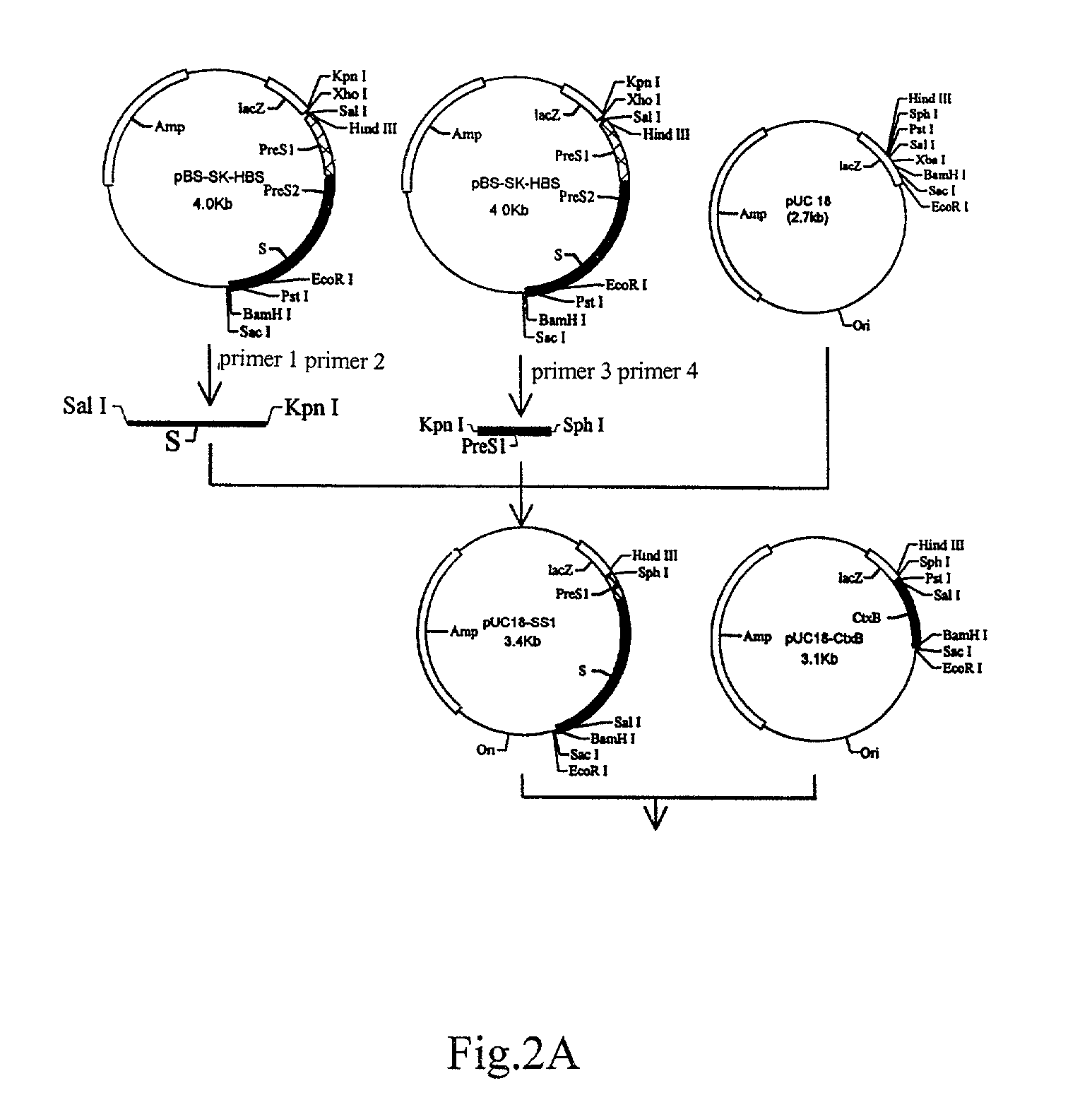
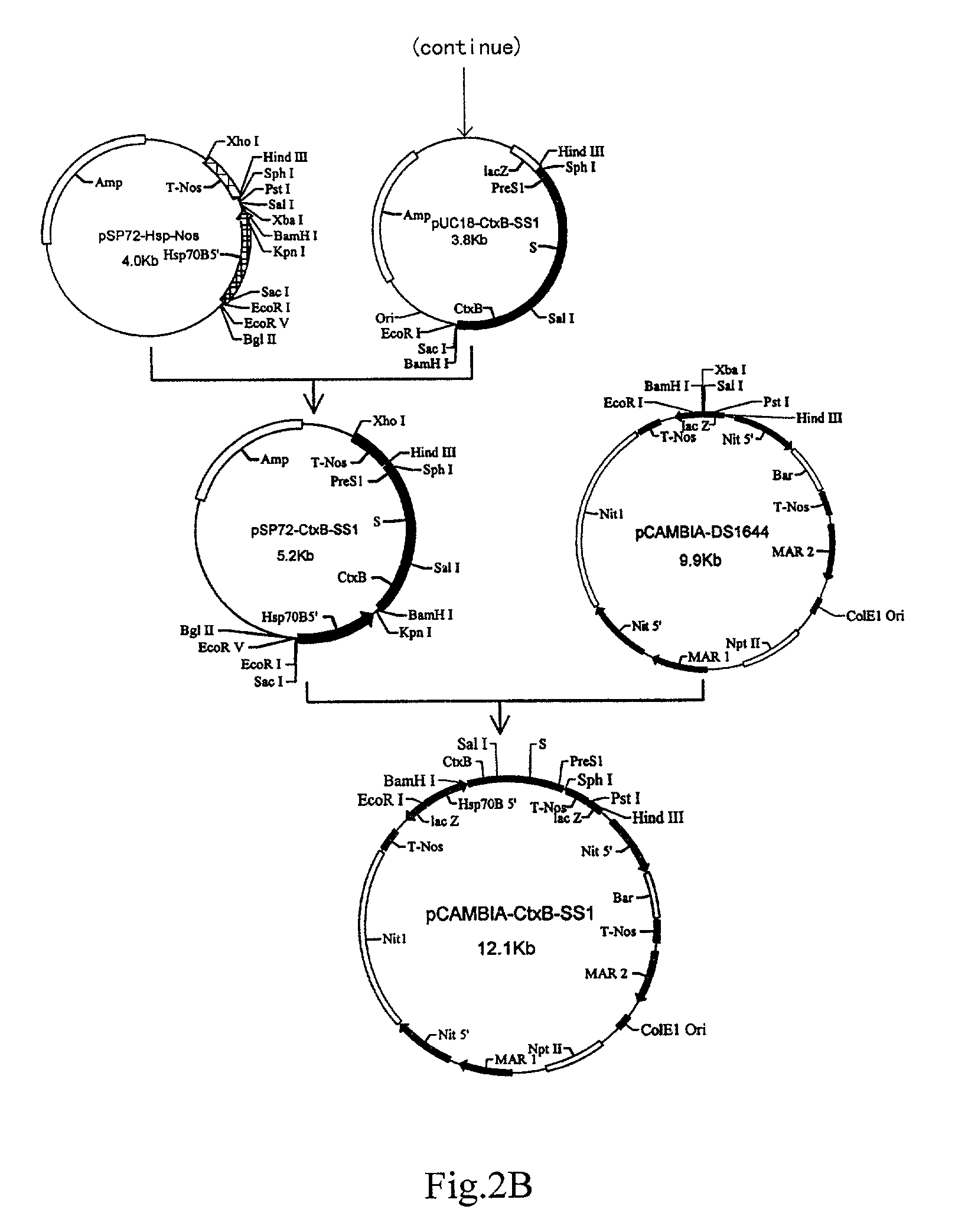
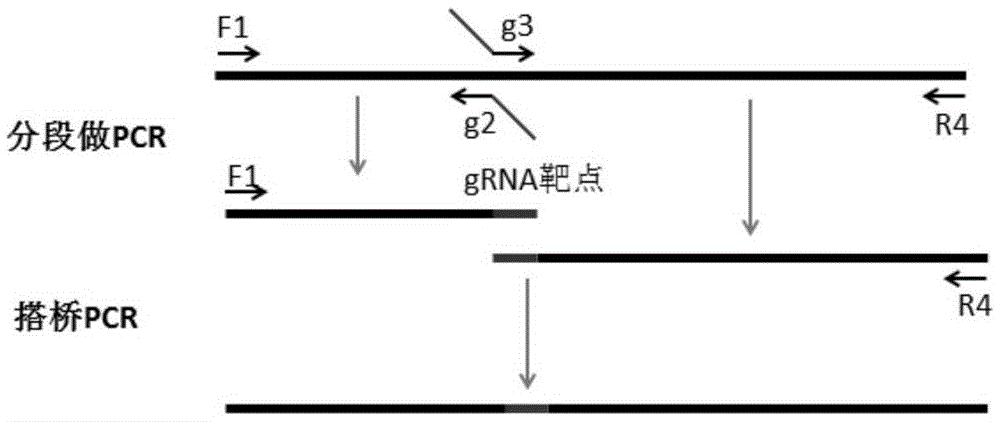
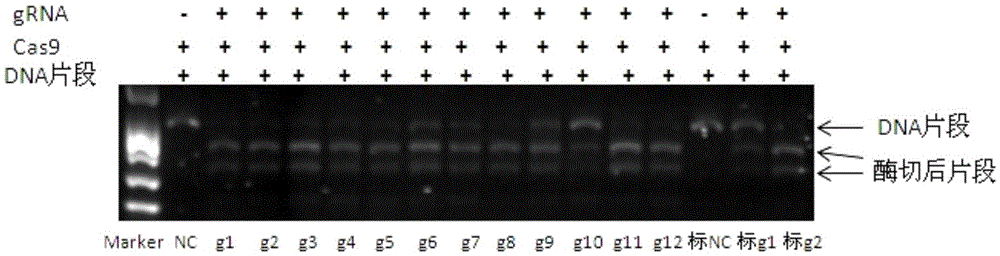
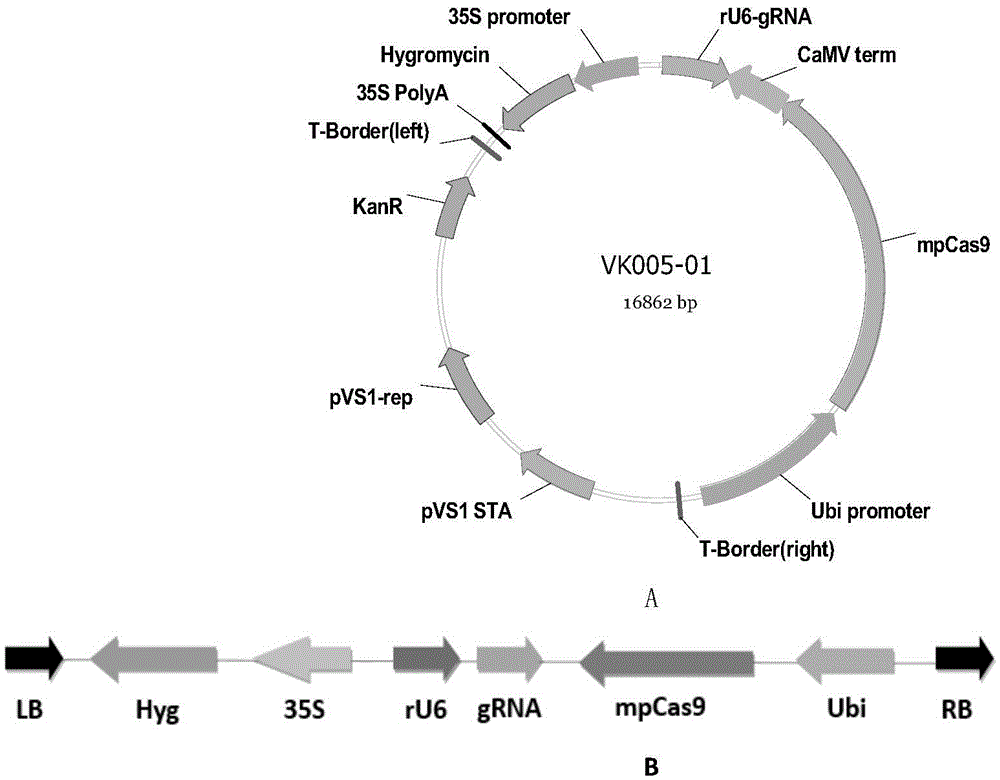
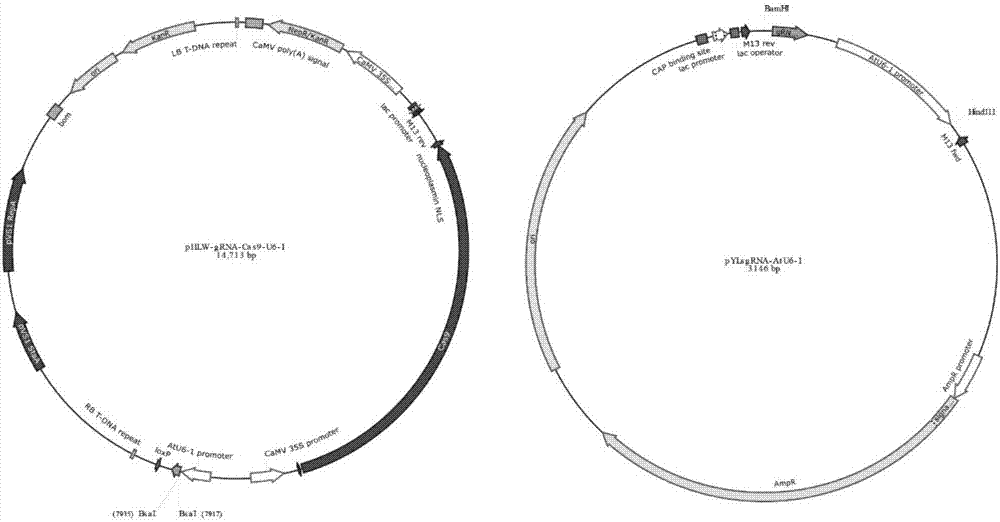
Patents
Literature
1959 results about "Genetics transformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic transformation: A process by which the genetic material carried by an individual cell is altered by the incorporation of foreign (exogenous) DNA into its genome.
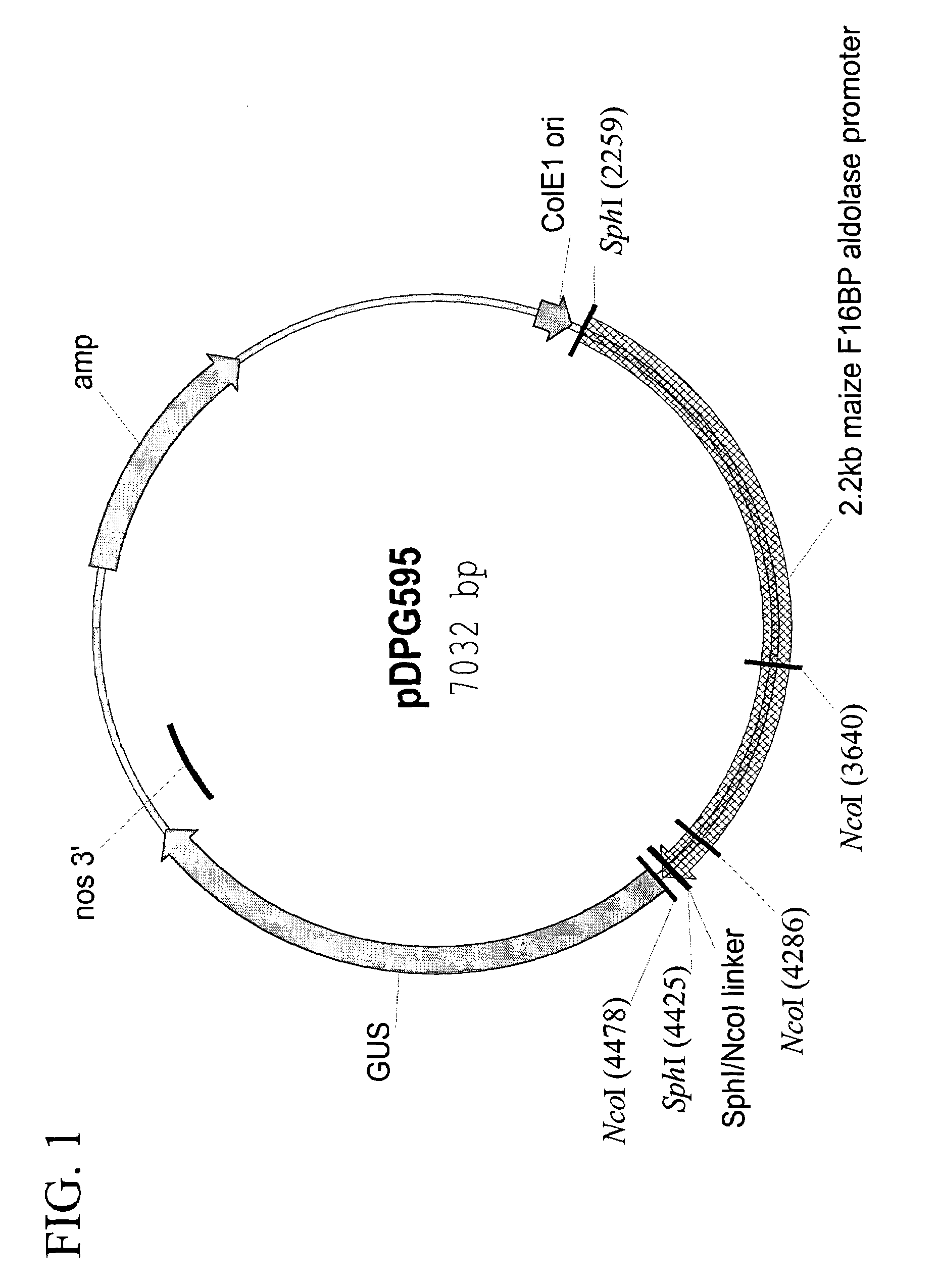
Maize chloroplast aldolase promoter compositions and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS7151204B2Simple compositionQuality improvementSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesFructoseTransgene
The current invention provides the promoter of the Zea mays nuclear gene encoding chloroplast-localized fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F16BP) aldolase. Compositions comprising this sequence are described, as are plants transformed with such compositions. Further provided are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the chloroplastic F16BP aldolase promoter by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods. The sequences of the invention represent a valuable new tool for the creation of transgenic plants, preferably having one or more added beneficial characteristics.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
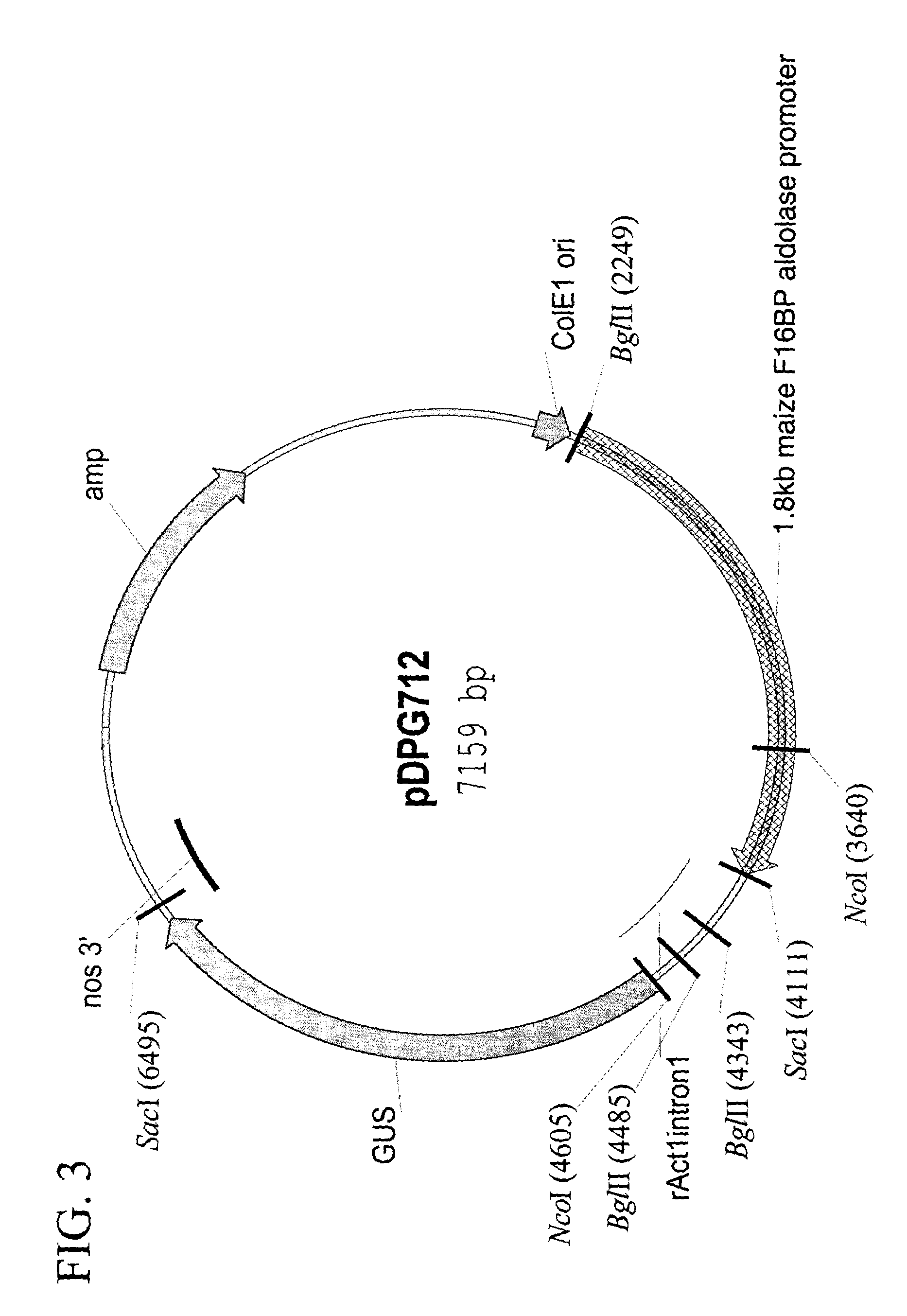
Rice actin 2 promoter and intron and methods for use thereof
The current invention provides regulatory regions from the rice actin 2 gene. In particular, the current invention provides the rice actin 2 promoter and actin 2 intron. Compositions comprising these sequences are described, as well as transformation constructs derived therefrom. Further provided are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the rice actin 2 intron and / or promoter directly by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods. The actin 2 sequences of the invention represent a valuable new tool for the creation of transgenic plants, preferably having one or more added beneficial characteristics.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Transgenic dunaliella salina as a bioreactor
Disclosed is a method for making a bioreactor comprising a foreign target gene, special selectable markers and Dunaliella Salina as host. It is prepared by the genetic transformation techniques that include introducing a foreign target gene into the cells of Dunaliella Salina and screening the transformed cells of Dunaliella Salina. The bioreactor of the present invention can be used as a safe and cheap production system for proteins of pharmaceutical interest including vaccines, especially oral products, in a large scale, because the cells of Dunaliella Salina are easy of genetic manipulation in preparation of the bioreactor, nontoxic and edible for humans and animals, and harmless to the environment.
Owner:XUE LEXUN +1
Maize RS81 promoter and methods for use thereof
The current invention provides the maize RS81 promoter. Compositions comprising this sequence are described, as are plants transformed with such compositions. Further provided are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the RS81 promoter by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods. The sequences of the invention represent a valuable new tool for the creation of transgenic plants, preferably having one or more added beneficial characteristics.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Preparation and use of plant embryo explants for transformation
ActiveUS20080280361A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEmbryoBiology
The present invention relates to excision of explant material comprising meristematic tissue from seeds, and storage of such material prior to subsequent use in plant tissue culture and genetic transformation. Methods for tissue preparation, storage, and transformation are disclosed, as is transformable meristem tissue produced by such methods, and apparati for tissue preparation.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Use of non-agrobacterium bacterial species for plant transformation
