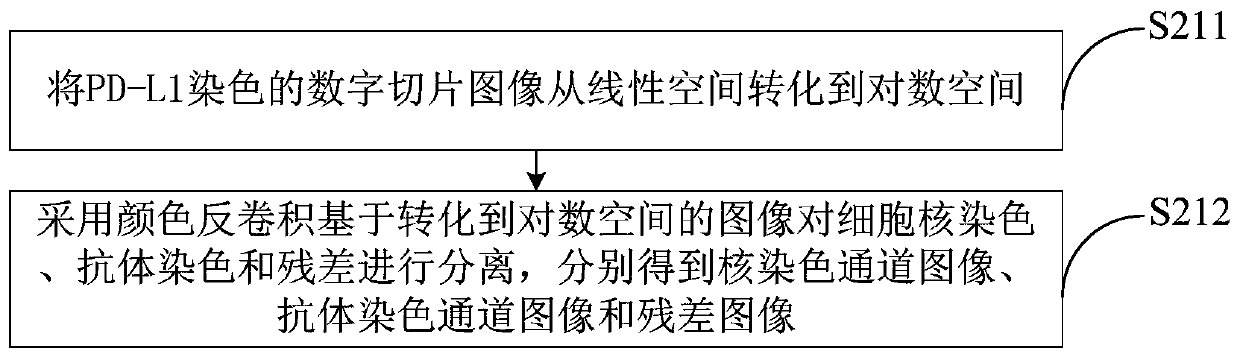
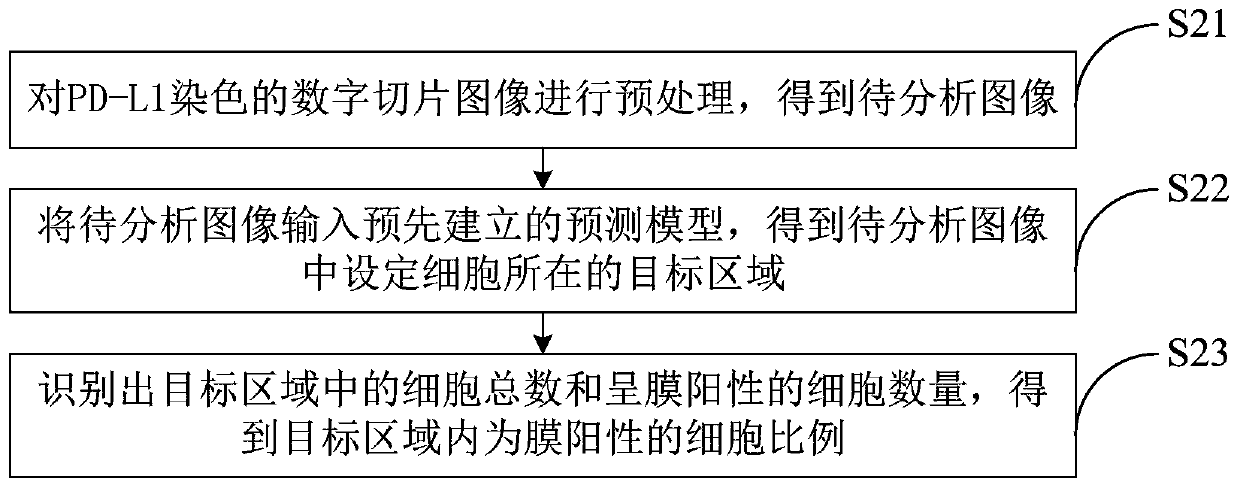
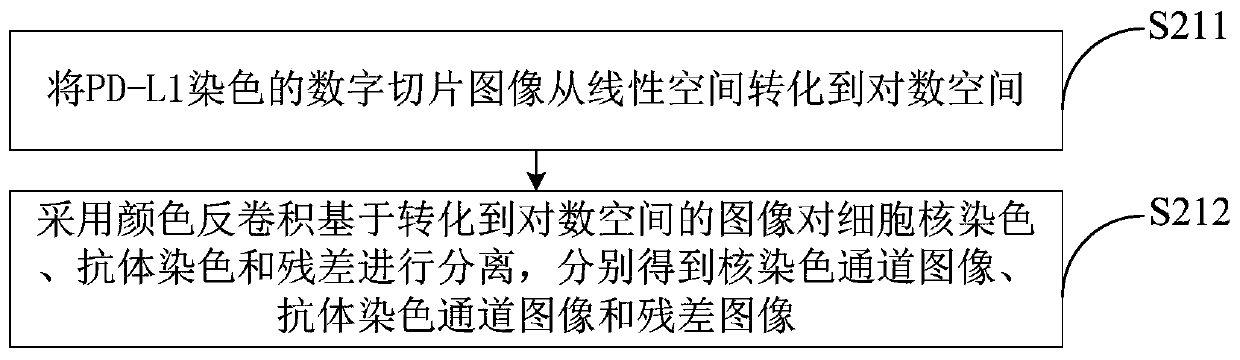
Automatic section reading method and system for PD-L1 antibody staining sections
InactiveCN109872335AReduce the workload of film readingQuick analysisImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyPD-L1
The present disclosure provides an automatic section reading method and system for PD-L1 antibody staining sections. Based on medical digitalimage analysis and processing, the PD-L1 immunohistochemical staining section can be automatically read. In detail, the method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: preprocessing the PD-L1 staining digital section image, and obtaining a to-be-analyzed image; inputting the to-be-analyzed image into a pre-established prediction model, and obtaining a target area corresponding to a set cell in the to-be-analyzed image; carrying out imageanalysis on the cell image of each set cell in the target area, identifying the total number of the cells in the target area and the number of the cells which are membrane-positive, and obtaining theproportion of the cells which are membrane-positive in the target area. Finally rapid, accurate and automatic section reading on the set cells is achieved.