The invention relates to methods for Rhizobia-mediated genetic transformation of plant cells, including soybean, canola, corn, and cotton cells. These include both VirD2-dependent and VirD2-independent methods. Bacterial species utilized include strains of Rhizobium sp., Sinorhizobium sp., and Mesorhizobium sp. Vectors for use in such transformation are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for acquiring aromatic rice strain by targeting Badh2 gene via CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology
InactiveCN105505979AScalableEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAromatic riceGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for acquiring an aromatic rice strain by targeting a Badh2 gene via CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology. The method comprises the following steps: separately targeting sequences, recognizable by Cas9, of every exon and intron of an aromatic gene by using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology and then cutting a genomic DNA sequence to initiate DNA restoration so as to obtain an afunctional Badh2 gene; with the callus of Indica rice, japonica rice or glutinous rice as a receptor material of genetic transformation and an mature embryo, young ear, ovary or the like as explant, carrying out induction so as to obtain a diploid callus, introducing a targeting vector into cells of the callus by using an Agrobacterium mediated transformation method, screening and identifying positive plants and separating the plants from a T1 colony so as to obtain an aromatic rice strain; and with anther, pollen, unfertilized ovary or the like as explant, carrying out induction so as to obtain a haploid callus, introducing the targeting vector into cells of the callus by using the Agrobacterium mediated transformation method, screening a positive callus, reduplicating the positive callus by using colchicine, carrying out differentiation to form seedlings and identifying genetic transformation positive plants so as to eventually obtain the aromatic rice strain.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Use of non-agrobacterium bacterial species for plant transformation
The invention relates to methods for Rhizobia-mediated genetic transformation of plant cells, including soybean, canola, corn, and cotton cells. These include both VirD2-dependent and VirD2-independent methods. Bacterial species utilized include strains of Rhizobium sp., Sinorhizobium sp., and Mesorhizobium sp. Vectors for use in such transformation are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for transforming rice into fragrant rice rapidly
InactiveCN105543228AGenetic stabilityRapid homozygousOxidoreductasesFermentationSelfingGene silencing
The invention discloses a method for transforming rice into fragrant rice rapidly. By means of the CRISPR / Case technology and related gene sequences in the rice fragrance metabolic process, a carrier is designed at the specific site, the element is transferred to non-fragrant rice through agrobacterium-mediated transformation, the gene is made to cause deletion mutation at the position of a fixed point, the gene is silent, fragrance cannot be normally metabolized and greatly accumulated, common rice is transformed into fragrant rice, then genetic transformation gene segments are separated from edited genes through selfing or hybridization, and the fragrant rice with the isozygoty capable of being stably inherited is rapidly obtained.
Owner:NINGXIA ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 as well as molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN103667309AClear functionGood effectBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteProtein
The invention provides a brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 as well as a molecular marker and application thereof. The brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and a cDNA (complementary Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The Bph9 gene is located between molecular markers InD2 and RM28466. The molecular markers closely linked with the gene also includes one of RM28438, InD28450, InD28453, InD14, InD28432, RM28481 and RM28486 which can be used for sieving the rice containing the brown planthopper resistant gene Bph9. The Bph9 gene belongs to the NBS-LRR (Nucleotide Binding Site-Leucine Rich Repeat) gene family; the encoded protein is related to the plant disease resistance; the Bph9 gene is transferred into common rice by virtue of genetic transformation and hybridization, and thus the resistance of rice to brown planthopper can be improved, so that the damage of brown planthopper is decreased, and the purposes of yield increase and yield stabilization are realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Compiling vector of kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN107446924AEfficient site-directed mutagenesisBacteriaHydrolasesAgricultural scienceActinidia
The invention discloses a compiling vector of a kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 as well as a construction method and application thereof. The compiling vector of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 established can quickly and simply perform efficient site-specific mutagenesis on the kiwi fruit gene, so that the blank of a gene fixed point compiling technology in kiwi fruit is filled. Experimental results verify that by means of agrobacterium-mediated kiwi fruit genetic transformation, the compiling vector of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 performs site-specific mutagenesis on two target spots of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS successfully, and meanwhile, an albefactedphenotype is induced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated large DNA fragment assembling method
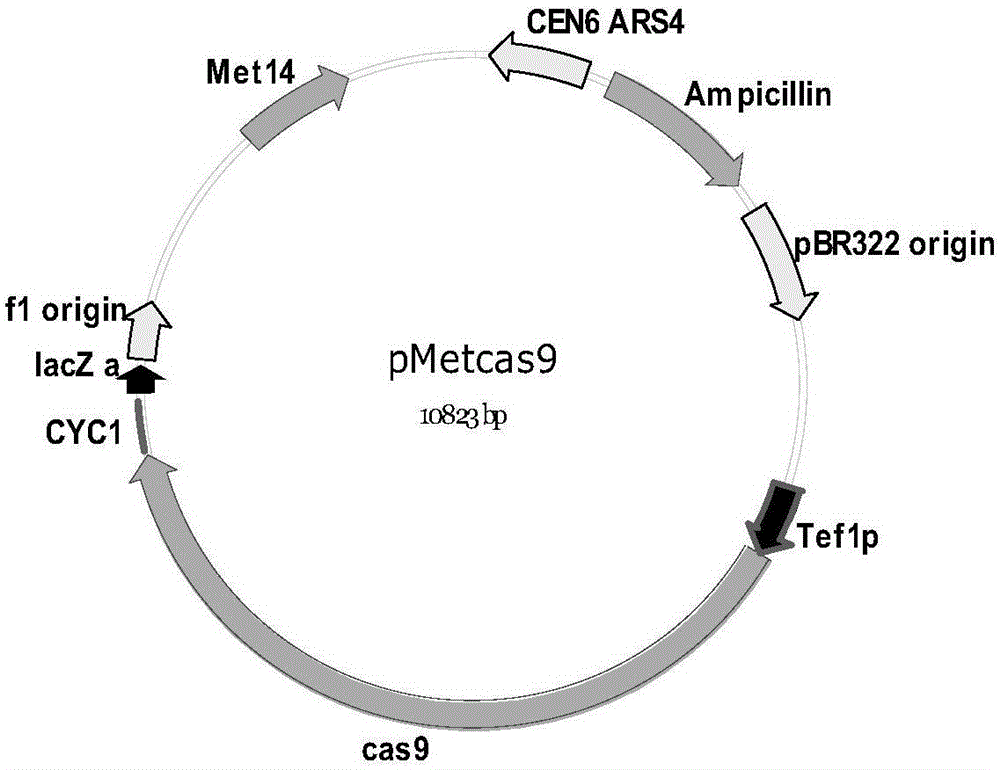
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9-mediated large DNA fragment assembling method. Specifically, the invention provides a nucleic acid construct capable of carrying out constitutive expression of Cas9 in yeast; the nucleic acid construct contains a yeast Tef1 promoter operationally connected with a Cas9 gene, a replication origin from pBR322 and a screening mark thereof, and a replication region from CEN6ARS4 and a screening mark thereof; and the nucleic acid construct is in the form of single-copy replication in the yeast and in the form of high-copy replication in Escherichia coli. The invention also provides a nucleic acid construct capable of carrying out constitutive expression of sgRNA in yeast, a nucleic acid construct used as a receptor vector and a DNA assembling method. According to the invention, two or more to-be-assembled large DNA fragments are successfully assembled in microzyme to form a large plasmid in one shot; so low-efficiency in-vitro digestion recovery, genetic transformation and the like of large DNA fragments are avoided, and the method provided by the invention is more convenient and efficient compared with traditional methods.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
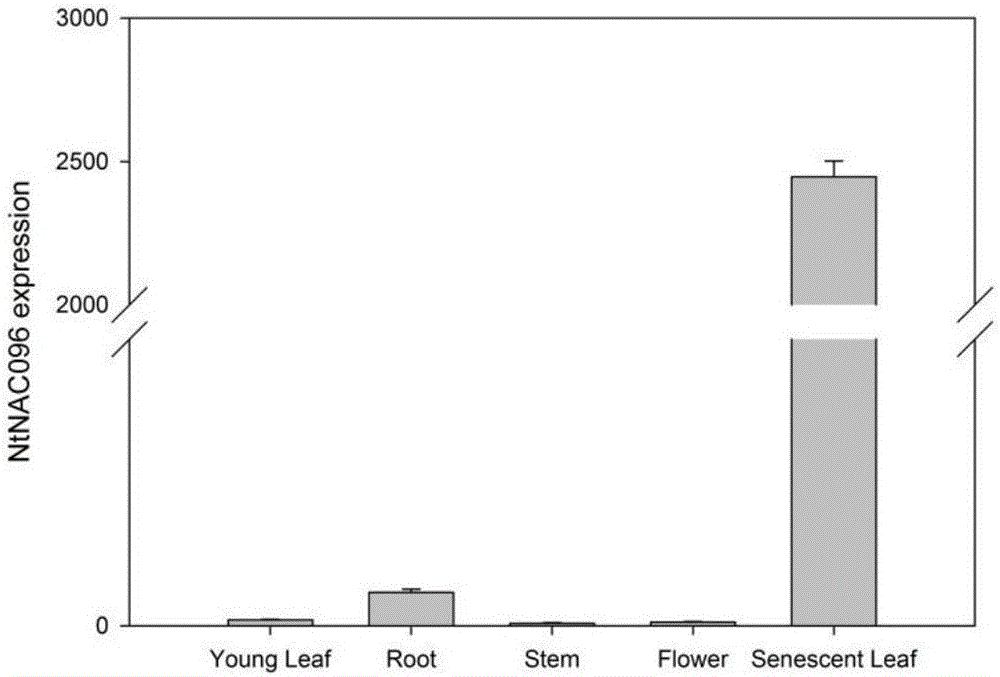
Application of tobacco NtNAC096 gene in control of tobacco aging
The invention provides application of a tobacco NtNAC096 gene in control tobacco aging, belonging to the field of tobacco biological control. The tobacco NtNAC096 gene can be used for regulating and controlling the aging of tobaccos significantly. The full length of a DNA sequence of a genome using the tobacco NtNAC096 gene c is 1203bp, and the genome consists of 3 exons and 2 introns. The application specifically comprises the following steps: (1) cloning the tobacco NtNAC096 gene, and performing sequence analysis; (2) performing expression analysis on the NtNAC096 gene; (3) performing function analysis on the tobacco NtNAC096 gene by establishing an over-expression vector of the tobacco NtNAC096 gene; and (4) designing target sites of the tobacco NtNAC096 gene by using a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology, establishing a NtNAC096 gene knockout vector, and performing genetic transformation on a tobacco variety, thereby obtaining a tobacco plant capable of delaying aging.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Molecular improvement method for lowering rice grain seed holding
ActiveCN106191107AReduce shatteringImprove work efficiencyPlant peptidesFermentationTransgenesisMolecular genetics
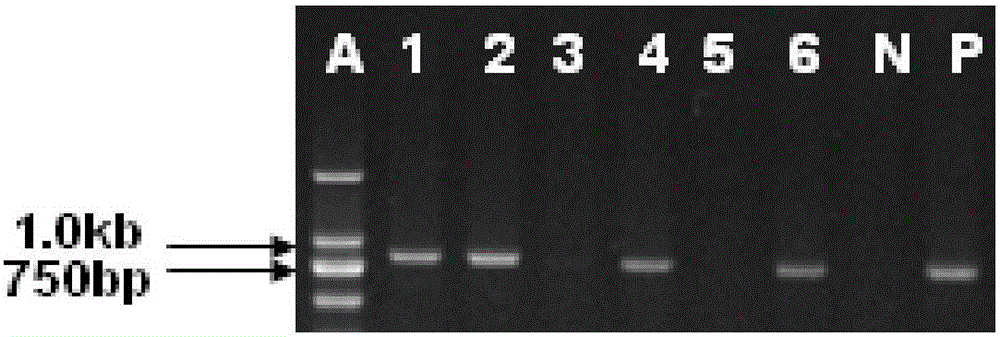
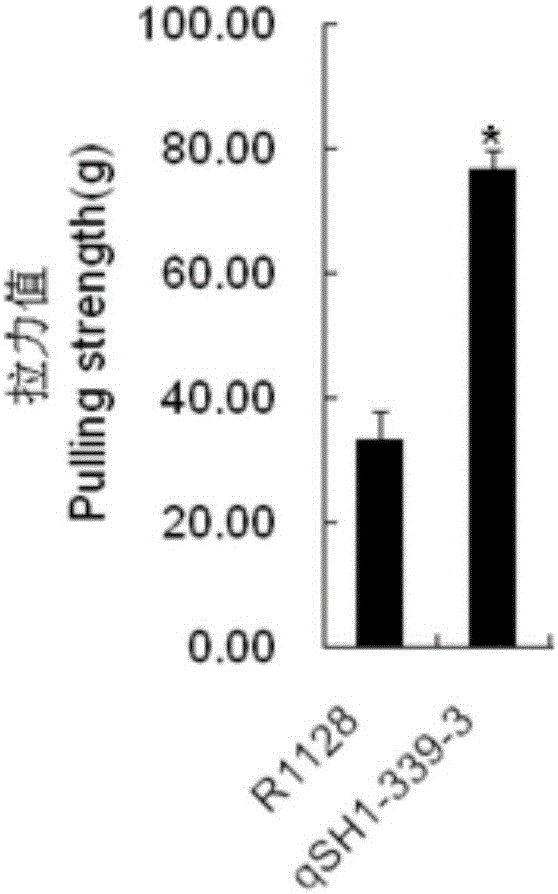
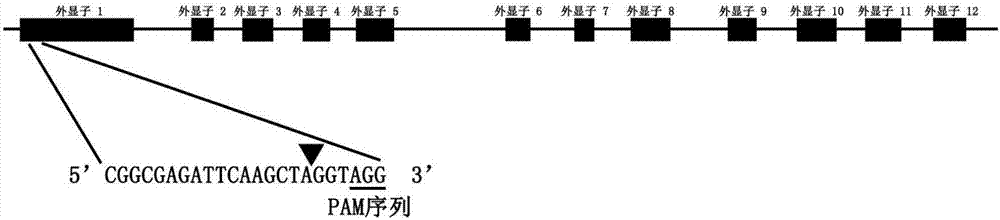
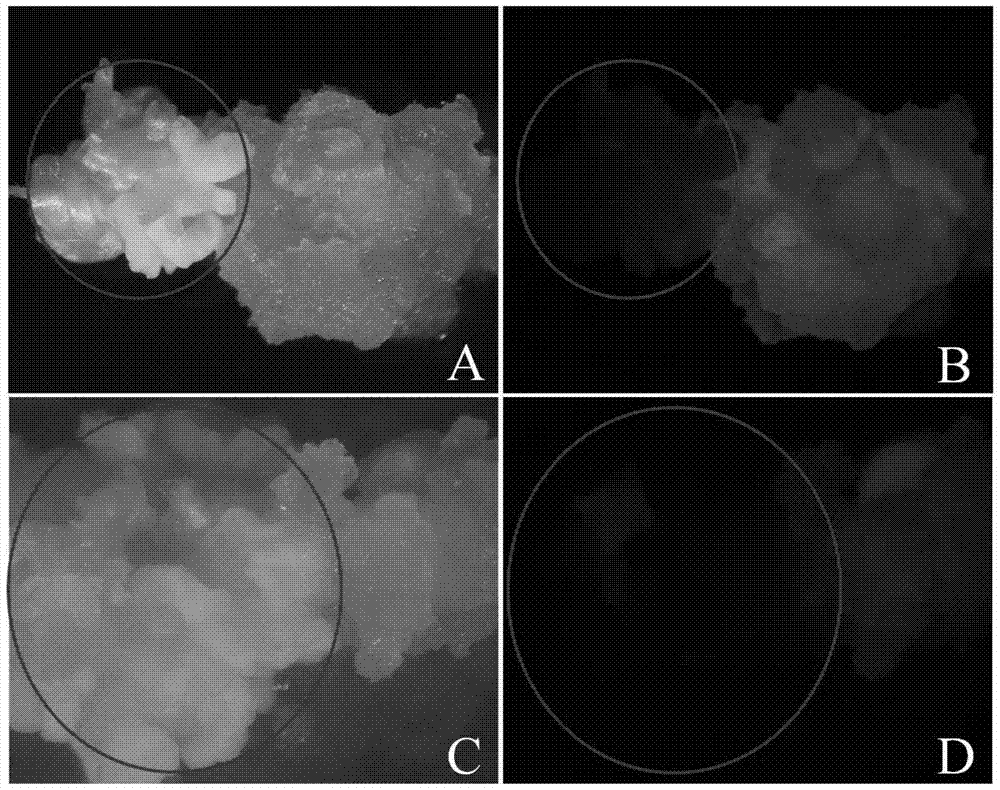
The invention discloses a molecular genetic improvement method for lowering rice seed holding by targeted modification on rice seed holding gene qSH1 by using a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) selecting an appropriate target; 2) establishing a vector containing the target spot sequence; 3) establishing a recombinant vector containing the target spot sequence by utilizing the vector; 4) introducing the recombinant vector into receptor rice to obtain a transgenic positive plant; 5) obtaining a targeted-mutation mutant plant by utilizing the transgenic positive plant; 6) carrying out additive-generation growth on the mutant plant to obtain a transgenic-component-free homozygous mutant plant; and 7) carrying out seed holding investigation by using the homozygous mutant plant to obtain the plant with obviously lower seed holding as the seed-holding-improved plant. The method has the advantages of high directionality, small genetic background changes and the like, can avoid the risks caused by genetic transformation, and can culture the new species and new combination of transgenic-component-free rice with obviously lower seed holding.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting arabidopsis ILK2 gene and application of sgRNA sequence
InactiveCN107236737AKnockout EfficientKnockout fastHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingArabidopsis thaliana
The invention discloses a sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting an arabidopsis ILK2 gene and application of the sgRNA sequence. The nucleotide sequence of the sgRNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. Two single-chain oligo DNA sequences are designed and synthesized according to a sgRNA guide sequence, a double chain is formed through annealing and is linked with a Cas9 carrier, a sgRNA coding sequence and a CRISPR system are introduced into Arabidopsis by using an agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation technique, a target sequence is shorn by a Cas9 protein under the guidance of sgRNA, and therefore, the knockout of an ILK2 gene is realized. According to the sgRNA sequence provided by the invention, the ILK2 gene can be knocked out or edited by virtue of a CRISPR-Cas9 system, so as to analyze the functions of the arabidopsis ILK2 gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for site-directed mutation of maize gene by means of CRISPR/Cas9 system
ActiveCN107022562AGood characterSite-directed mutagenesisPeptidesNucleic acid vectorDNA fragmentationA-DNA
The invention provides a method for site-directed mutation of a maize gene by means of a CRISPR / Cas9 system. An sgRNA sequence based on CRISPR / Cas9 is designed aiming at a target gene in maize, a DNA fragment for encoding the sgRNA sequence is connected to a vector carrying CRISPR / Cas9, and then maize transformation is conducted, so that site-directed mutation of a specific gene in maize is realized. Further, the vector containing CRISPR / Cas9 is transferred to an acceptor material carrying the target gene by means of a genetic transformation method, so as to obtain a site-directed mutation regeneration plant of the target gene. By the adoption of the method, site-directed mutation of a maize genome can be achieved. The method has the advantages that the experimental period is short, and operation is easy. Different target genes can be transformed in a site-directed mode by means of CRISPR / Cas9 systems with different targeting directions, a novel method is provided for improved breeding of maize, and the method is of great practical significance for maize trait improvement.
Owner:先正达集团股份有限公司
Cas9/RNA system and application thereof
InactiveCN107304435AEasy to synthesizeSpeed up breedingVectorsHydrolasesGenetic engineeringDouble stranded
The invention relates to genetic engineering transformation of nannochloropsis oculata and particularly relates to a method for carrying out genetic transformation by using Cas9 / CRISPR at a fixed point. A compound is formed by overexpressed Cas9 protein in the nannochloropsis oculata and gRNA, the Cas9 protein is used for carrying out site-specific cleavage on a genome double-stranded DNA under the guidance of the gRNA to cause gene mutation, and mutation is effectively screened by combining a sequencing technique. Fixed-point genetic engineering transformation is carried out on the nannochloropsis oculata by using a CRISPR / Cas technology, so that the algae species improvement efficiency of the nannochloropsis oculata can be significantly improved.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for regenerating plant strain using soybean cotyledonary node