Owner:志诺维思(北京)基因科技有限公司
Application of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 in preparation of medicines for treating non-small cell lung cancer
InactiveCN101732332AGrowth inhibitionImprove the quality of lifeOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsStainingImmunofluorescence staining
The invention relates to medicine application of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3, in particular to application of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 in preparation of medicines for treating a non-small cell lung cancer. In the invention, selecting a human non-small cell lung cancer cell strain (A549 lung adenocarcinoma, H460 large cell lung cancer and LTEP-78 lung squamous carcinoma) to be inoculated under the skin of a naked mouse, and observing the influence of the SPG-Rg3 on the non-small cell lung cancer; and carrying out CD34 immunohistochemistry staining and TUNEL immunofluorescence staining on tumor tissues, and observing the influence of the SPG-Rg3 on tumor angiogenesis and apoptosis. The inclusion proves that the 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 can remarkably inhibit the growth of the non-small cell lung cancer, has the action mechanism related with the promotion of the tumor apoptosis and the inhibition of the tumor angiogenesis and unobvious cooperation action when being combined with cyclophosphamide for application, and can be used for the clinical chemotherapy of the non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:北京鑫利恒医药科技发展有限公司
Efficient genetic transformation method of whole strain infection mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens in Rhododendron alpinum L
ActiveCN109207514AFill technology gapsSave seedsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsFiltrationHistochemical staining
The invention discloses an efficient genetic transformation method of whole strain infection method mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens of Rhododendron alpinum. The method mainly comprises the following steps: seed pre-culture, ultrasonic treatment, preparation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens bacterial solution, agrobacterium infection and vacuum filtration, co-culture, degerming washing, germination culture, GUS histochemical staining. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple operation, low experiment cost, short transformation period and high genetic transformation efficiencyof 61%, and can be applied to the genetic transformation of other plants of Rhododendron.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fully-automatic immune tissue chemical dyeing instrument
InactiveCN102116712AImprove experimental efficiencyImprove experimental precisionPreparing sample for investigationTemperature controlWater channel
The invention relates to a fully-automatic immune tissue chemical dyeing instrument which aims at the problems that the present immune tissue chemical dyeing experiment device generally adopts manual operation and has poor efficiency and low accuracy. An antibody holding device, a pipe taking and liquid filling device and a temperature control and heating device are arranged on a base of the fully-automatic immune tissue chemical dyeing instrument. The antibody holding device comprises an antibody pipe and a pipe support; screw threads are formed at the upper part of the lateral wall of a pipe body of the antibody body; and a piston is arranged in the pipe body. The pipe taking and liquid filling device comprises a transverse displacement device, a longitudinal displacement device and a vertical displacement device, wherein a sampler in the vertical displacement device is cylindrical, and screw threads matched with the lateral wall of the antibody pipe are formed on the inner wall of the sampler. The temperature control and heating device comprises a rack, a motor, a movable plate, a slice rack, a water channel and semiconductor heating plates; and each semiconductor heating plate corresponds to each slice in position. The fully-automatic immune tissue chemical dyeing instrument realizes the fully-automatic immune tissue chemical dyeing experiment and improves the experiment efficiency and the experiment precision without manual operation.
Owner:杭州依美洛克医学科技有限公司
Transgenic cultivation method of rice dedicated for starch medium
InactiveCN102550414AImprove gel propertiesHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureMolecular identificationOrganism
The invention relates to a transgenic cultivation method of rice dedicated for a starch medium. The method comprises the following steps: a mature embro of a rice species with a low content of alpha amylose is taken as an explant and is induced to form calluses; the calluses are subcultured to enter a proliferation period and are preculutured under a dark condition; the calluses are co-cultivated with agrobacterium tumefaciens for transformation and then transferred into a screening culture medium for being screened for three tims; resistant calluses are taken to be induced and differentiated into seedlings, and histochemical stain and molecular identification are performed to resistant plants to identify the differentiated plants containing target genes; the starch gelanitization property of selected transgenic plants is identified, and the transgenic plants which have the starch gelatinized and can form semi-solid gel after being cooled are selected and reserved; and expression stability of the starch gelatinization property of the plants is further evaluated, seed propagation is performed to the excellent plants with a stable starch gelatinization property, and finally dedicated rice for the starch medium is cultivated. The dedicated rice for the starch medium can be taken as a novel biological medium and be widely applied to scientific researches, food, medicine and chemical engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Drought-induced rice flower specific promoter and use thereof
The invention discloses a drought induced rice flower-specific promoter and application thereof. The promoter has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1, or a nucleotide sequence which can be hybridized with the sequence under highly rigorous conditions and has same functions. The promoter has flower tissue specificity and shows certain inductivity under drought induction conditions. By constructing a plant expression vector containing the promoter, the promoter is transformed into transgenic rice, the GUS histochemical staining and the RT-PCR detection are performed to a plurality of different tissues of a transgenic material such as ordinary leaves, sword-like leaves, flowers and so on under the drought induction conditions and the result proves the expression of a driving gene of the promoter in a rice flower tissue under the drought induction. The cloning of the promoter has greater practical significance on the research of male sterile strains of rice, and can be used for creating sterile lines of the rice and other plants and maintaining line-double-lines.
Owner:BEIJING KAITUO DNA BIOTECH RES CENT
Horizontal antigen retrieval
ActiveUS20100136612A1Prevent evaporationPoint becomes highPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingBiochemistryAntigen retrieval
The present invention relates to a method for enhancing immunoreactivity of a tissue or cell sample fixed in a fixing medium, a target retrieval composition and its use. The method comprises providing a carrier in a horizontal position, said carrier having thereon a tissue or cell sample, said tissue or cell sample being on top of the carrier; contacting substantially the tissue or cell sample side of the carrier with a buffered target retrieval solution, wherein the target retrieval solution remains otherwise exposed to the environment; heating the tissue or cell sample and the target retrieval solution to a temperature above 100° C. The invention furthermore concerns the automated immunohistochemical staining of said samples, in particular the reactivation of antigens masked by fixation.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Apparatus for automatic electric field immunohistochemical staining and method for automatic electric field immunohistochemical staining
ActiveUS20150233902A1Reliable applicationGuaranteed validityPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingStainingTissue sample
Acceleration and automation of immunohistochemical staining are achieved as follows: an automatic electric field immunohistochemical staining apparatus is configured to provided with a sample mounting unit, a solution supply unit, an electric field stifling unit, and a washing unit; the sample mounting unit on which a glass substrate with a tissue specimen fixed thereto is mounted and the electric field stirring unit that includes an upper electrode are operated in coordination to activate an antigen in the tissue specimen; the sample mounting unit and the solution supply unit containing various solutions are operated in coordination to supply a primary-antibody-containing solution to the tissue specimen; the sample mounting unit and the electric field stirring unit are operated in coordination to perform an antigen-antibody reaction of the antigen in the tissue specimen and a primary antibody; and the electric field stirring unit and the washing unit are operated in coordination.
Owner:GOVERNOR OF AKITA PREFECTURE +1
Efficient cell slide immunohistochemical method
InactiveCN104101701AImprove comparabilityImprove reliabilityMaterial analysisCell stainingPrinting ink