InactiveCN101176427AReduce humidityIncrease humidityCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsOrganogenesisHealth production
The invention relates to a method using the cotyledon node of soybeans as explant to perform soybean organogenesis and plant regeneration, belonging to the technical field of agricultural production. The invention is characterized in that based on the traditional tissue culture, the cotyledon node of soybeans is used as explant to perfect the regeneration system of organogenesis means. The invention has the advantages that based on the selection of effective disinfection technology for soybean seeds, the improvement and the optimization of various medium compositions is outstanding; through the verification of the tissue culture of conventional soybean varieties, the induction, the elongation and the rooting of multiple shoot are effectively promoted; the quality of aseptic seedlings and the differentiation rate of the multiple shoot are improved; the organogenesis and plant regeneration process of the cotyledon node of majority varieties are perfectly realized; solid technical support is provided for the genetic transformation and the molecular improvement of soybeans; and the invention has important practical significance to the effective breeding and health production of the soybeans in China.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Method for obtaining label-free transgenic plant
ActiveCN108753813AEasy to operateHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionLarge fragmentExpression gene
The invention discloses a method for obtaining label-free transgenic plant. The method is implemented by a CRISPR / Cas9 or CRISPR / Cpf1 system, and a vector of the CRISPR / Cas9 or CRISPR / Cpf1 system comprises a gene edited protein gene, a sgRNA of targeting the vector and a specific temporal and spatial expression gene promoter. The specific temporal and spatial expression gene promoter is not expressed during callus period, and the gene edited protein gene is expressed after genetic transformation is completed. The method provided by the invention has simple operation, and mainly aims at cropsor economic plants, especially plants that are perennial and vegetative propagated; large fragments of transgenic components are lost by splicing the vector, and the significance is great.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Method for regenerating plant from camellia callus
InactiveCN101558742ASimple recipeEasy to operatePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudCamellia sinensis
The invention mainly relates to a method for regenerating a plant from camellia callus. The method has the following steps: stripping off the inner and outer seed coats of a camellia fruit seed, and inoculating the seed to a 1 / 2MS culture medium; when a sterile seedling grows above 3 cm, inoculating the soft leaf of the young plant to a callus induction culture medium which is MS + 0.5mg.L 6-BA+1.0mg.L 2,4-D; when the callus grows to get a diameter about 1 cm, shifting the callus to a callus differentiation culture medium which is MS+mg.L 6-BA20+0.1mg.L I BA+ mg.L KT0.1; when an indefinite bud grows to 0.5 cm, carrying out the separation and inoculating to a strong bud culture medium which is MS + 0.2mg.L 6-BA+0.05mg.L NAA; and when a bud stick grows to 4 to 5 cm, cutting off the basal of the bud stick, immersing the basal of the bud stick in 1,000 g.L I BA, and then inoculating to a MW + 0.2mg.L I BA+0.2mg.L NAA culture medium. The method has the advantages that: the method has a simple culture medium recipe, a simple and convenient operating process, short culture time, high regeneration frequency and a high propagation expansion coefficient, and facilitates the large-scale production of rare camellia plants and the realization of the genetic transformation of exogenous genes.