The invention discloses an efficient cell slide immunohistochemical method. The method comprises the steps as follows: large-area glass slides and a culture dish which are subjected to sterilization disinfection treatment are matched for use, the glass slides are placed in the culture dish, cells are inoculated in the culture dish for cell slide, and immune cell histochemical staining identification is performed after cell culture is finished; and the immune cell histochemical staining identification comprises the steps as follows: a tool seal is used for dipping printing oil, a rubbing surface of the tool seal is covered with a cell slide surface of each glass slide, the glass slide is pressed to rub a cell staining area which has the same size with the rubbing surface of the tool seal and consists of printing ink frame strips, and if an area is short of printing ink, the area is filled up by a printing ink coating pen. The efficient cell slide immunohistochemical method can be used for large-scale and multi-sample medical scientific experiment and research.
Owner:SHUGUANG HOSPITAL AFFILIATED WITH SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
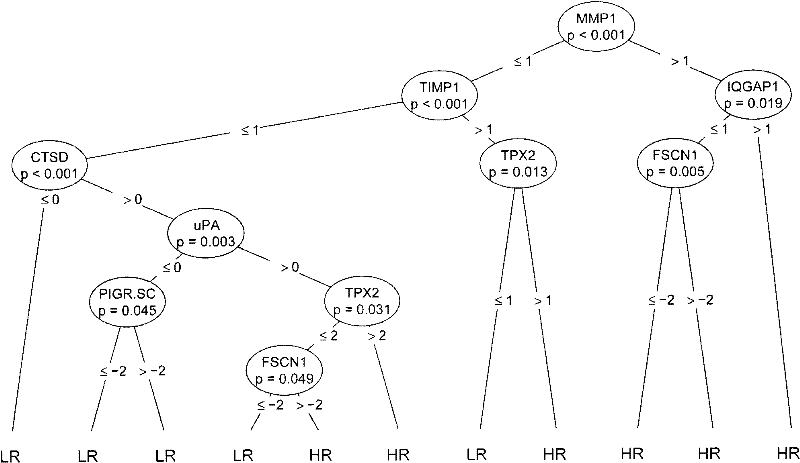
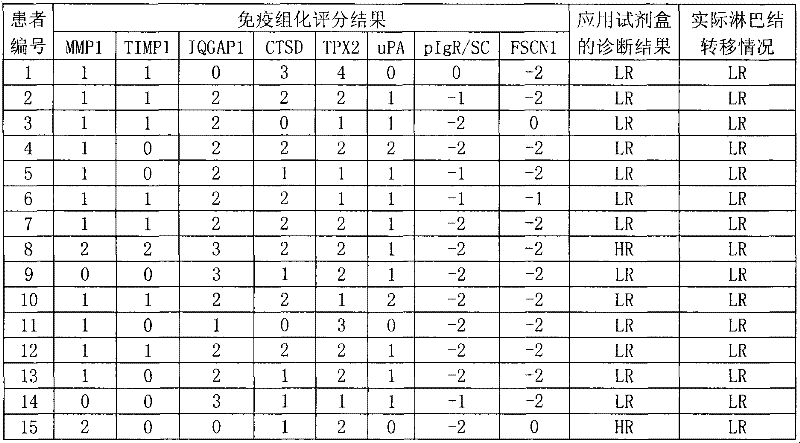
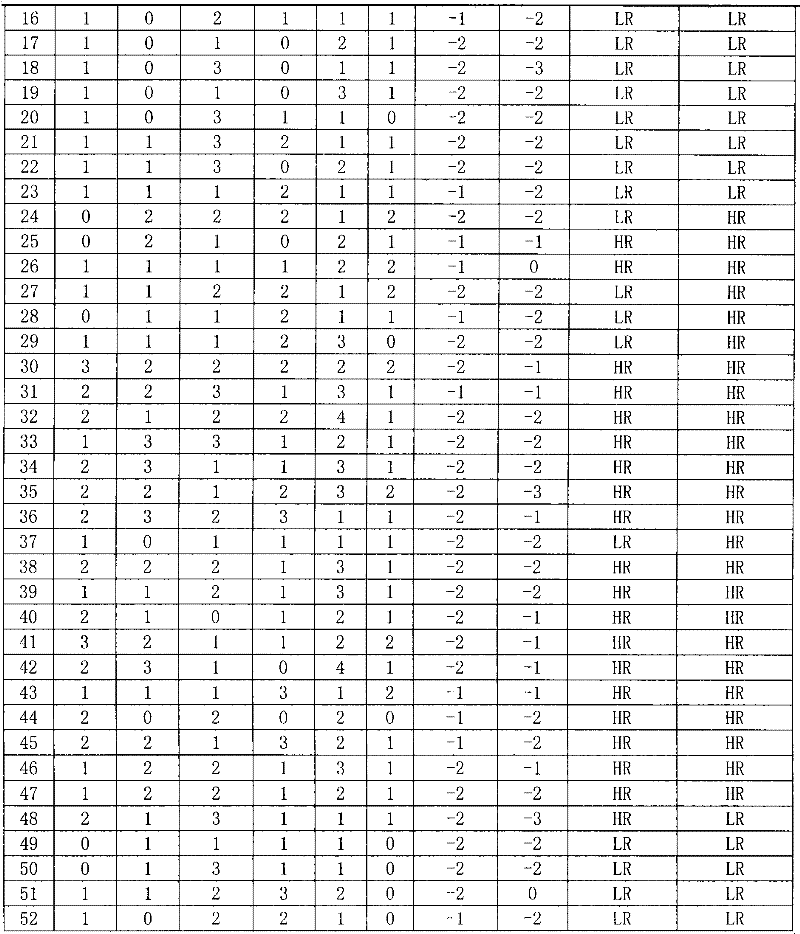
Reagent for auxiliarily diagnosing lung cancer lymph node metastasis
InactiveCN102445543AIncrease credibilityPracticalBiological testingStainingPolymeric immunoglobulin receptor
The invention discloses a reagent for auxiliarily diagnosing lung cancer lymph node metastasis, comprising 8 antibodies which are used for detecting 8 protein markers which are MMP1 (matrix metalloproteinase-1), TIMP1 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases metallopeptidase inhibitor 1), IQGAP1 (IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1), TPX2 (targeting protein for Xklp2), uPA (Urokinase-type plasminogen activator), Cathepsin-D, Fascin and pIgR / SC (polymeric immunoglobulin receptor / secretory component). By adopting the 8 antibodies and an immunohistochemical staining result, lung cancer lymph node metastasis can be auxiliarily diagnosed, and the reagent is expected to be used for the risk estimation of lung squamous cell cancer lymph node metastasis and the prognostic prediction. The reagent has high creditability, strong practicability and clinical use value based on the clinical routine immunohistochemical staining technology when the reagent is used for auxiliary diagnosis.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
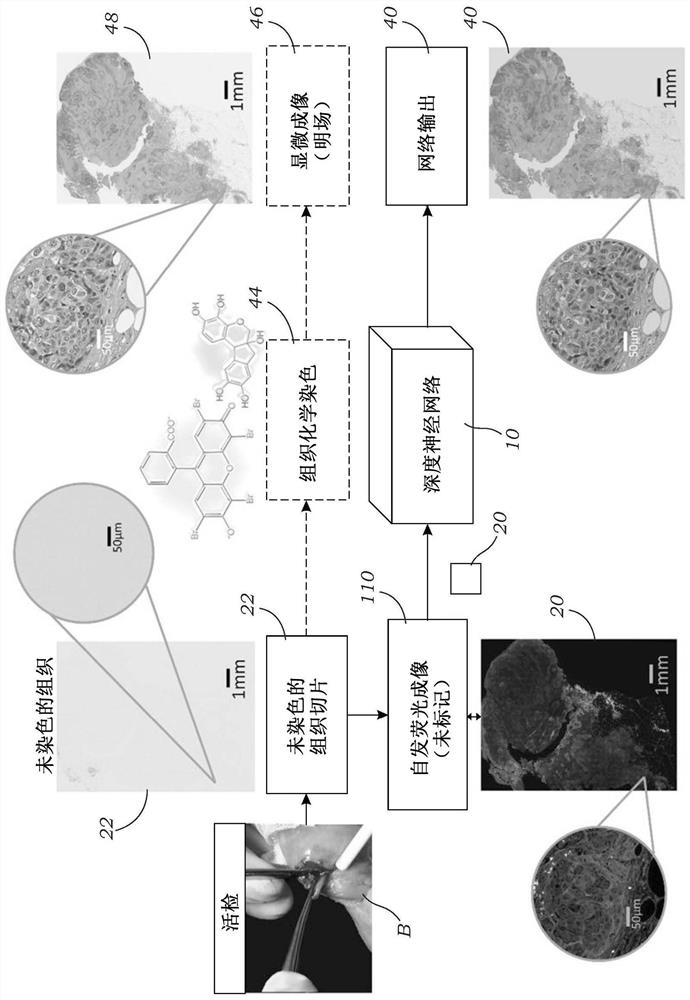
Method and system for digital staining of label-free fluorescence images using deep learning
PendingCN112106061AShorten the timeLow costImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageGenerative adversarial network
A deep learning-based digital staining method and system are disclosed that enables the creation of digitally / virtually-stained microscopic images from label or stain-free samples based on autofluorescence images acquired using a fluorescent microscope. The system and method have particular applicability for the creation of digitally / virtually-stained whole slide images (WSIs) of unlabeled / unstained tissue samples that are analyzes by a histopathologist. The methods bypass the standard histochemical staining process, saving time and cost. This method is based on deep learning, and uses, in oneembodiment, a convolutional neural network trained using a generative adversarial network model to transform fluorescence images of an unlabeled sample into an image that is equivalent to the brightfield image of the chemically stained-version of the same sample. This label-free digital staining method eliminates cumbersome and costly histochemical staining procedures and significantly simplifiestissue preparation in pathology and histology fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
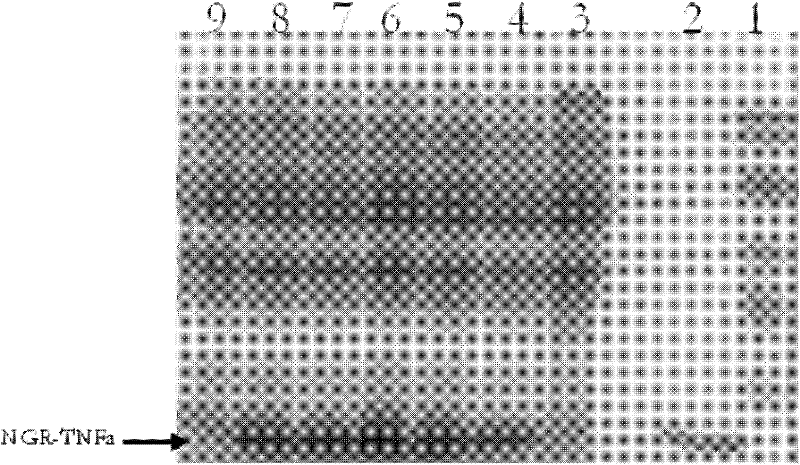
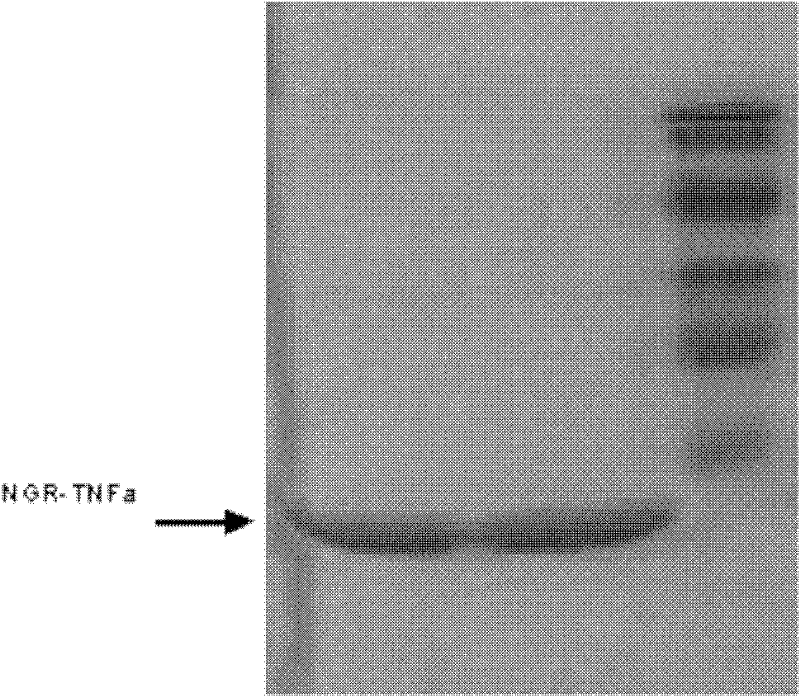
A kind of cd13 targeting peptide ngr and its application
ActiveCN102286074APeptide/protein ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsTarget peptideWilms' tumor
The invention provides NGR targeted peptide of CD13 (aminopeptidase N) and application thereof. The NGR targeted peptide has the amino acid sequence of CNGRVSTNGRC. The invention also provides a fusion protein NGR-TNF (tumor necrosis factor) alpha. The NGR-TNF alpha is the fusion protein formed by the NGR targeted peptide and a TNF alpha. The targeted peptide NGR of the CD13 is designed and screened by a conventional histochemical staining method; and then the NGR peptide is fused with a human TNF alpha by a gene recombination method to obtain the fusion protein NGR-TNF alpha. Through a greatamount of experimental analysis, people find that by the NGR-TNF alpha, the growth of tumor cell can be inhibited by inhibiting the growth of neovascularization in tumor in a targeted mode and the effect of resisting the tumor is achieved.