Owner:RES INST OF SUBTROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
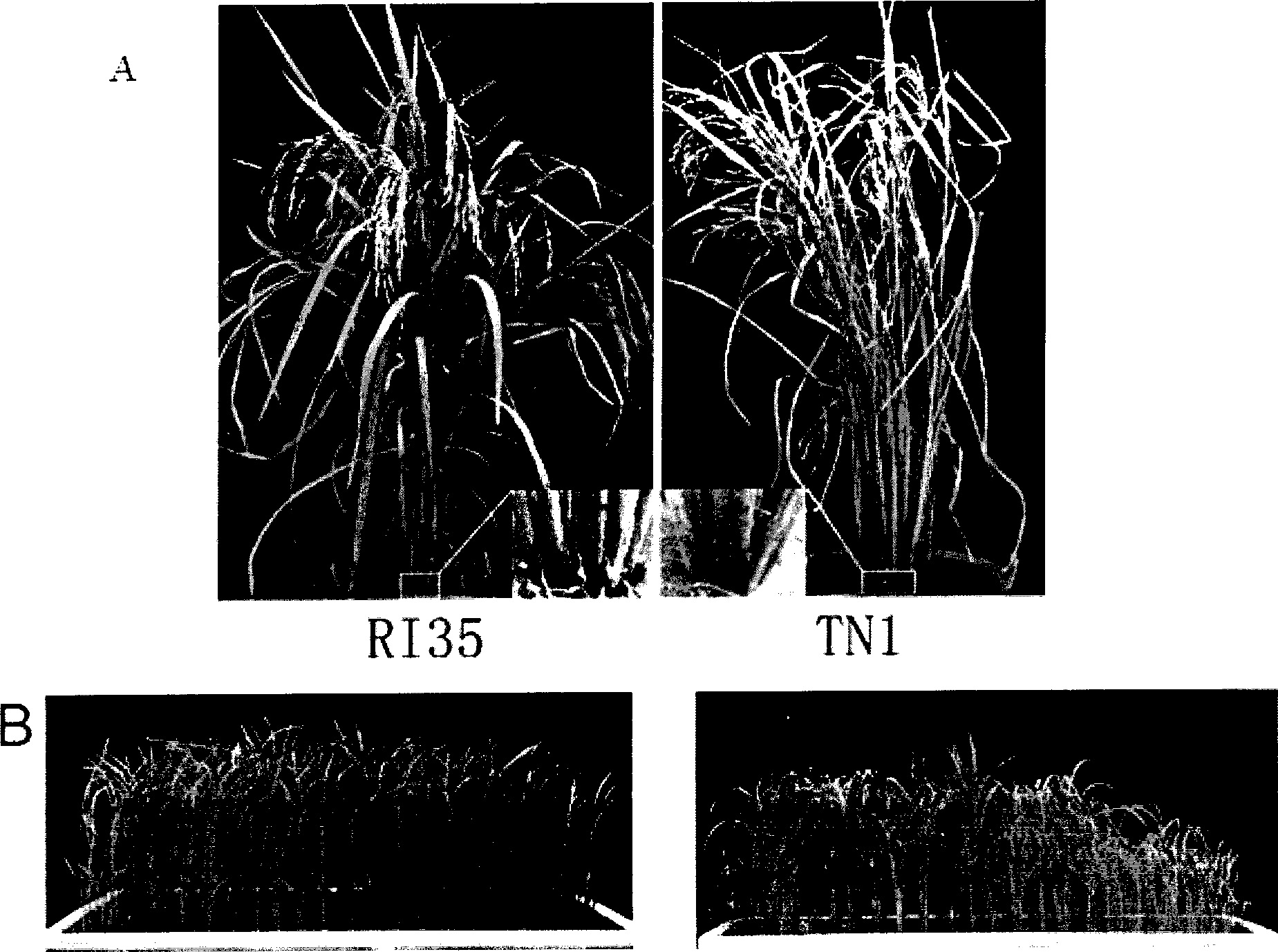
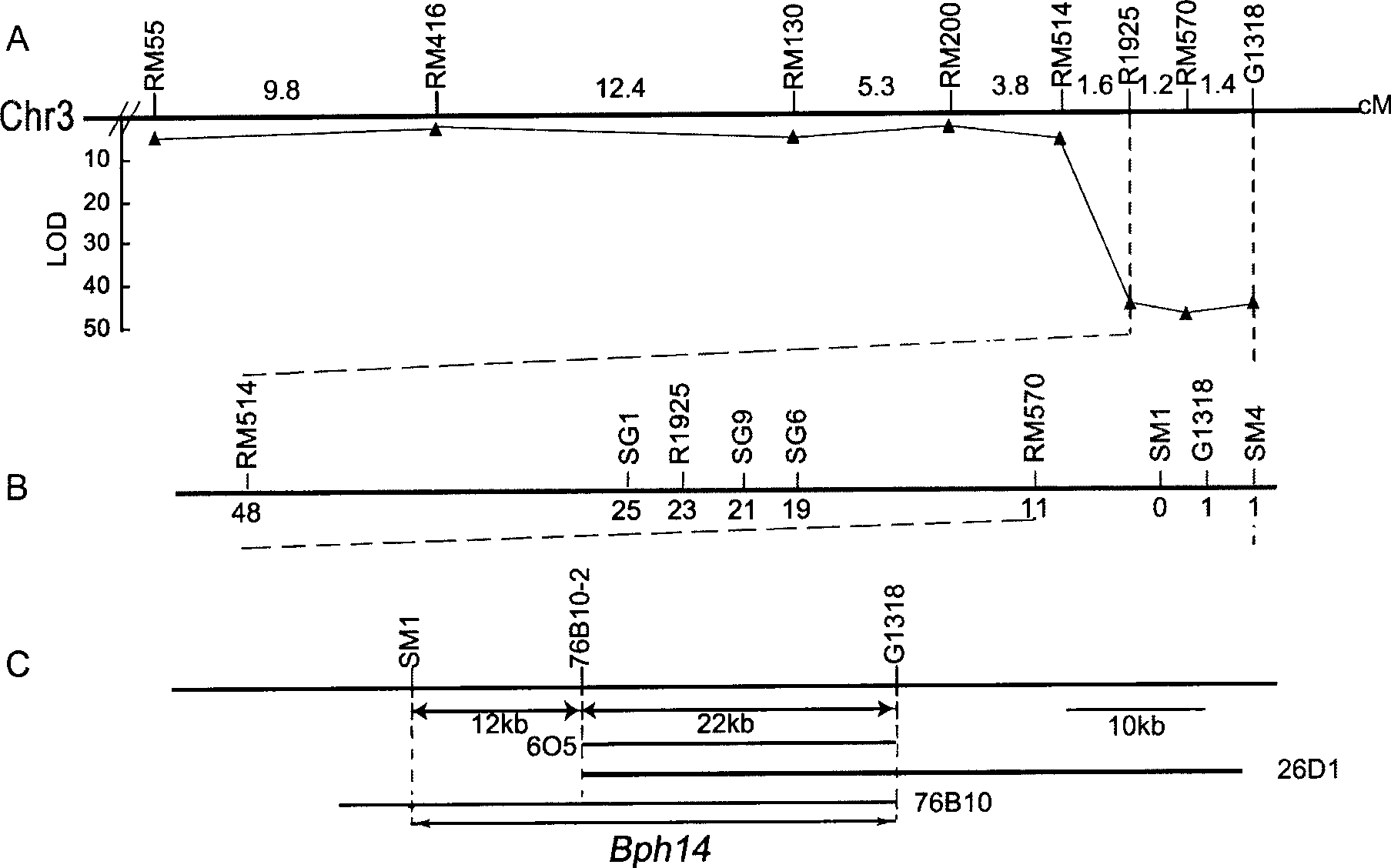
Brown planthopper resistant gene in rice and use thereof
The invention provides a brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 in rice. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and a cDNA sequence thereof is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The gene Bph14 of the invention belongs to CC-NBS-LRR gene family, and coded protein is related to plant disease resistance. The gene Bph14 has function of resisting the brown planthopper. Through genetic transformation and hybridization, the gene Bph14 is transferred into normal rice varieties, which can improve the resistance of the rice to the brown planthopper, thus reducing the damage caused by the brown planthopper and achieving the purposes of increasing and stabilizing the production of rice.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
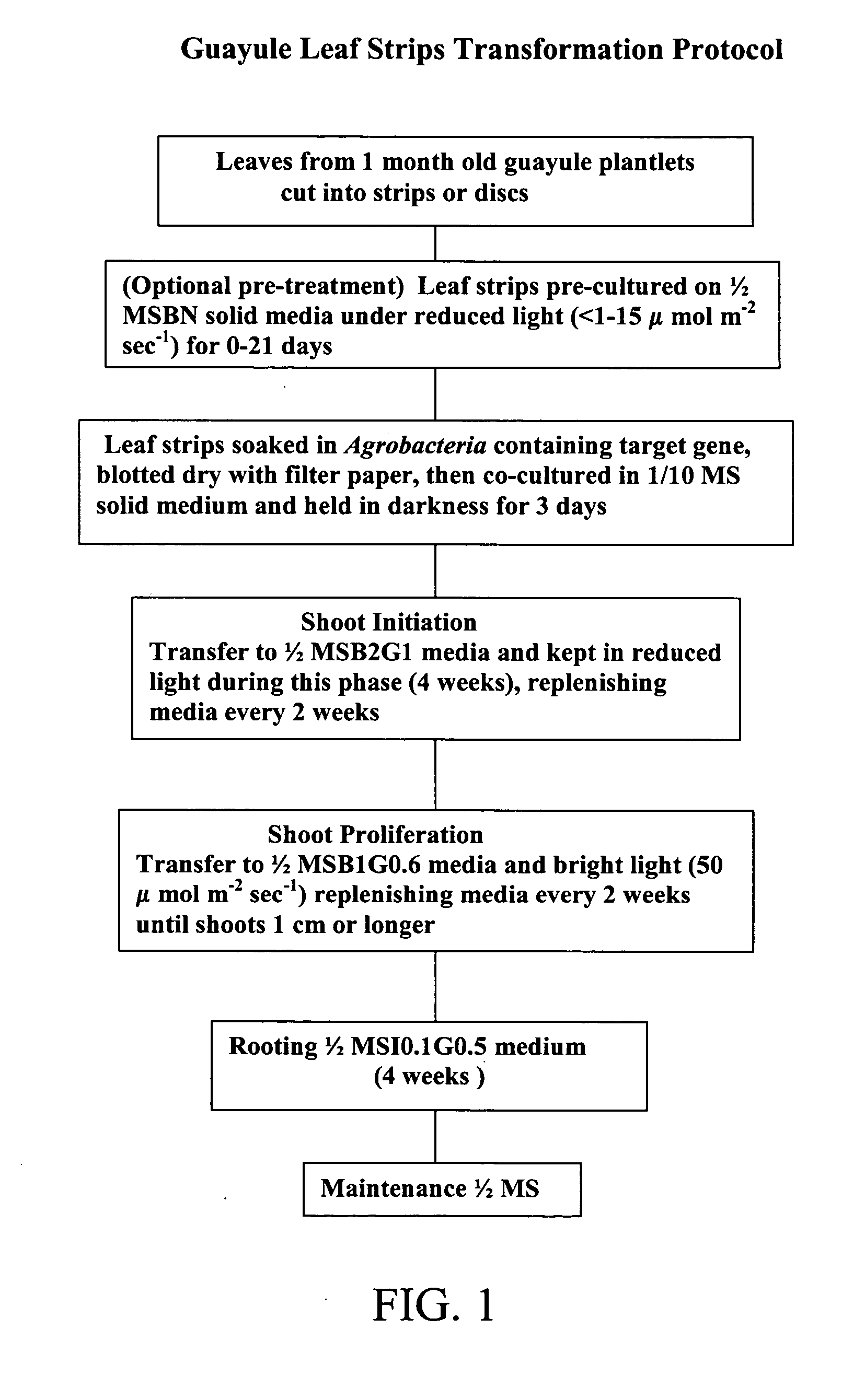
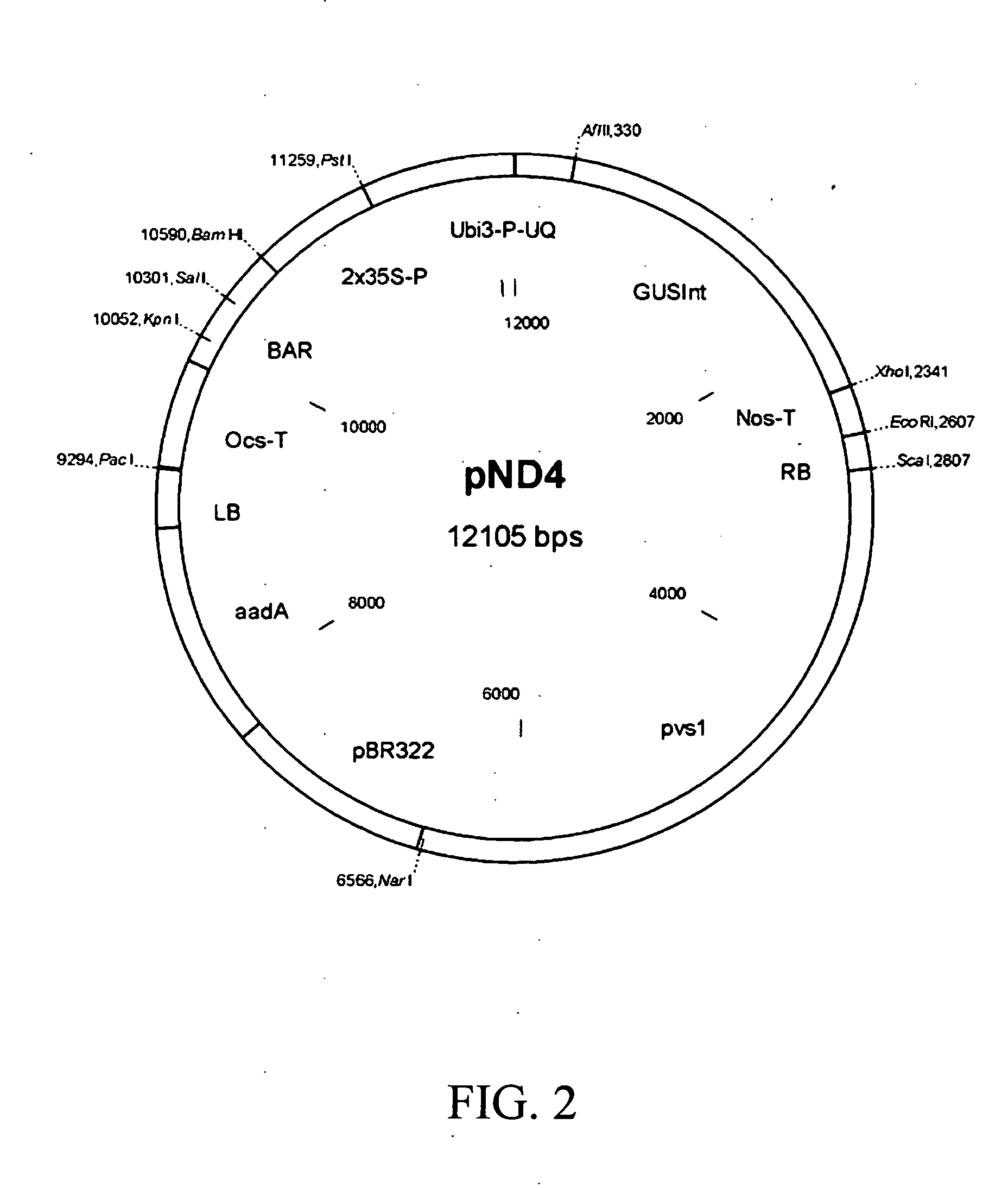
Transformation methods for Guayule using Agrobacterium and reduced light to slow metabolism and enhance recovery
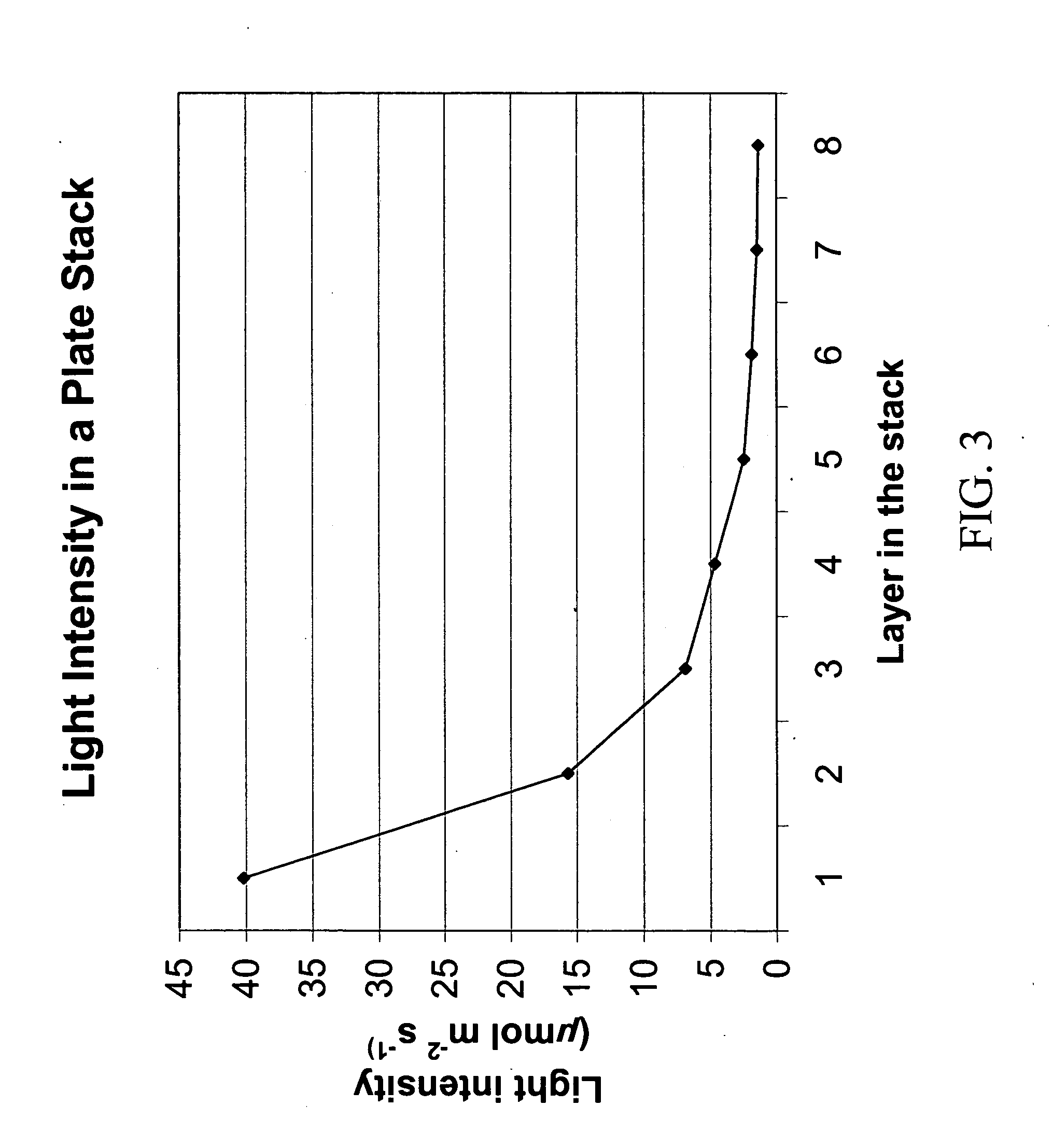
InactiveUS20060218660A1Increase productionLabor intensiveOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationParthenium argentatumGenetics
This invention is directed to a new technique of genetic transformation using low light conditions and leaf strips in the Guayule plant, Parthenium argentatum. The invention also relates to new lines of Guayule, created through this technique.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Method for agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sugarcane
InactiveCN102154364AOvercome serious shortfalls in conversionAddress serious deficienciesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMetal ArtifactTransformation efficiency
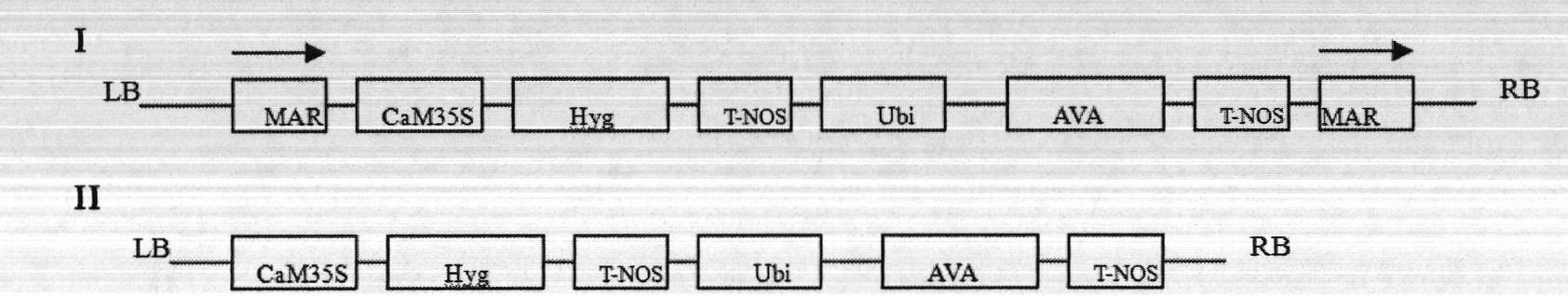
The invention discloses a method for agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sugarcane. The method comprises the steps: leading agrobacterium tumefaciens liquor carrying plant expression vectors to infect embryogenic callus of the sugarcane; and selecting and proliferating resistant calli to induce the resistant calli to obtain the resistant buds of the sugarcane, wherein matrix attachment region sequences are connected at two sides of a gene expression box of the plant expression vector. According to the method, MARs (metal artifact reduction) sequences are built at two sides of the gene expression box of the plant expression vector, thus greatly improving the exogenous gene transformation efficiency and seedling rate of the sugarcane, and being simple in process flow and low in cost.