Owner:优锐生物医药科技(深圳)有限公司
Tamarix hispida MYB transcription factor coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108342395AImprove salt toleranceStrong salt tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationWild typePlant genetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering breeding, and particularly relates to a tamarix hispida MYB transcription factor coding gene and application thereof. The tamarix hispida ThMYB gene provided by the invention can be used for improving salt resistance of plants or breeding salt-resistant transgenic plants. Overexpression and suppression expression vectors ofthe ThMYB gene are respectively constructed, transgenic tamarix hispida is obtained by transient infection, histochemical staining and physiological index measurement prove that an overexpression strain of the ThMYB gene has obvious salt resistance; when the ThMYB gene is transferred into arabidopsis, after transgenic T3-generation arabidopsis seeds are stressed by 150mM NaCl, an average germination rate of transgenic T3-generation arabidopsis seeds is 6.21 times of that of wild arabidopsis seeds, root lengths of the transgenic T3-generation arabidopsis seeds are 1.41 times of that of the wildtransgenic T3-generation arabidopsis seeds, and a fresh weight of the transgenic T3-generation arabidopsis seeds is 1.66 times of that of the wild transgenic T3-generation arabidopsis seeds. Both homologous and heterogenous overexpression results of the ThMYB gene show that the gene can obviously improve salt resistance of the transgenic plants and is an excellent gene for salt-resistant geneticengineering breeding.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Double-label immunohistochemical staining kit used for differential diagnosis of metastatic renal cell carcinoma
InactiveCN104297481ABe sensitiveMaintain propertiesMaterial analysisMetastatic renal cell cancerStaining
The invention relates to the technical field of immunohistochemical staining and particularly relates to a double-label immunohistochemical staining kit used for differential diagnosis of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. The kit comprises a DAB developing solution and a primary antibody formed by mixing a mixed solution of a PAX8 antibody and a CD10 antibody or / and an HRP enzyme-labeled secondary antibody. In order to overcome the disadvantages that the histological characteristics of the metastatic renal cell carcinoma are extremely easily confused with adrenal tumors, lung cancer, liver cancer, thyroid cancer and the like so that a definite diagnosis is not easy to make, a conventional immunohistochemical method is used for respectively detecting, more time and labor are consumed, the tissue amount of an aspiration biopsy specimen is not enough and the like, the same sensitivity and specificity when each antibody in the mixed antibody is singly stained are kept by using the method; and the double-label immunohistochemical staining kit also has the advantages that staining steps are few, the experiment time is short, the stability is high, an experiment result can be directly compared, and brought information amount is much higher than that of traditional single staining and the like, and especially has the remarkable advantages for biopsy pathological diagnosis with few specimen amounts.
Owner:卢洪胜
Cold-resistant anthurium transgenic culturing method
InactiveCN101643747AReduce manufacturing costEasy to industrializeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudCell budding
The invention relates to a cold-resistant anthurium transgenic culturing method which comprises the following steps of: selecting apical buds of a main-bred anthurium variety as explants; inducing calli; subculturing the calli till a fast proliferation period; carrying out 4 turns of selection by transferring the calli into a selection culture medium; selecting the resistant calli for induction and differentiation so as to obtain seedlings; carrying out histochemical staining and molecular detection on resistant plants; identifying the differentiated seedlings containing target genes; transferring the differentiated seedlings into a rooting culture medium so that the differentiated seedlings can grow into normal seedlings; determining cold resistance of selected transgenic plants; remaining the transgenic plants which are free from cold damage and grow well; continuing to grow the selected transgenic anthurium plants; assessing and verifying the expression stability of the cold resistance; carrying out proliferation on the stable and fine plants; and culturing the transgenic cold-resistant anthurium which resists the cold damage at low temperatures.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for cultivating rice with high resistant starch content
The invention relates to a method for cultivating rice with high resistant starch content, which comprises the steps: using mature embryos of a rice variety with 20%-25% of amylase content as explants to induce callus and to be sub-cultured till a multiplied proliferation period, performing pre-cultivation according to conditions, performing agrobacterium tumefaciens co-culture conversion, transferring converted mature embryos to a screening culture medium to be screened for three times, using resistant callus to induce and differentiate mature embryos into seedlings, performing marker gene histochemical staining and screened gene molecule detection to resistant plants, identifying differentiated seedlings inserted sequences and containing target genes ISA1, detecting the resistant starch content of selected transgenic plants, selecting and remaining transgenic plants with more than 10% of resistant starch content, continuing to plant and evaluating the expression stability of the resistant starch content, cultivating excellent plants with more than 10% of resistant starch content and finally cultivating the rice with high resistant starch content. The rice with high resistant starch content can be used for development of products special for diabetes and has important significance on implementation of dietotherapy of persons with diabetes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Non-isotonic preserving fluid for liquid-based thin-layer exfoliative cells
ActiveCN103461320AImprove the detection rateFacilitates histochemical stainingDead animal preservationMethyl aldehydeSodium phosphates
The invention discloses a non-isotonic preserving fluid for liquid-based thin-layer exfoliative cells, and is characterized by comprising the following raw materials by weight: 9-11 parts of methyl aldehyde, 13-16 parts of ethyl alcohol, 9-9.5 parts of glycine, 3-3.5 parts of carbamide, 1.8-2.2 parts of procaine hydrochloride, 1.3-1.6 parts of propylene glycol, 1.4-1.6 parts of dimethyl sulfoxide, 0.8-1.2 parts of sodium phosphate, 3.4-3.6 parts of trypsin, 0.1-0.3 part of acetic acid, 1-1.1 parts of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.3-0.32 part of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, and 51-52 parts of water. Compared with the prior art, the non-isotonic preserving fluid has the advantages as follows: buffer solution fixed cells by the formula of the non-isotonic preserving fluid facilitate histochemical stain; the solution utilizing the colligative property of a non-ionic solution splits red blood cells and dissolves mucus protein during the hydroformylation process, so that the microscopic examination background becomes clear, and the detection rate of positive cells is greatly improved.
Owner:安徽信灵检验医学科技股份有限公司
Rice cultivating method capable of improving resistant starch content
The invention relates to a rice cultivating method capable of improving resistant starch content, which includes the steps: taking a mature embryo of a rice variety with amylase content larger than 25% as an explant, inducing callus, subculturing to a multiplication period, preculturing under the condition of dark, conducting agrobacterium co-culture transformation, transferring to a screening medium to conduct three turns of screening, taking resistant callus to be induced to differentiate seedlings, conducting histochemical staining on marked genes of a resistant plant, conducting molecular detecting on screened genes of the resistant plant, identifying differentiation little seedlings containing a target gene starch synzyme ssIII-2 insertion sequence, conducting detecting of the resistant starch content of hot rice on selected transgenosis plants, selecting transgenosis plants with the resistant starch content larger than 10%, continuously planting, evaluating expression stability of the resistant starch content, and propagating excellent strains with the resistant starch content larger than 10% stably. The rice with improved resistant starch content has significant meaning on conducting dietotherapy for diabetes patients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Plant leaf specific expression promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN107815452AWon't cause escapeReduce material energy consumptionPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionGenomic DNADNA fragmentation
The present invention relates to a plant leaf specific expression promoter and application thereof. An upstream promoter of a highly-active cotton leaf specific expression gene screened by gene microarray data and RT-PCR is cloned on the basis of upland cotton Goker Coker 312 genomic DNA as a template to obtain a DNA fragment of about 2kb at the upstream of a translation initiation site. Pant expression vector pGhlsp::GUS for the promoter to drive GUS is constructed, arabidopsis thaliana is transformed by agrobacterium floral dip method, the arabidopsis thaliana is observed by GUS histochemical staining, results show that the gene is mainly specifically expressed in leaves, and hardly expressed in roots and stems, and the plant leaf specific expression promoter is a new leaf specific expression promoter.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
Mild constitutive expression promoter separated from populus tomentosa and application thereof
The invention discloses a mild constitutive expression promoter separated from populus tomentosa and application thereof. The mild constitutive expression promoter is a polynucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1. The invention further discloses a host cell and a recombination plant expression vector comprising the constitutive expression promoter. The constitutive promoter is converted into arabidopsis thaliana after connected with a GUS gene in an operable mode, and a transgene plant is obtained. GUS histochemical staining and GUS activity analysis prove that the separated promoter is a constitutive promoter which leads the GUS gene to carry out mild transcription or expression in various tissues of the plant and each development stage. The invention further discloses application of the constitutive promoter and the recombination plant expression vector comprising the constitutive promoter in the aspects of building transgenic plants, cultivating new plant species, establishing plant bioreactors, analyzing gene functions and the like.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Brassica napus L promoter pBnUnng0942890 and application thereof
ActiveCN109439663AImprove qualityGreat application potentialPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBrassicaGermplasm
The invention discloses brassica napus L promoter pBnUnng0942890 and application thereof. By cloning a promoter of a gene pBnUnng0942890 in the brassica napus L, a plant expression vector of a reporter gene GUS regulated by the promoter is constructed; by using an agrobacterium-mediated inflorescence impregnating method to transform arabidopsis, GUS histochemical staining is carried out on screened positive transgenic strains; the result shows that the pBnUnng0942890 has the functions of driving preferential expression of downstream genes in roots, flowers and seeds, and not expressing or realizing low expression in other tissues and organs. The promoter has good application potential in the aspects of improving crop quality by rapeseed transgene, artificially creating germplasm resourcesand the like.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Automatic slice reading method and automatic slice reading system for PD-L1 antibody staining slices
ActiveCN111242961AReduce the workload of film readingQuick analysisImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisRadiology
The invention provides an automatic slice reading method and an automatic slice reading system for PD-L1 antibody staining slices. The automatic slice reading of PD-L1 immunohistochemical staining slices is realized based on medical digital image analysis and processing. Specifically, the method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: preprocessing a PD-L1 dyed digital slice image; obtaining an image to be analyzed, inputting the to-be-analyzed image into a pre-established prediction model; obtaining a target area corresponding to set cells in the to-be-analyzed image; and carrying out image analysis on the cell image of each set cell in the target area, identifying the total number of cells in the target area and the number of cells with positive slice formation, obtaining the proportion of the cells with positive slice formation in the target area, and finally realizing rapid, accurate and automatic slice reading of the set cells.