Owner:广西作物遗传改良生物技术重点开放实验室
Method for high efficiency regeneration and genetic transformation of indica rice
InactiveCN102943090AFast growthShort conversion cycleFermentationGenetic engineeringRoom temperatureEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for high efficiency regeneration and genetic transformation of indica rice. The method comprises the following steps of (1) induction of calluses: an indica rice mature embryo or young embryo is used as an explant; (2) subculture multiplication of the calluses: light yellow granular calluses are selected and transferred to a subculture multiplication medium for cultivation; (3) preculture of the calluses; (4) agrobacterium mediated transformation of the embryonic calluses: the precultured calluses are transferred into an agrobacterium work bacterium liquid and immersed at a room temperature; (5) co-culture of the calluses and the agrobacterium; (6) screen of resistant calluses: the co-cultured calluses are screened to grow novel resistant calluses; (7) differentiation of the resistant calluses: the screened resistant calluses are inoculated in a differentiation medium; and (8) rootage of regeneration sprout: rooted transgenic plants are obtained. The method is simple and convenient in screening, has high efficiency, and improves the efficiency of genetic transformation of the indica rice. Three representative indica rice varieties are transferred; and the transformation rate of each indica rice variety is higher than 25%.
Owner:湖北省农业科学院
Method for generating resistance against citrus diseases caused by insects, fungi, oomycetes, bacteria or nematodes
ActiveUS20110119788A1Reduce accumulationAchieve resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNematodeWhole body
The invention consists in modifying the levels of accumulation and emission of monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes in citrus as a mechanism to achieve systemic resistance against pathogens or repellency against pests. The alteration of the content of d-limonene and other terpenes is achieved by genetic transformation via the introduction of a gene that encodes an enzyme with d-limonene synthase activity, from a citrus fruit or plant or from another living organism, in antisense or RNAi (RNA interference) configuration. Genetic modification is achieved either by Agrobacterium tumefaciens or any other method of genetic transformation of plants from protoplasts or explants. The construction is incorporated in citrus genotypes or related genera of the family Rutaceae in order to reduce the levels of accumulation and emission of the monoterpene and precursor compounds and / or derivatives, either of leaves or flowers and / or fruit.
Owner:INST VALENCIANO DE INVESTIGACIONES AGRARIAS IVIA
Method for establishing tissue culture regeneration system of camellia sinensis L.
InactiveCN104686332ASolve the problem of lack of seedlingsAvoid missingHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEmbryoCamellia sinensis
The invention discloses a method for establishing a tissue culture regeneration system of camellia sinensis L. and relates to a technical method for obtaining strain property stable camellia sinensis L. seedlings from the camellia sinensis L. by use of a vegetative rapid propagation technique. According to the method, the tissue culture regeneration system of camellia sinensis L. is established by taking the immaturate embryo of the camellia sinensis L. as the explant and by virtue of the steps of seed sterilization, embryo callus induction, differentiation culture, rooting culture, acclimatization and transplant and the like; as a result, the problem of shortage of good-quality seedlings of the camellia sinensis L. is solved, and a foundation also can be laid for developing the genetic transformation work of camellia sinensis L. in the future.
Owner:刘木娇
Low pressure gas accelerated gene gun
InactiveUS20070164133A1Easy to operateMaterial efficiencyFire rescueIntravenous devicesNanoparticleFree form
The present invention relates to a gene gun and its application for genetic transformation, medical therapeutic or cosmetic purposes. Particular designs of the gene gun allow the biological materials to be delivered to the plant epidermal cellular tissues, the skin of an animal or human-being via a solution or a pre-mixed with the high pressure gas loading system. Moreover, the biological materials delivered by the gene gun are applied either in encapsulated nanoparticles or in the free form without using particle carriers.
Owner:SONDLIN TECH CORP
In-vitro regeneration culture method for tea clones
InactiveCN102422810AReduce browning rateReduce browningPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShootCamellia sinensis
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method with vacuum infiltration assistance
InactiveCN103205459APerfect genetic transformation systemIncreased genetic transformation rateGenetic engineeringFermentationTi plasmidBiological activation
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses an agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method with vacuum infiltration assistance. The agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method includes: (1) induction and multiplication of embryonic callus of sugarcane core leaves, (2) activation and cultivation on agrobacterium tumefaciens with target genes, (3) agrobacterium infestation with vacuum infiltration assistance on embryonic callus of sugarcane core leaves, (4) resistant material screening and germination, and (5) resistant material verification. With the agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method, the agrobacterium can pass through the gaps among callus cells and enter deep cells on vacuum, and tiny wounds can be generated on the surfaces of the cells, so that phenolic substances are secreted by plants to activate shear and transfer of T-DNA (transferred deoxyribonucleic acid) in Ti plasmids. The agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation system is perfected. Genetic transformation rate of sugarcane is remarkably improved as compared with that of the prior art.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST
Gene for controlling rape plant type, molecular marker and application thereof
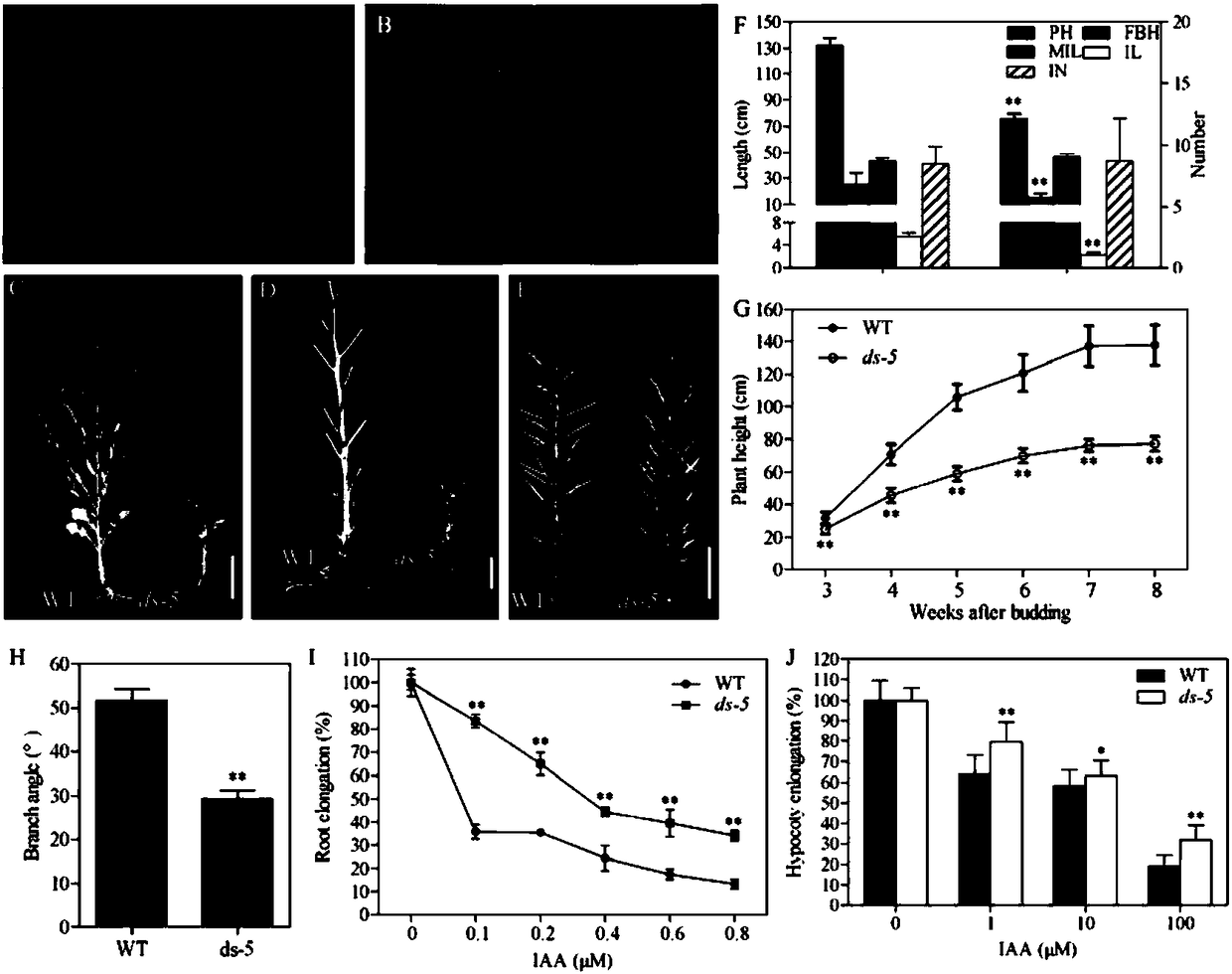
ActiveCN108239647AReduce plant heightSmall branch angleMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceRapeseed
The invention belongs to the field of rapeseed genetic engineering and relates to a gene for controlling a rape plant type, a molecular marker and an application thereof. The gene for controlling a rape plant type can control plant height, branching angles and leaf morphology. Through map-based cloning and genetic transformation, a gene BnaA3. IAA7 for controlling a rape plant type is cloned and verified. The gene is located on an A3 chromosome of a rape genome, codes an auxin protein and has a sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses a separated mutant geneBnaA3. Iaa7 of the gene BnaA3. IAA7. The mutant gene has a sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO: 4 and can significantly reduce the plant height and branching angles of rape. The mutant gene does not influence the yield per plant when improving the rape variety or the inbred plant type, and increases the yield per plant when improving the rape hybrid plant type. The invention also disclosesa related molecular marker.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com