Owner:BEIJING CANCER HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV CANCER HOSPITAL +1
Tamarix hispida COL (Constans-like) transcription factor encoding gene and application thereof
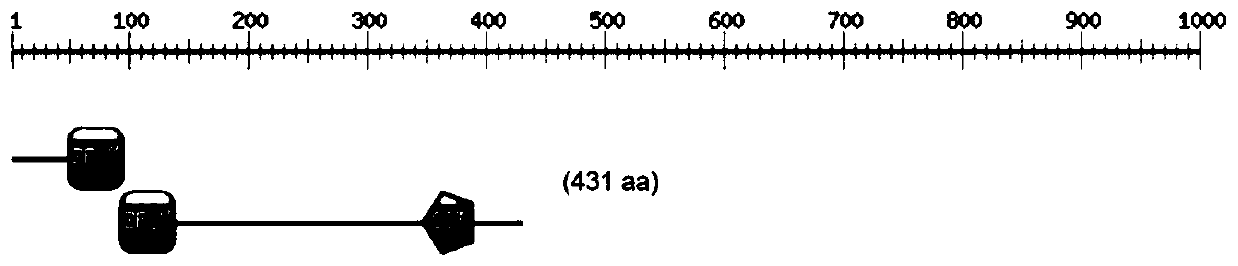
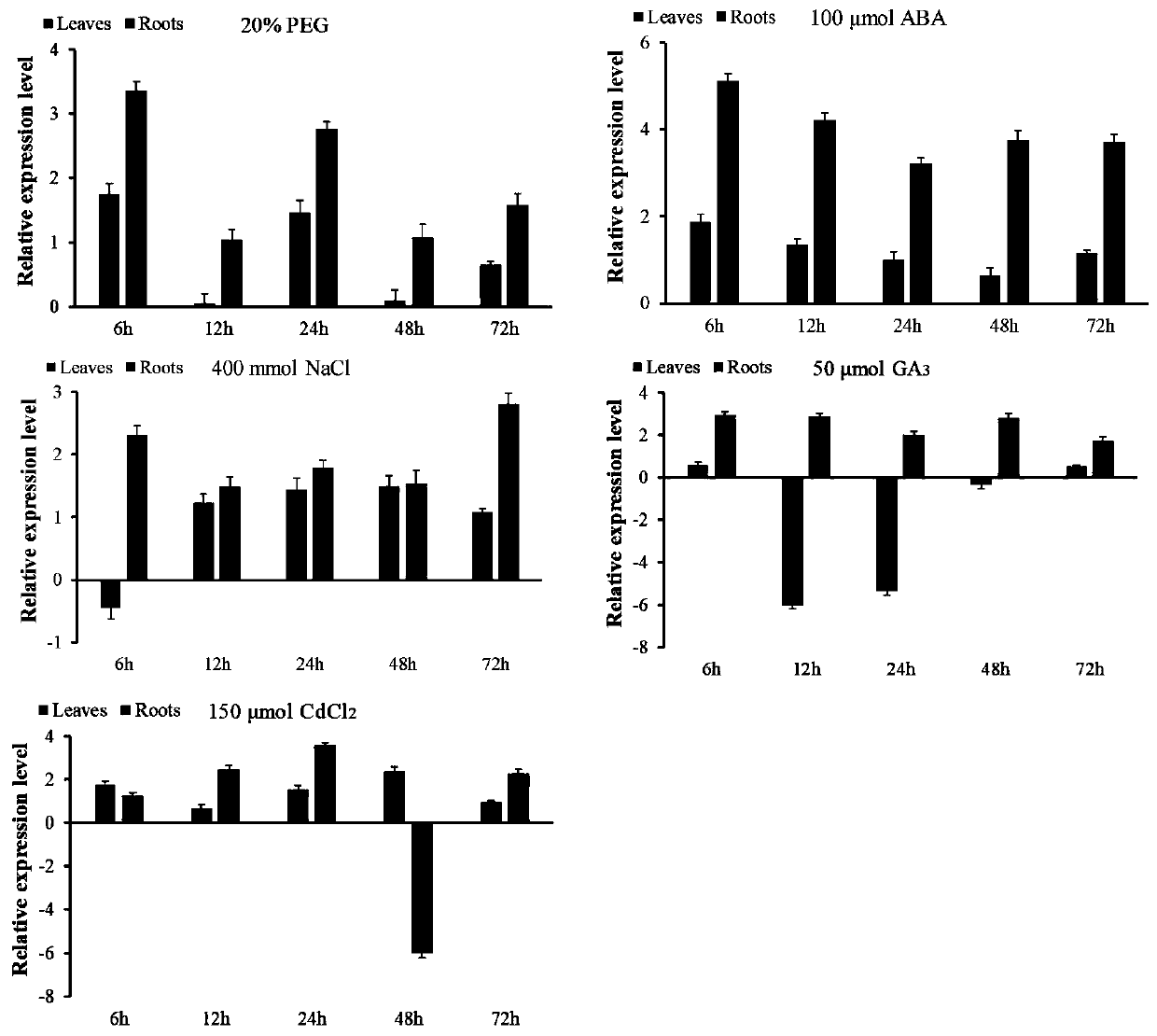
The invention relates to a tamarix hispida COL (Constans-like) transcription factor encoding gene and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering breeding. Inorder to solve the problem that a woody plant with good salt resistance can not be cultured through an existing tamarix hispida COL transcription factor encoding gene, the invention provides the tamarix hispida COL transcription factor encoding gene and the application thereof. The tamarix hispida COL transcription factor encoding gene is characterized in that the whole length of cDNA is 1296bp, and an amino acid sequence encoded by a cDNA sequence includes 431 amino acids which can be used for culturing salt-resistant transgenic plant varieties. An overexpression and suppression expression vector of the ThCOL gene is constructed, and transgenic tamarix hispida is obtained through instantaneous infection. Through experiments, including histochemistry staining, physiological index measurement and the like, a tamarix hispida ThCOL gene overexpression strain is discovered to own obvious salt resistance, and therefore, the tamarix hispida COL transcription factor encoding gene is a good gene used for forest salt resistance genetic engineering breeding.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com